Patents
Literature
80 results about "Specular component" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
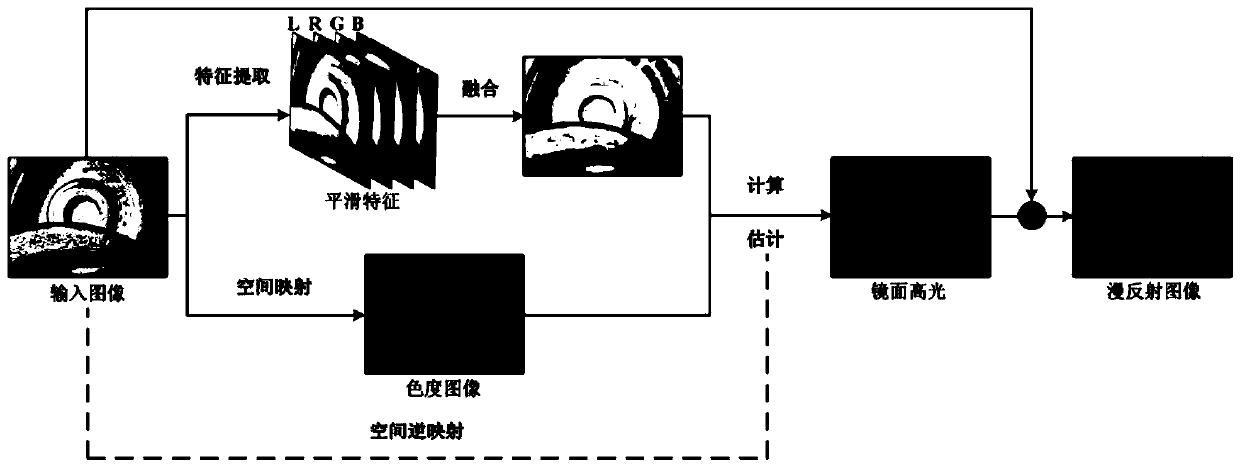
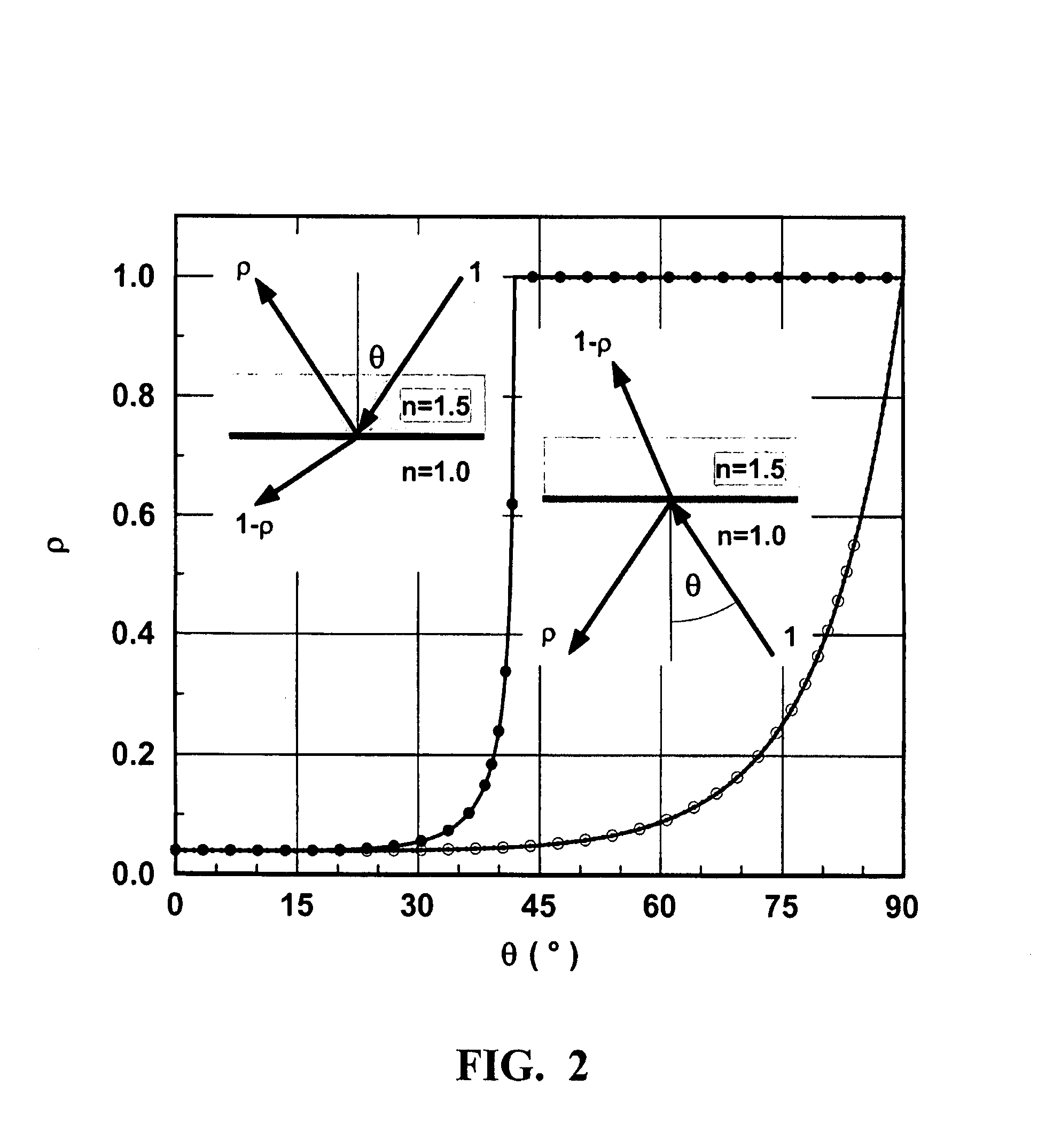
Specular Component The specular component is what makes a surface look shiny. ... This means that the specular component is usually a different color to the diffuse component. Most specular surfaces don't absorb anything, they just reflect all of the light, which means the specular color would be white.
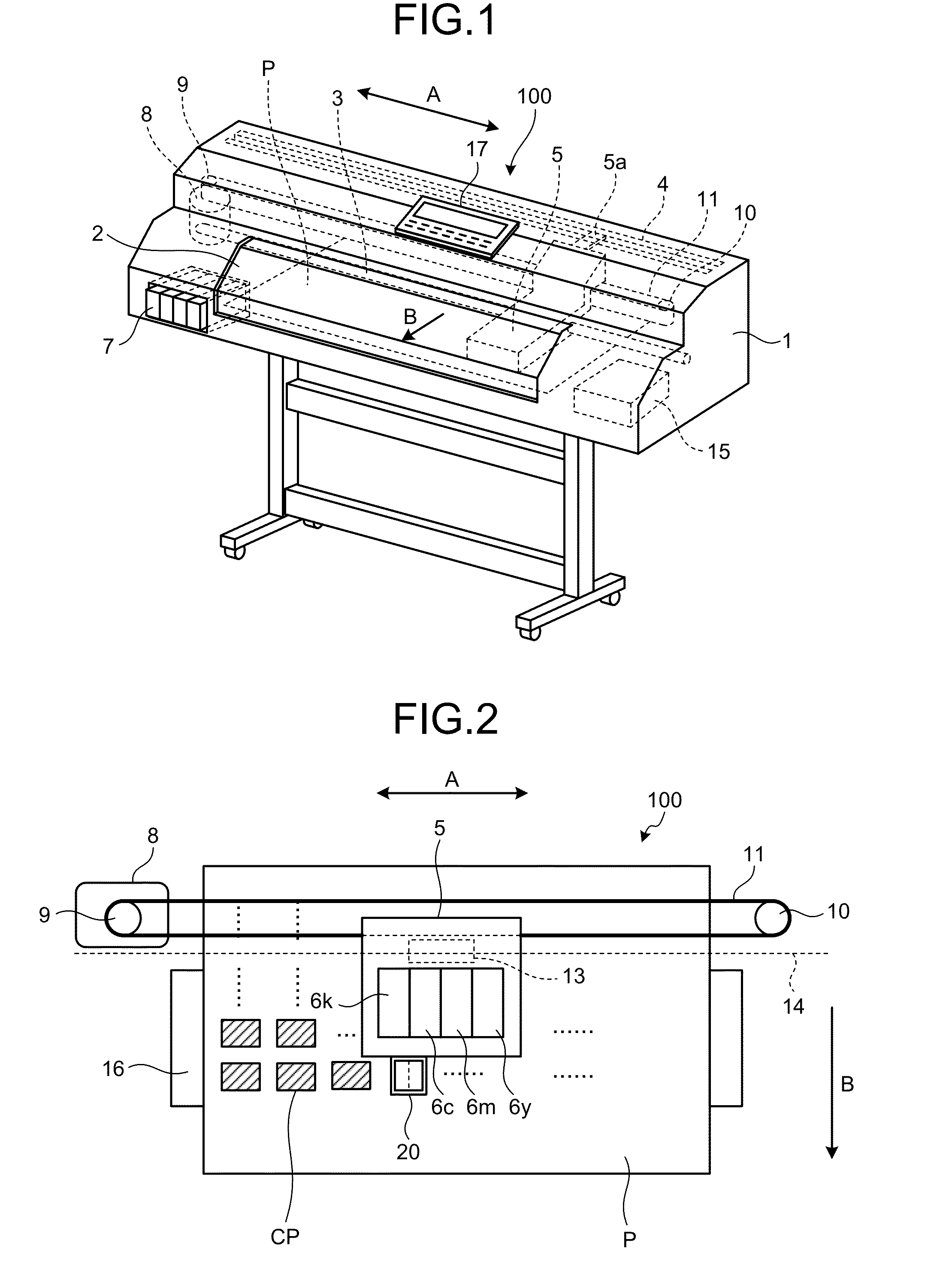
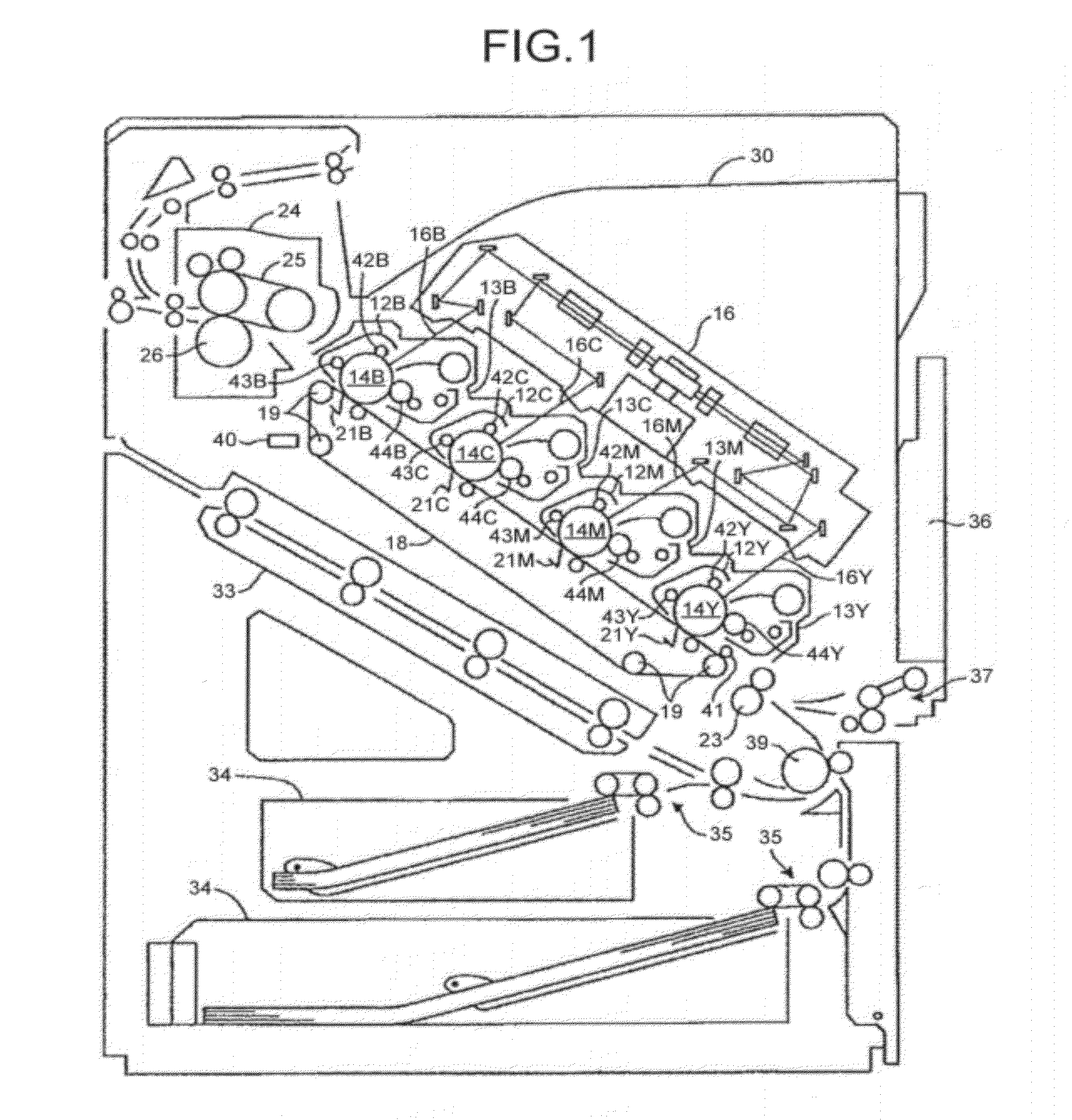
System for early detection of dental caries
ActiveUS20080170764A1Simple technologyDental toolsCharacter and pattern recognitionCementum cariesComputer vision
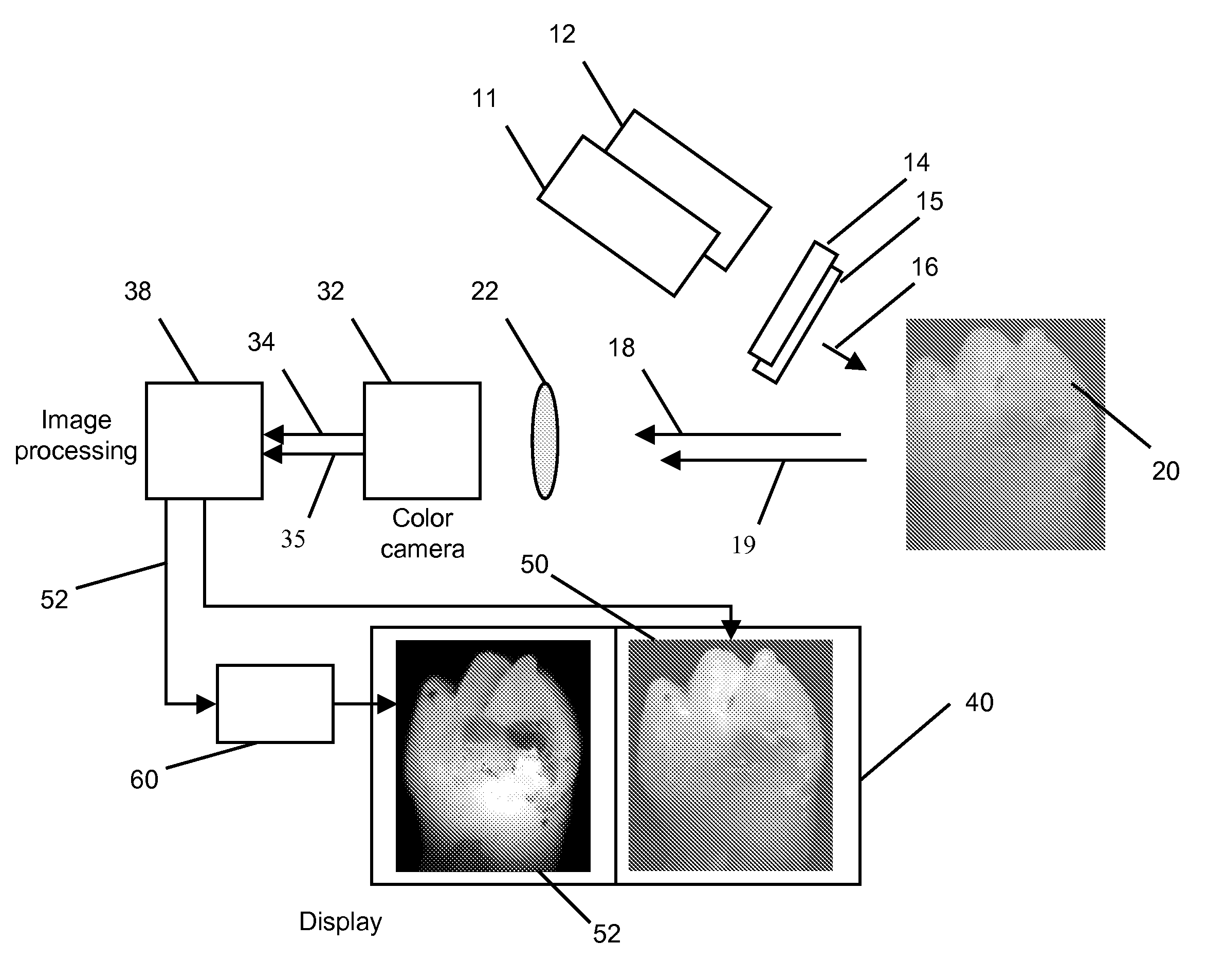
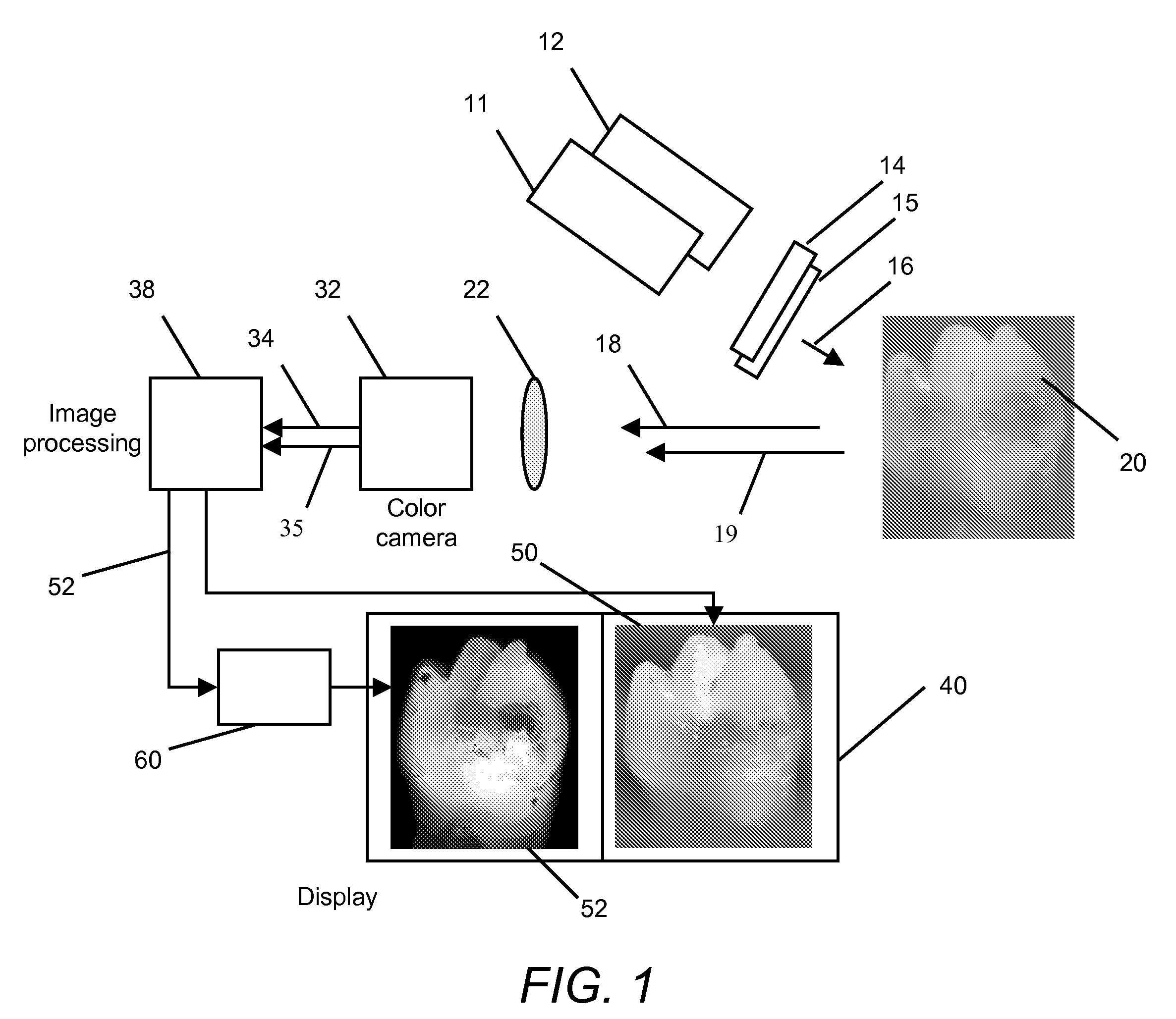
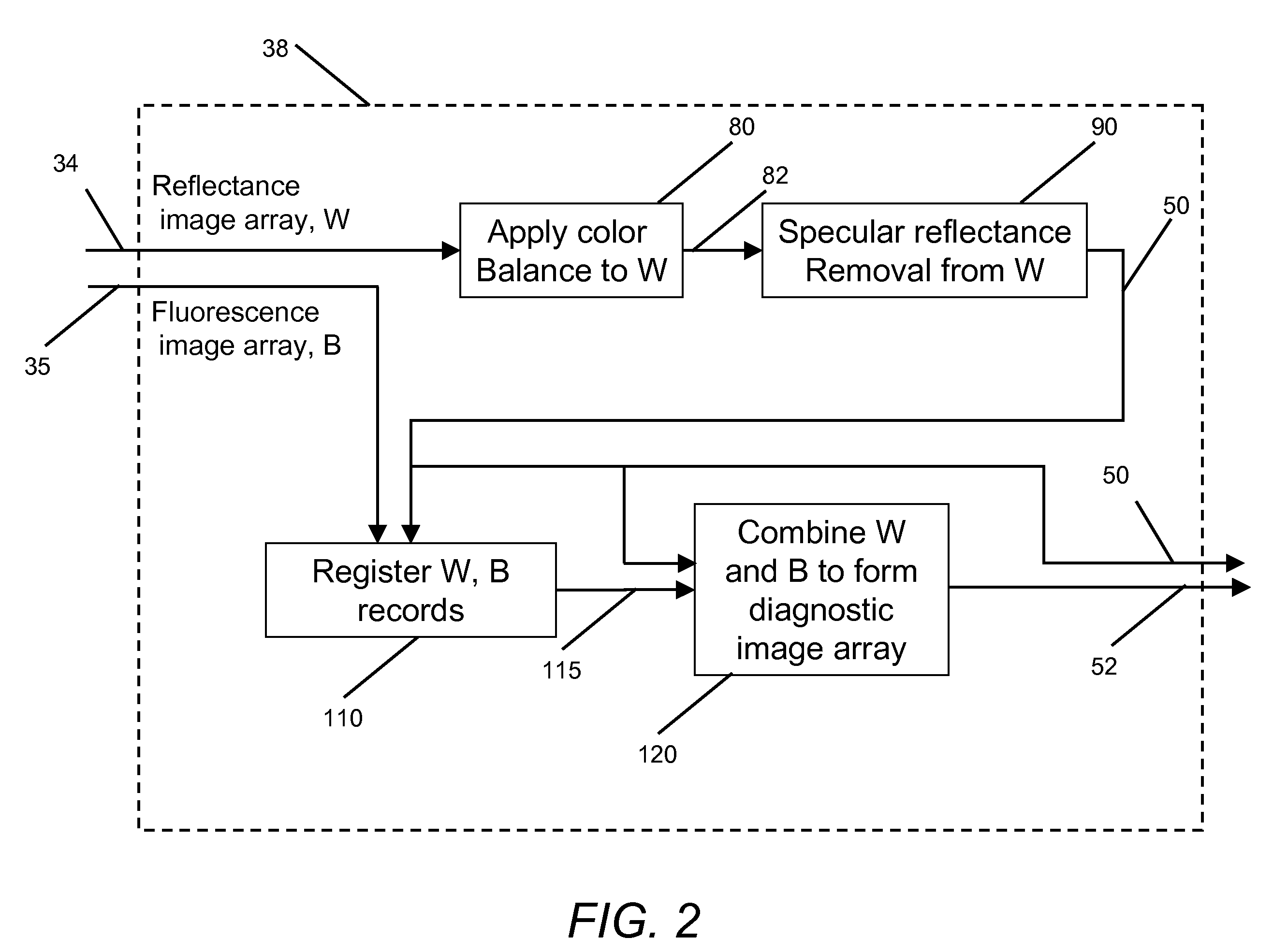
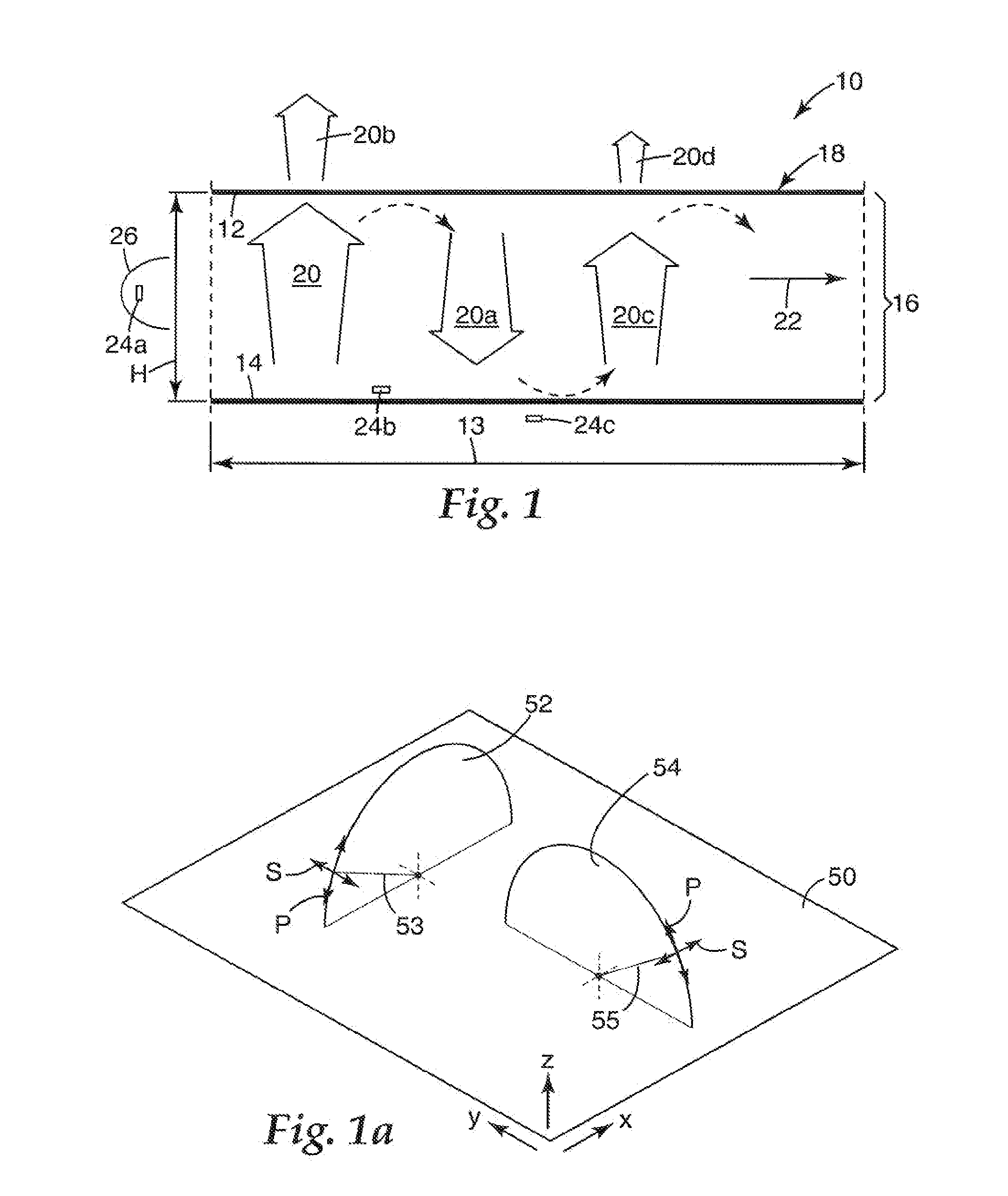
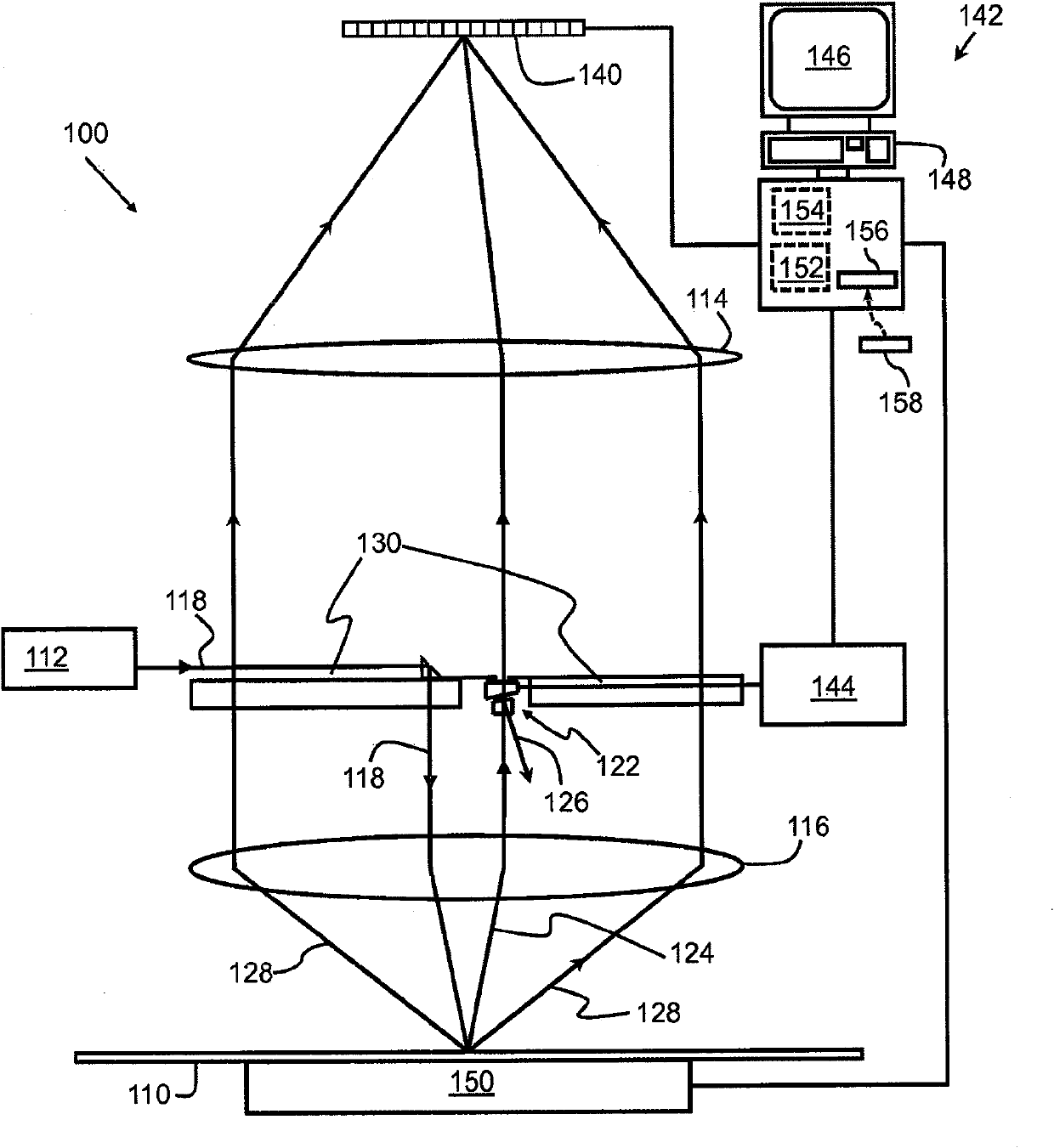
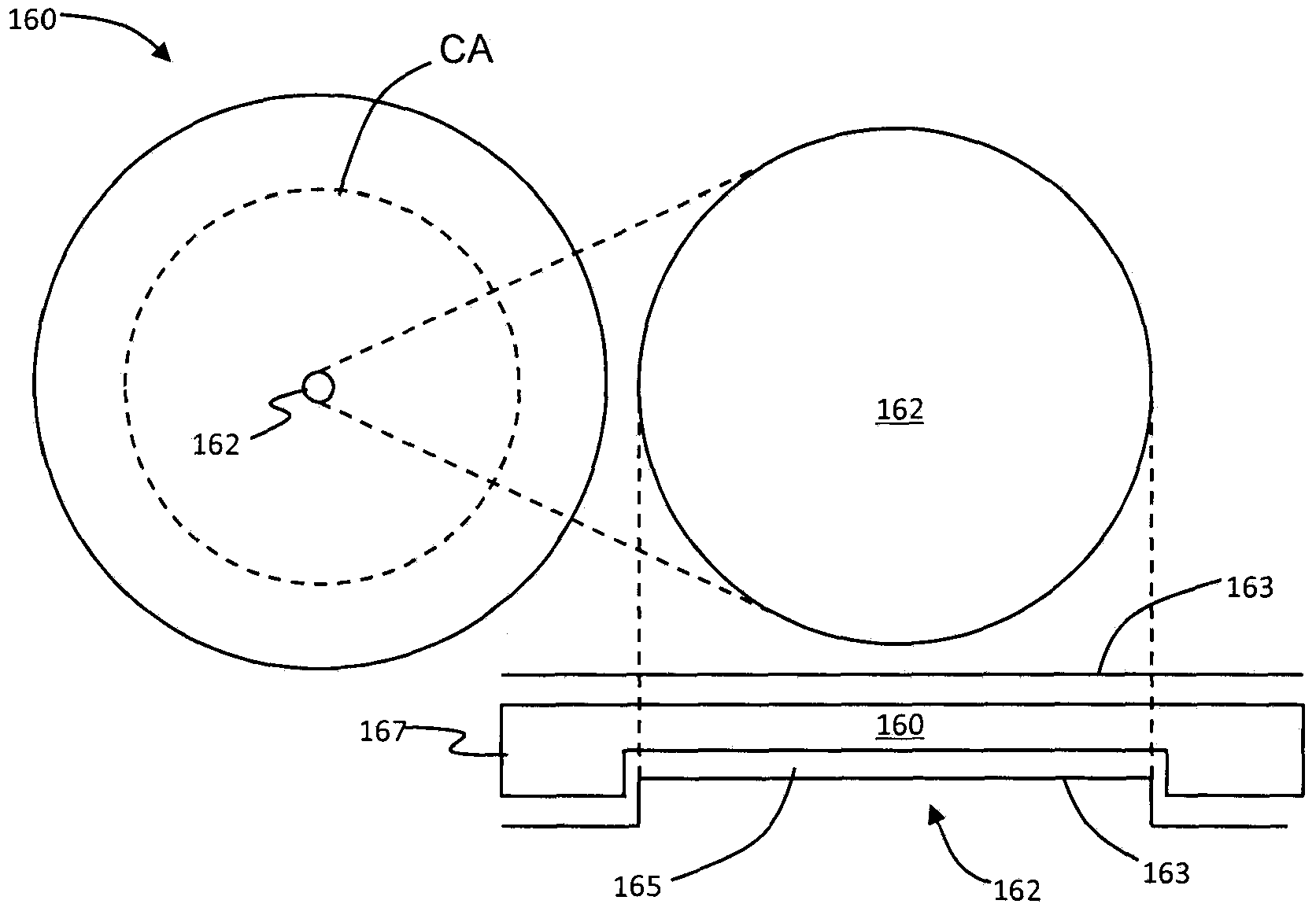
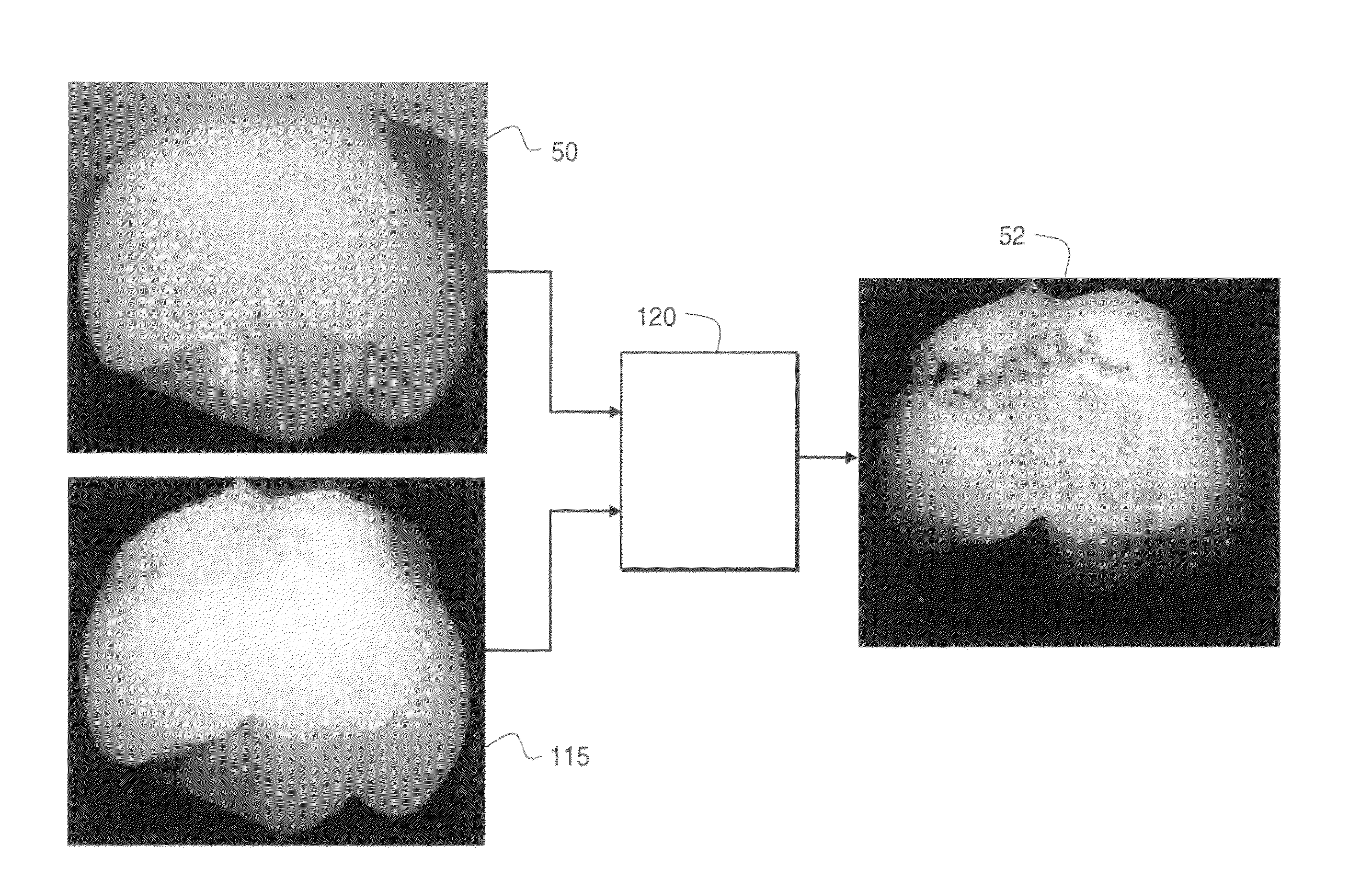
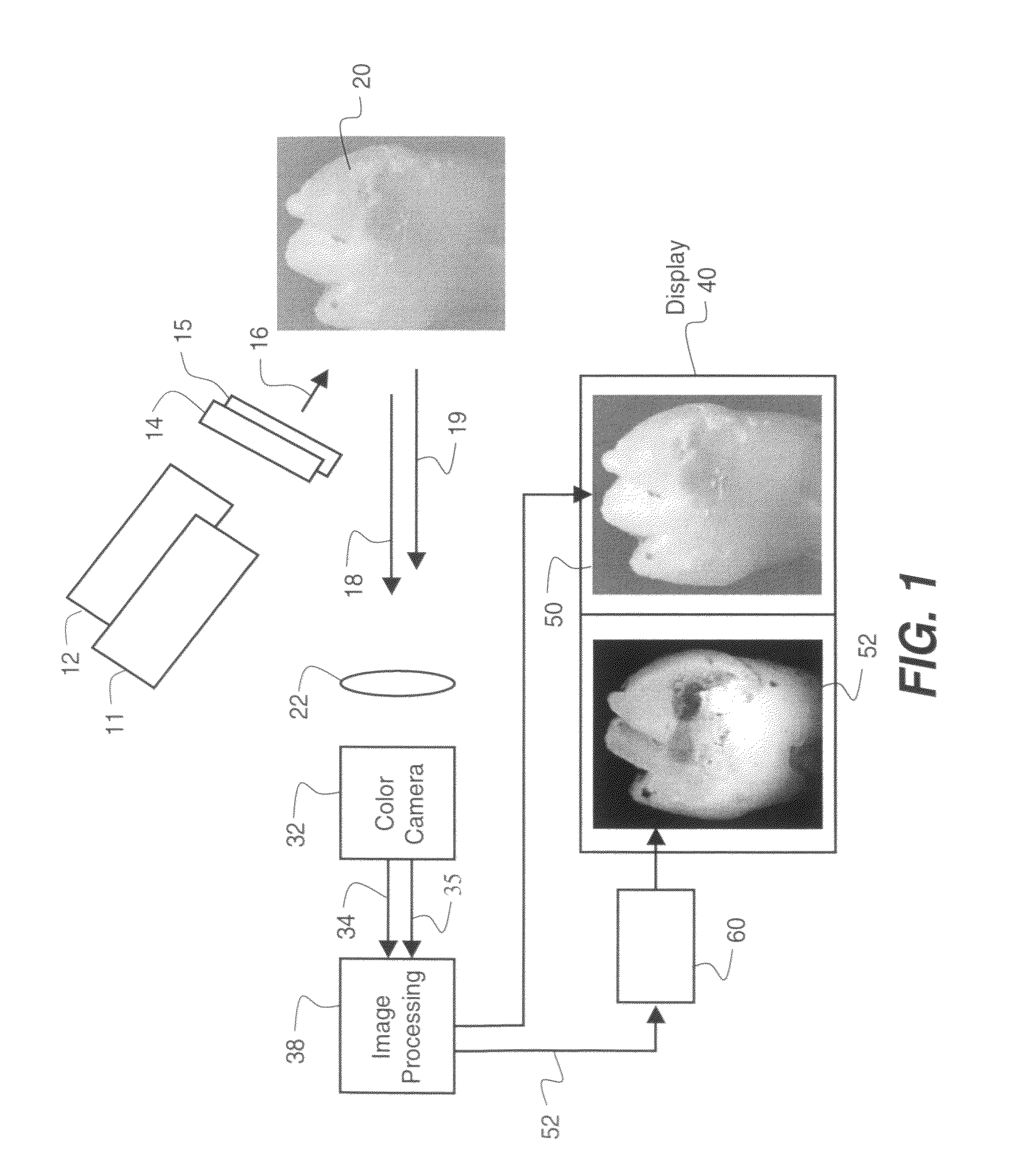
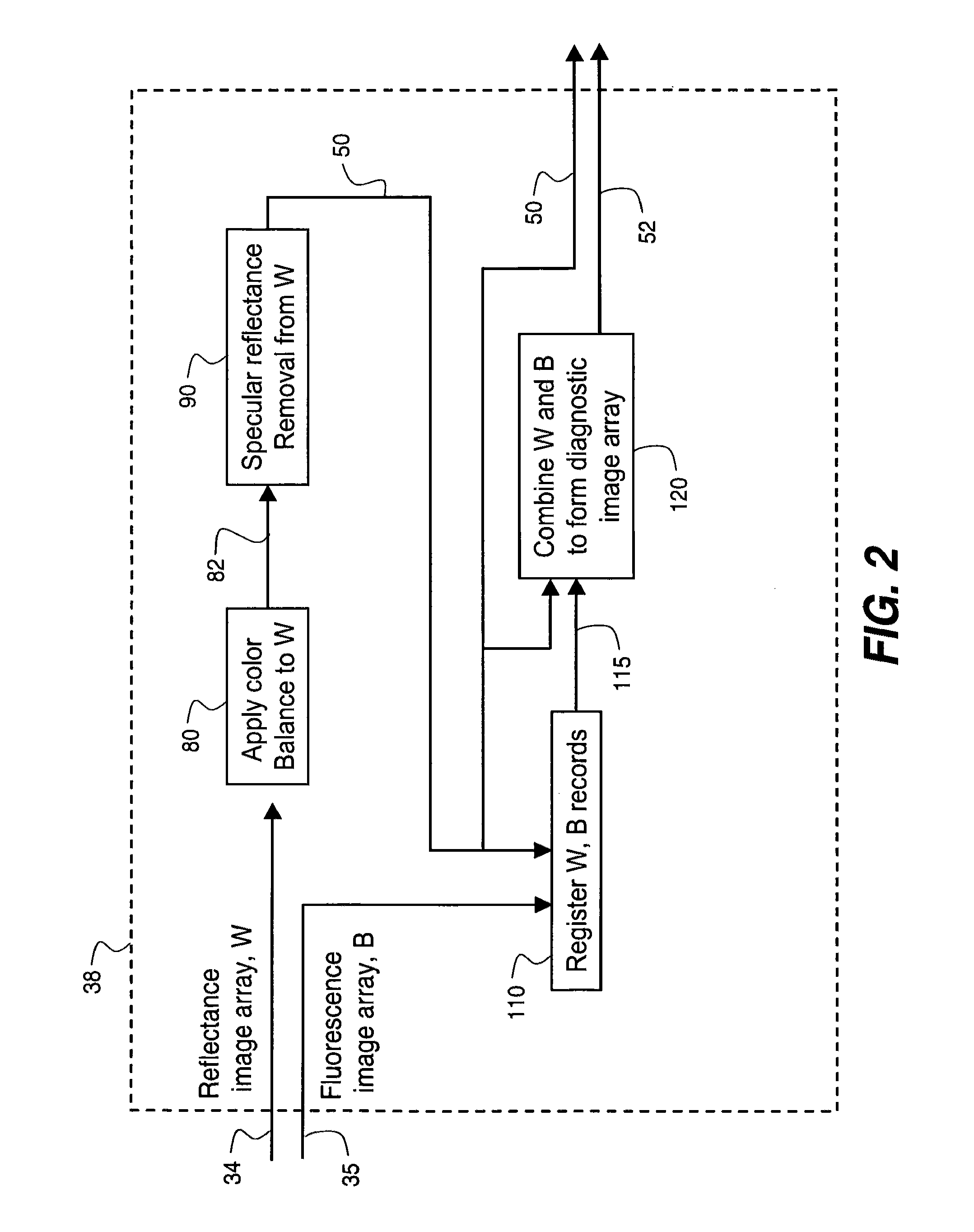
A method is disclosed for processing of images to detect dental caries, that includes the following steps. Directing incident light (16) toward a tooth (20), where this light excites a fluorescent emission from the tooth. Obtaining a fluorescence image (35) from the fluorescent light component (19), and obtaining a reflectance image (34) from the back-scattered light (18) from the tooth. Applying a color balance operation to the reflectance image. Removing the specular reflectance components from the color balanced reflectance image (82) to give a back-scattered reflectance image (50). Registering the fluorescent image with the back-scattered reflectance image. Combining the registered fluorescent image (115) with the back-scattered reflectance image to provide a diagnostic image (52).
Owner:CARESTREAM DENTAL TECH TOPCO LTD
Recycling backlights with semi-specular components
ActiveUS20100238686A1Improve output performanceHollow light guidesIlluminated signsBack reflectorInjection point
A hollow light-recycling backlight has a “semi-specular” component providing a balance of specularly and diffusely reflected light improving the uniformity of the light output. The component may be arranged on the reflectors (1021), (1014) or inside the cavity (1016). This balance is achieved by designing the component's “transport ratio” defined by (F−B) / (F+B), (F and B are the amounts of incident light scattered forwards and backwards respectively by the component in the plane of the cavity) to lie in a certain range. Furthermore, the product of the front and back reflector “hemispherical” reflectivities should also lie in a given range. Alternatively, the “cavity transport value”, a measure of how well the cavity can spread injected light from the injection point to distant points in the cavity should lie in a further range and the “hemispherical” reflectivity of the back reflector should be >0.7.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Methods for identifying, separating and editing reflection components in multi-channel images and videos
