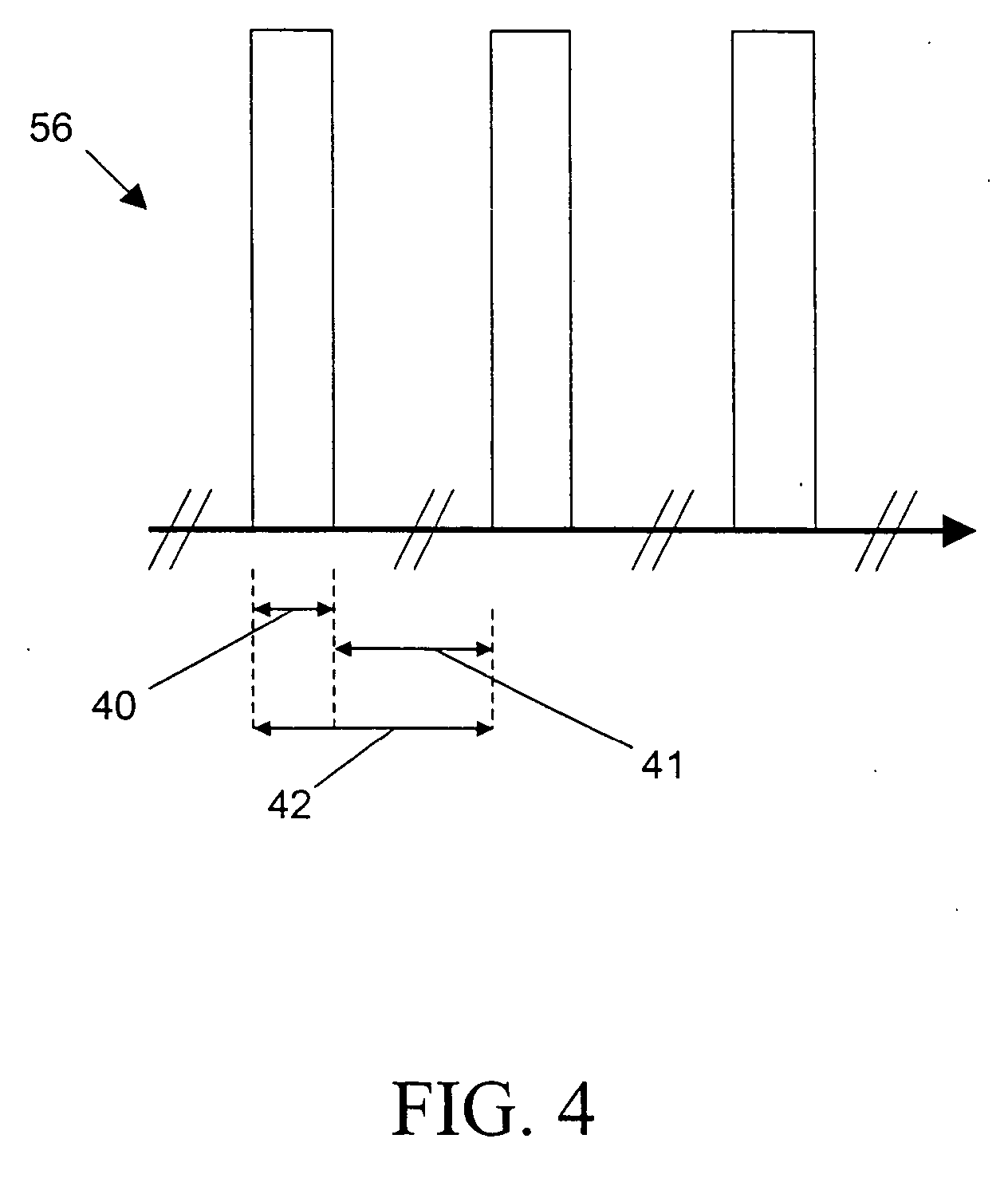
Patents
Literature
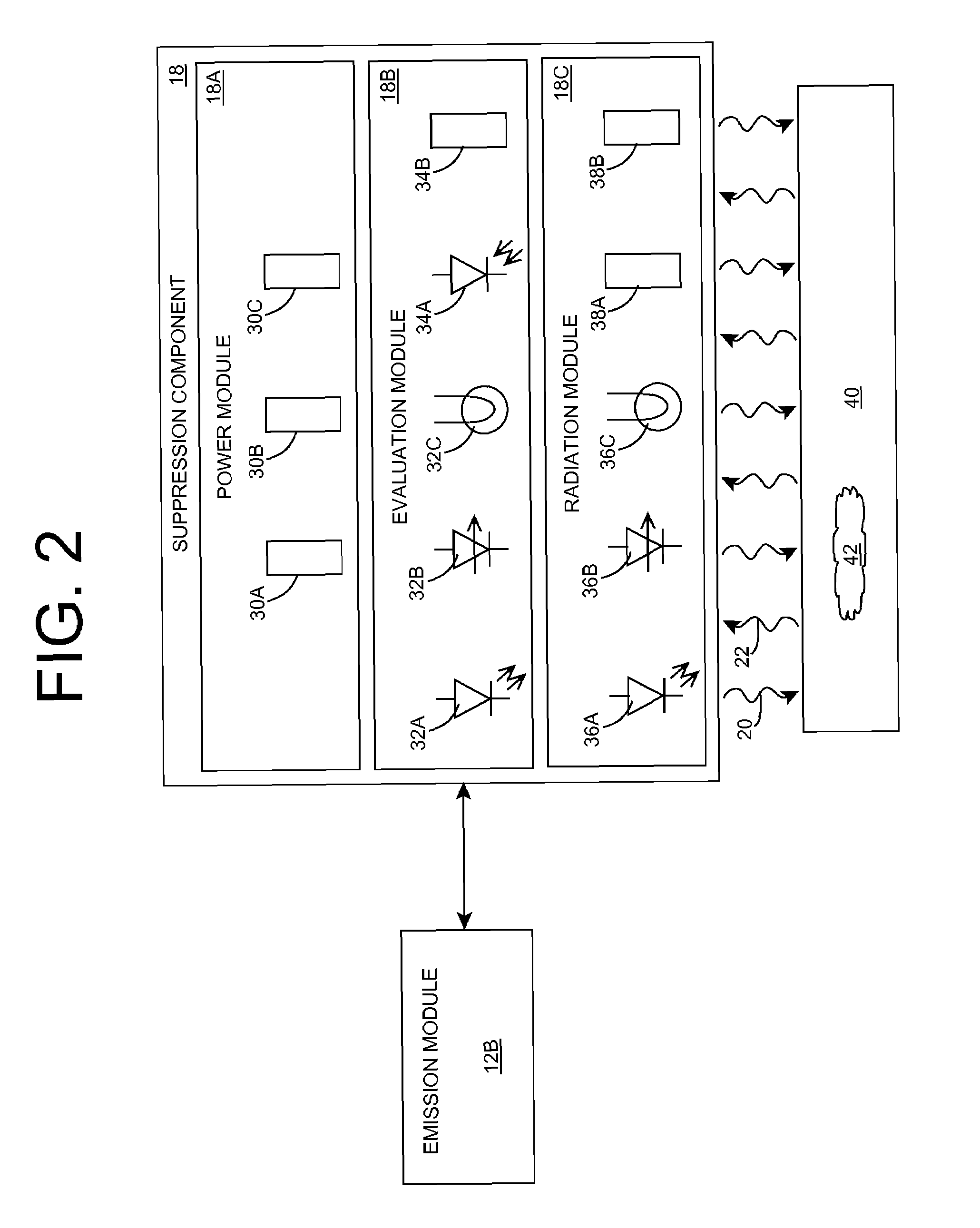
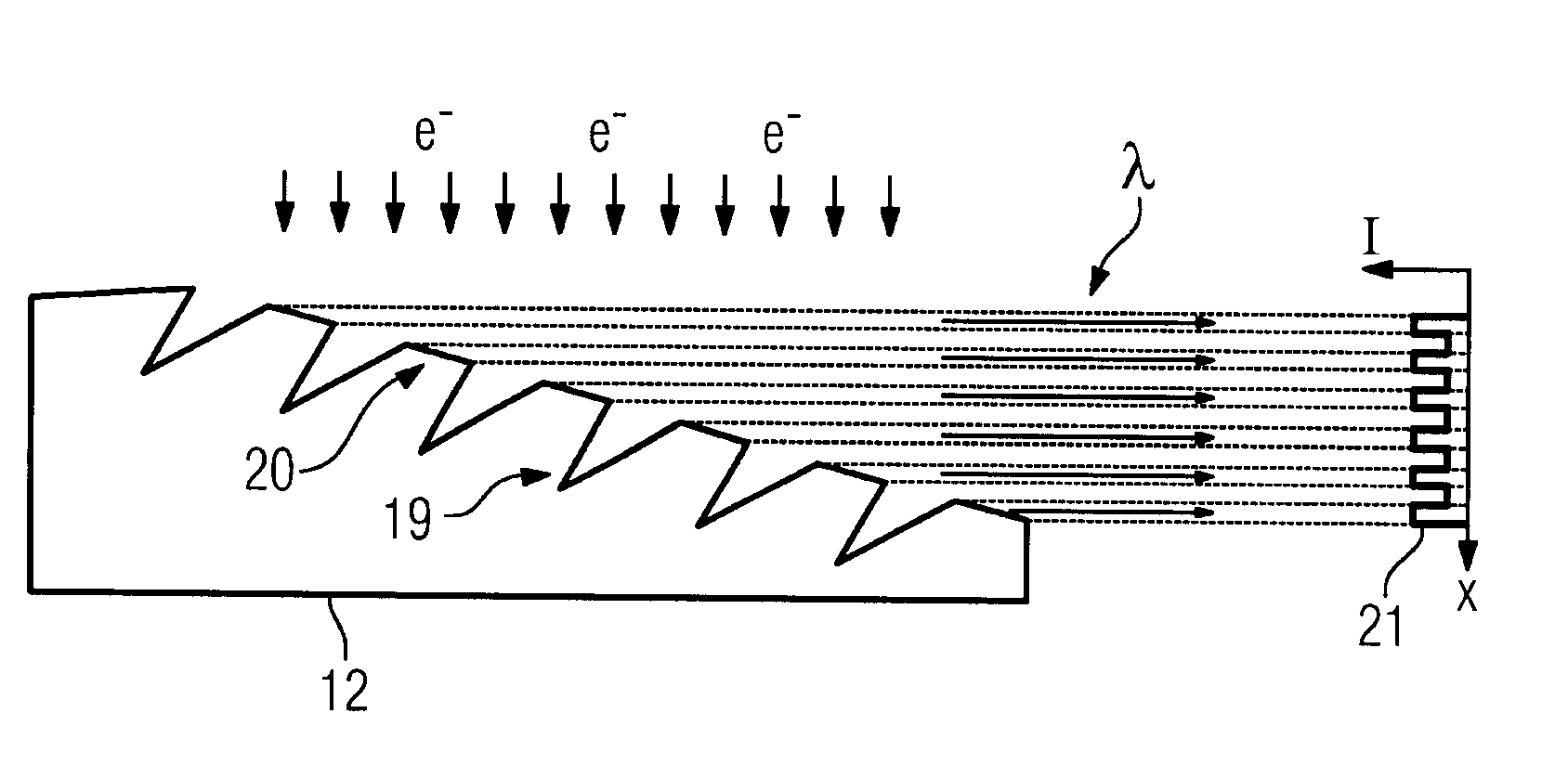
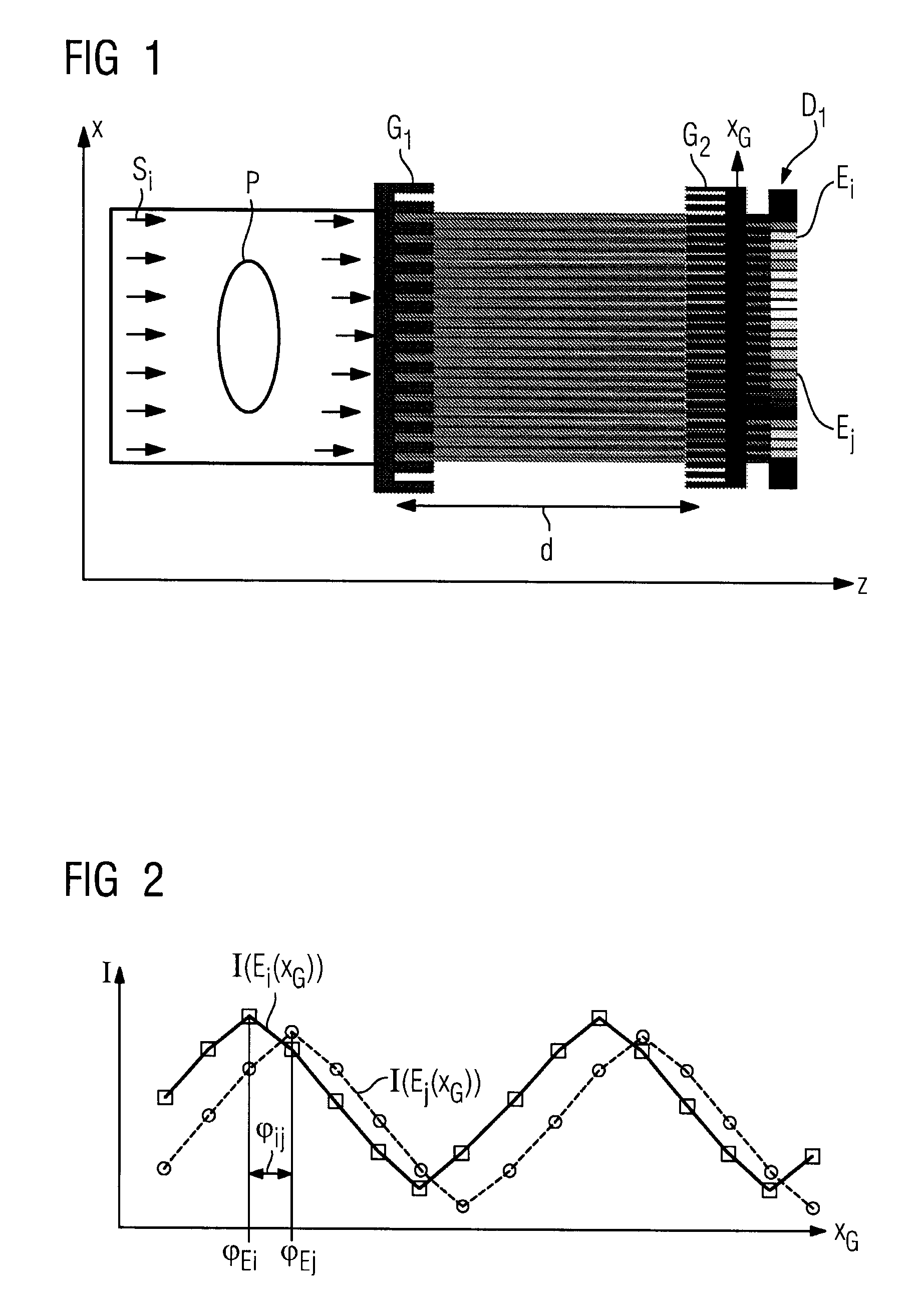
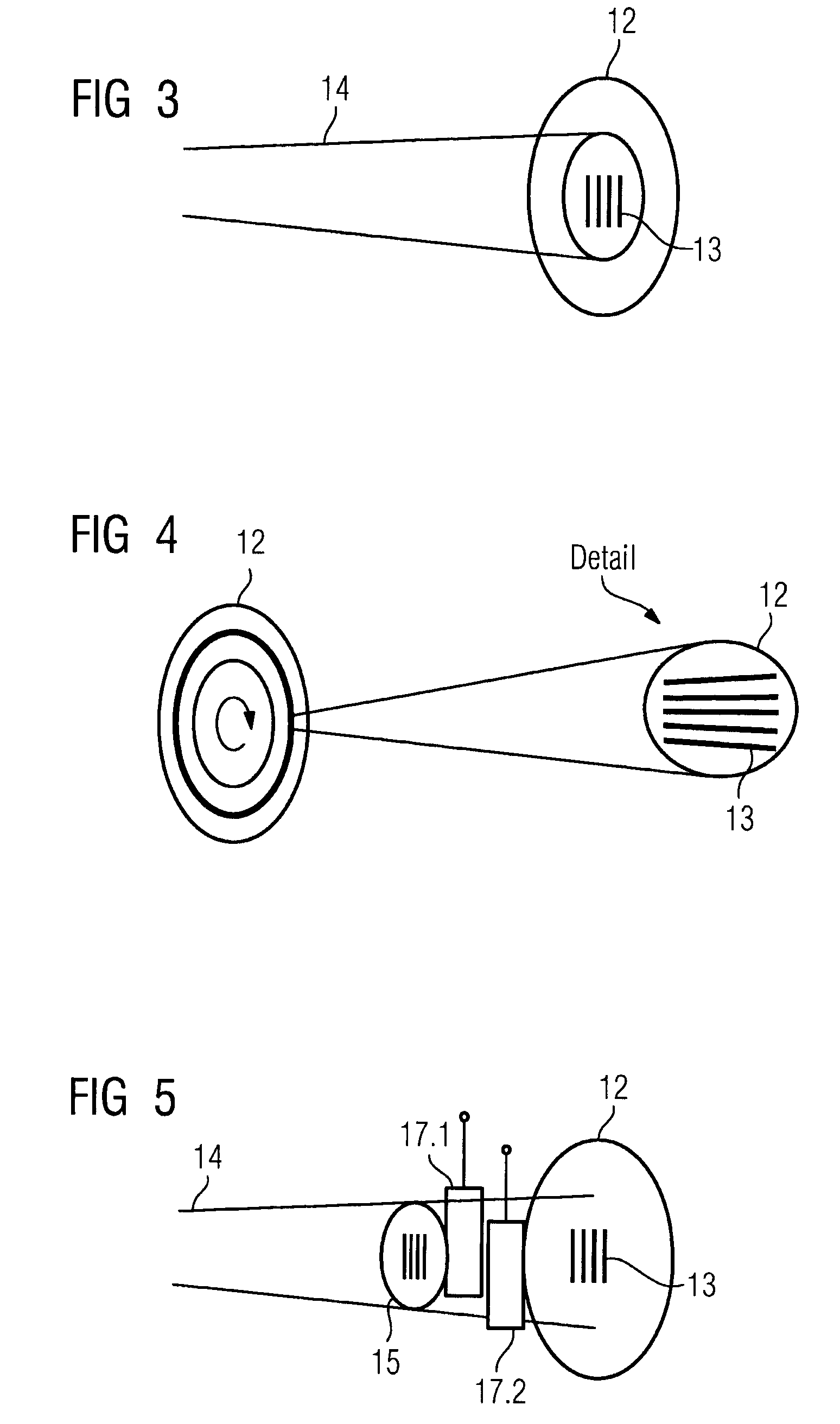
639 results about "Radiation emission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Radiation is the emission of energy as electromagnetic waves or as moving subatomic particles, especially high-energy particles which cause ionization. Radiation can also be defined as the mode of traveling energy through space. Radiation can occur via either waves or particles. Radiation can go through space as well as through some materials.
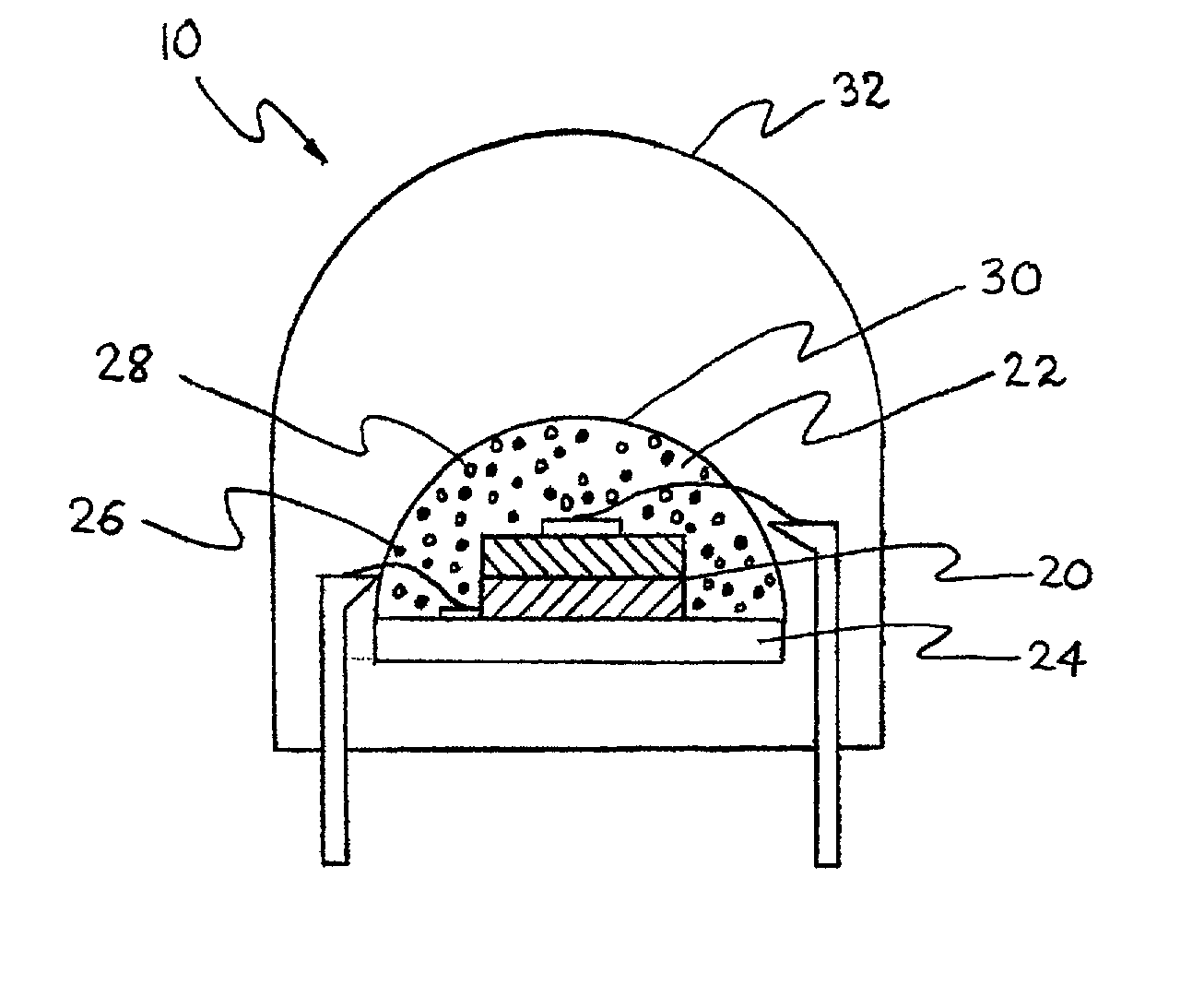
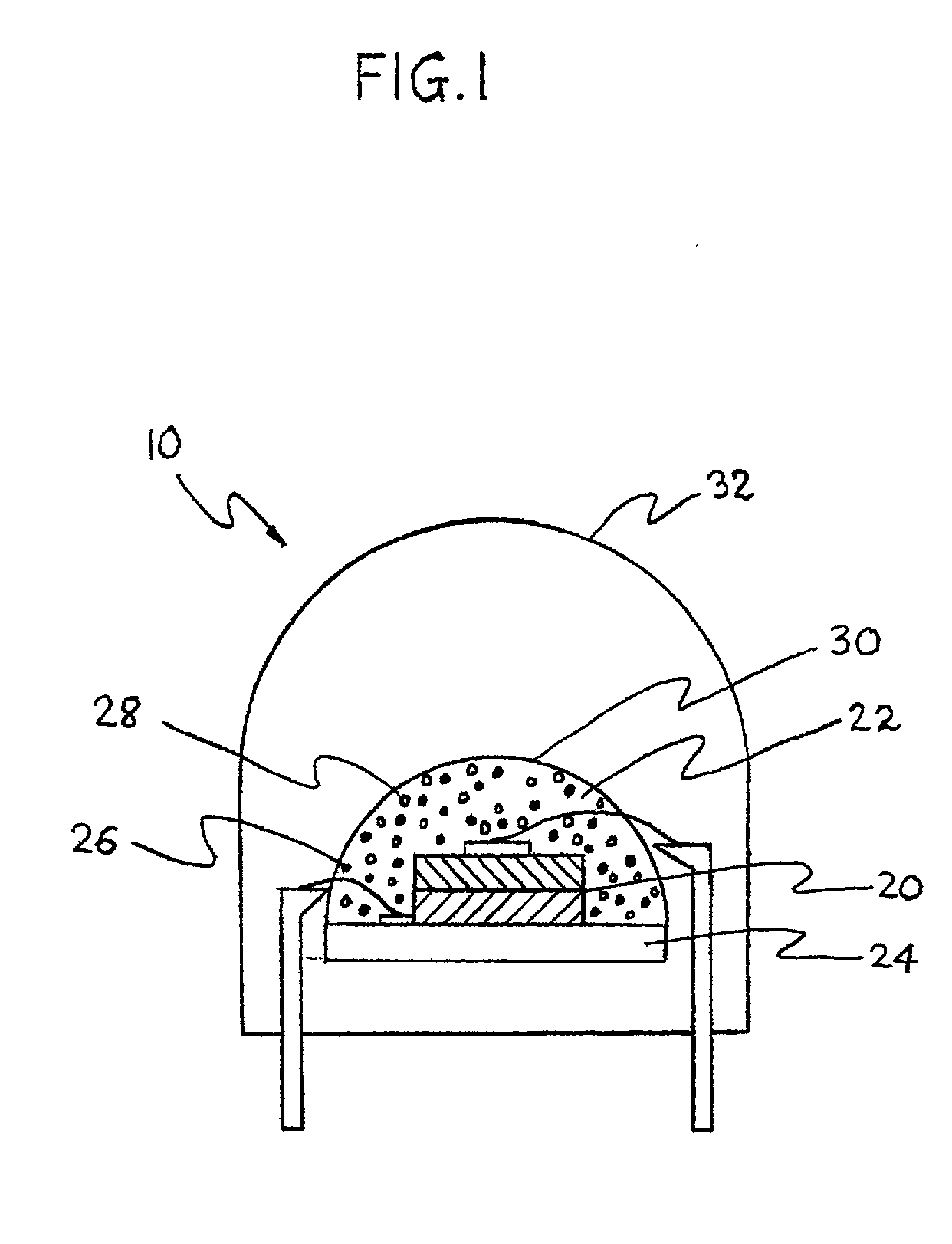
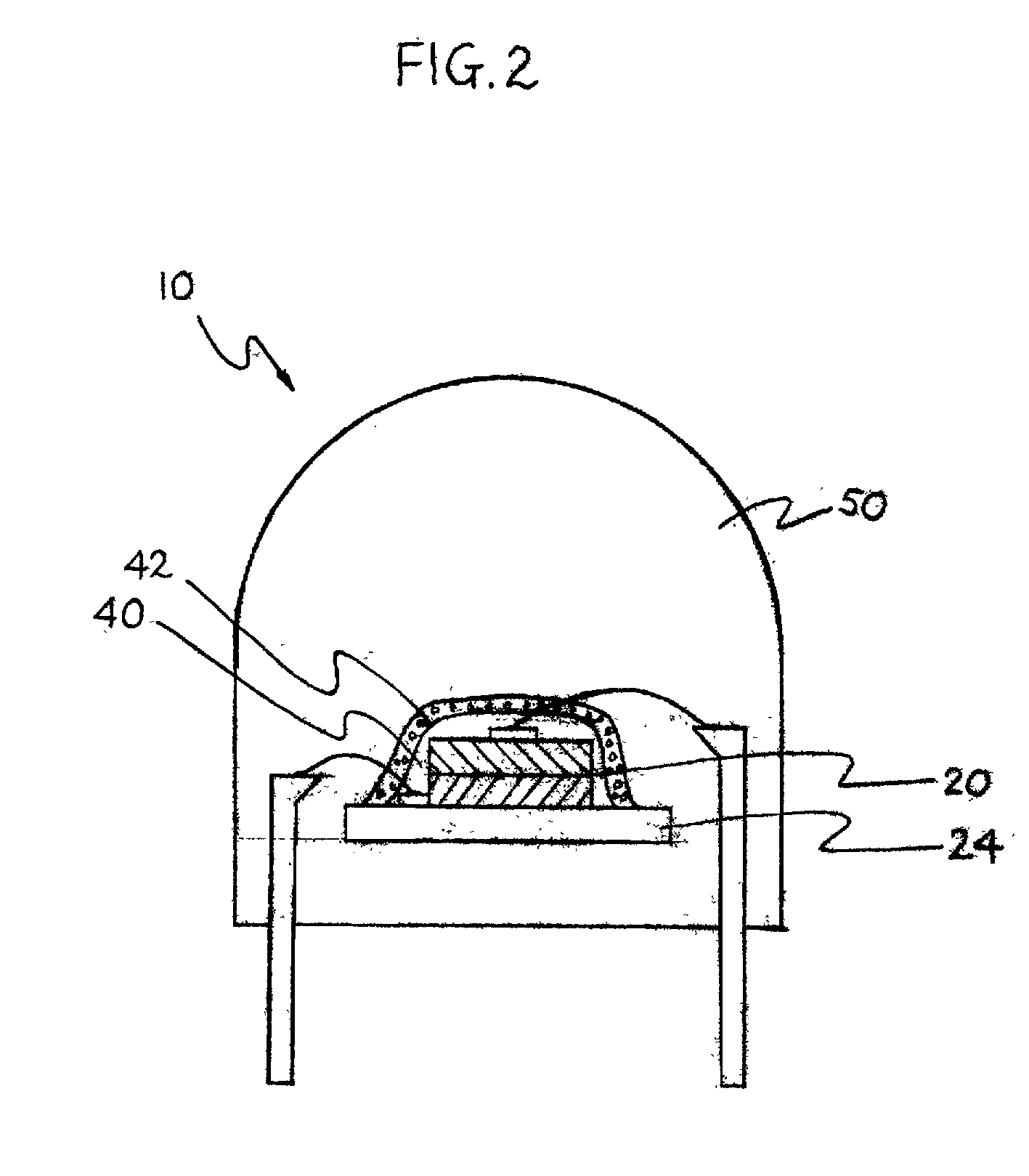
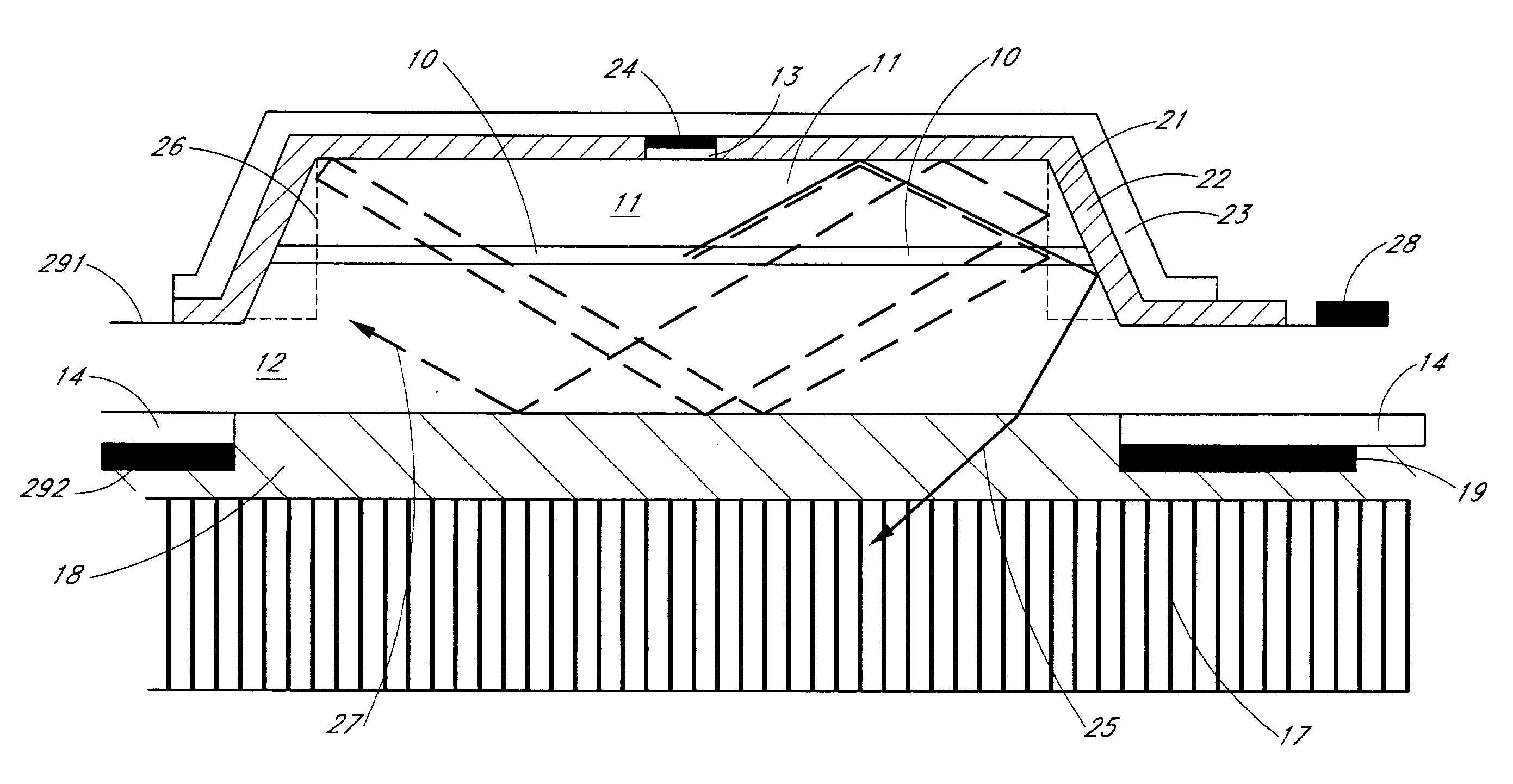
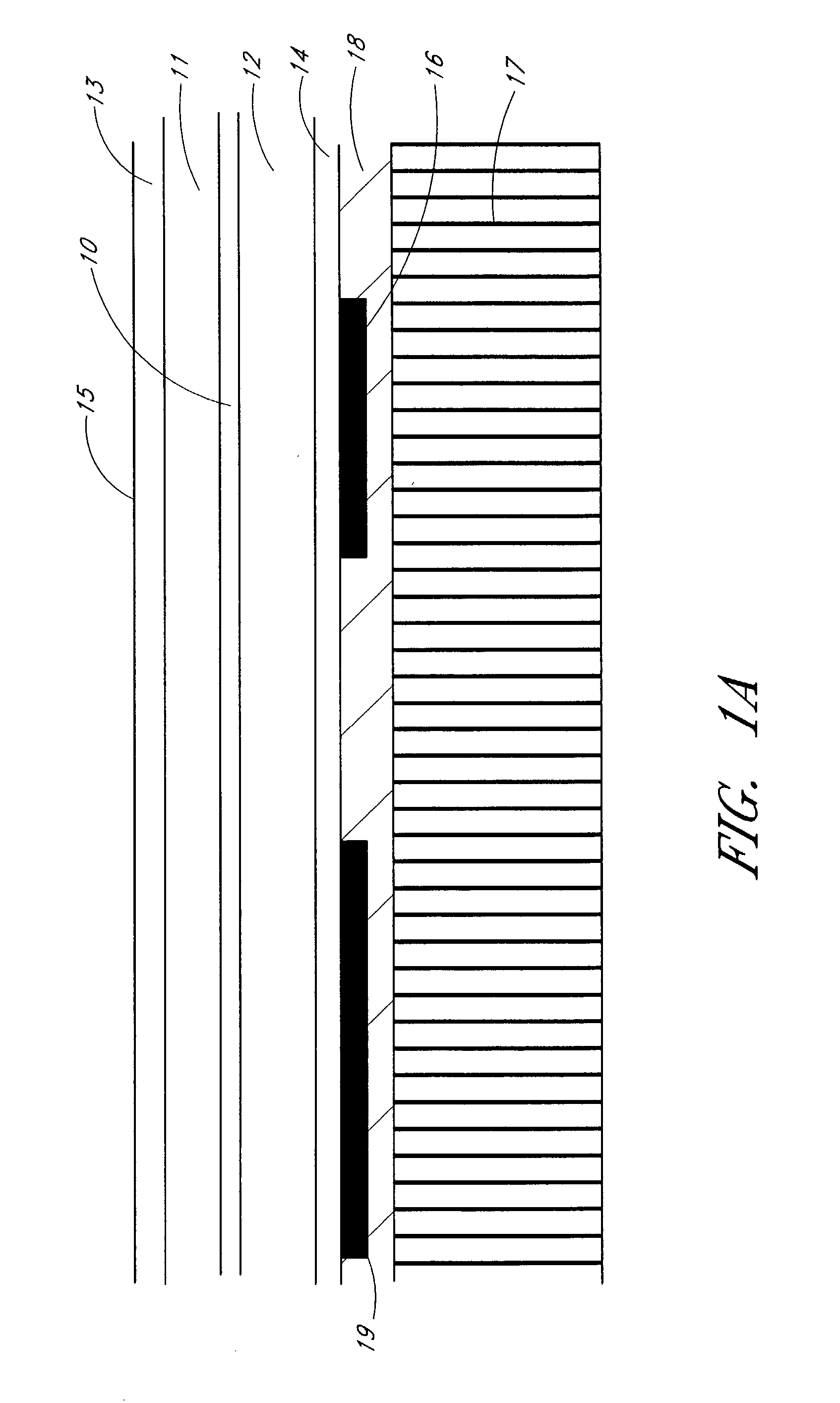
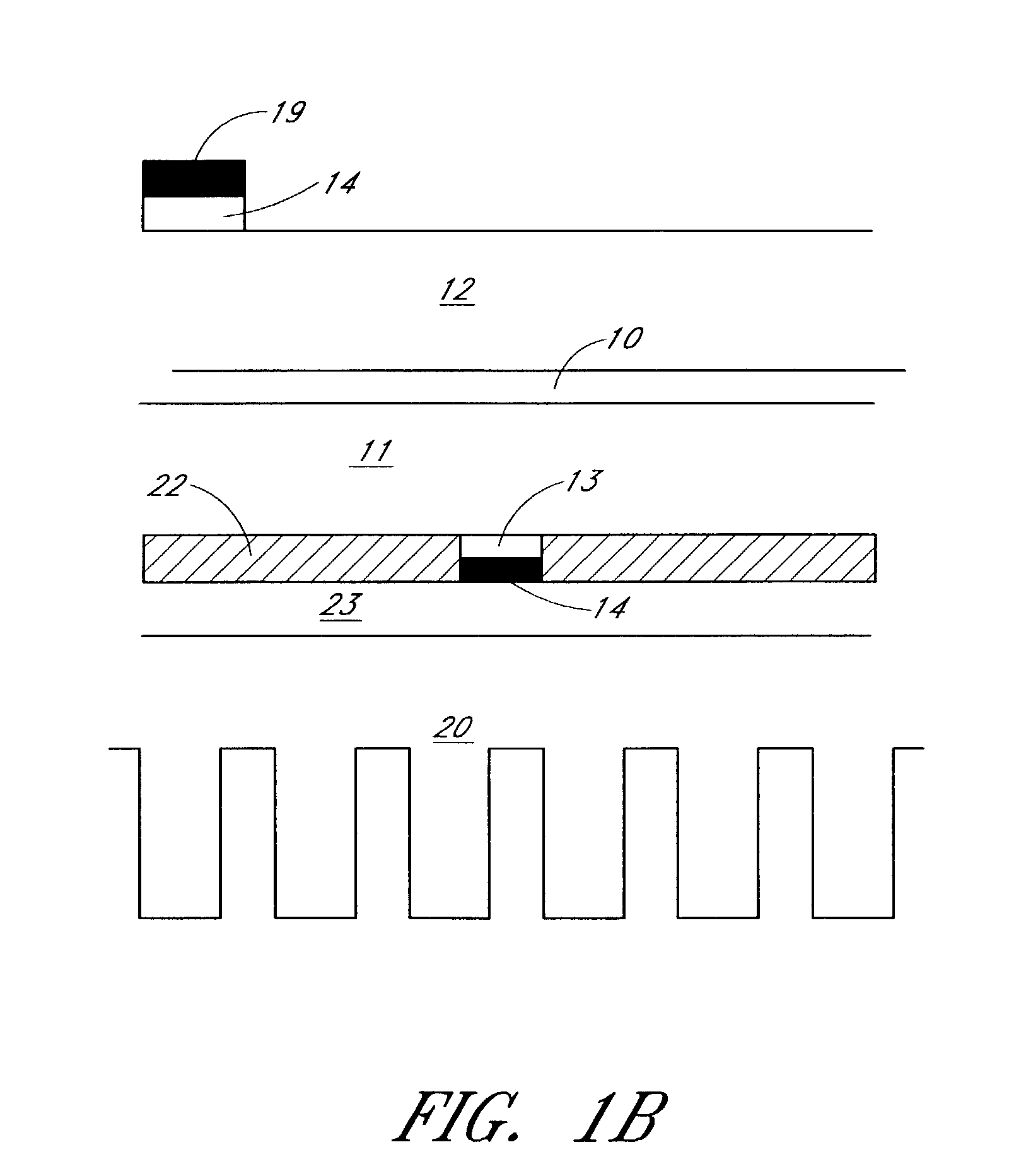
UV reflectors and UV-based light sources having reduced UV radiation leakage incorporating the same
InactiveUS20020180351A1Uniform colorUniform light intensityIncadescent screens/filtersMirrorsRadiation leakagePhosphor
UV reflectors incorporated in UV LED-based light sources reduce the amount of UV radiation emission into the surroundings and increase the efficiency of such light sources. UV reflectors are made of nanometer-sized particles having a mean particle diameter less than about one-tenth of the wavelength of the UV light emitted by the UV LED, dispersed in a molding or casting material surrounding the LED. Other UV reflectors are series of layers of materials having alternating high and low refractive indices; each layer has a physical thickness of one quarter of the wavelength divided by the refractive index of the material. Nanometer-sized textures formed on a surface of the multilayered reflector further reduce the emission of UV radiation into the surroundings. UV LED-based light sources include such a multilayered reflector disposed on an encapsulating structure of a transparent material around a UV LED, particles of a UV-excitable phosphor dispersed in the transparent material. Alternatively, the transparent material also includes nanometer-sized particles of a UV-radiation scattering material.
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
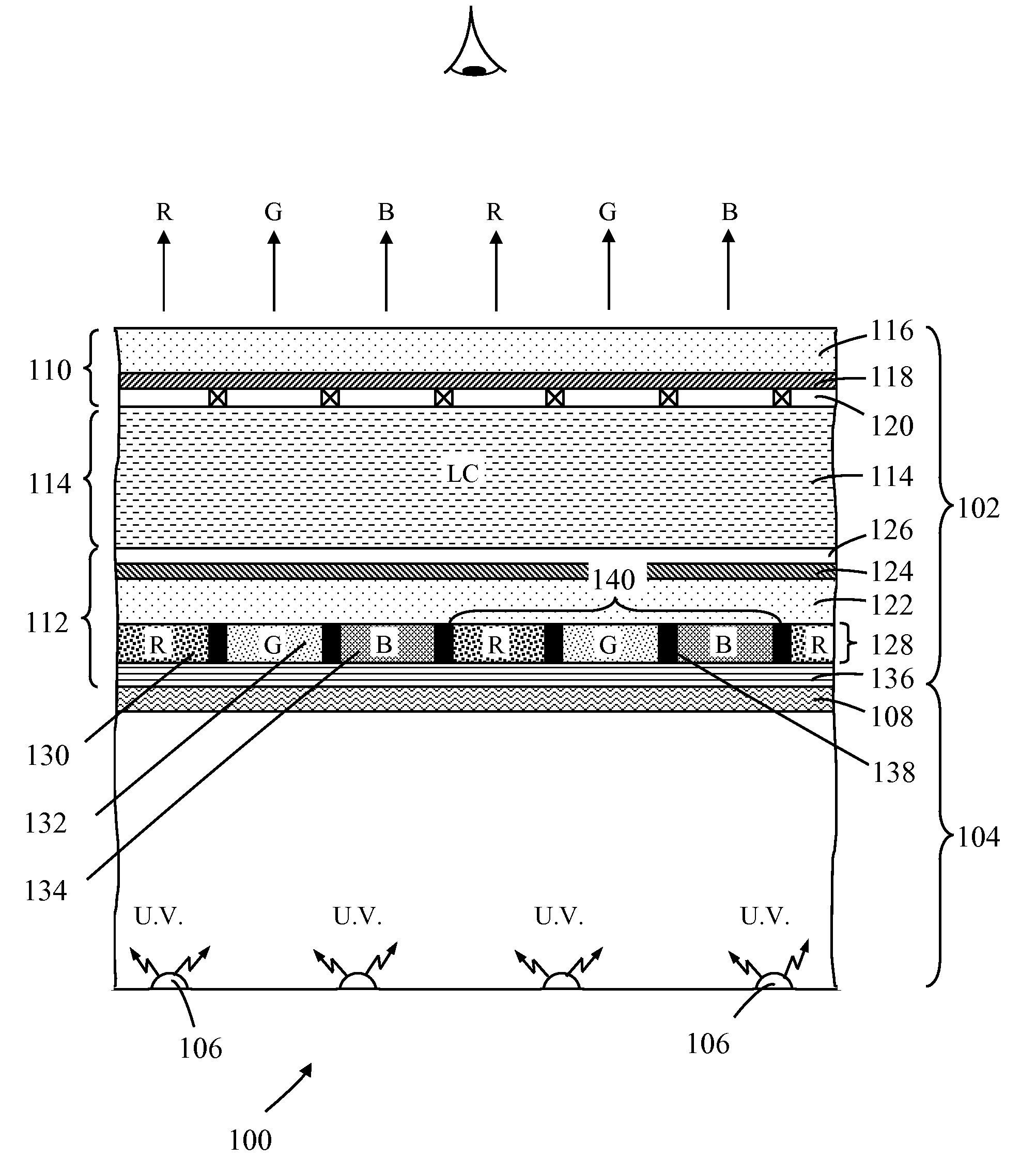
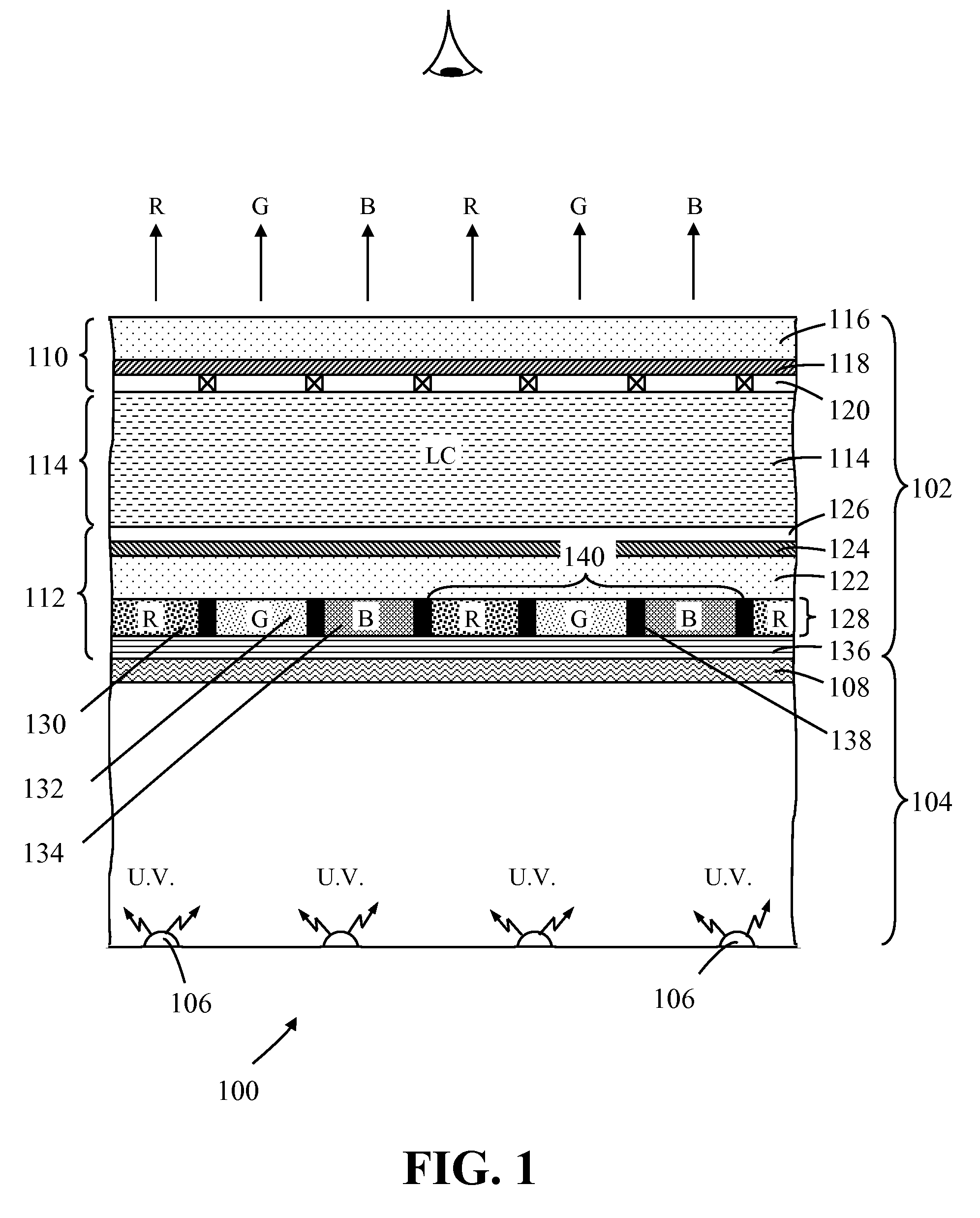
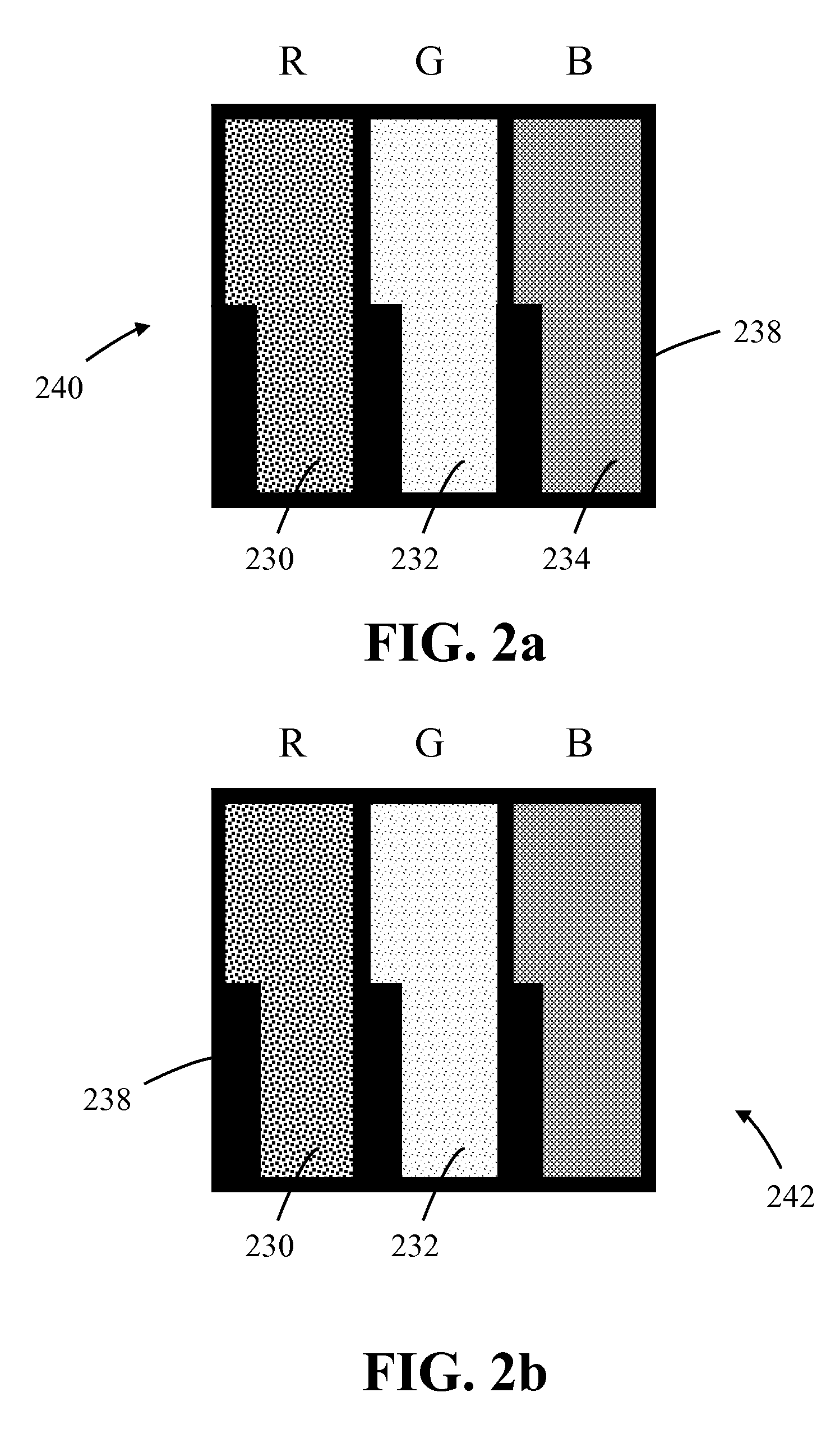
Photoluminescence color display
A photoluminescence color display comprises a display panel that displays red, green and blue pixel areas, an excitation source operable to generate excitation radiation for operating the display, and a photoluminescence color-element plate. The color-element plate comprises at least one photoluminescence material, such as a phosphor material or quantum dots, that is operable to emit light corresponding to red, green and blue pixel areas of the display in response to said excitation radiation. Additionally, the photo-luminescence color display comprises a wavelength selective filter that is provided between the color-element plate and the excitation source. The filter has a transmission characteristic that allows the passage of excitation radiation from the excitation source to excite the at least one photoluminescence material whilst preventing the passage of photoluminescence light back to the excitation source thereby prevent cross contamination of light among the different pixel areas of the display.
