Patents
Literature
76 results about "Radiation scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Scattering of electromagnetic radiation is caused by the interaction of radiation with matter resulting in the reradiation of part of the energy to other directions not along the path of the incidint radiation. Scattering effectively removes energy from the incident beam.
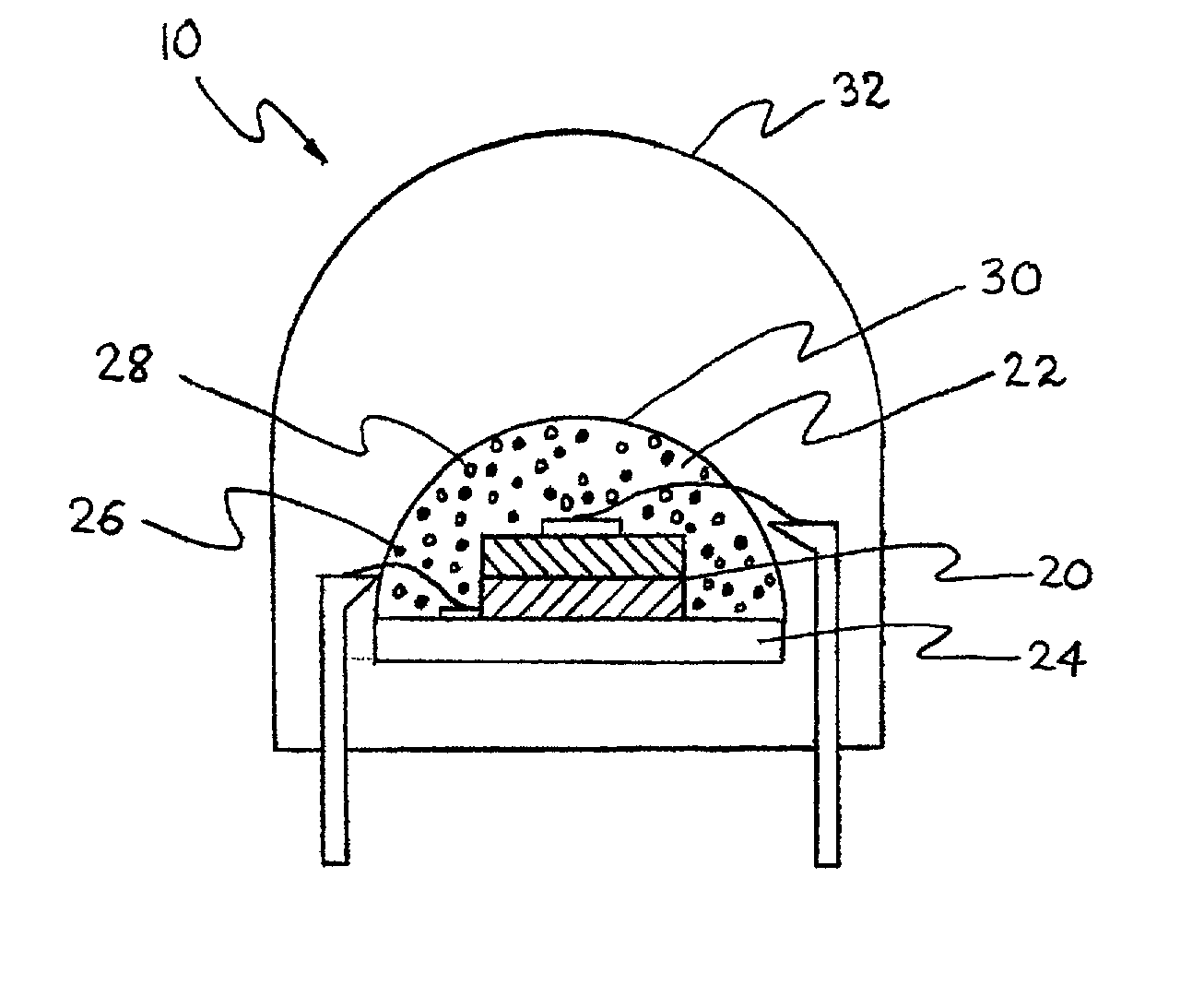
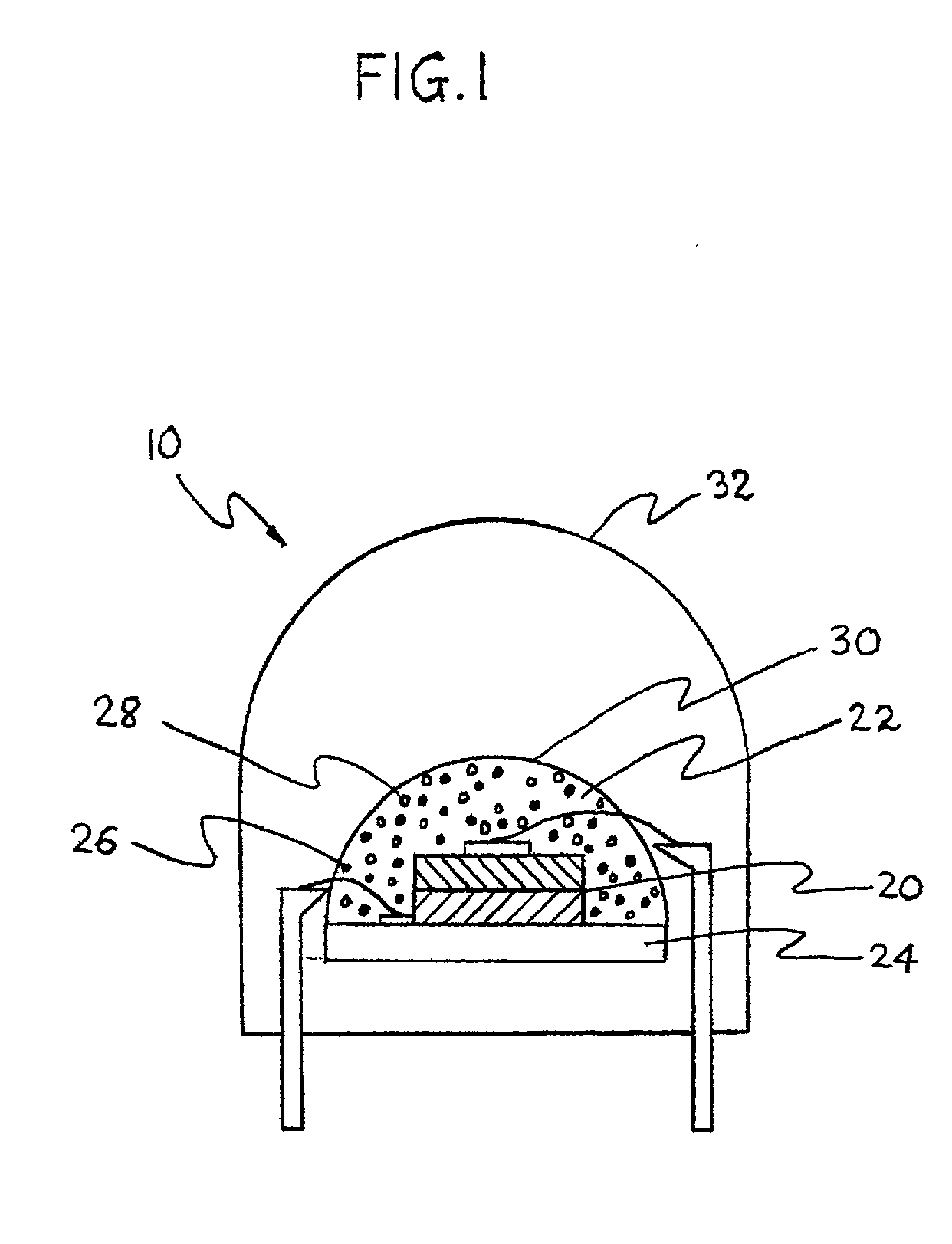
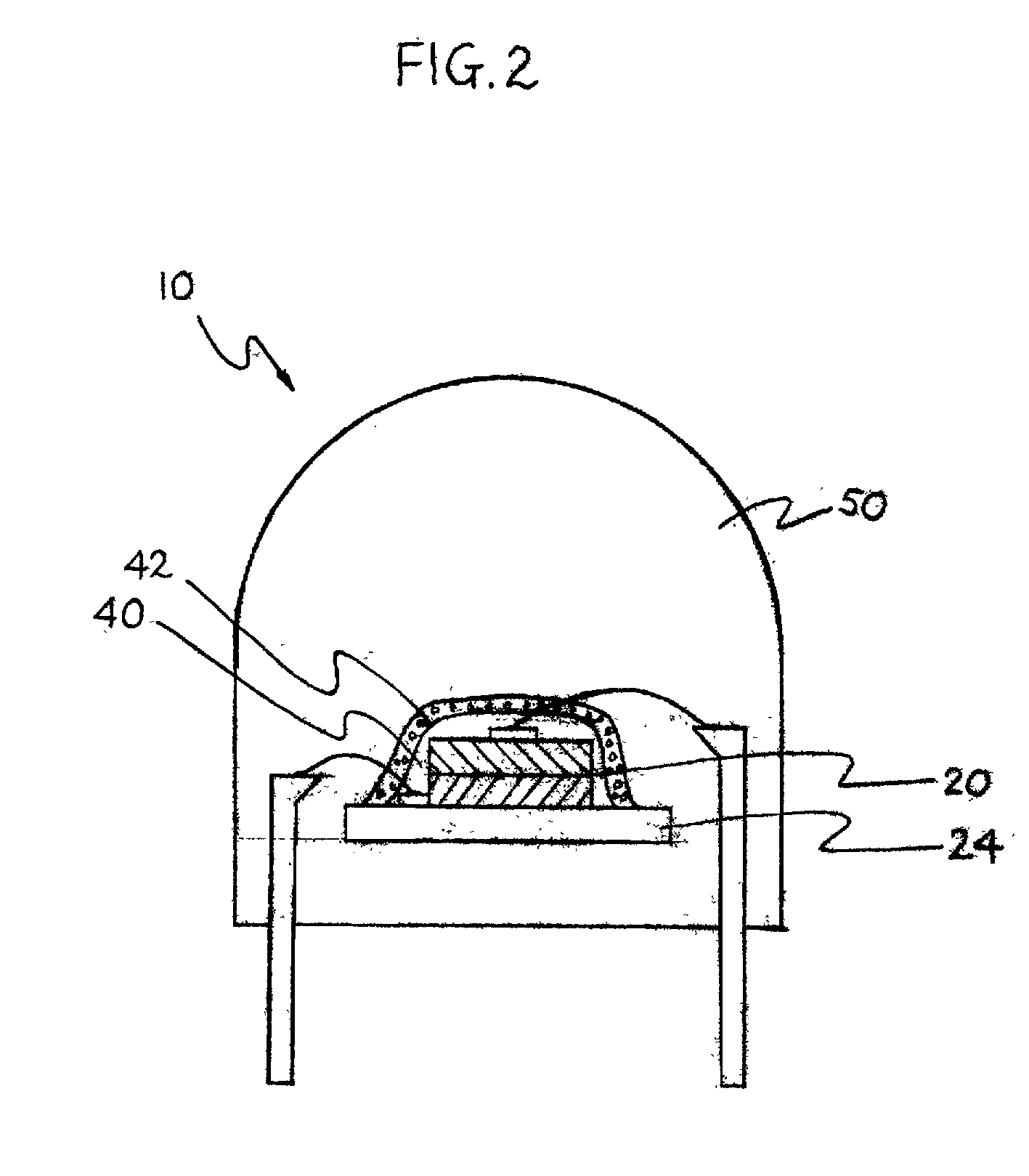
UV reflectors and UV-based light sources having reduced UV radiation leakage incorporating the same
InactiveUS20020180351A1Uniform colorUniform light intensityIncadescent screens/filtersMirrorsRadiation leakagePhosphor
UV reflectors incorporated in UV LED-based light sources reduce the amount of UV radiation emission into the surroundings and increase the efficiency of such light sources. UV reflectors are made of nanometer-sized particles having a mean particle diameter less than about one-tenth of the wavelength of the UV light emitted by the UV LED, dispersed in a molding or casting material surrounding the LED. Other UV reflectors are series of layers of materials having alternating high and low refractive indices; each layer has a physical thickness of one quarter of the wavelength divided by the refractive index of the material. Nanometer-sized textures formed on a surface of the multilayered reflector further reduce the emission of UV radiation into the surroundings. UV LED-based light sources include such a multilayered reflector disposed on an encapsulating structure of a transparent material around a UV LED, particles of a UV-excitable phosphor dispersed in the transparent material. Alternatively, the transparent material also includes nanometer-sized particles of a UV-radiation scattering material.
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
Electromagnetic radiation attenuating and scattering member with improved thermal stability
ActiveUS6912049B2Improve thermal stabilityLower requirementPhotometry using reference valueDiffusing elementsInvarSpectralon
The present invention provides a thermally stable reference member comprising, at least one radiation attenuating element and at least one radiation scattering element. The radiation attenuating element comprising at least one aperture for transmission of radiation therethrough. The attenuating and scattering elements placed in series so that radiation transmitted through the reference member passes through each of the attenuating and scattering elements. The attenuating and scattering elements of the reference member may further comprise a thermally stable mount to hold the elements in a selected position relative to each other, and in relation to an instrument, or the elements may be bonded together. The radiation attenuating element may be comprised of a material selected from the group consisting of INVAR, tungsten, brass, and a material substantially non-transparent for incident radiation, and the radiation scattering element may be comprised of a radiation scattering material selected from the group consisting of opalescent glass, SPECTRALON, PTFE, ZERODUR, fused silica, quartz, sapphire, diamond, and a transparent material with essentially low thermal expansion.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Apparatus for differentiating blood cells using back-scatter
InactiveUS6869569B2Material thermal conductivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhotodetectorRed blood cell
Blood cells of interest are readily distinguishable from other blood cells and look-a-like particles found in a blood sample by their back-scatter signature. A preferred method for differentiating platelets in a blood sample is to irradiate the cells and particles, one at a time, with a beam of radiation, and to detect back-scattered (reflected) radiation using a plurality of optical fibers to transmit the back-scattered radiation to a high-gain photodetector, e.g. a photomultiplier tube. Preferably, the back-scatter signal so obtained is combined with a second signal representing, for example, either the level of forward-scatter within a prescribed, relatively narrow angular range, or the level of side-scattered radiation, or the level of attenuation of the cell-irradiating beam caused by the presence of the irradiated cell or particle in the beam, or the electrical impedance of the irradiated cell or particle, to differentiate the cells of interest. The method and apparatus of the invention are particularly useful in differentiating platelets and basophils in a blood sample.
