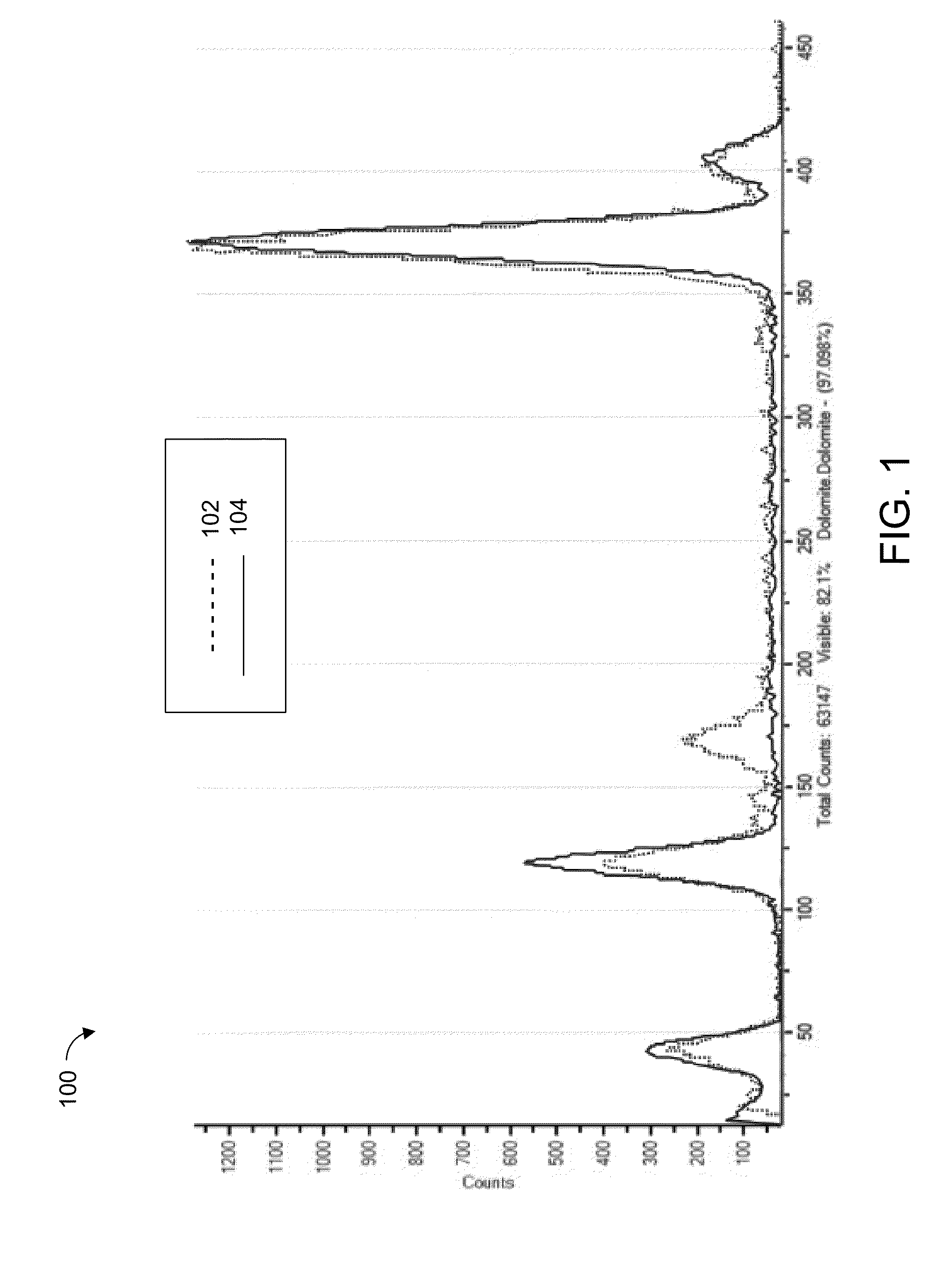
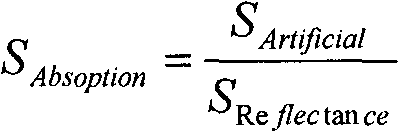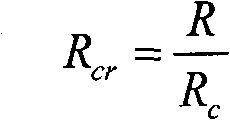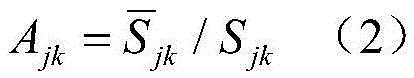Patents
Literature
79 results about "Mineral identification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Minerals can be identified by their physical characteristics. The physical properties of minerals are related to their chemical composition and bonding. Some characteristics, such as a mineral’s hardness, are more useful for mineral identification.
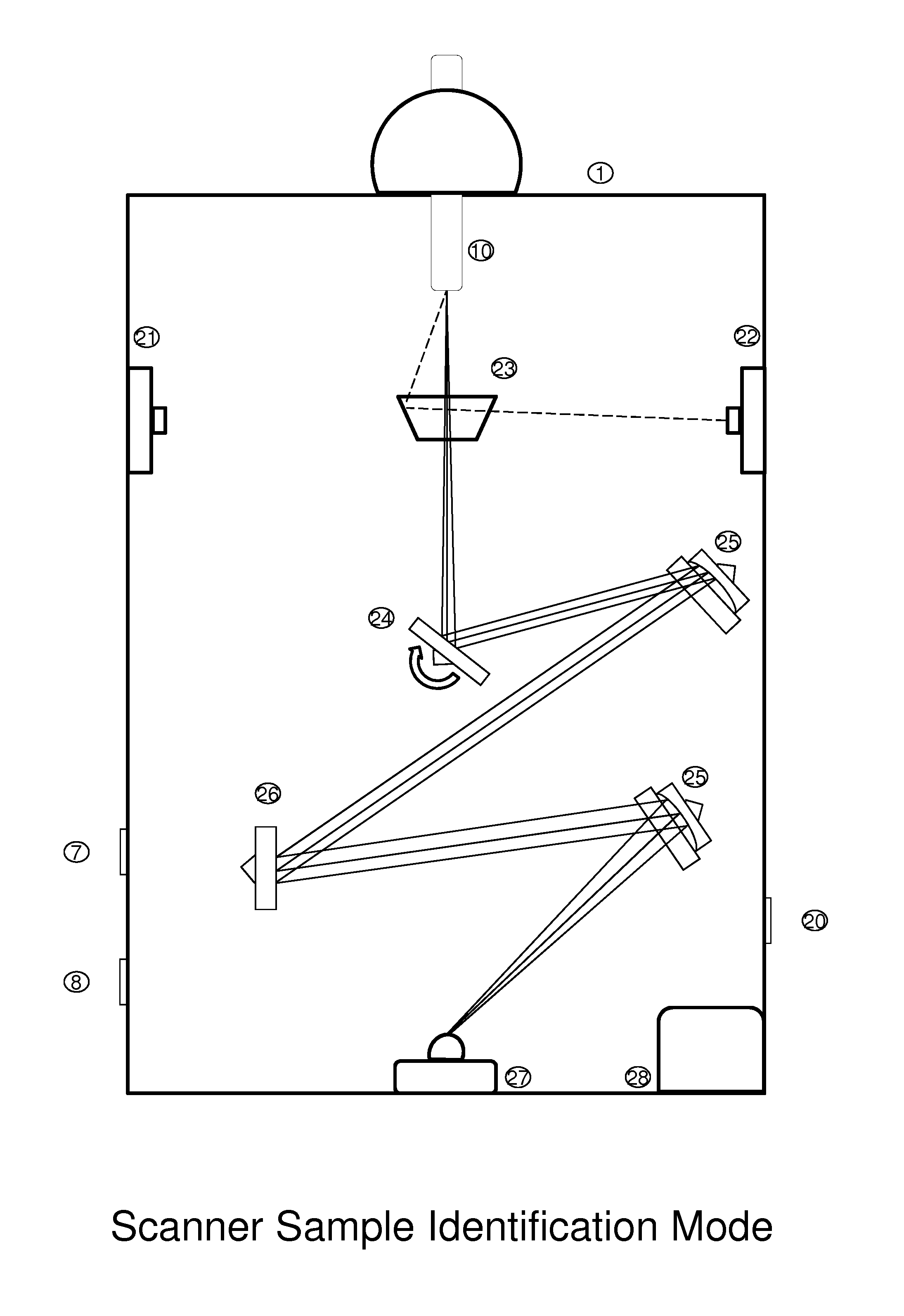
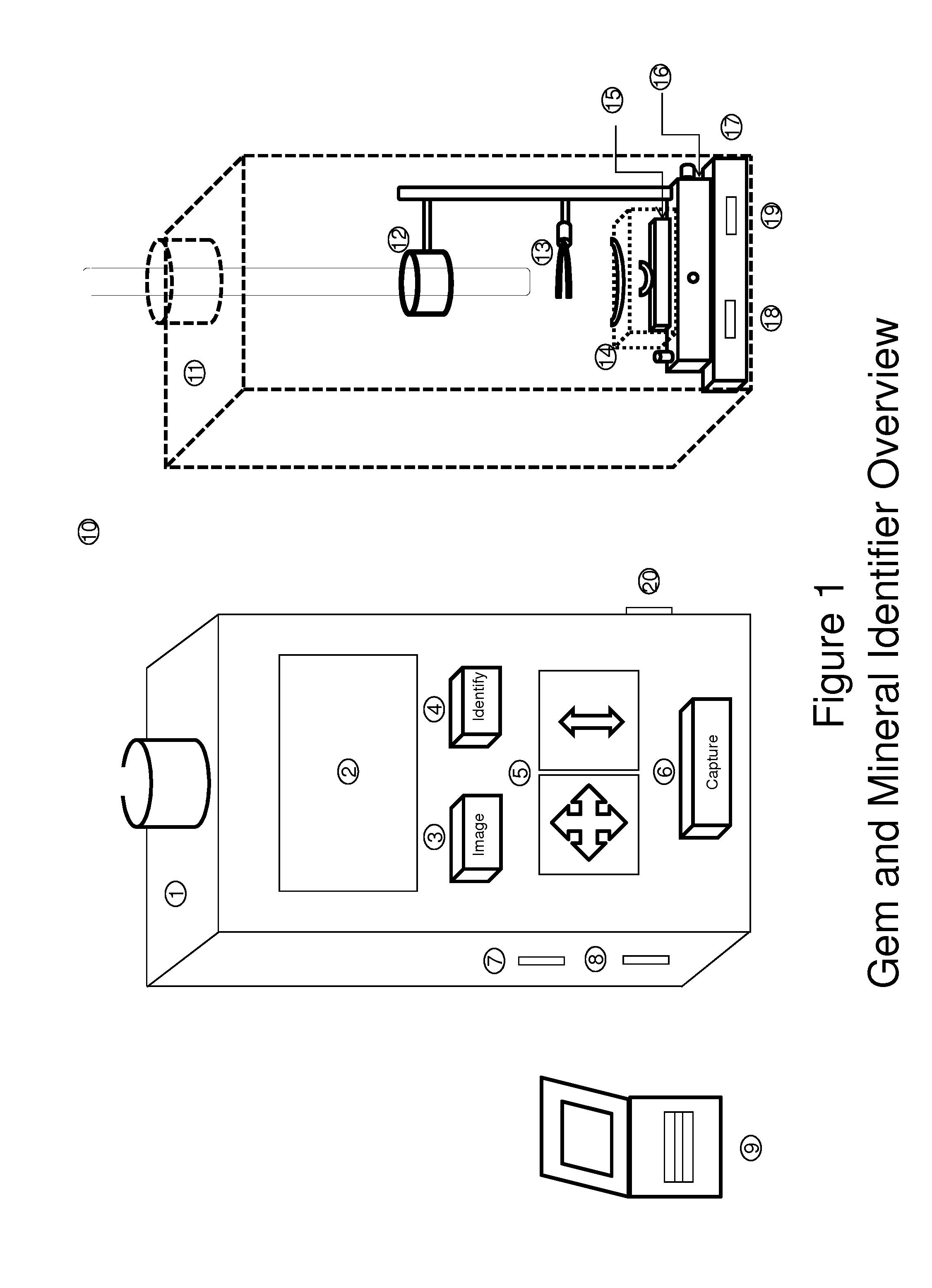
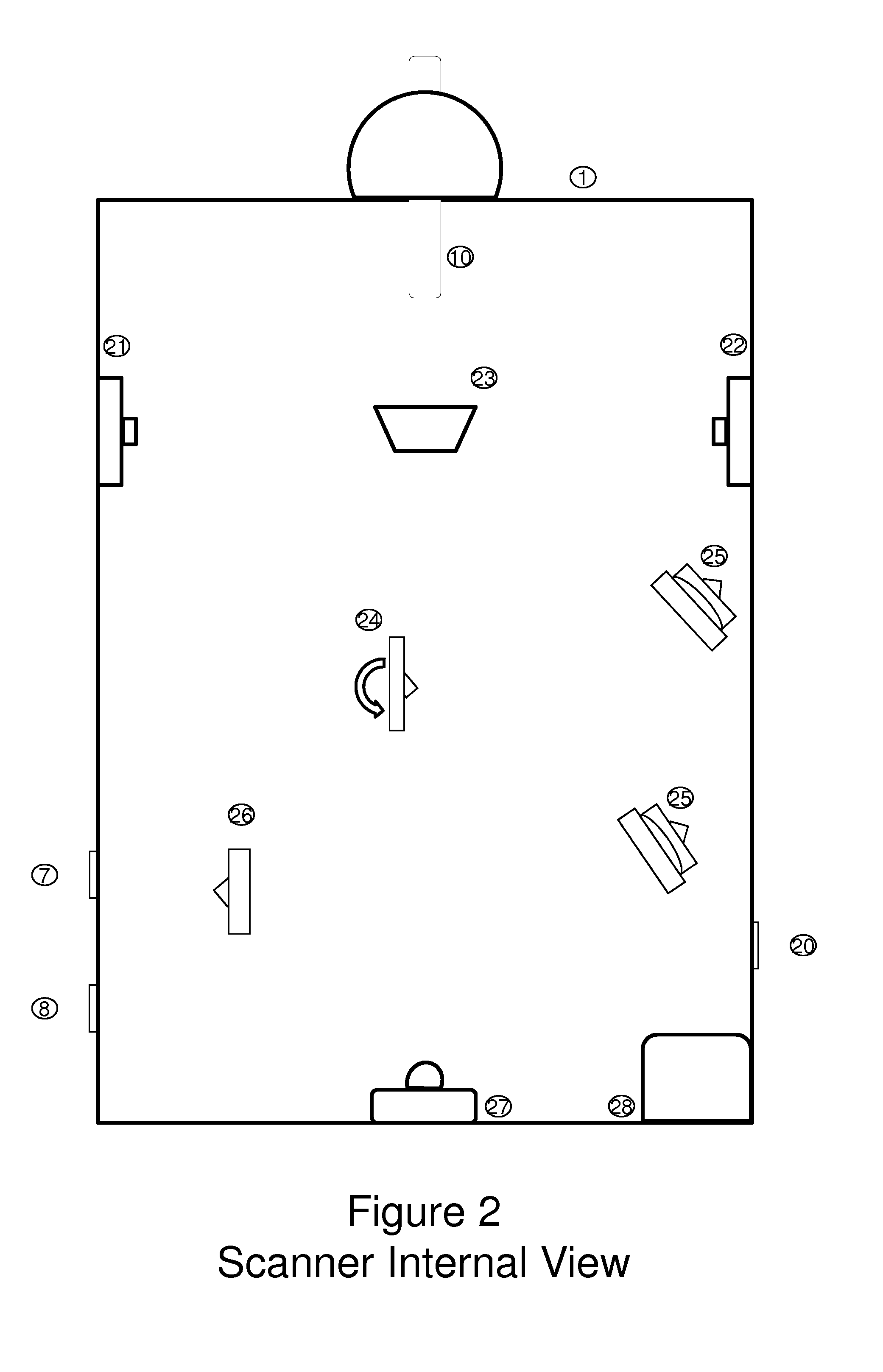
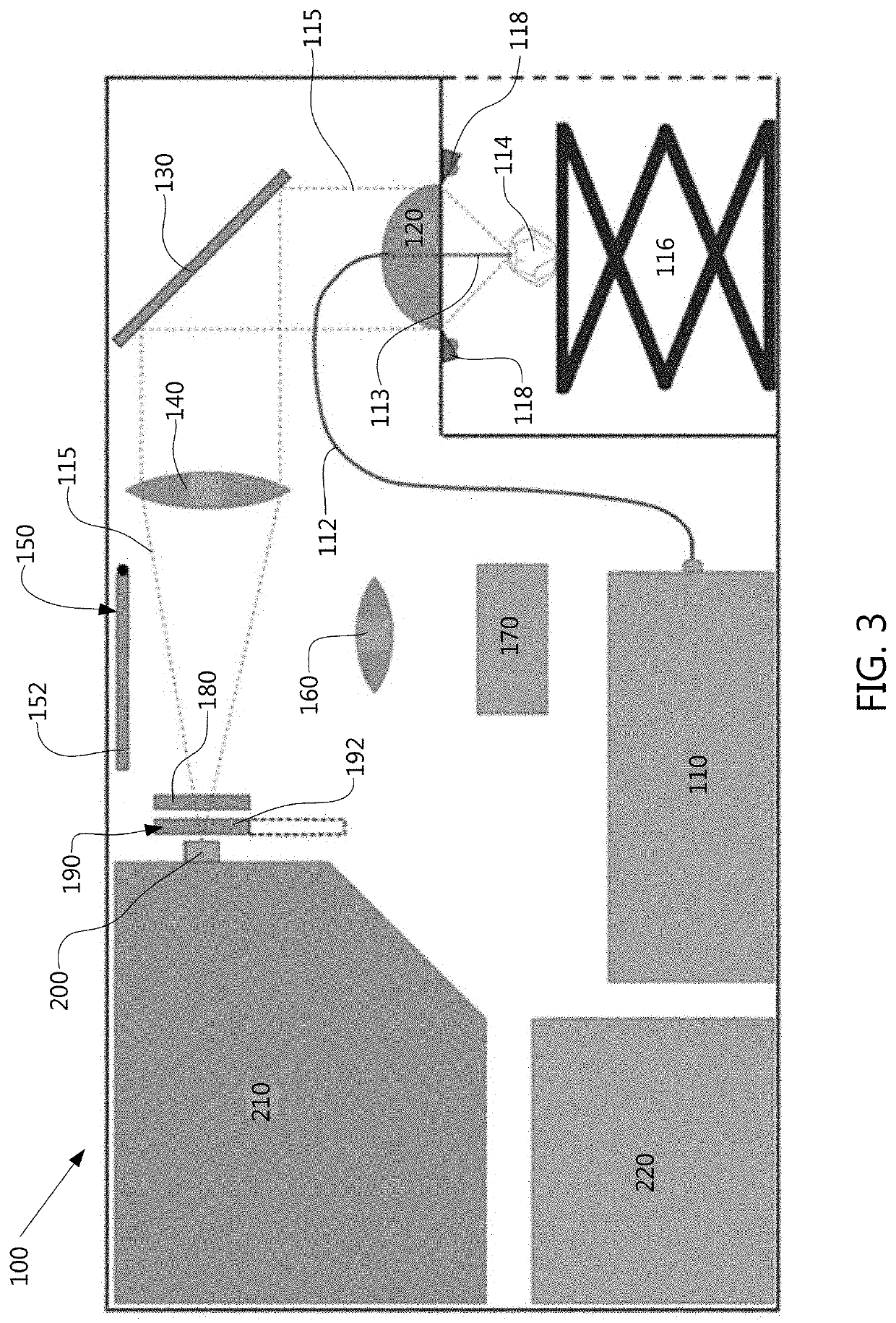
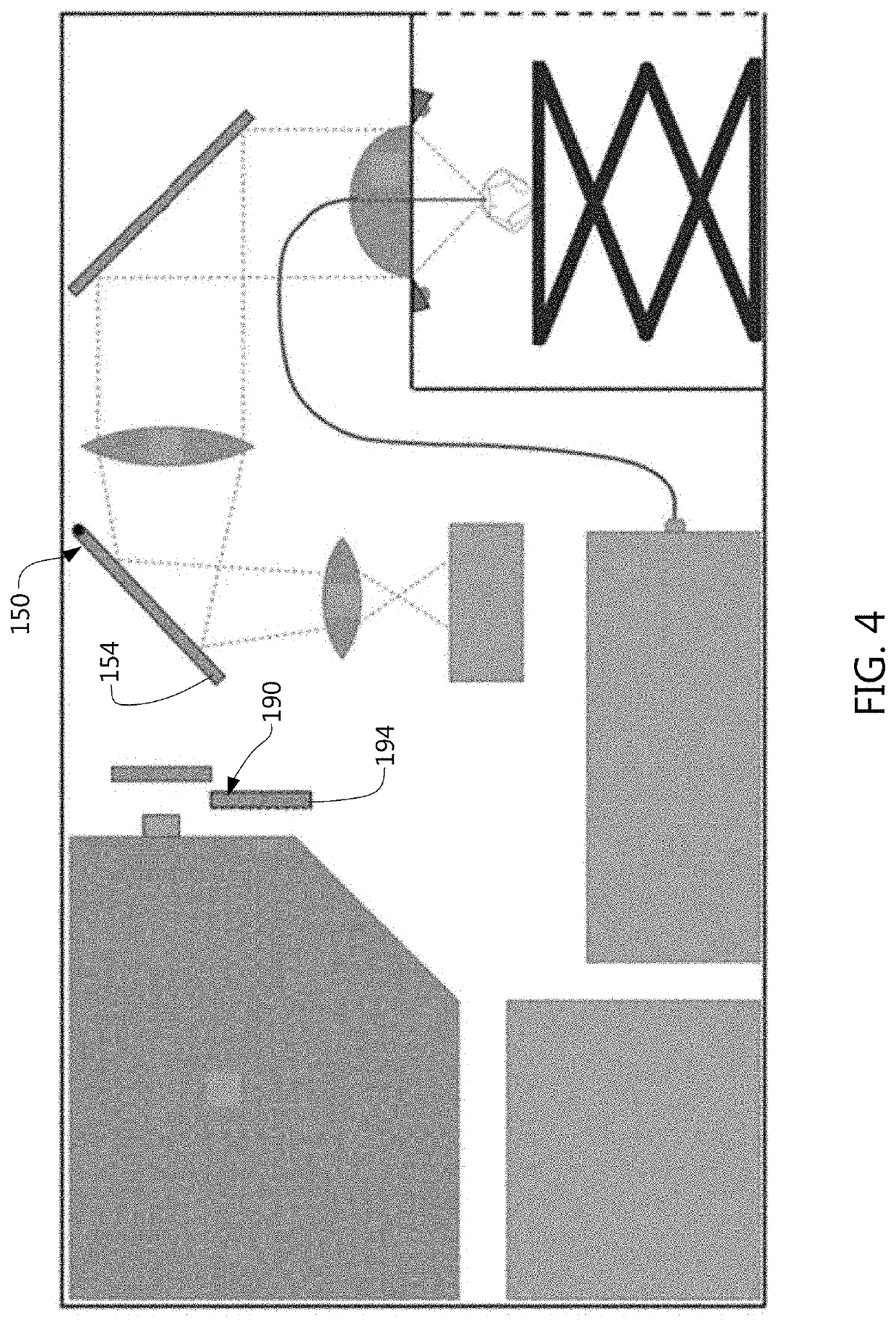
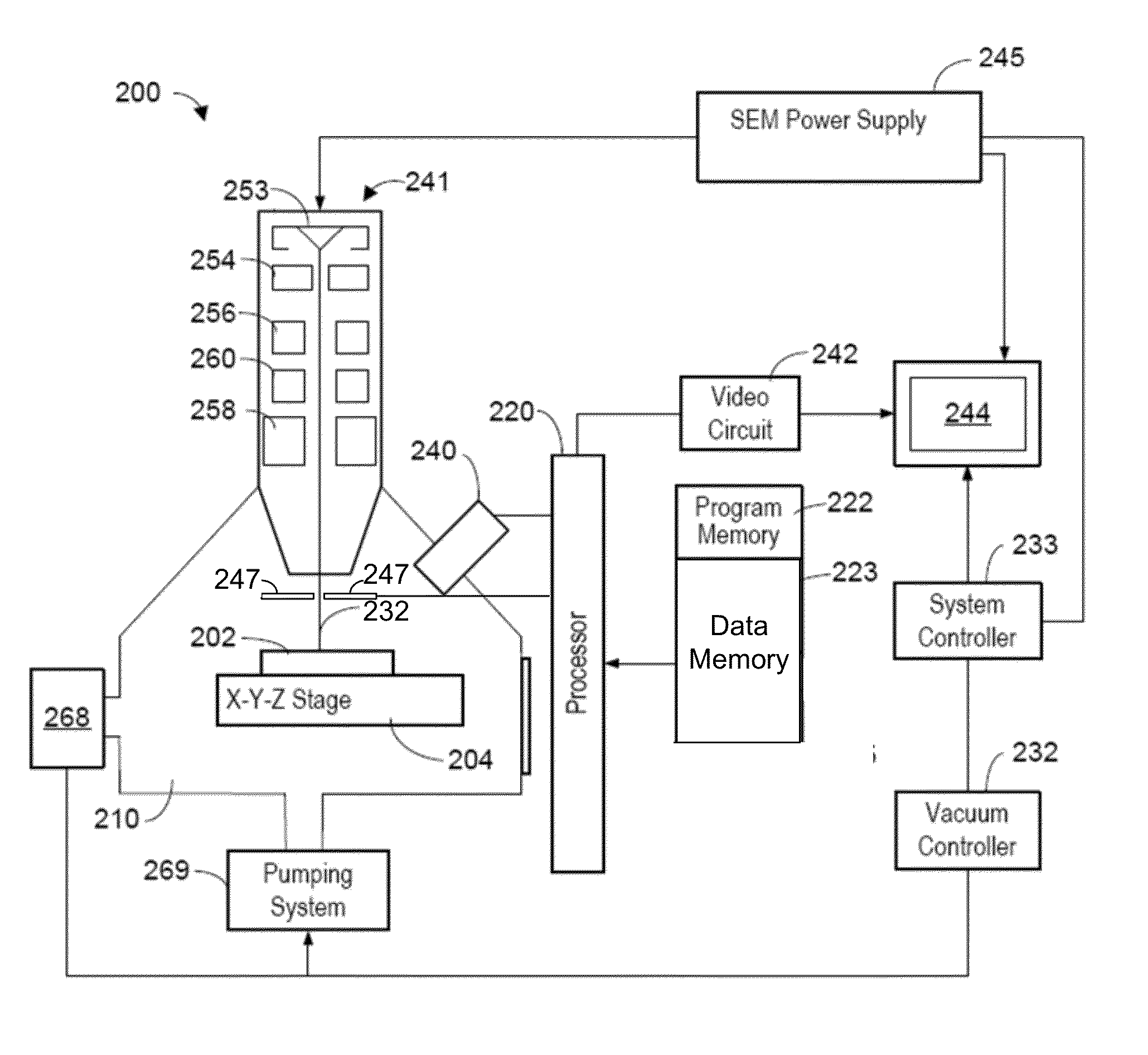
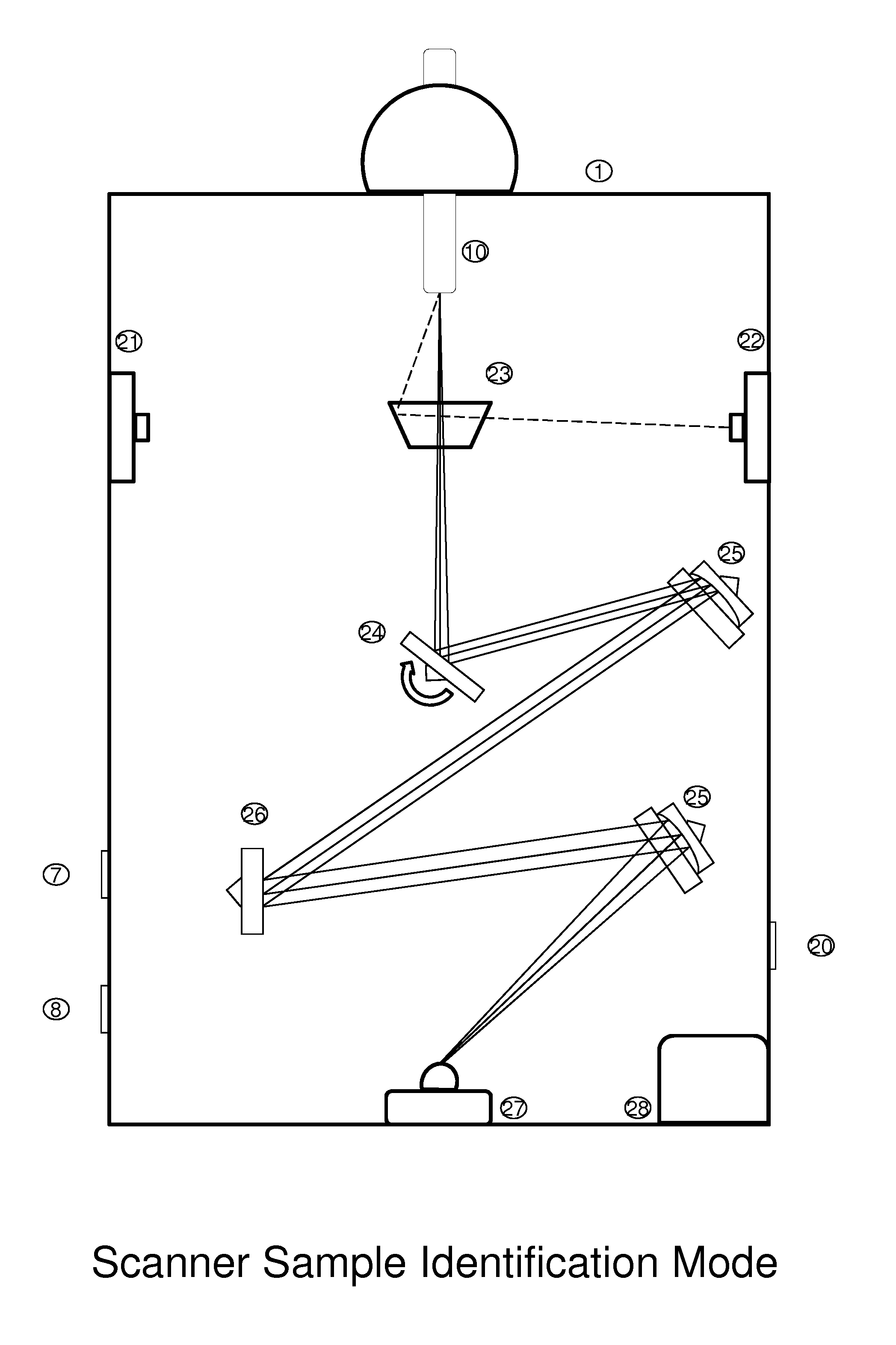
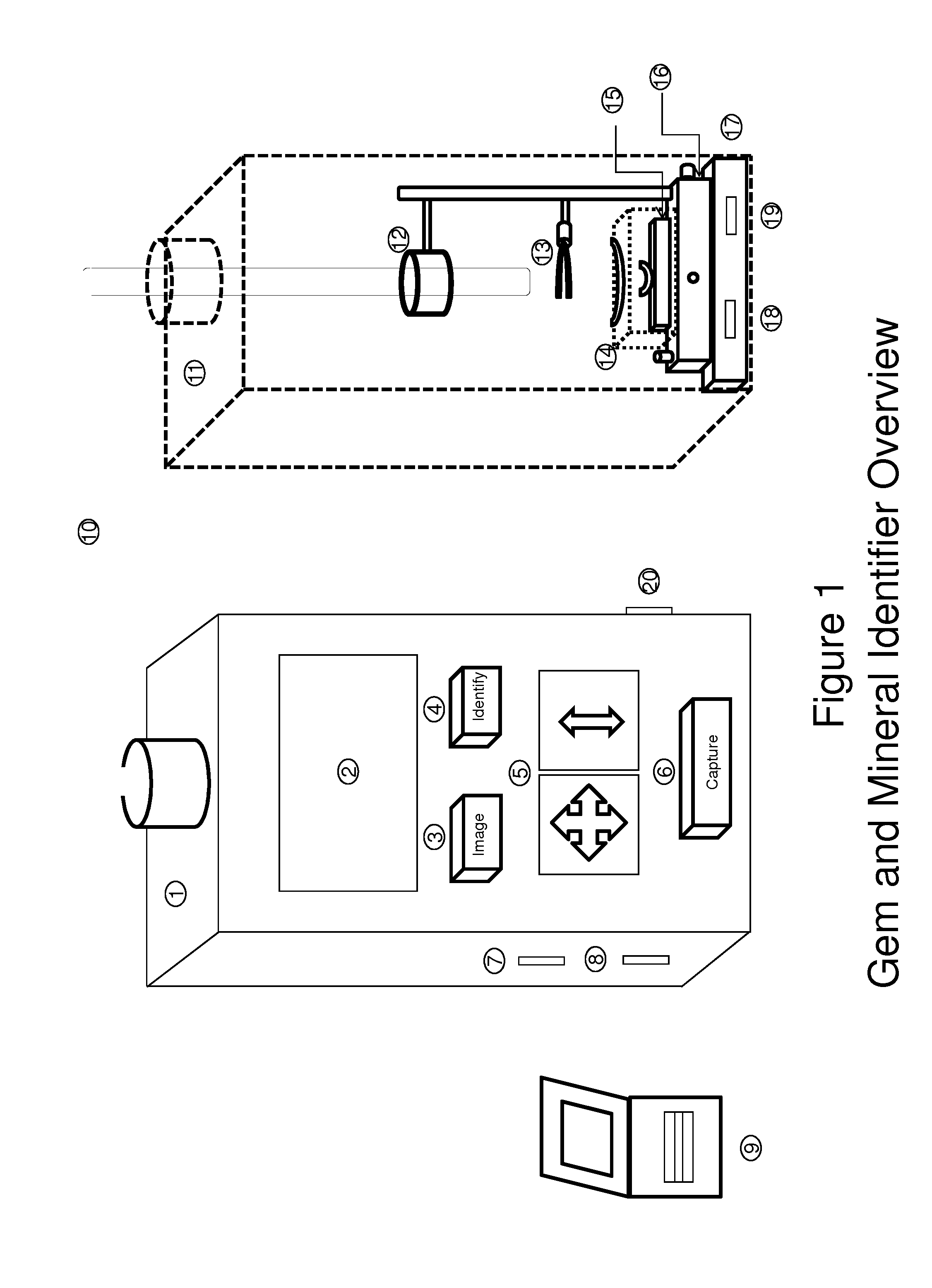
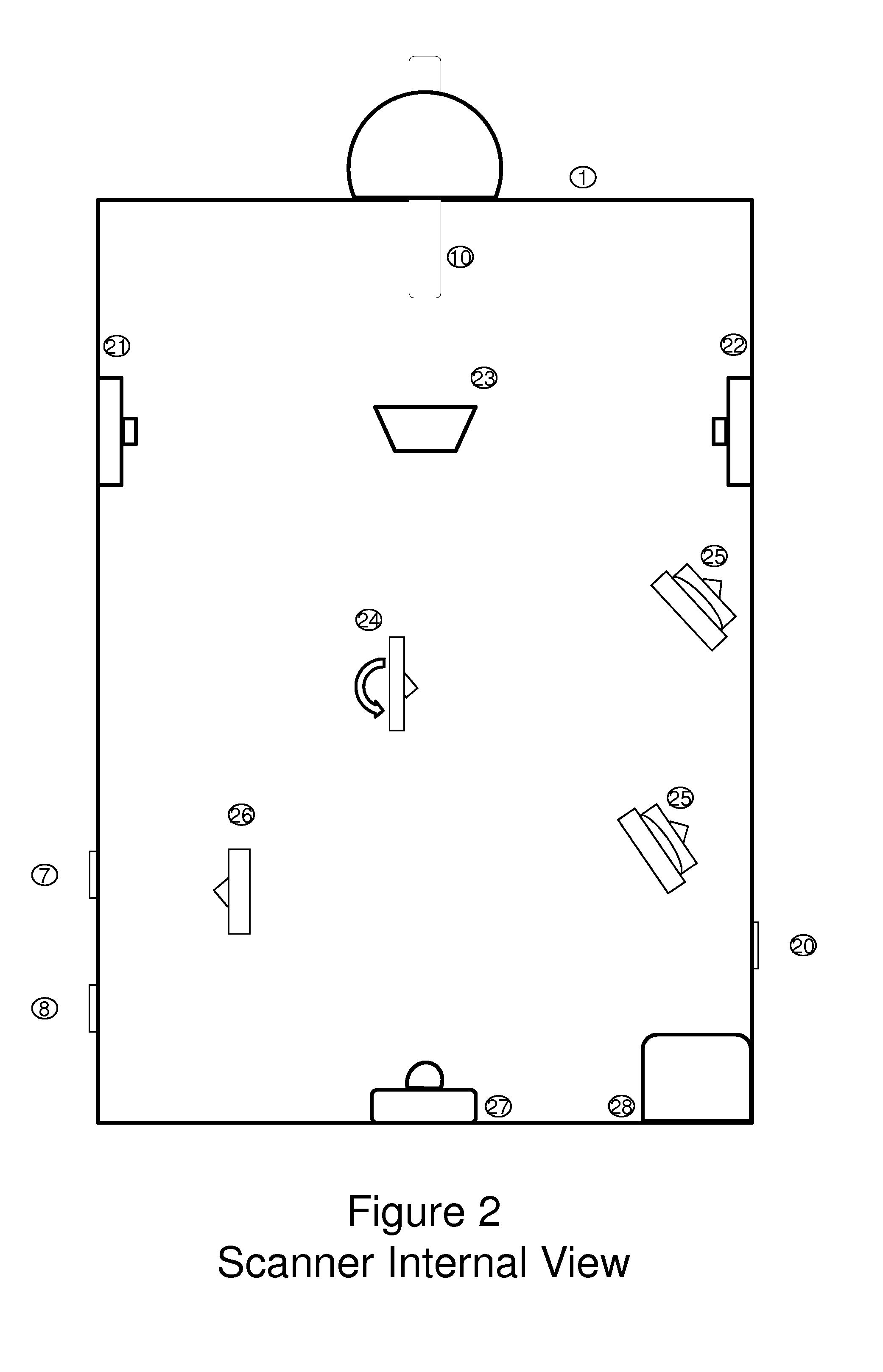
Universal tool for automated gem and mineral identification and measurement
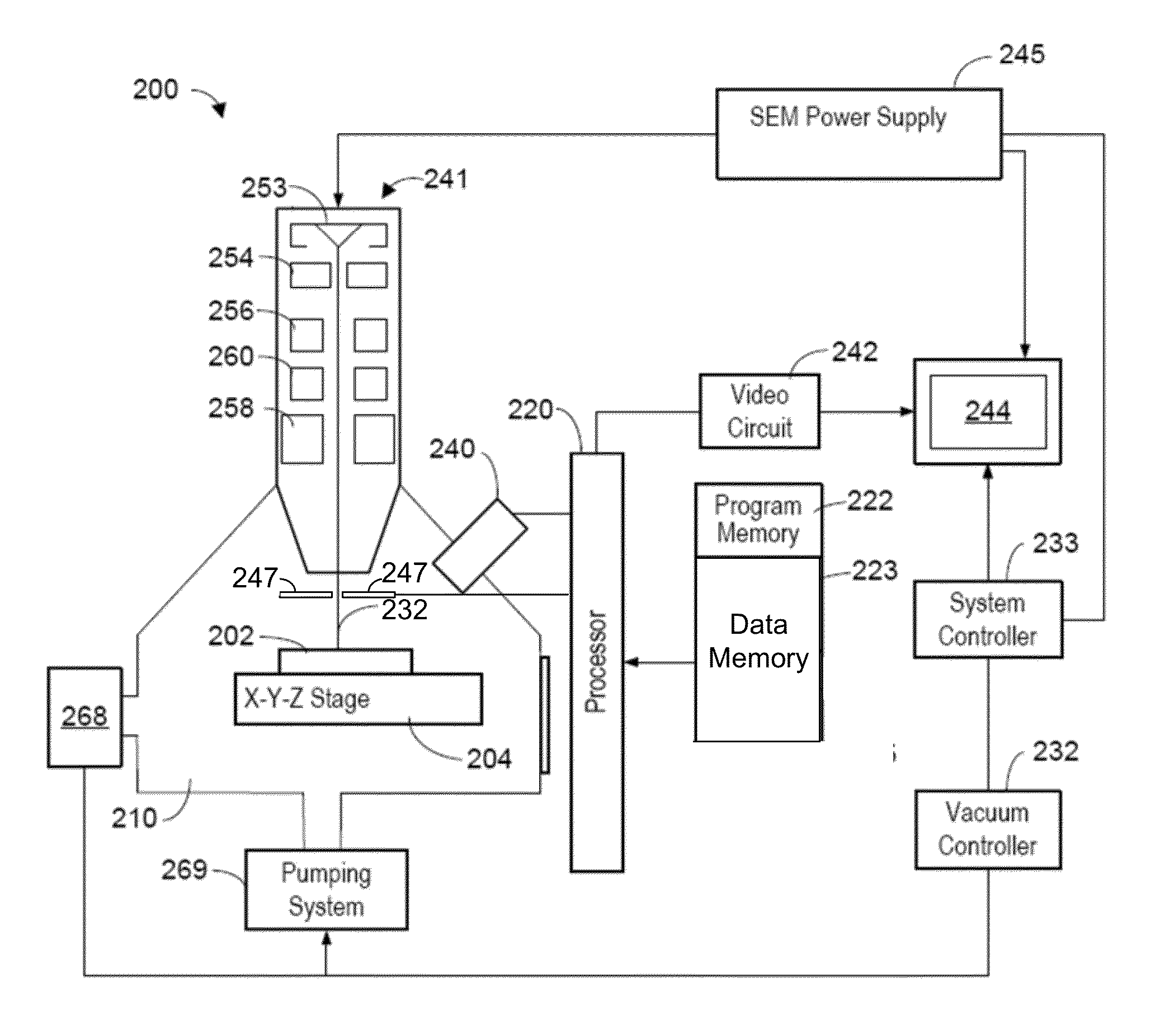
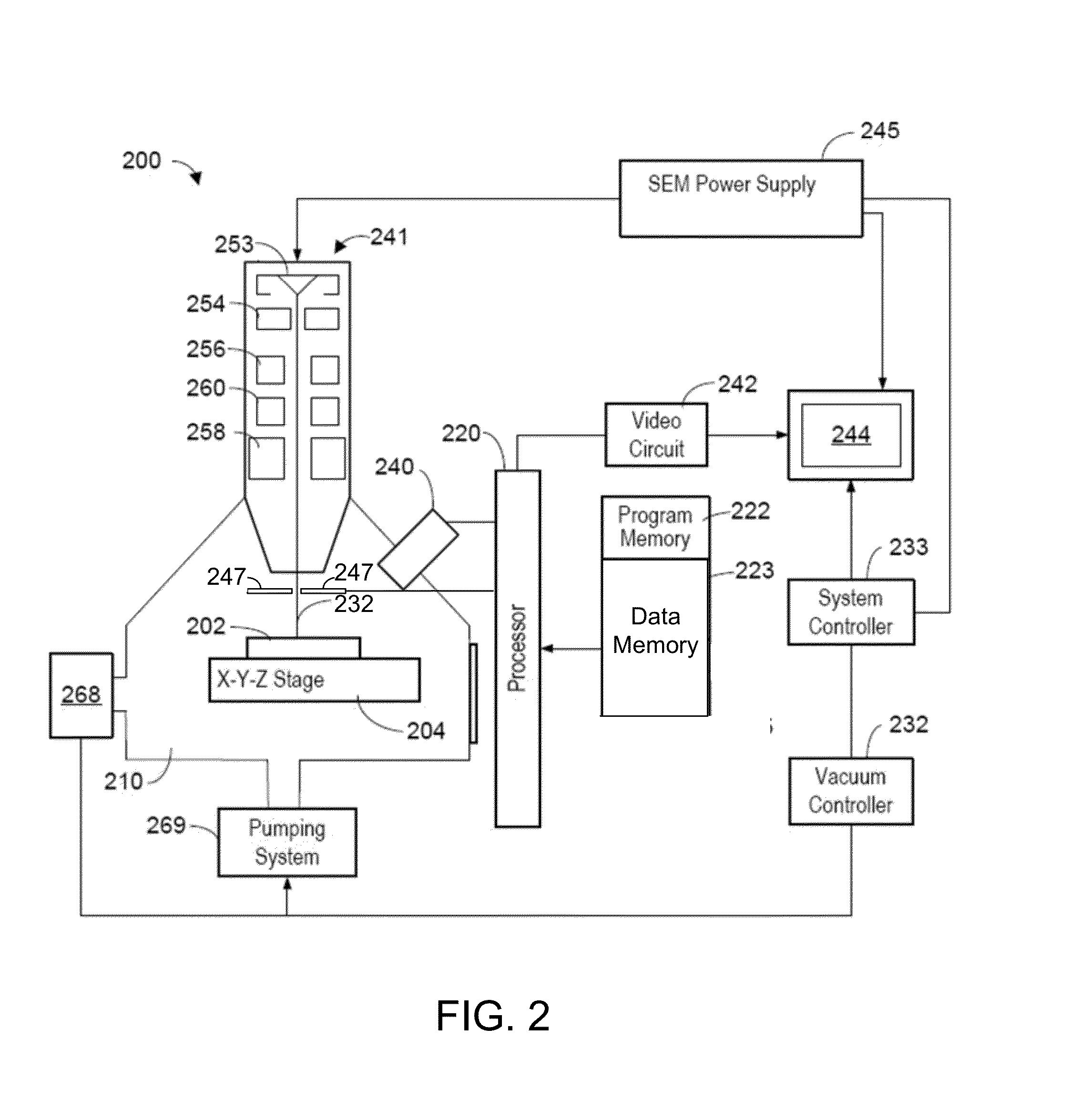
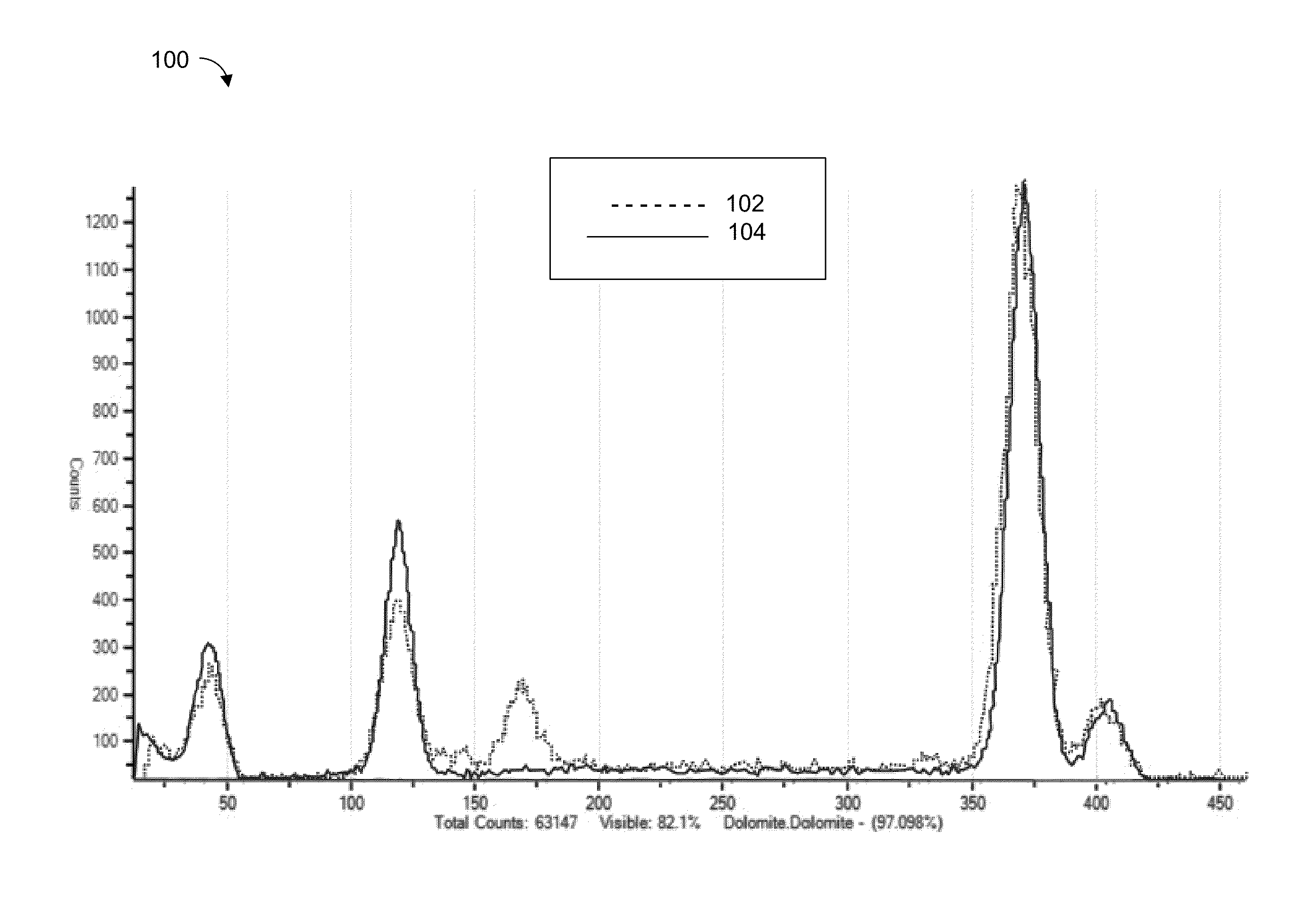
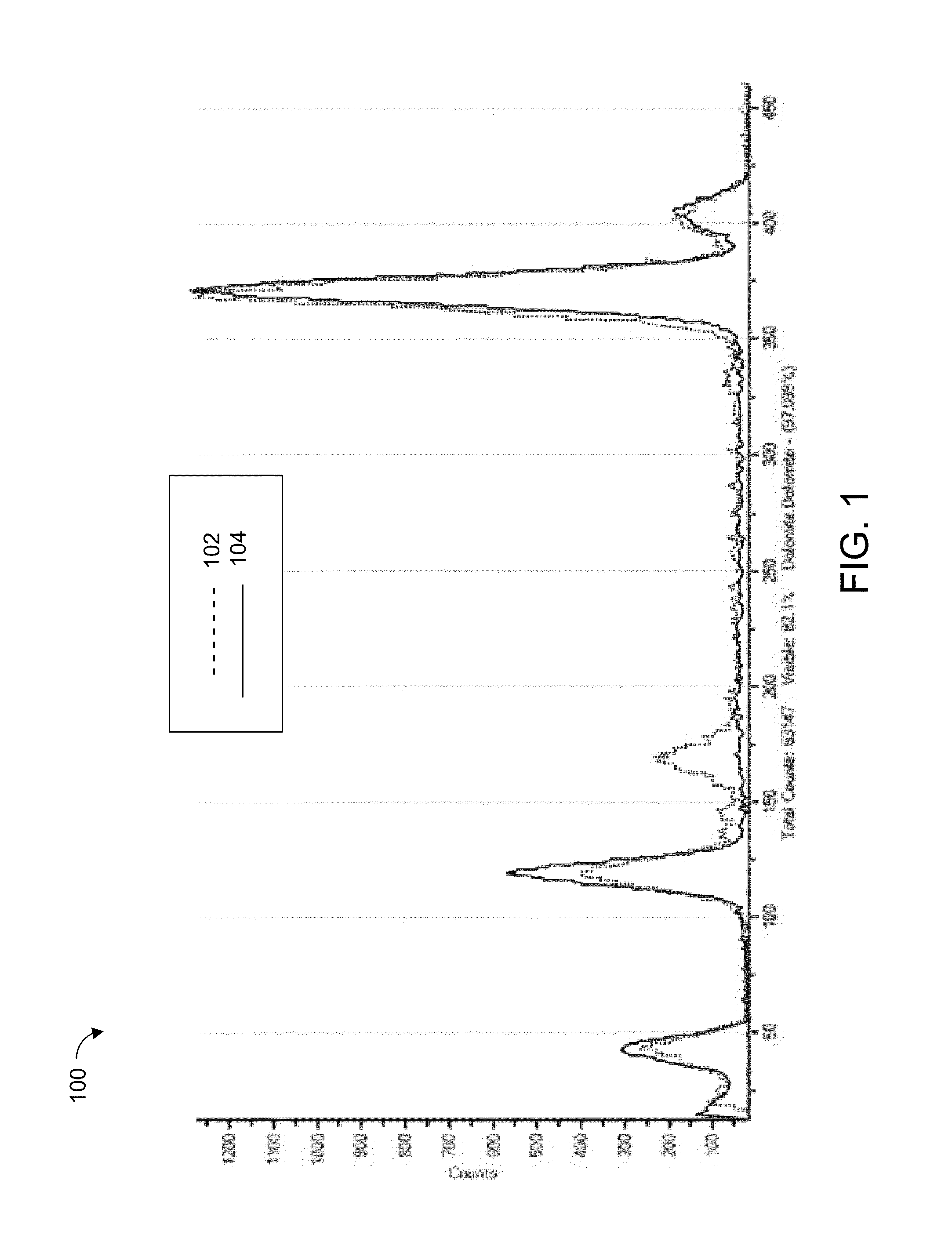
ActiveUS20130321792A1The process is fast and accurateRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringTelecommunications linkCommunication link
A tool employs Raman spectroscopy, optical imaging, physical measurements, smart software applications, and custom databases for automated on-site gem and mineral identification, measurement, and authenticity verification. Operators with no technical expertise can perform on-site, fast, nondestructive gem and mineral characterization. A custom smart application for data handling and processing enables applicability with a variety of processors. Automated generation of Raman spectral signatures and subsequent correlation to spectral fingerprints of known materials enables gem and mineral identification and verification in field settings. A single tool provides high resolution digital optical imaging and physical measurement capabilities, enables comprehensive sample characterization and reporting that currently requires multiple tools and significant labor. The Tool also provides the capability for sample analysis, requiring an additional level of technical expertise, to be done remotely at another location by the transmission of the data via a communications link. A rechargeable battery pack is included.