Owner:INTEMATIX
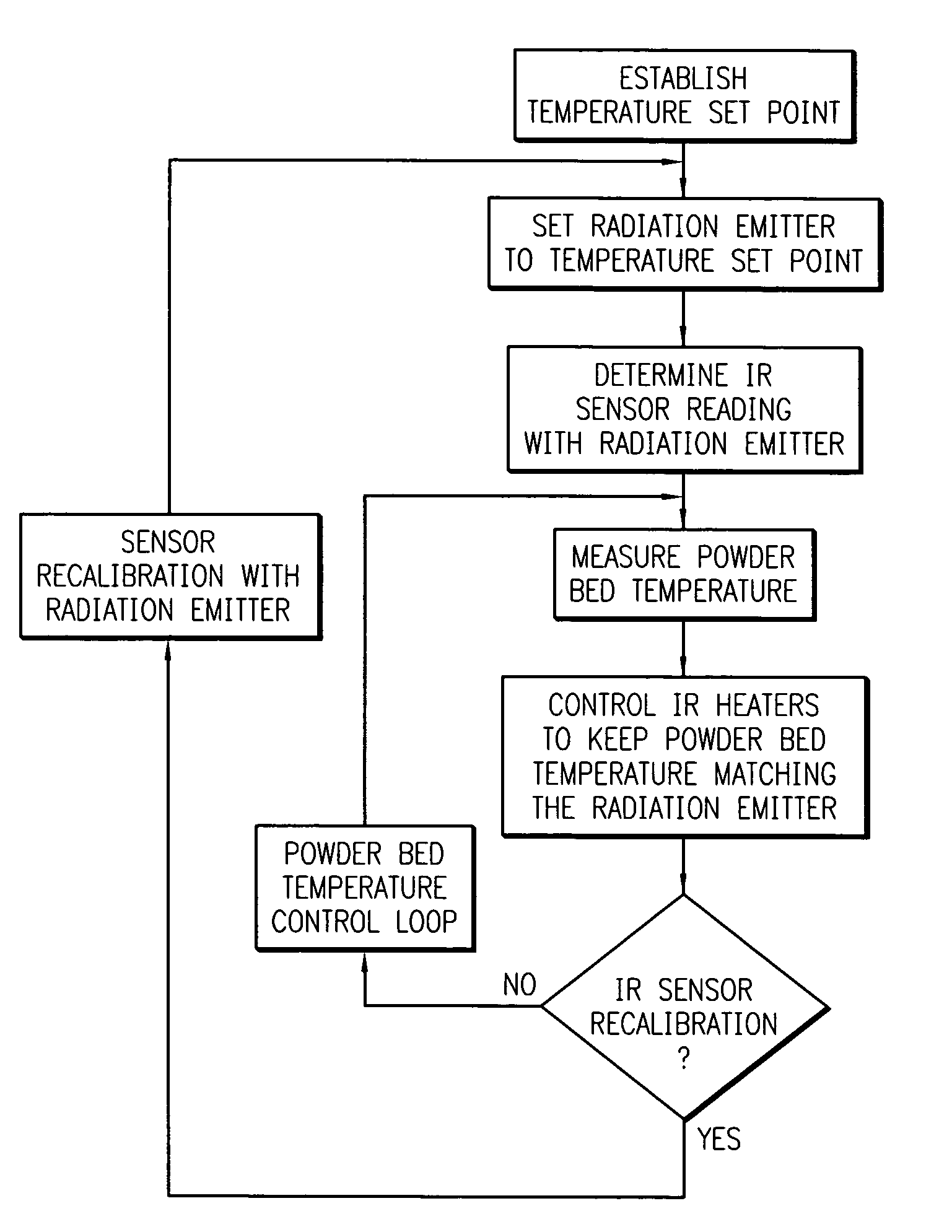
Continuous calibration of a non-contact thermal sensor for laser sintering
ActiveUS6930278B1Accurate monitoringHighly consistent mechanical propertyAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyAcousticsLaser
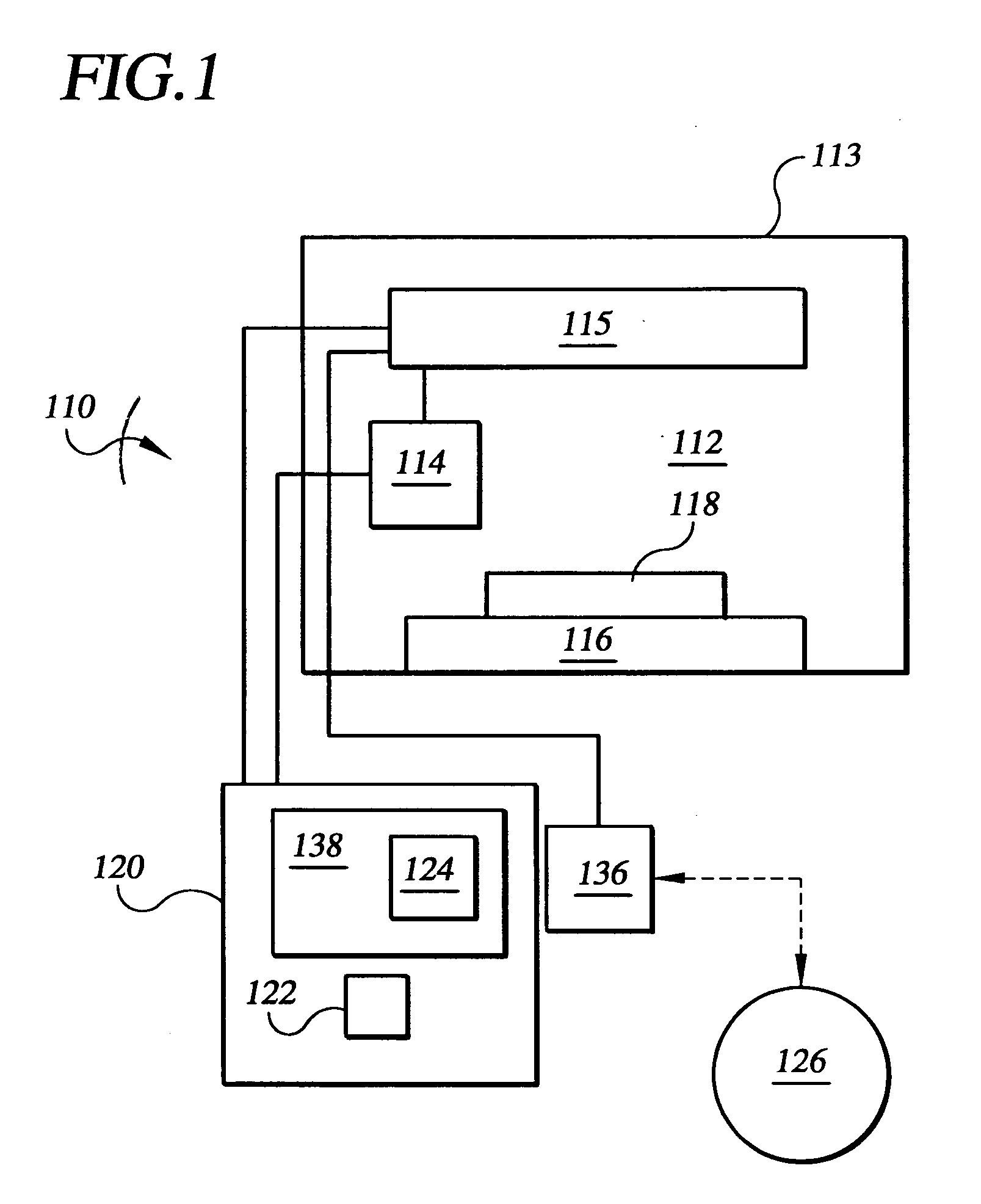
An apparatus and a method of using the apparatus wherein a radiation emitter is positioned adjacent a sensor apparatus within a process chamber in a laser sinter system that emits radiation to the sensor apparatus and a calibration apparatus receives readings from the sensor apparatus to compare temperature sensings received from the sensor apparatus with set emission signals from the radiation emitter to adjust the temperature sensings to calibrate the sensor apparatus during the forming of a three-dimensional article. The calibration is done repeatedly during the build process of the three-dimensional article.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Shaped biocompatible radiation shield and method for making same
InactiveUS7109505B1Reduce low energy radiationPrevent regenerationRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsRadiosurgeryProximate
A radiation applicator system is structured to be mounted to a radiation source for providing a predefined dose of radiation for treating a localized area or volume, such as the tissue surrounding the site of an excised tumor. The applicator system includes an applicator and an adapter. The adapter is formed for fixedly securing the applicator to a radiation source, such as a radiosurgery system which produces a predefined radiation dose profile with respect to a predefined location along the radiation producing probe. The applicator includes a shank and an applicator head, wherein the head is located at a distal end of the applicator shank. A proximate end of the applicator shank couples to the adapter. A distal end of the shank includes the applicator head, which is adapted for engaging and / or supporting the area or volume to be treated with a predefined does of radiation. The applicator can include a low energy radiation filter inside of the applicator head to reduce undesirable low energy radiation emissions. A biocompatible radiation shield may be coupled to the outer surface of the applicator head to block radiation emitted from a portion of the radiation probe, in order to shield an adjacent location or vital organ from any undesired radiation exposure. A plurality of applicators having applicator heads and radiation shields of different sizes and shapes can be provided to accommodate treatment sites of various sizes and shapes.
