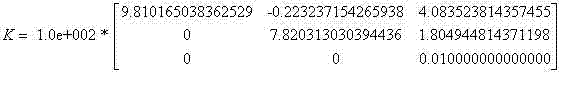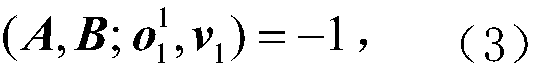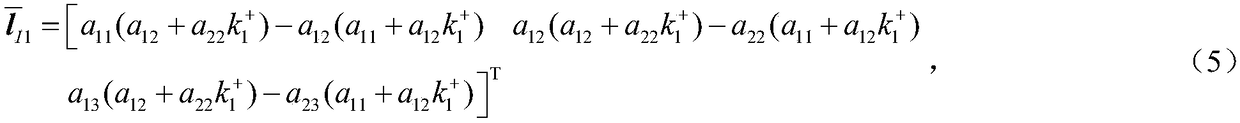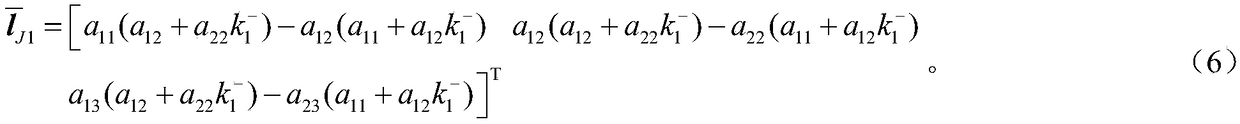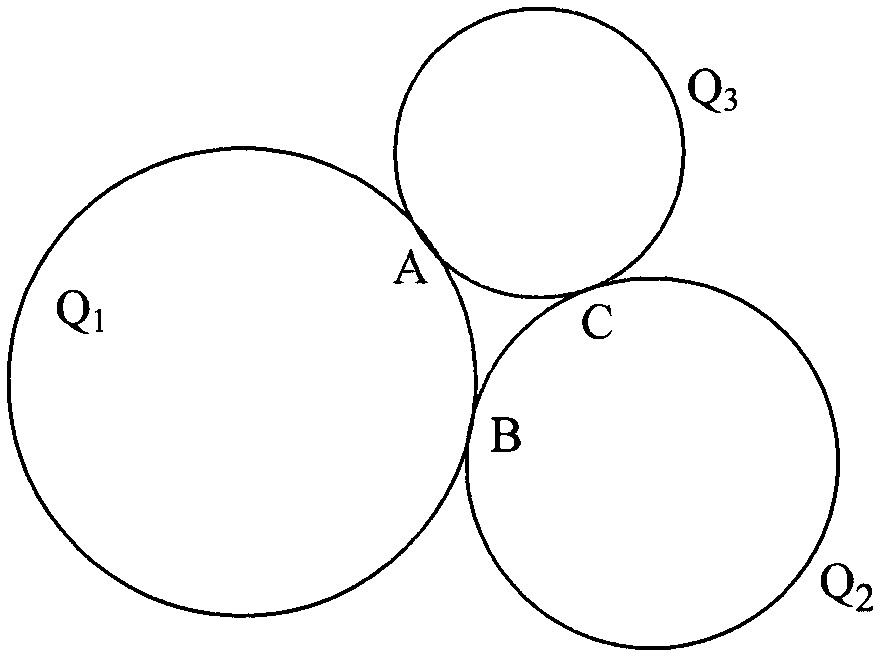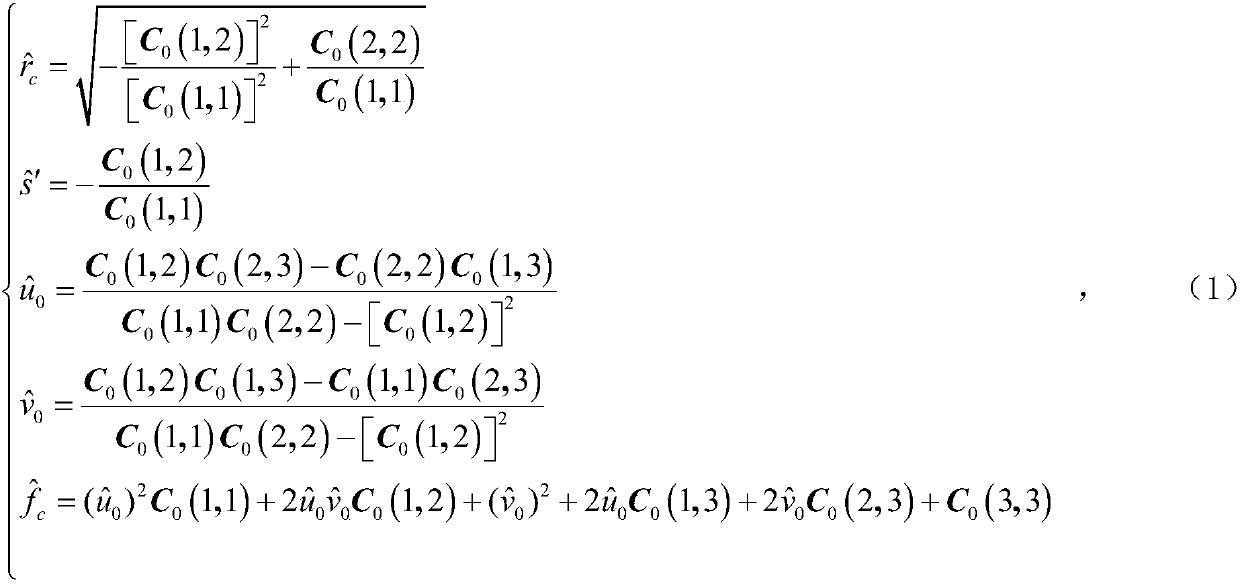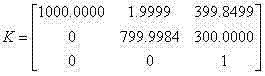Patents
Literature
60results about How to "Physical scale is not required" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
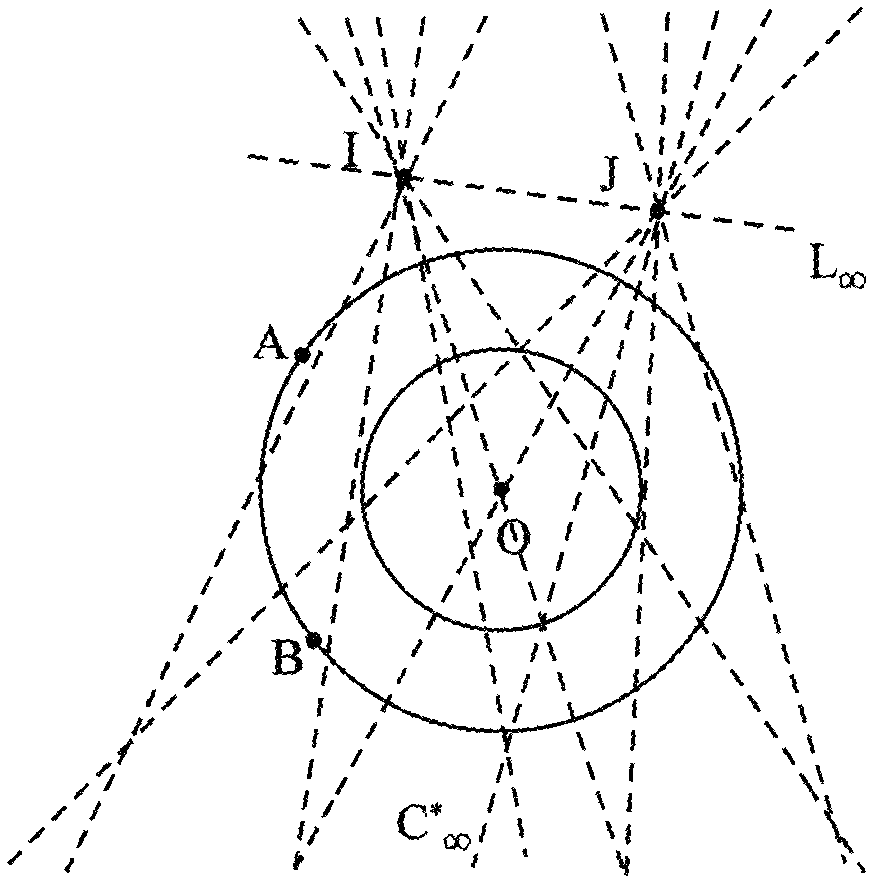
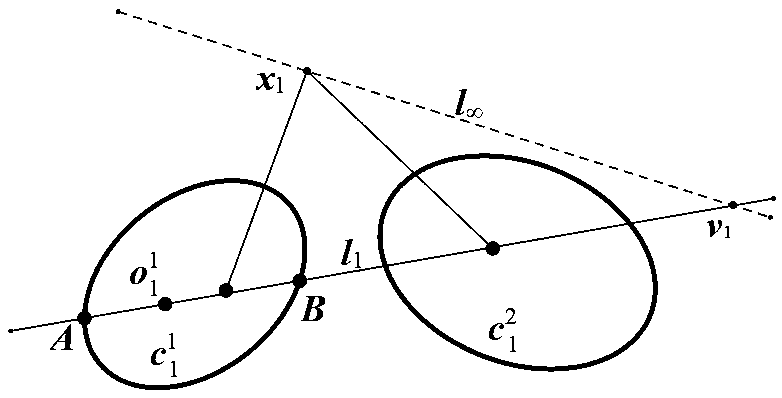
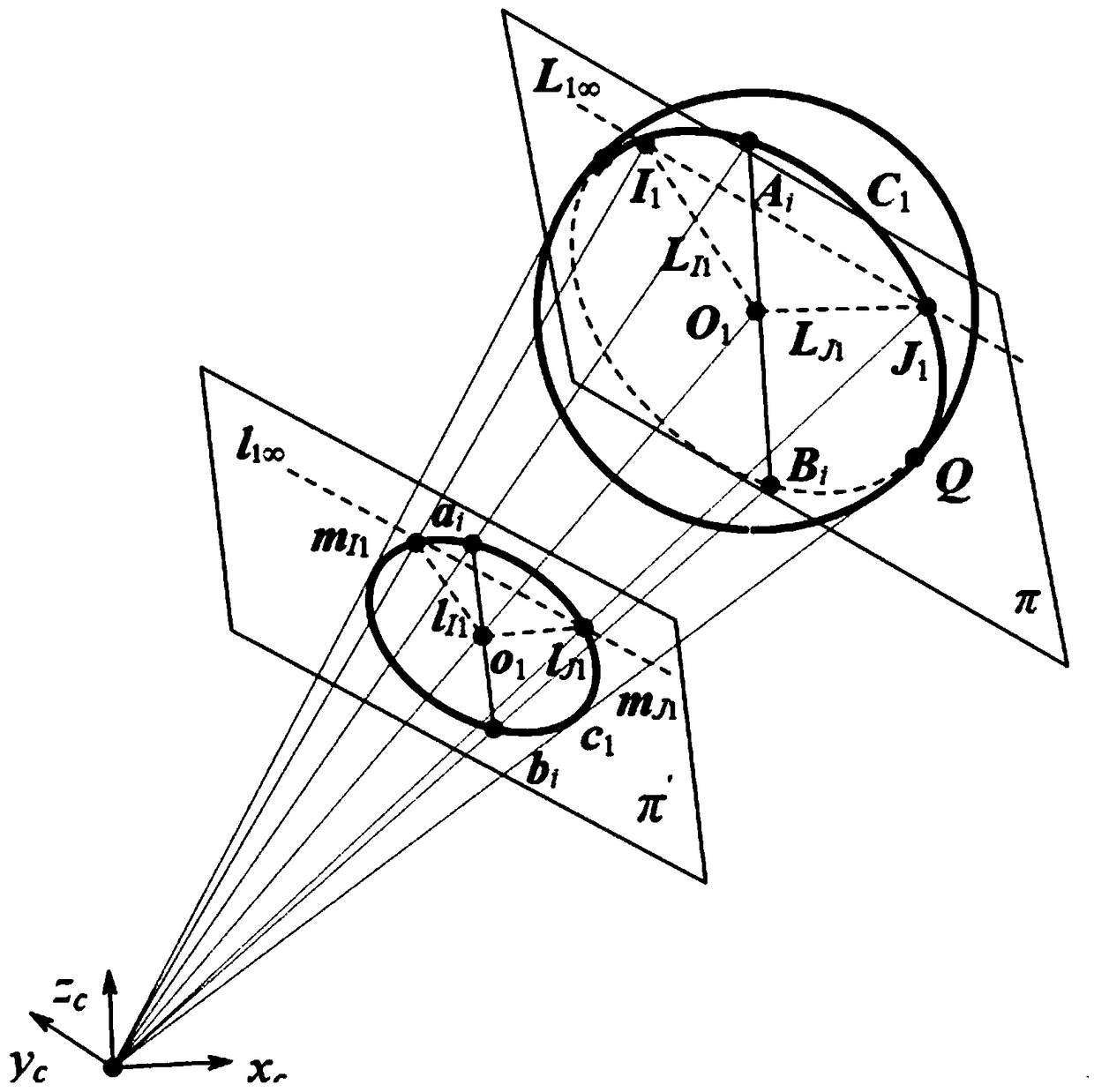
Solving camera intrinsic parameter by using image of center of sphere and orthogonality
InactiveCN104835144AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisIntrinsicsConstraint matrix
The invention relates to a method for solving camera intrinsic parameter by using the image of the center of a sphere and orthogonality. The method comprises: firstly, taking three pictures of a calibrated sphere from different directions and reading the images, extracting coordinates of three quadratic curves from the three images; according to imaging process of the sphere and the center of the sphere under the camera, solving to obtain image coordinates of three centers of spheres, and according to projections of the centers of spheres, calculating end points on orthogonal directions, and finally by using the end points on orthogonal directions, solving images of absolute conics, and according to the images of quadratic curves, and solving a constraint matrix of camera intrinsic parameters, so as to obtain the camera intrinsic parameter. By using the spheres which are targets, full-automatic calibration can be realized, and errors caused by measurement in a calibration process are reduced. Since the quadratic curve is a simpler and more global element, and projection contours of the spheres can be completely extracted from the images, calibration precision is improved in a camera calibration process.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method of calibrating paracatadioptric camera using image of single sphere and circular points
InactiveCN106327504AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisVanishing lineSurface contour
The present invention relates to a method for calibrating a paracatadioptric camera using the images of a single sphere and circular points. According to the method, two different points are selected from the image of the sphere, so that two vanishing points are obtained; a straight line where the two vanishing points are located is a vanishing line, the images of the vanishing line and the image of the sphere intersect with the images of the circular points, and three images can provide the images of three circular points; and the inner parameters of the camera are solved through using the constraint of the images of the circular points for an absolute conic curve image. The method specifically includes the following steps of: fitting a mirror surface contour projection equation and a target projection equation; estimating an antipodal sphere image; determining the images of the circular points; and solving the inner parameters of the paracatadioptric camera. In a process of solving the inner parameters of the paracatadioptric camera, five inner parameters of the paracatadioptric camera are solved by using three images of a target shoot by the paracatadioptric camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Linear solving of video camera internal parameters by utilizing two intersected same circles and common tangent
The invention relates to linear solving of video camera internal parameters by utilizing two intersected same circles and a common tangent, and the method is a drone composed of two intersected same circles and the common tangent and used for calibrating video cameras. The drone is shoot for six images from different directions; elliptic equations and characteristic points are extracted from the images, and intersection point of two ovals are solved; vanishing points on image planes at the orthogonal direction is obtained according to perpendicular bisector of circle center line segment connecting the two circles and the common tangent of the two intersected circles and cross ratio of collinear four points; and the video camera internal parameters are performed with linear solving by utilizing the vanishing points at the orthogonal direction and restraint of images of an absolute conic. By utilizing the drone, full-automatic calibration can be achieved, and error caused by measurement during the calibration process is reduced. Circle is an element which is more concise and global, and accordingly calibration accuracy is improved during the calibration process.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for solving intrinsic parameters of camera by using three non-concentric circles
InactiveCN103106650AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisComputer visionIntrinsic metric
