Patents
Literature
139 results about "Linear prediction coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
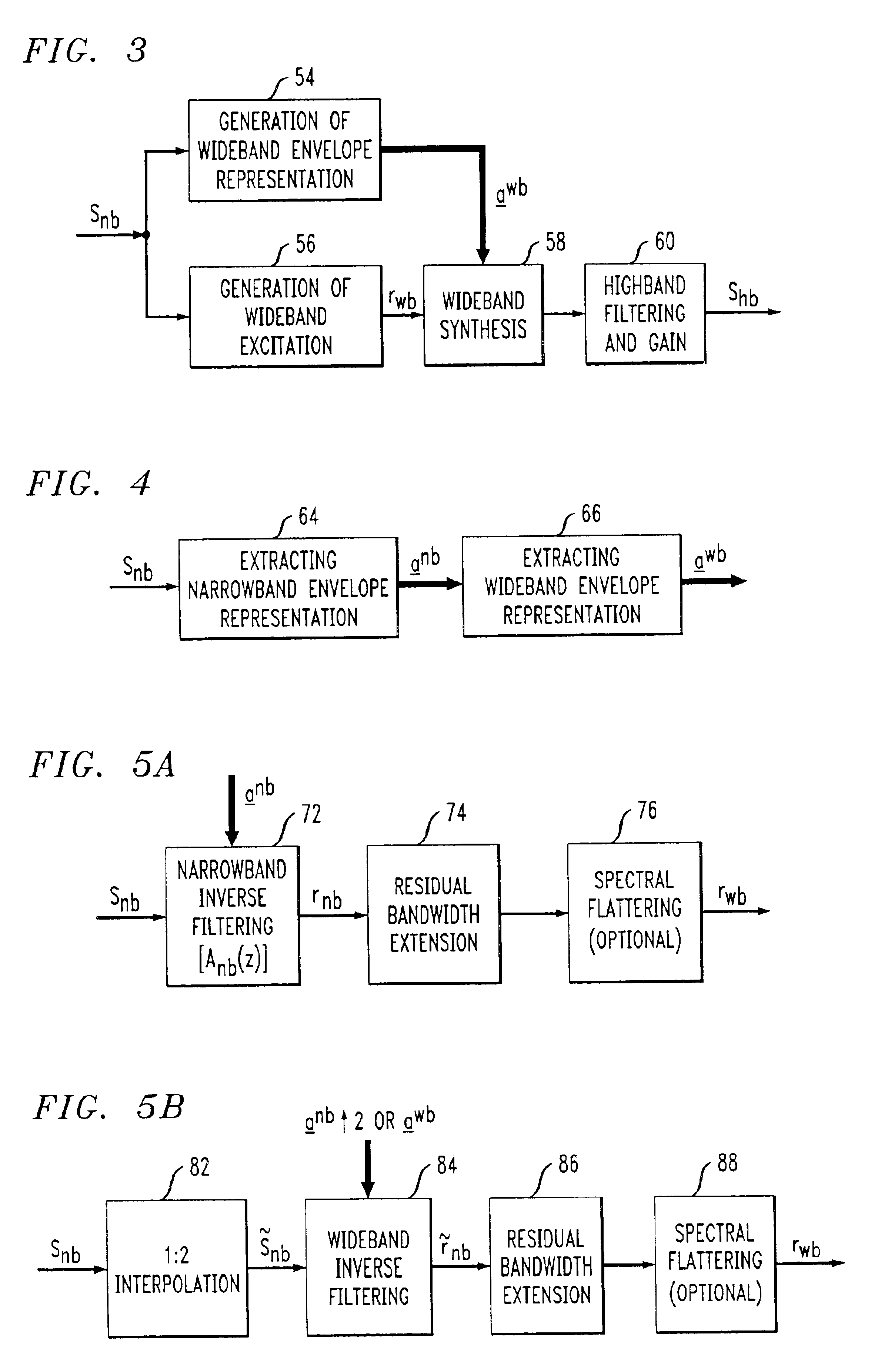
System for bandwidth extension of Narrow-band speech
InactiveUS6895375B2Quality improvementEasy to useDigital computer detailsElectric digital data processingNarrowband speechLinear prediction coefficient
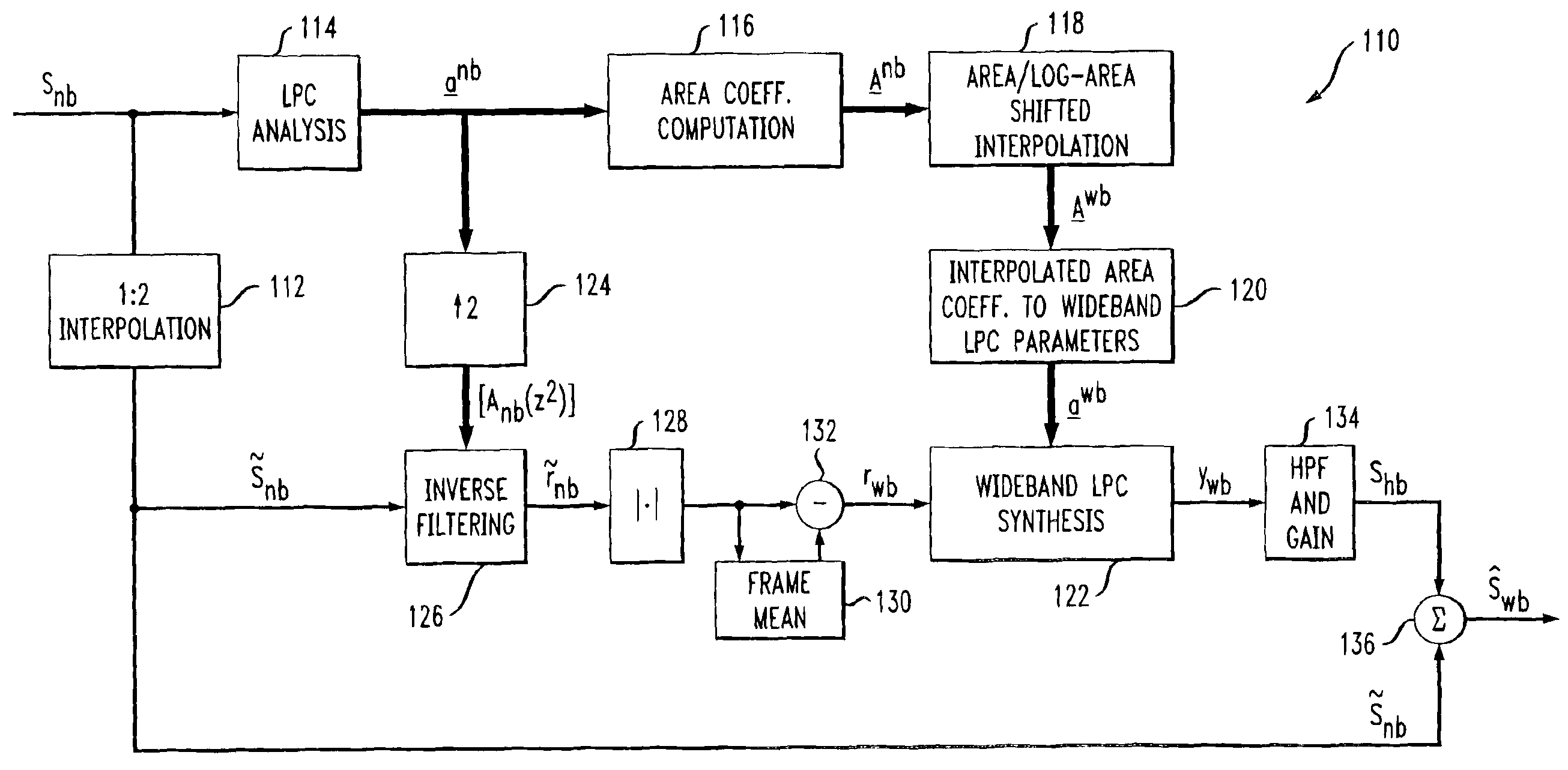
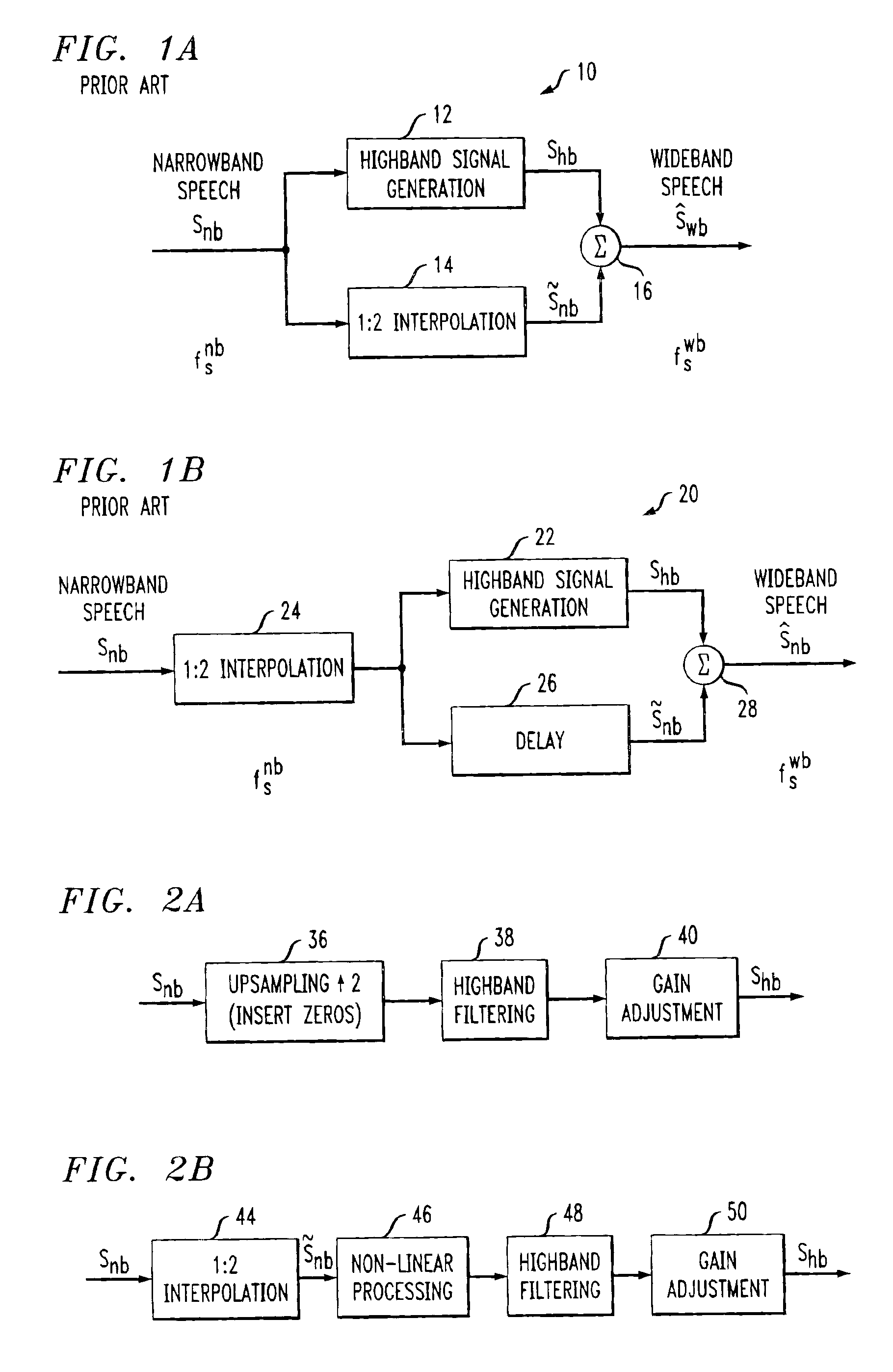
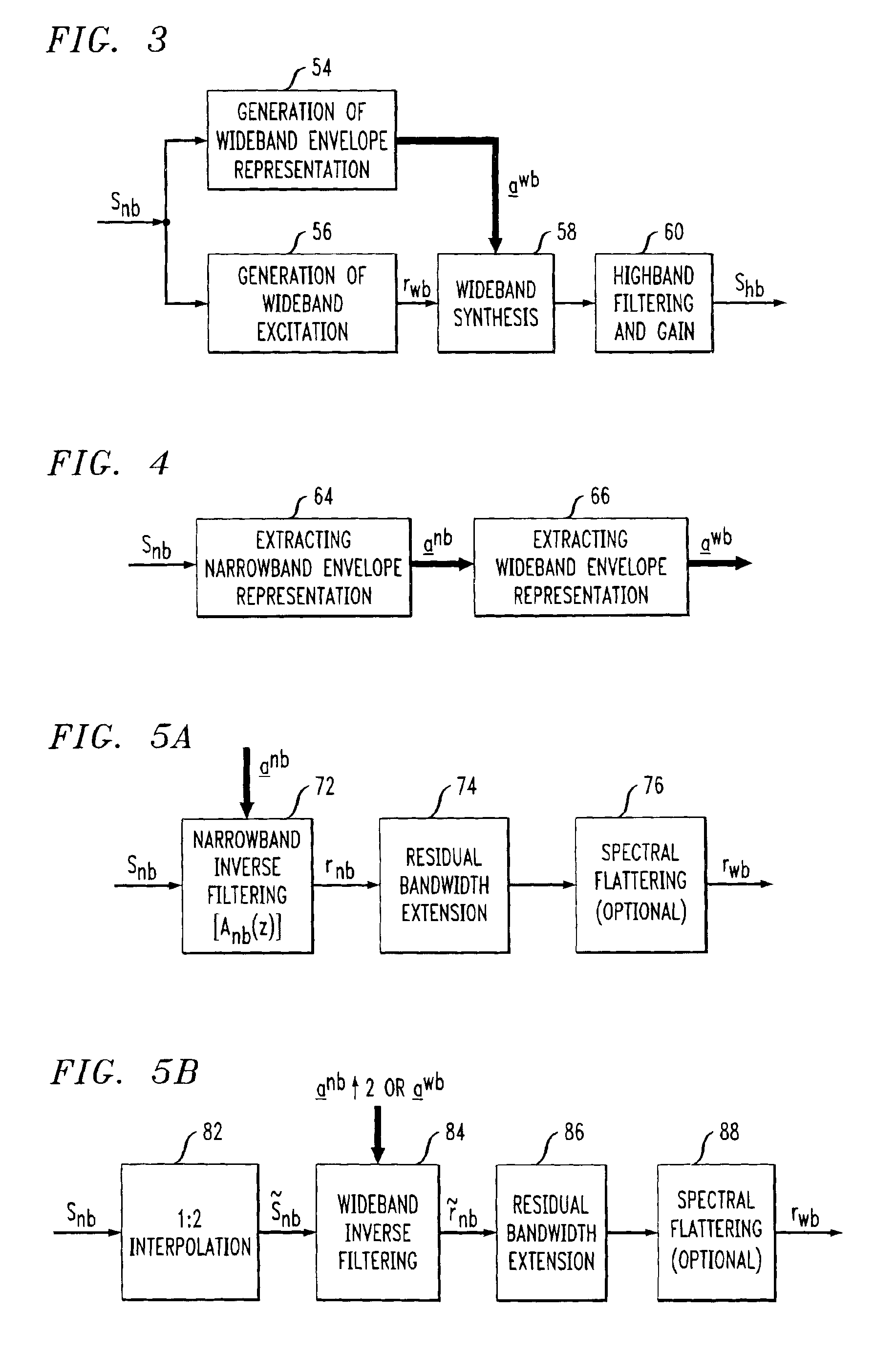
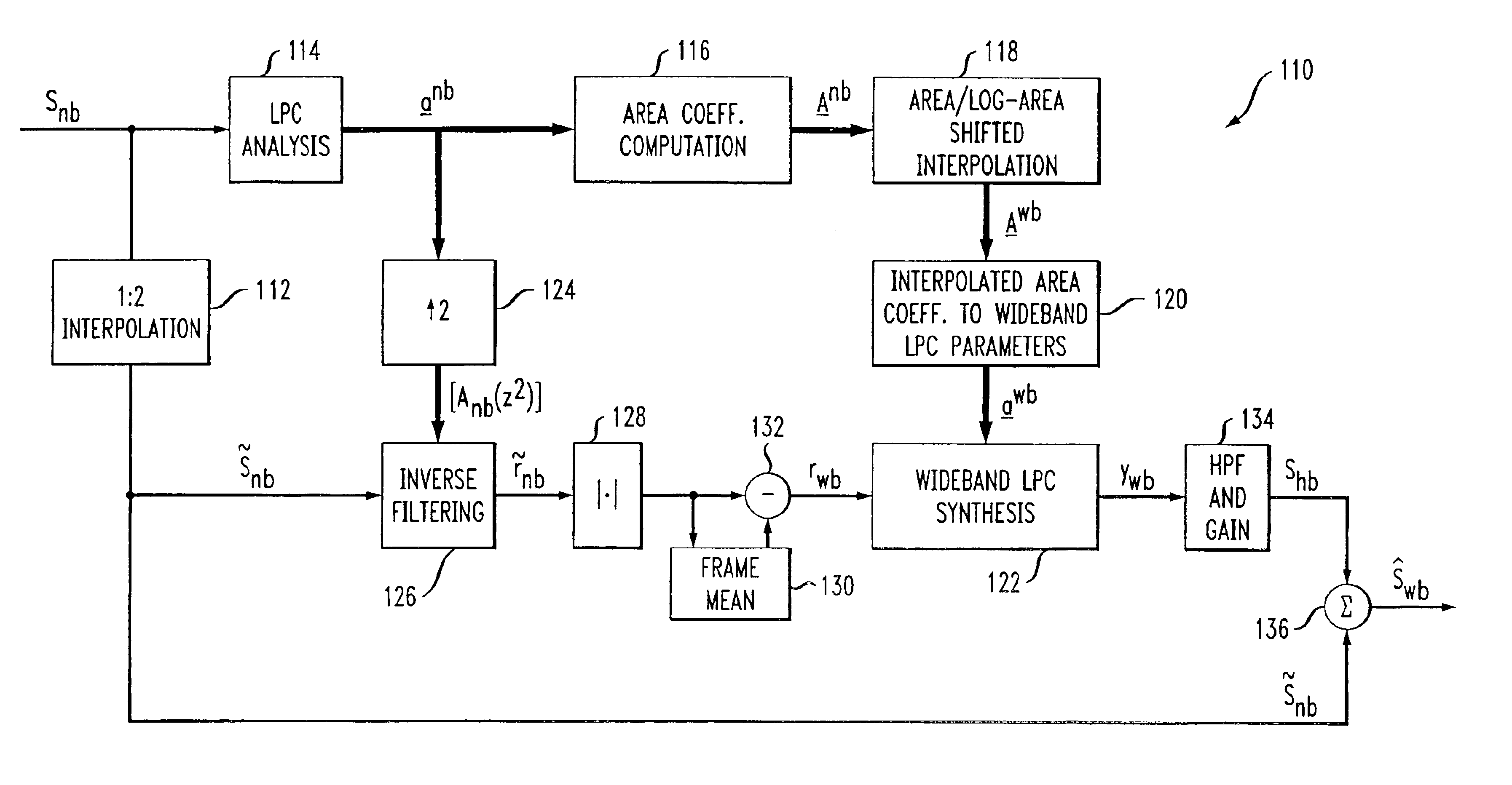
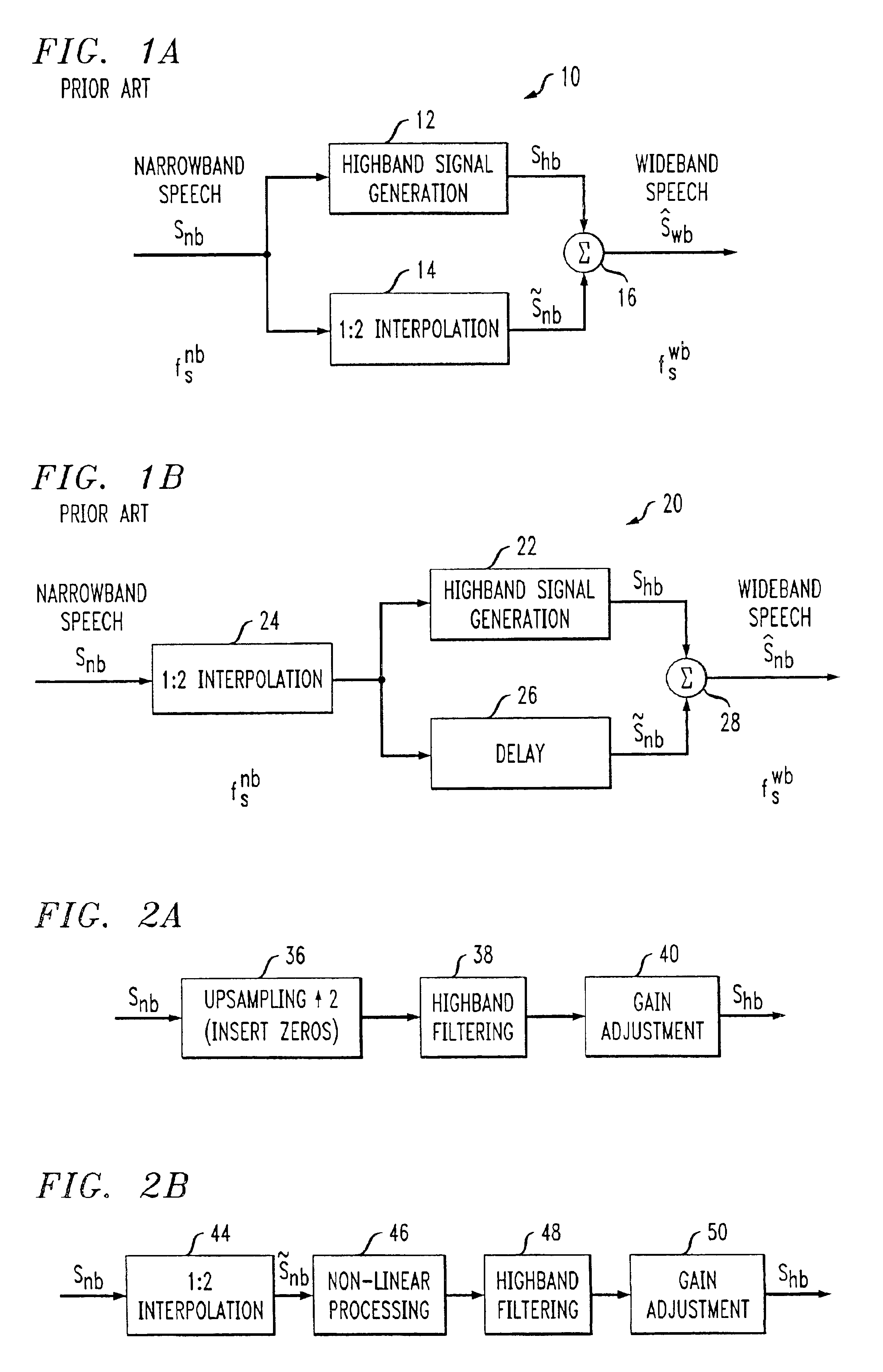
A system and method are disclosed for extending the bandwidth of a narrowband signal such as a speech signal. The method applies a parametric approach to bandwidth extension but does not require training. The parametric representation relates to a discrete acoustic tube model (DATM). The method comprises computing narrowband linear predictive coefficients (LPCs) from a received narrowband speech signal, computing narrowband partial correlation coefficients (parcors) using recursion, computing Mnb area coefficients from the partial correlation coefficient, and extracting Mwb area coefficients using interpolation. Wideband parcors are computed from the Mwb area coefficients and wideband LPCs are computed from the wideband parcors. The method further comprises synthesizing a wideband signal using the wideband LPCs and a wideband excitation signal, highpass filtering the synthesized wideband signal to produce a highband signal, and combining the highband signal with the original narrowband signal to generate a wideband signal. In a preferred variation of the invention, the Mnb area coefficients are converted to log-area coefficients for the purpose of extracting, through shifted-interpolation, Mwb log-area coefficients. The Mwb log-area coefficients are then converted to Mwb area coefficients before generating the wideband parcors.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
Speech recognition system
InactiveUS7266496B2Improve execution speedLow costSpeech recognitionLinearityLinear prediction coefficient
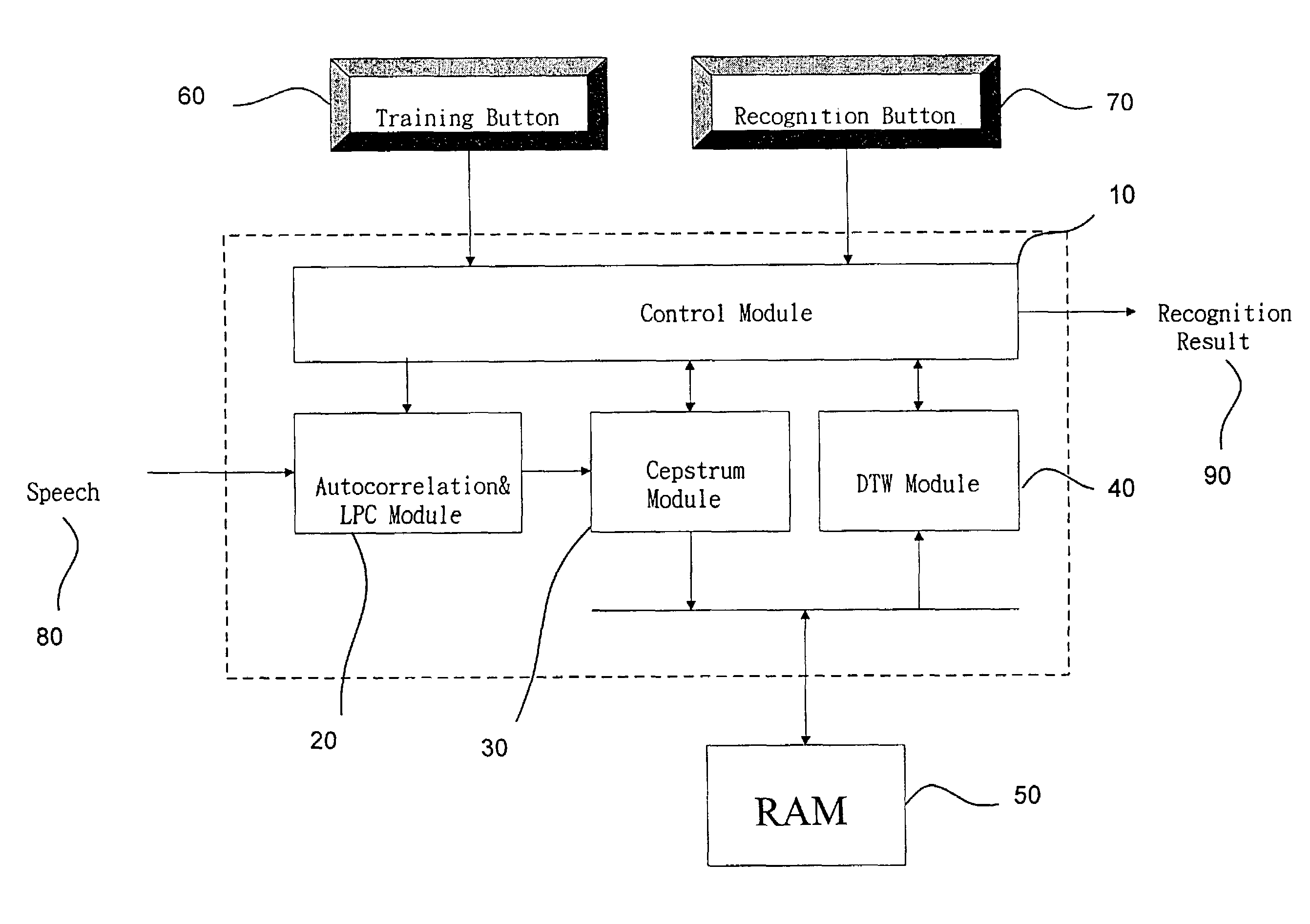
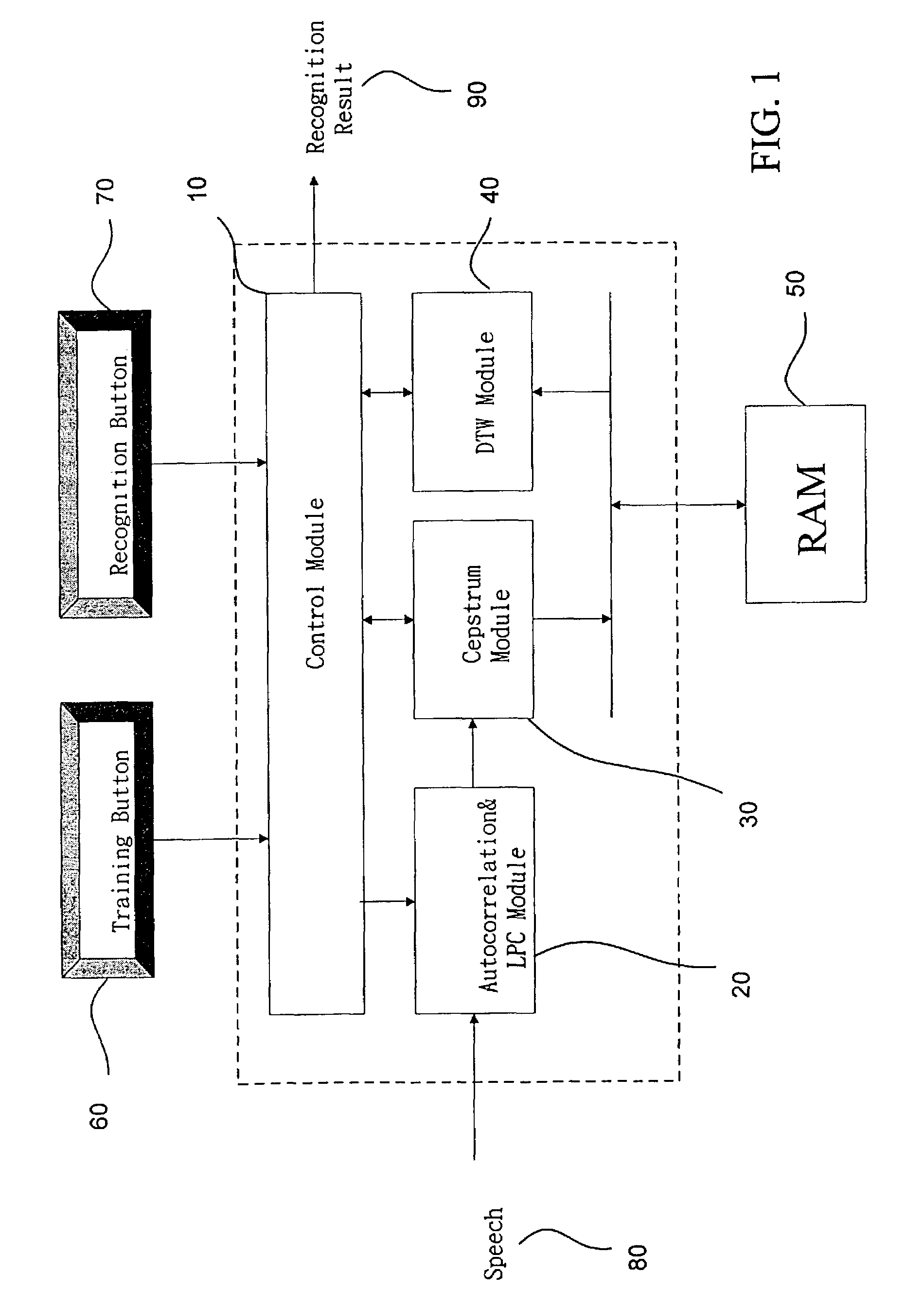
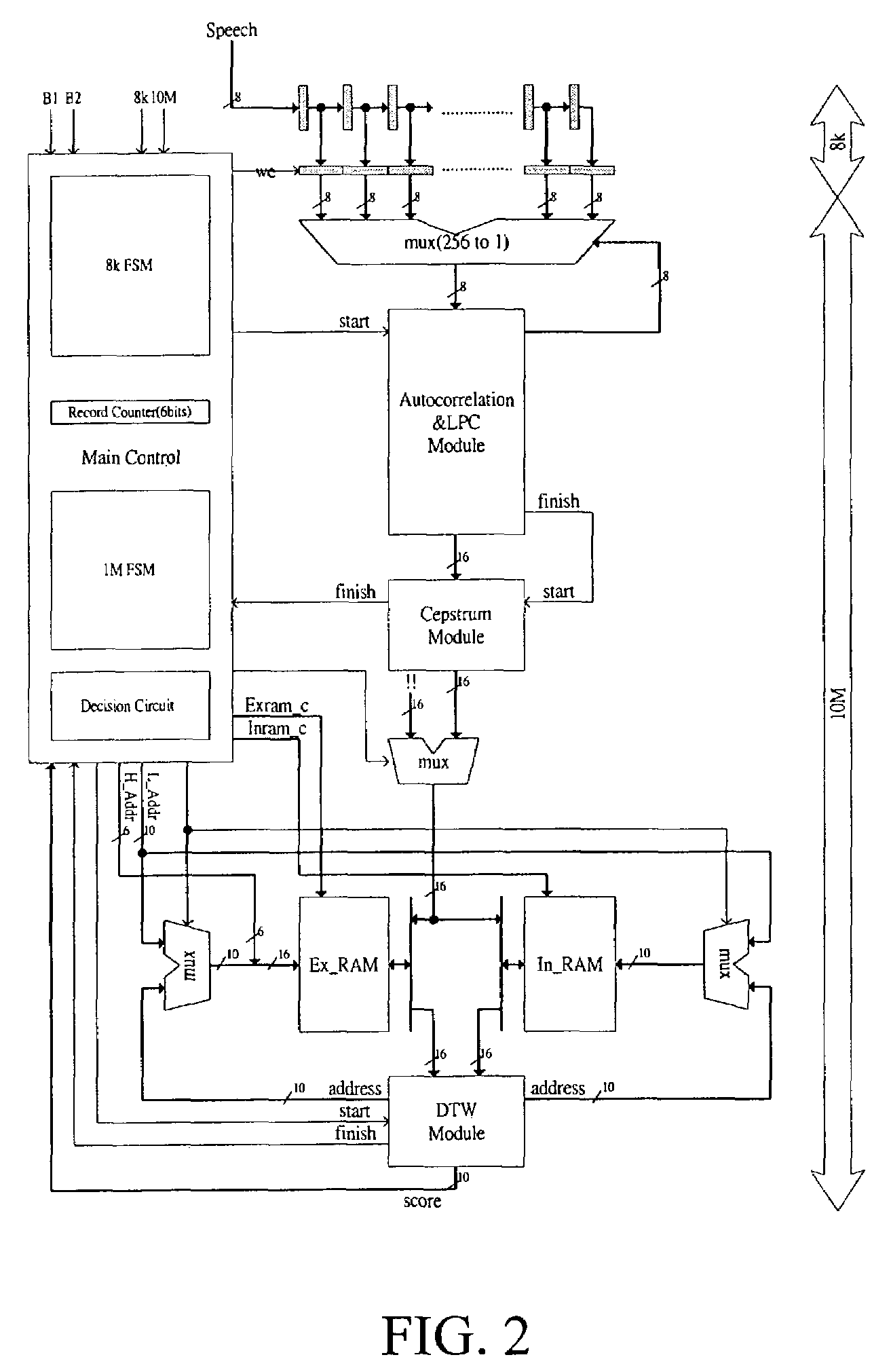
The present invention discloses a complete speech recognition system having a training button and a recognition button, and the whole system uses the application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) architecture for the design, and also uses the modular design to divide the speech processing into 4 modules: system control module, autocorrelation and linear predictive coefficient module, cepstrum module, and DTW recognition module. Each module forms an intellectual product (IP) component by itself. Each IP component can work with various products and application requirements for the design reuse to greatly shorten the time to market.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Method of bandwidth extension for narrow-band speech
InactiveUS6988066B2Quality improvementEasy to useDigital computer detailsElectric digital data processingPattern recognitionNarrowband speech
A system and method are disclosed for extending the bandwidth of a narrowband signal such as a speech signal. The method applies a parametric approach to bandwidth extension but does not require training. The parametric representation relates to a discrete acoustic tube model (DATM). The method comprises computing narrowband linear predictive coefficients (LPCs) from a received narrowband speech signal, computing narrowband partial correlation coefficients (parcors) using recursion, computing Mnb area coefficients from the partial correlation coefficient, and extracting Mwb area coefficients using interpolation. Wideband parcors are computed from the Mwb area coefficients and wideband LPCs are computed from the wideband parcors. The method further comprises synthesizing a wideband signal using the wideband LPCs and a wideband excitation signal, highpass filtering the synthesized wideband signal to produce a highband signal, and combining the highband signal with the original narrowband signal to generate a wideband signal. In a preferred variation of the invention, the Mnb area coefficients are converted to log-area coefficients for the purpose of extracting, through shifted-interpolation, Mwb log-area coefficients. The Mwb log-area coefficients are then converted to Mwb area coefficients before generating the wideband parcors.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
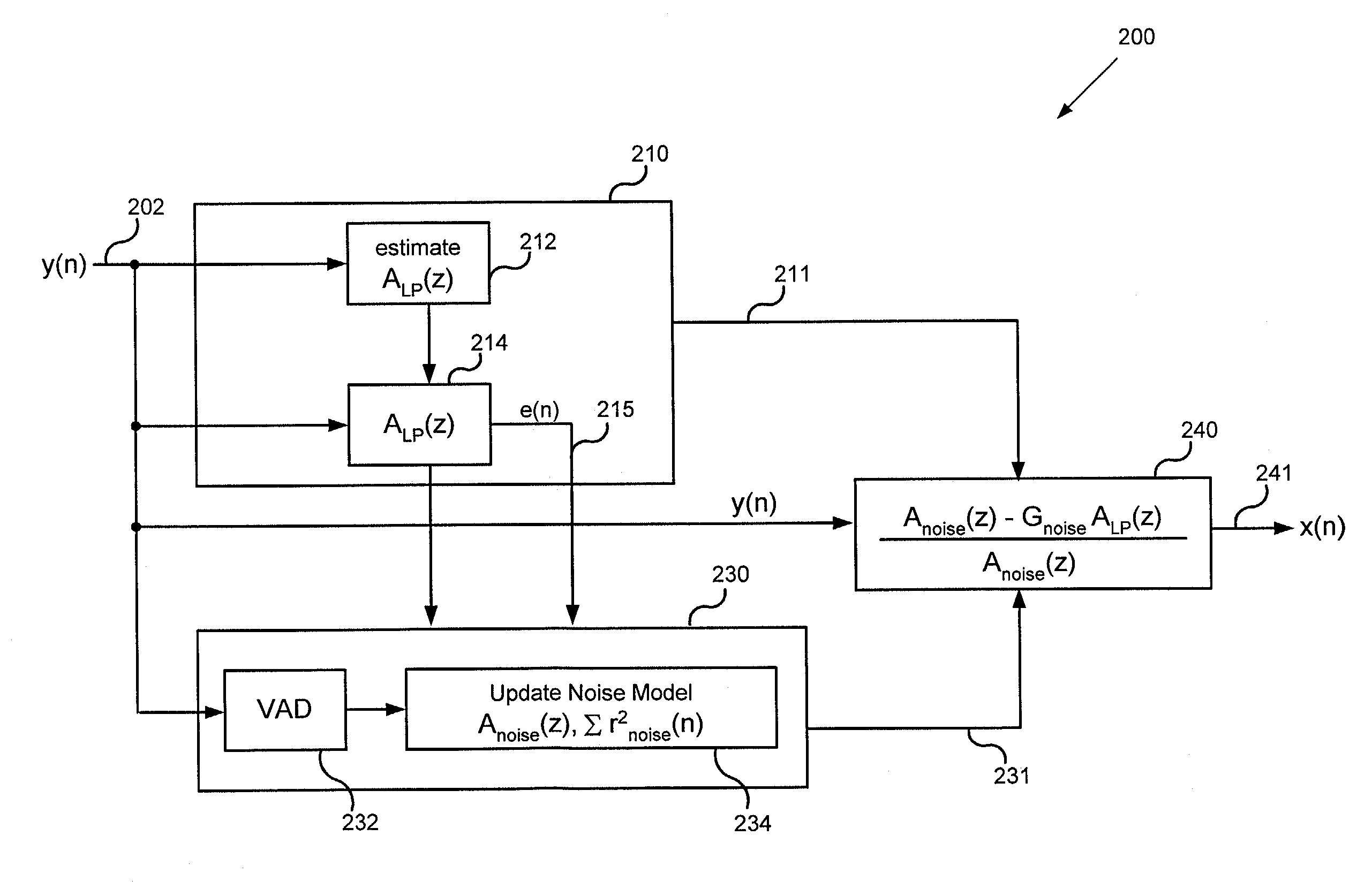
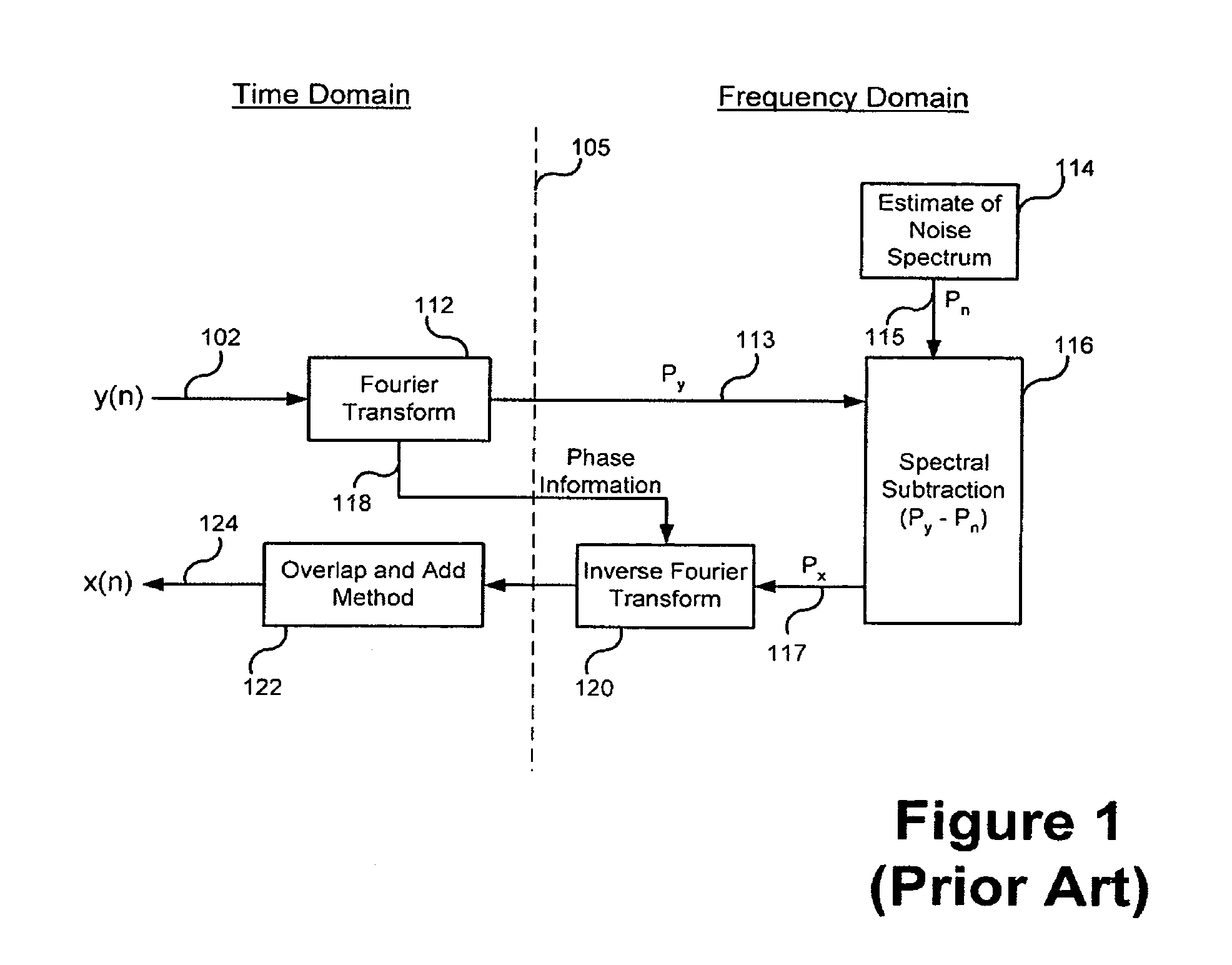
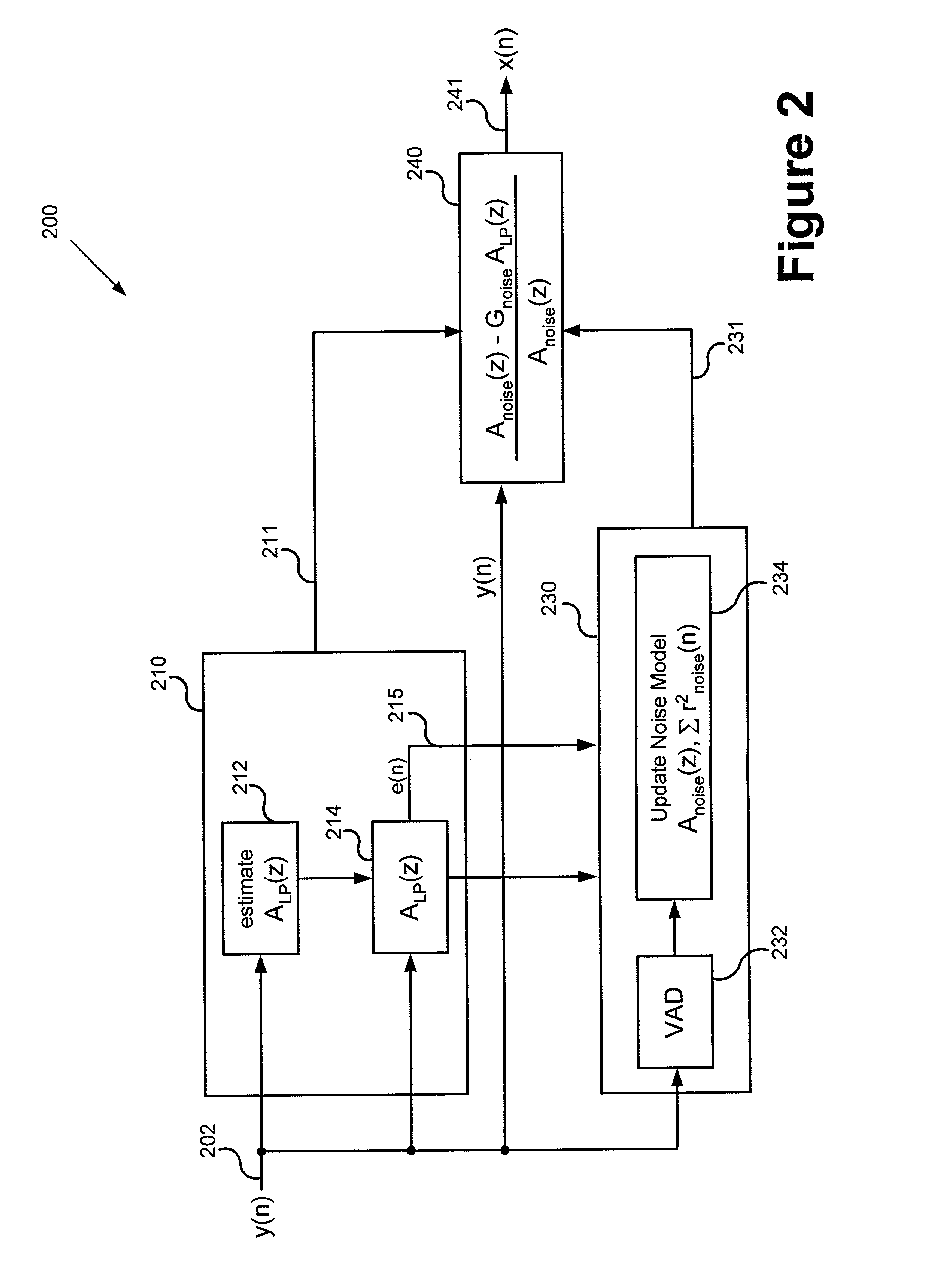