Owner:CARL ZEISS STIFTUNG DOING BUSINESS CARL ZEISS
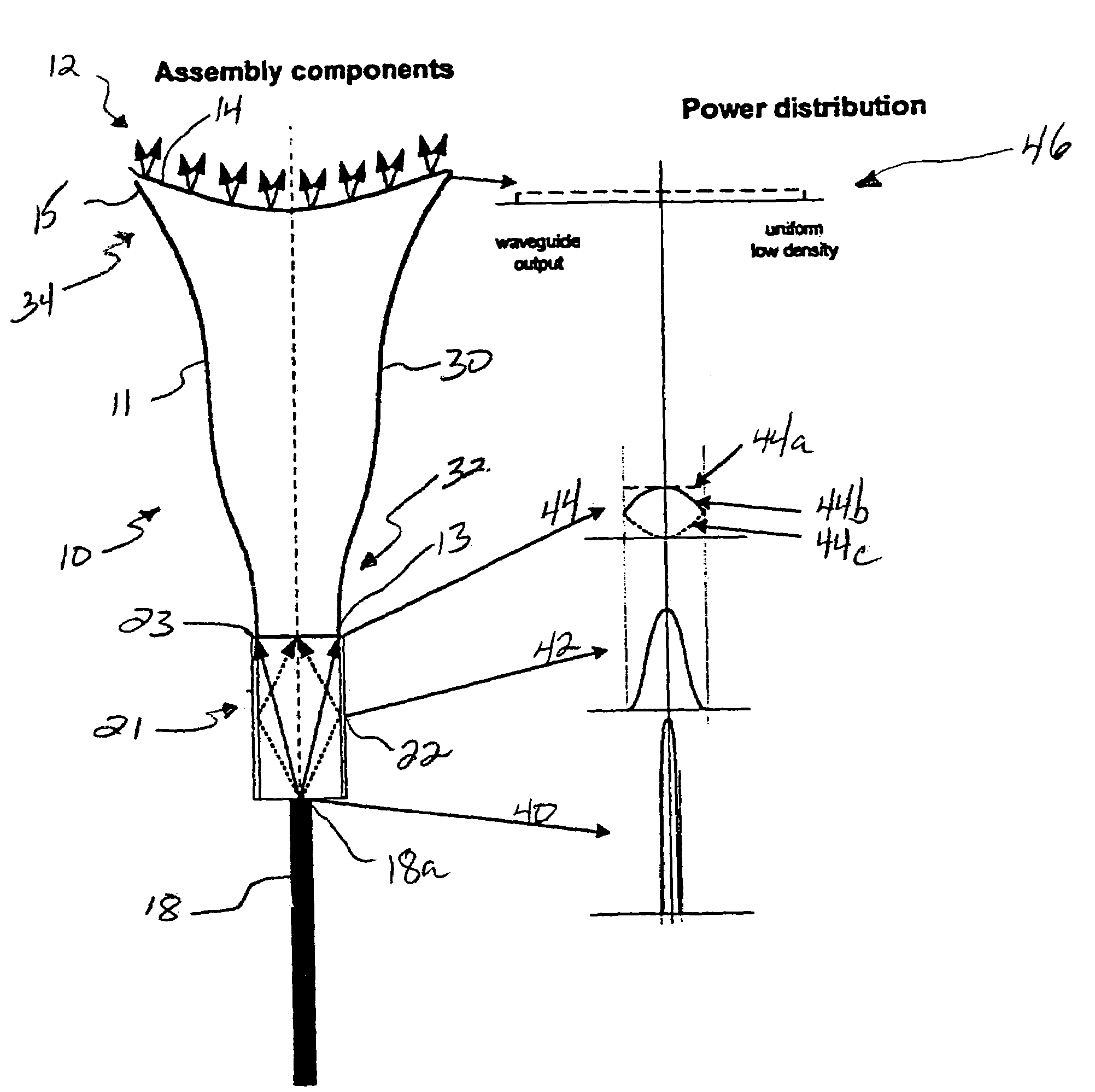
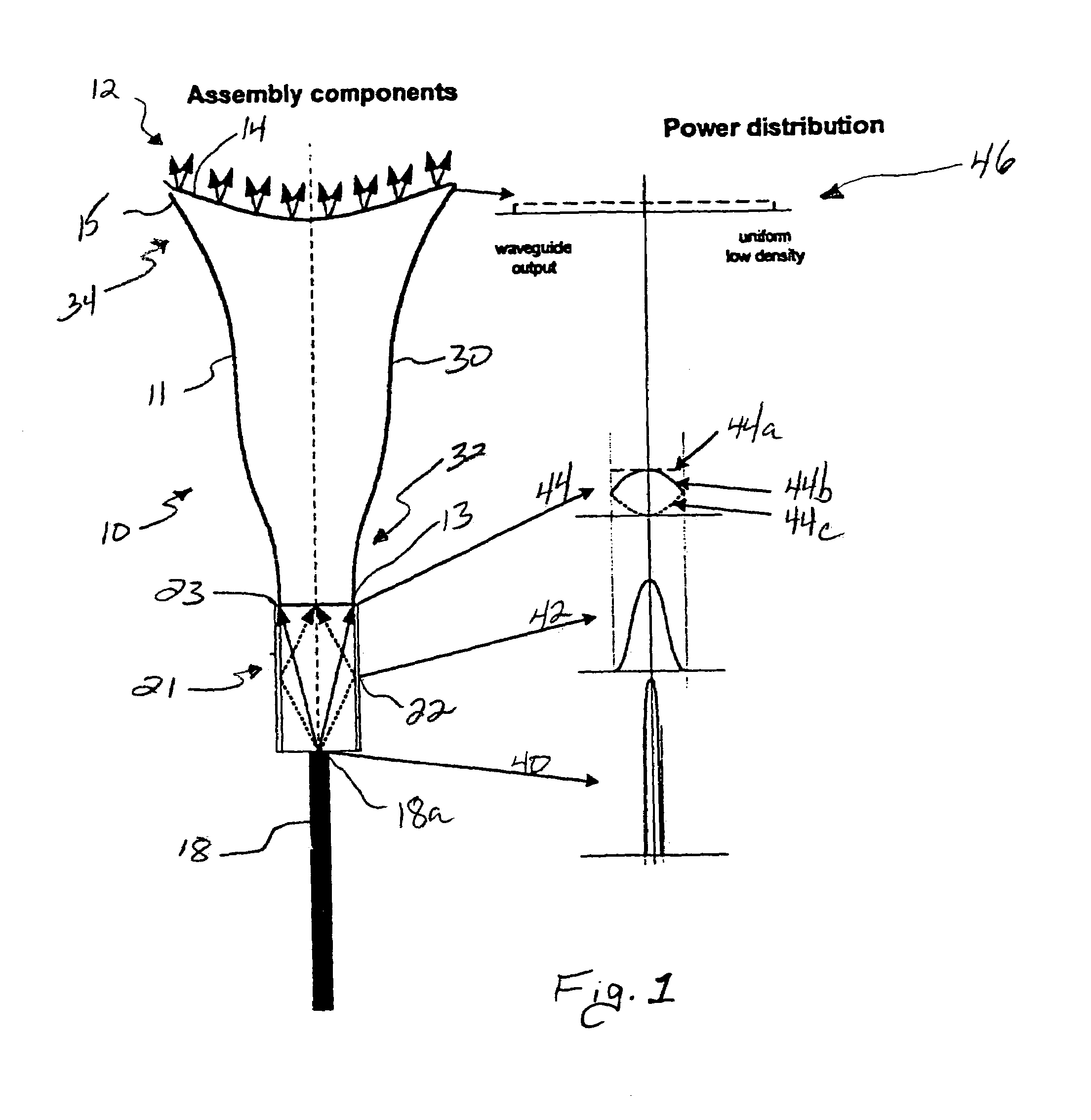
Radiation emitting apparatus with spatially controllable output energy distributions
InactiveUS6942658B1Loss of optical powerEvenly distributedSurgical instrument detailsCoupling light guidesFiberOptoelectronics
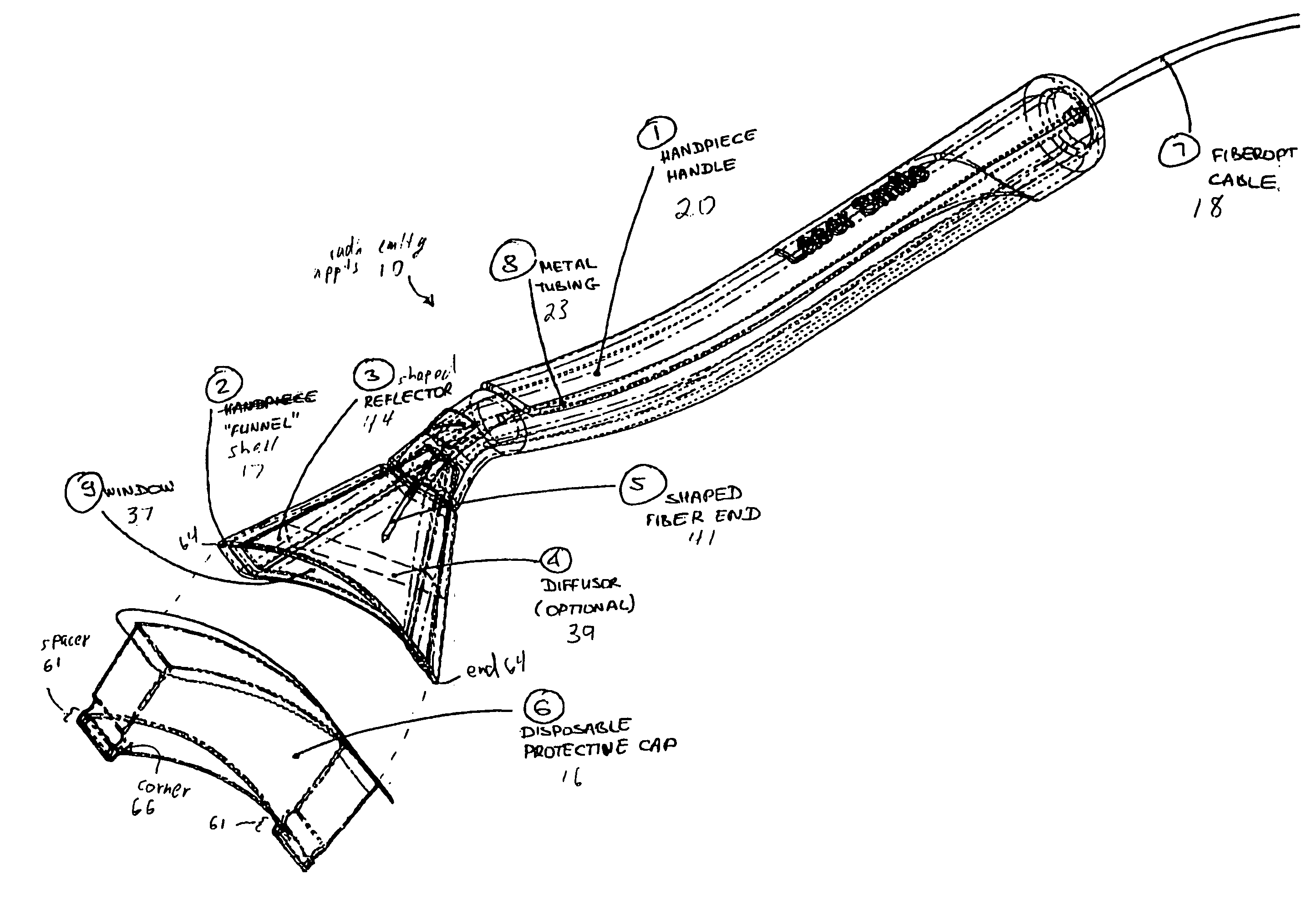
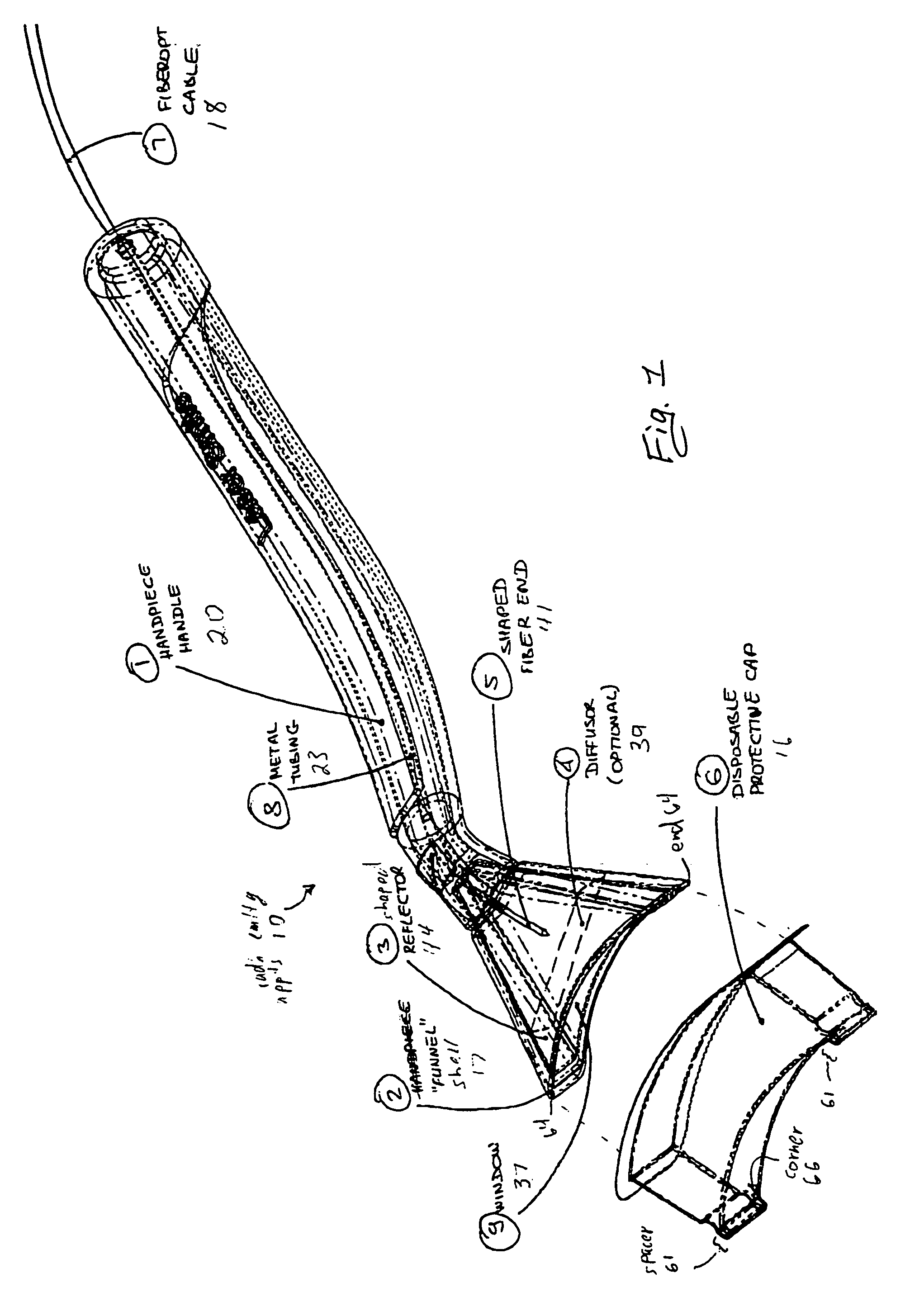
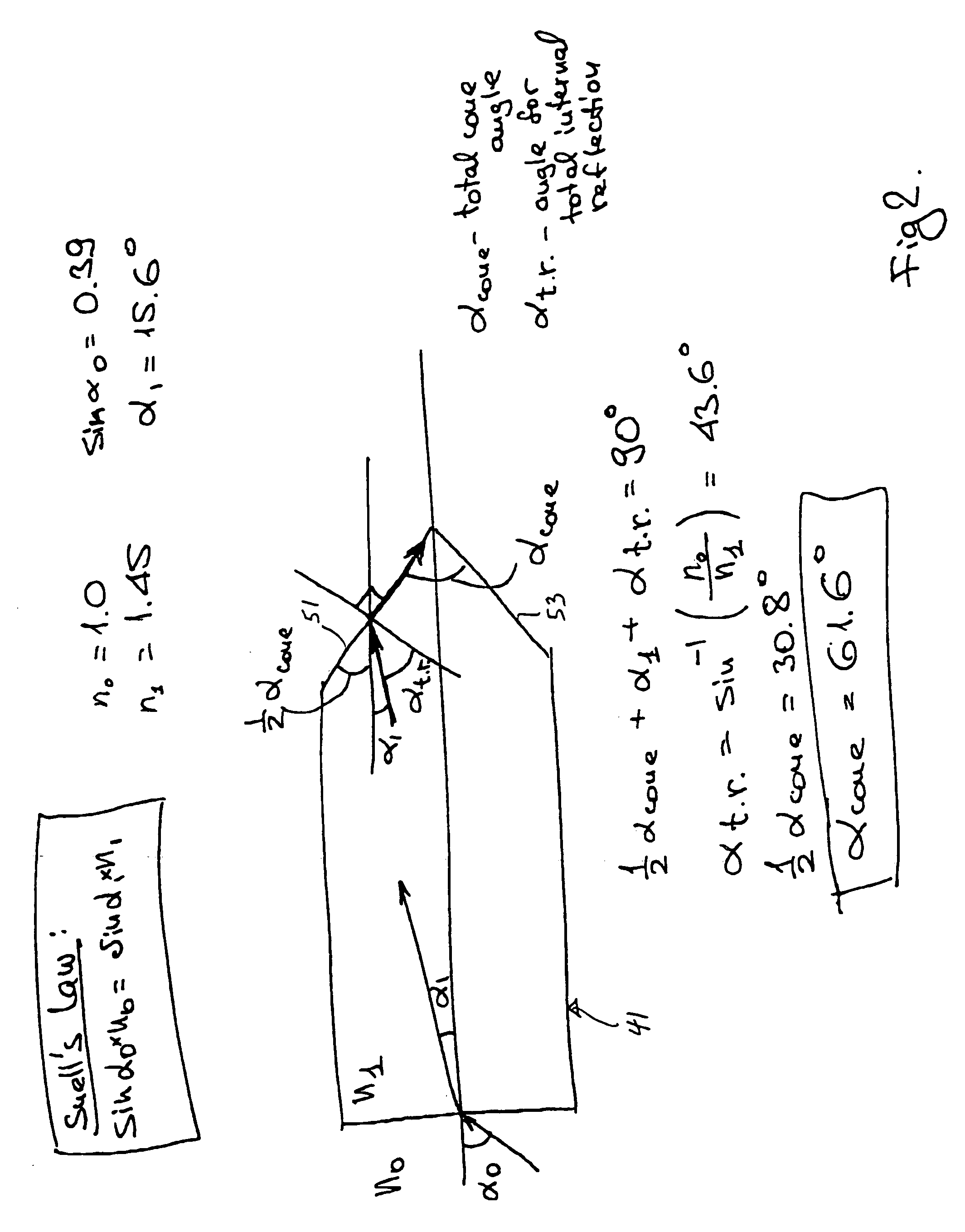
A laser handpiece is disclosed, including a fiber optic end having a non-cylindrical shape and further including a reflector surrounding a portion of the fiber optic end. The reflector is shaped to direct laser energy emitted from the fiber optic end in a direction away from the laser handpiece and toward a treatment site.
Owner:BIOLASE TECH INC
Full spectrum endpoint detection
InactiveUS6969619B1Simplifies parameterPromote useSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesFrequency spectrumOptoelectronics
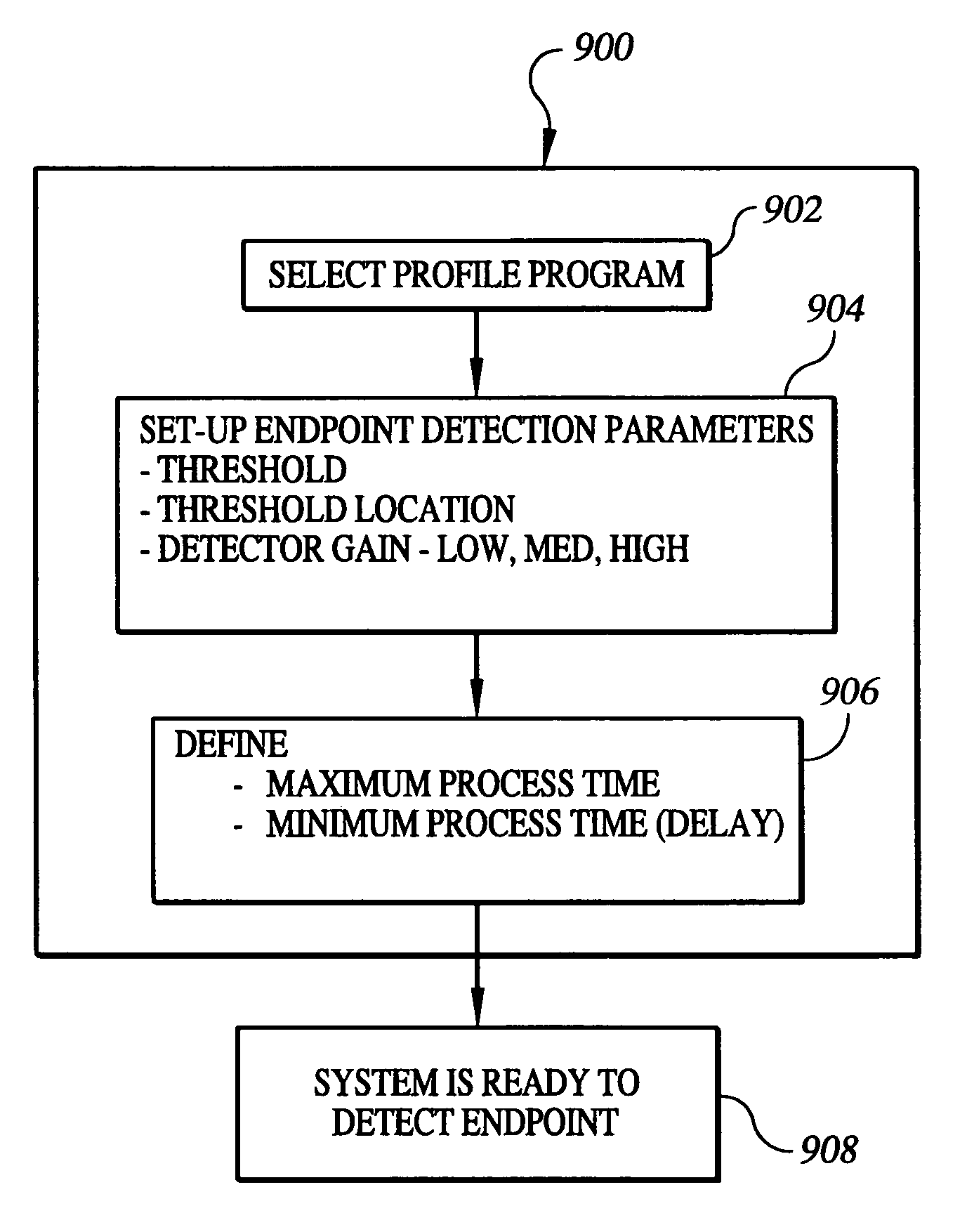
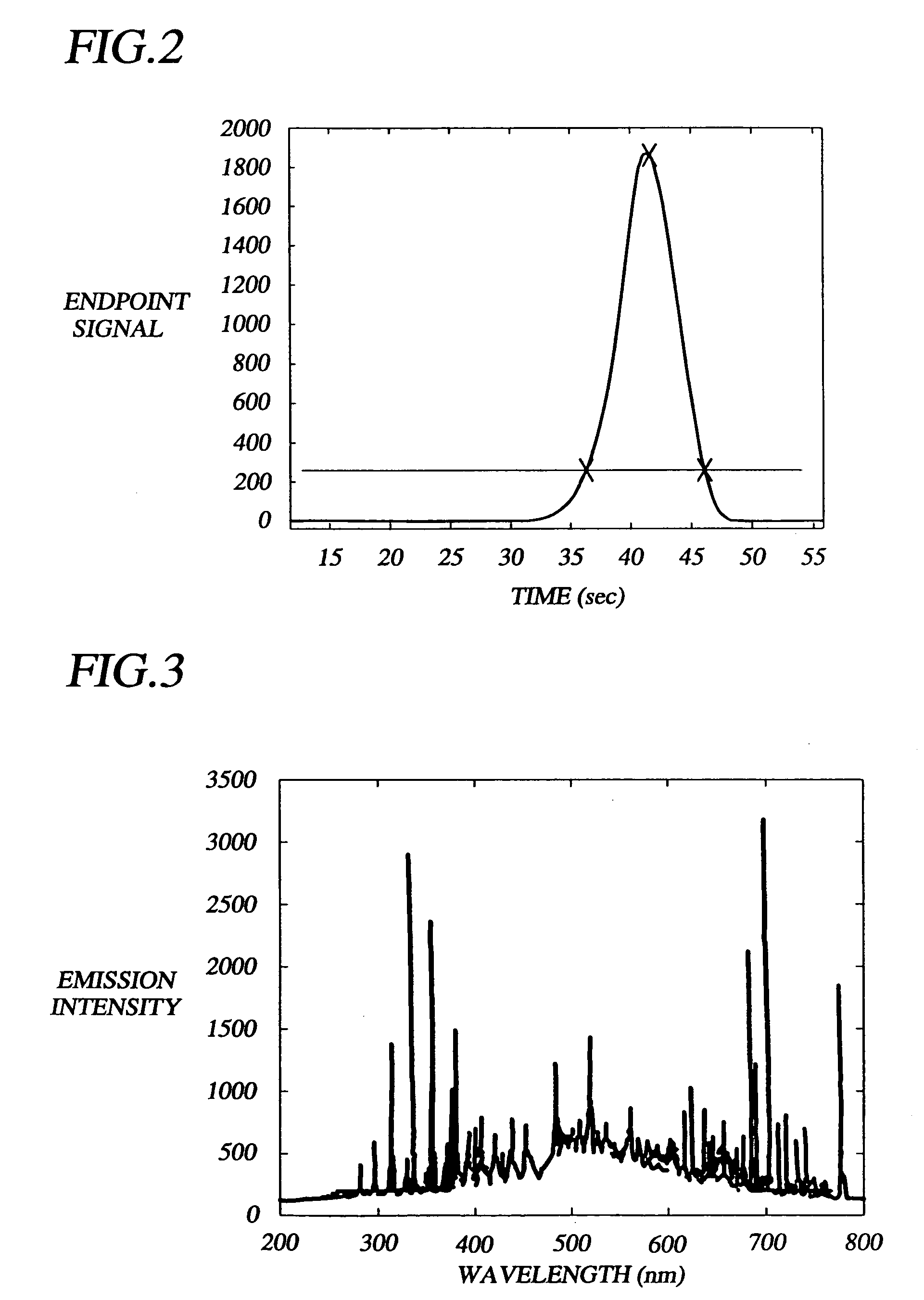
A method of endpoint detection during plasma processing of a semiconductor wafer comprises processing a semiconductor wafer using a plasma, detecting radiation emission from the plasma during the semiconductor processing, and tracking data points representing changes in spectra of the radiation as a function of time during the semiconductor processing. At any point prior to or during processing a plurality of profiles are provided, each profile representing a different processing condition affecting detection of the desired plasma processing endpoint of the semiconductor wafer. After selecting a desired profile, a first set of parameters are input, representing simplified values for determining when changes in spectra of the radiation indicate that plasma processing of the semiconductor wafer reaches a desired endpoint. The selected profile converts the input first set of parameters into a larger, second set of parameters, and then applies the second set of parameters to an algorithm that converts data points from the spectra of the radiation as a function of time into an endpoint curve. The method then uses the algorithm to track changes in spectra of the radiation as a function of time and determine when plasma processing of the semiconductor wafer reaches a desired endpoint.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Apparatus, methods and processes for sorting particles and for providing sex-sorted animal sperm
ActiveUS20070117086A1Low powerHigh incidenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImage resolutionManipulator
Owner:XY
Trachea tube with germicidal light source
ActiveUS7159590B2Reduce riskReduce needTracheal tubesMedical devicesAntibiotic YBiological activation
A tube for insertion into a trachea having a germicidal light source that is positioned above a cuff that holds the tube in place in the trachea. Activation of the germicidal light source causes an radiation emission that kills undesired bacteria that is fostered by the tube and the cuff, reducing the patient's risk of associated disease, and reducing the need for antibiotics.
