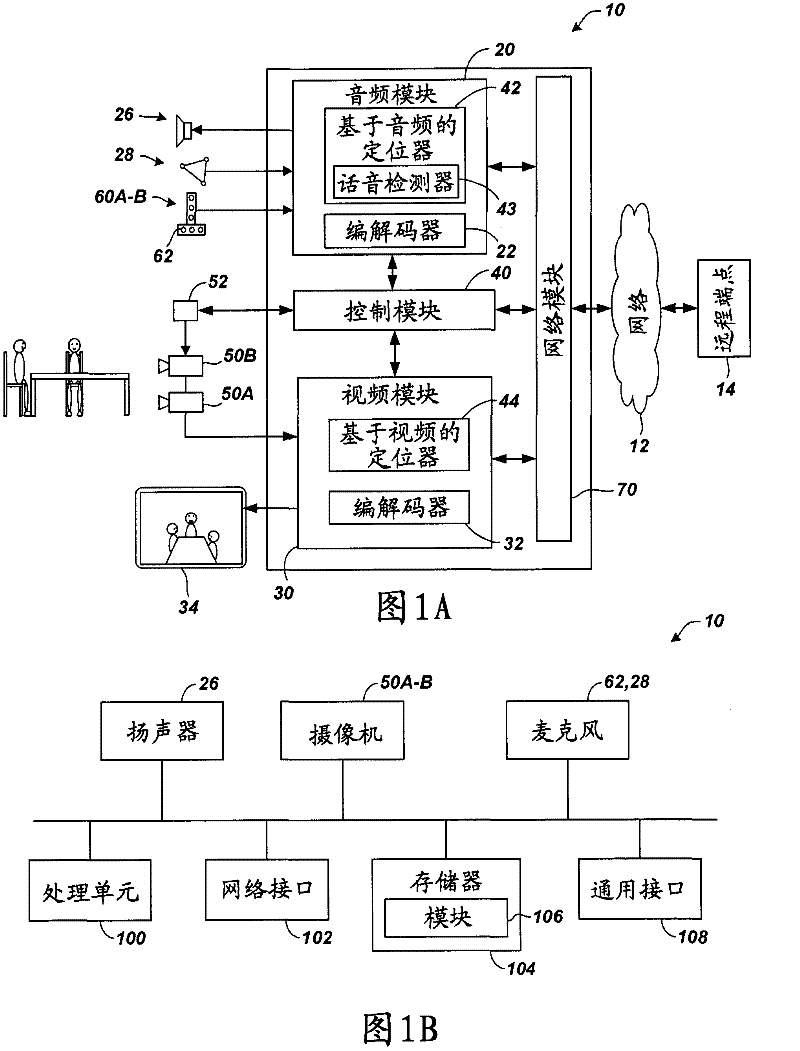
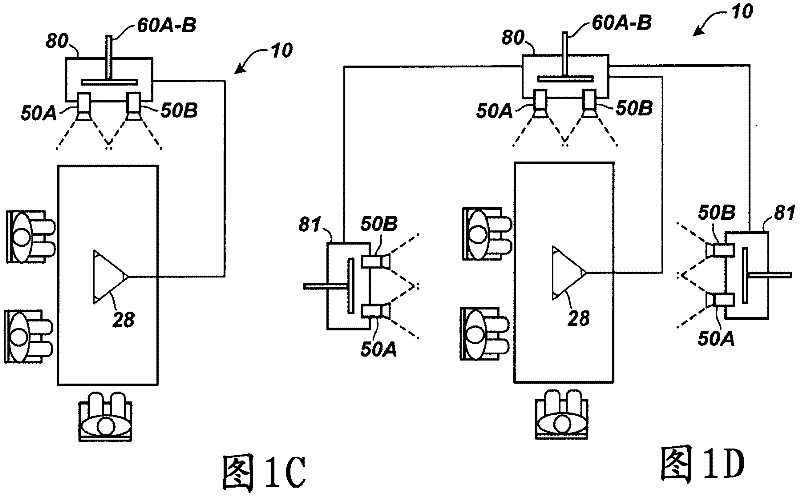
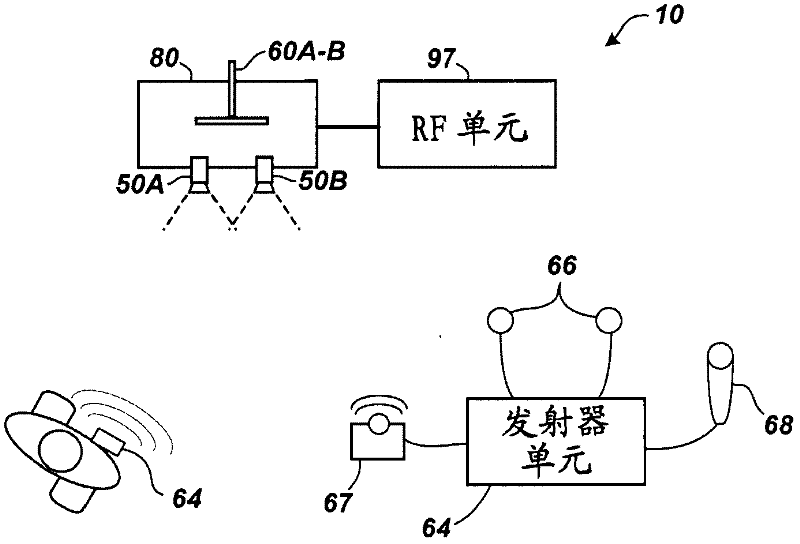
Patents
Literature
863 results about "View camera" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
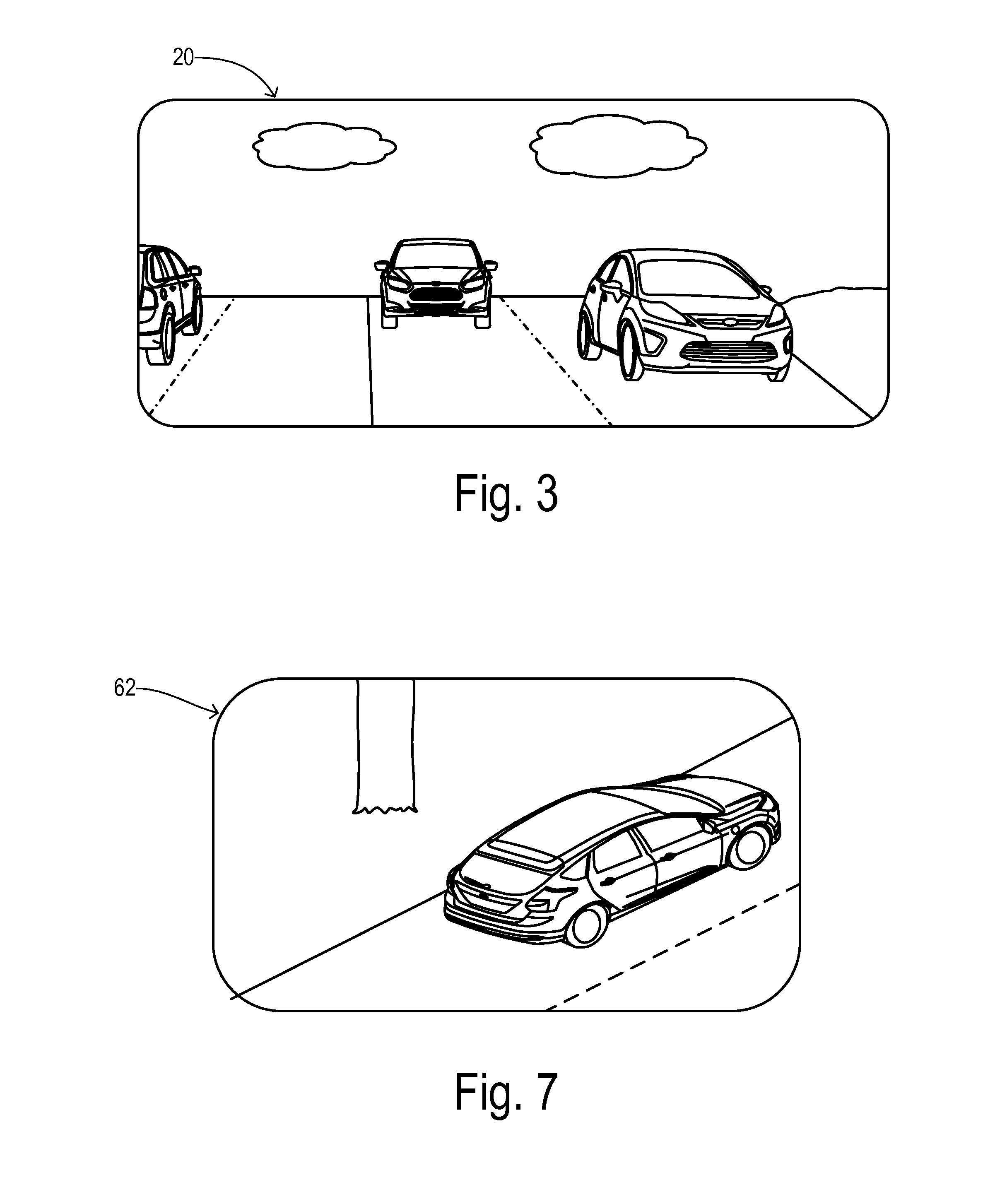
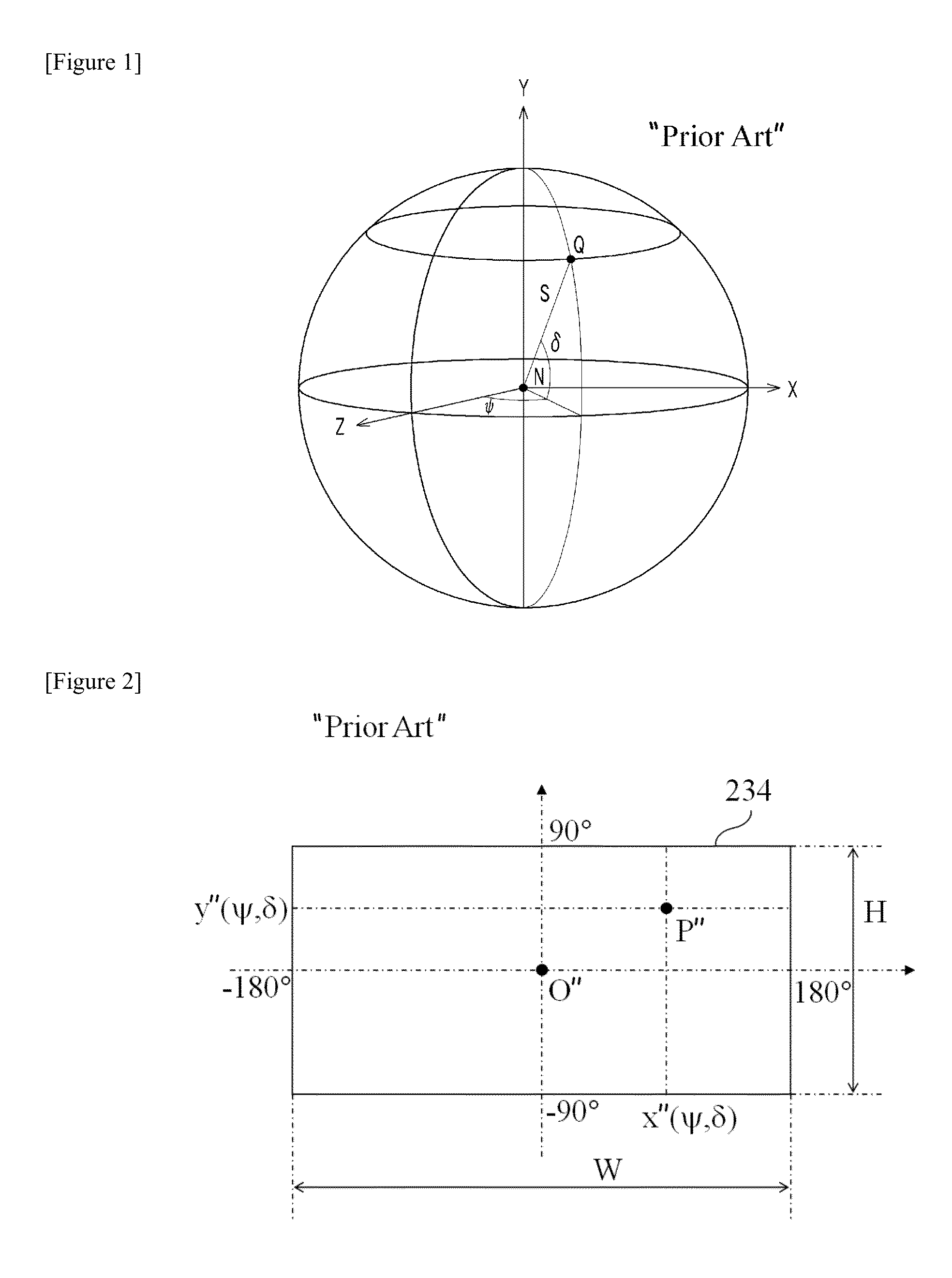
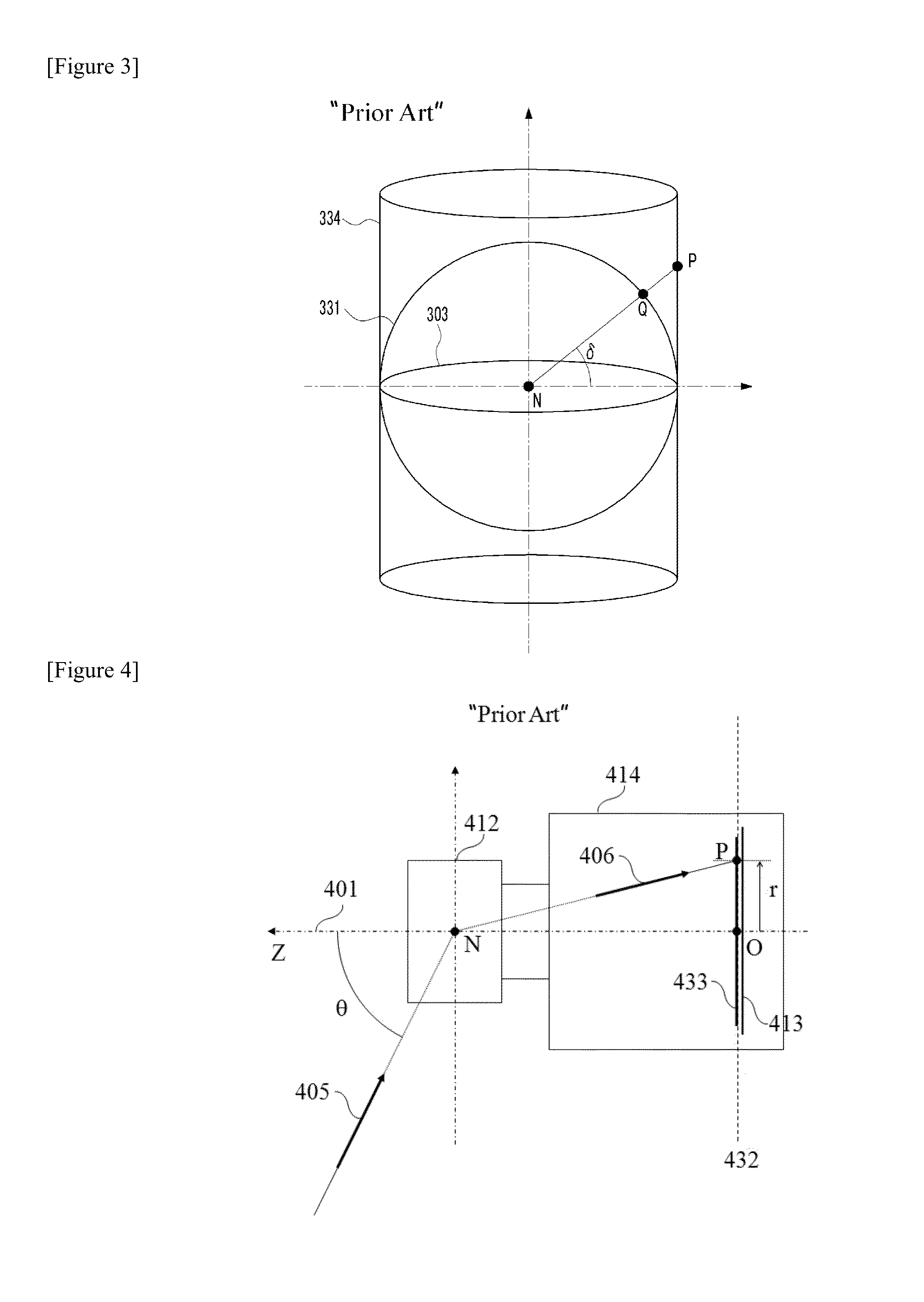
A view camera is a large format camera in which the lens forms an inverted image on a ground glass screen directly at the plane of the film. The image viewed is exactly the same as the image on the film, which replaces the viewing screen during exposure.
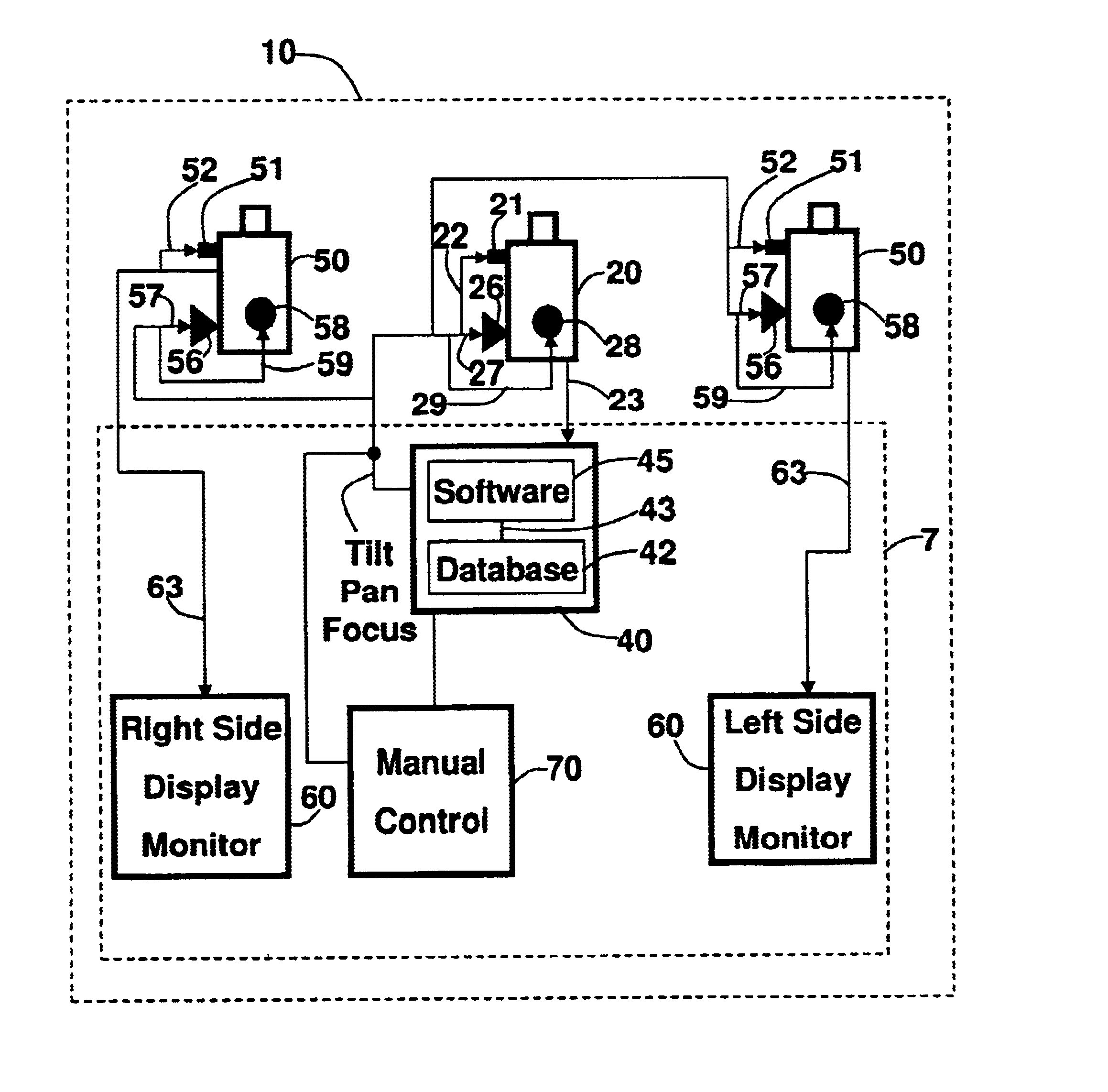
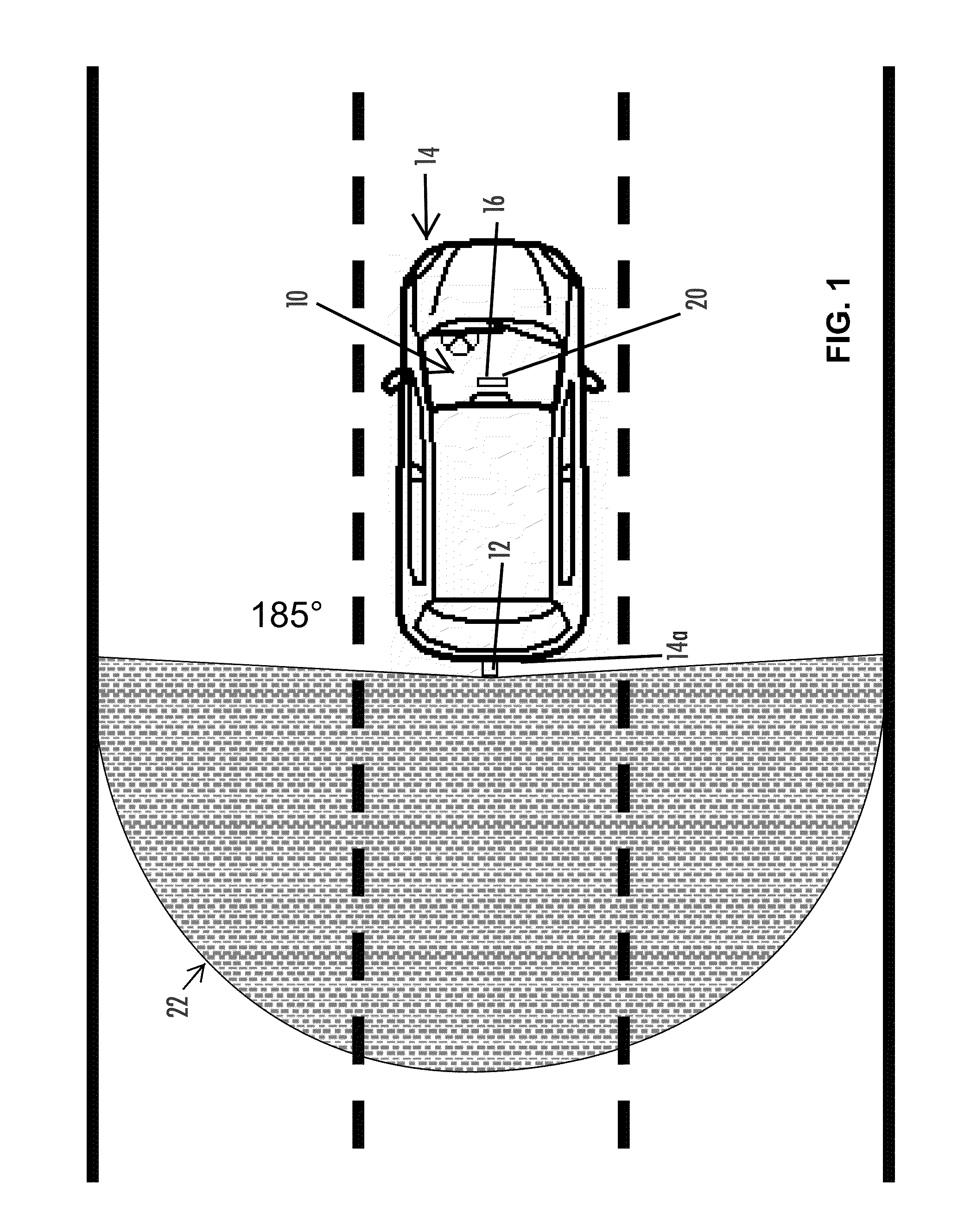
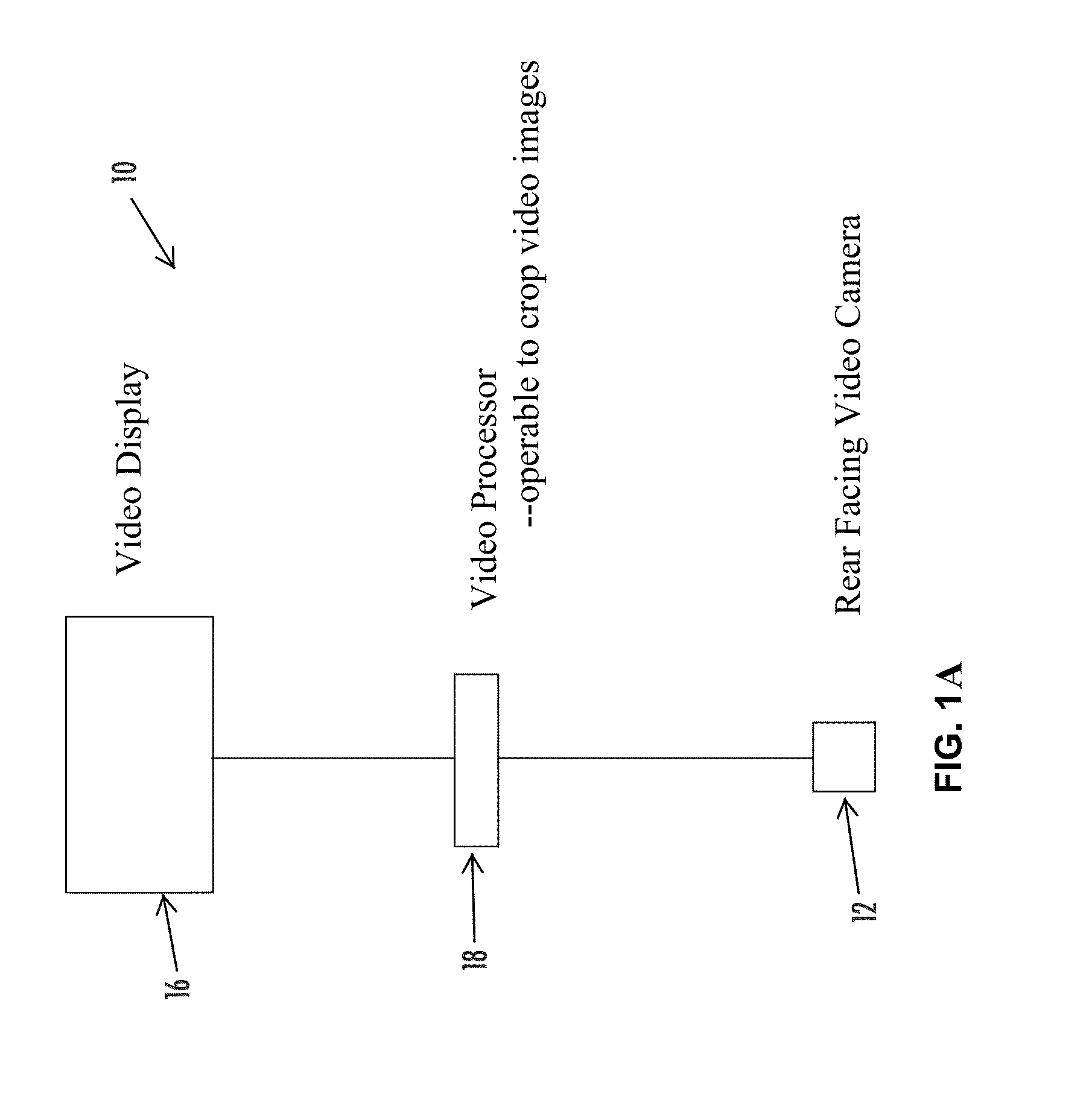
Tractor-trailer viewing system
InactiveUS6690413B1Improved viewing systemQuality improvementTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionView cameraArticulated vehicle
This invention relates to motor vehicles, and, more particularly, to a rear viewing system for tractor-trailer vehicles. An automated, universal trailer rear viewing system that is integrated in its entirety on the head or pulling portion of a pivotally connected articulated vehicle. The system includes: (a) at least one image capturing device mounted on the tractor designed to tilt, pan and focus on a target object or an area around the trailer; (b) a computer located inside the tractor coupled to the image capturing device; (c) an image capturing and comparative software program loaded into the memory of the computer capable of processing the image file of the target object transmitted from the image capturing device, and capable of generating control commands to the image capturing device so that an image of the target object is maintained as the system is activated; (d) at least one adjustable viewing camera also coupled to the computer that automatically adjusts the viewing camera tilting, panning and focusing according to the movement of the image capturing device; and, (e) at least one display monitor located near the driver that is coupled to the viewing camera so that the image seen thereby may be seen by the driver.
