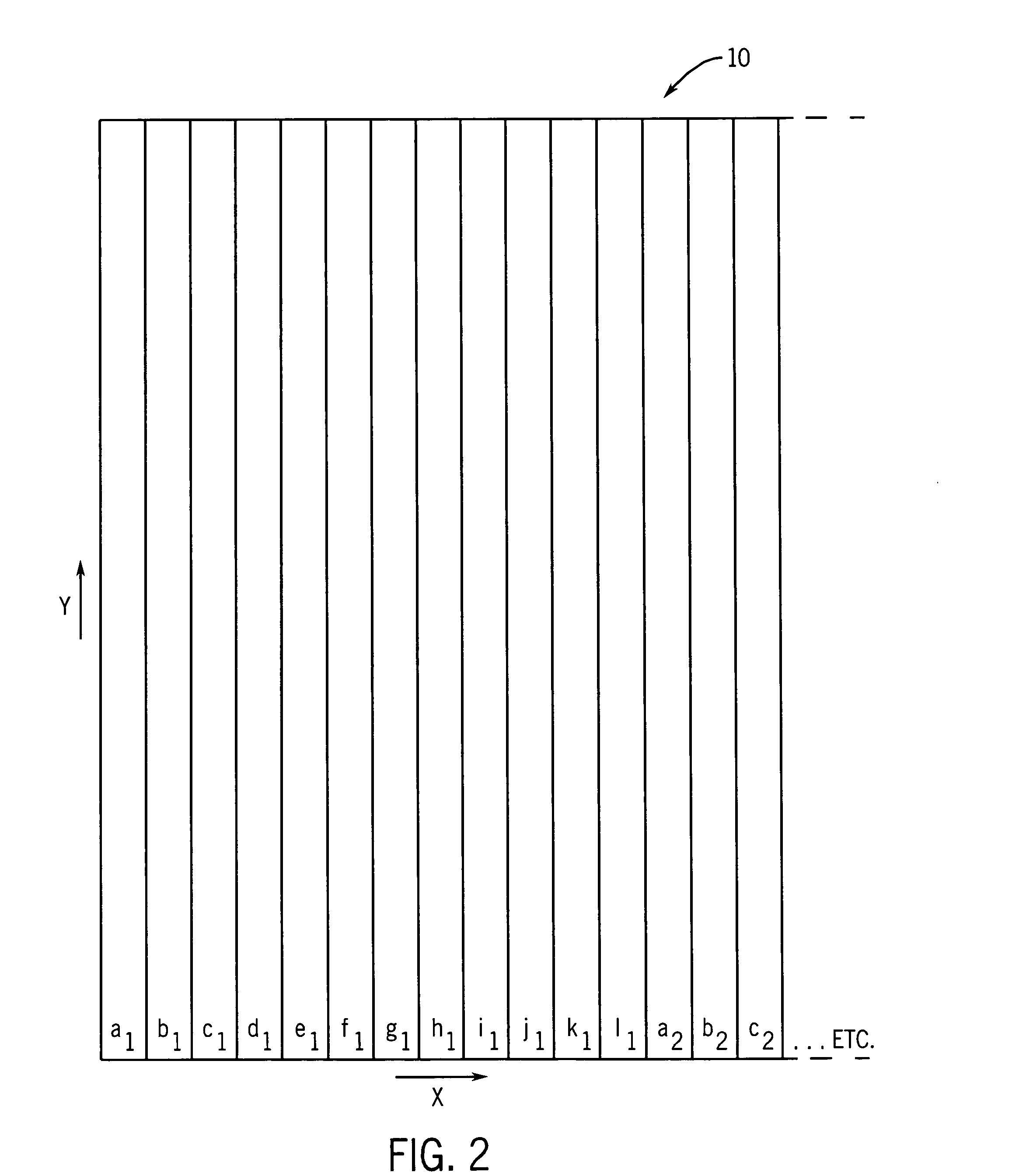Patents
Literature
77results about How to "Reduce image degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
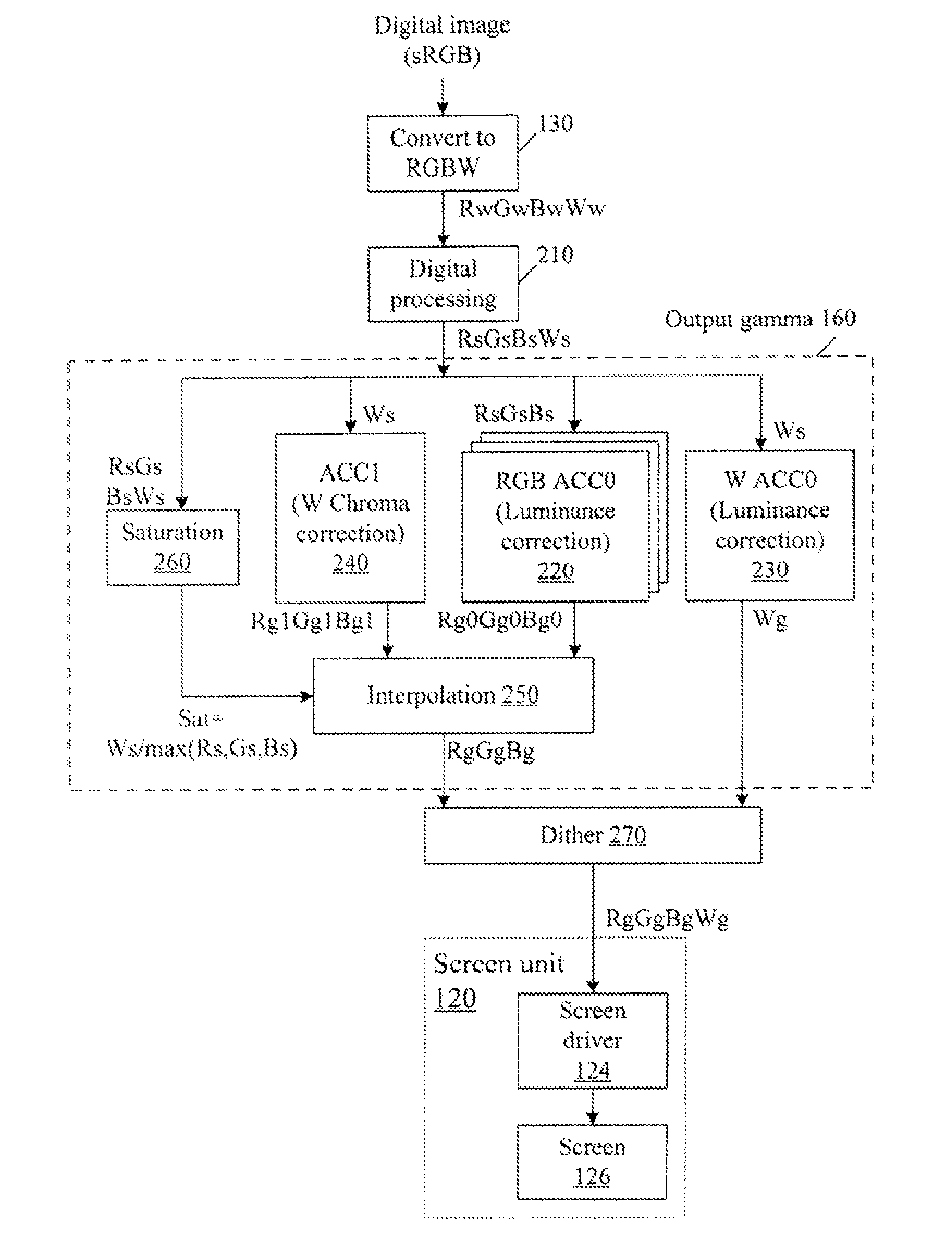
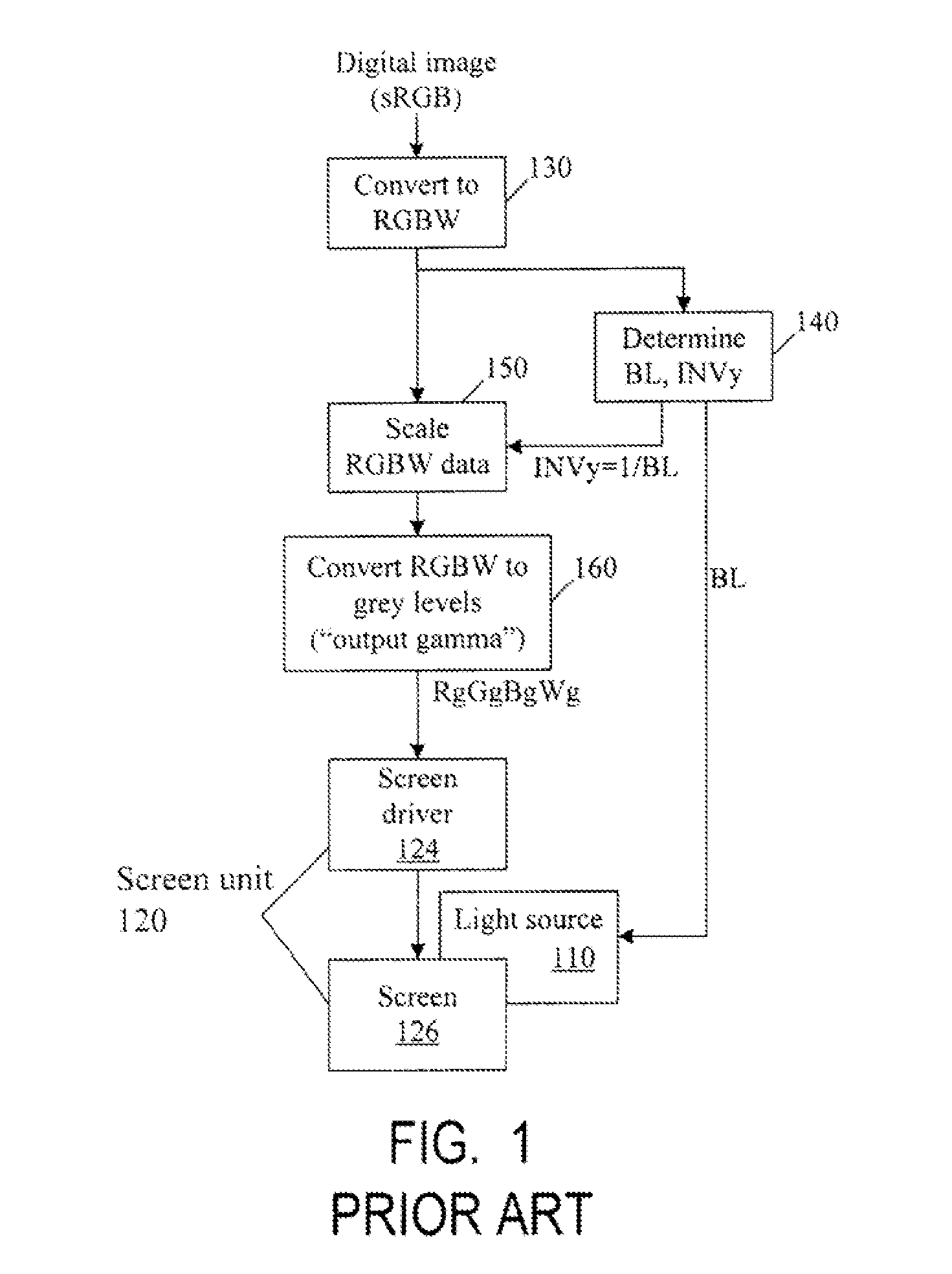
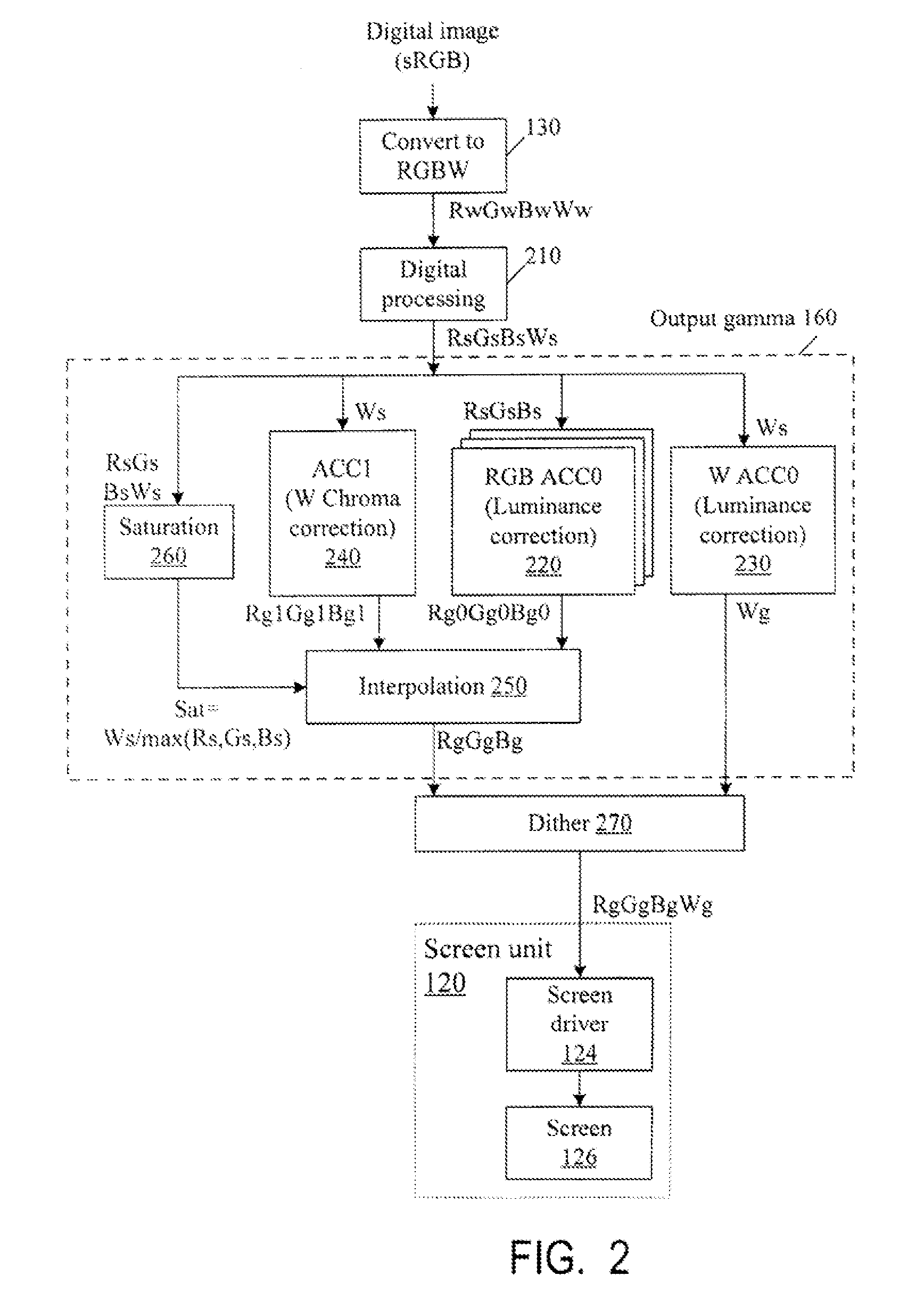
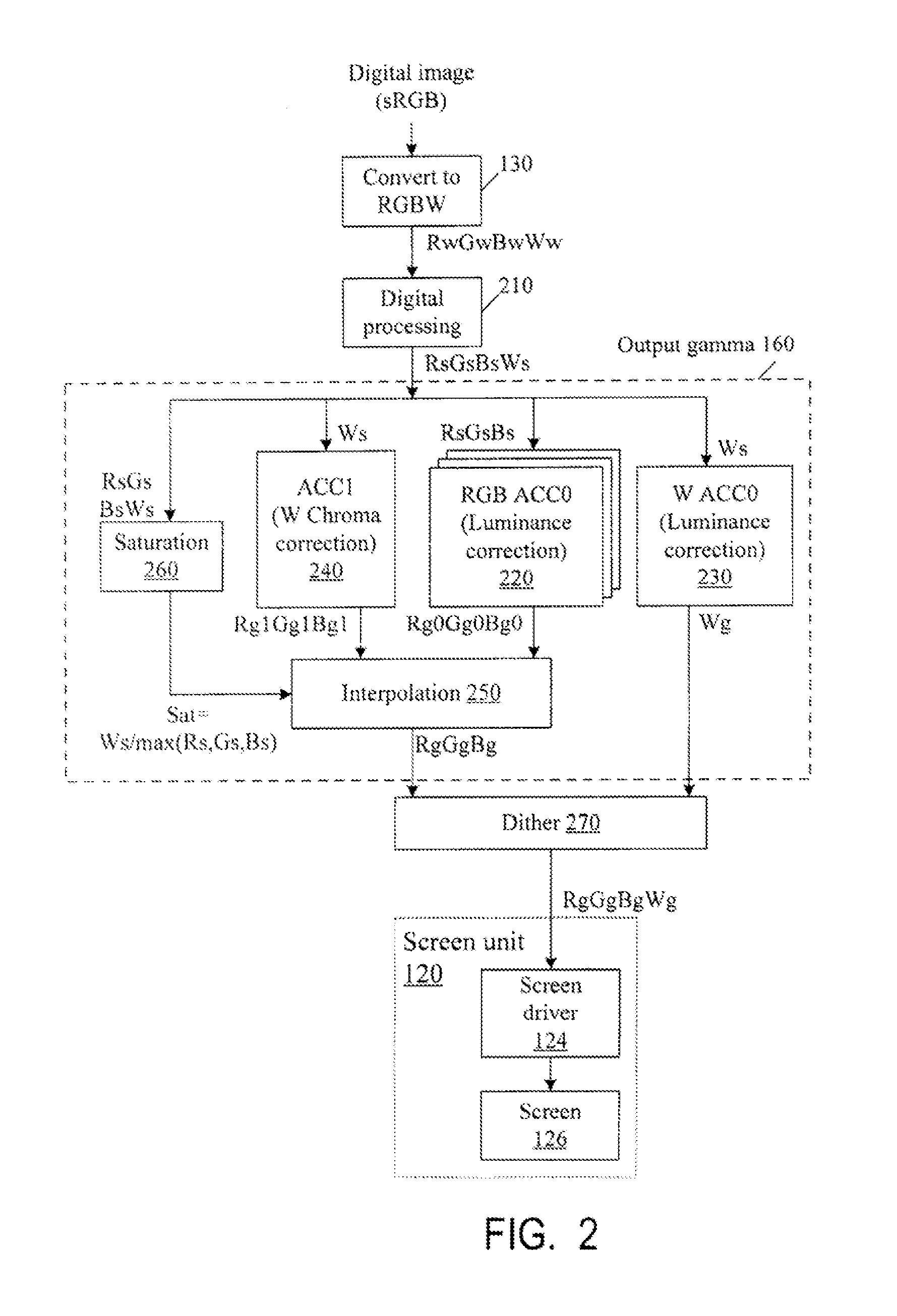
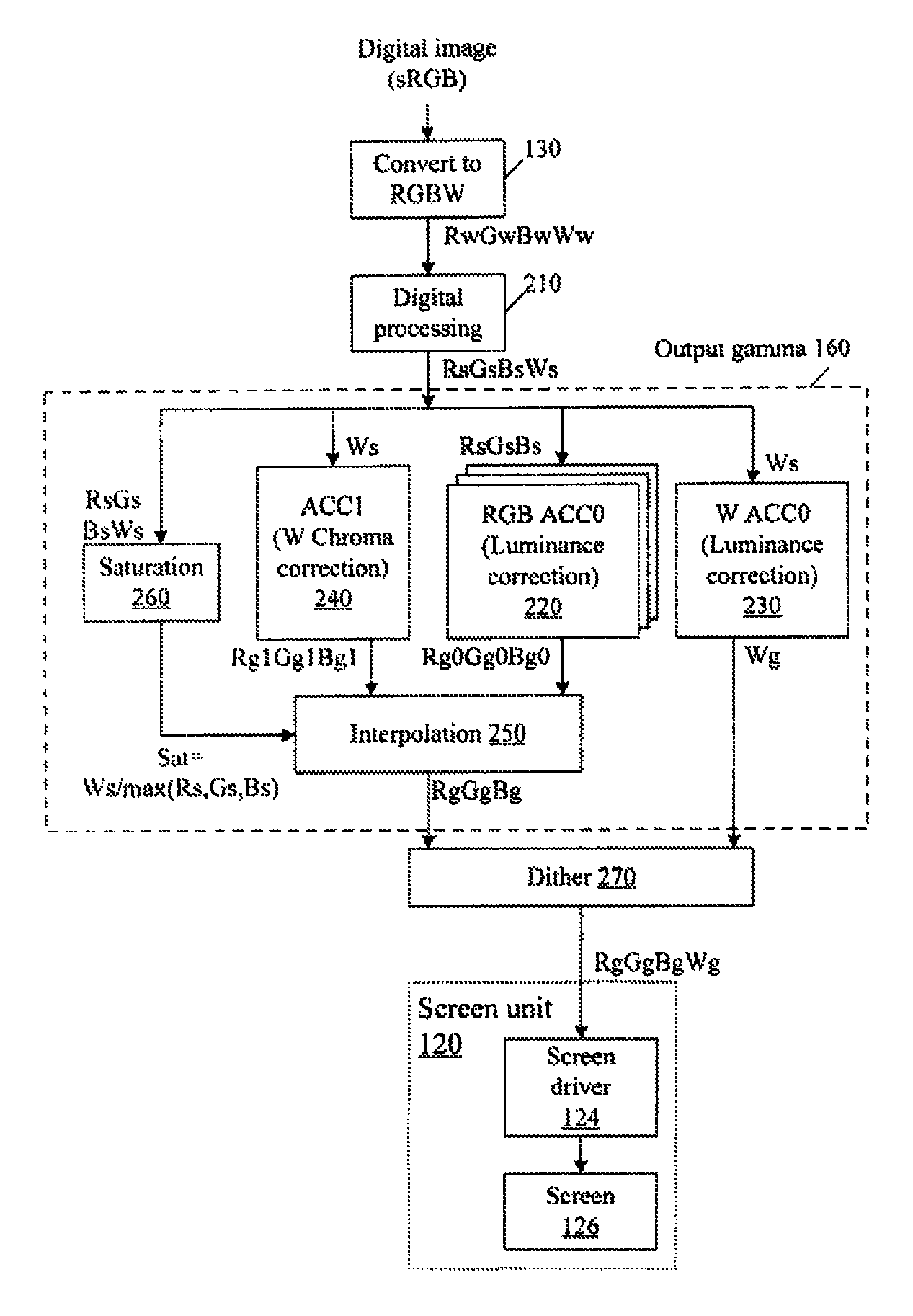
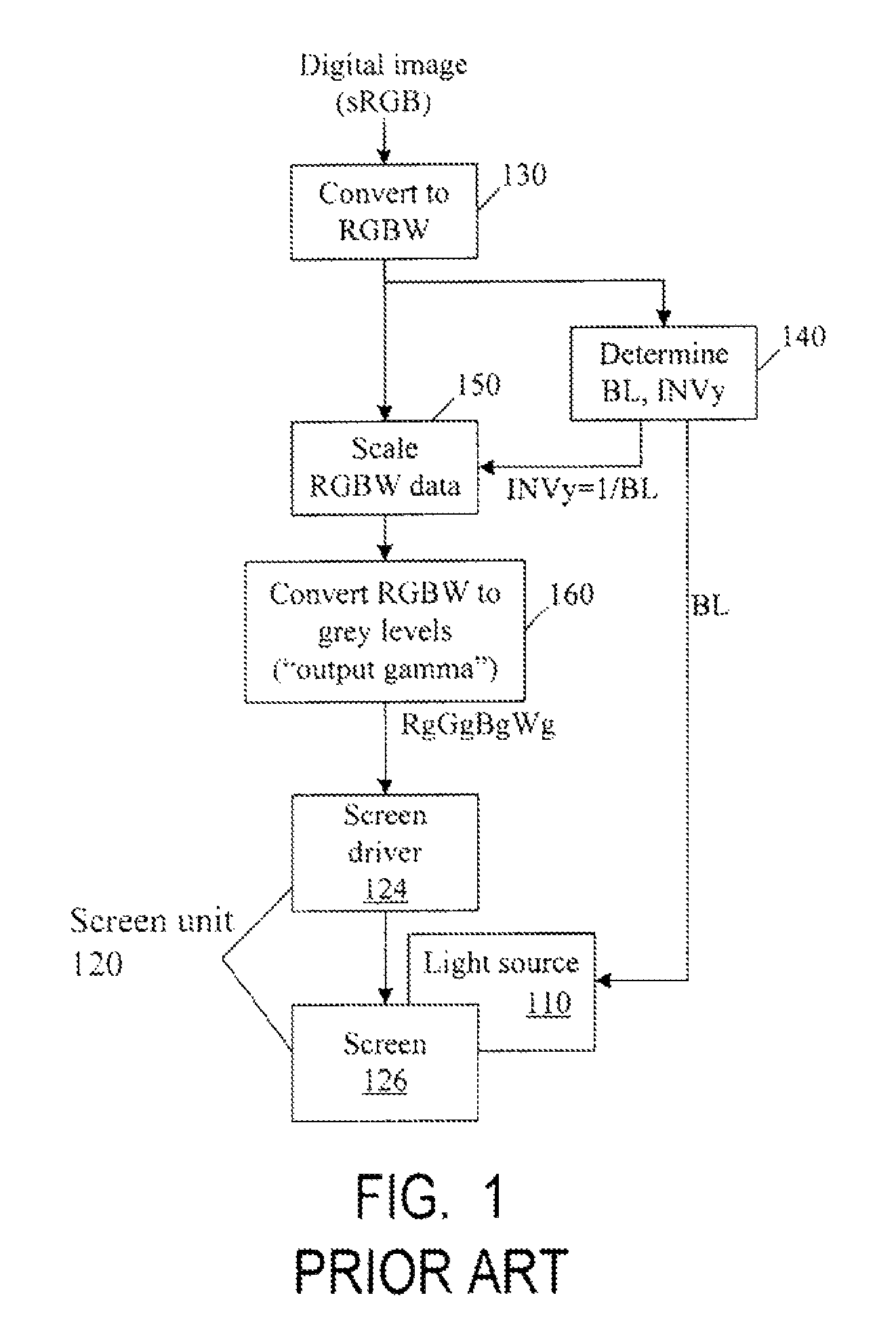
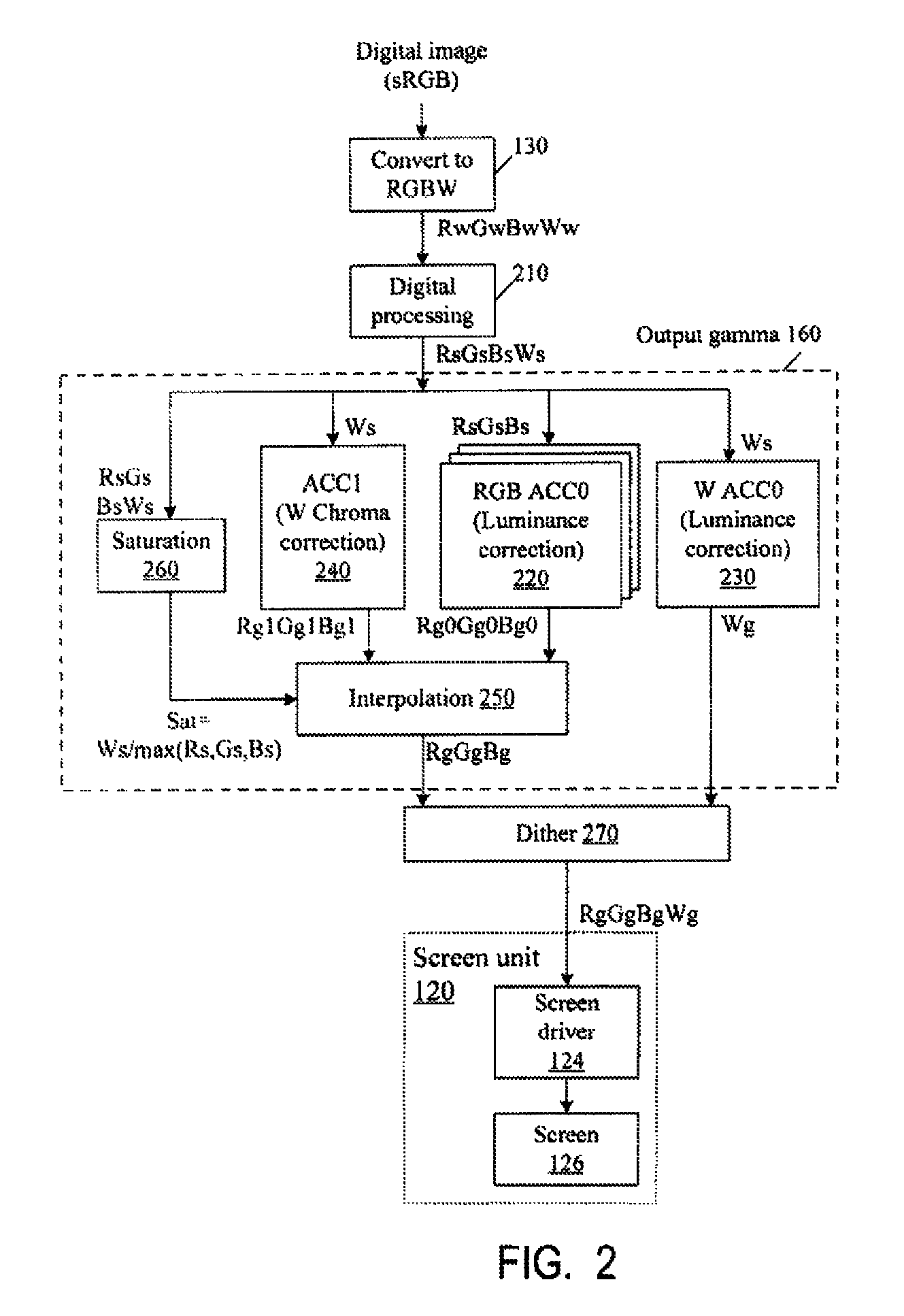
Color correction to compensate for displays' luminance and chrominance transfer characteristics
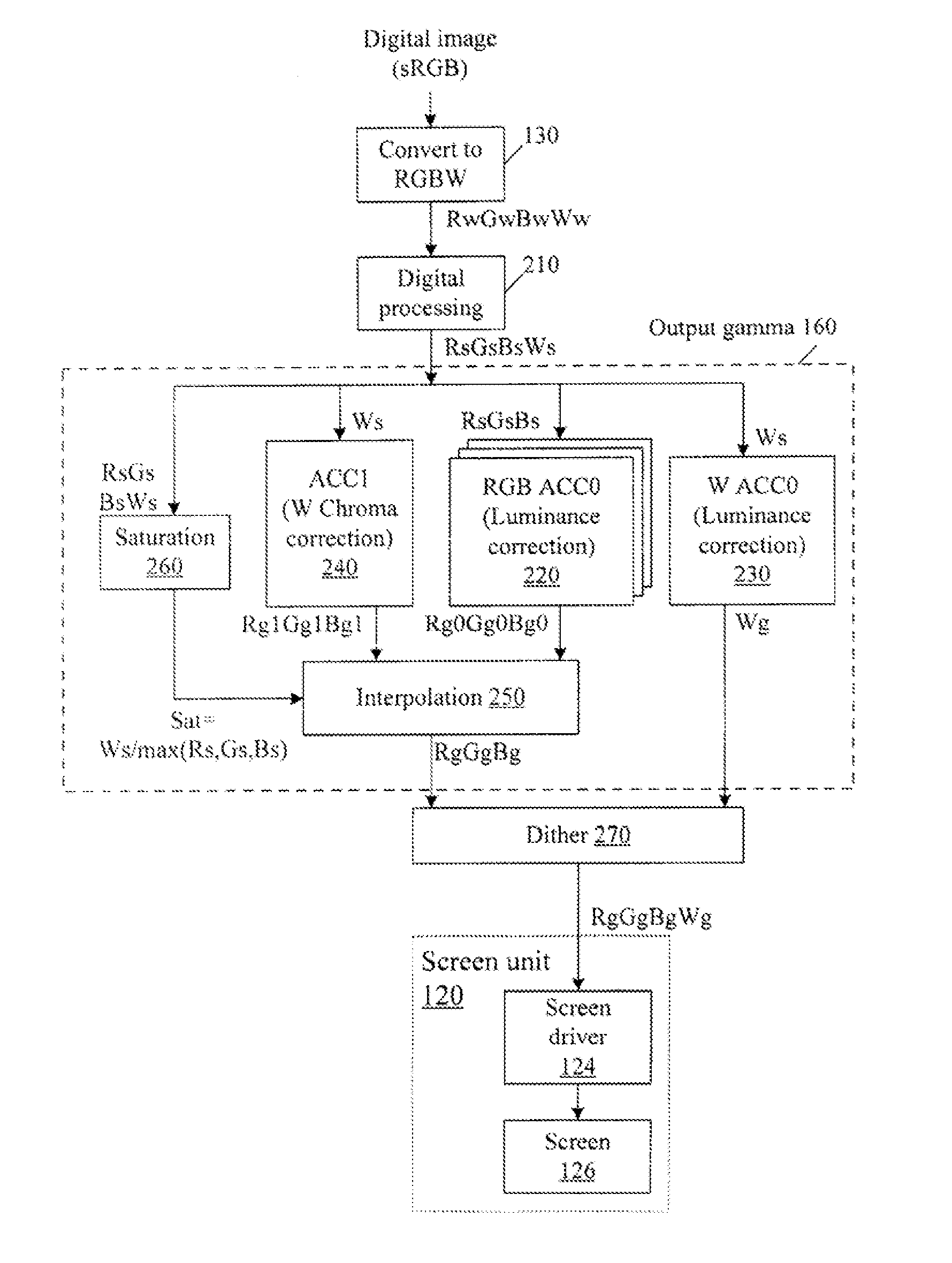
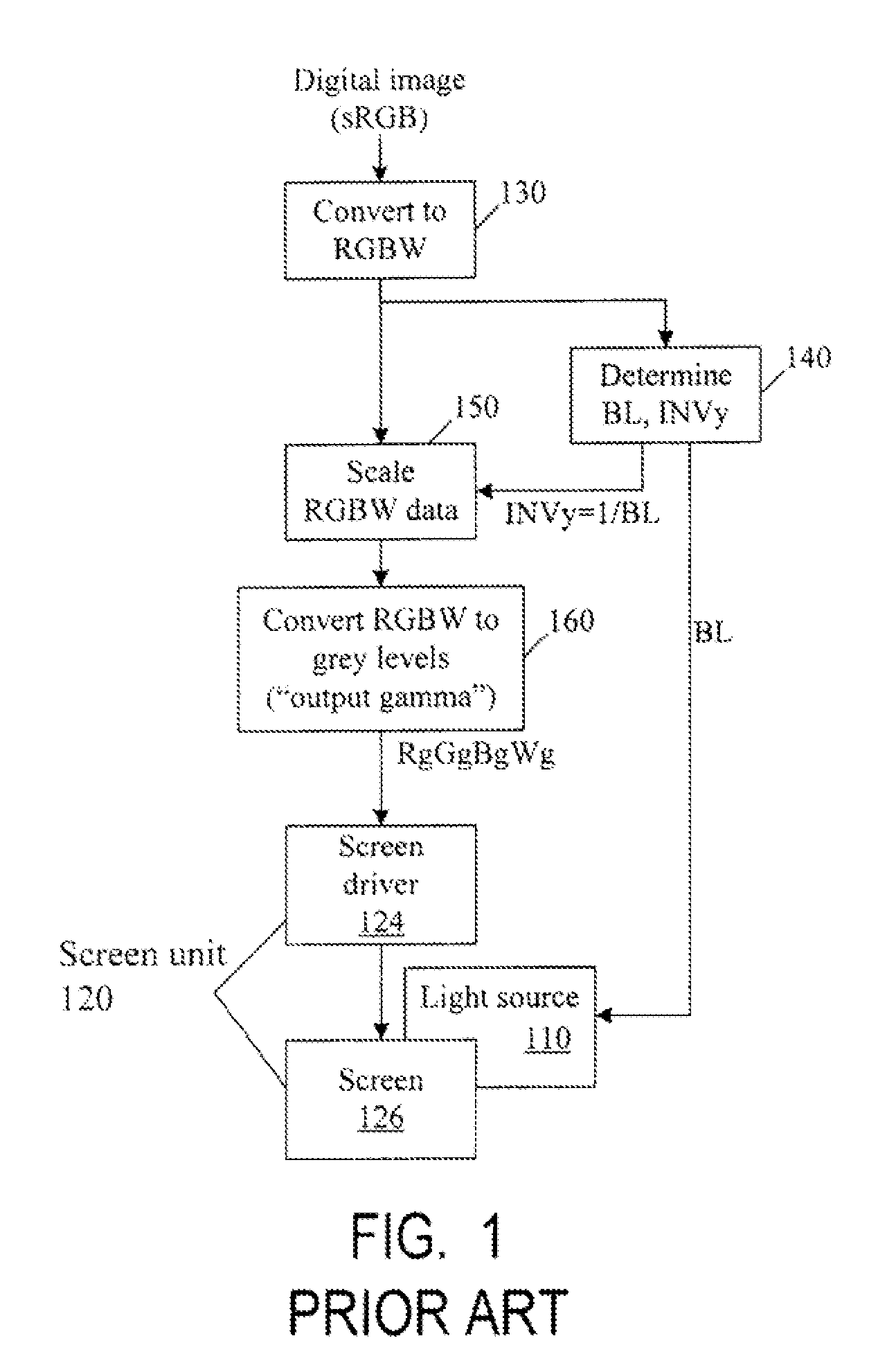
ActiveUS20110149166A1Image degradation can be highIncrease brightnessTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsColor correctionDisplay device
Displays are provided with circuitry performing color correction to compensate for the displays' luminance and chrominance transfer characteristics. Some techniques are suitable for RGBW displays and for subpixel-rendered displays. Some displays include an external light source (e.g. a backlight unit in LCDs), and the color correction is coordinated with dynamic control of the light source.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Multimodal Imaging System, Apparatus, and Methods
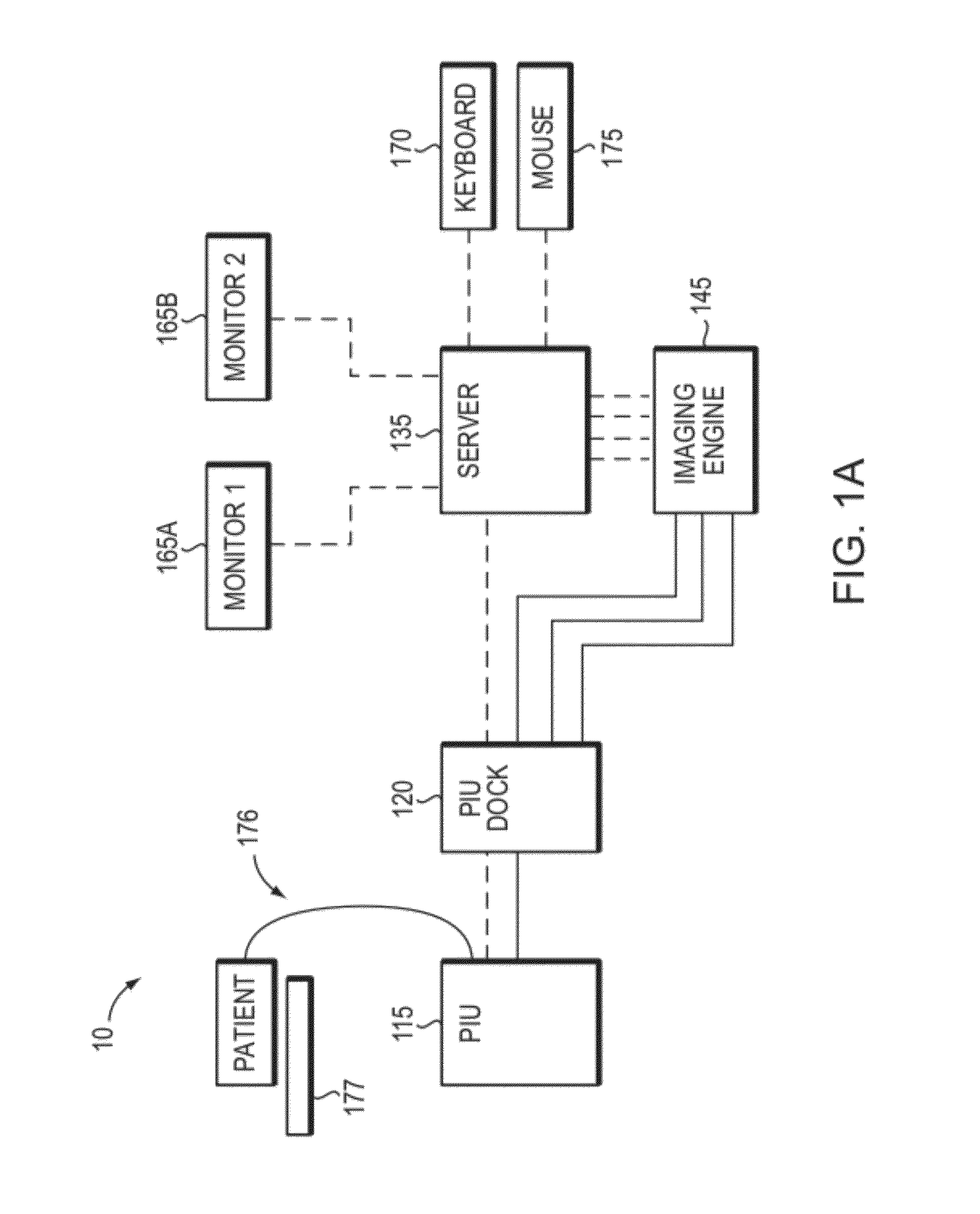
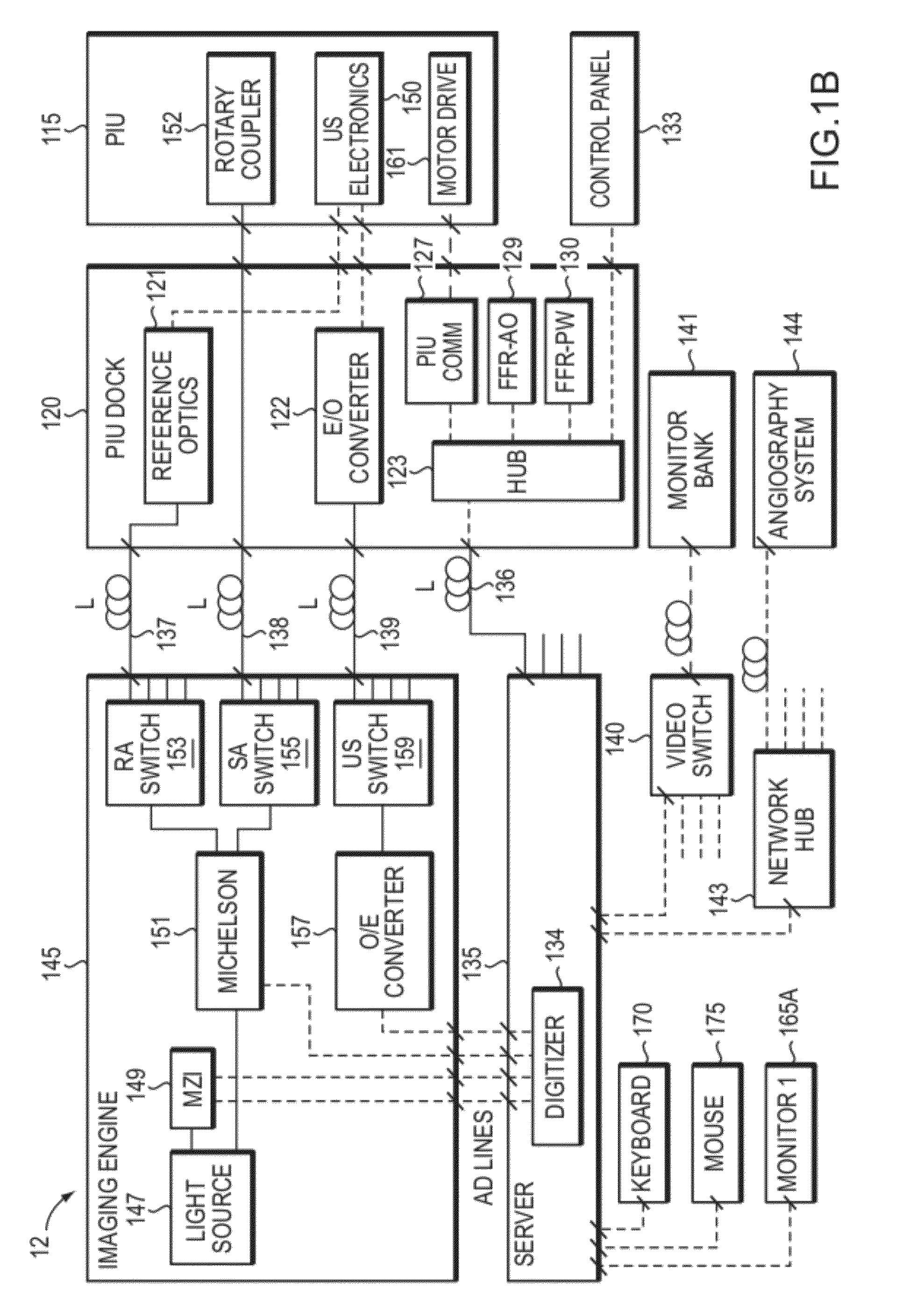
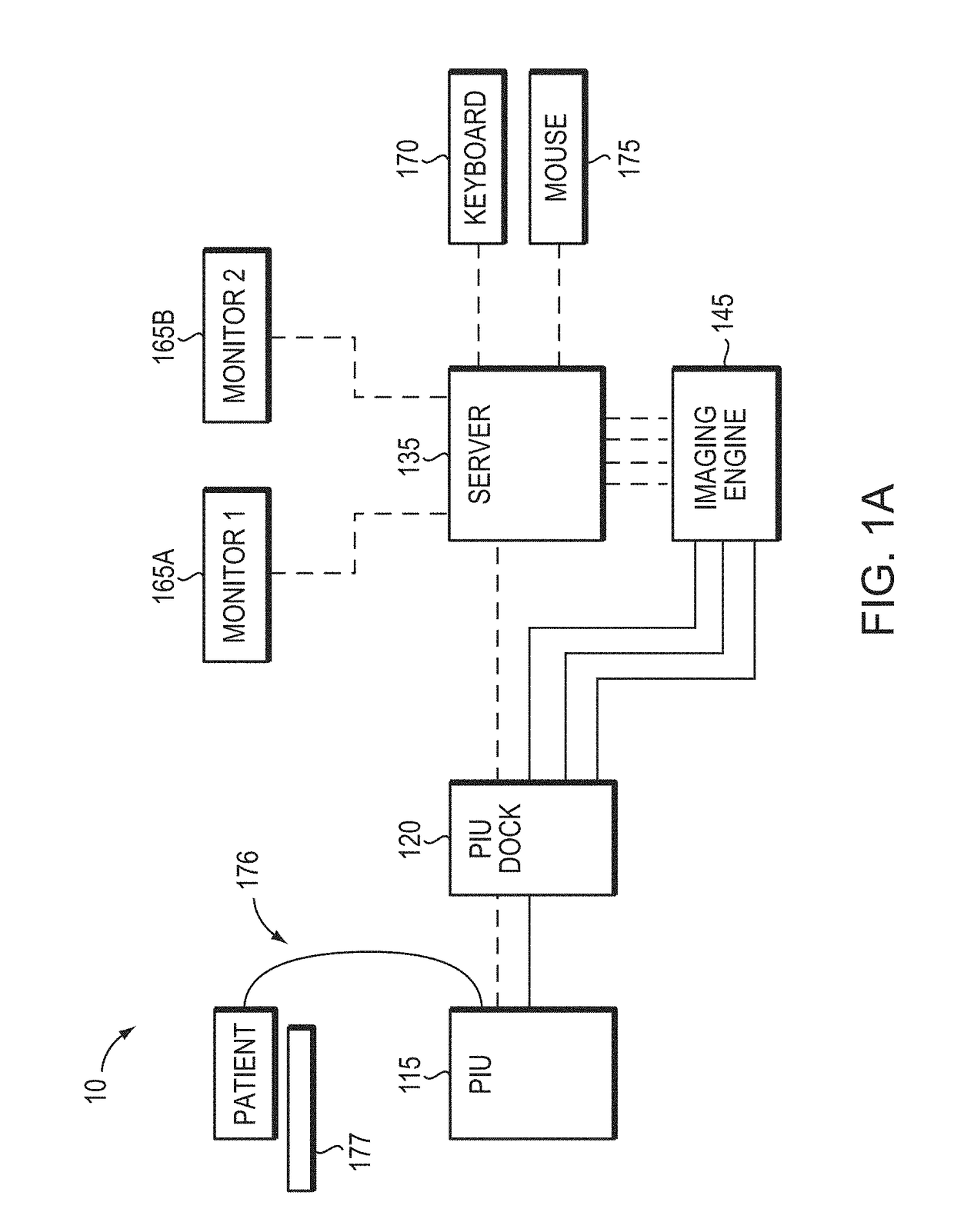
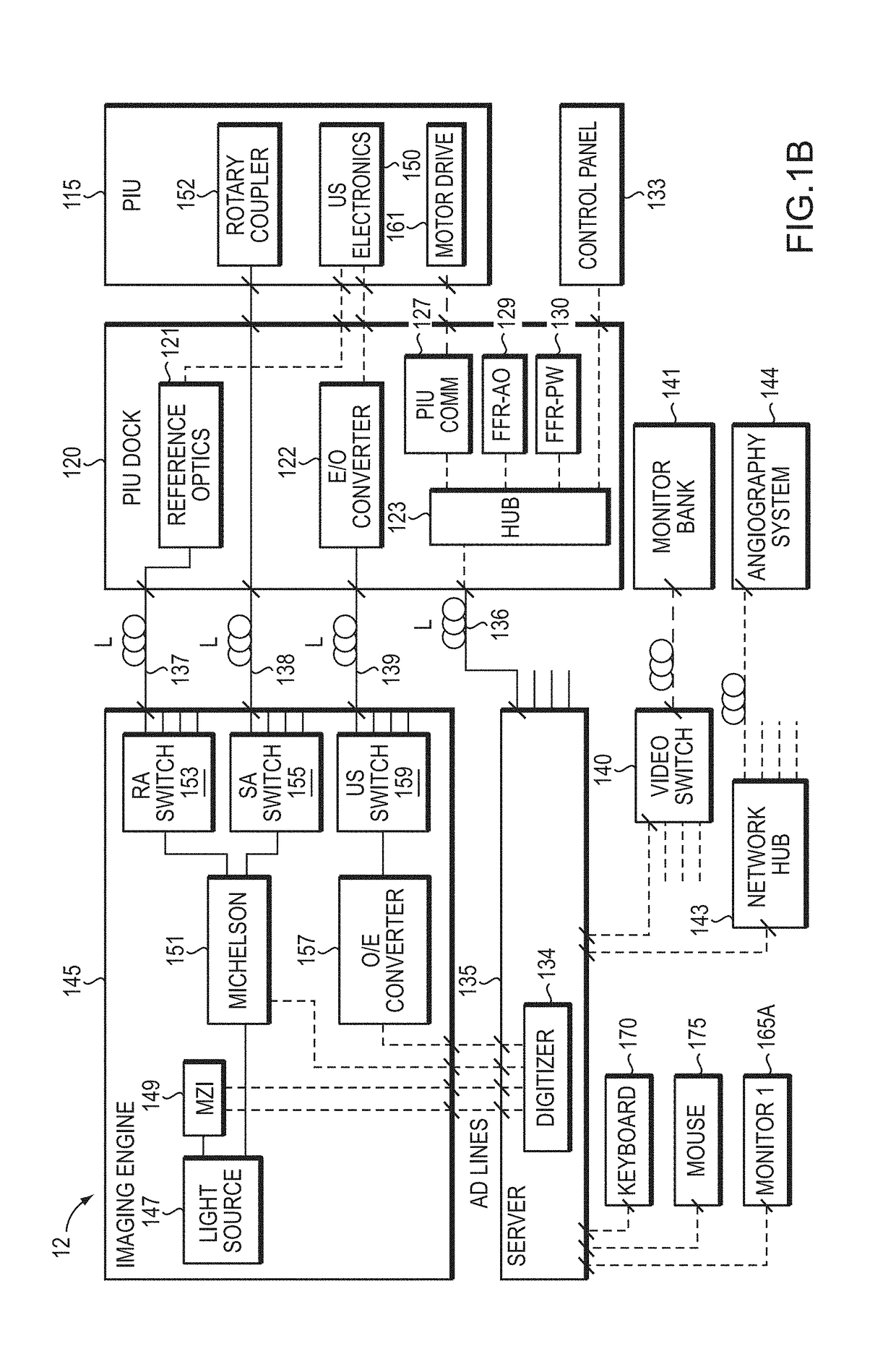
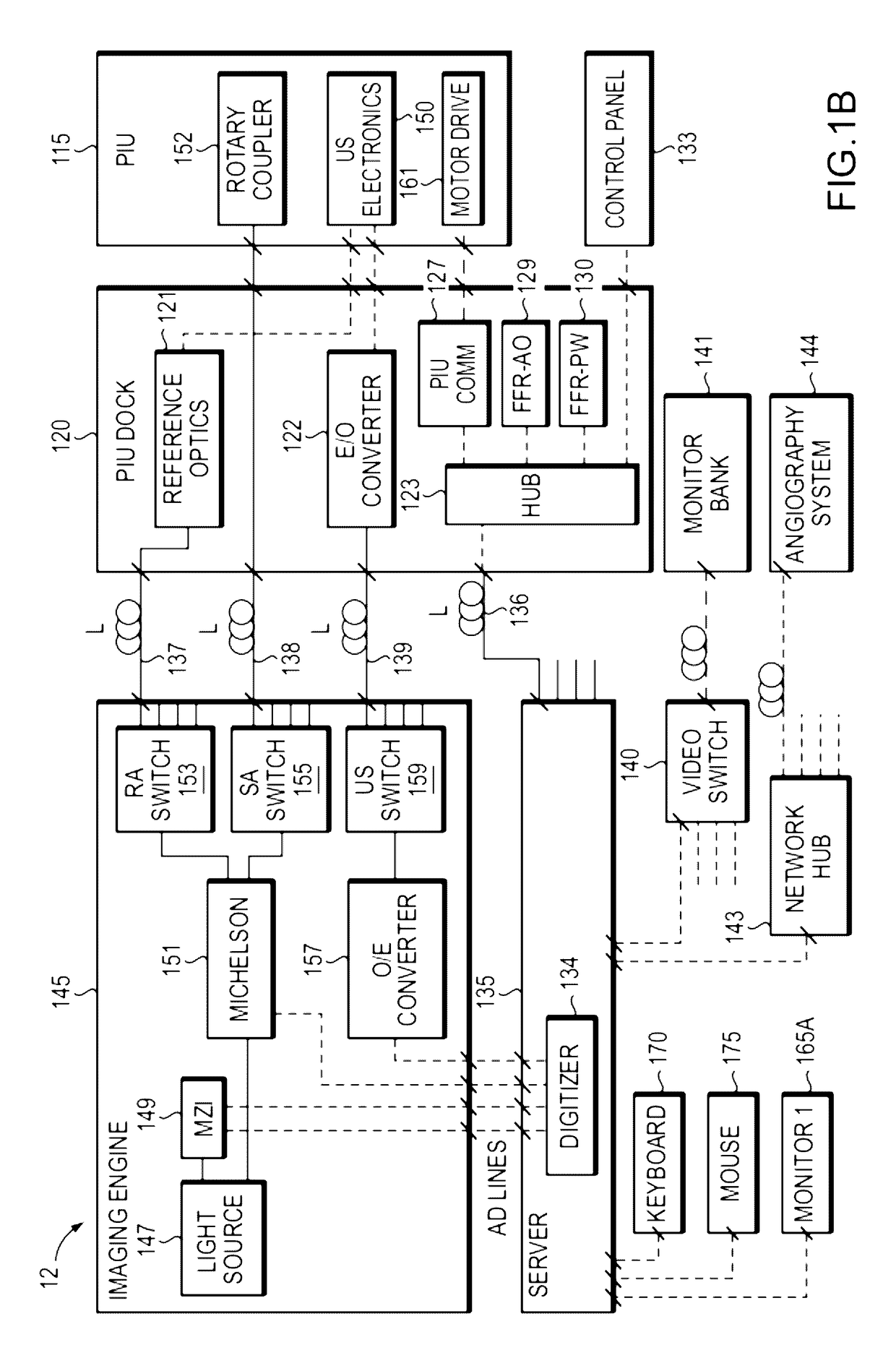
In part, the invention relates to an image data collection system. The system can include an interferometer having a reference arm that includes a first optical fiber of length of L1 and a sample arm that includes a second optical fiber of length of L2 and a first rotary coupler configured to interface with an optical tomography imaging probe, wherein the rotary coupler is in optical communication with the sample arm. In one embodiment, L2 is greater than about 5 meters. The first optical fiber and the second optical fiber can both be disposed in a common protective sheath. In one embodiment, the system further includes an optical element configured to adjust the optical path length of the reference arm, wherein the optical element is in optical communication with the reference arm and wherein the optical element is transmissive or reflective.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Color correction to compensate for displays' luminance and chrominance transfer characteristics
ActiveUS20110148910A1Reducing table sizeIncrease image brightnessCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingColor correctionDisplay device
Displays are provided with circuitry performing color correction to compensate for the displays' luminance and chrominance transfer characteristics. Some techniques are suitable for RGBW displays and for subpixel-rendered displays. Some displays include an external light source (e.g. a backlight unit in LCDs), and the color correction is coordinated with dynamic control of the light source.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
