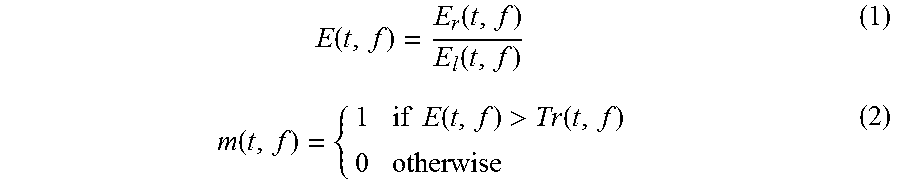Patents
Literature
53 results about "Linear predictive analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Linear predictive analysis is a simple form of first-order extrapolation: if it has been changing at this rate then it will probably continue to change at approximately the same rate, at least in the short term. This is equivalent to fitting a tangent to the graph and extending the line.
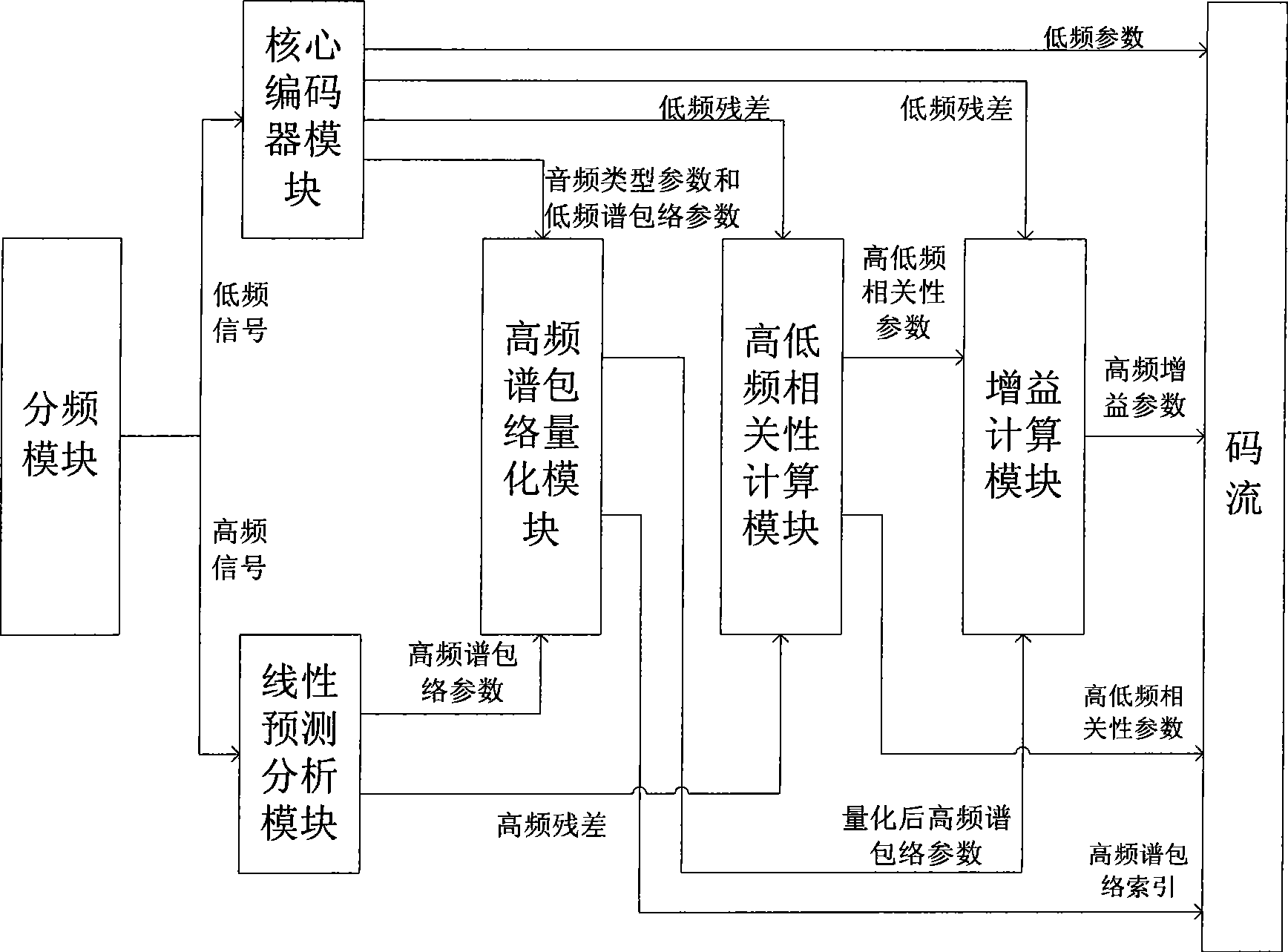
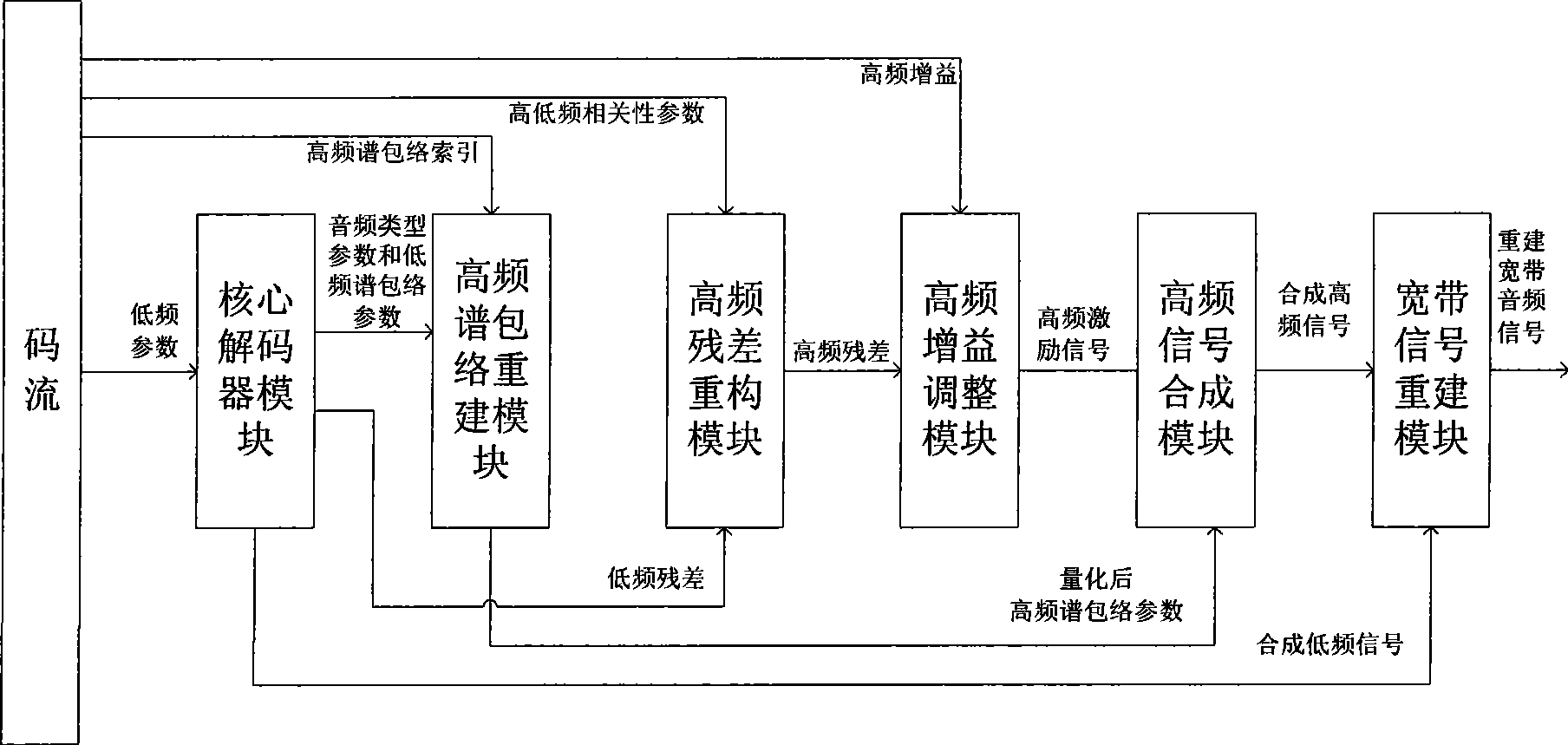
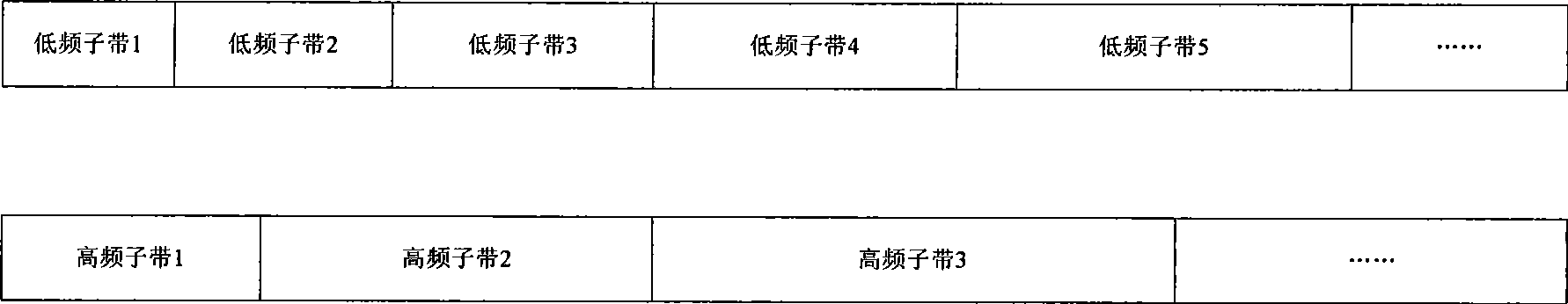
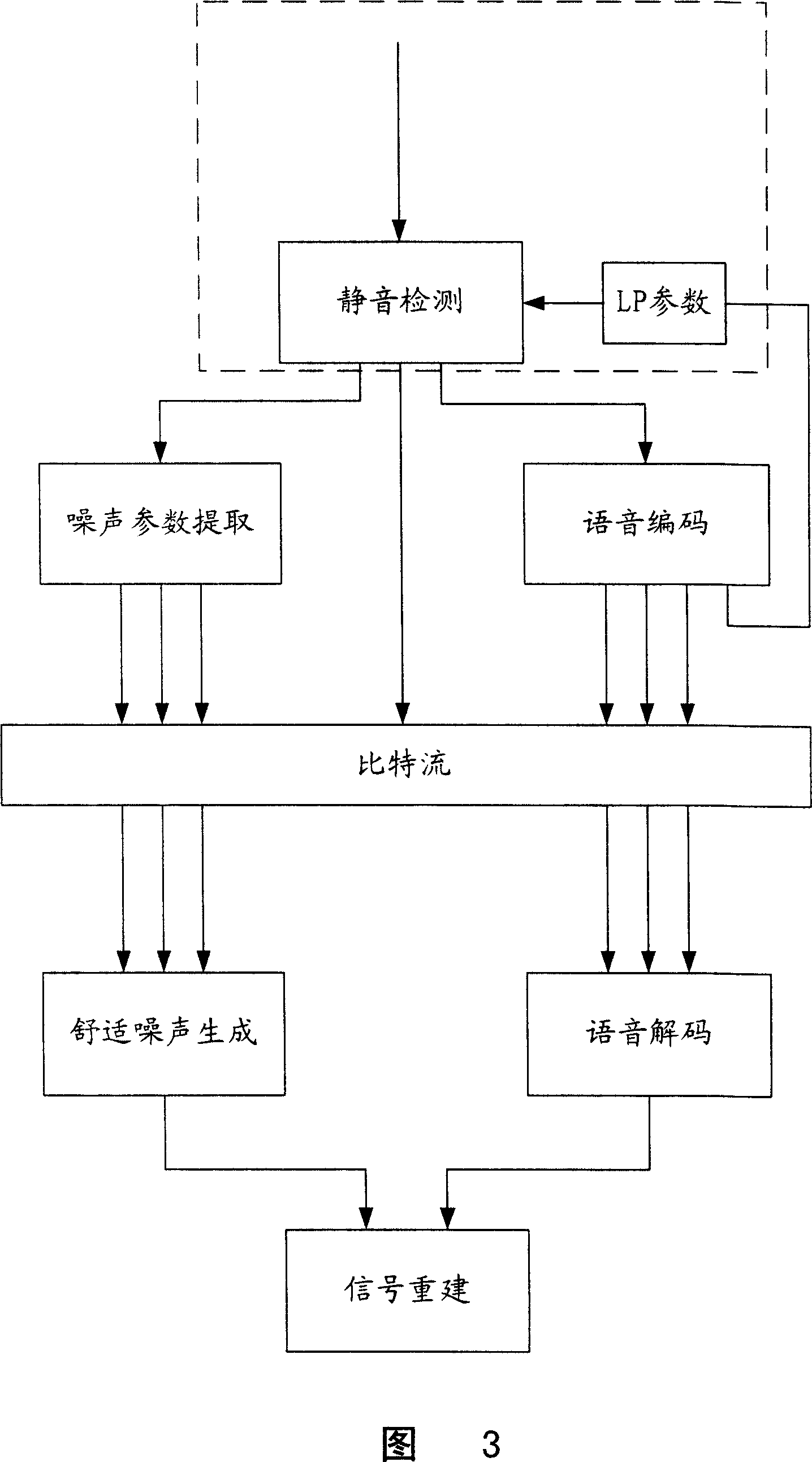
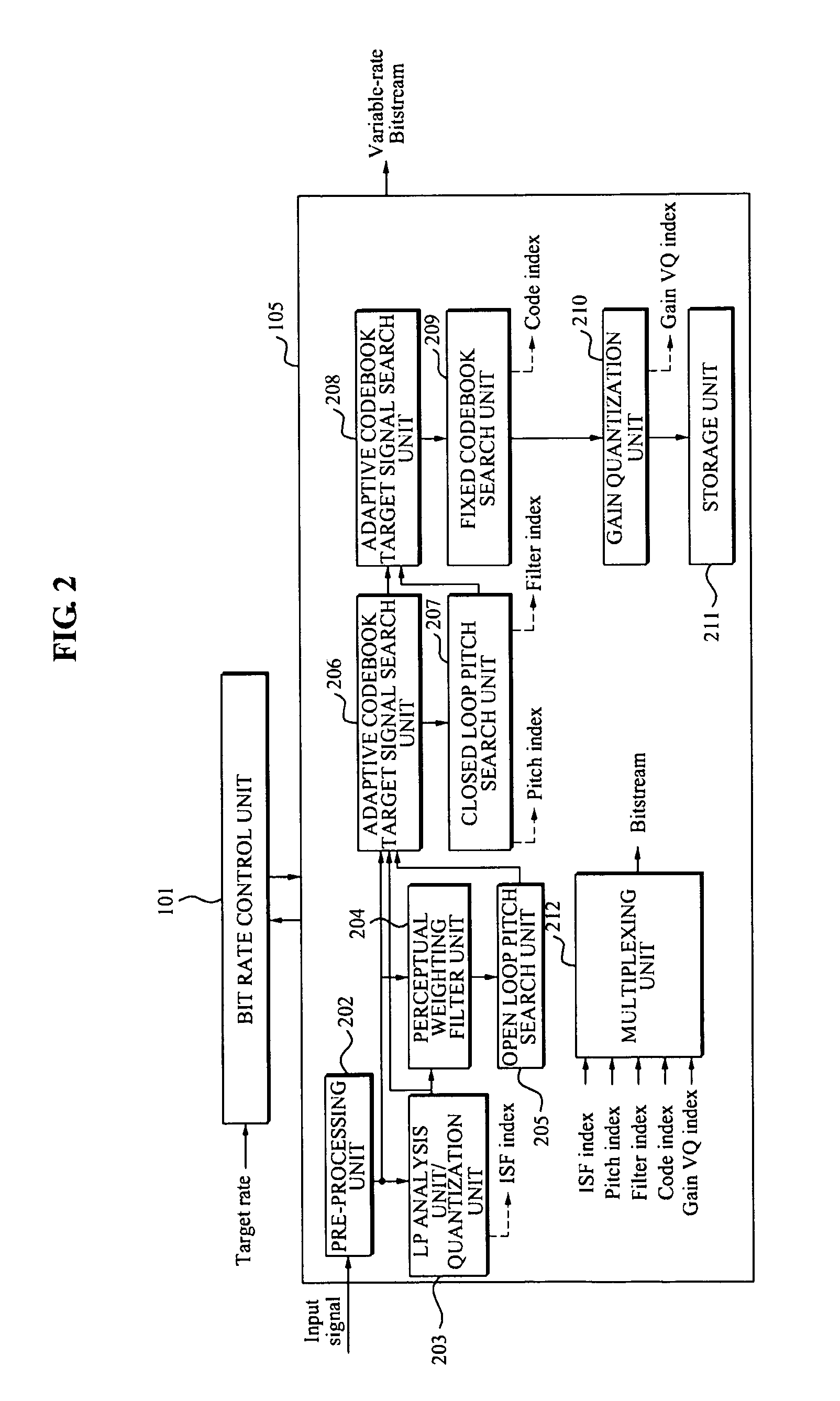
Audio bandwidth expansion coding and decoding devices
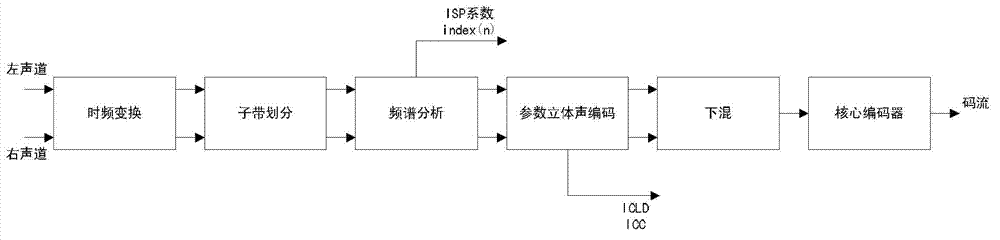
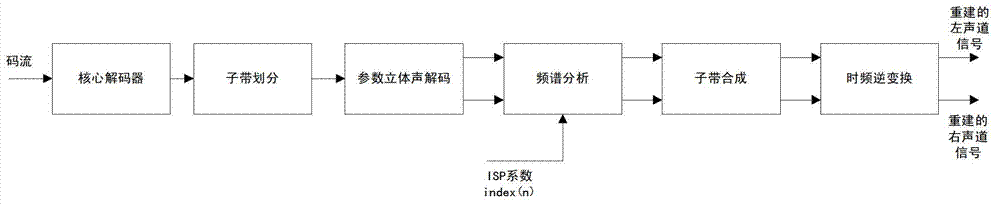
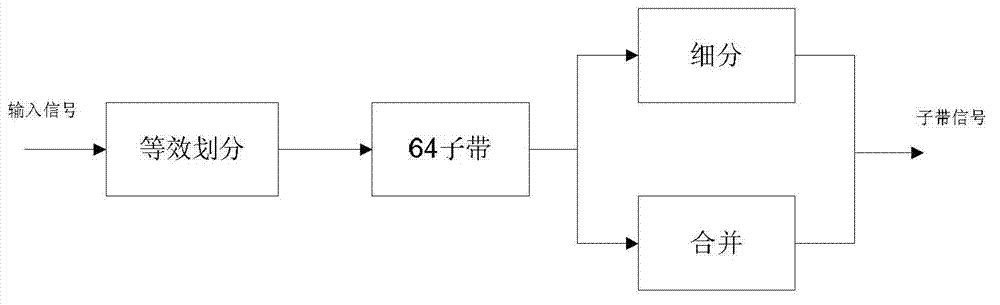
ActiveCN101521014AImprove decoding qualityQuality improvementSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumAudio signal
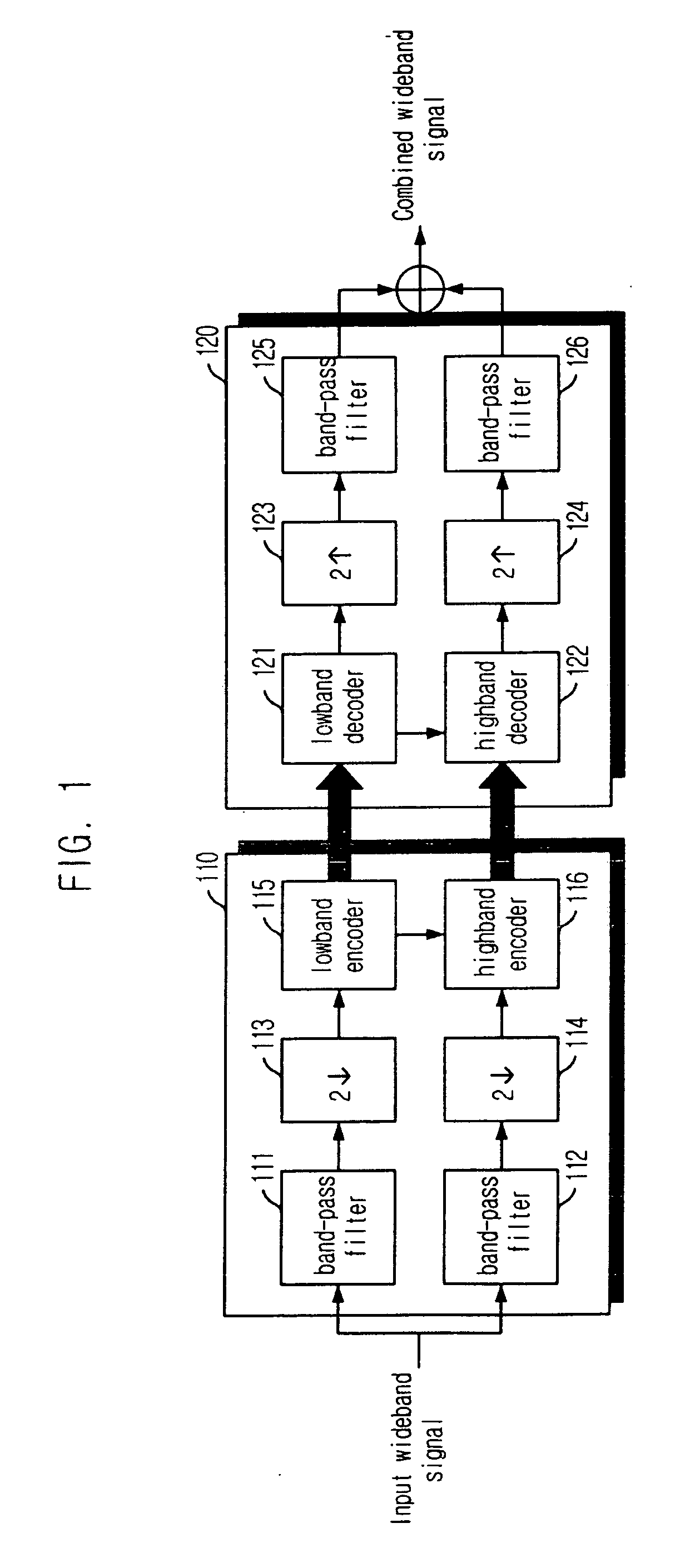
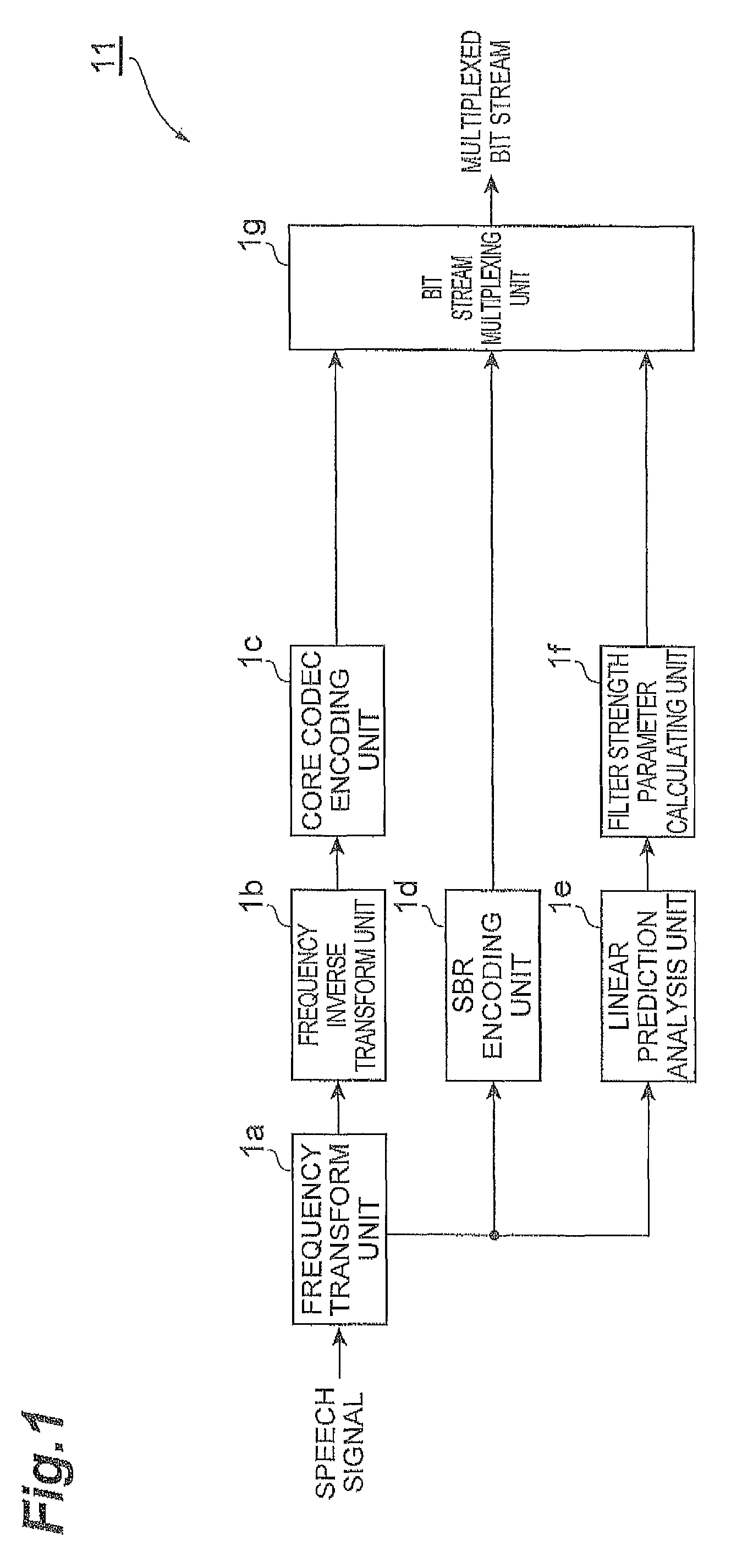
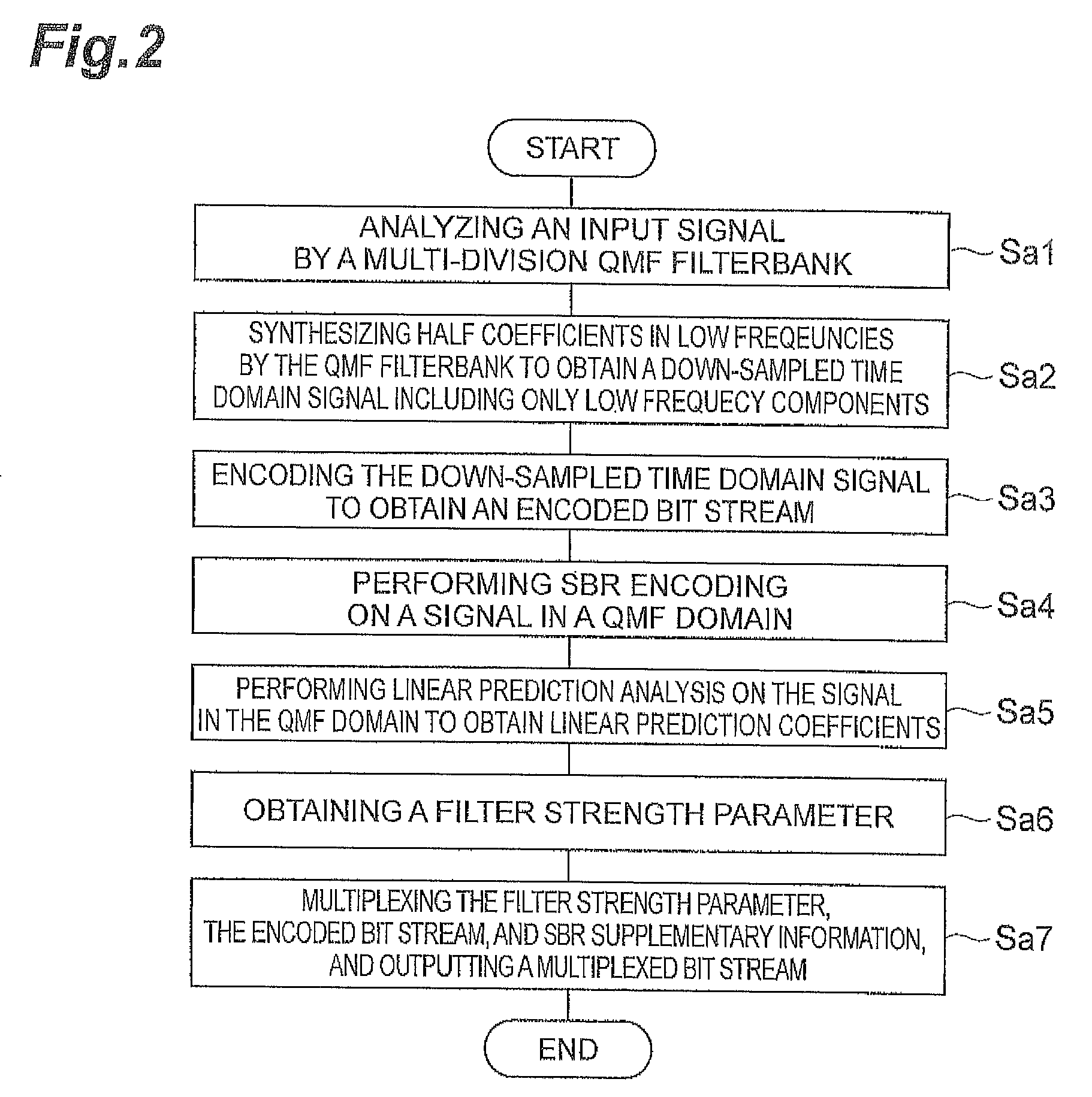
The invention provides audio bandwidth expansion coding and decoding devices which can reconstruct a high frequency signal by using the lower code rate so as to improve the quality of the output audio signal. The audio bandwidth expansion coding device comprises a frequency division module, a core coder module, a linear prediction analysis module, a spectrum envelope quantization module, a high and low frequency correlation computation module and a gain computation module; and the audio bandwidth expansion decoding device comprises a core decoder module, a high-frequency spectrum envelope reconstruction module, a high-frequency residual error reconstruction module, a high-frequency gain adjustment module, a high-frequency signal synthesis module and a wideband signal reconstruction module.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
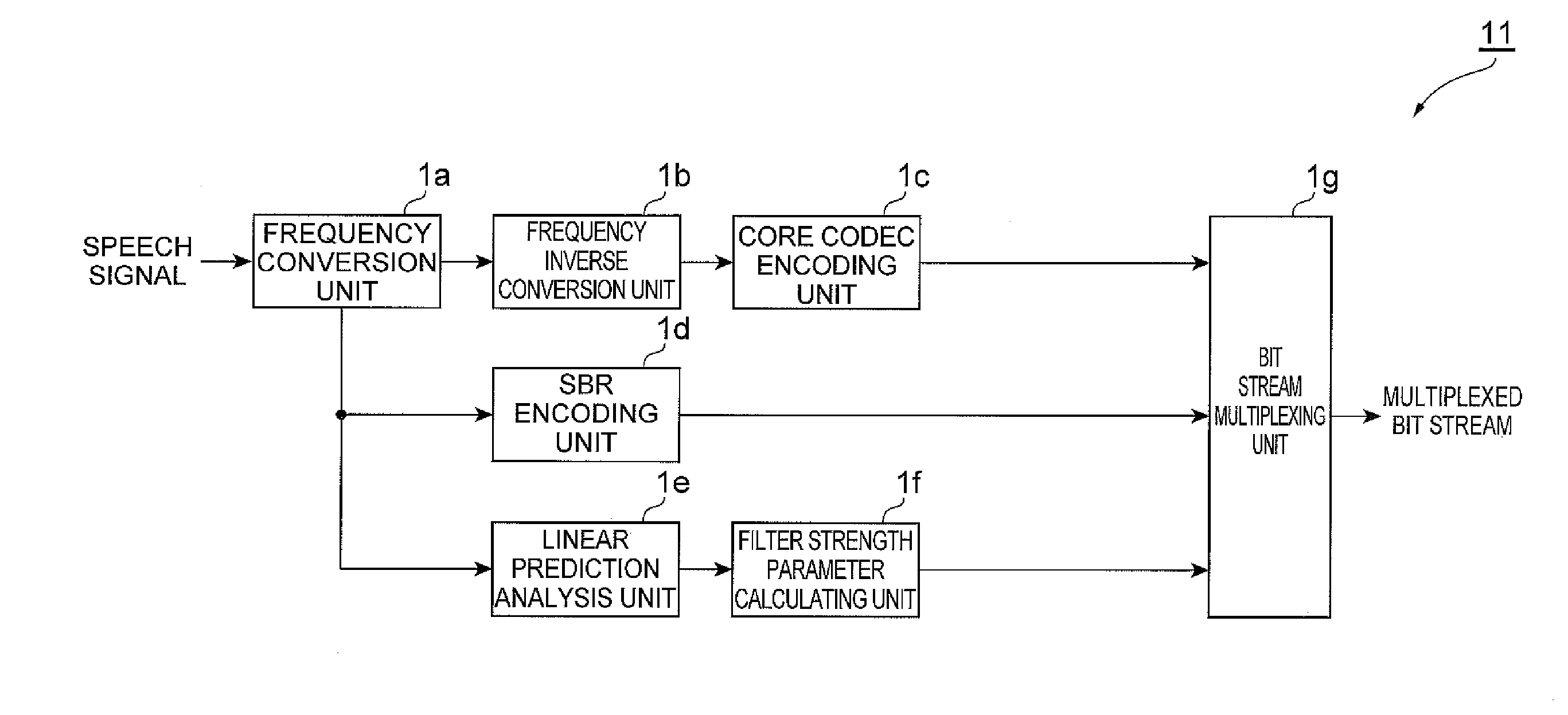
Speech encoding/decoding device
ActiveUS20120010879A1Increase bitrateImprove subjective qualitySpeech analysisCovariance methodComputer science
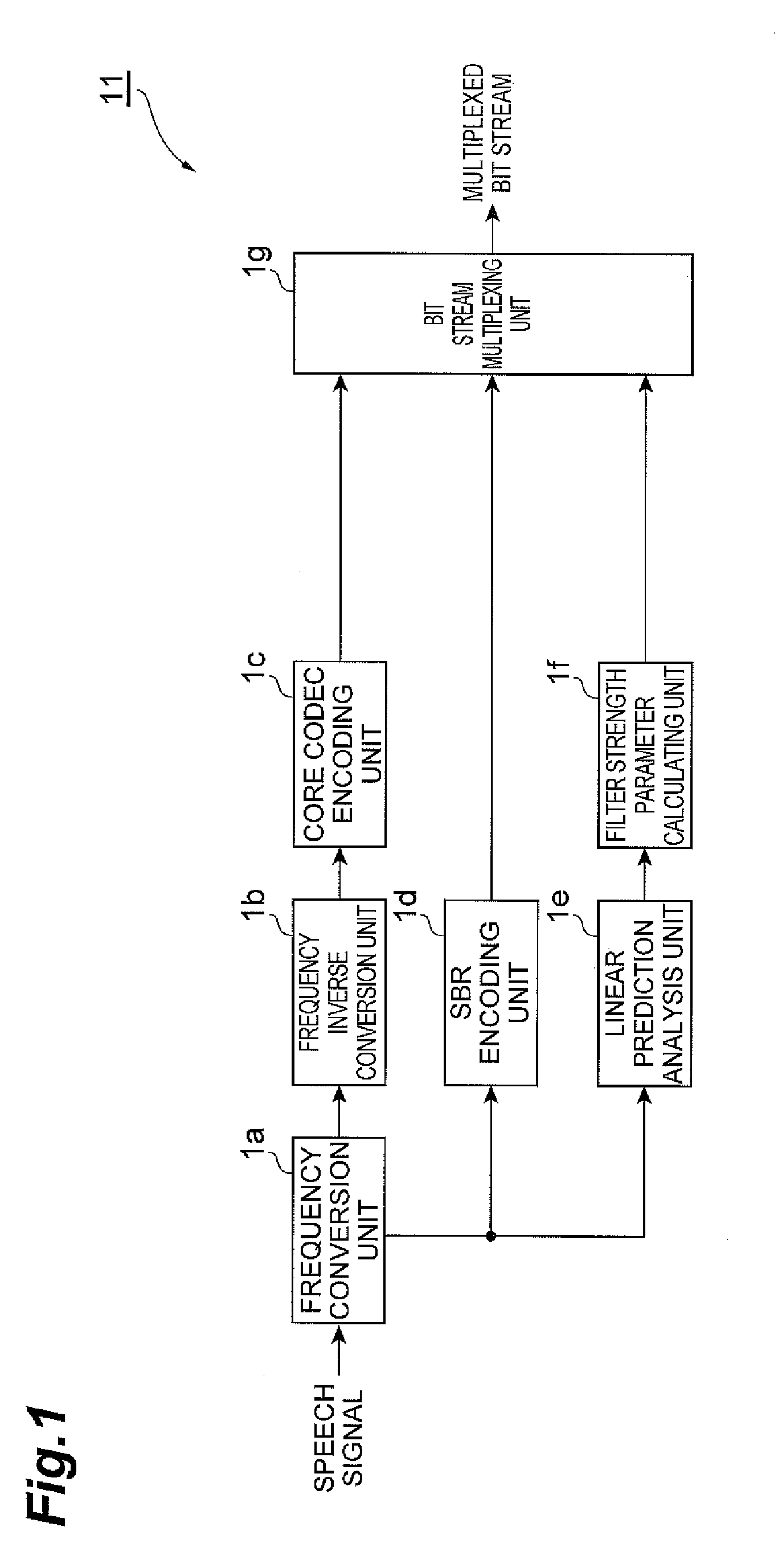
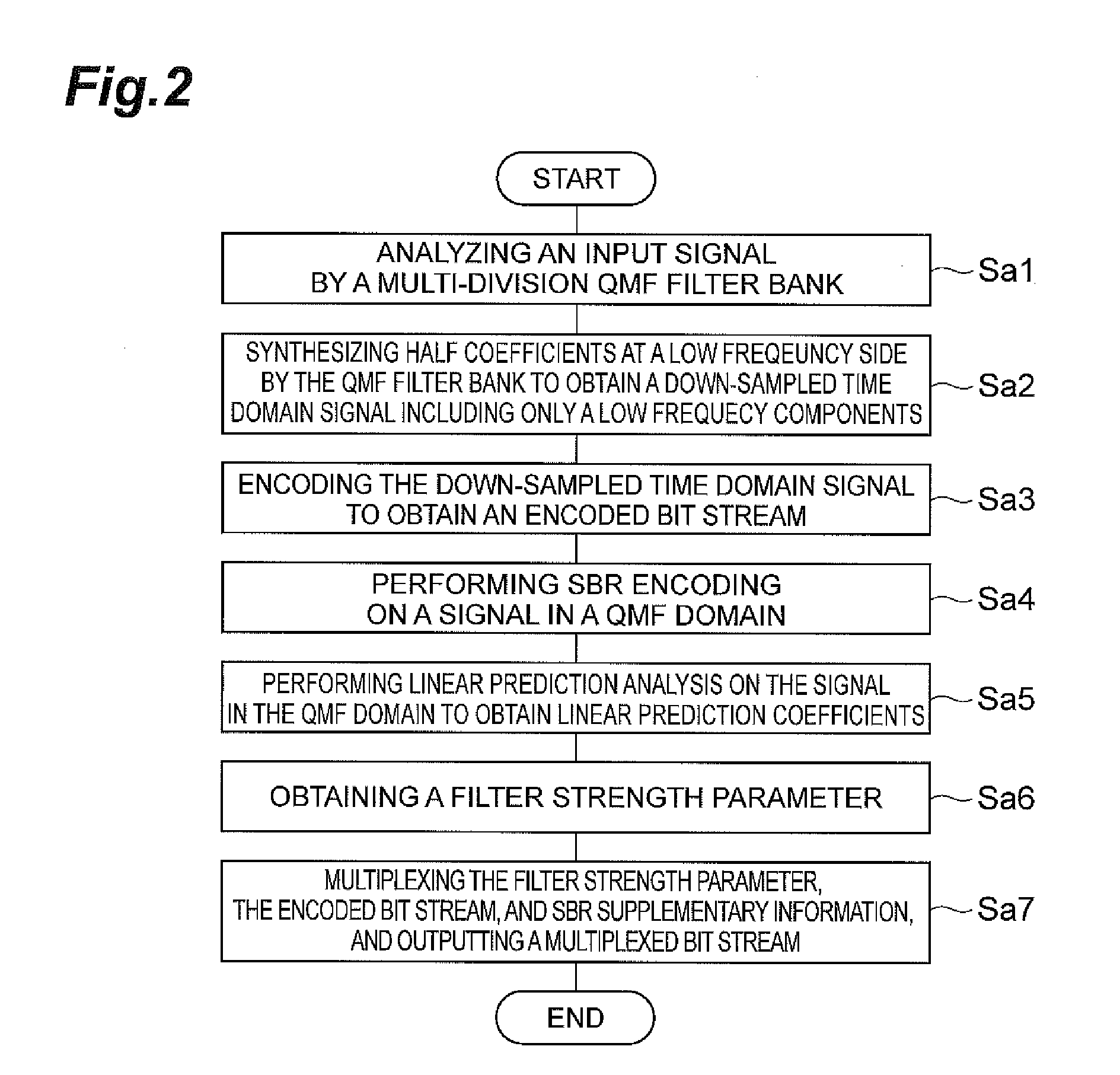
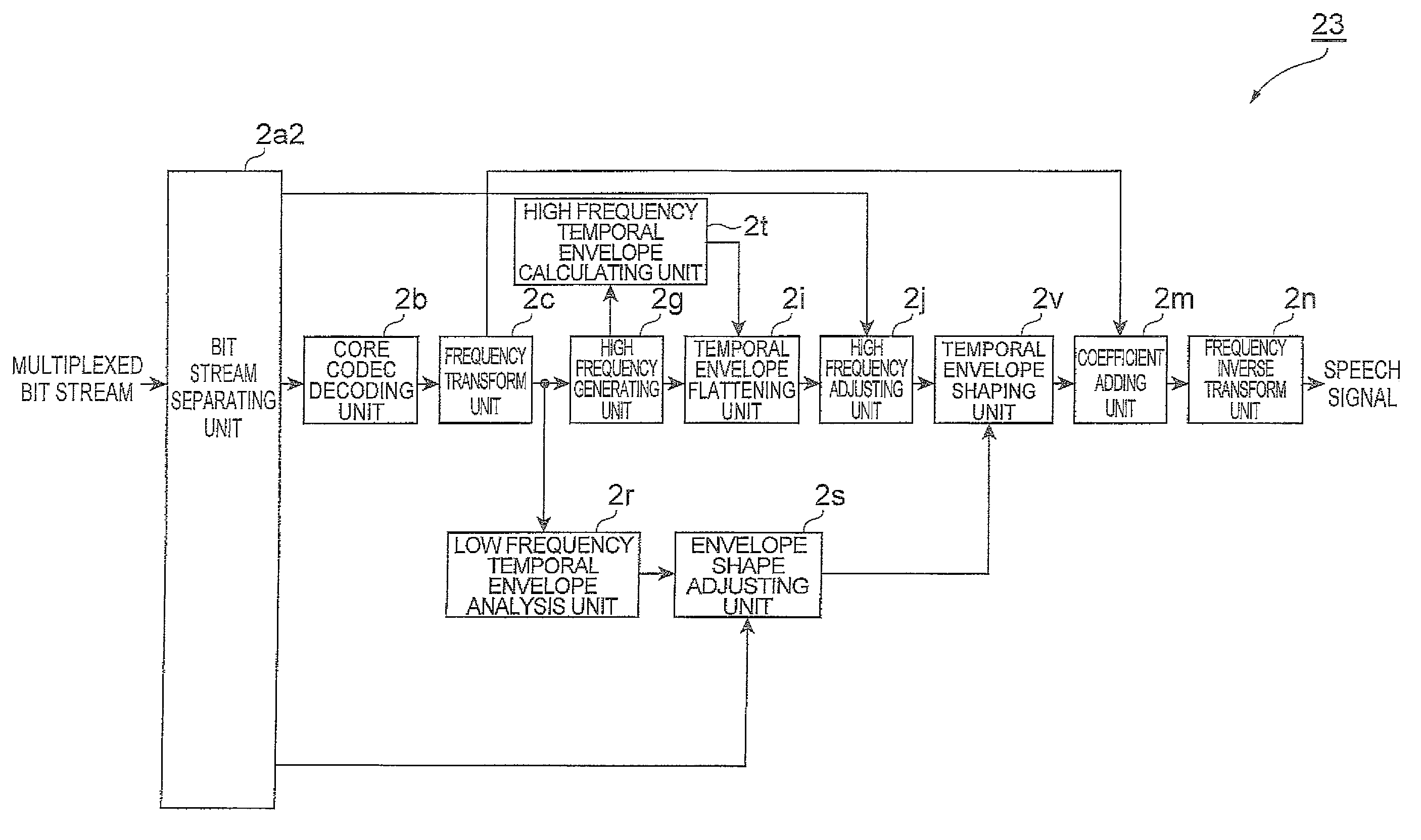
A linear prediction coefficient of a signal represented in a frequency domain is obtained by performing linear prediction analysis in a frequency direction by using a covariance method or an autocorrelation method. After the filter strength of the obtained linear prediction coefficient is adjusted, filtering may be performed in the frequency direction on the signal by using the adjusted coefficient, whereby the temporal envelope of the signal is transformed. This reduces the occurrence of pre-echo and post-echo and improves the subjective quality of the decoded signal, without significantly increasing the bit rate in a band extension technique in the frequency domain represented by SBR.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Signal modification method for efficient coding of speech signals
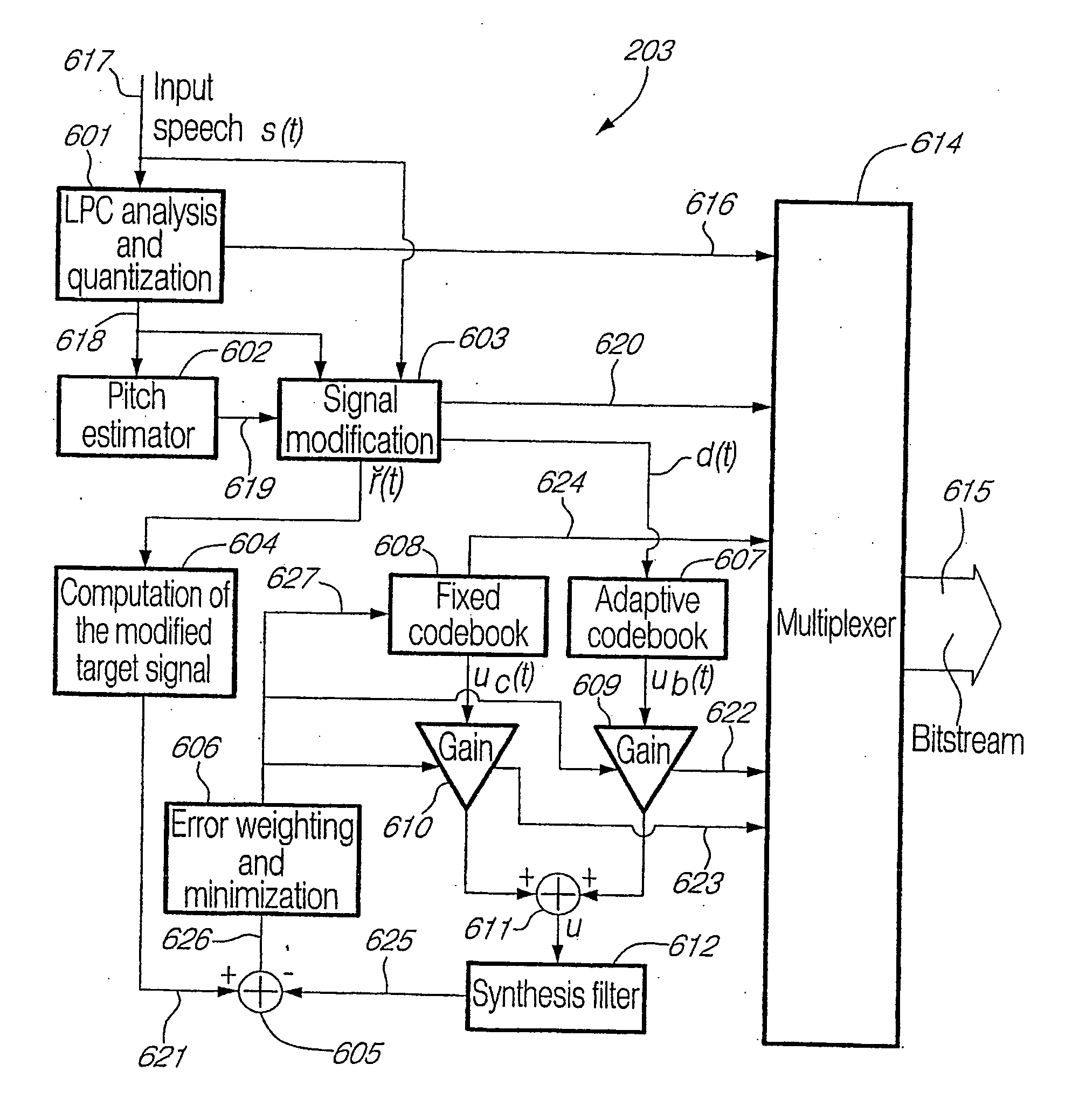
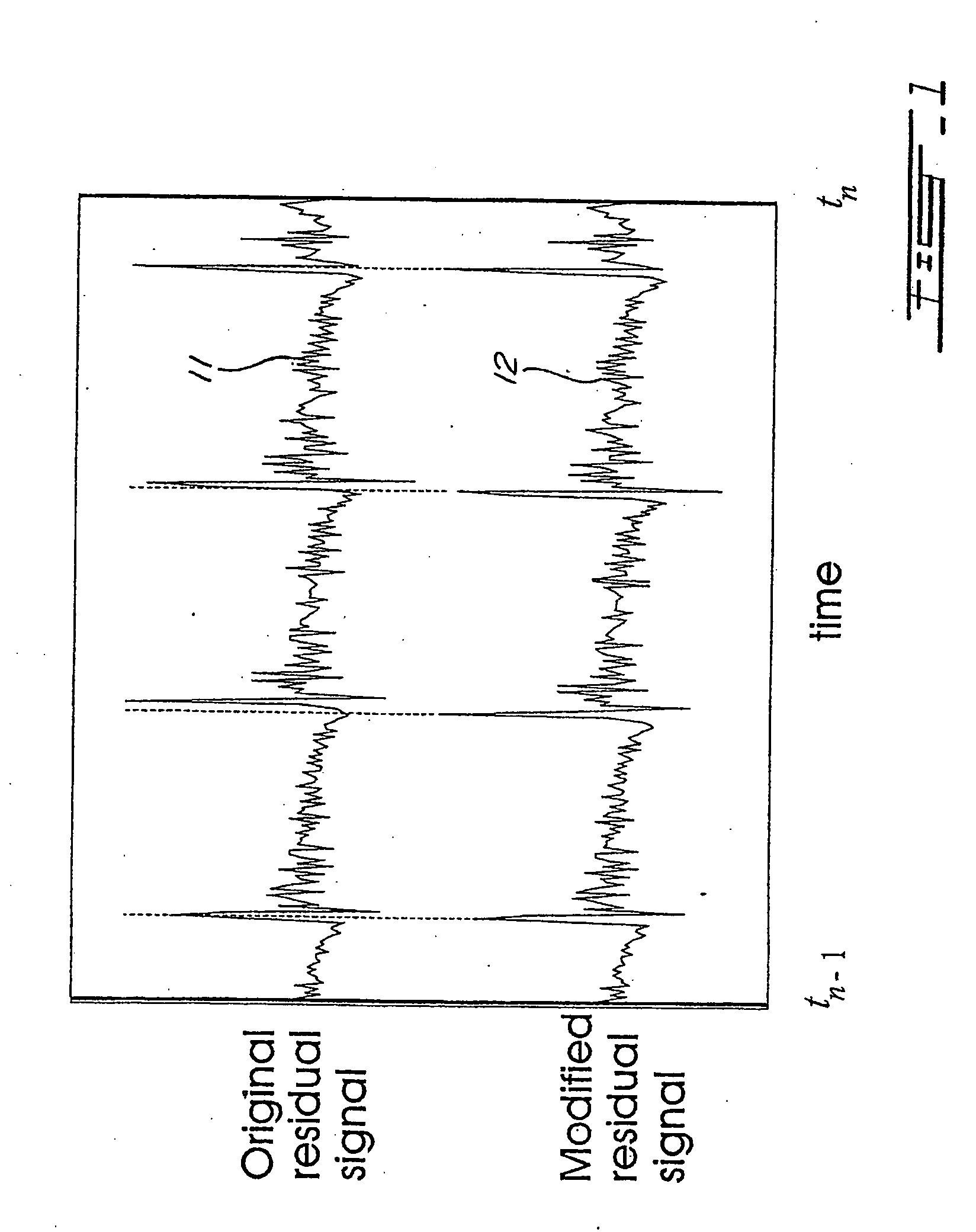
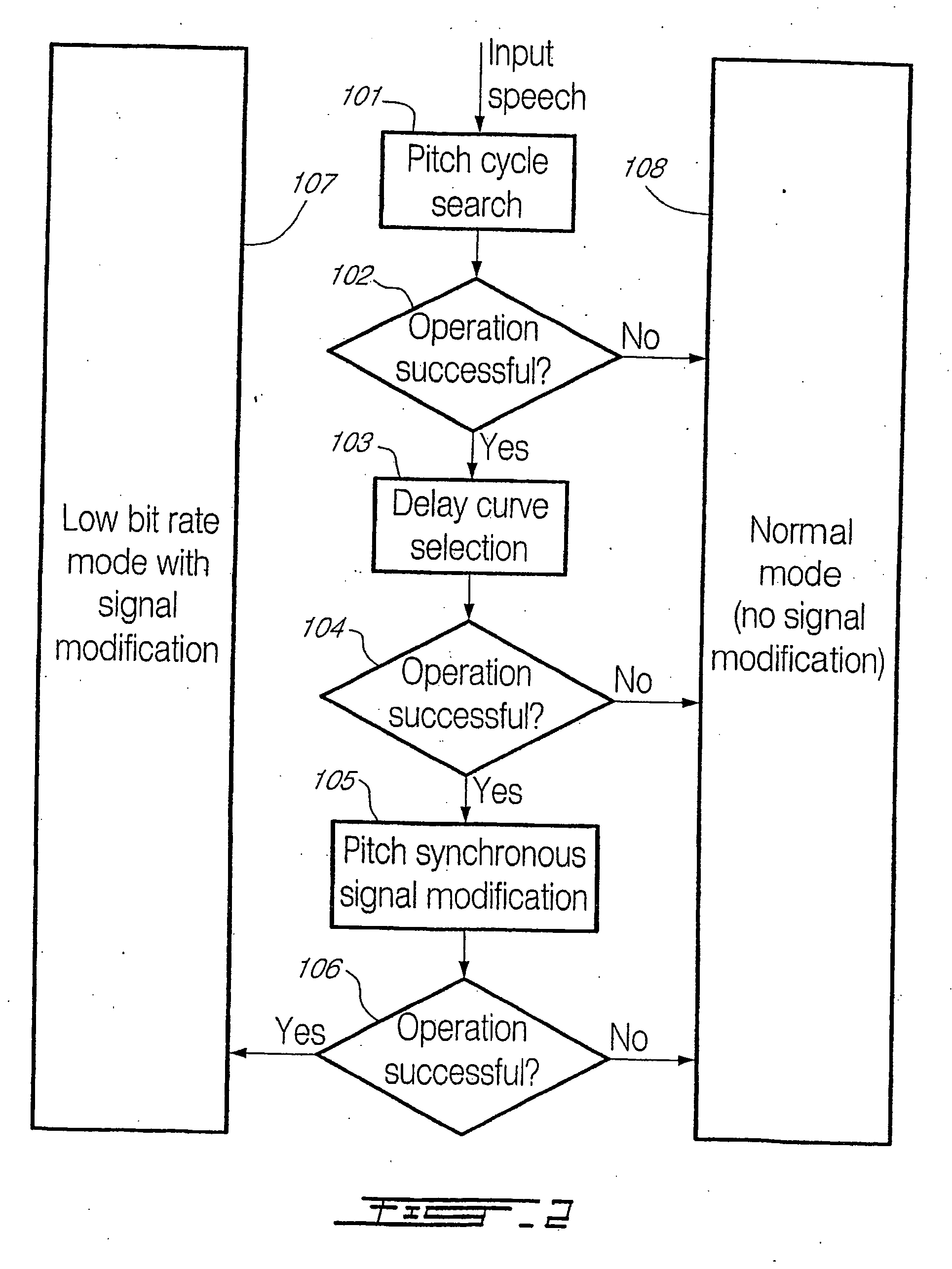
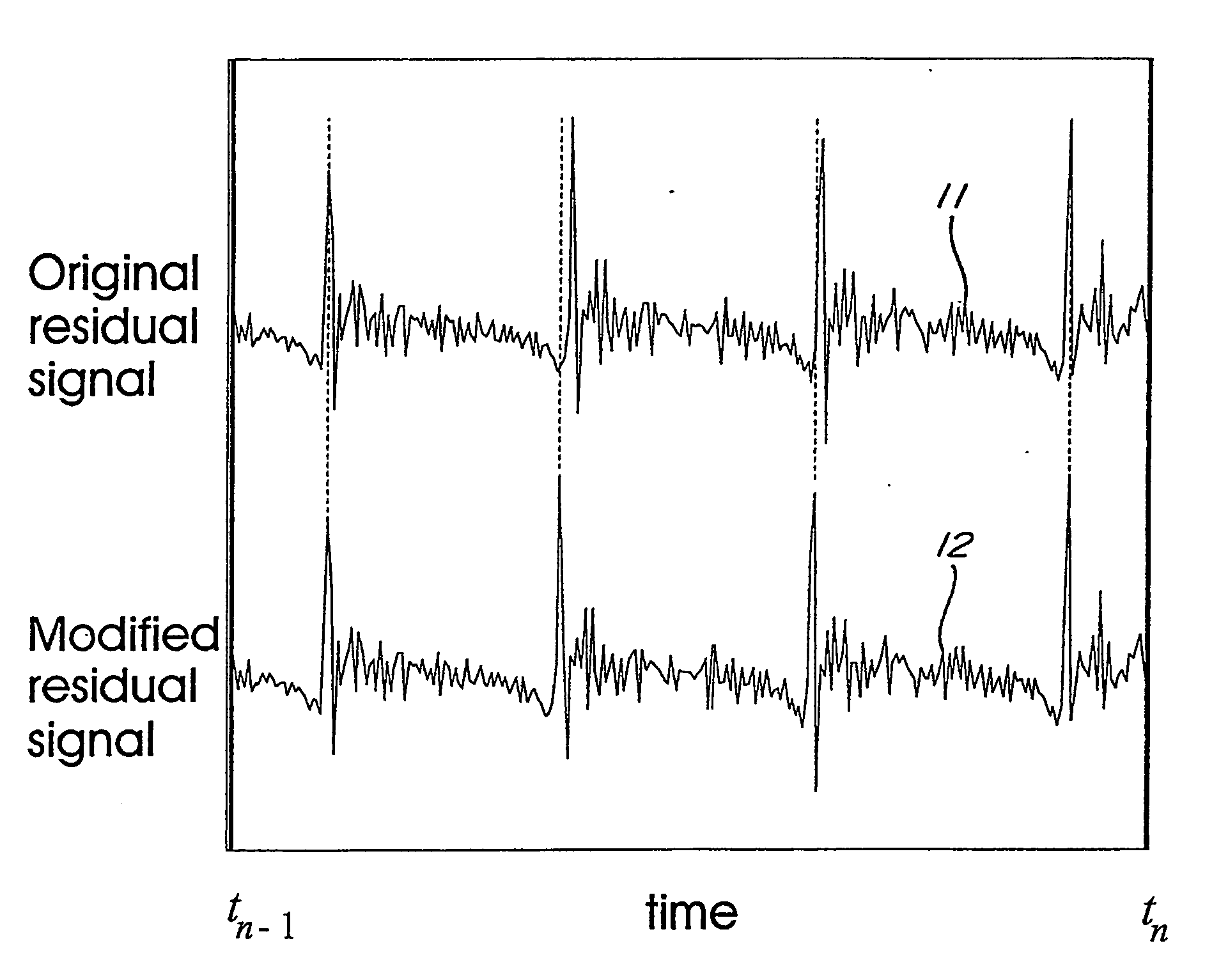
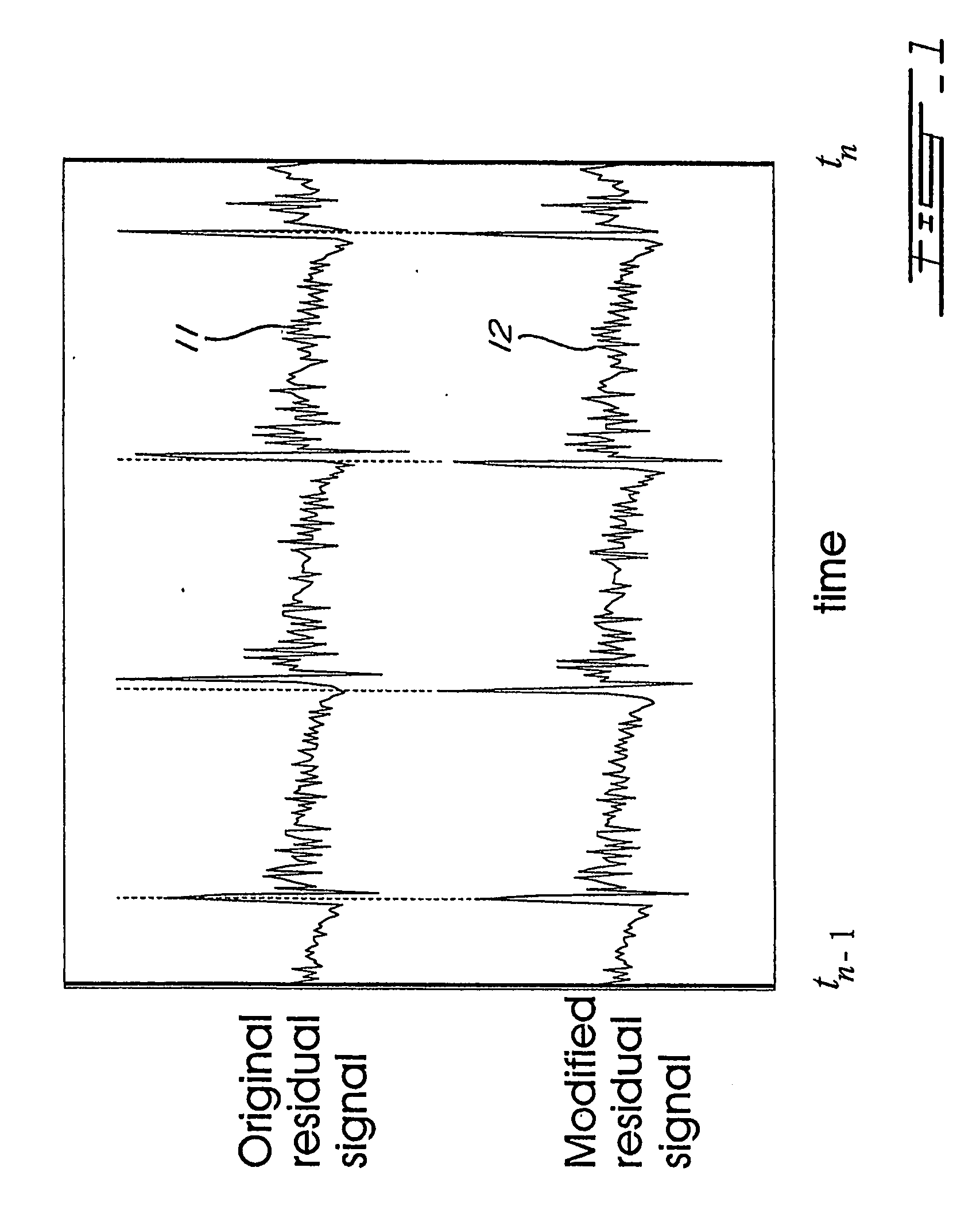
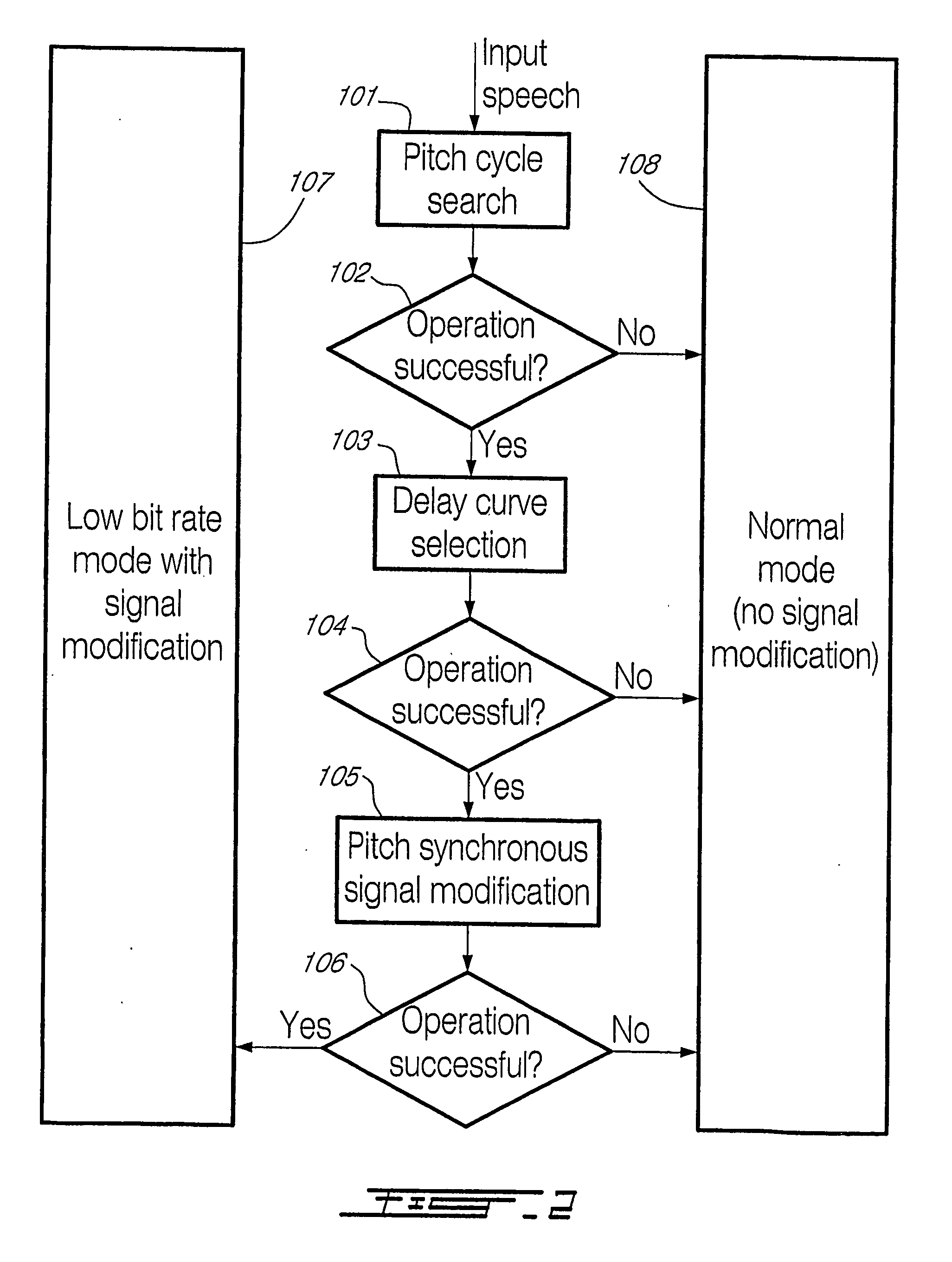