Owner:RIFE ROBERT W
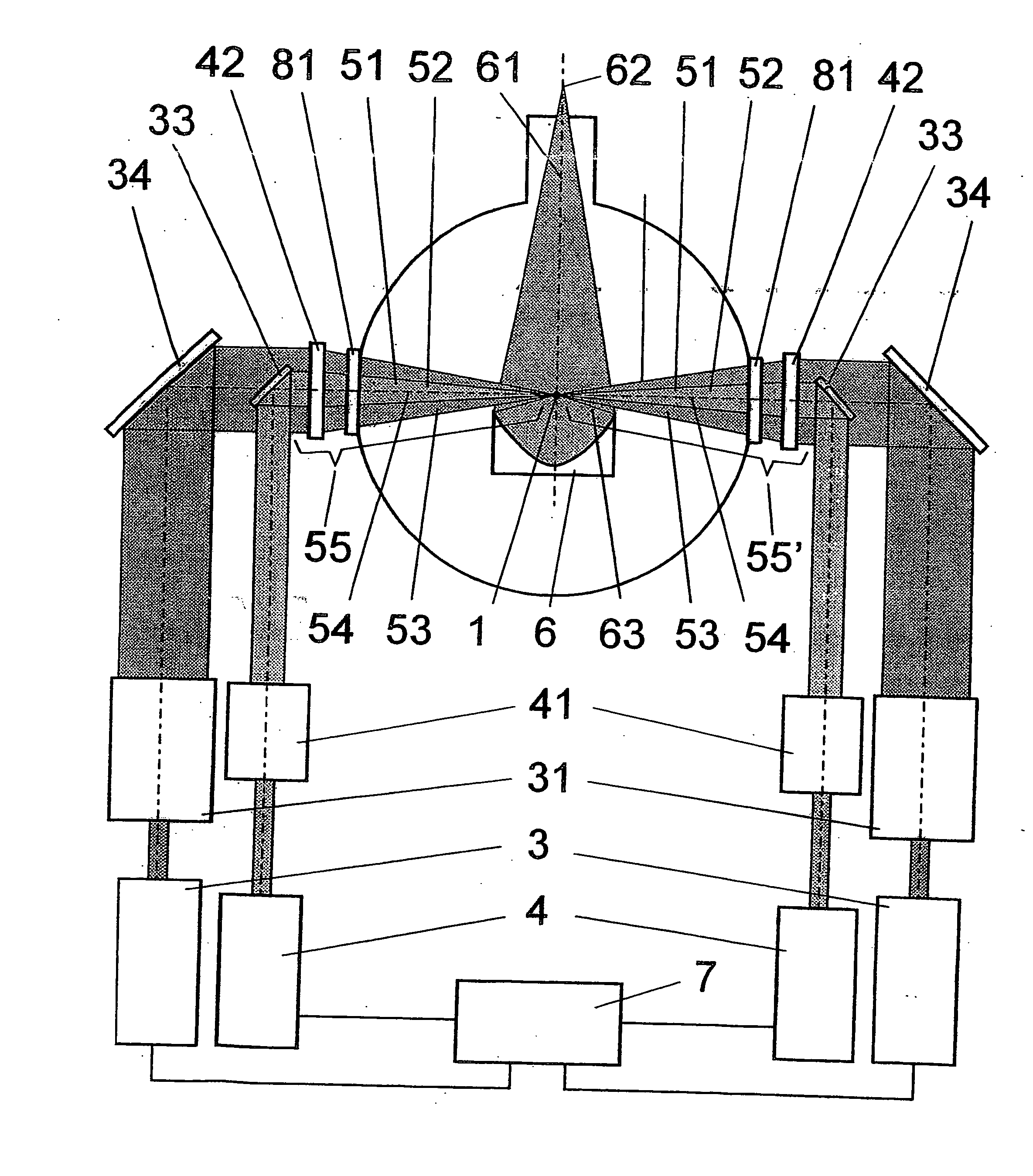
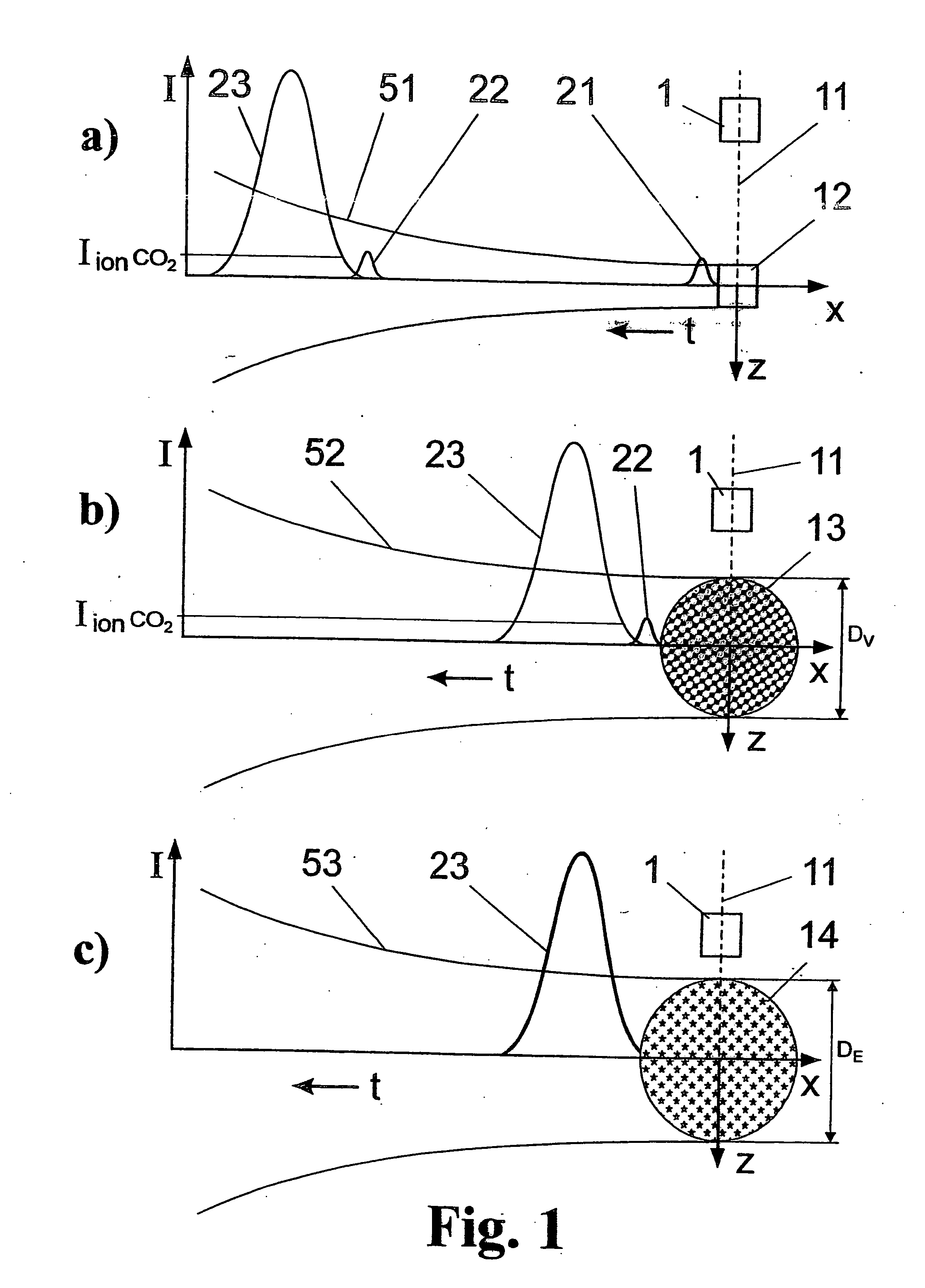
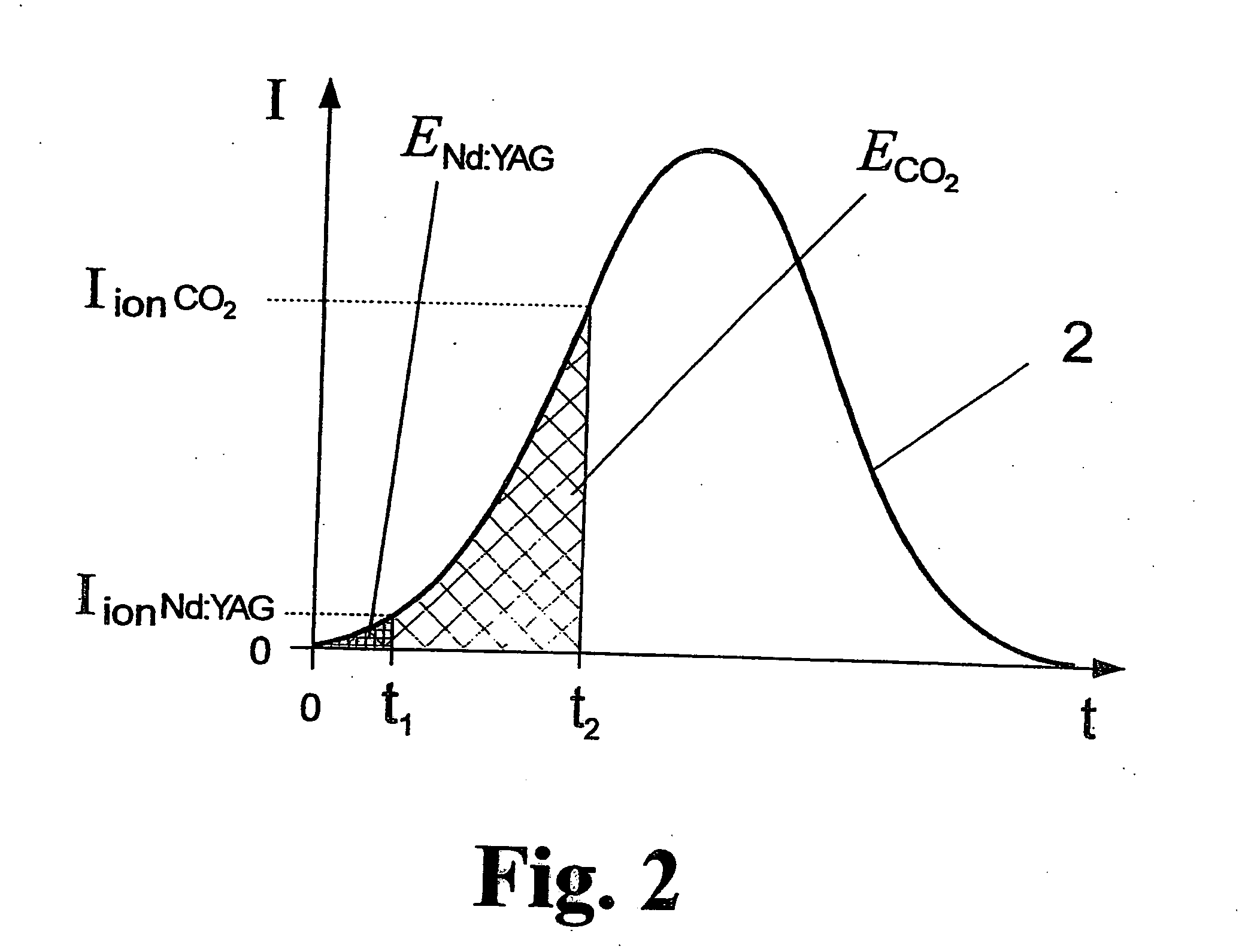
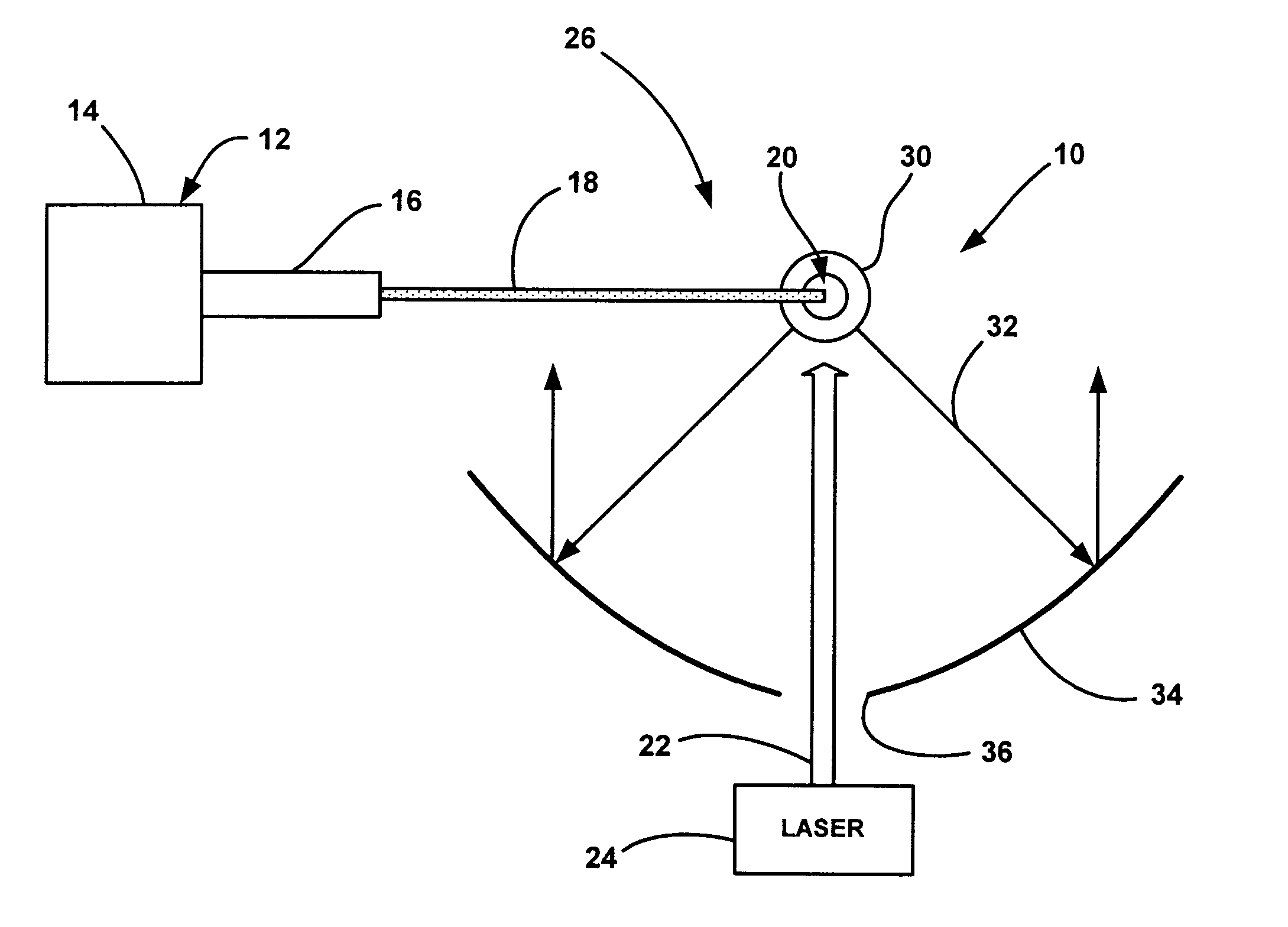
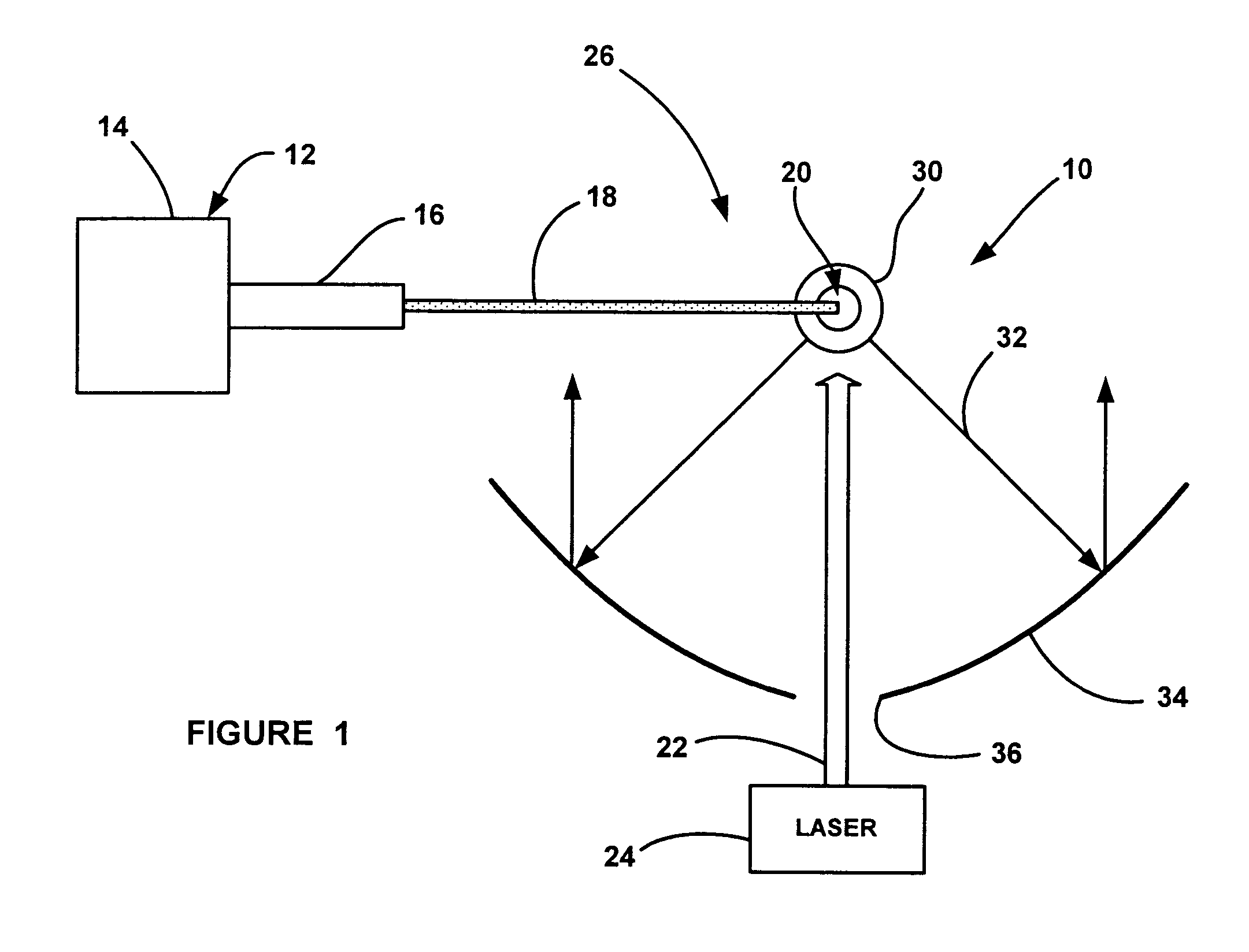
Method and arrangement for the efficient generation of short-wavelength radiation based on a laser-generated plasma
InactiveUS20060215712A1Losses in the main pulse (e.g., due to transmission) are minimizedLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialIon densityElectromagnetic radiation
The invention is directed to a method and an arrangement for the efficient generation of intensive short-wavelength radiation based on a plasma. The object of the invention is to find a novel possibility for the generation of intensive short-wavelength electromagnetic radiation, particularly EUV radiation, which permits the excitation of a radiation-emitting plasma with economical gas lasers (preferably CO2 lasers). This object is met, according to the invention, in that a first prepulse for reducing the target density is followed by at least a second prepulse which generates free electrons in the target by multiphoton ionization after a virtually complete recombination of free electrons generated by the first prepulse has taken place due to a long-lasting expansion of the target for reducing the target density, and the main pulse of a gas laser with a low critical electron density typical for its wavelength is directed to the target immediately after the second prepulse when the second prepulse in the expanded target, whose ion density corresponds to the critical electron density of the gas laser, has created enough free electrons so that an efficient avalanche ionization is triggered by the main pulse of the gas laser until reaching the ionization level for the desired radiation emission of the plasma.
Owner:XTREME TECH
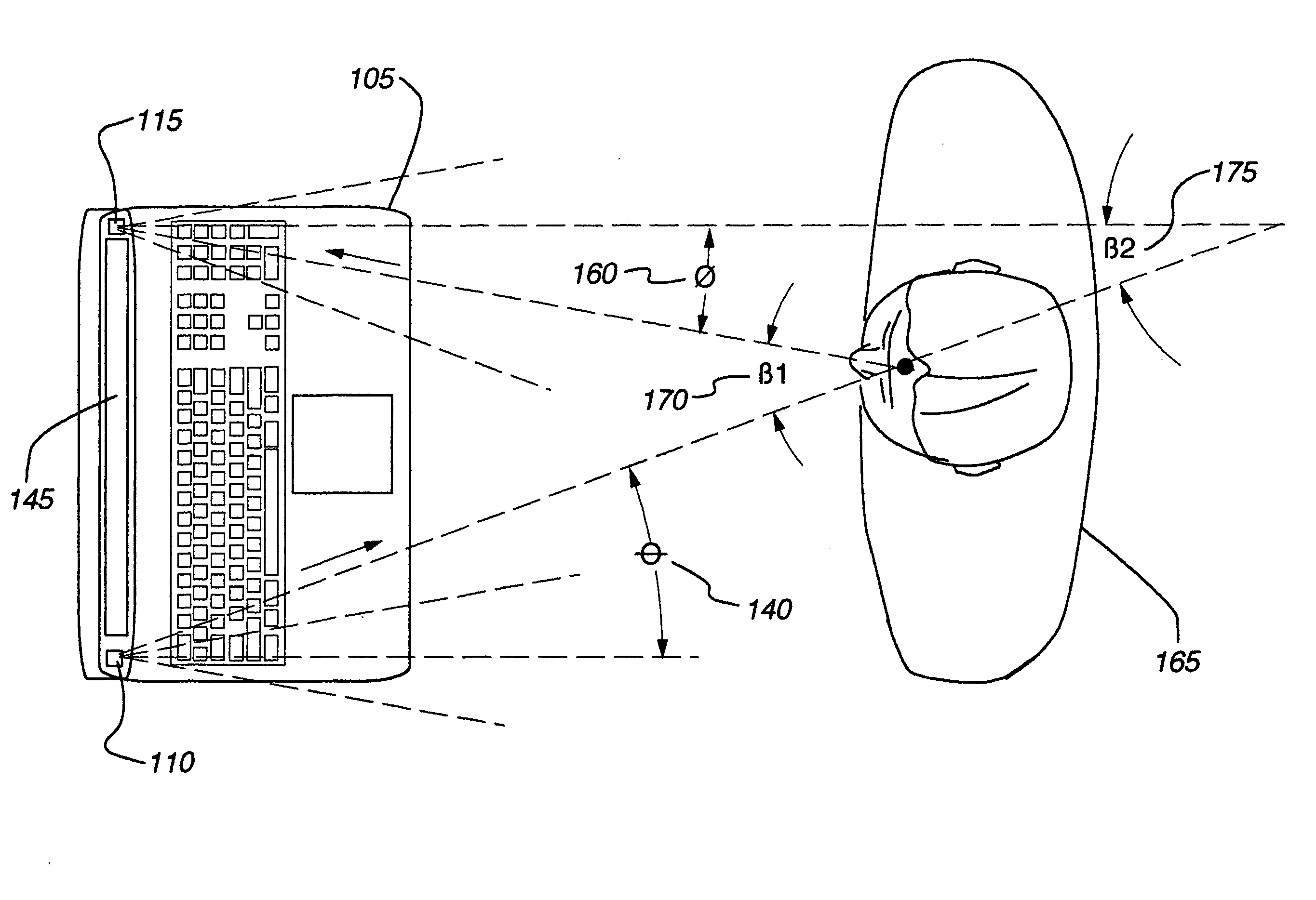
Method and apparatus for remotely detecting presence
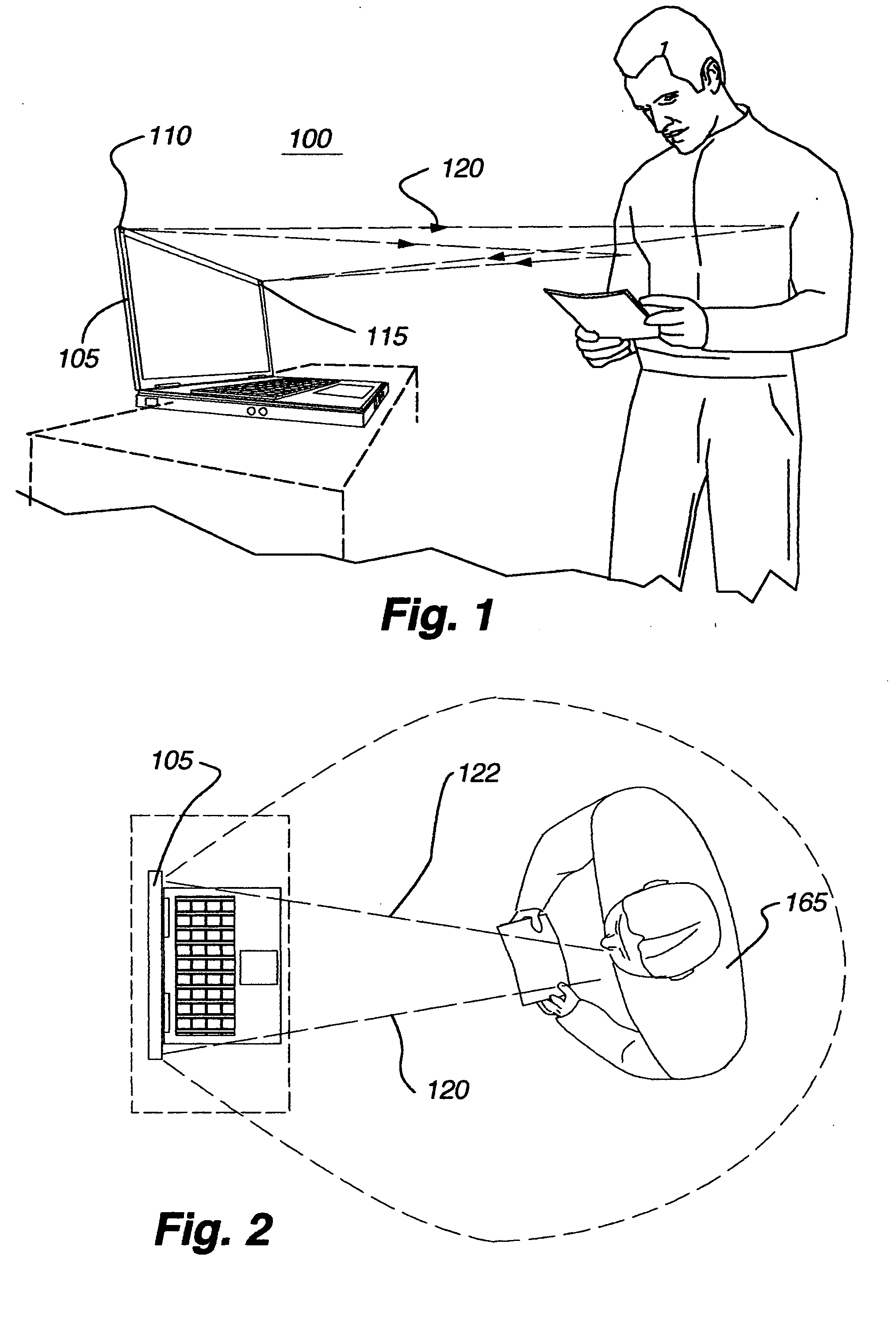
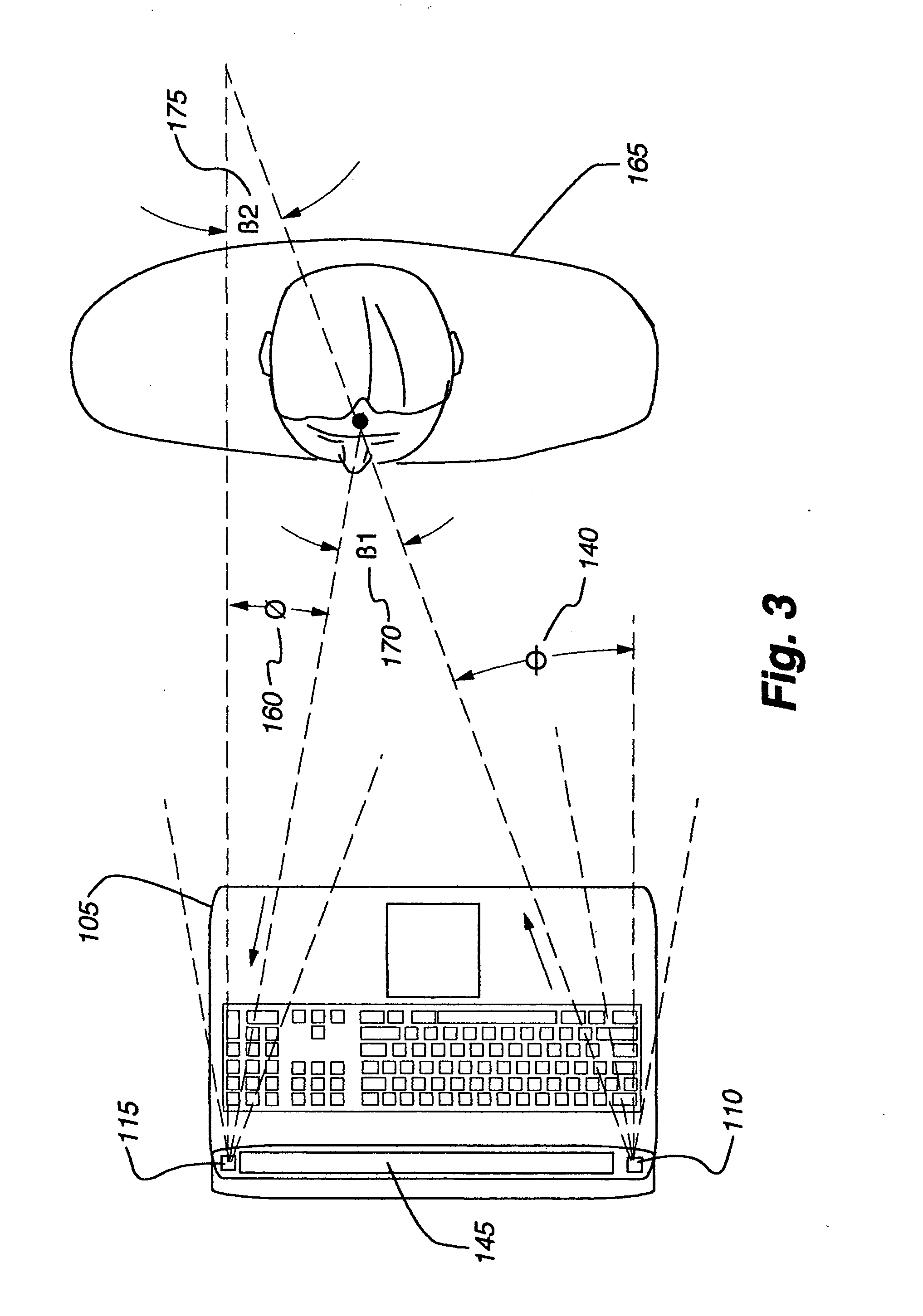
ActiveUS20060290921A1Minimize power consumptionImprove user experienceAngle measurementOptical rangefindersElectric forceEngineering
An apparatus for detecting a person's presence without requiring the person to provide auditory or tactile input. The invention may be incorporated into an electronic device, such as a desktop computer or notebook computer. The embodiment may employ a variety of radiation emissions to determine when a person enters the embodiment's field of detection and, in response to the person entering, activate the electronic device. This may prove particularly useful where, for example, the electronic device consumes significant power and / or may suffer deleterious effects if left active for too long.
