Patents
Literature
437results about "Investigating jewels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
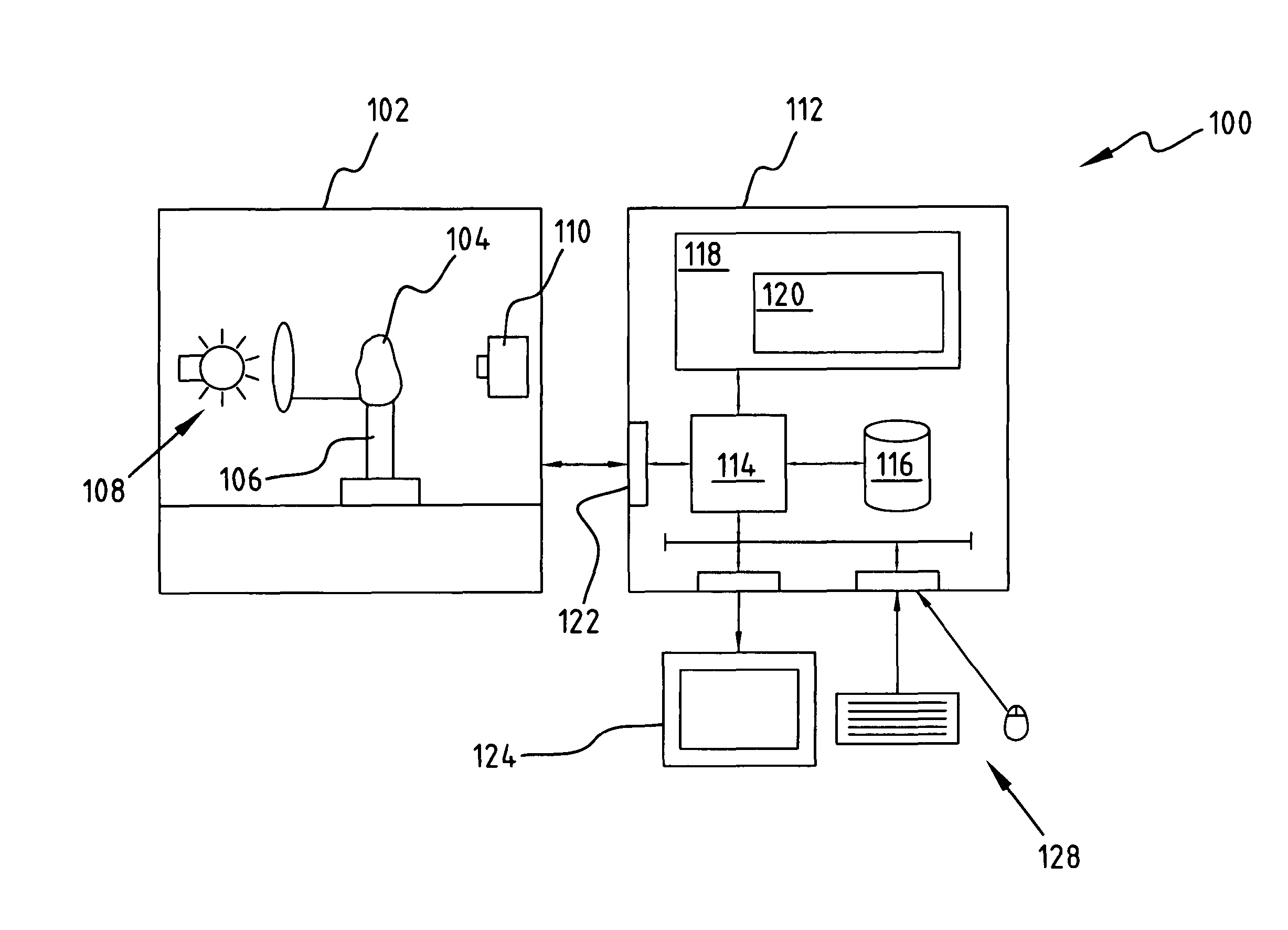
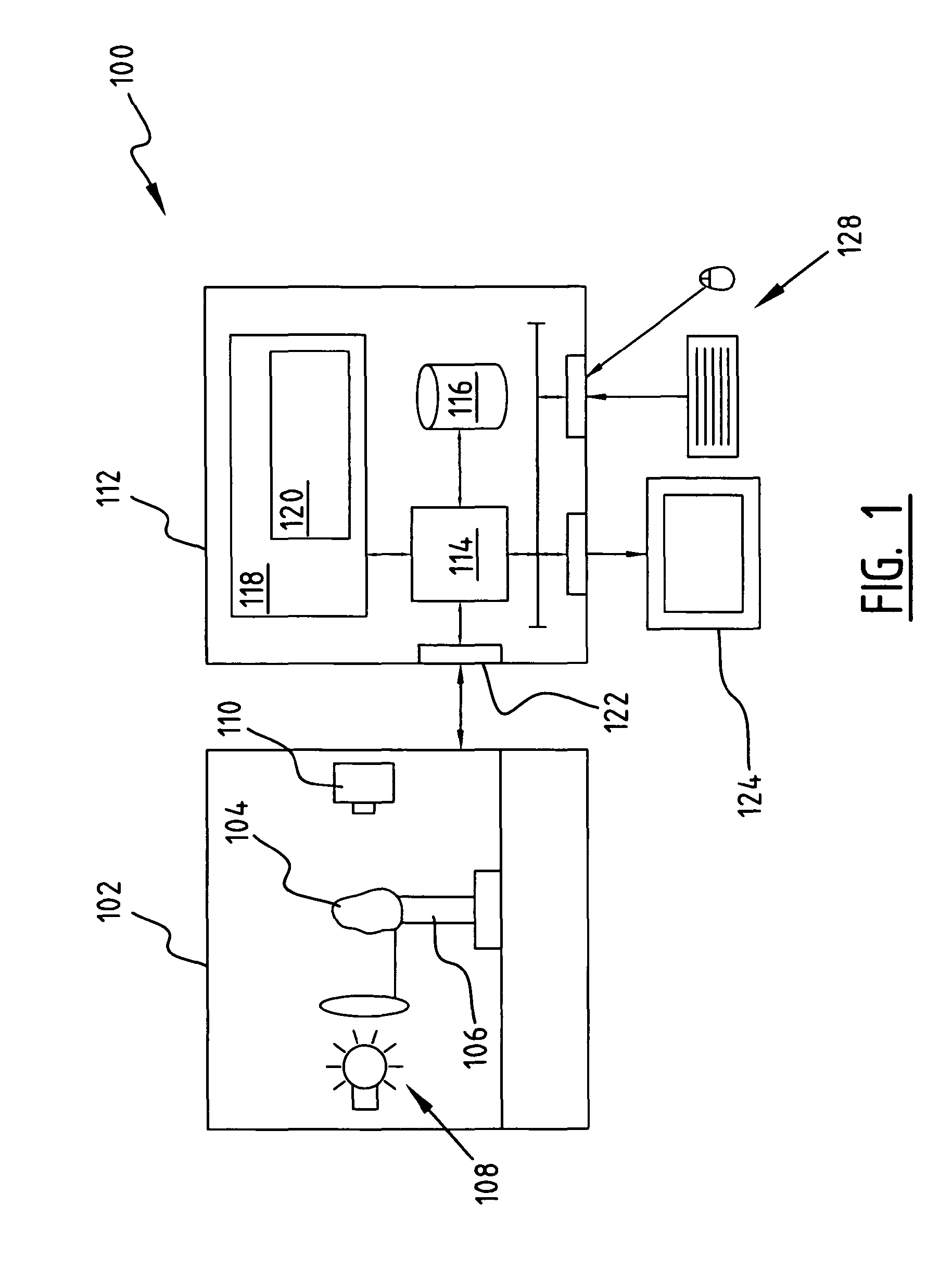
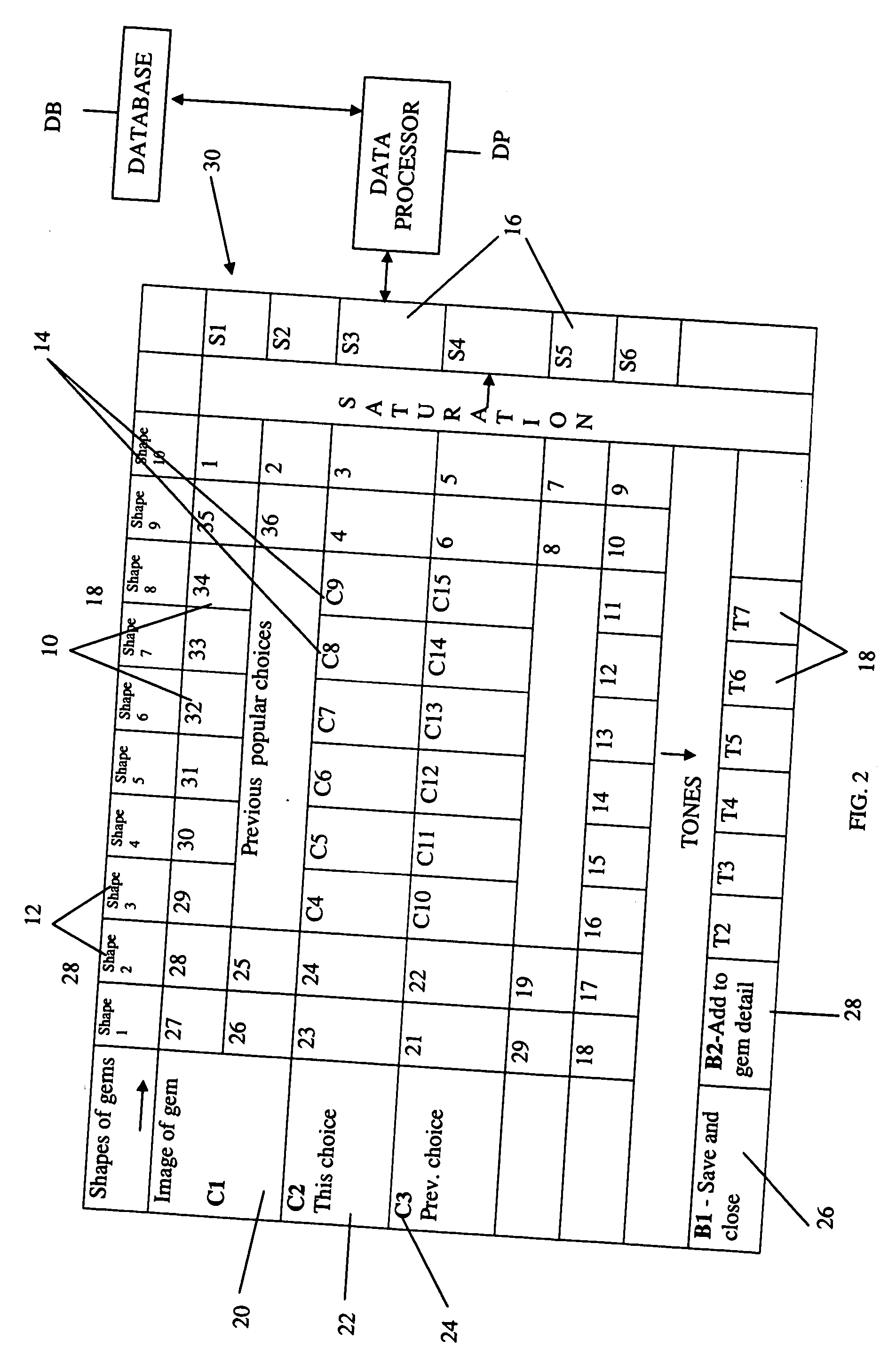
Method and associated apparatus for the standardized grading of gemstones
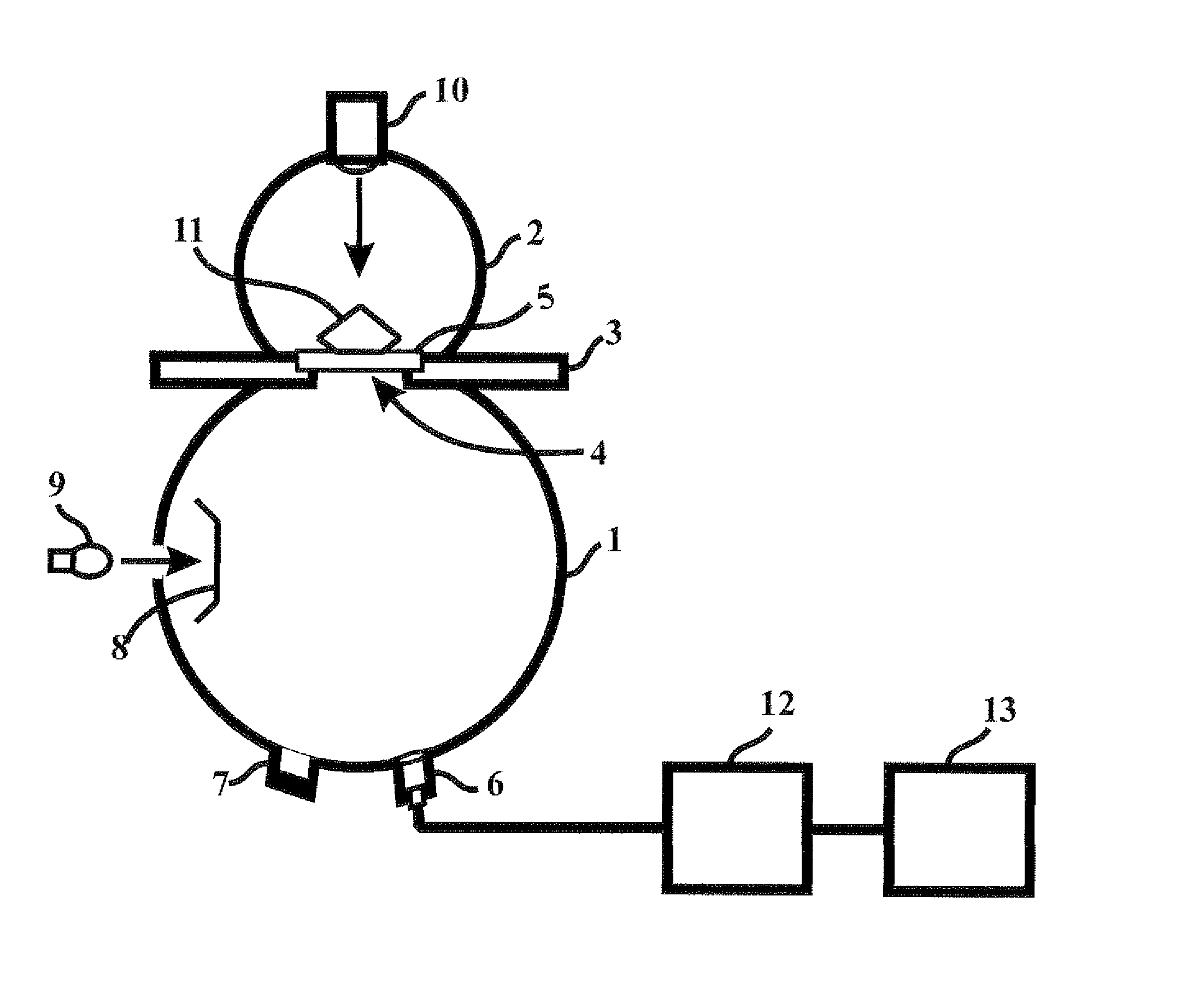
InactiveUS6980283B1Process safetyInvestigating jewelsSpecial data processing applicationsSpectral responseData set
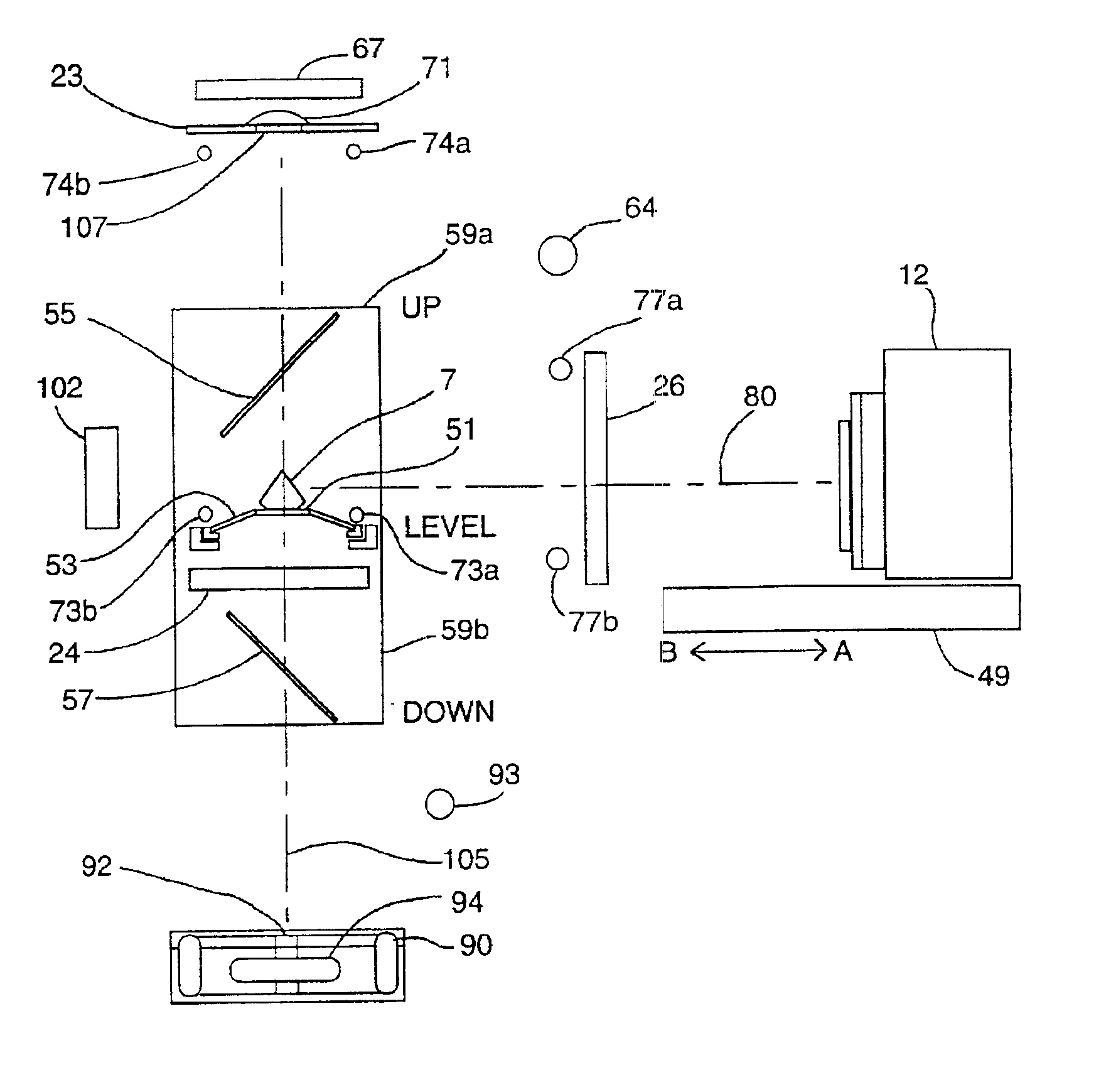
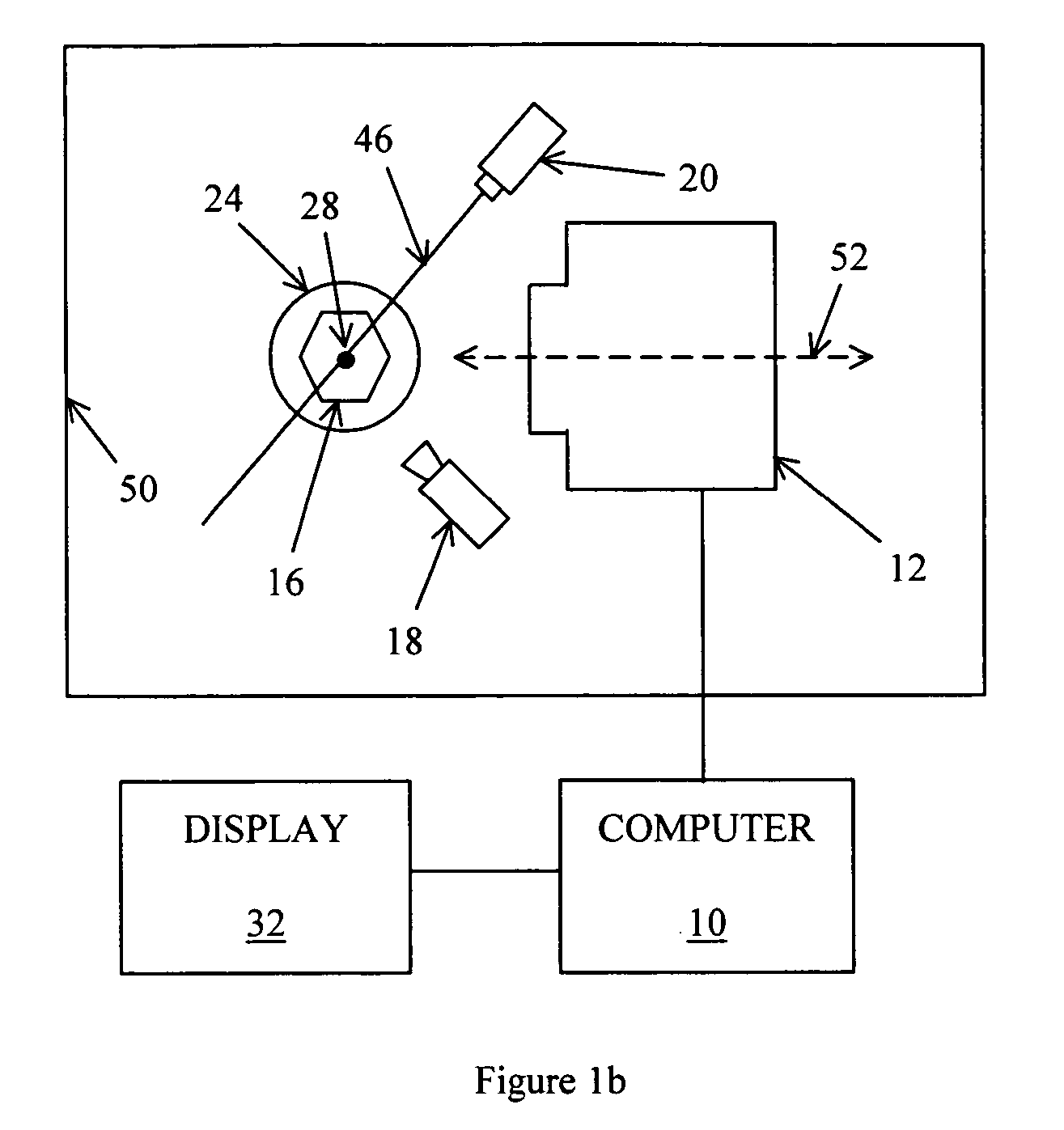
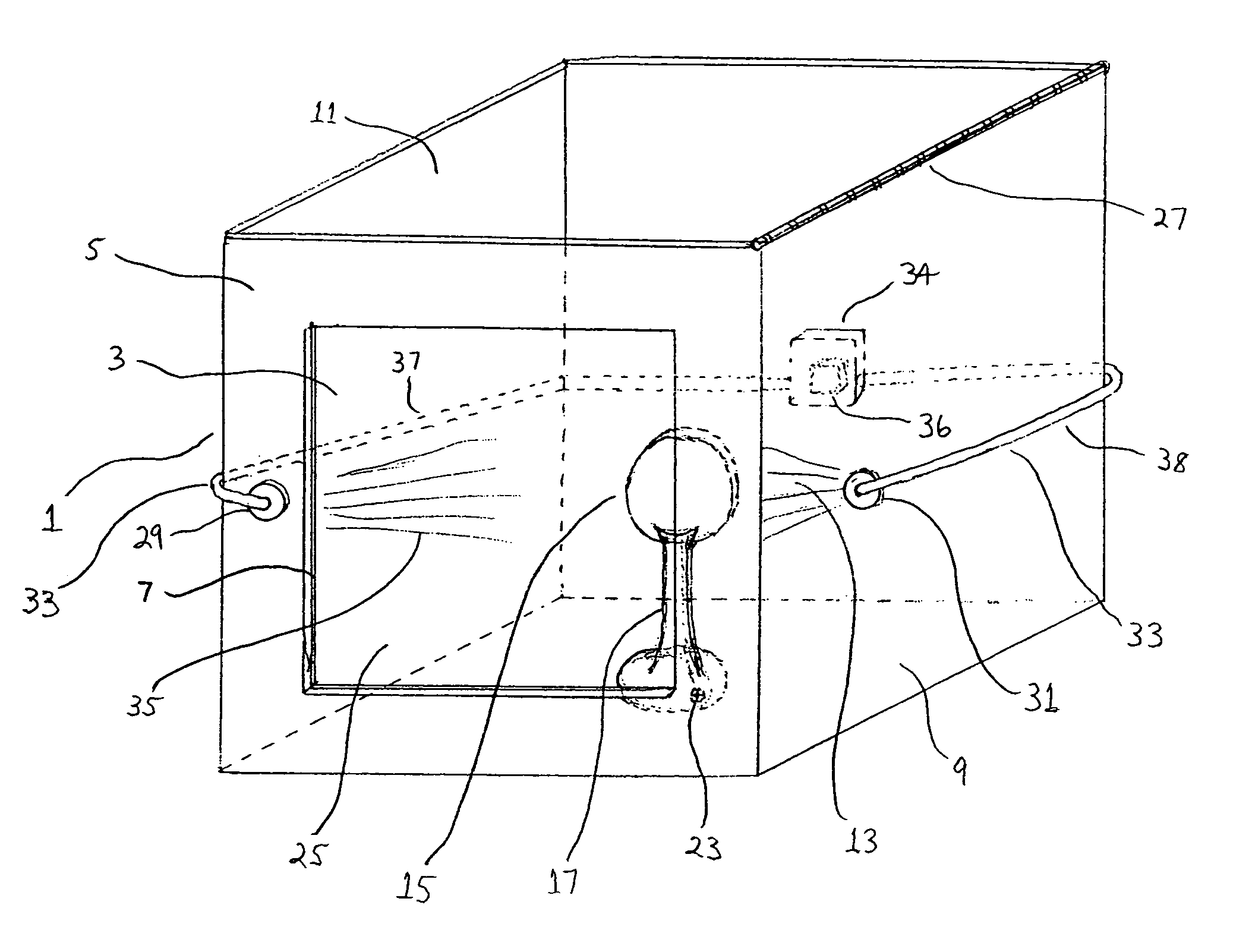
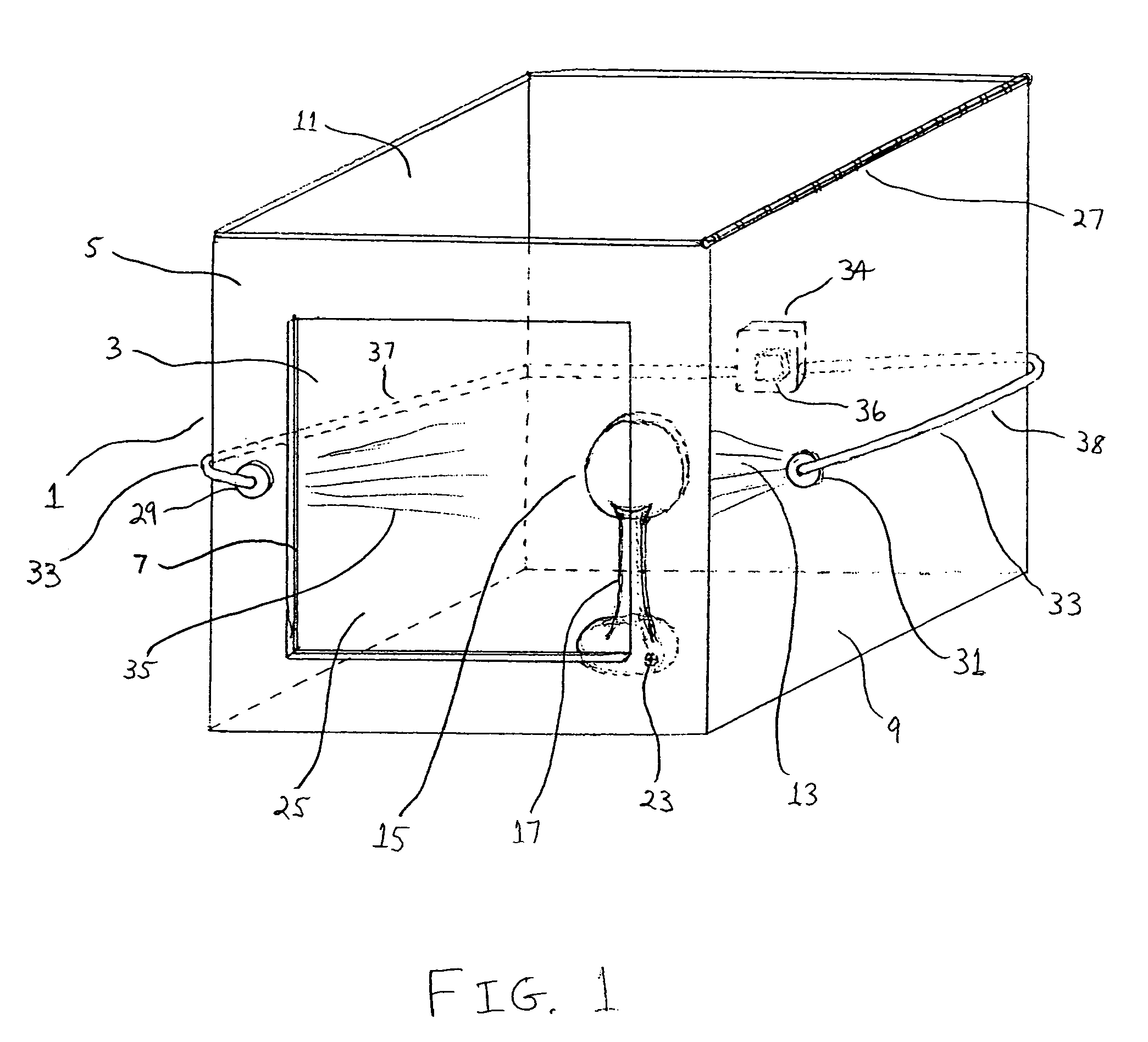
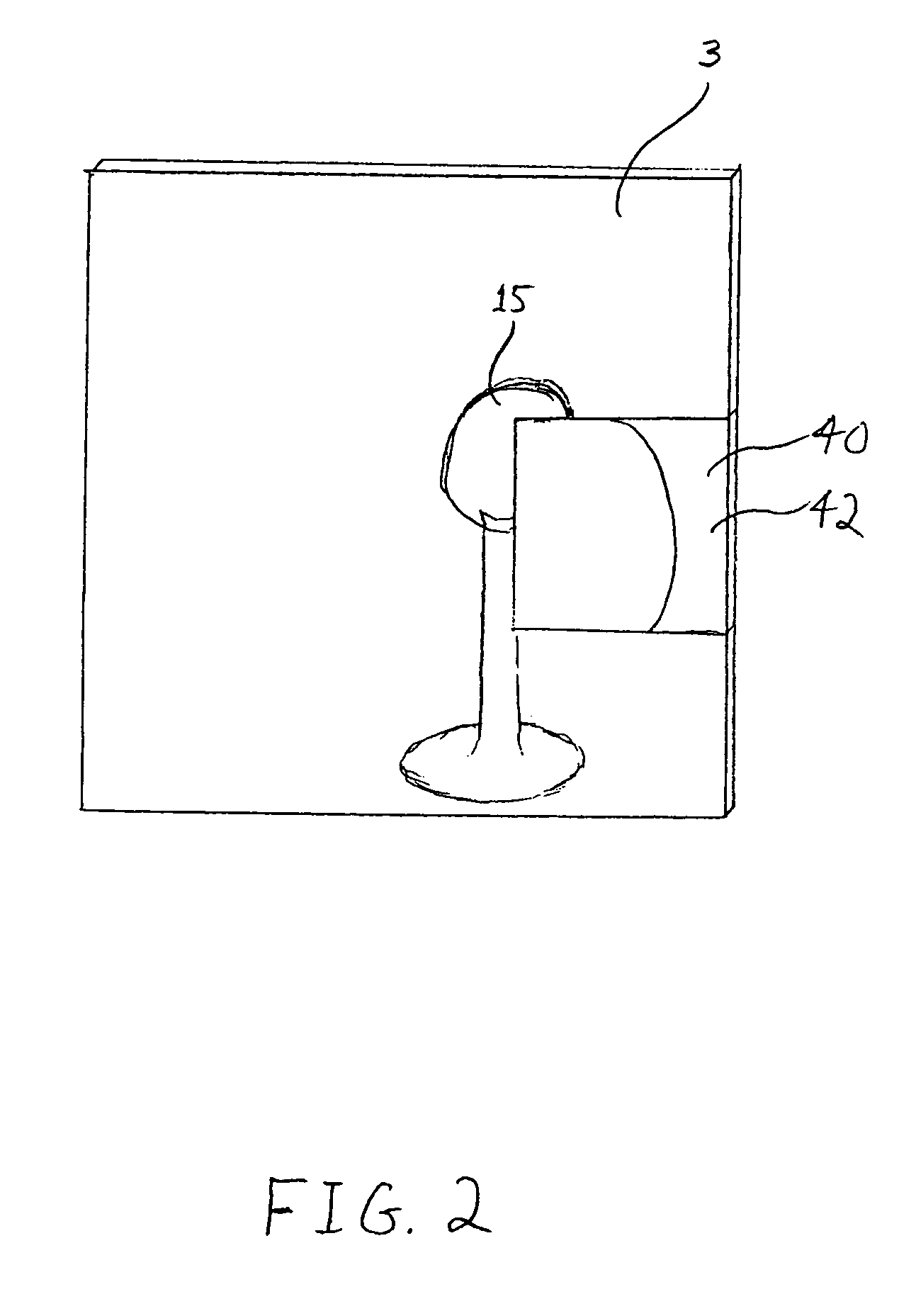
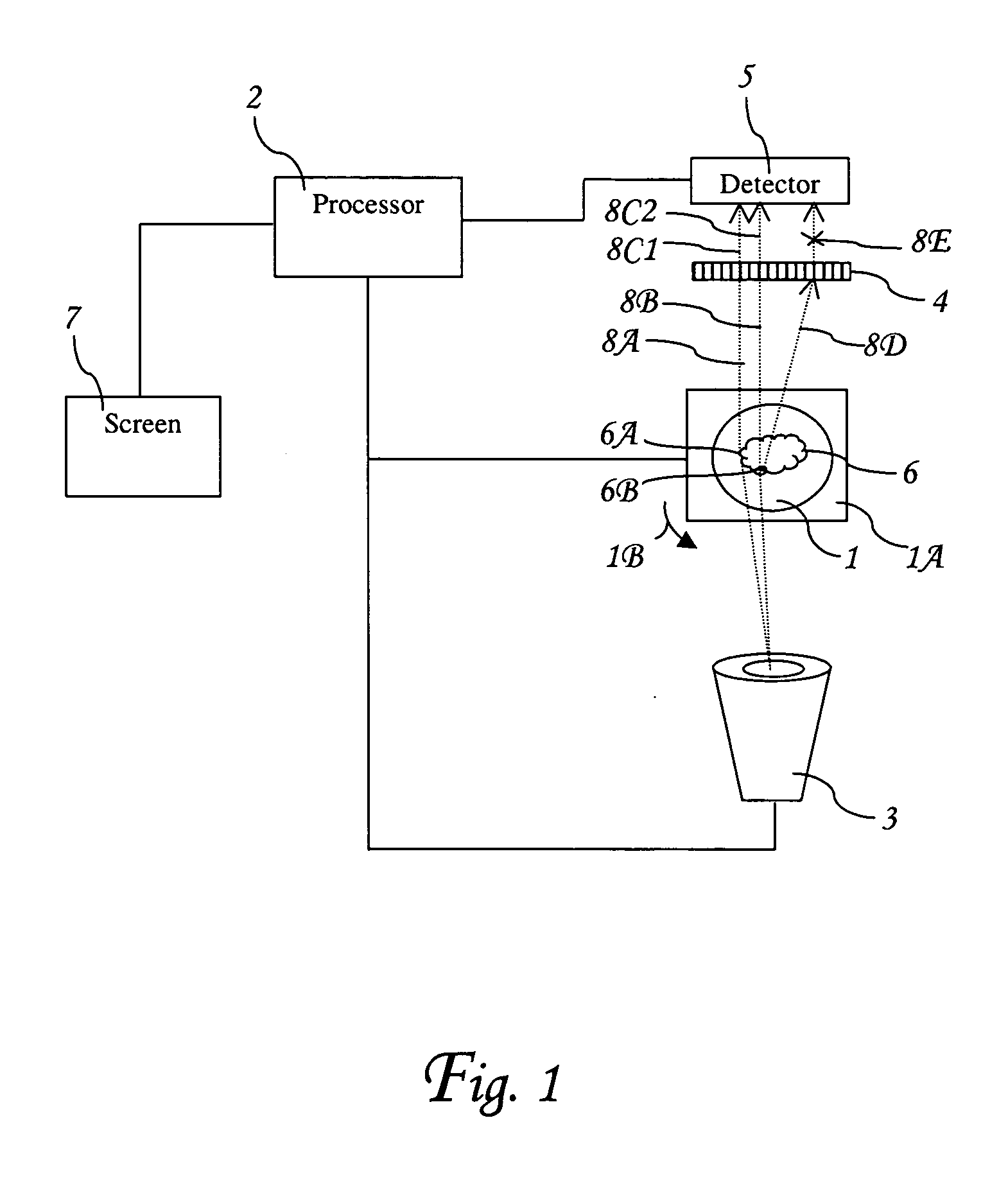
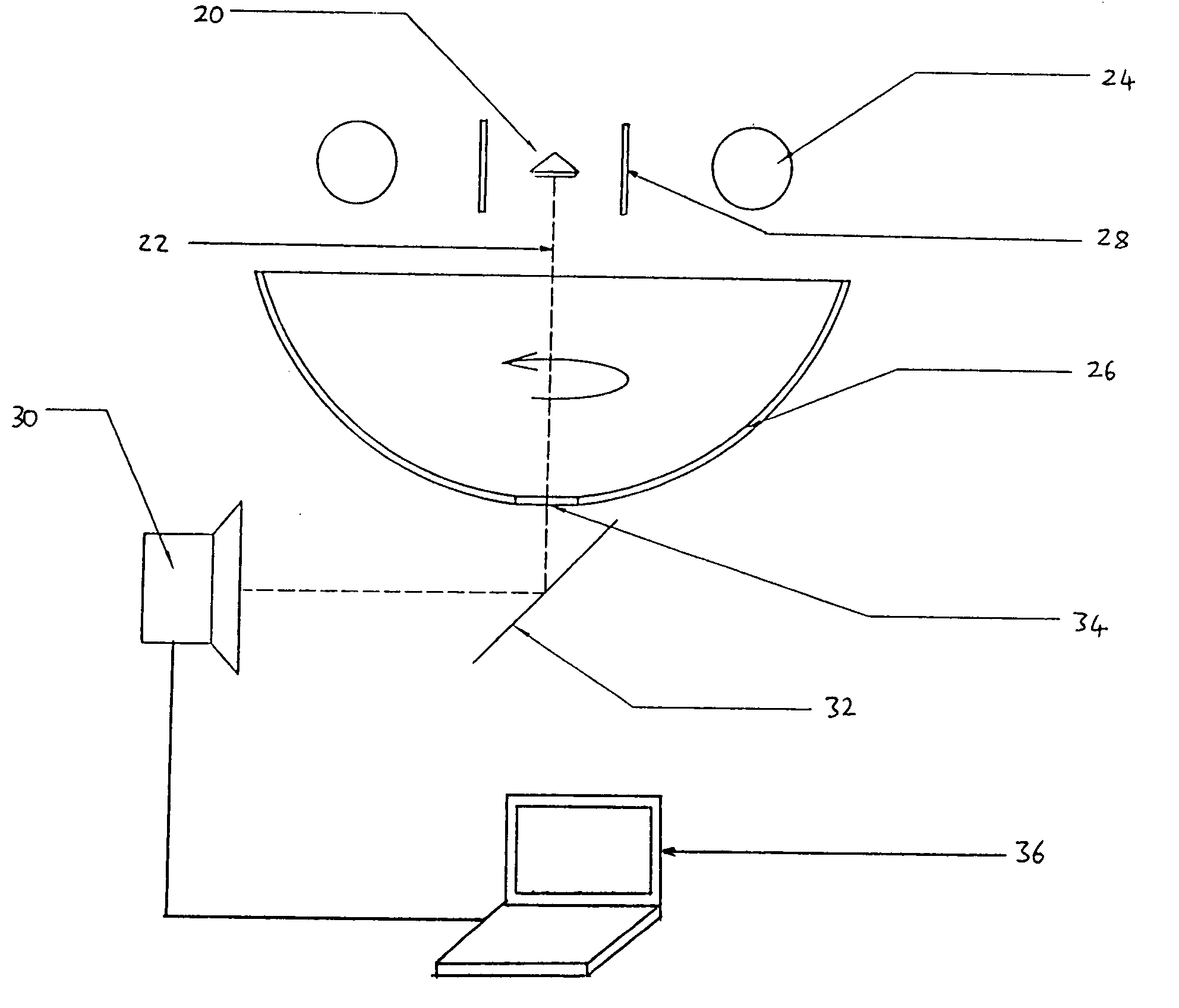
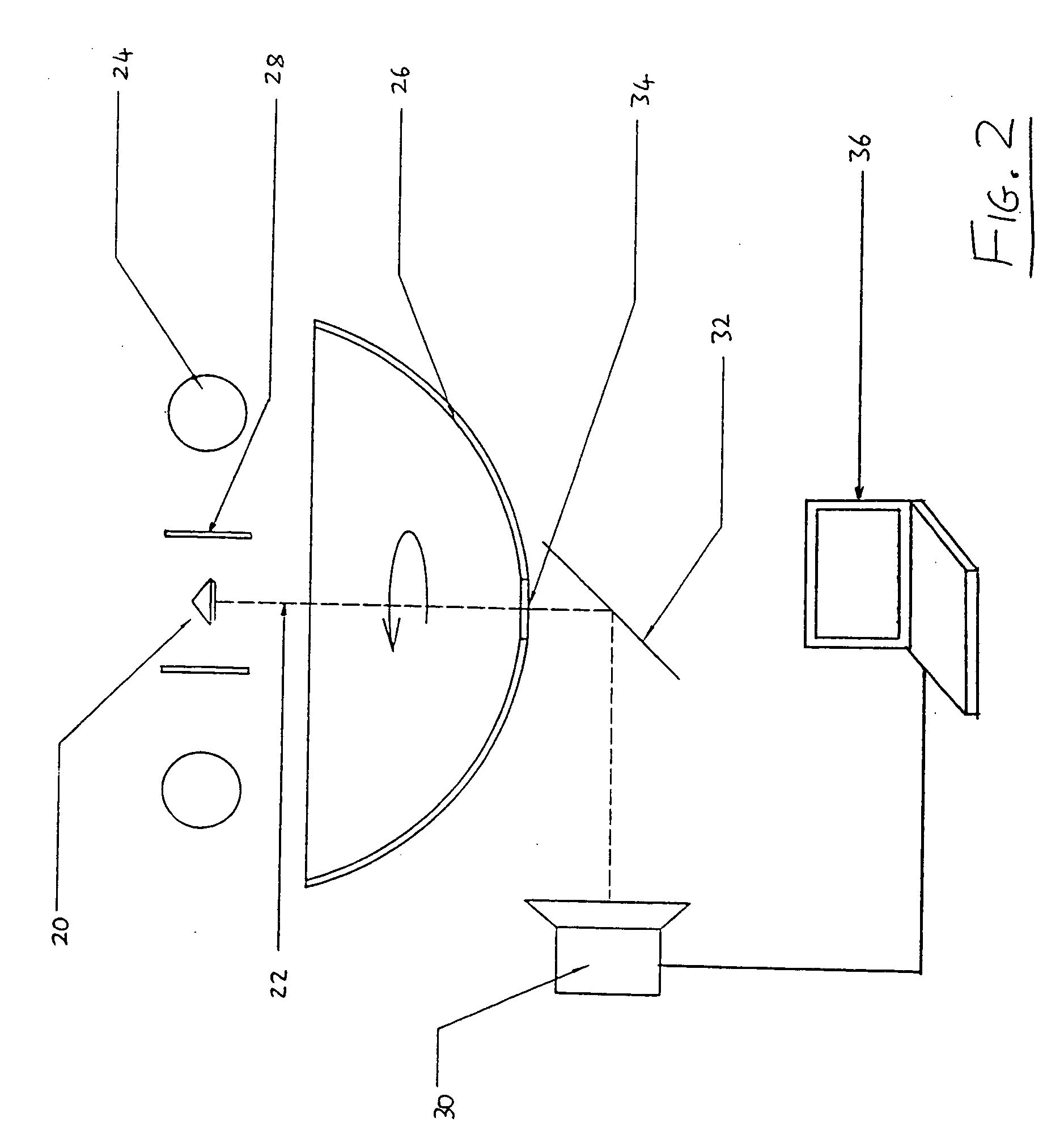
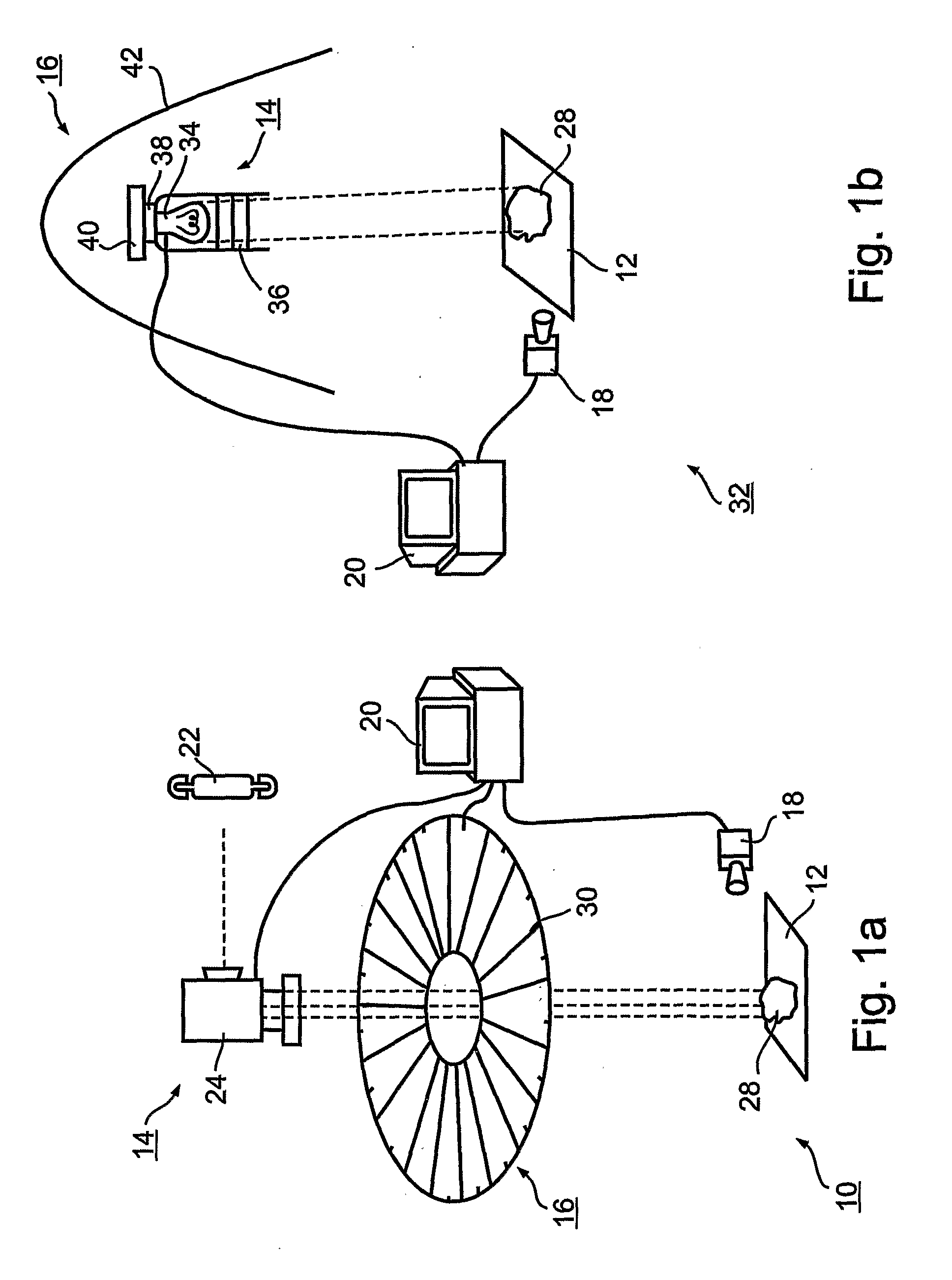
A method and associated apparatus (5) for the standardized grading of gemstones is provided. The system gauges the spectral response of a gemstone subject to a plurality of incident light sources (77, 64, 90, 92, 102) within an imaging apparatus. The operation of the imaging apparatus is controlled by an instruction set of a local station control data processor (12). Light energy data is captured in the form of pixel data sets via a charge coupled device of the imaging apparatus of the local station (8). The control data processor data of the local station is operably linked to analysis station (14). Gemstones qualities are analyzed by the plurality of light sources (92, 90, 102) of the imaging apparatus (5) and quantified relative to model pixel data sets of the database and recorded for future reference therein.
Owner:IMAGESTATISTICS
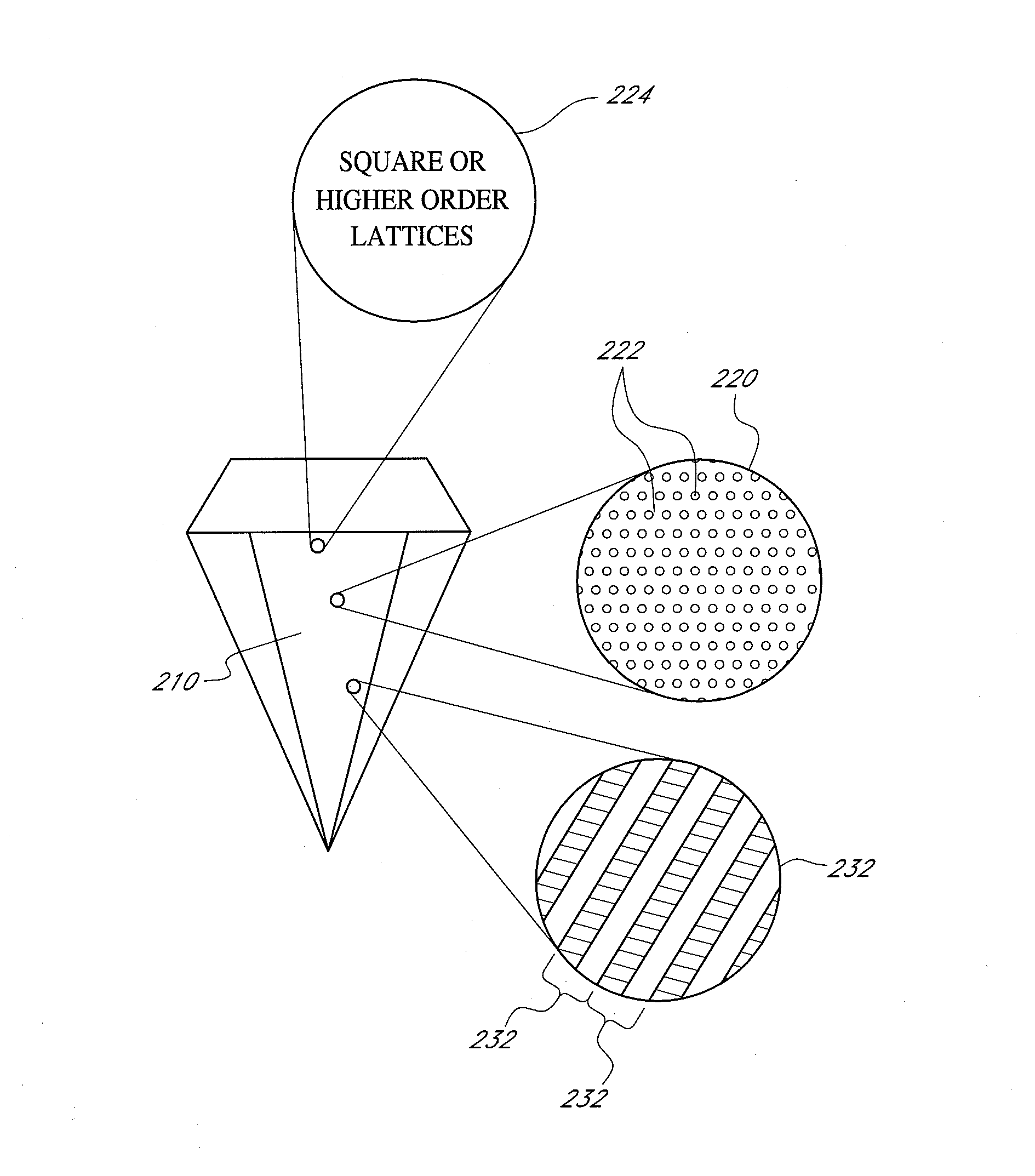
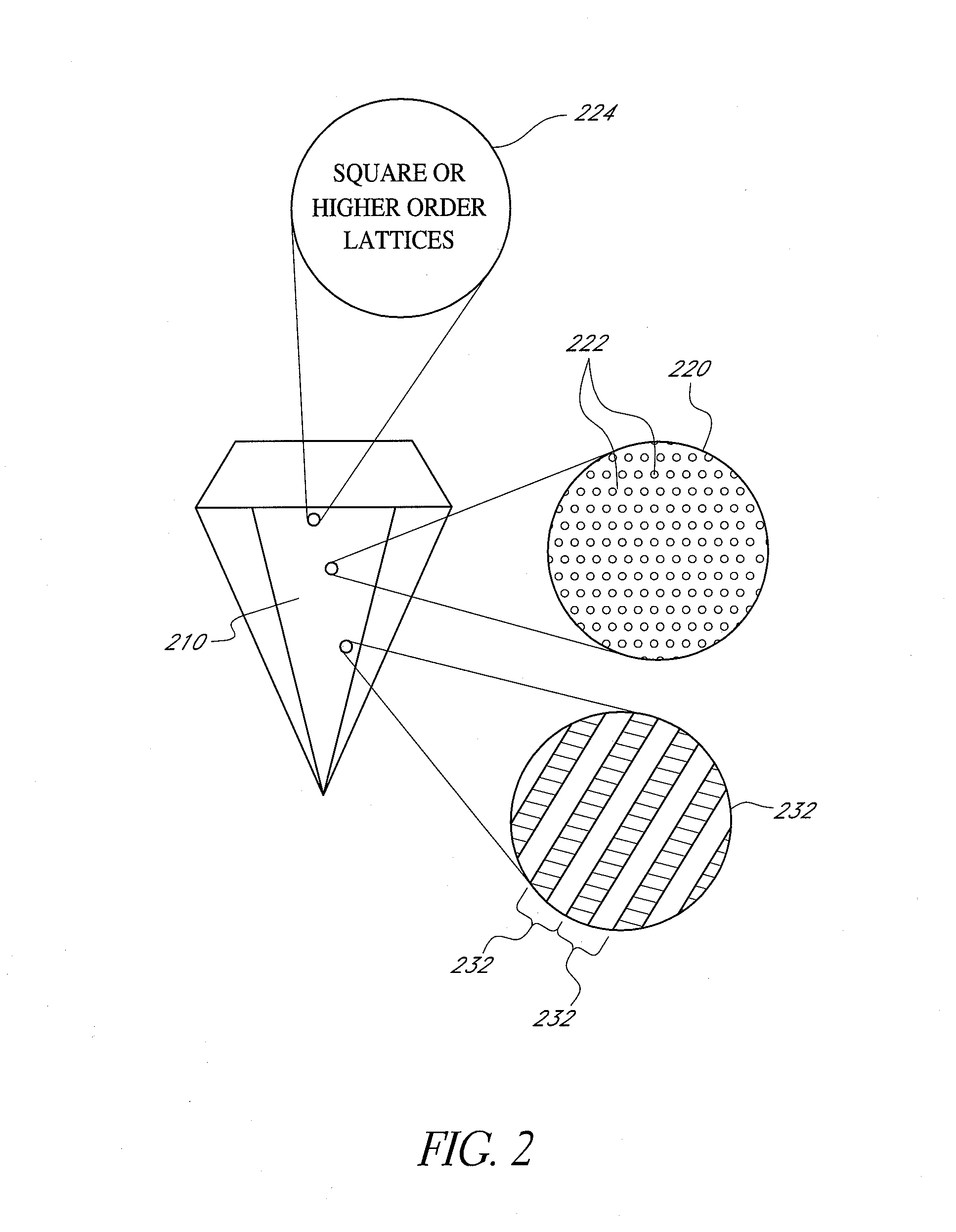
