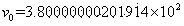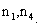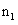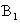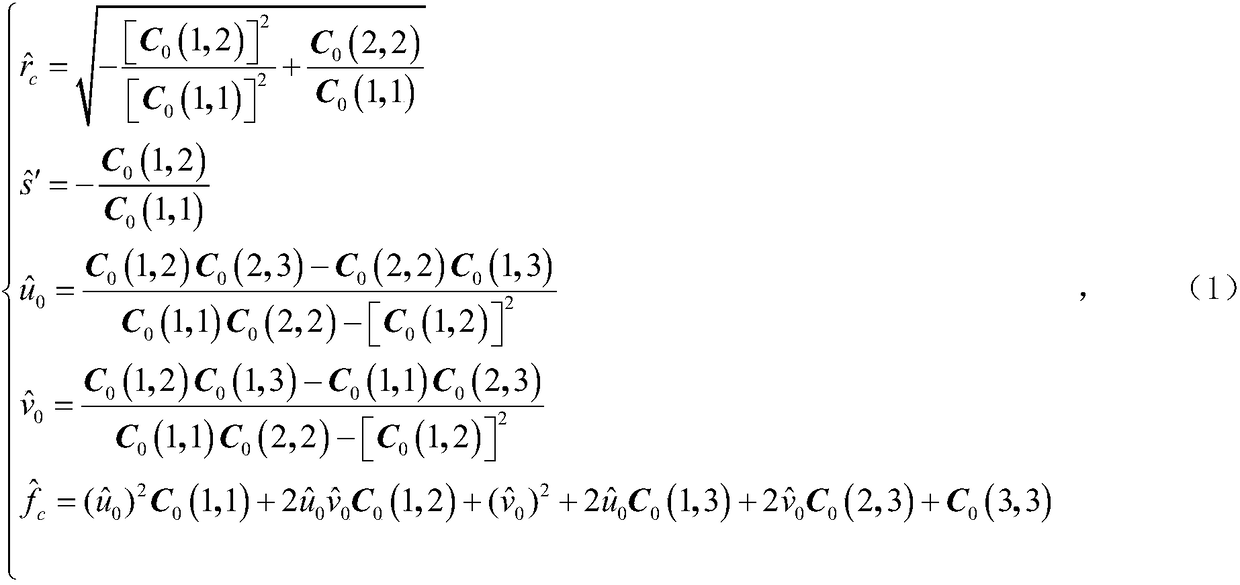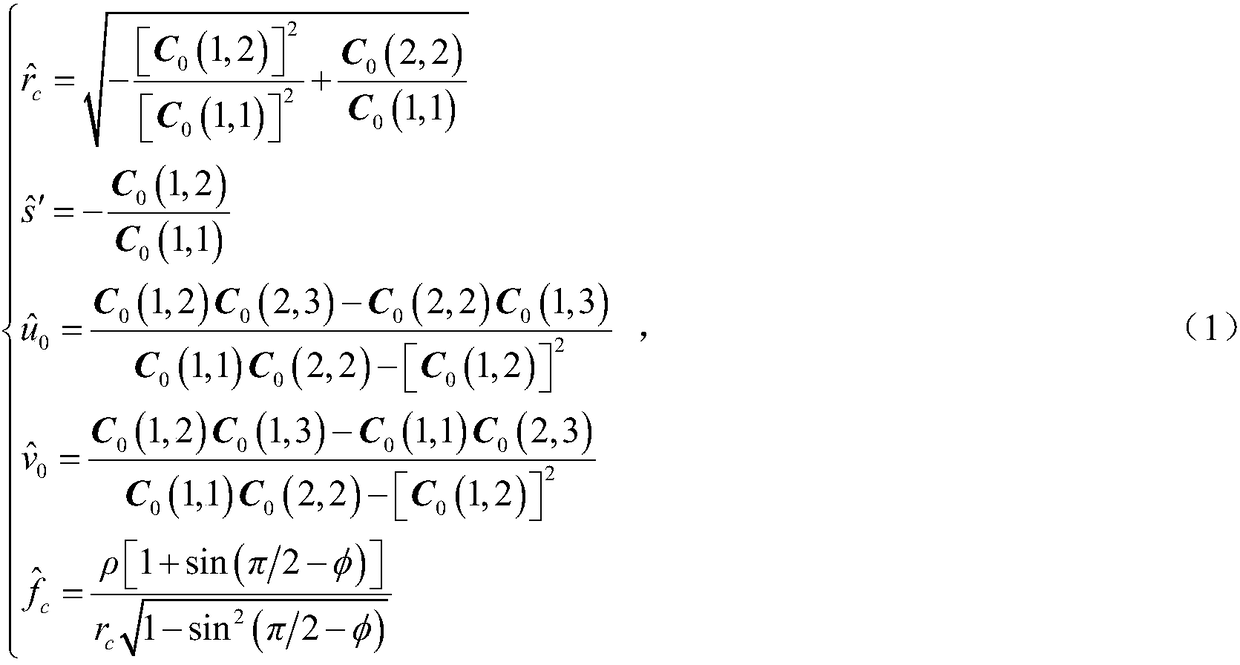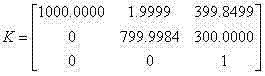Patents
Literature
68 results about "Absolute conic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
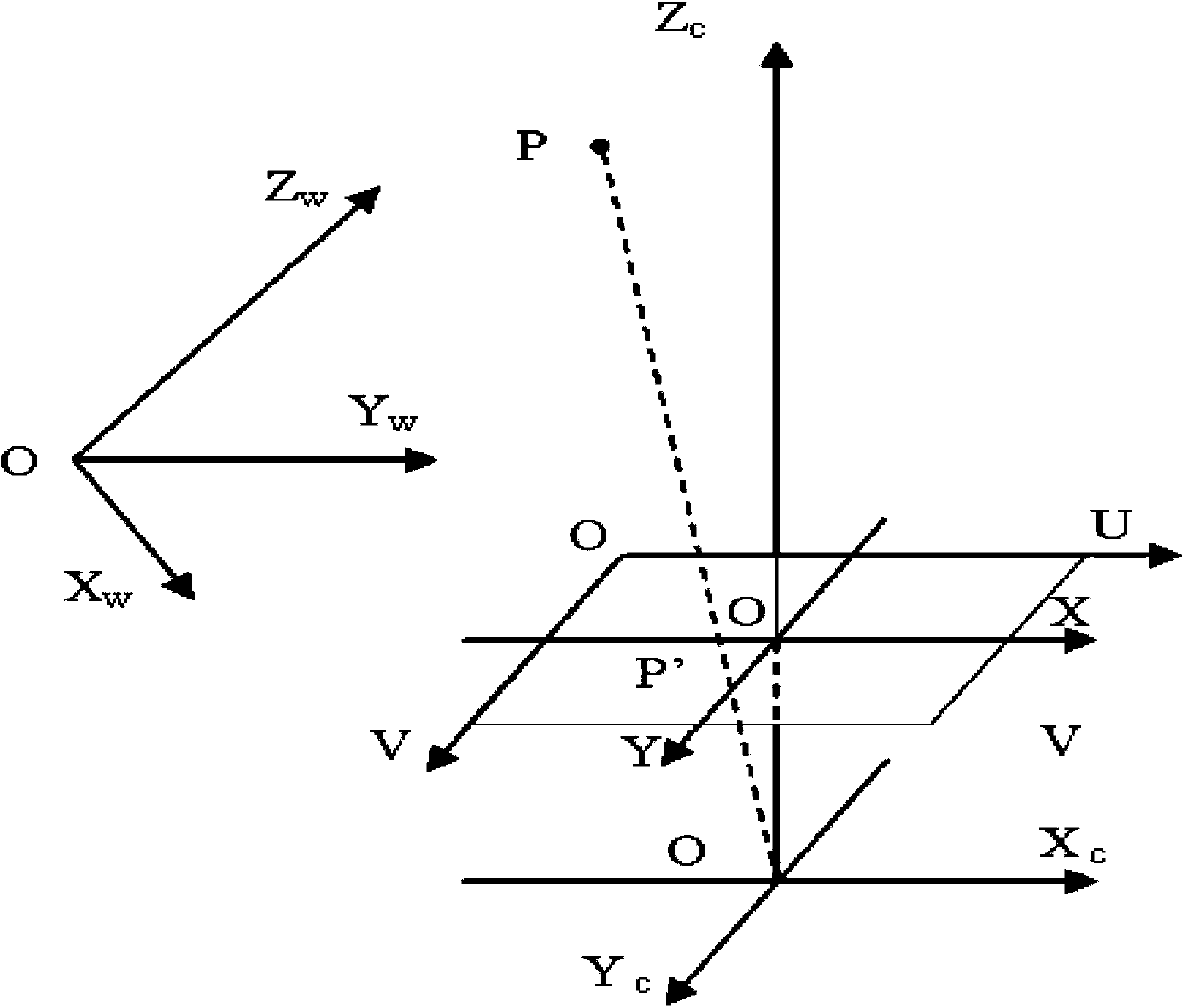
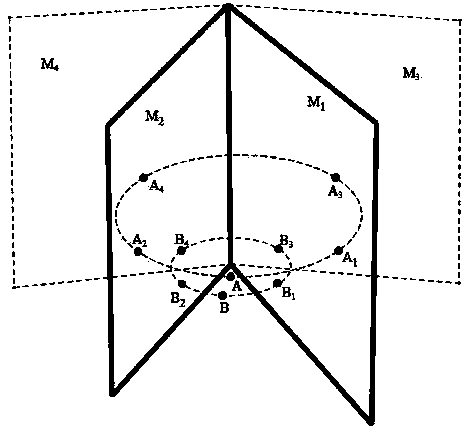
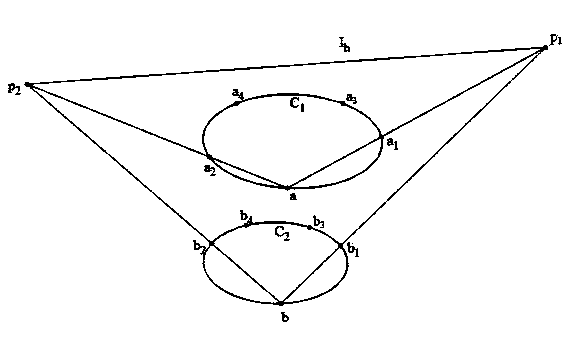
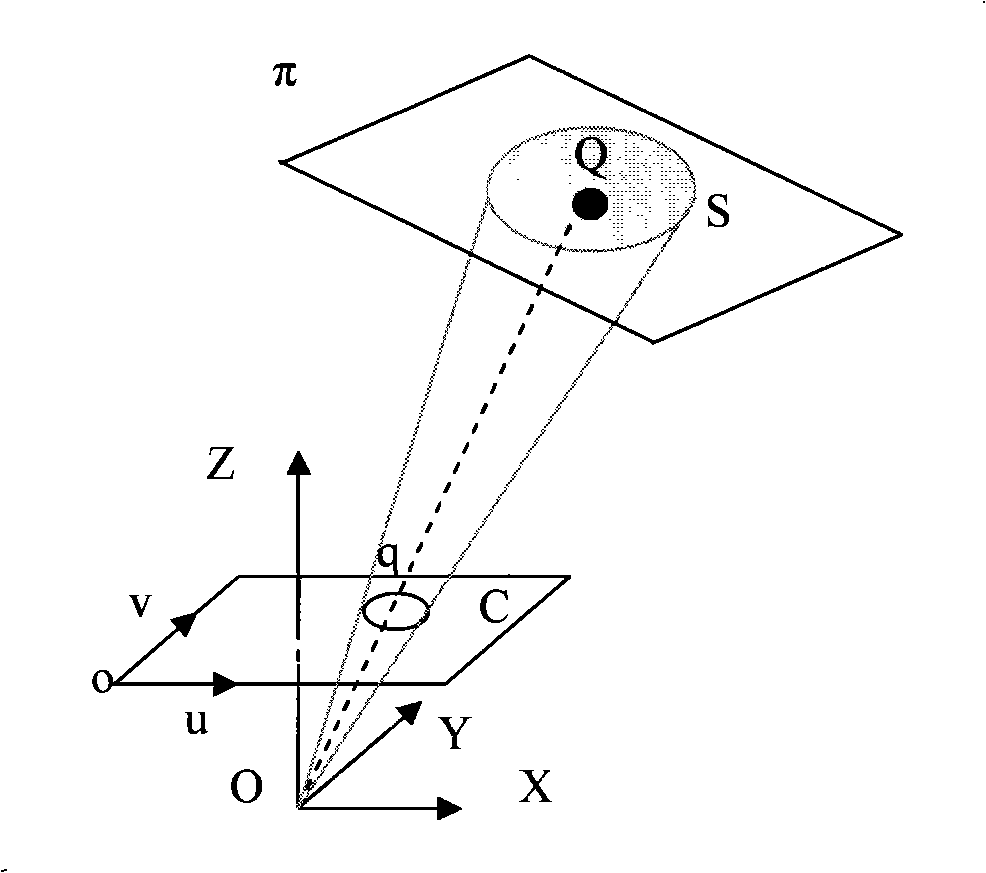
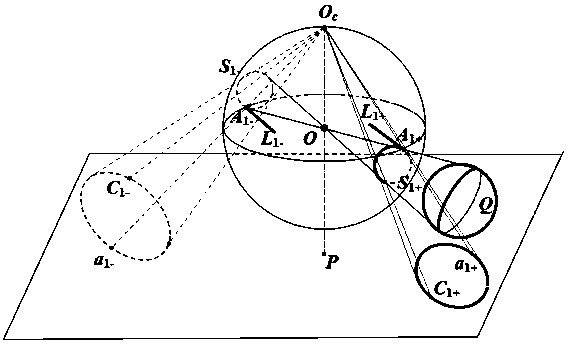
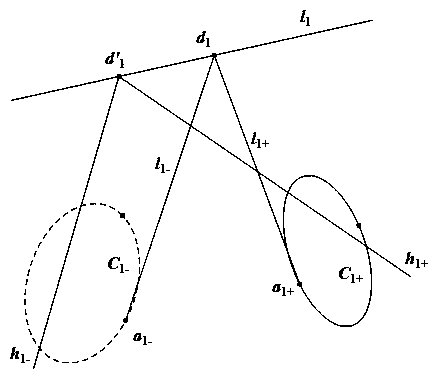
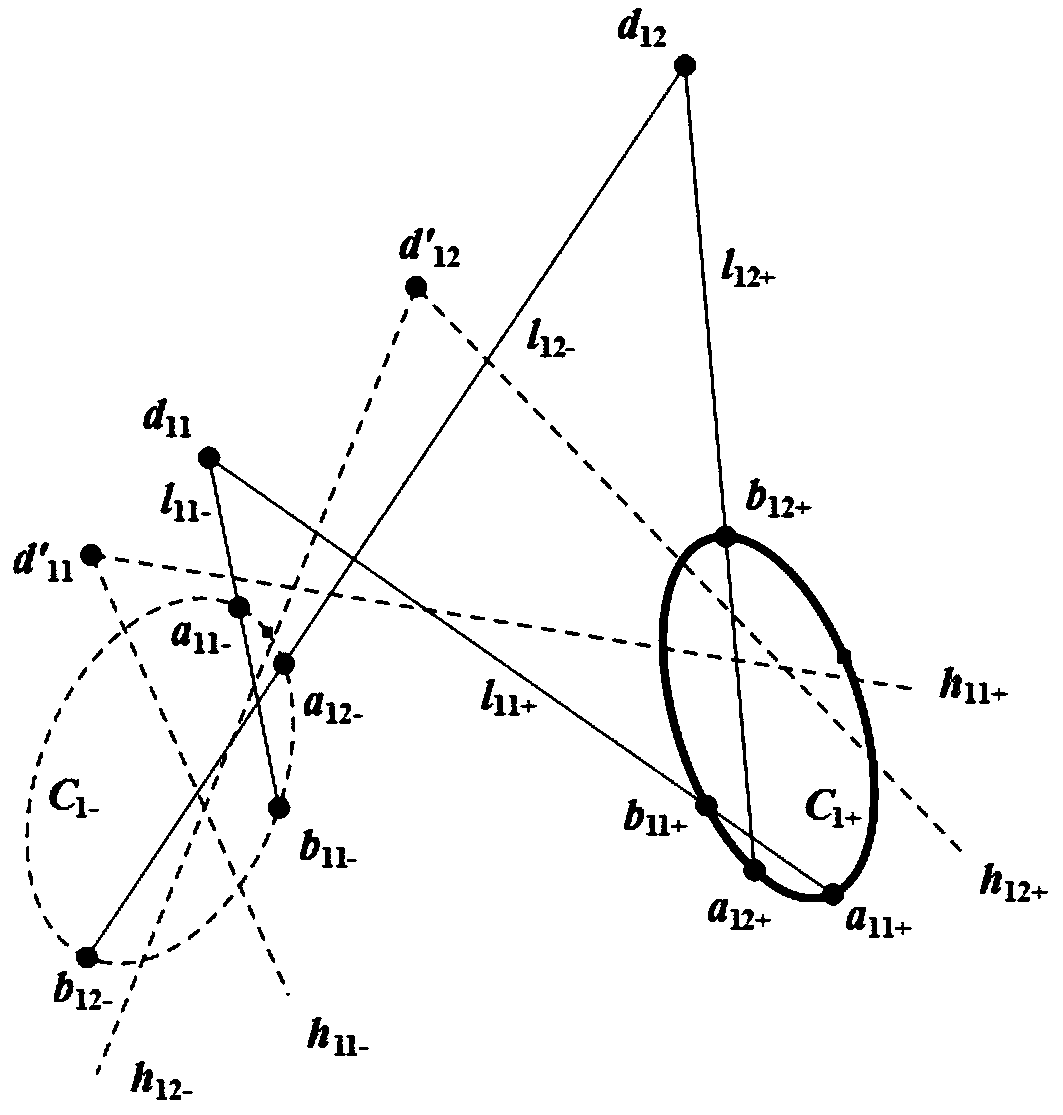
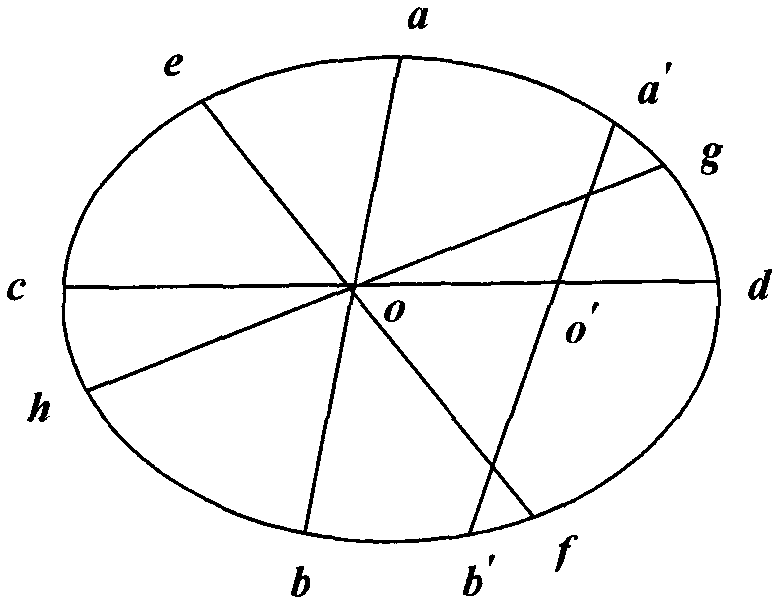
The image of the absolute conic. One of the most important concepts for self-calibration is the Absolute Conic (AC) and its projection in the images (IAC) F2. Since it is invariant under Euclidean transformations (see Section 2.2.3), its relative position to a moving camera is constant.
Method for calibrating camera
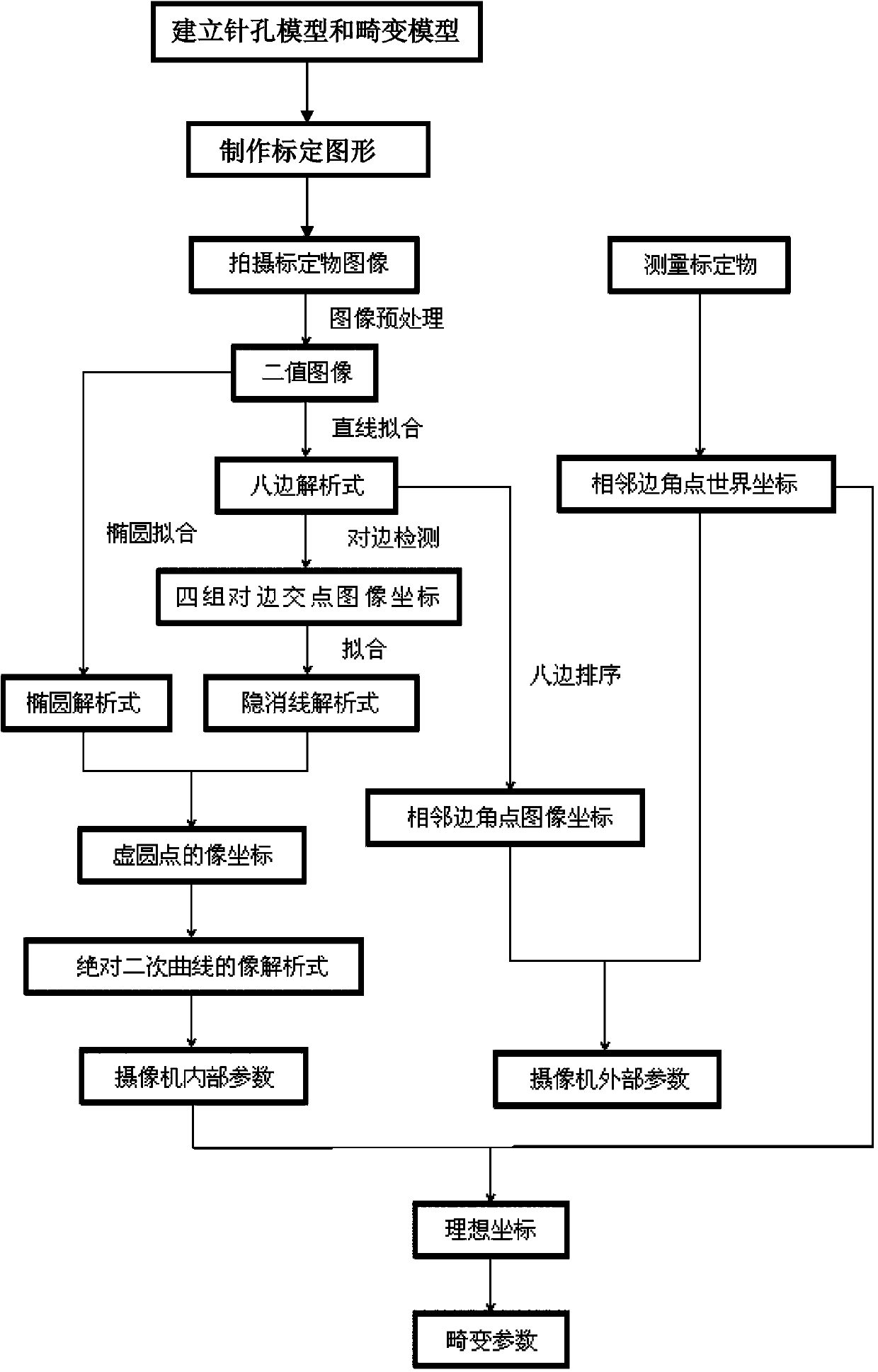
The invention provides a method for calibrating a camera. According to a camera calibration line circle method, a circle and an inscribed regular octagon of the circle are used as calibration objects for calibrating the camera. The circle and the inscribed regular octagon of the circle are used as the calibration objects, the camera is used for shooting the calibration objects from three different angles, three calibration object images are obtained, the calibration process is based on the shooting geometric principle, according to the relevance of the image of an absolute conic and the inside parameter of the camera, a hidden line intersects with an ellipse to obtain a circular point, an absolute conic equation is further obtained, and the inside parameter of the camber is obtained finally. An outside parameter is calibrated according to a radial array binding principle, an overdetermined equation is solved to obtain the outside parameter of the camera, at last, the radial distortion of the camera is considered, the distortion parameter of the camera is further obtained, and distortion compensation is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Solving camera intrinsic parameter by using image of center of sphere and orthogonality
InactiveCN104835144AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisIntrinsicsConstraint matrix
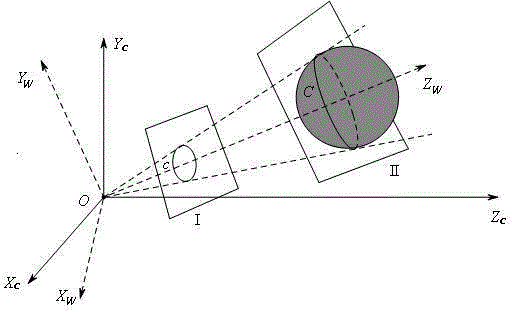
The invention relates to a method for solving camera intrinsic parameter by using the image of the center of a sphere and orthogonality. The method comprises: firstly, taking three pictures of a calibrated sphere from different directions and reading the images, extracting coordinates of three quadratic curves from the three images; according to imaging process of the sphere and the center of the sphere under the camera, solving to obtain image coordinates of three centers of spheres, and according to projections of the centers of spheres, calculating end points on orthogonal directions, and finally by using the end points on orthogonal directions, solving images of absolute conics, and according to the images of quadratic curves, and solving a constraint matrix of camera intrinsic parameters, so as to obtain the camera intrinsic parameter. By using the spheres which are targets, full-automatic calibration can be realized, and errors caused by measurement in a calibration process are reduced. Since the quadratic curve is a simpler and more global element, and projection contours of the spheres can be completely extracted from the images, calibration precision is improved in a camera calibration process.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method of calibrating paracatadioptric camera using image of single sphere and circular points
InactiveCN106327504AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisVanishing lineSurface contour
The present invention relates to a method for calibrating a paracatadioptric camera using the images of a single sphere and circular points. According to the method, two different points are selected from the image of the sphere, so that two vanishing points are obtained; a straight line where the two vanishing points are located is a vanishing line, the images of the vanishing line and the image of the sphere intersect with the images of the circular points, and three images can provide the images of three circular points; and the inner parameters of the camera are solved through using the constraint of the images of the circular points for an absolute conic curve image. The method specifically includes the following steps of: fitting a mirror surface contour projection equation and a target projection equation; estimating an antipodal sphere image; determining the images of the circular points; and solving the inner parameters of the paracatadioptric camera. In a process of solving the inner parameters of the paracatadioptric camera, five inner parameters of the paracatadioptric camera are solved by using three images of a target shoot by the paracatadioptric camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method of determining intrinsic parameters of parabolic catadioptric camera through linearity of two mutually-shielded spheres
InactiveCN104217435APhysical scale is not requiredNo need to know world coordinatesImage analysisCatadioptric cameraImage plane