The invention relates to a method for marking intrinsic parameters of a camera by solving an image of a circular point, wherein the image of the circular point is solved by solving a plane vanishing line by using any three non-concentric circles on a plane and by using centers of the three non-concentric circles. According to the method for solving the intrinsic parameters of the camera by using the three non-concentric circles, three images are shot in different directions by a target, image curves of the three circles on each image and coordinates of the images of each three centers are extracted, a homogeneous coordinate of the plane vanishing line is obtained by using relation of a pole and a polarline formed by the centers and the vanishing line according to the theory of the pole and the polarline and through solving three simple linear equations, the image of the circular point is solved by solving an intersection point between the vanishing line and the image of any of the three circles, and then the five intrinsic parameters of the camera is determined by building a constraint equation about the intrinsic parameters of the camera by using the image of the circular point. Due to the fact that a curve of the second degree is a simple and an overall element, solving the vanishing line by fitting the curve of the second degree is higher in stability than solving the vanishing line by fitting a point and a plane. The method for solving the intrinsic parameters of the camera by using the three non-concentric circles is high in application value.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method of calibrating parabolic catadioptric camera by use of single sphere and orthogonal vanishing point
InactiveCN106447731AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisCatadioptric cameraImage edge
The invention relates to a method of calibrating a parabolic catadioptric camera by use of a single sphere and an orthogonal vanishing point. The method is characterized in that only a sphere element is used. Firstly, the edge points of a mirror surface contour projection and the edge points of a target image are extracted from an image, a mirror surface contour projection and a sphere image projection are obtained by fitting based on a least square method. Secondly, antipodal image points are obtained according to the relationship between image points and antipodal image points thereof, and an antipodal sphere image of a sphere image is fitted out; two different points are taken from the sphere image, and the antipodal image points of the two points are calculated out; the two groups of antipodal image points provide a group of orthogonal vanishing points; and six groups of points (there are two different points in each group) are taken from the sphere image to obtain six group of orthogonal vanishing points. Finally, the intrinsic parameters of the camera are calculated based on the constraint of the orthogonal vanishing points on the intrinsic parameters of the camera; and in the process of calculation, five intrinsic parameters of the parabolic catadioptric camera are calculated using one image of a shooting target of the parabolic catadioptric camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for linearly solving camera inner parameter by using two identical intersected ellipses
The invention relates to a method for linearly solving camera inner parameters by using two identical intersected ellipses. According to the method, a target drone which is formed by two identical intersected ellipses sharing the same main axis and which is calibrated by a camera is adopted; five images of the target drone are shot in different directions; an ellipse equation is extracted from the images and the intersection points of the two ellipse are solved; end points in the planes of the images in the orthogonal directions are obtained according to the polarity principle and the property of the cross ration of four straight lines; and camera inner parameters are linearly solved by using the end points in the orthogonal directions and the constraint of the images of absolute conics. With the adoption of the target drone in the method, the full-automatic calibration can be implemented, the error caused by the measurement in the calibration process is reduced, and the calibration precision in the calibration process of the camera is improved as the conic is a simpler and more global-oriented element.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for solving intrinsic parameters of parabolic catadioptric camera linearly by utilizing three unparallel straight lines in space
InactiveCN102982551AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisIntersection of a polyhedron with a lineCatadioptric camera
The invention relates to a method for solving intrinsic parameters of a parabolic catadioptric camera linearly by utilizing three unparallel straight lines in a space. The method comprises the steps that a target consisting of the three unparallel straight lines in the space and used for automatic calibration of the parabolic catadioptric camera is utilized; the parabolic catadioptric camera is used to shoot an image of the target; the linear parabolic catadioptric image is a quadratic curve; target image points are extracted from the image; curvilinear equations are fitted; an intersection point of every two curves is solved; images of three pairs of circular ring points on a plane of the image are obtained according to a polar principle and a diameter concyclic center attribute; and the parameters in the camera are solved by utilizing linear restriction of the images of the circular ring points on an absolute conic. With the adoption of the target in the method, full automatic calibration can be realized, and errors due to measurement in a calibration process are reduced. As the straight lines are elements which are more concise and global, the calibration accuracy is improved in the calibration process of the camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for calibrating parabolic refraction and reflection camera via single ball and parallel circle properties