InactiveUS20070132759A1Preserve textureReduce specular reflectionImage enhancementImage analysisStructure from motionRgb image
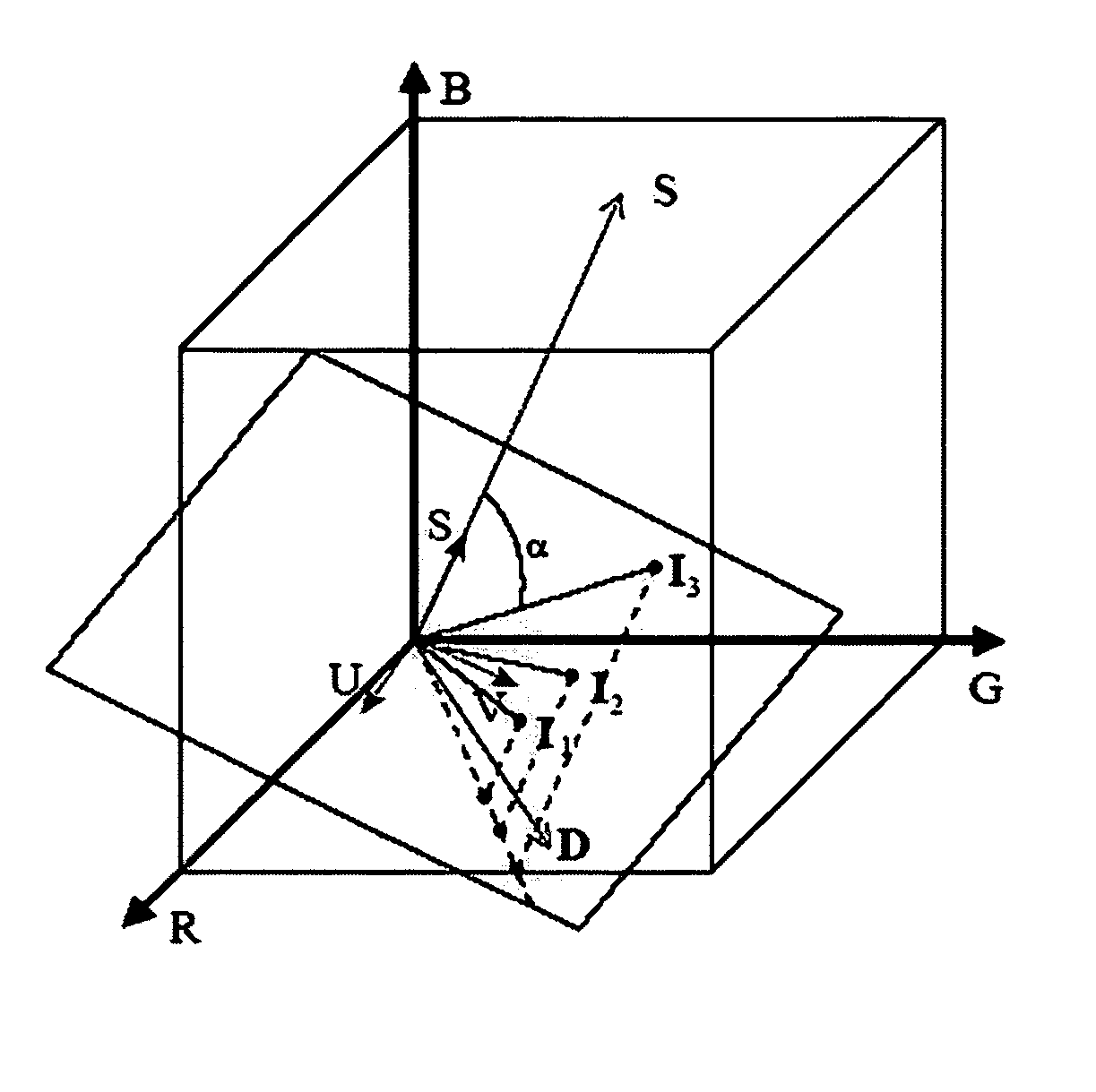
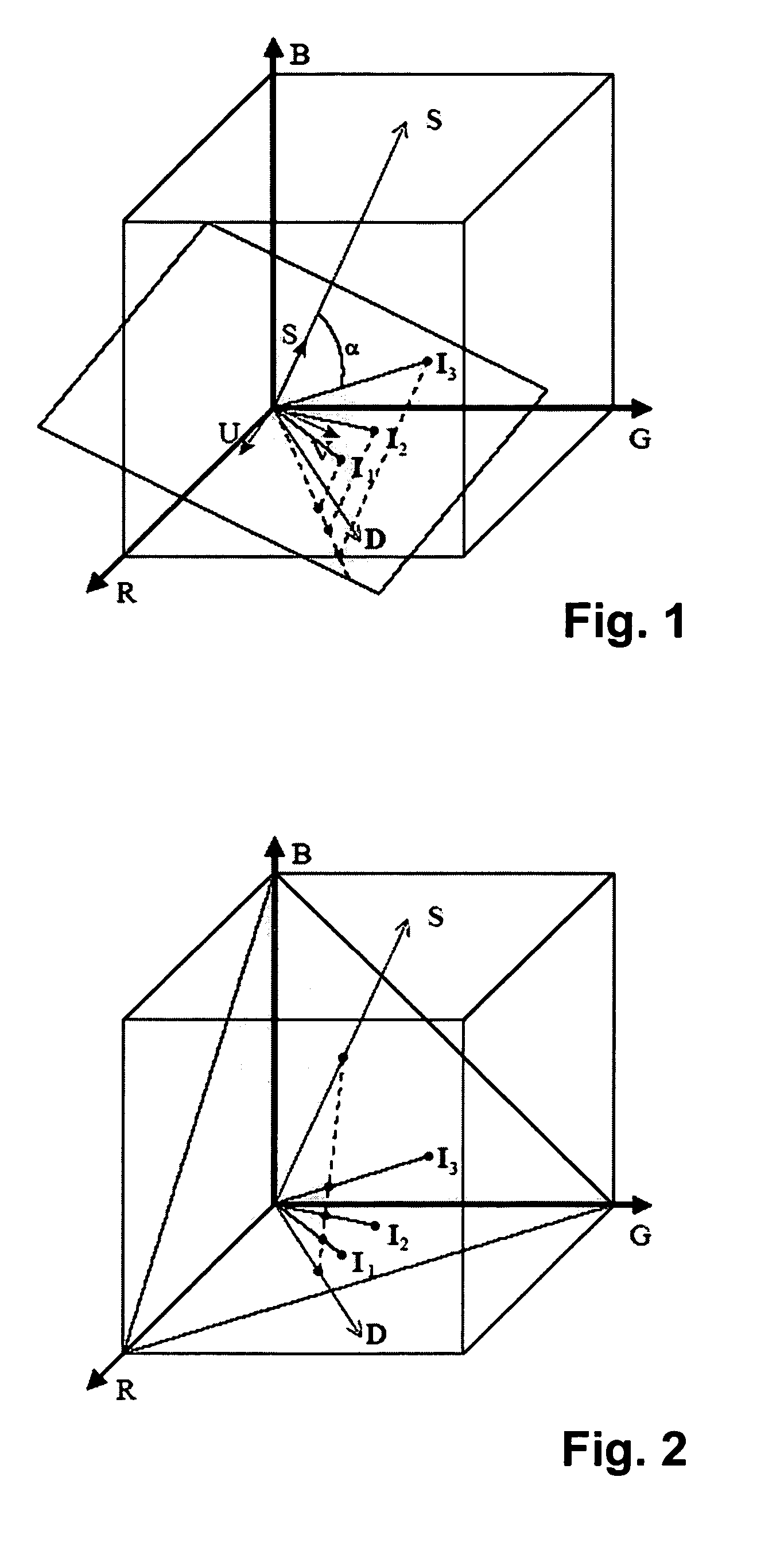
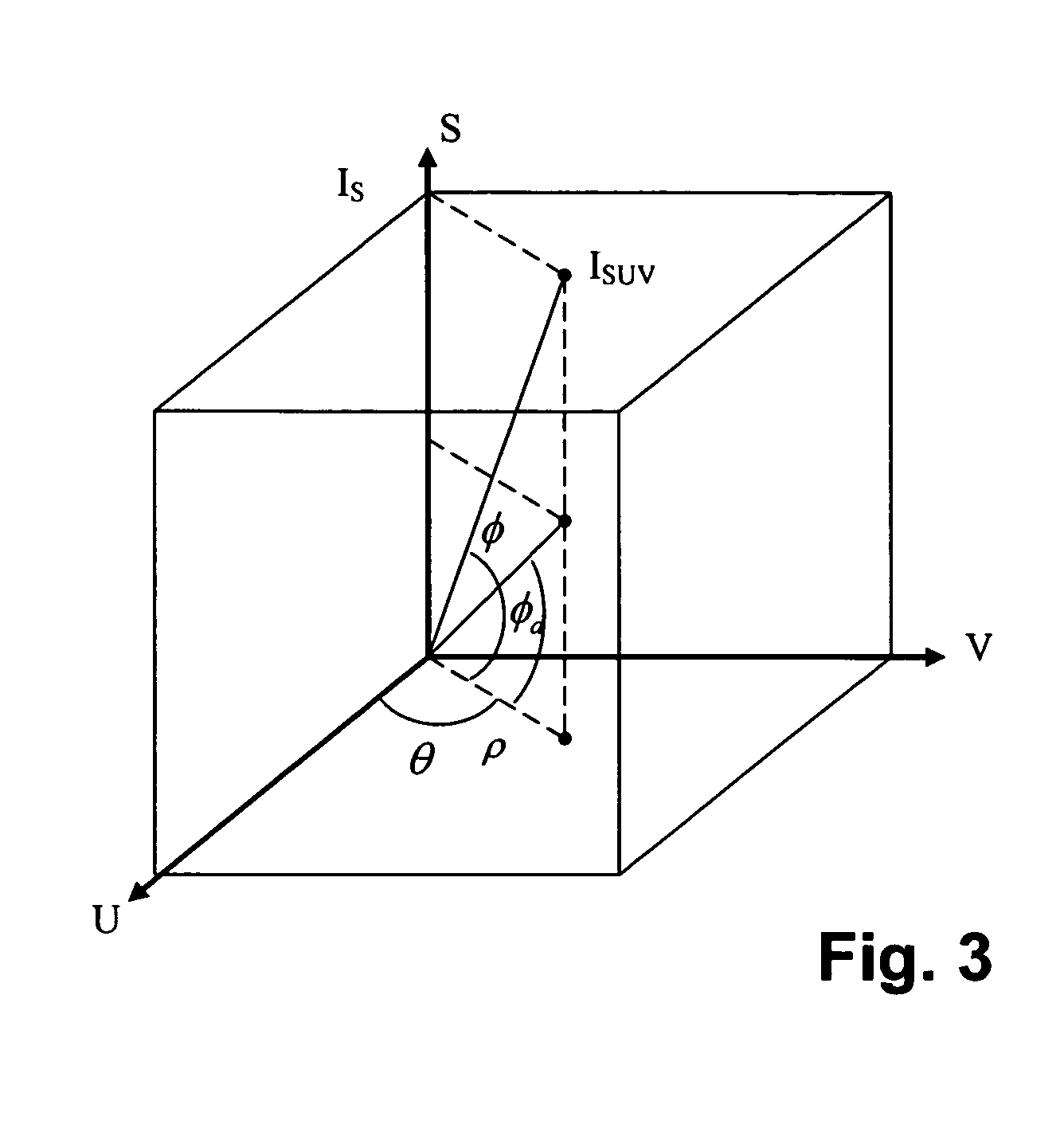
The present invention presents a framework for separating specular and diffuse reflection components in images and videos. Each pixel of the an M-channel input image illuminated by N light sources is linearly transformed into a new color space having (M-N) channels. For an RGB image with one light source, the new color space has two color channels (U,V) that are free of specularities and a third channel (S) that contains both specular and diffuse components. When used with multiple light sources, the transformation may be used to produce a specular invariant image. A diffuse RGB image can be obtained by applying a non-linear partial differential equation to an RGB image to iteratively erode the specular component at each pixel. An optional third dimension of time may be added for processing video images. After the specular and diffuse components are separated, dichromatic editing may be used to independently process the diffuse and the specular components to add or suppress visual effects. The (U,V) channels of images can be used as input to 3-D shape estimation algorithms including shape-from-shading, photometric stereo, binocular and multinocular stereopsis, and structure-from-motion.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Interferometric defect detection and classification
InactiveCN102089616APhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansRelative phaseControl system
Systems and methods for using common-path interferometric imaging for defect detection and classification are described. An illumination source generates and directs coherent light toward the sample. An optical imaging system collects light reflected or transmitted from the sample including a scattered component and a specular component that is predominantly undiffracted by the sample. A variablephase controlling system is used to adjust the relative phase of the scattered component and the specular component so as to change the way they interfere at the image plane. The resultant signal is compared to a reference signal for the same location on the sample and a difference above threshold is considered to be a defect. The process is repeated multiple times each with a different relative phase shift and each defect location and the difference signals are stored in memory. This data is used to calculate an amplitude and phase for each defect.
