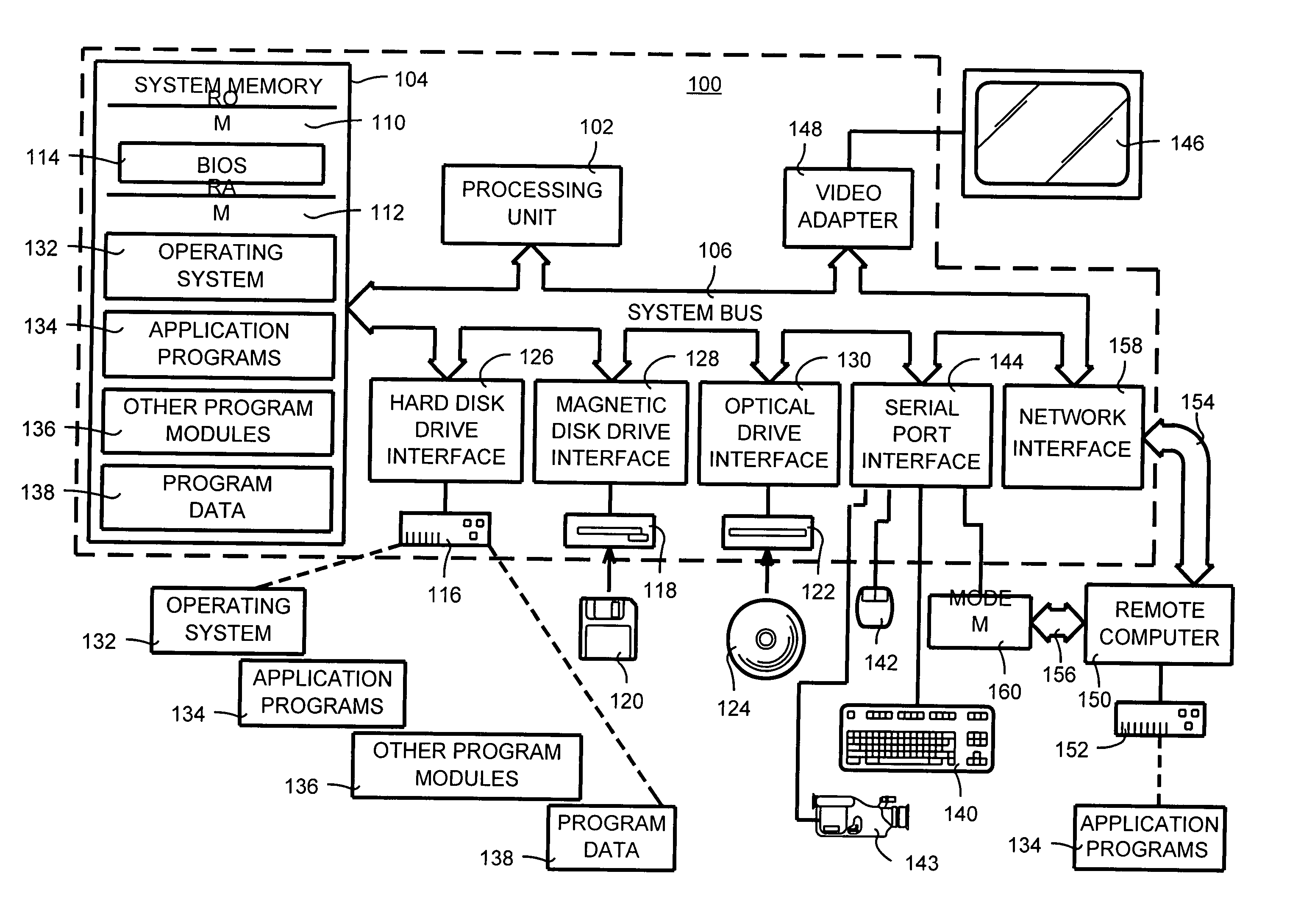
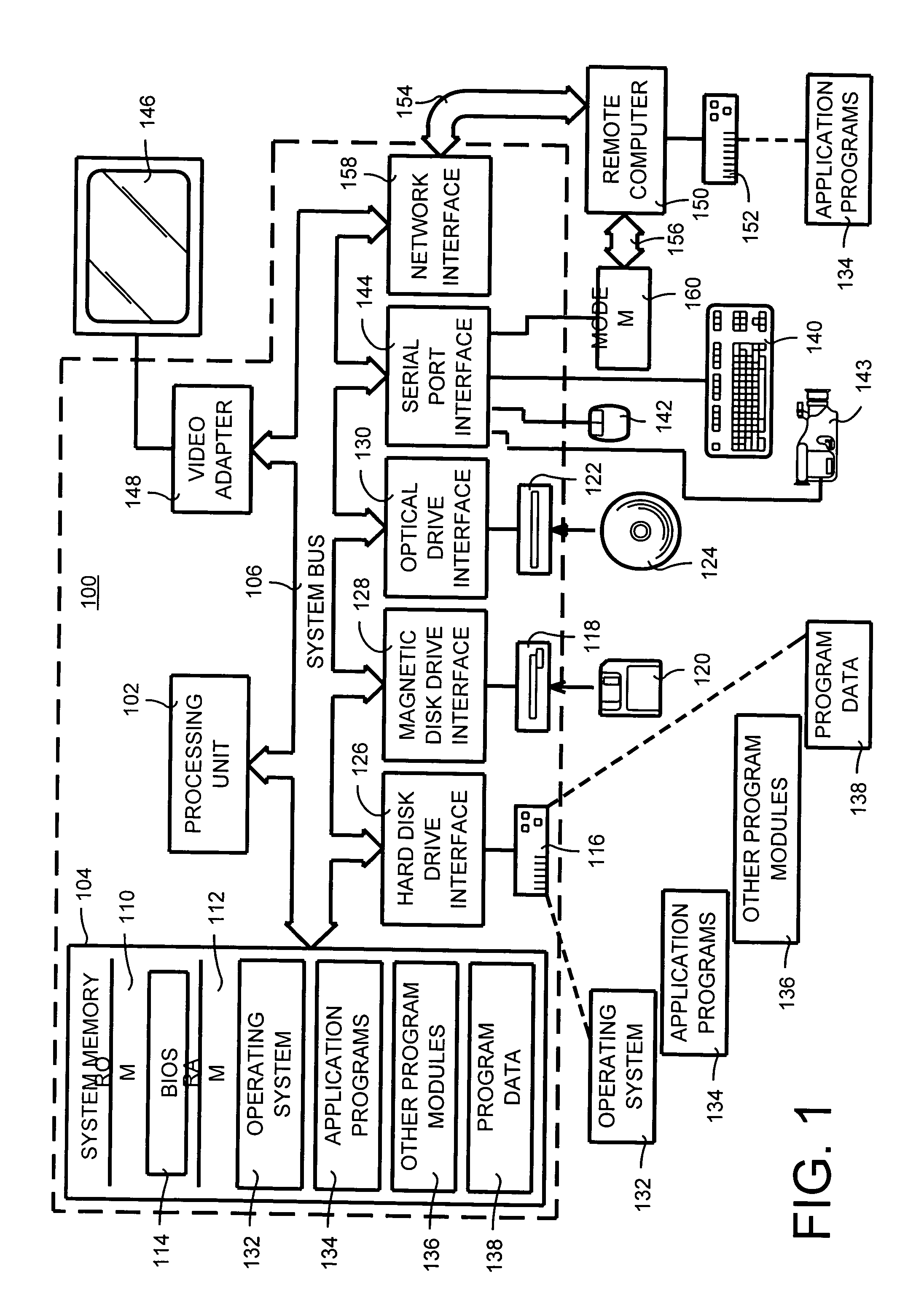
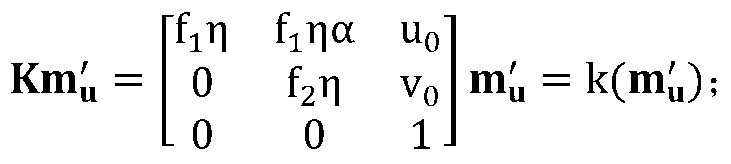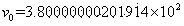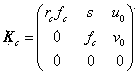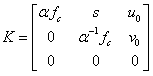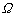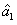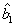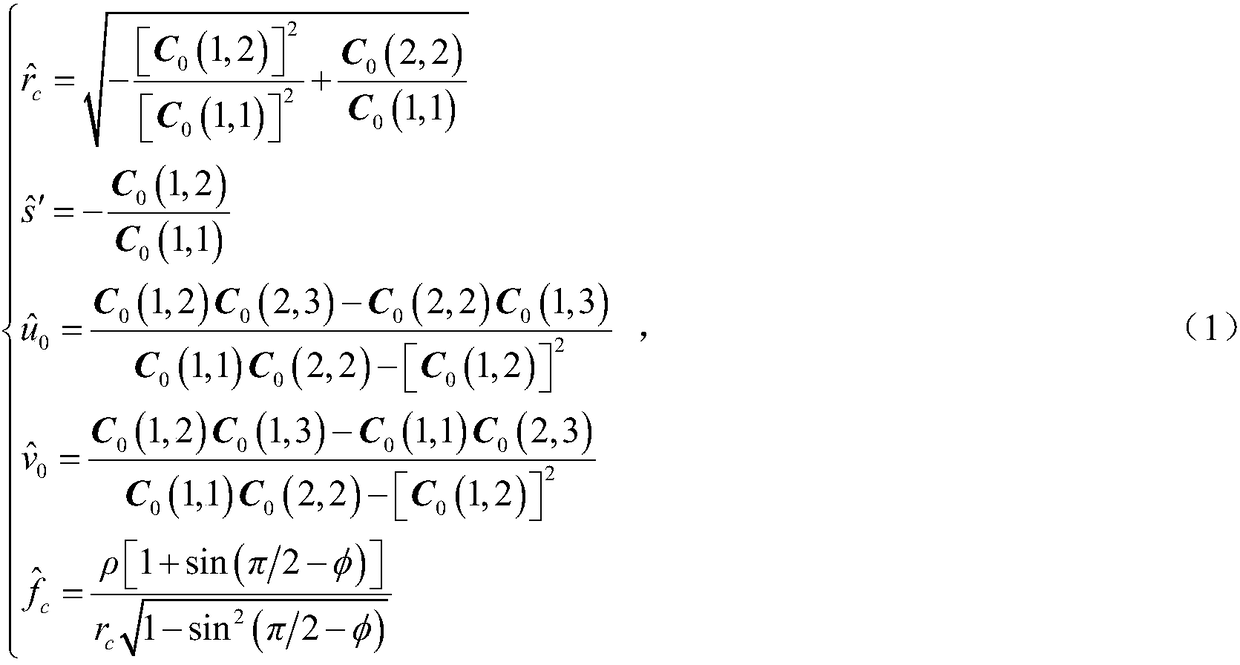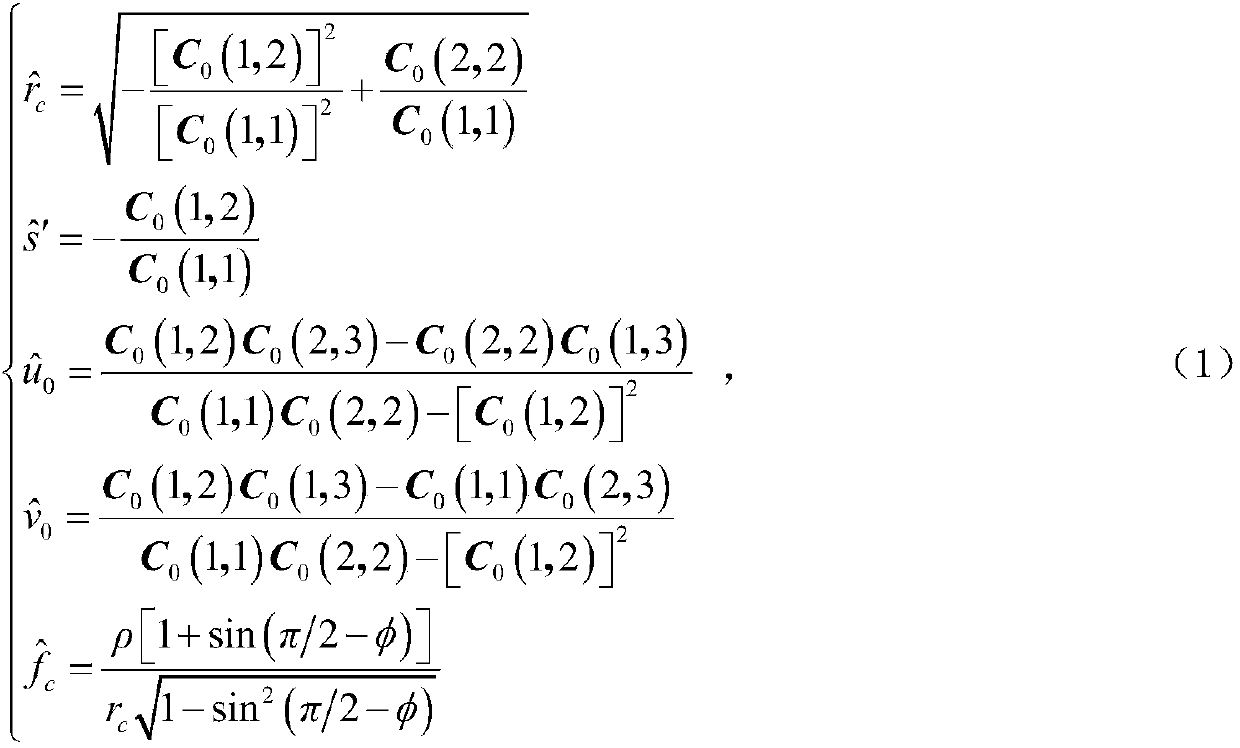Patents
Literature
67 results about "Catadioptric camera" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
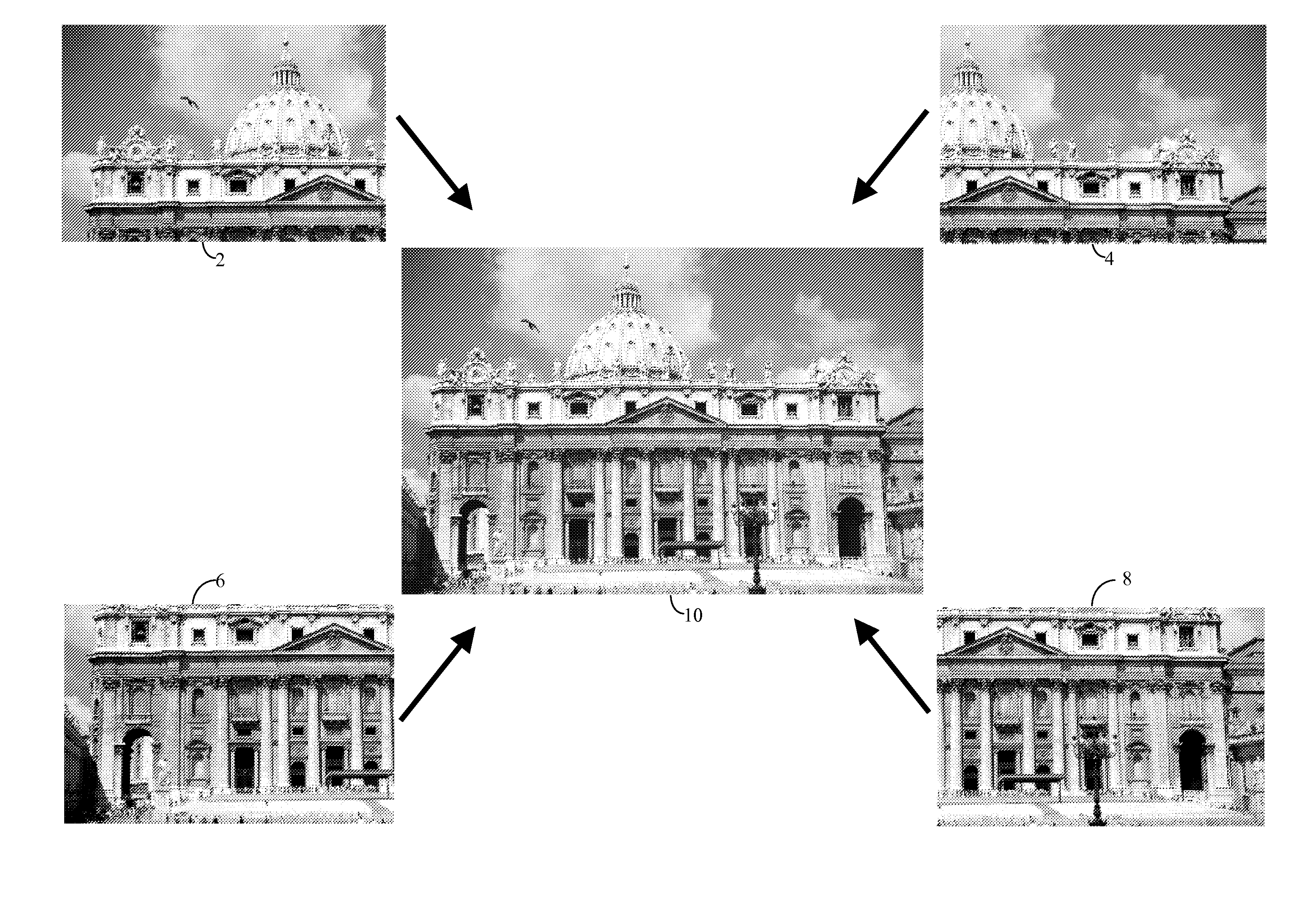
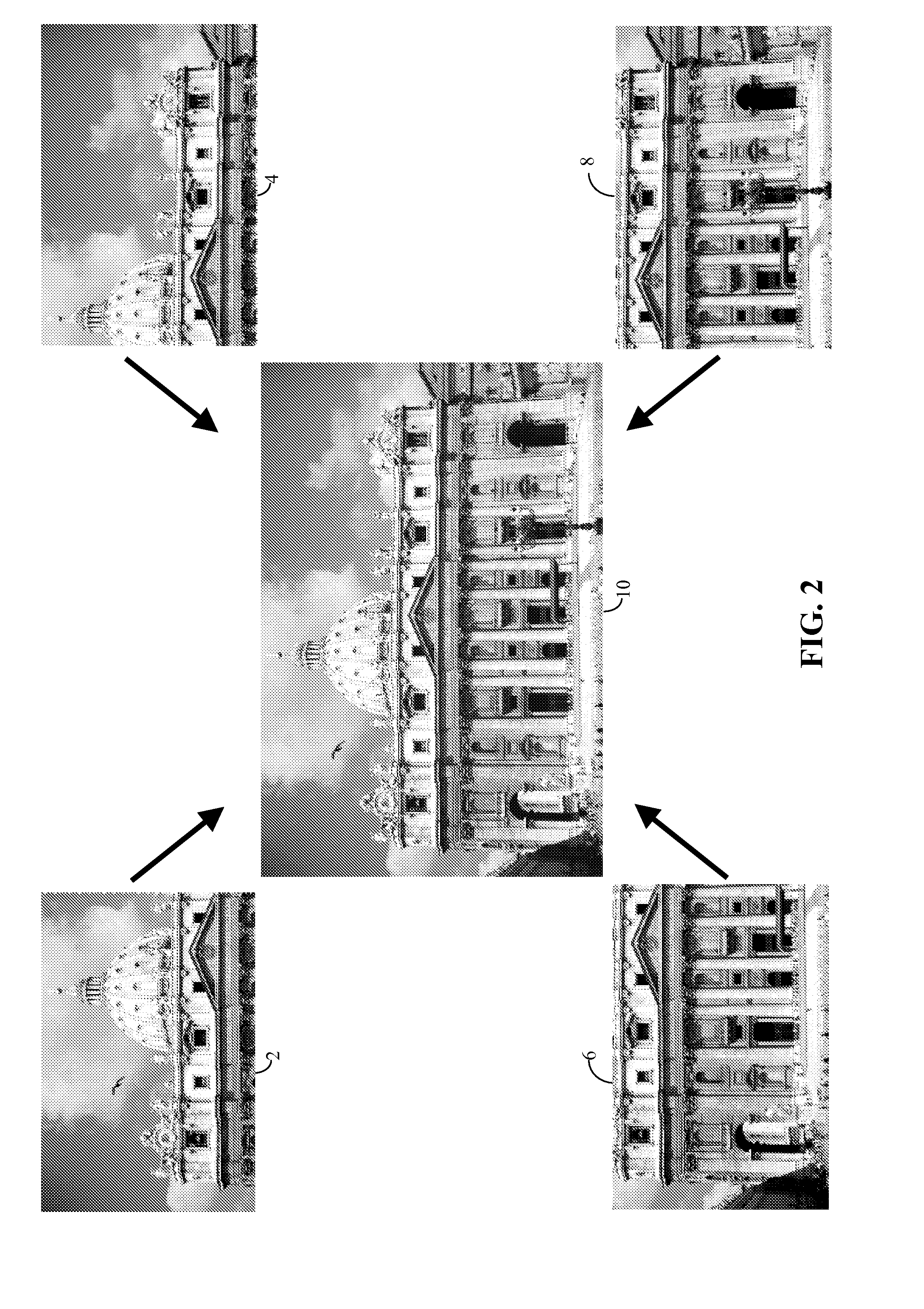
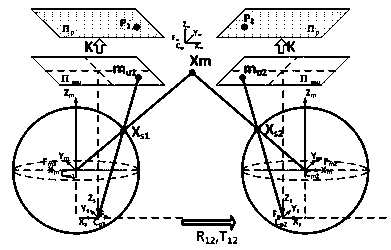
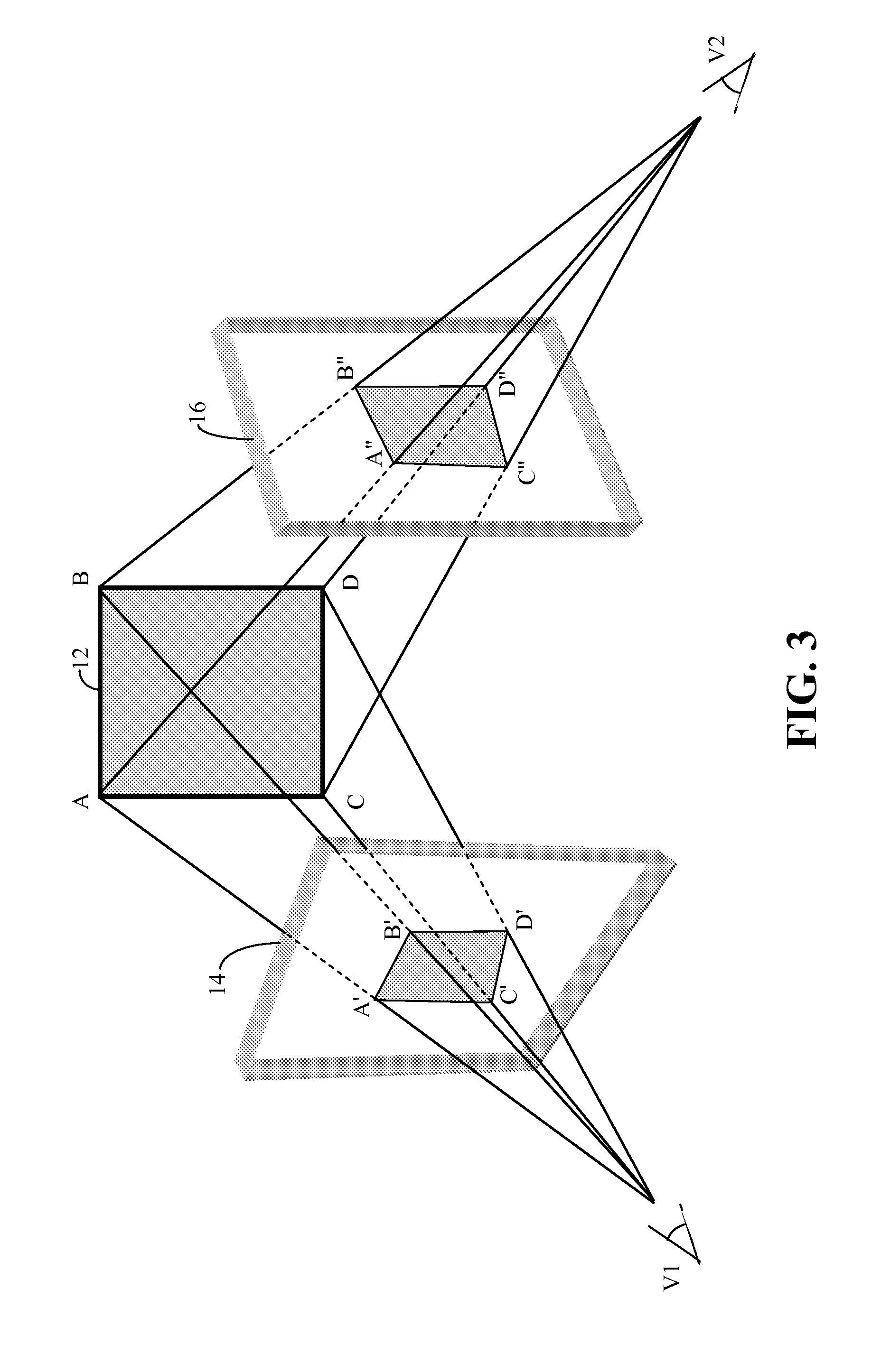
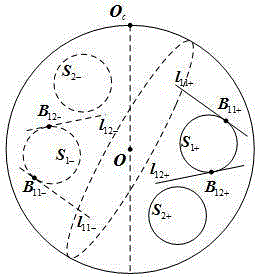
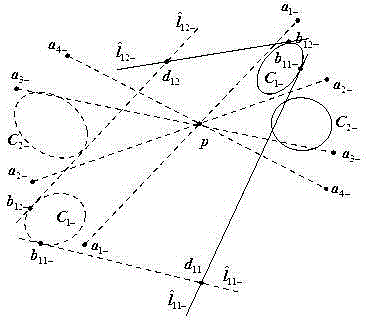
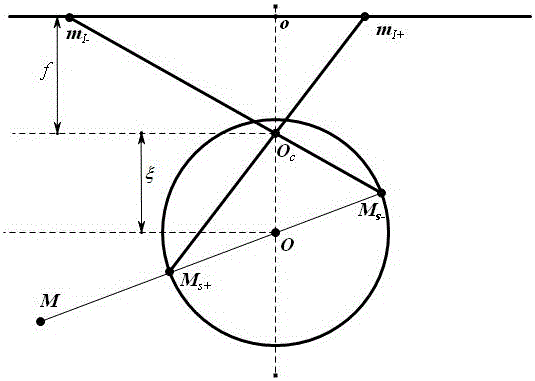
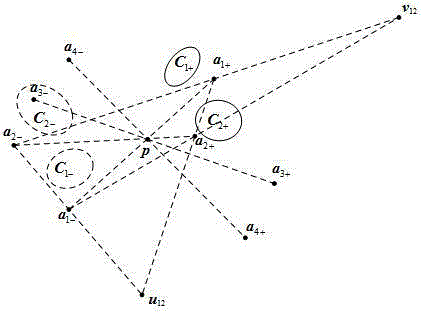
Context and Epsilon Stereo Constrained Correspondence Matching
InactiveUS20130002828A1Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionParallaxGreek letter epsilon
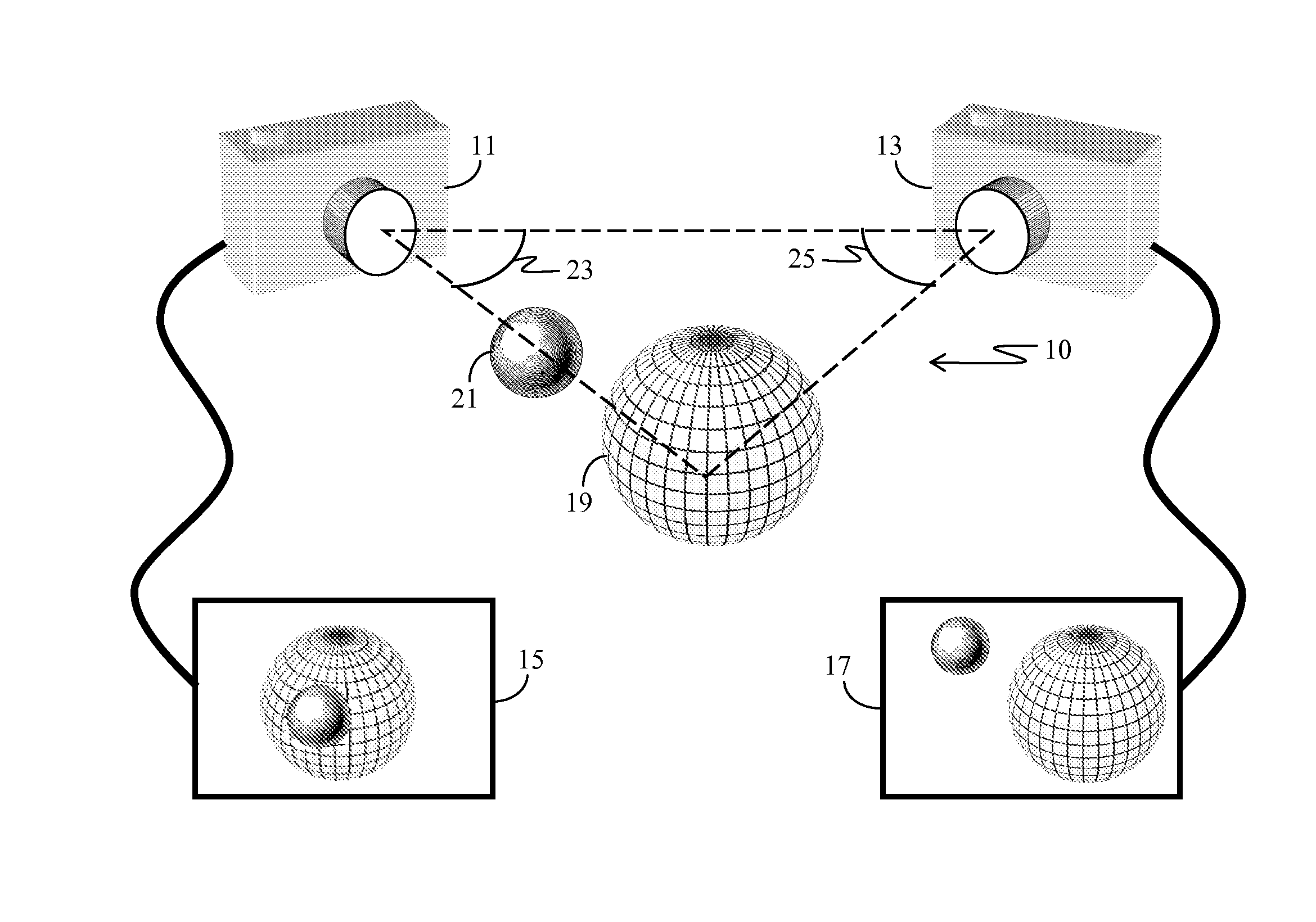
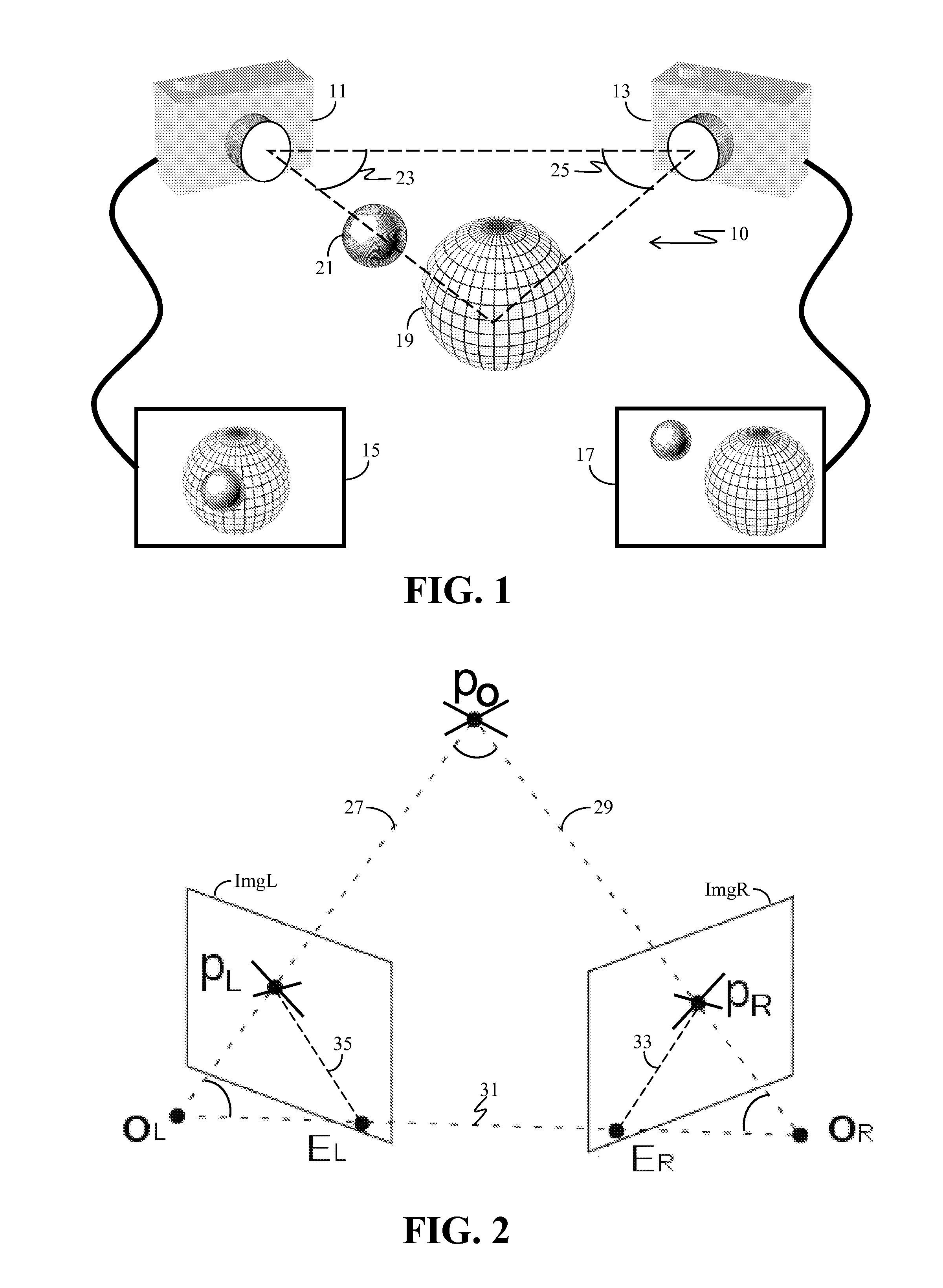
A catadioptric camera having a perspective camera and multiple curved mirrors, images the multiple curved mirrors and uses the epsilon constraint to establish a vertical parallax between points in one mirror and their corresponding reflection in another. An ASIFT transform is applied to all the mirror images to establish a collection of corresponding feature points, and edge detection is applied on mirror images to identify edge pixels. A first edge pixel in a first imaged mirror is selected, its 25 nearest feature points are identified, and a rigid transform is applied to them. The rigid transform is fitted to 25 corresponding feature points in a second imaged mirror. The closes edge pixel to the expected location as determined by the fitted rigid transform is identified, and its distance to the vertical parallax is determined. If the distance is not greater than predefined maximum, then it is deemed correlate to the edge pixel in the first imaged mirror.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Ray Image Modeling for Fast Catadioptric Light Field Rendering
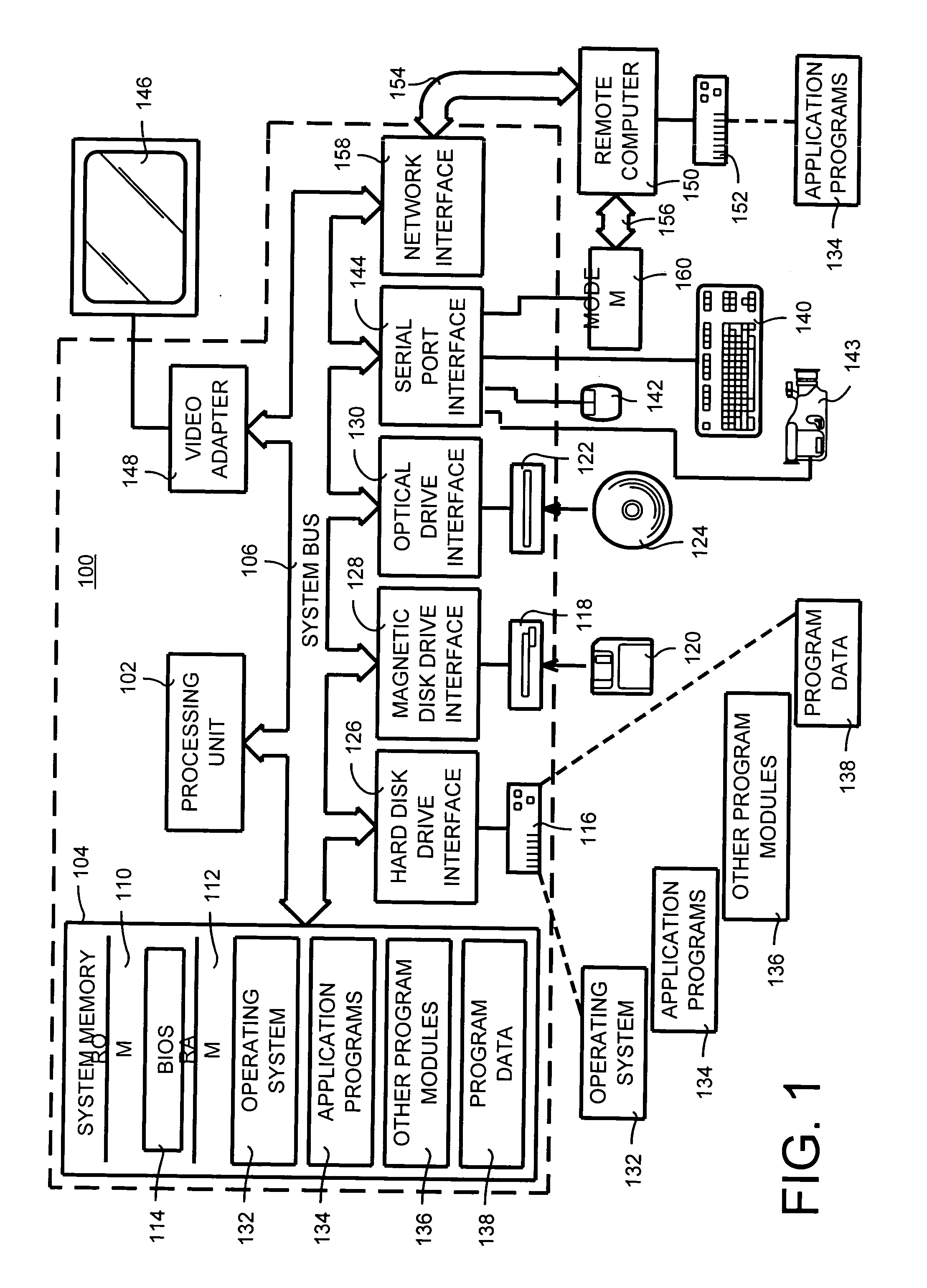
A catadioptric camera creates images light fields from a 3D scene by creating ray images defined as 2D arrays of ray-structure picture-elements (ray-xels). Each ray-xel capture light intensity, mirror-reflection location, and mirror-incident light ray direction. A 3D image is then rendered from the ray images by combining the corresponding ray-xels.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
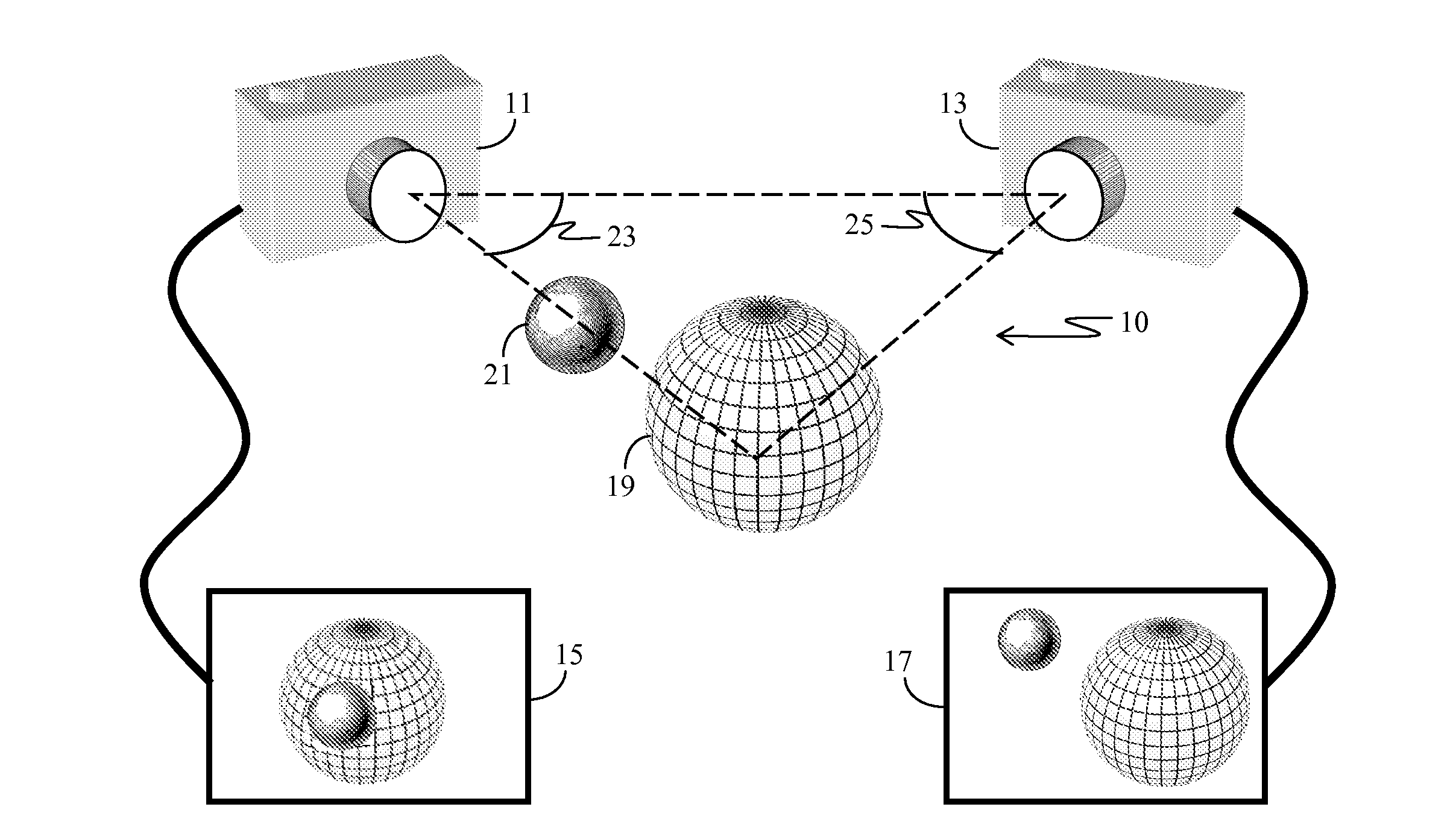
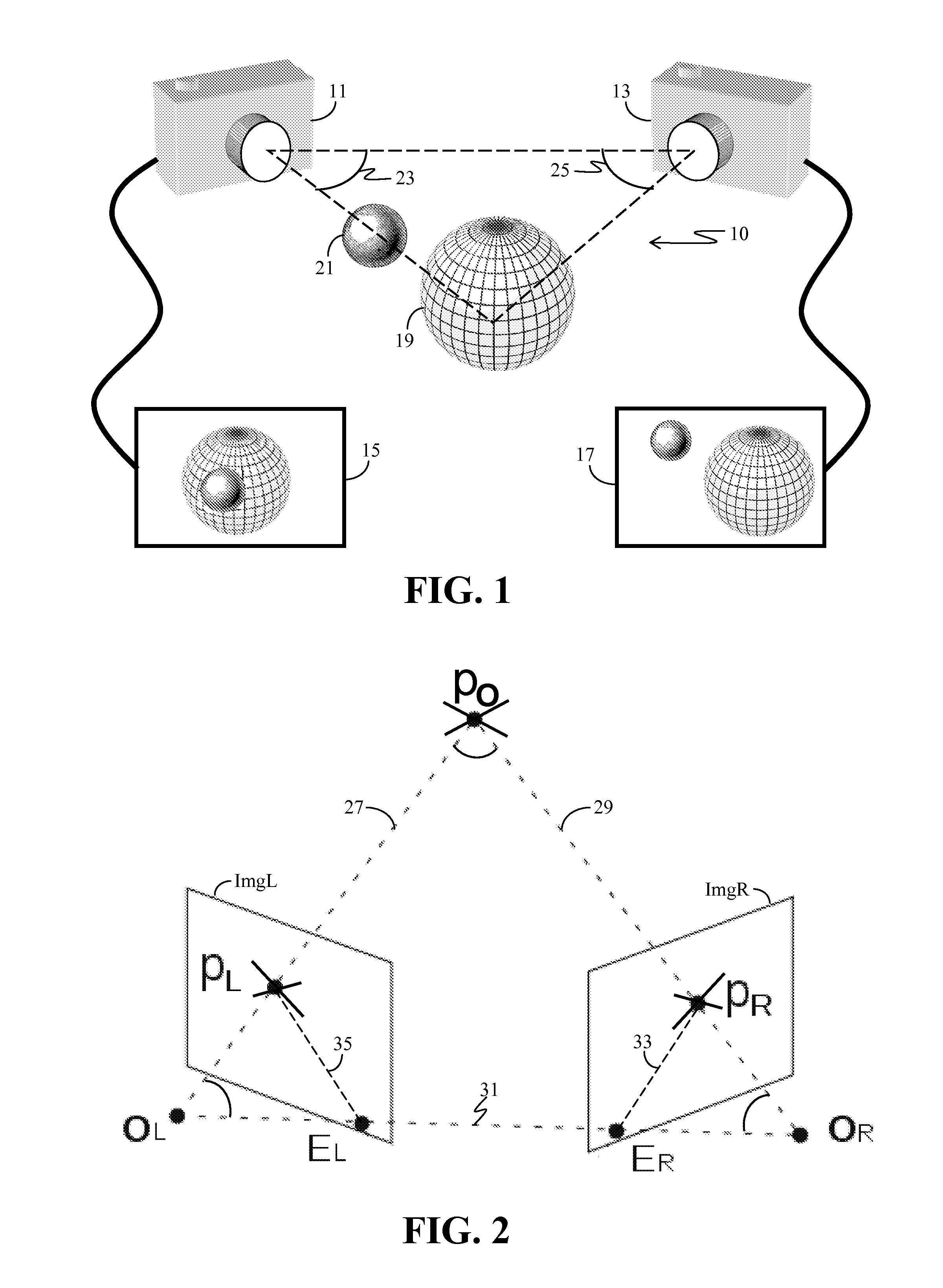
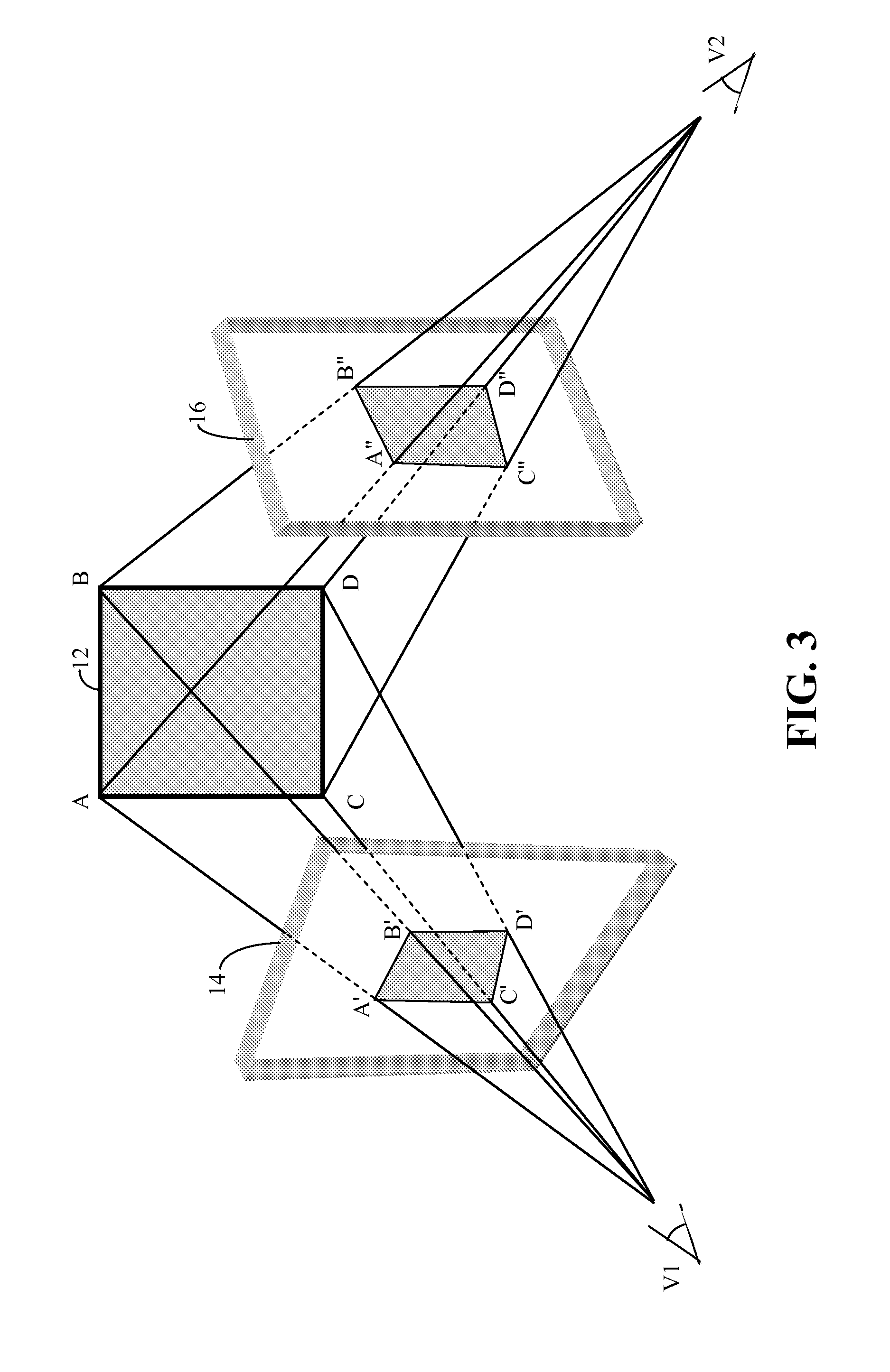
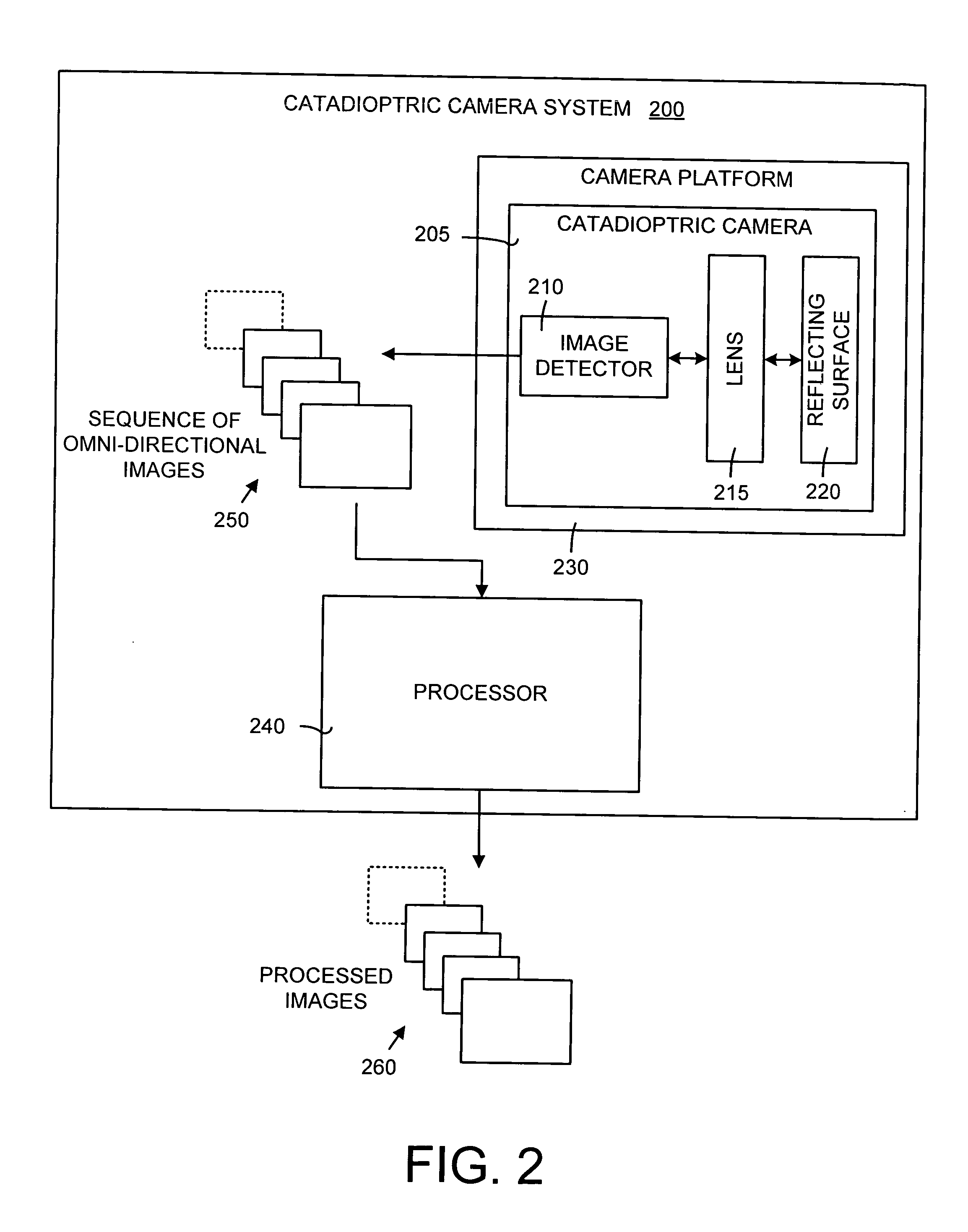
Self-calibration for a catadioptric camera
InactiveUS6870563B1Easy to useAccurate CalibrationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionView camera
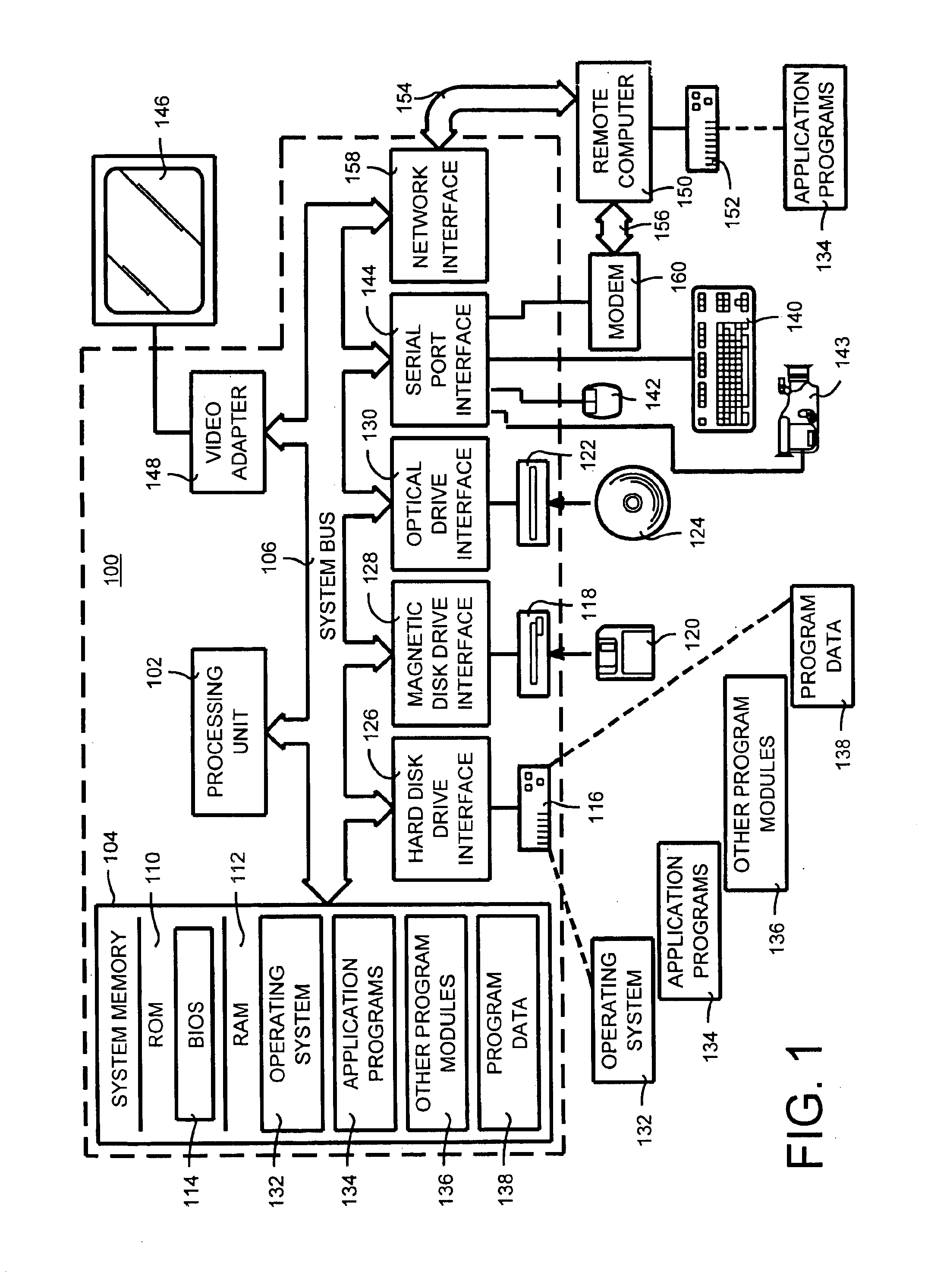
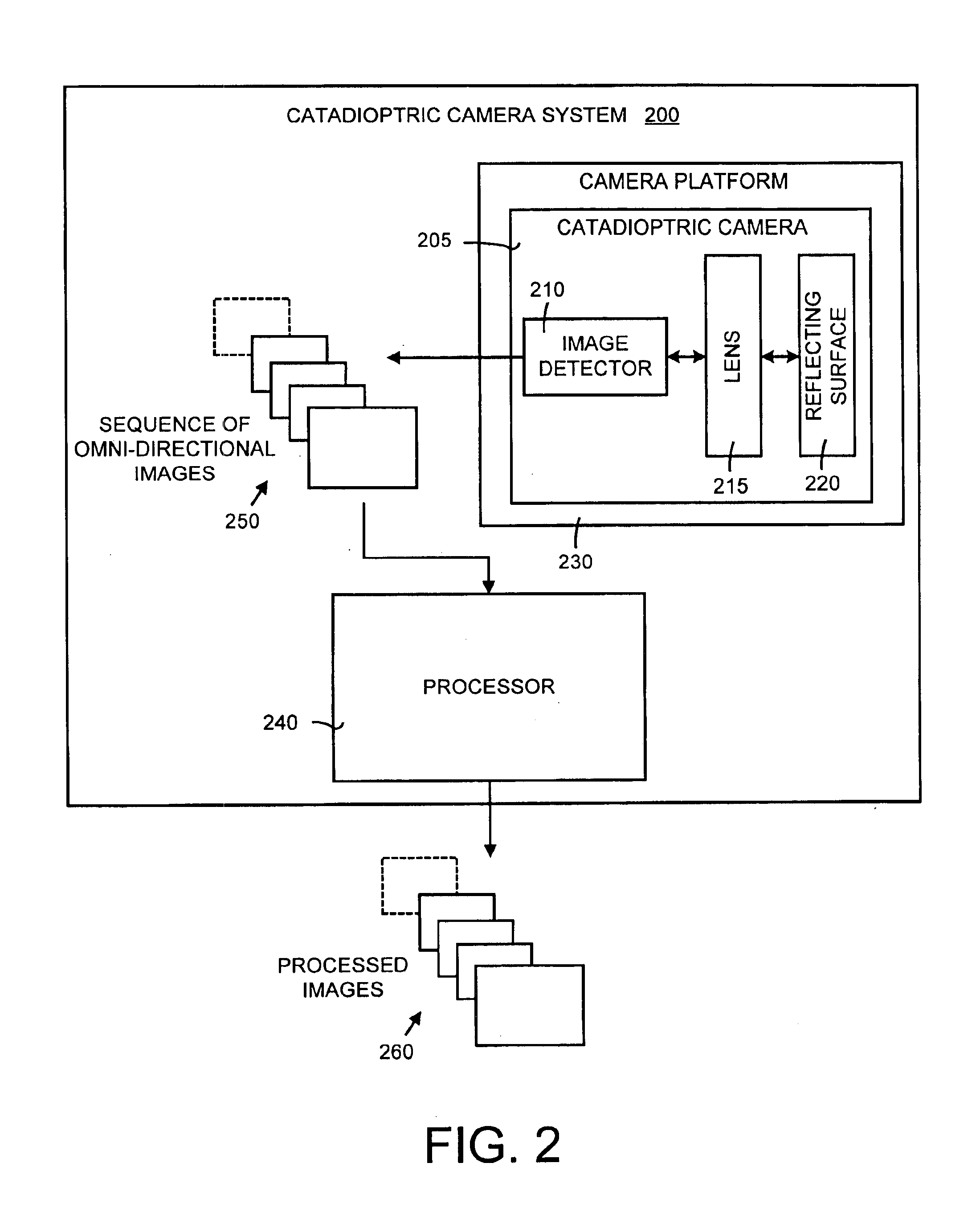
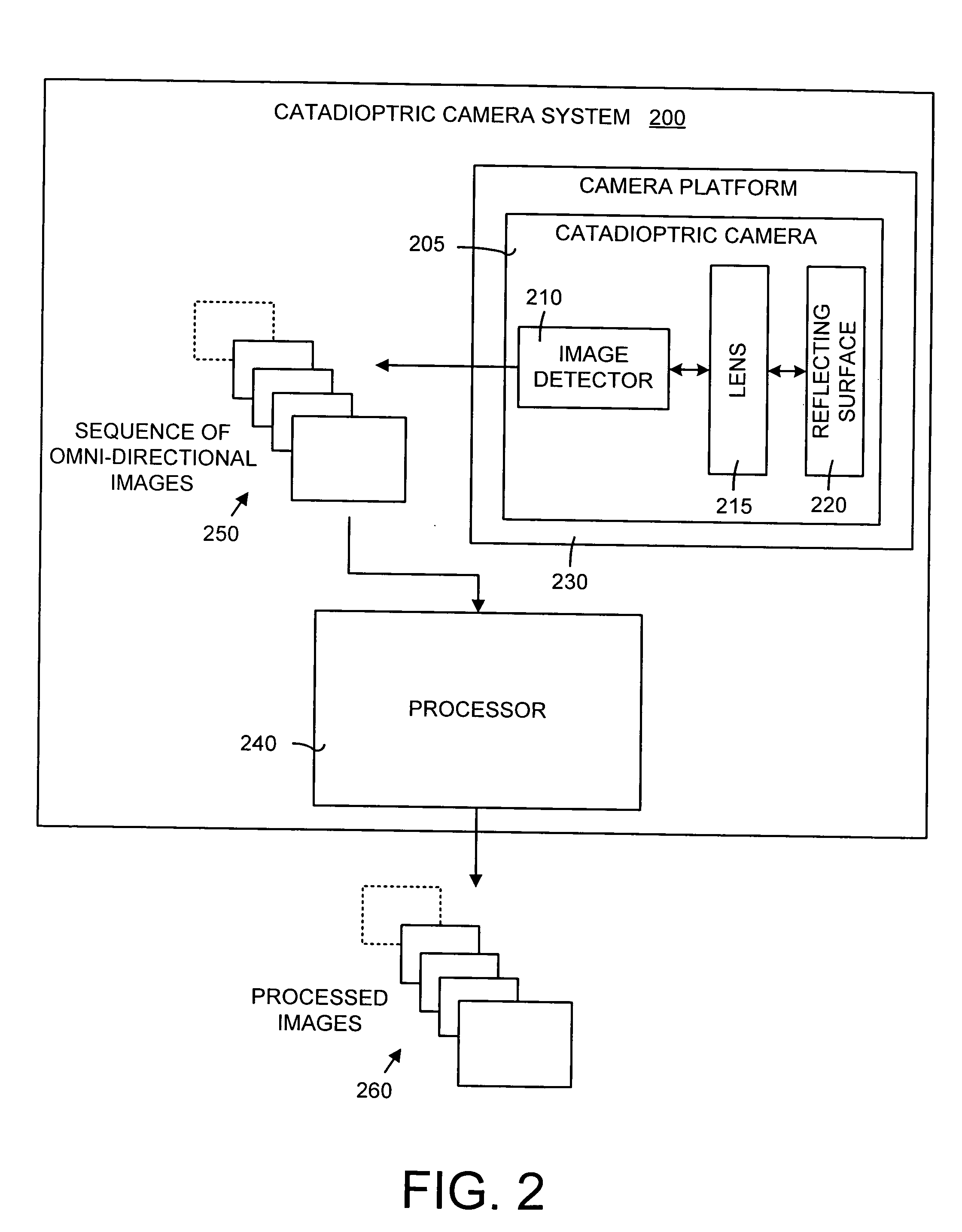
A method and a system for self-calibrating a wide field-of-view camera (such as a catadioptric camera) using a sequence of omni-directional images of a scene obtained from the camera. The present invention uses the consistency of pairwise features tracked across at least a portion of the image collection and uses these tracked features to determine unknown calibration parameters based on the characteristics of catadioptric imaging. More specifically, the self-calibration method of the present invention generates a sequence of omni-directional images representing a scene and tracks features across the image sequence. An objective function is defined in terms of the tracked features and an error metric (an image-based error metric in a preferred embodiment). The catadioptric imaging characteristics are defined by calibration parameters, and determination of optimal calibration parameters is accomplished by minimizing the objective function using an optimizing technique. Moreover, the present invention also includes a technique for reformulating a projection equation such that the projection equation is equivalent to that of a rectilinear perspective camera. This technique allows analyses (such as structure from motion) to be applied (subsequent to calibration of the catadioptric camera) in the same direct manner as for rectilinear image sequences.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
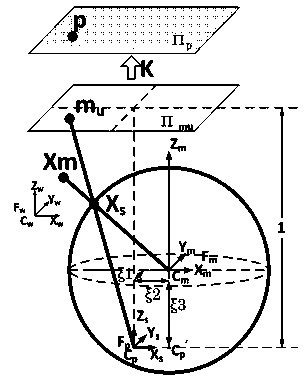
Unified model of catadioptric omnidirectional camera and calibration method thereof
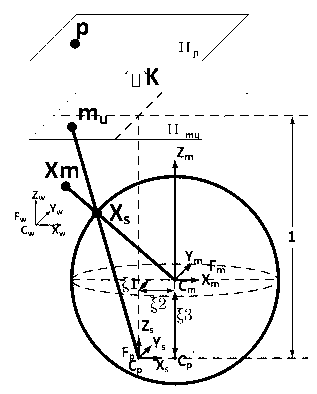