InactiveCN106651956AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisIntersection of a polyhedron with a lineImage plane
A method for calibrating a parabolic refraction and reflection camera via single ball and parallel circle properties is disclosed. In a parabolic refraction and reflection system, two small parallel circles are formed when a ball is projected onto a unit visual ball for a first time. The two parallel circles in a space have two pairs of conjugated virtual intersection points, and two conjugated virtual intersection points that are collinear with a point at infinity on a plane where space circles are positioned are circular ring points. An image of the circular ring points is obtained on an image plane according to colinearity of the image of the circular ring points and a vanishing point; three images provide images of three groups of circular ring points. Intrinsic parameters of the camera are solved via constraints posed on an absolute conic image by the images of the circular ring points. The method specifically comprises the following steps: a mirror surface contour projection equation and a target projection equation are fitted, an antipodal sphere image of a sphere image is estimated, the images of the circular ring points are determined, and the intrinsic parameters of the parabolic refraction and reflection camera are solved.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Calibration of parabolic refraction and reflection camera through Veronese mapping and checkerboard
InactiveCN105513063APhysical scale is not requiredNo need to know locationImage enhancementImage analysisCholesky decompositionVanishing line
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a parabolic refraction and reflection camera through the Veronese mapping and a checkerboard. The method is characterized in that the target of the method is formed by a known checkerboard in the space. The method comprises the specific steps of during the solving process of the internal parameters of a parabolic refraction and reflection camera, shooting 3 images by the parabolic refraction and reflection camera; obtaining three homography matrixes through the Veronese mapping so as to solve a vanishing point for any straight line; solving another vanishing point based on the relationship between antipodal points and harmonic conjugates, wherein the connecting line of the two vanishing points is a vanishing line; according to the intersection points of the vanishing line with the image of the straight line namely a quadratic curve, solving the image of three sets of circular points; based on the constraint of the image of circular points on the image of the absolute quadratic curve, solving the internal parameters of the parabolic refraction and reflection camera through the Cholesky decomposition.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for solving parameters in parabolic catadioptric camera through three unparallel straight lines in checkerboard
InactiveCN103942784AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisGeometric propertyCross-ratio
The invention relates to a method for linearly solving parameters in a parabolic catadioptric camera through three unparallel straight lines in a checkerboard. The method is characterized in that only linear elements are utilized, and a template is composed of the three unparallel straight lines on the checkerboard; parabolic catadioptric images of the straight lines are quadratic curves, the parabolic catadioptric camera is used for taking an image of a target, image points of the target are extracted from the image first, fitting is conducted to obtain the curve equation, and the intersection points of every two curves are solved, six sets of orthogonal fading points on the image plane are then obtained according to the geometric properties of a circle and the cross ratio invariance property, and the parameters in the parabolic catadioptric camera are linearly solved for constraints on images of the absolute quadratic curves through the orthogonal fading points. According to the method, the target can be calibrated in a full-automatic mode, and errors caused by measurement in the calibration process are reduced. Due to the fact that the straight lines are the simpler and more comprehensive elements, calibration accuracy is improved in the calibration process of the camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for calibrating parabolic catadioptric camera by using properties of single sphere and circle tangent line
InactiveCN107644445AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisCatadioptric cameraVanishing line
The invention discloses a method for calibrating a parabolic catadioptric camera by using properties of a single sphere and a circle tangent line. The method is characterized by taking a sphere in a space as a target. The method comprises the specific steps of: firstly, shooting three pictures containing the sphere from different positions by means of the parabolic catadioptric camera; secondly, acquiring antipodal image points according to relationship between image points and antipodal image points thereof in a parabolic catadioptric unit visual sphere model, so as to estimate an antipodal sphere image of a sphere image; thirdly, selecting a point from the sphere images, wherein a tangent line of each image point about the corresponding sphere image and a tangent line of the corresponding antipodal image point about the corresponding antipodal sphere image intersect at an image vanishing point through definition of the antipodal image points, an intersection point of the image vanishing point about polar lines of the sphere image and the antipodal sphere image is an image vanishing point, a straight line where the two image vanishing points are located is an image vanishing line,an intersection point of the image vanishing line and the sphere image is an image of circular points, and the three pictures provide the images of three groups of circular points; and finally, solving inner parameters of the camera by utilizing the constraint of the images of the circular points for an absolute conic curve image.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for linearly solving intrinsic parameters of camera by aid of two concentric circles