Owner:MOORE MICHAEL S
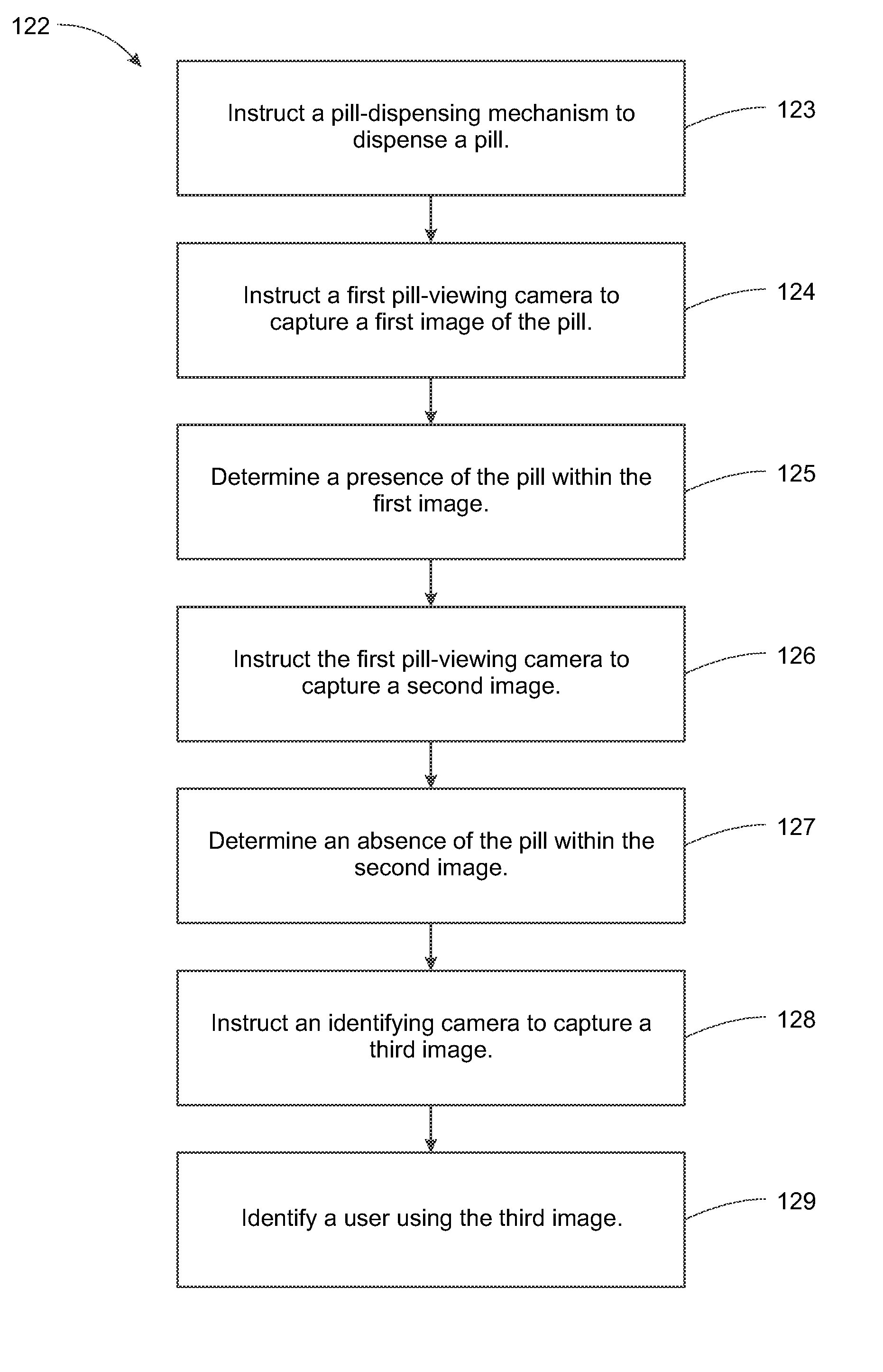
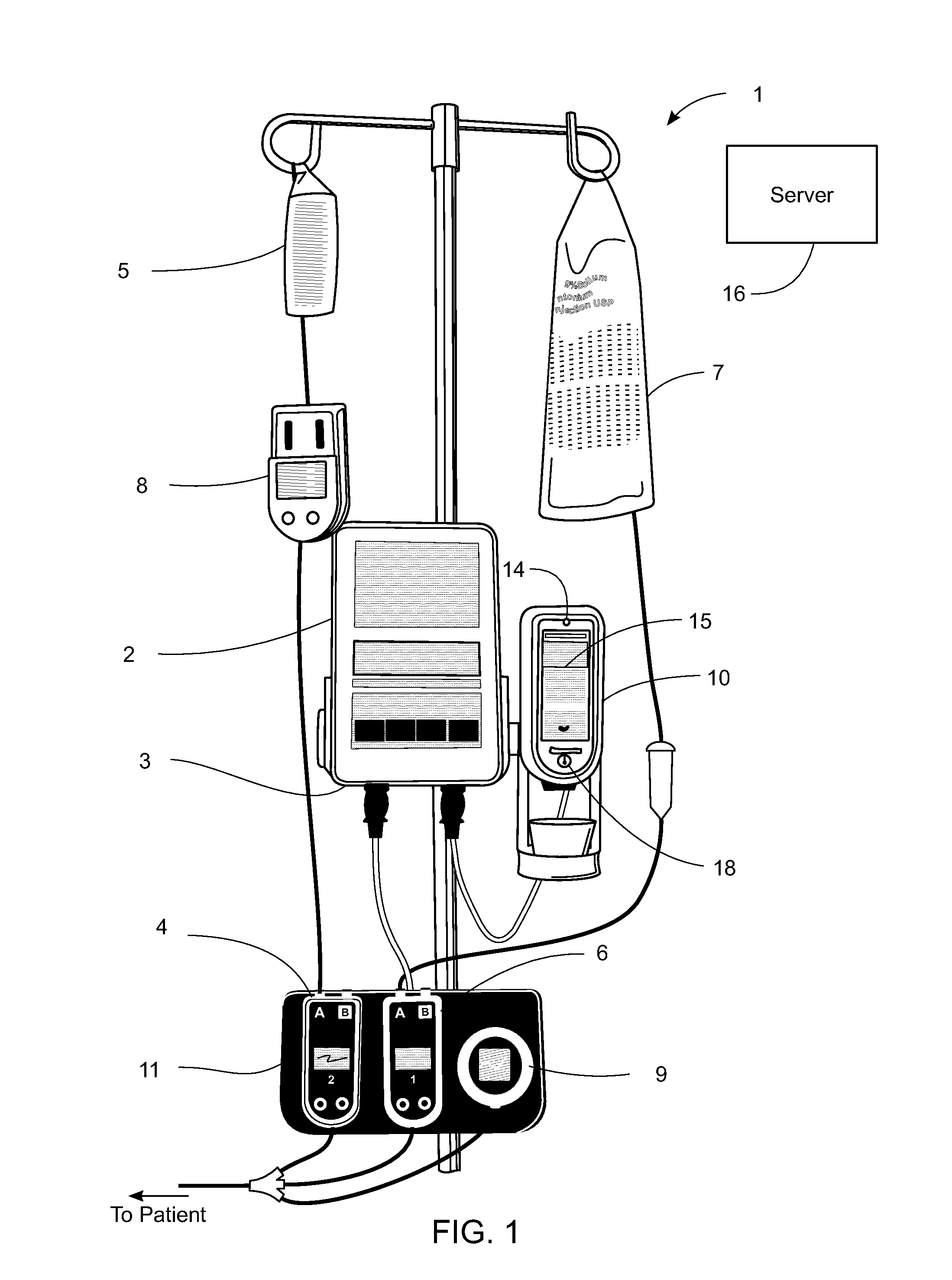
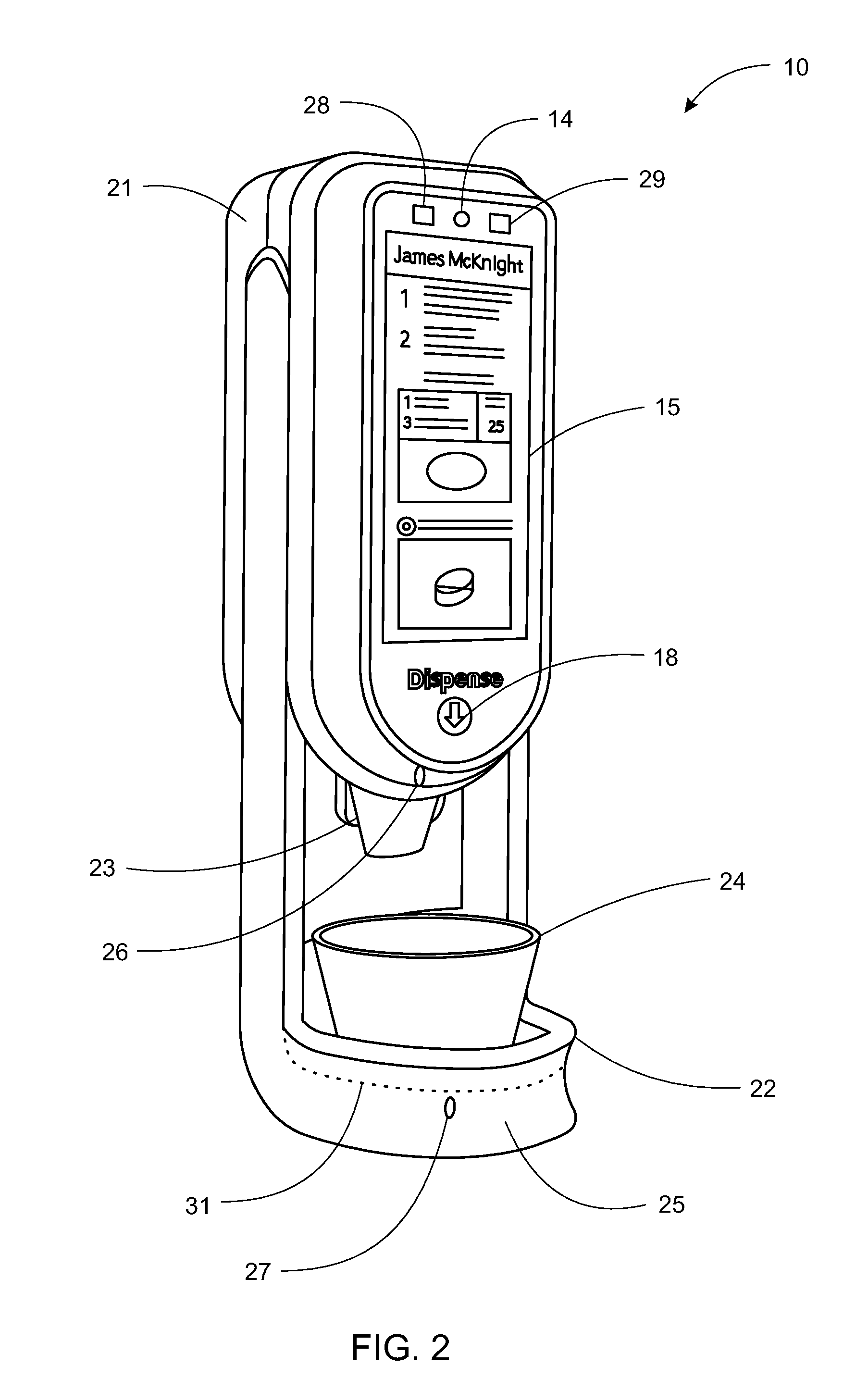
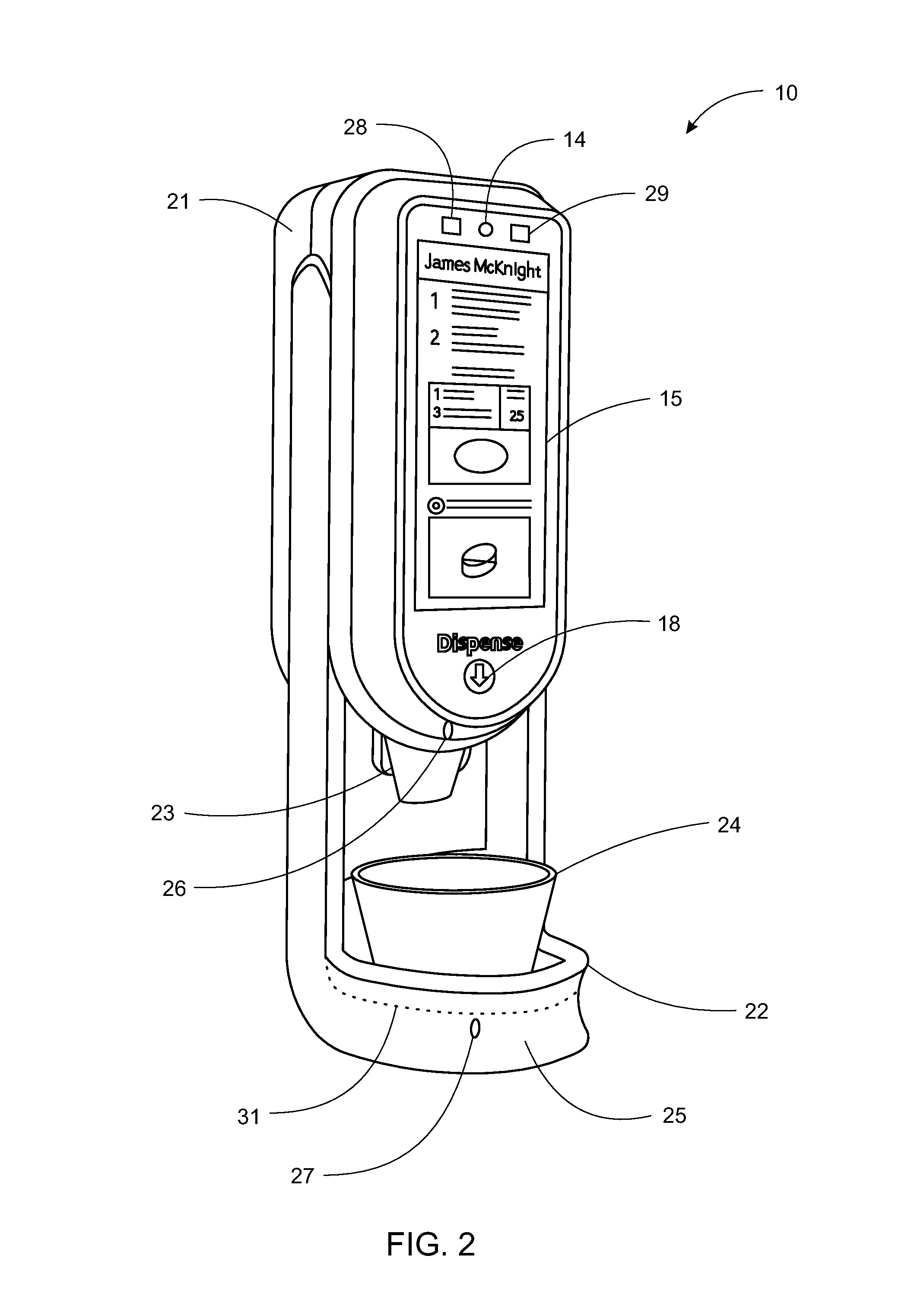
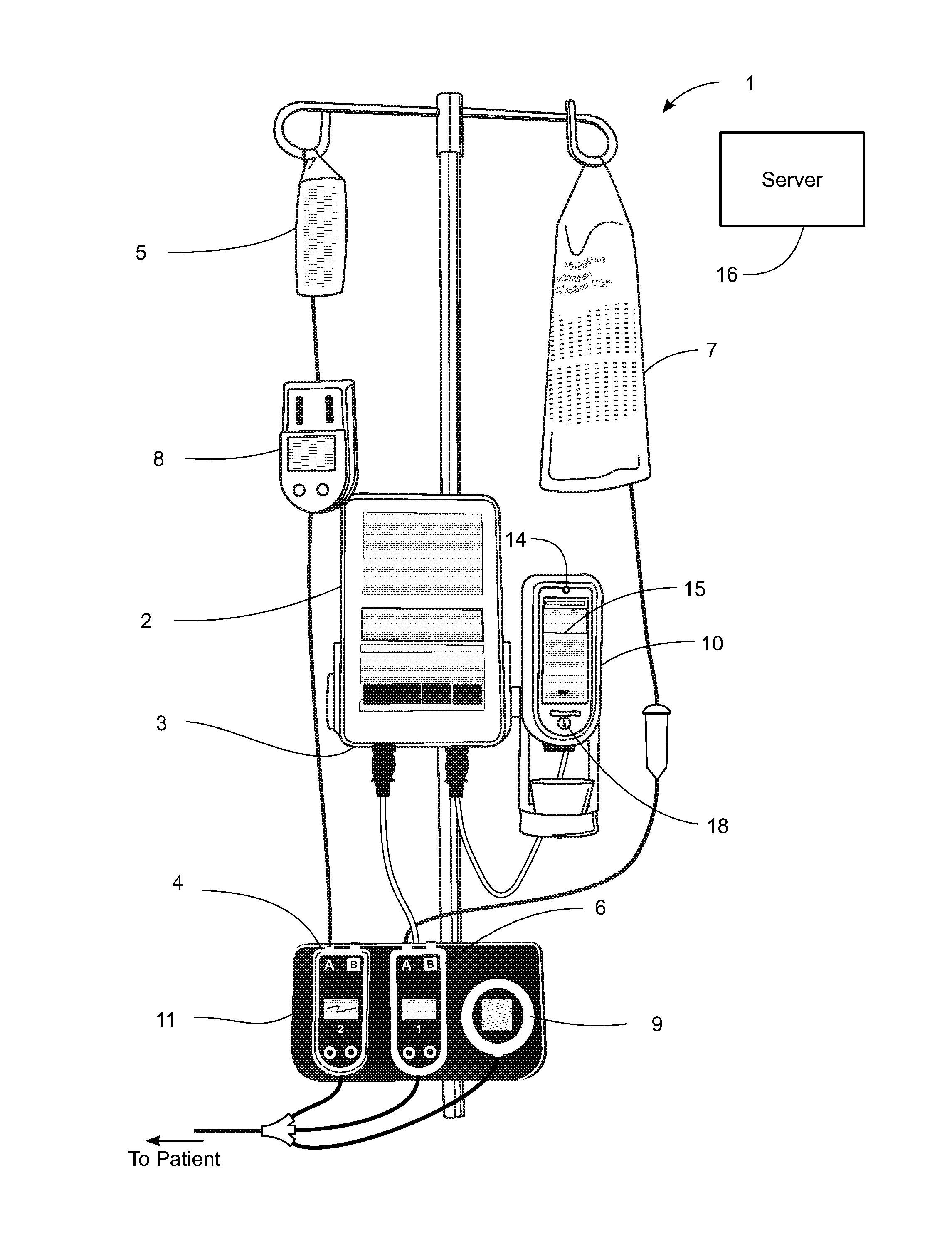
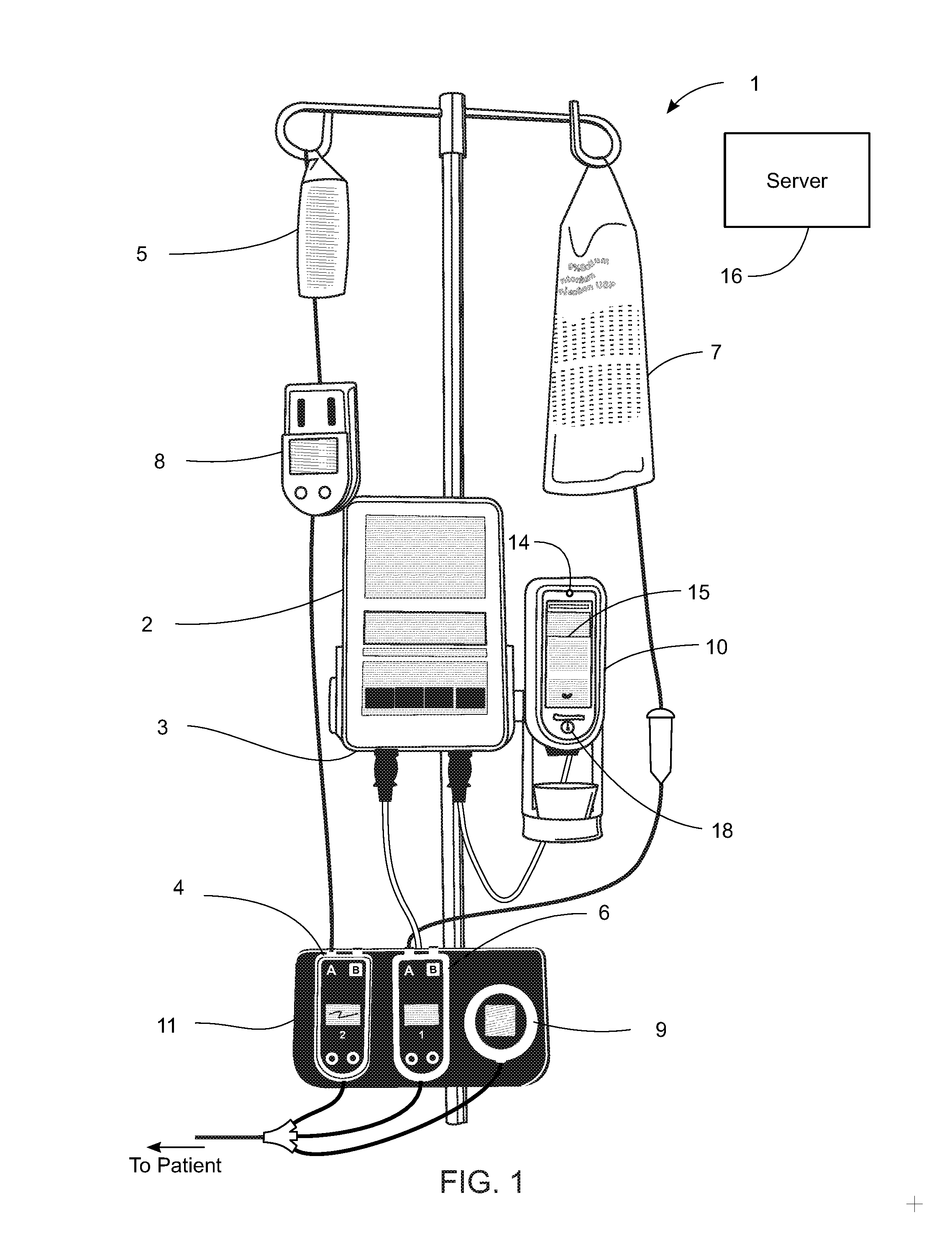
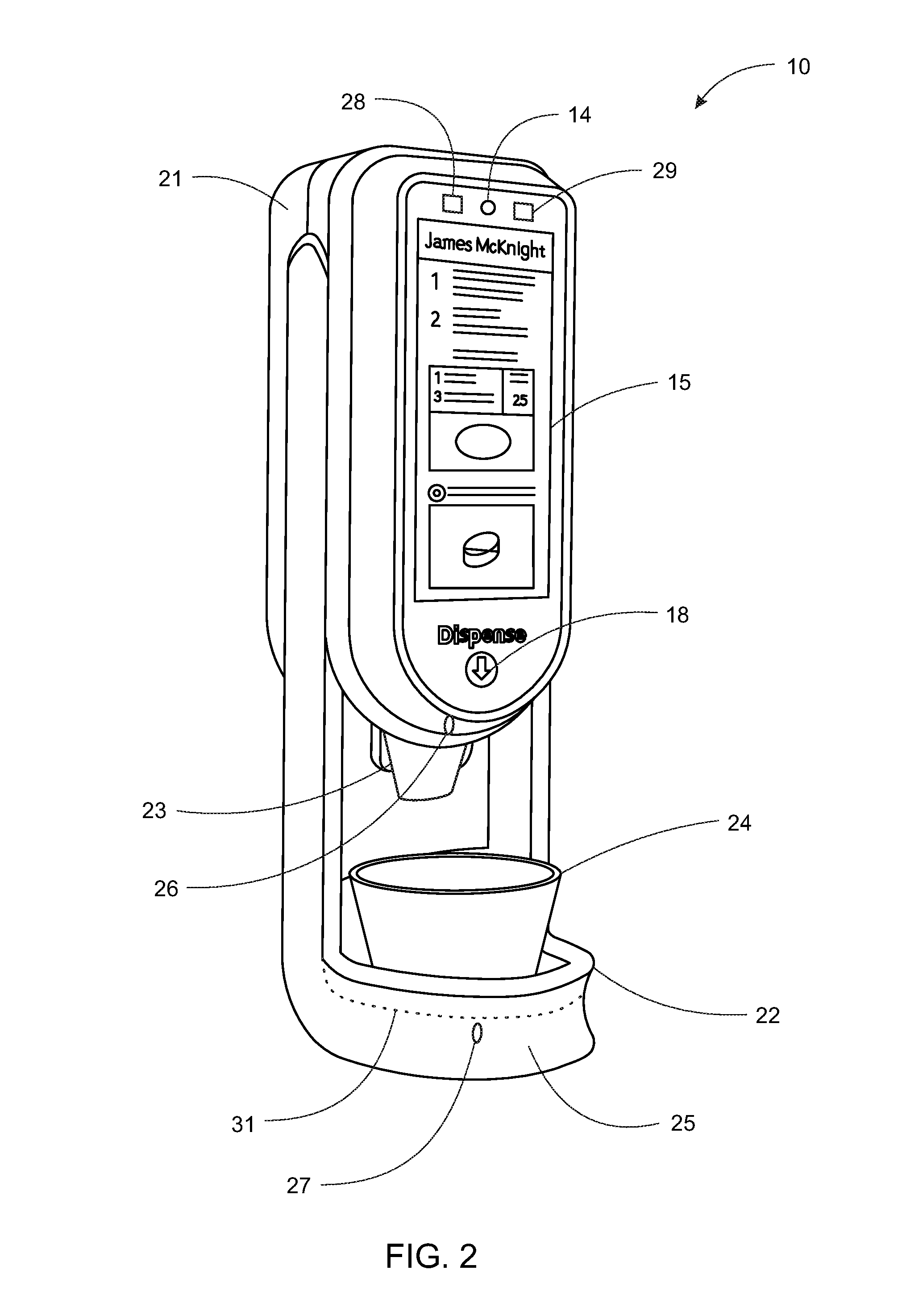
System, Method, and Apparatus for Dispensing Oral Medications
A pill dispenser includes a housing, a pill-dispensing mechanism, a receptacle, a pill-viewing camera, an identifying camera, one or more processors, and a storage medium (e.g., a memory). The pill-dispensing mechanism is coupled to an opening of the housing. The first pill-viewing camera is positioned to capture an image of the receptacle, and the identifying camera is positioned to capture an image of an area adjacent to the housing. The one or more processors are in operative communication with the pill-dispensing mechanism, the pill-viewing camera, and the identifying camera. The storage medium stores processor-executable instructions for: instructing the pill-dispensing mechanism to dispense a pill; instructing the pill-viewing camera to capture a first image of the pill to determine a presence of the pill; instructing the pill-viewing camera to capture a second image to determine an absence of the pill; and instructing the identifying camera to capture a third image.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
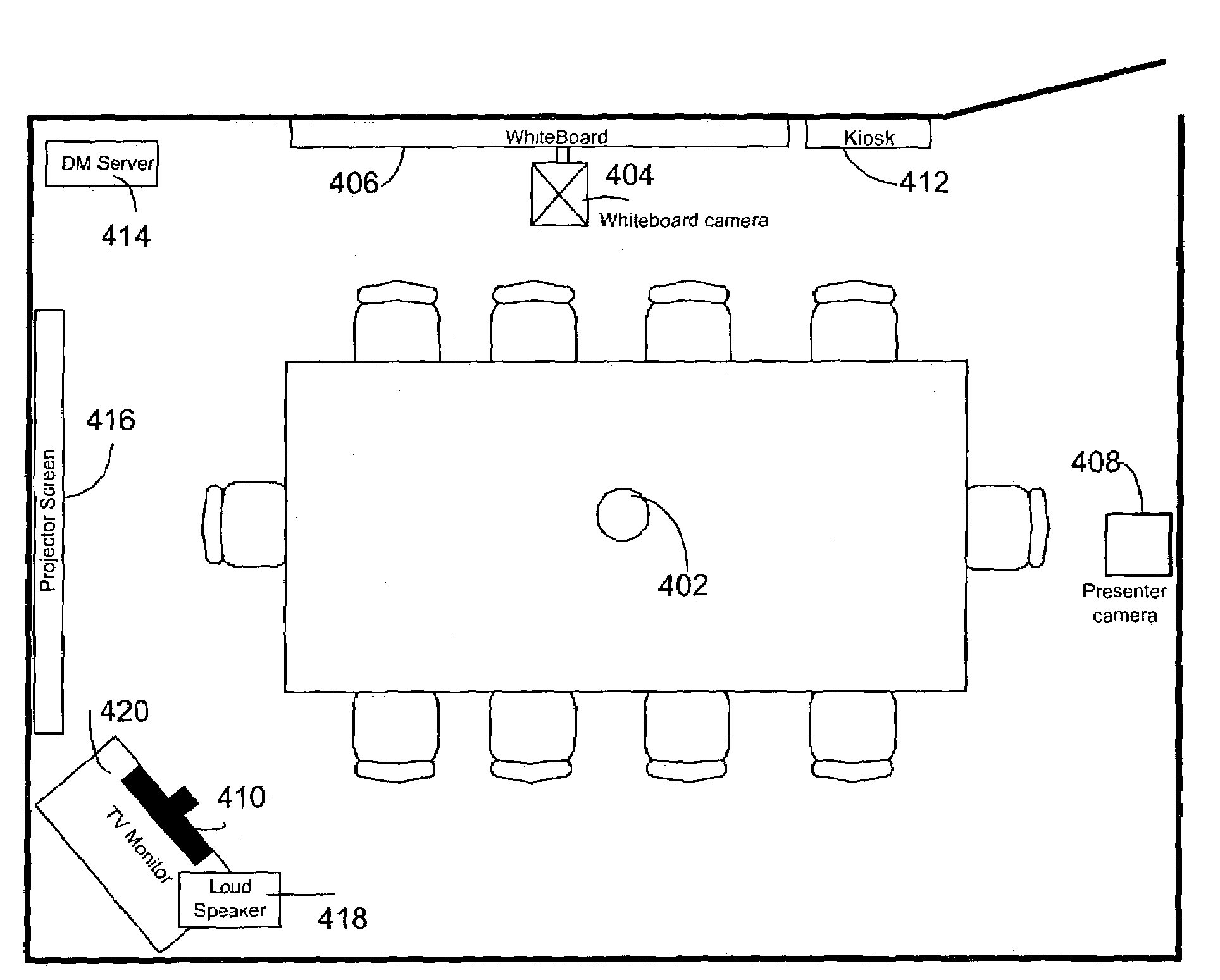
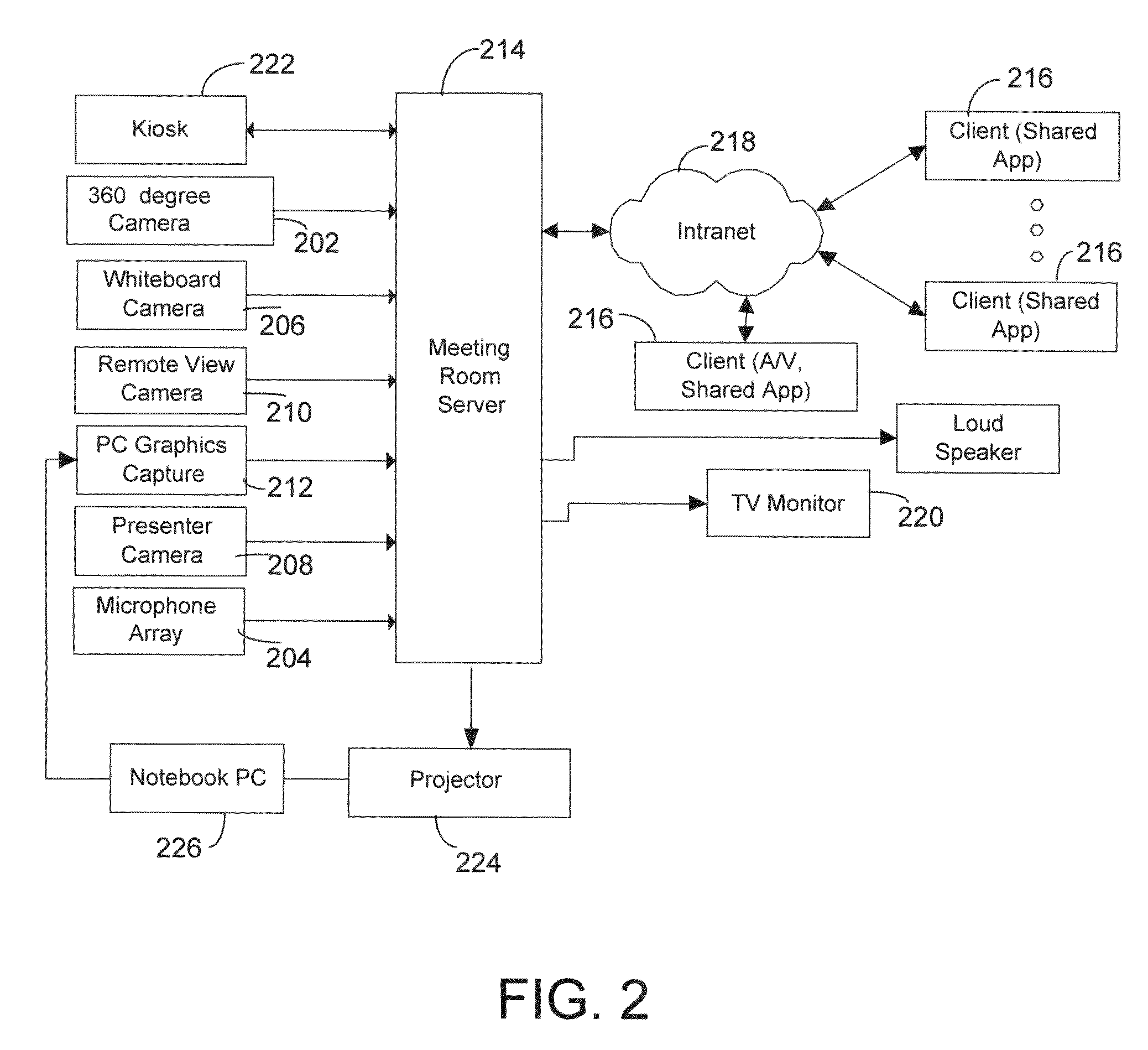
System and method for distributed meetings
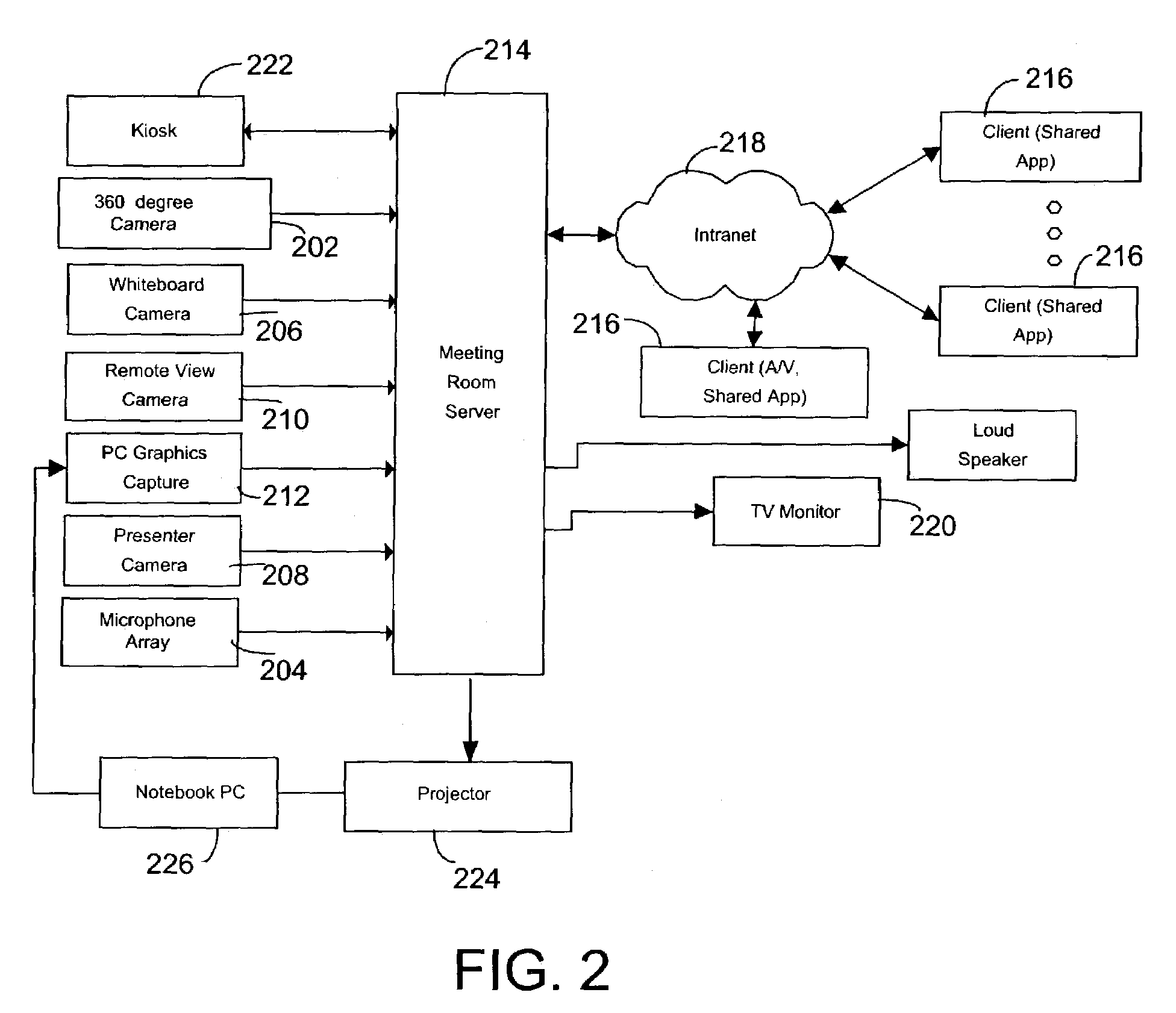
InactiveUS7428000B2Rich browsingQuick ViewTelevision system detailsTelevision conference systemsWhiteboardView camera
A system and method for teleconferencing and recording of meetings. The system uses a variety of capture devices (a novel 360° camera, a whiteboard camera, a presenter view camera, a remote view camera, and a microphone array) to provide a rich experience for people who want to participate in a meeting from a distance. The system is also combined with speaker clustering, spatial indexing, and time compression to provide a rich experience for people who miss a meeting and want to watch it afterward.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Rear obstruction detection
A method is provided using a system mounted in a vehicle. The system includes a rear-viewing camera and a processor attached to the rear-viewing camera. When the driver shifts the vehicle into reverse gear, and while the vehicle is still stationary, image frames from the immediate vicinity behind the vehicle are captured. The immediate vicinity behind the vehicle is in a field of view of the rear-viewing camera. The image frames are processed and thereby the object is detected which if present in the immediate vicinity behind the vehicle would obstruct the motion of the vehicle. The processing is preferably performed in parallel for a plurality of classes of obstructing objects using a single image frame of the image frames.
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
Videoconferencing endpoint having multiple voice-tracking cameras
ActiveCN102256098ATelevision conference systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionView cameraComputer science
A videoconferencing apparatus automatically tracks speakers in a room and dynamically switches between a controlled, people-view camera and a fixed, room-view camera. When no one is speaking, the apparatus shows the room view to the far-end. When there is a dominant speaker in the room, the apparatus directs the people-view camera at the dominant speaker and switches from the room-view camera to the people-view camera. When there is a new speaker in the room, the apparatus switches to the room-view camera first, directs the people-view camera at the new speaker, and then switches to the people-view camera directed at the new speaker. When there are two near-end speakers engaged in a conversation, the apparatus tracks and zooms-in the people-view camera so that both speakers are in view.