The invention relates to a method of determining intrinsic parameters of a parabolic catadioptric camera through linearity of two mutually-shielded spheres. The method comprises the following steps that five images of a target are shot from different directions by utilizing the parabolic catadioptric camera, parabolic catadioptric images of the target are two intersected quadratic curves, boundary pixel point coordinates and image point coordinates of the five target images are extracted from the images, antipodal image points are obtained according to the relation between the image points and the antipodal image points, curve equations are respectively fitted, two groups of antipodal image points are formed by two actual points of intersection of a sphere image and two actual points of intersection of an antipodal sphere image, through definition of the antipodal image points, the two groups of antipodal image points provide one group of orthogonal direction end points on an image plane, and the intrinsic parameters of the camera are solved by utilizing constraint linearity of the orthogonal direction end points on an absolute conic image. By utilizing the target in the invention, full-automatic calibration can be implemented, and errors caused by measurement in a calibration process are reduced. Projection contour lines of the spheres can be completely extracted in the image, so that the calibration precision of the camera is improved.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Pose measuring method based on coaxial circle characteristics of target
ActiveCN104517291AImprove fitting accuracySimplify the measurement stepsImage analysisPicture interpretationEllipsePoint projection
The invention relates to a pose measuring method based on coaxial circle characteristics of a target and belongs to the technical field of computer vision measurement. The pose measuring method is characterized in that the target is provided with coaxial circle characteristics, curve extraction and ellipse fitting technologies are combined to obtain two coaxial circular projection equations in an image, and circular point projection coordinates and vanishing line equation of a target plane are obtained by means of relation of absolute conic, vanishing line and circular points in projection geometry of the circle characteristics; by means of the polar line-pole theorem, circular center projection coordinates of two coaxial circles are obtained by the vanishing line equation of the plane, and pose and position information of the target is solved by taking the actual distance of the coaxial circles as prior condition and combining the projection of the circular points and the projection coordinates of the circular centers. The pose measuring method based on the coaxial circle characteristics of the target has the advantages that measuring of target pose is completed by means of a single target image of coaxial circle characteristics, so that the pose measuring method is simple to operate and applicable to measurement in real time. Meanwhile, without manual intervention, high-precision measurement is realized.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Solving parabolic catadioptric camera parameters through two intersected straight lines in space
InactiveCN103106661AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisCatadioptric cameraHarmonic conjugate
The invention relates to a method to solve parabolic catadioptric camera parameters through two intersected straight lines in space. The method is that a target (a calibration object) composed of the two intersected straight lines in the space is used for self-calibration of a parabolic catadioptric camera. Three images of the target are shot by the parabolic catadioptric camera from different directions. A parabolic catadioptric image of a straight line is a quadric curve. Boundary pixel point coordinates and image point coordinates of the three target images are extracted from the images to respectively fit curvilinear equations. Images of disappeared points on image planes along the orthogonal direction are obtained according to that images of harmonic conjugates and two parallel straight lines are intersected to one point. Camera parameters are solved by utilizing the linear constraint of the images on the orthogonal direction on an image of an absolute conic. By utilizing the method, the target can be fully and automatically calibrated, and errors caused by measurement in the calibration process are reduced. Because a straight line is a more concise and more global element, calibration precision of the camera in the calibration process is improved.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Linear solving of video camera internal parameters by utilizing two intersected same circles and common tangent
The invention relates to linear solving of video camera internal parameters by utilizing two intersected same circles and a common tangent, and the method is a drone composed of two intersected same circles and the common tangent and used for calibrating video cameras. The drone is shoot for six images from different directions; elliptic equations and characteristic points are extracted from the images, and intersection point of two ovals are solved; vanishing points on image planes at the orthogonal direction is obtained according to perpendicular bisector of circle center line segment connecting the two circles and the common tangent of the two intersected circles and cross ratio of collinear four points; and the video camera internal parameters are performed with linear solving by utilizing the vanishing points at the orthogonal direction and restraint of images of an absolute conic. By utilizing the drone, full-automatic calibration can be achieved, and error caused by measurement during the calibration process is reduced. Circle is an element which is more concise and global, and accordingly calibration accuracy is improved during the calibration process.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for solving camera inner parameters by utilizing bimirror device and circular point characteristics