InactiveCN102999895AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisIntrinsic metricVideo camera
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a camera by means of solving images of two vanishing points in orthogonal directions or images of circular points by the aid of two concentric circles on a plane and two points which are positioned on one of the circles but are not positioned on the same diameter. The method includes that three images for a target are taken from different directions, and coordinates of a curve and coordinates of two points on each image are extracted; points, which correspond to an image of a circle center and images of two points relative to the circle center, on each curve are computed, and the two vanishing points in the orthogonal directions are acquired from intersection points of straight lines; and a vanishing line on each image can be acquired by implementing a theory of dual quadratic curves of the circular points, the images of the circular points are intersection points of images of the vanishing lines and the circles, constraint equations of the images of the vanishing points in the orthogonal directions or the images of the circular points relative to intrinsic parameters of the camera are established, and the five intrinsic parameters of the camera can be linearly solved. The method has the advantages that full-automatic calibration can be realized owing to the target, errors caused by measurement in a calibration procedure are reduced; and the quadratic curves are concise and comprehensive elements, and accordingly the precision is improved in the calibration procedure.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Camera intrinsic parameters determined by utilizing projected coordinate and epipolar line of centres of circles
InactiveCN102930551AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisLinear methodsImage plane
The invention relates to a target for determining camera intrinsic parameters. The target is characterized in that the target is composed of at least three centers of any non-concentric circles in a plane, and the specific steps comprises estimating coordinates of images of the centers of the circles, and estimating vanishing line of the images in the plane by utilizing polarity principle to realize a linear method for camera intrinsic parameters. According to the target for determining the camera intrinsic parameters, three images are taken for the target from different directions, curvilinear equation for each image is extracted, the images of the centers of the circles and equations of the vanishing line on the images are figured out, intersections between the vanishing line and the images of the circles are images of ring points, constraint equations for the images of the ring points, which is related to the camera intrinsic parameters, are established, and matrix for the camera intrinsic parameters of is linearly solved. The target disclosed in the invention can be utilized to realize full-automatic calibration, so that errors caused by measurement in the calibration process are reduced. A quadratic curve is a more simple and globalized element, thereby improving the precision in the calibration process.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Image calibration parabolic refraction and reflection camera using double-ball tangent image and annular points
InactiveCN105279758AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisImage calibrationFully automatic
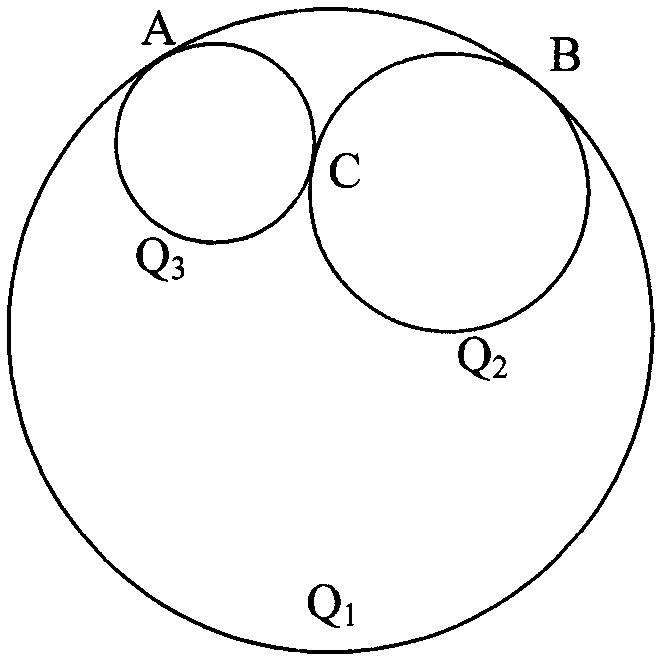
The invention relates to an image calibration parabolic refraction and reflection camera using a double-ball tangent image and annular points. The parabolic refraction and reflection camera is used for shooting an image using double balls as a target, and in addition, the target images are tangent. A main point is determined through three groups of antipodal image points correspondingly formed by solid and virtual intersecting points in the ball image of the refraction and reflection image and the solid and virtual intersecting points of an antipodal ball image; on the basis of obtaining the main point, the disappearance line of the double balls on a located plane of two groups of parallel projection small circles on a unit visual ball is solved, so that the images of the annular points on the plane are determined; and finally, the restriction of the images of the annular points on parameters in the camera are used for solving the rest parameters in the camera. The method provided by the invention can be used for realizing the fully-automatic calibration; and the errors due to measurement in the calibration process are reduced. The projection contour line of the ball can be completely extracted in the image, so that the calibration precision of the camera is improved.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for calibrating parabolic reflex camera by using properties of conjugate diameters of straight line and circle