Owner:焕・J・郑
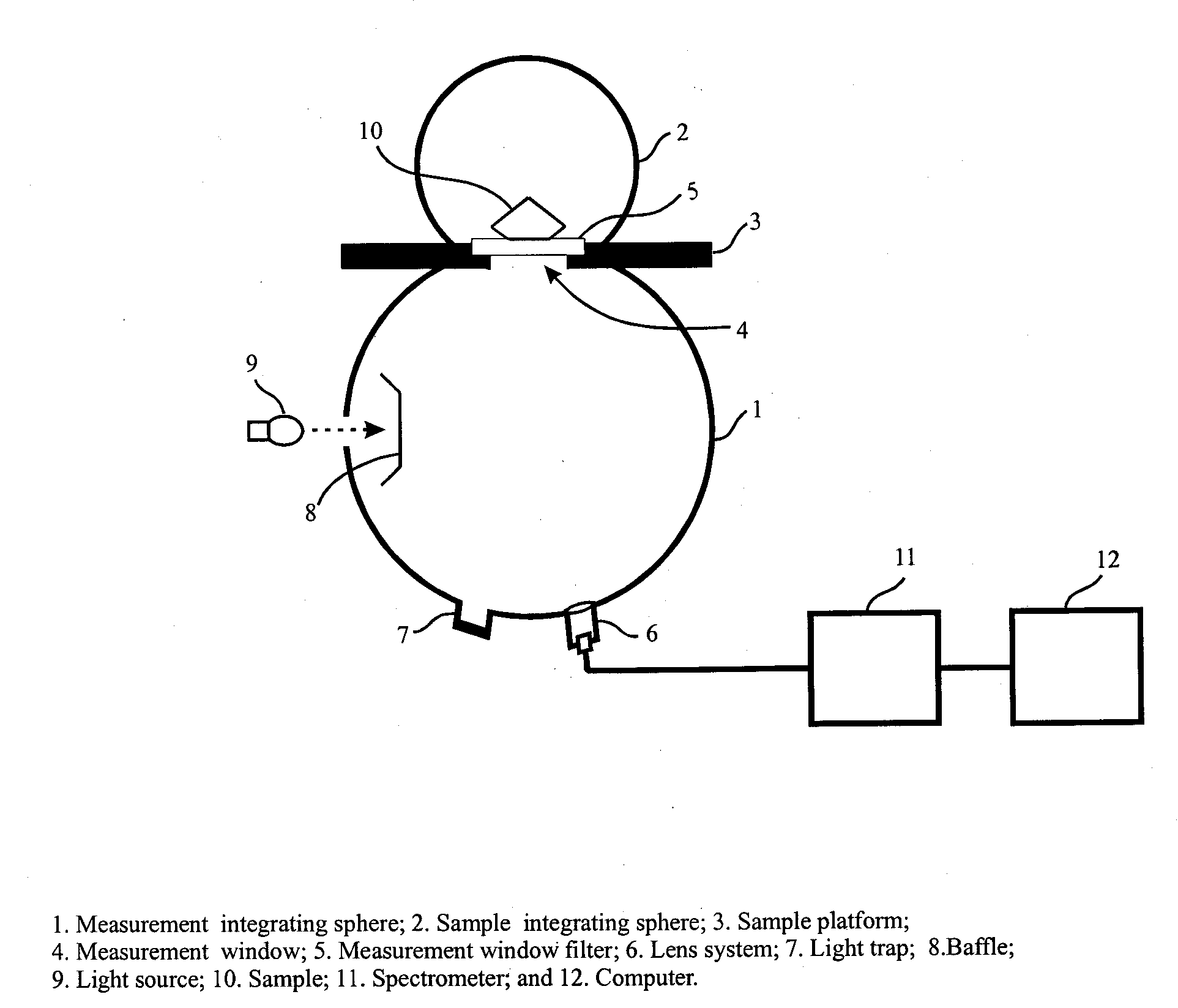
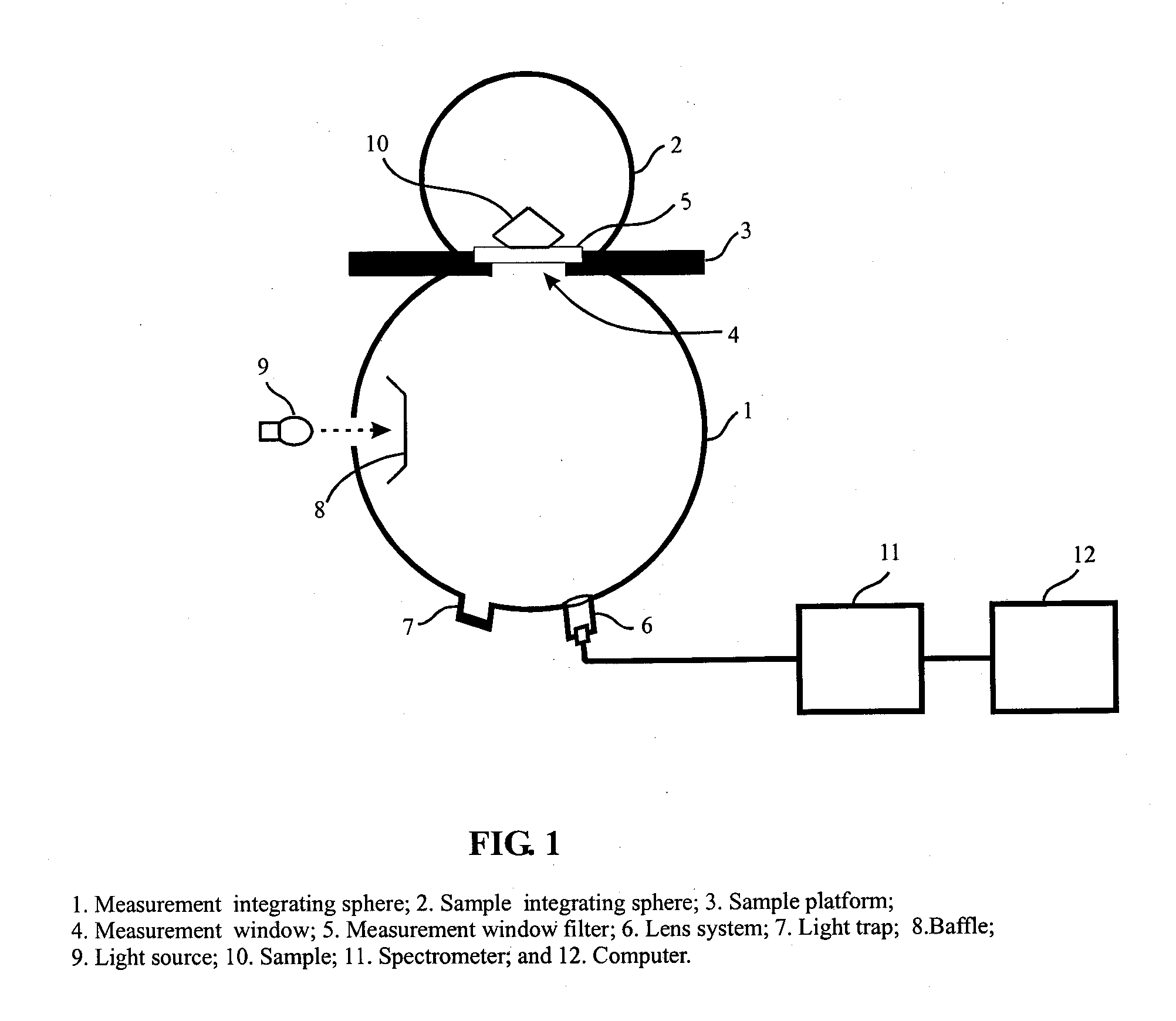
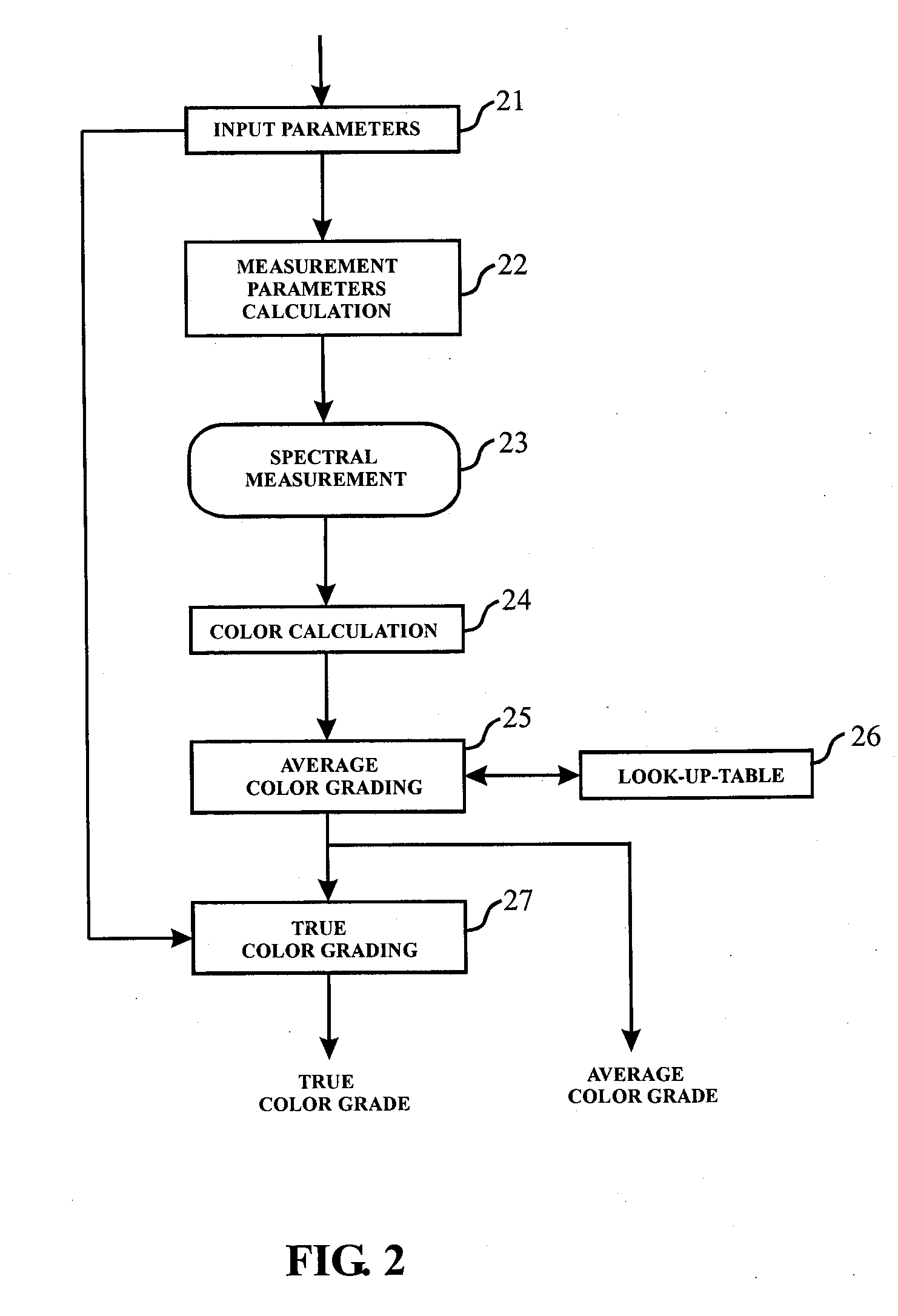
Apparatus and method for color measurement and color grading of diamonds, gemstones and the like
InactiveUS20080204705A1Accurate measurementReduce manufacturing costPhotometryInvestigating jewelsDiffuse illuminationFluorescence
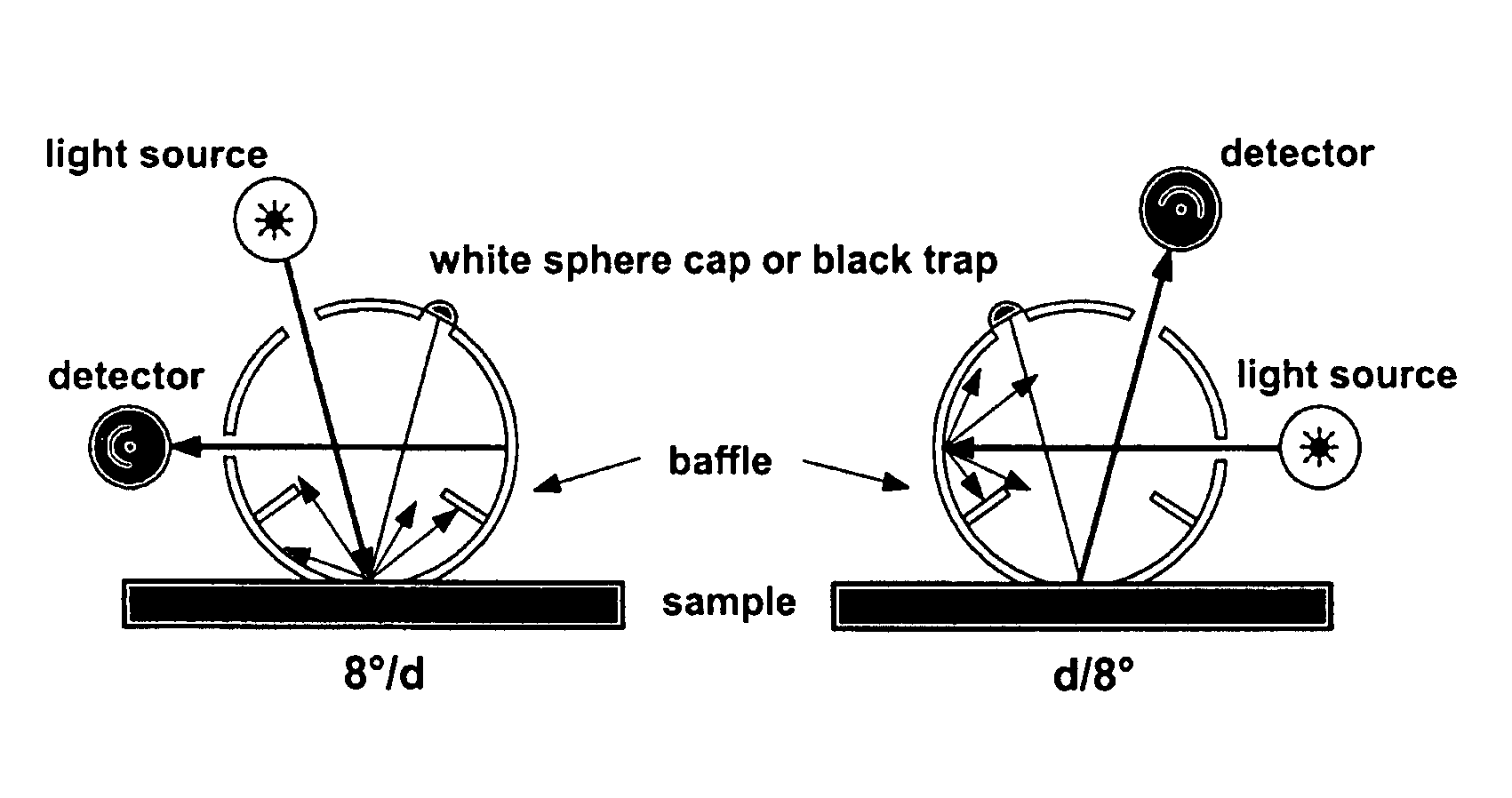
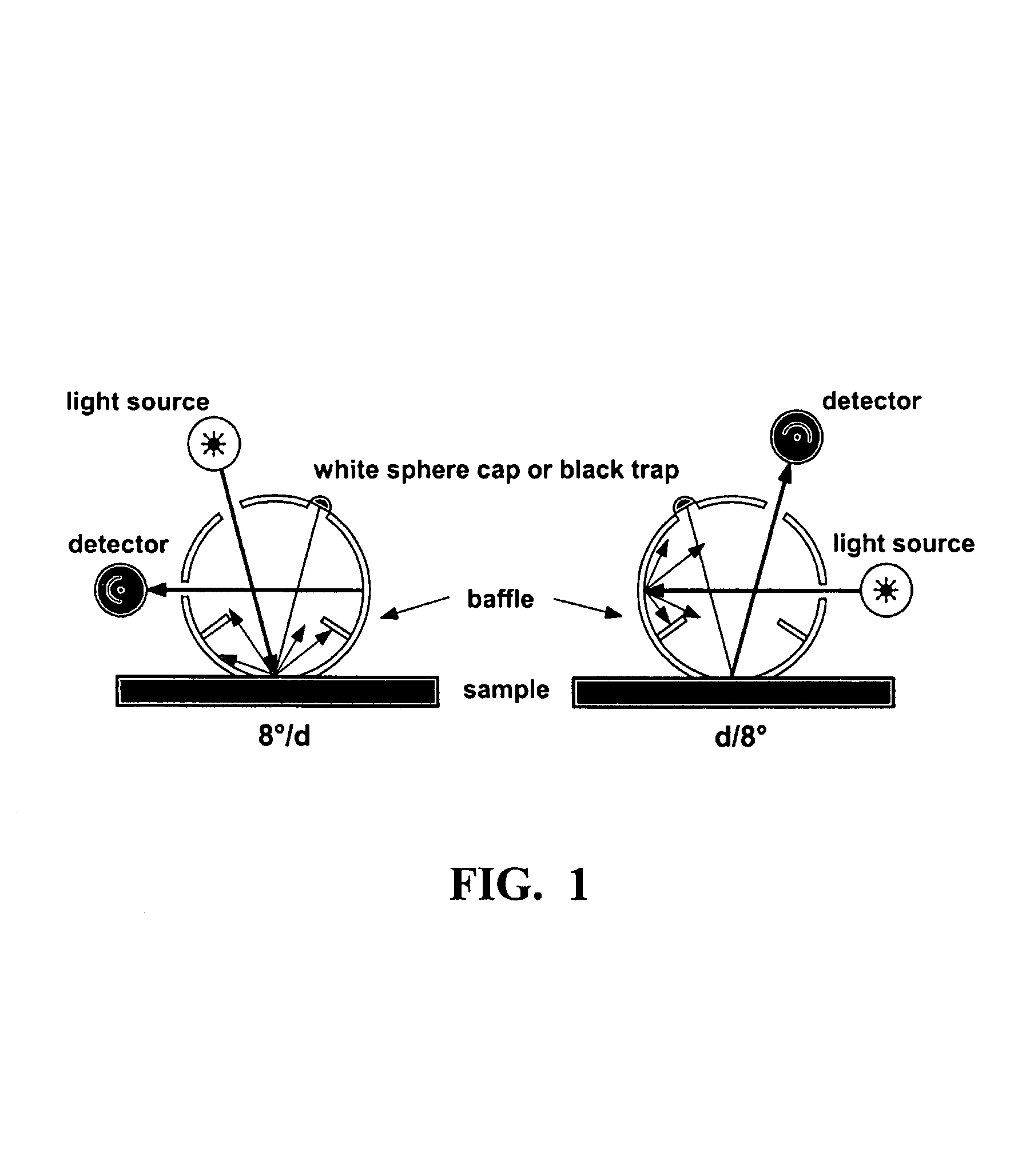
The present invention discloses an apparatus and method for color measurement and color grading of faceted gemstones, diamonds and the like. The apparatus comprises a spectrometer, a computer, and a dual integrating sphere measurement arrangement comprising a measurement integrating sphere, a sample integrating sphere, a sample platform, a filter, a lens system, a baffle and a light source. The measurement geometry of the dual integrating sphere measurement arrangement is diffuse illumination and 8 degree viewing with the specular component excluded, plus diffuse white background provided by the sample integrating sphere. The sample integrating sphere encloses a sample to provide a constant environment for simulating the visual color grading environment. A novel three-step calibration insures an accurate spectral measurement of the sample inside the measurement integrating sphere. The computer controls the spectrometer and provides measurement parameters calculated from the physical parameters of the measured sample, including, but not limited to, shape, dimensions, refractive index, intensity of fluorescence and cut grade. The computer then calculates the spectral reflectance and calorimetric data, and determines an average color grade by checking a look-up-table that represents the relationship between the CIELAB coordinate and the average color grade. The computer also determines a true color grade based upon the average color grade and the physical parameters, using mathematical analyses and algorithms.
