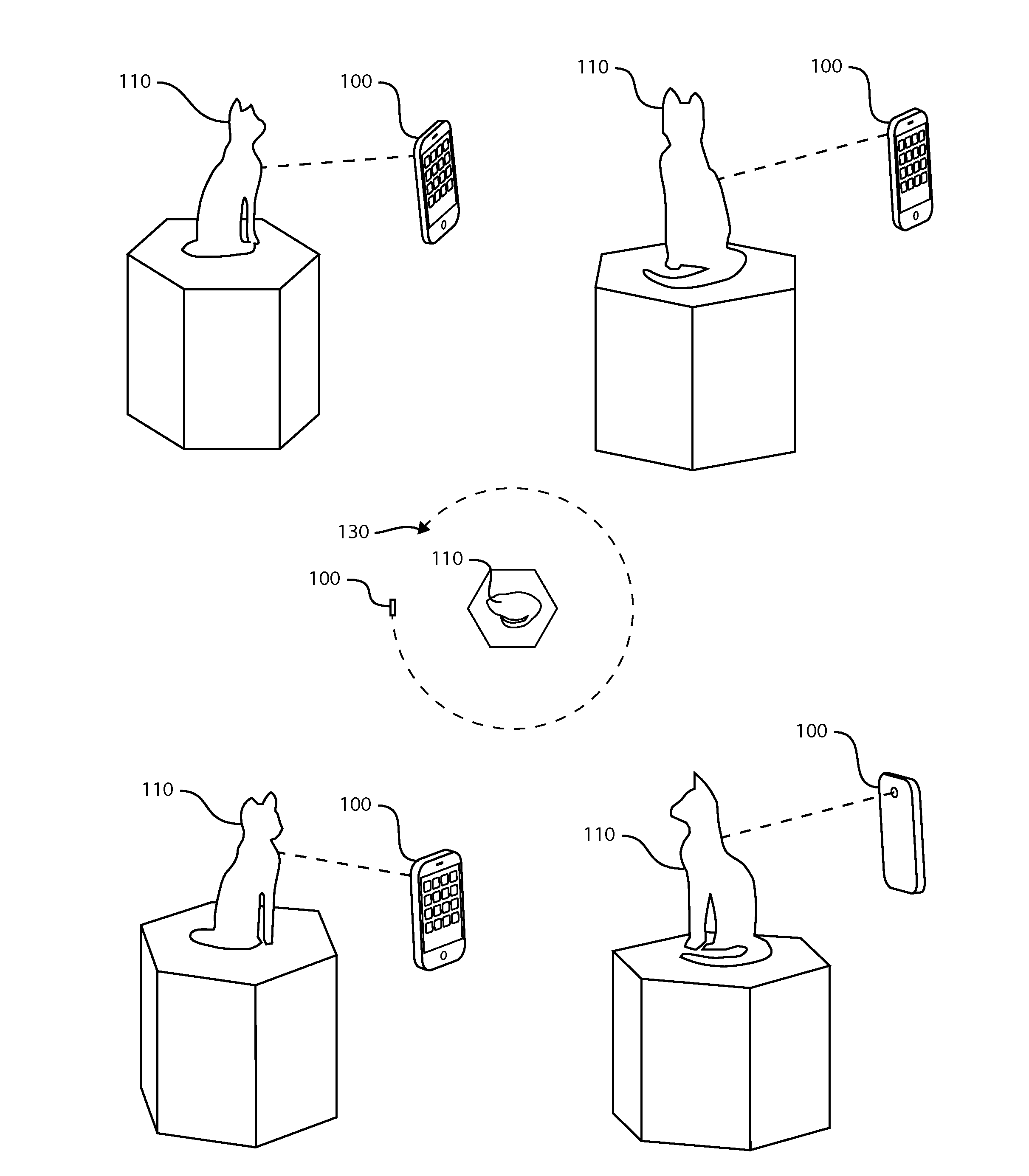
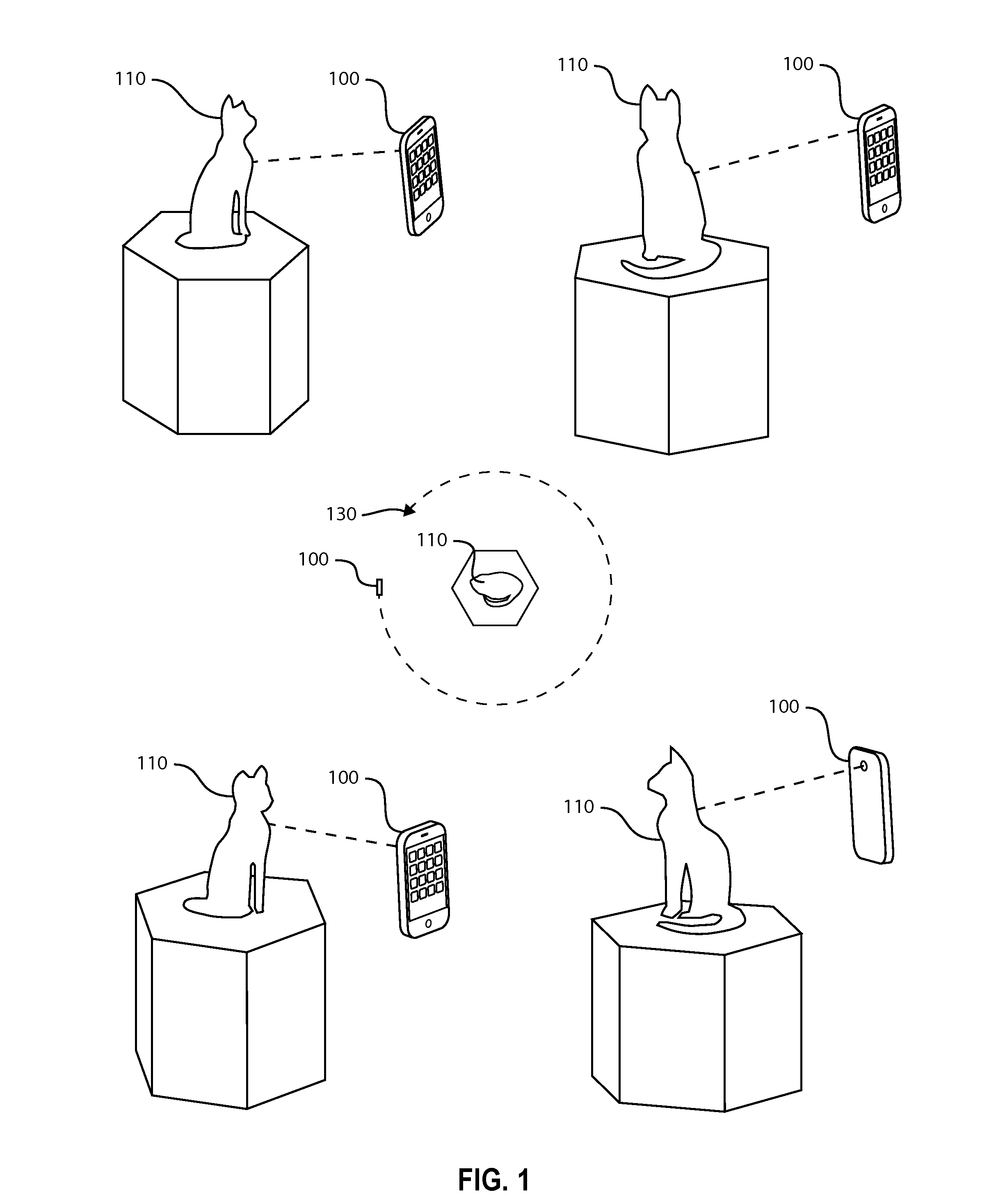
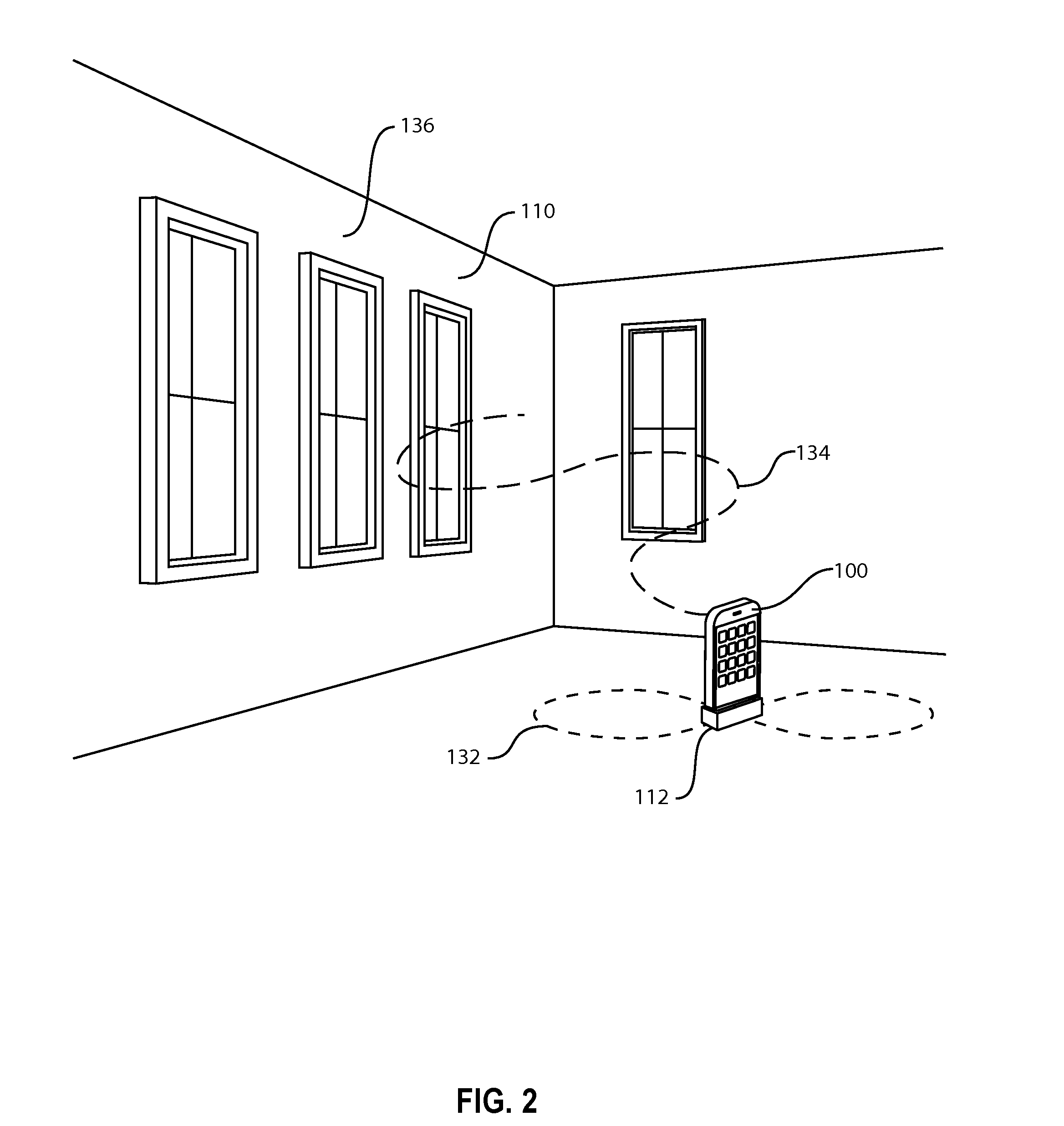
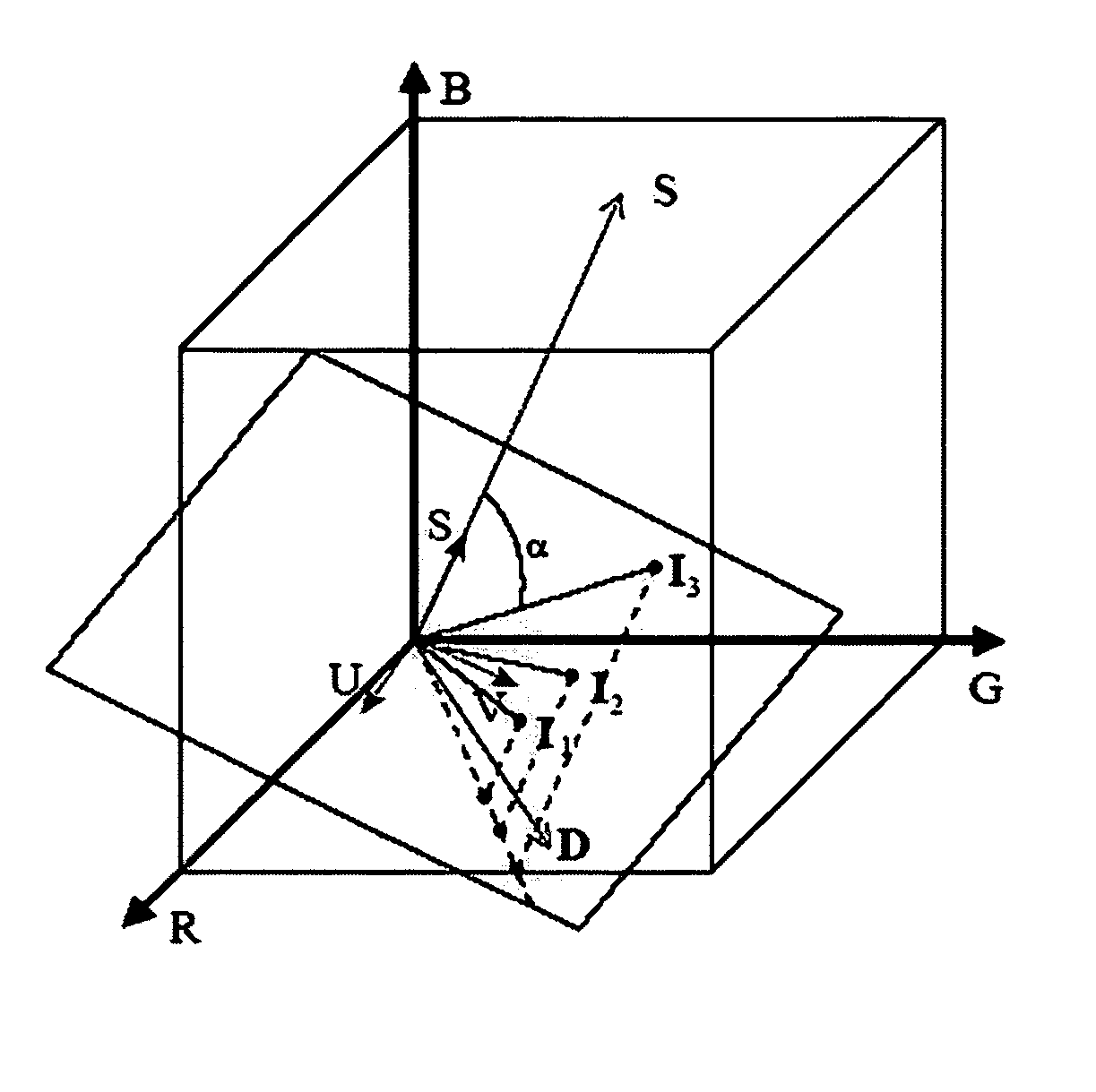
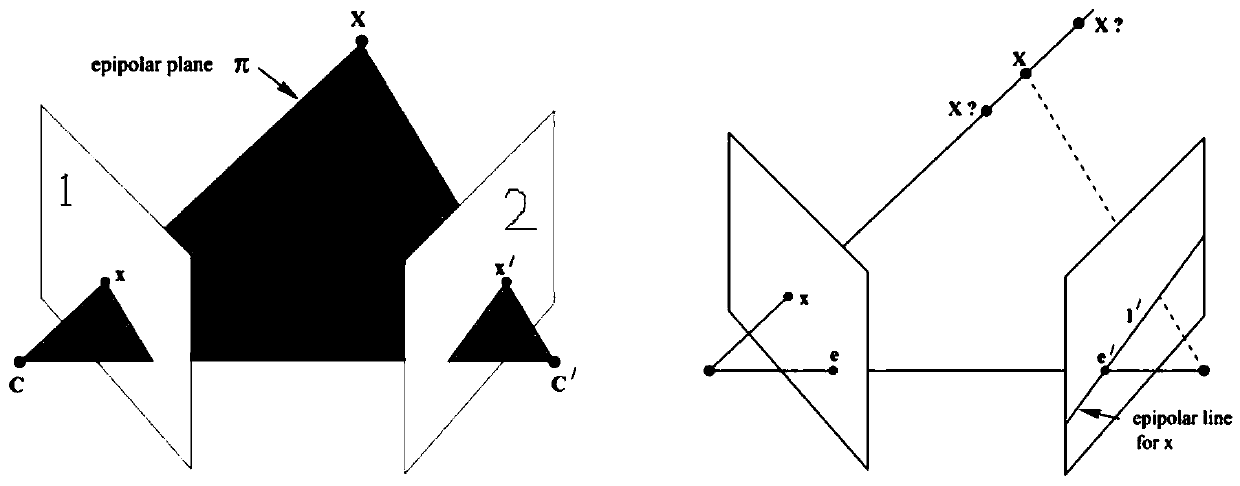Patents
Literature
77 results about "Structure from motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
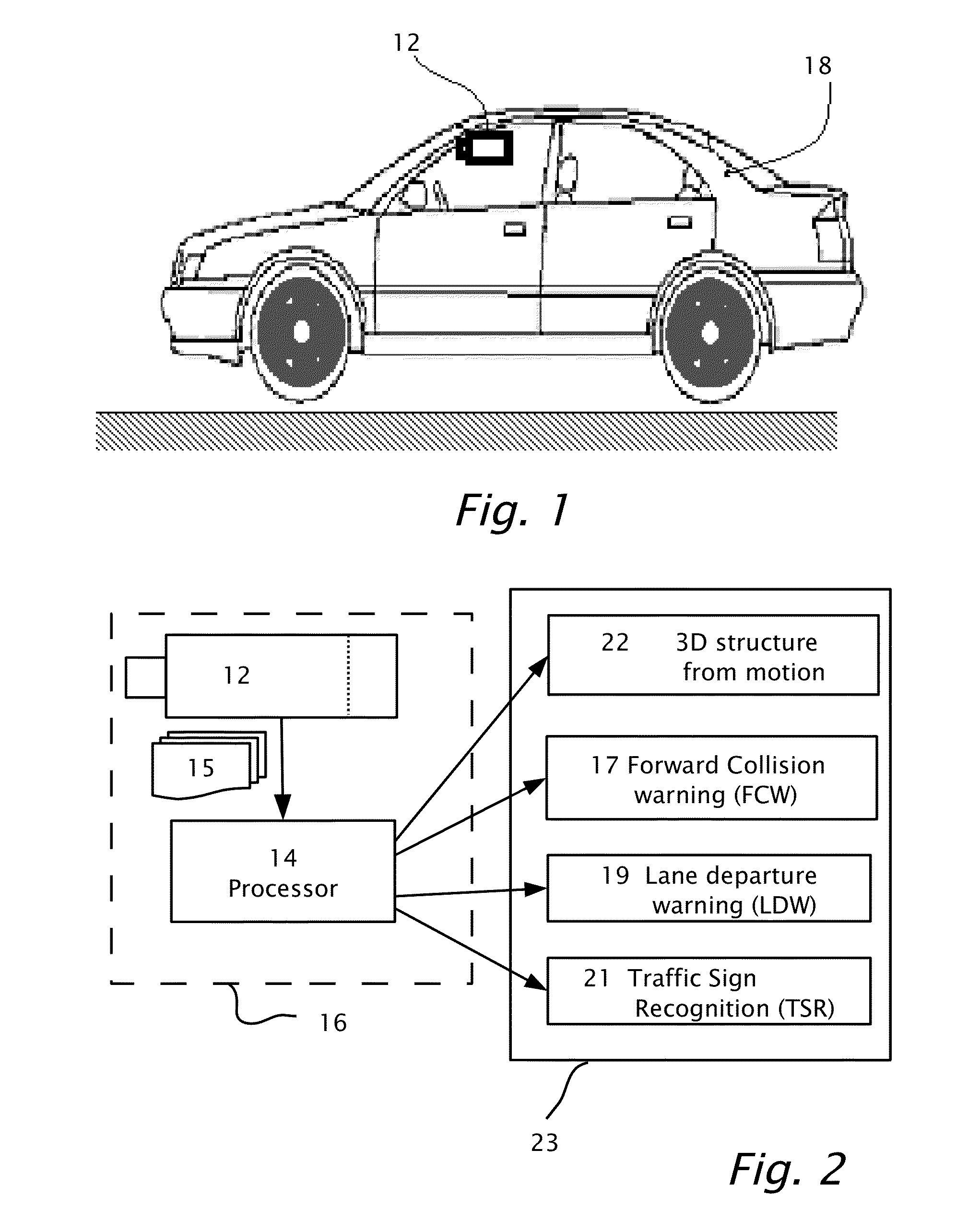
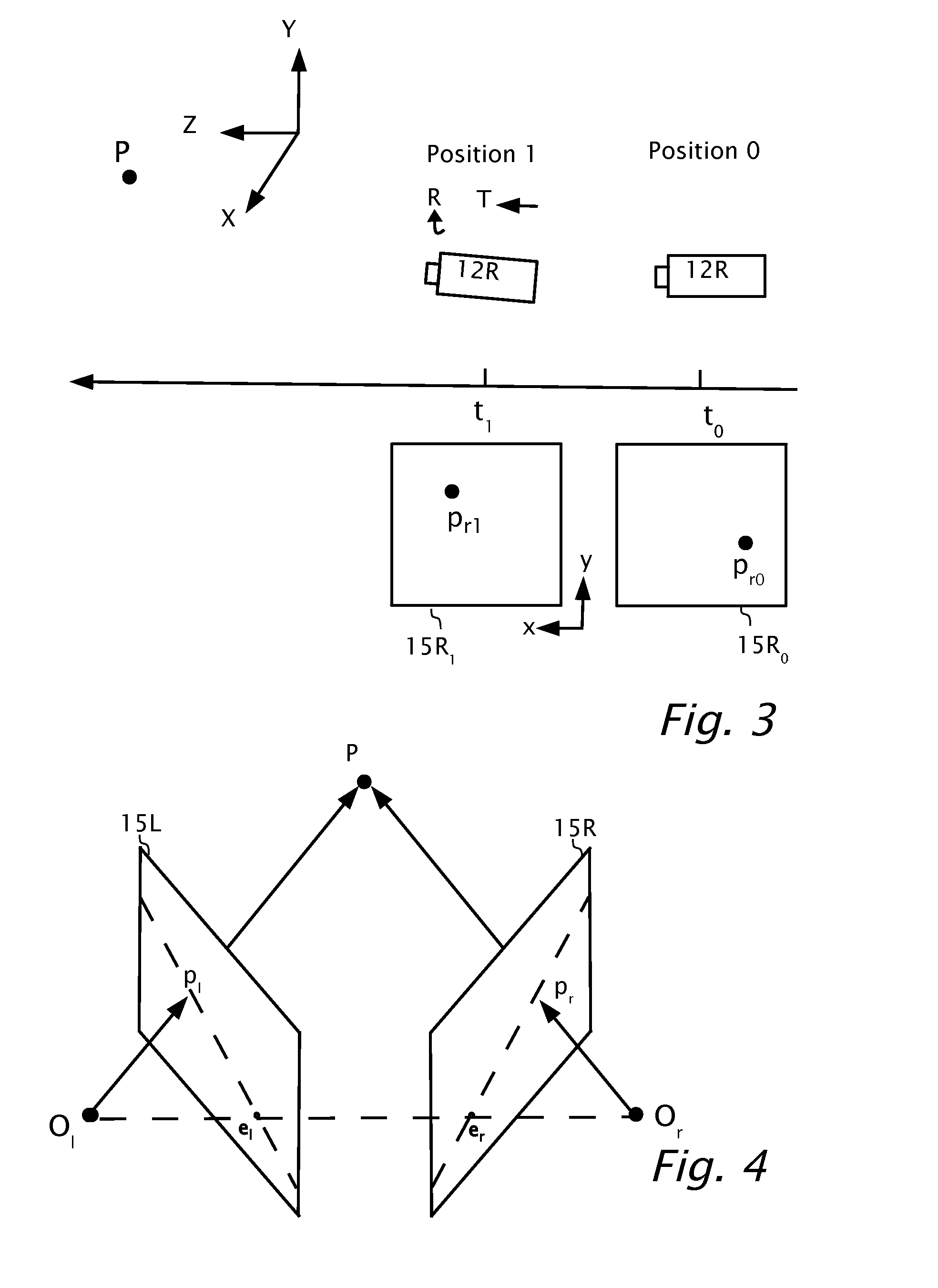
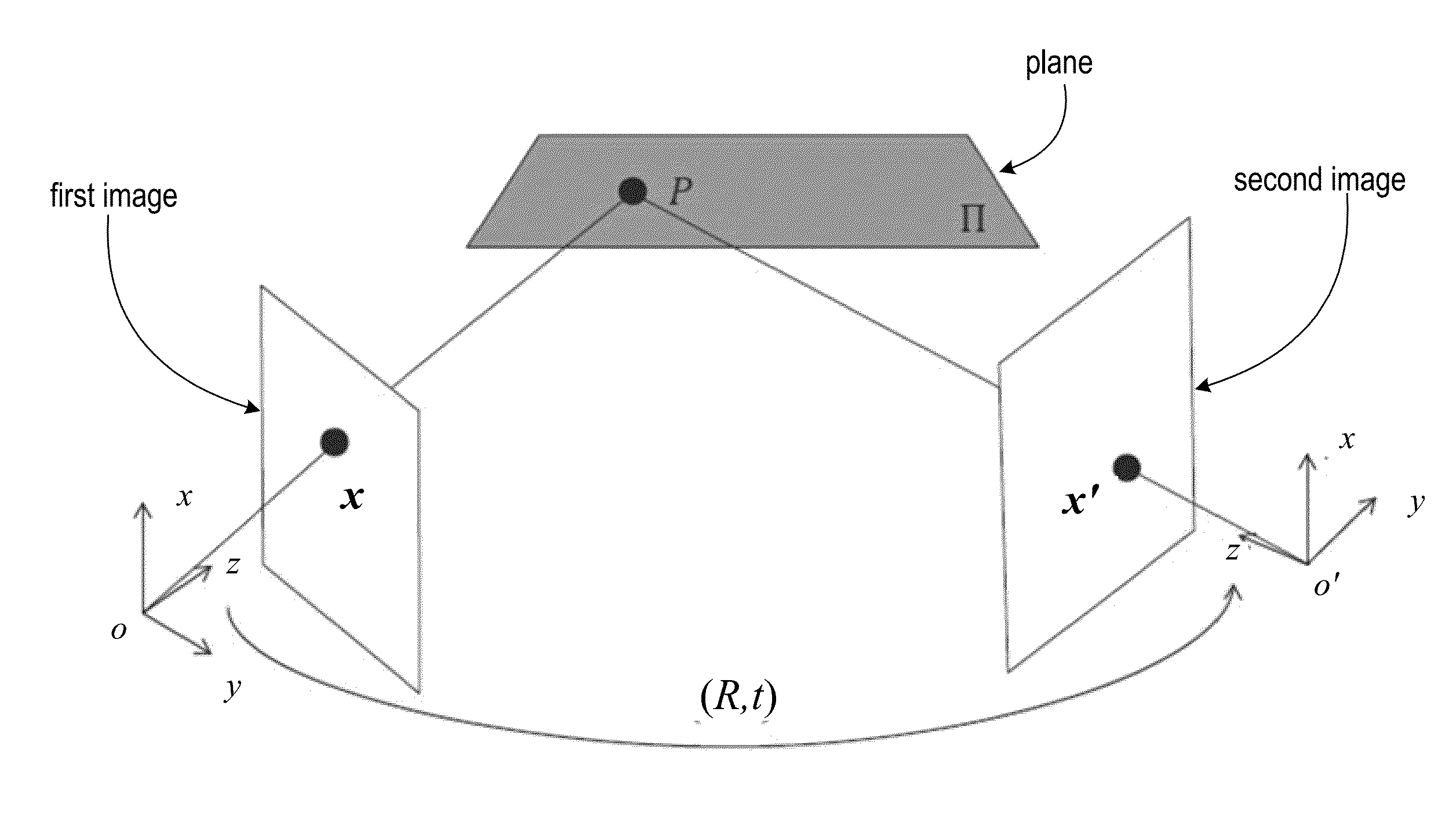
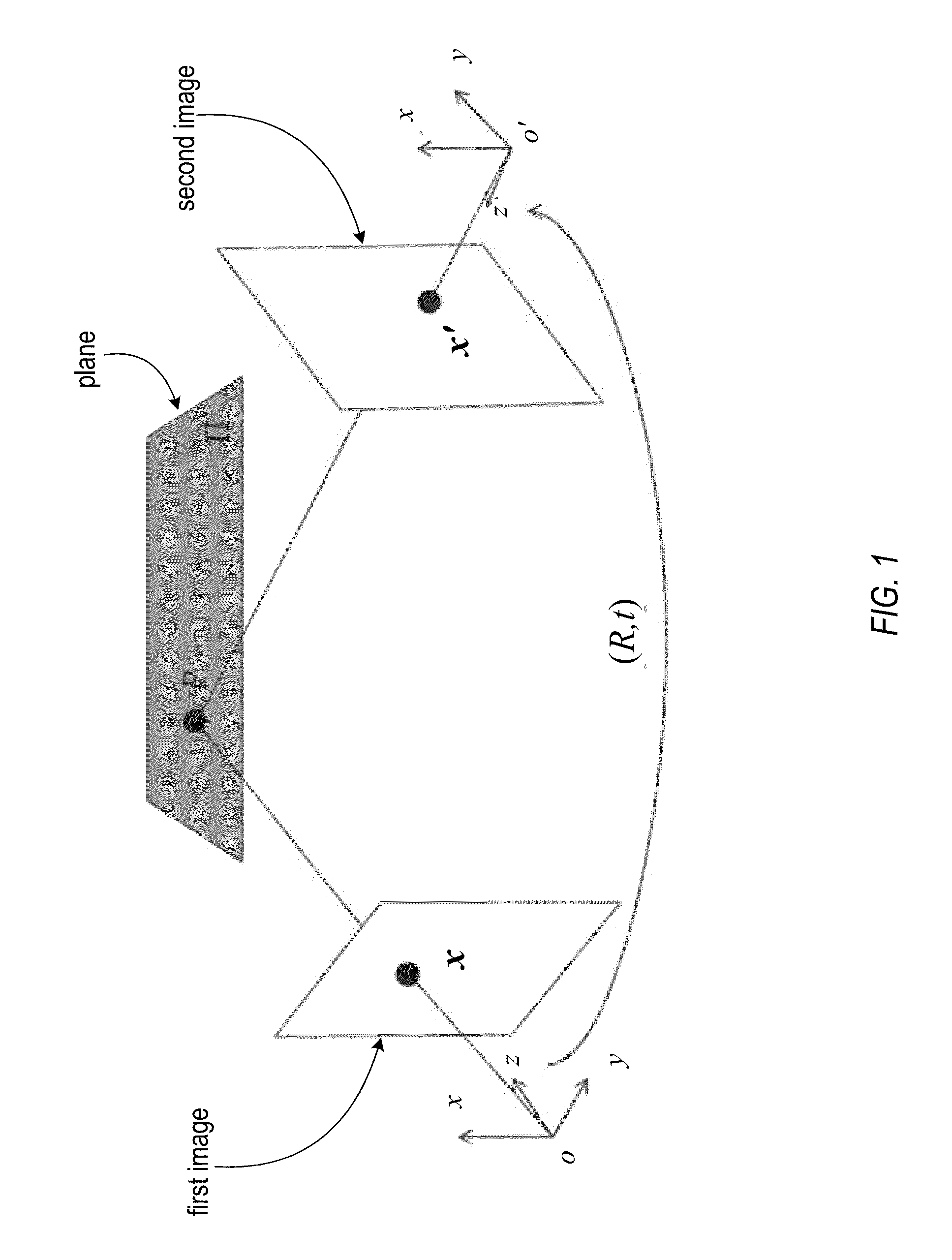
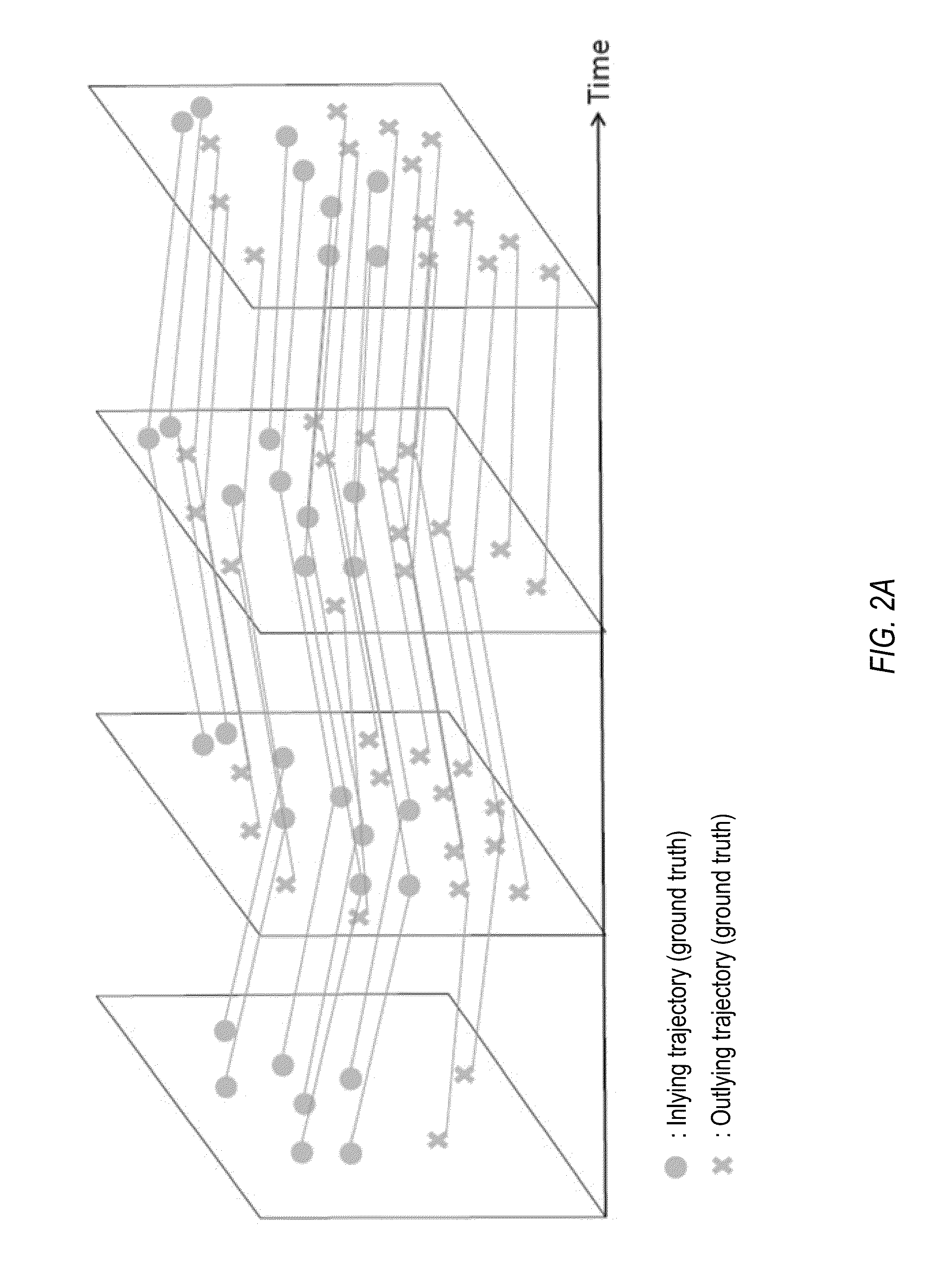
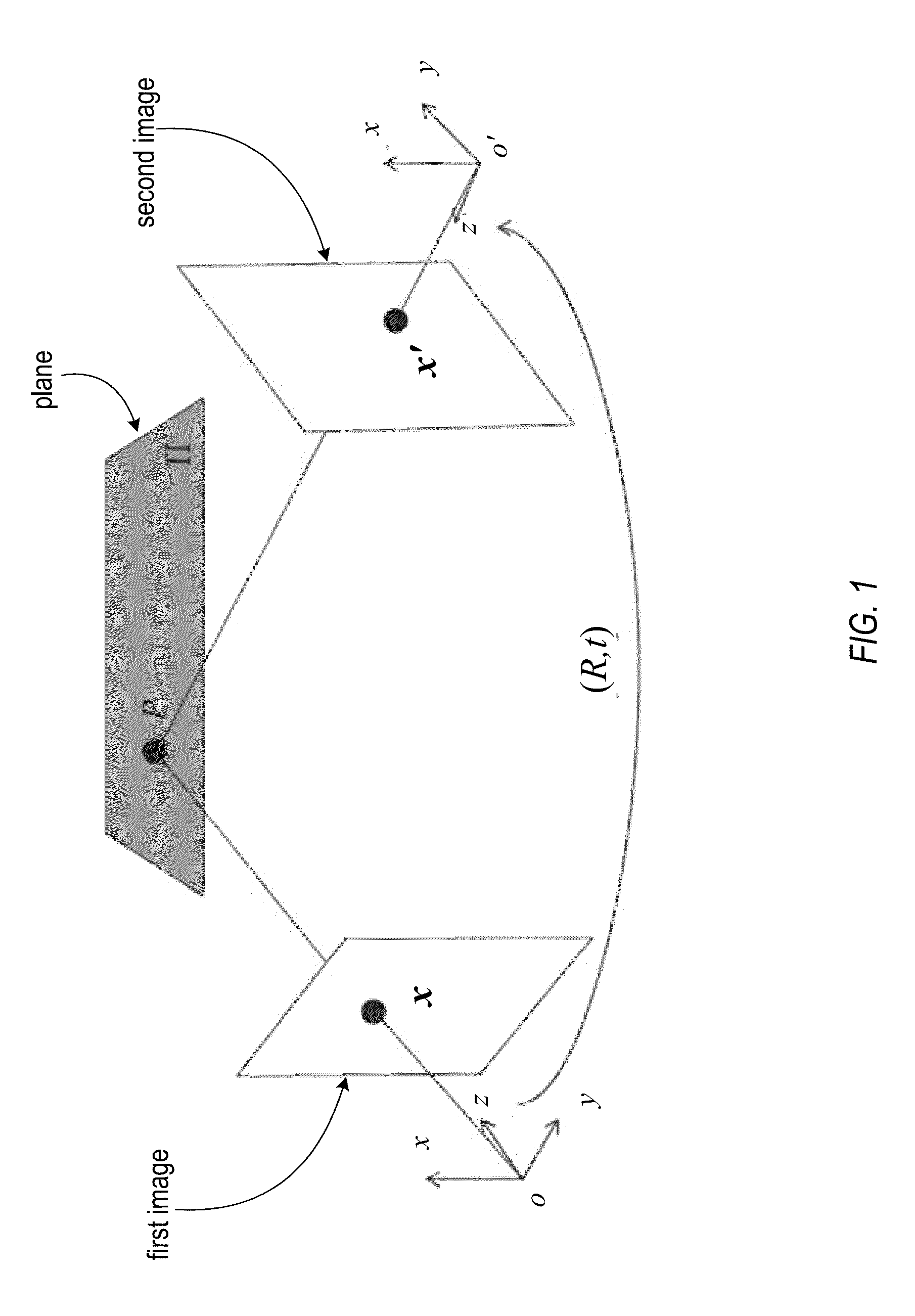
Structure from motion (SfM) is a photogrammetric range imaging technique for estimating three-dimensional structures from two-dimensional image sequences that may be coupled with local motion signals. It is studied in the fields of computer vision and visual perception. In biological vision, SfM refers to the phenomenon by which humans (and other living creatures) can recover 3D structure from the projected 2D (retinal) motion field of a moving object or scene.
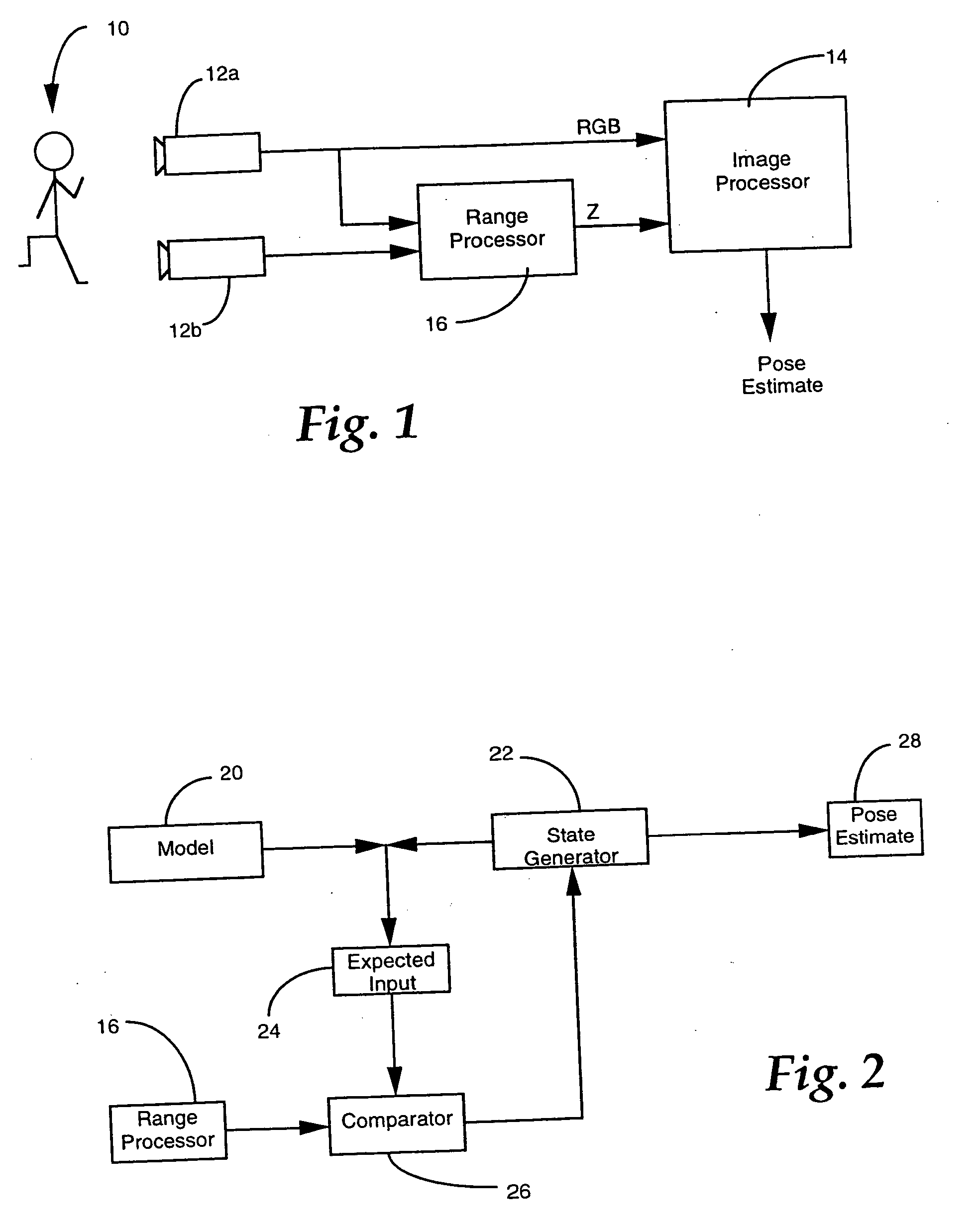
Three dimensional object pose estimation which employs dense depth information
InactiveUS7003134B1Accurate estimateImprove tracking performanceImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsStructure from motion
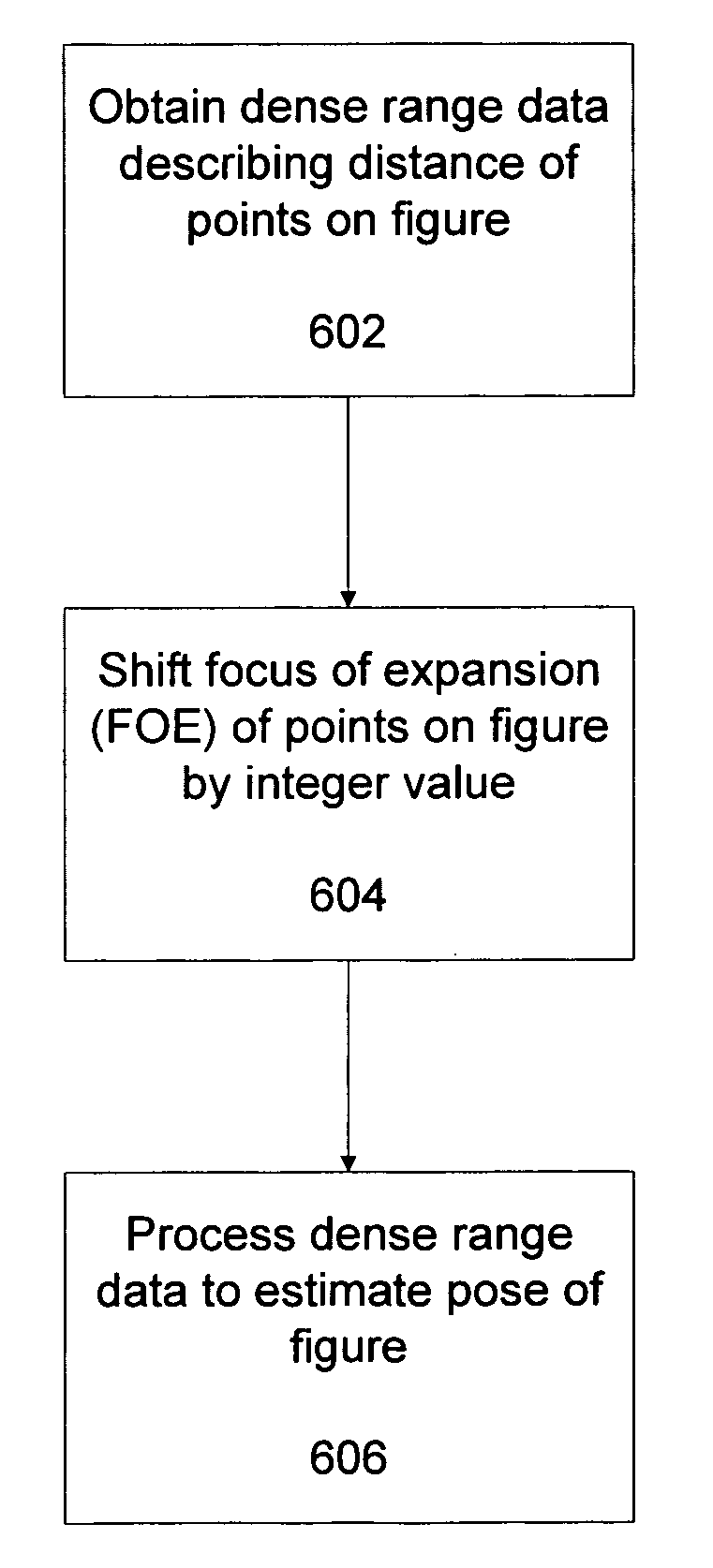
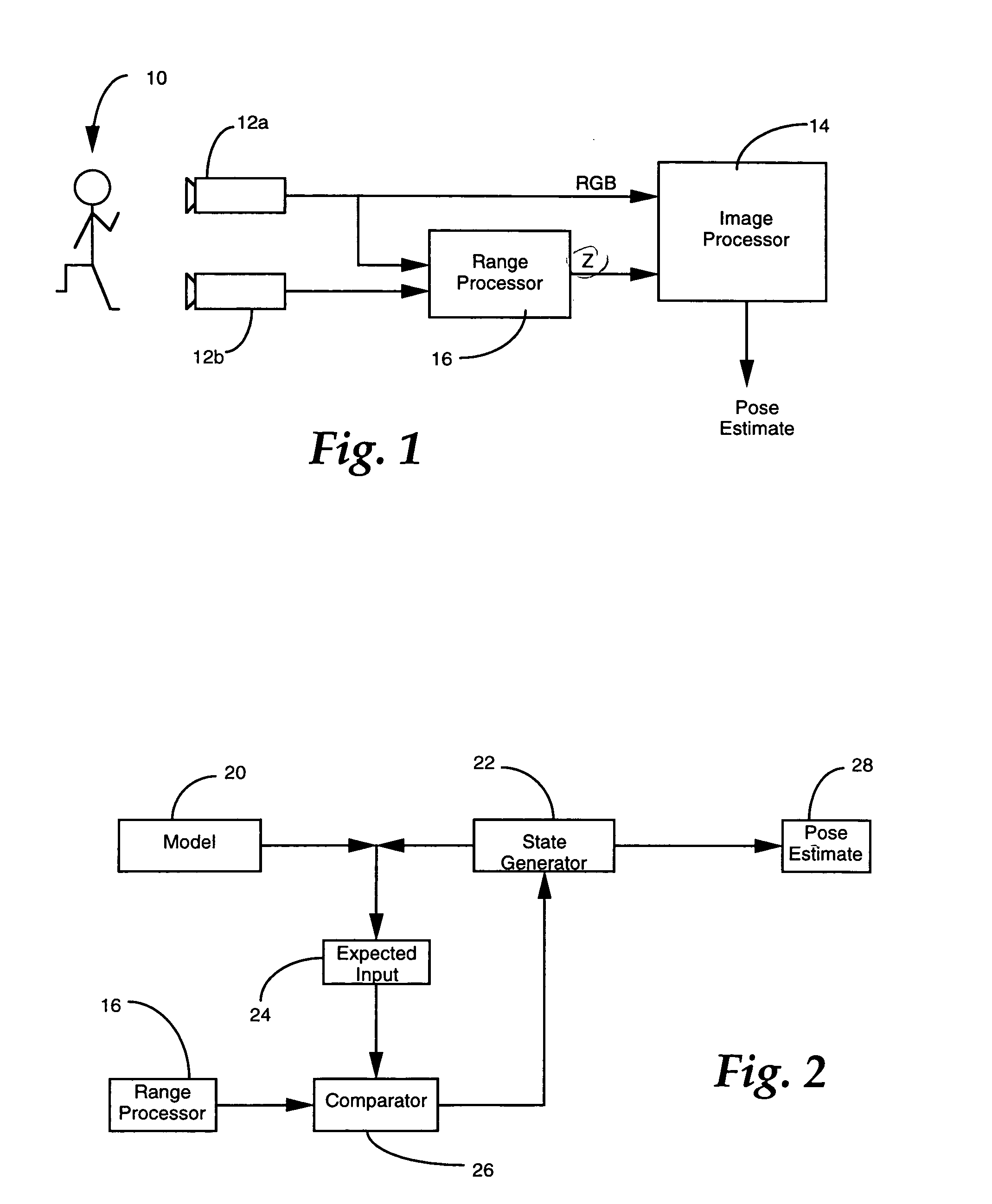
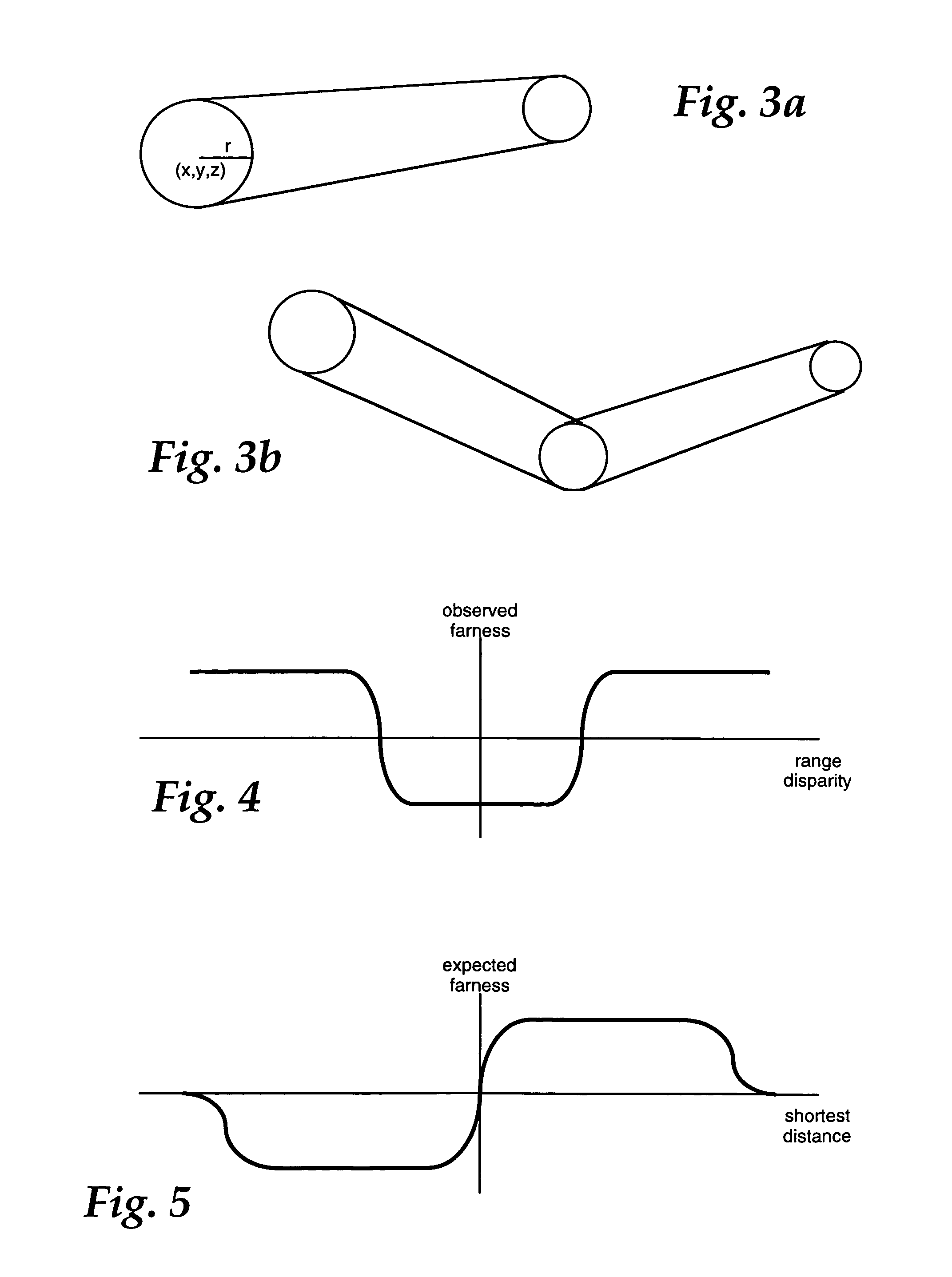
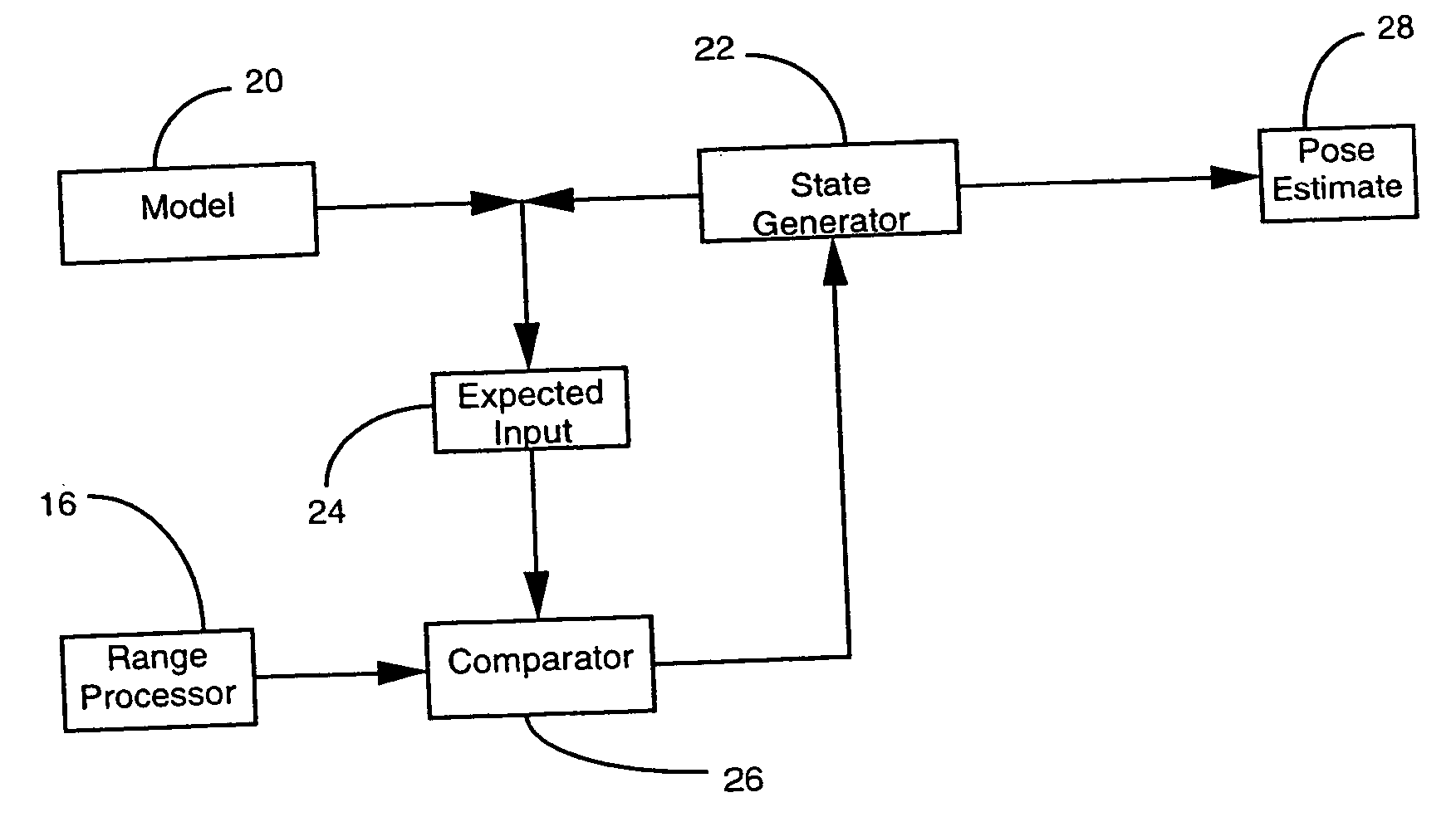
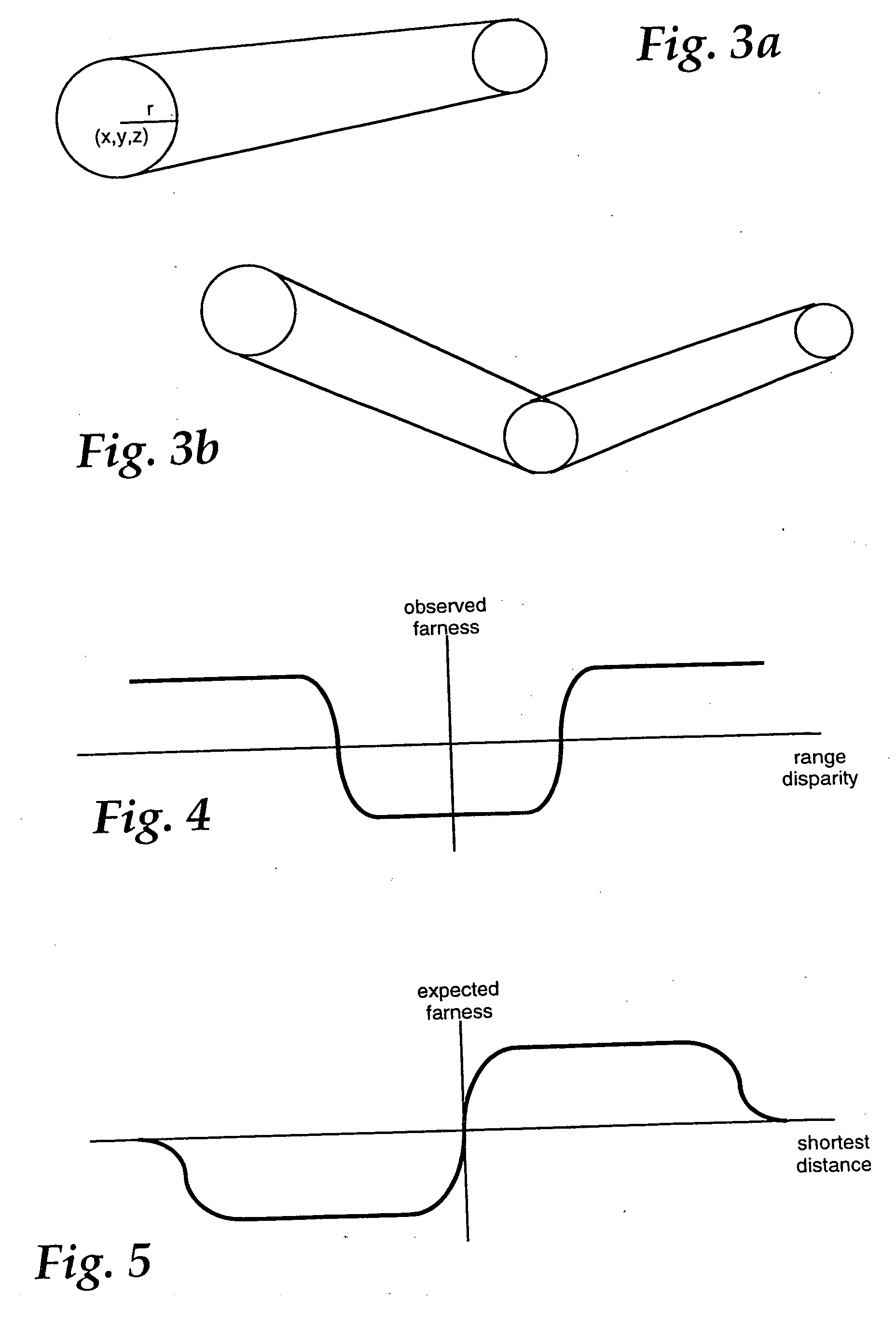
Dense range data obtained at real-time rates is employed to estimate the pose of an articulated figure. In one approach, the range data is used in combination with a model of connected patches. Each patch is the planar convex hull of two circles, and a recursive procedure is carried out to determine an estimate of pose which most closely correlates to the range data. In another aspect of the invention, the dense range data is used in conjunction with image intensity information to improve pose tracking performance. The range information is used to determine the shape of an object, rather than assume a generic model or estimate structure from motion. In this aspect of the invention, a depth constraint equation, which is a counterpart to the classic brightness change constraint equation, is employed. Both constraints are used to jointly solve for motion estimates.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Three dimensional object pose estimation which employs dense depth information
InactiveUS20050265583A1Improve pose tracking performanceAccurate representationImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsStructure from motion
Dense range data obtained at real-time rates is employed to estimate the pose of an articulated figure. In one approach, the range data is used in combination with a model of connected patches. Each patch is the planar convex hull of two circles, and a recursive procedure is carried out to determine an estimate of pose which most closely correlates to the range data. In another aspect of the invention, the dense range data is used in conjunction with image intensity information to improve pose tracking performance. The range information is used to determine the shape of an object, rather than assume a generic model or estimate structure from motion. In this aspect of the invention, a depth constraint equation, which is a counterpart to the classic brightness change constraint equation, is employed. Both constraints are used to jointly solve for motion estimates.