Owner:SHAPIRO FREDERICK W
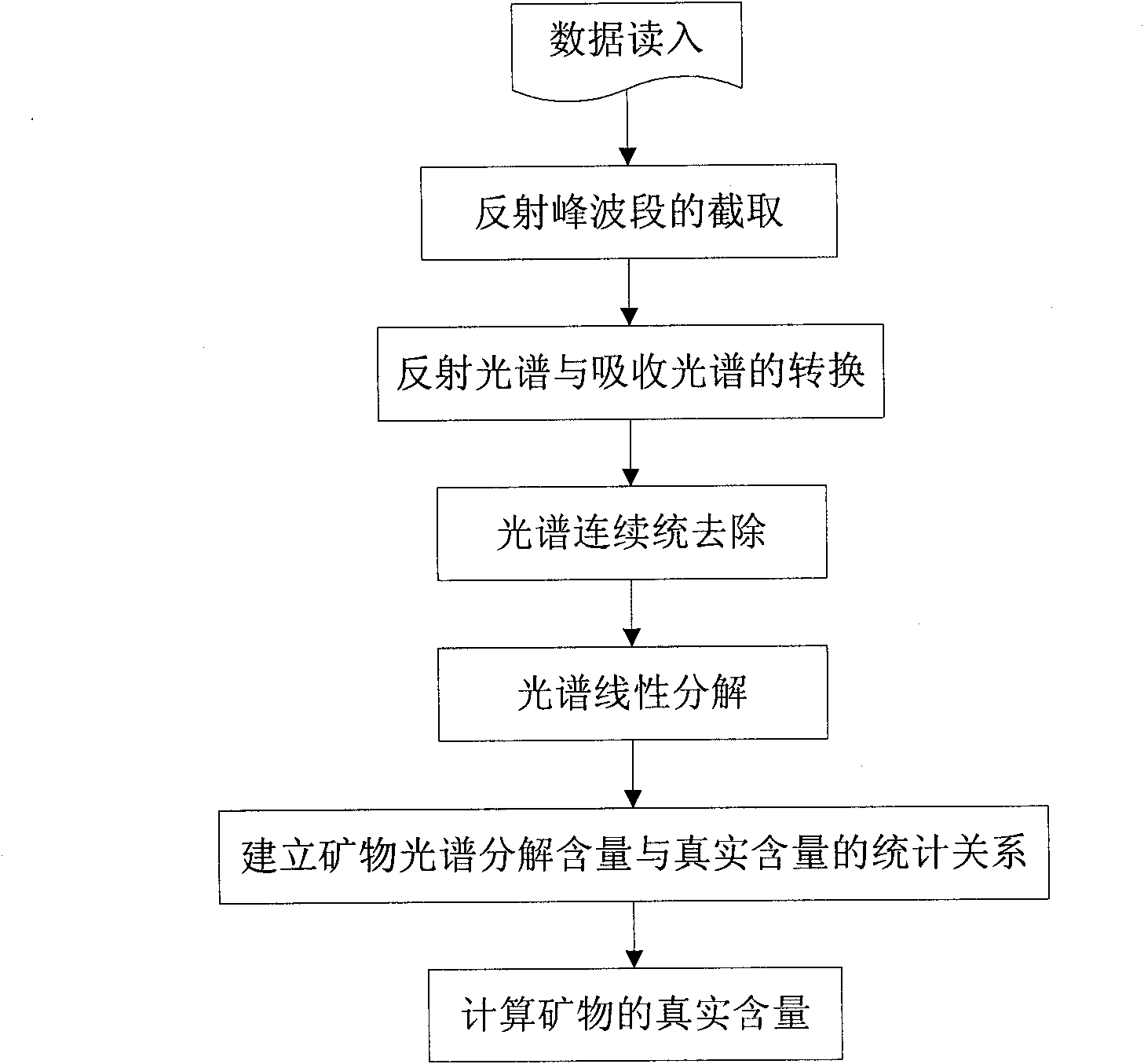
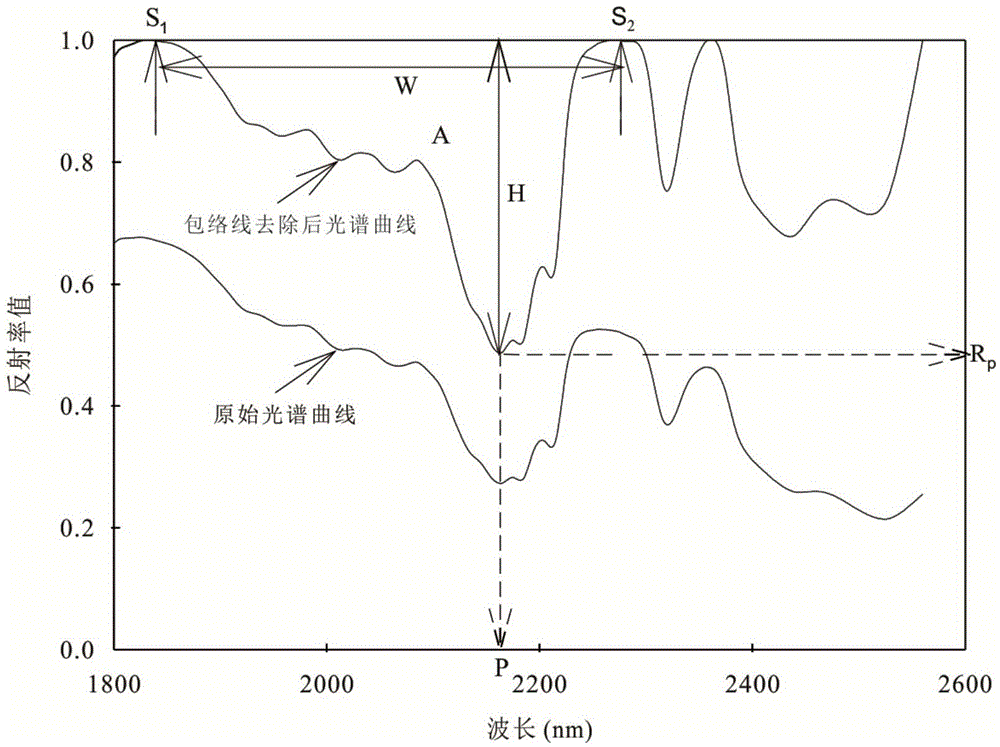
Spectral reflectance peak decomposition based quantitative inversion method of hyperspectral remote sensing mineral content
InactiveCN101887012AFully excavatedImprove quantificationColor/spectral properties measurementsAction spectrumReflectance spectroscopy
The invention relates to a spectral reflectance peak decomposition based quantitative inversion method of the hyperspectral remote sensing mineral content. The method comprises the seven steps of: 1. reading data in; 2. intercepting a reflection peak band; 3. converting a reflectance spectrum and an absorption spectrum; 4. carrying out continuum removal on the spectrums; 5. linearly decomposing the spectrums to obtain the mineral spectrum decomposition content; 6. establishing a statistical relationship between the mineral spectrum decomposition content and the real content; and 7. converting the calculated mineral spectrum decomposition content in the step 5 into the real mineral content according to the established statistical relationship in the step 6. The invention can not only be applied to hyperspectral data which is not covered by a mineral absorption spectrum band, but also can be used for hyperspectral data which is covered by the mineral absorption spectrum band in the spectrum band range, carries out quantitative mineral content inversion by comprehensively applying a spectral reflectance peak and an absorption spectrum band and improves the inversion precision and the inversion accuracy. The invention has practical value and broad application potential in the field of hyperspectral remote sensing mineral identification.
Owner:CHINA AERO GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY & REMOTE SENSING CENT FOR LAND & RESOURCES +1
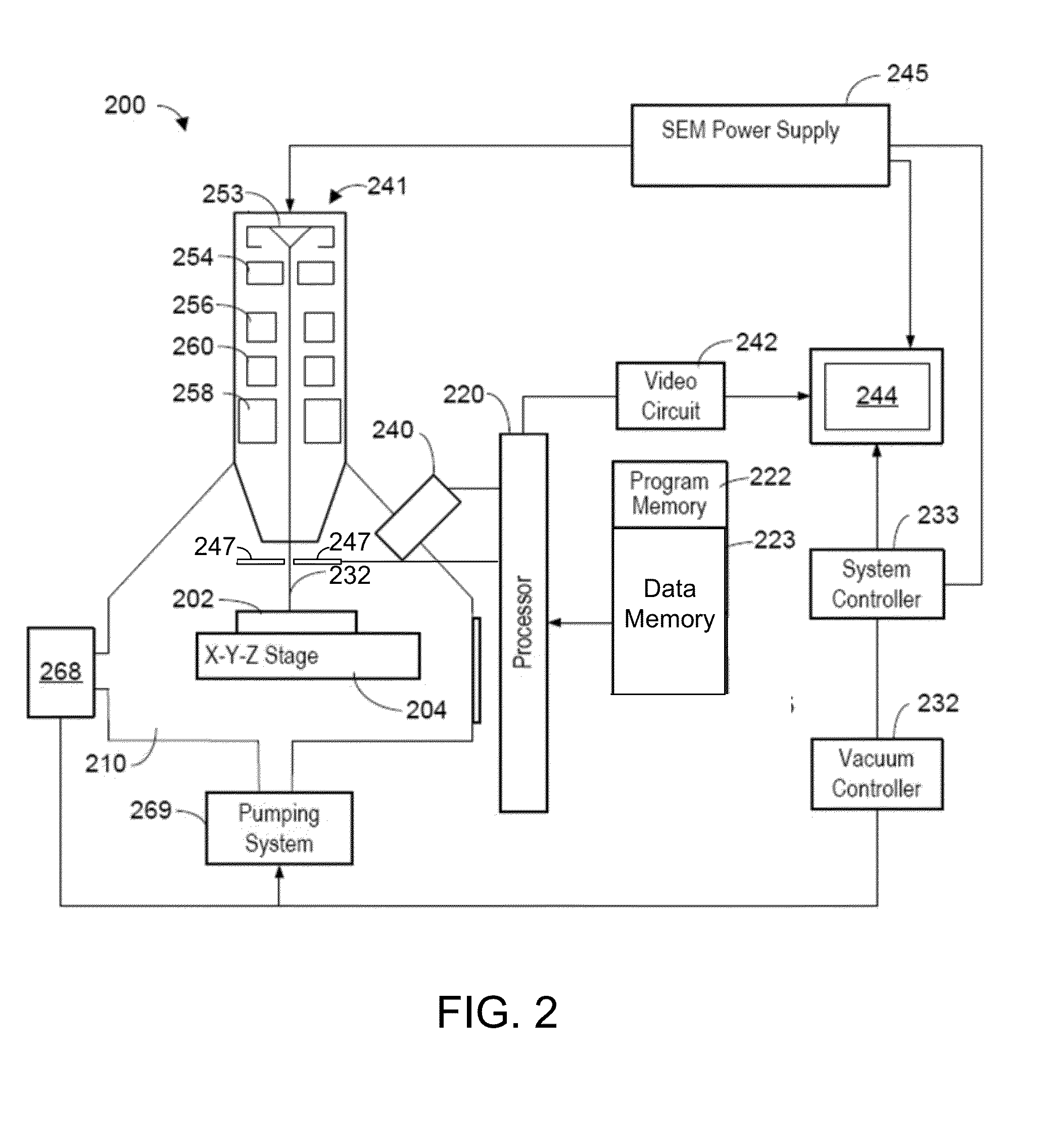
Mineral identification using mineral definitions including variability
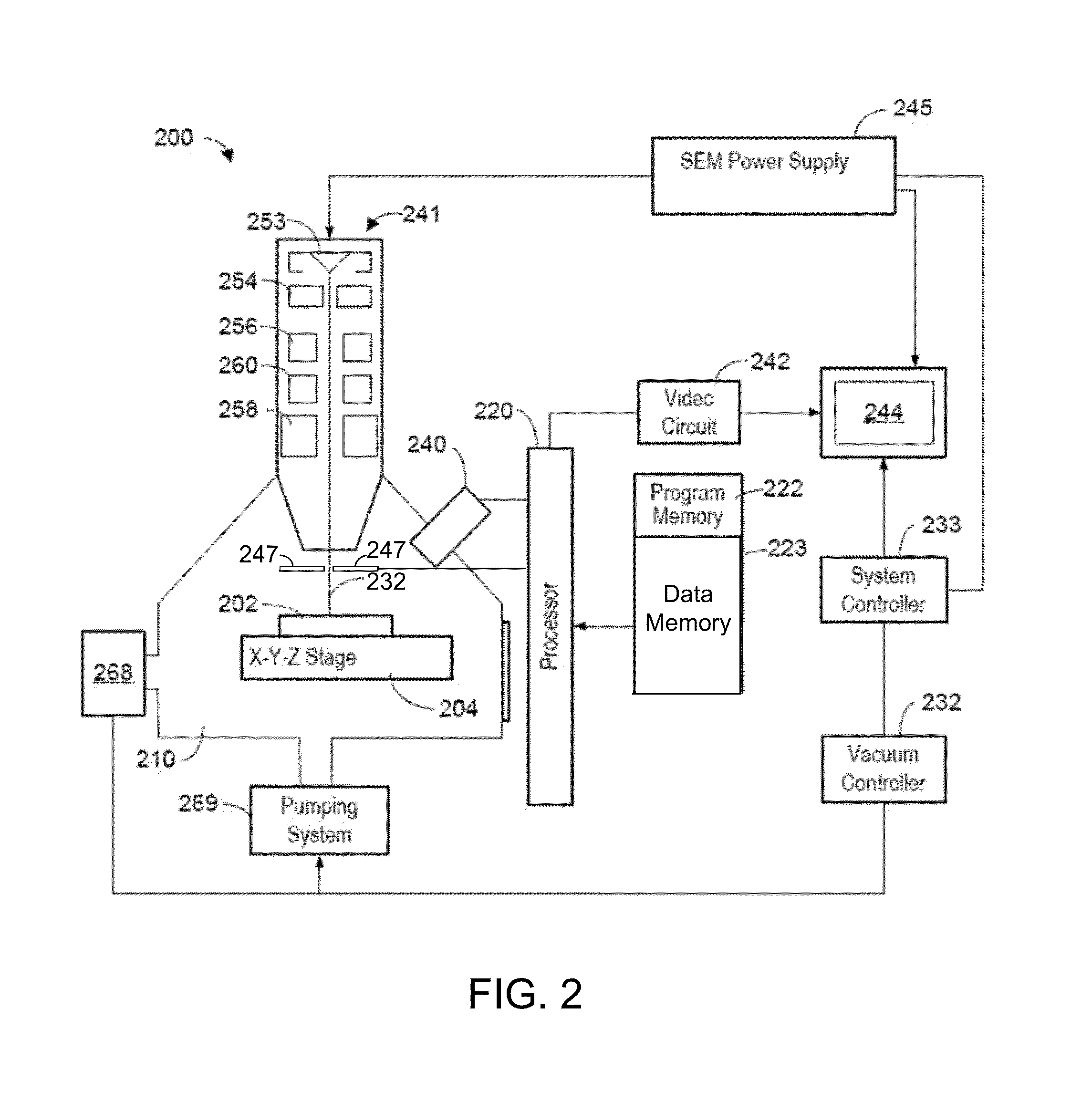
ActiveUS8937282B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationGamma-ray/x-ray microscopesX-rayMineral identification
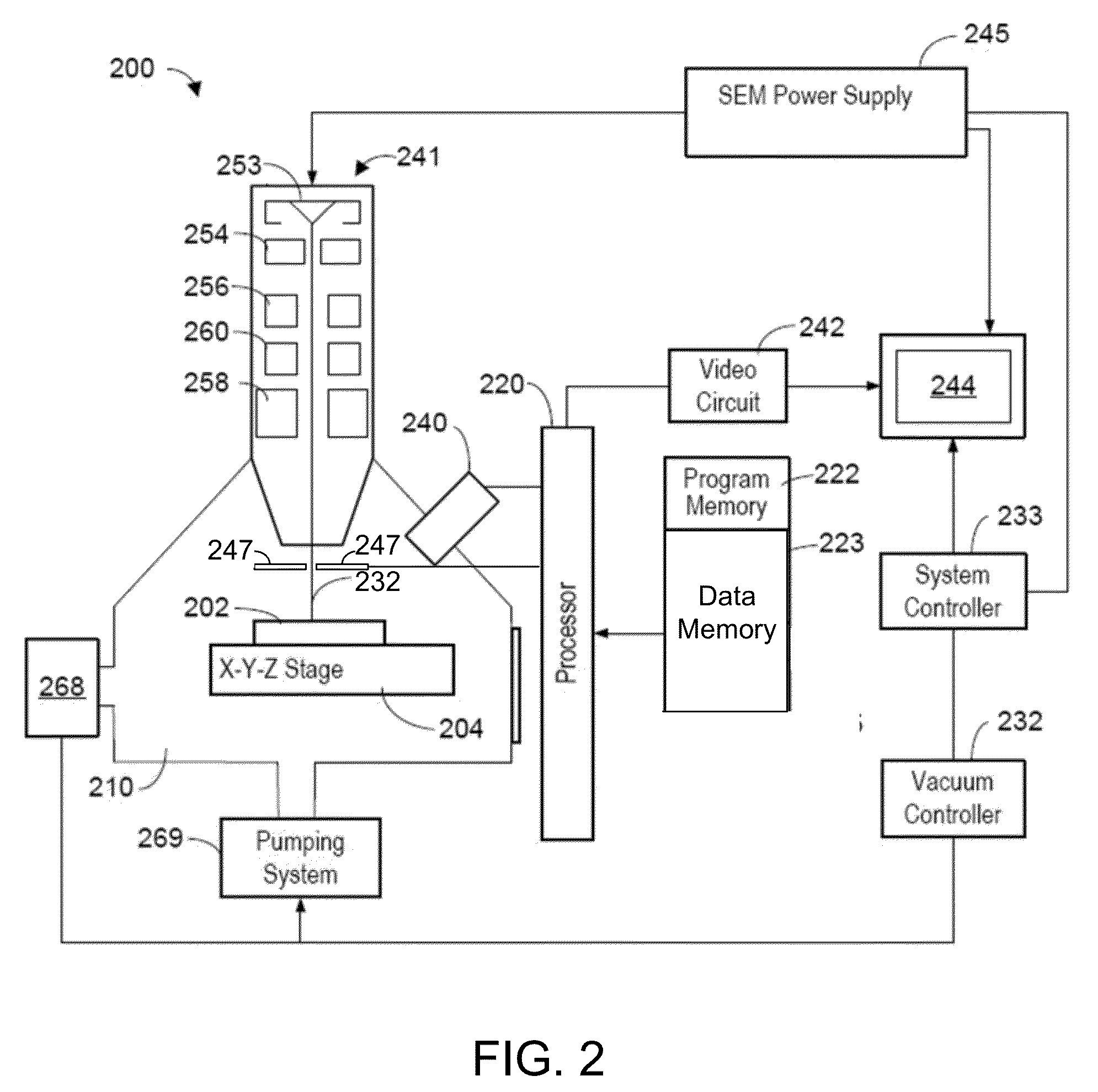
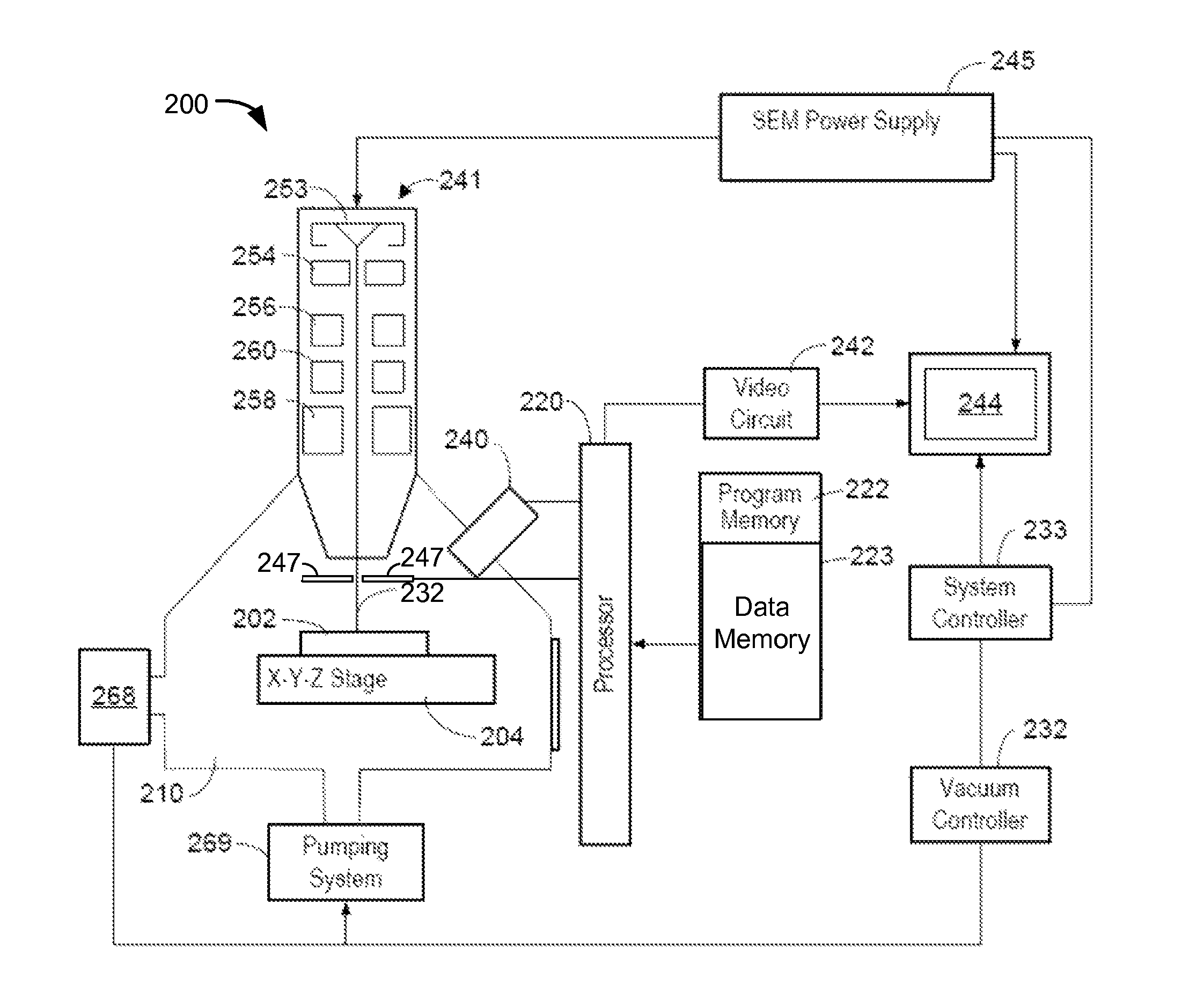
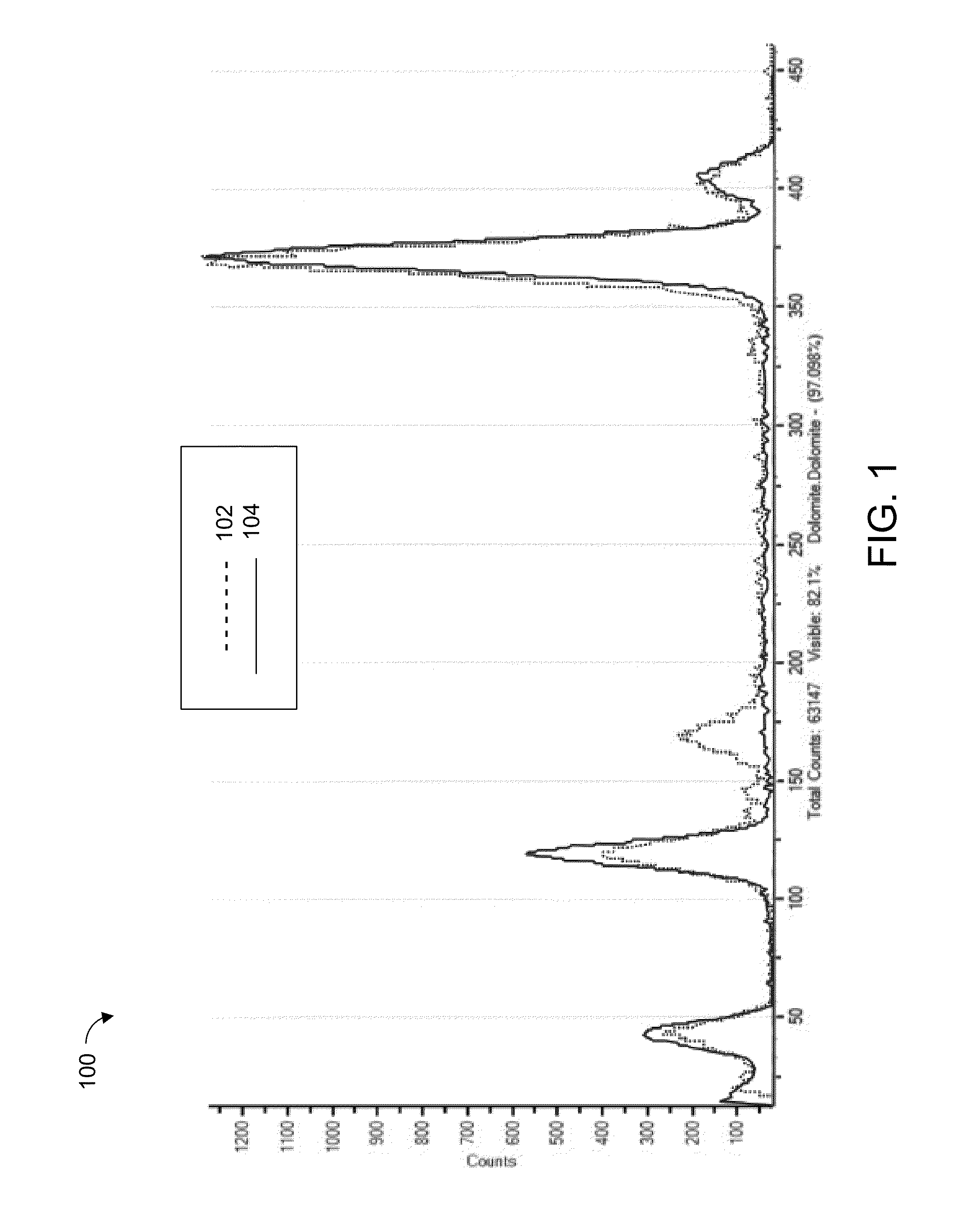
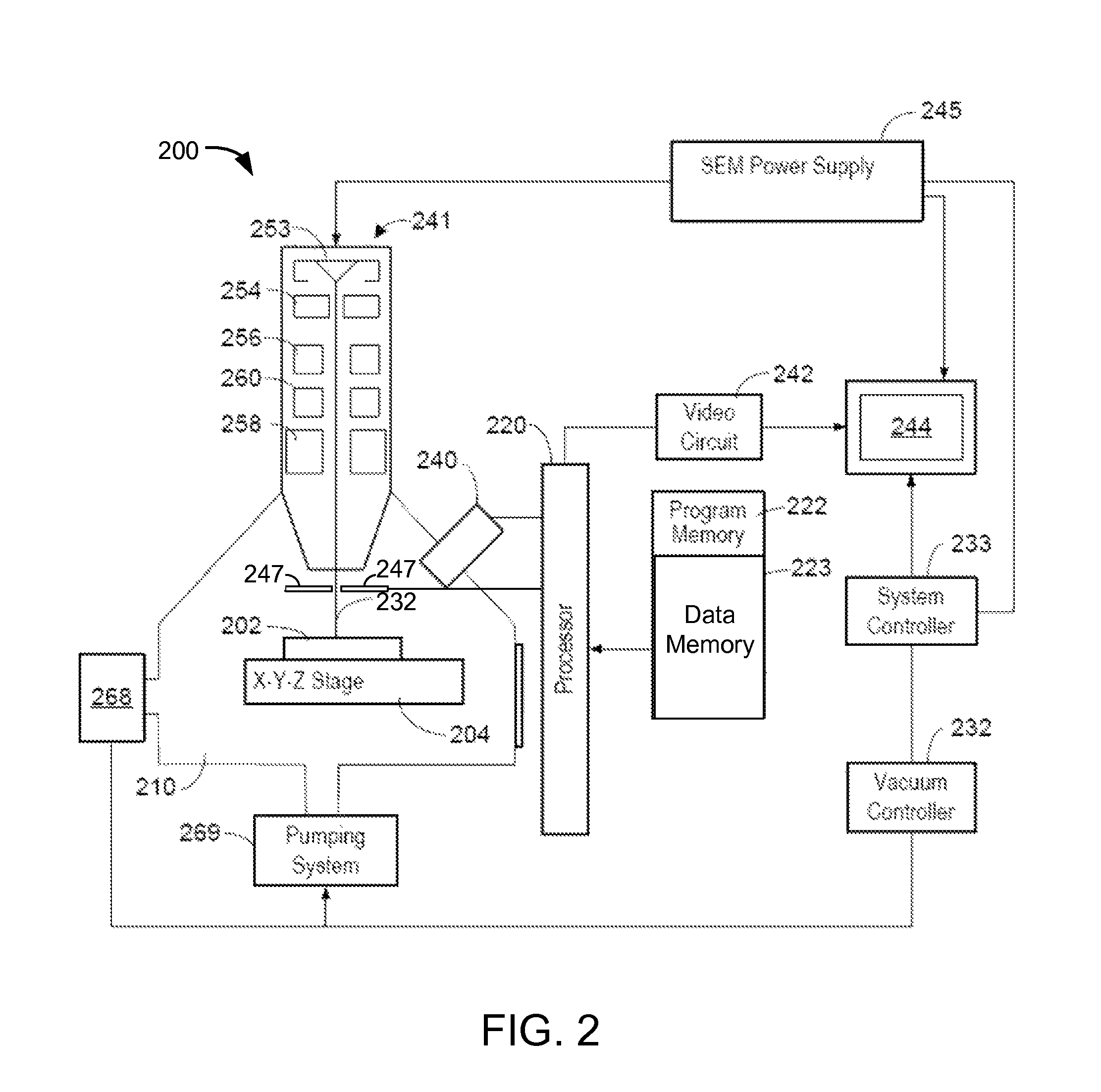
An improved mineral analysis system includes mineral definitions that include not only characteristics of the minerals, but also variability in those characteristics. The variabilities allow the calculation of ranges of expected values for different quality of measurements, for example, for different numbers of x-ray counts. Match probabilities can therefore be calculated to more accurately determine the composition of a mineral sample.