For determining a long-term-prediction delay parameter characterizing a long term prediction in a technique using signal modification for digitally encoding a sound signal, the sound signal is divided into a series of successive frames, a feature of the sound signal is located in a previous frame, a corresponding feature of the sound signal is located in a current frame, and the long-term-prediction delay parameter is determined for the current frame while mapping, with the long term prediction, the signal feature of the previous frame with the corresponding signal feature of the current frame. In a signal modification method for implementation into a technique for digitally encoding a sound signal, the sound signal is divided into a series of successive frames, each frame of the sound signal is partitioned into a plurality of signal segments, and at least a part of the signal segments of the frame are warped while constraining the warped signal segments inside the frame. For searching pitch pulses in a sound signal, a residual signal is produced by filtering the sound signal through a linear prediction analysis filter, a weighted sound signal is produced by processing the sound signal through a weighting filter, the weighted sound signal being indicative of signal periodicity, a synthesized weighted sound signal is produced by filtering a synthesized speech signal produced during a last subframe of a previous frame of the sound signal through the weighting filter, a last pitch pulse of the sound signal of the previous frame is located from the residual signal, a pitch pulse prototype of given length is extracted around the position of the last pitch pulse of the sound signal of the previous frame using the synthesized weighted sound signal, and the pitch pulses are located in a current frame using the pitch pulse prototype.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Highband speech coding apparatus and method for wideband speech coding system
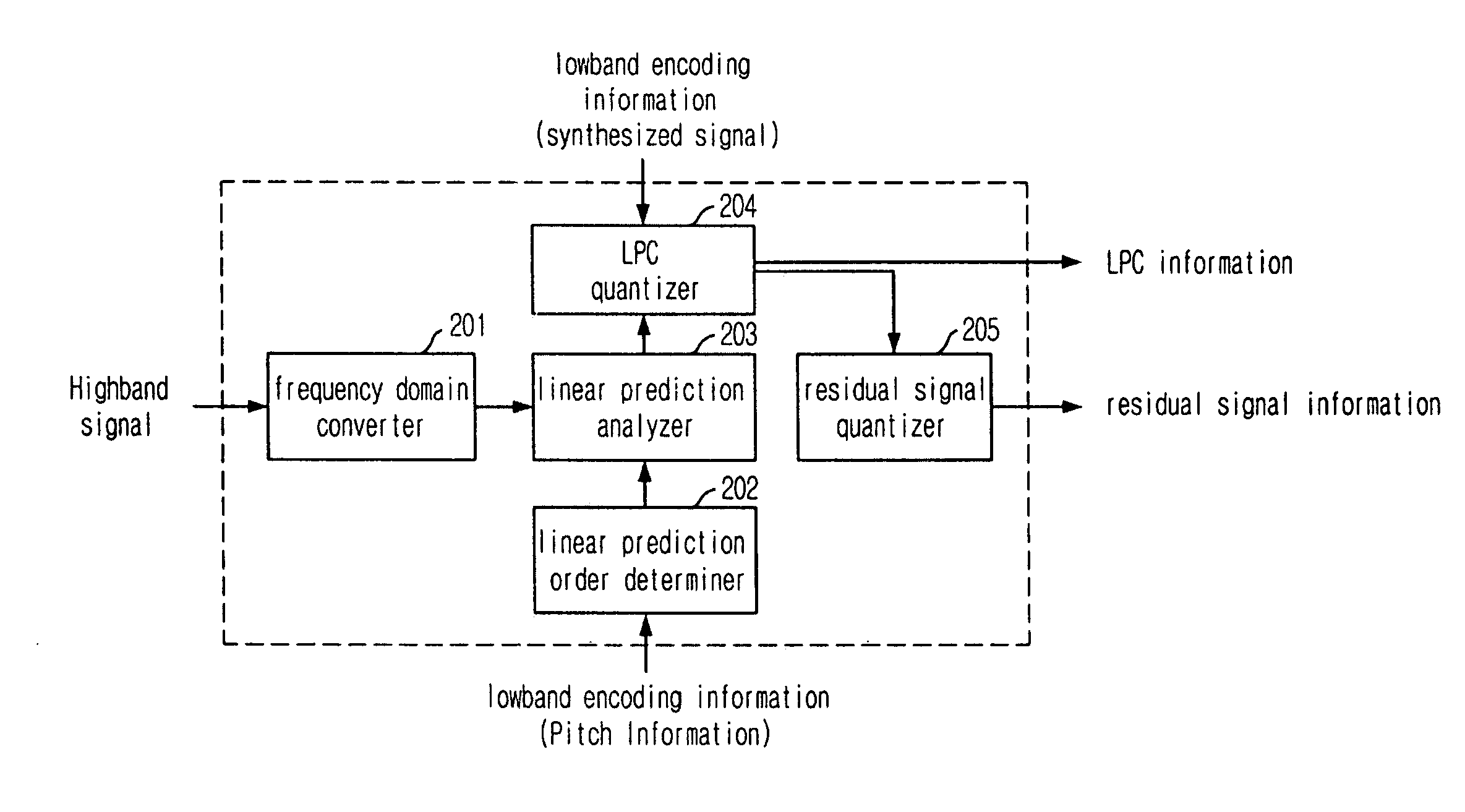
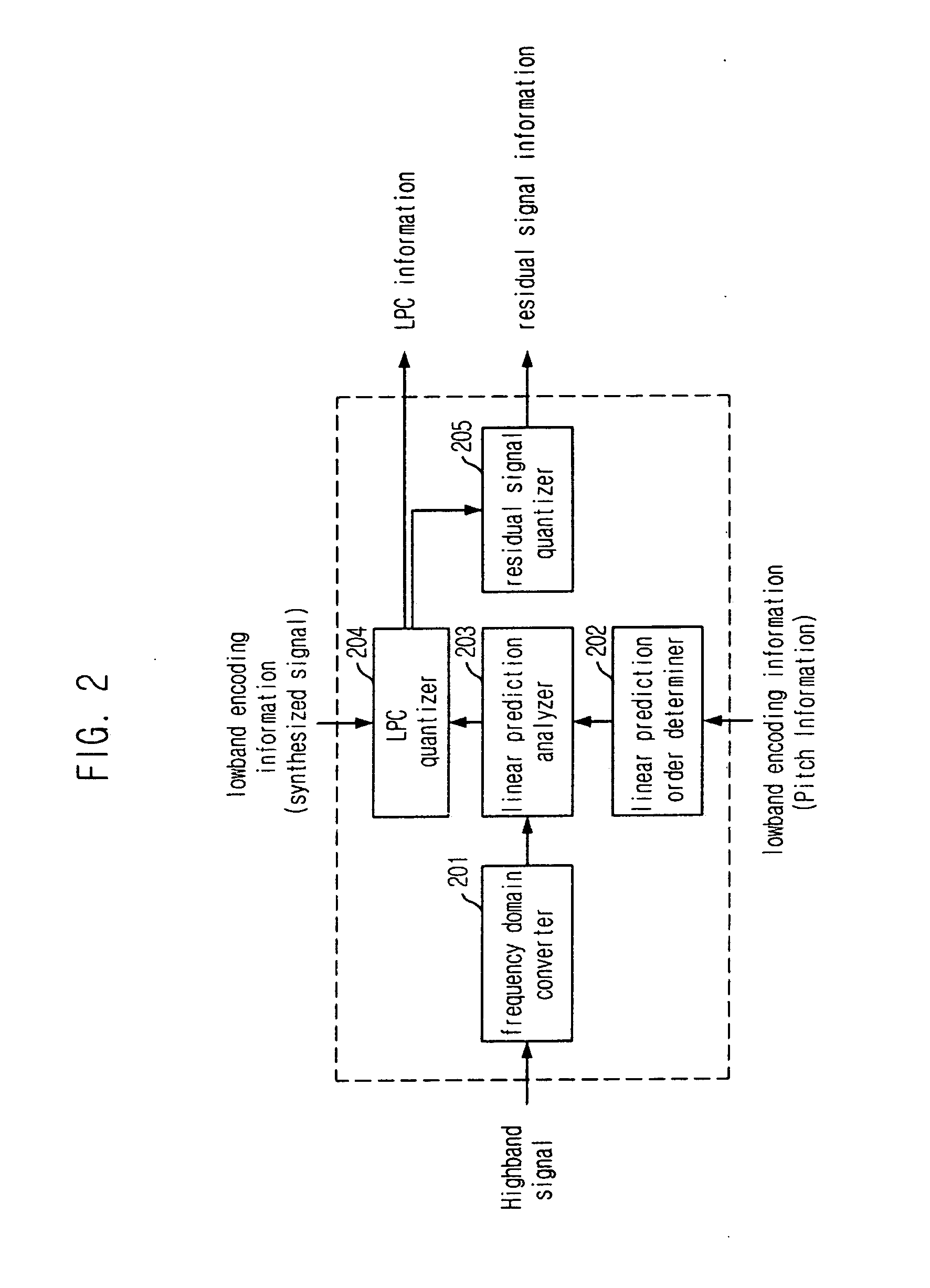
Provided is a highband coding apparatus and method for a wideband coding system. The coding apparatus and method can reduce a pre-echo phenomenon by encoding the highband based on lowband encoding information and Temporal Noise Shaping technique. A highband encoding apparatus includes: a domain converter for converting the domain of an input highband signal into a frequency domain; a linear prediction order determiner for determining a linear prediction order based on the lowband encoding information; a linear prediction analyzer for analyzing a highband signal of the frequency domain based on the determined linear prediction order to thereby generate a linear prediction coefficient; a linear prediction coefficient quantizer for quantizing the linear prediction coefficient based on the lowband encoding information; and a residual signal quantizer for obtaining a residual signal by dequantizing the quantized linear prediction coefficient and quantizing the residual signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
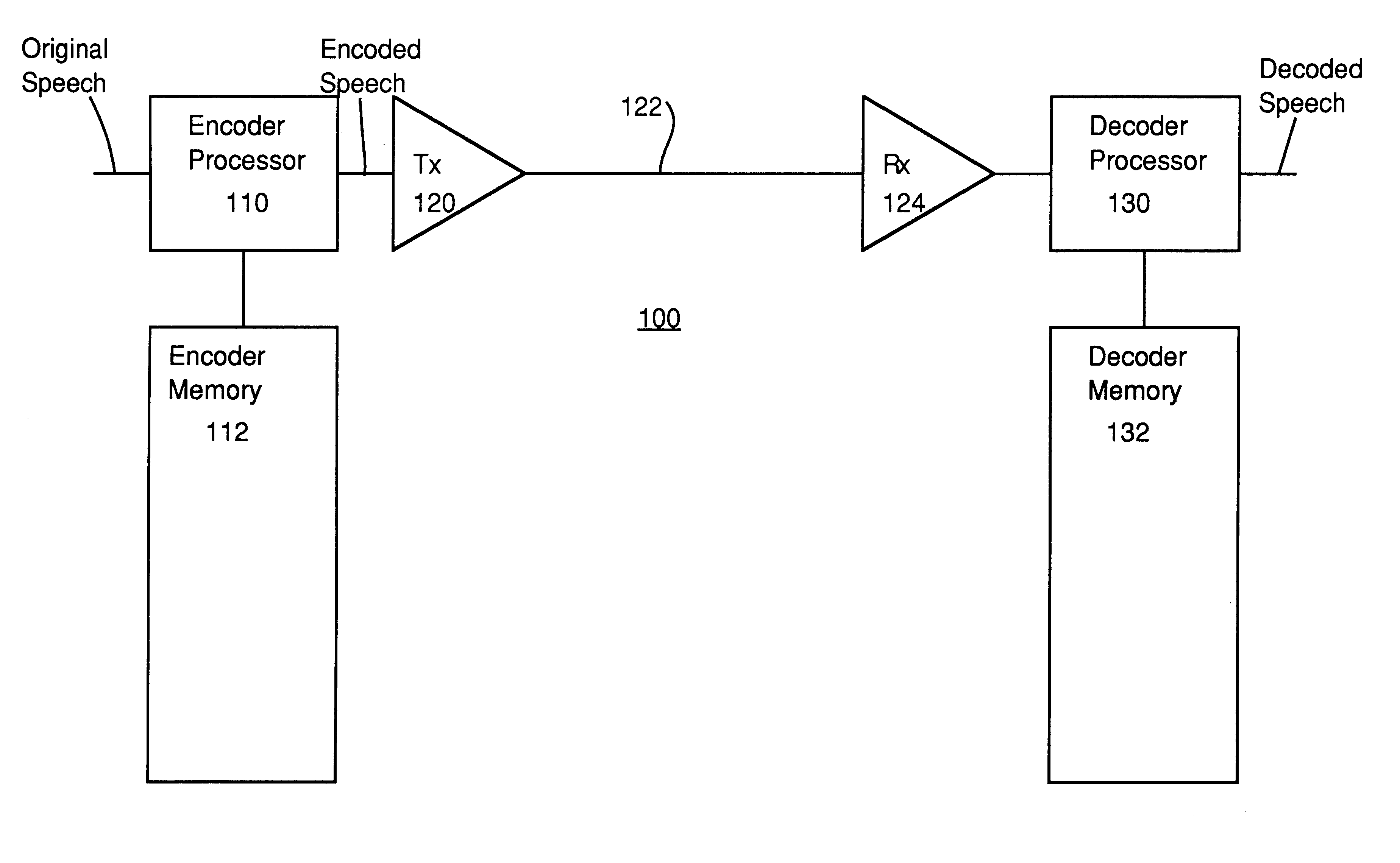
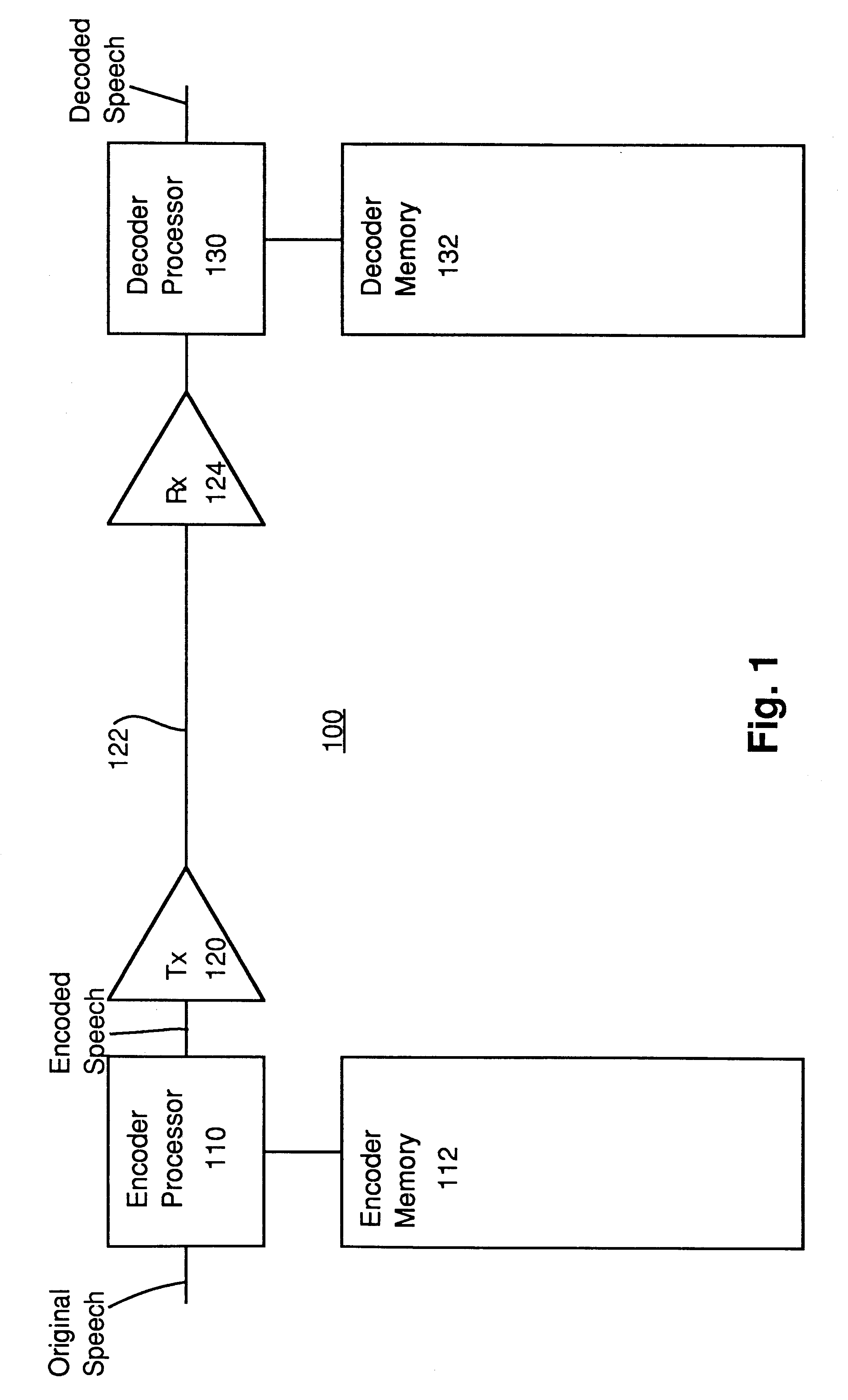
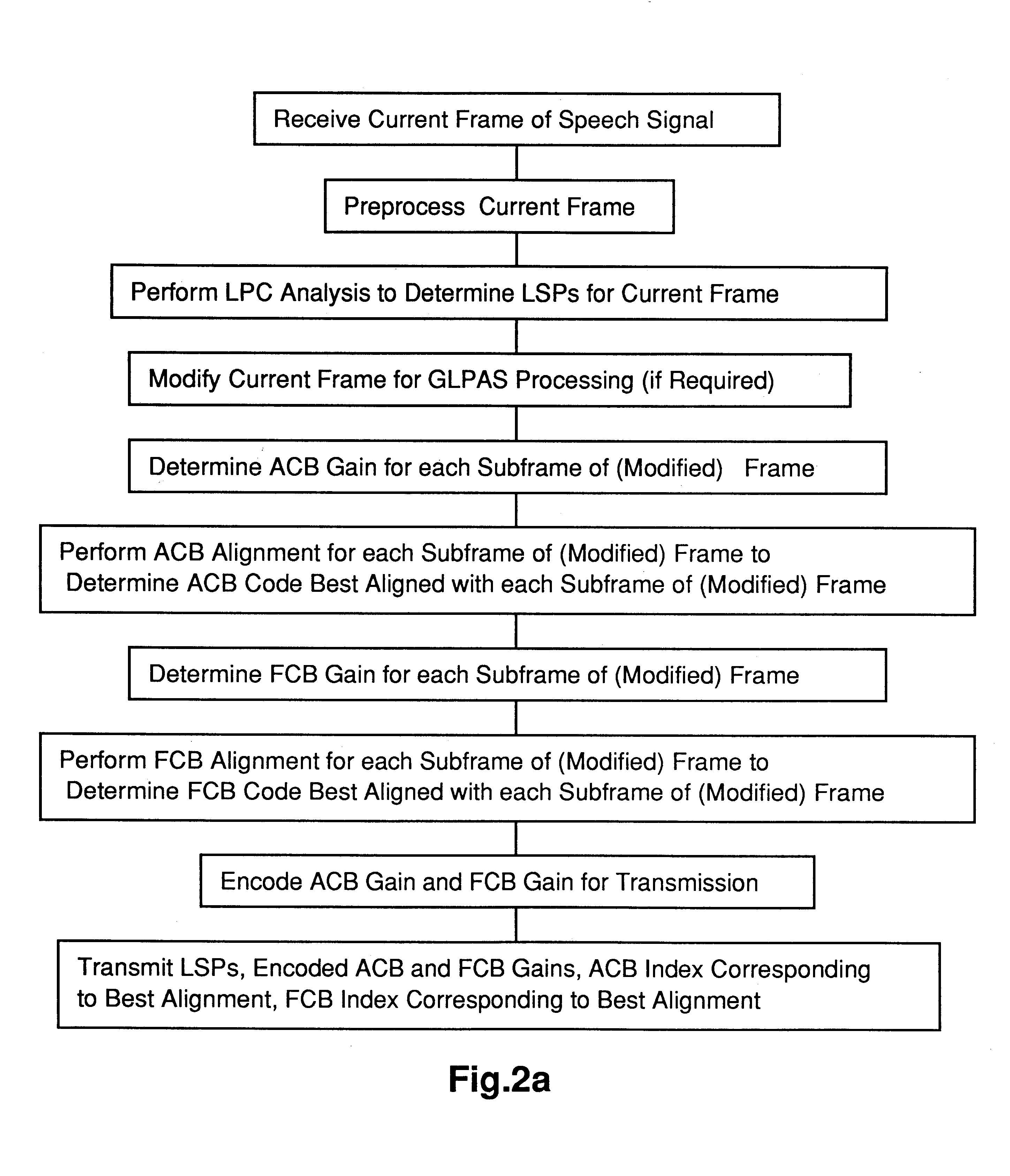
Methods and apparatus for efficient quantization of gain parameters in GLPAS speech coders
InactiveUS6240385B1Improve coding efficiencySpeech analysisFluid pressure measurementTrellis quantizationSpeech code
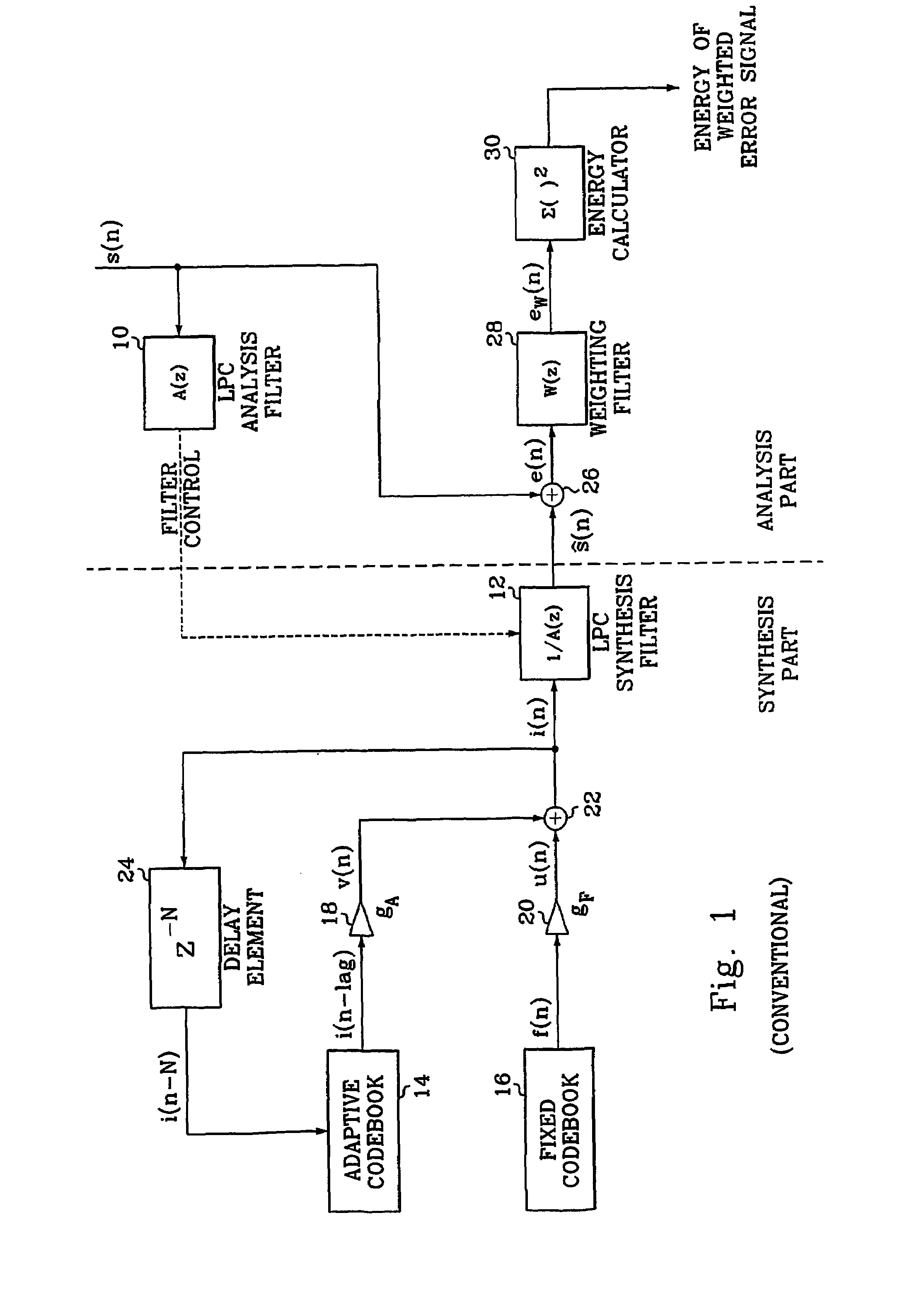