The invention relates to a method for solving camera inner parameters by utilizing a bimirror device and circular point characteristics. The bimirror device is specifically composed of two rectangular plane mirrors, the two plane mirrors are perpendicular to a plane formed by bottom edges of the two plane mirrors, and the bimirror device is used for a camera self-calibration device. The method includes the steps of shooting three images including an image of an object and four images formed in the plane mirrors of the object, extracting characteristic points from the images, arranging one set of corresponding characteristic points on one circle, enabling points at infinity in the direction of the two real plane mirrors to be on the same straight line, calling the straight line as an infinity straight line, calling images of the infinity straight line as a vanishing line, regarding the intersection point of the projection of the circle and the vanishing line as the image of a circular point, setting six sets of constraint equations of the image of the circular point on an absolute conic image by utilizing the three images, and solving the camera inner parameters in a linear mode.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Solving parabolic catadioptric camera parameters through one straight line in space
The invention relates to a method to solve parabolic catadioptric camera parameters through one straight line in space. The method is that a calibration object composed of the straight line in the space is used for self-calibration of a parabolic catadioptric camera. Three images of the calibration object are shot by the parabolic catadioptric camera from different directions. A parabolic catadioptric image of a straight line is a quadric curve. Boundary pixel point coordinates and image point coordinates of the three calibration objects images are extracted from the images to respectively fit curvilinear equations. Images of circular ring points on image planes are obtained according to a polarity principle. Camera parameters are solved by utilizing the linear constraint of the images on the circular ring points on an image of an absolute conic. By utilizing the method, the calibration object can be fully and automatically calibrated, and errors caused by measurement in the calibration process are reduced. Because a straight line is a more concise and more global element, calibration precision of the camera in the calibration process is improved.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for linearly solving camera inner parameter by using two identical intersected ellipses
The invention relates to a method for linearly solving camera inner parameters by using two identical intersected ellipses. According to the method, a target drone which is formed by two identical intersected ellipses sharing the same main axis and which is calibrated by a camera is adopted; five images of the target drone are shot in different directions; an ellipse equation is extracted from the images and the intersection points of the two ellipse are solved; end points in the planes of the images in the orthogonal directions are obtained according to the polarity principle and the property of the cross ration of four straight lines; and camera inner parameters are linearly solved by using the end points in the orthogonal directions and the constraint of the images of absolute conics. With the adoption of the target drone in the method, the full-automatic calibration can be implemented, the error caused by the measurement in the calibration process is reduced, and the calibration precision in the calibration process of the camera is improved as the conic is a simpler and more global-oriented element.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Video camera parameter calibration method by adopting single circle as marker
InactiveCN101334894ASimple and accurate determinationRealize fully automatic calibrationImage analysisUsing optical meansAutonomous Navigation SystemCalculation error
The invention relates to a calibration method for the intrinsic parameters of a camera by adopting a single circle as a calibration object; the method comprises the following steps that: first, three different images of a calibration object are shot by using a camera; then an image point location of a circular point of each image is identified; by utilizing the image point of the three groups of the circular points, projection curve equation of absolute conic is fitted; finally, all intrinsic parameters of the camera are calculated in a way linearly, including a principal point location, aspect ratio and tilt factor. The method of the invention can identify all intrinsic parameter of the camera once, and can realize automatic calibration and reduce calculation error caused by human intervention, and is particularly applicable to a non-contact type industrial inspection and an autonomous navigation system based on vision.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for solving intrinsic parameters of parabolic catadioptric camera linearly by utilizing three unparallel straight lines in space