Owner:FEI CO
Mineral standard sample used for nanometer CT, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105067395AFill vacancyRealize one-time calibrationPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationMineral particlesMineral identification
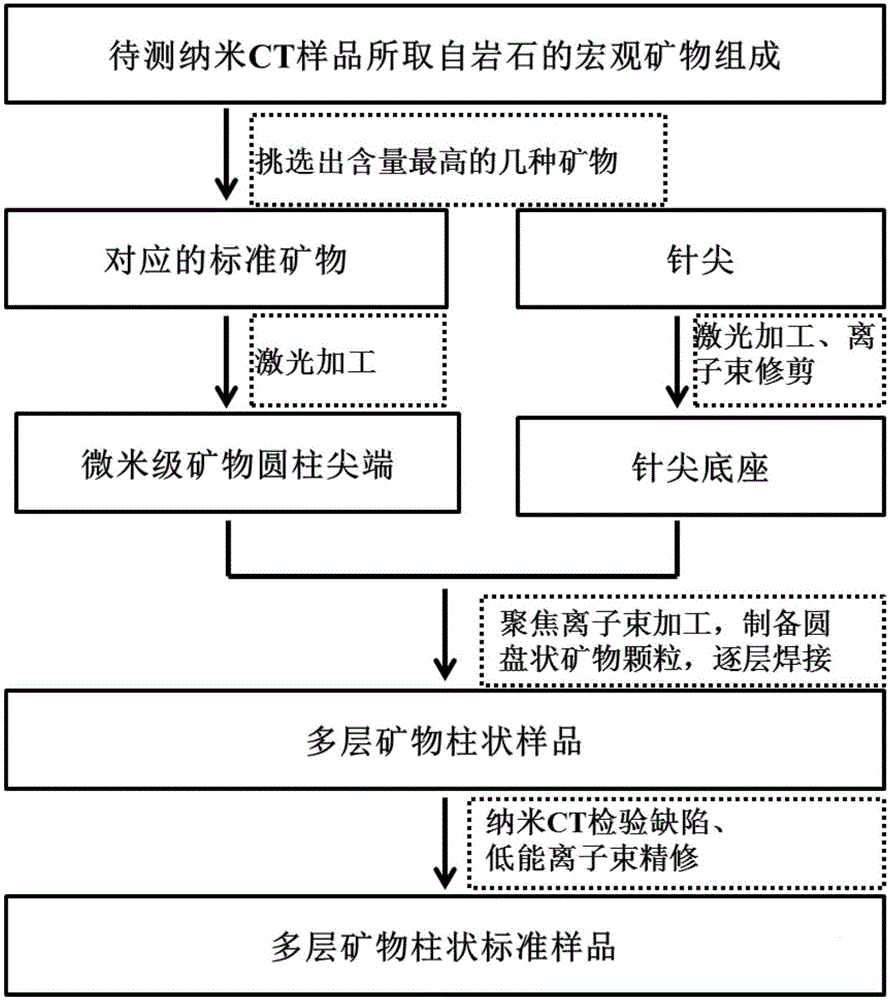
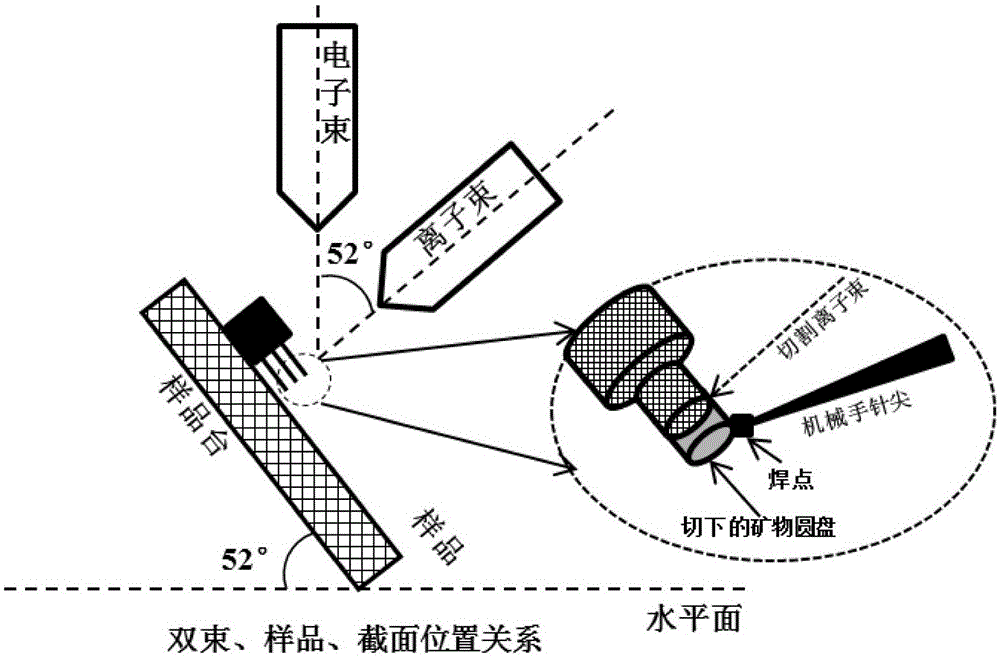
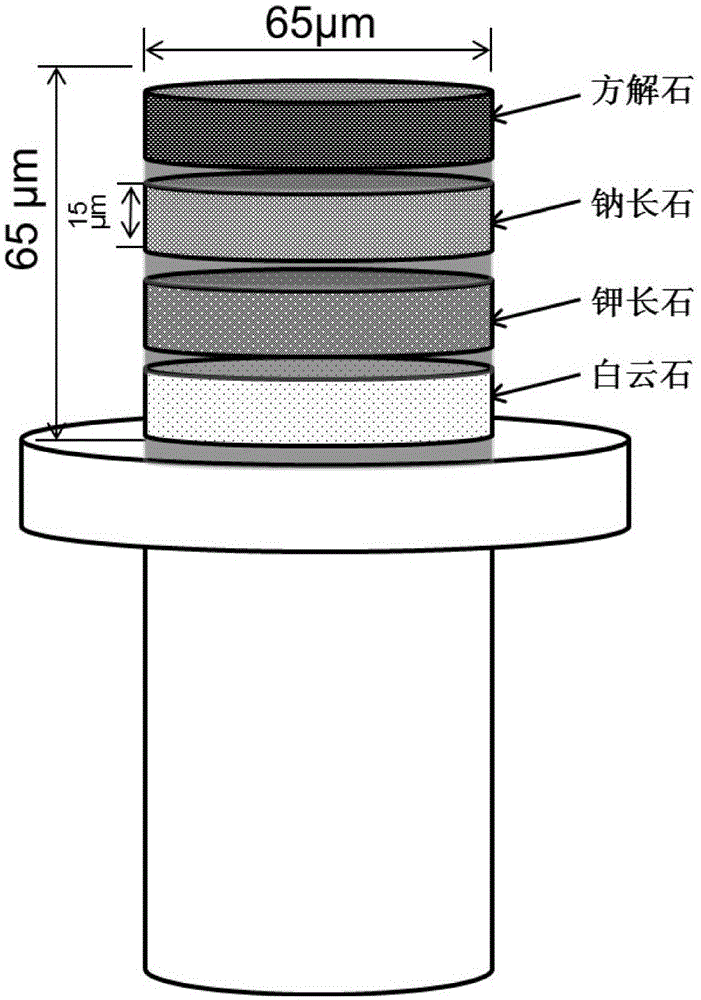
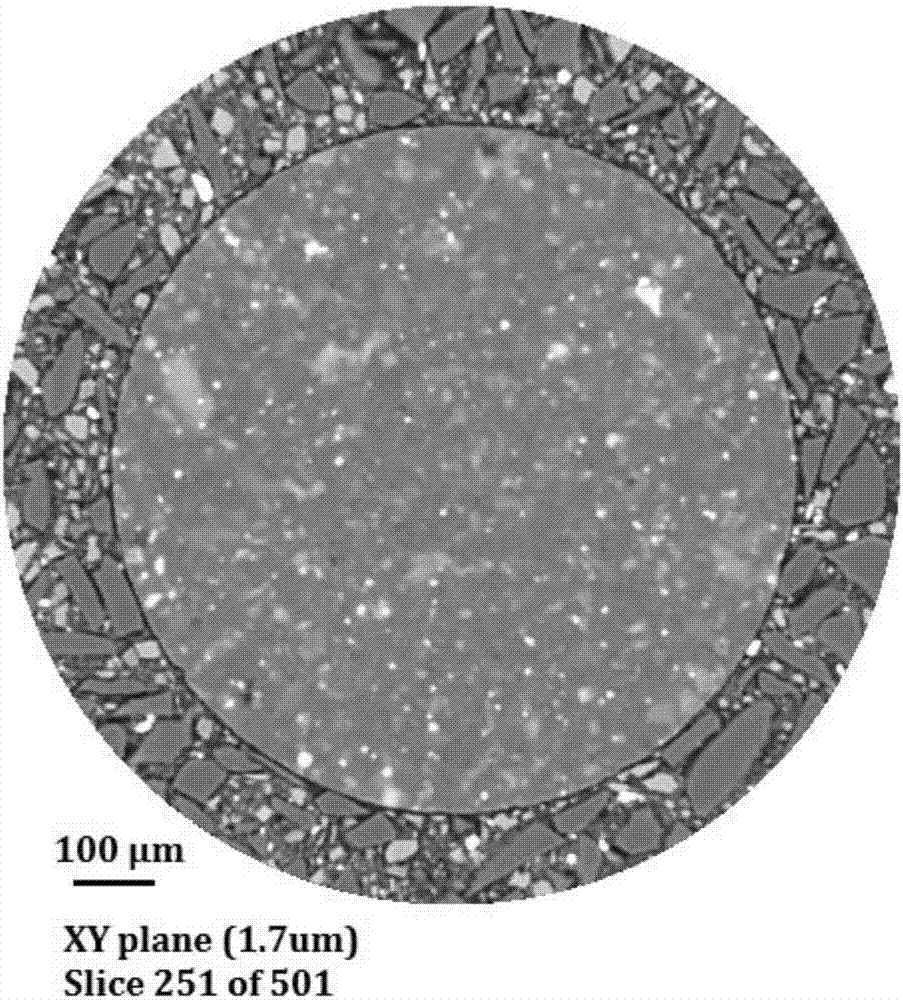
The invention provides a mineral standard sample used for nanometer CT, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method of the mineral standard sample comprises the following steps: selecting standard mineral particles according to the mineral composition of a rock to be measured; respectively processing at least one of the selected standard mineral particles to form mineral sample discs; and welding one of the mineral sample discs to a pedestal, and stacking and welding all the mineral sample discs to form the mineral standard sample. When the mineral standard sample is used in mineral analysis, mineral identification is carried out by using the gray scale information of the standard mineral sample and a rock sample to make unknown mineral particles in the rock sample identified and calibrated, so the three dimensional distribution, the volume proportions and the mineral particle dimension distribution of corresponding mineral components in the rock sample are obtained. The method effectively fills up the gap in preparation methods of like standard samples, and meets urgent demands of microscopic three dimensional mineral analysis in the petroleum geology field.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
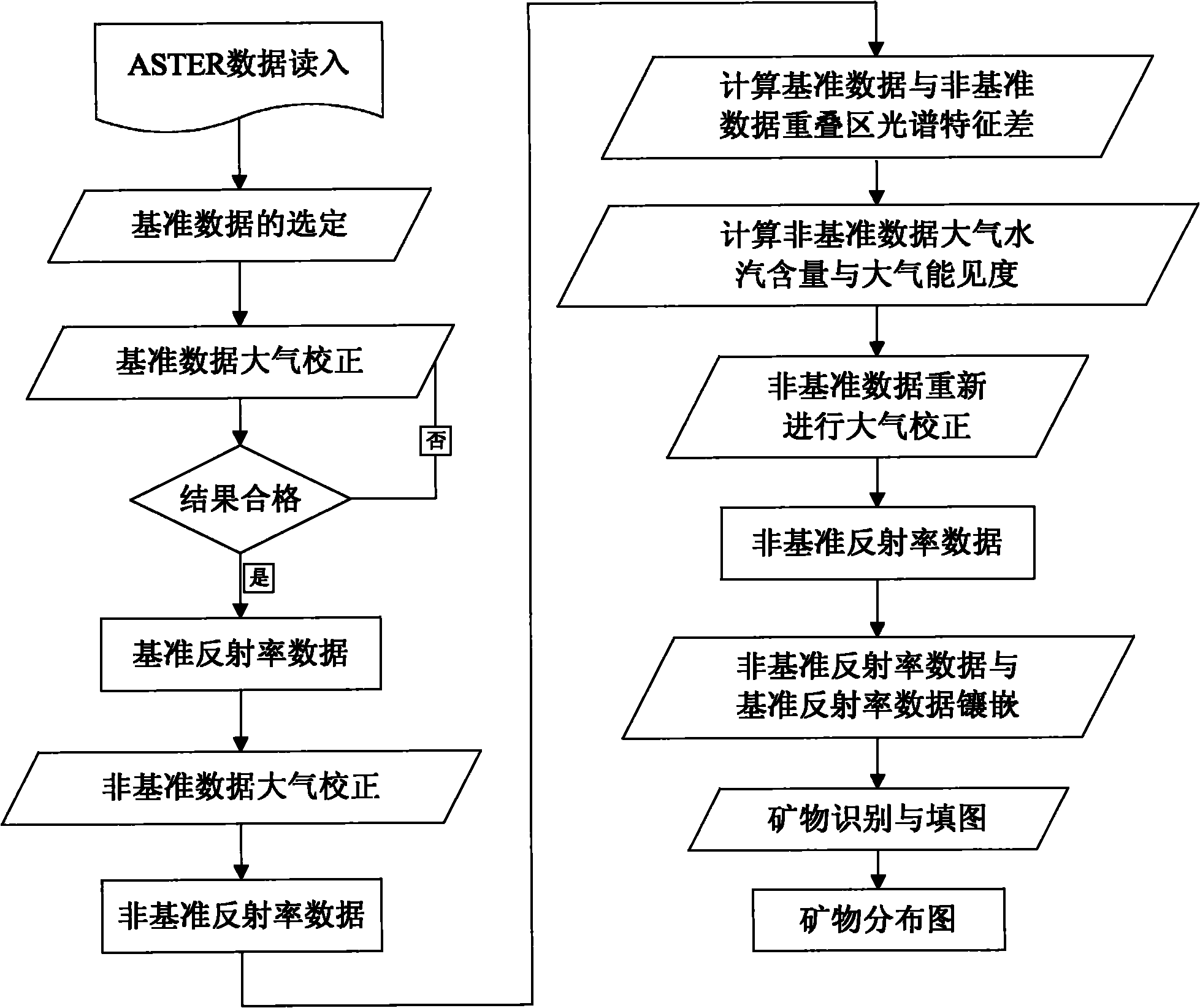
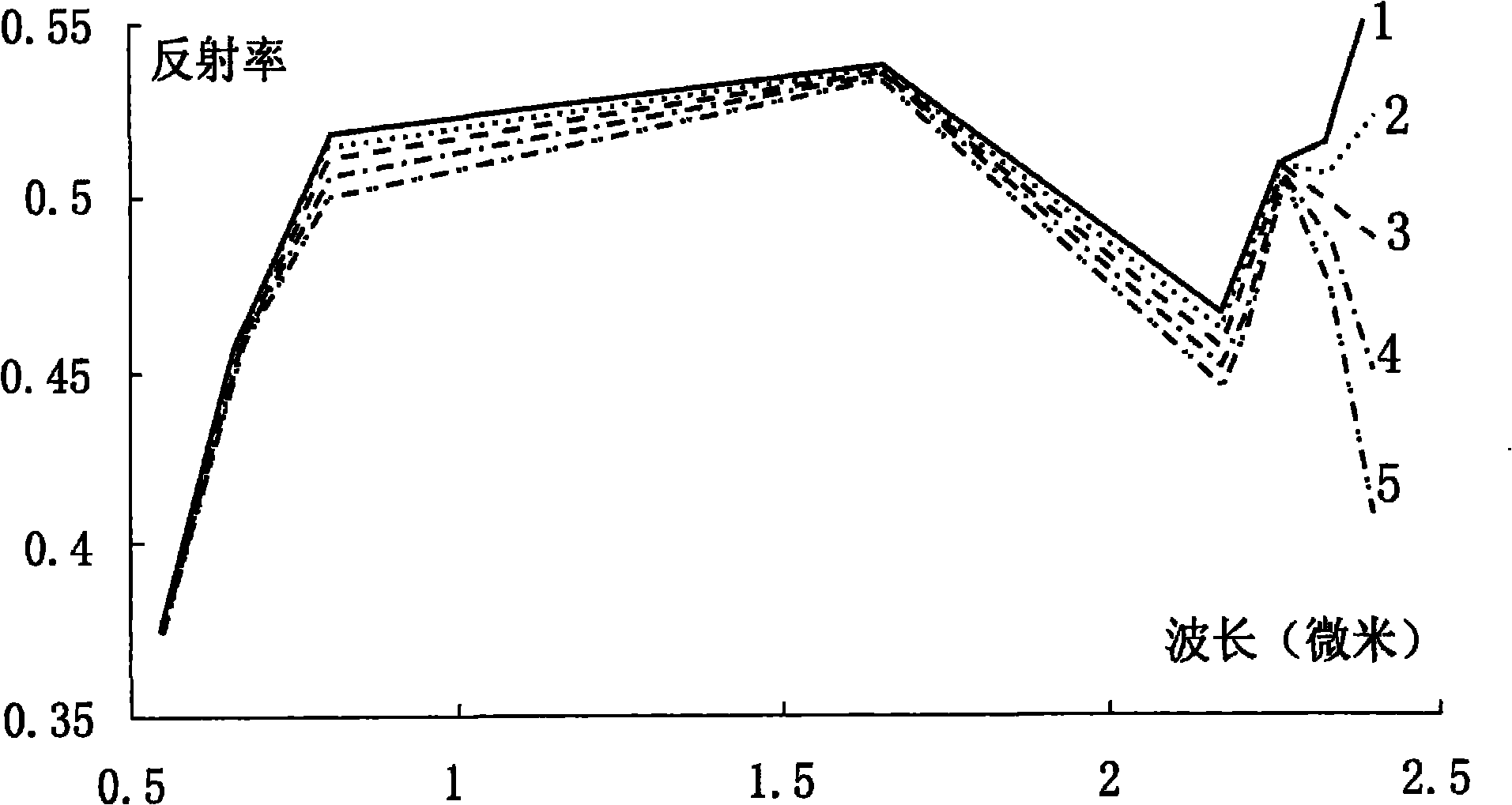
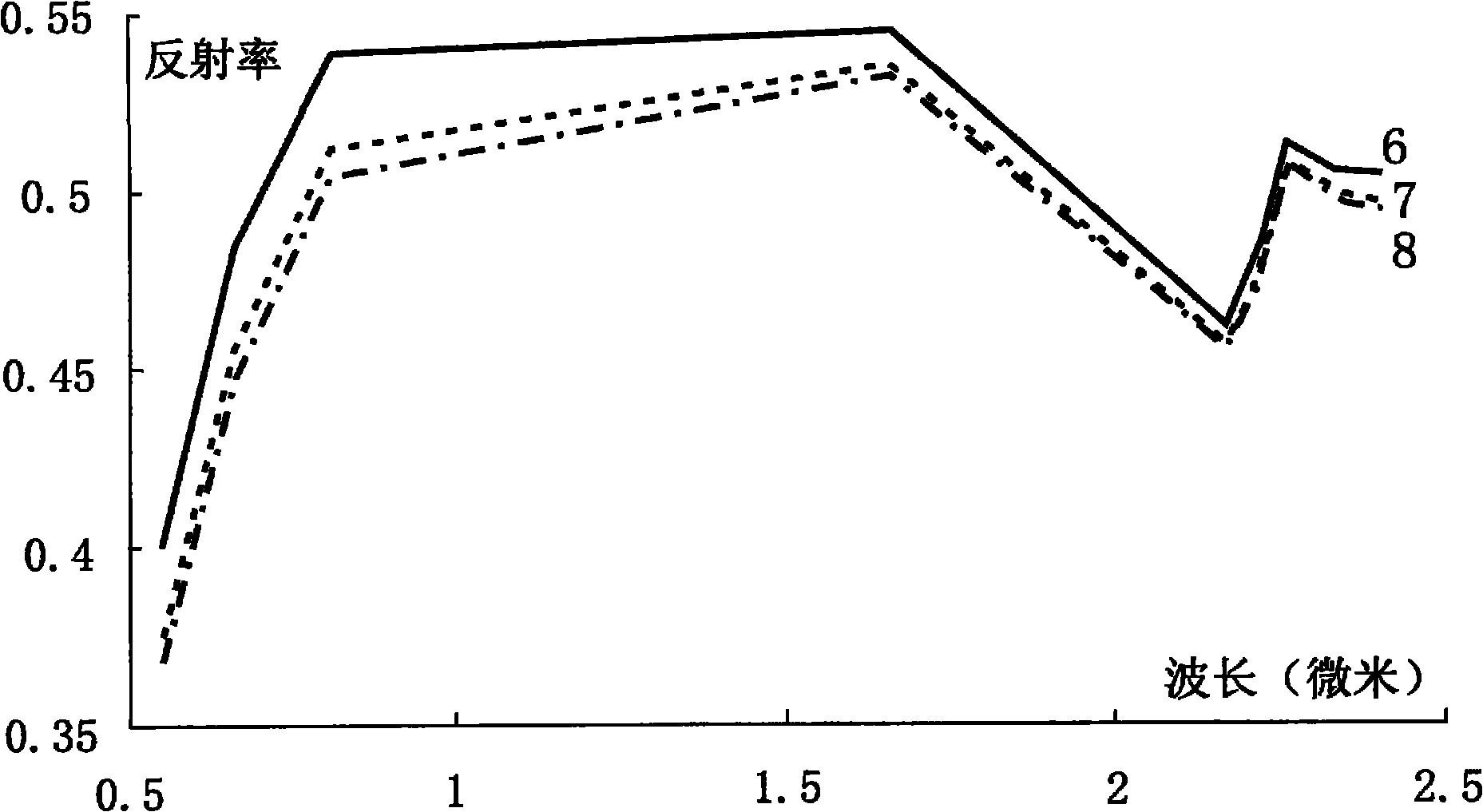
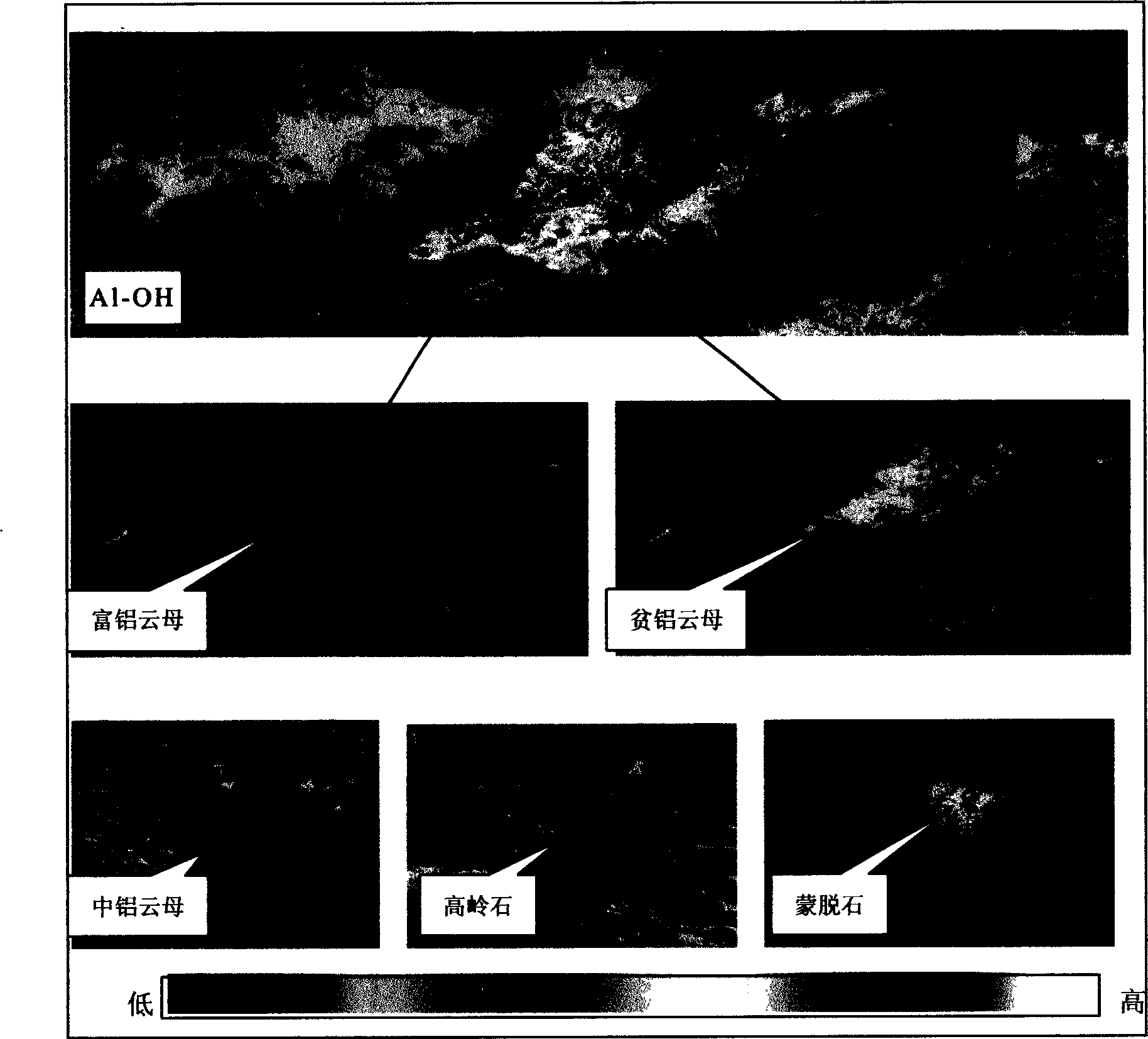
Atmospheric correction and regional mineral map spotting method utilizing multi-scene ASTER (Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer) remote sensing data
InactiveCN101871884AEliminate differencesScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsBaseline dataSensing data
The invention relates to an atmospheric correction and regional mineral map spotting method utilizing multi-scene ASTER (Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer) remote sensing data, comprising the following nine steps of: (1) reading in ASTER data; (2) selecting reference data, wherein one-scene data is selected from multi-scene data as a reference for atmospheric correction; (3) carrying out the atmospheric correction on the reference data to obtain reference reflectivity data; (4) carrying out atmospheric correction on non-reference data to obtain non-reference reflectivity data; (5) calculating the overlay region spectral characteristic difference of the reference reflectivity data and the non-reference reflectivity data; (6) calculating the atmospheric water vapor content and the atmospheric visibility of the non-reference data; (7) newly carrying out the atmospheric correction on the non-reference data by utilizing the calculated atmospheric water vapor content and the atmospheric visibility to obtain non-reference reflectivity data; (8) carrying out inlaying treatment on the multi-scene reflectivity data including the reference data and the non-reference data; and (9) carrying out mineral identification and map spotting by utilizing spectral indexes. The method effectively eliminates inlaid gaps among the multi-scene data, thereby realizing the regional mineral map spotting.
Owner:CHINA AERO GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY & REMOTE SENSING CENT FOR LAND & RESOURCES