Linear prediction based noise suppression
Various time-domain noise suppression methods and devices for suppressing a noise signal in a speech signal are provided. For example, a time-domain noise suppression method comprises estimating a plurality of linear prediction coefficients for the speech signal, generating a prediction error estimate based on the plurality of prediction coeficients, generating an estimate of the speech signal based on the plurality of linear prediction coefficients, using a voice activity detector to determine voice activity in the speech signal, updating a plurality of noise parameters based on the prediction error and if the voice activity detector determines no voice activity in the speech signal, generating an estimate of the noise signal based on the plurality of noise parameters, and passing the speech signal through a filter derived from the estimate of the noise signal and the estimate of the speech signal to generate a clean speech signal estimate.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC +1
Speech encoding/decoding device
ActiveUS20120010879A1Increase bitrateImprove subjective qualitySpeech analysisCovariance methodComputer science
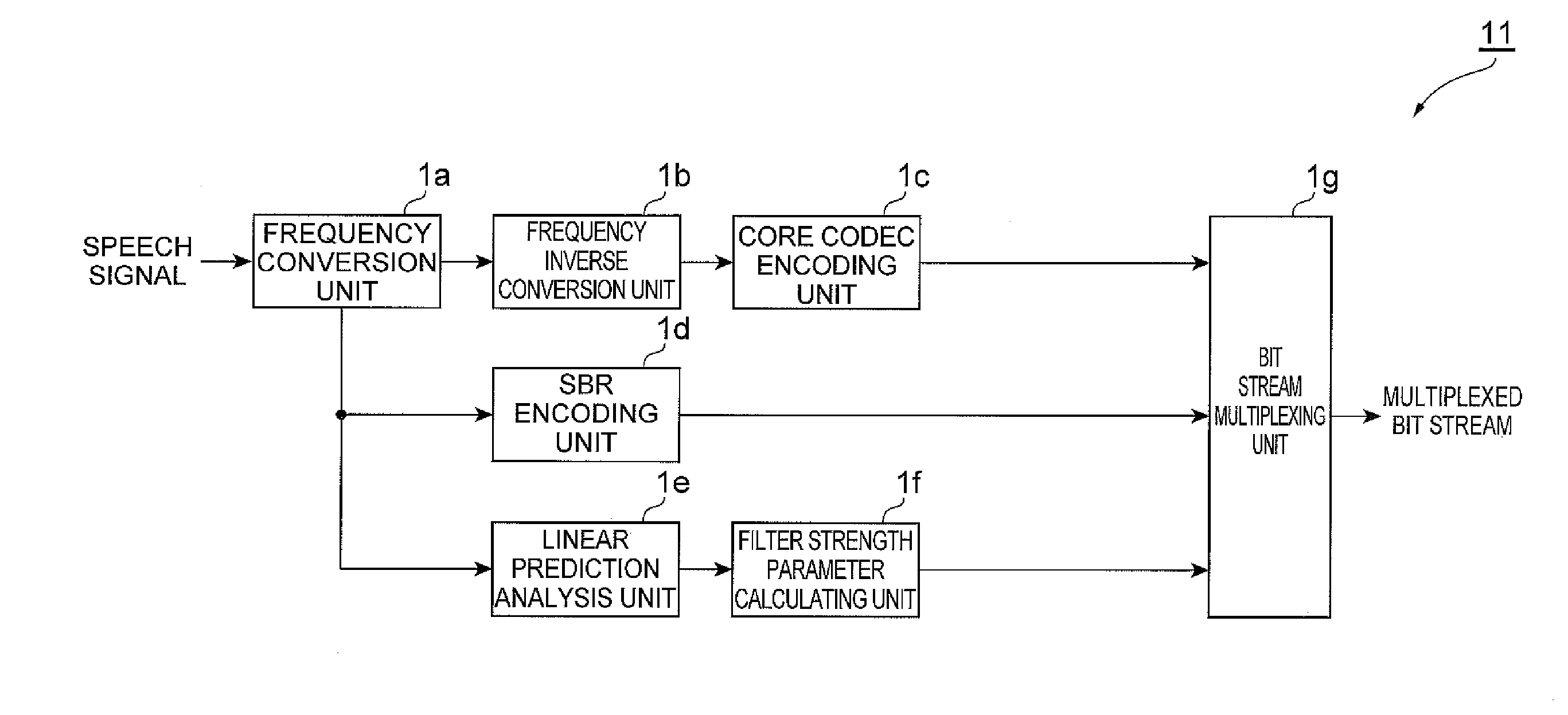
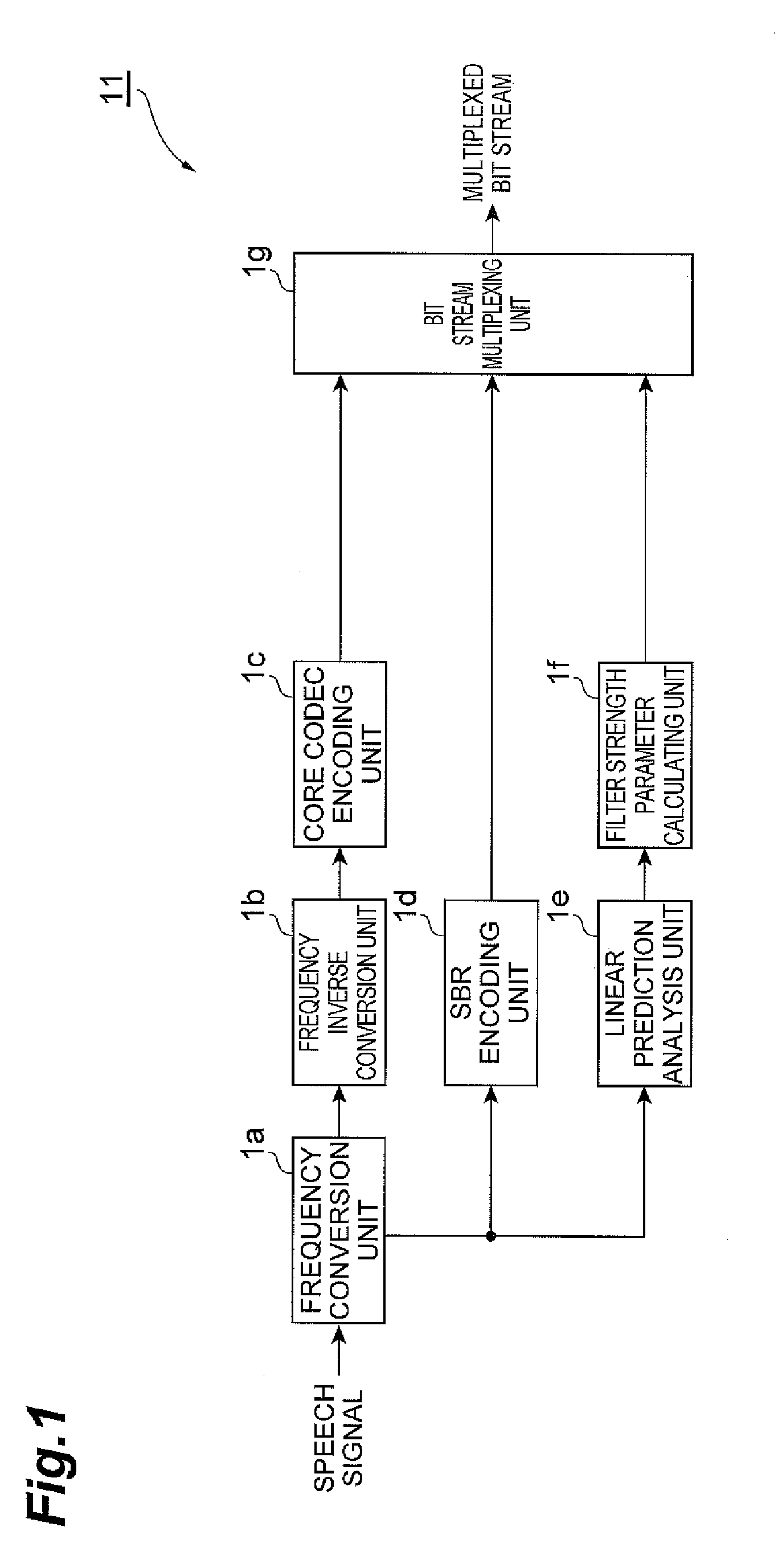
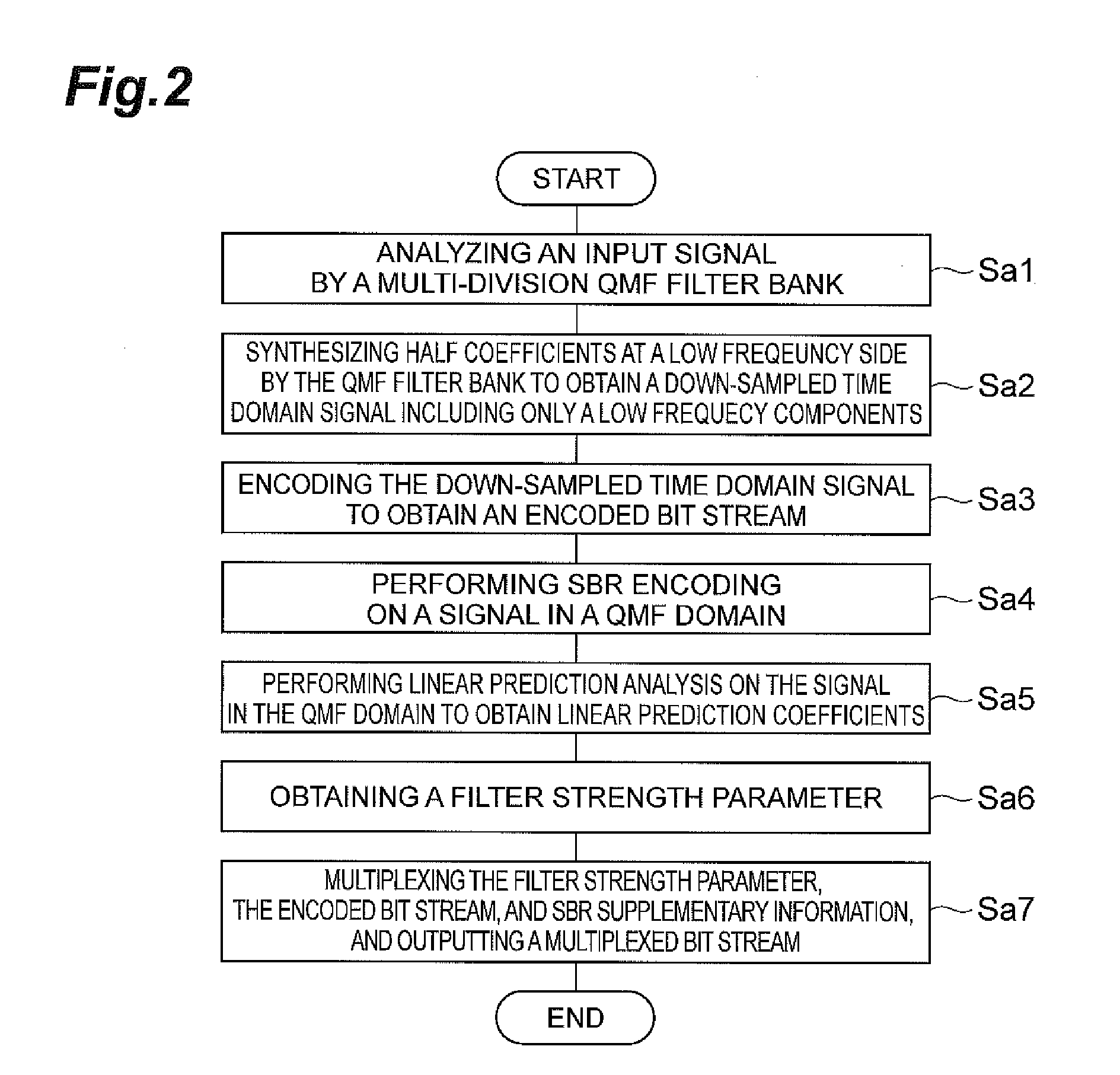
A linear prediction coefficient of a signal represented in a frequency domain is obtained by performing linear prediction analysis in a frequency direction by using a covariance method or an autocorrelation method. After the filter strength of the obtained linear prediction coefficient is adjusted, filtering may be performed in the frequency direction on the signal by using the adjusted coefficient, whereby the temporal envelope of the signal is transformed. This reduces the occurrence of pre-echo and post-echo and improves the subjective quality of the decoded signal, without significantly increasing the bit rate in a band extension technique in the frequency domain represented by SBR.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
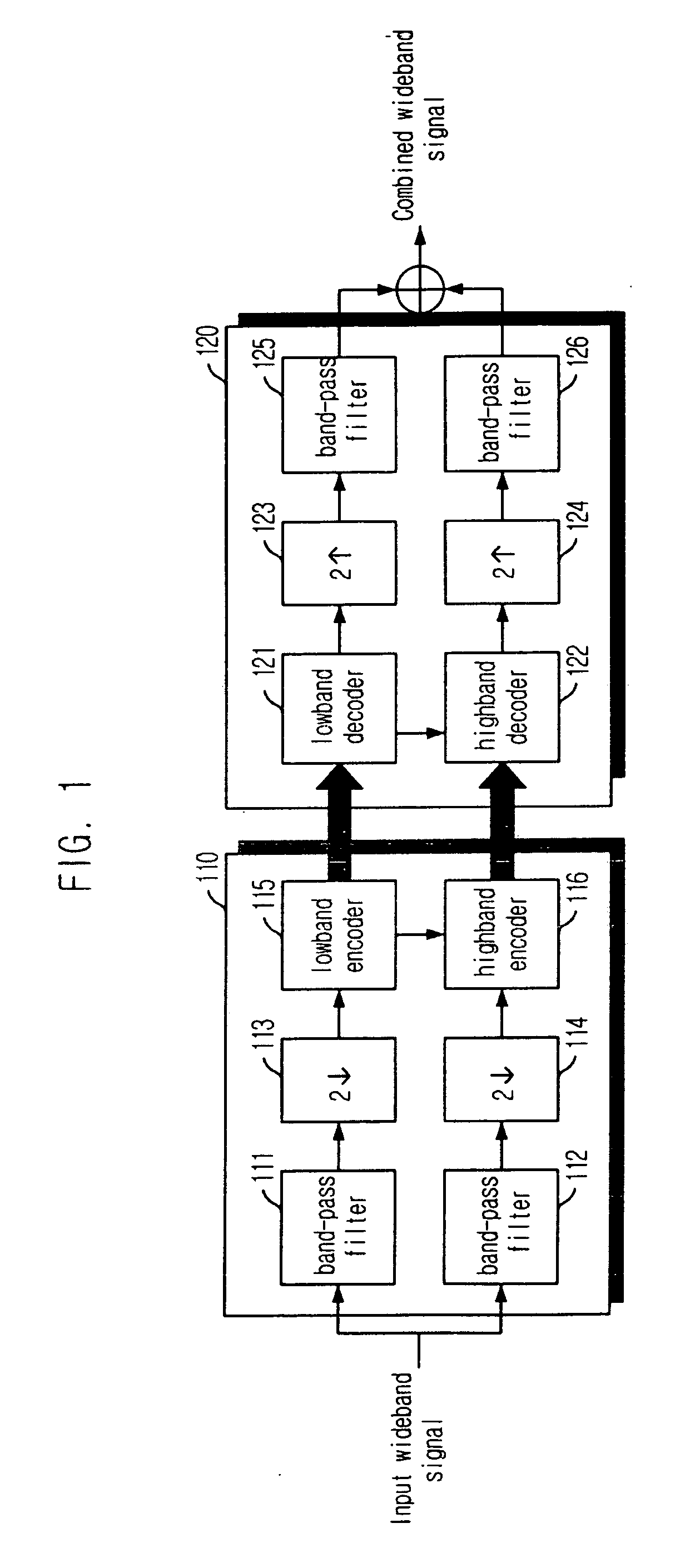
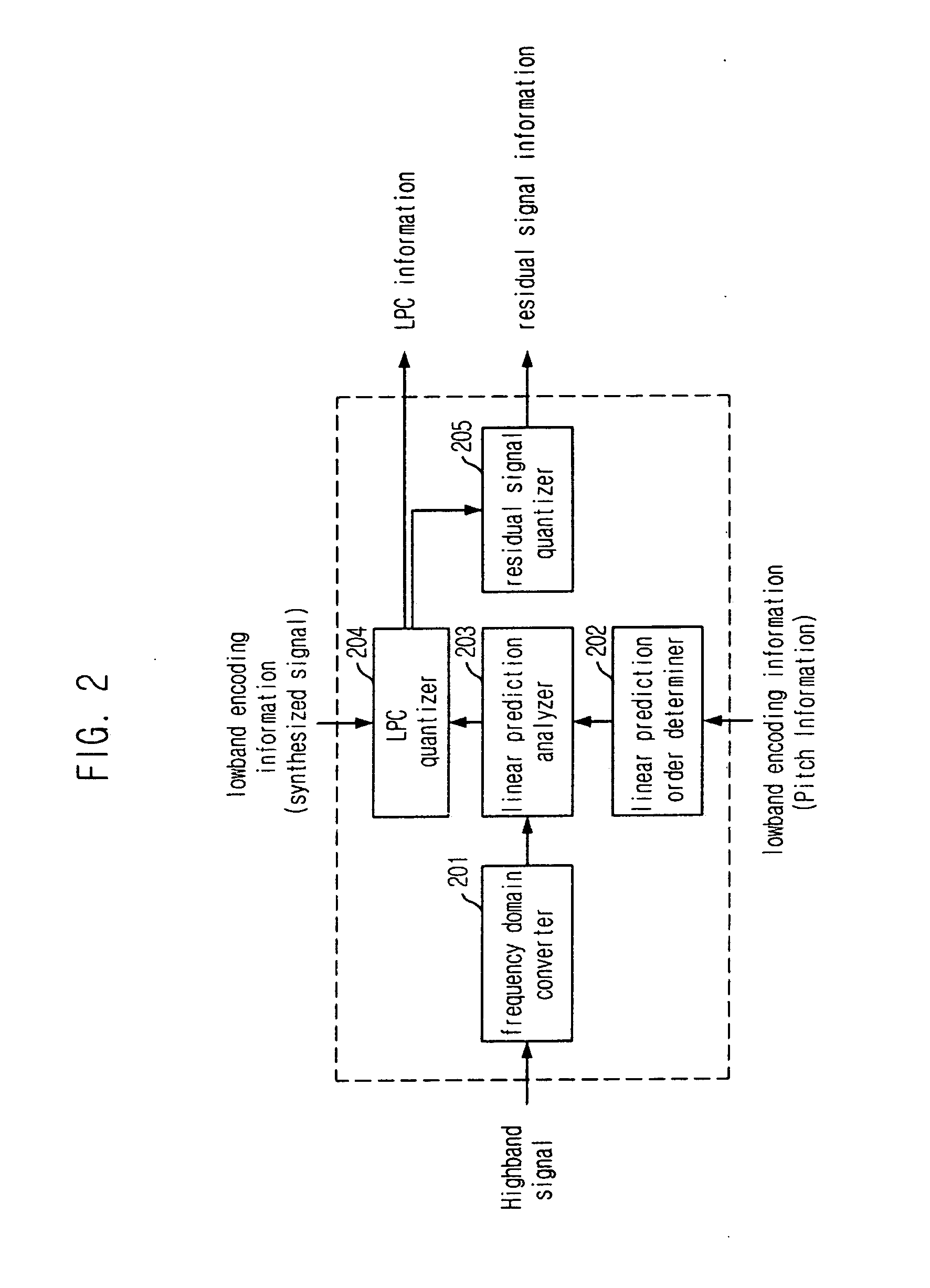
Highband speech coding apparatus and method for wideband speech coding system
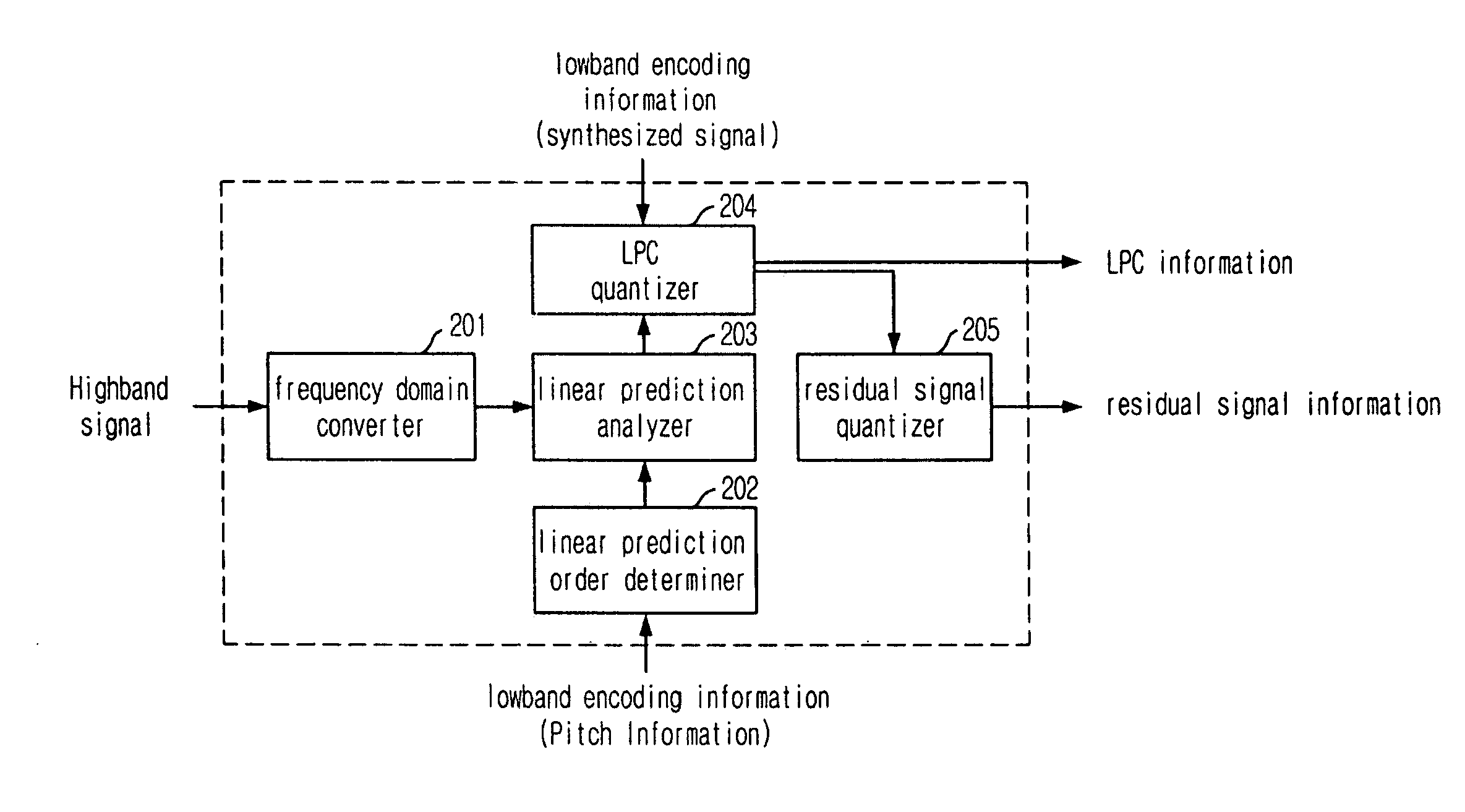
Provided is a highband coding apparatus and method for a wideband coding system. The coding apparatus and method can reduce a pre-echo phenomenon by encoding the highband based on lowband encoding information and Temporal Noise Shaping technique. A highband encoding apparatus includes: a domain converter for converting the domain of an input highband signal into a frequency domain; a linear prediction order determiner for determining a linear prediction order based on the lowband encoding information; a linear prediction analyzer for analyzing a highband signal of the frequency domain based on the determined linear prediction order to thereby generate a linear prediction coefficient; a linear prediction coefficient quantizer for quantizing the linear prediction coefficient based on the lowband encoding information; and a residual signal quantizer for obtaining a residual signal by dequantizing the quantized linear prediction coefficient and quantizing the residual signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
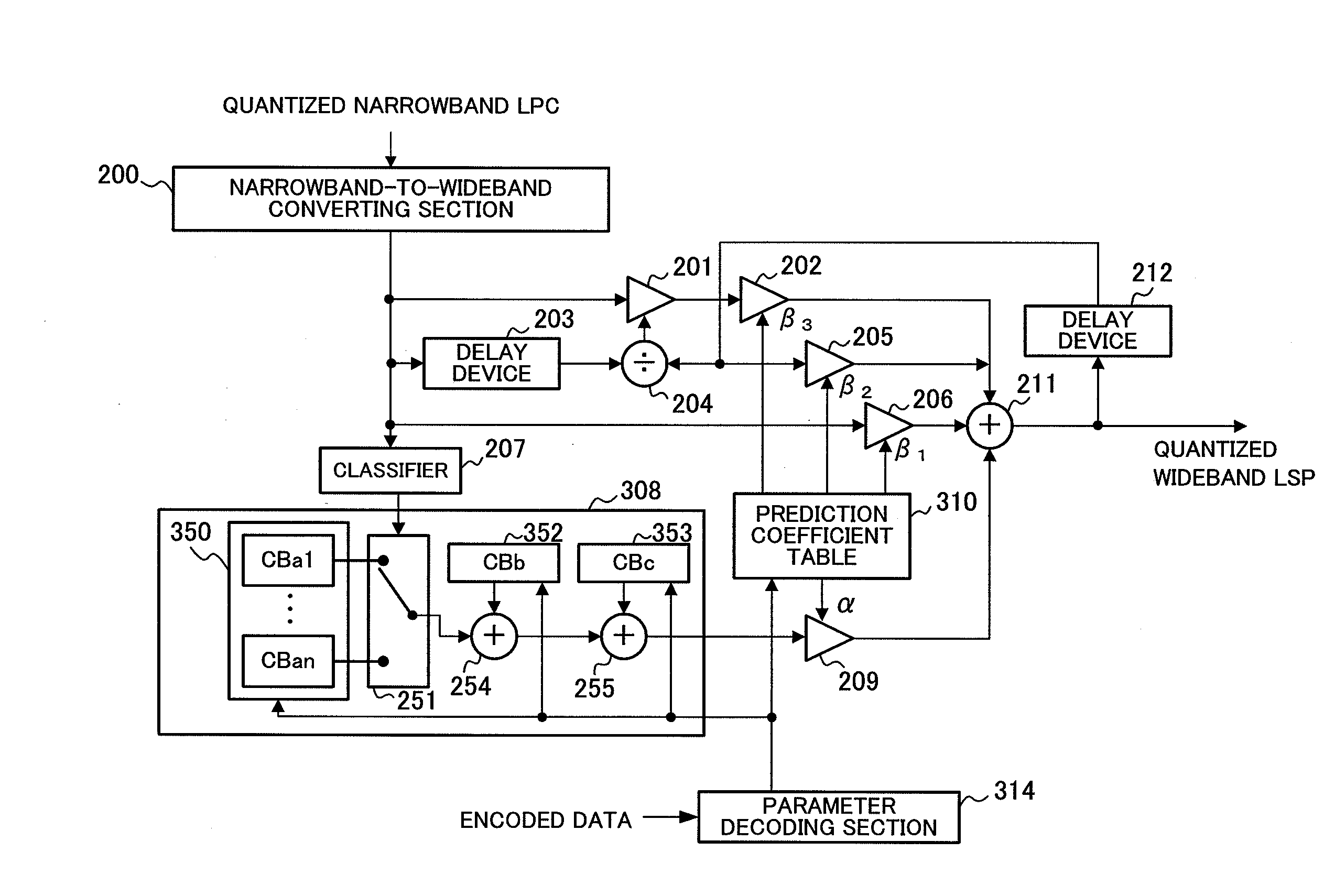
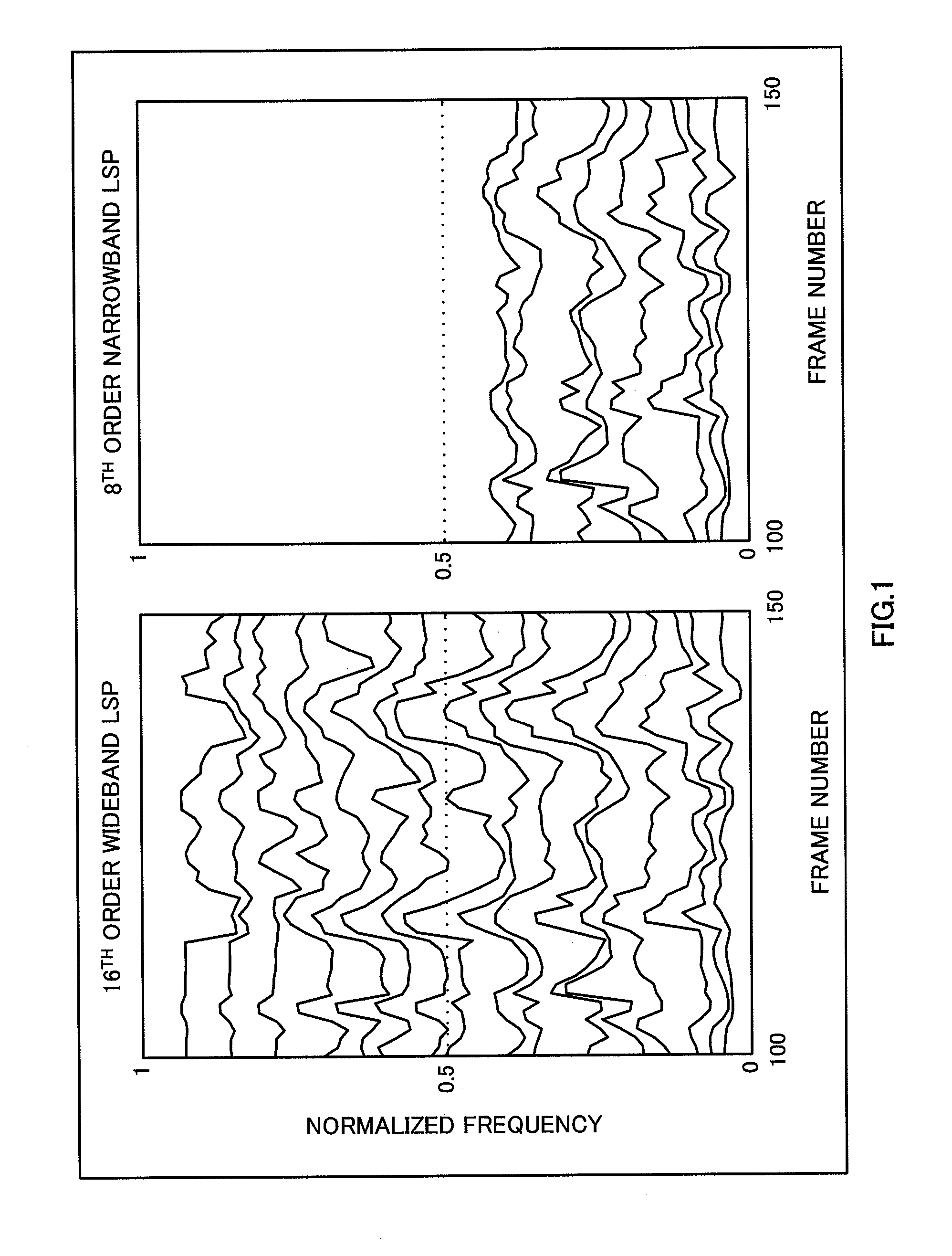
Scalable Encoding Apparatus, Scalable Decoding Apparatus, Scalable Encoding Method, Scalable Decoding Method, Communication Terminal Apparatus, and Base Station Apparatus
ActiveUS20080059166A1Improve Quantization EfficiencyImprove efficiencySpeech analysisComputer architectureTerminal equipment
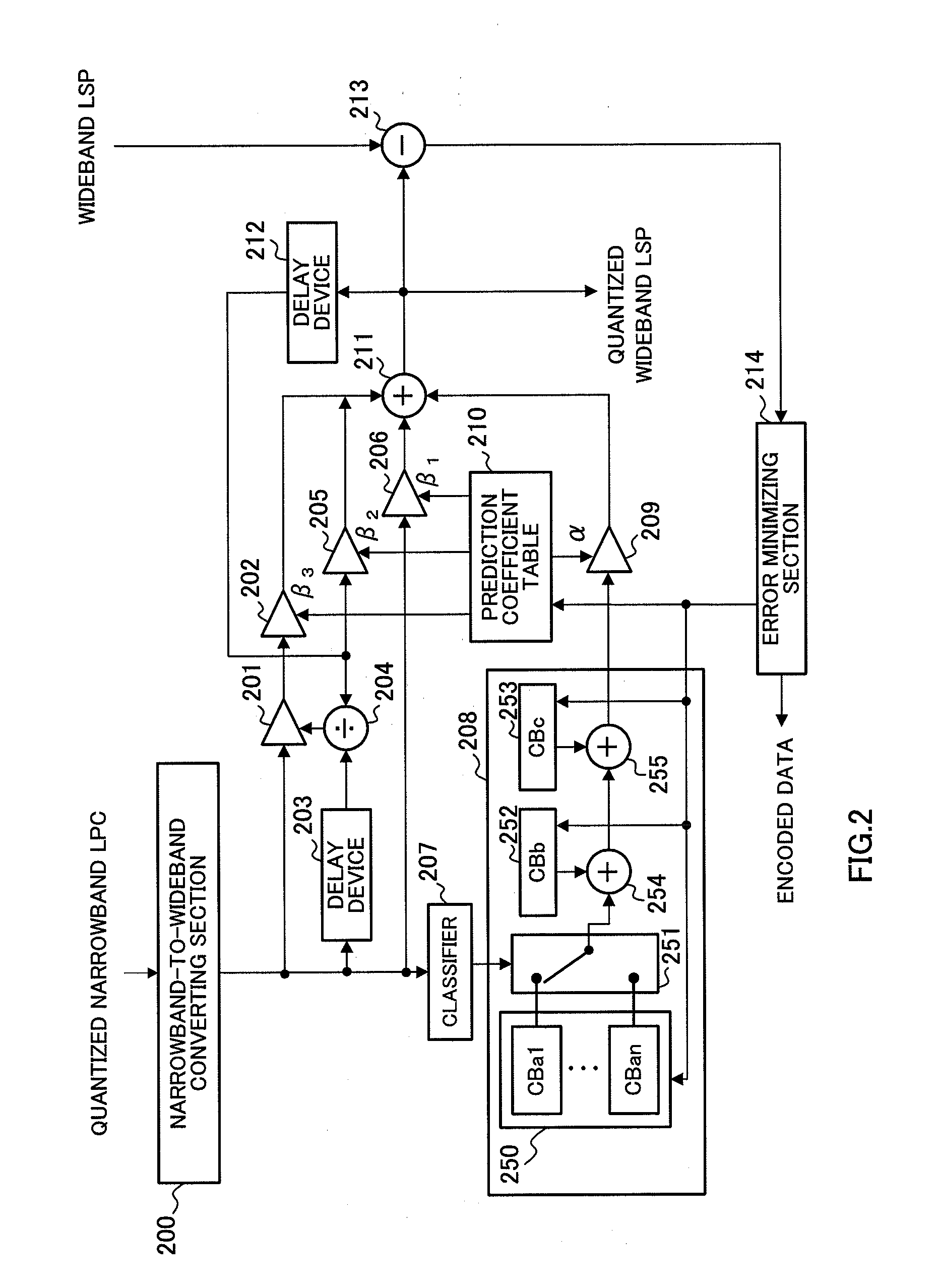
A scalable encoding apparatus, a scalable decoding apparatus and the like are disclosed which can achieve a band scalable LSP encoding that exhibits both a high quantization efficiency and a high performance. In these apparatuses, a narrow band-to-wide band converting part (200) receives and converts a quantized narrow band LSP to a wide band, and then outputs the quantized narrow band LSP as converted (i.e., a converted wide band LSP parameter) to an LSP-to-LPC converting part (800). The LSP-to-LPC converting part (800) converts the quantized narrow band LSP as converted to a linear prediction coefficient and then outputs it to a pre-emphasizing part (801). The pre-emphasizing part (801) calculates and outputs the pre-emphasized linear prediction coefficient to an LPC-to-LSP converting part (802). The LPC-to-LSP converting part (802) converts the pre-emphasized linear prediction coefficient to a pre-emphasized quantized narrow band LSP as wide band converted, and then outputs it to a prediction quantizing part (803).