InactiveCN102982551AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisIntersection of a polyhedron with a lineCatadioptric camera
The invention relates to a method for solving intrinsic parameters of a parabolic catadioptric camera linearly by utilizing three unparallel straight lines in a space. The method comprises the steps that a target consisting of the three unparallel straight lines in the space and used for automatic calibration of the parabolic catadioptric camera is utilized; the parabolic catadioptric camera is used to shoot an image of the target; the linear parabolic catadioptric image is a quadratic curve; target image points are extracted from the image; curvilinear equations are fitted; an intersection point of every two curves is solved; images of three pairs of circular ring points on a plane of the image are obtained according to a polar principle and a diameter concyclic center attribute; and the parameters in the camera are solved by utilizing linear restriction of the images of the circular ring points on an absolute conic. With the adoption of the target in the method, full automatic calibration can be realized, and errors due to measurement in a calibration process are reduced. As the straight lines are elements which are more concise and global, the calibration accuracy is improved in the calibration process of the camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for calibrating parabolic refraction and reflection camera via single ball and parallel circle properties
InactiveCN106651956AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisIntersection of a polyhedron with a lineImage plane
A method for calibrating a parabolic refraction and reflection camera via single ball and parallel circle properties is disclosed. In a parabolic refraction and reflection system, two small parallel circles are formed when a ball is projected onto a unit visual ball for a first time. The two parallel circles in a space have two pairs of conjugated virtual intersection points, and two conjugated virtual intersection points that are collinear with a point at infinity on a plane where space circles are positioned are circular ring points. An image of the circular ring points is obtained on an image plane according to colinearity of the image of the circular ring points and a vanishing point; three images provide images of three groups of circular ring points. Intrinsic parameters of the camera are solved via constraints posed on an absolute conic image by the images of the circular ring points. The method specifically comprises the following steps: a mirror surface contour projection equation and a target projection equation are fitted, an antipodal sphere image of a sphere image is estimated, the images of the circular ring points are determined, and the intrinsic parameters of the parabolic refraction and reflection camera are solved.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for inferring intrinsic parameters of camera by utilizing bimirror device and Laguerre theorem
The invention discloses a method used for camera self-calibration by utilizing two rectangular plane mirrors, wherein the two plane mirrors are vertical to a plane formed by bottom edges of the two plane mirrors. The method comprises the following specific steps of shooting three images including an object and four images of the object, formed in the plane mirrors; extracting feature points from the images; acquiring end points of the plane mirrors in a normal direction by utilizing the plane mirror imaging principle; acquiring end points of the two plane mirrors in a mirror plane direction by utilizing the property of cross ratio; finally, acquiring images of circular points according to the deduction of the Laguerre theorem; establishing six groups of constraint equations of the images of the circular points to absolute conic images by utilizing the three images; and linearly solving the intrinsic parameters of a camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for calibrating parabolic catadioptric camera by using properties of single sphere and circle tangent line
InactiveCN107644445AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisCatadioptric cameraVanishing line
The invention discloses a method for calibrating a parabolic catadioptric camera by using properties of a single sphere and a circle tangent line. The method is characterized by taking a sphere in a space as a target. The method comprises the specific steps of: firstly, shooting three pictures containing the sphere from different positions by means of the parabolic catadioptric camera; secondly, acquiring antipodal image points according to relationship between image points and antipodal image points thereof in a parabolic catadioptric unit visual sphere model, so as to estimate an antipodal sphere image of a sphere image; thirdly, selecting a point from the sphere images, wherein a tangent line of each image point about the corresponding sphere image and a tangent line of the corresponding antipodal image point about the corresponding antipodal sphere image intersect at an image vanishing point through definition of the antipodal image points, an intersection point of the image vanishing point about polar lines of the sphere image and the antipodal sphere image is an image vanishing point, a straight line where the two image vanishing points are located is an image vanishing line,an intersection point of the image vanishing line and the sphere image is an image of circular points, and the three pictures provide the images of three groups of circular points; and finally, solving inner parameters of the camera by utilizing the constraint of the images of the circular points for an absolute conic curve image.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for solving intrinsic parameters of camera by circular motion in double-plane-mirror device