High spectrum multiple end element linear fitting mineral identification and mineralizing indication method
InactiveCN1595110AOvercome the shortcomings of low precisionColor/spectral properties measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsCorrelation coefficientModel parameters
This invention provides a highlight spectrum multiple-end linear fitted mineral identification and mineralization indicate method which is based on mineral theory and wall rock alteration characteristics and chooses the alteration mineral indicating different kinds of mineral to form multiple-end compound. The selected multiple-end mineral group is linear fitted and any picture element correlation coefficient is made to be the maximum of the fitted mineral. In the highlight spectrum picture process, it uses matrix calculation to do multiple linear regressions fit and the fit parameter vector A serves as distribution weigh in the compound of the different ends. The weigh serves as the probability existed in the end and at same time denotes the relative abundance of the distribution end. It uses different end content as mineral model parameters and makes color graph and displays mineral distribution and identifies the mineral according to the larger weigh value.
Owner:CHINA AERO GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY & REMOTE SENSING CENT FOR LAND & RESOURCES
Layered lineage identification method for high spectrum mineral
InactiveCN1595203AAdapt to the needs of drawingIntelligentOptical prospectingOptical detectionMineral identificationLighting spectrum
This invention establishes a mineral identification layer spectrum system which is mineral macro-taxonomy to mineral kind to detail mineral to mineral variation, according to the different grade of characteristic light spectrum parameters in the mineral mixed light spectrum. It concludes and valuates some common light spectrum parameters stability and the relative weigh in the mineral identification and establishes the light spectrum identification method and identification database of the more than twenty kinds of etching minerals. This invention integrates the mineral light spectrum knowledge of professional person into the identification of the mineral based on effectively solving the light spectrum change or variation and makes the general operation person can identify the minerals and realizes the intelligence, batch process and the scale utility of mineral area charting of high light spectrum remote sensor mineral identification.
Owner:CHINA AERO GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY & REMOTE SENSING CENT FOR LAND & RESOURCES
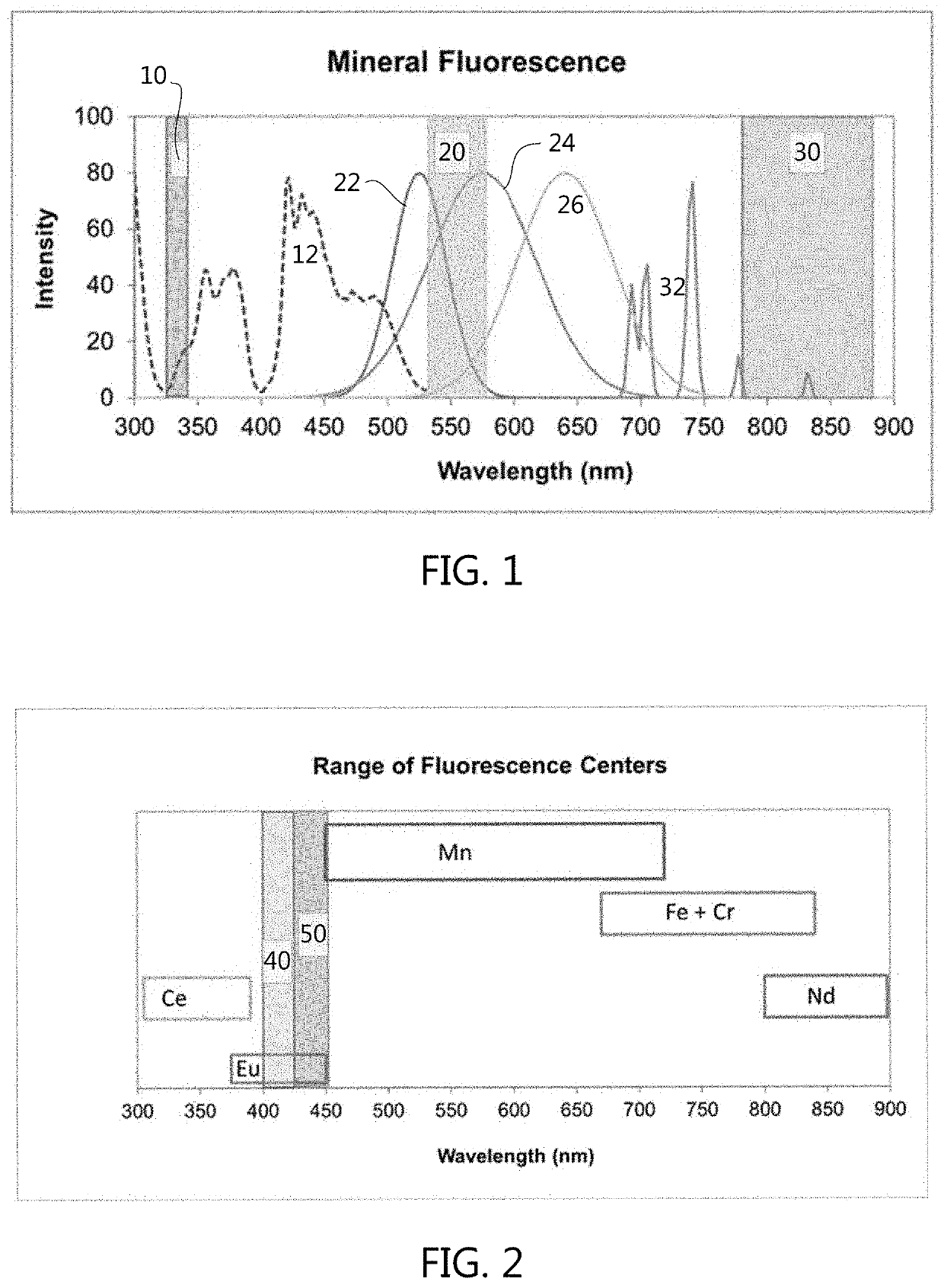
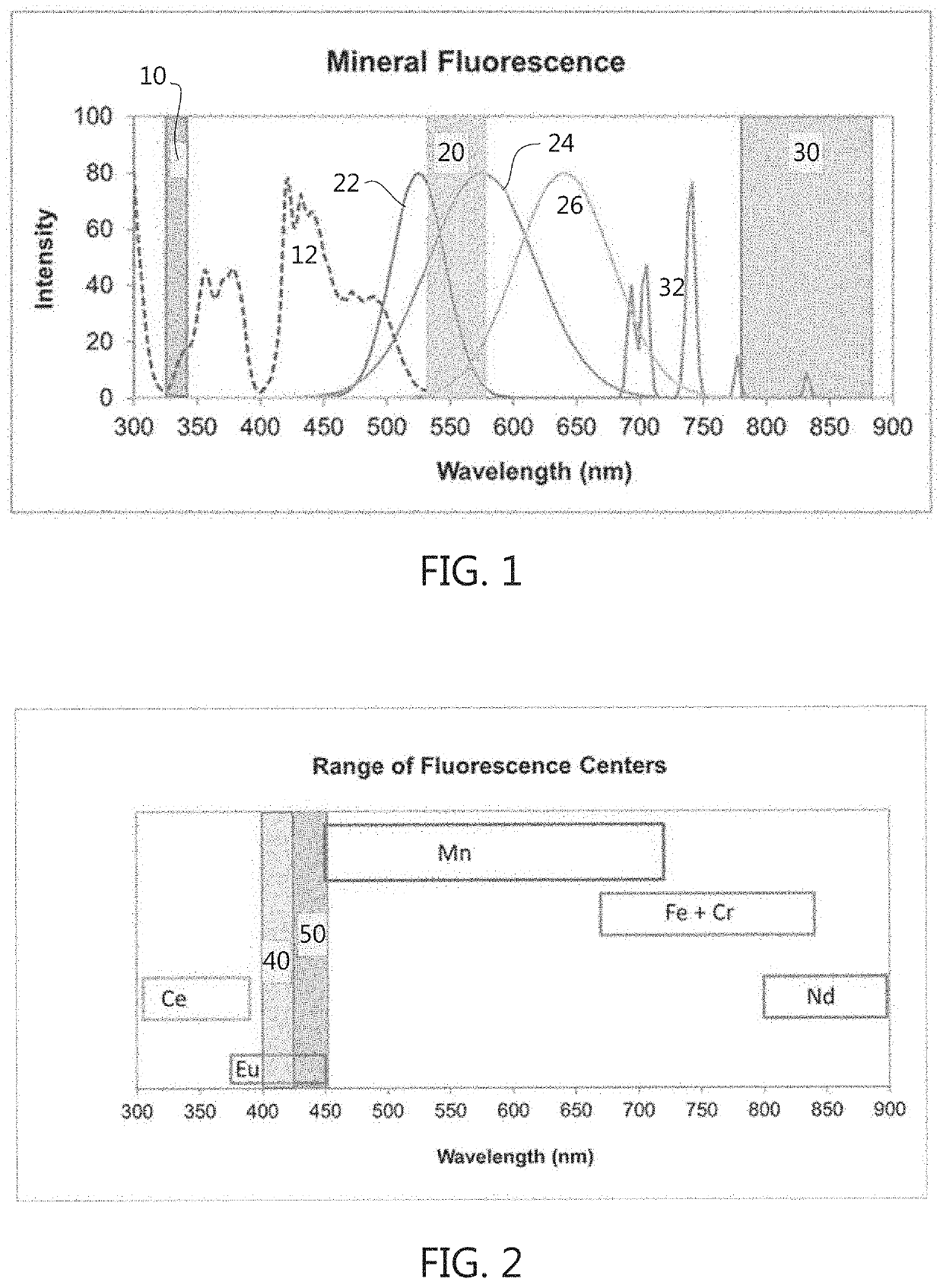
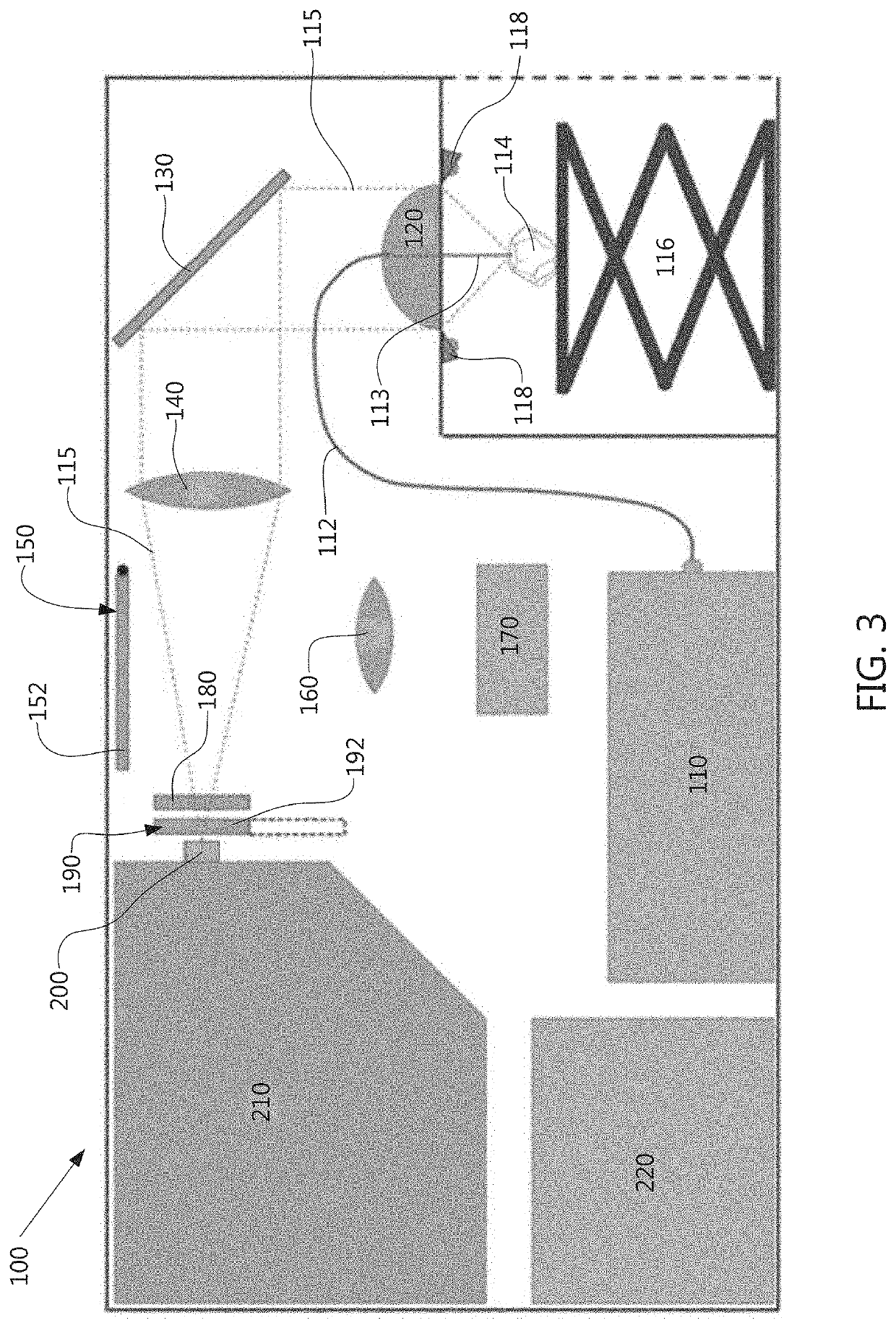
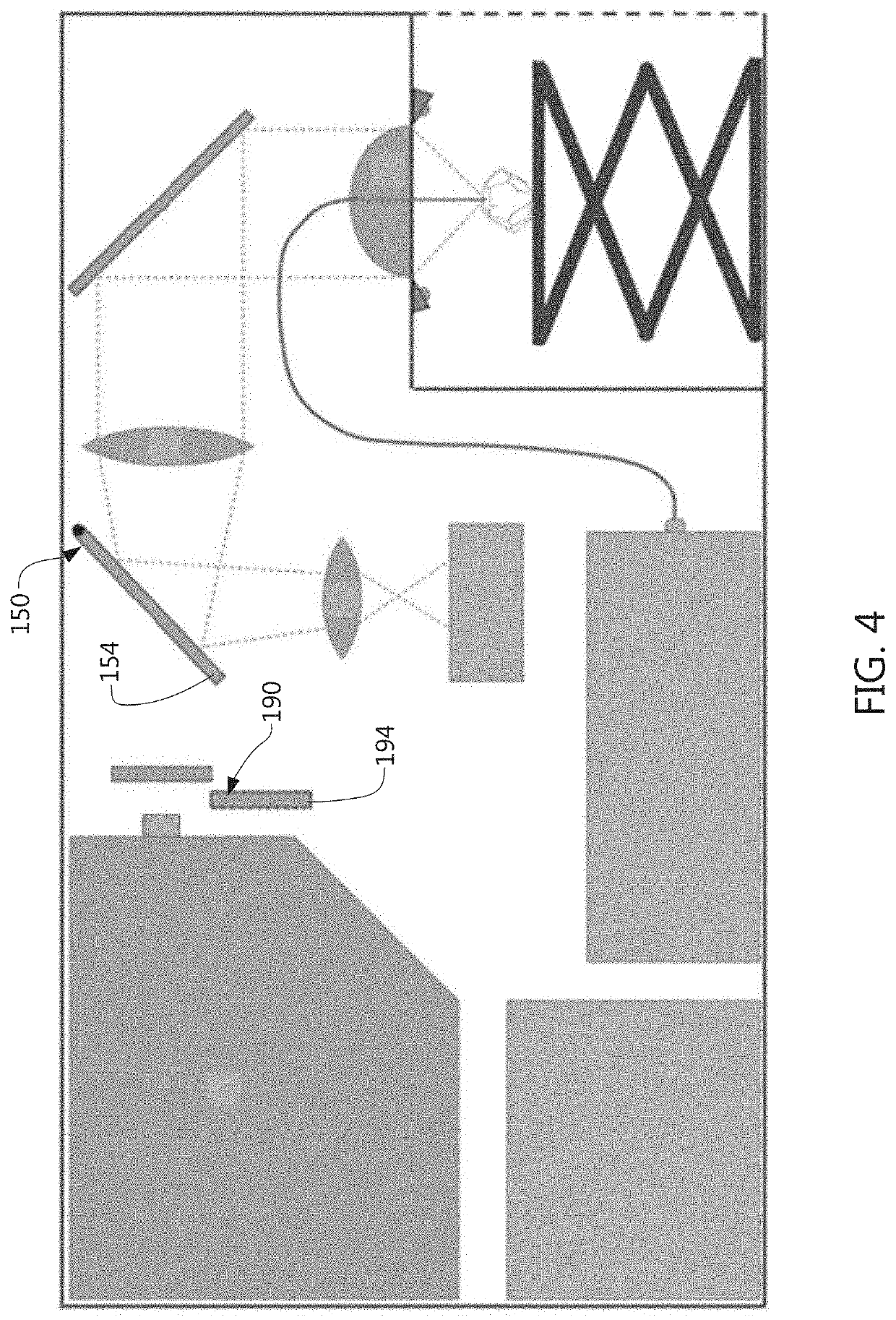
Raman Spectroscopy for Minerals Identification
A method for identifying minerals and other materials illuminates a mineral with monochromatic light for an illumination duration and collects scattered light using a Raman spectrometer detector and an aggregated or average Raman spectrum data is determined. True Raman spectrum data is determined by subtracting a blank spectrum. The true Raman spectrum data is compared to reference spectrums to identify the mineral or material. A display or output of one or more of: (a) a name and / or chemical composition of one or more identified minerals; (b) the true Raman spectrum data; and (c) the one or more reference spectrums; are provided. The monochromatic light preferably has a wavelength in the range of about 400 nm to about 425 nm and the Raman spectrometer detector is adapted to detect a Raman-shift range of about 100 cm−1 to about 1400 cm−1.