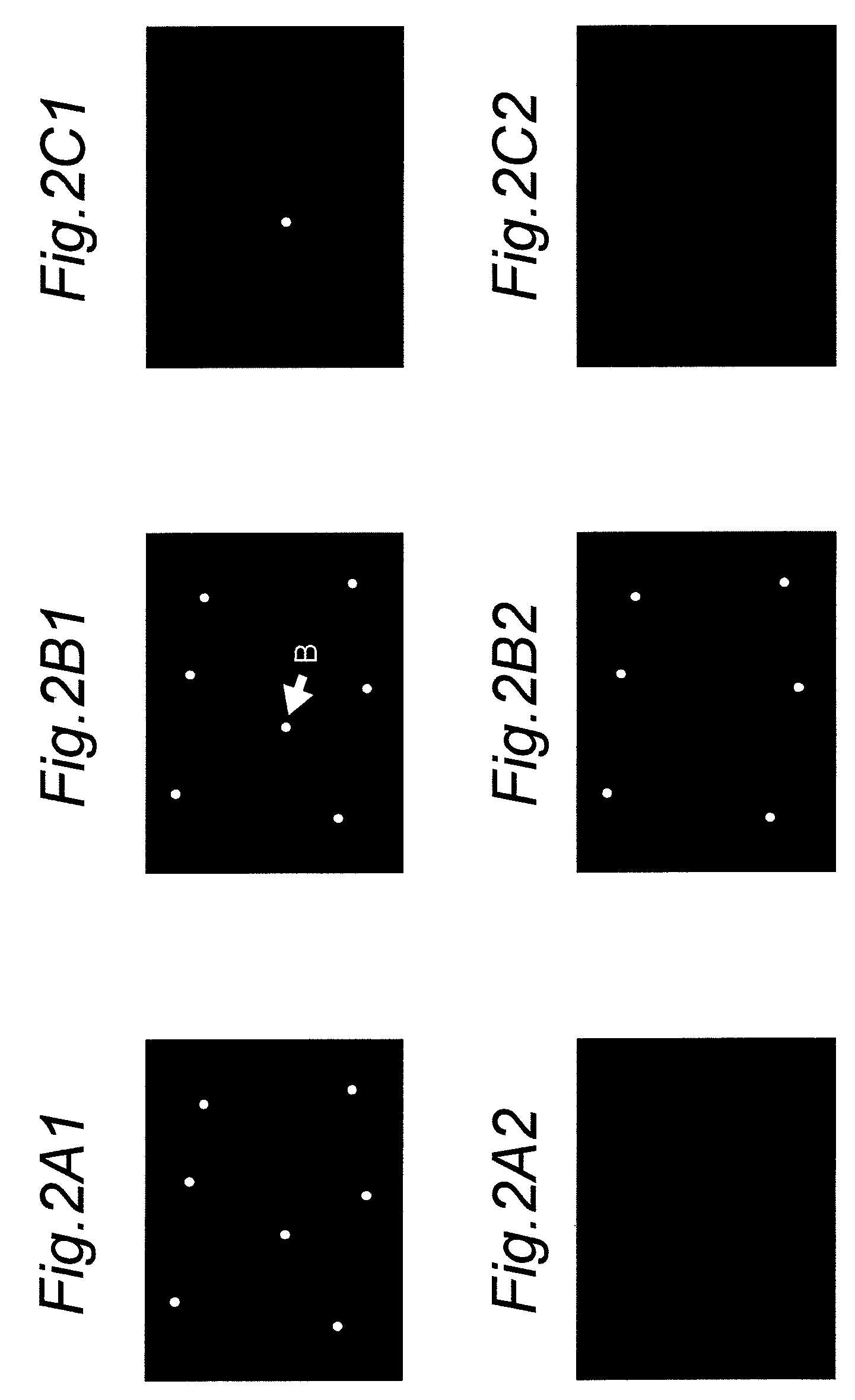
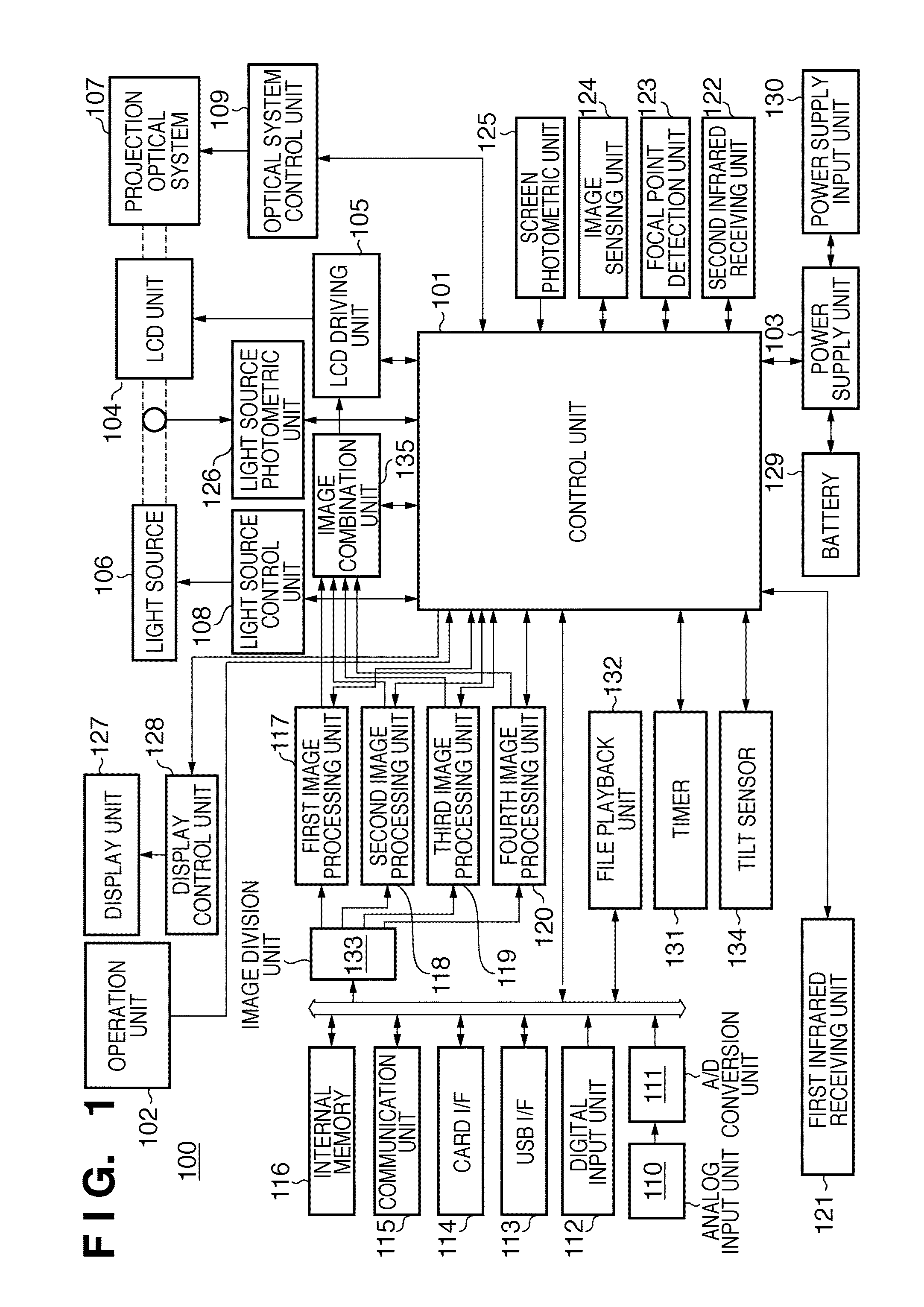
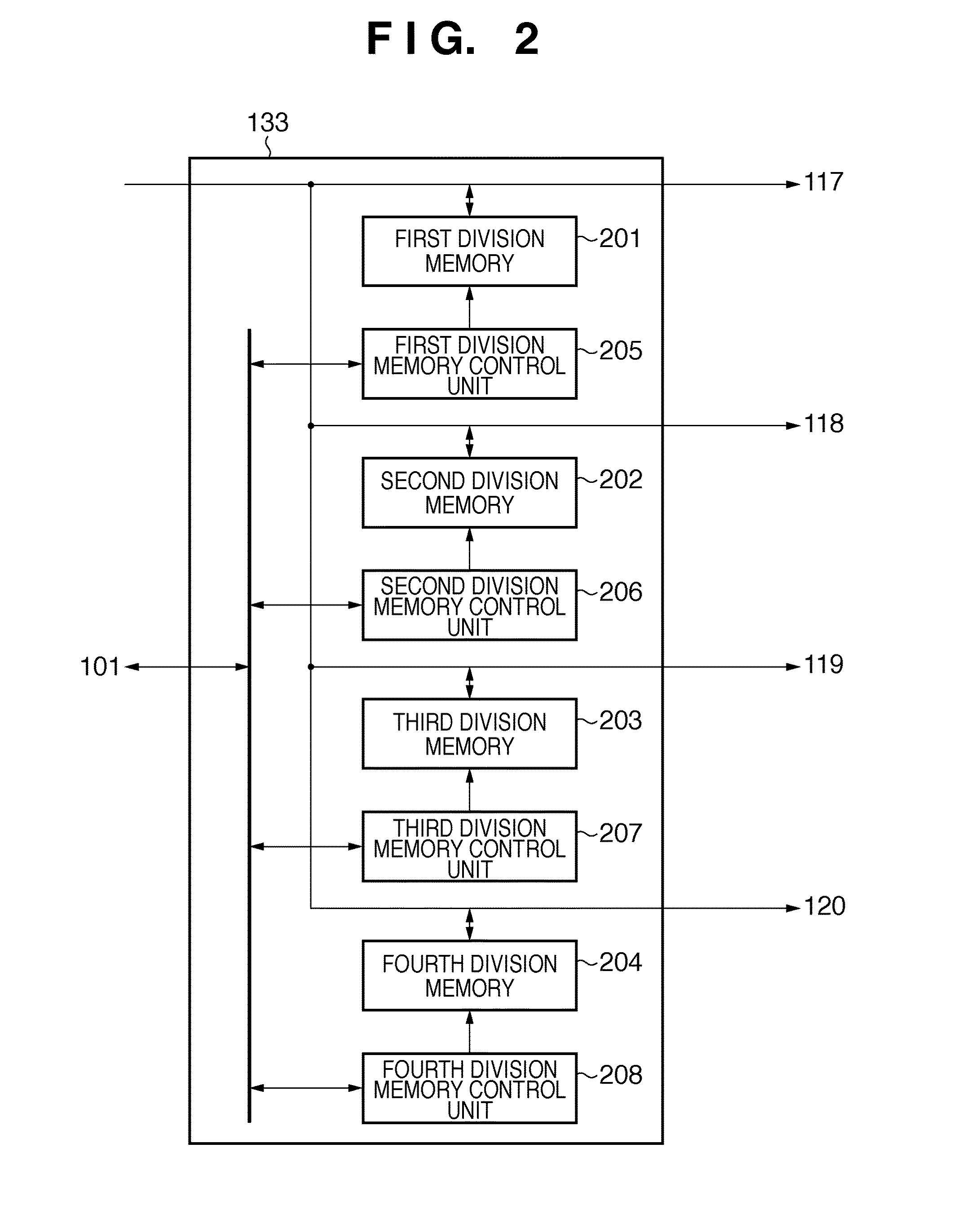
Image projecting apparatus and image projecting method
InactiveUS7967445B2Lower performance requirementsReduce image degradationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging processingLuminous flux
Owner:RICOH KK
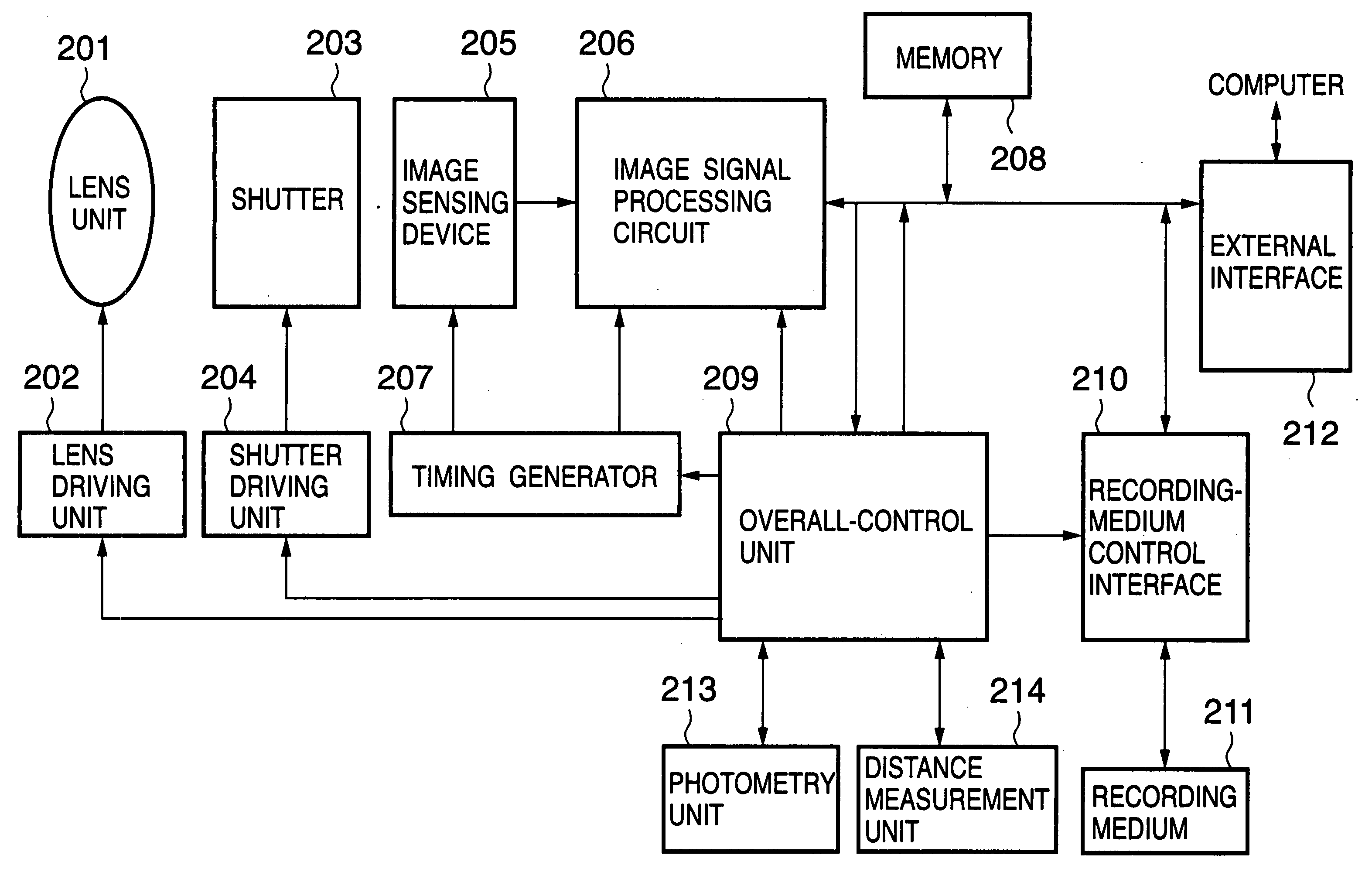
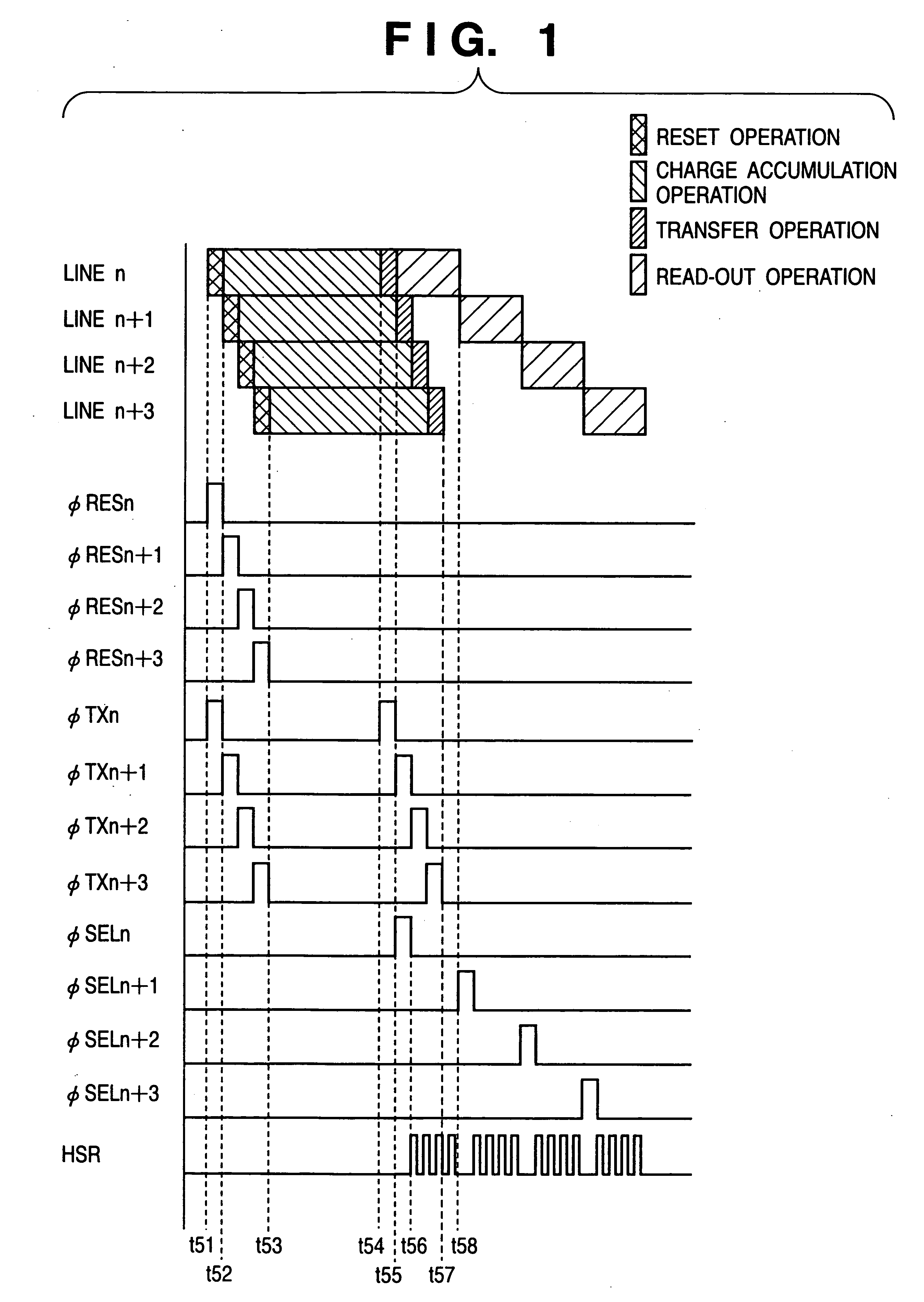
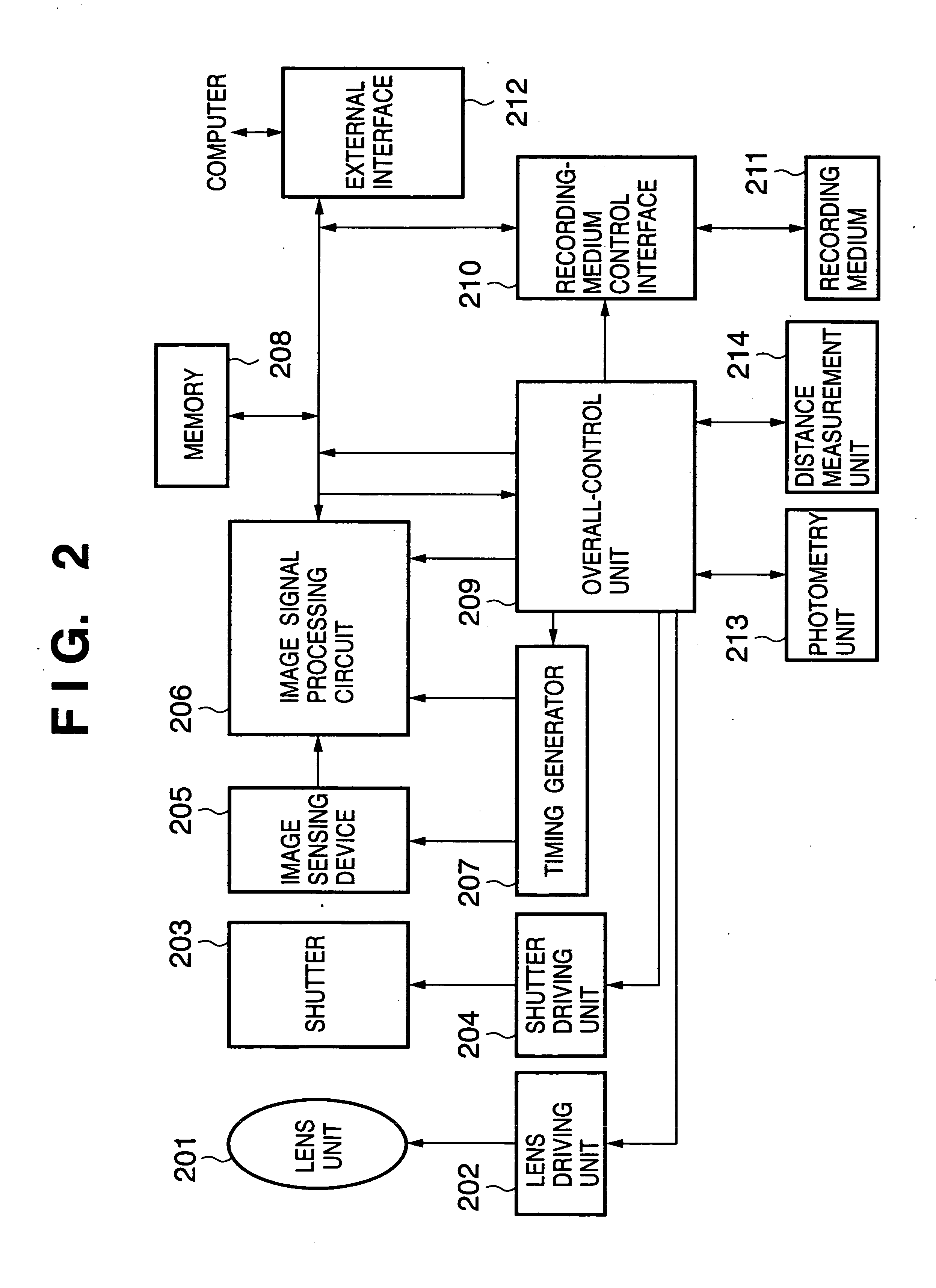
Image sensing apparatus and method of controlling same
InactiveUS20050128324A1Reduce image degradationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsTransfer modeEngineering
Disclosed is an image sensing apparatus comprising a plurality of two-dimensionally arrayed pixels each having a photodiode and a floating depletion area for temporarily storing a charge signal that has accumulated in the photodiode; an output unit that outputs the charge signal, which has been transferred to the floating depletion area, successively pixel by pixel; a scanning unit having a reset mode for resetting the photodiodes and floating depletion areas successively by prescribed unit, a first transfer mode for transferring the charge signal, which has accumulated in the photodiodes, to the floating depletion areas successively by the prescribed unit at prescribed time intervals upon lapse of a prescribed period of time from start of reset, and a second transfer mode for transferring the charge signal, which has been transferred to the floating depletion areas, to the output unit. Before operation of the second transfer mode is performed with respect to a plurality of the prescribed units, the scanning unit transfers the charge signal, which has accumulated in the photodiodes, to the floating depletion areas successively by the prescribed unit at the prescribed time intervals with respect to the
Owner:CANON KK
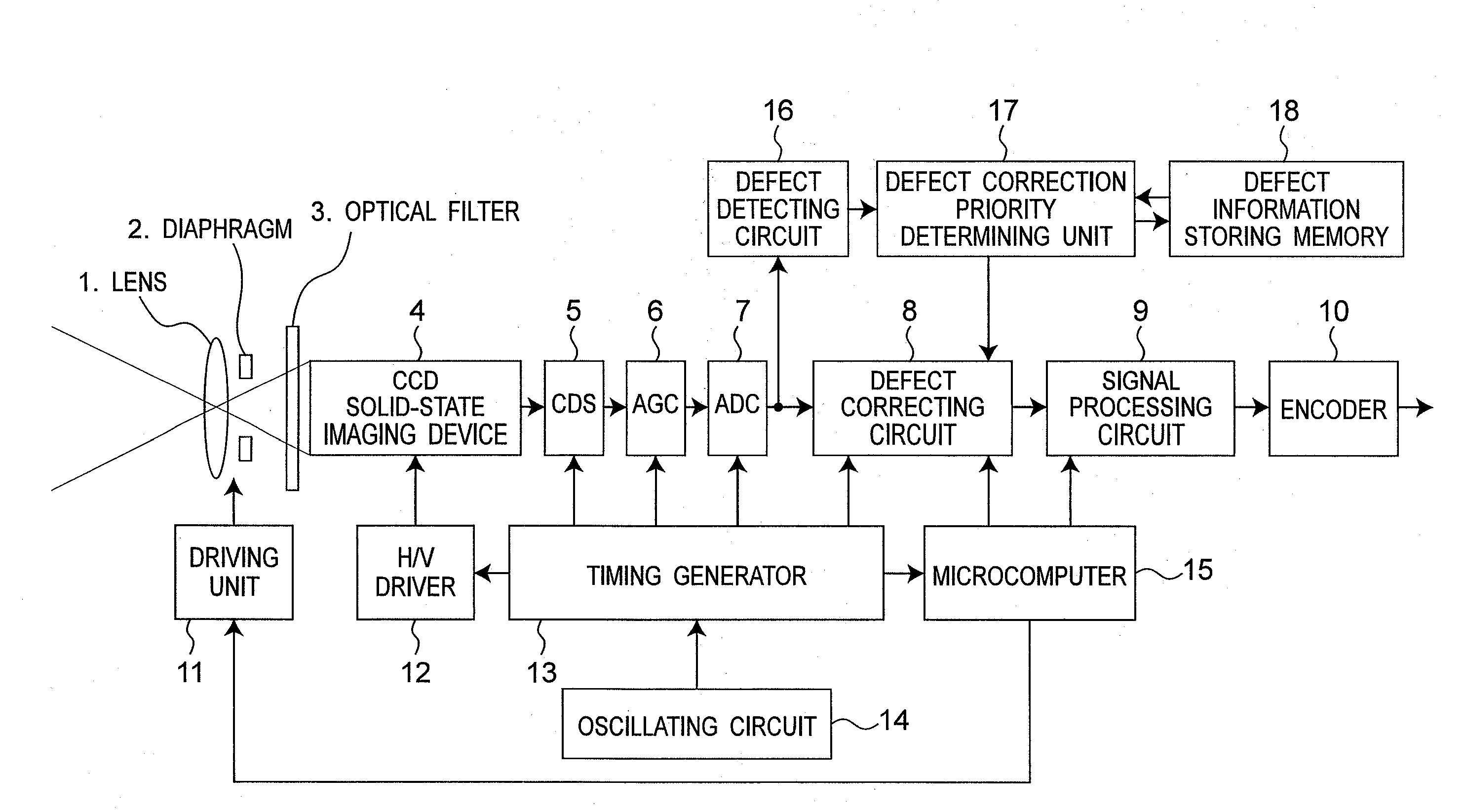
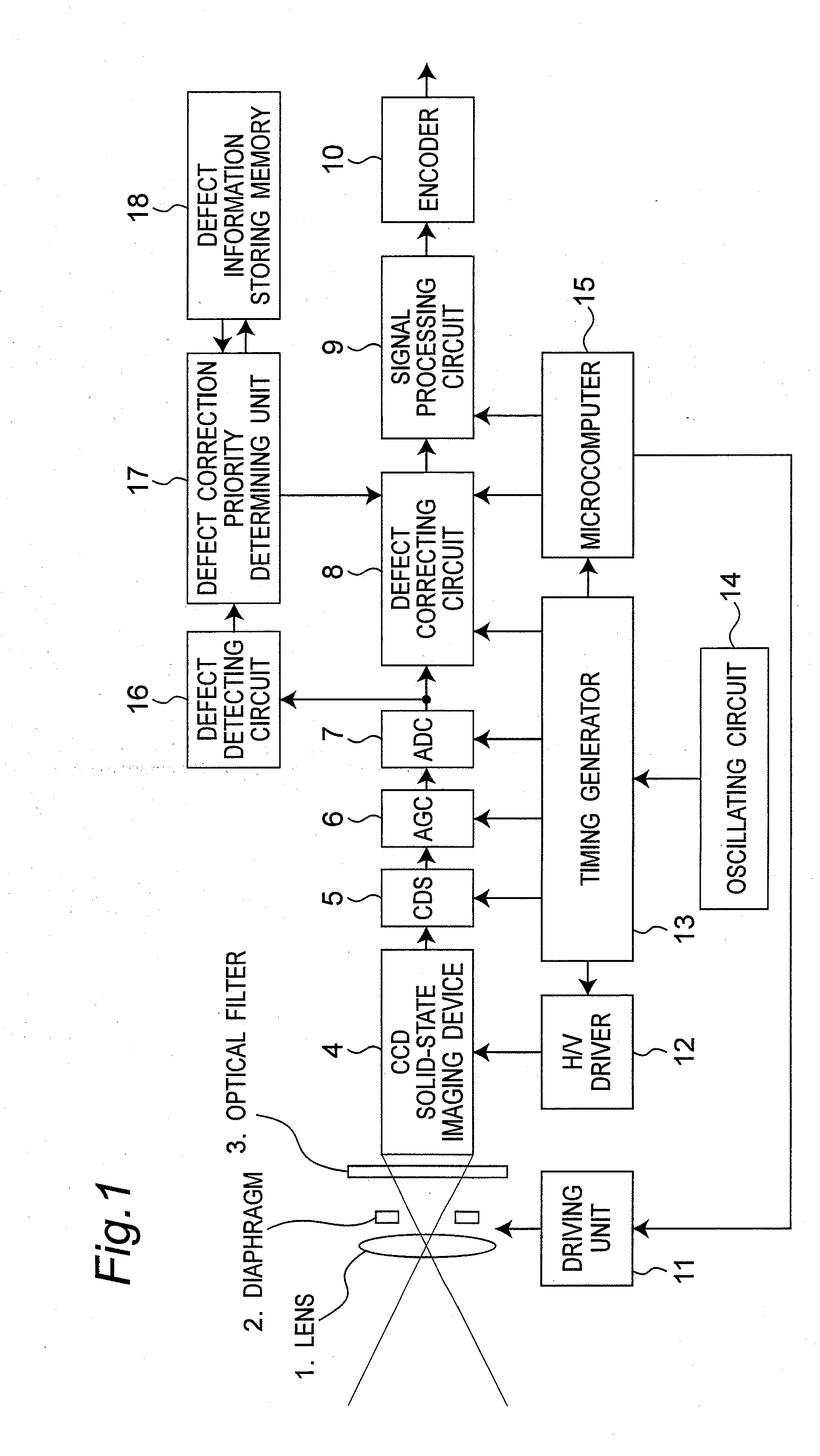
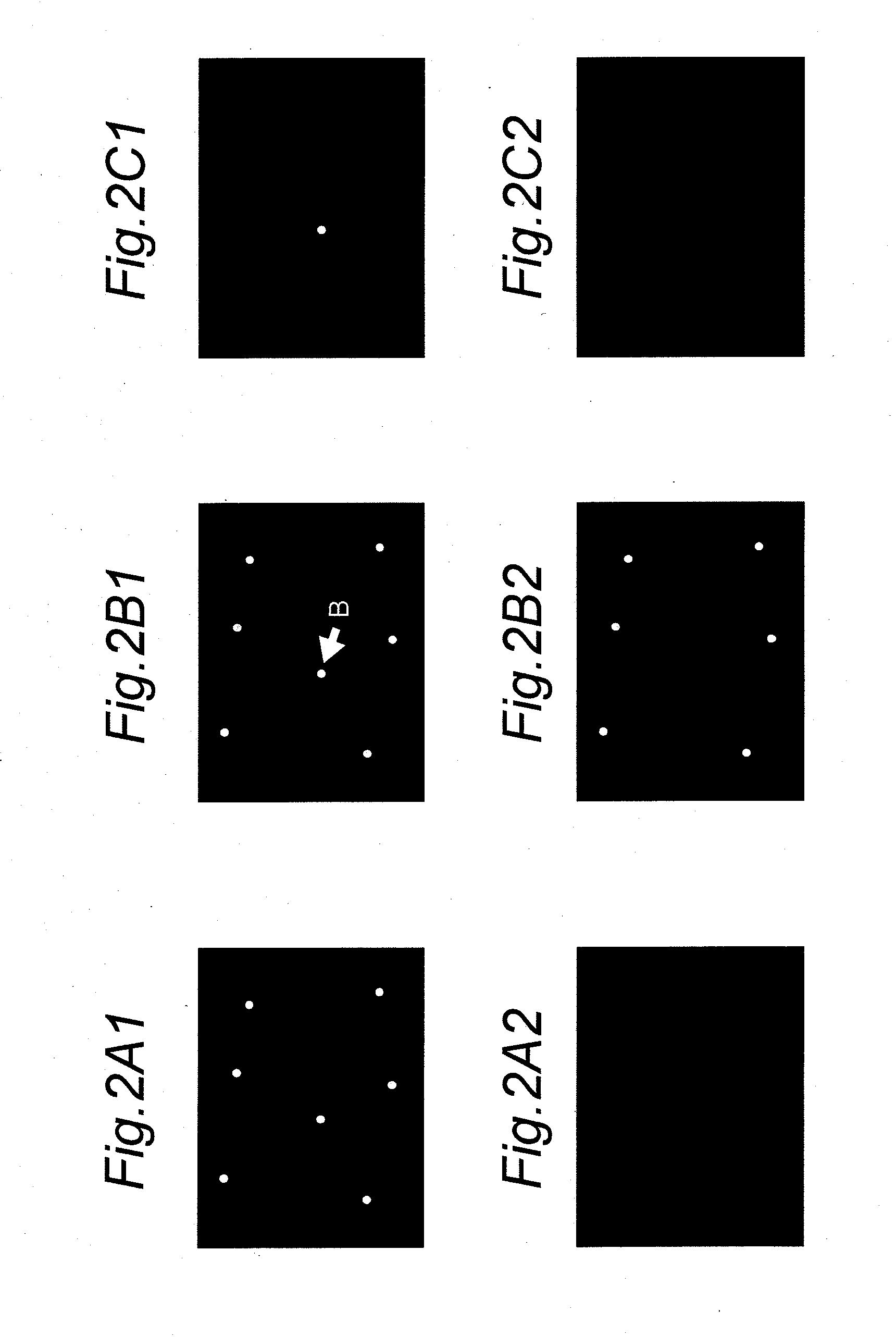
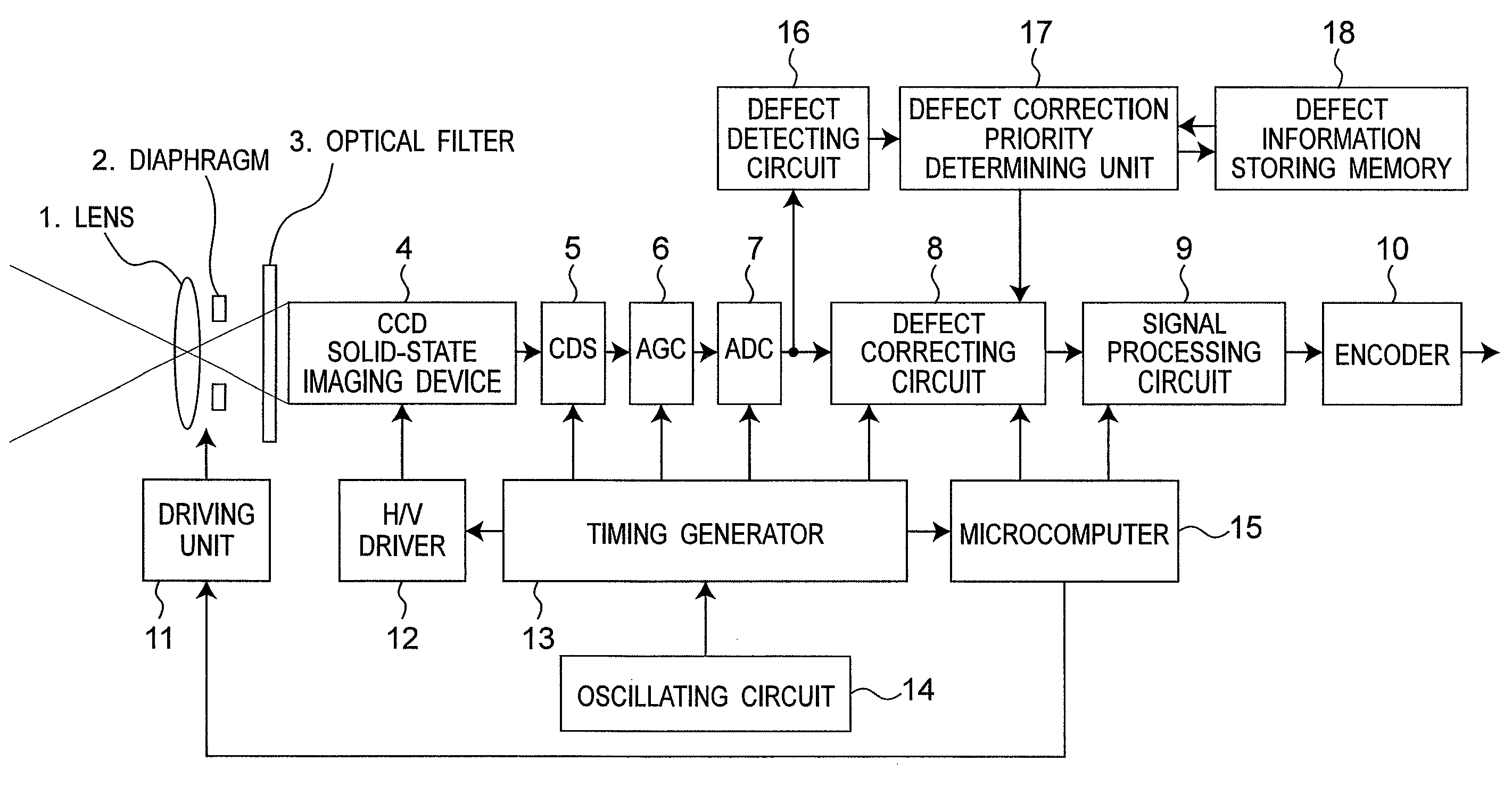
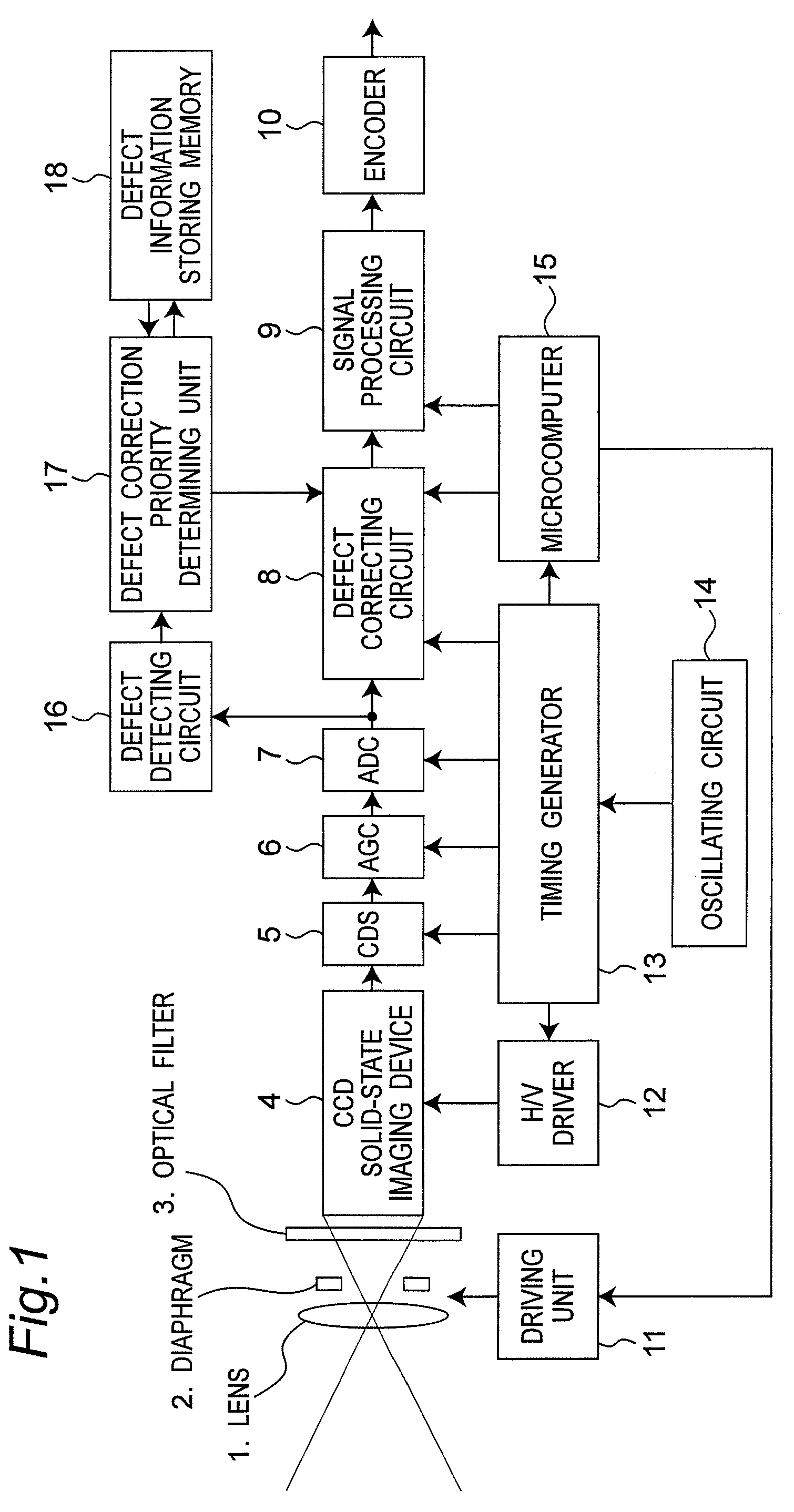
Defective pixel detecting device, defective pixel detecting method, record medium storing a program for detecting defective pixels, and imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20100073526A1Reduce image degradationReduce adverse effectsTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImaging SignalImage signal
A defective pixel detecting device determining defective pixels as correction targets in an imaging device that produces image signals is provided, and the device includes: defect information storage configured to store priority of defective pixels to be corrected; a defective pixel detector configured to detect defective pixels by comparing levels of imaging signals from the imaging device with a predetermined detection level; a priority setter configured to set priority of the detected defective pixels, based on the levels of the imaging signals of the