Patents
Literature
31results about How to "Cost of apparatus can be reduced" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
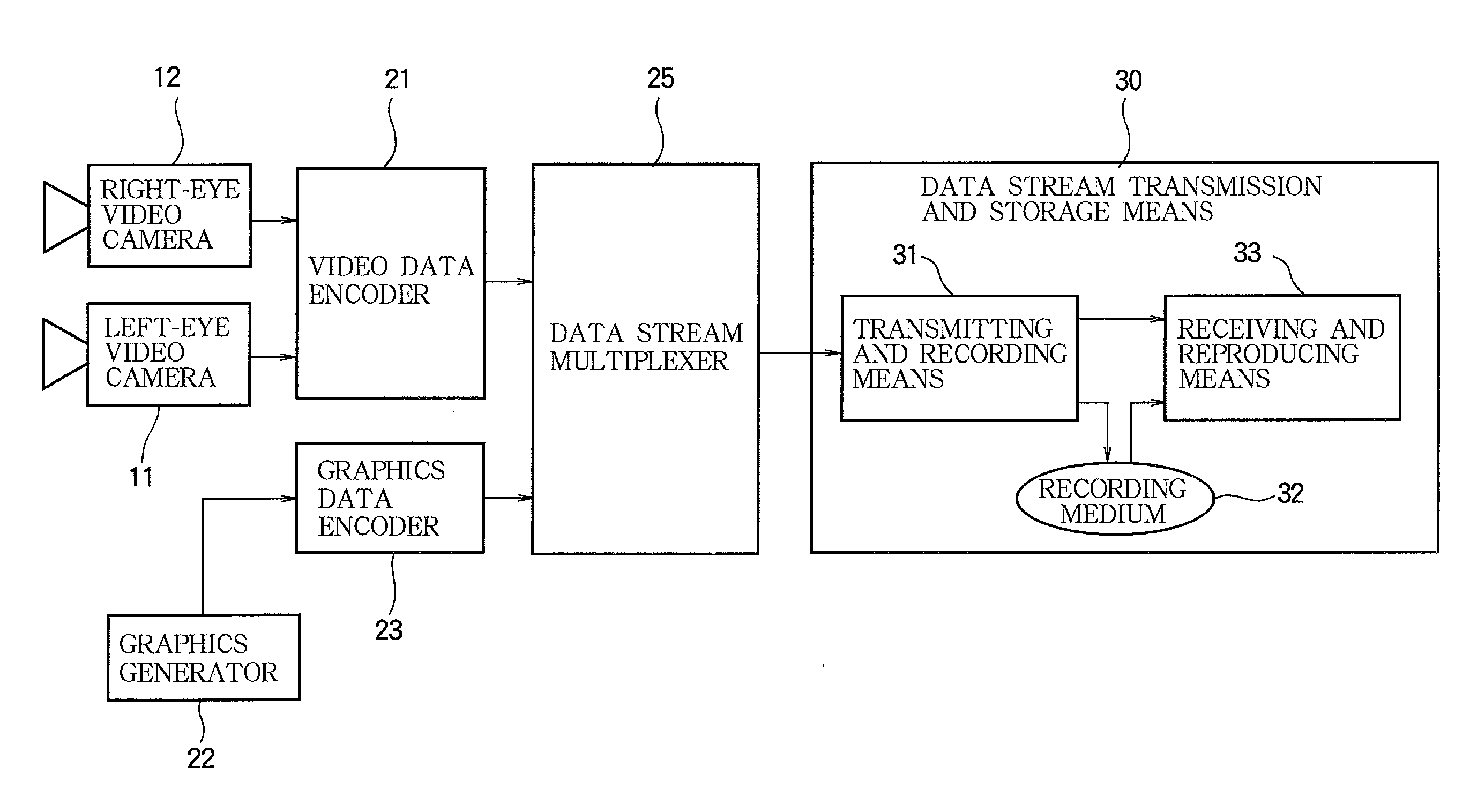
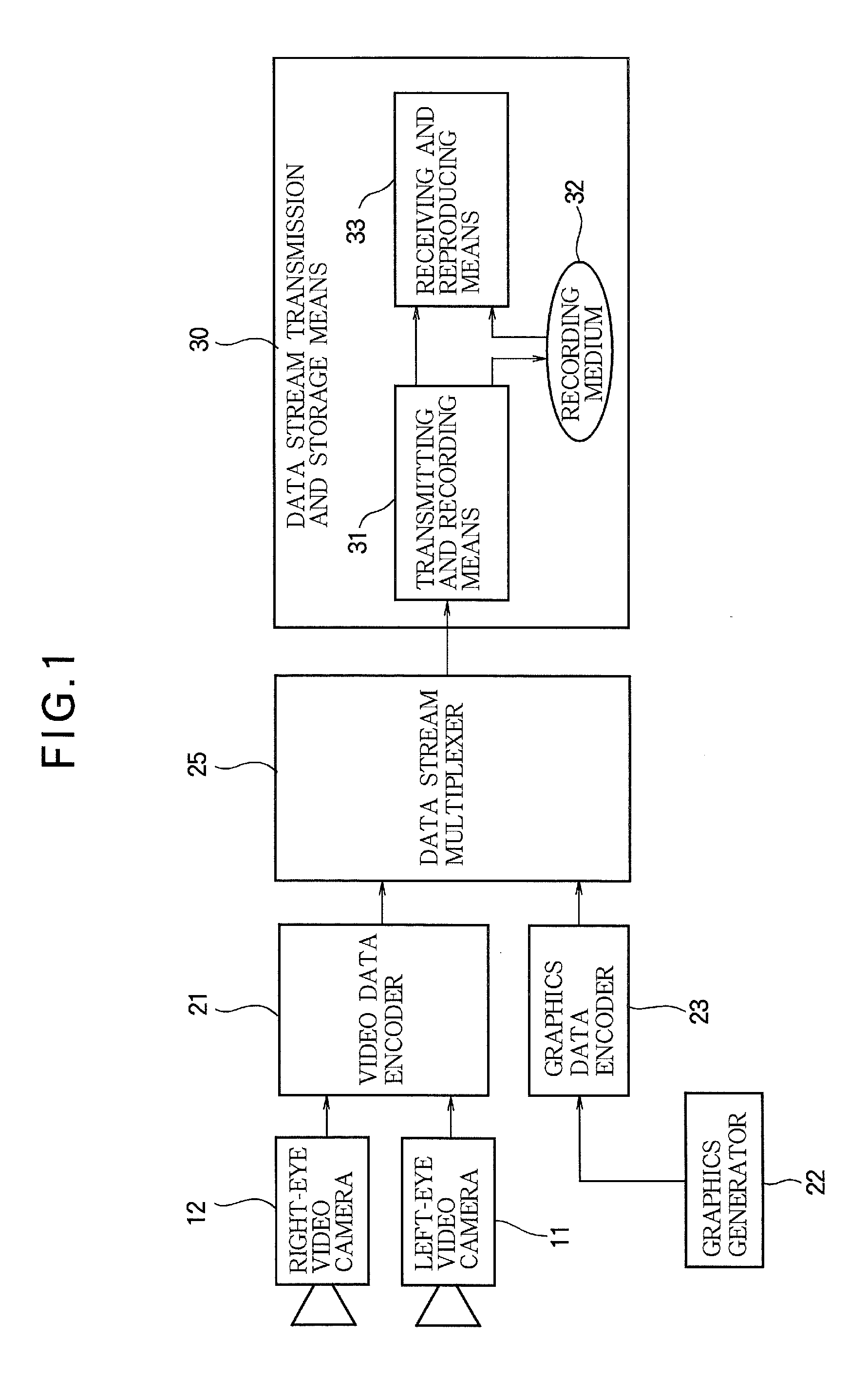
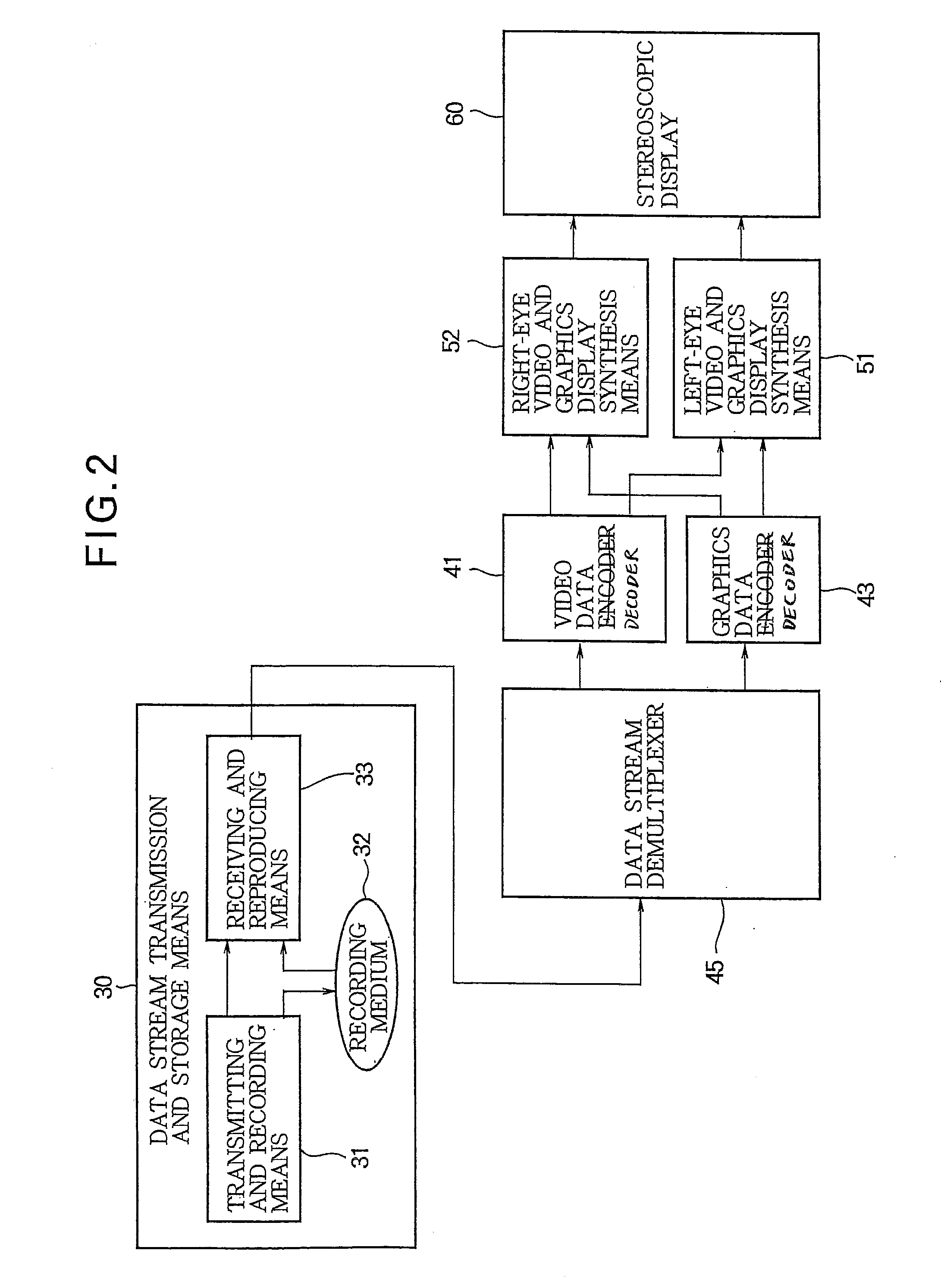
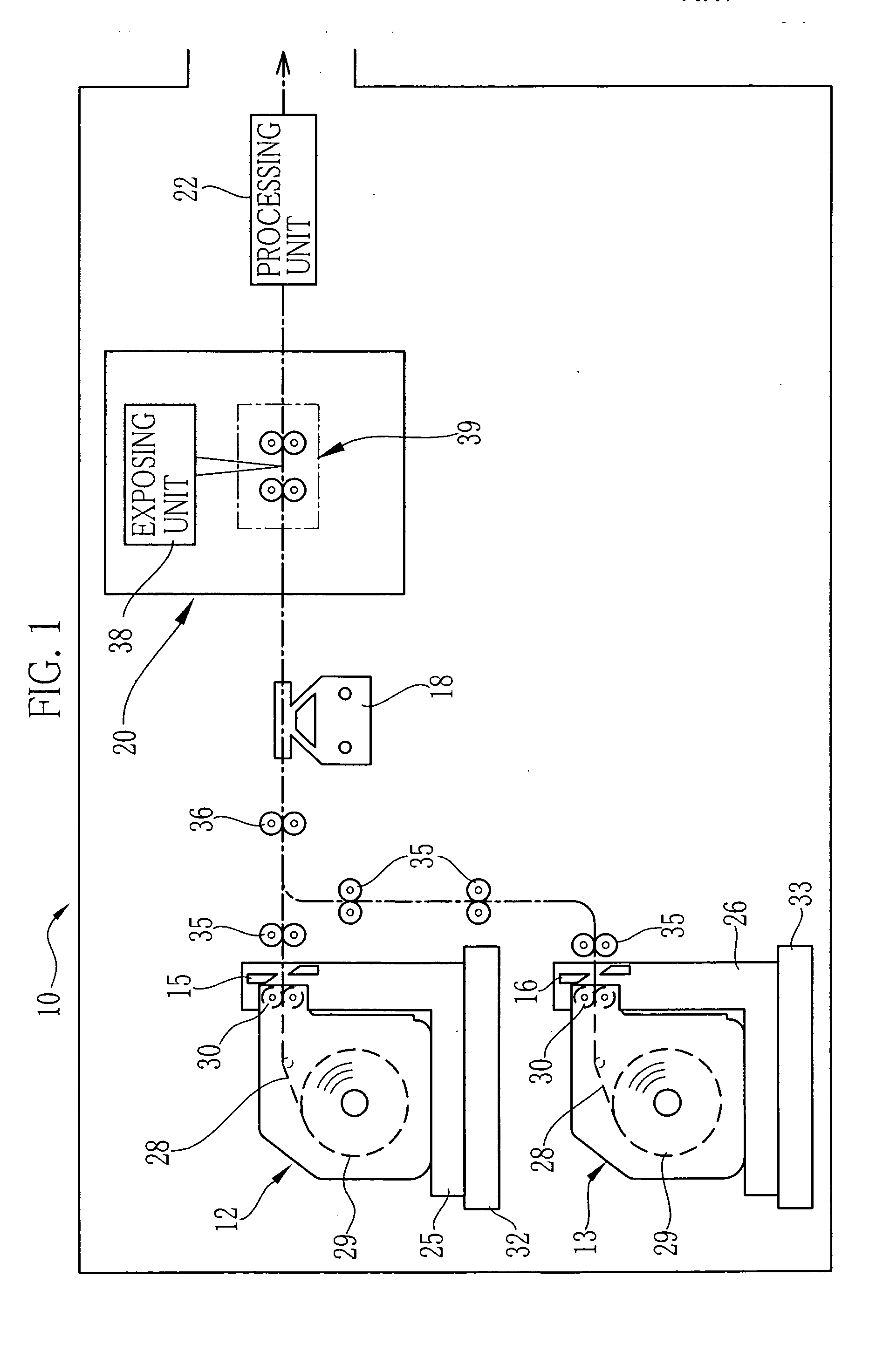
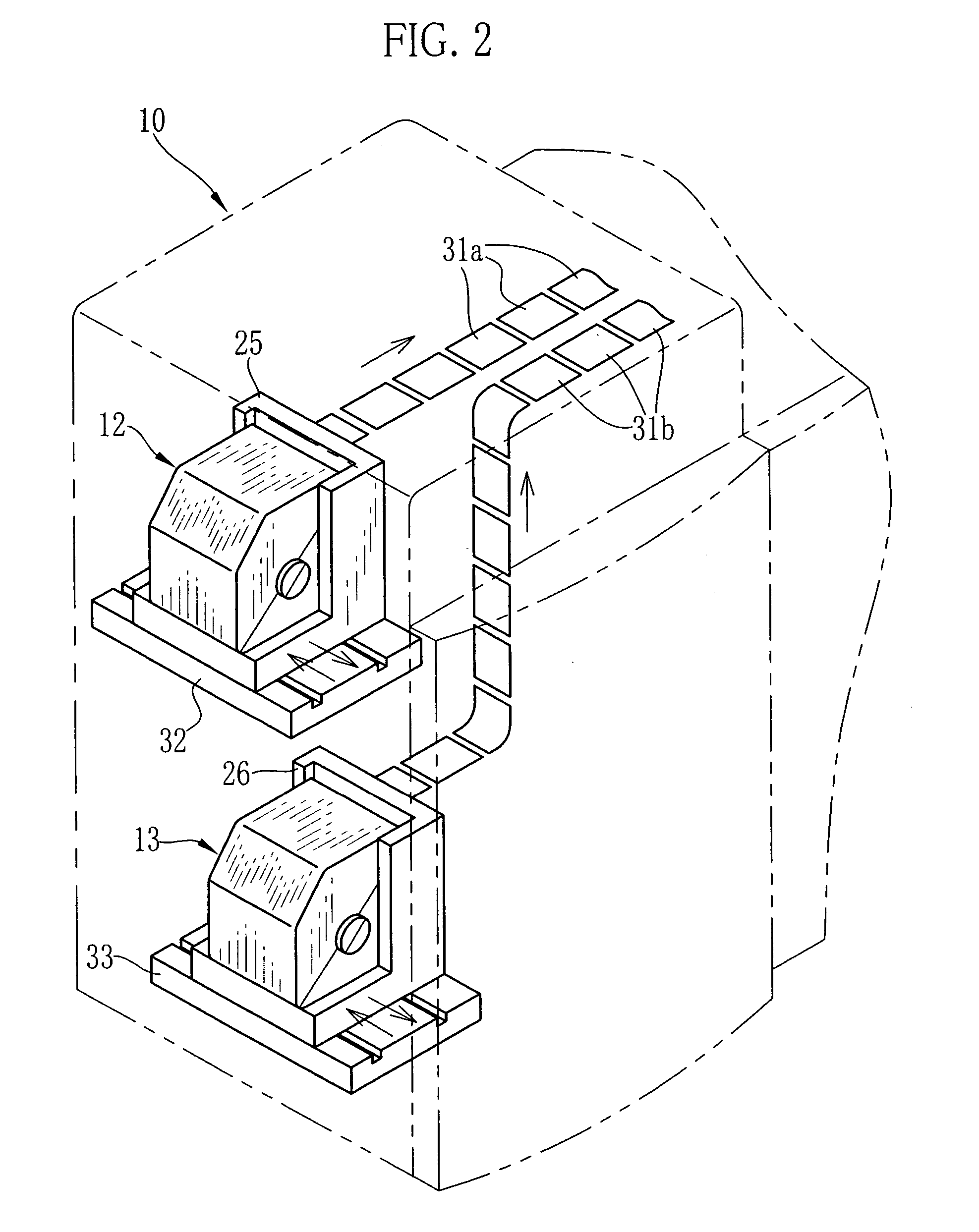
Video encoding device, video encoding method, video reproducing device, video reproducing method, video recording medium, and video data stream
InactiveUS20110069153A1Increase freedomReduce data volumeDigital video signal modificationSteroscopic systemsStereoscopic videoData stream
In a system for visualizing a stereoscopic image by displaying separate video images for the left and right eyes, sub-picture data (GRD) is created for the left eye and displayed superimposed on left-eye video data (VDD) as a left-eye sub-picture without change. The right-eye sub-picture (106) is displayed by shifting the horizontal positions at which the sub-picture data created for the left eye is displayed by prescribed widths. For example, the sub picture may include a plurality of objects (GRD-1, GRD-2, . . . , GRD-N); shift widths (108, 110) of the horizontal positions of the left and right ends of the objects are individually set and stored in the sub-picture data for displaying the objects for the right eye. A sub-picture superimposed on a stereoscopic video image can thereby be rendered in the depth direction, and the data size of the sub-picture and the amount of computation required for its display can be reduced.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
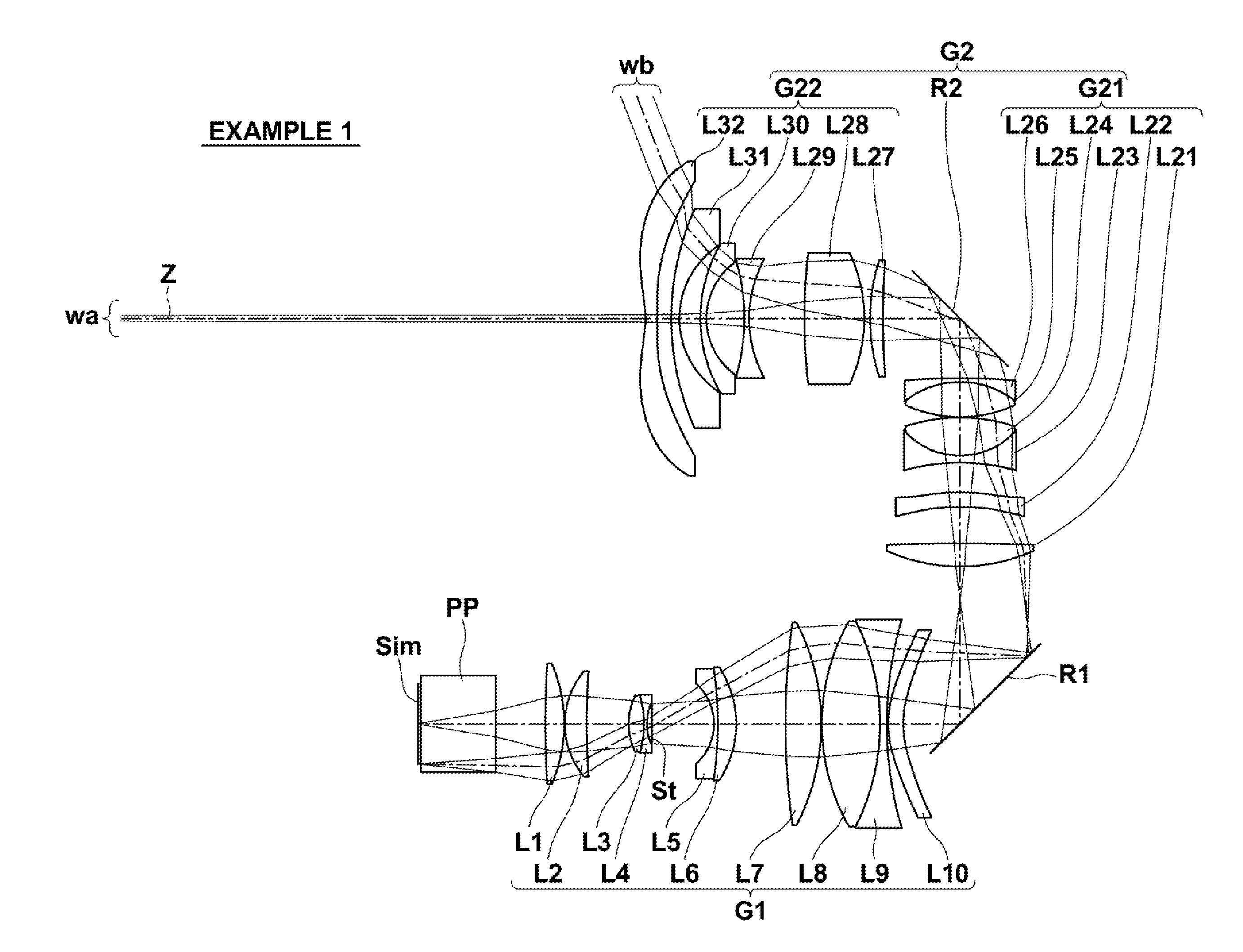
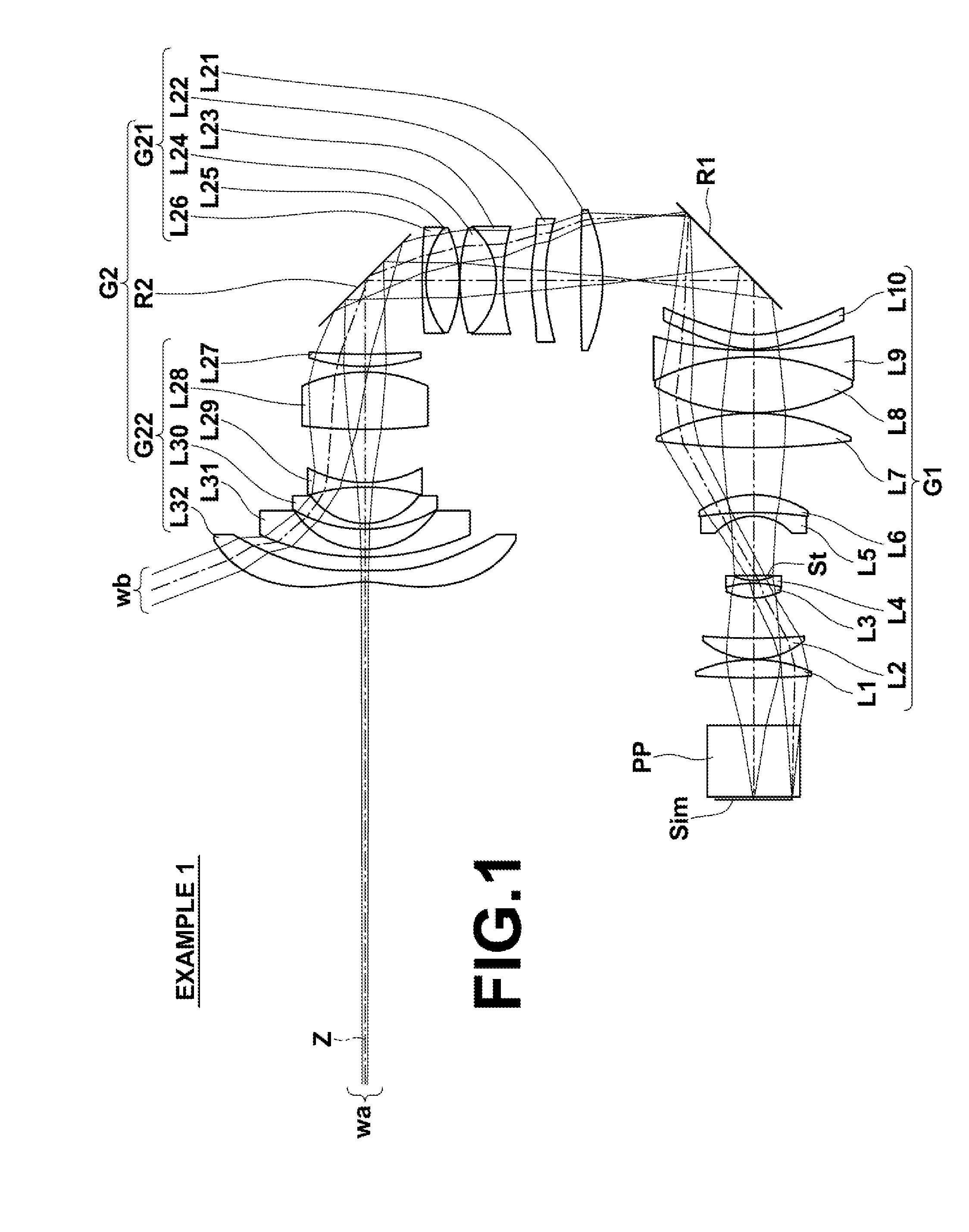
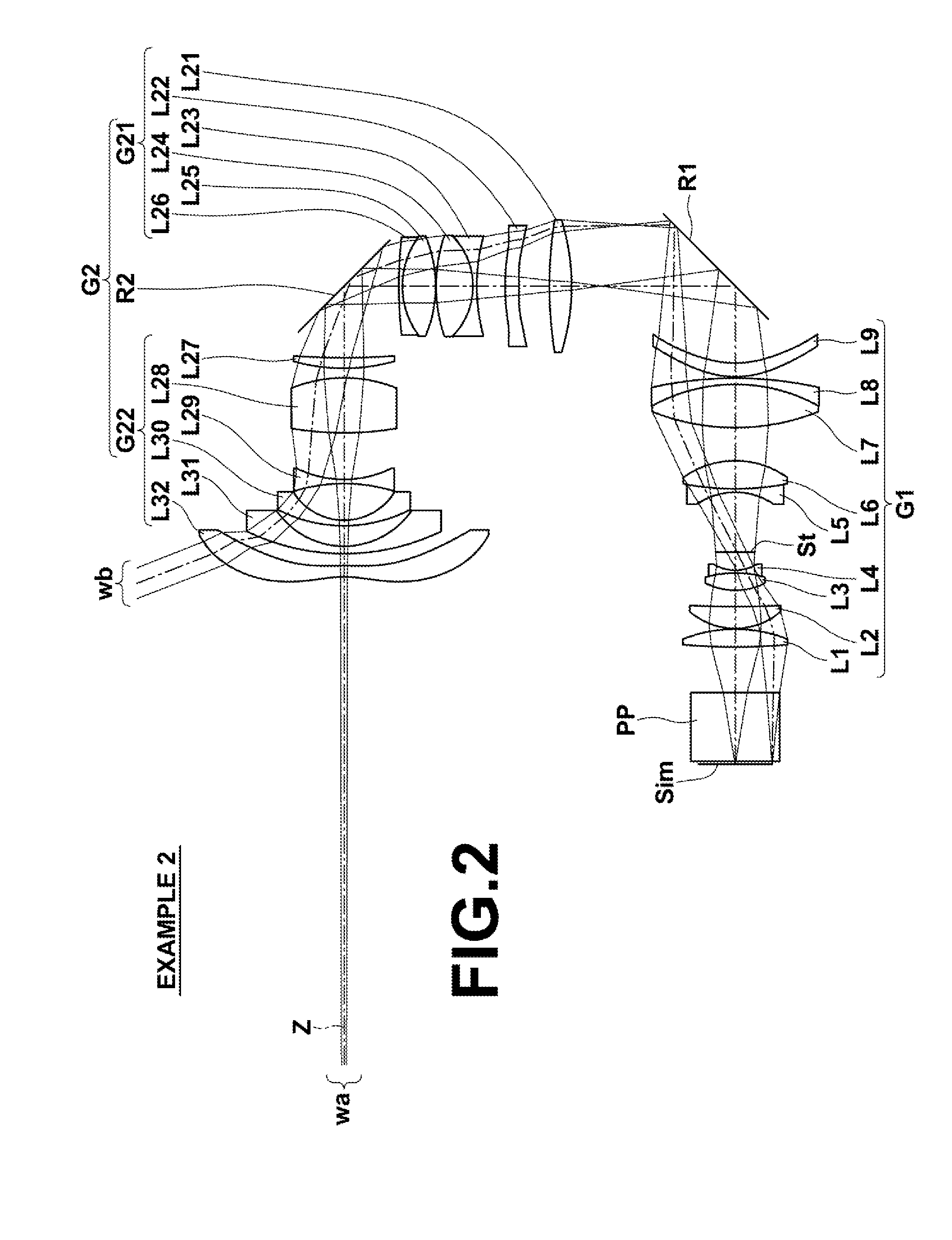
Projection optical system and projection type display device
ActiveUS20160246034A1Improve image qualityCost of apparatus can be reducedProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesIntermediate imageDisplay device
A projection optical system is constituted by, in order from the reduction side, a first optical system constituted by a plurality of lenses for forming an image displayed by image display elements as an intermediate image, and a second optical system constituted by a plurality of lenses for forming the intermediate image on a magnification side conjugate plane. Conditional Formula (1) below is satisfied.8.20<Imφ·f2 / f2<20.00 (1)
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
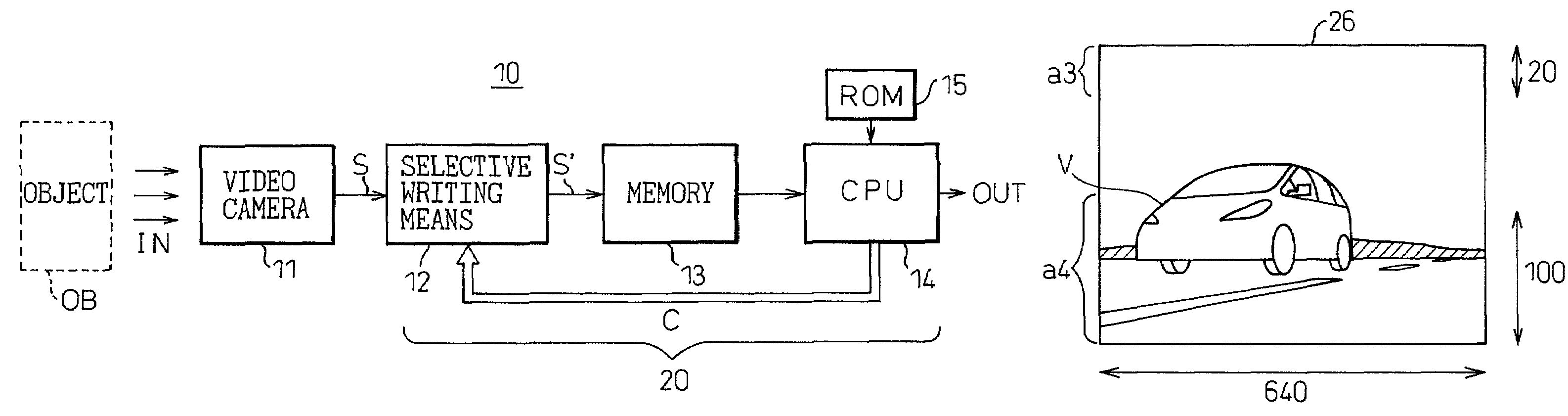
Image processing apparatus for selectively storing specific regions of an image
InactiveUS7365779B2Solve large capacityCost of apparatus can be reducedImage enhancementTelevision system detailsHigh densityImaging processing