Method and system for laser marking in the volume of gemstones such as diamonds
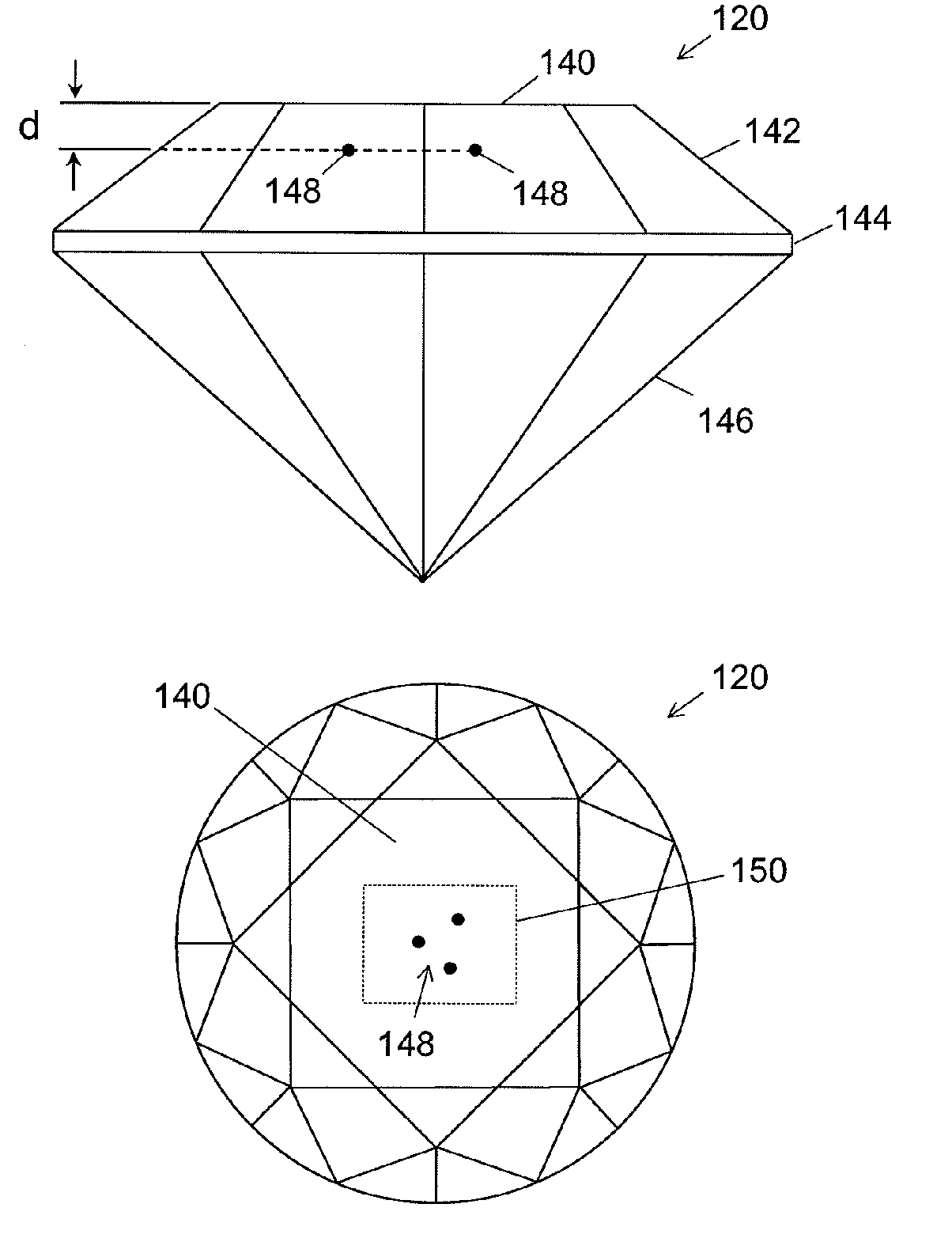
ActiveUS20060196858A1Suitable contrastImprove image contrastLight effect designsInvestigating jewelsMagnifying glassGemstone
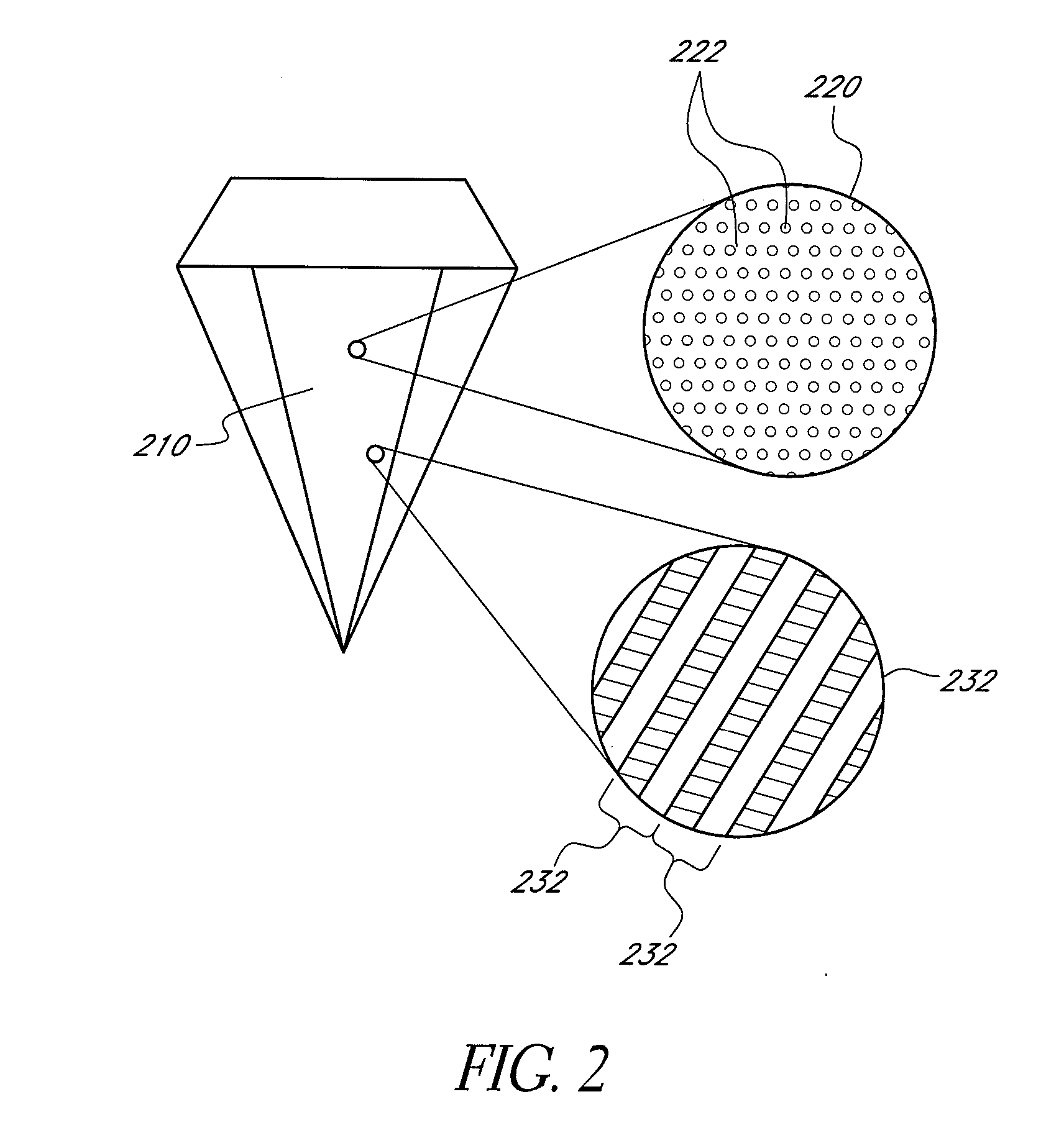
A method and an apparatus for laser marking indicia in the volume of gemstones such as diamonds, the indicia being made up of a plurality of microscopic dot-shaped marks whose build-up can be initiated by exposing naturally-occurring internal defects or impurities in the volume of a gemstone to a tightly focused train of laser pulses. Authentication data is encoded in the gemstone from the relative spatial arrangement of the dot-shaped marks that form the indicium. Taking advantage of the presence of otherwise invisible defects in the gemstone allows for inscribing indicia with laser pulses carrying energies substantially lower than the threshold energy required for inscribing in the volume of a perfect gemstone material. The marking process is then much less susceptible to inflict damages to the surface of the gemstone, and the marking can be performed using a broad variety of femtosecond laser systems. The dot-shaped marks engraved at a depth below the surface of a gemstone can be made undetectable with the unaided eye or with a loupe by limiting their individual size to a few micrometres, while devising indicia made up of only a few marks. As a result, the marking does not detract from the appearance and value of the gemstone. The procedure for laser marking accounts for the random spatial distribution of the defects present in natural gemstones as well as for their strongly localized character. The presence of an indicium can be detected by using a dedicated optical reader that can be afforded by every jewellery store.
