Patents
Literature
686results about How to "Control precision" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
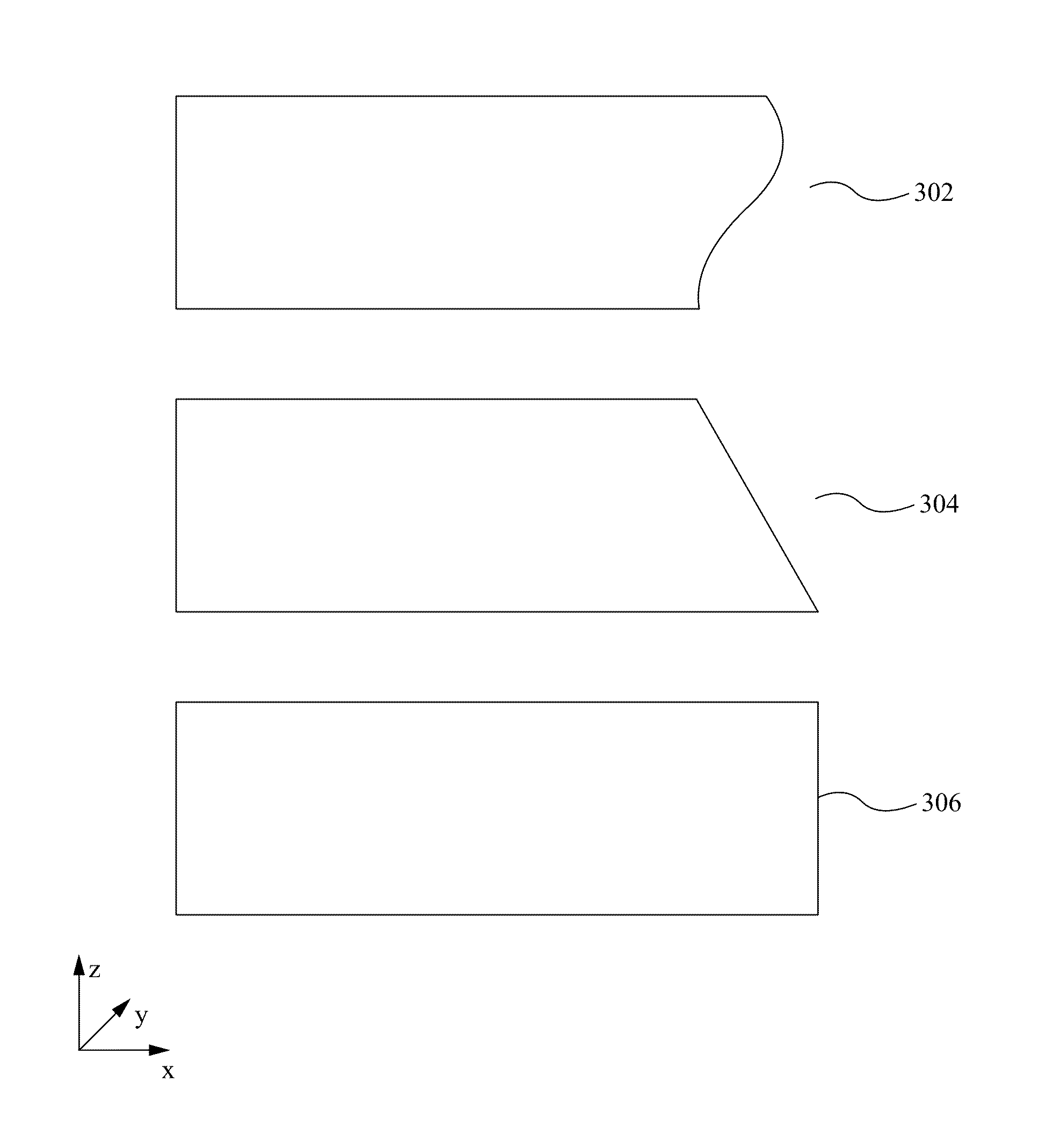
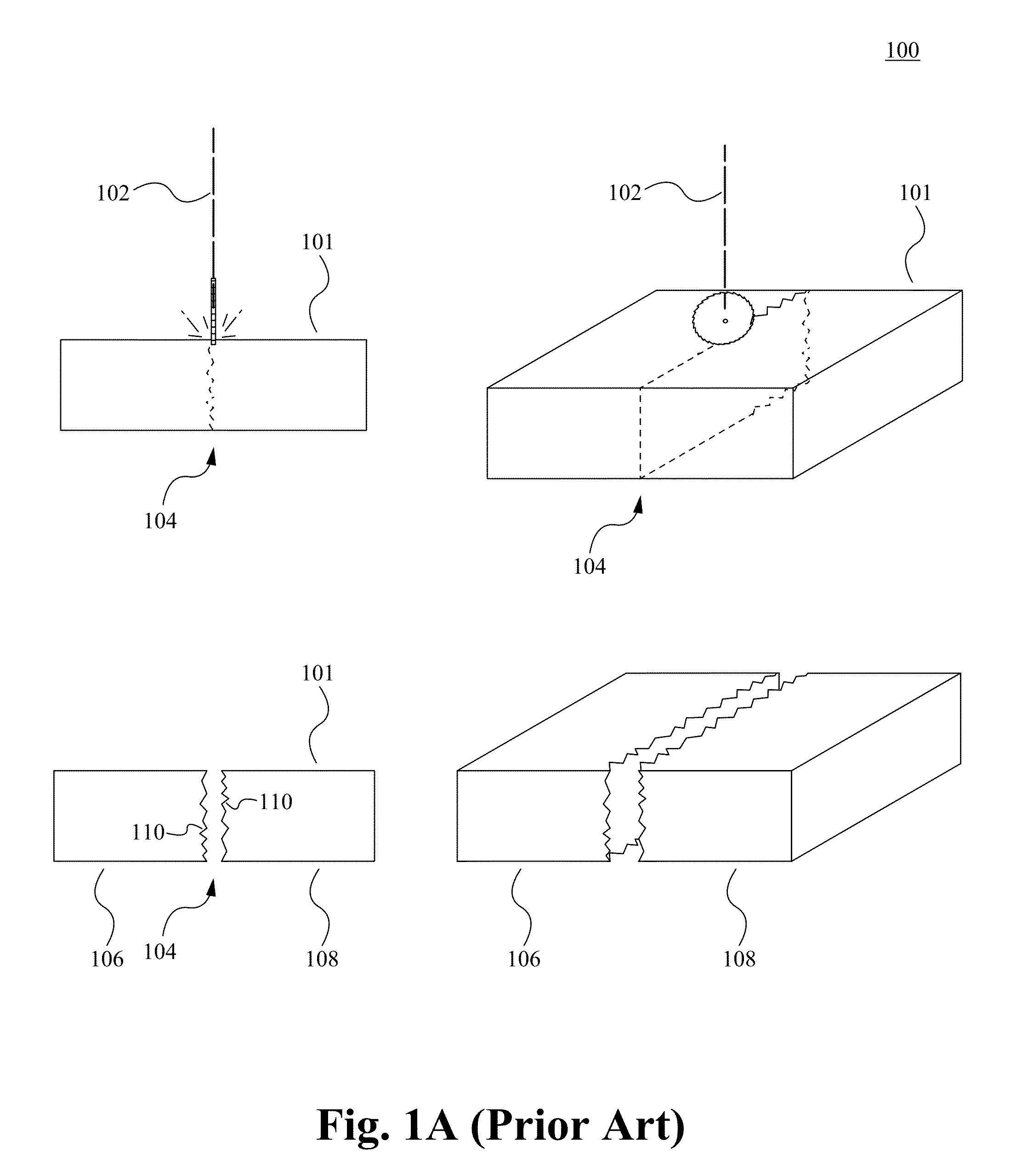
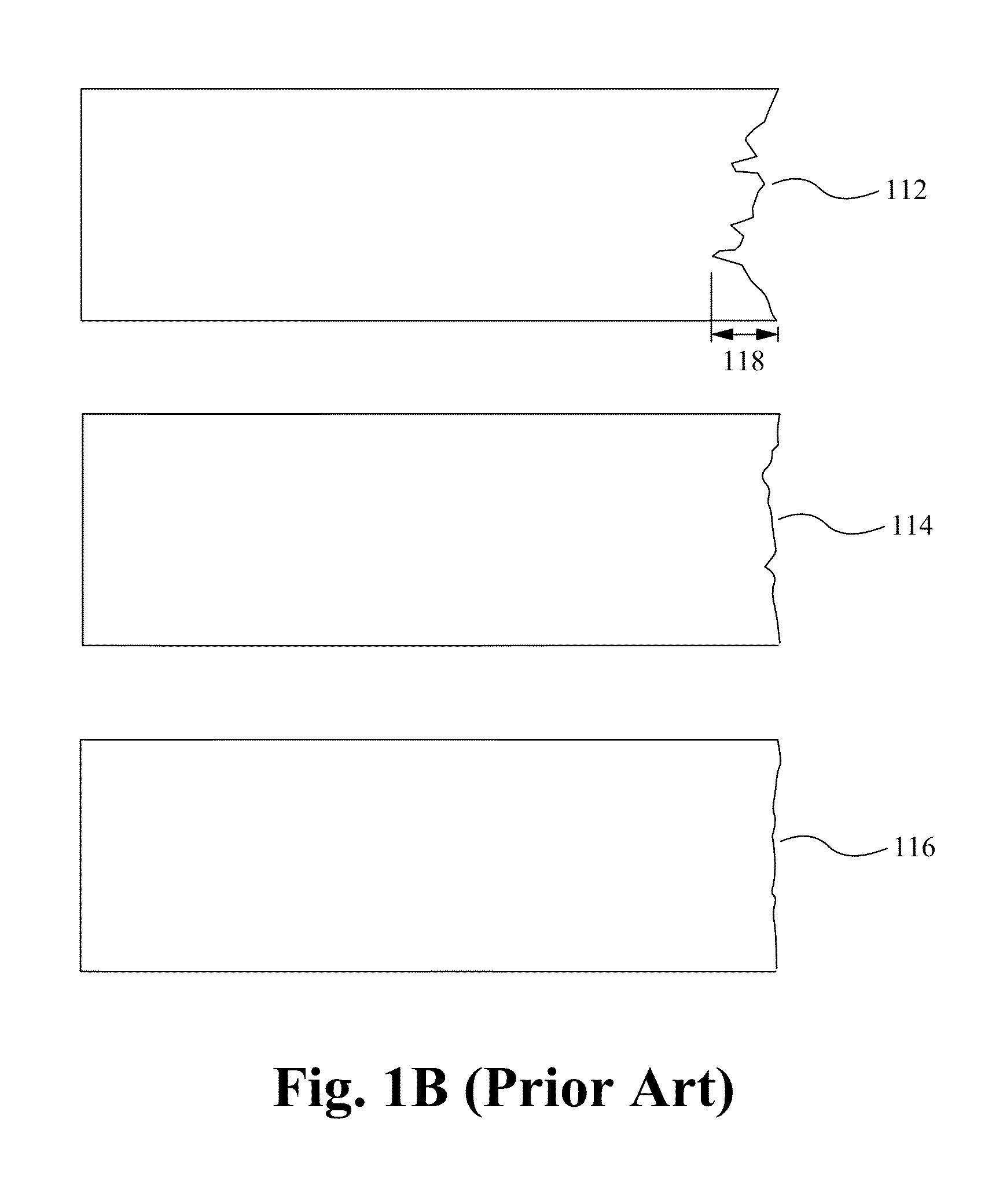
Cutting of brittle materials with tailored edge shape and roughness
InactiveUS20140027951A1Control precisionAuxillary shaping apparatusGlass severing apparatusBiomedical engineeringLaser beams
The method of and device for cutting brittle materials with tailored edge shape and roughness are disclosed. The methods can include directing one or more tools to a portion of brittle material causing separation of the material into two or more portions, where the as-cut edge has a predetermined and controllable geometric shape and / or surface morphology. The one or more tools can comprise energy (e.g., a femtosecond laser beam or acoustic beam) delivered to the material without making a physical contact.
Owner:COHERENT INC +1
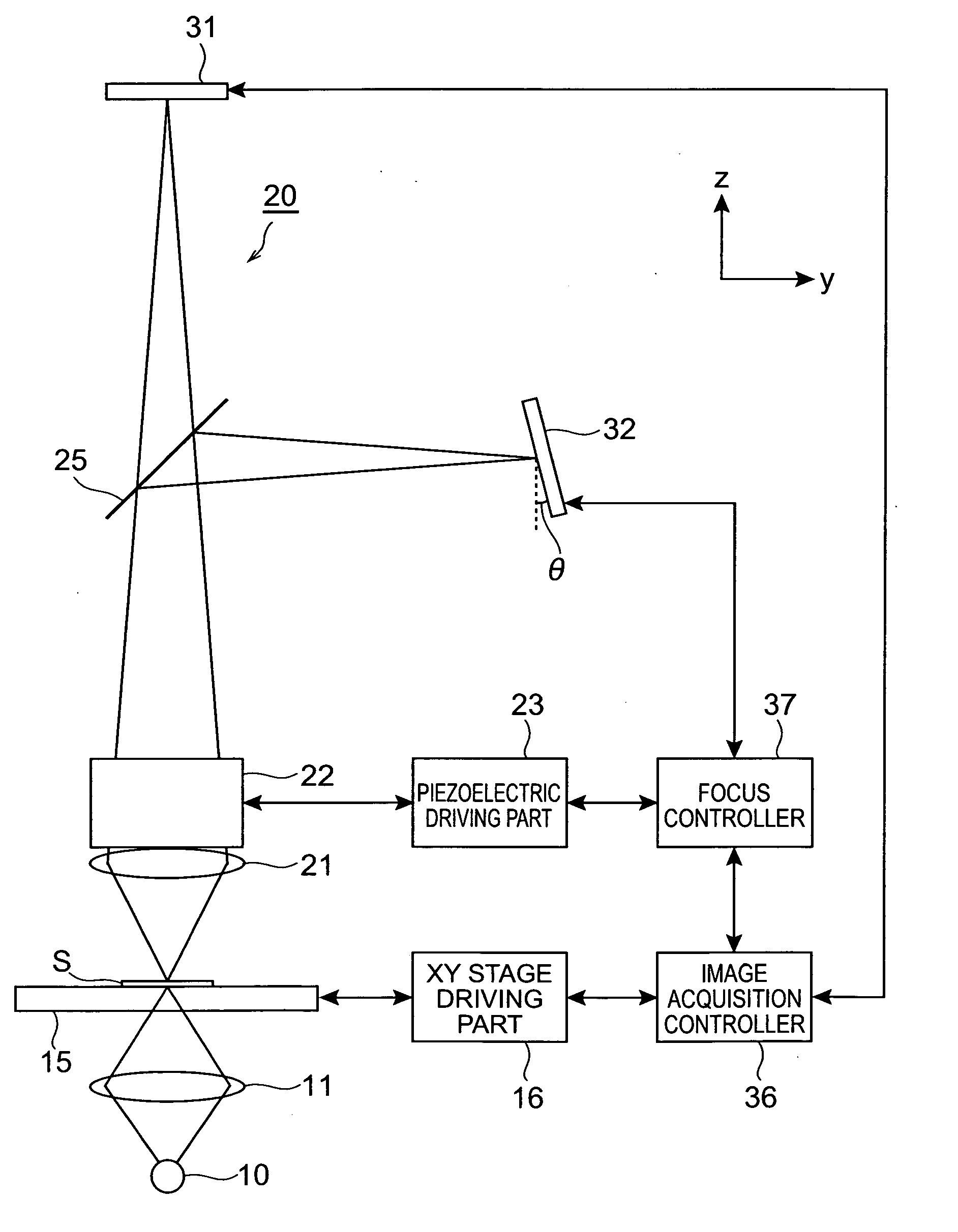
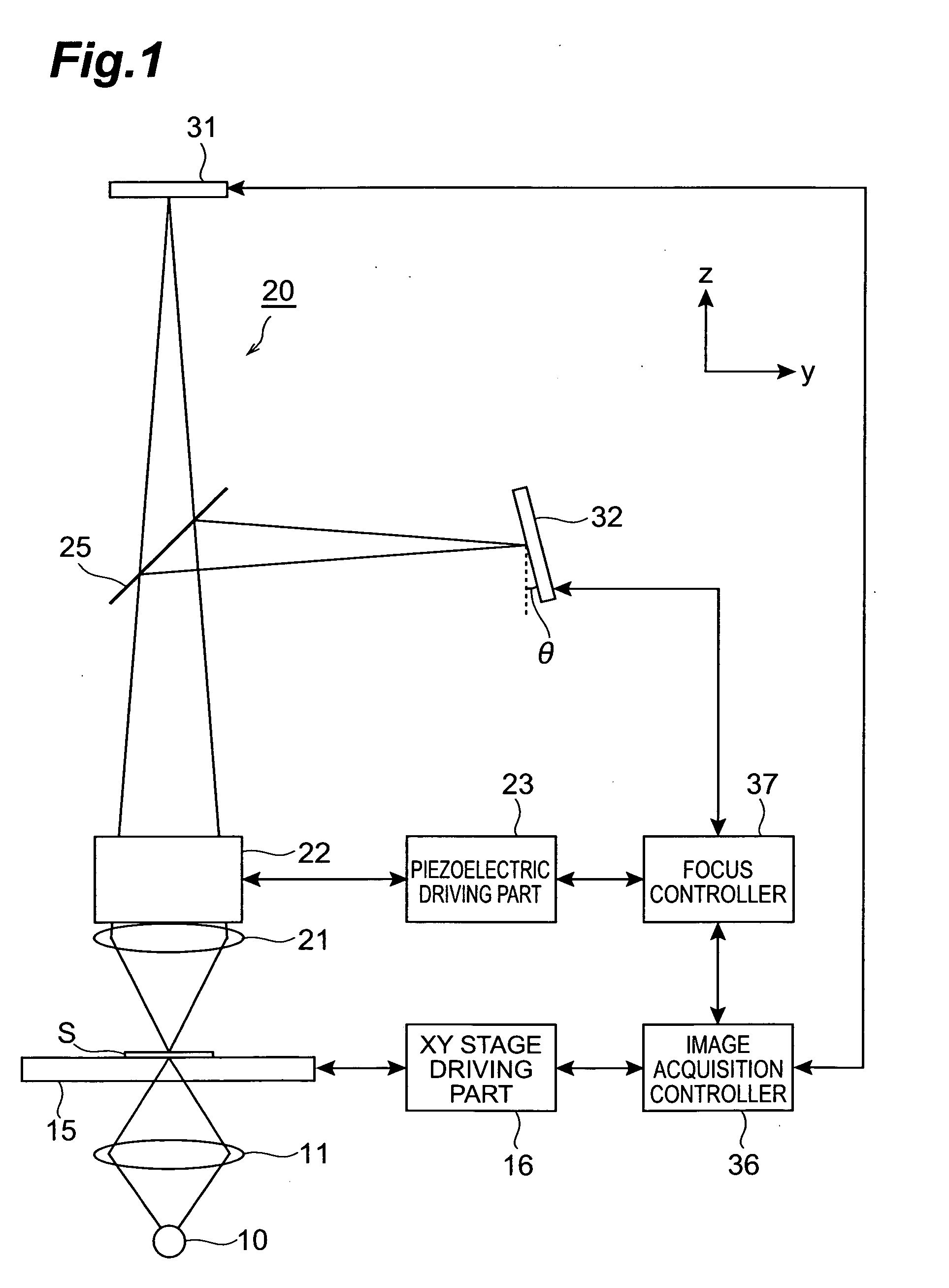
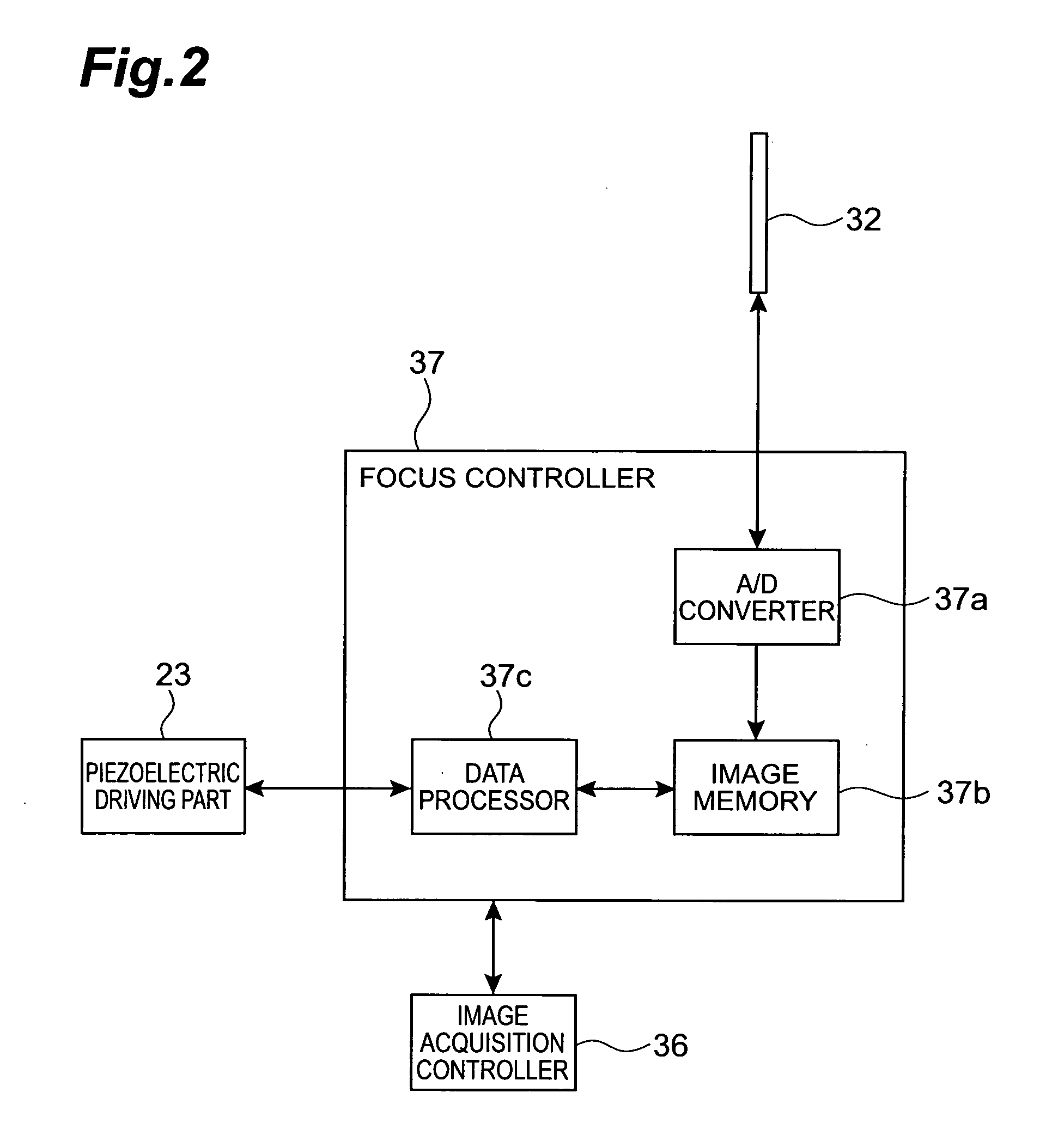
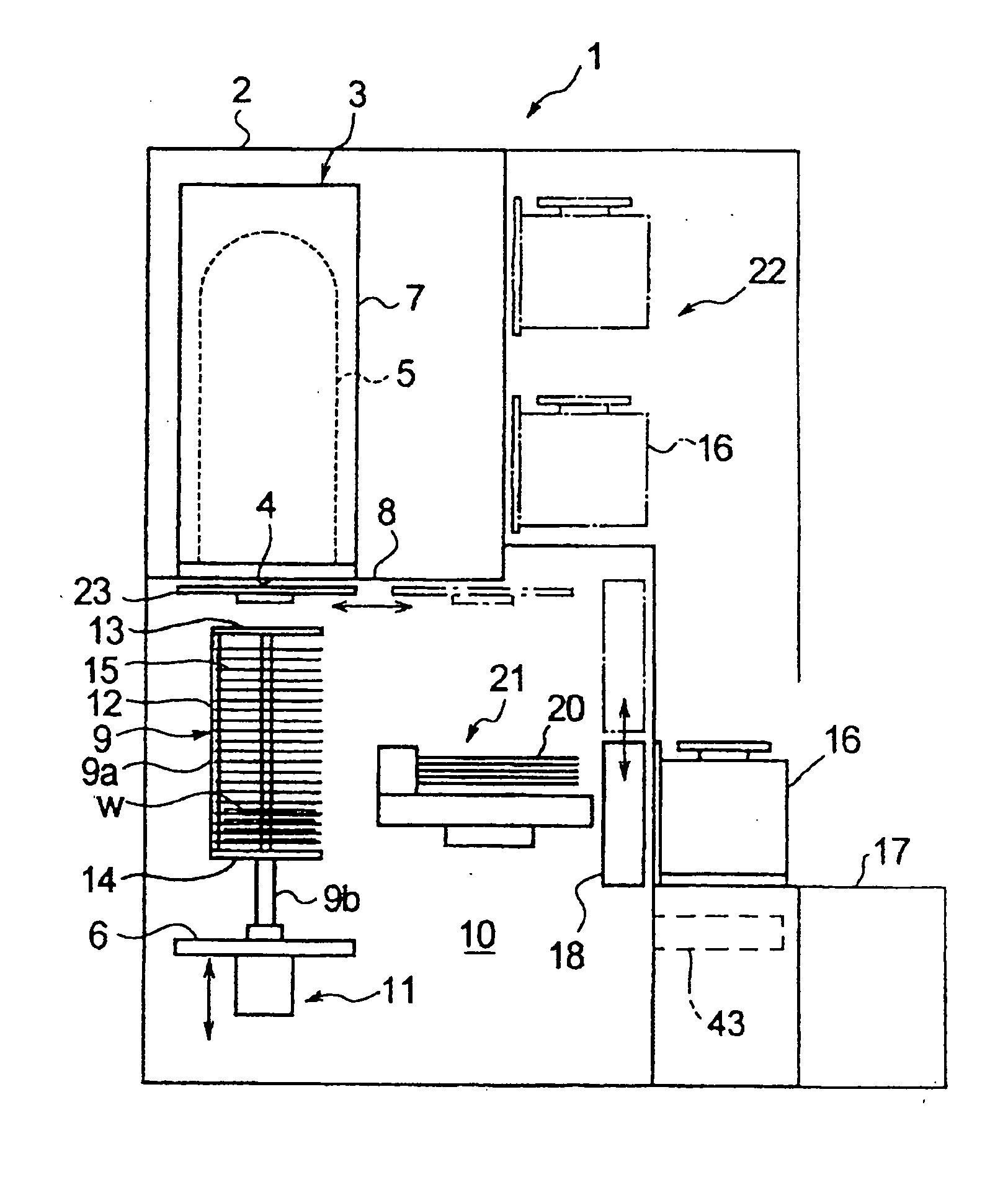
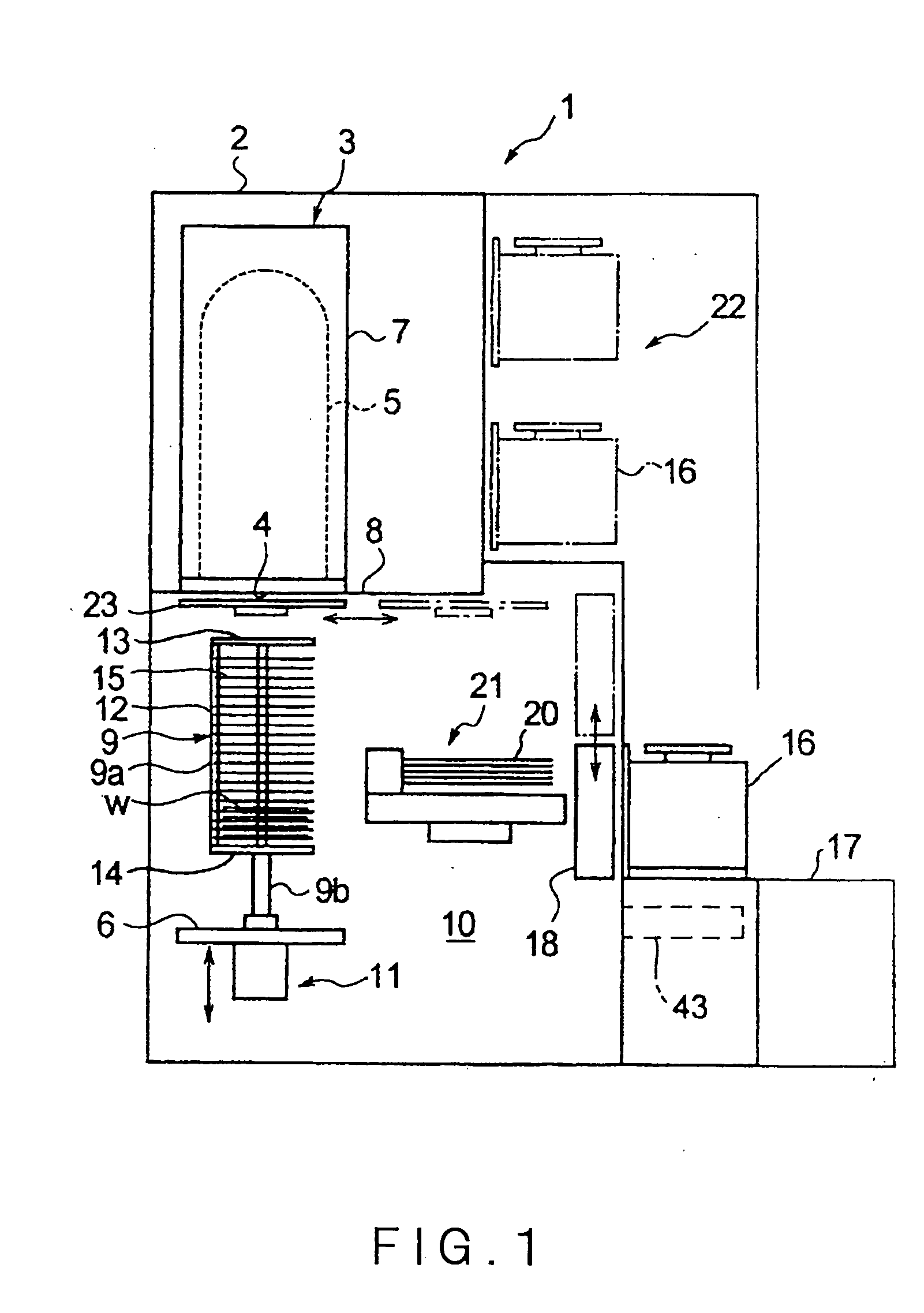
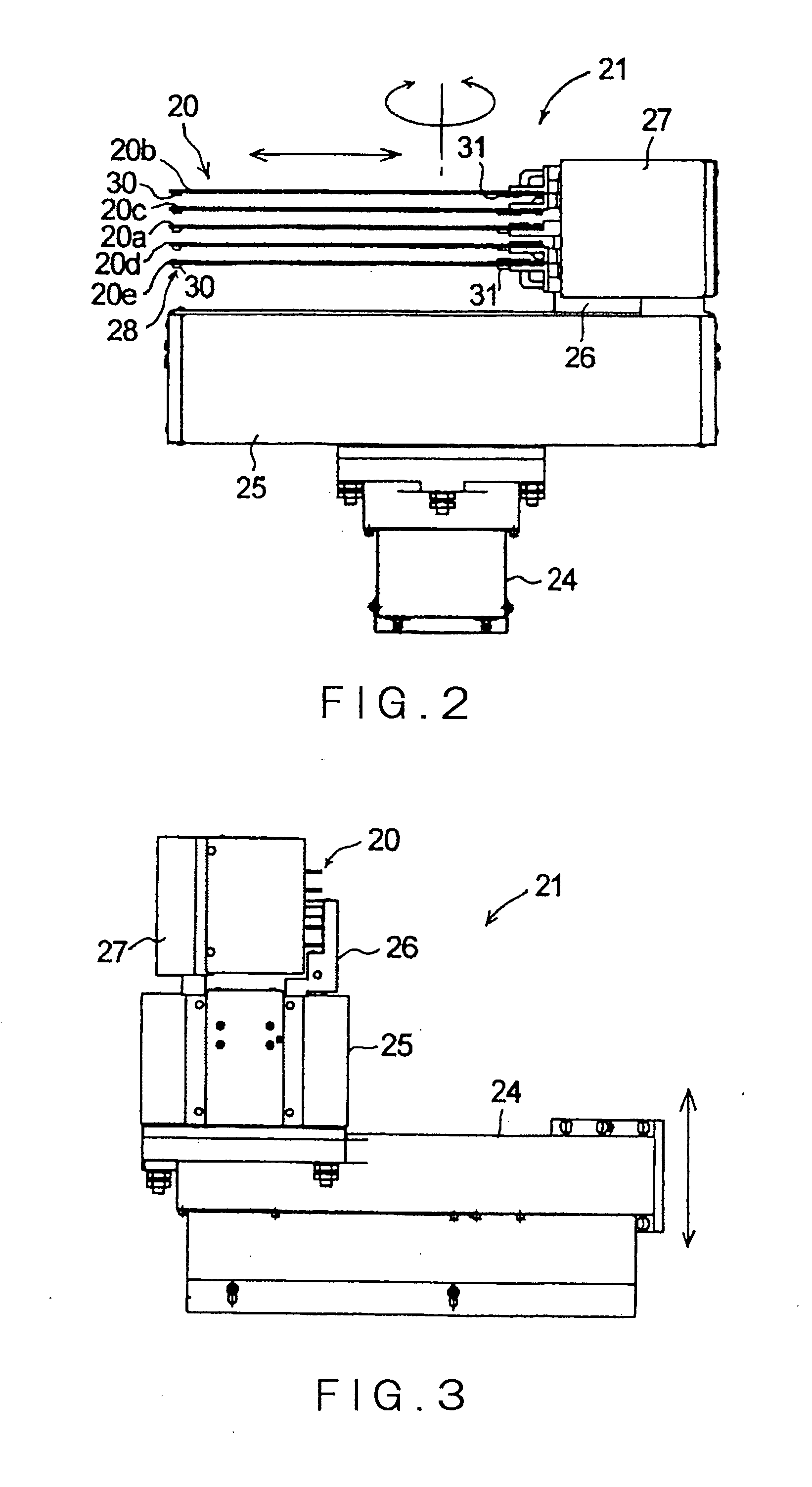
Microscope system
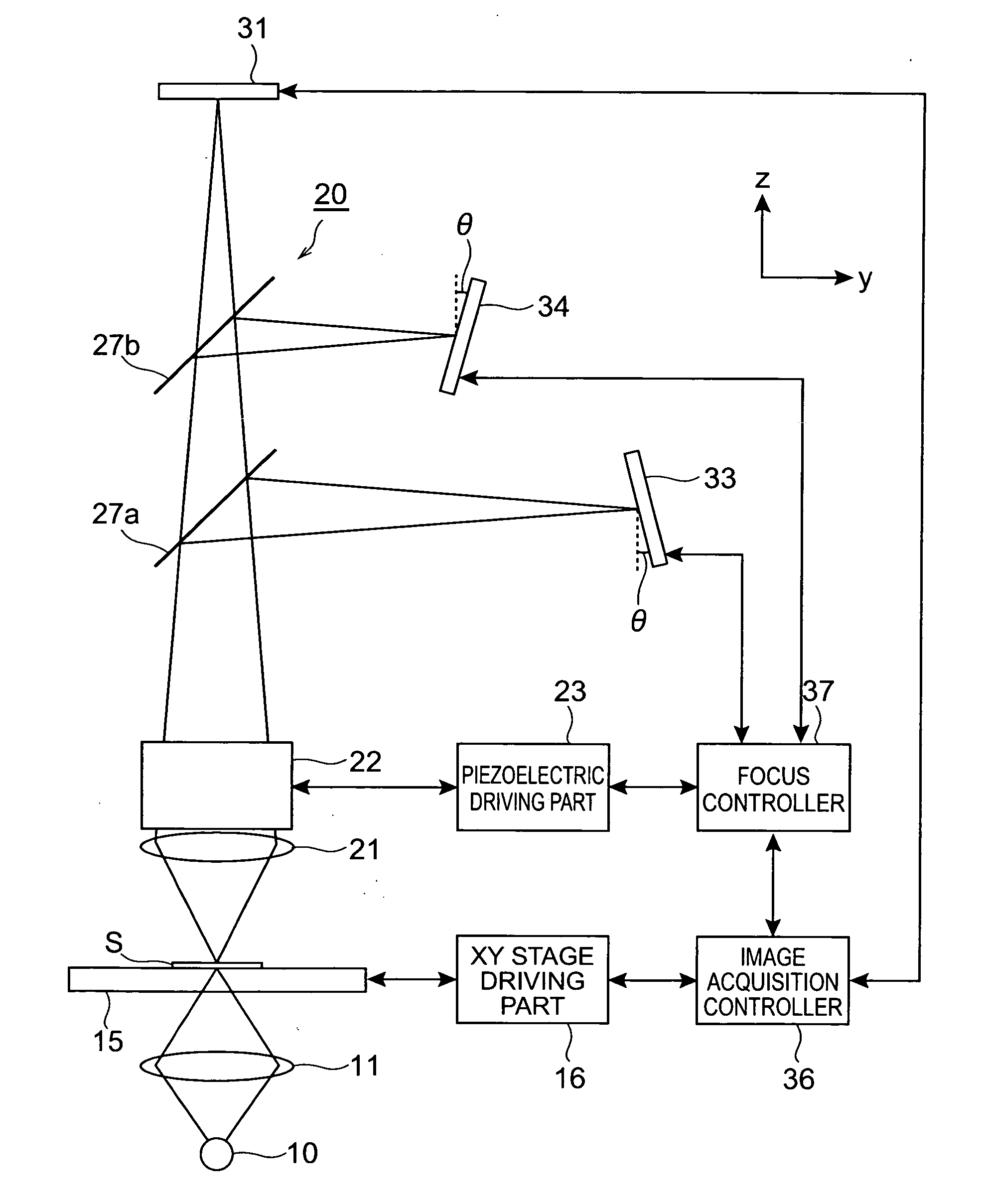