Owner:POLYCOM INC
Augmented reality display system and method for vehicle
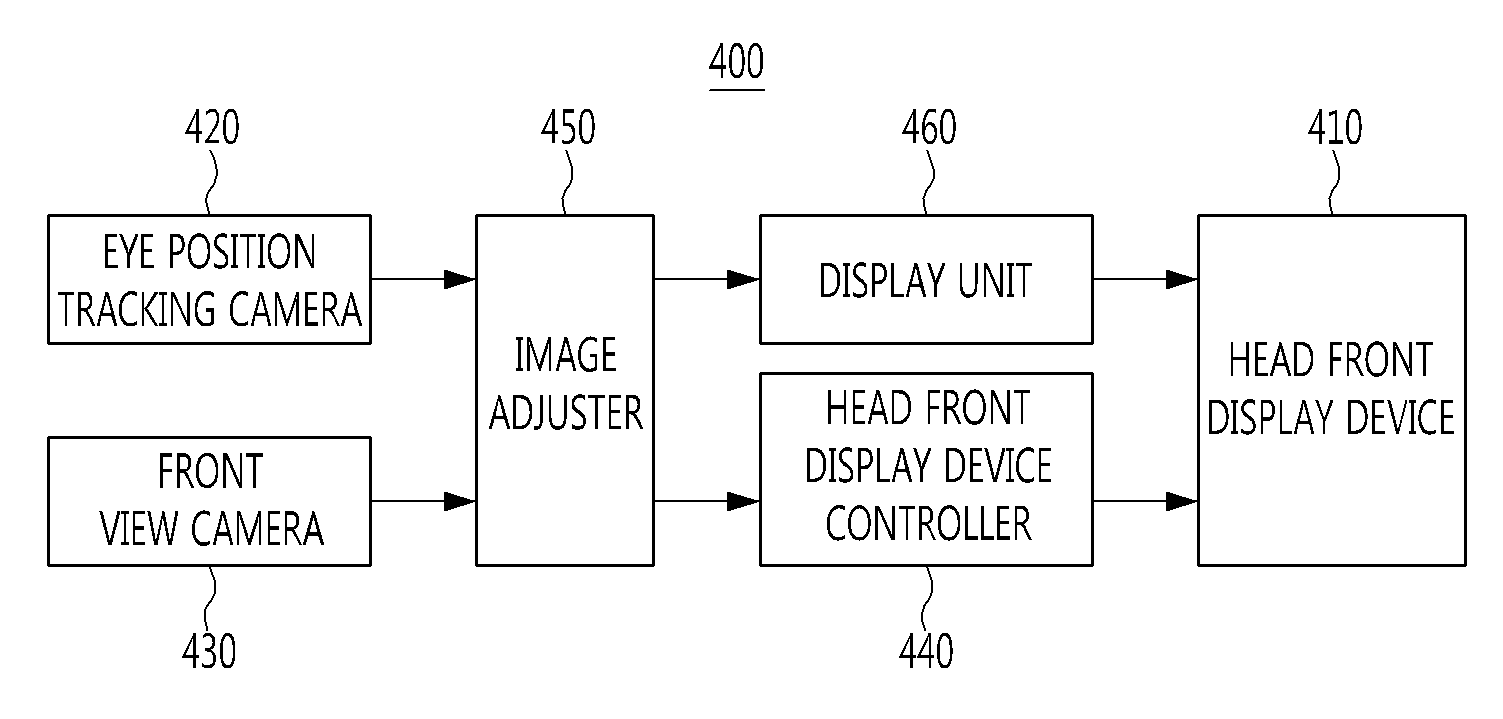
ActiveUS20120154441A1Intuitive informationRoad vehicles traffic controlAcquiring/recognising eyesDriver/operatorView camera
A system includes a head front display device, an eye position tracking camera to track movement of a driver's irises, a front view camera to take a picture of a front view of the driver, a head front display device controller to implement at least one of an angle change, forward movement, backward movement, upward movement, downward movement, leftward movement, and rightward movement of the head front display device, an image adjuster to adjust an object displayed on the head front display device in association with an object of an actual view seen through the front window of the vehicle based on positions of the driver's irises obtained through the eye position tracking camera and an image of the front view obtained by the front view camera, and a display unit controlled by the image adjuster and configured to display information on the head front display device.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
System, method, and apparatus for dispensing oral medications
A pill dispenser includes a housing, a pill-dispensing mechanism, a receptacle, a pill-viewing camera, an identifying camera, one or more processors, and a storage medium (e.g., a memory). The pill-dispensing mechanism is coupled to an opening of the housing. The first pill-viewing camera is positioned to capture an image of the receptacle, and the identifying camera is positioned to capture an image of an area adjacent to the housing. The one or more processors are in operative communication with the pill-dispensing mechanism, the pill-viewing camera, and the identifying camera. The storage medium stores processor-executable instructions for: instructing the pill-dispensing mechanism to dispense a pill; instructing the pill-viewing camera to capture a first image of the pill to determine a presence of the pill; instructing the pill-viewing camera to capture a second image to determine an absence of the pill; and instructing the identifying camera to capture a third image.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
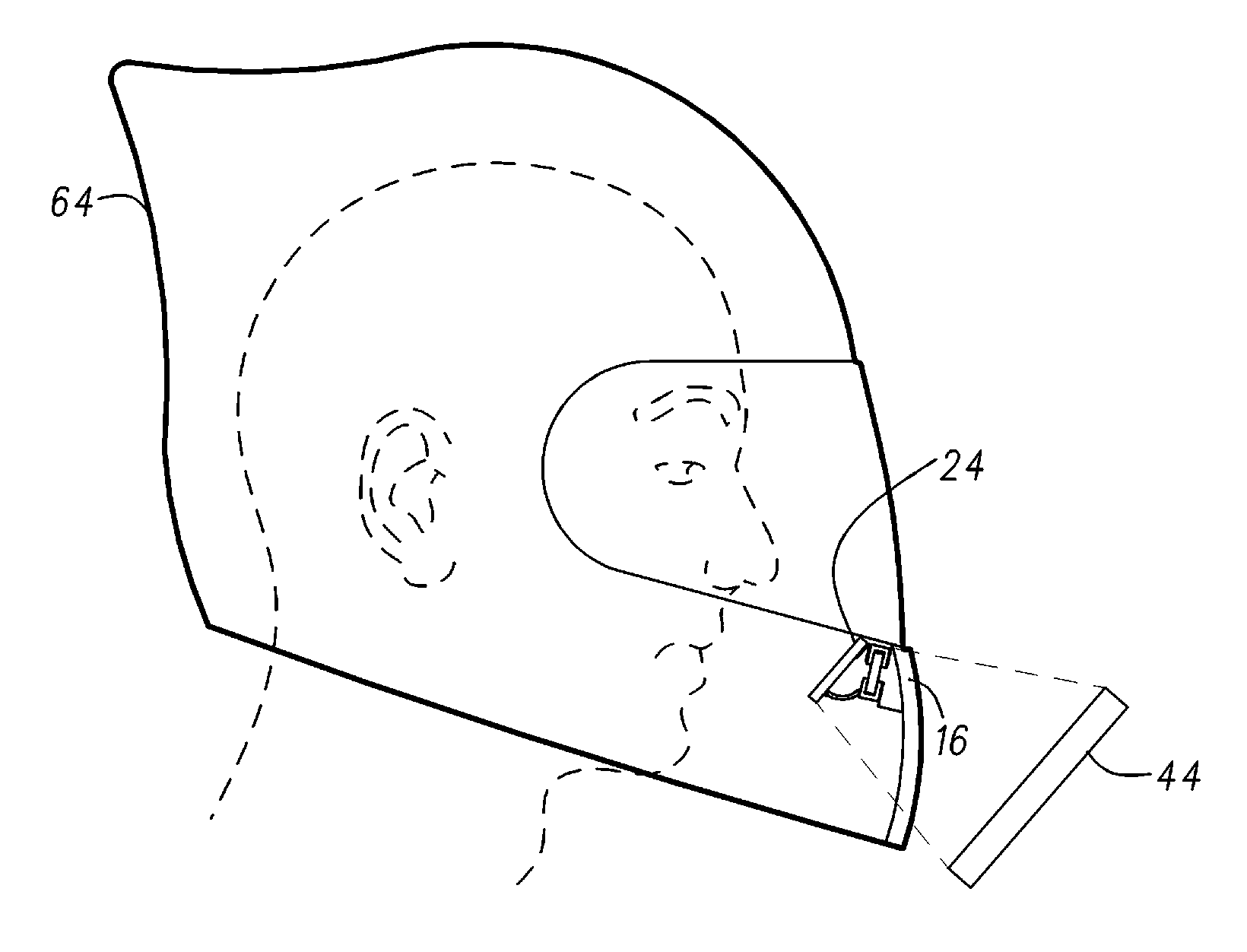
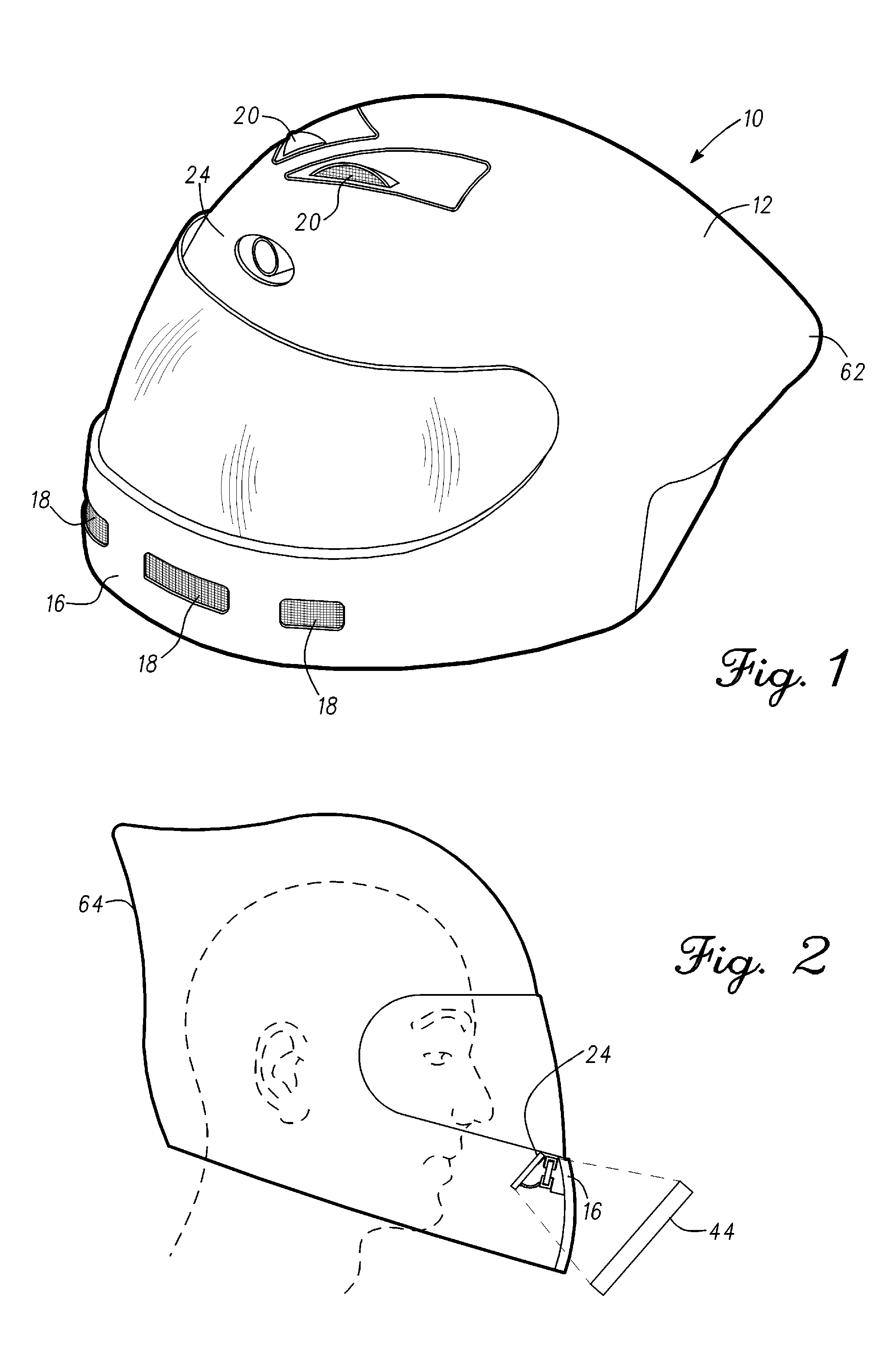
Augmented reality motorcycle helmet
InactiveUS20130305437A1Inertial resistance is smallReduce liftScene recognitionHatsHead movementsGyroscope
An augmented-reality helmet comprises a full-face motorcycle helmet with a look-down micro-display that projects a virtual image in-line with the helmet's chin bar. In order to accommodate the power requirements, the helmet includes a battery pack mounted at the base of the motorcyclist's skull. A wind turbine charges the batteries. Exhaust from the turbine is then deducted through the helmet to cool the battery pack and / or the motorcyclist's head. The turbine is controllable so that it can operate as a circulating fan to provide ventilation. A digital gyroscope provides a control input to a controller for operating a steerable headlight of the motorcycle to track the rider's head movements; and provides acceleration output to an algorithm that will contact emergency responders if the rider is non-responsive after a collision. A 170 degree rear-view camera is mounted within an aerodynamic fairing on the back of the helmet.
