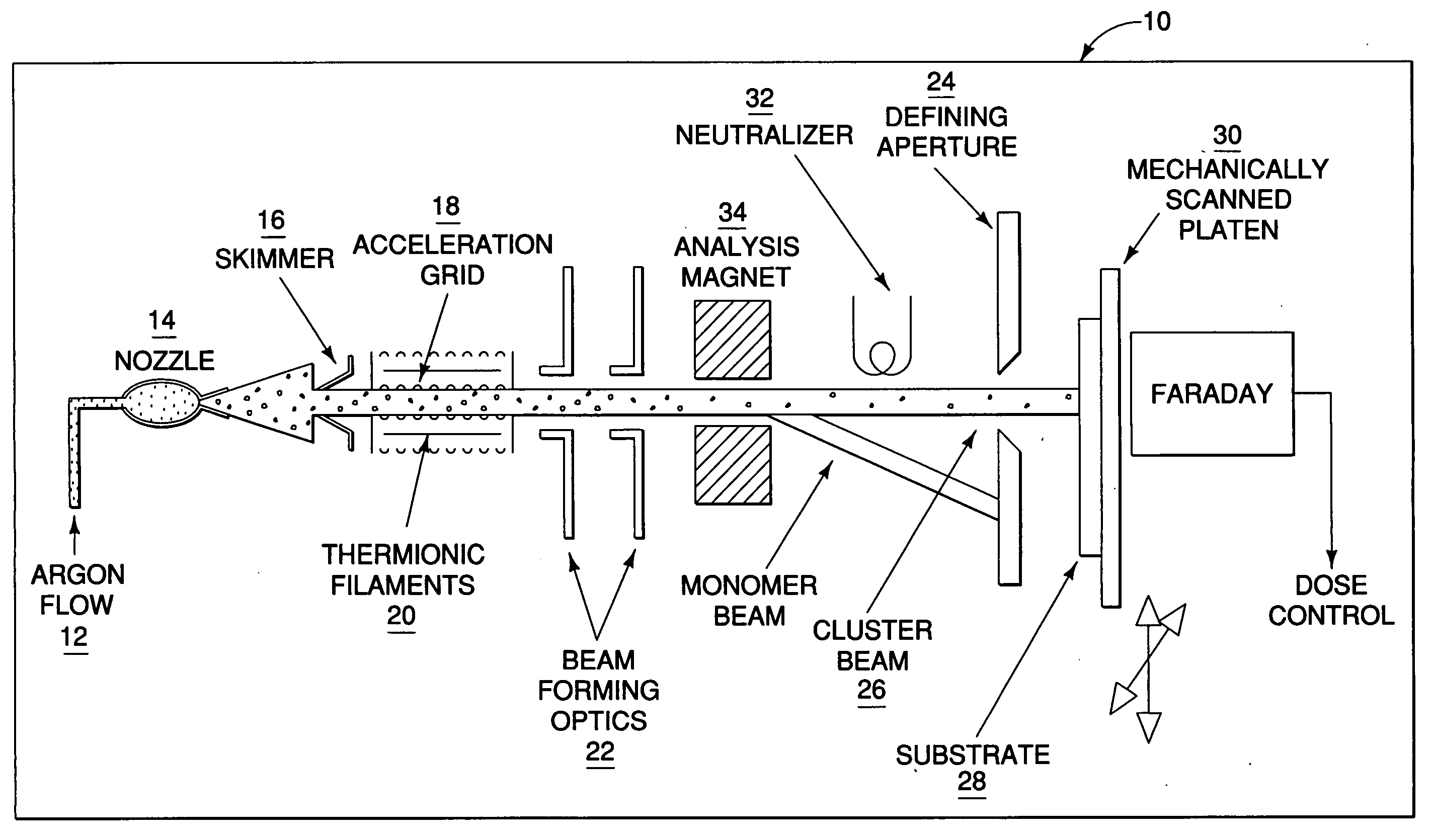
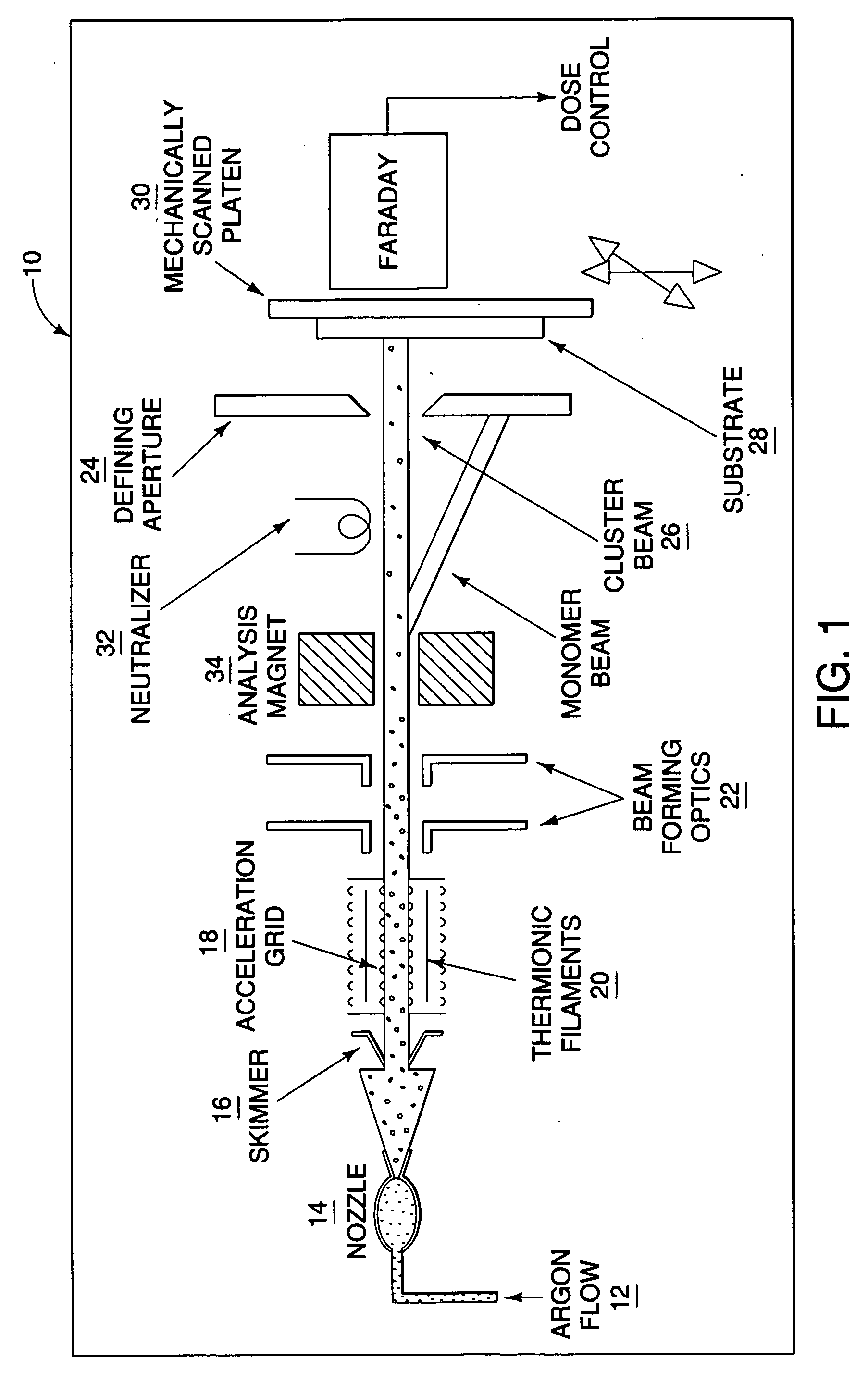
Patents
Literature
688 results about "Gemstone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A gemstone (also called a gem, fine gem, jewel, precious stone, or semi-precious stone) is a piece of mineral crystal which, in cut and polished form, is used to make jewelry or other adornments. However, certain rocks (such as lapis lazuli and opal) and occasionally organic materials that are not minerals (such as amber, jet, and pearl) are also used for jewelry and are therefore often considered to be gemstones as well. Most gemstones are hard, but some soft minerals are used in jewelry because of their luster or other physical properties that have aesthetic value. Rarity is another characteristic that lends value to a gemstone.
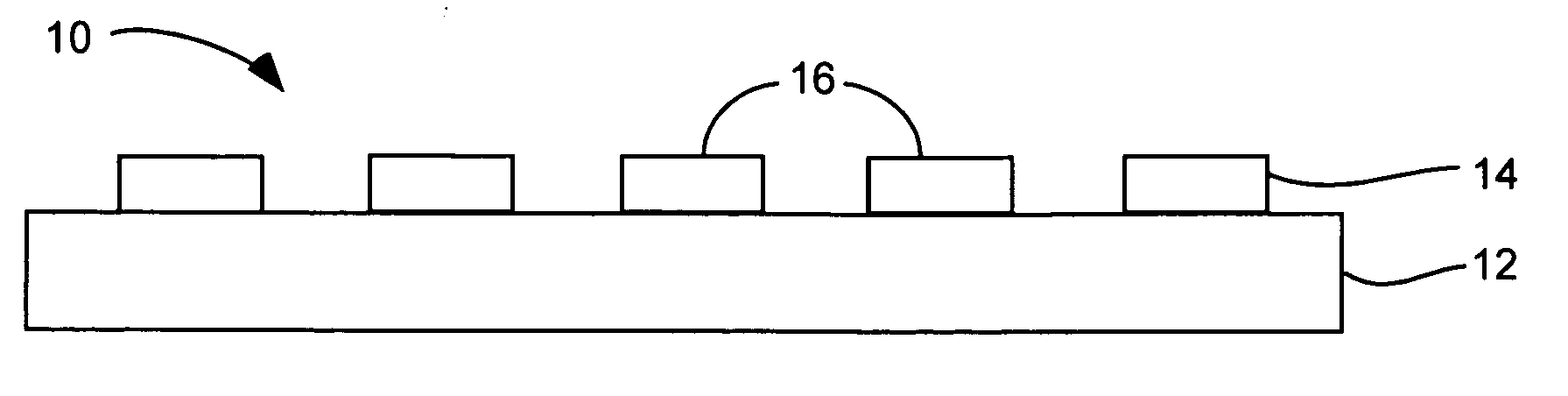
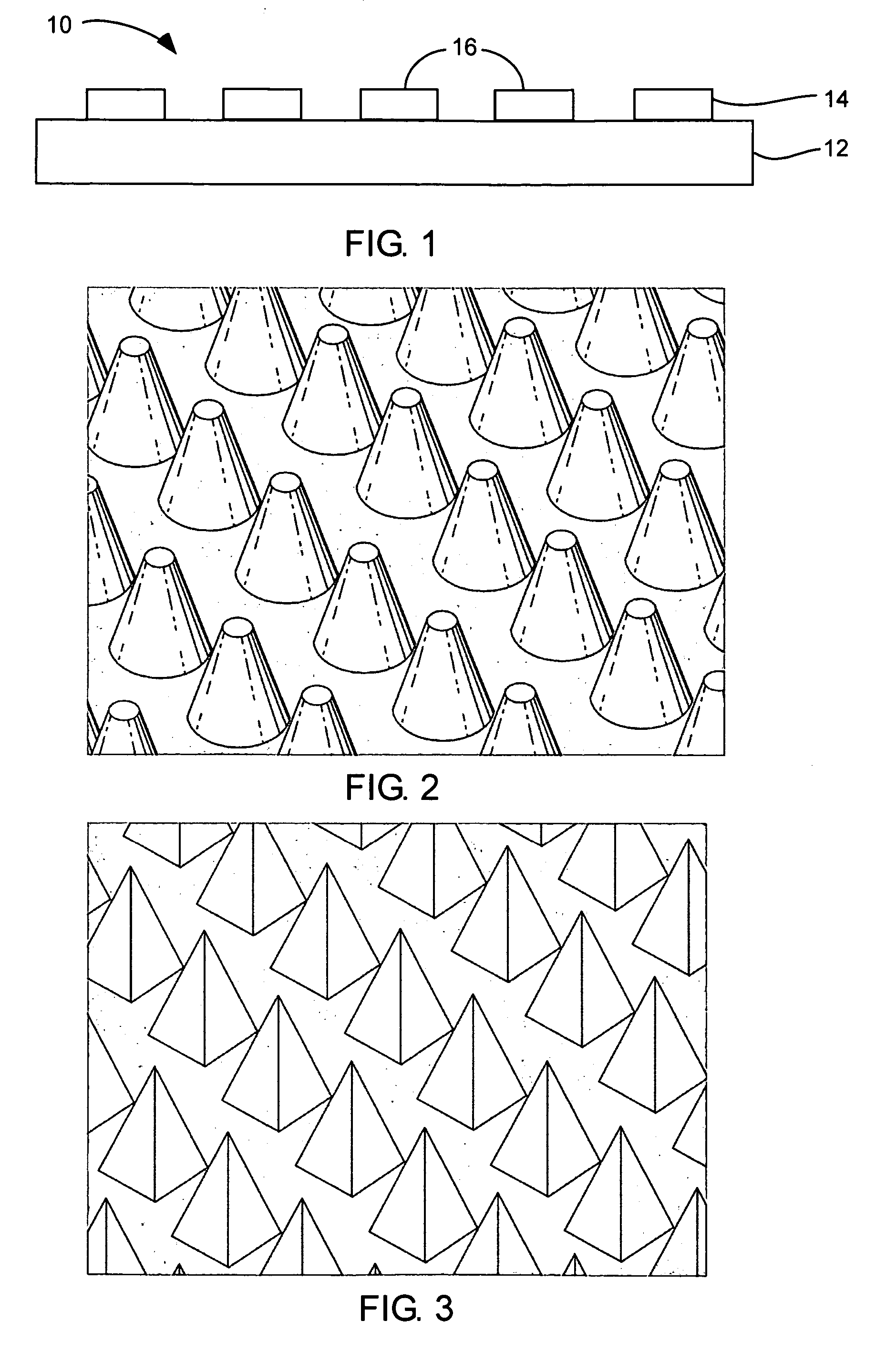
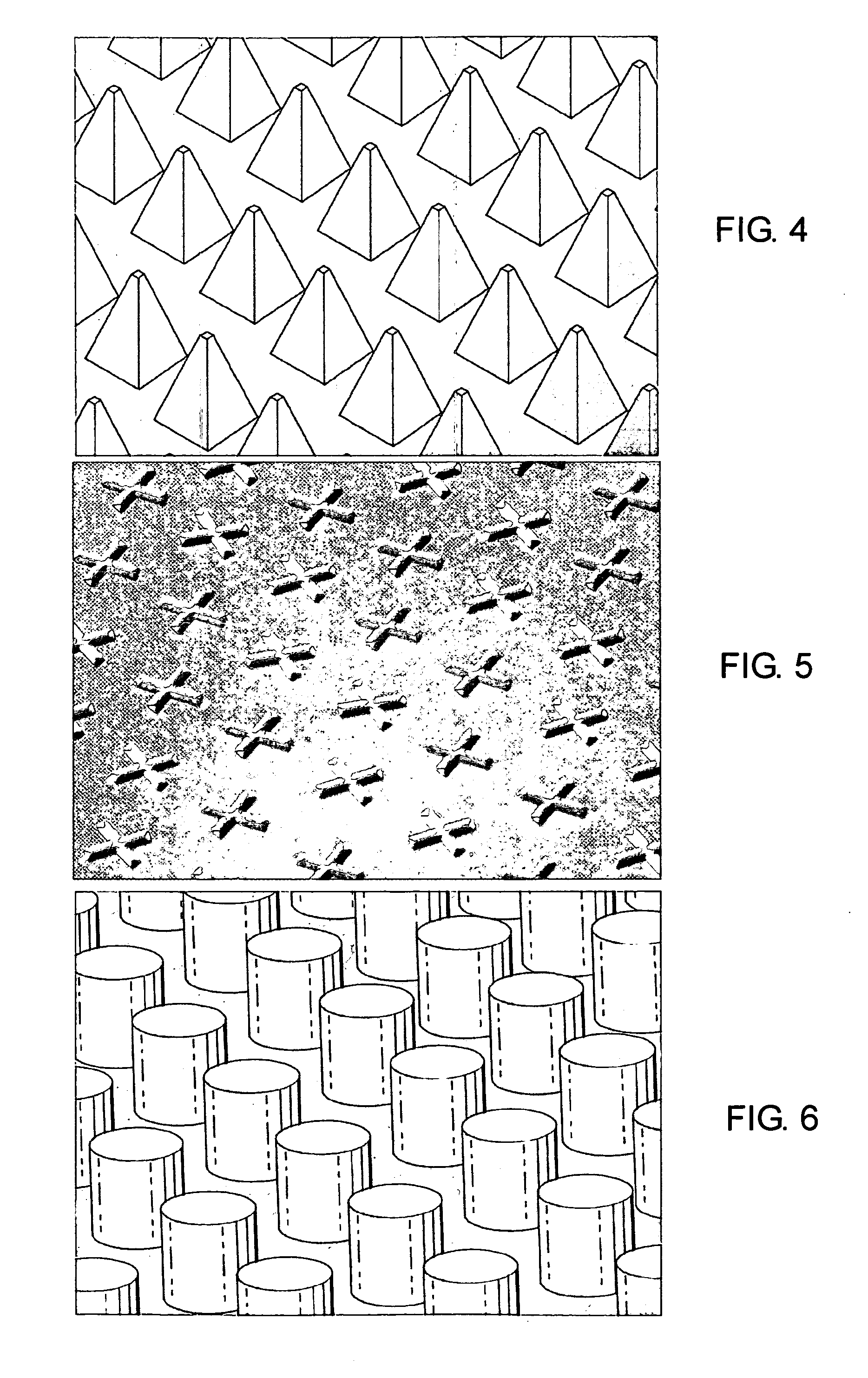
Fixed abrasive tools and associated methods
InactiveUS20050227590A1Easy to remove debrisAdequate material removal rateAbrasion apparatusPlane surface grinding machinesScreen printingMostly True
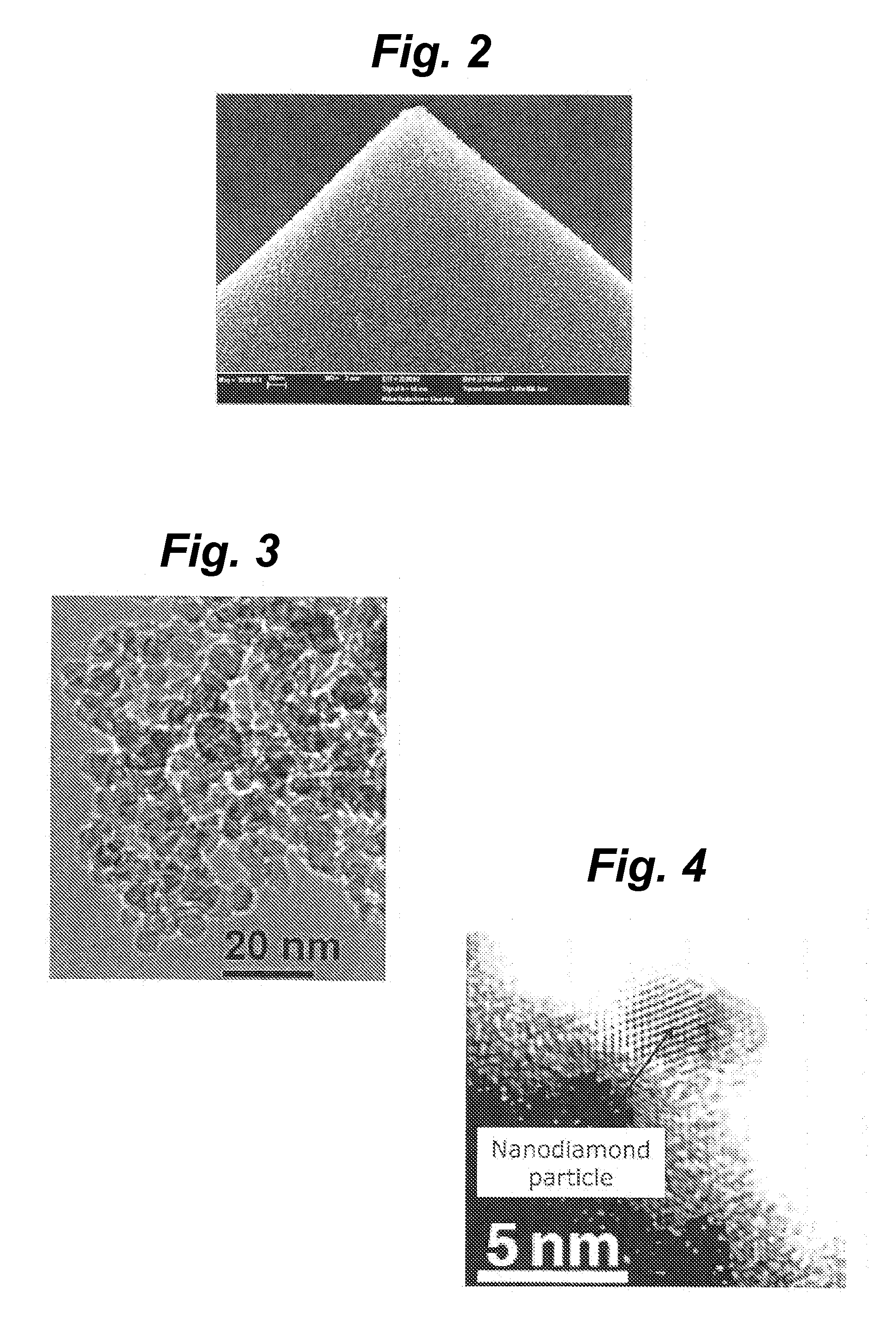
A fixed abrasive tool incorporating nanodiamond particles is described and disclosed. A fixed abrasive tool can include a polishing layer on a substrate. The polishing layer can include an organic matrix with nanodiamond particles therein. The polishing layer can be formed in a wide variety of configurations, depending on the specific polishing application. Most often, the polishing layer can include a plurality of projections which can have a wide variety of configurations in order to achieve a particular polishing performance. Nanodiamond particles used in the present invention can have a particle size from about 1 nm to about 50 nm, and preferably about 2 nm to about 10 nm. Optionally, the nanodiamond particles can include a carbonaceous coating. Such fixed abrasive tools can be formed by screen printing of a slurry of nanodiamond particles and an organic binder to form a predetermined three-dimensional pattern. Other methods can also be used to form the disclosed nanodiamond fixed abrasive tools. These fixed abrasive tools are particularly suitable for polishing expensive workpieces such as silicon wafers, integrated circuitry, gemstones, and hard drive platters.
Owner:SUNG CHIEN MIN
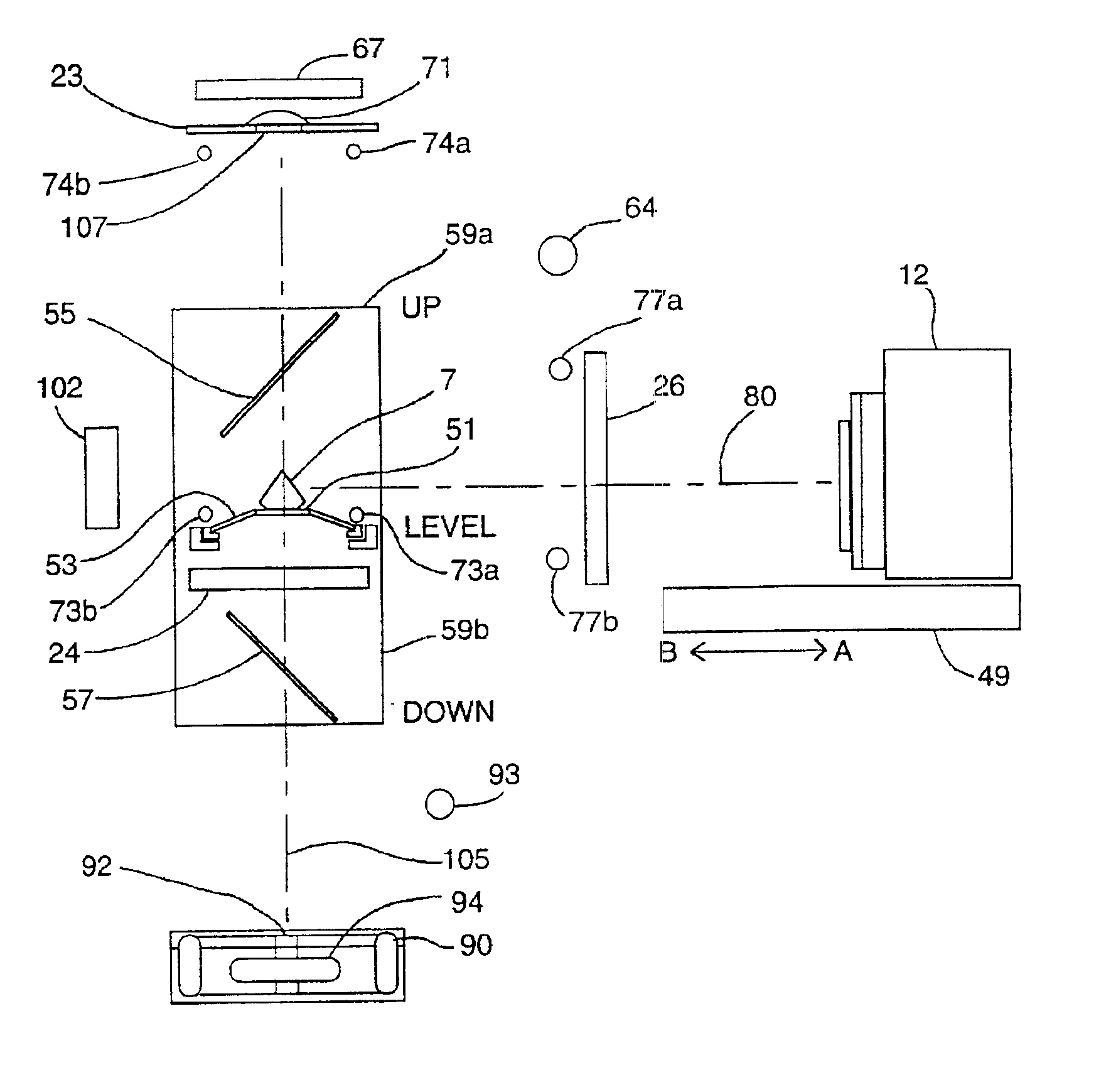
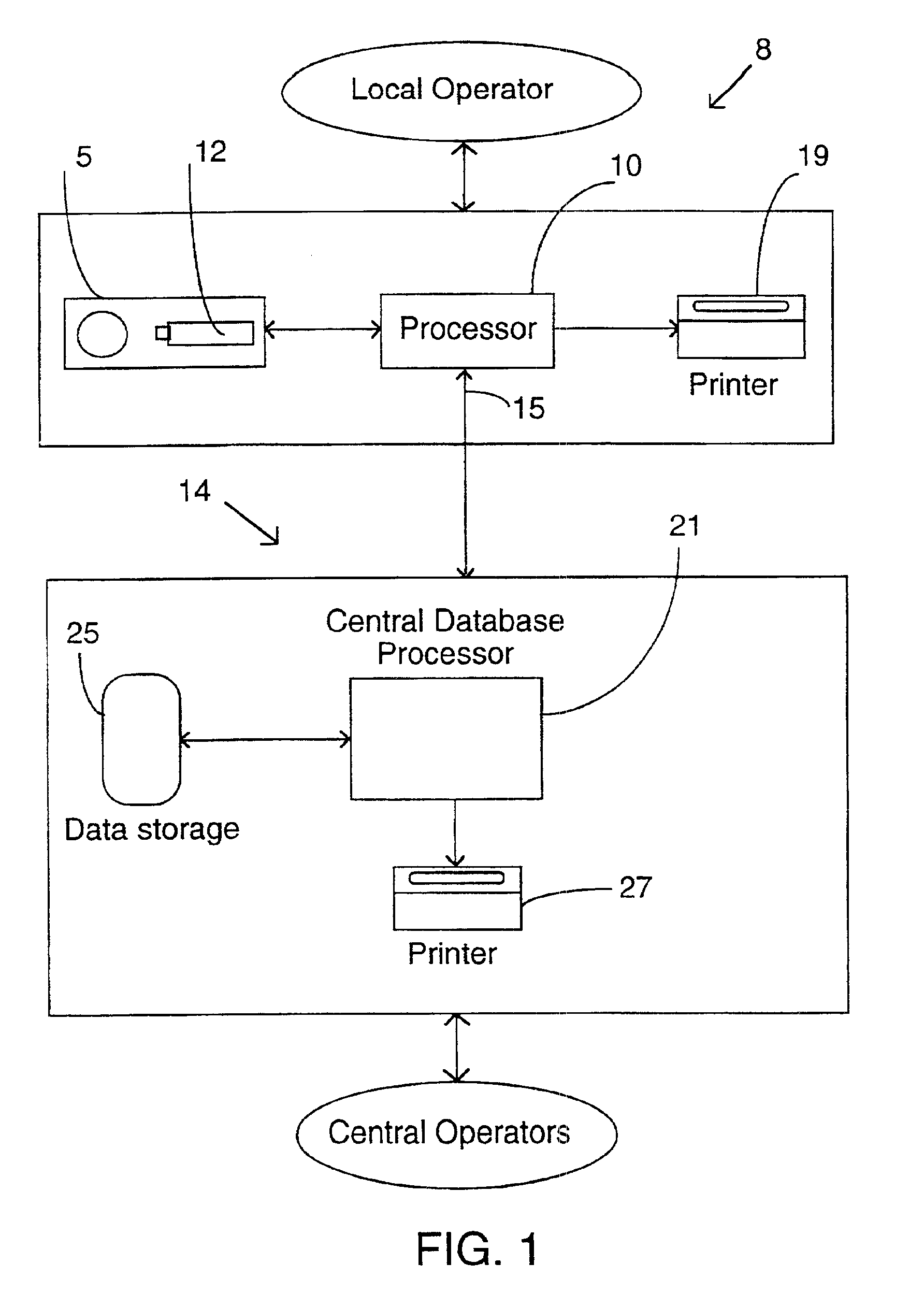
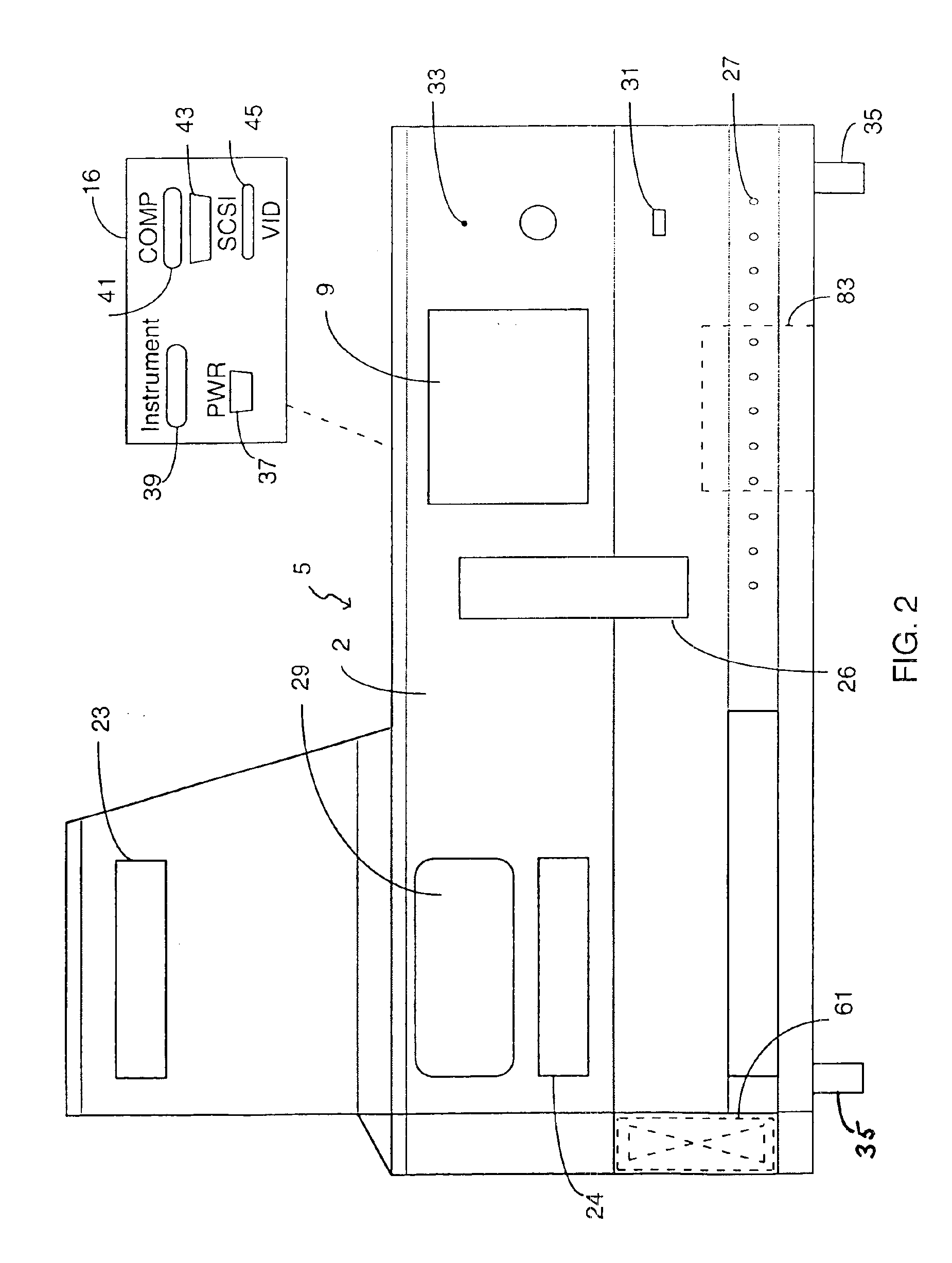
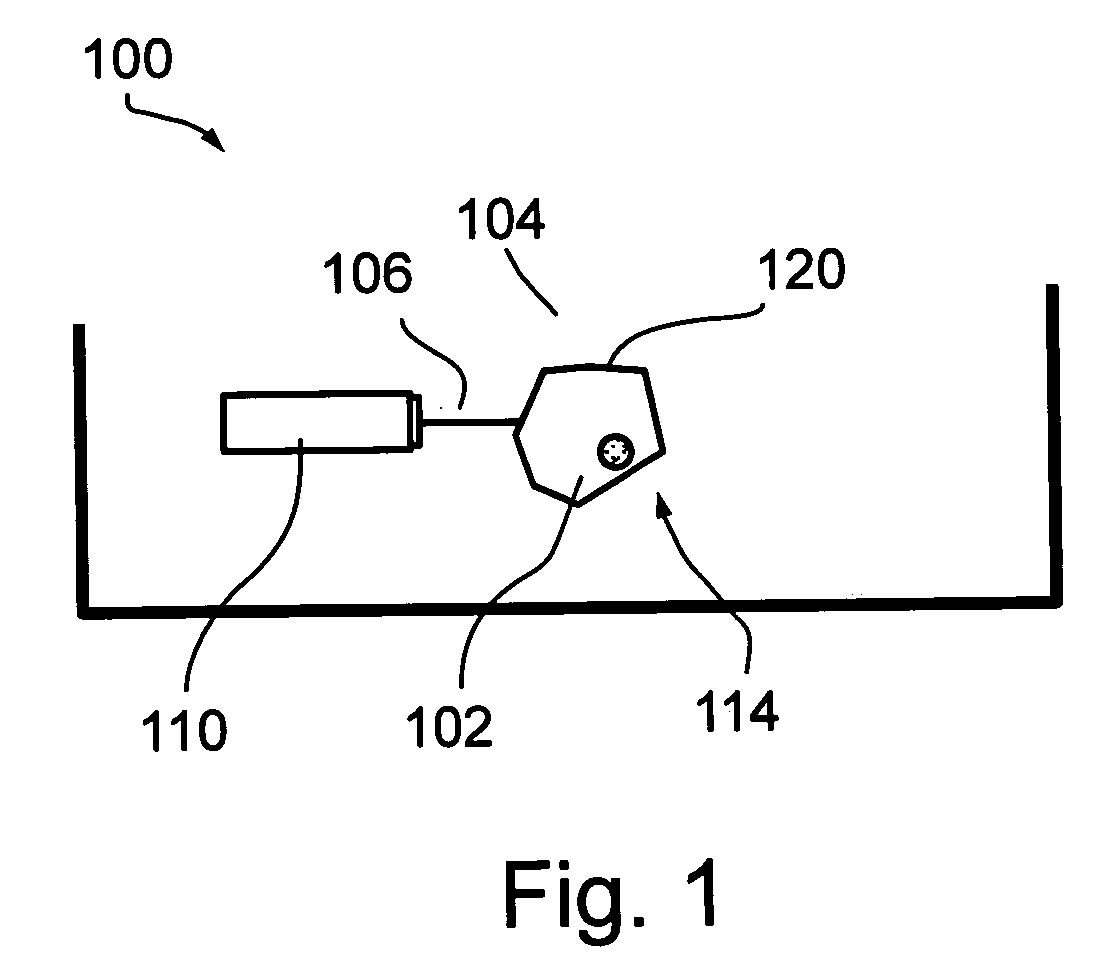
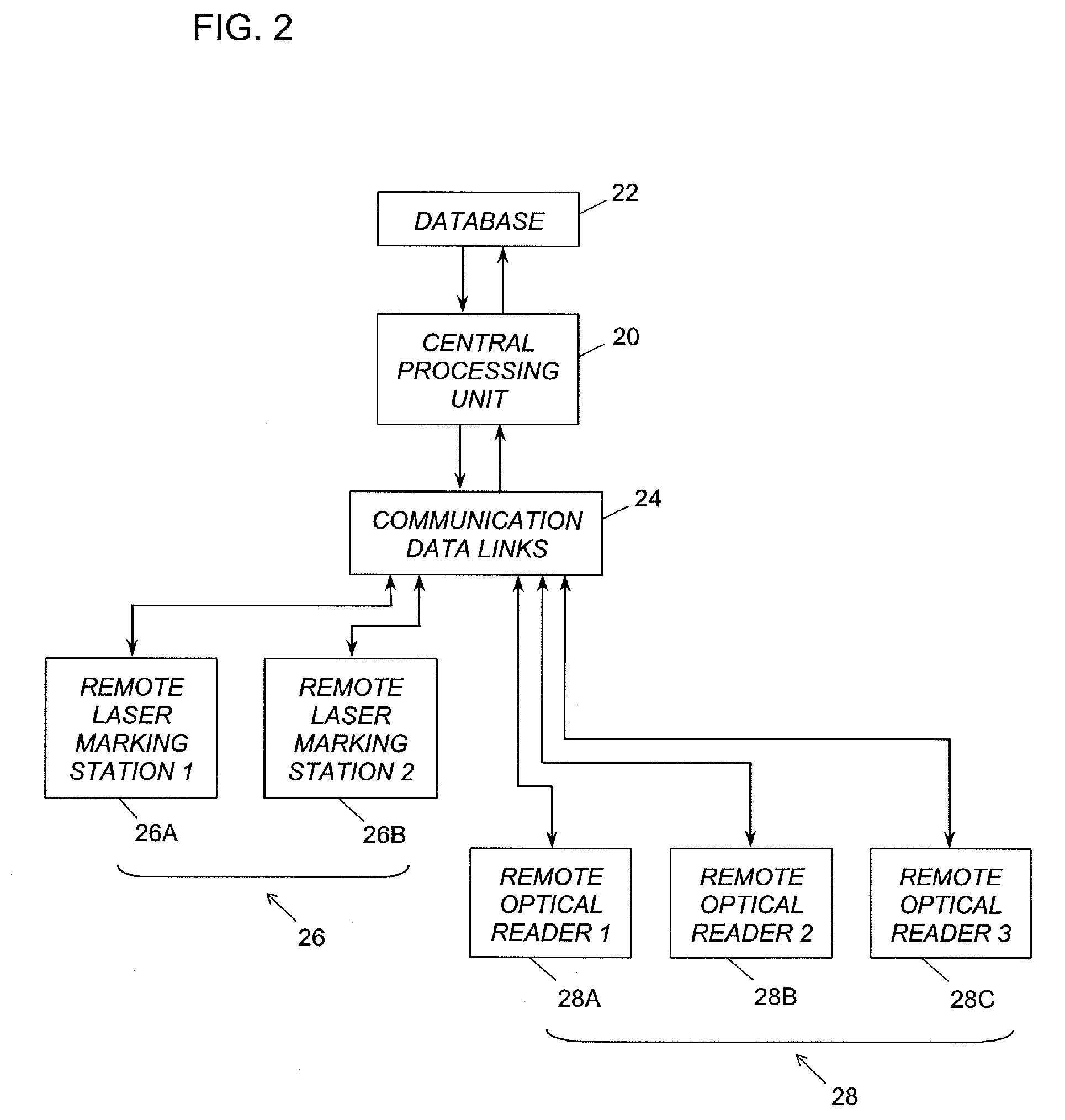
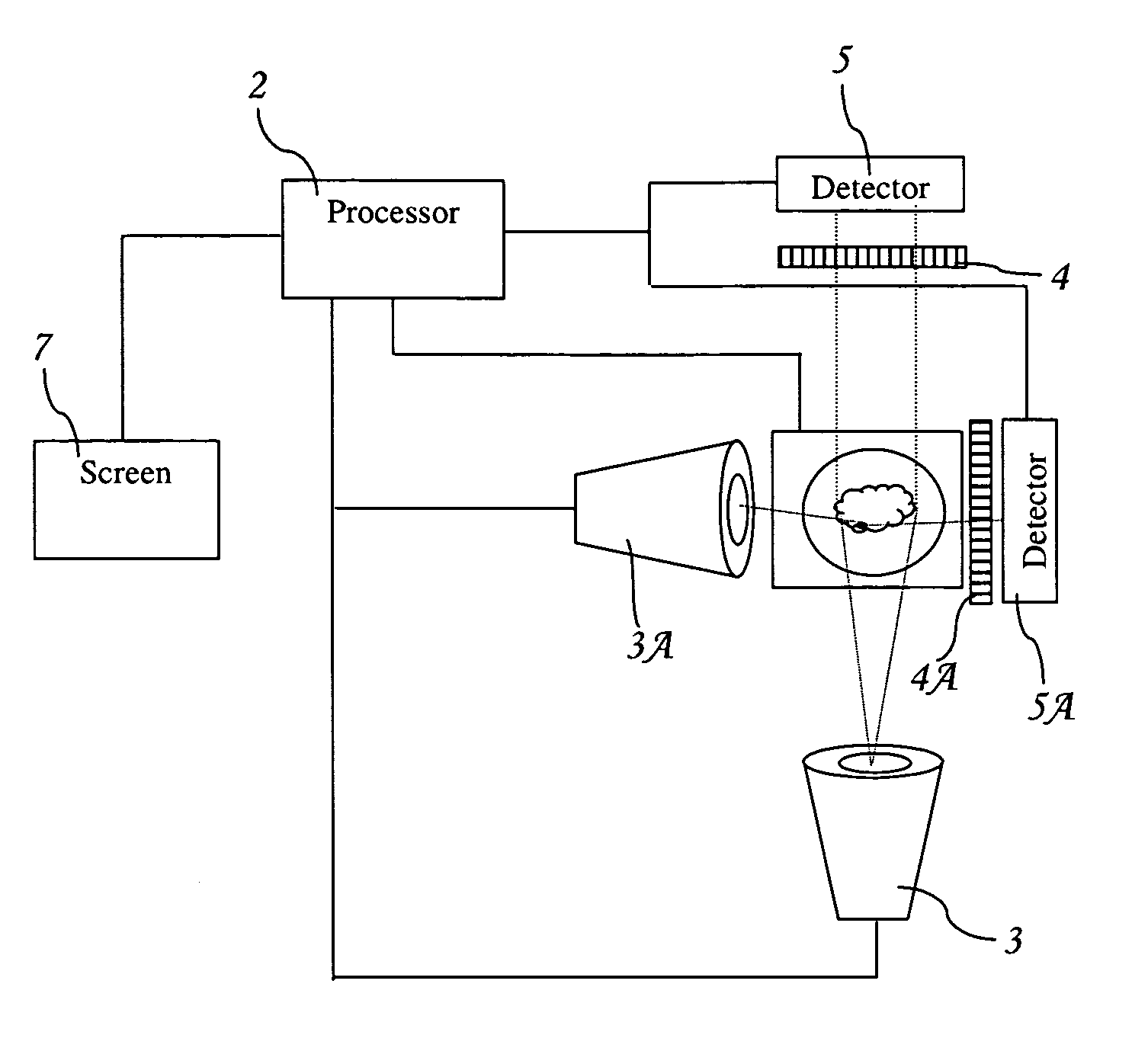
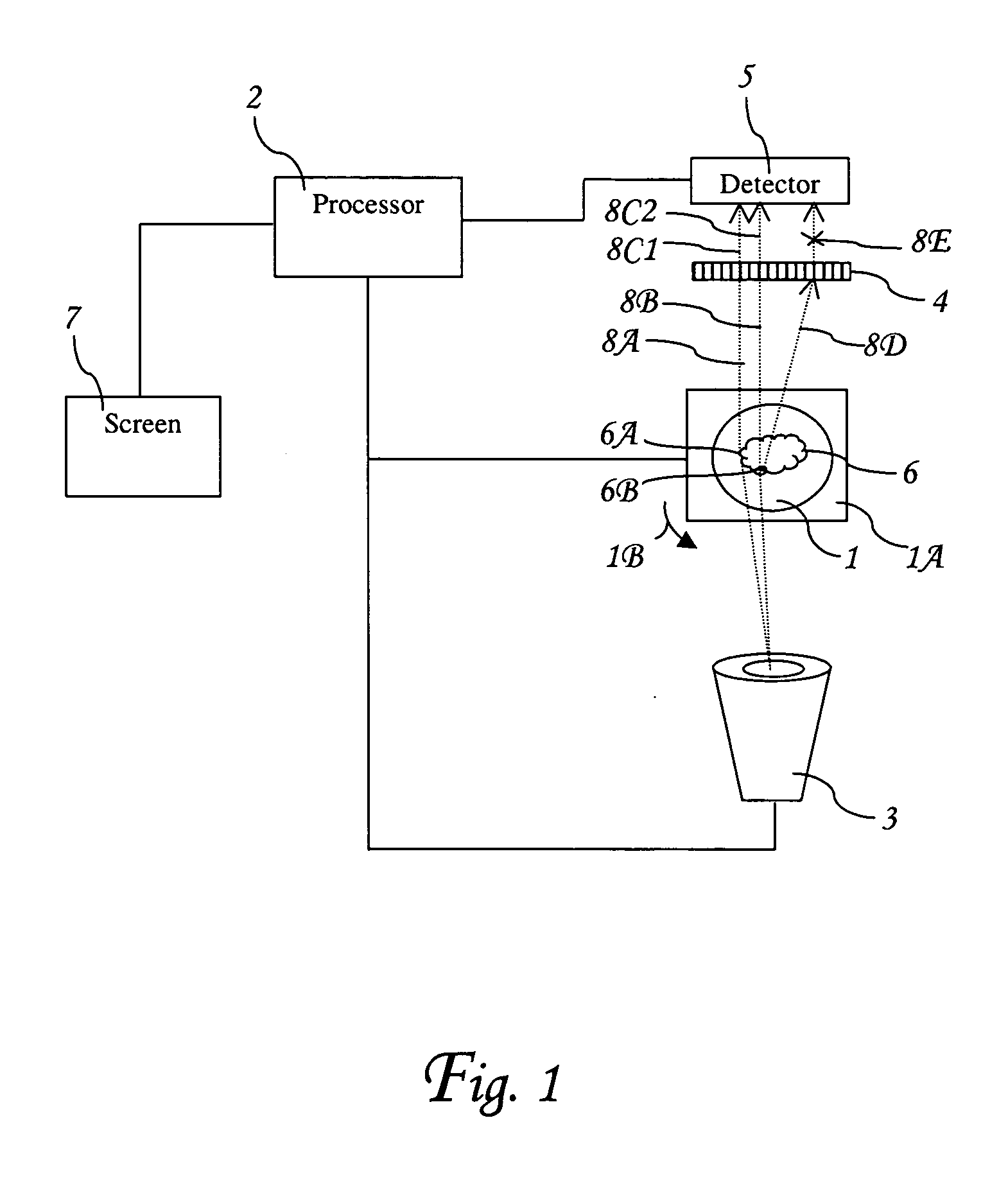
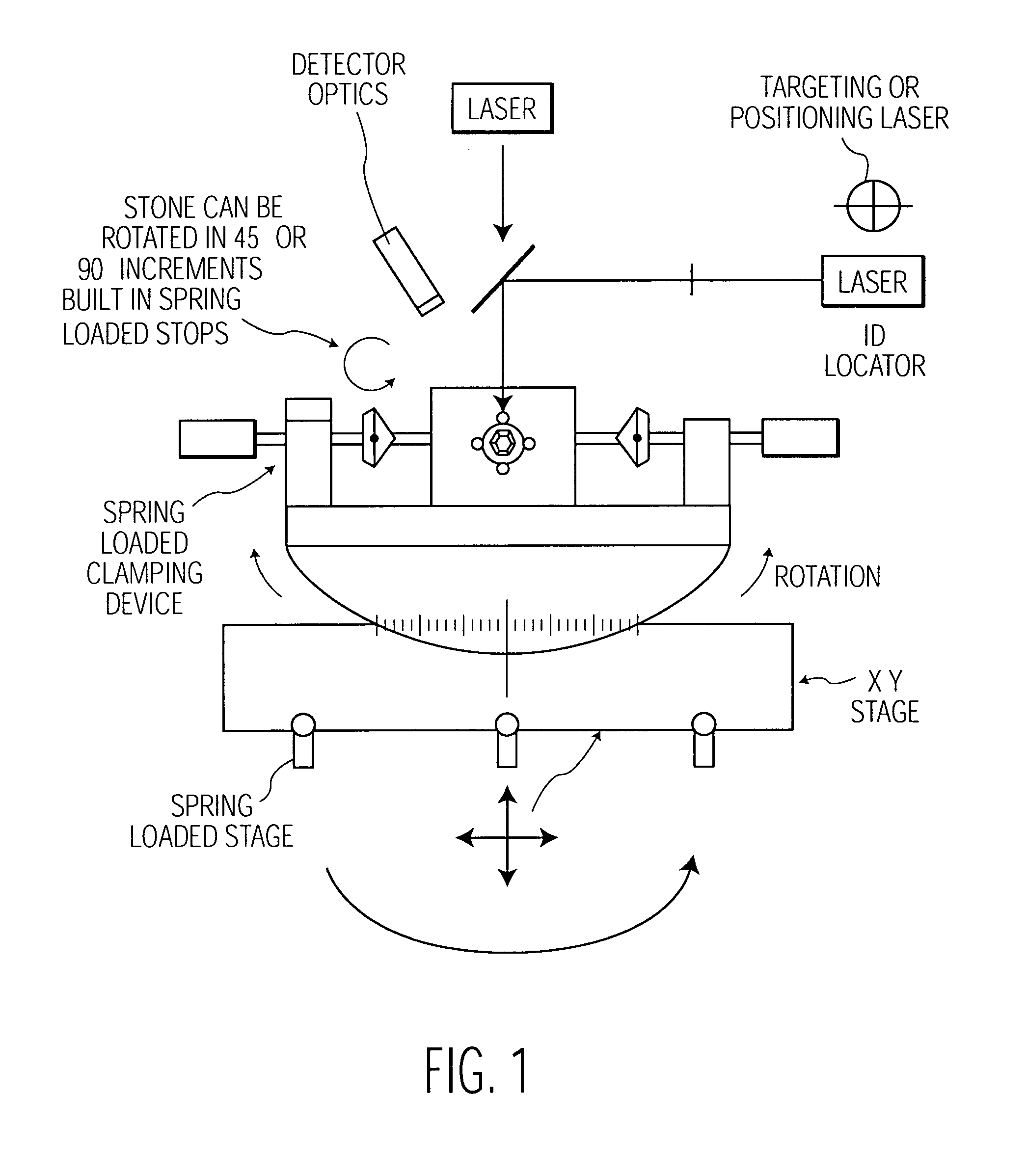
Method and associated apparatus for the standardized grading of gemstones
InactiveUS6980283B1Process safetyInvestigating jewelsSpecial data processing applicationsSpectral responseData set