Owner:GEMOLOGICAL INST OF AMERICA INC
Marking diamond
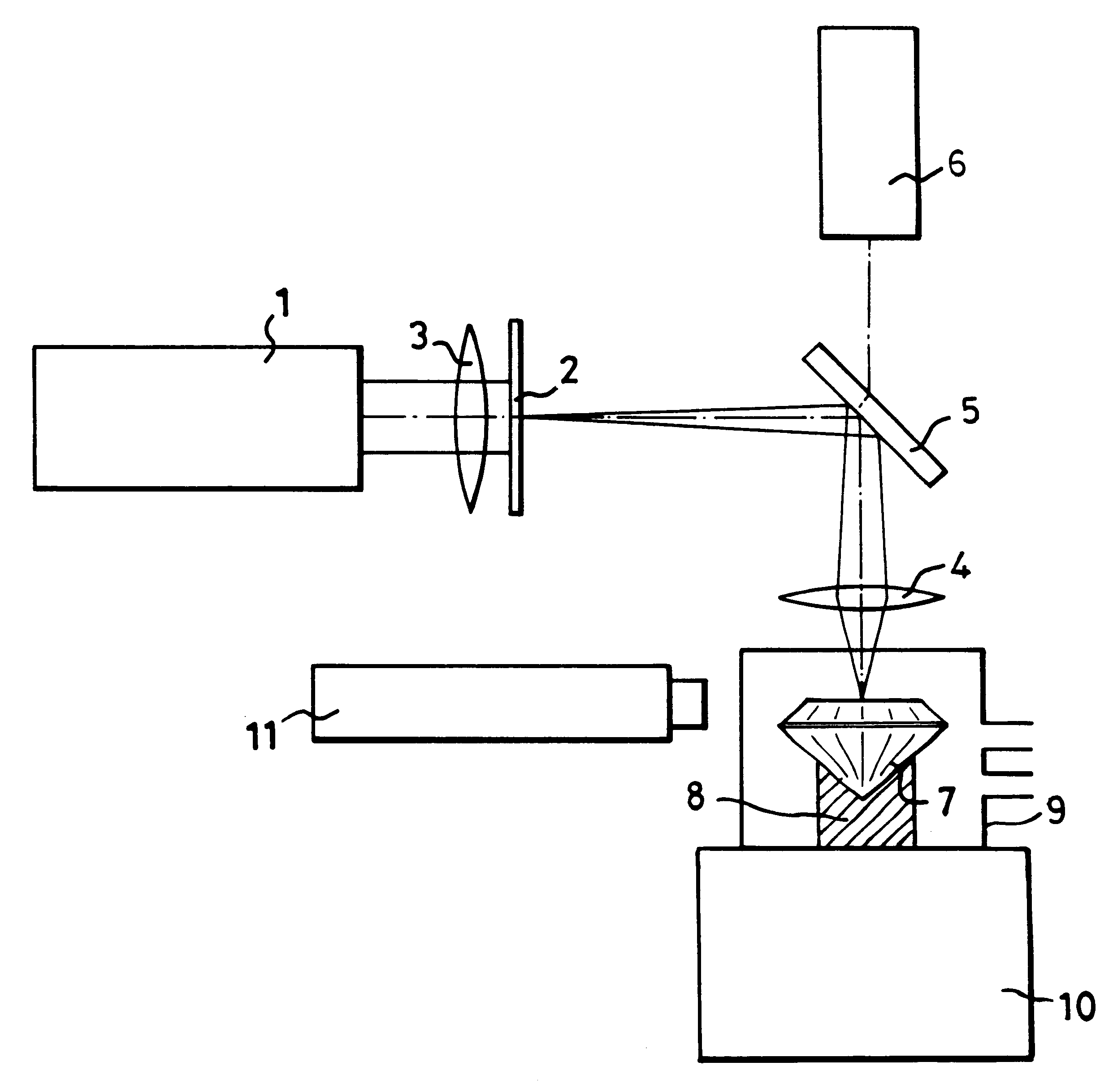
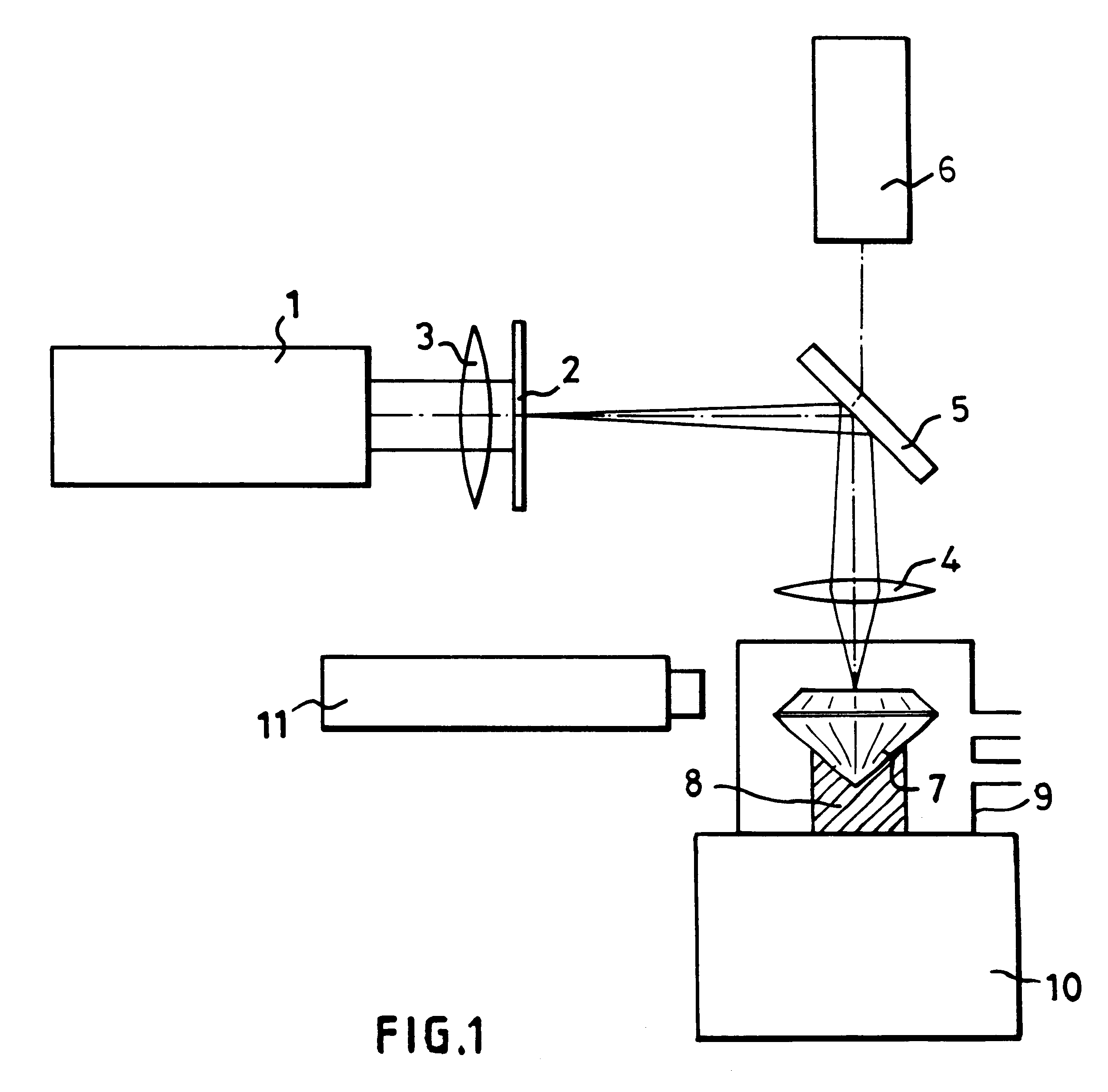
InactiveUS6187213B1Avoid overall overheatingAvoid necessityBranding equipmentPolycrystalline material growthMicroscopic observationGemstone
In order to produce on the table of a diamond gemstone (7), an information mark which is invisible to the naked eye using a x10 loupe, an ultraviolet laser (1) having a wavelength of 193 nm is used in association with a mask (2) to irradiate the surface of the stone (7) at a fluence of less than 2 J / cm2 per pulse and with not fewer than 100 pulses, in the presence of air which reacts with the diamond (7) and causes the mark to be formed without any darkening which is visible when viewing using a microscope.
Owner:GERSAN ESTAB
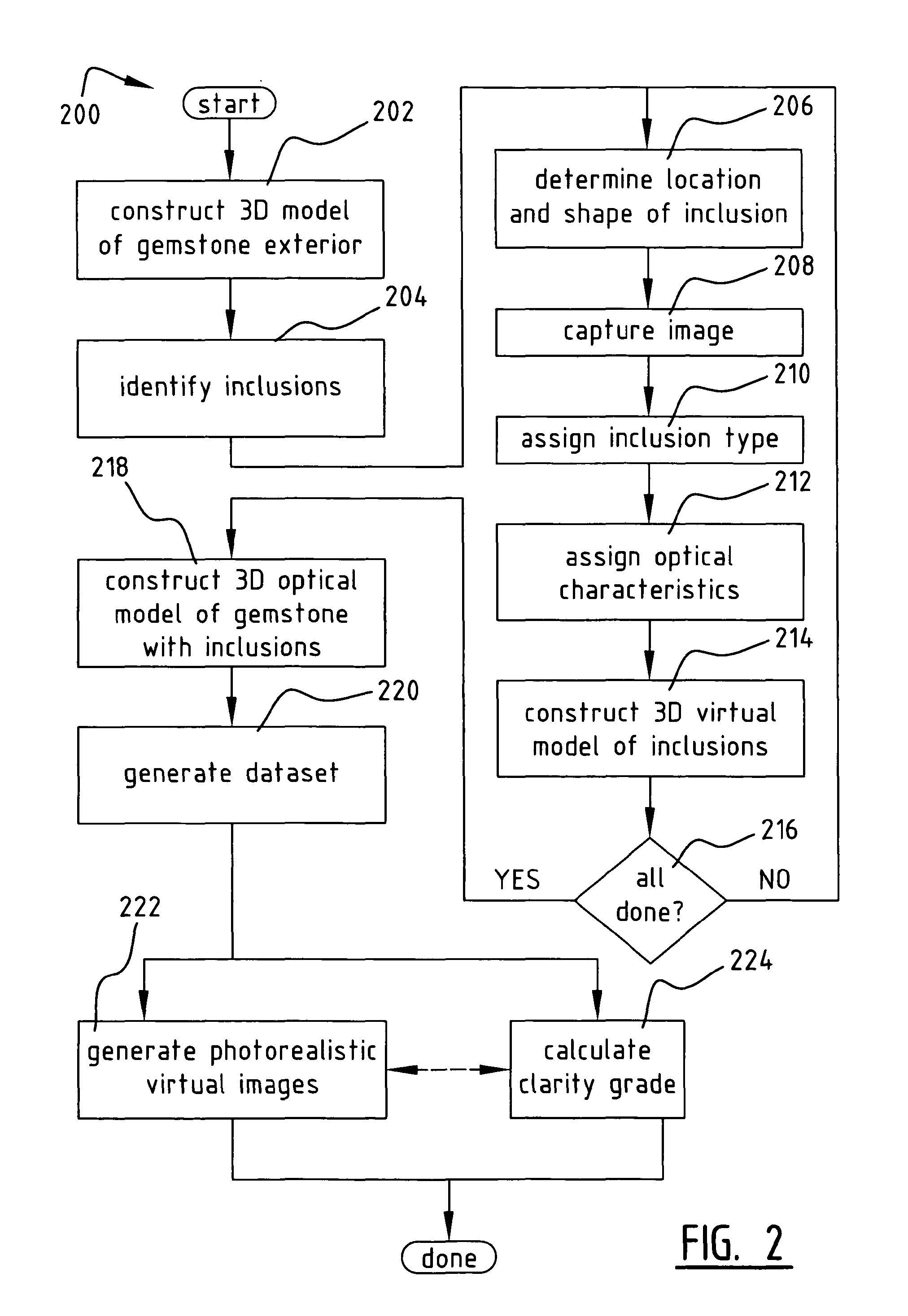
Method and System for Improved Optical Modeling of Gemstones
ActiveUS20100250201A1Reduce deficiencyImproved virtual optical modelingInvestigating jewelsOptically investigating flaws/contamination3d shapesOptical property
A method of constructing a virtual model of a gemstone including the steps of performing measurements of the gemstone to construct a three-dimensional (3D) model of an exterior surface of the gemstone; identifying one or more visible inclusions within an interior volume of the gemstone; for each identified inclusion, performing the steps of determining a location and 3D shape of the inclusion within the interior volume of the gemstone; capturing at least one image of the inclusion; using the at least one image to determine relevant optical characteristics of the inclusion; and constructing a 3D virtual model of the inclusion, said model including the 3D shape of the inclusion and optical properties of the inclusion based upon said optical characteristics; constructing a 3D virtual model of the gemstone which includes the 3D virtual model of the exterior surface of the gemstone and the 3D virtual models of the one or more visible inclusions within the interior volume of the gemstone; and generating a dataset representing said 3D virtual model, wherein said dataset may be used in subsequent computer analysis to provide a user with information relating to a visual characteristic of the gemstone.
Owner:IDEAL SCOPE
Method for evaluation of a gemstone
ActiveUS20080231833A1Reliably foundWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationRefractive indexGemstone
An apparatus for determining location of at least one inclusion in a gemstone having a first refractive index, comprising:a container adapted for containing a material having a second refractive index,a holder operative to support a gemstone in the material when the container contains the material;an illuminator positioned and adapted to illuminate said gemstone when disposed within said material in said container, with illumination at which said gemstone and said material have their respective first and second indices;a detector that detects illumination from the illuminated gemstone and said material and produces signals responsive thereto;a controller that receives the signals and is operative to determine a location of an inclusion in the gemstone based on the signals; anda system, operative to reduce the presence within said material, at least when the gemstone is disposed therein, of any substance other than inclusions, having a third refractive index.
Owner:GALATEA
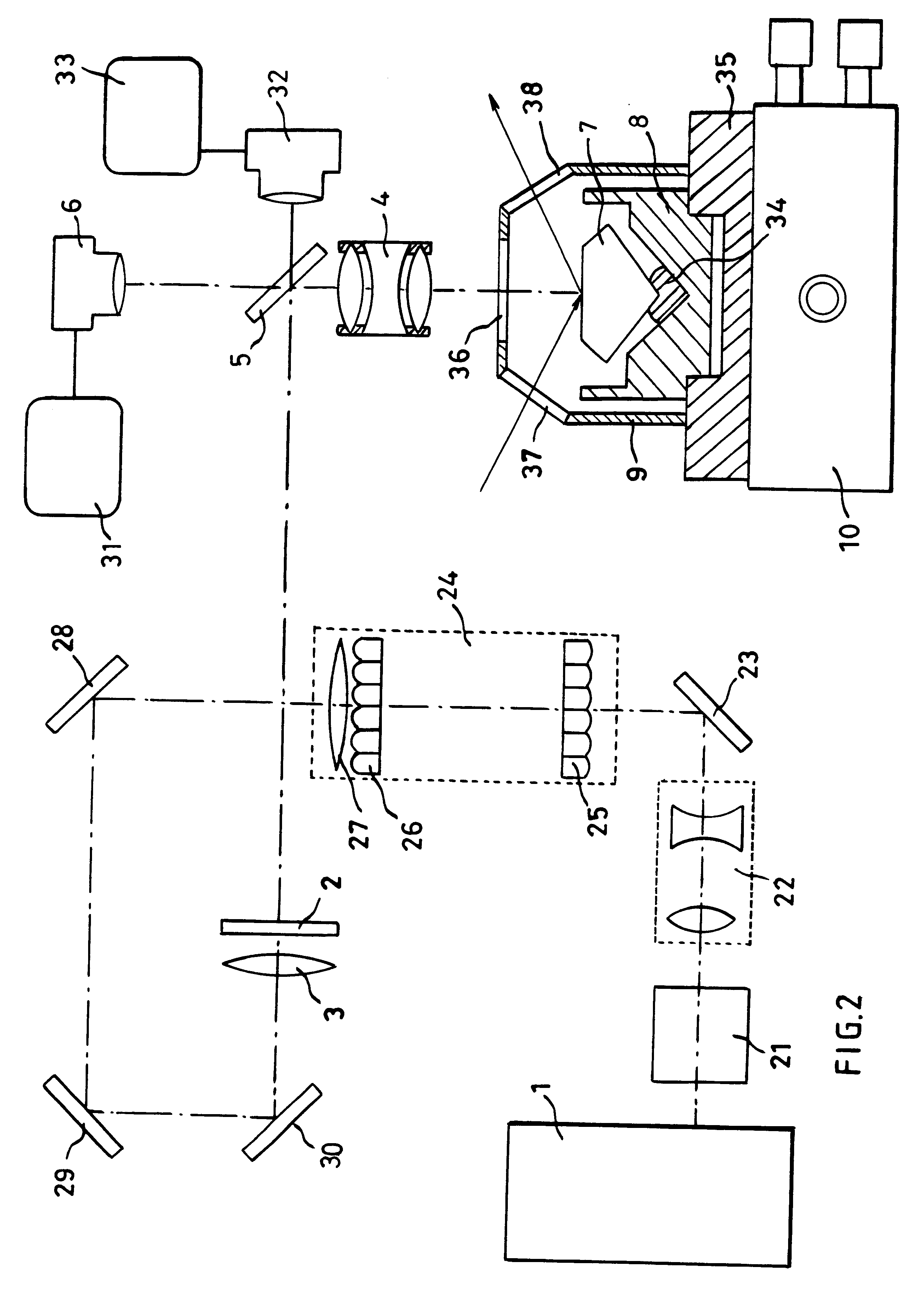
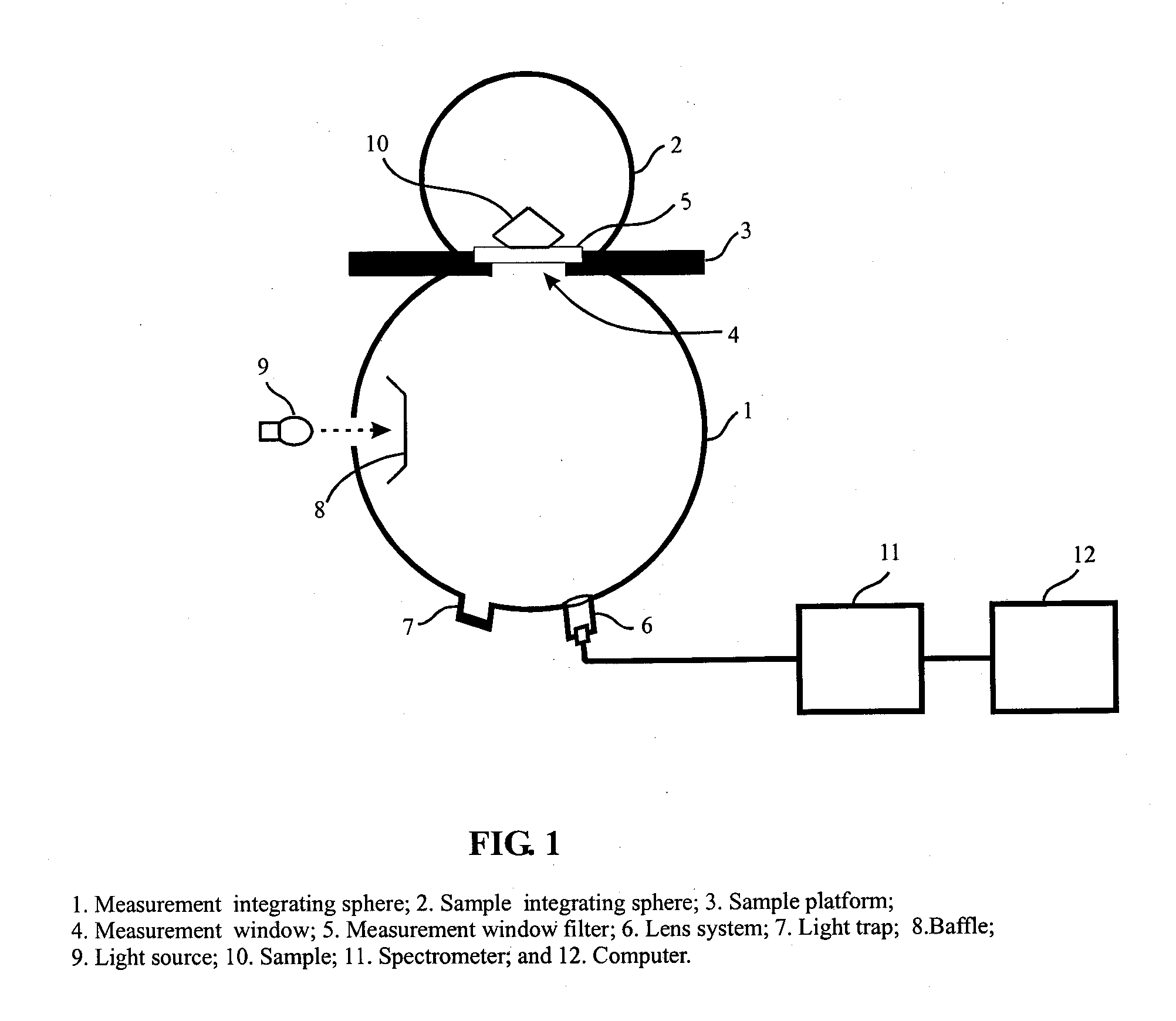
Apparatus and method for color measurement and color grading of diamonds, gemstones and the like
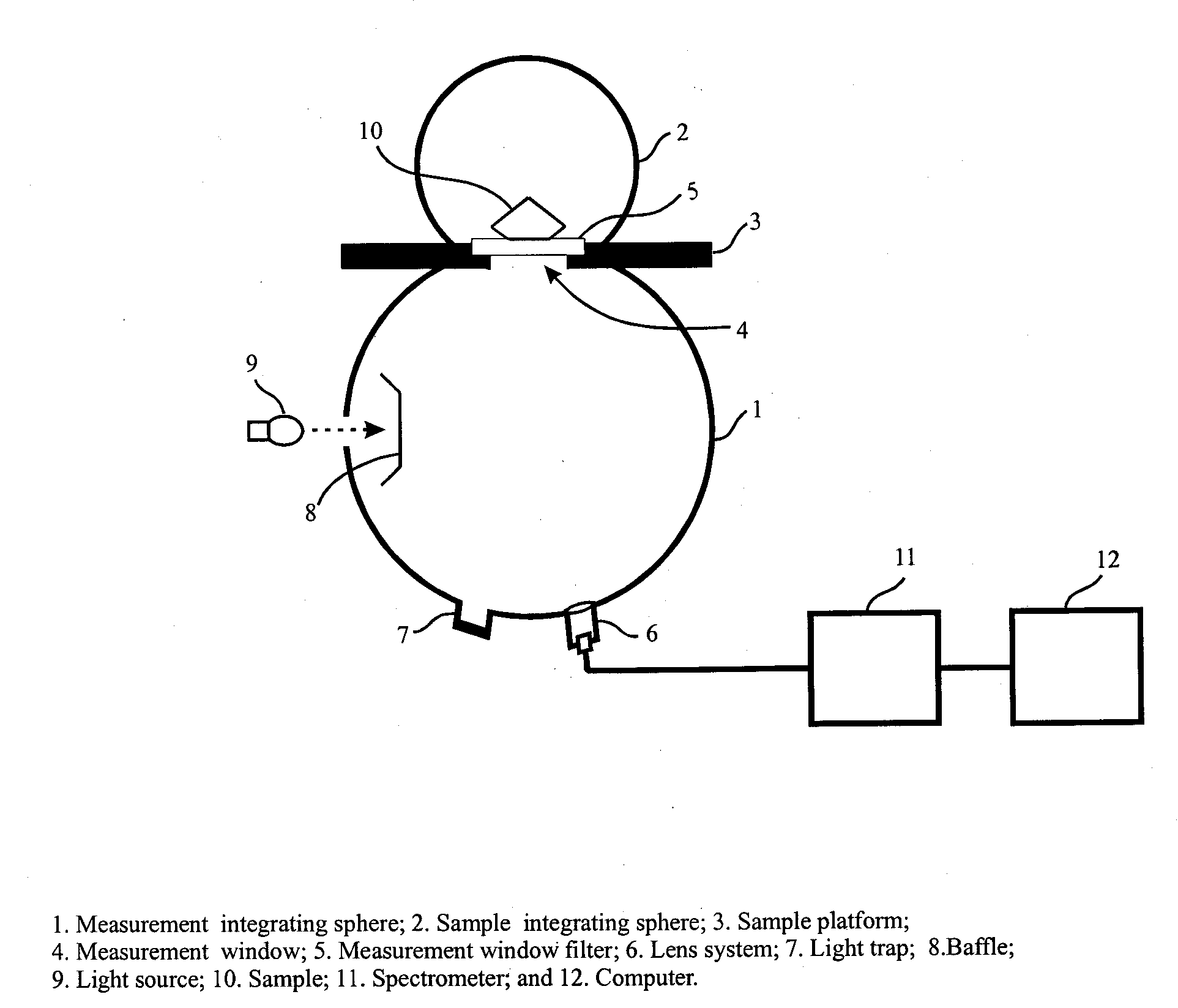
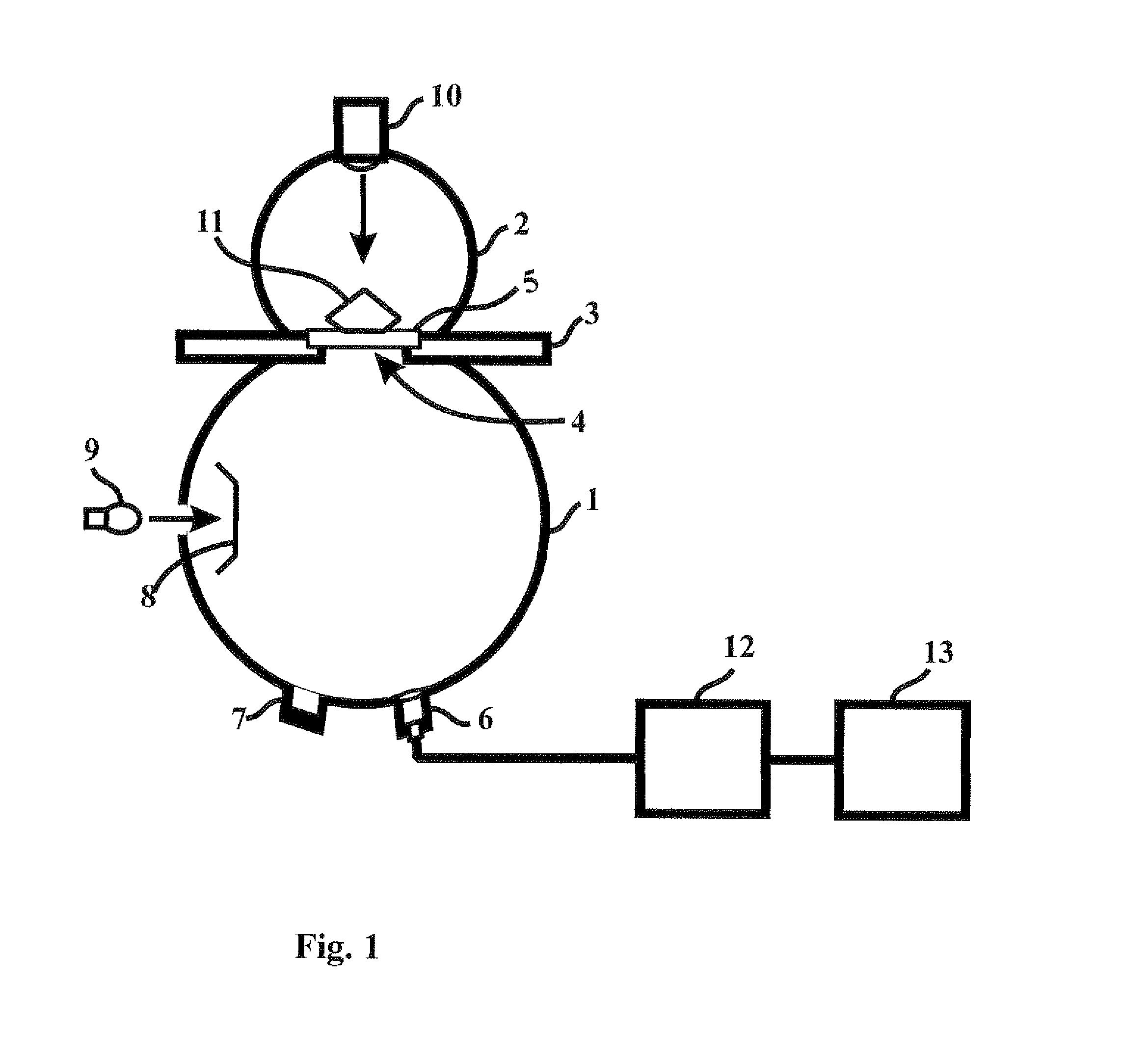
InactiveUS20080204705A1Accurate measurementReduce manufacturing costPhotometryInvestigating jewelsDiffuse illuminationFluorescence
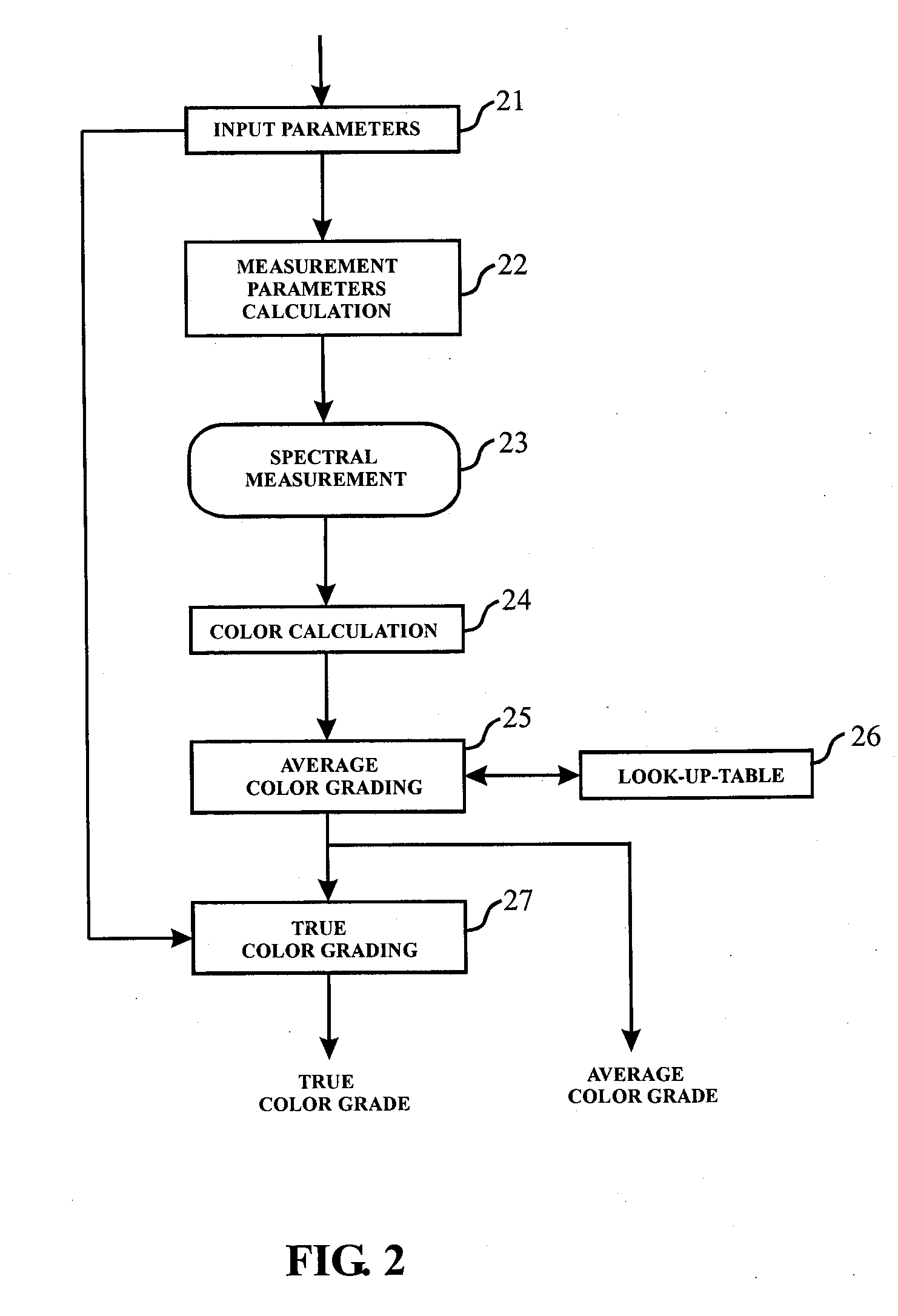
The present invention discloses an apparatus and method for color measurement and color grading of faceted gemstones, diamonds and the like. The apparatus comprises a spectrometer, a computer, and a dual integrating sphere measurement arrangement comprising a measurement integrating sphere, a sample integrating sphere, a sample platform, a filter, a lens system, a baffle and a light source. The measurement geometry of the dual integrating sphere measurement arrangement is diffuse illumination and 8 degree viewing with the specular component excluded, plus diffuse white background provided by the sample integrating sphere. The sample integrating sphere encloses a sample to provide a constant environment for simulating the visual color grading environment. A novel three-step calibration insures an accurate spectral measurement of the sample inside the measurement integrating sphere. The computer controls the spectrometer and provides measurement parameters calculated from the physical parameters of the measured sample, including, but not limited to, shape, dimensions, refractive index, intensity of fluorescence and cut grade. The computer then calculates the spectral reflectance and calorimetric data, and determines an average color grade by checking a look-up-table that represents the relationship between the CIELAB coordinate and the average color grade. The computer also determines a true color grade based upon the average color grade and the physical parameters, using mathematical analyses and algorithms.