InactiveCN107657645AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisReflexConjugate diameters
The present invention discloses a method for calibrating a parabolic reflex camera by using the properties of conjugate diameters of a straight line and a circle. Firstly, an edge point of a target image and an edge point of a mirror contour projection of one image are extracted from three images, and the mirror contour projection is obtained by least square fitting. A point is taken on a line image, and an antipodal image point is obtained. An intersection of a tangent of the image point to a line image and a tangent of the antipodal image point to the line image is a vanishing point. Two heterogeneous points are taken on the line image, two vanishing points are obtained, and a vanishing line is determined by the two vanishing points. An intersection of a polar of the vanishing points tothe line image and the vanishing line and the vanishing points form a group of orthogonal vanishing points, and six groups of orthogonal vanishing points are provided by the three images. Finally, theconstraint of an absolute quadratic curve image with the orthogonal vanishing points is used to solve camera internal parameters.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Calibrating a catadioptric camera by using the property of an infinitely distant point with respect to a circular pole line
InactiveCN109325983AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisAbsolute conicSpherical image
A method for calibrating a catadioptric camera by using the property of an infinitely distant point with respect to a circular pole line is characterized in that a ball in space is used as a target. The method comprises the following steps of firstly extracting edge points of a target image and edge points of a mirror contour projection of one image from three images respectively; secondly, according to the relation between the image point and its extension point, obtaining the extension point, and then fitting the extension spherical image of the spherical image; taking two different points on the spherical image and obtaining the opposite extension points of the two points; according to the definition of topological points and the properties of circles, using the two sets of topologicalpoints to provide a vanishing point; taking two dissimilar points from the spherical image, and obtaining two vanishing points. Wherein the straight line of the two vanishing points is the vanishing line; finally, obtaining the camera intrinsic parameters by using the constraint of the orthogonal vanishing point to the absolute conic image.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
A method for calibrating a catadioptric camera using properties of a single sphere and a conjugate diameter
InactiveCN109360248AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisCatadioptric cameraConjugate diameters
A method for calibrating a catadioptric camera using properties of a single sphere and a conjugate diameter is characterized in that only spherical elements are used. Firstly, the edge points of the target image and the edge points of the specular contour projection of one image are extracted from three images respectively, and the specular contour projection and the spherical image projection areobtained by least square fitting. Secondly, according to the relation between the image point and its extension point, the extension point is obtained, and then the extension spherical image of the spherical image is fitted. According to the property of the conjugate diameter of a circle, the intersection point of the polar line of the vanishing point with respect to the spherical image and the contrastive spherical image is a set of orthogonal vanishing points. Two sets of orthogonal vanishing points can be obtained by choosing two sets of different points on the spherical image. All the orthogonal vanishing points corresponding to a plane only provide two constraints for the image of absolute conic and six constraints for three images. Finally, the camera intrinsic parameters are obtained by using the constraint of the orthogonal vanishing point to the absolute conic image.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for calibrating parabolic refraction-reflection camera via intersection image of two spheres and images of circular ring points
InactiveCN105303570AEasy to makeWith occlusion effectImage analysisPartition of unityIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a parabolic refraction-reflection camera via an intersection image of two spheres and images of circular ring points. The parabolic refraction-reflection camera shoots a target to obtain one image, a main point is determined via four groups of antipodal image points corresponding to solid and virtual intersection points in a spherical image in the refraction-reflection image and solid and virtual intersection points of an antipodal spherical image, a disappearance line of a plane, where two small parallel projection circles are placed in a unit visual sphere, of the two spheres is solved, images of the circular ring points in the plane are determined, and finally, the circular ring points are used to solve other inner parameters of the camera according to limitations of the inner parameters. The method of the invention can be used to realize full-automatic calibration, and reduce errors caused by measurement in the calibration process. Due to the fact that the projection contours of the spheres can be completely extracted from the images, the calibration precision of the camera is improved.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for calibrating a pinhole camera by using a public autopolar triangle and an orthogonal vanishing point of a separation circle