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
Classification of speech and music using linear predictive coding coefficients
InactiveUS20050159942A1Electrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisLinear predictive codingLinearity
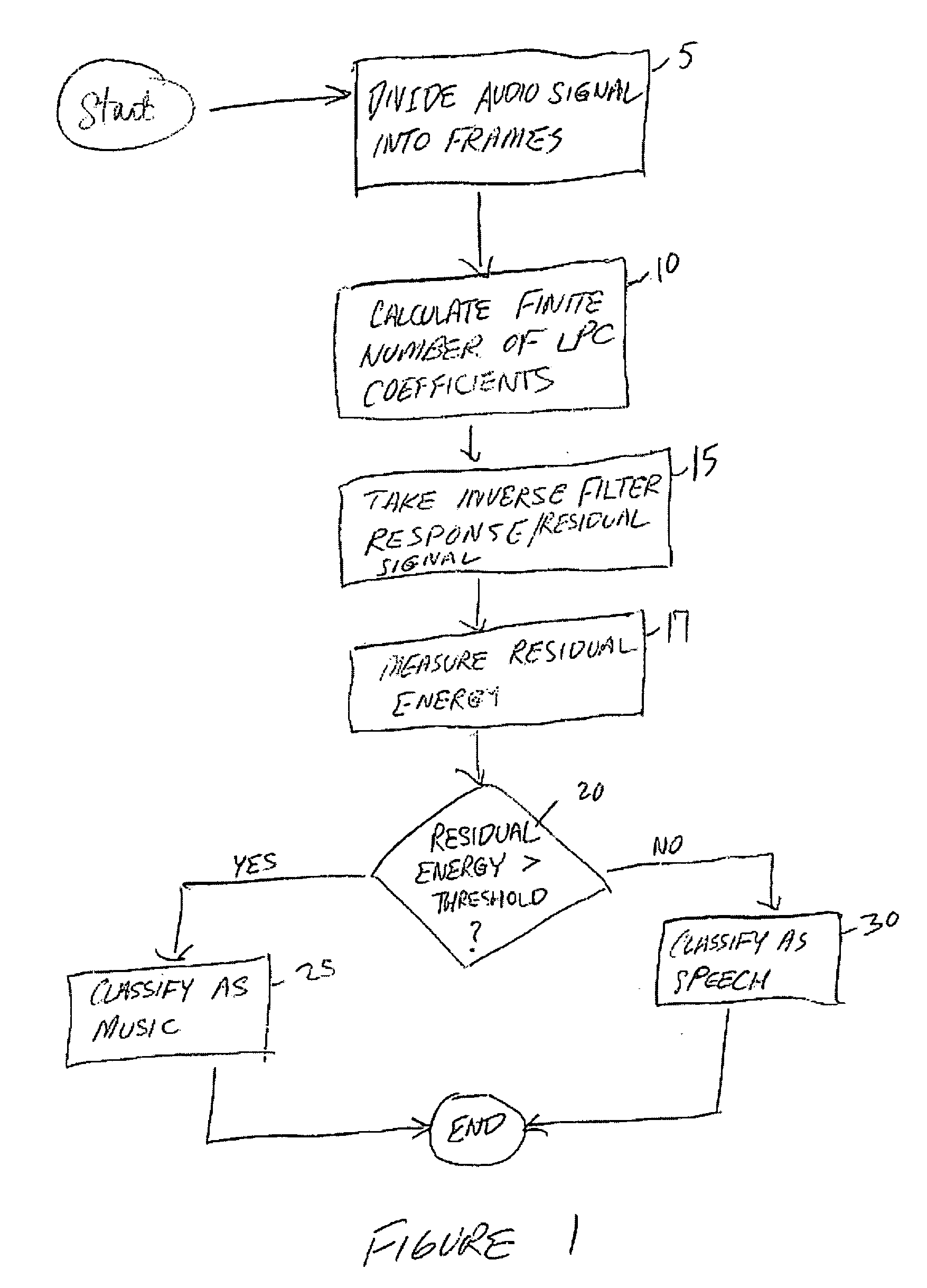
Presented herein are systems and methods for classifying an audio signal. The audio signal is classified by calculating a plurality of linear prediction coefficients (LPC) for a portion of the audio signal; inverse filtering the portion of the audio signal with the plurality of linear prediction coefficients (LPC), thereby resulting in a residual signal; measuring the residual energy of the residual signal; and comparing the residual energy to a threshold.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
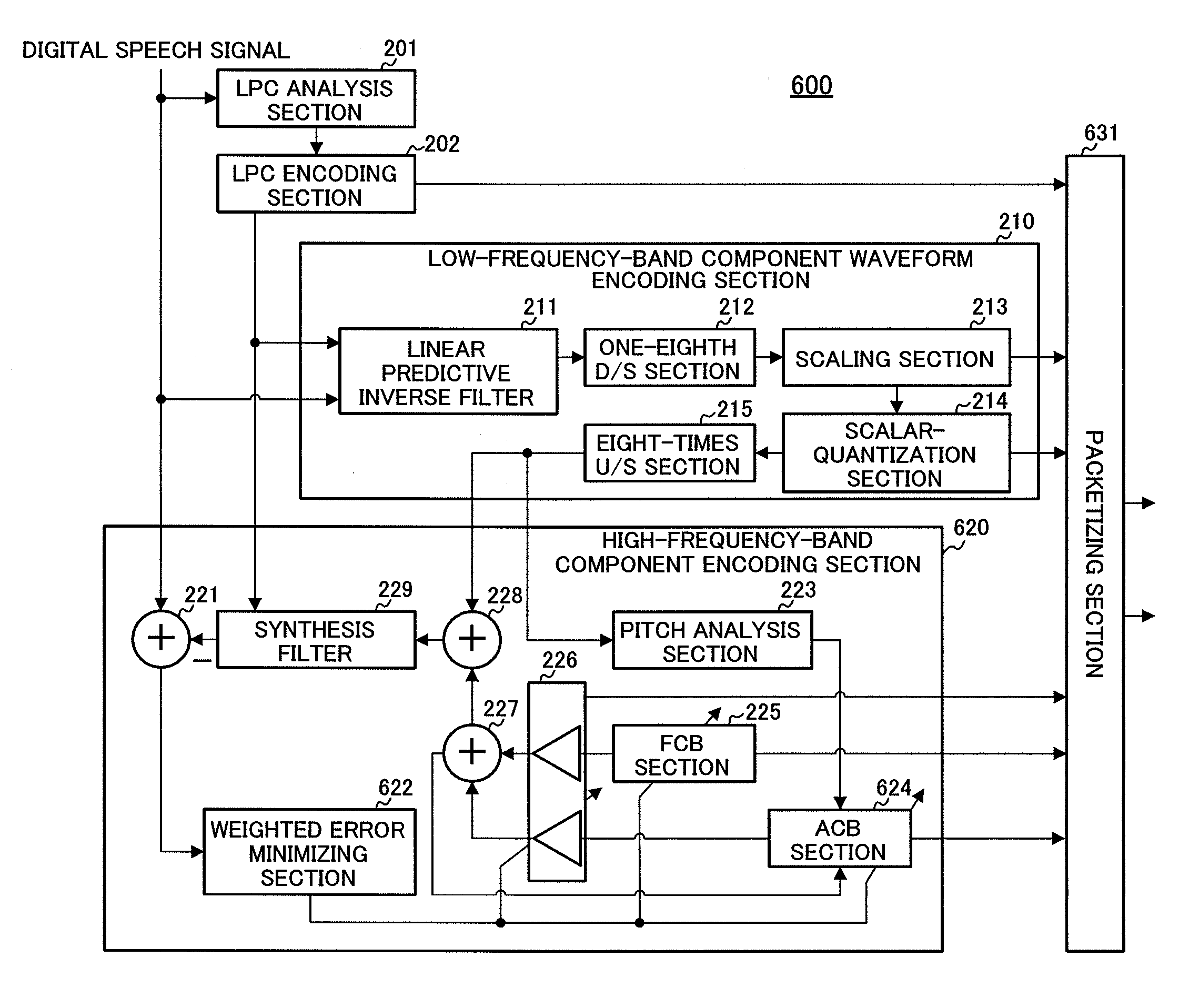
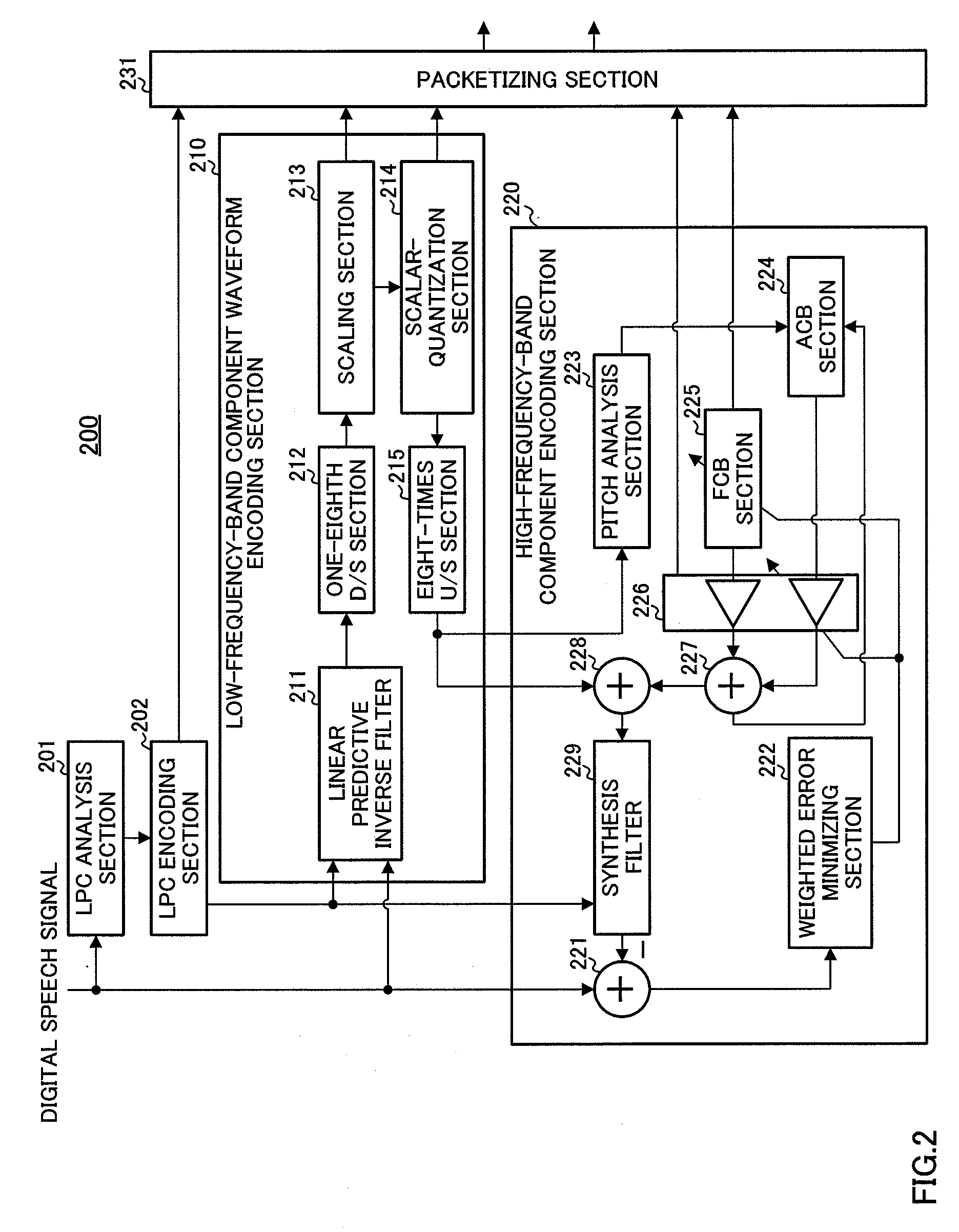
Low-frequency-band component and high-frequency-band audio encoding/decoding apparatus, and communication apparatus thereof
InactiveUS7848921B2Improve voice qualityError propagationSpeech analysisLow frequency bandCommunication device
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
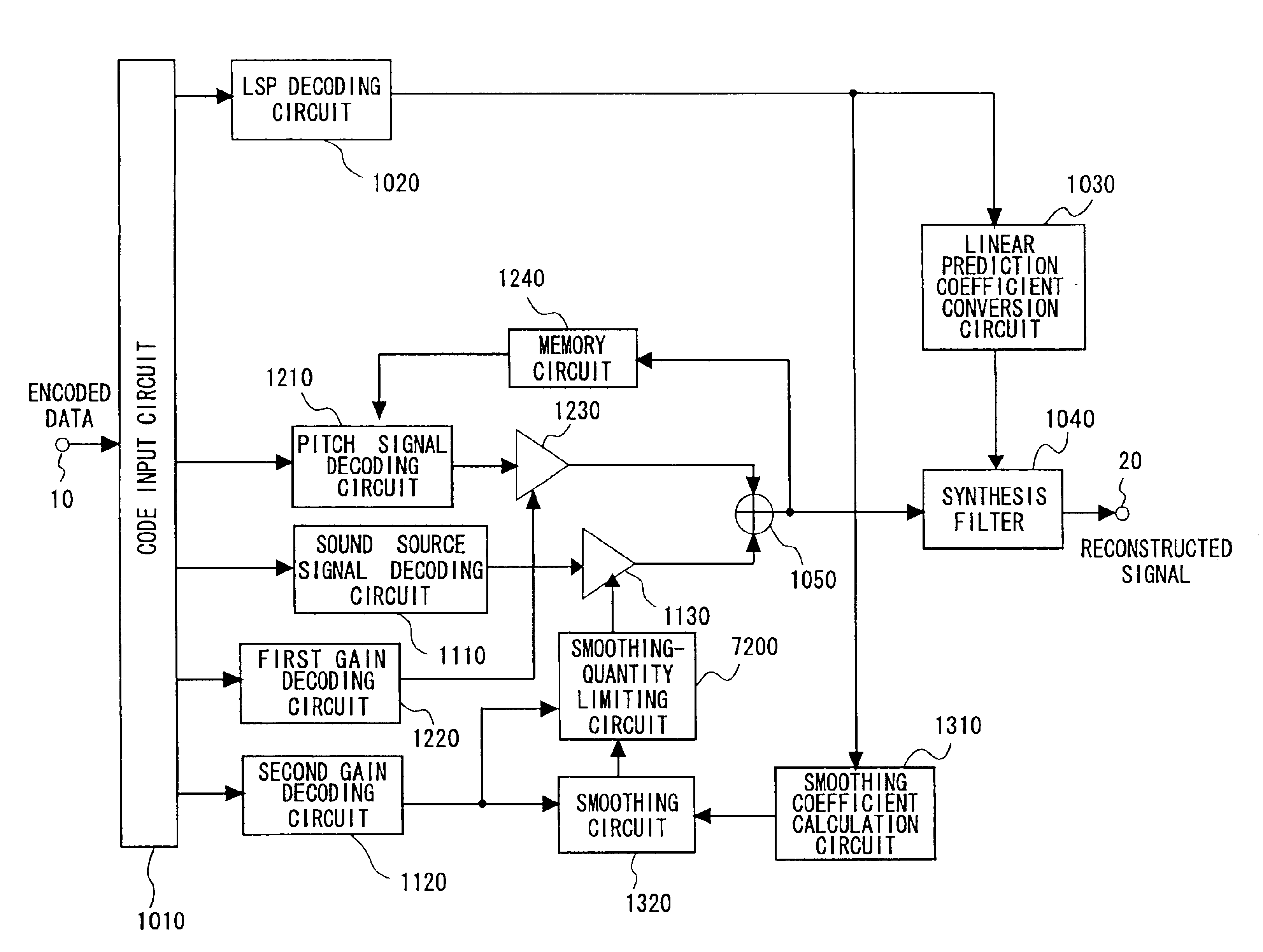
Speech signal decoding method and apparatus, speech signal encoding/decoding method and apparatus, and program product therefor
InactiveUS6910009B1Avoid it happening againSpeech analysisCode conversionSound sourcesExcitation signal
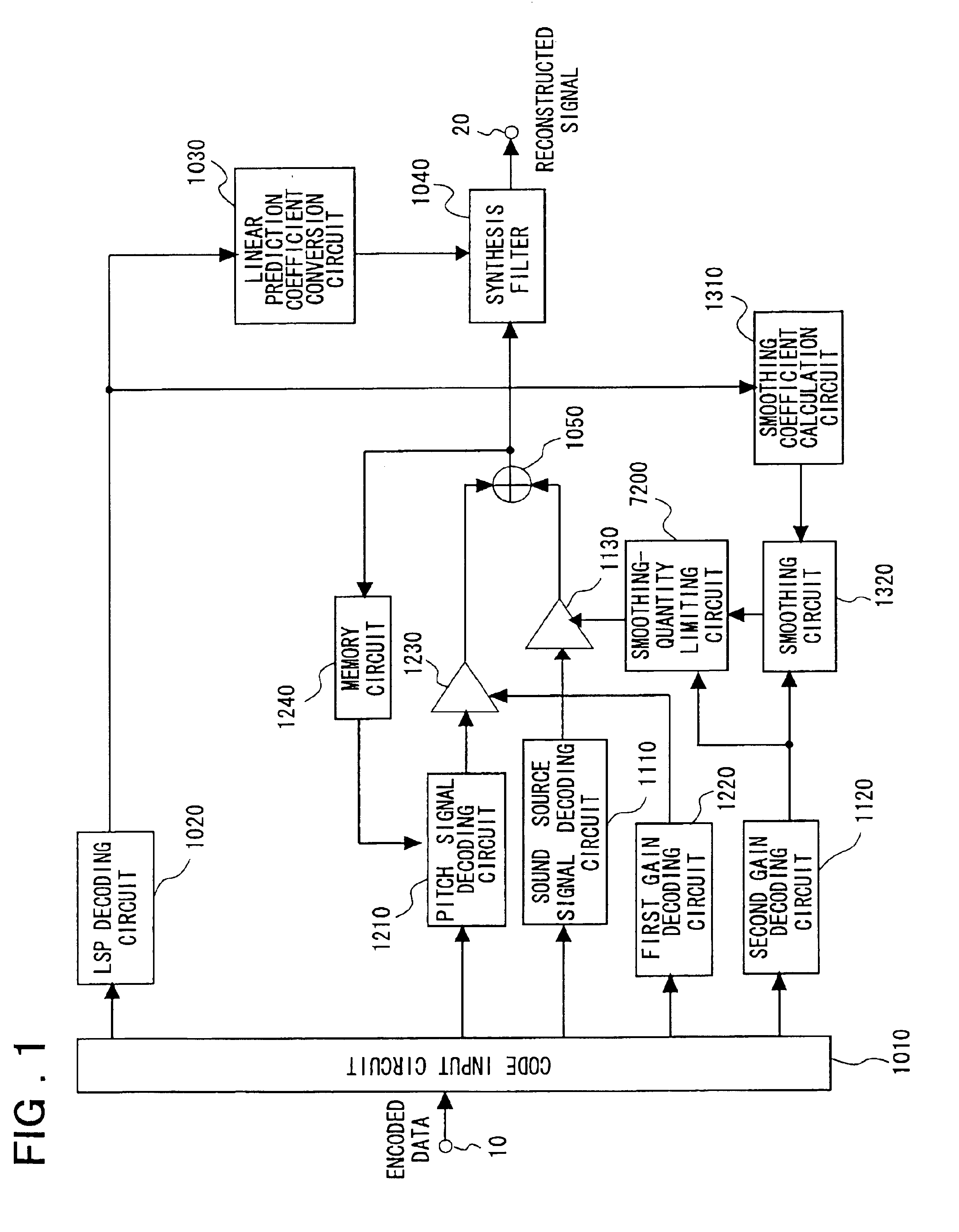
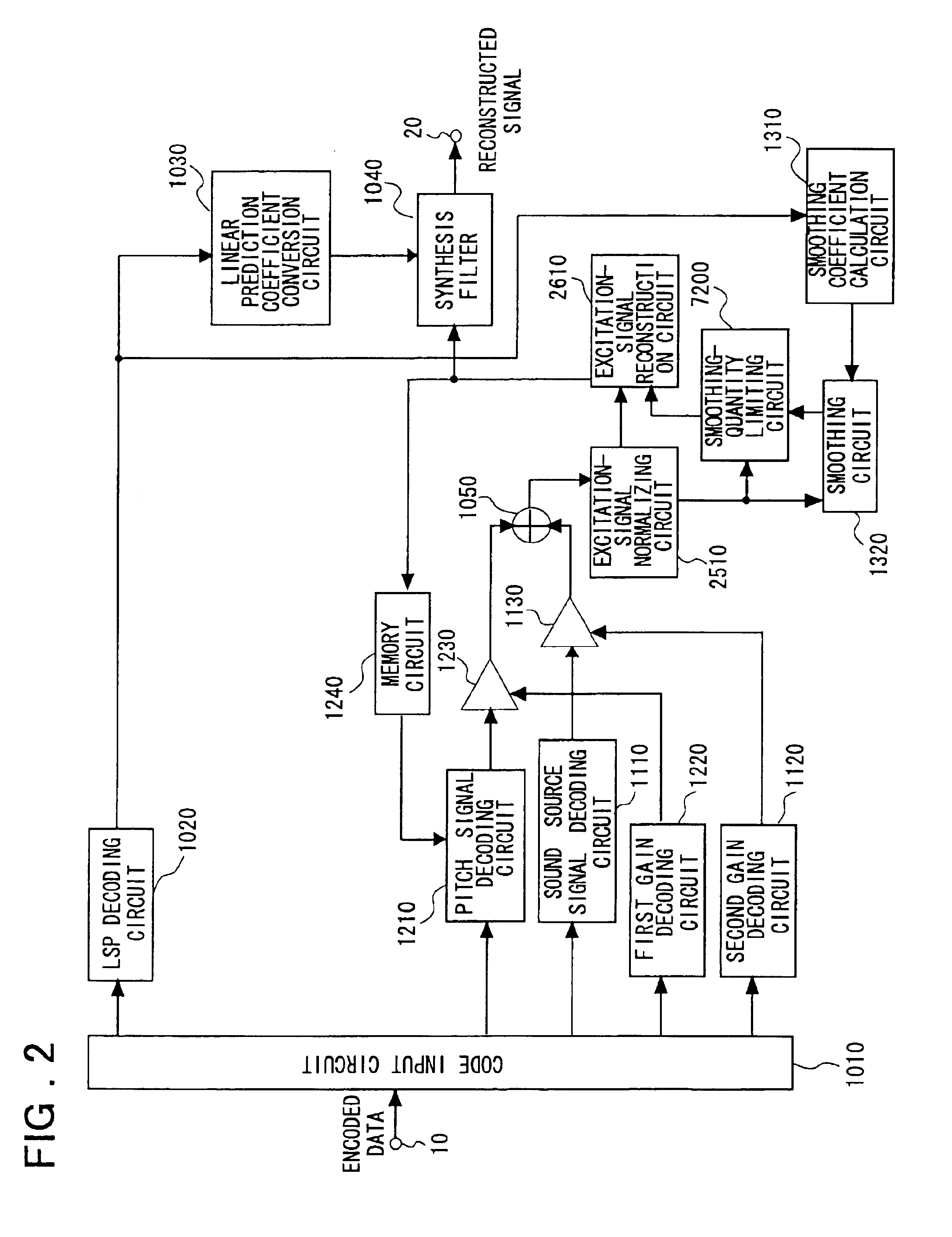
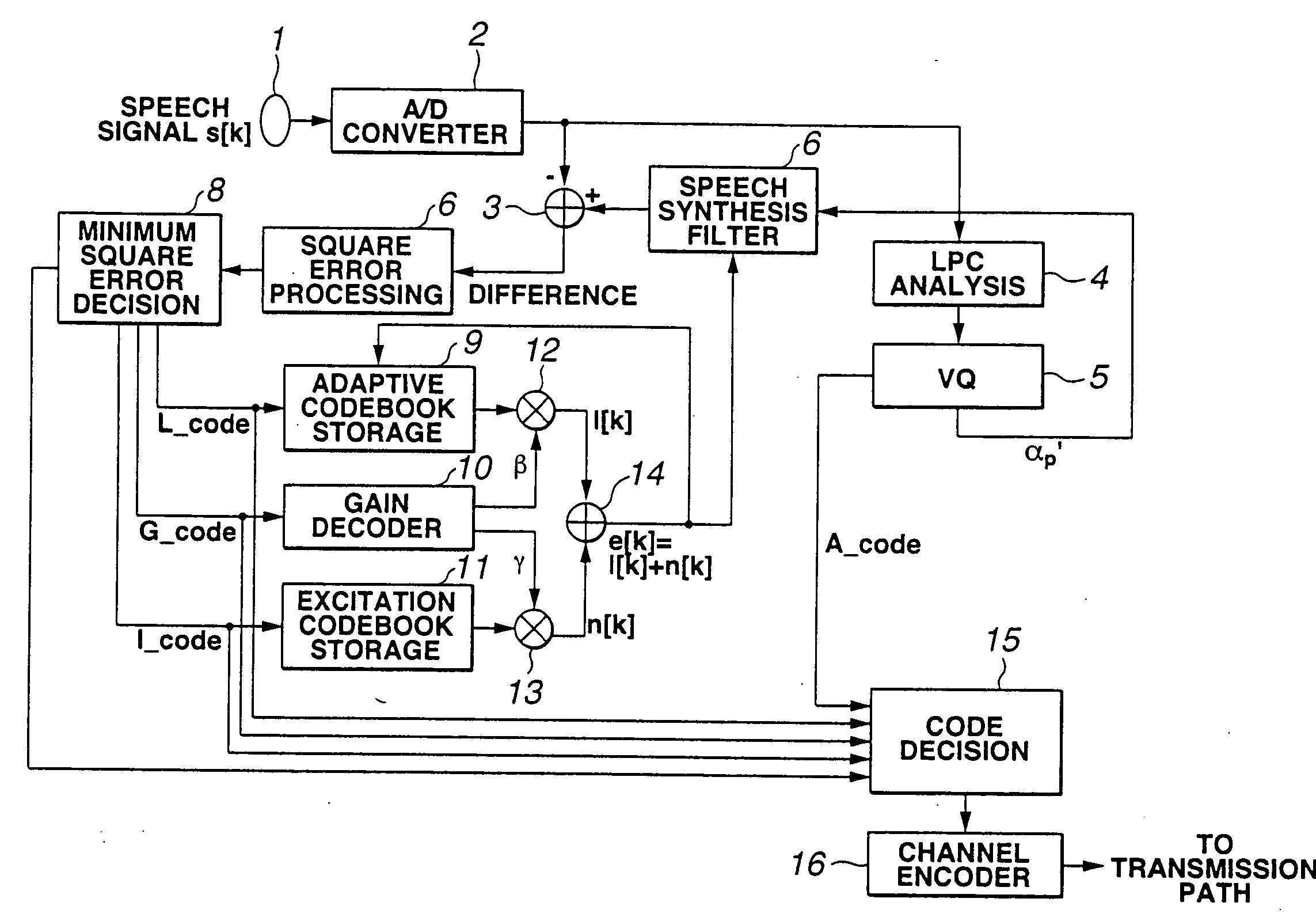
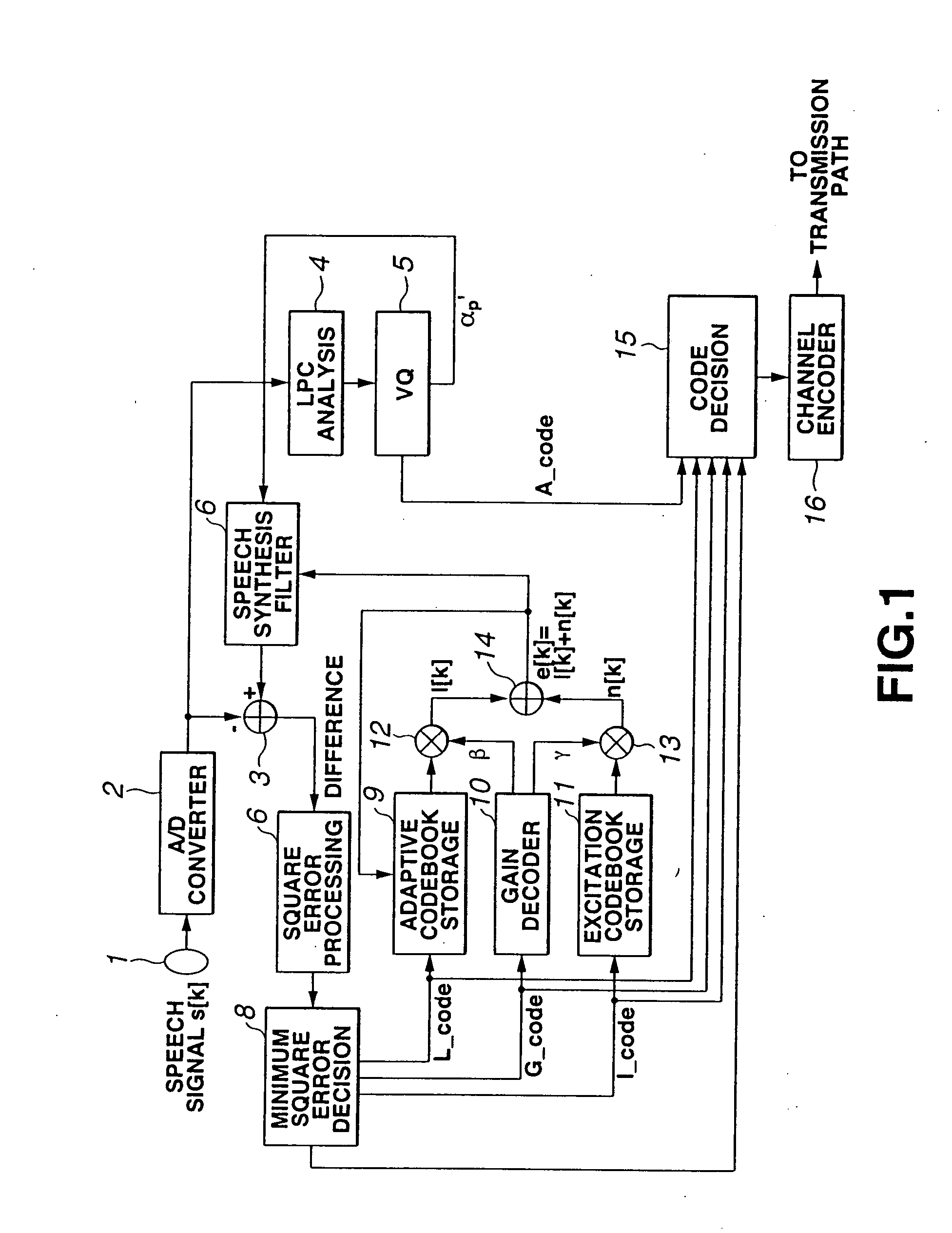
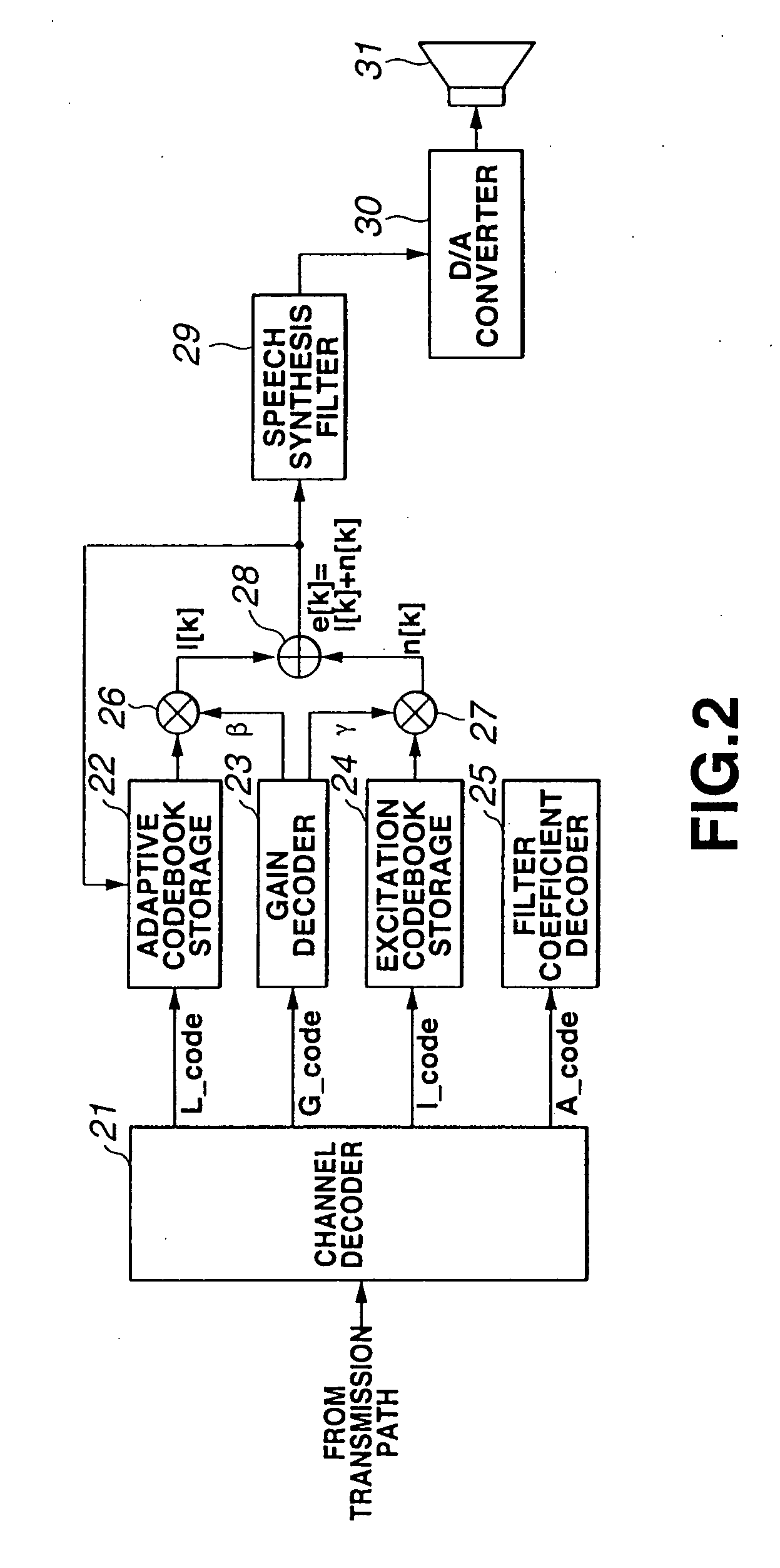
The quality of reconstructed speech on which background noise is superimposed is improved in a speech signal decoding apparatus for generating a speech signal by driving a filter, which is constituted by linear prediction coefficients, by an excitation signal. A smoothing circuit smoothes sound source gain in a noise segment using sound source gain that was obtained in the past. A smoothing-quantity limiting circuit calculates an amount of fluctuation represented by dividing, by the sound source gain, the absolute value of the difference between the sound source gain and the sound source gain that has been smoothed, and limits the value of the smoothed gain in such a manner that the amount of fluctuation will not exceed a certain threshold value.
Owner:NEC CORP
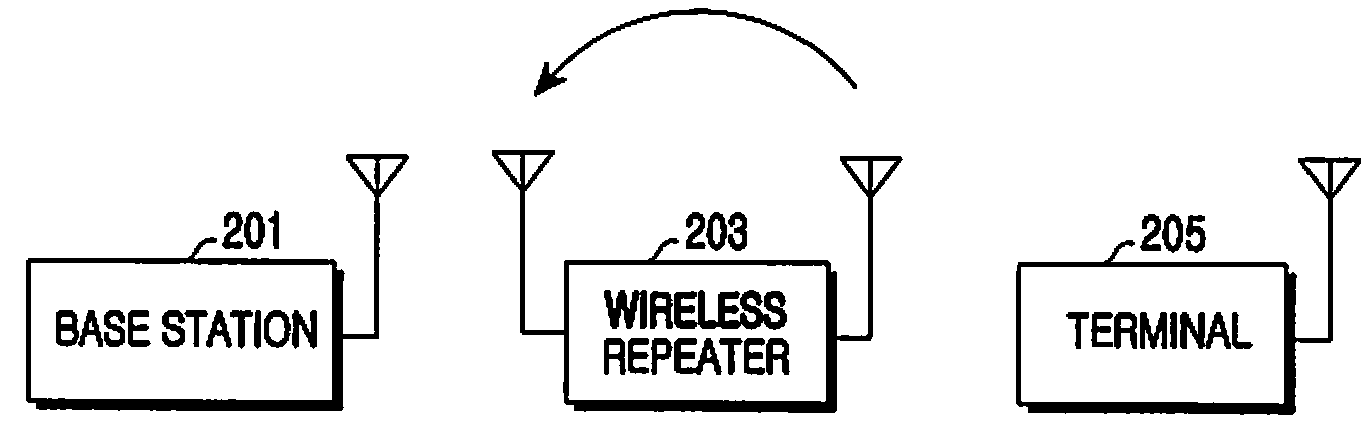
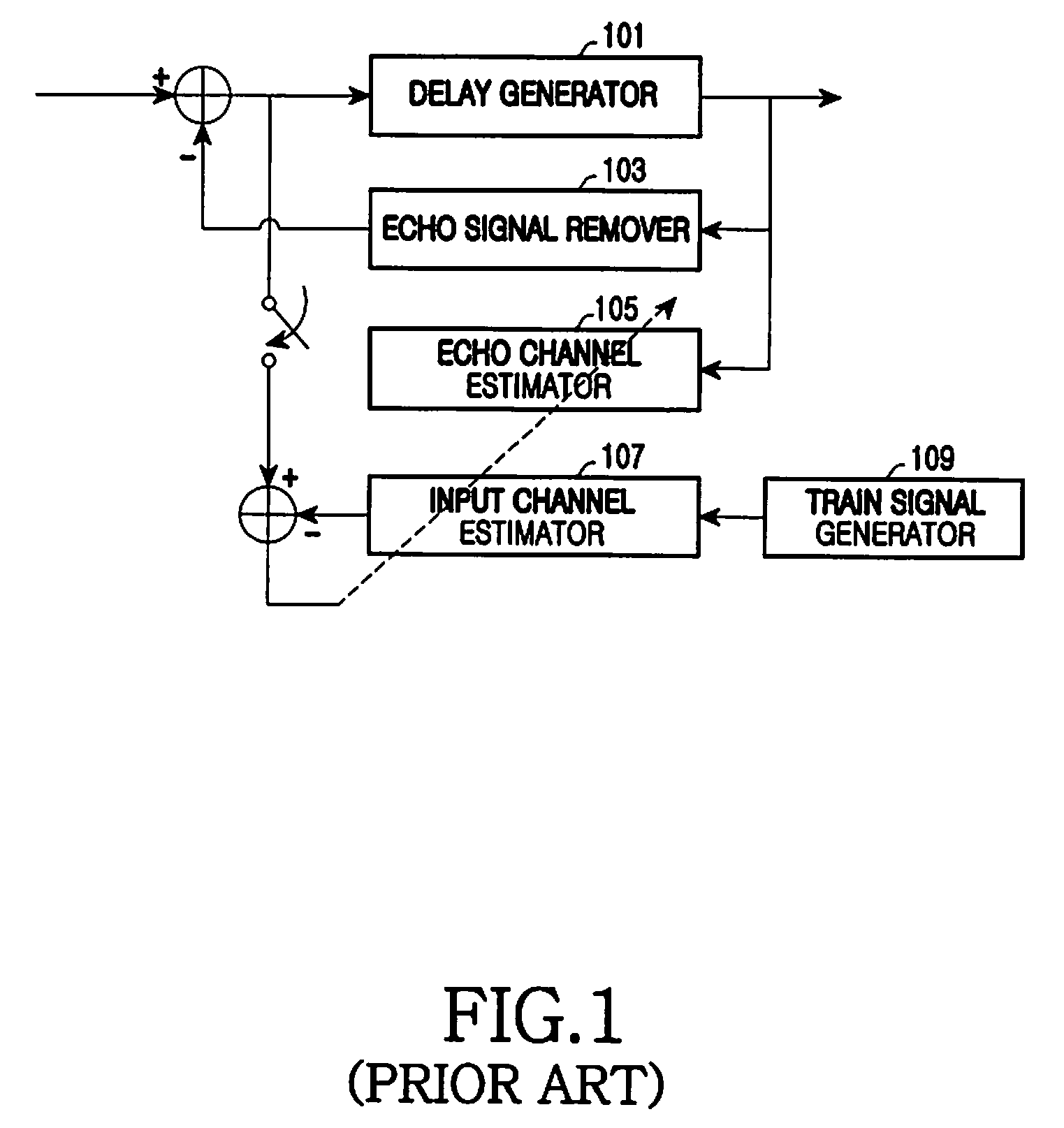
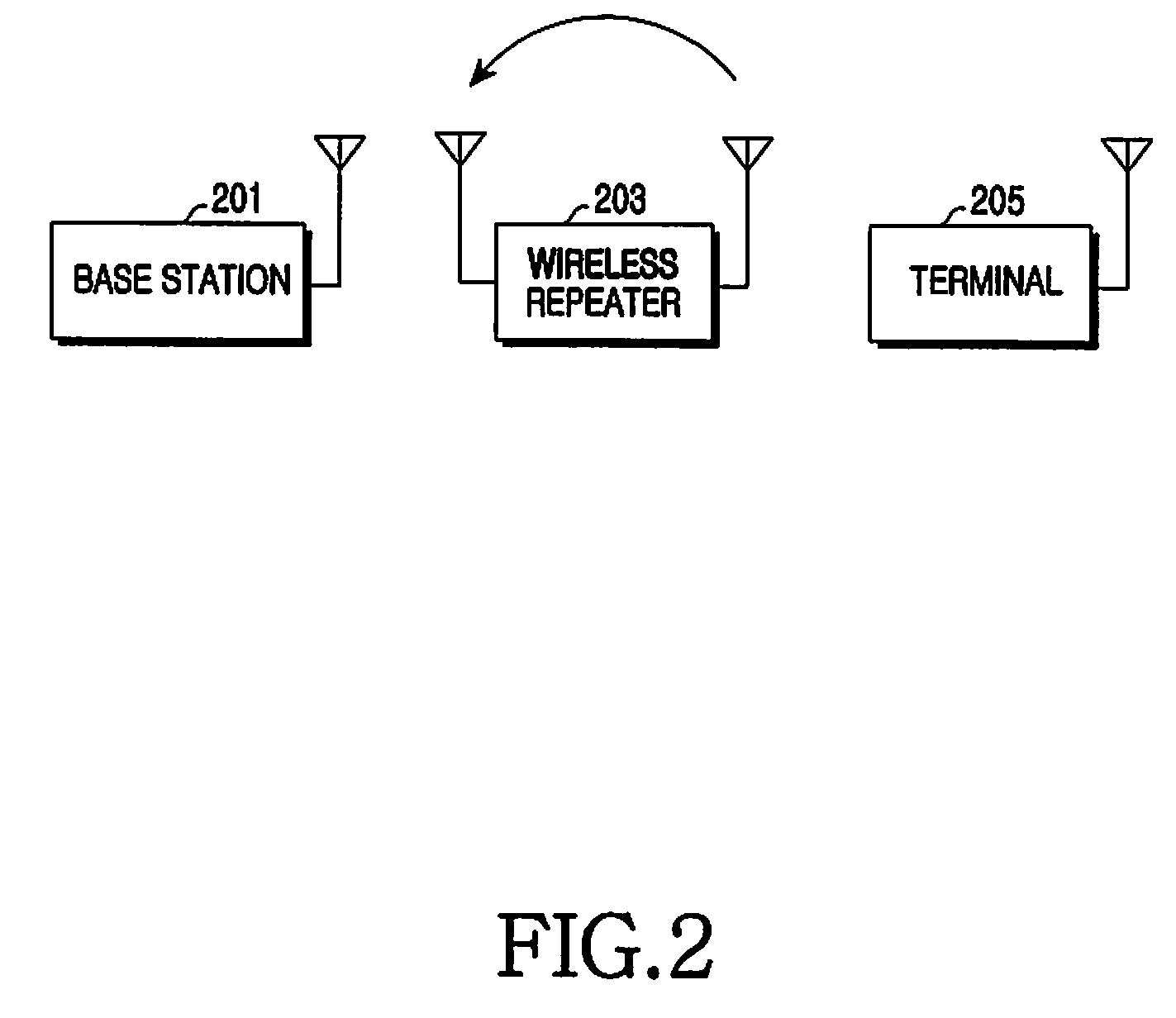
Method and apparatus for estimating/removing echo signal using channel coefficient predicting technique in multi-carrier system
A method and an apparatus are provided for estimating and removing interference of a signal at a wireless repeater operating in a multi-carrier system. In the method, a current echo channel linear prediction coefficient, which represents a coefficient between a current train signal section and a previous train signal section, is estimated using a current echo channel coefficient estimated in the current train signal section and a previous echo channel coefficient generated in the previous train signal section. A next echo channel coefficient is estimated using the current echo channel coefficient, the previous echo channel coefficient, and the current echo channel linear prediction coefficient. An echo channel coefficient outside a train signal section is estimated using the current echo channel coefficient and the next echo channel coefficient.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Wide-band speech coder/decoder and method thereof
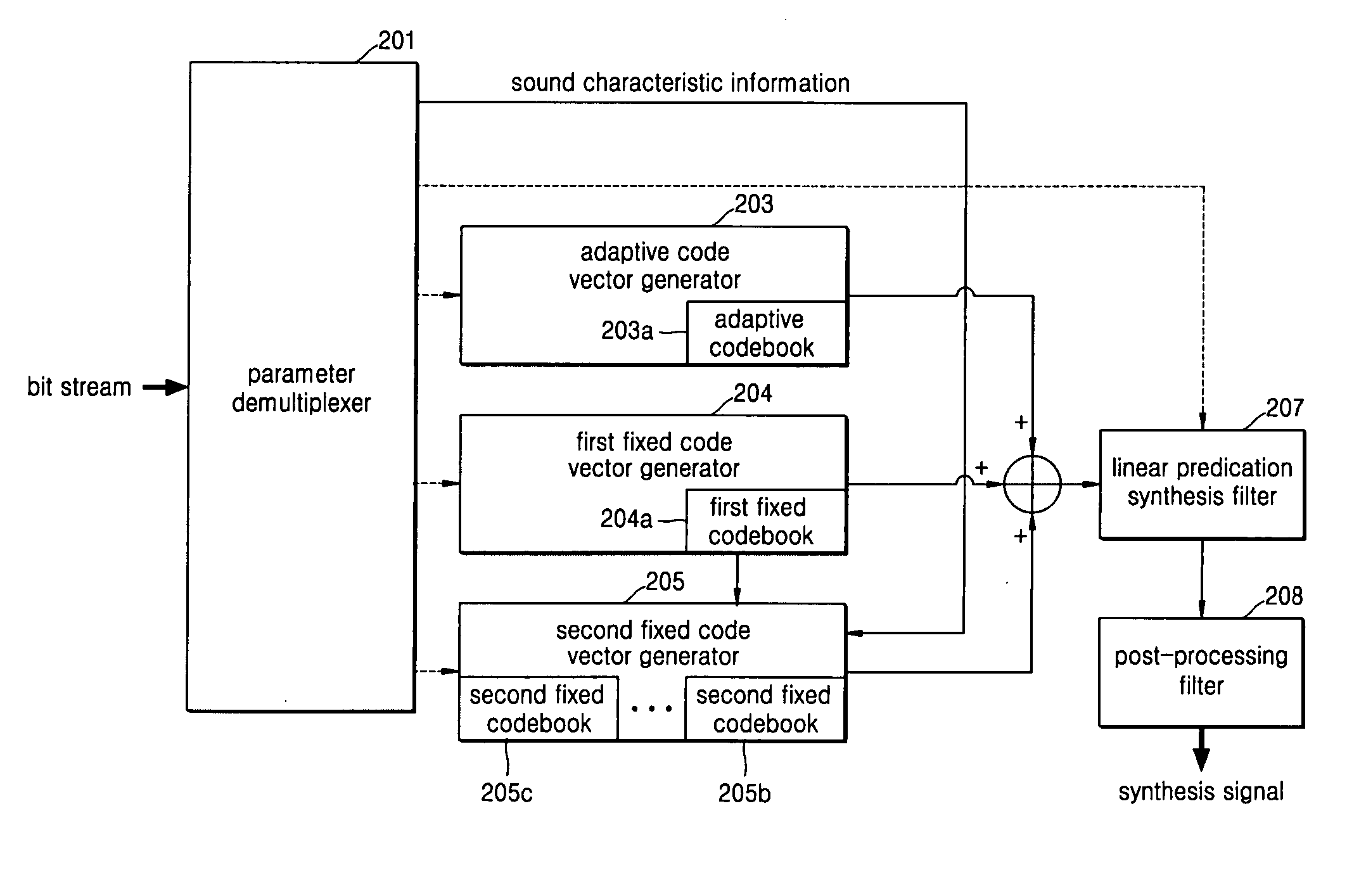
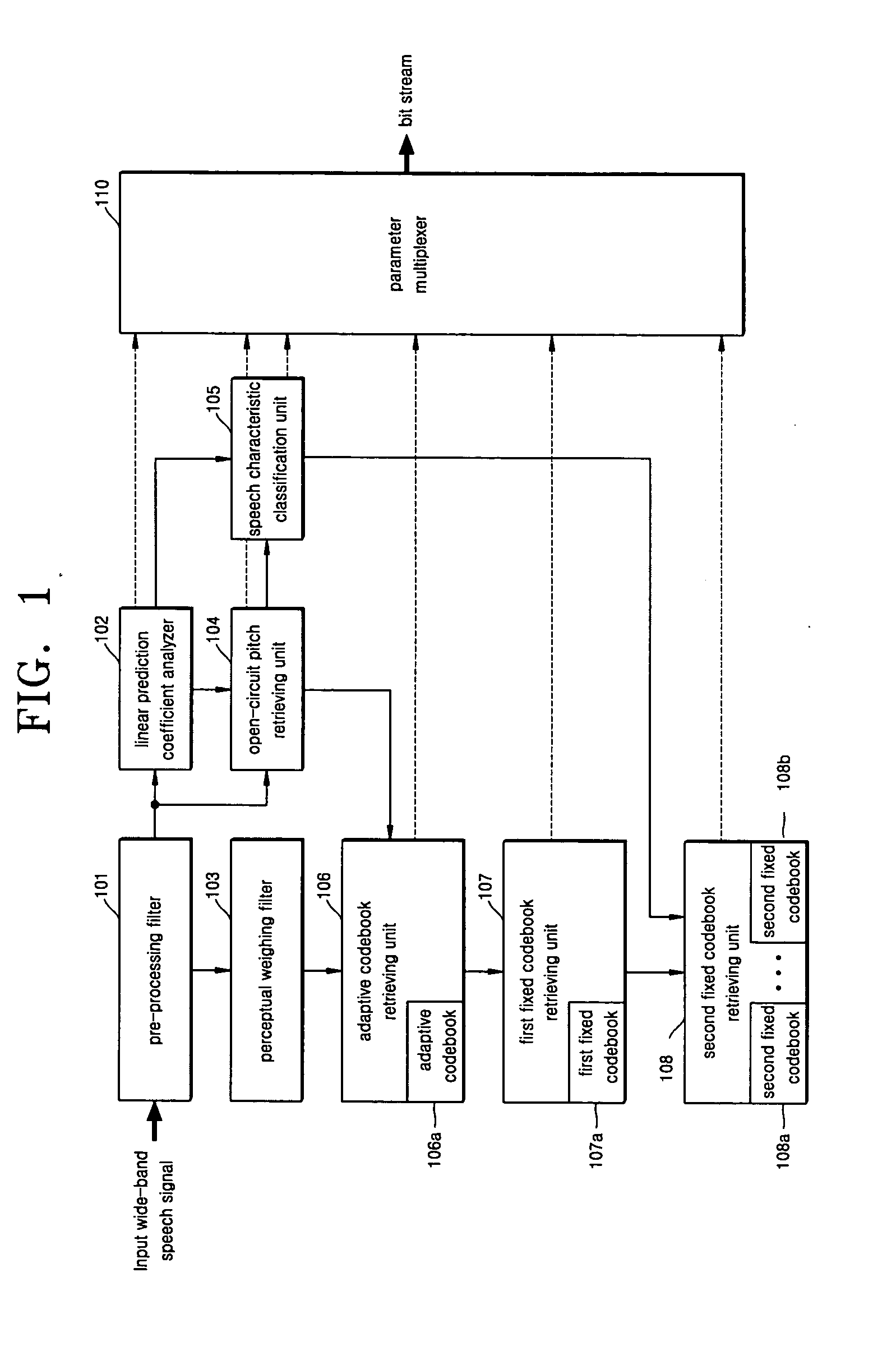
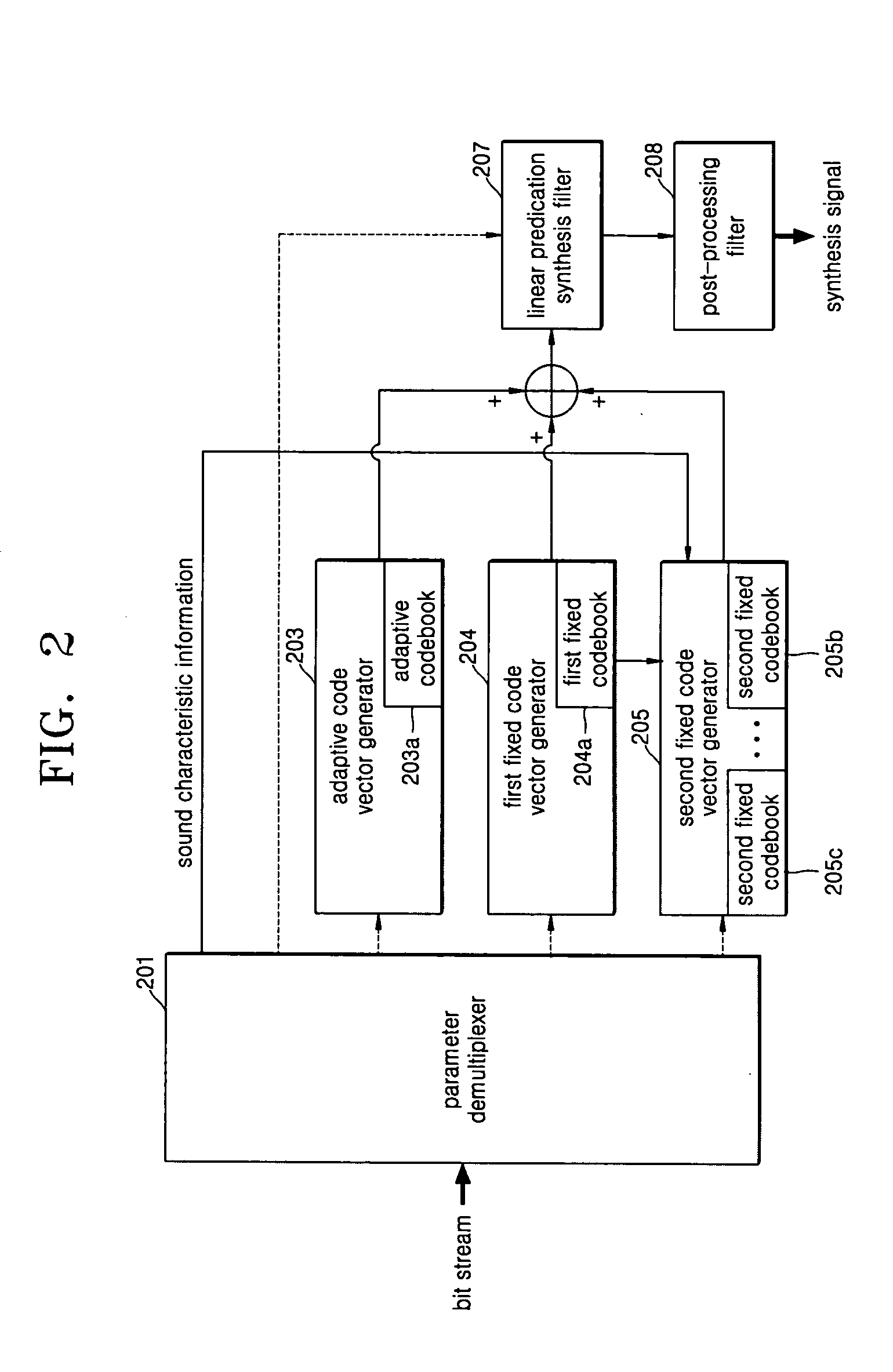
InactiveUS20050010402A1Improve voice qualitySmall amount of calculationSpeech analysisMultiplexingTarget signal