The invention discloses a unified model of a catadioptric omnidirectional camera and a calibration method thereof. The unified model of the catadioptric omnidirectional camera is formed by a virtual unit ball, a virtual viewpoint, a normalization plane and an imaging plane. On the basis of the unified model, a plurality of calibration plate images acquired through the catadioptric omnidirectional camera are utilized to calibrate the parameters of the model and the pose relationship between a calibration board and the catadioptric omnidirectional camera. On the condition that misalignment of the catadioptric omnidirectional camera exists, precision of the model is far higher than that of a unified imaging model of a traditional single view point catadioptric camera. Compared with other non-single-view-point imaging model, the model is simple in imaging model, strong in operability, quick in optimizing speed, and good in precision and noise-resistant performance. The calibration method is high in accuracy and convenient to operate, and is quick in non-linear optimized speed due to original value calculation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Camera model and calibration procedure for omnidirectional paraboloidal catadioptric cameras
InactiveUS7362969B2Enhances calibration modelImage enhancementImage analysisOmnidirectional antennaCatadioptric camera
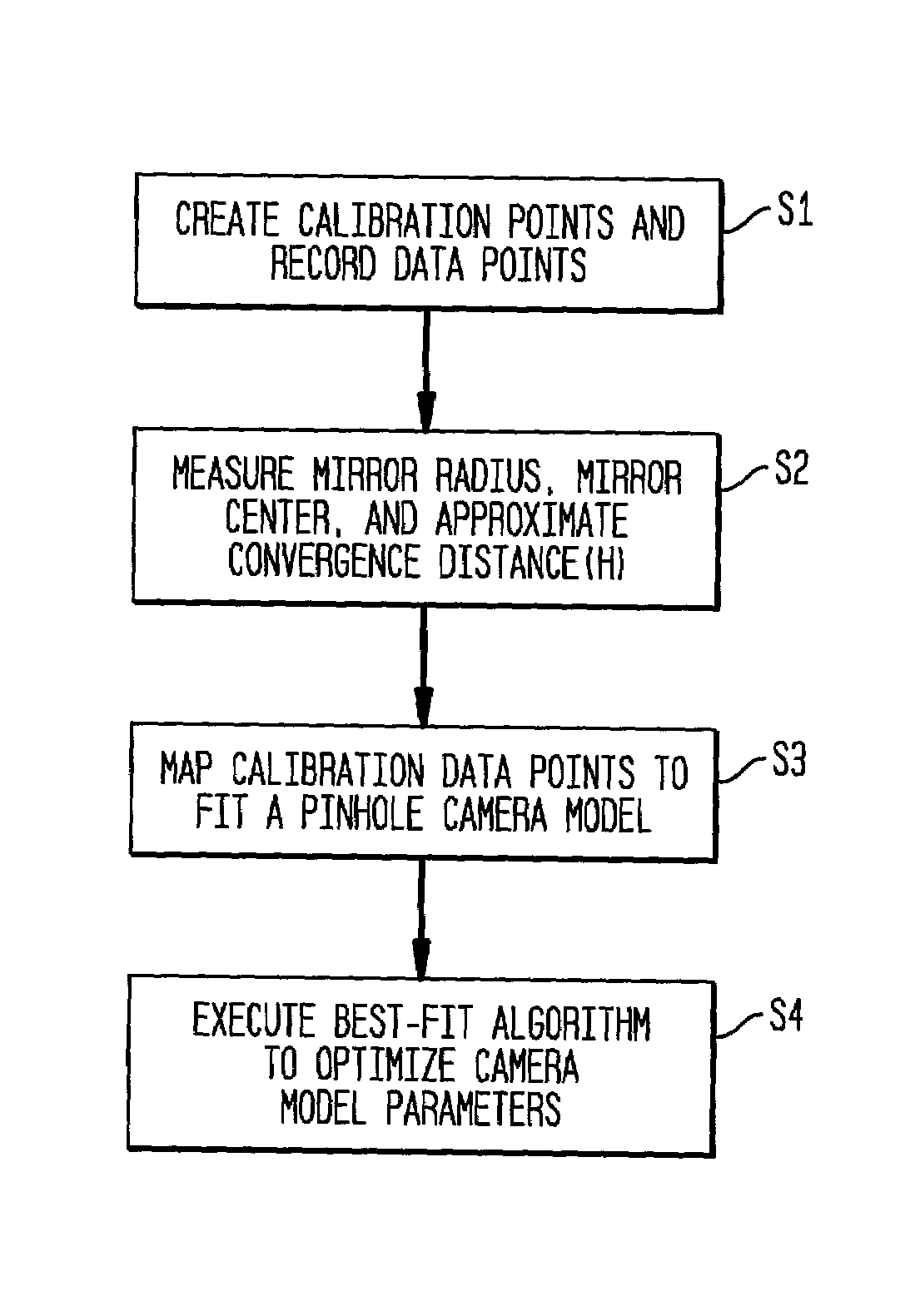
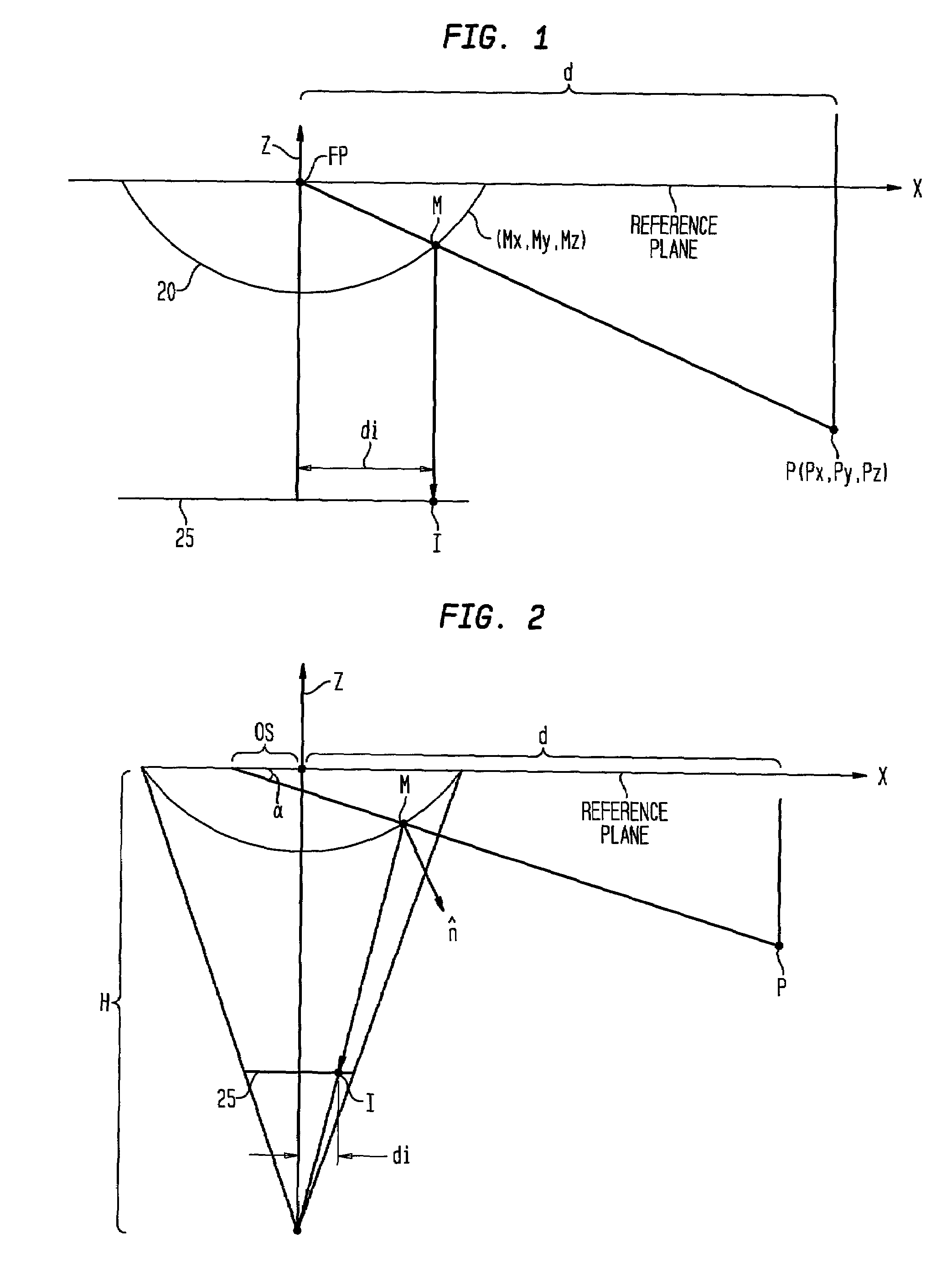
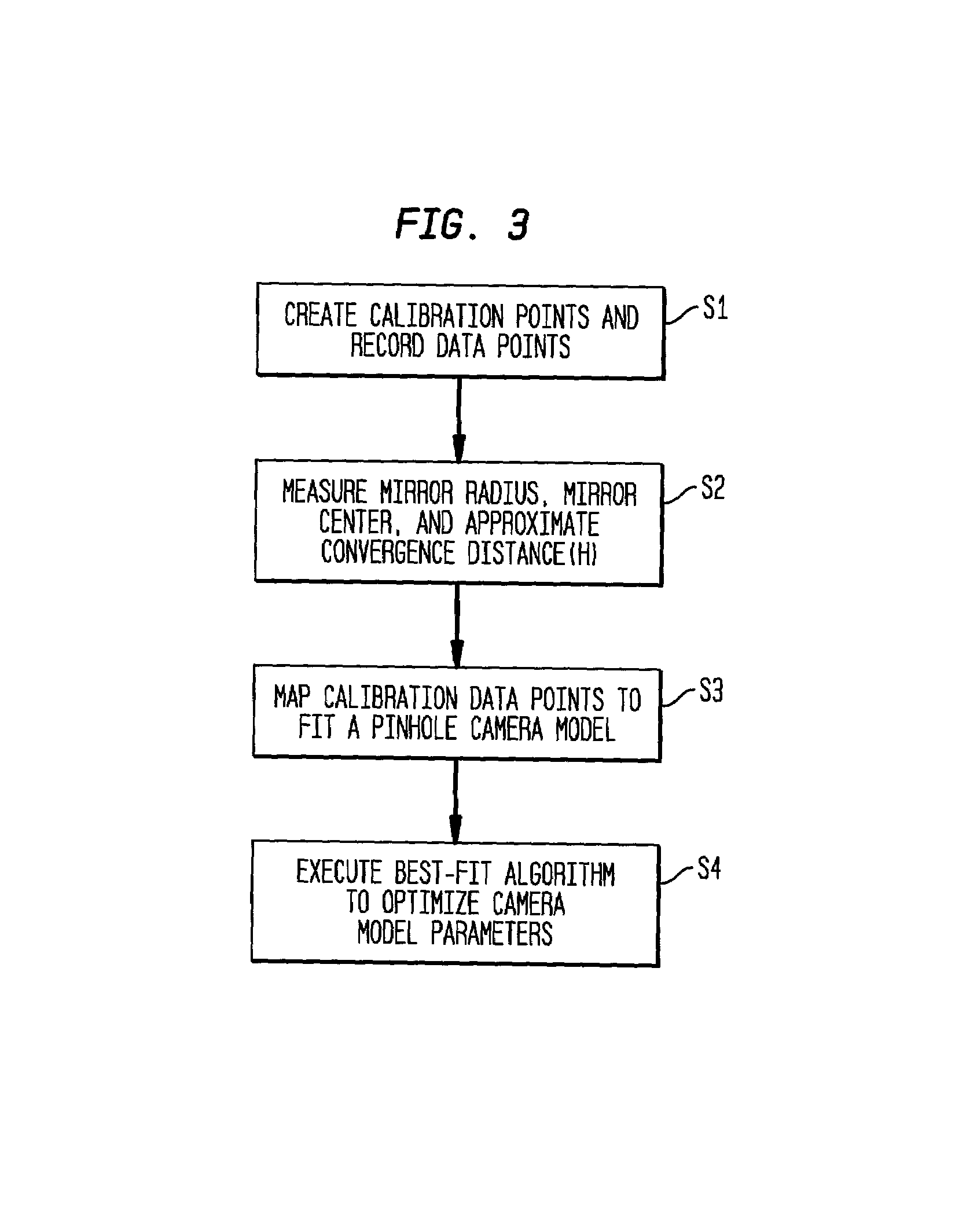
A paraboloidal catadioptric camera is calibrated by relaxing the assumption of an ideal system to account for perspective projection, radial distortion, and mirror misalignment occurring within the camera system. Calibration points, which are small and visually distinct objects, are distributed at fixed locations within an environment. Omnidirectional images are captured by the catadioptric camera at different locations of the environment. Data points are obtained by identifying the location of the calibration points in each captured image. An optimization algorithm best-fits the data points to a perspective camera model in order to derive parameters, which are used to calibrate the catadioptric camera.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
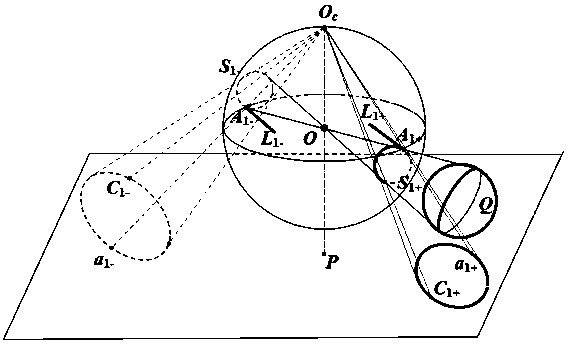
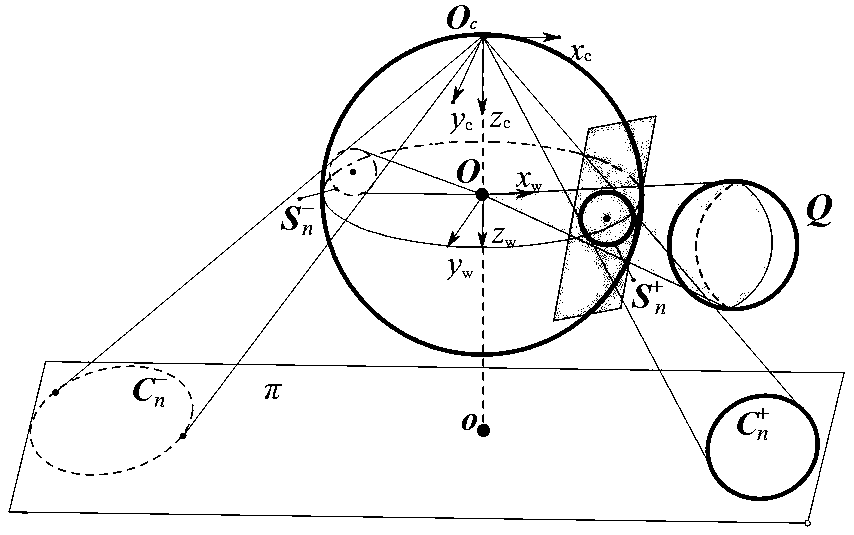
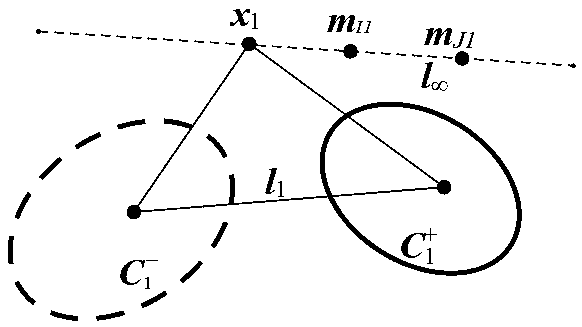
Method of determining intrinsic parameters of parabolic catadioptric camera through linearity of two mutually-shielded spheres
InactiveCN104217435APhysical scale is not requiredNo need to know world coordinatesImage analysisCatadioptric cameraImage plane
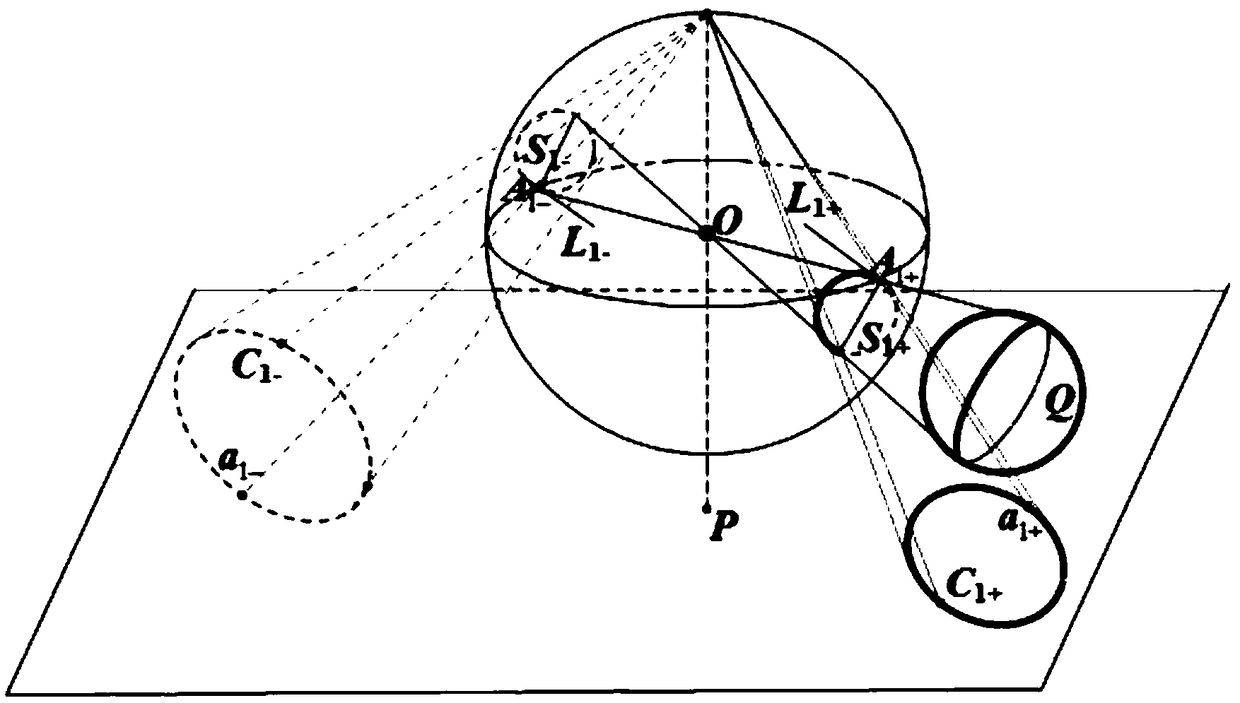
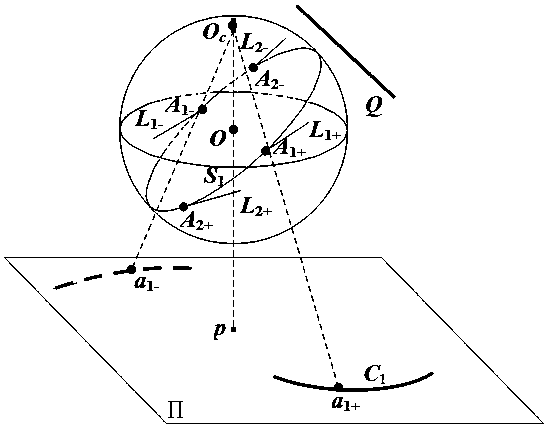
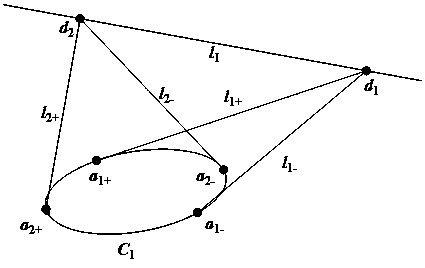
The invention relates to a method of determining intrinsic parameters of a parabolic catadioptric camera through linearity of two mutually-shielded spheres. The method comprises the following steps that five images of a target are shot from different directions by utilizing the parabolic catadioptric camera, parabolic catadioptric images of the target are two intersected quadratic curves, boundary pixel point coordinates and image point coordinates of the five target images are extracted from the images, antipodal image points are obtained according to the relation between the image points and the antipodal image points, curve equations are respectively fitted, two groups of antipodal image points are formed by two actual points of intersection of a sphere image and two actual points of intersection of an antipodal sphere image, through definition of the antipodal image points, the two groups of antipodal image points provide one group of orthogonal direction end points on an image plane, and the intrinsic parameters of the camera are solved by utilizing constraint linearity of the orthogonal direction end points on an absolute conic image. By utilizing the target in the invention, full-automatic calibration can be implemented, and errors caused by measurement in a calibration process are reduced. Projection contour lines of the spheres can be completely extracted in the image, so that the calibration precision of the camera is improved.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
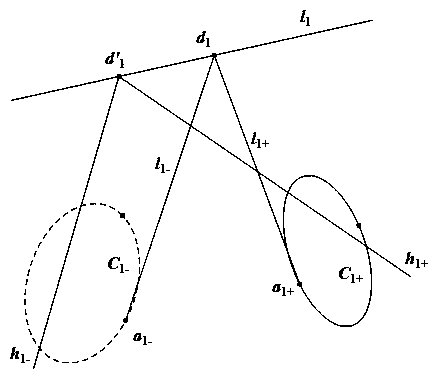
Solving parabolic catadioptric camera parameters through two intersected straight lines in space
InactiveCN103106661AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisCatadioptric cameraHarmonic conjugate
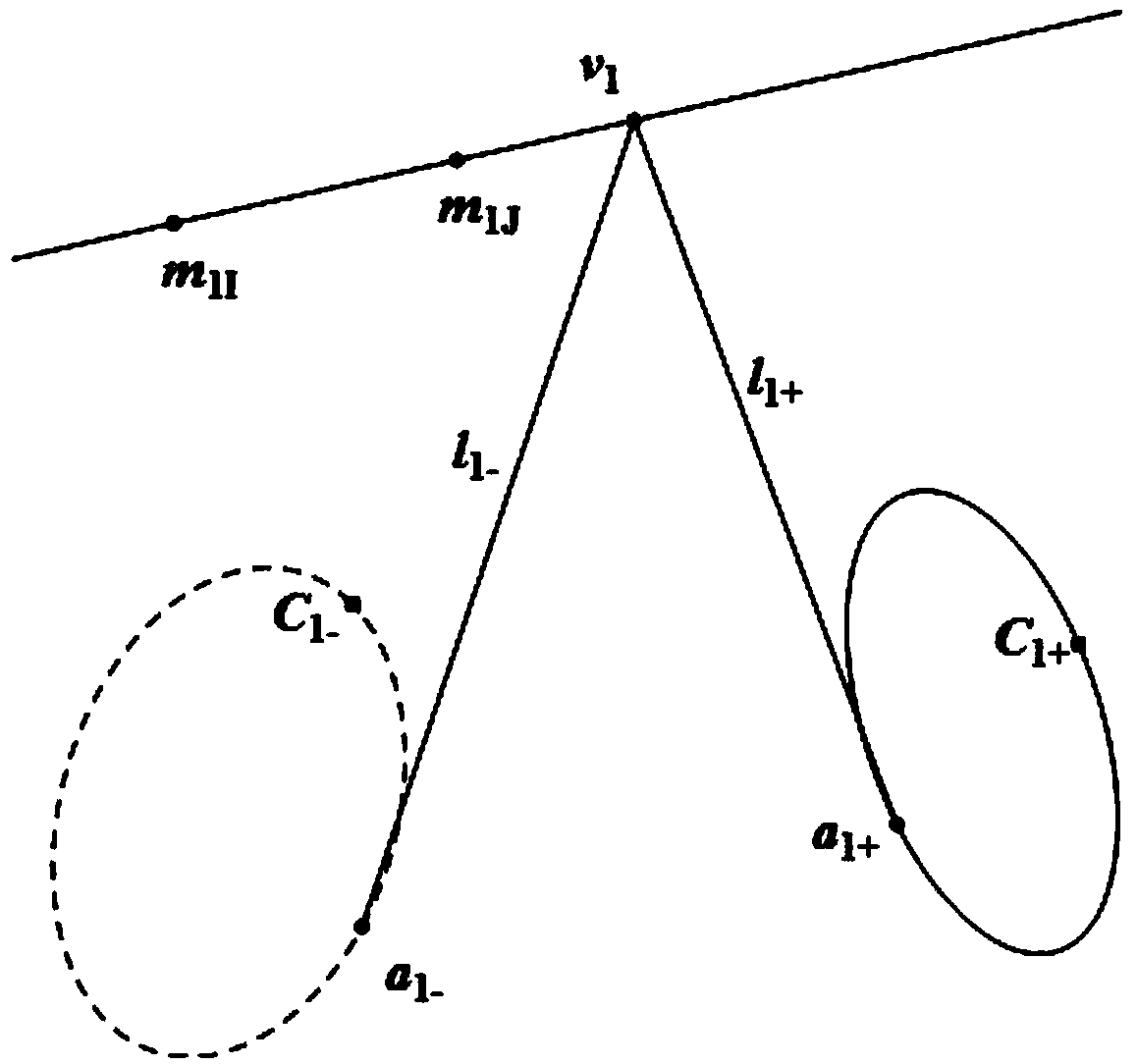
The invention relates to a method to solve parabolic catadioptric camera parameters through two intersected straight lines in space. The method is that a target (a calibration object) composed of the two intersected straight lines in the space is used for self-calibration of a parabolic catadioptric camera. Three images of the target are shot by the parabolic catadioptric camera from different directions. A parabolic catadioptric image of a straight line is a quadric curve. Boundary pixel point coordinates and image point coordinates of the three target images are extracted from the images to respectively fit curvilinear equations. Images of disappeared points on image planes along the orthogonal direction are obtained according to that images of harmonic conjugates and two parallel straight lines are intersected to one point. Camera parameters are solved by utilizing the linear constraint of the images on the orthogonal direction on an image of an absolute conic. By utilizing the method, the target can be fully and automatically calibrated, and errors caused by measurement in the calibration process are reduced. Because a straight line is a more concise and more global element, calibration precision of the camera in the calibration process is improved.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