Owner:LIU YAN
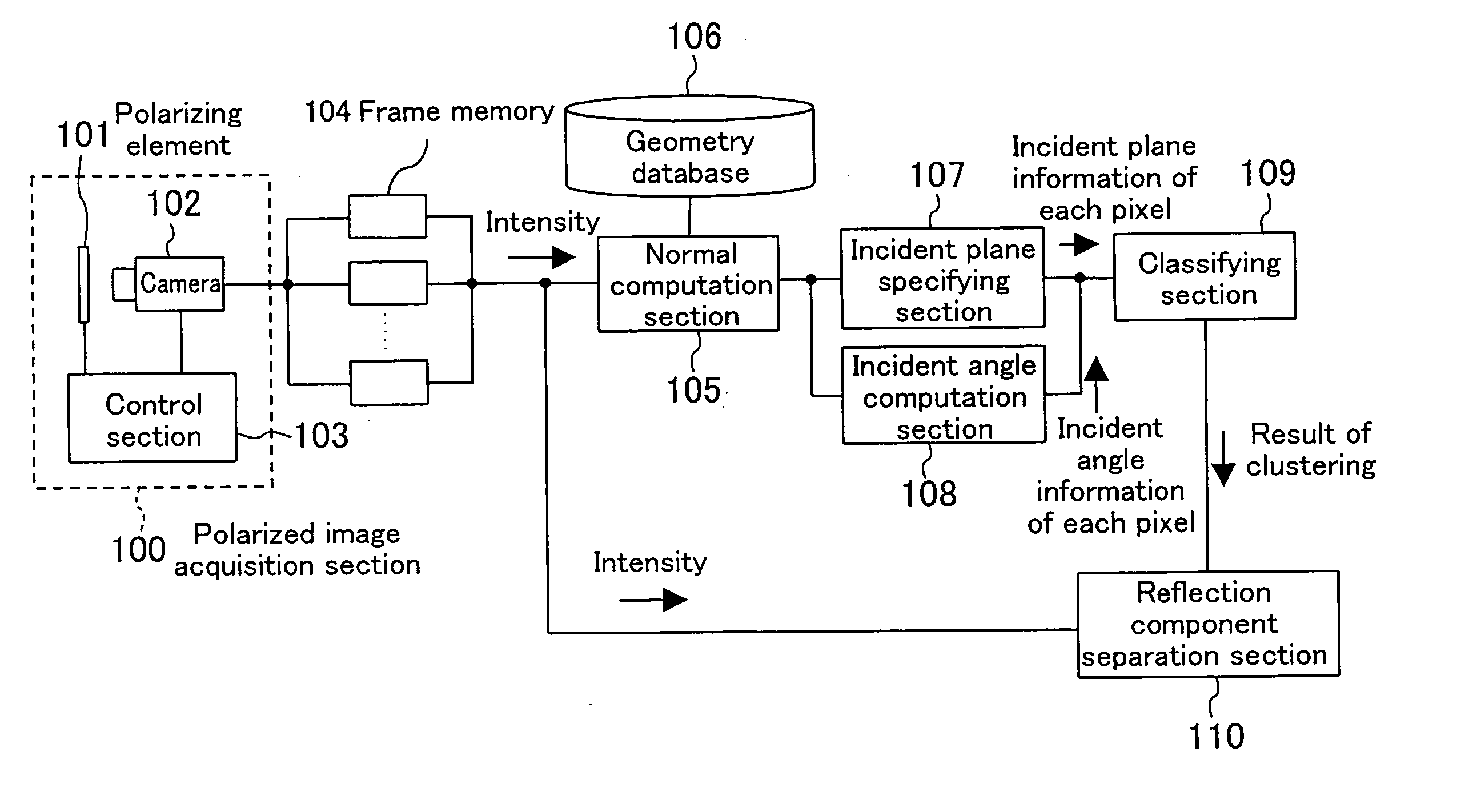
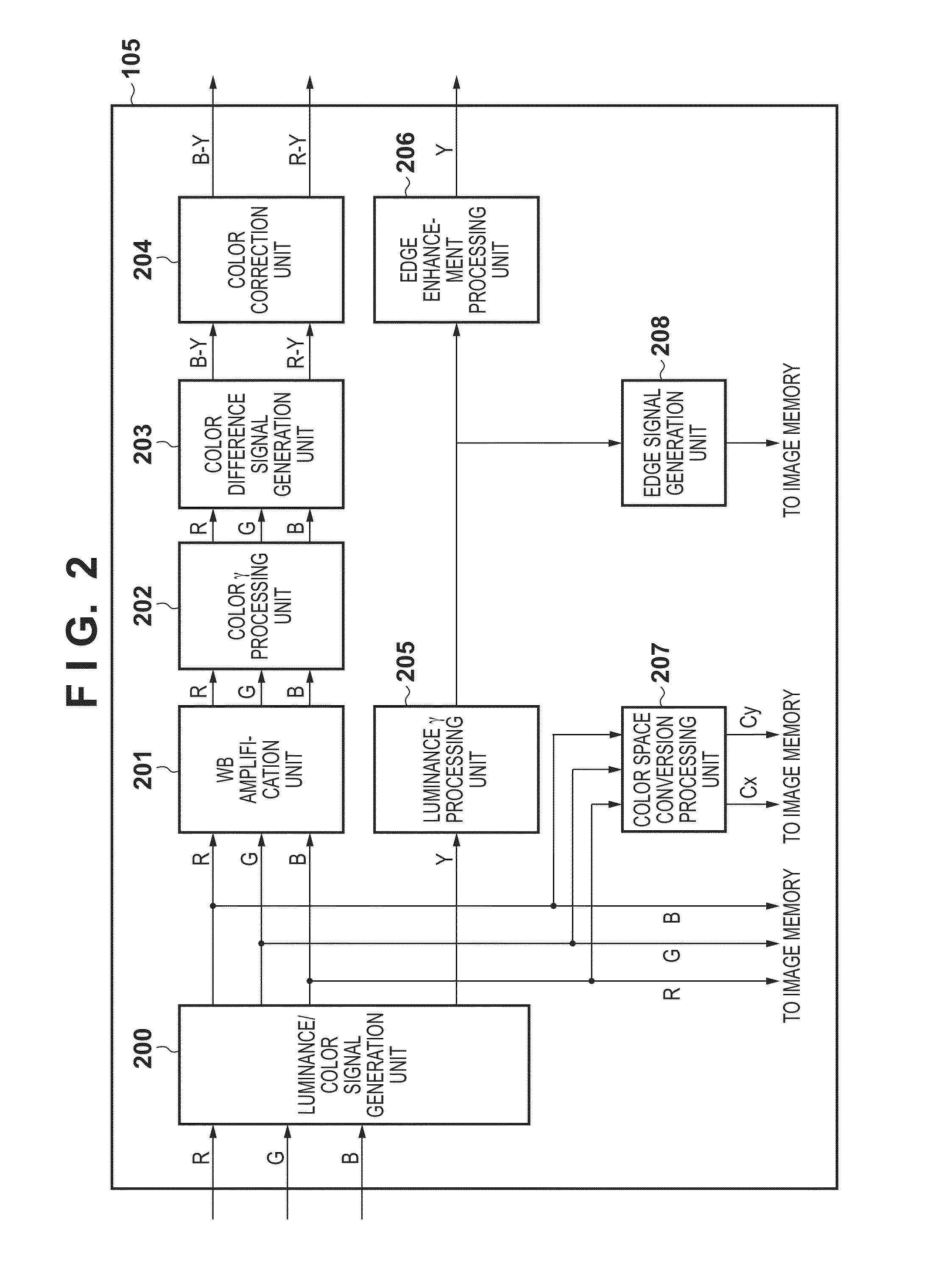
Image processing method, image processor, and image processing program
InactiveUS20070222781A1Image enhancementCathode-ray tube indicatorsImaging processingDiffuse reflection
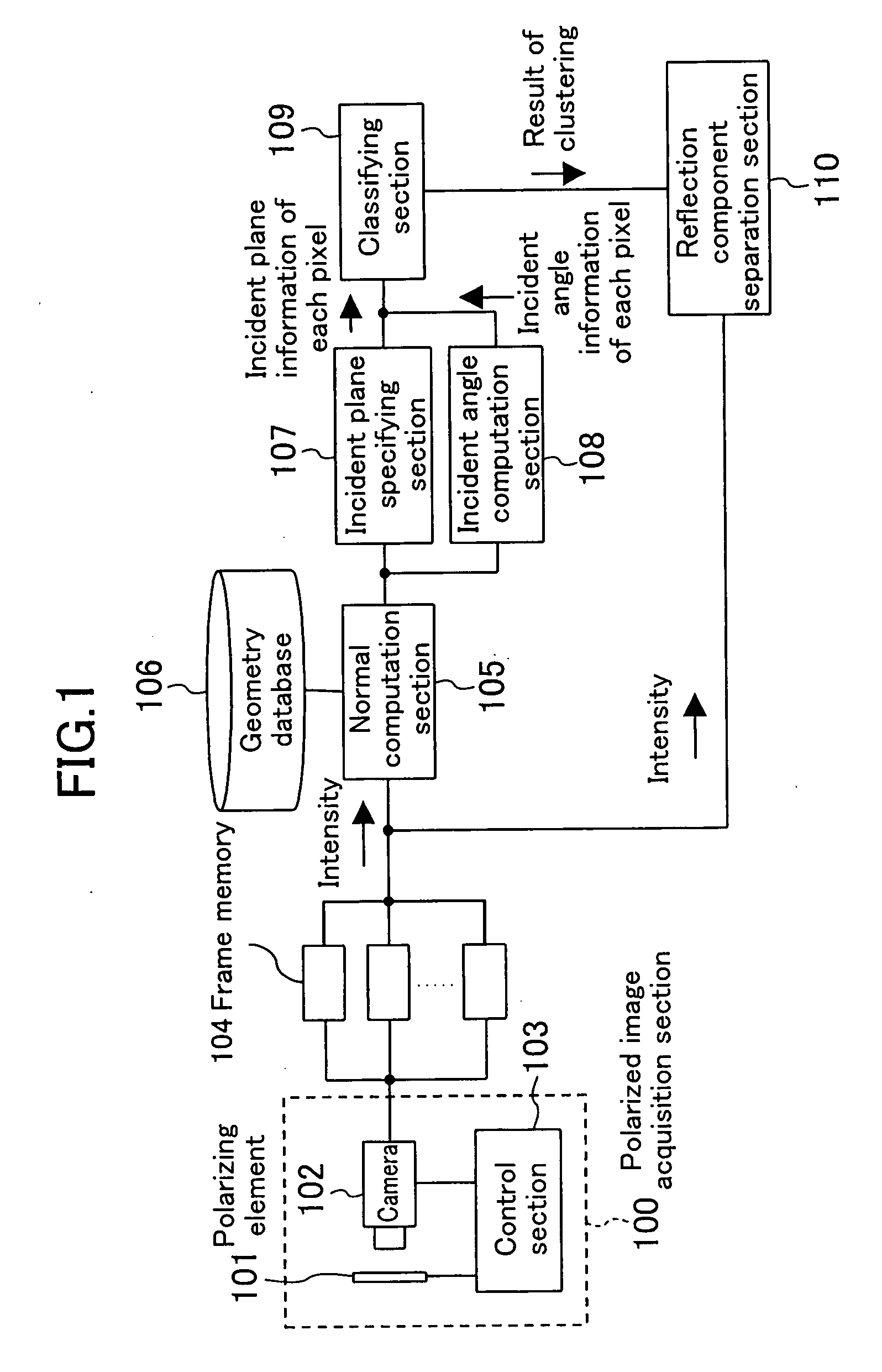
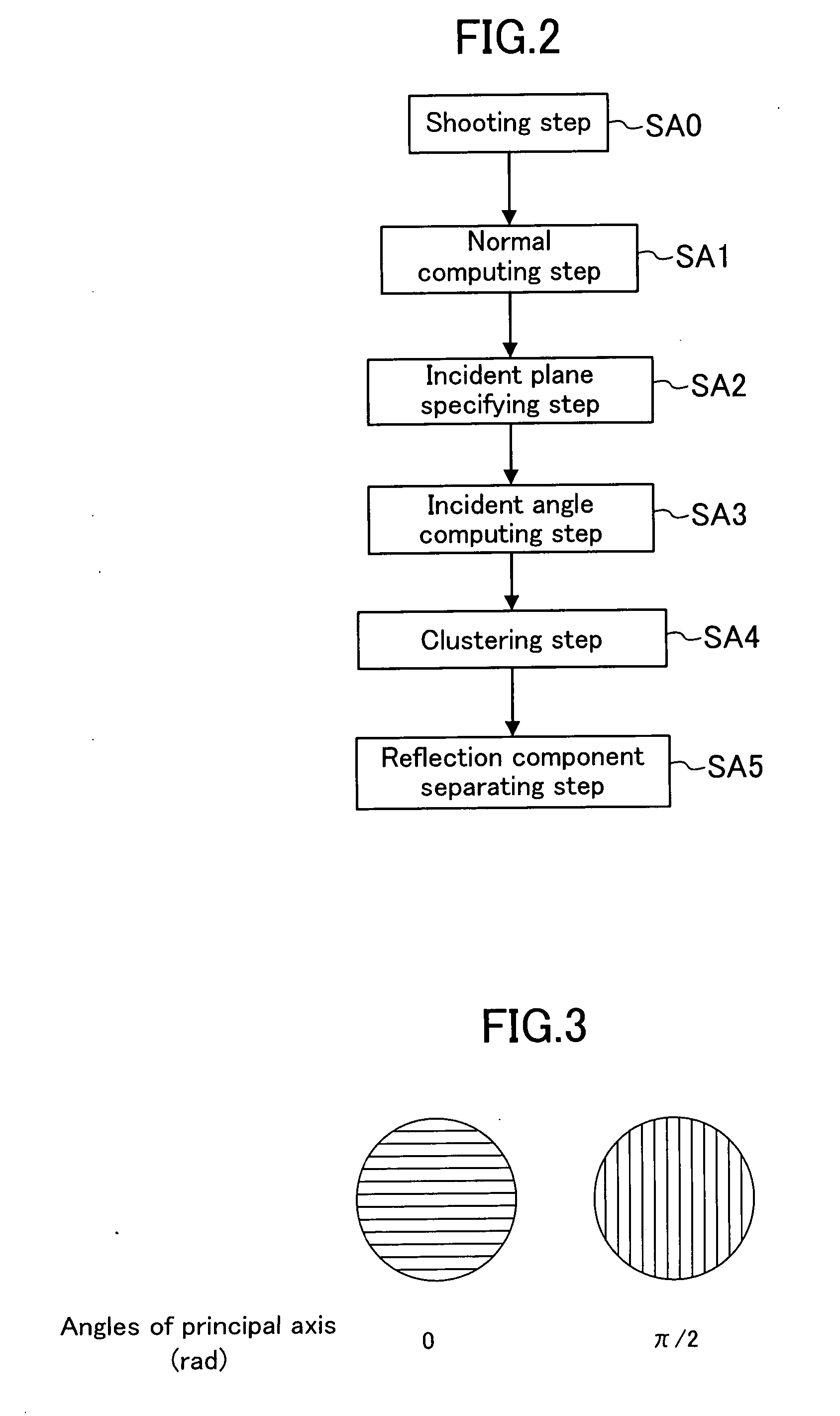
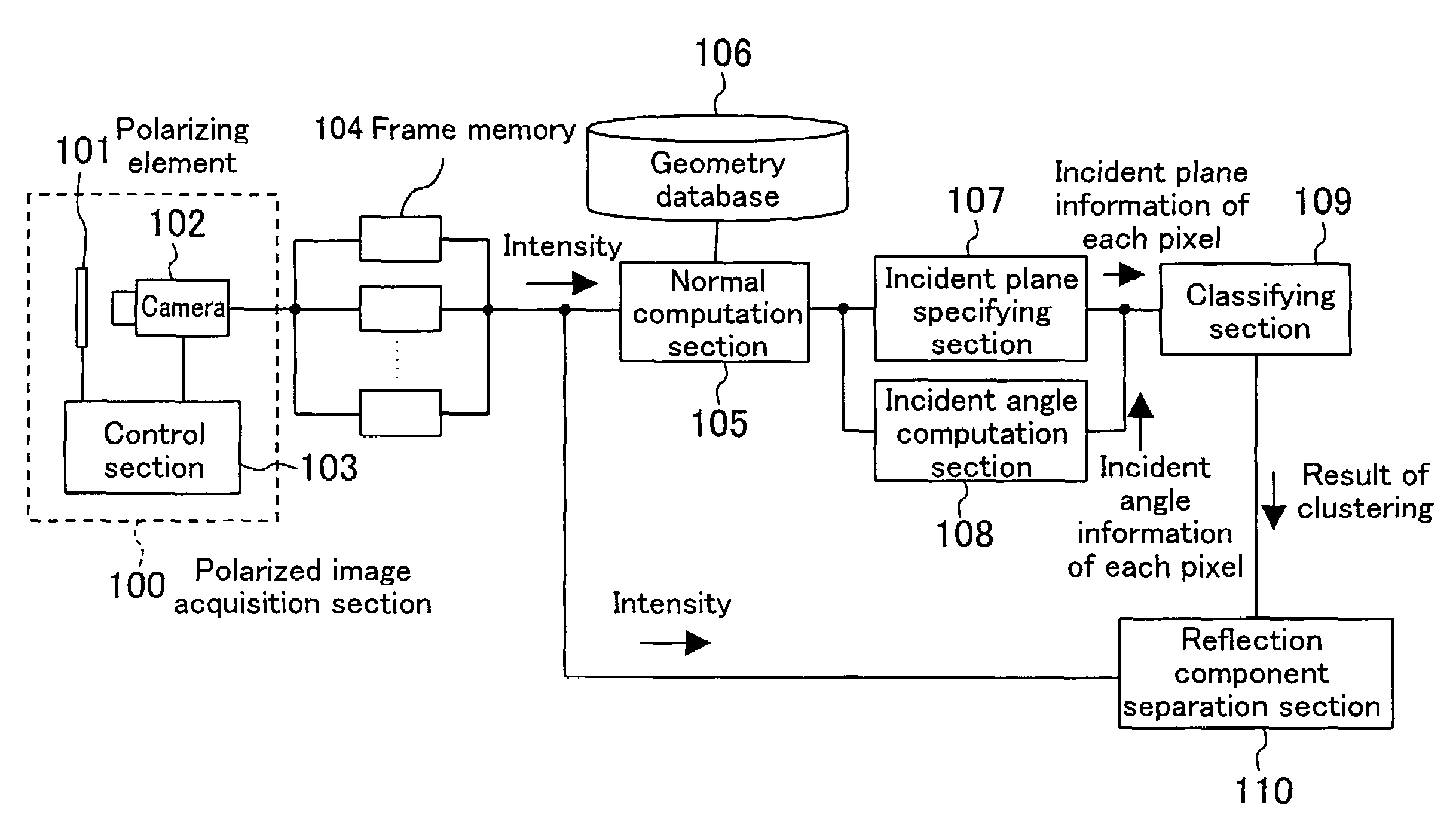
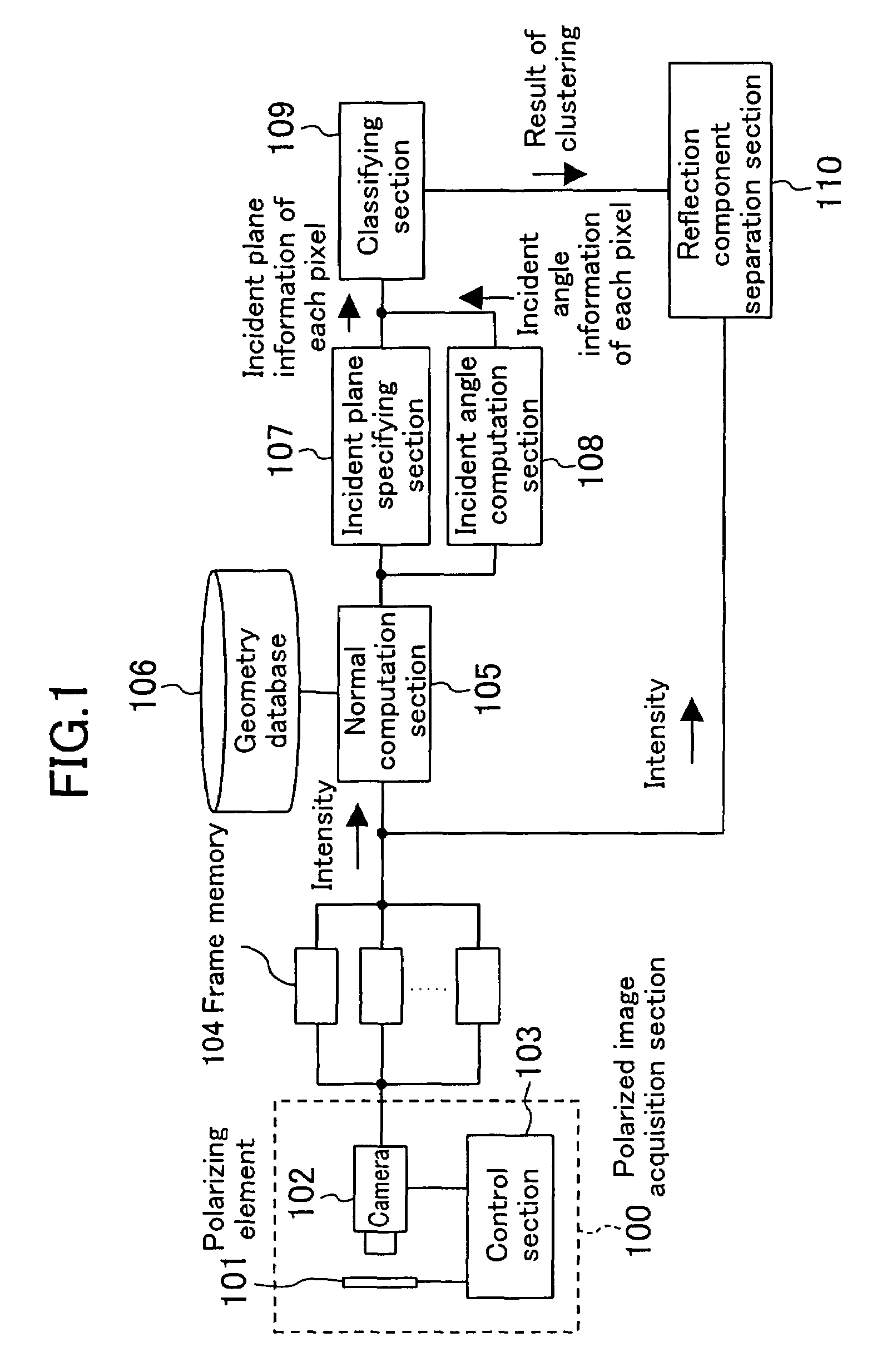
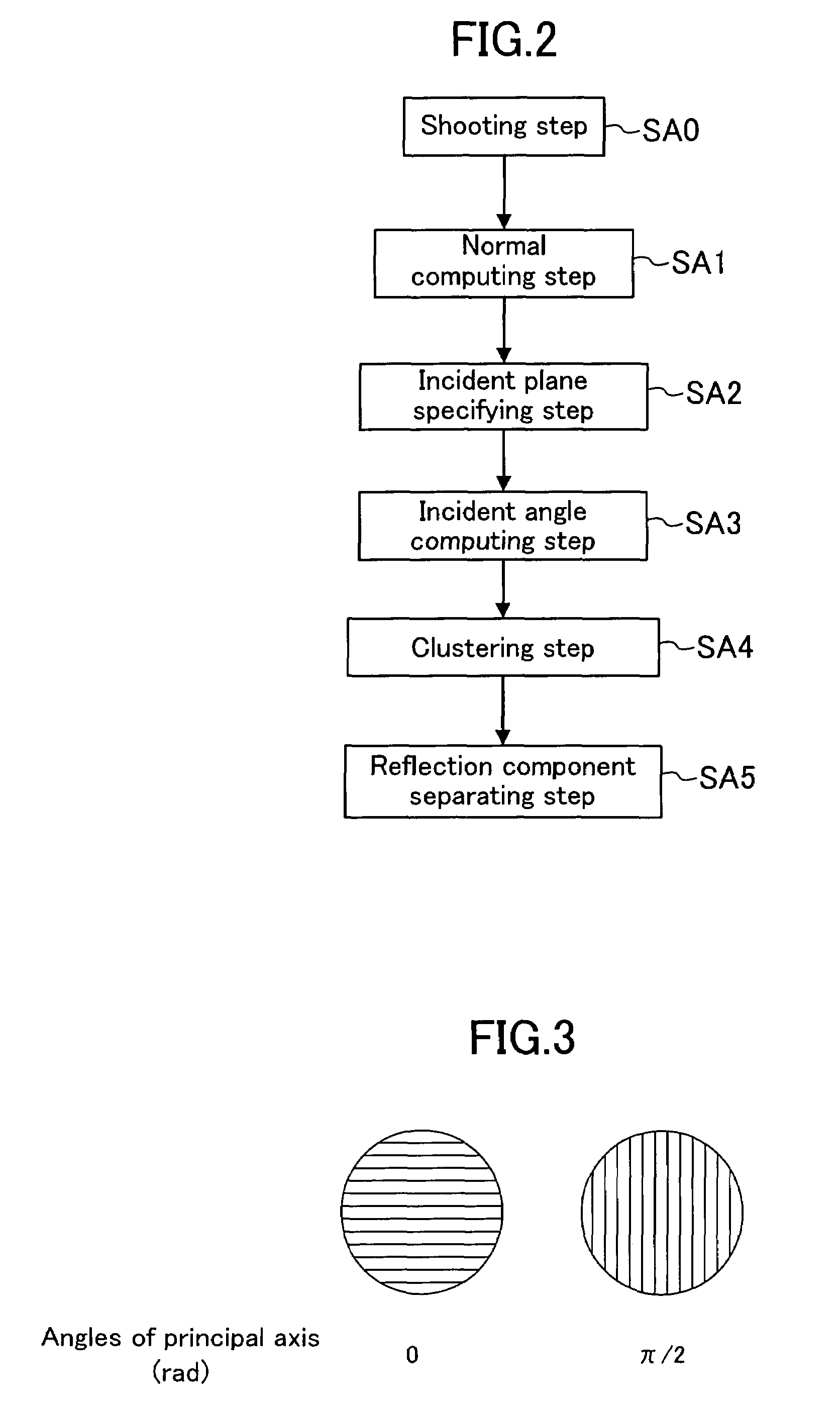
A polarized image acquisition section shoots a subject through a polarizing element operable to set principal axes of which directions are different from each other. An incident plane specifying section specifies an incident plane of each pixel, and an incident angle computation section computes an incident angle of each pixel. A classifying section clusters pixels similar to each other in both incident plane and incident angel. A reflection component separation section performs reflection component separation on each clustered pixel set on the assumption of probabilistic independence between the diffuse reflection component and the specular reflection component.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Image processing device, image processing method and image processing program
ActiveUS20110164811A1Improve accuracyEasy to identifyImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionAlbedoImaging processing
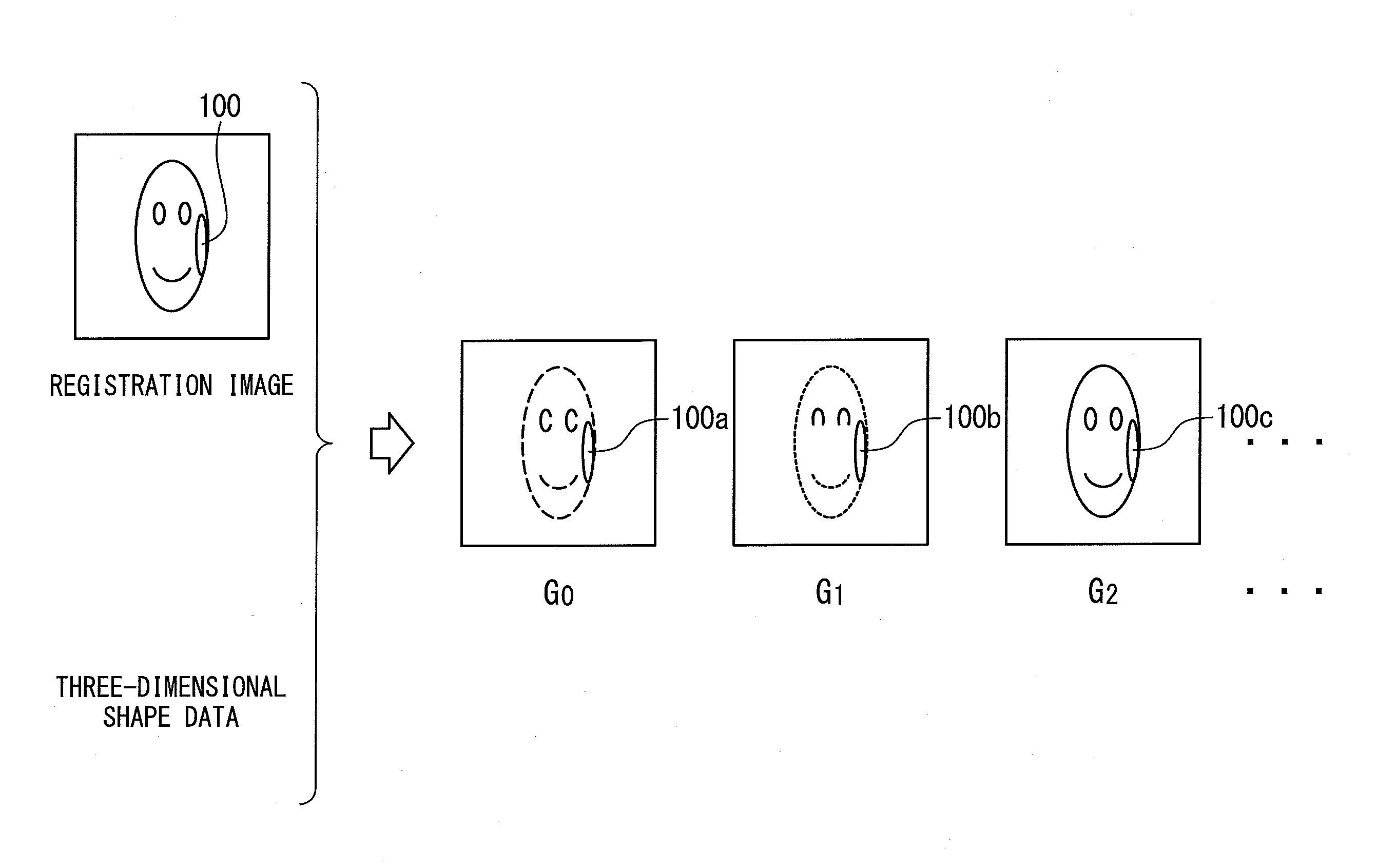
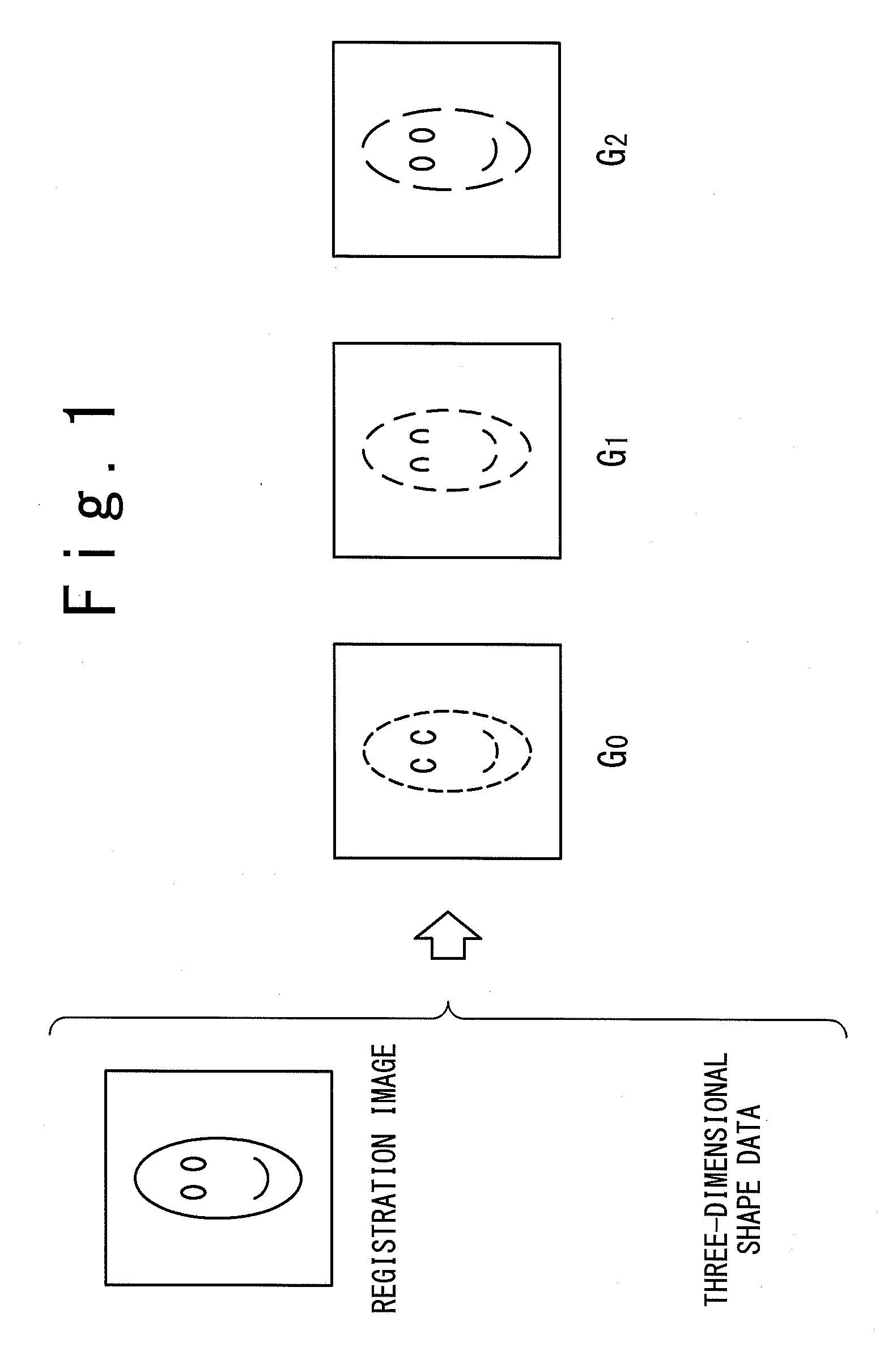
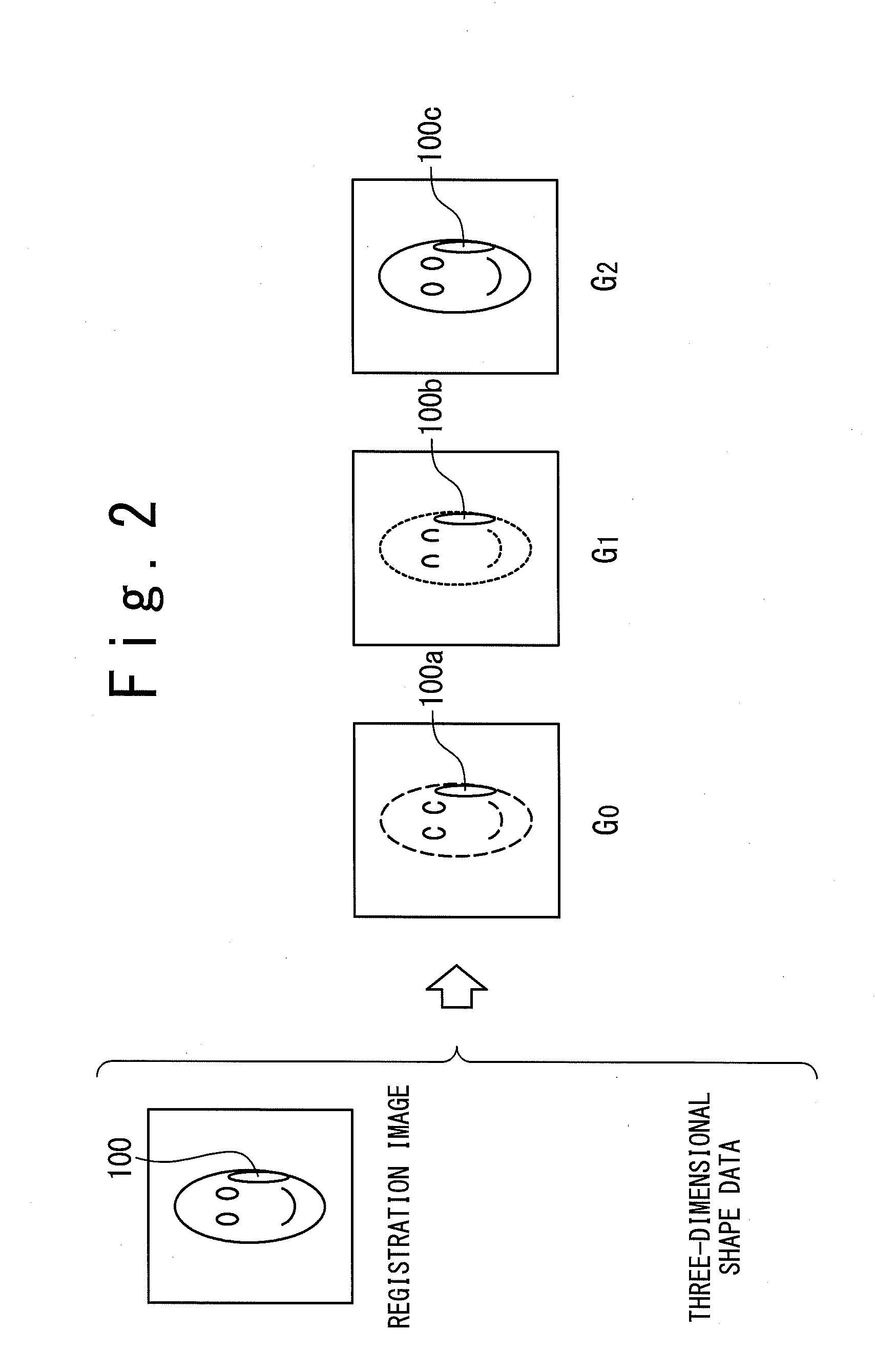
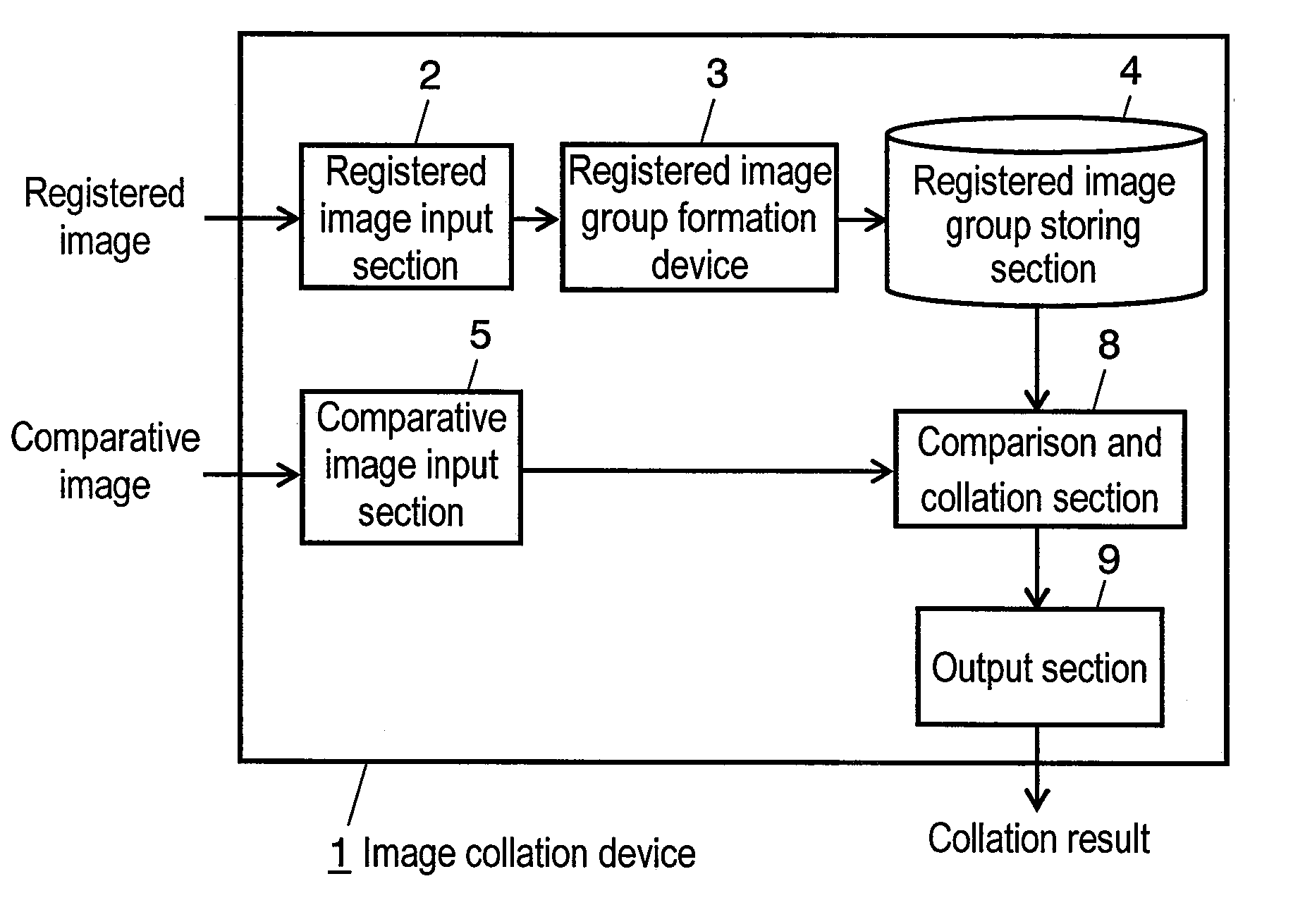
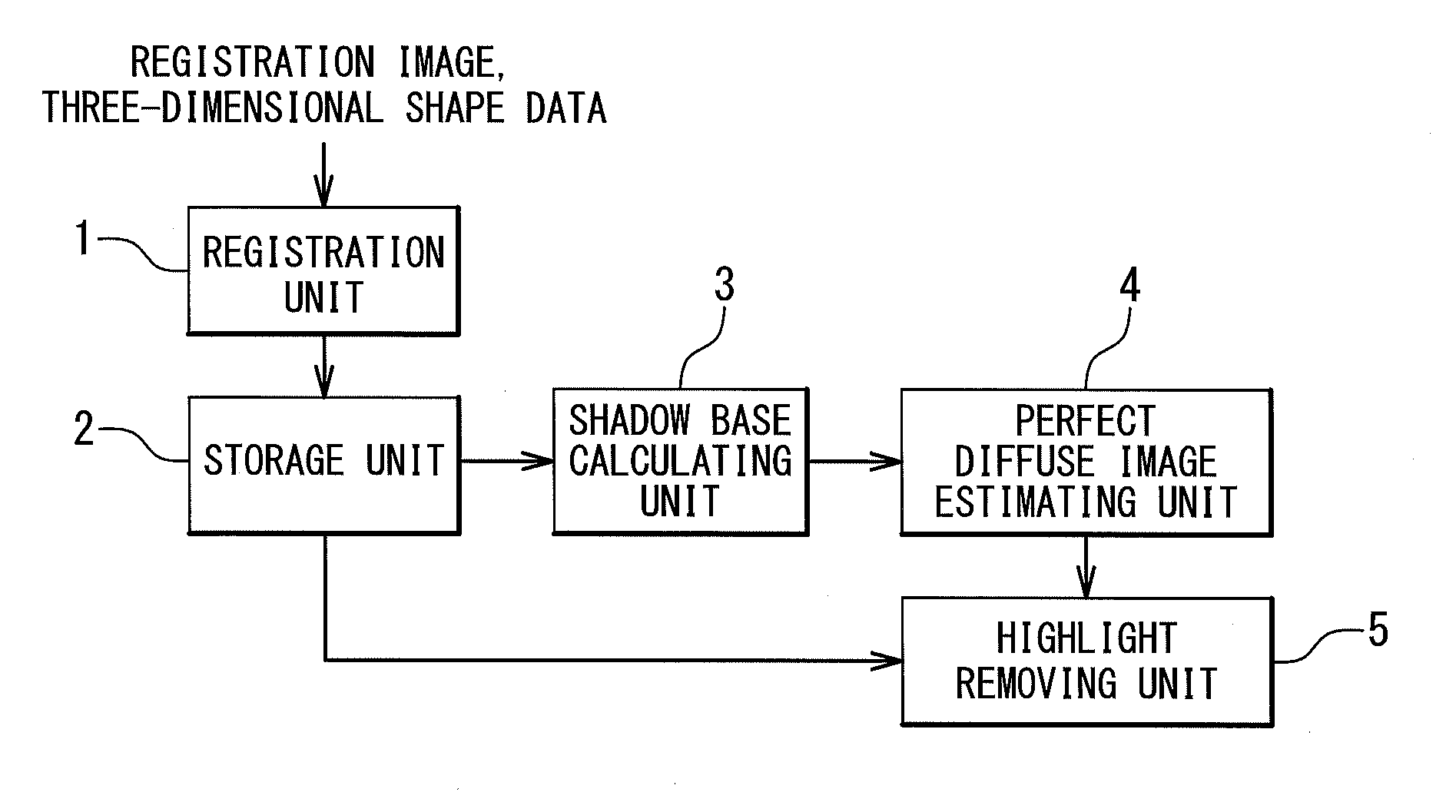
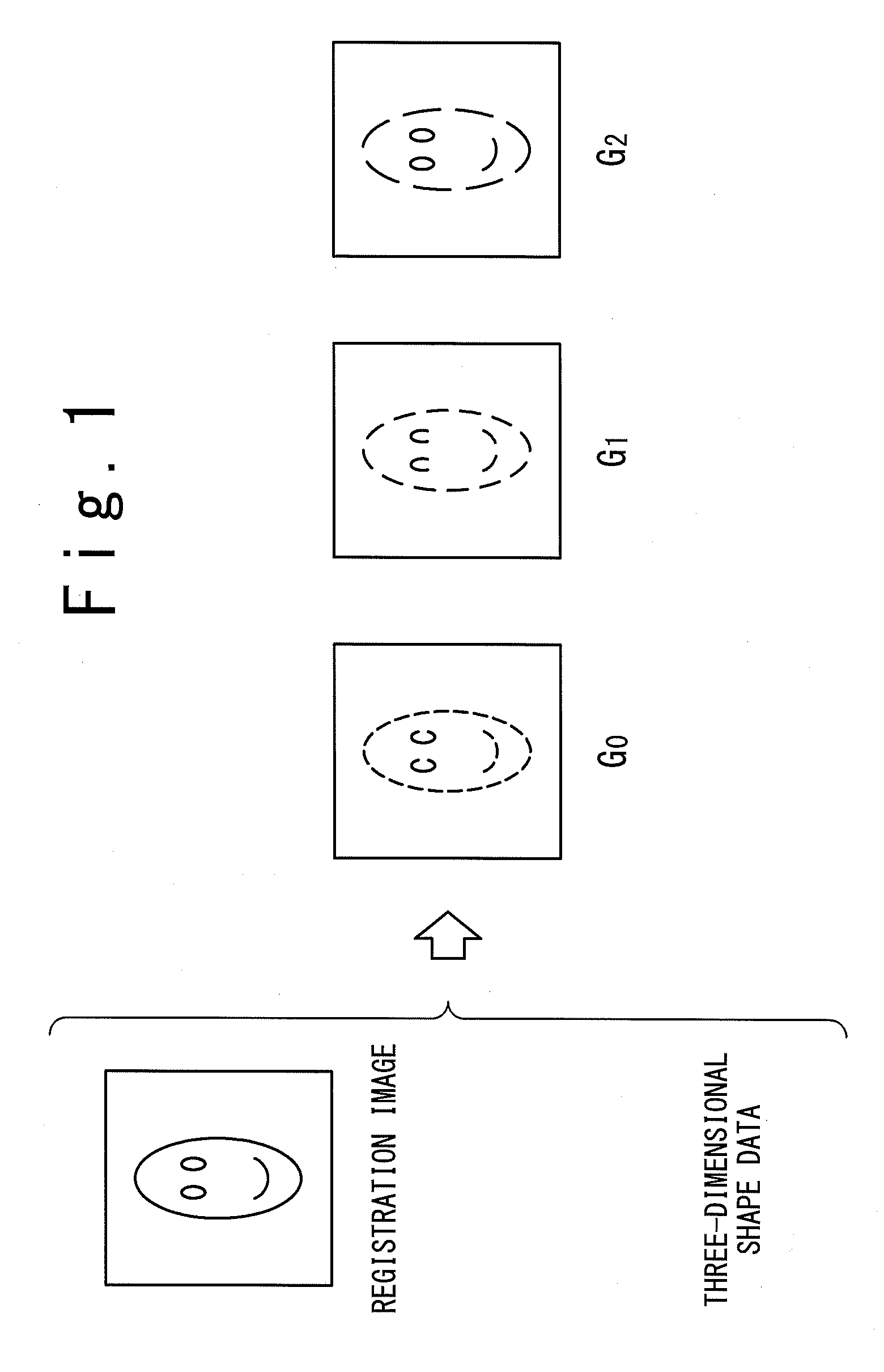
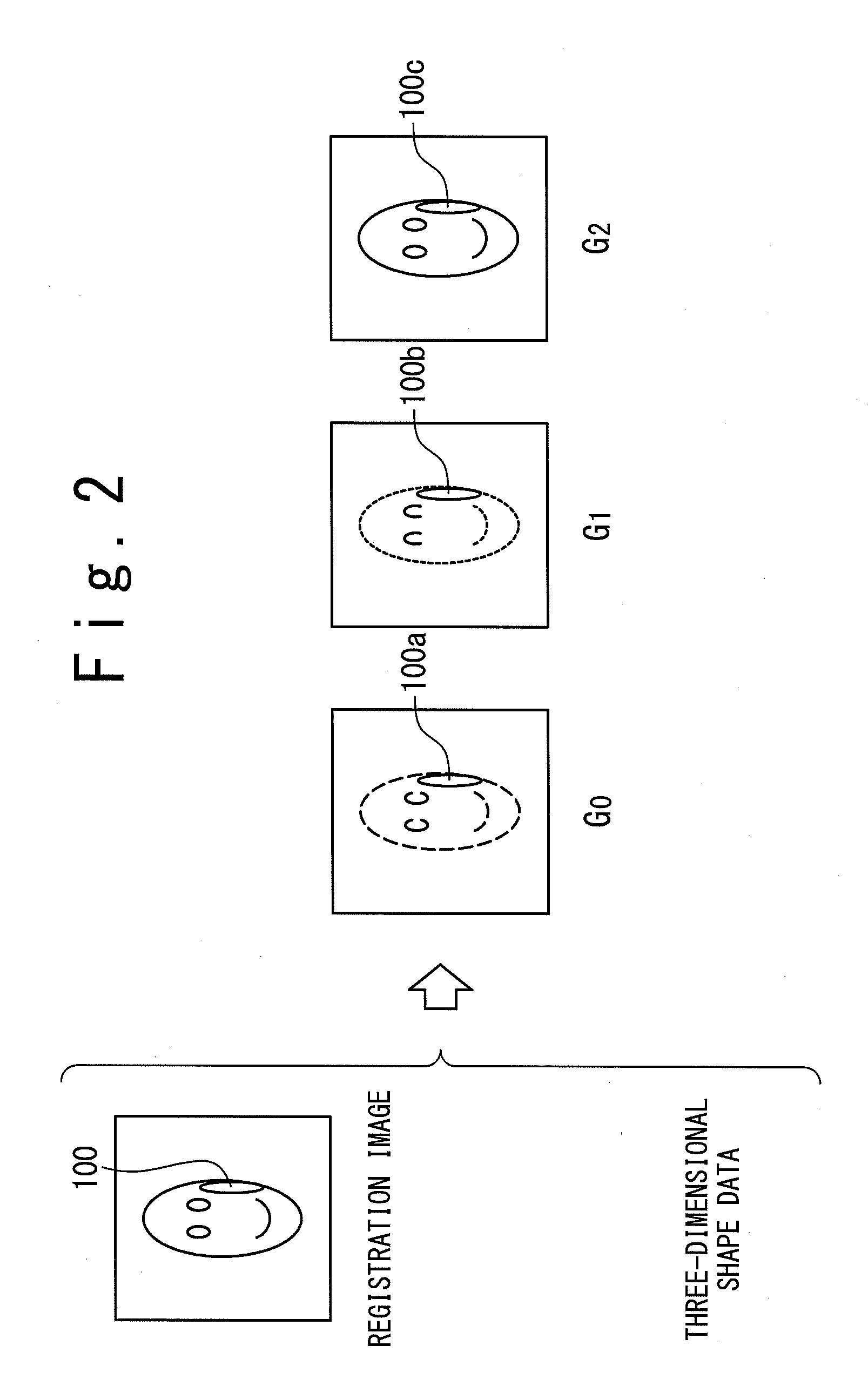
An image processing device calculates, from a registration image representing a photographed object and three-dimensional shape data in which respective points of a three-dimensional shape of the object are correlated with pixels of the registration image, by assuming uniform albedo, a shadow base vector group having components from which an image under an arbitrary illumination condition can be generated through linear combination. A shadow in the registration image is estimated with using the vector group. A perfect diffuse component image including the shadow is generated, and based on the image a highlight removal image is generated in which a specular reflection component is removed from the registration image. Thus, an image recognition system generates illumination base vectors from the highlight removal image and thereby can obtain the illumination base vectors based on which an accurate image recognition process can be carried out without influence of a specular reflection.
Owner:NEC CORP
Chroma-keyed specular texture mapping in a graphics processor
A graphics system includes a graphics controller for rendering polygons with specular highlighting (glare) based on a comparison of texel color values from a texture map to a range of color values. The graphics processor includes range registers for storing the range of color values and color comparators for comparing a texel color value to the range of colors stored in the range registers. The range of color values used in the comparison corresponds to the range of colors of those portions of a texture for which specular highlighting is appropriate, such as metallic surfaces off which light reflects. If a texel color value to be applied to a screen pixel is within the range of colors defined for specular highlighting, the graphics processor adds an appropriate specular component to the texel value.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Thermoplastic polycarbonate compositions with improved optical surface quality, articles made therefrom and method of manufacture
A thermoplastic composition contains a polycarbonate resin, an aromatic vinyl copolymer, an impact modifier and a mineral filler, wherein the composition has a lightness L* of greater than or equal to about 70 under one or more of CIE D65, CWF-2 or C illumination using a 2° observer at 360 to 750 nanometers (nm), including specular components. Alternatively, a thermoplastic composition may contain a polycarbonate resin, a vinyl aromatic copolymer, an impact modifier and a mineral filler, and less than or equal to about 400 parts per million iron, by weight of the composition. An article may be formed by molding, extruding, shaping or forming such a composition to form the article.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Methods for identifying, separating and editing reflection components in multi-channel images and videos