InactiveCN109559351AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisPinhole cameraIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a pinhole camera by using a public autopolar triangle and an orthogonal vanishing point of a separation circle. Firstly, edge points of a target imageare extracted from the image, and a circular image equation is obtained through least square method fitting. According to the fact that any two separated circular images have a unique public self-polar triangle, a group of corresponding poles and polar lines of the pair of separated circular images can be obtained. Meanwhile, the polar line is an image passing through the circle centers of the two circles, and the polar point is a vanishing point. Wherein the vanishing point has a polar line relative to the separated circle image, the polar line passes through the image of the circle center and the circle image and is intersected with the two points, the image of the circle center and the vanishing point in the polar line direction can be obtained by utilizing the property of harmonizingand conjugating the two intersected points and the image of the circle center, and the obtained two vanishing points are a group of orthogonal vanishing points. Therefore, six groups of orthogonal vanishing points can be obtained from the six images, and the internal parameters of the pinhole camera are solved by using the constraint of the orthogonal vanishing points and the image of the absolutequadratic curve.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method of utilizing projection matrix of Veronese mapping checkerboard to calibrate central catadioptric camera
InactiveCN106558082AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage enhancementImage analysisHat matrixAngular point
The present invention relates to a method of utilizing a projection matrix of a Veronese mapping checkerboard to calibrate a central catadioptric camera. The method comprises the steps of using the central catadioptric camera to shoot a target image, and extracting the image points corresponding to the checkerboard in the space; utilizing the Veronese mapping to expand the coordinates, and using a DLT-similarity method to estimate the projection matrix linearly; utilizing the projection matrix to solve the parameters in the camera. By utilizing the method of the present invention, no physical scale requirement is required, the points are easy to select, the point sources are abundant, the calibration errors caused by the data errors during a calibration process are reduced, and the one-to-one correspondence of the image points and the angular points of the space checkerboard can be controlled, thereby improving the calibration precision of the camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
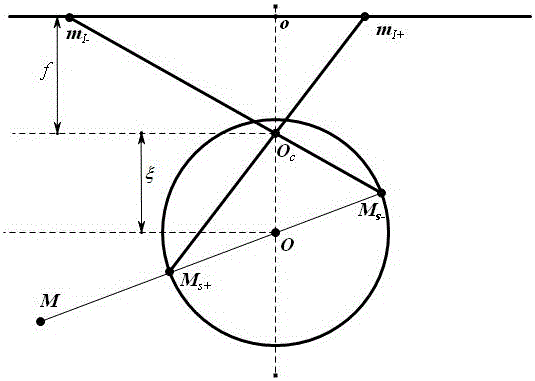
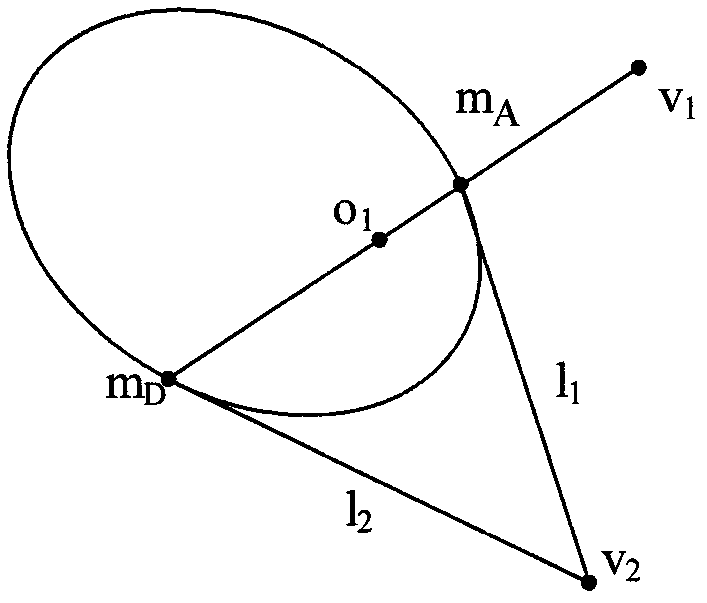
Method for qualitatively calibrating pinhole camera by utilizing single ball and asymptotic line
ActiveCN108921904AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisPinhole cameraPinhole camera model
The invention relates to a method for qualitatively calibrating a pinhole camera by utilizing a single ball and an asymptotic line, characterized in that a ball element is utilized only. Firstly, pixel coordinates of target image edge points are extracted from three images and a ball image equation is obtained by adopting least square fitting. On the basis of the obtained ball image equation, an asymptotic line of a ball image is solved. The asymptotic line of the ball image is namely a polar line of an image of a circular point about the ball image, thus an image of a circle center is determined according to a polarity principle, orthogonal end points can be obtained by virtue of the image of the circle center, and the three images provide six groups of orthogonal end points. Finally, intrinsic parameters of the camera are solved by utilizing constraints of the orthogonal end points on an absolute conic image. The method comprises the following specific steps: fitting a target projection equation, estimating the asymptotic line of the ball image, determining the orthogonal end points, and solving the intrinsic parameters of the pinhole camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for linearly solving intrinsic parameters of camera by aid of three tangent circles
InactiveCN102999896AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisCross-ratioIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for calibrating a parabolic camera through a public autopolar triangle and a circular ring point of a single sphere
InactiveCN109523598AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage enhancementImage analysisCatadioptric cameraLeast squares