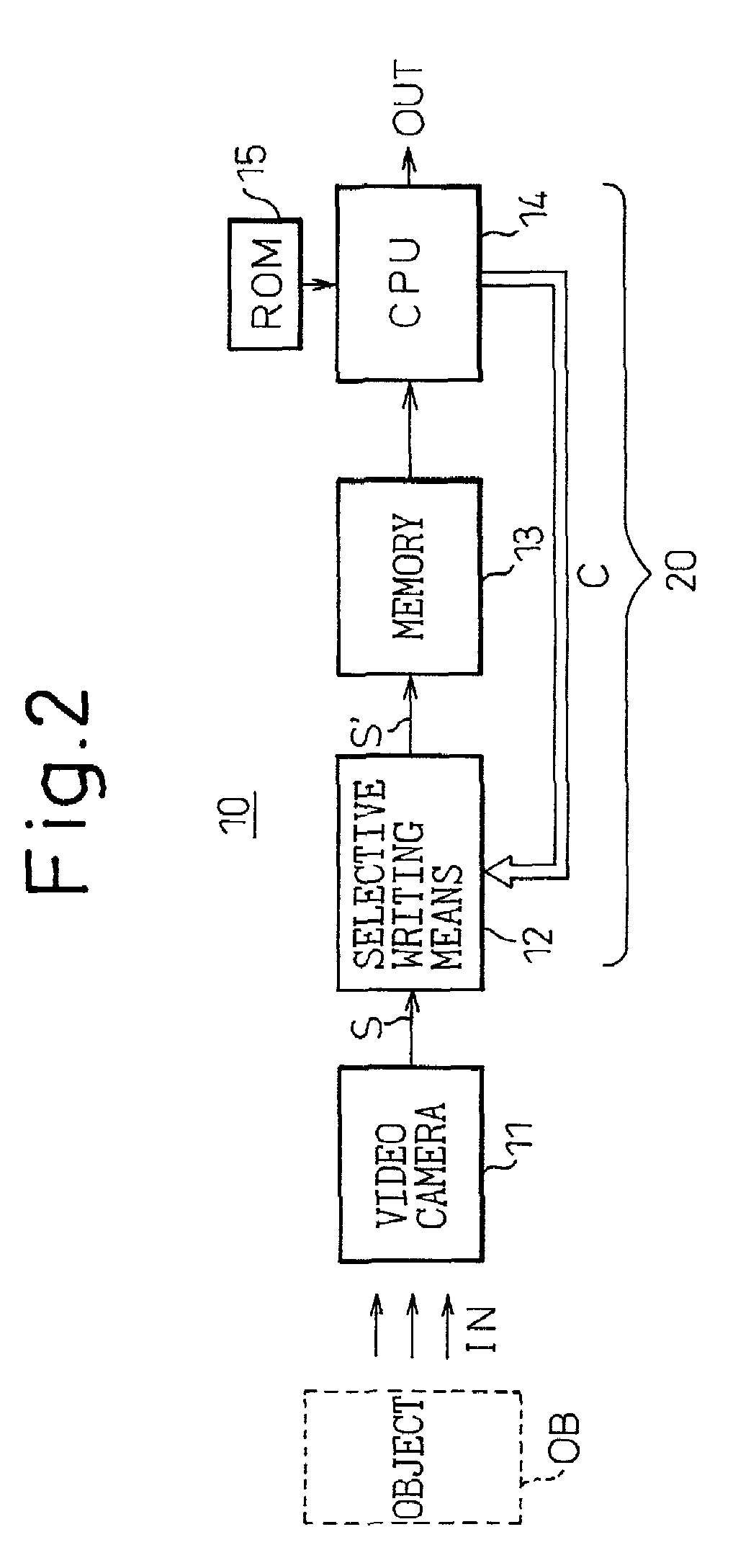
The invention provides an image processing apparatus that can reduce the memory capacity of a memory forming part of the image processing apparatus and can correct the optical axis misalignment of a video camera in a simple manner. The image processing apparatus 10, which comprises a video camera 11, a memory 13 for storing an image signal supplied from the video camera, and a CPU 14 for performing prescribed processing on the image signal read out of the memory, includes a selective writing means 12 for selecting only a designated portion of the image signal in accordance with a select command C from the CPU, and for writing only the selected portion as a selected image signal S′ into the memory 13. The image processing apparatus further includes a switching means for selecting the pixel data to be stored in the memory by switching between high-density pixel data covering a designated range centralized in a horizontal direction of the image and relatively low-density pixel data covering a full image range. The switching means is capable of switching in accordance with vehicle speed.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
Method and apparatus for the analysis of material composition
InactiveUS6907107B1Low production costCost of apparatus can be reducedX-ray spectral distribution measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor materialsMechanical engineering
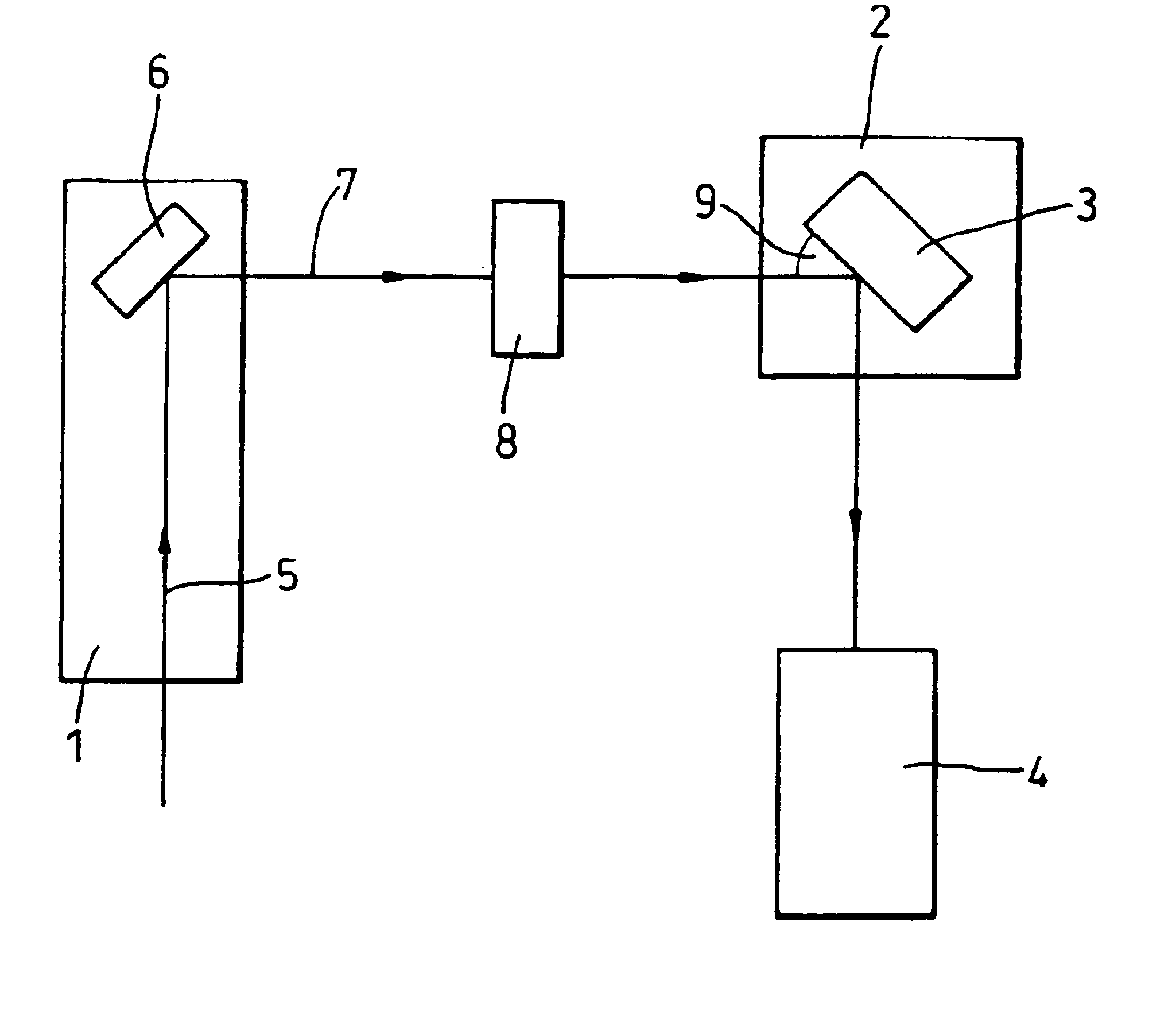
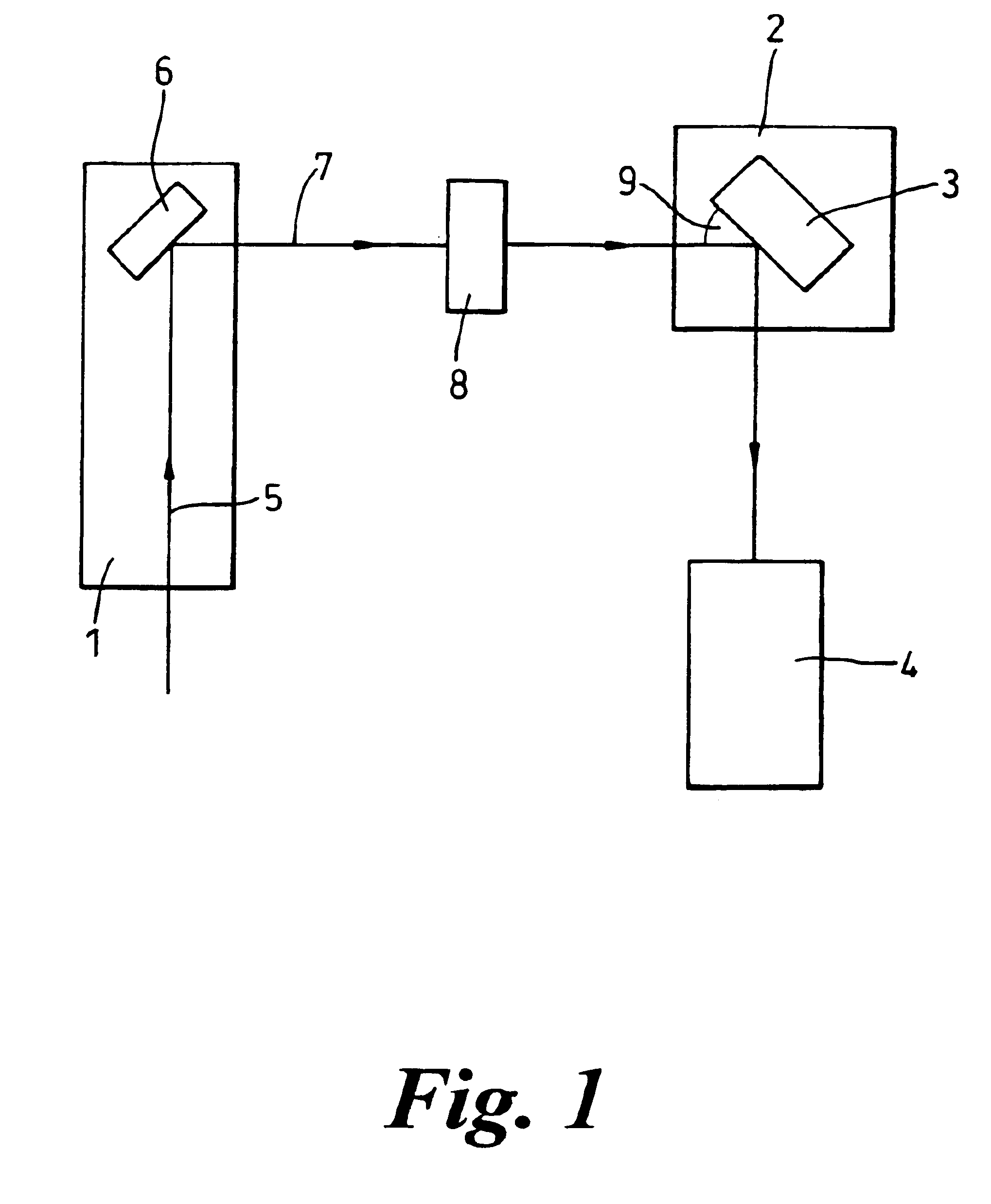
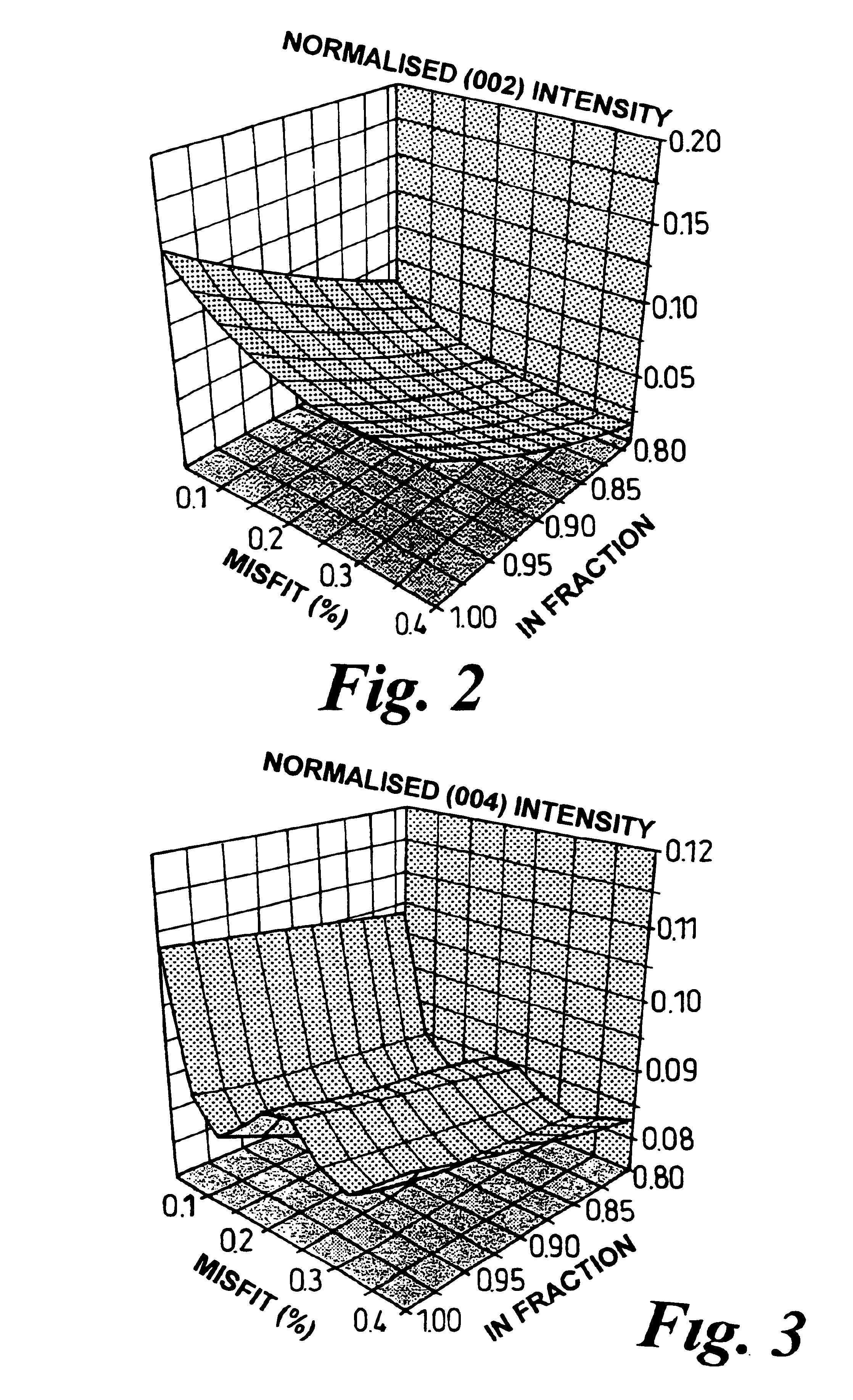
A method is provided of analysing the composition of a semiconductor material (3) comprising irradiating the material with energy from an energy source (1) which energy is diffracted from the material, detecting one or more portions of the diffracted energy, and analysing the or each detected portion to obtain a parameter indicative of the intensity of the or each portion. The or each portion of the diffracted energy detected may be a quasi-forbidden reflection diffracted from the material, e.g. may be a (002) reflection diffracted from the material, or a (006) reflection. The detection of the or each portion of the diffracted energy may take place at one or more detection angles (9), or at all angles of reflection / transmission of the diffracted energy source, or at a range of angles around one or more detection angles. The energy source may comprise a beam of x-rays produced by an x-ray tube (2), and one or more detectors (4) may be used to detect the or each portion of the diffracted energy.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
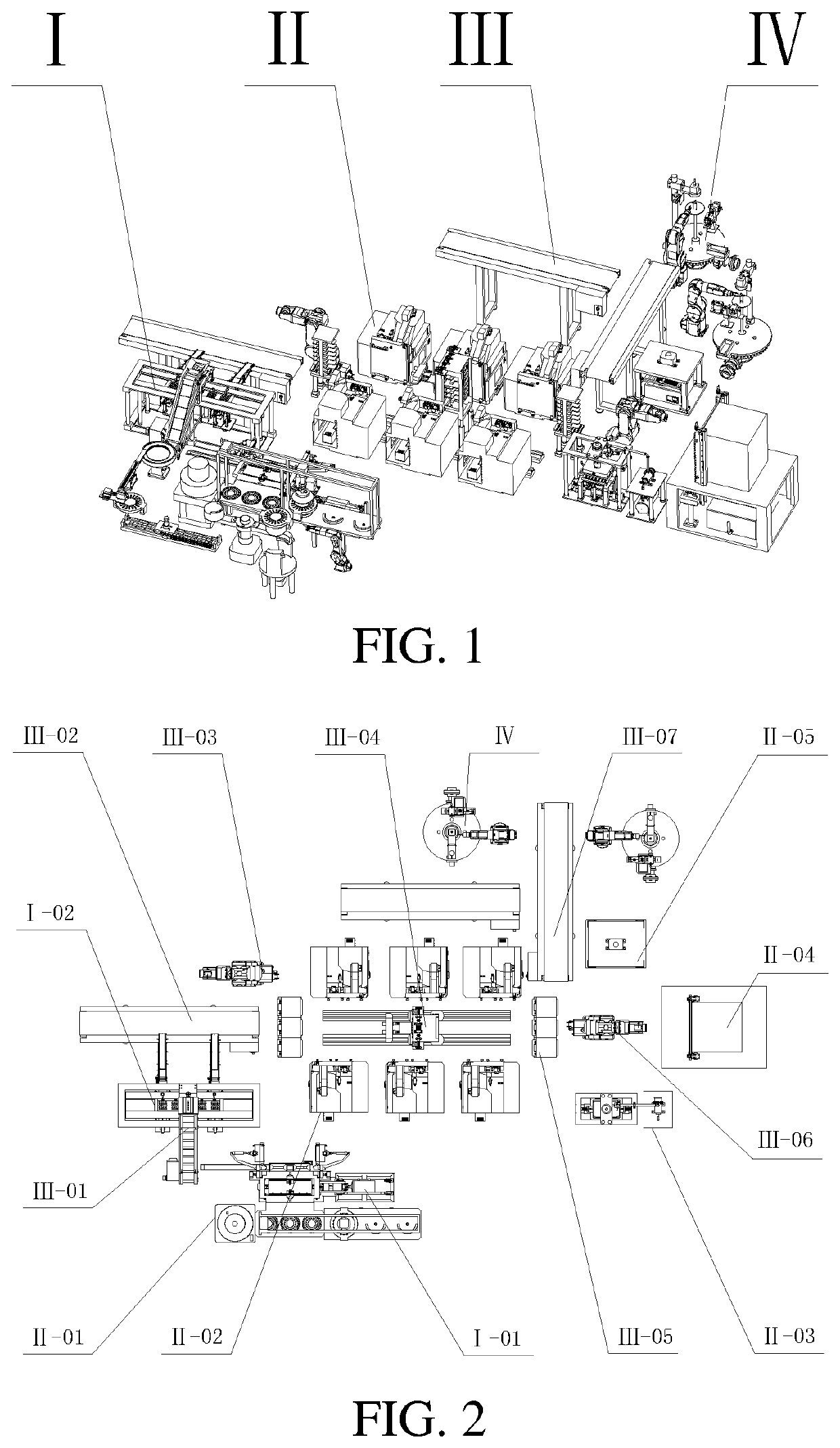