Owner:INTEL CORP
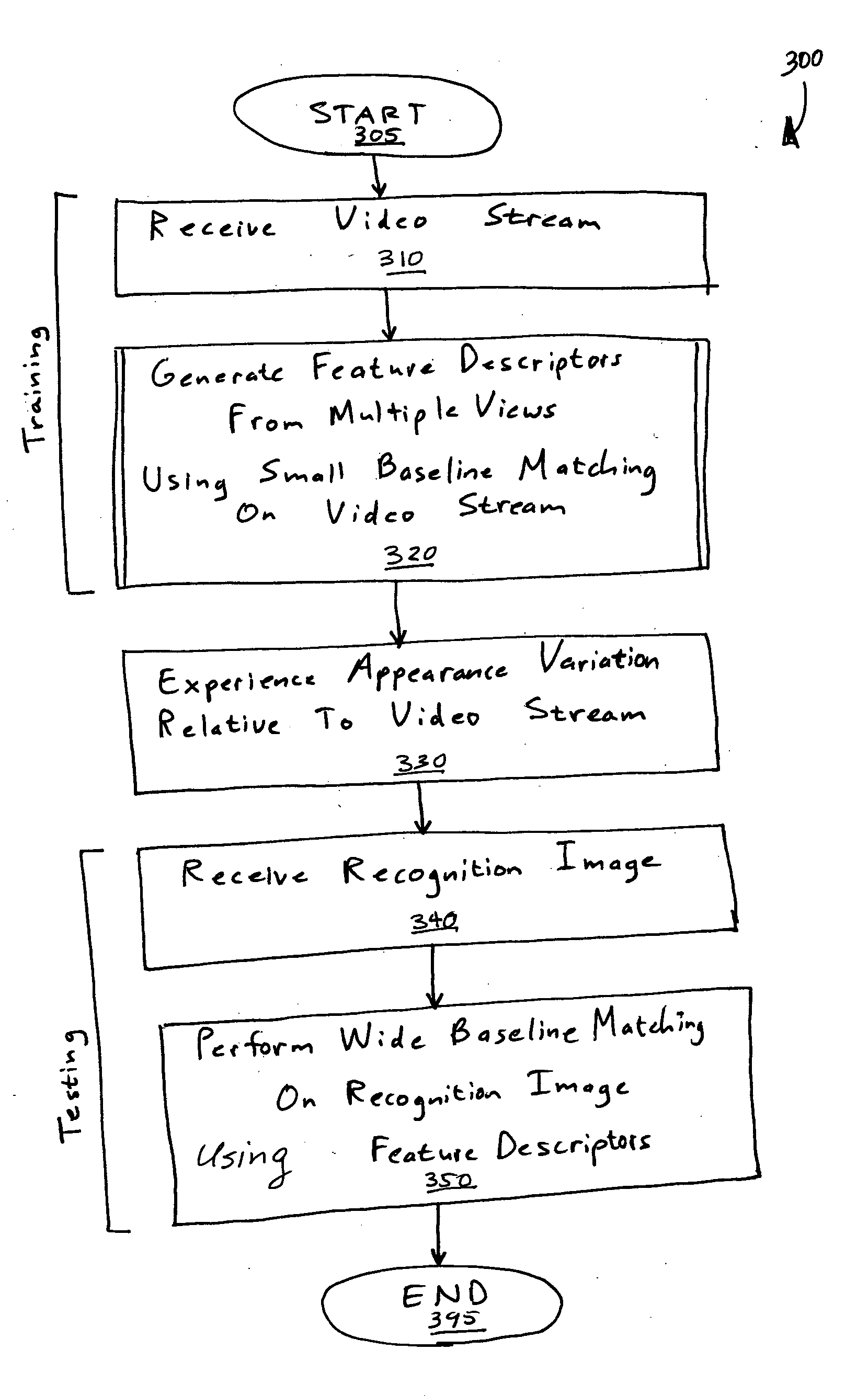
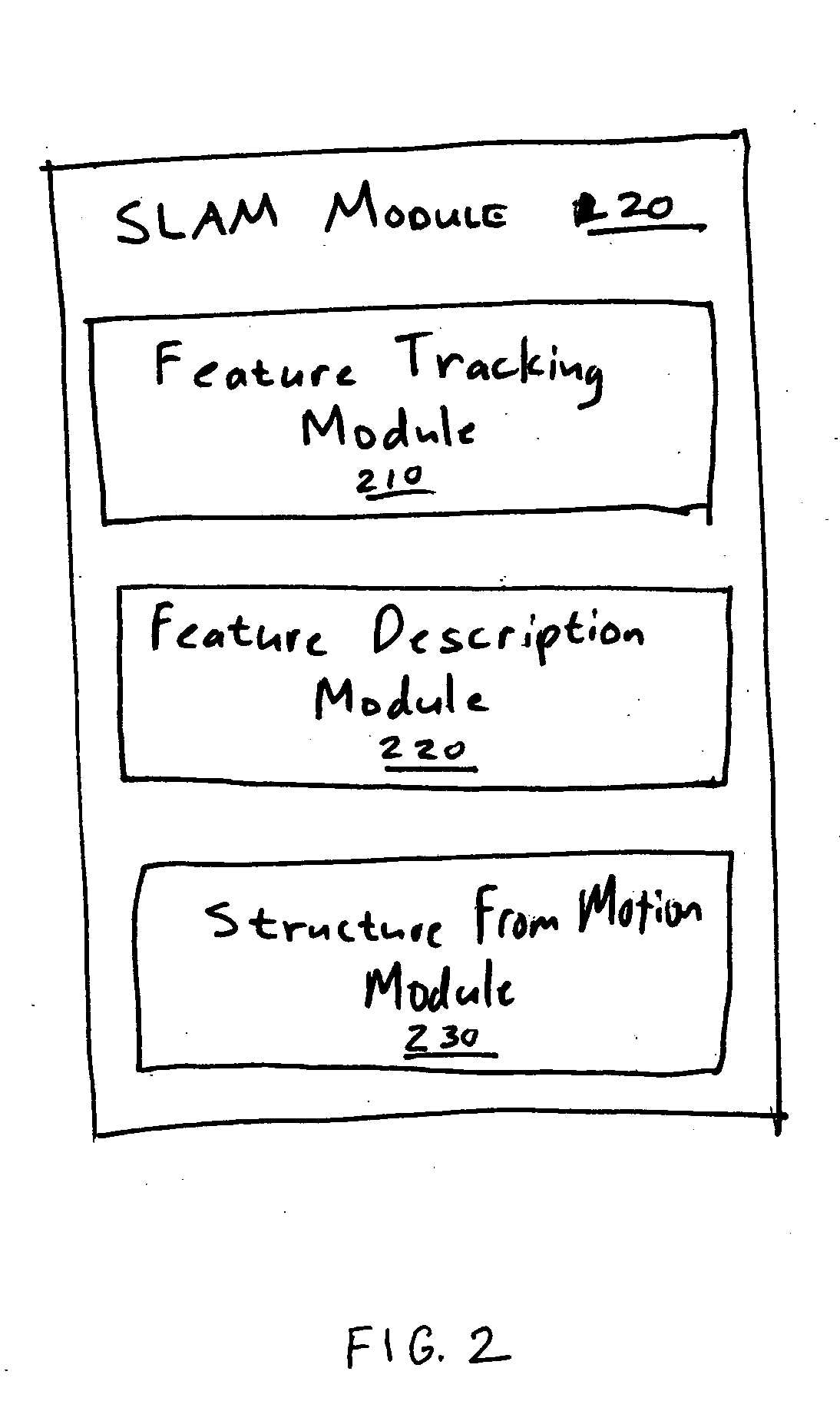
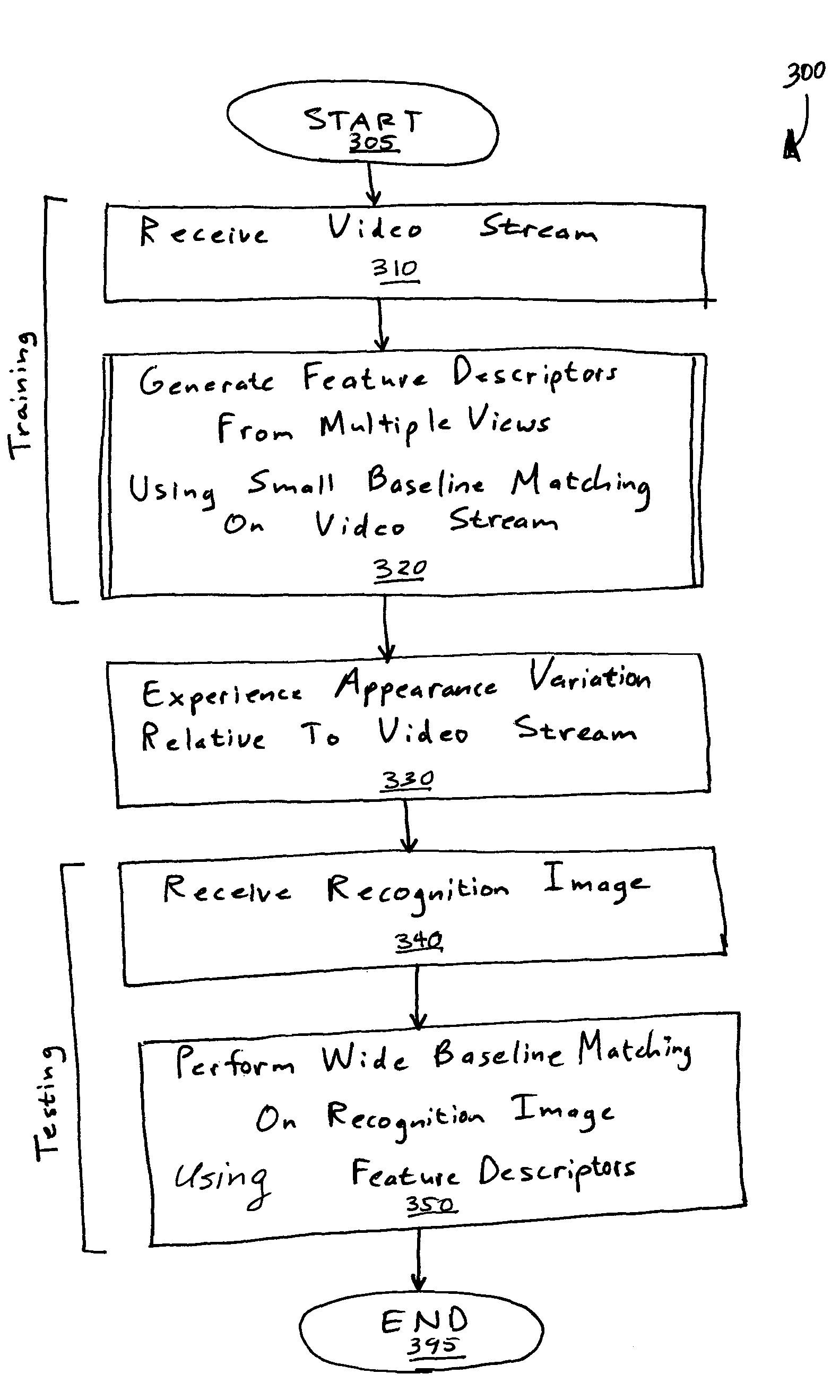
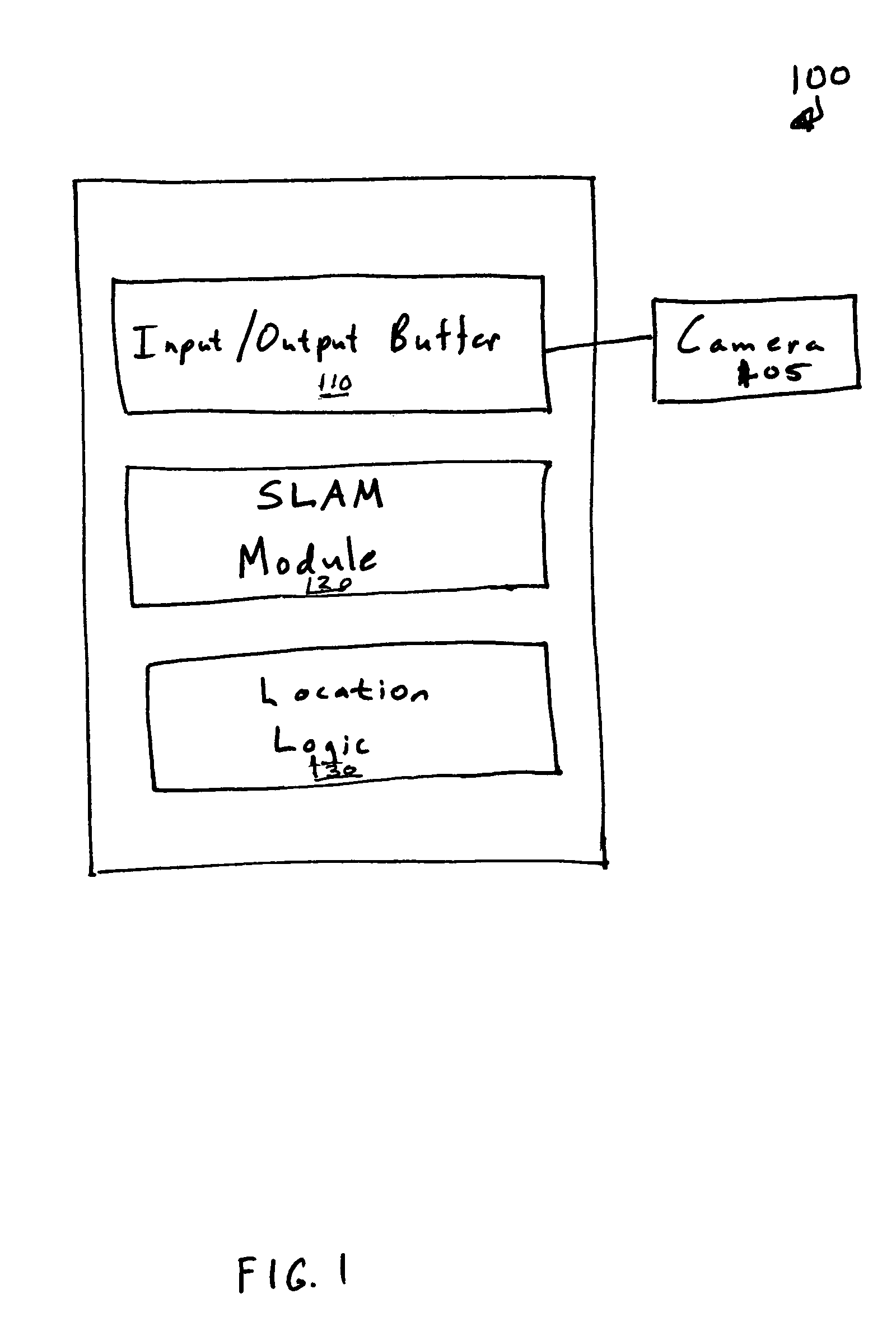
Simultaneous localization and mapping using multiple view feature descriptors
InactiveUS20050238200A1Efficiently build necessary feature descriptorReliable correspondenceThree-dimensional object recognitionKaiman filterKernel principal component analysis
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) utilizes multiple view feature descriptors to robustly determine location despite appearance changes that would stifle conventional systems. A SLAM algorithm generates a feature descriptor for a scene from different perspectives using kernel principal component analysis (KPCA). When the SLAM module subsequently receives a recognition image after a wide baseline change, it can refer to correspondences from the feature descriptor to continue map building and / or determine location. Appearance variations can result from, for example, a change in illumination, partial occlusion, a change in scale, a change in orientation, change in distance, warping, and the like. After an appearance variation, a structure-from-motion module uses feature descriptors to reorient itself and continue map building using an extended Kalman Filter. Through the use of a database of comprehensive feature descriptors, the SLAM module is also able to refine a position estimation despite appearance variations.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
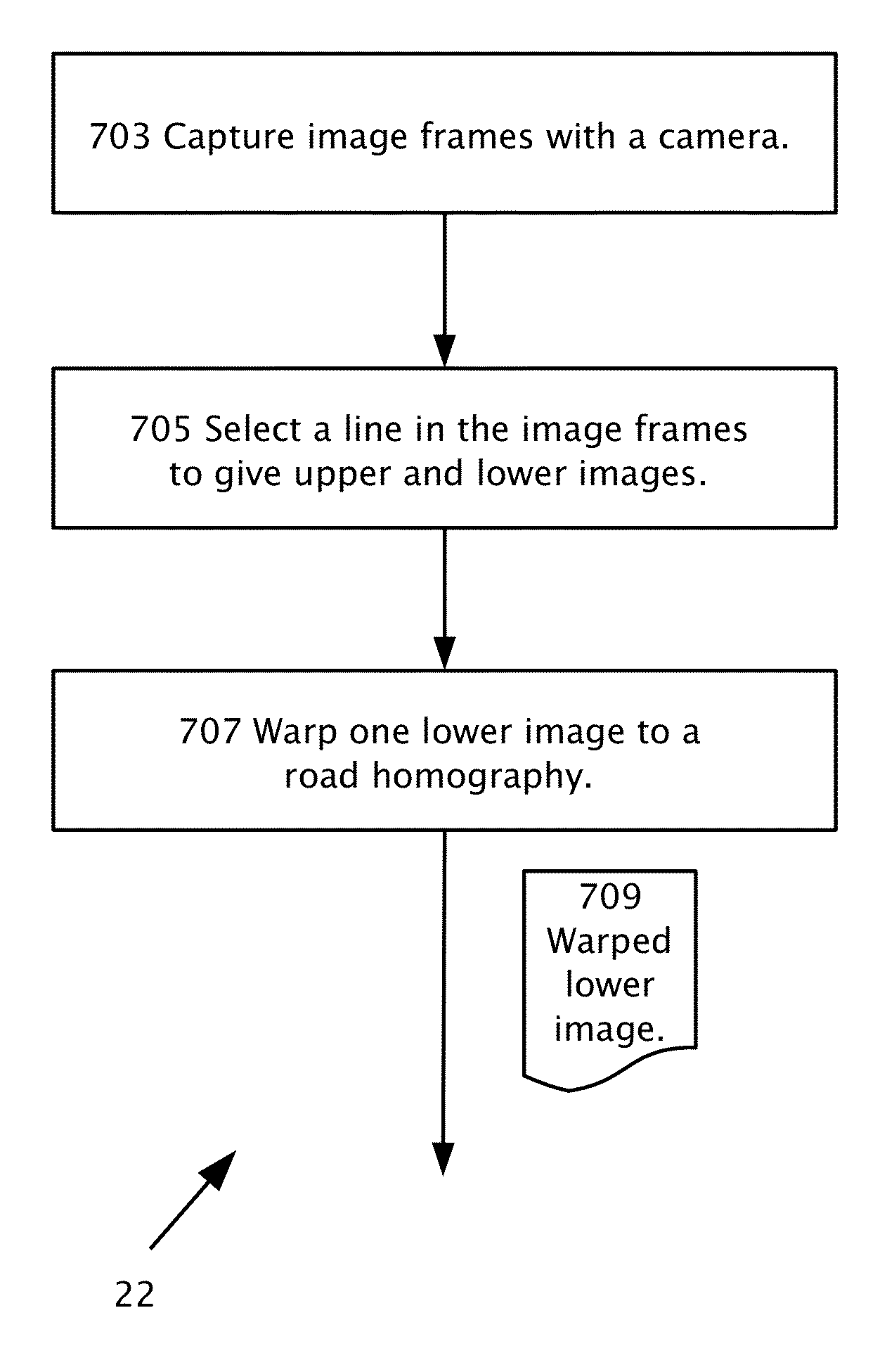
Dense structure from motion
ActiveUS20140161323A1Reduce image resolutionReduce resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisStructure from motionHomography
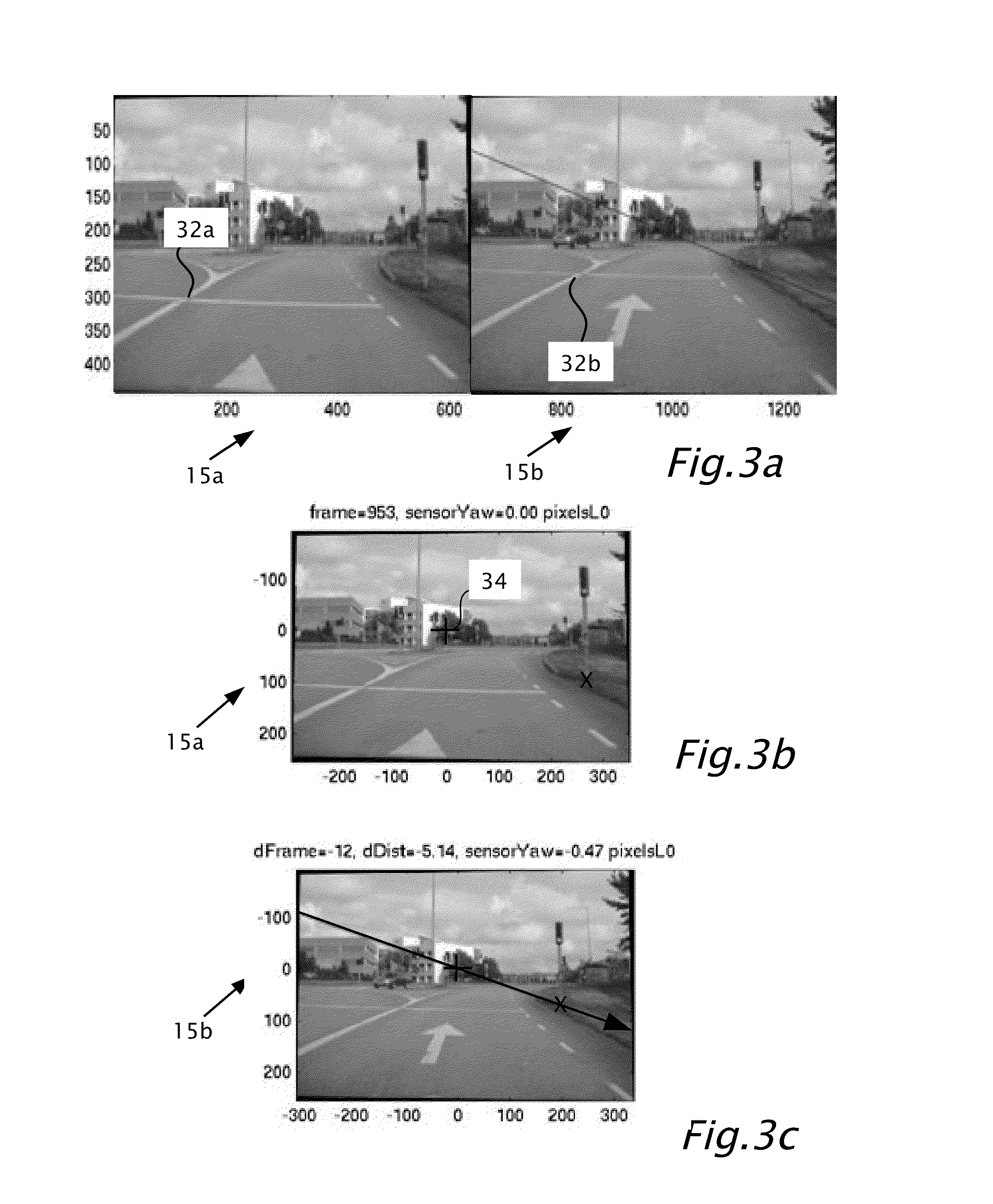
Determining three-dimensional structure in a road environment using a system mountable in a host vehicle including a camera connectible to a processor. Multiple image frames are captured in the field of view of the camera. In the image frames, a line is selected below which the road is imaged. The line separates between upper images essentially excluding images of the road and lower images essentially including images of the road. One or more of the lower images is warped, according to a road homography to produce at least one warped lower image. The three-dimensional structure may be provided from motion of a matching feature within the upper images or from motion of a matching feature within at least one of the lower images and at least one warped lower image.