Owner:APPLE INC
Quantum photodetectors, imaging apparatus and systems, and related methods
ActiveUS20080156993A1Material analysis by optical meansMagnetic property measurementsRadioactive tracerPhotodetector
A camera sub-module is provided for providing tomographic imaging of radiation emissions generated internally by a body. The camera sub-module includes a radiation-emitting layer having a radioactive source for emitting transmission emissions, and at least one radiation-detection layer for contemporaneously detecting and permitting differentiation between the transmission emissions and emissions generated internal to an imaged body administered with a positron-emitting radiotracer. Also provided herein are imaging systems, scanners, and other apparatus and methods.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
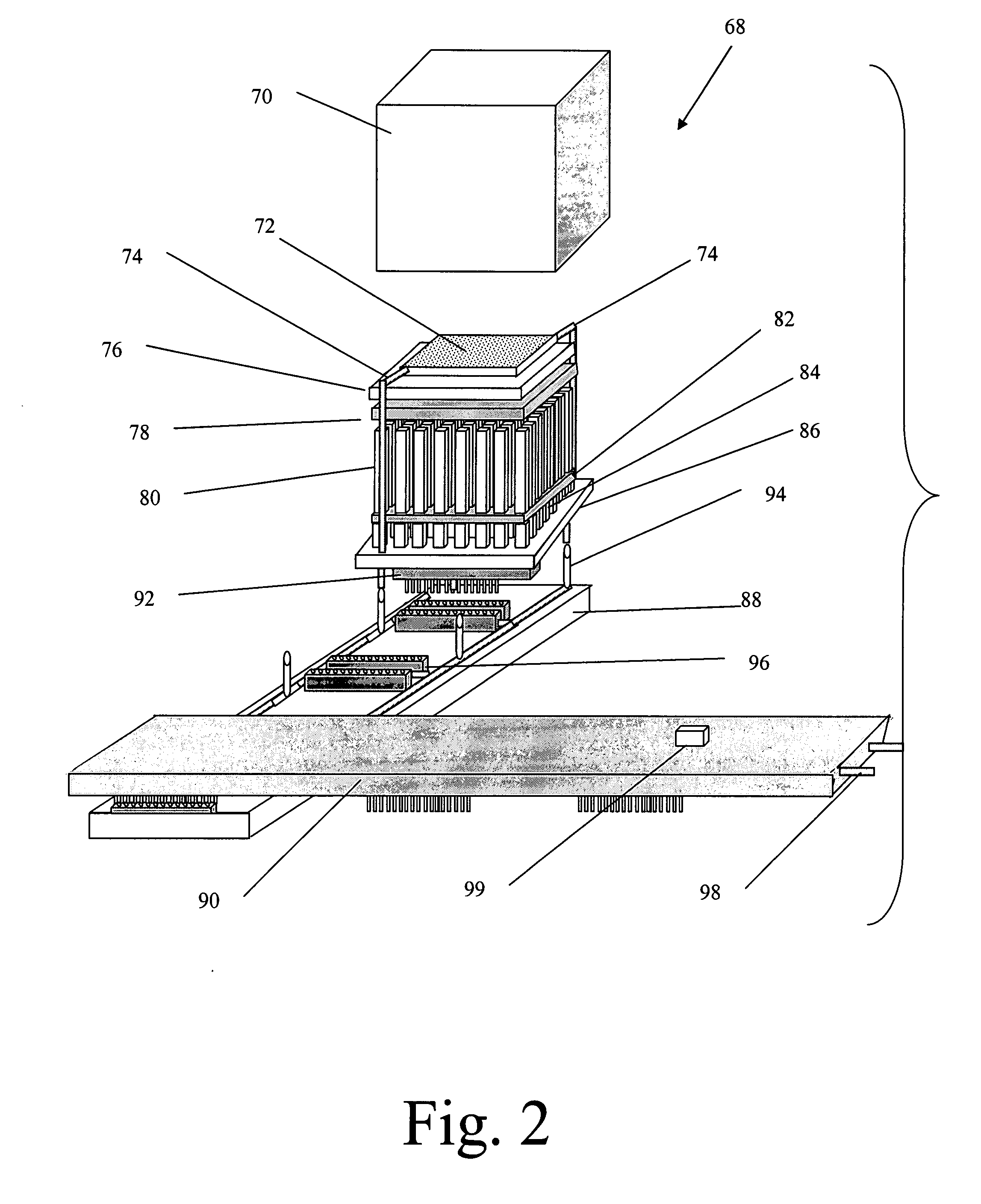
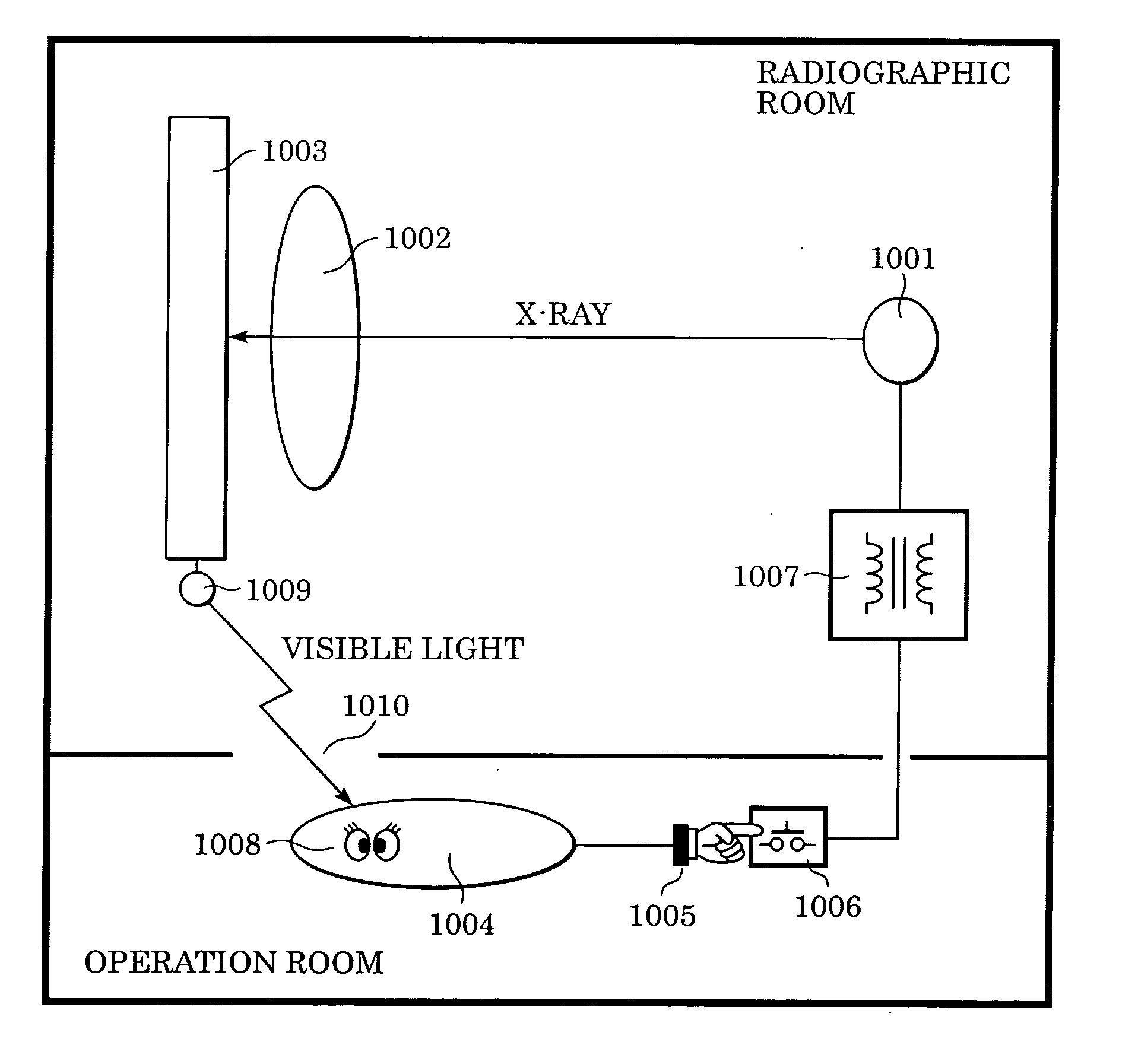
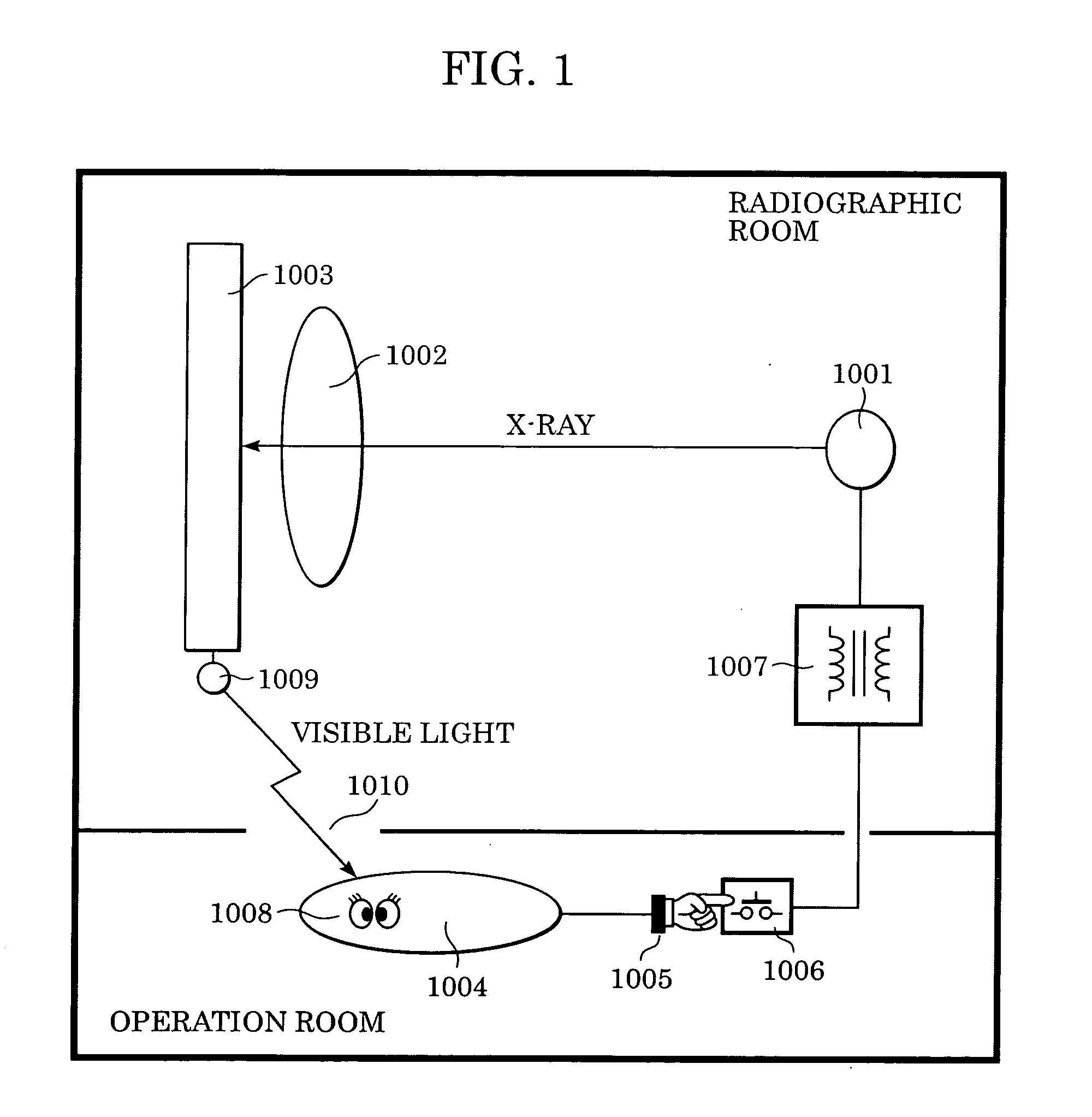
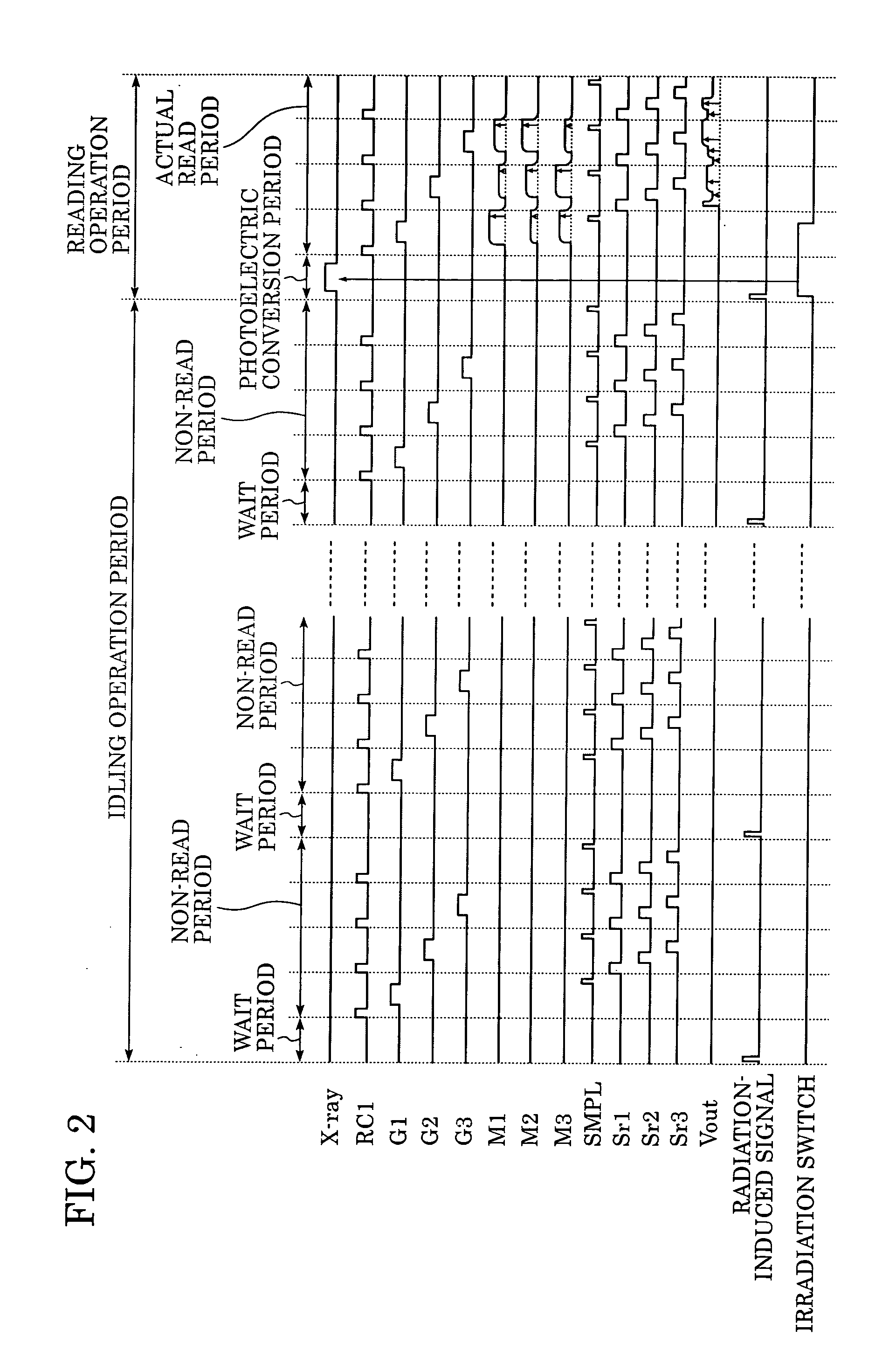
Radiation imaging apparatus and control method therefor
InactiveUS20050220269A1Stably performing radiographyAvoid delayX-ray apparatusRadiation diagnosticsX-rayOpto electronic
A lamp emits pulse-shaped visible light when a wait period begins. If a radiation emission switch is not pressed in the wait period, X-ray radiation is not emitted from an X-ray source, and no charges are accumulated in photoelectric conversion elements of an X-ray imaging apparatus. In a non-read period, although signals are sequentially read from the photoelectric conversion elements, an output signal does not change. When the radiation emission switch is pressed in synchronization with a radiation-induced signal in a certain wait period, the X-ray source emits X-rays. After irradiation of X-rays, a photoelectric conversion period transitions to an actual read period. In the photoelectric conversion period, X-rays are emitted and transmitted X-ray information of a patient are accumulated in the photoelectric conversion elements of the X-ray imaging apparatus. In the actual read period, the accumulated information is read.
Owner:CANON KK
Sensor detecting reflected light and method for its manufacture
ActiveUS7030359B2Simply and effectively accomplishedSuppressing optical “ crosstalk ”Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsSolid-state devicesLight emitterRadiation
A reflected-light sensor includes a light emitter for emitting radiation onto an object to be measured and an optical receiver for receiving the reflected radiation from the object. The sensor includes a carrier for the light emitter and the optical receiver and a glass layer arranged on the carrier. The glass layer has transparent areas arranged above the light emitter and the optical receiver and light absorbing areas located in between.
Owner:SARTORIUS LAB INSTR GMBH & CO KG
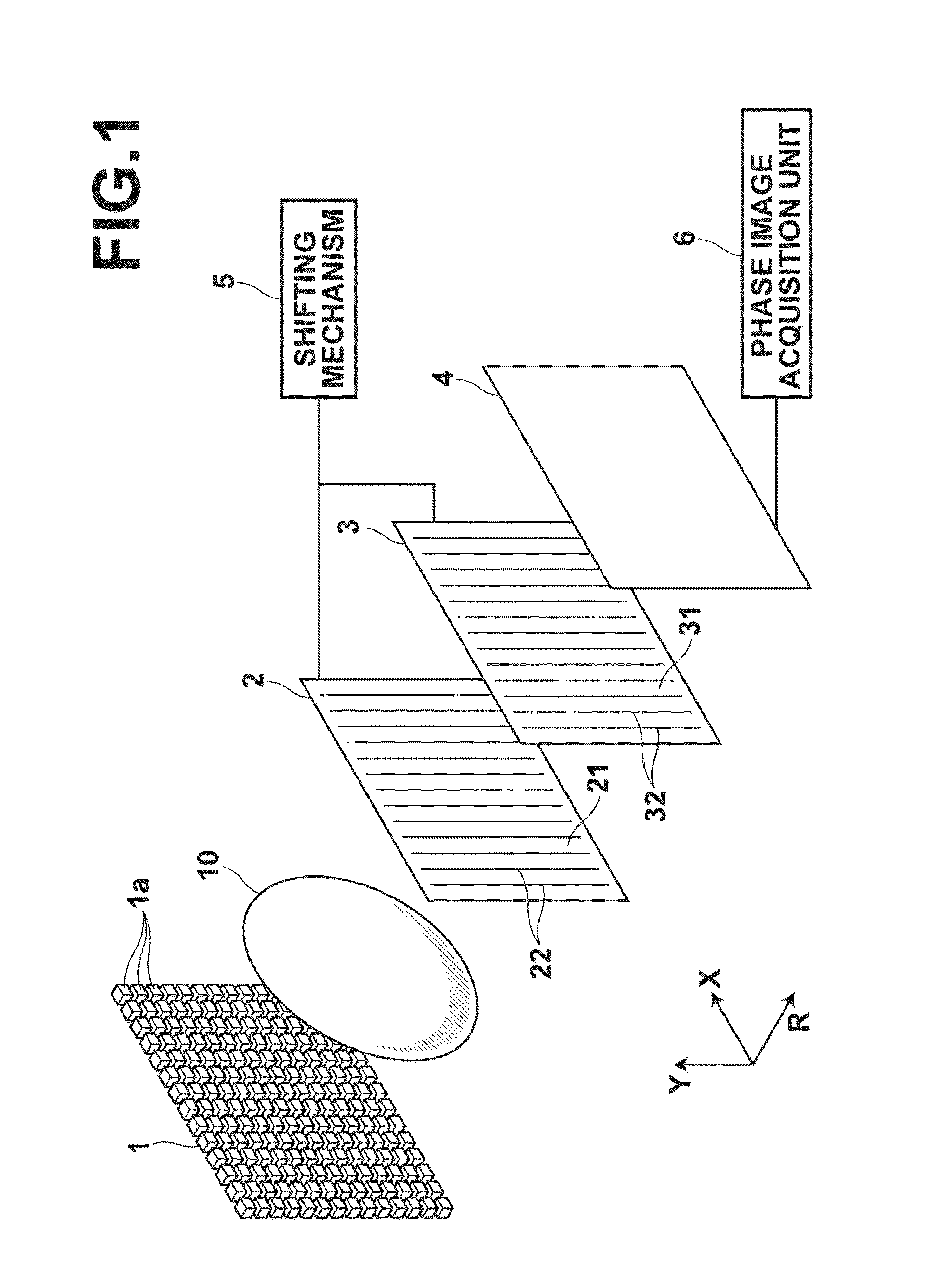
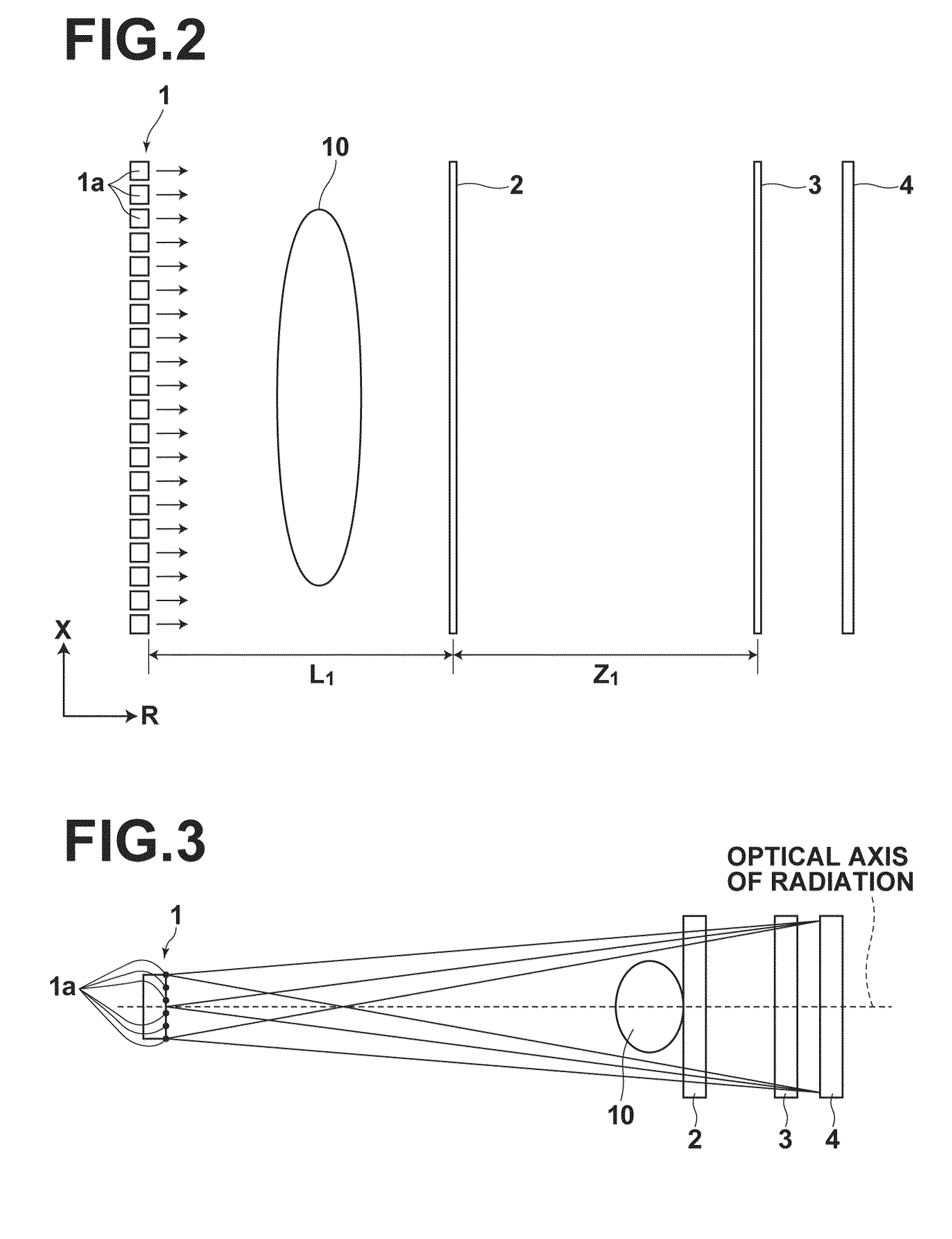
Radiation phase contrast imaging apparatus
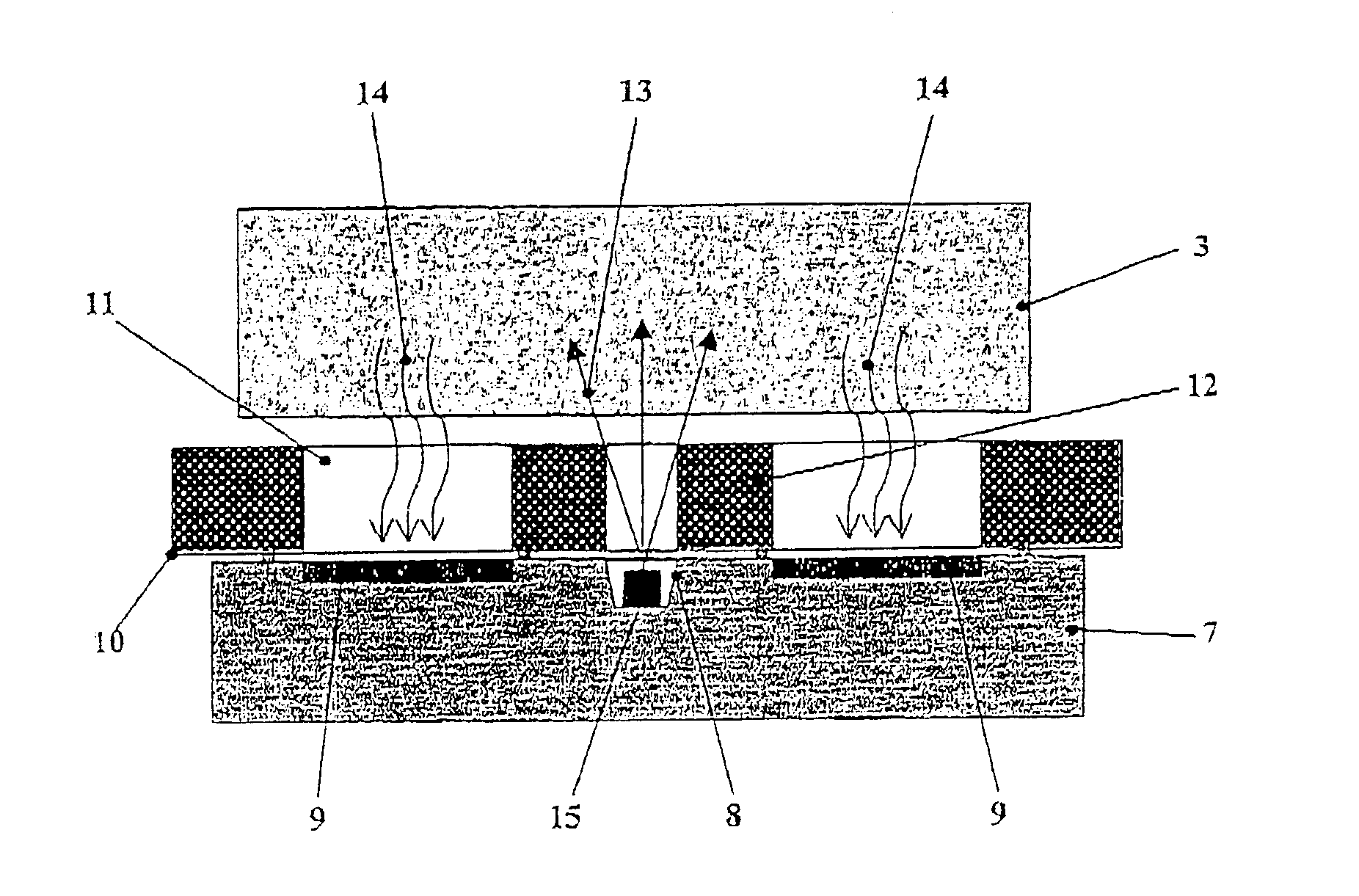
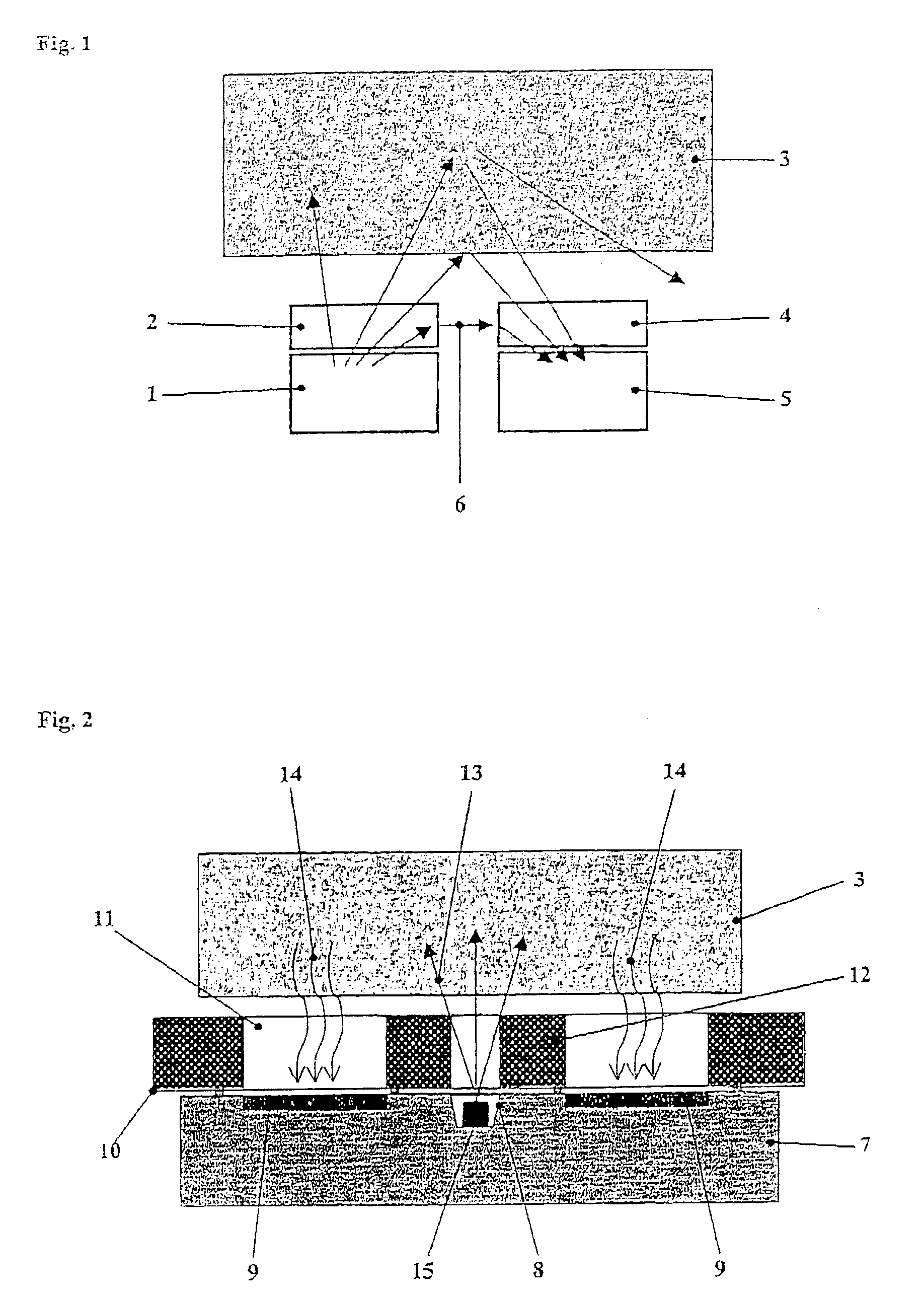
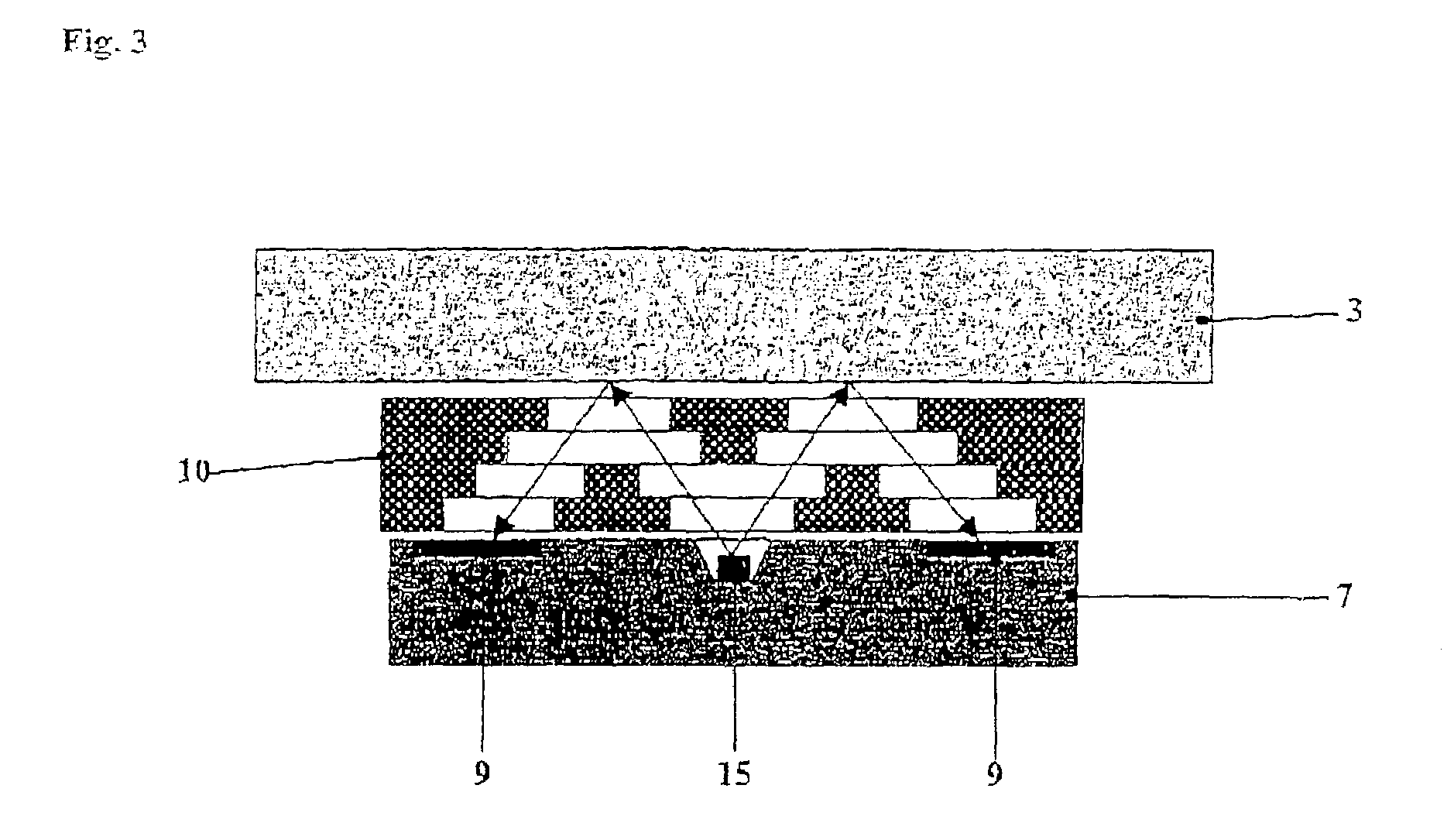
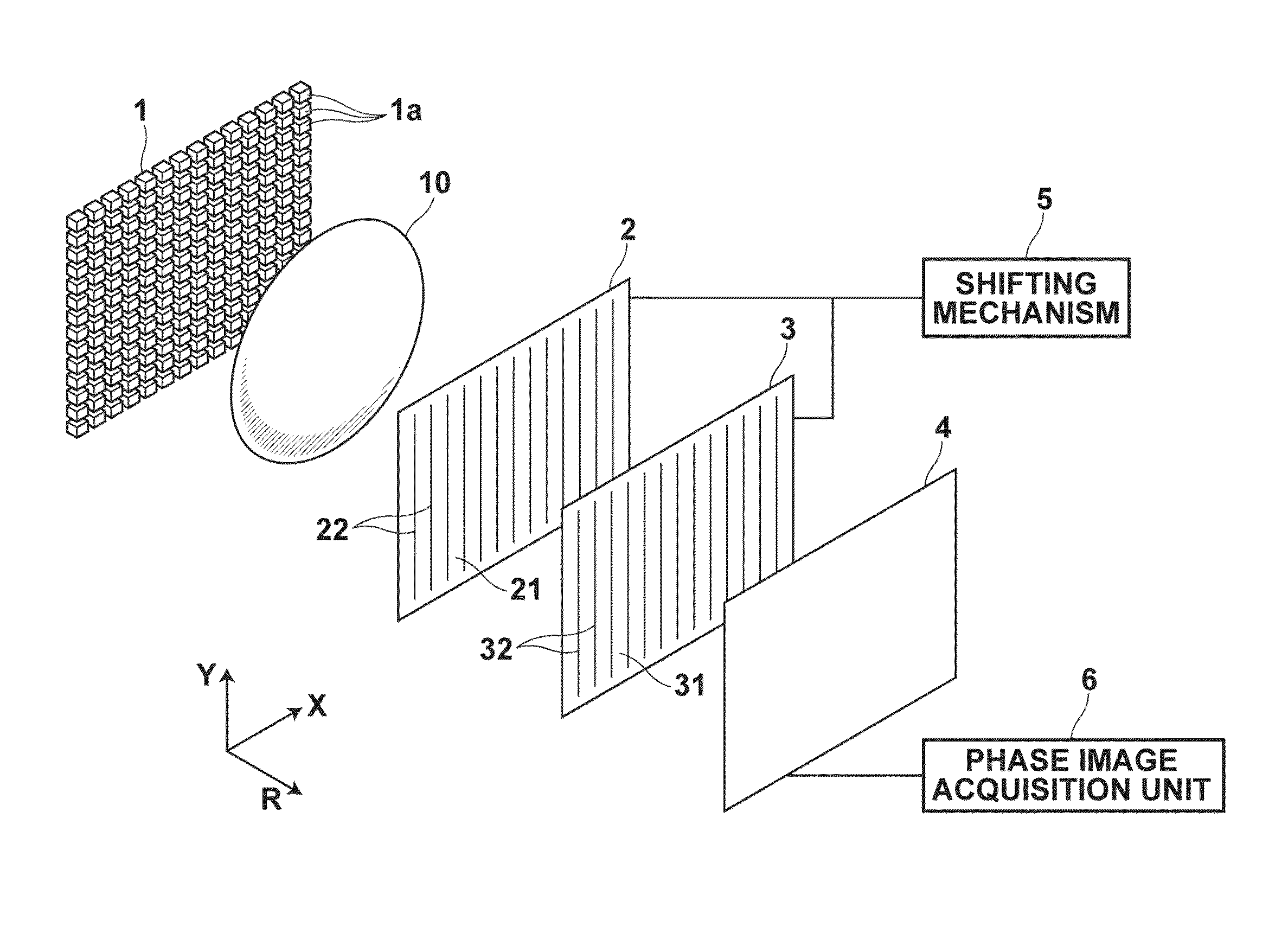
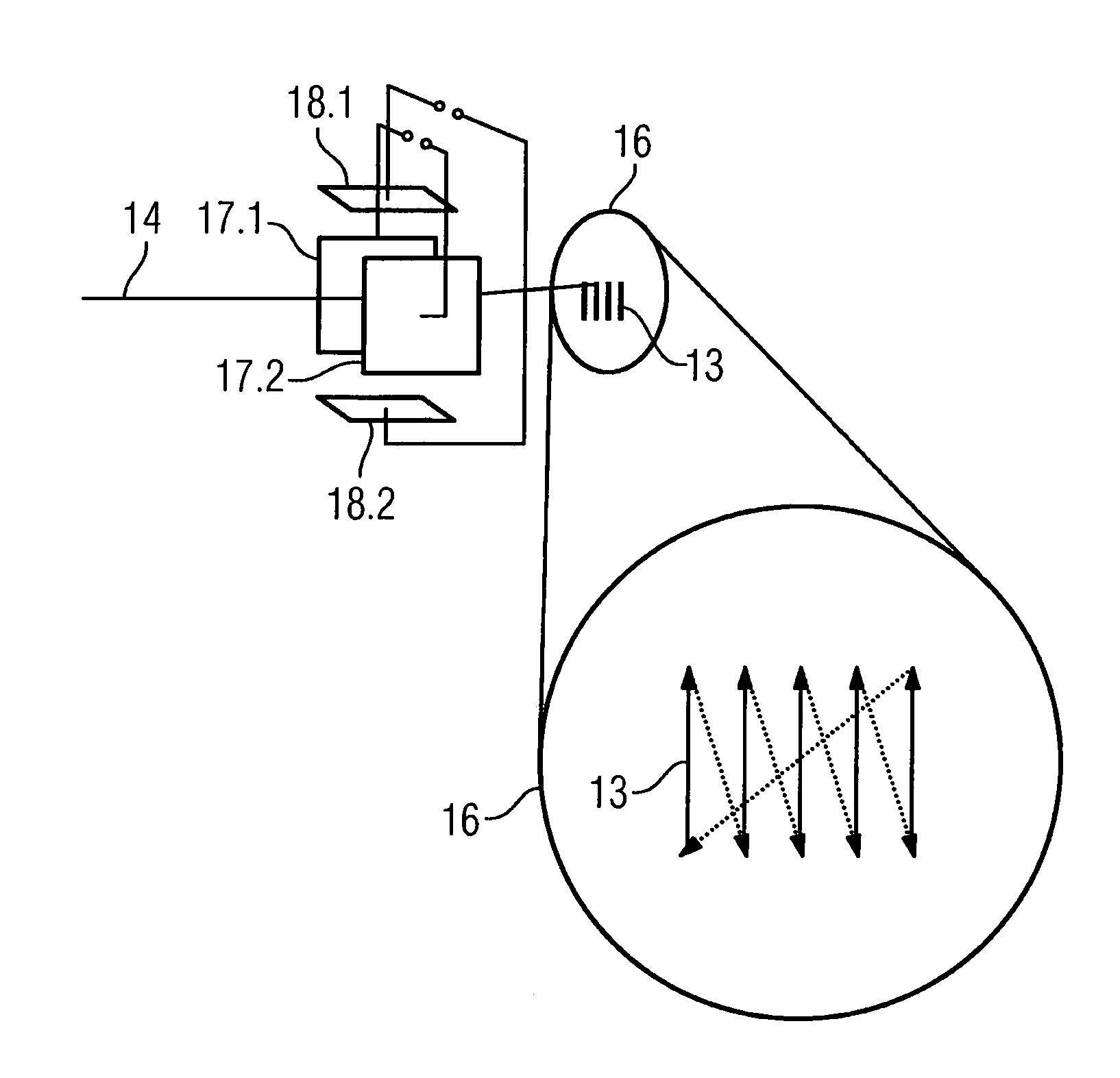
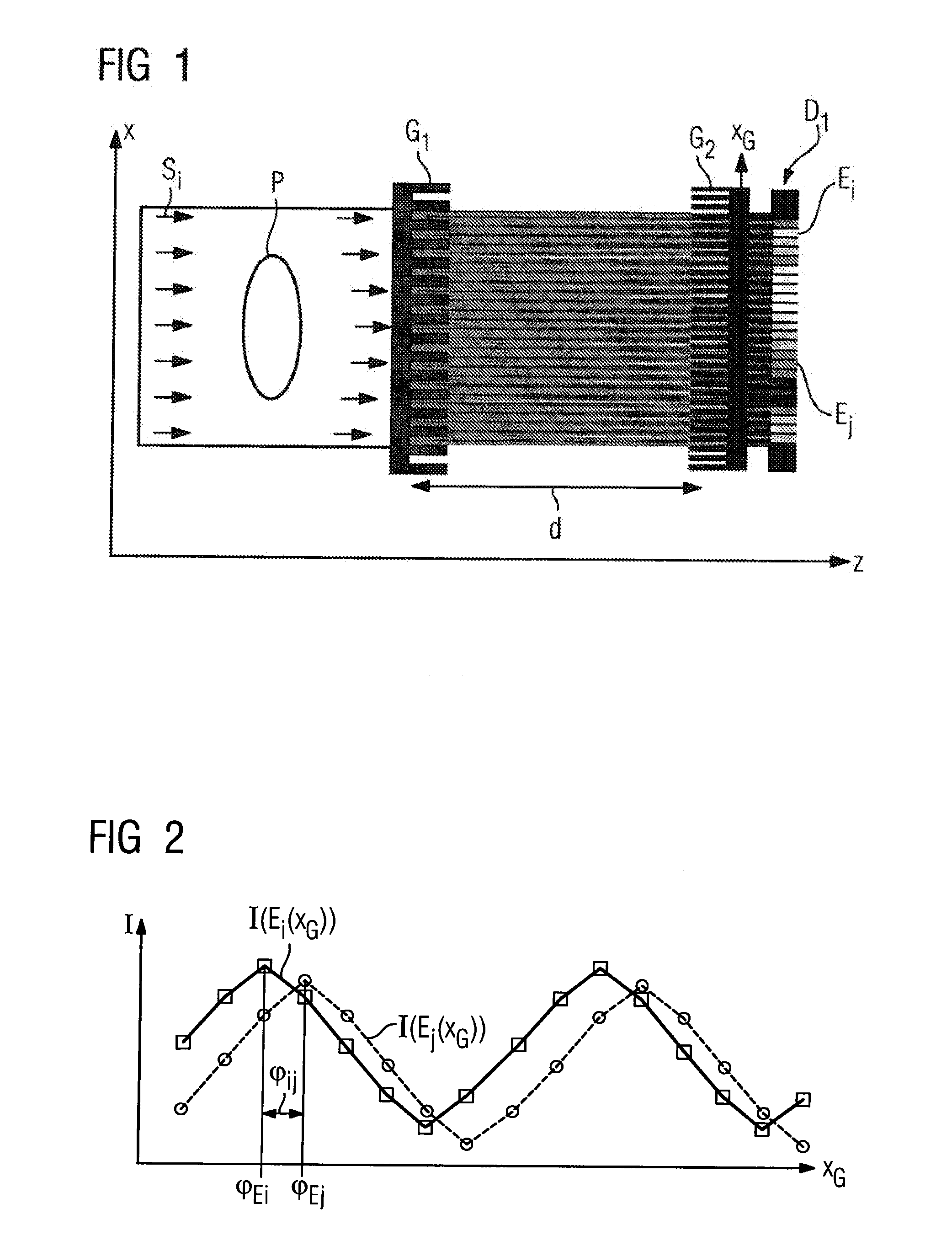