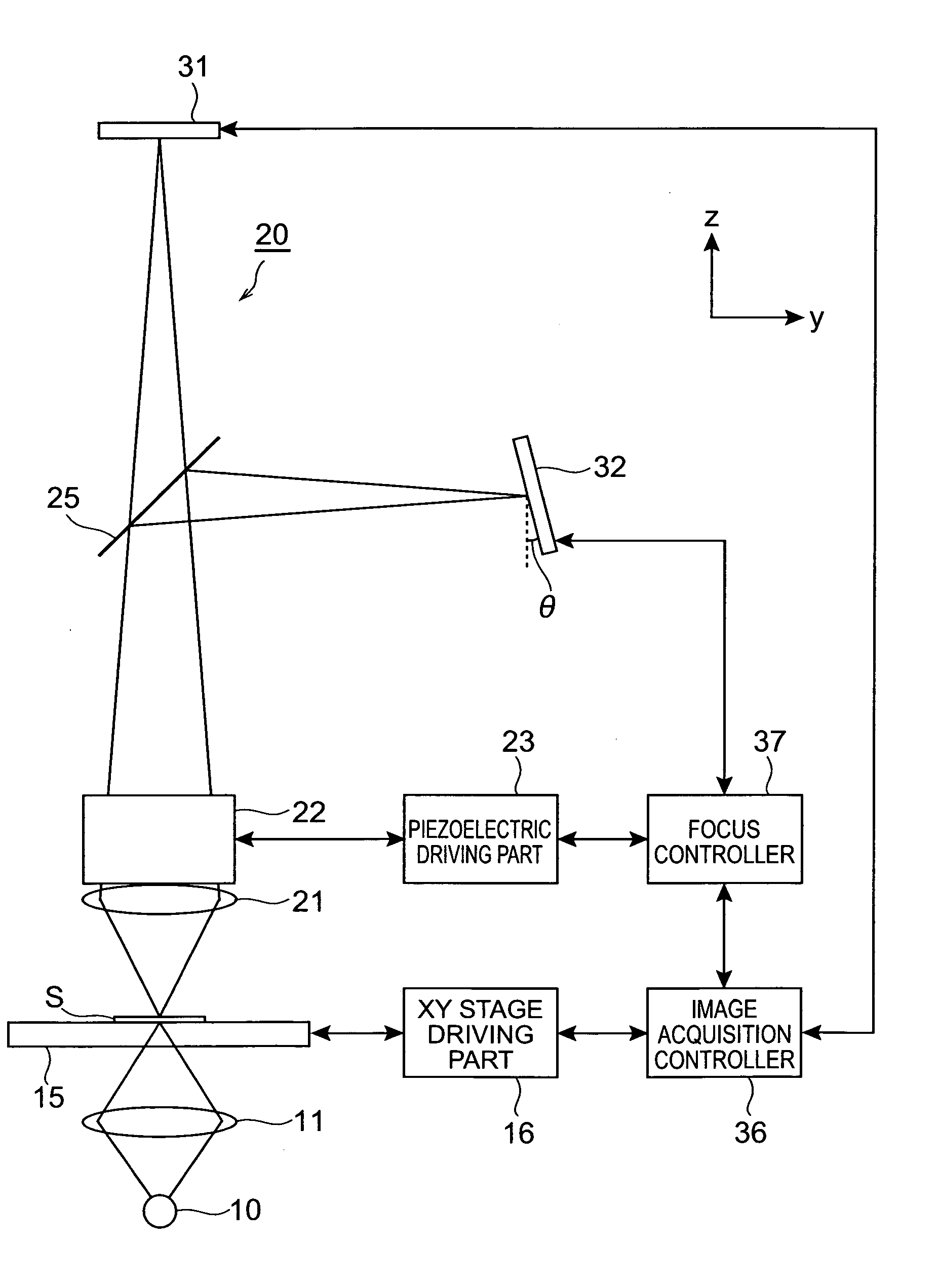
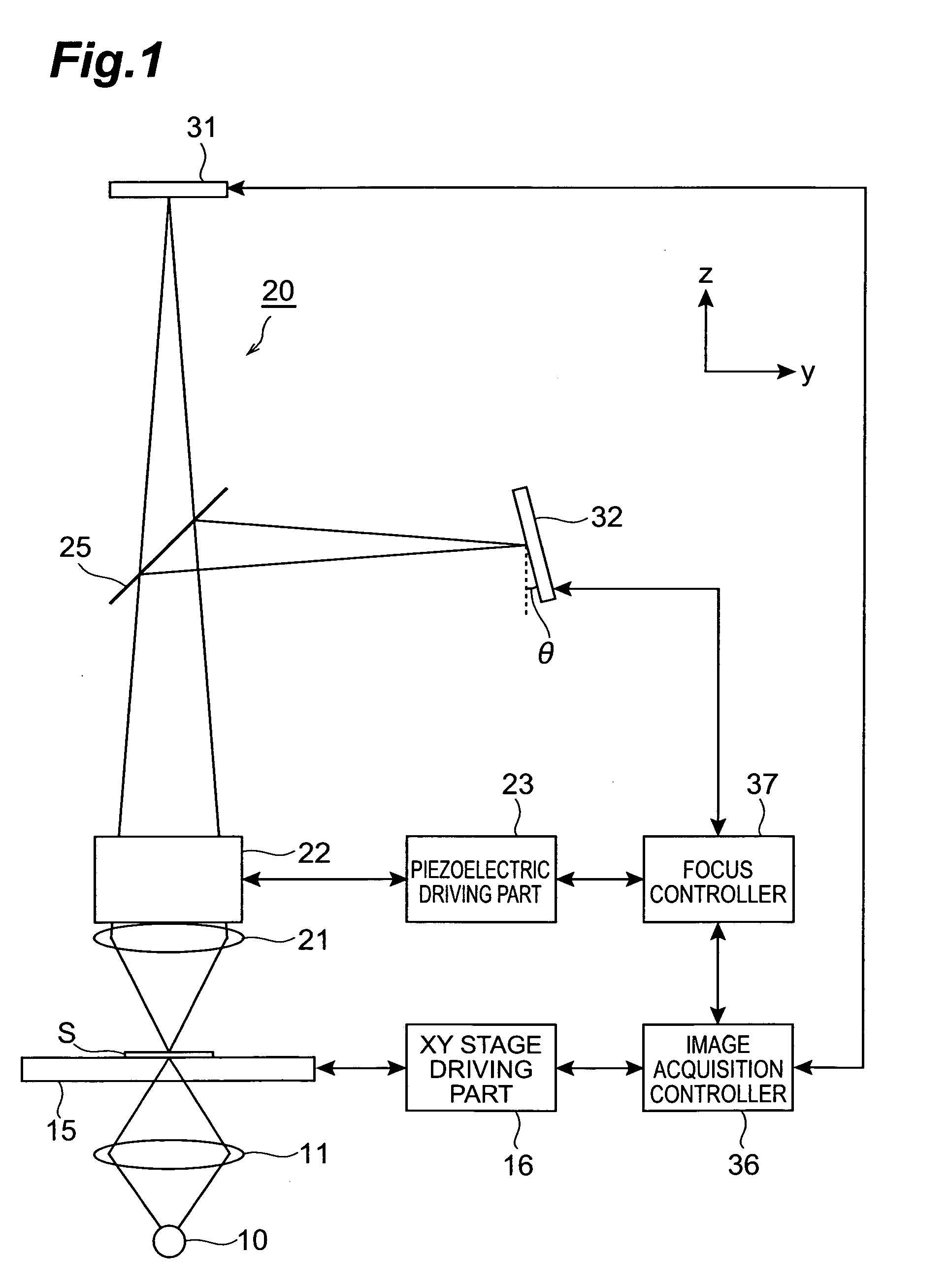
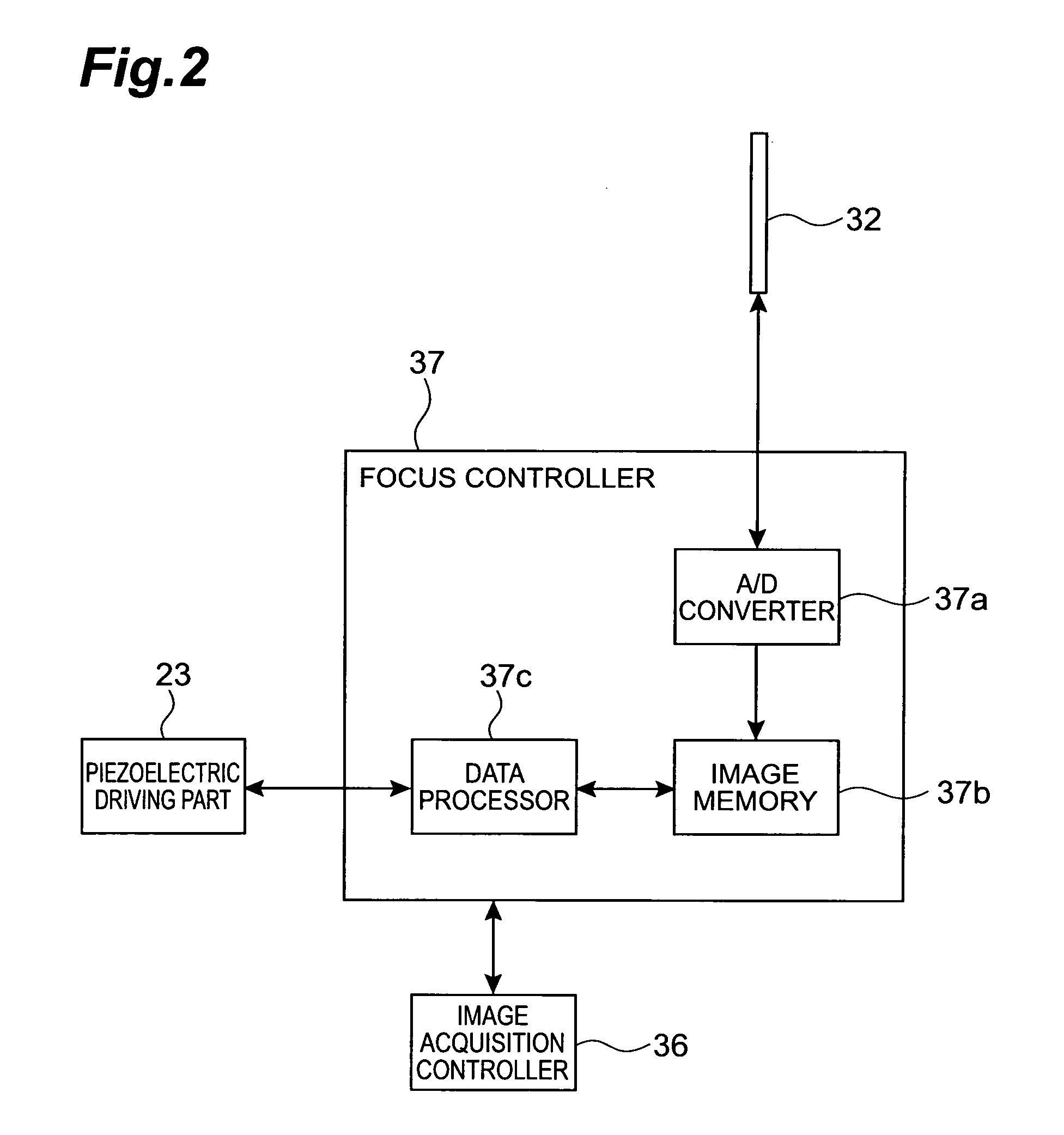
ActiveUS20050258335A1Suitable performanceControl precisionMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesBeam splitterPhotovoltaic detectors
A microscope system comprises a light guiding optical system 20 containing an objective lens 21 and a beam splitter 25 for splitting an optical image of a sample S to a first optical path and a second optical path, a photodetector 31 disposed on the first optical path used to acquire an image of the sample S, and a CCD camera 32 disposed on the second optical path for acquiring a two-dimensional image for focus control. The camera 32 is disposed being inclined at an angle of θ with respect to the optical path so that the optical path length in the light guiding optical system 20 varies along the z-axis direction. The image acquired by the camera 32 is analyzed by a focus controller 37, and the focal point for image pickup with respect to the sample S is controlled on the basis of the analysis result. Accordingly, there can be implemented a microscope system in which image acquisition of the sample and focus control for image pickup can be simultaneously performed.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