Owner:LIU YAN
Capture and display of image of three-dimensional object
InactiveUS20060066877A1Realistic viewing experienceSimple modelInvestigating jewelsUsing optical meansElement modelMultiple perspective
A system and method for modeling three-dimensional objects such as diamonds and other gemstones. A three-dimensional finite-element model obtained by, for example, analysis of boundaries of the object in photographs taken from multiple perspectives with frontal lighting or silhouette lighting, or by analysis of structured-light photographs of the object taken from multiple perspectives, is combined with color or grayscale information obtained from photographs of the object. Enhanced or “false” color can be used to improve the viewing experience or to emphasize particular features of the object. A computer can rotate the model about arbitrary axes according to the desires of a viewer.
Owner:BENZANO DANIEL
Enhancing the optical characteristics of a gemstone
Various embodiments described herein comprise a gemstone or other piece of jewelry, which incorporates one or more diffractive optical elements to enhance the fire displayed by the gemstone. In certain embodiments, the diffractive optical element comprises a diffraction grating etched on one or more facets of the gemstone.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method and system for laser marking in the volume of gemstones such as diamonds
A method and an apparatus for laser marking indicia in the volume of gemstones such as diamonds, the indicia being made up of a plurality of microscopic dot-shaped marks whose build-up can be initiated by exposing naturally-occurring internal defects or impurities in the volume of a gemstone to a tightly focused train of laser pulses. Authentication data is encoded in the gemstone from the relative spatial arrangement of the dot-shaped marks that form the indicium. Taking advantage of the presence of otherwise invisible defects in the gemstone allows for inscribing indicia with laser pulses carrying energies substantially lower than the threshold energy required for inscribing in the volume of a perfect gemstone material. The marking process is then much less susceptible to inflict damages to the surface of the gemstone, and the marking can be performed using a broad variety of femtosecond laser systems. The dot-shaped marks engraved at a depth below the surface of a gemstone can be made undetectable with the unaided eye or with a loupe by limiting their individual size to a few micrometers, while devising indicia made up of only a few marks. As a result, the marking does not detract from the appearance and value of the gemstone. The procedure for laser marking accounts for the random spatial distribution of the defects present in natural gemstones as well as for their strongly localized character. The presence of an indicium can be detected by using a dedicated optical reader that can be afforded by every jewellery store.
Owner:GEMOLOGICAL INST OF AMERICA INC
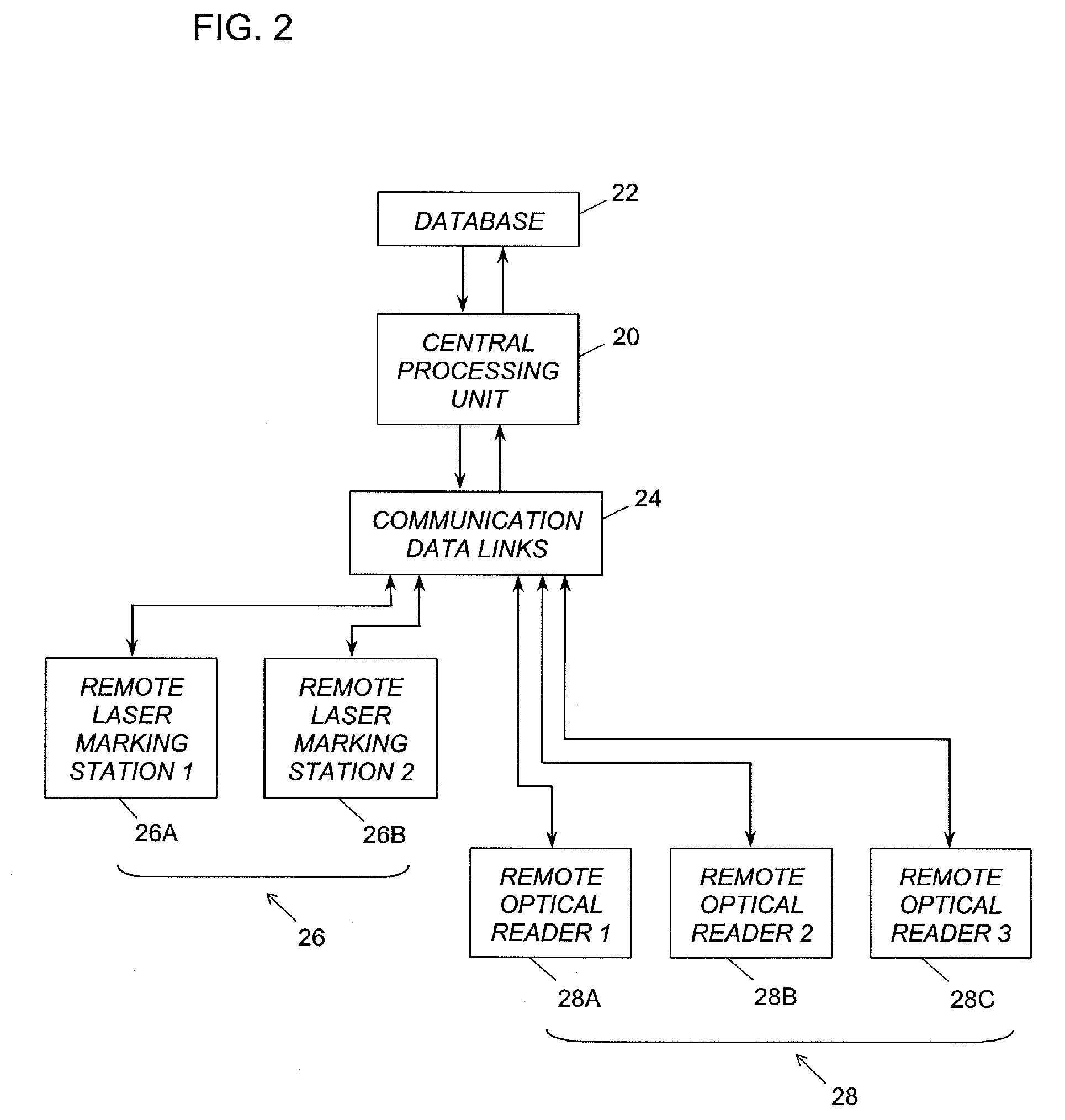
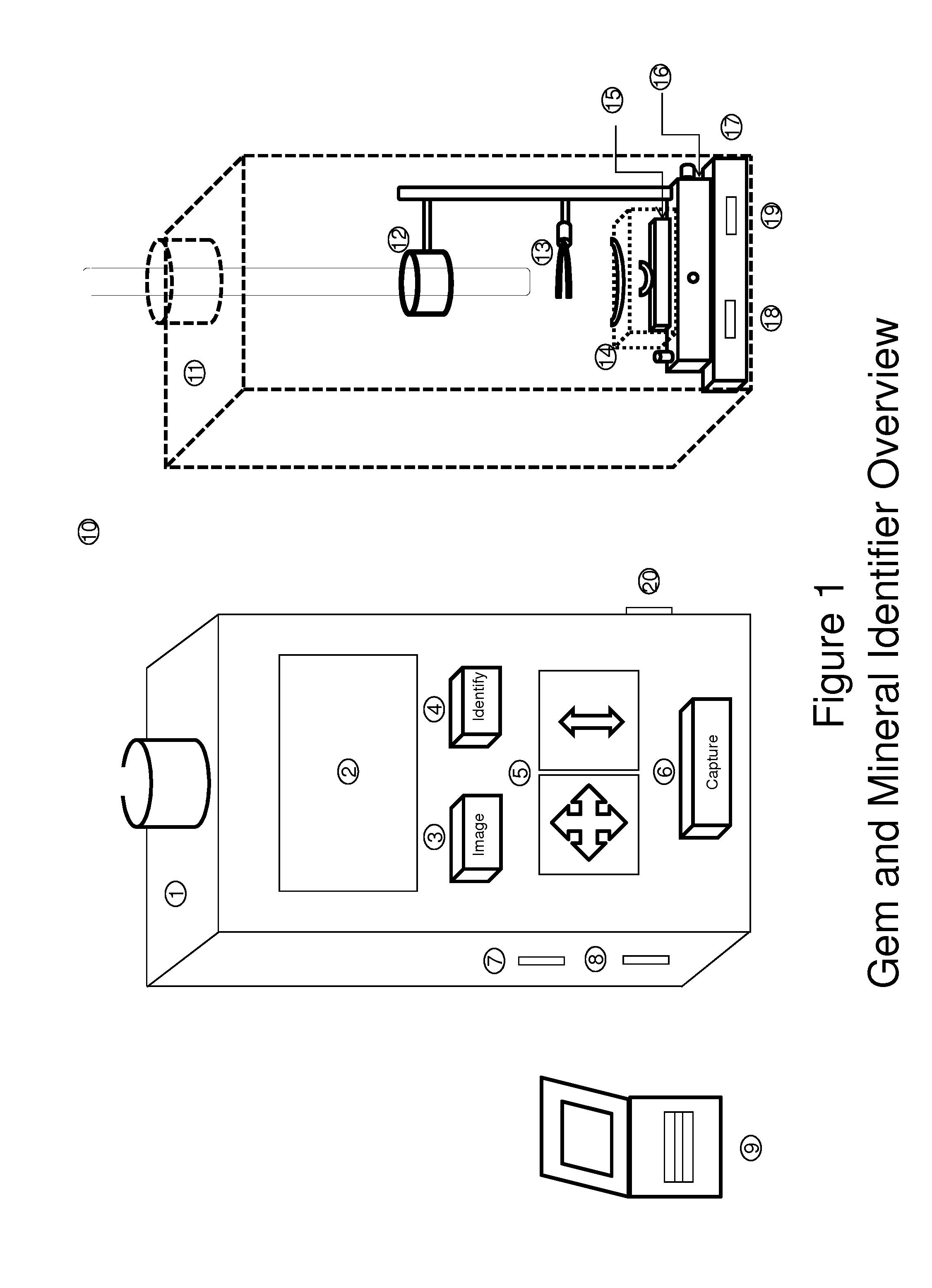
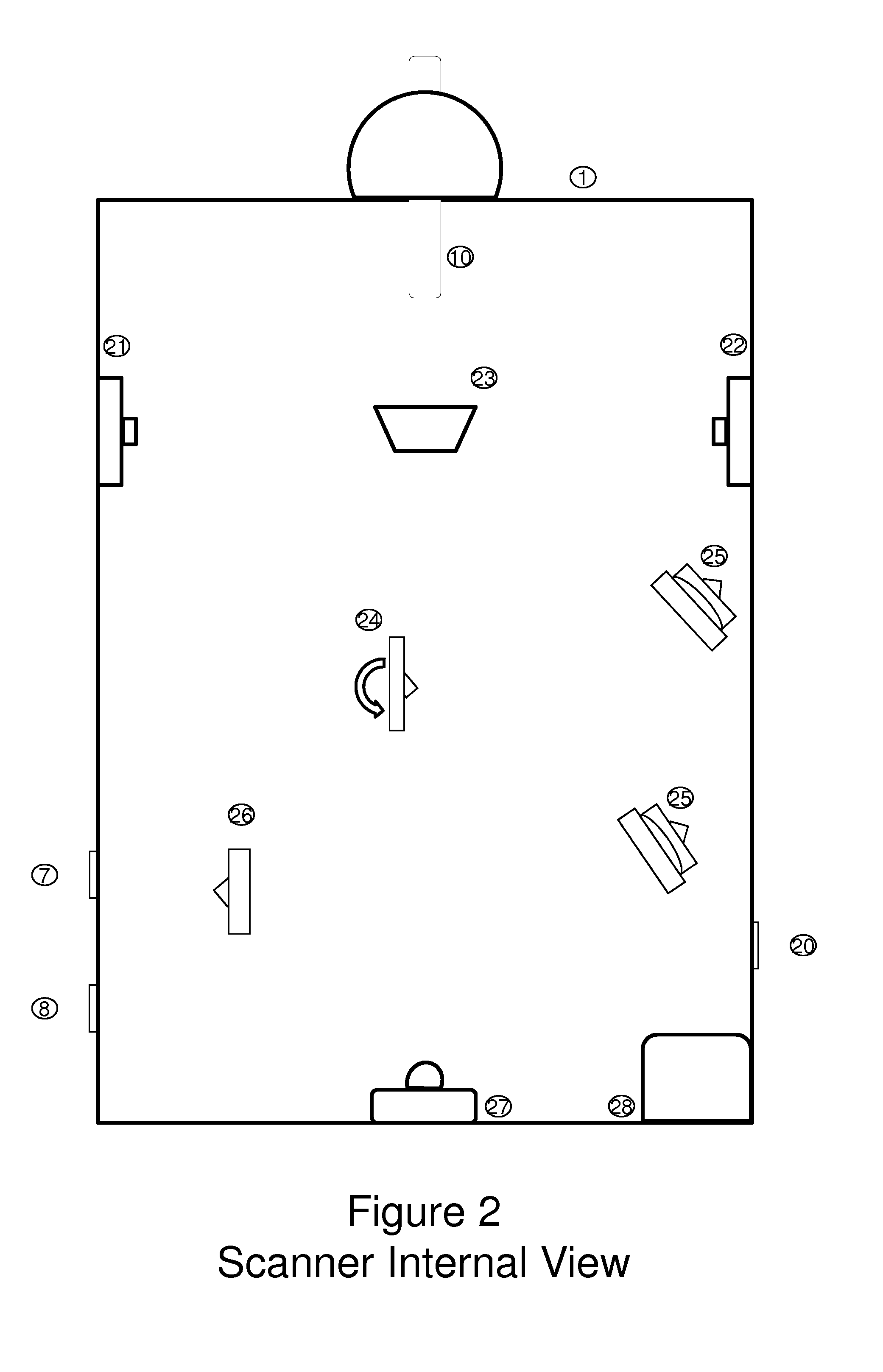
Universal tool for automated gem and mineral identification and measurement
ActiveUS20130321792A1The process is fast and accurateRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringTelecommunications linkCommunication link
A tool employs Raman spectroscopy, optical imaging, physical measurements, smart software applications, and custom databases for automated on-site gem and mineral identification, measurement, and authenticity verification. Operators with no technical expertise can perform on-site, fast, nondestructive gem and mineral characterization. A custom smart application for data handling and processing enables applicability with a variety of processors. Automated generation of Raman spectral signatures and subsequent correlation to spectral fingerprints of known materials enables gem and mineral identification and verification in field settings. A single tool provides high resolution digital optical imaging and physical measurement capabilities, enables comprehensive sample characterization and reporting that currently requires multiple tools and significant labor. The Tool also provides the capability for sample analysis, requiring an additional level of technical expertise, to be done remotely at another location by the transmission of the data via a communications link. A rechargeable battery pack is included.
Owner:SHAPIRO FREDERICK W
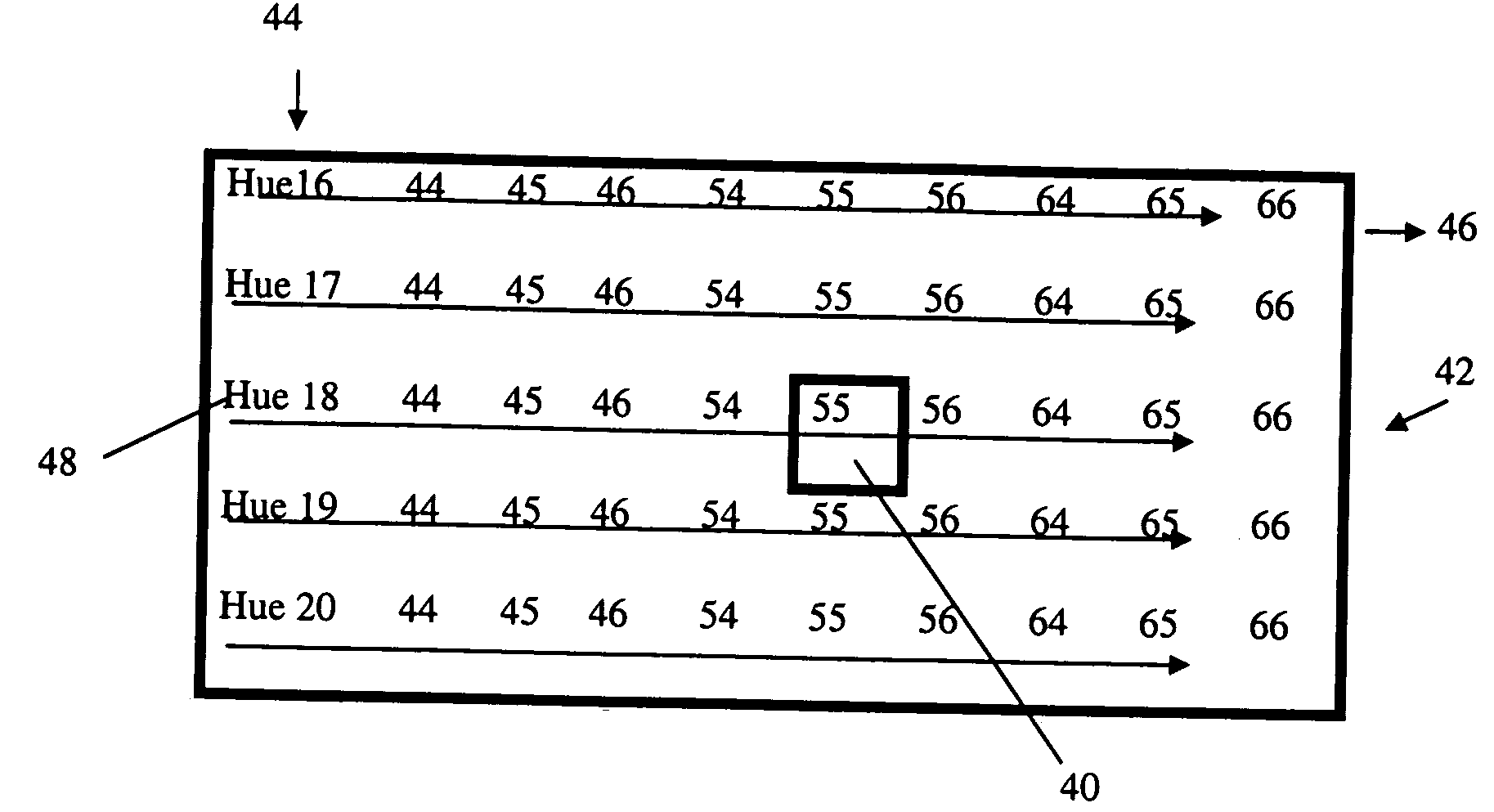
Method for digital color grading of gems and communication thereof
ActiveUS20050149369A1Precise definitionProduct appraisalCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual comparisonThe Internet
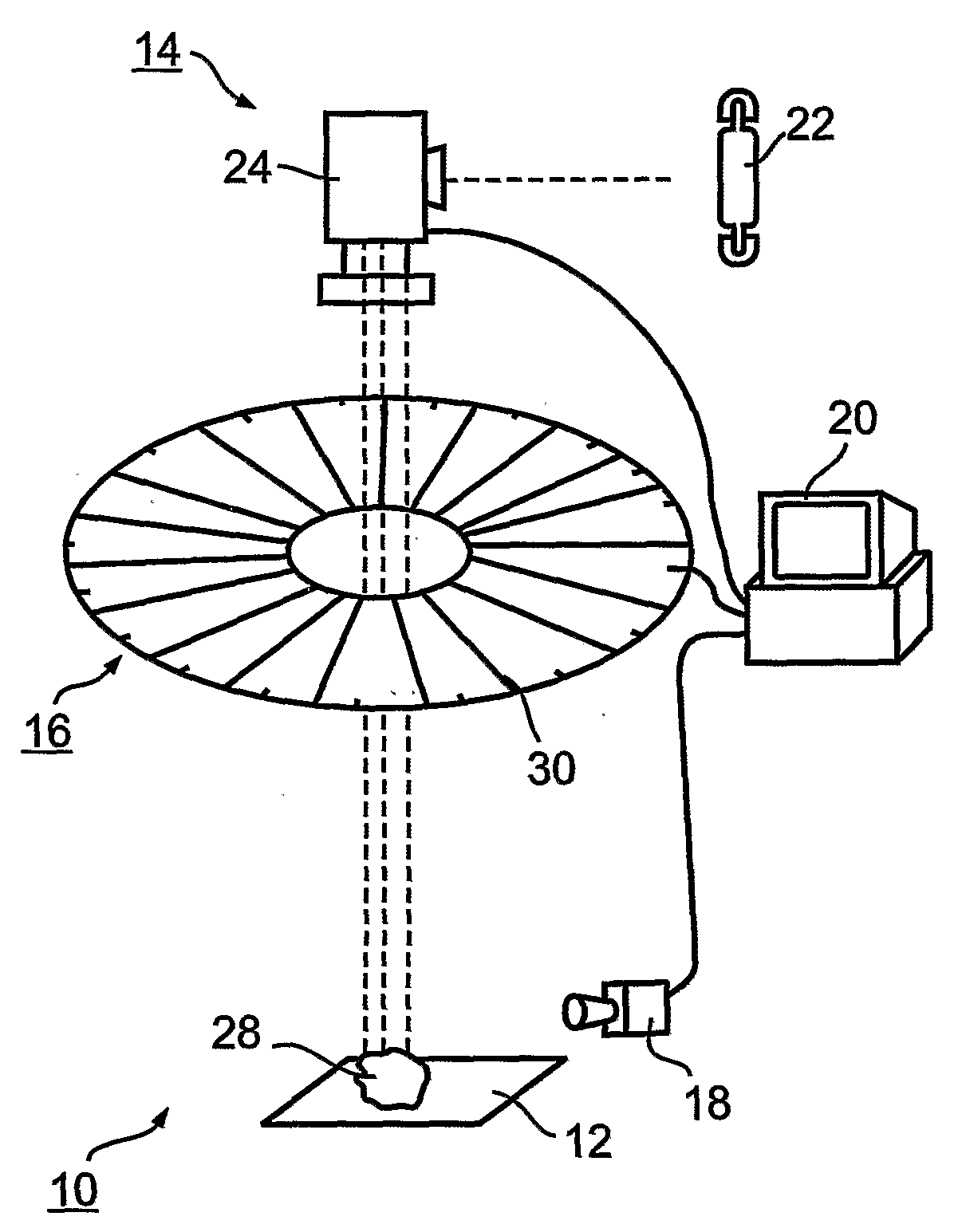
A computer based expert system and method of grading gems by their inherent properties of shape and color, including hue-tone-saturation. Each of the properties is variable over a practical range derived from a data-base; the database prepared by digital methods from real gems. The grading is conducted interactively on-screen by visual comparison to the image of a real target gem, and the result, translated into alpha-numeric code, can be communicated by phone or via the Internet to any other user of the same system and database. The communicated code can be reconstructed by the system into an identical gem image, enabling remote discussion and evaluation of the same target gem, including matching and pairing of gems. A practical embodiment of the grading system and method is described, including application modes specifically aimed at gems and diamonds.
Owner:SEVDERMISH MENAHEM
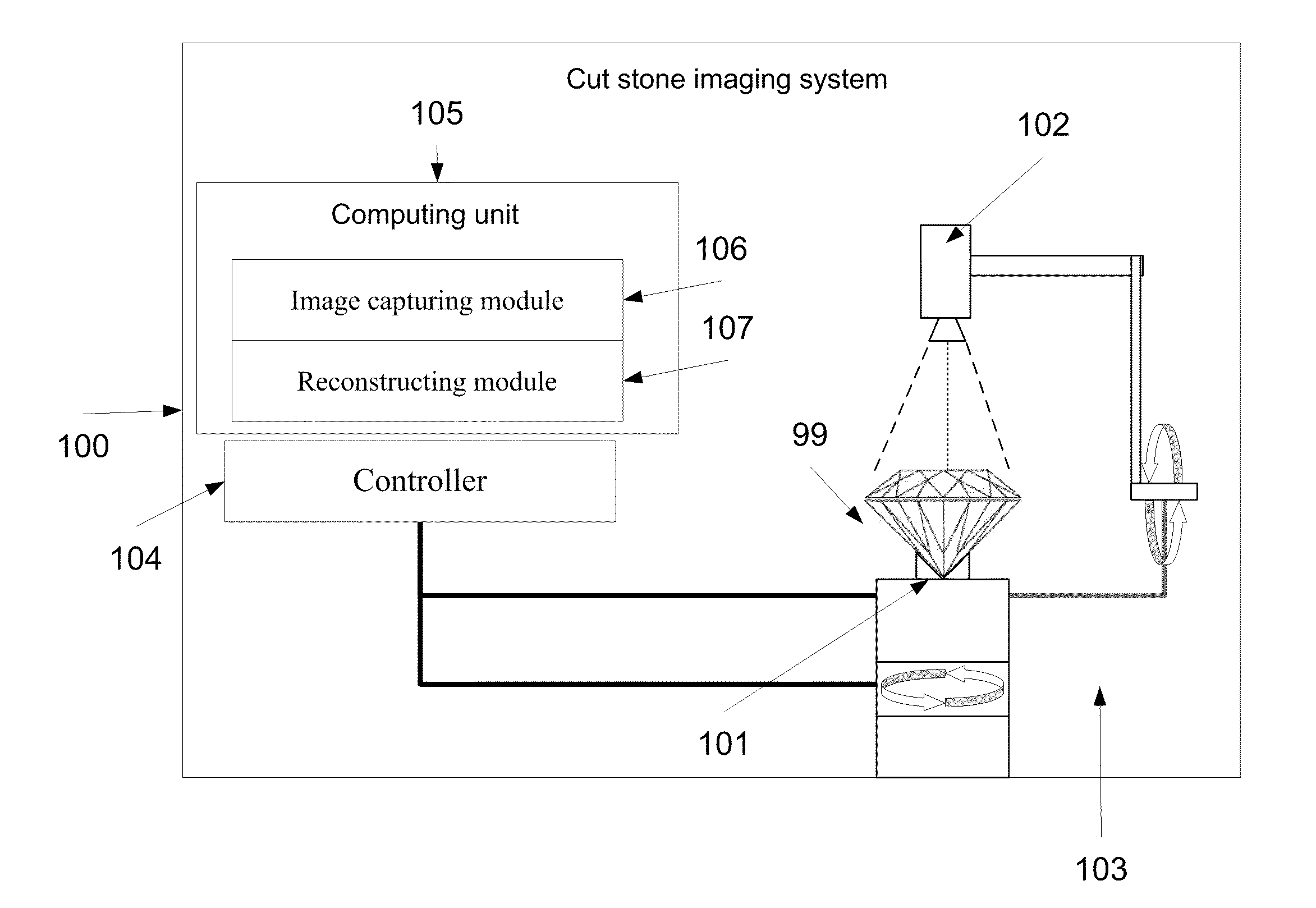
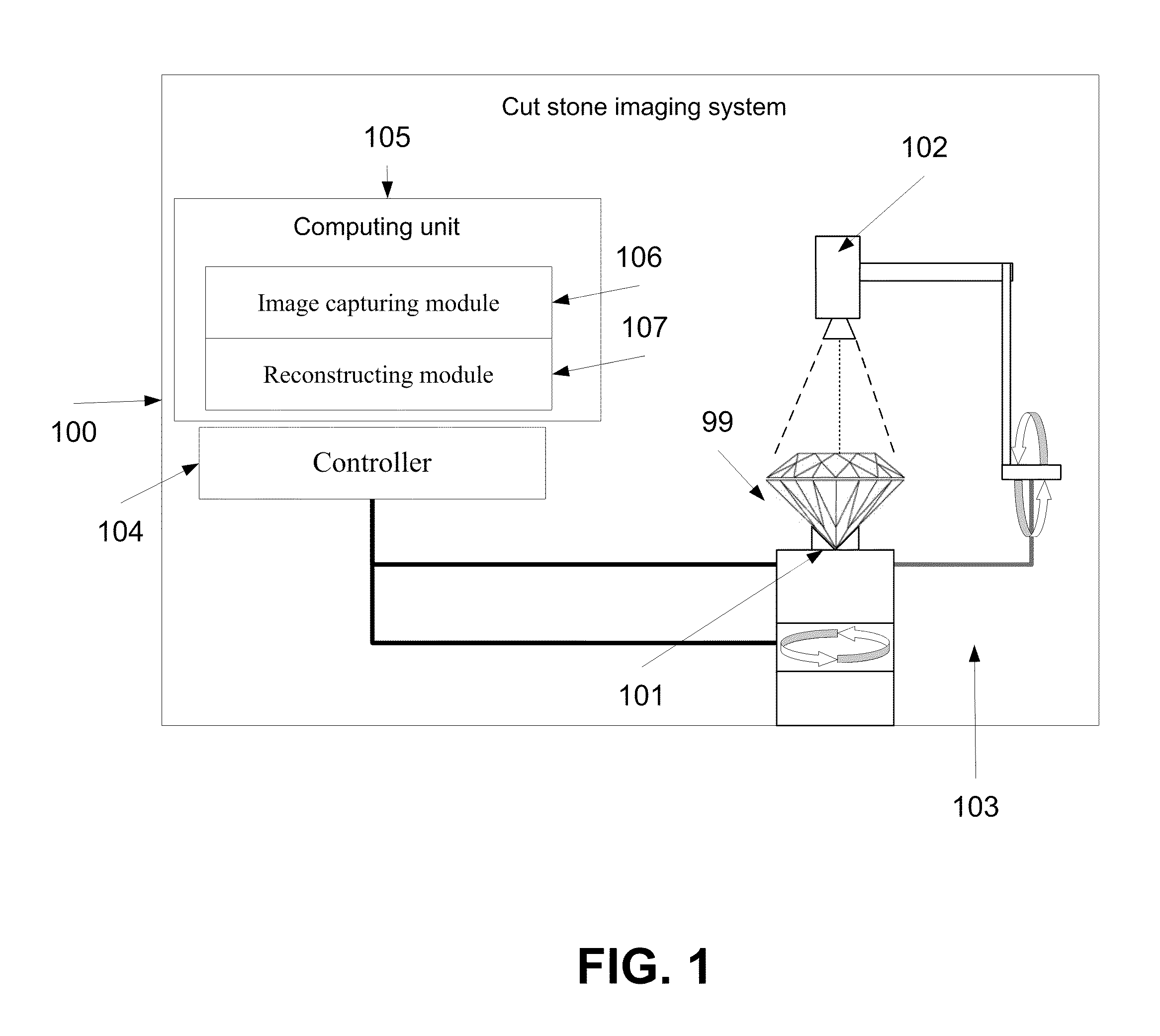
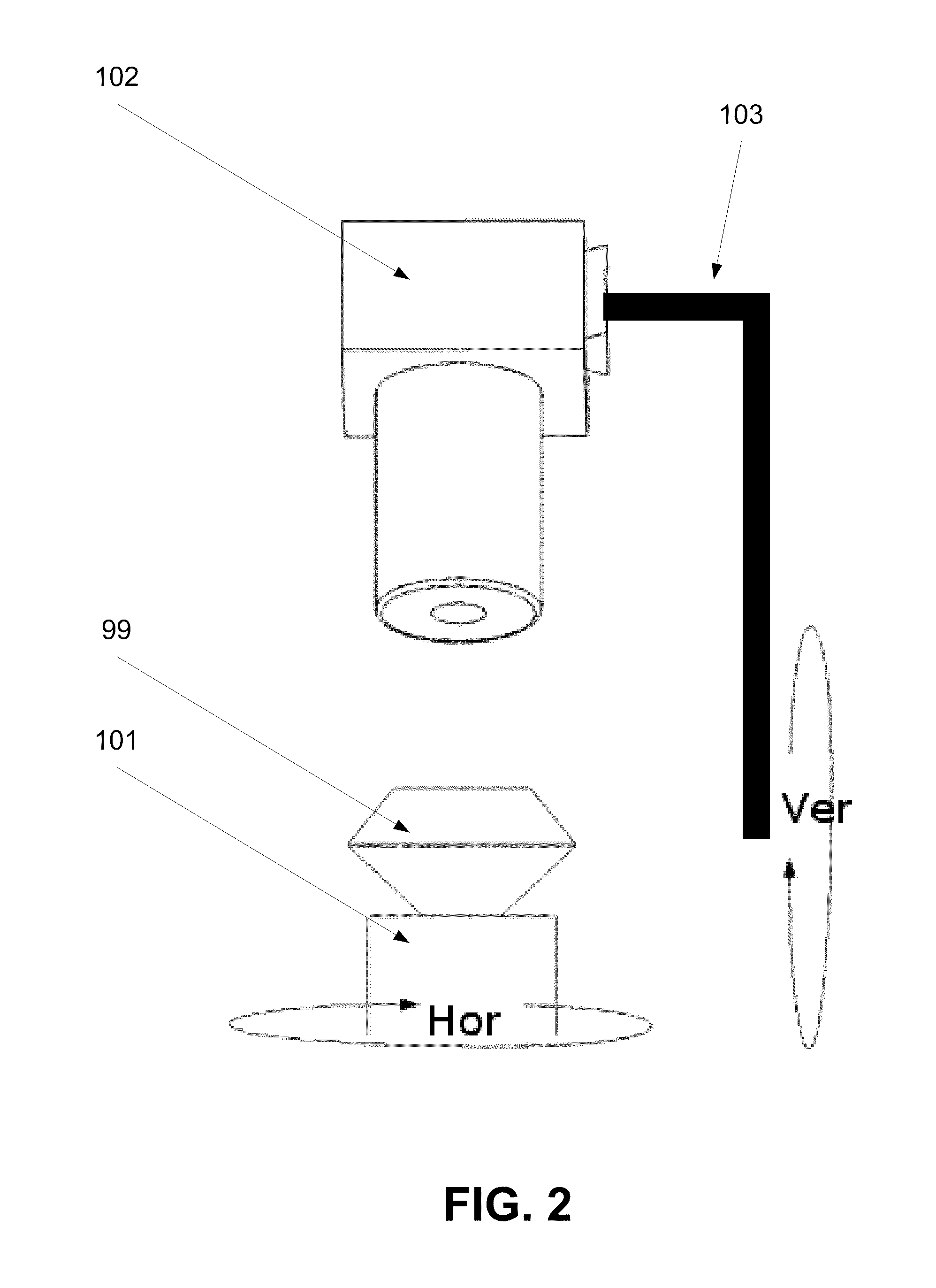
Methods and systems of imaging cut stones
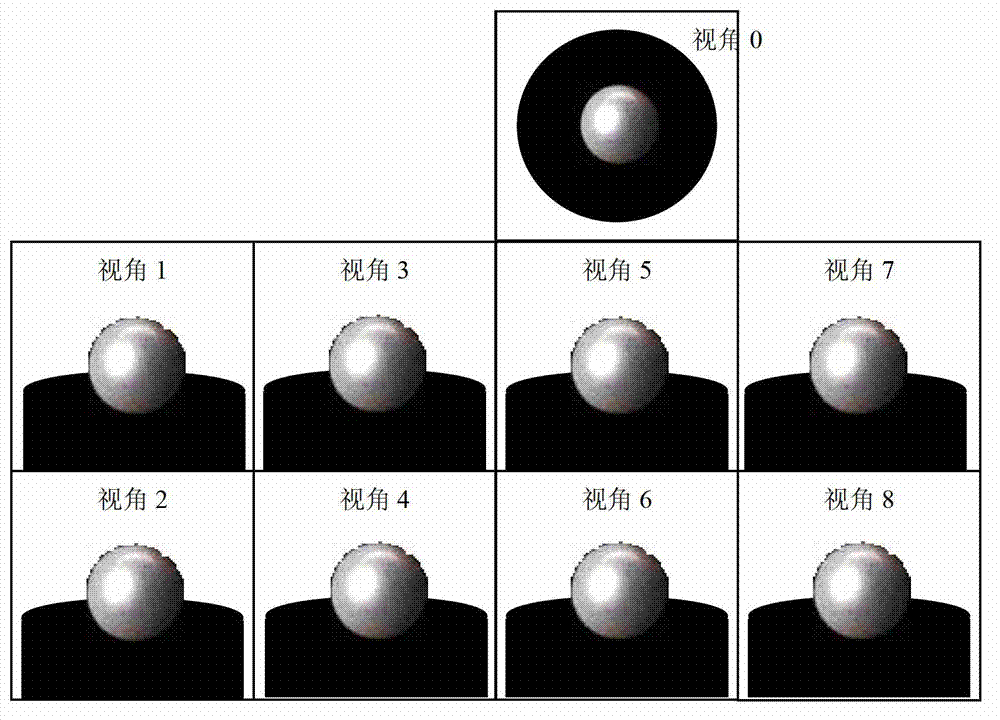
ActiveUS20120007971A1Increase exposureImage enhancementTelevision system detailsMethod of imagesVolumetric model
A method of imaging a cut stone. The method comprises a) identifying an orientation of a cut stone, b) creating a volumetric model of the cut stone according to the orientation, c) capturing a plurality of images of the cut stone from a plurality of viewing angles around the cut stone, d) cropping a plurality of segments depicting the cut stone from the plurality of images using the volumetric model, and e) generating a volumetric image of the cut stone from the plurality of segments.