Owner:COULTER INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Electromagnetic radiation attenuating and scattering member with improved thermal stability
ActiveUS20040008343A1Photometry using reference valueDiffusing elementsThermal expansionRadiation scattering
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Multilayer optical display device
A multilayer optical device which comprises one or more radiation scattering layers, radiation absorption layers, tint layers, interfacial layers, adhesive layers, protective layers, matte, non-reflective, anti-glare, antistatic or embossed surface layers, focusing layers and supporting layers is described. Interfacial layers, adhesive layers, protective layers, tint layers, matte, non-reflective, anti-glare, antistatic or embossed surface layers, focusing layers and supporting layers may be optional in some embodiments of the invention. The device is used to display an image which is projected either in the transmission or reflection mode.
Owner:COOPER TERENCE ALFRED +1
Particle ID with narrow angle detectors
InactiveUS7072038B2Continuous monitoringOptimize disinfectionMaterial analysis by optical meansParticle size analysisParticle physicsRadiation scattering
A method for the identification of unknown particles contained in a fluid. The method utilizes a source of radiation and at least one radiation detector to measure the radiation scattered by an unknown particle in the fluid. The measurement for the unknown particle is compared with a standard radiation scattering pattern capable of uniquely identifying a previously identified particle and the unknown particle is identified based upon the comparison.
Owner:QUIST GREGORY M +1
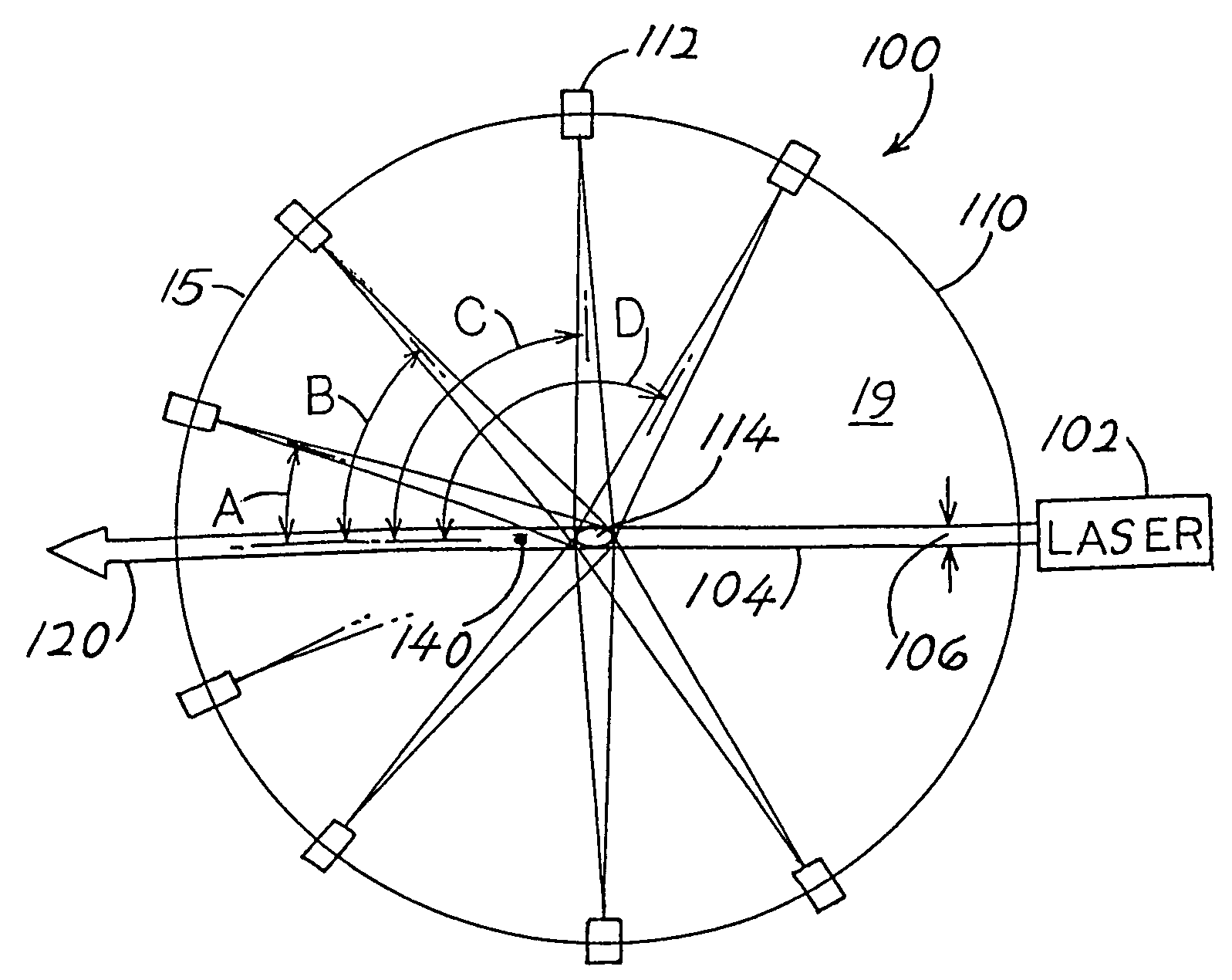
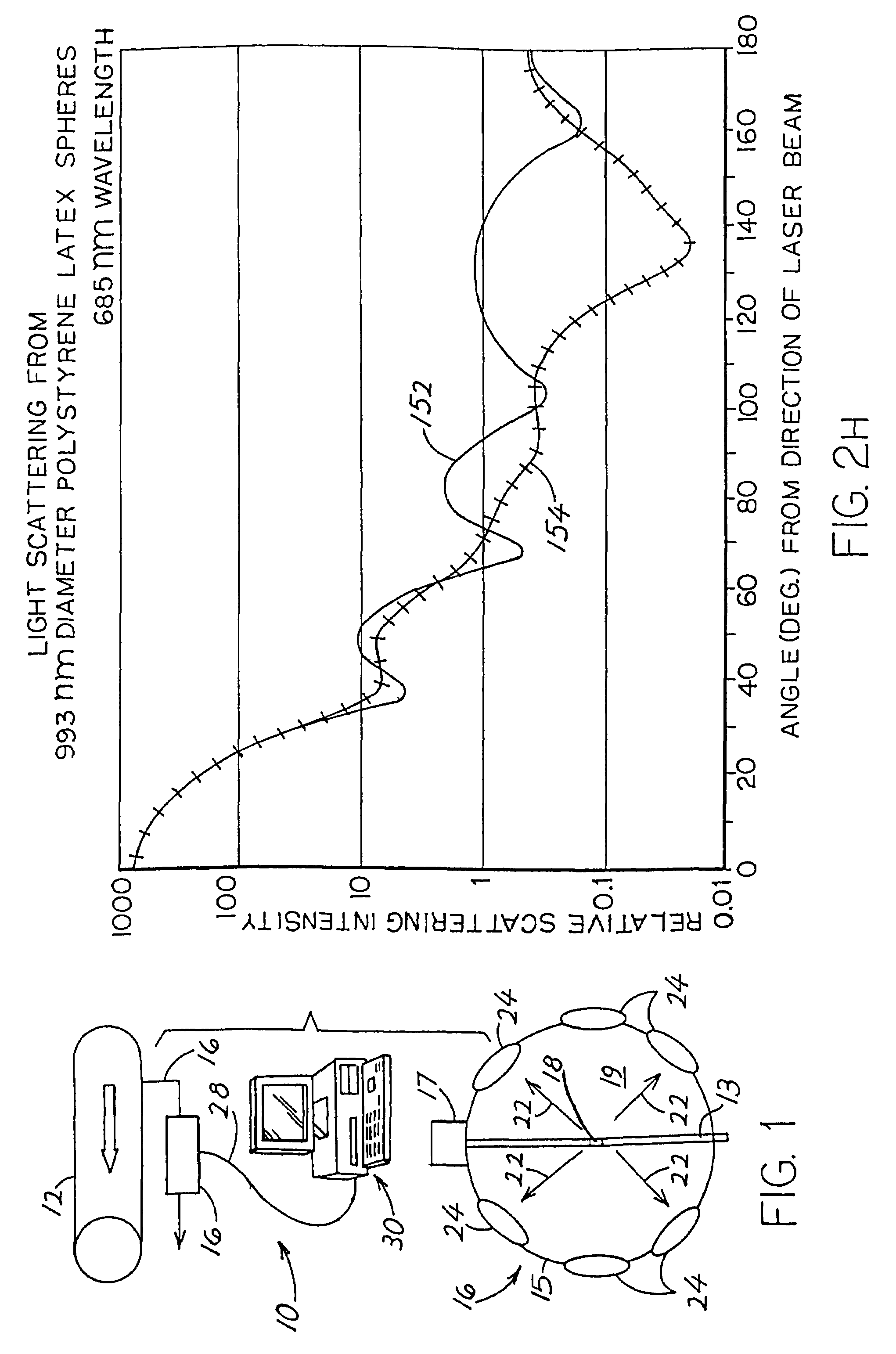
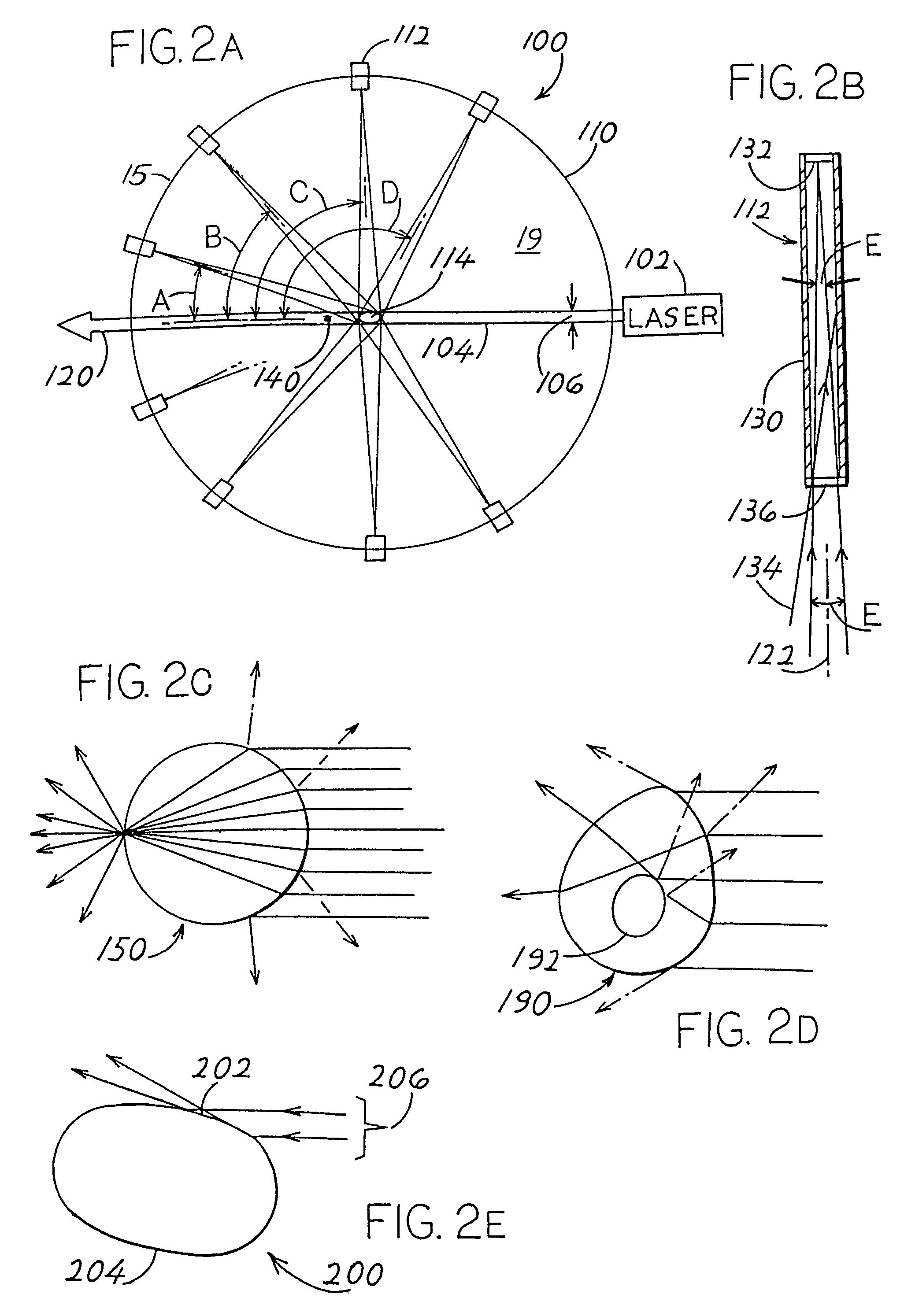
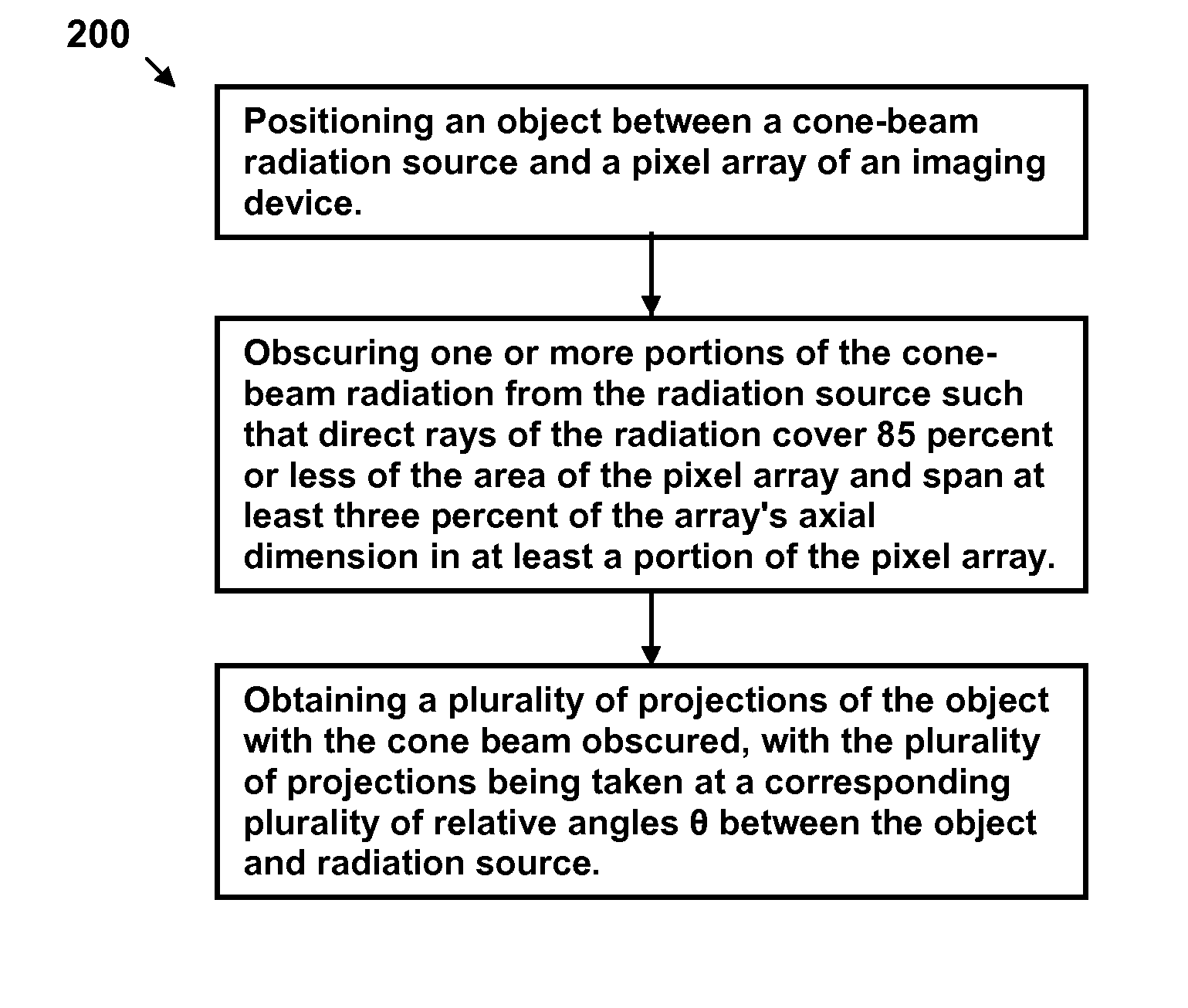
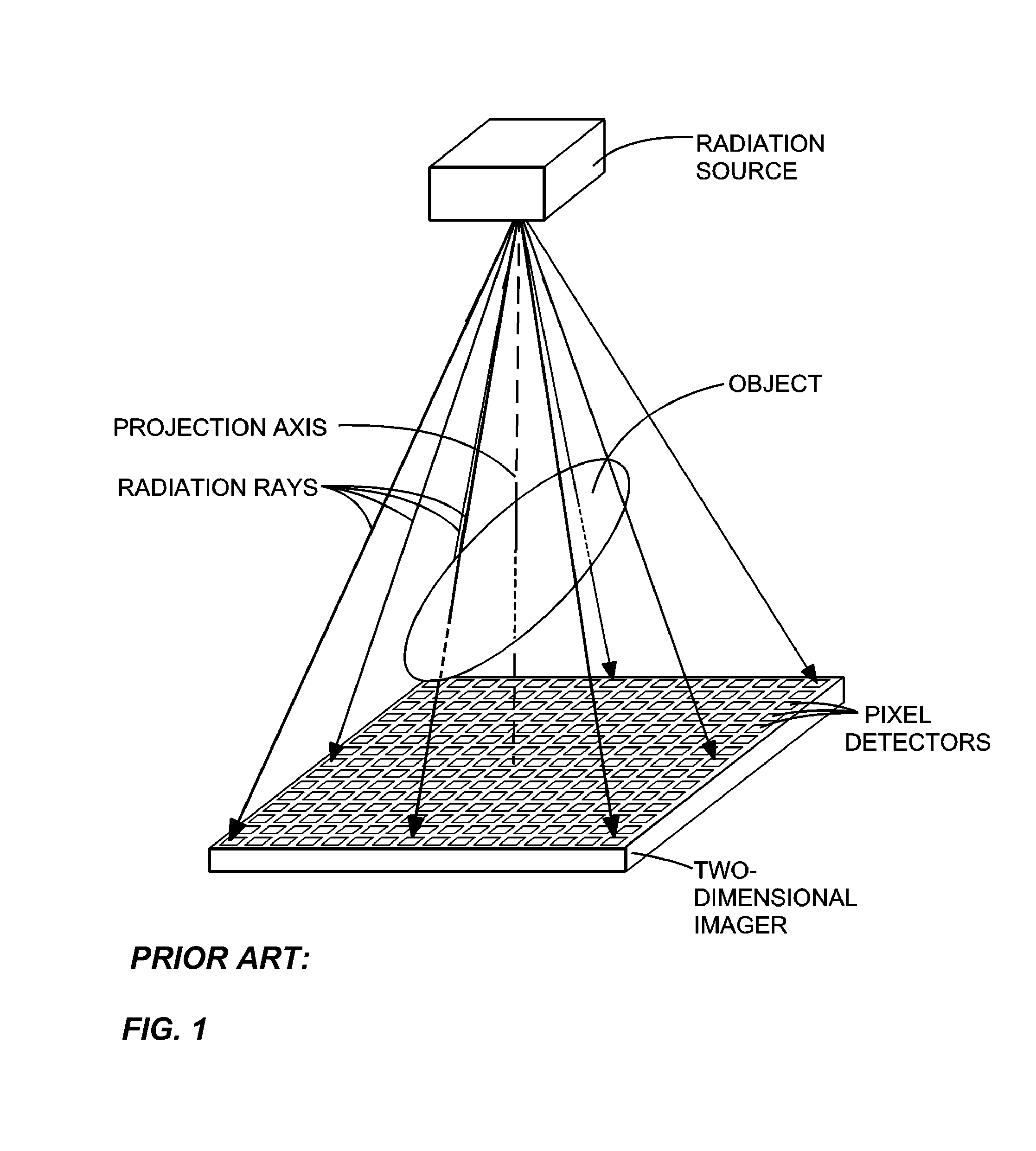
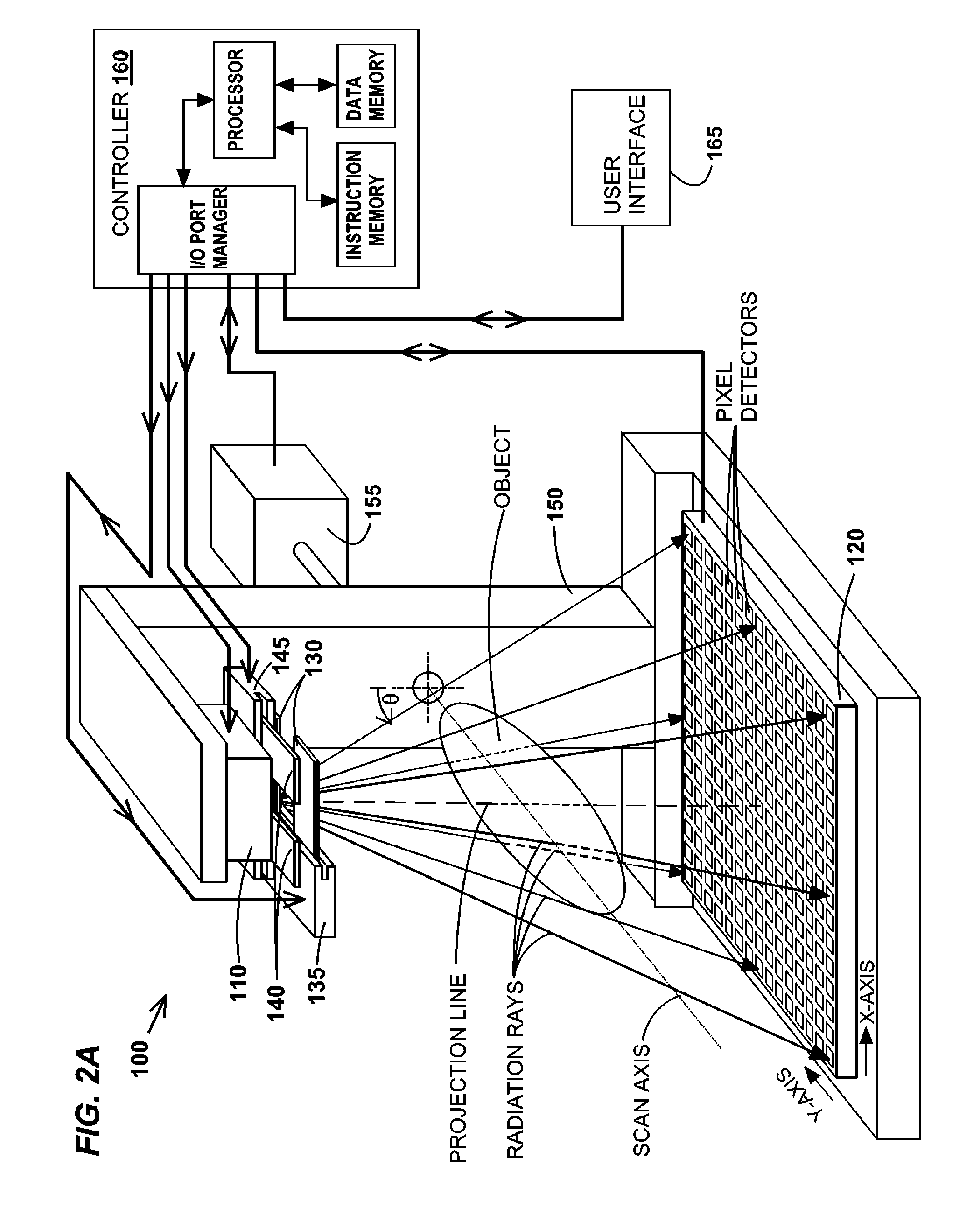
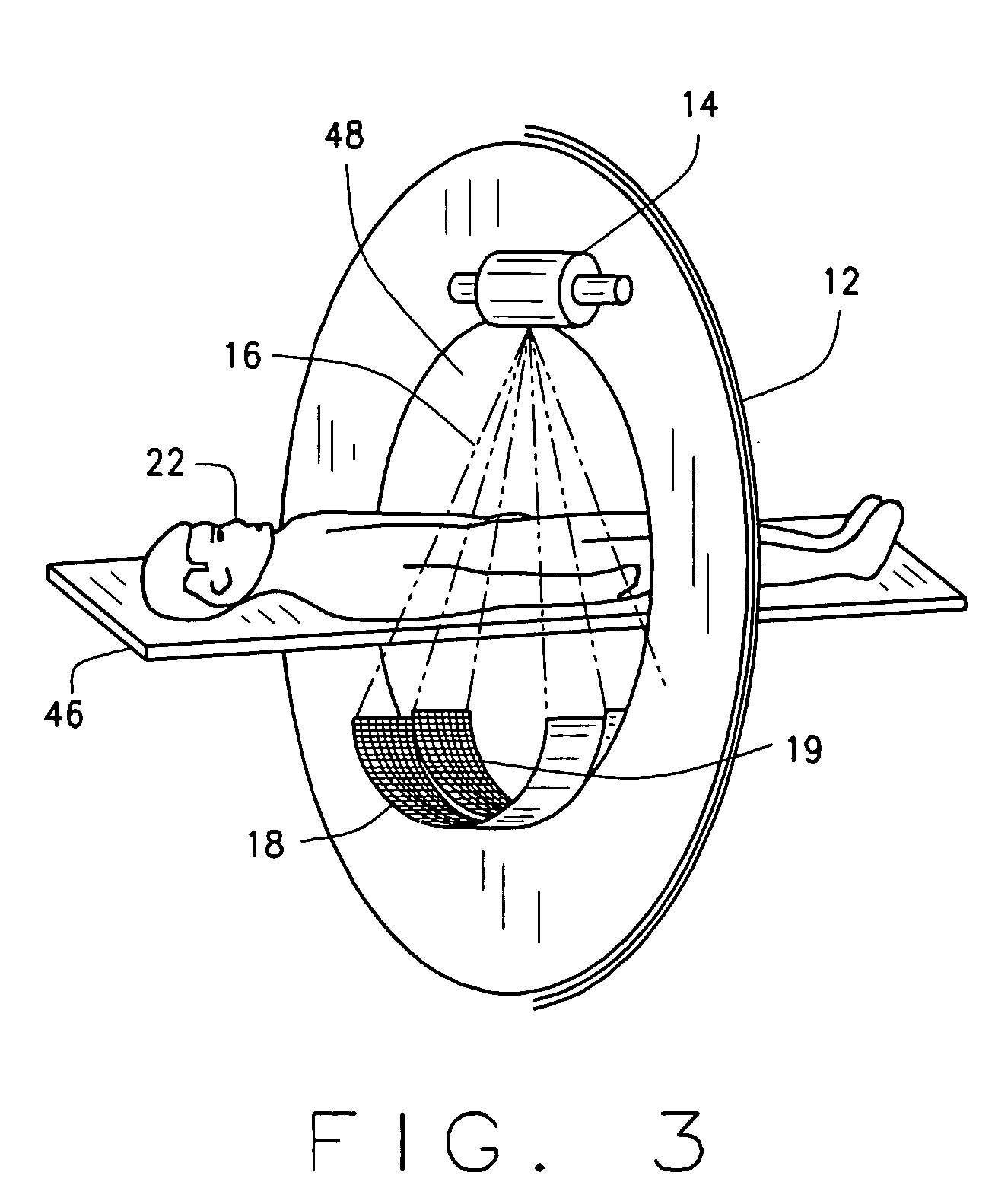
Methods, apparatus, and computer-program products for increasing accuracy in cone-beam computed tomography
ActiveUS8009794B2Reduce errorsImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSources of errorTomography
Disclosed are methods, systems, and computer-product programs for increasing accuracy in cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) by obscuring portions of the radiation source so that the radiation only passes through the specific areas of the patient related to the regions-of-interest to the doctor. The obscuring action causes less radiation scattering to occur in the patient's body, thereby reducing a major source of error in the image accuracy caused by scattered radiation. Scattered radiation received by detector pixels that are obscured by direct-line of sight radiation may be used to estimate the scattered radiation in the un-obscured portion, which can be used to further increase the accuracy of the image.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
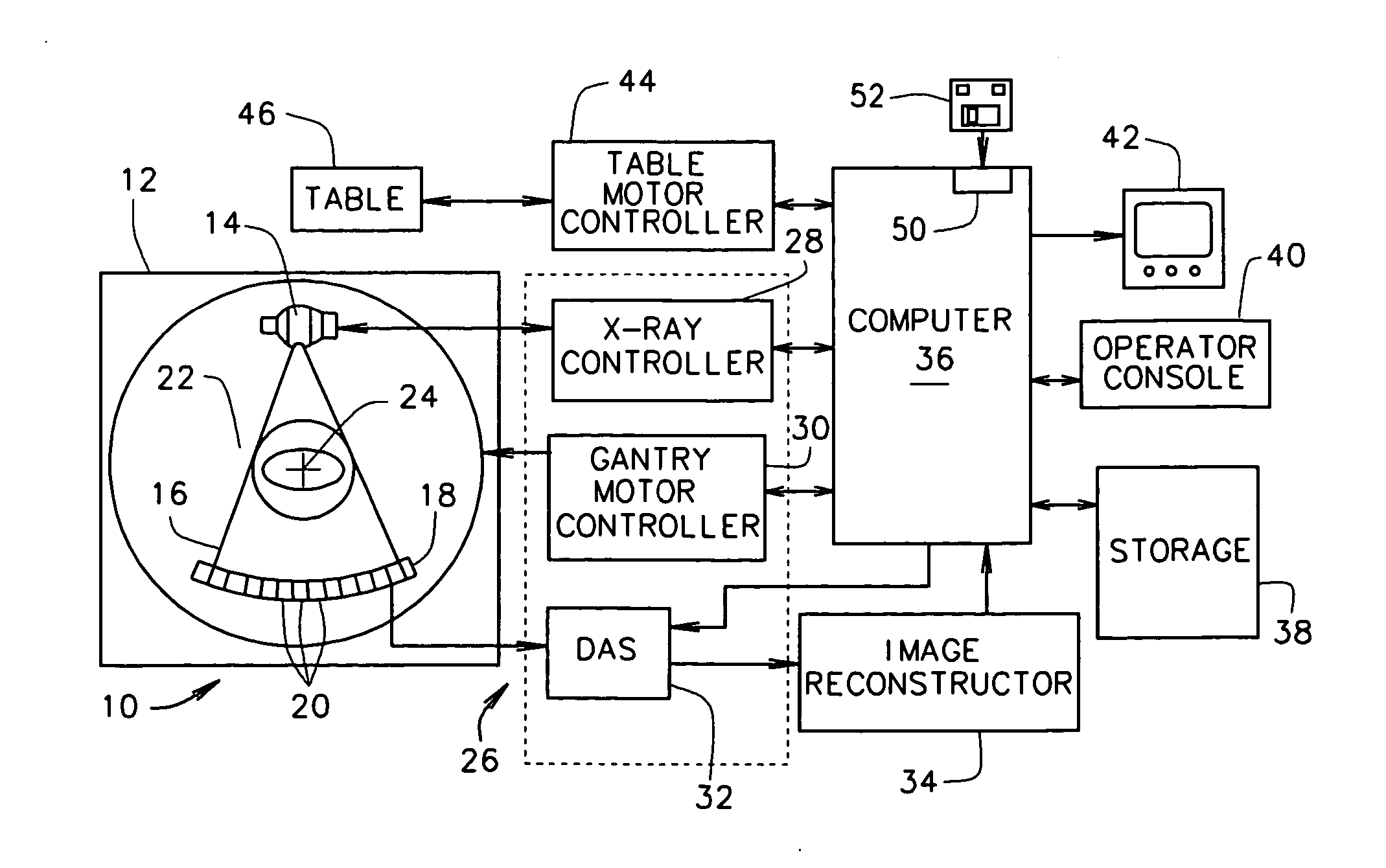
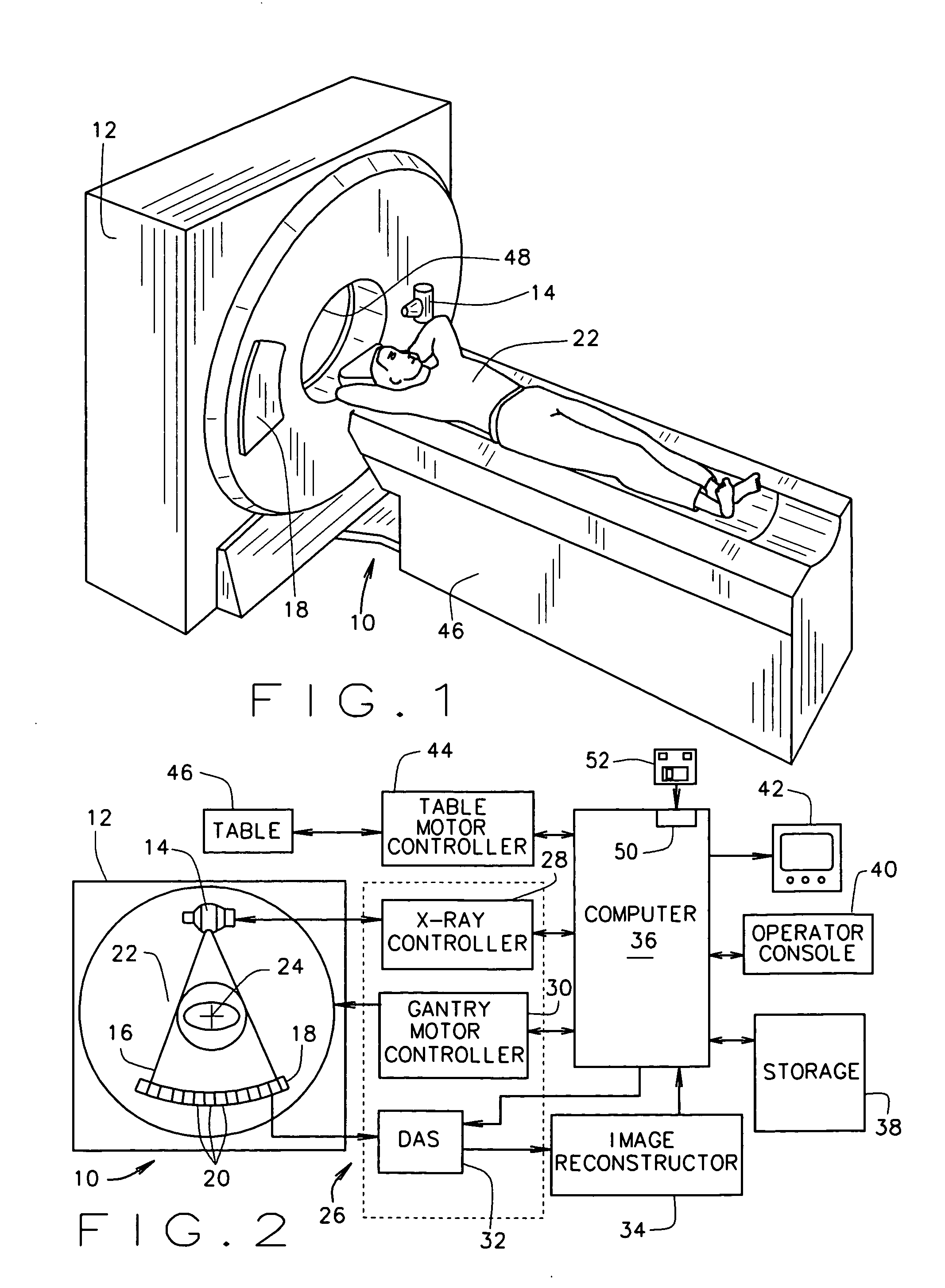
Multidetector CT imaging method and apparatus with reducing radiation scattering
ActiveUS20050147201A1Reduce image degradationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingMultidetector ctMulti slice ct
A method for scanning an object to reduce image degradation includes scanning the object in a helical mode using a multi-slice CT imaging system having a plurality of detector arrays arranged along a z-axis direction and a radiation source having a beam focal spot. The method further includes wobbling the focal spot of the radiation source in the z-axis direction during the scanning to selectively preferentially illuminate individual detector arrays through the scanned object for each view. Data is collected from each detector array for each view only when the detector array from which data is being collected is selectively illuminated.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
UV-radiation protectant compositions
A substantially aqueous composition comprising one or more particle encapsulated sunscreen active agents, at least one volatile additive, and at least one UV-radiation scattering agent, whereby the composition provides an SPF greater than 30.