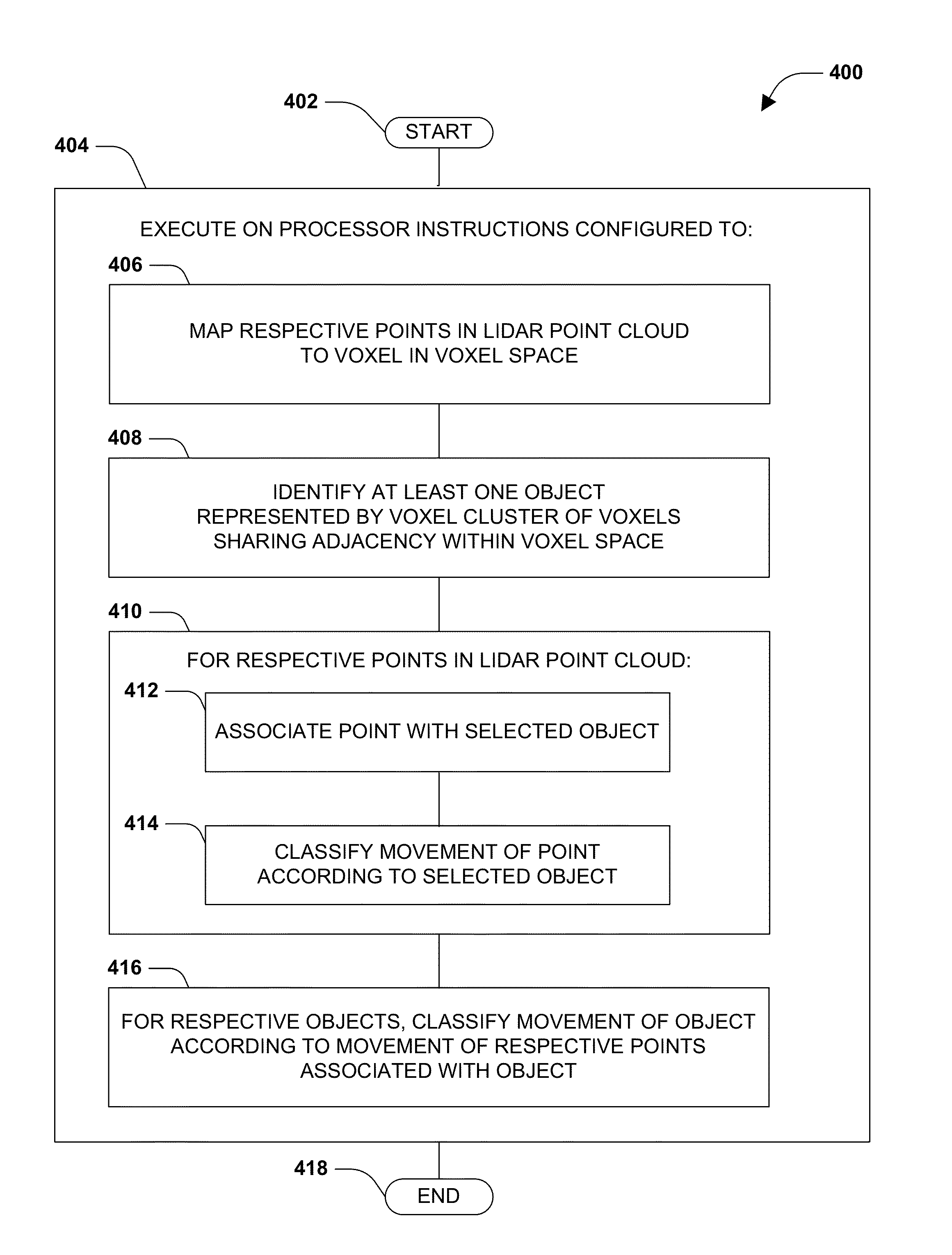
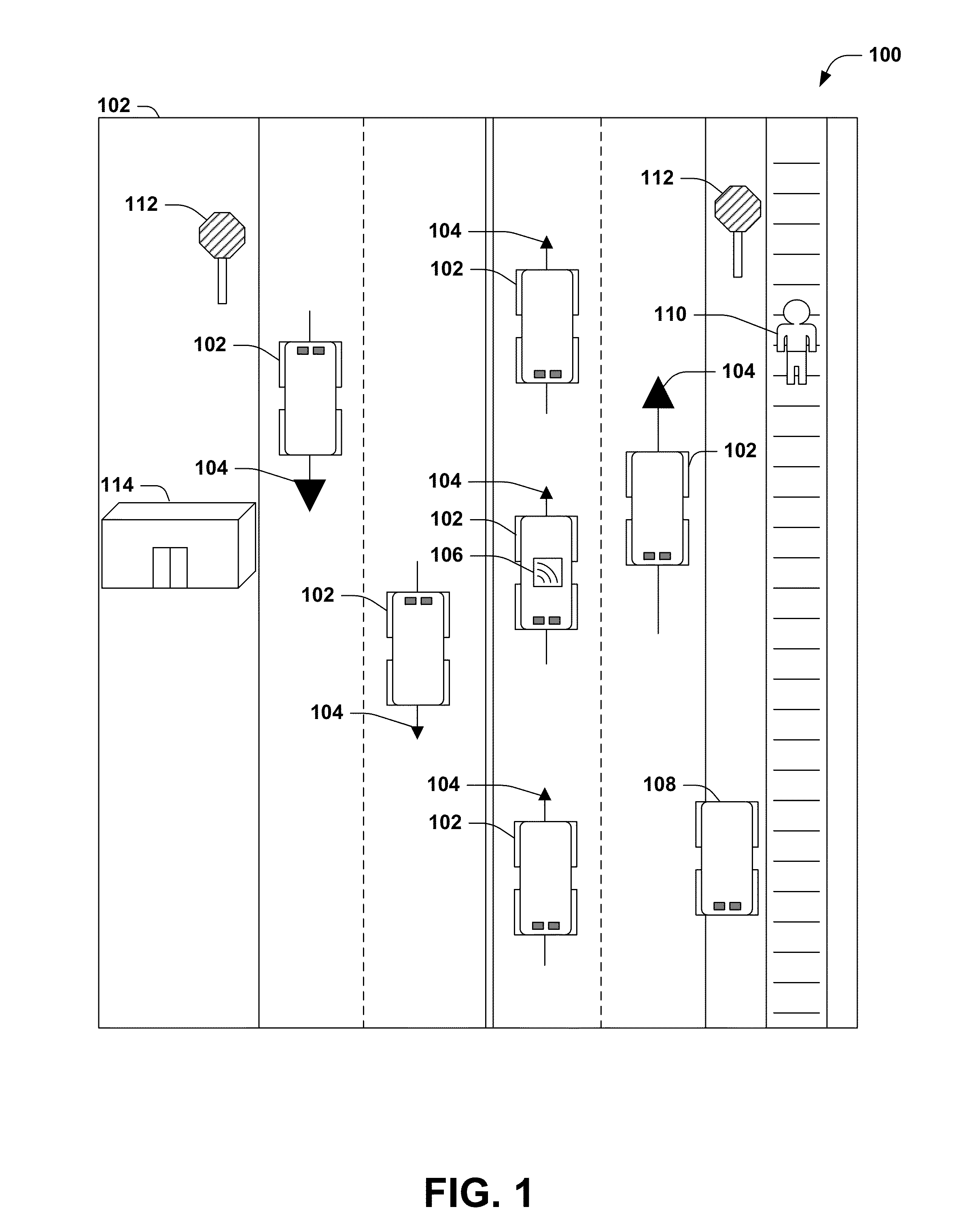
Lidar-based classification of object movement
ActiveUS20140368807A1Precise processControl precisionScene recognitionDevices using optical meansMarine navigationParallax
Within machine vision, object movement is often estimated by applying image evaluation techniques to visible light images, utilizing techniques such as perspective and parallax. However, the precision of such techniques may be limited due to visual distortions in the images, such as glare and shadows. Instead, lidar data may be available (e.g., for object avoidance in automated navigation), and may serve as a high-precision data source for such determinations. Respective lidar points of a lidar point cloud may be mapped to voxels of a three-dimensional voxel space, and voxel clusters may be identified as objects. The movement of the lidar points may be classified over time, and the respective objects may be classified as moving or stationary based on the classification of the lidar points associated with the object. This classification may yield precise results, because voxels in three-dimensional voxel space present clearly differentiable statuses when evaluated over time.