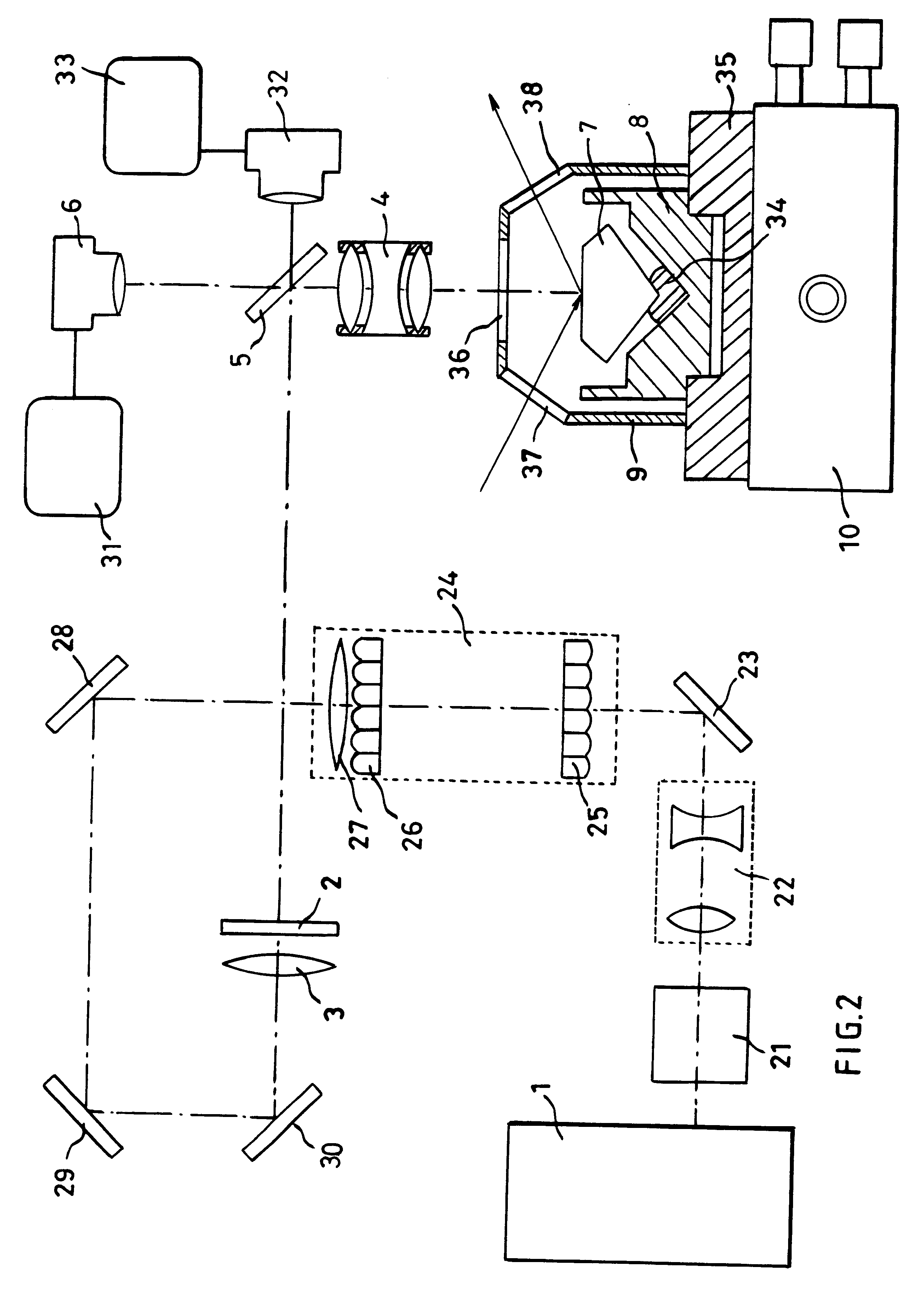
A method and associated apparatus (5) for the standardized grading of gemstones is provided. The system gauges the spectral response of a gemstone subject to a plurality of incident light sources (77, 64, 90, 92, 102) within an imaging apparatus. The operation of the imaging apparatus is controlled by an instruction set of a local station control data processor (12). Light energy data is captured in the form of pixel data sets via a charge coupled device of the imaging apparatus of the local station (8). The control data processor data of the local station is operably linked to analysis station (14). Gemstones qualities are analyzed by the plurality of light sources (92, 90, 102) of the imaging apparatus (5) and quantified relative to model pixel data sets of the database and recorded for future reference therein.
Owner:IMAGESTATISTICS
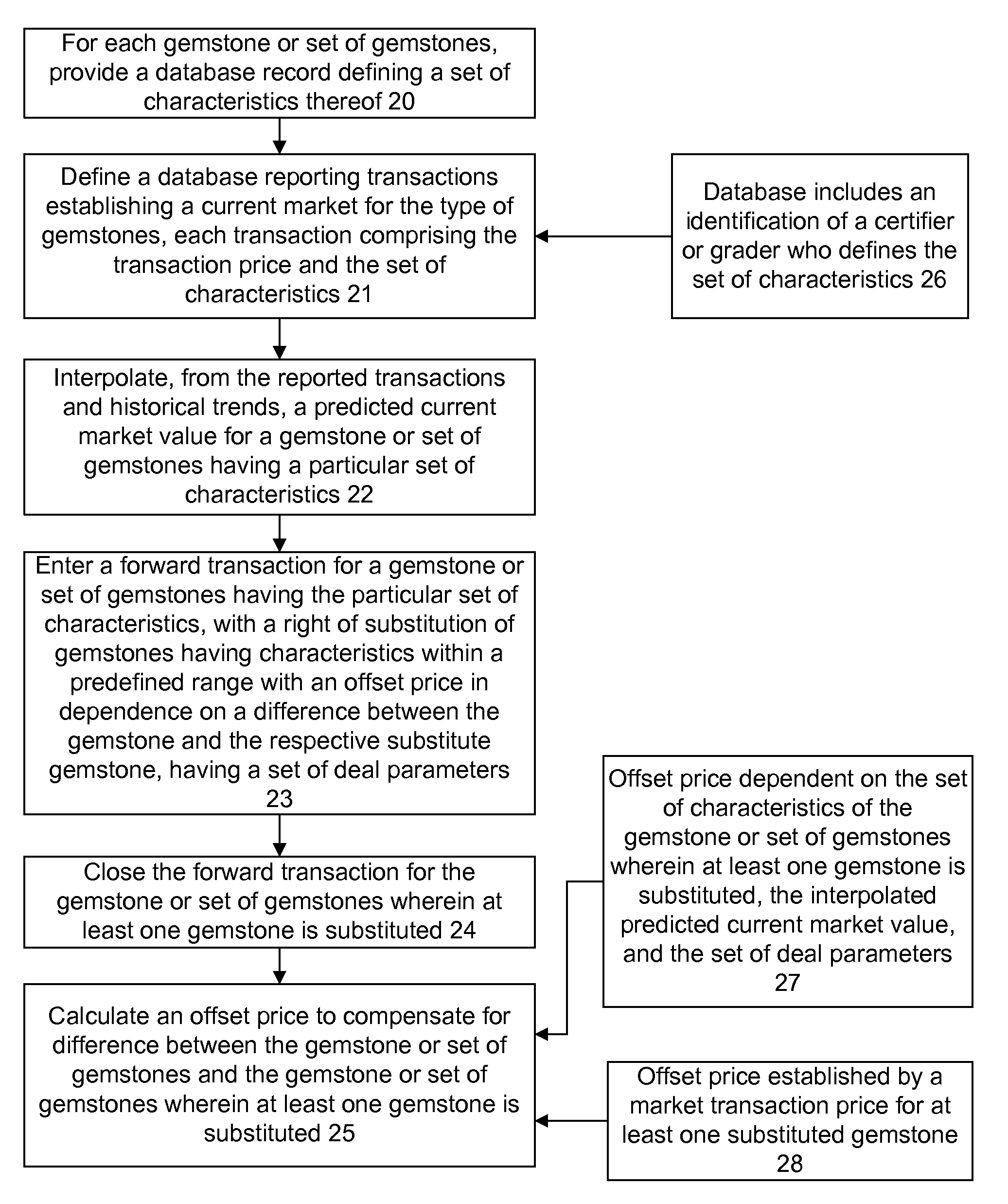
Database system and method for tracking goods
InactiveUS20090070273A1High market valueImprove liquidityComplete banking machinesFinanceGemstoneData mining
An online database method, comprising marking a plurality of gemstones with respective identifiers; maintaining a database linking the identifiers with at least a portion of at least one of a transaction history and a subjective description of the plurality of gemstones; updating the database with an economic value based on transactions involving respective gemstones; determining normalization parameters for extracting objective parameters determinative of value for each of a plurality of gemstones from the respective subjective description of the gemstones; and predicting a market value for a respective gemstone based on the subjective description of the respective gemstone, the normalization parameters, and the transaction history of a plurality of gemstones.
Owner:MORYTO WILLIAM
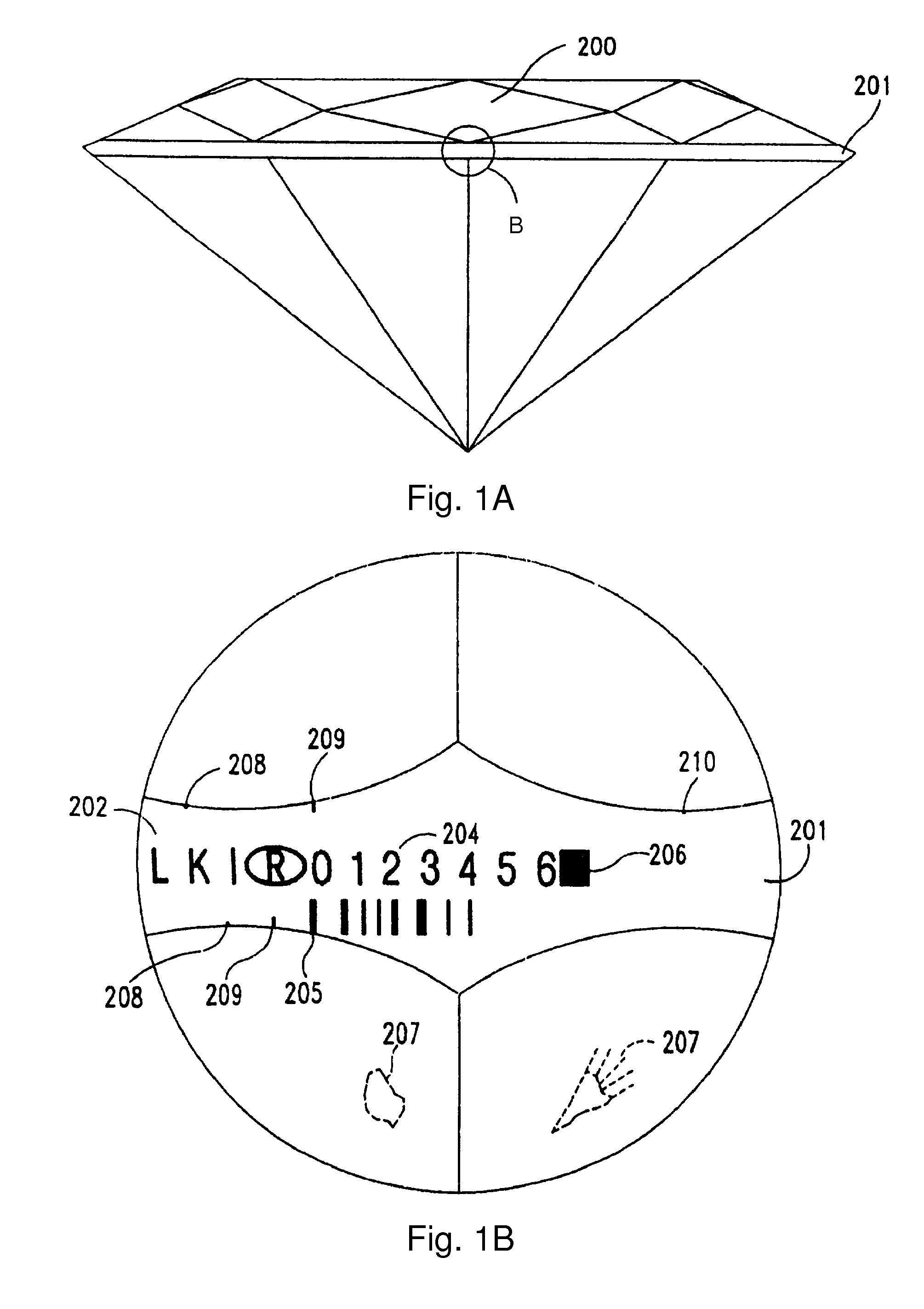
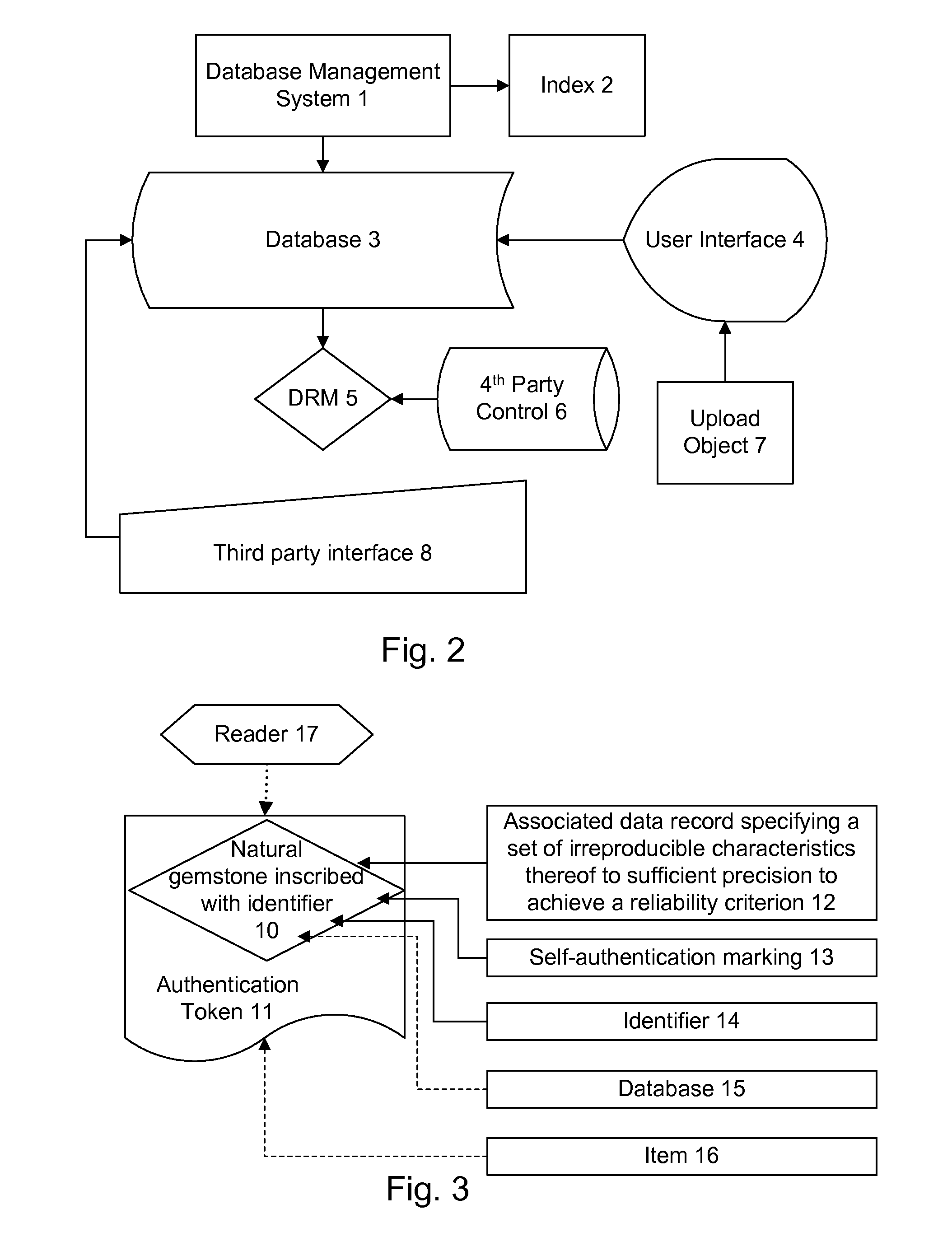
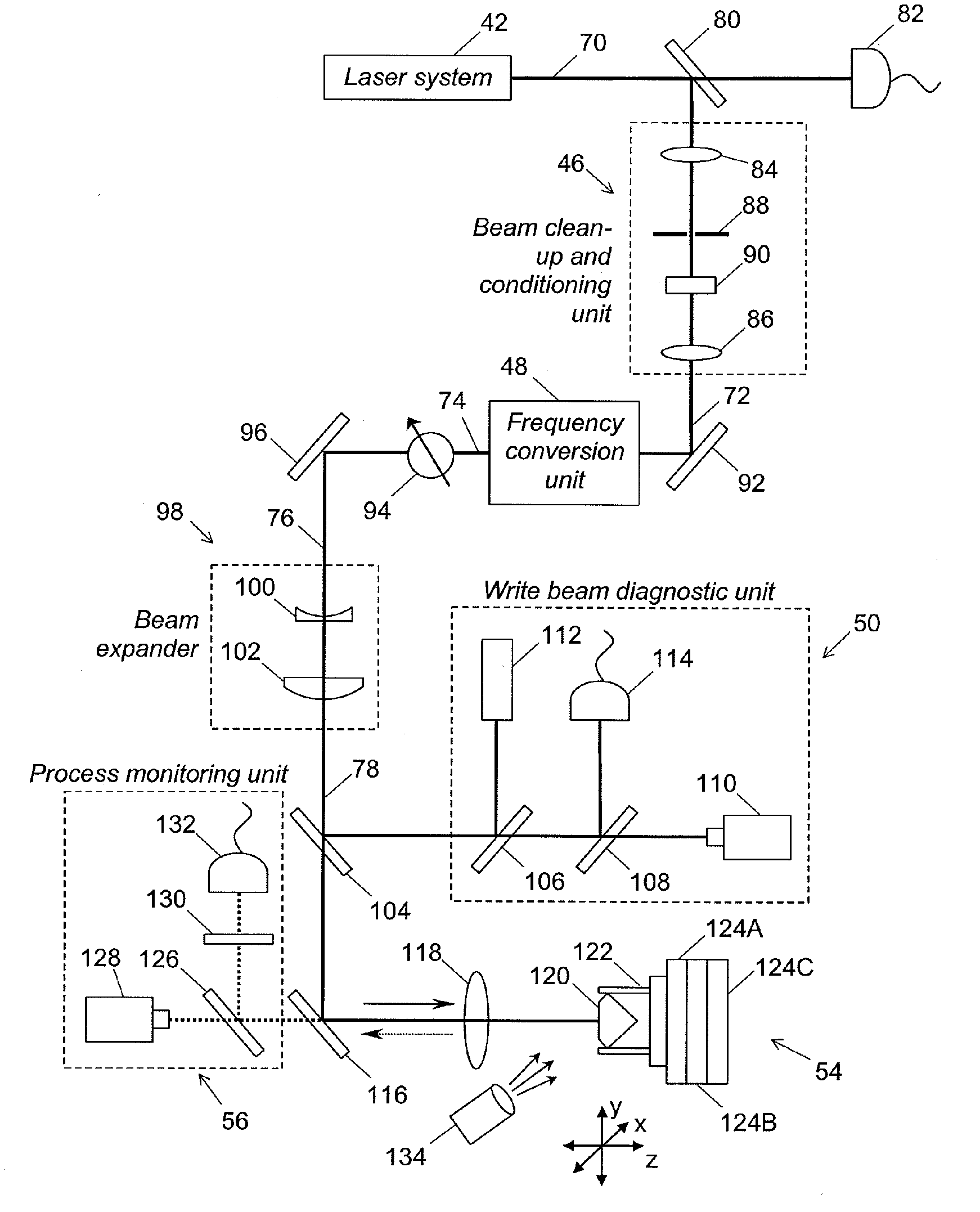
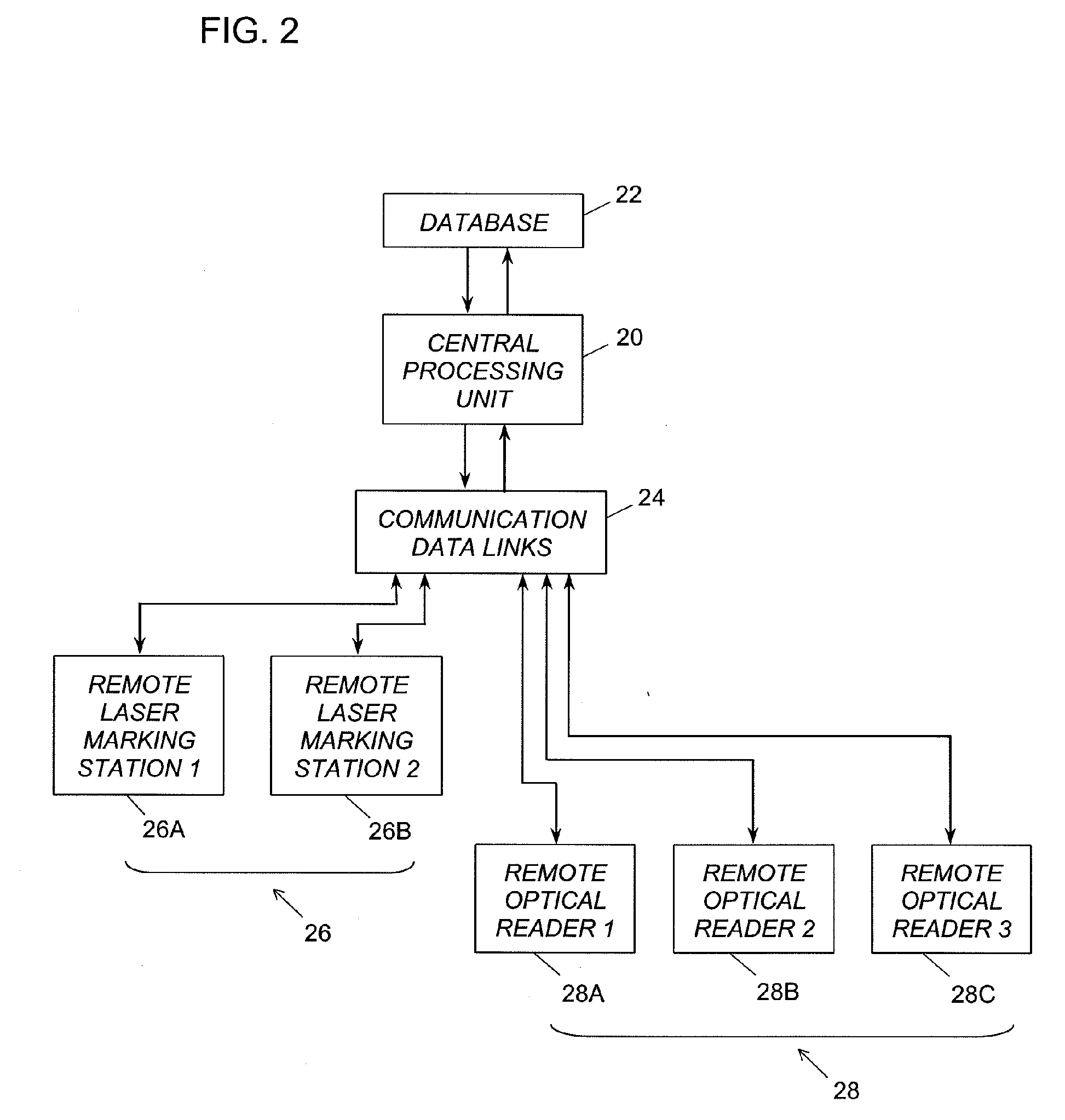
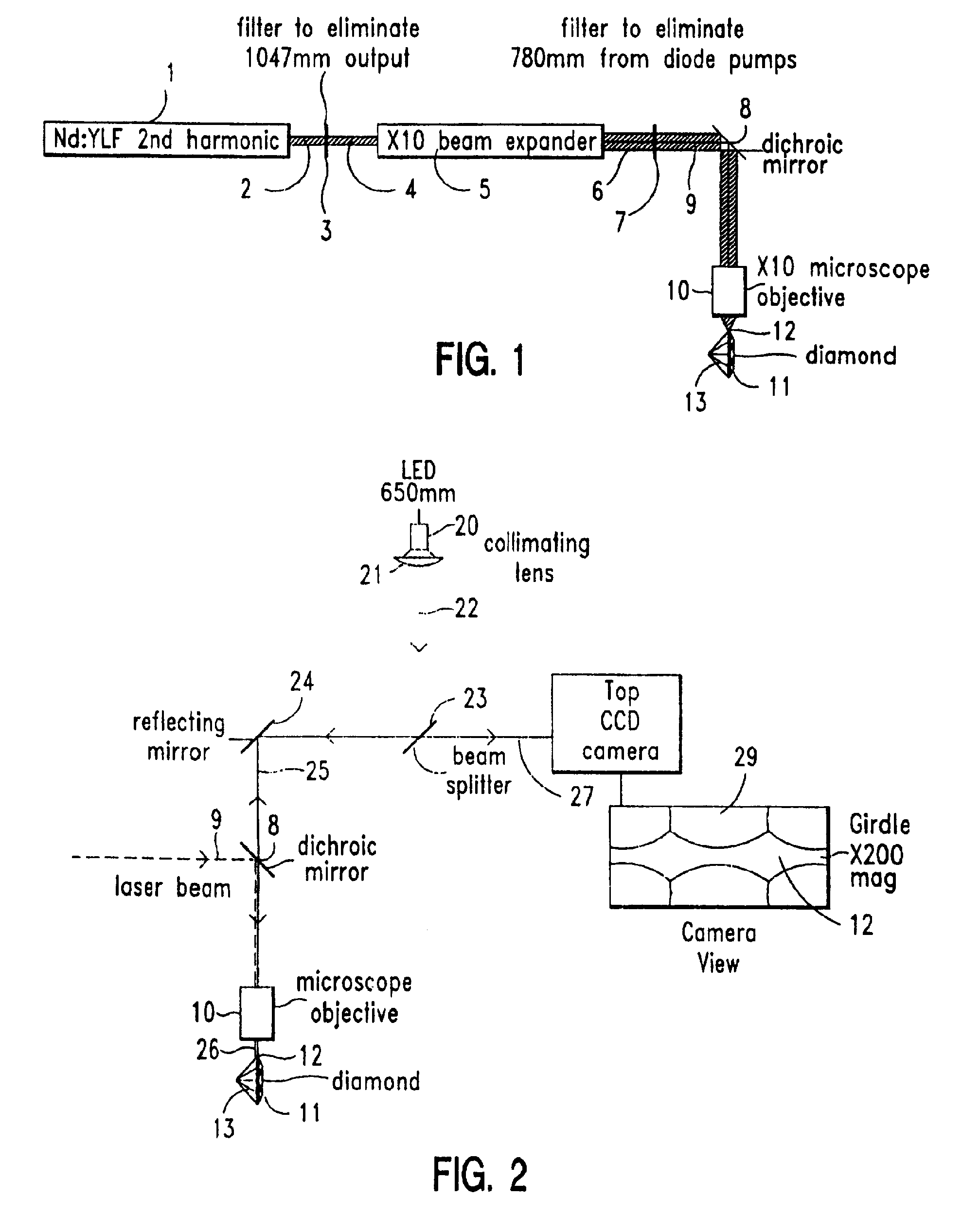
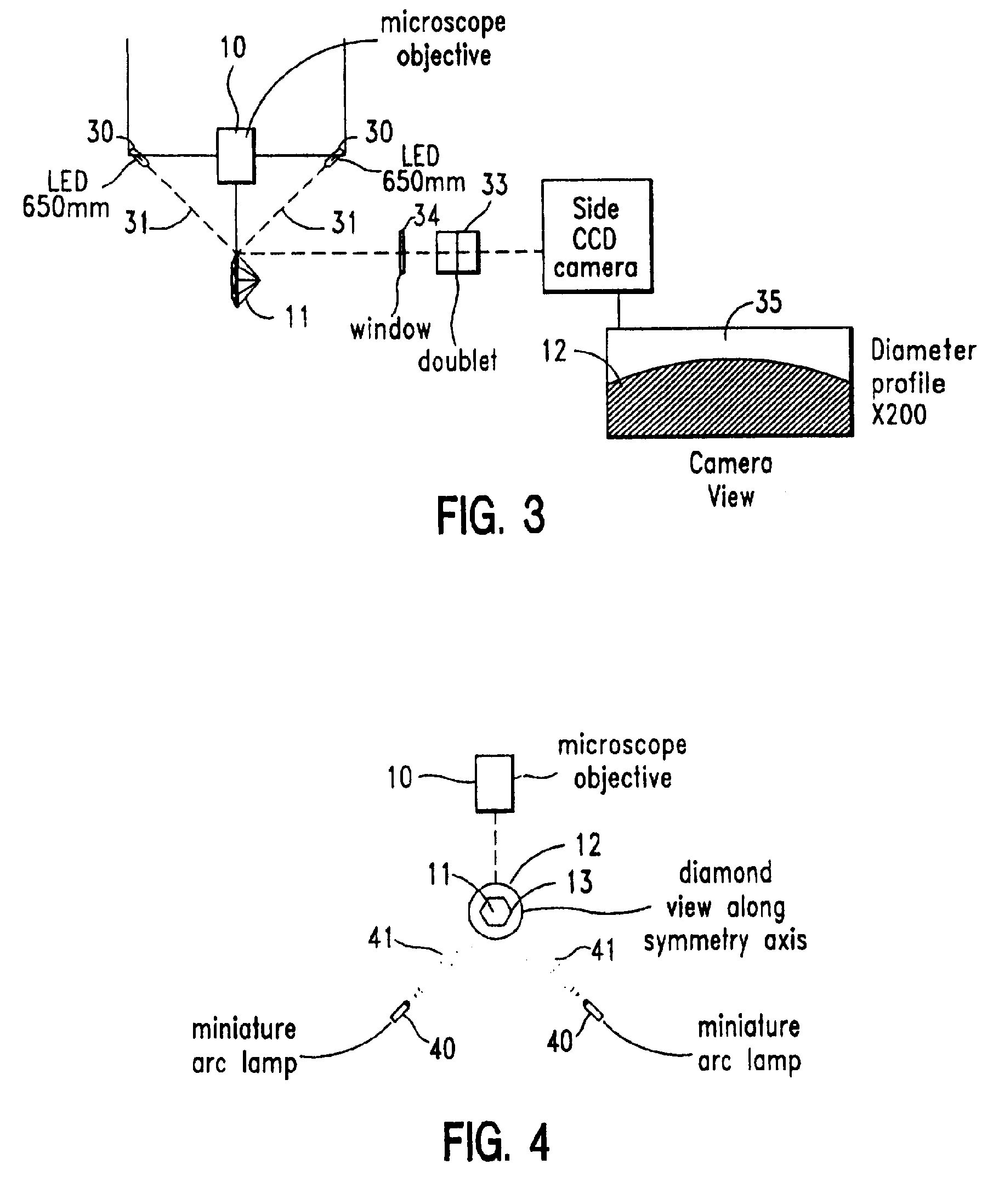
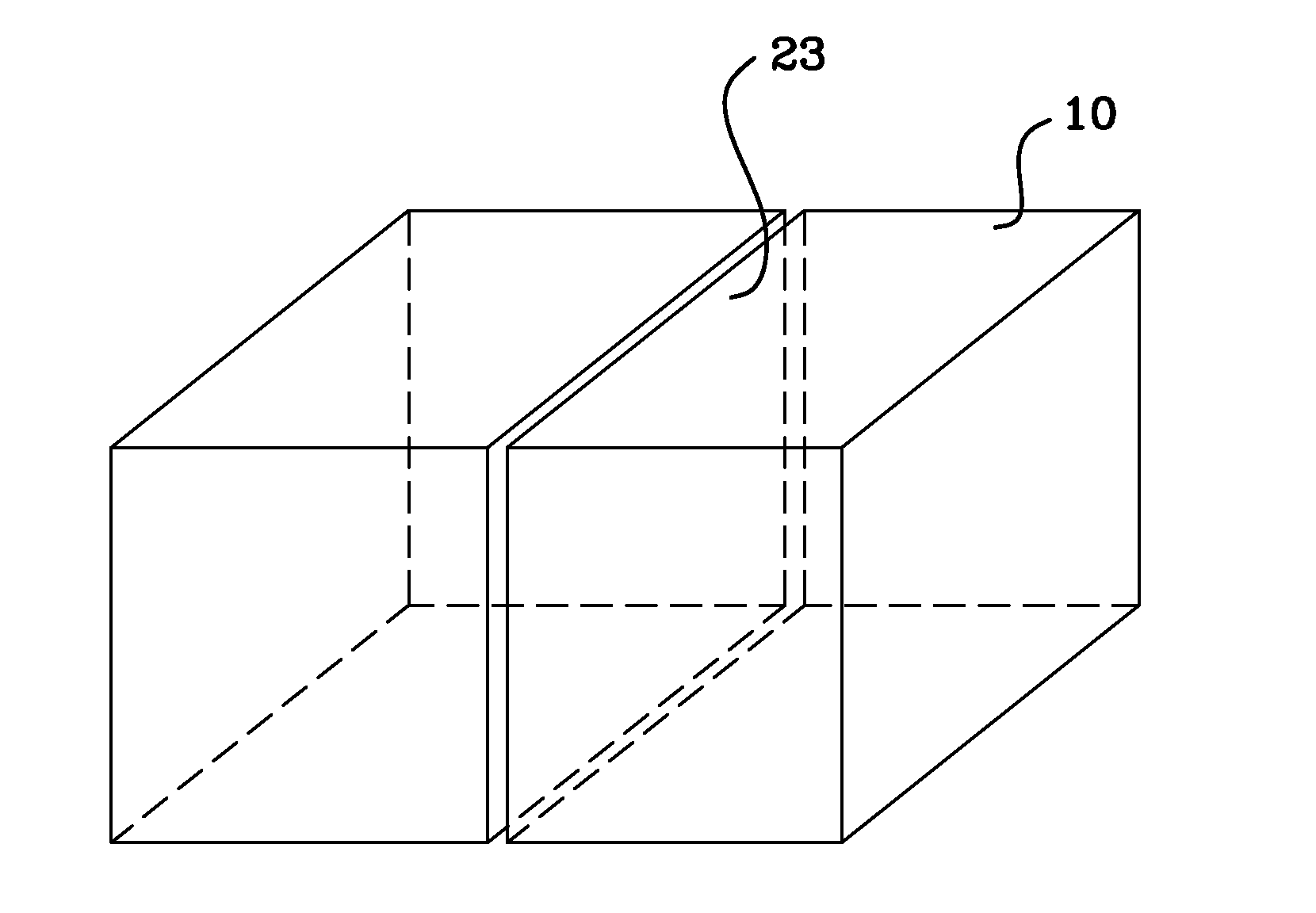
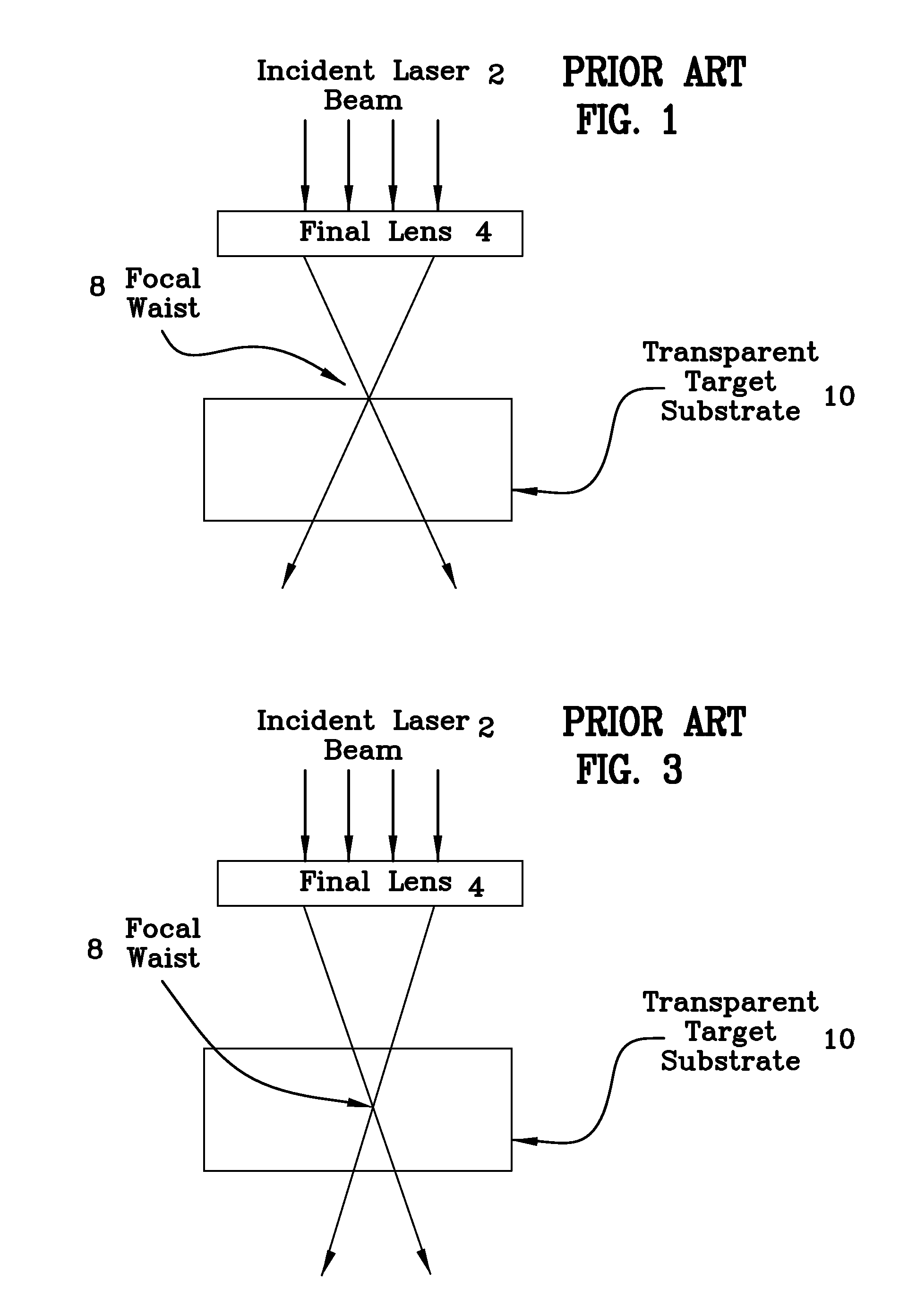
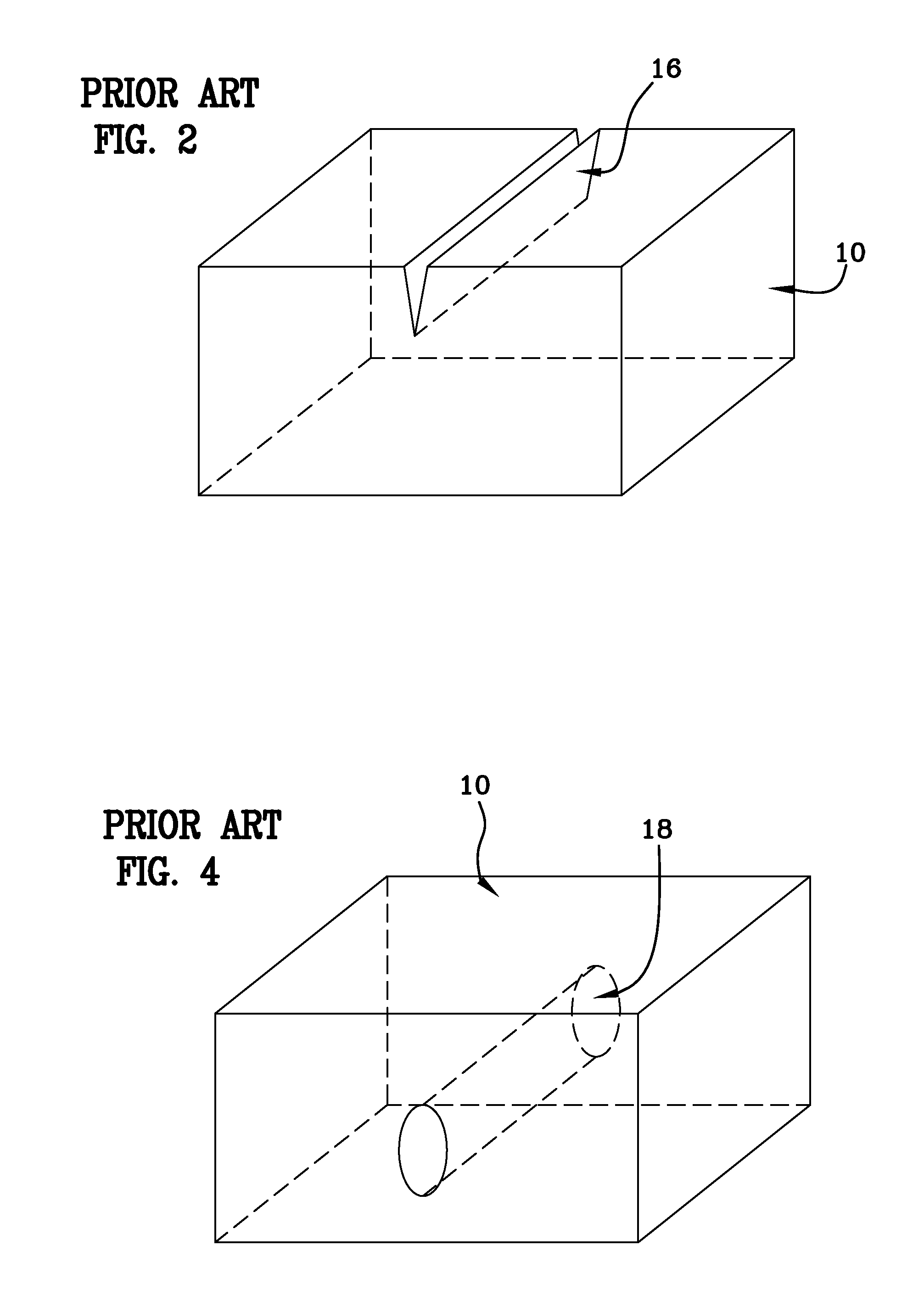
Method and system for laser marking in the volume of gemstones such as diamonds
ActiveUS20060196858A1Suitable contrastImprove image contrastLight effect designsInvestigating jewelsMagnifying glassGemstone