InactiveUS20100246765A1Cost of apparatus can be reducedLow costRadiation/particle handlingMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationGratingElectron source
A radiation phase contrast imaging apparatus, including a radiation emission unit having a plurality of electron sources for emitting electron beams, and a target for emitting radiation through collision of electron beam emitted from each electron source, a first grating in which grating structures for diffracting radiation are disposed periodically, a second grating in which grating structures for transmitting and shielding radiation are disposed periodically, and a radiation image detector for detecting radiation transmitted through the second grating, in which the first and second gratings are disposed in an optical axis direction of the radiation so as to be able to substantially superimpose each image of the first grating formed based on radiation corresponding to each electron source on a surface of the second grating, and the radiation corresponding to each electron source forms each phase image of the same subject on the radiation image detector.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Phototherapy device for illuminating the periphery of a wound and phototherapy system incorporating the same
Owner:MEDX HEALTH
Laser-produced plasma EUV light source with pre-pulse enhancement
InactiveUS20040264512A1Laser using scattering effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBeam splitterHigh energy
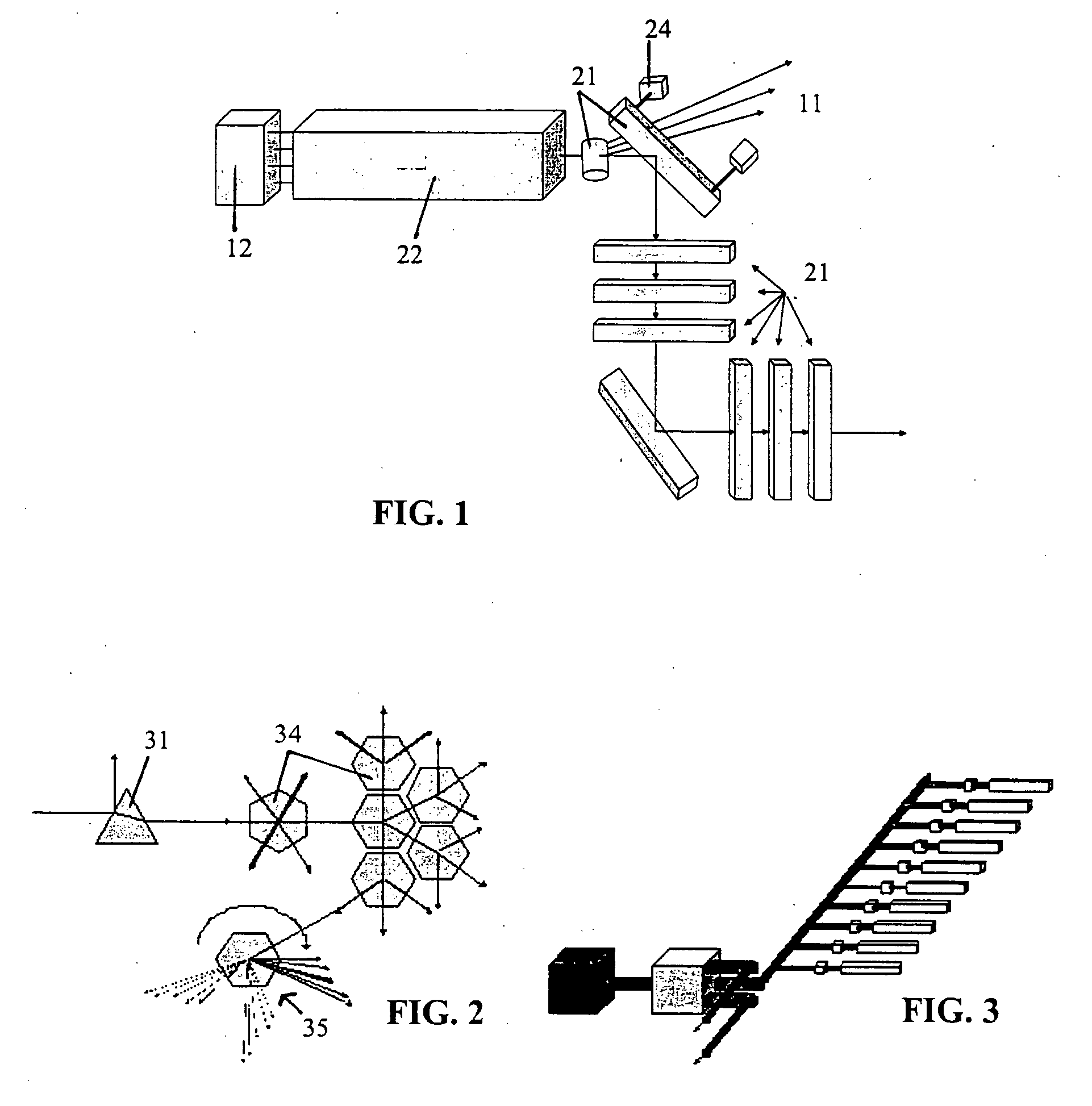
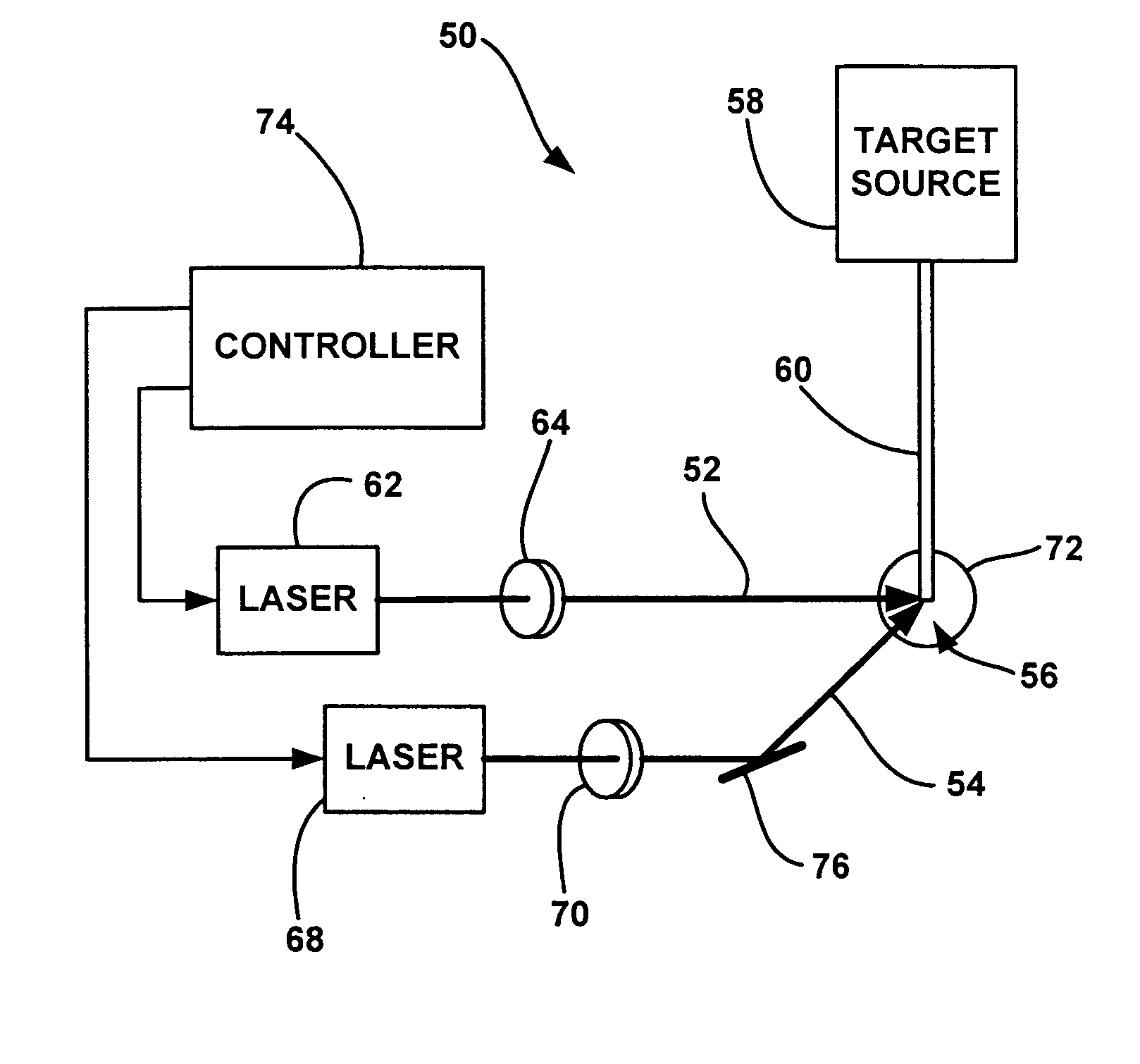
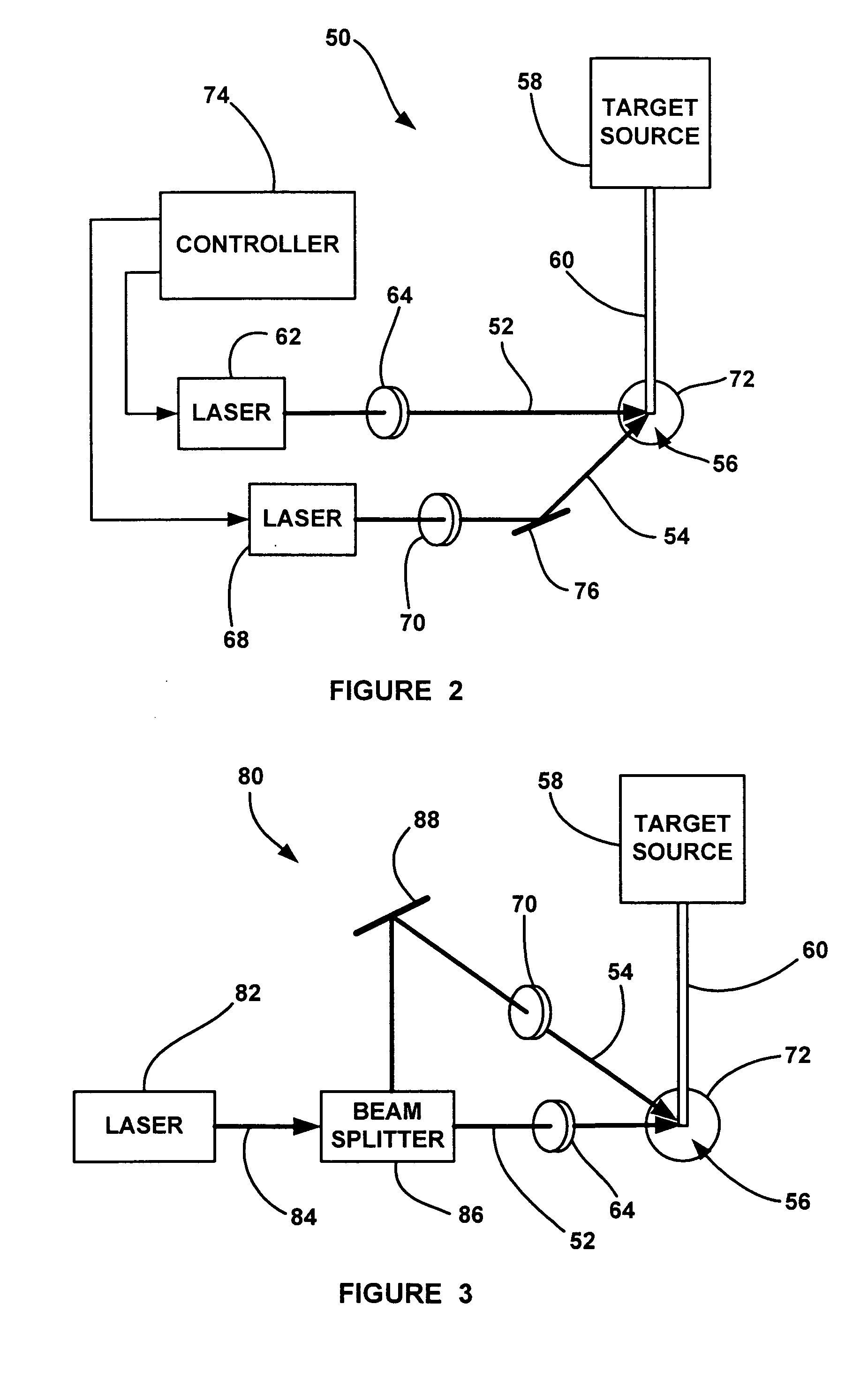
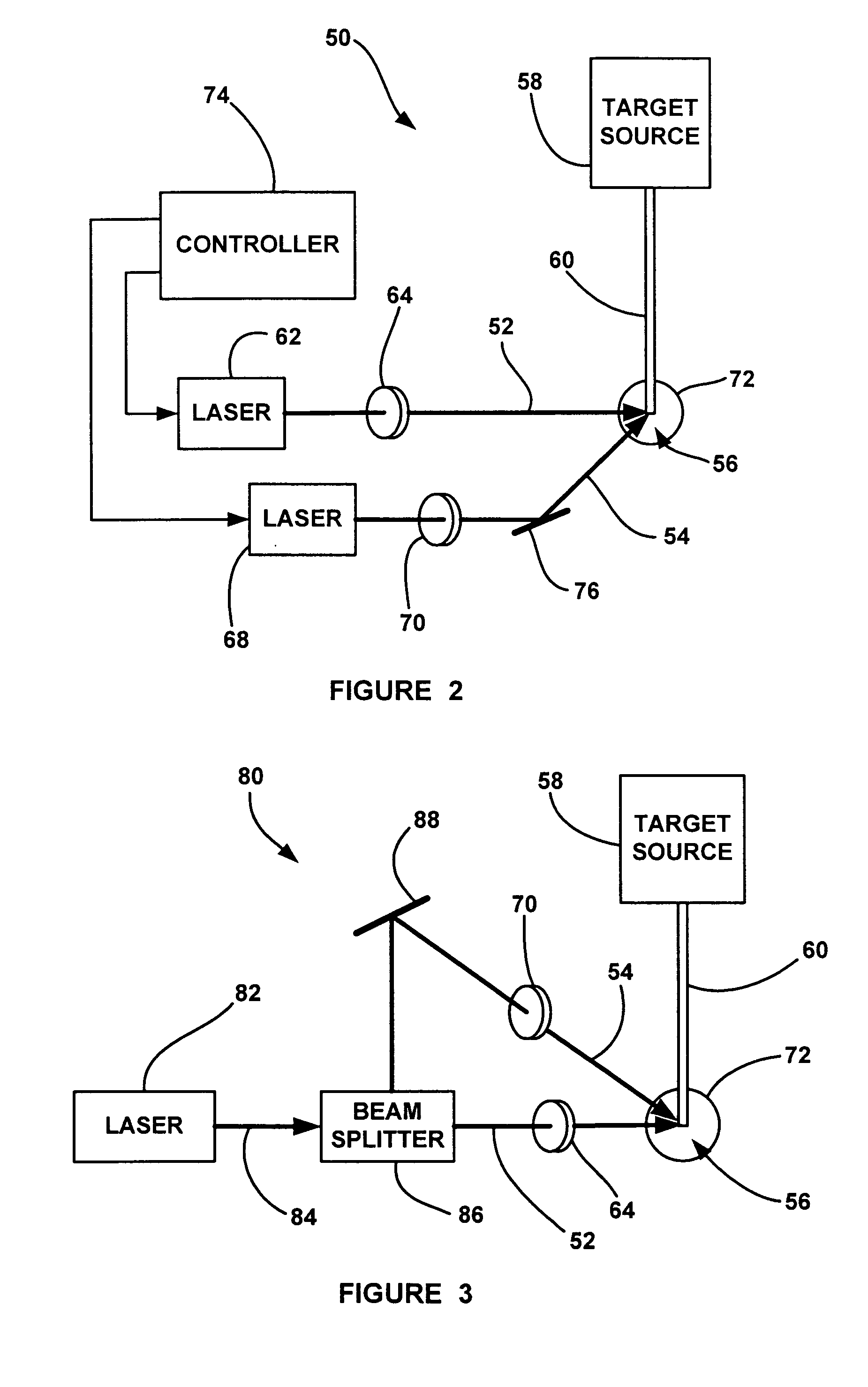
An EUV radiation source that employs a low energy laser pre-pulse and a high energy laser main pulse. The pre-pulse generates a weak plasma in the target area that improves laser absorption of the main laser pulse to improve EUV radiation emissions. High energy ion flux is reduced by collisions in the localized target vapor cloud generated by the pre-pulse. Also, the low energy pre-pulse arrives at the target area 20-200 ns before the main pulse for maximum output intensity. The timing between the pre-pulse and the main pulse can be reduced below 160 ns to provide a lower intensity of the EUV radiation. In one embodiment, the pre-pulse is split from the main pulse by a suitable beam splitter having the proper beam intensity ratio, and the main pulse is delayed to arrive at the target area after the pre-pulse.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Ionic shield for devices that emit radiation
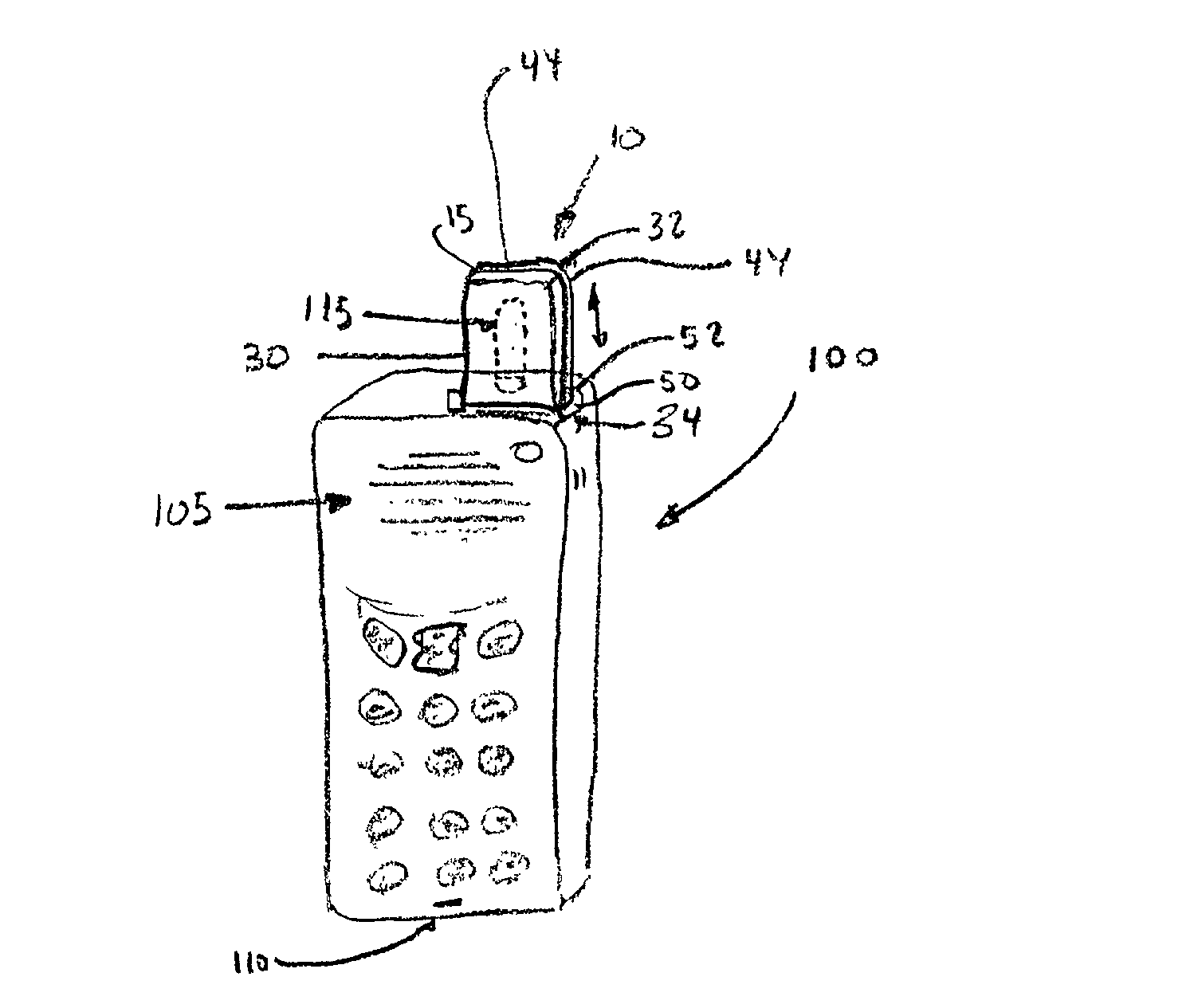
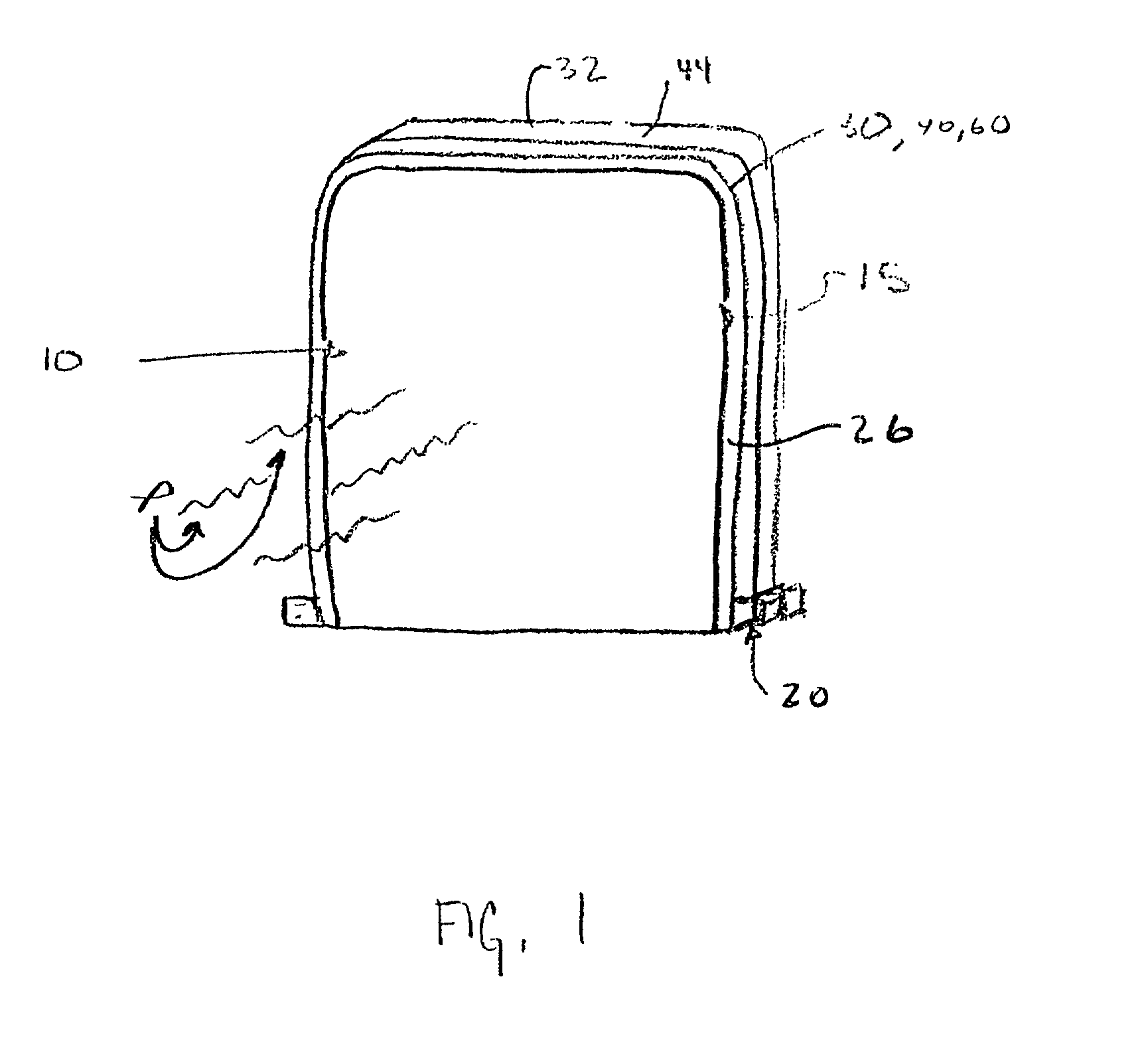
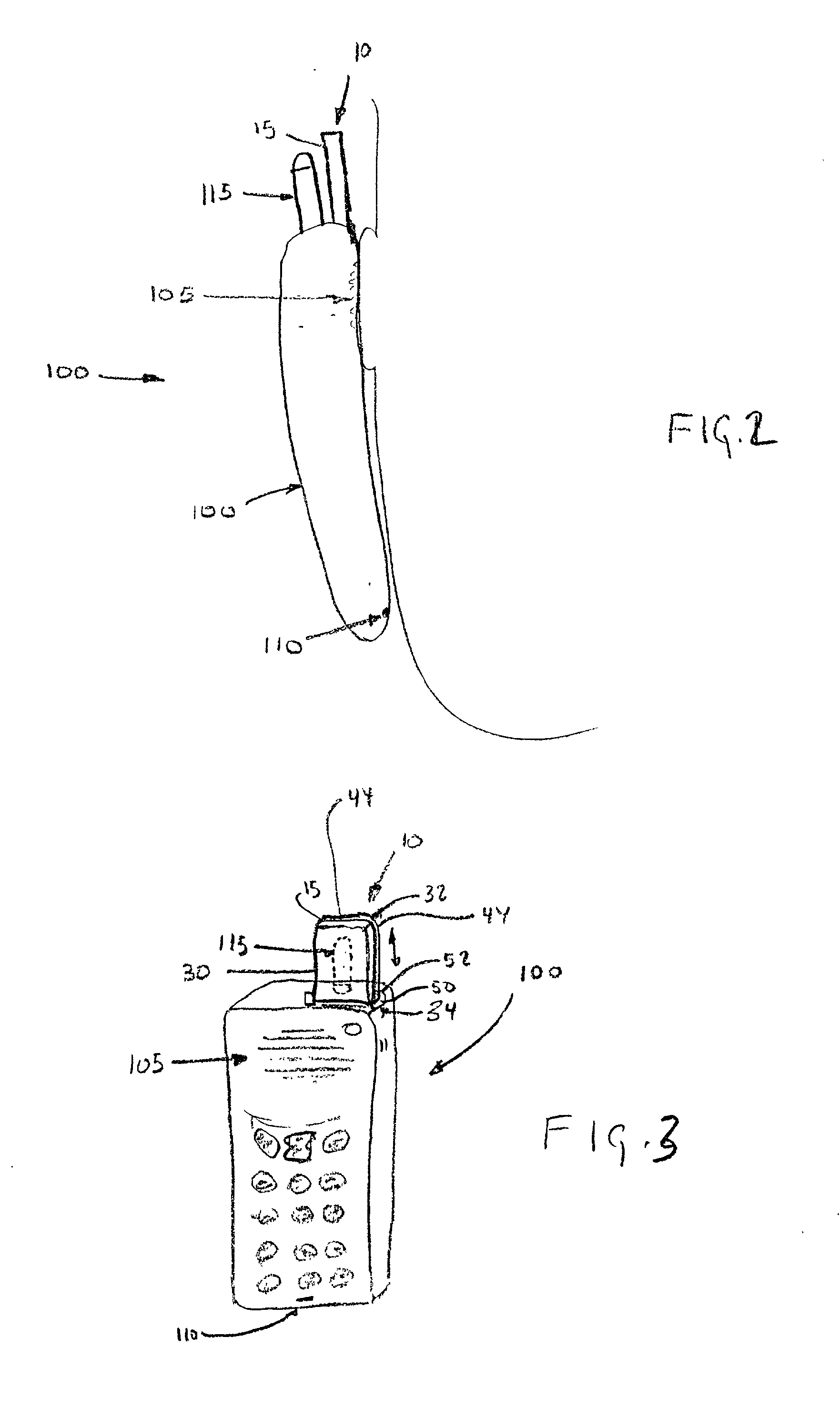
InactiveUS20020089464A1Antenna supports/mountingsAntenna couplingsRadiation shieldCellular telephone
A radiation shield, for use in association with a device, such as a cellular telephone, having a radiation emitter, comprising a barrier positioned between a source of radiation and an object to be shielded, the barrier including means for converting radiation into ionic motion, to, in turn, dissipate the radiation and preclude the radiation from reaching an object to be shielded. The invention further comprises methods associated with the shielding of a user from radiation.