Owner:UBER TECH INC
Microscope system
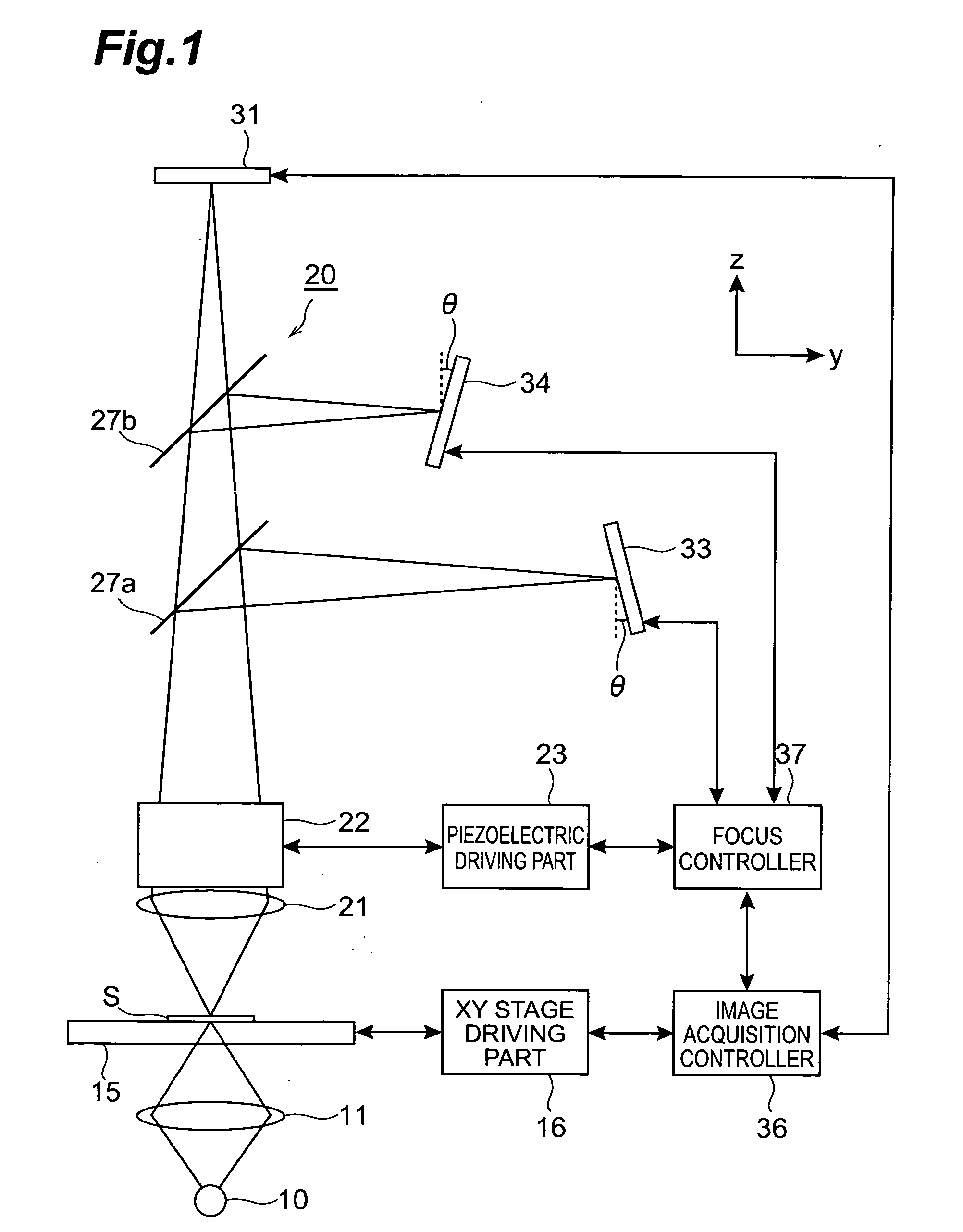
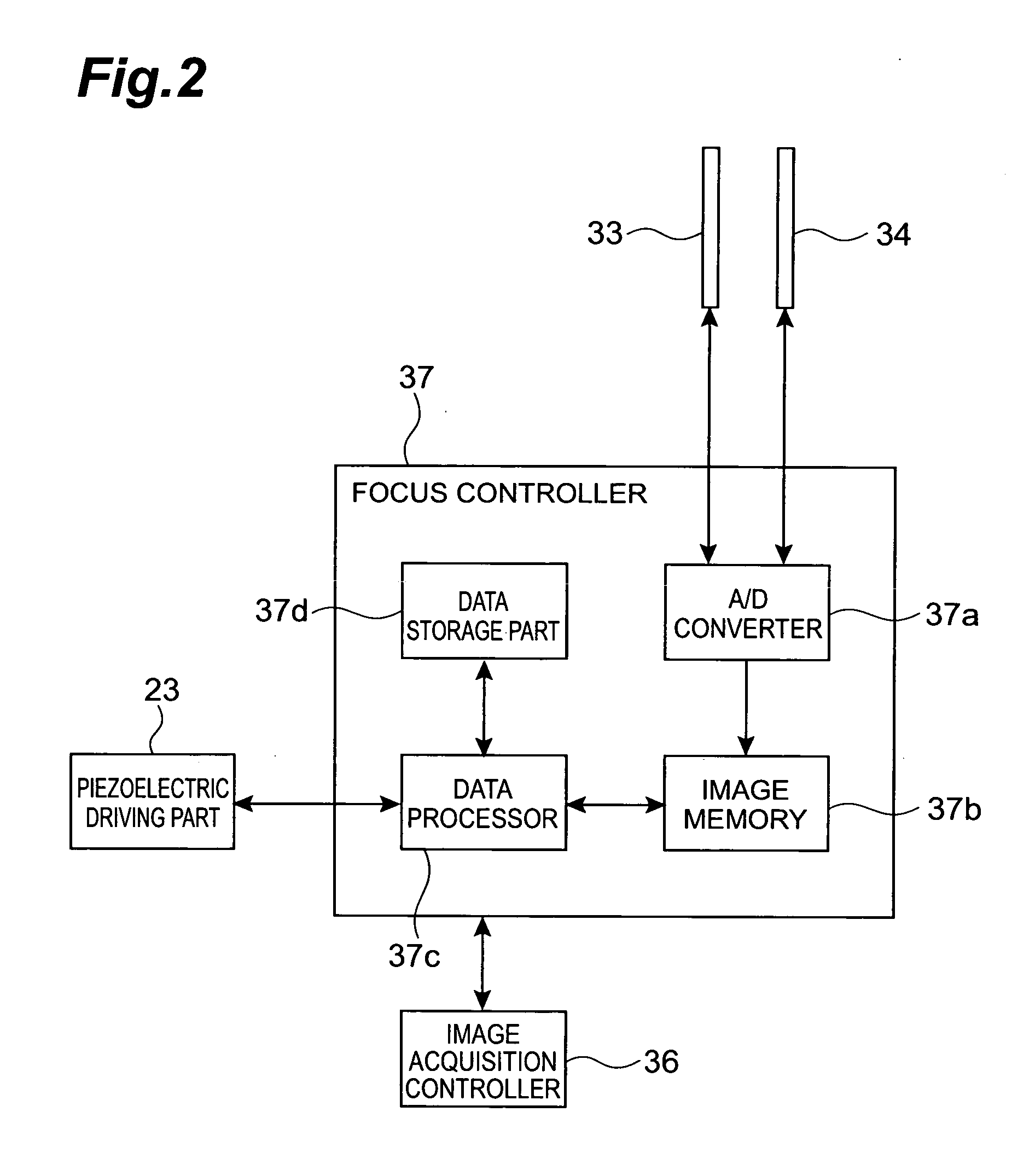
InactiveUS20050270611A1High precisionImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer security arrangementsPhotovoltaic detectorsBeam splitter
A microscope system is constructed by a light guiding optical system 20 having an objective lens 21 and beam splitters 27a and 27b for splitting an optical image of a sample S, a photodetector 31 for acquiring an image of the sample S, and two CCD cameras 33 and 34 for focus control disposed on optical paths split by the beam splitters 27a and 27b. The cameras 33 and 34 are disposed being inclined with respect to the optical path so that the optical paths thereof in the light guiding optical system 20 vary along a z-axis direction in opposite directions to each other. Images acquired by these cameras 33 and 34 are analyzed in a focus controller 37, and the image pickup focal point to the sample S is controlled on the basis of the analysis result, whereby the focus control when an image of the sample is acquired can be suitably performed.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Selective laser melting forming molten bath real-time monitoring device and monitoring method
ActiveCN106363171AImprove yieldEasy to controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyForming processesPulsed laser
The invention relates to a selective laser melting forming molten bath real-time monitoring device and a monitoring method, and belongs to the technical field of 3D printing additive manufacturing. The selective laser melting forming molten bath real-time monitoring device and the monitoring method can monitor the molten bath temperature, the shape and the area in the SLM forming process in real time, conduct online assessment on the forming precision and the laser power and feed back the result. According to the adopted technical scheme, a melting forming laser system and a pulsed laser are arranged on the top of a forming cavity, a piece of transparent glass is arranged in the center of the top of the forming cavity, a laser lens tube is arranged above the transparent glass, and the pulsed laser is connected with the laser lens tube through an optical fiber. A lifting frame is arranged in the forming cavity, lifting mechanisms are arranged on the two sides of the lifting frame, and cameras are arranged at the bottom of the lifting frame in the mode of different angles. The melting forming laser system, the pulsed laser, the lifting mechanisms and the cameras are connected with a master control system. The selective laser melting forming molten bath real-time monitoring device and the monitoring method are widely used for real-time monitoring of a selective laser melting forming molten bath.
Owner:山西阳宸中北科技有限公司
Method for forming control of long joist axial line of composite material stiffened wall panel
The invention belongs to technologies of composite material forming, and relates to a method for forming control of a long joist axial line of a composite material stiffened wall panel in an aviation aircraft. The method is a fixture method suitable for forming control of long joist axial lines of various types, such as a T shape, an I shape, a J shape and the like, of long joist composite material stiffened wall panels. A forming fixture mainly comprises a long joist forming mold A and a long joist forming mold B, a skinned curing mold, a cushion block and an axial line positioning mold. The two ends of the long joist forming mold A are designed to be dovetail-shaped and are closed matched with the axial line positioning mold to control the deviation of a long joist in the length direction of the axial line; and the axial line positioning mold is fixed on the skinned curing mold through positioning pins to control left and right deviations of the long joist axial line. By the forming fixture method, the molding surface quality and the position accuracy of a long joist product are effectively improved, and the long joist axial line is prevented from deviation.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Transfer head and transfer system for semiconductor light-emitting device and method for transferring semiconductor light-emitting device
ActiveUS20180277524A1Increase clamping forcePrecise control for alignmentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransfer systemDisplay device
The present invention relates to a display device and, more particularly, to a transfer head for a semiconductor light-emitting device applied to the display device and a method for transferring a semiconductor light-emitting device. The transfer head for a semiconductor light-emitting device, according to the present invention, comprises: a base substrate; and an electrode unit disposed on the base substrate to generate an electrostatic force by charging an un-doped semiconductor layer of the semiconductor light-emitting device with electric charges, wherein the base substrate and the electrode unit are formed of light-transmitting materials so that at least a part of the semiconductor light-emitting device is viewable through the base substrate and the electrode unit in sequence.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Broadside subsection integrated construction method
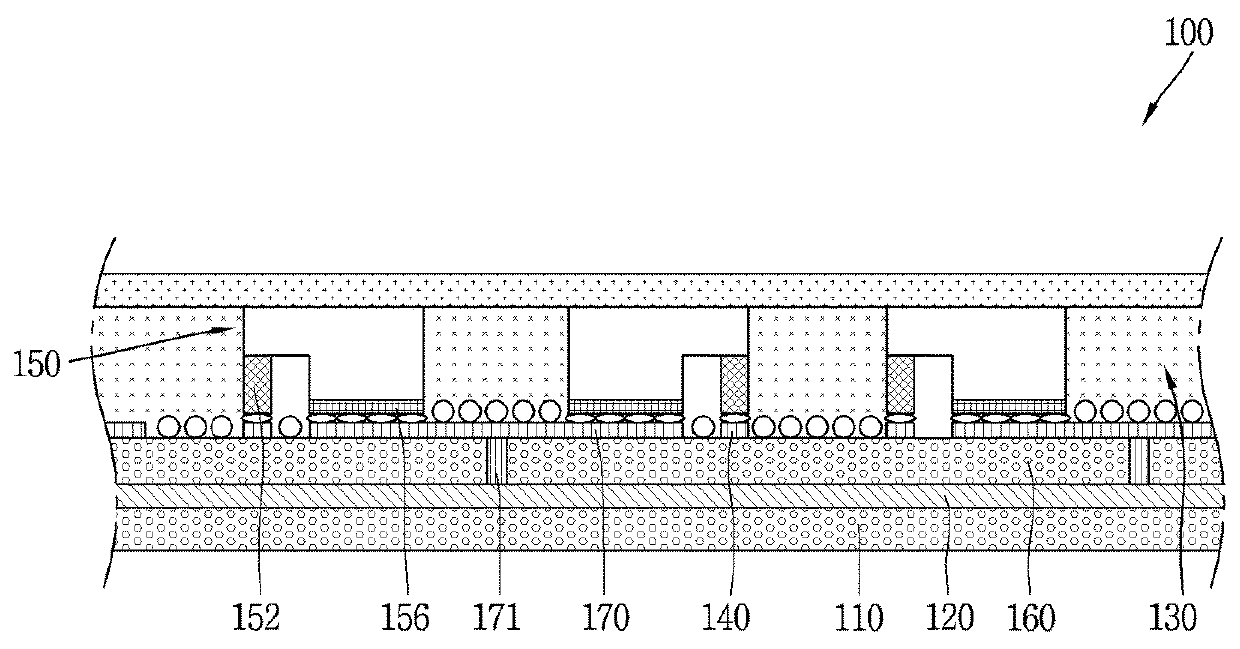
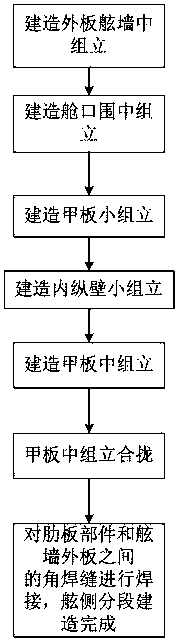
InactiveCN108177730AControl positioning welding accuracyAvoid wastingVessel partsEngineeringIntermediate product
The invention discloses a broadside subsection integrated construction method, and belongs to the technical field of ship construction. The broadside subsection integrated construction method comprises the following steps that 1, a planking bulwark middle assembly is constructed by taking a planking as a base face; 2, a hatch coaming middle assembly is constructed by taking a midship longitudinalwall as a base face; 3, a deck small assembly is constructed by taking the upper surface of a deck as a base face; 4, taking a longitudinal wall splicing plate as a base face, a rib plate part is mounted on an inner longitudinal wall splicing plate to form an inner longitudinal wall small assembly; 5, the deck small assembly is overturned by 90 degrees to be folded with the inner longitudinal wallsmall assembly so as to form a deck middle assembly; 6, the planking is overturned by 180 degrees and then hoisted to the top of the deck middle assembly to be folded, and the hatch coaming middle assembly is transversally moved and folded to the side face of the deck middle assembly, so that a broadside subsection is formed; and 7, the broadside subsection is overturned by 180 degrees, and welding is completed. A planking bulwark and a hatch coaming are integrally constructed, the integrity of the ship section intermediate product is expanded, the precision of ship construction is improved,and the efficiency of ship construction is improved.