A method and an apparatus for laser marking indicia in the volume of gemstones such as diamonds, the indicia being made up of a plurality of microscopic dot-shaped marks whose build-up can be initiated by exposing naturally-occurring internal defects or impurities in the volume of a gemstone to a tightly focused train of laser pulses. Authentication data is encoded in the gemstone from the relative spatial arrangement of the dot-shaped marks that form the indicium. Taking advantage of the presence of otherwise invisible defects in the gemstone allows for inscribing indicia with laser pulses carrying energies substantially lower than the threshold energy required for inscribing in the volume of a perfect gemstone material. The marking process is then much less susceptible to inflict damages to the surface of the gemstone, and the marking can be performed using a broad variety of femtosecond laser systems. The dot-shaped marks engraved at a depth below the surface of a gemstone can be made undetectable with the unaided eye or with a loupe by limiting their individual size to a few micrometres, while devising indicia made up of only a few marks. As a result, the marking does not detract from the appearance and value of the gemstone. The procedure for laser marking accounts for the random spatial distribution of the defects present in natural gemstones as well as for their strongly localized character. The presence of an indicium can be detected by using a dedicated optical reader that can be afforded by every jewellery store.
Owner:GEMOLOGICAL INST OF AMERICA INC
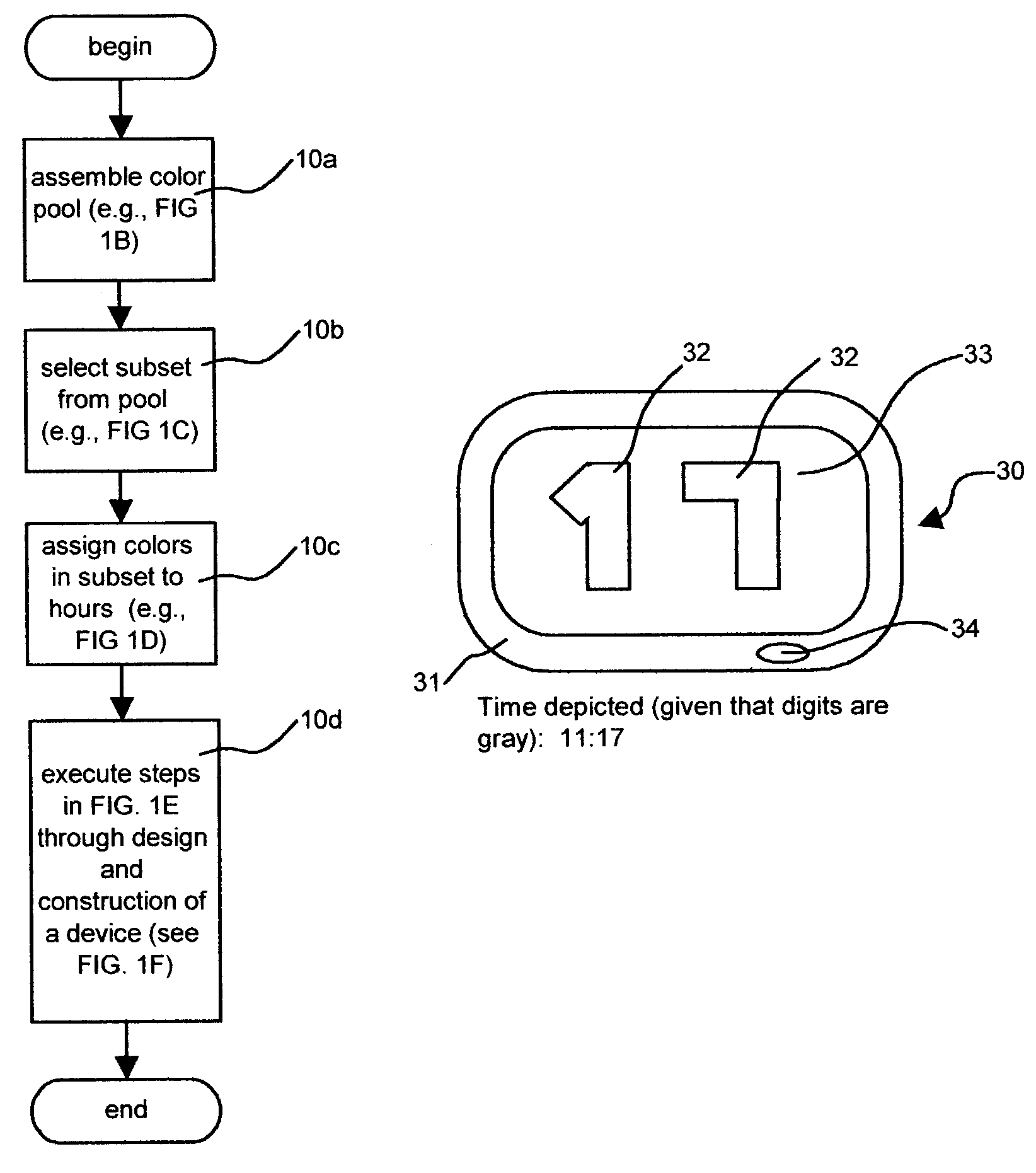
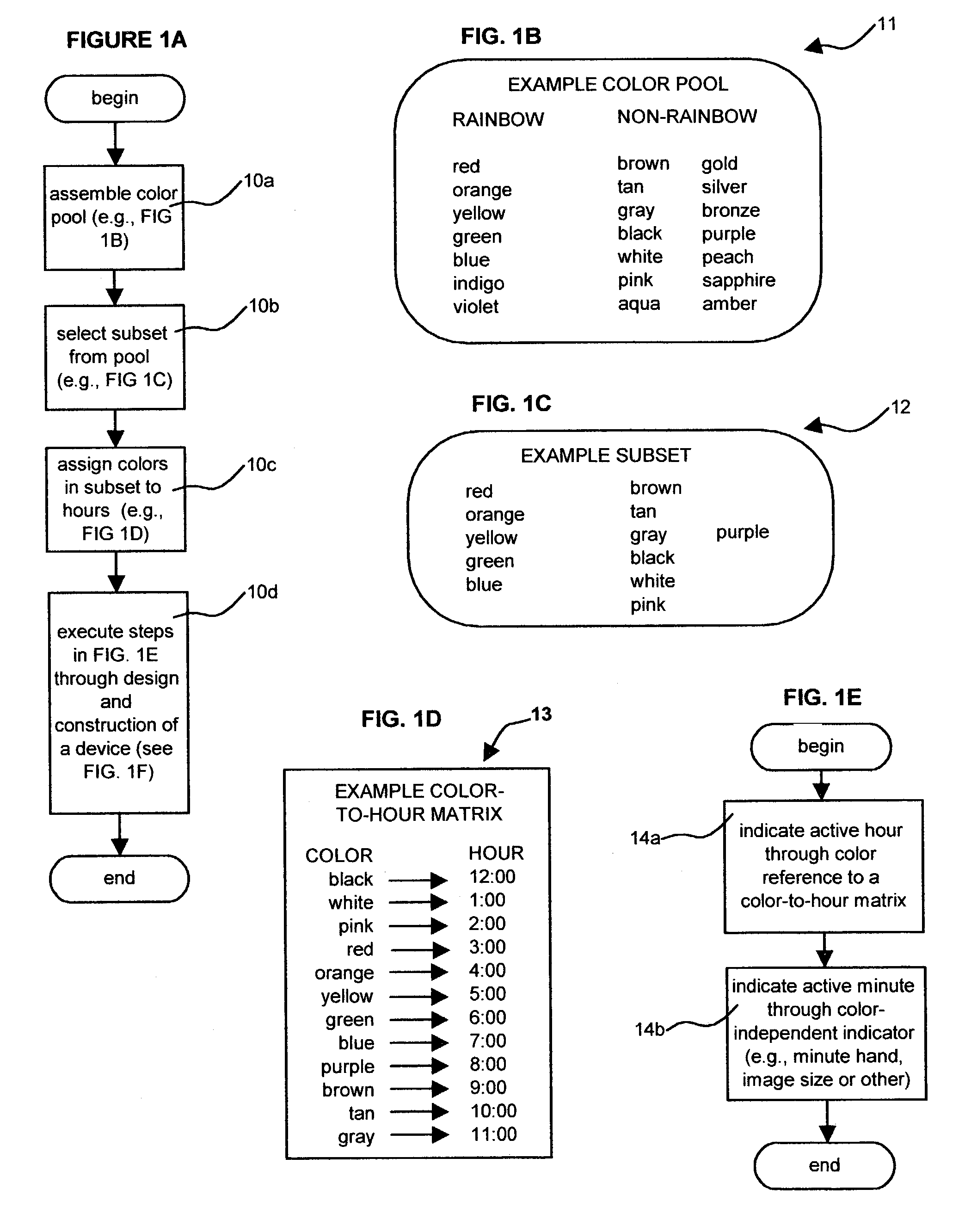
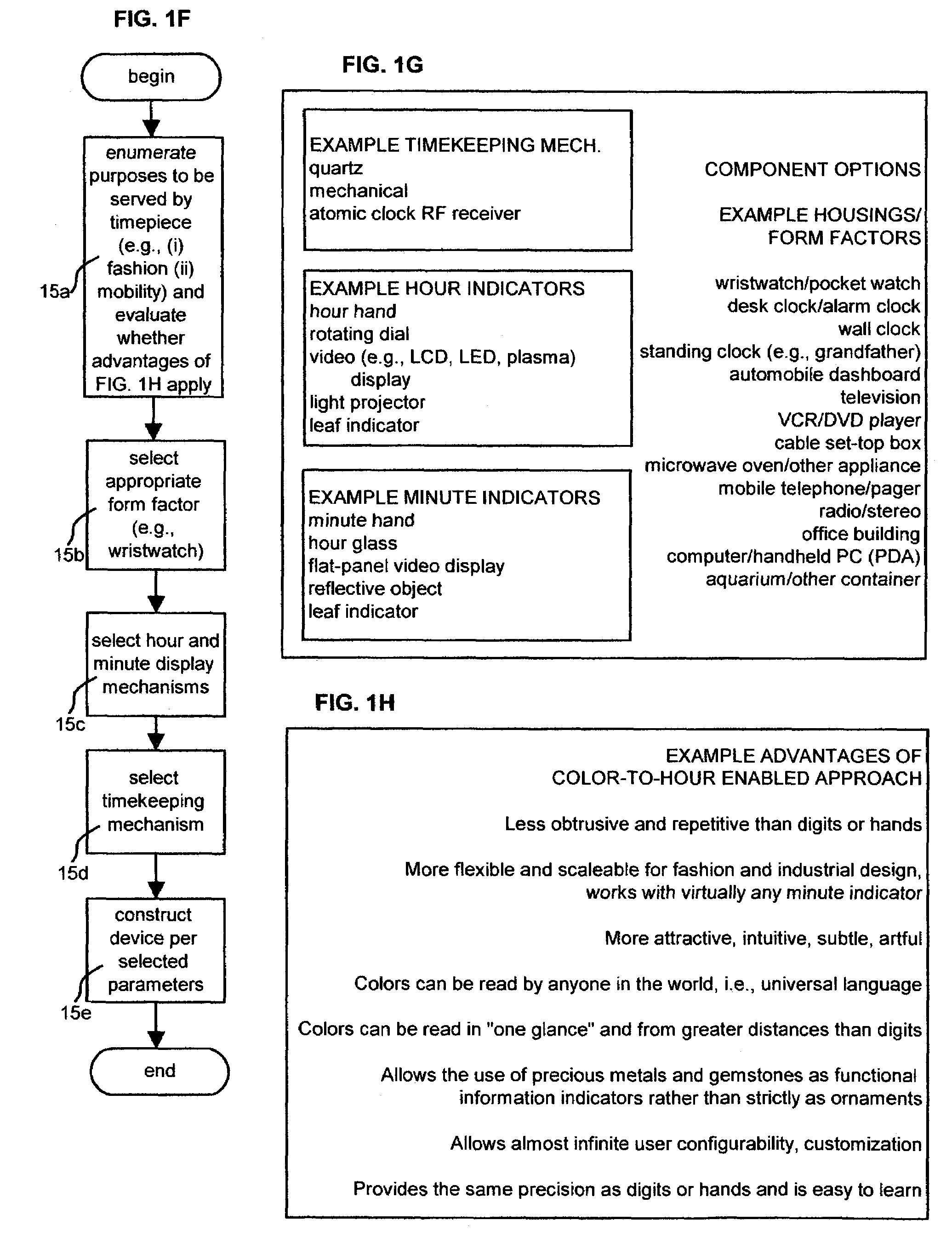
Time display system, method and device
InactiveUS7079452B2Eliminate needReduce the burden onVisual indicationElectrophonic musical instrumentsDisplay deviceThe Internet
A time display device (“TDD”)—equally adaptable to watches, clocks, computers, phones, and vehicles—indicates the current hour of the day by displaying a color that refers an observer to the disclosed color-to-hour matrix, thereby eliminating the traditional hour hand or digit altogether. Alternately adaptable to months, the system may be used with both mechanical and electronic displays. Various disclosed minute indicators provide minute indication by shape, complexity, company logo, air bubbles, or other novel methods. Environmental sensors allow switching between functions. TDD appearance is user-customizable via Internet. Birthstones, gemstones, and precious metals are alternately used as stand-alone time indicators.
Owner:SEARCH & SOCIAL MEDIA PARTNERS
System and method for gemstone microinscription
ActiveUS20080006615A1Minimize damageEasy to controlArc welding apparatusElectron beam welding apparatusGemstoneControl space
A gemstone micro-inscription system, comprising an energy source, a spatial light modulator, and a control, the control controlling a spatial light pattern modulation of the spatial light modulator, wherein the spatial light modulator exposes a photoresist on the gemstone, which selectively impedes an etching process to produce a pattern on the gemstone corresponding to the spatial light modulation pattern.