defective pixels detected by the defective pixel detector; and a correction target determiner configured to newly determine defective pixels to be corrected based on the priority of the defective pixels out of the defective pixels that are currently detected by the defective pixel detector and the defective pixels to be corrected stored in the defect information storage, determining priority of the newly determined defective pixels to be corrected, and storing the priority of the newly determined defective pixels to be corrected in the defect information storage.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Defective pixel detecting device, defective pixel detecting method, record medium storing a program for detecting defective pixels, and imaging apparatus
ActiveUS8169514B2Reduce adverse effectsEnough can be detectedTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsSetterPriority setting
A defective pixel detecting device determining defective pixels as correction targets in an imaging device that produces image signals is provided, and the device includes: defect information storage configured to store priority of defective pixels to be corrected; a defective pixel detector configured to detect defective pixels by comparing levels of imaging signals from the imaging device with a predetermined detection level; a priority setter configured to set priority of the detected defective pixels, based on the levels of the imaging signals of the defective pixels detected by the defective pixel detector; and a correction target determiner configured to newly determine defective pixels to be corrected based on the priority of the defective pixels out of the defective pixels that are currently detected by the defective pixel detector and the defective pixels to be corrected stored in the defect information storage, determining priority of the newly determined defective pixels to be corrected, and storing the priority of the newly determined defective pixels to be corrected in the defect information storage.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
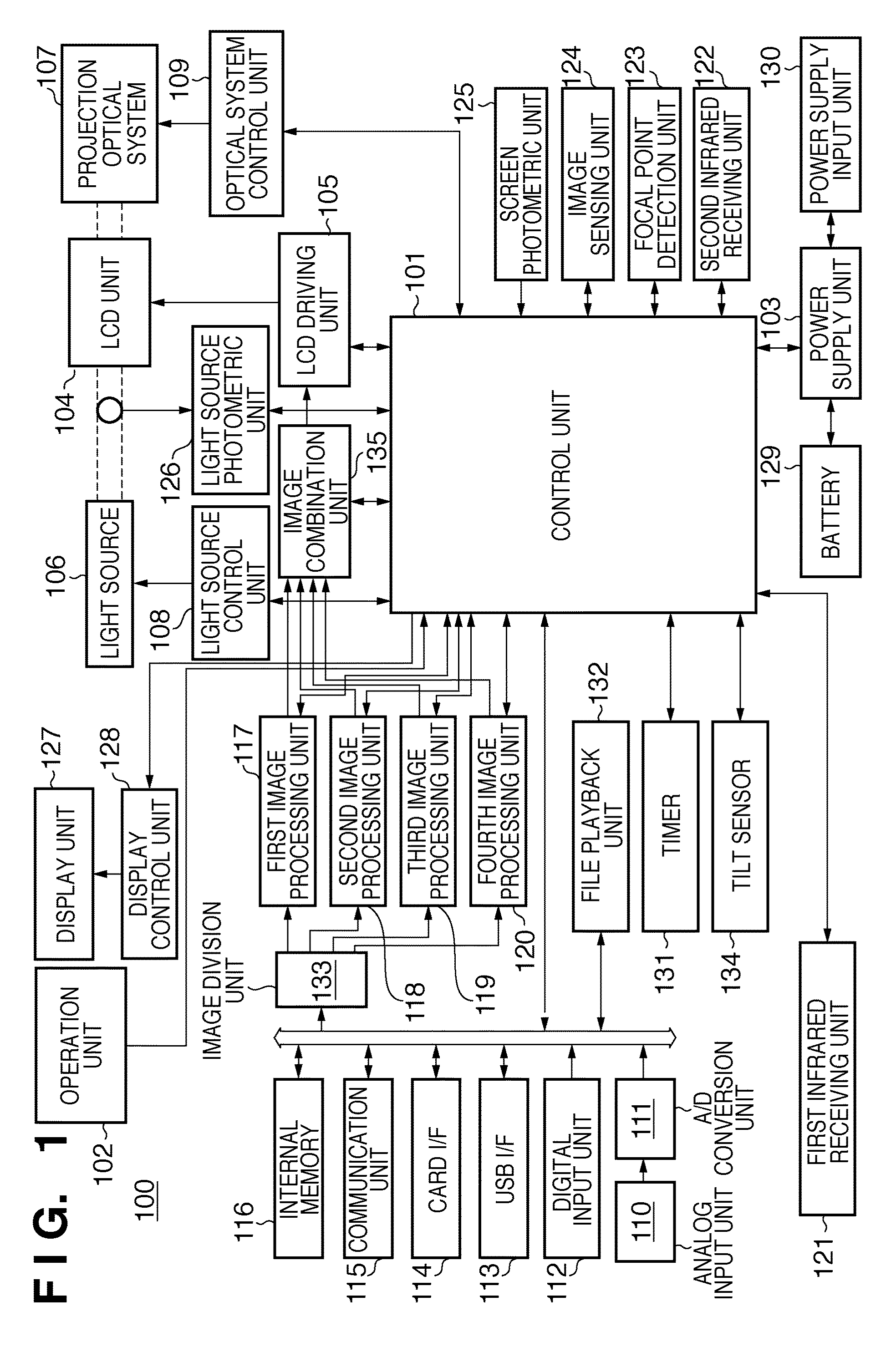
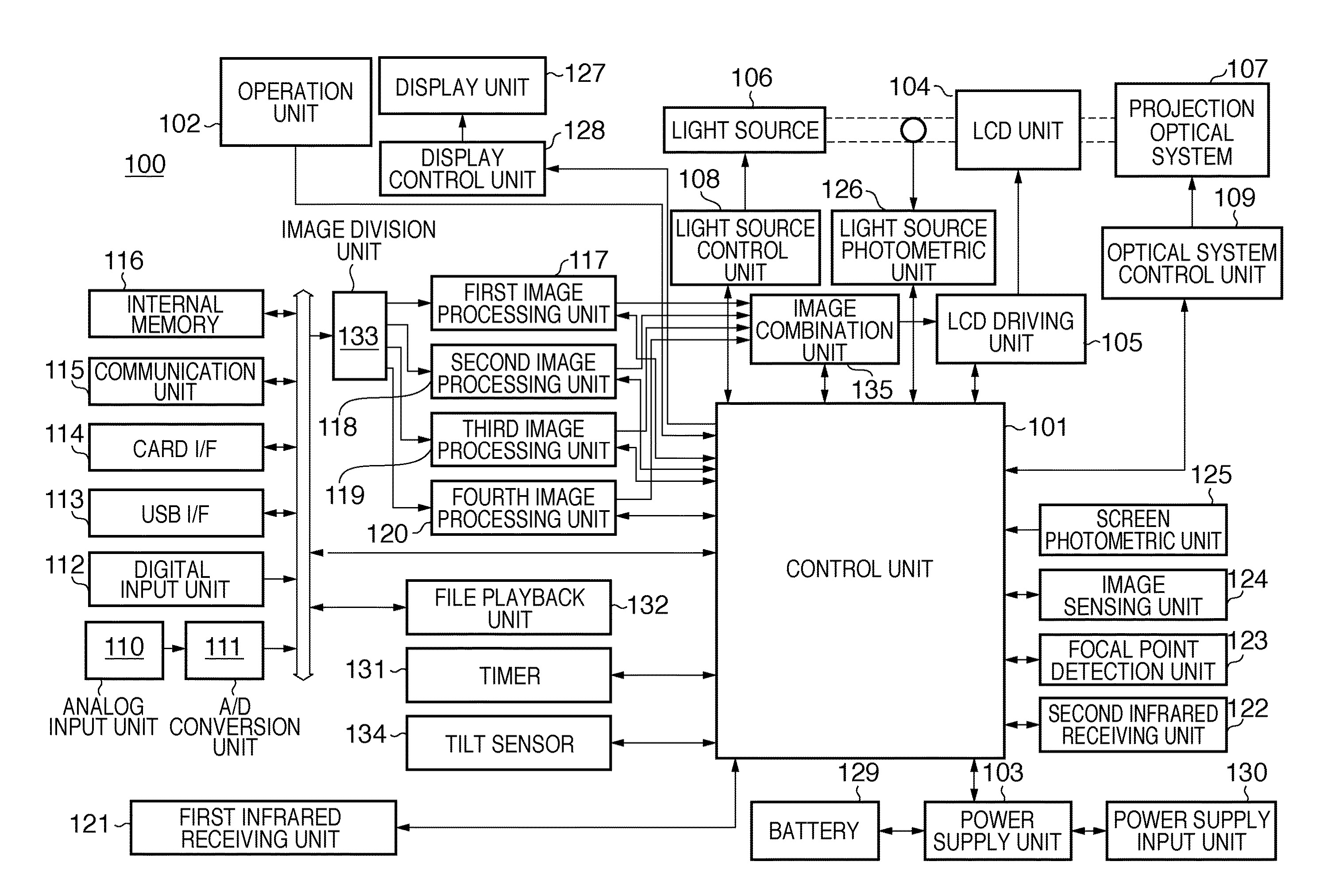
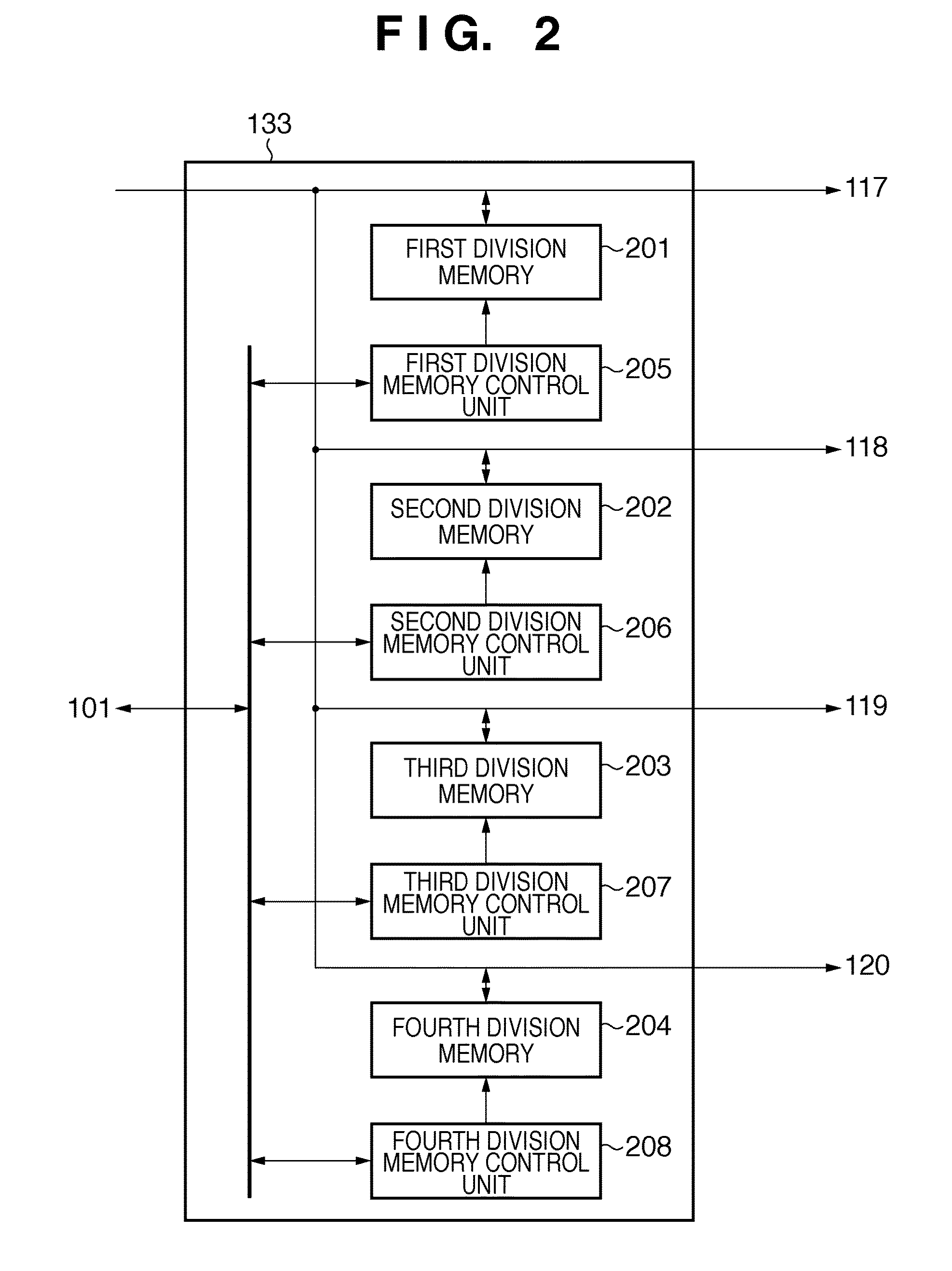
Projection apparatus and control method thereof
ActiveUS20110285971A1Reduce time spentReduce image degradationTelevision system scanning detailsPulse generatorProjection planeImage signal
A projection apparatus which projects an image onto a projection plane based on an input image signal, the apparatus comprises: a division unit configured to divide an image represented by the input image signal into a plurality of regions; a deformation unit configured to deform various types of shapes of the images divided by the division unit; a combination unit configured to combine the images deformed by the deformation unit; and a projection unit configured to project the image combined by the combination unit onto the projection plane.
Owner:CANON KK
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