A wide-band speech coder and a method thereof and a wide-band speech decoder and a method thereof are provided. The wide-band speech coder includes a speech characteristic classification unit, which stipulates a characteristic of speech corresponding to a current frame statistically using an open-circuit pitch value and a linear prediction coefficient in which a wide-code speech signal to be coded is perceptual weigh filtered, an adaptive codebook retrieving unit, which retrieves a pitch delay value around the open-circuit pitch value, calculates a pitch gain value, generates an adaptive codebook contribution signal corresponding to the retrieved pitch delay value, and outputs a difference between the generated adaptive codebook contribution signal and the perceptual weigh filtered signal as a first fixed codebook target signal, a first fixed codebook retrieving unit, which obtains a first fixed codebook index that can express the first fixed codebook target signal most properly, and a first fixed codebook gain value, generates a first fixed codebook contribution signal corresponding to the retrieved index, and outputs a difference between the first generated fixed codebook contribution signal and the first fixed codebook target signal as a second fixed codebook target signal, a second fixed codebook retrieving unit, which includes at least two second fixed codebooks according to a speech characteristic, selects a second fixed codebook according to the speech characteristic, and retrieves second fixed codebook indices that can express the second fixed codebook target signal most properly, and second fixed codebook gain values, and a parameter multiplexer, which quantizes and multiplexes the speech characteristic information, the pitch delay value, the pitch gain value, the first fixed codebook index, the first fixed codebook gain value, the second fixed codebook indices, and the second fixed codebook gain values, makes them as a bit stream, and transmits the bit stream to an external speech decoding terminal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
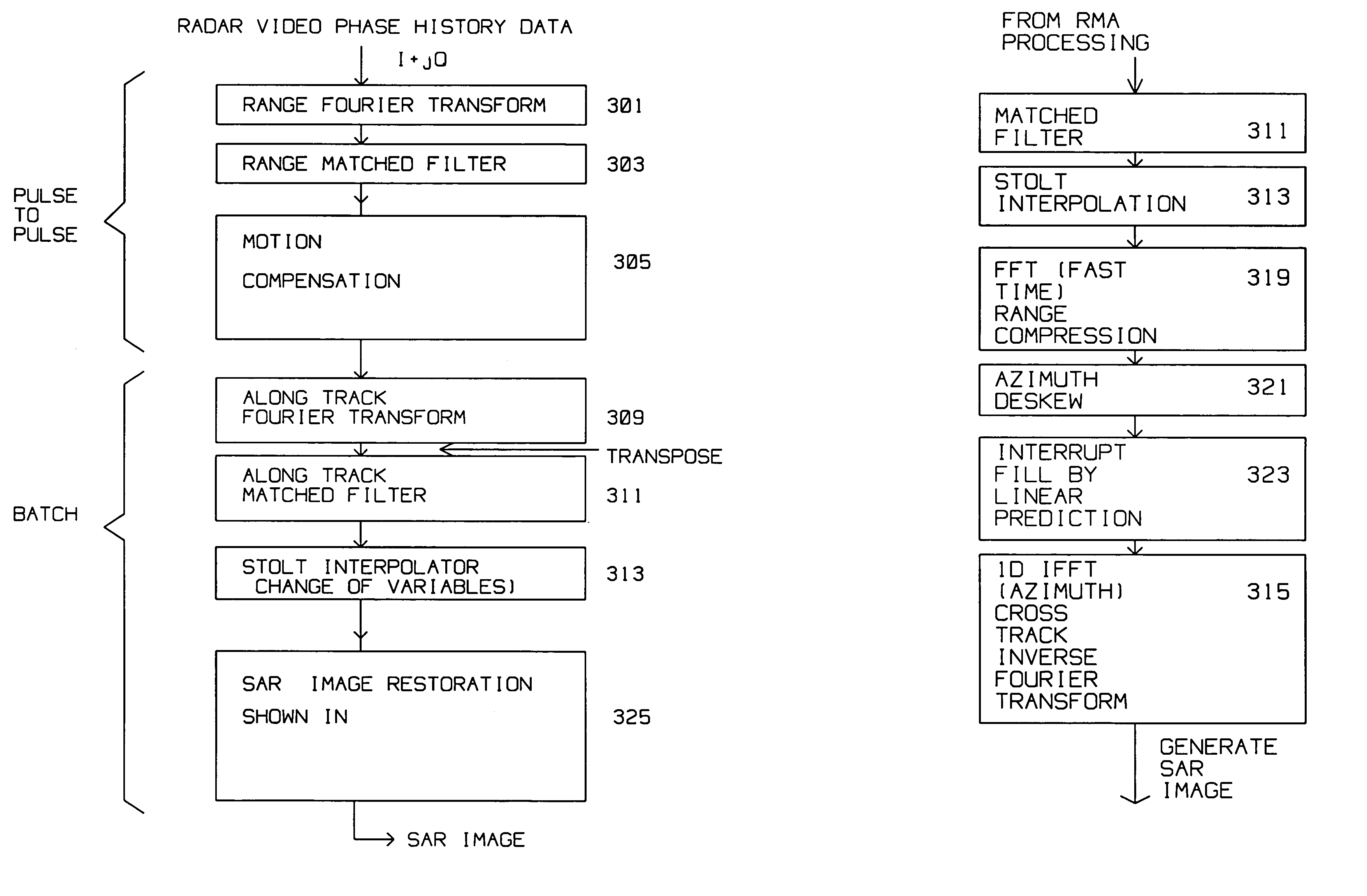
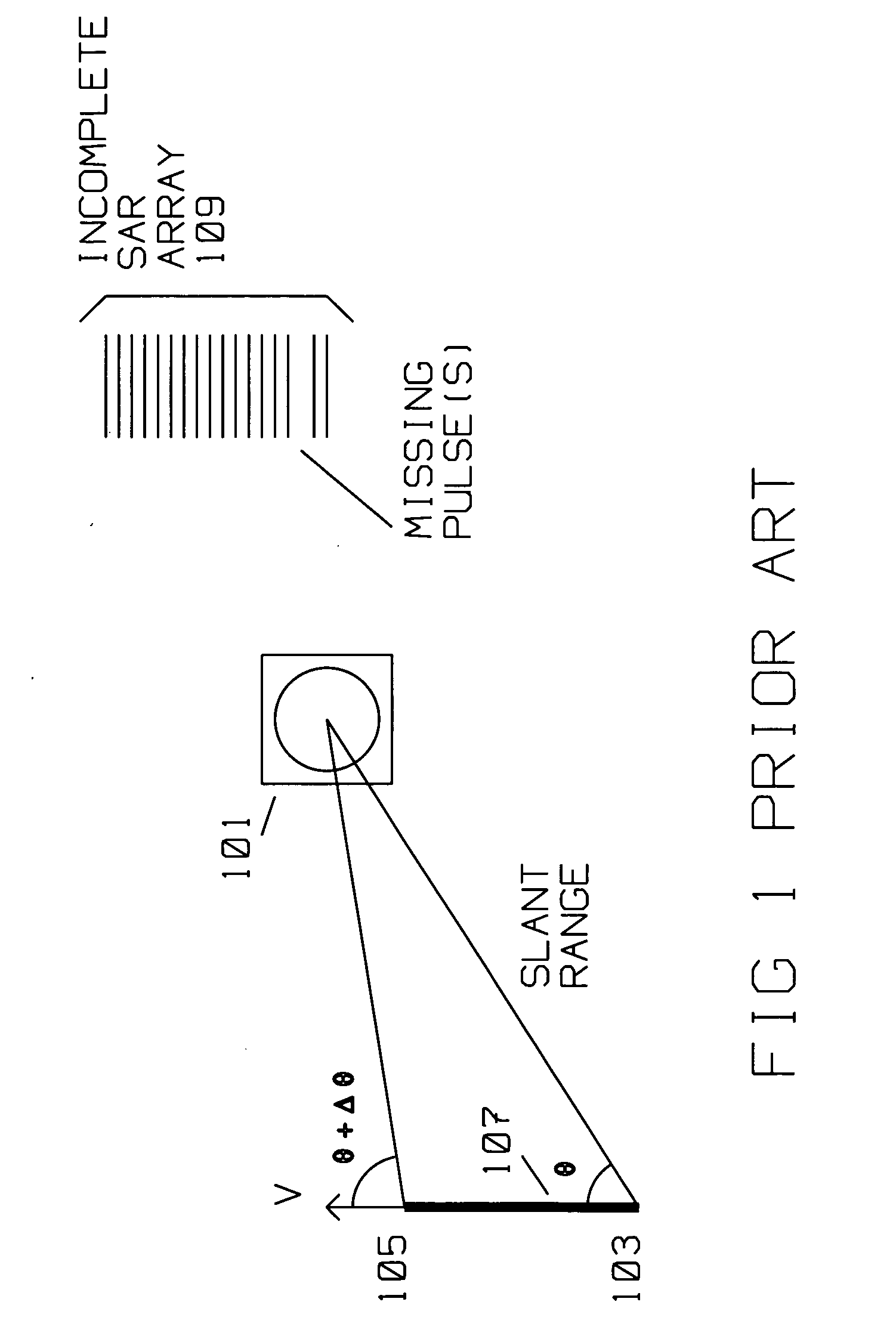
Interrupt SAR image restoration using linear prediction and Range Migration Algorithm (RMA) processing
SAR images are improved by a method for acquiring a synthetic aperture image from a sequence of periodic pulse returns where the sequence of periodic pulse returns is interspersed with interrupts, i.e. missing pulses. The interrupts mark the start and end of one or more segments, where the segments contain the periodic pulse returns form the SAR image. The method comprises the steps of:converting said pulse returns into a digital stream;performing an azimuth deskew on said digital stream to obtain a deskewed digital stream;forming a forward-backward data matrix from the deskewed digital stream for one or more segments;forming an average segment covariance from the forward-backward data matrix;computing a model order for the average segment covariance;computing one or more linear prediction coefficients using data contained in the forward backward data matrix, and model order;using the linear prediction coefficients to compute missing pulse returns belonging within the interrupts.The computation for extrapolating the missing pulse returns is introduced after the Stolt interpolator in RMA processing. In computing the model order, eigenvalues are found and compared to a threshold. Roots of a linear prediction polynomial are computed, then stabilized to obtain stabilized roots. Linear prediction coefficients are reconstituted using the stabilized roots. Sub-bands are used to decrease computing time for the missing pulse returns.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method and an apparatus for processing a signal
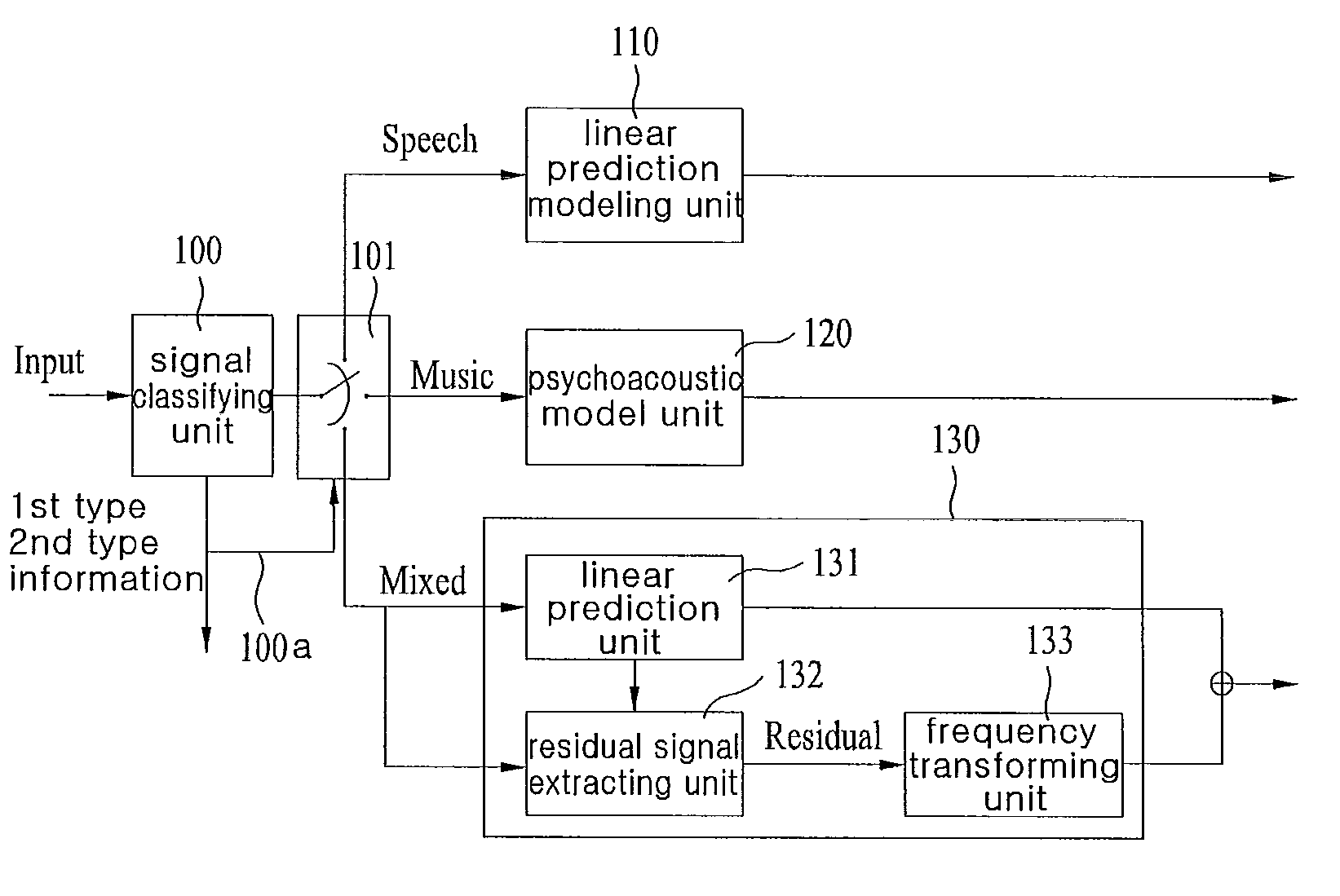
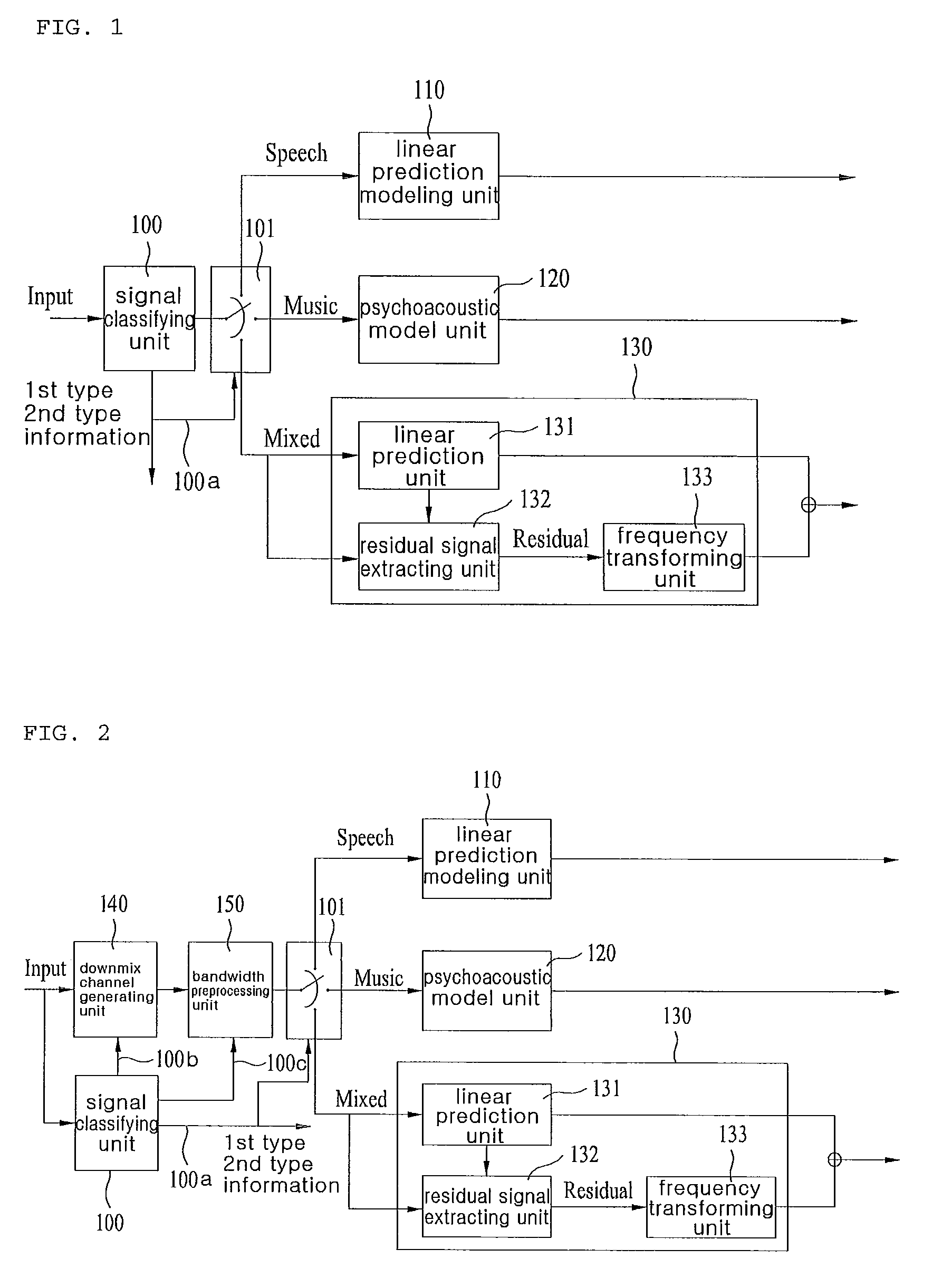
ActiveUS20100070272A1Improve efficiencySpeech analysisTime-division multiplexLinear prediction codingFrequency spectrum
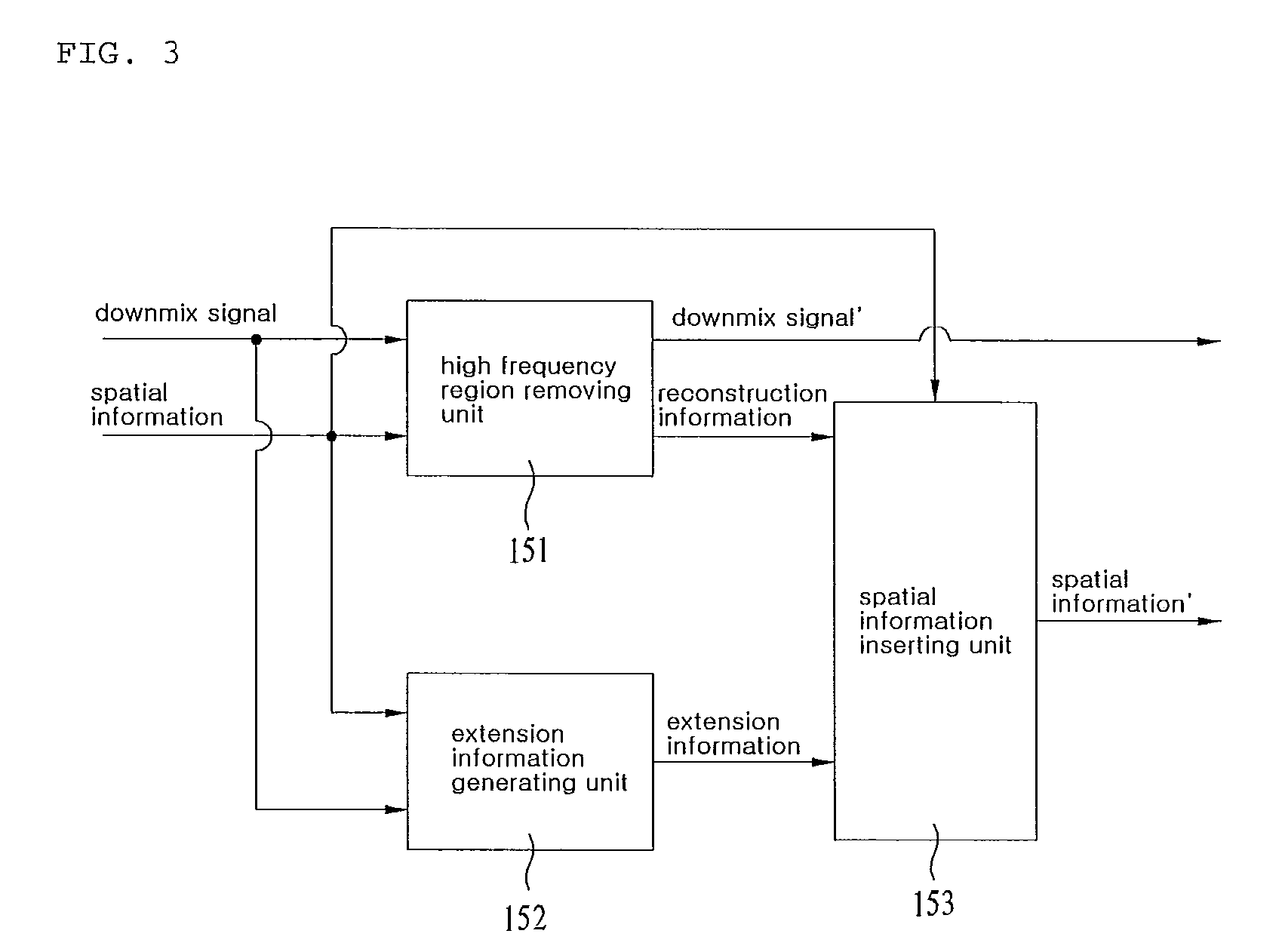
An apparatus for processing an encoded signal and method thereof are disclosed, by which an audio signal can be compressed and reconstructed in higher efficiency. An audio signal processing method includes the steps of identifying whether a coding type of the audio signal is a music signal coding type using first type information, if the coding type of the audio signal is not the music signal coding type, identifying whether the coding type of the audio signal is a speech signal coding type or a mixed signal coding type using second type information, if the coding type of the audio signal is the mixed signal coding type, extracting spectral data and a linear predictive coefficient from the audio signal, generating a residual signal for linear prediction by performing inverse frequency conversion on the spectral data, reconstructing the audio signal by performing linear prediction coding on the linear predictive coefficient and the residual signal, and reconstructing a high frequency region signal using an extension base signal corresponding to a partial region of the reconstructed audio signal and band extension information. Accordingly, various kinds of audio signals can be encoded / decoded in higher efficiency.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Perceptual coding of audio signals using separated irrelevancy reduction and redundancy reduction