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
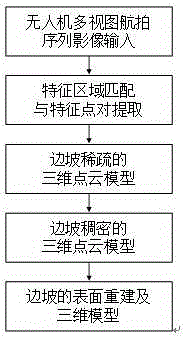
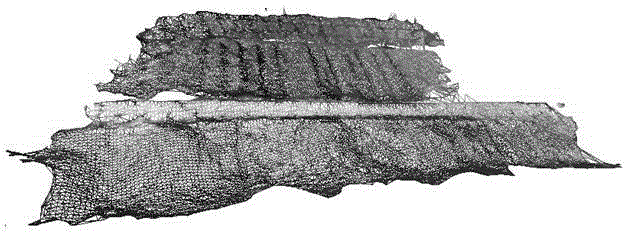
Unmanned aerial vehicle aerial photography sequence image-based slope three-dimension reconstruction method
InactiveCN105184863AReduce in quantityReduce texture discontinuities3D modellingVisual technologyStructure from motion
The invention relates to an unmanned aerial vehicle aerial photography sequence image-based slope three-dimension reconstruction method. The method includes the following steps that: feature region matching and feature point pair extraction are performed on un-calibrated unmanned aerial vehicle multi-view aerial photography sequence images through adopting a feature matching-based algorithm; the geometric structure of a slope and the motion parameters of a camera are calculated through adopting bundle adjustment structure from motion and based on disorder matching feature points, and therefore, a sparse slope three-dimensional point cloud model can be obtained; the sparse slope three-dimensional point cloud model is processed through adopting a patch-based multi-view stereo vision algorithm, so that the sparse slope three-dimensional point cloud model can be diffused to a dense slope three-dimensional point cloud model; and the surface mesh of the slope is reconstructed through adopting Poisson reconstruction algorithm, and the texture information of the surface of the slop is mapped onto a mesh model, and therefore, a vivid three-dimensional slope model with high resolution can be constructed. The unmanned aerial vehicle aerial photography sequence image-based slope three-dimension reconstruction method of the invention has the advantages of low cost, flexibility, portability, high imaging resolution, short operating period, suitability for survey of high-risk areas and the like. With the method adopted, the application of low-altitude photogrammetry and computer vision technology to the geological engineering disaster prevention and reduction field can be greatly prompted.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
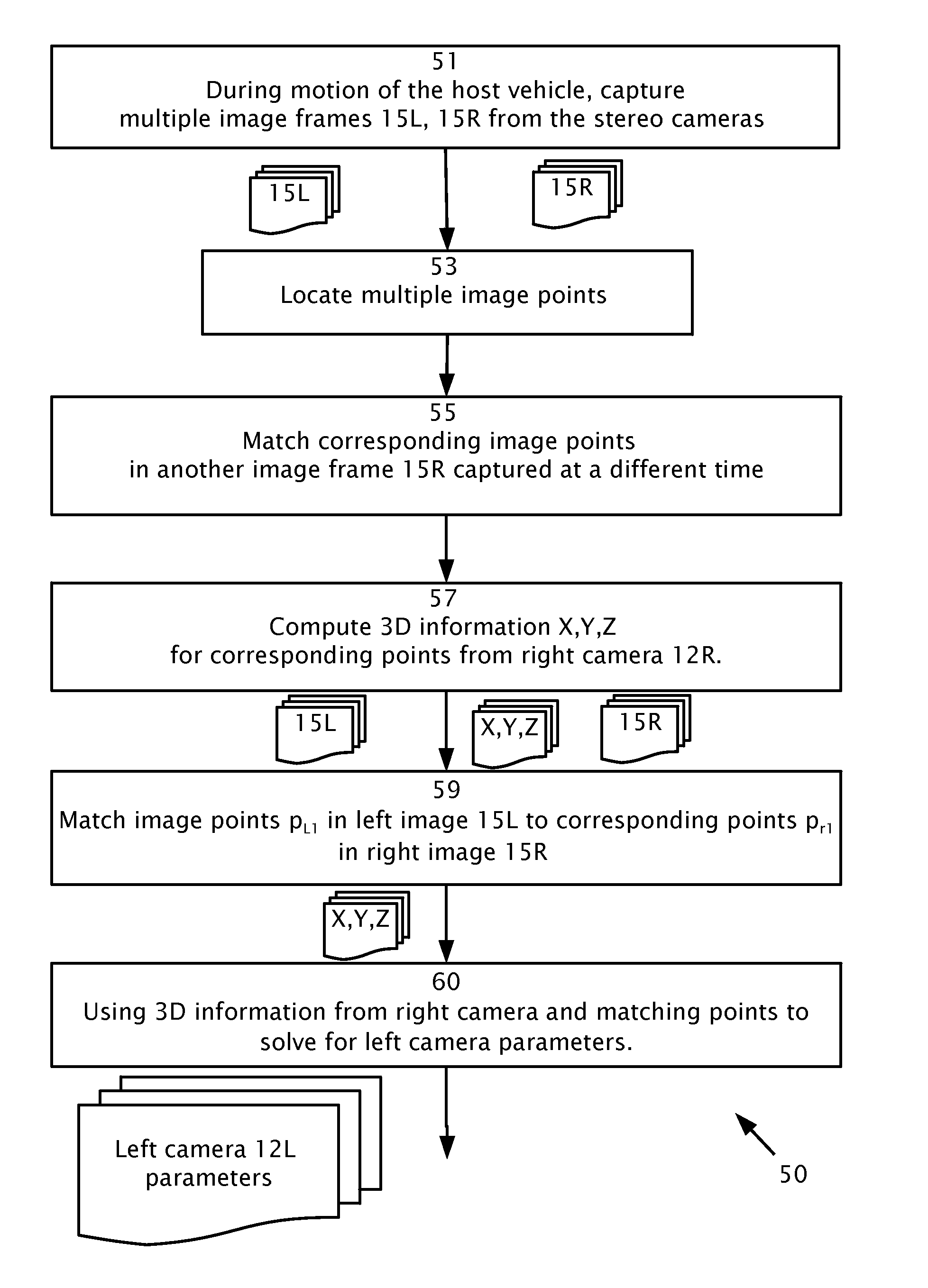
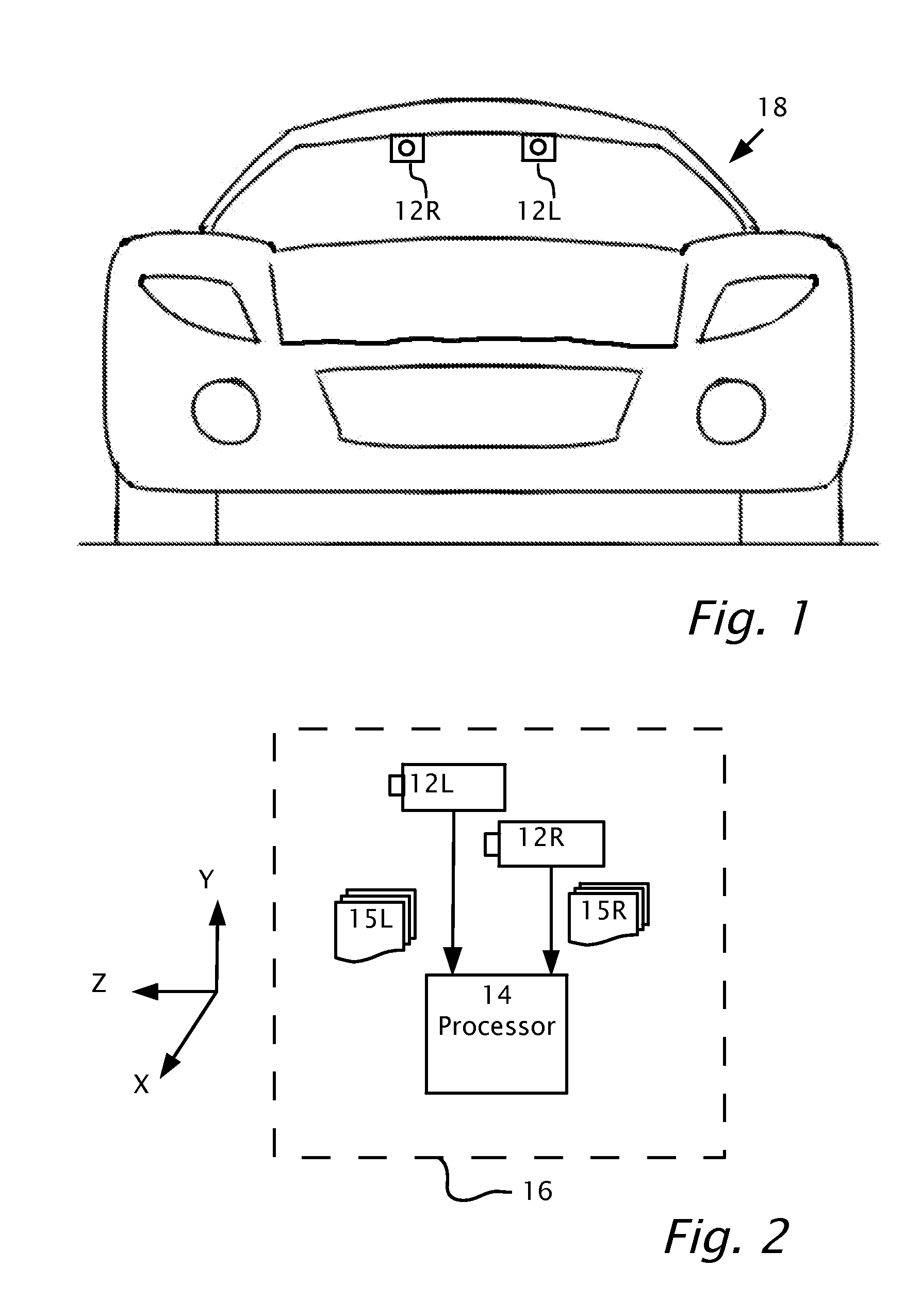
Stereo auto-calibration from structure-from-motion
Auto-calibration of stereo cameras installable behind the windshield of a host vehicle and oriented to view the environment through the windshield. Multiple first image points are located of one of the first images captured from the first camera at a first time and matched with first image points of at least one other of the first images captured from the first camera at a second time to produce pairs of corresponding first image points respectively in the first images captured at the different times. World coordinates are computed from the corresponding first image points. Second image points in the second images captured from the second camera are matched to at least a portion of the first image points. The world coordinates as determined from the first camera are used, to solve for camera parameters of the second camera from the matching second image points of the second camera.
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
Plane-based Self-Calibration for Structure from Motion
Robust techniques for self-calibration of a moving camera observing a planar scene. Plane-based self-calibration techniques may take as input the homographies between images estimated from point correspondences and provide an estimate of the focal lengths of all the cameras. A plane-based self-calibration technique may be based on the enumeration of the inherently bounded space of the focal lengths. Each sample of the search space defines a plane in the 3D space and in turn produces a tentative Euclidean reconstruction of all the cameras that is then scored. The sample with the best score is chosen and the final focal lengths and camera motions are computed. Variations on this technique handle both constant focal length cases and varying focal length cases.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Method and system for 3D capture based on structure from motion with pose detection tool
Method and System for 3D capture based on SFM with simplified pose detection is disclosed. This invention provides a straightforward method to directly track the camera's motion (pose detection) thereby removing a substantial portion of the computing load needed to build the 3D model from a sequence of images.
Owner:JOVANOVIC DEJAN +4
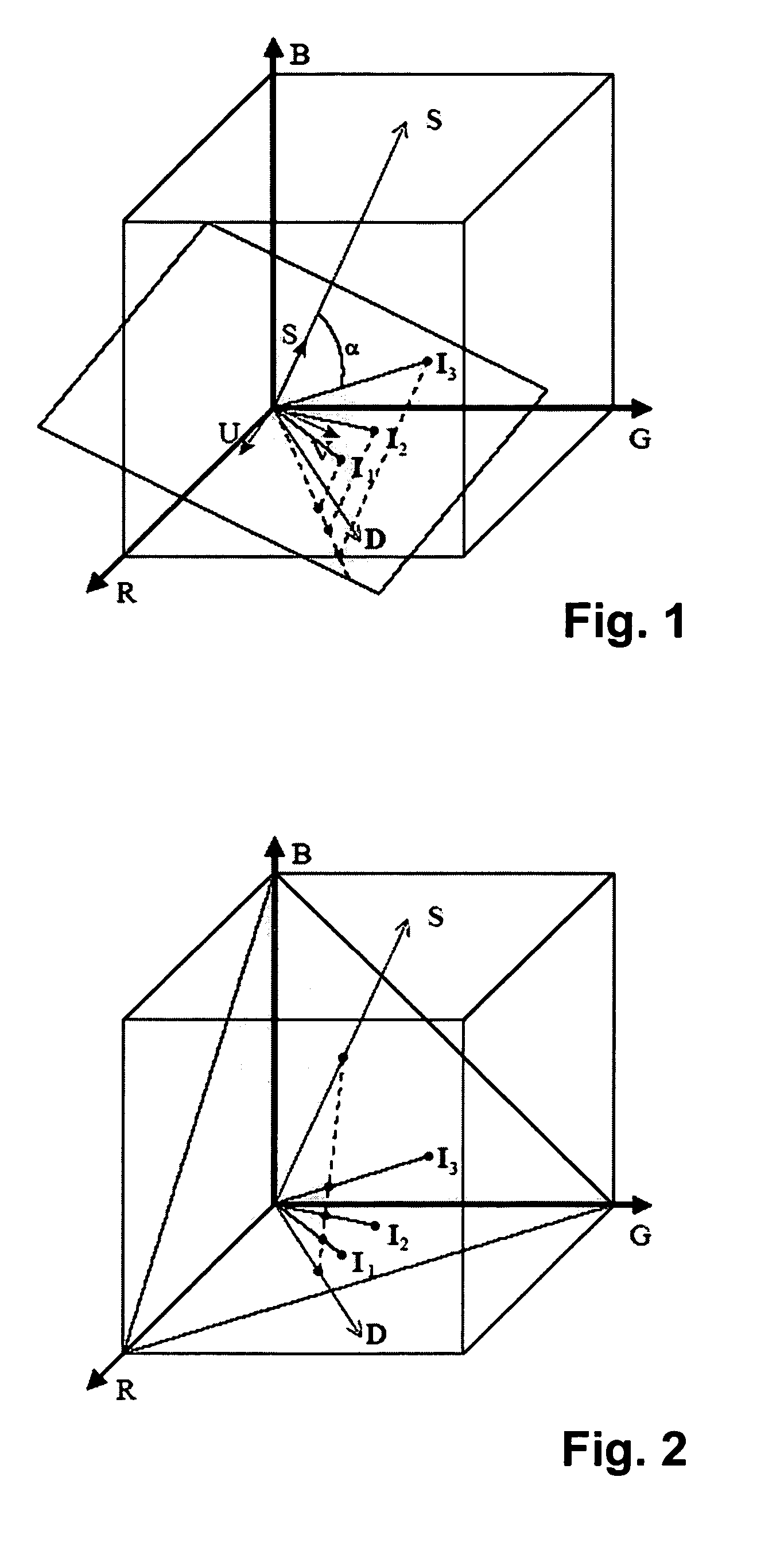
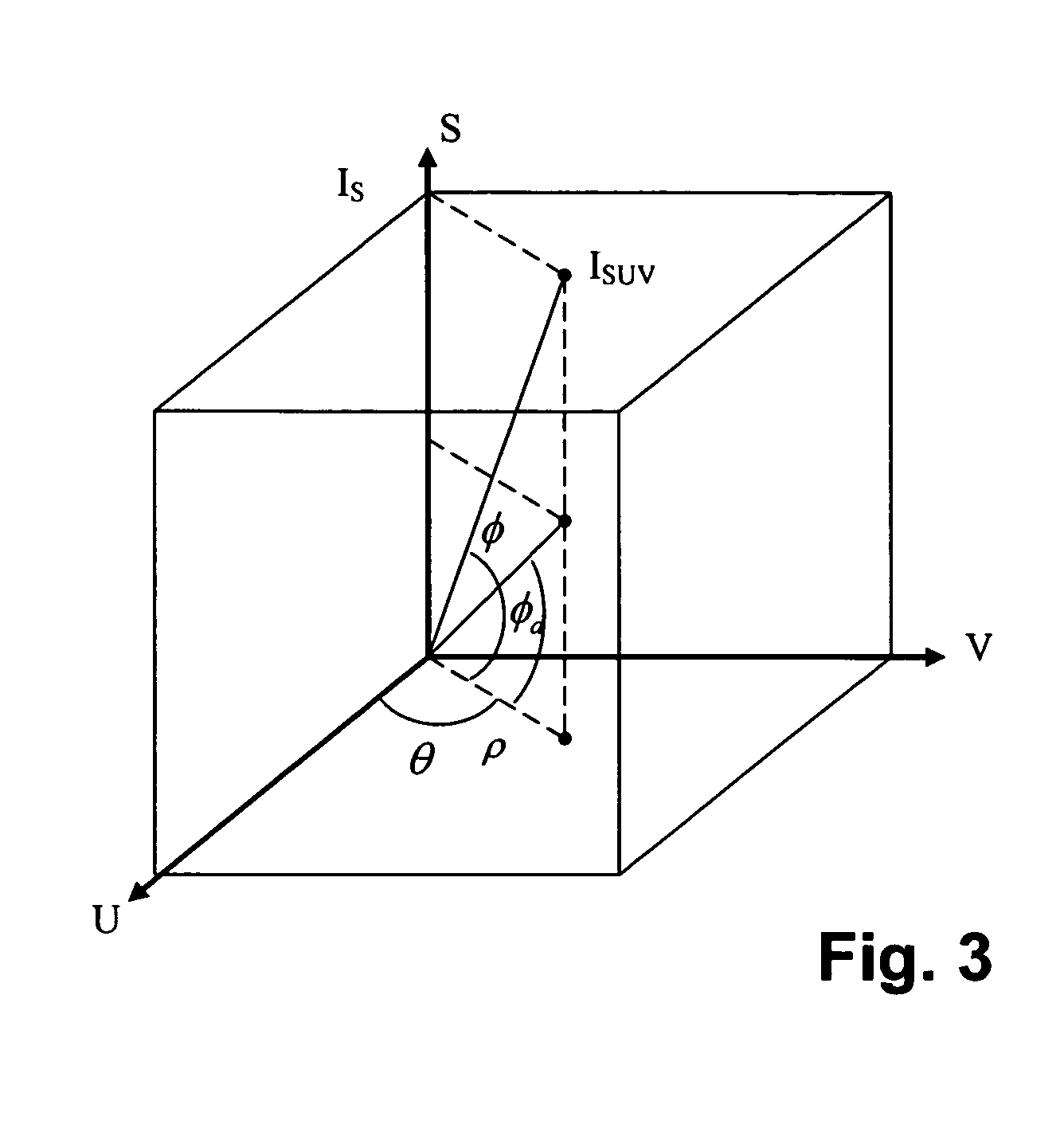
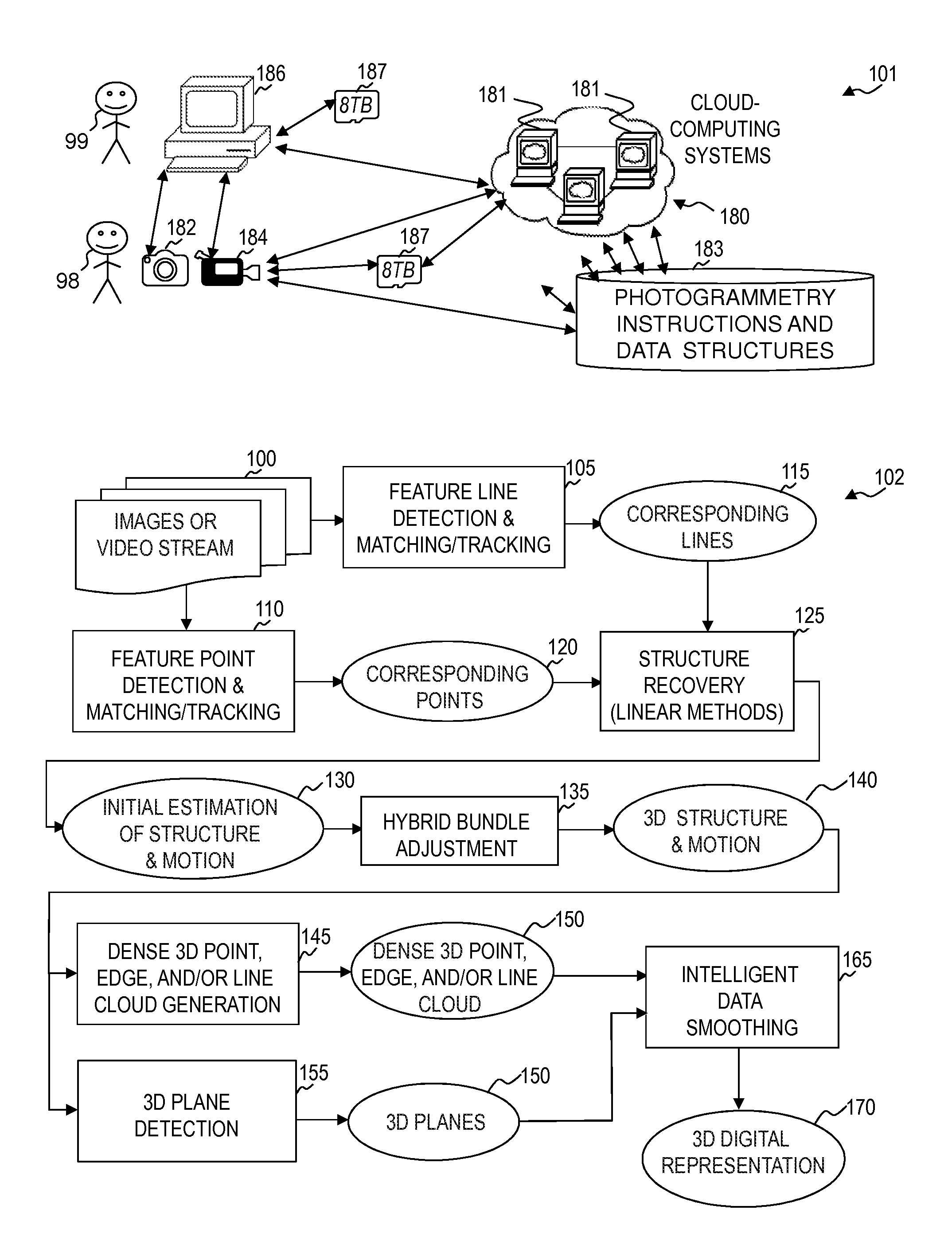
Methods for identifying, separating and editing reflection components in multi-channel images and videos
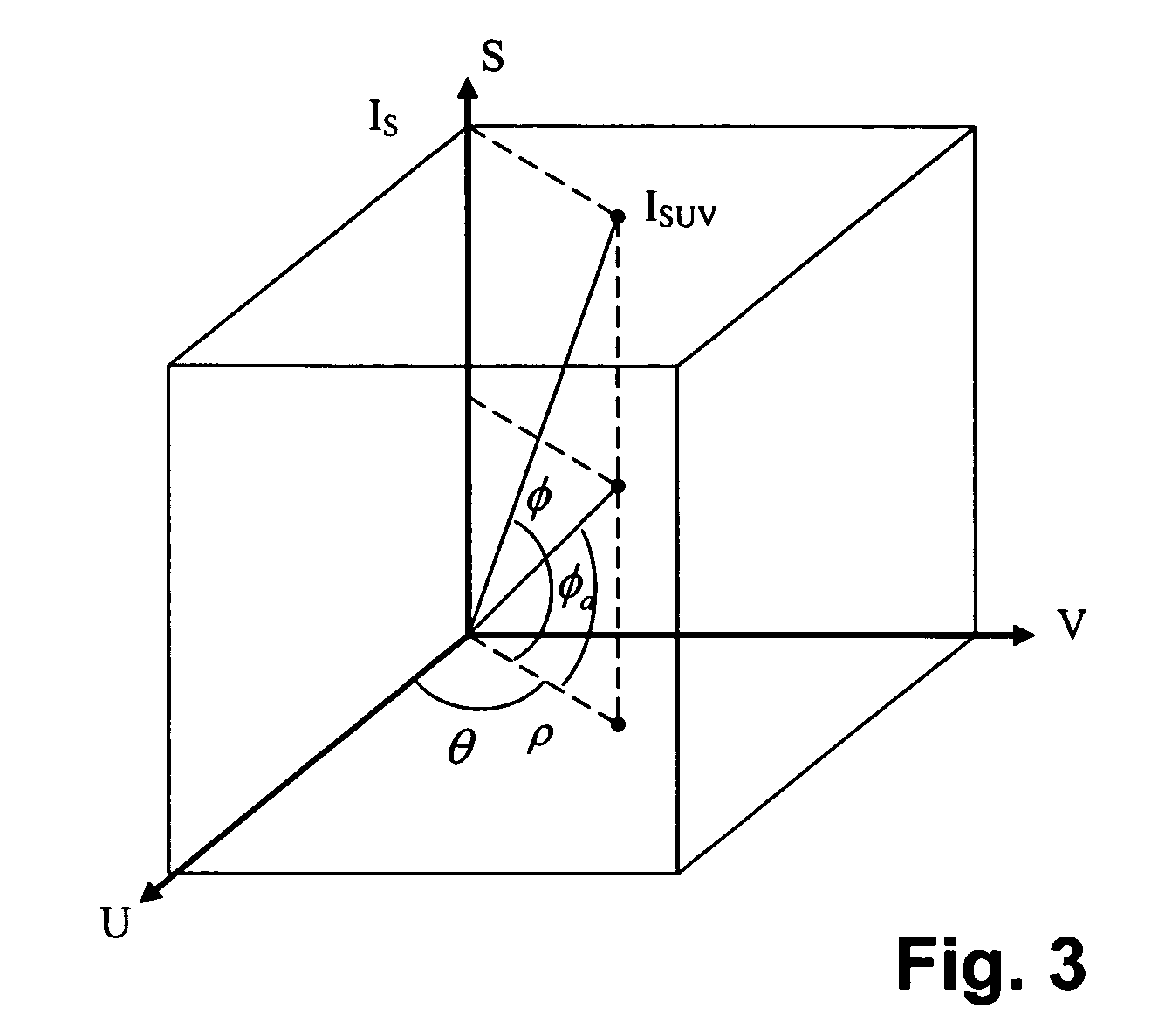
InactiveUS20070132759A1Preserve textureReduce specular reflectionImage enhancementImage analysisStructure from motionRgb image
The present invention presents a framework for separating specular and diffuse reflection components in images and videos. Each pixel of the an M-channel input image illuminated by N light sources is linearly transformed into a new color space having (M-N) channels. For an RGB image with one light source, the new color space has two color channels (U,V) that are free of specularities and a third channel (S) that contains both specular and diffuse components. When used with multiple light sources, the transformation may be used to produce a specular invariant image. A diffuse RGB image can be obtained by applying a non-linear partial differential equation to an RGB image to iteratively erode the specular component at each pixel. An optional third dimension of time may be added for processing video images. After the specular and diffuse components are separated, dichromatic editing may be used to independently process the diffuse and the specular components to add or suppress visual effects. The (U,V) channels of images can be used as input to 3-D shape estimation algorithms including shape-from-shading, photometric stereo, binocular and multinocular stereopsis, and structure-from-motion.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
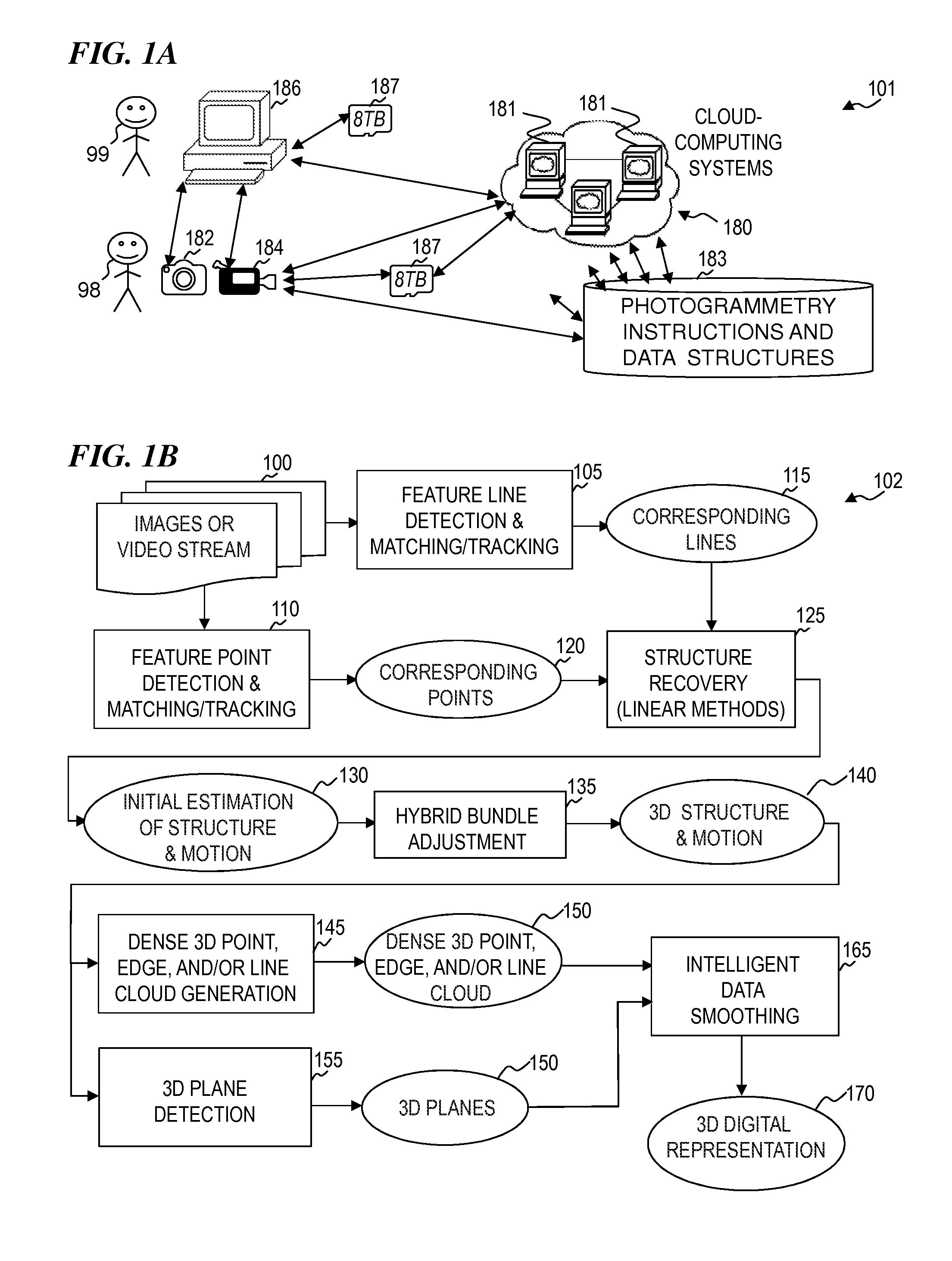
Photogrammetric methods and devices related thereto
InactiveUS20160239976A1Accurate measurementExcessive overall dimensionImage enhancementImage analysisStructure from motionImage capture
The inventions herein relate generally to improvements in photogrammetry and devices suitable for obtaining such improvements. Some embodiments use only a single passive image-capture device to obtain overlapping 2D images, where such images at least partially overlap with regard to at least one object of interest in a scene. Such images can be processed using methods incorporating structure from motion algorithms. Accurate 3D digital representations of the at least one object of interest can be obtained. Substantially accurate measurements and other useful information regarding the at least one object of interest are obtainable from the methodology herein.