The invention relates to a method for solving intrinsic parameters of a camera by circular motion in a double-plane-mirror device. The device is composed of two plane mirrors and a pinhole camera, and space points and reflection image points thereof in the plane mirrors are located on a same space circle. The method includes: shooting an object and three images of four reflection images of the object in the plane mirrors, extracting features points from the images, and fitting a curvilinear equation; acquiring an image of the circle center by the aid of symmetrical property of reflection point groups relative to the plane mirrors and tangential property of a curve at the feature points, and then utilizing relation among poles and polar lines to obtain a vanishing line on an image plane, namely an image of a line at infinity; acquiring an interaction of the vanishing line and the curve, namely an image of a circular point, creating six constraint equations of the image of the circular point relative to an absolute conic image, and linearly solving intrinsic parameters of the camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method of solving intrinsic parameters of camera with regular pentagonal prismatic table
The invention discloses a target used for self-calibrating of a camera and consisting of a regular prismatic table with regular pentagonal bottom surfaces. A method comprises the particular steps as follows: characteristic points on the upper bottom surface and the two side faces of the regular positive pentagonal prismatic table are extracted from an image; coordinates of vanishing points on a plane of the image are solved according to attributes that an intersection point of two parallel straight lines is an infinite point, and a simulacrum of the infinite point is the vanishing point, and according to the attribute of a cross ratio of four collinear points; intrinsic parameters of the camera are solved linearly according to constraint of the orthogonal vanishing points on an absolute conic; two images of the target are shot in different directions; the coordinates of the characteristic points on the images are extracted; the orthogonal vanishing points on the upper bottom surface and the two side faces of the regular positive pentagonal prismatic table are calculated; constraint equations of the orthogonal vanishing points relevant to the intrinsic parameters of the camera are established; and matrixes of the intrinsic parameters of the camera are solved linearly. With the adoption of the target, full automatic calibration can be realized, and errors due to measuring in a calibrating process are reduced. The vanishing points are more concise and global elements, and the accuracy is improved in the calibrating process.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
A method for calibrating a catadioptric camera using properties of a single sphere and a conjugate diameter
InactiveCN109360248AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisCatadioptric cameraConjugate diameters
A method for calibrating a catadioptric camera using properties of a single sphere and a conjugate diameter is characterized in that only spherical elements are used. Firstly, the edge points of the target image and the edge points of the specular contour projection of one image are extracted from three images respectively, and the specular contour projection and the spherical image projection areobtained by least square fitting. Secondly, according to the relation between the image point and its extension point, the extension point is obtained, and then the extension spherical image of the spherical image is fitted. According to the property of the conjugate diameter of a circle, the intersection point of the polar line of the vanishing point with respect to the spherical image and the contrastive spherical image is a set of orthogonal vanishing points. Two sets of orthogonal vanishing points can be obtained by choosing two sets of different points on the spherical image. All the orthogonal vanishing points corresponding to a plane only provide two constraints for the image of absolute conic and six constraints for three images. Finally, the camera intrinsic parameters are obtained by using the constraint of the orthogonal vanishing point to the absolute conic image.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Camera self-calibration method based on absolute quadratic curve image
ActiveCN109064516ACalibration is simple, convenient and practicalGet rid of the bondageImage analysisEssential matrixImaging processing