InactiveUS7110953B1Conserving transmitted bitsGuaranteed normal transmissionSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumTemporal resolution
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Signal compression method and apparatus
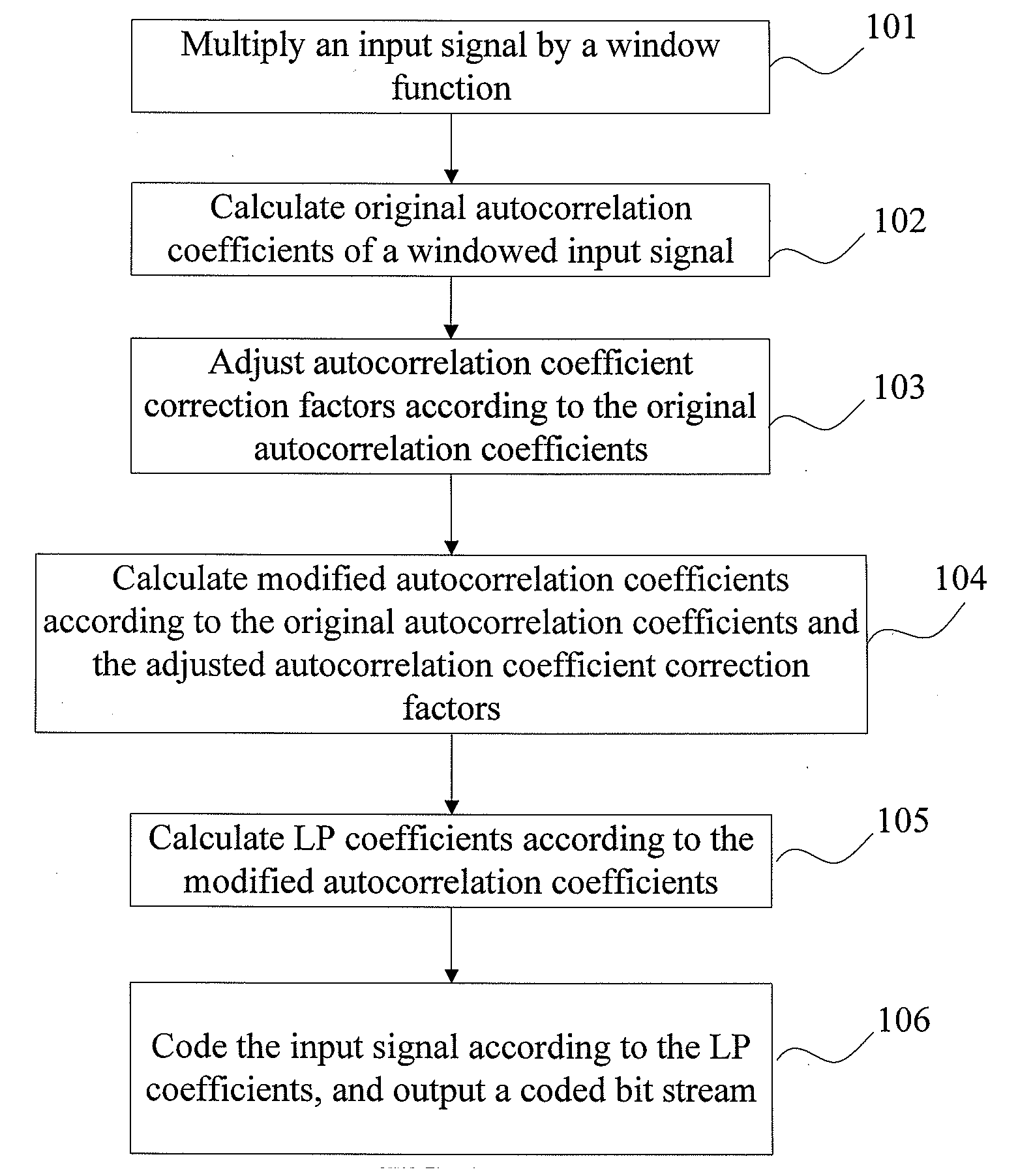
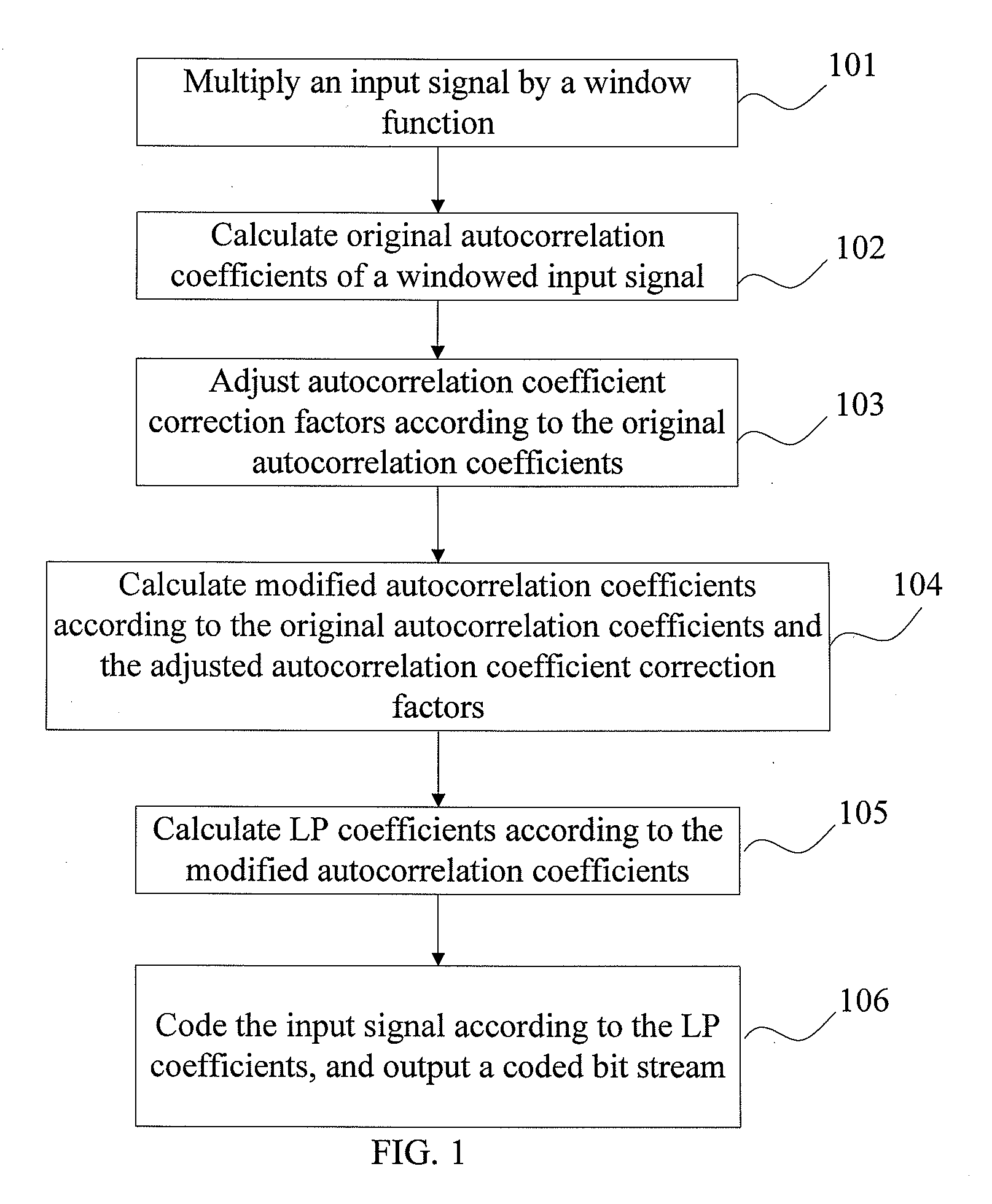
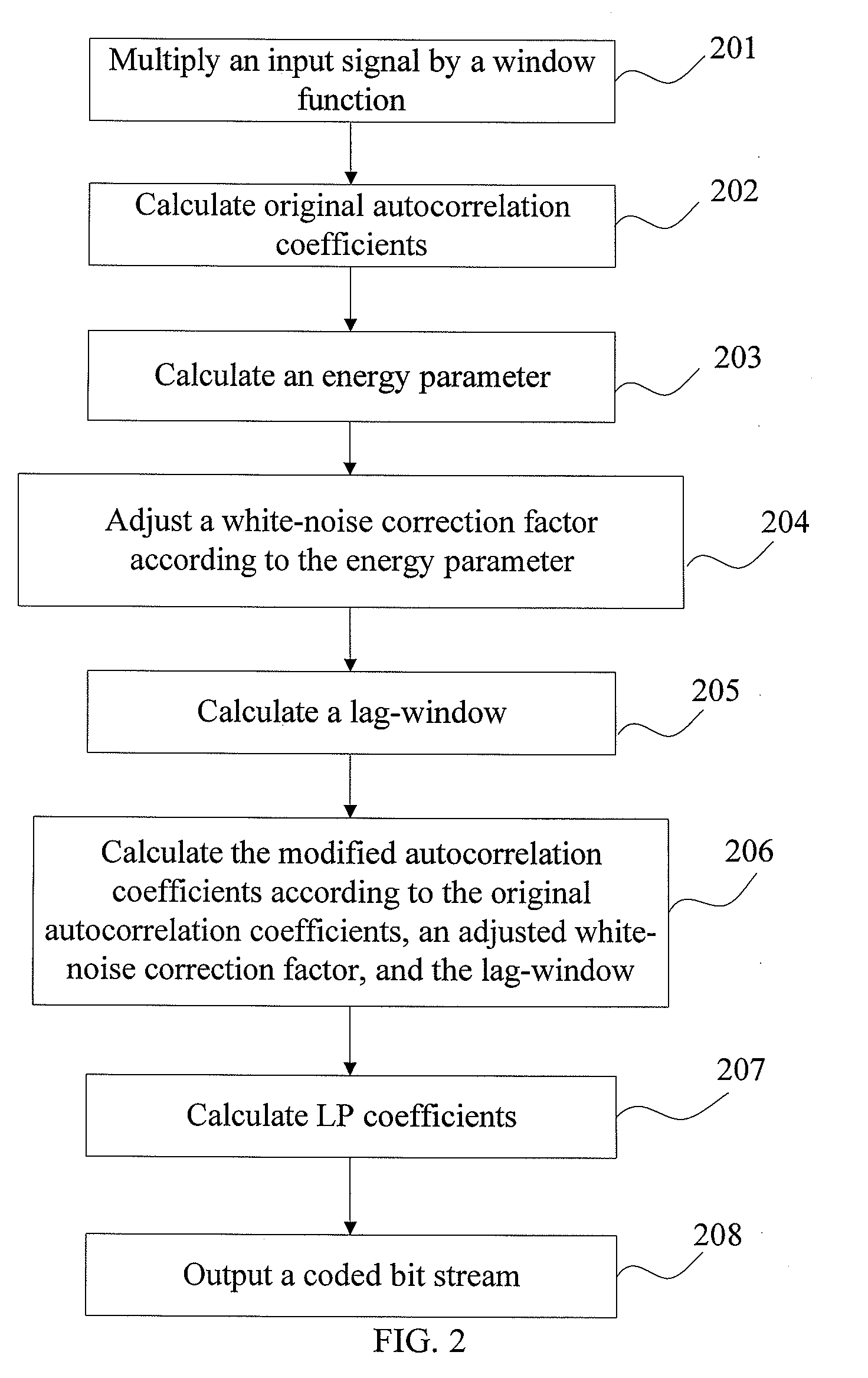
ActiveUS20100169086A1Improve compression efficiencyEasy to operateSpeech analysisCode conversionSelf correlationSignal compression
A signal compression method includes: multiplying an input signal by a window function, calculating original autocorrelation coefficients of a windowed input signal. The method also includes calculating a white-noise correction factor or a lag-window according to the original autocorrelation coefficients, and calculating modified autocorrelation coefficients according to the original autocorrelation coefficients, the white-noise correction factor and the lag-window. The method further includes calculating linear prediction coefficients according to the modified autocorrelation coefficients, and outputting a coded bit stream according to the linear prediction coefficients.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Three-dimensional acoustic processor which uses linear predictive coefficients
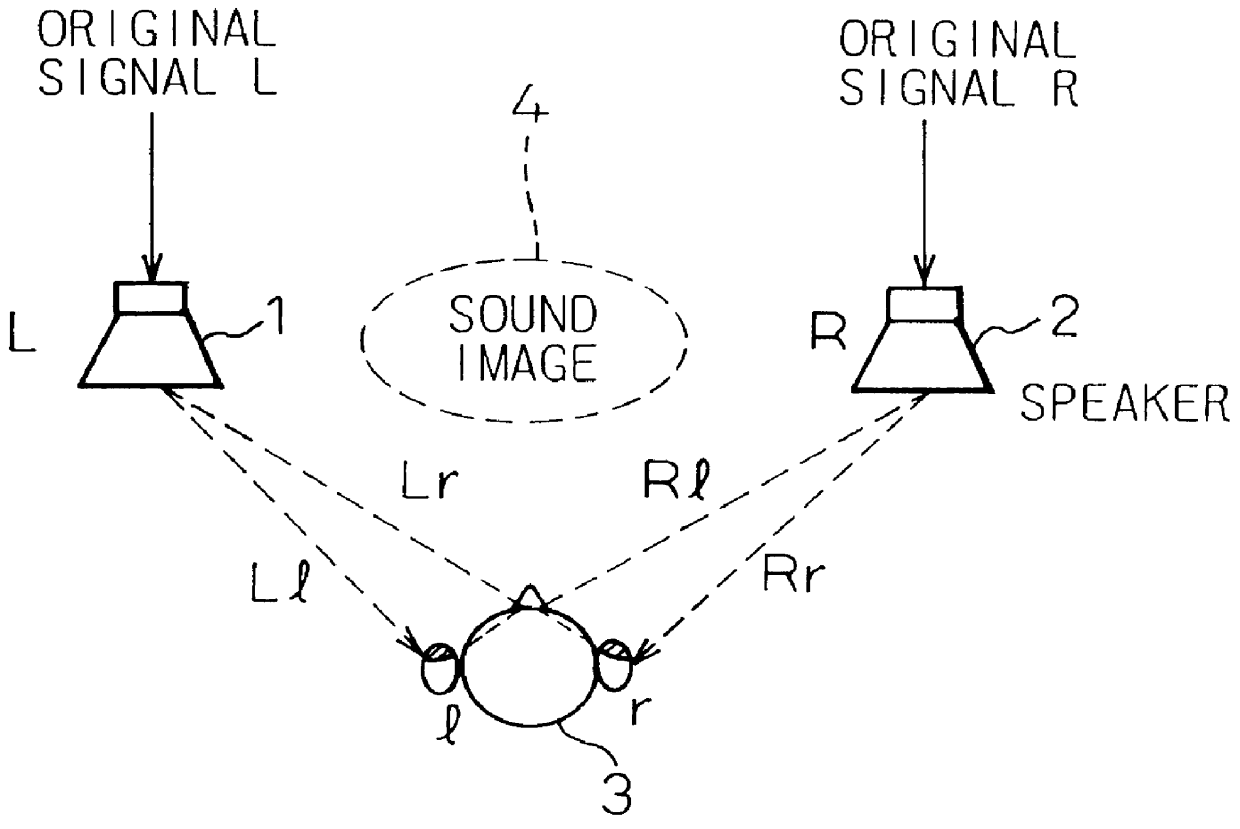
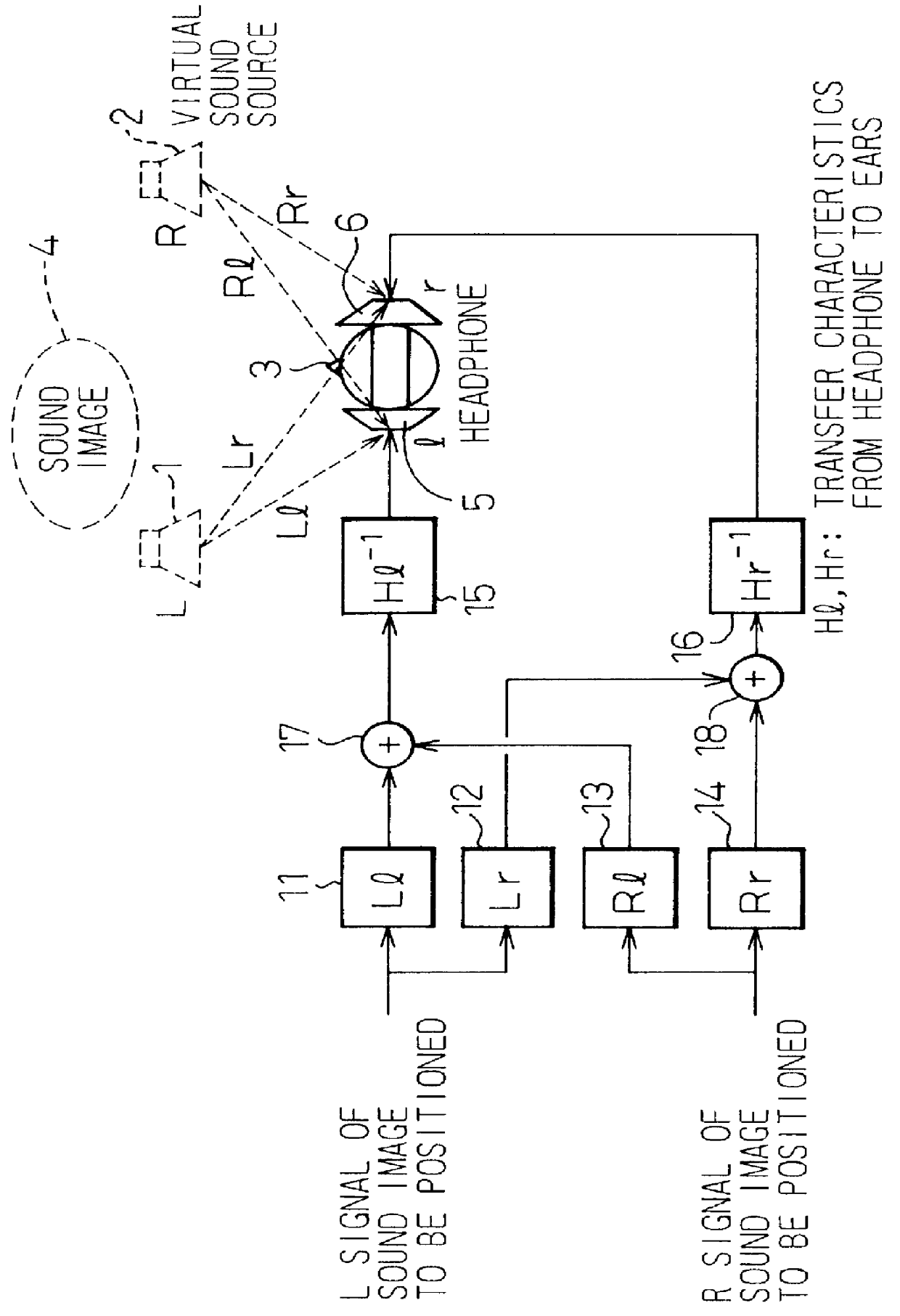
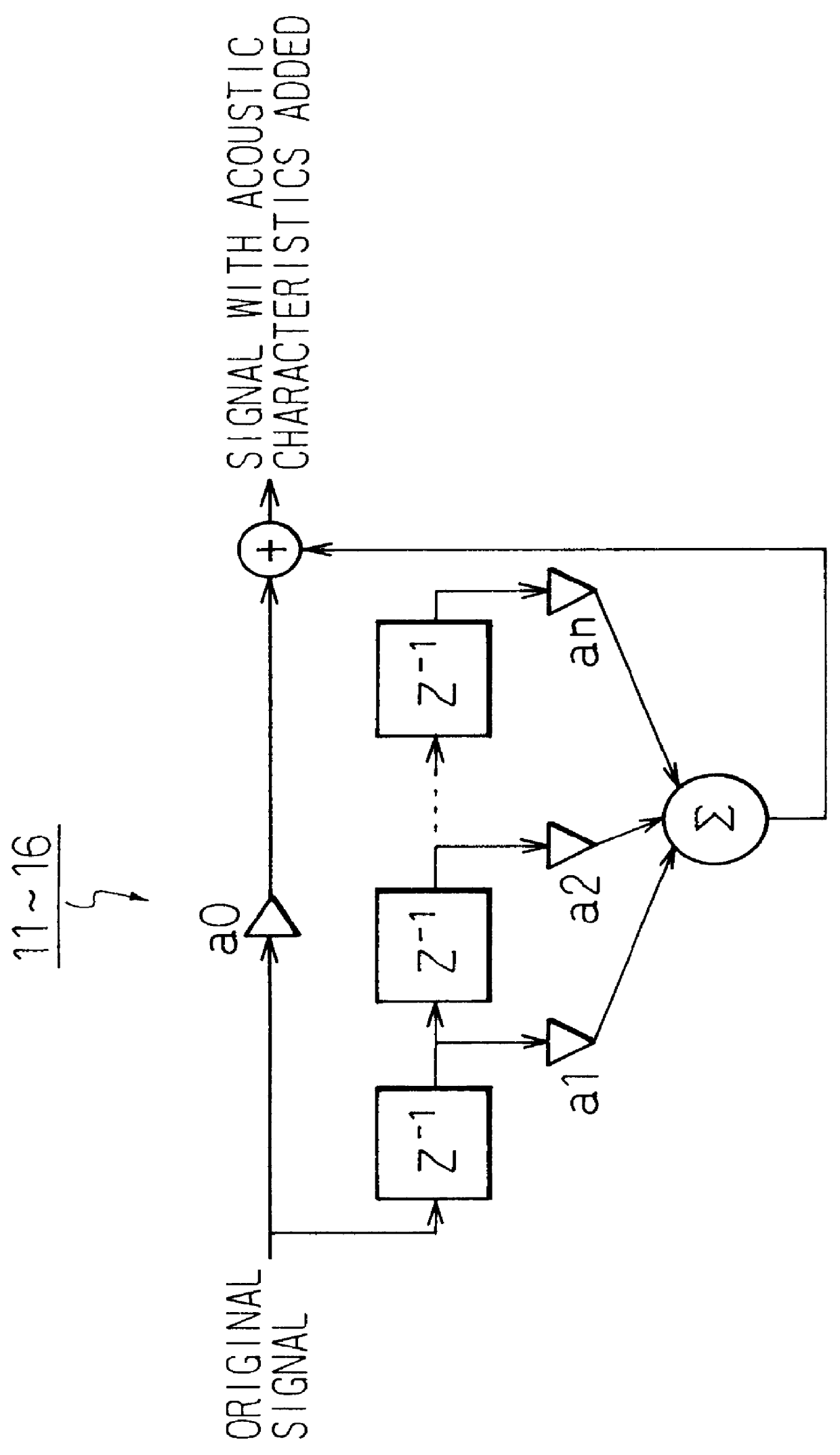
InactiveUS6269166B1Reduce amountAvoid complex processTwo-channel systemsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsHeadphonesAcoustic effect
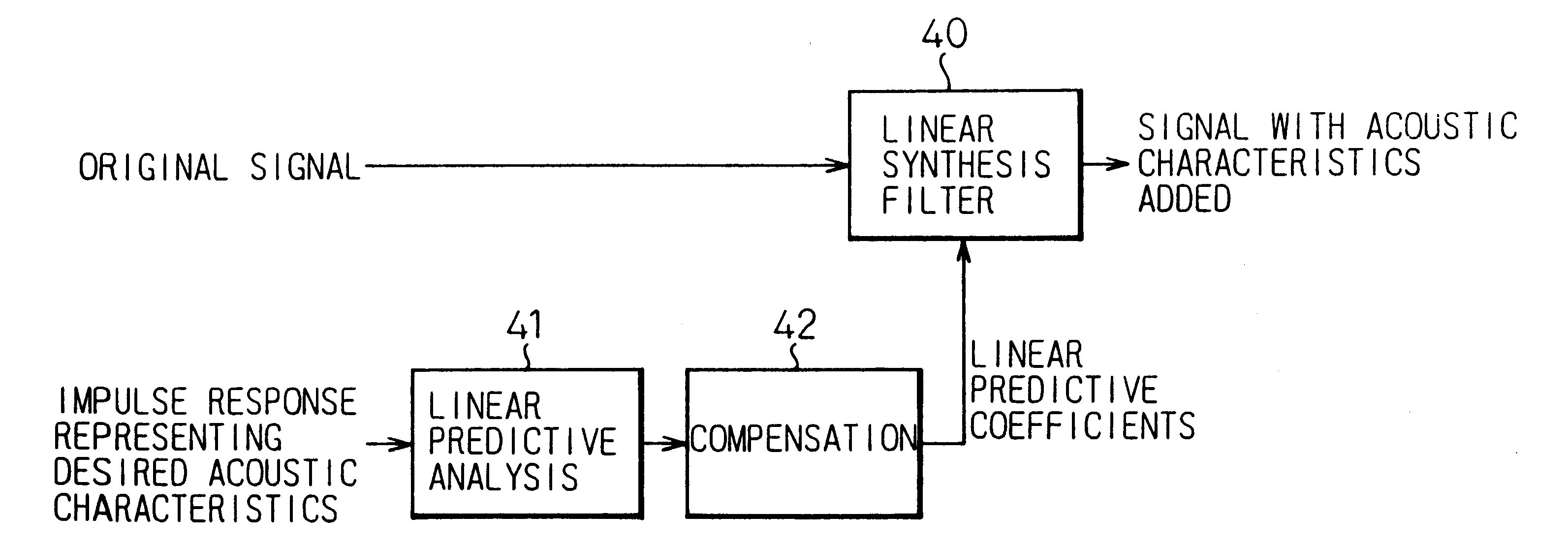
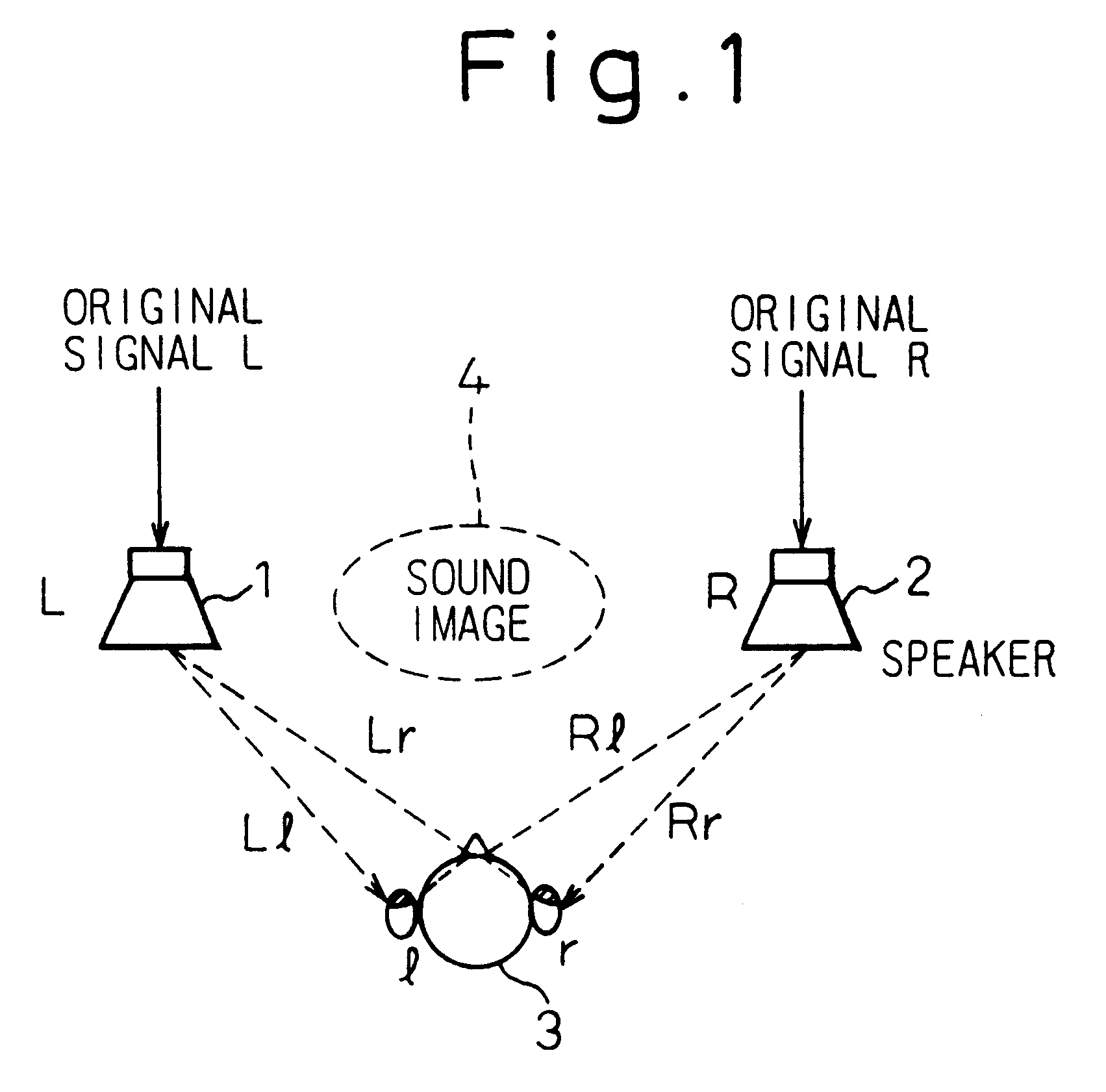
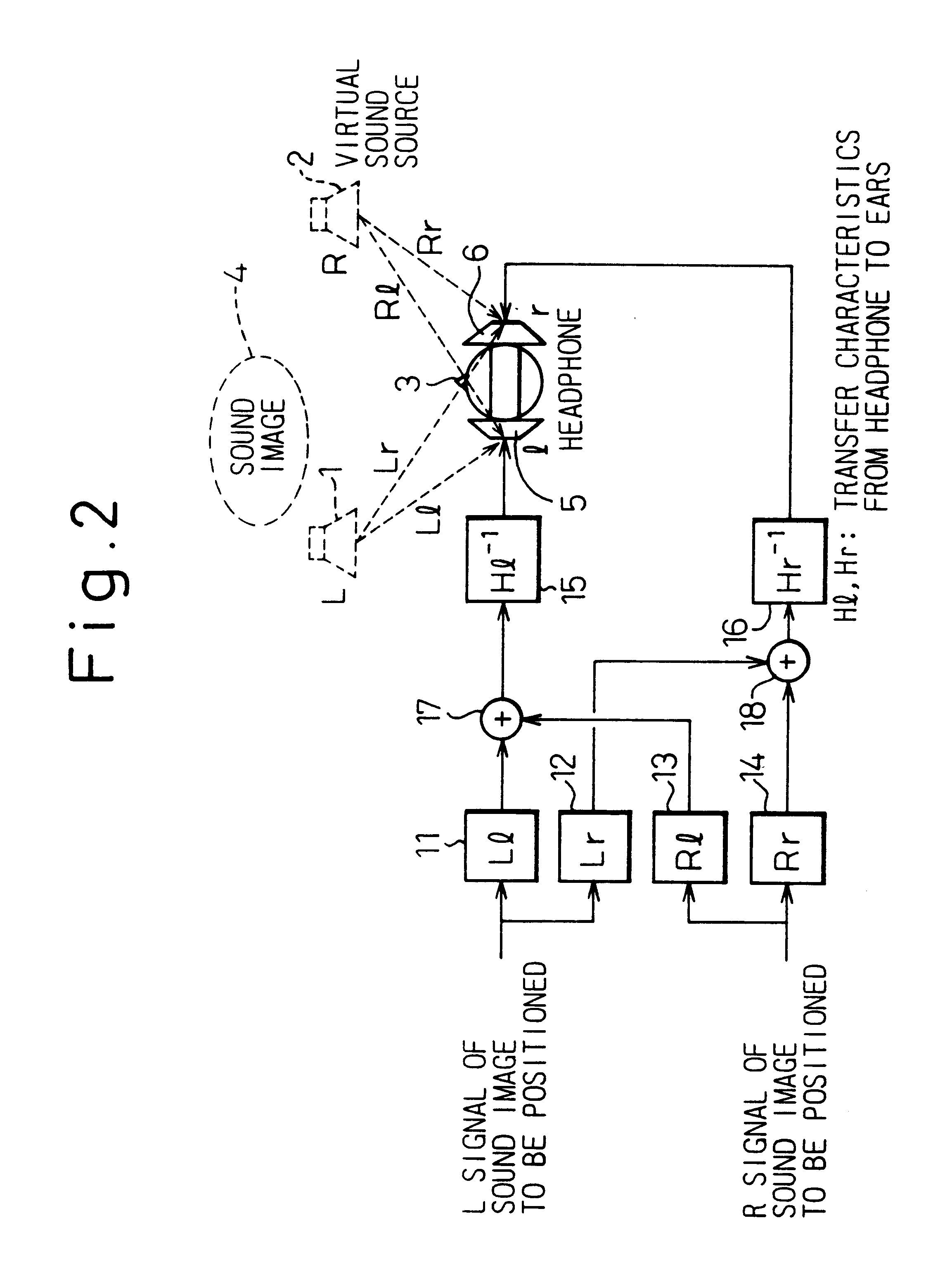
To provide a three-dimensional acoustic effect to a listener in a reproduction field, via a headphone in particular, a three-dimensional acoustic apparatus is formed by a linear synthesis filter having filter coefficients that are the linear predictive coefficients obtained by performing a linear predictive analysis on an impulse response which represents the acoustic characteristics to be added to the original signal to achieve this effect. By passing the signal through this acoustic characteristics adding filter, the desired acoustic characteristics are added to the original signal, and by dividing the power spectrum of the impulse response of these acoustic characteristics into critical bandwidths and performing this linear predictive analysis based on impulse signal determined based from power spectrum signals representing the signal sound of each of these critical bandwidths, the filter coefficients of the linear synthesis filter are determined.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Interrupt SAR implementation for range migration (RMA) processing
ActiveUS20070159376A1Reduce restrictionsEnhance the imageRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRange migrationComplete sequence
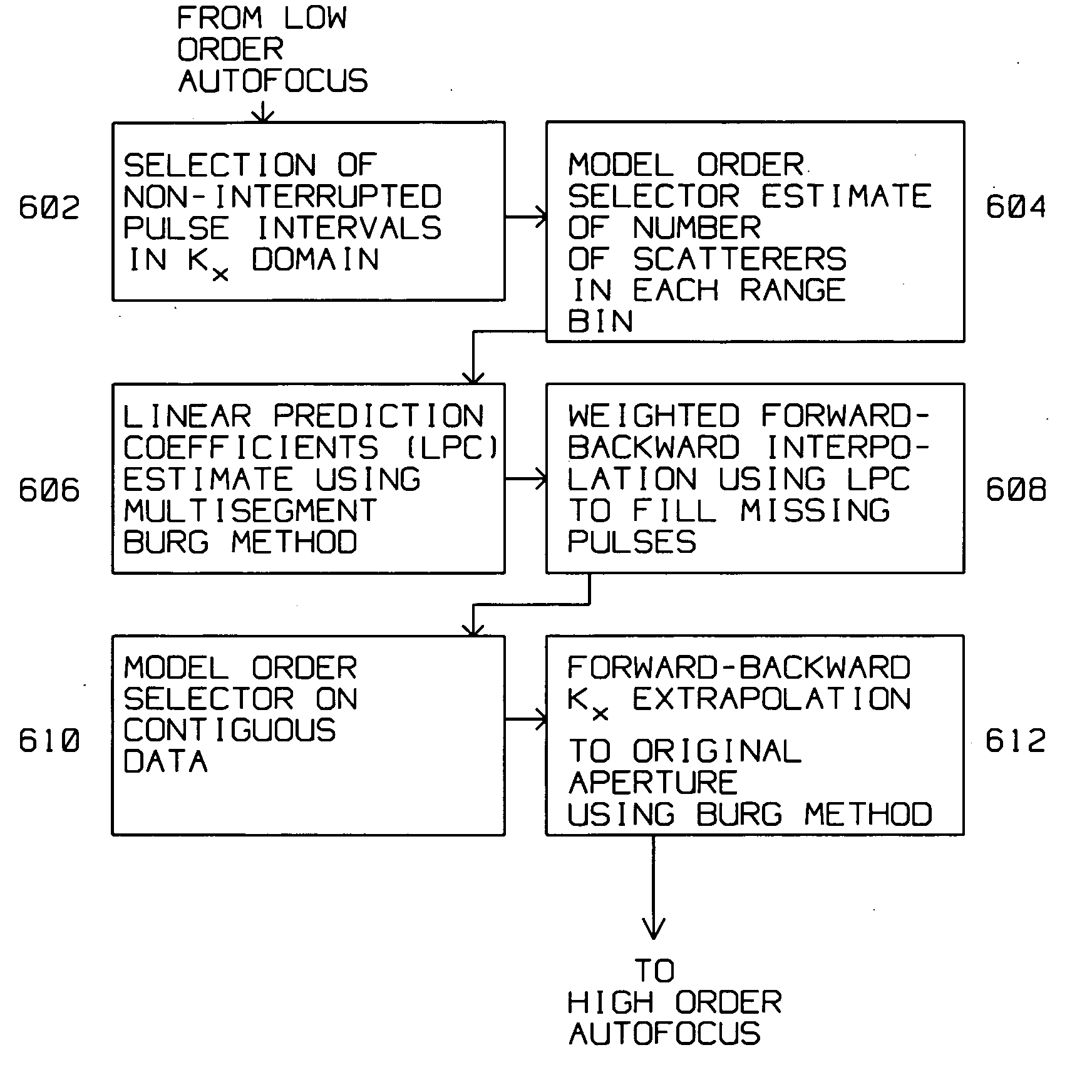
A moving radar (405) generates a synthetic aperture image from an incomplete sequence of periodic pulse returns. The incomplete sequence of periodic pulse returns has one or more missing pulses. The radar converts the incomplete sequence of pulse returns into a digital stream. A computer (403) processes the digital stream by computing an along track Fourier transform (402), a range compression (408), an azimuth deskew (410) and an image restoration and auto focus (412). The image restoration and autofocus (412) utilizes a low order autofocus (501), a gap interpolation using a Burg algorithm (503), and a high order autofocus (505) for generating an interpolated sequence. The interpolated sequence contains a complete sequence of periodic pulse returns with uniform spacing for generating the synthetic aperture image. The image restoration and autofocus (412) computes a linear prediction coefficients estimate using the Burg Algorithm (606). The linear prediction coefficients estimate (606) is used to compute a weighted forward-backward interpolation to generate the complete sequence of periodic pulse returns (608).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Kernel fuzzy c-means speech emotion identification method combined with secondary identification of support vector machine