Owner:POINTIVO
Method for 3D modelling based on structure from motion processing of sparse 2D images
ActiveUS20180276885A1Improve accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisCluster algorithmStructure from motion
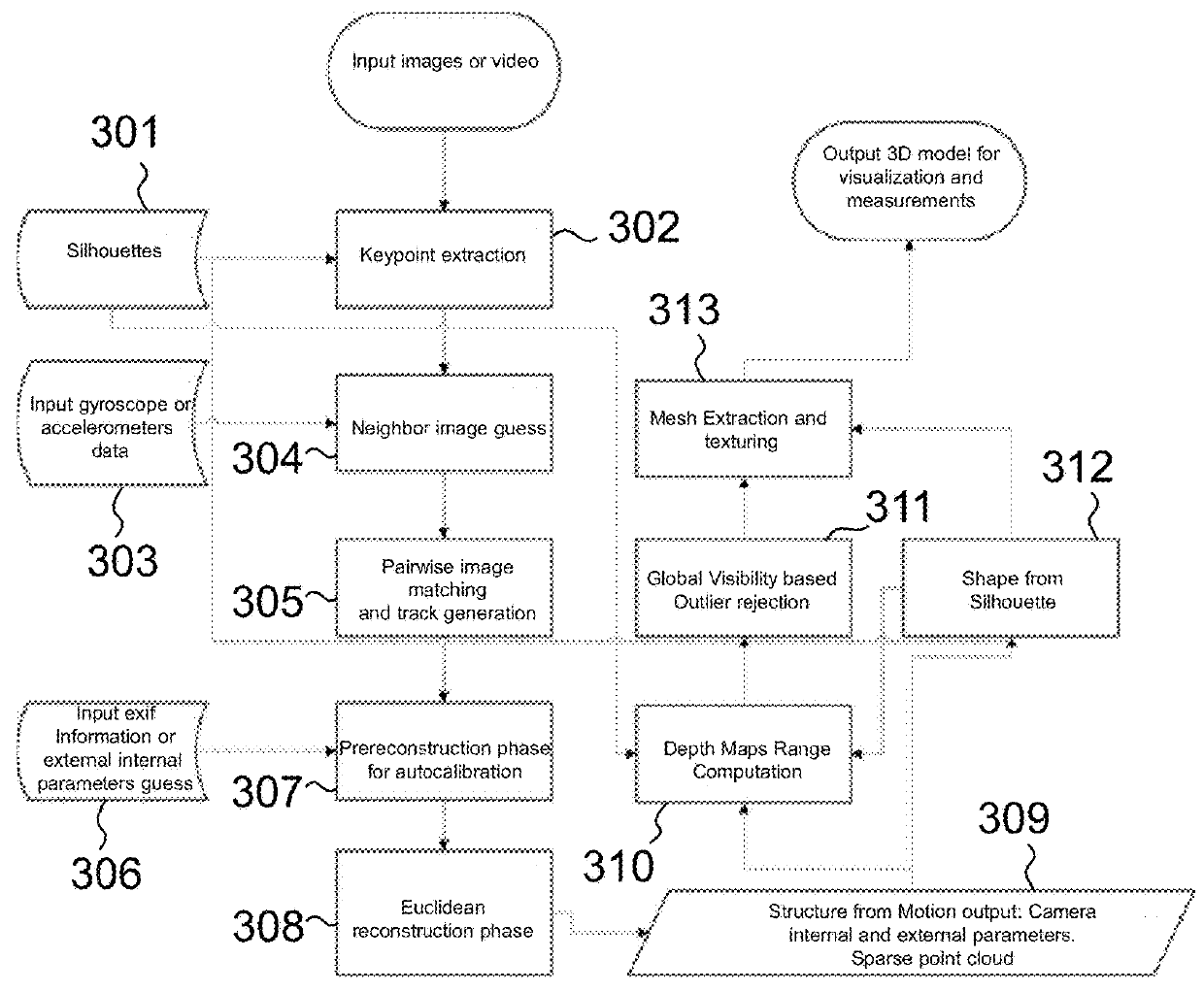
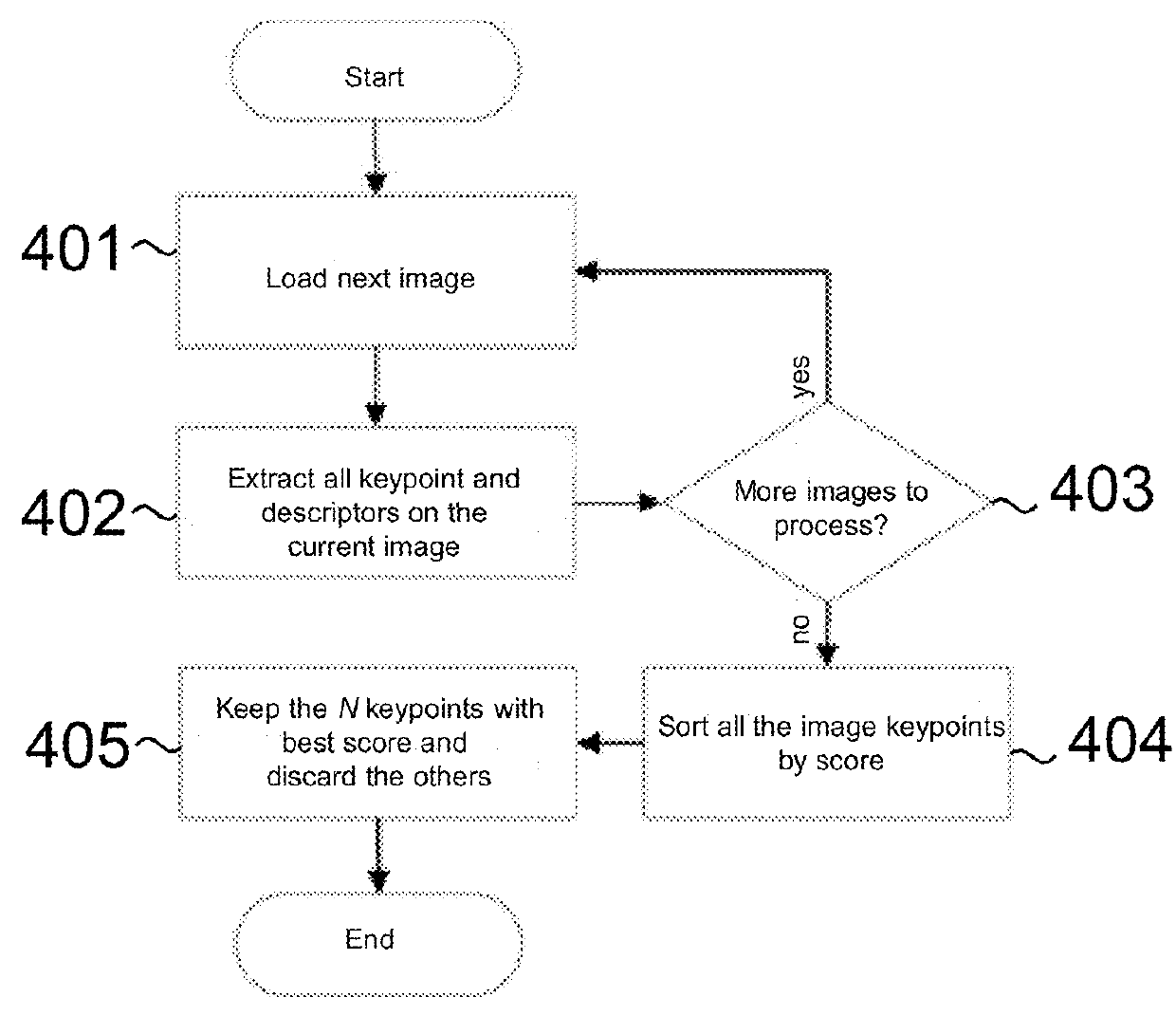
A method based on Structure from Motion for processing a plurality of sparse images acquired by one or more acquisition devices to generate a sparse 3D points cloud and of a plurality of internal and external parameters of the acquisition devices includes the steps of collecting the images; extracting keypoints therefrom and generating keypoint descriptors; organizing the images in a proximity graph; pairwise image matching and generating keypoints connecting tracks according maximum proximity between keypoints; performing an autocalibration between image clusters to extract internal and external parameters of the acquisition devices, wherein calibration groups are defined that contain a plurality of image clusters and wherein a clustering algorithm iteratively merges the clusters in a model expressed in a common local reference system starting from clusters belonging to the same calibration group; and performing a Euclidean reconstruction of the object as a sparse 3D point cloud based on the extracted parameters.
Owner:3DFLOW SRL
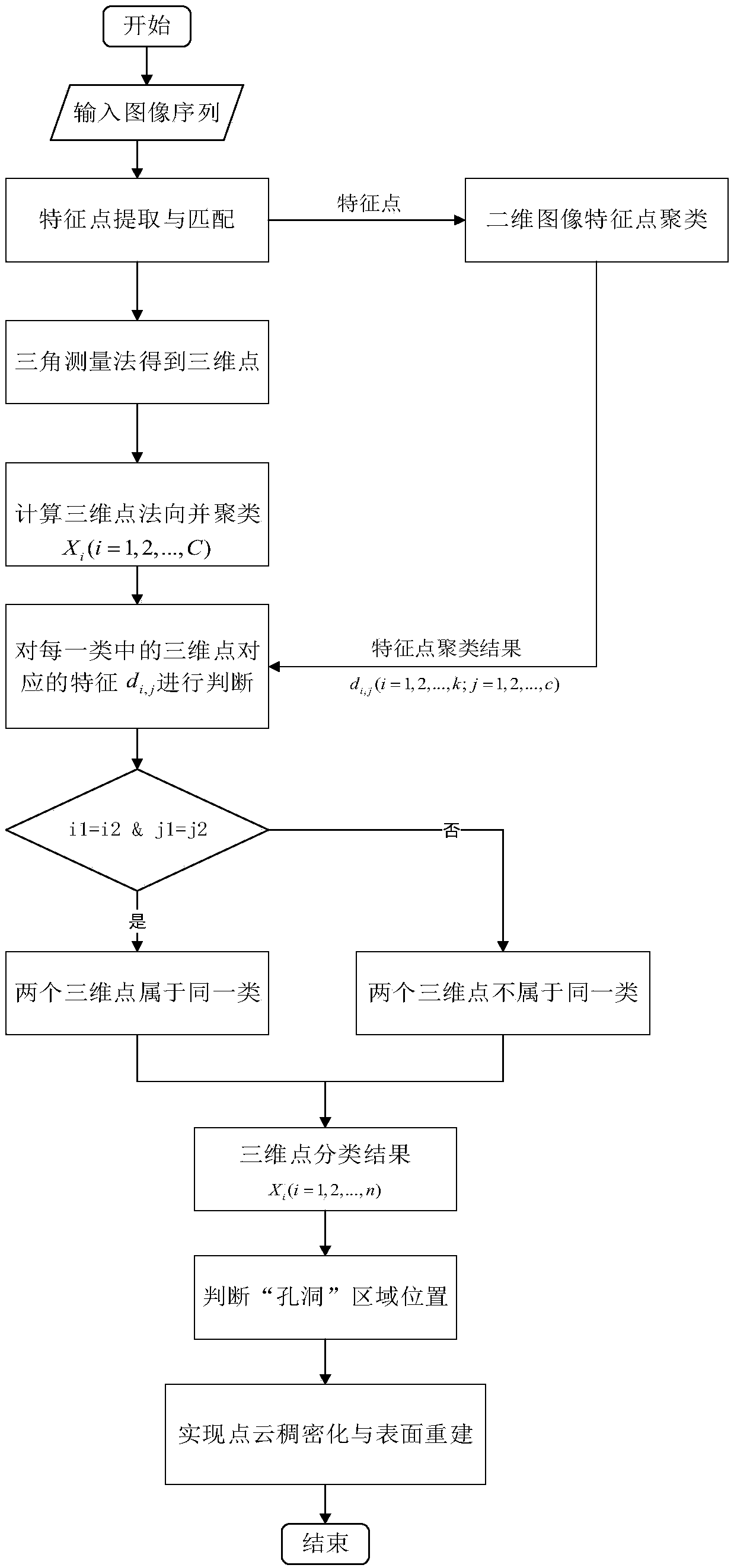
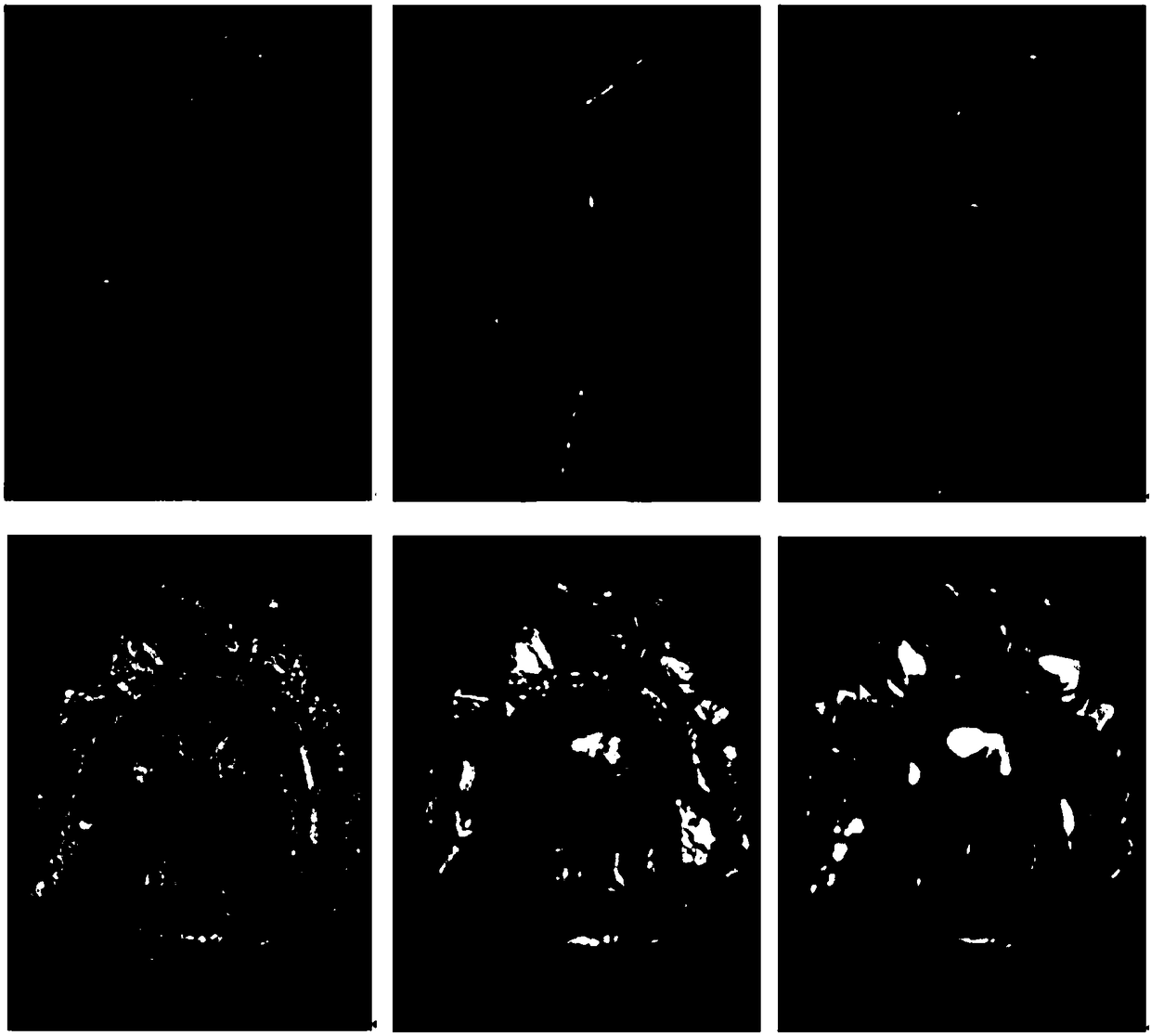
Target reconstruction method based on geometric constraint
ActiveCN108090960AImproved point cloud resultsImprove integrityImage enhancementImage analysisStructure from motionPoint cloud
The invention relates to a target reconstruction method based on a geometric constraint and belongs to the computer vision field. The method comprises the following steps of through a structure from motion (SFM) method, acquiring initial point cloud; through image characteristic point clustering, acquiring a classification result of characteristic points, wherein the classification result means aneighborhood relation of similar portions in an image; carrying out normal characteristic clustering of the initial point cloud, and using a corresponding relation between the classification result ofthe image characteristic points and an initial point cloud clustering result to define a geometric structure of the initial point cloud; using the geometric structure to acquire a sparse portion in the initial point cloud, defining the portion as a ''hole'', and then using a combined structure constraint of a ''hole'' area to carry out fitting of a space plane and a curved surface through an RANSAC method and a least square method; and sampling a fitted surface, adding an acquired three-dimensional point into the initial point cloud so as to acquire a dense point cloud model, and finally using a Poisson surface to reconstruct and acquire a three-dimensional model of a target. Through an experiment result, implementation of the method is verified and a good effect is achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Simultaneous localization and mapping using multiple view feature descriptors
InactiveUS7831094B2Efficiently build necessary feature descriptorReliable correspondenceThree-dimensional object recognitionKaiman filterKernel principal component analysis
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method and system for 3D capture based on structure from motion with simplified pose detection
Owner:SMART PICTURE TECH
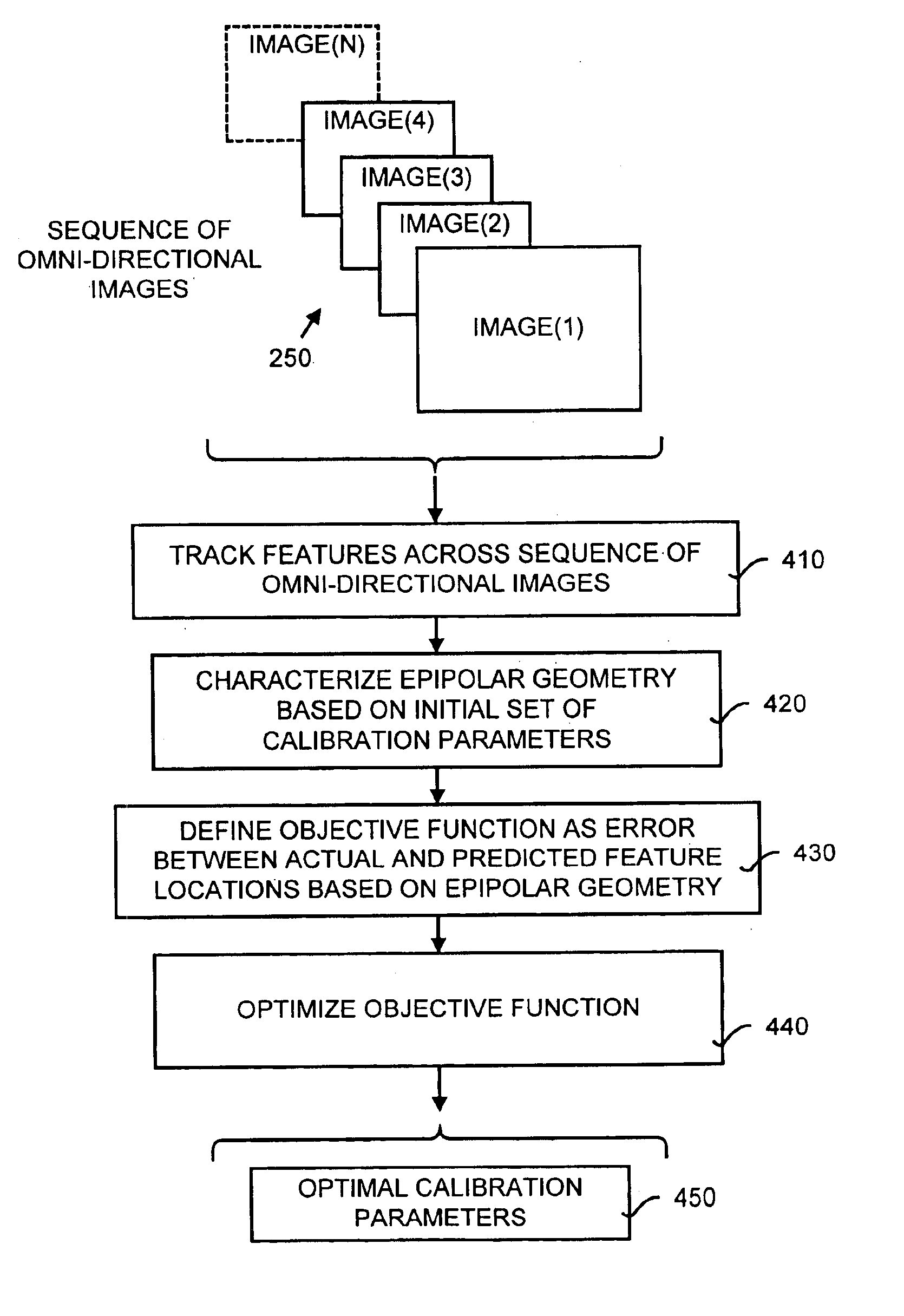
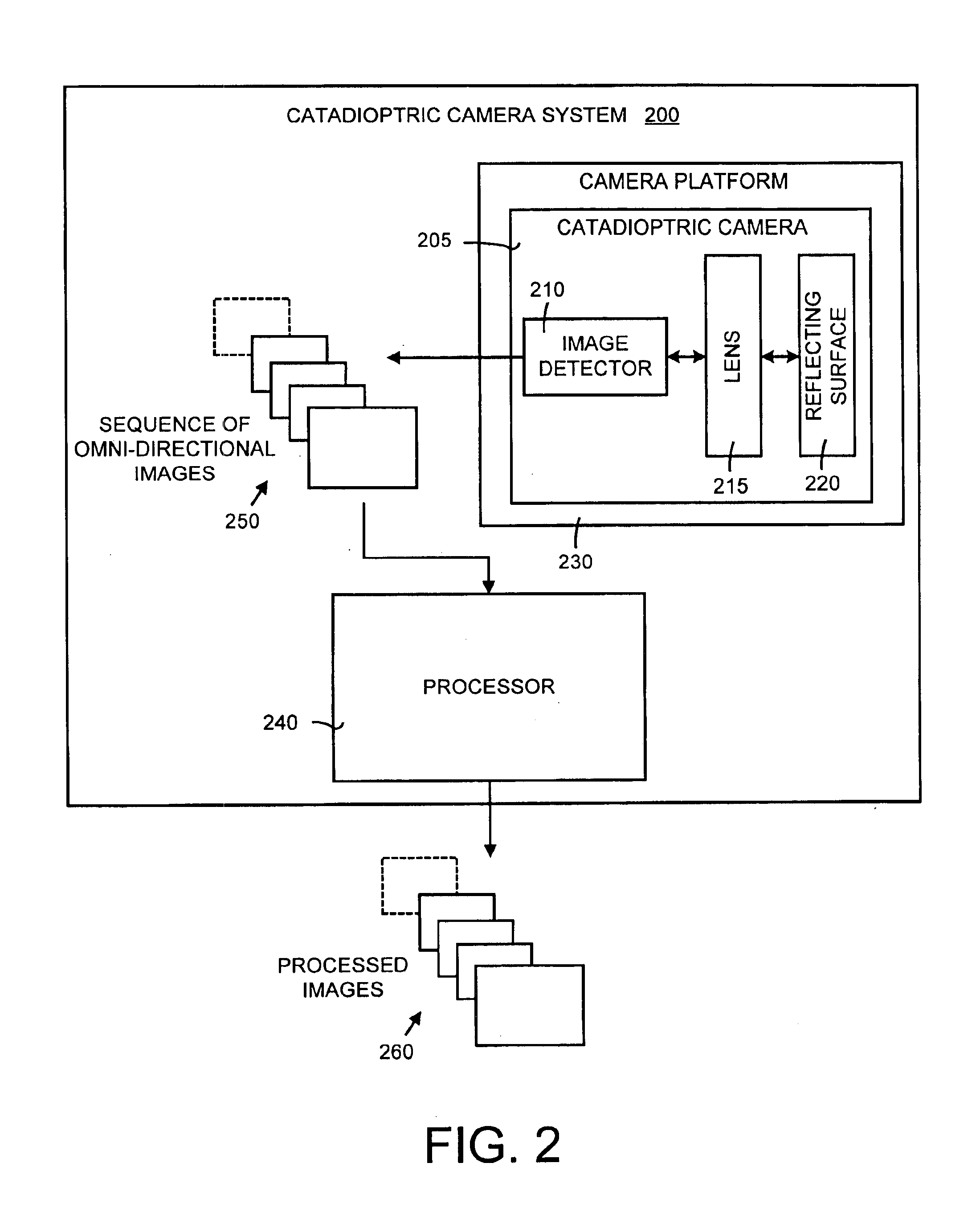
Self-calibration for a catadioptric camera
InactiveUS6870563B1Easy to useAccurate CalibrationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionView camera
A method and a system for self-calibrating a wide field-of-view camera (such as a catadioptric camera) using a sequence of omni-directional images of a scene obtained from the camera. The present invention uses the consistency of pairwise features tracked across at least a portion of the image collection and uses these tracked features to determine unknown calibration parameters based on the characteristics of catadioptric imaging. More specifically, the self-calibration method of the present invention generates a sequence of omni-directional images representing a scene and tracks features across the image sequence. An objective function is defined in terms of the tracked features and an error metric (an image-based error metric in a preferred embodiment). The catadioptric imaging characteristics are defined by calibration parameters, and determination of optimal calibration parameters is accomplished by minimizing the objective function using an optimizing technique. Moreover, the present invention also includes a technique for reformulating a projection equation such that the projection equation is equivalent to that of a rectilinear perspective camera. This technique allows analyses (such as structure from motion) to be applied (subsequent to calibration of the catadioptric camera) in the same direct manner as for rectilinear image sequences.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
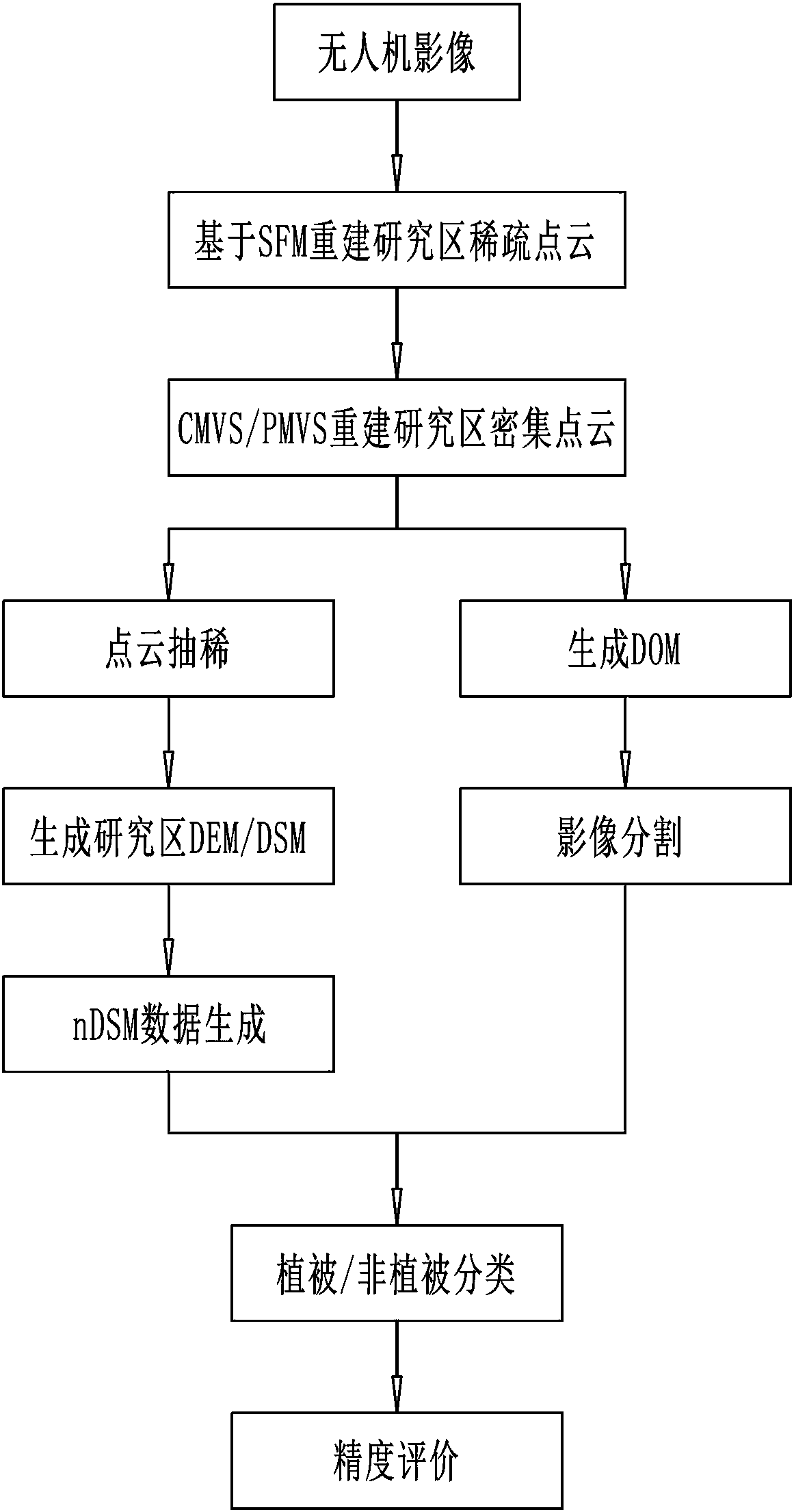
Urban vegetation classification method based on unmanned aerial vehicle images and reconstructed point cloud
ActiveCN108363983AHigh precisionImprove classification efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionStructure from motionPoint cloud
The present invention provides an urban vegetation classification method based on unmanned aerial vehicle images and reconstructed point cloud. The method comprises the steps of: performing point cloud reconstruction of original unmanned aerial vehicle images; generating nDSM (normalized digital surface model) information of a research area; performing vegetation index calculation based on visiblelight; and performing classification discrimination of image objects. The method provided by the invention reconstructs point cloud of the research area based on a structure from motion (SFM) and cluster multi-view stereo (CMVS) and based on a patch-based multi-view stereo (PMVS) algorithm, performs filtering and interpolation to generate a digital elevation model (DEM) of the research area and the nDSM, and combines image spectral information to perform classification extraction of urban vegetations with different heights; an image analysis method facing the objects is employed to achieve differentiation of the categories of vegetations with different heights according to spectral information such as the nDSM information, normalized green-red difference indexes (NGRDI) and visible lightwave band difference vegetation indexes (VDVI) so as to greatly improve the differentiation precision.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