In methods and apparatus for encoding a gain parameter in a generalized linear predictive analysis-by-synthesis (GLPAS) coder, a subframe gain parameter is determined for each of a plurality of successive subframes of a frame, and a quantized frame gain parameter is determined for each frame using a delayed decision quantizer operating on the subframe gain parameters. The subframe gain parameters may be treated as components of a gain vector and the gain vector may be vector quantized to determine the quantized frame gain parameter. Encoder parameters are efficiently aligned with decoder parameters to ensure proper end-to-end operation. Alternatively, tree quantization or trellis quantization may be applied to the subframe gain parameters to determine the quantized frame gain parameter. The methods and apparatus are particularly applicable to low bit rate speech coding.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
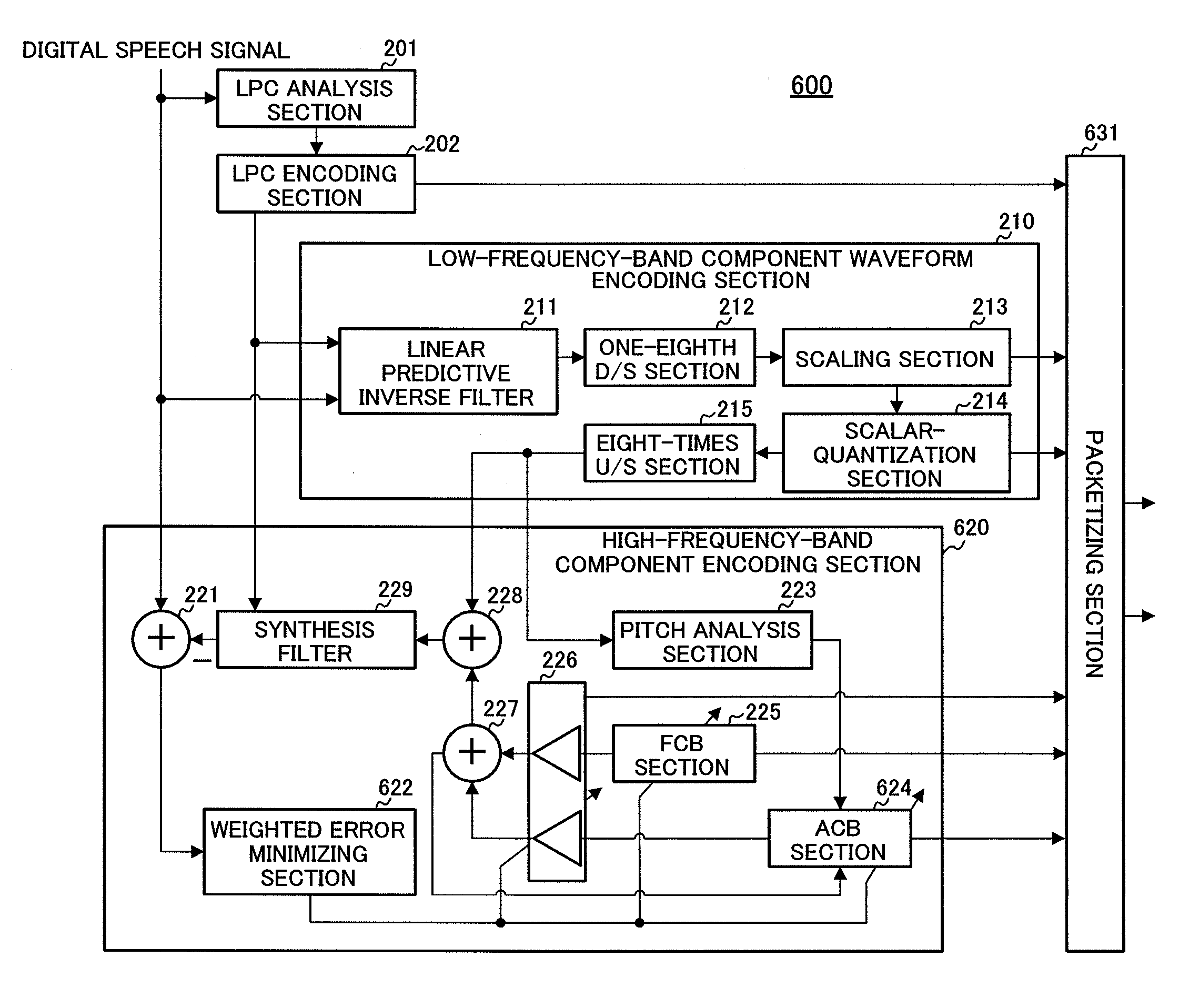
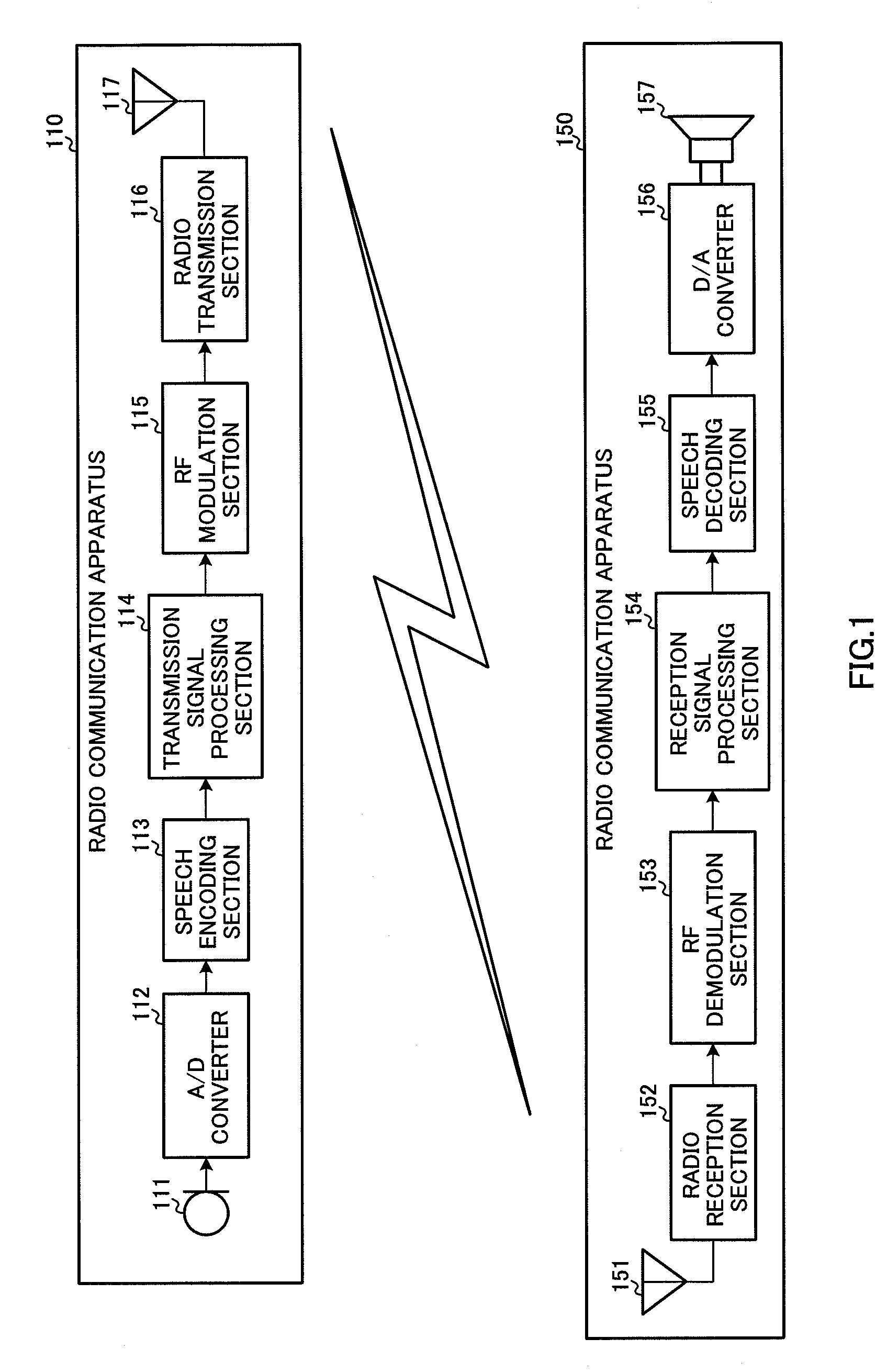
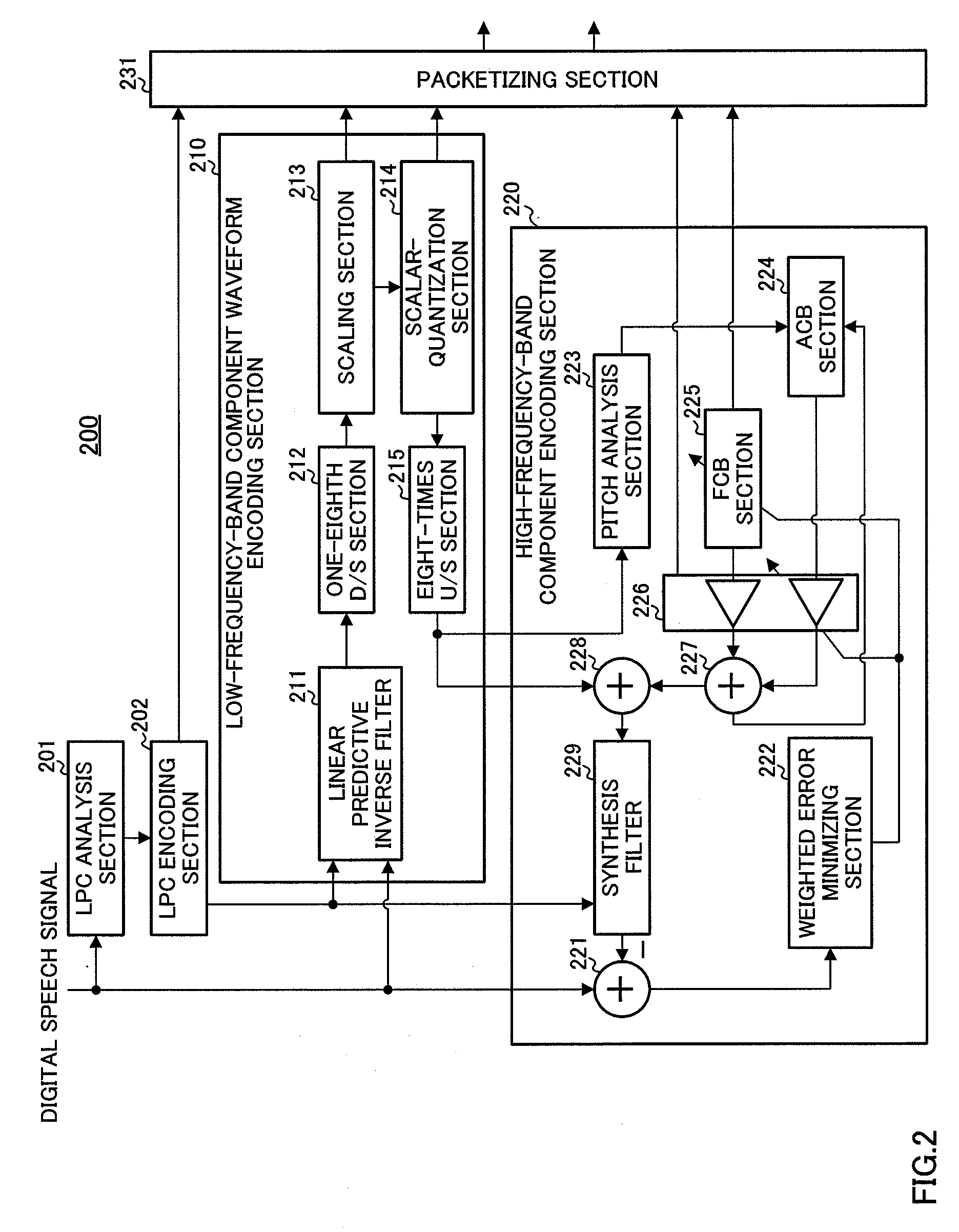
Low-frequency-band component and high-frequency-band audio encoding/decoding apparatus, and communication apparatus thereof
InactiveUS7848921B2Improve voice qualityError propagationSpeech analysisLow frequency bandCommunication device
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
Three-dimensional acoustic processor which uses linear predictive coefficients
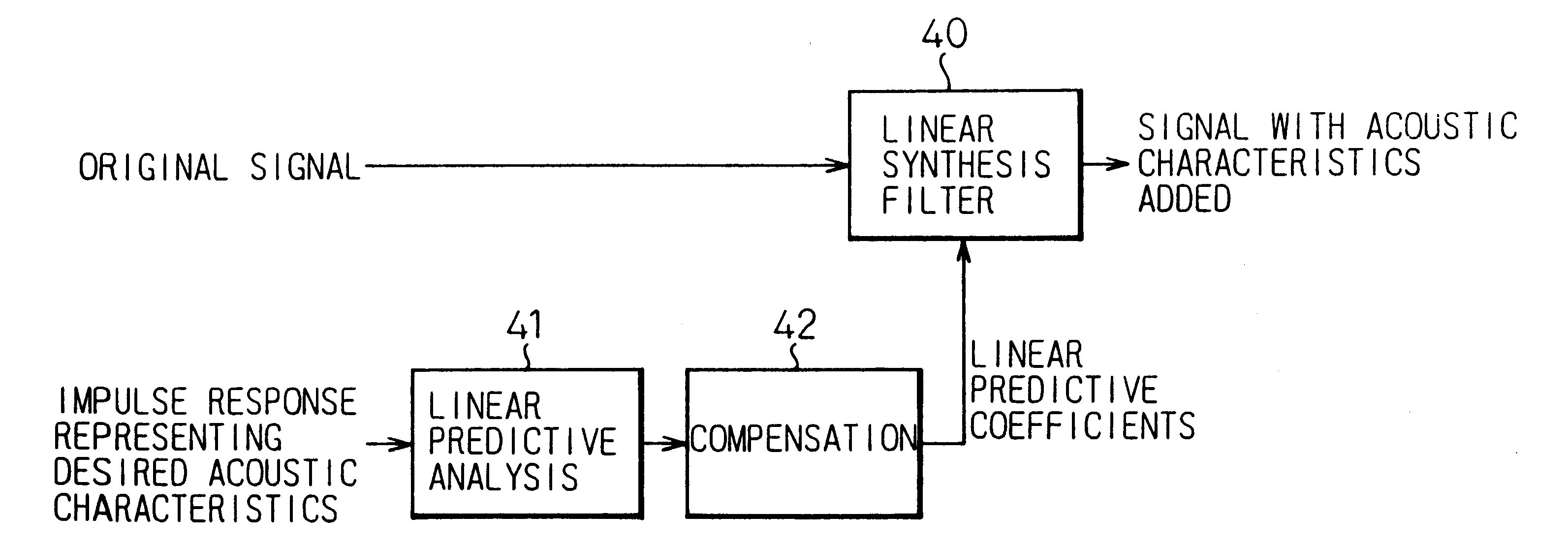
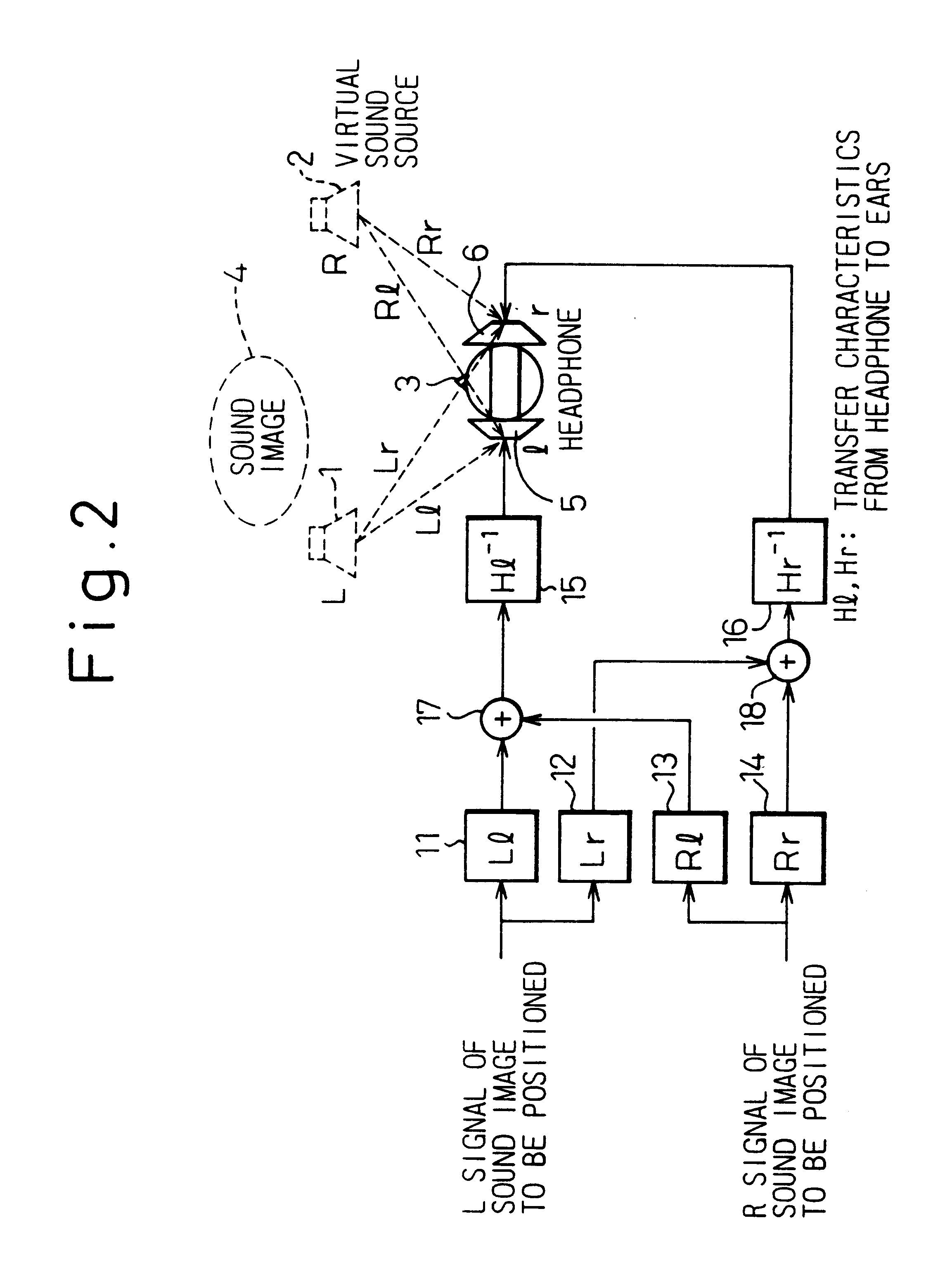
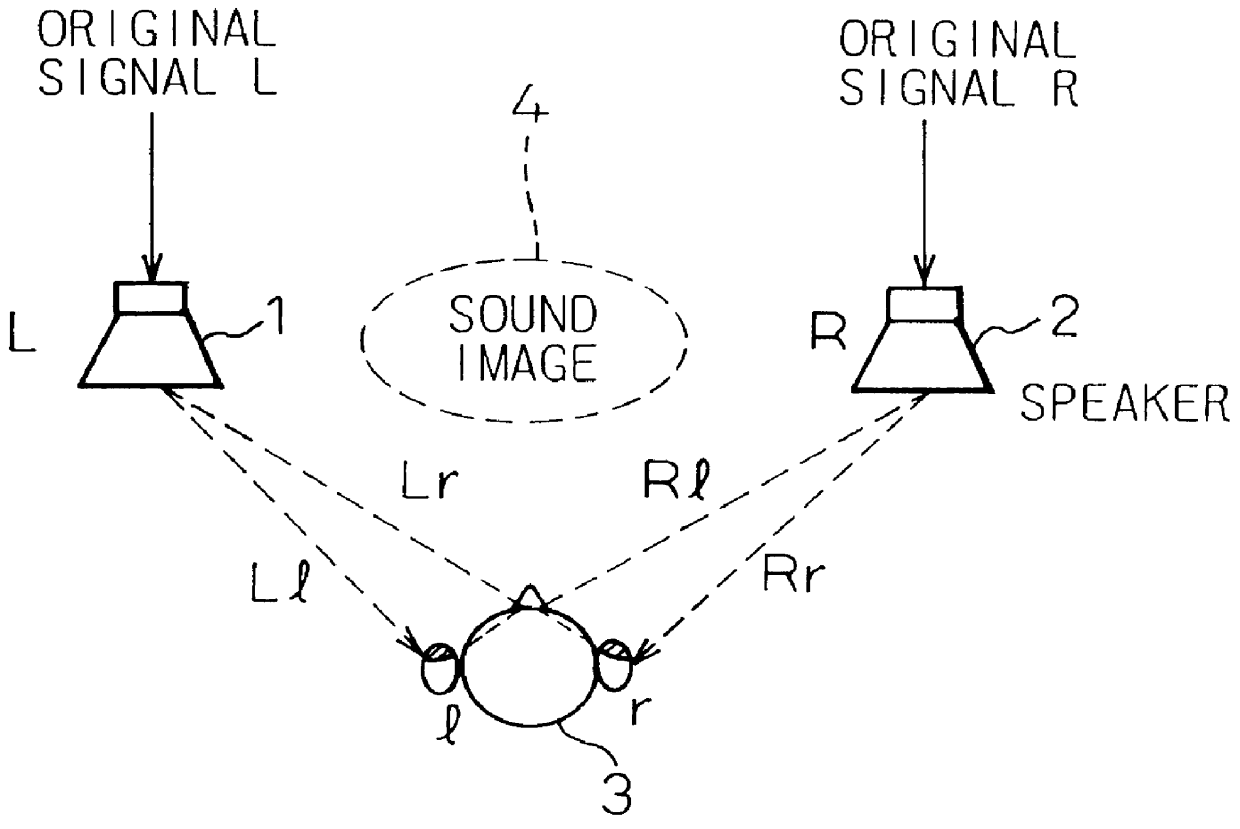
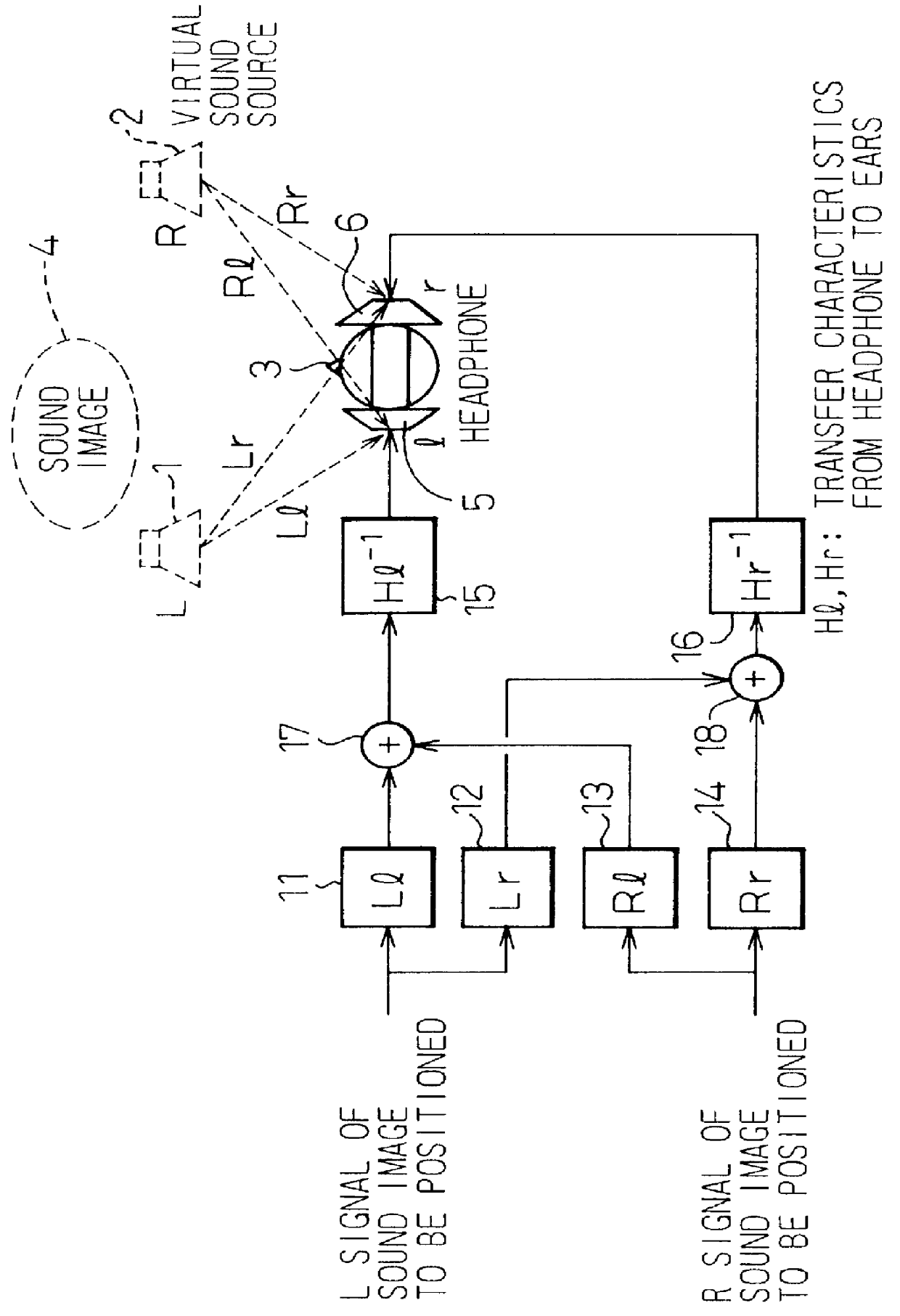
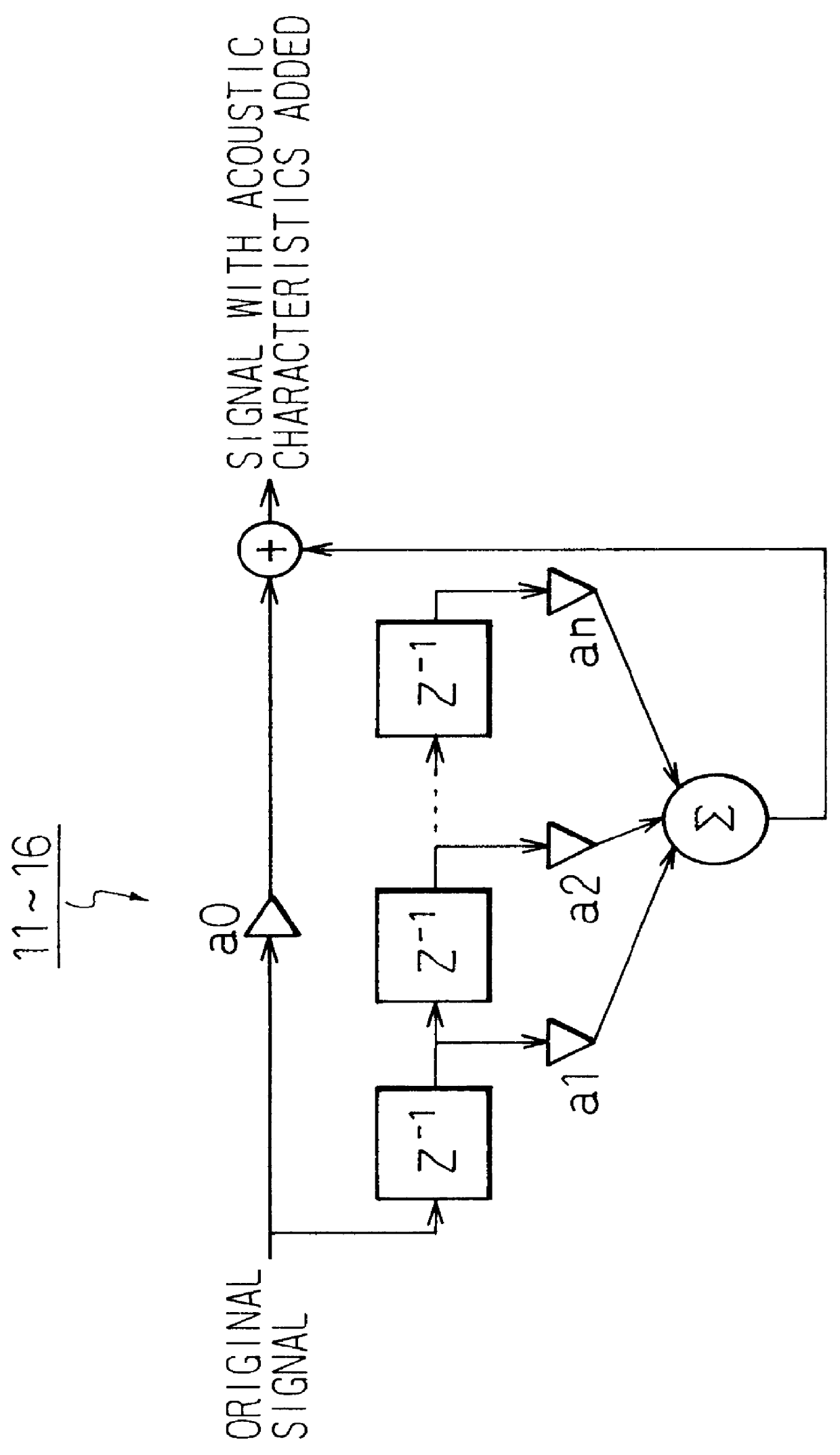
InactiveUS6269166B1Reduce amountAvoid complex processTwo-channel systemsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsHeadphonesAcoustic effect
To provide a three-dimensional acoustic effect to a listener in a reproduction field, via a headphone in particular, a three-dimensional acoustic apparatus is formed by a linear synthesis filter having filter coefficients that are the linear predictive coefficients obtained by performing a linear predictive analysis on an impulse response which represents the acoustic characteristics to be added to the original signal to achieve this effect. By passing the signal through this acoustic characteristics adding filter, the desired acoustic characteristics are added to the original signal, and by dividing the power spectrum of the impulse response of these acoustic characteristics into critical bandwidths and performing this linear predictive analysis based on impulse signal determined based from power spectrum signals representing the signal sound of each of these critical bandwidths, the filter coefficients of the linear synthesis filter are determined.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Multi-channel signal encoding and decoding
ActiveUS7283957B2Reduce bitrateImprove sound qualityTime-division multiplexSpeech synthesisPattern recognitionChannel correlation
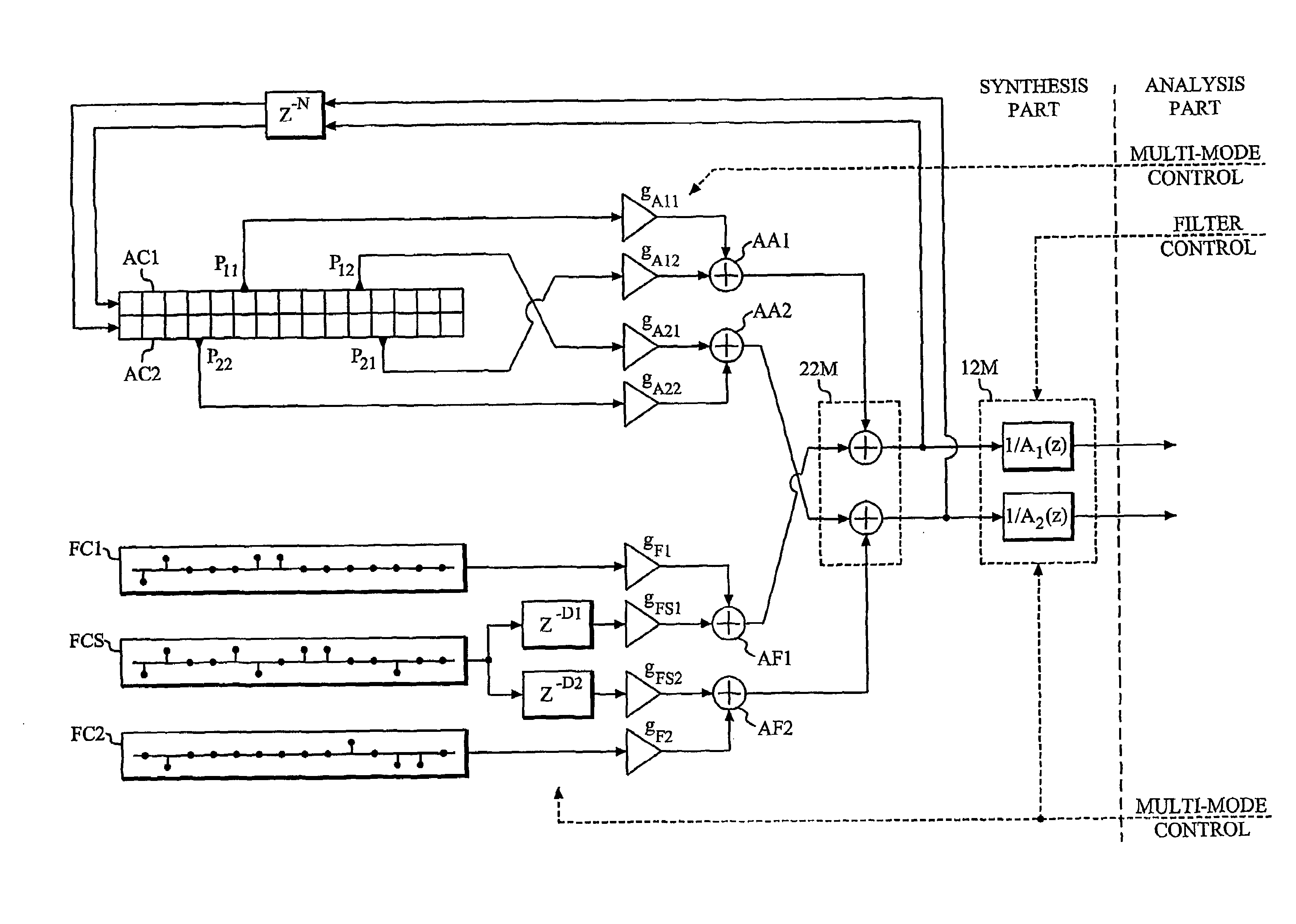
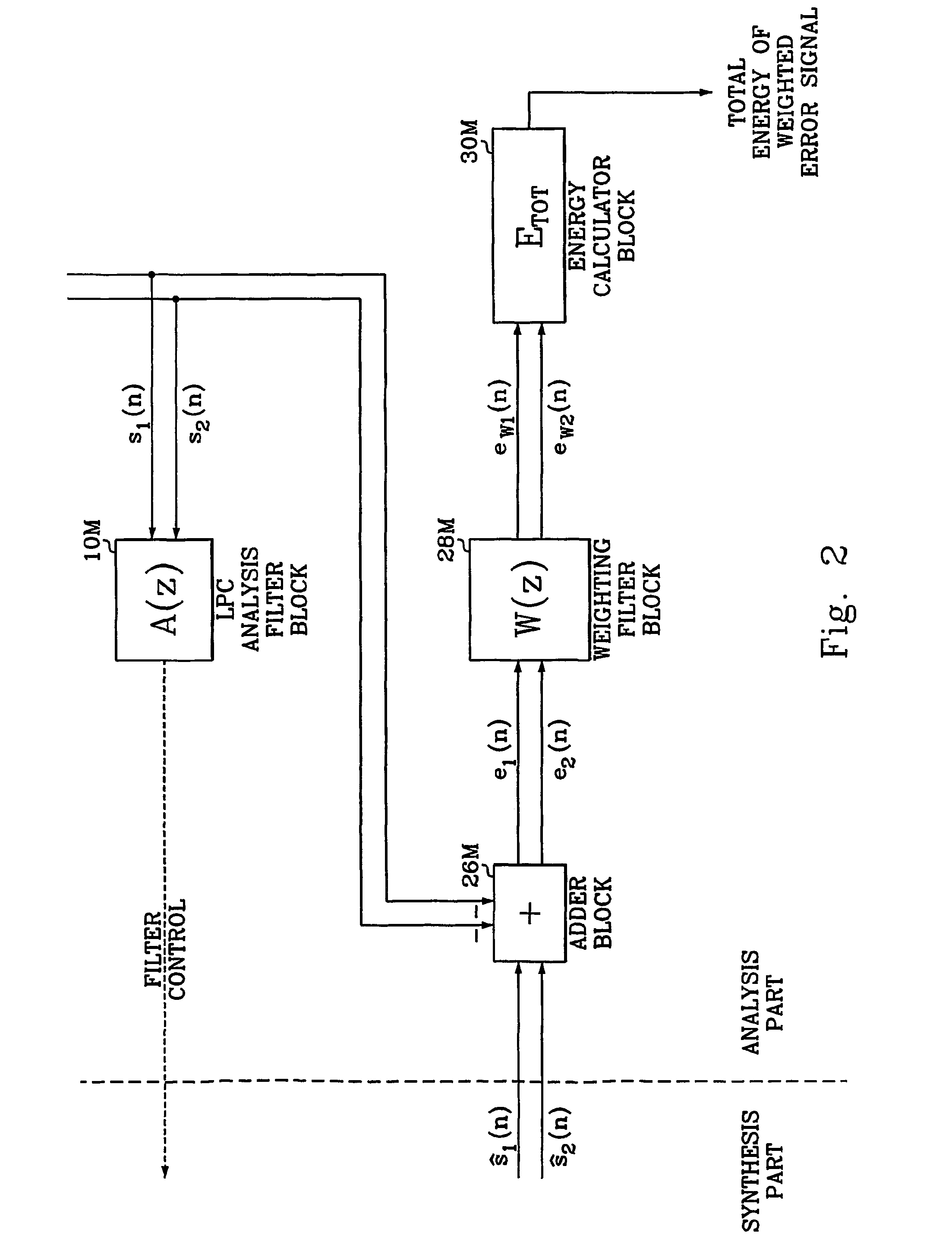
A multi-channel linear predictive analysis-by-synthesis signal encoding method detects (S26, S27) inter-channel correlation and select one of several possible encoding modes (S24, S29, S30) based on the detected correlation.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Encoding and decoding method and encoding and decoding device for enhancing dual-track voice frequency and tone quality