Owner:SKULLY
Pill Dispenser
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
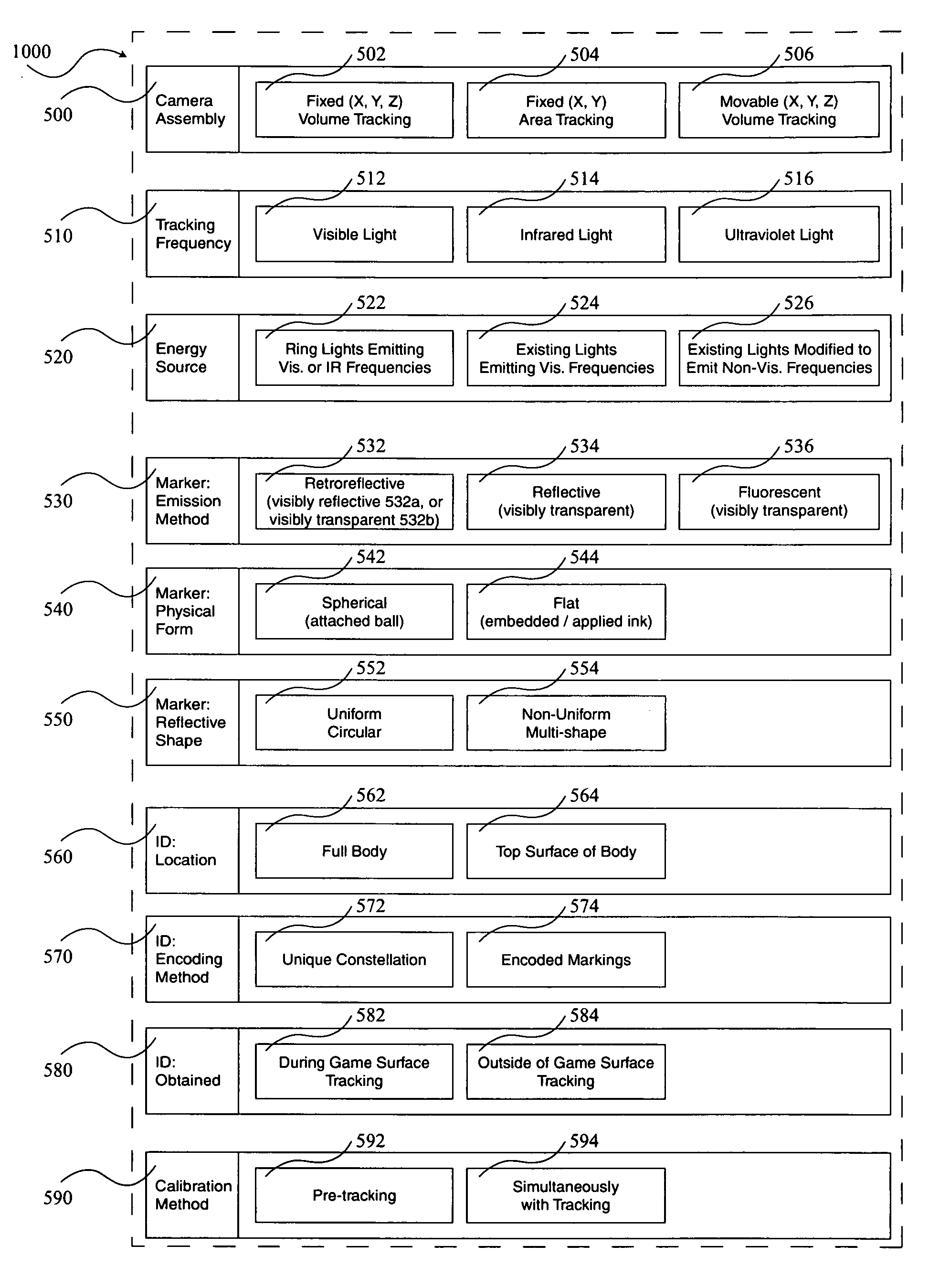
Optimizations for live event, real-time, 3D object tracking
InactiveUS20090046152A1Maximized manufacturingMaximized installation costTelevision system detailsImage analysisView cameraIce hockey
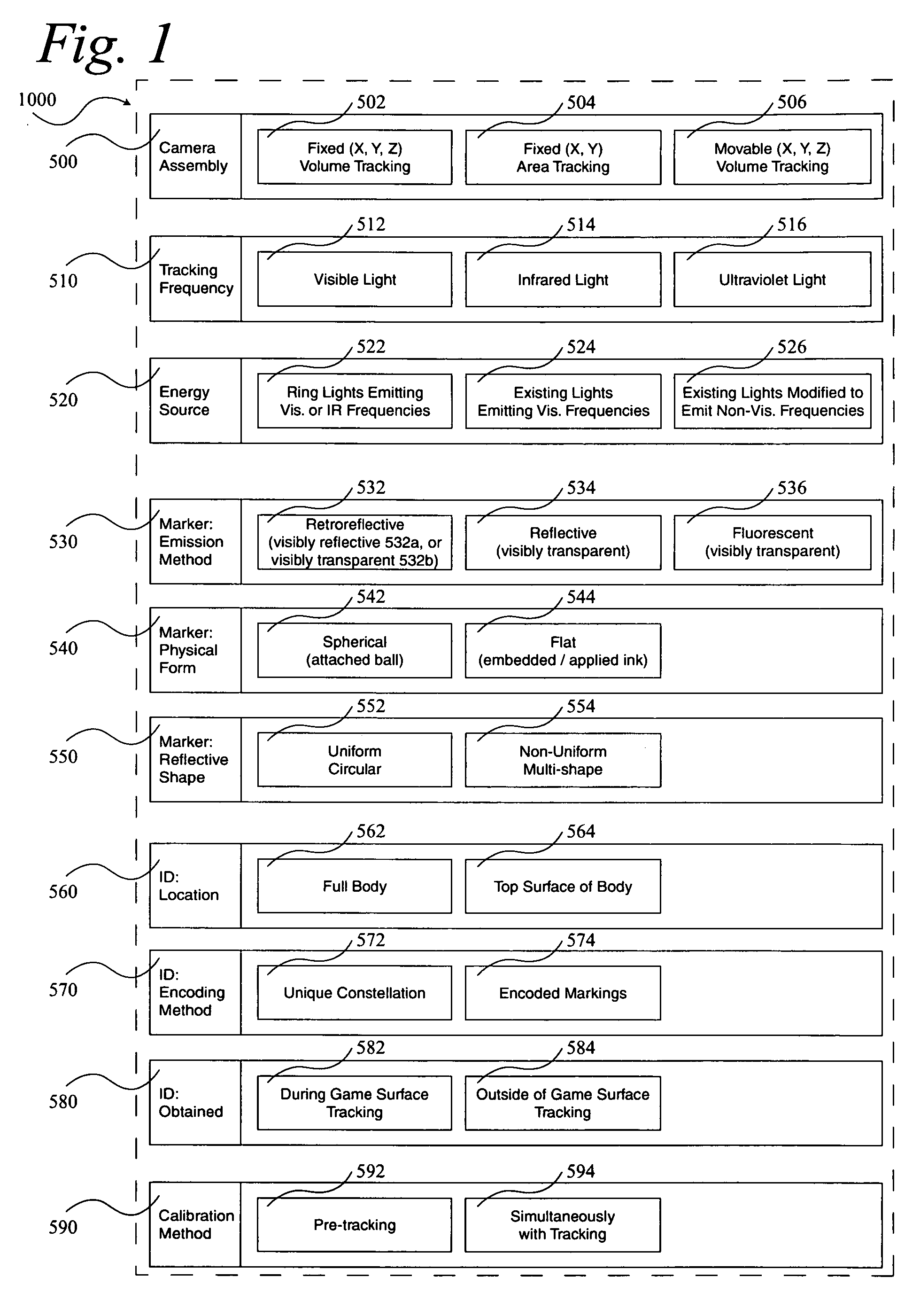
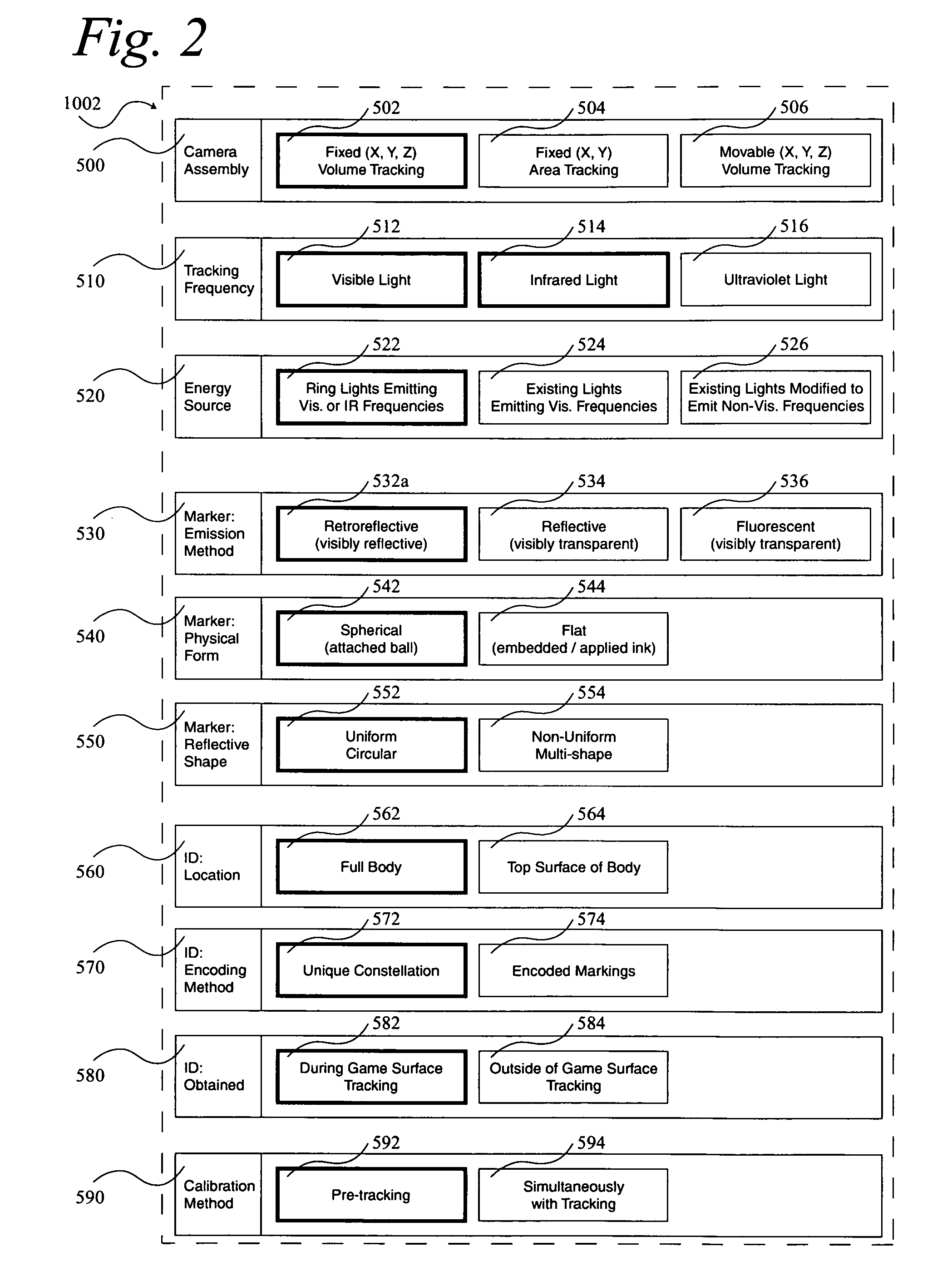
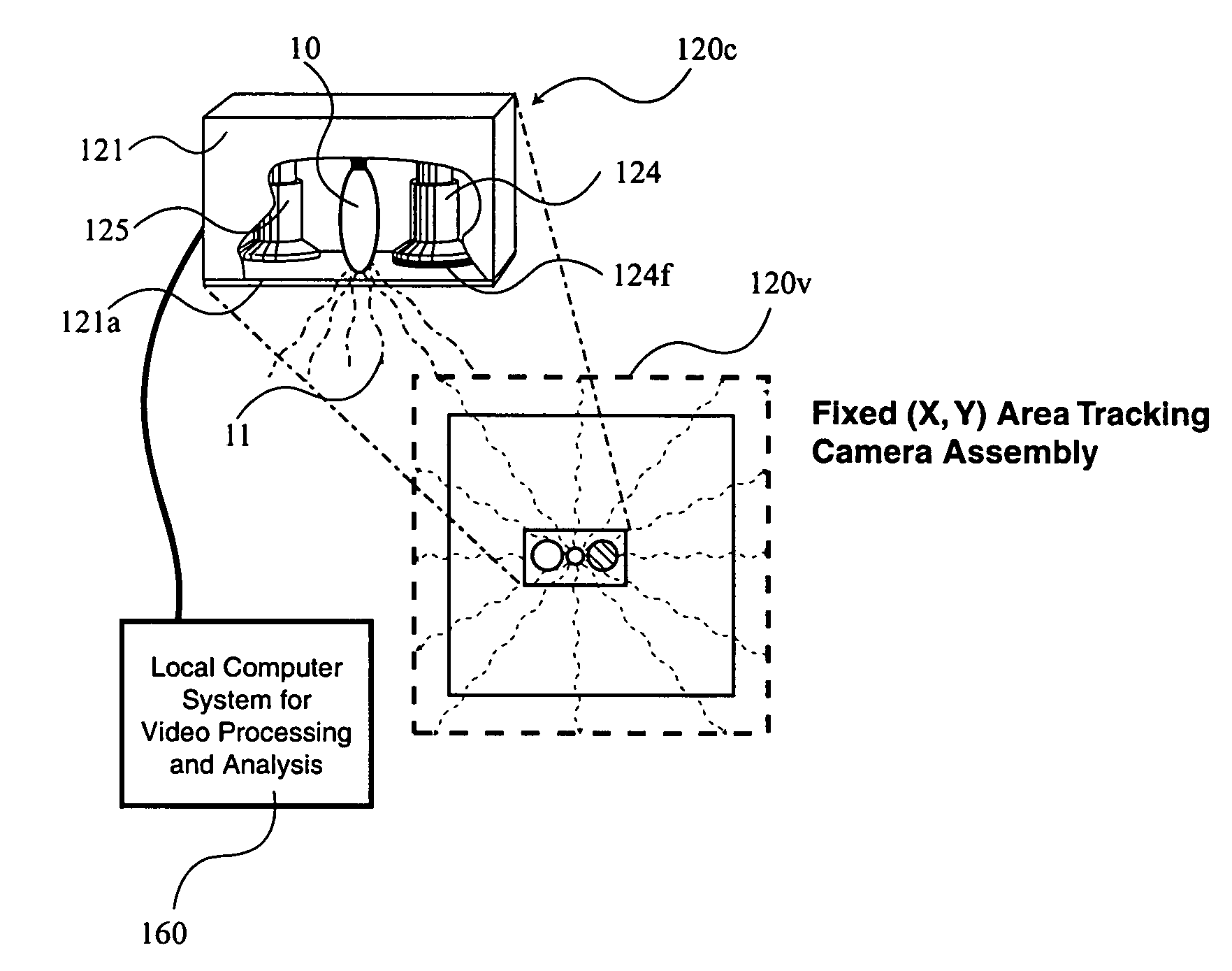
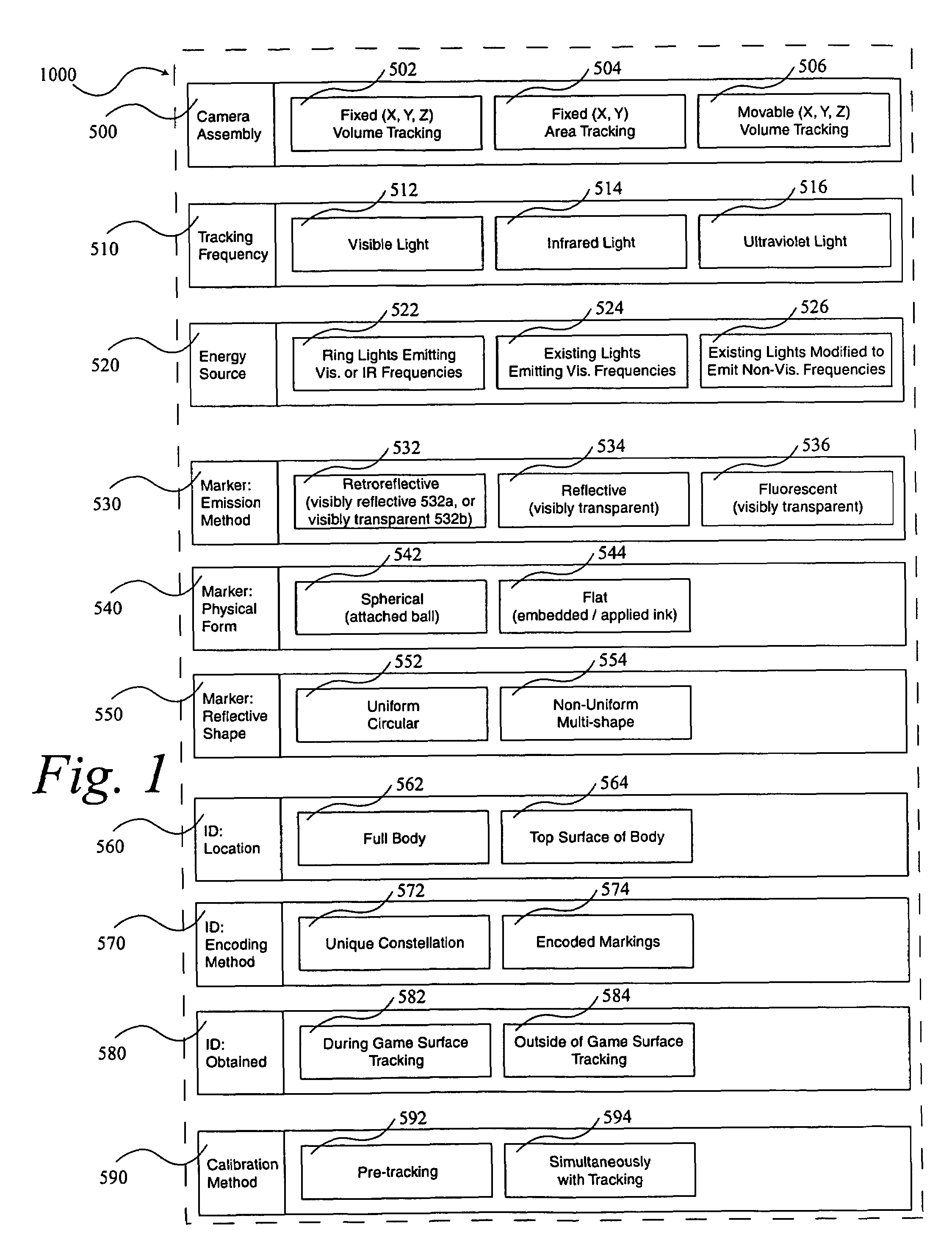
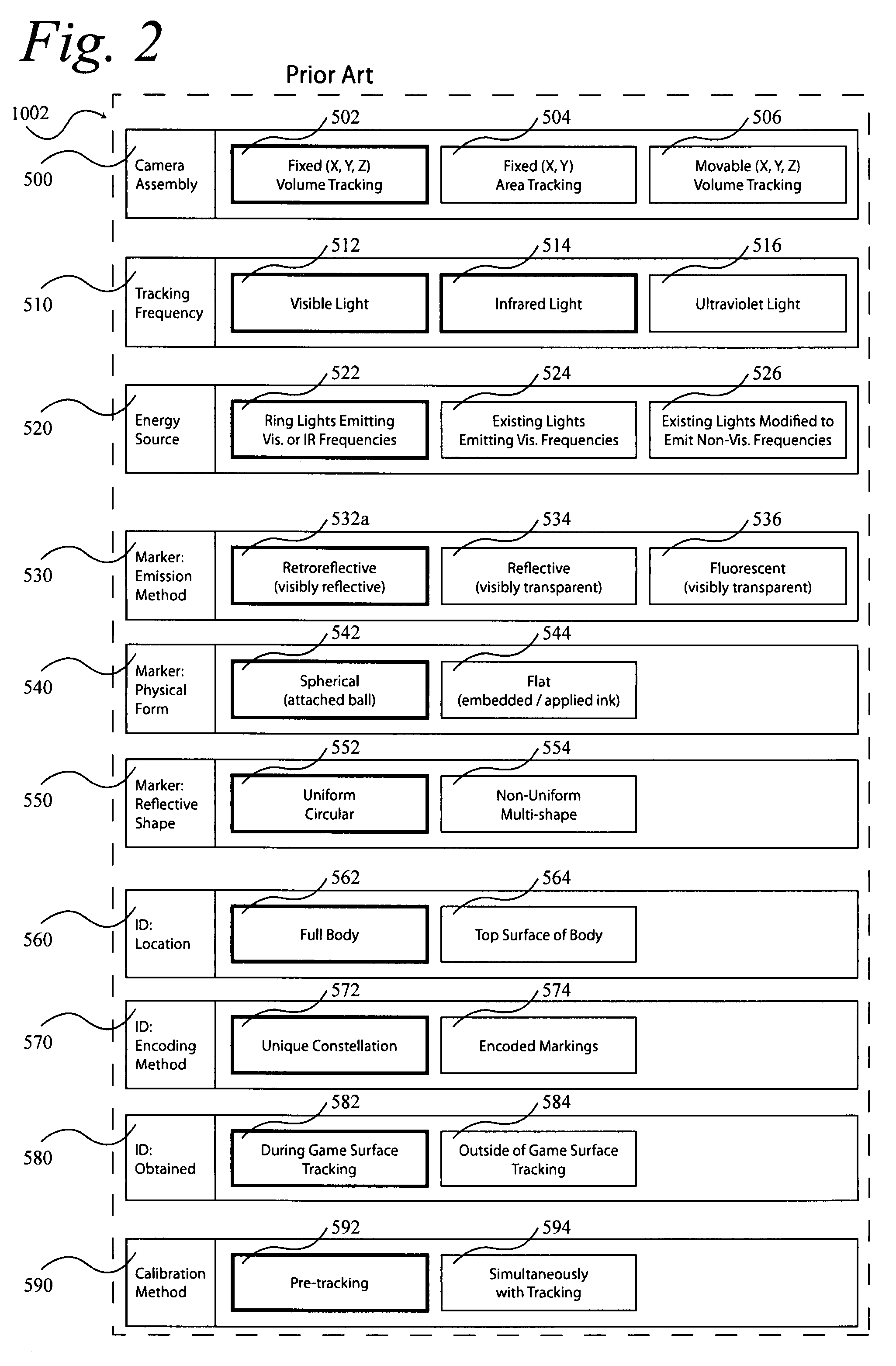
A system 1000, and its alternates 1002 through 1022, for automatically tracking and videoing the movements of multiple participants and objects during an event. System 1000 and its alternates comprise a scalable area tracking matrix of overhead tracking cameras 120c, whose individual field-of-views 120v combine to form a contiguous view 504m of the performance area where the event is being held. As participants 110, and all other necessary objects such as 103 (e.g. a puck in ice-hockey) and 104 (e.g. a stick in ice-hockey) move about during the event, computer 160 analyzes the images from contiguous view 504m to create a real-time tracking database at least including participant and object centroid locations respective to the performance area, and preferably including their identities matched to these ongoing locations. System 1000 and its alternates then employ the real-time database to automatically direct, without operator intervention, one or more side-view cameras such as 140-a, 140-b, 140-c and 140-d, to maintain optimal viewing of the event. The participants and objects may additionally be marked with encoded or non-encoded, visible or non-visible markers, either denoting centroid locations visible from their upper surfaces, and / or non-centroid locations visible from perspective views. The encoded markers are preferably placed on upper surfaces and detectable by computer 160 as it analyzes the images from contiguous overhead field-of-view 504m, thus providing participant and object identities to correspond with ongoing locations, further enhancing algorithms for subsequently controlling side-view cameras 140-a through 140-d. The non-encoded markers are preferably placed on multiple non-centroid locations at least on the participants that are then adjustably viewable by system 1000 and its alternates as the system uses the determined locations of each participant from the overhead view to automatically adjust one or more side-view cameras to tightly follow the participant. The resulting images from side-view cameras 140-a through 140-d may then be subsequently processed to determine the non-encoded marker locations, thus forming a three dimensional model of each participant and objects movements.
Owner:MAXX HLDG
Optimizations for live event, real-time, 3D object tracking
InactiveUS7483049B2Maximized manufacturingMaximized installation costImage enhancementTelevision system detailsView cameraImaging analysis
During a sporting or similar event, participants and objects are automatically tracked using a scalable matrix of fixed, non-adjustable overhead cameras that form a view of the entire performance area. The participants and objects are identified with attached visible or non-visible markers that are detected using image analysis. A real-time database of two-dimensional movement locations is created from the resulting information, which is then used to automatically direct multiple fixed, adjustable side-view cameras for capturing and recording the event. Image analysis of this side-view video detects additional markers providing a three-dimensional model of the participants and objects.