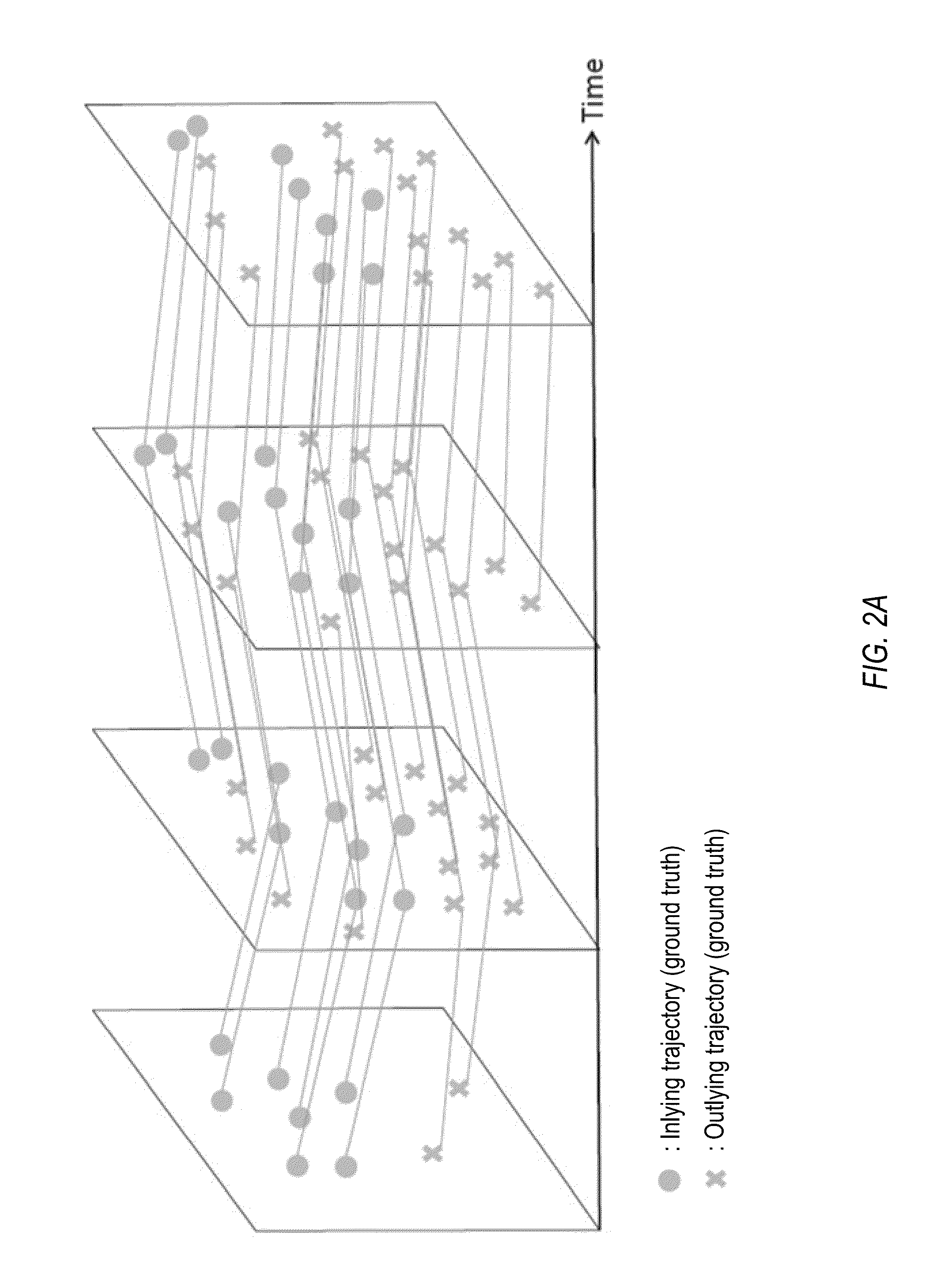
Real-time camera position estimation with drift mitigation in incremental structure from motion
ActiveUS20180315221A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionStructure from motionPoint cloud
A system provides camera position and point cloud estimation 3D reconstruction. The system receives images and attempts existing structure integration to integrate the images into an existing reconstruction under a sequential image reception assumption. If existing structure integration fails, the system attempts dictionary overlap detection by accessing a dictionary database and searching to find a closest matching frame in the existing reconstruction. If overlaps are found, the system matches the images with the overlaps to determine a highest probability frame from the overlaps, and attempts existing structure integration again. If overlaps are not found or existing structure integration fails again, the system attempts bootstrapping based on the images. If any of existing structure integration, dictionary overlap detection, or bootstrapping succeeds, and if multiple disparate tracks have come to exist, the system attempts reconstructed track merging.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
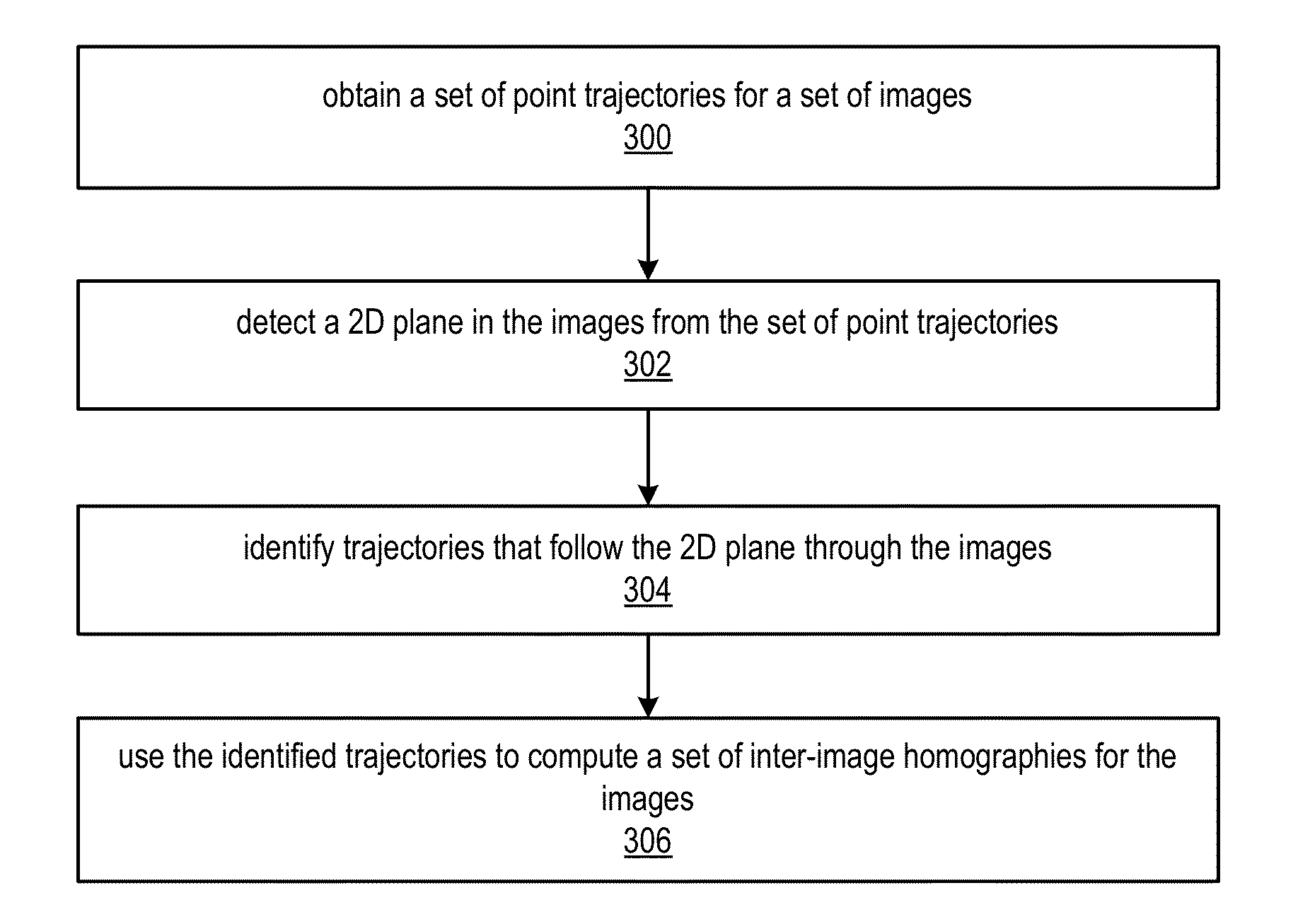
Plane Detection and Tracking for Structure from Motion
Plane detection and tracking algorithms are described that may take point trajectories as input and provide as output a set of inter-image homographies. The inter-image homographies may, for example, be used to generate estimates for 3D camera motion, camera intrinsic parameters, and plane normals using a plane-based self-calibration algorithm. A plane detection and tracking algorithm may obtain a set of point trajectories for a set of images (e.g., a video sequence, or a set of still photographs). A 2D plane may be detected from the trajectories, and trajectories that follow the 2D plane through the images may be identified. The identified trajectories may be used to compute a set of inter-image homographies for the images as output.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Methods for identifying, separating and editing reflection components in multi-channel images and videos
InactiveUS7689035B2Reduce specular reflectionImage enhancementImage analysisStructure from motionRgb image
The present invention presents a framework for separating specular and diffuse reflection components in images and videos. Each pixel of the an M-channel input image illuminated by N light sources is linearly transformed into a new color space having (M−N) channels. For an RGB image with one light source, the new color space has two color channels (U,V) that are free of specularities and a third channel (S) that contains both specular and diffuse components. When used with multiple light sources, the transformation may be used to produce a specular invariant image. A diffuse RGB image can be obtained by applying a non-linear partial differential equation to an RGB image to iteratively erode the specular component at each pixel. An optional third dimension of time may be added for processing video images. After the specular and diffuse components are separated, dichromatic editing may be used to independently process the diffuse and the specular components to add or suppress visual effects. The (U,V) channels of images can be used as input to 3-D shape estimation algorithms including shape-from-shading, photometric stereo, binocular and multinocular stereopsis, and structure-from-motion.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Super pixel-based target reconstruction method
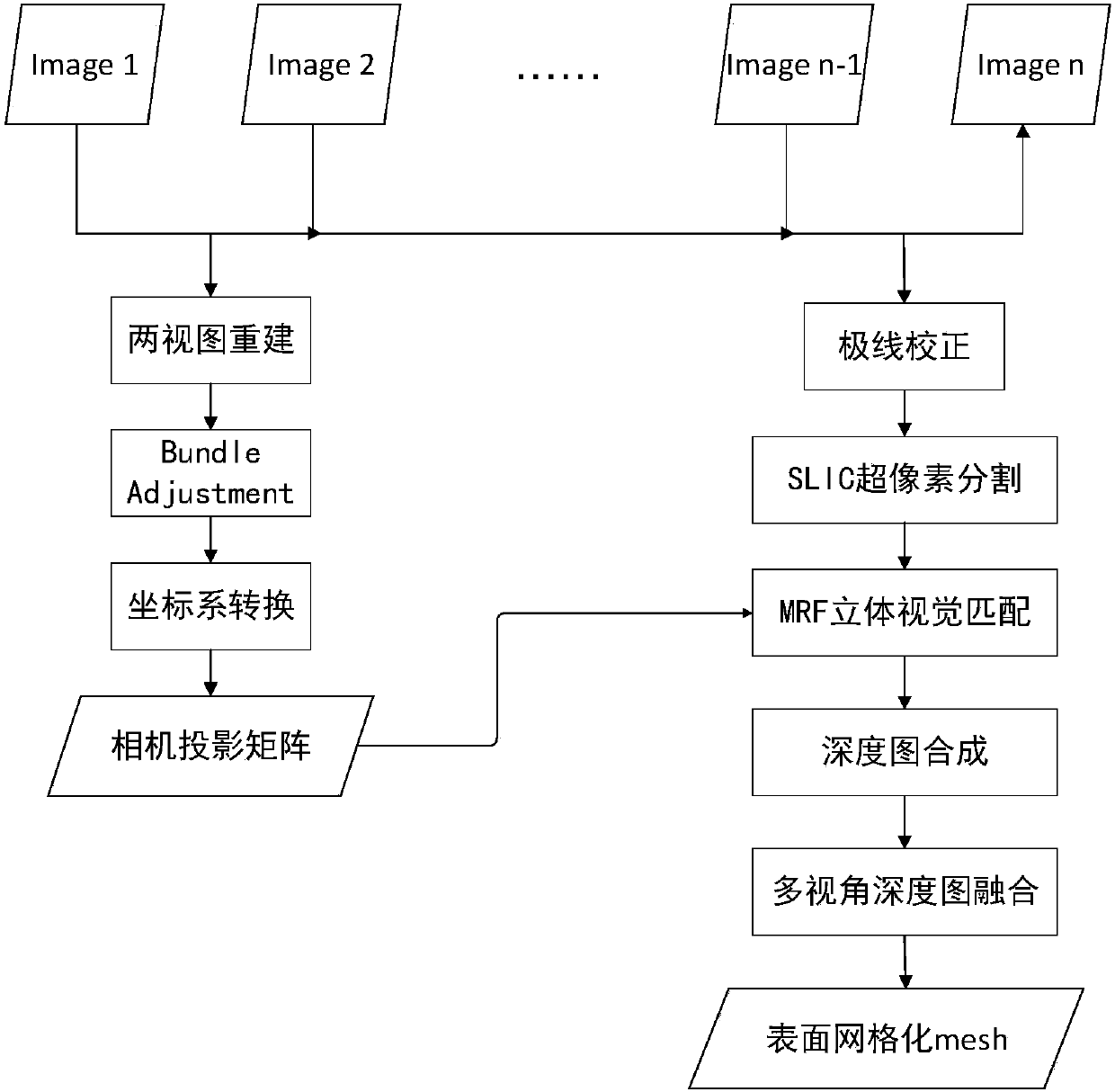
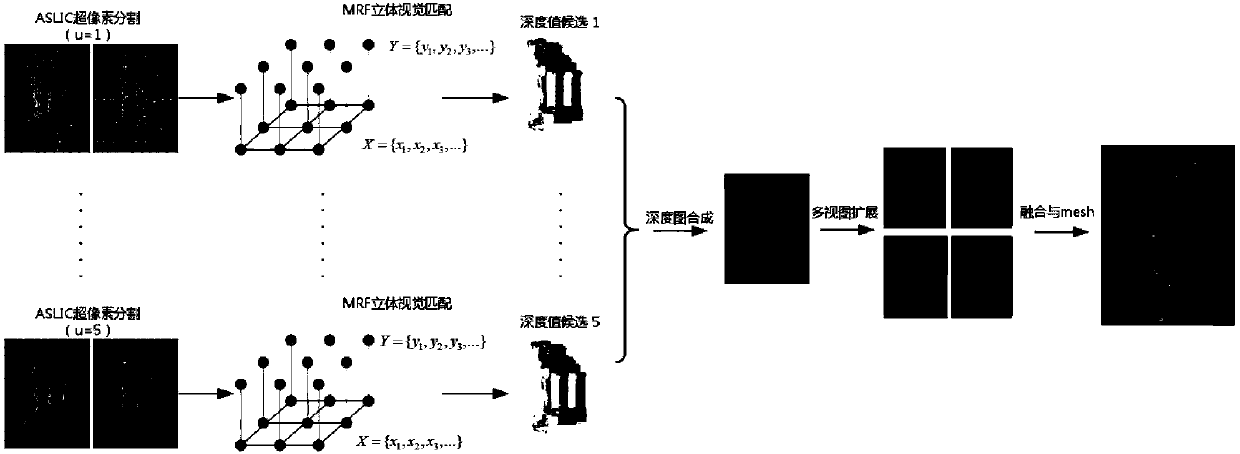
ActiveCN108038905ASimplify the matching processRobustImage analysisGeometric image transformationHat matrixComputation complexity
The invention provides a super pixel-based target reconstruction method. The method is formed by structure-from-motion (SFM) projection matrix estimation, multi-view stereoscopic vision matching undersuper pixels and synthesis and fusion of depth graphs. A specific process includes the six major steps of: step 1, reading an image sequence, and utilizing a structure-from-motion method to estimatea camera projection matrix; step 2, carrying out super-pixel segmentation on image pairs; step 3, calculating possible depth values for each super pixel; step 4, utilizing an MRF model to select optimal depth values of the super pixels; step 5, creating a multi-scale super-pixel framework; and step 6, carrying out depth graph fusion and surface meshing. According to the method, a disadvantage of insufficient precision of super pixel-based stereoscopic vision matching is overcome, advantages that the same is high in robustness for noises and brightness deviations, can accurately provide targetcontour information, and is low in calculation complexity are utilized, better reconstruction results can be achieved for both texture regions and non-texture regions, and universality is high. The method has broad application backgrounds.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
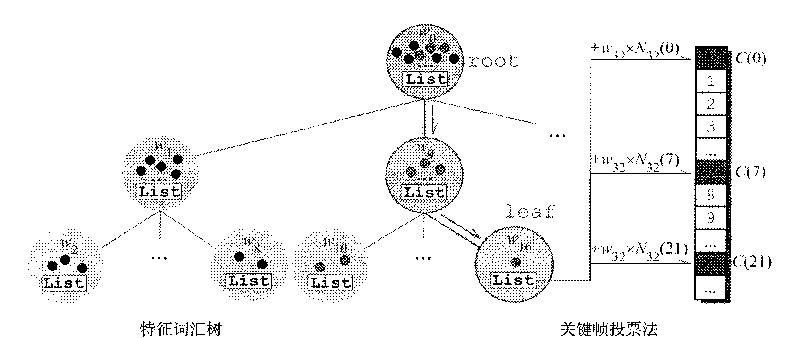
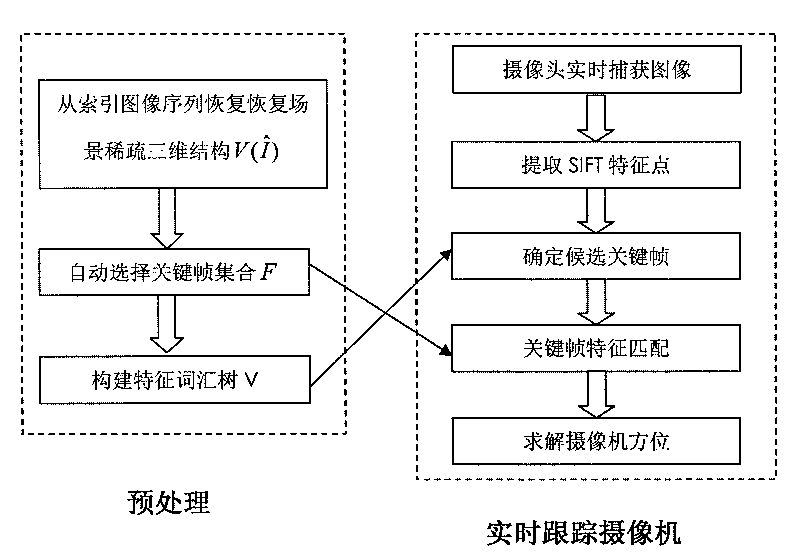
Real-time video camera tracking method based on key frames
InactiveCN101763647AQuick fixImprove computing efficiencyImage analysisStructure from motionEnergy functional