Owner:CERAMTEC
Organism growth suppression using ultraviolet radiation
ActiveUS20070205382A1Suppress and prevent growthGrowth inhibitionRadiation pyrometryFire rescueBiological bodyBiofilm
A solution for suppressing organism growth using ultraviolet radiation generated by solid state ultraviolet radiation emitters, such as ultraviolet diodes is provided. The invention includes a connection structure that includes a plurality of solid state ultraviolet radiation emitters disposed thereon. Each of the plurality of solid state ultraviolet radiation emitters emits ultraviolet radiation having a wavelength less than or equal to four hundred nanometers to harm a target organism that may be present on a surface. In one embodiment, the connection structure comprises a two-dimensional mesh that may be placed adjacent an air filter, incorporated in a cover, and / or moved with respect to a surface, such as the interior of an air duct. In this manner, the invention can suppress and / or prevent the growth of organisms, such as biofilms and mold, in locations that are susceptible to such growth.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Organism growth suppression using ultraviolet radiation
ActiveUS7553456B2Suppress and prevent growthGrowth inhibitionLavatory sanitoryFire rescueBiological bodyBiofilm
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Focus detector arrangement and method for generating contrast x-ray images
ActiveUS7817777B2Improve utilizationRaise the ratioImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayX-ray
In a focus detector arrangement and method for an x-ray apparatus for generating projection or tomographic phase-contrast images of an examination subject, a beam of coherent x-rays is generated by an anode that has areas of different radiation emission characteristics arranged in bands thereon, that proceed parallel to grid lines of a phase grid that is used to generate the phase-contrast images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Volumetric image formation from optical scans of biological tissue with multiple applications including deep brain oxygenation level monitoring
InactiveUS20080177163A1Low costSimple cuttingCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostics using tomographyOptical radiationProperty value
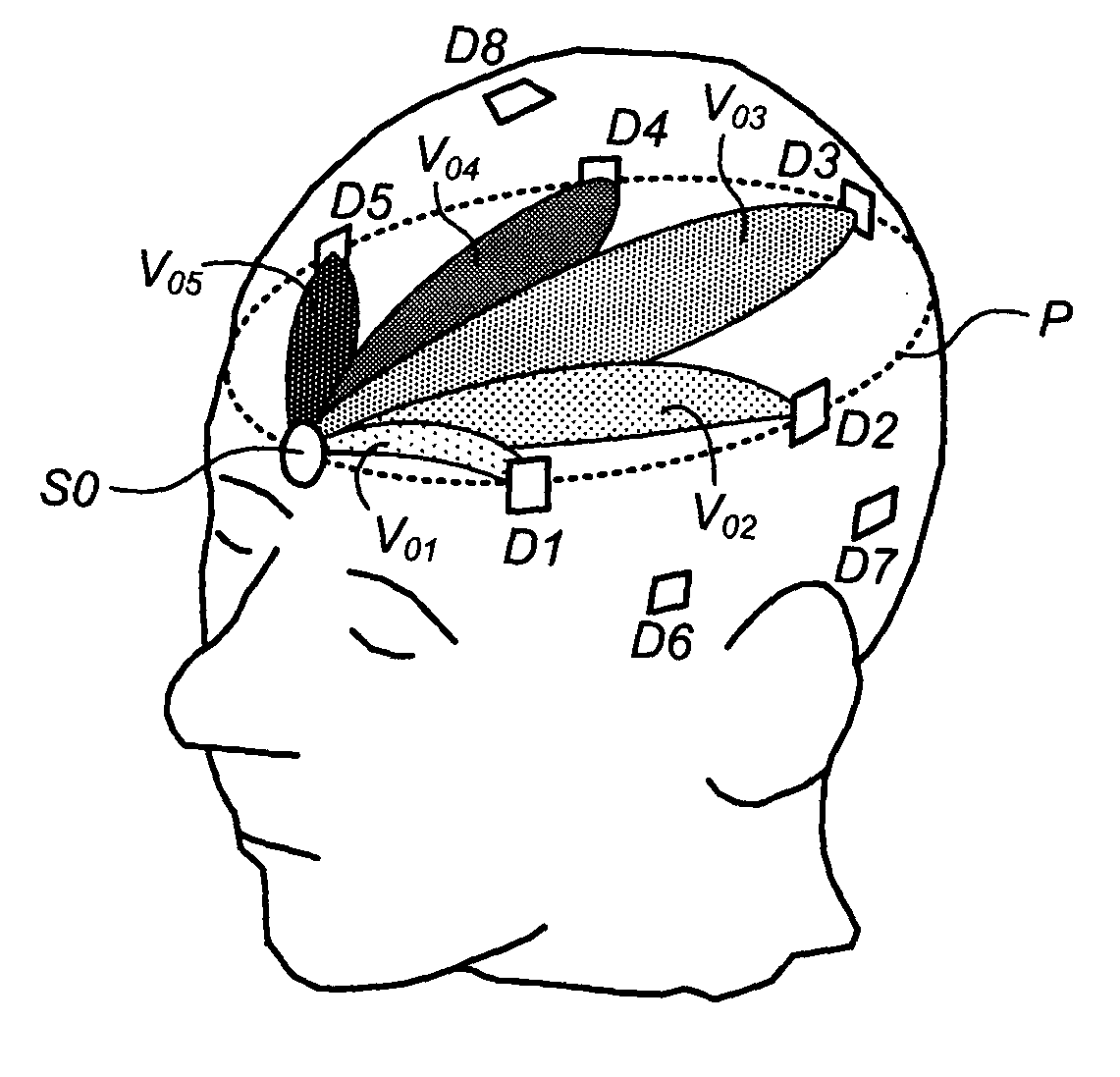
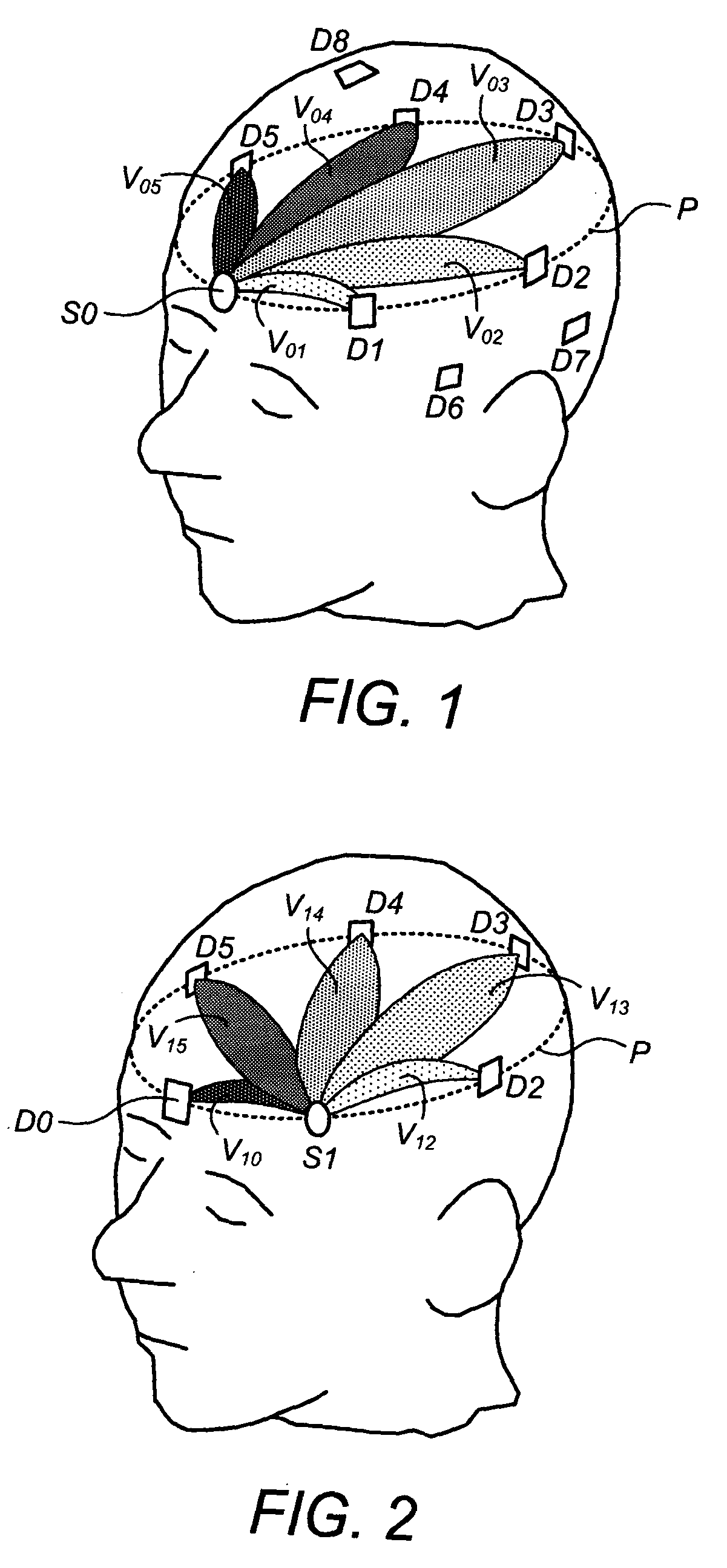
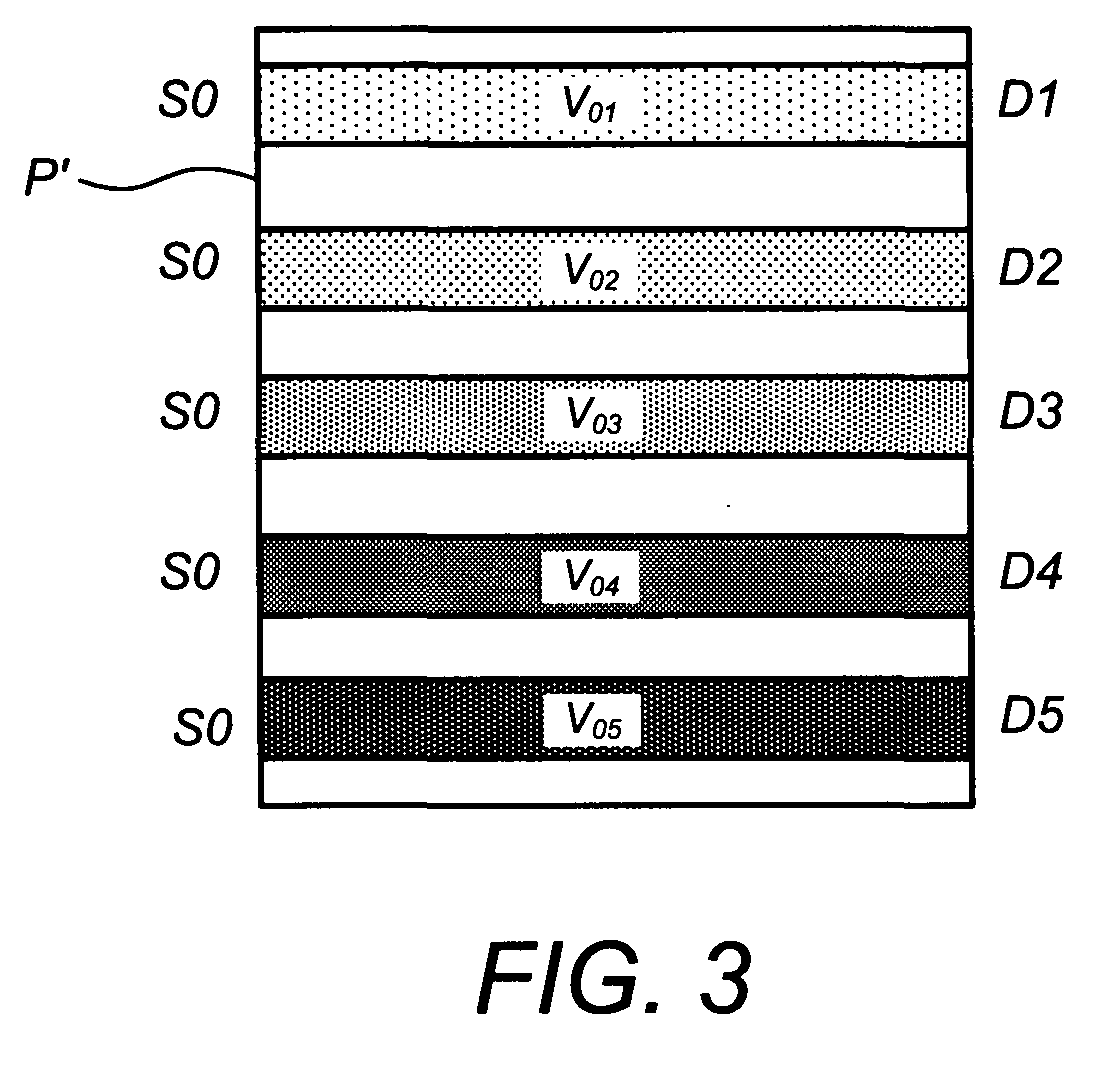
Methods, systems, and related computer program products for non-invasive monitoring of a biological volume, such as a human brain, are described. In one preferred embodiment, each of a plurality of optical sources emits optical radiation into the biological volume each of a plurality of optical detectors detects optical radiation impinging thereupon from the biological volume. The optical measurements are processed to compute a requisite property value associated with each source-detector pair. For each source-detector pair, a volumetric basis region corresponding thereto is weighted by the requisite property value, the volumetric basis region being predetermined and representative of an estimated subvolume of the biological volume encountered by optical radiation emitted from that source and propagating to that detector. The weighted volumetric basis regions are accumulated into a volumetric cumulative array, and a display output is generated based at least in part on the volumetric cumulative array.
Owner:O2 MEDTECH
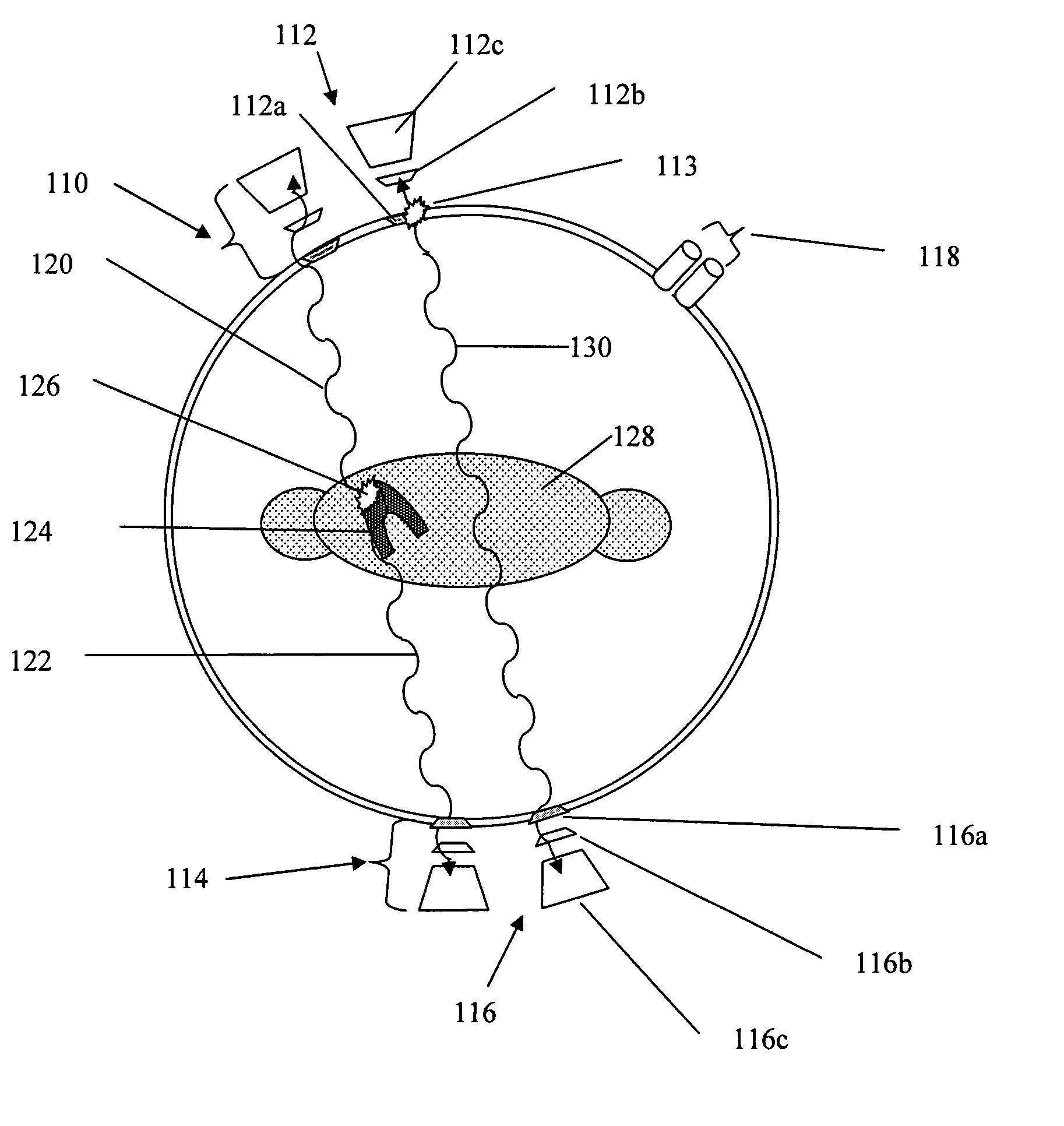
Liquid-jet/liquid droplet initiated plasma discharge for generating useful plasma radiation
InactiveUS6998785B1Reduce harmReduce debris generationRadiation pyrometryElectric arc lampsLiquid jetX ray spectra
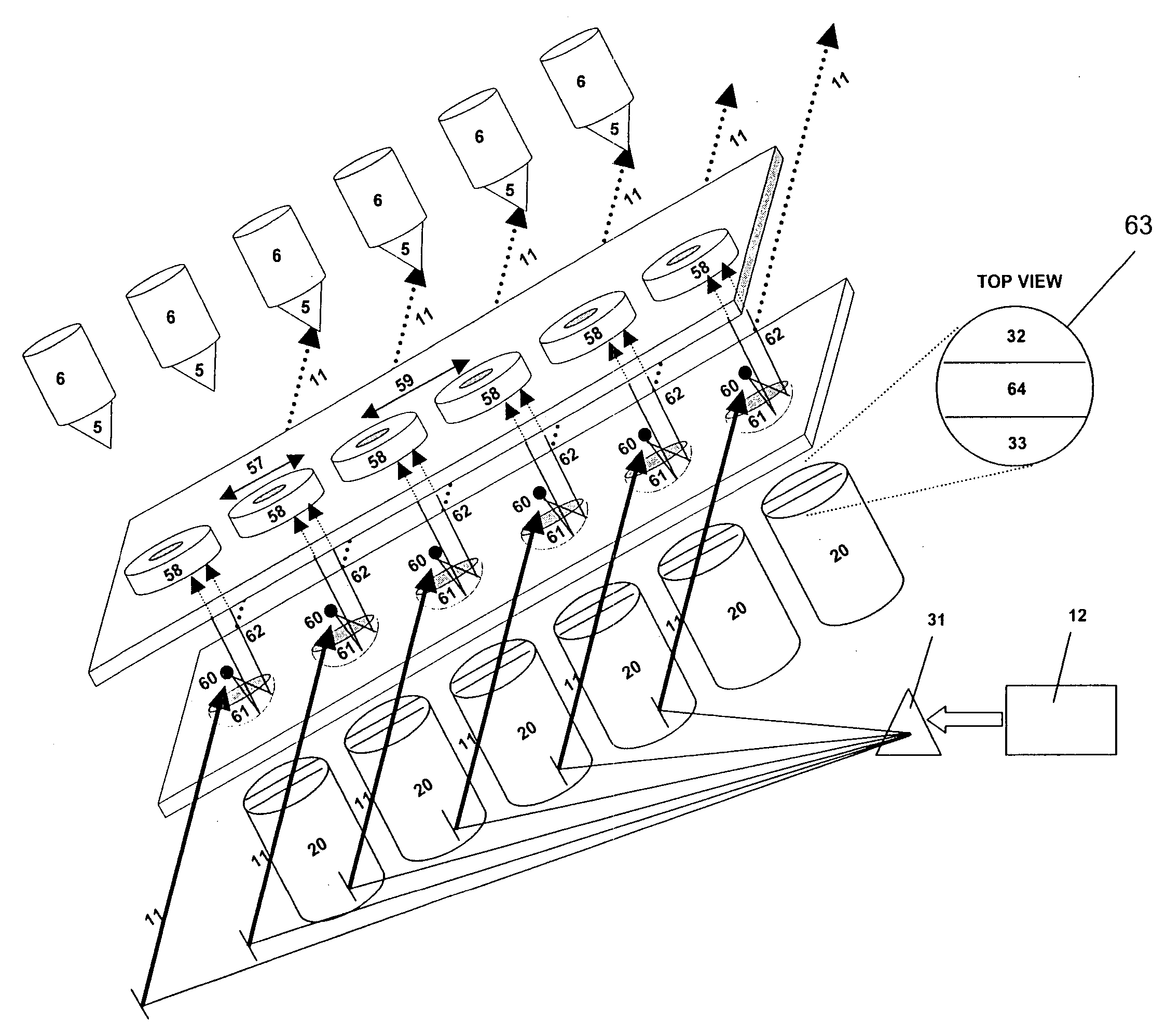
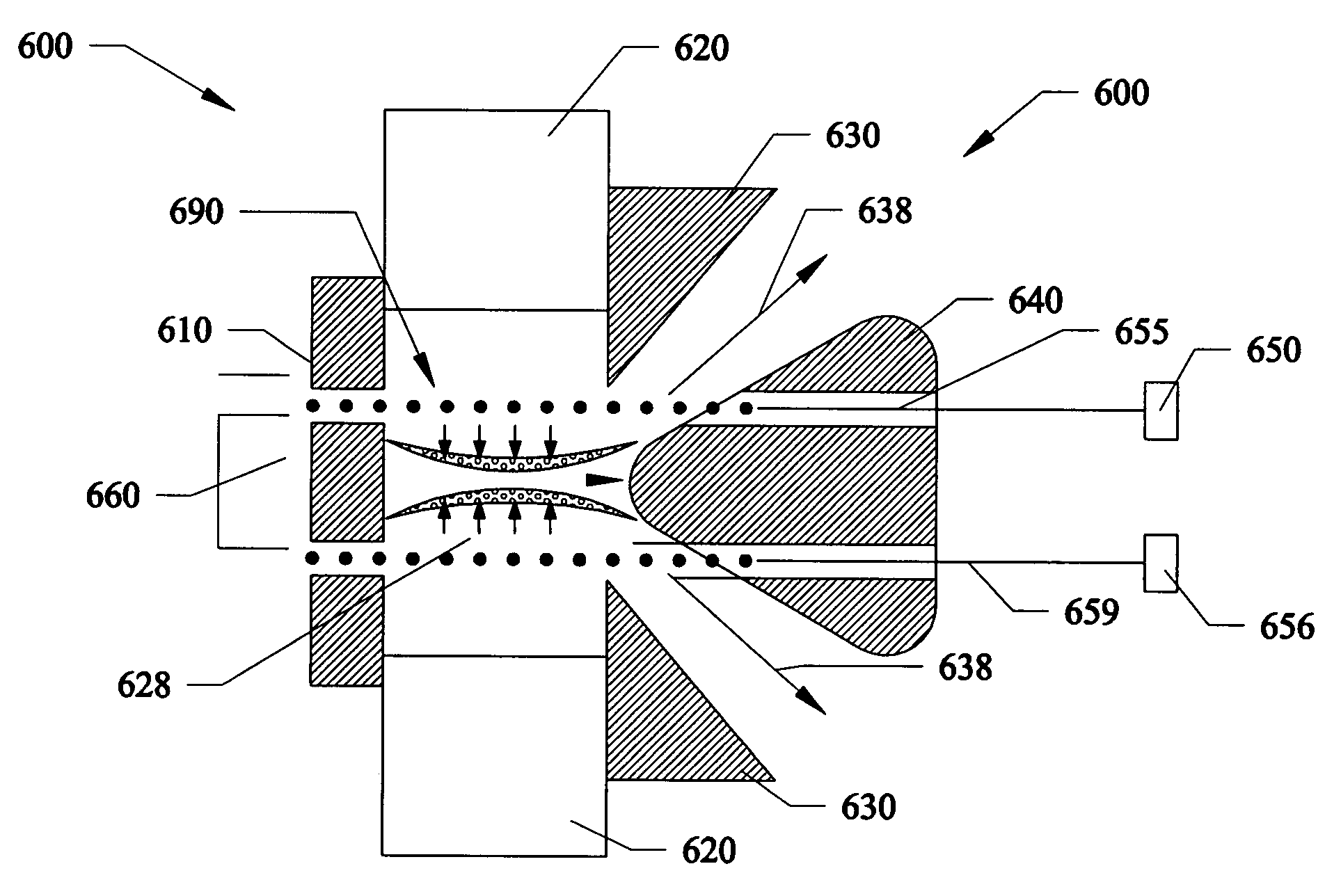
Plasma discharge sources for generating emissions in the VUV, EUV and X-ray spectral regions. Embodiments can include running a current through liquid jet streams within space to initiate plasma discharges. Additional embodiments can include liquid droplets within the space to initiate plasma discharges. One embodiment can form a substantially cylindrical plasma sheath. Another embodiment can form a substantially conical plasma sheath. Another embodiment can form bright spherical light emission from a cross-over of linear expanding plasmas. All the embodiments can generate light emitting plasmas within a space by applying voltage to electrodes adjacent to the space. All the radiative emissions are characteristic of the materials comprising the liquid jet streams or liquid droplets.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
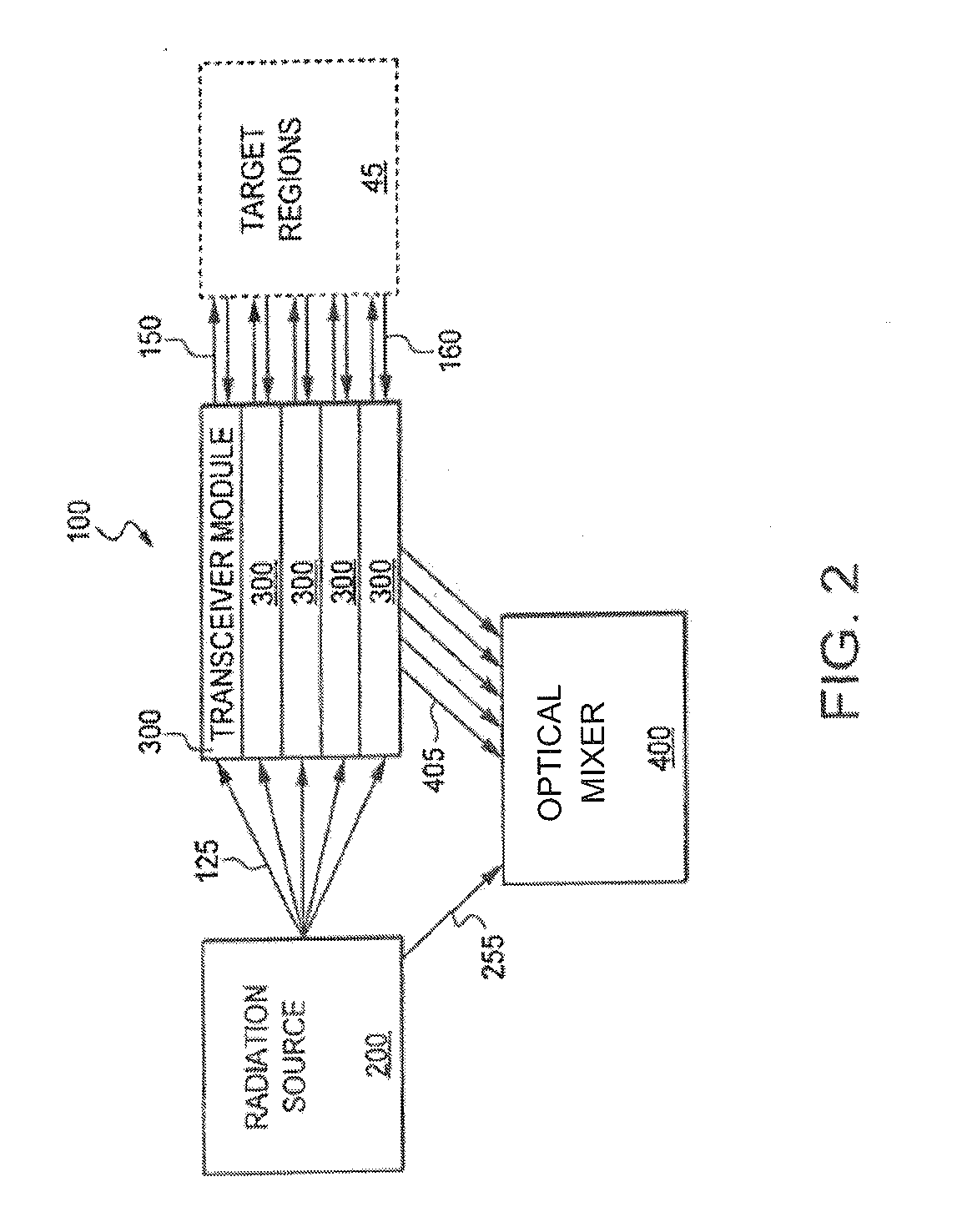
Laser Wind Velocimeter With Multiple Radiation Sources
ActiveUS20120206712A1Improve reading accuracyImprove timelinessWind motor combinationsMachines/enginesTransceiverAtmospheric sciences
A system and method for measuring wind velocities are provided. A laser wind velocimeter with a radiation source includes a fiber laser. All optical signals, transmitted and received, are conveyed by optical fibers. An amplifier amplifies a source laser, which is then transmitted to one or more transceivers. The one or more transceivers, each projecting along a different axis, and each with a single optical fiber input / output interface act as both the transmission device to focus the radiation at a target region, and as the receiving system for collecting reflected radiation. The one or more transceivers transmit radiation to the target region. A portion of the reflected radiation collected by the receiving system is analyzed to determine the Doppler shift, which can me used to measure wind velocity
Owner:RD2 LLC
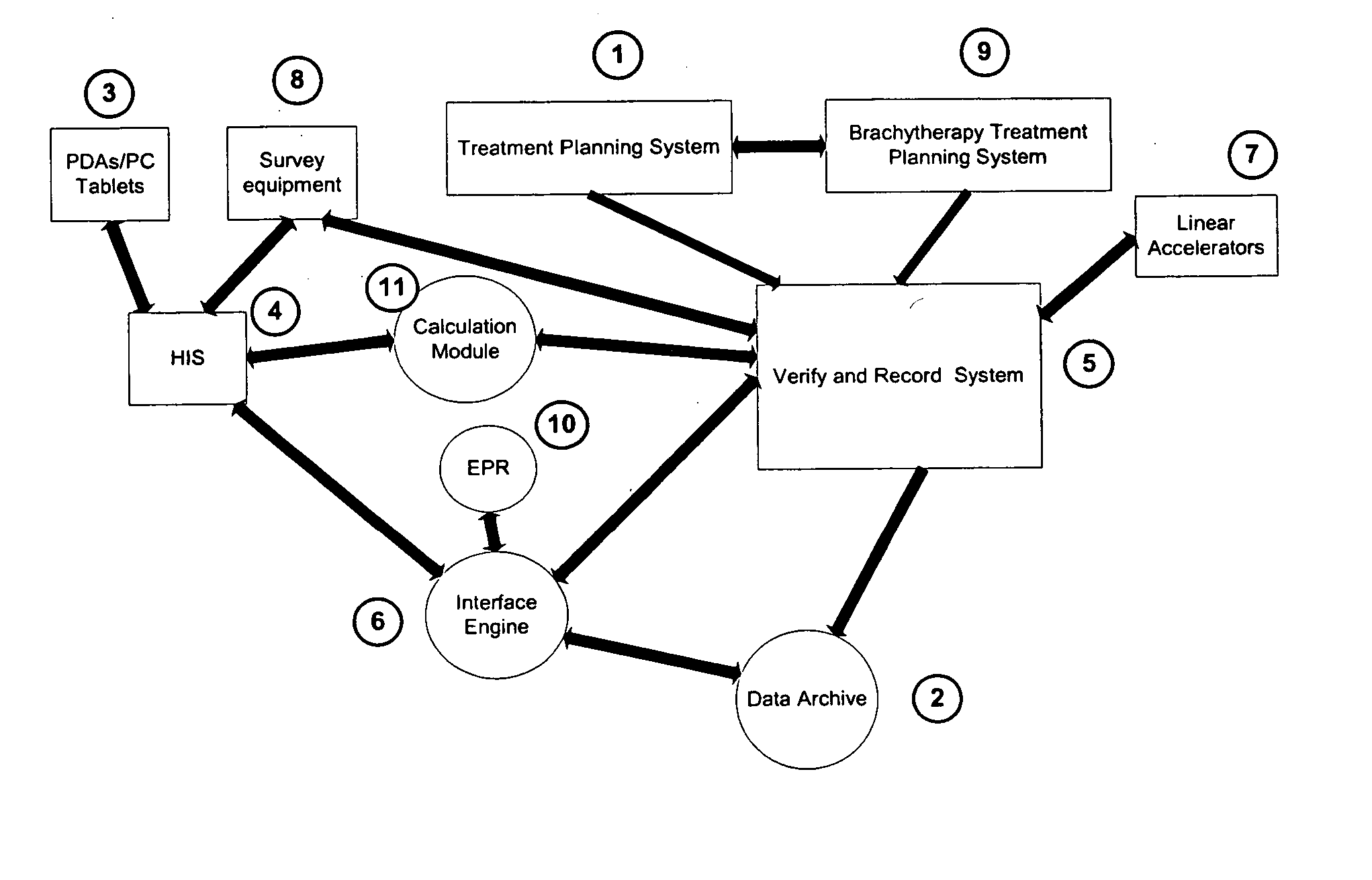
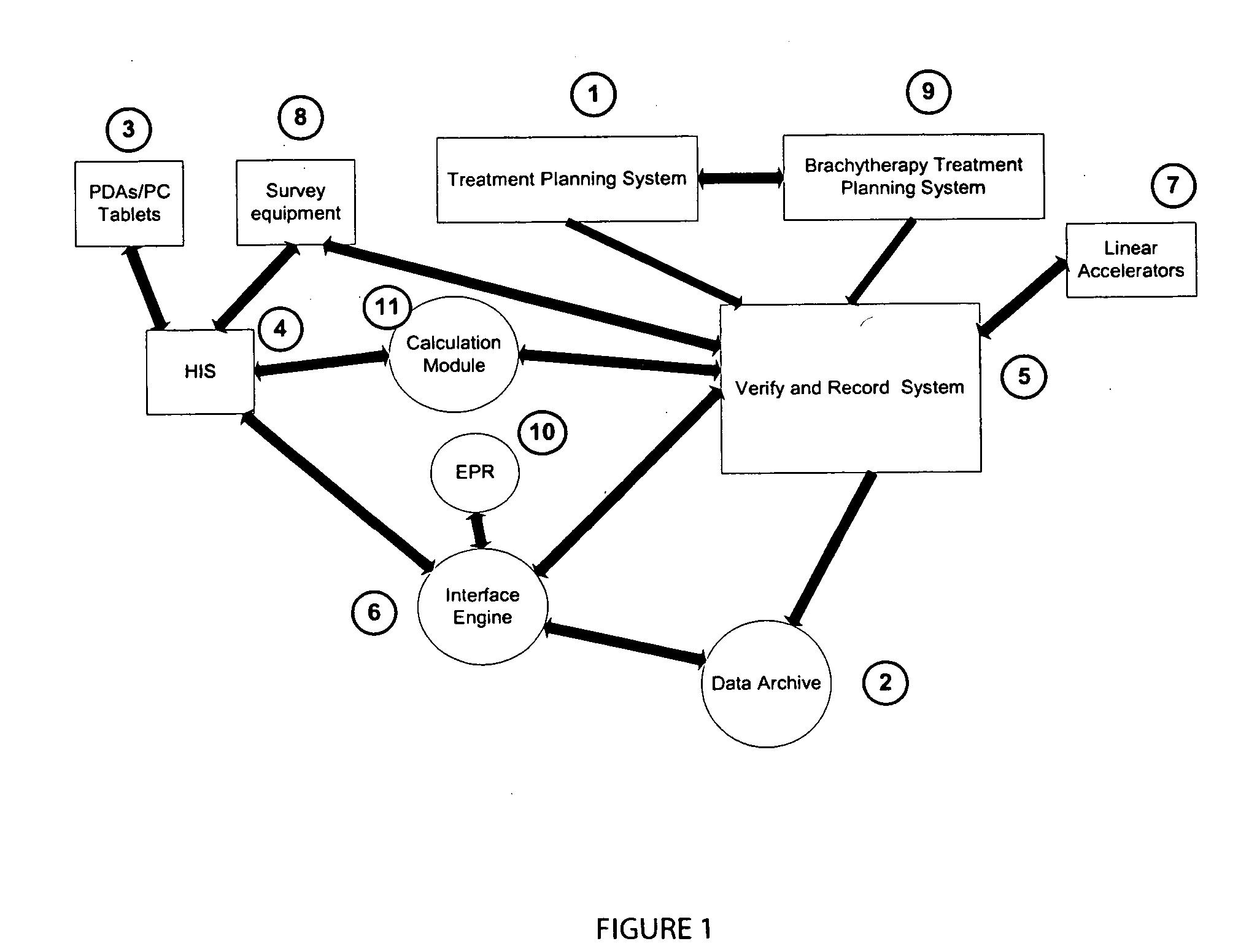
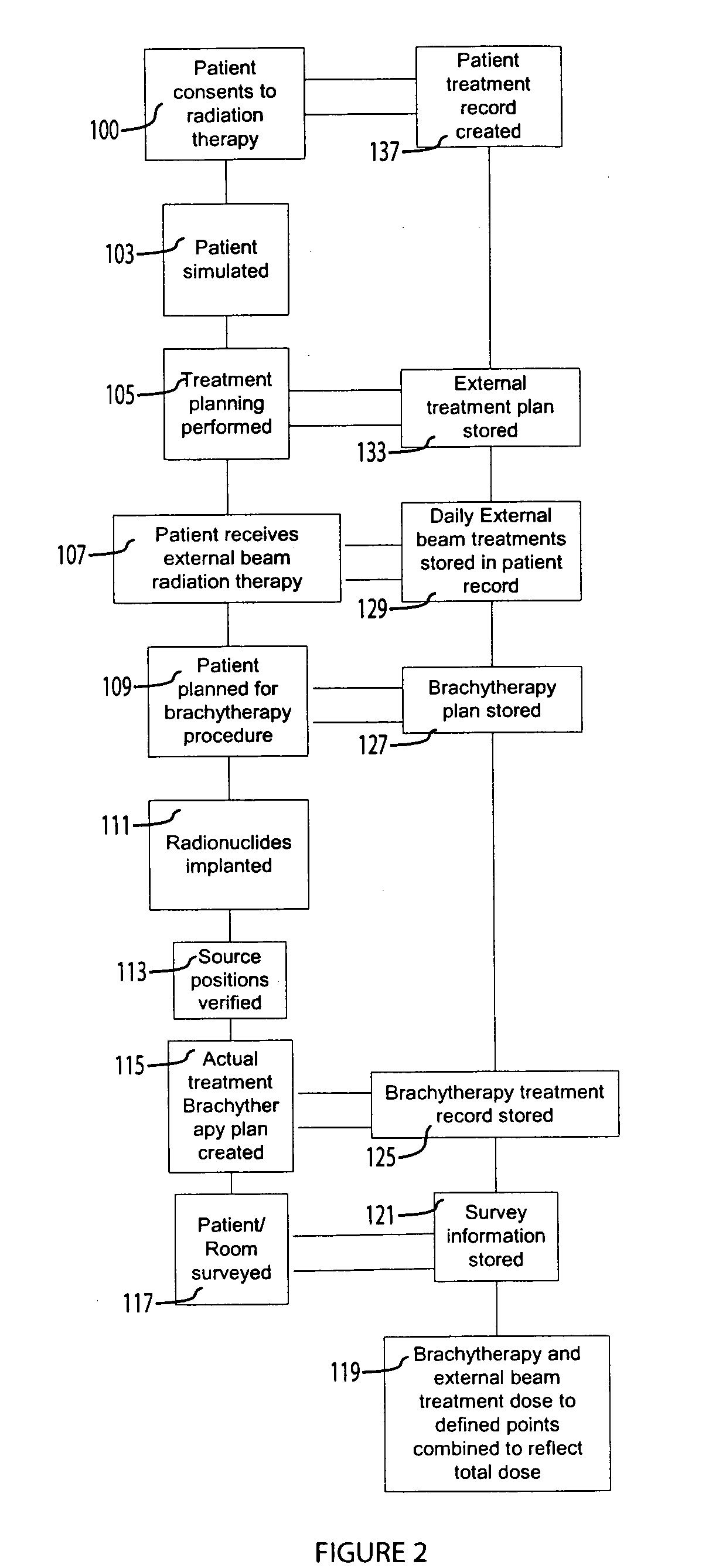
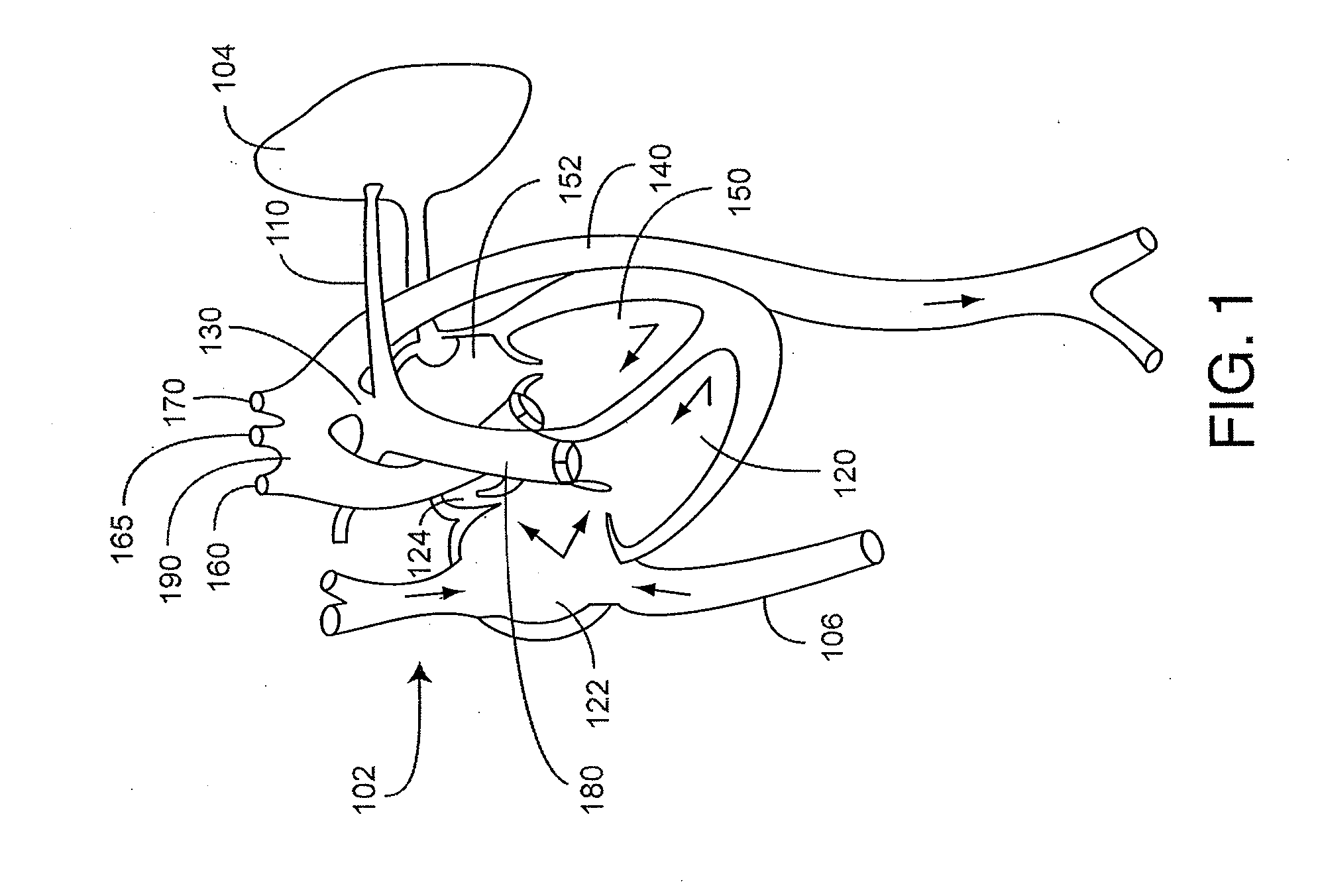
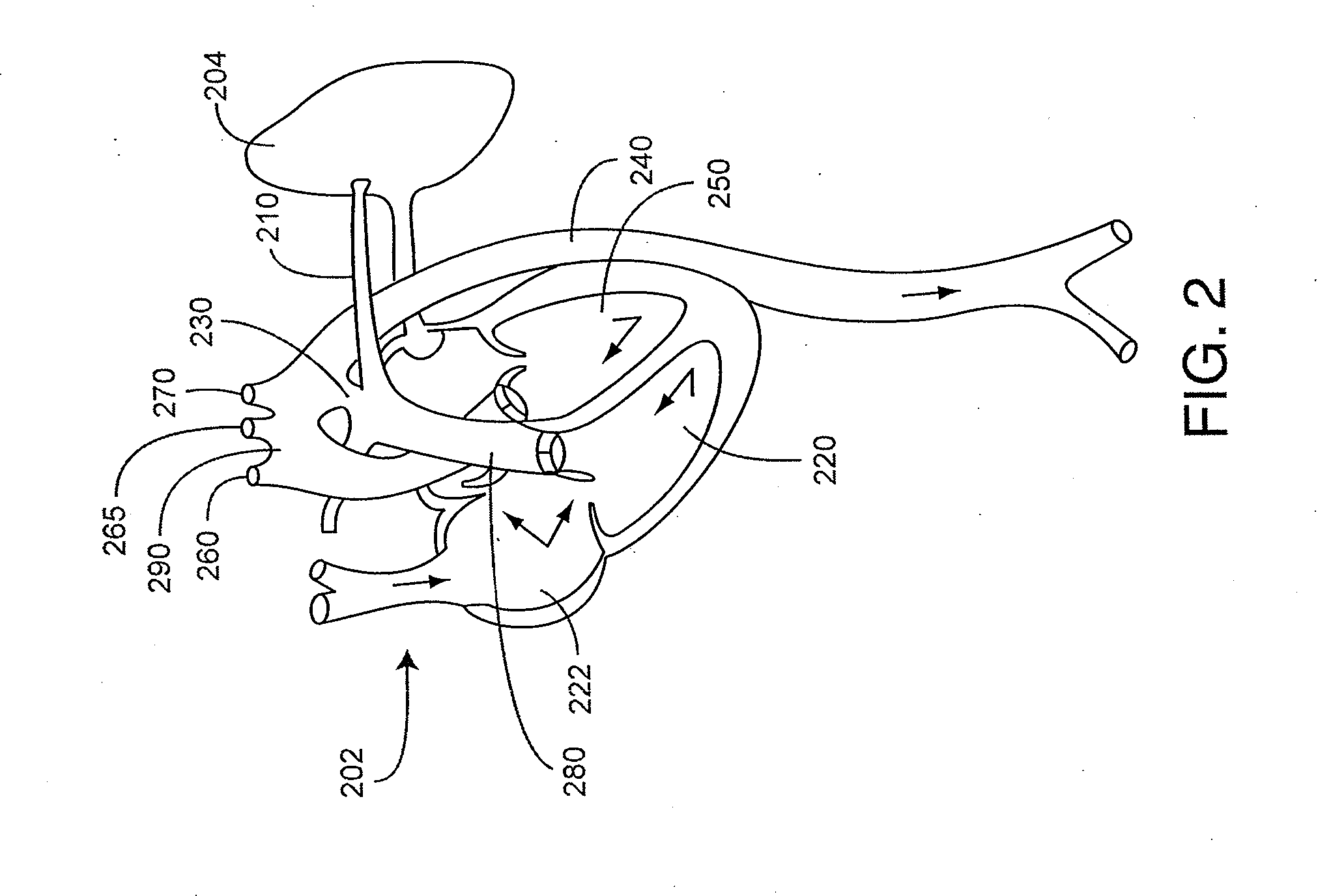
System for processing patient radiation treatment data
InactiveUS20050027196A1Convenient treatmentEasy to useRadiation diagnosticsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyAnatomic regionRadiation emission