Owner:HUDONG ZHONGHUA SHIPBUILDINGGROUP
Assembling precision control method of single-body blades in blisk of electron beam welding structure
InactiveCN102837160AImprove assembly accuracy before weldingBreak through the key technical difficulties that the weld seam gap is less than 0.1mmWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesEngineeringWeld line
The invention belongs to the field of machining and particularly relates to an assembling precision control method of single-body blades in a blisk of an electron beam welding structure. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: firstly, machining the single-body blades; designing convex technical circular platforms at blades tip parts of blade blanks; utilizing five coordinate milling centers to simultaneously mill welding surfaces and blade body modeled faces of the blades; dividing the single-body blades into seven groups to be clamped on a specific welding clamp, so as to finally control an assembling error to be within 0.05 mm; and after assembling, carrying out subsequent electron beam welding. According to the assembling precision control method disclosed by the invention, a reasonable blade forging blank structure design, integrated precise machining of blade references and welding surfaces, predication before welding of welding deformation of the blades, pre-compensation before welding, reasonable design of an assembling and welding clamp, and precise assembling of the blades on the clamp before welding, and the like are applied, so that the assembling precision of the blades before the welding is greatly improved, and the key technical difficulty that the gap between welding lines is ensured to be less than 0.1mm before electron beams are welded is broken through; and the after-welding precision of the blisk of the electron beam welding structure is controlled, an industrial blank is filled and the researching cost and the researching period are reduced at the same time.
Owner:SHENYANG LIMING AERO-ENGINE GROUP CORPORATION
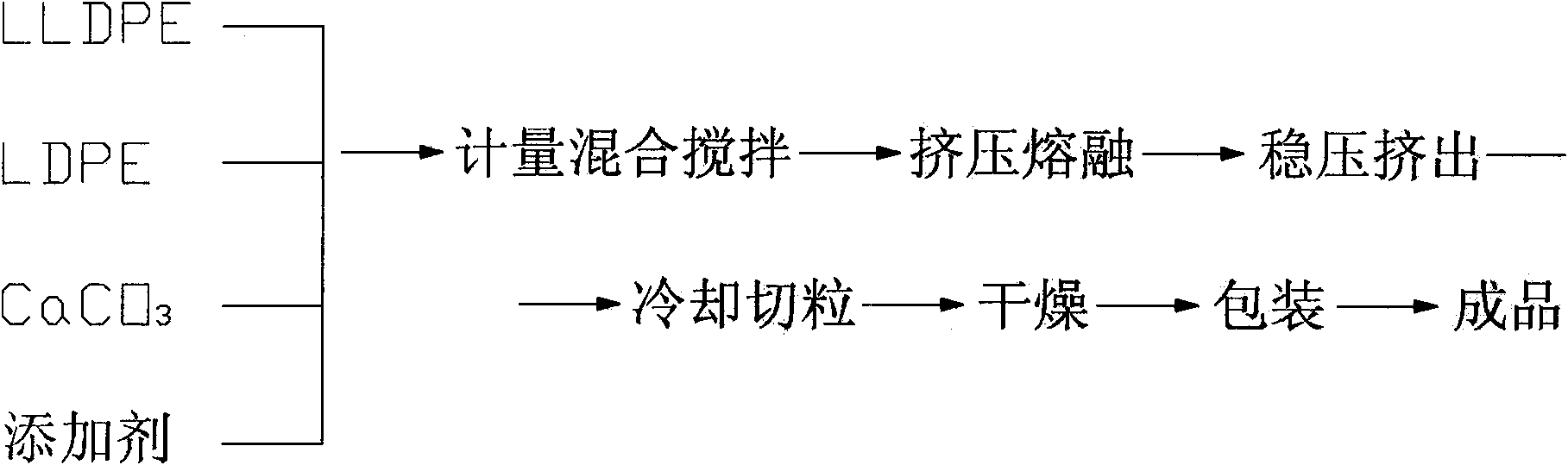
Ultrathin high porosity film and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an ultrathin high porosity film and a preparation method thereof. The film comprises the following components by weight percent: 40-50% of : PE(LLDPE / LDPE), 45-55% of calcium carbonate and 3-5% of modified additives (plastic additive and film forming additive). The preparation method of the invention comprises the following steps: (1) breathable film master batch process flow and (2) breathable film process flow. The product of the invention can replace imported products, thus reducing the production cost of the breathable film, improving the current dilemma of foreignmonopoly, filling the domestic blank to develop and produce the breathable film material with independent intellectual property rights and having practical and great economic benefit and social benefit.
Owner:ZHEJIANG YUEHAN TECH BREATHABLE MATERIAL
Microscope system
ActiveUS7232980B2Suitable performanceControl precisionMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceBeam splitterPhotodetector
A microscope system comprises a light guiding optical system 20 containing an objective lens 21 and a beam splitter 25 for splitting an optical image of a sample S to a first optical path and a second optical path, a photodetector 31 disposed on the first optical path used to acquire an image of the sample S, and a CCD camera 32 disposed on the second optical path for acquiring a two-dimensional image for focus control. The camera 32 is disposed being inclined at an angle of θ with respect to the optical path so that the optical path length in the light guiding optical system 20 varies along the z-axis direction. The image acquired by the camera 32 is analyzed by a focus controller 37, and the focal point for image pickup with respect to the sample S is controlled on the basis of the analysis result. Accordingly, there can be implemented a microscope system in which image acquisition of the sample and focus control for image pickup can be simultaneously performed.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
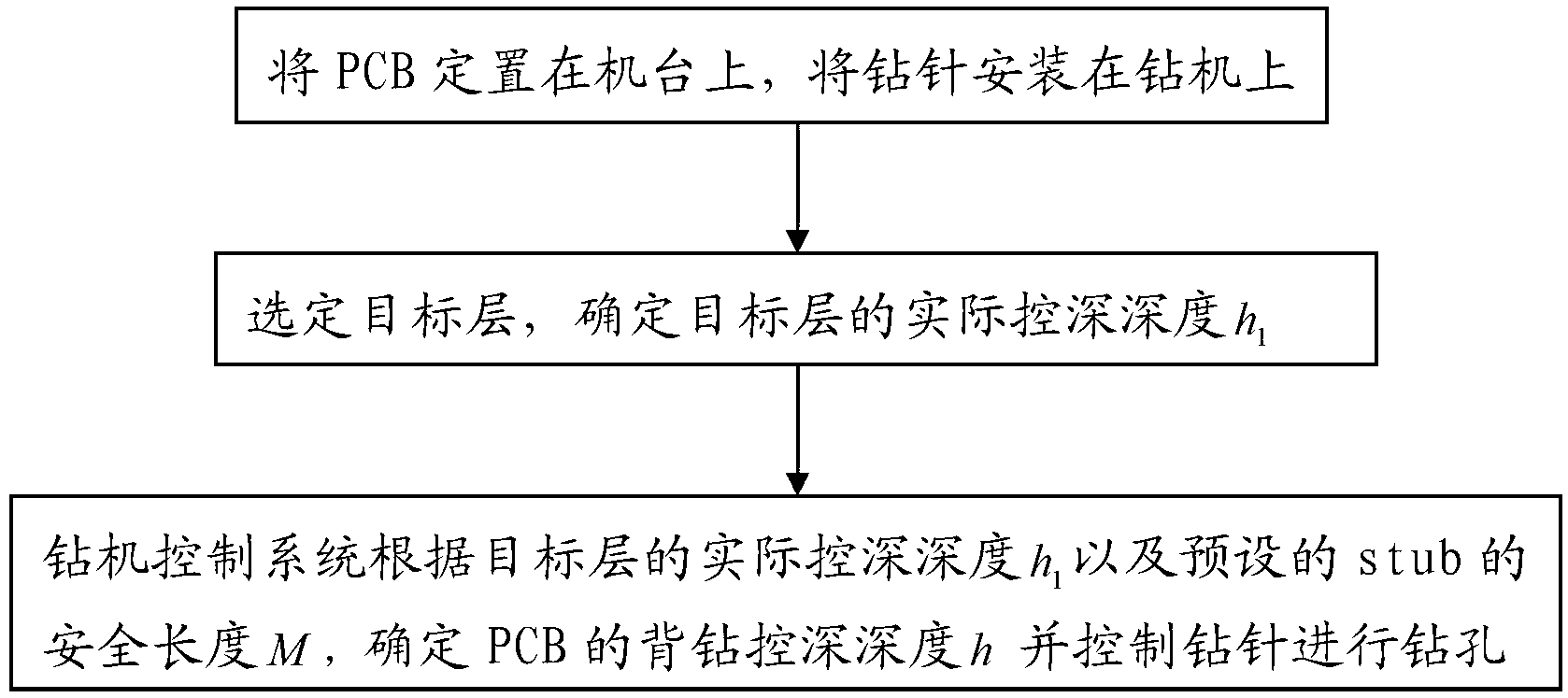
PCB (printed circuit board) back drilling method
The invention relates to a PCB (printed circuit board) back drilling method. The PCB back drilling method comprises the following steps: fixing a PCB on a machine table, and mounting a drill bit on a drilling machine; selecting a target layer, and determining an actual control depth h1 of the target layer; and determining a back drilling control depth h of the PCB according to the actual control depth h1 of the target layer and a preset safety length M of a stub and controlling the drill bit to drill a hole drilling machine control system. According to the PCB back drilling method, influence of thickness uniformity of the board, cone height of a drill tip and copper / tin-plating process variation on the accuracy of the control depth can be reduced; and through introduction of the safety length M of the stub, the precision of the PCB back drilling control depth h can be effectively controlled, thus achieving precision control of the stub and eliminating adverse effects of the stub on a signal.
Owner:GUANGZHOU FASTPRINT CIRCUIT TECH
Installation method of ship single shafting without setting front bearing of stern shaft tube
ActiveCN101723057AControl precisionGuaranteed accuracyVessel partsMedial axisPulp and paper industry
The invention discloses an installation method of ship single shafting without setting a front bearing of a stern shaft tube, mainly comprising the following steps of: determining the position of a boring hole of a bearing installing hole by using a tail datum point and a head datum point on a shafting central line as datum and adopting an illumination method; positioning a middle bearing by using the central point of a bearing installing hole at the front end of the stern shaft tube and the central point of the bearing installing hole at the back end as the datum and adopting the illumination method; and hoisting a stern shaft, a central shaft and a main machine and then connecting the central shaft with the stern shaft into single shafting. The invention initially positions the central bearing through adopting the illumination method twice to ensure that the installation precision of the ship single shafting without setting the front bearing of the stern shaft tube is effectively controlled, and can enhance the installation efficiency, ensure the installation precision of the shafting and accord with the requirements of the ship design, and the shafting installed by the installation method can run more stably so as to ensure the using safety of the bearing and the main machine.
Owner:JIANGNAN SHIPYARD GRP CO LTD
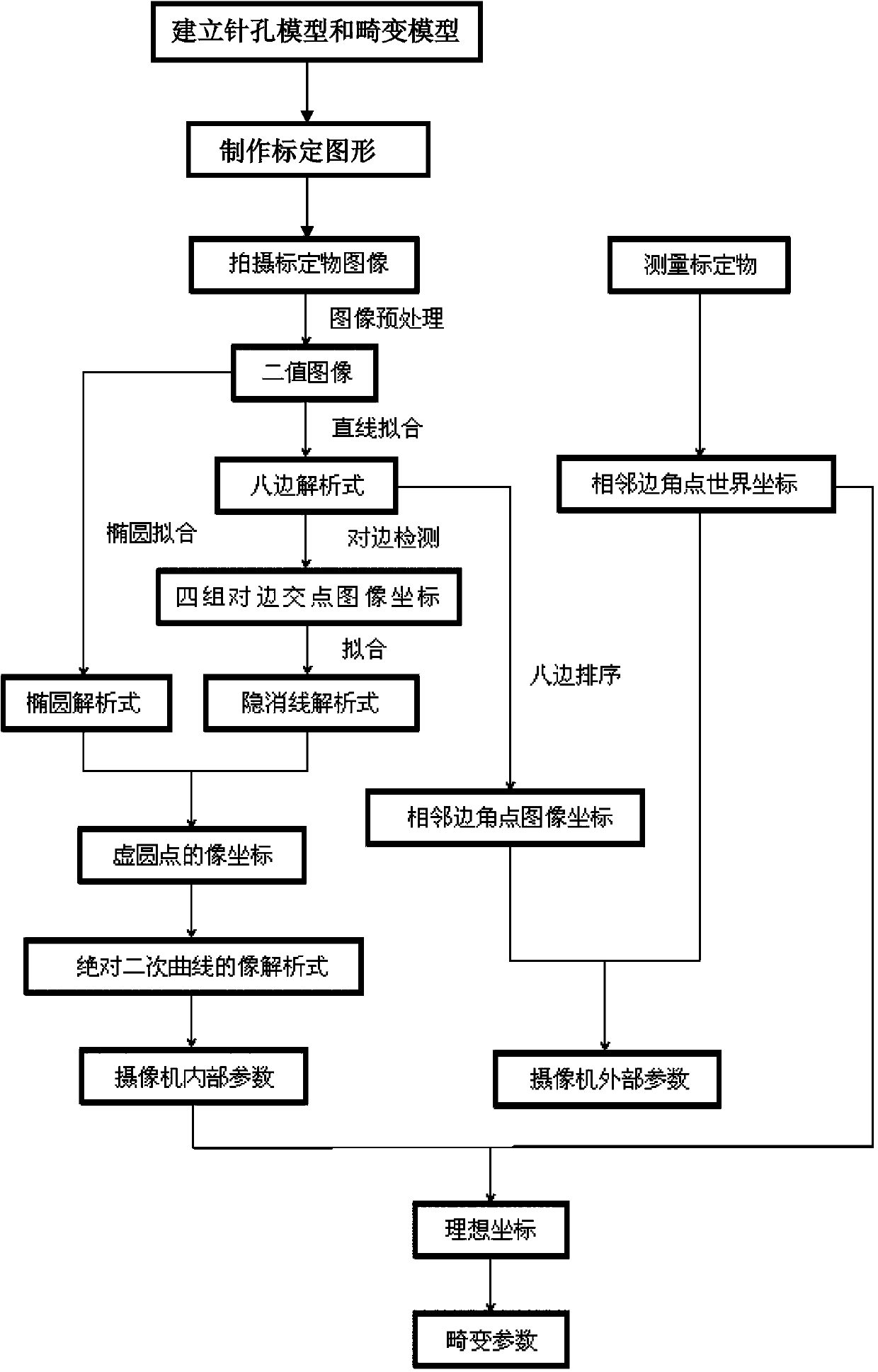
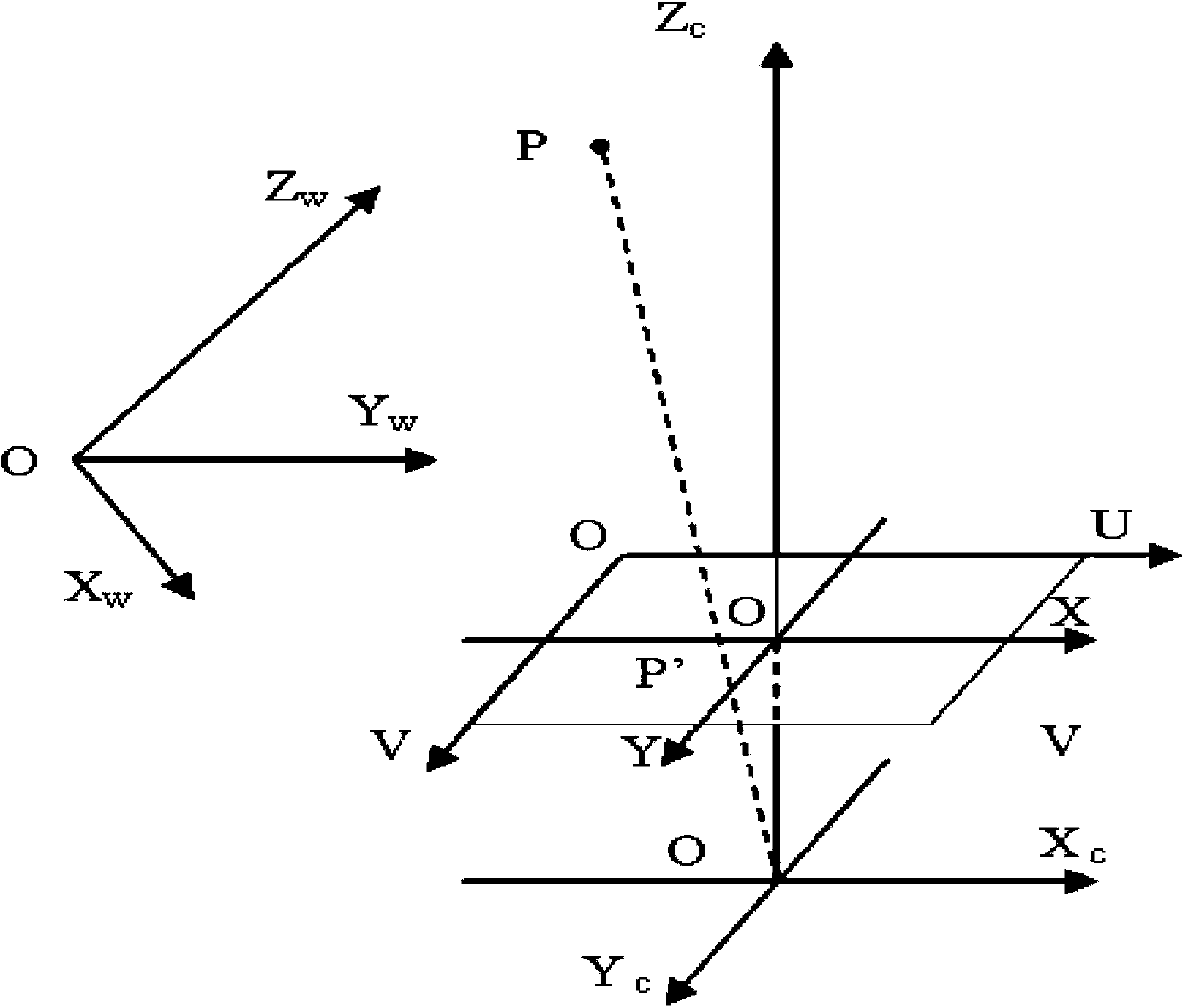
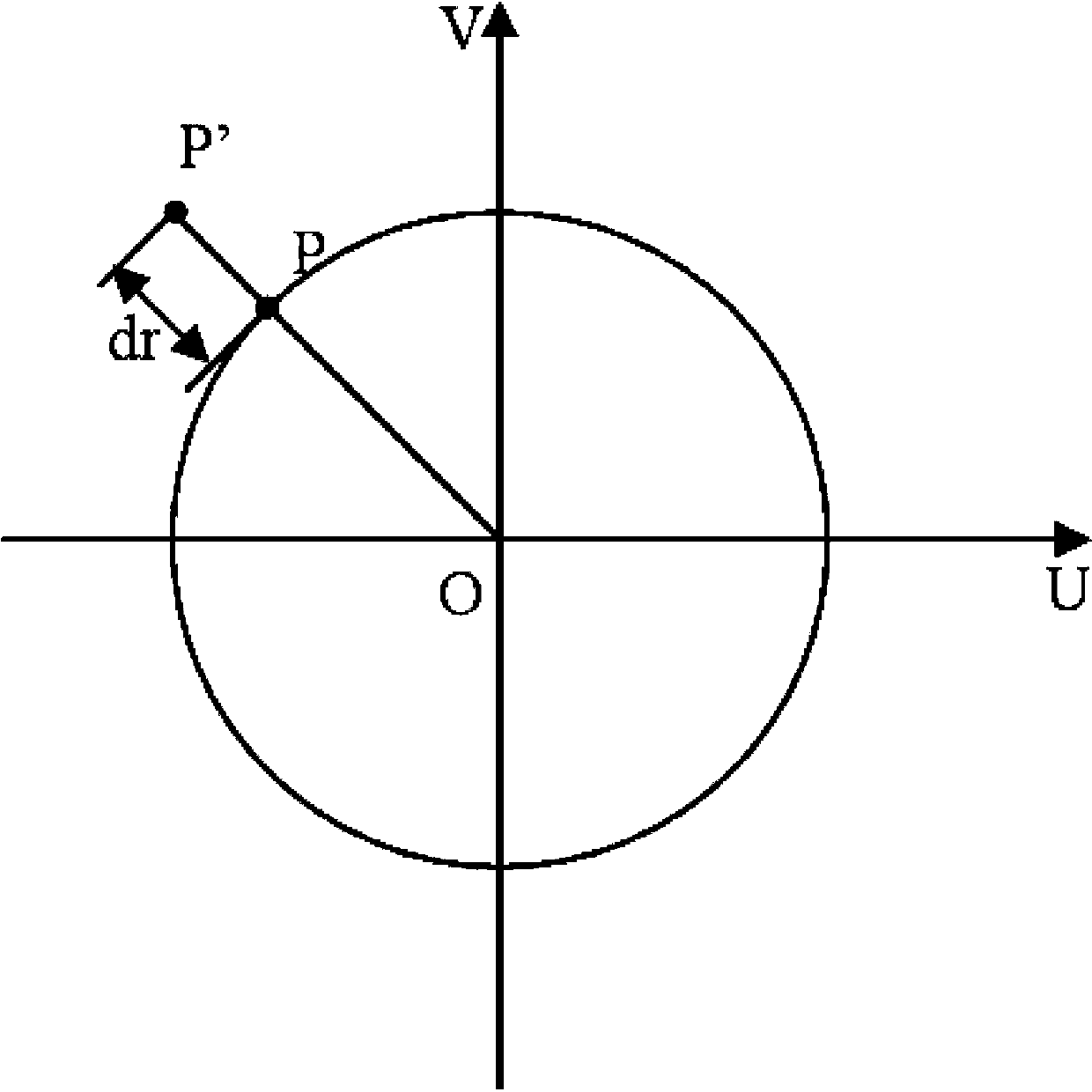
Method for calibrating camera
The invention provides a method for calibrating a camera. According to a camera calibration line circle method, a circle and an inscribed regular octagon of the circle are used as calibration objects for calibrating the camera. The circle and the inscribed regular octagon of the circle are used as the calibration objects, the camera is used for shooting the calibration objects from three different angles, three calibration object images are obtained, the calibration process is based on the shooting geometric principle, according to the relevance of the image of an absolute conic and the inside parameter of the camera, a hidden line intersects with an ellipse to obtain a circular point, an absolute conic equation is further obtained, and the inside parameter of the camber is obtained finally. An outside parameter is calibrated according to a radial array binding principle, an overdetermined equation is solved to obtain the outside parameter of the camera, at last, the radial distortion of the camera is considered, the distortion parameter of the camera is further obtained, and distortion compensation is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Machining process of middle-long thin-wall blades
ActiveCN103008741AReduce cumulative errorReduce processing stress deformationMilling equipment detailsEngineeringMachining process
The invention discloses a machining process of middle-long thin-wall blades, which belongs to the technical field of machining of blades. The machining process is implemented by a detailed process of integrated rough machining and integrated fine machining, wherein the integrated rough machining comprise the specific steps of rough machining of each surface of a blade tip, each surface of a blade root and a molded surface of a steam passage; and the integrated fine machining comprises the specific steps: semifinishing of each surface of the blade tip and each surface of the blade root, fine machining of each surface of the blade tip, each surface of the blade root and each residue, semifinishing of the steam passage and fine machining of the steam passage. According to the machining process of the middle-long thin-wall blades, the operation is simple and convenient, the use is convenient and fast, the cost is low, the machining efficiency is high, and the operation is easy and labor-saving; and the deformation of the middle-long thin-wall blades is controlled within 0 to 0.8mm, the normal machining of a subsequent mold correction process is facilitated, and the machining of each blade is finished once.