The invention discloses a camera self-calibration method based on an absolute conic image, belonging to the technical field of image processing and camera calibration. The method comprises the following steps: extracting feature points and feature lines, calculating images of vanishing points, vanishing lines and imaginary circles; according to the image of the vanishing point and the imaginary circle, the image of the absolute quadratic curve is calculated and the intrinsic parameter matrix of the camera is obtained. The rotation matrix is calculated by using the orthogonal property of the rotation matrix, and the translation vector is calculated by using the position of the camera center in the world coordinate system. The Euler angle of the camera is calculated by comparing the erasingline calculated by perspective projection model with the erasing line obtained by fitting the erasing points. Normalization algorithm is used to solve the basic matrix, determine the constraint relationship between different images, and complete camera self-calibration. The invention has the advantages of designing a new target, which is simple, convenient and practical to calibrate, has wide practicability, improves the accuracy of data processing, and reduces the influence of coordinate transformation on data.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for solving internal parameters of planar catadioptric video camera according to property of orthogonal vanishing point
The invention relates to a method for solving internal parameters of a planar catadioptric video camera according to property of an orthogonal vanishing point. The video camera consists of two plane mirrors and a pinhole video camera, wherein the two plane mirrors are perpendicular to a plane formed by bottom edges of the two plane mirrors. An object and three images formed through four-time catoptric imaging of the object in the plane mirrors are shot, and feature points are extracted from the images. The orthogonal vanishing points are solved by utilizing symmetry of a reflection point set relative to the plane mirrors and the harmonic conjugate property, a constraint equation of the orthogonal vanishing point with respect to an absolute conic image is established, and the internal parameters of the planar catadioptric video camera are linearly solved.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for qualitatively calibrating pinhole camera by utilizing single ball and asymptotic line
ActiveCN108921904AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisPinhole cameraPinhole camera model
The invention relates to a method for qualitatively calibrating a pinhole camera by utilizing a single ball and an asymptotic line, characterized in that a ball element is utilized only. Firstly, pixel coordinates of target image edge points are extracted from three images and a ball image equation is obtained by adopting least square fitting. On the basis of the obtained ball image equation, an asymptotic line of a ball image is solved. The asymptotic line of the ball image is namely a polar line of an image of a circular point about the ball image, thus an image of a circle center is determined according to a polarity principle, orthogonal end points can be obtained by virtue of the image of the circle center, and the three images provide six groups of orthogonal end points. Finally, intrinsic parameters of the camera are solved by utilizing constraints of the orthogonal end points on an absolute conic image. The method comprises the following specific steps: fitting a target projection equation, estimating the asymptotic line of the ball image, determining the orthogonal end points, and solving the intrinsic parameters of the pinhole camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Common self-polar triangle and orthogonal vanishing point calibration parabolic camera for a single sphere
InactiveCN109360247AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisHarmonic conjugateVanishing point
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a parabolic camera by using a common self-polar triangle and an orthogonal vanishing point of a single sphere. Firstly, the edge points of spherical image and the edge points of specular contour projection are extracted from this image respectively. According to the fact that any two separate spherical images have a unique common self-polar triangle, a set of poles and poles corresponding to the spherical image and its extension can be obtained. At the same time, this polar line is an image of the center of the two spheres, and this pole is a vanishing point. The vanishing point has a polar line on the ball image; A polar line passes through the image of the center of a sphere and intersects the image of the sphere at two points. The imageof the center of the sphere and the vanishing point can be obtained by using the image of the intersection point and the center of the sphere and the property of harmonic conjugate of the vanishing point in the direction of the polar line. The two vanishing points are a set of orthogonal vanishing points. Then six sets of orthogonal vanishing points can be obtained from six images, and the intrinsic parameters of the parabolic camera can be obtained by using the constraint of the orthogonal vanishing points and the image of the absolute conic.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Calibrating a catadioptric camera of a primer by using a single ball and a parallel circular tangent property
InactiveCN109325982AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisComplex mathematical operationsPartition of unityCatadioptric camera