Owner:SARIN COLOR TECH
Method and System for Improved Optical Modeling of Gemstones
ActiveUS20140107986A1Reduce deficiencyImproved virtual optical modelingInvestigating jewelsOptically investigating flaws/contamination3d shapesOptical property
A method of constructing a virtual model of a gemstone including the steps of performing measurements of the gemstone to construct a three-dimensional (3D) model of an exterior surface of the gemstone; identifying one or more visible inclusions within an interior volume of the gemstone; for each identified inclusion, performing the steps of determining a location and 3D shape of the inclusion within the interior volume of the gemstone; capturing at least one image of the inclusion; using the at least one image to determine relevant optical characteristics of the inclusion; and constructing a 3D virtual model of the inclusion, said model including the 3D shape of the inclusion and optical properties of the inclusion based upon said optical characteristics; constructing a 3D virtual model of the gemstone which includes the 3D virtual model of the exterior surface of the gemstone and the 3D virtual models of the one or more visible inclusions within the interior volume of the gemstone; and generating a dataset representing said 3D virtual model, wherein said dataset may be used in subseguent computer analysis to provide a user with information relating to a visual characteristic of the gemstone.
Owner:IDEAL SCOPE
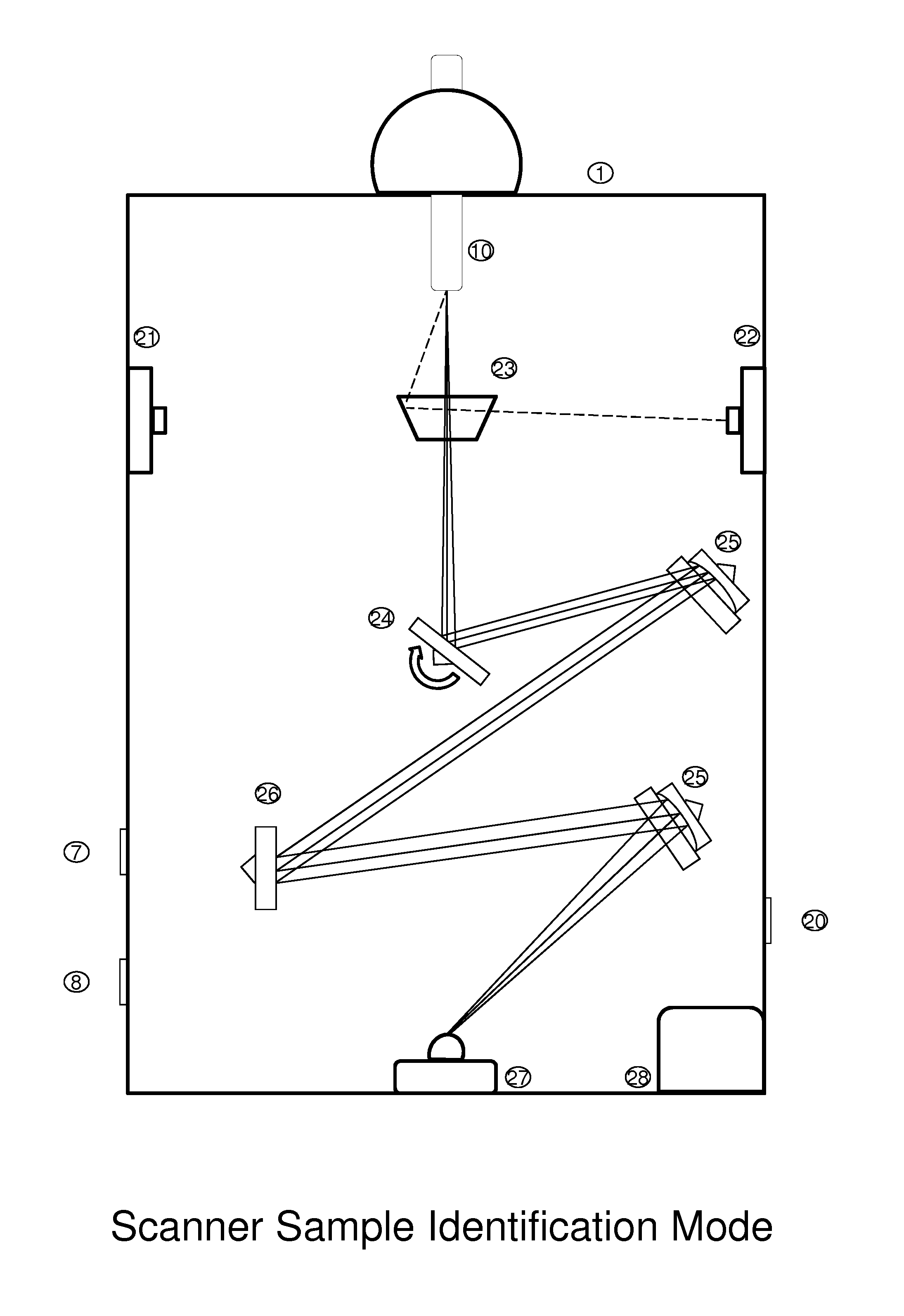
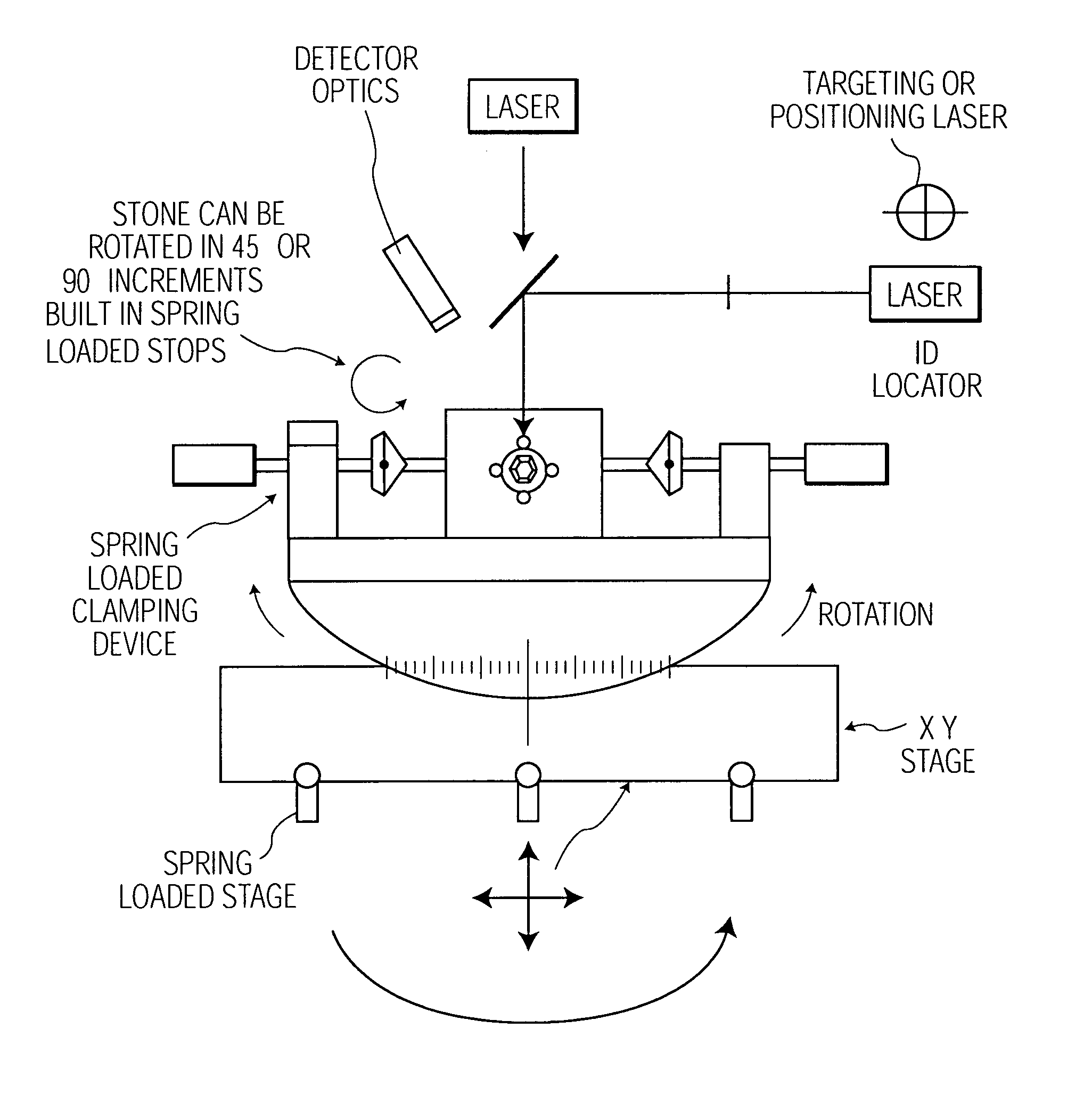
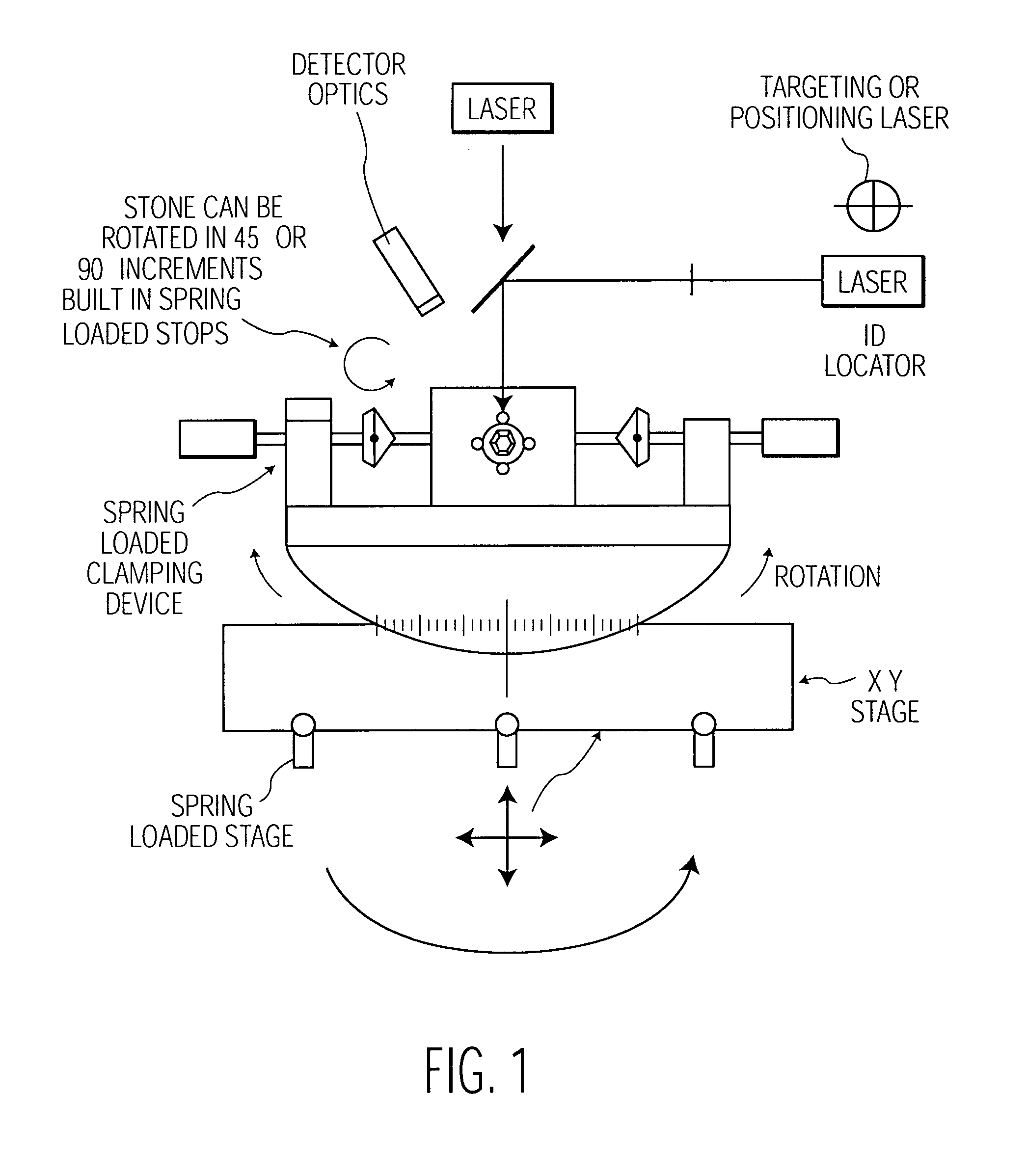
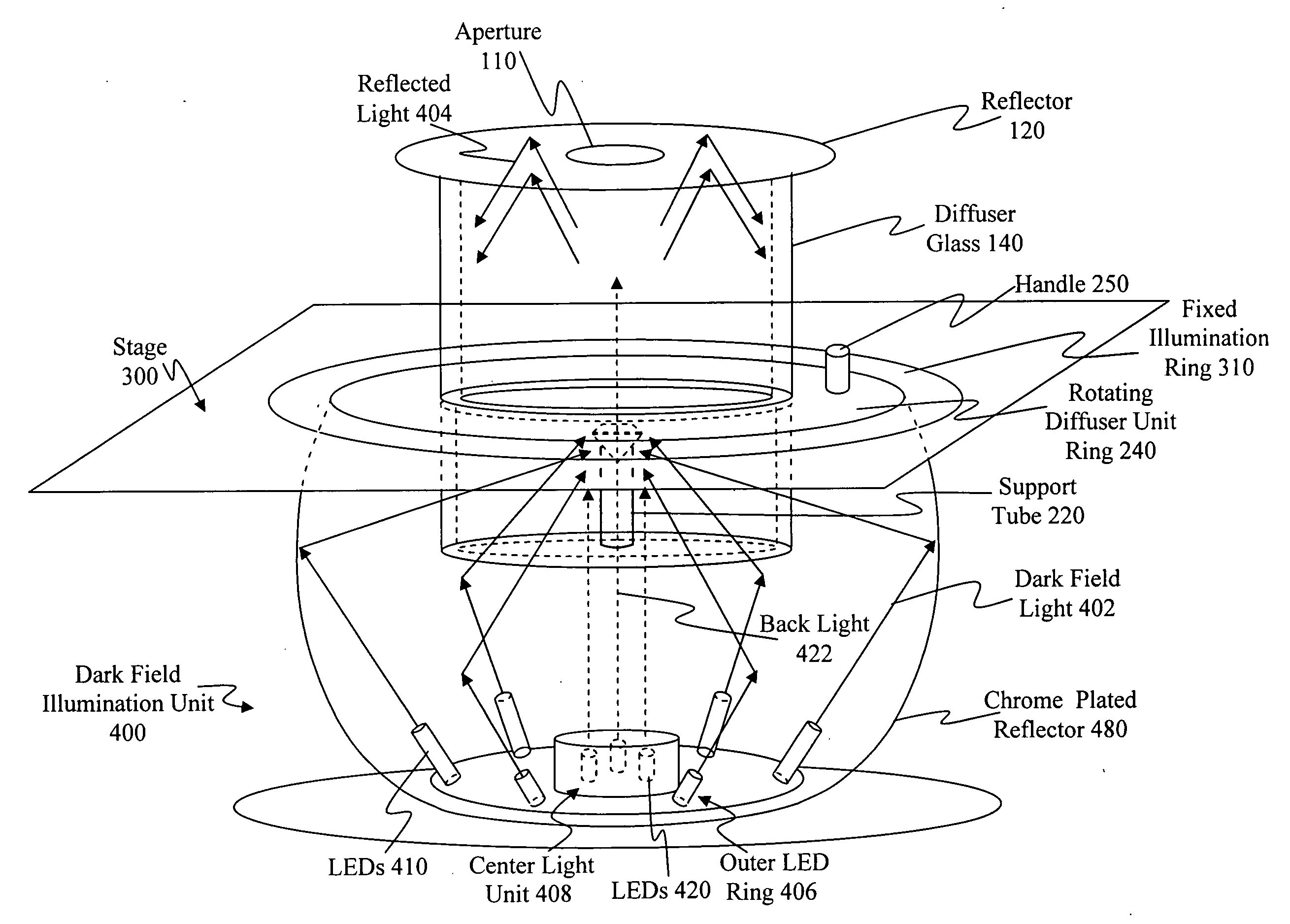
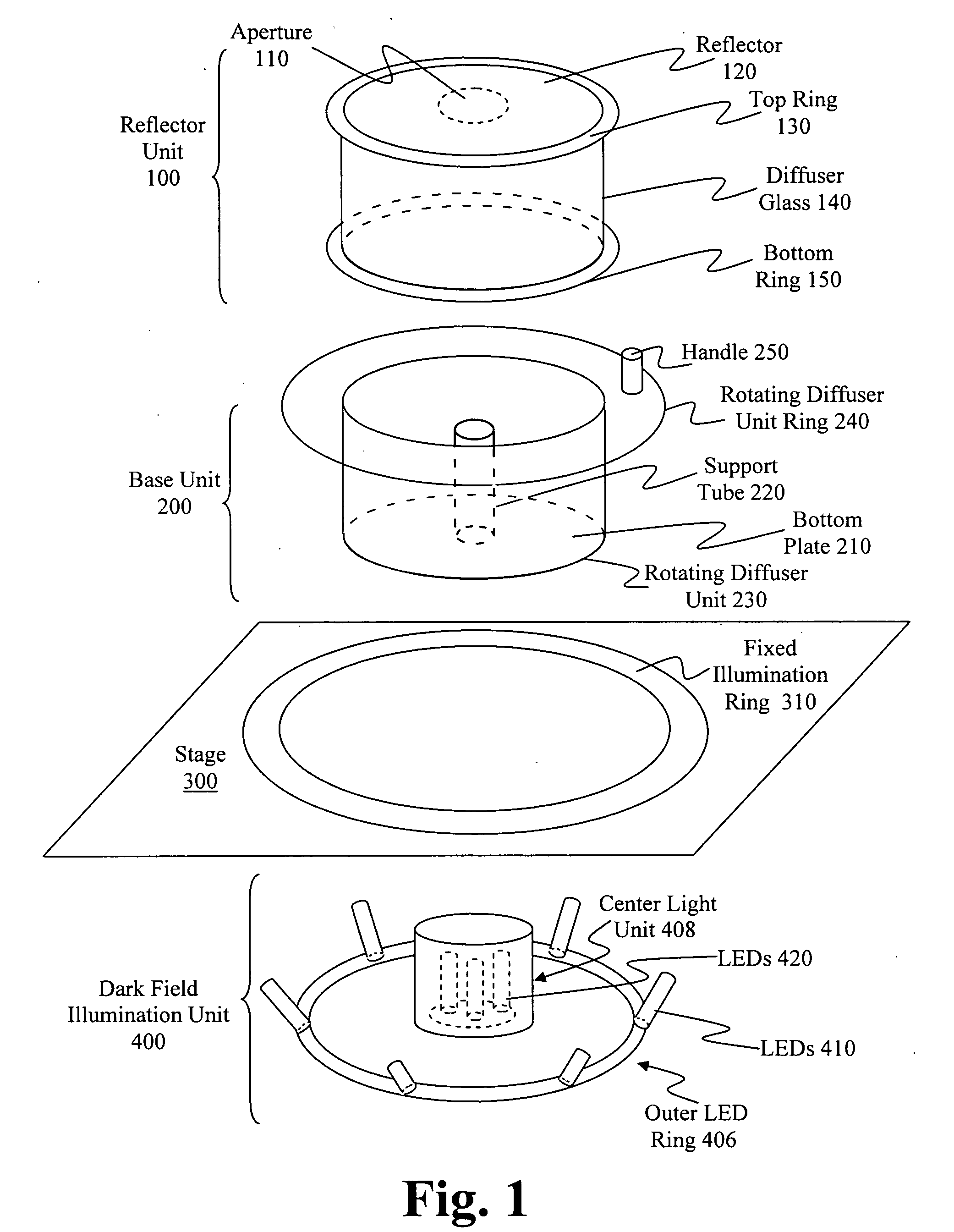
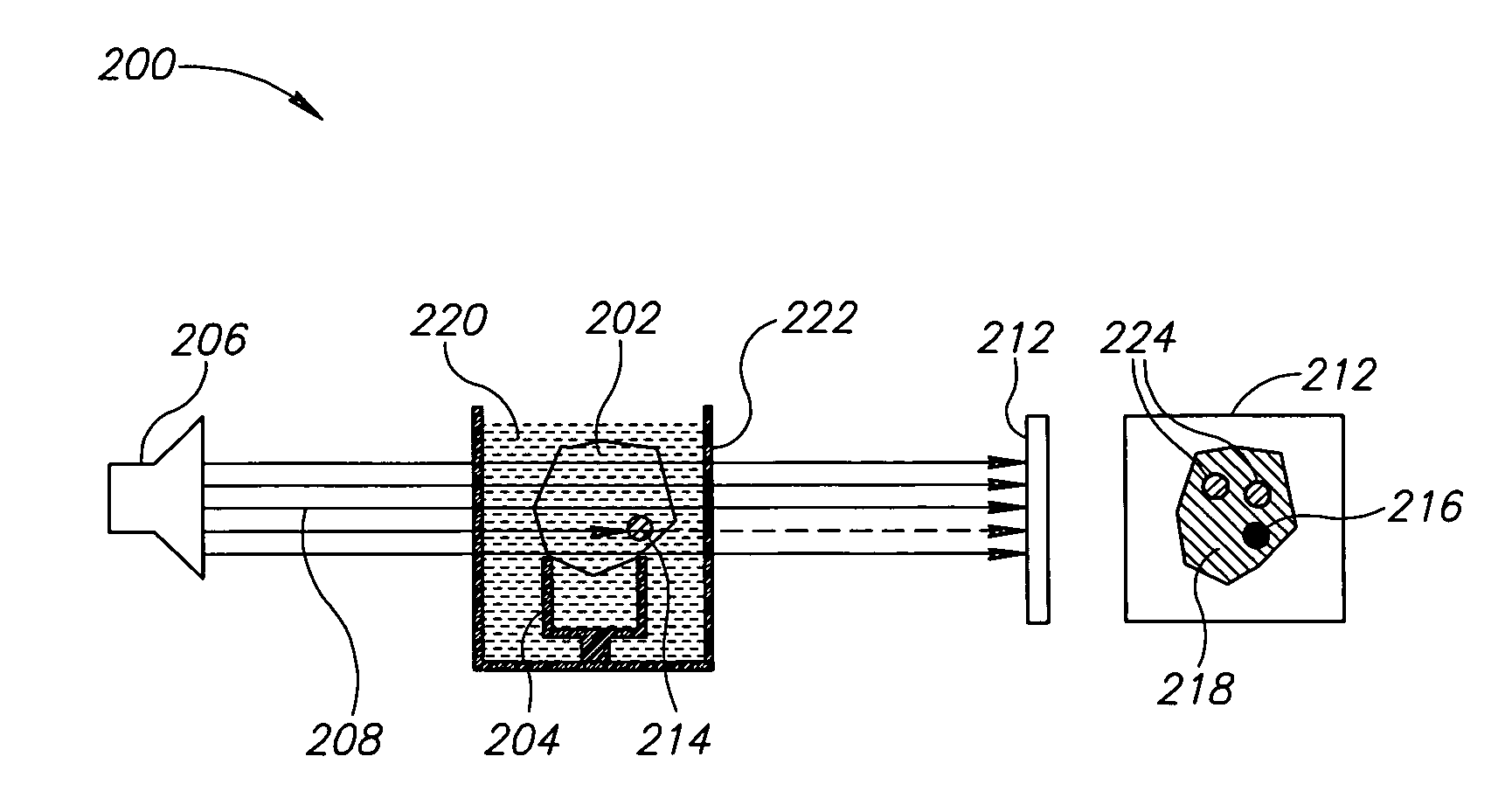
Method and apparatus for object viewing, observation, inspection, identification, and verification
In an object verifier having a housing and an object holder, an object may be placed in the object holder for observation by an operator. The object is illuminated using a collimated beam of white light that is generated by a light generator. The collimated beam of white light is passed through a beam splitter with the two portions of the collimated beam of white light presented to the object at a 90 degree angle one from the other. The interior of the housing includes a reflective surface for maximal illumination of the object. The observer may view the illuminated object through a viewing window and / or through a magnification window. The magnification window provides for the viewing of the object in greater detail.
Owner:BOCK JOEL N +2
System and method for three-dimensional location of inclusions in a gemstone
InactiveUS20060062446A1Rapid and cost-effectiveInvestigating moving sheetsHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-rayLaser beams
The present invention presents a non-destructive method and means of obtaining either the inner portion or the outer contour of a two-dimensional or three-dimensional model of the outer contours of a gemstone. The method comprising the steps of placing the gemstone on a holder such that the gemstone to be scanned is located in a radiation path comprising inter alia at least one emitter and at least one detector synchronized by a processor; radiating said gemstone by means of said emitter; detecting the emitted irradiation by means of said detector; processing said detection such that a two-dimensional in-scan of said gemstone is obtained by means of said processor; displacing the gemstone in respect to said emitter and said detector; repeating steps (b) through (e) for a plurality of predetermined displacements; and, if a three-dimensional model is required, integrating the obtained multiple two-dimensional in-scans into a three-dimensional model of the gemstone's outer contours; wherein the emitter is an irradiation delivery device, selected from a group consisting of either monochromatic or white light, UV or IR emitters; X-ray radiation source and / or collimator of the same; NMR, CT, NQR and / or MIR scatters; beta radiation emission devices; gamma radiation emission devices; laser beam cannons; photons cannons; microwave or RF emitters; sonic or ultrasonic emitters or any combination thereof.