The invention discloses a real-time video camera tracking method based on key frames, which comprises the following steps: (1) capturing an index image sequence, and restoring a sparse three-dimensional characteristic point structure of a scene by a method of inferring a structure from movement; (2) giving the index image sequence and the sparse three-dimensional characteristic point structure, and automatically selecting the key frames by optimizing an energy function related to the key frames; (3) in the real-time video camera tracking process, for each frame of real-time input image, firstly, quickly positioning a candidate key frame similar to the real-time input image from the key frame set by a characteristic word tree method of image recognition; and (4) matching the characteristic points abstracted on the real-time input image with the characteristic points on the candidate key frame, obtaining the corresponding three dimensional coordinates of the characteristic points on the image, and calculating the directionality parameters of the video camera. The invention has high calculating efficiency and stable solving result, and the video camera tracking result obtained by the method can be directly used for the applications of reality enhancement, virtual interaction and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
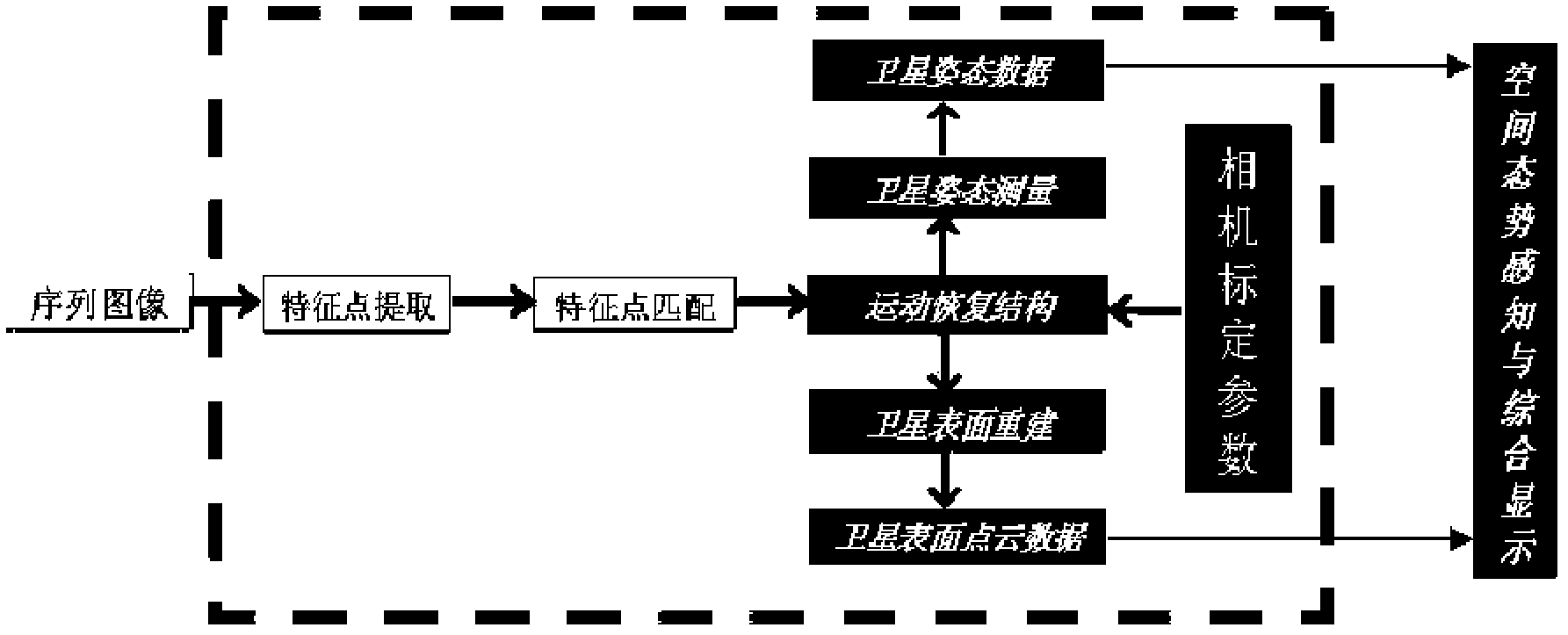
Satellite relative attitude measuring method based on structure from motion
InactiveCN102607534ARealize identificationImplement trackingPicture interpretationNumerical stabilityStructure from motion
The invention discloses a satellite relative attitude measuring method based on a structure from motion. The satellite relative attitude measuring method includes a first step, respectively extracting SIFT (scale invariant feature transform) feature points of inputted sequence images; a second step, matching the obtained SIFT feature points; a third step, realizing the structure from motion according to the matched feature points; a fourth step, optimizing structural parameters of the structure from motion by a light beam adjustment method; a fifth step, carrying out three-dimensional reconstruction according to the matched feature points and the optimized structural parameters of the structure from motion; and a sixth step, comprehensively displaying a spatial environment according to effective three-dimensional feature points and the structural parameters of the structure from motion. By the aid of the satellite relative attitude measuring method, relative attitudes of an observed satellite target can be effectively measured according to standard test data, satellite simulation data of a STK (satellite tool kit) ontrack satellite simulation platform and ground semi-physical simulation data, and the measurement precision for constructing a system and stability of computed numerical values can be improved by the aid of the light beam adjustment method.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
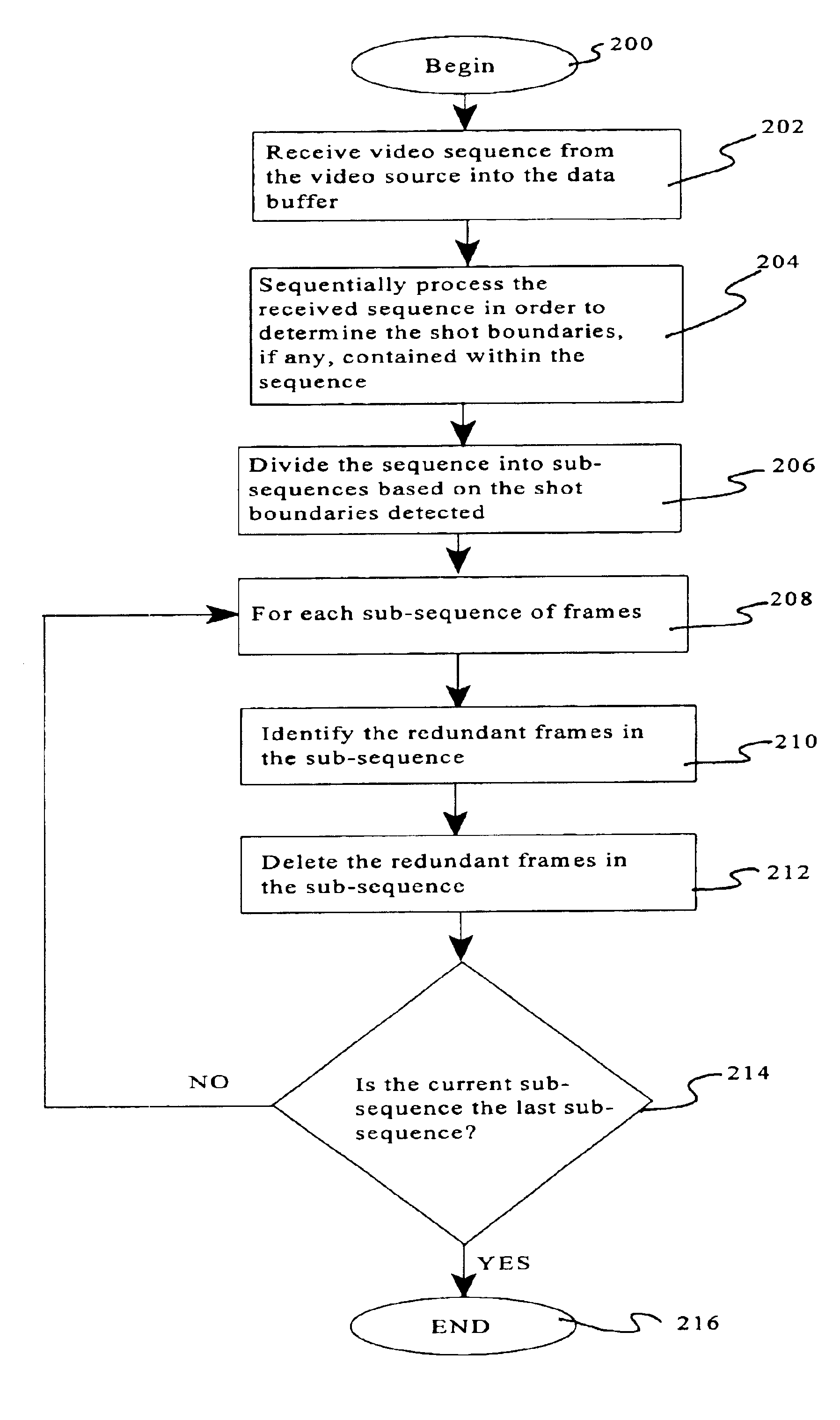
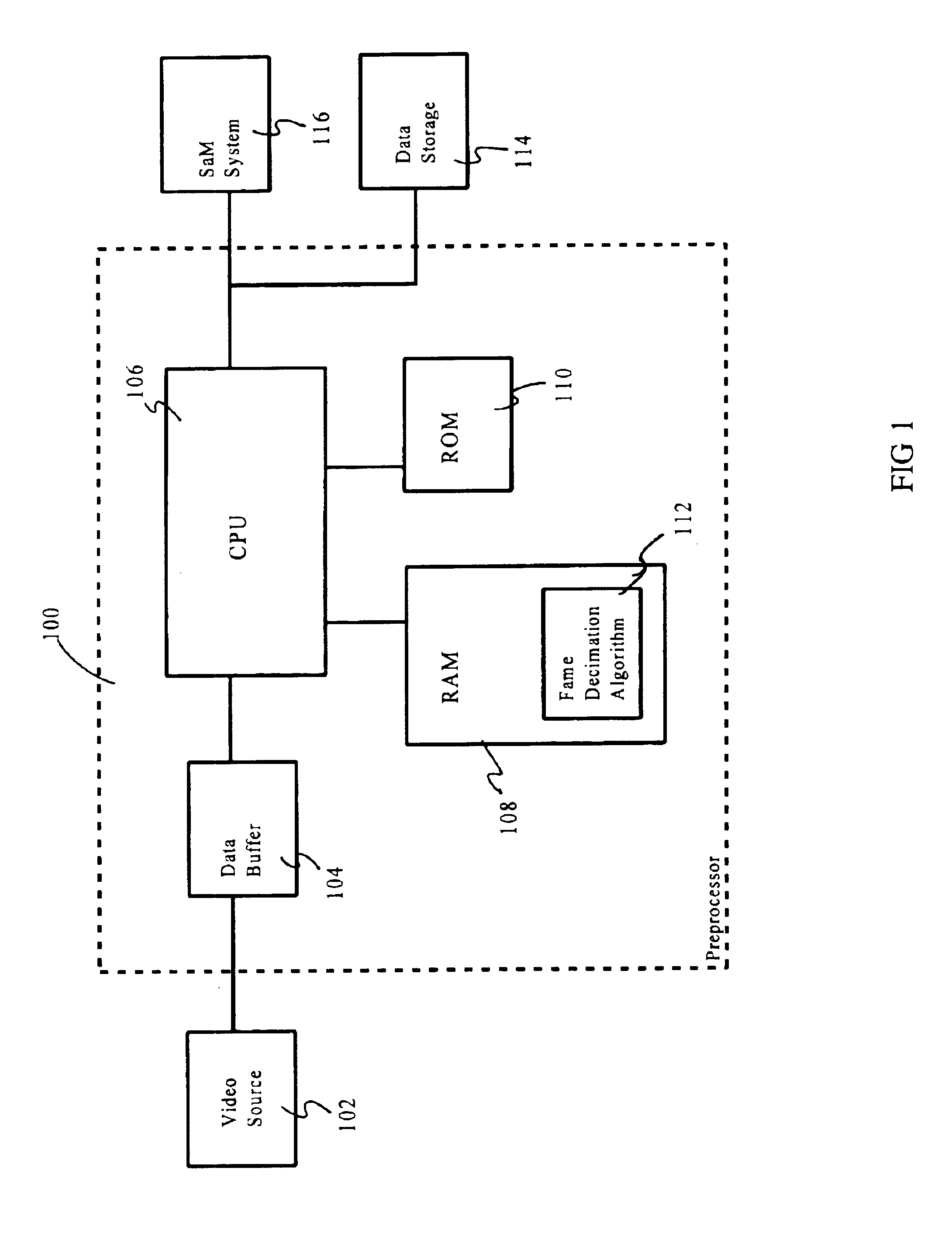
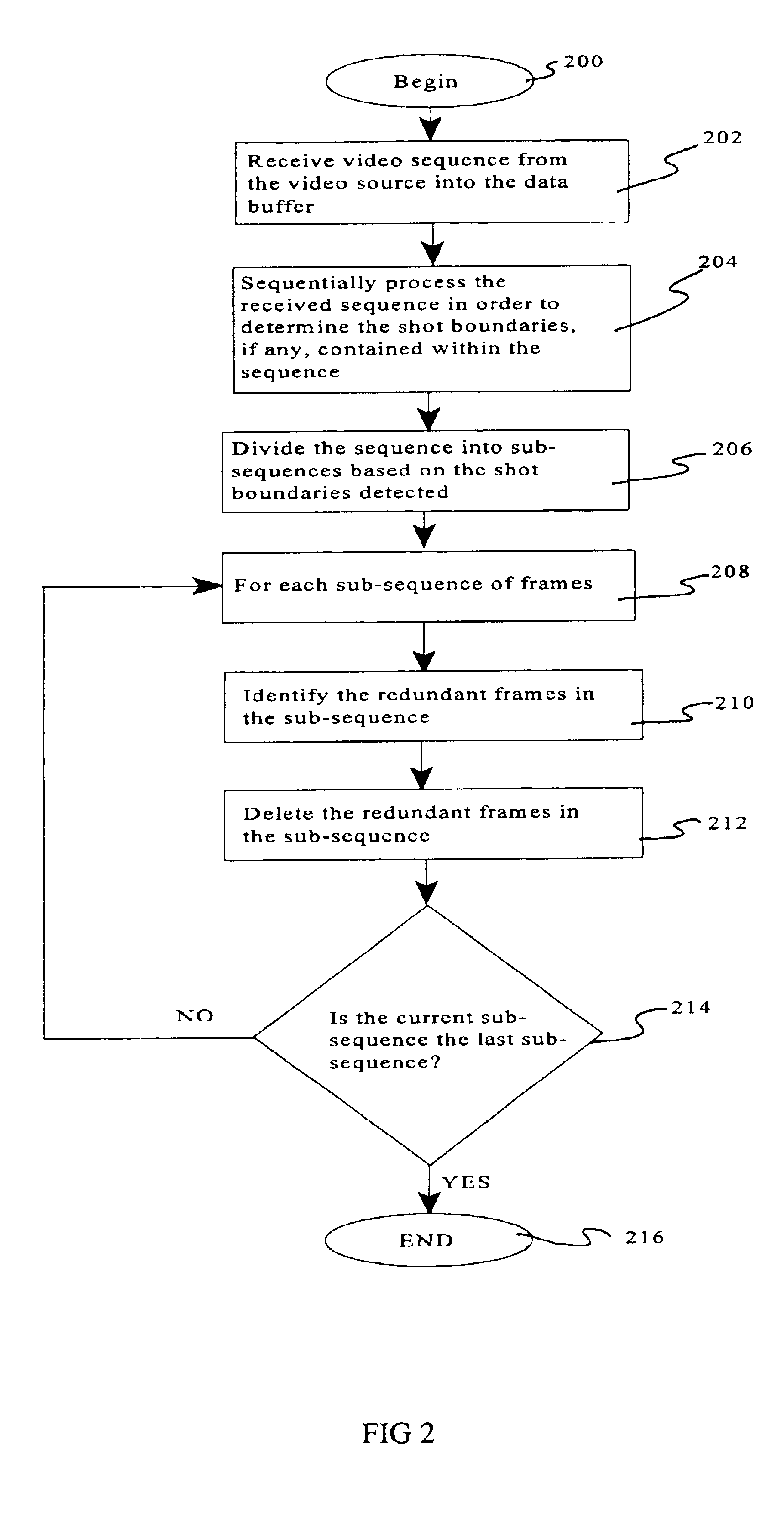
Frame decimation for structure from motion
InactiveUS6952212B2Image enhancementTelevision system detailsStructure from motionComputer graphics (images)
A preprocessing mechanism automatically processes a video sequence in order to obtain a set of views suitable for structure from motion (SaM) processing. The preprocessor employs a frame decimation algorithm which removes redundant frames within the video sequence based on motion estimation between frames and a sharpness measure. The motion estimation can be performed either globally or locally. The preprocessor can be configured to process static video sequences (i.e., previously acquired / captured) to select a minimal subsequence of sharp views form the video sequence, or to process the frames of a video sequence as they are being captured to discard frames which are redundant. In either configuration, the goal of the preprocessor is to select a minimal sequence of sharp views tailored for SaM processing.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Indoor environment reconstruction method based on monocular camera
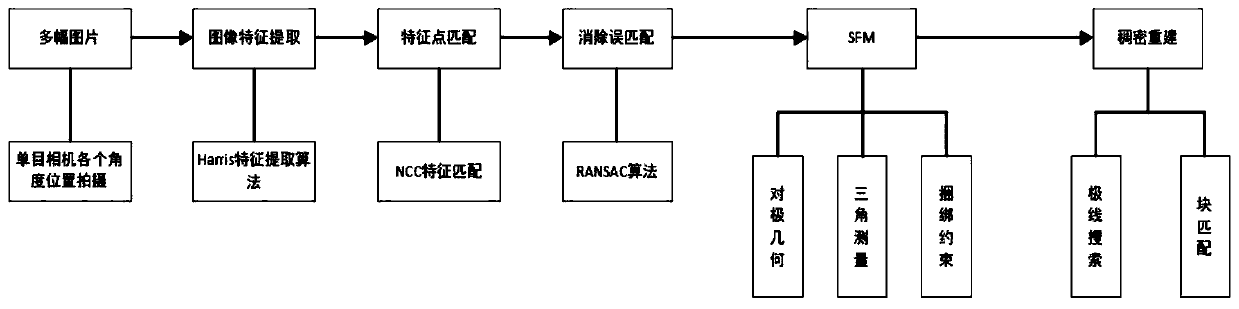
PendingCN110021065AReduce complexityGood reconstructionImage enhancementImage analysisFeature point matchingPoint match
The invention discloses an indoor environment reconstruction method based on a monocular camera, and the method comprises the steps: shooting indoor photos at different angles and positions through the monocular camera, extracting the characteristics of each image through a Harris corner detection algorithm, and obtaining the characteristic point of each image; performing feature point matching onany two pictures with similar shooting positions to obtain a matched feature point pair set of all the images; due to the fact that mismatching feature point pairs exist in matching, mismatching feature point pairs in the matching feature point pair set are eliminated; through a motion inference structure SFM, reconstructing a sparse point cloud for the photo with the mismatching feature point pair eliminated; carrying out dense point cloud reconstruction on the sparse point cloud, reconstructing all point clouds in the scene, and recovering the indoor scene environment. According to the method, the complexity of a common feature extraction method is reduced through a feature extraction algorithm with higher speed, feature point matching is carried out through a kd tree, sparse three-dimensional point cloud is reconstructed according to a geometric method, and a better reconstruction effect is realized through a dense reconstruction algorithm in the later period.
Owner:杨晓春
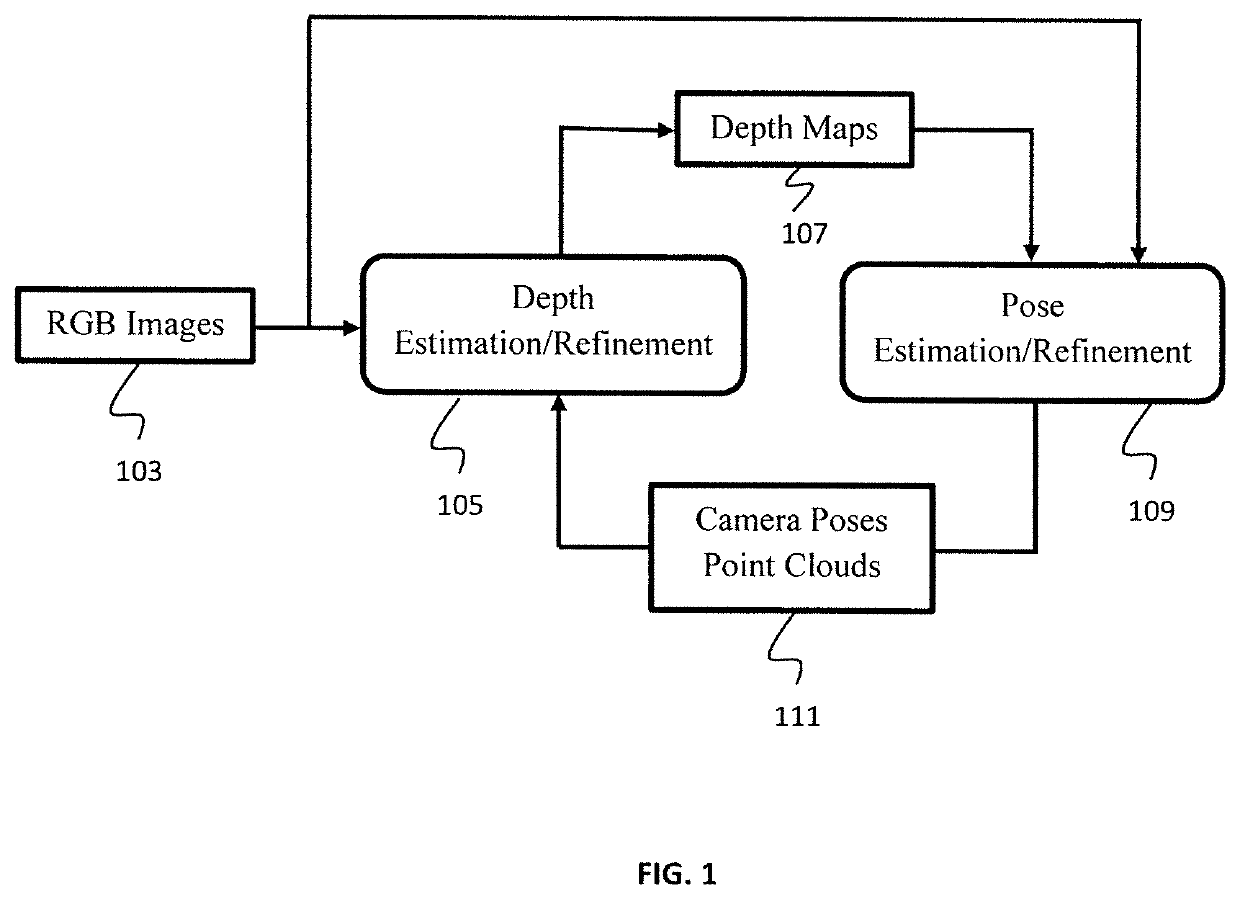
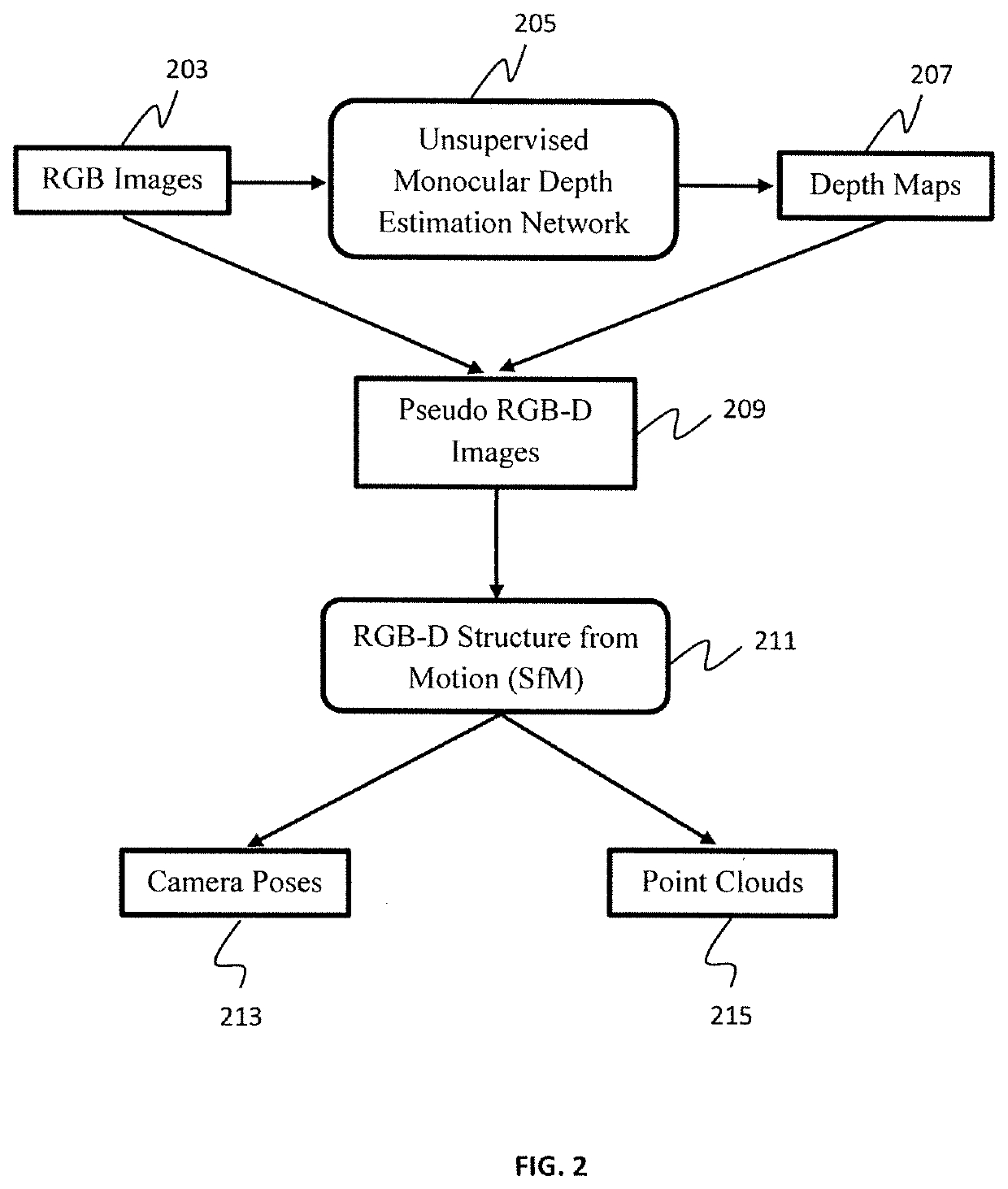
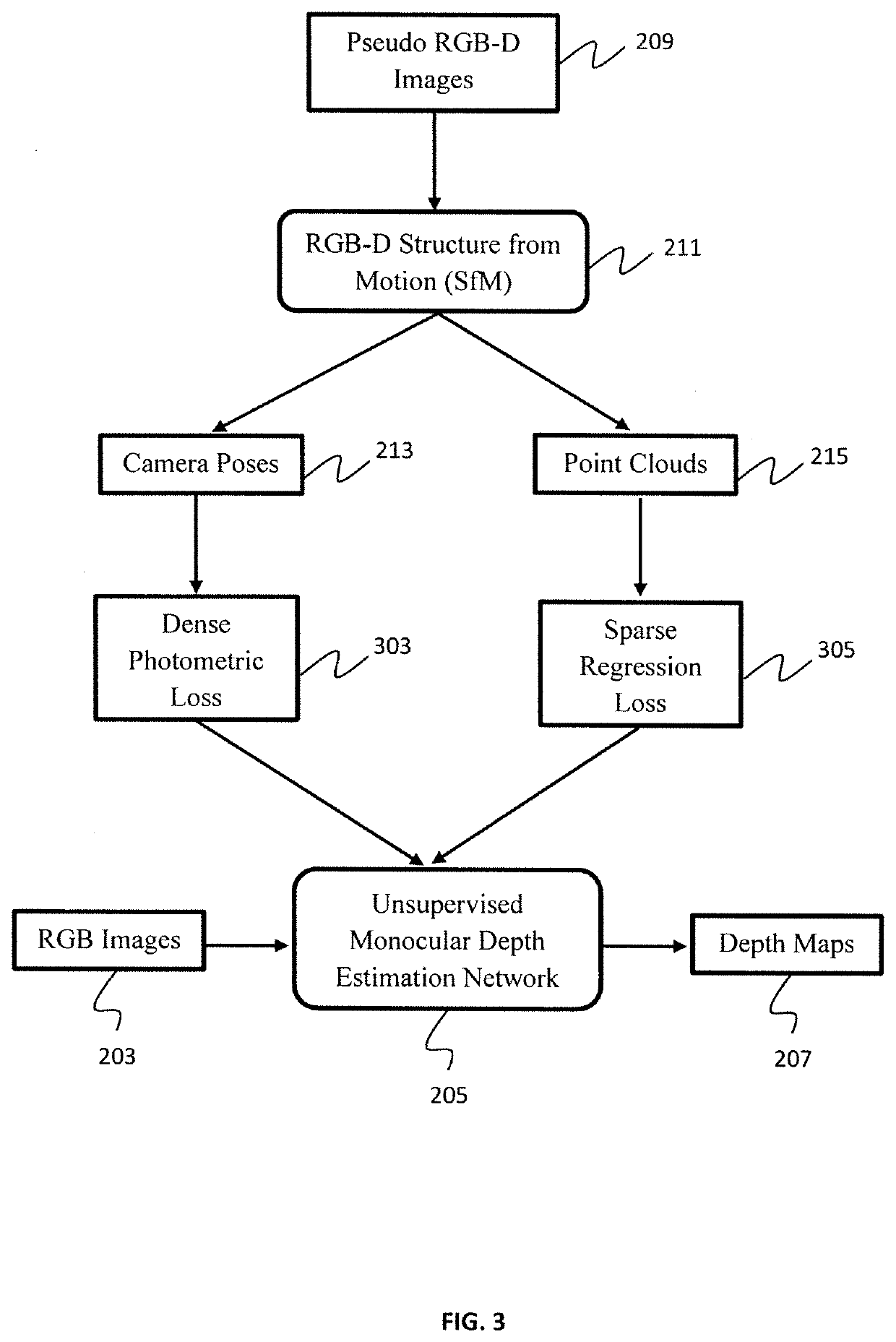
Pseudo rgb-d for self-improving monocular slam and depth prediction
A method for improving geometry-based monocular structure from motion (SfM) by exploiting depth maps predicted by convolutional neural networks (CNNs) is presented. The method includes capturing a sequence of RGB images from an unlabeled monocular video stream obtained by a monocular camera, feeding the RGB images into a depth estimation / refinement module, outputting depth maps, feeding the depth maps and the RGB images to a pose estimation / refinement module, the depths maps and the RGB images collectively defining pseudo RGB-D images, outputting camera poses and point clouds, and constructing a 3D map of a surrounding environment displayed on a visualization device.