Owner:MSD CONSUMER CARE INC
System and method for visualizing needle entry into a body
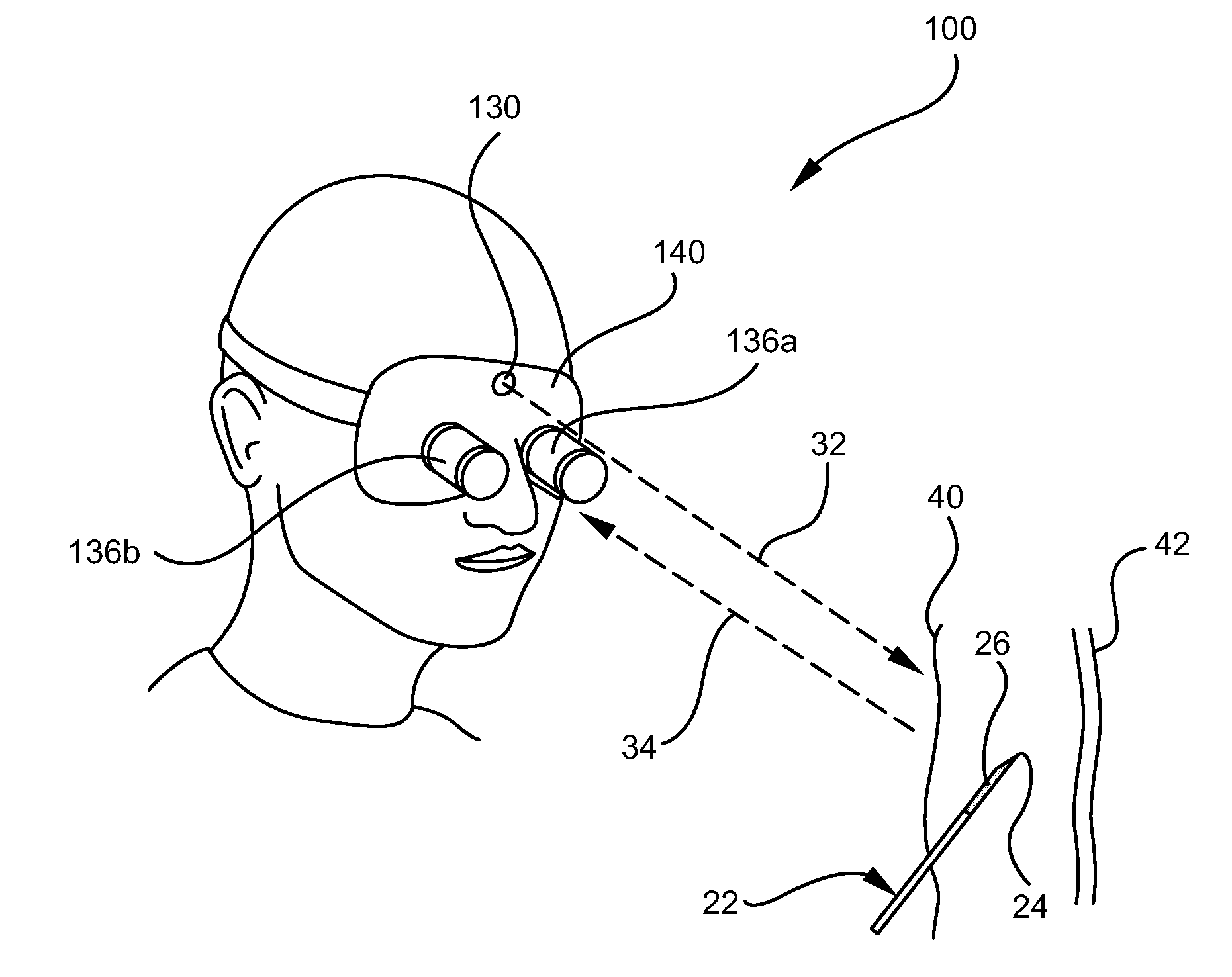
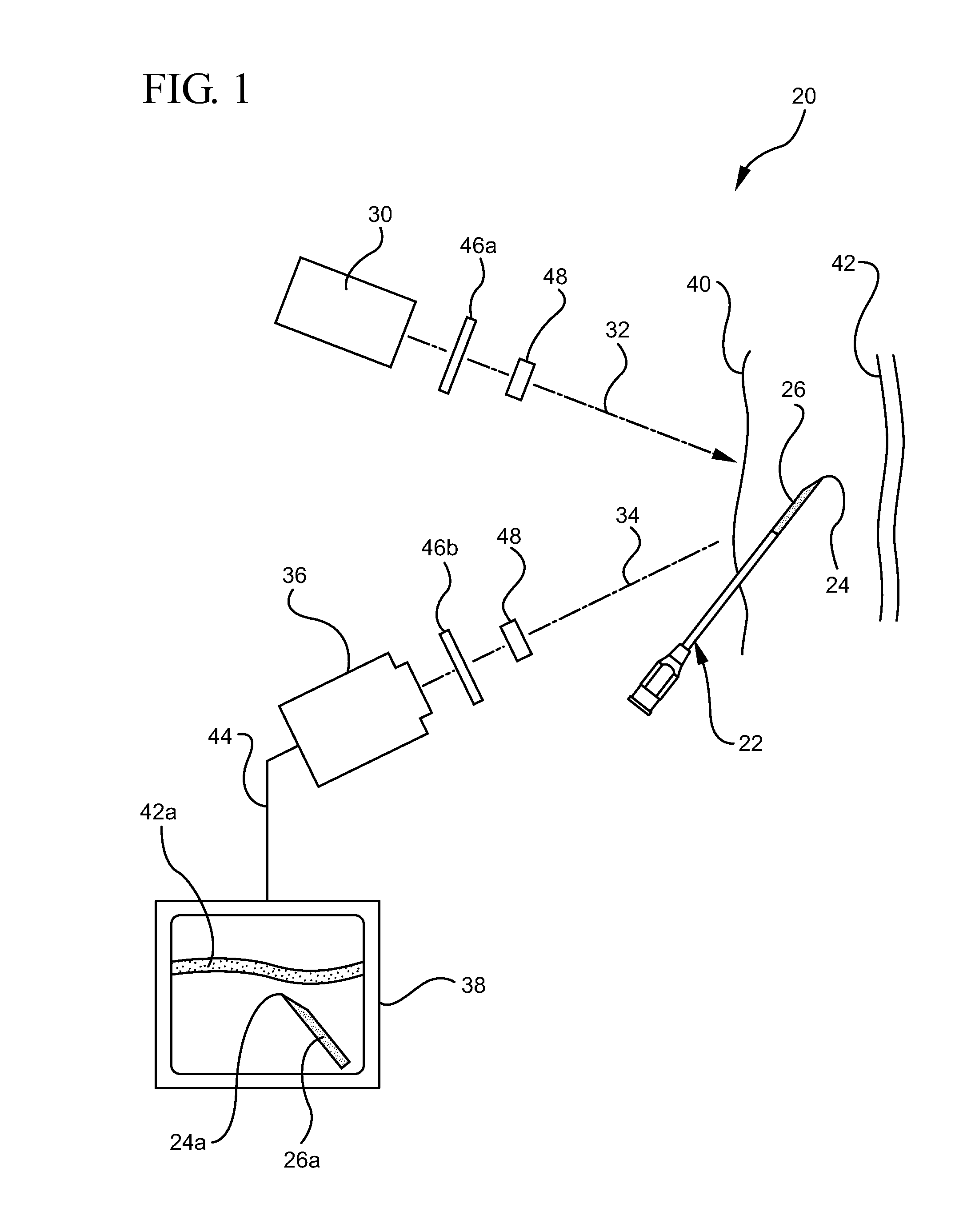
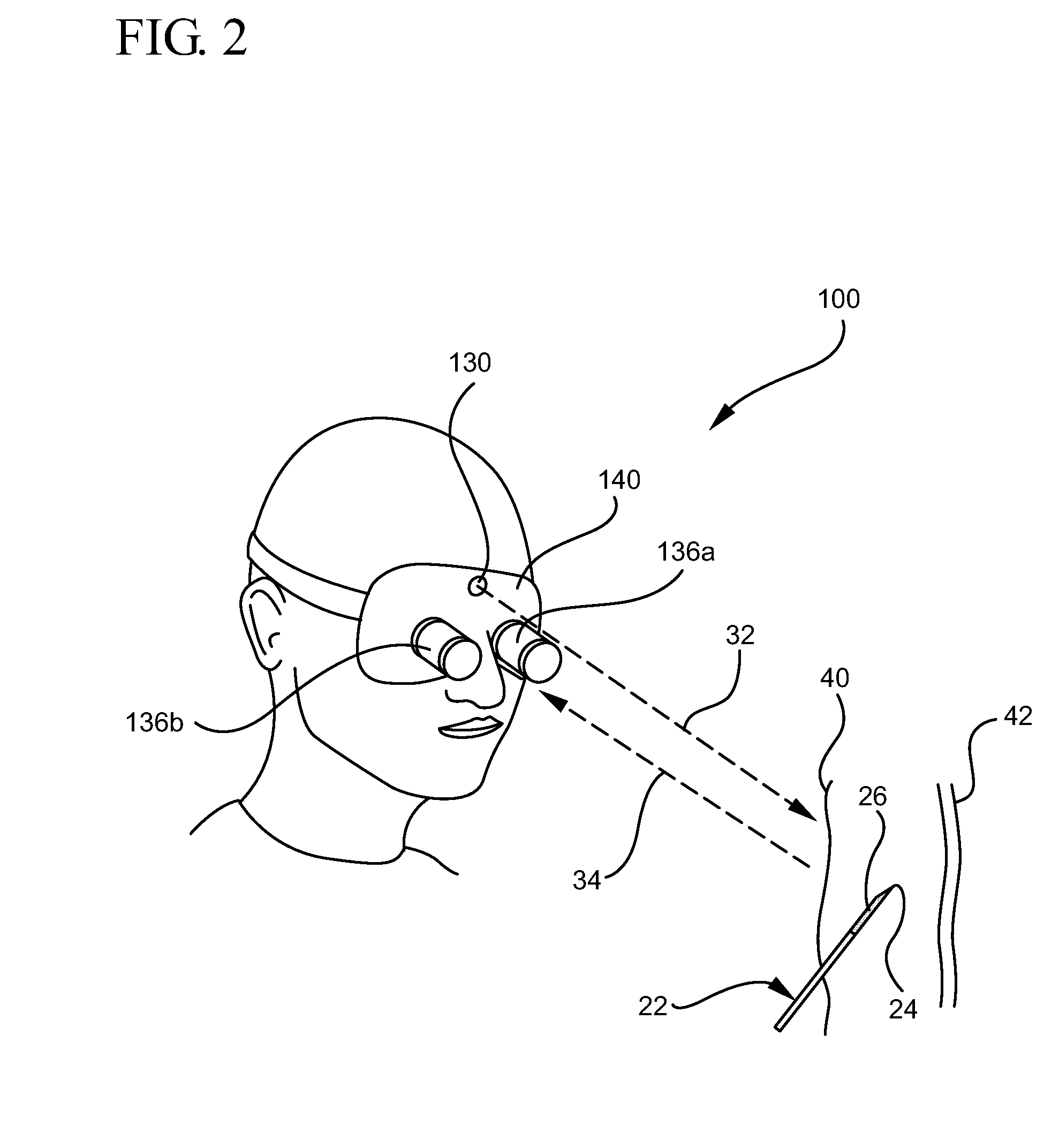
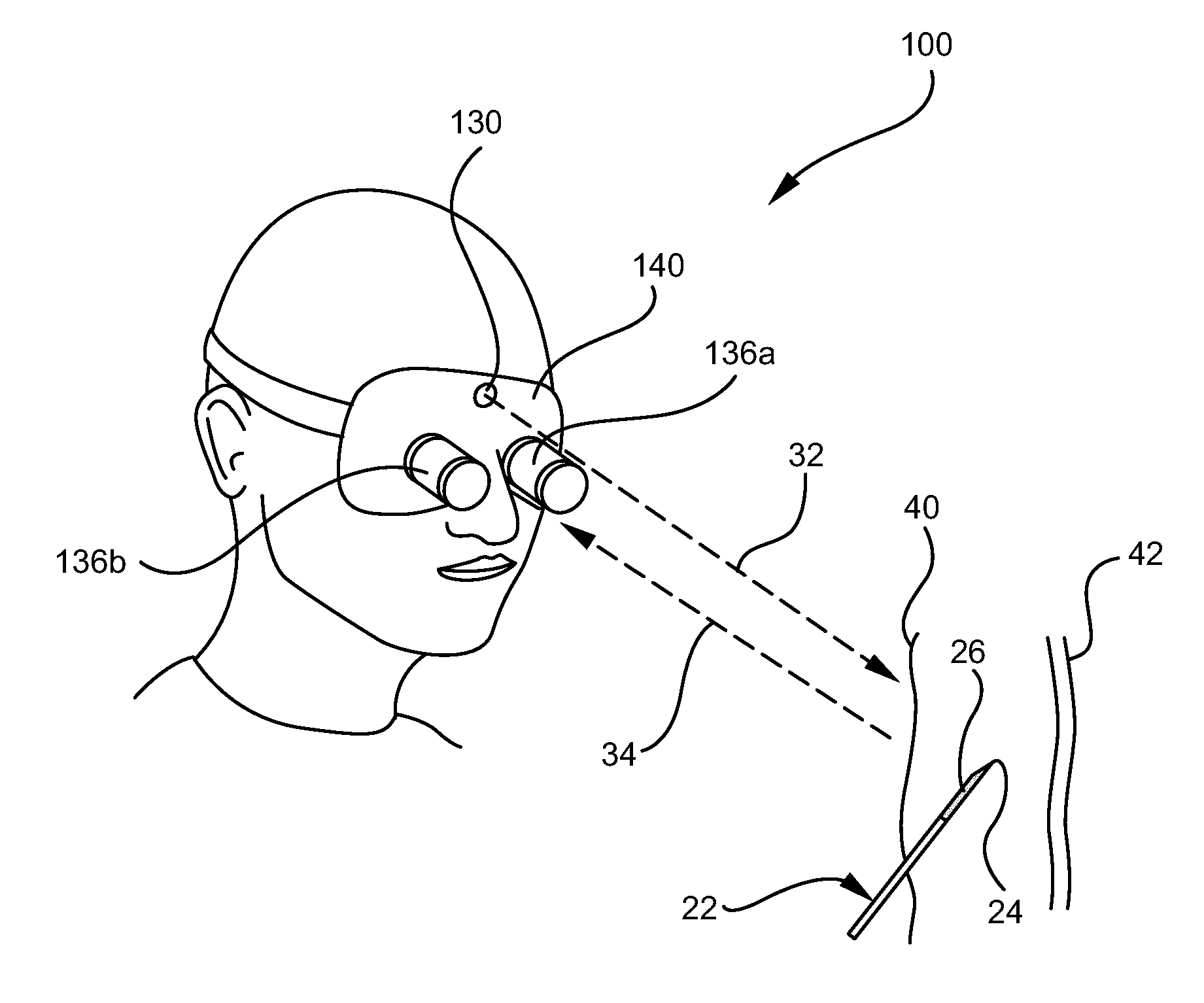
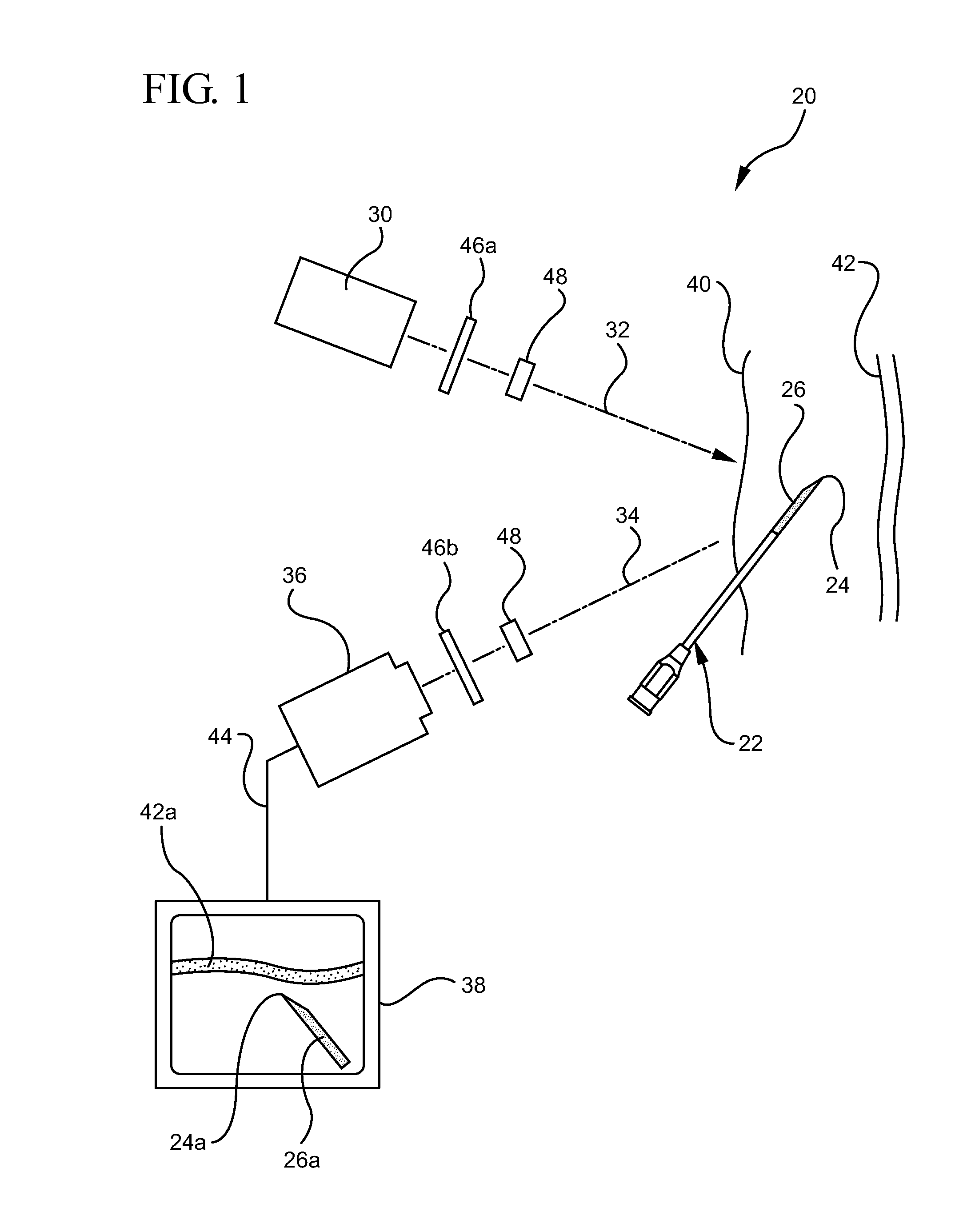
ActiveUS20110009738A1Performed accurately and rapidlyDiagnostics using lightSurgical needlesAnatomical structuresMedicine
A system for visualizing needle entry into a body is presented. The system includes a needle for entering a body. The needle is coated with a radiation scattering coating on at least a portion of the needle. The system additionally includes a radiation visualization device which detects reflected radiation directed at a target body and enables medical personnel to view anatomical structures such as a blood vessel along with the inserted needle within a body.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
A system and method of determining a position of a radiation scattering/reflecting element
A method and system for determining the position of a radiation scattering / reflecting element, where the radiation emitter is provided at a surface of a radiation transmissive element an on which radiation is incident. This incident radiation is scattered / diffused / reflected by the scattering / reflecting element and guided by the transmissive element toward a detector able to determine the position of the element.