Owner:SICHUAN MIANZHU XINKUN MACHINERY MAKING
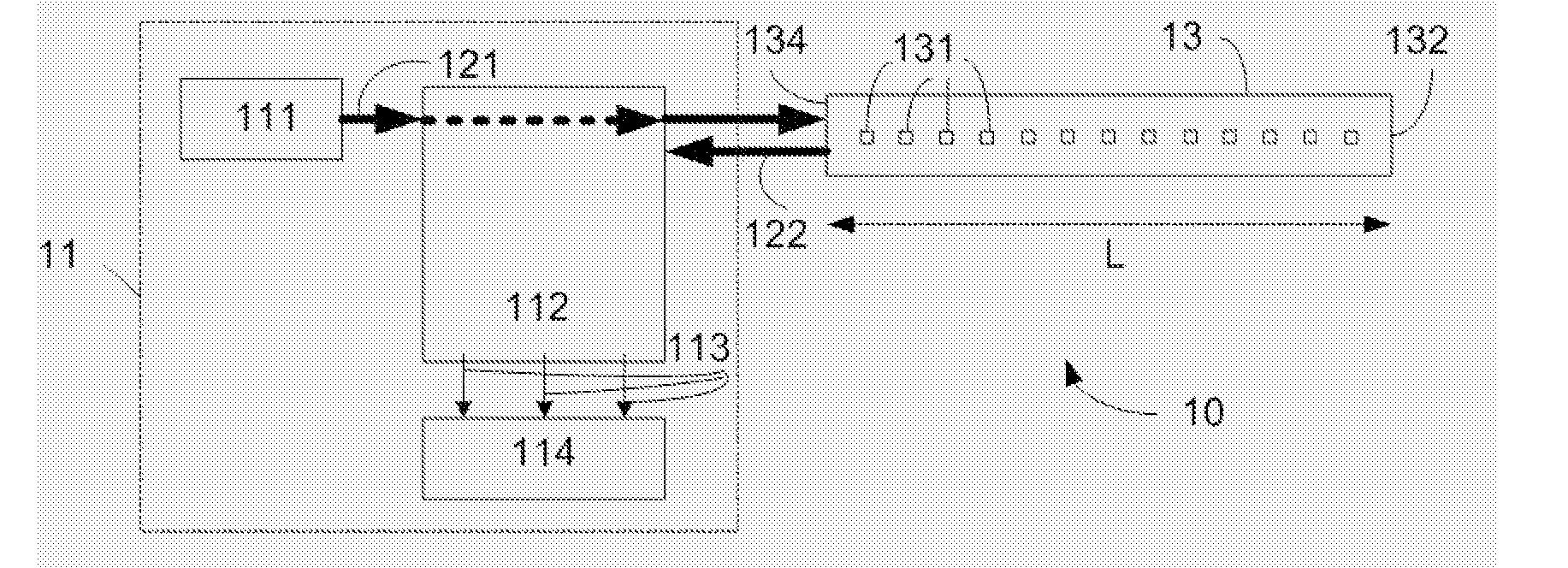
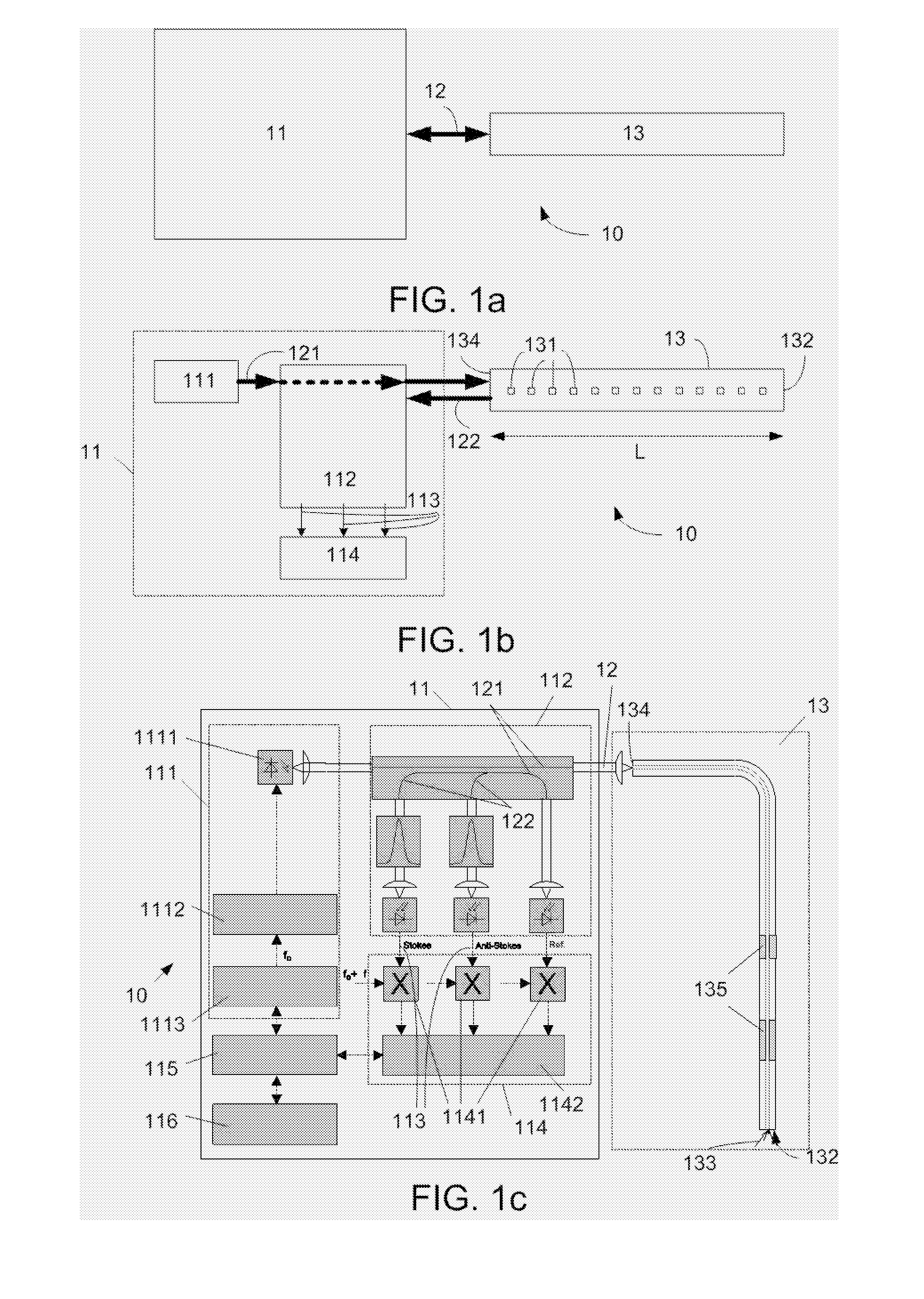
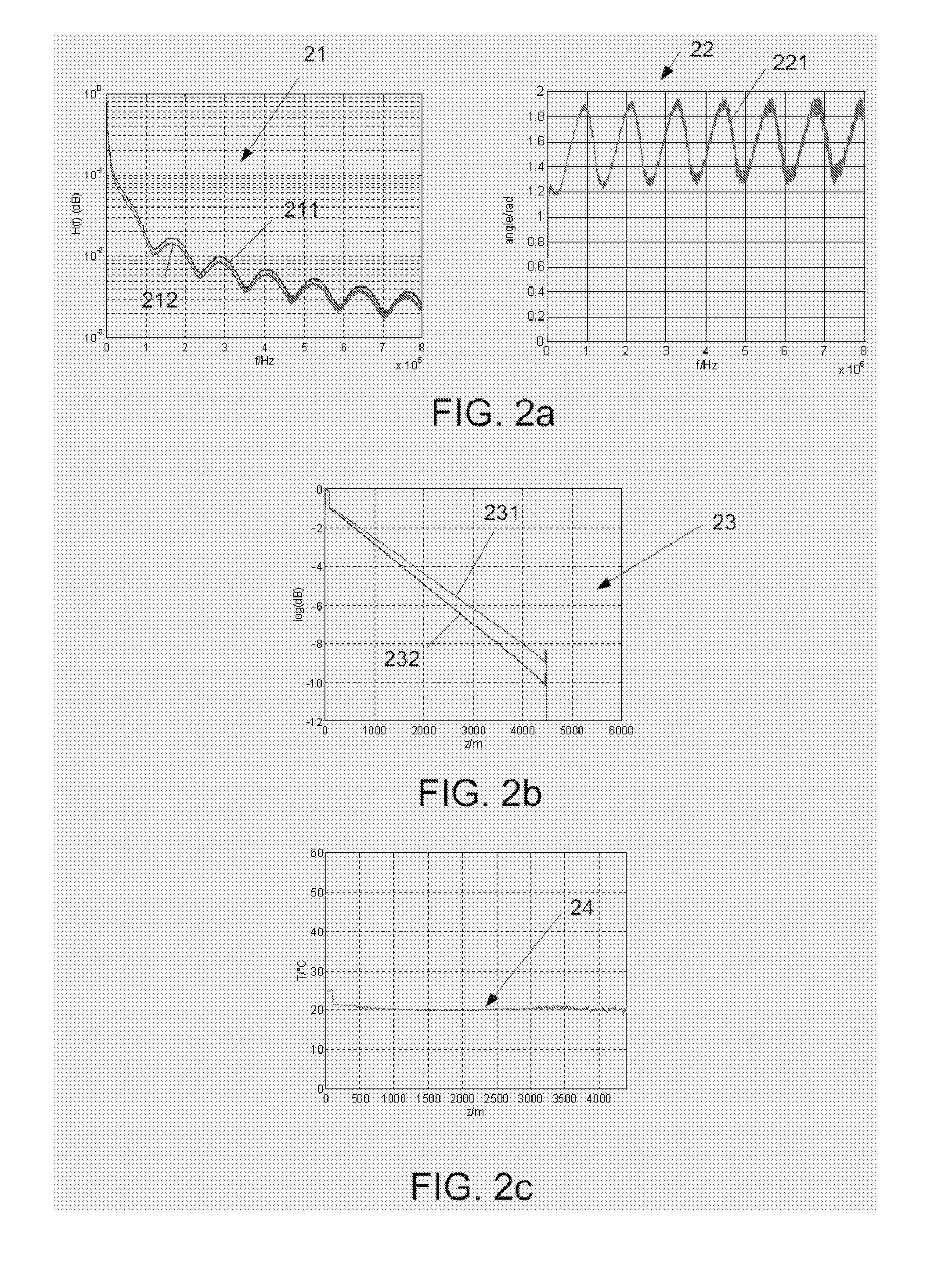
Calibrating An Optical FMCW Backscattering Measurement System
ActiveUS20090240455A1High precisionSuitable for automationRadiation pyrometryTesting/calibration apparatusElectric signalAccuracy and precision
The object of the invention is to provide a method of calibrating an optical FMCW backscattering measurement system that improves the precision of the measurement. The problem is solved by a method comprising the steps of A. Converting said received sensor signal to a complex received electrical signal as a function of said modulation frequency fm, said complex received electrical signal being represented by a magnitude part and a phase angle part as a function of said modulation frequency fm; B. Performing a transformation of said received electrical signal to provide a backscattering signal as a function of location between said first and second ends of said sensor and beyond said second end; C. From said backscattering signal as a function of location determining characteristics of a curve representative of said backscattering signal beyond said second end; D. Correcting said magnitude part of said received electrical signal and said phase angle part of said received electrical signal in a predetermined dependence of said curve; and E. Repeating step B) on the basis of the corrected received electrical signal.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS GMBH