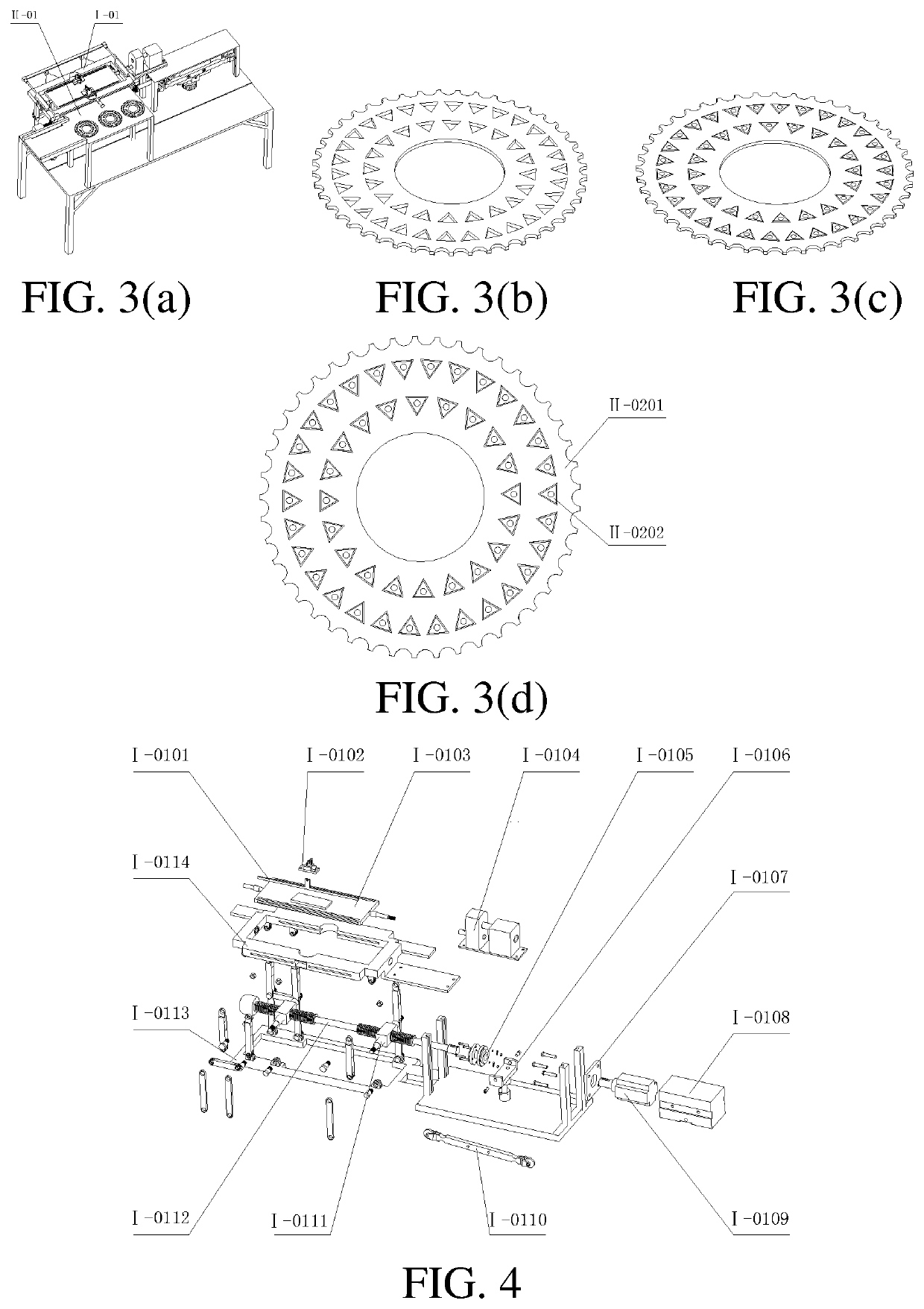
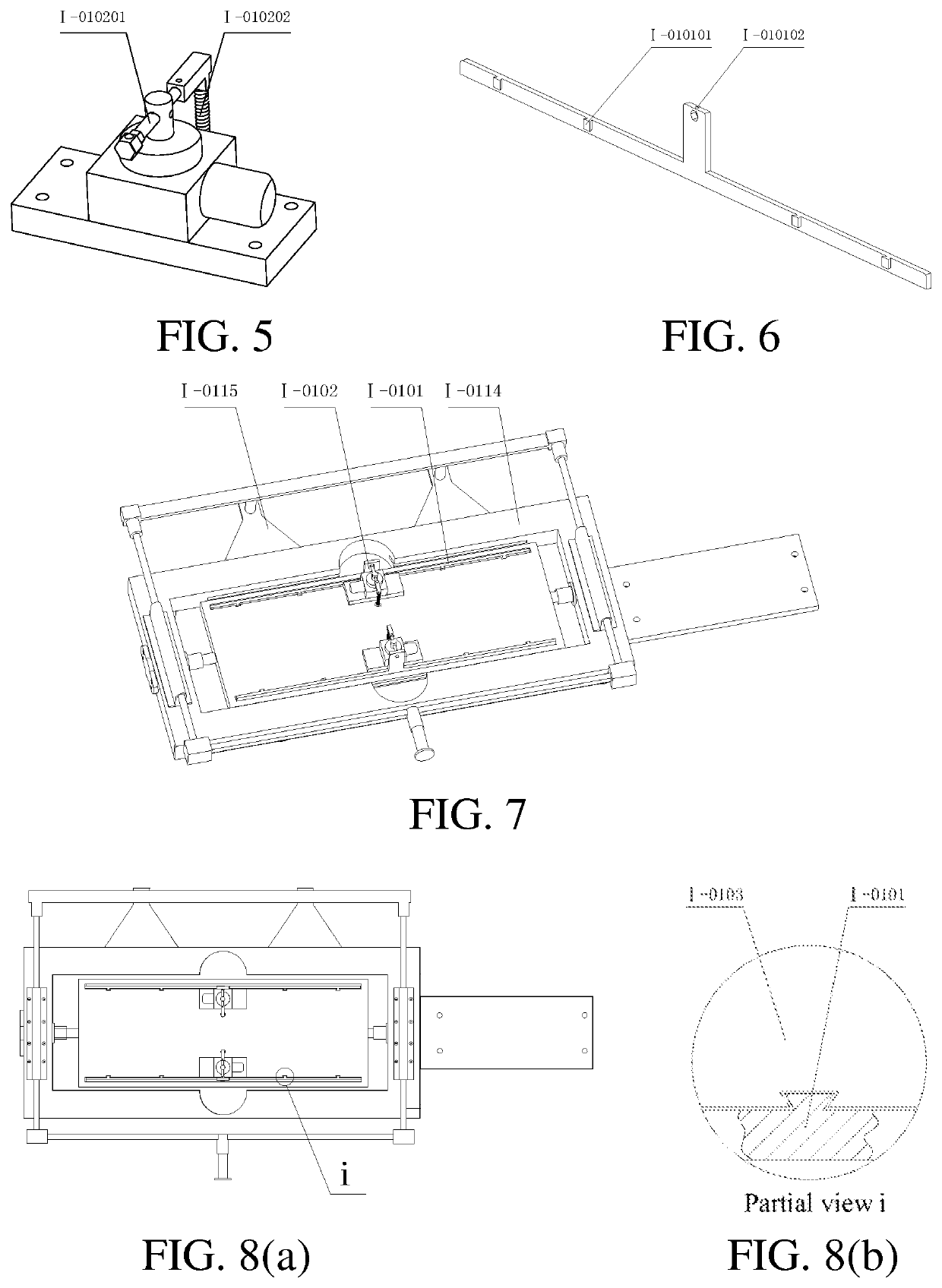
Carbide blade grinding forming processing production line
ActiveUS20220055171A1Simplifies blade conveying processHigh degree of automationEdge grinding machinesGrinding feed controlTool bitProduction line
The present disclosure provides a carbide blade grinding forming processing production line, relates to the field of blade processing in forming, and provides a production line for grinding forming processing of a carbide blade with inscribed circular holes, which has functions of blade grinding forming processing, blade cleaning and drying and detection of external dimension of a formed blade, and has an automatic loading and uninstalling function. In most processing course of the blade, the cutter head is taken as a carrier, and an overturning device is configured to overturn a whole cutter die box, such that integral end surface overturning of the cutter head in the cutter die box after single end surface grinding is realized, and blade filling processes in different processing links are reduced.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY +1
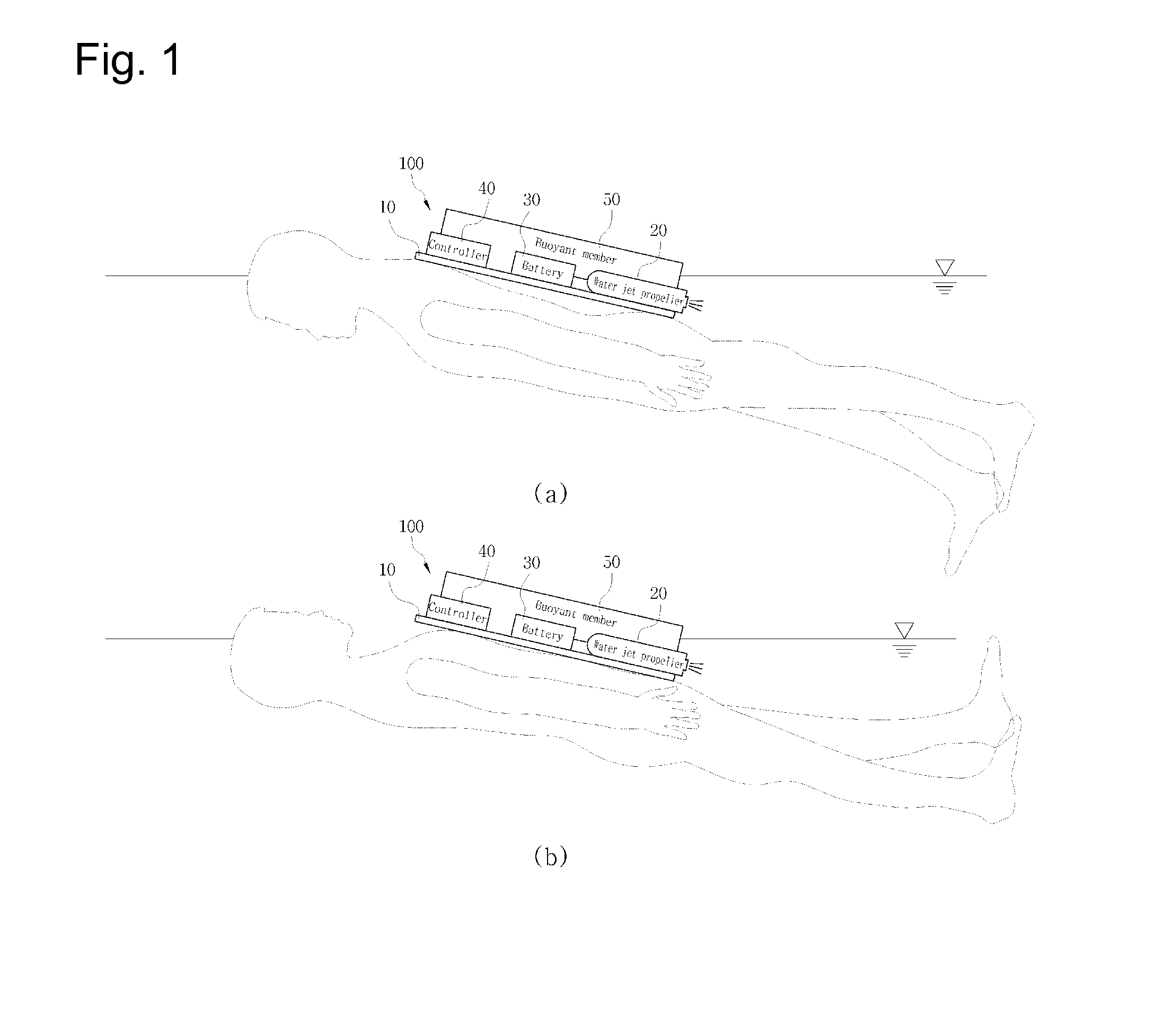
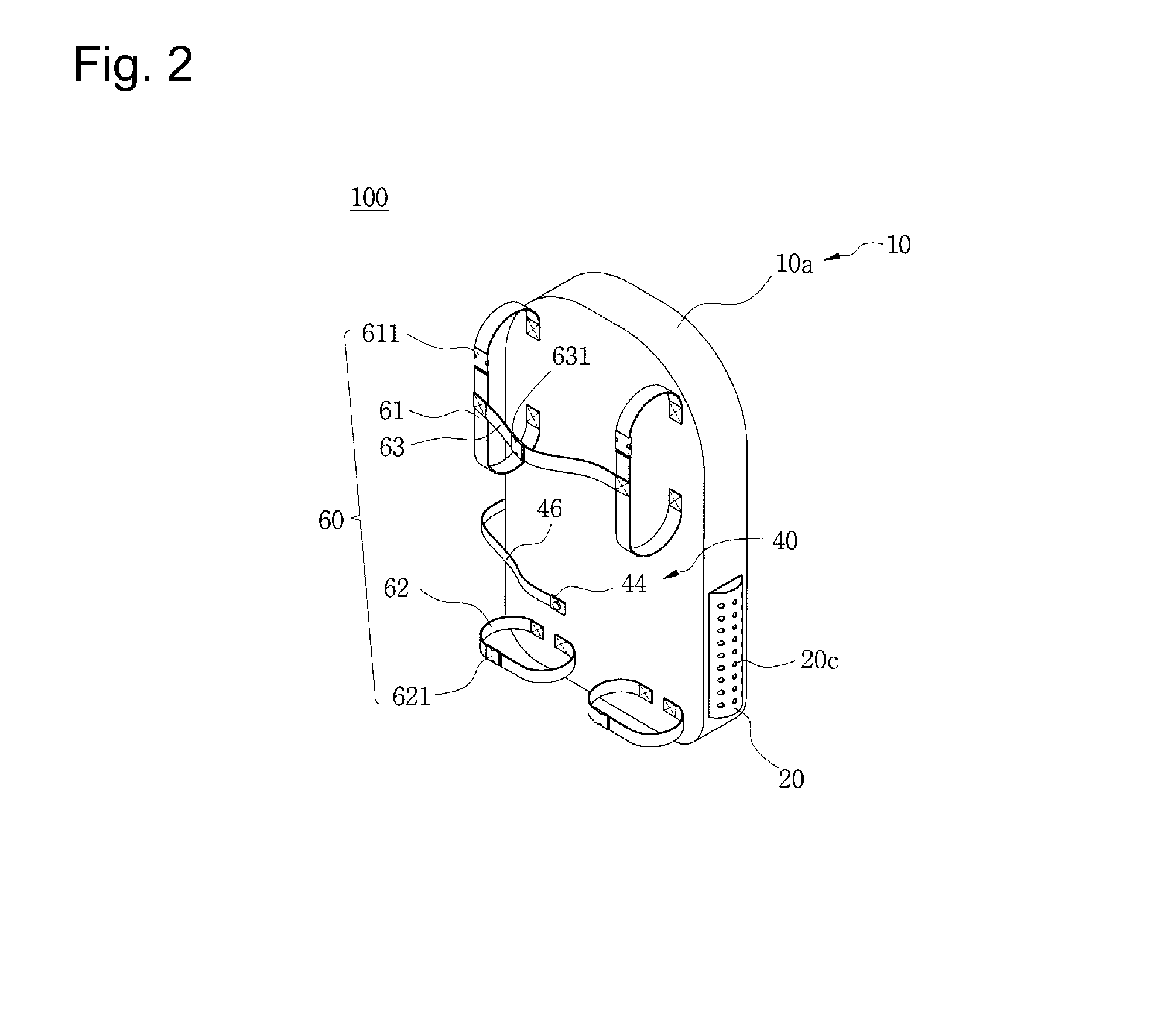
Swimming aid apparatus worn on the body
InactiveUS20140273672A1Simple configurationIncreased durabilitySwimming frameworkPropulsive elementsBiological bodyPropeller
The present invention relates to a swimming aid apparatus worn on the body. The swimming aid apparatus worn on the body according to the present invention is worn by the user to provide propulsive force so that the user can enjoy swimming. Also, a water jet propeller may be used and stably operated without breaking down or being damaged by underwater living organisms or foreign substances. The swimming aid apparatus worn on the body according to the present invention includes: a body frame worn on the user's body; a water jet propeller fixed to the body frame to spray water, thereby generating propulsive force; a battery connected to the water jet propeller to supply power; and a controller controlling the operation of the water jet propeller.
Owner:LEE SUNG JONG
Method of detecting failure or anomaly of sensor terminal
ActiveUS20170241958A1Cost of apparatus can be reducedReduce manpower costVibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEngineeringSeismic exploration