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
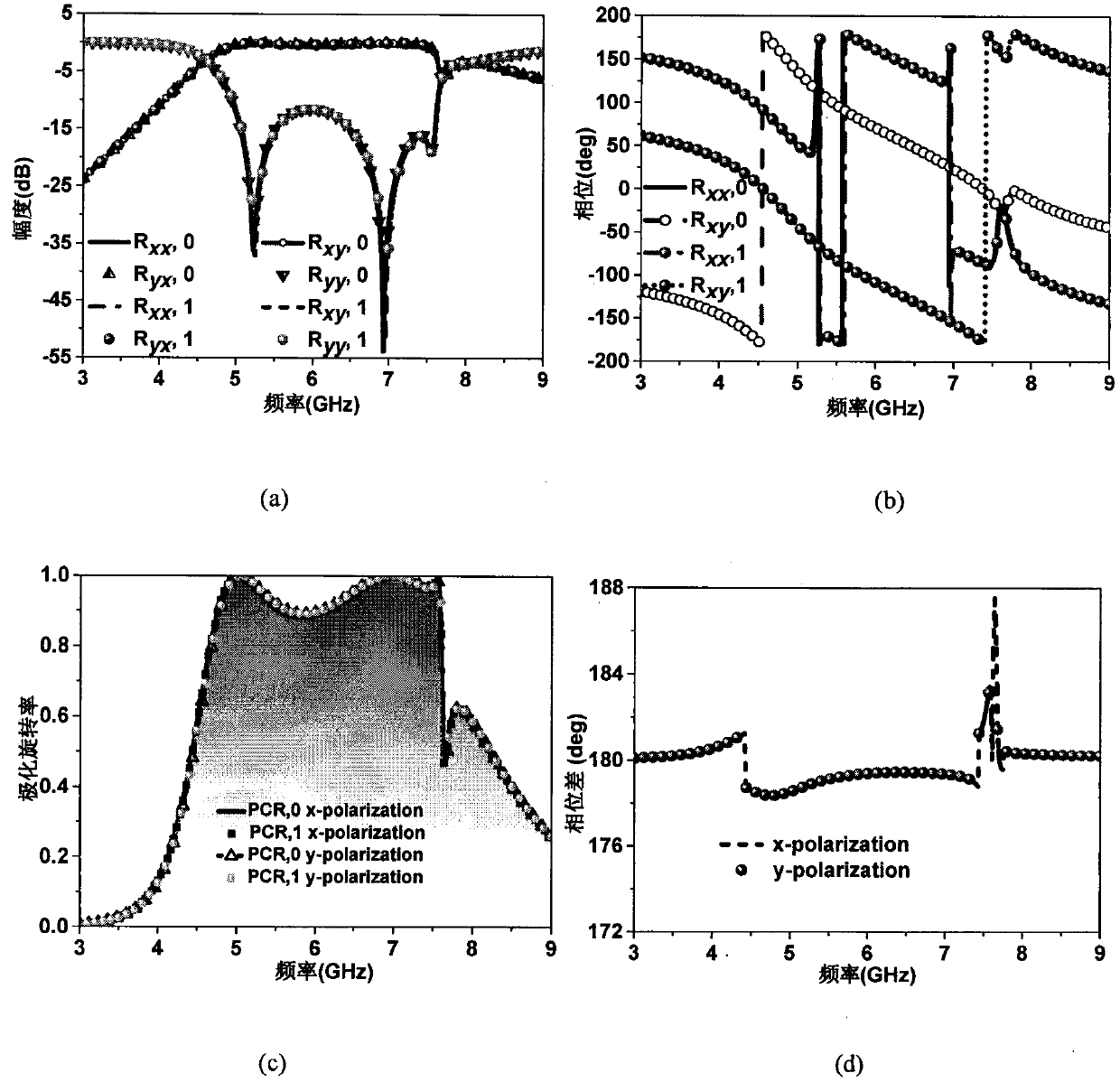
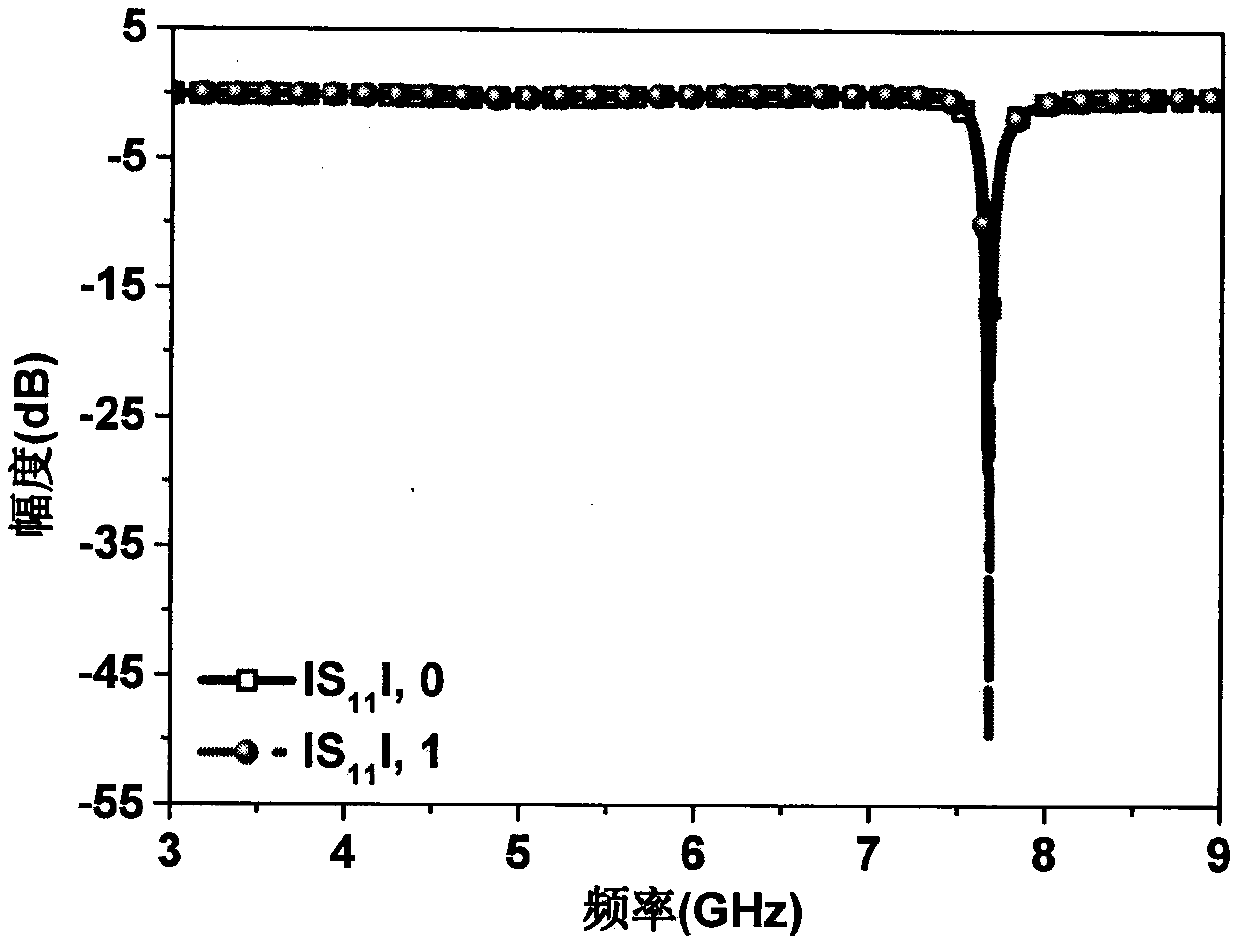
Radiation scattering regulated 1-bit excitable digital coding metasurface
The invention provides an exciteable digital coding metasurface unit of a cuboid structure, the upper surface and the lower surface of the exciteable digital coding metasurface unit are square, and the exciteable digital coding metasurface unit comprises a dielectric plate, a dielectric plate upper surface metal patch, a dielectric plate lower surface metal patch, a metal probe penetrating throughthe upper surface and the lower surface of the dielectric plate and an SMA interface in the lower surface of the dielectric plate. 1bit coding is carried out on the metasurface unit and a 90-degree rotating unit of the metasurface unit, and a 1bit excitable digital coding metasurface array is formed through a chessboard array. The single-station RCS of 10 dB is reduced to cover 4.88 GHz to 7.36 GHz, the maximum reduction amount exceeds 30 dB, and the radiation bandwidth covers 7.59 GHz to 7.64 GHz. Linear polarization, left-handed circular polarization and single-beam and four-beam radiationcan be realized through different excitation conditions. According to the method, the 1bit digital coding metasurface can be excited, the working characteristics of the digital coding metasurface areexpanded, and the application range of the metasurface is greatly expanded.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
Simulation method used for woodland complex scene high-spectrum remote sensing data
InactiveCN101477197AApproximately goodWave based measurement systemsSpecial data processing applicationsSensing dataSky
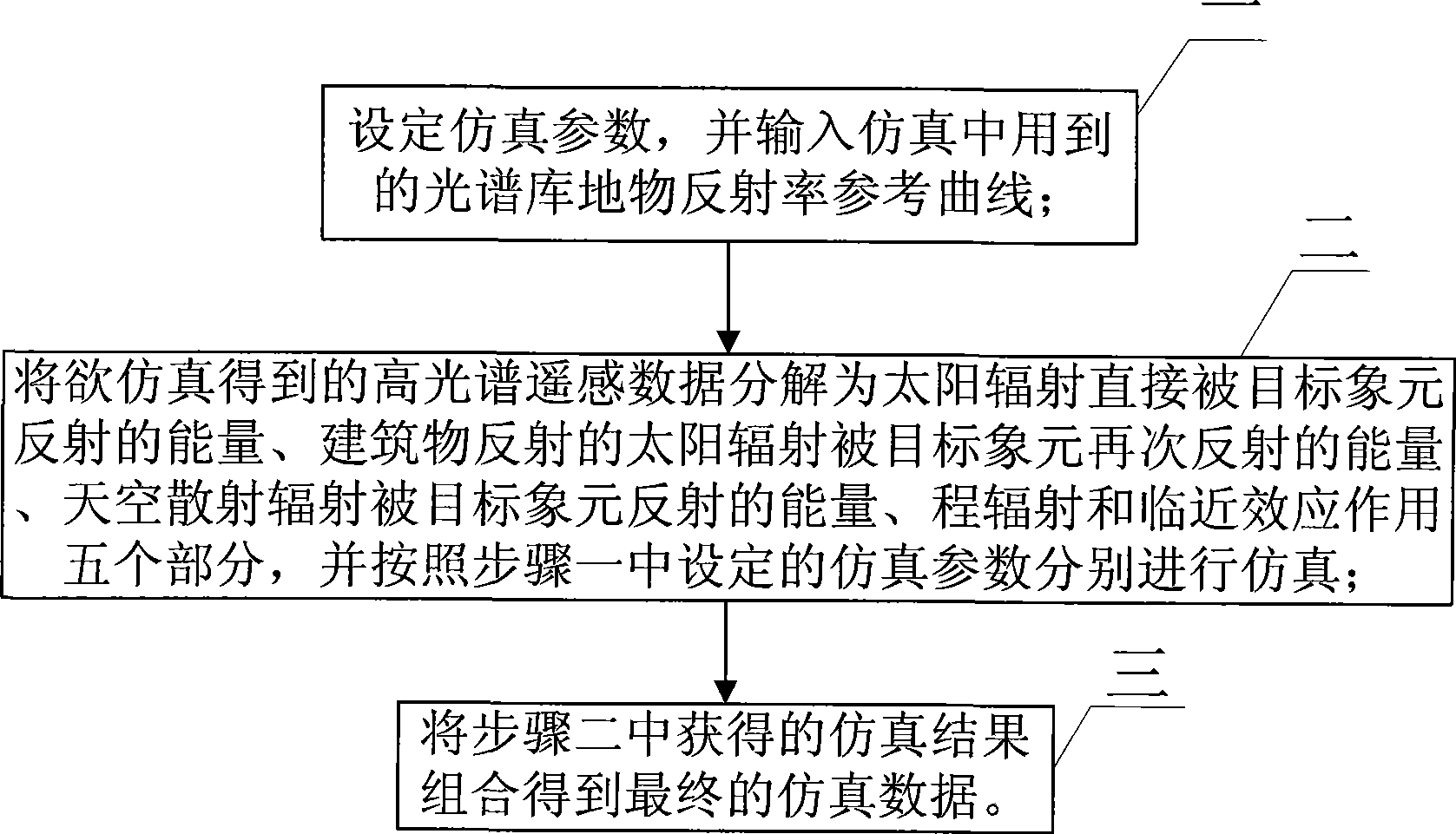
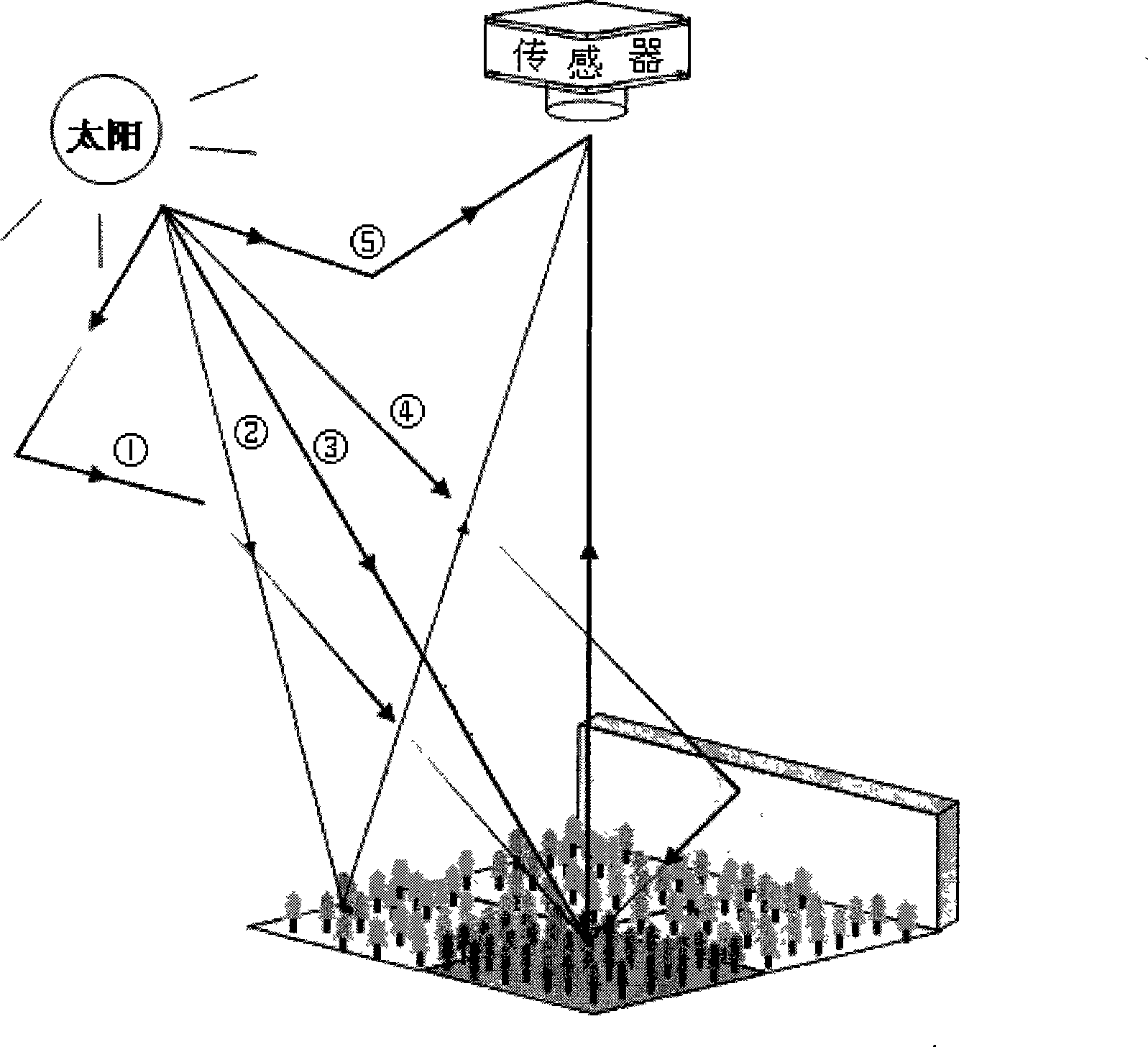
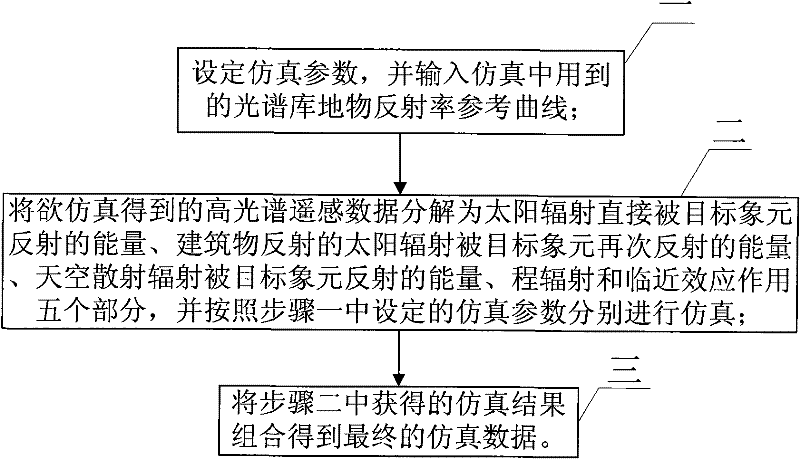
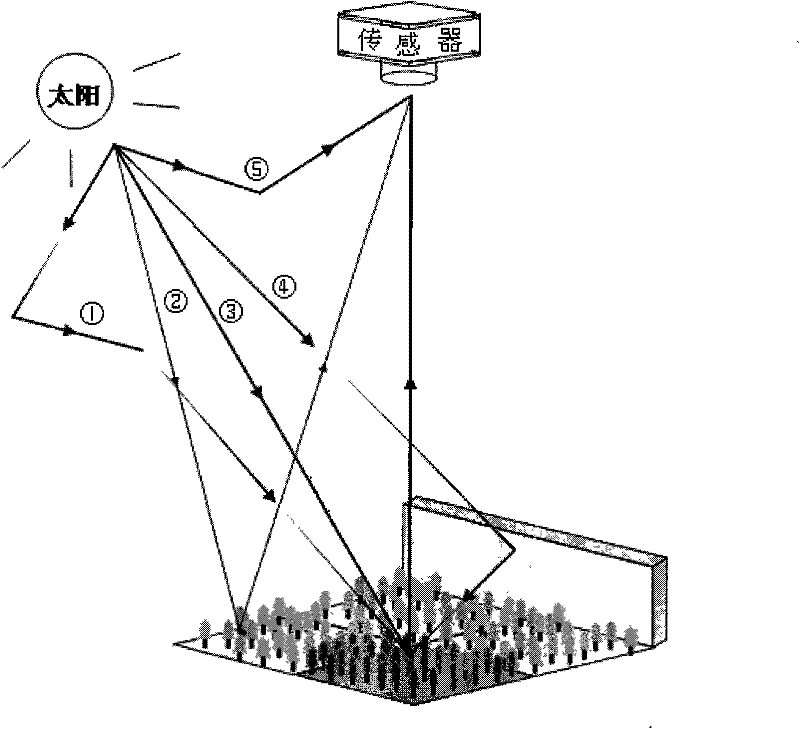
The invention provides a method for emulating high spectroscopic remote sensing data used in a woodland complex scene, relates to the technical field of high spectroscopic remote sensing data emulation, and solves the problem that the prior method for emulating the high spectroscopic remote sensing data is not applicable to the high spectroscopic remote sensing data under the condition that a tall building exists near the woodland as height factor of a ground object is not considered. The method comprises the following steps: 1, setting an emulation parameter, and inputting a reference curve of ground and object reflectivity of a spectrum library used in emulation; 2, resolving high spectroscopic remote sensing data to be acquired in emulation into energy of solar radiation directly reflected by a target pixel element, energy of building reflected solar radiation which is reflected by the target pixel element once again, energy of sky radiation scattering which is reflected by the target pixel element, path radiation and proximity effect, and carrying out emulation respectively according to the emulation parameter in the step 1; and 3, combining emulation results acquired in the step 2 to acquire the final emulation data. The method provides economic and high-quality emulation data for research of post-processing of the high spectroscopic remote sensing data.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Multidetector CT imaging method and apparatus with reducing radiation scattering
ActiveUS7187748B2Reduce image degradationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingMultidetector ctMulti slice ct
A method for scanning an object to reduce image degradation includes scanning the object in a helical mode using a multi-slice CT imaging system having a plurality of detector arrays arranged along a z-axis direction and a radiation source having a beam focal spot. The method further includes wobbling the focal spot of the radiation source in the z-axis direction during the scanning to selectively preferentially illuminate individual detector arrays through the scanned object for each view. Data is collected from each detector array for each view only when the detector array from which data is being collected is selectively illuminated.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
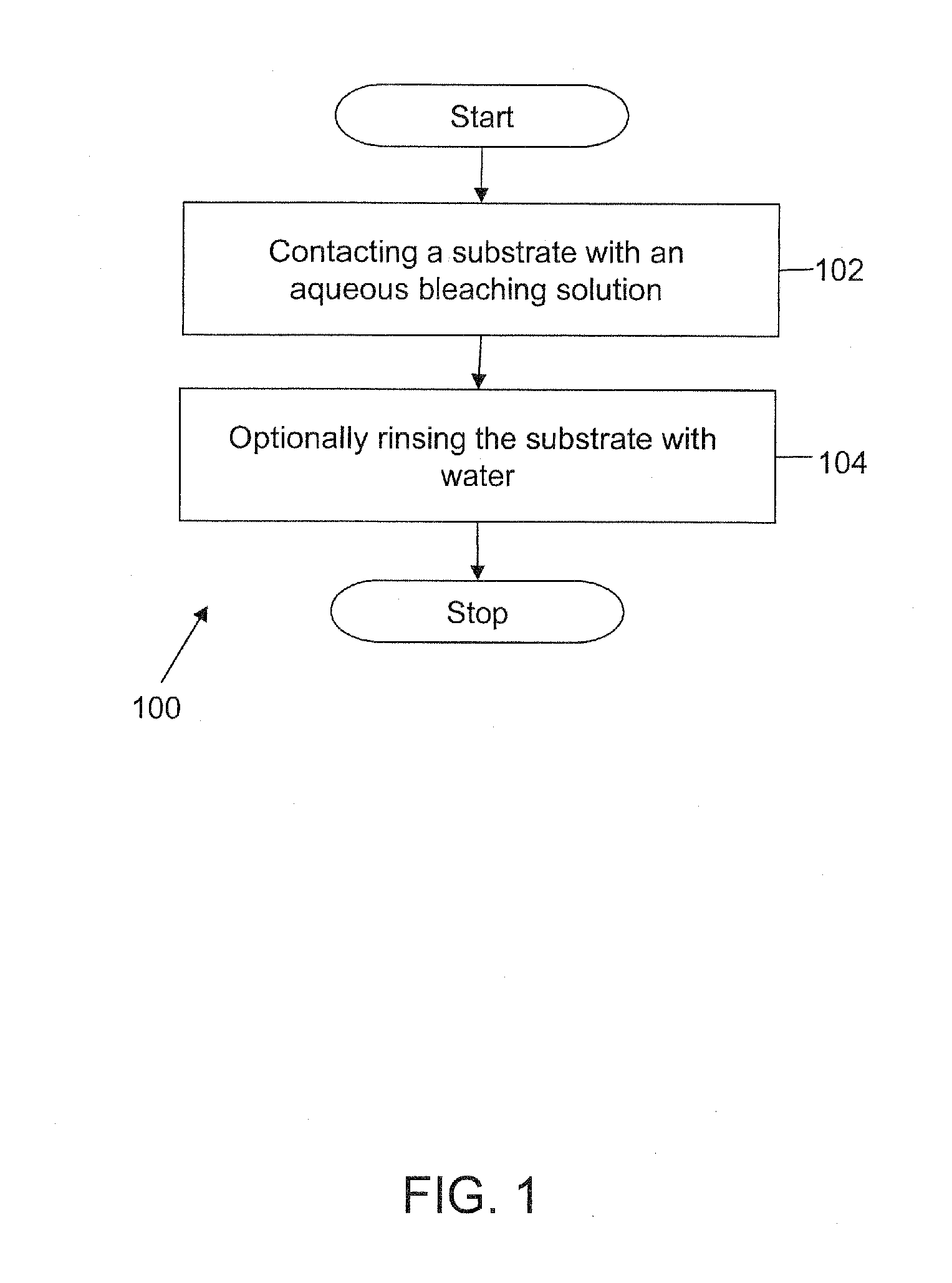
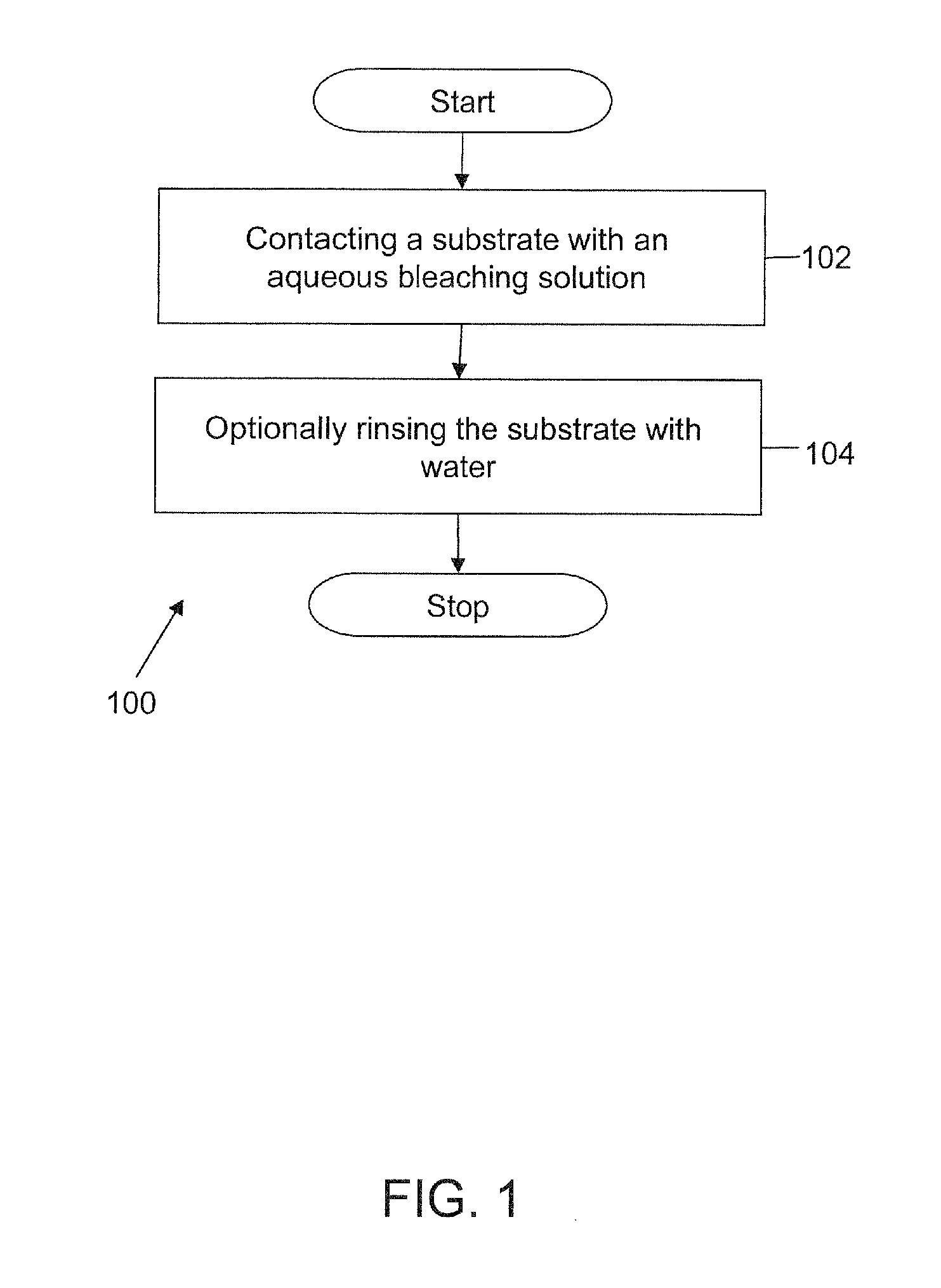
Oxidizing Bleach Composition
The invention provides an aqueous bleaching solution for substrate treatment. The aqueous bleaching solution features a source of oxidant and a plurality of optically functional nanoparticles. The optically functional nanoparticles are nanoparticles in the range of about 0.1 nanometers to about 400 nanometers in size. The aqueous bleaching solution may optionally include one or more an oxidant-stable surfactants and optionally, one or more oxidant-stable polymers, and adjuncts. The optically functional nanoparticles are extremely stable in the aqueous bleaching solution and remain substantially suspended in the aqueous bleaching solution due to their extremely small size despite having an average density greater than that of the bleaching solution. The optically functional nanoparticles provide at least one optical functional benefit to the bleaching solution owing to their uniform and stable suspension throughout the solution, including such benefits as uniform light absorption, light and radiation scattering, fluorescent emission, phosphorescent emission, coloration, and visual aesthetic benefits and the like. Further, optically functional benefits include those benefits provided to a substrate or surface treated with the aqueous bleaching solutions whereby the optically functional property is transferred either temporarily or permanently to the substrate or surface following contact with bleaching solutions containing the optically functional nanoparticles.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
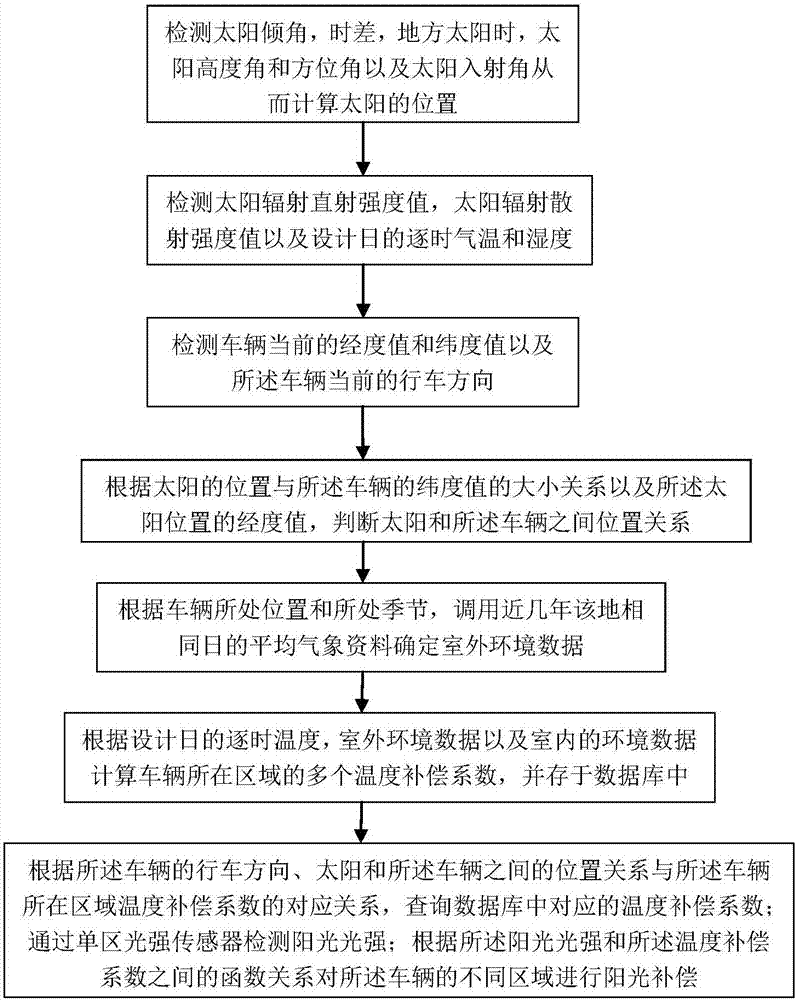
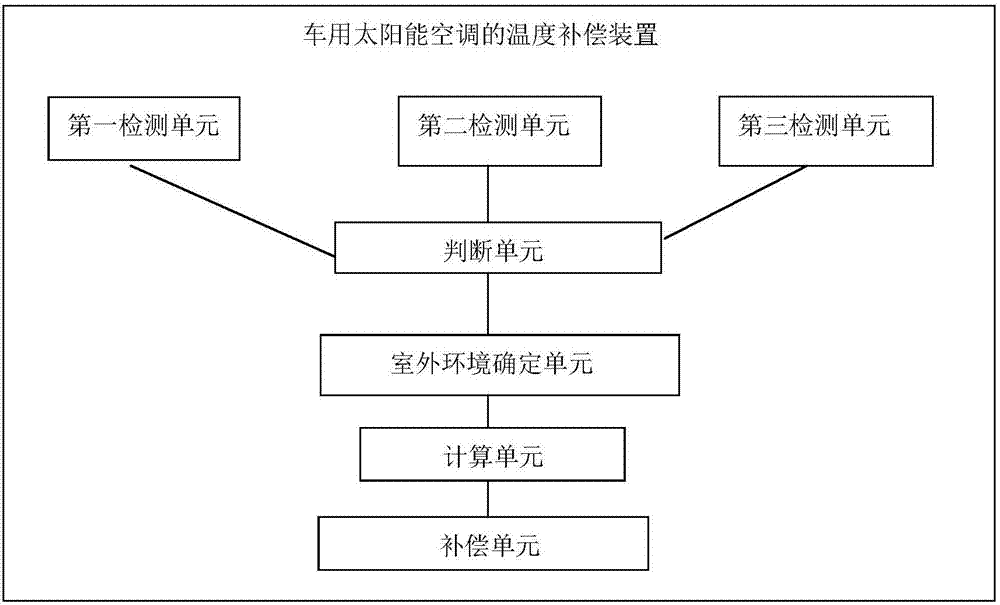
Temperature compensation method and system of solar air conditioner for car
ActiveCN106864205ALow costReduce complexityAir-treating devicesVehicle heating/cooling devicesLongitudeEngineering
Provided are a temperature compensation method and system of a solar air conditioner for a car. The method comprises the steps that 1, the position of the sun is detected; 2, the sun radiation perpendicular incidence intensity value, the sun radiation scattering intensity value and designed hourly temperature and humidity are detected; 3, the current longitude value and latitude value and the running direction of the car are detected; 4, the position relation between the sun and the car is judged; 5, outdoor environment data is determined; 6, a plurality of temperature compensation coefficients of the area where the car is located are calculated and stored in a database; 7, the corresponding temperature compensation coefficients in the database are queried, the sun light intensity is detected through a single-area light intensity sensor, and sunlight compensation is carried out on different areas of the car according to the function relation between the sunlight intensity and the temperature compensation coefficients and serves as temperature compensation. According to the method, the light intensity and temperature are coupled, therefore, general use of the solar air conditioner for the car is achieved, and the cost and achieving complexity of the multi-temperature-zone automatic conditioner are reduced.