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a catadioptric camera of a primer by using a single ball and a parallel circular tangent property, which is characterized in that only the ball element is used; firstly, the edge points of specular contour projection and target image are extracted from three images respectively, and the specular contour projection and spherical image projection areobtained by least square fitting; secondly, according to the relationship between the image point and its extension point, the extension point is obtained, and then the extension spherical image of the spherical image is fitted; a point on the spherical image is taken and the topological point is found; by defining the topological points and the properties of parallel circles, the above set of topological points provides a vanishing point; in a parabolic catadioptric system, the sphere is projected onto the unit sphere for the first time to form two small parallel circles, two parallel circles on different faces have two pairs of conjugate imaginary intersection points, in which the two conjugate imaginary intersection points which are collinear with the infinity point of the plane in which the circle is located are ring points. Finally, the camera intrinsic parameters are obtained by using the constraint of the image of the torus point to the image of the absolute conic curve.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
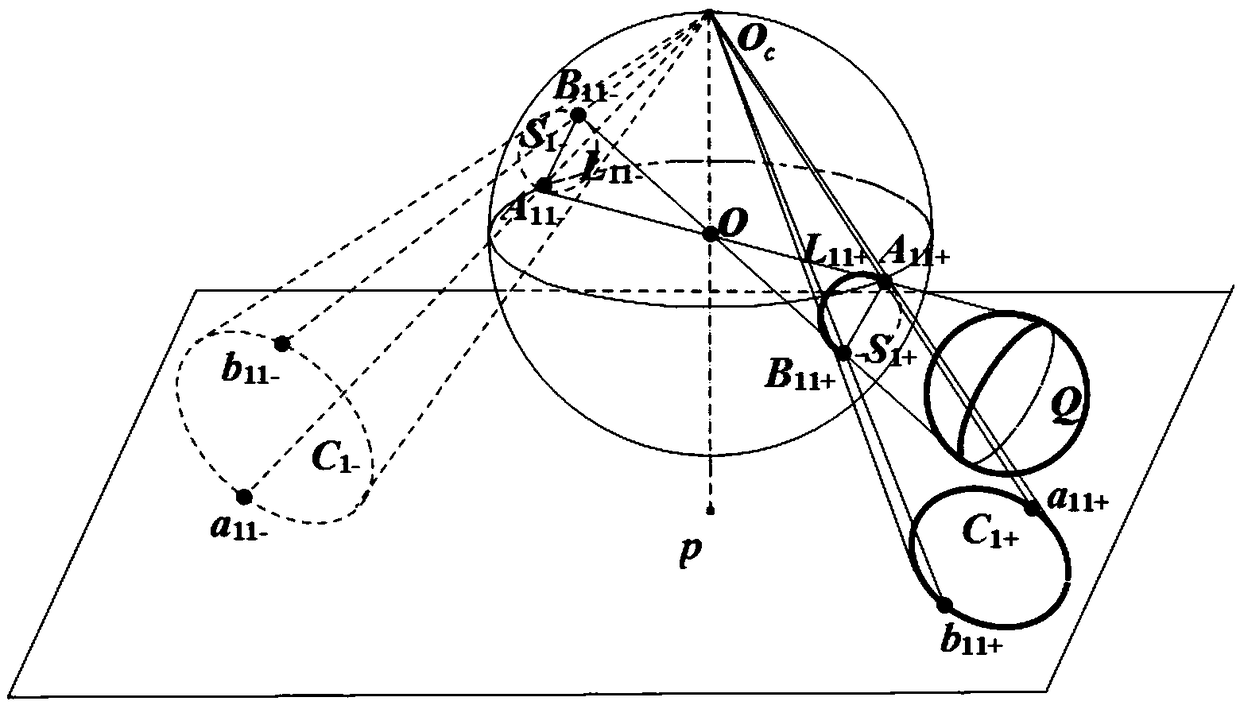
Method for calibrating central catadioptric camera through three balls at different spatial positions
InactiveCN107958468AEasy to makeHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisCatadioptric cameraAbsolute conic
The invention discloses a method for calibrating the central catadioptric camera through three balls at different spatial positions, and the method is characterized in that the method just employs theball elements. The method comprises the steps: extracting points on an image from a captured ball image, carrying out the fitting of ball images corresponding to the three balls, and solving the pixels corresponding to the centers of small circles formed by the projection of the three balls on a unit virtual globe; solving a polar line of the circle centers relative to the ball images through therelation between a polar point and the polar line; solving two intersection points of the ball images and the polar line, i.e., the images of circle points; obtaining an absolute conic through the images of the obtained six circle points, finally carrying out the decomposition of the absolute conic, and carrying out the inversion to obtain the internal parameters of the camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for solving camera inner parameters by using dot matrix template and orthogonality
The invention relates to a method for solving camera inner parameters by using a dot matrix template and orthogonality. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, taking out a physical coordinate of a dot matrix in a template; extracting a matching point in an image; estimating a homography matrix between the image and the template; supposing the slopes of two non-parallel and non-orthogonal straight lines in a template plane; calculating to obtain the slope of a straight slope orthogonal with the straight lines in the template plane; further calculating a coordinate of an in infinite point of the two groups of orthogonal straight lines; obtaining orthogonal end points through perspective projection transformation; shooting at least three images according to the relationship of the orthogonal end points and an absolute conic image so as to linearly solve the camera inner parameters. With the adoption of the template in the method, the full-automatic calibration can be implemented, and the measurement error in the calibration process is reduced.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
A method for calibrating the reflex camera by using the properties of a single sphere and the midpoint of the chord
InactiveCN109215089AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisReflexIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a catadioptric camera of a primer by using properties of a single ball and a midpoint of a chord. Firstly, the edge points of the specular contour projection and the target image are extracted from the image, and the specular contour projection and the spherical image projection are obtained by least square fitting. Secondly, according to the relationship between the image point and its extension point, the extension point is obtained, and then the extension spherical image of the spherical image is fitted. Two different points are taken from the spherical image, and the two points' topological points are obtained. From the definition of topological points and the properties of circles, the two sets of pairs of topological points can determine the midpoint of the upper chord of the sphere image. The image of the center of a circle is determined according to the properties of the two points on the spherical image with respect to the polar line of the spherical image and the midpoint of the chord. The polar line of the center of a circle with respect to the spherical image is the shadow cancellation line, and the intersection point ofthe shadow cancellation line and the spherical image is the image of a circular ring point. Three images provide three sets of images of circular ring points. Finally, the camera intrinsic parametersare obtained by using the constraint of the image of the torus point to the image of the absolute conic curve.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method of solving intrinsic parameters of camera with two center-sharing and principal axis orthonormal intersected identical ellipses