There is disclosed a method of detecting failures or anomalies of a large number of sensor terminals without using manpower or expensive equipment in the seismic exploration business. The method includes preparing a plurality of sensor terminals having sensors that detect vibrations from outside, the plurality of sensor terminals receiving the vibrations and outputting vibration reception signals, and comparing a first vibration reception signal output by a first sensor terminal with a second vibration reception signal output by a second sensor terminal, thereby detecting if one of the first sensor and the second sensor is failed or anomalous.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Register mark dtection apparatus
InactiveUS20100165343A1Cost of apparatus can be reducedLow costMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionLight beamOptoelectronics
A register mark detecting apparatus detects a transparent register mark printed on a conveyed transparent web. The register mark detecting apparatus includes a light source, a parallel light flux irradiation optical system, a collective optical system, a knife-edge, and a light receiving element. The parallel light flux irradiation optical system converts a light flux from the light source into a parallel light flux to irradiate a transparent web with the parallel light flux. The collective optical system collects the light flux transmitted through the transparent web. The knife-edge is disposed near a back focus of the collective optical system. The knife-edge interrupts the light flux going straight in the transparent web and causes only the light flux refracted by being transmitted through the transparent register mark to pass by. The light receiving element receives the light flux transmitted through the knife-edge.
Owner:TAIYO ELECTRIC IND
Auto feed, copy and print apparatus for information storage disks and method of the same
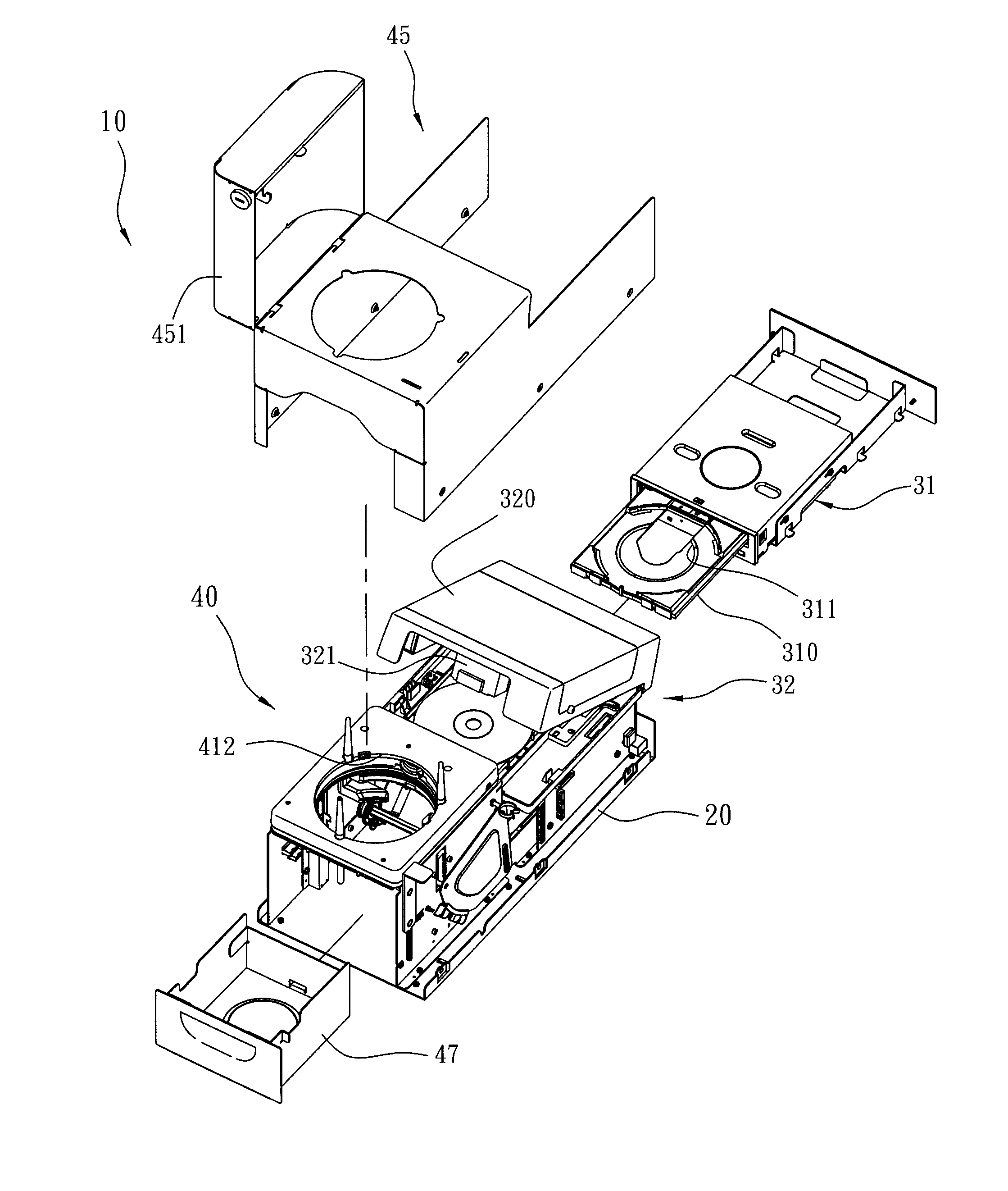
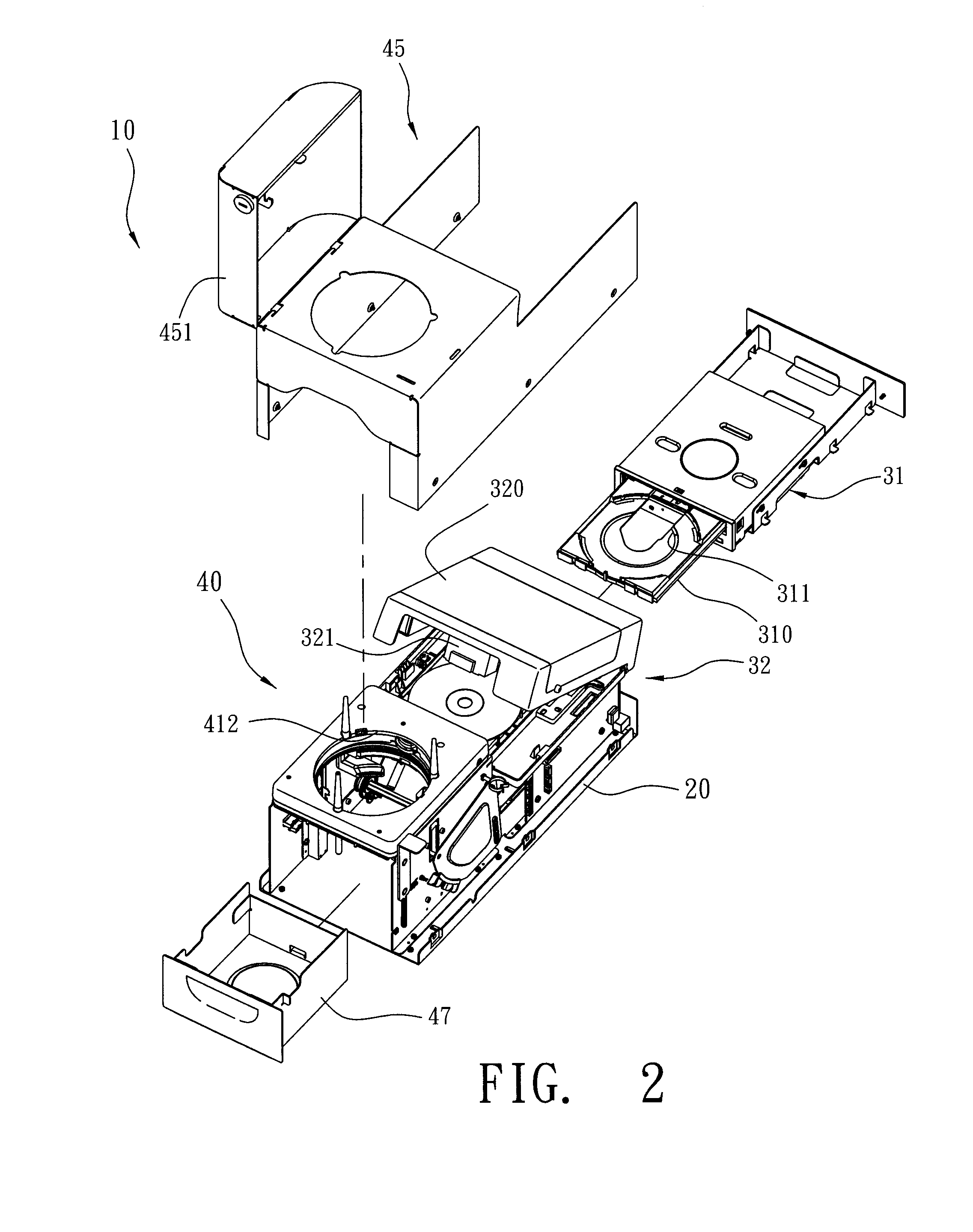
InactiveUS20080123476A1Shorten the timeCost of apparatus can be reducedRecord information storageOptical recording/reproducingComputer scienceInformation storage
An auto feed, copy and print apparatus for information storage disks and a method of the same are disclosed. The apparatus includes a frame, a read / write and print device and a feeding device. The read / write and print device and the feeding device are mounted on the frame. The feeding apparatus feeds a disk once by gravity onto a tray of the read / write and print device. The tray retracts so as to perform copy and print disk cover operations. The Method includes steps of providing disks, using a feeding device to support the disks and feeds a single disk once by gravity, receiving the disk on a tray, retracting the tray with the disk into a read / write and print device, and using the read / write and print apparatus to write data into the disk and print the disk's cover.