The invention relates to a kernel fuzzy c-means speech emotion identification method combined with the secondary identification of a support vector machine. The kernel fuzzy c-means speech emotion identification method comprises the following steps of: firstly, using a Mel-frequency cepstral coefficient to map to a high dimension characteristic space by a nonlinear kernel function; obtaining a clustering center by utilizing the kernel fuzzy c-means and using the clustering center as a code book quantized by a vector; then estimating a sample category label by an average fuzzy weighted minimum vector quantized error rule; and after estimating the label, carrying out secondary identification on pleasure and anger by utilizing a support vector machine method and a linear prediction coefficient. The kernel fuzzy c-means speech emotion identification method is an important composition part for automatically identifying the emotion in a man-machine interactive system, is a first step of carrying out emotional interaction between the machine and a person and has important application prospect for a system which uses people as the design center.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Music identifying method and system
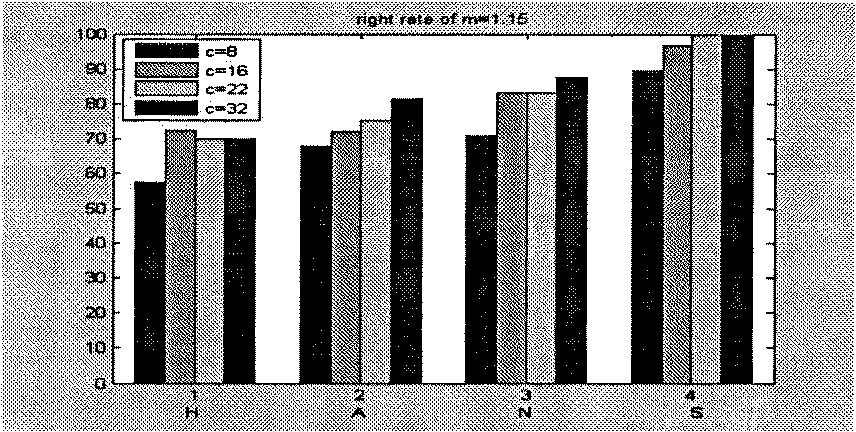
ActiveCN106919662AImprove recognition resultsImprove noise immunitySpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorPerceptual linear prediction
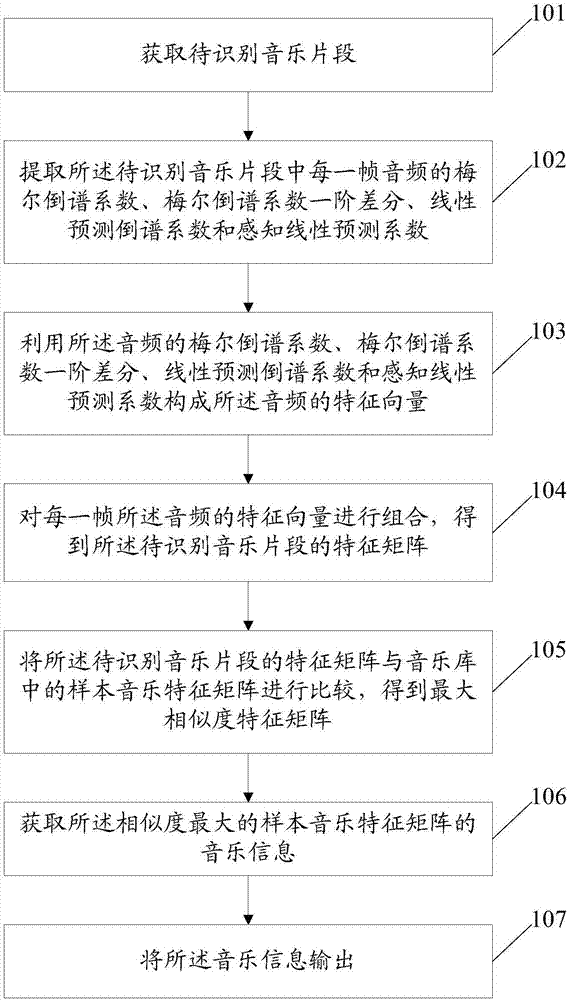
The invention discloses a music identifying method and system. The method comprises steps of acquiring a to-be-identified music clip, extracting a mel-frequency cepstrum coefficient of each frame of the to-be-identified music clip, a mel-frequency cepstrum coefficient first difference, a linear prediction cepstrum coefficient and a sensing linear prediction coefficient, forming an audio feature vector according to the above coefficients of the audio, combing feature vectors of each frame audio to achieve a feature matrix of the to-be-identified music clip, comparing the feature matrix of the to-be-identified music clip and a feature matrix of a sampling music in a music library to achieve a maximum-similarity feature matrix, acquiring music information of a maximum sampling music feature matrix, and outputting the music information. The maximum-similarity feature matrix belongs to a sampling music having the maximum similarity to the to-be-identified music. The music identifying method and system have great noise resisting property and great identifying efficiency and ideal identifying effect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Three-dimensional acoustic processor which uses linear predictive coefficients
InactiveUS6023512AReduce amountAvoid complex processTwo-channel systemsStereophonic arrangmentsHeadphonesAcoustic effect
To provide a three-dimensional acoustic effect to a listener in a reproduction field, via a headphone in particular, a three-dimensional acoustic apparatus is formed by a linear synthesis filter having filter coefficients that are the linear predictive coefficients obtained by performing a linear predictive analysis on an impulse response which represents the acoustic characteristics to be added to the original signal to achieve this effect. By passing the signal through this acoustic characteristics adding filter, the desired acoustic characteristics are added to the original signal, and by dividing the power spectrum of the impulse response of these acoustic characteristics into critical bandwidths and performing this linear predictive analysis based on impulse signal determined based from power spectrum signals representing the signal sound of each of these critical bandwidths, the filter coefficients of the linear synthesis filter are determined.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
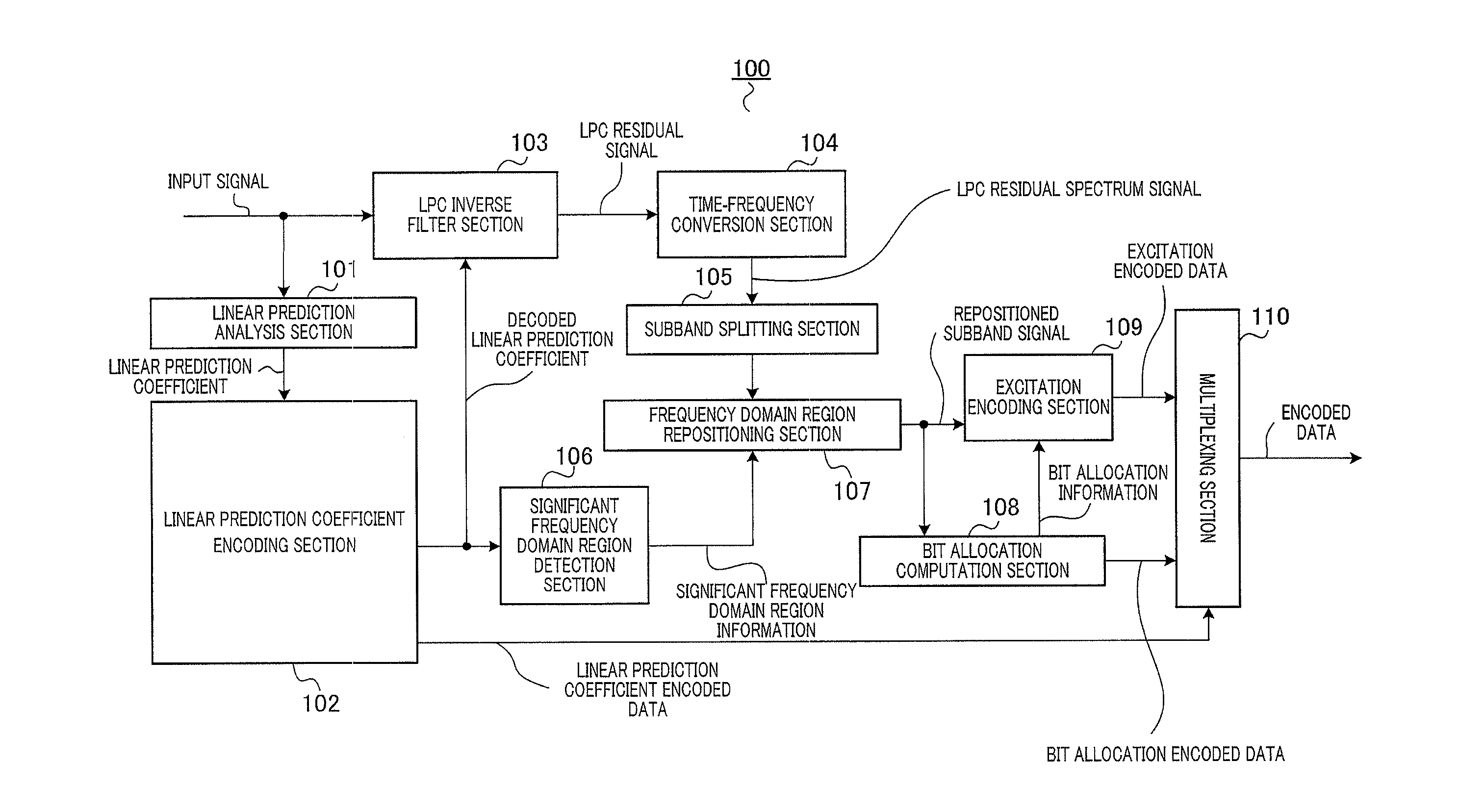
Speech/audio encoding apparatus, speech/audio decoding apparatus, and methods thereof
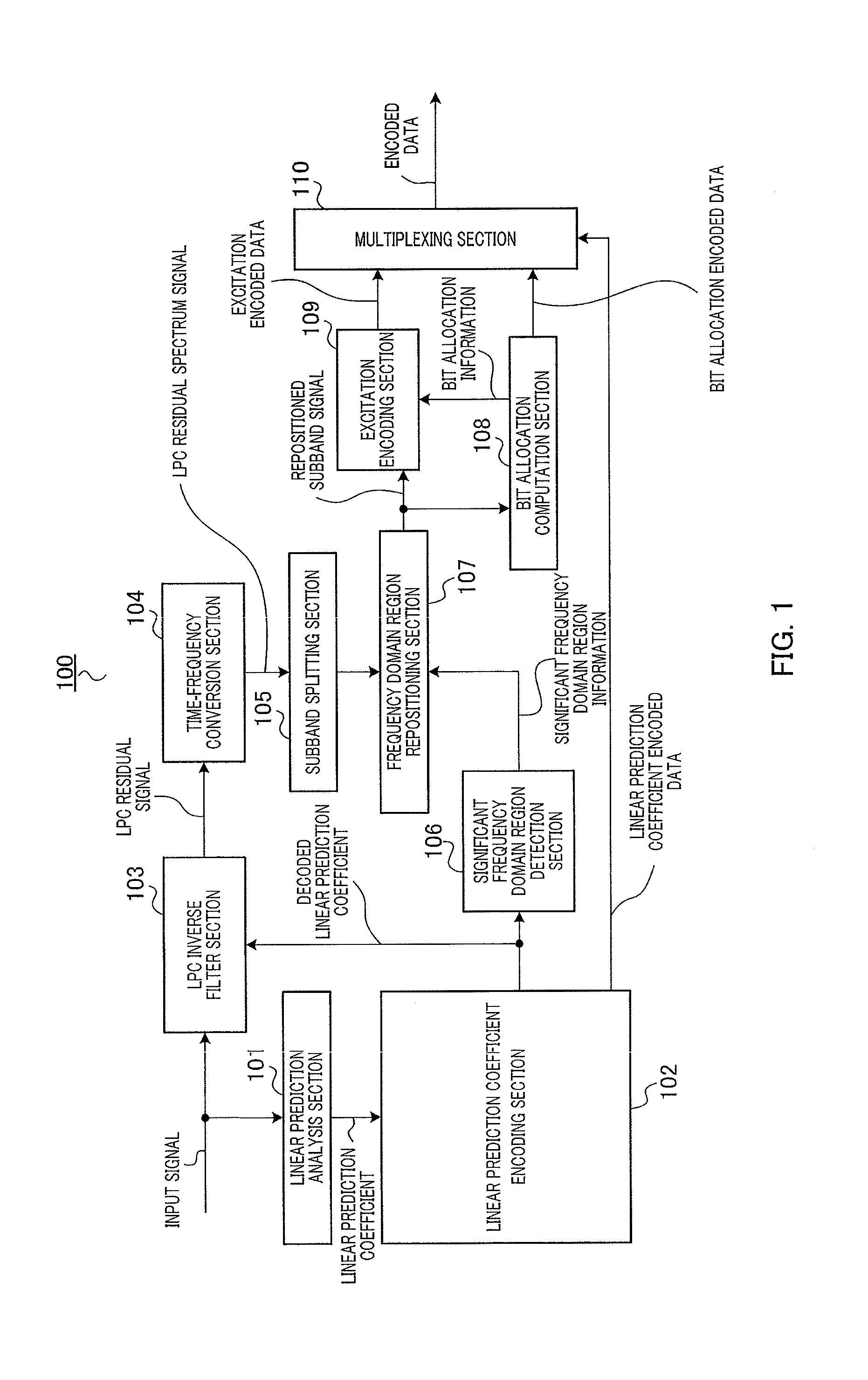
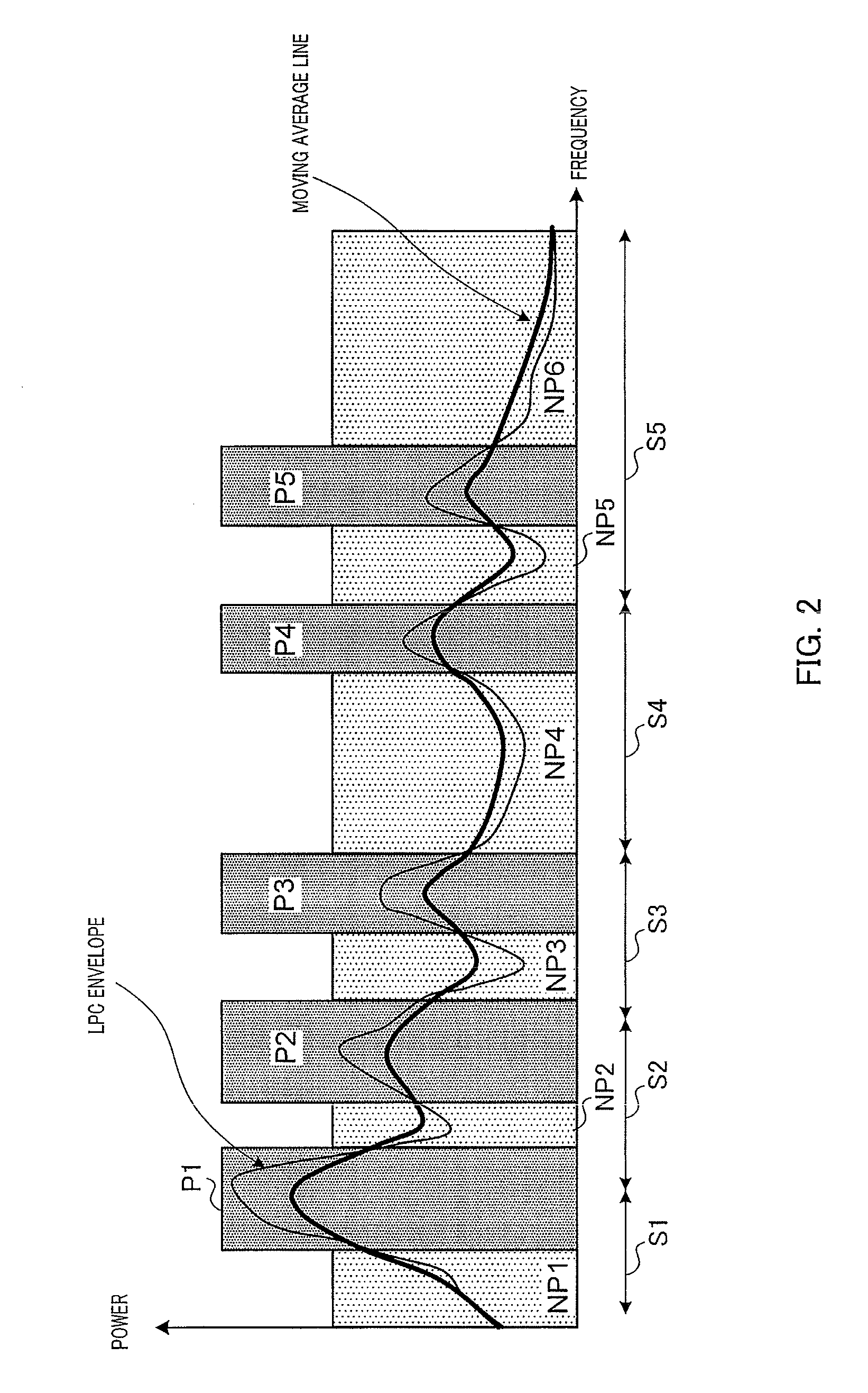
Provided is a speech / audio encoding apparatus with which it is possible to code a significant frequency domain region with high precision, and to enable high audio quality. A speech / audio encoding apparatus codes a linear prediction coefficient. A significant frequency domain region detection unit identifies a frequency domain region which is aurally significant from the linear prediction coefficient. A frequency domain region repositioning unit repositions the significant frequency domain region which is identified by the significant frequency domain region detection unit. A bit allocation computation unit determines a coding bit allocation on the basis of the significant frequency domain region which is repositioned by the frequency domain region repositioning unit.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Noise filling without side information for celp-like coders