Apparatus method for monitoring the I-Q phase bias in an I-Q quadrature modulation transmitter
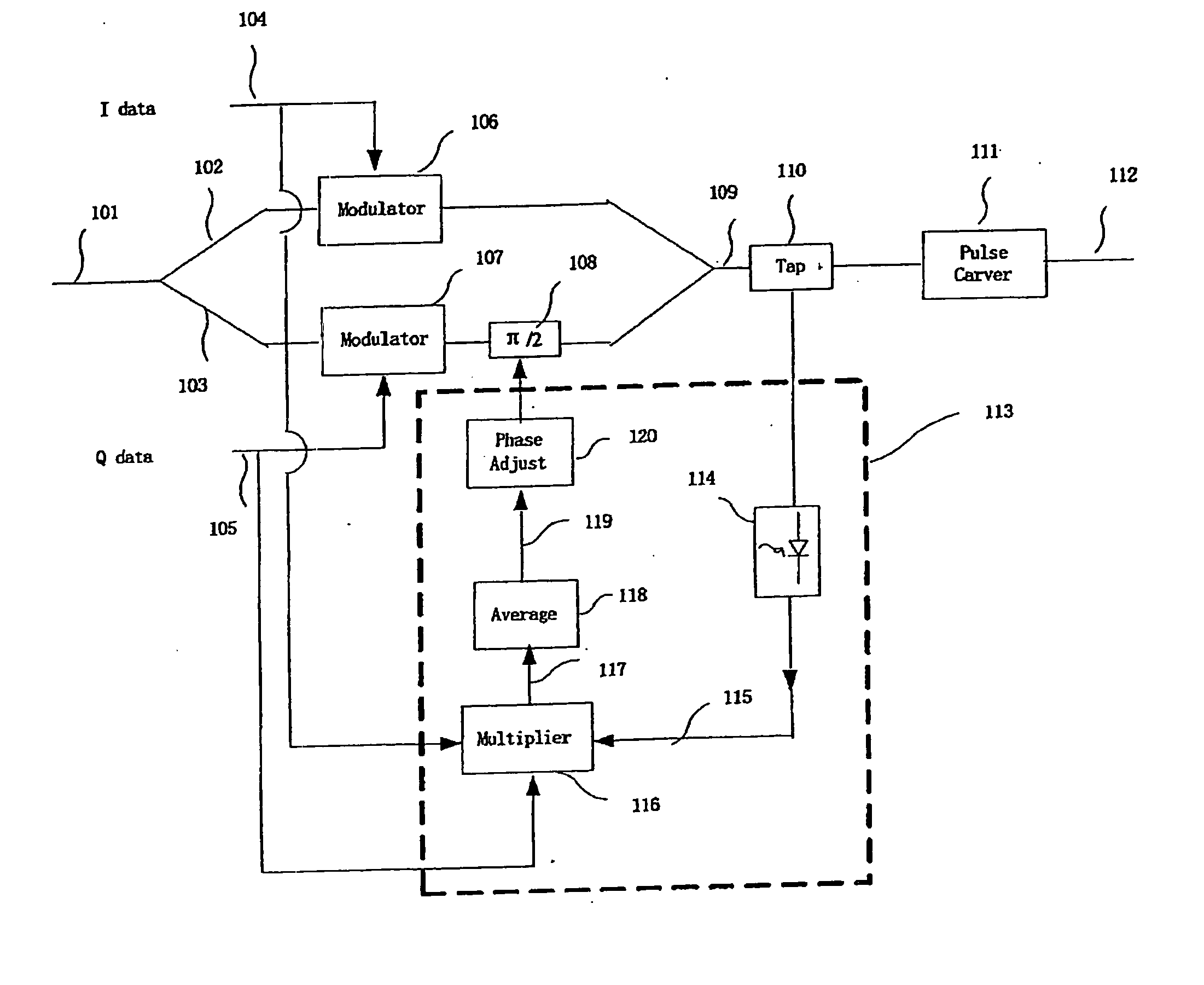
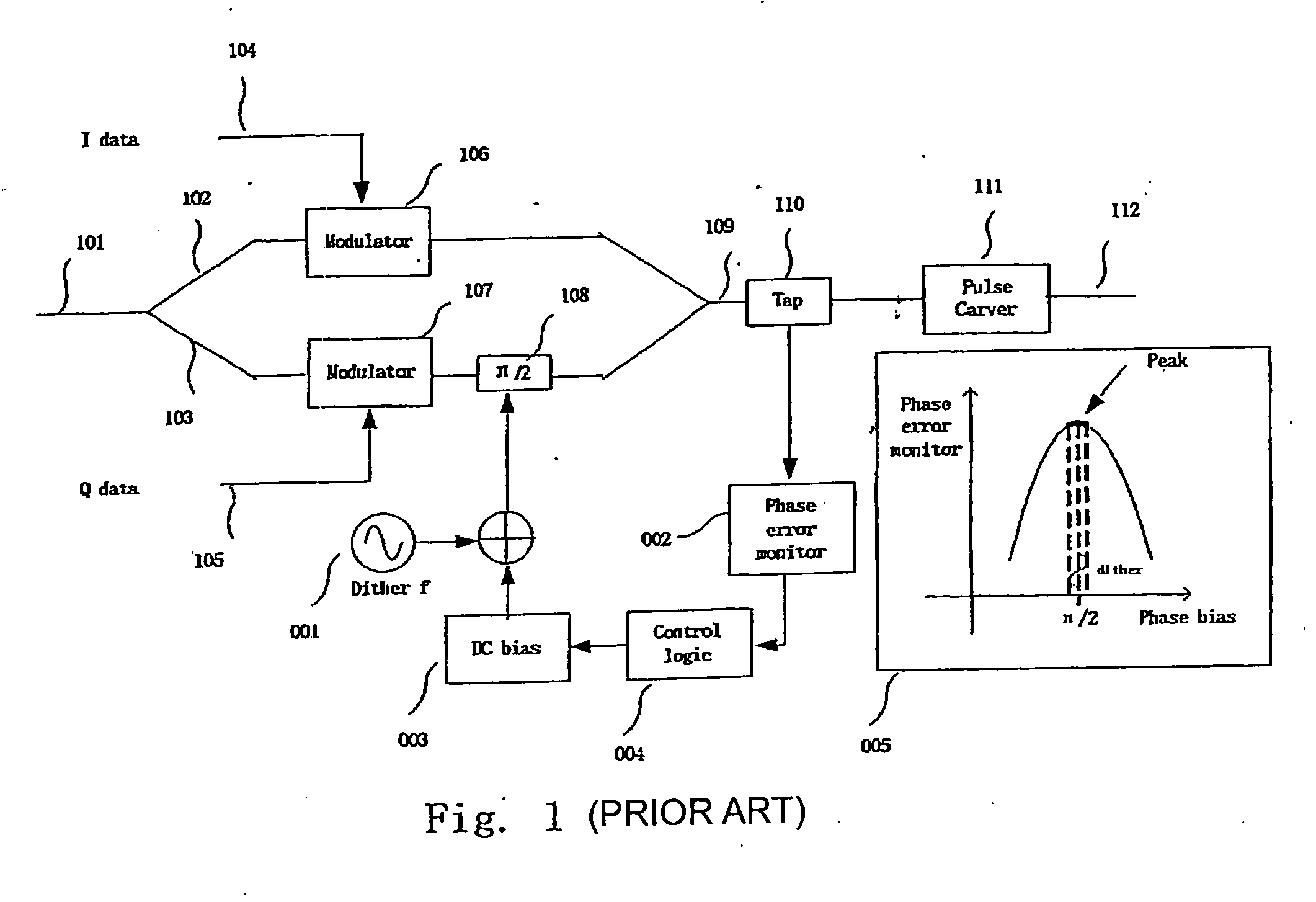
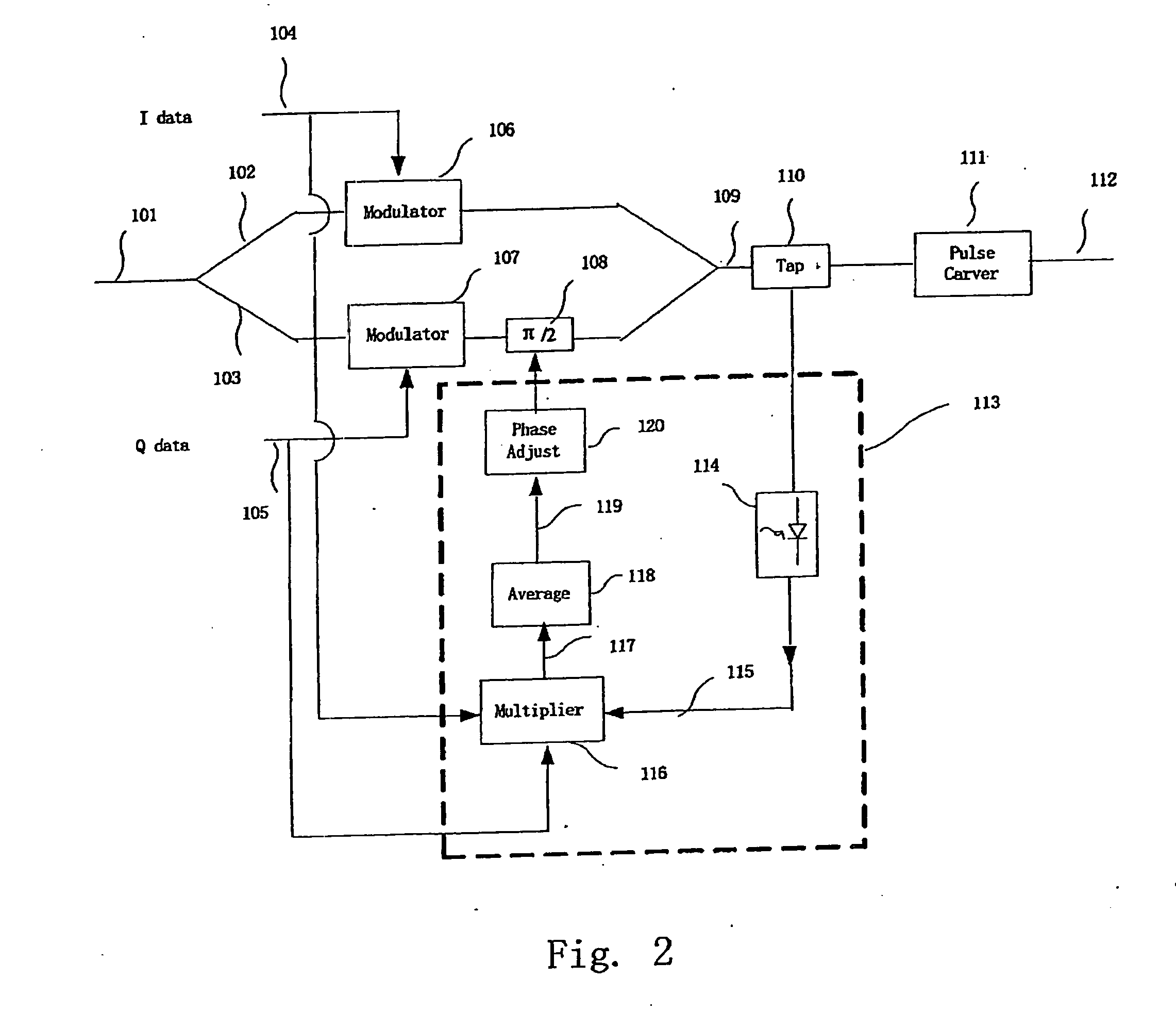
InactiveUS20070230617A1High precisionControl precisionAngle modulationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsQuadrature modulationTransmitter
An apparatus and a method for a I-Q quadrature modulation transmitter monitor a phase bias between an I branch and a Q branch of the I-Q quadrature modulation transmitter. The I-Q quadrature modulation transmitter includes the I-branch, the Q-branch equipped with a phase bias, and a tap. The apparatus is installed between the tap and the phase bias, and monitors the phase between the I branch and the Q branch which phase is introduced by the phase bias. The apparatus includes the following components: a module squarer, receiving signal from the tap and outputting a module square of the received signal; a multiplier, to multiplying data of the I-branch, data of the Q-branch and the module square to output a multiplied signal; and an averager, averaging the multiplied signal output by the multiplier. The phase between the I branch and the Q branch may be corrected according to monitoring results.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
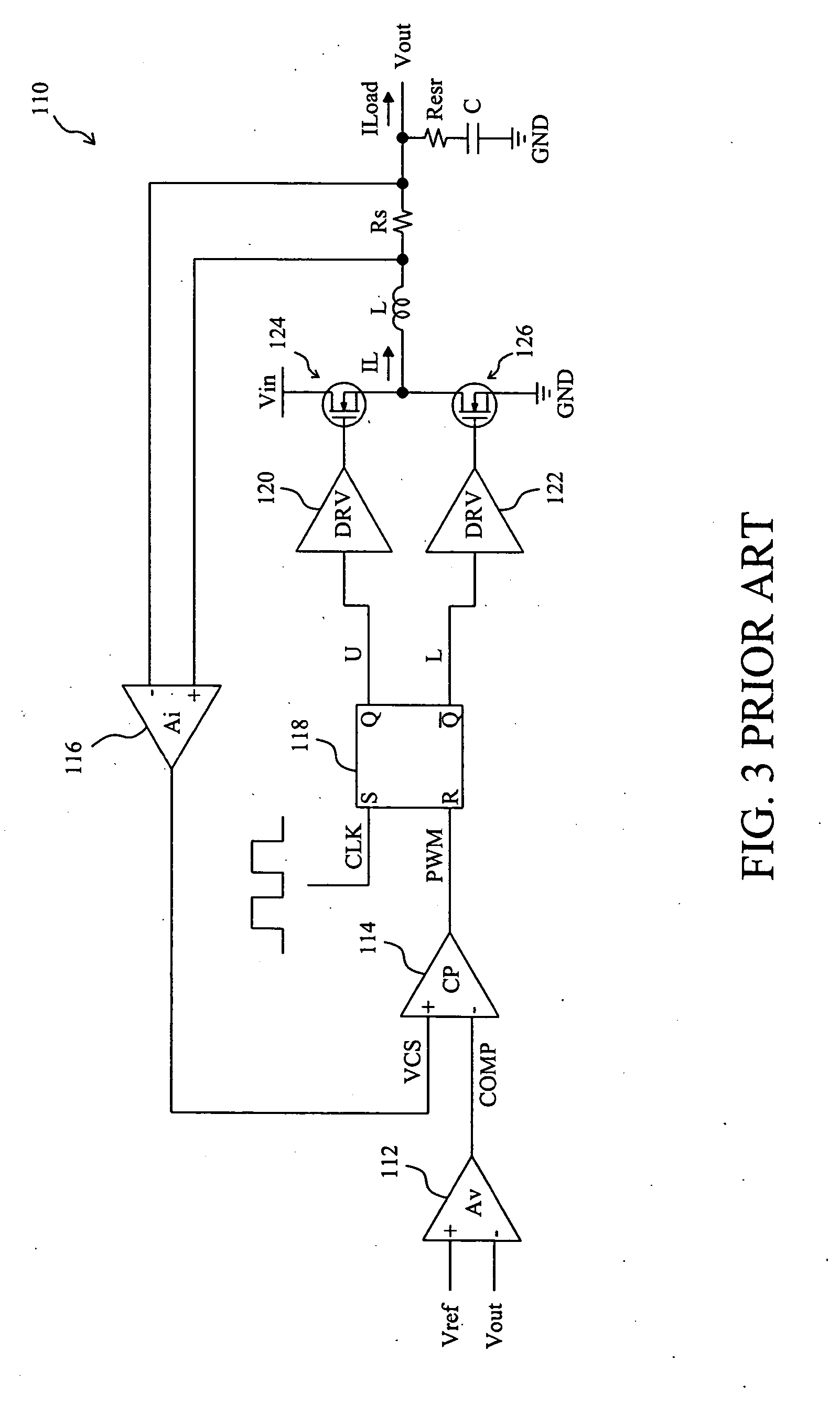
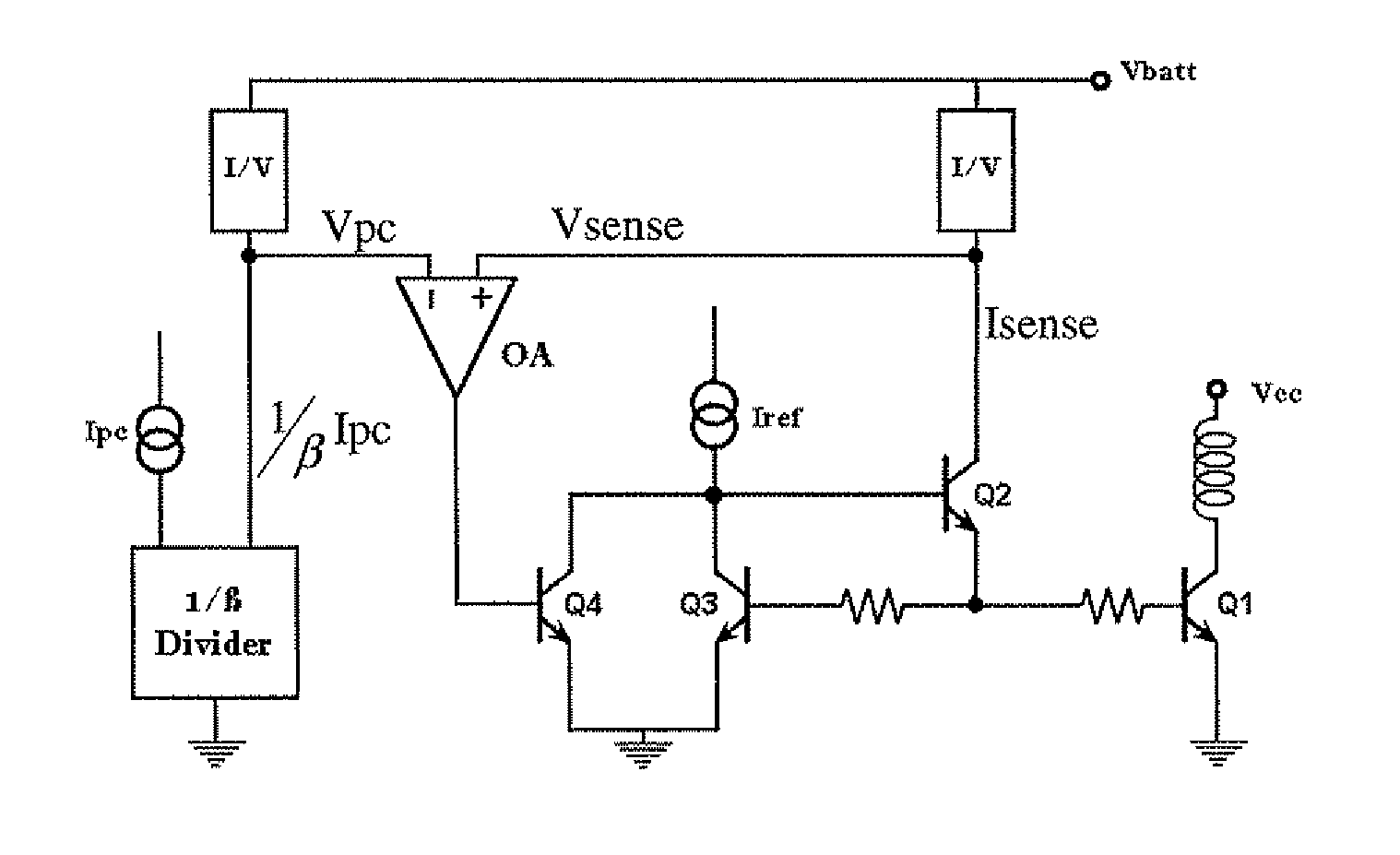
Low-gain current-mode voltage regulator
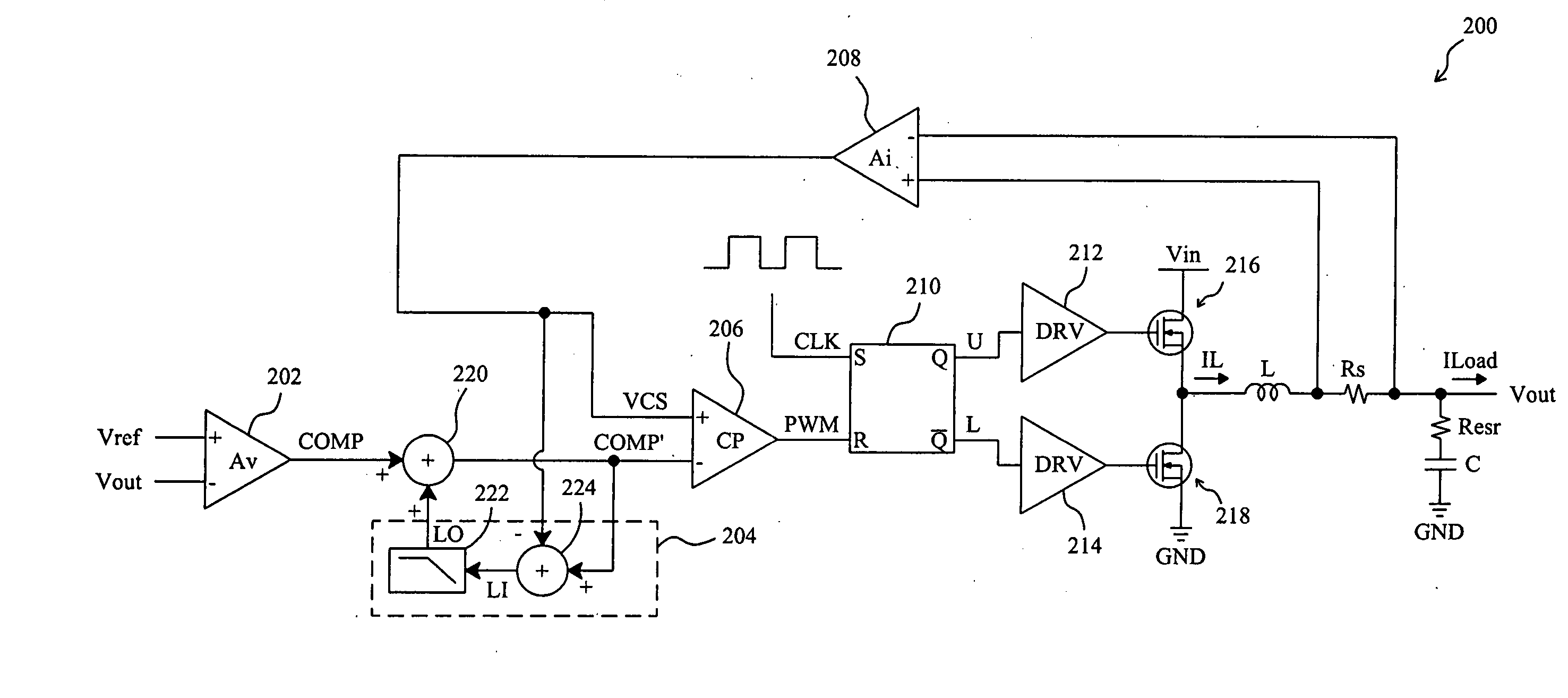
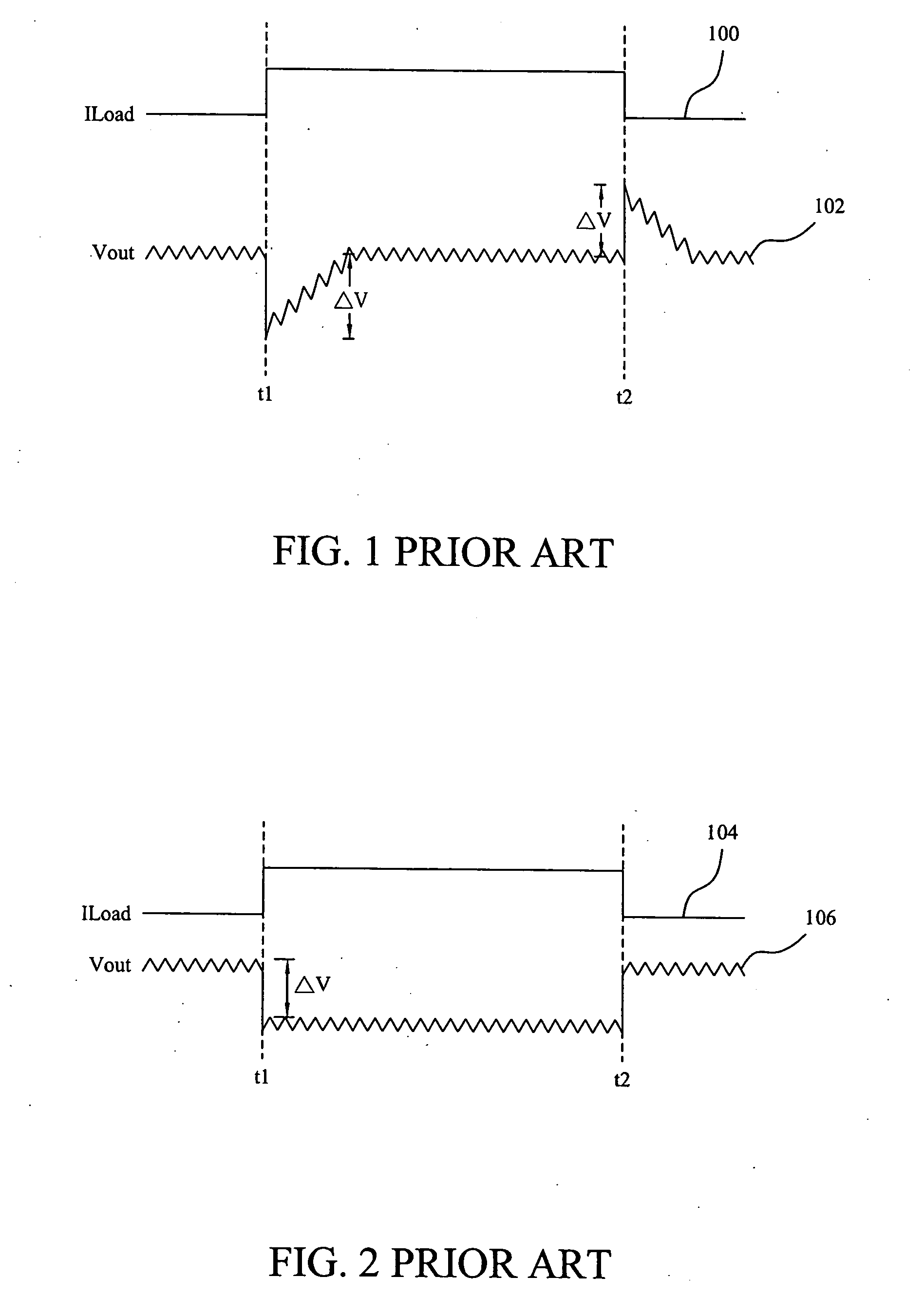