The invention discloses a target used for self-calibrating of a camera and consisting of two center-sharing and principal axis orthonormal intersected identical ellipses. A method comprises the particular steps that peripheral points of the ellipses are extracted from an image; elliptic equations are fitted to solve simulacra of intersection points of the two ellipses; vanishing points in orthogonal directions of a plane of the image are obtained according to the attribute of a cross ratio of four collinear points and to the fact that two parallel straight lines are intersected at an infinite point; coordinates of simulacra of circular ring points are solved through a Laguerre theorem inferentially; and intrinsic parameters of the camera are solved by the constraint of image points of the circular ring points and a simulacrum of an absolute conic. With the adoption of the target, full automatic calibrating can be realized, and errors due to measuring in a calibrating process are reduced. As the absolute conic is a more concise and global element, the calibration accuracy is improved in the camera calibrating process.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
A method for calibrating a parabolic reflex camera using a straight line and a circular polar line
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a parabolic reflex camera using a straight line and a circular polar line. Firstly, the edge points of the target image are extracted from three images respectively, and the line image equation is obtained by least square fitting. On the basis of obtaining the equation of line image, the asymptotic line of line image is solved. Because the asymptotic line of the line image is the polar line of the circular point image with respect to the line image, according to the polar matching principle, the polar line of the circular point image with respect to the line image intersects with the image of the center of the circle, so as to determine the image of the center of the circle. The orthogonal vanishing points can be obtained from the image ofthe center of the circle. Three images provide six sets of orthogonal vanishing points. Finally, the camera intrinsic parameters are obtained by using the constraint of the orthogonal vanishing pointto the absolute conic image. Specific steps include: fitting the target projection equation, estimating the asymptote of the line image, determining the orthogonal vanishing point, and solving the internal parameters of the parabolic reflex camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for linear solving of intrinsic parameters of camera by using circle divided into eight equal parts
InactiveCN103106649APhysical scale is not requiredEasy to makeImage analysisIntrinsic metricVanishing line
The invention relates to a method for camera calibration by using a circle divided into eight equal parts in a plane. According to the method for linear solving of intrinsic parameters of a camera by using a circle divided into eight equal parts, three images are shot in different directions by a target, image curves of the circles on the images, four images of diameter ends and coordinates of images of circle centers are extracted, coordinates of two vanishing points in the mutual orthogonal direction can be calculated according to the property that images of the circle centers and the images of points on the diameters and the images of the vanishing points relative to the circle in the diameter image direction are mutual harmonic conjugate points, a linear constraint equation about an absolute conic is built by using the two vanishing points in the mutual orthogonal direction on the three images and according to the property of a pair of harmonic conjugate points of the two vanishing points on vertical lines relative to the absolute conic, and then the linear solving of the five intrinsic parameters of the camera is achieved. Due to the fact that a curve of the second degree is a simple and an overall element, solving the vanishing line by fitting the curve of the second degree is higher in stability than solving the vanishing line by fitting a point and a plane. The method for the linear solving of the intrinsic parameters of the camera by using the circle divided into the eight equal parts is high in application value.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
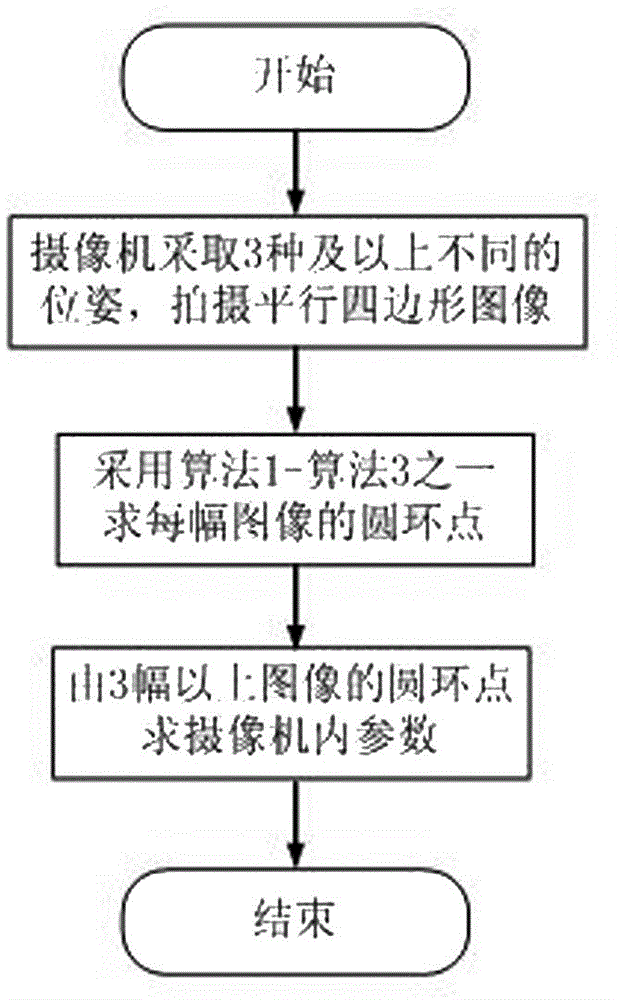
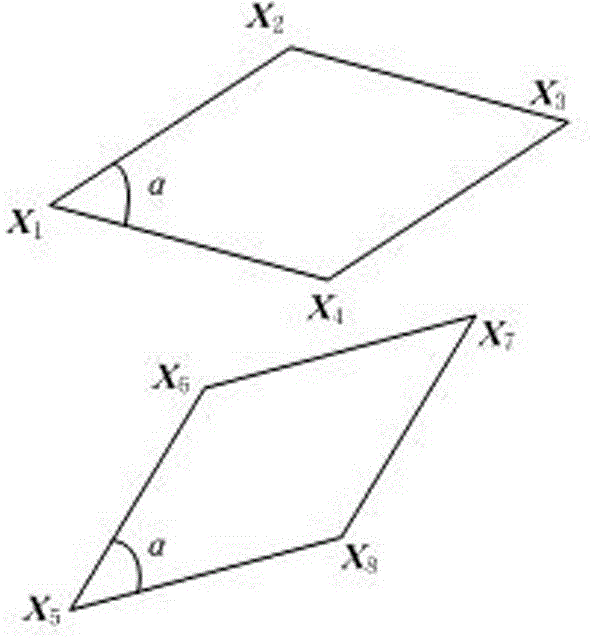
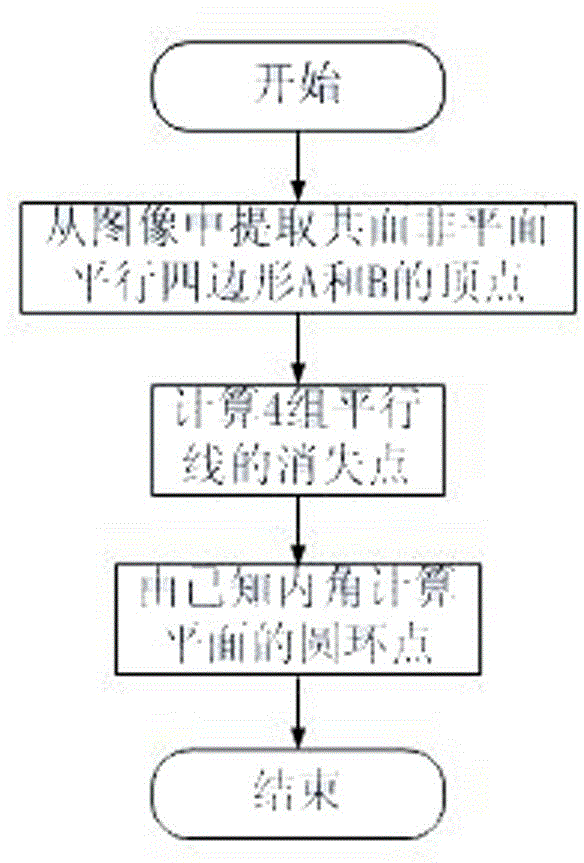
Method for calibrating intrinsic parameters of camera through parallelograms
The invention relates to the field of computer vision measurement, in particular to a method for calibrating intrinsic parameters of a camera through parallelograms, wherein the method is used for building the relations between the image pixel positions of the camera and the positions of scenes. According to the method, calibrating requirements are low, use is flexible and convenient, and high applicability is achieved. The method comprises the following steps that (1) three or more poses are adopted for the camera, and a parallelogram image is taken in each pose; (2) according to the relations between the number and the positions of the parallelograms in each parallelogram image, a calibrating scheme is determined; (3) according to the different calibrating schemes in the step (2), the coordinates of a circular point of the image taken in each pose are obtained; (4) an equation set about the IAC is established, and linear solving is conducted; (5) Cholesky decomposition is conducted on an obtained absolute conic parameter matrix so that an inverse matrix of an intrinsic parameter matrix of the camera can be obtained, and the intrinsic parameter matrix of the camera can be determined through inversion.
Owner:WUXI PROFESSIONAL COLLEGE OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com