Owner:MAXX HLDG
Smart vehicle sun visor
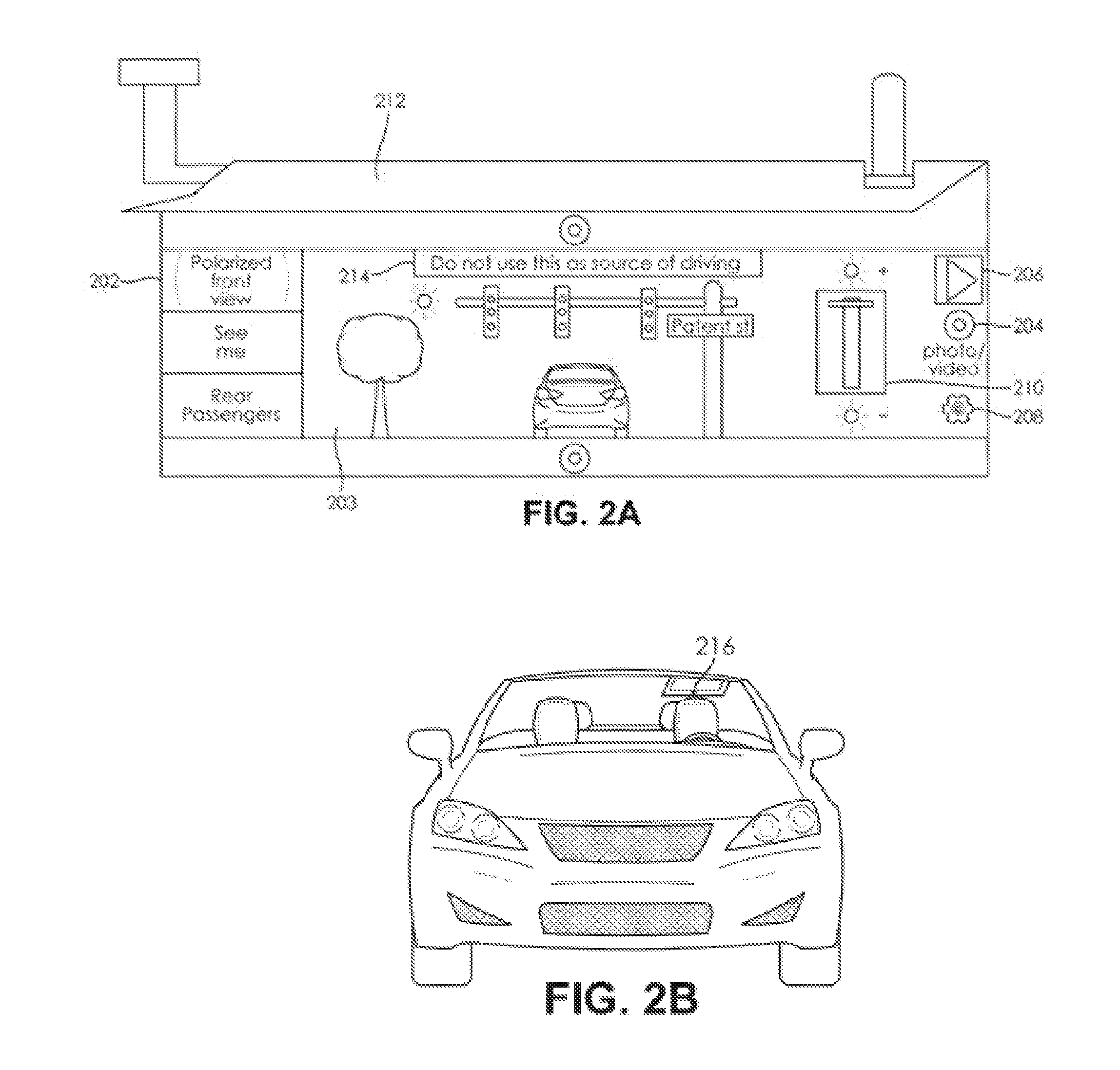
ActiveUS20170013188A1Reduce glareEliminate glareInput/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsDistractionVisibility
A vehicle sun visor system with a touch screen display is configured to display video feed from one or more cameras. A front facing polarized and / or photochromic camera shows the area of view which is normally blocked by the deployed sun visor, allowing the user to view traffic lights, road signs, etc. without the distraction of glare. Software image processing may also be used to reduce glare and improve visibility. In addition, the sun visor system also has a “see-me” camera which allows the user to use the screen as a mirror, and one or more rear-view cameras which can be used to see the passenger area of a vehicle through the touch-screen display. Any of the cameras may be used to take photos or videos, which may be viewed on the display and transmitted wirelessly to other electronic devices or cloud storage.
Owner:BE TOPNOTCH LLC
System and method for distributed meetings
InactiveUS20090046139A1Rich browsingImprove experienceTelevision conference systemsSubstation equipmentWhiteboardView camera
A system and method for teleconferencing and recording of meetings. The system uses a variety of capture devices (a novel 360° camera, a whiteboard camera, a presenter view camera, a remote view camera, and a microphone array) to provide a rich experience for people who want to participate in a meeting from a distance. The system is also combined with speaker clustering, spatial indexing, and time compression to provide a rich experience for people who miss a meeting and want to watch it afterward.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
External Monitoring System for Securing Driver's Field of Vision for Vehicles
InactiveUS20080055411A1Reduce air resistanceColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsDriver/operatorView camera
Disclosed therein is an external monitoring system, which includes cameras mounted at both sides of the front and rear of a vehicle and on side view mirrors, display devices for outputting images in a driver's front sight direction through the cameras, and controller for controlling the display devices. The display devices are mounted on a dash board of the upper portion of an instrument cluster or on the dash board of the upper portion of a steering wheel and are adjustable in their location laterally to allow the driver to gaze the front to the maximum. The external monitoring system includes: front and rear view cameras disposed at both side ends of the front and rear of the vehicle; side view cameras mounted on both side view mirrors of the vehicle in such a way as to be directed to the rear of the vehicle; at least two display devices for receiving and outputting signals inputted through the front and rear view cameras and the side view cameras; a holding device mounted on the dash board of the upper portion of the instrument cluster for moving the display devices laterally and fixing them; and a controller for converting the image output from the front and rear view cameras and the side view cameras and controlling brightness of a screen and zoom-in and zoom-out of the cameras.
Owner:LEE DONG WOOK
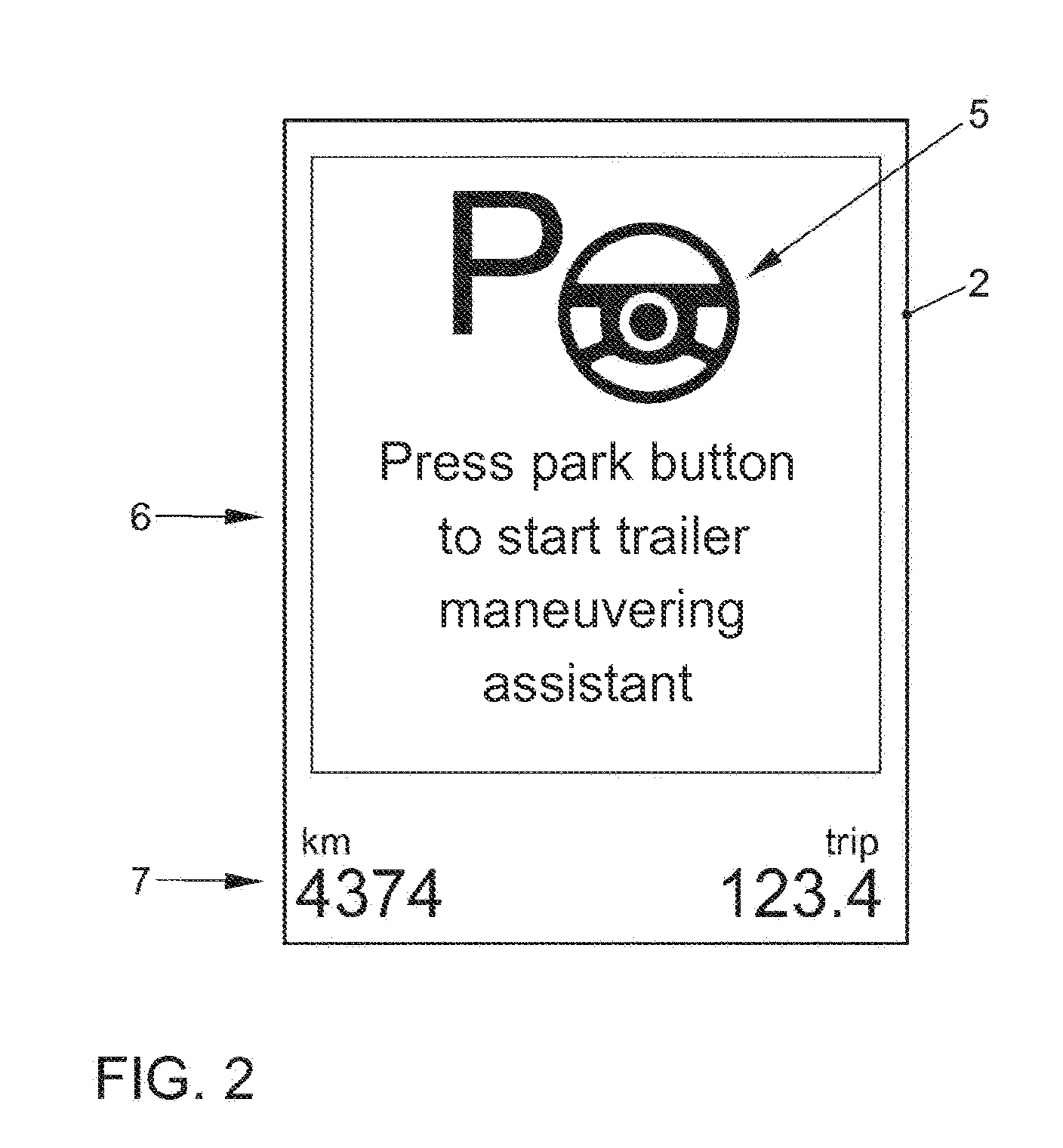
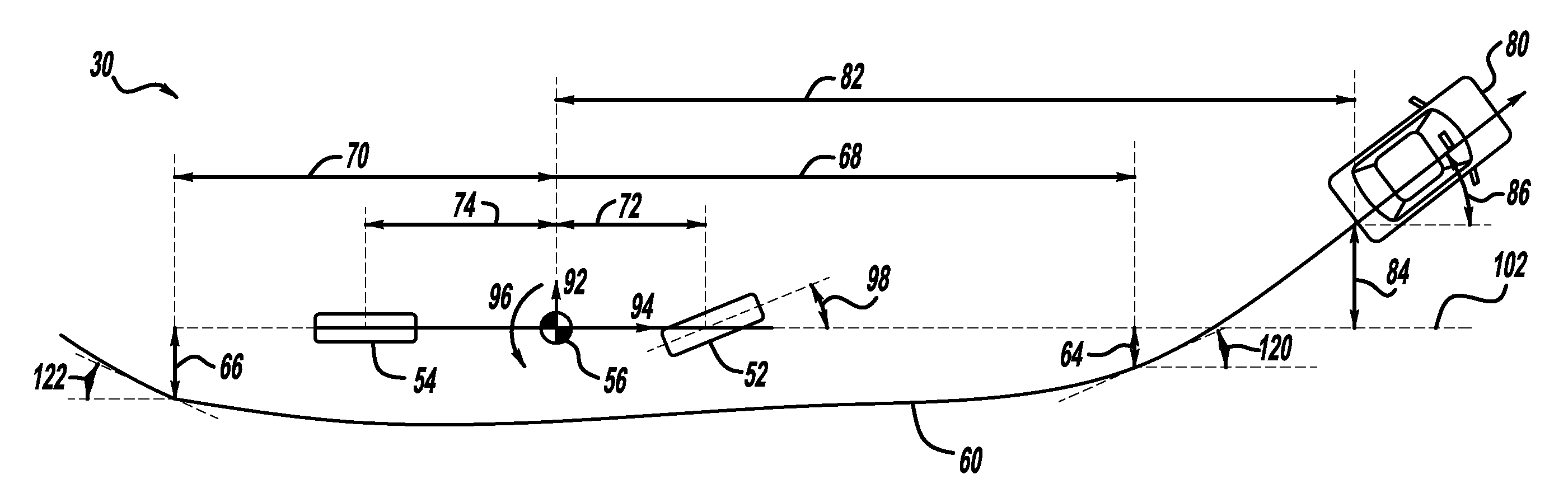
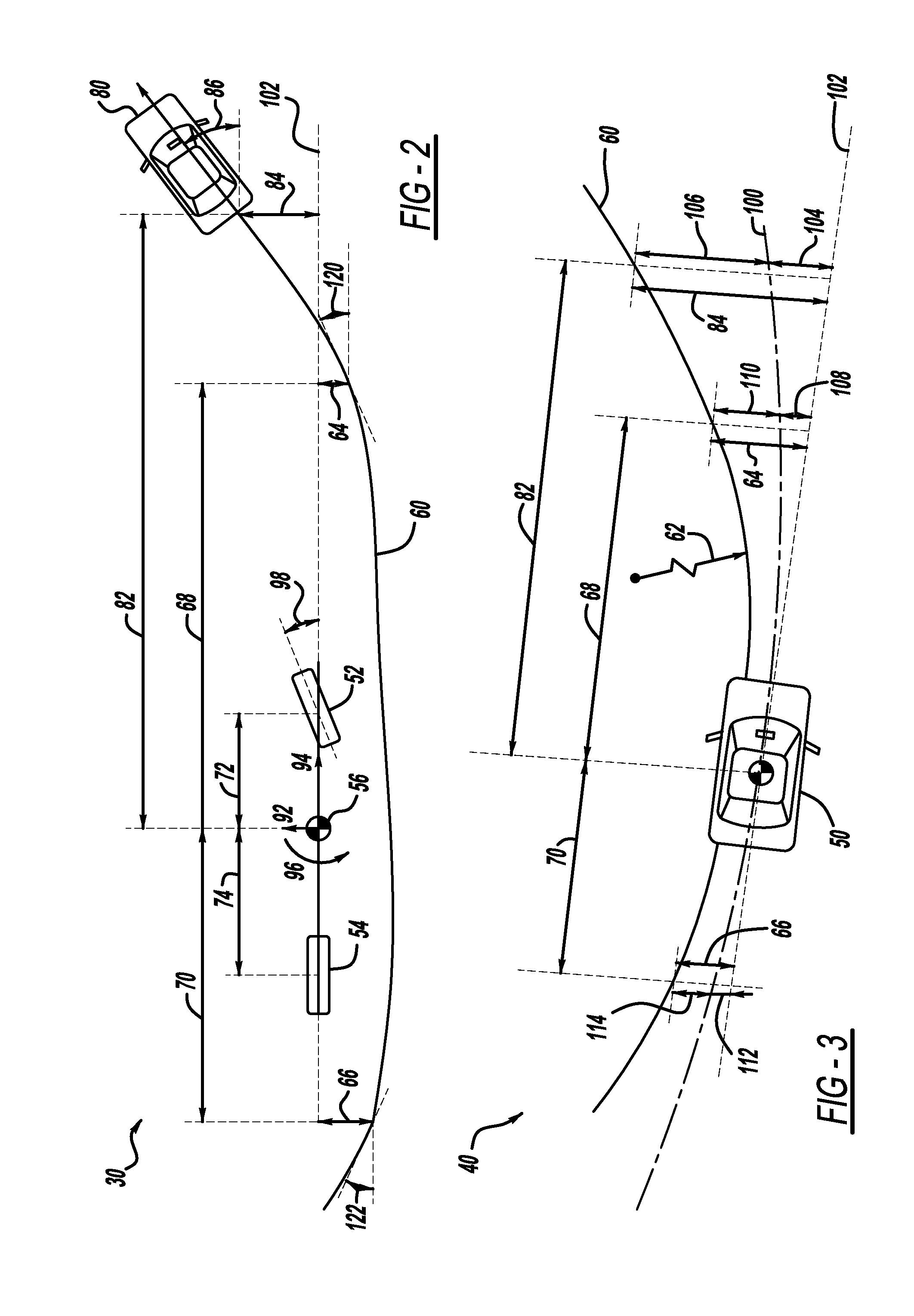
Method and device for maneuvering a trailer
ActiveUS20150149040A1Easy to operateDigital data processing detailsSteering initiationsView cameraActive steering
A method and a device for maneuvering a combination of a towing vehicle and a trailer, wherein the trailer is connected to the towing vehicle by a non-steerable tow-bar, and the towing vehicle observes the rear surroundings, including the trailer, by a rear-view camera. The method includes the steps: a) determining the actual articulation of the trailer relative to the towing vehicle; b) determining the length of the tow-bar and the maximum articulation of the trailer; c) inputting the intended articulation of the trailer; d) reversing the towing vehicle with at least active steering support until the intended articulation of the trailer is reached; e) fixing the direction of travel predetermined by the intended articulation; f) maneuvering the towing vehicle with at least active steering support while maintaining the predetermined direction of travel until an eventual parking position is reached.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN AG
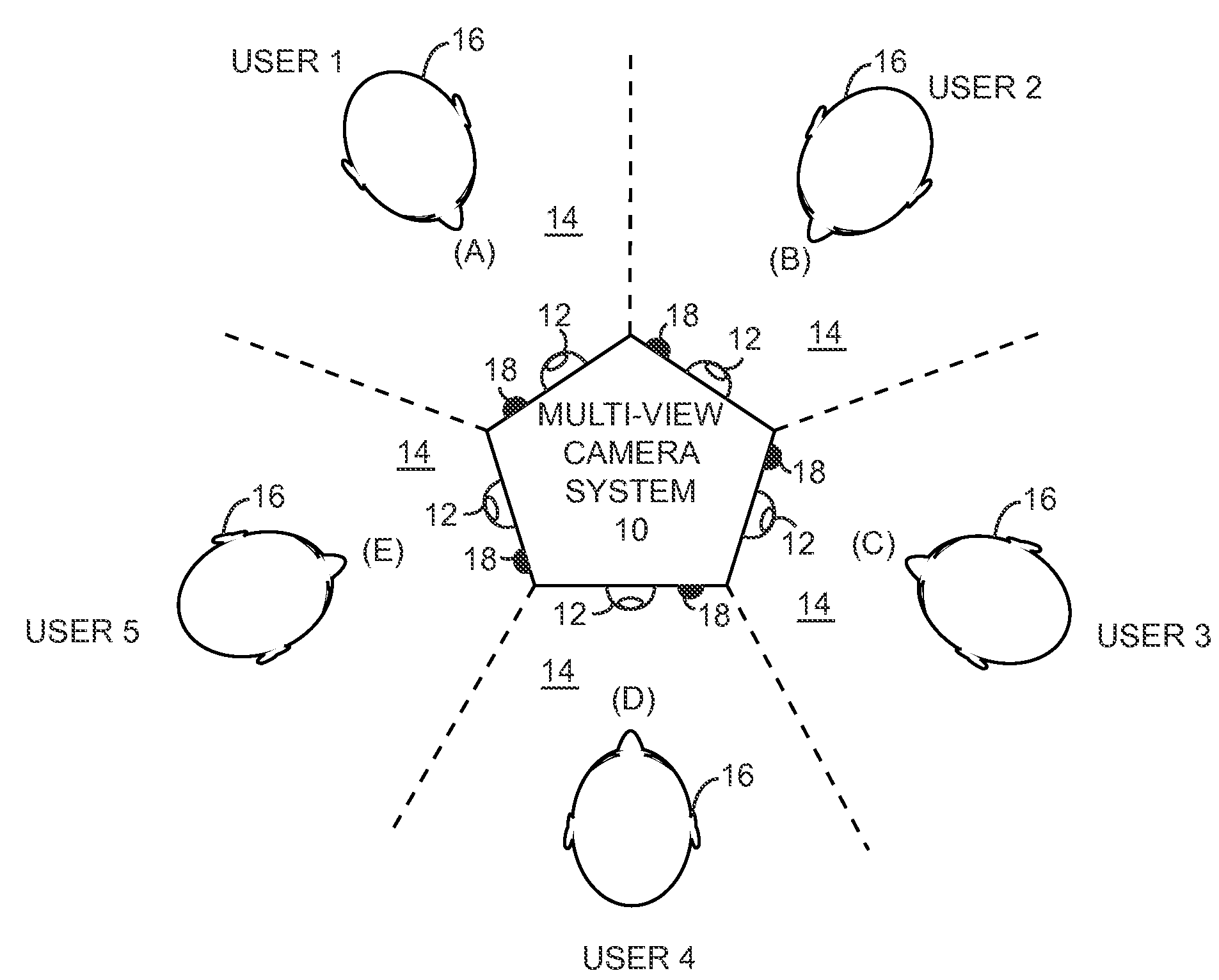
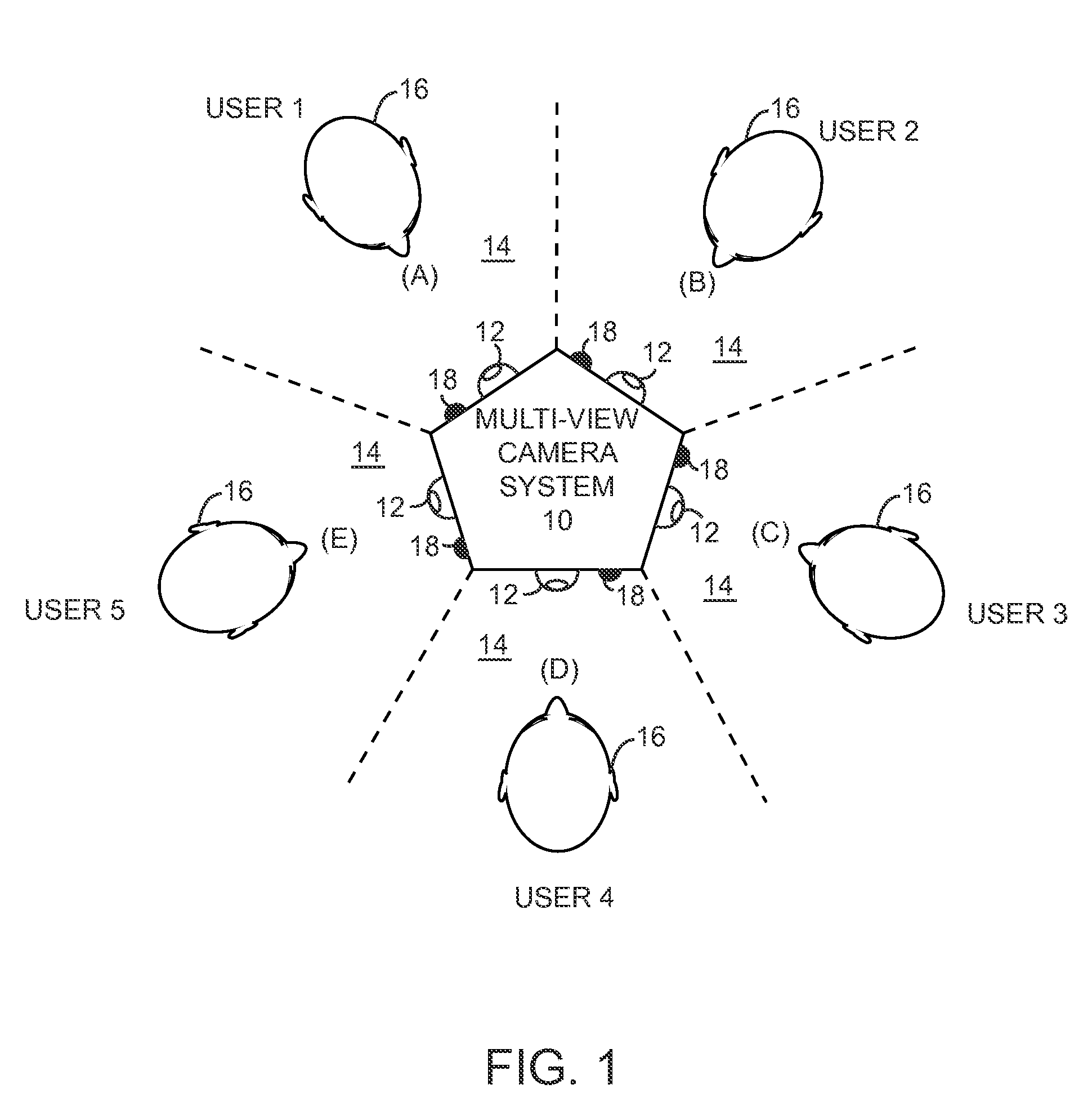
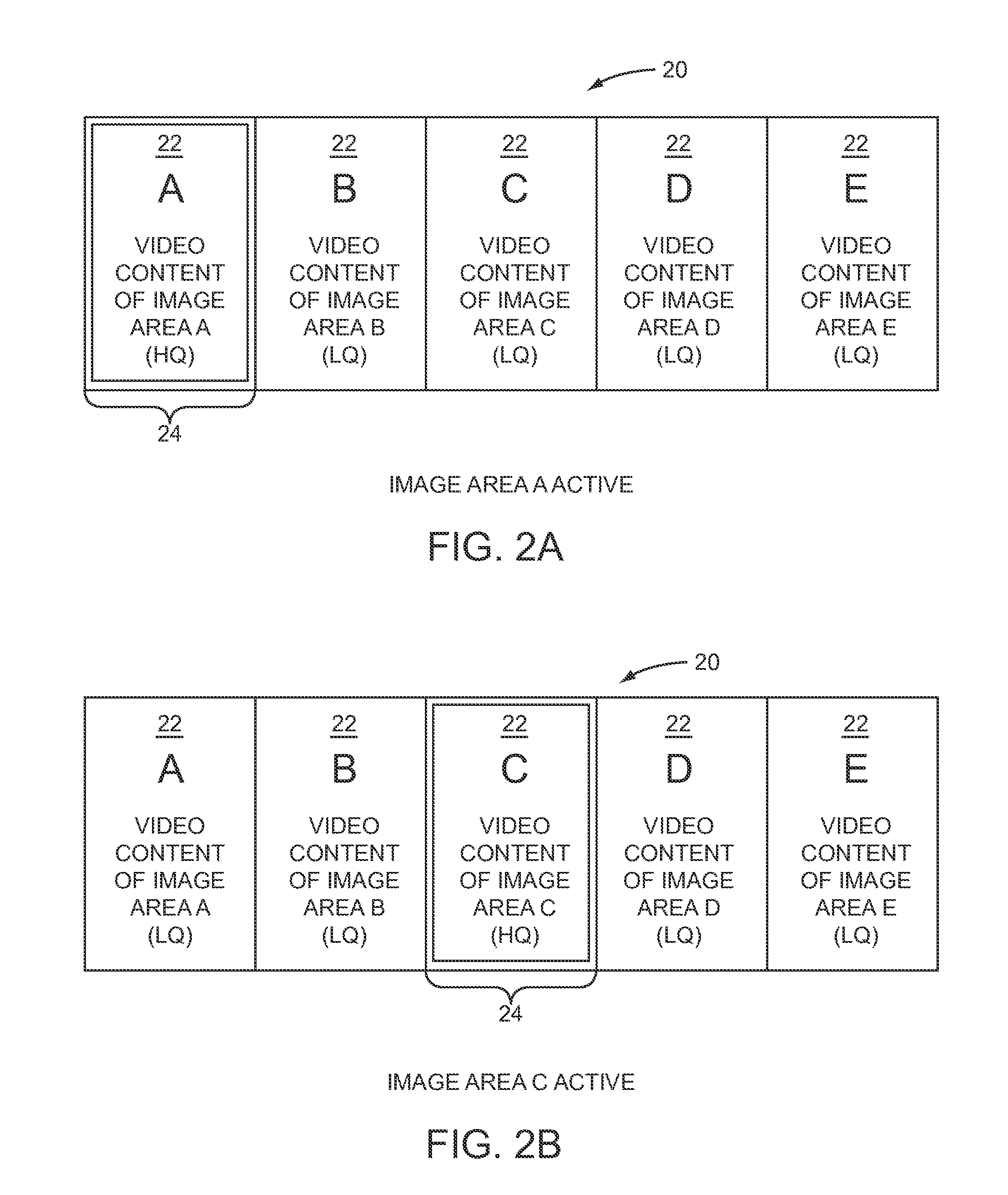
Scalable video encoding in a multi-view camera system
ActiveUS20100157016A1Low level of qualityQuality improvementTelevision conference systemsTwo-way working systemsView cameraVideo encoding
Owner:APPLE INC
Image capturing apparatus, image processing apparatus, and method thereof
An image processing apparatus and method relate to an imaging process which is applied to image data captured by an image capturing apparatus such as a multi-eye camera, multi-view camera, and the like. The image processing apparatus and method generates synthetic image data which focused on a curved focus surface by compositing multi-view image data captured from multi-viewpoints.