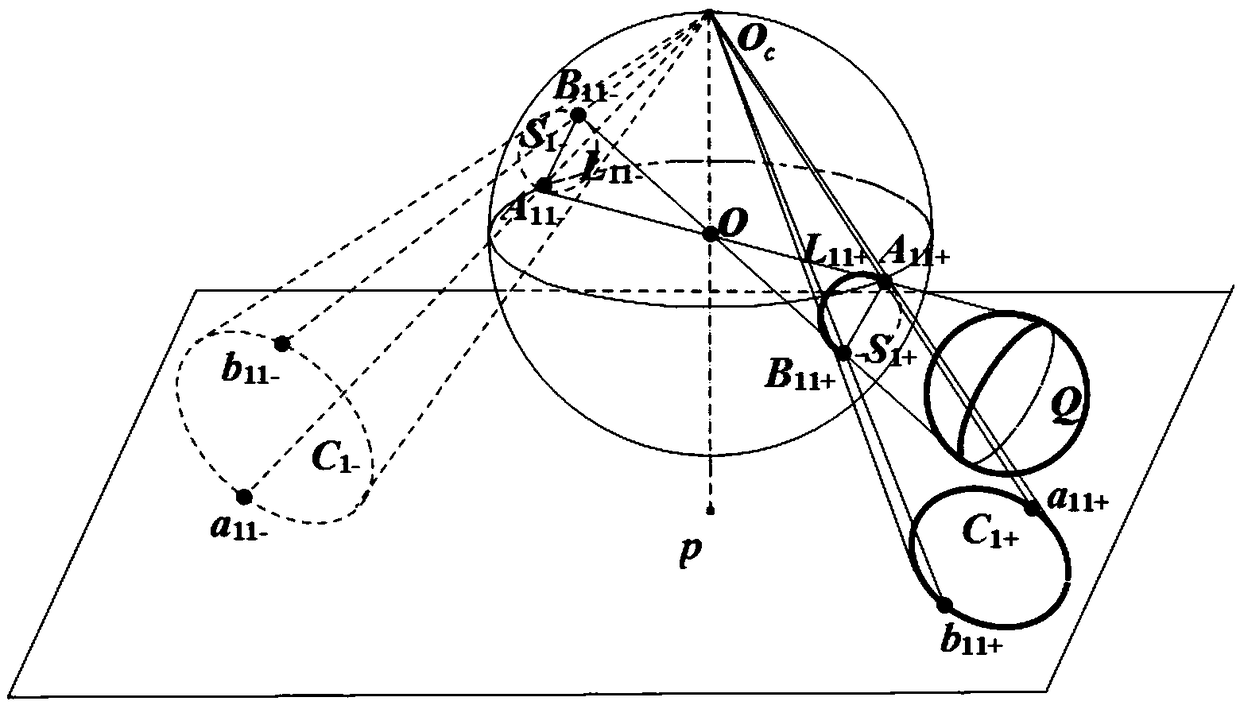
Method for calibration of parabolic catadioptric camera by employing ball image and common self-polar triangles
The present invention relates to a method for calibration of a parabolic catadioptric camera by employing a ball image and common self-polar triangles. A ball in a space is employed as a calibration object to fit a mirror surface contour projection equation and a ball image equation under a parabolic catadioptric camera and calculate an antipodal ball image equation and an equation of an image ofa great circle having a center of a circle being coincided with a center of a circle of a unit virtual ball and being parallel with a projection small circle of the ball on a unit visual ball model, two common poles, corresponding to two common self-polar triangles formed by the ball image and the antipodal ball image, of the image of the great circle are connected with two common poles to solve avanishing line, a relation of the projection of the circle and the vanishing line is employed to solve the images of circular ring points, and three images are shot to obtain images of the three circular ring points, and the images of the circular ring points and the constraint of the internal parameter matrix of the camera are employed to complete calibration of the camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method of calibrating parabolic catadioptric camera by use of single sphere and orthogonal vanishing point
InactiveCN106447731AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisCatadioptric cameraImage edge
The invention relates to a method of calibrating a parabolic catadioptric camera by use of a single sphere and an orthogonal vanishing point. The method is characterized in that only a sphere element is used. Firstly, the edge points of a mirror surface contour projection and the edge points of a target image are extracted from an image, a mirror surface contour projection and a sphere image projection are obtained by fitting based on a least square method. Secondly, antipodal image points are obtained according to the relationship between image points and antipodal image points thereof, and an antipodal sphere image of a sphere image is fitted out; two different points are taken from the sphere image, and the antipodal image points of the two points are calculated out; the two groups of antipodal image points provide a group of orthogonal vanishing points; and six groups of points (there are two different points in each group) are taken from the sphere image to obtain six group of orthogonal vanishing points. Finally, the intrinsic parameters of the camera are calculated based on the constraint of the orthogonal vanishing points on the intrinsic parameters of the camera; and in the process of calculation, five intrinsic parameters of the parabolic catadioptric camera are calculated using one image of a shooting target of the parabolic catadioptric camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Solving parabolic catadioptric camera parameters through one straight line in space
The invention relates to a method to solve parabolic catadioptric camera parameters through one straight line in space. The method is that a calibration object composed of the straight line in the space is used for self-calibration of a parabolic catadioptric camera. Three images of the calibration object are shot by the parabolic catadioptric camera from different directions. A parabolic catadioptric image of a straight line is a quadric curve. Boundary pixel point coordinates and image point coordinates of the three calibration objects images are extracted from the images to respectively fit curvilinear equations. Images of circular ring points on image planes are obtained according to a polarity principle. Camera parameters are solved by utilizing the linear constraint of the images on the circular ring points on an image of an absolute conic. By utilizing the method, the calibration object can be fully and automatically calibrated, and errors caused by measurement in the calibration process are reduced. Because a straight line is a more concise and more global element, calibration precision of the camera in the calibration process is improved.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Self-calibration for a catadioptric camera
InactiveUS20050099502A1Easy to useAccurate CalibrationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsView cameraWide field