InactiveUS7689035B2Reduce specular reflectionImage enhancementImage analysisStructure from motionRgb image
The present invention presents a framework for separating specular and diffuse reflection components in images and videos. Each pixel of the an M-channel input image illuminated by N light sources is linearly transformed into a new color space having (M−N) channels. For an RGB image with one light source, the new color space has two color channels (U,V) that are free of specularities and a third channel (S) that contains both specular and diffuse components. When used with multiple light sources, the transformation may be used to produce a specular invariant image. A diffuse RGB image can be obtained by applying a non-linear partial differential equation to an RGB image to iteratively erode the specular component at each pixel. An optional third dimension of time may be added for processing video images. After the specular and diffuse components are separated, dichromatic editing may be used to independently process the diffuse and the specular components to add or suppress visual effects. The (U,V) channels of images can be used as input to 3-D shape estimation algorithms including shape-from-shading, photometric stereo, binocular and multinocular stereopsis, and structure-from-motion.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
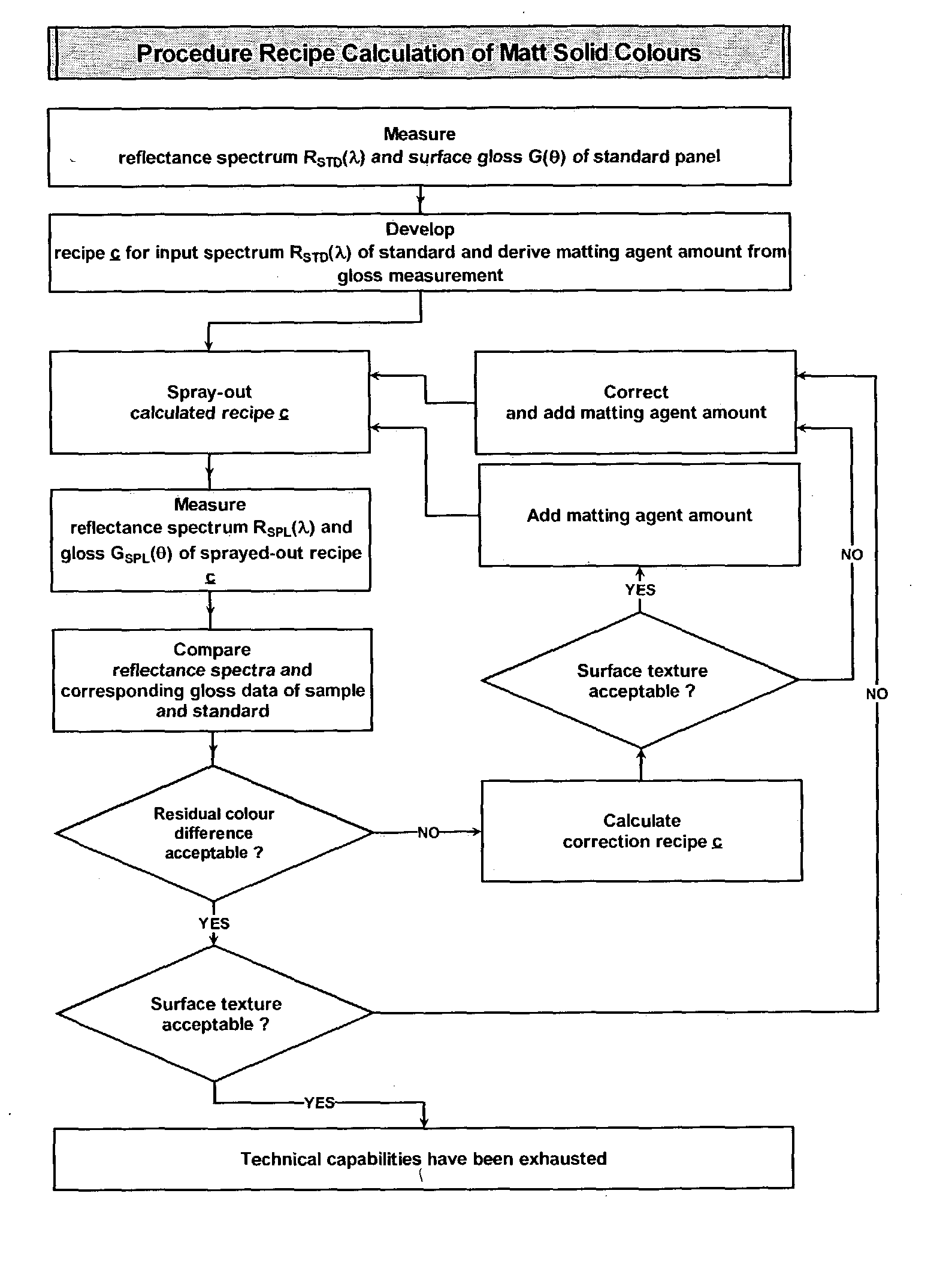
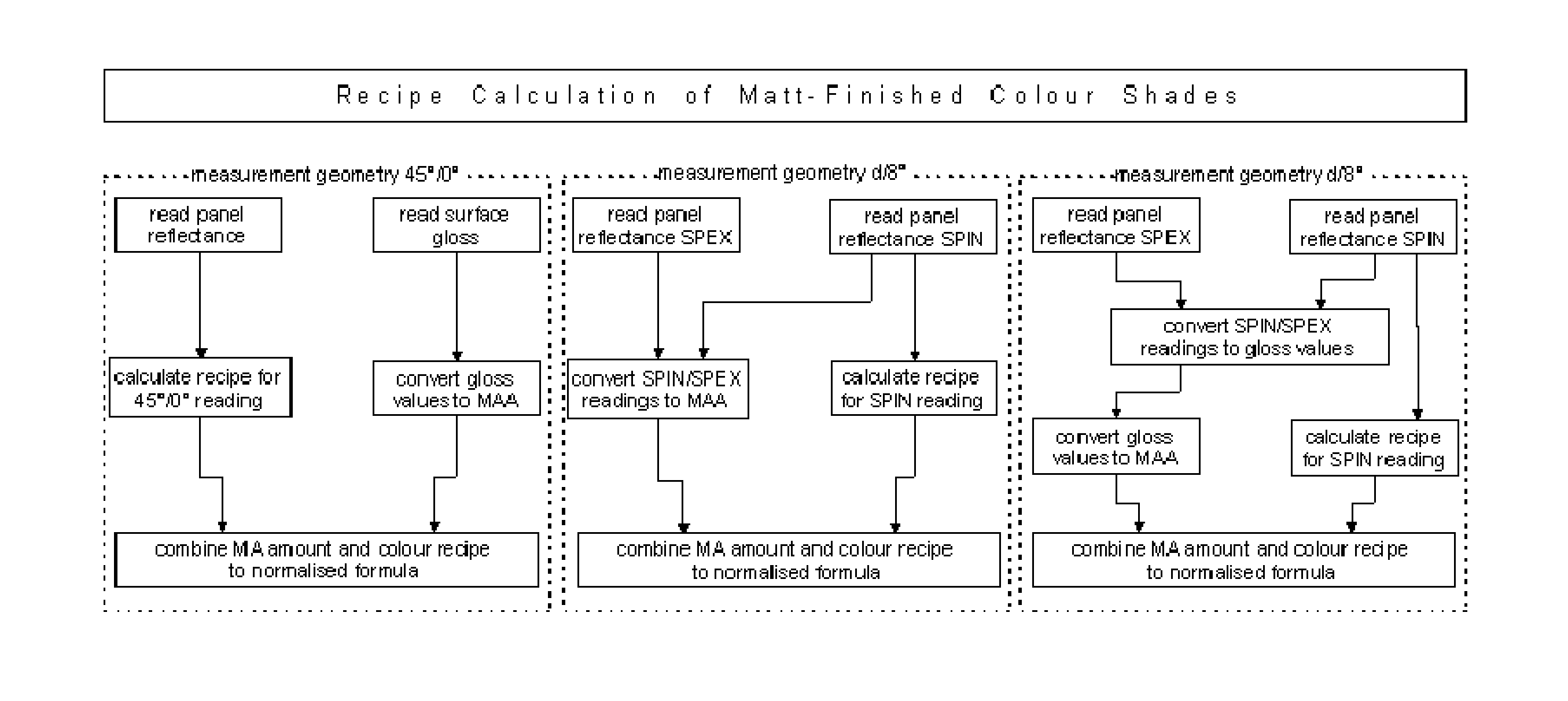
Recipe calculation method for matt color shades
ActiveUS20040252883A1Scattering properties measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringSpecular component
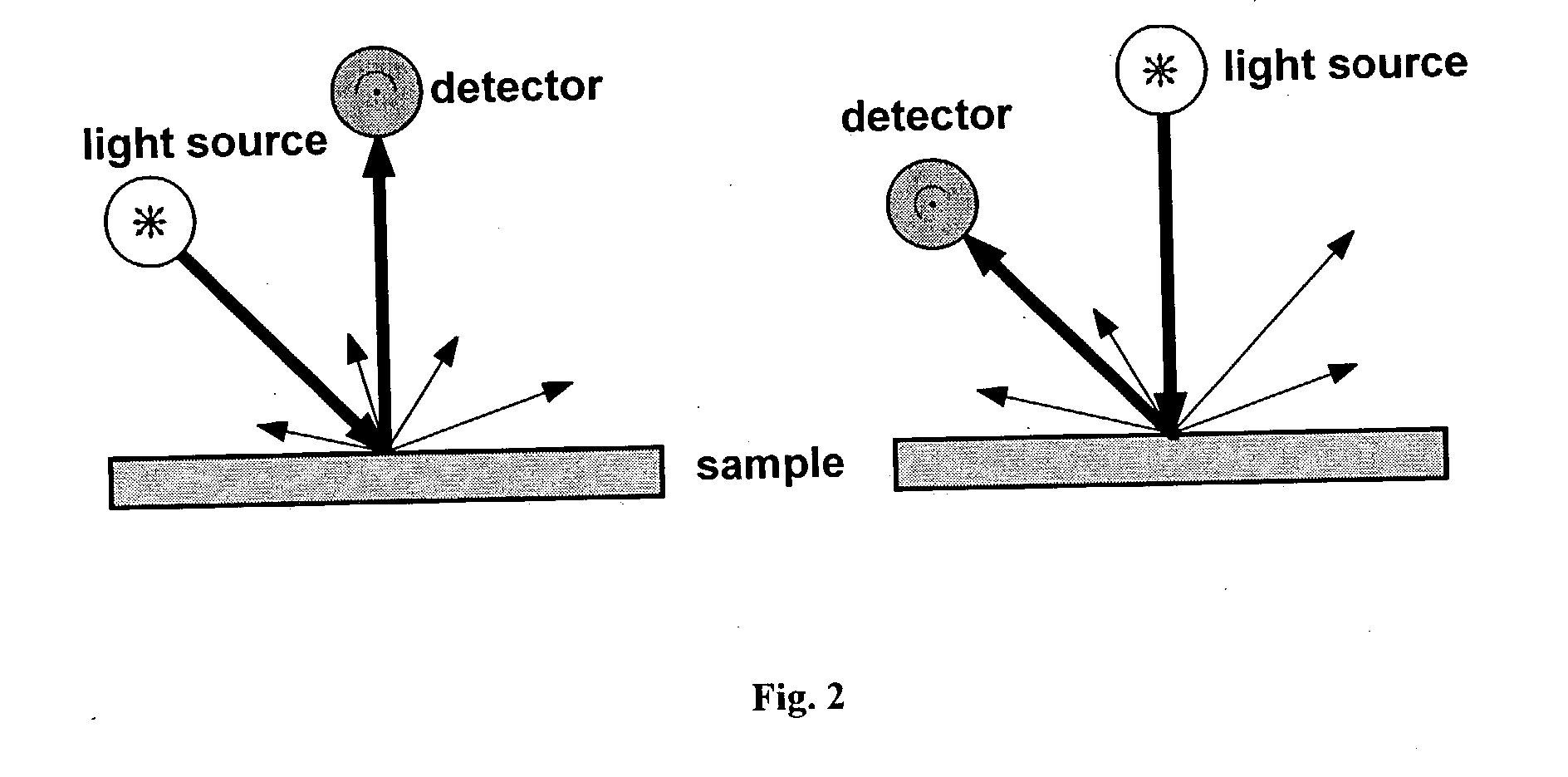
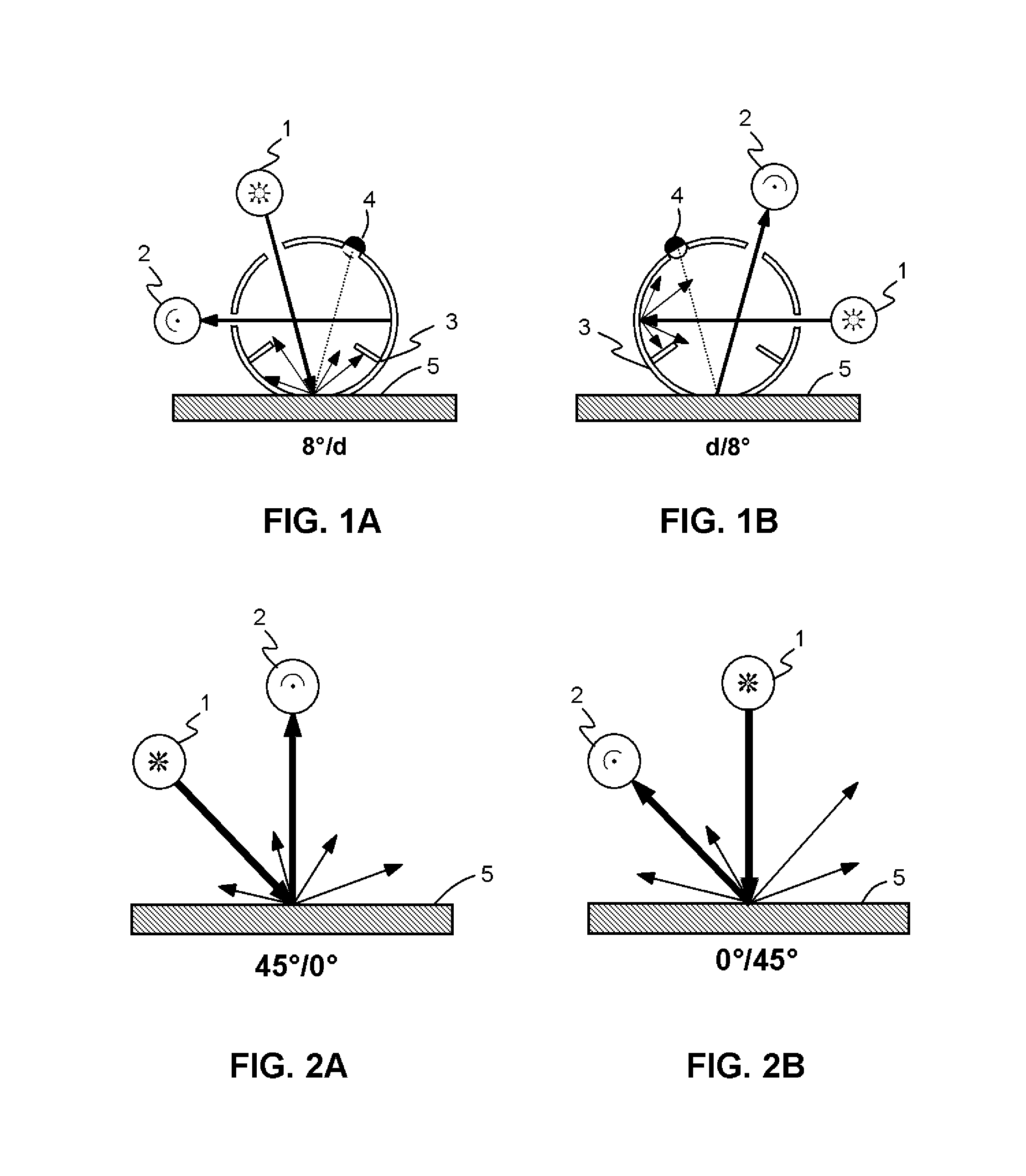
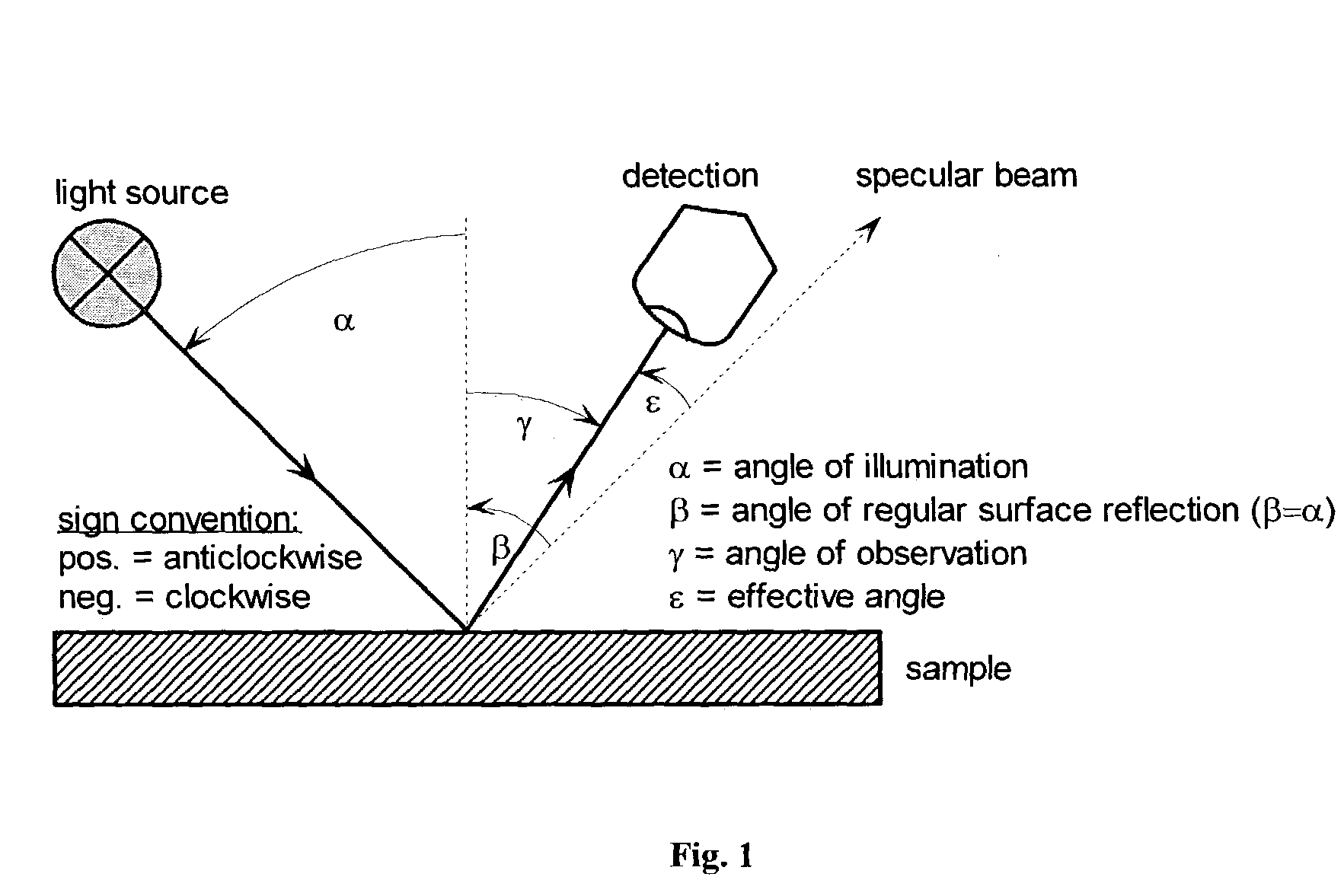
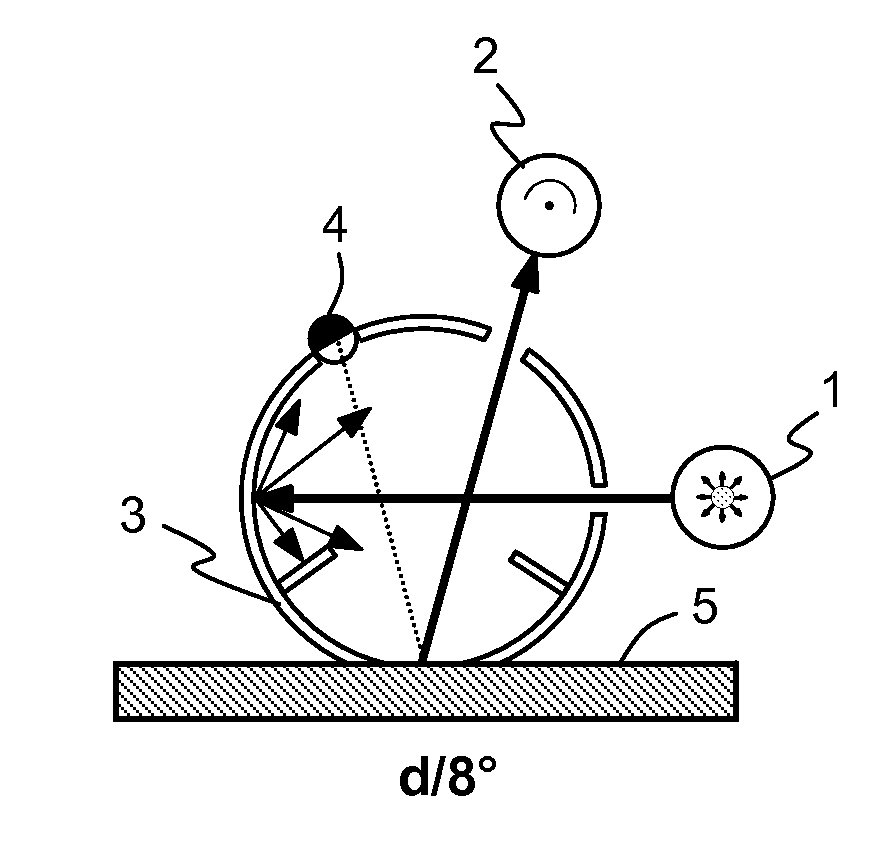
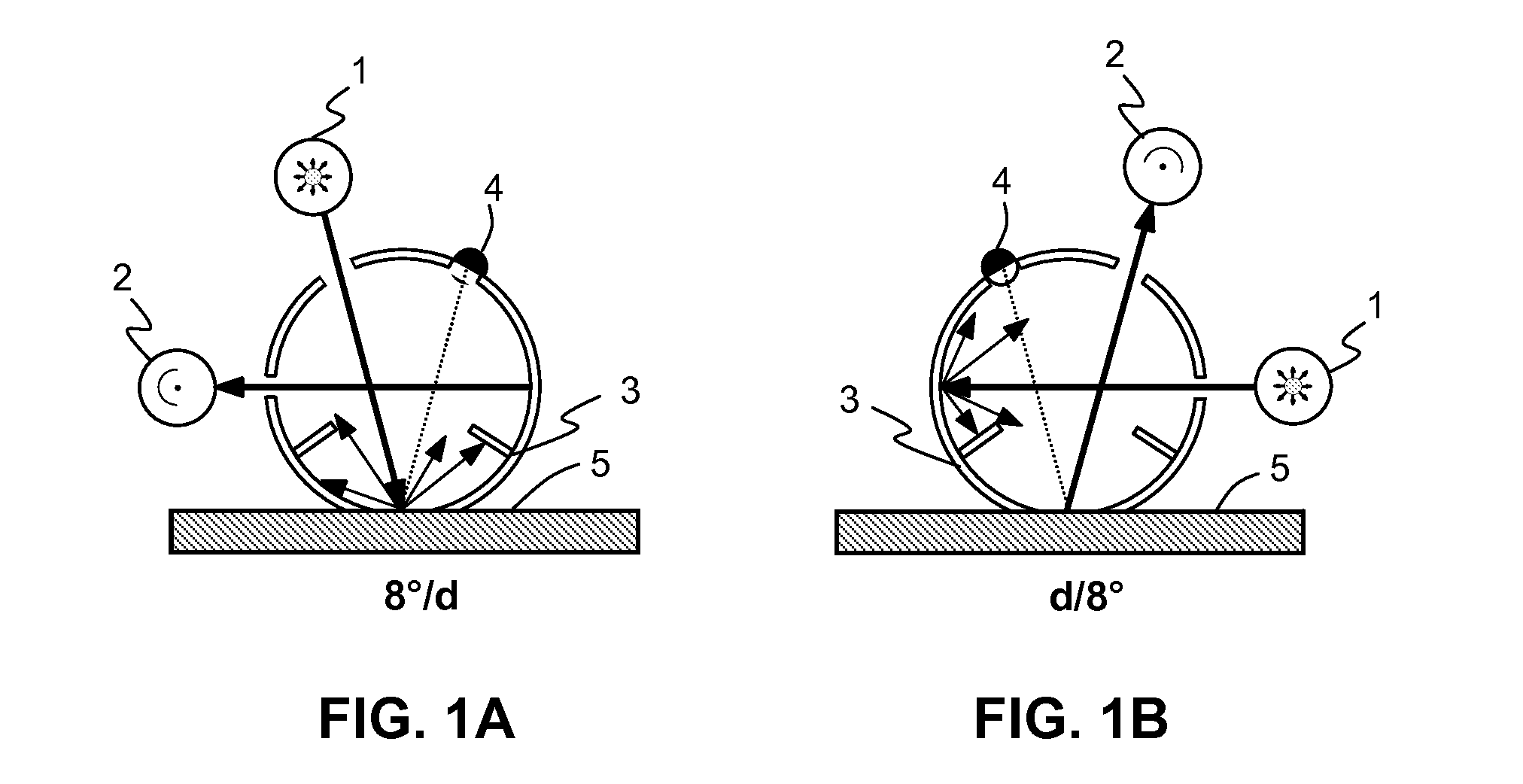
The present invention provides a colour recipe calculation method for matt finished, solid colour shades, by means of which it is possible to determine the proportion of matting agents in a colour recipe in a manner decoupled from the actual calculation of the recipe and is based on a conventional spectrophotometric characterization of a matt sample using a standardised 45° / 0° measurement geometry along with an established gloss measurement, or alternatively using a spectrophotometer equipped with a d / 8° measurement geometry and analyzing readings taken with the specular component included and excluded.
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
Glossiness determining device, color measuring device, image forming apparatus, and glossiness determination method
A glossiness determining device includes: a light source; a two-dimensional sensor that receives reflected light containing a specular reflection component of a subject illuminated by the light source, and outputs an image of the subject; and a determining unit that determines glossiness of the subject by using a saturated image, which is the image of the subject output by the two-dimensional sensor and in which pixel values of a partial area are saturated.
Owner:RICOH KK
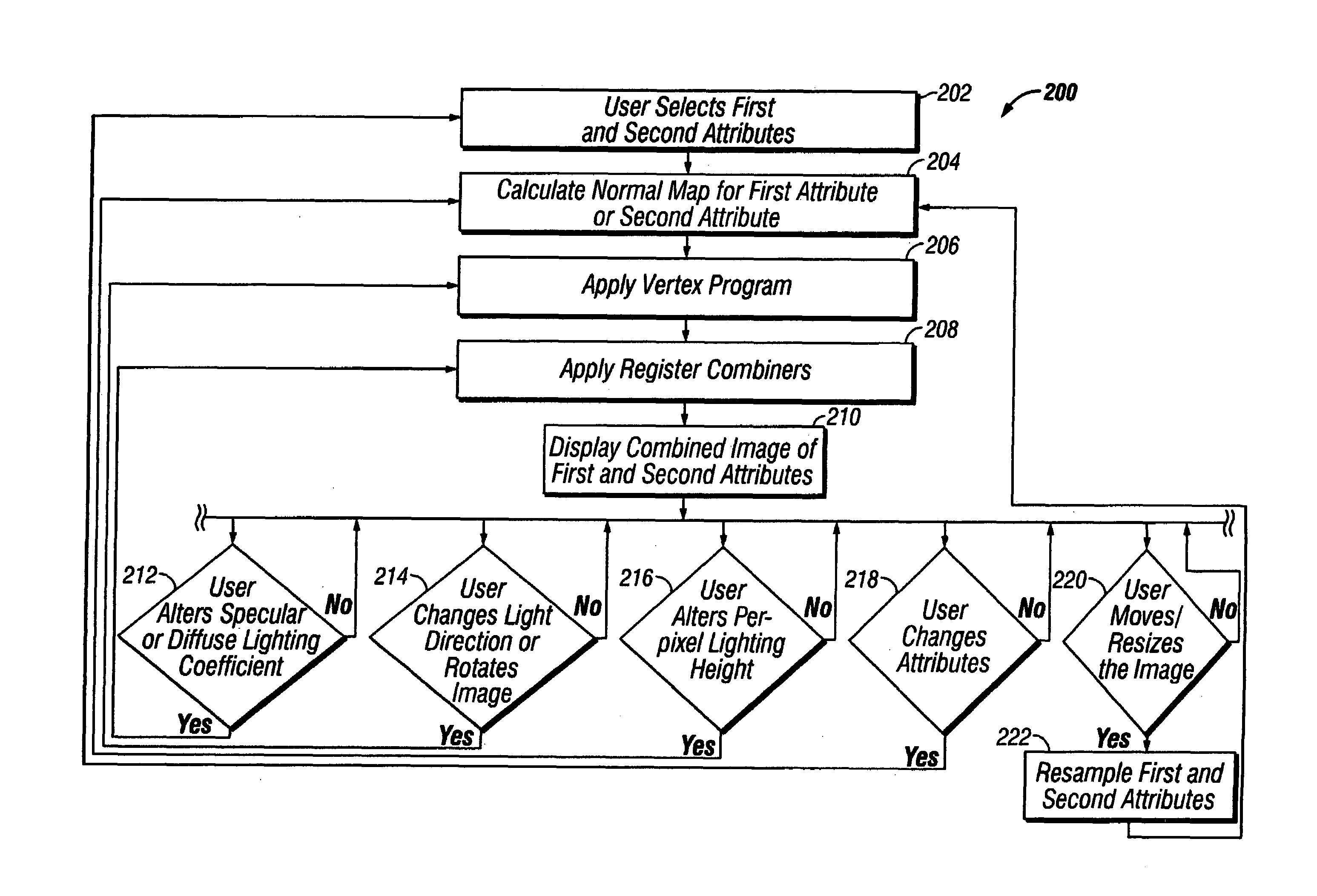
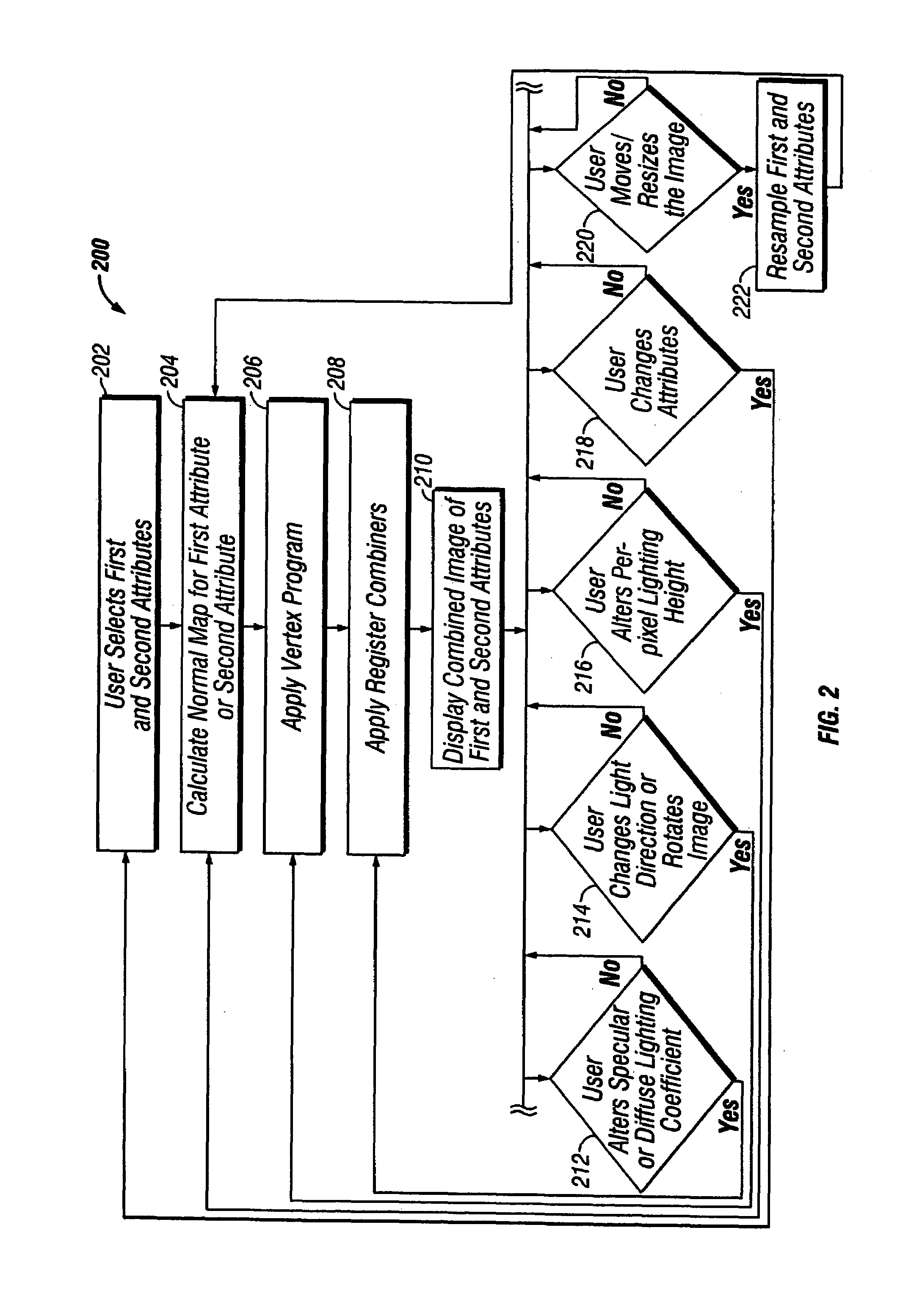
System and method for real-time co-rendering of multiple attributes
ActiveUS7298376B2Provides illusionDrawing from basic elementsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Multiple attribute
An apparatus and method for enhancing the combined image of multiple attributes without compromising the image of either attribute. The combined image of the multiple attributes is enhanced for analyzing a predetermined property revealed by the attributes. The combined image can be interactively manipulated to display each attribute relative to an imaginary light source or highlighted using a specular component. The method and apparatus are best described as particularly useful for analytical, diagnostic and interpretive purposes.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS CORP
Colour recipe calculating method for matt colour standards
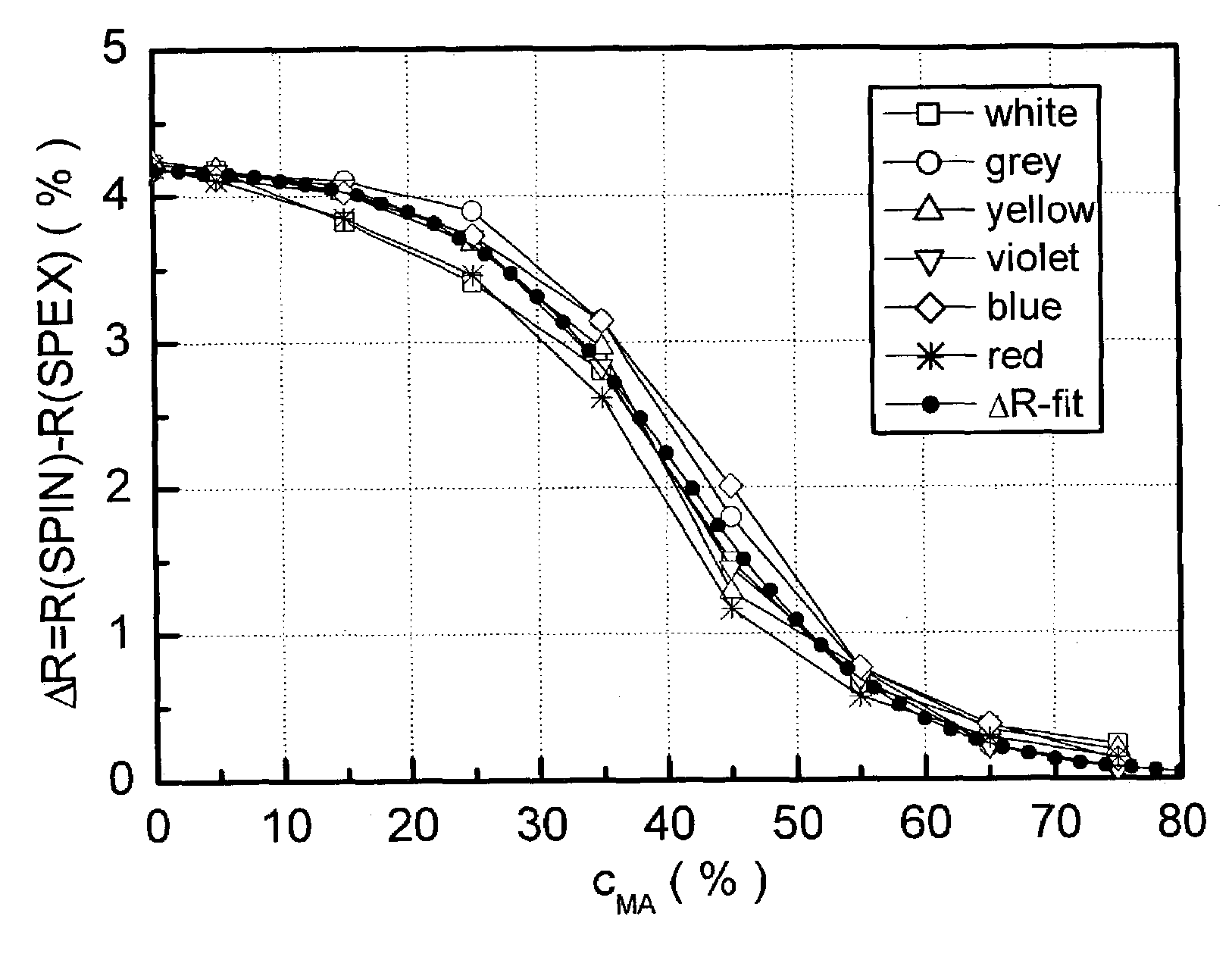