Owner:徐州兴梁农业发展有限公司
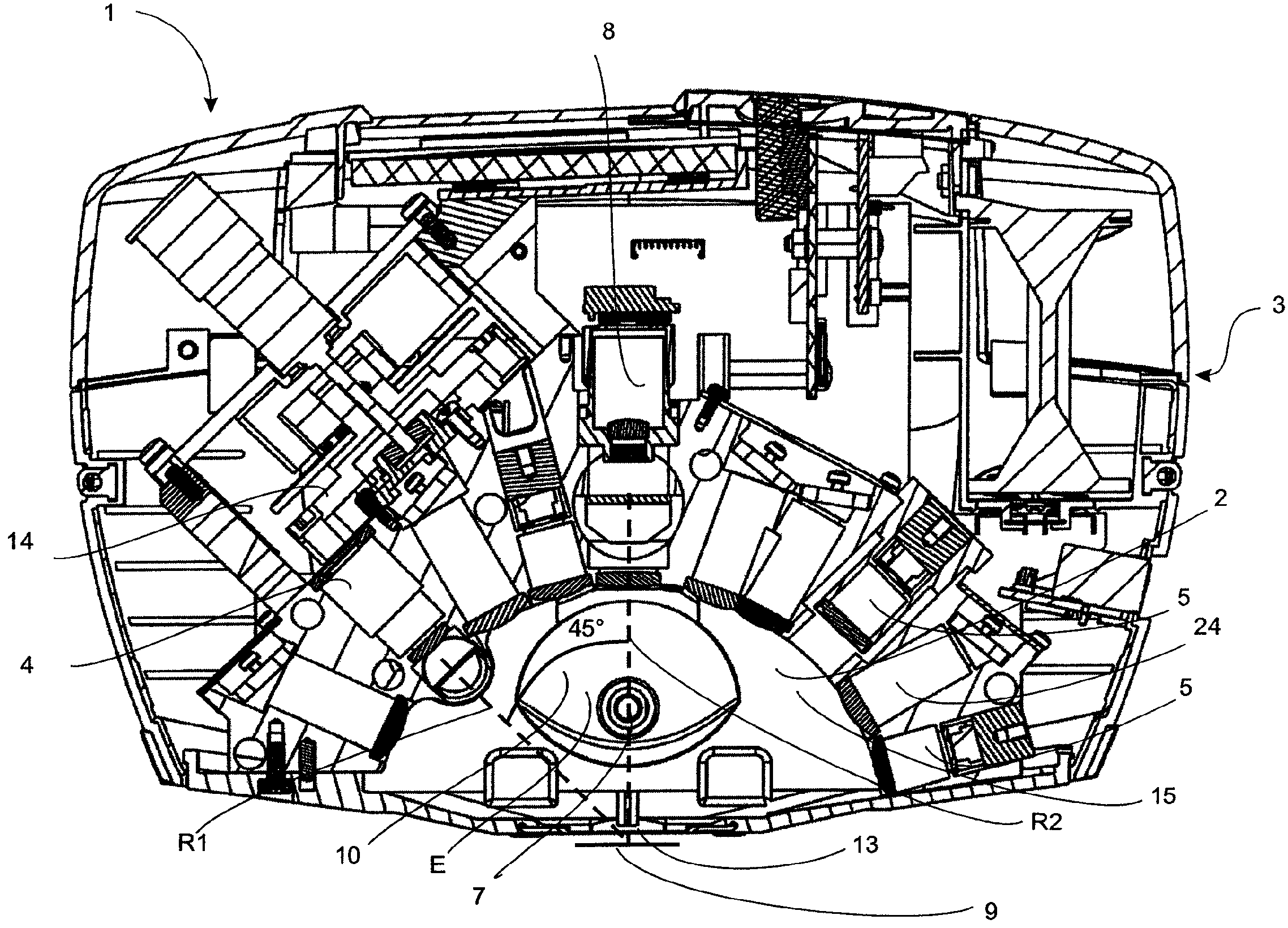
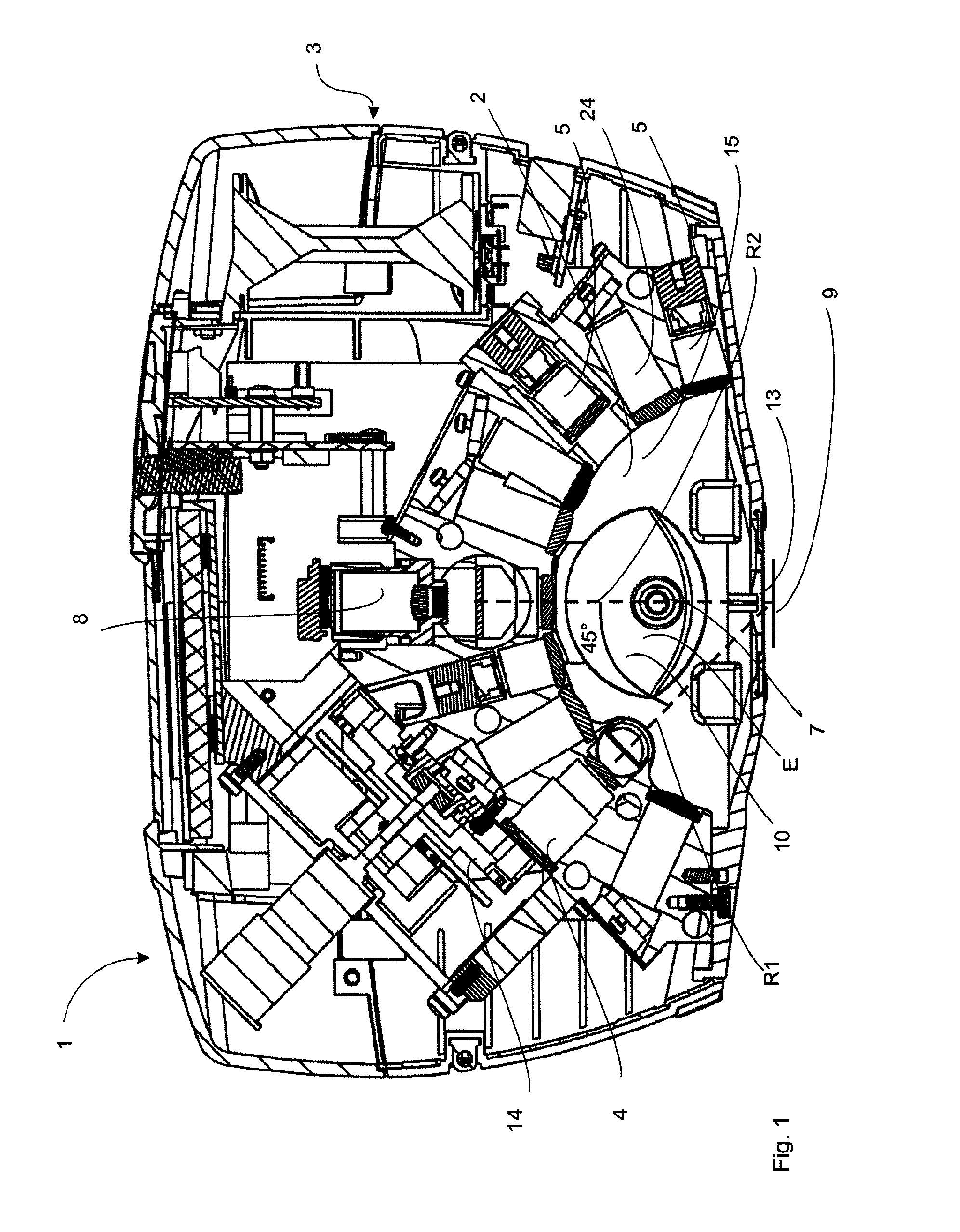
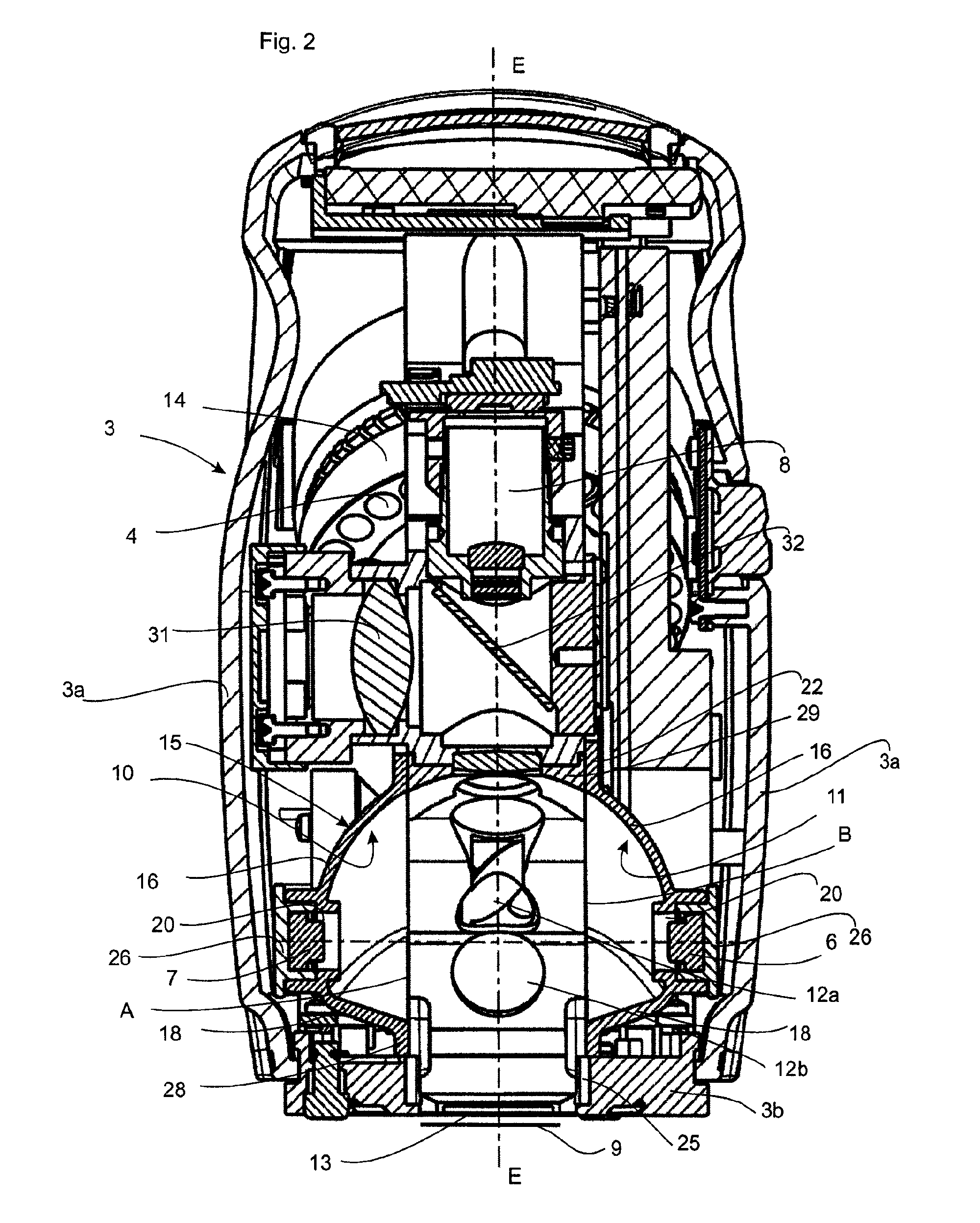
Apparatus for analysing surface properties with indirect illumination
ActiveUS7741629B2Avoid mixingUndesirable mixing can be preventedInvestigating moving sheetsScattering properties measurementsRadiation scatteringScattering radiation
An apparatus (1) for analysing surface properties, comprising a first radiation device (4) which emits radiation directly onto a surface (9) to be analyzed, a first illumination device (6, 7) for indirectly illuminating the surface (9) to be analyzed, a first radiation detector device (8) which receives at least part of the radiation thrown back from the surface (9) to be analyzed and outputs at least one signal which is characteristic of this part of the radiation. According to the invention, a radiation scattering device (10, 11) is provided which is at least partially illuminated by the first illumination device (6, 7) and which transmits scattered radiation onto the surface (9) to be analyzed.
Owner:BYK GARDNER
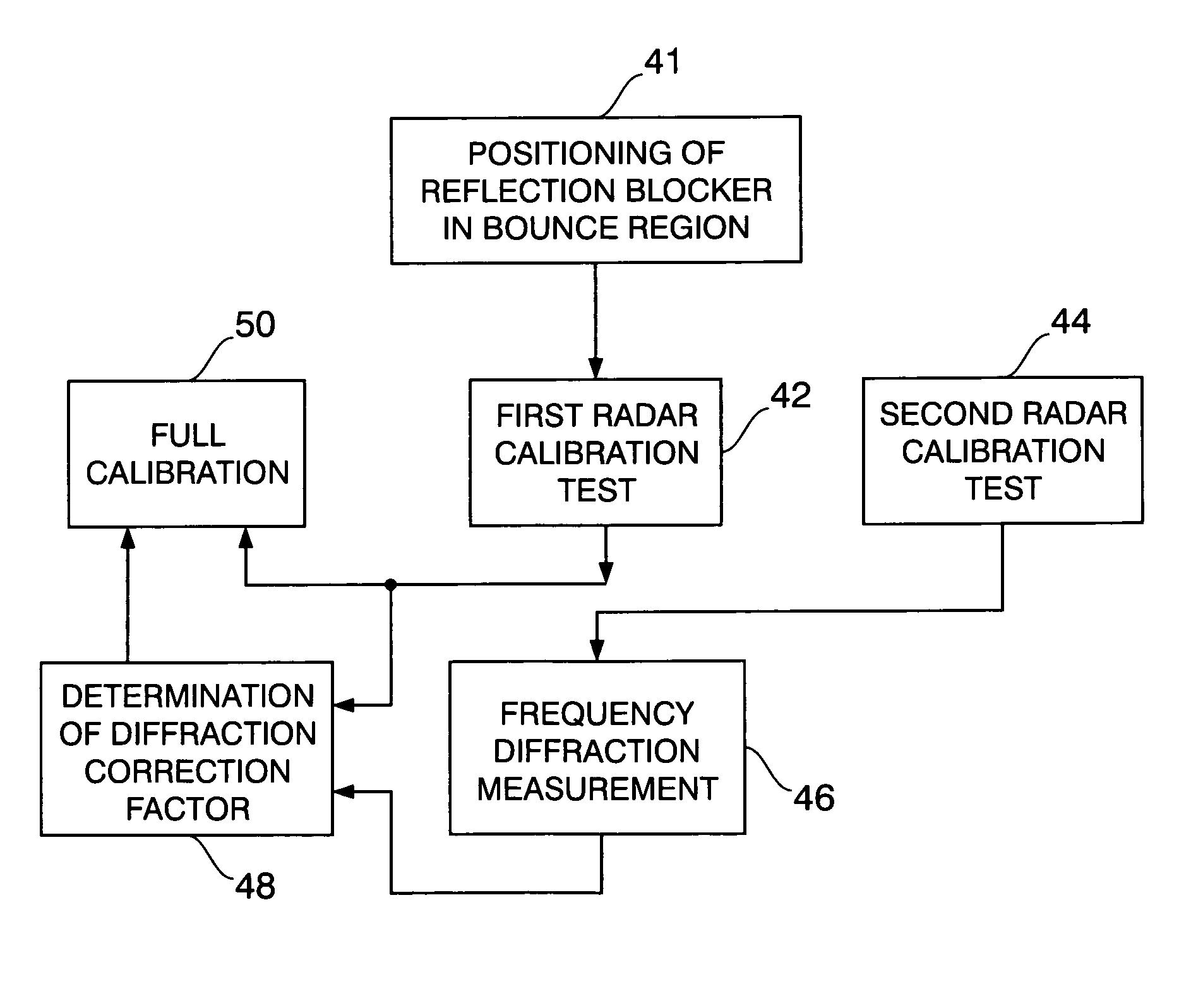
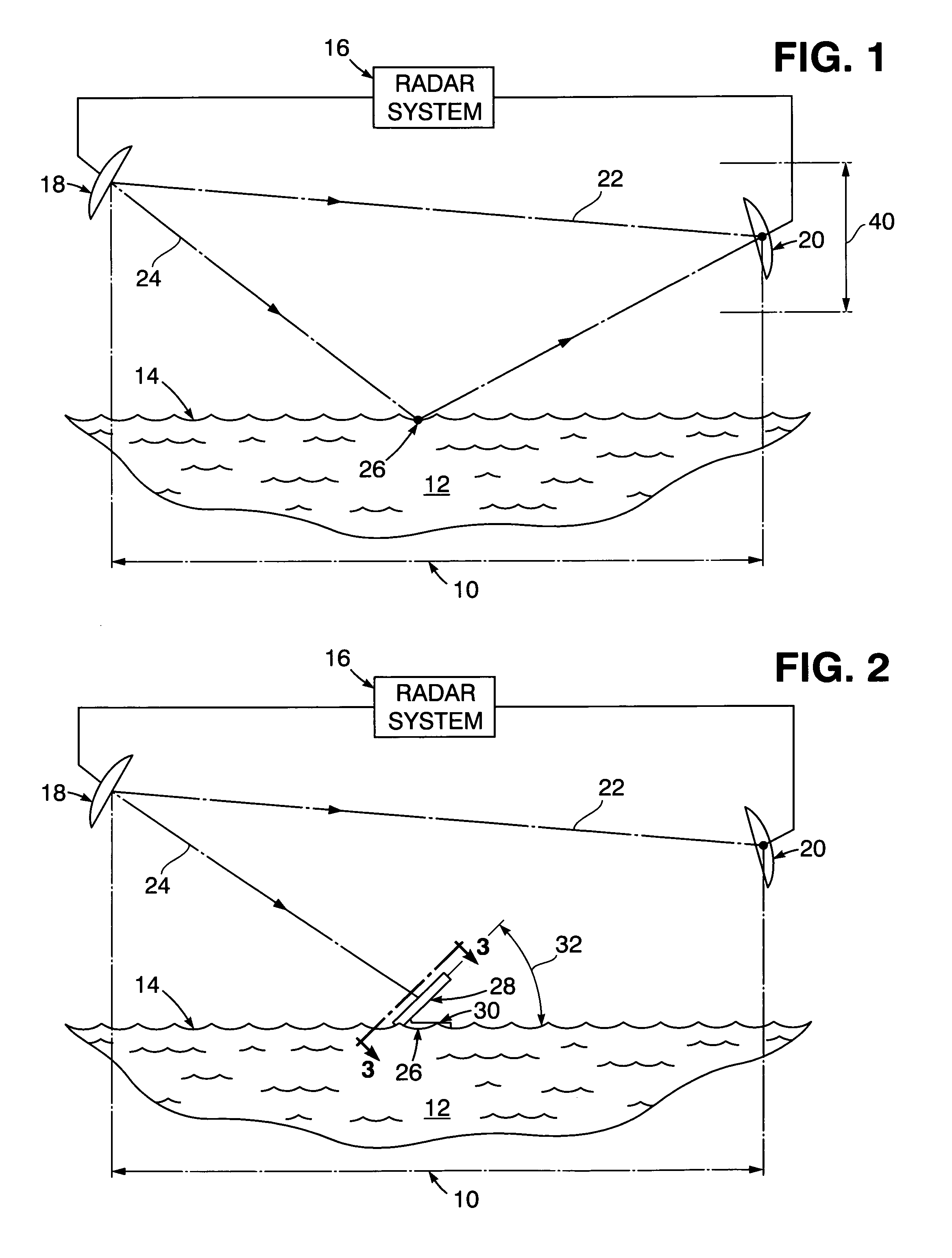
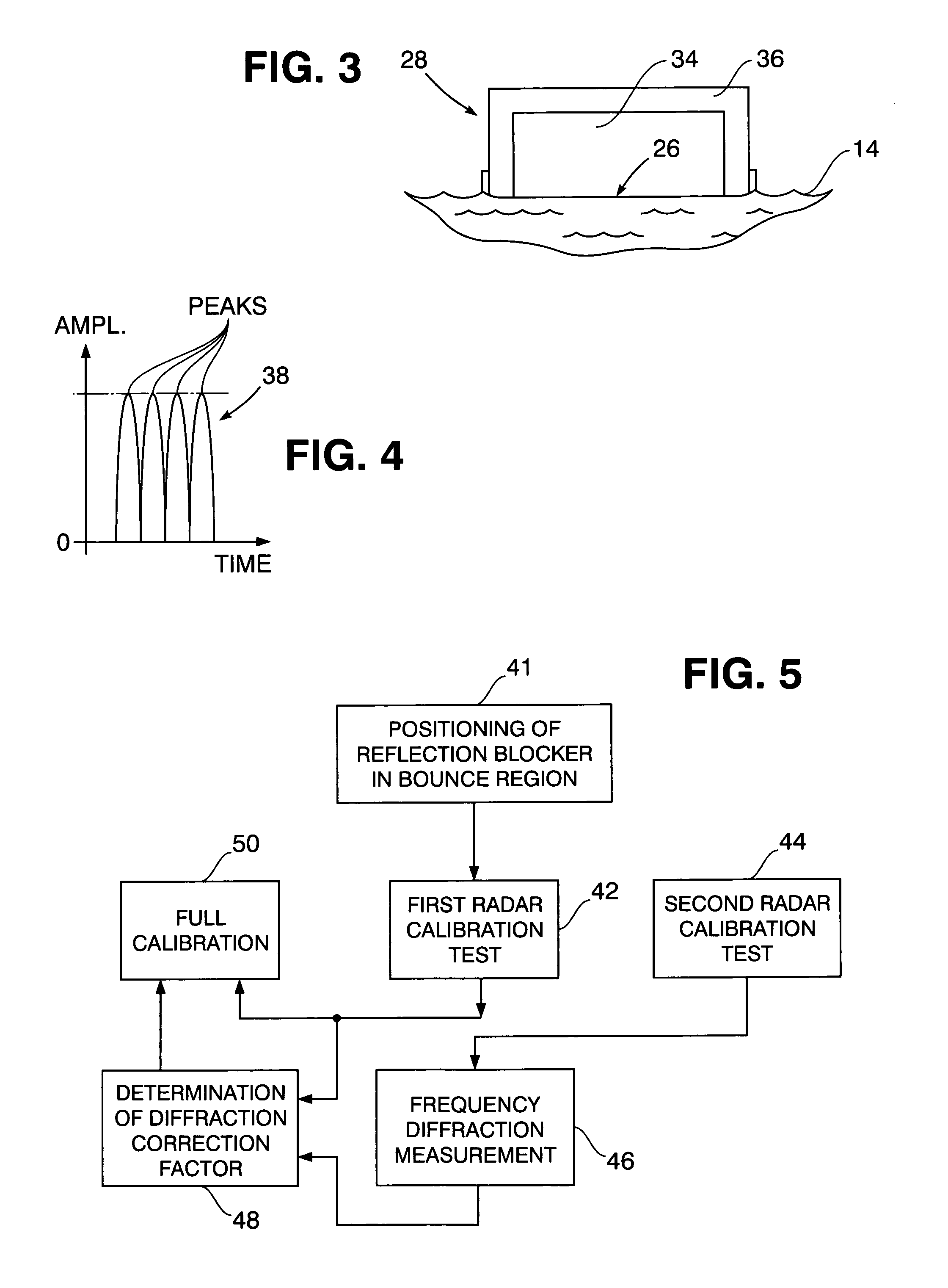
In-situ calibration of radar frequency measurement
InactiveUS7138941B1Eliminate radiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsMeasurement test
Frequency calibration of a bi-static type of radar system is performed by positioning radar transmitter and receiver in spaced relation to each other over a targeted seawater surface from which radar radiation along a forward radiation scattering path is reflected toward the receiver while radar energy is also radiated along a direct path to the receiver by-passing the seawater during sequential frequency measurement tests to determine a frequency diffraction factor. A radiation blocking barrier is positioned by a floating support at a reflection location at an angular position on the seawater surface for intersection by the forward scattering path to block reflection of radar energy radiation toward the receiver during one of the measurement tests.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Radiation scattering integrated low-RCS radome and design method thereof
InactiveCN111430903ARealize the designAchieve optimizationRadiating element housingsMachine learningStochastic gradient descentAlgorithm
The invention relates to the technical field of radomes, and discloses a radiation scattering integrated low-RCS radome and a design method thereof, and the method comprises the following steps: optimizing the arrangement of a plurality of phase units on a transmission-type metasurface of the radome through a stochastic gradient descent method; optimizing the objective function of the phase unit arrangement by using a stochastic gradient descent method to obtain optimal phase arrangement; obtaining the optimal phase arrangement according to the optimized objective function, carrying out the fitting between the sizes of the phase units and the phase relation of the phase units through employing an artificial neural network, and finding out the patch sizes corresponding to a plurality of phase units; and designing the transmission-type metasurface of the radome according to the patch sizes corresponding to a plurality of phase units and the optimal arrangement so as to obtain the radiation scattering integrated low-RCS radome. The radome and the design method thereof solve the problem of RCS reduction in a working band and are simple in implementation method, low in cost and high inpracticability.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
X-Ray Backscatter Imaging of an Object Embedded in a Highly Scattering Medium
ActiveUS20140254764A1High energyHigh strengthMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationConstructionsShaped beamConfocal
An apparatus and associated method for obtaining a three-dimensional representation of a target object within a fluid-carrying conduit, such as a hydrocarbon exploration or production well, using high energy photons is provided. The representation is essentially a three-dimensional image that achieves visualization of the shape of the target object despite the intervening opaque fluids located between the imaging tool and the object. In one specific though non-limiting embodiment, a narrow, pencil-shaped beam of radiation is scanned in coordination with a similarly narrow detector field-of-view in order to sample the radiation-scattering properties of only a small volume of material at any given time. The result is a clearer to visualization with a greater viewing depth.