A method and a system for self-calibrating a wide field-of-view camera (such as a catadioptric camera) using a sequence of omni-directional images of a scene obtained from the camera. The present invention uses the consistency of pairwise features tracked across at least a portion of the image collection and uses these tracked features to determine unknown calibration parameters based on the characteristics of catadioptric imaging. More specifically, the self-calibration method of the present invention generates a sequence of omni-directional images representing a scene and tracks features across the image sequence. An objective function is defined in terms of the tracked features and an error metric (an image-based error metric in a preferred embodiment). The catadioptric imaging characteristics are defined by calibration parameters, and determination of optimal calibration parameters is accomplished by minimizing the objective function using an optimizing technique.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
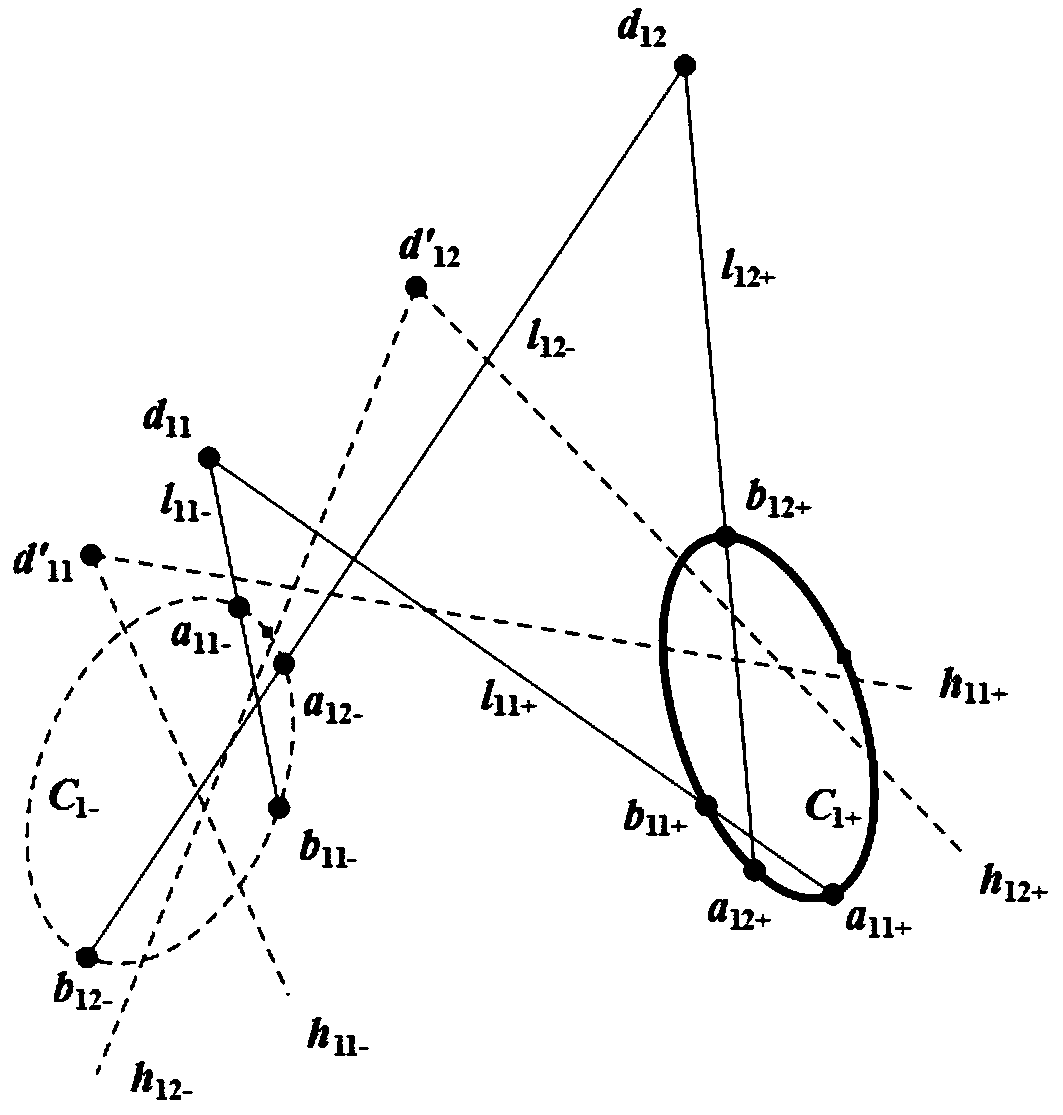
Method for solving intrinsic parameters of parabolic catadioptric camera linearly by utilizing three unparallel straight lines in space
InactiveCN102982551AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisIntersection of a polyhedron with a lineCatadioptric camera
The invention relates to a method for solving intrinsic parameters of a parabolic catadioptric camera linearly by utilizing three unparallel straight lines in a space. The method comprises the steps that a target consisting of the three unparallel straight lines in the space and used for automatic calibration of the parabolic catadioptric camera is utilized; the parabolic catadioptric camera is used to shoot an image of the target; the linear parabolic catadioptric image is a quadratic curve; target image points are extracted from the image; curvilinear equations are fitted; an intersection point of every two curves is solved; images of three pairs of circular ring points on a plane of the image are obtained according to a polar principle and a diameter concyclic center attribute; and the parameters in the camera are solved by utilizing linear restriction of the images of the circular ring points on an absolute conic. With the adoption of the target in the method, full automatic calibration can be realized, and errors due to measurement in a calibration process are reduced. As the straight lines are elements which are more concise and global, the calibration accuracy is improved in the calibration process of the camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for solving parameters in parabolic catadioptric camera through three unparallel straight lines in checkerboard
InactiveCN103942784AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisGeometric propertyCross-ratio
The invention relates to a method for linearly solving parameters in a parabolic catadioptric camera through three unparallel straight lines in a checkerboard. The method is characterized in that only linear elements are utilized, and a template is composed of the three unparallel straight lines on the checkerboard; parabolic catadioptric images of the straight lines are quadratic curves, the parabolic catadioptric camera is used for taking an image of a target, image points of the target are extracted from the image first, fitting is conducted to obtain the curve equation, and the intersection points of every two curves are solved, six sets of orthogonal fading points on the image plane are then obtained according to the geometric properties of a circle and the cross ratio invariance property, and the parameters in the parabolic catadioptric camera are linearly solved for constraints on images of the absolute quadratic curves through the orthogonal fading points. According to the method, the target can be calibrated in a full-automatic mode, and errors caused by measurement in the calibration process are reduced. Due to the fact that the straight lines are the simpler and more comprehensive elements, calibration accuracy is improved in the calibration process of the camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
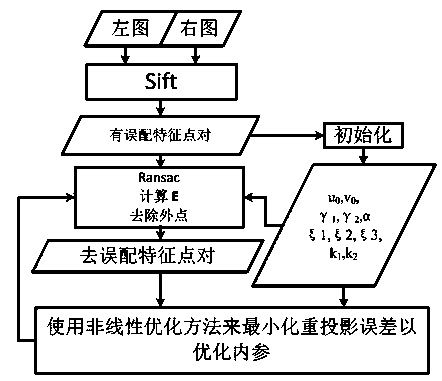
Catadioptric camera self-calibration method based on generalized unified model
The invention discloses a catadioptric camera self-calibration method based on a generalized unified model. The method includes the following steps that a left catadioptric panorama and a right catadioptric panorama which are clearly imaged are acquired in different positions of the same scene through a catadioptric camera; SIFT feature points of the left catadioptric panorama and the right catadioptric panorama are extracted, and feature point matching is performed; internal parameters of the generalized unified model are initialized; an essential matrix E is calculated out through epipolar geometry, the accuracy is improved through RANSAC in the calculating process of E, and meanwhile external points are removed; the reprojection errors of the feature points are minimized through a nonlinear optimization LevenbergMarquardt method; the internal parameters are optimized continuously till the reprojection errors are smaller than preset threshold values, and the robustness and the accurate result are obtained through optimization. According to the method, the internal parameters of the generalized unified model and the relation between the two positions can be calibrated just through the two panoramas in different positions, calibration is performed fully automatically, and the method has the advantages of being convenient and fast to use, easy to operate and high in accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for calibrating parabolic catadioptric camera by using properties of single sphere and circle tangent line