Owner:LIU MING HSUN
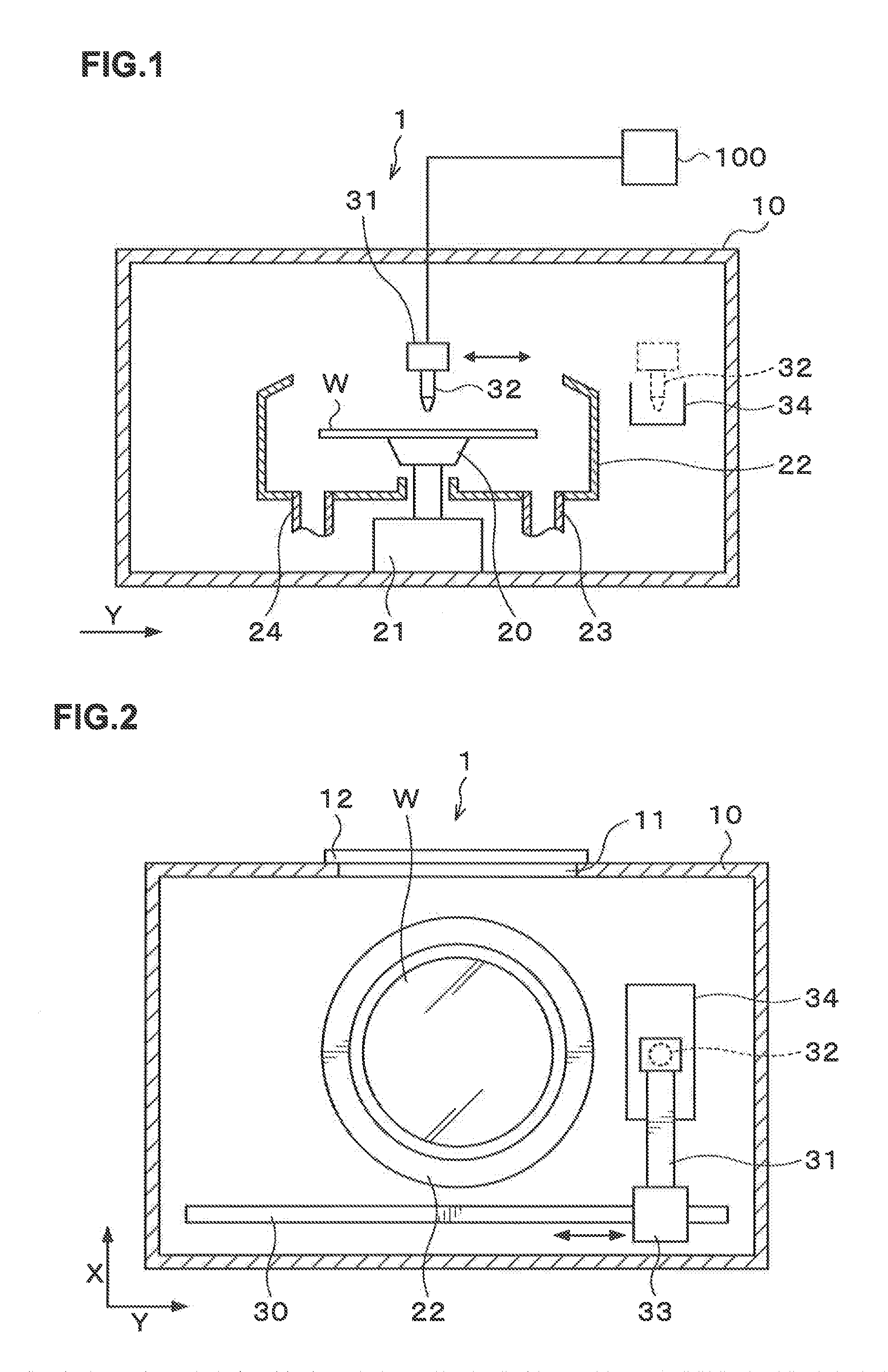
Treatment solution supply method, non-transitory computer storage medium and treatment solution supply apparatus
InactiveUS20130112628A1Reduce defectsSimple configurationSemi-permeable membranesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesForeign matterEngineering
A treatment solution supply method of the present invention is for supplying a treatment solution from a treatment solution supply source to a treatment solution supply unit supplying the treatment solution to a substrate, wherein a supply pipe connected to the treatment solution supply unit is provided with a filter collecting foreign matter in the treatment solution and not allowing the foreign matter to be released therefrom, and the treatment solution flowing in the supply pipe is caused to pass through the filter in a reciprocation manner at least one time and then supplied to the treatment solution supply unit, so that the foreign matter in the treatment solution can be sufficiently removed and the collected foreign matter never mixes again into the treatment solution.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
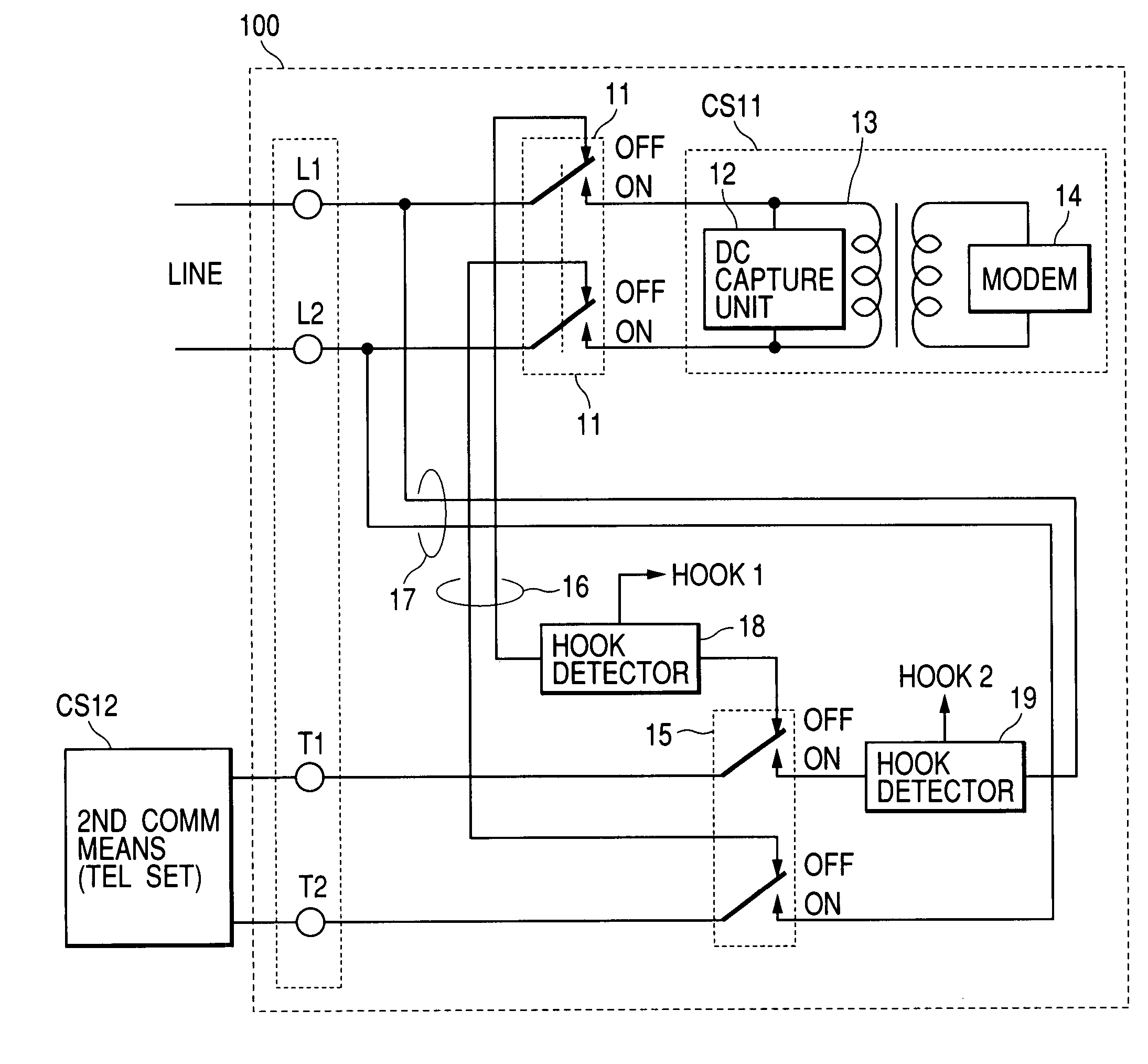
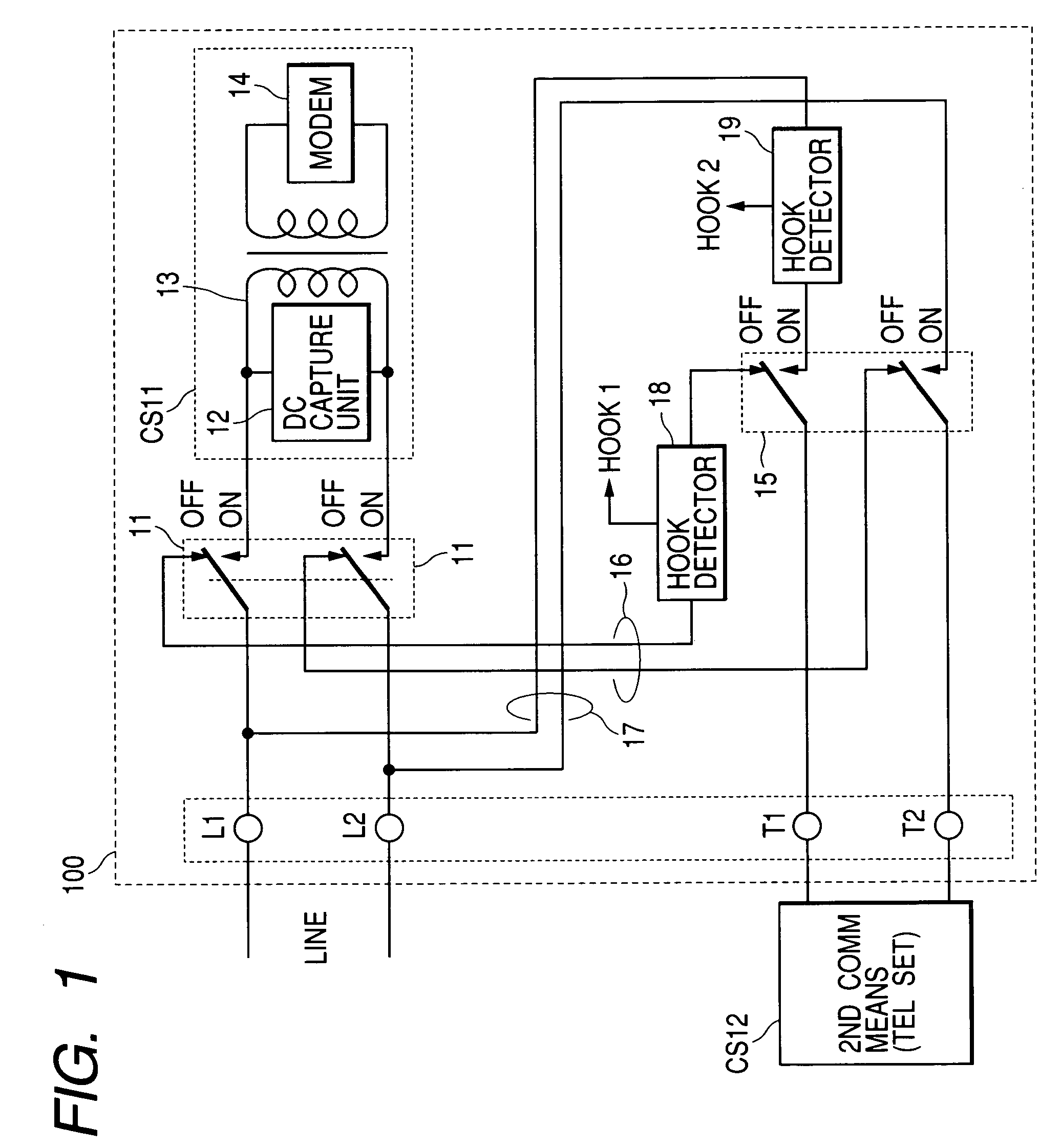
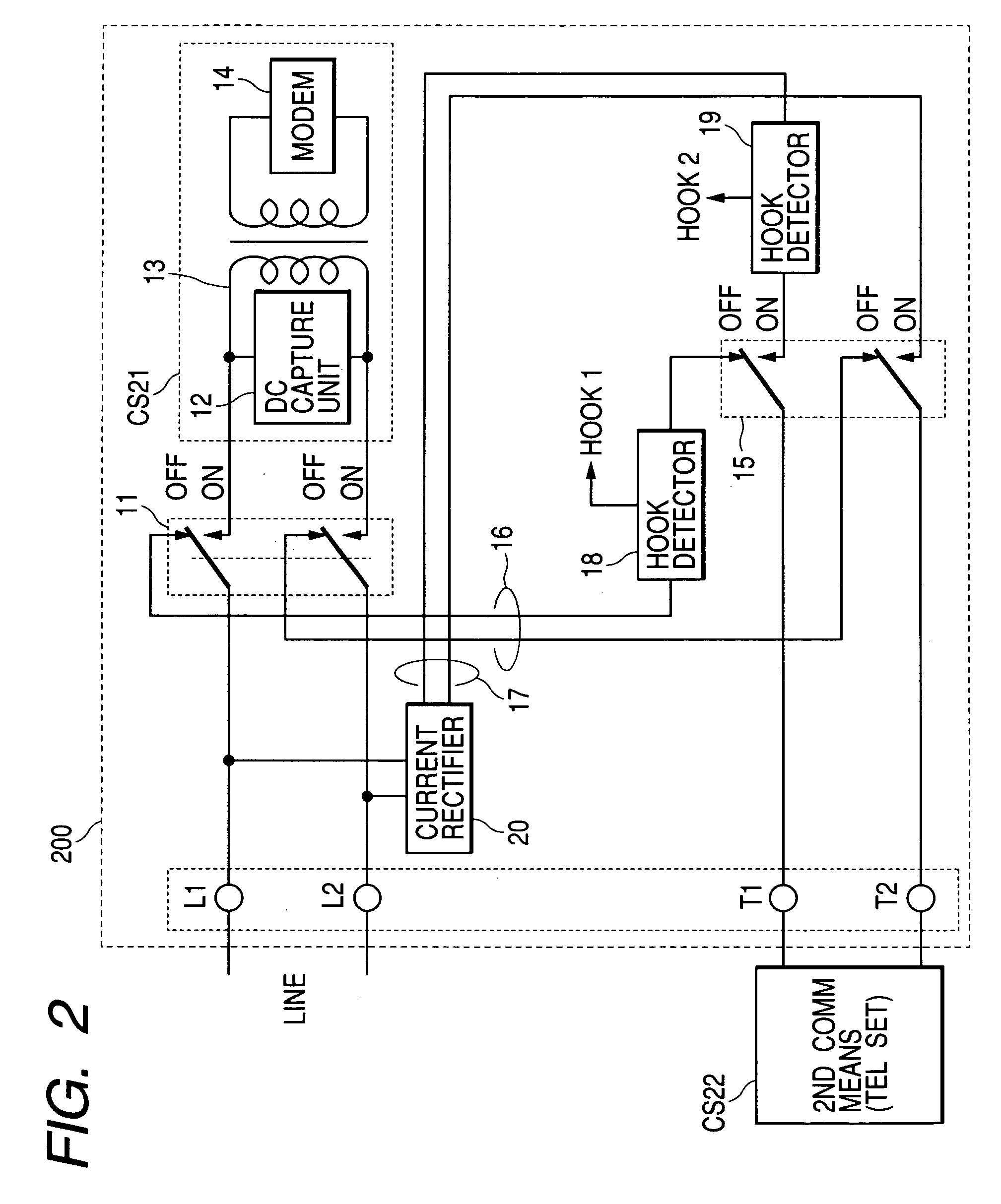
Communication apparatus
InactiveUS7092499B2Low costSave spacePictoral communicationLine monitoring circuitsCommunication deviceTelecommunications equipment
Disclosed is a communication apparatus connected to an analog public line, which can be actualized at low costs and can save its space. This communication apparatus includes a first communication means connected to a telephone line, for performing communications, and a connecting means for connecting a second communication means connected to the telephone line via the first communication means and thus performing communications. In this communication apparatus, the first communication means has a first switch means for connecting the telephone line to the first communication means or the second communication means, a first route means for connecting the second communication means to the telephone line via the first switch means, a second route means for connecting the second communication means directly to the telephone line, a second switch means for connecting the second communication means to the first route means or the second route means, a first hook detecting means connected to the first route means, and a second hook detecting means connected between the telephone line on the second route means and the second switch means.
Owner:CANON KK
Polishing apparatus, polishing head and polishing method
InactiveUS20060057942A1Improve flatnessInhibit productionPolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesRetaining ringCost cutting
A polishing apparatus comprises a polishing plate (24), an abrasive cloth (25) attached to the surface of the polishing plate (24), a chuck (19) for holding and pressing one surface of a wafer (39) against the abrasive cloth (25), and a circular retaining ring (23) concentrically arranged on the periphery of the chuck (19). The retaining ring (23) is rotatable and vertically movable with respect to the chuck (19), and is pressed against the abrasive cloth (25) during the lapping step. The retaining ring (23) is lifted upward during the final polishing step, thereby preventing lapping grains from being brought into the final polishing stage. Accordingly, lapping and final polishing can be successively conducted using the same polishing head. With this structure, cost cutting of the apparatus can be realized, since lapping and final polishing are successively conducted using the same polishing head without bringing the lapping grains used for lapping into the final polishing stage.