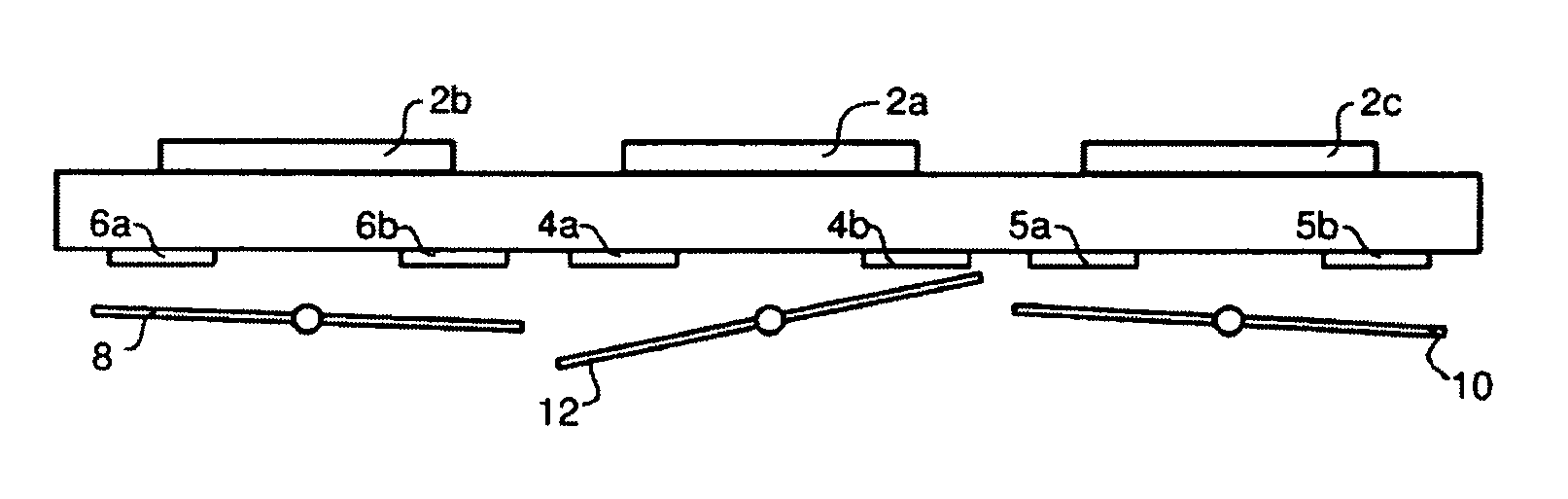
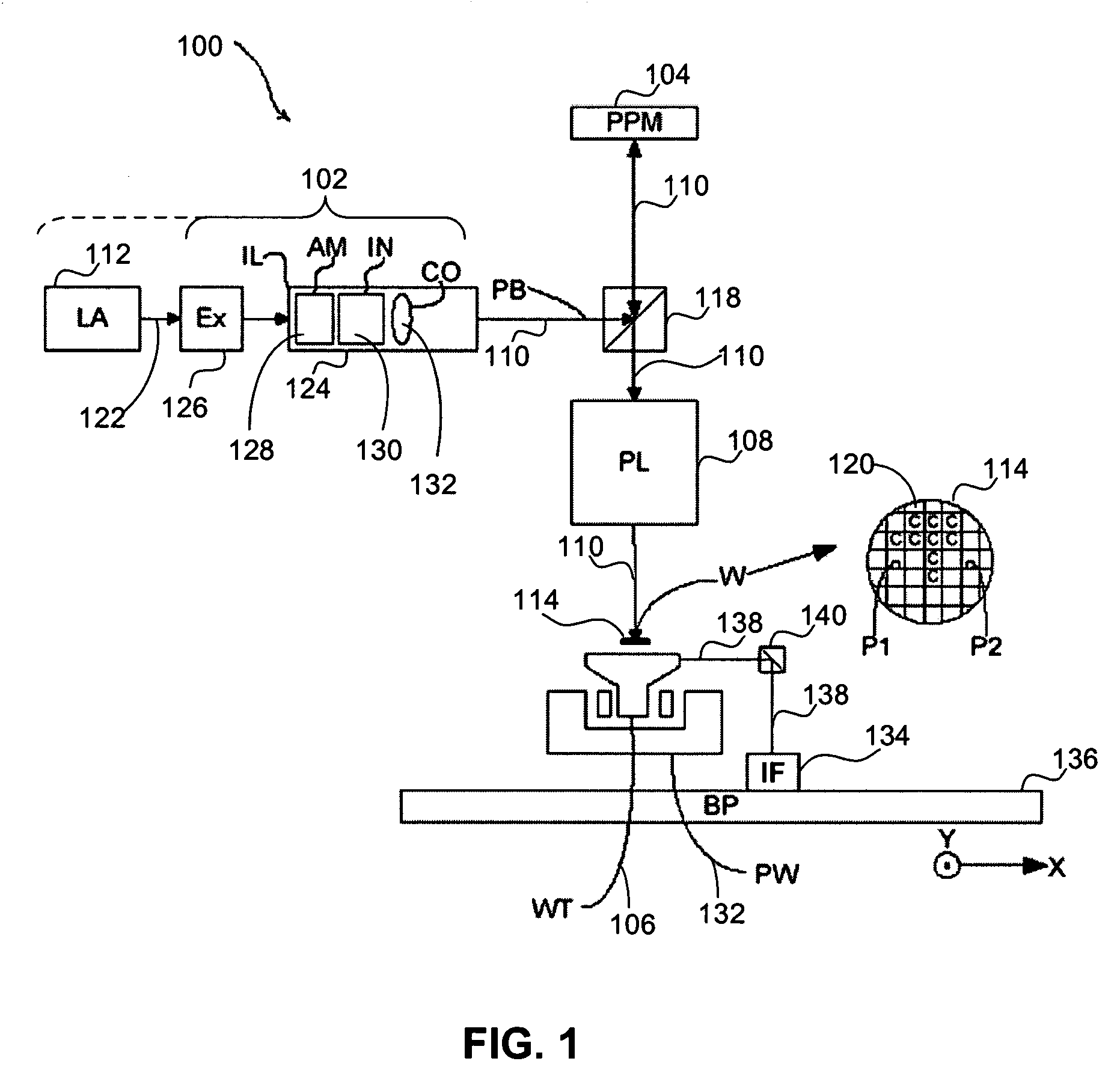
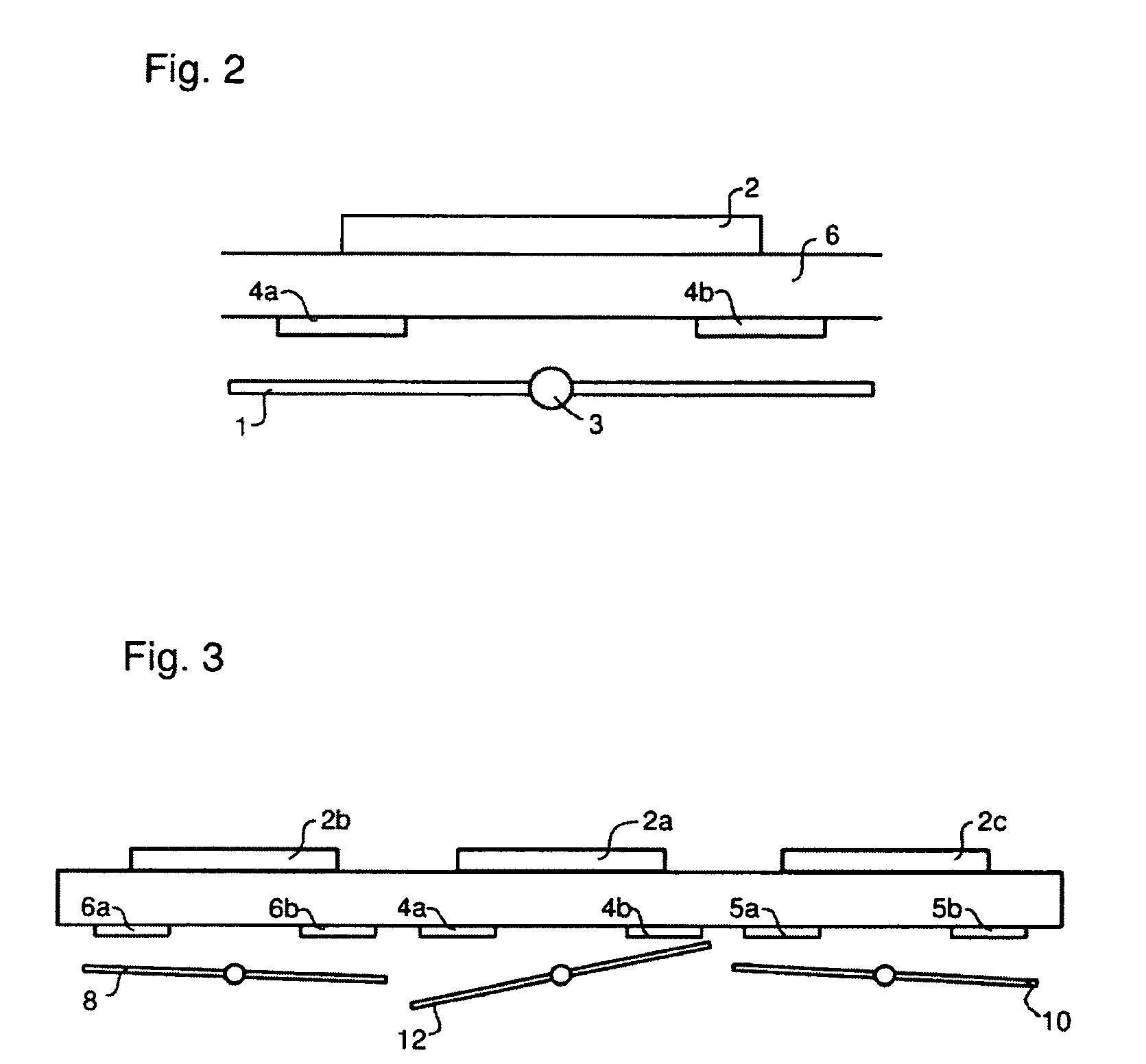
ActiveUS7053981B2Efficient and flexibleReduce image degradationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusControl systemControl signal
A lithographic apparatus and method are used to pattern a substrate. The system and method includes an illumination system for supplying a projection beam of radiation, an array of individually controllable elements for imparting the projection beam with a pattern in its cross-section, and a substrate table for supporting the substrate during an exposure operation. A projection system projects the patterned beam onto a target portion of the substrate. A control system sends a control signal for setting each said individually controllable elements to a desired state. A compensation device for adjusting the control signal applied to a first individually controllable element based on the control signal to be applied to at least one other individually controllable element. This can be done to reduce image degradation arising from cross-talk between individually controllable elements.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method and apparatus for data entry for a liquid crystal display
InactiveUS7573466B1Enhance the imageIncrease reflectionInput/output processes for data processingAcoustic wave reradiationLiquid-crystal displayTouchscreen
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
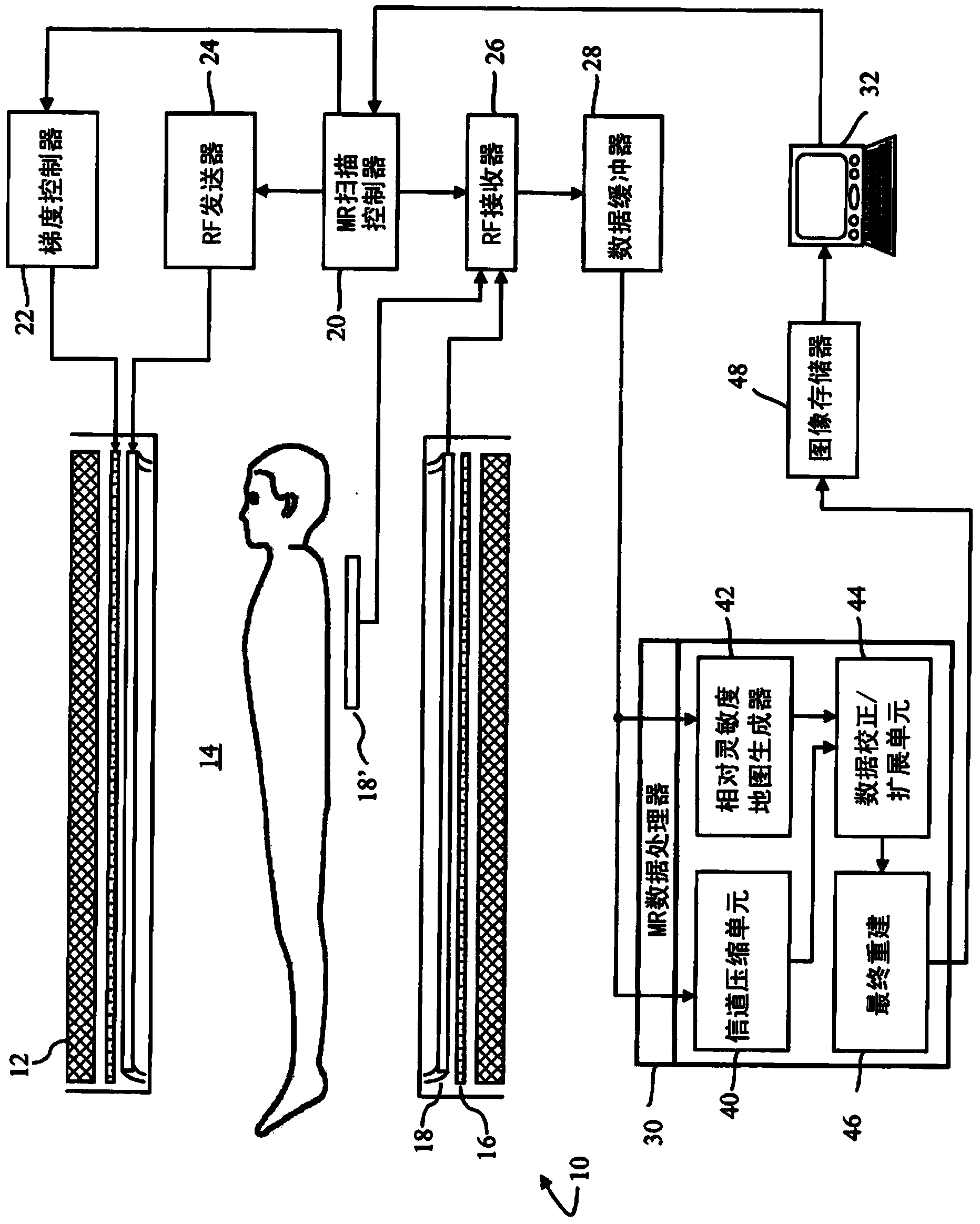
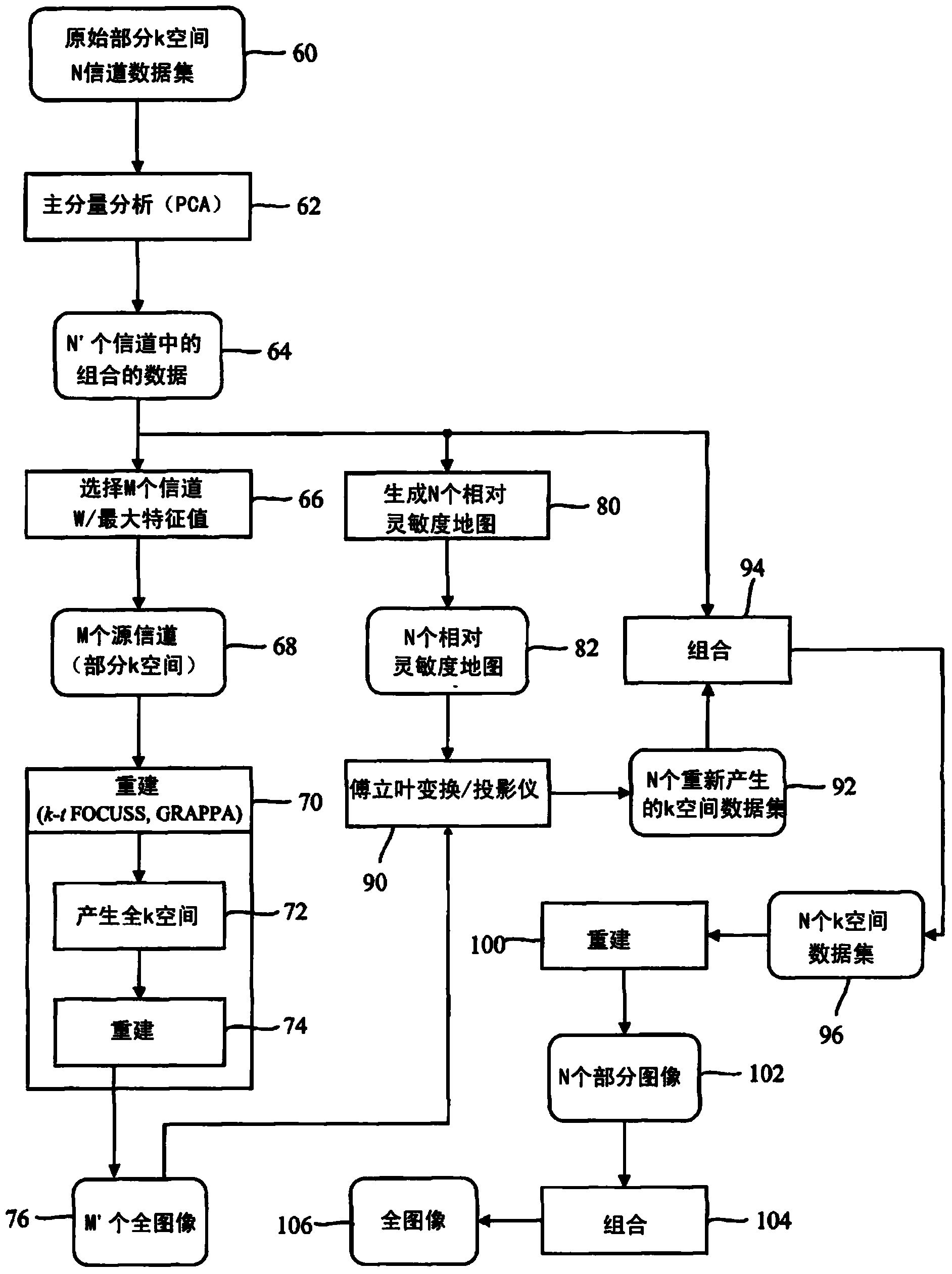
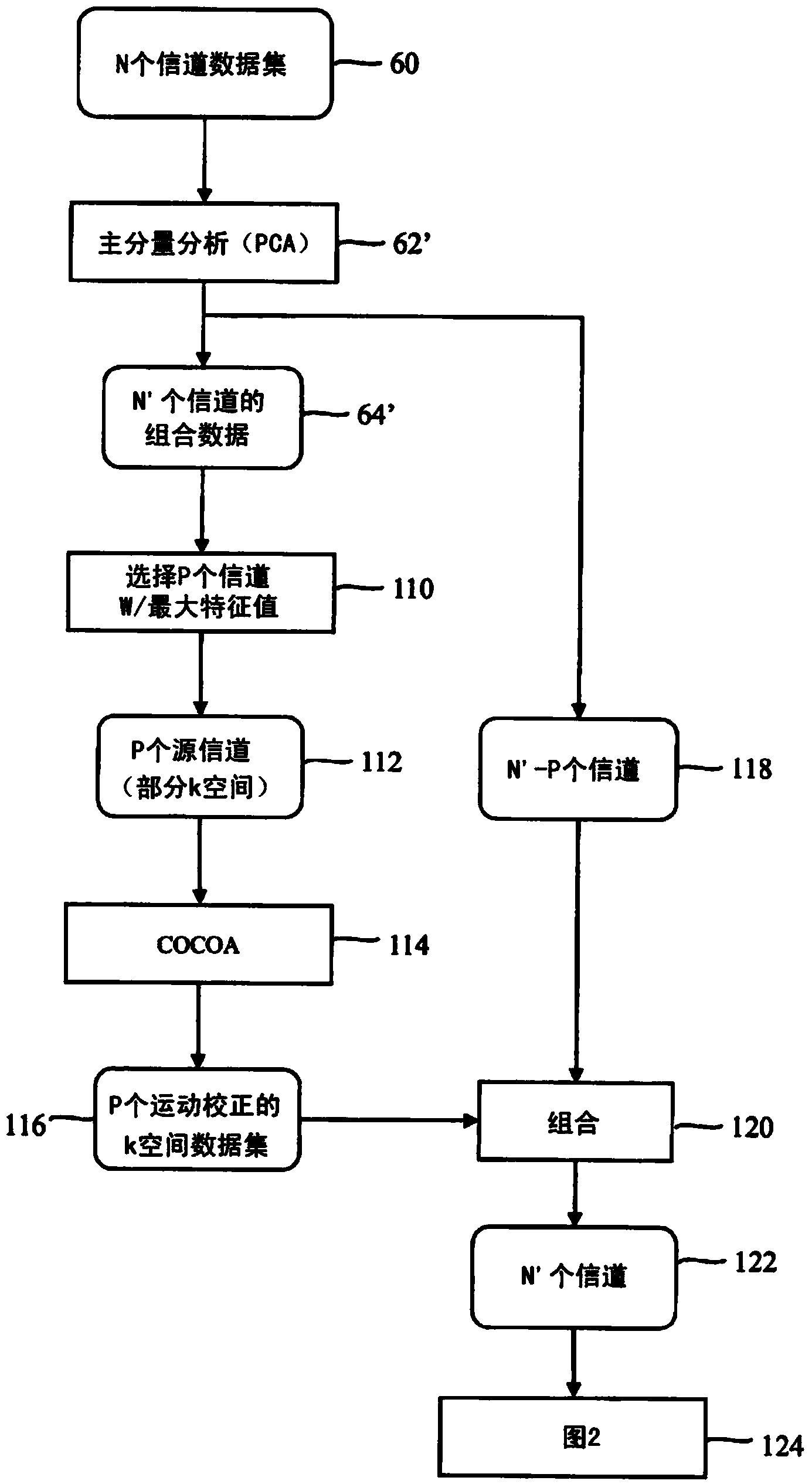
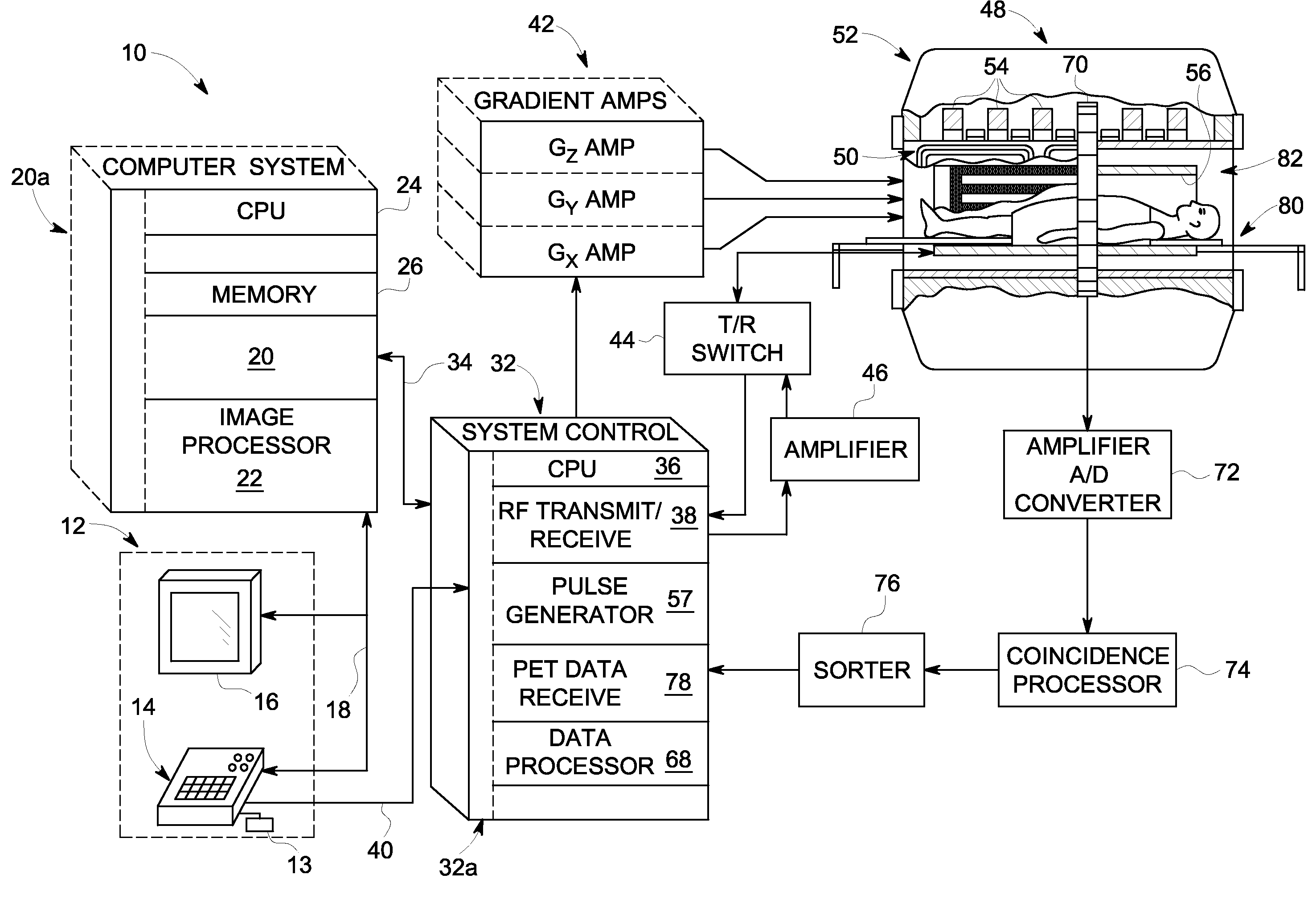
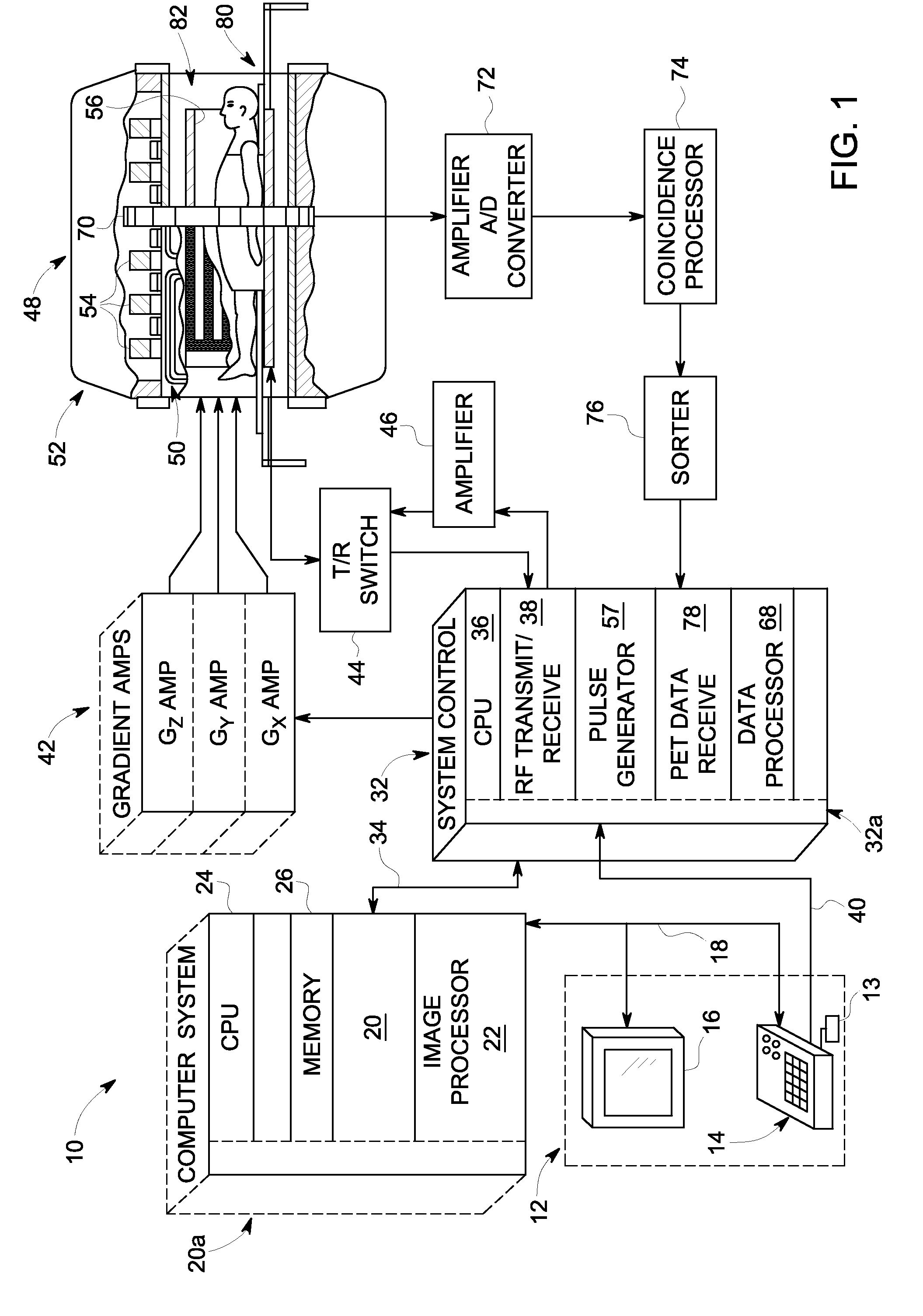
A MRI method of faster channel-by-channel reconstruction without image degradation
InactiveCN103430038AReduce rebuild timeReduce image degradationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsImage representationImage degradation
A plurality of coil elements (18, 18') and corresponding receivers (26) define a plurality of channels, each carrying a corresponding partial k-space data set (60, 64). One or more processors (30) generate (80) a first image representation (76) based on the plurality of partial k-space data sets, generate a relative sensitivity map (82) for each of the channels, project (90) the first image representation (76) with each of the relative sensitivity maps (82) to generate a plurality of recreated k-space data sets (92), and each partial k-space data and the corresponding recreated k-space data set are combined to generate substituted k-space data sets (96). The substituted k-space data sets are reconstructed (100) into a plurality of images (102) which are combined (104) to create a final image (106).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Apparatus, method, and computer program for processing image, and recording medium storing the computer program
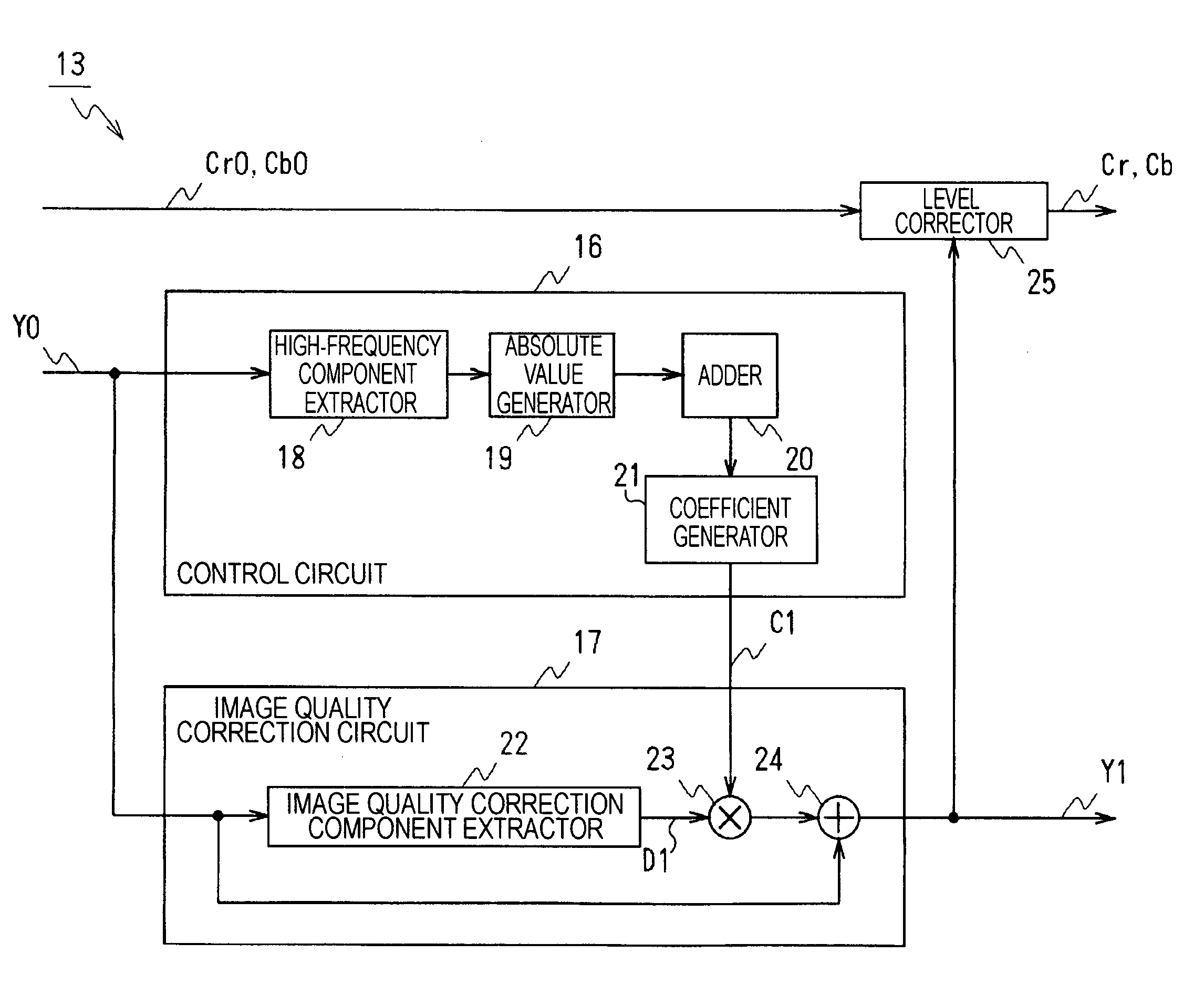
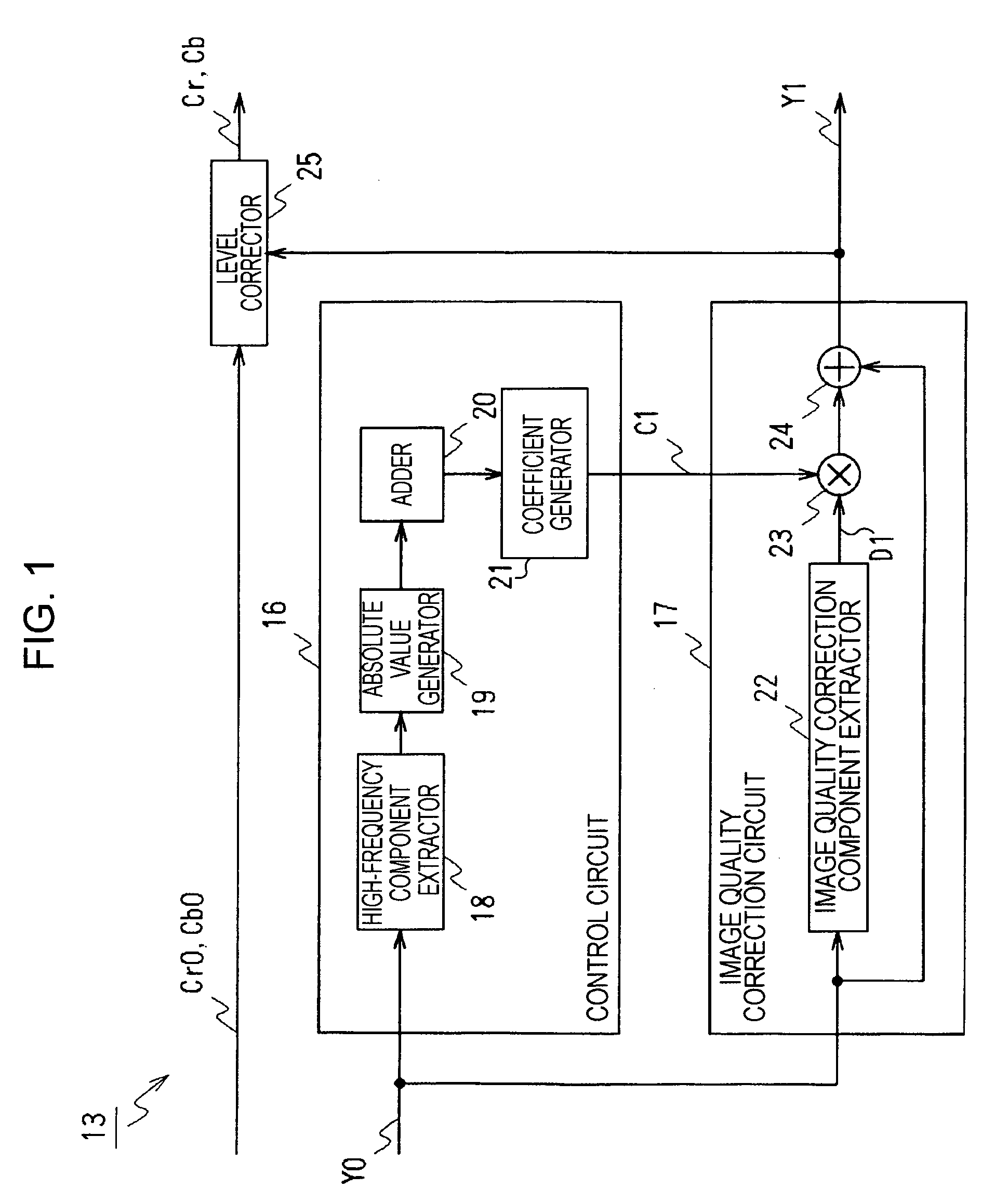
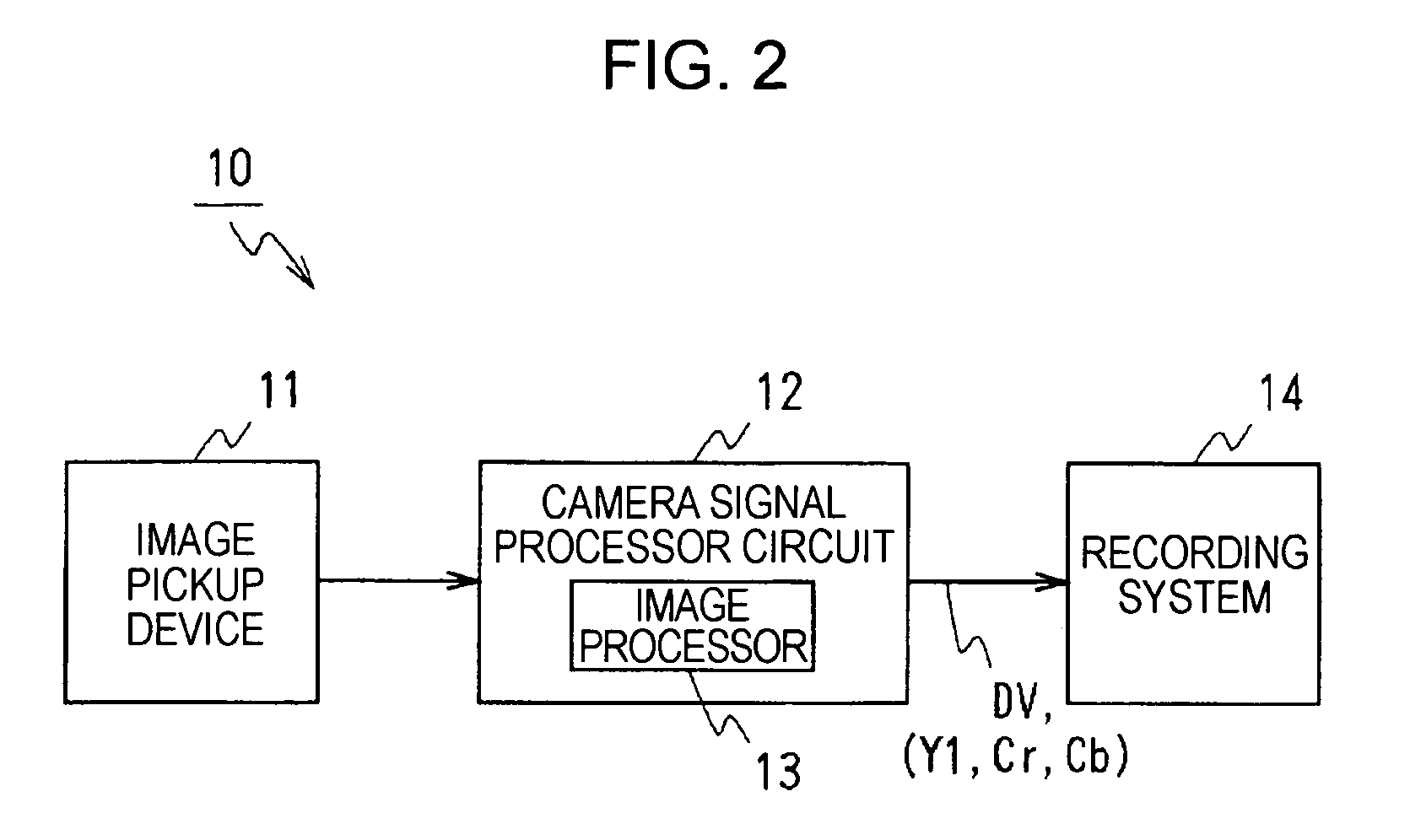