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a parabolic camera by using a public autopolar triangle and a circular ring point of a single sphere. Firstly, edge points of a target image are extracted from the image, and a spherical image equation is obtained through least square method fitting. According to the fact that any two separated spherical images have a unique public self-polar triangle, a group of corresponding poles and polar lines of the spherical images and the antipodal spherical images can be obtained. Meanwhile, the polar line is an image passing through the sphere centersof the two spheres, and the polar point is a vanishing point. Wherein the sphere image and the antipodal sphere image have four imaginary intersection points, one pair of conjugate complex points isan image of a circular point, and the image of the circular point can be determined according to the collinear property of the image of the circular point and the vanishing point, so that the constraint of the image of the circular point and the image of the absolute quadratic curve is utilized to solve the internal parameters of the parabolic catadioptric camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for calibrating parabolic catadioptric camera by using separated two-ball image and orthogonal vanishing point
InactiveCN105354840AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisCatadioptric cameraComputer science
The present invention relates to a method for calibrating a parabolic catadioptric camera by using a separated two-ball image and an orthogonal vanishing point. The method comprises: firstly, using the parabolic catadioptric camera to shoot an image of a target, wherein the target is two balls with separated projections on an image plane; obtaining an antipodal image point according to a relationship between an image point and the antipodal image point of the image point, thereby estimating an antipodal ball image of the two-ball image in a catadioptric image, and solving intersection points of the two-ball image and intersection points of the antipodal ball image of the two-ball image; secondly, determining the orthogonal vanishing point according to four groups of virtual antipodal image points correspondingly formed by virtual intersection points of the ball image and the antipodal ball image; and finally, solving an intrinsic parameter of the parabolic catadioptric camera by using constraint of the orthogonal vanishing point on the intrinsic parameter of the camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for calibrating parabolic type catadioptric camera by using straight line and circular point image
InactiveCN107610184AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisCatadioptric cameraVanishing line
Provided is a method for calibrating a parabolic type catadioptric camera by using a straight line and a circular point image, and the method is characterized in that a straight line in the space is taken as a target. The method includes firstly shooting three straight-line-containing images from different positions by means of the parabolic type catadioptric camera, extracting the edge point of the mirror surface contour projection and the edge point of the target image, and obtaining a mirror surface contour projection and a straight line image by means of the least square fitting; taking one point on the line image, and obtaining an antipodal image point, wherein the intersection point of the image point and the antipodal image point relative to the tangent line of the line image is a vanishing point; taking two different points from the line image to obtain two vanishing points; determining one vanishing line with the two vanishing points, wherein the intersection point of the vanishing line and the line image is the image of the circular point, and three images provide three groups of images of the circular point; and finally, solving the internal parameters of the camera through the constraint of the images of the circular point on the absolute quadratic curve image.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for solving camera inner parameters by using dot matrix template and orthogonality
The invention relates to a method for solving camera inner parameters by using a dot matrix template and orthogonality. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, taking out a physical coordinate of a dot matrix in a template; extracting a matching point in an image; estimating a homography matrix between the image and the template; supposing the slopes of two non-parallel and non-orthogonal straight lines in a template plane; calculating to obtain the slope of a straight slope orthogonal with the straight lines in the template plane; further calculating a coordinate of an in infinite point of the two groups of orthogonal straight lines; obtaining orthogonal end points through perspective projection transformation; shooting at least three images according to the relationship of the orthogonal end points and an absolute conic image so as to linearly solve the camera inner parameters. With the adoption of the template in the method, the full-automatic calibration can be implemented, and the measurement error in the calibration process is reduced.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for calibrating parabolic catadioptric camera by using tangential two-ball image and orthogonal vanishing points
InactiveCN105354839AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage enhancementImage analysisTangential projectionCatadioptric camera