Owner:SUMCO TECHXIV
Electrophoretic chip and a method of electrophoresis
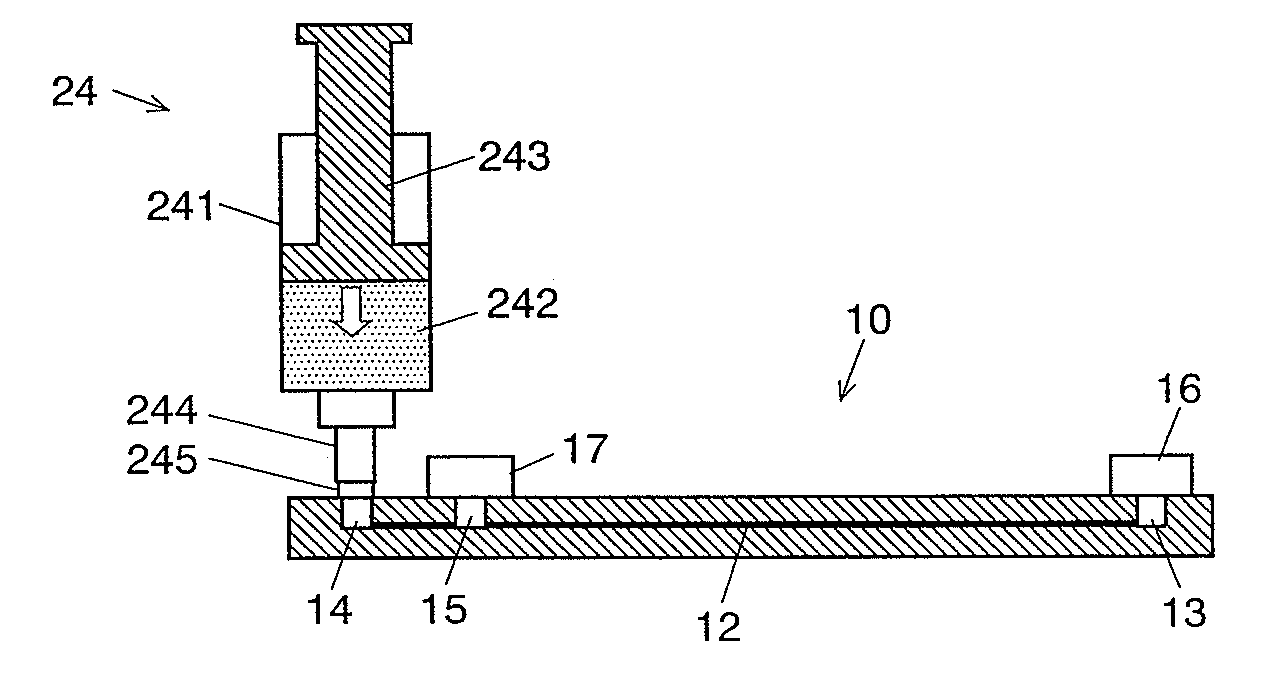
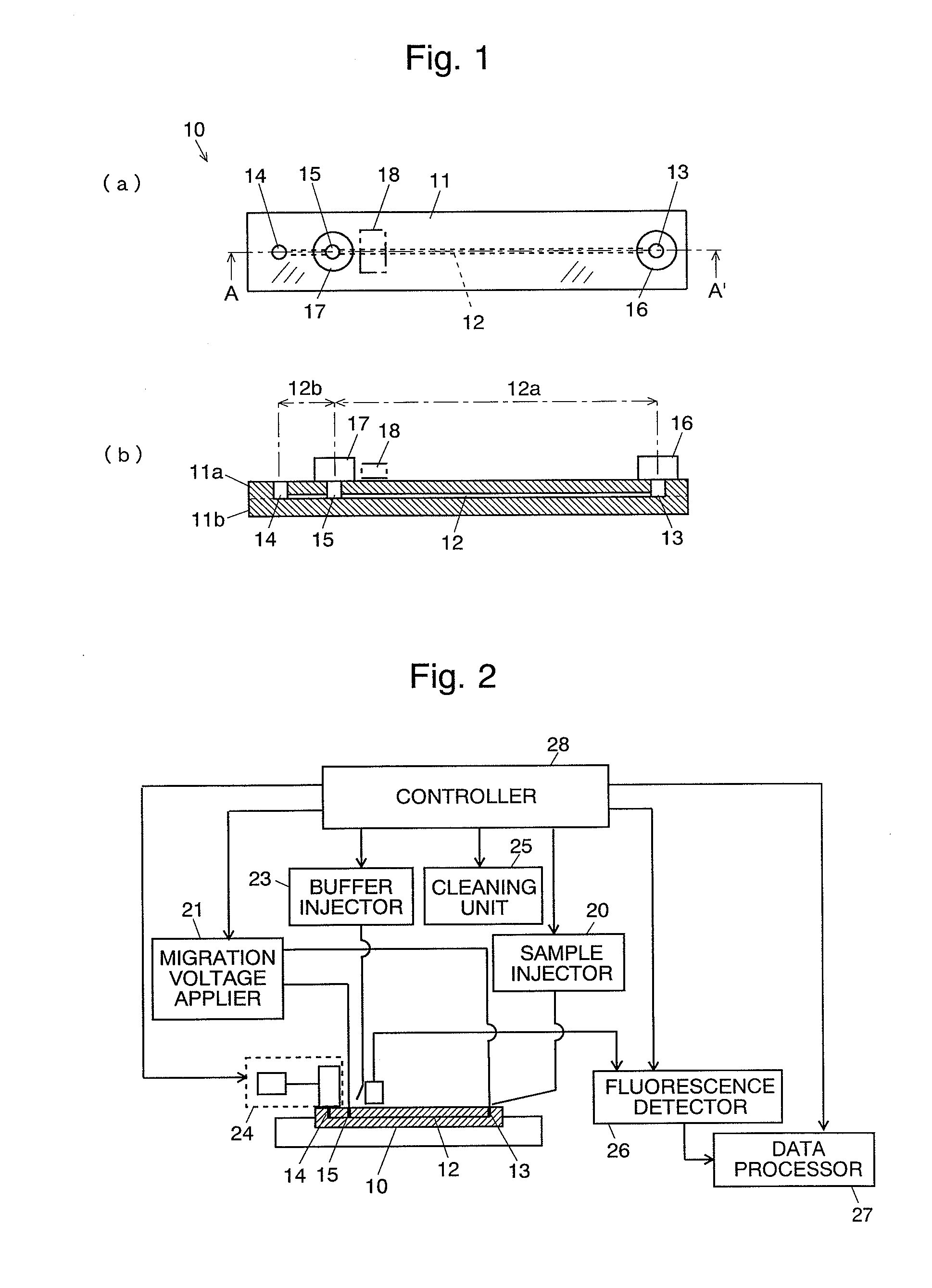
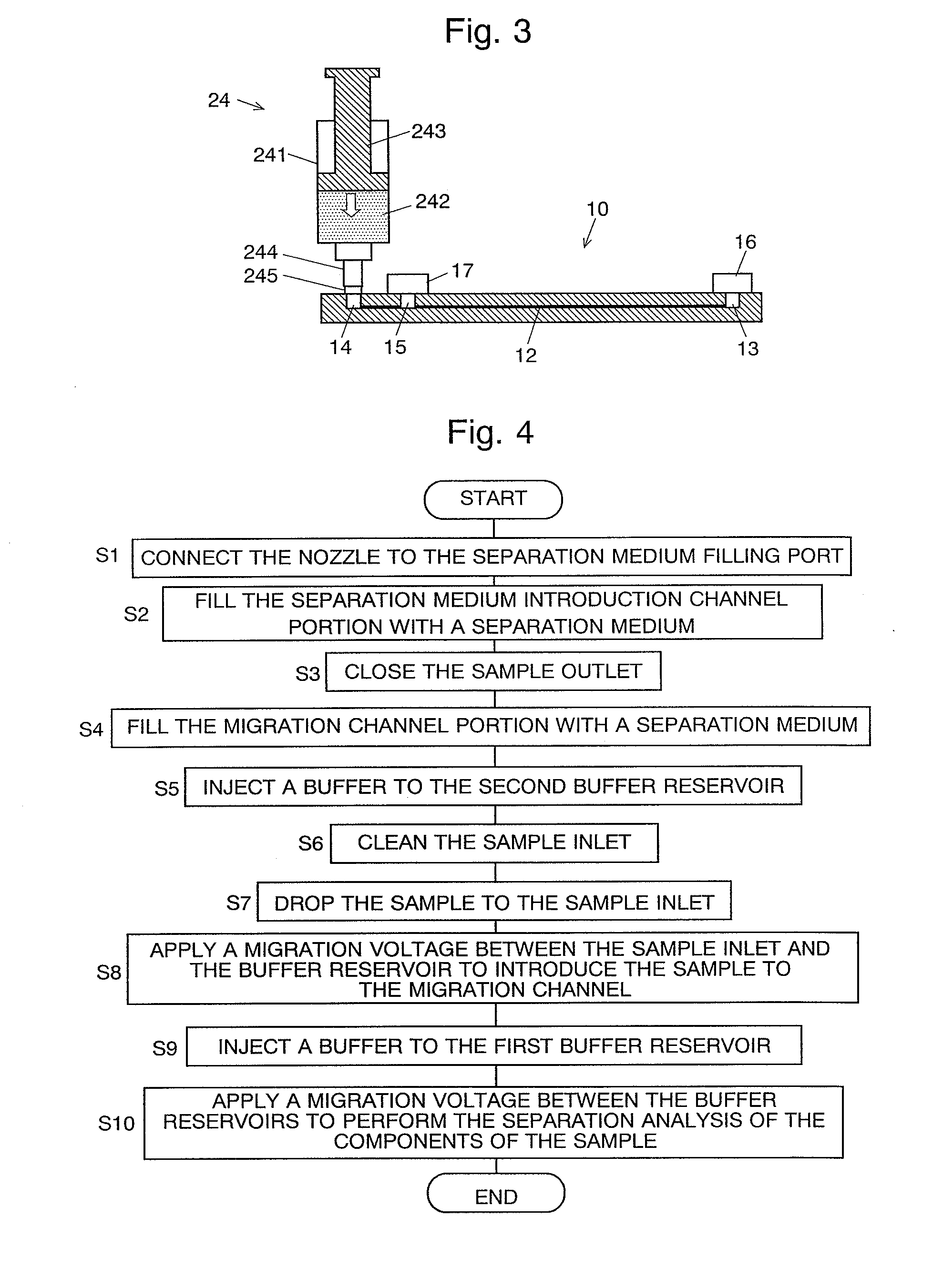
ActiveUS20100116661A1Low costHigh positioning accuracySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectrophoresisEngineering
A channel (12) is formed inside a transparent substrate (11), and the two ends are respectively connected to a sample inlet (13) and a separation medium filling port (14) both open to outside, and a sample outlet (15) which is open to outside is provided on the channel (12). The portion between the sample inlet (13) and the sample outlet (15) is a separation channel portion (12a), and the portion between the sample outlet (15) and the separation medium filling port (14) is a separation medium introduction channel portion (12b). A separation medium supplier is connected to the separation medium filling port (14) and the separation medium introduction channel portion (12b) is filled with a separation medium. Then a sample is dropped to the sample inlet (13), with the sample medium supplier still connected, to introduce the sample to the separation channel portion (12a). And then, buffer liquid is poured in buffer reservoirs (16) and (17) and a migration voltage is applied to perform a migration analysis. Since an analysis can be repeatedly performed with the sample medium supplier kept connected, it is not necessary to disconnect the supplier from the electrophoretic chip each time a migration is performed.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Method and system for fabricating a semiconductor device
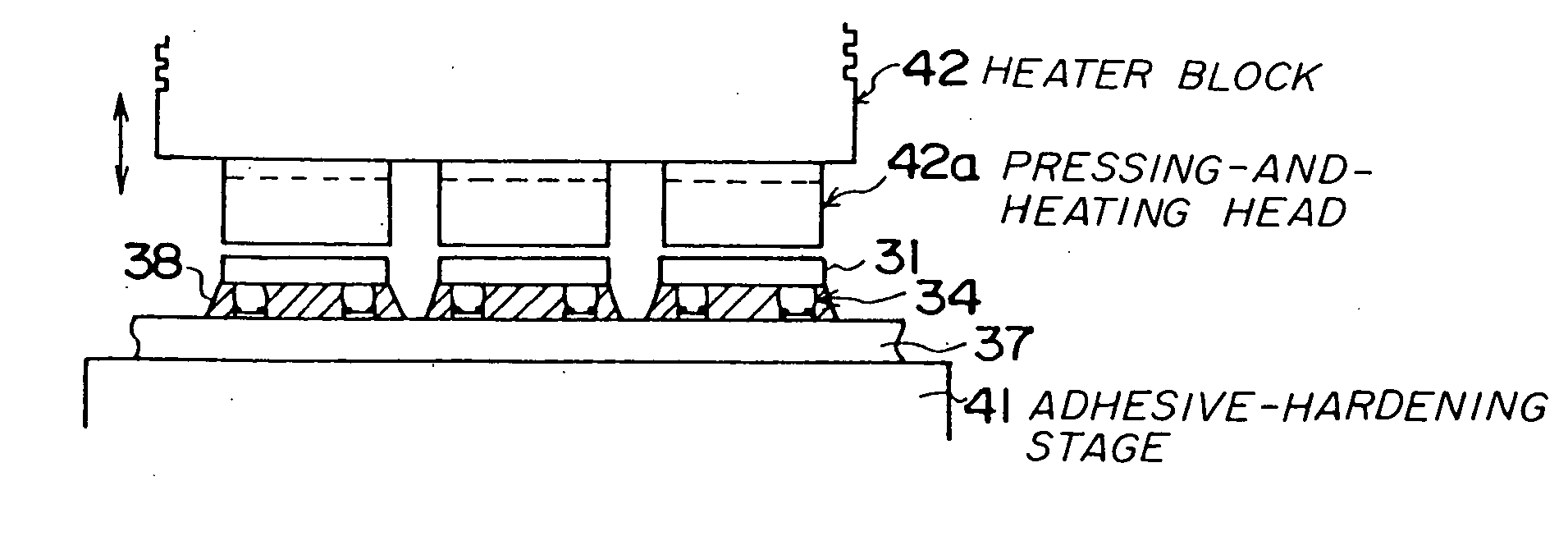
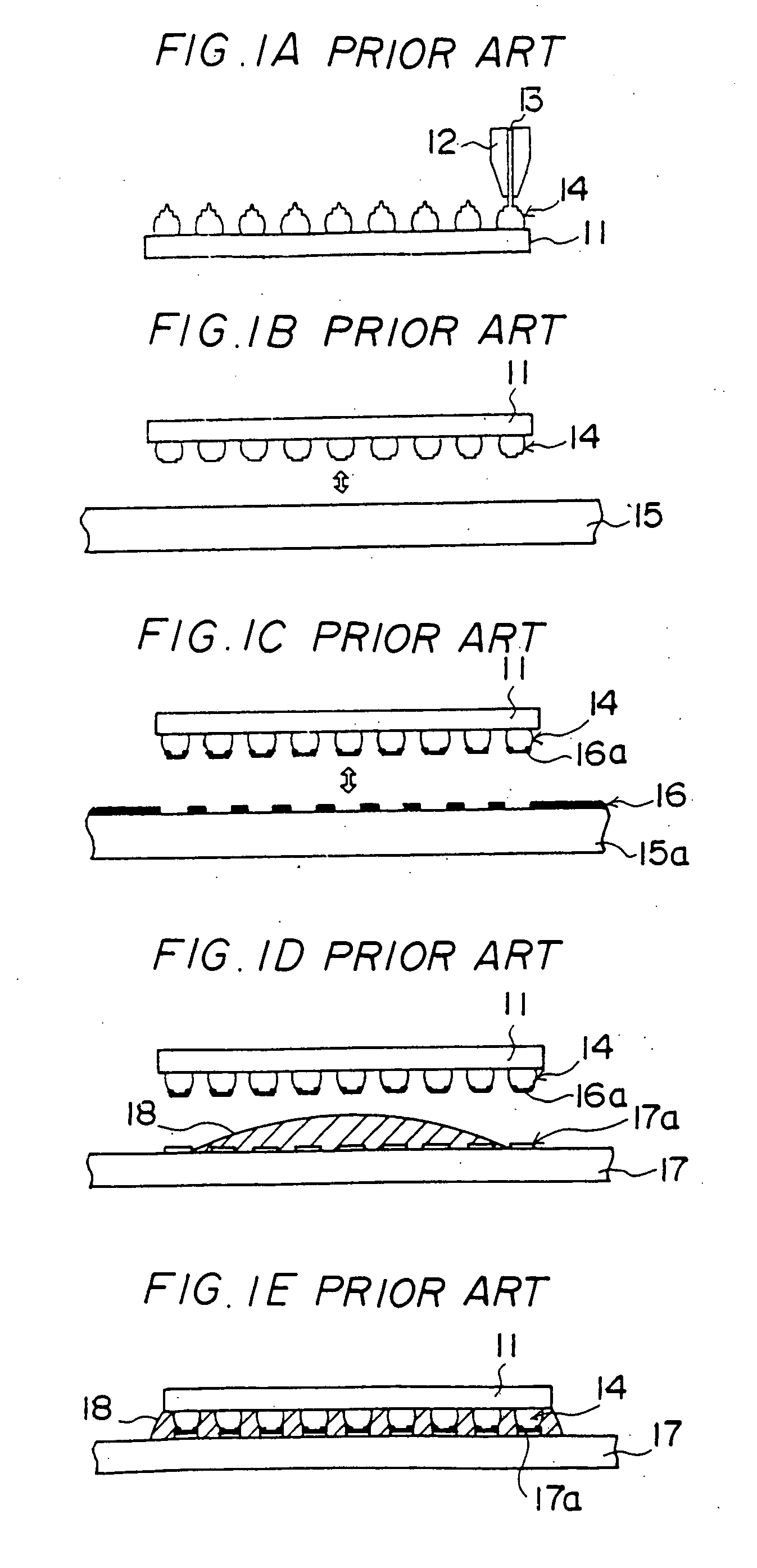
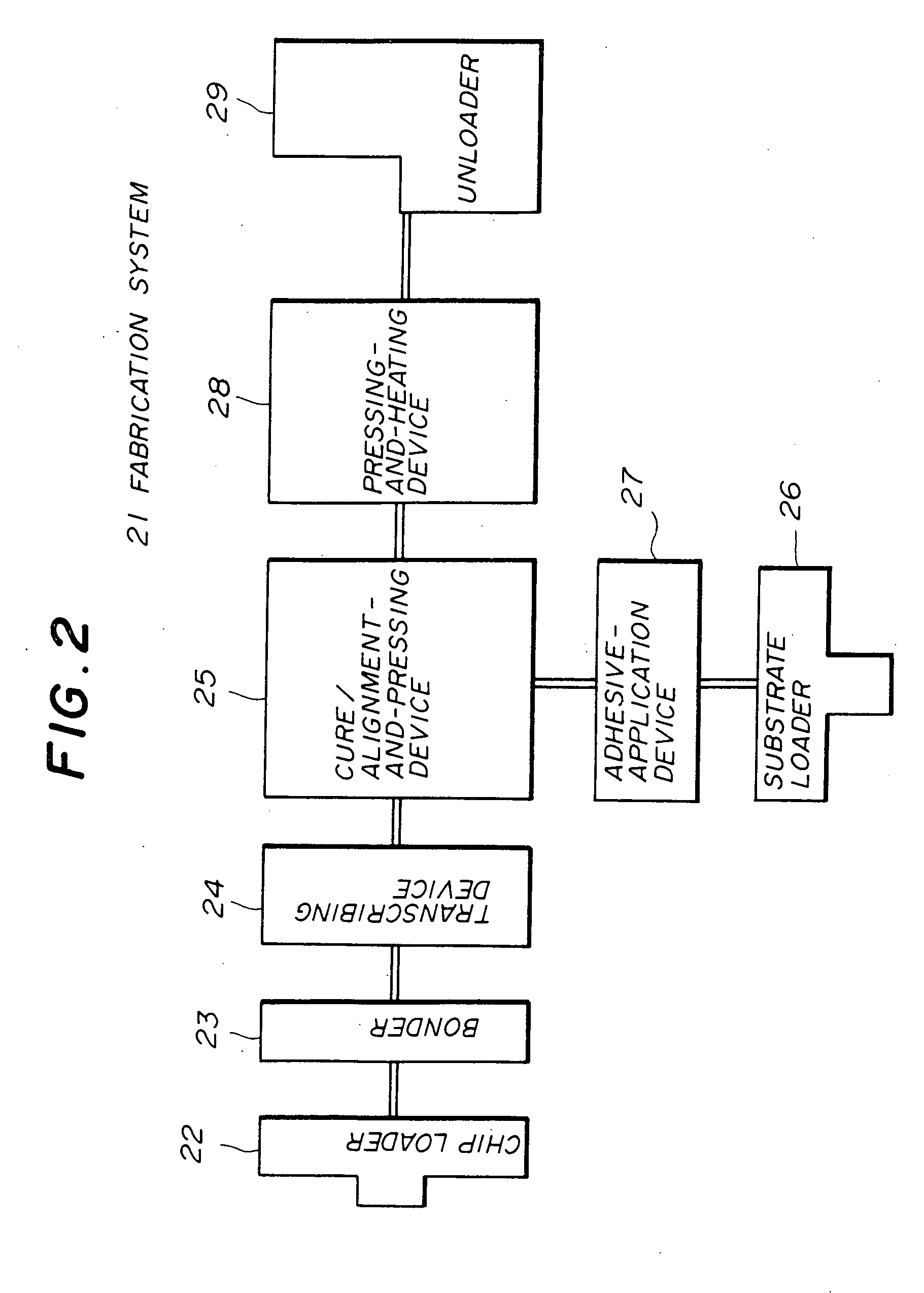
InactiveUS20070261233A1Perfect flip-chip connectionCost of apparatus can be reducedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAdhesiveDevice material
A fabrication method of a semiconductor device is disclosed. The method includes the following steps. First, a given number of projection electrodes are formed on each of a given number of semiconductor chips, and a thermosetting insulating adhesive is applied to areas of mounting parts where the semiconductor chips are to be mounted on a substrate. Second, the thermosetting insulating adhesive on the substrate is heated with a half-thermosetting temperature. Third, the semiconductor chips are aligned to the mounting parts of the substrate and a first fixing of the semiconductor chips is performed with a first pressure. Fourth, the substrate, on which the semiconductor chips are fixed, is heated with a thermosetting temperature of the thermosetting insulating adhesive, and a second fixing of the semiconductor chips is performed with a second pressure.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
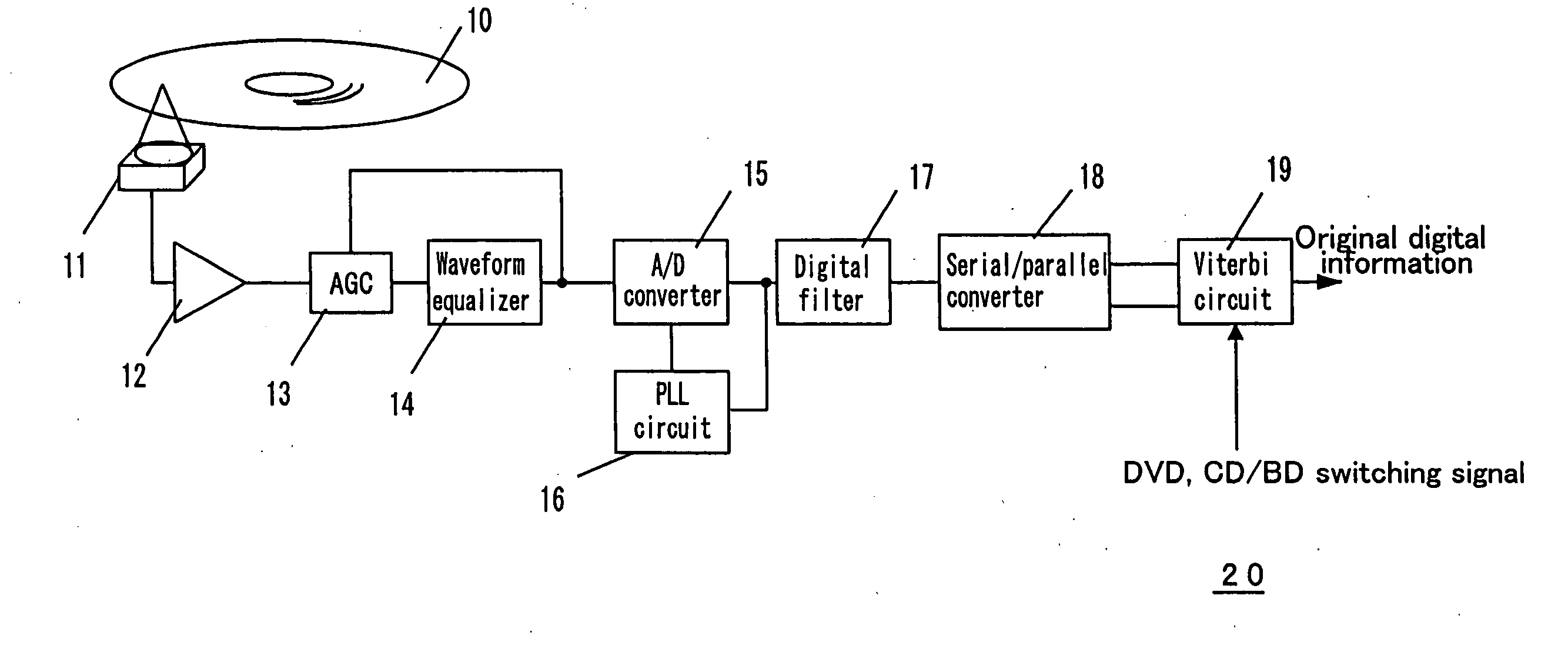
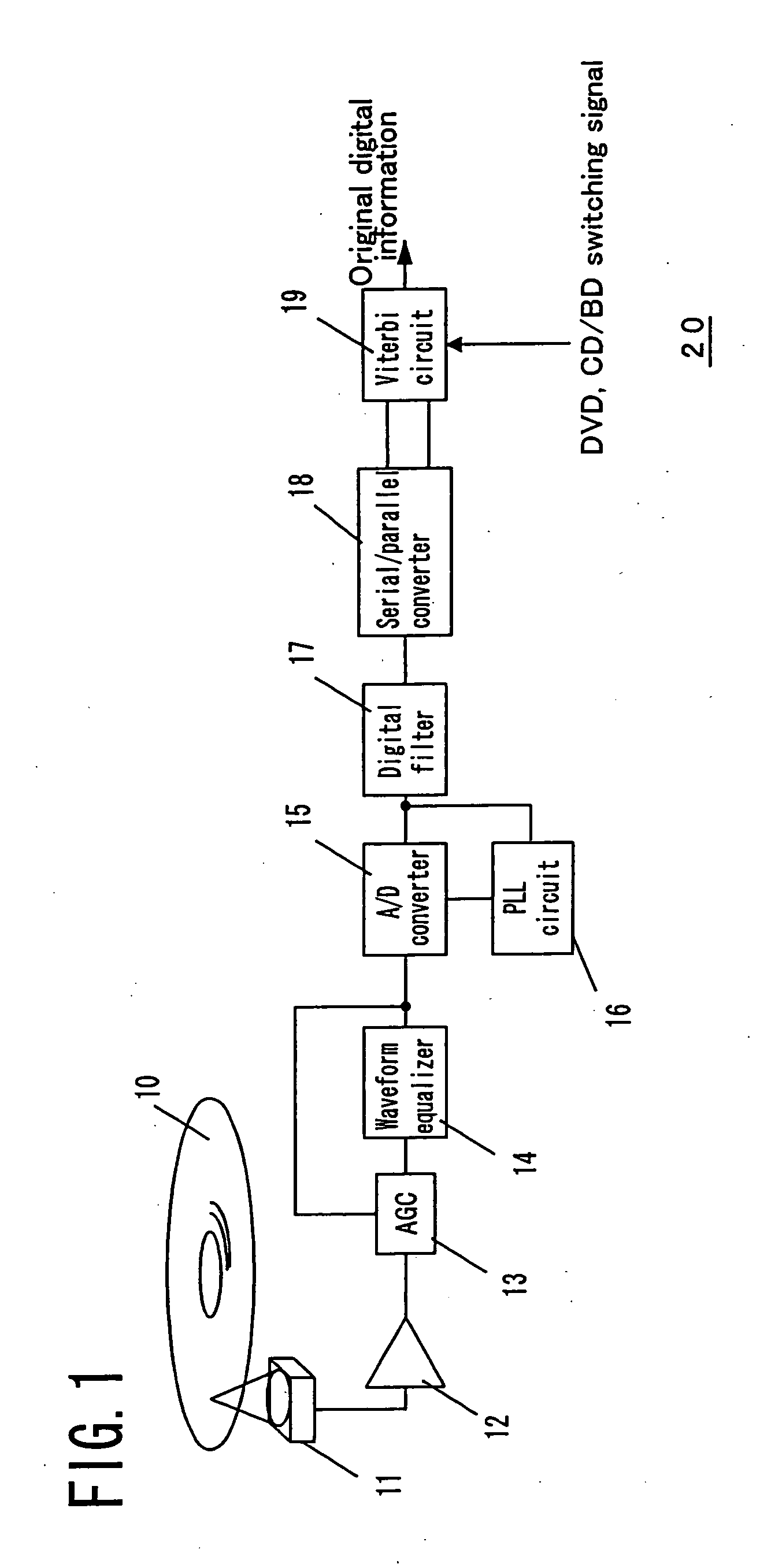
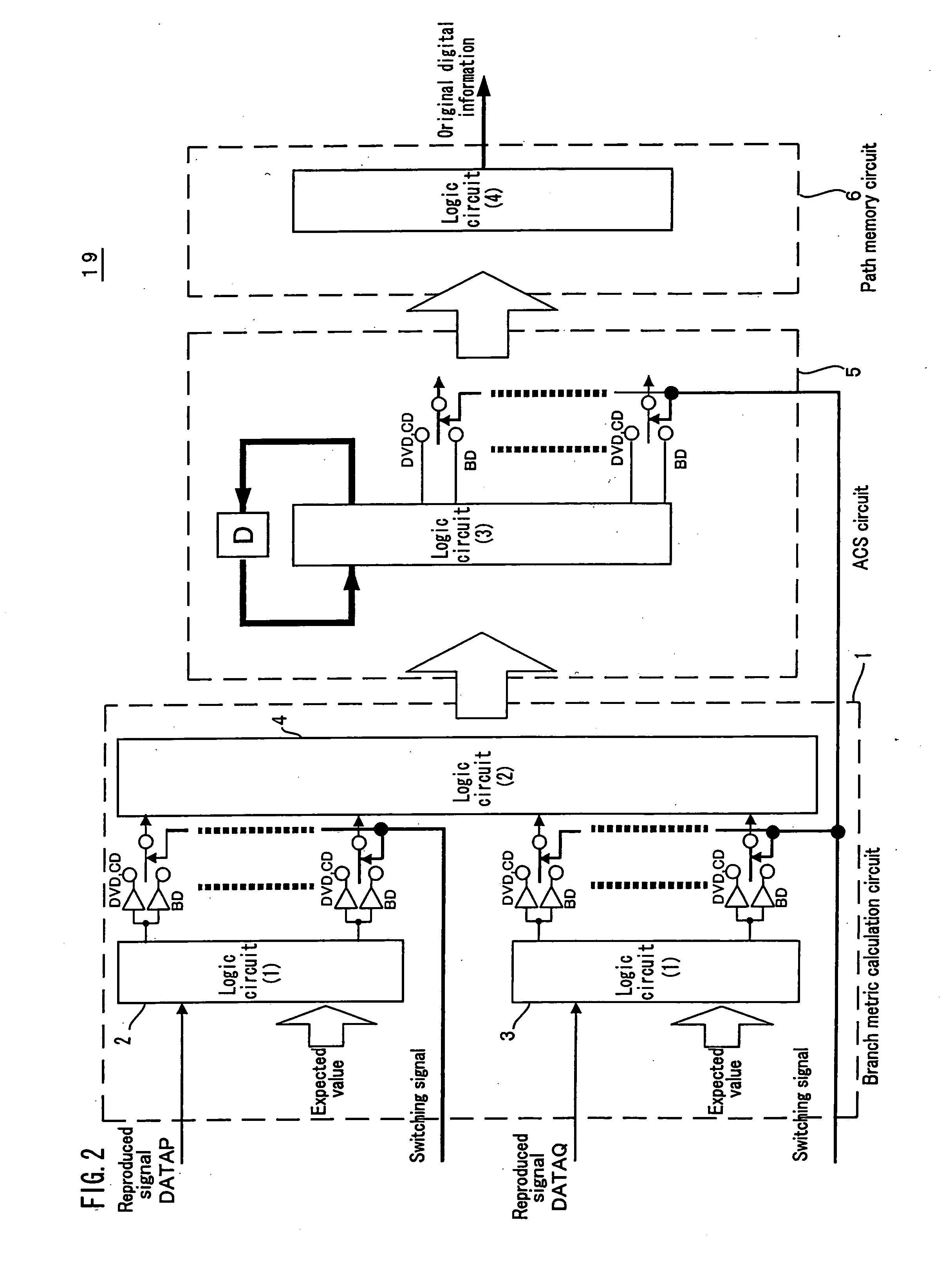
Maximum likelihood encoding apparatus, maximum likelihood encoding method, program and reproduction apparatus
InactiveUS20050138534A1Improve transfer rateReduce circuit sizeData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesArtificial intelligenceRecording media
A maximum likelihood encoding apparatus is provided, which is constructed to be compatible with a plurality of signals reproduced from a plurality of recording media having a plurality of types. The apparatus comprises a path metric value generation section for generating a plurality of path metric values corresponding to a recording medium having one of the plurality of types based on a type signal indicating the one of the plurality of types, and a path memory section for detecting digital information from a signal reproduced from the recording medium having the one of the plurality of types based on the plurality of path metric values.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Electric device and printing apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20140002517A1Cost of apparatus can be reducedSimple configurationVisual presentationOther printing apparatusKey pressingElectrical devices