Owner:LAZARE KAPLAN INT
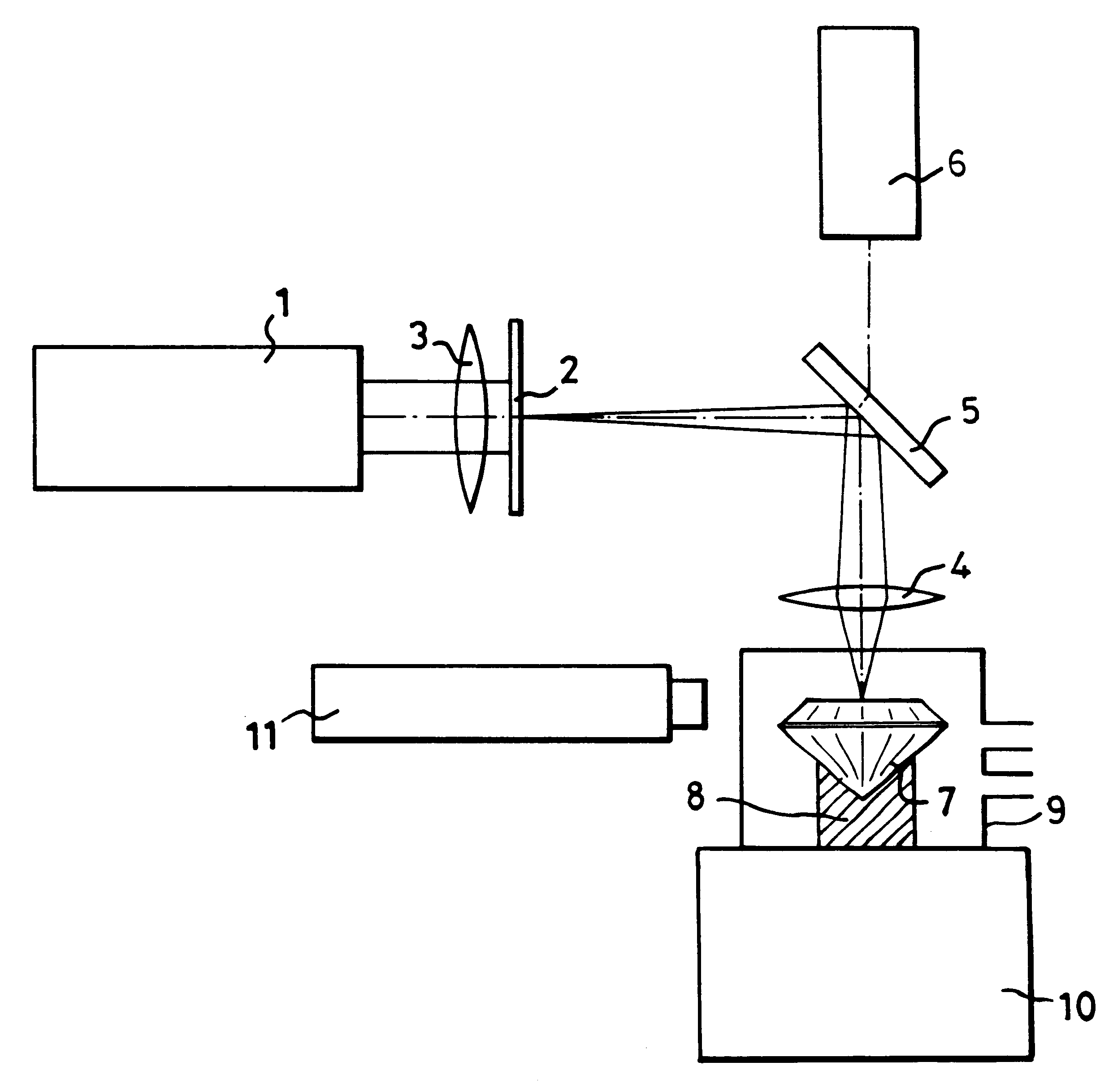
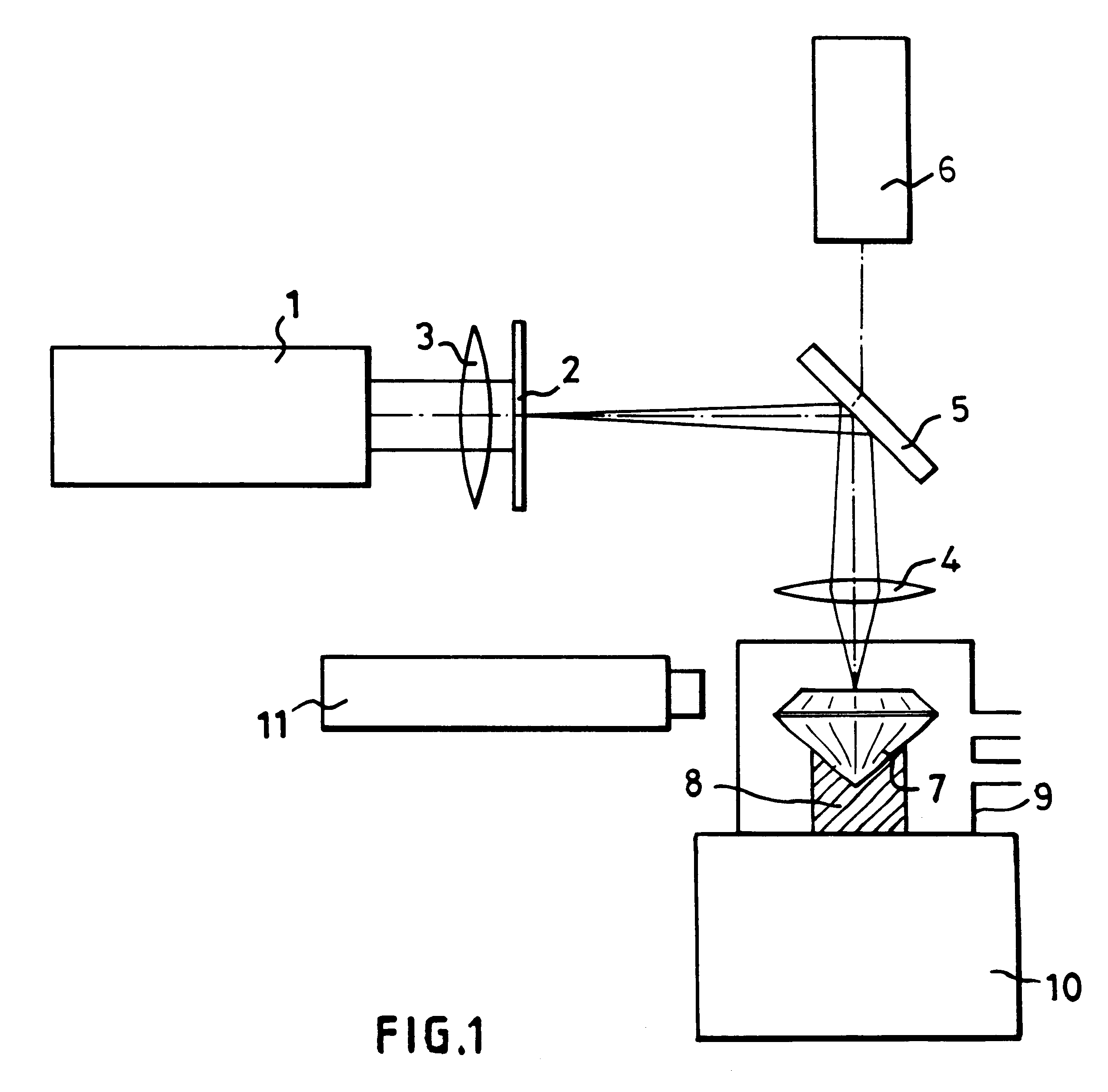
Marking diamond
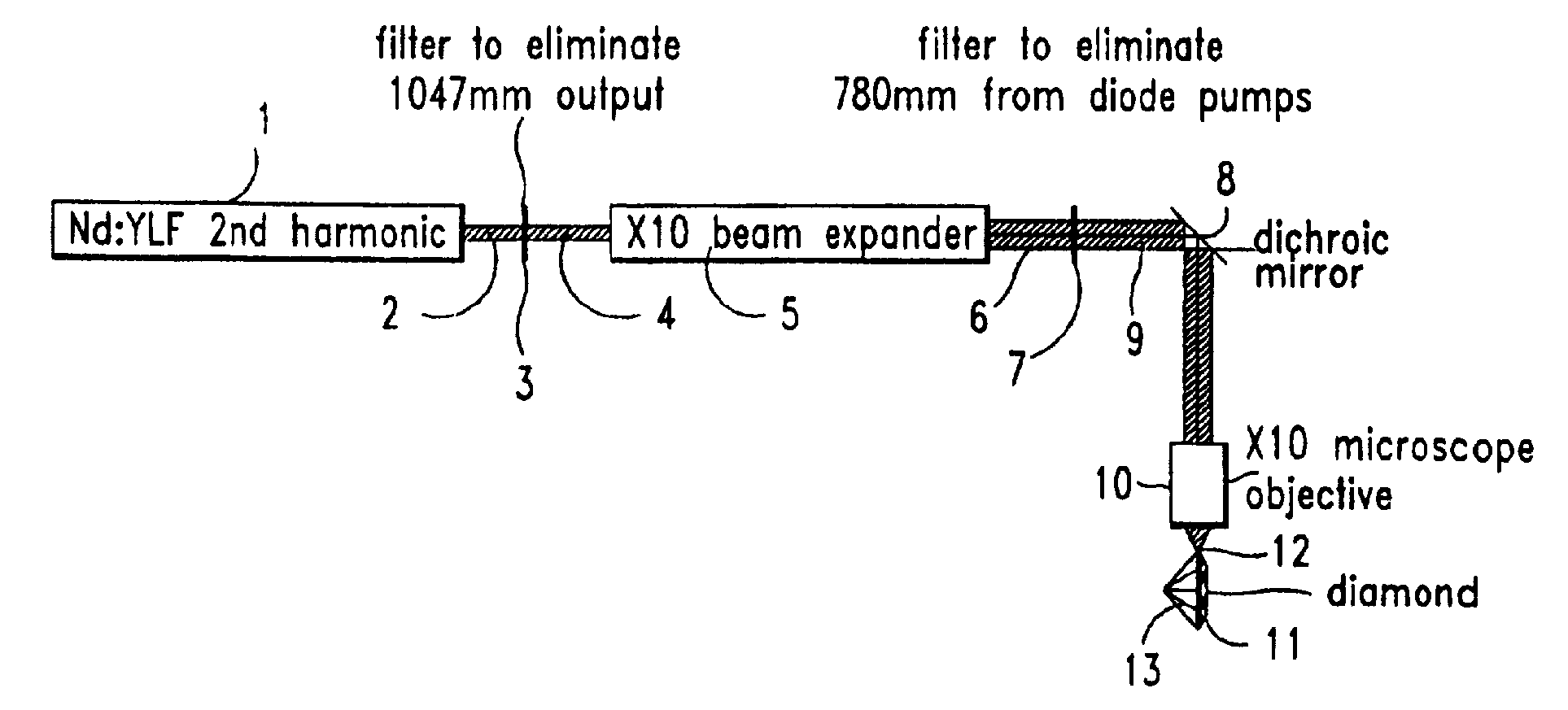
InactiveUS6187213B1Avoid overall overheatingAvoid necessityBranding equipmentPolycrystalline material growthMicroscopic observationGemstone
In order to produce on the table of a diamond gemstone (7), an information mark which is invisible to the naked eye using a x10 loupe, an ultraviolet laser (1) having a wavelength of 193 nm is used in association with a mask (2) to irradiate the surface of the stone (7) at a fluence of less than 2 J / cm2 per pulse and with not fewer than 100 pulses, in the presence of air which reacts with the diamond (7) and causes the mark to be formed without any darkening which is visible when viewing using a microscope.
Owner:GERSAN ESTAB
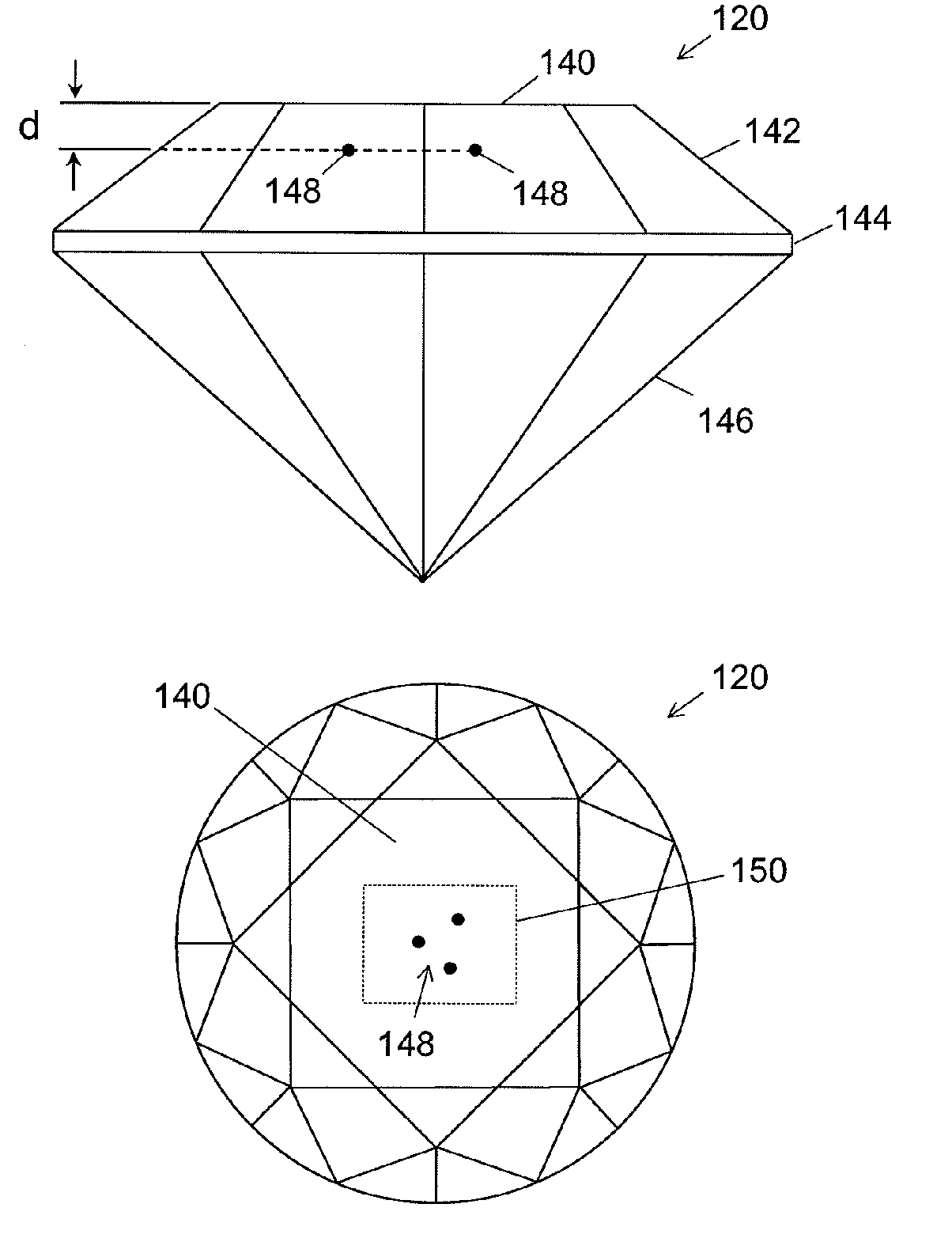
Method and System for Improved Optical Modeling of Gemstones
ActiveUS20100250201A1Reduce deficiencyImproved virtual optical modelingInvestigating jewelsOptically investigating flaws/contamination3d shapesOptical property
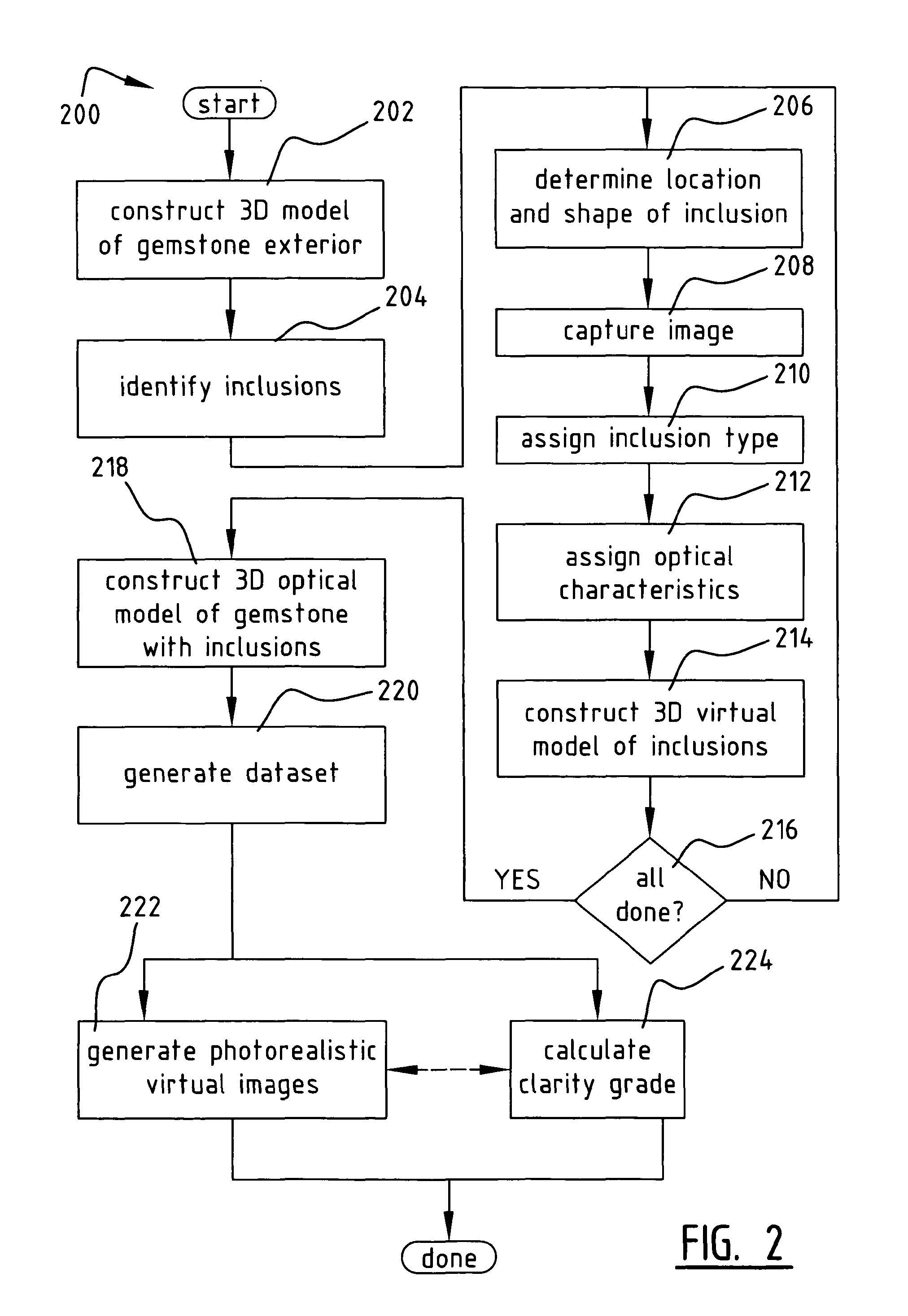
A method of constructing a virtual model of a gemstone including the steps of performing measurements of the gemstone to construct a three-dimensional (3D) model of an exterior surface of the gemstone; identifying one or more visible inclusions within an interior volume of the gemstone; for each identified inclusion, performing the steps of determining a location and 3D shape of the inclusion within the interior volume of the gemstone; capturing at least one image of the inclusion; using the at least one image to determine relevant optical characteristics of the inclusion; and constructing a 3D virtual model of the inclusion, said model including the 3D shape of the inclusion and optical properties of the inclusion based upon said optical characteristics; constructing a 3D virtual model of the gemstone which includes the 3D virtual model of the exterior surface of the gemstone and the 3D virtual models of the one or more visible inclusions within the interior volume of the gemstone; and generating a dataset representing said 3D virtual model, wherein said dataset may be used in subsequent computer analysis to provide a user with information relating to a visual characteristic of the gemstone.
Owner:IDEAL SCOPE
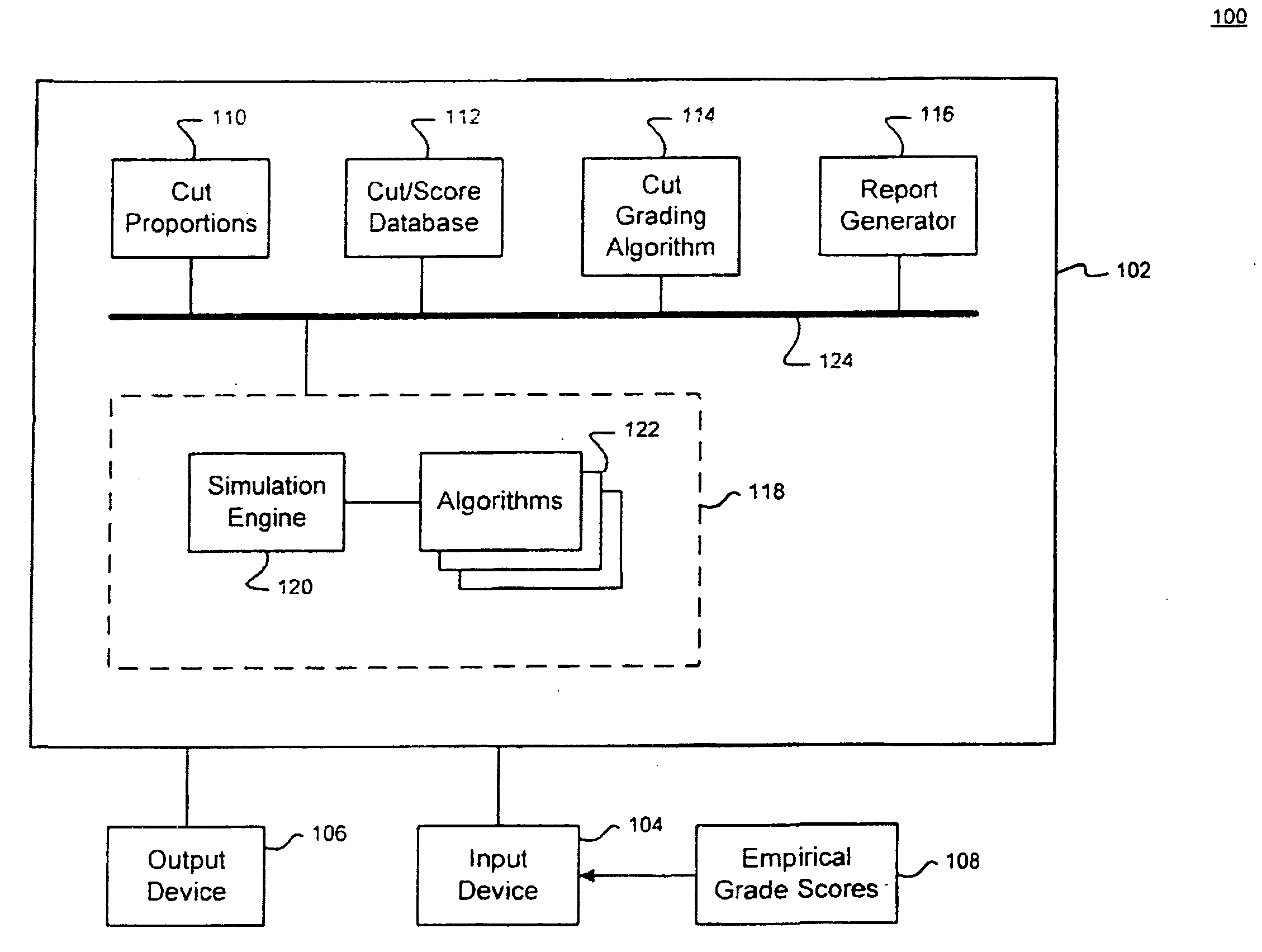
System and method for gemstone cut grading
ActiveUS20060074588A1Accurate predictionSuitable for useBy zone-melting liquidsDigital computer detailsGemstoneScore method
A system for grading the cut of a diamond utilizes a number of appearance metrics to generate scores for a number of cut components that affect cut quality. These cut components include brightness, fire, scintillation, overweight, durability, polish, and symmetry. The cut grading system employs a cut grading algorithm that processes the individual scores obtained for the cut components to generate an overall cut grade for the diamond. The scoring methodology and the cut grading algorithm are designed to emulate actual observation grading such that the overall cut grade represents a fair indication of the cut quality of the diamond. In one practical embodiment, the cut grading system is fully automated and computer-implemented.
Owner:GEMOLOGICAL INST OF AMERICA INC
Method for evaluation of a gemstone
ActiveUS20080231833A1Reliably foundWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationRefractive indexGemstone
An apparatus for determining location of at least one inclusion in a gemstone having a first refractive index, comprising:a container adapted for containing a material having a second refractive index,a holder operative to support a gemstone in the material when the container contains the material;an illuminator positioned and adapted to illuminate said gemstone when disposed within said material in said container, with illumination at which said gemstone and said material have their respective first and second indices;a detector that detects illumination from the illuminated gemstone and said material and produces signals responsive thereto;a controller that receives the signals and is operative to determine a location of an inclusion in the gemstone based on the signals; anda system, operative to reduce the presence within said material, at least when the gemstone is disposed therein, of any substance other than inclusions, having a third refractive index.
Owner:GALATEA
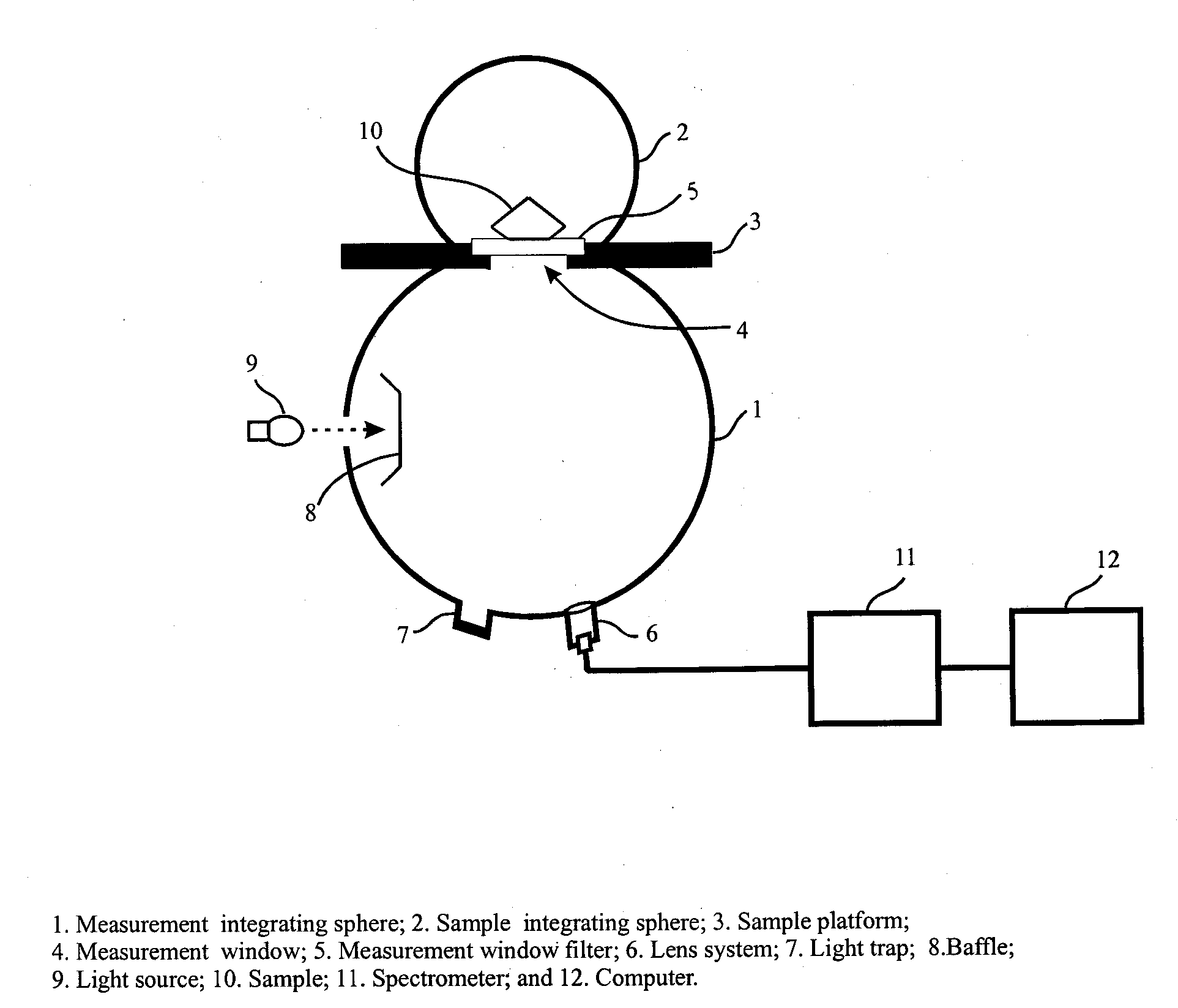
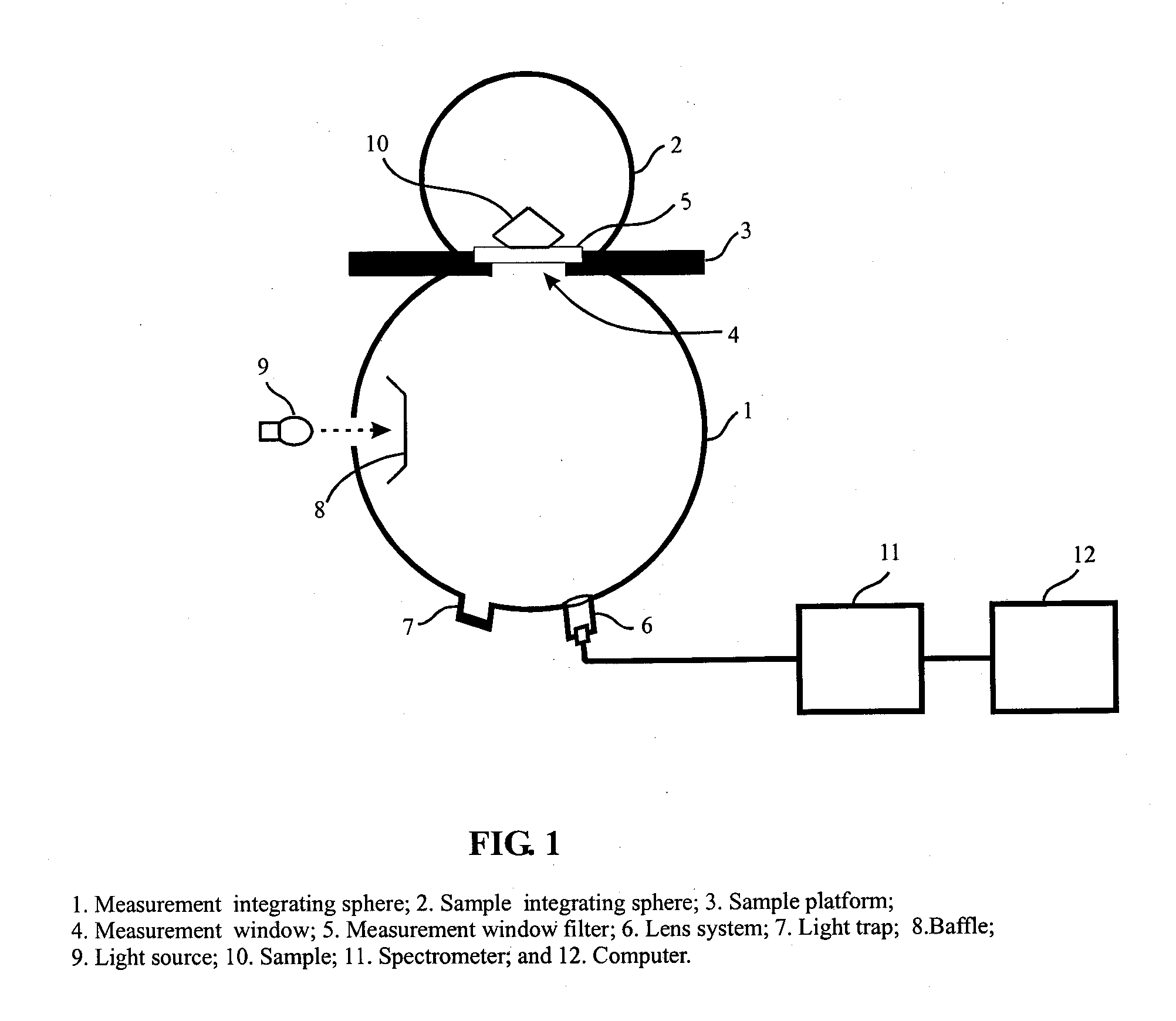
Apparatus and method for color measurement and color grading of diamonds, gemstones and the like
InactiveUS20080204705A1Accurate measurementReduce manufacturing costPhotometryInvestigating jewelsDiffuse illuminationFluorescence
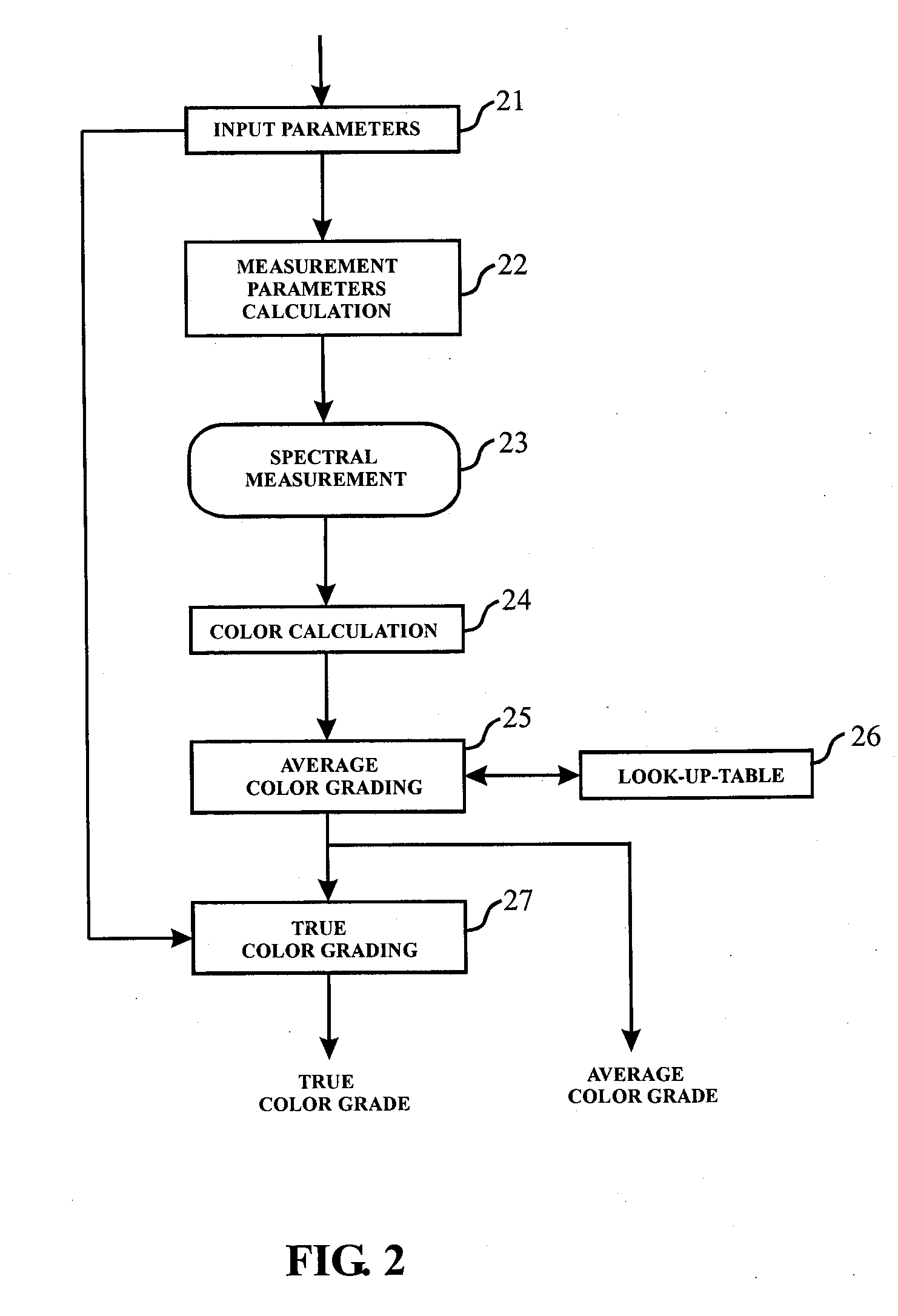
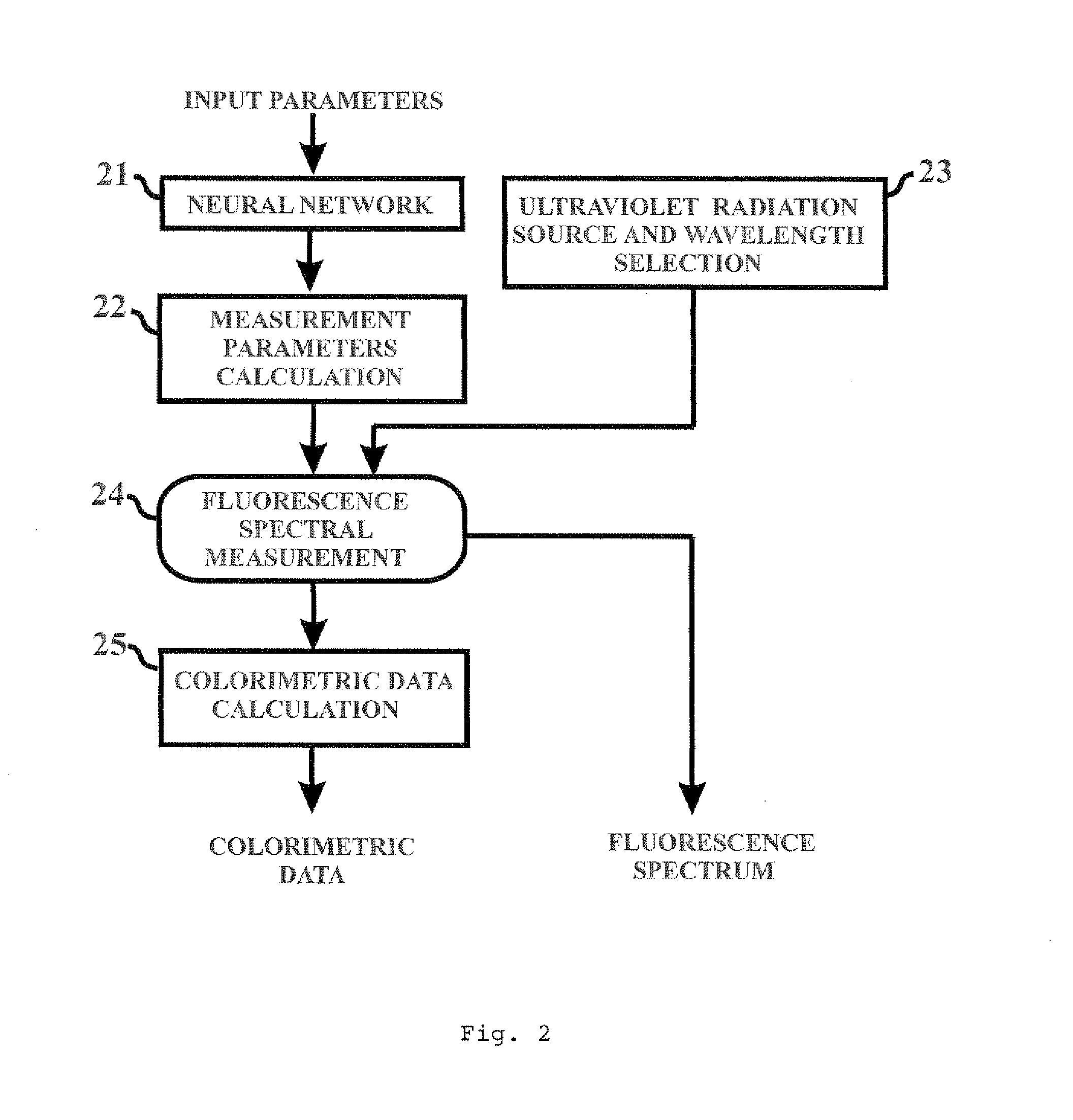
The present invention discloses an apparatus and method for color measurement and color grading of faceted gemstones, diamonds and the like. The apparatus comprises a spectrometer, a computer, and a dual integrating sphere measurement arrangement comprising a measurement integrating sphere, a sample integrating sphere, a sample platform, a filter, a lens system, a baffle and a light source. The measurement geometry of the dual integrating sphere measurement arrangement is diffuse illumination and 8 degree viewing with the specular component excluded, plus diffuse white background provided by the sample integrating sphere. The sample integrating sphere encloses a sample to provide a constant environment for simulating the visual color grading environment. A novel three-step calibration insures an accurate spectral measurement of the sample inside the measurement integrating sphere. The computer controls the spectrometer and provides measurement parameters calculated from the physical parameters of the measured sample, including, but not limited to, shape, dimensions, refractive index, intensity of fluorescence and cut grade. The computer then calculates the spectral reflectance and calorimetric data, and determines an average color grade by checking a look-up-table that represents the relationship between the CIELAB coordinate and the average color grade. The computer also determines a true color grade based upon the average color grade and the physical parameters, using mathematical analyses and algorithms.