Owner:CANON KK
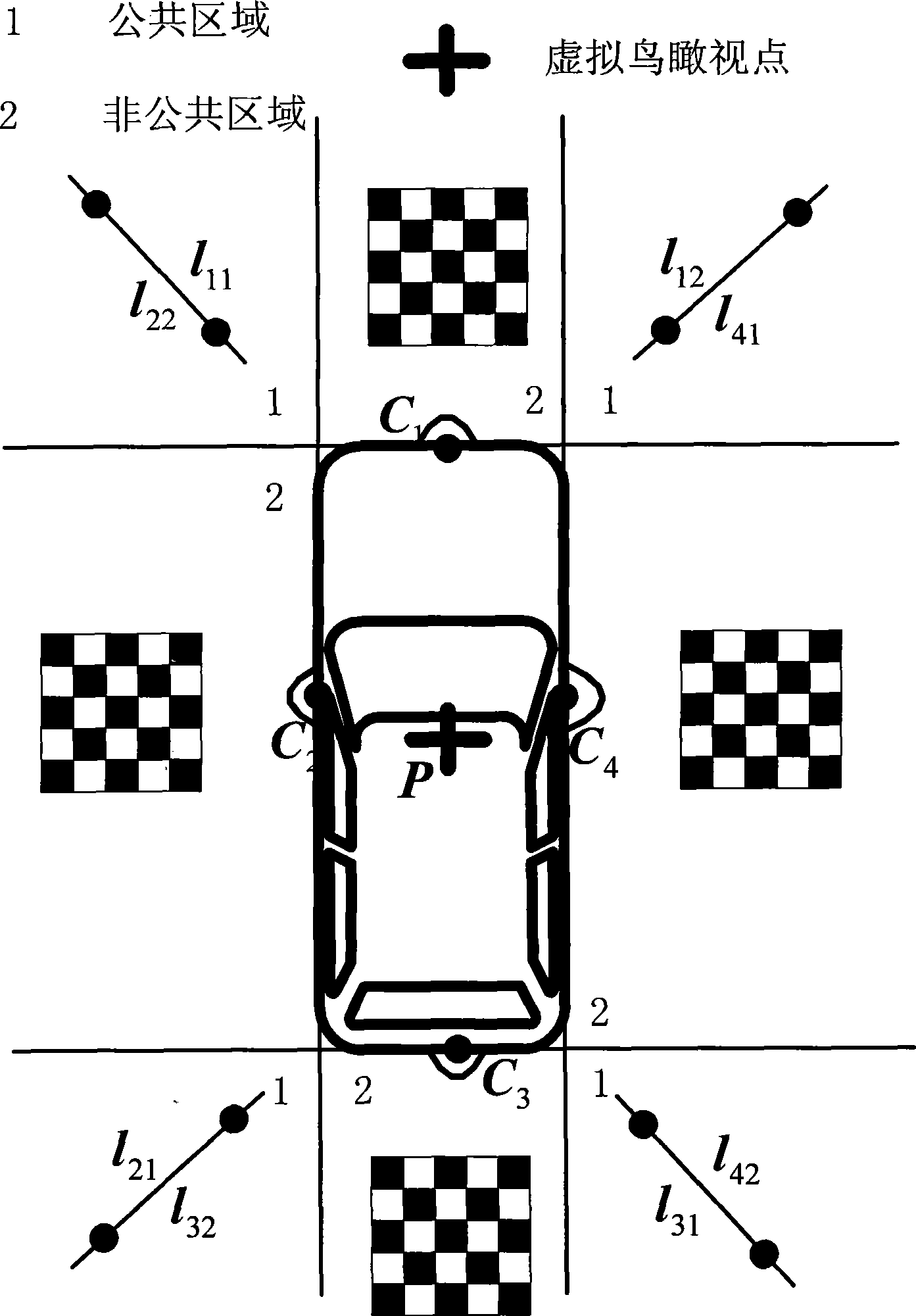
Panoramic view vision auxiliary parking system demarcating method
InactiveCN101425181AGood panoramic bird's eye view effectSimple methodImage analysisSystem integrationView camera
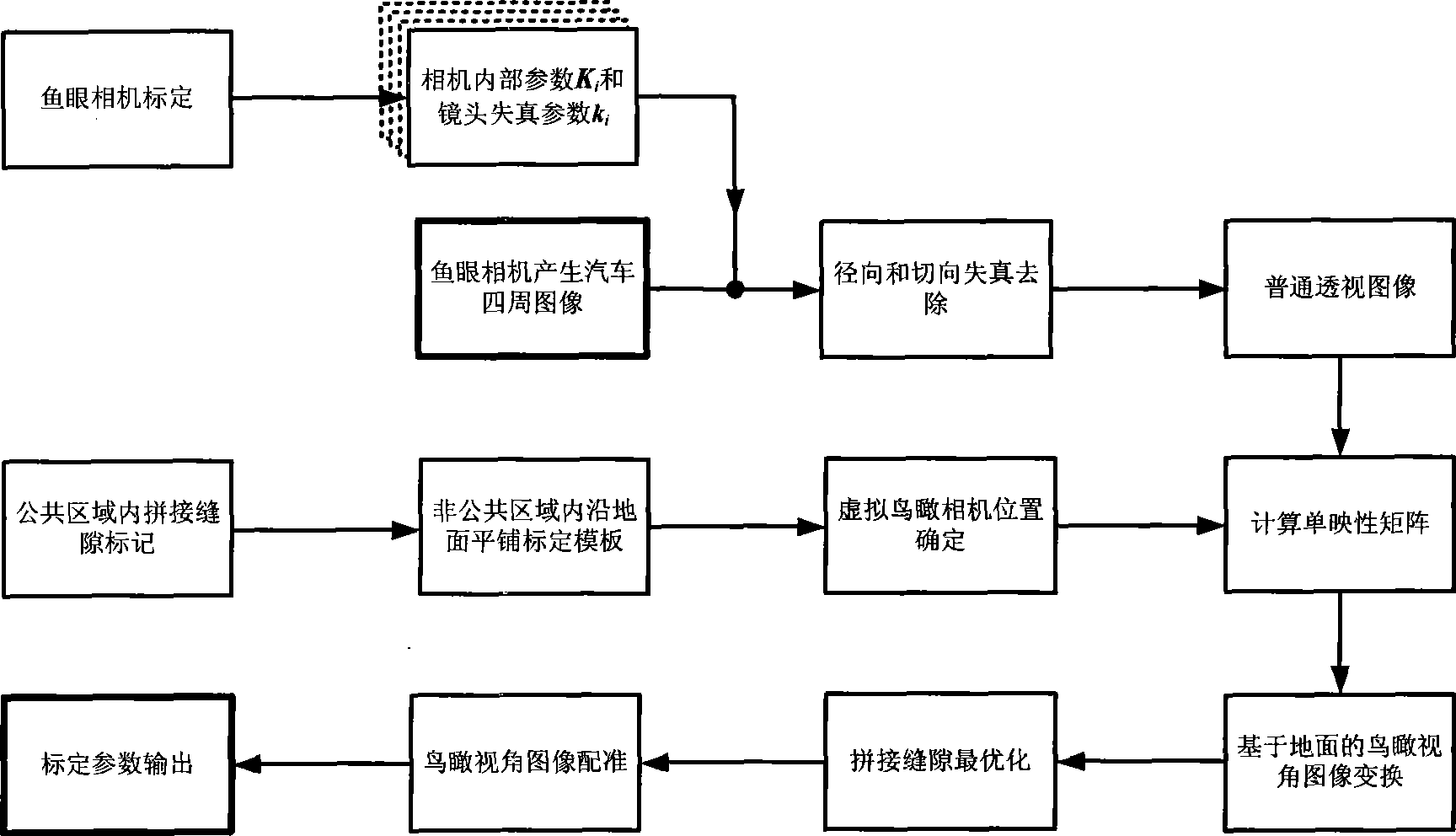
The invention discloses a parking method for a panoramic optical aid parking system, which uses images generated by at least two wide-angle fisheye cameras installed at the periphery of an automobile for generating a virtual aerial view image at a certain height at the top of the automobile. The method comprises the following steps: model parameters of the wide-angle fisheye cameras are calculated; a certain straight line in a public view field is identified as a splice seam; the position of a world coordinate system in a non-public view field is identified; the position of a visual aerial view camera is fixed; a single-mapping transformation matrix based on the ground level is calculated; the position of the splice position is totally optimized; position parameters among all images under the visual aerial view camera are calculated. The method has the advantages of low requirement to equipment, simple process, and no dependence on relative positions among cameras and accurate posture parameters, and reduces the complexity of system integration; calculated parameters during real-time work can be provided by one-time parking; and the method has favorable peripheral panoramic aerial view effect of automobiles.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and apparatus for obtaining panoramic and rectilinear images using rotationally symmetric wide-angle lens
The present invention provides mathematically accurate image processing algorithms for extracting natural looking panoramic images and distortion-free rectilinear images from images acquired using a camera equipped with a wide-angle lens which is rotationally symmetric about an optical axis and devices implementing such algorithms. Imaging systems using this method can be used not only in security•surveillance applications for indoor and outdoor environments, but also in diverse areas such as video phone for apartment entrance door, rear view camera for vehicles, visual sensor for unmanned aerial vehicles and robots, camera phone, PC camera, and broadcasting camera. Also, it can be used to obtain panoramic or rectilinear photographs using a digital camera.
Owner:NANOPHOTONICS CO LTD
Robot global path planning method based on deeply enhanced learning
ActiveCN107065881AMake up for deficienciesStrong real-timePosition/course control in two dimensionsNerve networkView camera
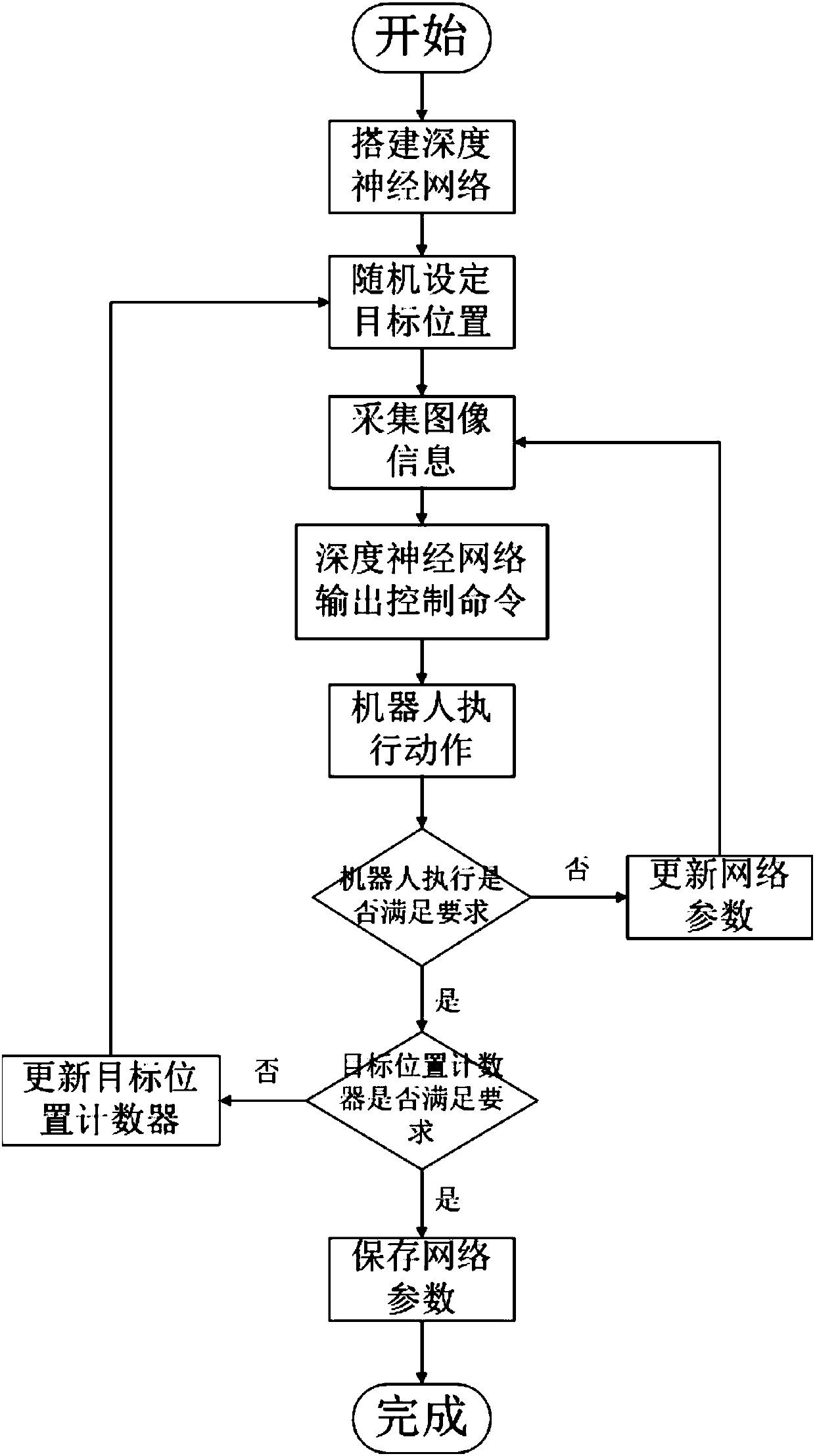
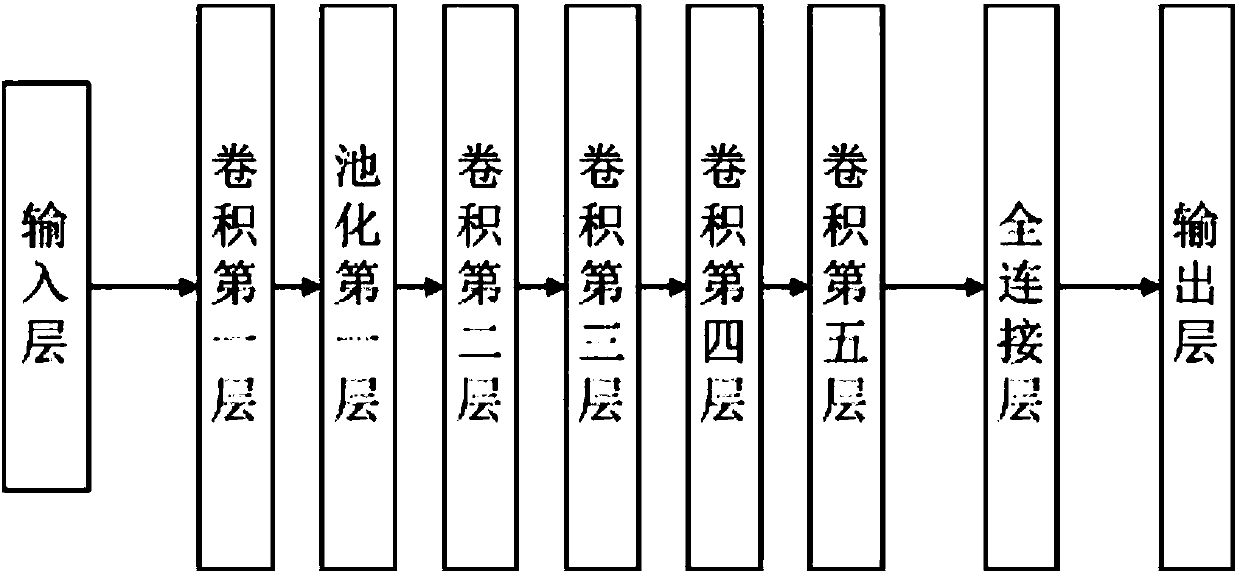
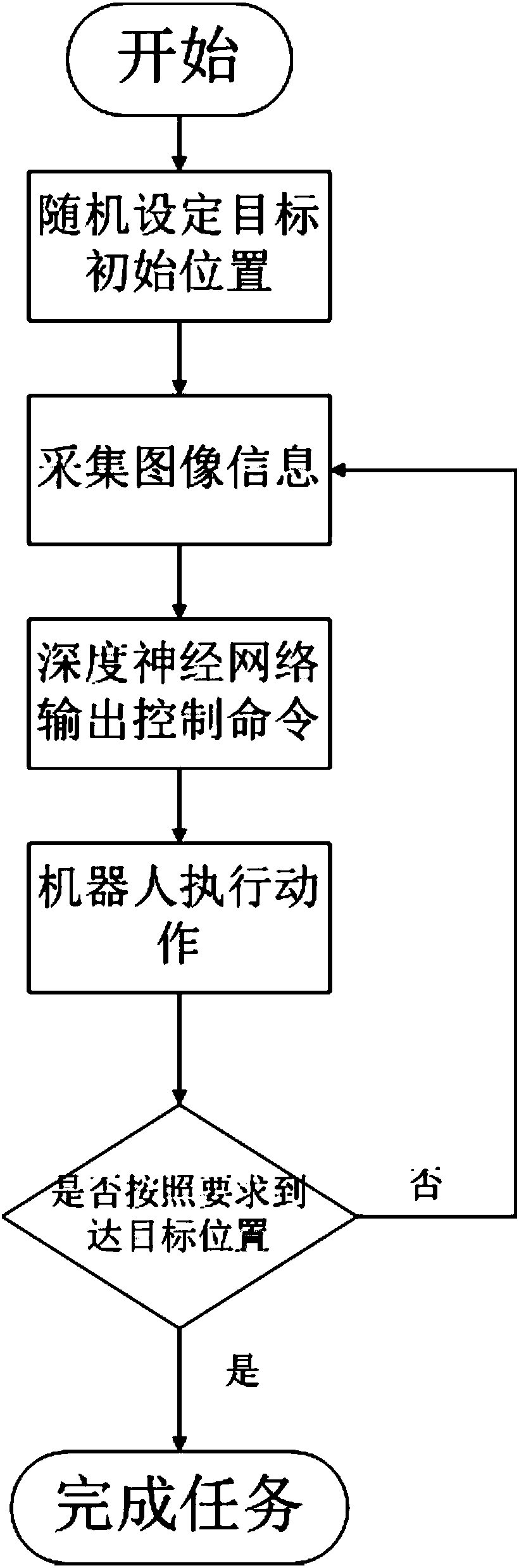
The invention proposes a robot global path planning method based on deeply enhanced learning, which belongs to the robot learning and global path planning technology fields. The method comprises: in the training session: firstly, installing a top-view camera in a scenario; constructing a deep neural network; after a training path is created, outputting the executing actions by the deep neural network according to the images photographed by the camera; and according to the execution effect of the actions, optimizing the parameters of the deep neural network; then, updating the position of a target; performing different path planning trainings to obtain a final deep neural network; and in the execution session: outputting the executing actions for the robot by the final deep neural network according to the images photographed by the camera so that the robot executes the actions; and if the robot reaches the position of the target after its execution of the actions, then, completing the global path planning by the robot. The method of the invention is very practical in use, does not require manual participation, or the entrance of a scenario for constructing an environment map in advance. The method can be applied to multiple scenarios at a low cost.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Systems and methods for initializing motion tracking of human hands
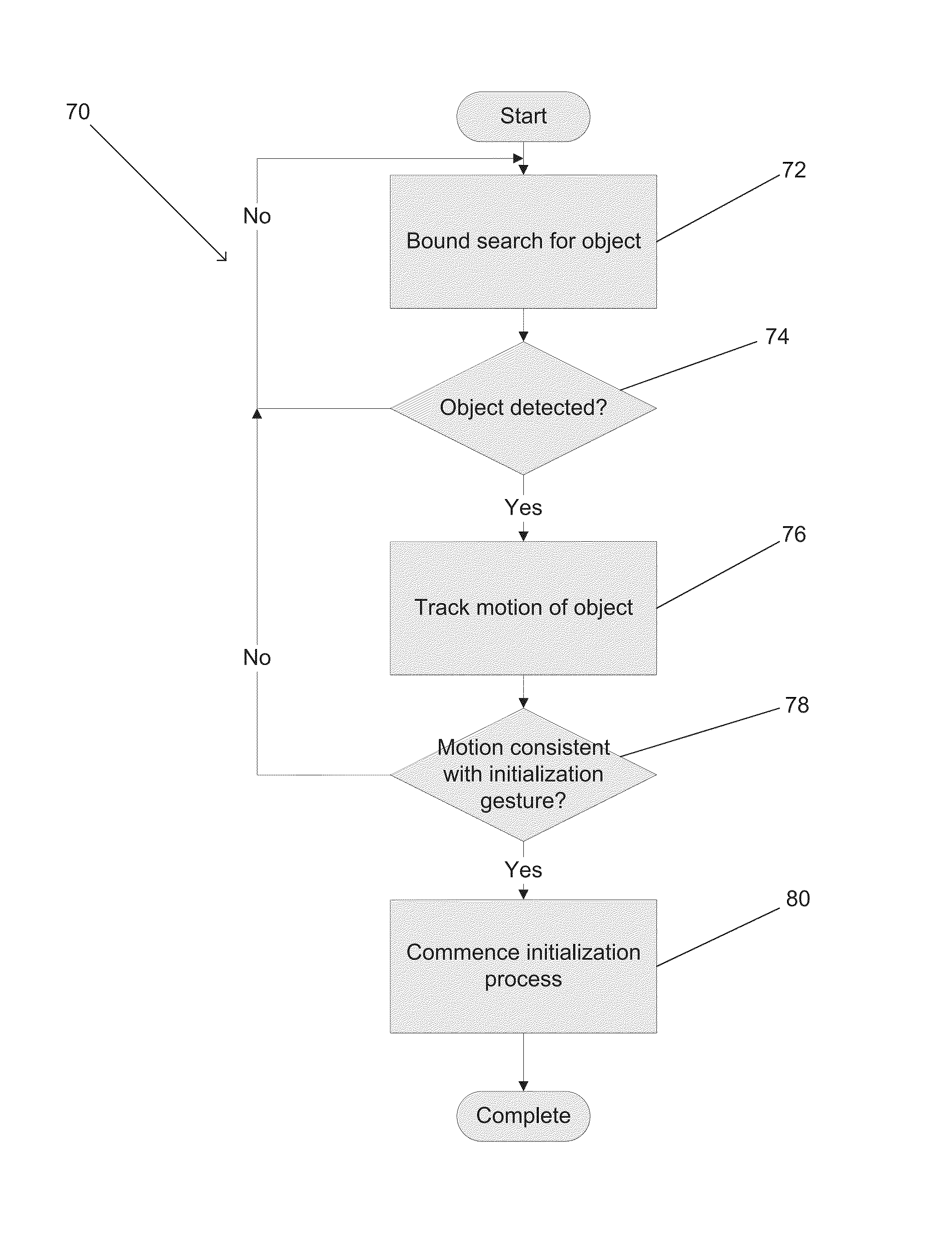
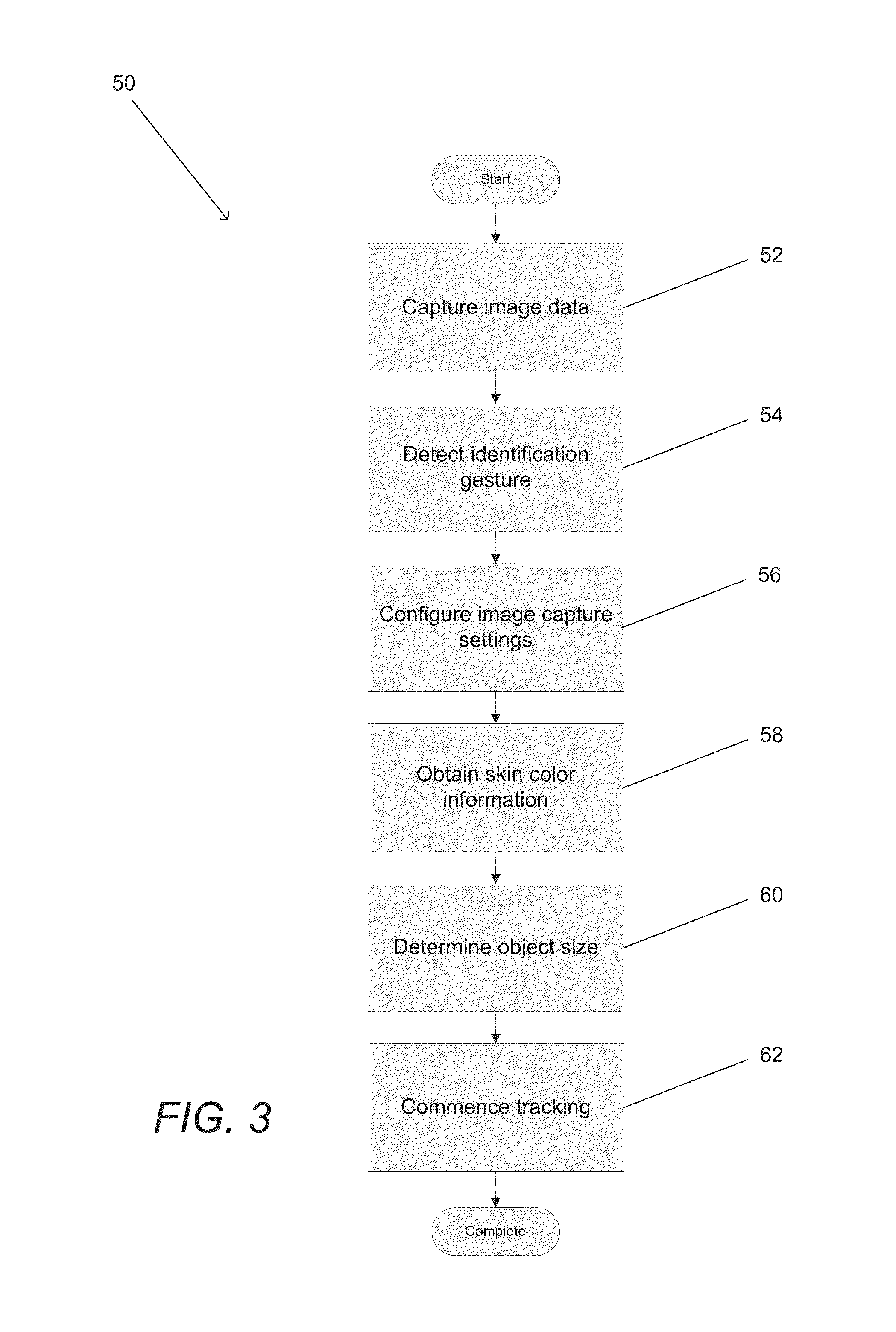
Systems and methods for initializing motion tracking of human hands within bounded regions are disclosed. One embodiment includes: a processor; reference and alternate view cameras; and memory containing a plurality of templates that are rotated and scaled versions of a base template. In addition, a hand tracking application configures the processor to: obtain reference and alternate view frames of video data; generate a depth map; identify at least one bounded region within the reference frame of video data containing pixels having distances from the reference camera that are within a specific range of distances; determine whether any of the pixels within the at least one bounded region are part of a human hand; track the motion of the part of the human hand in a sequence of frames of video data obtained from the reference camera; and confirm that the tracked motion corresponds to a predetermined initialization gesture.