InactiveCN107644445AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisCatadioptric cameraVanishing line
The invention discloses a method for calibrating a parabolic catadioptric camera by using properties of a single sphere and a circle tangent line. The method is characterized by taking a sphere in a space as a target. The method comprises the specific steps of: firstly, shooting three pictures containing the sphere from different positions by means of the parabolic catadioptric camera; secondly, acquiring antipodal image points according to relationship between image points and antipodal image points thereof in a parabolic catadioptric unit visual sphere model, so as to estimate an antipodal sphere image of a sphere image; thirdly, selecting a point from the sphere images, wherein a tangent line of each image point about the corresponding sphere image and a tangent line of the corresponding antipodal image point about the corresponding antipodal sphere image intersect at an image vanishing point through definition of the antipodal image points, an intersection point of the image vanishing point about polar lines of the sphere image and the antipodal sphere image is an image vanishing point, a straight line where the two image vanishing points are located is an image vanishing line,an intersection point of the image vanishing line and the sphere image is an image of circular points, and the three pictures provide the images of three groups of circular points; and finally, solving inner parameters of the camera by utilizing the constraint of the images of the circular points for an absolute conic curve image.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Planar catadioptric camera internal parameter solving method based on spatial parallel circles
The invention relates to a planar catadioptric camera internal parameter solving method based on spatial parallel circles. The camera internal parameters are solved according to the properties of linearity of the spatial parallel circles in a planar catadioptric system. The device comprises two rectangular planar mirrors and one pinhole camera, and spatial points and reflection image points of the planar mirrors are on the same spatial circle; the two spatial parallel circles are provided with four crossed conjugate imaginary intersection points which are circular points of two conjugate complex points collinear to the infinity of the plane where the spatial parallel circles located. Three images including an object and four reflected images in the planar images are captured, two groups of feature points are extracted and quadric curves are fitted, and one vanishing point of an image plane is solved through the symmetry of a reflecting point group about the planar mirrors. Two groups of conjugate imaginary intersection points of the quadric curves are solved through the image plane, the image coordinates of the circular points is acquired according to the collinearity of the circular points and the vanishing point, the limitation of an image of the circular points corresponding to an absolute quadric curve image is established, and the camera internal parameters are solved in a linear manner.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Ray image modeling for fast catadioptric light field rendering
InactiveUS8432435B2MirrorsTelevision signal transmission by single/parallel channels3d imageSpecular reflection
A catadioptric camera creates image light fields from a 3D scene by creating ray images defined as 2D arrays of ray-structure picture-elements (ray-xels). Each ray-xel captures light intensity, mirror-reflection location, and mirror-incident light ray direction. A 3D image is then rendered from the ray images by combining the corresponding ray-xels.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
A method for calibrating a catadioptric camera using properties of a single sphere and a conjugate diameter
InactiveCN109360248AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisCatadioptric cameraConjugate diameters
A method for calibrating a catadioptric camera using properties of a single sphere and a conjugate diameter is characterized in that only spherical elements are used. Firstly, the edge points of the target image and the edge points of the specular contour projection of one image are extracted from three images respectively, and the specular contour projection and the spherical image projection areobtained by least square fitting. Secondly, according to the relation between the image point and its extension point, the extension point is obtained, and then the extension spherical image of the spherical image is fitted. According to the property of the conjugate diameter of a circle, the intersection point of the polar line of the vanishing point with respect to the spherical image and the contrastive spherical image is a set of orthogonal vanishing points. Two sets of orthogonal vanishing points can be obtained by choosing two sets of different points on the spherical image. All the orthogonal vanishing points corresponding to a plane only provide two constraints for the image of absolute conic and six constraints for three images. Finally, the camera intrinsic parameters are obtained by using the constraint of the orthogonal vanishing point to the absolute conic image.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for calibrating parabolic catadioptric camera by using separate image of double balls and image of circular point