ActiveUS7903148B2Reduce image degradationAccurate qualityTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer hardwareImaging processing
An image processing apparatus includes an image quality correction circuit for correcting an image quality of input video data by enhancing the input video data and a control circuit for controlling the image quality correction circuit. The control circuit detects a signal level of a high-frequency component of the input video data and controls the image quality correction circuit in response to the signal level detection result so that the degree of enhancement of the input video data is increased in response to an increase in the signal level of the high-frequency component.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Multimodal Imaging System, Apparatus, and Methods
ActiveUS20170188831A1Easy to operateImprove usabilityOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryOptical tomographyCollection system
In part, the invention relates to an image data collection system. The system can include an interferometer having a reference arm that includes a first optical fiber of length of L1 and a sample arm that includes a second optical fiber of length of L2 and a first rotary coupler configured to interface with an optical tomography imaging probe, wherein the rotary coupler is in optical communication with the sample arm. In one embodiment, L2 is greater than about 5 meters. The first optical fiber and the second optical fiber can both be disposed in a common protective sheath. In one embodiment, the system further includes an optical element configured to adjust the optical path length of the reference arm, wherein the optical element is in optical communication with the reference arm and wherein the optical element is transmissive or reflective.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
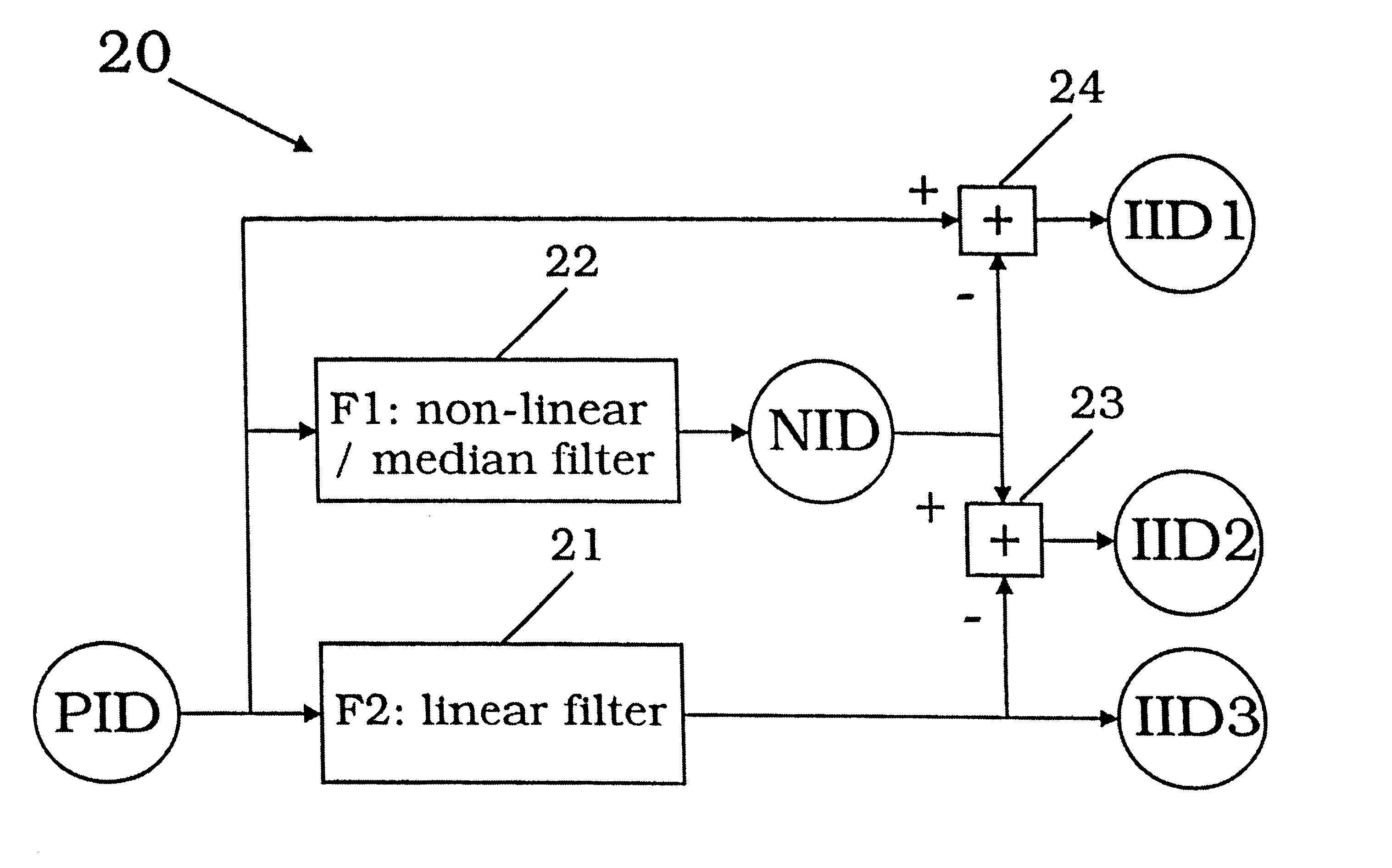
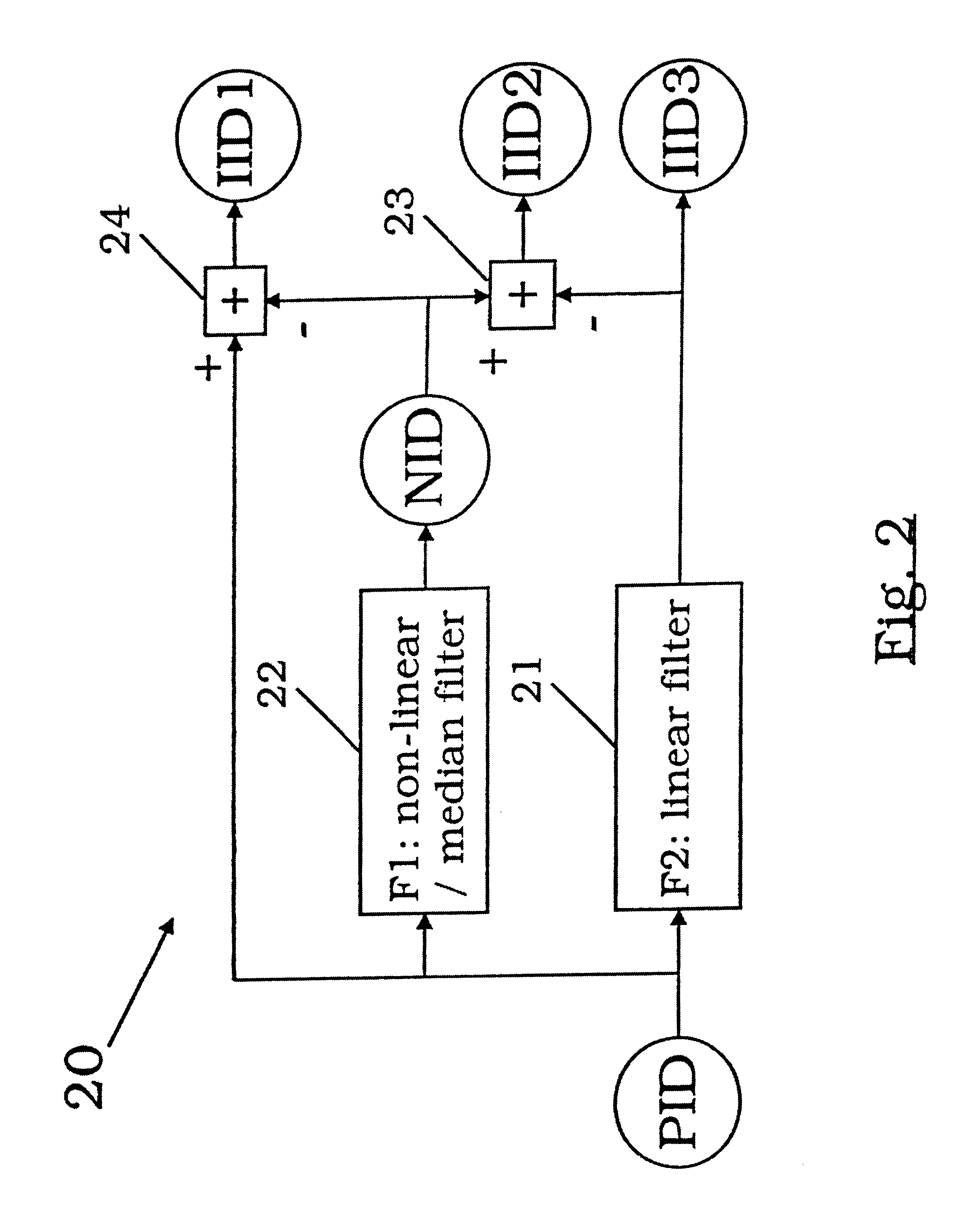
Method for processing compressed image data for reducing blocking artifacts
InactiveUS6847739B2Reducing blocking artefactReduce image degradationImage enhancementImage analysisFine structurePattern recognition
A method for post-processing compressed image data for reducing blocking artifacts is suggested, in which a set of primary image data (PID) is decomposed into data sets (IID1, IID2) containing the fine structure of the image with structure being smaller than the blocking artifacts and without the blocking artifacts and structures being larger than or comparable to the blocking artifacts as well as the blocking artifacts, respectively. In the decomposition of the primary image data (PID) a non-linear filtering process (F1) is involved. After decomposition of the primary image data (PID) a filtering process (F3) can be applied to the set of intermediate image data (IID2) containing larger details of the image as well as the blocking artifacts. Therefore, in the process of filtering out the blocking artifacts, the fine structure of the image is not influenced.