ActiveUS20140350895A1Reduce processing timeAttractive priceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceScattering properties measurementsMeasuring instrumentSpins
The invention relates to a method for colour recipe calculation for matt colour standards with the steps: A) experimentally determining reflection spectra R(exp) of the colour standard, comprising a first reflection spectrum (SPIN) and a second reflection spectrum (SPEX), with an integrating sphere colour measurement instrument, wherein said first reflection spectrum (SPIN) is obtained at (A1) d / 8°—geometry with the specular component included, and said second reflection spectrum (SPEX) is obtained at (A2) d / 8°—geometry with the specular component excluded; B1) calculating a recipe for the matt colour standard based on the experimentally determined reflection spectrum R(exp) with the specular component included, which has been corrected for the specular component, or B2) comparing the experimentally determined reflection spectrum R(exp) with the specular component included, en which has been corrected for the specular component, with reflection spectra associated to colour recipes of a colour recipe database for glossy colour shades and identifying from said colour recipe database a stored reflection spectrum which comes closest to the experimentally determined reflection spectrum R(exp) of the matt colour standard, as well as the associated colour recipe; C) converting reflection spectra data of the experimentally determined reflection spectra (SPIN, SPEX) of the matt colour standard to gloss values, and D) converting the gloss values obtained to the amount of matting agent (MAA) with the assistance of previously prepared calibration curves for the available colorant system.
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
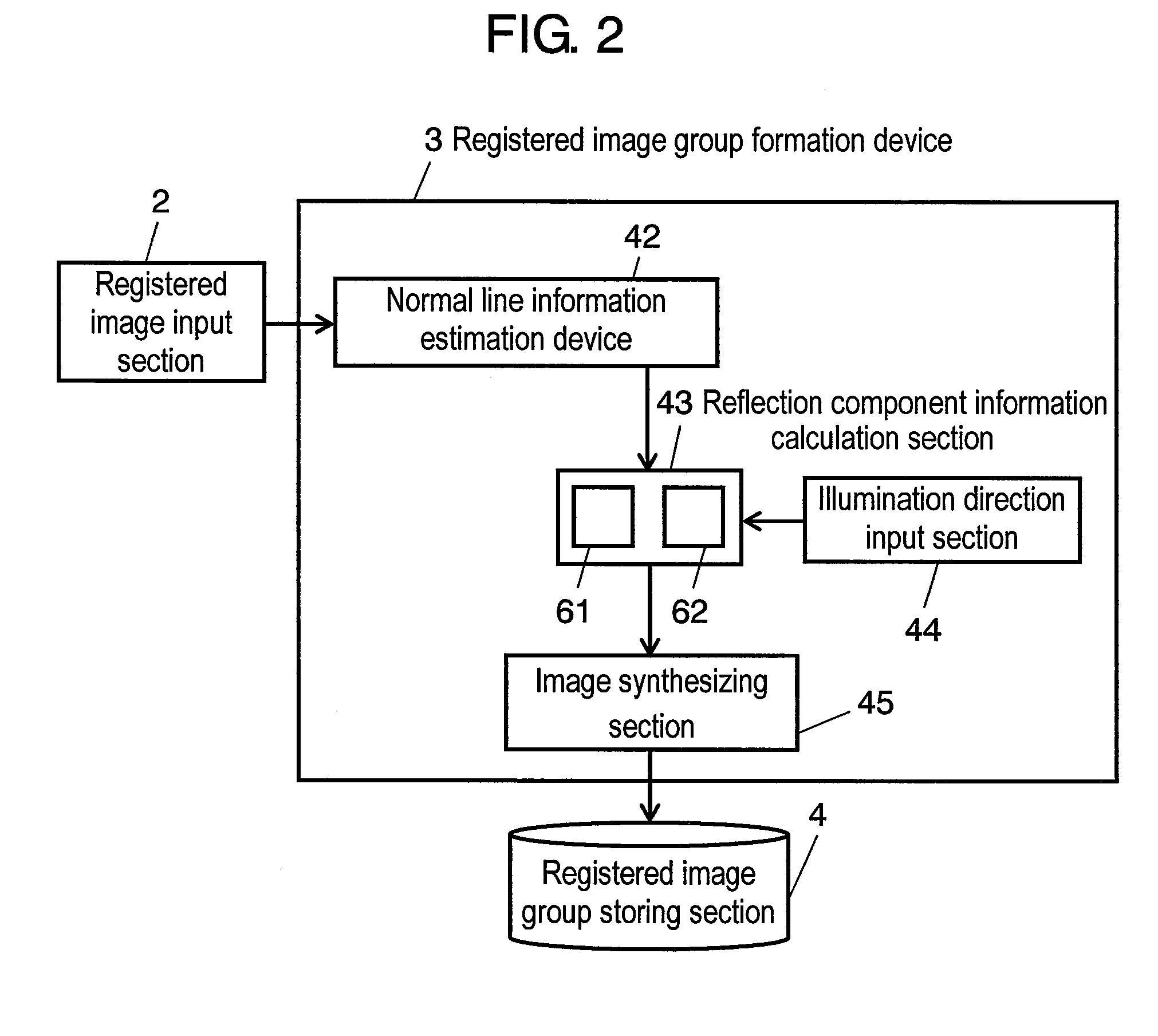
Normal line information estimation device, registered image group formation device and image collation device, and normal line information estimation method
InactiveUS20090208108A1High authentication rateHigh rateImage enhancementImage analysisImage estimationEstimation methods
A normal line information estimation device for estimating normal line information of an object from an image of the object. The normal line information estimation device includes an illumination direction estimation section for estimating an illumination direction with respect to the object in the image from a luminance value of the image; a normal line information estimation section for estimating the normal line information of the object in the image based on the illumination direction; and a specular reflection component estimation section for estimating a specular reflection component of the image from the normal line information of the object and the illumination direction with respect to the object. The normal line information estimation section estimates the normal line information again from the image from which a specular reflection component has been removed in the specular reflection component section.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Image processing device, image processing method and image processing program
ActiveUS8457389B2Improve accuracyEasy to identifyImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingAlbedo
An image processing device calculates, from a registration image representing a photographed object and three-dimensional shape data in which respective points of a three-dimensional shape of the object are correlated with pixels of the registration image, by assuming uniform albedo, a shadow base vector group having components from which an image under an arbitrary illumination condition can be generated through linear combination. A shadow in the registration image is estimated with using the vector group. A perfect diffuse component image including the shadow is generated, and based on the image a highlight removal image is generated in which a specular reflection component is removed from the registration image. Thus, an image recognition system generates illumination base vectors from the highlight removal image and thereby can obtain the illumination base vectors based on which an accurate image recognition process can be carried out without influence of a specular reflection.