Owner:LIU YAN
Capture and display of image of three-dimensional object
InactiveUS20060066877A1Realistic viewing experienceSimple modelInvestigating jewelsUsing optical meansElement modelMultiple perspective
A system and method for modeling three-dimensional objects such as diamonds and other gemstones. A three-dimensional finite-element model obtained by, for example, analysis of boundaries of the object in photographs taken from multiple perspectives with frontal lighting or silhouette lighting, or by analysis of structured-light photographs of the object taken from multiple perspectives, is combined with color or grayscale information obtained from photographs of the object. Enhanced or “false” color can be used to improve the viewing experience or to emphasize particular features of the object. A computer can rotate the model about arbitrary axes according to the desires of a viewer.
Owner:BENZANO DANIEL
Lightweight dry refractory
A dry refractory composition having superior insulating value. The dry refractory composition also may have excellent resistance to molten metals and slags. The composition includes filler lightweight material, which may be selected from perlite, vermiculite, expanded shale, expanded fireclay, expanded alumina silica hollow spheres, bubble alumina, sintered porous alumina, alumina spinel insulating aggregate, calcium alumina insulating aggregate, expanded mulllite, cordierite, and anorthite, and matrix material, which may be selected from calcined alumina, fused alumina, sintered magnesia, fused magnesia, silica fume, fused silica, silicon carbide, boron carbide, titanium diboride, zirconium boride, boron nitride, aluminum nitride, silicon nitride, Sialon, titanium oxide, barium sulfate, zircon, a sillimanite group mineral, pyrophyllite, fireclay, carbon, and calcium fluoride. The composition also may include dense refractory aggregate, which may be selected from calcined fireclay, calcined Chamotte, a sillimanite group mineral, calcined bauxite, pyrophyllite, silica, zircon, baddeleyite, cordierite, silicon carbide, sintered alumina, fused alumina, fused silica, sintered mullite, fused mullite, fused zirconia, sintered zirconia mullite, fused zirconia mullite, sintered magnesia, fused magnesia, sintered spinel, and fused spinel refractory grog, a heat activated bonding agent, and a dust suppressant.
Owner:ALLIED MINERAL PROD
Method and apparatus for machining diamonds and gemstones using filamentation by burst ultrafast laser pulses
InactiveUS20150121960A1Efficient cuttingLess-waste is producedBlowing machine gearingsFine working devicesNon ablativeFilamentation
A non-ablative laser machining method and apparatus for cutting facets of a diamond, using a material machining technique involving filamentation by burst ultrafast laser pulses well suited to mass production. Coupled with 3D modeling and the computerized laser machining system, complex geometric surfaces can be created on the diamond. The facets of the diamond need not be planar in configuration, and may incorporate acute as well as oblique angles. This method minimizes the need for diamond polishing, speeds up production, and realizes great reductions in the quantity of lost material from the cutting process.
Owner:ROFIN SINAR TECH
Method and system for laser marking in the volume of gemstones such as diamonds
A method and an apparatus for laser marking indicia in the volume of gemstones such as diamonds, the indicia being made up of a plurality of microscopic dot-shaped marks whose build-up can be initiated by exposing naturally-occurring internal defects or impurities in the volume of a gemstone to a tightly focused train of laser pulses. Authentication data is encoded in the gemstone from the relative spatial arrangement of the dot-shaped marks that form the indicium. Taking advantage of the presence of otherwise invisible defects in the gemstone allows for inscribing indicia with laser pulses carrying energies substantially lower than the threshold energy required for inscribing in the volume of a perfect gemstone material. The marking process is then much less susceptible to inflict damages to the surface of the gemstone, and the marking can be performed using a broad variety of femtosecond laser systems. The dot-shaped marks engraved at a depth below the surface of a gemstone can be made undetectable with the unaided eye or with a loupe by limiting their individual size to a few micrometers, while devising indicia made up of only a few marks. As a result, the marking does not detract from the appearance and value of the gemstone. The procedure for laser marking accounts for the random spatial distribution of the defects present in natural gemstones as well as for their strongly localized character. The presence of an indicium can be detected by using a dedicated optical reader that can be afforded by every jewellery store.
Owner:GEMOLOGICAL INST OF AMERICA INC
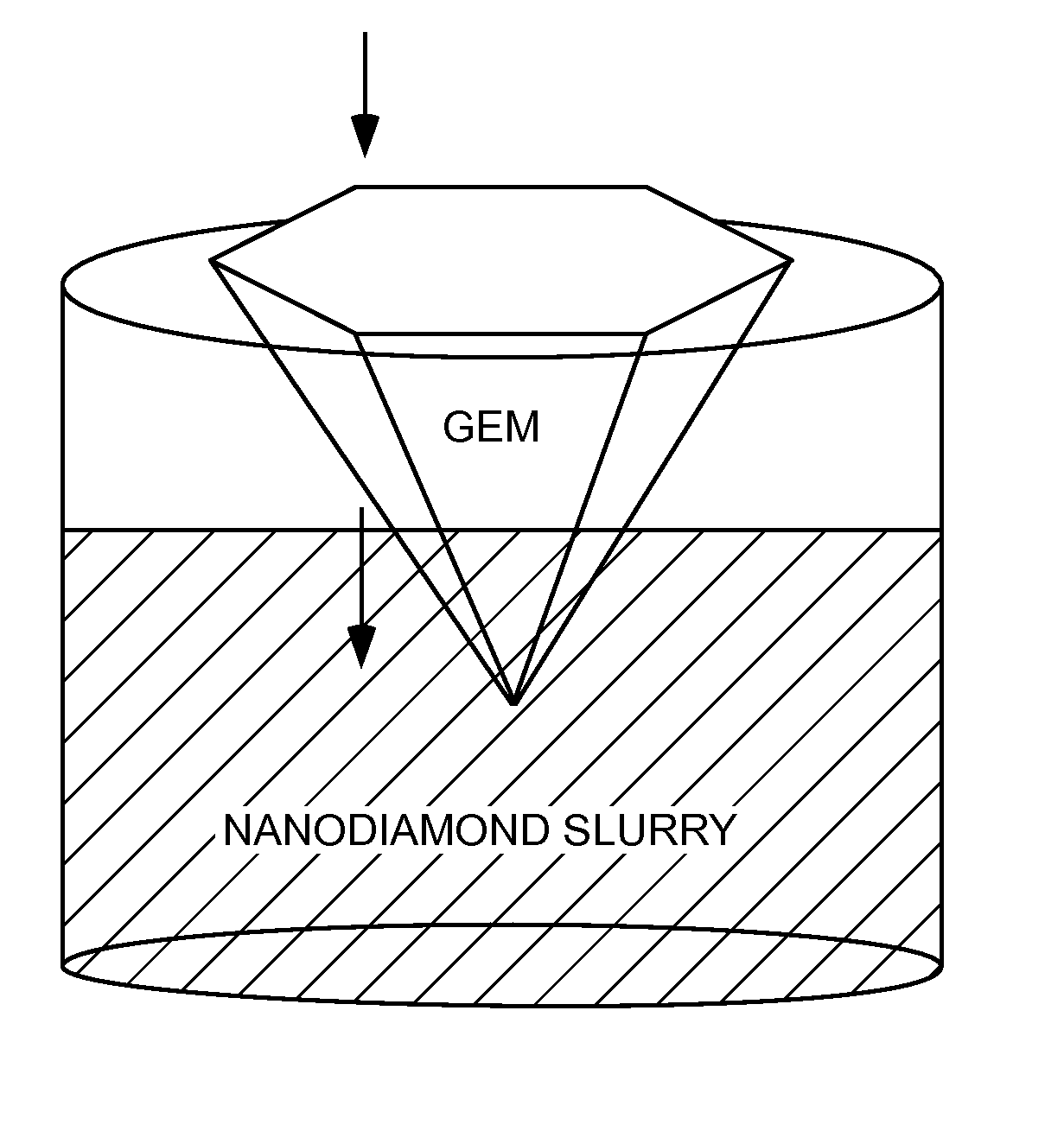
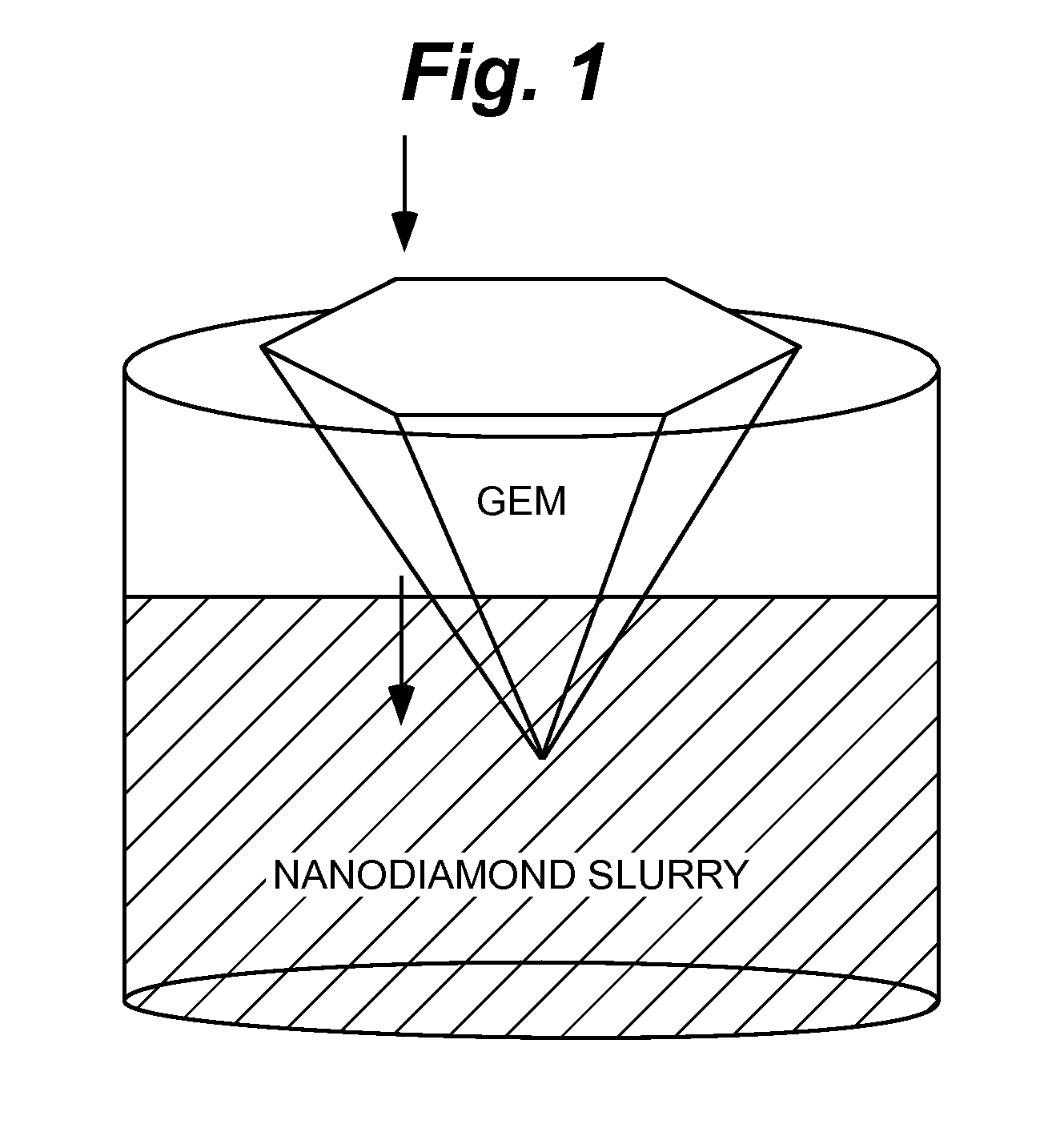
Method for producing nanocrystalline diamond coatings on gemstones and other substrates
ActiveUS20100068503A1Reduce usageEasy to storeElectric discharge heatingLayered productsGemstoneSlurry
A method to apply nano-crystalline diamond onto a selected substrate, including preparing Nanodiamond slurry of nanodiamond particles dispersed in a medium. The medium may include a liquid or a sol-gel. The selected substrate is immersed in the Nanodiamond slurry for a predetermined period of time. Then the substrate is removed from the slurry. The substrate is then dried with a flow of inert gas. The substrate is left coated with a coating of the nanodiamond particles that are highly adherently held by van der Waals forces.
Owner:ARYAMOND SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Method and System for Improved Optical Modeling of Gemstones
ActiveUS20140107986A1Reduce deficiencyImproved virtual optical modelingInvestigating jewelsOptically investigating flaws/contamination3d shapesOptical property
A method of constructing a virtual model of a gemstone including the steps of performing measurements of the gemstone to construct a three-dimensional (3D) model of an exterior surface of the gemstone; identifying one or more visible inclusions within an interior volume of the gemstone; for each identified inclusion, performing the steps of determining a location and 3D shape of the inclusion within the interior volume of the gemstone; capturing at least one image of the inclusion; using the at least one image to determine relevant optical characteristics of the inclusion; and constructing a 3D virtual model of the inclusion, said model including the 3D shape of the inclusion and optical properties of the inclusion based upon said optical characteristics; constructing a 3D virtual model of the gemstone which includes the 3D virtual model of the exterior surface of the gemstone and the 3D virtual models of the one or more visible inclusions within the interior volume of the gemstone; and generating a dataset representing said 3D virtual model, wherein said dataset may be used in subseguent computer analysis to provide a user with information relating to a visual characteristic of the gemstone.
Owner:IDEAL SCOPE
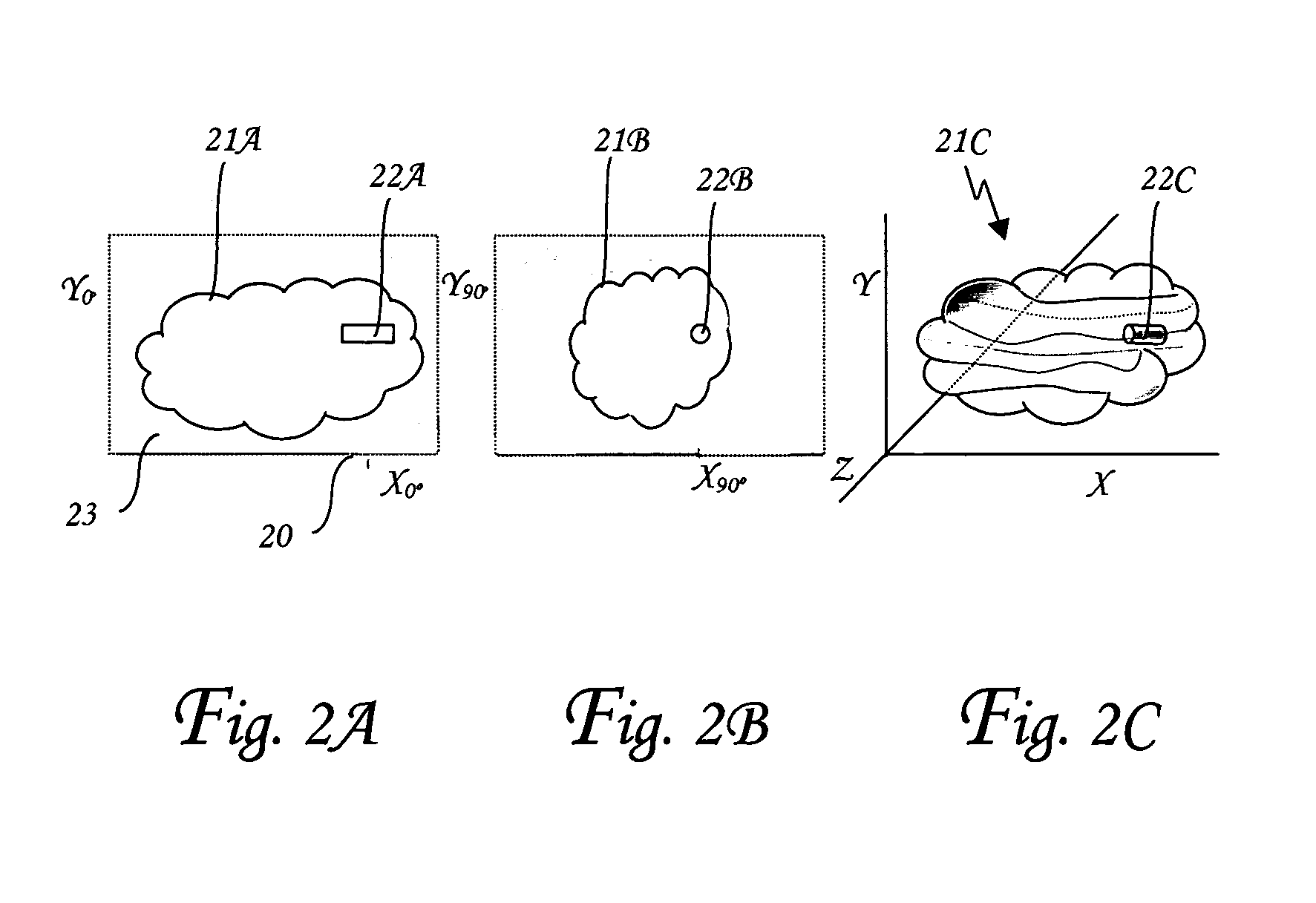
System and method for three-dimensional location of inclusions in a gemstone
InactiveUS20060062446A1Rapid and cost-effectiveInvestigating moving sheetsHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-rayLaser beams
The present invention presents a non-destructive method and means of obtaining either the inner portion or the outer contour of a two-dimensional or three-dimensional model of the outer contours of a gemstone. The method comprising the steps of placing the gemstone on a holder such that the gemstone to be scanned is located in a radiation path comprising inter alia at least one emitter and at least one detector synchronized by a processor; radiating said gemstone by means of said emitter; detecting the emitted irradiation by means of said detector; processing said detection such that a two-dimensional in-scan of said gemstone is obtained by means of said processor; displacing the gemstone in respect to said emitter and said detector; repeating steps (b) through (e) for a plurality of predetermined displacements; and, if a three-dimensional model is required, integrating the obtained multiple two-dimensional in-scans into a three-dimensional model of the gemstone's outer contours; wherein the emitter is an irradiation delivery device, selected from a group consisting of either monochromatic or white light, UV or IR emitters; X-ray radiation source and / or collimator of the same; NMR, CT, NQR and / or MIR scatters; beta radiation emission devices; gamma radiation emission devices; laser beam cannons; photons cannons; microwave or RF emitters; sonic or ultrasonic emitters or any combination thereof.
Owner:PORAT ZVI
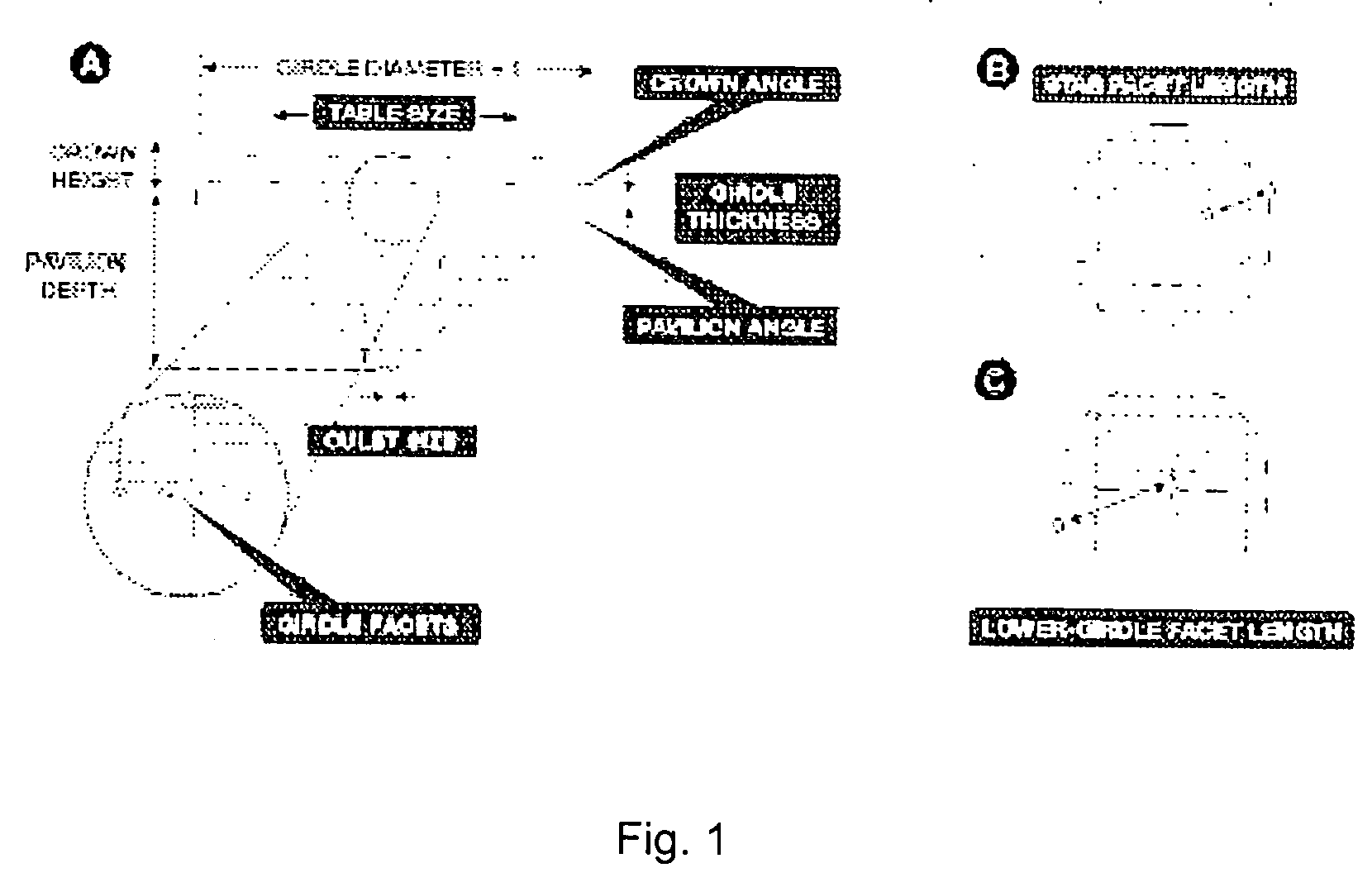
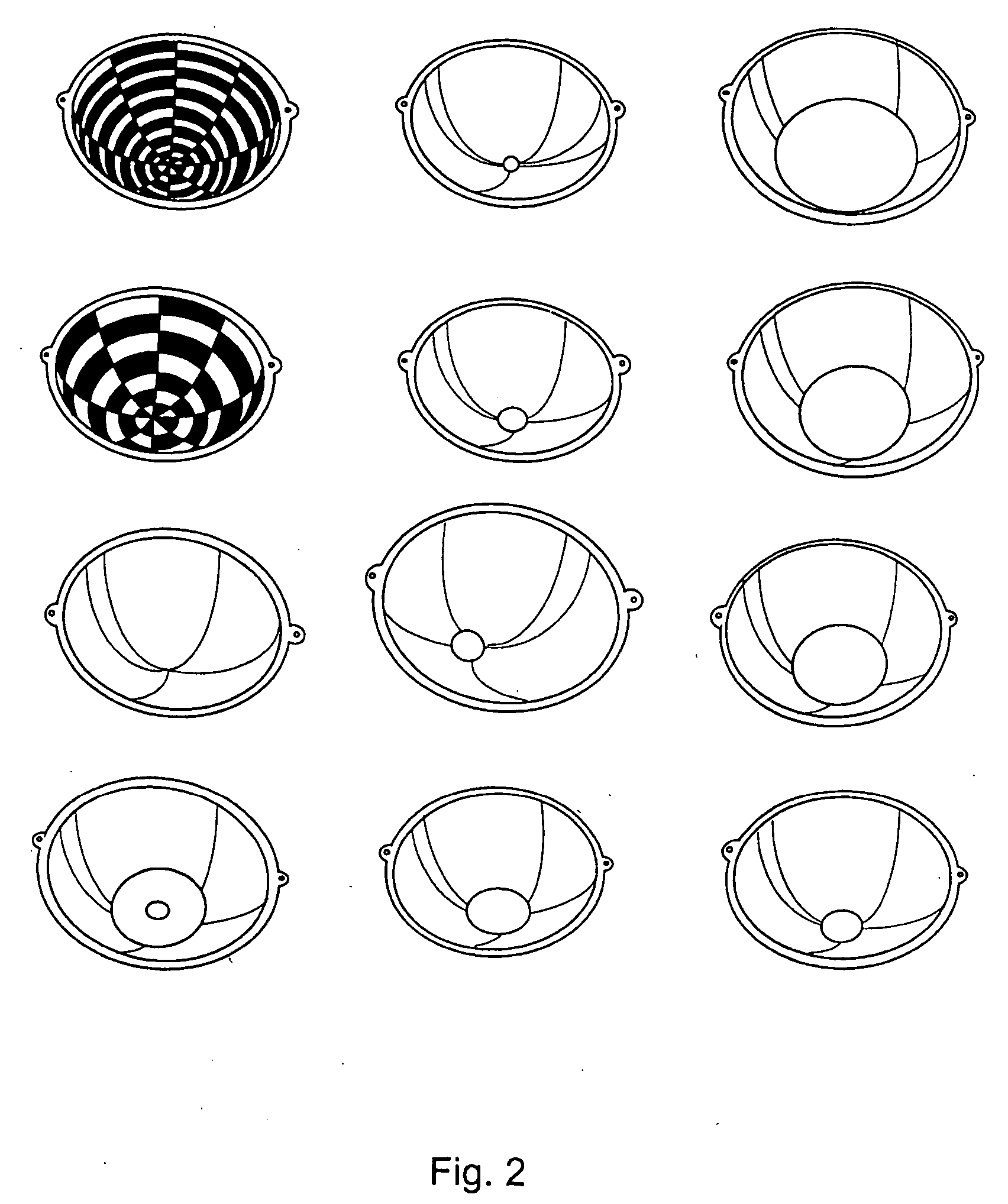
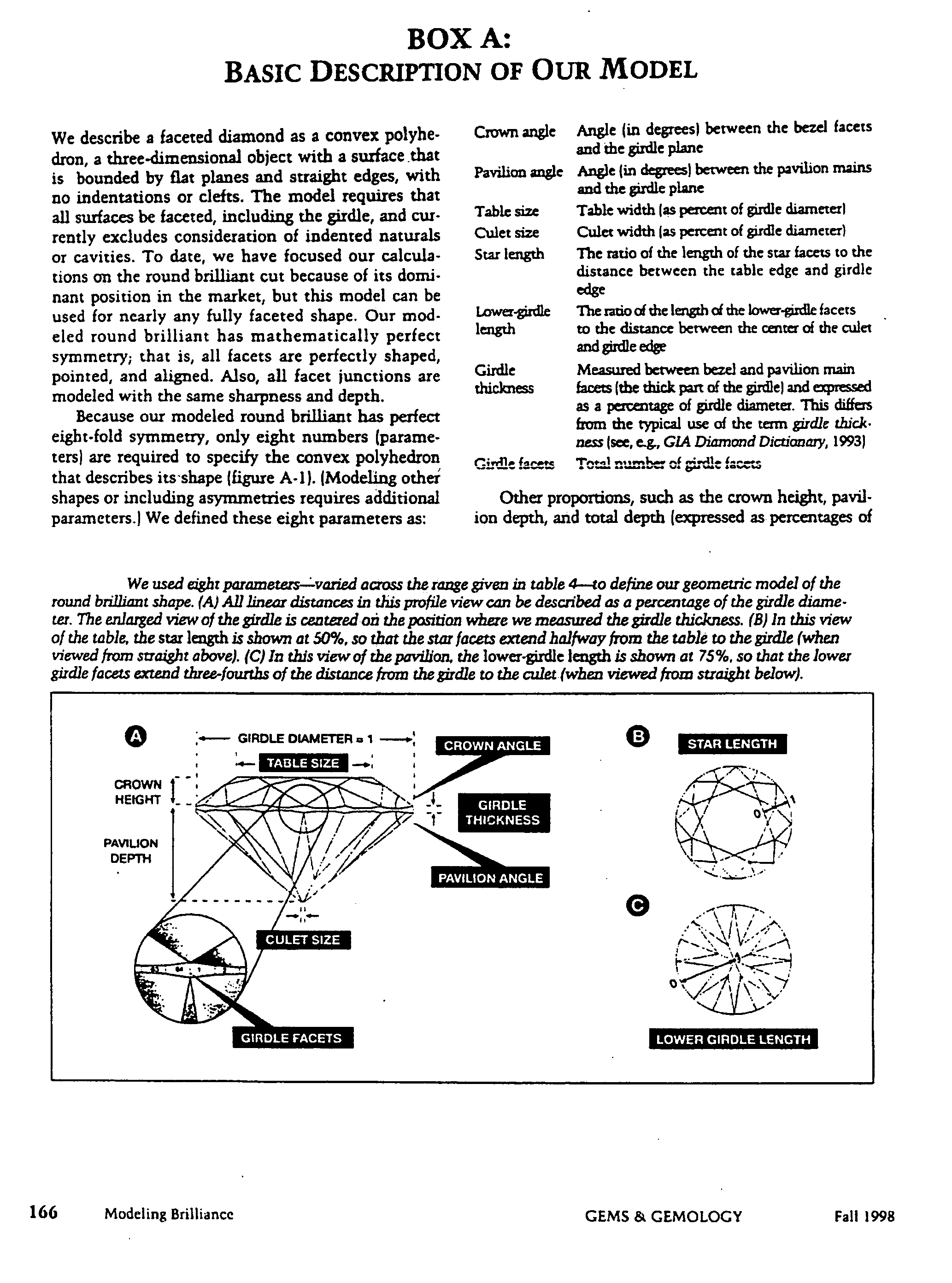
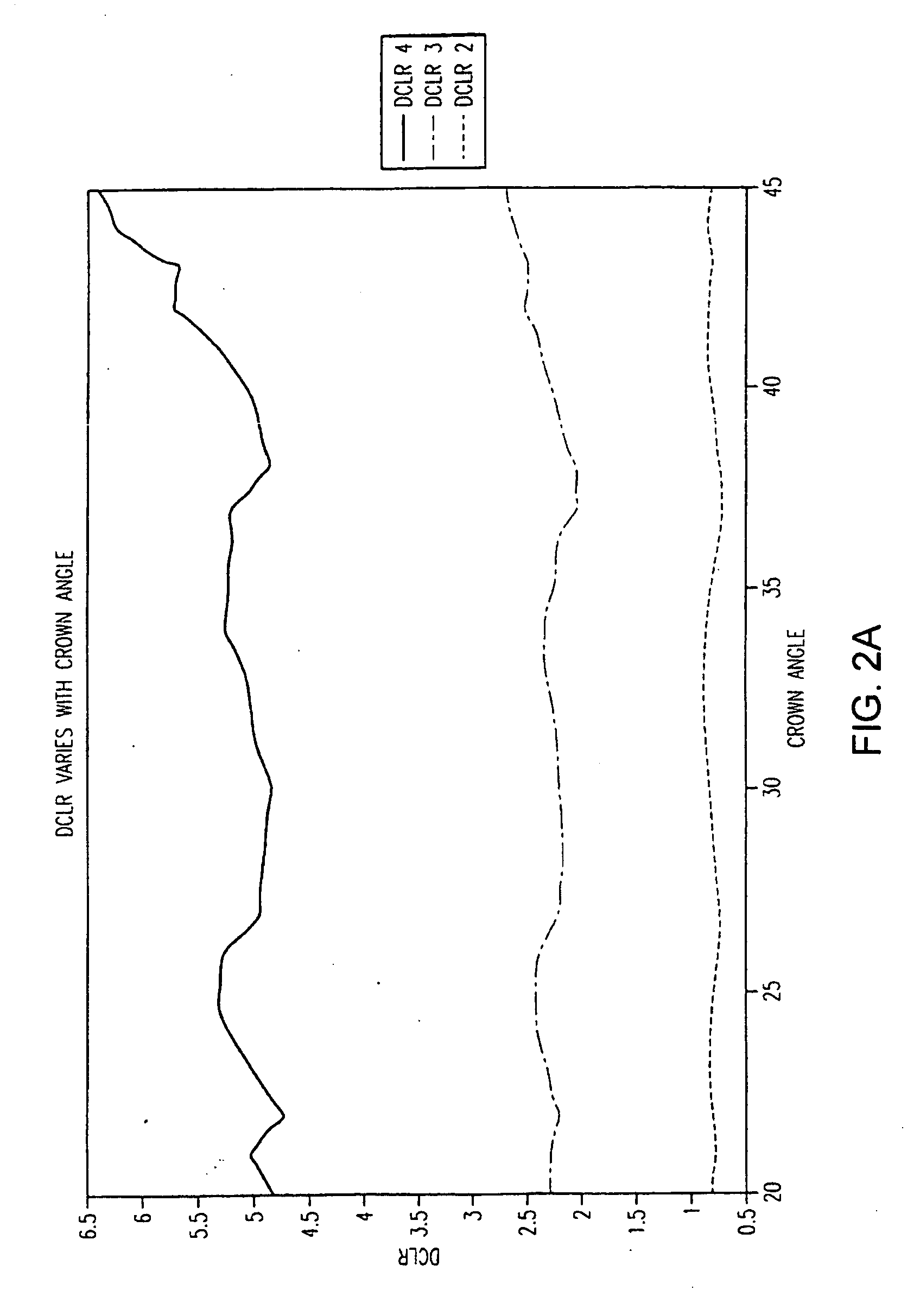
Systems and methods for evaluating the appearance of a gemstone
Of the “four C's,” cut has historically been the most complex to understand and assess. This application presents a three-dimensional mathematical model o study the interaction of light with a fully faceted, colorless, symmetrical round-brilliant-cut diamond. With this model, one can analyze how various appearance factors (brilliance, fire, and scintillation) depend on proportions. The model generates images and a numerical measurement of the optical efficiency of the round brilliant-called DCLR—which approximates overall fire. DCLR values change with variations in cut proportions, in particular crown angle, pavilion angle, table size, star facet length, culet size, and lower girdle facet length. The invention describes many combinations of proportions with equal or higher DCLR than “Ideal” cuts, and these DCLR ratings may be balanced with other factors such as brilliance and scintillation to provide a cut grade for an existing diamond or a cut analysis for prospective cut of diamond rough.