Owner:VISURAY INTECH LTD
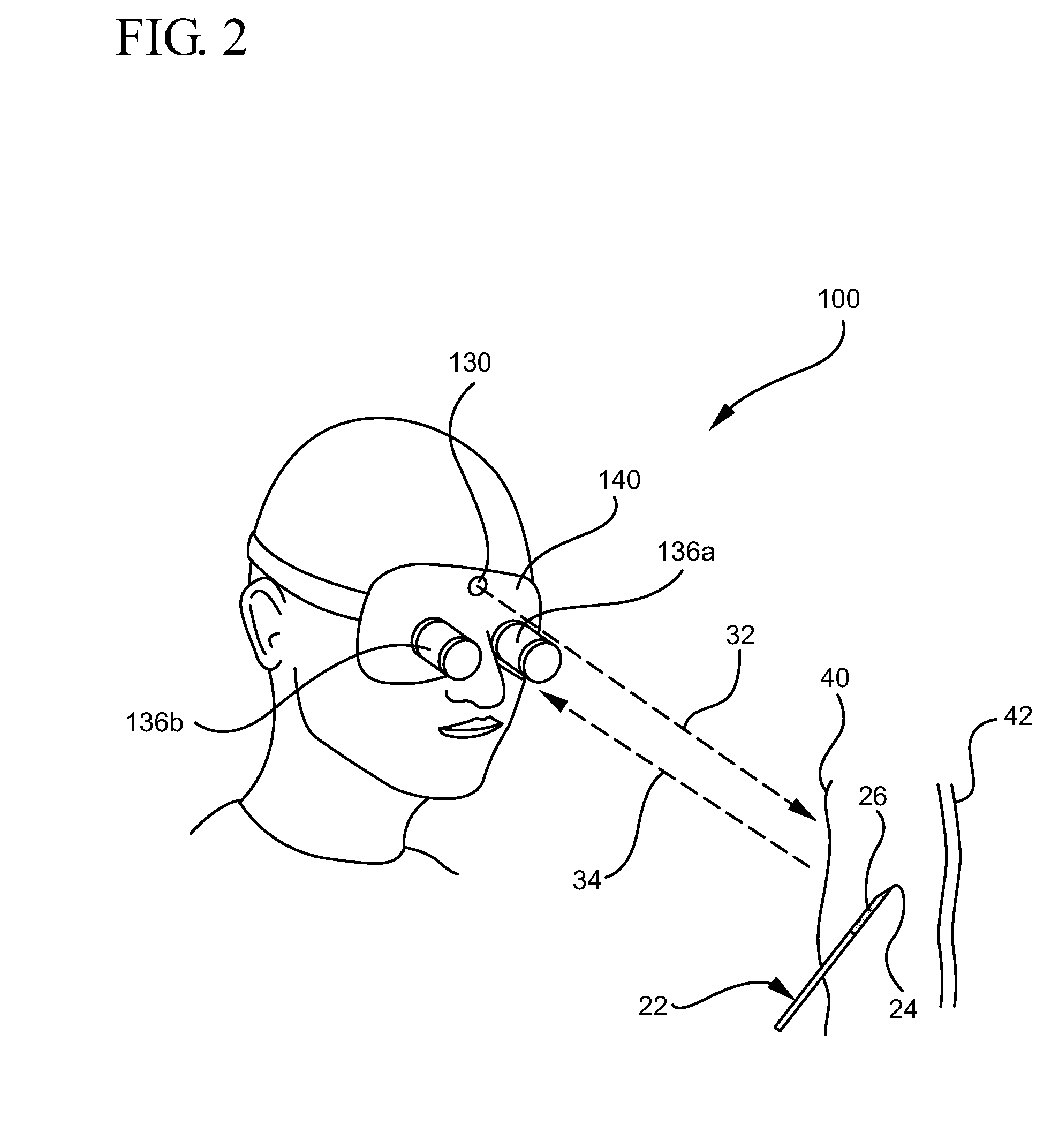
System and method for visualizing needle entry into a body
ActiveUS8311615B2Performed accurately and rapidlyDiagnostics using lightSurgical needlesAnatomical structuresRadiation scattering
A system for visualizing needle entry into a body is presented. The system includes a needle for entering a body. The needle is coated with a radiation scattering coating on at least a portion of the needle. The system additionally includes a radiation visualization device which detects reflected radiation directed at a target body and enables medical personnel to view anatomical structures such as a blood vessel along with the inserted needle within a body.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
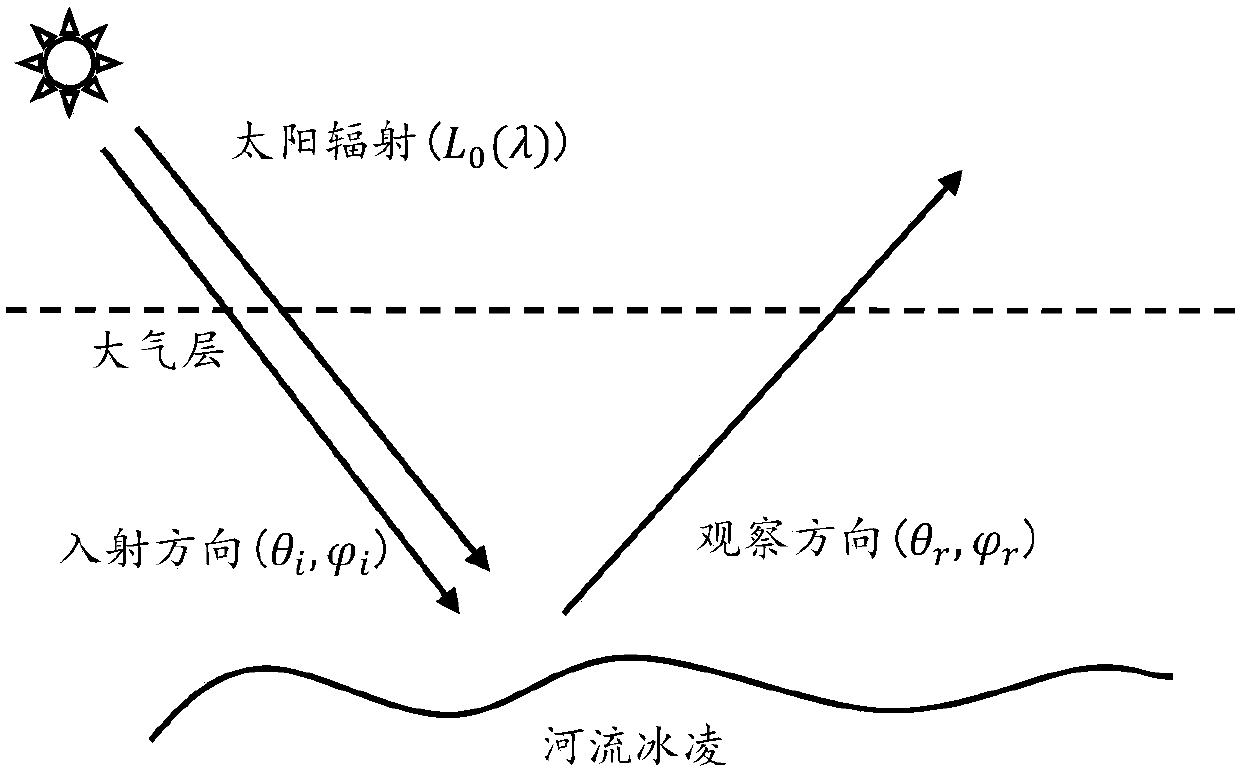
Method for calculating scattering characteristic of river ice infrared waveband
ActiveCN107247038AReduce calculation errorsImprove accuracyScattering properties measurementsEarth observationKnowledge Field
The invention discloses a method for calculating scattering characteristic of a river ice infrared waveband, and belongs to the field of target and environmental infrared radiation scattering characteristic research. The problems that a scattering model has low calculation accuracy and low practicability in engineering because the fact that the river ice has the characteristics of strong directional scattering and strong scattering radiation brightness is not considered are solved. The method comprises the following steps: dividing BRDF on the surface of river ice into two parts, namely diffusion reflection BRDFdiff and specular reflection BRDFspec, and calculating the diffusion reflection BRDFdiff and the specular reflection BRDFspec separately to obtain the BRDF on the surface of the river ice; according to the BRDF on the surface of the river ice, the wavelength of incident solar radiation, the incident direction and the observation direction, calculating the radiation brightness after the river ice is scattered; and according to the radiation brightness, calculating the scattering radiation brightness after the scattering radiation brightness of the river ice is absorbed by atmosphere through the observation direction. The method is used for calculating the scattering radiation brightness of the river ice under solar radiation exposure during earth observation.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Increased absorption-measurement accuracy through windowing of photon-transit times to account for scattering in continuous webs and powders
InactiveUS8527212B2Accurate and more calibrationAccurate measurementRadiation pyrometryInvestigating moving sheetsPhoton transmissionMean free path
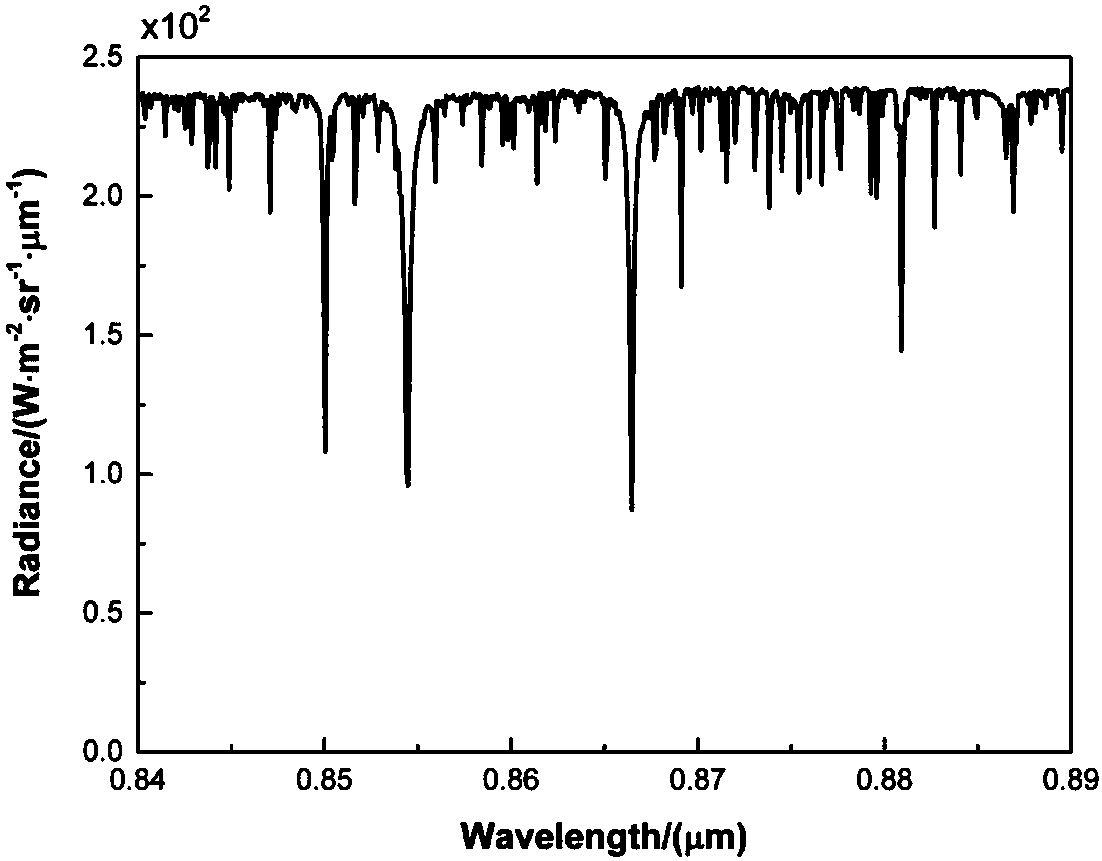
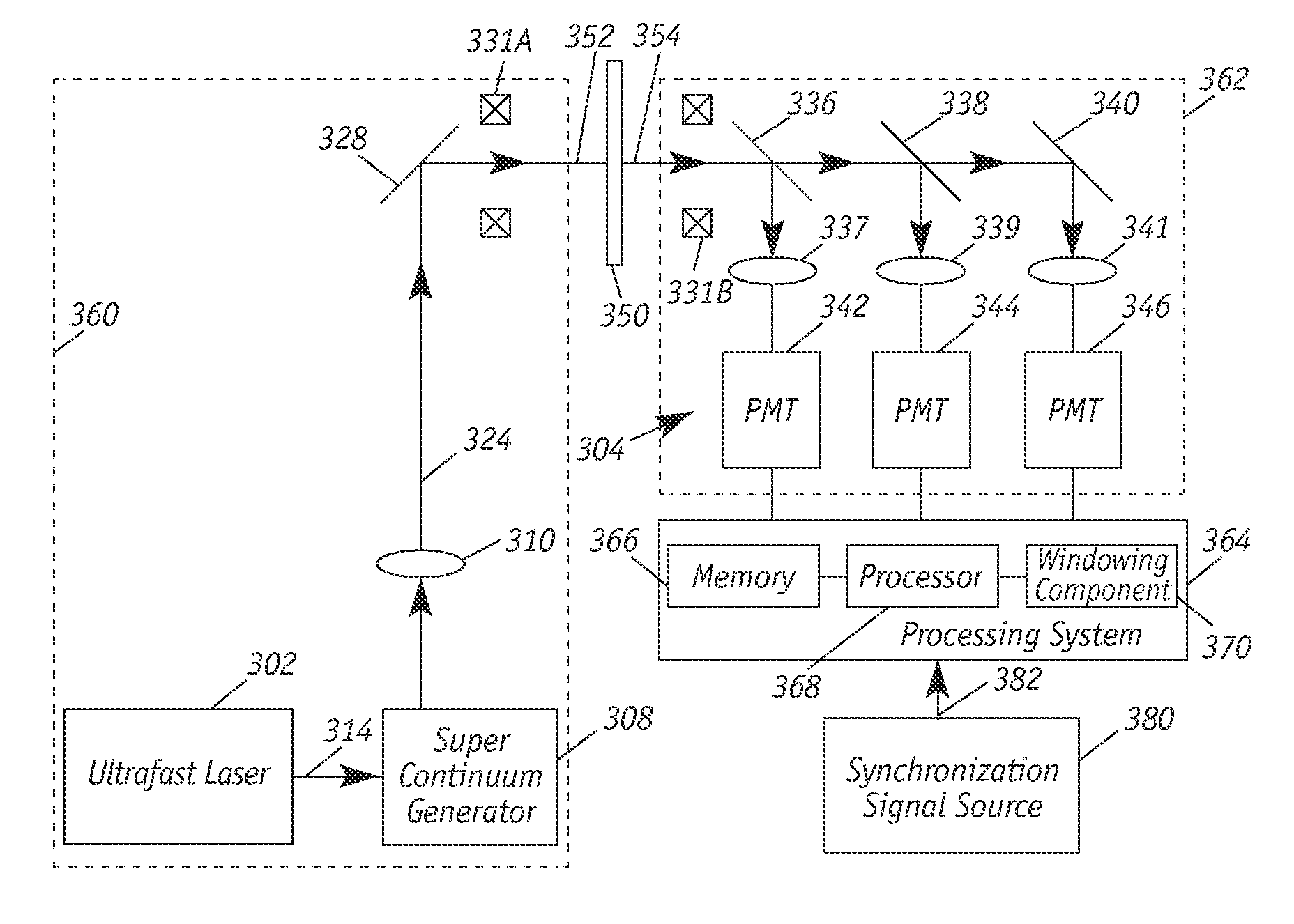
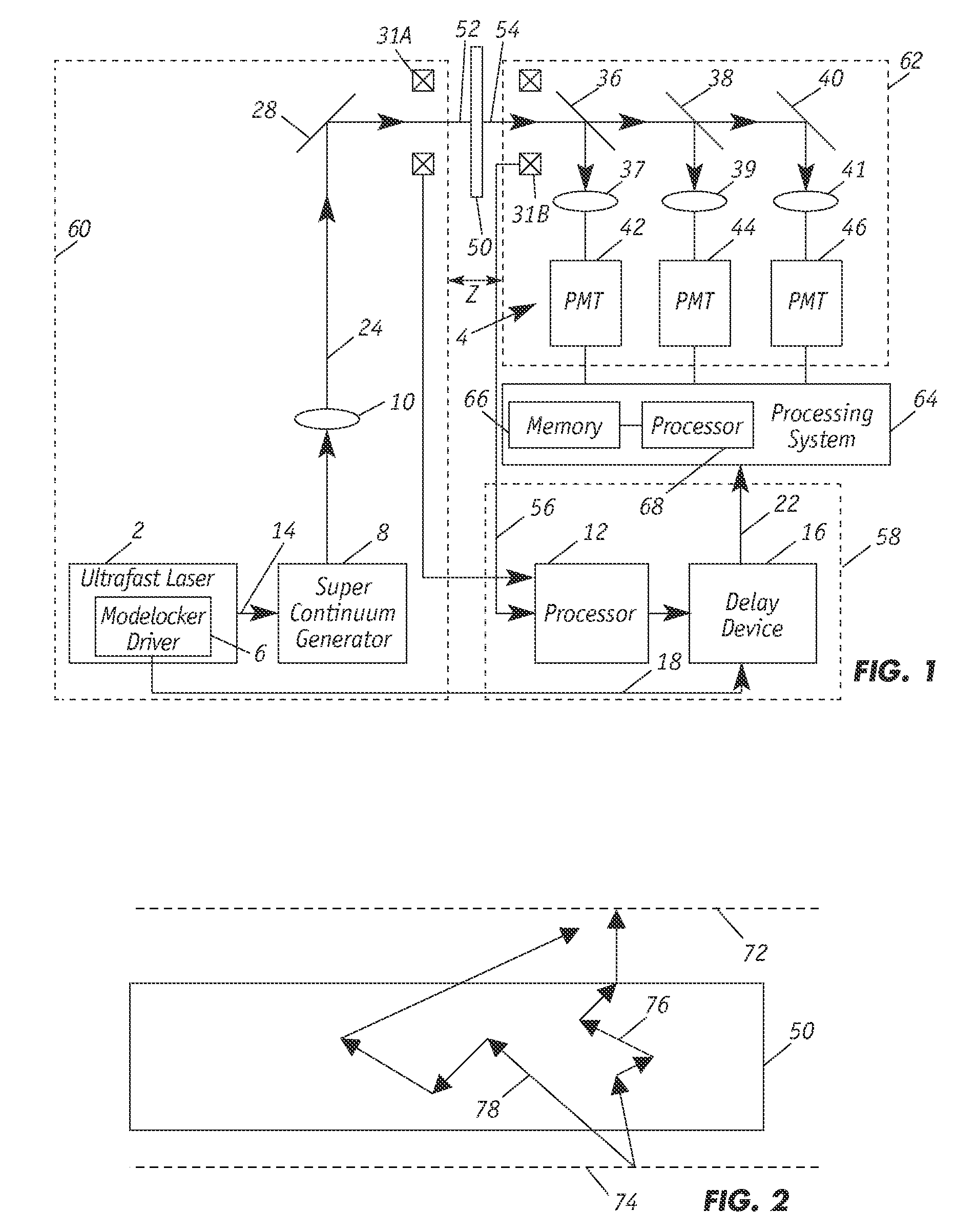
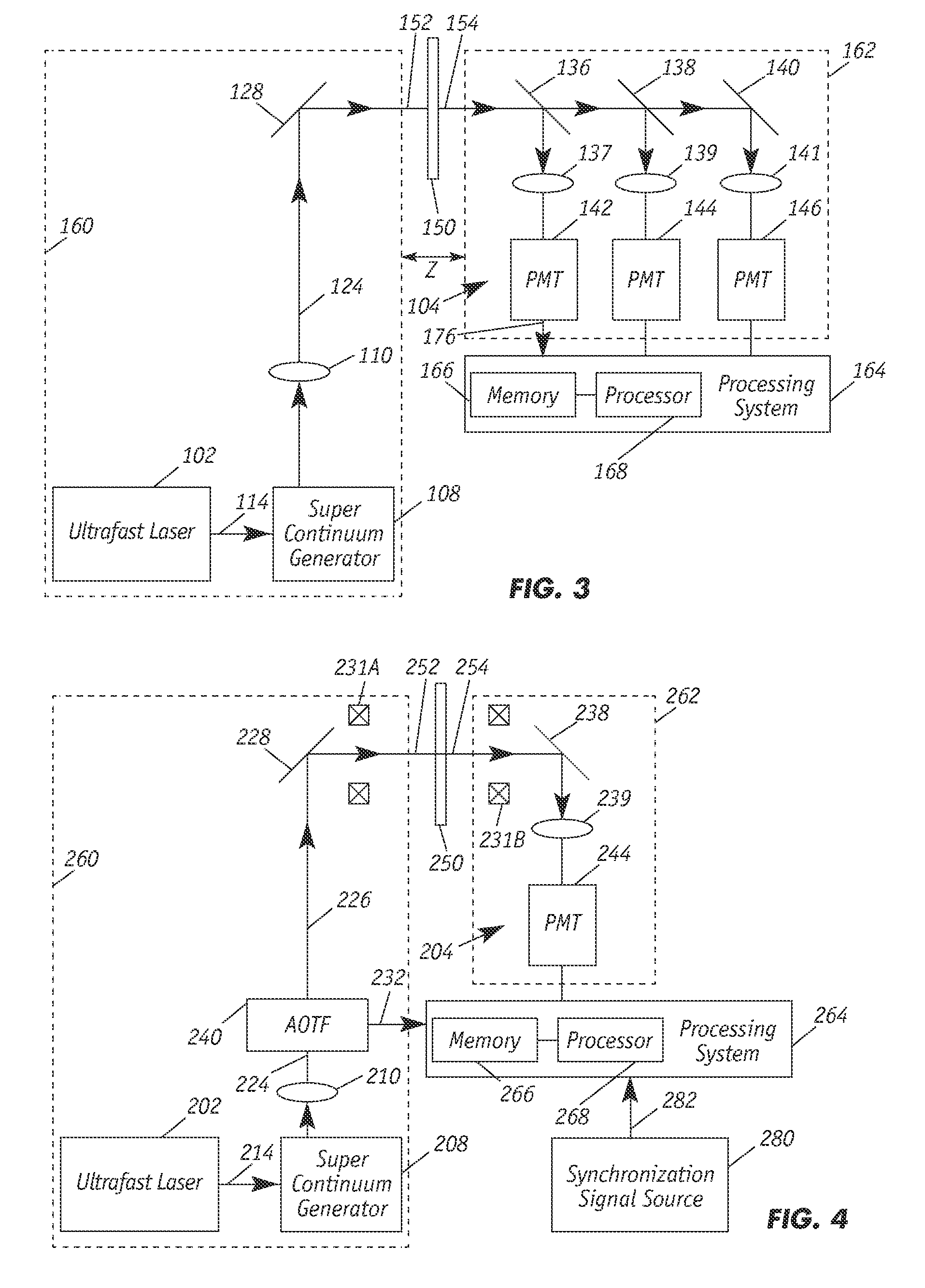
Radiation scattering is one of the main contributors to the uncertainty of near infrared (NIR) measurements. Enhanced absorption-measurement accuracy for NIR sensors is achieved by using a combination of NIR spectroscopy and time-of-flight techniques to select photons that are the result of a given mean free path within a moving sample target. By measuring absorption as a function of path length or by windowing signals that are attributable to excessive scattering of NIR radiation within the sample, this technique affords the calculation of more accurate and more universal calibrations. The NIR sensor employs short or ultra-short laser pulses to create NIR that is directed to the moving sample and emerging radiation is detected over time. Windowing effectively truncates non-contributing measurements.