Owner:BARTHOLOMEW PAUL
Mineral Identification Using Mineral Definitions Including Variability
ActiveUS20140117230A1Improve mineral identificationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSpecial data processing applicationsX-rayMineral identification
An improved mineral analysis system includes mineral definitions that include not only characteristics of the minerals, but also variability in those characteristics. The variabilities allow the calculation of ranges of expected values for different quality of measurements, for example, for different numbers of x-ray counts. Match probabilities can therefore be calculated to more accurately determine the composition of a mineral sample.
Owner:FEI CO
Modularized rock core component spectral imaging scanning system
The invention discloses a modularized rock core component spectral imaging scanning system, which comprises a light source unit, a sample unit, and a spectrometer unit; the light source unit emits a light beam with a wide spectral line; the sample unit bears a rock core sample; the rock core sample born on the sample unit are uniformly exposed in the light beam with a wide spectral line emitted by the light source unit; light generated by diffuse reflection of the rock core sample enters the spectrometer unit; and the spectrometer unit performs spectral imaging according to the entered diffuse reflection light. Through the rock core component imaging spectra formed by the combination of image scanning technology with spectral light splitting technology, the modularized rock core component spectral imaging scanning system of embodiments of the invention not only provides the spatial form distribution of the rock core sample, but also provides sample spectral information accurate to pixel points in the imaging field of view, can assist in mineral identification, analysis, result visualization and post-treatment, and provides a new experimental platform for rock core mineral component analysis.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
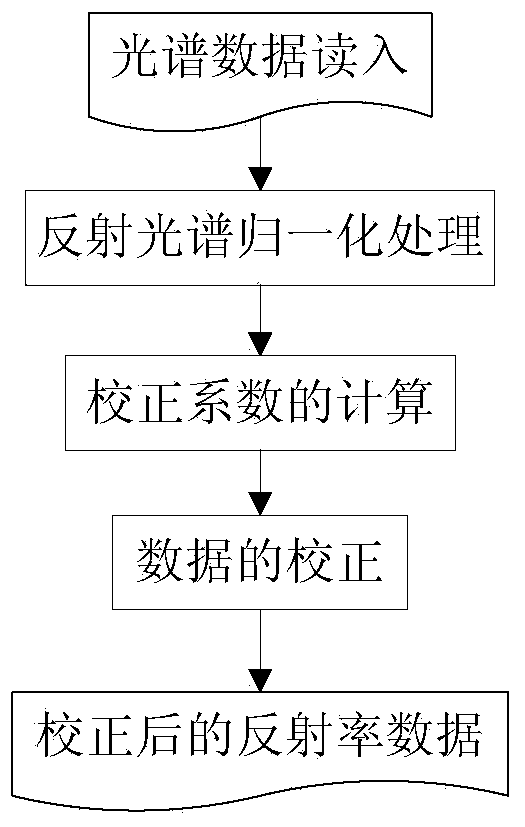
Spectral correction method of imaging spectrum reflectivity data
InactiveCN103592235AReduce leak rateReduce mistakesColor/spectral properties measurementsMineral identificationAtmospheric radiative transfer codes
A spectral correction method of imaging spectrum reflectivity data comprises the following steps: 1, reading in the spectrum data; 2, normalizing a reflection spectrum; 3, calculating a correction coefficient; and 4, correcting the data. The method can be used for correcting the imaging spectrum reflectivity data generated after the spectral reconstruction by utilizing an atmospheric radiative transfer model in order to reduce the error and reduce the information extraction leakage rate. The method has a practical value and a wide application prospect in the hyperspectral remote-sensing mineral identification field.
Owner:CHINA AERO GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY & REMOTE SENSING CENT FOR LAND & RESOURCES
Mineral identification method based on full-spectrum-segment hyperspectral remote sensing data
ActiveCN110261329ASolve problemsResolve identifiabilityColor/spectral properties measurementsPattern recognitionSpectral curve
A mineral identification method based on full-spectrum-segment hyperspectral remote sensing data is disclosed. The method comprises the following steps of (1) reading hyperspectral data in different wave band ranges; (2) carrying out minimum noise separation on an image and carrying out data dimensionality reduction; (3) calculating an information entropy of a pixel in a minimum noise separation result obtained in the step (2), setting a threshold value and extracting the pixel with a small information entropy; (4) corresponding the pixel extracted in the step (3) to an original image according to a pixel position, acquiring spectral characteristic parameter, and comparing with and marking the spectral characteristic parameter of a mineral spectral curve in a spectral library; (5) inputting a marked sample into a learning device and training the learning device to obtain a mineral identification result of each single wave band range; and (6) based on a main body majority voting method, fusing each wave band range identification result and completing full-spectrum-segment mineral identification. By using the method of the invention, higher identification accuracy can be acquired when prior information of an identification area is less, and full-spectrum-segment data can be used to make an identification result be comprehensive and accurate.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Mineral identification using sequential decomposition into elements from mineral definitions
ActiveUS20140117229A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesDecompositionMineral identification
Mineral definitions each include a list of elements, each of the elements having a corresponding standard spectrum. To determine the composition of an unknown mineral sample, the acquired spectrum of the sample is sequentially decomposed into the standard spectra of the elements from the element list of each of the mineral definitions, and a similarity metric computed for each mineral definition. The unknown mineral is identified as the mineral having the best similarity metric.
Owner:FEI CO
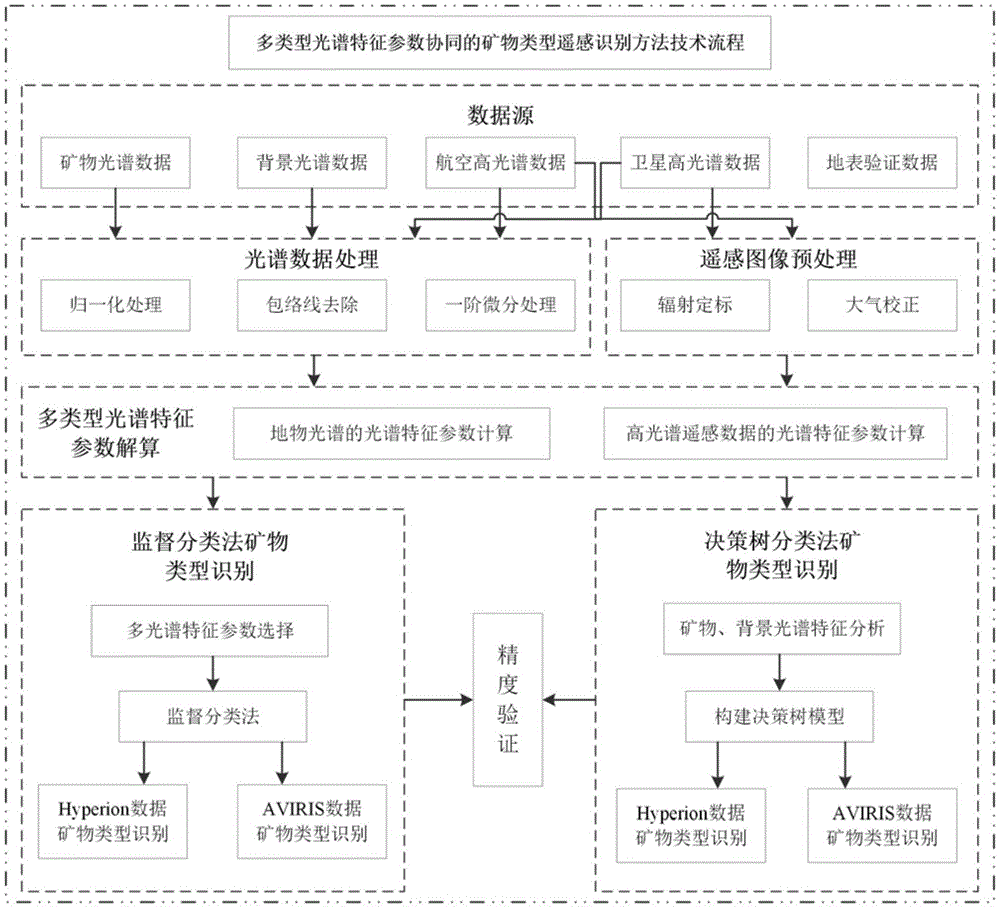
Mineral type remote sensing recognition method based on multi-type spectral feature parameter collaboration
InactiveCN105606537AReduce or attenuate the mixed spectrumReduce or weaken spectral distortionColor/spectral properties measurementsStatistical analysisMineral mapping
The invention discloses a mineral type remote sensing recognition method based on multi-type spectral feature parameter collaboration. The method includes the steps of: a. conducting spectral re-building on hyperspectral data; b. for different hyperspectral data, conducting spectrum resampling on typical mineral spectral data according to different sampling intervals; c. firstly conducting envelope removal treatment on hyperspectral data and a typical mineral spectrum, and then extracting multi-type spectral feature parameters respectively; d. calculating the information amount of different spectral feature parameter combinations through an optimum index factor, determining an optimum spectral feature parameter combination, and conducting mineral mapping experiment based on pattern recognition method; and e. firstly carrying out statistical analysis on the multi-type spectral feature parameters of the typical mineral spectrum, then referring to spectral feature parameter values corresponding to mineral end members in the hyperspectral data, constructing a research area mineral type recognition decision tree model, and conducting mineral mapping experiment. The mineral type remote sensing recognition method provided by the invention has high integral mineral recognition precision.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
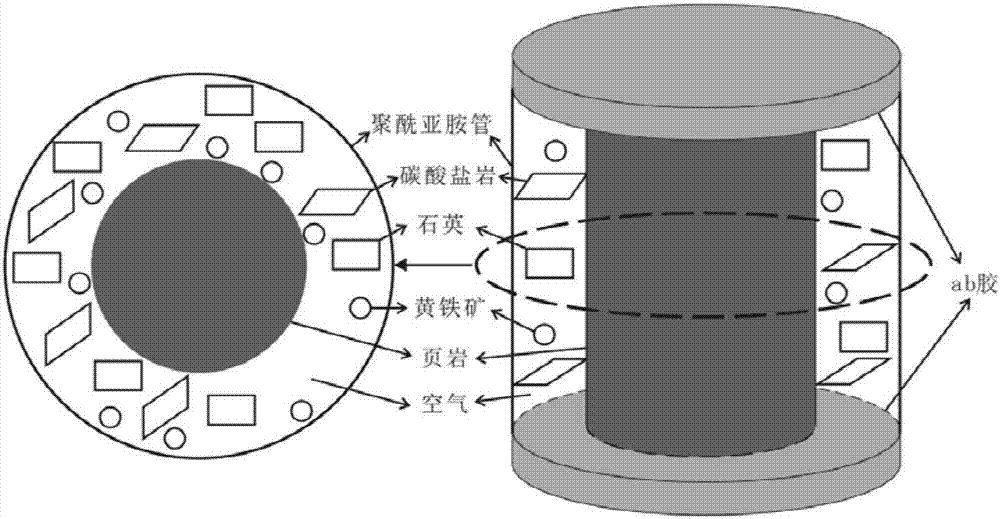
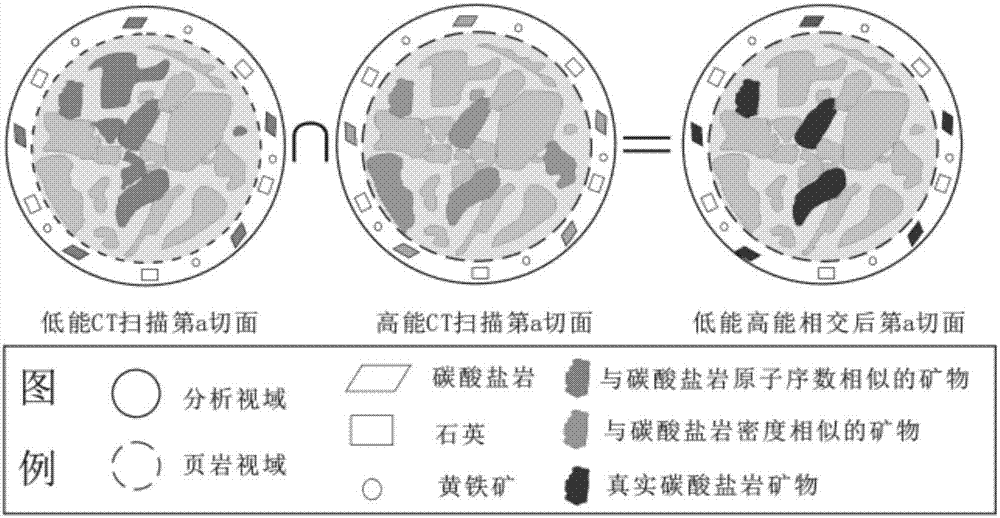
Device and method for quantitative recognition of rock sample of rock mineral by using dual-energy micron CT
ActiveCN106950231AEasy to makeNo damageMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationComputed tomographyThree-dimensional space
The invention mainly belongs to the field of petroleum and gas and digital rock physics, and particularly relates to a device and method for quantitative recognition of a rock sample of a rock mineral by using a dual-energy micron CT. The rock sample device comprises a rock sample and a standard sample formed by one or more rock sample components; and the rock mineral is identified by using a dual-energy micron CT rock sample scanning device and a gray-scale segmentation method. The device has the characteristics that sample preparation is simple, a sample is free of an injury, the mineral identification accuracy rate is high, three-dimensional spatial distribution characteristics of the mineral can be reflected, and the technical problem that the accuracy of rock mineral identification in the three-dimensional space is low in the prior art is solved.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
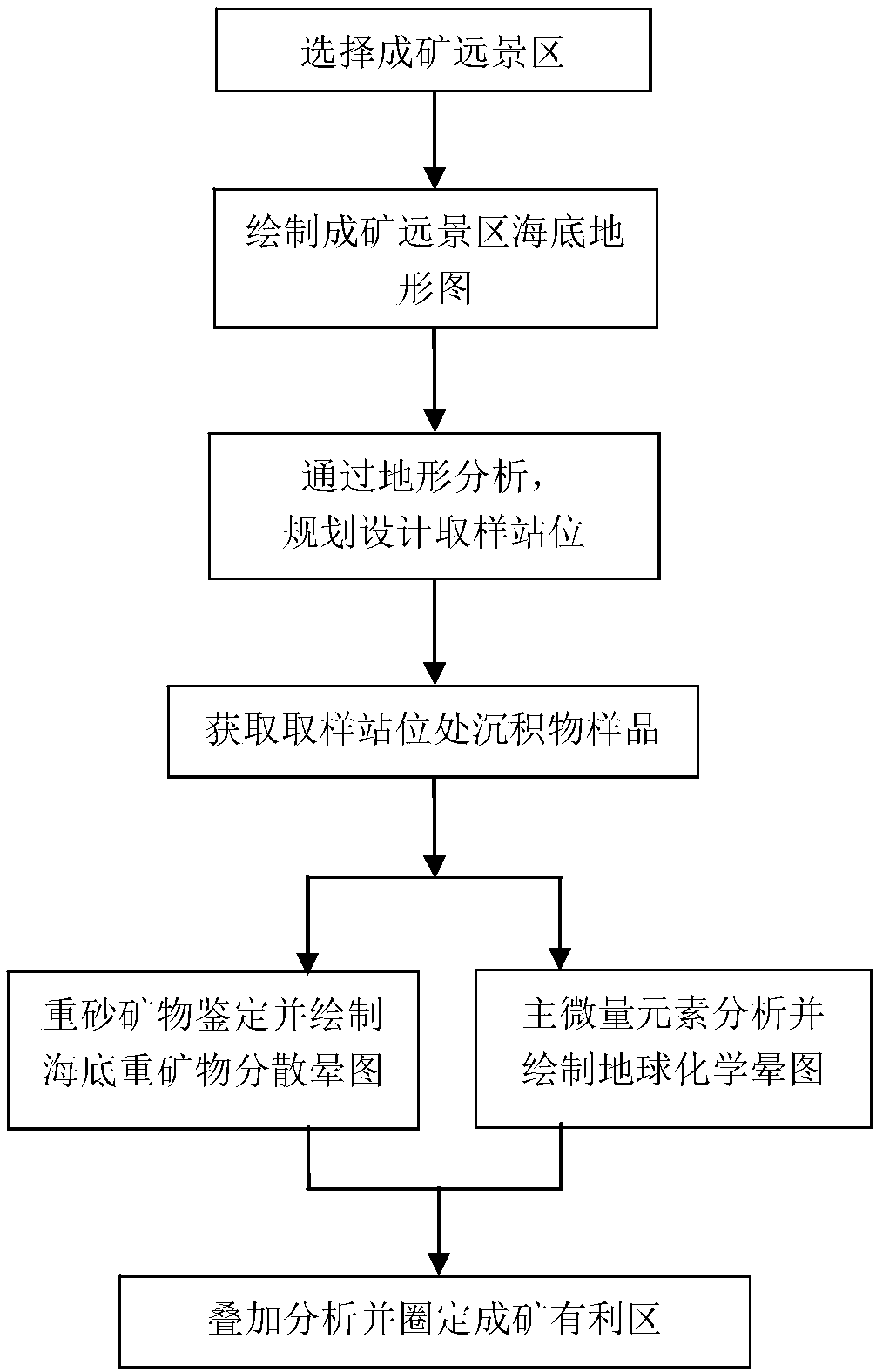
Seabed sulfide ore prospecting method based on topographic analysis
ActiveCN109188556AReasonable and efficient layoutImprove rationalityGeological measurementsOcean bottomSeabed sediment
The invention discloses a seabed sulfide ore prospecting method based on topographic analysis, which comprises the following steps: step 1: selecting a mineralizing prospect area; step 2: searching for topographic data of the mineralizing prospect area and drawing a topographic map of the seabed; step 3: analyzing the topographic map of the seabed, and planning and designing a sampling station; step 4: obtaining a sediment sample at the sampling station position in the step 3; step 5: performing heavy sand mineral identification and main trace element analysis on the sediment sample, and drawing a seabed heavy mineral dispersion halo map and a geochemical halo map; step 6: performing overlay analysis on the seabed heavy mineral dispersion halo map and the geochemical halo map, and defininga favorable mineralization area in combination with the topographic analysis. The method in the invention optimizes and innovates the sampling station setting of the seabed sediment, and the samplingstation setting is more reasonable and effective; combined with the heavy mineral and geochemical methods, a better detection effect is achieved for the inactive hydrothermal zone concealed sulfide and secondary enrichment mineralization; and the cost is low compared with other methods.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR
Universal tool for automated gem and mineral identification and measurement
ActiveUS9075015B2The process is fast and accurateRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringTelecommunications linkRechargeable battery pack
A tool employs Raman spectroscopy, optical imaging, physical measurements, smart software applications, and custom databases for automated on-site gem and mineral identification, measurement, and authenticity verification. Operators with no technical expertise can perform on-site, fast, nondestructive gem and mineral characterization. A custom smart application for data handling and processing enables applicability with a variety of processors. Automated generation of Raman spectral signatures and subsequent correlation to spectral fingerprints of known materials enables gem and mineral identification and verification in field settings. A single tool provides high resolution digital optical imaging and physical measurement capabilities, enables comprehensive sample characterization and reporting that currently requires multiple tools and significant labor. The Tool also provides the capability for sample analysis, requiring an additional level of technical expertise, to be done remotely at another location by the transmission of the data via a communications link. A rechargeable battery pack is included.