An embodiment of this invention relates to an electric device capable of controlling a plurality of elements with an inexpensive, simple configuration, and a printing apparatus using the same. In this embodiment, an operation unit of the printing apparatus switches the states of a plurality of general purpose input / output ports between low-level signal output, high-level signal output, and input high impedance for each time set in a timer by an MPU. This allows LED light emission control and switch key press detection. Also, output ports used for LED light emission control, and input ports used for key press detection are shared using general purpose input / output ports to realize LED light emission control and switch key press detection with a configuration simpler than the conventional configuration.
Owner:CANON KK
Hydrogen recovery method
ActiveUS20180318749A1Reduce operating costsCost of apparatus can be reducedProductsGas treatmentRecovery methodHydrogen
Provided is a hydrogen recovery method such that highly concentrated hydrogen gas can be obtained efficiently by adsorbing and removing hydrocarbon gas such as carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and methane, using a relatively low pressure, from pyrolysis gas obtained by heat treating biomass. The present invention is the method for recovering hydrogen from pyrolysis gas obtained by heat treating biomass, characterized by including: a first purifying step of adsorbing and removing gas that mainly includes carbon dioxide under pressure from the pyrolysis gas to purify the pyrolysis gas; and a second purifying step of further adsorbing and removing gas that includes carbon dioxide under pressure from purified gas obtained by the first purifying step at a pressure lower than the pressure in the first purifying step to purify the purified gas in order to recover hydrogen from the purified gas.
Owner:JBEC CO LTD +1
Plasma surface treating method and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20050121305A1Cost of apparatus can be reducedReduce power consumptionElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPulse voltageCorona discharge
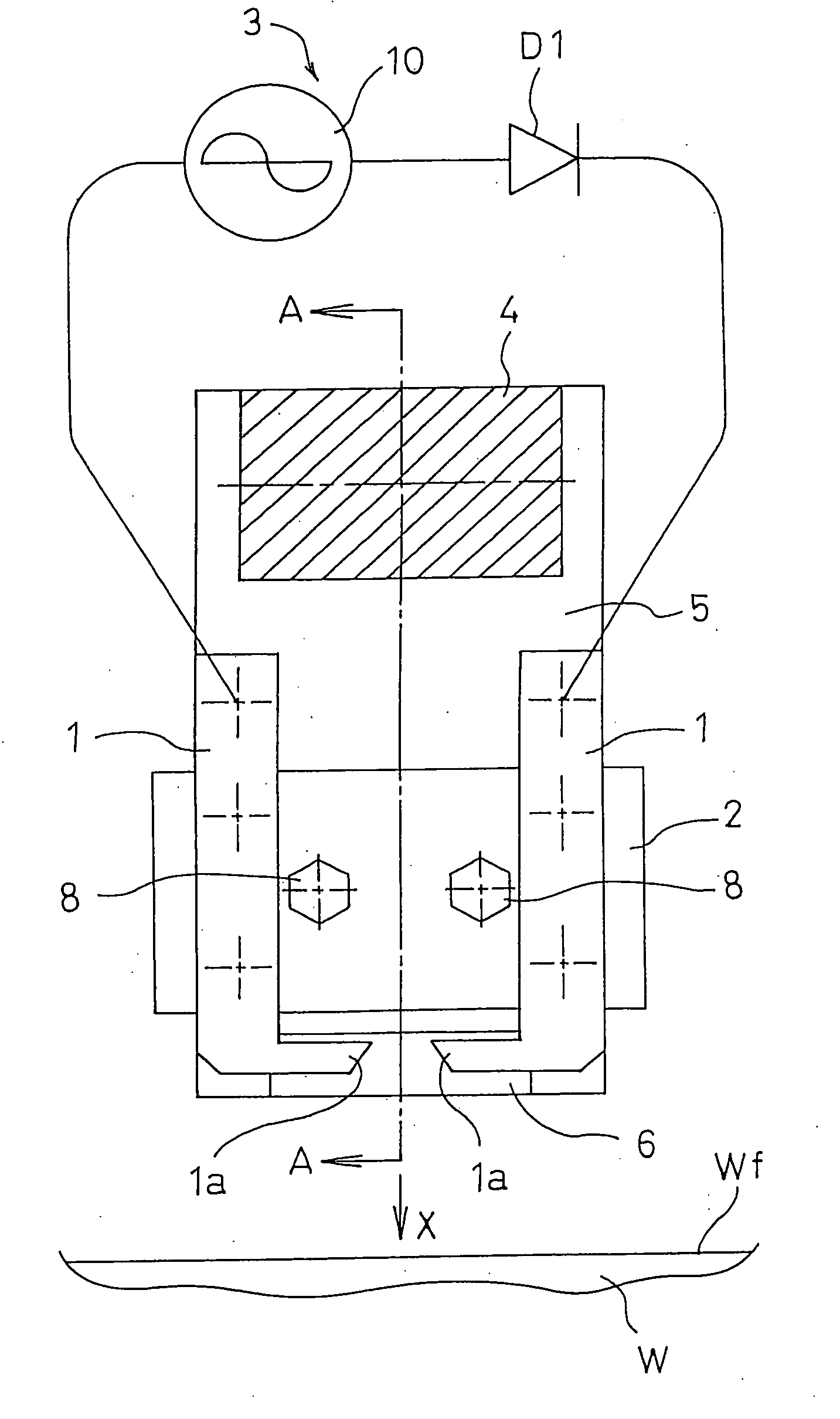
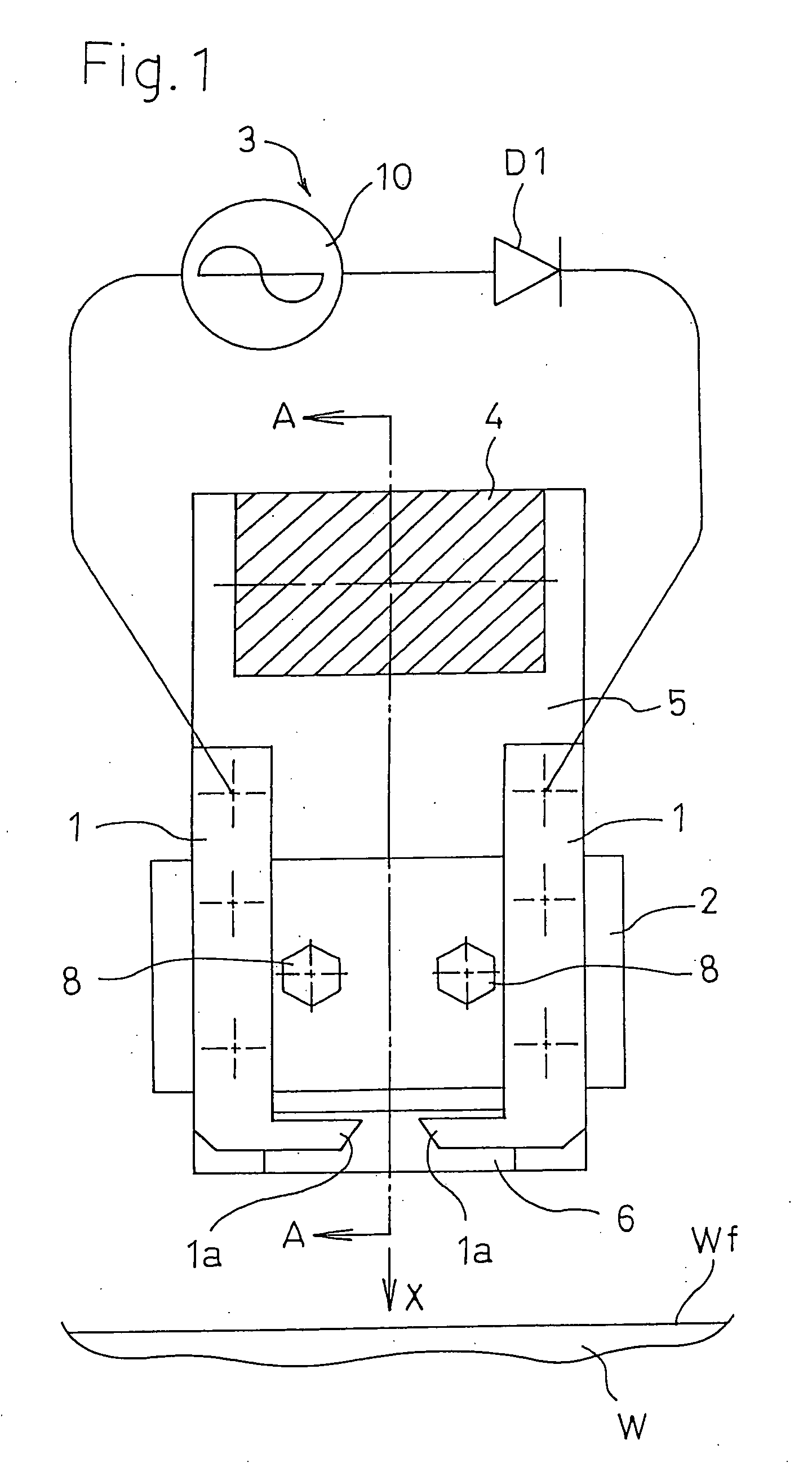
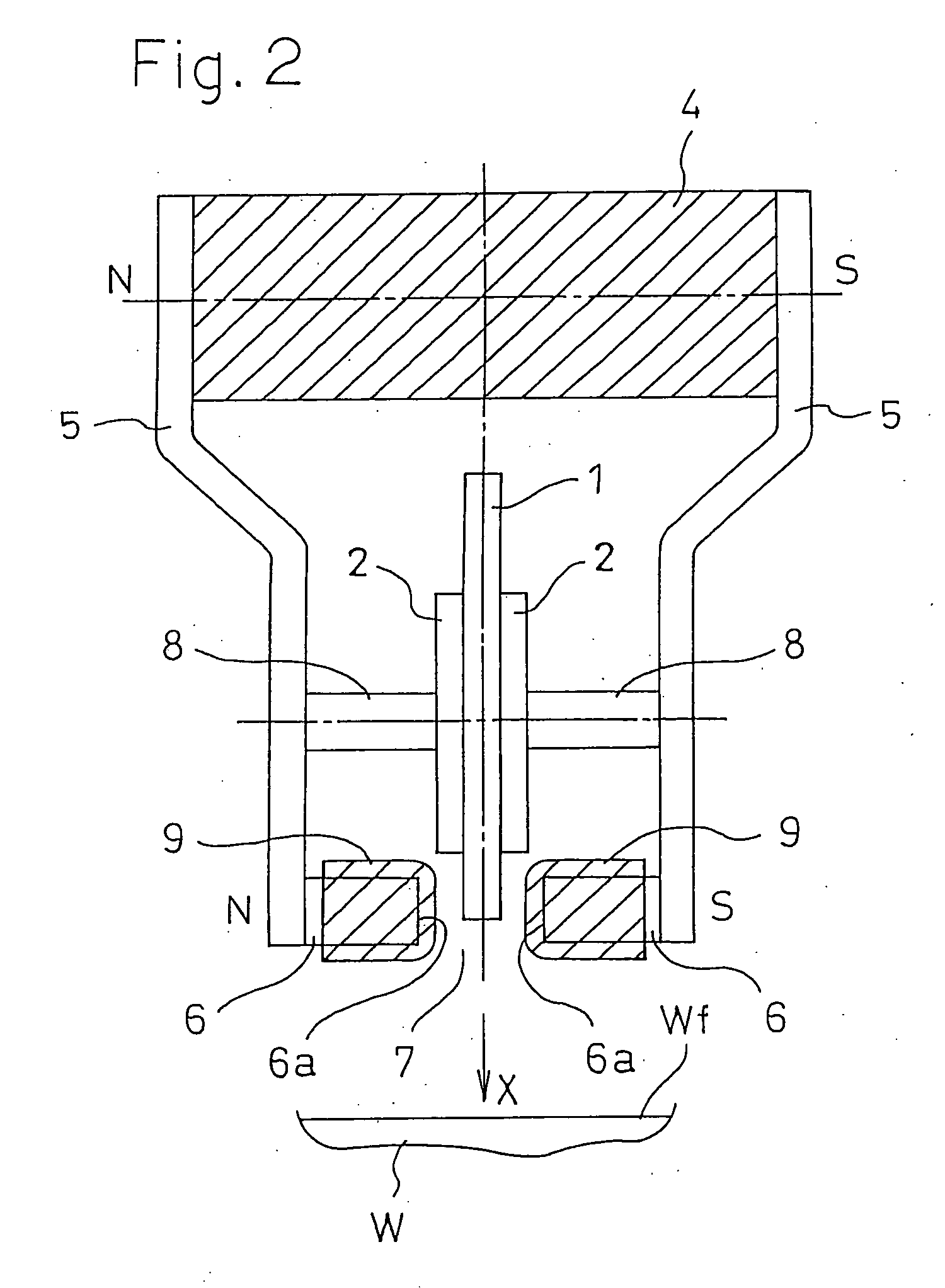
Without requiring ejection of air or the like, the amount and area of irradiation of excited species to a workpiece surface can be increased, the whole surface can be uniformly irradiated, and the loss of effective excited species can be suppressed, whereby the treatment performance and the treatment efficiency can be remarkably improved. In a method in which a pulse voltage is applied to a pair of opposing discharge electrodes 1, 1 to produce corona discharge between pointed ends 1a, 1a, and excited species including plasma are produced by the corona discharge, thereby conducting a surface treatment, a magnetic field is formed in the vicinity of the pointed ends 1a, 1a of the discharge electrodes 1, 1, by magnetic field forming means configured by a permanent magnet 4, magnetic members 5, and pole pieces 6, and the excited species are irradiated toward the surface Wf of a workpiece W by a Lorentz force which acts as a pushing force on charged particles moving in the magnetic field, thereby conducting a surface treatment.