Owner:PORAT ZVI
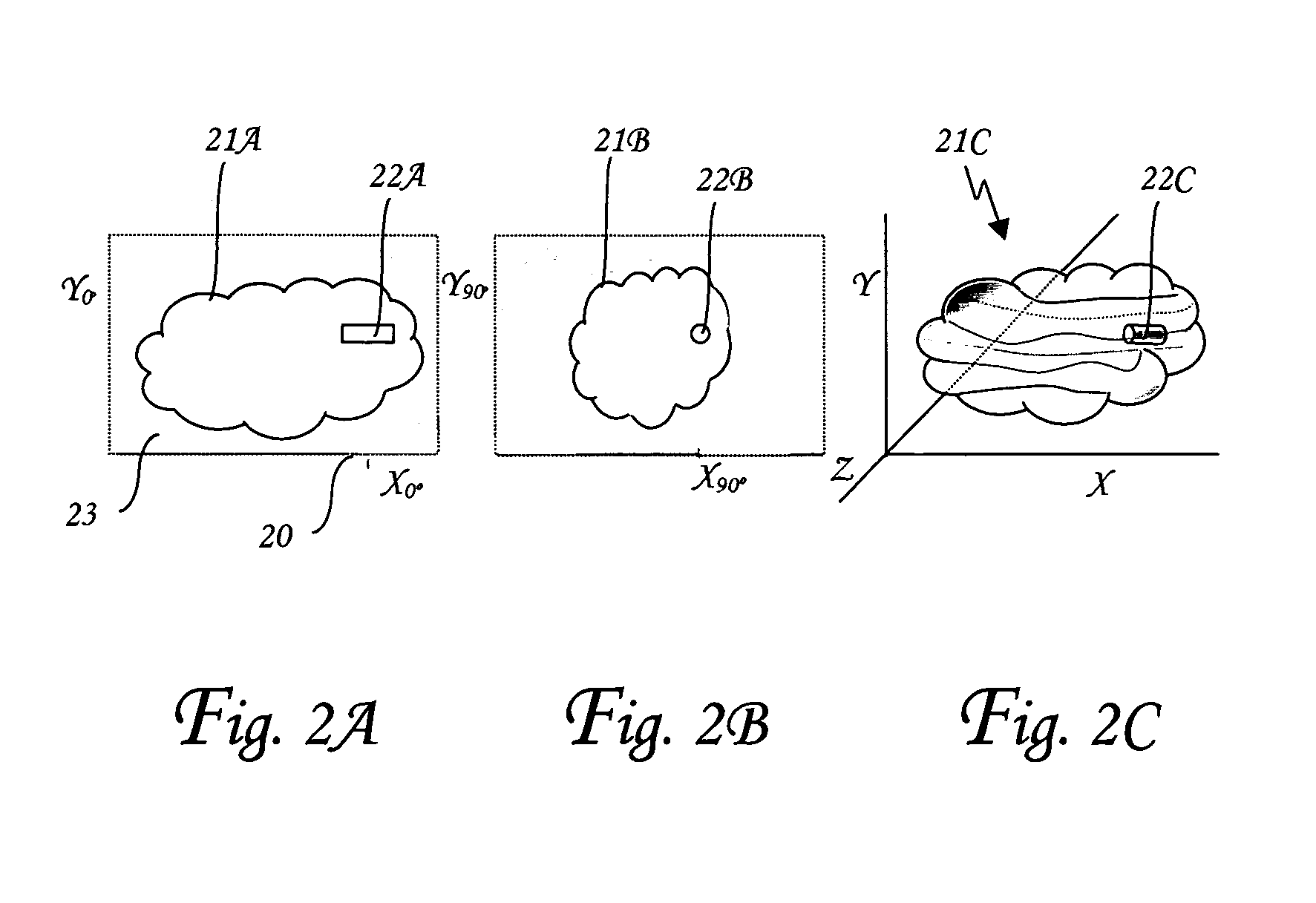
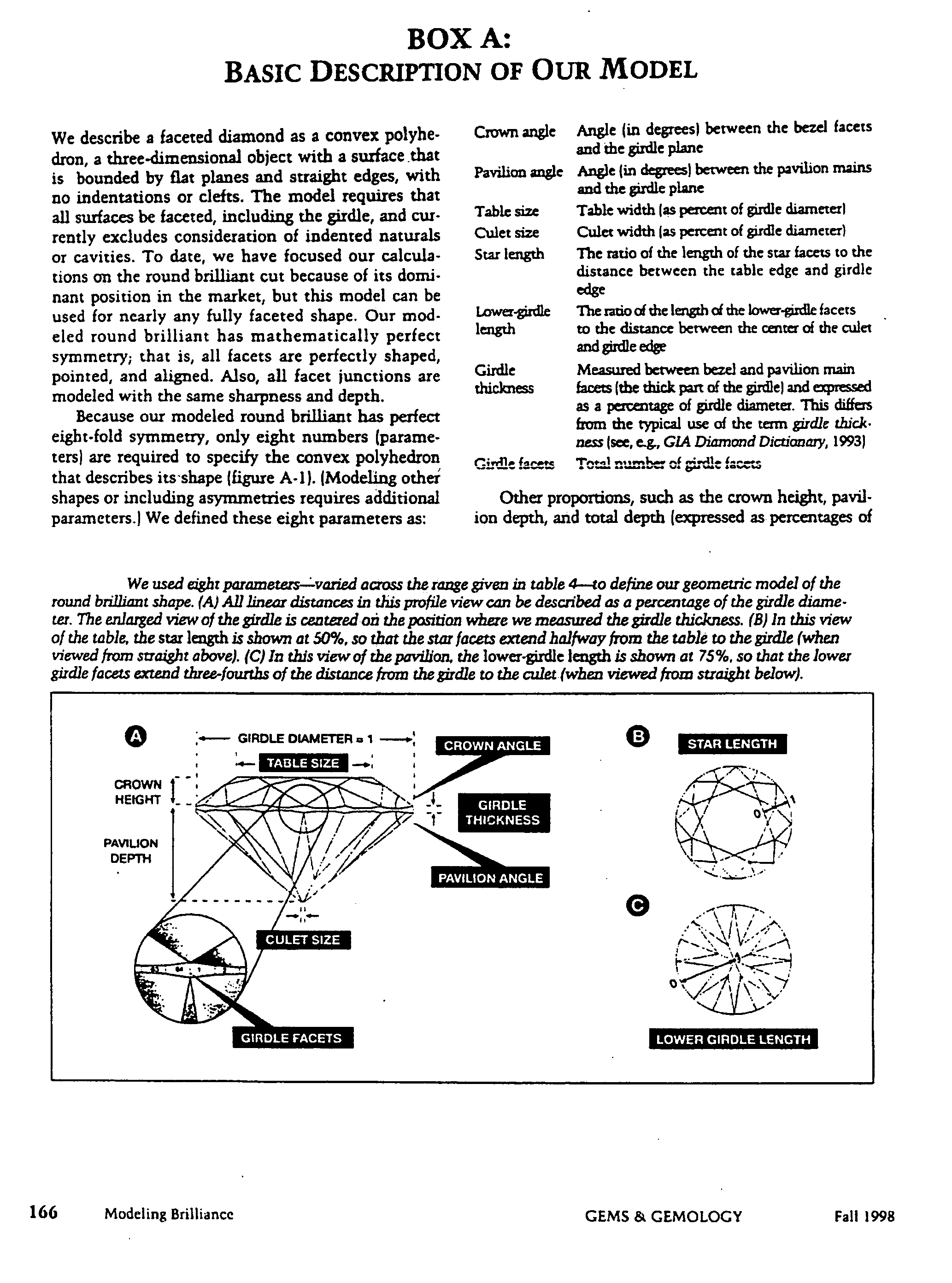
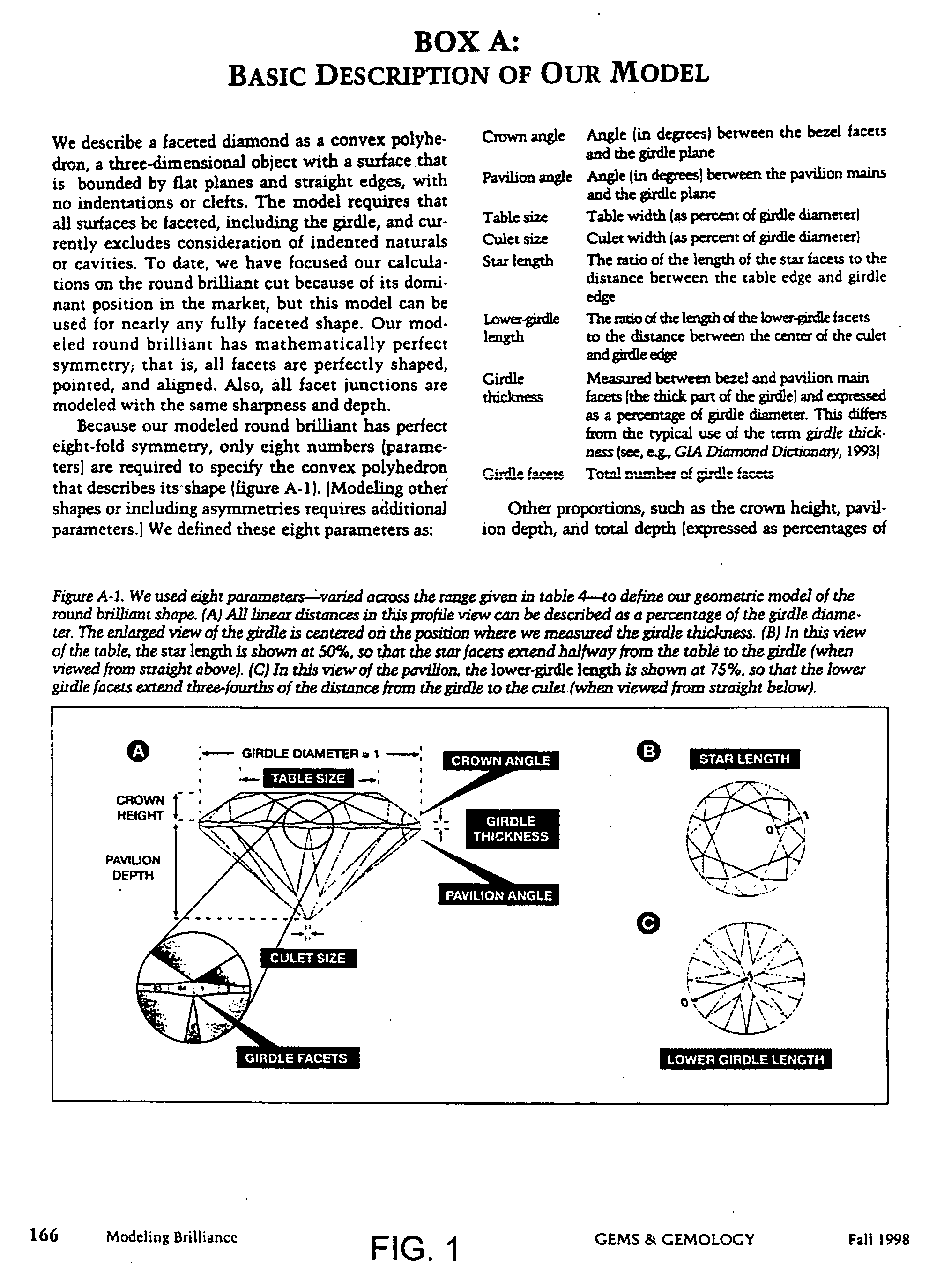
Systems and methods for evaluating the appearance of a gemstone
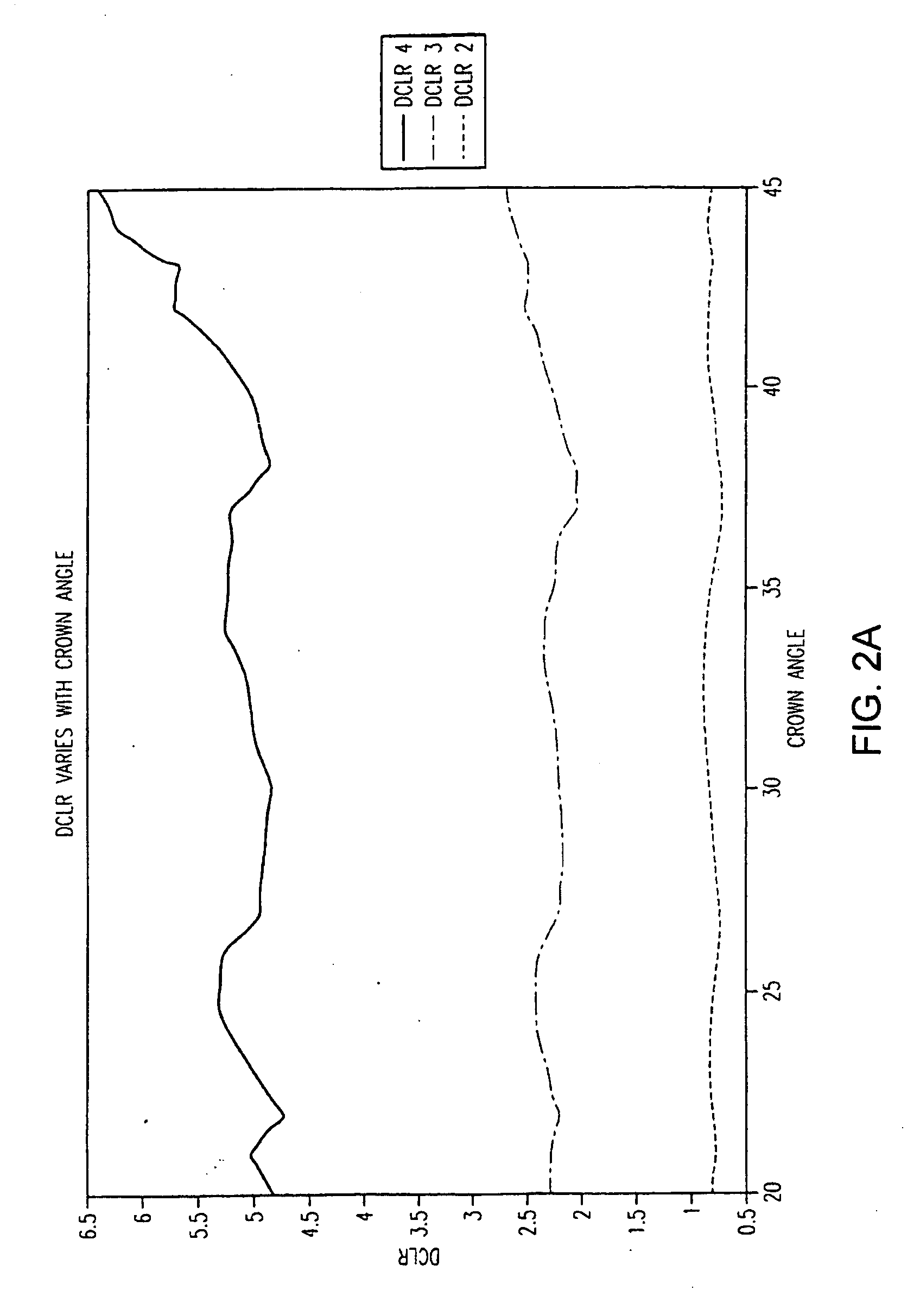
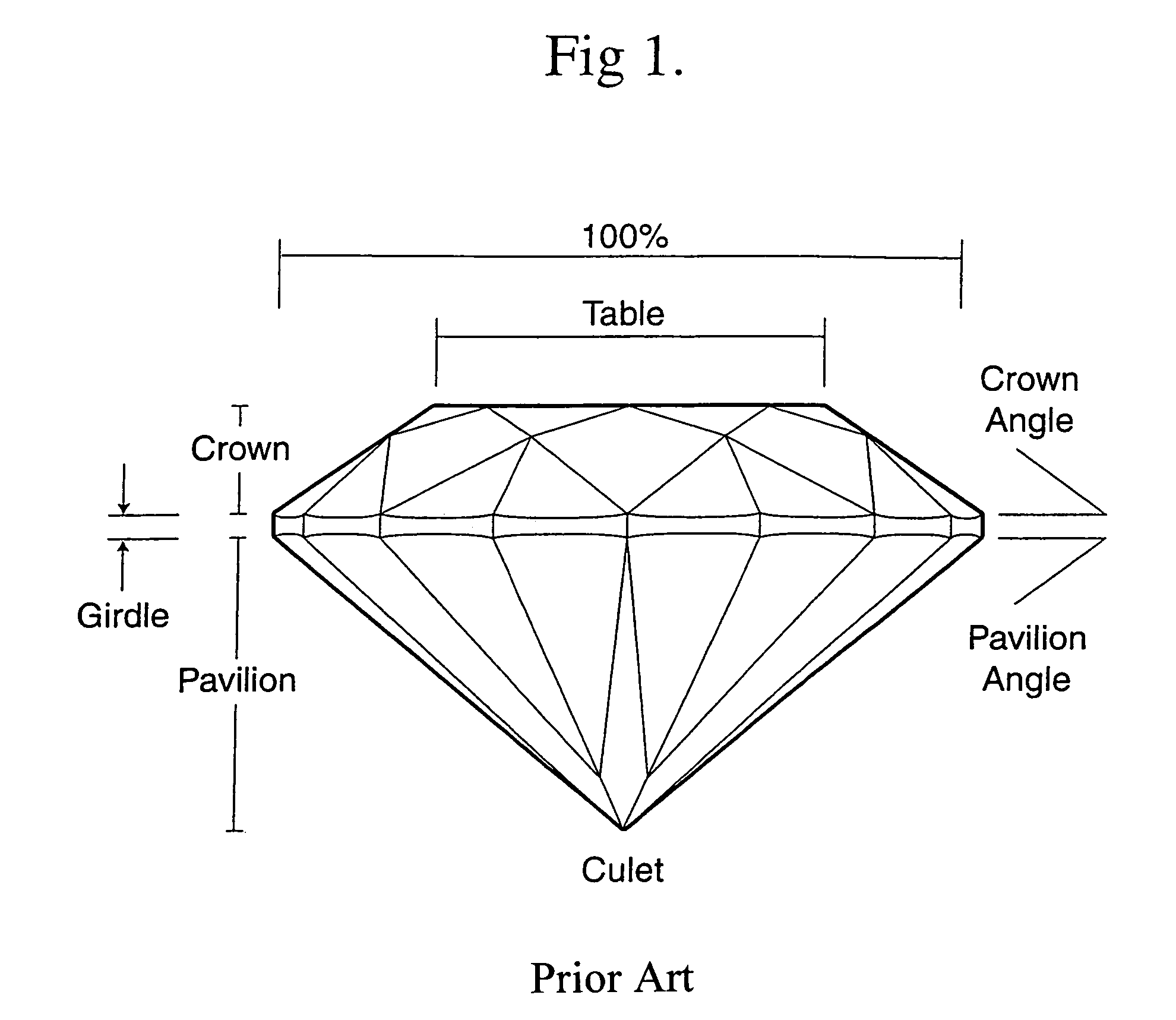
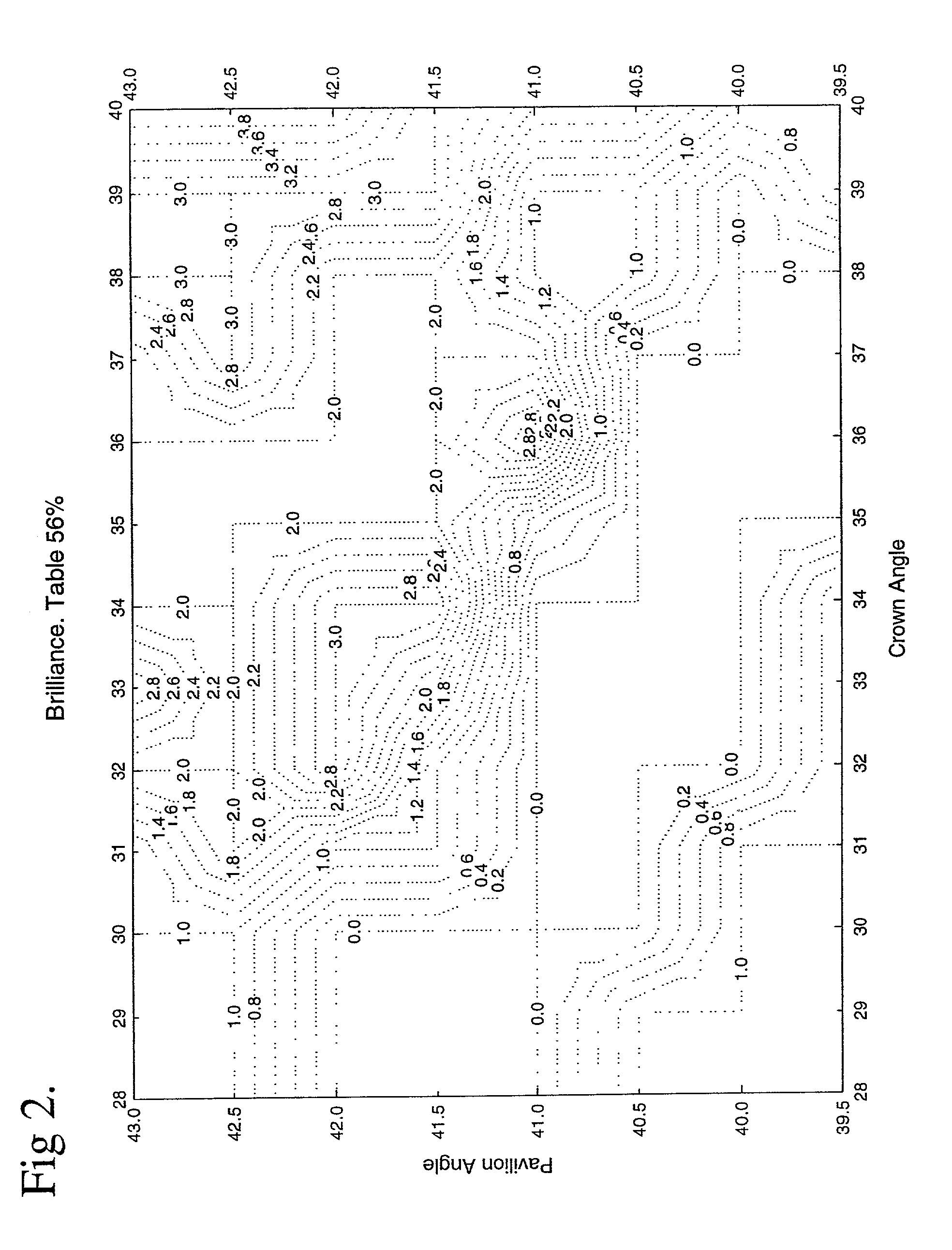
Of the “four C's,” cut has historically been the most complex to understand and assess. This application presents a three-dimensional mathematical model o study the interaction of light with a fully faceted, colorless, symmetrical round-brilliant-cut diamond. With this model, one can analyze how various appearance factors (brilliance, fire, and scintillation) depend on proportions. The model generates images and a numerical measurement of the optical efficiency of the round brilliant-called DCLR—which approximates overall fire. DCLR values change with variations in cut proportions, in particular crown angle, pavilion angle, table size, star facet length, culet size, and lower girdle facet length. The invention describes many combinations of proportions with equal or higher DCLR than “Ideal” cuts, and these DCLR ratings may be balanced with other factors such as brilliance and scintillation to provide a cut grade for an existing diamond or a cut analysis for prospective cut of diamond rough.
Owner:GEMOLOGICAL INST OF AMERICA INC
System and method for analysis of gemstones
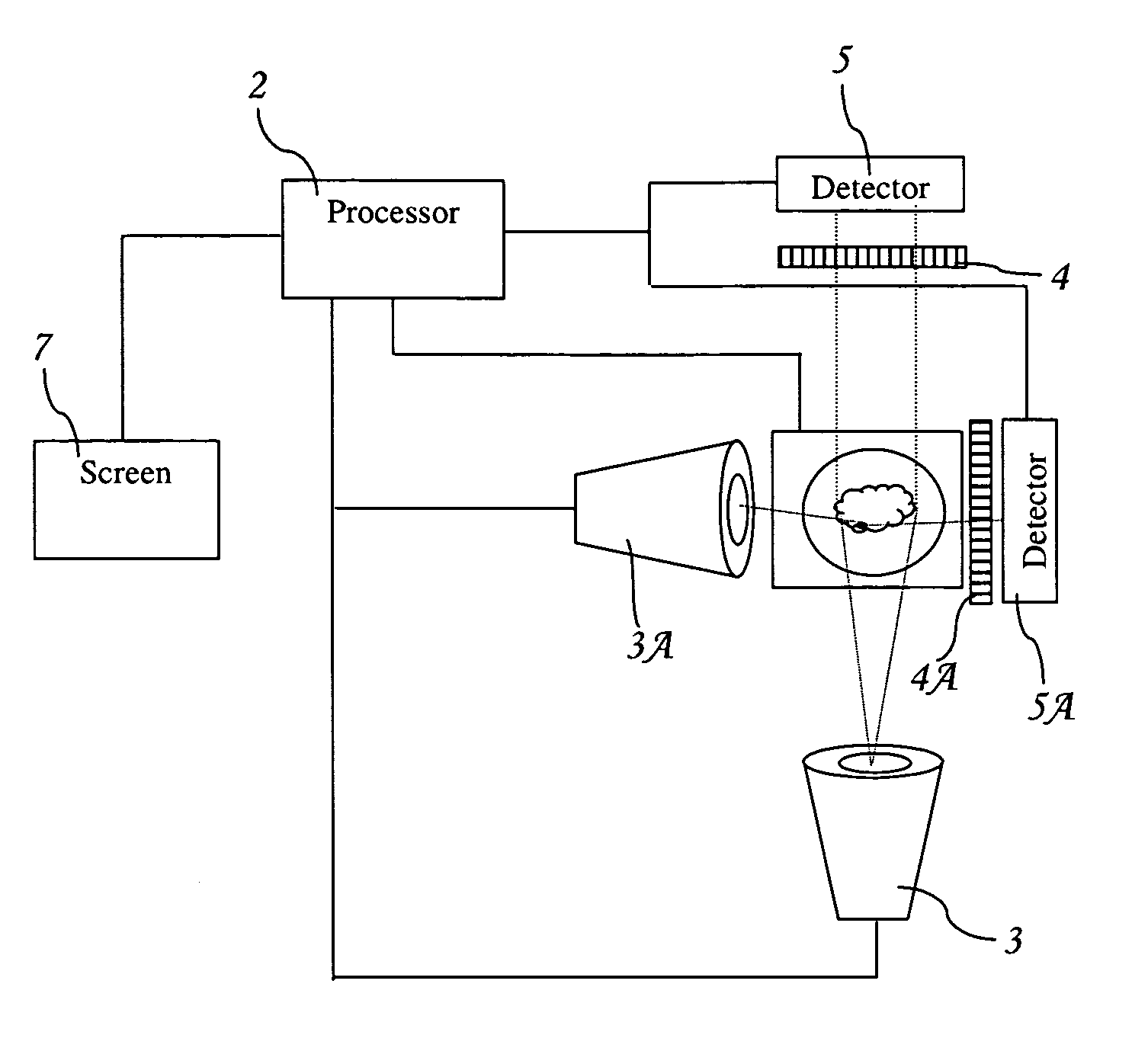
InactiveUS7557917B1Reduce detection limitRapid analysis cycleRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSpectral emissionChemical composition
A system for analyzing the chemical composition of a sample, comprising exciting a portion of the sample to generate atomic spectral emissions; a spectrometer for determining atomic emission characteristics; processor for receiving an output from the spectrometer, analyzing said output to determine atomic composition, said processor predicting at least one of (i) an origin of the sample, (ii) a treatment applied to said sample, (iii) a composition of the sample, and (iv) a feedback signal for controlling a process. Calibration samples are also provided for standardizing readings from the spectrometer.
Owner:AMERICAN GEMOLOGICAL LAB
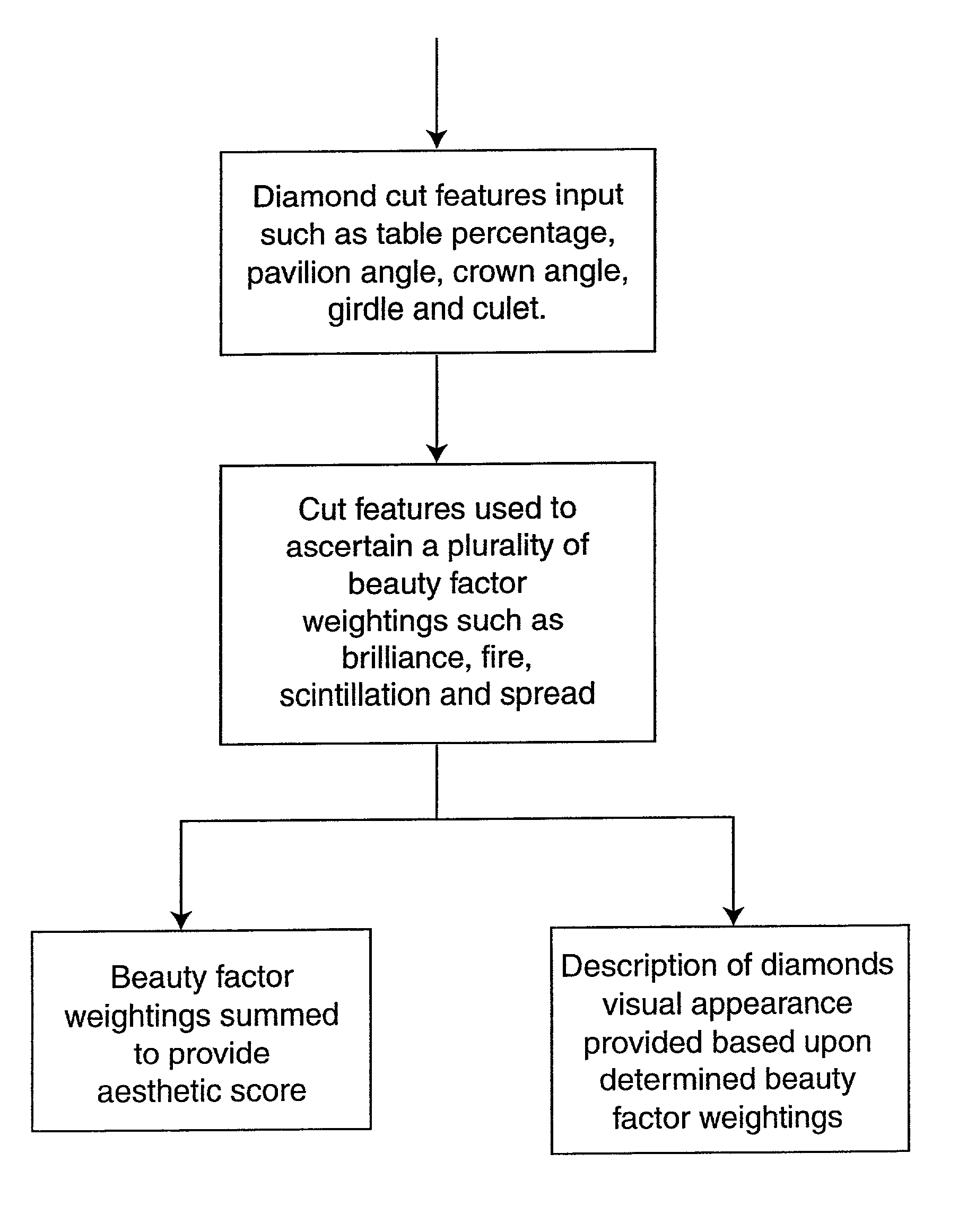
Computer implemented method, computer program product, and system for gem evaluation
InactiveUS7251619B2Improve diamond beautyGive flexibilityInvestigating jewelsApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingQuality ratingEvaluation system
System and method for providing a gem assessment based upon proportional parameter values relating to the proportions of a gem, such as a diamond. A gem cut quality rating is provided. The system and method are particularly suited for use in an online environment or may be utilized in conjunction with rough diamond analysis instruments in order to provide cutters with greater guidance as to the most appropriate dimensions to cut rough diamonds in order to maximize the yield of a rough diamond and to also produce a diamond of an acceptable grade.
Owner:GARRY IAN HOLLOWAY
Method and apparatus for examining a diamond
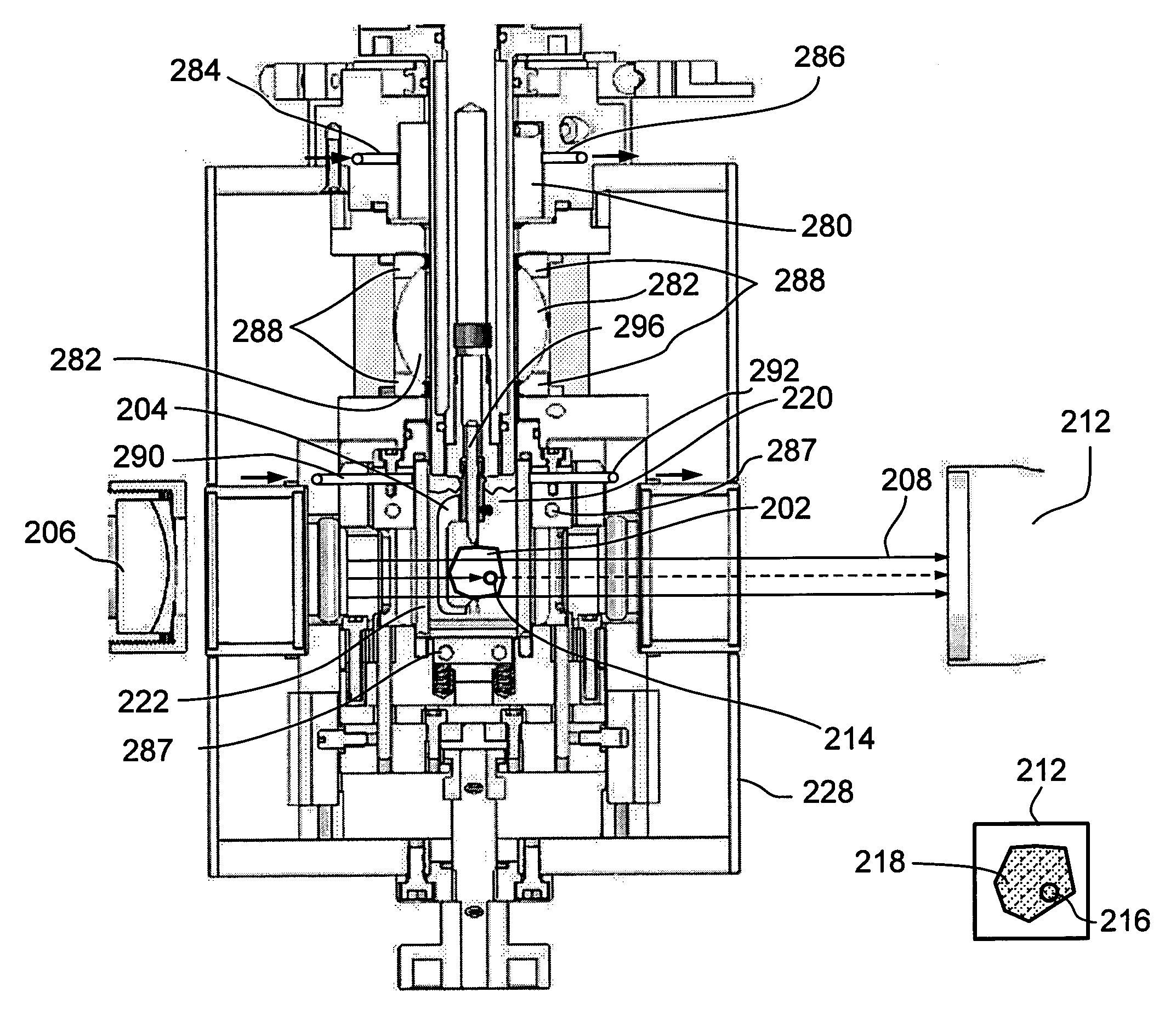
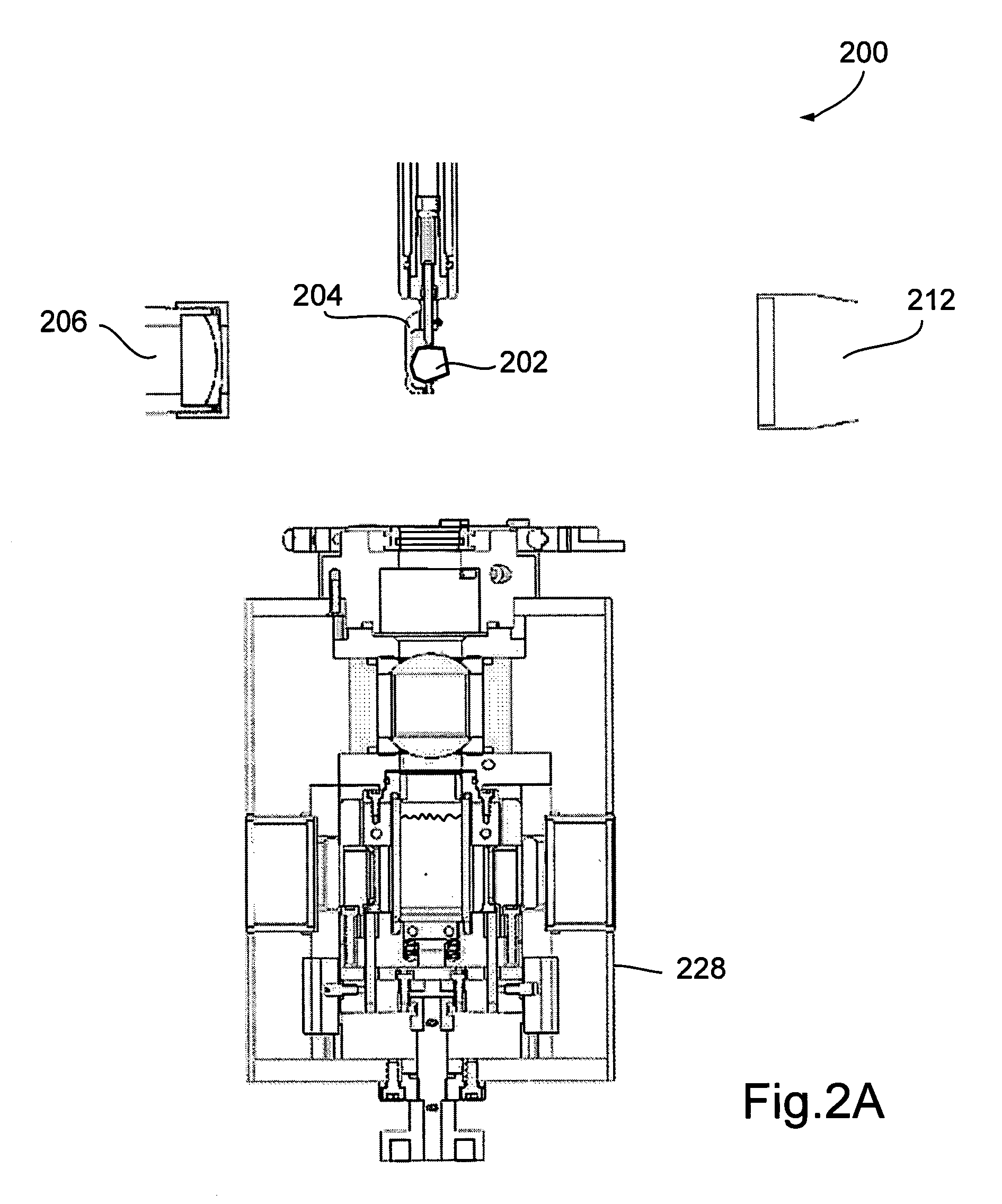
ActiveUS7259839B2Accurate judgmentAvoid the needInvestigating jewelsPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsMicrometerFaceting
Prior methods of measuring diamond proportions in order to construct a complete model, such as a three dimensional virtual wire-frame model, of a diamond have been found to be inadequate. In particular, there has been no commercially available, automated and objective method for measuring the dimensions of a diamond with similar or greater accuracy as compared with the accuracy that can be achieved with manual gauges or micrometers. The present invention provides a method of measuring a physical characteristic of a facet of a diamond, such as the location of one or more points on an edge of a facet. The method comprises illuminating the diamond to visually distinguish a facet from adjacent facets when viewed from a predetermined location, and then capturing an image of the diamond as viewed from this predetermined location. The image is then analyzed to determine the location of at least one point located on an edge of a facet by identifying a discontinuity in the properties of light transmitted from the diamond to the viewing location.