The present invention relates to a method for calibrating a parabolic catadioptric camera by using a tangential two-ball image and orthogonal vanishing points. The method comprises: firstly using a parabolic catadioptric camera to shoot two images of a target, wherein the target is two balls with tangential projections on an image plane; in each image, obtaining an antipodal image point according to a relationship between an image point and the antipodal image point of the image point, thereby estimating an antipodal ball image of the two-ball image in a catadioptric image, and solving real and virtual intersection points of the two-ball image and real and real and virtual intersection points of the antipodal ball image; secondly, determining three groups of orthogonal vanishing points according to three groups of antipodal image points correspondingly formed by the intersection points of the ball image and the intersection points of the antipodal ball image, wherein six groups of orthogonal vanishing points can be determined from the two images; and finally, solving an intrinsic parameter of the camera by using constraint of the orthogonal vanishing points on the intrinsic parameter of the camera. By using the method provided by the present invention, full-automatic calibration can be realized, so that errors caused by measurement in a calibration process are reduced. Because projection contour lines of the balls in the image can be completely extracted, so that calibration precision of the camera is improved.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
A method for calibrating the reflex camera by using the properties of a single sphere and the midpoint of the chord
InactiveCN109215089AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisReflexIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a catadioptric camera of a primer by using properties of a single ball and a midpoint of a chord. Firstly, the edge points of the specular contour projection and the target image are extracted from the image, and the specular contour projection and the spherical image projection are obtained by least square fitting. Secondly, according to the relationship between the image point and its extension point, the extension point is obtained, and then the extension spherical image of the spherical image is fitted. Two different points are taken from the spherical image, and the two points' topological points are obtained. From the definition of topological points and the properties of circles, the two sets of pairs of topological points can determine the midpoint of the upper chord of the sphere image. The image of the center of a circle is determined according to the properties of the two points on the spherical image with respect to the polar line of the spherical image and the midpoint of the chord. The polar line of the center of a circle with respect to the spherical image is the shadow cancellation line, and the intersection point ofthe shadow cancellation line and the spherical image is the image of a circular ring point. Three images provide three sets of images of circular ring points. Finally, the camera intrinsic parametersare obtained by using the constraint of the image of the torus point to the image of the absolute conic curve.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method of solving intrinsic parameters of camera with two center-sharing and principal axis orthonormal intersected identical ellipses
The invention discloses a target used for self-calibrating of a camera and consisting of two center-sharing and principal axis orthonormal intersected identical ellipses. A method comprises the particular steps that peripheral points of the ellipses are extracted from an image; elliptic equations are fitted to solve simulacra of intersection points of the two ellipses; vanishing points in orthogonal directions of a plane of the image are obtained according to the attribute of a cross ratio of four collinear points and to the fact that two parallel straight lines are intersected at an infinite point; coordinates of simulacra of circular ring points are solved through a Laguerre theorem inferentially; and intrinsic parameters of the camera are solved by the constraint of image points of the circular ring points and a simulacrum of an absolute conic. With the adoption of the target, full automatic calibrating can be realized, and errors due to measuring in a calibrating process are reduced. As the absolute conic is a more concise and global element, the calibration accuracy is improved in the camera calibrating process.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for calibrating parabolic catadioptric camera using spatial straight lines
InactiveCN107993267AEasy accessPhysical scale is not requiredImage enhancementDrawing from basic elementsPartition of unityCatadioptric camera
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a parabolic catadioptric camera using spatial straight lines. The camera is calibrated using three straight lines in space as targets. First, in a unit virtual globe model, three non-parallel lines in space are projected and are projected onto an image plane to form three intersecting quadratic curves, and because the two quadratic curves intersectat two real intersecting points, the two intersecting points form a straight line. However, due to the presence of noise, the three straight lines do not intersect at one point but form a triangle. The center of gravity of the triangle can be considered as the approximate principal point on the image plane. Secondly, epipolar lines of the principal point about the three quadratic curves are solved respectively; as can be learnt from the relationship between the epipolar lines of poles, the epipolar line of the principal point with respect to the quadratic curve is a vanishing line, and each vanishing line and the corresponding quadratic curve are intersected at an image of two ring points, and thus intrinsic parameters of the camera are solved.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com