Owner:BBK BIO +2
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS6996359B2Cost of apparatus can be reducedIncrease productivityWorkpiece holdersOther angling devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
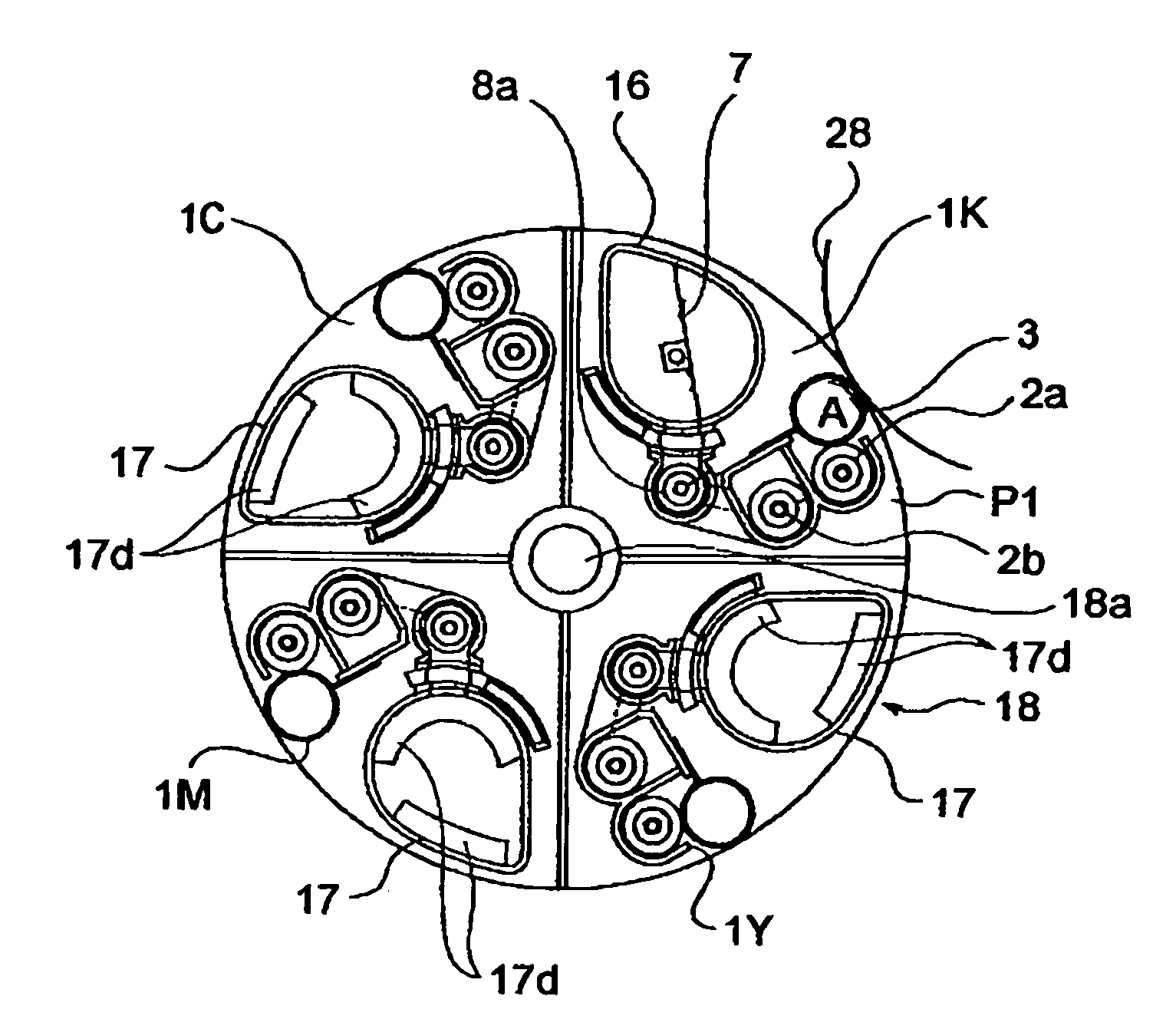
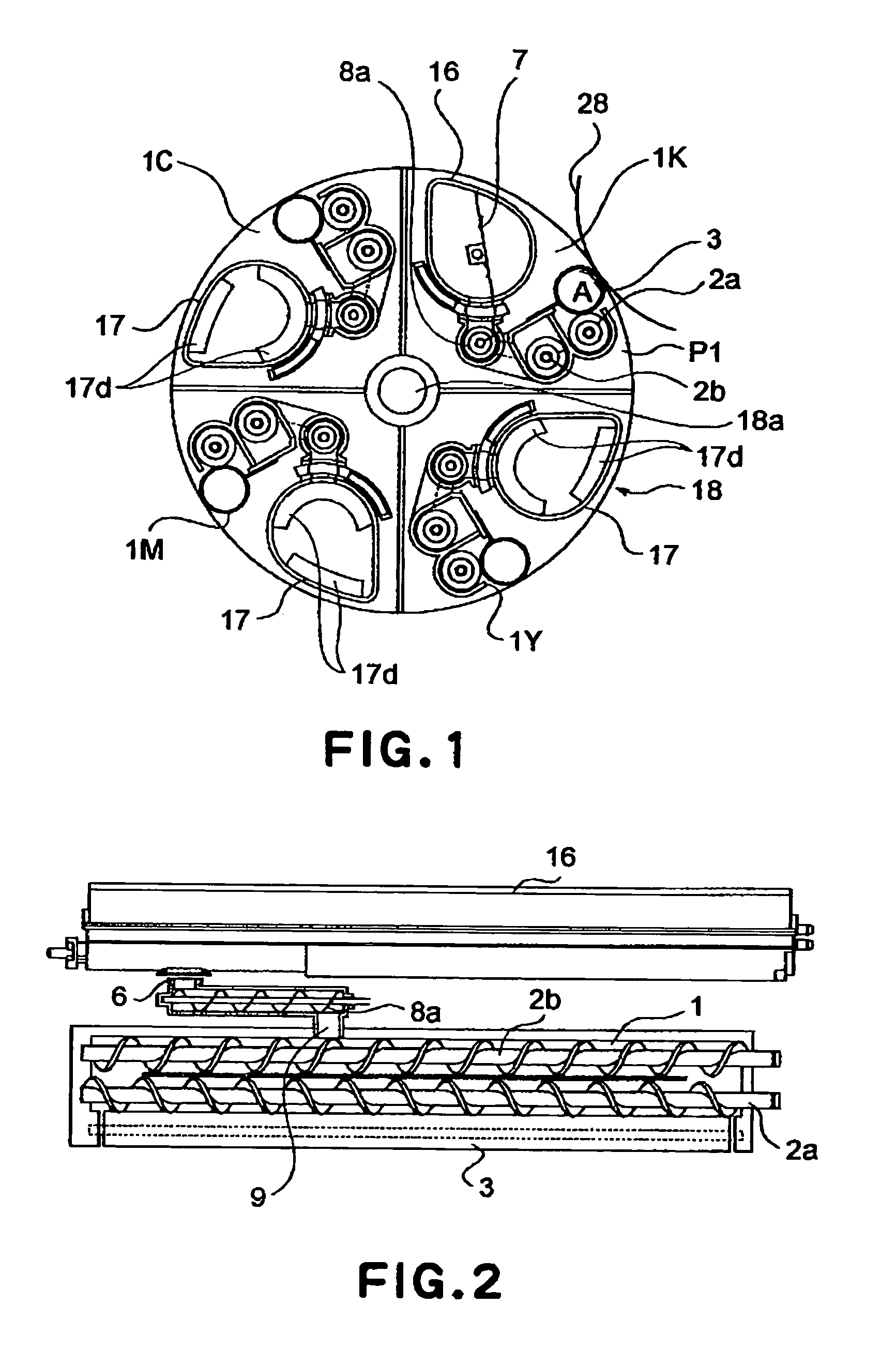
An image forming apparatus includes a first developing device and a second developing device for developing an electrostatic latent image formed on an image bearing member and a developing portion; a rotatable member supporting the first and second developing devices, the rotatable member being rotatable along a path through the developing portion; a first developer supply container and a second developer supply container, supported on the rotatable member, for supplying developer into the first developing device and into the second developing device; wherein the developer in the first developer supply container is fed using rotation of the rotatable member, whereas the developer in the second developer supply container is fed without using rotation of the rotatable member.
Owner:CANON KK
Device and method for recording and/or reproducing data onto/from information recording medium by using near-field light and information recording medium
InactiveUS20100118665A1Layer deterioratesSimple optical configurationCombination recordingRecord information storageLaser lightComputer science
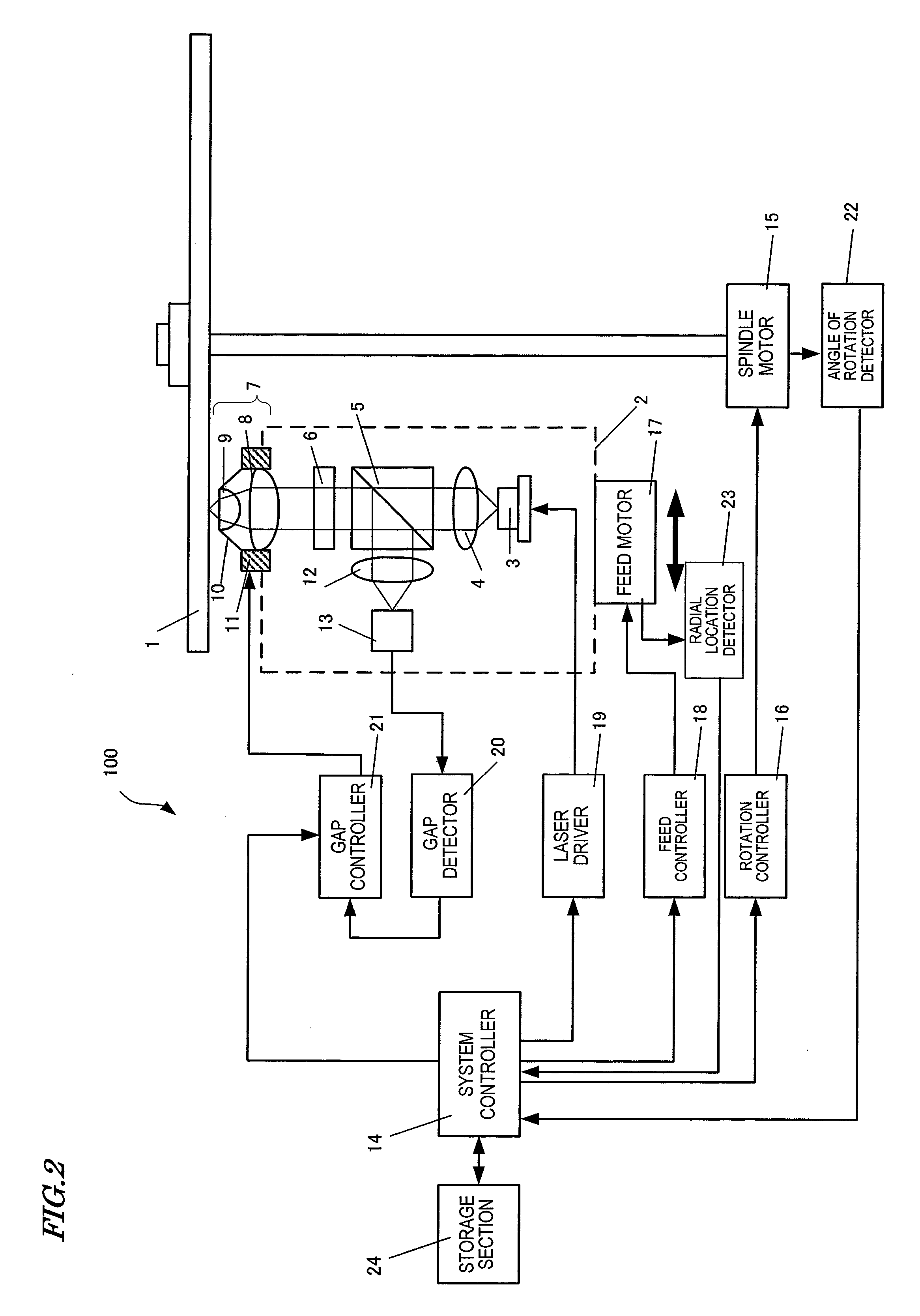
An apparatus 100 according to the present invention is designed to read and / or write data from / on an information recording medium 1 using near-field light. The apparatus 100 includes: a light source 3 for emitting laser light; a condensing section 7 for producing the near-field light based on the laser light; a detecting section 22, 23 for detecting the relative positions of the condensing section 7 and the information recording medium 1; and a control section 14 for controlling the position of the condensing section 7. In starting a gap servo operation, the control section 14 controls the position of the condensing section 7 so that the gap servo operation is started at a different location on the information recording medium 1 from any other location where the gap servo operation has ever been started.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Teaching apparatus, transport system, and method for measuring positioning pins
ActiveUS20180251299A1Suppresses inclinationPrecise positioningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStorage devicesTransport systemEngineering
Owner:MURATA MASCH LTD
Apparatus and Method for Processing a Recording Medium with Embedded Information
InactiveUS20120224231A1Cost of apparatus can be reducedRealize the operationVisual presentation using printersCharacter and pattern recognitionIntegrated processingEmbedded system
An apparatus for processing a recording medium with embedded information comprises: a passage mechanism including a first passage, a loop passage and recording medium conveying rollers, wherein a first opening and a second opening of the loop passage are connected to the tail end of the first passage; a first guide mechanism configured to selectively communicate the first passage with the first opening or the second opening of the loop passage; and a processing device including a magnetic head and a print head which are arranged in the first passage, wherein the magnetic head is arranged at a side of a recording medium inlet / outlet port which is adjacent to a leading end of the first passage. A method for processing the recording medium with embedded information is also disclosed. According to the apparatus and method for processing the recording medium mentioned above, the recording medium can be turned over automatically during moving through the loop passage, so that the printing on both sides of the recording medium can be realized by one single print head, and thus a comprehensive process on the recording medium with embedded information is realized, and the cost of the apparatus is reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG NEW BEIYANG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Surface cleaning apparatus with two-stage collection
ActiveUS20200305672A1Reduced Power RequirementsCost of apparatus can be reducedAutomatic obstacle detectionTravelling automatic controlSurface cleaningEnvironmental engineering
The present disclosure provides a surface cleaning apparatus that mechanically removes liquid and debris from a brushroll and stores the mechanically-removed liquid and debris onboard the apparatus in a first collection area. The surface cleaning apparatus also collects further liquid and debris from the brushroll by a source of suction including a vacuum motor or a pump and stores the collected liquid and debris onboard the apparatus in a second collection area.
Owner:BISSELL INC
Heating unit, erasing device, and information erasing and recording apparatus
InactiveUS20080246829A1Efficient heatingCost of apparatus can be reducedRecording apparatusPower drive mechanismsHeat sensitiveEngineering
A heating unit is disclosed that heats a heat-sensitive medium. The heating unit includes a heat generating body that converts electric energy into heat energy; a fixed member to which the heat generating body is fixed; and a holding member that directly holds the fixed member while contacting at least a part of the fixed member.
Owner:RICOH KK +1
Chemical bath deposition (CBD) apparatus
ActiveUS20130152856A1Simple processSave energyLiquid surface applicatorsSpray nozzlesEngineeringChemical vapor deposition
A chemical bath deposition (CBD) apparatus includes a first cap, a second cap, and a solution input / output device. The second cap is arranged corresponding to the first cap so as to form a deposition space. The solution input / output device is located in the first cap so as to feed a solution into / out of the deposition space. The position of the solution input / output device is fixed, or the solution input / output device is movable in the deposition space.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Image recording apparatus and recording-material feeding method
InactiveUS20050185013A1Prevent scanning unevennessEasy to controlPrinting mechanismsRecording apparatusComputer printingImage recording
A feeder is provided inside an exposure section of a photographic printer. First and second feed-roller pairs are respectively disposed at an upstream side and a downstream side of an exposing position of the feeder. A first nip roller of the first feed-roller pair and a second nip roller of the second feed-roller pair are movable between a nip position for nipping paper sheets, and a release position for releasing the nip thereof. The second nip roller is moved to the nip position after an anterior end of the paper sheet situated at the most upstream side has passed the second nip roller. The first nip roller is moved to the release position before a posterior end of the paper sheet situated at the most downstream side leaves the first nip roller.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Method for recovering hydrogen from biomass pyrolysis gas
ActiveUS20190201836A1Reduce operating costsCost of apparatus can be reducedReactant parameters controlWaste processingChemistryCarbon dioxide
A method for recovering hydrogen which is capable of efficiently recovering high concentration hydrogen gas by adsorbing and removing hydrocarbon gas such as carbon dioxide from biomass pyrolysis gas under a relatively low pressure, and also capable of storing the recovered high concentration hydrogen gas, preferably, in a cartridge type container that can be used as is as a hydrogen storing container for an apparatus equipped with a fuel cell. The method includes a first purifying stare of purifying biomass pyrolysis gas and a second purifying stage of purifying the obtained purified gas under a pressure equal to or less than the pressure in the first purifying stage to recover gas that contains hydrogen, and further includes a hydrogen storing stage of feeding the gas containing hydrogen recovered in the second purifying stage into the container filled with a hydrogen storage alloy and storing high purity hydrogen.
Owner:JAPAN BLUE ENERGY +1
Electrical switch apparatus having two interrupters, such as a busbar disconnector and a grounding disconnector, and including common actuator means for the movable contacts of the interrupters
InactiveUS20100089732A1Reduce distanceSmall sizeContact driving mechanismsContact operating partsActuatorControl theory
A switch apparatus comprising two interrupters, such as a busbar disconnector and a grounding disconnector. Common actuator means are provided for the movable contacts of the interrupters, for permitting one of the interrupters to be opened while holding the other interrupter closed, and vice versa, which enables the strokes performed by the movable contacts to be crossed.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
Method and apparatus for desalinating and concentrating sea water, desalinated deep water and concentrated deep water
InactiveUS7008516B2Short separationIncrease ratingsDrying using combination processesGeneral water supply conservationWater desalinationHeat conducting
According to a method of desalinating sea water, sea water sampled from deep sea is injected into a decompression chamber of a reduced pressure tank having a steam chamber, steam at an atmospheric pressure superheated to a boiling temperature or higher by high-frequency heating is supplied to the steam chamber at a surrounding of the decompression chamber at an interval of a heat conducting wall therebetween, water in the sea water is evaporated by heating sea water in the decompression chamber and the evaporated water is condensed to thereby provide fresh water. Concentrated sea water remains in the decompression chamber and therefore, the method can be utilized also as a method of concentrating sea water. Salt can be obtained by further evaporating the water of the concentrated sea water as necessary.
Owner:KOZUKA YOSHINOBU
Vane pump
InactiveUS20220178369A1Cost of apparatus can be reducedReduce manufacturing costRotary piston pumpsRotary piston liquid enginesEngineeringCam
A vane pump is provided with: a pump housing having an accommodating concave portion; and a pump cartridge accommodated in the accommodating concave portion, wherein the pump cartridge has: a rotor; a plurality of vanes received in a plurality of slits formed in the rotor; a cam ring formed with a cam face on an inner circumference of the cam ring; and a first side plate provided at the opposite side from a bottom surface of the accommodating concave portion such that the cam ring is located therebetween, the first side plate has a first projected portion projected radially outward, and the pump cartridge is anchored to the pump housing via the first projected portion.
Owner:KYB CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com