A system records and documents both external beam radiation therapy and radiation from implanted sources applied to an anatomical area, in a comprehensive consolidated record of radiation treatment that also documents detected radiation emission levels from internal patient sources measured externally to the patient. A system processes data concerning patient radiation treatment. The system includes an input processor for receiving data identifying a first radiation dose received by a particular anatomical part of a patient, from a radiation source external to a patient and a second radiation dose, received by the particular anatomical part of the patient from a radiation source internal to the patient. A data processor combines data representing the first and second dose to provide a combined dose value. A storage processor stores the combined value in a record associated with the patient
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS HEALTH SERVICES CORPORAT
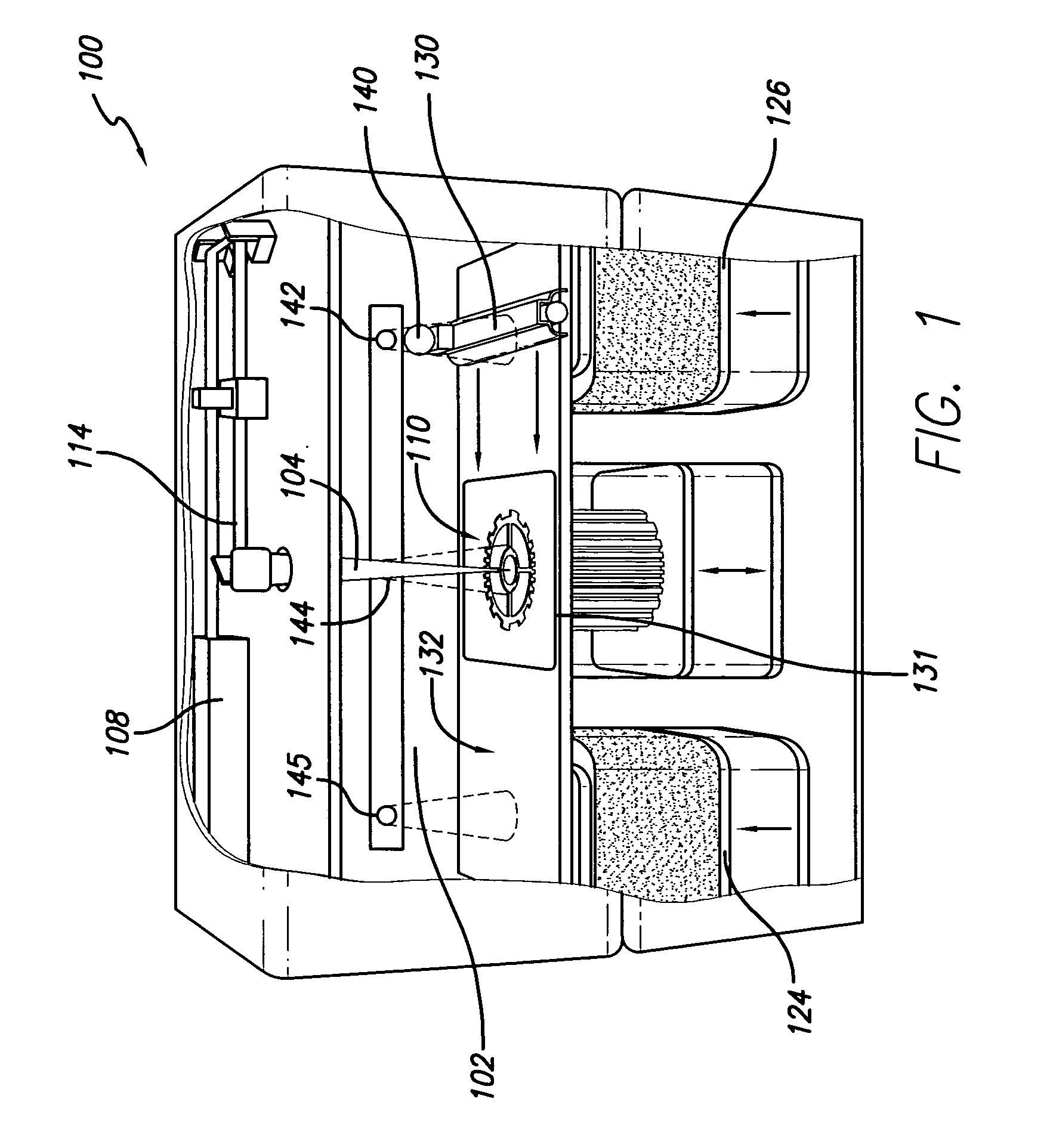
Flash curing in selective deposition modeling
InactiveUS20050253308A1Reduce heatReduce power consumptionAdditive manufacturing apparatusWood working apparatusSelective depositionOxygen
A flash curing system for solid freeform fabrication which generates a plurality of radiation emitting pulses that forms a planar flash. The planar flash initiates curing of a curable material dispensed by a solid freeform fabrication apparatus. The radiation emitting pulses have a high peak power value that releases a sufficient quantity of free radicals from the photoinitiator to initiate curing and overcome the problem of oxygen inhibition. Substantially less power is consumed and less heat generated by the flash curing system compared to conventional continuous emission curing systems.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Congenital heart disease monitor
ActiveUS20080071155A1Health-index calculationMedical automated diagnosisUltrasound attenuationOptical radiation
A congenital heart disease monitor utilizes a sensor capable of emitting multiple wavelengths of optical radiation into a tissue site and detecting the optical radiation after attenuation by pulsatile blood flowing within the tissue site. A patient monitor is capable of receiving a sensor signal corresponding to the detected optical radiation and calculating at least one physiological parameter in response. The physiological parameter is measured at a baseline site and a comparison site and a difference in these measurements is calculated. A potential congenital heart disease condition in indicated according to the measured physiological parameter at each of the sites or the calculated difference in the measured physiological parameter between the sites or both.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Laser-produced plasma EUV light source with pre-pulse enhancement
InactiveUS6973164B2Improves laser absorption of laserLess likely to damageLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBeam splitterVapor cloud
An EUV radiation source that employs a low energy laser pre-pulse and a high energy laser main pulse. The pre-pulse generates a weak plasma in the target area that improves laser absorption of the main laser pulse to improve EUV radiation emissions. High energy ion flux is reduced by collisions in the localized target vapor cloud generated by the pre-pulse. Also, the low energy pre-pulse arrives at the target area 20–200 ns before the main pulse for maximum output intensity. The timing between the pre-pulse and the main pulse can be reduced below 160 ns to provide a lower intensity of the EUV radiation. In one embodiment, the pre-pulse is split from the main pulse by a suitable beam splitter having the proper beam intensity ratio, and the main pulse is delayed to arrive at the target area after the pre-pulse.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Focus detector arrangement and method for generating contrast x-ray images
ActiveUS20090154640A1Improved dose utilizationRaise the ratioImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayX-ray
In a focus detector arrangement and method for an x-ray apparatus for generating projection or tomographic phase-contrast images of an examination subject, a beam of coherent x-rays is generated by an anode that has areas of different radiation emission characteristics arranged in bands thereon, that proceed parallel to grid lines of a phase grid that is used to generate the phase-contrast images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method of manufacturing surface textured high-efficiency radiating devices and devices obtained therefrom
InactiveUS20030075723A1Reduce power consumptionImprove Outcoupling EfficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActive matrixEmission efficiency
The present invention relates to radiation, preferably light emitting, devices with a high radiation emission efficiency and to fabricating these as small devices in an array of such devices. In one embodiment, the emitting devices can be placed in dense arrays. In another embodiment, outcoupling efficiency of the devices is improved, which leads to a reduced power consumption for a given radiation output power. In another embodiment, the speed of the radiation is increased, hence the serial bandwidth per optical channel is increased. The invention further relates to light emitting devices that exhibit uniform radiation emission characteristics. The light emitting devices (diodes, LEDs) of the present invention can be used for applications wherein two-dimensional LED arrays, particularly low-power arrays, are useful, such as in display technology. Active matrix displays relying on liquid crystals (e.g. integrated on CMOS circuitry) could be replaced by LED arrays. Dense and bright one-dimensional LED arrays are useful for example for printing and copying. Also for single LED applications it is important to have a maximum of photons escaping from the light emitting surface. The intensity of light per unit area (the brightness) is larger, and this is useful in many applications. Furthermore, the packaging cost can be reduced. In order to achieve a large global efficiency, many conventional LEDs need an elaborate package that includes a cavity with mirrors, because the light is emitted from more than one surface of the LED.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com