InactiveCN102737647ARecovery DetailsSubjective sound quality is goodSpeech analysisTwo-channel systemsDecoding methodsFrequency spectrum
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Three-dimensional acoustic processor which uses linear predictive coefficients
InactiveUS6023512AReduce amountAvoid complex processTwo-channel systemsStereophonic arrangmentsHeadphonesAcoustic effect
To provide a three-dimensional acoustic effect to a listener in a reproduction field, via a headphone in particular, a three-dimensional acoustic apparatus is formed by a linear synthesis filter having filter coefficients that are the linear predictive coefficients obtained by performing a linear predictive analysis on an impulse response which represents the acoustic characteristics to be added to the original signal to achieve this effect. By passing the signal through this acoustic characteristics adding filter, the desired acoustic characteristics are added to the original signal, and by dividing the power spectrum of the impulse response of these acoustic characteristics into critical bandwidths and performing this linear predictive analysis based on impulse signal determined based from power spectrum signals representing the signal sound of each of these critical bandwidths, the filter coefficients of the linear synthesis filter are determined.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
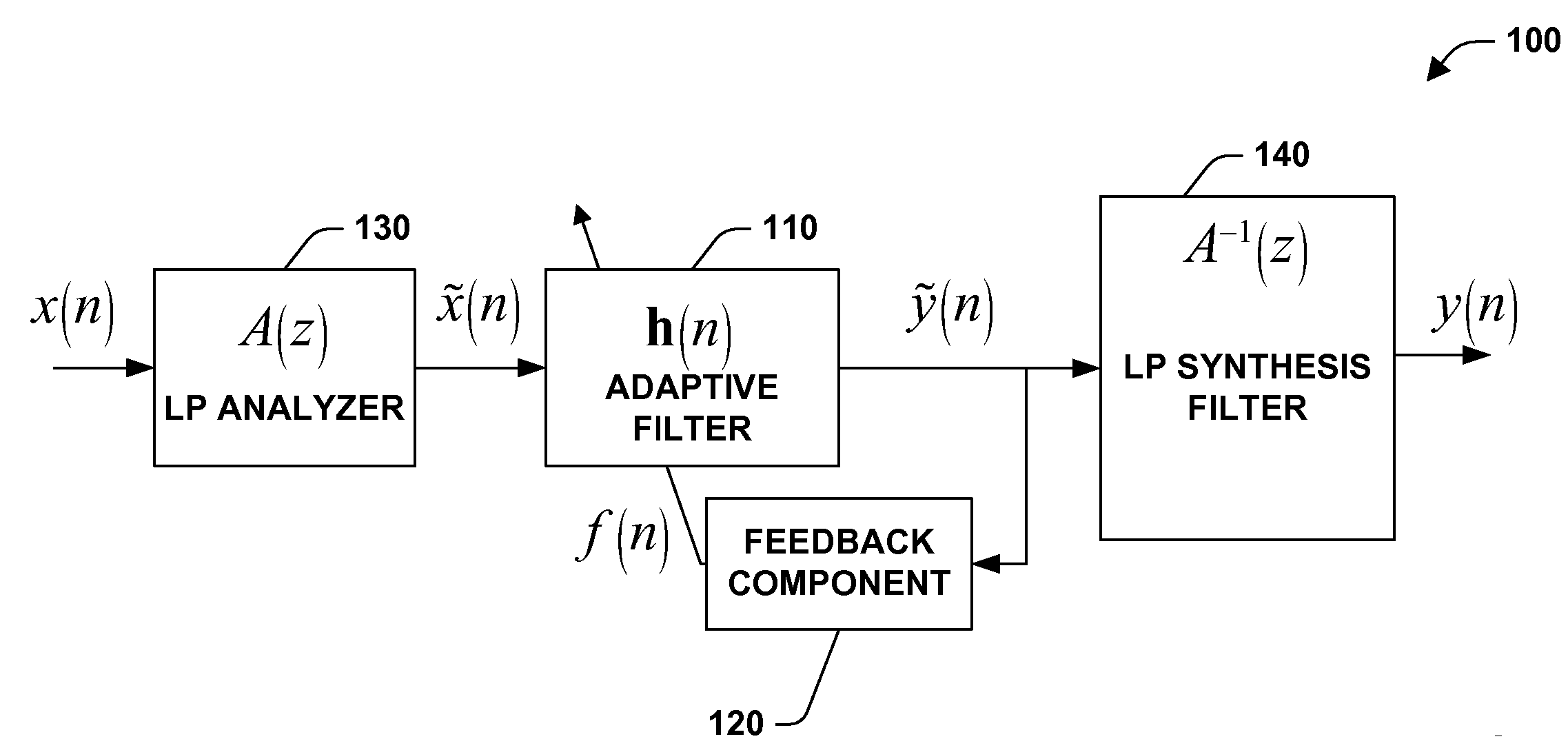
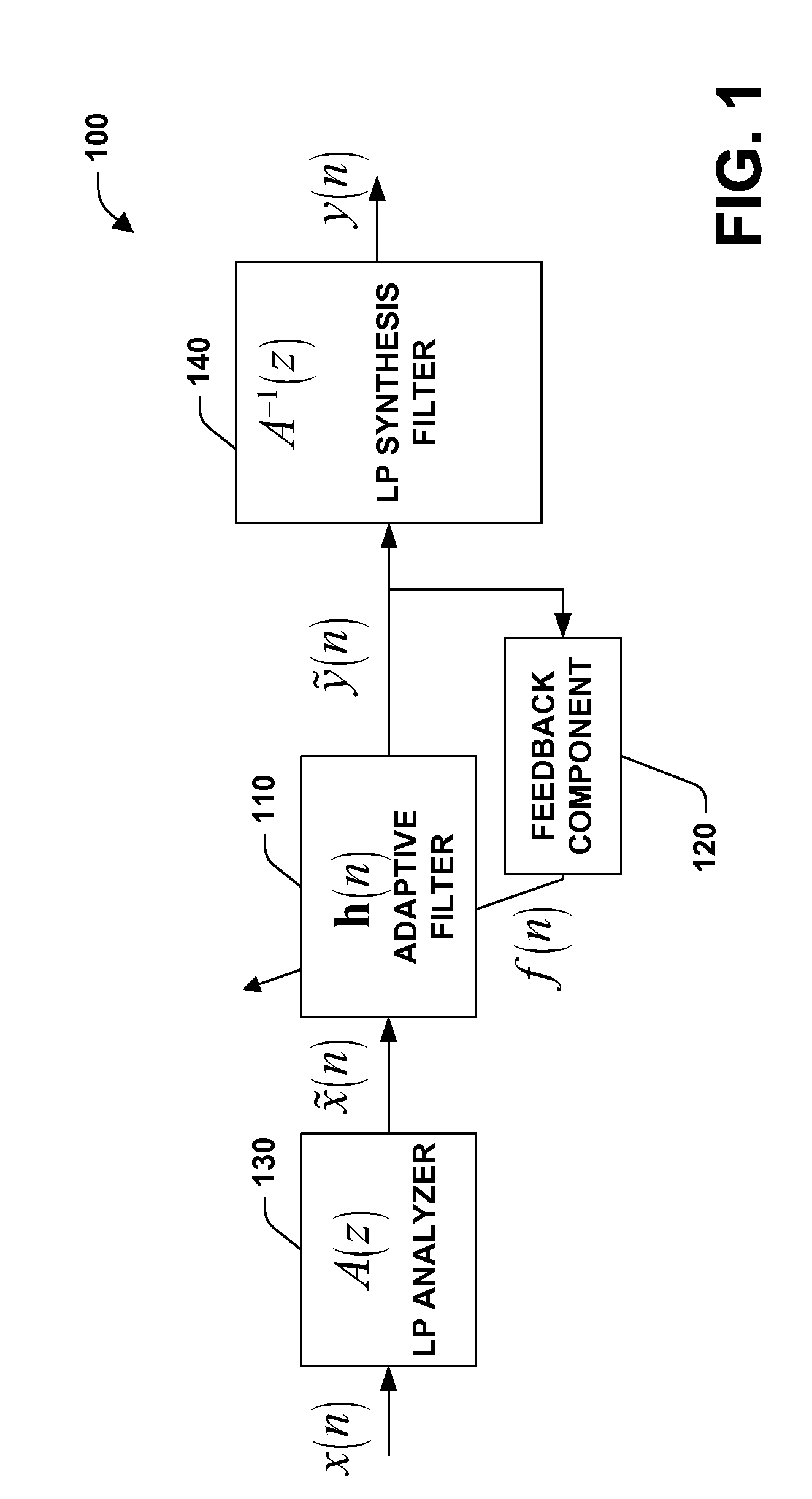
Microphone array signal enhancement
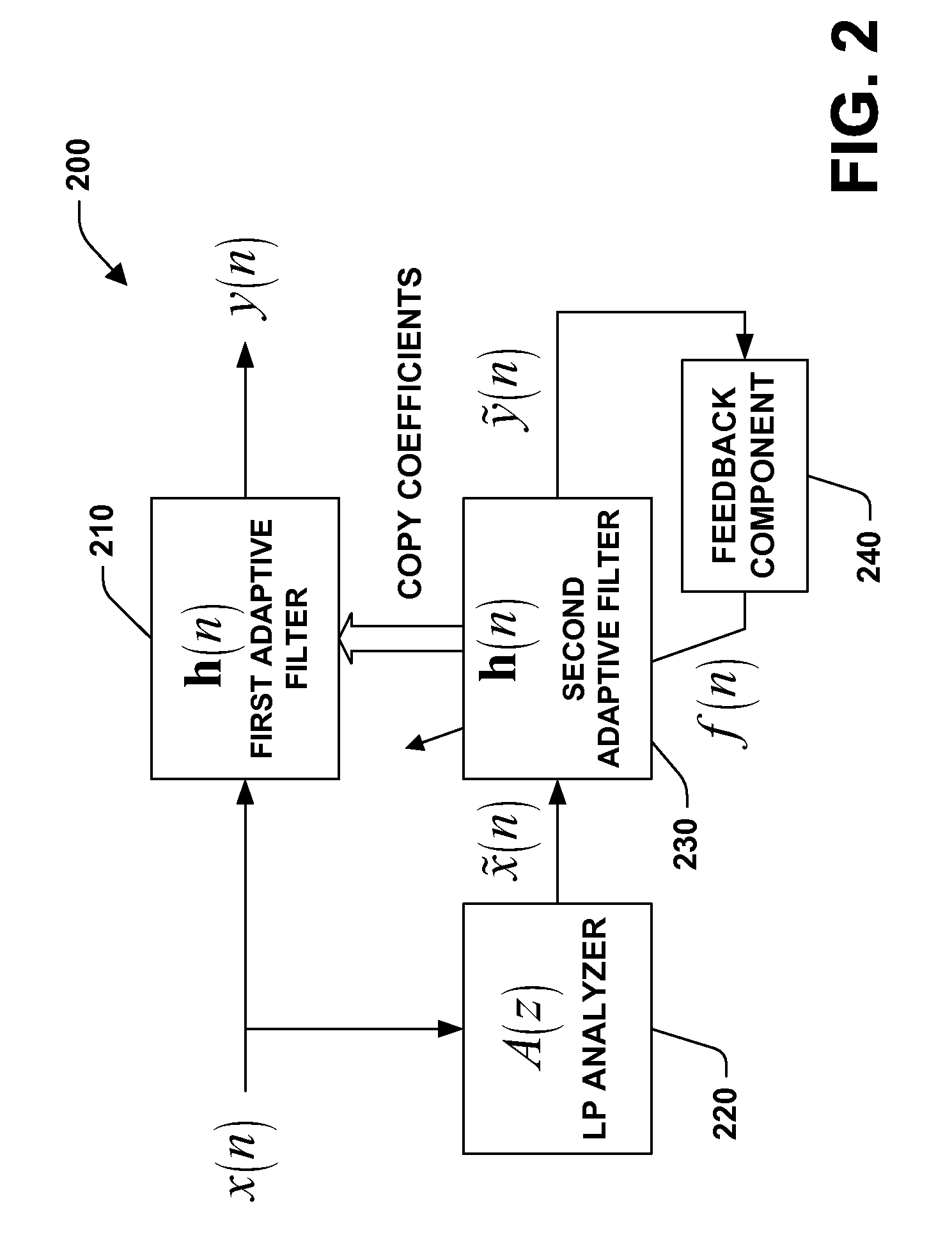
InactiveUS20060198538A1Quality improvementEnhance signal(s)Digitally weighted transducing elementsEar treatmentAdaptive filterEngineering
A system and method facilitating signal enhancement utilizing an adaptive filter is provided. The invention includes an adaptive filter that filters an input based upon a plurality of adaptive coefficients and modifies the adaptive coefficients based on a feedback output. A feedback component provides the feedback output based, at least in part, upon a non-linear function of the acoustic reverberation reduced output. Optionally, the system can further include a linear prediction (LP) analyzer and / or a LP synthesis filter. The system can enhance signal(s), for example, to improve the quality of speech that is acquired by a microphone by reducing reverberation. The system utilizes, at least in part, the principle that certain characteristics of reverberated speech are measurably different from corresponding characteristics of clean speech. The system can employ a filter technology (e.g., reverberation reducing) based on a non-linear function, for example, the kurtosis metric.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
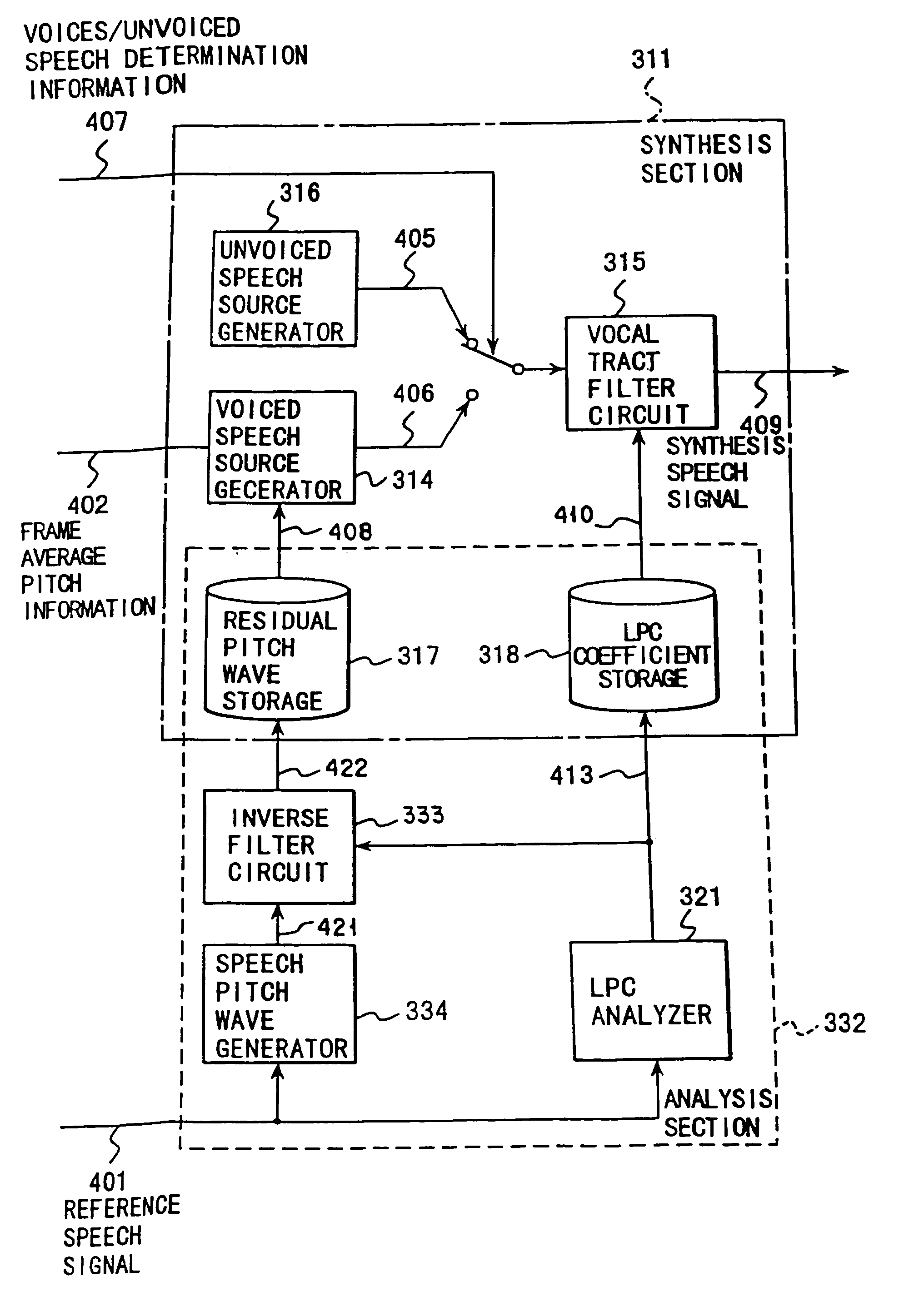
Speech synthesis method
A speech synthesis method subjects a reference speech signal to windowing to extract a speech pitch wave having a window function of a window length double a pitch period of the reference speech signal from the reference speech signal. A linear prediction coefficient is generated by subjecting the reference speech signal to a linear prediction analysis. The speech pitch wave is subjected to inverse-filtering based on the linear prediction coefficient to produce a residual pitch wave, which is then stored as information of a speech synthesis unit in a voiced period in a storage. Speech using the information of the speech synthesis unit is then synthesized.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Signal modification method for efficient coding of speech signals