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
Surface stationary array coil structure for multi-modality imaging
ActiveUS20150025358A1Reduce image degradationImprove image qualityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringEngineeringPet mr imaging
A stand-alone MR or hybrid PET-MR imaging system incorporating a surface stationary RF coil structure is disclosed. The imaging system includes a support assembly comprising a cradle to accommodate a subject and a bridge to receive the cradle and provide for translation therealong to enable an acquisition of imaging data. An RF coil structure is positioned between the bridge and the cradle, and includes a base portion, a cover portion, and an array of RF coil elements positioned on the cover portion. The cover portion includes contoured features that enable placement of RF coil elements in proximity to a subject and to provide a constant and uniform gap between the RF elements and the cradle. The RF coil structure also includes structural elements that support the cradle when rolling over the array of RF coil elements without deforming the RF coil elements.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
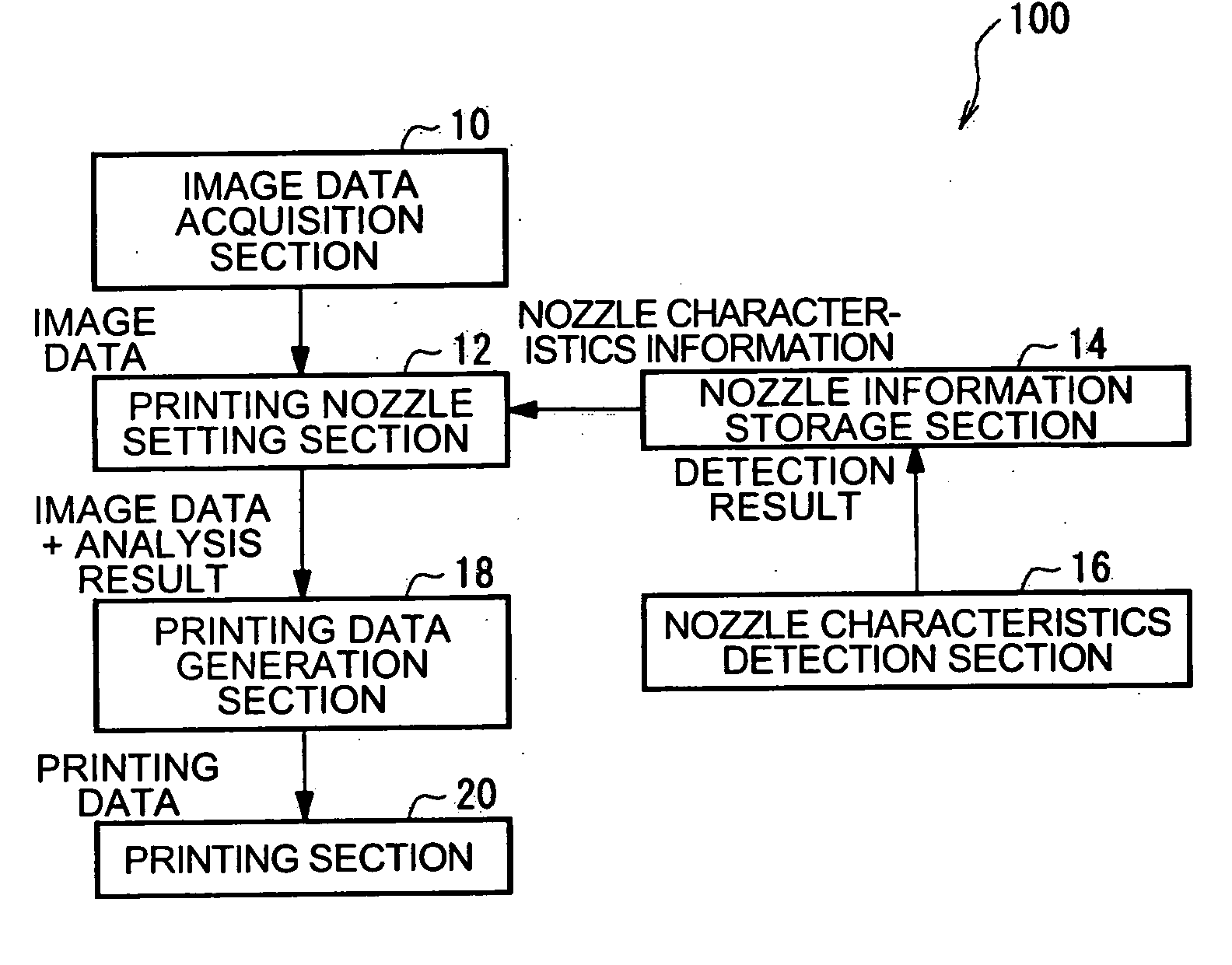
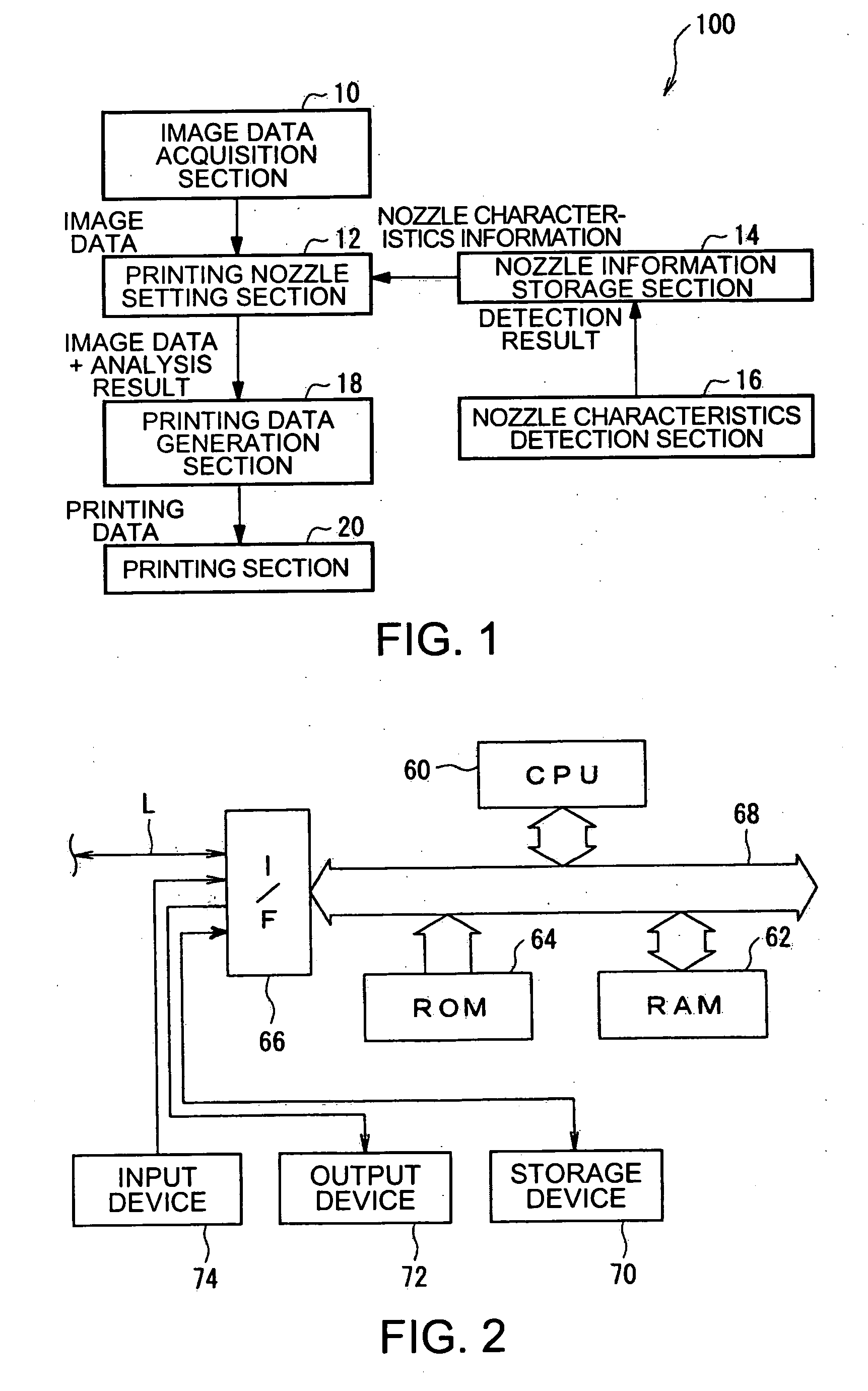
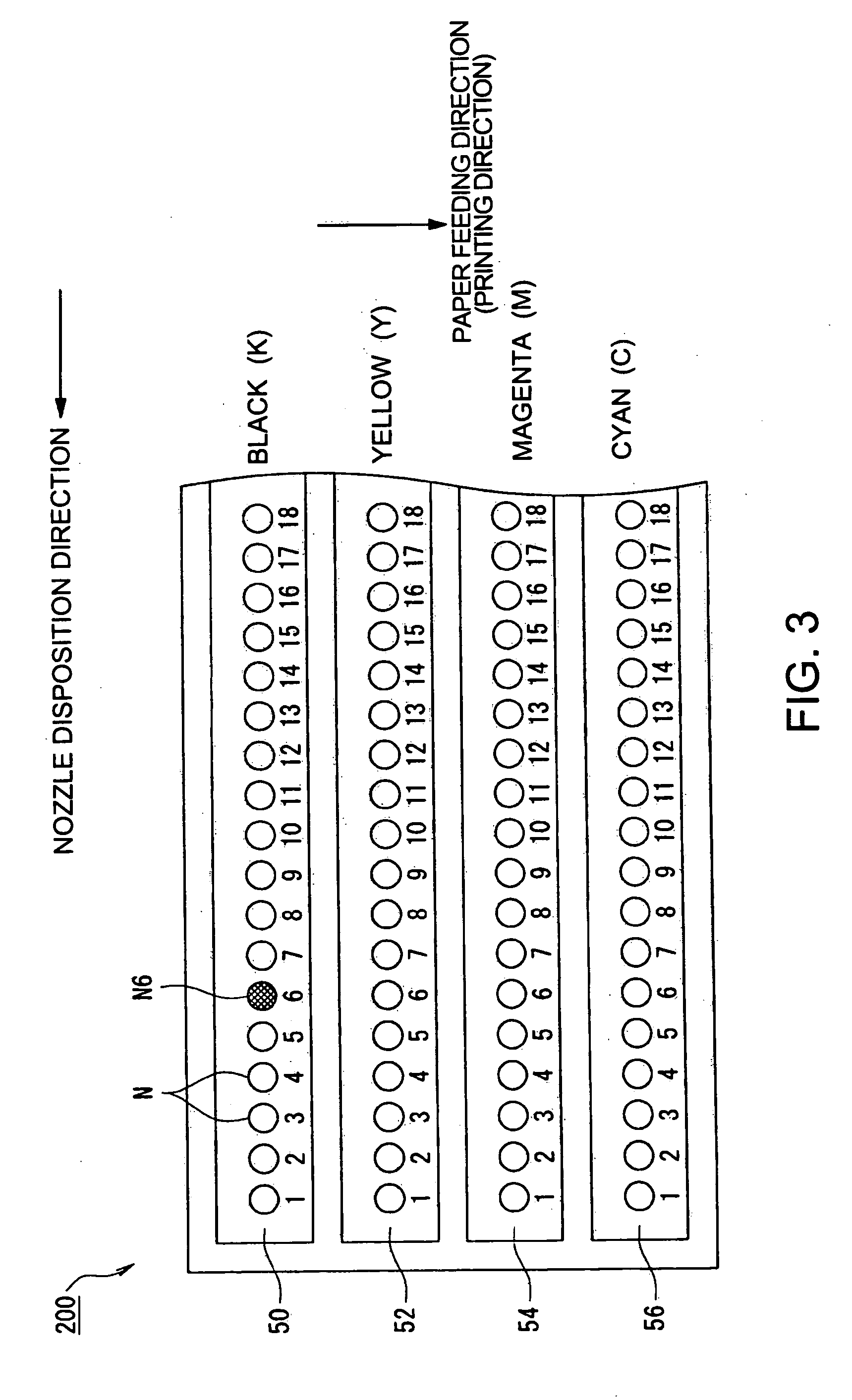
Printing device, printing device control, program and method, and printing data generation device, program and method
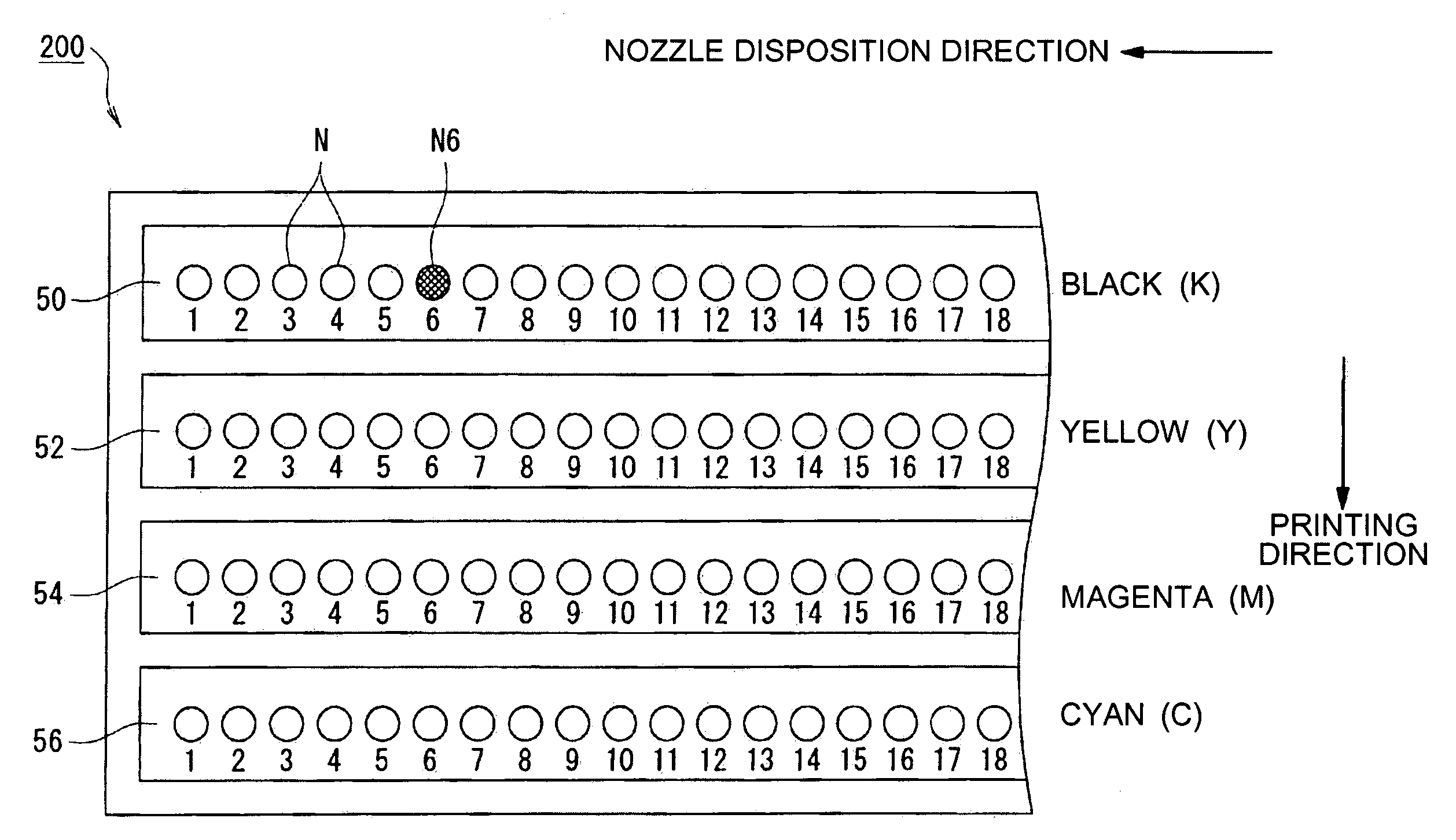
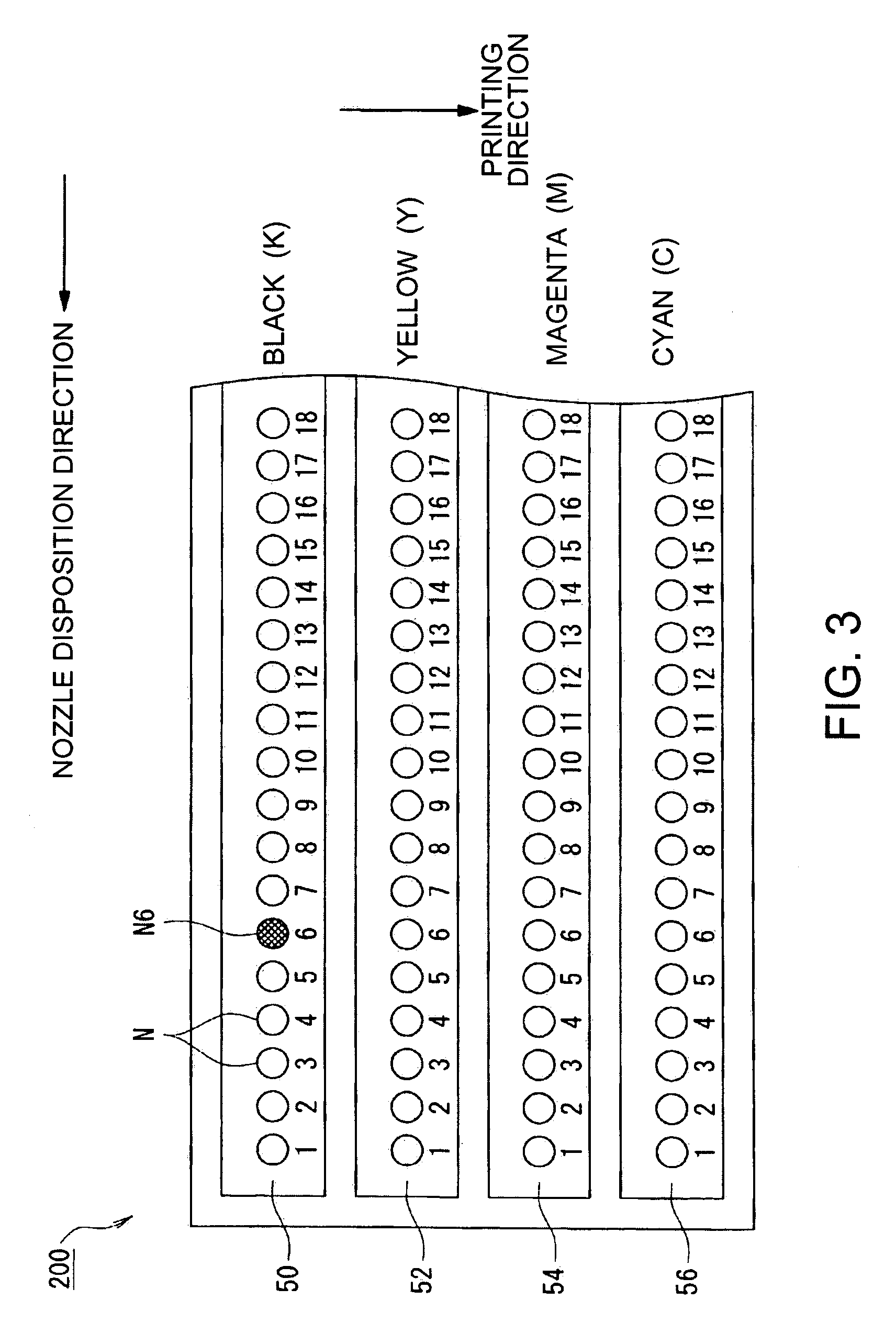
InactiveUS20060125860A1Stopping image degradationReduce image degradationTypewritersOther printing apparatusComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
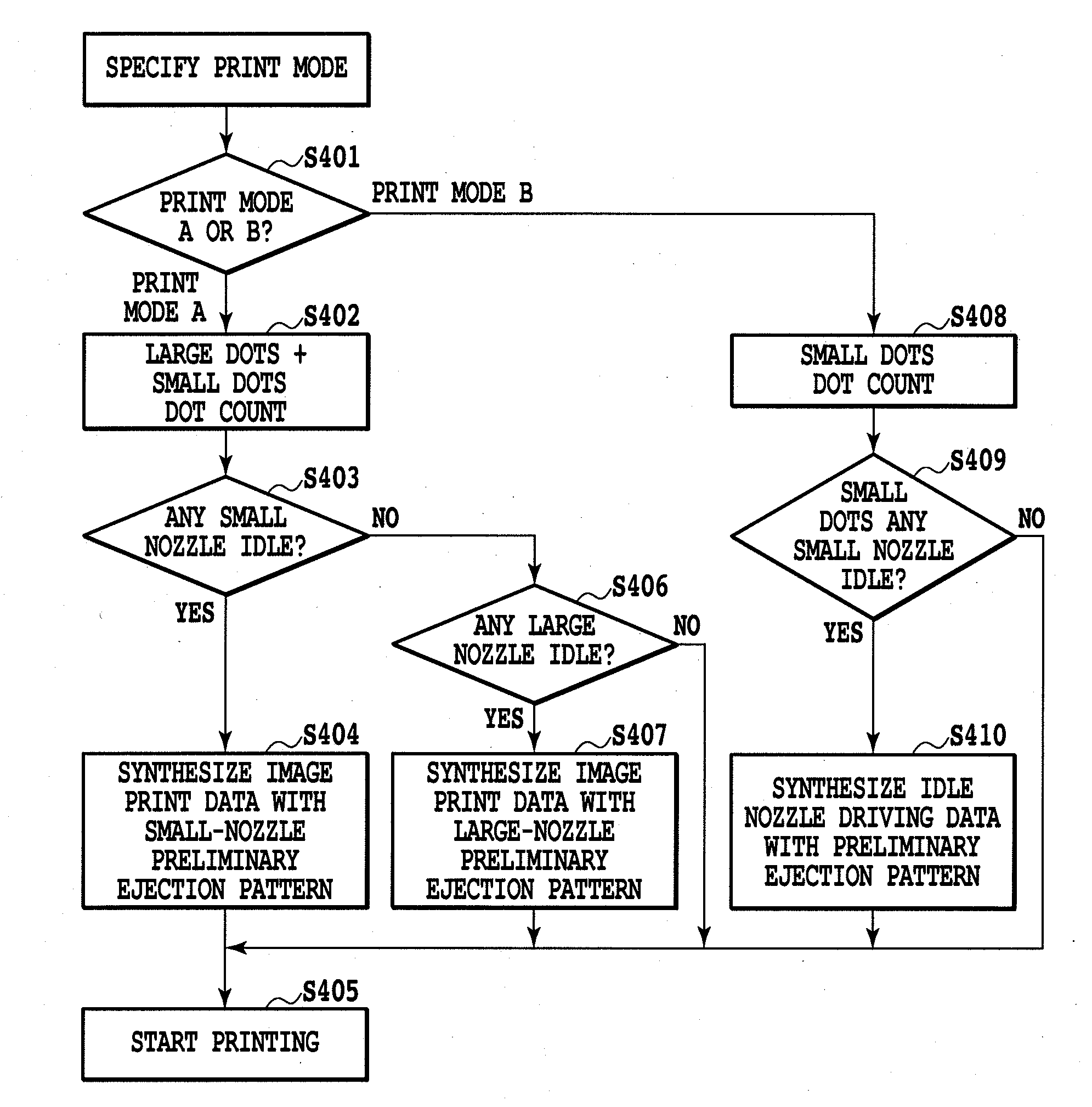
A printing device including: an image data acquisition unit acquiring image data corresponding to pixels of the image; a printing data generation unit generating, based on the acquired image data, printing data including information about dot formation details based on the pixels for each of the nozzles; a nozzle information storage unit storing information about nozzles whose dot formation details are different from predetermined dot formation details; and a printing unit printing, based on the printing data, the image onto a printing medium using a printing head. By referring to the nozzle information storage unit, the printing data generation unit generates printing data providing a lower resolution for the image to be printed by at least either the nozzle of different dot formation details or neighboring nozzles compared with a resolution of the image data acquired by the image data acquisition unit corresponding to the nozzle used for printing.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Projection apparatus and control method thereof
ActiveUS8529069B2Reduce time spentReduce image degradationTelevision system scanning detailsPulse generatorProjection planeImage signal
A projection apparatus which projects an image onto a projection plane based on an input image signal, the apparatus comprises: a division unit configured to divide an image represented by the input image signal into a plurality of regions; a deformation unit configured to deform various types of shapes of the images divided by the division unit; a combination unit configured to combine the images deformed by the deformation unit; and a projection unit configured to project the image combined by the combination unit onto the projection plane.
Owner:CANON KK
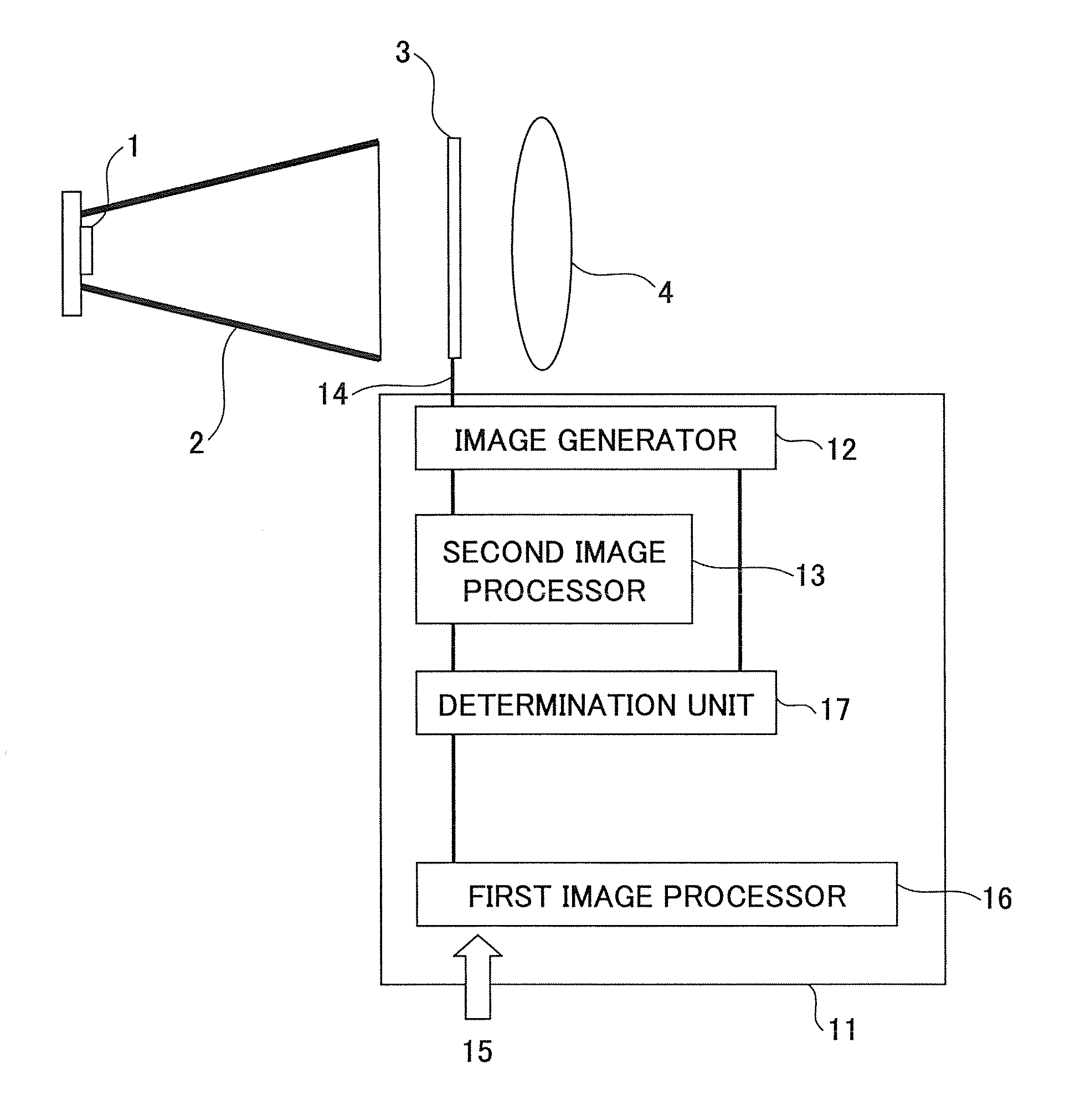
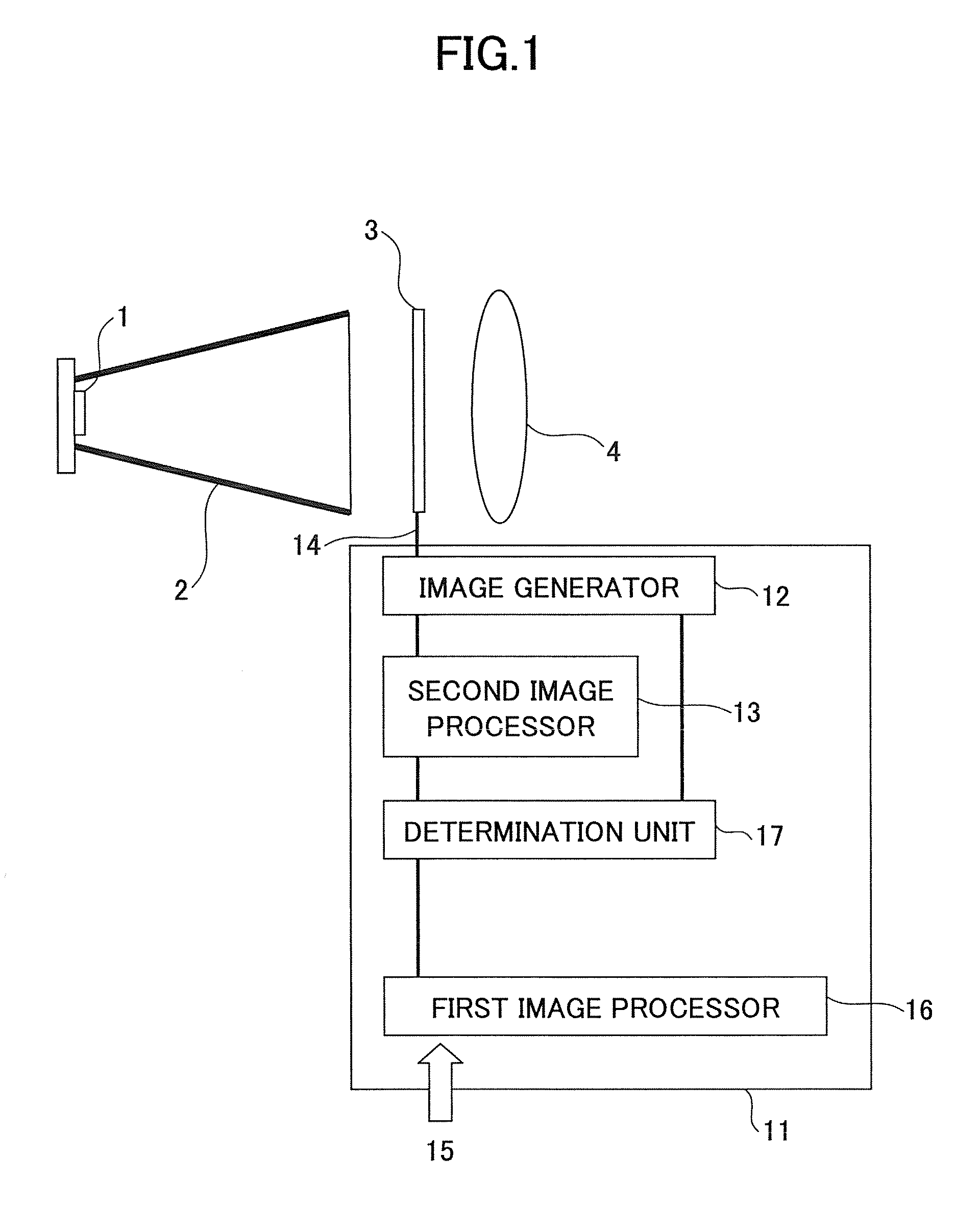
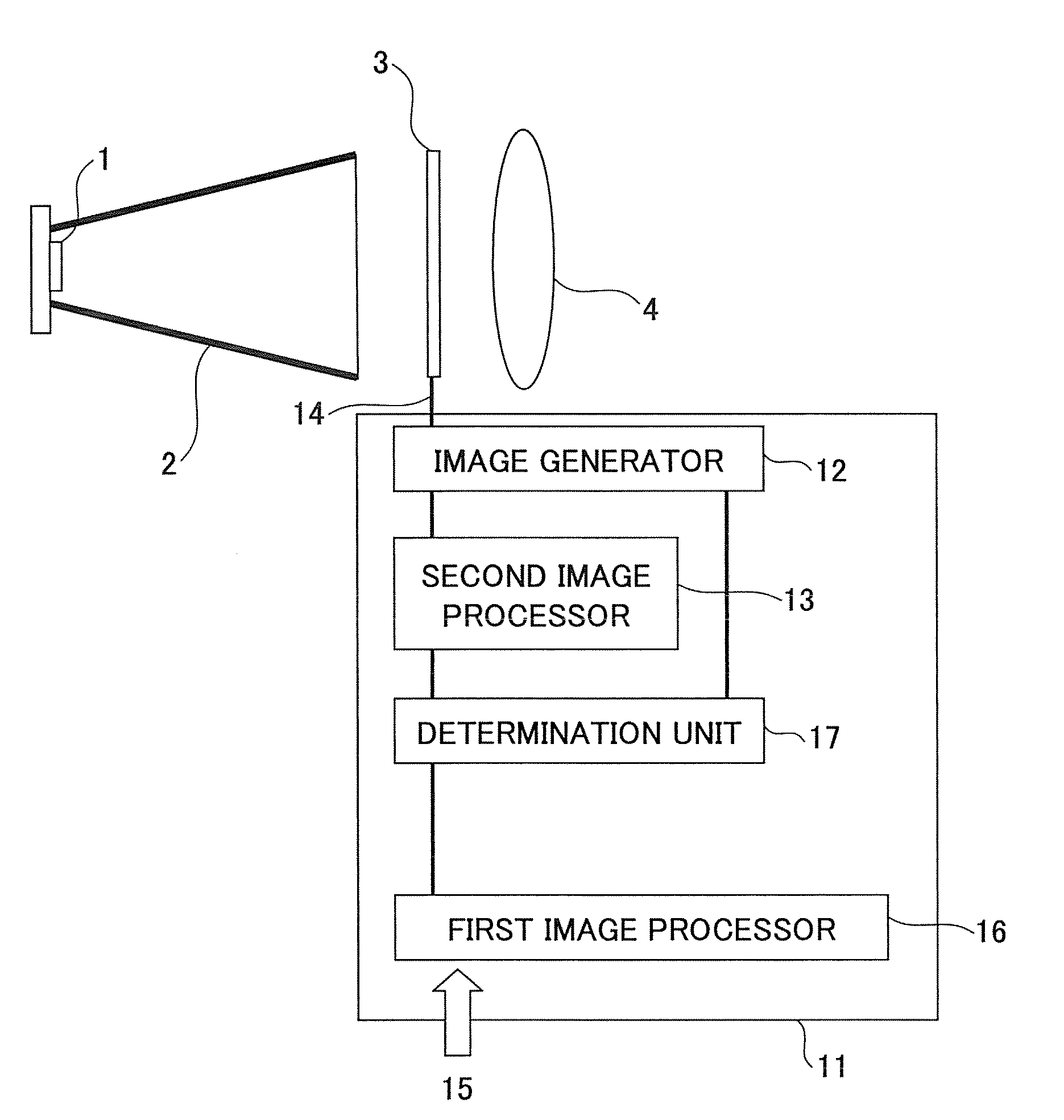
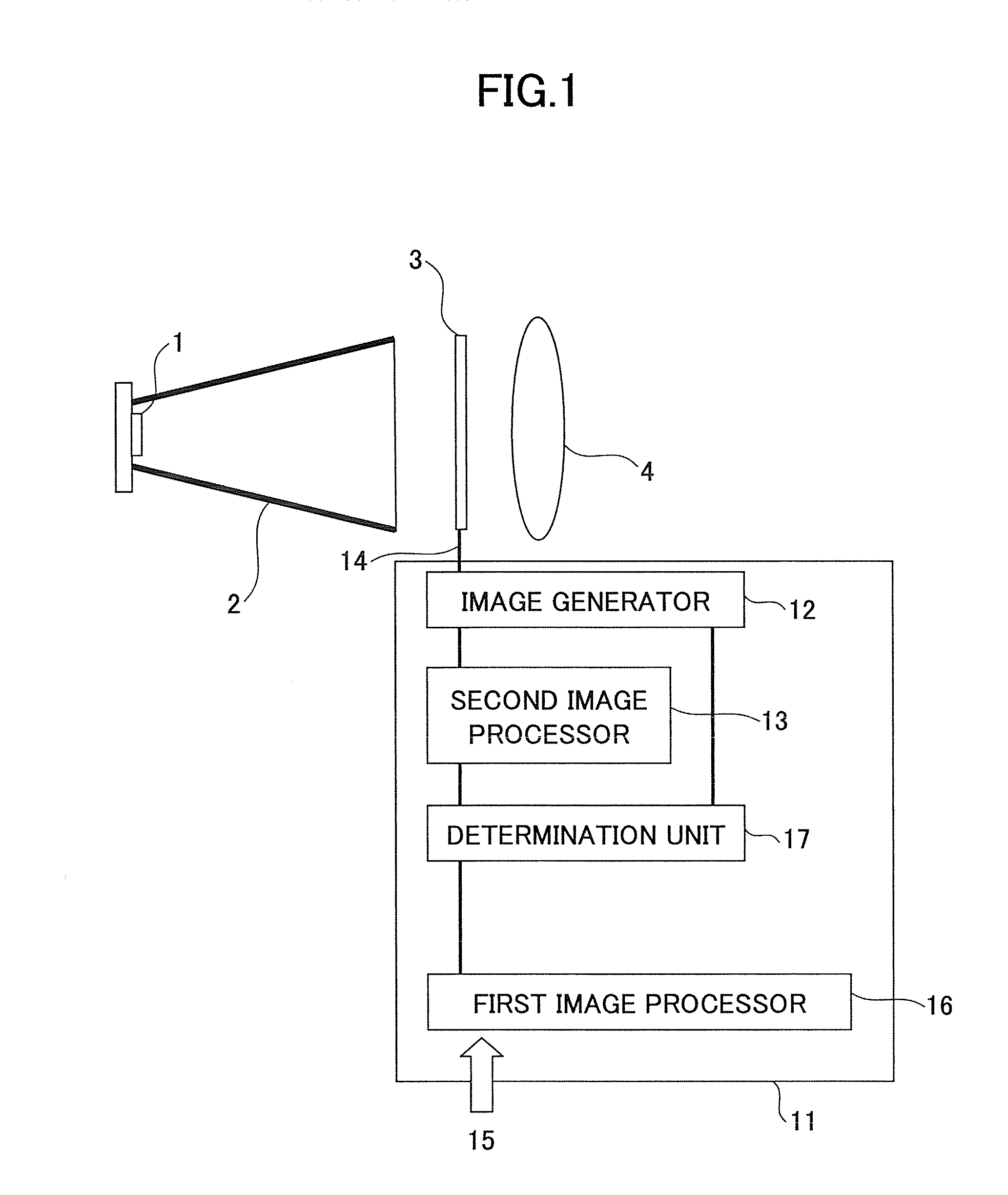
Image projecting apparatus and image projecting method
InactiveUS20080117387A1Eliminate the problemLower performance requirementsTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging processingLuminous flux
An image projecting apparatus enables the formation of a projected image faithful to original image information by reducing degradation in the projected image due to decrease in imaging performance of a projection optical system. Image information is processed by an image processing device, which includes a first and a second image processor. A light modulating device modulates a flux of light emitted by an illumination optical system based on the processed image information. The modulated flux of light is projected on a screen by a projection optical system. If the image information processed by the first image processor in a pixel region is not within a representable modulation range of the light modulating device, the image information is processed by the second image processor.