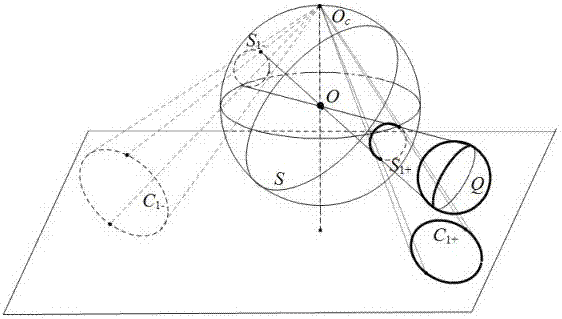
InactiveCN105321181APhysical scale is not requiredHigh precisionImage analysisMedicineComputer graphics (images)
The present invention relates to a method for calibrating a parabolic catadioptric camera by using a separate image of double balls and an image of a circular point. An image of double balls used as targets is shot by using the parabolic catadioptric camera, and the targets are separated on an image plane. A main point of an intrinsic parameter of the camera is determined by four groups of imaginary antipodal image points, which are correspondingly formed by imaginary intersection points of ball images in the catadioptric image and imaginary intersection points of antipodal ball images; on the basis of obtaining the main point, vanishing lines of planes where two groups of parallel projection small circles of double balls on a unit virtual ball are positioned are solved, so that the image of the circular point on the plane is determined and finally, other intrinsic parameter of the camera are solved by using the constraint of image of the circular point to the intrinsic parameter of the camera. According to the method provided by the present invention, full automatic calibration can be implemented, and errors caused by measurement in the calibration process are reduced. Since all the projection contour lines of the balls in the image can be extracted, thereby improving the calibration accuracy of the camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Context and epsilon stereo constrained correspondence matching
InactiveUS8773513B2Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionParallaxComputer graphics (images)
A catadioptric camera having a perspective camera and multiple curved mirrors, images the multiple curved mirrors and uses the epsilon constraint to establish a vertical parallax between points in one mirror and their corresponding reflection in another. An ASIFT transform is applied to all the mirror images to establish a collection of corresponding feature points, and edge detection is applied on mirror images to identify edge pixels. A first edge pixel in a first imaged mirror is selected, its nearest feature points are identified, and a rigid transform is applied to them. The rigid transform is fitted to corresponding feature points in a second imaged mirror. The closest edge pixel to the expected location as determined by the fitted rigid transform is identified, and its distance to the vertical parallax is determined. If the distance is not greater than predefined maximum, then it is deemed correlate to the edge pixel in the first imaged mirror.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Camera device and method for shooting light having at least two wavelength bands
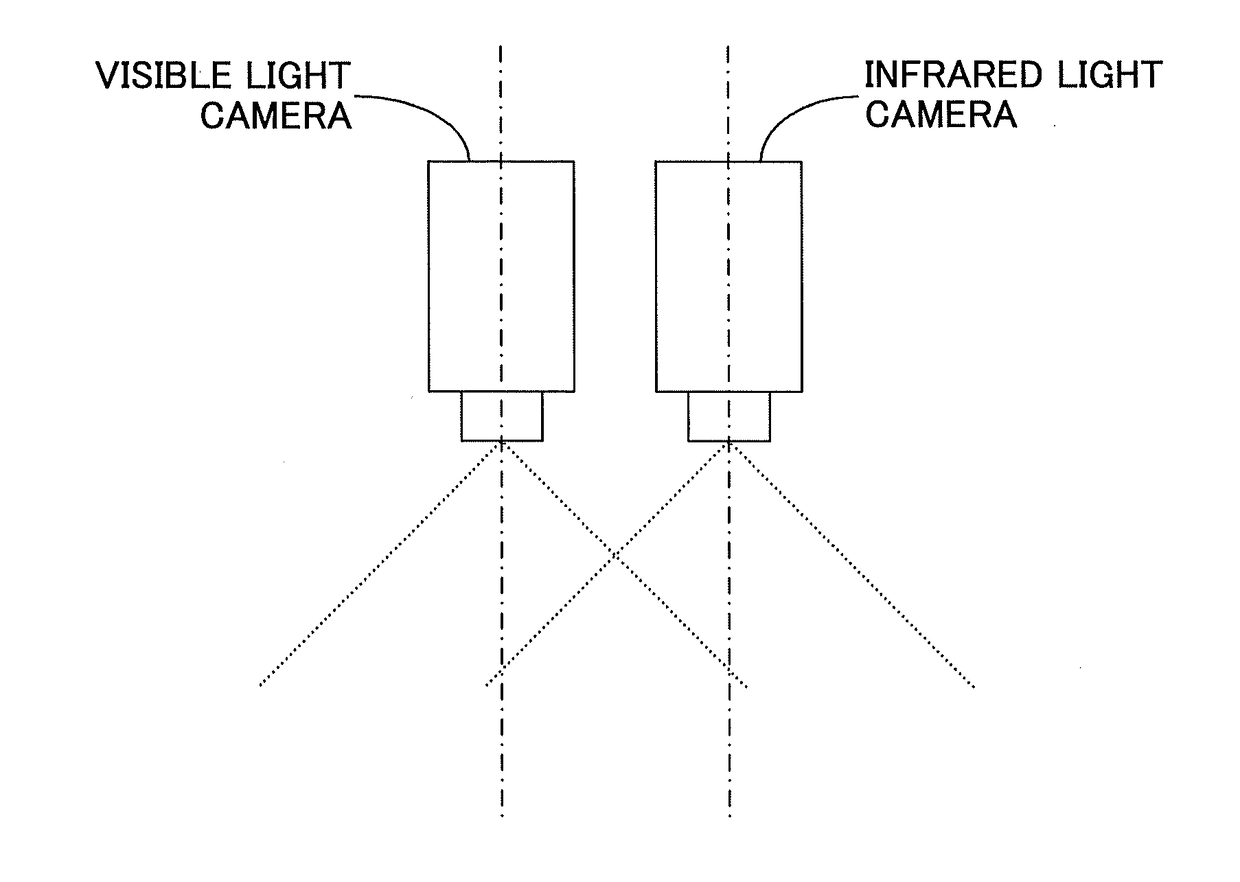
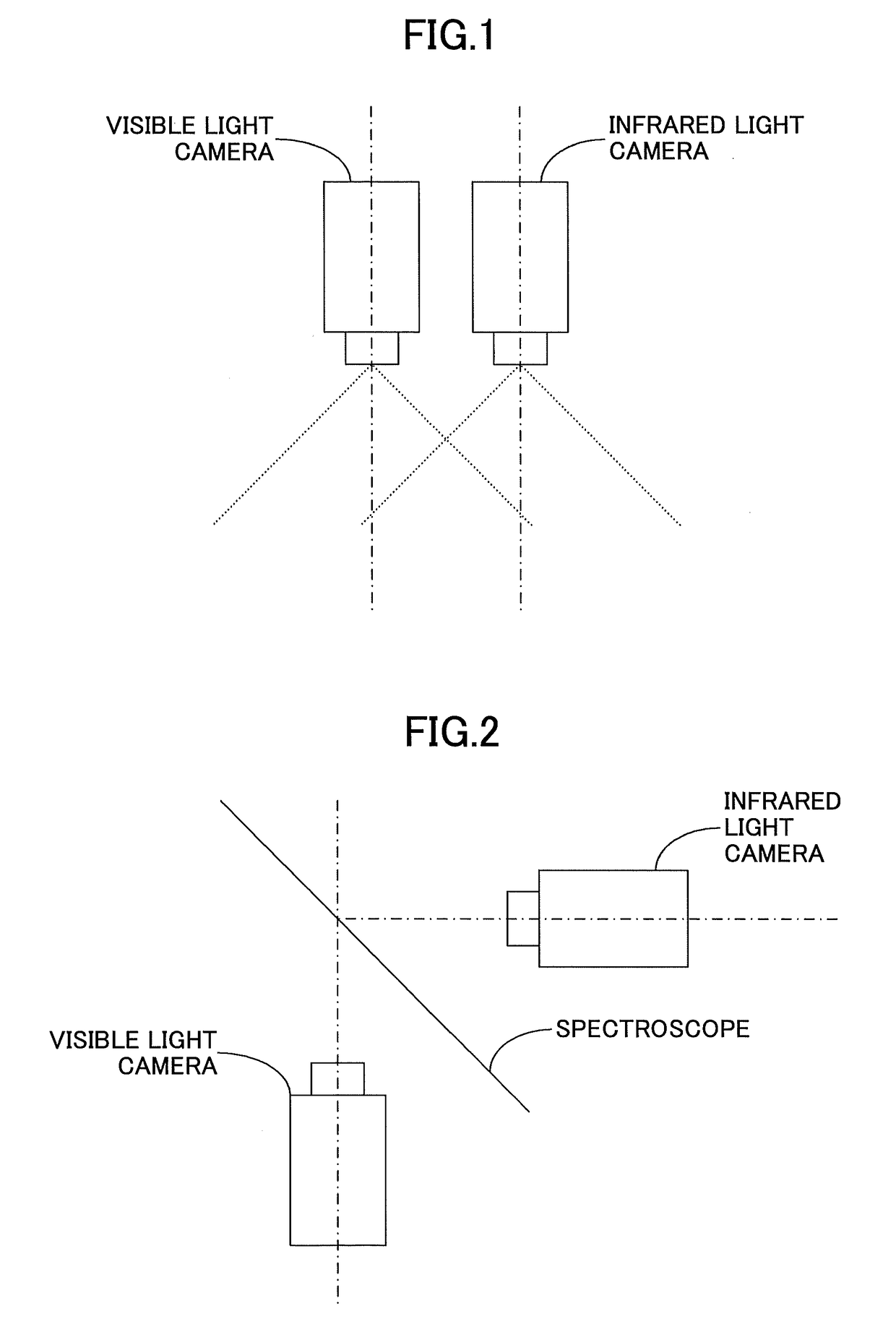
ActiveUS20180249910A1Exclude influenceReduce the amount of solutionSensorsTelemetric patient monitoringFisheye lensCatadioptric camera
Camera device and method for shooting light having at least two wavelength bands are disclosed. The camera device includes a first camera containing a first lens for receiving light having a first wavelength band; a second camera including a second lens for receiving light having a second wavelength band which is different from the first wavelength band, the second lens being disposed facing the first lens of the first camera; and a parabolic mirror set between the first camera and the second camera, able to let the light having the first wavelength band penetrate therethrough, and at the same time, reflect the light having the second wavelength band. The first camera is a non-fisheye camera. The first lens is a non-fisheye lens. The second camera and the parabolic mirror form a catadioptric camera. The aperture stop of the non-fisheye lens coincides with the focal point of the parabolic mirror.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method of utilizing projection matrix of Veronese mapping checkerboard to calibrate central catadioptric camera
InactiveCN106558082AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage enhancementImage analysisHat matrixAngular point