For determining a long-term-prediction delay parameter characterizing a long term prediction in a technique using signal modification for digitally encoding a sound signal, the sound signal is divided into a series of successive frames, a feature of the sound signal is located in a previous frame, a corresponding feature of the sound signal is located in a current frame, and the long-term-prediction delay parameter is determined for the current frame while mapping, with the long term prediction, the signal feature of the previous frame with the corresponding signal feature of the current frame. In a signal modification method for implementation into a technique for digitally encoding a sound signal, the sound signal is divided into a series of successive frames, each frame of the sound signal is partitioned into a plurality of signal segments, and at least a part of the signal segments of the frame are warped while constraining the warped signal segments inside the frame. For searching pitch pulses in a sound signal, a residual signal is produced by filtering the sound signal through a linear prediction analysis filter, a weighted sound signal is produced by processing the sound signal through a weighting filter, the weighted sound signal being indicative of signal periodicity, a synthesized weighted sound signal is produced by filtering a synthesized speech signal produced during a last subframe of a previous frame of the sound signal through the weighting filter, a last pitch pulse of the sound signal of the previous frame is located from the residual signal, a pitch pulse prototype of given length is extracted around the position of the last pitch pulse of the sound signal of the previous frame using the synthesized weighted sound signal, and the pitch pulses are located in a current frame using the pitch pulse prototype.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
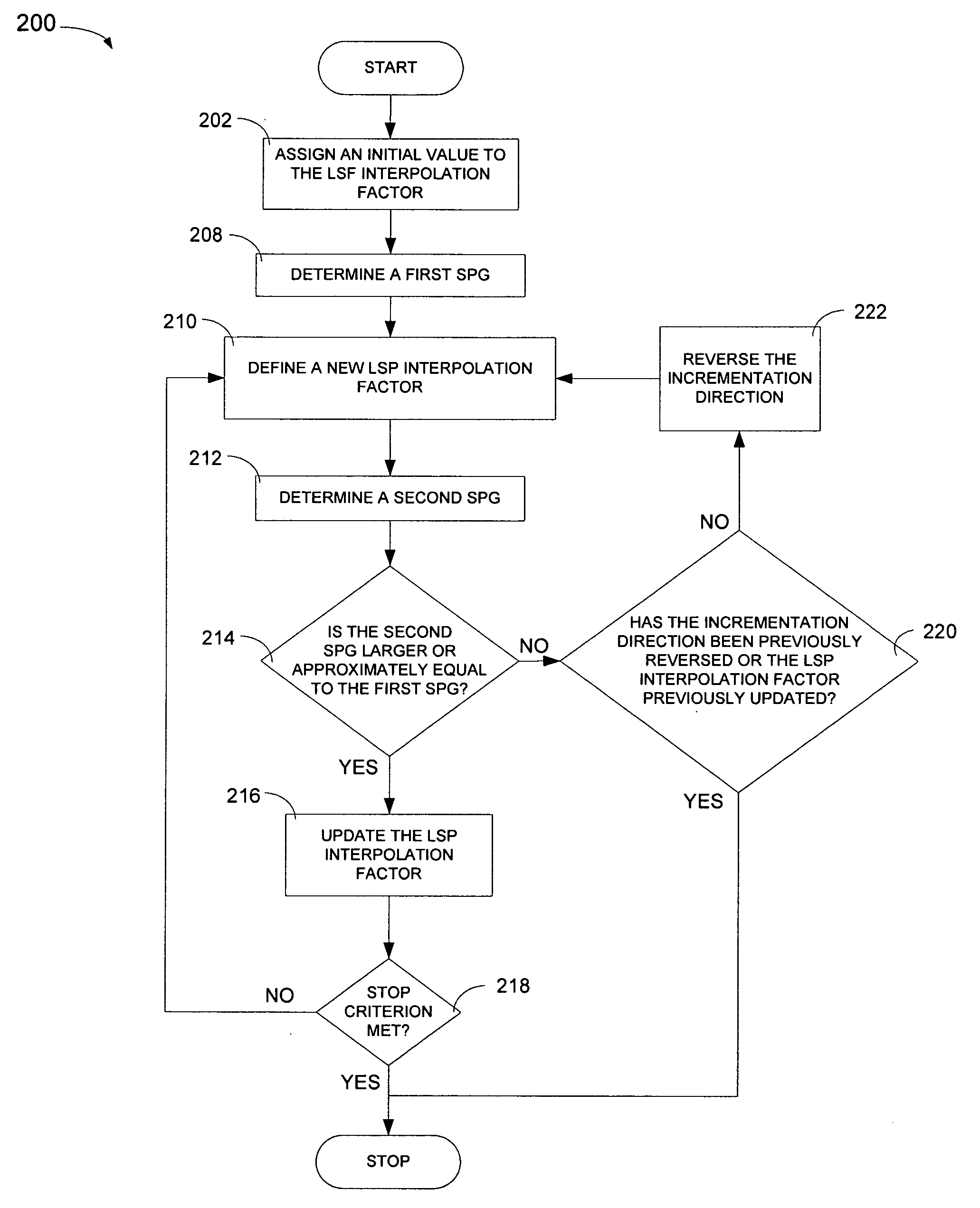
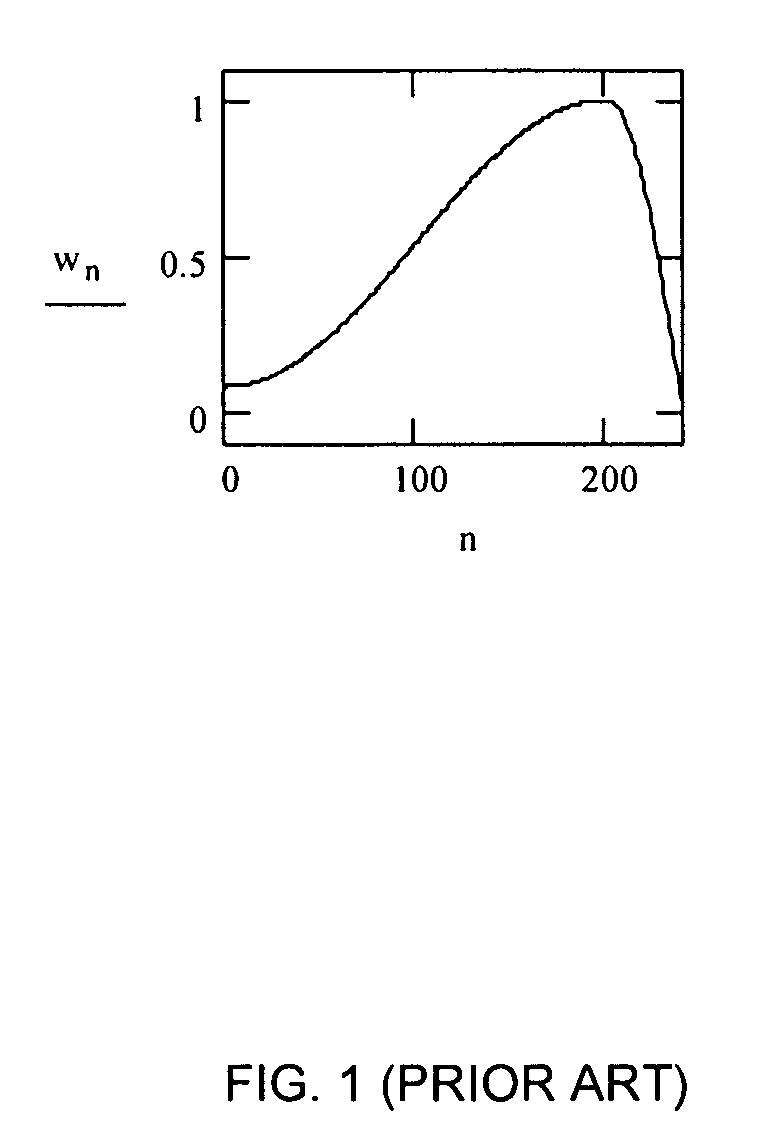
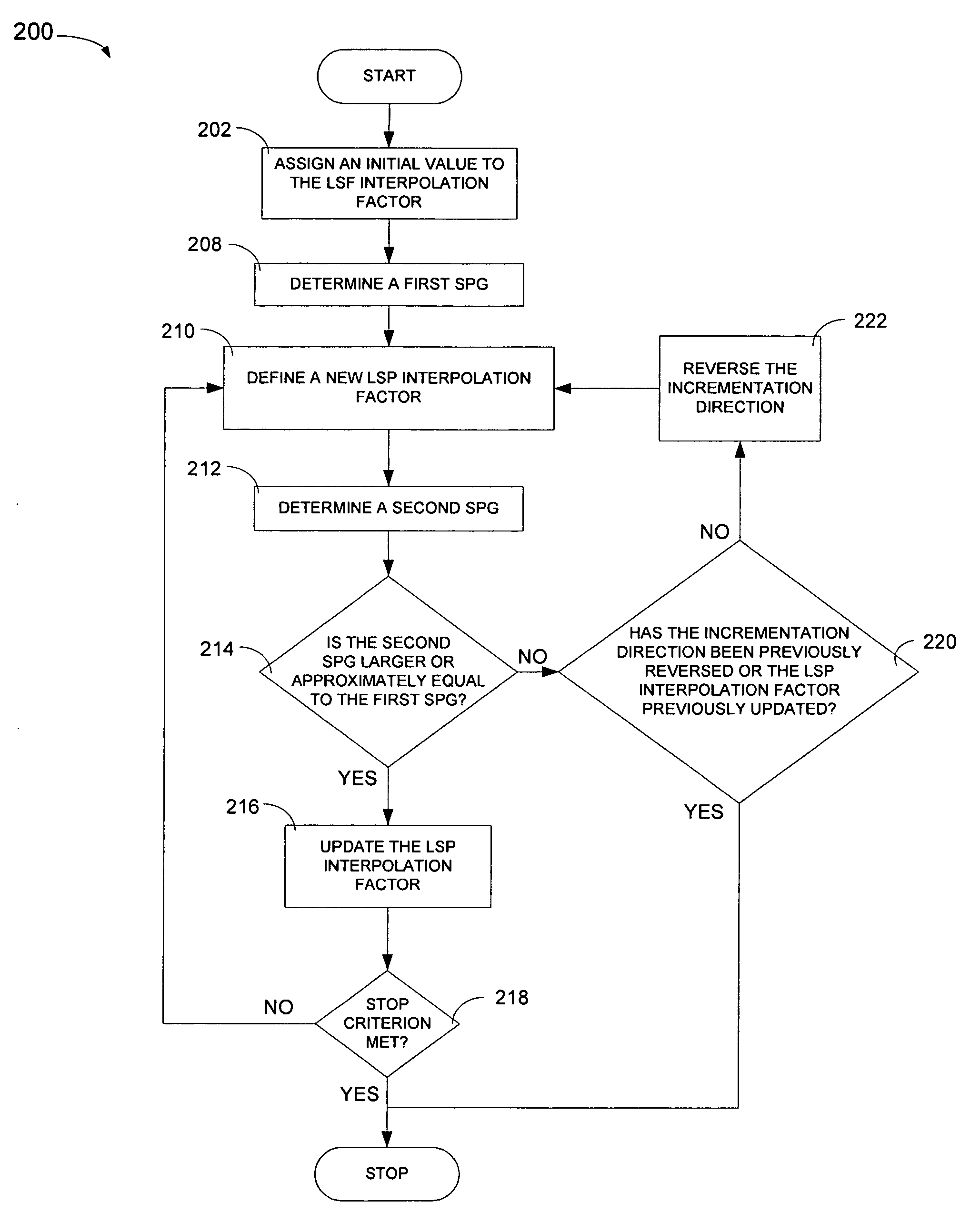
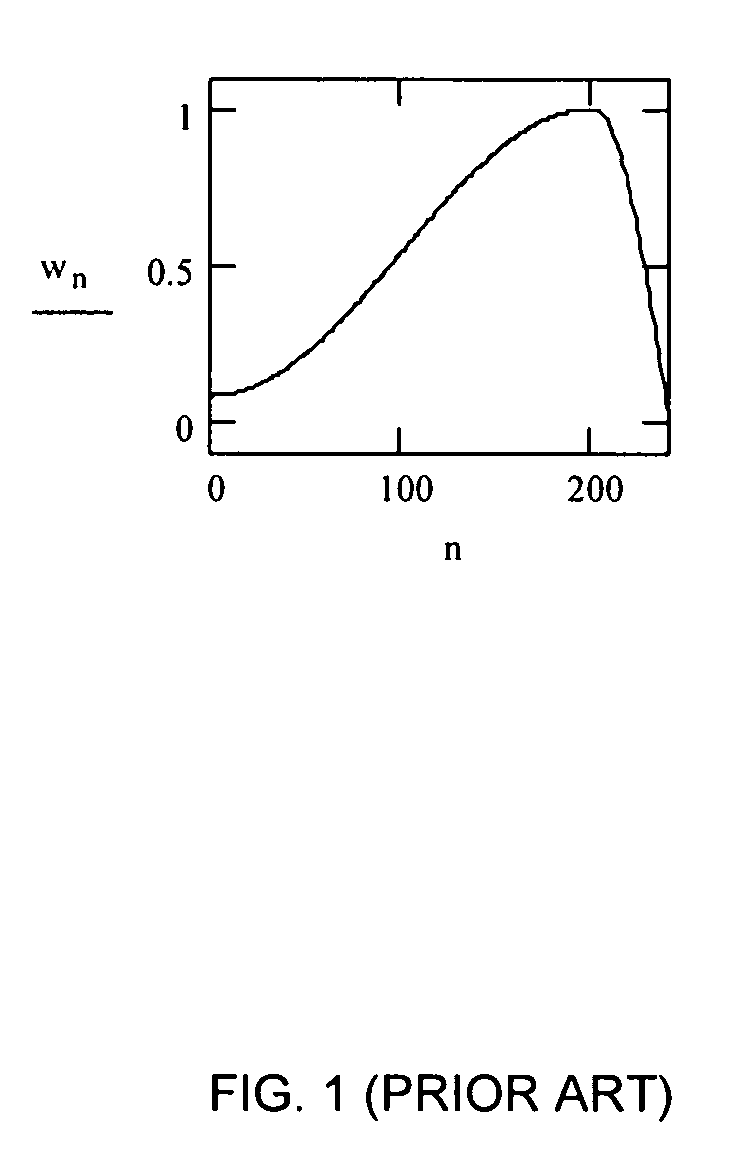
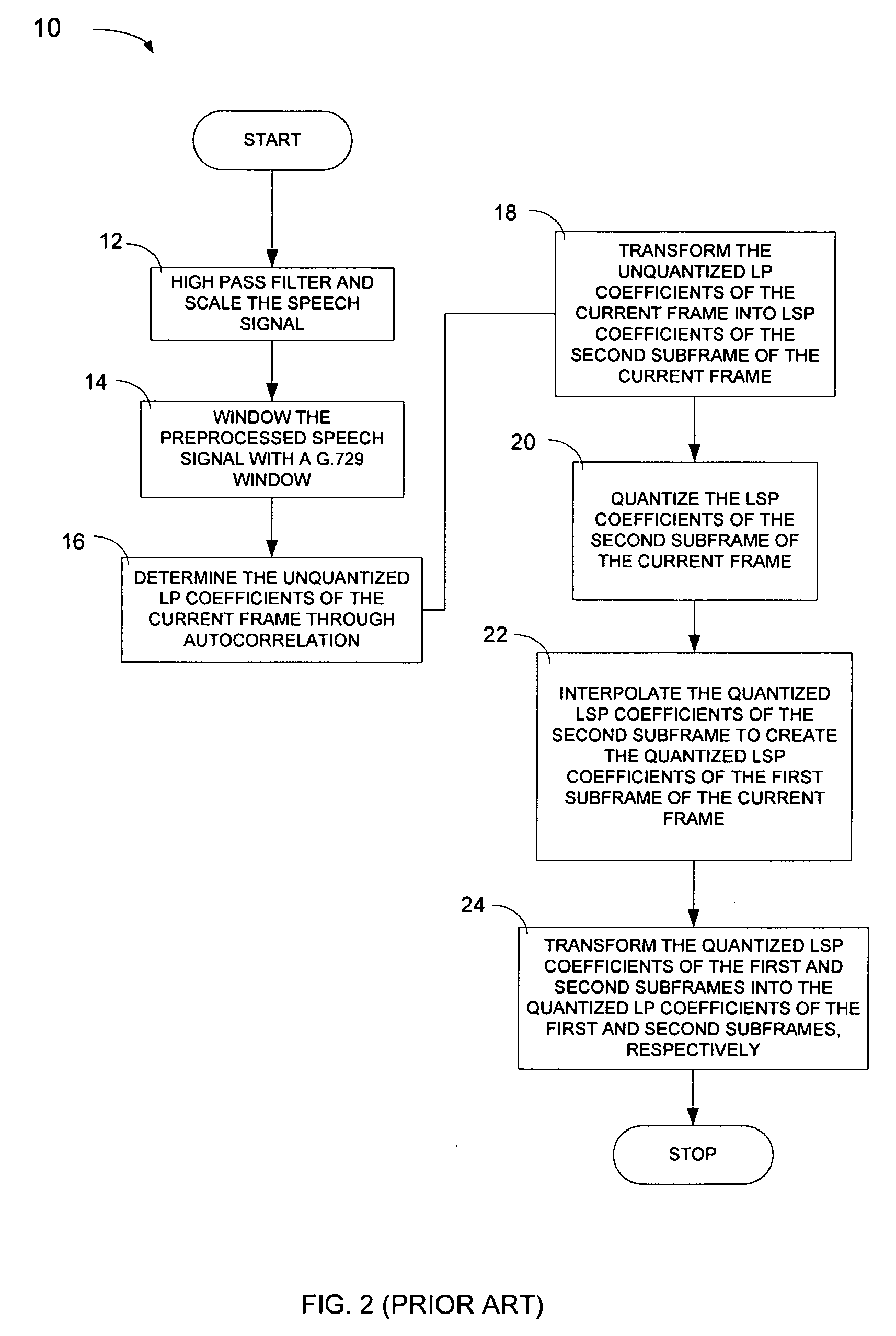
Optimized windows and interpolation factors, and methods for optimizing windows, interpolation factors and linear prediction analysis in the ITU-T G.729 speech coding standard
Alternate window optimization procedures and / or LSP interpolation factor optimization procedures are used to improve the ITU-T G.729 speech coding standard (the “Standard”) by replacing the window used by the Standard with an optimized window and / or replacing the LSP interpolation factor used by the standard with an optimized LSP interpolation factor. Optimized windows created using the alternate window optimization procedure and / or optimized LSP interpolation factors created using the LSP interpolation factor optimization procedure yield improvements in the objective quality of synthesized speech produced by the Standard. In many cases, improvements are obtained using shorter windows, which results in reduced computational cost and / or smaller future buffering requirements, which results in lowered coding delay. The improved Standard, procedures, and optimized windows and LSP interpolation factors can all be implemented as computer readable software code and in optimization devices.