Owner:SHAPIRO FREDERICK W
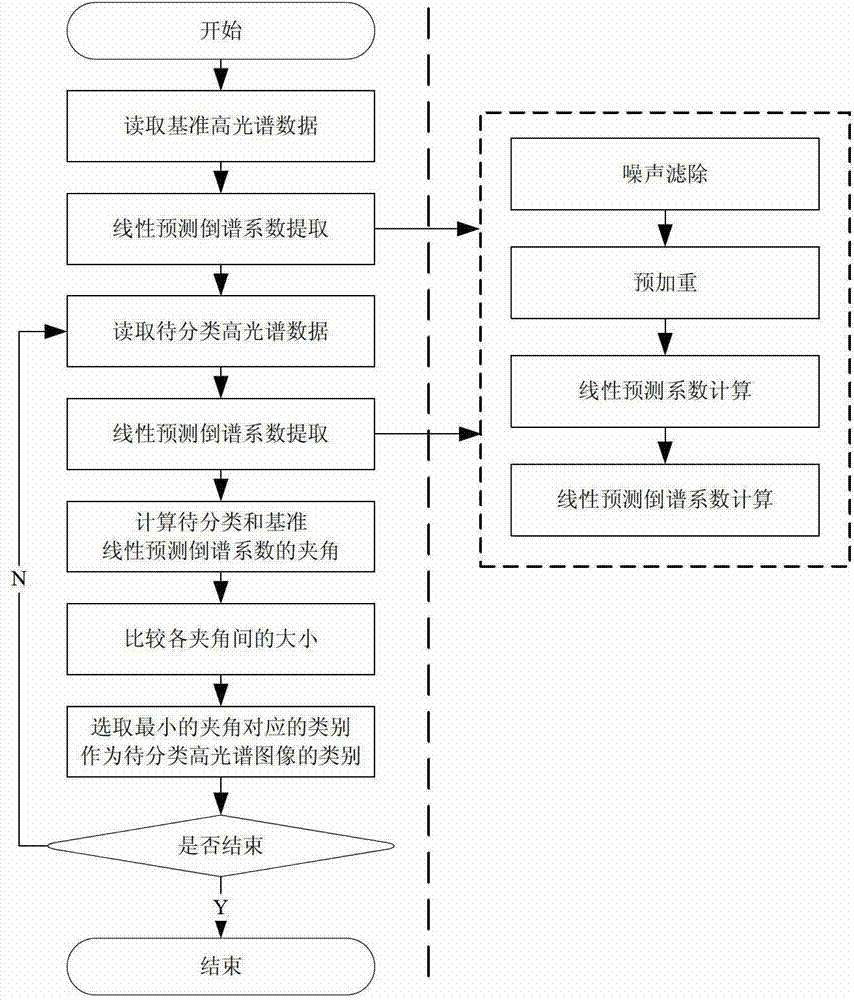
High-spectrum image classification method based on linear prediction cepstrum coefficient
InactiveCN102880861AOvercoming the Huges phenomenonReduce distractionsCharacter and pattern recognitionClassification methodsHyperspectral image classification
The invention discloses a high-spectrum image classification method based on linear prediction cepstrum coefficient, and solves the shortages in the prior that the complexity is high, real-time capability is bad, Huges phenomenon exists, prior information of a sample is needed, and wide application is difficult to realize. The method provided by the invention applies the linear prediction cepstrum coefficient in voice signal identification in spectrum data of a spectrum image and comprises the following steps: firstly, performing spectrum noise filtering on the high-spectrum data; secondly, performing pre-emphasis on the spectrum data subjected to the noise filtering for enhancing characteristics of the spectrum data; after that, utilizing Levinson-Durbin algorithm for solving a linear prediction coefficient and converting the linear prediction coefficient to the linear prediction cepstrum coefficient; and finally, matching the linear prediction cepstrum coefficient, and performing description with vector quantity included angles, wherein the smaller the included angles, the higher the similarity between classification results and standard surface configurations is. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of low complexity, high real-time capability, good classification effect and no-prior-information for the sample, and can be applied in aspects such as surface features classification and mineral identification of the high-spectrum image, etc.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
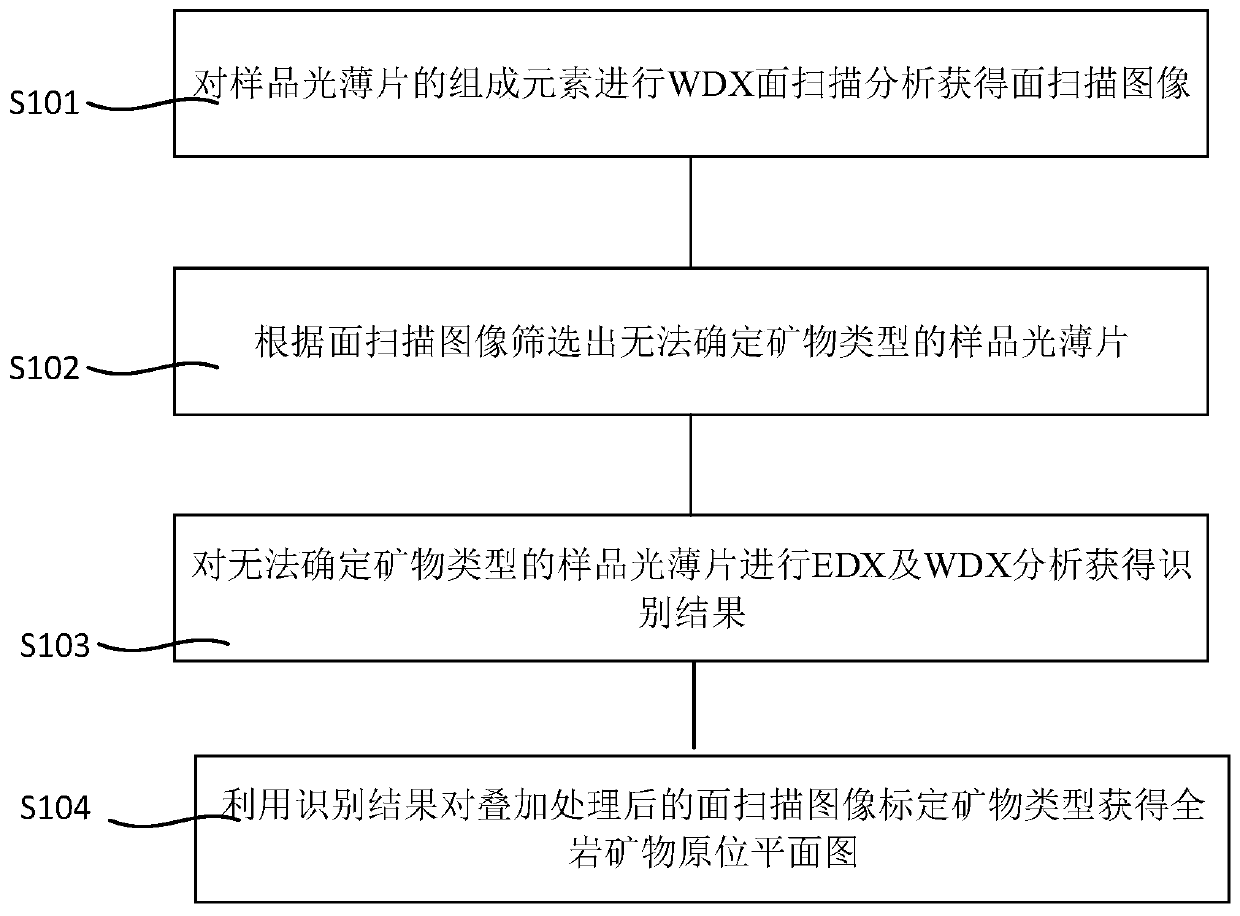
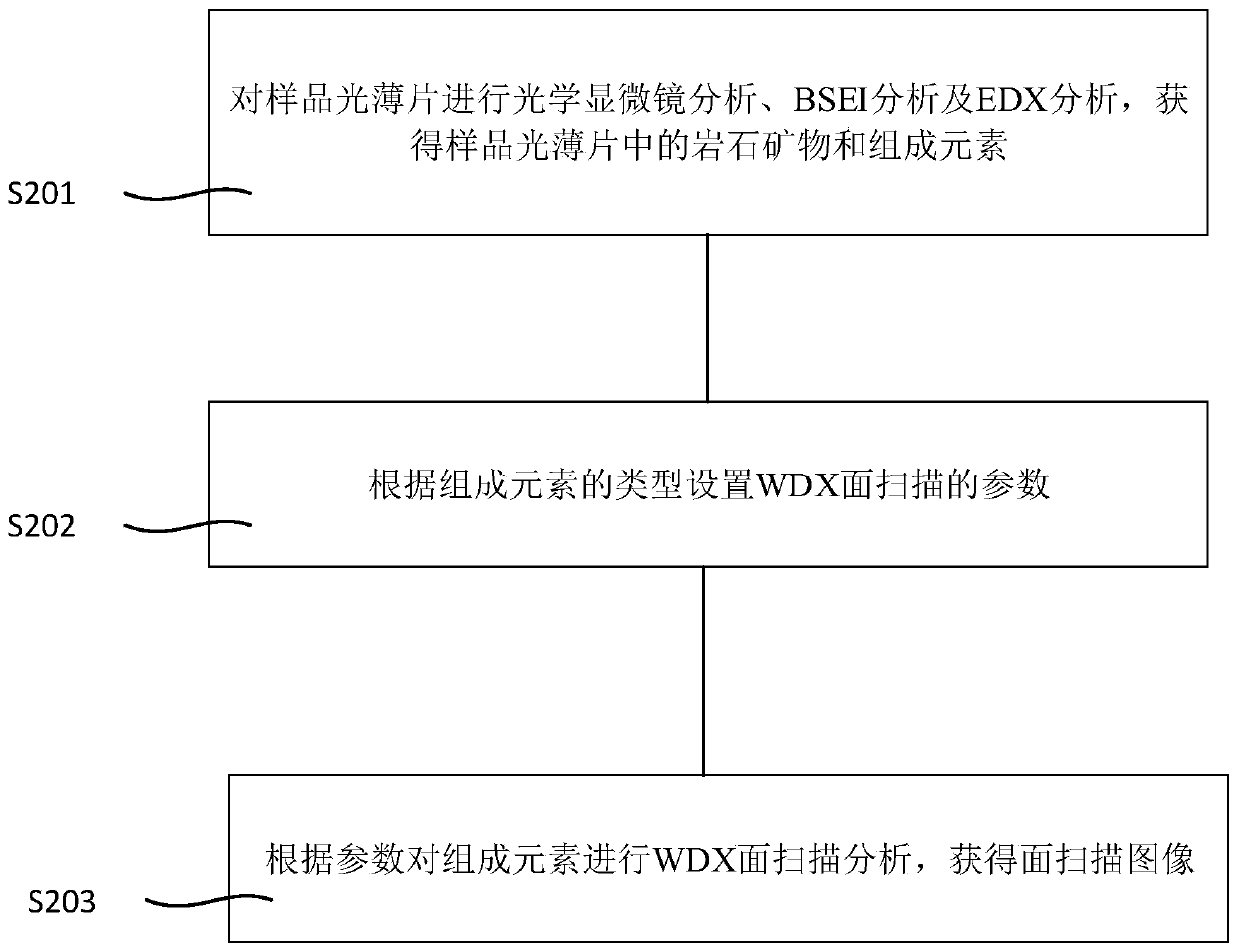
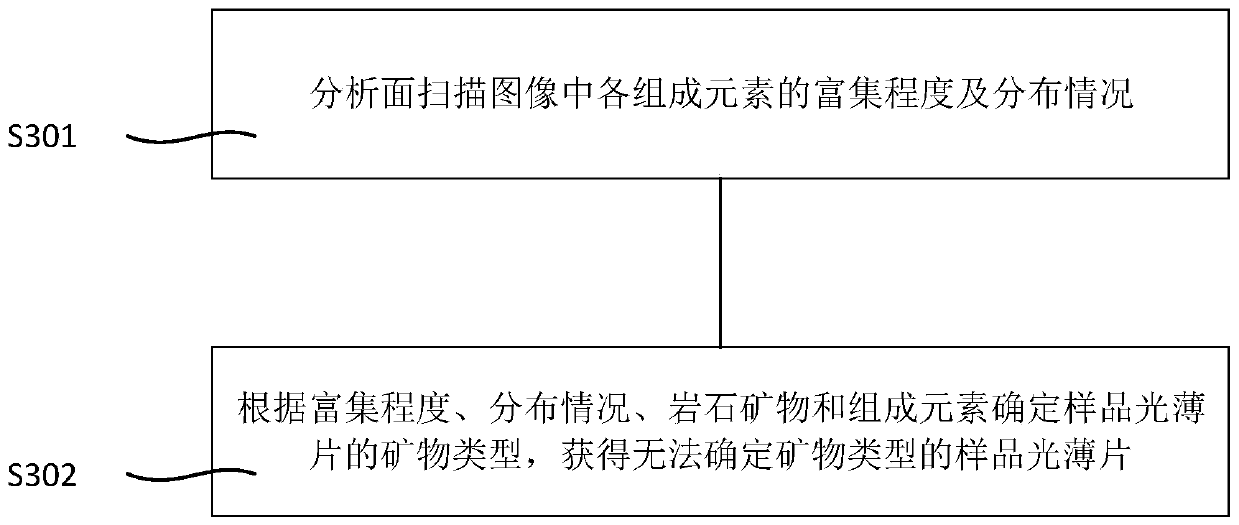
EPMA-WDX total rock mineral identification and plane imaging method and device
PendingCN111189864AComprehensive recognitionAccurate identificationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionImage calibrationMineral identification
The invention provides an EPMA-WDX total rock mineral identification and plane imaging method and device. The method comprises the steps of: conducting WDX surface scanning analysis on constituent elements of a sample light sheet to obtain a surface scanning image; according to the surface scanning image, screening out a sample light sheet which cannot determine the mineral type; carrying out EDXand WDX analysis on the sample light sheet which cannot determine the mineral type to obtain an identification result; and calibrating the mineral type of the surface scanning image subjected to superposition processing by using the identification result to obtain a total rock mineral in-situ planar graph. The finally formed in-situ total rock mineral plane distribution diagram is very accurate, visual and objective.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Mineral identification using sequential decomposition into elements from mineral definitions
ActiveUS9048067B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesDecompositionMineral identification
Mineral definitions each include a list of elements, each of the elements having a corresponding standard spectrum. To determine the composition of an unknown mineral sample, the acquired spectrum of the sample is sequentially decomposed into the standard spectra of the elements from the element list of each of the mineral definitions, and a similarity metric computed for each mineral definition. The unknown mineral is identified as the mineral having the best similarity metric.
Owner:FEI CO
Mineral identification method based on reflection spectrum
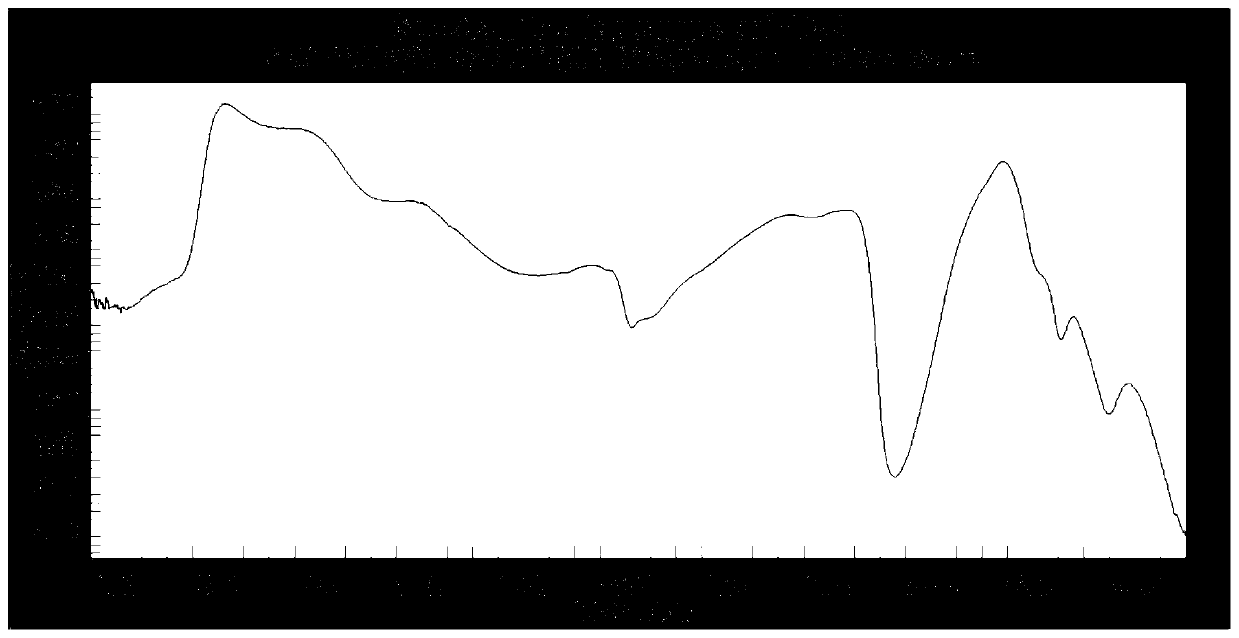
InactiveCN109959624ASolve the accuracy problemResolution timeColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectrographLength wave
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of mineral identification, proposes a mineral identification method based on reflection spectrum. The method comprises the following steps: S1, carrying out data measurement; to be specific, measuring a plurality of sampling points in a sample by using a spectrograph to obtain a measurement value; S2, carrying out data processing; to be specific,acquiring a spectral waveform of each sampling point based on the measurement value of each sampling point in the S1, carrying out splicing correction, and then carrying out equalization to obtain aspectral waveform of the sample; S3, carrying out mineral identification; to be specific, carrying out calculation on the spectral waveform data of the sample in the S2 to obtain the position of a characteristic valley, carrying out standard matching on typical minerals in a spectrum database based on the wavelength of the characteristic valley to obtain a matched mineral, and then comparing the spectral waveform of the matched mineral with the spectral waveform of the sample to obtain minerals that may exist in the sample; and S4, carrying out data calculation; to be specific, carrying out fitting calculation on the minerals that may exist in the sample to obtain mineral compositions in the sample and relative content of all compositions. Therefore, problems of low recognition precision and long recognition time in the prior art are solved.
Owner:中国黄金集团石湖矿业有限公司
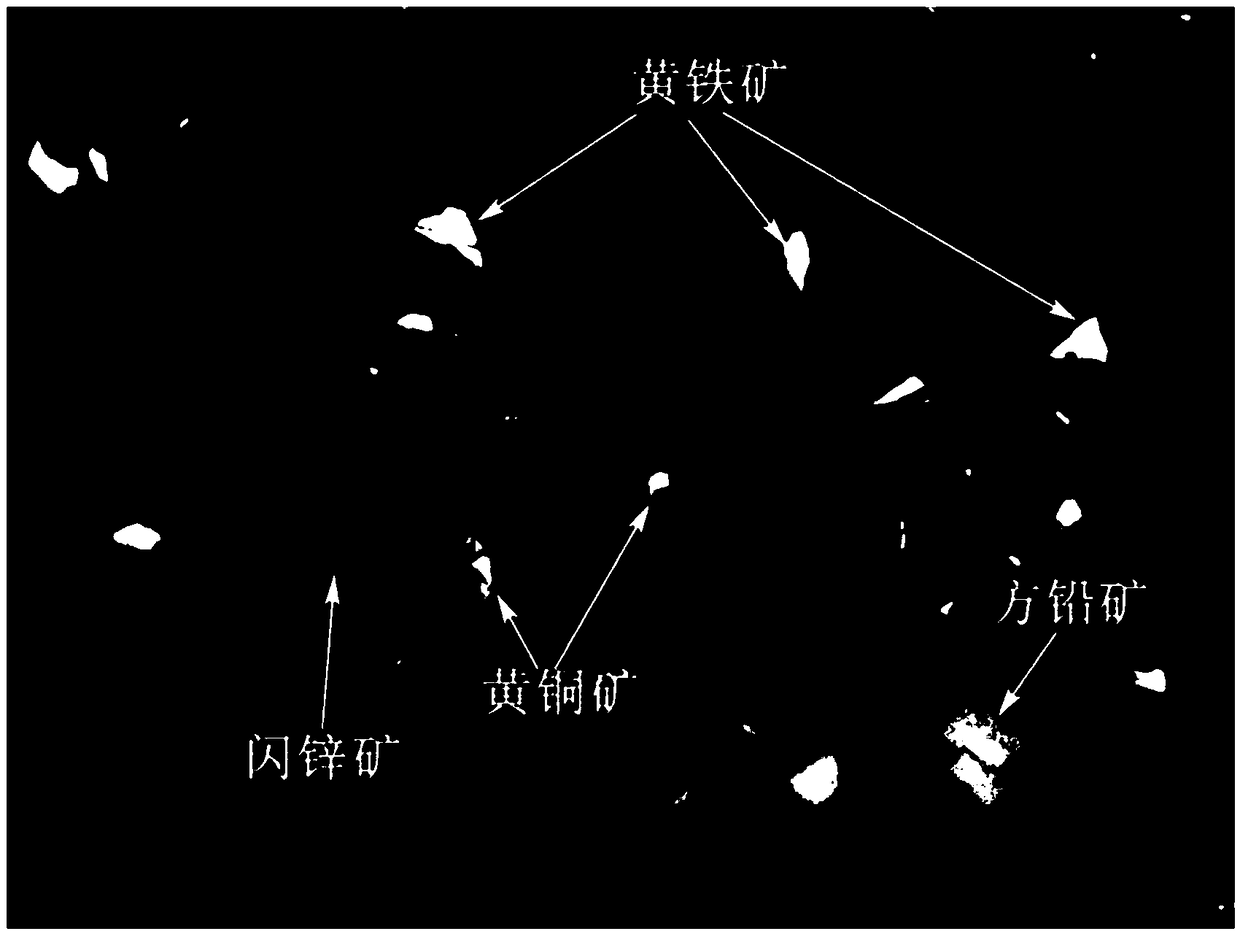
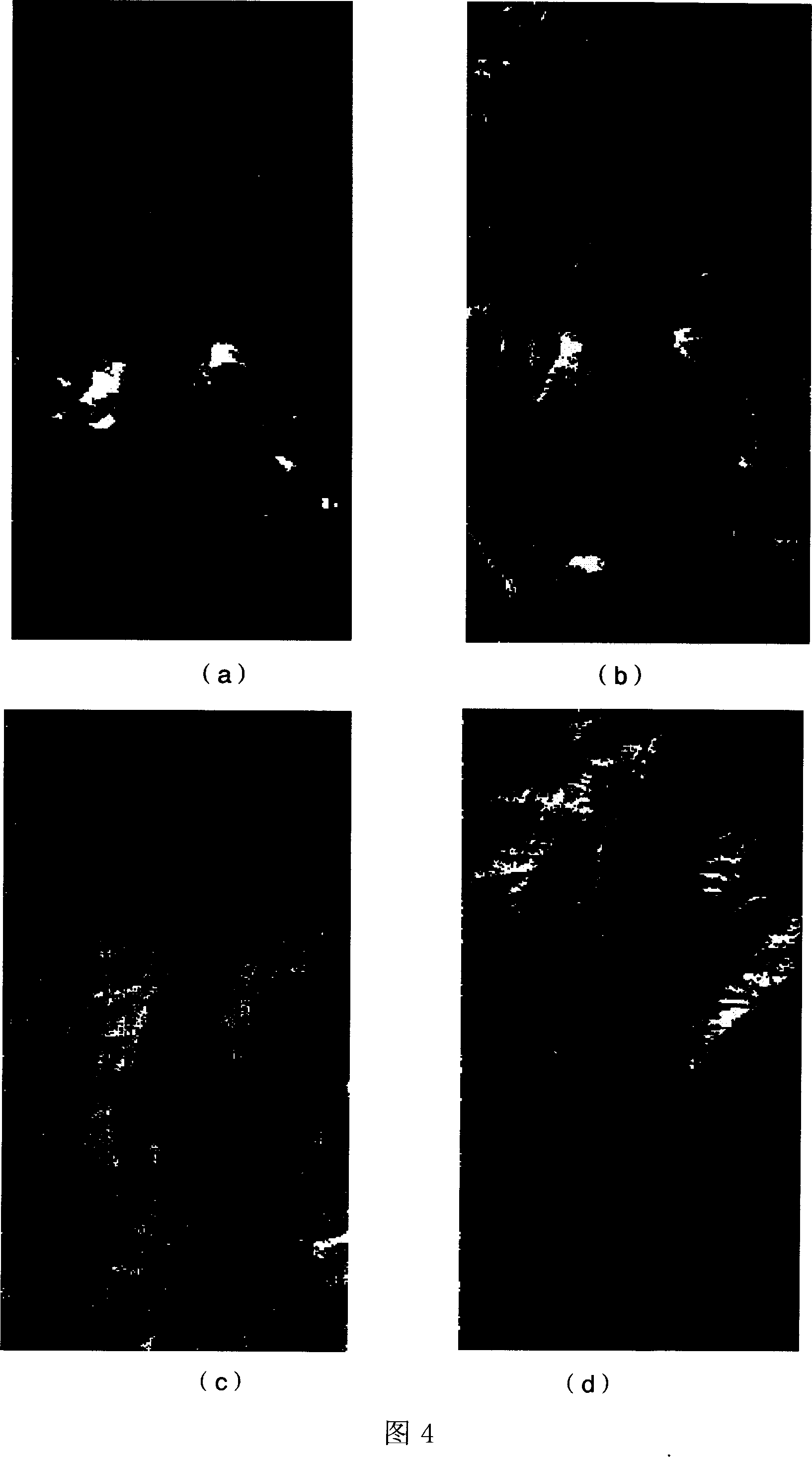
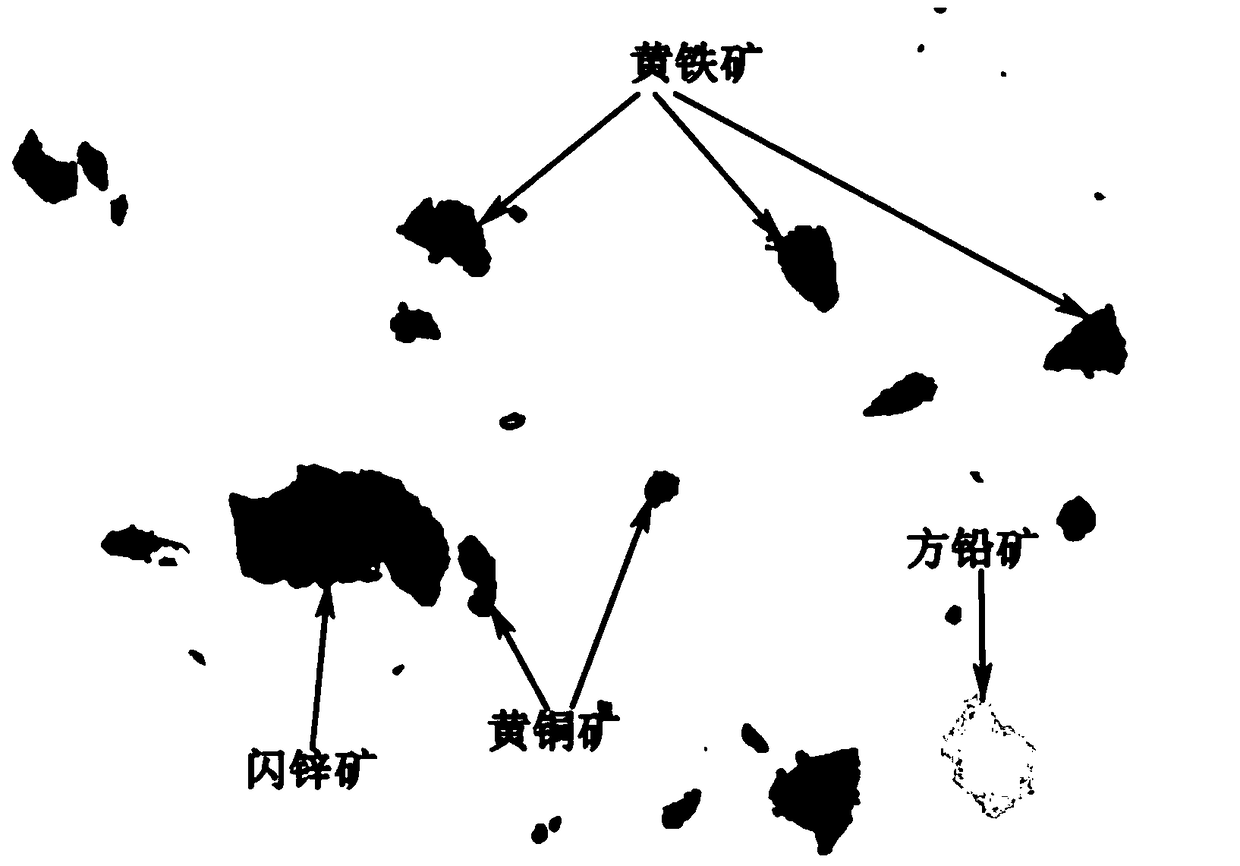
Automatic recognition method for optical microscopic images of metal sulfide minerals
PendingCN109117759AEfficient identificationAccurate identificationAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsMicroscopic imageGray level
The invention discloses an automatic identification method for optical microscopic images of metal sulfide minerals. The prepared rock and mineral sample light sheet is placed on a stage of an opticalmicroscope. The HSV value of each metal sulfide in the image is measured by CCD, and the database of HSV value of metal sulfide is established as the standard of automatic identification of metal sulfide. The metallic sulfide particles are extracted from the samples and their HSV values are measured. According to the HSV value of the mineral particles in the image, the established mineral database is used as a standard to identify the mineral particles, and different minerals are painted with different pseudo-colors to show the difference, thus completing the automatic identification of metalsulphides. The method can effectively solve the problem that the mineral gray level is close to the difficult to distinguish, can accurately and effectively identify the metal sulfide of the rock andmineral samples, and can improve the accuracy of mineral identification.