The present invention relates to a method of utilizing a projection matrix of a Veronese mapping checkerboard to calibrate a central catadioptric camera. The method comprises the steps of using the central catadioptric camera to shoot a target image, and extracting the image points corresponding to the checkerboard in the space; utilizing the Veronese mapping to expand the coordinates, and using a DLT-similarity method to estimate the projection matrix linearly; utilizing the projection matrix to solve the parameters in the camera. By utilizing the method of the present invention, no physical scale requirement is required, the points are easy to select, the point sources are abundant, the calibration errors caused by the data errors during a calibration process are reduced, and the one-to-one correspondence of the image points and the angular points of the space checkerboard can be controlled, thereby improving the calibration precision of the camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Self-calibration for a catadioptric camera
InactiveUS20050099501A1Easy to useAccurate CalibrationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionWide field
A method and a system for self-calibrating a wide field-of-view camera (such as a catadioptric camera) using a sequence of omni-directional images of a scene obtained from the camera. The present invention uses the consistency of pairwise features tracked across at least a portion of the image collection and uses these tracked features to determine unknown calibration parameters based on the characteristics of catadioptric imaging. More specifically, the self-calibration method of the present invention generates a sequence of omni-directional images representing a scene and tracks features across the image sequence. An objective function is defined in terms of the tracked features and an error metric (an image-based error metric in a preferred embodiment). The catadioptric imaging characteristics are defined by calibration parameters, and determination of optimal calibration parameters is accomplished by minimizing the objective function using an optimizing technique.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
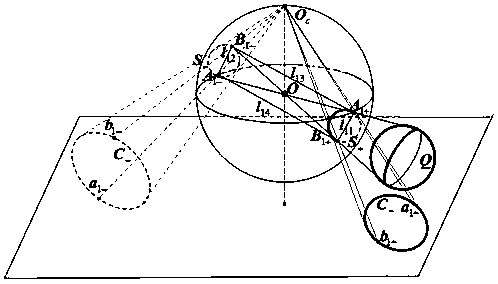
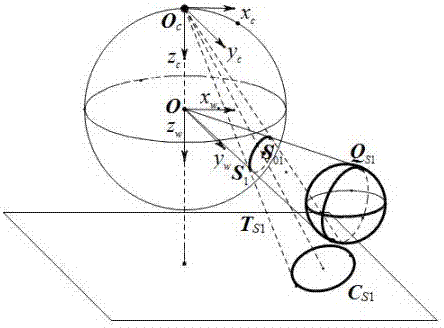
Calibrating a catadioptric camera of a primer by using a single ball and a parallel circular tangent property
InactiveCN109325982AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisComplex mathematical operationsPartition of unityCatadioptric camera
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a catadioptric camera of a primer by using a single ball and a parallel circular tangent property, which is characterized in that only the ball element is used; firstly, the edge points of specular contour projection and target image are extracted from three images respectively, and the specular contour projection and spherical image projection areobtained by least square fitting; secondly, according to the relationship between the image point and its extension point, the extension point is obtained, and then the extension spherical image of the spherical image is fitted; a point on the spherical image is taken and the topological point is found; by defining the topological points and the properties of parallel circles, the above set of topological points provides a vanishing point; in a parabolic catadioptric system, the sphere is projected onto the unit sphere for the first time to form two small parallel circles, two parallel circles on different faces have two pairs of conjugate imaginary intersection points, in which the two conjugate imaginary intersection points which are collinear with the infinity point of the plane in which the circle is located are ring points. Finally, the camera intrinsic parameters are obtained by using the constraint of the image of the torus point to the image of the absolute conic curve.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for calibrating a parabolic camera through a public autopolar triangle and a circular ring point of a single sphere
InactiveCN109523598AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage enhancementImage analysisCatadioptric cameraLeast squares
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a parabolic camera by using a public autopolar triangle and a circular ring point of a single sphere. Firstly, edge points of a target image are extracted from the image, and a spherical image equation is obtained through least square method fitting. According to the fact that any two separated spherical images have a unique public self-polar triangle, a group of corresponding poles and polar lines of the spherical images and the antipodal spherical images can be obtained. Meanwhile, the polar line is an image passing through the sphere centersof the two spheres, and the polar point is a vanishing point. Wherein the sphere image and the antipodal sphere image have four imaginary intersection points, one pair of conjugate complex points isan image of a circular point, and the image of the circular point can be determined according to the collinear property of the image of the circular point and the vanishing point, so that the constraint of the image of the circular point and the image of the absolute quadratic curve is utilized to solve the internal parameters of the parabolic catadioptric camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for calibrating central catadioptric camera through three balls at different spatial positions
InactiveCN107958468AEasy to makeHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisCatadioptric cameraAbsolute conic