Owner:CHU WAI CHUNG +1
Multi-channel signal encoding and decoding
ActiveUS7263480B2Gross bitrateHigh mono-qualityFrequency-division multiplexSpeech synthesisComputer scienceSignal encoding
A multi-channel linear predictive analysis-by-synthesis signal encoding method determines (S1) a leading channel and encodes the leading channel as an embedded bitstream. Thereafter trailing channels are encoded as a discardable bitstream exploiting cross-correlation to the leading channel.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
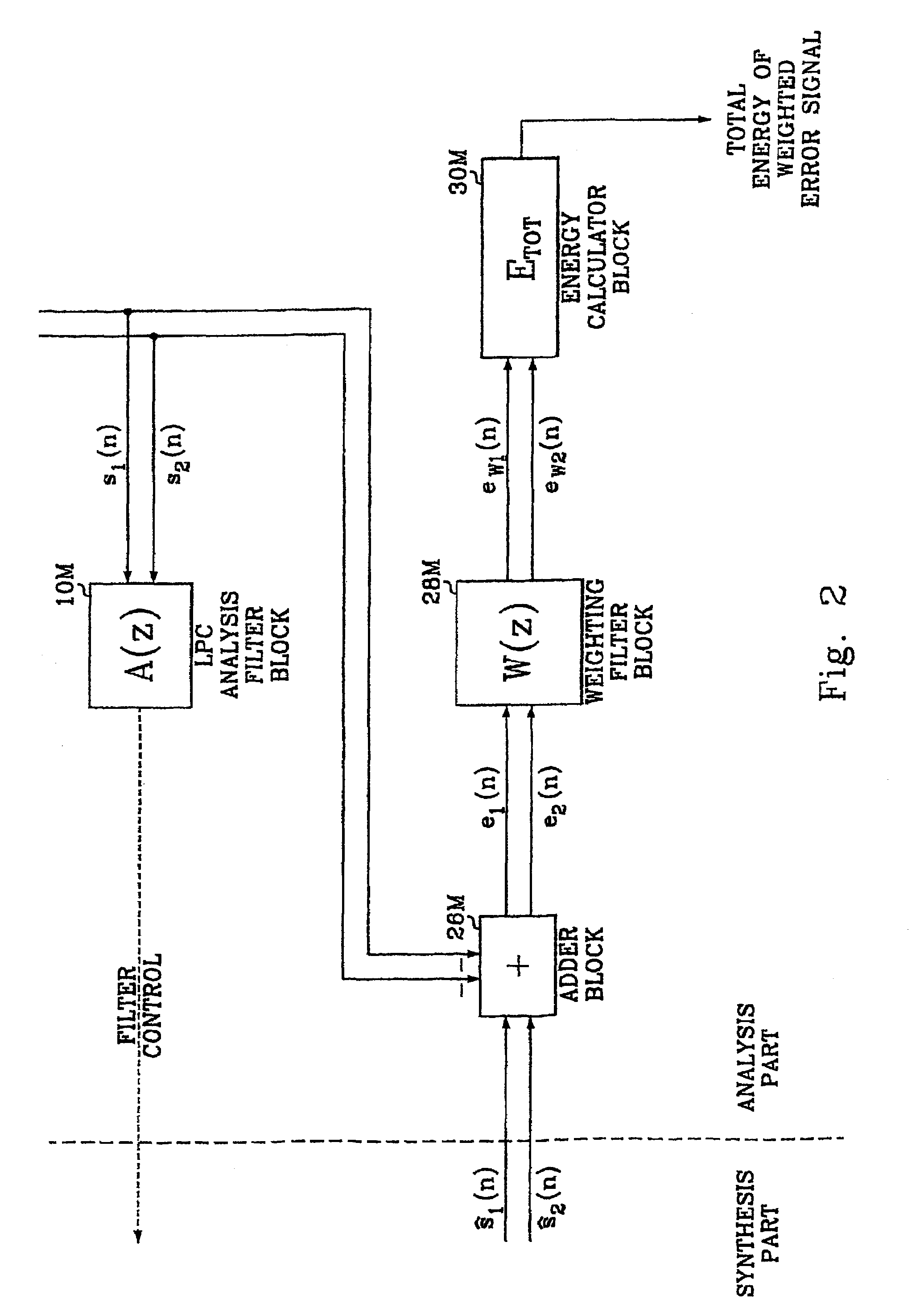
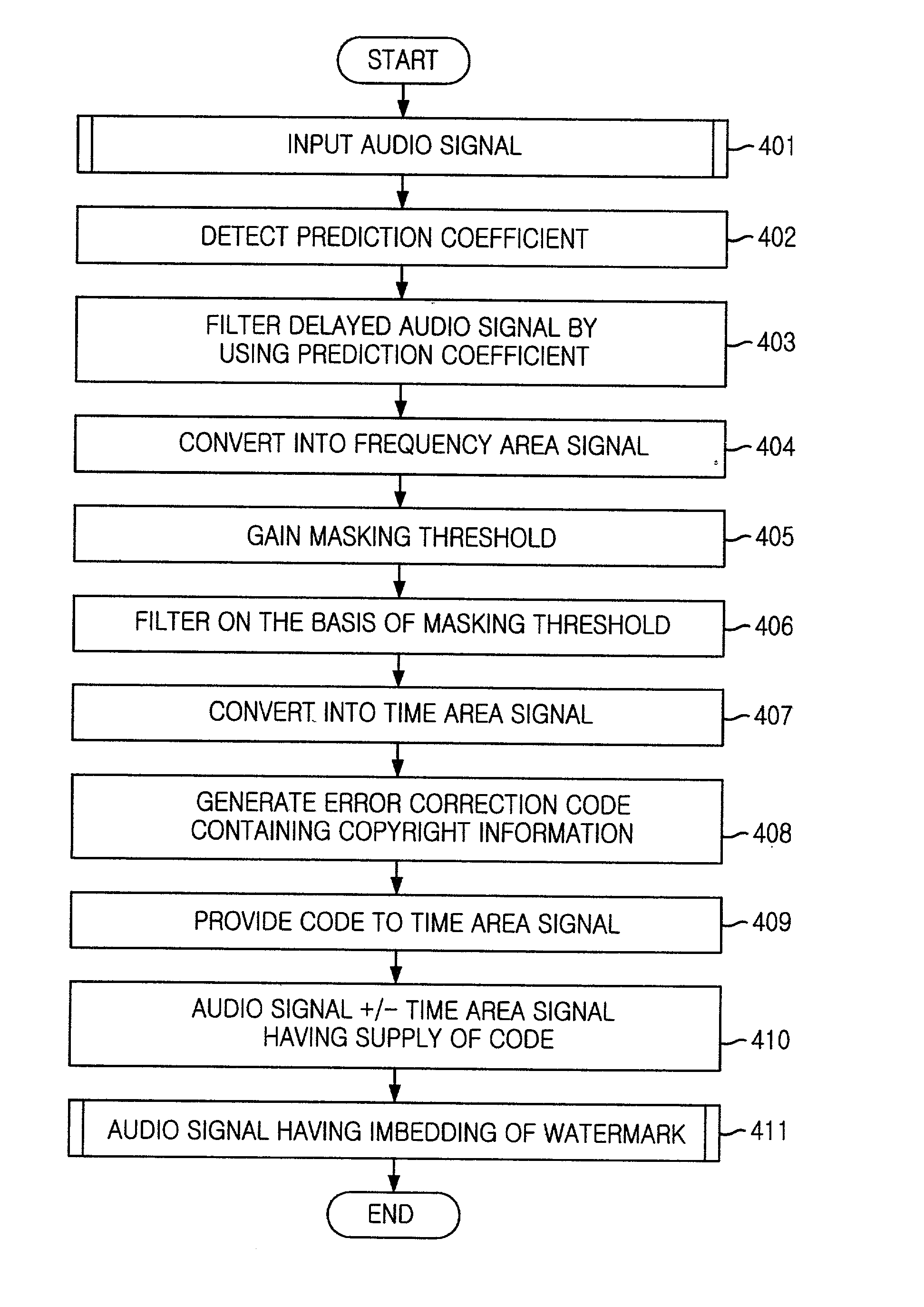
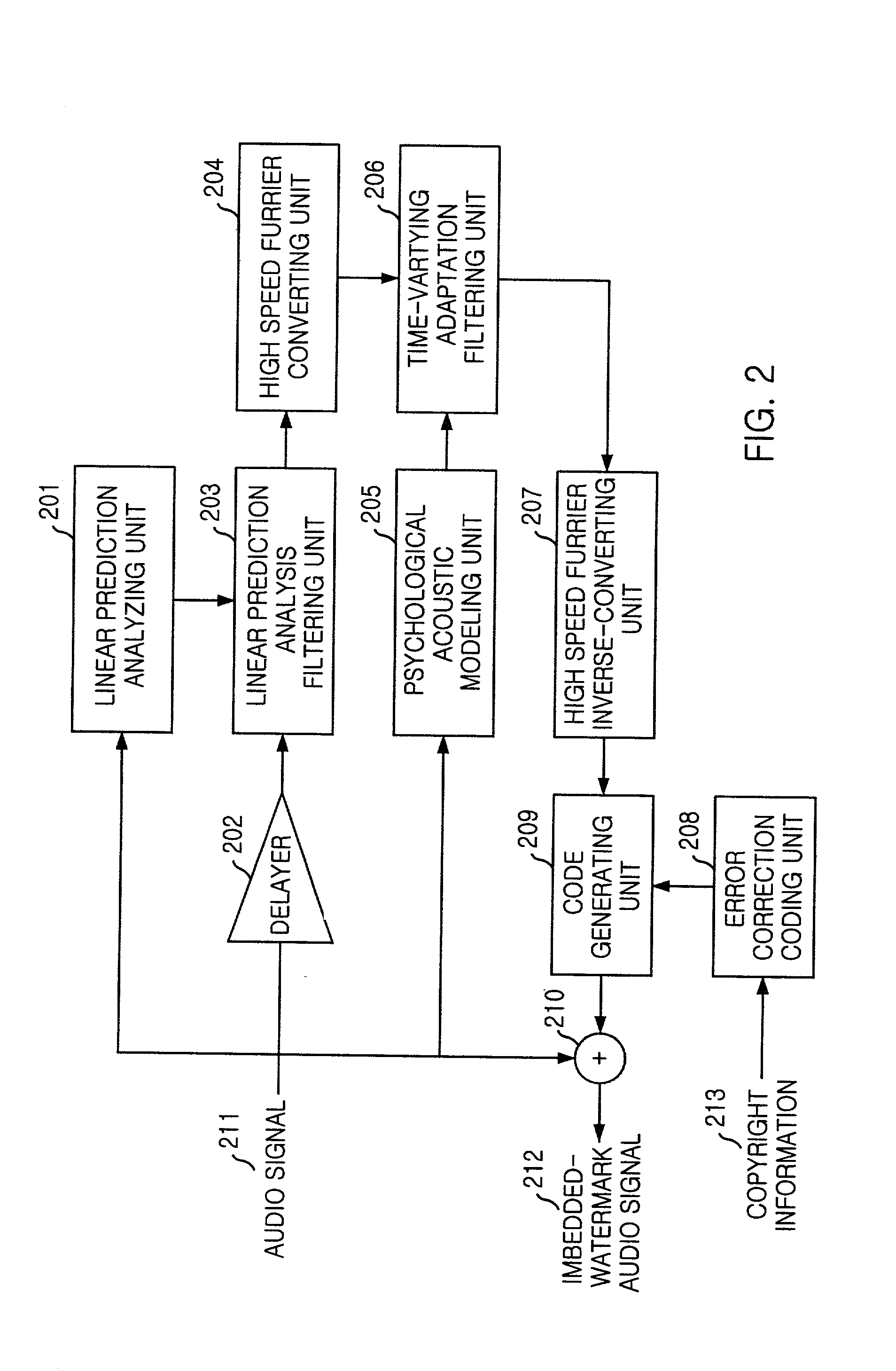
Apparatus and method for watermark embedding and detection using linear prediction analysis
InactiveUS20020087863A1User identity/authority verificationSpeech analysisSignal qualityRead through
In the apparatus and method for a watermark embedding and detection through a linear prediction analysis, and a record medium capable of being read through a computer having a writing of a program to realize the inventive method, in which a quality of a signal does not drop, even after an imbedding of a watermark by using a signal based on a changed shape of an original signal through a use of a linear prediction analysis, with a watermark signal to be imbedded in a digital signal, but also the watermark signal containing copyright information can be detected even though an optional attack is applied thereto.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
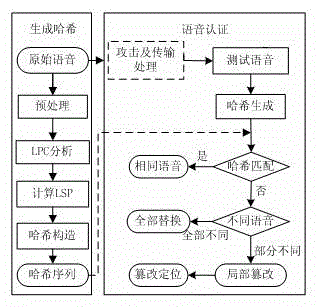
Phonetic empathy Hash content authentication method capable of implementing tamper localization
InactiveCN102915740ASimple structureImprove authentication efficiencySpeech analysisVoice communicationLine spectral pairs
The invention relates to a phonetic empathy Hash content authentication method capable of implementing tamper localization. The method comprises the following steps: pre-processing a voice signal, carrying out 10-order linear prediction analysis on each frame of the voice signal, and acquiring an LSP (line spectral pair) coefficient through the discrete Fourier transformation as the empathy characteristics; grouping the voice data in sequence, combining LSP coefficient weighted expectations of each group of the voice data as the final authentication data, and compressing the authentication data volume through a Hash structure; and finally, quickly authenticating the voice contents through the Hash match. The method can keep robustness for the operations such as changing the sound volume, resounding and resampling, is sensitive to malicious operations such as replacement and deletion, can accurately locate the tamper area, has the characteristics of low authentication data volume and high operation efficiency, and is suitable for resource-limited voice communication terminals.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
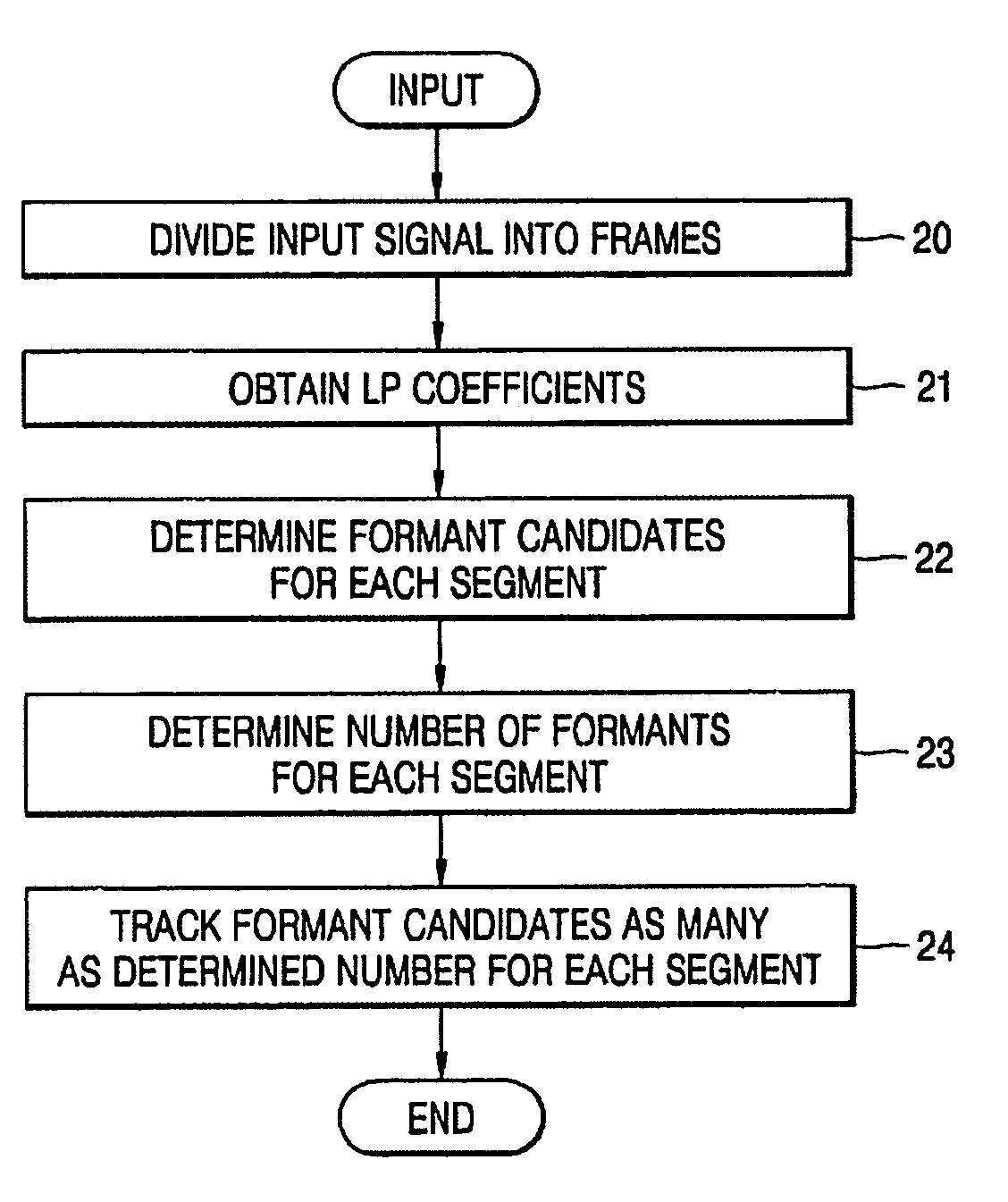
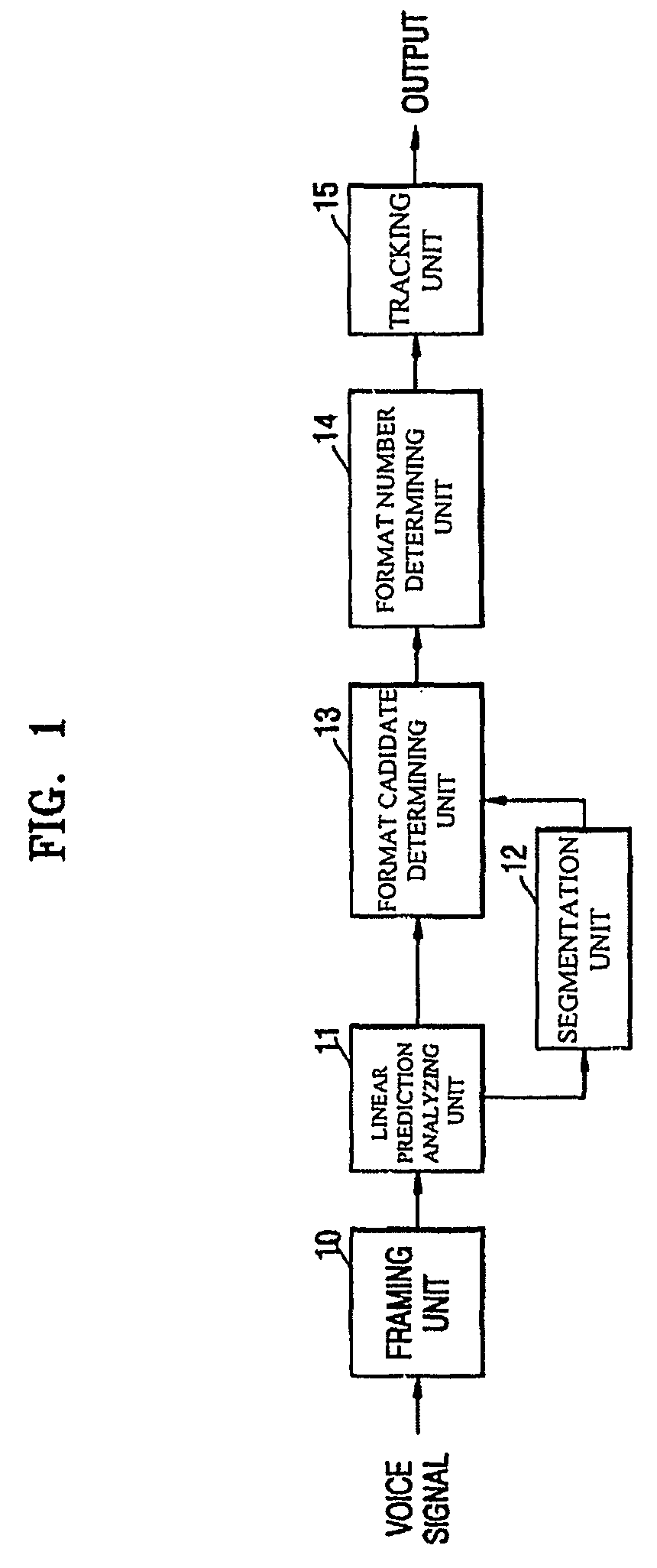
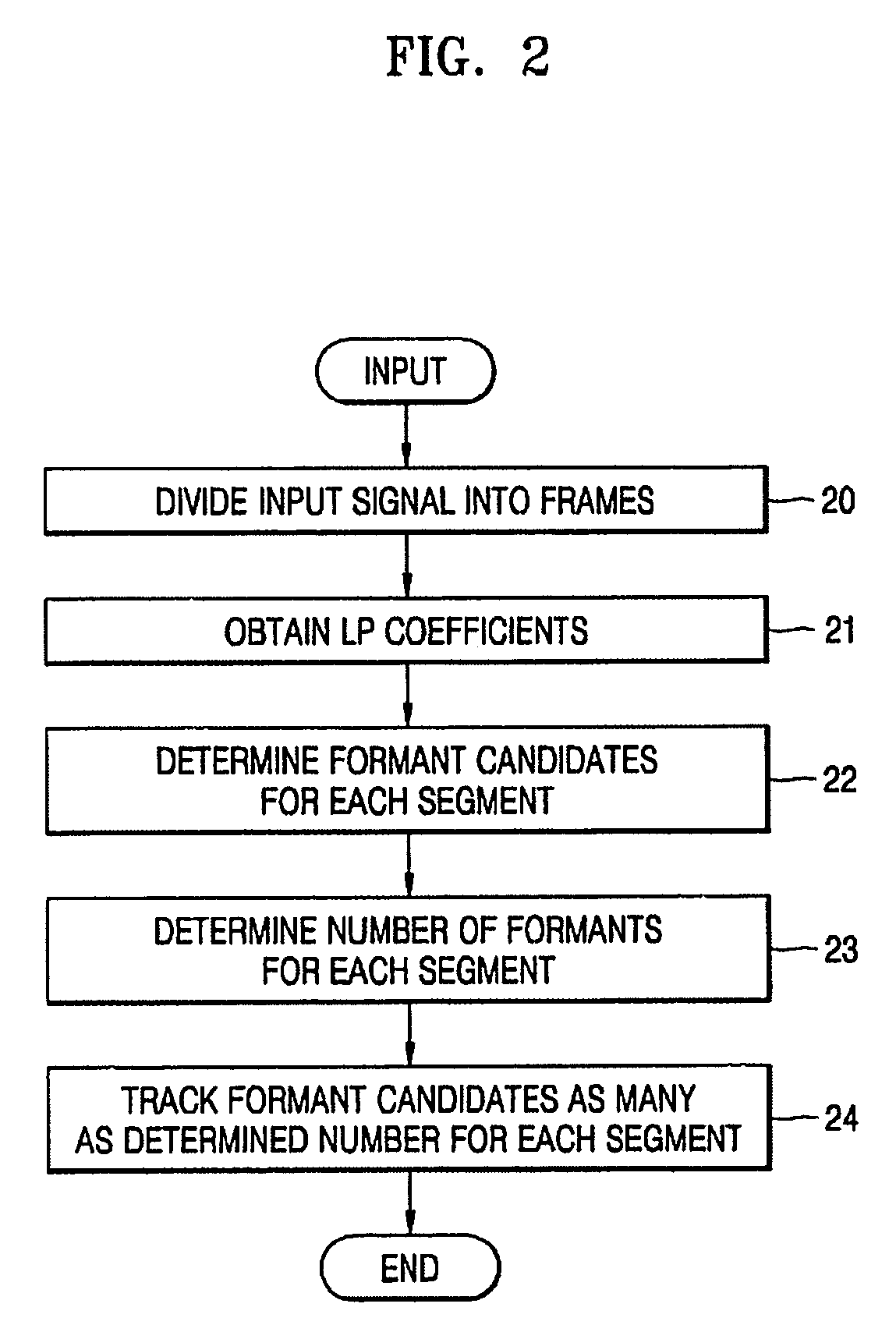
Formant tracking apparatus and formant tracking method
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optimized windows and interpolation factors, and methods for optimizing windows, interpolation factors and linear prediction analysis in the ITU-T G.729 speech coding standard
InactiveUS20070055504A1Reduce window sizeFuture buffering requirementSpeech analysisObjective qualitySpeech code
Alternate window optimization procedures and / or LSP interpolation factor optimization procedures are used to improve the ITU-T G.729 speech coding standard (the “Standard”) by replacing the window used by the Standard with an optimized window and / or replacing the LSP interpolation factor used by the standard with an optimized LSP interpolation factor. Optimized windows created using the alternate window optimization procedure and / or optimized LSP interpolation factors created using the LSP interpolation factor optimization procedure yield improvements in the objective quality of synthesized speech produced by the Standard. In many cases, improvements are obtained using shorter windows, which results in reduced computational cost and / or smaller future buffering requirements, which results in lowered coding delay. The improved Standard, procedures, and optimized windows and LSP interpolation factors can all be implemented as computer readable software code and in optimization devices.
Owner:CHU WAI CHUNG +1
Speech encoding/decoding device
ActiveUS8655649B2Increase bitrateImprove subjective qualitySpeech analysisFrequency spectrumCovariance method
A linear prediction coefficient of a signal represented in a frequency domain is obtained by performing linear prediction analysis in a frequency direction by using a covariance method or an autocorrelation method. After the filter strength of the obtained linear prediction coefficient is adjusted, filtering may be performed in the frequency direction on the signal by using the adjusted coefficient, whereby the temporal envelope of the signal is shaped. This reduces the occurrence of pre-echo and post-echo and improves the subjective quality of the decoded signal, without significantly increasing the bit rate in a bandwidth extension technique in the frequency domain represented by spectral band replication.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Skin Evaluating Method And Skin Evaluation
InactiveUS20070276206A1Condition the skinImprove textureVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringPattern recognitionFundamental frequency
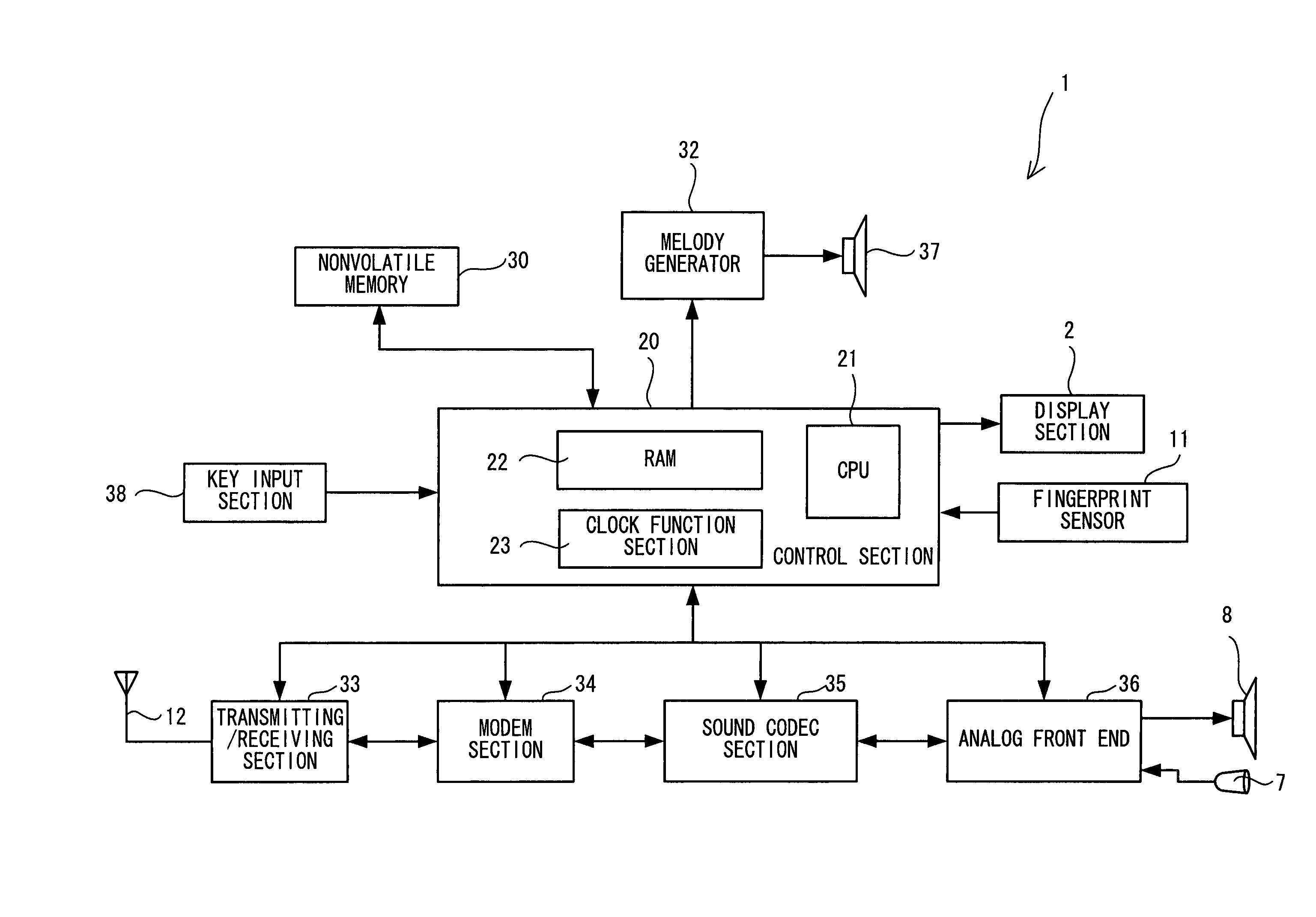
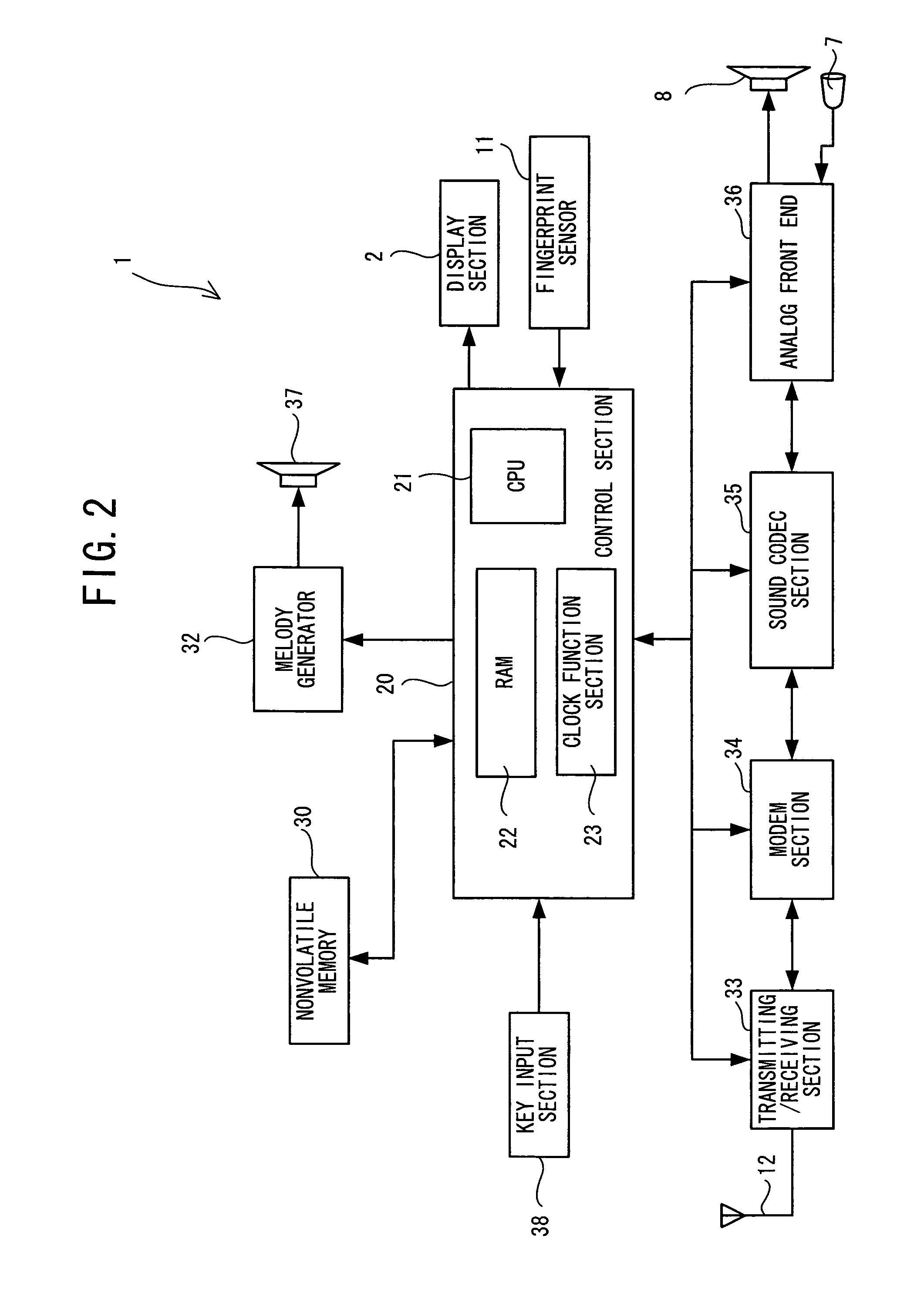
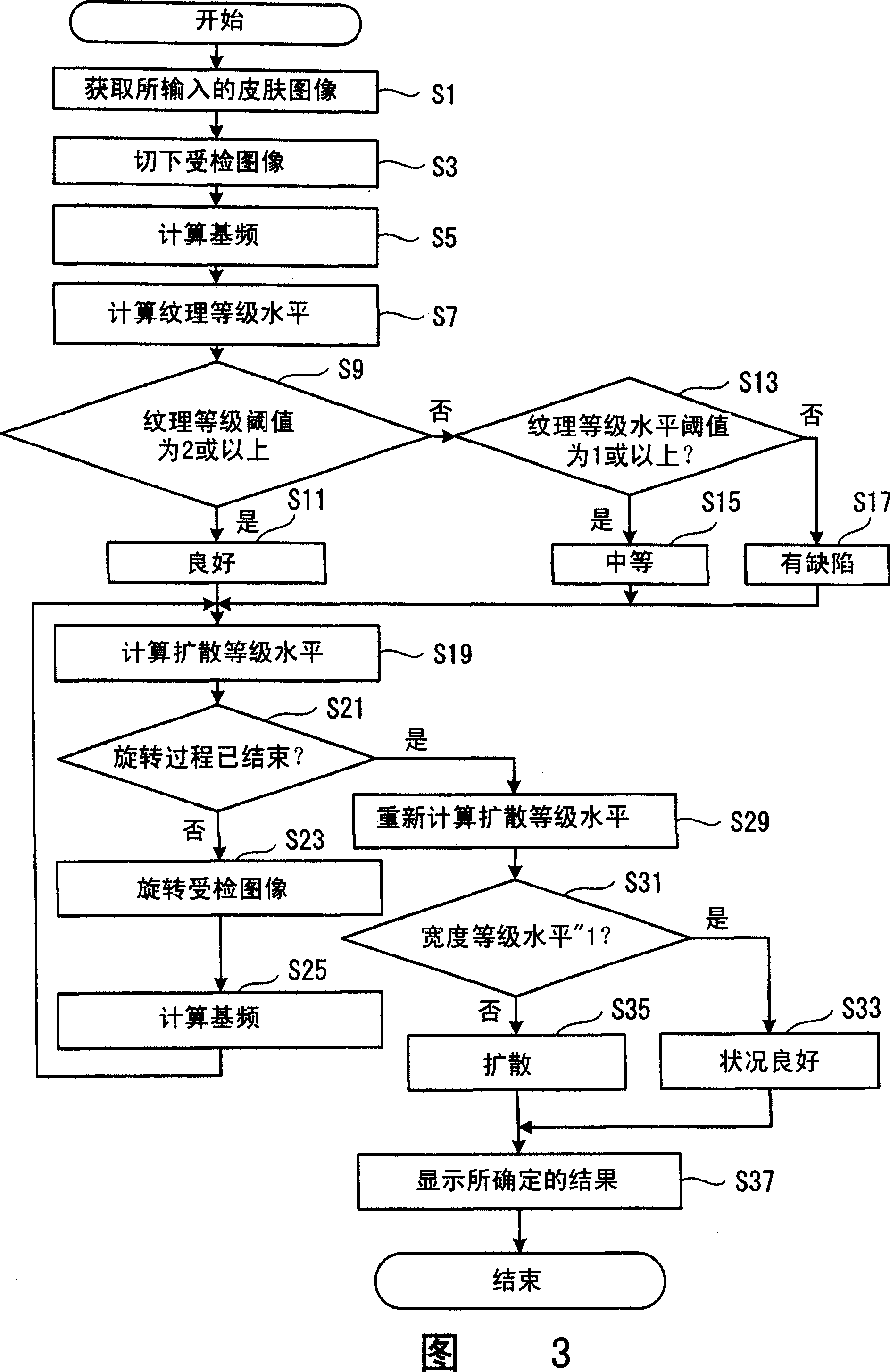
A part of the image input from a fingerprint sensor (S1) is cut out (S3), and a fundamental frequency is calculated by using second-order linear predictive analysis (S5). A total value S of the fundamental frequencies in a direction x and a direction y is calculated so as to be used as a grading scale of fineness in texture (S7). A prepared threshold is compared with the grading scale S obtained at S7, and the fineness in texture of a skin condition is evaluated in three grades (S9 to S17). Further, a ratio of the fundamental frequency of the subject image in the direction x to the fundamental frequency in the direction y is calculated so as to be used as a grading scale relating to texture running (S19). Similar grading scales are obtained by rotating the image, and the texture running is determined into two grades based on the grading scales (S31 to S35). Results of determining the fineness in texture and the texture running are displayed on a display screen (S37).