ActiveUS20150332696A1Consume less bandwidthQuality improvementSpeech analysisPattern recognitionNoise level
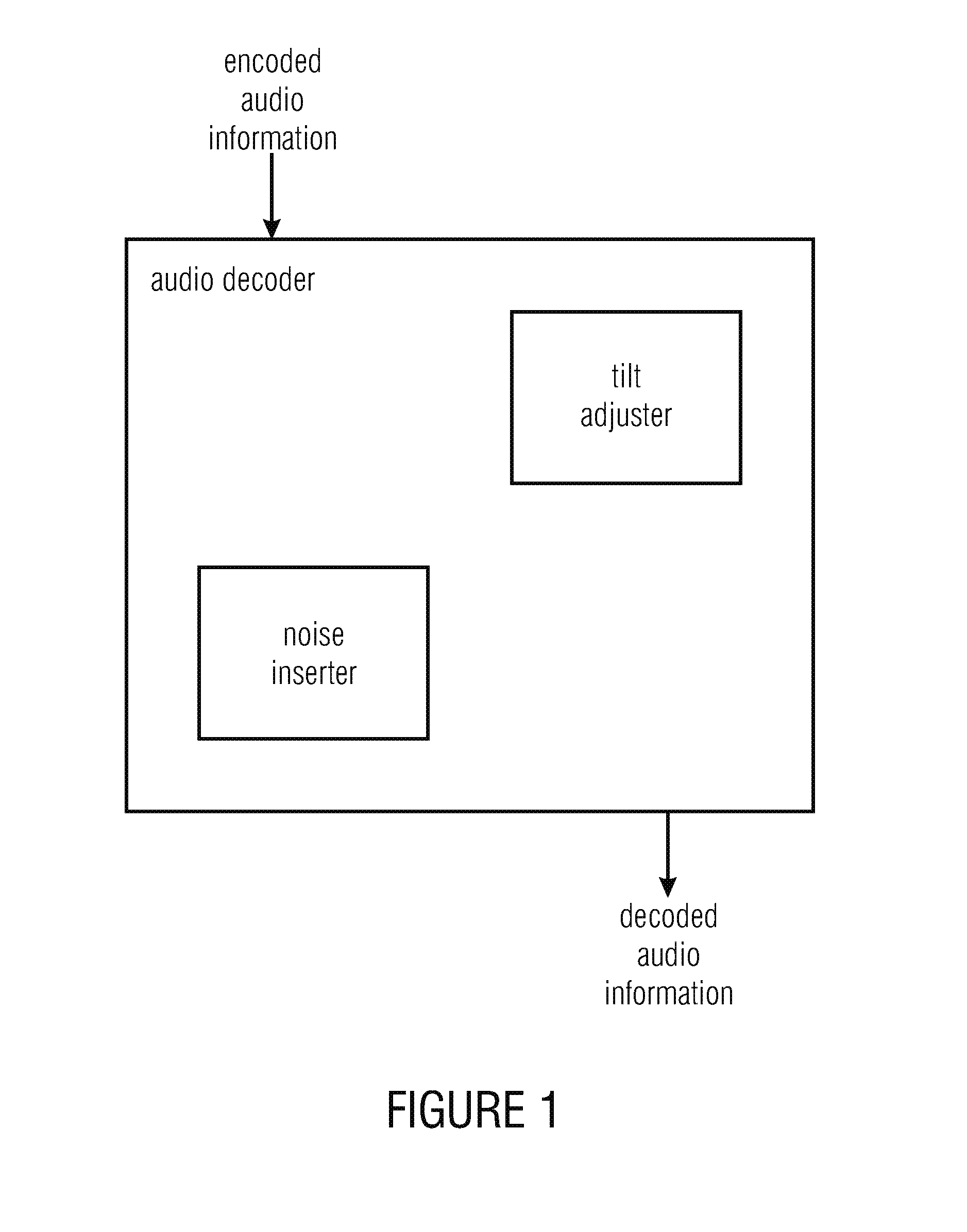
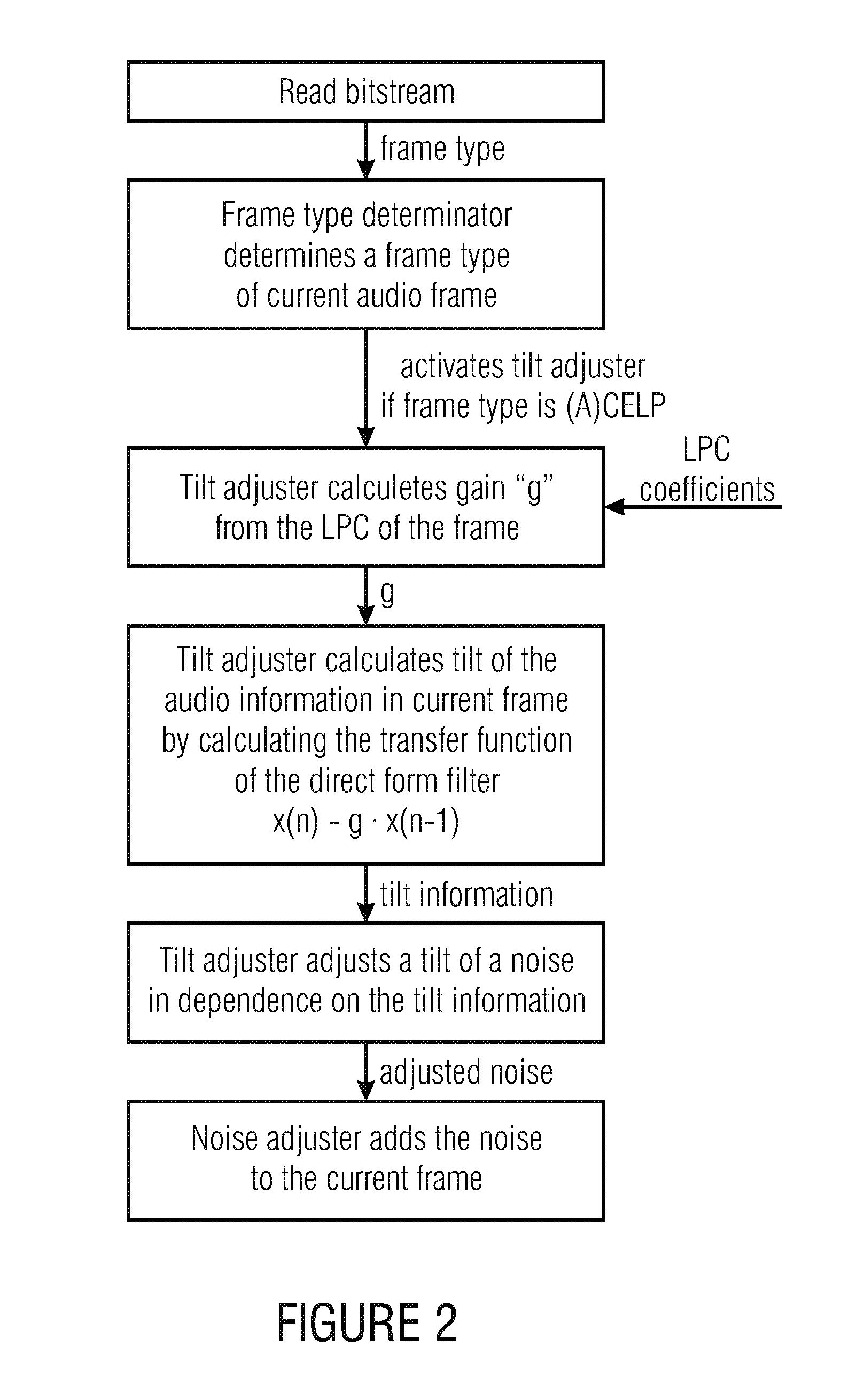
An audio decoder provides a decoded audio information on the basis of an encoded audio information including linear prediction coefficients (LPC) and includes a tilt adjuster to adjust a tilt of a noise using linear prediction coefficients of a current frame to acquire a tilt information and a noise inserter configured to add the noise to the current frame in dependence on the tilt information. Another audio decoder includes a noise level estimator to estimate a noise level for a current frame using a linear prediction coefficient of at least one previous frame to acquire a noise level information; and a noise inserter to add a noise to the current frame in dependence on the noise level information provided by the noise level estimator. Thus, side information about a background noise in the bit-stream may be omitted. Methods and computer programs serve a similar purpose.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
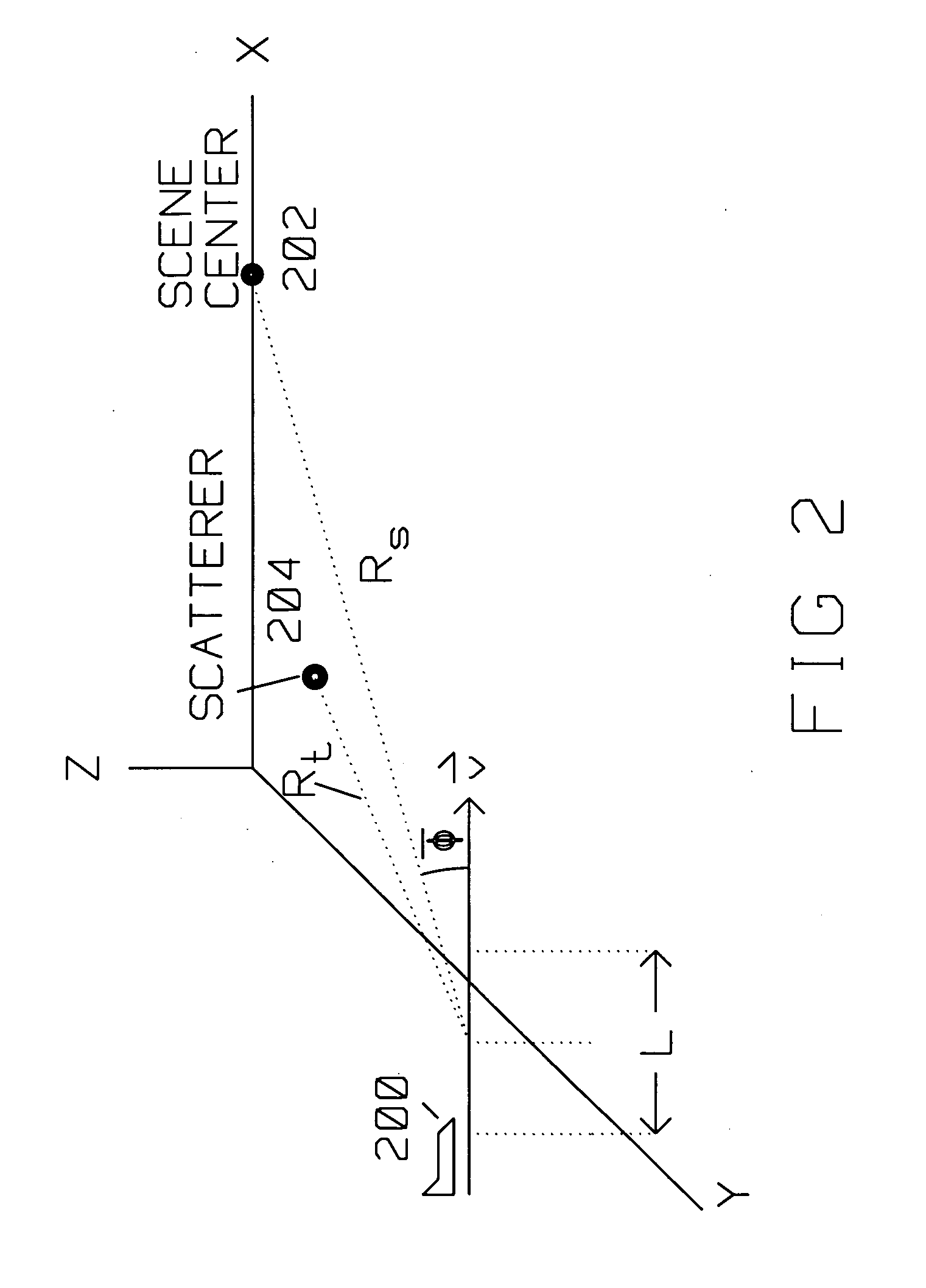
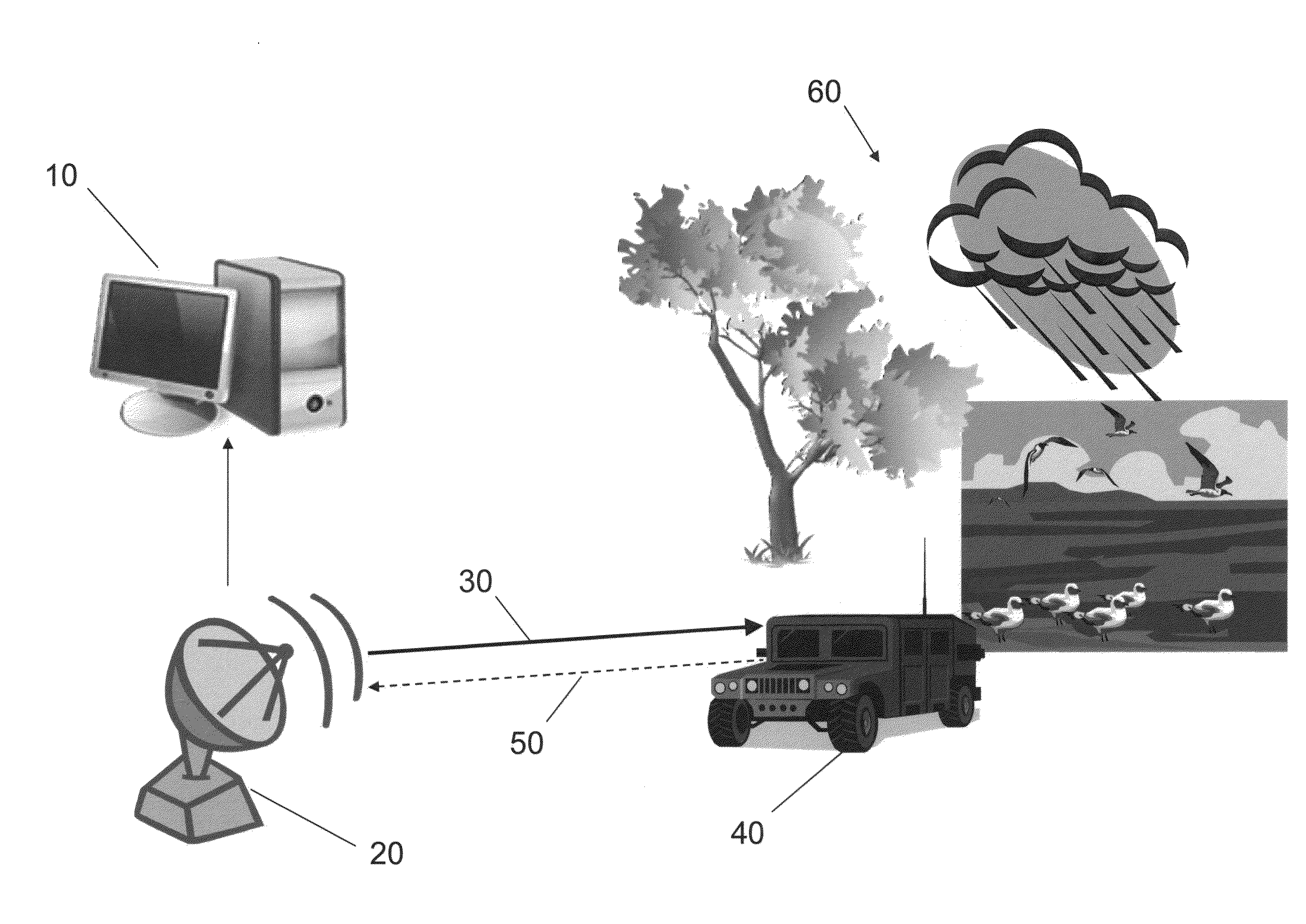
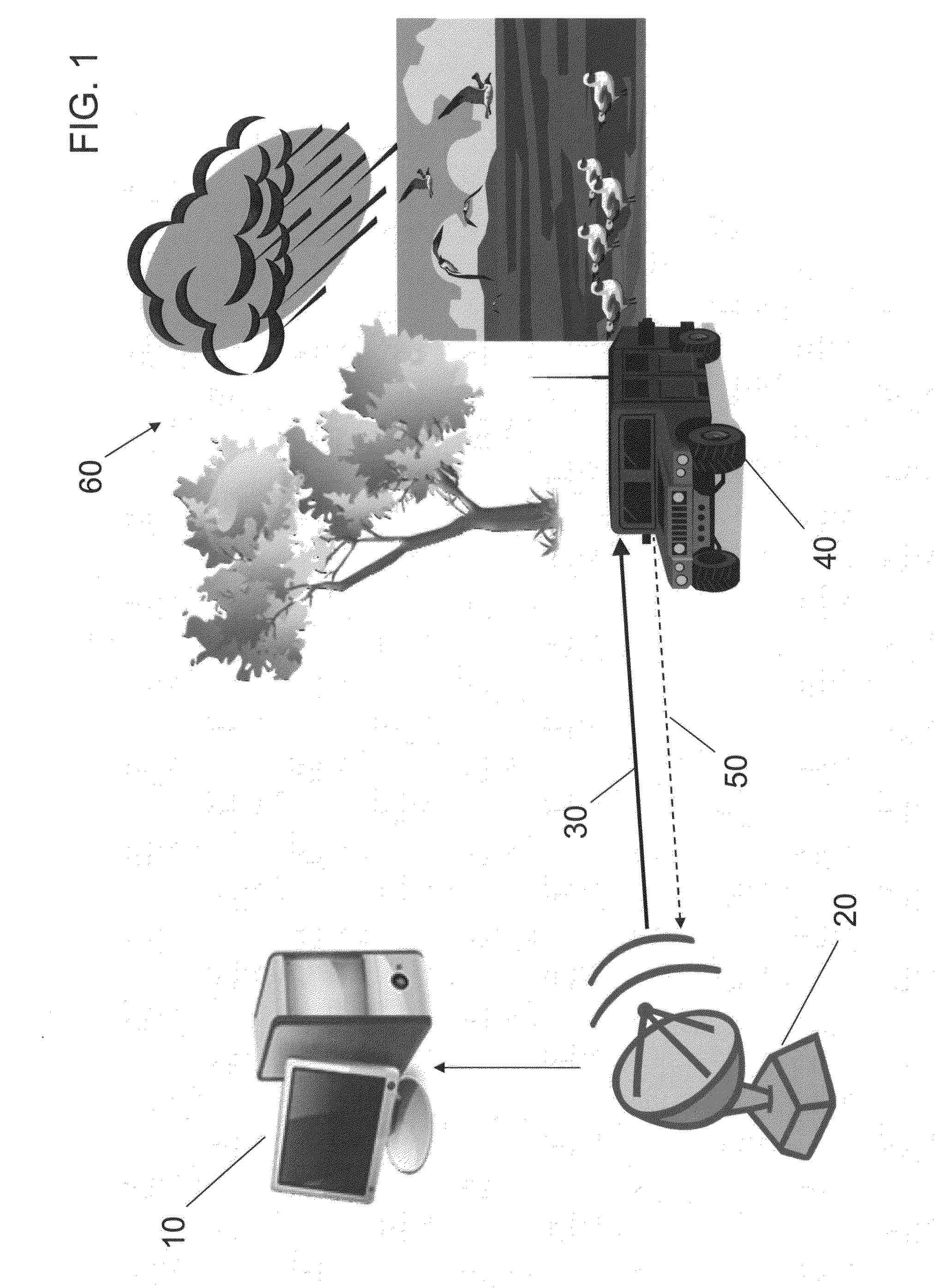
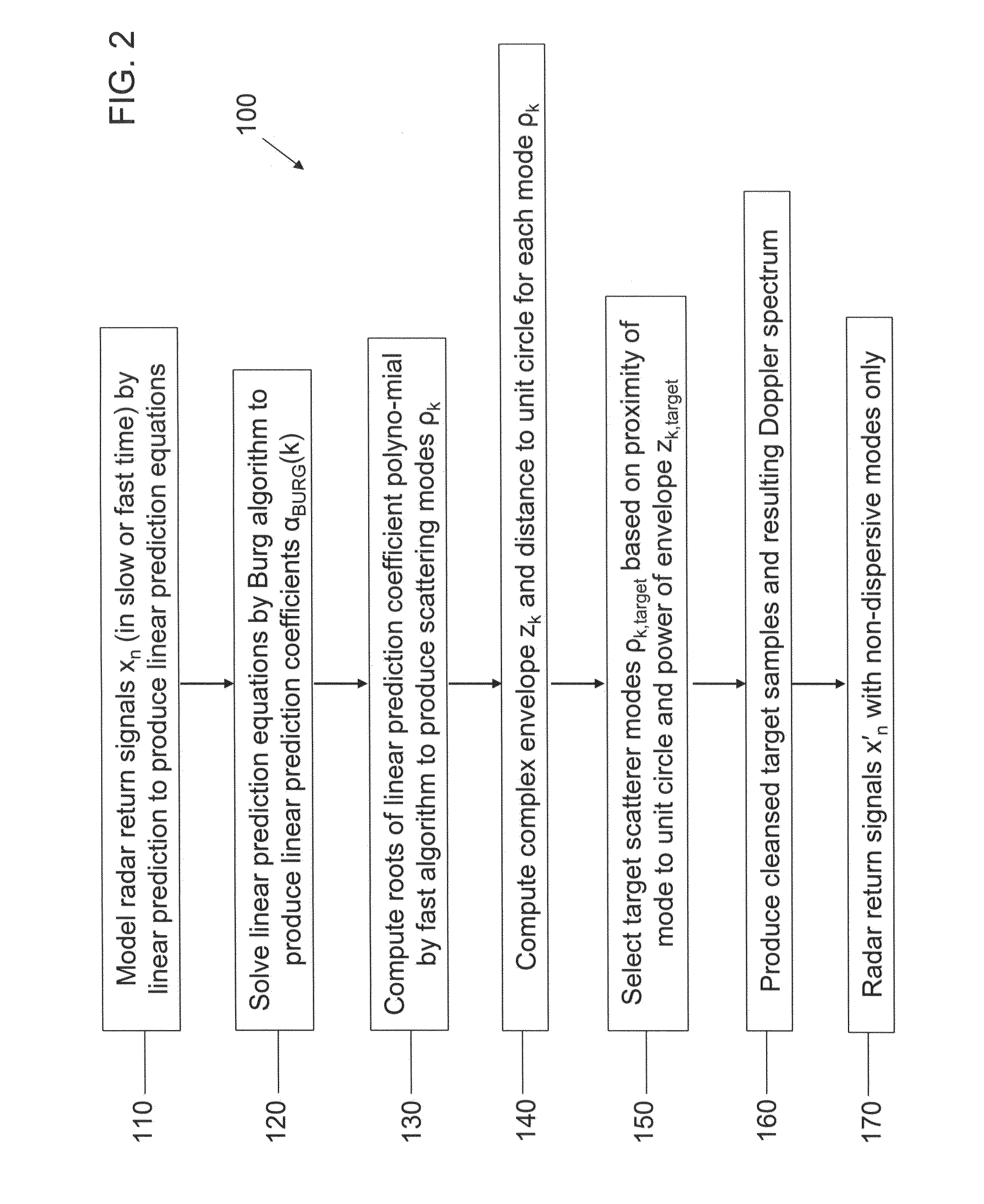
Enhanced target detection using dispersive vs non-dispersive scatterer signal processing
ActiveUS20130194130A1Improve target detectionIncreased Doppler resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionProcessing elementLinearity
A method of target discrimination and identification, on a computer including a processing unit and a non-volatile storage device, from a radar signal having a plurality of radar return signals, is presented. The method includes: modeling, on the computer, the radar return signals by linear prediction to produce linear prediction equations; solving, on the computer, the linear prediction equations by the Burg algorithm to produce linear prediction coefficients for a linear prediction coefficient polynomial; computing, on the computer, roots of the linear prediction coefficient polynomial to produce scattering modes; computing, on the computer, a distance of each of the scattering modes to a unit circle; computing, on the computer, a complex envelope for each mode of the scattering modes; and selecting, on the computer, target scattering modes from among the scattering modes based on the distance of the mode to the unit circle and the complex envelope of the mode.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
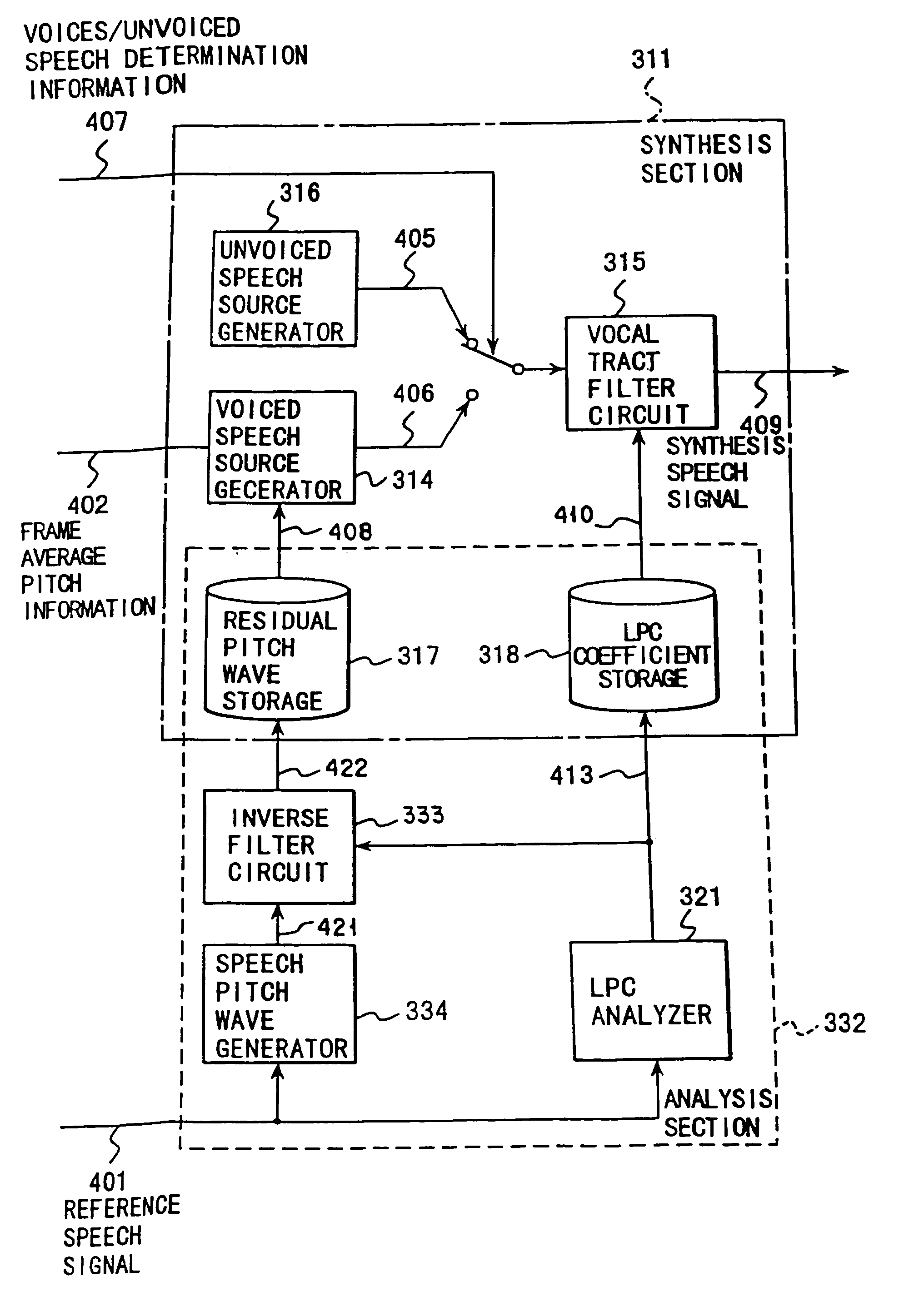
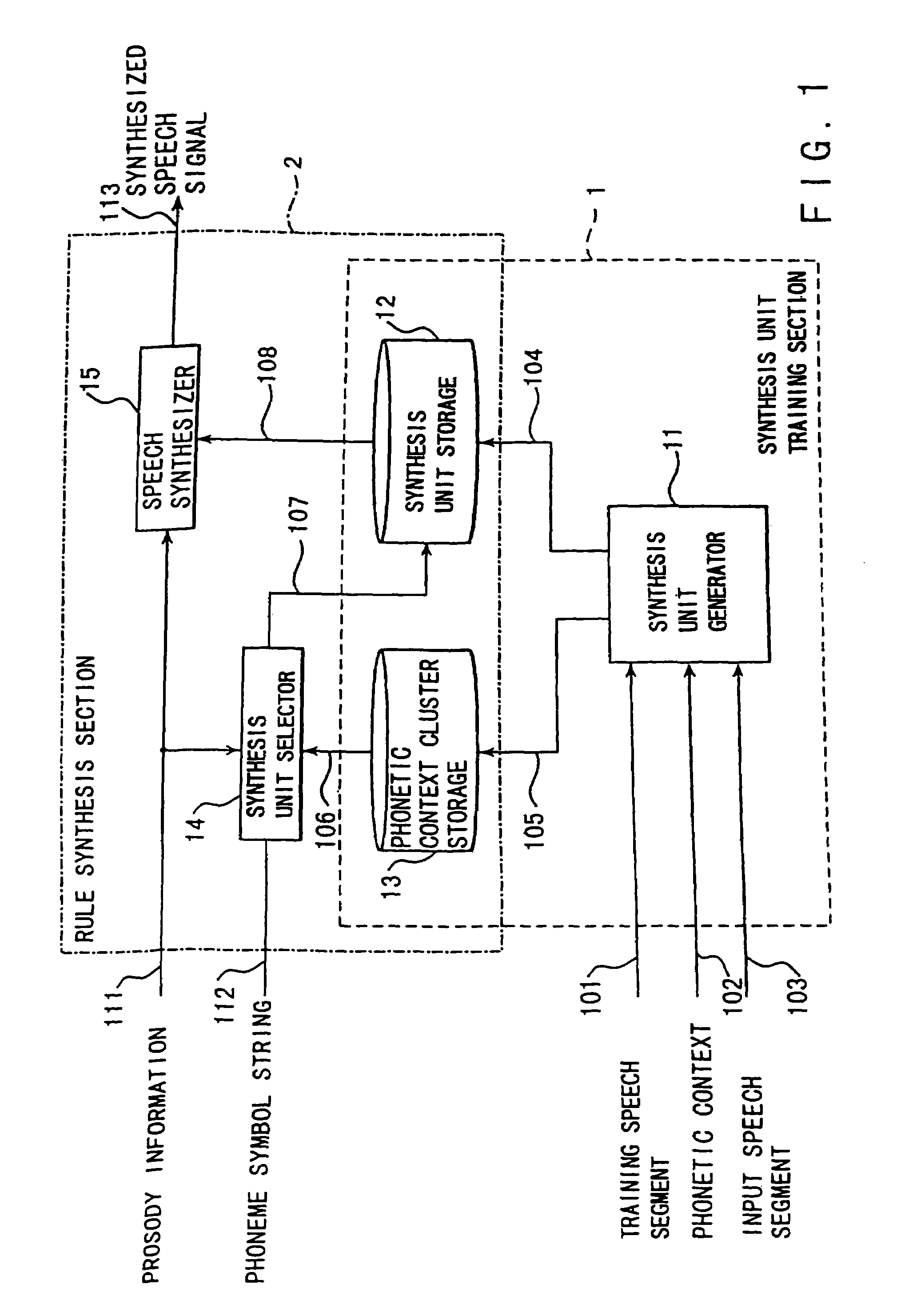
Speech synthesis method
A speech synthesis method subjects a reference speech signal to windowing to extract a speech pitch wave having a window function of a window length double a pitch period of the reference speech signal from the reference speech signal. A linear prediction coefficient is generated by subjecting the reference speech signal to a linear prediction analysis. The speech pitch wave is subjected to inverse-filtering based on the linear prediction coefficient to produce a residual pitch wave, which is then stored as information of a speech synthesis unit in a voiced period in a storage. Speech using the information of the speech synthesis unit is then synthesized.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
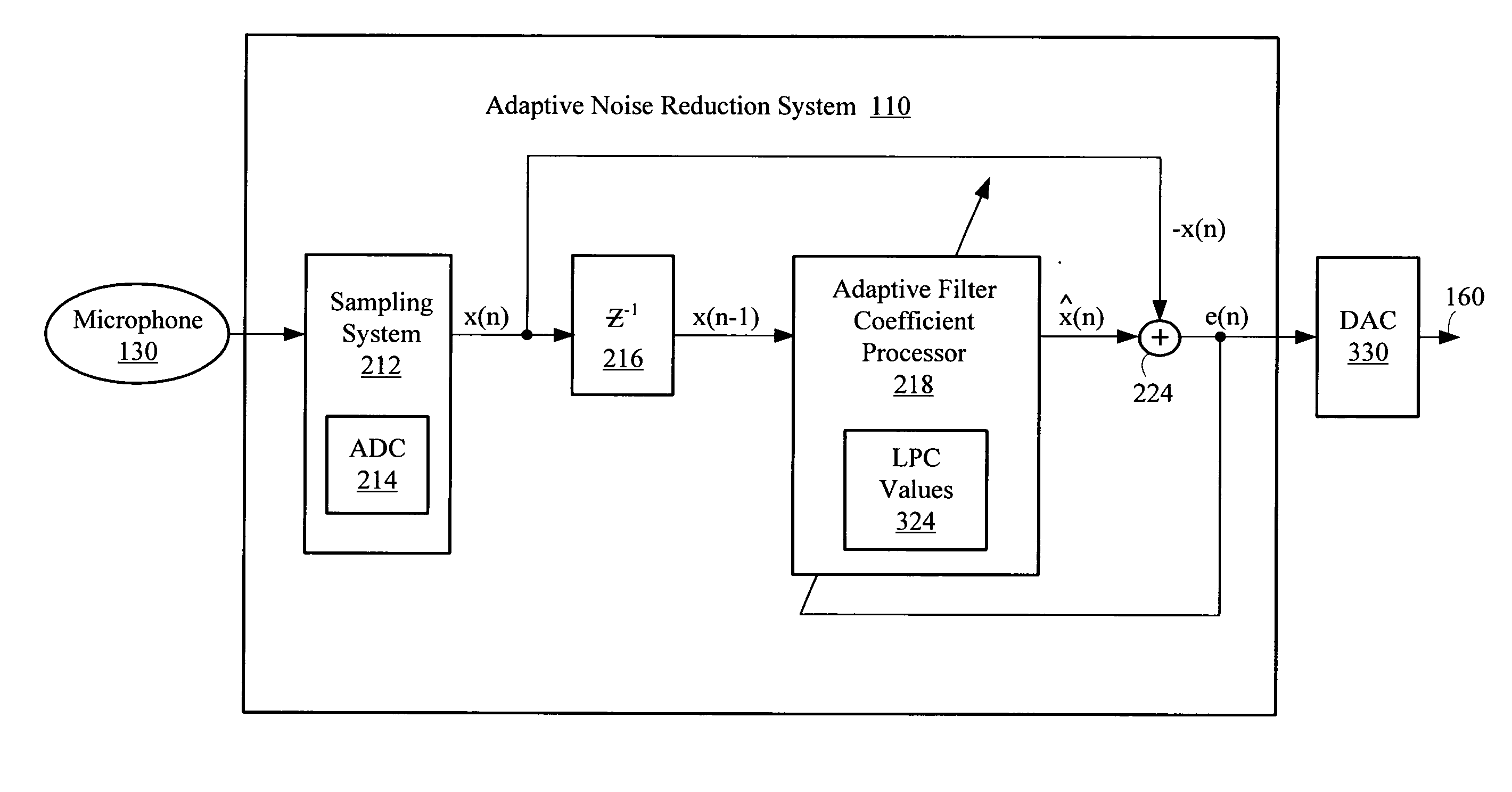
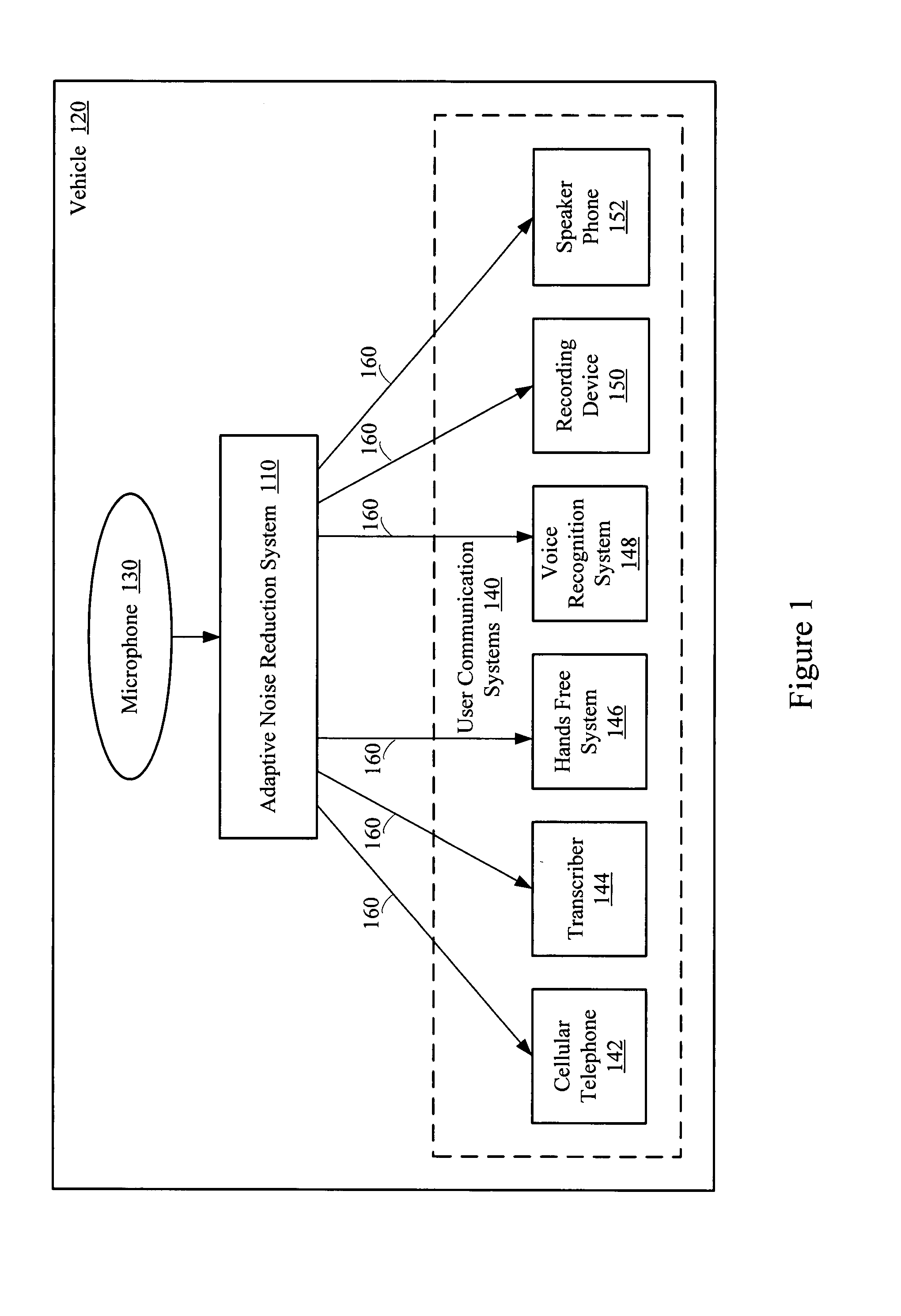
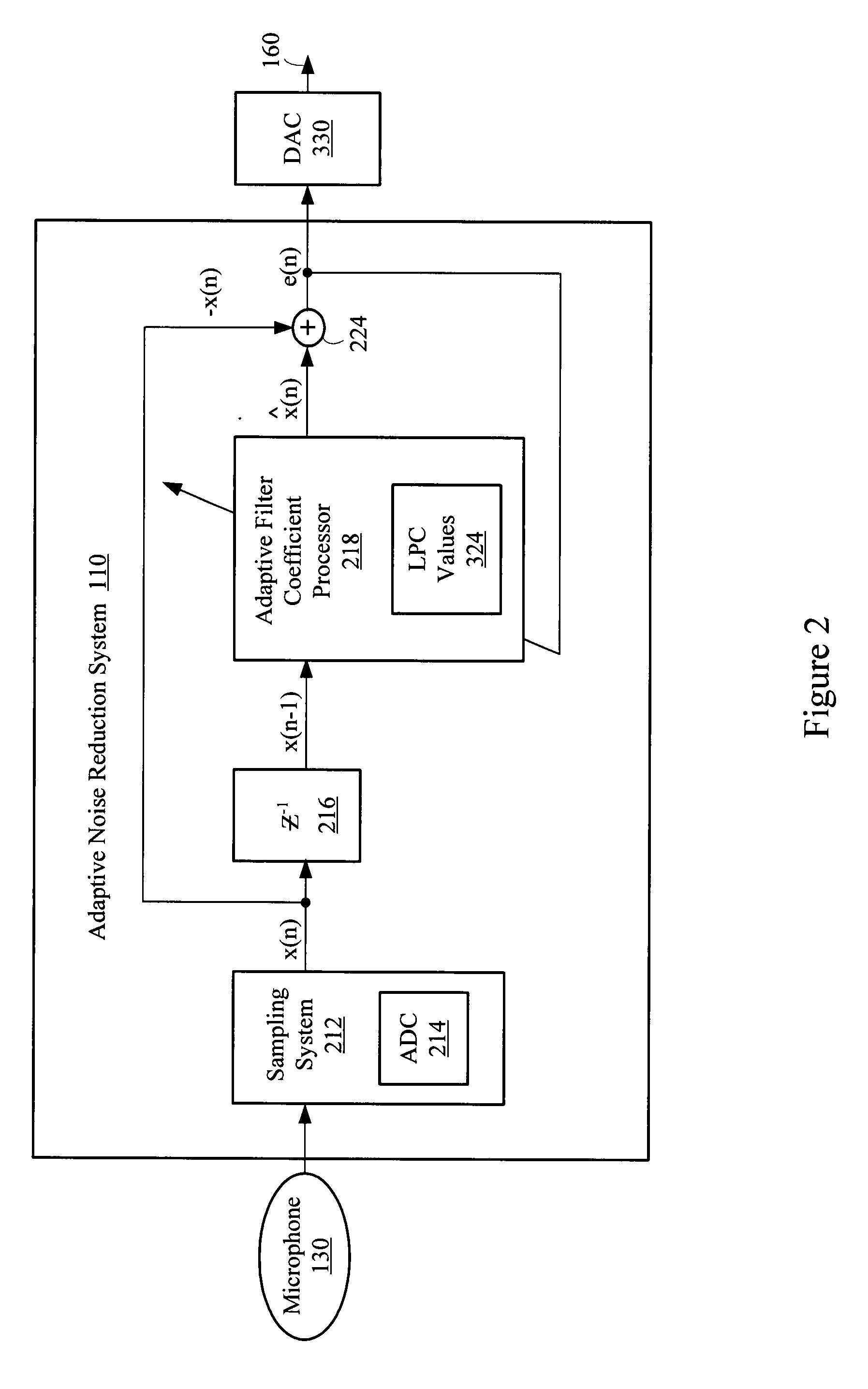
Adaptive LPC noise reduction system
ActiveUS20080285773A1Reduce low frequency noiseLimited setEar treatmentSpeech analysisNoise reductionNoise suppression
A noise suppression system reduces low-frequency noise in a speech signal using linear predictive coefficients in an adaptive filter. A digital filter may update or adapt a limited set of linear predictive coefficients on a sample-by-sample basis. The linear predictive coefficients may be used to provide an error signal based on a difference between the speech signal and a delayed speech signal. The error signal represents an enhanced speech signal having attenuated and normalized low-frequency noise components.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Sensing Hash value extracting method and sensing Hash value authenticating method for voice sensing Hash authentication