Owner:BEIJING MINING & METALLURGICAL TECH GRP CO LTD
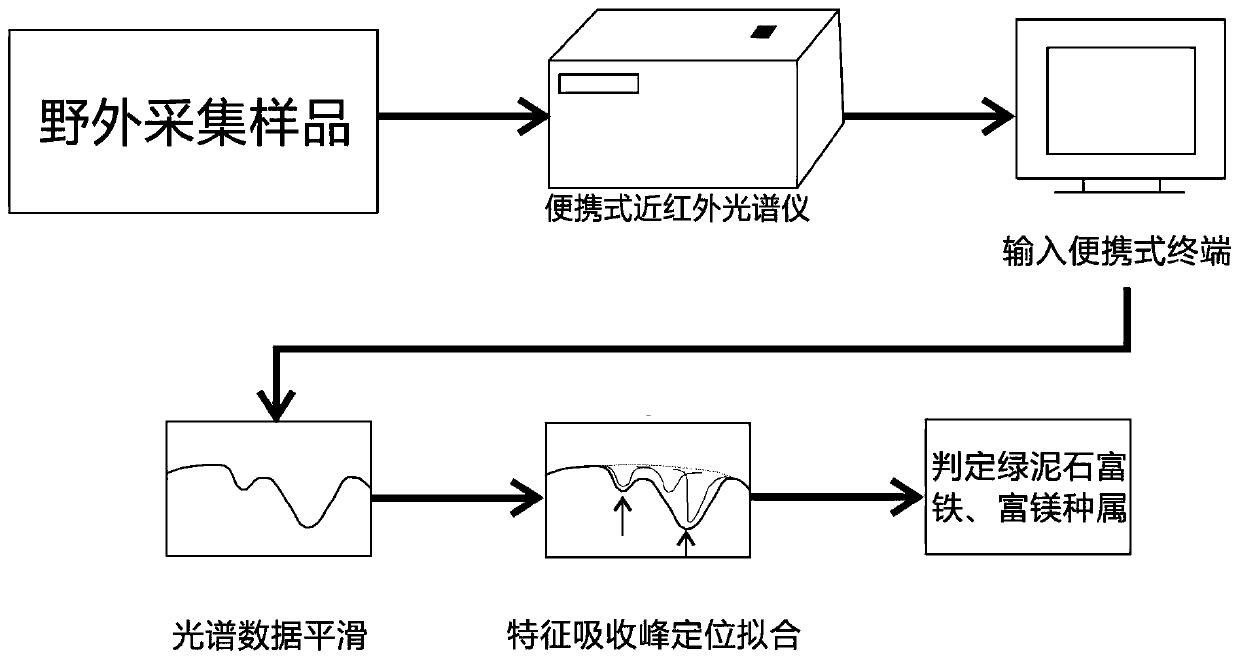
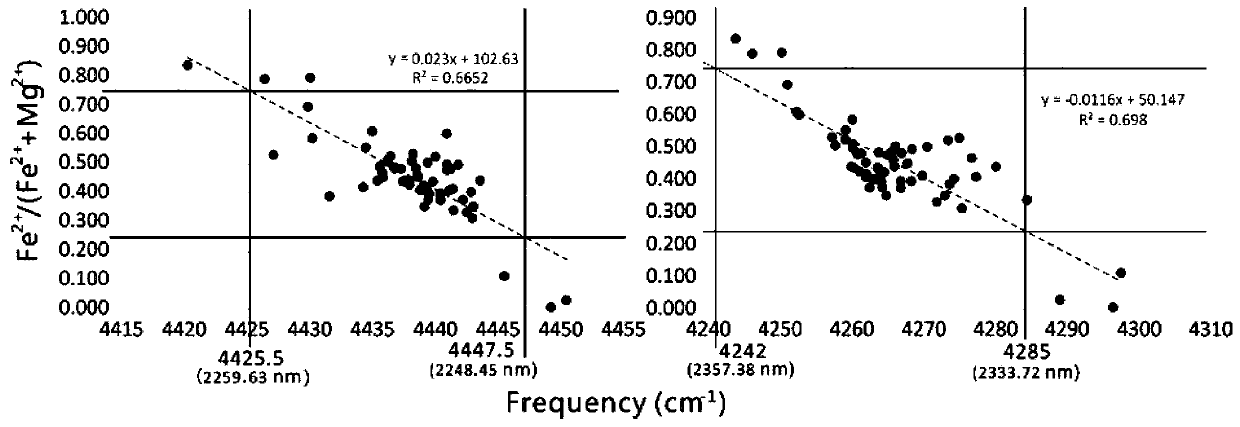
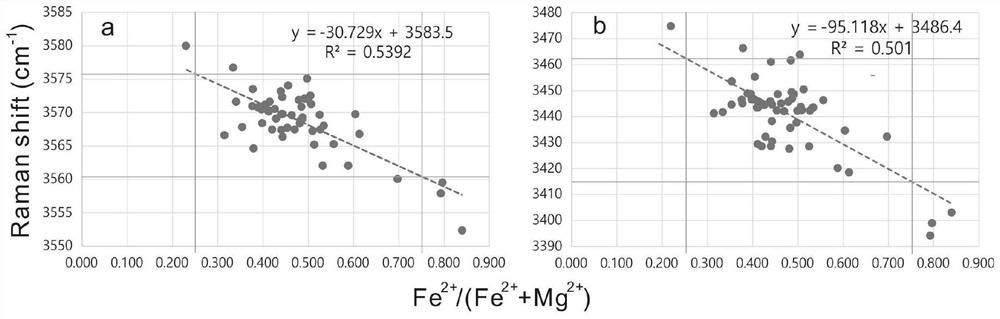
Chlorite mineral species identification method based on near infrared reflectance spectroscopy
ActiveCN110618106ATo meet the needs of rapid identification of chlorite mineral subspeciesLow preparation costMaterial analysis by optical meansStatistical relationData treatment
The invention belongs to the technical field of chlorite mineral identification and discloses a chlorite mineral species identification method based on near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a near infrared reflection spectrum of a field chlorite mineral species through nondestructive surface measurement; performing smooth denoising processing on spectrum data, and determining a characteristic absorption peak by adopting Gaussian-Lorentzian function fitting; performing spectral curve smoothing data preprocessing on the near infrared reflection spectrum data in a data processing terminal, and performing peak-differentiating and imitating on the characteristic absorption peak of the curve subjected to a spectrum data smoothing link; and according to a linear statistical relationship between a position of the characteristic absorption peak and content of iron in chlorite, rapidly identifying the subspecies type of a chlorite mineral according to the position of the characteristic absorption peak. The method disclosed by the invention can enable field staff to obtain subspecies information of the chlorite mineral in an alteration zone in real time, shortens time required by laboratory rock and mineral identification, eliminates a sample preparation step, is time-saving and labor-saving and also saves fund.
Owner:XIAN CENT OF GEOLOGICAL SURVEY CGS
Raman Spectroscopy for Minerals Identification
ActiveUS20200064191A1Reducing sample-heatingRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryOptical spectrometerSpectrograph
An apparatus for identifying materials. The apparatus includes a laser device adapted to produce monochromatic light in the wavelength range of about 400 nm to about 425 nm, a first set of optical components for focusing the laser light on a material sample positioned on a sample stage, a second set of optical components for transmitting light reflected from the material sample, and a spectrograph adapted to receive light reflected from the material sample via at least part of the second set of optical components and adapted to collect data in the Raman shift range of about 100 cm−1 to about 1400 cm−1. The first set of optical components includes a fiber optic cable adapted to transmit the laser light to the material sample. The second set of optical components includes an objective lens having an opening adapted to receive the fiber optic cable.
Owner:BARTHOLOMEW PAUL
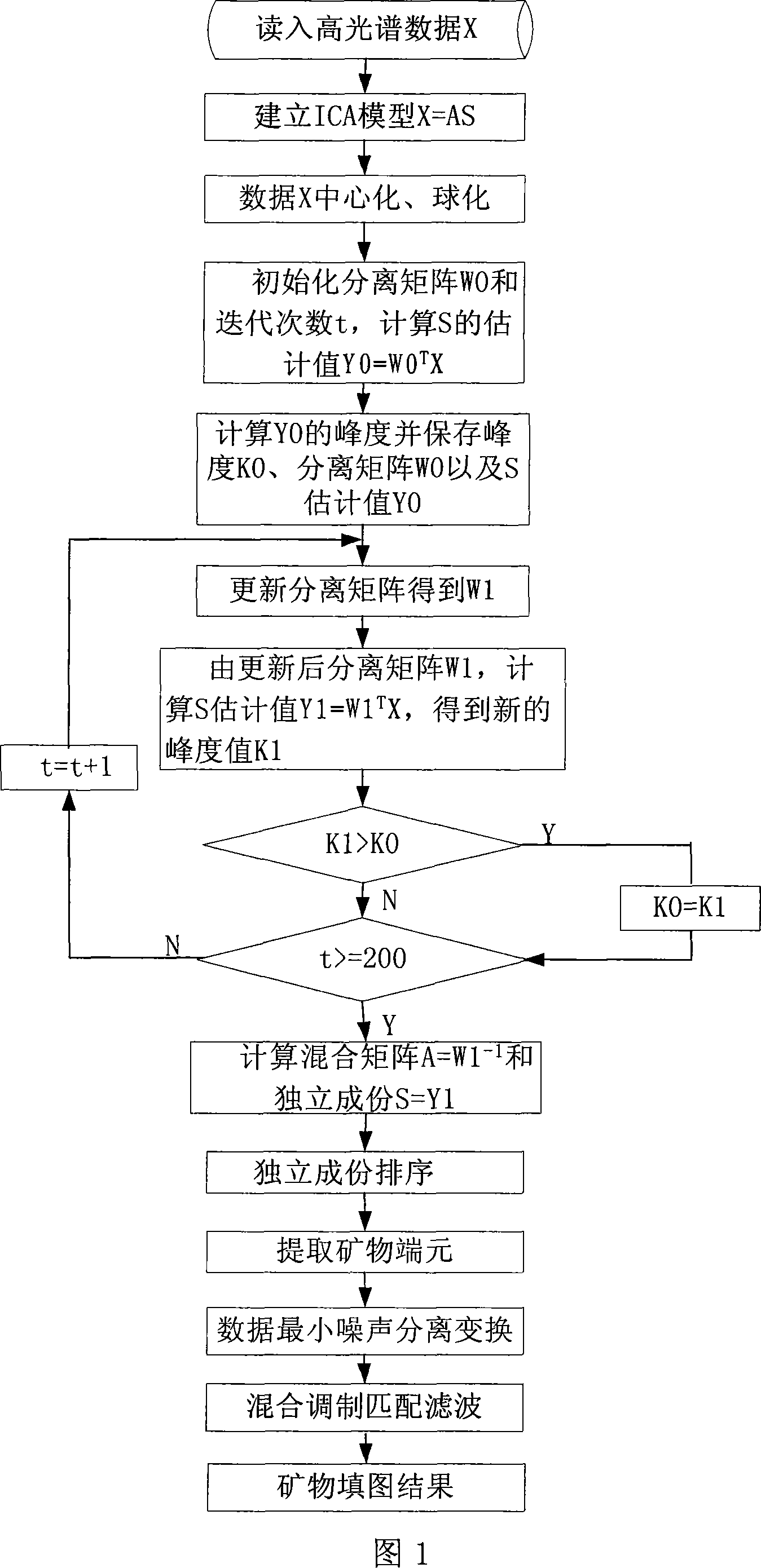
High spectrum mineral map plotting method
InactiveCN101109658AImprove mapping accuracyInsufficient prior knowledge to limitSpectrum investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsPrior informationData center
The invention relates to a method for mapping mineral by taking use of the statistics characteristics of data without prior information for a high spectrum data, which comprises the following procedures: reading in the high spectrum data, centralizing the data, sphericalizing the data, setting up an analysis model of independent components, rating the independent components, extracting end members of mineral, min. noise separating and transforming, mixing, modulating, matching and filtering, mapping mineral. The method allows to extract end members of eroded mineral based on the analysis model of independent component by taking use the hi-order statistics feature of data themselves without unknowing any prior information, and to map eroded mineral by a way based on mixing, modulating, matching and filtering. The method avoids in the mineral identification the influence of uncertainness of spectrum feature of mineral caused by spectrum mixing, illumination, and mineralizing condition, combines the restricting condition of end-member content to be positive and 1 in the linear mixing decomposition theory, has effectively improves the detection limit for mineral and mapping mineral accuracy.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
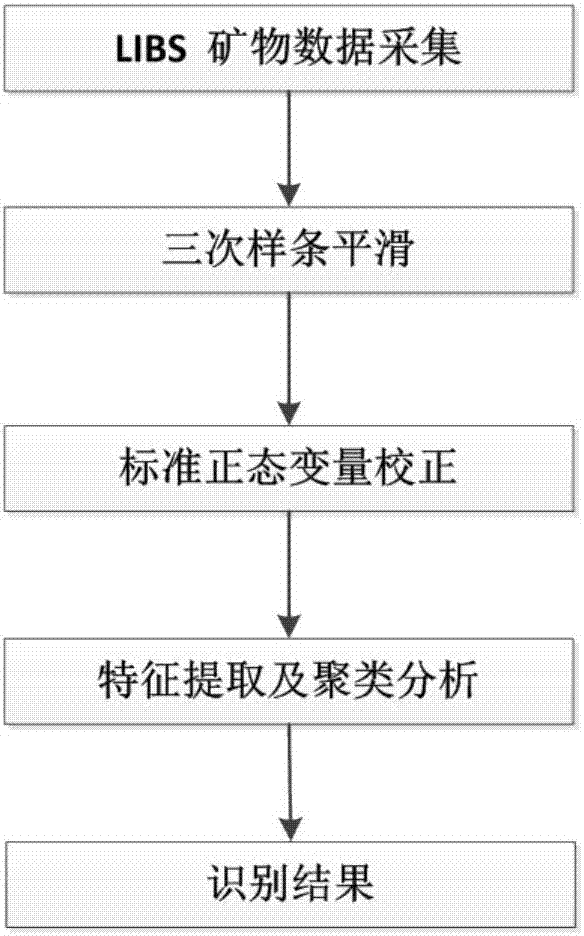
Mineral identification method based on laser-induce breakdown spectroscopy and linear discriminant analysis
InactiveCN107305187AReal-time measurementHigh sensitivityAnalysis by thermal excitationData acquisitionLaser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
The invention belongs to the field of geological prospecting and specifically relates to a mineral identification method based on laser-induce breakdown spectroscopy and linear discriminant analysis. The method comprises the following steps: 1) collecting data on the basis of an LIBS (Laser-induced Breakdown Spectroscopy) optical system; 2) adopting a cubic spline interpolation algorithm for correcting various spectrogram wavelengths, thereby causing the collected data be consistent; 3) performing standard normal variable correction on the smoothed spectroscopic data, thereby acquiring a spectrum after the standard normal variable correction; 4) utilizing a linear discriminant analysis method to perform feature extraction and clustering analysis on the spectroscopic data after the standard normal variable correction. According to the method, the quick and accurate analysis and discrimination for a mineral sample can be realized in the manner of collecting a certain quantity of analysis samples for forming a training sample and adopting a statistic mode algorithm for acquiring the inherent space structure information of the sample.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF URANIUM GEOLOGY
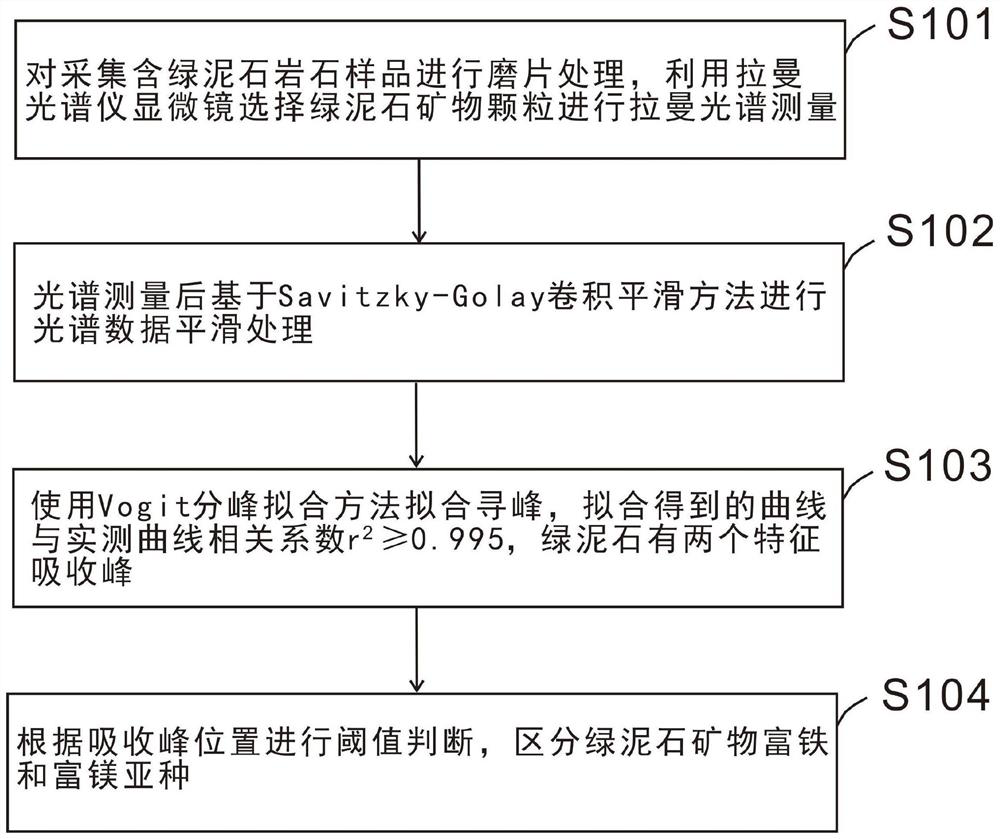
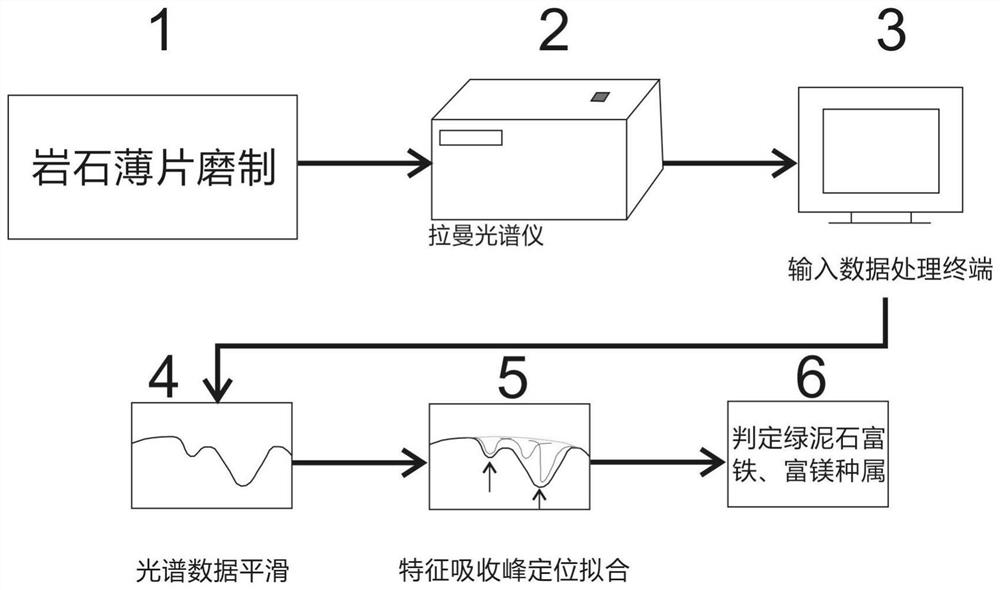
Chlorite mineral variety identification method based on Raman spectroscopy
PendingCN112362636ATo meet the needs of rapid identification of chlorite mineral subspeciesEliminate tedious calculation stepsPreparing sample for investigationRaman scatteringSpectral curvePhysical chemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of chlorite mineral identification, and discloses a chlorite mineral variety identification method based on Raman spectroscopy. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a Raman spectrum of a chlorite mineral sheet; carrying out smooth denoising processing on the spectral data, and determining the position of a characteristic absorption peak by adopting Voigt function fitting; carrying out spectrum curve smooth data preprocessing on the raman spectral data in a data processing terminal, and carrying out peak position fitting and positioning of thecharacteristic absorption peak on a curve passing through a spectrum data smooth link; and quickly identifying the subspecies category of the chlorite mineral according to the linear statistical relationship between the position of the characteristic absorption peak and the chlorite iron content and the position of the characteristic absorption peak. The relative iron and magnesium content information of the chlorite mineral in an alteration zone is obtained through Raman spectroscopy, the time required for obtaining the iron and magnesium content through a traditional electronic probe methodis shortened, time and labor are saved, and meanwhile expenditure is saved.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Mineral identification using mineral definitions having compositional ranges
ActiveUS9091635B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationMineral identificationComputer science
Determining the composition of a mineral sample entails comparing measurements of a sample to mineral definitions and determining a similarity metric. The mineral definition includes a subspace of compositional values defined by end members. The similarity metric is related to a projection of the measured data point onto the subspace or onto an extension of the subspace.
Owner:FEI CO
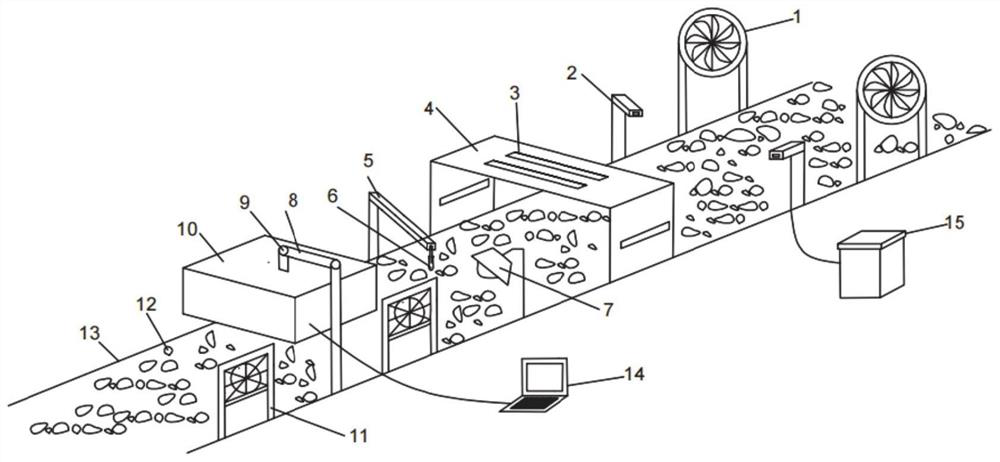
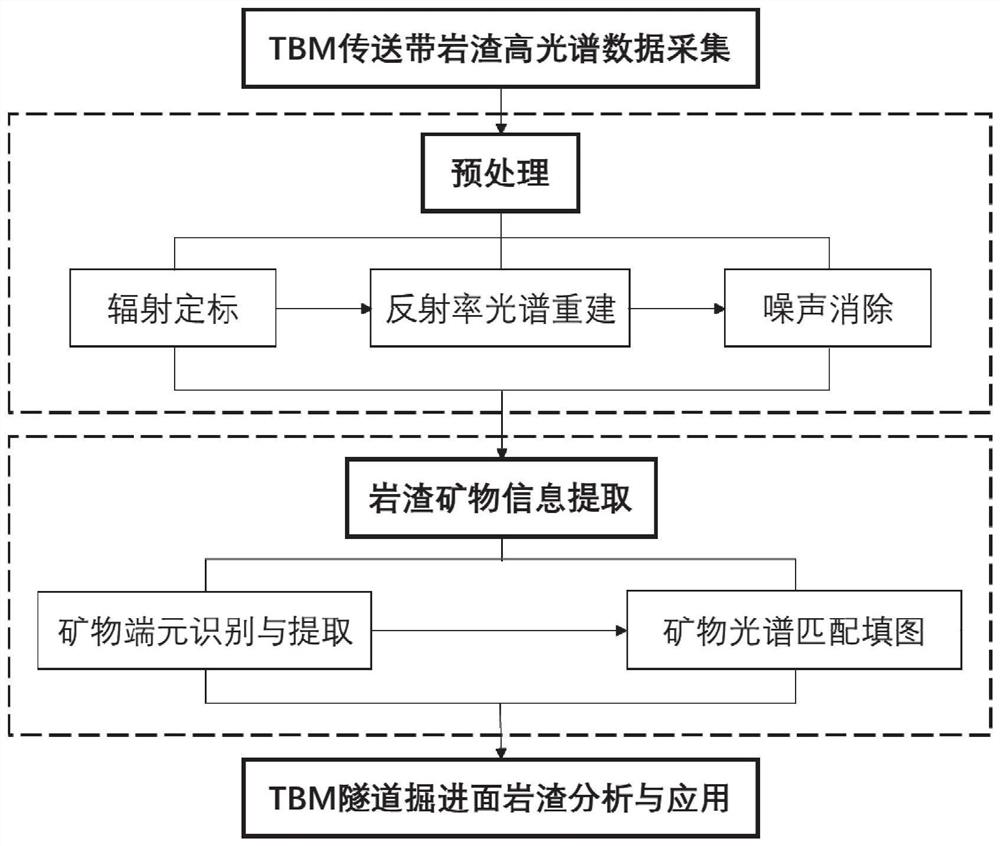
TBM tunnel carrying type rock slag mineral recognition system and method based on hyperspectral imaging
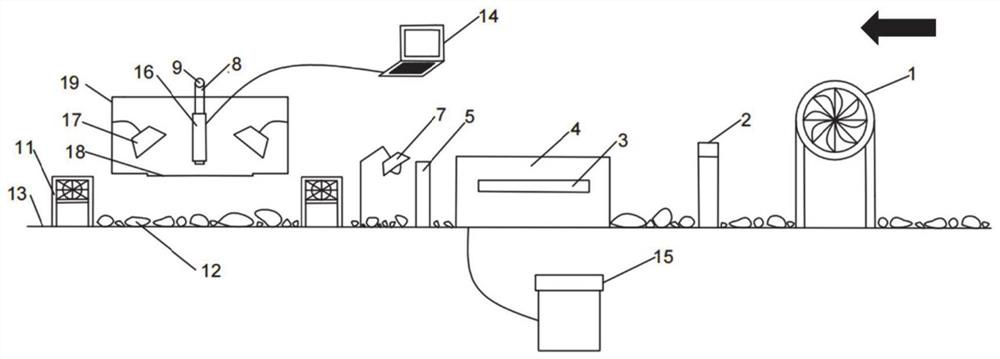
ActiveCN113310949ATimely adjustment of TBM mechanical parametersGuaranteed scanning image qualityPreparing sample for investigationScattering properties measurementsLithologyPhysical chemistry
The invention provides a TBM tunnel carrying type rock slag mineral recognition system and method based on hyperspectral imaging. The system comprises a conveying belt, a rock slag cleaning device, a rock slag drying device and a hyperspectral imaging device are sequentially arranged above the conveying belt, the hyperspectral imaging device is connected with a mechanical control device, and the mechanical control device is arranged beside the conveying belt for adjusting the position and the height of the hyperspectral imaging device on the conveying belt; the hyperspectral imaging device is connected with the processor, and the processor is configured to match lithology according to rock slag spectral information collected by the hyperspectral imaging device and perform quantitative identification on the mineral content of the rock slag. According to the method, the mineral content information of the rock slag can be quickly analyzed in real time.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Mixed pixel decomposition and end member extraction method
InactiveCN102346853ACalculation speedHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionInformation processingDecomposition
The invention relates to a mixed pixel decomposition and end member extraction method. Remote sensing refers to the modern application technology which obtains surface information through sensors on various platforms run in the upper air or an outer space, and obtains the shape, the location, the spatial distribution, the category, the nature and the like of a surface object through an information processing method. The remote sensing is originated from 1960s, and integrates aerospace, computer, sensor, information processing and other technologies. An obtained remote sensing image contains rich spectral and spatial information, and is widely applied to a plurality of aspects, such as environment monitoring, surveying and mapping, geological rock and mineral identification, agriculture, forestry, archaeology, tourism, military affairs and the like.
Owner:张灵芝
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com