The invention discloses a method for calibrating the central catadioptric camera through three balls at different spatial positions, and the method is characterized in that the method just employs theball elements. The method comprises the steps: extracting points on an image from a captured ball image, carrying out the fitting of ball images corresponding to the three balls, and solving the pixels corresponding to the centers of small circles formed by the projection of the three balls on a unit virtual globe; solving a polar line of the circle centers relative to the ball images through therelation between a polar point and the polar line; solving two intersection points of the ball images and the polar line, i.e., the images of circle points; obtaining an absolute conic through the images of the obtained six circle points, finally carrying out the decomposition of the absolute conic, and carrying out the inversion to obtain the internal parameters of the camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
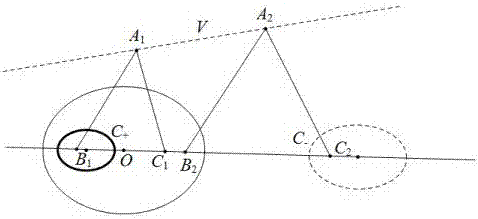
Method for calibrating parabolic catadioptric camera by using separated two-ball image and orthogonal vanishing point
InactiveCN105354840AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisCatadioptric cameraComputer science
The present invention relates to a method for calibrating a parabolic catadioptric camera by using a separated two-ball image and an orthogonal vanishing point. The method comprises: firstly, using the parabolic catadioptric camera to shoot an image of a target, wherein the target is two balls with separated projections on an image plane; obtaining an antipodal image point according to a relationship between an image point and the antipodal image point of the image point, thereby estimating an antipodal ball image of the two-ball image in a catadioptric image, and solving intersection points of the two-ball image and intersection points of the antipodal ball image of the two-ball image; secondly, determining the orthogonal vanishing point according to four groups of virtual antipodal image points correspondingly formed by virtual intersection points of the ball image and the antipodal ball image; and finally, solving an intrinsic parameter of the parabolic catadioptric camera by using constraint of the orthogonal vanishing point on the intrinsic parameter of the camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
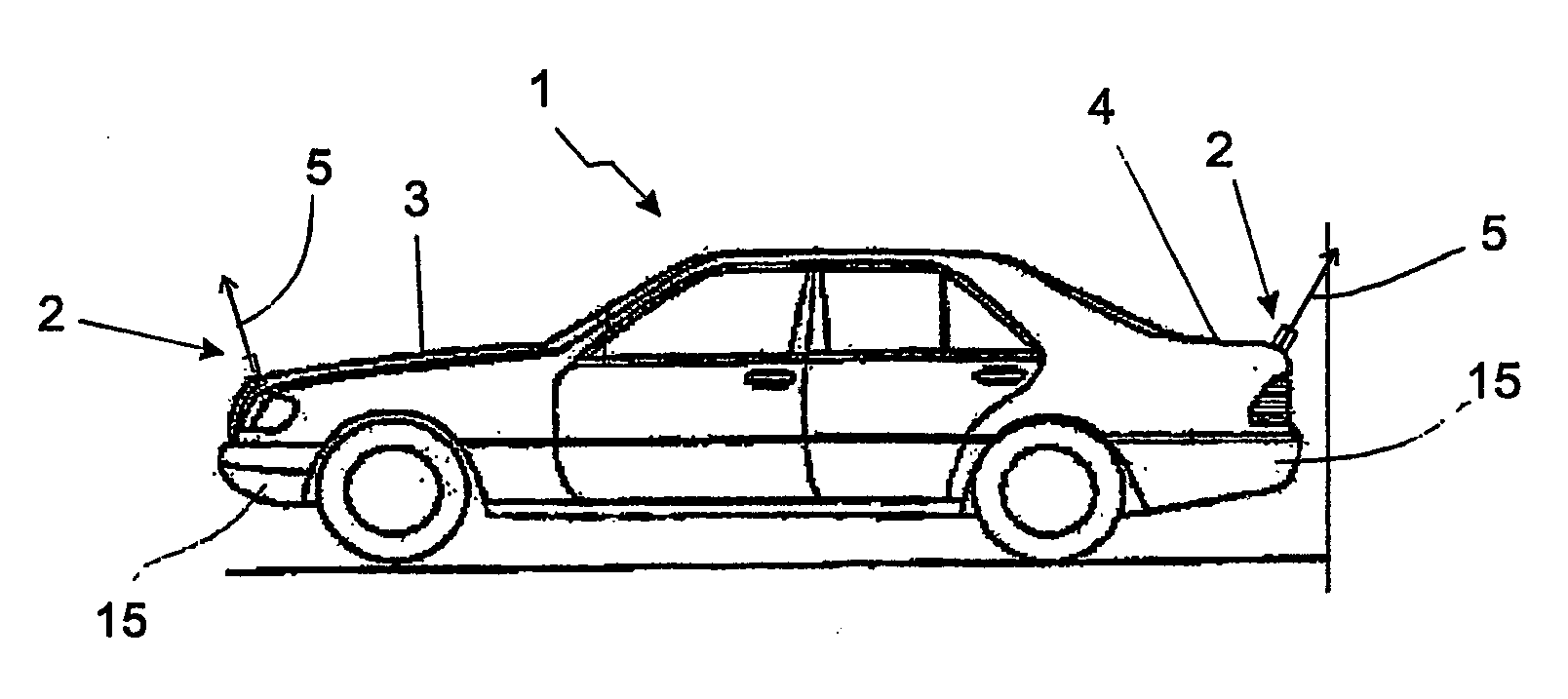
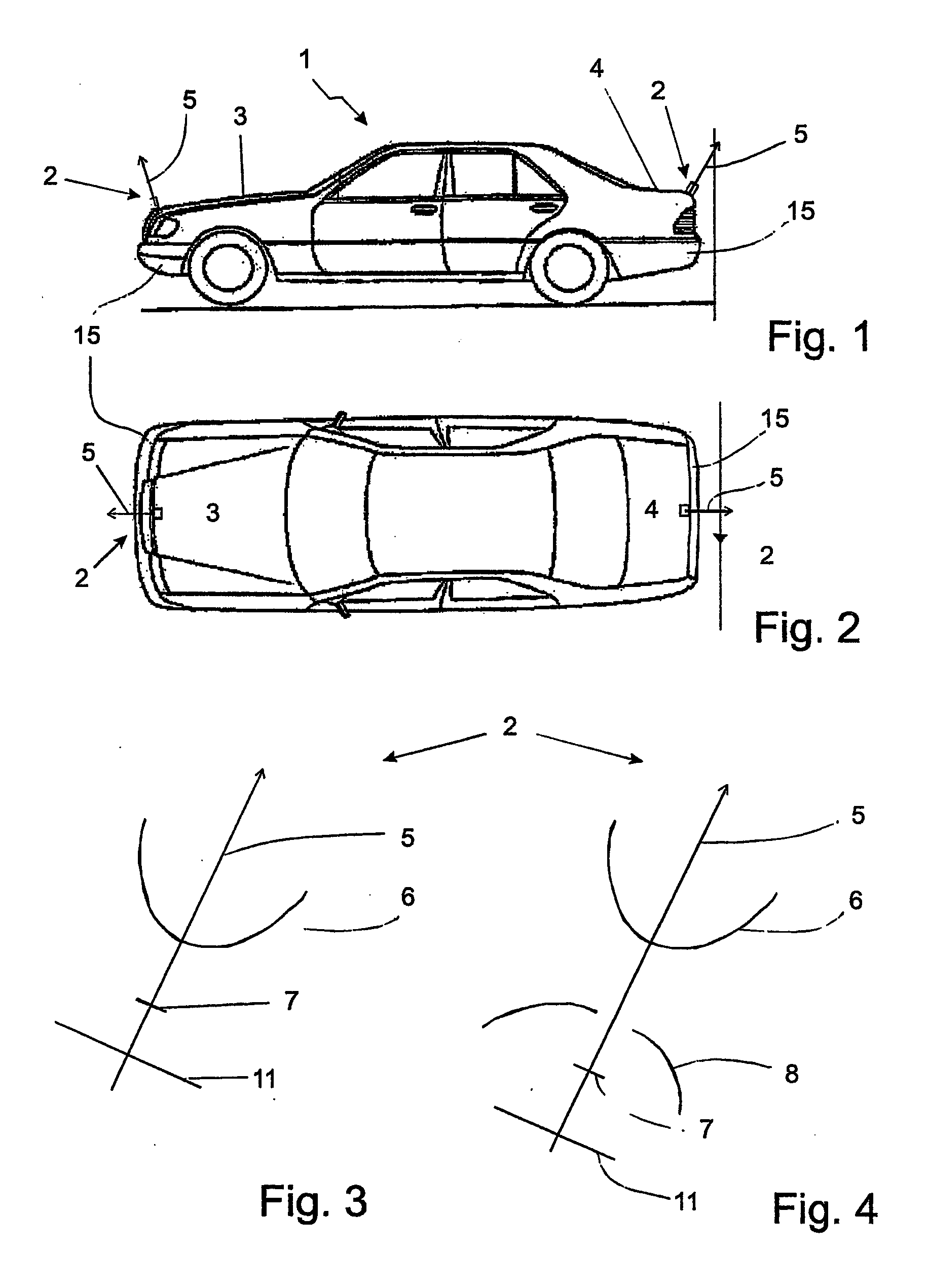
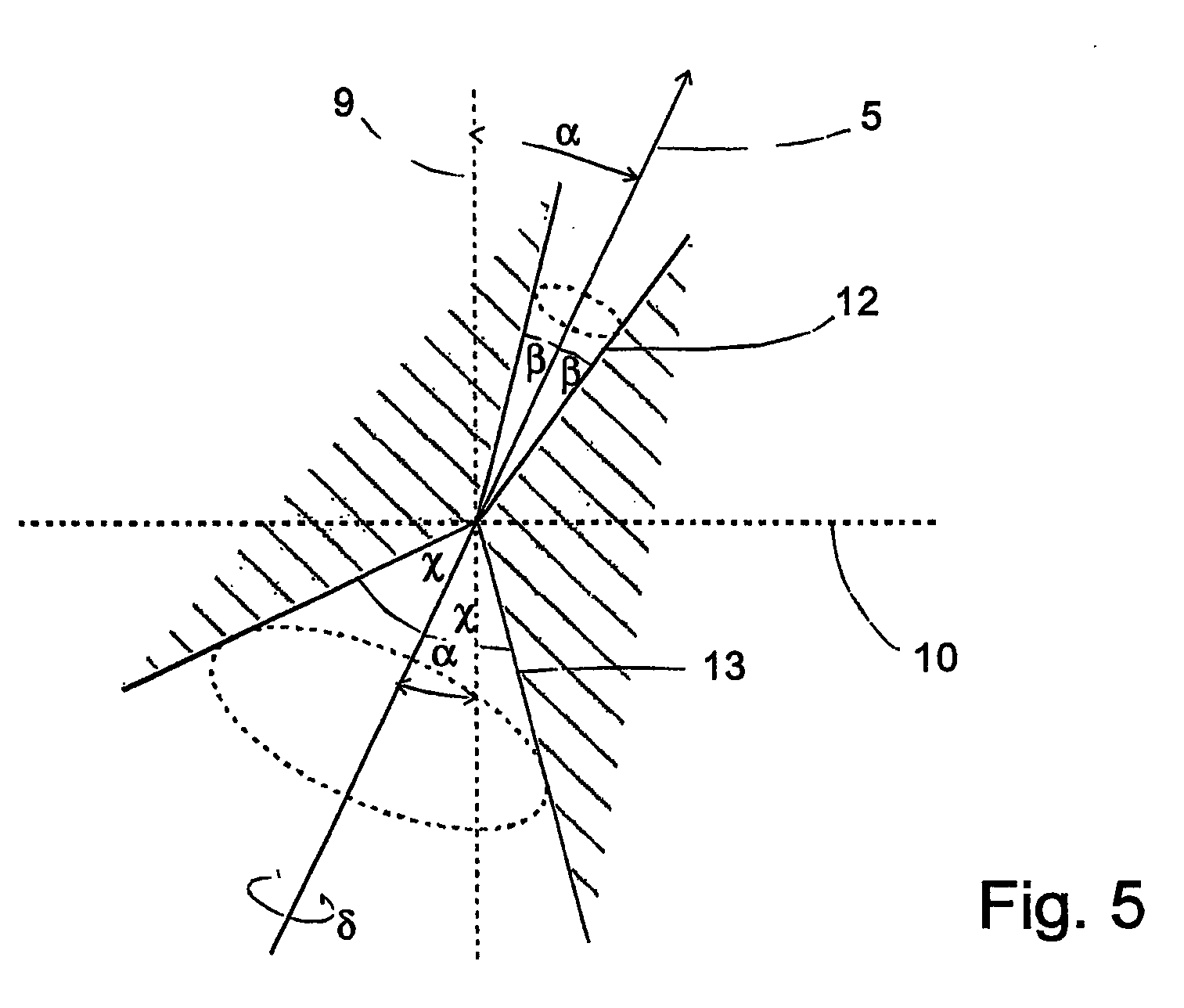
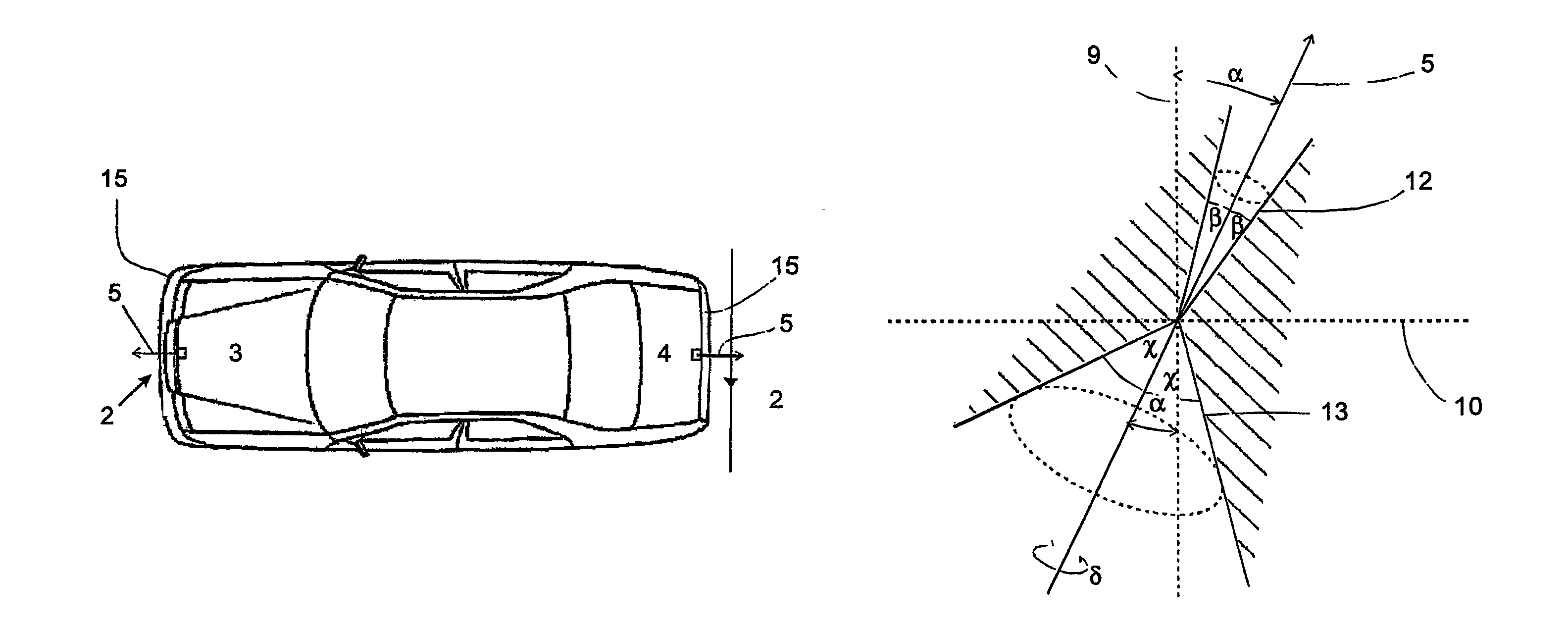
Vehicle comprising a catadioptric camera
InactiveUS20060078328A1Improved spatial monitoringIncrease spacingPrintersIndication of parksing free spacesOptical axisCatadioptric camera
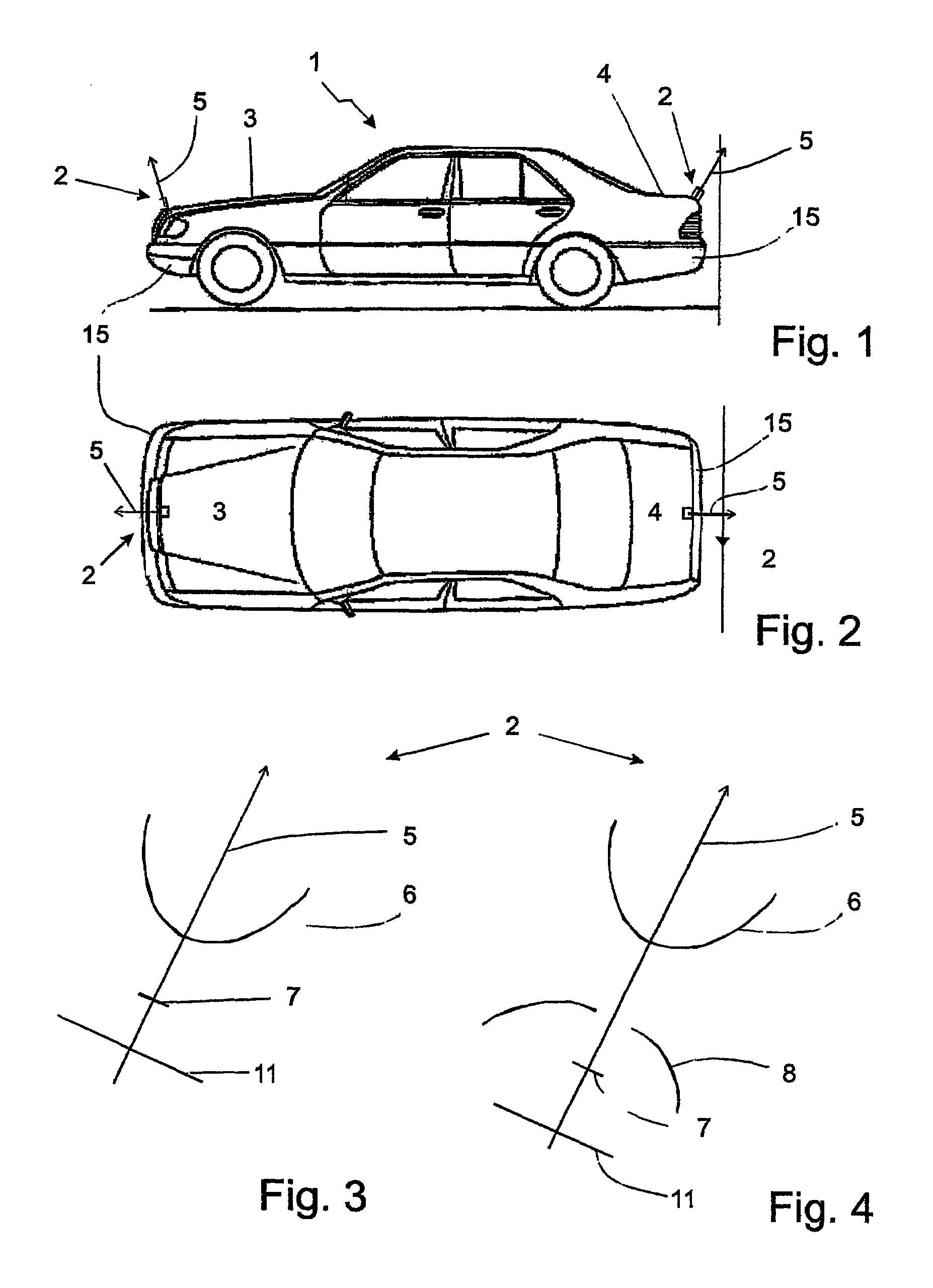
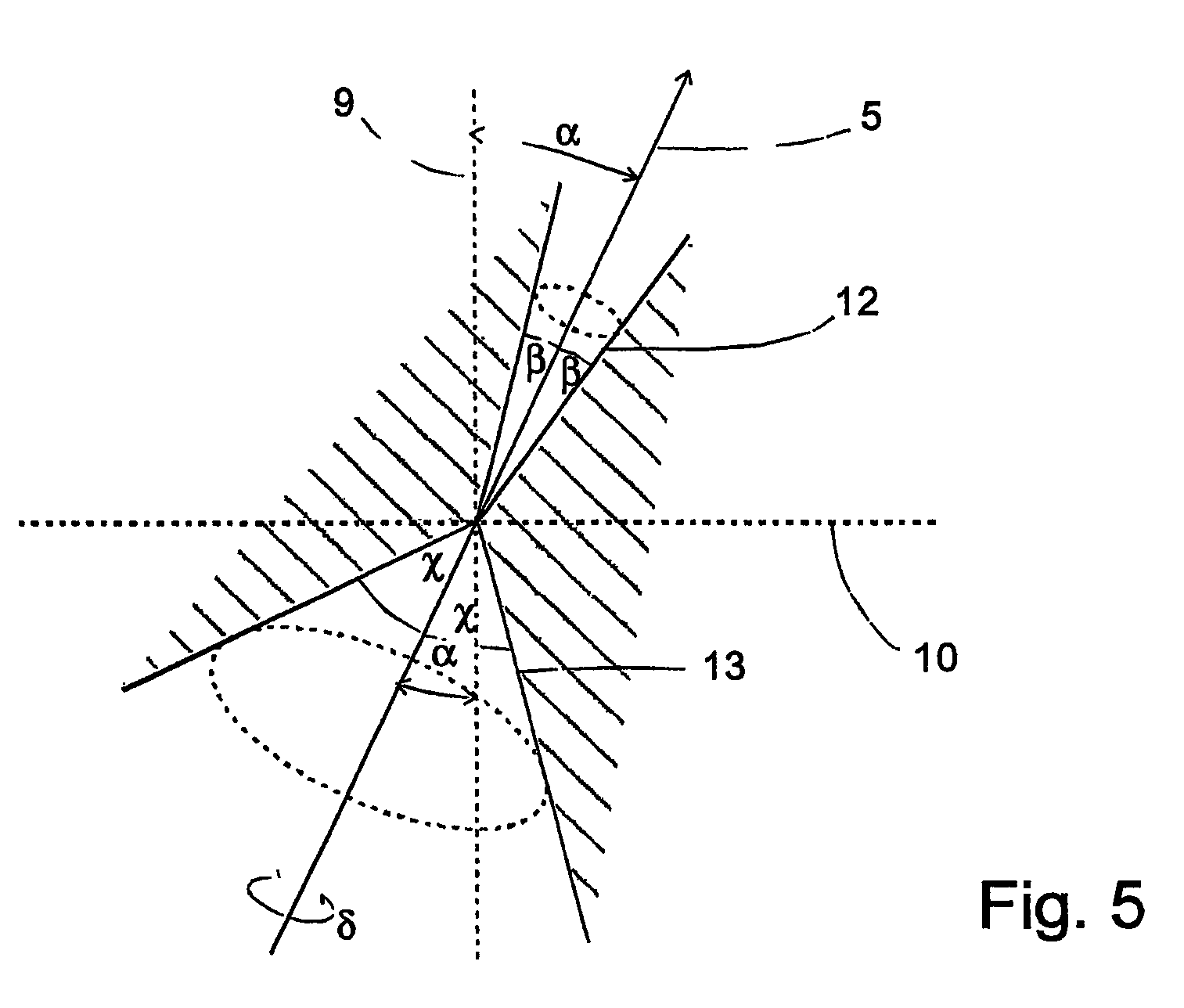
The invention relates to a vehicle (1) comprising at least one catadioptric camera (2), which is mounted on the vehicle and which has an optical axis (5) and at least one first mirror (6) that is arranged on the optical axis. The optical axis (5) of the camera (2) is slanted relative to a vertical (9).
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Method for calibrating parabolic type catadioptric camera by using straight line and circular point image
InactiveCN107610184AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisCatadioptric cameraVanishing line
Provided is a method for calibrating a parabolic type catadioptric camera by using a straight line and a circular point image, and the method is characterized in that a straight line in the space is taken as a target. The method includes firstly shooting three straight-line-containing images from different positions by means of the parabolic type catadioptric camera, extracting the edge point of the mirror surface contour projection and the edge point of the target image, and obtaining a mirror surface contour projection and a straight line image by means of the least square fitting; taking one point on the line image, and obtaining an antipodal image point, wherein the intersection point of the image point and the antipodal image point relative to the tangent line of the line image is a vanishing point; taking two different points from the line image to obtain two vanishing points; determining one vanishing line with the two vanishing points, wherein the intersection point of the vanishing line and the line image is the image of the circular point, and three images provide three groups of images of the circular point; and finally, solving the internal parameters of the camera through the constraint of the images of the circular point on the absolute quadratic curve image.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Vehicle with a catadioptric camera
The invention relates to a vehicle (1) comprising at least one catadioptric camera (2), which is mounted on the vehicle and which has an optical axis (5) and at least one first mirror (6) that is arranged on the optical axis. The optical axis (5) of the camera (2) is slanted relative to a vertical (9).
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com