Owner:HONEYWELL ASCA INC
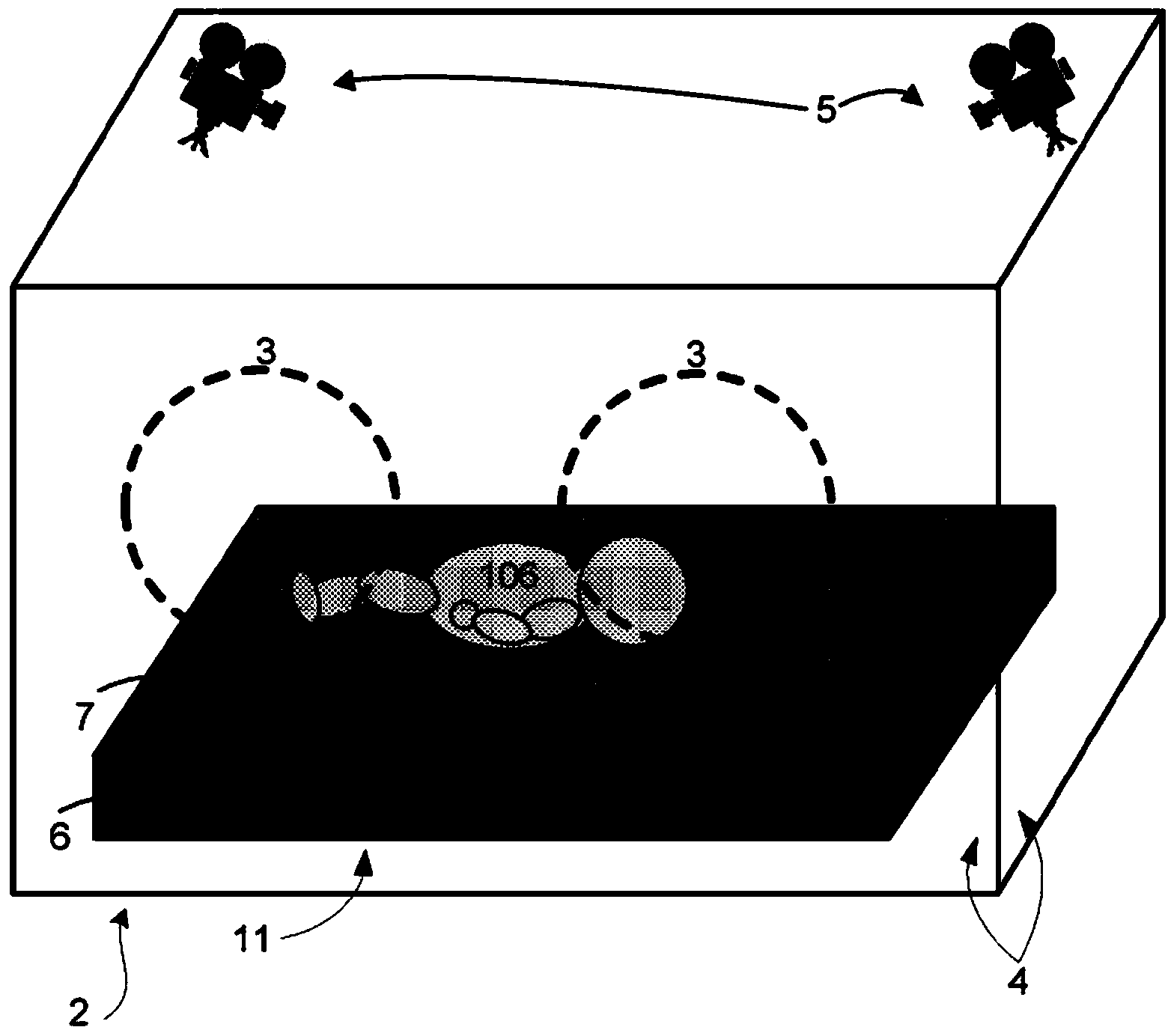
Incubator illumination
ActiveCN103813770ABaby-incubatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringCamera imageSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Monitoring of infants in an incubator may use cameras to measure vital signs and other medical parameters, including oxygen saturation of arterial blood. However, the images obtained by these cameras suffer from a reduced signal-to-noise ratio due to specular reflectance from light reflecting off the skin of the infant. By including radiation scattering structures within the incubator walls and light sources arranged along the edges of the incubator walls, diffuse illumination may be achieved, specular reflectance may be reduced, and the above-mentioned adverse affects on the signal-to-noise ratio of the camera images may be avoided and / or reduced.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
A Simulation Method for Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data of Complex Woodland Scenes
InactiveCN101477197BApproximately goodWave based measurement systemsSpecial data processing applicationsSensing dataSky
The invention provides a method for emulating high spectroscopic remote sensing data used in a woodland complex scene, relates to the technical field of high spectroscopic remote sensing data emulation, and solves the problem that the prior method for emulating the high spectroscopic remote sensing data is not applicable to the high spectroscopic remote sensing data under the condition that a tall building exists near the woodland as height factor of a ground object is not considered. The method comprises the following steps: 1, setting an emulation parameter, and inputting a reference curve of ground and object reflectivity of a spectrum library used in emulation; 2, resolving high spectroscopic remote sensing data to be acquired in emulation into energy of solar radiation directly reflected by a target pixel element, energy of building reflected solar radiation which is reflected by the target pixel element once again, energy of sky radiation scattering which is reflected by the target pixel element, path radiation and proximity effect, and carrying out emulation respectively according to the emulation parameter in the step 1; and 3, combining emulation results acquired in the step 2 to acquire the final emulation data. The method provides economic and high-quality emulation data for research of post-processing of the high spectroscopic remote sensing data.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Radiation scatter protection system
A radiation scatter protection system designed to attach to an X-ray table to limit exposure to radiation for both medical staff and patient. The radiation scatter protection system includes an arm board adapted to be disposed around an arm of the patient; an arm board shielding including one large sheet of shielding extending downward from the X-ray table and a plurality of additional sheets of shielding, removably mounted to the arm board; a sand bag shield including a plurality of sheets of top shielding and a plurality of sheets of bottom shielding which connect to an elongated, cylindrical sandbag; a side curtain shield hanging from the X-ray table; and a throw shield.
Owner:BAIRD DAVID A +2
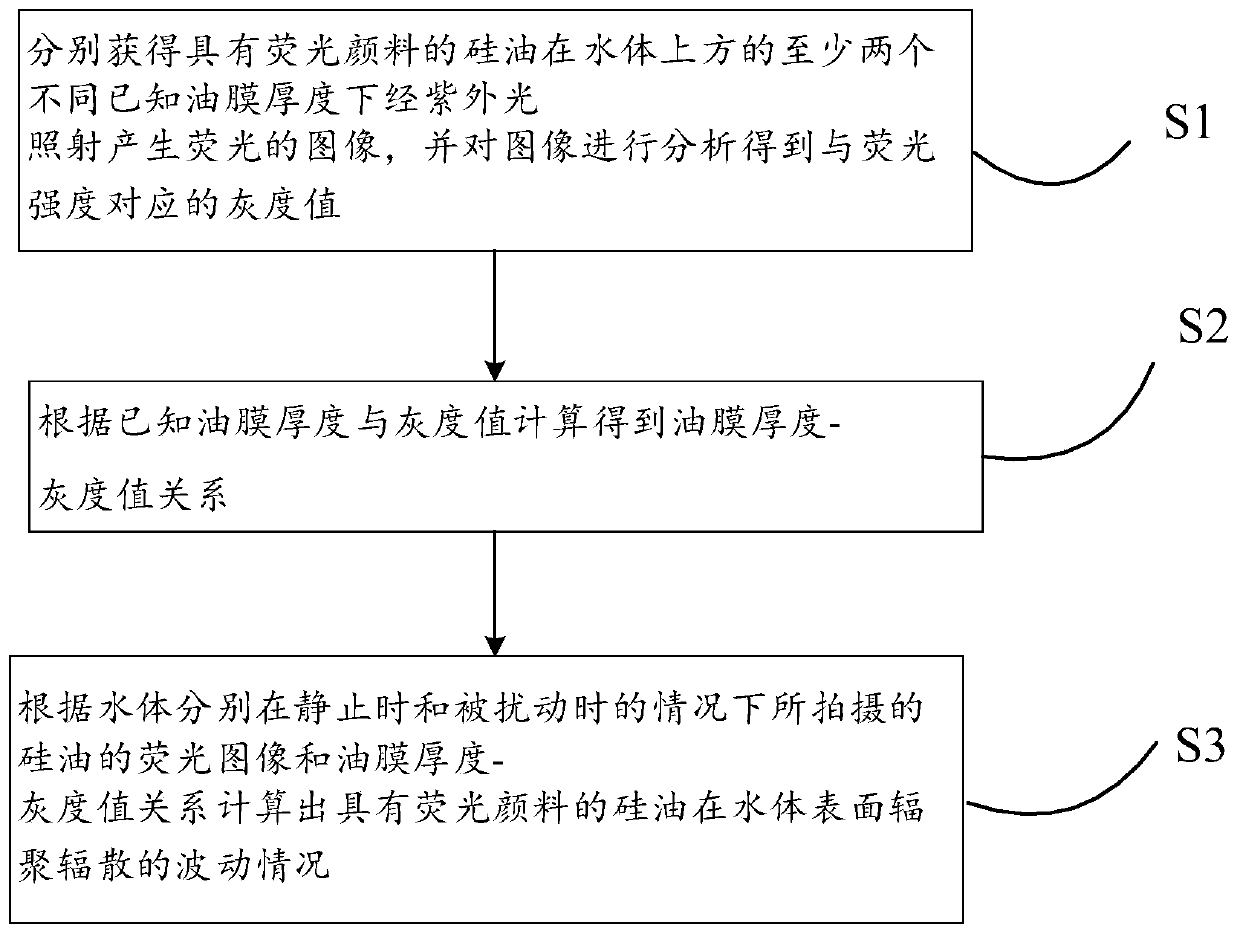
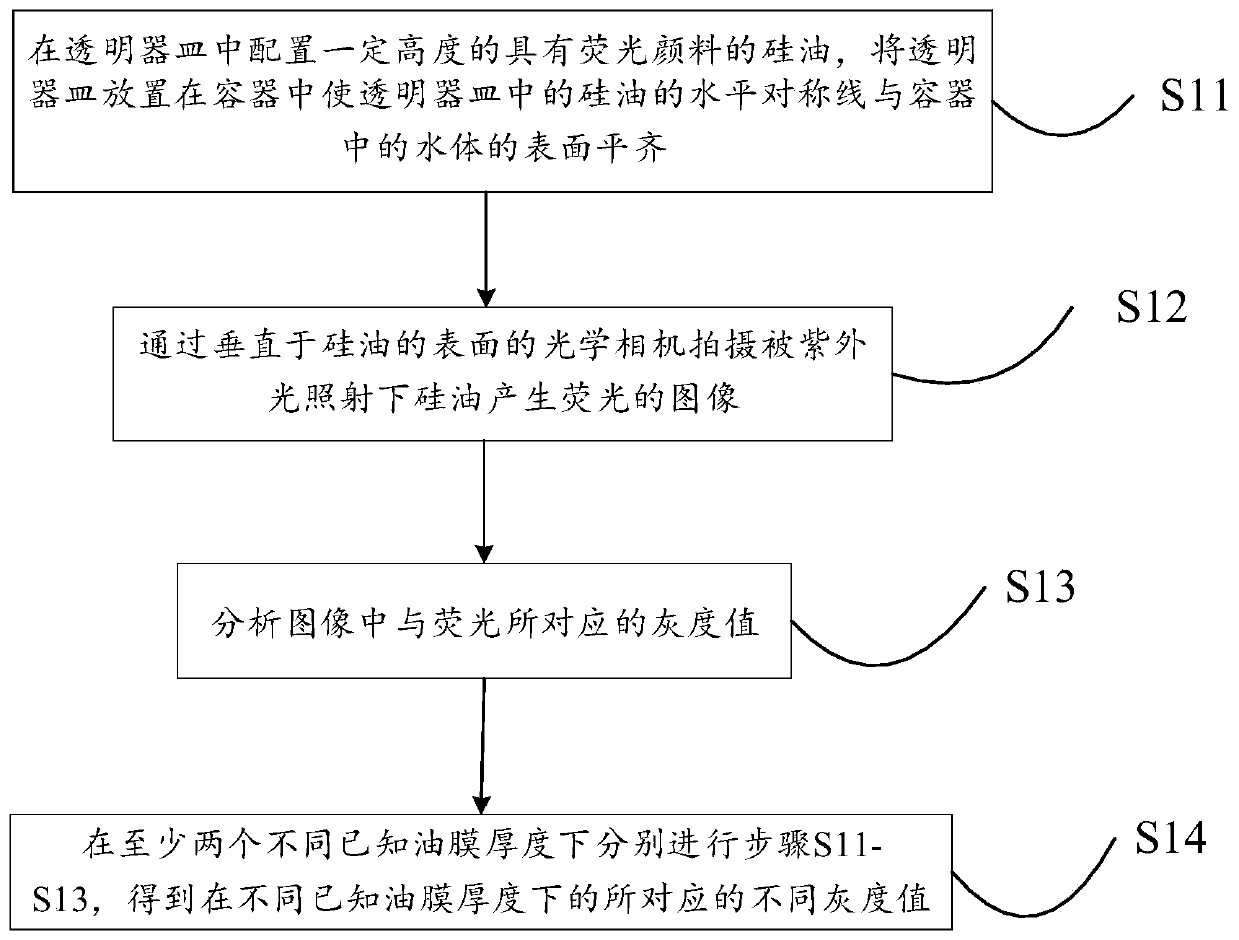
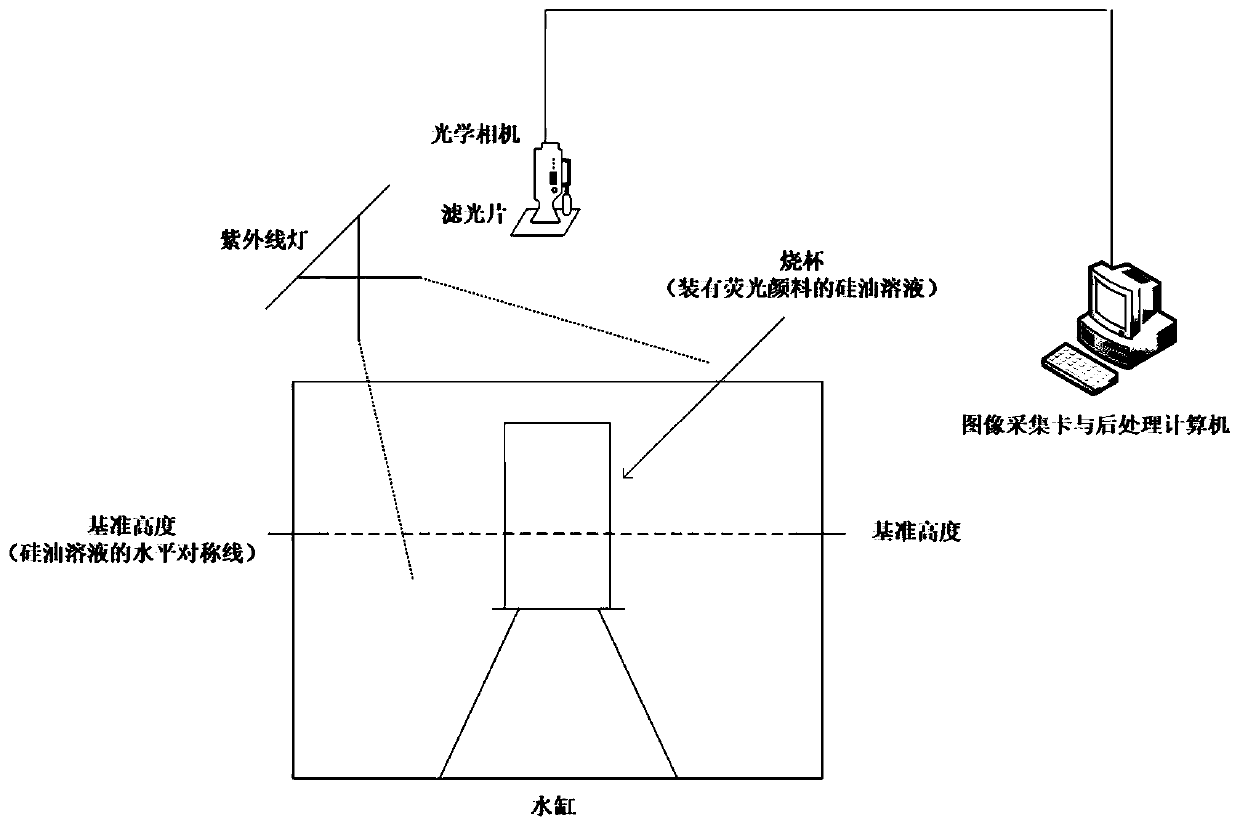
Flow field radiation gathering and radiation scattering measurement method based on oil film fluorescence brightness
ActiveCN111220588AOvercome limitationsReduce restrictionsFluorescence/phosphorescencePhoto irradiationRadiation scattering