Owner:GEMOLOGICAL INST OF AMERICA INC
System and method for analysis of gemstones
InactiveUS7557917B1Reduce detection limitRapid analysis cycleRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSpectral emissionChemical composition
A system for analyzing the chemical composition of a sample, comprising exciting a portion of the sample to generate atomic spectral emissions; a spectrometer for determining atomic emission characteristics; processor for receiving an output from the spectrometer, analyzing said output to determine atomic composition, said processor predicting at least one of (i) an origin of the sample, (ii) a treatment applied to said sample, (iii) a composition of the sample, and (iv) a feedback signal for controlling a process. Calibration samples are also provided for standardizing readings from the spectrometer.
Owner:AMERICAN GEMOLOGICAL LAB
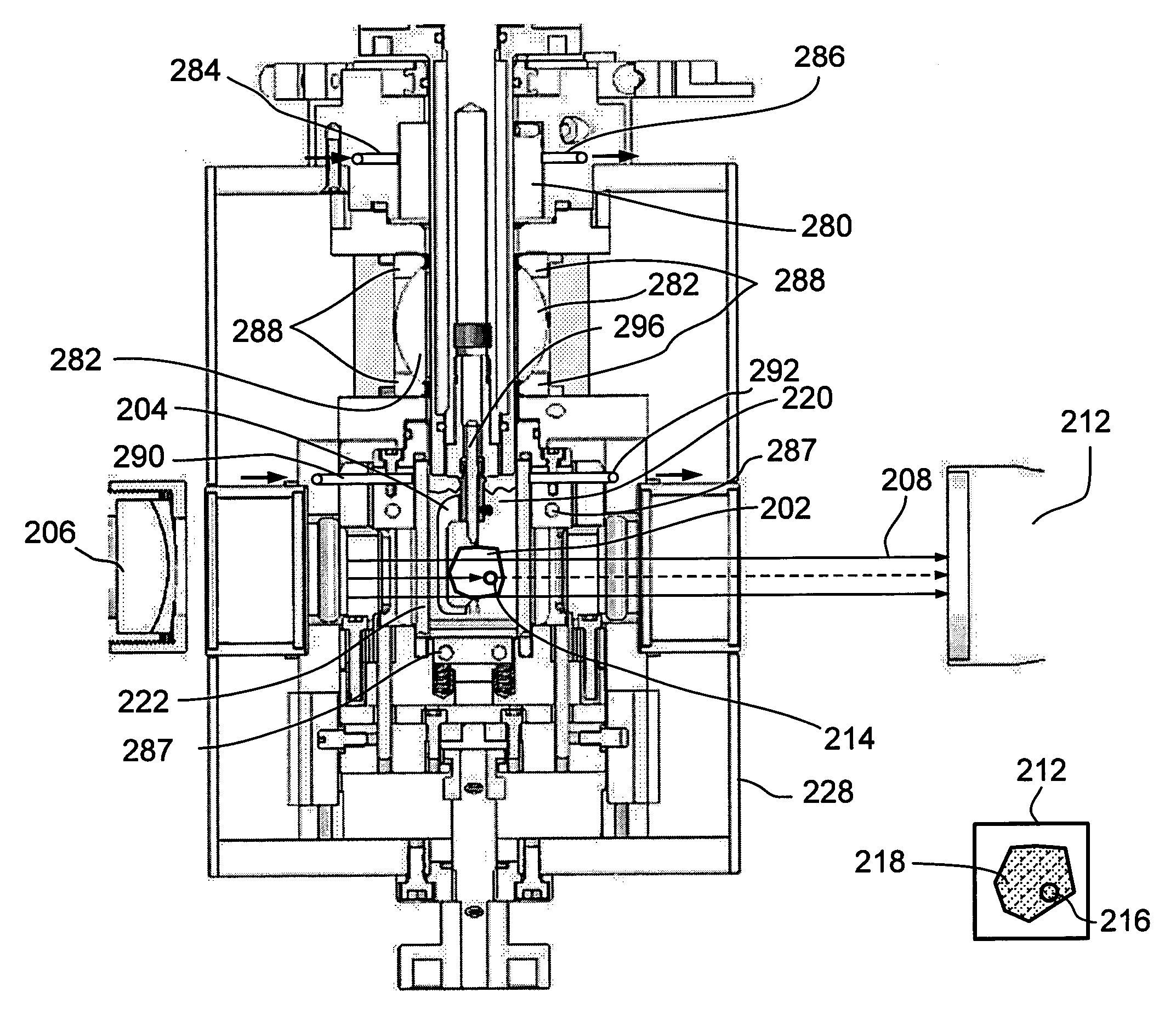
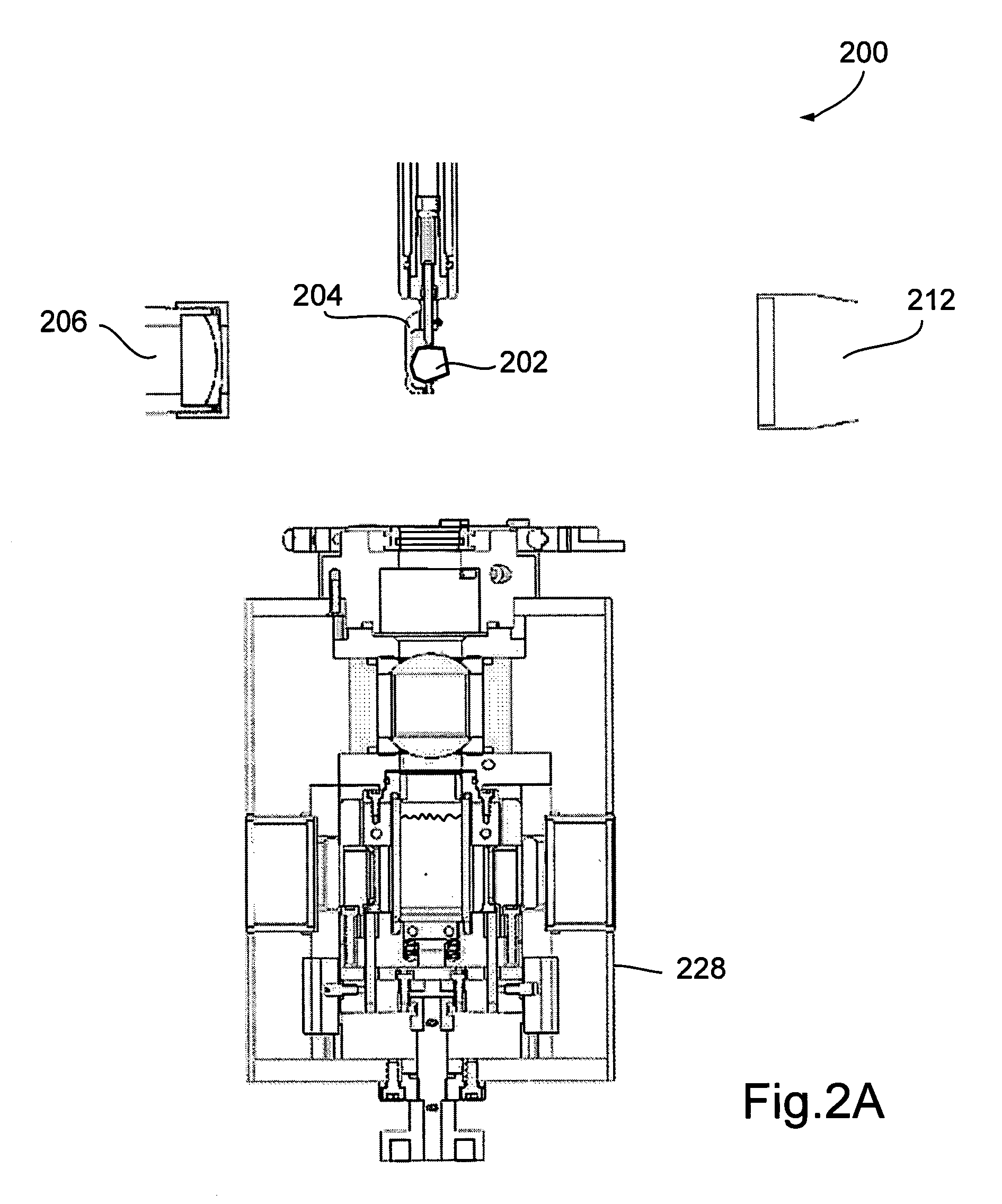
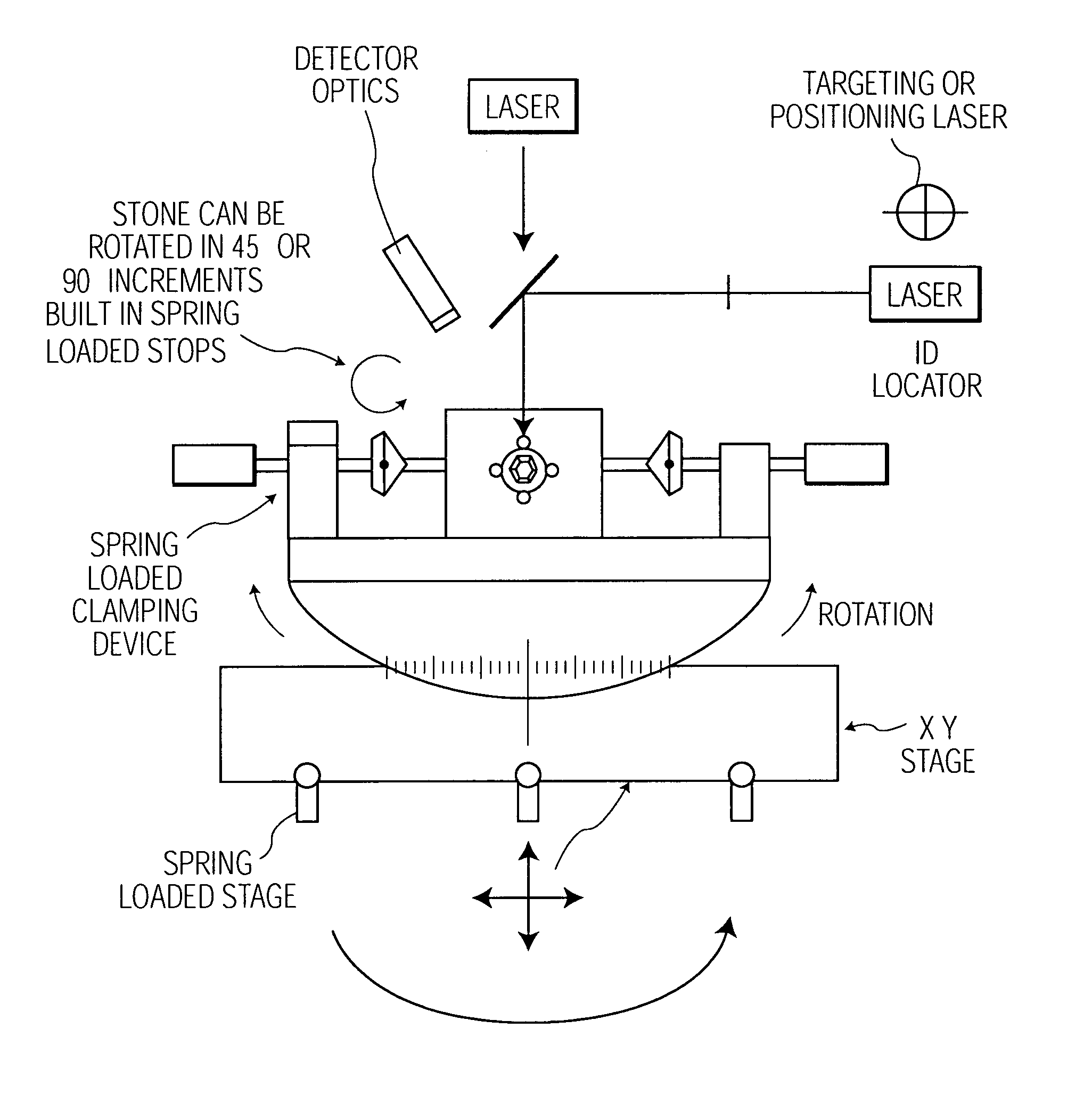
Modified apparatus and method for assessment, evaluation and grading of gemstones
InactiveCN102216760AConfidenceImprove reliabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationInvestigating jewelsInformation processingGemstone
An apparatus (10) for assessment, evaluation and grading of gemstones has a stage (11) upon which a gemstone may be supported. The stage is enclosed in a housing (15) that is impervious to light. There is at least one light source (14) located in the housing which is adapted to project incident light onto the gemstone. Means for rotating and tilting the stage so as to vary the orientation of the gemstone to the incident light are also present. A digital camera (16) is located in the housing adjacent the or each light source and is adapted to take images of the gemstone based on reflection and / or refraction of the incident light. The apparatus also includes information processing means for calibrating and analysing the images.; The information processing means is programmed with instruction sets for assessing one or more of colour, cut, clarity, scintillation, brilliance, lustre, dispersion and sheen. The gemstone is supported upon the stage by securing means (17) engaging the gemstone at its bottom surface.
Owner:OPAL PRODUCERS AUSTRALIA LTD
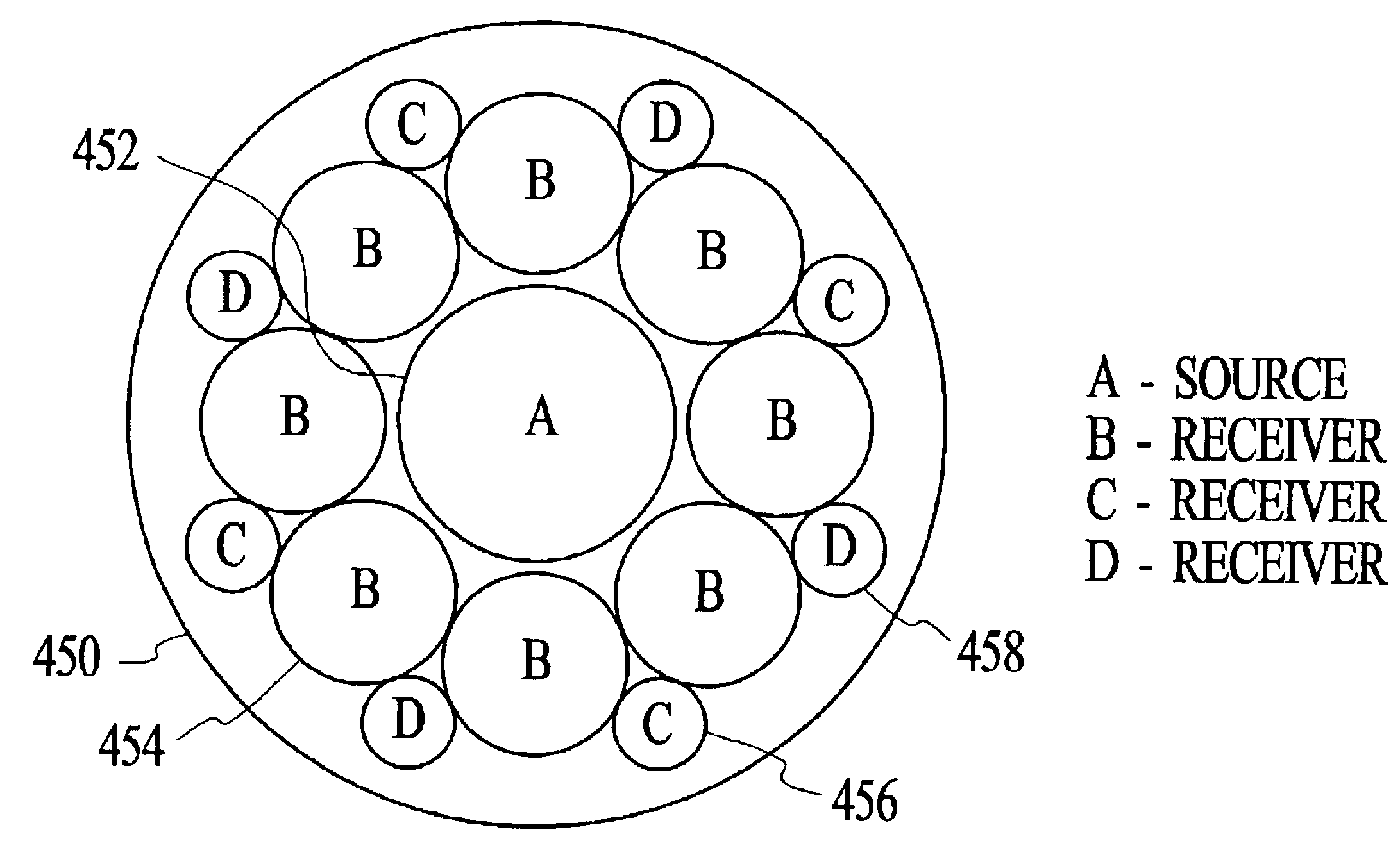
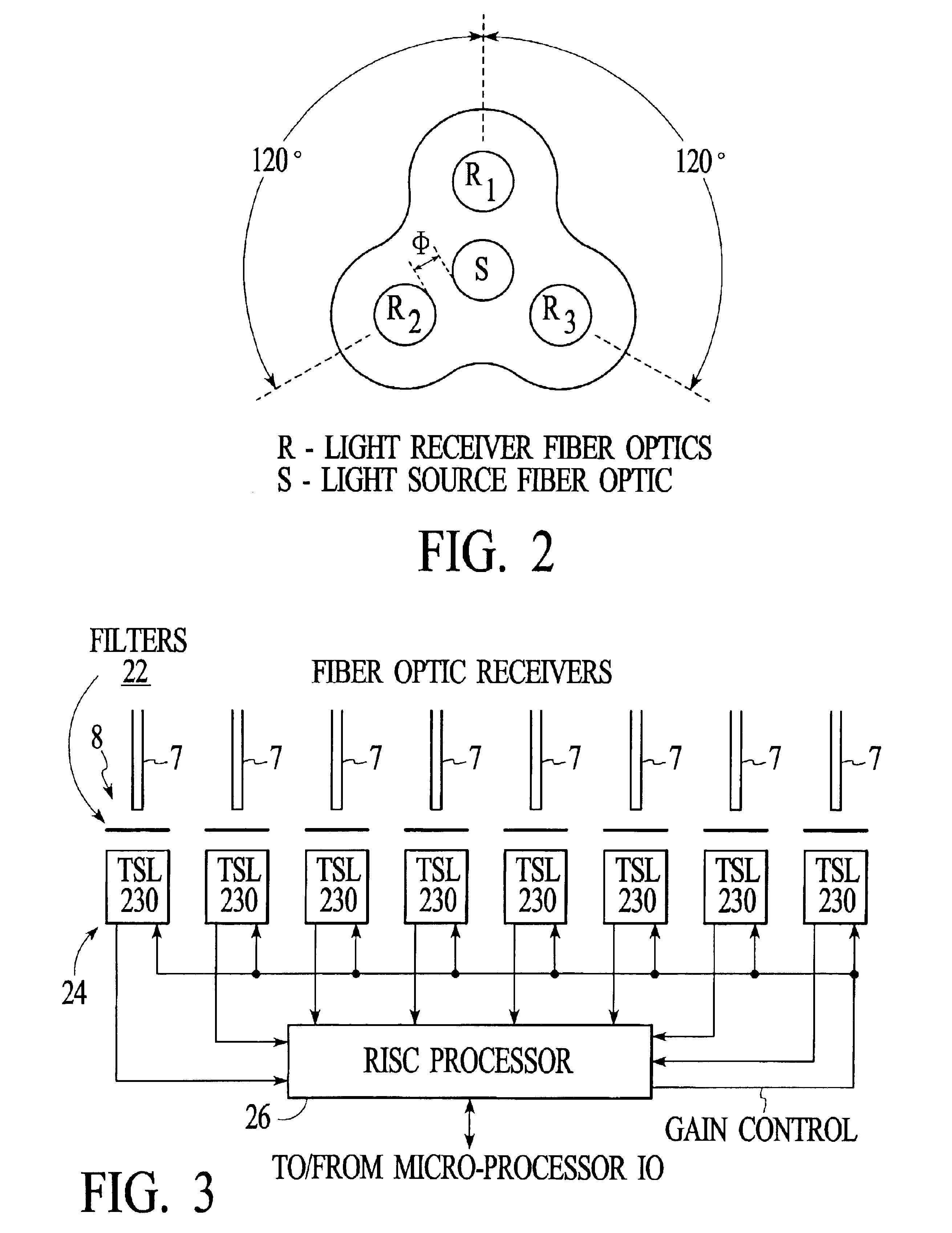
Methods for characterizing gems or precious stones using a probe having a plurality of light receivers
InactiveUS6958810B2Minimal problemMinimizing heightRadiation pyrometryScattering properties measurementsFiberOptical property
Optical characteristic measuring systems and methods such as for determining the color or other optical characteristics of teeth are disclosed. Perimeter receiver fiber optics are spaced apart from a source fiber optic and receive light from the surface of the object / tooth being measured. Light from the perimeter fiber optics pass to a variety of filters. The system utilizes the perimeter receiver fiber optics to determine information regarding the height and angle of the probe with respect to the object / tooth being measured. Under processor control, the optical characteristics measurement may be made at a predetermined height and angle. Various color spectral photometer arrangements are disclosed. Translucency, fluorescence, gloss and / or surface texture data also may be obtained. Audio feedback may be provided to guide operator use of the system. The probe may have a removable or shielded tip for contamination prevention. A method of producing dental prostheses based on measured data also is disclosed. Measured data also may be stored and / or organized as part of a patient data base.
Owner:JJL TECH +1
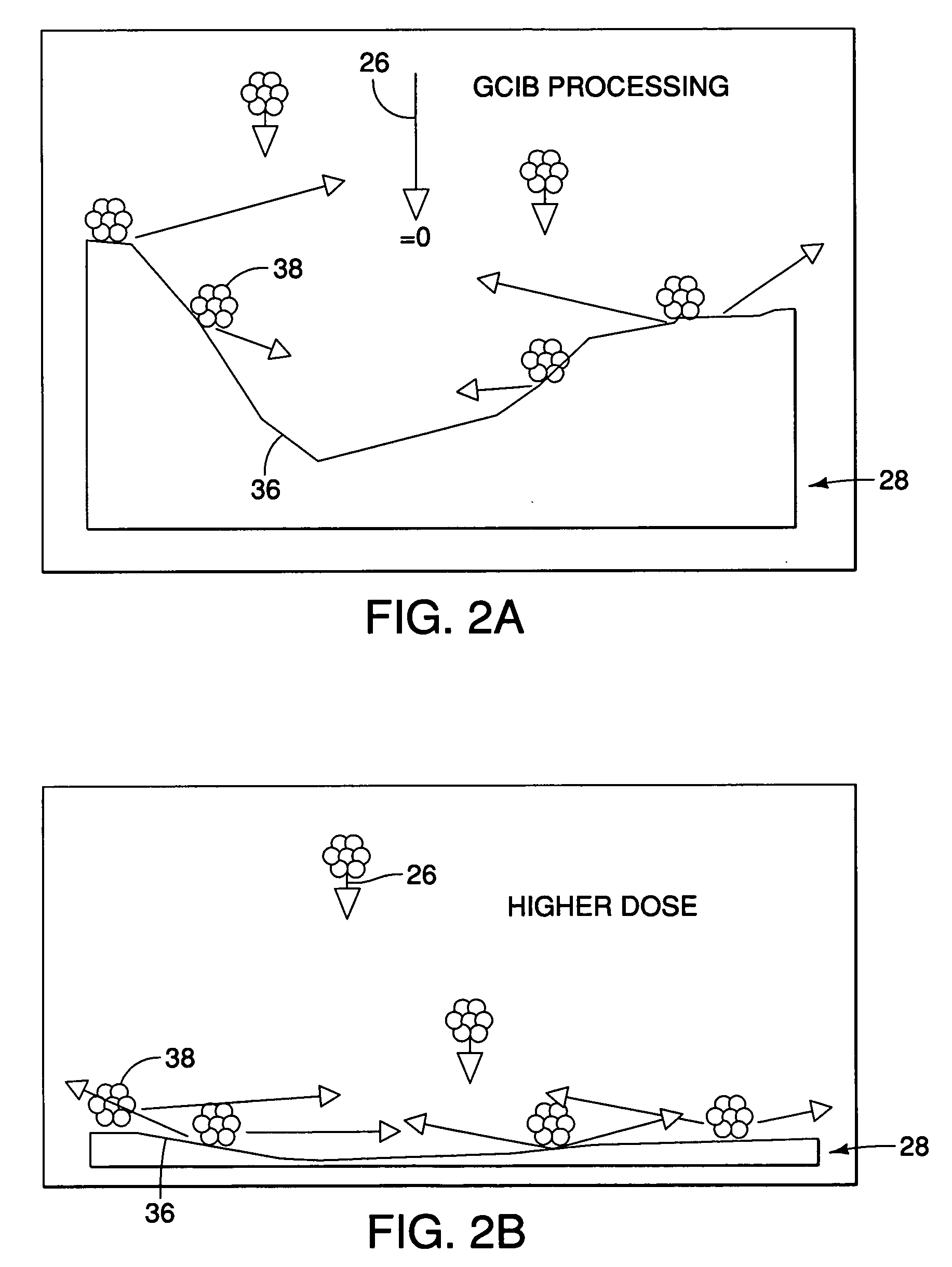
Apparatus and method for polishing gemstones and the like
InactiveUS20060102854A1Increase throughput timeReduce errorsEdge grinding machinesRadiation/particle handlingGas cluster ion beamElectron bombardment
The invention comprises a two-step process for achieving an ultra-polish finish on materials such as gemstones and the like by first performing a chemical-mechanical polishing of the material using an intermetallic material as the grinding medium followed by a gas cluster ion beam (GCIB) treatment. The intermetallic grinding wheel is formed of carbide-forming metals in the form of intermetallics consisting of one kind or more of elements selected from the group of Al, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Ru, Rh, Pd, Os, Ir and Pt, and one kind or more of elements selected from the group of Ti, V, Zr, Nb, Mo, Hf, Ta and W. The gas cluster ion beams are comprised of gas clusters having nano-sized aggregates of materials that are gaseous under conditions of standard temperature and pressure. Such clusters can be ionized by electron bombardment or other means, permitting the gas clusters to be formed into directed beams of known and controllable energy. The larger sized gas clusters are the most useful because the larger sized gas clusters are able to carry substantial energy per cluster ion, while yet having only modest energy per atom or molecule.
Owner:NEOGI JAYANT +1
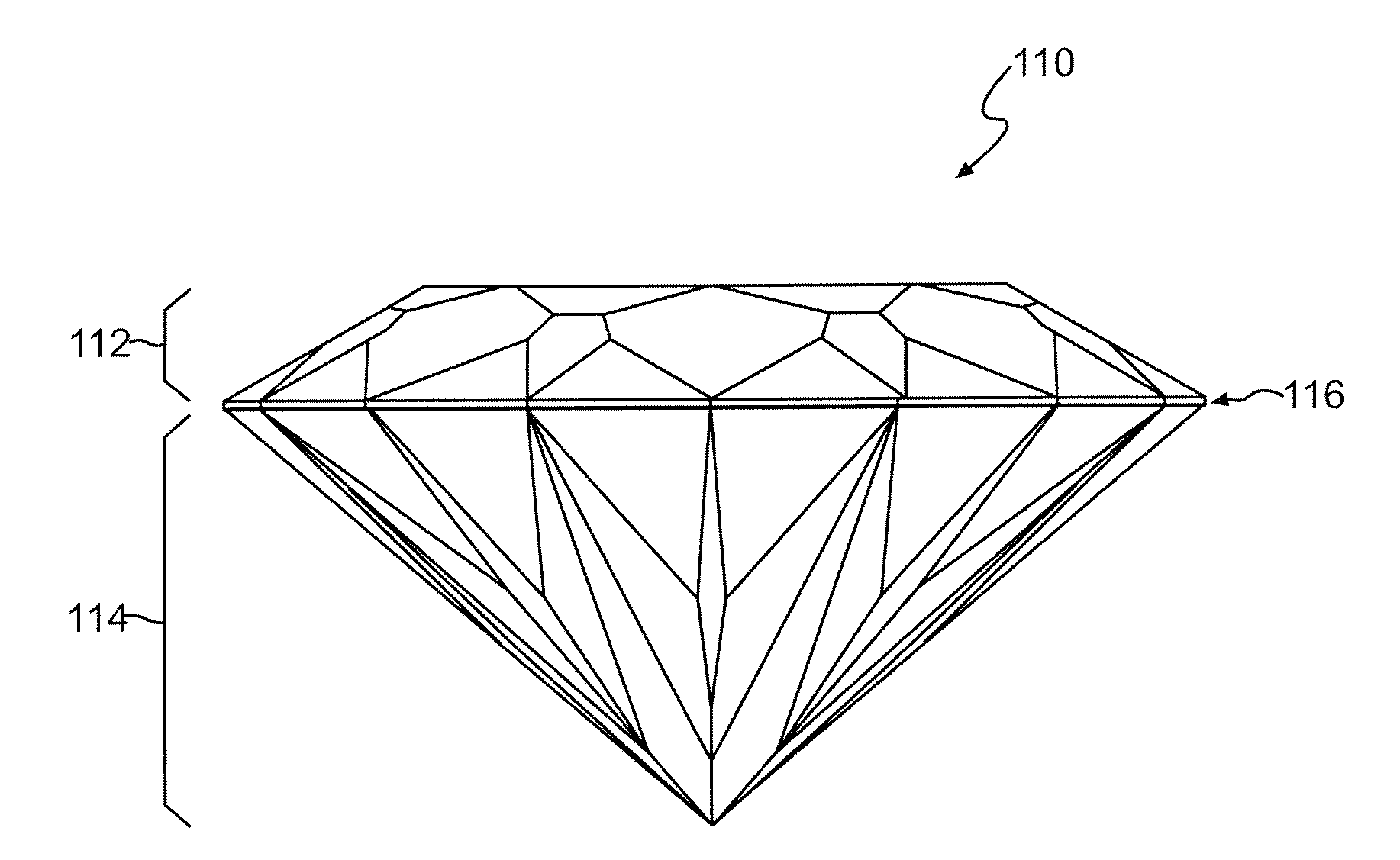
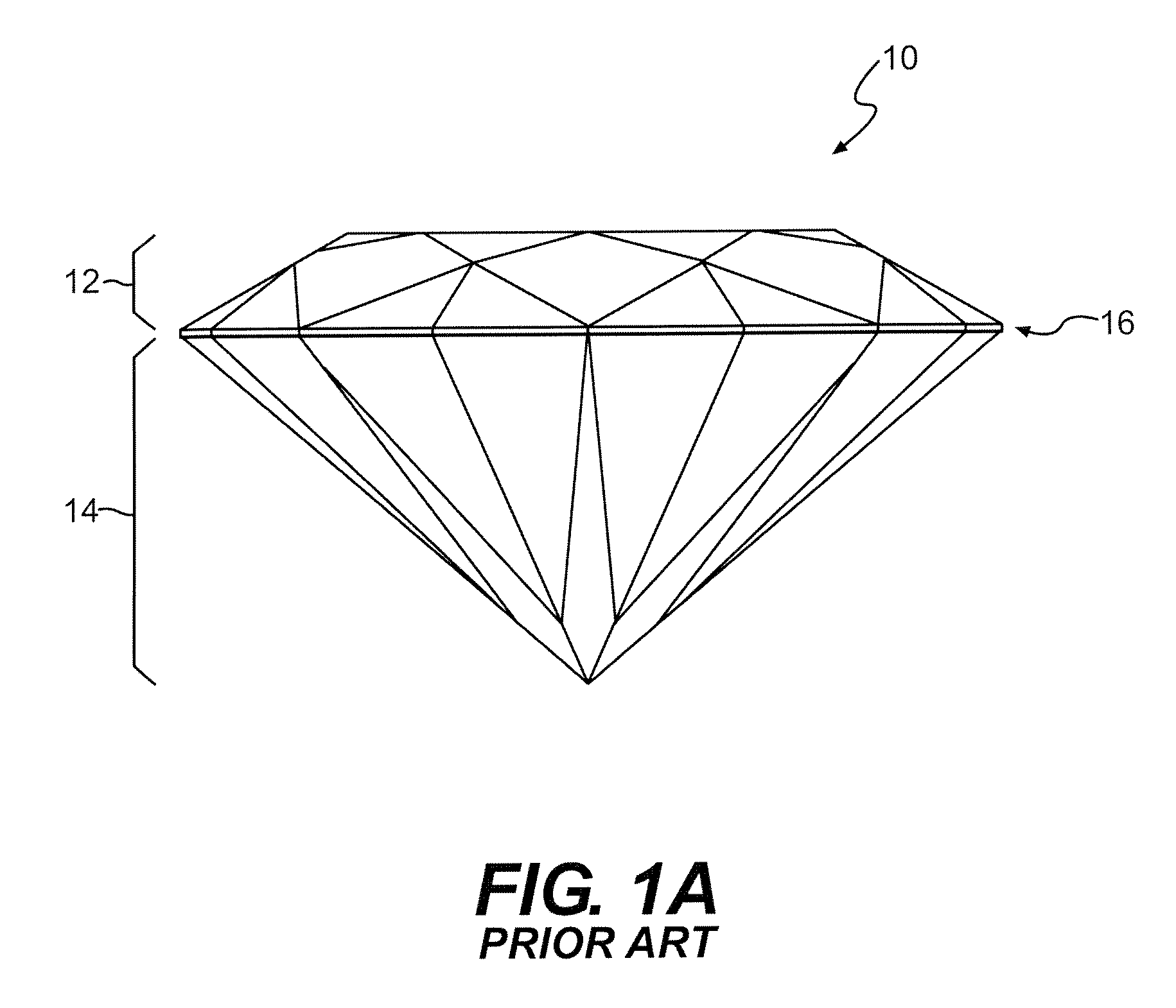
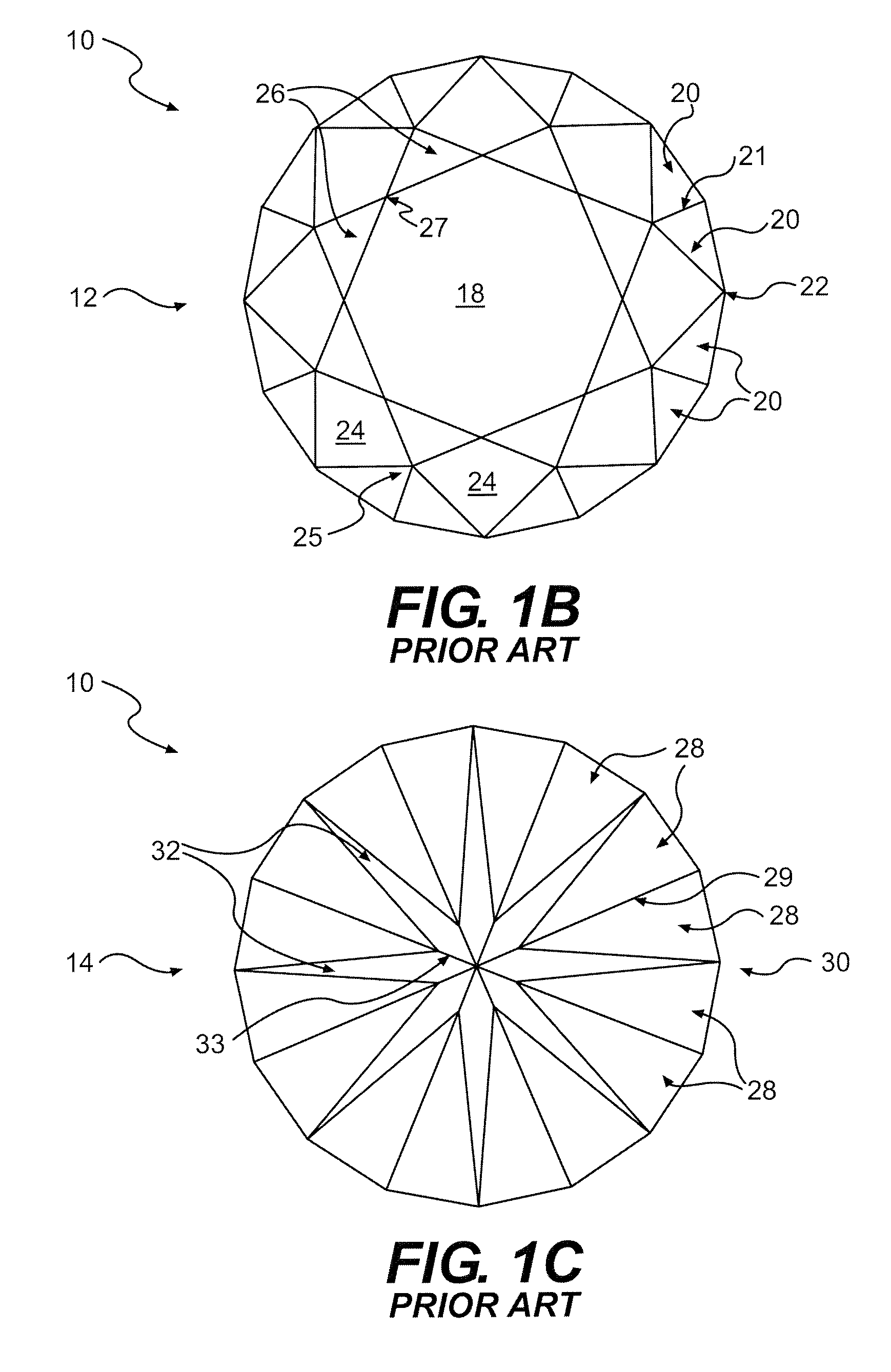
Gemstone Facet Configuration
A gemstone can include a crown portion having a table facet, a plurality of trapezoidal facets, a plurality of irregular-hexagonal facets, a plurality of irregular-pentagonal facets, and a plurality of triangular crown-facets. The gemstone can also include a pavilion portion having a plurality of first kite facets, a plurality of irregular-quadrilateral facets, a plurality of second kite facets, and a plurality of triangular pavilion-facets.