Owner:KAYA DYNAMICS LLC
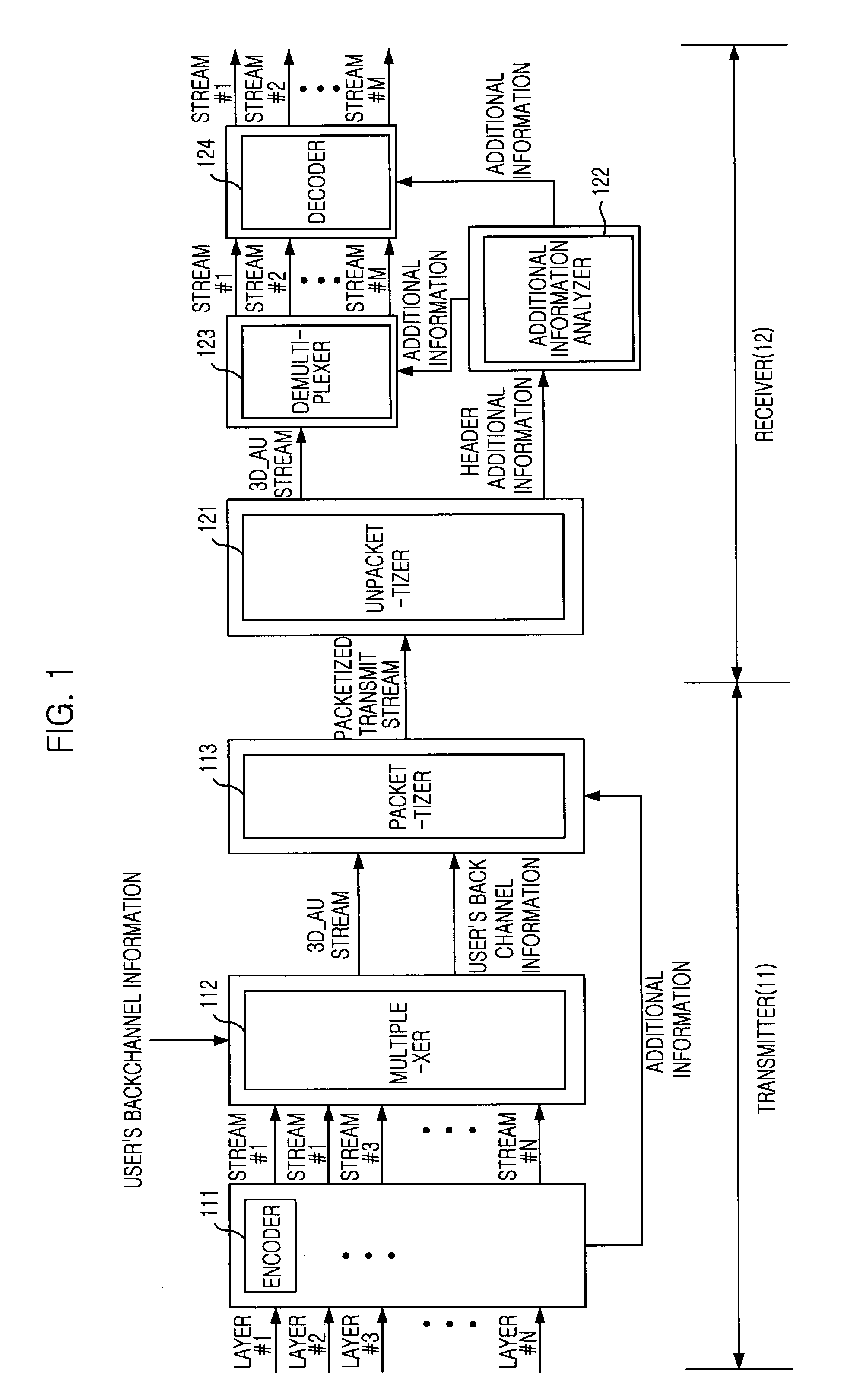
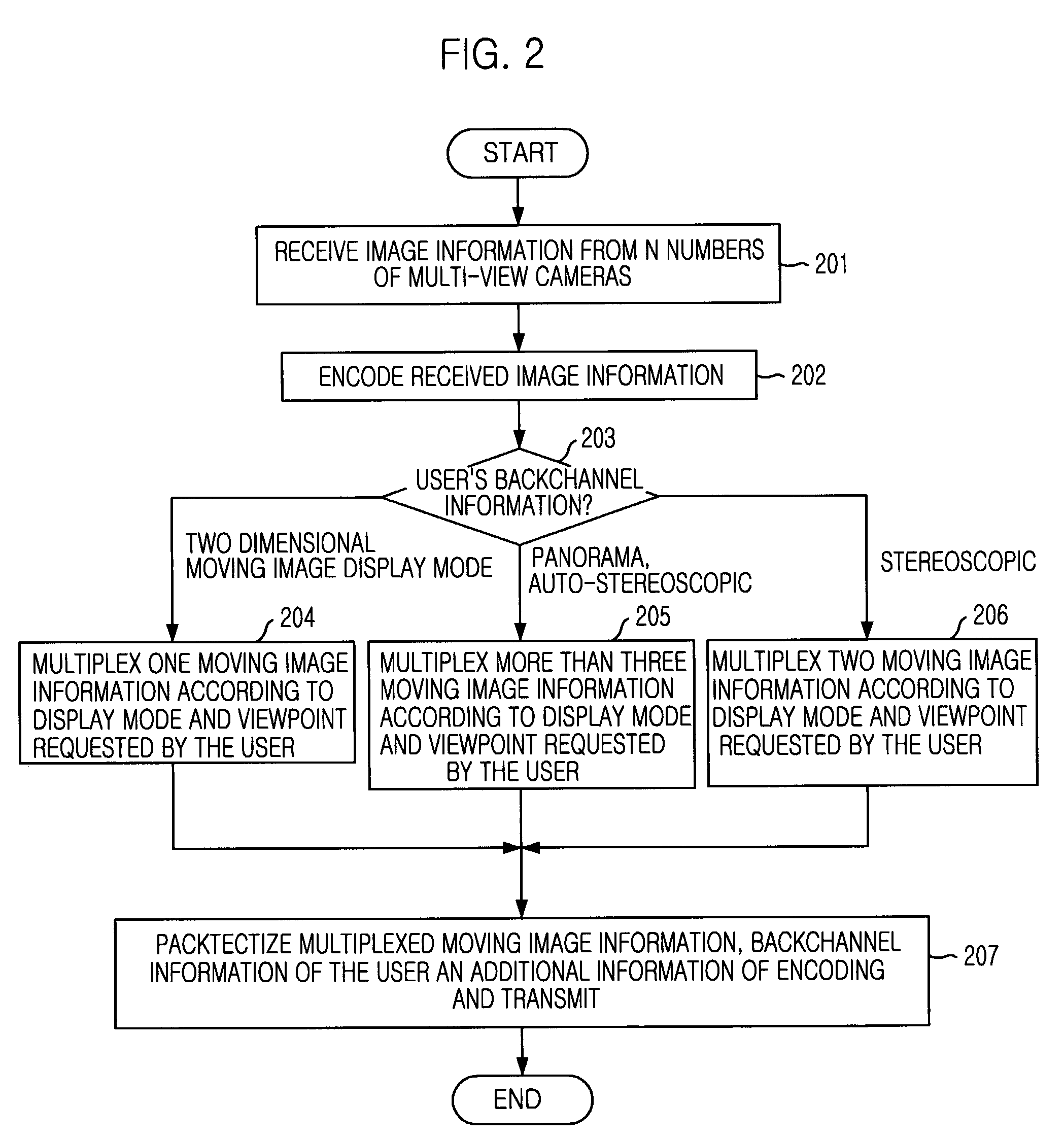
Method and apparatus for multiplexing multi-view three-dimensional moving picture
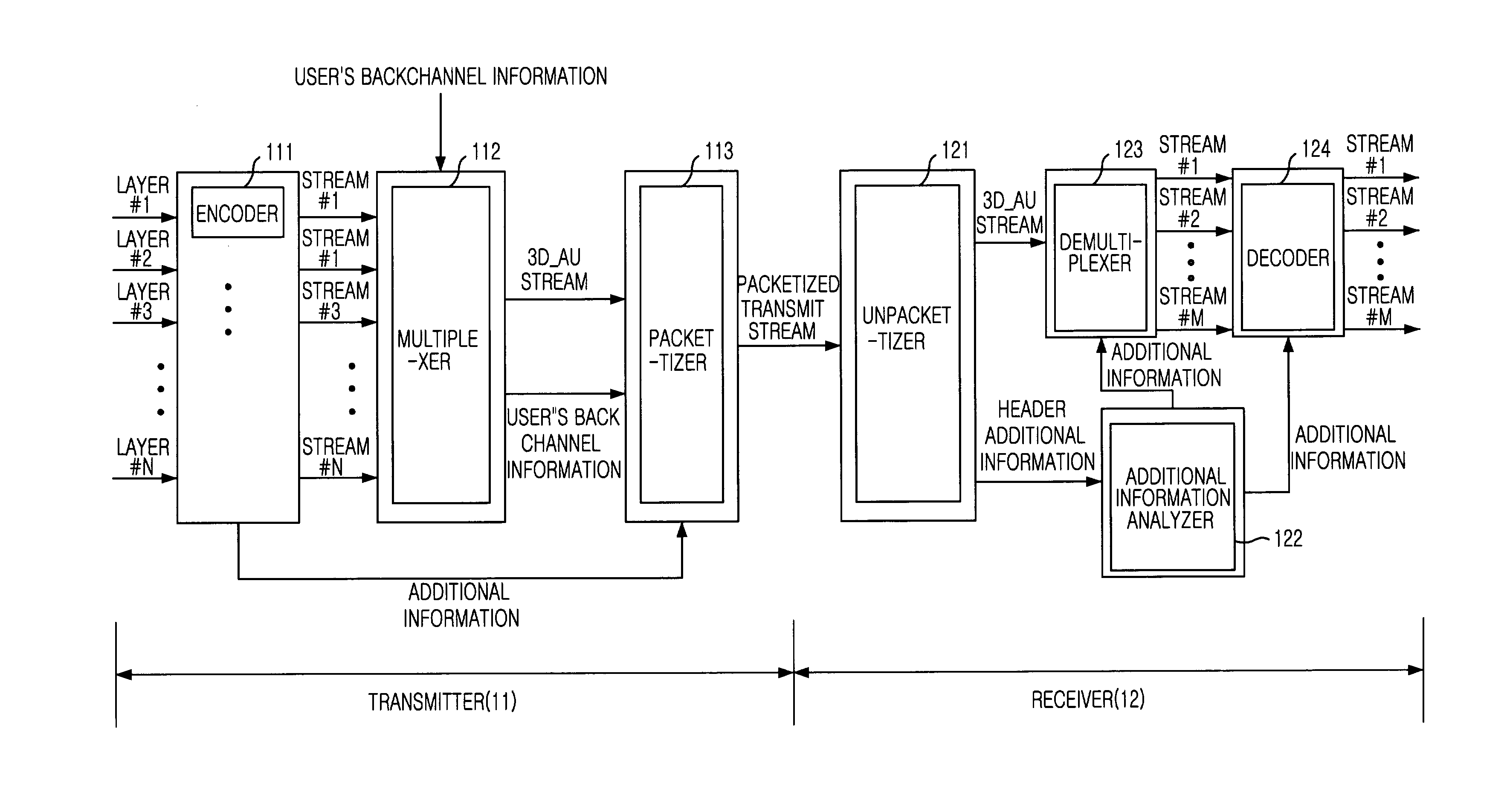
ActiveUS7136415B2Pulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMultiplexingTemporal information
An apparatus and method for multiplexing a multi-view three-dimensional moving picture according to a user's request is disclosed. The apparatus multiplexes a multi-view three-dimensional moving pictures by receiving moving pictures and information inputted from multi-view cameras and generating multi-view encoded streams corresponding to received moving pictures and information, receiving back channel information of the user, selecting necessary multi-view encoded streams according to the back channel information and multiplexing the selected multi-view encoded streams by a frame or a field having same time information. The present invention can effectively process the multi-view three-dimensional moving picture according to the display mode and system environment requested from the user by simplifying a synchronization process.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Portable wireless rearview camera system for a vehicle
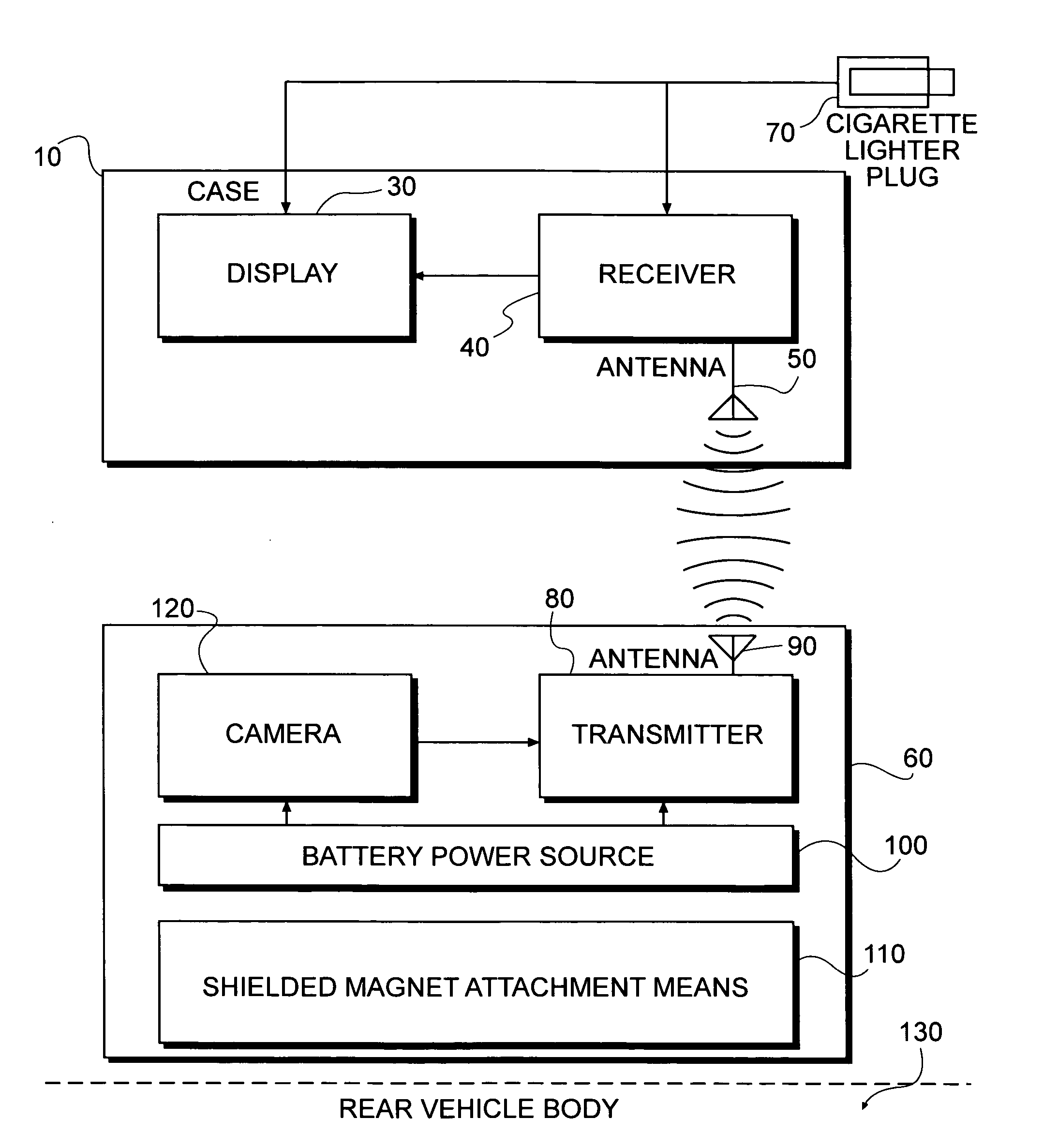
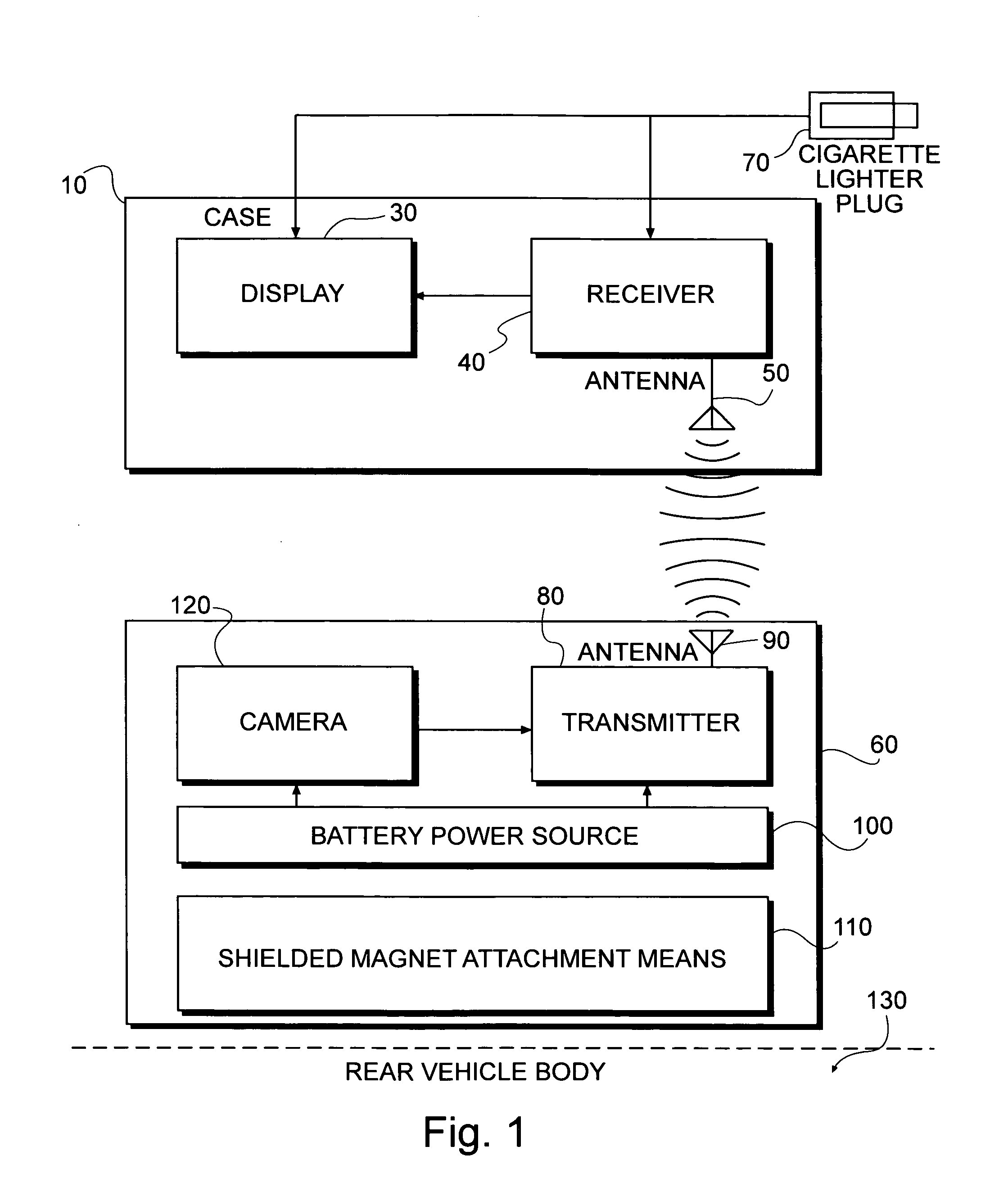
InactiveUS20060098094A1Eliminate needGood adhesionColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsComputer hardwareView camera
A portable wireless rearview camera system for vehicles is provide that is comprised of a movable weather resistant camera housing unit that wirelessly transmits images to the movable display unit. The weather resistant camera housing unit comprises a video camera to capture images behind the vehicle and a wireless transmitter to transmit the images to the movable display unit. The camera housing unit is connected to the vehicle or its attached trailer by a shielded magnet, which can easily be removed for use on another vehicle or to prevent its theft. The movable display unit comprises a wireless receiver coupled with a video monitor to display the images transmitted from the rear view camera to provide the vehicle's driver with a real time image of what is behind the vehicle.