Owner:NEC CORP
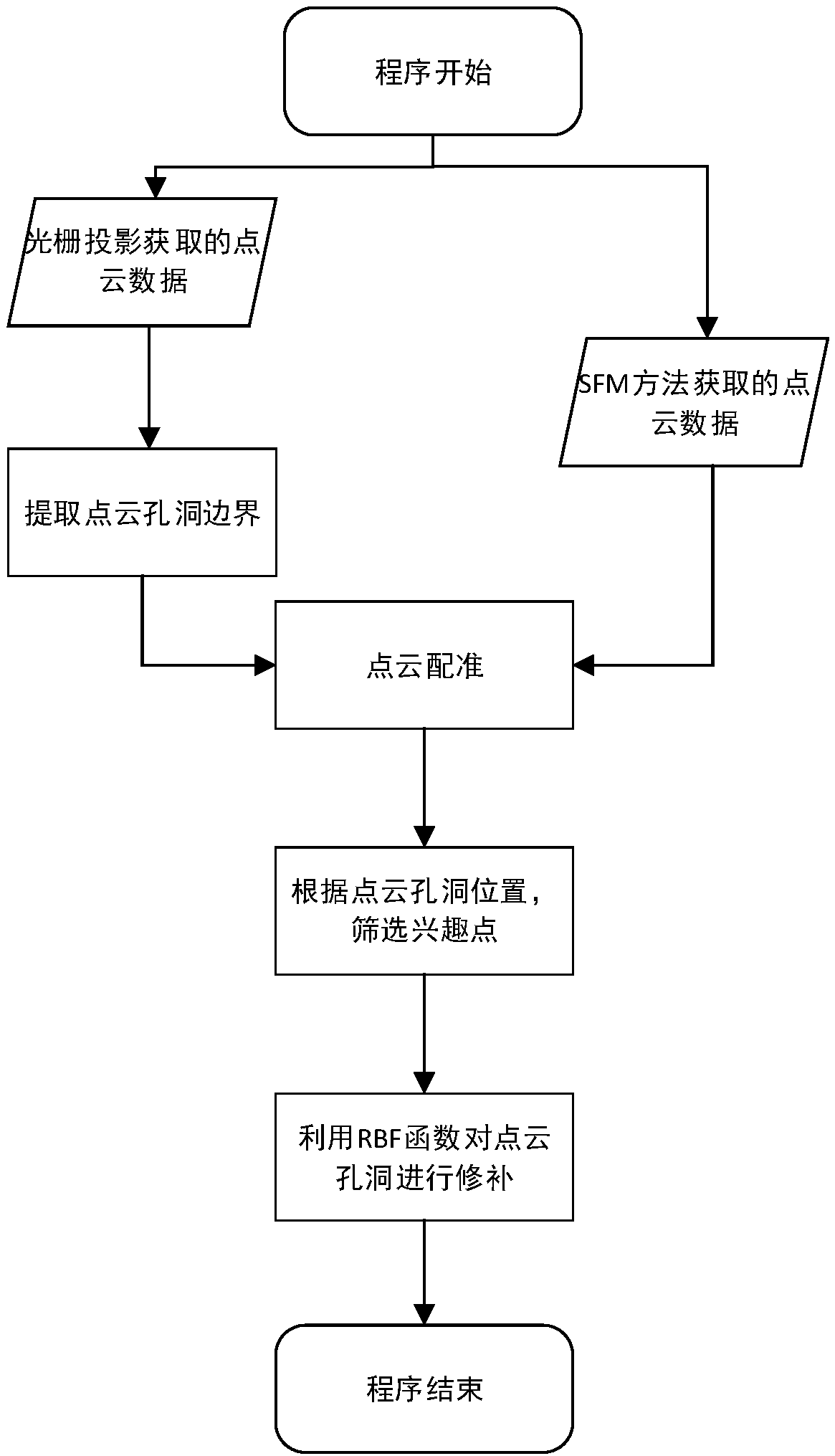
Point cloud hole repairing method based on SFM
The invention discloses a point cloud hole repairing method based on SFM (Structure From Motion), which includes the following steps: (1) acquiring point cloud data through the grating projection method and the SFM method, and extracting the boundary points of a 3D point cloud hole according to point cloud 2D phase information acquired using the grating projection method; (2) registering a point cloud data set acquired using the SFM method and a point cloud data set acquired using the grating projection method; (3) acquiring the supplement points of the hole area in the point cloud acquired using the grating projection method from the data set acquired using the SFM method; and (4) based on the supplement points, using a radial basis function to further repair the hole. The algorithm is robust. The repair effect is highly precise. More detail information of an object can be restored.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
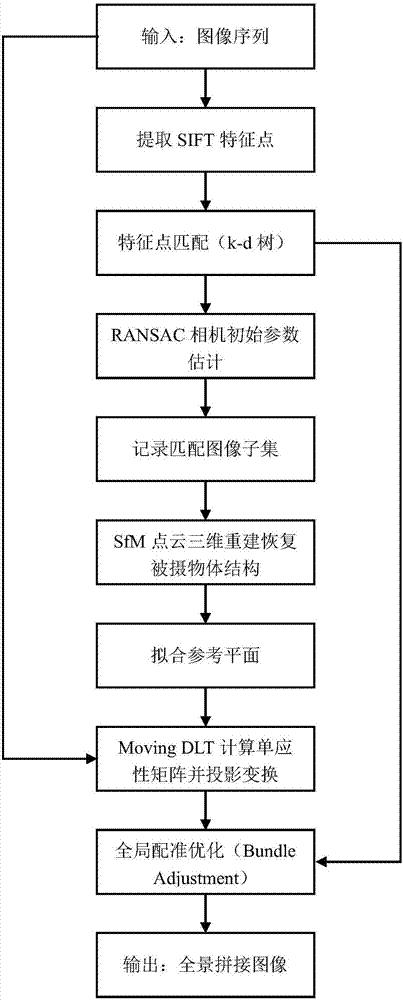
Sequence image's automatic splicing method based on three-dimension reconstruction
InactiveCN107240067ARealize automatic splicingPromote reductionImage enhancementImage analysisStructure from motionPoint cloud
The invention relates to a sequence image's automatic splicing method based on three-dimension reconstruction. The method comprises the following steps: extracting the scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) feature points respectively from N inputted images; based on the matching condition of the feature points, selecting m candidate matching images corresponding to each image to structure a candidate matching image set; performing three-dimension reconstruction to the candidate matching image set through the use of the structure from motion (SfM) algorithm to obtain a reflected and projected three-dimension plane; seeking the two-dimension reference plane corresponding to the three-dimension plane and projecting it to a designated two-dimension coordinate plane; seeking the mirror distortion parameter of each image and optimizing the splicing effect between adjacent images. Compared with the prior art, the invention is based on the three-dimension point cloud reconstruction method to restore the three-dimension structure of a photographed object and is able to solve the problems with the sequence image splicing when the images and the photographed object cannot meet the homograph restrain conditions, eliminates the homograph distortion of the inputted images and improves the image splicing quality.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Simple techniques for three-dimensional modeling
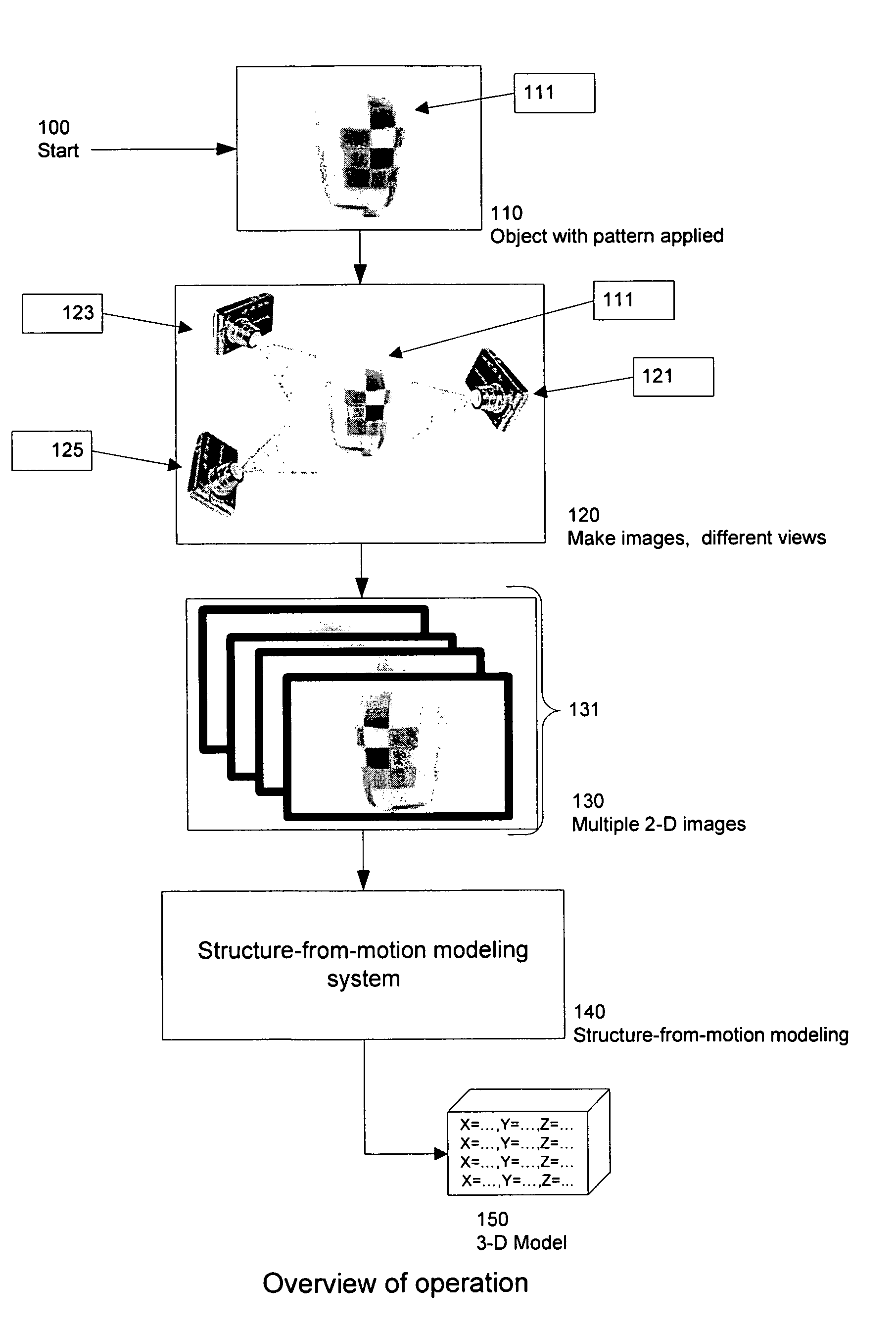
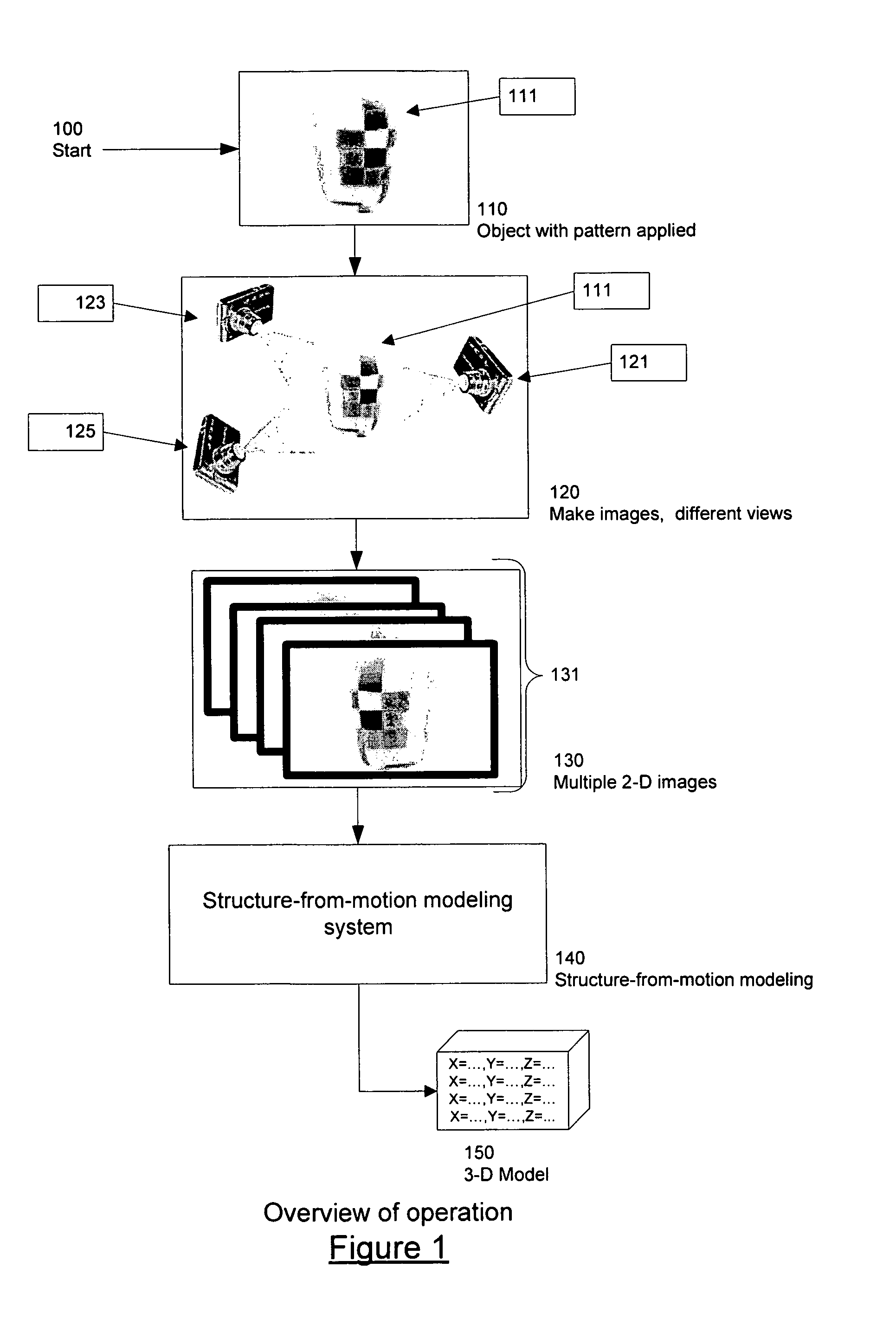
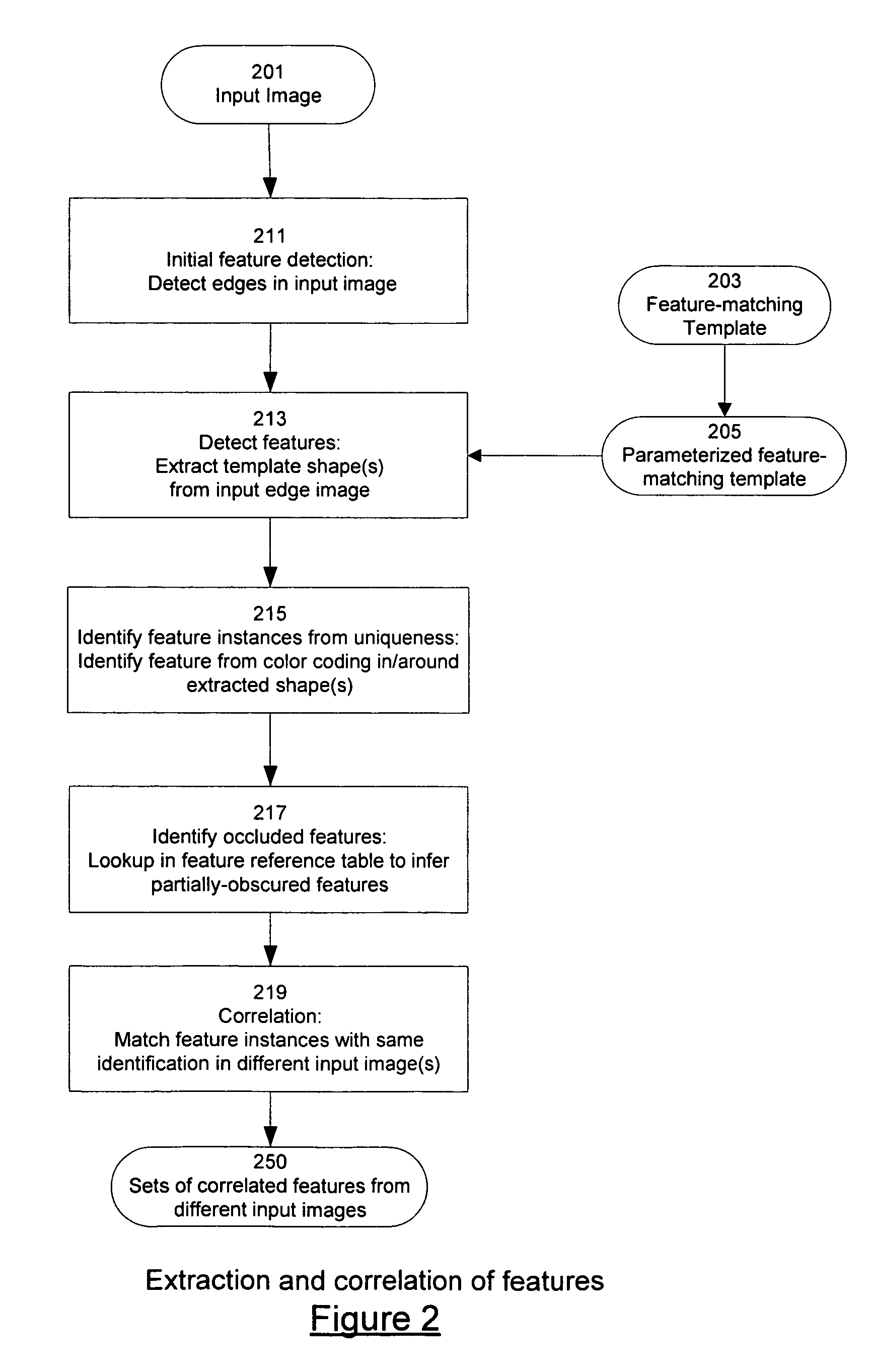
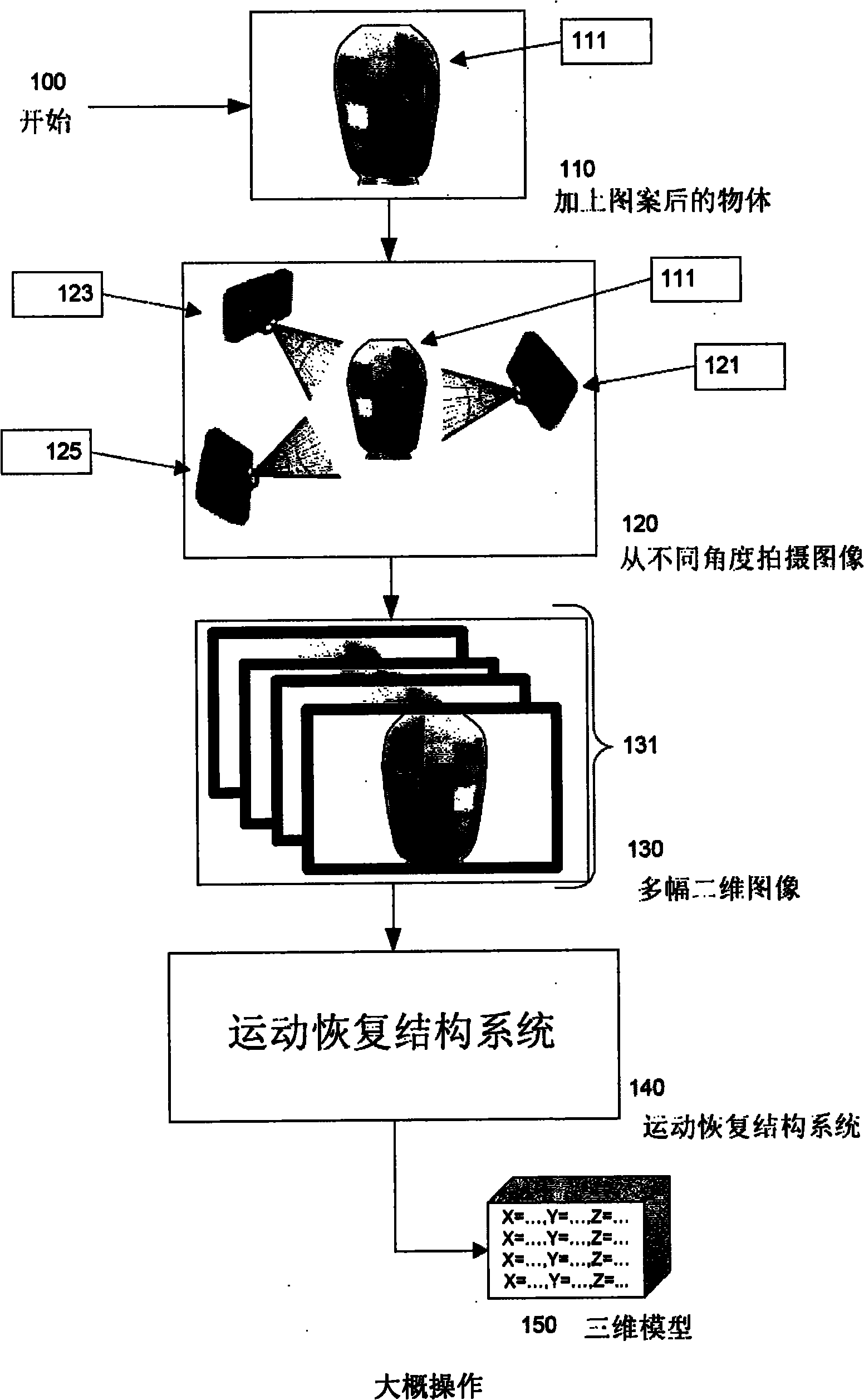
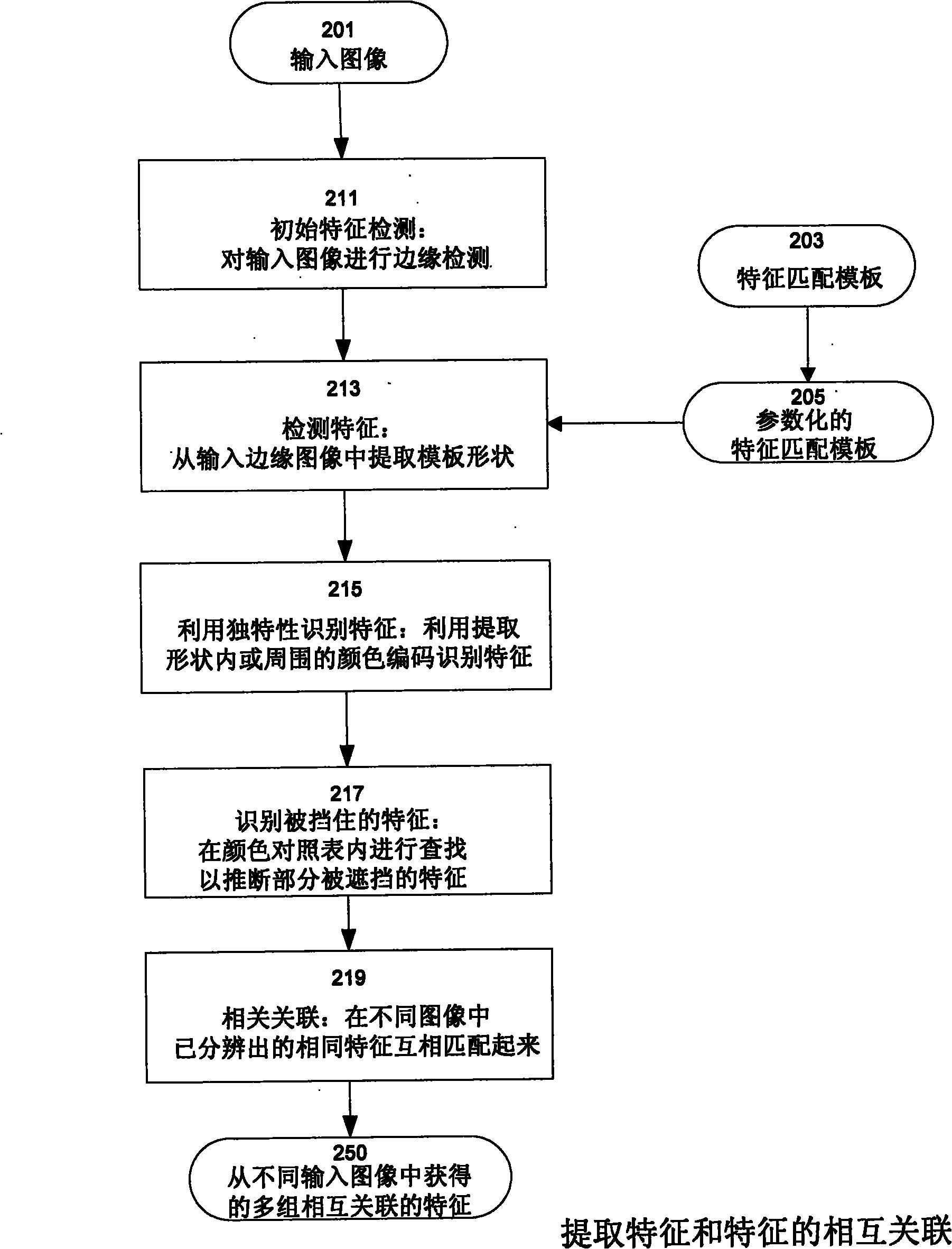
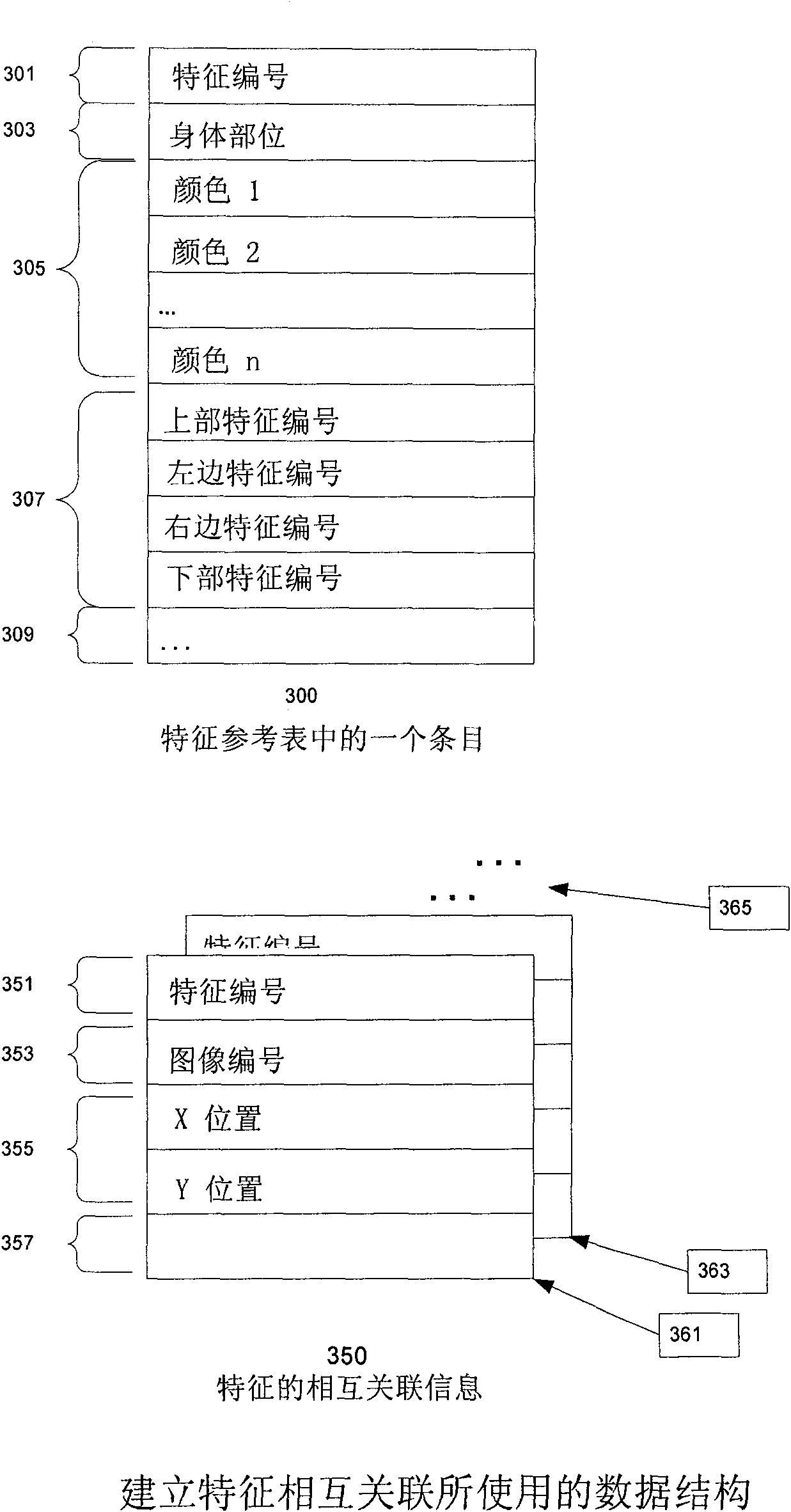
ActiveUS8571698B2Quality improvementImage enhancementImage analysisStructure from motionDimensional modeling
Techniques which employ structure-from-motion modeling techniques to produce 3-D models of any desired accuracy of any surface I the techniques, a pattern is applied to the surface to be modeled The pattern includes elements which are unique within the pattern as applied to the surface and which have a density in the pattern such that when two-dimensional images are made of the surface, correlatable features having the density required for the desired accuracy may be extracted from the two dimensional images In one example of the techniques, a consumer may make the images required to produce a model of his or her body by donning a garment with a pattern having the necessary uniqueness and density, and then using any digital camera to take pictures of their body wearing the garment The model may then be produced from the pictures.
Owner:NETVIRTA
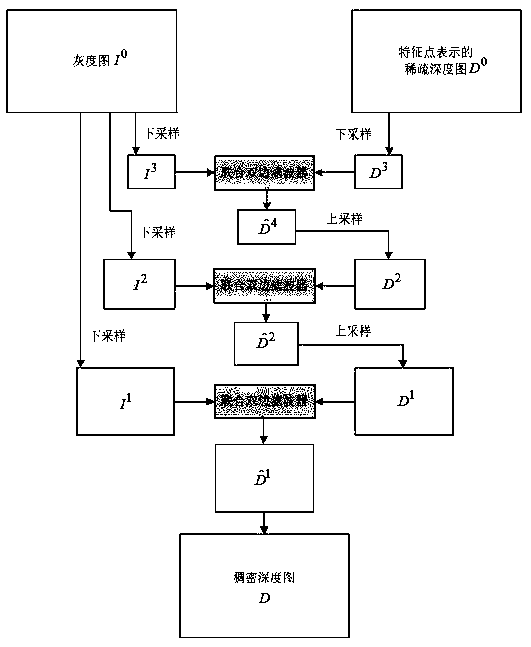
Quick depth restoring method for three-dimensional reconstruction
ActiveCN108062769ARecovery is efficient and accurateImprove computing efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisSimultaneous localization and mappingStructure from motion
The invention relates to the technical field of stereo vision in computer vision, and particularly to a depth restoring method for three-dimensional reconstruction. After depths of sparse characteristic points in an image are obtained through a structure from motion (SFM), depth is diffused based on the sparse characteristic points and a gray scale image through multilayer down-sampling and a double-side filter. An accurate depth map is quickly restored from low resolution to high resolution and from rough to fine in a layered manner. The method has advantages of accurate result and low calculating amount. The sparse characteristic points which are obtained through calculation in the system can be restored to the dense depth map by means of a simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) system based on a characteristic point method, thereby reconstructing the three-dimensional dense map.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Simple techniques for three-dimensional modeling
The invention provides techniques which employ structure-from-motion modeling techniques to produce 3-D models of any desired accuracy of any surface. In the techniques, a pattern is applied to the surface to be modeled. The pattern includes elements which are unique within the pattern as applied to the surface and which have a density in the pattern such that when two-dimensional images are made of the surface, correlatable features having the density required for the desired accuracy may be extracted from the two dimensional images. In one example of the techniques, a consumer may make the images required to produce a model of his or her body by donning a garment with a pattern having the necessary uniqueness and density, and then using any digital camera to take pictures of their body wearing the garment. The model may then be produced from the pictures.
Owner:NETVIRTA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com