Owner:NEC CORP
Thermoplastic polycarbonate compositions with improved optical surface quality, articles made therefrom and method of manufacture
A thermoplastic composition contains a polycarbonate resin, an aromatic vinyl copolymer, an impact modifier and a mineral filler, wherein the composition has a lightness L* of greater than or equal to about 70 under one or more of CIE D65, CWF-2 or C illumination using a 2° observer at 360 to 750 nanometers (nm), including specular components. Alternatively, a thermoplastic composition may contain a polycarbonate resin, a vinyl aromatic copolymer, an impact modifier and a mineral filler, and less than or equal to about 400 parts per million iron, by weight of the composition. An article may be formed by molding, extruding, shaping or forming such a composition to form the article.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Recipe calculation method for matt color shades
ActiveUS7158672B2Scattering properties measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer visionSpecular component
The present invention provides a color recipe calculation method for matt finished, solid color shades, by means of which it is possible to determine the proportion of matting agents in a color recipe in a manner decoupled from the actual calculation of the recipe and is based on a conventional spectrophotometric characterization of a matt sample using a standardised 45° / 0° measurement geometry along with an established gloss measurement, or alternatively using a spectrophotometer equipped with a d / 8° measurement geometry and analyzing readings taken with the specular component included and excluded.
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
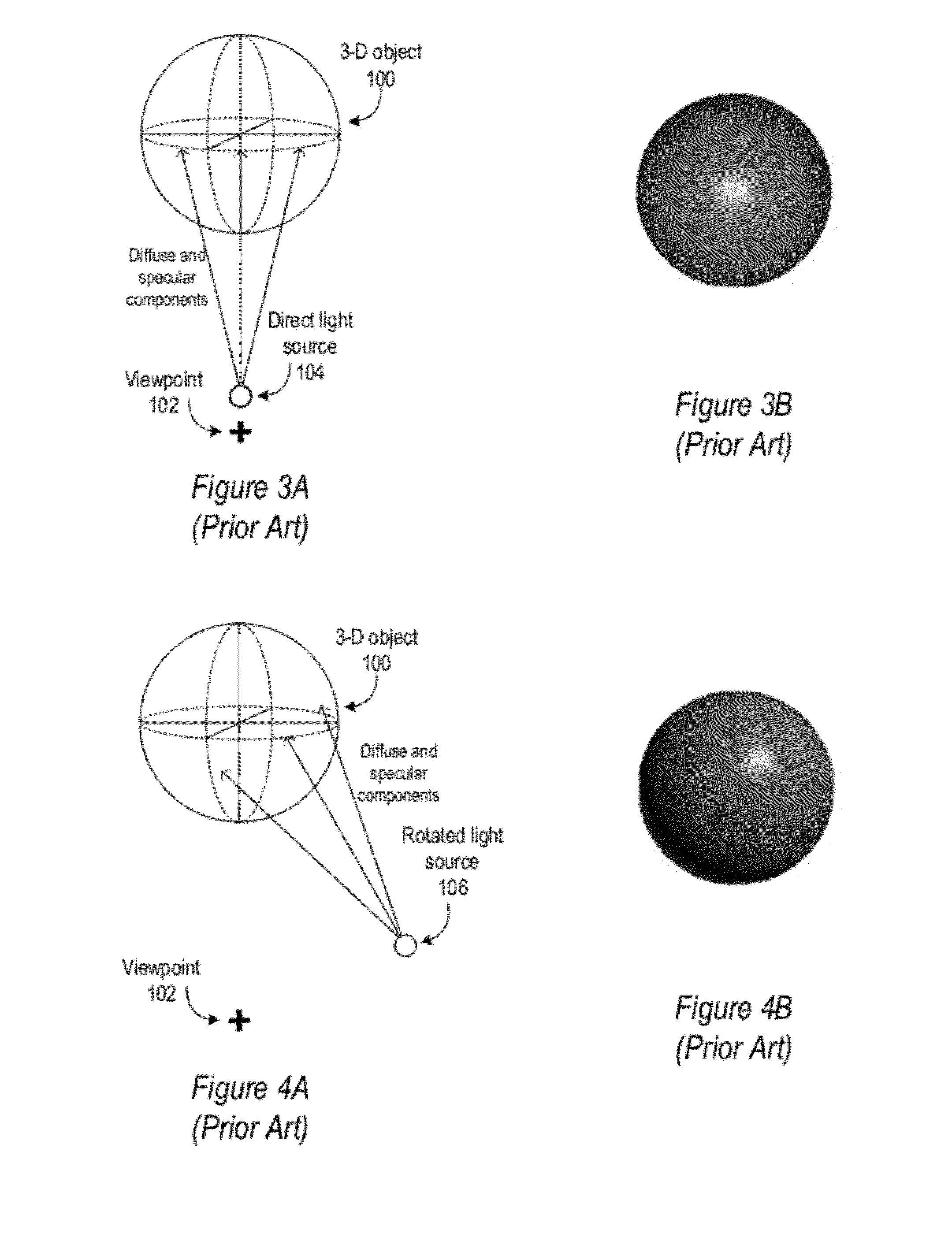
Method and apparatus for illuminating objects in 3-D computer graphics
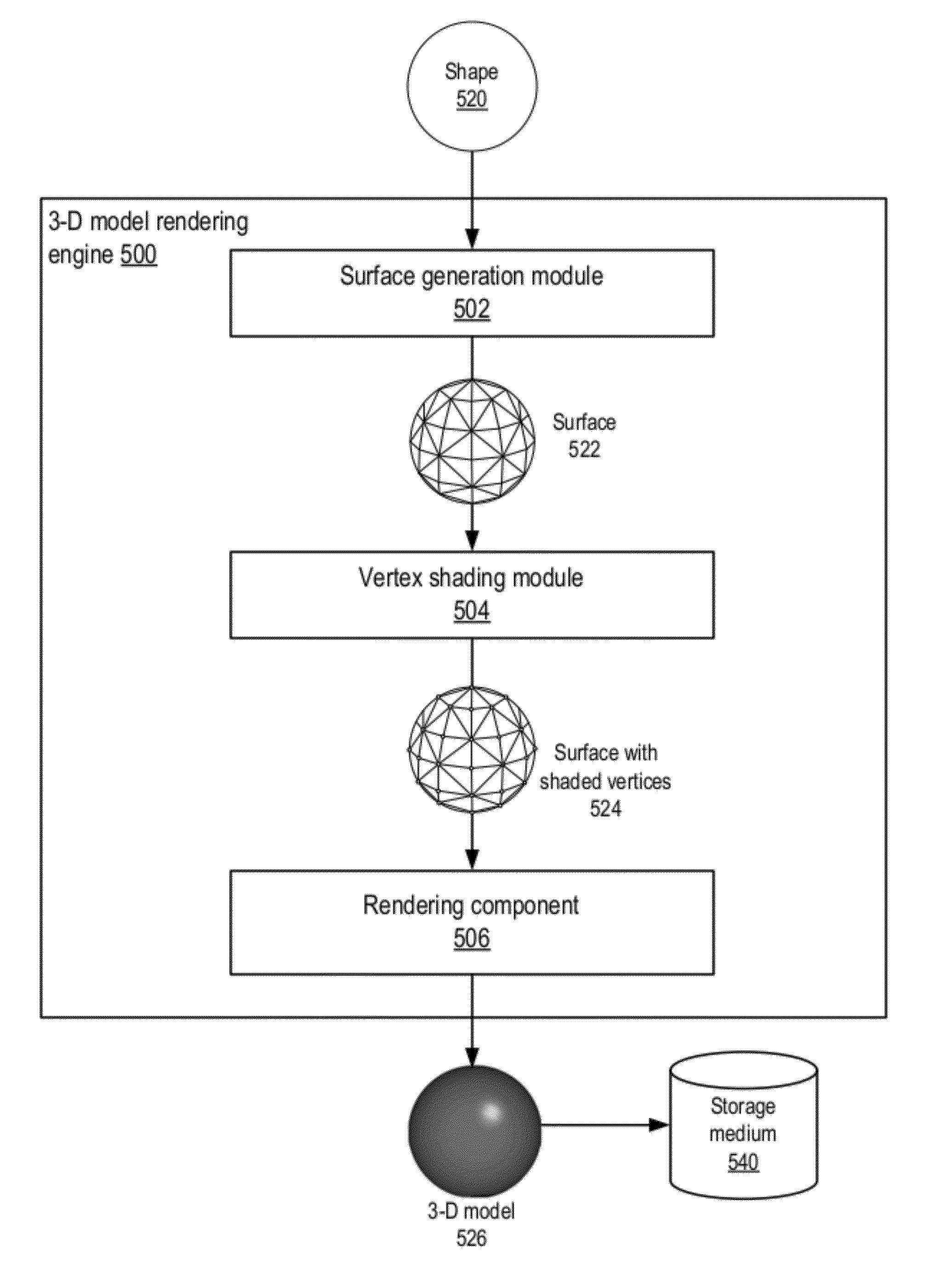
ActiveUS8294713B1Convenient lightingAvoid problems3D-image rendering3D modellingGraphicsEffect light
A method and apparatus for illuminating objects in 3-D computer graphics are described in which a single equation that employs two light sources is used to perform vertex shading. In the vertex shading equation, a direct light source is used to calculate a diffuse component of the lighting, while a rotated light source is used to calculate a specular component of the lighting. Using a single equation that employs two different light sources may provide better lighting for portions of object(s) when compared to conventional vertex shading techniques, while doing so at the same or similar computational cost as conventional techniques that use a single light source to calculate the diffuse and specular components.
Owner:ADOBE INC
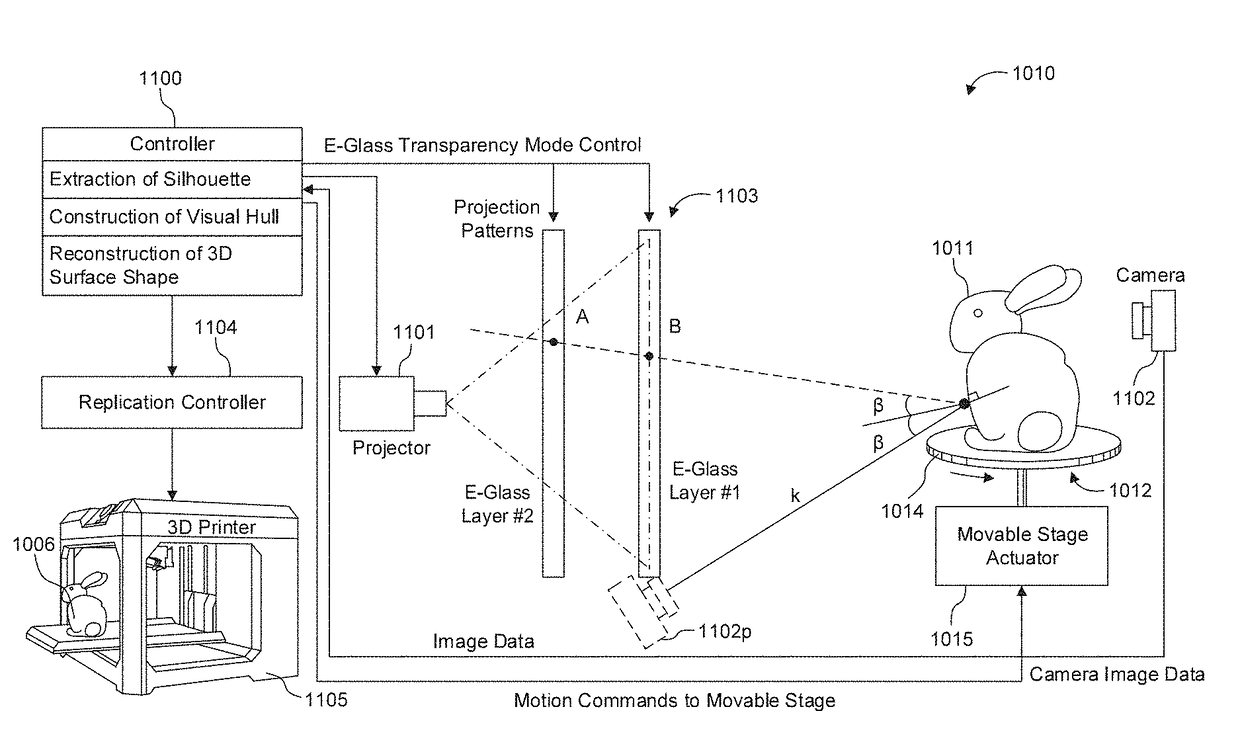
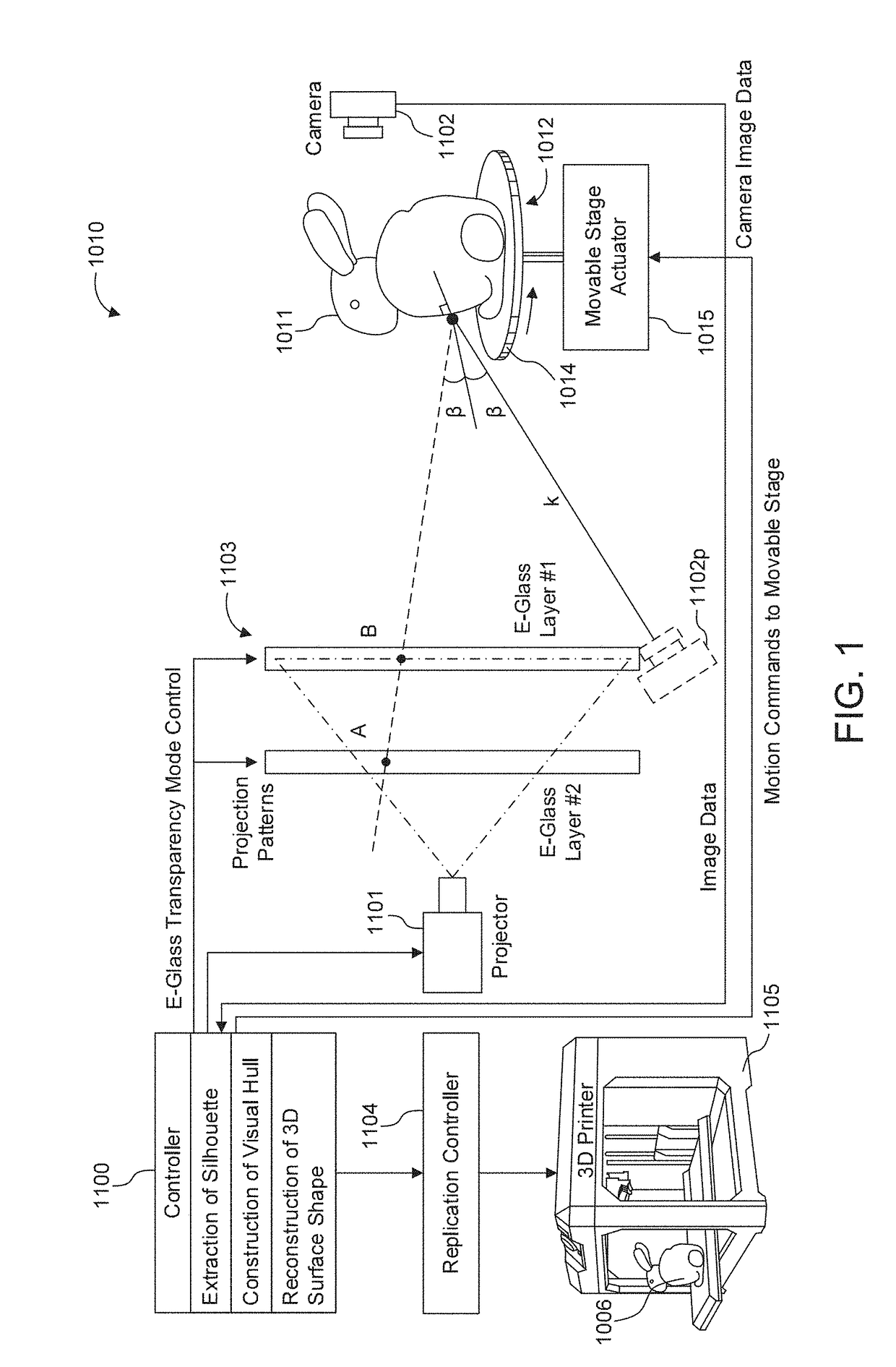
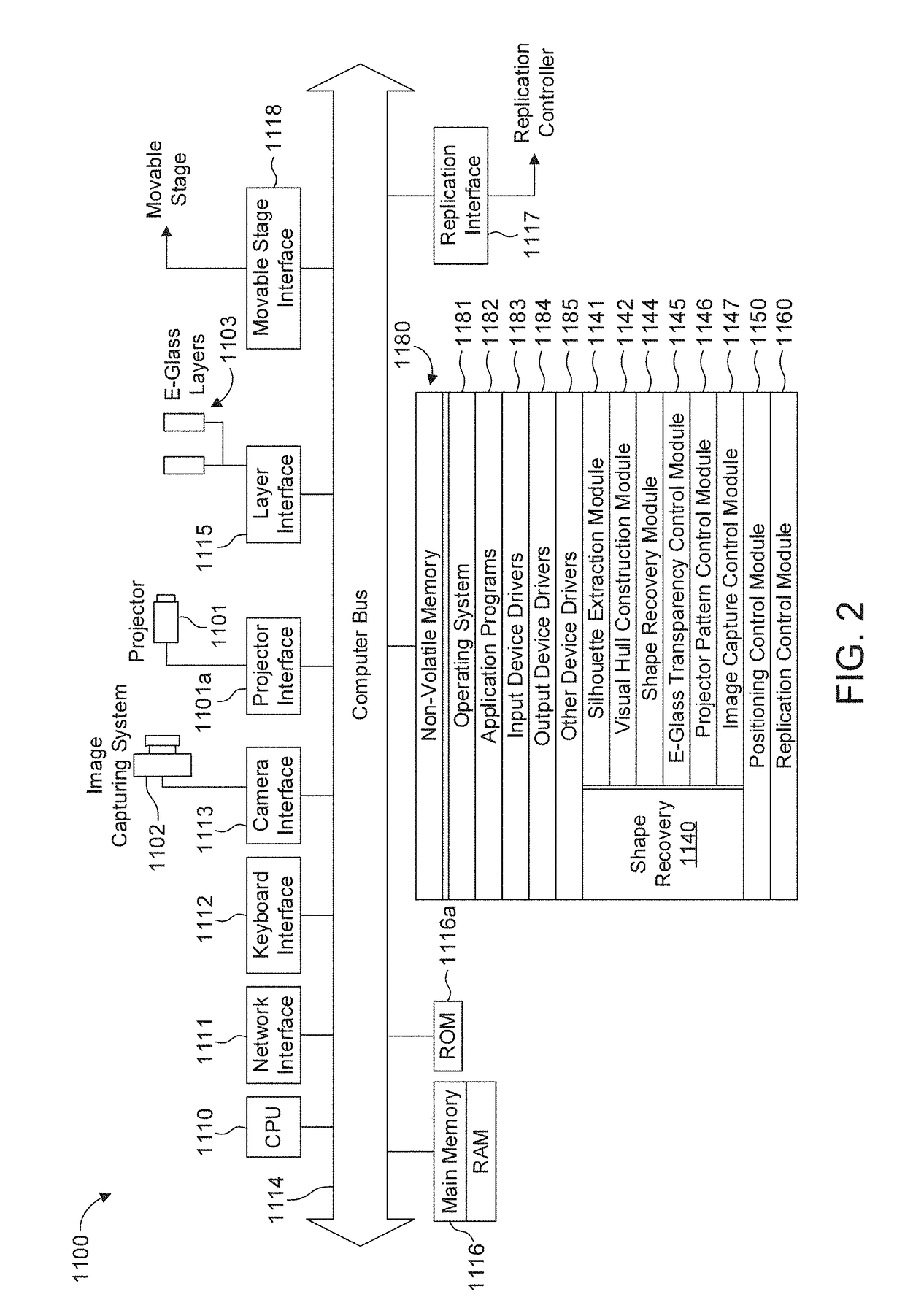
Shape reconstruction using electronic light diffusing layers (e-glass)
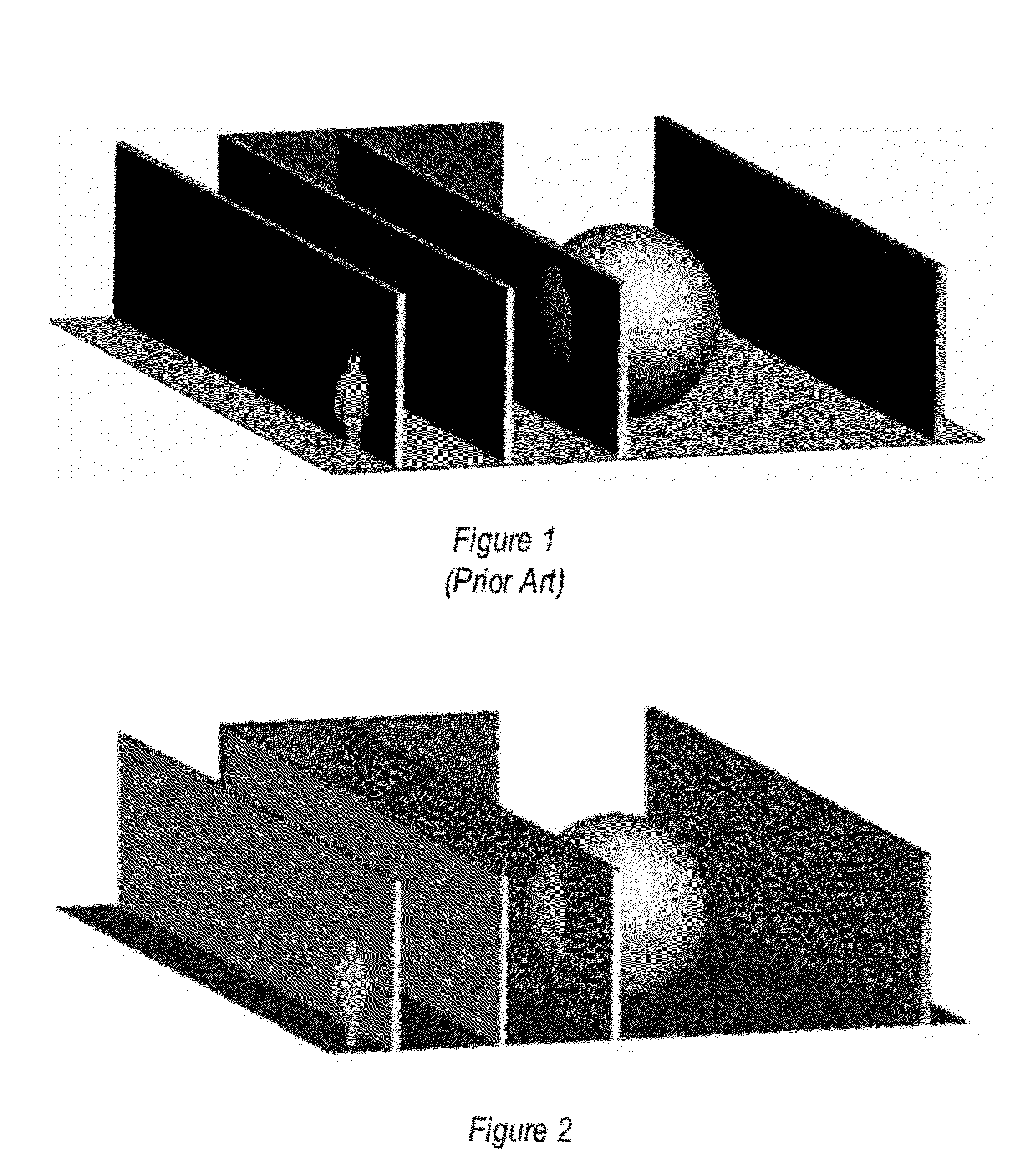
ActiveUS20170302902A1Accurate silhouette extractionSimple methodImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelDiffuse reflection
Shape measurement of a specular object even in the presence of multiple intra-object reflections such as those at concave regions of the object. Silhouettes of the object are extracted, by positioning the object between a camera and a background. A visual hull of the object is reconstructed based on the extracted silhouettes, such as by image capture of shadows of the object projected onto a screen, and image capture of reflections by the surface of the object of coded patterns onto the screen. The visual hull is used to distinguish between direct (single) reflections of the coded patterns at the surface of the object and multiple reflections. Only the direct (single) reflections are used to triangulate camera rays and light rays onto the surface of the object, with multiple reflections being excluded. The 3D surface shape may be derived by voxel carving of the visual hull, in which voxels along the light path of direct reflections are eliminated. For surface reconstruction of heterogeneous objects, which exhibit both diffuse and specular reflectivity, variations in the polarization state of polarized light may be used to separate between a diffuse component of reflection and a specular component.