Owner:LOTT MADISON
Lane fusion system using forward-view and rear-view cameras
ActiveUS20120062747A1Character and pattern recognitionColor television detailsCamera imageVehicle dynamics
A method and system for computing lane curvature and a host vehicle's position and orientation relative to lane boundaries, using image data from forward-view and rear-view cameras and vehicle dynamics sensors as input. A host vehicle includes cameras at the front and rear, which can be used to detect lane boundaries such as curbs and lane stripes, among other purposes. The host vehicle also includes vehicle dynamics sensors including vehicle speed and yaw rate. A method is developed which computes lane curvature and the host vehicle's position relative to a lane reference path, where the lane reference path is derived from the lane boundaries extracted from a fusion of the front and rear camera images. Mathematical models provided in the disclosure include a Kalman filter tracking routine and a particle filter tracking routine.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
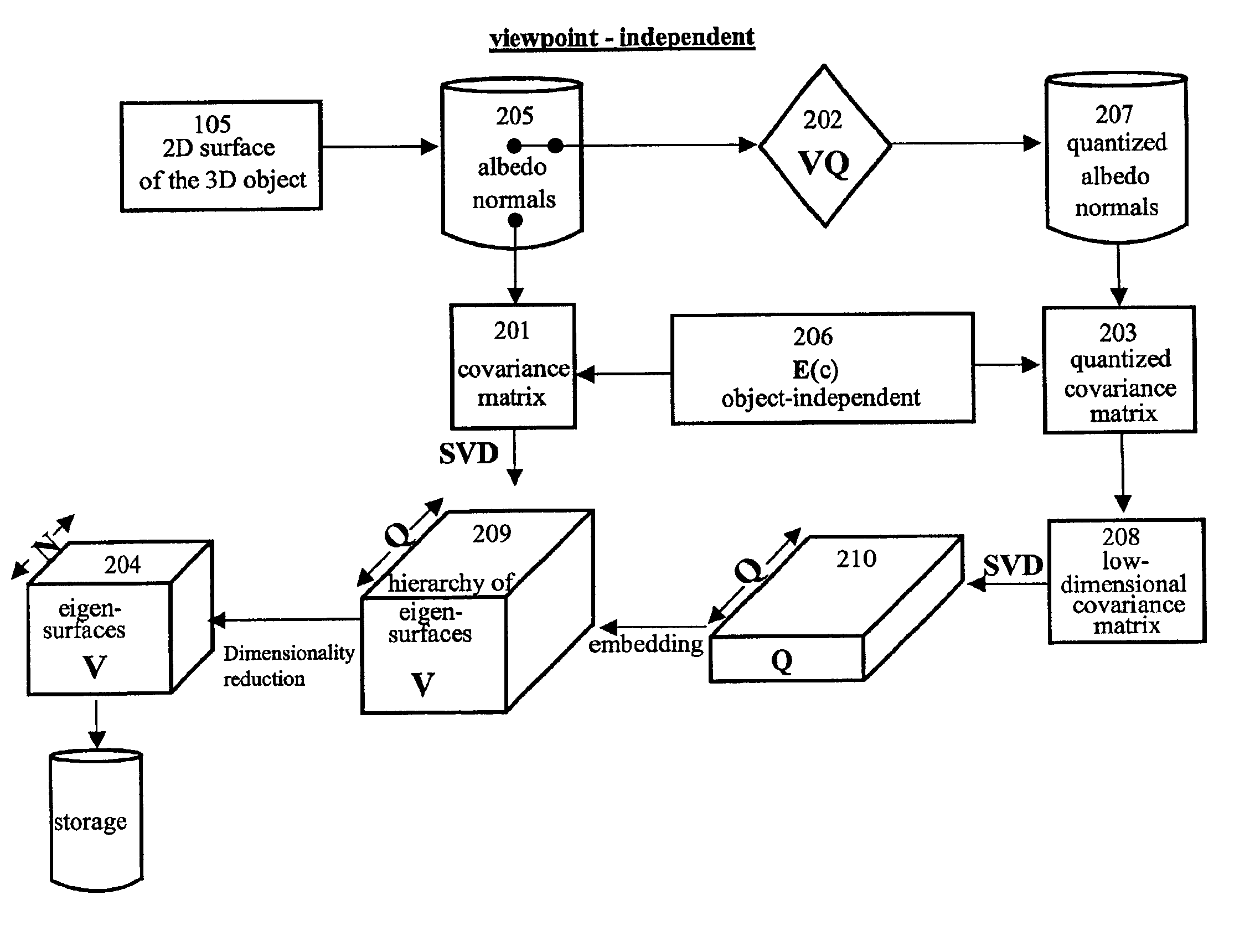
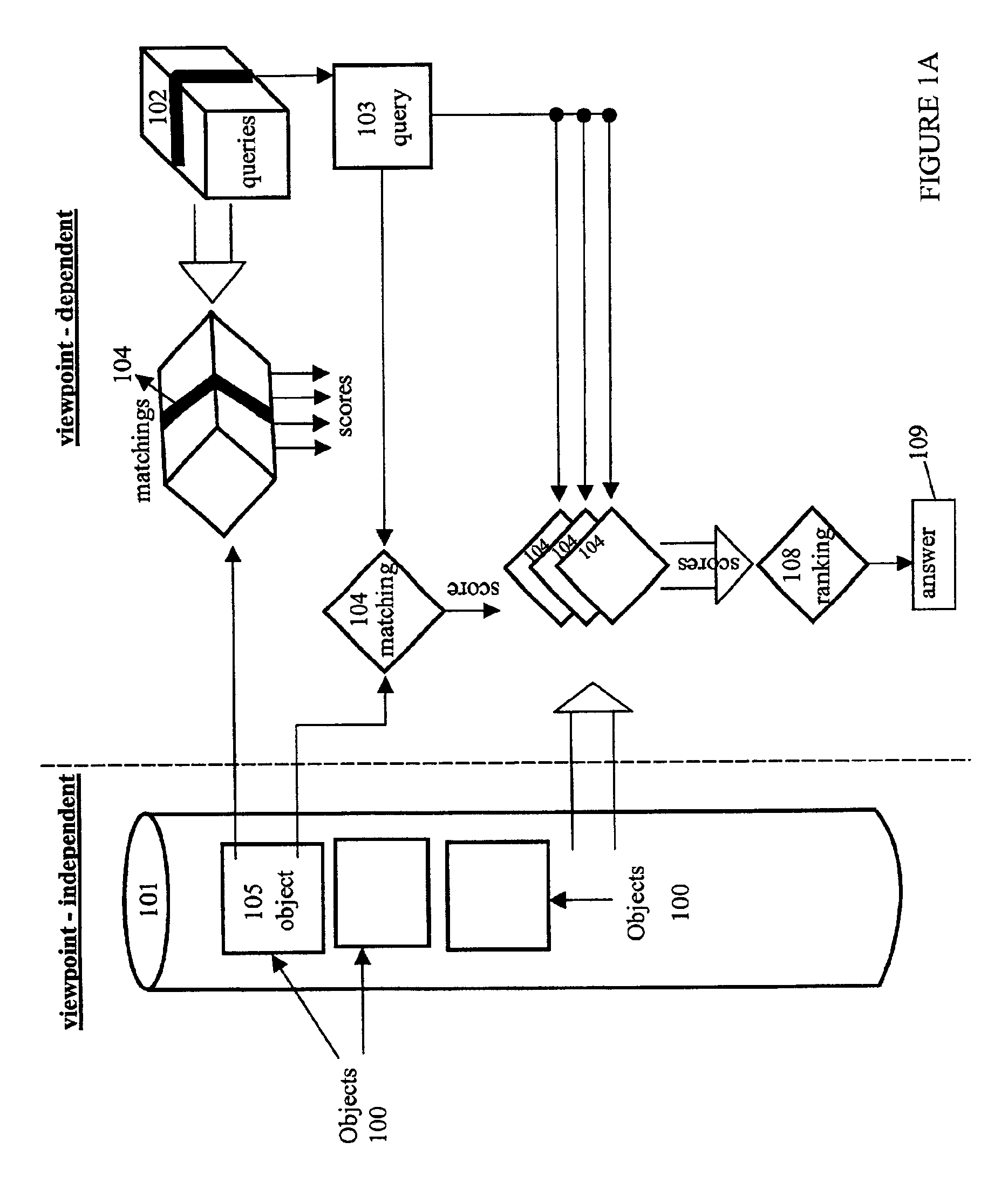
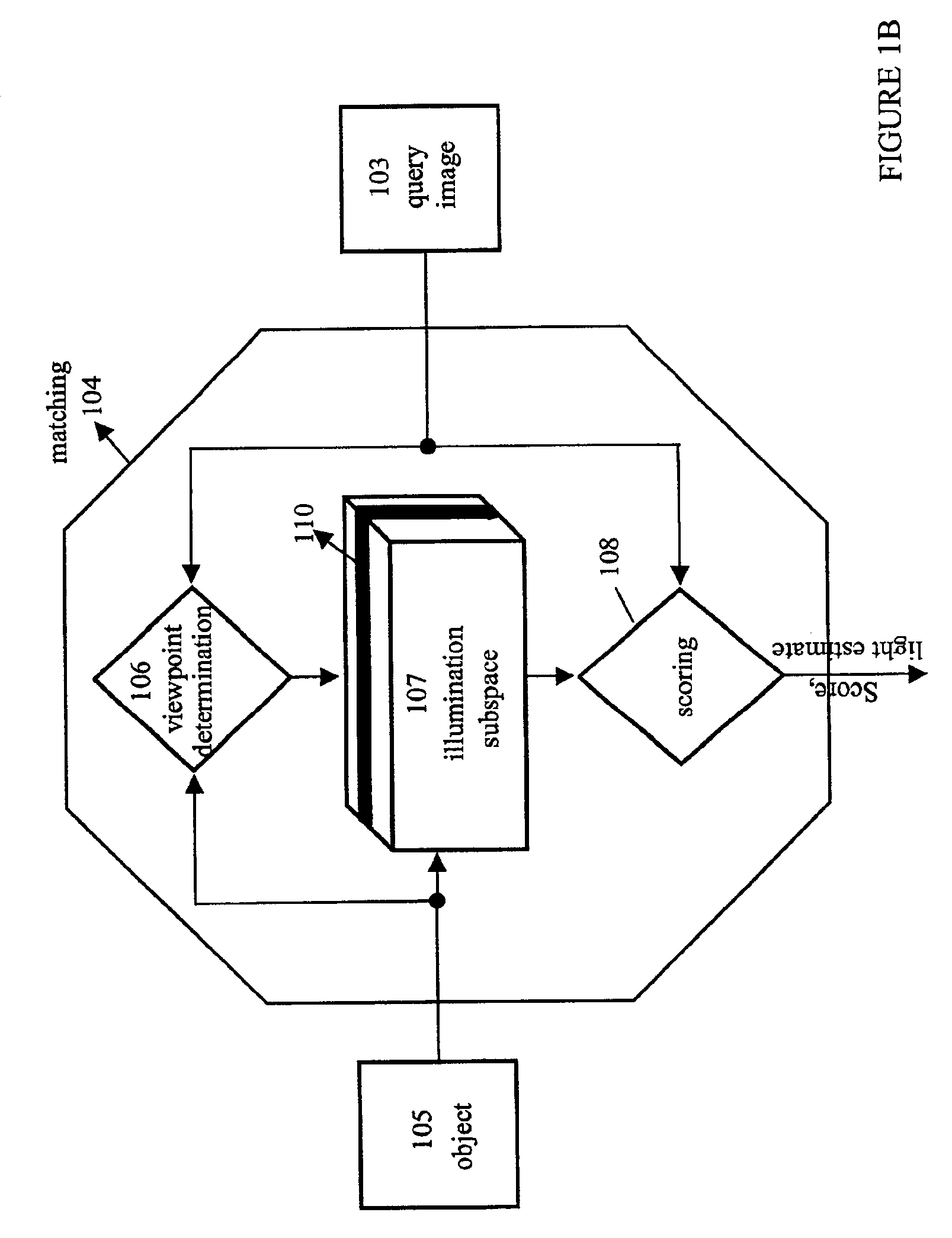
Fast optimal linear approximation of the images of variably illuminated solid objects for recognition
InactiveUS6888960B2Solve the lack of precisionComputationally efficientImage analysisImage codingViewpointsView camera
An efficient computation of low-dimensional linear subspaces that optimally contain the set of images that are generated by varying the illumination impinging on the surface of a three-dimensional object for many different relative positions of that object and the viewing camera. The matrix elements of the spatial covariance matrix for an object are calculated for an arbitrary pre-determined distribution of illumination conditions. The maximum complexity is reduced for the model by approximating any pair of normal-vector and albedo from the set of all such pairs of albedo and normals with the centers of the clusters that are the result of the vector quantization of this set. For an object, a viewpoint-independent covariance matrix whose complexity is large, but practical, is constructed and diagonalized off-line. A viewpoint-dependent covariance matrix is computed from the viewpoint-independent diagonalization results and is diagonalized online in real time.
Owner:NEC CORP
Rear view camera system using rear view mirror location
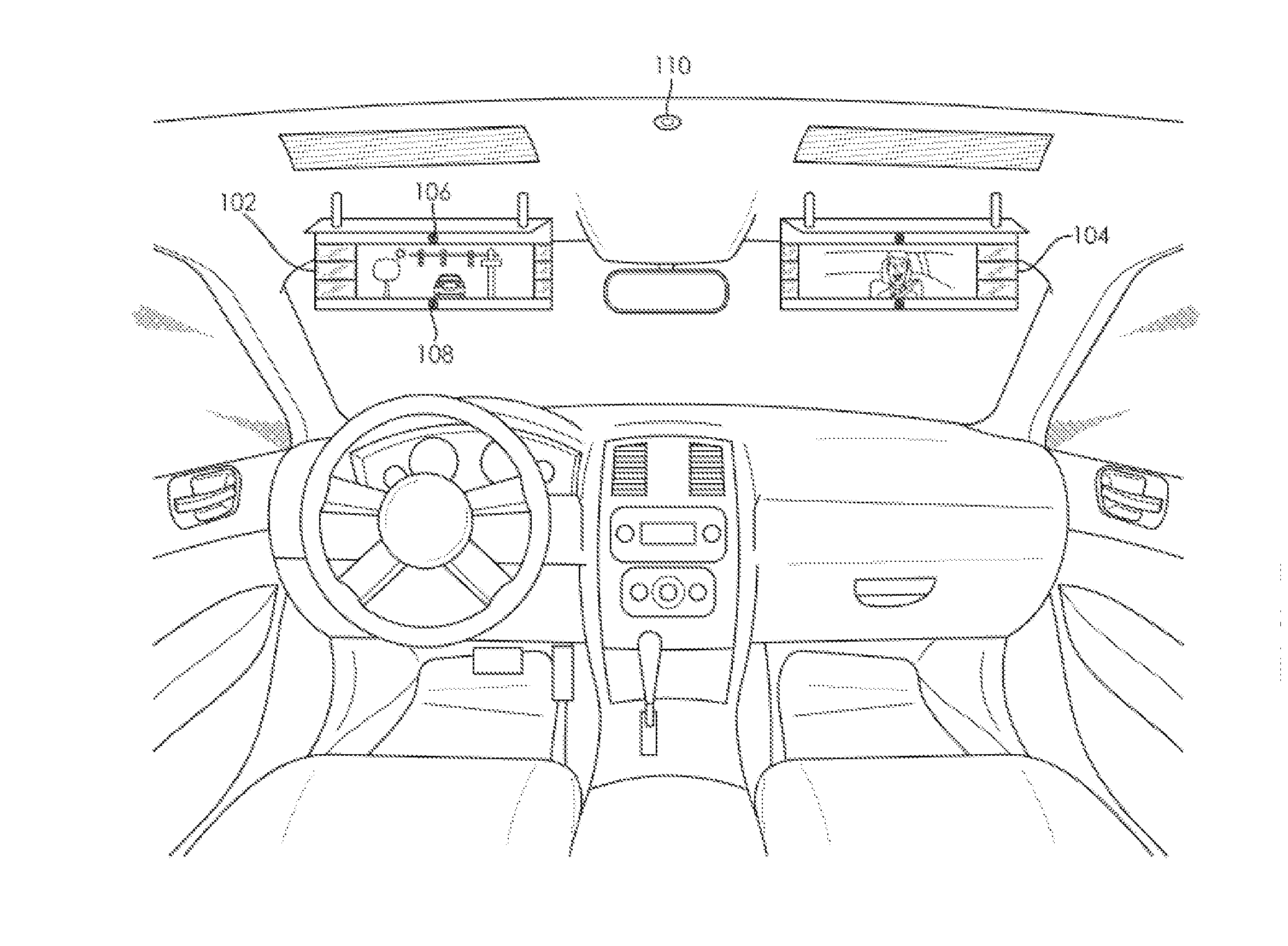
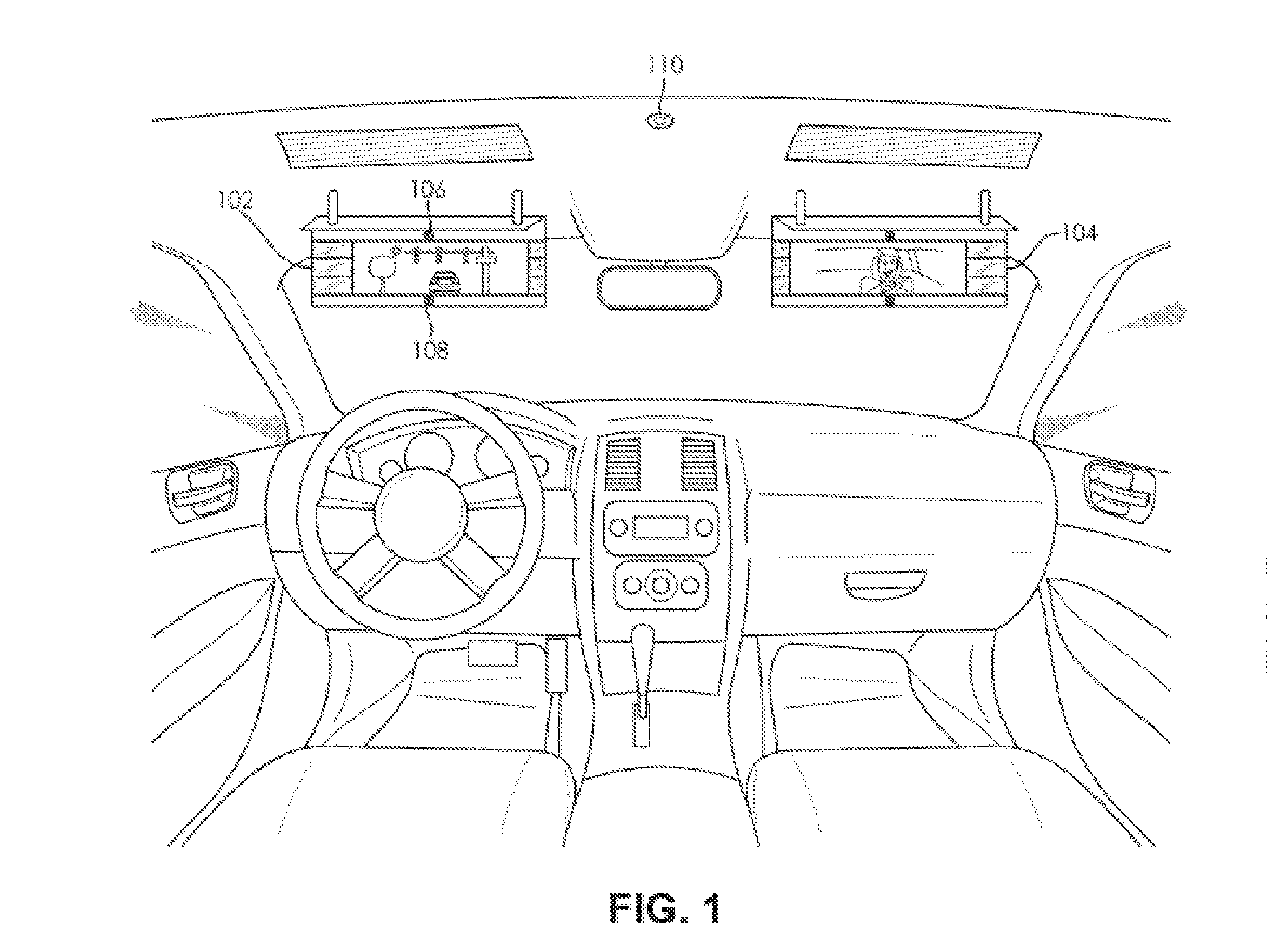
ActiveUS20140340516A1Improve their frame of referenceColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsMobile vehicleIntegrator
A rearward viewing system for an automotive vehicle comprises an image display mounted proximate to a front windshield of the vehicle. An exterior image sensor captures a first image directed externally of the vehicle with a first field of view. An internal image sensor captures a second image directed internally of the vehicle with a second field of view. An image integrator merges the first and second images according to a predetermined alignment of the first and second fields of view, wherein the second image is muted in the merged image so that the first image is emphasized when displayed on the image display.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
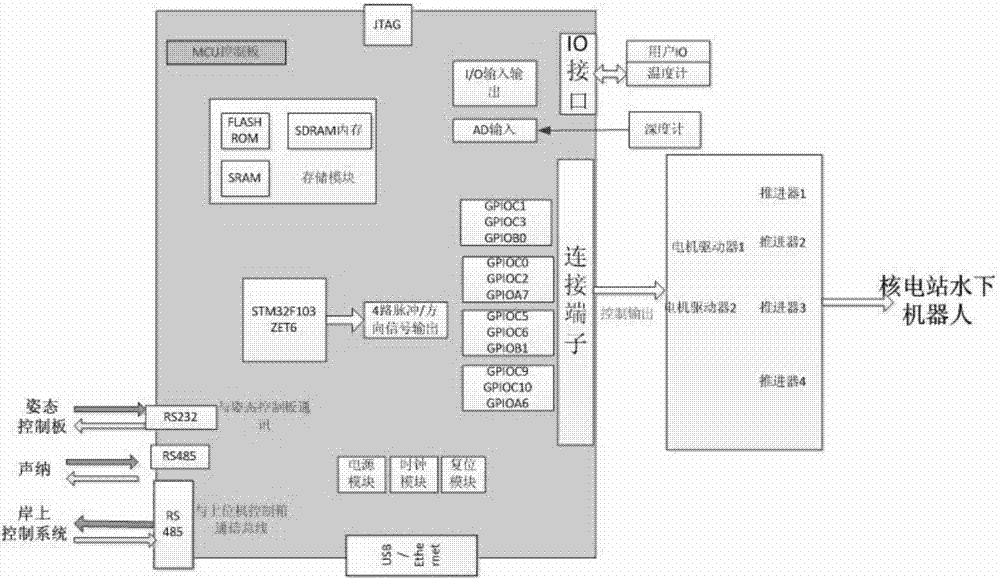
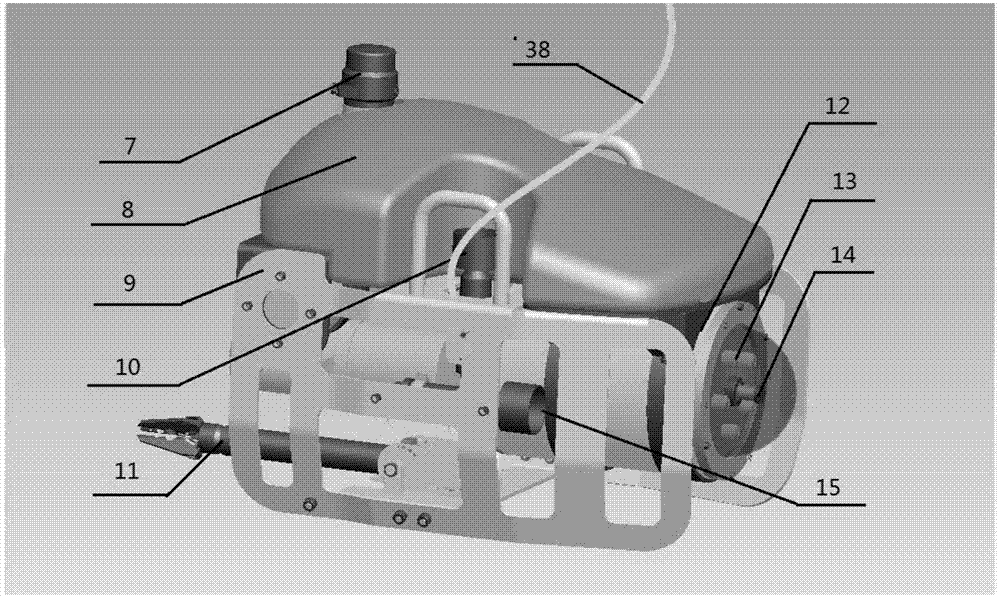
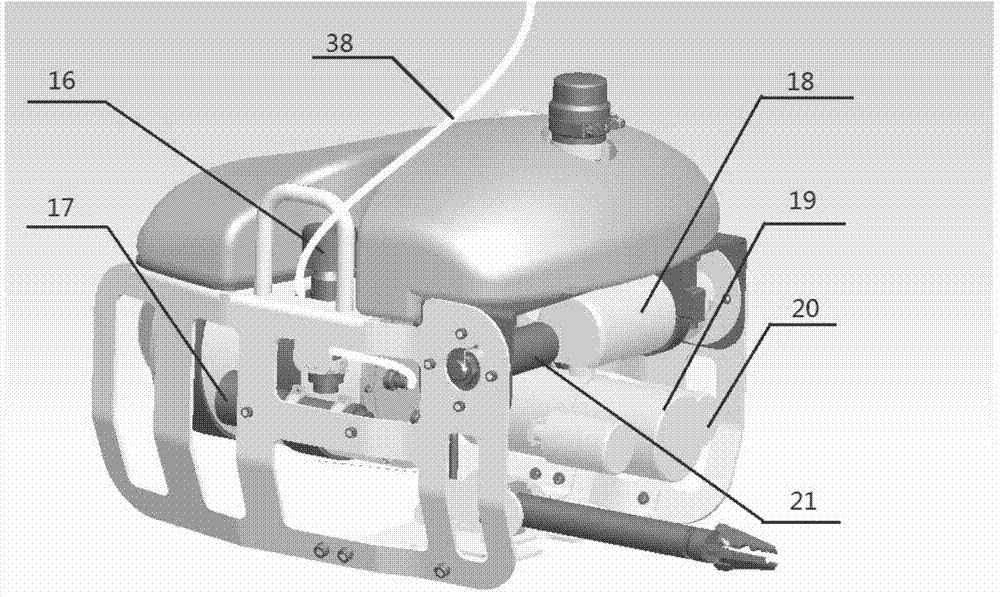
Microminiature operation underwater robot of nuclear power plant
The invention relates to a microminiature operation underwater robot of a nuclear power plant, and the robot comprises an underwater robot body and an onshore control system, wherein two propellers are respectively arranged in the horizontal and vertical directions of the robot body, a depth gauge is arranged on the right side of the front part of the robot body, a manipulator is arranged at the bottom in front of the robot body, and a sonar is arranged on the top of the robot body; a control cabin is arranged in the middle rear part of the robot body; an outer cabin is sealed by a transparent glass cover, and is provided with a rearview camera and an auxiliary lighting light-emitting diode (LED) lamp; a front-view camera system is arranged at the front part of the robot body, and comprises a zooming radiation resistant camera tube, a tripod head and a lighting lamp; a video image and control signal is transmitted to the onshore control system through a shield cable; and the control system comprises a movement control rod, a manipulator control button, a keyboard, a main display screen and a speed governing knob. The microminiature operation underwater robot of the nuclear power plant is used for the monitoring and the simple foreign body fishing of a core pool, a spent fuel pool and a component pool of the nuclear power plant.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and apparatus for obtaining panoramic and rectilinear images using rotationally symmetric wide-angle lens
InactiveUS20150062292A1Television system detailsGeometric image transformationCamera phoneView camera
The present invention provides mathematically accurate image processing algorithms for extracting natural looking panoramic images and distortion-free rectilinear images from images acquired using a camera equipped with a wide-angle lens which is rotationally symmetric about an optical axis and devices implementing such algorithms. Imaging systems using this method can be used not only in security•surveillance applications for indoor and outdoor environments, but also in diverse areas such as video phone for apartment entrance door, rear view camera for vehicles, visual sensor for unmanned aerial vehicles and robots, camera phone, PC camera, and broadcasting camera. Also, it can be used to obtain panoramic or rectilinear photographs using a digital camera.
Owner:KWEON GYEONGIL
Imaging and display system for vehicle
ActiveUS20150251602A1Increase awarenessEasy to identifyRoad vehicles traffic controlColor television detailsView cameraEngineering
A vehicular vision system includes first, second, third and fourth cameras having respective forward, rearward, sideward and sideward fields of view. A video processor is operable to process second image data captured by the second or rearward viewing camera. A video display screen displays video images derived, at least in part, from captured second image data. The video processor includes an image processor operable for machine vision analysis of first image data captured by the first or forward viewing camera. During a reversing maneuver of the vehicle, the video display screen displays video images derived, at least in part, from captured second image data. During forward travel of the vehicle and responsive to the image processor processing captured first image data to detect a road sign ahead of the vehicle, an image or iconistic representation of the detected road sign is displayed by the video display screen.
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS INC
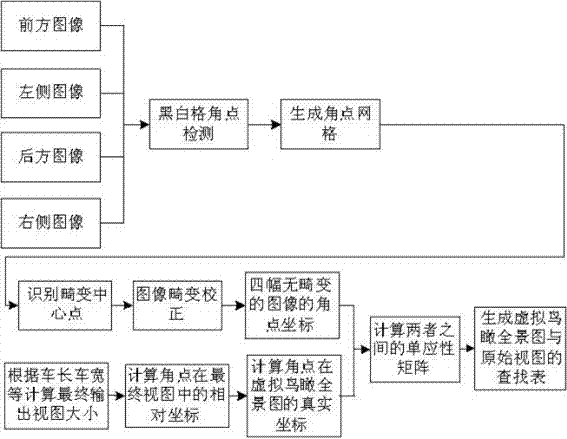
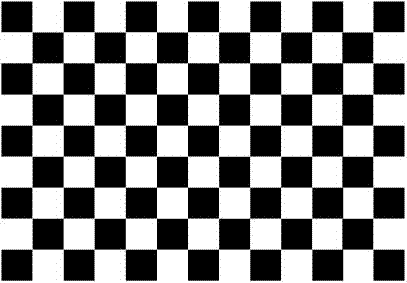
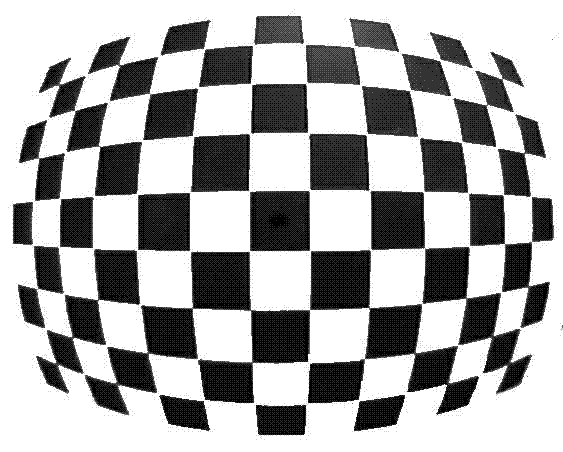
Automatically calibration method based on black and white grid corner matching
The invention discloses an automatically calibration method based on black and white grid corner matching. The method includes adopting black and white calibrating cloth as a calibrating model, respectively detecting image corners by an improved harris corner detection calculation, building position relations between corners and forming a corner network; performing distortion correction and matching to images; calculating corner position in non-distorting images and homographic matrix of corner real position in final virtual full view bird's-eye view; and performing view changing according to virtual bird's-eye view camera position and homographic matrix, calculating corresponding relation between image points in the coordinate system and the original images, and then forming a lookup table. The automatically calibration method adopting the improved harris corner detection calculation is simple and practical, can well judge corner position relation, and forms a correct corner network; and the automatically calibration method adopting lookup table function can generate output images after the images are calibrated, is fast, and can well meet real-time need.
Owner:FORYOU GENERAL ELECTRONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com