Owner:DDS
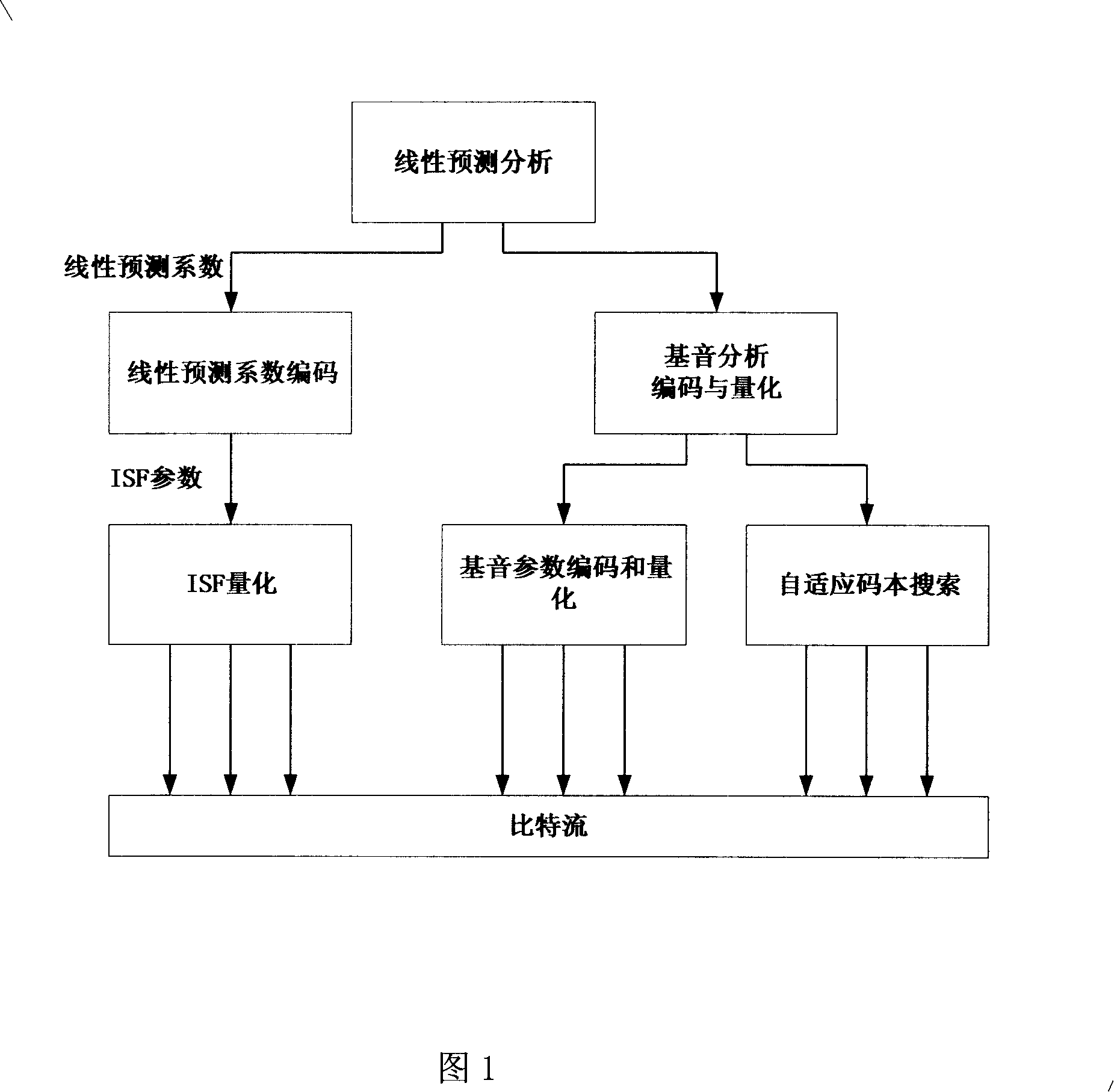
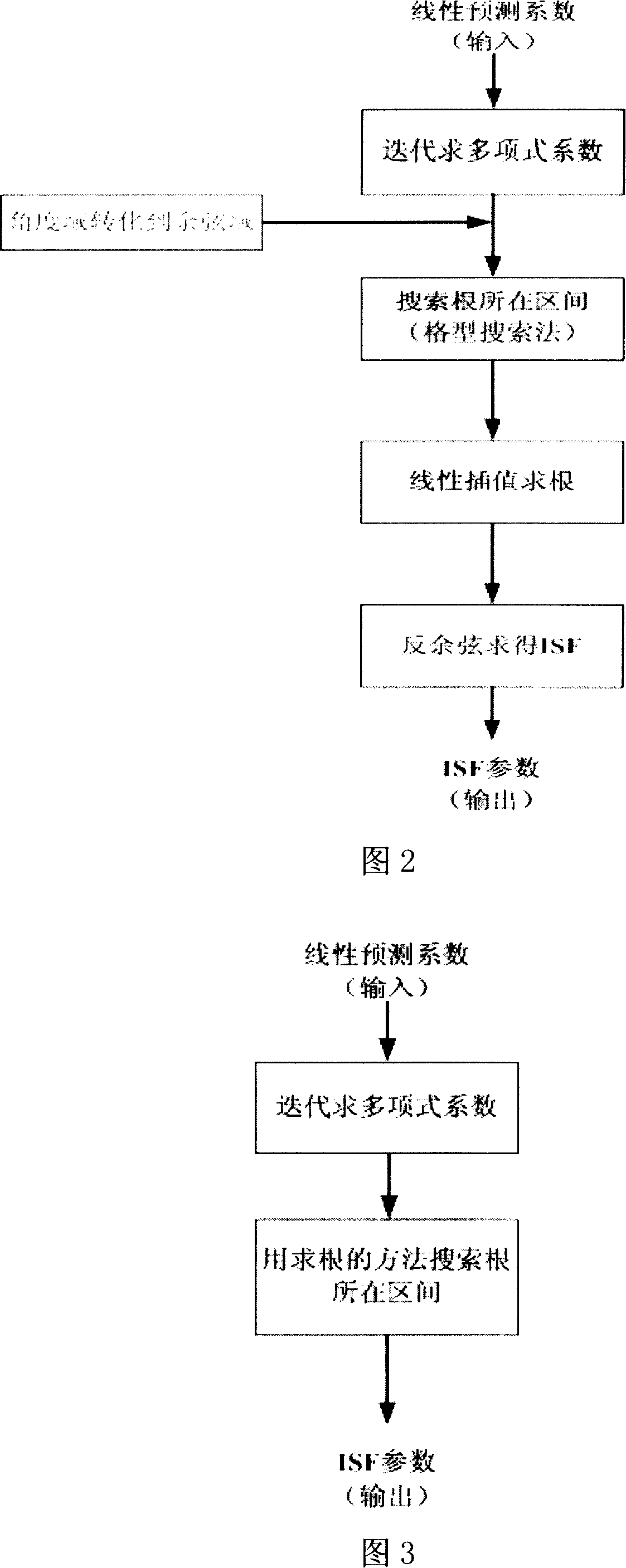
Method for determining ISF parameter in linear predication analysis
The method for determining ISF parameter in linear prediction analysis includes: deriving the polynome coefficient by iteration method, searching the interval where the root is at to obtain ISF parameter. Advantage: simple operation and suitable to audio / voice coding.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Mute test method and device
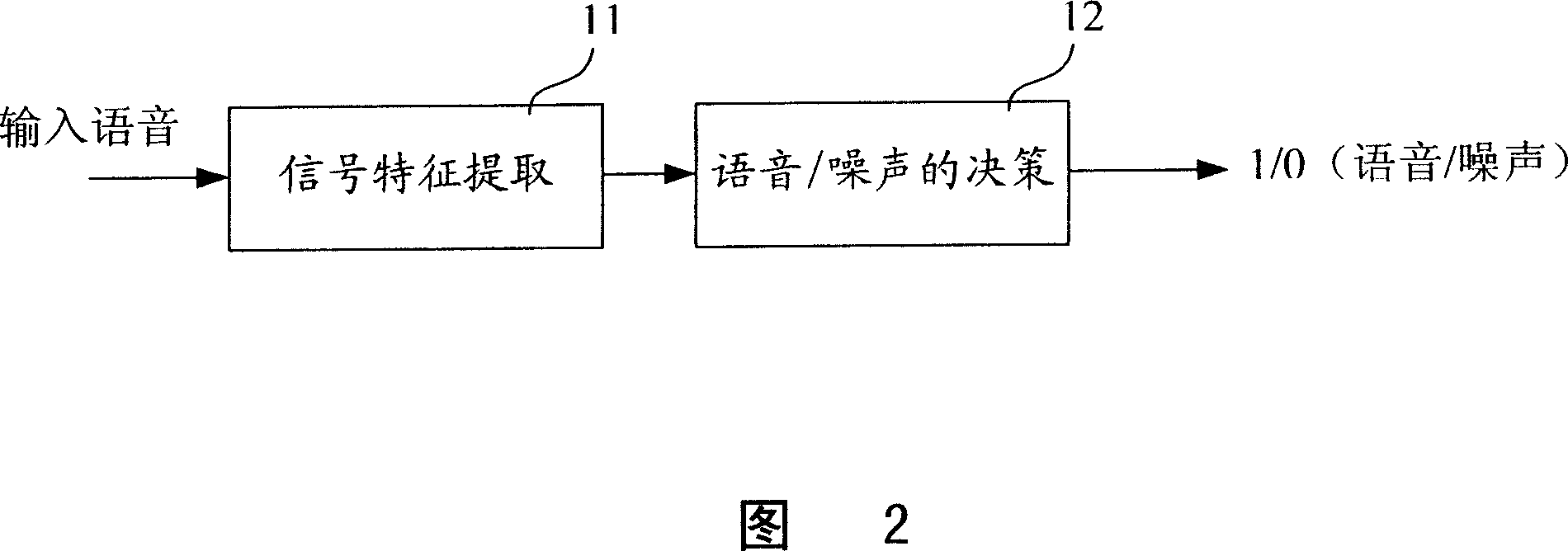
ActiveCN101149921AImprove detection rateReduce complexitySpeech analysisPre treatmentAudio frequency
The method detecting mute, avoiding excess linear prediction analysis to audio-frame only containing noise and having good detection rate and low complexity, includes: (1) pre-treating the first frame audio-frequency; (2) receiving next frame audio as current audio frame; (3) computing linear prediction weighting energy according to N-order linear prediction coefficient, in which N is a natural number; (4) predicting whether there is a voice signal according to the linear prediction weighing energy, if 'yes' which presents that the current frame is voice, going on next step, if 'no' which presents that the current frame is noise, turning to step (6); (5) linear predicting and analyzing current frame to obtain the N-order linear prediction coefficient of the frame itself to substitute the N-order linear prediction coefficient in original step (3); (6) judging whether current frame is the last one in frame series, if 'yes', ending, if 'no', turning to step (2).
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Skin evaluating method and skin evaluating device
InactiveCN1942137AAccurate evaluationEasy accessVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringThree levelSkin texture
A part of the image inputted (S1) from a fingerprint sensor is segmented (S3), and the fundamental frequency is computed by second-order linear prediction analysis (S5). The sum (S) of the fundamental frequencies in the x and y directions is computed and used as a judgment measure of the texture degree (S7). A predetermined threshold and the measure S determined in S7 are compared, and the degree of skin texture is evaluated to one of three levels (S9 to S17). The ratio between the fundamental frequencies in the x and y directions of the object image is computed and used as an evaluation measure of the texture flow (S19). The image is rotated, and a similar evaluation measure is determined. Based on these measures, the texture flow is judged at one of two levels (S31 to S35). The results of the judgment on the texture degree and the texture flow are displayed on a display screen (S37).
Owner:DDS
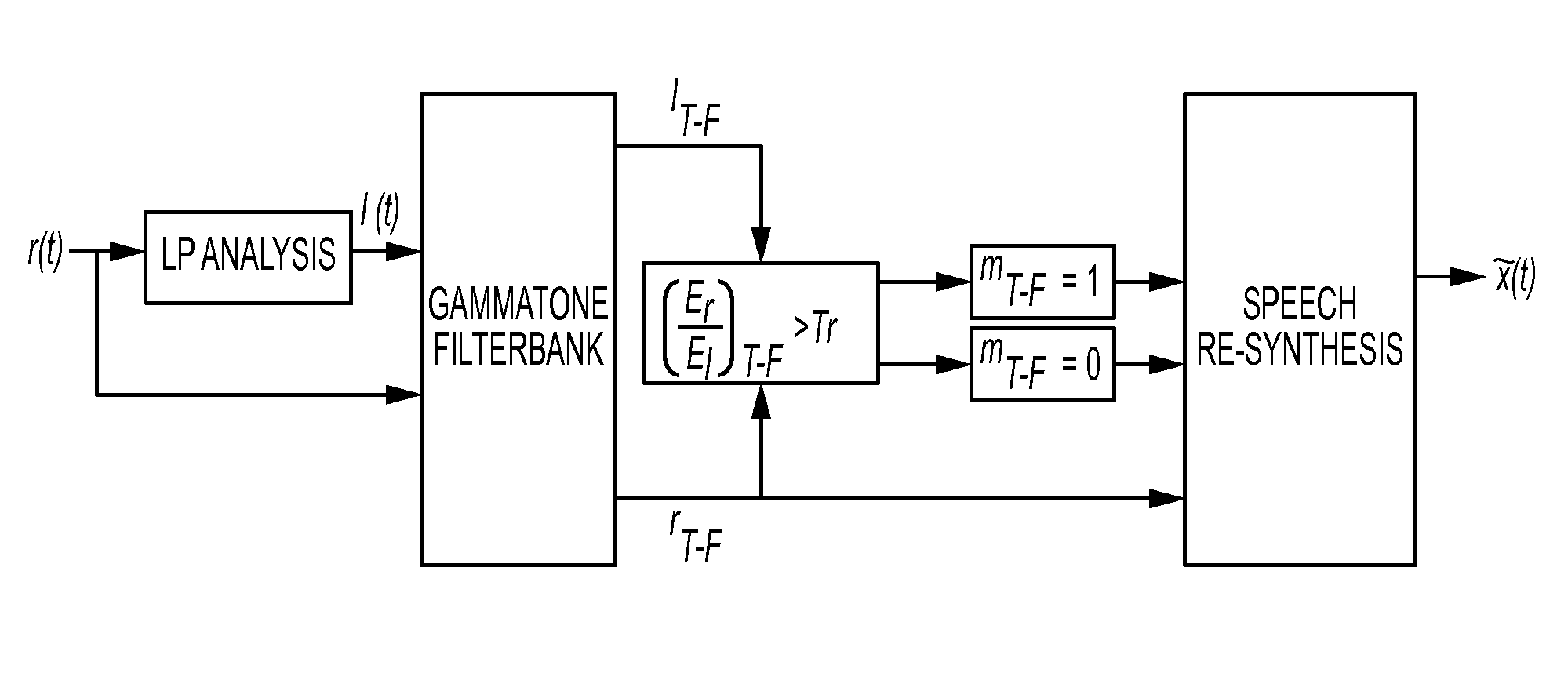
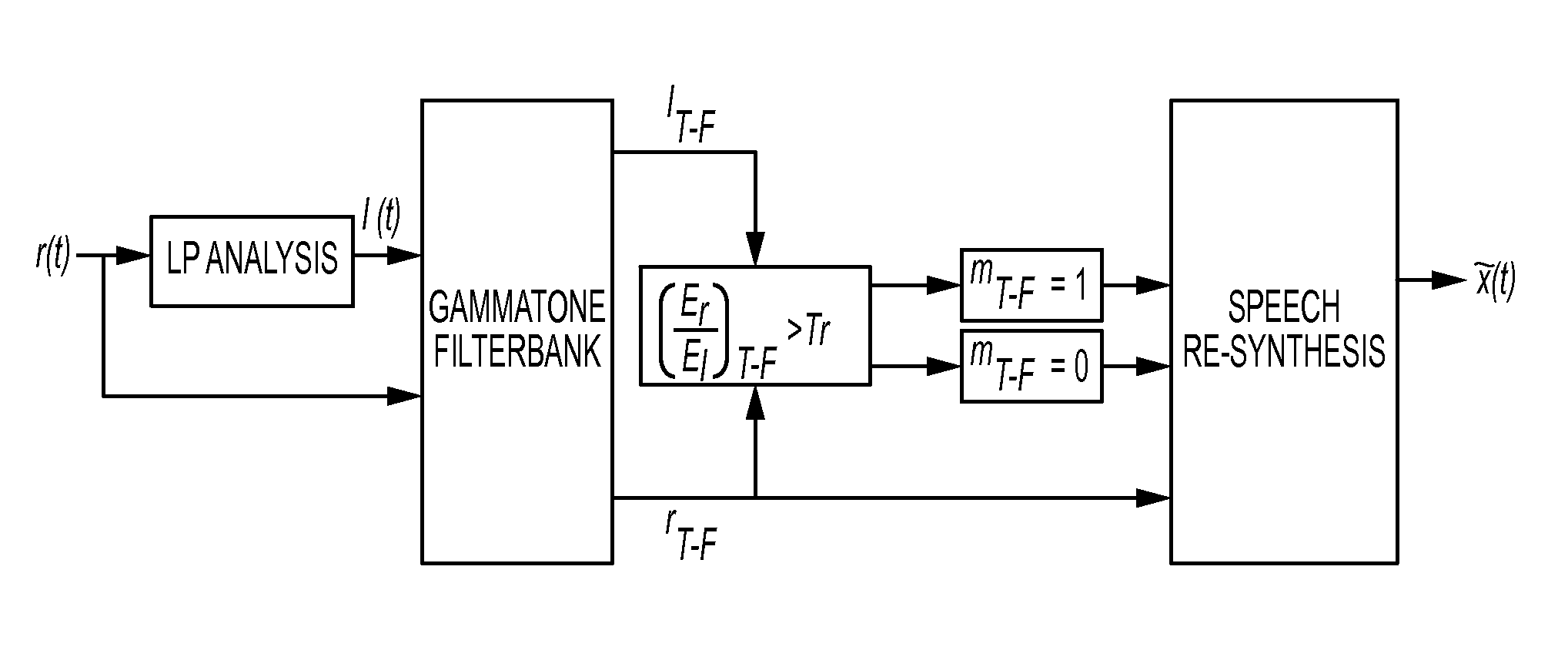
Enhancement of reverberant speech by binary mask estimation
ActiveUS9538297B2Enhancing reverberant speech recognition performanceImproving reverberant speech identificationSpeech analysisLine-transmissionEstimation methodsSpeech identification
The invention is directed to a single channel mask estimation method capable of improving reverberant speech identification for CI users. The method is based on the energy of the reverberant signal and the residual signal computed from linear prediction (LP) analysis. The mask is estimated by comparing the energy ratio of the two signals at different frequency bins with an adaptive threshold. As the threshold is updated for each frame of speech based on the energy ratios of the reverberant and LP residual signals computed from previous frames, it is amenable for real-time implementation. It can thus be used as a specialized (for reverberant environments) sound coding strategy used for cochlear implant applications.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
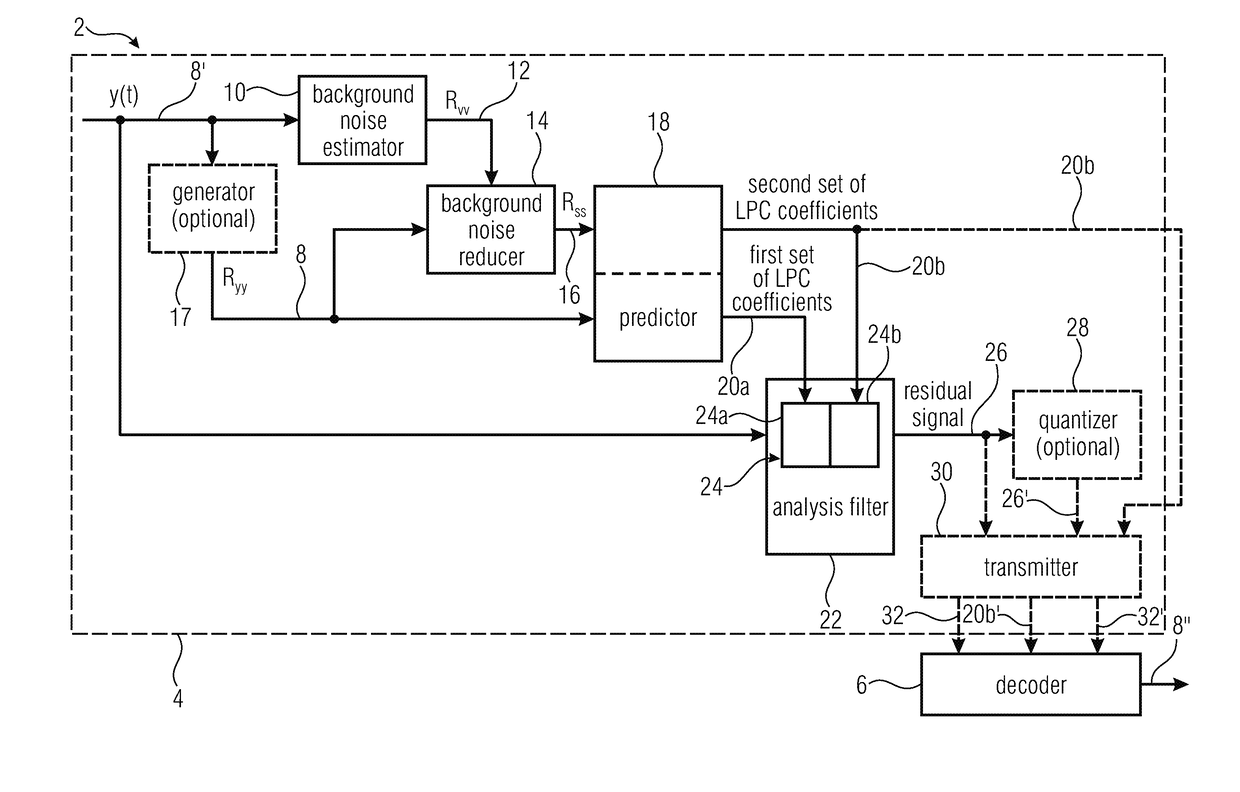
Encoder and method for encoding an audio signal with reduced background noise using linear predictive coding
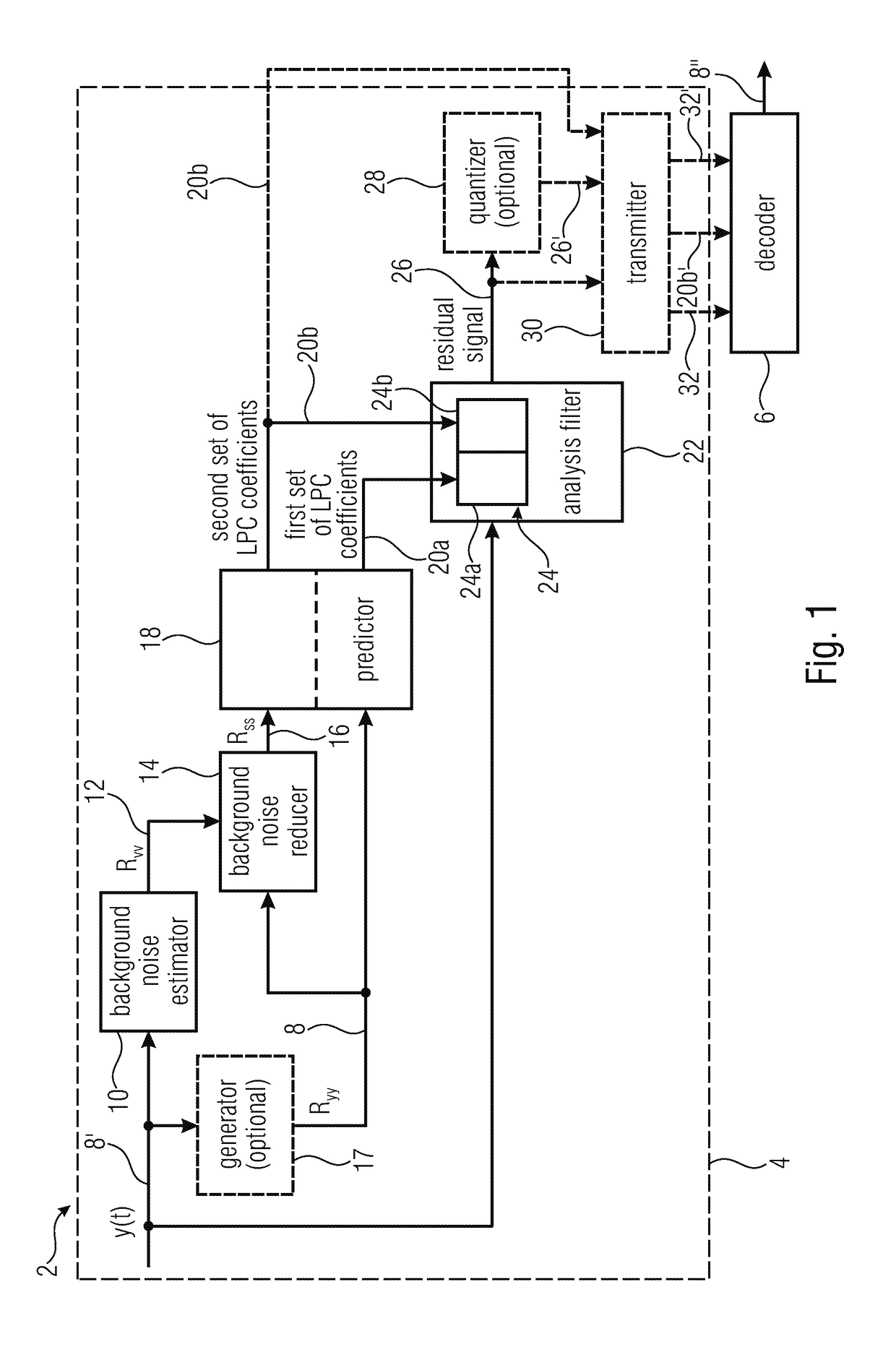
ActiveUS20180204580A1Improve signal processing capabilitiesImprove processing speedSpeech analysisTime domainReducer