Owner:CANON KK
Recycling backlights with semi-specular components
ActiveUS8608363B2Improve output performanceHollow light guidesIlluminated signsBack reflectorInjection point
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Ultrasound diagnostic apparatus, method of transmitting and receiving ultrasonic wave, and program for transmitting and receiving ultrasonic wave
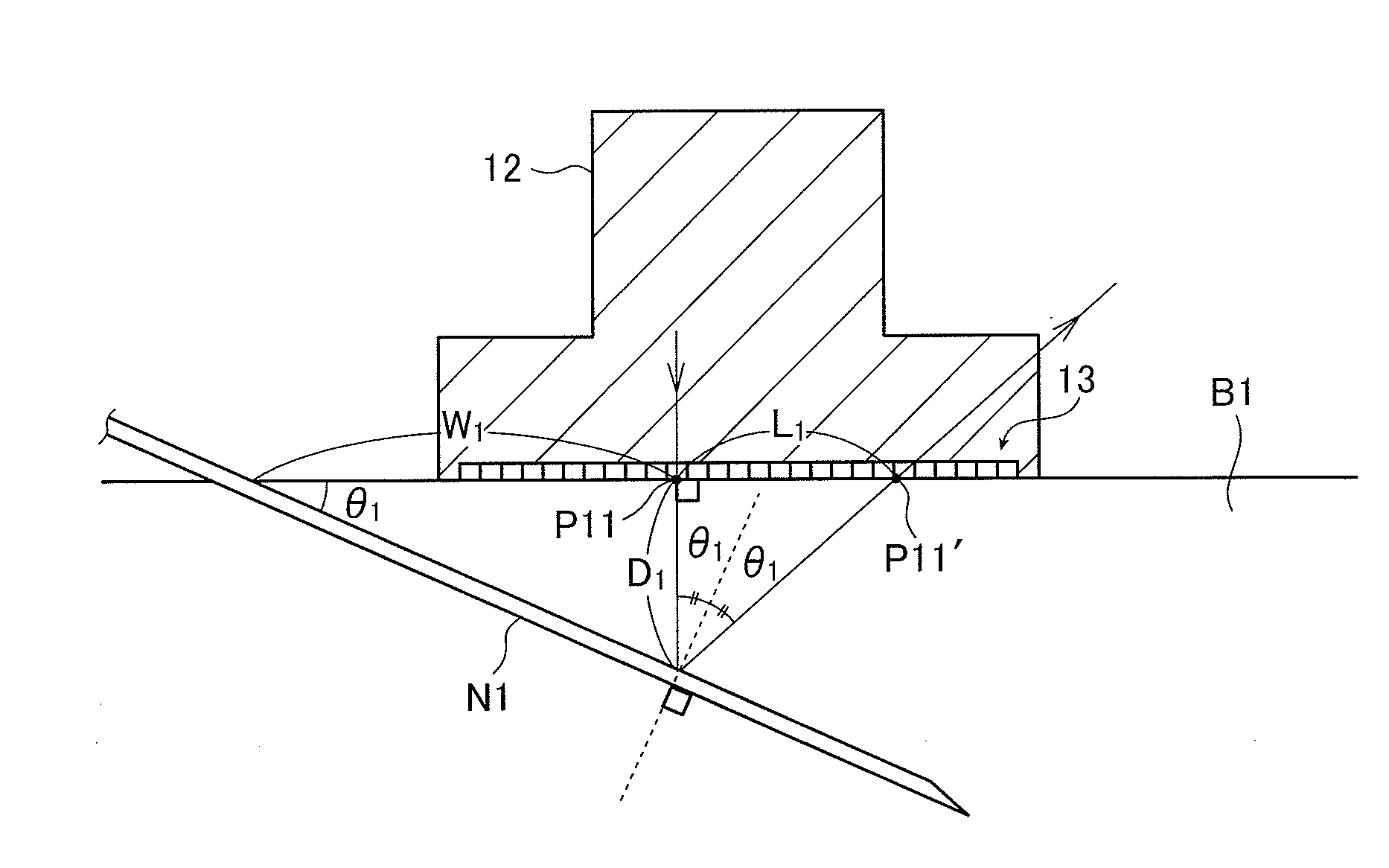
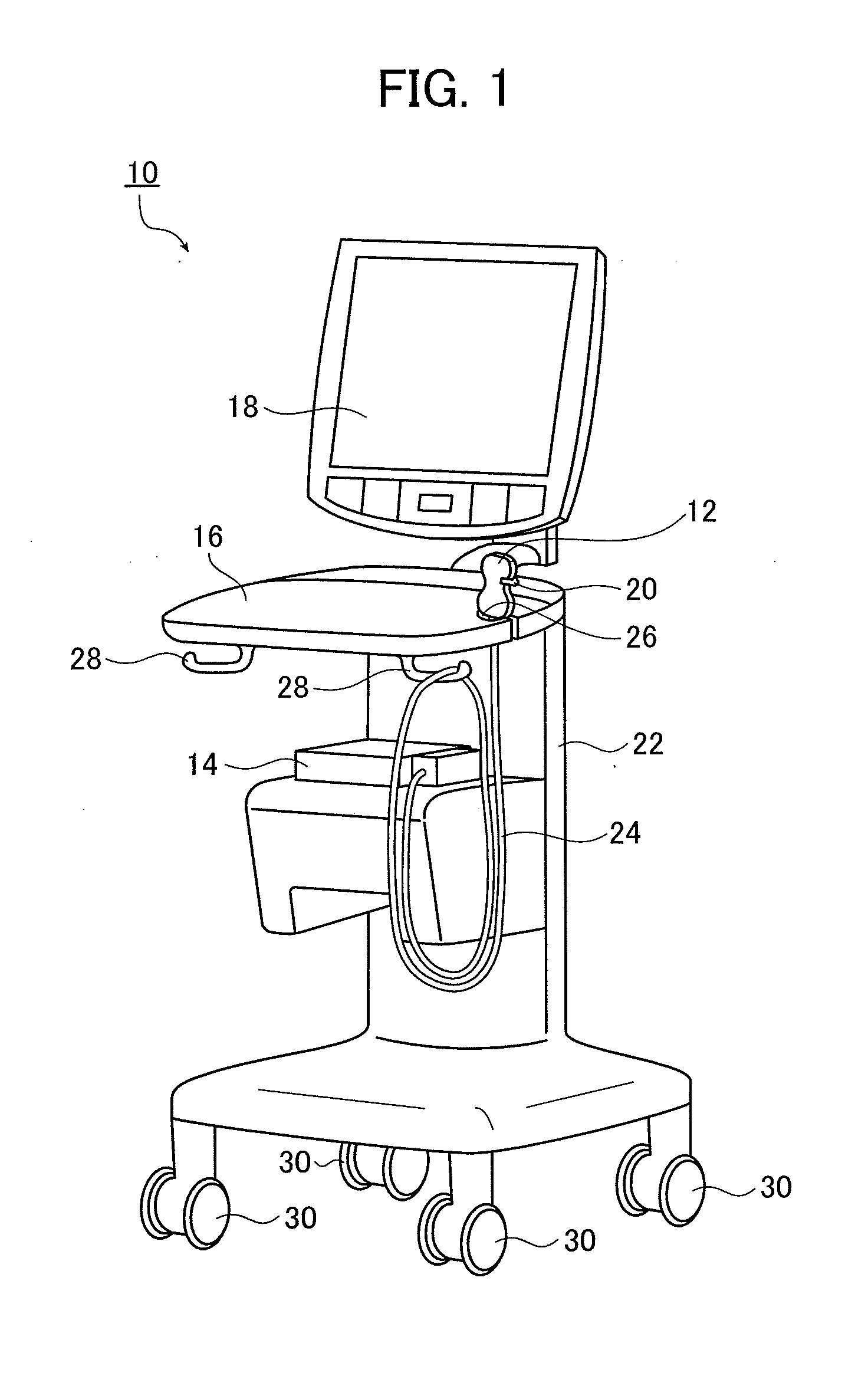
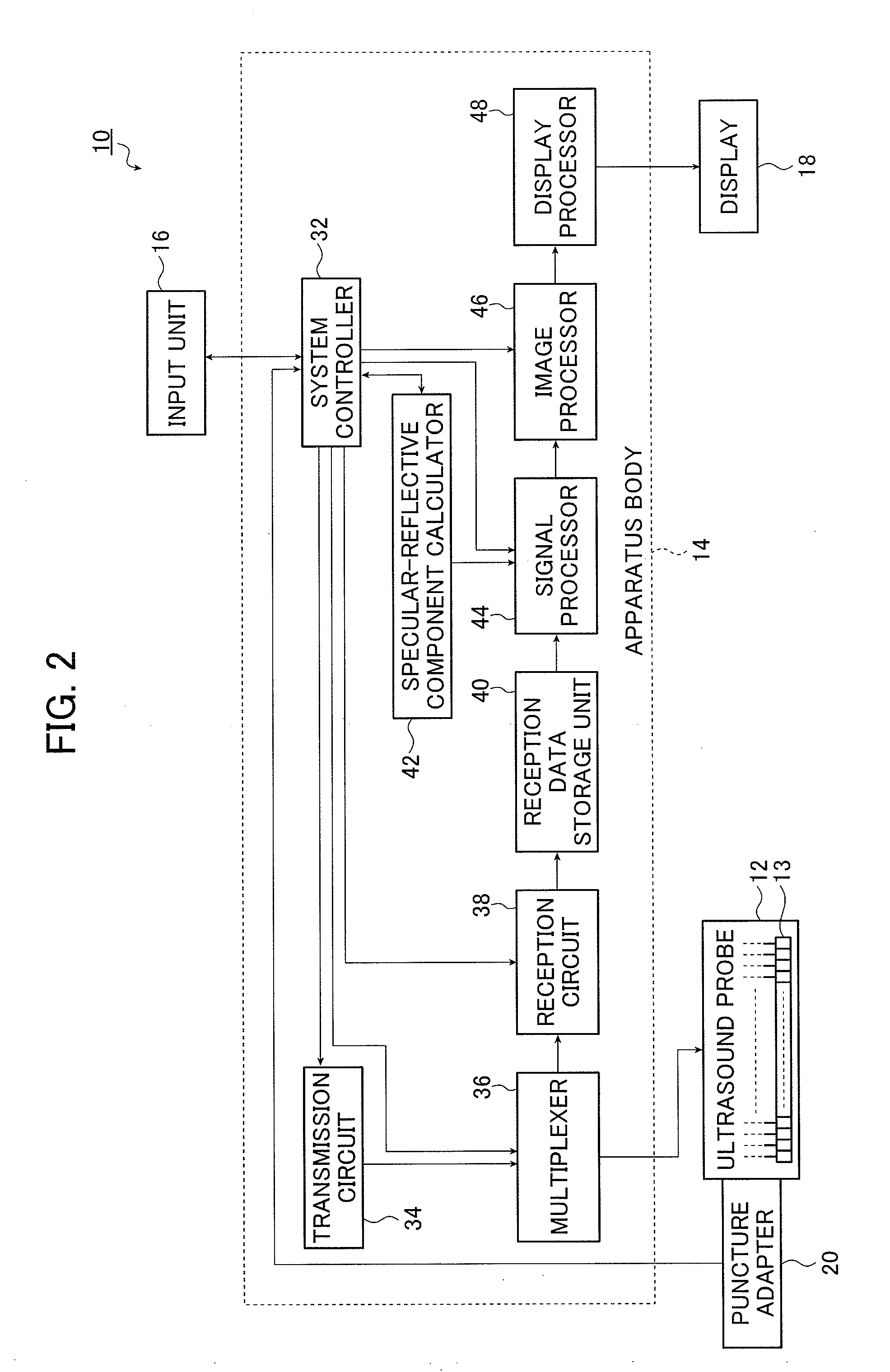
ActiveUS20120226164A1High strengthIncrease awarenessUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesUltrasonic beamSonification
An ultrasound diagnostic apparatus includes plural ultrasound transducers which perform transmission and reception of ultrasonic waves toward a target site of a subject containing a puncture needle. A method of transmitting and receiving an ultrasonic wave uses the ultrasound transducers. The apparatus and the method form an ultrasonic beam to be transmitted from a transmit aperture set on the ultrasound transducers, acquire information relating to a specular-reflective component of the ultrasonic beam in the puncture needle, set a first receive aperture different from the transmit aperture set on the ultrasound transducers on the basis of the information relating to the specular-reflective component of the ultrasonic beam, and process an ultrasonic echo signal received by the ultrasound transducers using the first receive aperture.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Image processing method, image processor, and image processing program
A polarized image acquisition section shoots a subject through a polarizing element operable to set principal axes of which directions are different from each other. An incident plane specifying section specifies an incident plane of each pixel, and an incident angle computation section computes an incident angle of each pixel. A classifying section clusters pixels similar to each other in both incident plane and incident angle. A reflection component separation section performs reflection component separation on each clustered pixel set on the assumption of probabilistic independence between the diffuse reflection component and the specular reflection component.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Phase-controlled model-based overlay measurement systems and methods
Overlay measurement systems and methods are disclosed that control the relative phase between the scattered and specular components of light to amplify weak optical signals before detection. The systems and methods utilize model-based regressional image processing to determine overlay errors accurately even in the presence of inter-pattern interference.
Owner:JSMSW TECH
System for early detection of dental caries
A method is disclosed for processing of images to detect dental caries, that includes the following steps. Directing incident light (16) toward a tooth (20), where this light excites a fluorescent emission from the tooth. Obtaining a fluorescence image (35) from the fluorescent light component (19), and obtaining a reflectance image (34) from the back-scattered light (18) from the tooth. Applying a color balance operation to the reflectance image. Removing the specular reflectance components from the color balanced reflectance image (82) to give a back-scattered reflectance image (50). Registering the fluorescent image with the back-scattered reflectance image. Combining the registered fluorescent image (115) with the back-scattered reflectance image to provide a diagnostic image (52).
Owner:CARESTREAM DENTAL TECH TOPCO LTD
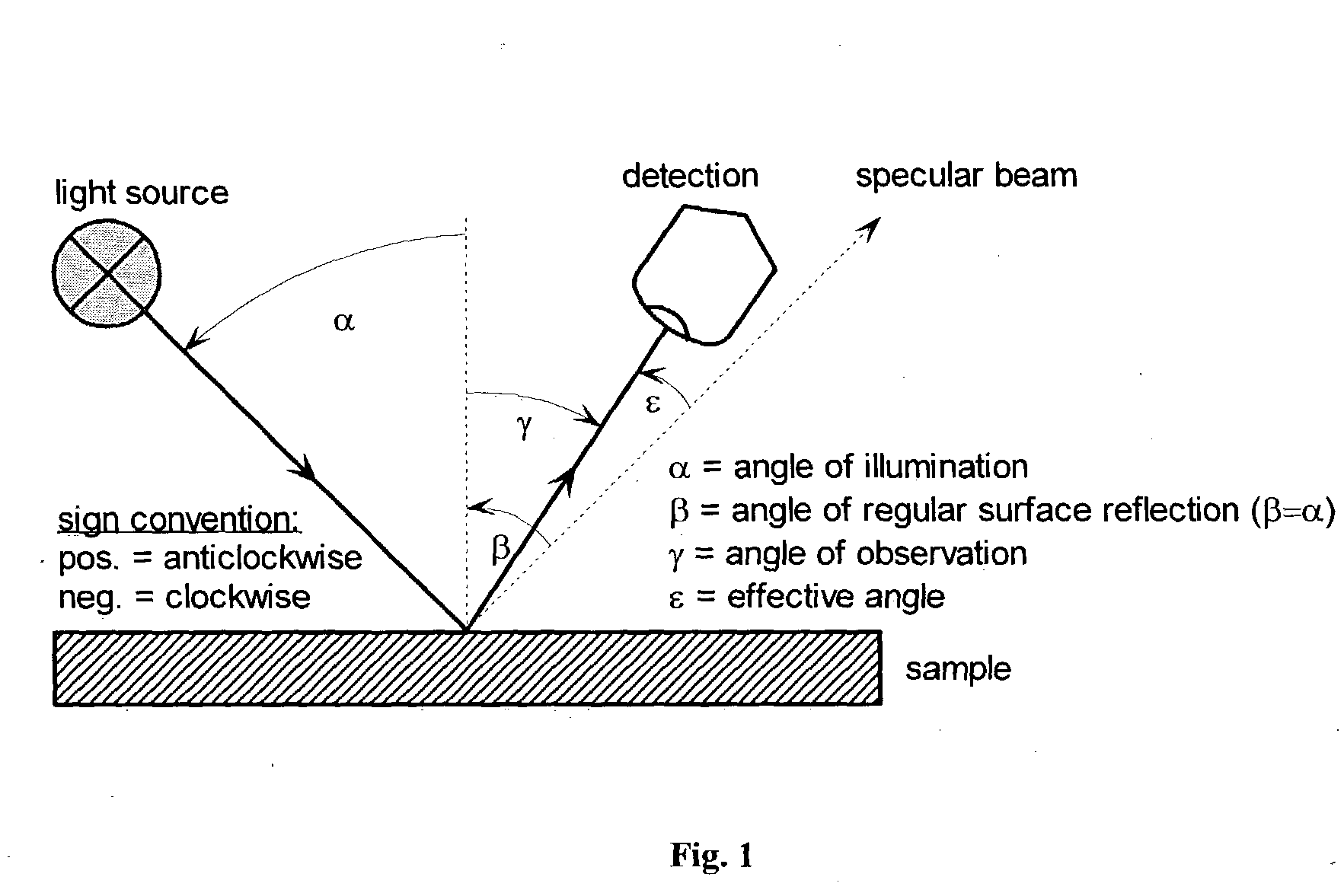
Method for determining the surface gloss of a colour standard
InactiveUS20140327912A1Reduce in quantityScattering properties measurementsSpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsFunctional RelationshipSpecular component
The invention relates to a method for determining the gloss of a colour standard comprising the following steps: A) experimentally determining reflection spectra R(exp) of the colour standard, comprising a first reflection spectrum and a second reflection spectrum, with an integrating sphere colour measurement instrument, wherein said first reflection spectrum is obtained at (A1) d / 8-geometry with the specular component included, and said second reflection spectrum is obtained at (A2) d / 8-geometry with the specular component excluded, and B) converting reflection spectra data of the experimentally determined reflection spectra R(exp) of the colour standard to gloss values by: B1) acquiring the difference reflection spectrum ΔR of the experimentally determined reflection spectrum R(exp) with the specular component included (A1) and the reflection spectrum R (exp) with the specular component excluded (A2), and B2) determining the gloss values corresponding to said difference reflection spectrum ΔR with the assistance of previously prepared calibration curves, representing the functional relationship between the difference reflection spectrum ΔR and the gloss values measured at one or more gloss angles.
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
A method for removing highlight of image in natural scene
ActiveCN111080686AEstimated Specular Reflection CoefficientGood effectImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Radiology
The invention discloses a method for removing highlight of an image in a natural scene, which comprises the following steps: decomposing an original image by using a robust sparse decomposition methodto obtain low-frequency information representing brightness change and color change of the image; converting the original image from a color space to a chrominance space, and estimating a specular reflection coefficient in the chrominance space by using low-frequency information; and calculating a specular reflection component by using the estimated specular reflection coefficient, removing the calculated specular reflection component from the original image, and converting the specular reflection component into a color space to obtain a highlight-removed image. According to the method, specular reflection can be accurately separated; the method has the advantages that the artifacts cannot be introduced during highlight elimination, the image cannot become blurred, the optimal highlight removal effect is achieved in a natural scene, and in addition, details and structural information of the original image are greatly reserved in some challenging scenes containing complex textures or saturated pixels.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Non-destructive method of determining the refractive index of clear coats
InactiveUS7248350B2Phase-affecting property measurementsScattering properties measurementsNon destructiveDifferential spectrum
The invention is directed to a method for determining repairability of an original clear coat applied over a darkly pigmented substrate with a corresponding repair clear coat used in repairing damaged original vehicle coatings. The method non-destructively determines the refractive indices of the original clear coat and the corresponding repair clear coats by acquiring the reflection spectrum of these coats with a spectrophotometer with d / 8° measurement geometry with and without the specular components followed by determining the refractive indices with the assistance of the differential spectrum between the reflection spectrums with and without the specular components, and then comparing the refractive indices to determine difference between these refractive indices, wherein when the difference between the refractive indices of the original arid repair clear coats is within an acceptable range, the repair clear coat is used for repairing the original clear coat.
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
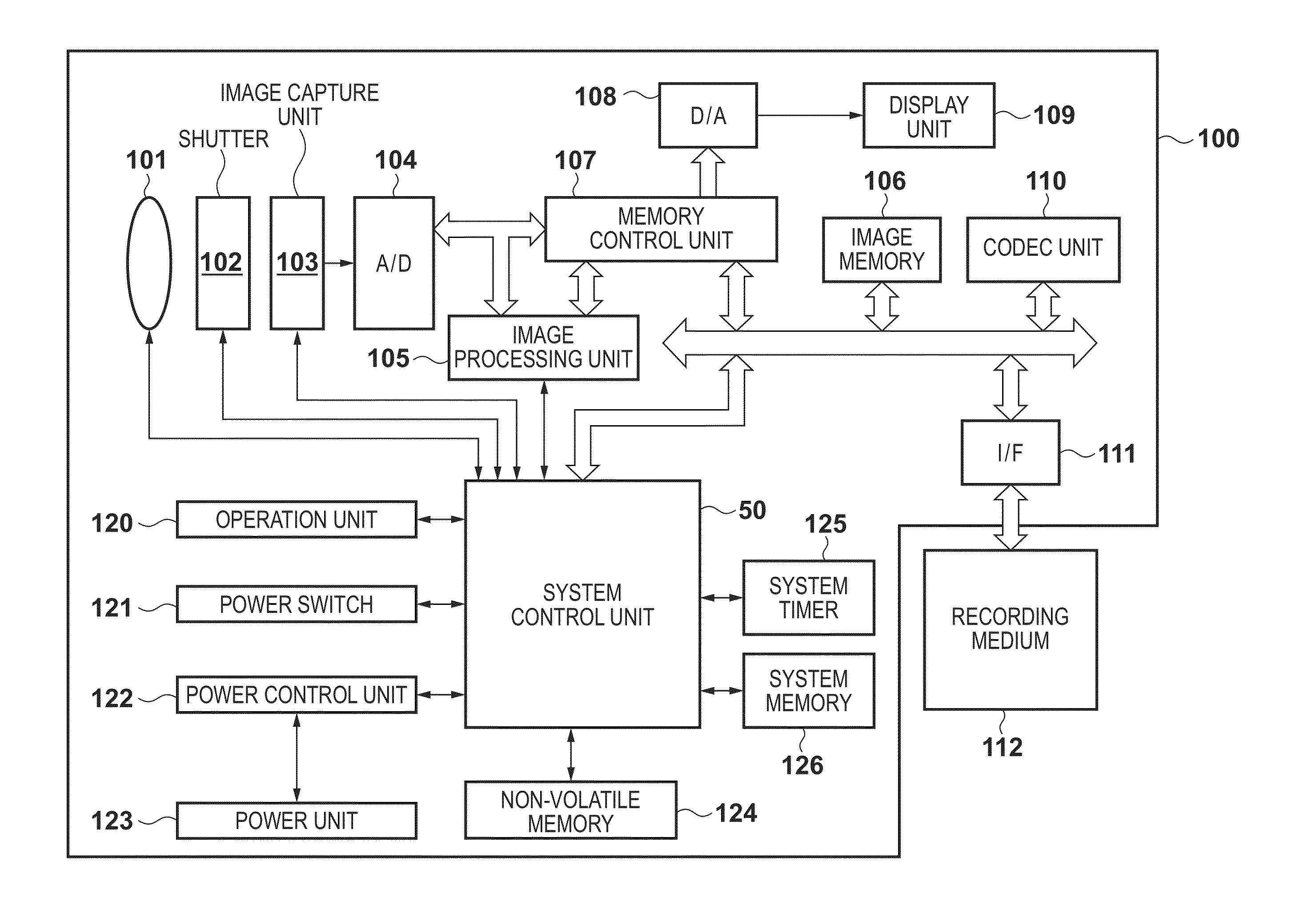
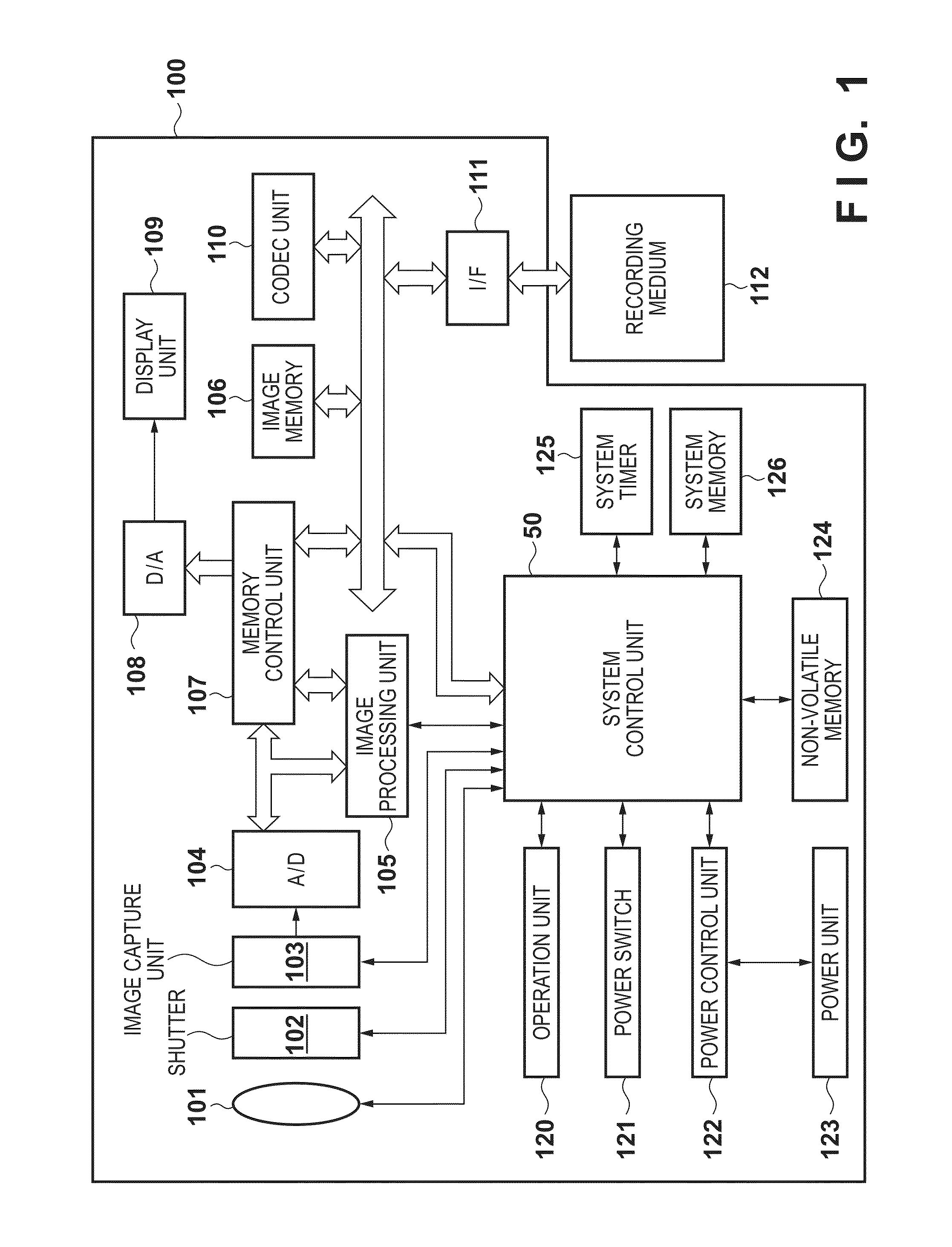
Image processing apparatus and control method therefor
InactiveUS20130342724A1Accurate white balance gainTrue colorColor signal processing circuitsImaging processingSpecular component
An image processing apparatus is provided that allows accurate white balance gains to be obtained by accurately estimating the illuminant colors of various objects in an image. The white balance gains are obtained based on values of white pixels that have been extracted from an input image and have colors included in an extraction range, and the white balance gains are obtained based on specular reflection components included in the input image, are mixed in accordance with a mix ratio. The mix ratio is determined in accordance with, for example, a degree of reliability of extraction of the white pixels.
Owner:CANON KK
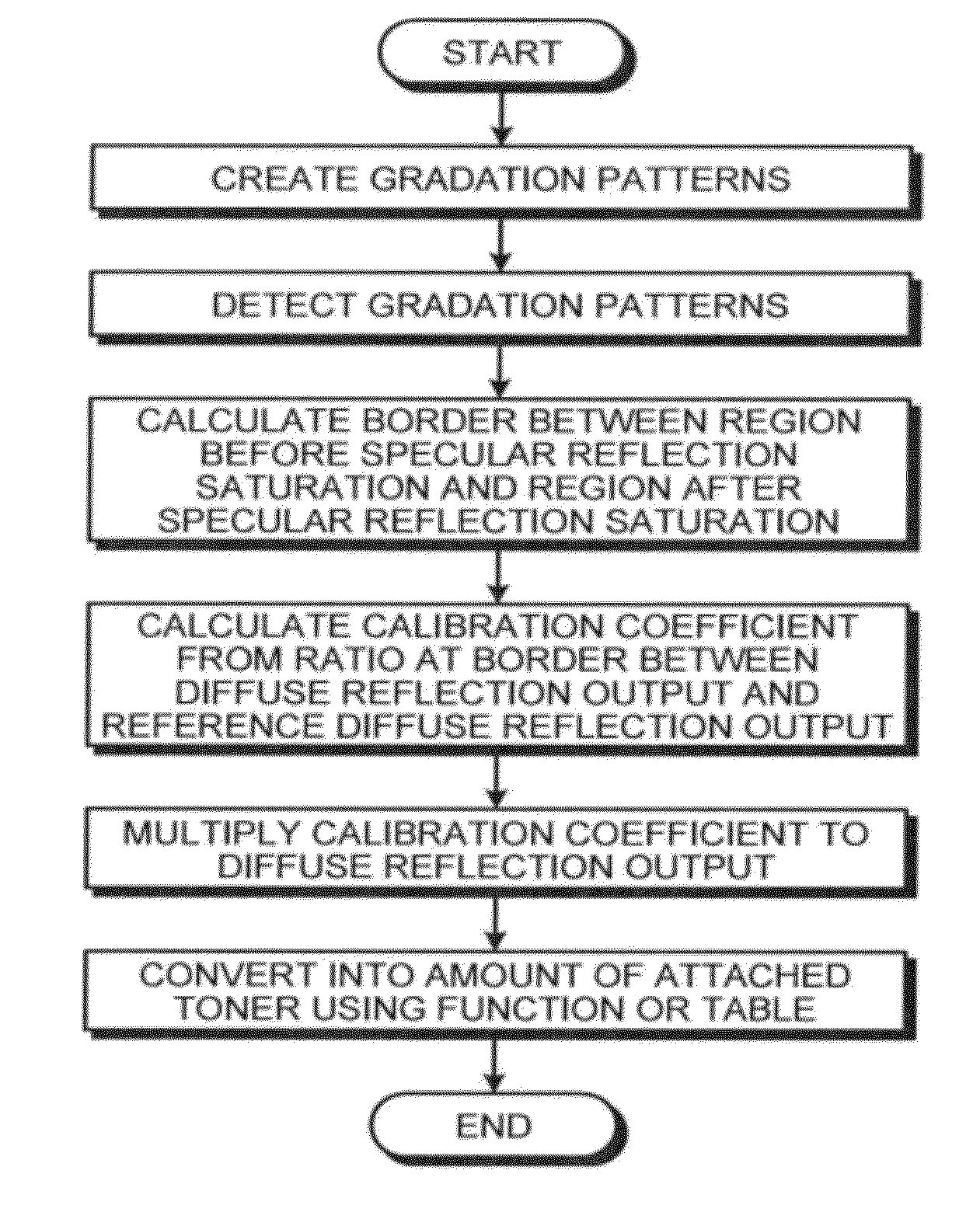
Diffuse reflection output conversion method, attached powder amount conversion method, and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20120315056A1Material analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansDiffuse reflectionSpecular component
In an embodiment, a diffuse reflection output conversion method is executed in an apparatus detecting a plurality of gradation patterns. The apparatus includes a light emitter and light receiver, and detects specular reflection and diffuse reflection simultaneously. A region before specular reflection saturation is a region where the specular reflection component decreases and saturates at minimum level. A diffuse reflection detector is calibrated by: obtaining a diffuse reflection output resulting from an amount of attached powder at a border between the region before specular reflection saturation and the region after specular reflection saturation; calculating a ratio between the diffuse reflection output and a reference diffuse reflection output calculated in advance as a calibration coefficient; and multiplying a diffuse reflection output obtained from the gradation patterns by the calibration coefficient calculated at the calculating.
Owner:RICOH KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com