Owner:HOLLOWAY GARRY IAN +1
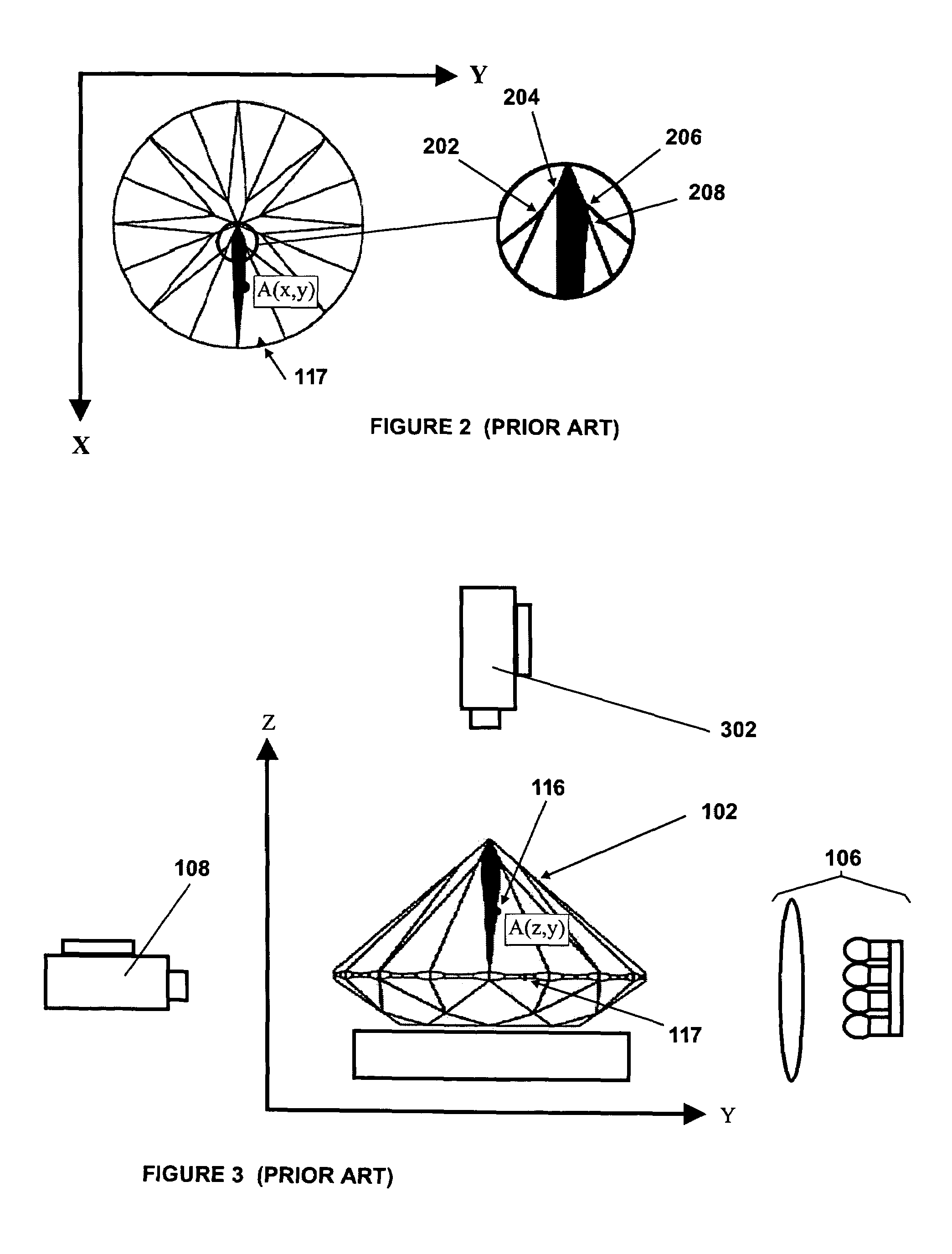
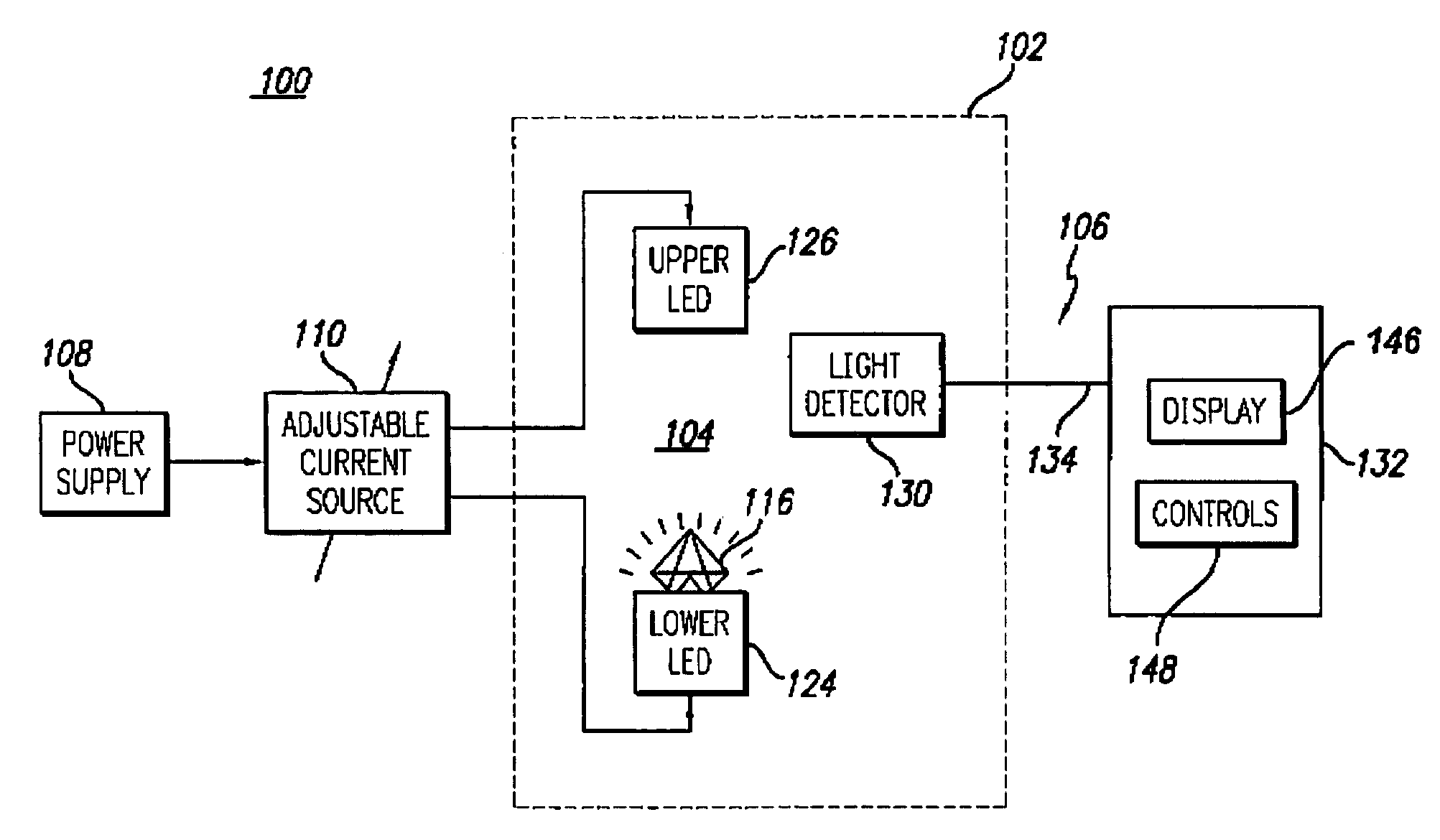
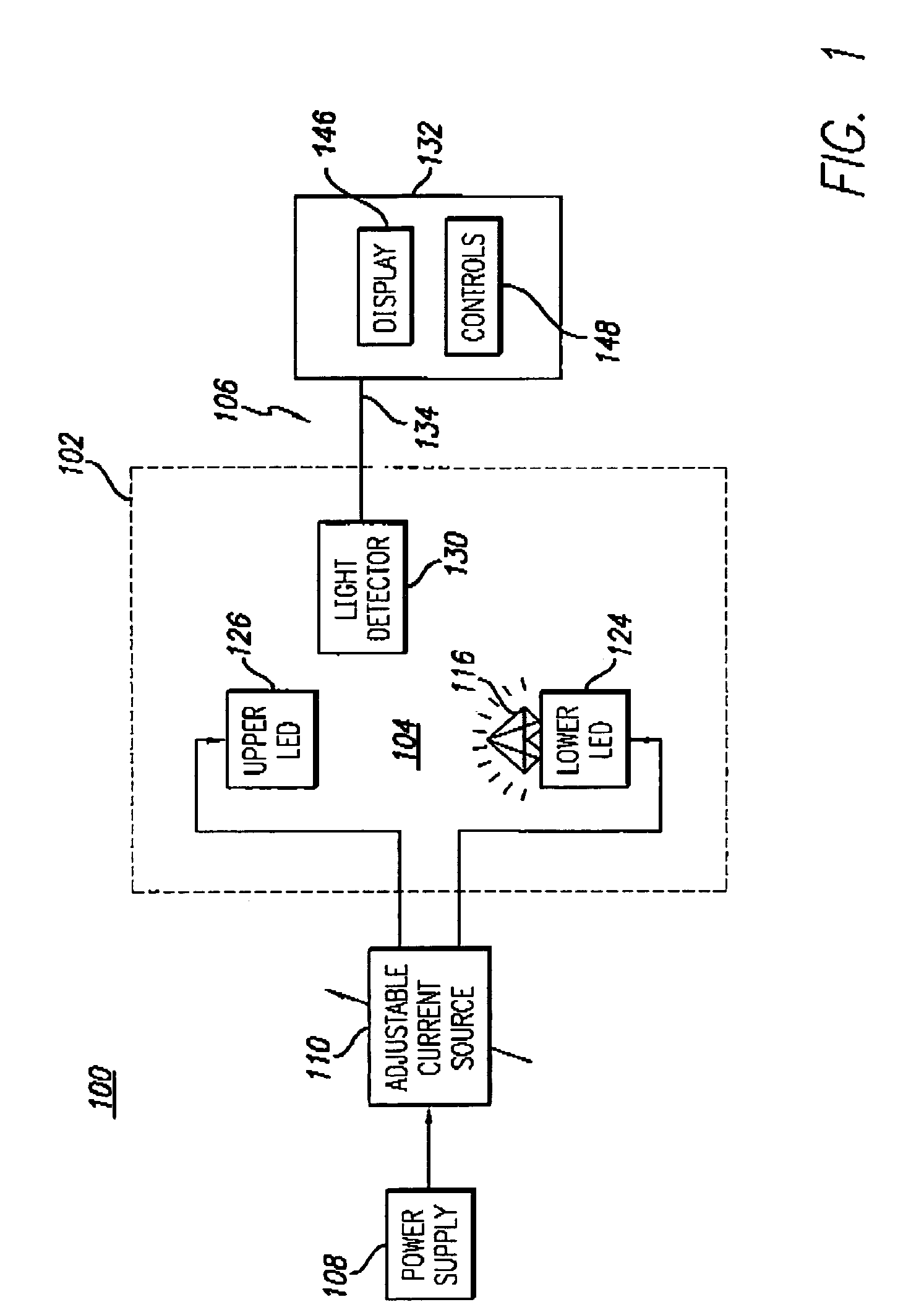
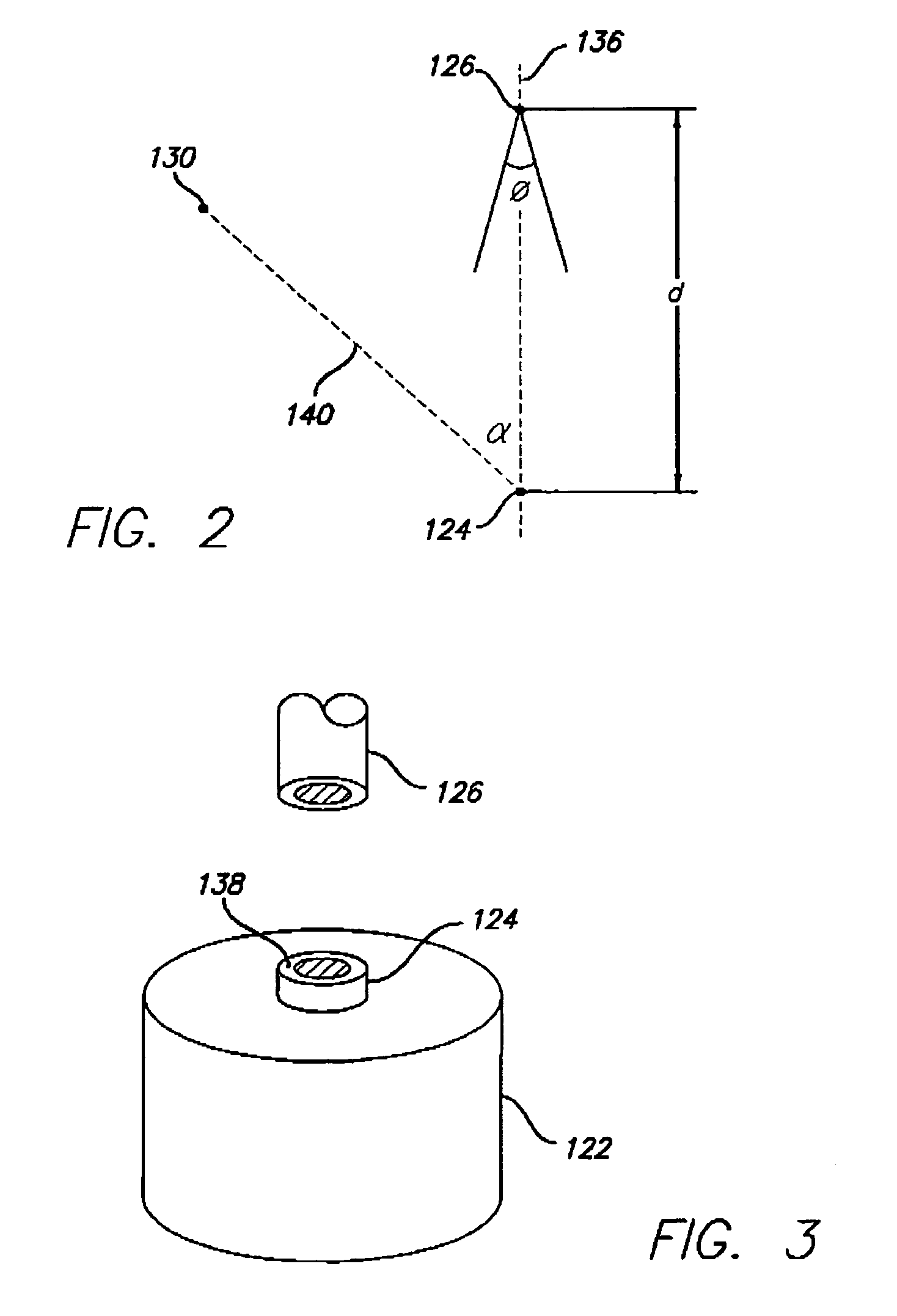
Fluorescence measuring device for gemstones
A gemstone fluorescence measuring device according to the invention generally includes an ultraviolet (“UV”) emission chamber, a UV radiation source, and a light meter assembly. The UV radiation source includes an upper light emitting diode (“LED”) and a lower LED that radiate a gemstone under test from both above and below the gemstone. The UV radiation source provides both trans-radiation and direct radiation to the gemstone, and the UV radiation source has an adjustable intensity, thus facilitating calibration of the fluorescence measuring device. The light meter assembly includes a light detector that detects the visible light emitted from the gemstone under test in response to the UV radiation. The light detector is configured to simulate the spectral characteristics of the human eye. The fluorescence measuring device converts the measured visible light into a numerical lux reading, which can then be converted into a fluorescence grade for the gemstone under test.
Owner:GEMOLOGICAL INST OF AMERICA INC
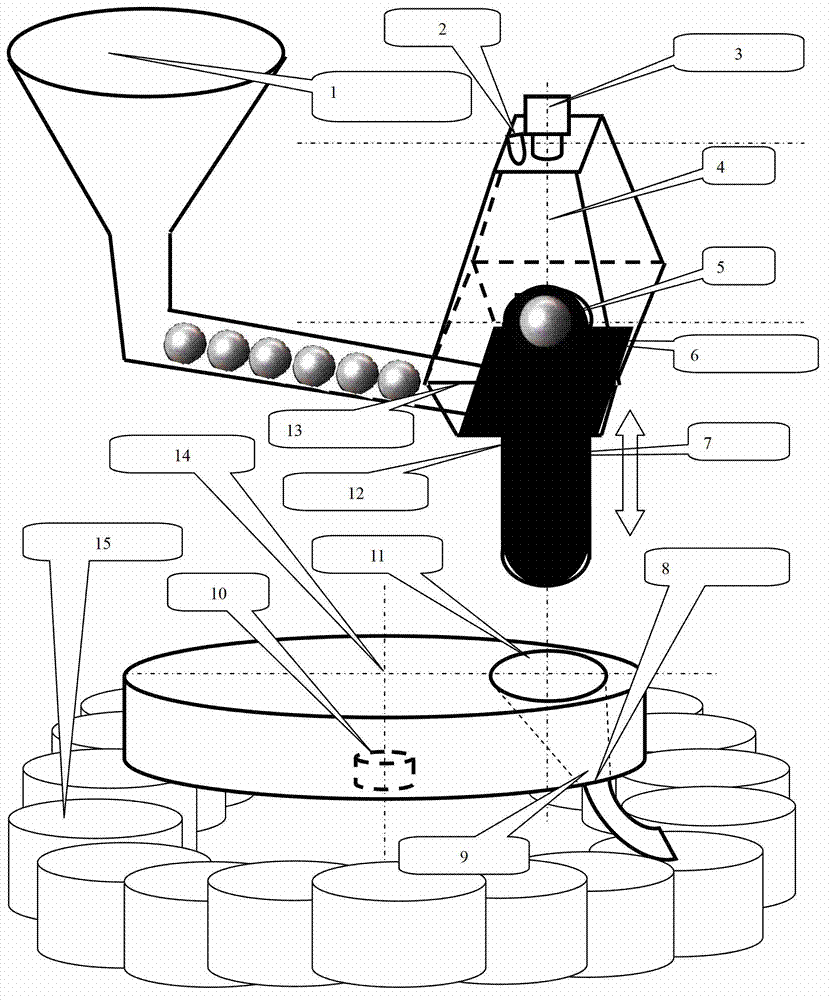
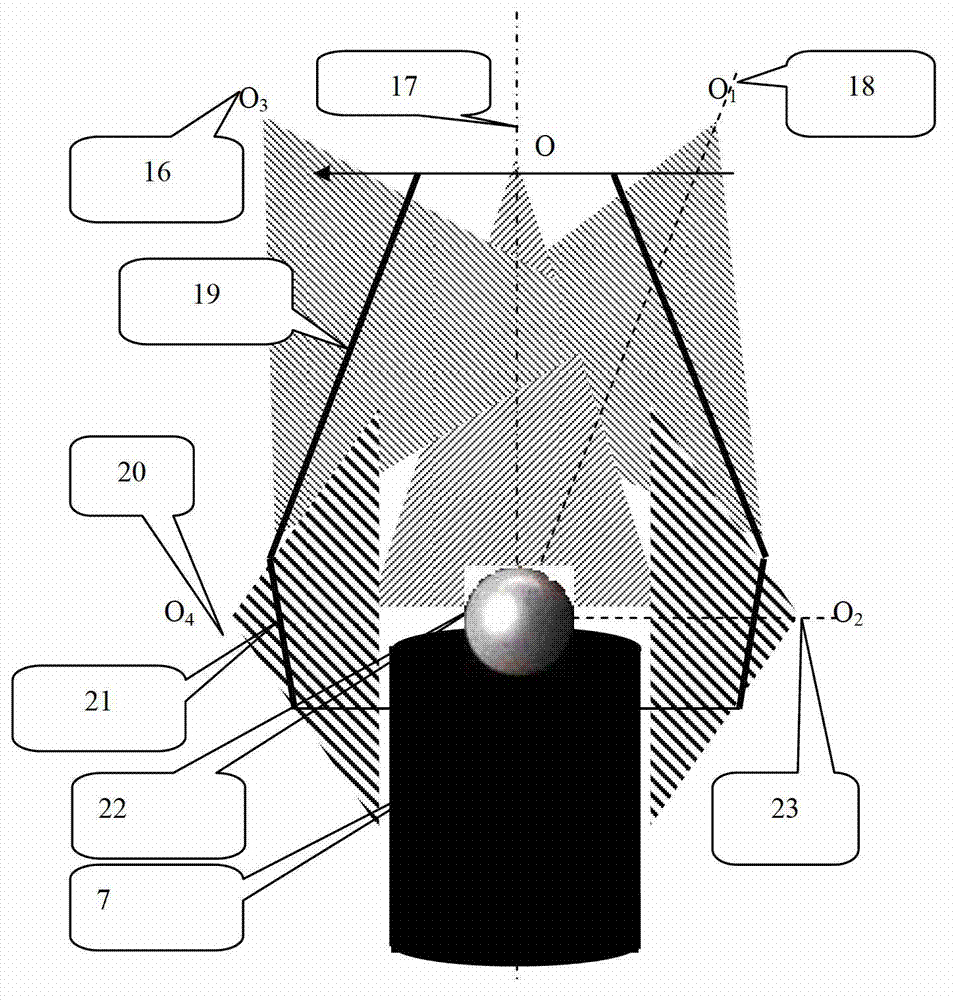
Device for automatically grading pearls on line according to size and shape on basis of monocular multi-view machine vision
ActiveCN102928431ASimplify complexityImprove detection efficiencyInvestigating jewelsUsing optical meansMachine visionImaging processing
The invention relates to a device for automatically grading pearls on line according to the size and the shape on the basis of monocular multi-view machine vision. The device comprises a flow line, a monocular multi-view machine vision device and a microprocessor, wherein the flow line is used for automatically detecting and classifying pearls and comprises a feeding action mechanism, an inspection action mechanism, a discharging action mechanism, a classifying action mechanism and a classifying execution mechanism; the multi-view machine vision device is used for shooting images of pearls to be detected; and the microprocessor is used for carrying out image processing, detecting, identifying and classifying on the pearls to be detected and coordinately controlling coordinated action of the action mechanisms. The device for automatically grading the pearls on line according to the size and the shape on the basis of the monocular multi-view machine vision, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of simple mechanism, low manufacturing cost, capability of meeting the detection of quality indexes, such as size and shape, high grading efficiency, convenience for use and maintenance and high automation degree.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Apparatus and method for fluorescence spectral and color measurements of diamonds, gemstones and the like
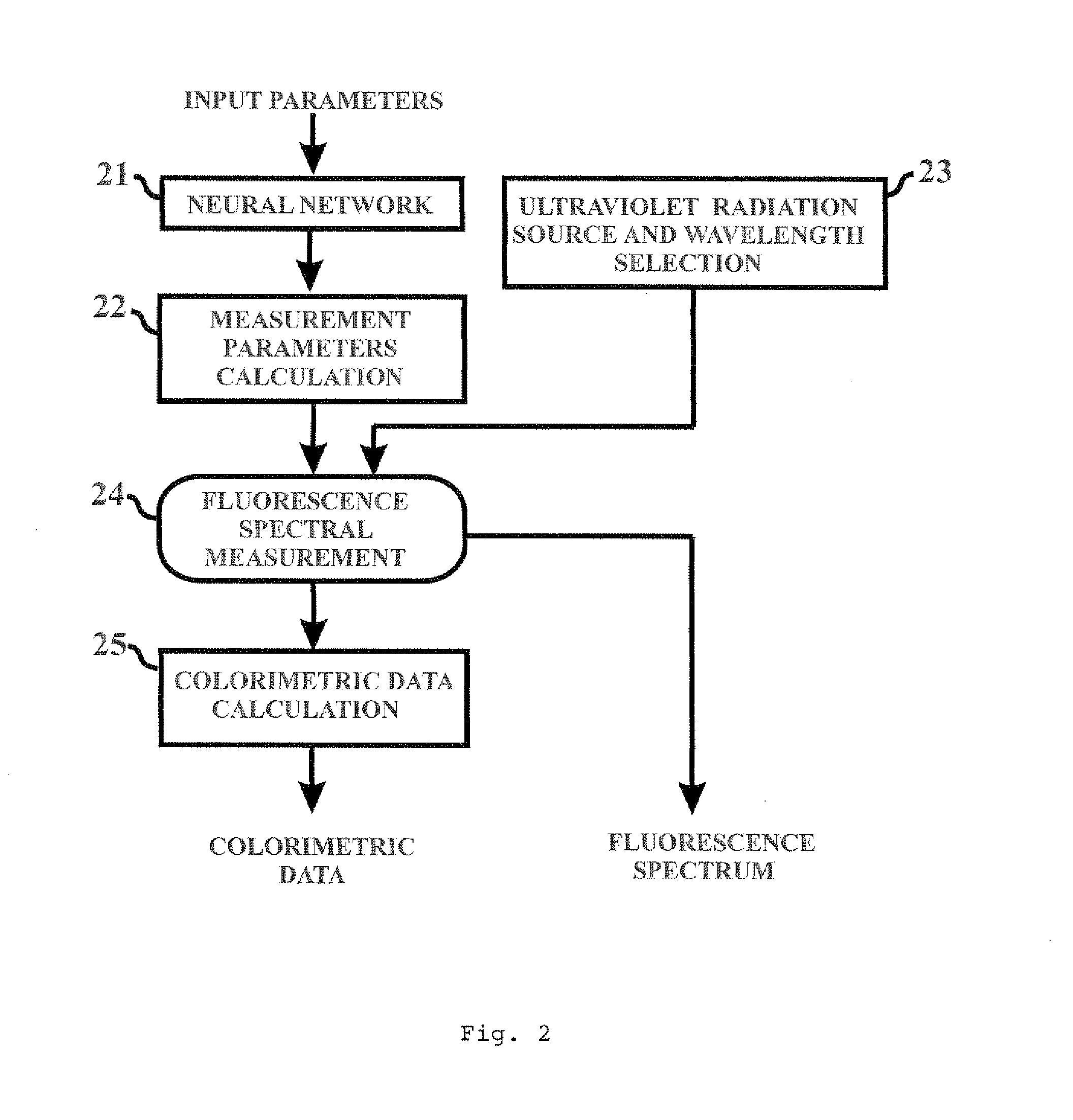
InactiveUS8878145B1Accurate measurementReduce manufacturing costInvestigating jewelsFluorescence/phosphorescenceUltravioletUltraviolet radiation
An apparatus and method for fluorescence spectral and color measurements of diamonds, gemstones and the like. The apparatus comprises a spectrometer, and computer and a dual integrating sphere measurement arrangement comprising a measurement integrating sphere, a sample integrating sphere, a sample platform, a lens system, a baffle, an ultraviolet radiation source on the top of the sample integrating sphere, and another light source attached to the measurement integrating sphere. The sample on the sample platform is radiated by the ultraviolet radiation source on the top of the measurement integrating sphere. The sample emits fluorescent light into the measurement integrating sphere, and the fluorescent light is received by the lens system. The spectrometer separates the fluorescent light into spectral signals, and the computer calculates the fluorescence spectrum and colorimetric data.