Disclosed are a sensing Hash value extracting method and a sensing Hash value authenticating method for voice sensing Hash authentication. According to the characteristics of LPC (linear prediction coefficients), robustness of an LPC method is improved by optimizing the LPC method and performing three steps of optimizing and blocking of the LPC and disintegrating matrix of parameters after blocking, the optimized LPC are high in robustness and calculating efficiency, and robustness of a sensing Hash sequence formed is improved as well. The sensing Hash value calculated by the optimized LPC maintains the advantages of good instantaneity of a simple LPC method while having good robustness for attacks to the voice during transmission.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
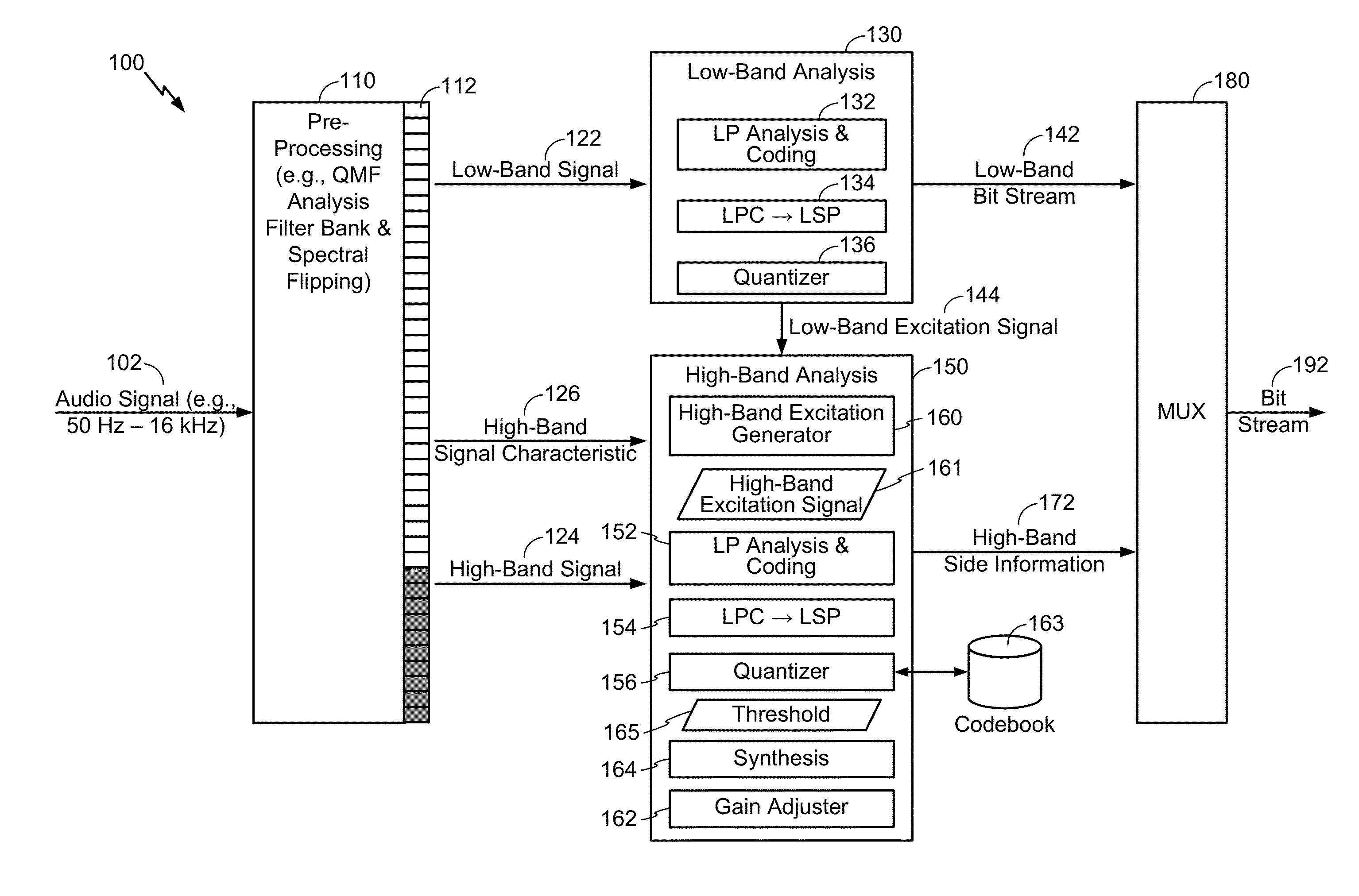
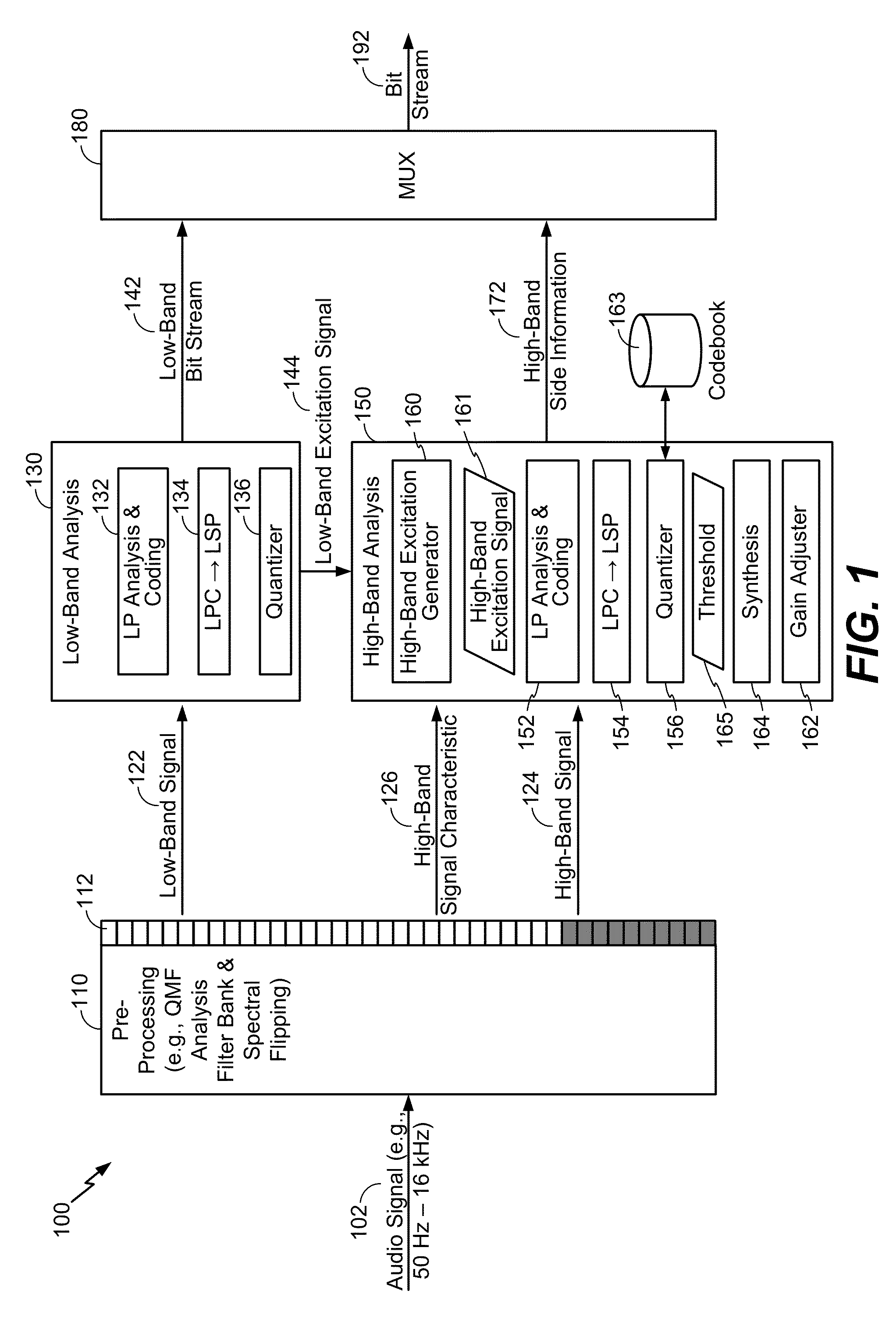
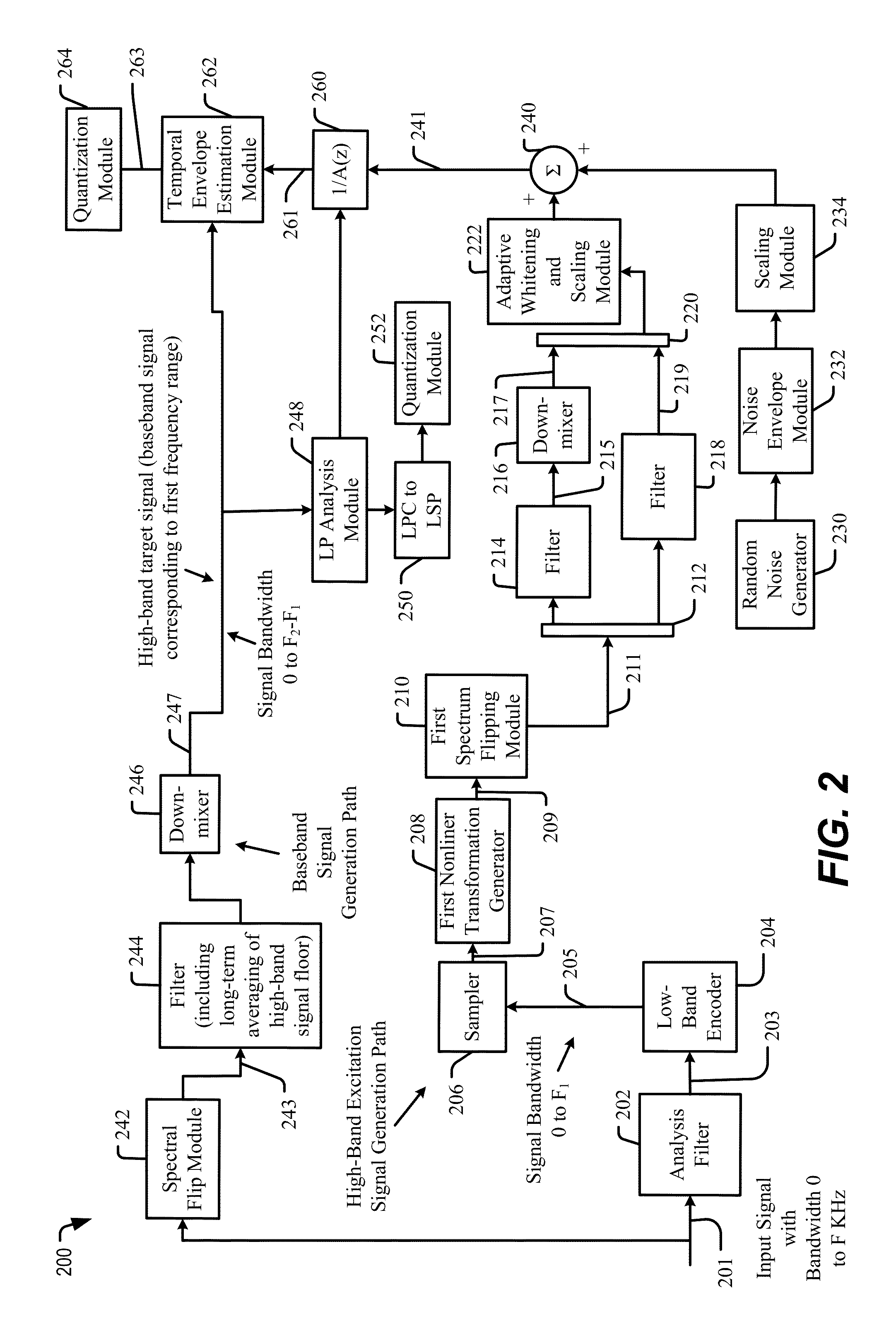
Temporal gain adjustment based on high-band signal characteristic
The present disclosure provides techniques for adjusting a temporal gain parameter and for adjusting linear prediction coefficients. A value of the temporal gain parameter may be based on a comparison of a synthesized high-band portion of an audio signal to a high-band portion of the audio signal. If a signal characteristic of an upper frequency range of the high-band portion satisfies a first threshold, the temporal gain parameter may be adjusted. A linear prediction (LP) gain may be determined based on an LP gain operation that uses a first value for an LP order. The LP gain may be associated with an energy level of an LP synthesis filter. The LP order may be reduced if the LP gain satisfies a second threshold.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
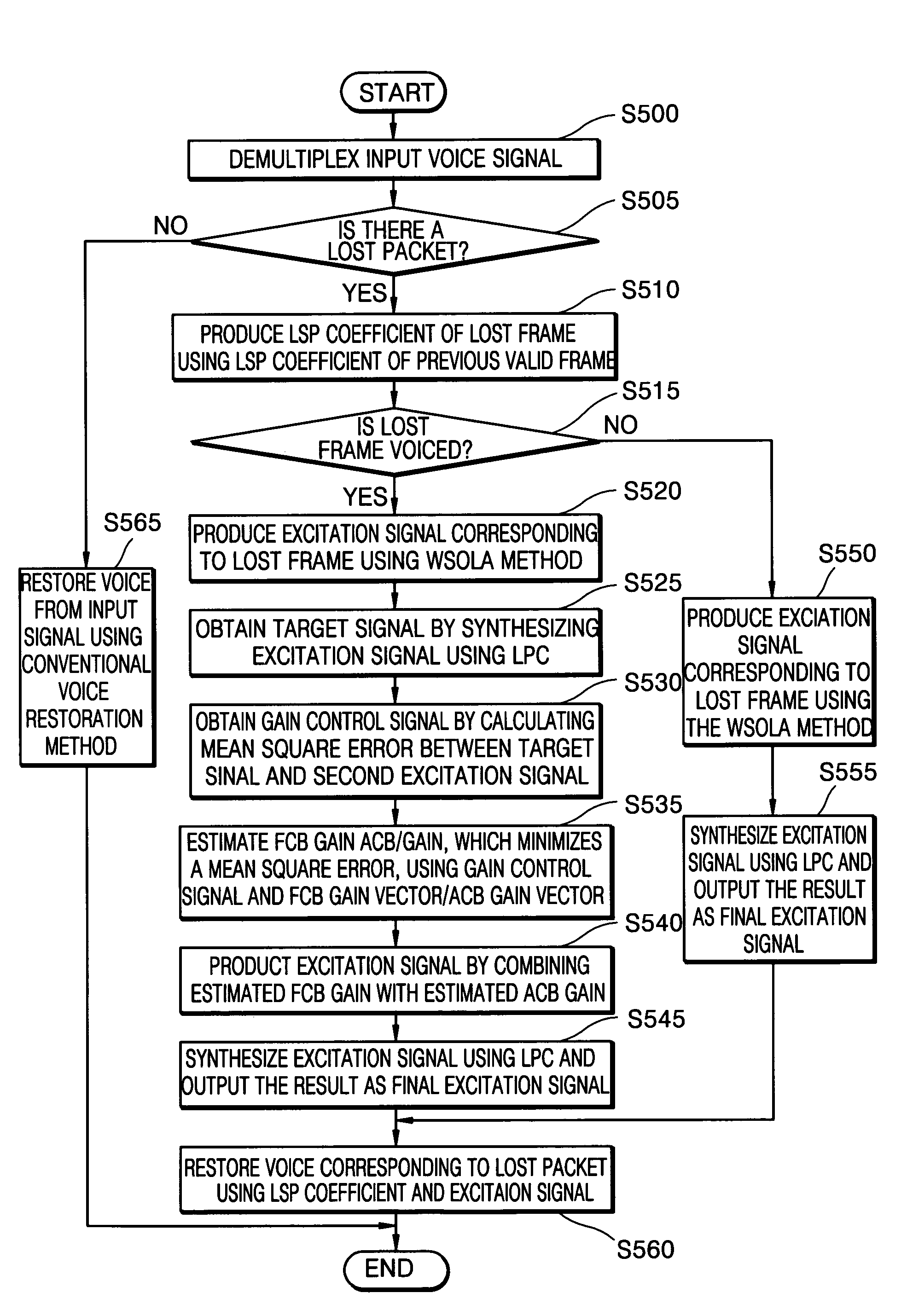
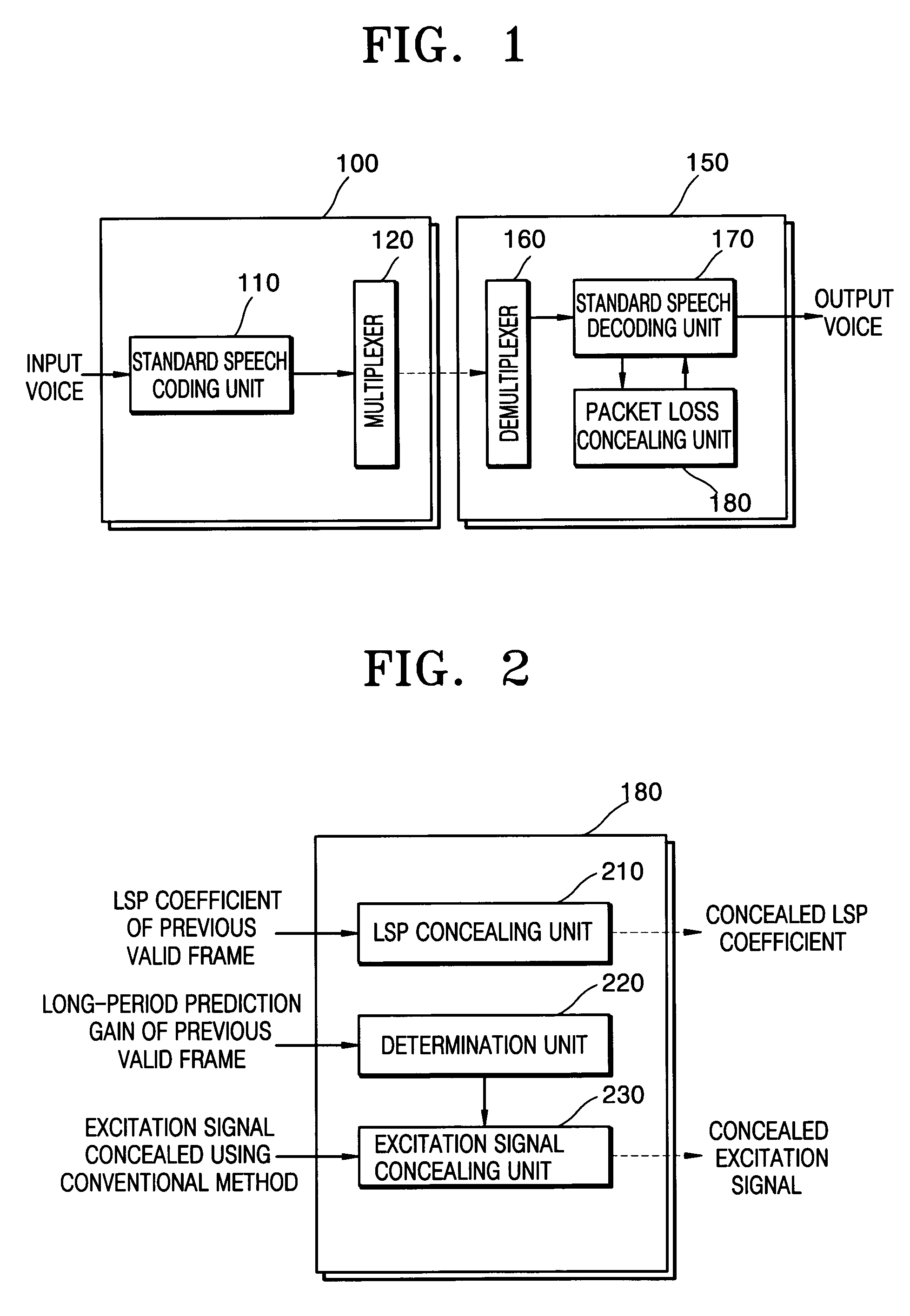
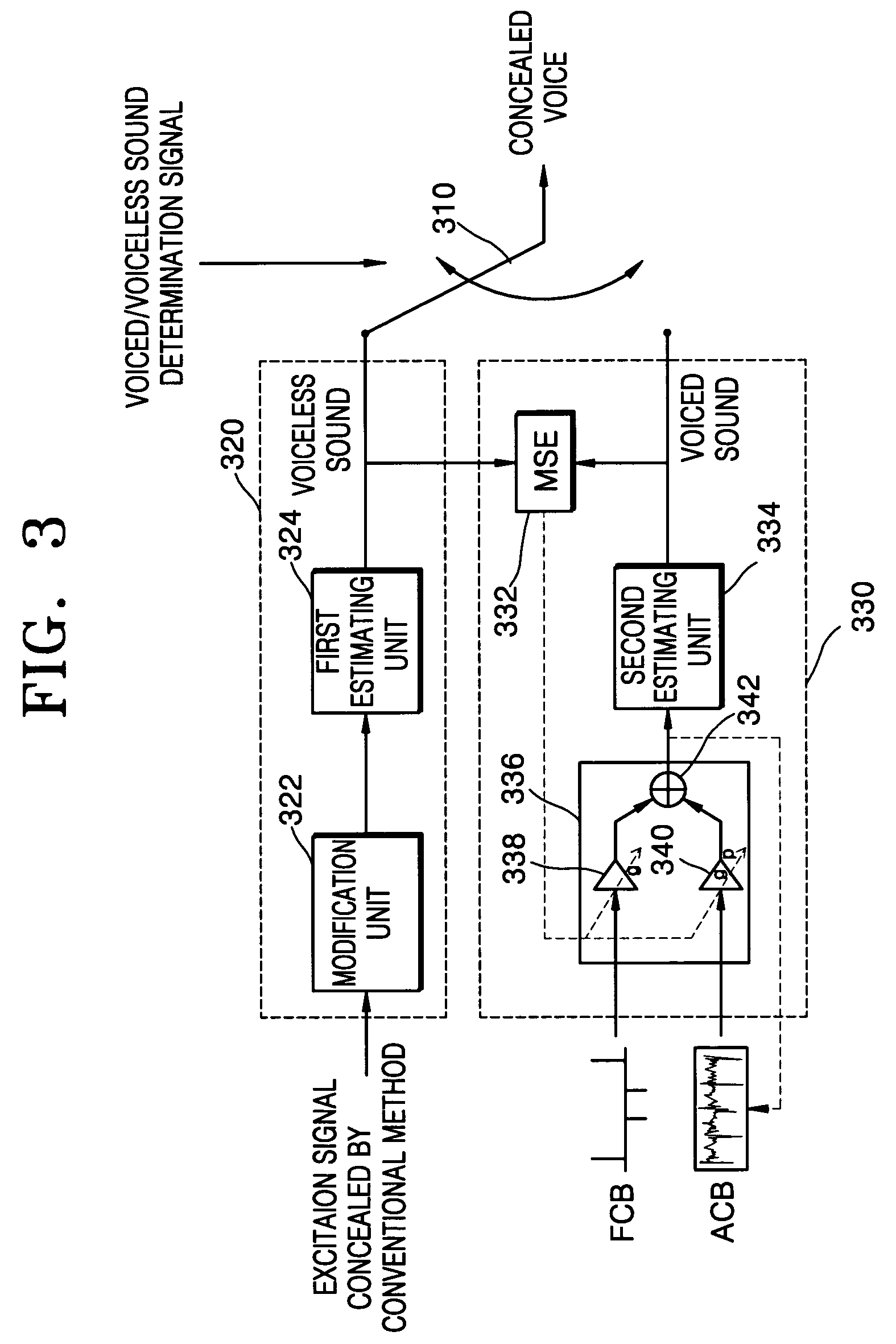
Speech restoration system and method for concealing packet losses
Provided are a speech restoration system and method for concealing packet losses. The system includes a demultiplexer that demultiplexes an input bit stream and divides the input bit stream into several packets; a packet loss concealing unit that produces and outputs a linear spectrum pair (LSP) coefficient representing the vocal tract of voice and an excitation signal corresponding to a lost frame, when a packet loss occurs; and a speech restoring unit that synthesizes voice using the packets input from the demultiplexer, outputs the result as restored voice, and synthesizes voice corresponding to a lost packet using the LSP coefficient and the excitation signal input from the packet loss concealing unit and outputs the result as restored voice when the lost packet is detected, wherein the packet loss concealing unit repeats linear prediction coefficients (LPCs) of a last-received valid frame, produces a first excitation signal for the lost frame using a time scale modification (TSM) method, when the lost frame is voiceless, and produces a second excitation signal by re-estimating a gain parameter based on the first excitation signal, when the lost frame is voiced.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and apparatus for speech data
InactiveUS20080027720A1Improve sound qualityRelatively small errorSpeech analysisSound qualityMultiple category
There is disclosed a speech processing device in which prediction taps for finding prediction values of the speech of high sound quality are extracted from the synthesized sound obtained on affording linear prediction coefficients and residual signals, generated from a preset code, to a speech synthesis filter, speech of high sound quality being higher in sound quality than the synthesized sound, and in which the prediction taps are used along with preset tap coefficients to perform preset predictive calculations to find the prediction values of the speech of high sound quality. The speech of high sound quality is higher in sound quality than the synthesized sound. The device includes a prediction tap extracting unit (45) for extracting, from the synthesized sound, the prediction taps used for predicting the speech of high sound quality, as target speech, the prediction values of which are to be found, and a class tap extraction unit (46) for extracting class taps, used for classifying the target speech to one of a plurality of classes, from the above code. The device also includes a classification unit (47) for finding the class of the target speech based on the class taps, acquisition unit for acquiring the tap coefficients associated with the class of the target speech from among the tap coefficients as found on learning from class to class, and a prediction unit (49) for finding the prediction values of the target speech using the prediction taps and the tap coefficients associated with the class of the target speech.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com