Owner:RICOH KK
Methods, systems, and computer-program products to estimate scattered radiation in cone-beam computerized tomographic images and the like
ActiveUS20080025458A1Reduce image degradationReduce artifactsReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTomographyWide band
Disclosed are imaging systems, methods, and computer program products that generate estimates of scattered radiation in tomographic imaging systems, such as cone-beam computerized tomography (CBCT) systems, and the like. In an exemplary embodiment, a first group of projections is taken of an object with the radiation covering a wide band of the object, and a second group of projections is taken of the object with the radiation covering a narrower band of the object. The projections of the second group cover less of the object, but have less scattered radiation. The scattered radiation within the narrower band may be estimated from differences between projections from the first and second groups, or from representations thereof.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG +1
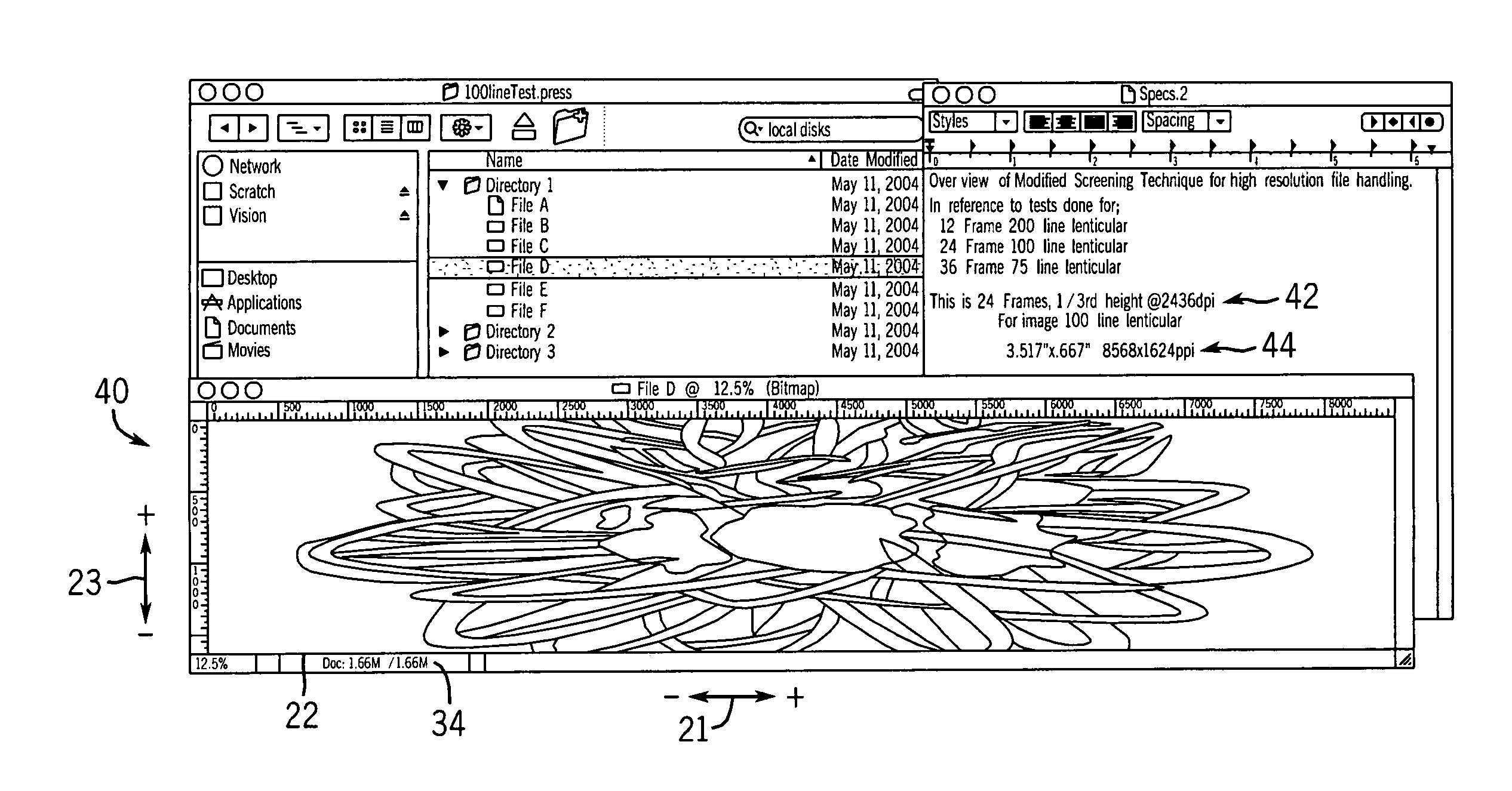
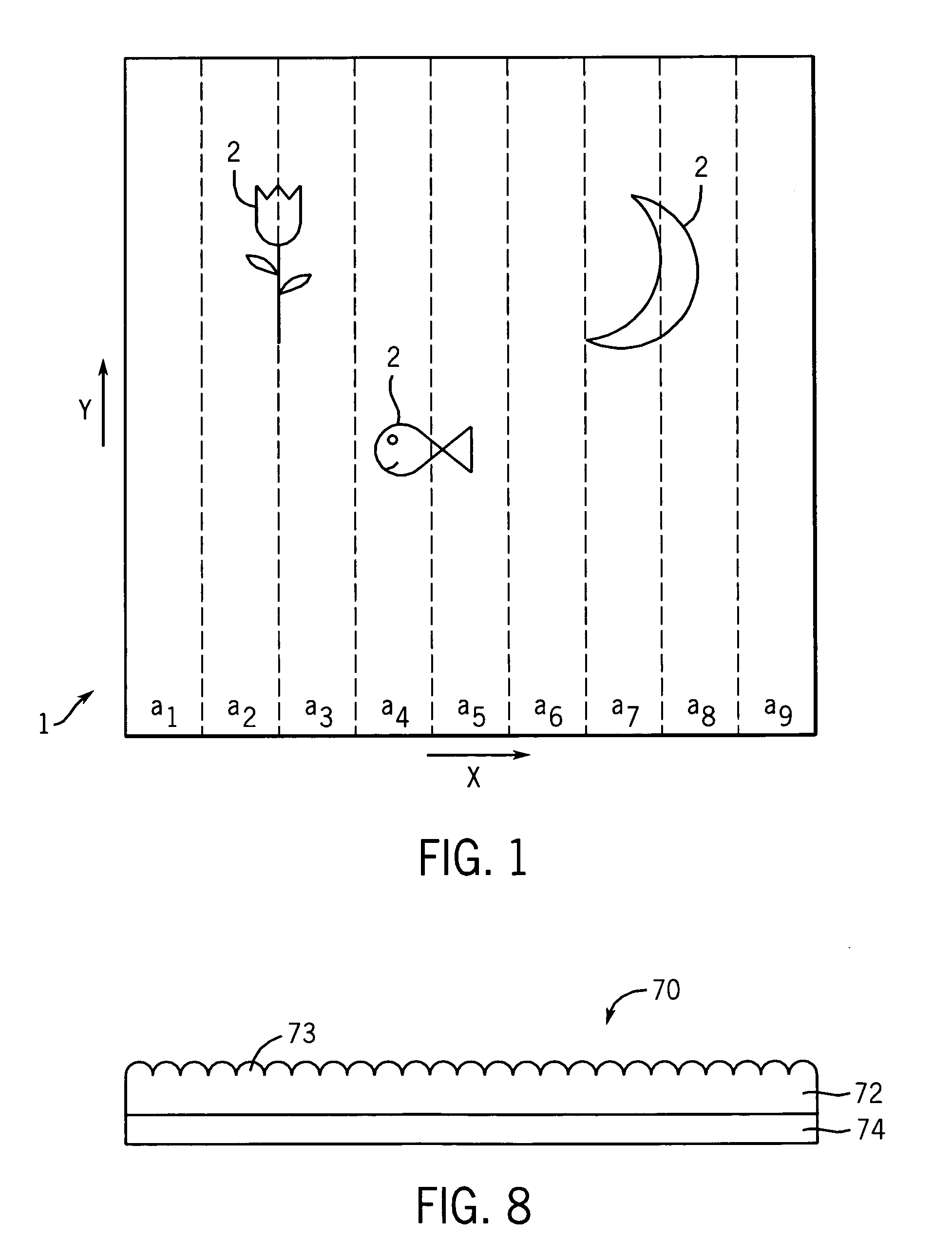
Lenticular imaging file manipulation method
InactiveUS20050271292A1Dot gain is reducedReduce image degradationCharacter and pattern recognitionSteroscopic systemsGratingInterlaced video
A lenticular interlaced image file manipulation / screening method is disclosed. Frame files (which may or may not have already have been compressed) can be fractionally scaled in a coextending lenticular direction to obtain fractionally scaled frame files. Alternatively, frame files can be interlaced to create an interlaced frame file, which can be fractionally scaled. Prior to output, a screened interlaced frame file can then be normalized in a coextending lenticular direction to normalize the initial fractional scaling in the coextending lenticular direction. The invention permits manipulation of work files used to create a lenticular image so as to decrease lenticular image frame memory usage and file handling time, increase the number of frames in a lenticular image for use with high resolution output devices, and increase lenticular image quality.
Owner:NAT GRAPHICS
Color correction to compensate for displays' luminance and chrominance transfer characteristics
ActiveUS9049410B2Image degradation can be highIncrease brightnessTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsColor correctionDisplay device
Displays are provided with circuitry performing color correction to compensate for the displays' luminance and chrominance transfer characteristics. Some techniques are suitable for RGBW displays and for subpixel-rendered displays. Some displays include an external light source (e.g. a backlight unit in LCDs), and the color correction is coordinated with dynamic control of the light source.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Anamorphic three-perforation imaging system
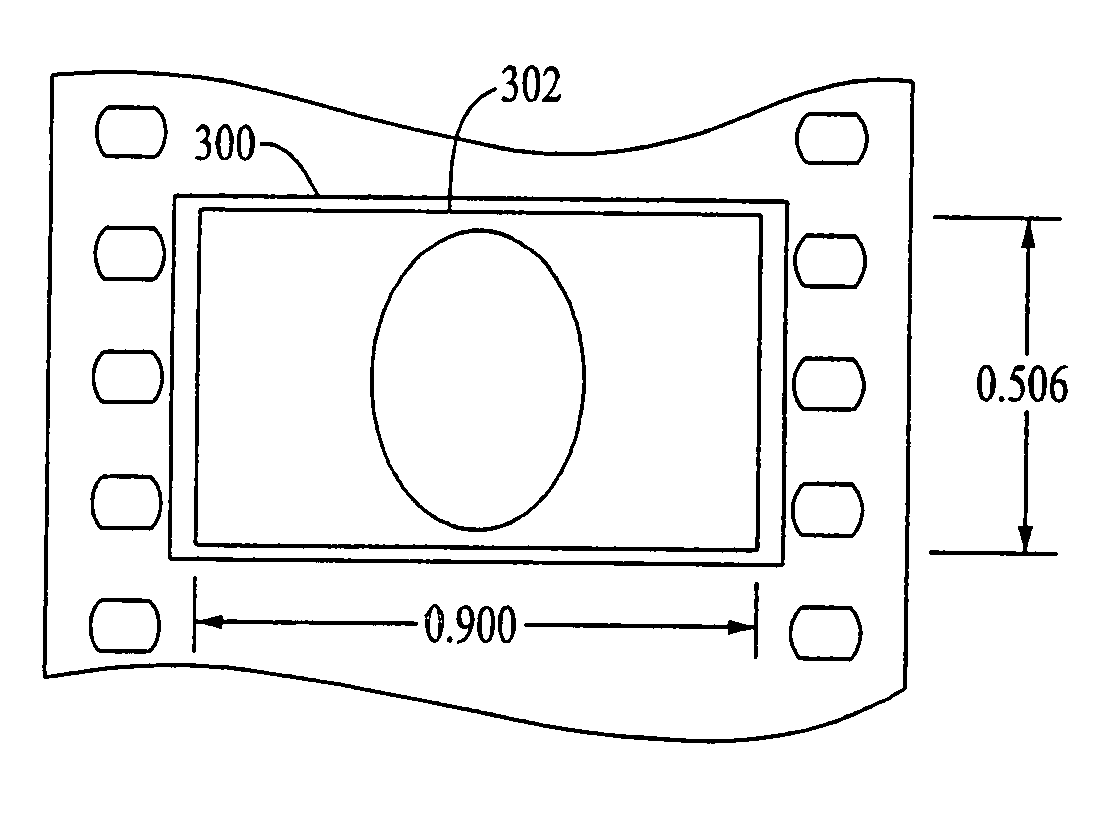
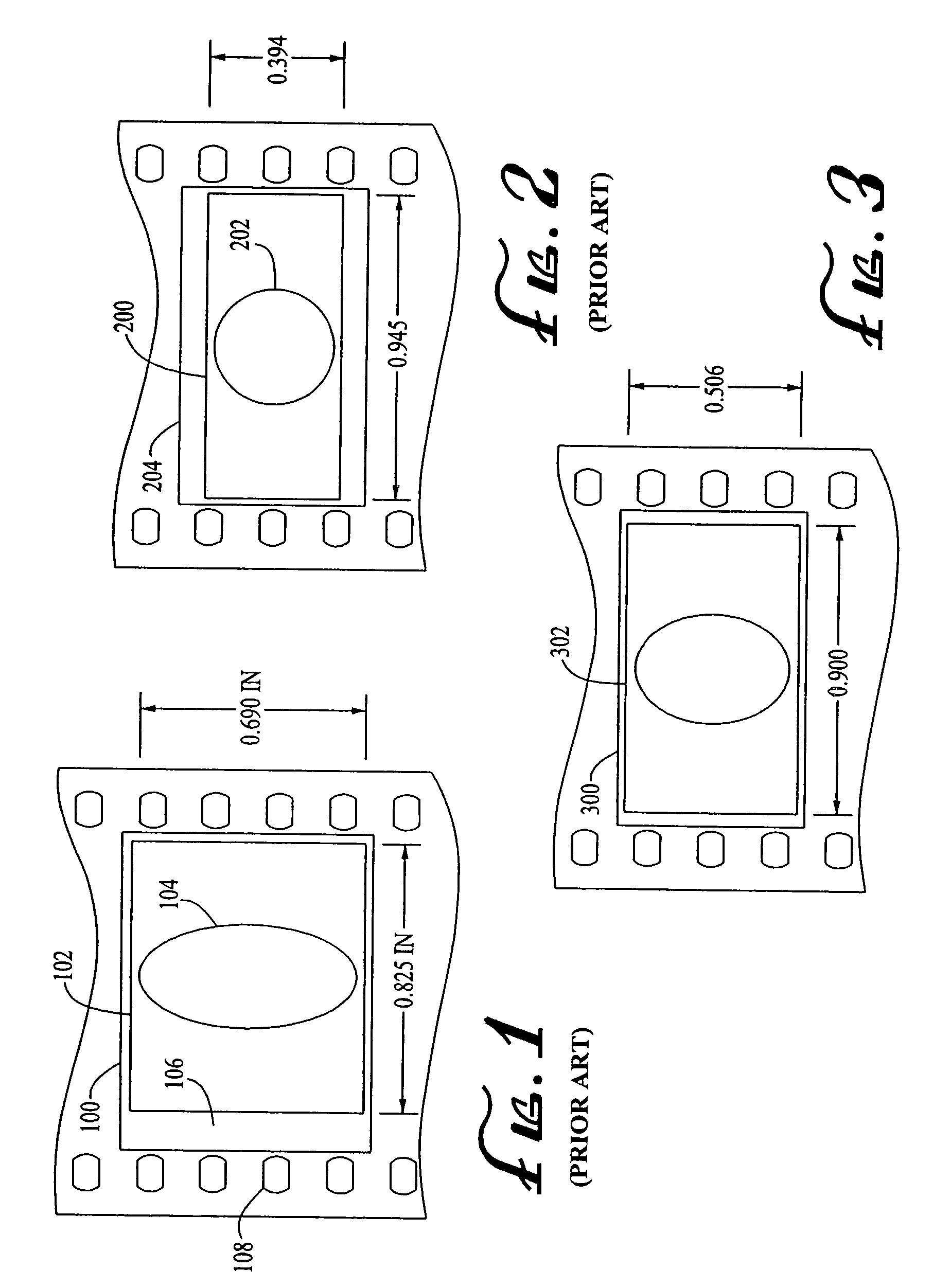
ActiveUS7148947B2Reduce image degradationMaximize image capture areaProjectorsRecord information storageDigital imagingComputer graphics (images)
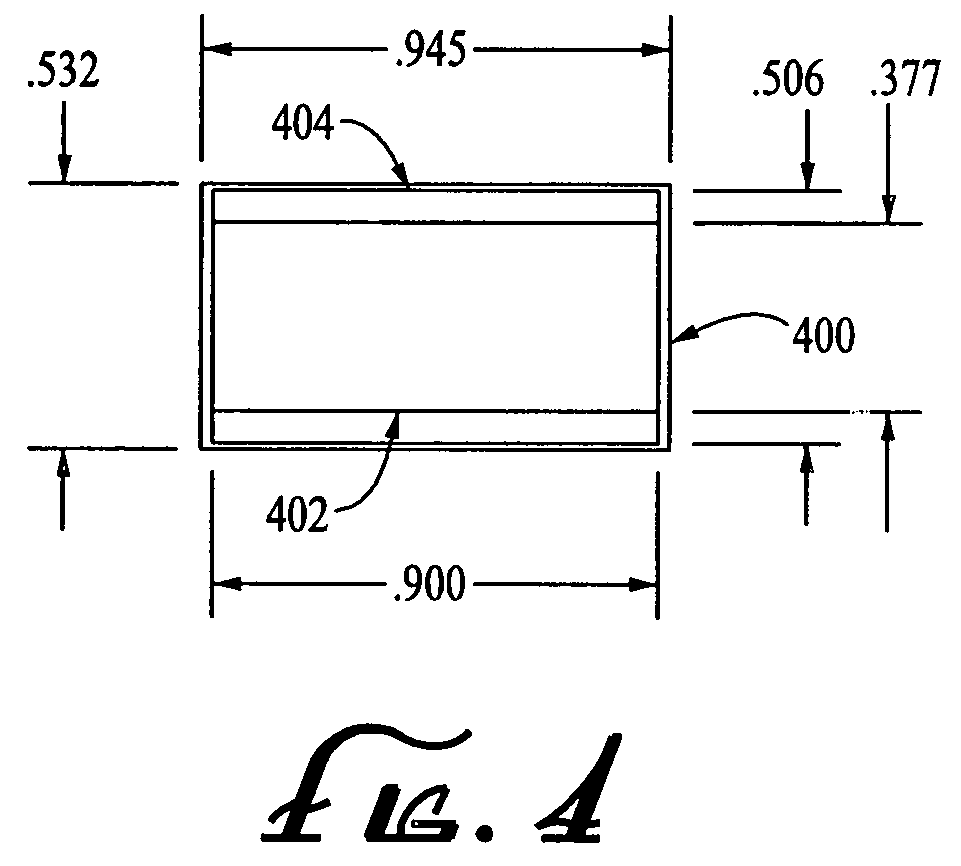
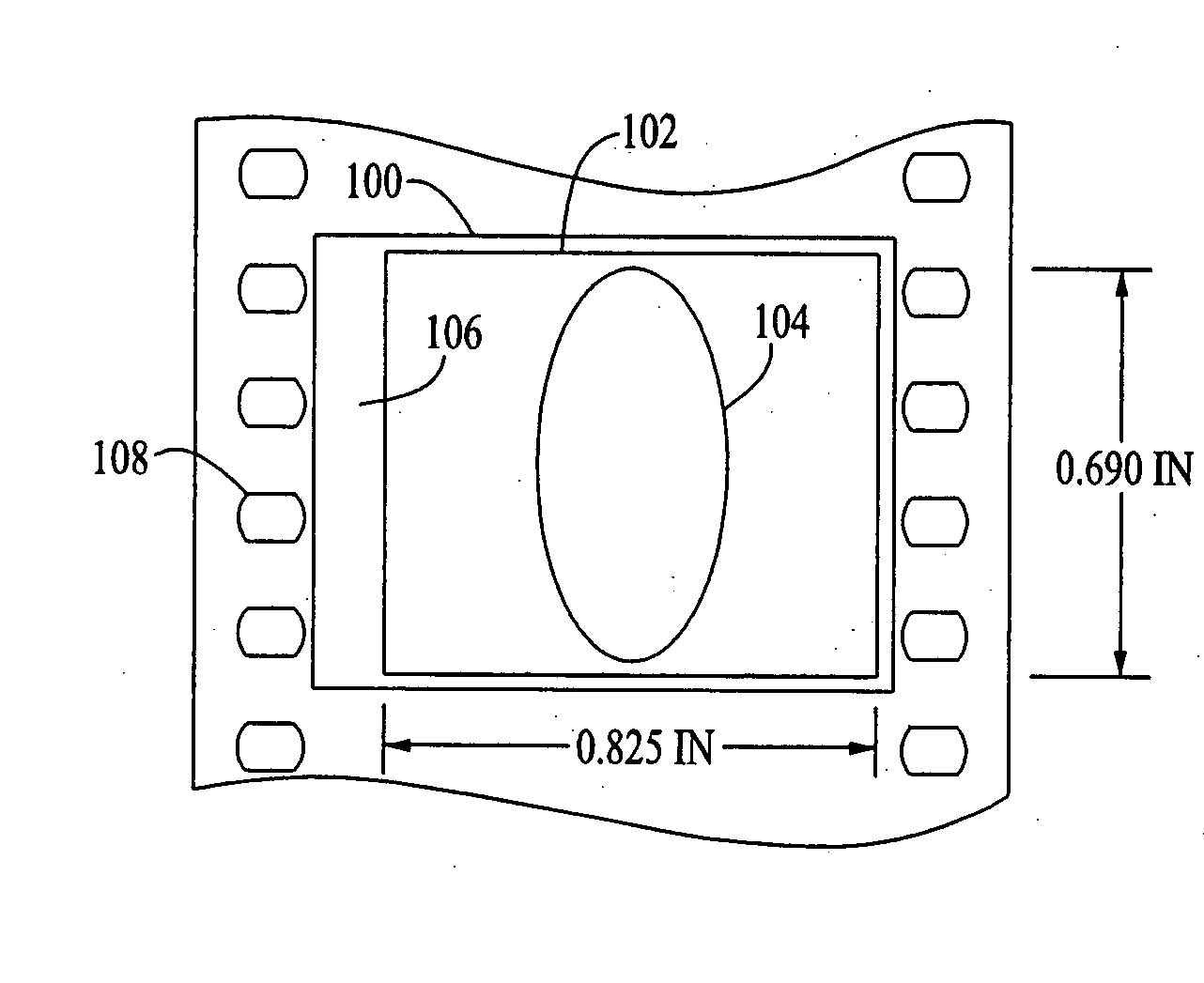
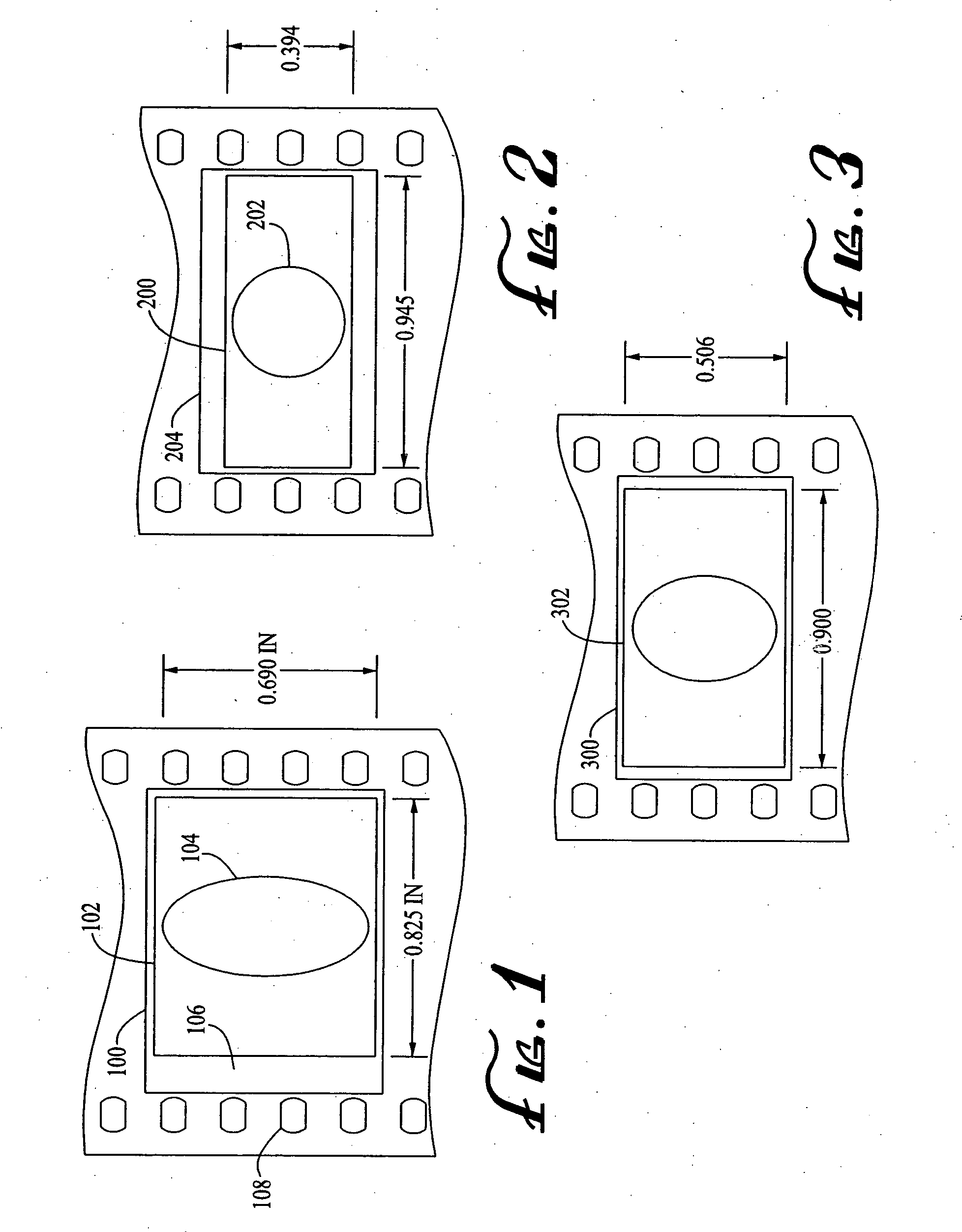
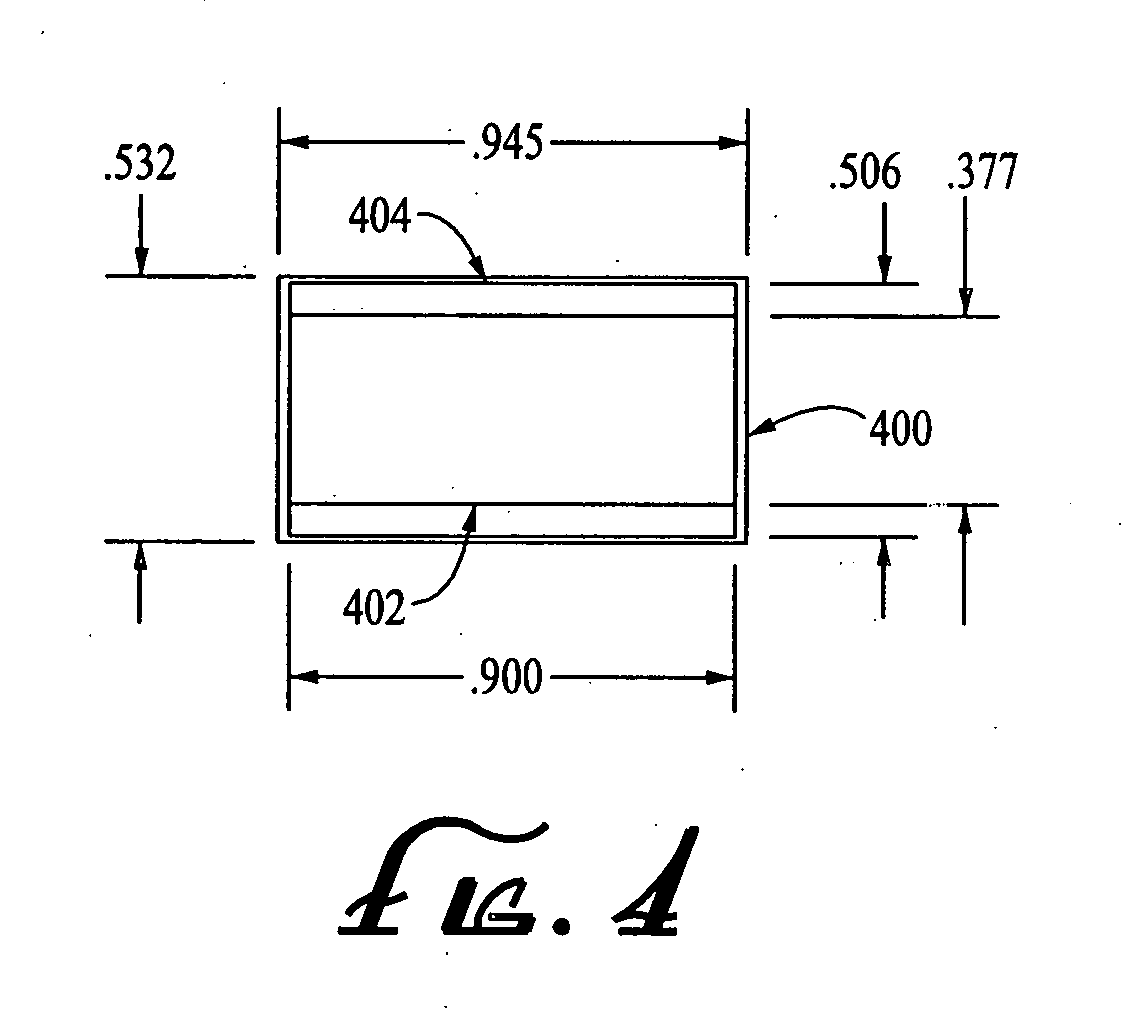
An anamorphic imaging system is disclosed which maximizes the use of available image area to minimize display magnification and image degradation due to display magnification, reduces the amount of anamorphic squeeze during photography to lower image degradation due to anamorphosis, and in film applications, utilizes a film frame that is only three perforations in height to reduce the amount of original film needed. The frame for either film or digital applications has an aspect ratio of approximately 16:9, is contained within the total available frame area of a three-perforation frame or digital imager, and is sized to maximize image area. In preferred embodiments, the image capture area is approximately 0.900 inches wide by approximately 0.506 inches tall.