The invention discloses a flow field radiation gathering and radiation scattering measurement method based on oil film fluorescence brightness, and the method comprises the following steps: respectively obtaining images of fluorescence generated by silicone oil with fluorescent pigment through ultraviolet irradiation under at least two different known oil film thicknesses above a water body, and analyzing the images to obtain a gray value corresponding to the fluorescence intensity; performing calculating according to the known oil film thickness and the gray value to obtain an oil film thickness-gray value relation; and calculating the fluctuation condition of radiation gathering and radiation scattering of the silicone oil with the fluorescent pigment on the surface of the water body according to the relation between the oil film thickness-gray value and the fluorescent images of the silicone oil shot when the water body is static and disturbed. According to the method, the detectionintuition is enhanced, the cost is low, the amount of data needing to be processed is small, the post-processing steps are simple, and the difficulty is greatly reduced. Quantitative analysis can beconveniently carried out on the fluctuation intensity of surface fluid radiation gathering and radiation scattering, and certain help is provided for summarizing the law of the fluid surface radiationgathering and radiation scattering phenomenon caused by underwater or water surface navigation bodies.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
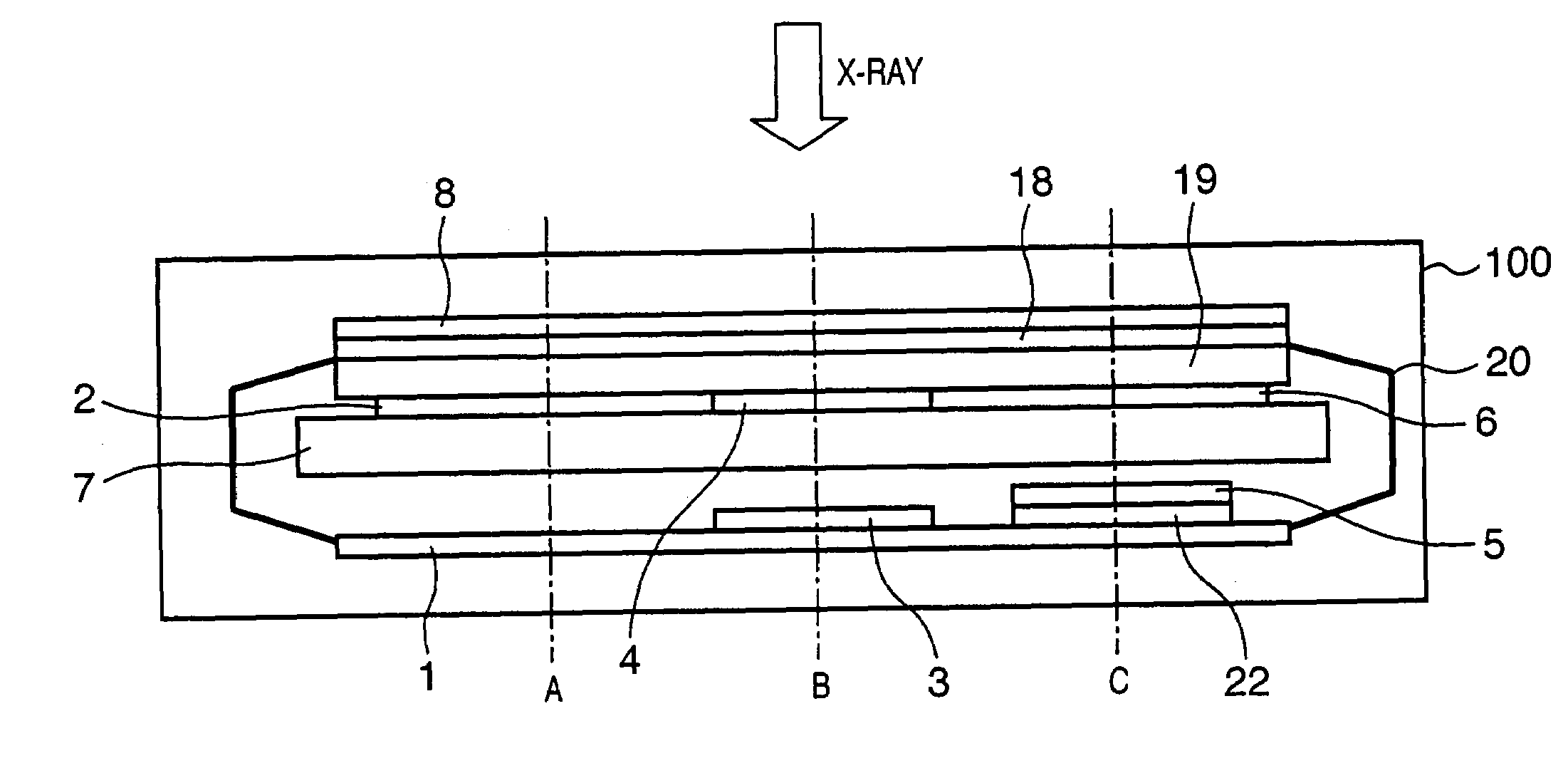
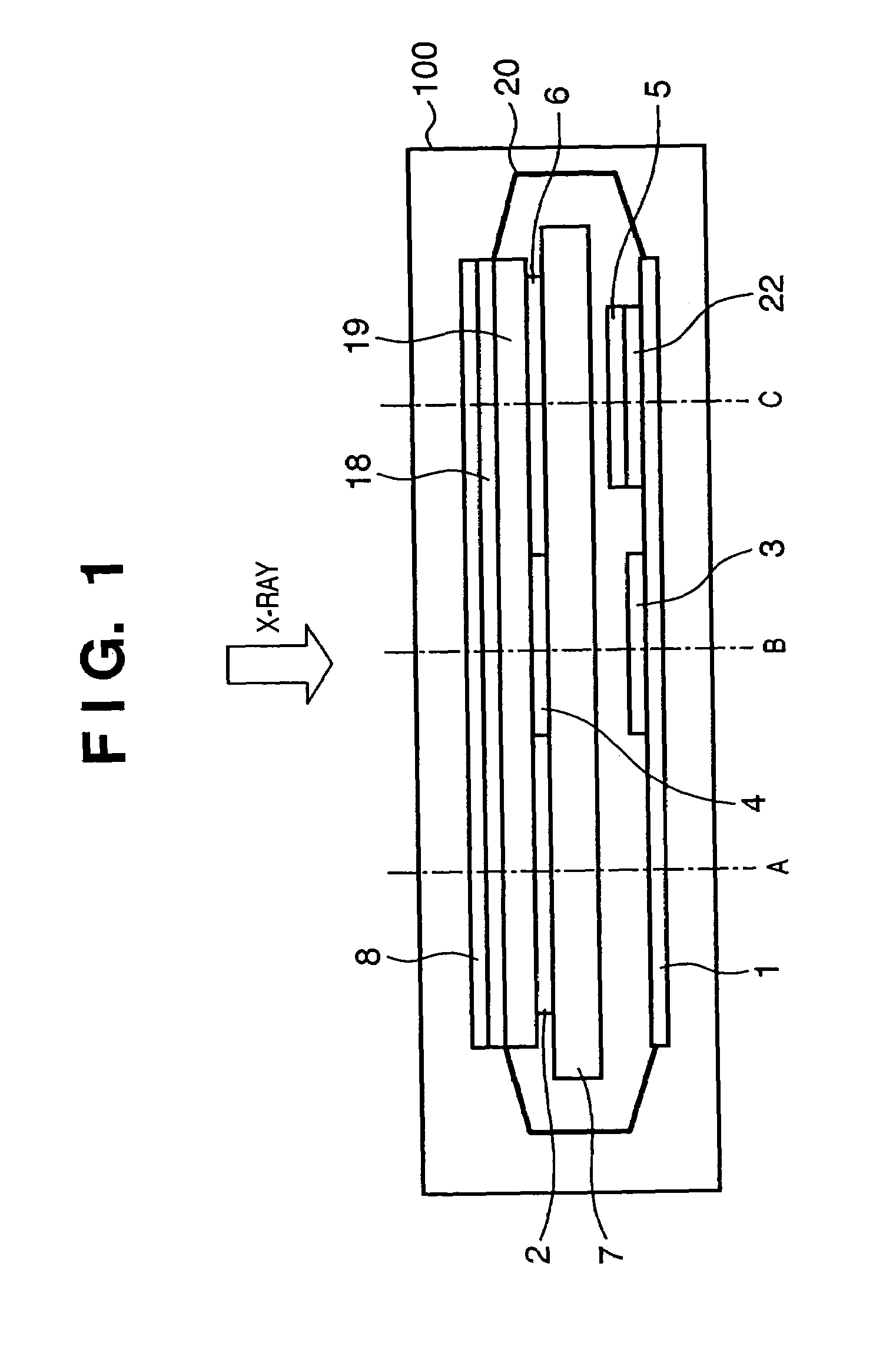
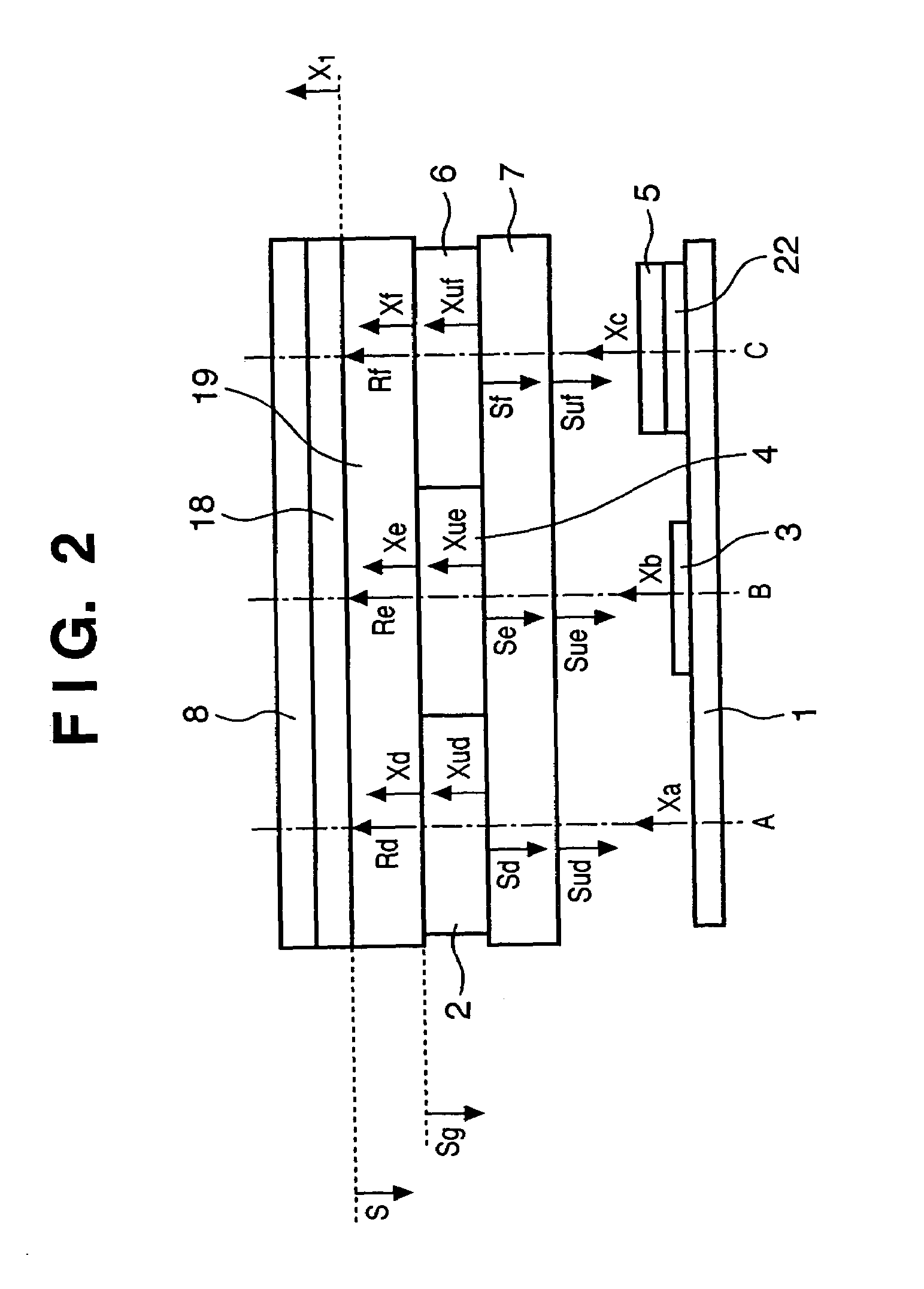
Radiographic apparatus
InactiveUS7053378B2Backscatter can be reducedHolding down weightSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation scatteringImage signal
A radiographic apparatus includes photoelectric converter elements for converting a radiographic image of an object into image signals and a shield member for shielding the photoelectric converter elements from scattered rays arising within the radiographic apparatus from radiation passing through the photoelectric converter elements. The shield member has a plurality of areas, in which at least one of a radiation transmittivity and a radiation scattering probability varies.
Owner:CANON KK
Oxidizing bleach composition
The invention provides an aqueous bleaching solution for substrate treatment. The aqueous bleaching solution features a source of oxidant and a plurality of optically functional nanoparticles. The optically functional nanoparticles are nanoparticles in the range of about 0.1 nanometers to about 400 nanometers in size. The aqueous bleaching solution may optionally include one or more an oxidant-stable surfactants and optionally, one or more oxidant-stable polymers, and adjuncts. The optically functional nanoparticles are extremely stable in the aqueous bleaching solution and remain substantially suspended in the aqueous bleaching solution due to their extremely small size despite having an average density greater than that of the bleaching solution. The optically functional nanoparticles provide at least one optical functional benefit to the bleaching solution owing to their uniform and stable suspension throughout the solution, including such benefits as uniform light absorption, light and radiation scattering, fluorescent emission, phosphorescent emission, coloration, and visual aesthetic benefits and the like. Further, optically functional benefits include those benefits provided to a substrate or surface treated with the aqueous bleaching solutions whereby the optically functional property is transferred either temporarily or permanently to the substrate or surface following contact with bleaching solutions containing the optically functional nanoparticles.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
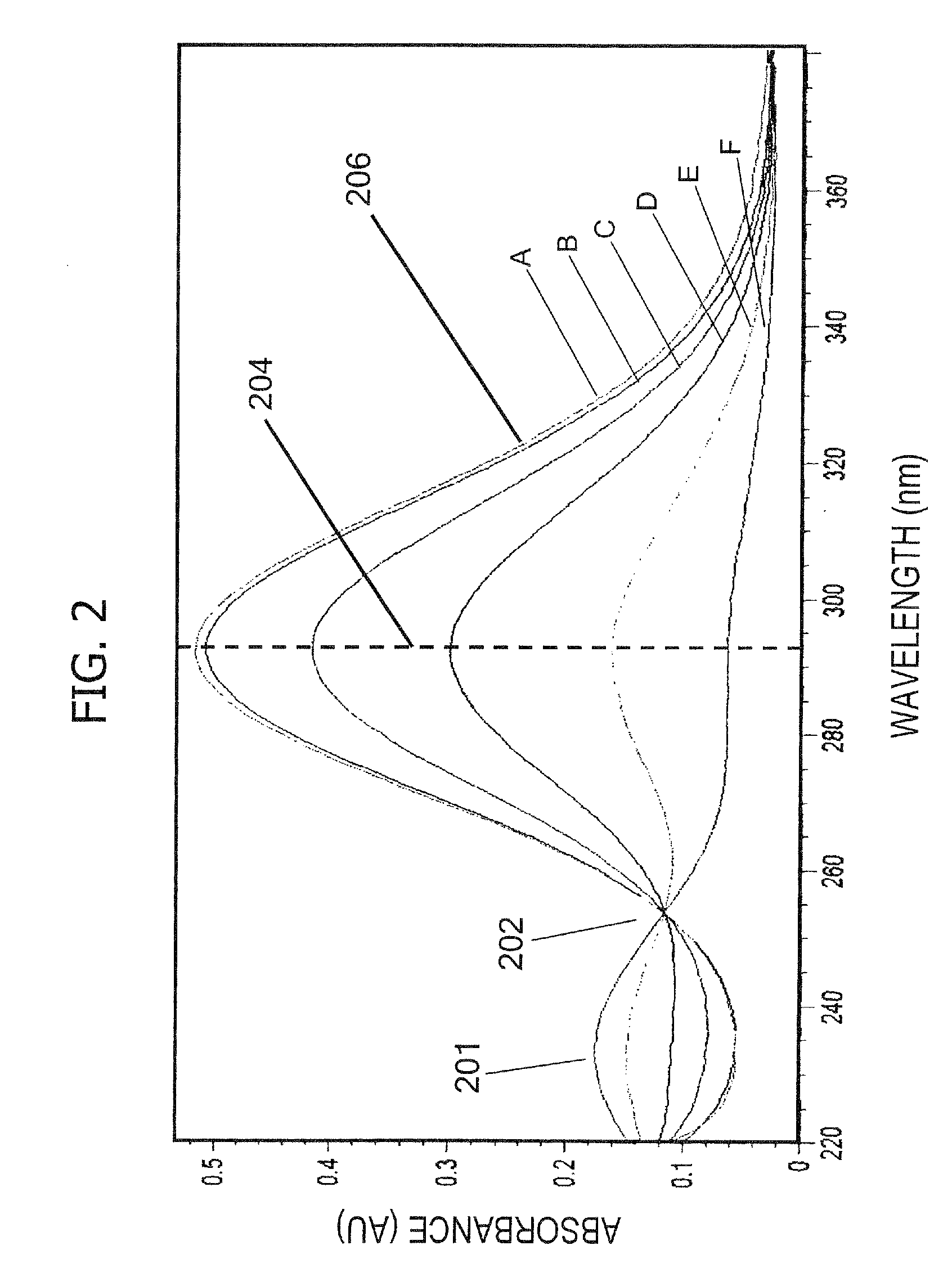
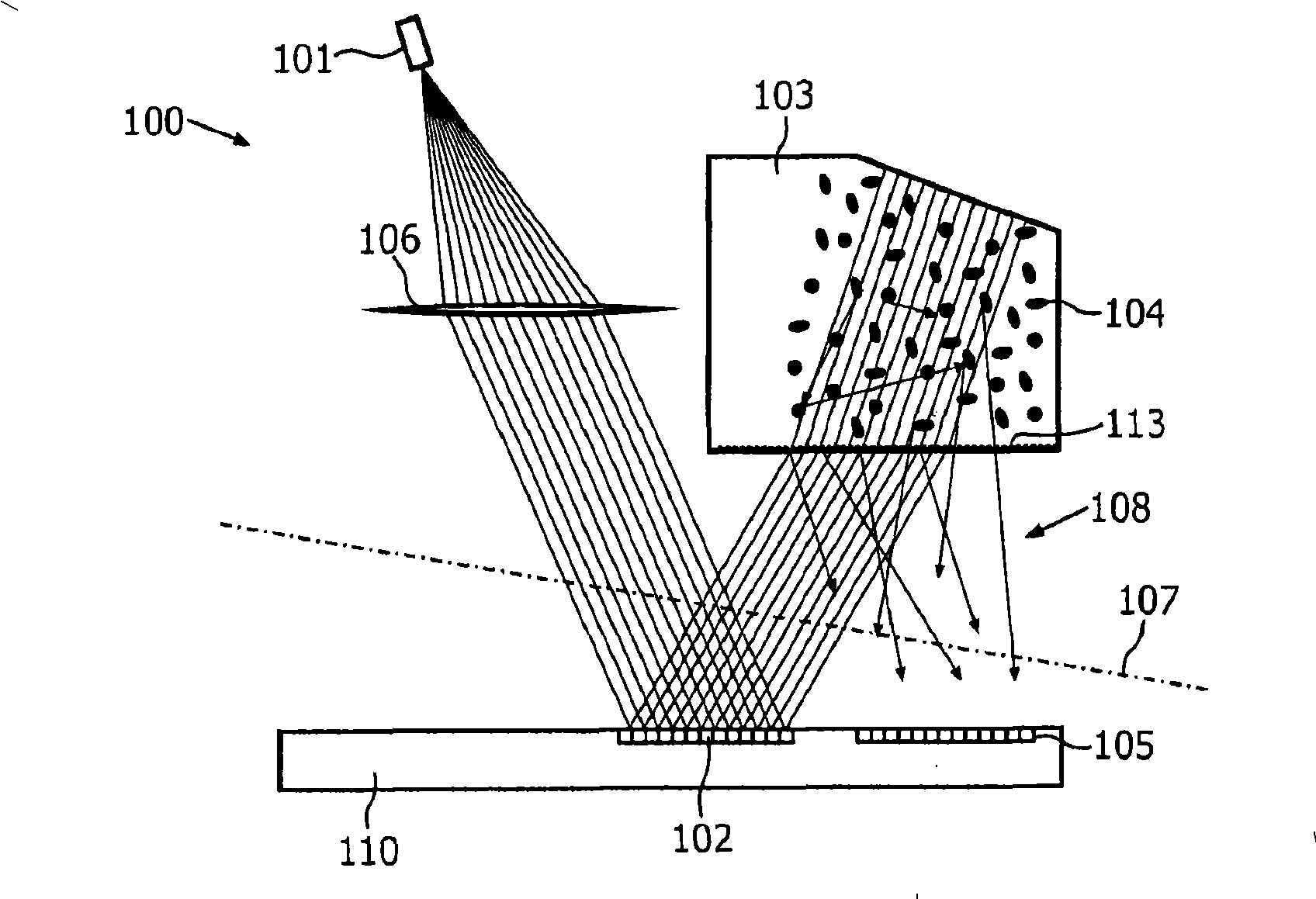
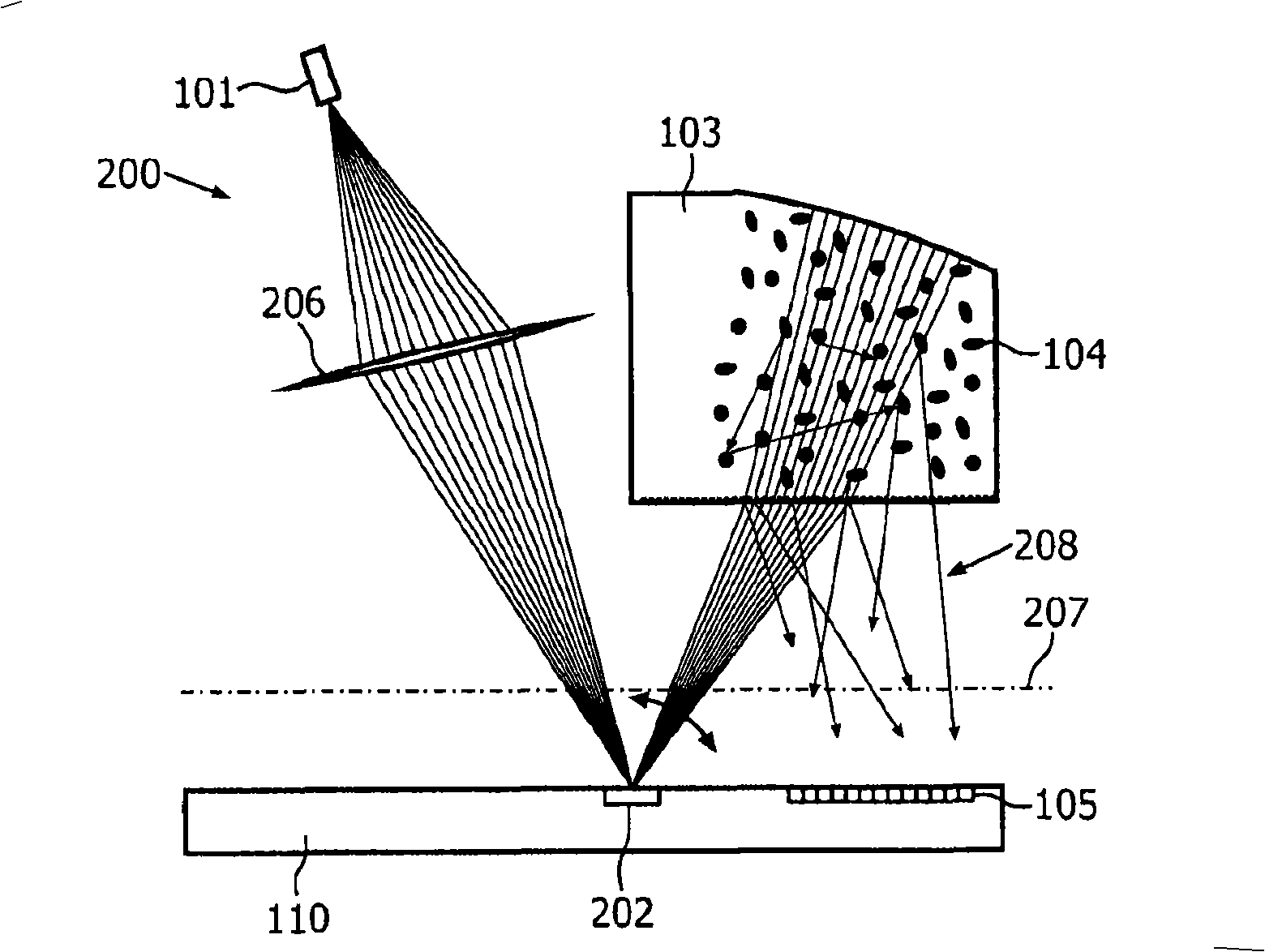
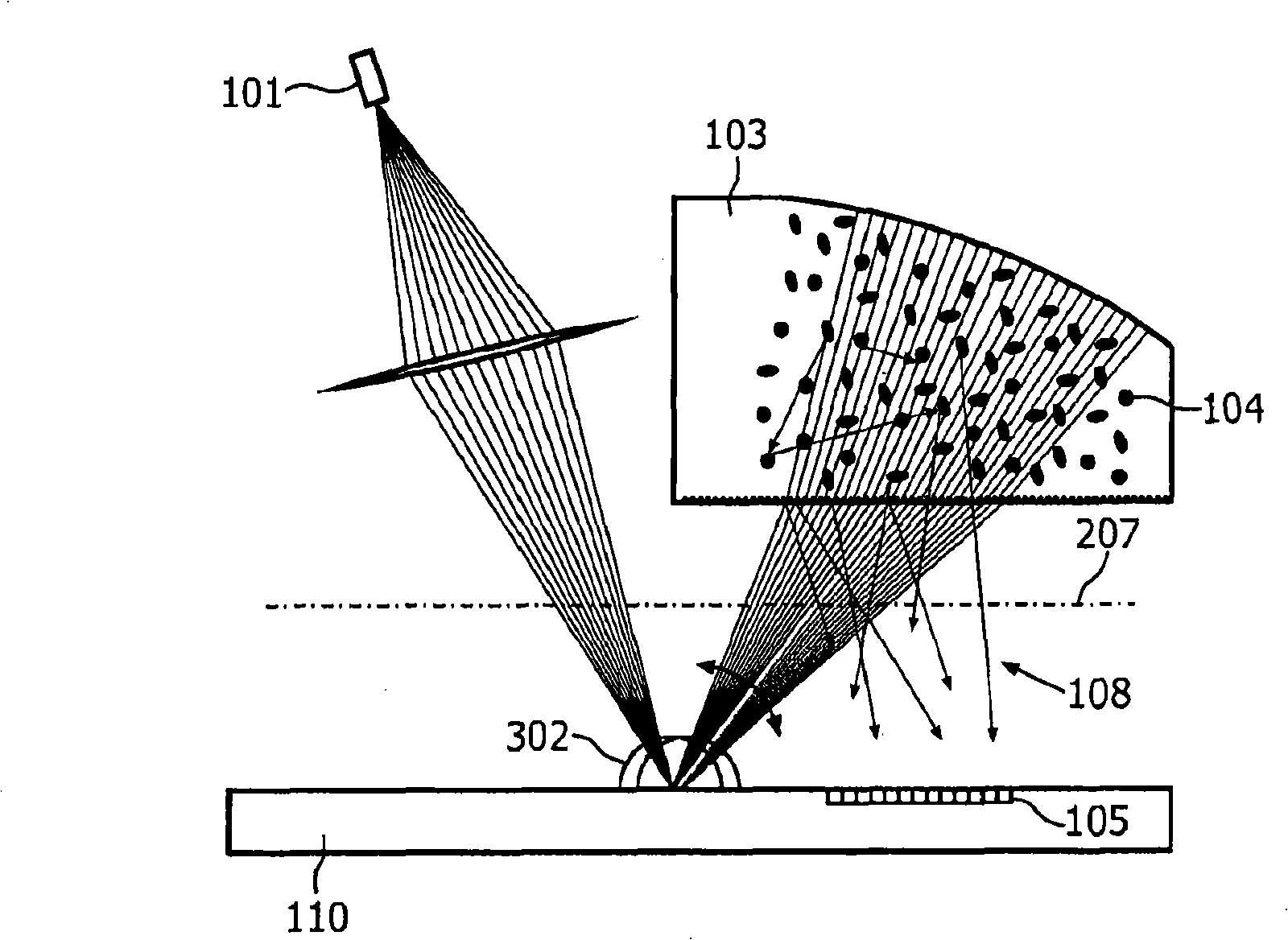
Integrated PUF
InactiveCN101292465AEasy alignmentEasy to manufactureDiffusing elementsUser identity/authority verificationSpeckle patternOptoelectronics
In a device for providing challenge-response pairs a radiation detection element, a challenge-modifying element and preferably also a light source are arranged on the same side of an imaginary plane, which separates said radiation-detecting element from a radiation scattering element. Hence, generation of a speckle pattern having a desired minimum speckle size is facilitated and a more easily assembled device is provided.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com