Owner:CHARLES & COLVARD
Drag-and-drop customization of jewelry
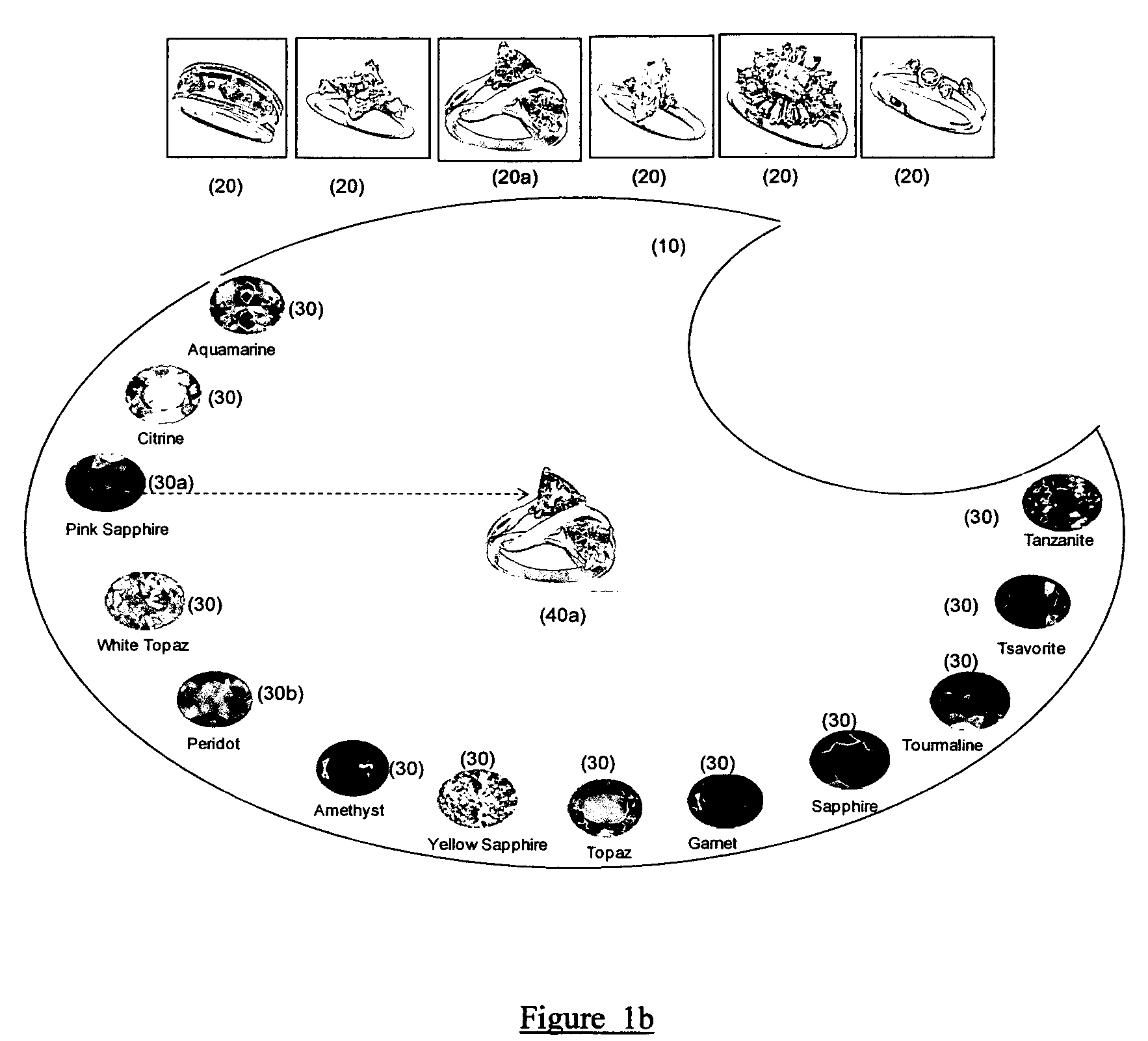
An inventive method and system for allowing visitors of a web site to customize design elements into a final unique design through the use of an intuitive drag-and-drop or click-and-place method of assembly is presented. The inventive method and system enable better simulation of the highly visual, interactive, experimental and iterative creative design process employed by people when building artistic designs including jewelry. The drag-and-drop or click-and-place technique of putting gemstones into settings is analogous to an artist creating a painting by iteratively picking up a particular paint color with a paintbrush and placing the selected paint on a particular spot on a canvas.
Owner:FACETAB OF YOU
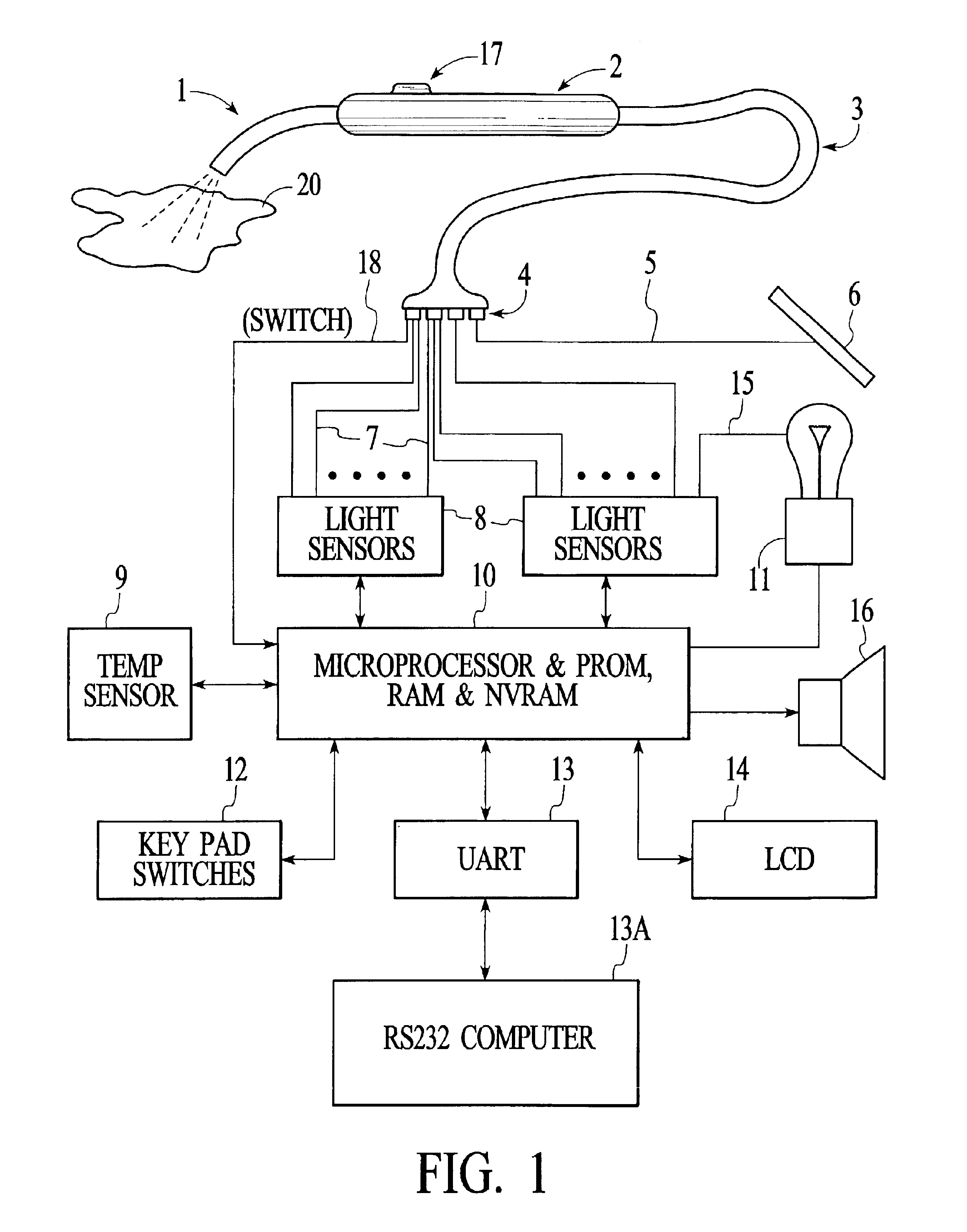
Fluorescence measuring device for gemstones
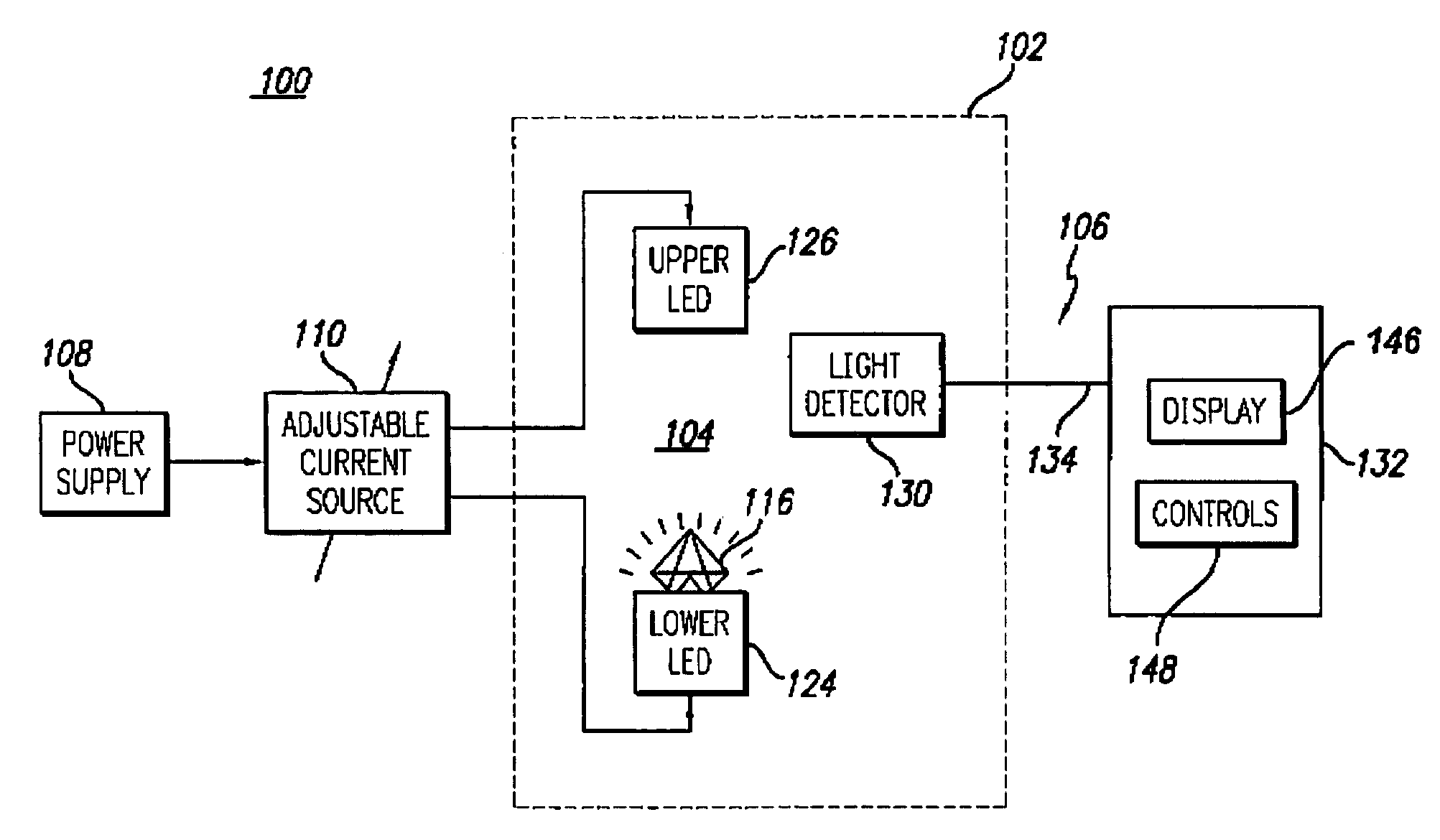
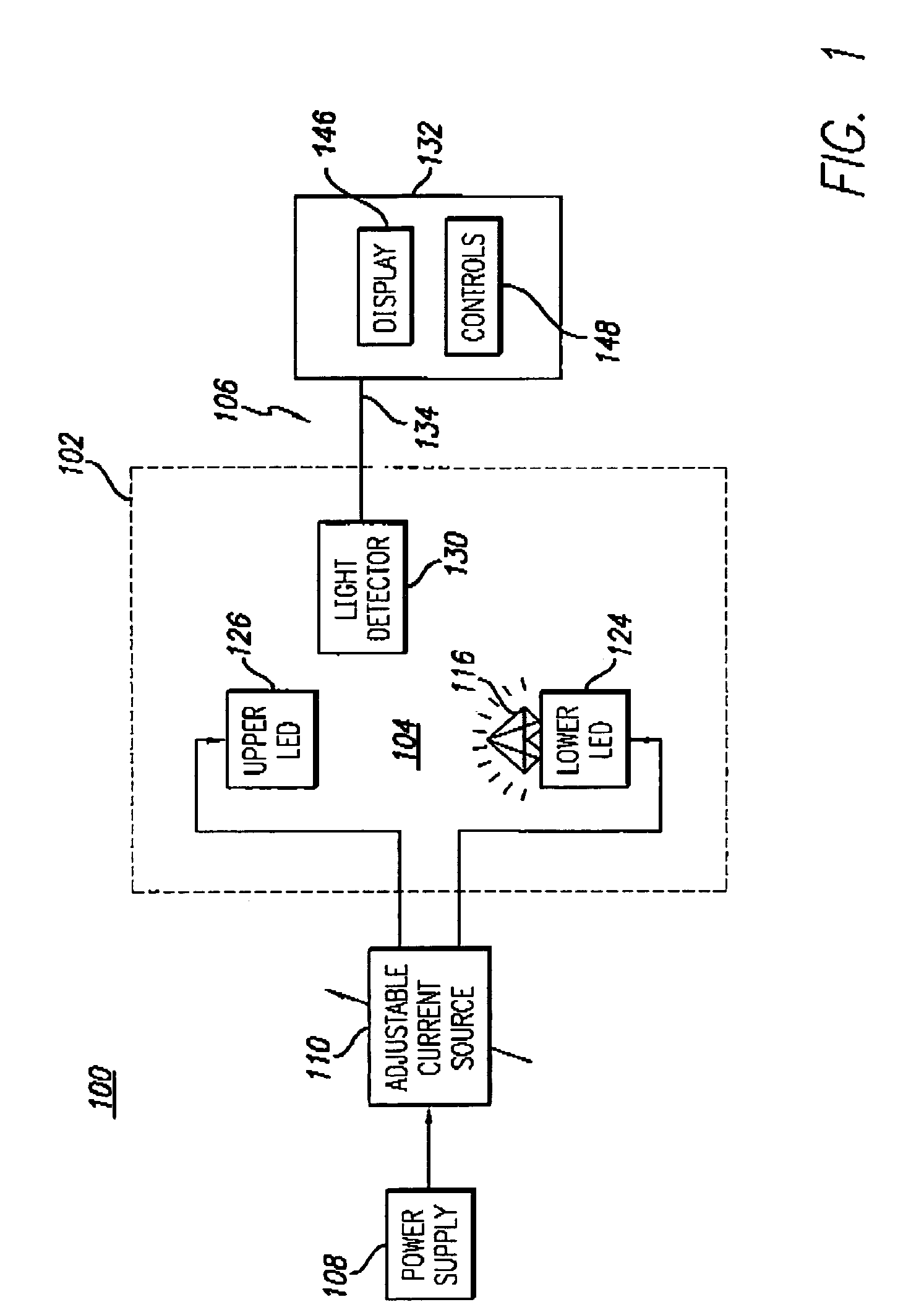
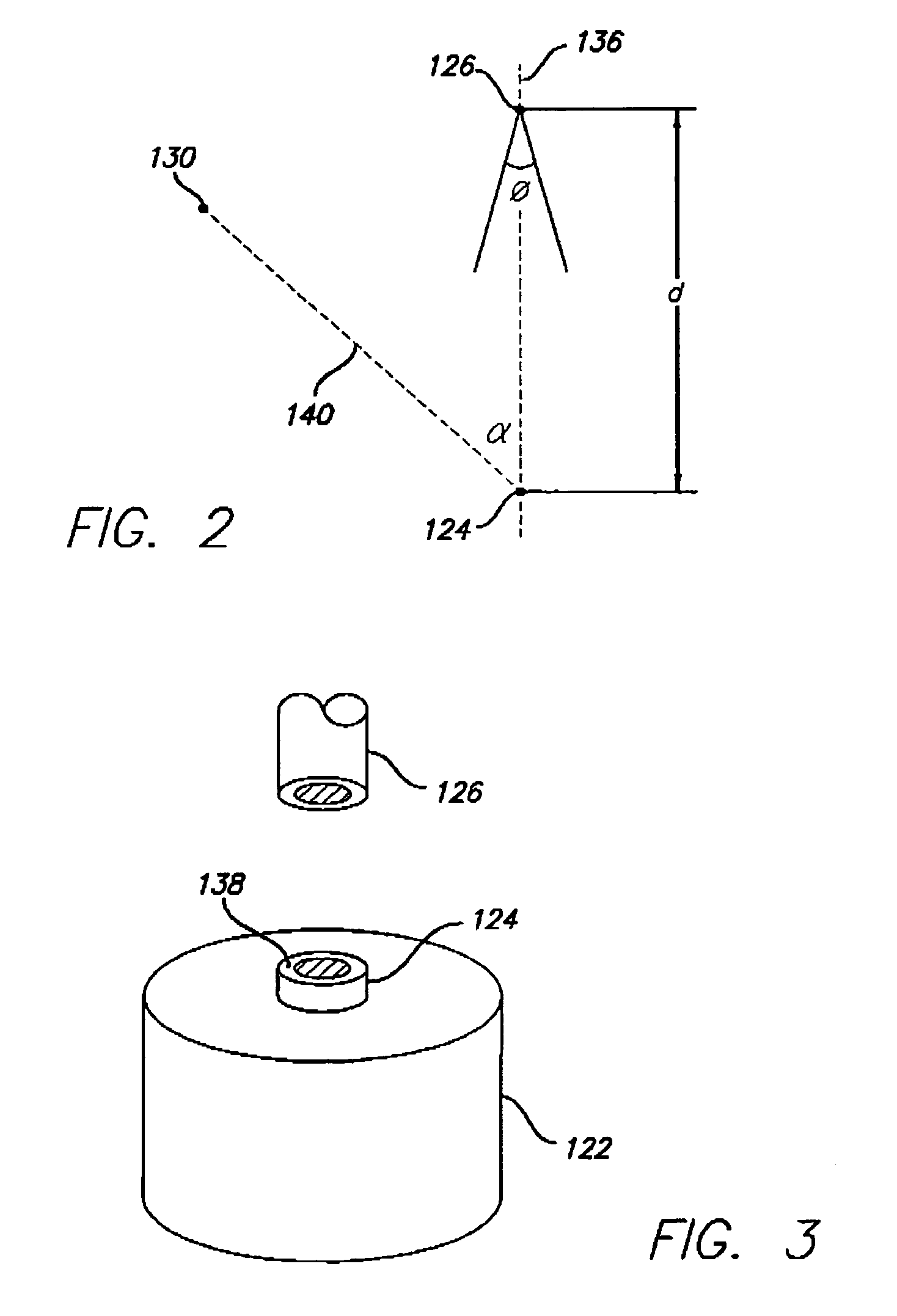
A gemstone fluorescence measuring device according to the invention generally includes an ultraviolet (“UV”) emission chamber, a UV radiation source, and a light meter assembly. The UV radiation source includes an upper light emitting diode (“LED”) and a lower LED that radiate a gemstone under test from both above and below the gemstone. The UV radiation source provides both trans-radiation and direct radiation to the gemstone, and the UV radiation source has an adjustable intensity, thus facilitating calibration of the fluorescence measuring device. The light meter assembly includes a light detector that detects the visible light emitted from the gemstone under test in response to the UV radiation. The light detector is configured to simulate the spectral characteristics of the human eye. The fluorescence measuring device converts the measured visible light into a numerical lux reading, which can then be converted into a fluorescence grade for the gemstone under test.
Owner:GEMOLOGICAL INST OF AMERICA INC
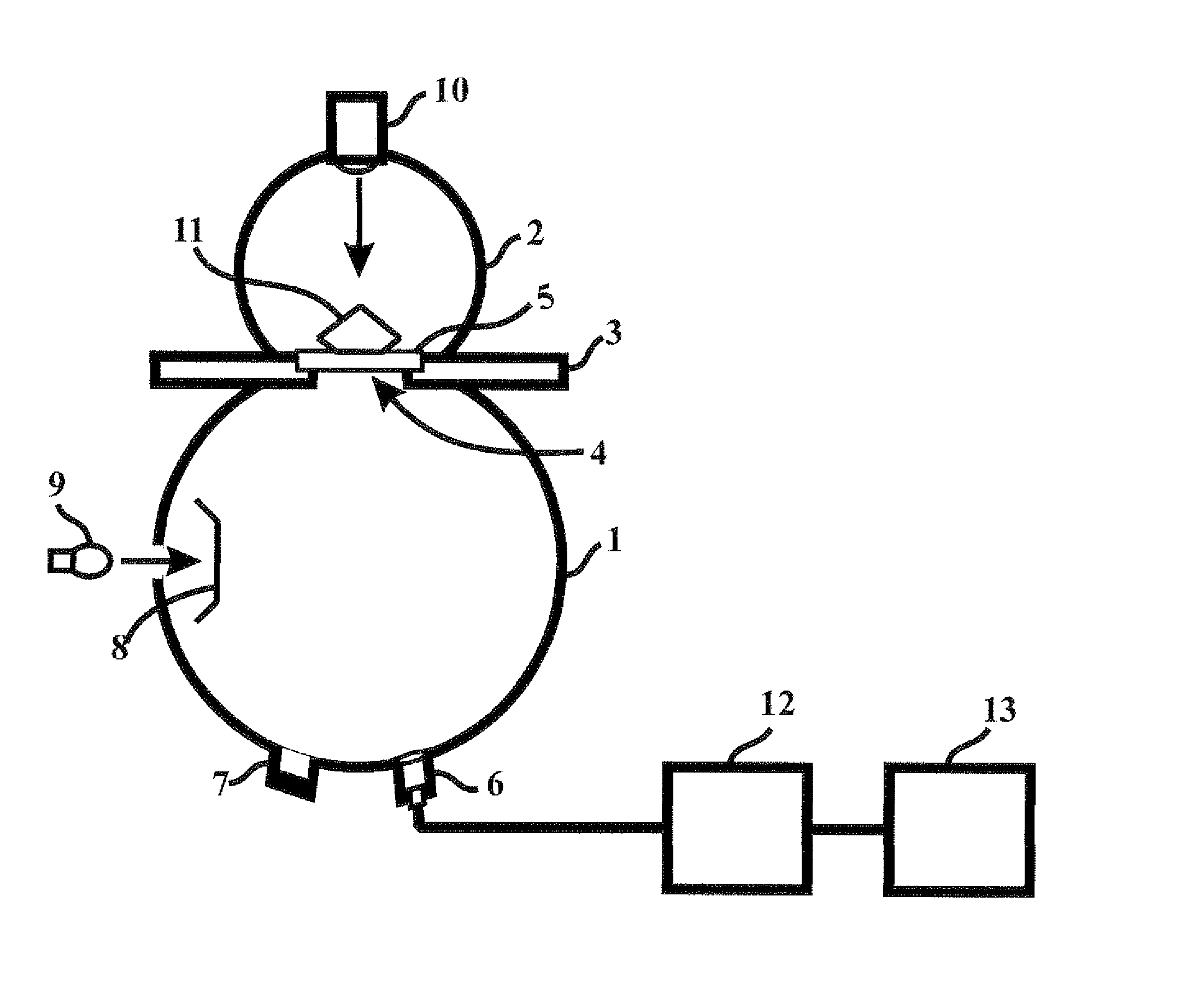
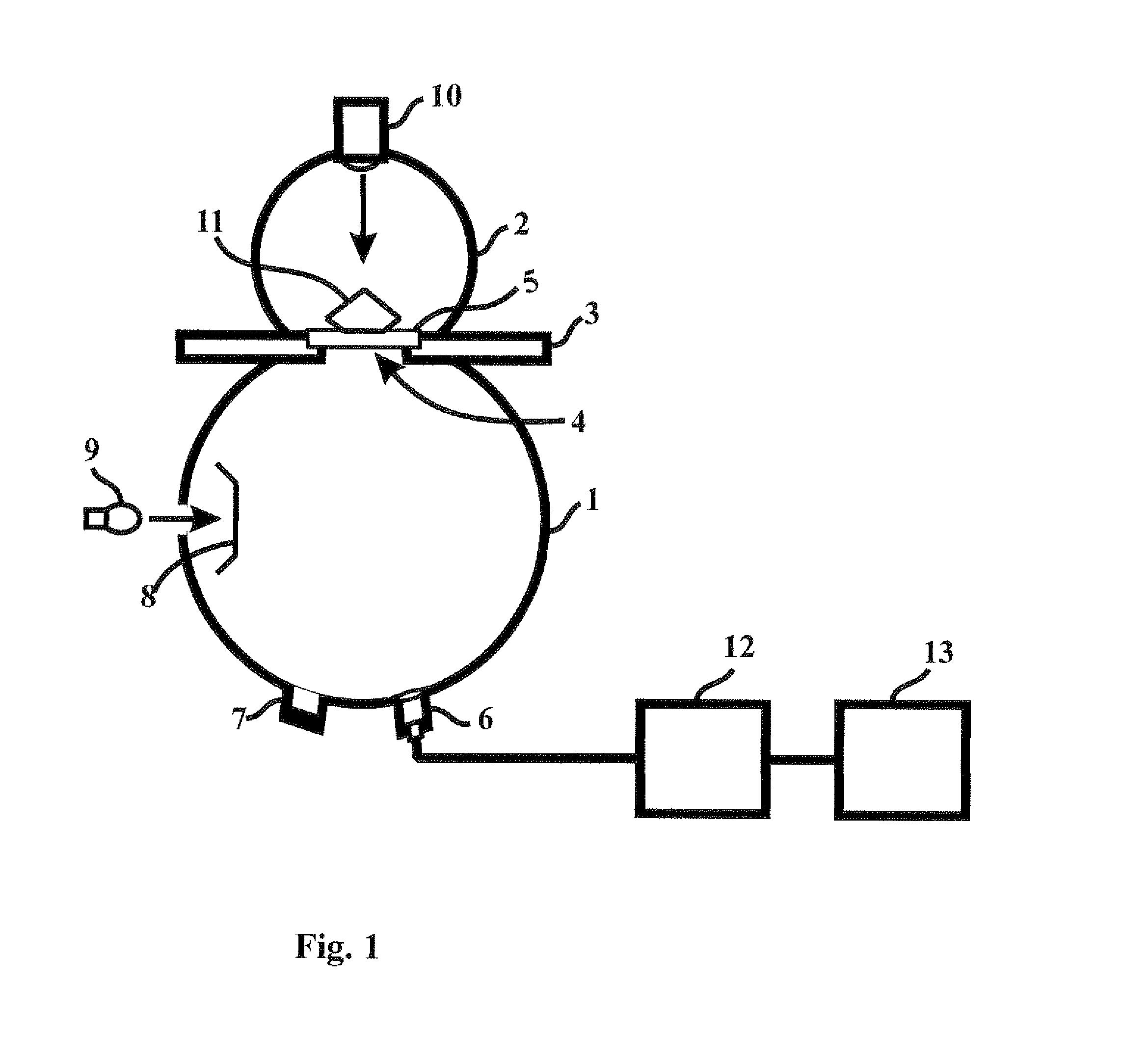
Apparatus and method for fluorescence spectral and color measurements of diamonds, gemstones and the like
InactiveUS8878145B1Accurate measurementReduce manufacturing costInvestigating jewelsFluorescence/phosphorescenceUltravioletUltraviolet radiation
An apparatus and method for fluorescence spectral and color measurements of diamonds, gemstones and the like. The apparatus comprises a spectrometer, and computer and a dual integrating sphere measurement arrangement comprising a measurement integrating sphere, a sample integrating sphere, a sample platform, a lens system, a baffle, an ultraviolet radiation source on the top of the sample integrating sphere, and another light source attached to the measurement integrating sphere. The sample on the sample platform is radiated by the ultraviolet radiation source on the top of the measurement integrating sphere. The sample emits fluorescent light into the measurement integrating sphere, and the fluorescent light is received by the lens system. The spectrometer separates the fluorescent light into spectral signals, and the computer calculates the fluorescence spectrum and colorimetric data.