Owner:PANAVISION INT LP +1
Ink jet printing apparatus and ink jet printing method
InactiveUS20100328385A1Image degradationLower jetOther printing apparatusData designElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:CANON KK
Method and apparatus for improving image appearance
InactiveUS7024049B2Good lookingEasy to readGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionProbit model
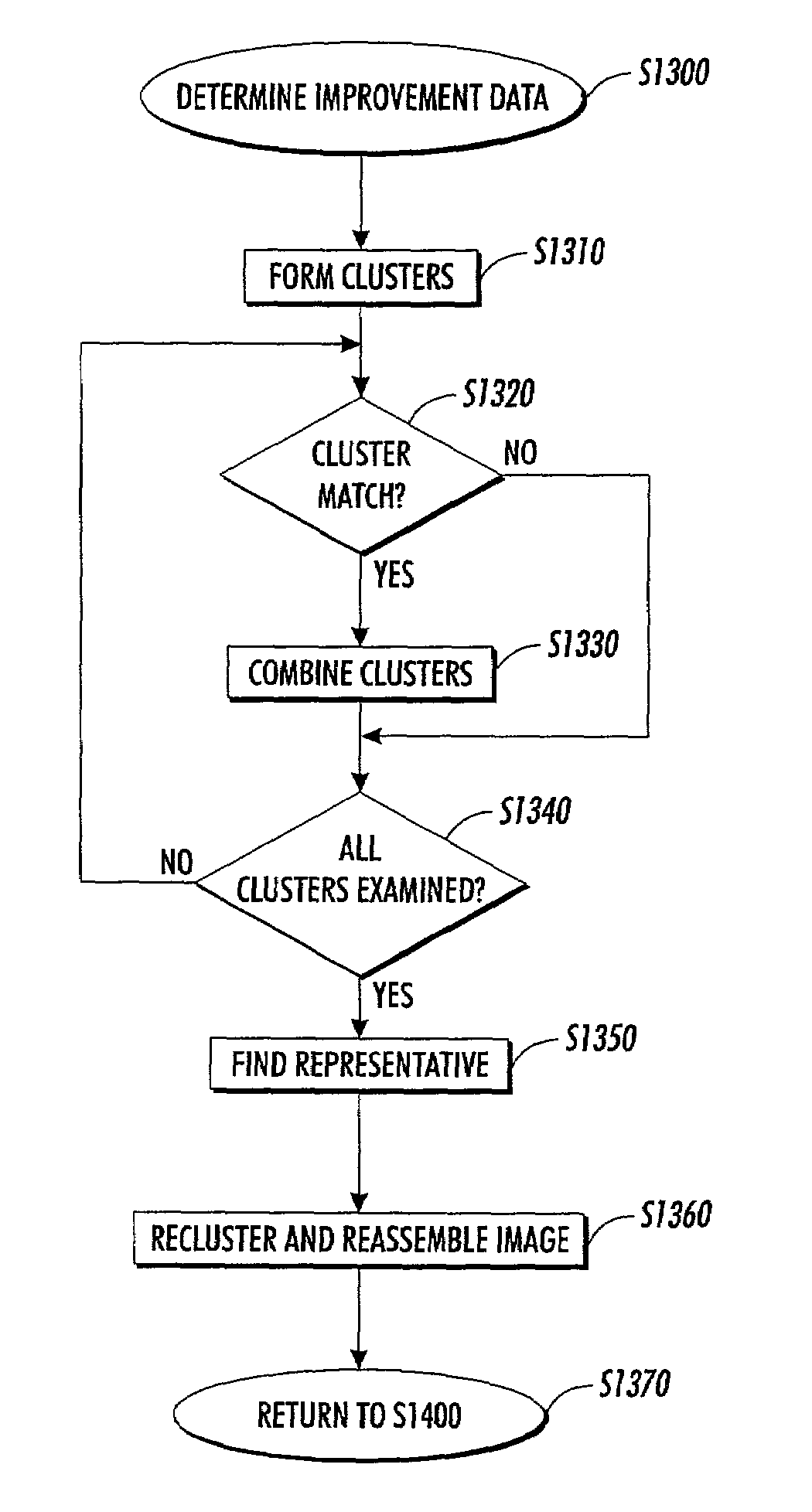
Connected components of dark pixels are clustered from across the image. A “most likely” representative image for each cluster of images is determined, with likelihood determined by a probabilistic model of the image capturing process. An a priori (prior) probability distributions on bitmaps may be used to determine the most likely representative images. For example, a priori probability distributions based on so-called chain codes are implemented. The representative images are used to cluster connected components. Clustering may be repeated. The output page is assembled by replacing each member of a cluster of images by that cluster's representative image.
Owner:XEROX CORP
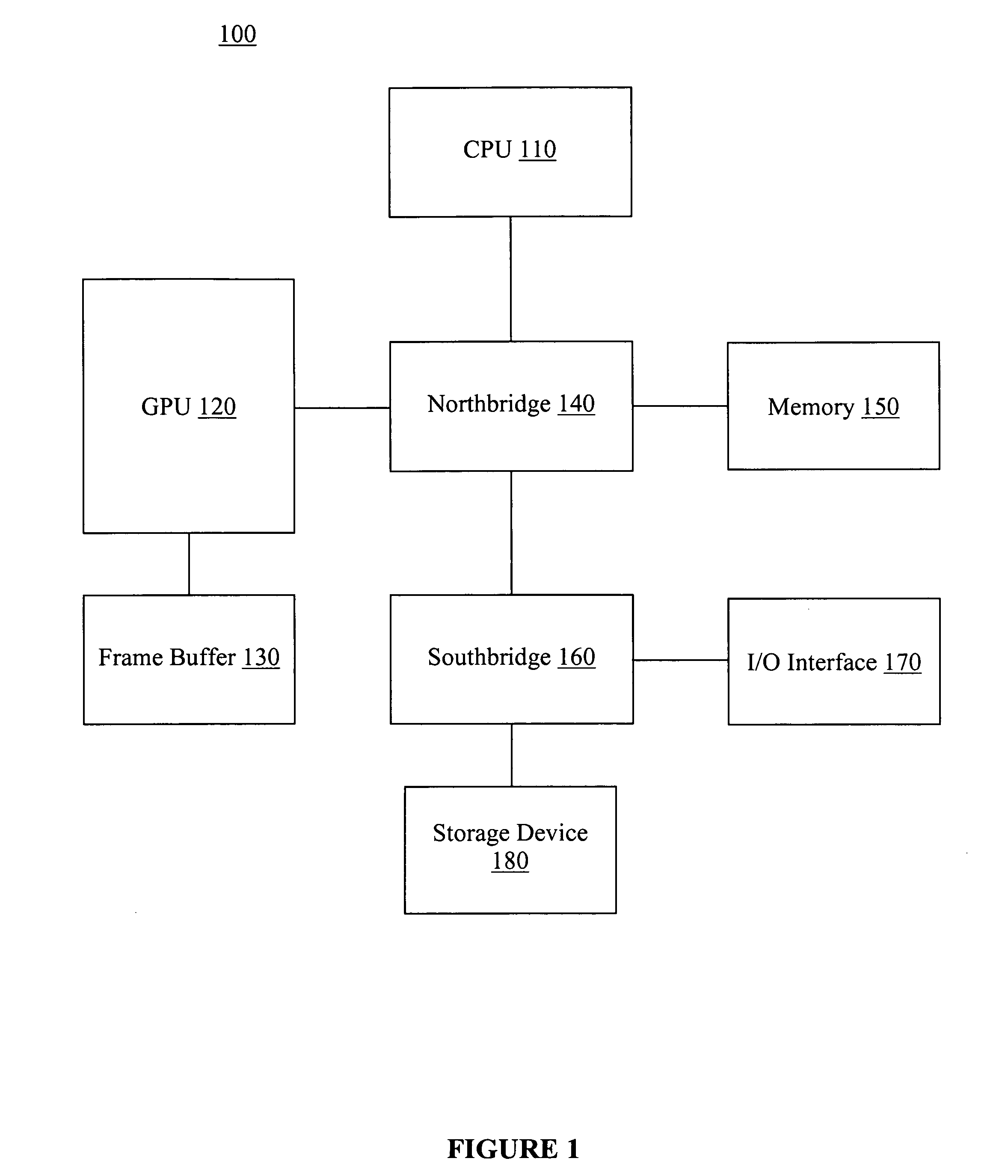
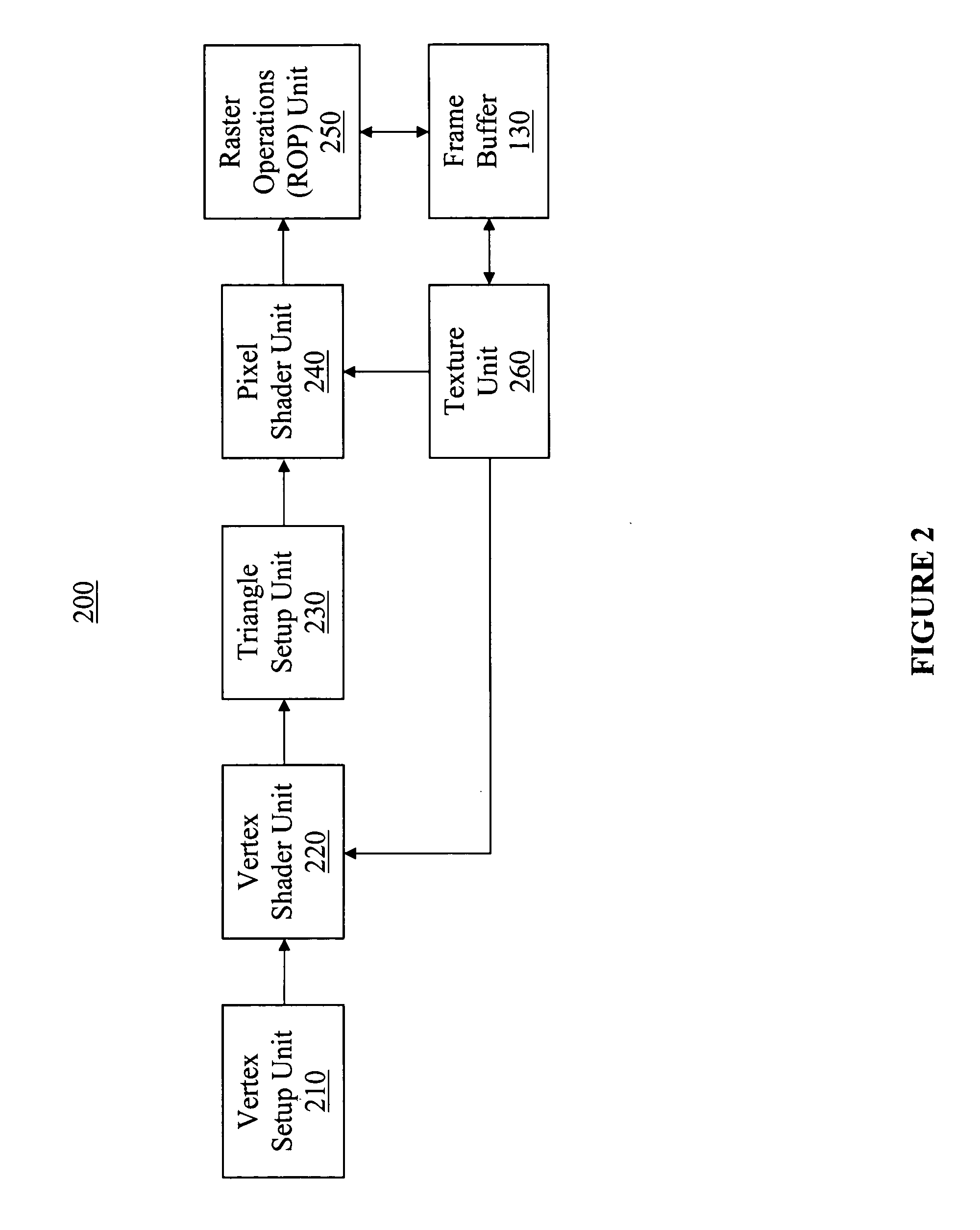
Method and user interface for enhanced graphical operation organization
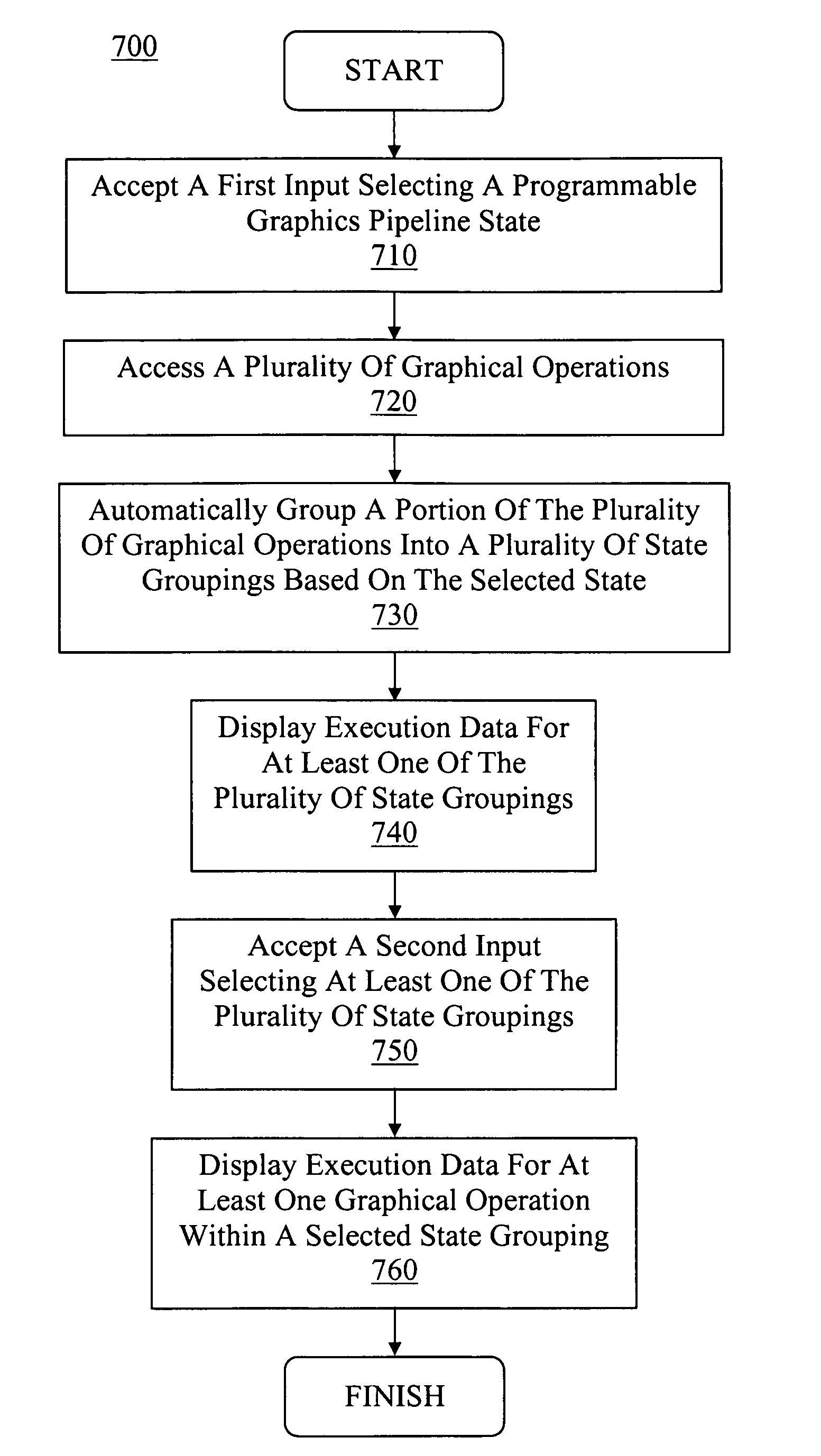
ActiveUS20080030511A1Reduced execution timeImprove performanceError detection/correctionProcessor architectures/configurationGraphicsUser interface
A computer-implemented method and user interface for organizing graphical operations and displaying performance data of a graphics processing pipeline. More specifically, embodiments provide a convenient and effective mechanism for enhancing graphics processing by automatically determining and grouping graphical operations with similar state attributes relating to one or more units of the graphics pipeline. As such, pipeline adjustments for reducing execution time of one graphical operation may benefit other graphical operations with similar state attributes, thereby reducing the number of pipeline adjustments and allowing more careful selection of graphical operations to increase performance and reduce image degradation. Also, the display of the grouped graphical operations also provides information for determining the troublesome operations. In one embodiment, the groups are ranked by their respective execution time. Additionally, other forms of performance data may be displayed for graphical operations with similar state attributes, thereby providing additional information to guide enhancement operations.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
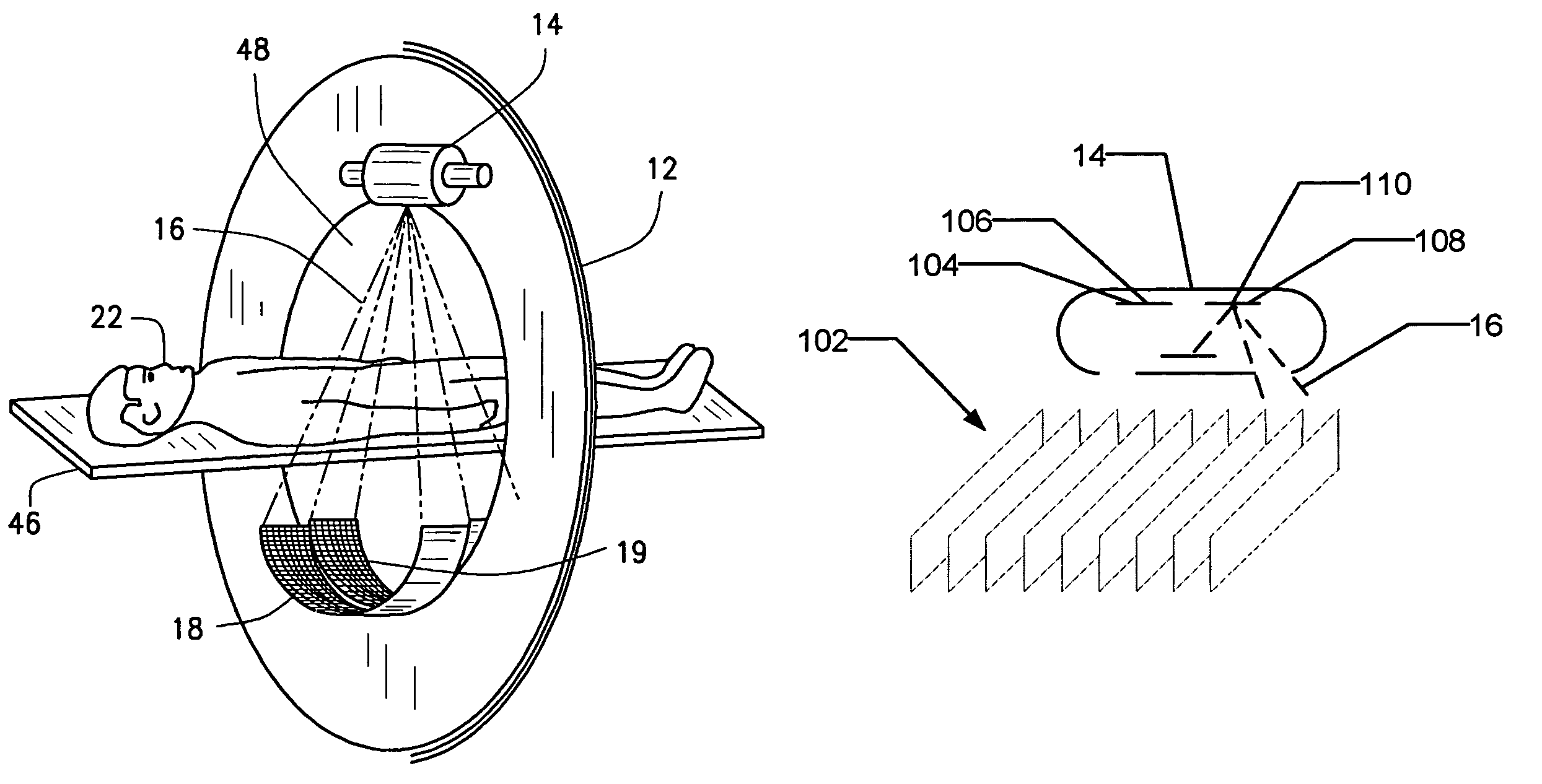
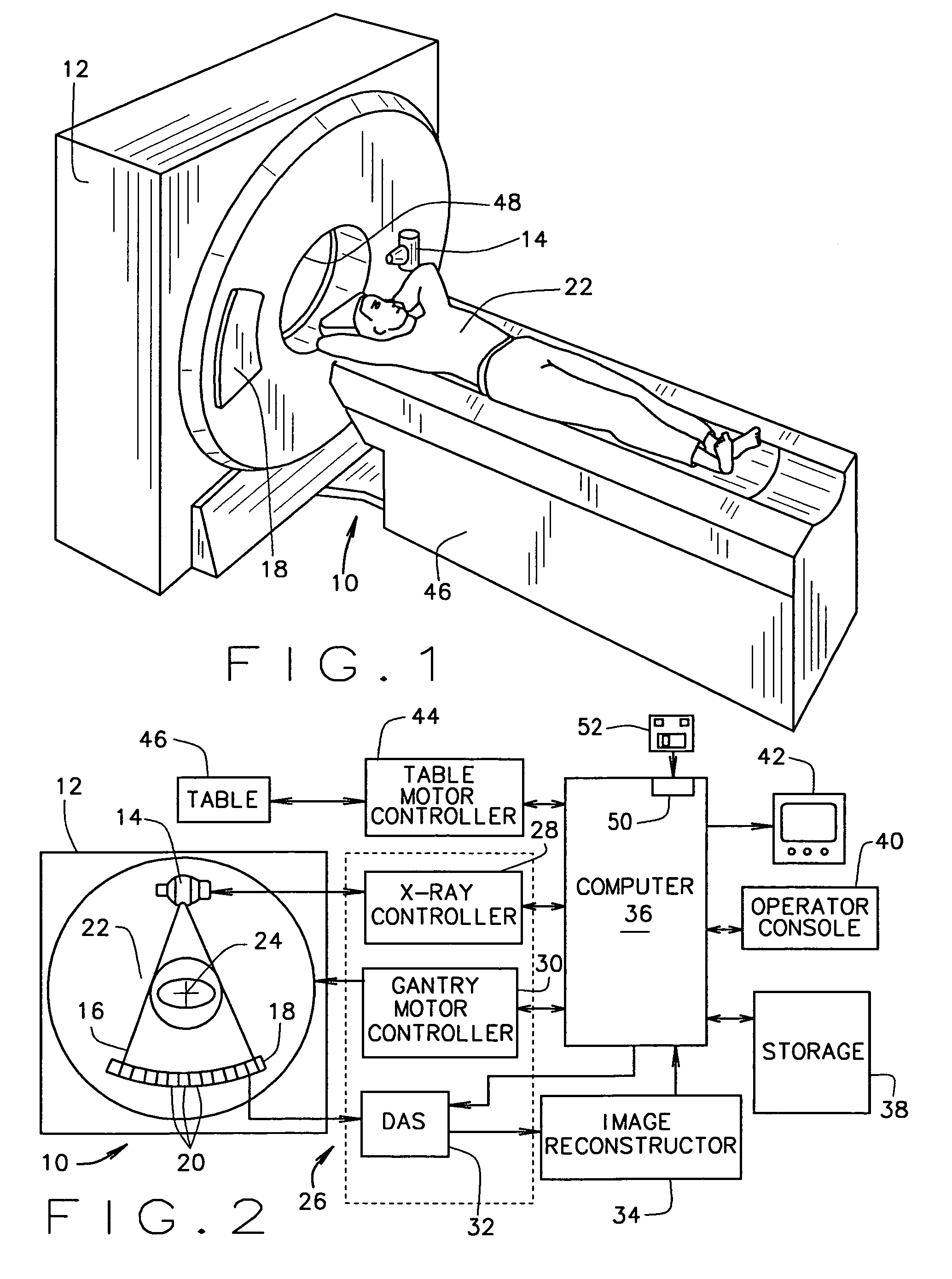
Multidetector CT imaging method and apparatus with reducing radiation scattering
ActiveUS7187748B2Reduce image degradationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingMultidetector ctMulti slice ct
A method for scanning an object to reduce image degradation includes scanning the object in a helical mode using a multi-slice CT imaging system having a plurality of detector arrays arranged along a z-axis direction and a radiation source having a beam focal spot. The method further includes wobbling the focal spot of the radiation source in the z-axis direction during the scanning to selectively preferentially illuminate individual detector arrays through the scanned object for each view. Data is collected from each detector array for each view only when the detector array from which data is being collected is selectively illuminated.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Printing device, printing device control program and method, and printing data generation device, program, and method
InactiveUS7438375B2Stopping image degradationReduce image degradationOther printing apparatusImaging qualityEngineering
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Anamorphic three-perforation imaging system
ActiveUS20050225726A1Reduce image degradationMaximize image capture areaProjectorsRecord information storageDigital imagingComputer graphics (images)
An anamorphic imaging system is disclosed which maximizes the use of available image area to minimize display magnification and image degradation due to display magnification, reduces the amount of anamorphic squeeze during photography to lower image degradation due to anamorphosis, and in film applications, utilizes a film frame that is only three perforations in height to reduce the amount of original film needed. The frame for either film or digital applications has an aspect ratio of approximately 16:9, is contained within the total available frame area of a three-perforation frame or digital imager, and is sized to maximize image area. In preferred embodiments, the image capture area is approximately 0.900 inches wide by approximately 0.506 inches tall.
Owner:PANAVISION INT LP +1
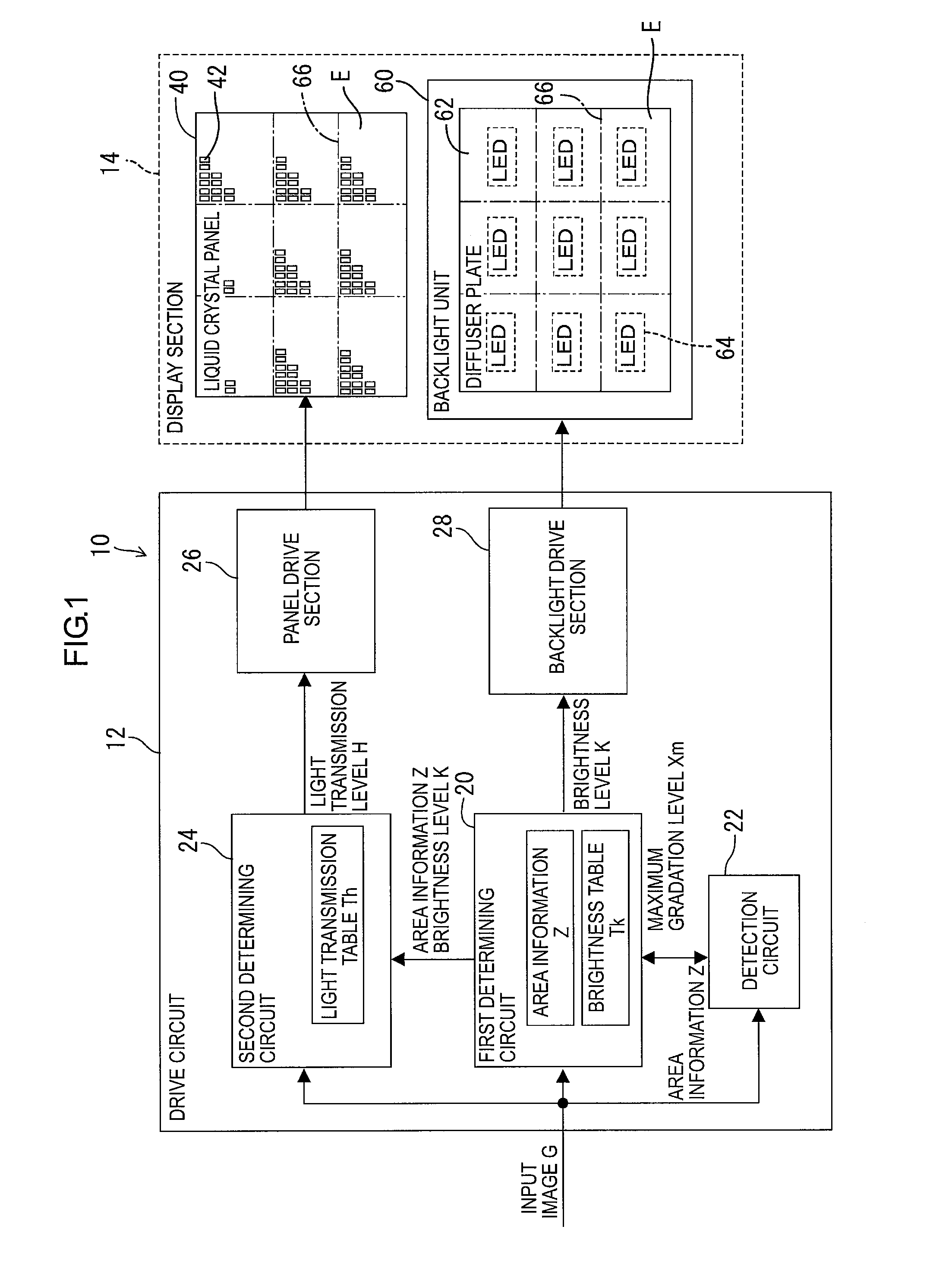
Drive circuit, drive method, and display device
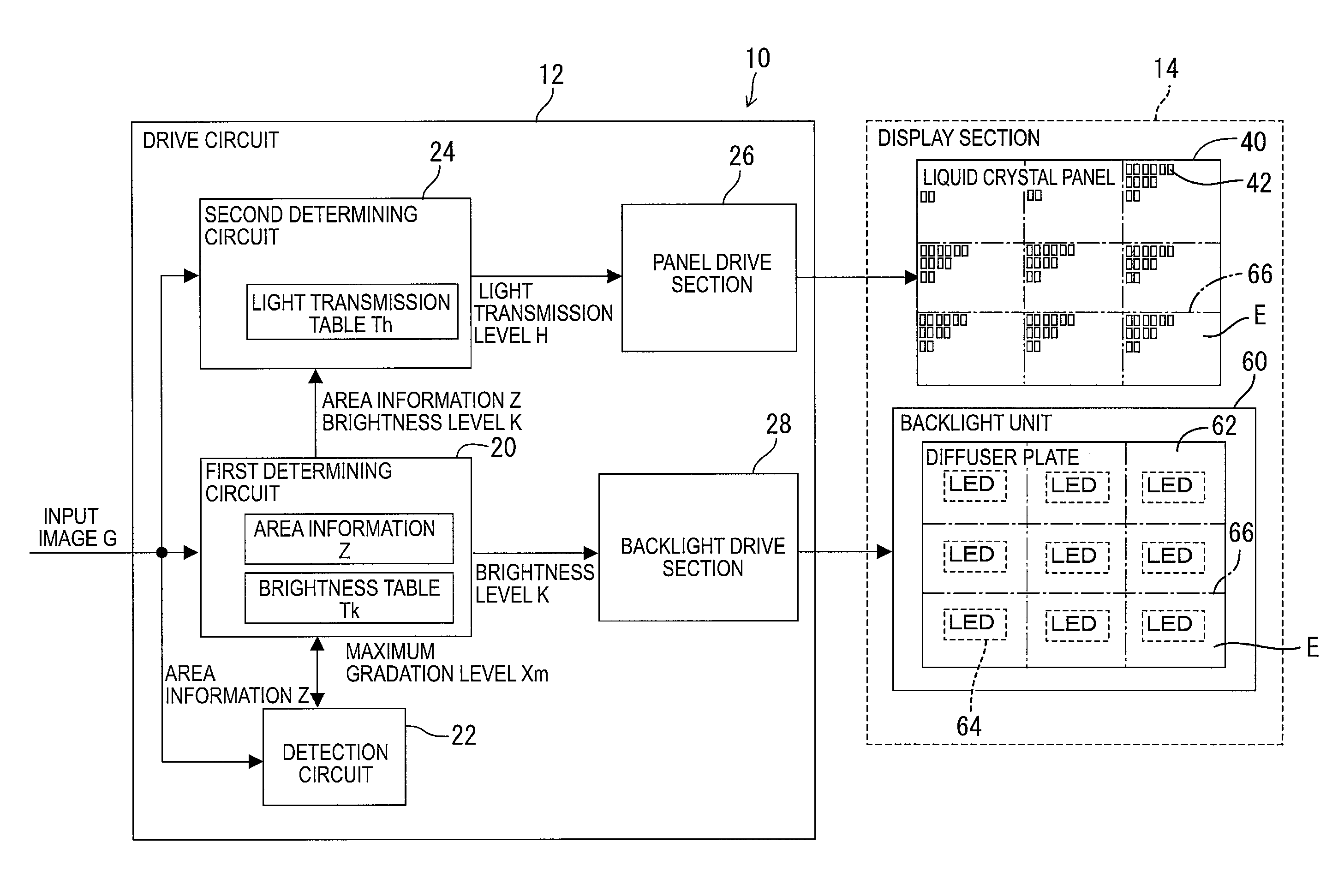
InactiveUS20130162700A1Improve responsivenessReduce image degradationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingCritical levelDisplay device
A drive circuit is configured to drive a display panel including pixels and a backlight including LEDs. The display panel includes a critical light transmission level that is a minimum level for causing each pixel to respond in a predetermined time upon an input of an image. The drive circuit includes first and second circuits. The first circuit is configured to divide the image into areas and determine brightness levels of the LEDs for the areas based on the image. The second circuit is configured to determine a light transmission level based on the image and the brightness levels such that the level is higher than the critical level.
Owner:SHARP KK
Multimodal imaging system, apparatus, and methods
ActiveUS9610064B2Easy to operateImprove usabilityOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryOptical tomographyCollection system
In part, the invention relates to an image data collection system. The system can include an interferometer having a reference arm that includes a first optical fiber of length of L1 and a sample arm that includes a second optical fiber of length of L2 and a first rotary coupler configured to interface with an optical tomography imaging probe, wherein the rotary coupler is in optical communication with the sample arm. In one embodiment, L2 is greater than about 5 meters. The first optical fiber and the second optical fiber can both be disposed in a common protective sheath. In one embodiment, the system further includes an optical element configured to adjust the optical path length of the reference arm, wherein the optical element is in optical communication with the reference arm and wherein the optical element is transmissive or reflective.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com