Owner:LIU YAN
Reflected dark field method and apparatus
Owner:GEMOLOGICAL INST OF AMERICA INC
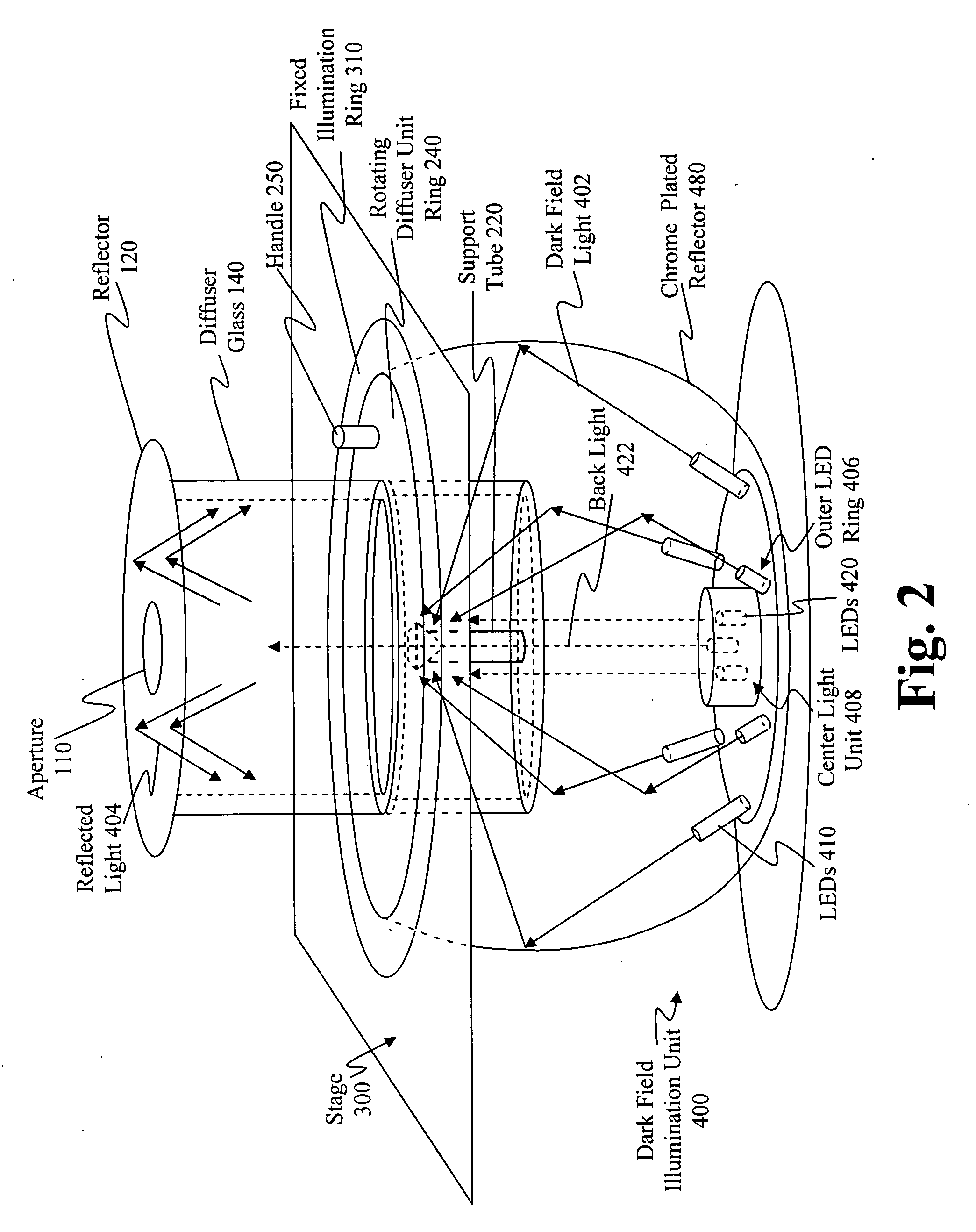
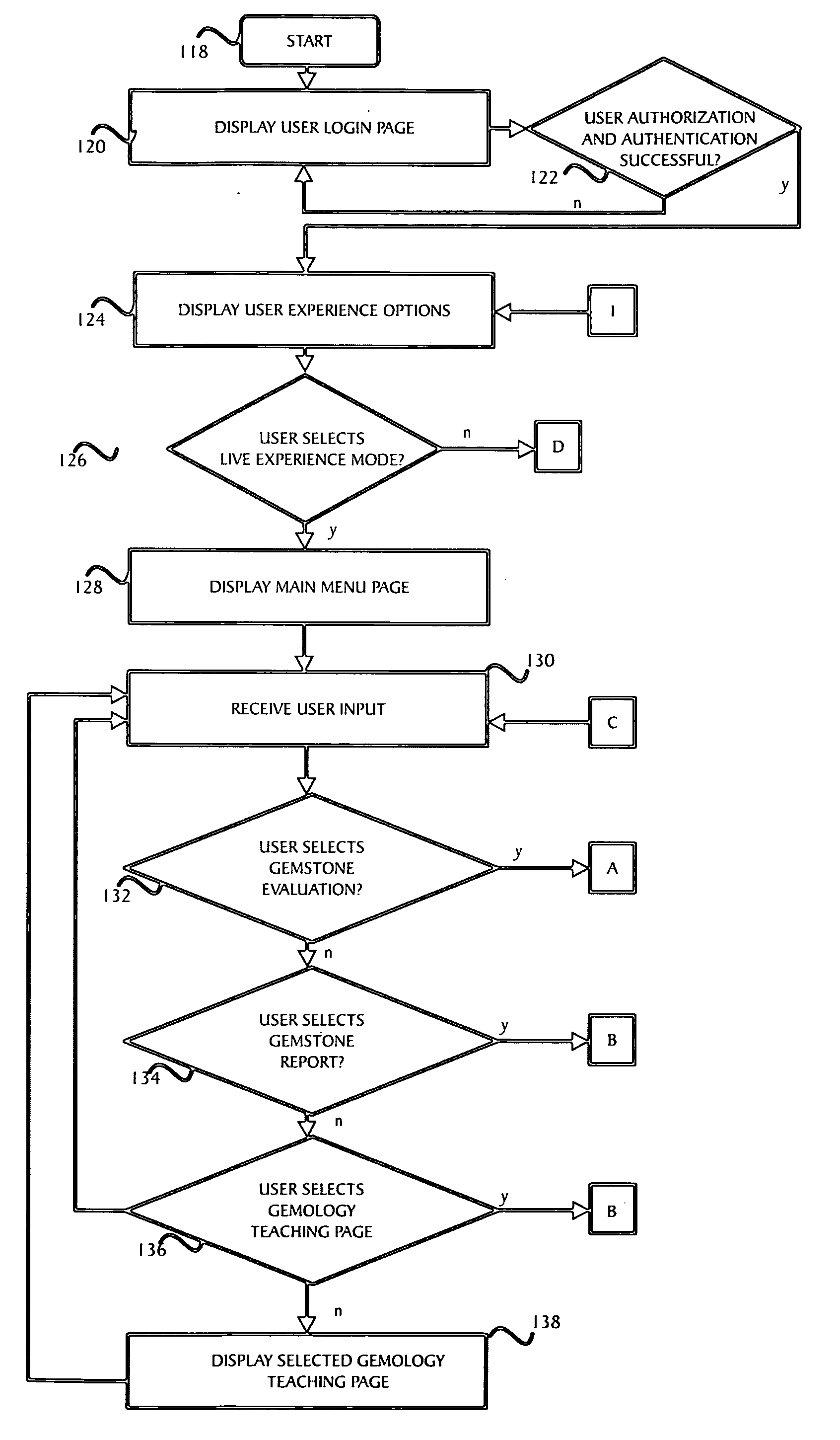
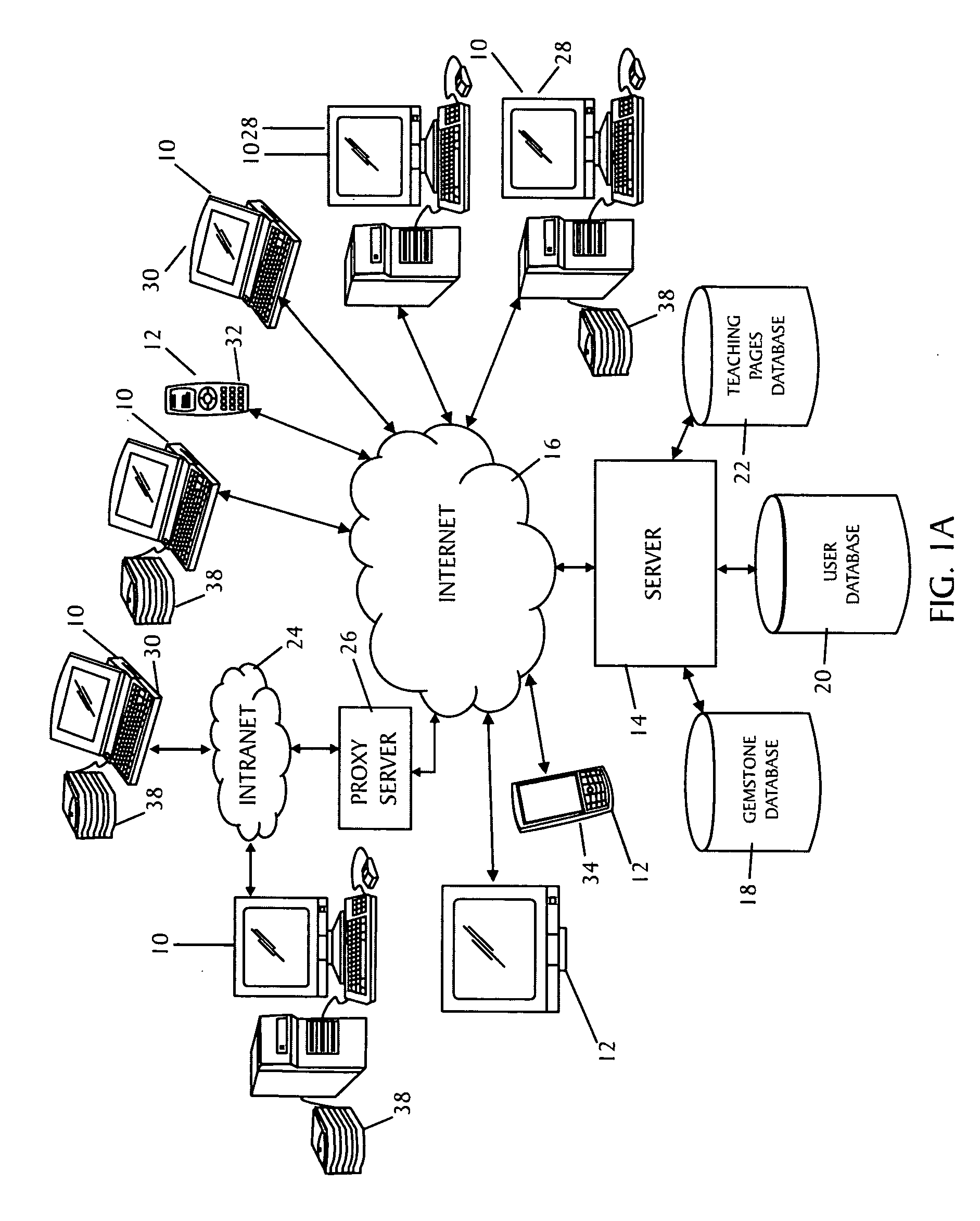
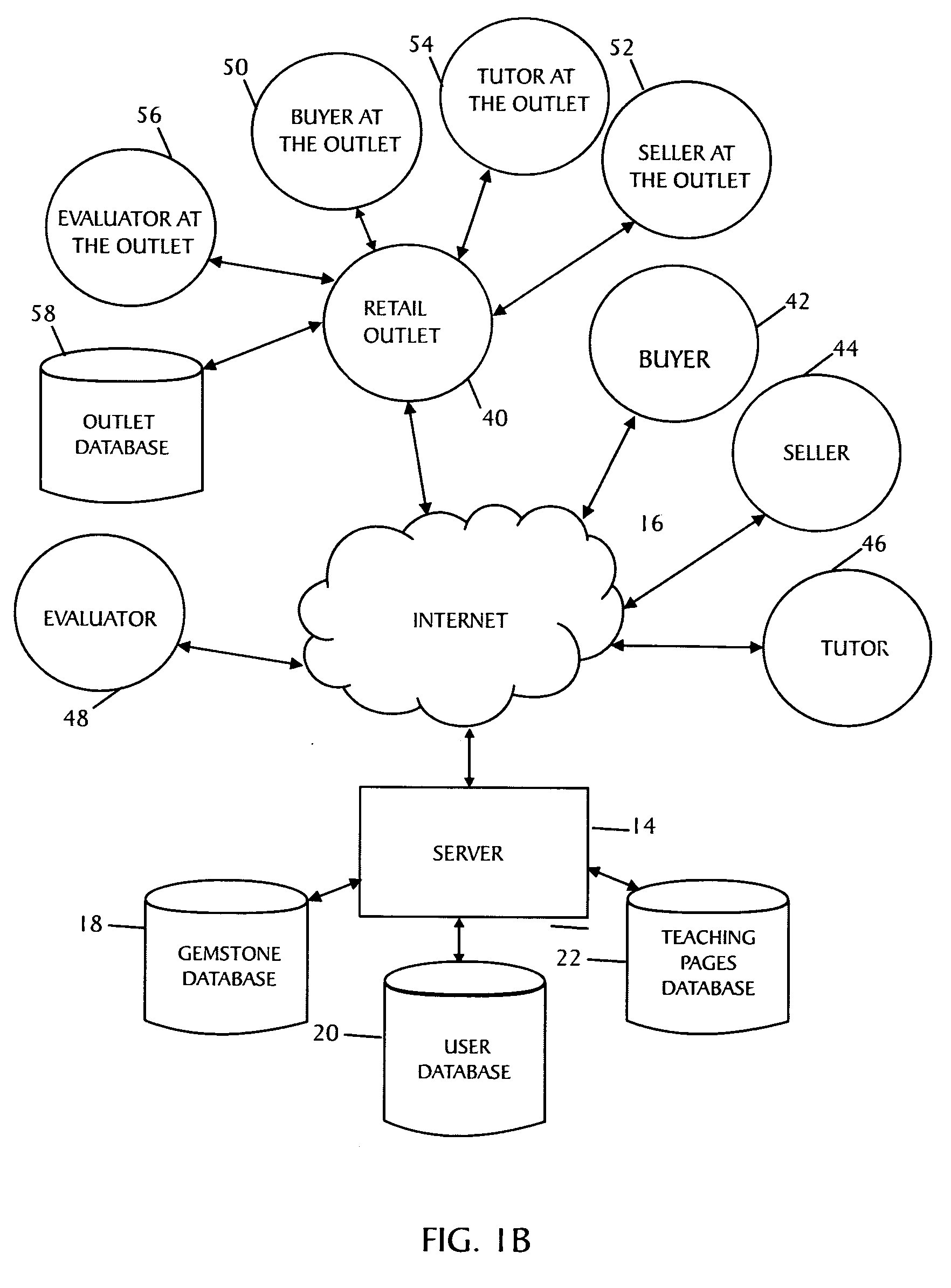
Apparatus, a method, and a system for gemstone evaluation and gemology tutoring over the internet
A method of evaluating a gemstone over the internet is described that includes providing a server computer, providing access to an internet enabled device that is connectable to an apparatus capable of capturing an image of a gemstone, connecting the device to a second device through the server, and transmitting data over the internet of a received image of the gemstone to determine one or more optical properties of the gemstoneThe method includes examining and purchasing a diamond or gemstone online, examining a diamond online and purchasing it at a retail establishment, conferencing with the seller and / or other persons online to examine the diamond online, and purchasing it online or at a retail establishment.A system for gemstone evaluation over the internet is also included. The system comprises a server computer having a client device connectable to the internet for transmitting gemstone images and evaluating data, means for processing an image of a gemstone received from the apparatus to determine one or more optical properties of the gemstone, and means for presenting, on the display, the received image of the gemstone and representations of the determined one or more optical properties.
Owner:SARIN COLOR TECH
Enhancing the optical characteristics of a gemstone
ActiveUS8033136B2Increase and control fireIncrease and control and brillianceInvestigating jewelsDiffraction gratingsOptical propertyDiffraction grating
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for evaluation of a gemstone
A method of determining the position of inclusions in a gemstone, comprising:(a) placing the gemstone within a material having a refractive index within 0.5, optionally 0.2 or 0. 1, of that of the gemstone;(b) illuminating the gemstone and imaging the illuminated gemstone; and(c) determining the position of inclusions based on images of the inclusions in the images.
Owner:GALATEA
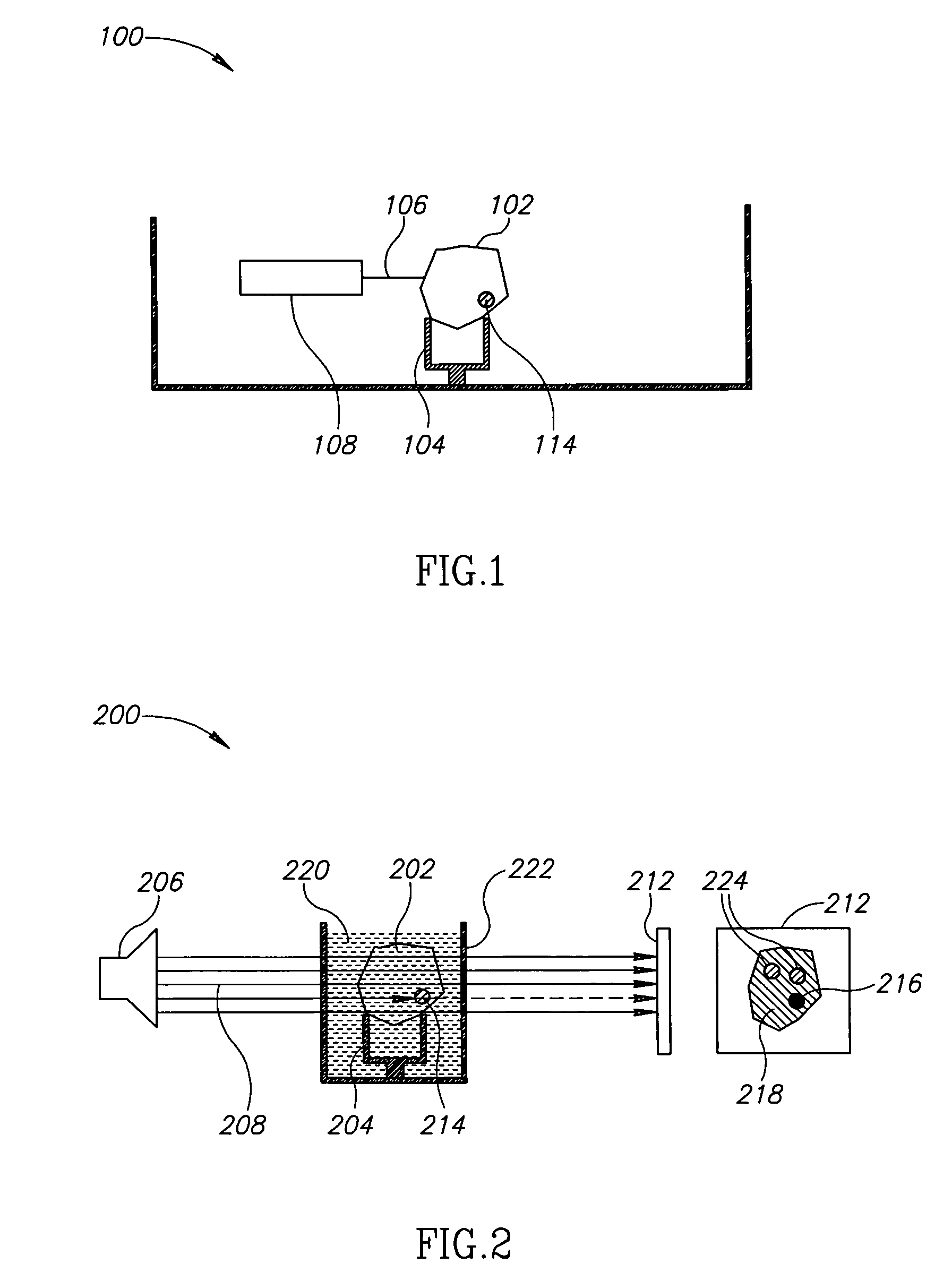
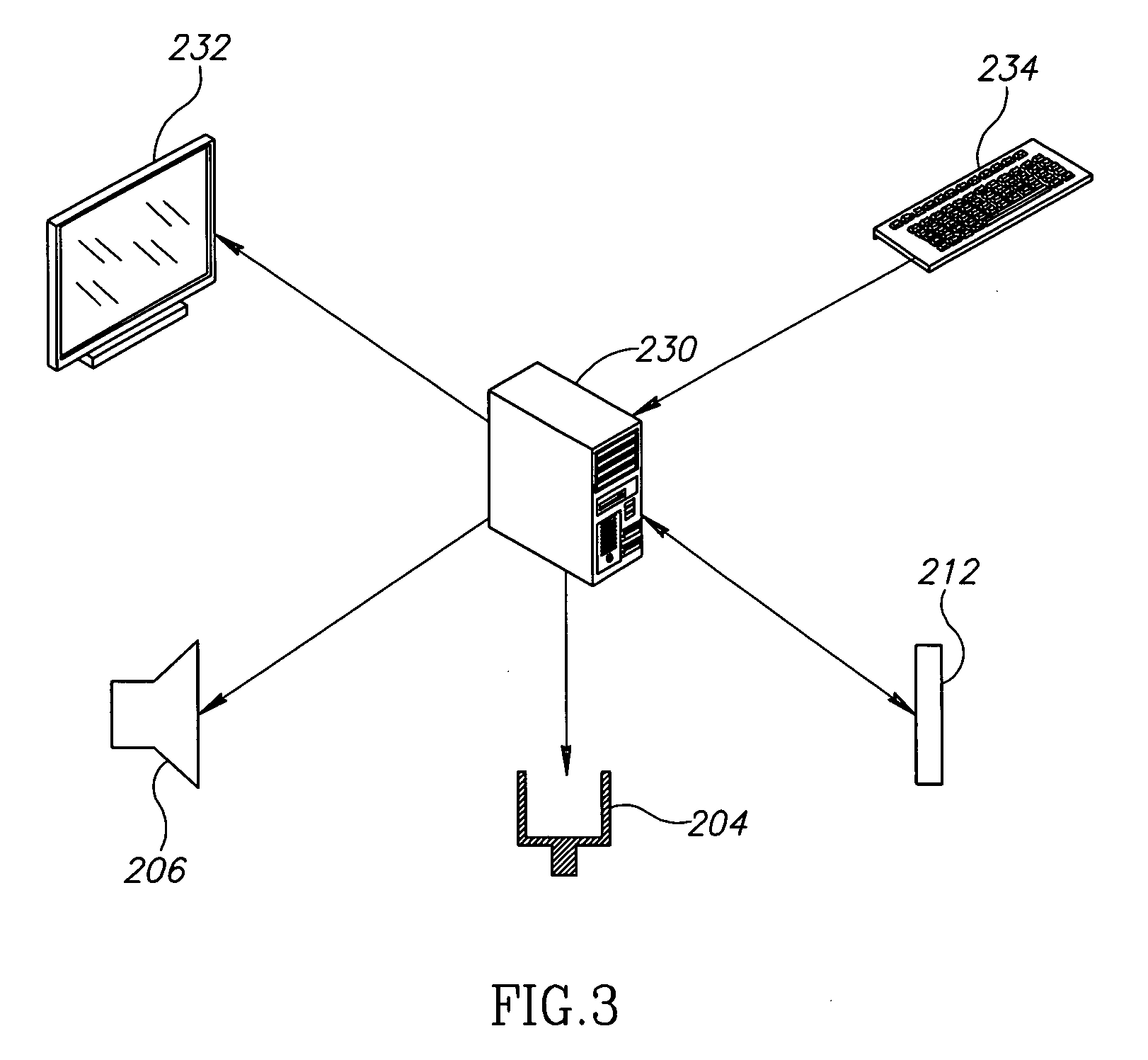
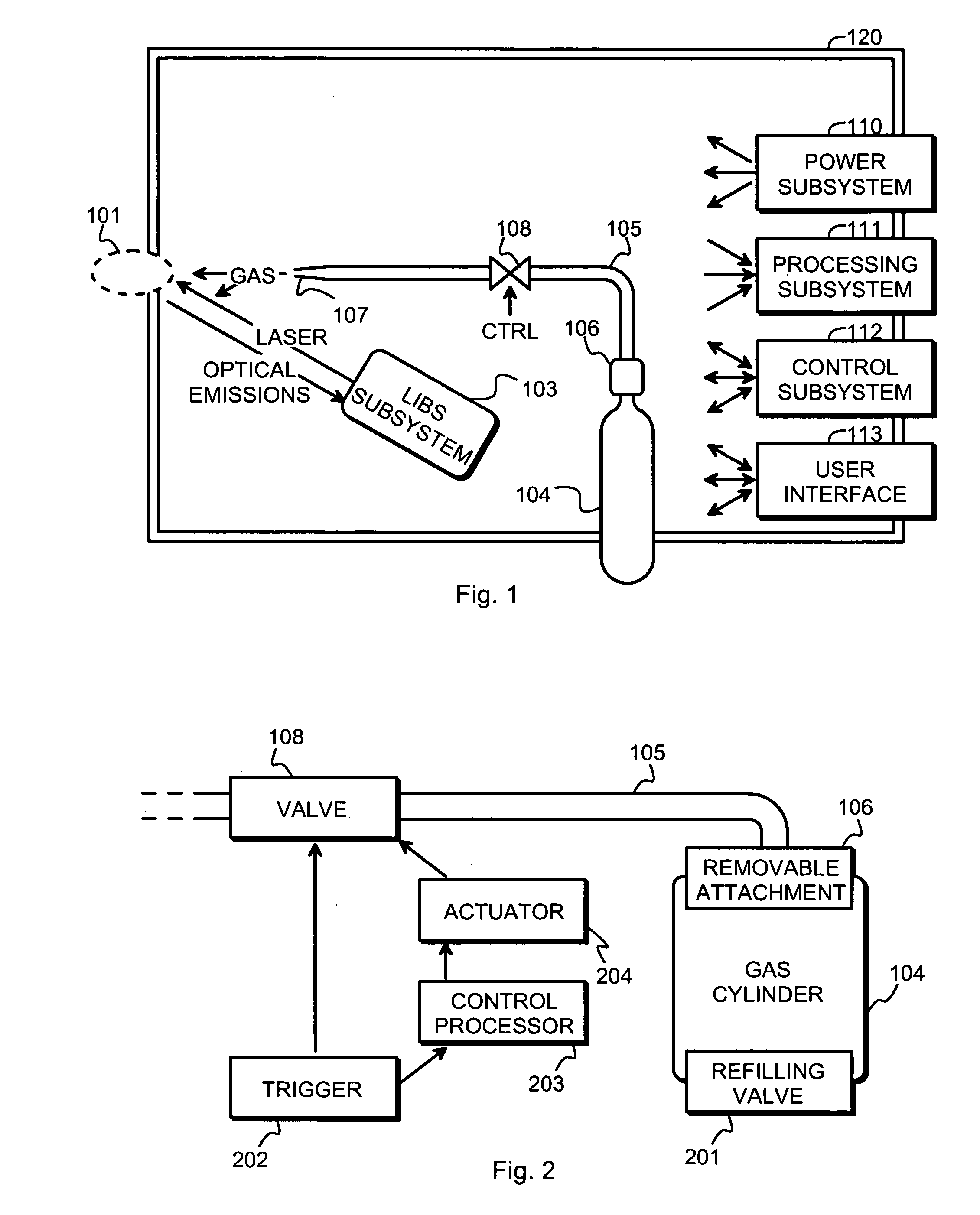
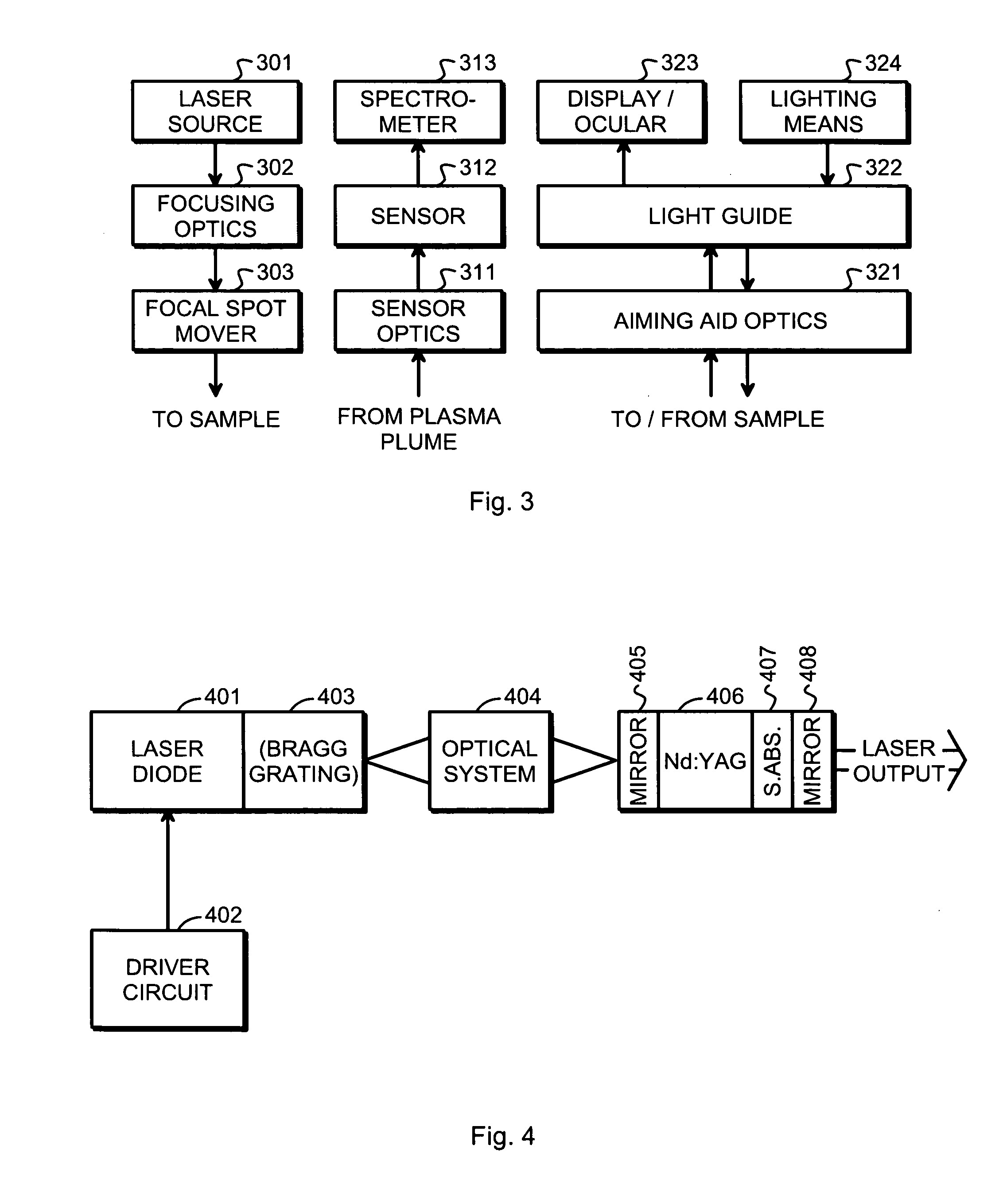
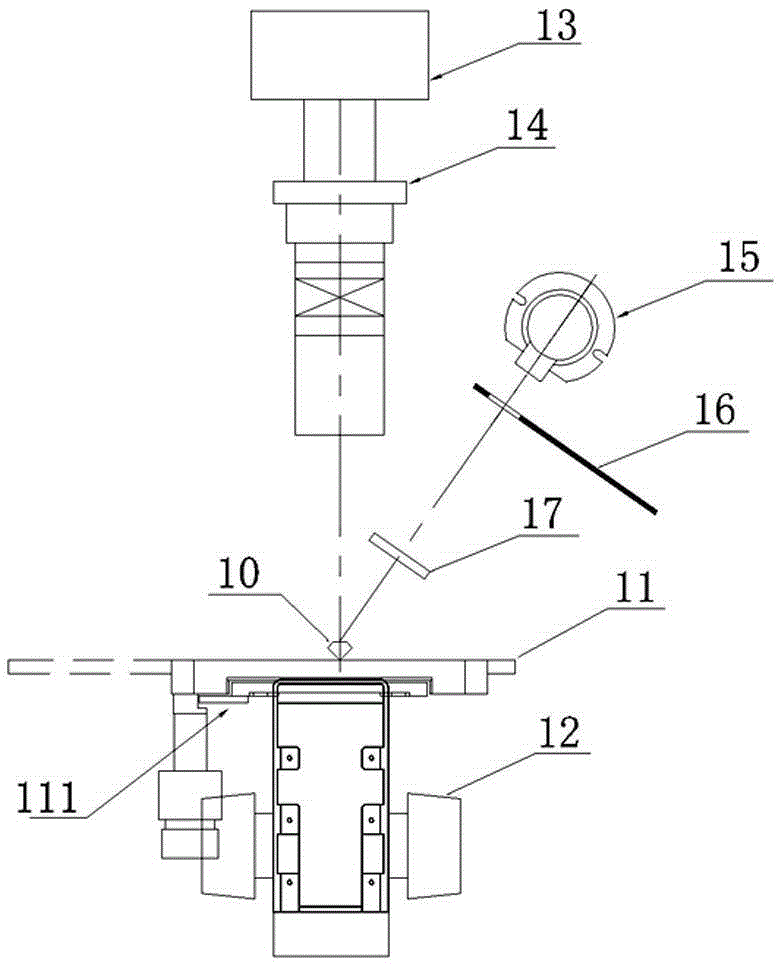
Method and arrangement for non-destructive composition analysis of delicate samples
ActiveUS20060262302A1Easy to useOperating conditionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationNon destructiveComposition analysis
An arrangement and a method are provided for non-destructively analyzing the composition of a delicate sample. The value of the sample depends at least partly on absence of visual defects. A laser source (301) produces a pulsed laser beam, and focusing optics (302) focus said pulsed laser beam into a focal spot on the sample. A sensor (312) receives and detects optical emissions from particles of the sample excited by said pulsed laser beam. A processing subsystem (111) produces information of the composition of the sample based on the optical emissions detected by said sensor (312).
Owner:HITACHI HIGH TECH ANALYTICAL SCI FINLAND OY
Method and detection device used for distinguishing natural gemstone and synthetic gemstone
InactiveCN105352929AEasy to detectEasy to operateInvestigating jewelsFluorescence/phosphorescenceGreen yellowUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses a method and a detection device used for distinguishing natural gemstone and synthetic gemstone. The method comprises following steps: continuous wave band ultraviolet light with a wavelength ranging from 220 to 360nm is used for irradiating sample surfaces; sample surfaces and surface right lower regions are irradiated; fluorescence and phosphorescence are excited so as to form fluorescence images capable of reflecting growth of the irradiated regions, and phosphorescence illuminate images are formed when irradiation is shut down; image characteristic difference is obtained via observation based on the fluorescence images and the phosphorescence illuminate images so as to determine that the detected samples are natural gemstone or synthetic gemstone; if the images are not capable of emitting phosphorescence and blue white fluorescence, and horny growth patterns are observed, the detected samples are natural gemstone; if the images are capable of emitting phosphorescence, blue green or yellow green fluorescence, and layered growth structures and octagonal growth structures are observed, the detected samples are synthetic gemstone. According to the method, only the surface regions of gemstone are irradiated without influences by other factors, and it is possible to determine the detected samples are natural or synthetic based on patterns, or fluorescence, or phosphorescence generated by the gemstone samples.
Owner:SHENZHEN JEWELRY RES INST NAT GEMS & JEWELRY TECH ADMINISTATIVE CENT
Apparatus for generating data for determining a property of a gemstone and methods and computer programs for determining a property of a gemstone
InactiveUS20050036132A1Compact and lightweight formEasily and accurately and objectively measurableInvestigating jewelsMaterial testing goodsAxis of symmetryGemstone
Owner:SARIN COLOR TECH
Assessment of diamond color
InactiveUS20090182520A1Quality of colorImprove assessment accuracyInvestigating jewelsSpecial data processing applicationsDiamond colorComputer science
Disclosed are methods and devices for assessing the colors of diamonds. In embodiments, the color of finished diamonds cut from a given rough diamond is assessed by analyzing the effect on light interacting with the rough diamond to give a reasonable (that is to say commercially significant) assessment of the color quality of the finished diamond.
Owner:PLATFORM DEV & INVESTMENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com