It is shown an encoder for encoding an audio signal with reduced background noise using linear predictive coding. The encoder includes a background noise estimator configured to estimate background noise of the audio signal, a background noise reducer configured to generate background noise reduced audio signal by subtracting the estimated background noise of the audio signal from the audio signal, and a predictor configured to subject the audio signal to linear prediction analysis to obtain a first set of linear prediction filter (LPC) coefficients and to subject the background noise reduced audio signal to linear prediction analysis to obtain a second set of linear prediction filter (LPC) coefficients. Furthermore, the encoder includes an analysis filter composed of a cascade of time-domain filters controlled by the obtained first set of LPC coefficients and the obtained second set of LPC coefficients.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method and apparatus for encoding/decoding speech signal
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
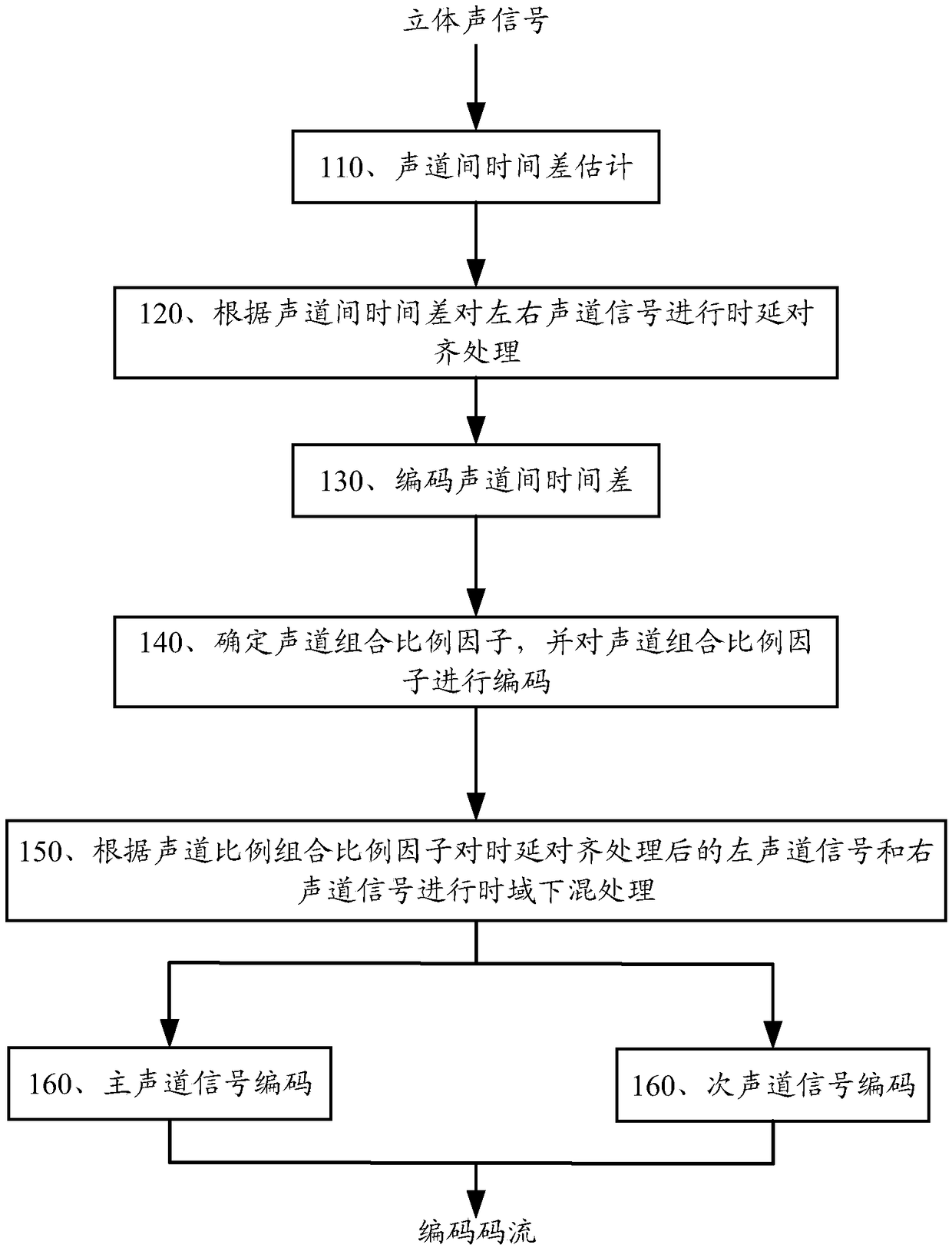
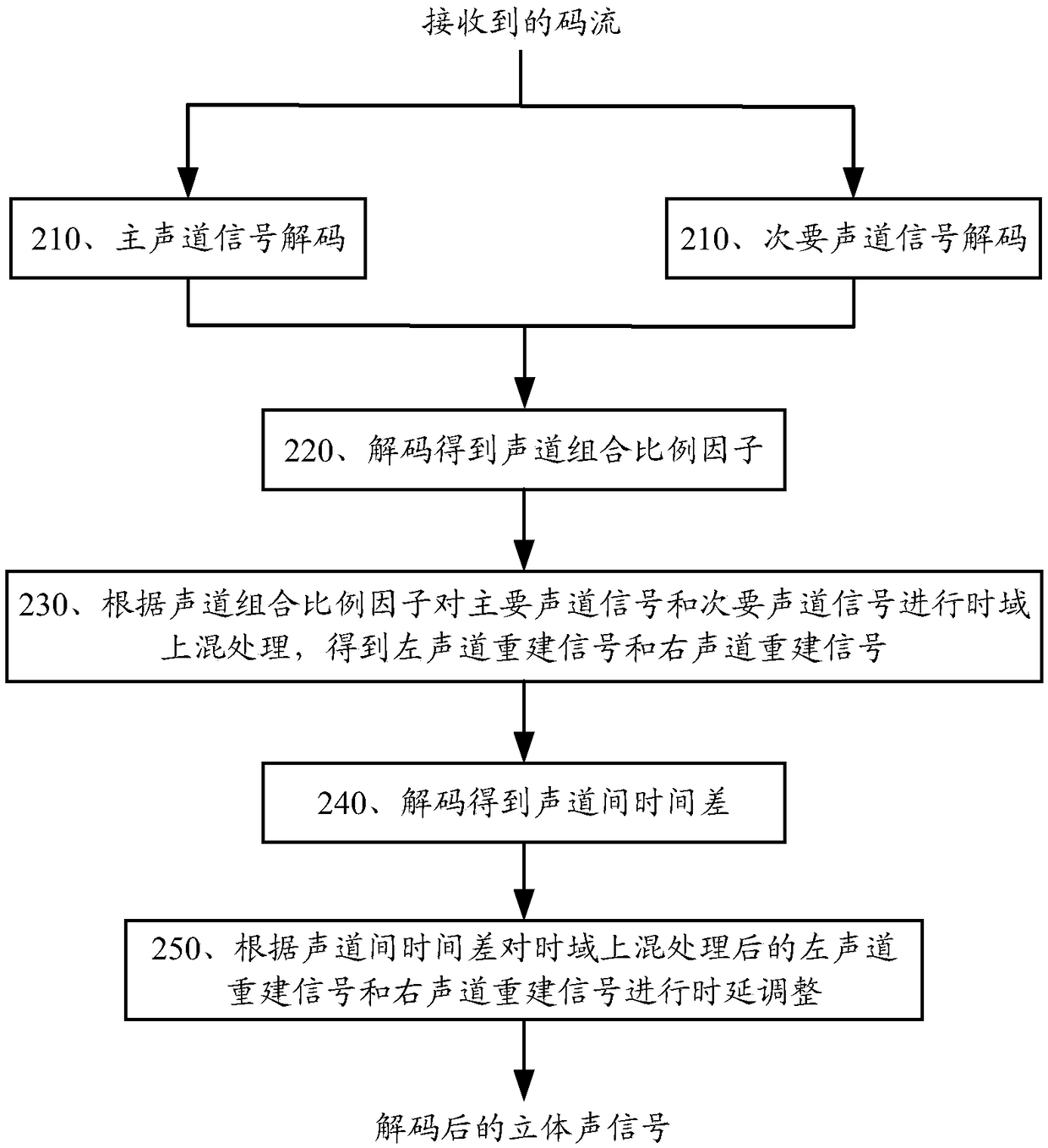
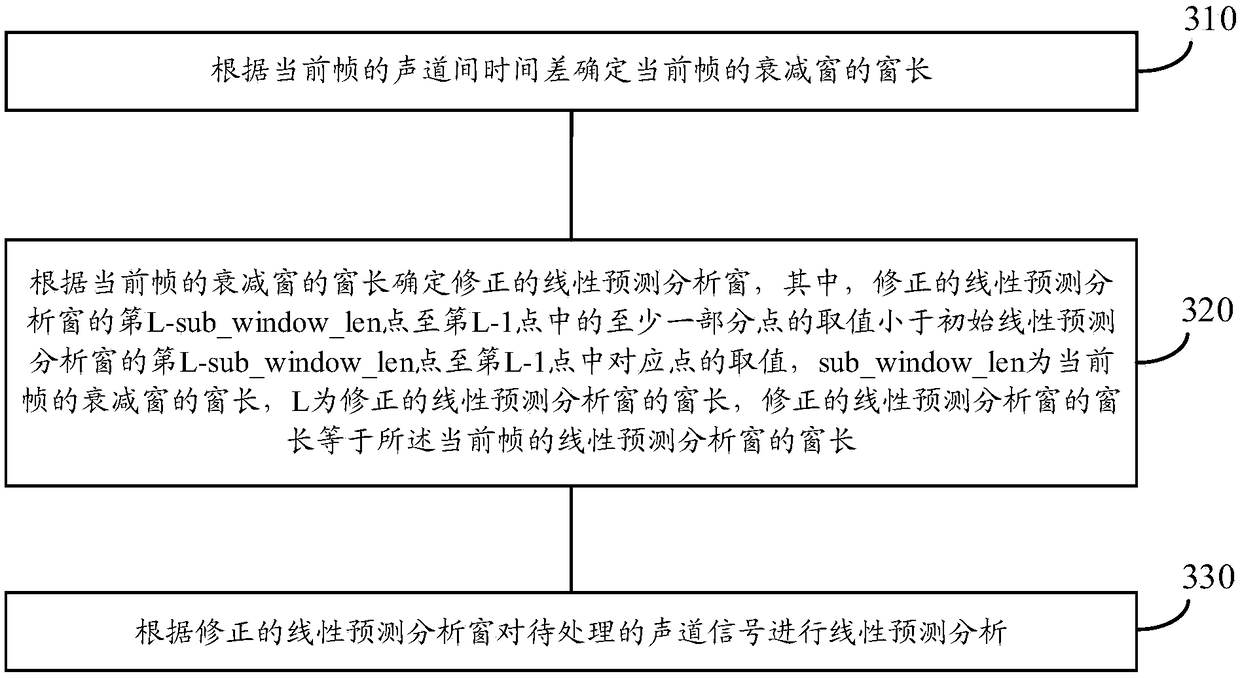
Encoding method and encoding apparatus for stereo signal
Provided are an encoding method and encoding apparatus for a stereo signal. The method comprises determining a window length of an attenuating window of a current frame according to an inter-channel time difference of the current frame; determining a corrected linear prediction analysis window according to the window length of the attenuating window of the current frame, wherein values of at leastsome of the points between an (L sub_window_len)th point and an (L 1)th point in the corrected linear prediction analysis window are lower than values of corresponding points between the (L sub_window_len)th point and the (L 1)th point in an initial linear prediction analysis window, sub_window_len is the window length of the attenuating window of the current frame, L is a window length of the corrected linear prediction analysis window, and the window length of the corrected linear prediction analysis window is equal to the window length of a linear prediction analysis window of the currentframe; and performing linear prediction analysis on a channel signal to be processed according to the corrected linear prediction analysis window. The accuracy of linear prediction can be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method for high quality audio transcoding
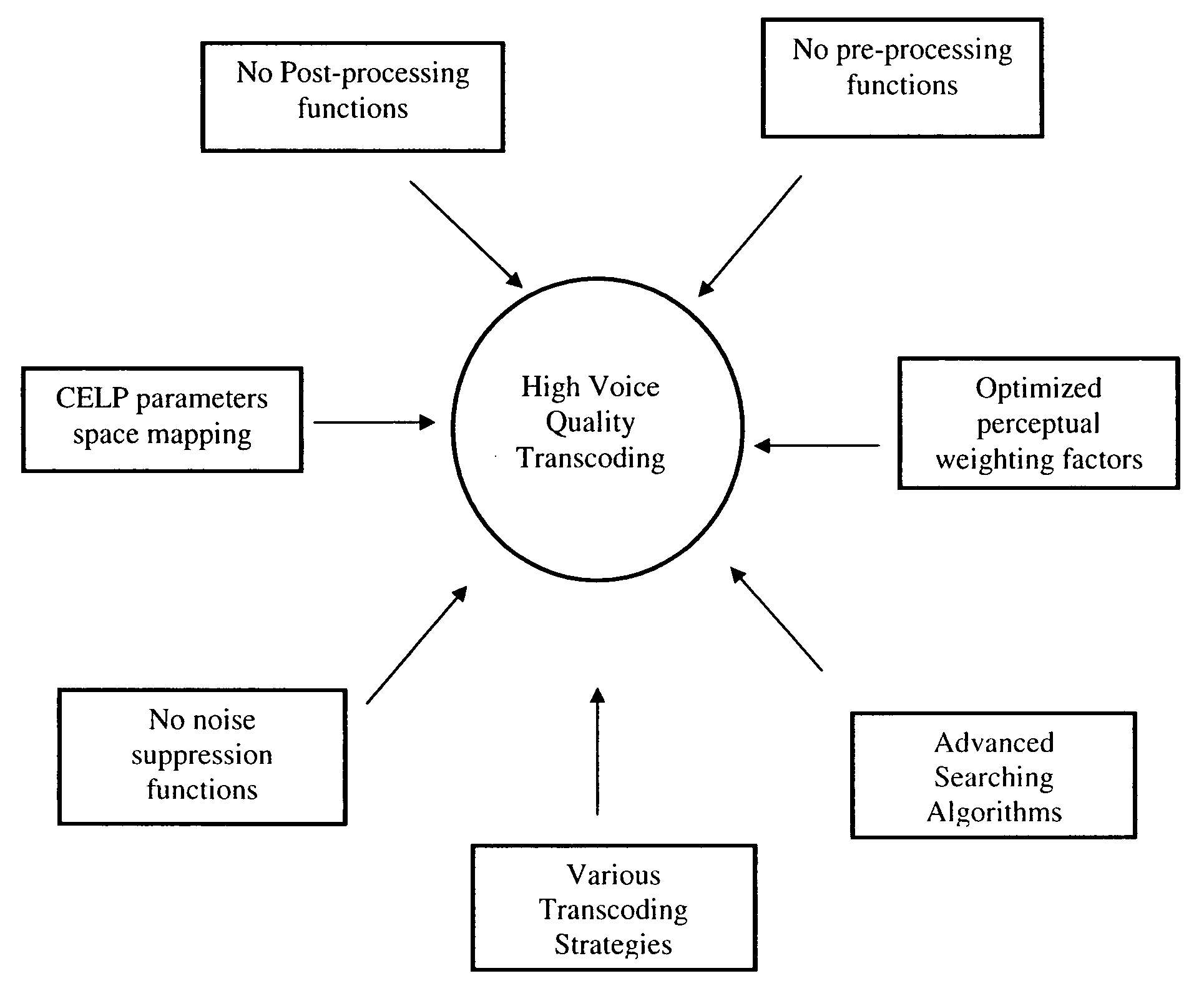
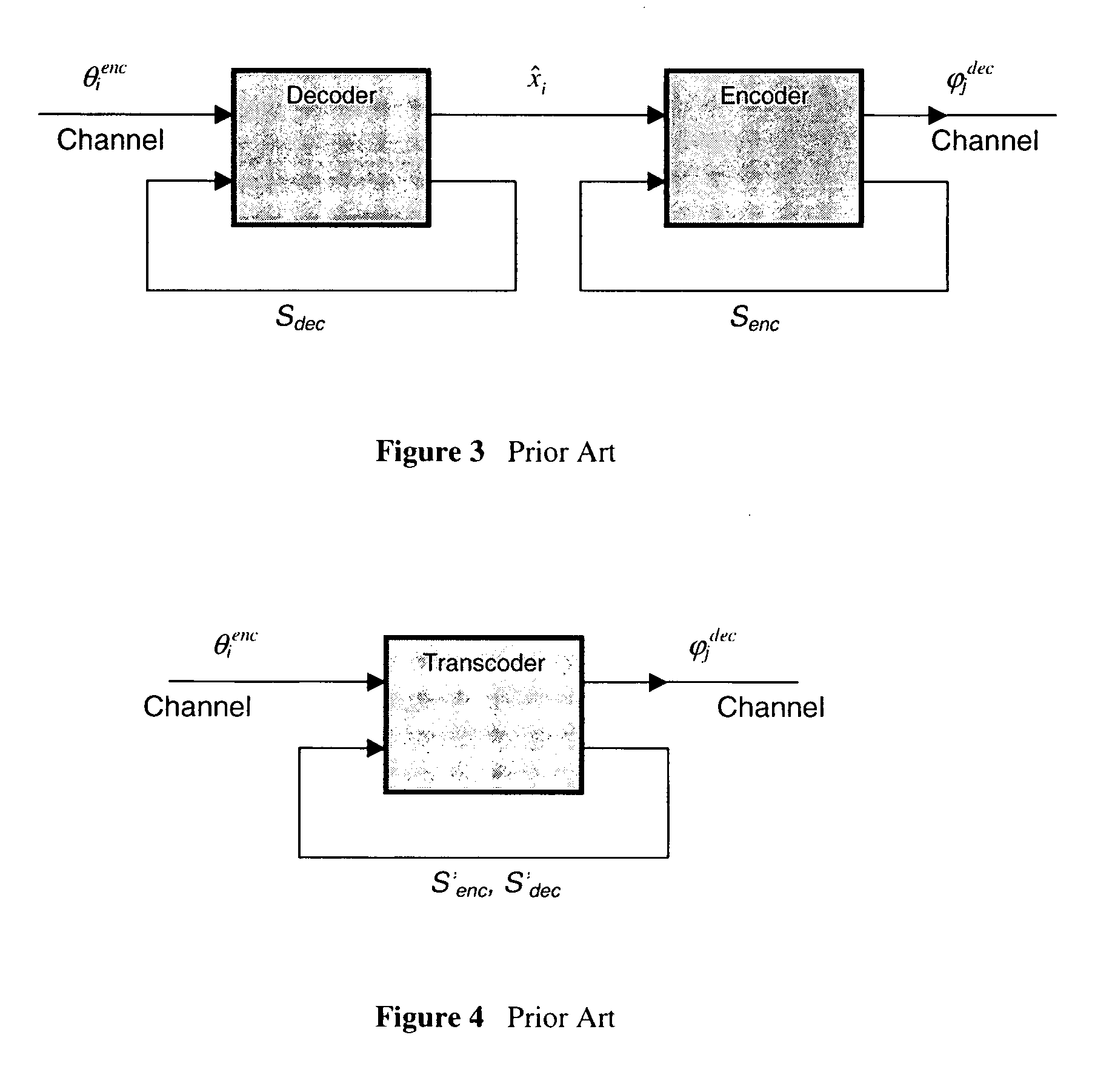
InactiveUS20080195384A1Improve sound qualityReduce complexitySpeech analysisTime-division multiplexTranscodingSpeech code
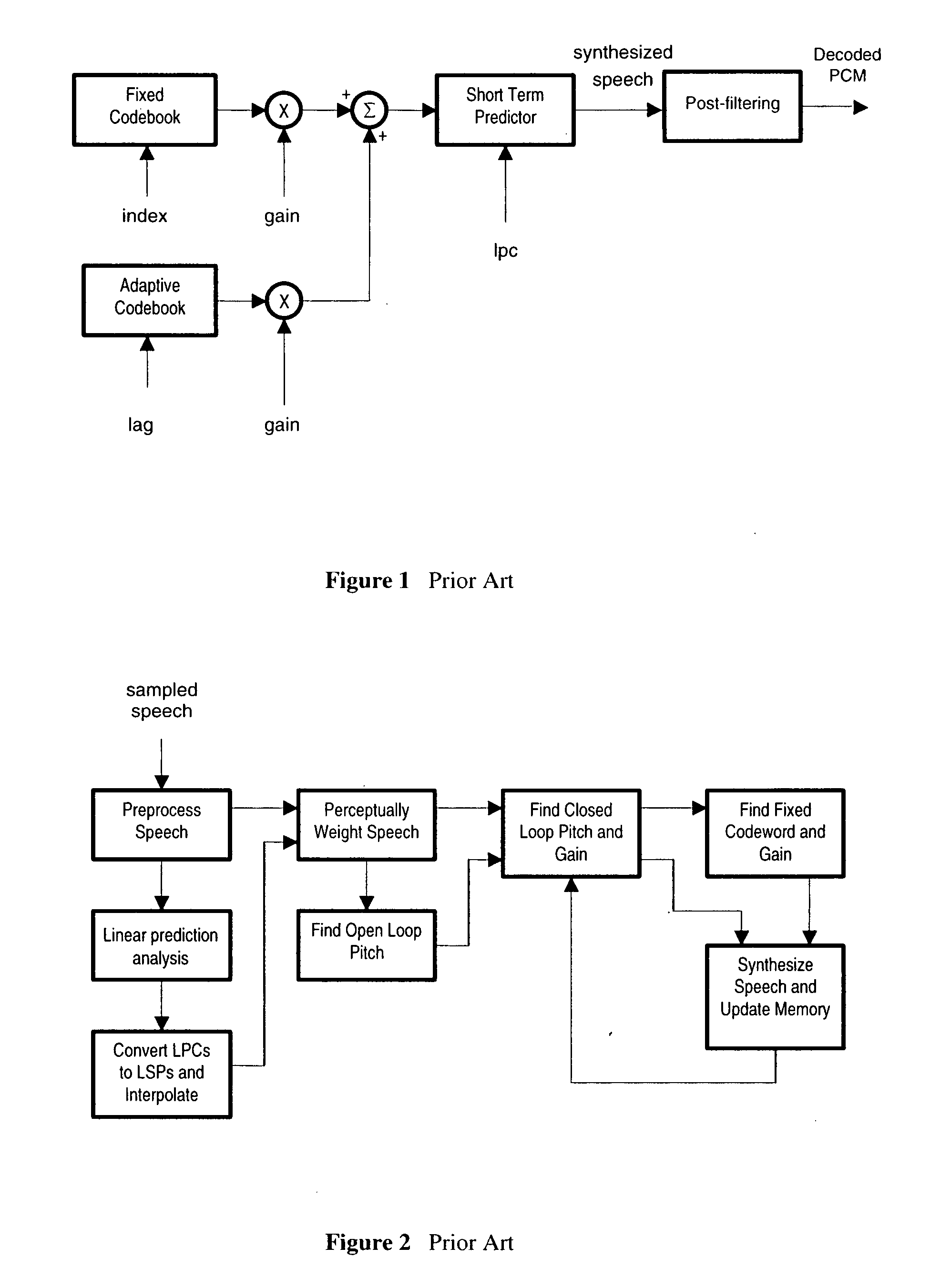
A method and apparatus for a voice transcoder that converts a bitstream representing frames of data encoded according to a first voice compression standard to a bitstream representing frames of data according to a second voice compression standard using perceptual weighting that uses tuned weighting factors, such that the bitstream of a second voice compression standard to produce a higher quality decoded voice signal than a comparable tandem transcoding solution. The method includes pre-computing weighting factors for a perceptual weighting filter optimized to a specific source and destination codec pair, pre-configuring the transcoding strategies, mapping CELP parameters in the CELP parameter space according to the selected coding strategy, performing Linear Prediction analysis if specified by the transcoding strategy, perceptually weighting the speech using with tuned weighting factors, and searching for adaptive codebook and fixed-codebook parameters to obtain a quantized set of destination codec parameters.
Owner:ONMOBILE GLOBAL LTD
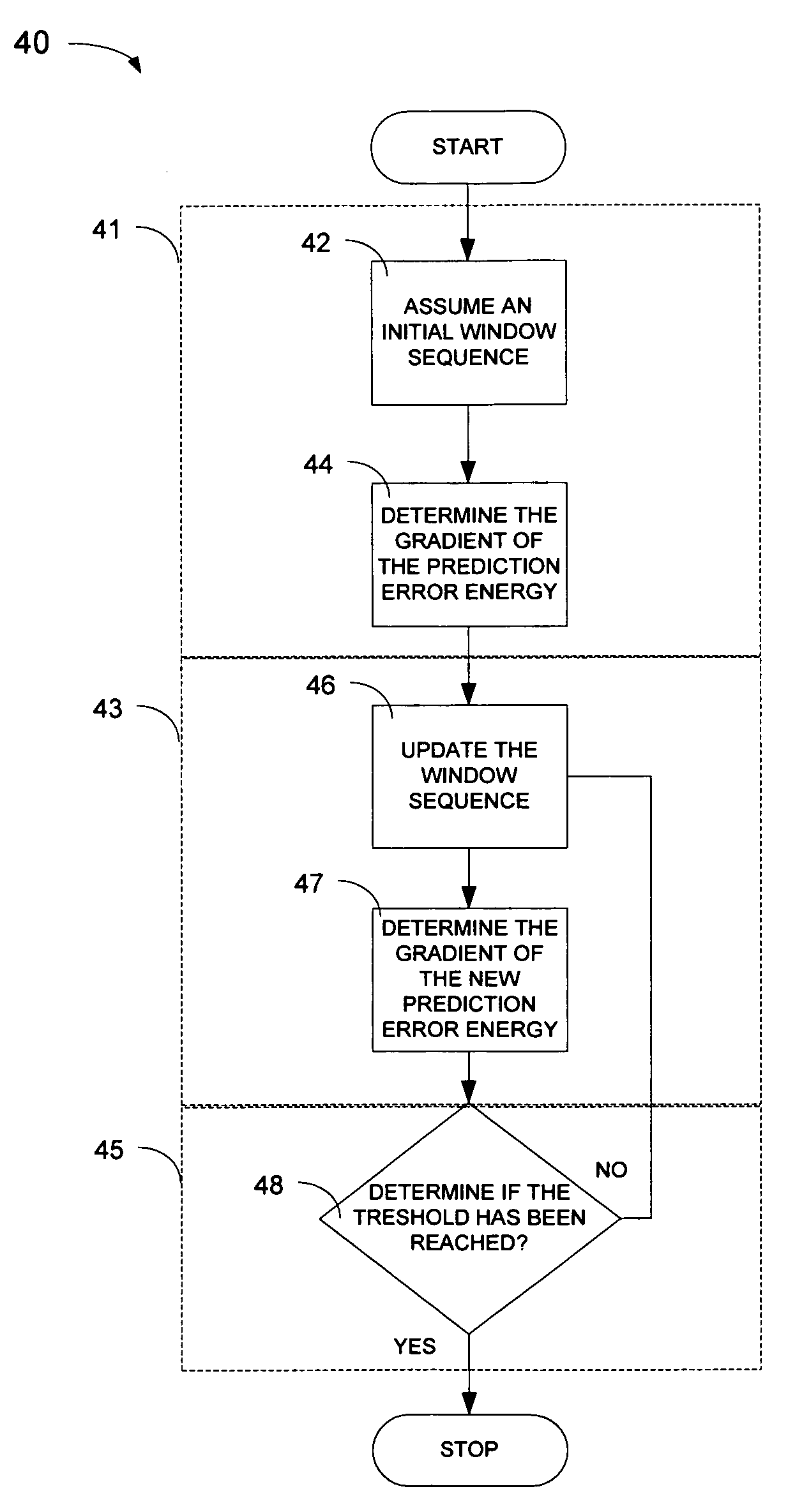
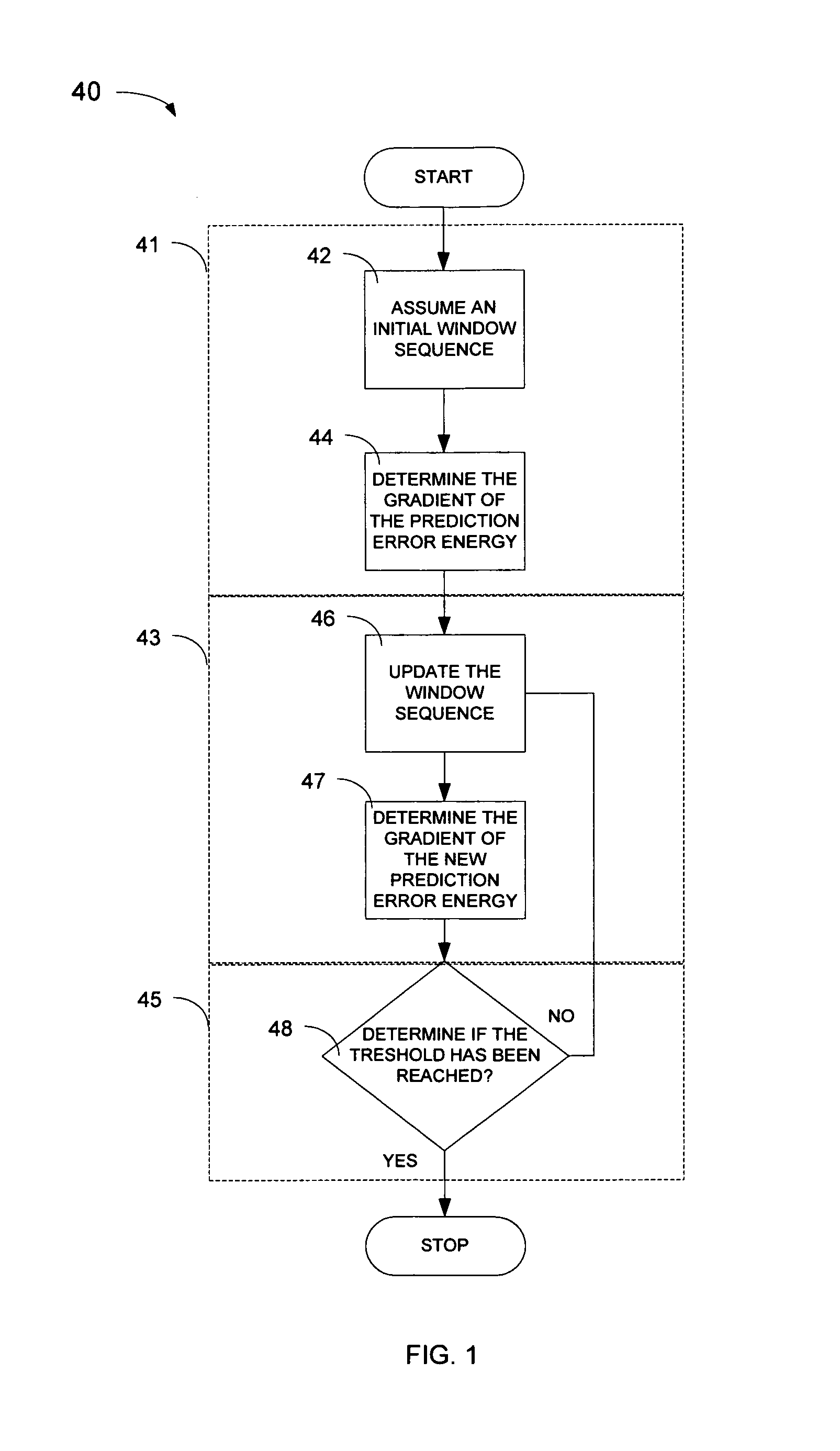
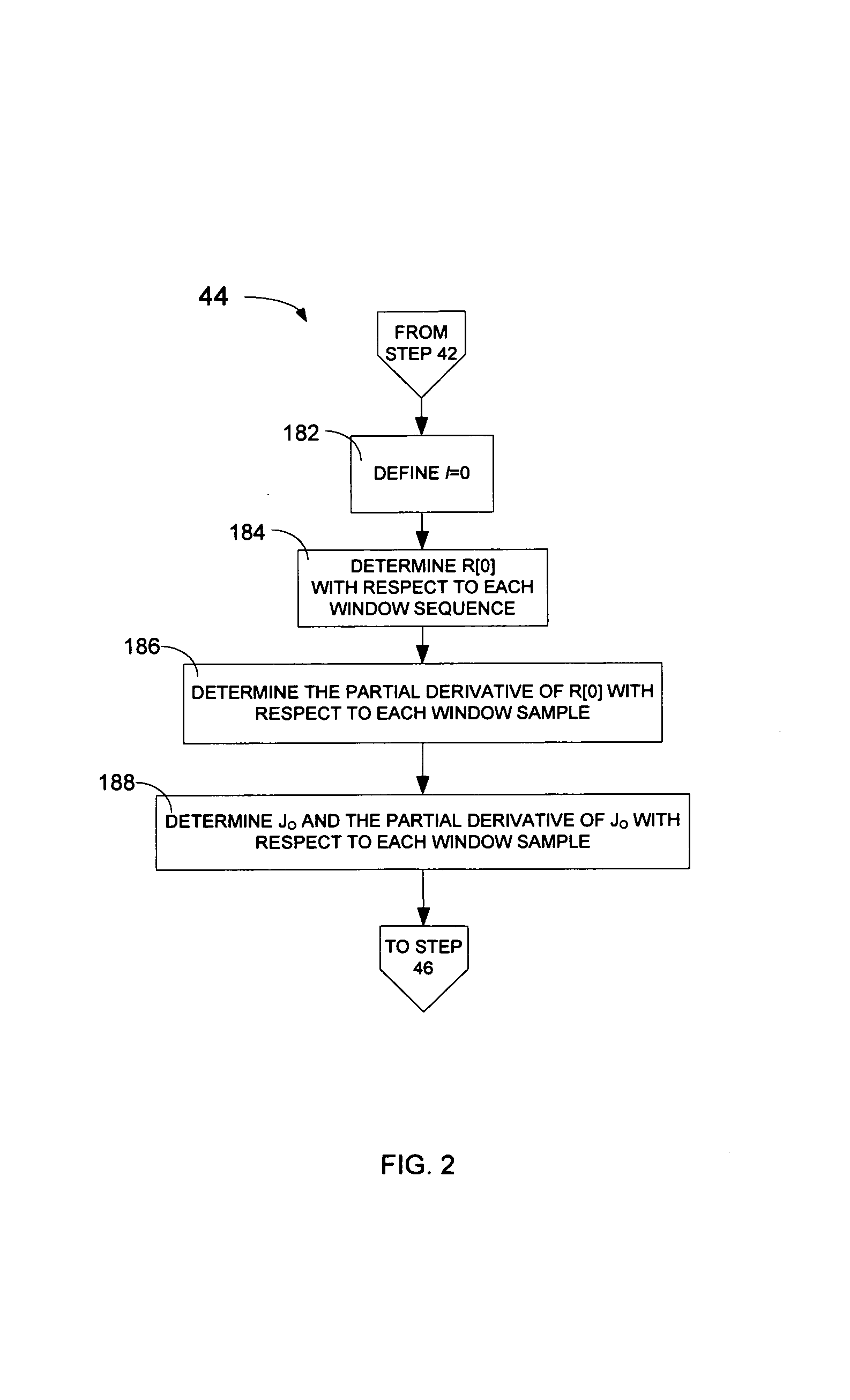
Method and apparatus for gradient-descent based window optimization for linear prediction analysis
The shape of windows used during linear predictive analysis can be optimized through the use of gradient-descent based window optimization procedures. Window optimization may be achieved fairly precisely through the use of a primary optimization procedure, or less precisely through the use of an alternate optimization procedure. Both optimization procedures use the principle of gradient-descent to find a window sequence that will either minimize the prediction error energy or maximize the segmental prediction gain. However, the primary optimization procedure uses a Levinson-Durbin based algorithm to determine the gradient while the alternate optimization procedure uses an estimate of the gradient based on the basic definition of a derivative. These optimization procedures can be implemented as computer readable software code. Additionally, the optimization procedures may be implemented in a window optimization device which generally includes a window optimization unit and may also include an interface unit.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com