Owner:LIU YAN
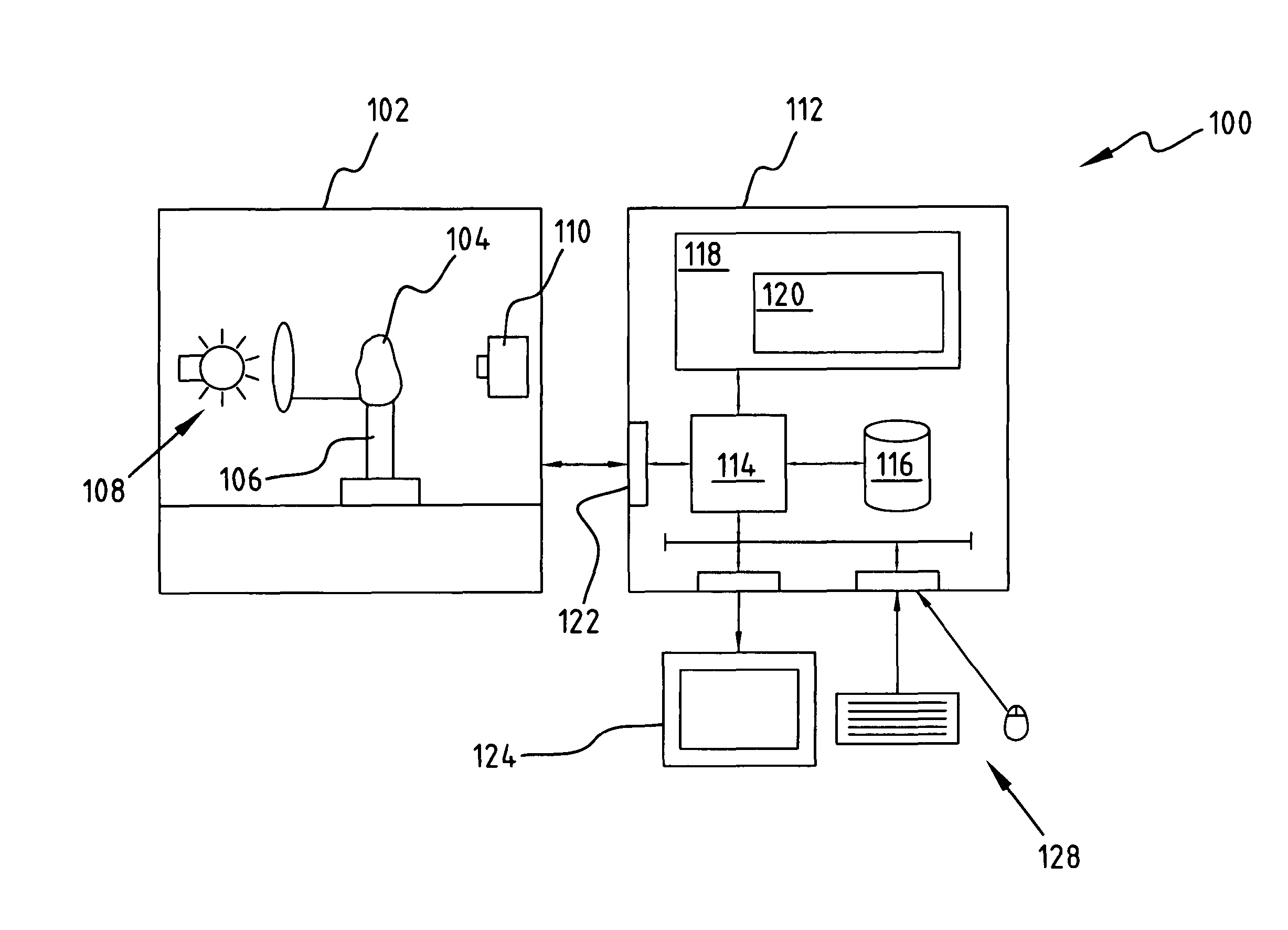
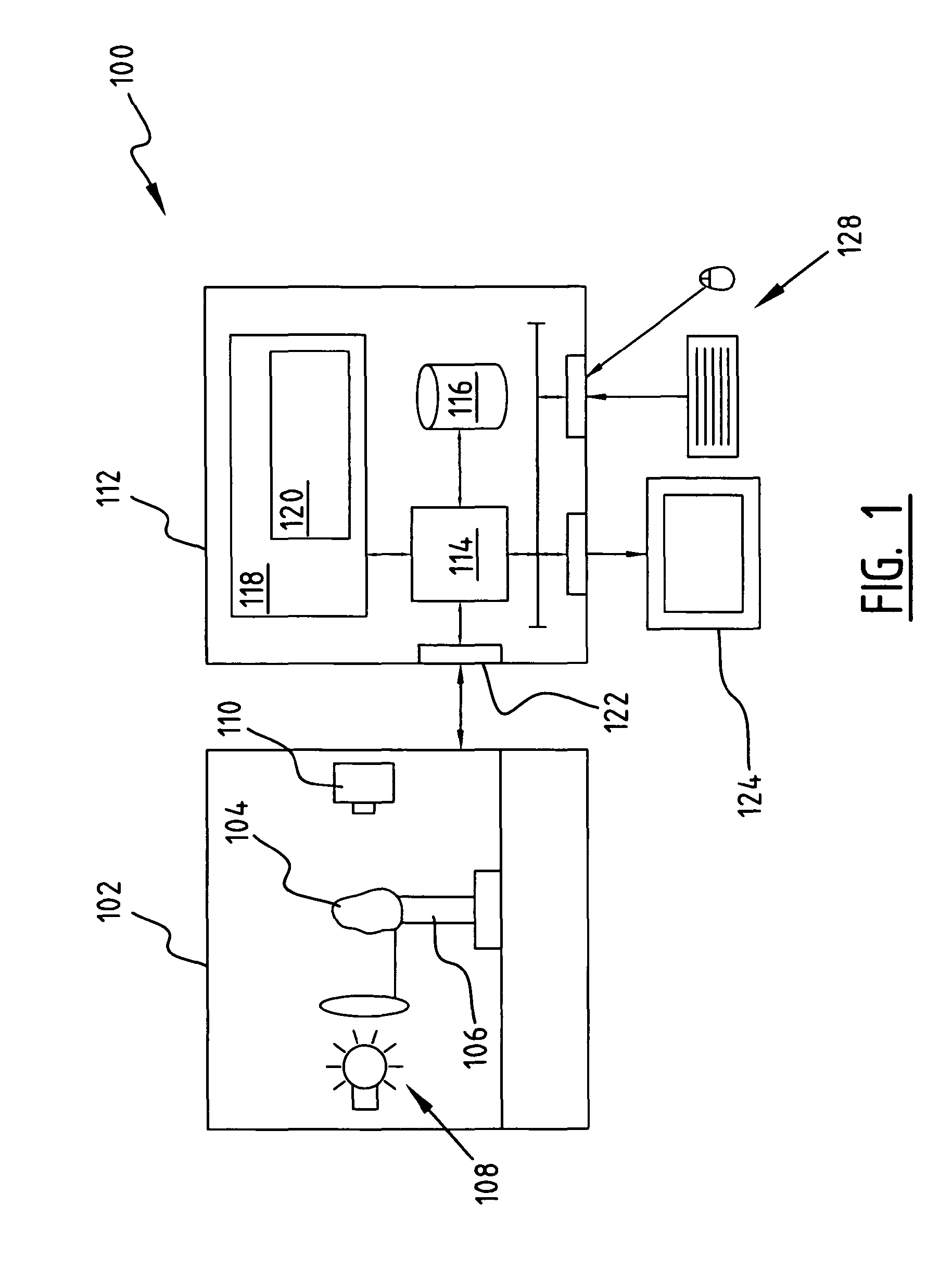
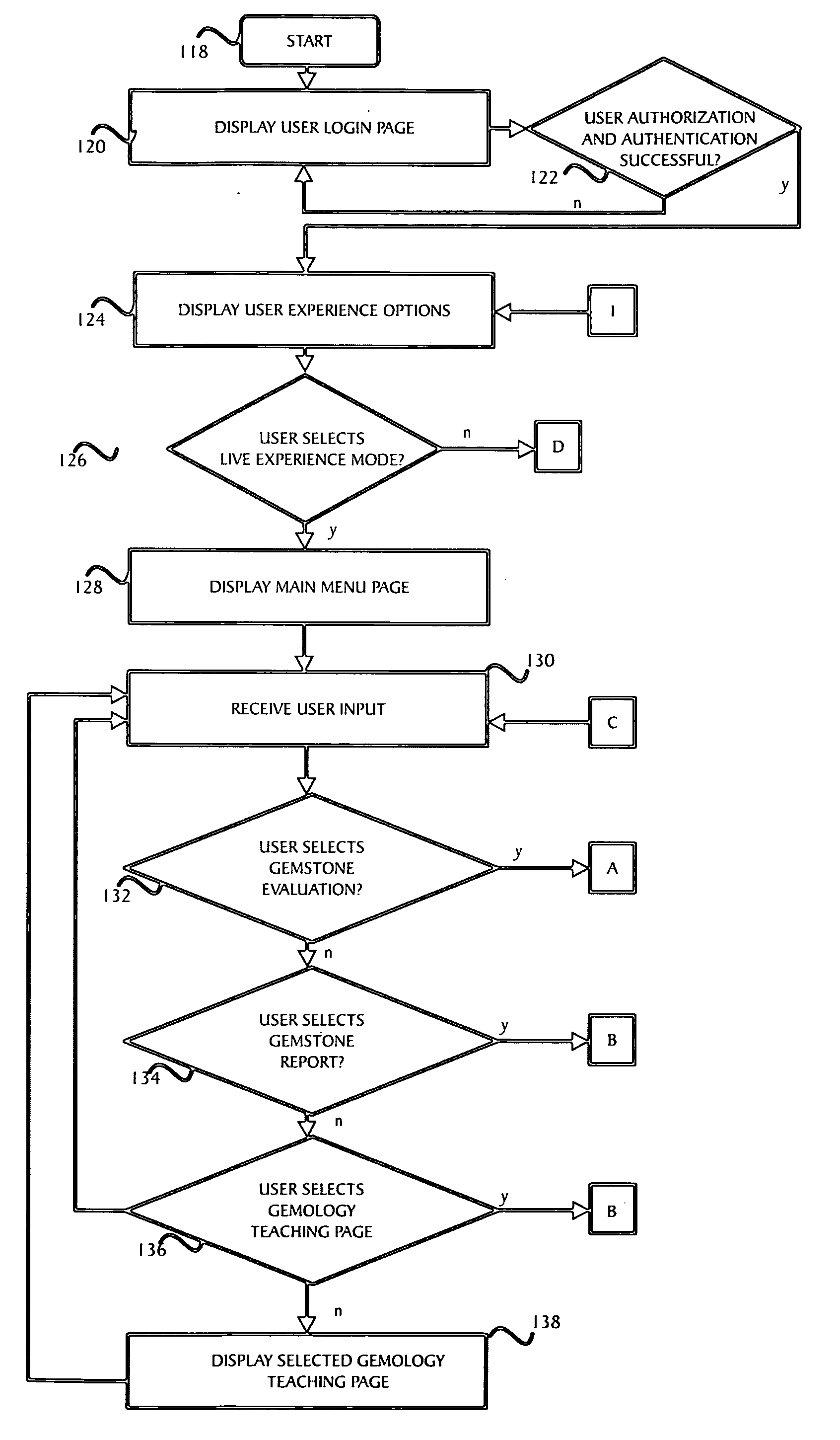
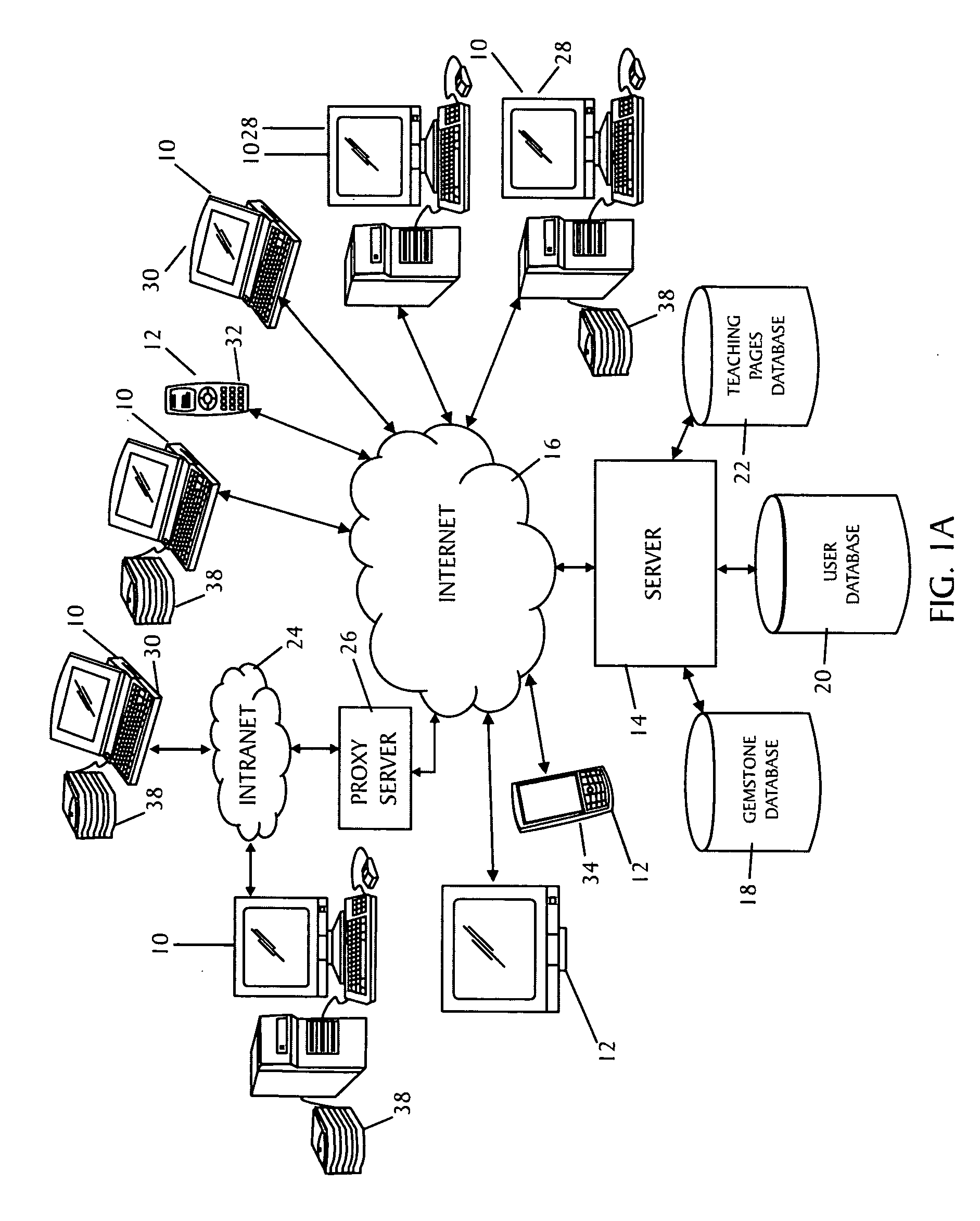
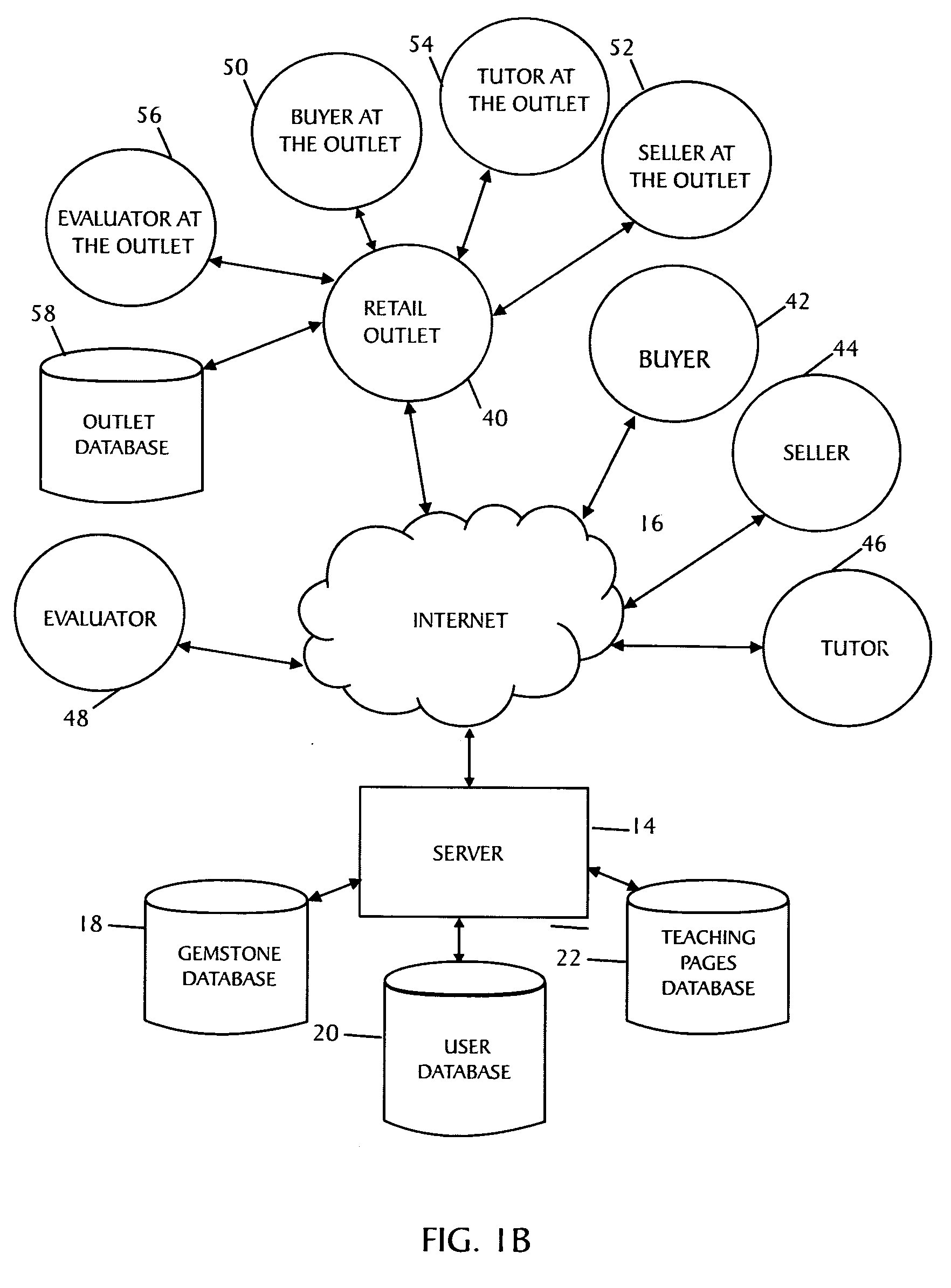
Apparatus, a method, and a system for gemstone evaluation and gemology tutoring over the internet
A method of evaluating a gemstone over the internet is described that includes providing a server computer, providing access to an internet enabled device that is connectable to an apparatus capable of capturing an image of a gemstone, connecting the device to a second device through the server, and transmitting data over the internet of a received image of the gemstone to determine one or more optical properties of the gemstoneThe method includes examining and purchasing a diamond or gemstone online, examining a diamond online and purchasing it at a retail establishment, conferencing with the seller and / or other persons online to examine the diamond online, and purchasing it online or at a retail establishment.A system for gemstone evaluation over the internet is also included. The system comprises a server computer having a client device connectable to the internet for transmitting gemstone images and evaluating data, means for processing an image of a gemstone received from the apparatus to determine one or more optical properties of the gemstone, and means for presenting, on the display, the received image of the gemstone and representations of the determined one or more optical properties.
Owner:SARIN COLOR TECH
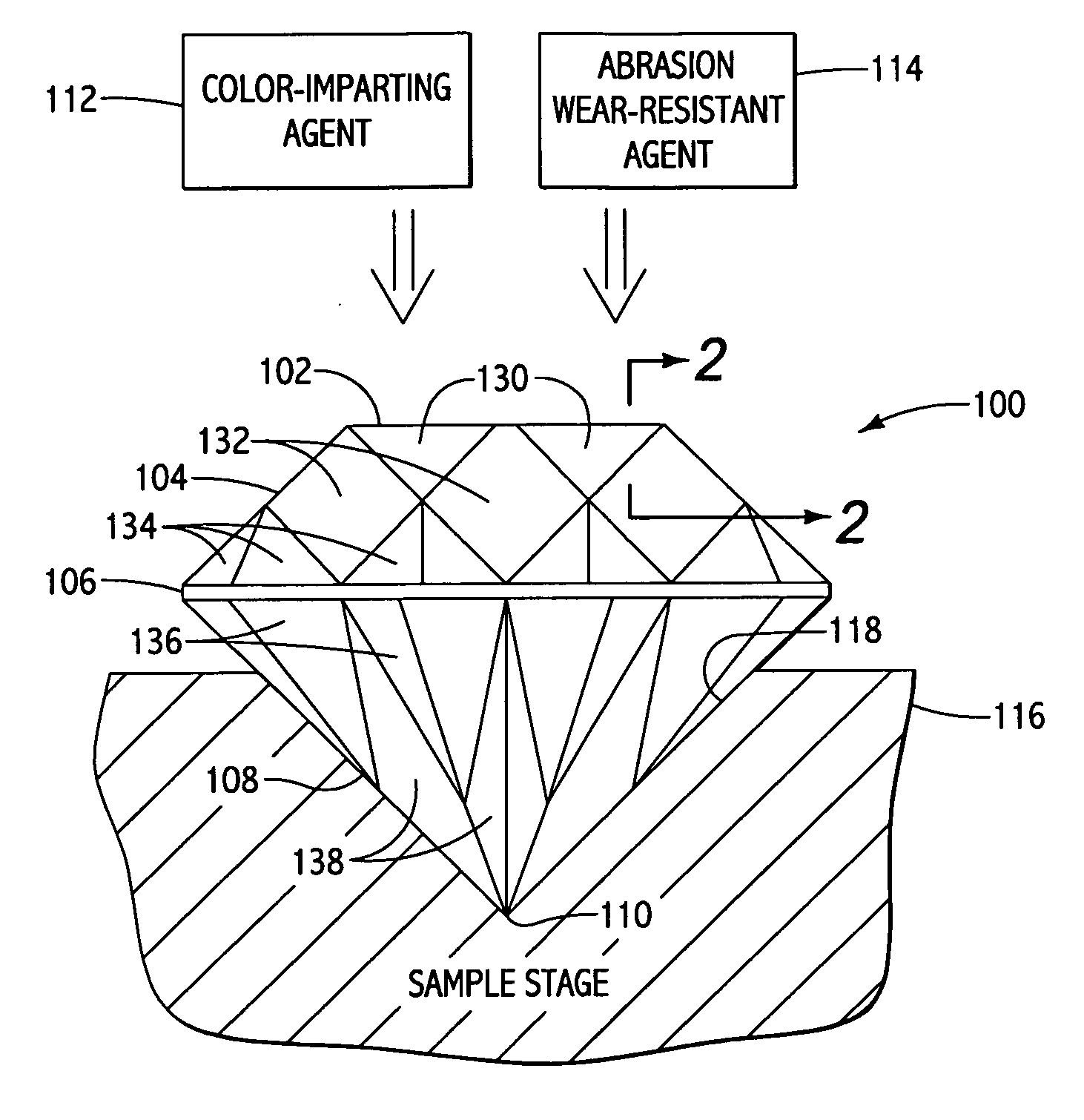
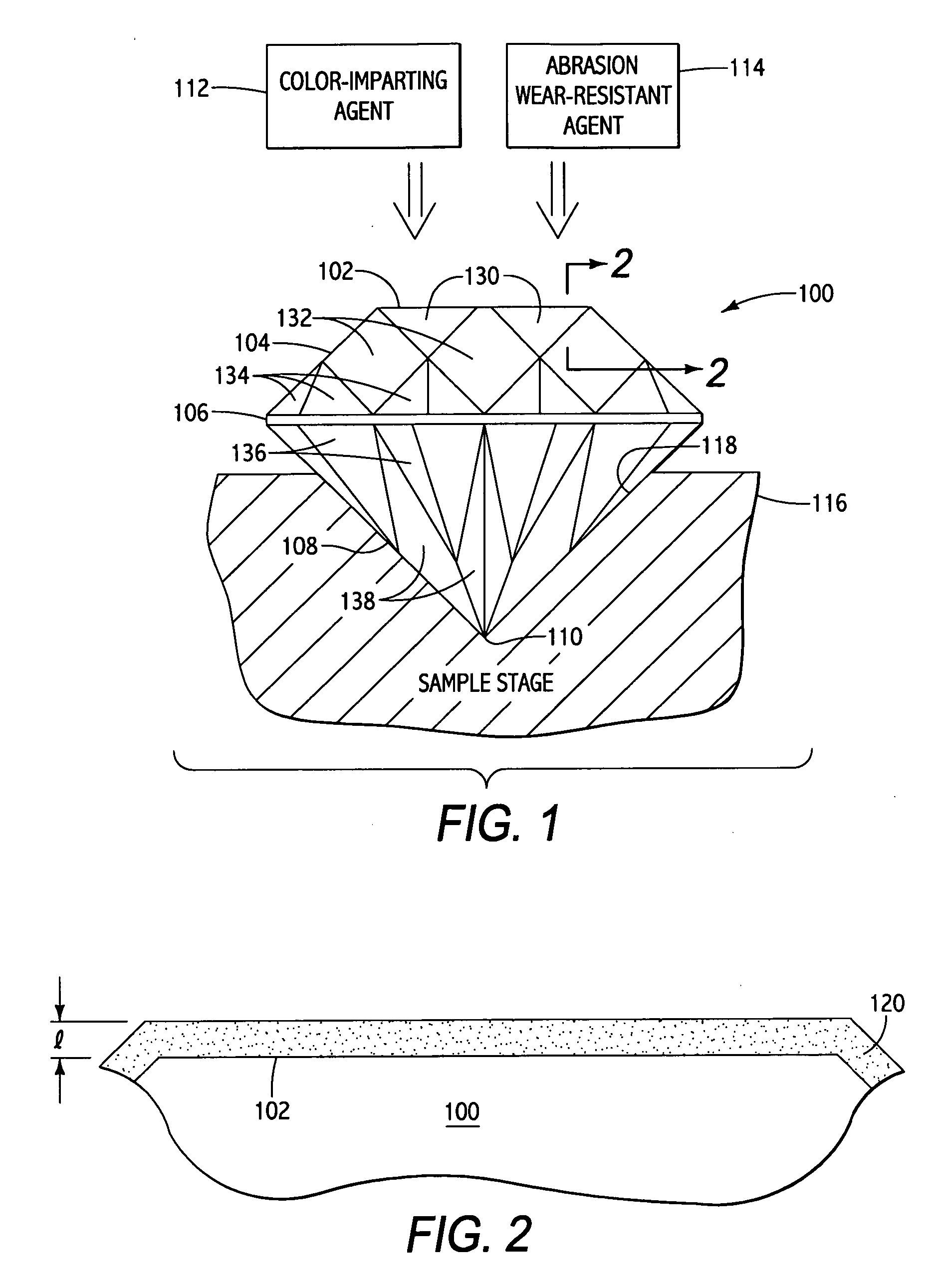
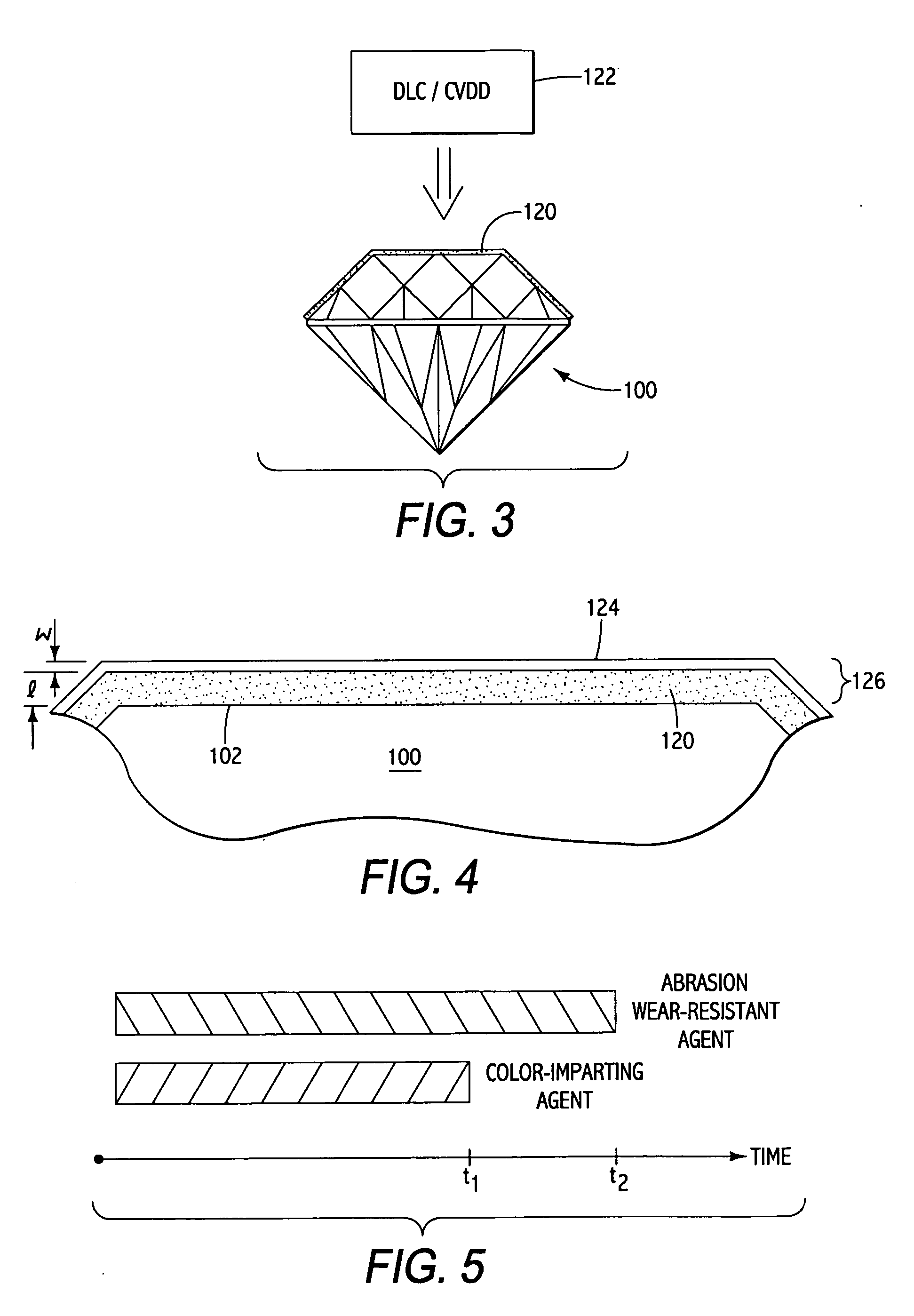
Abrasion resistant coatings with color component for gemstones and such
ActiveUS20060182883A1Provide wear resistancePretreated surfacesLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingDiamond-like carbonInterference phenomenon
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided methods for imparting abrasion wear resistant color to “gemstones” by providing an integrated coating consisting of the color imparting agent and the abrasion wear resistant agent. The color imparting agent may provide the perception of color via interference phenomena or via bulk absorption phenomena. Abrasion wear resistance may be provided by integrating any of the materials such as DLC (diamond-like carbon), CVD diamond (CVDD), alumina, polymer-based materials, nitrides and carbonitrides. Abrasion wear resistant properties of DLC or CVDD may be further improved, in addition to improvement of other mechanical properties and inducing hydrophobicity, by incorporating certain elements into the deposited film.
Owner:ARYAMOND SINGAPORE PTE LTD
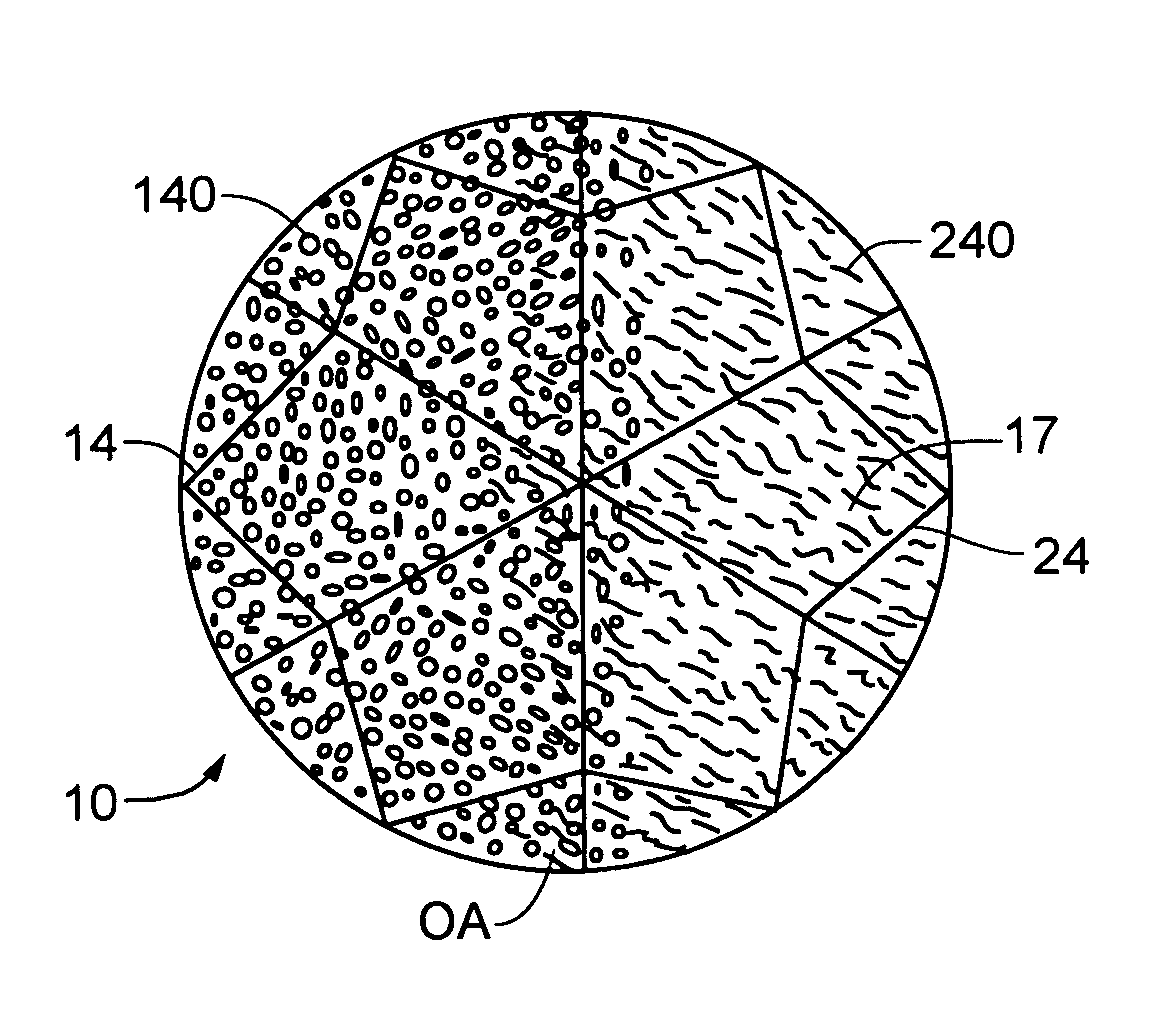
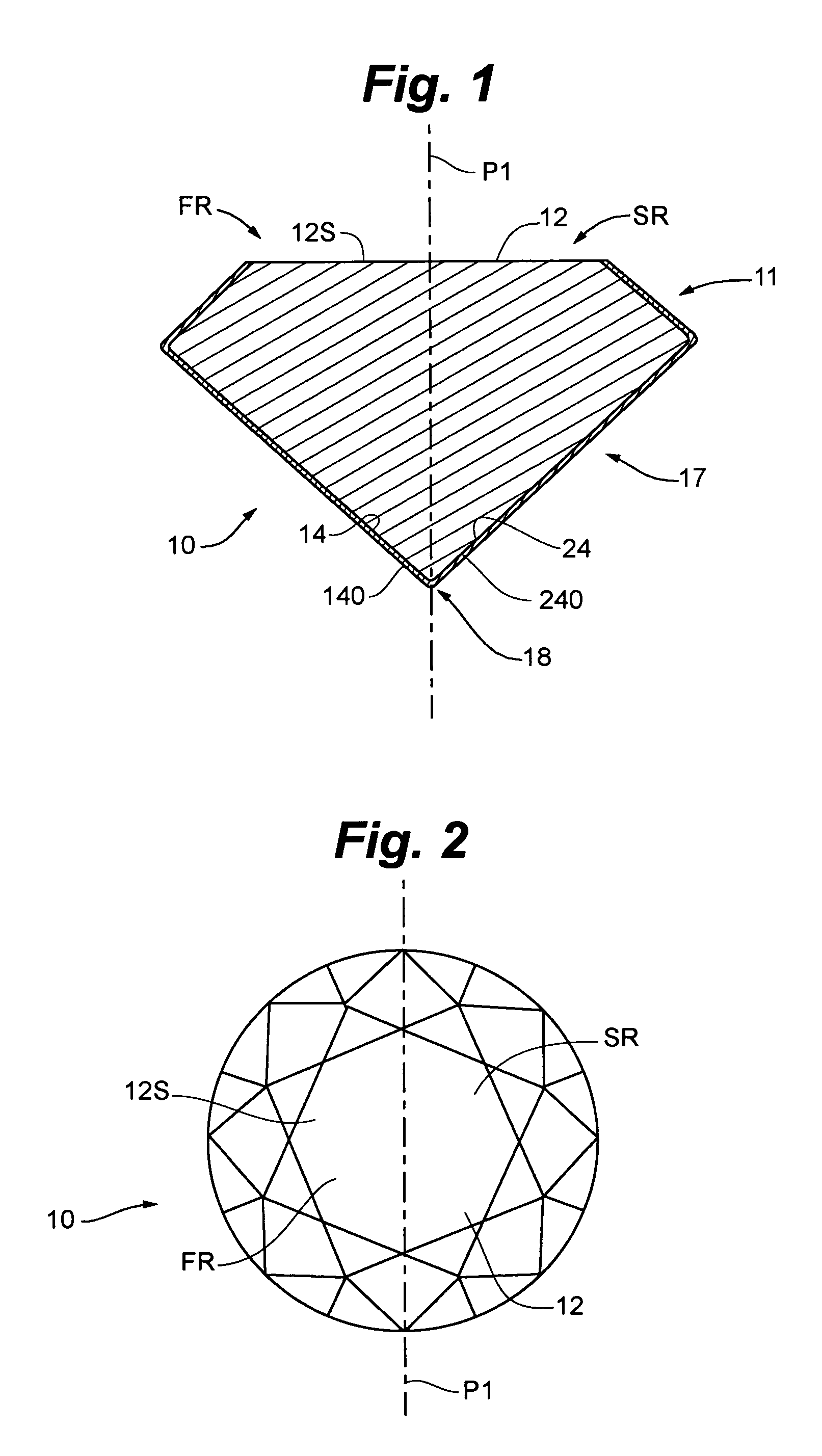
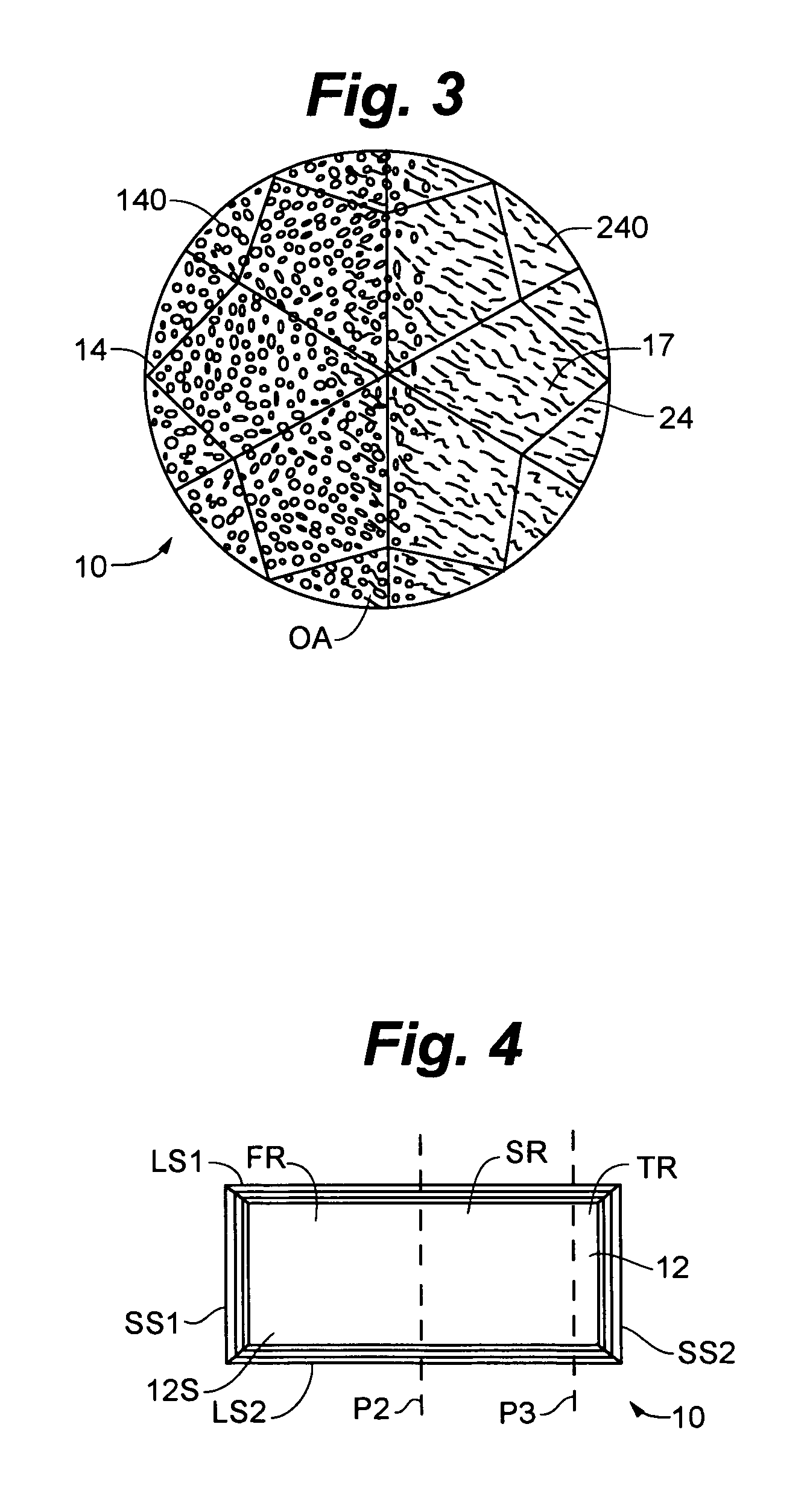
Multi-color gemstones and gemstone coating deposition technology
The invention provides a gemstone or a decorative object having at least one surface bearing a thin film coating. In some embodiments, there is provided a gemstone having an appearance characterized by at least two different color zones, where such two zones are of different colors. In other embodiments, two different areas of a single (e.g., integral, one-piece) gemstone carry coatings of different composition, and the resulting appearance of the gemstone is characterized by the stone exhibiting substantially a single uniform body color that is different than the body color the stone would exhibit if it were coated only with one or the other of the coatings. Also provided are new deposition techniques.
Owner:AZOTIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com