ActiveUS20080024100A1Control precisionPrecise controlDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationLow gainInductor
In a low-gain current-mode voltage regulator having a PWM comparator in response to the varying output voltage and inductor current of the voltage regulator to produce a PWM signal to regulate the output voltage, an offset signal is derived from a subtraction between the inputs of the PWM comparator, and the offset signal is injected into the PWM comparator to cancel the output offset of the voltage regulator.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH +1
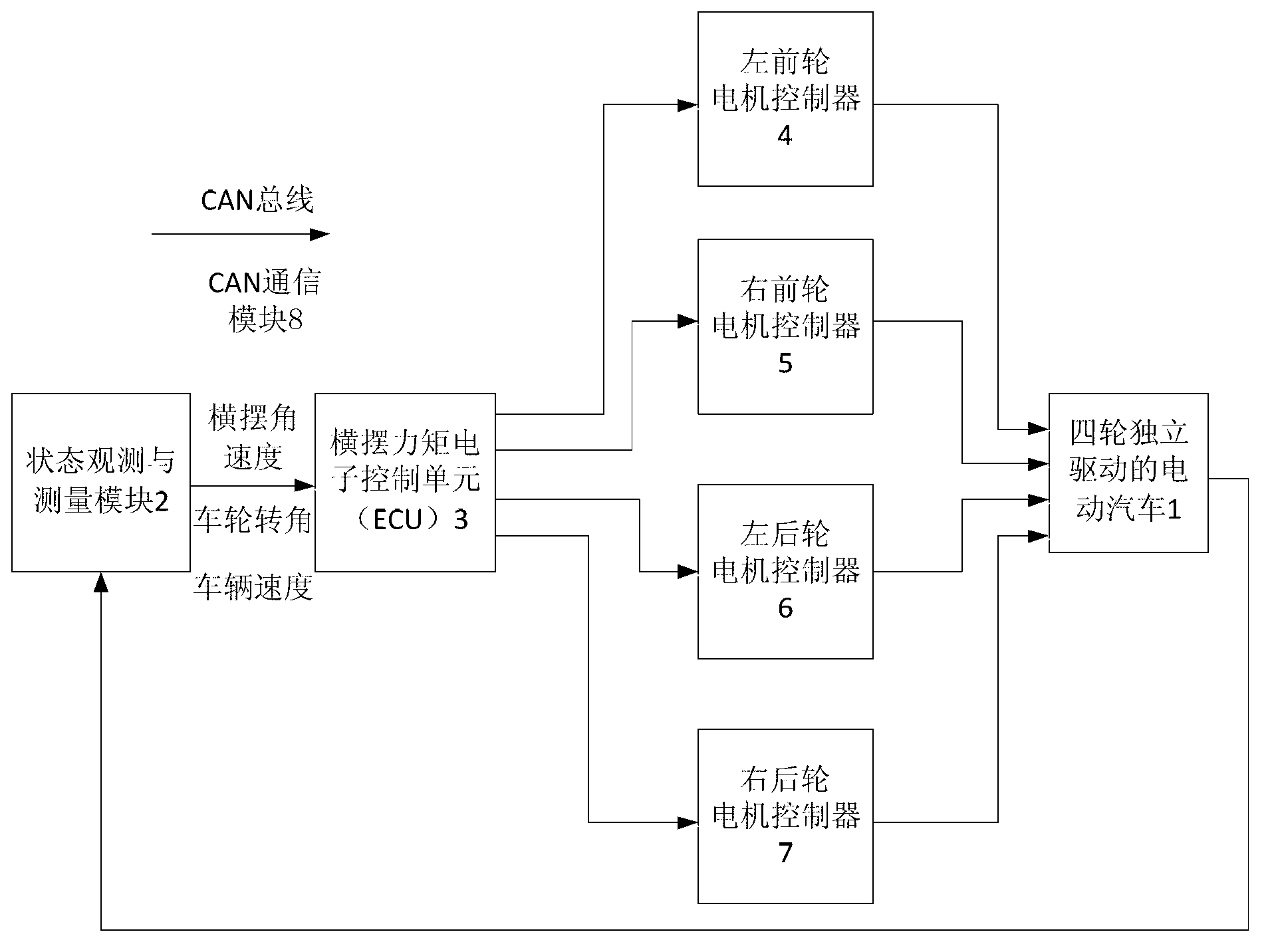
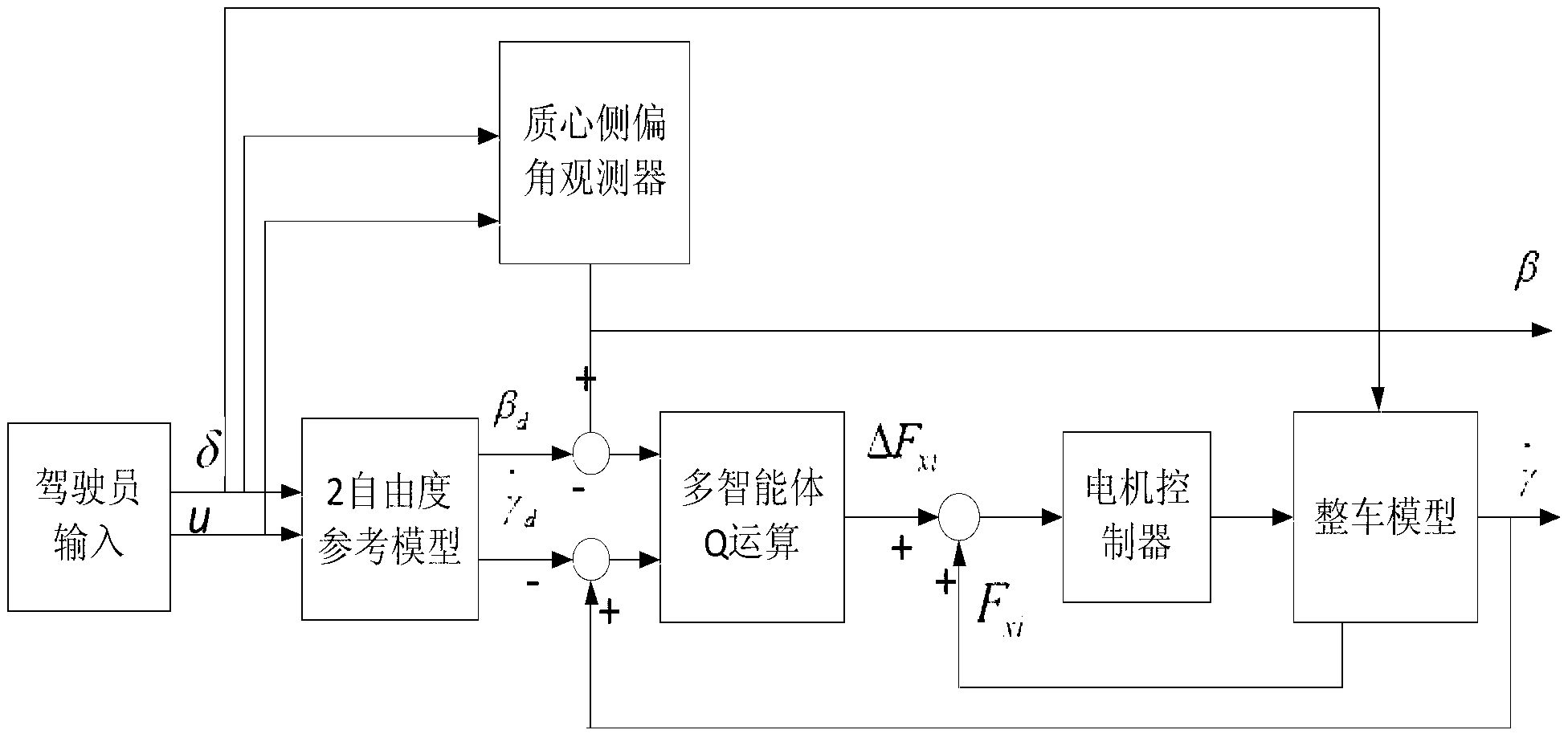
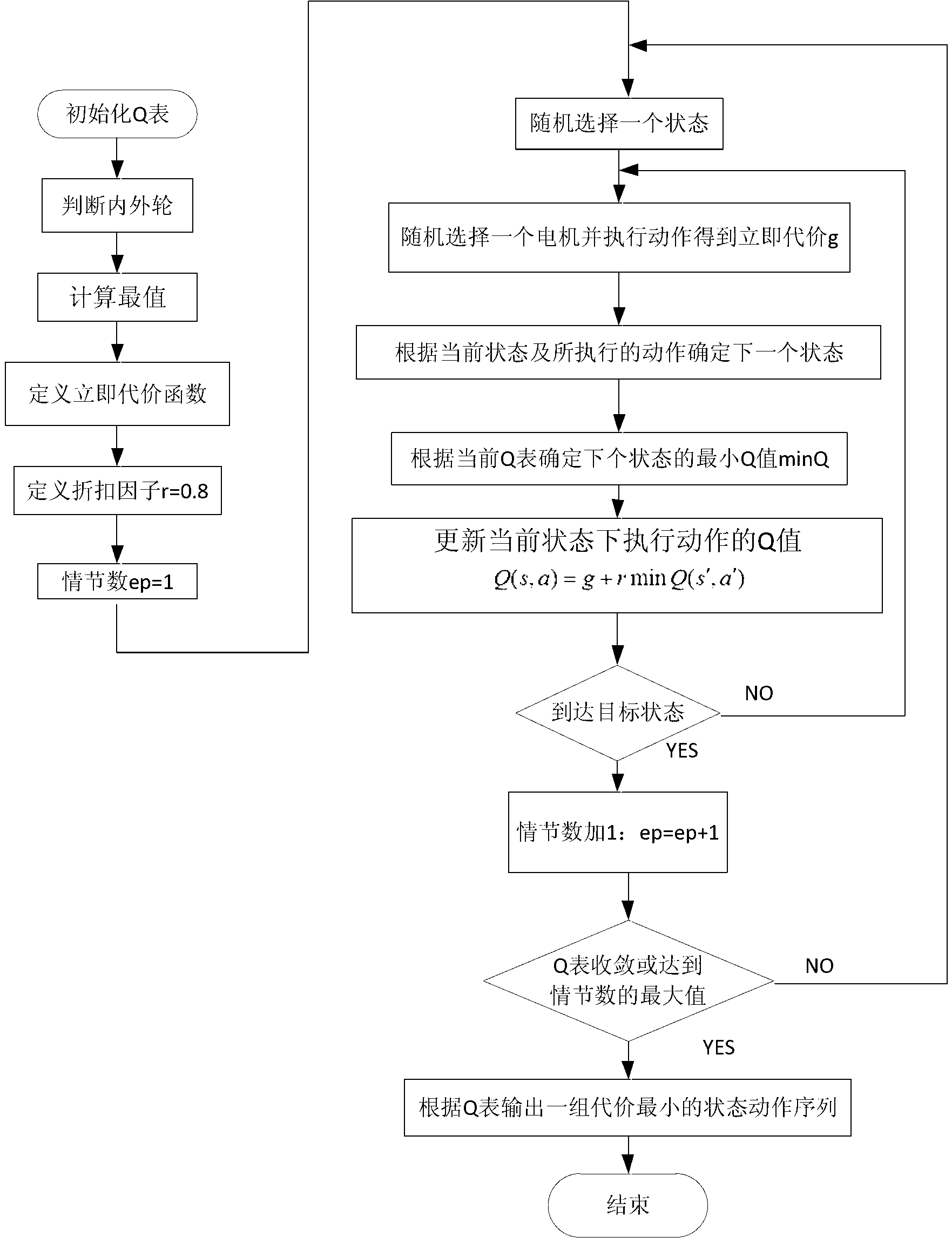
Yawing moment control method of individual driven electromobile based on multi-agent
InactiveCN103057436AImprove adaptabilitySmooth transitionSpeed controllerElectric energy managementLinear elementElectric machinery
The invention discloses a yawing moment control method of an individual driven electromobile based on a multi-agent. The yawing moment control method includes enabling a yawing moment electric control unit to ba a regulating controller of every motor of the individual driven electromobile to obtain a turning intention and a driving state of a driver in real time through a state observation and measurement module; obtaining torque adjusting motion sequence which is needed by four-wheel of the individual electromobile through a reinforced learning Q-algorithm which is based on a multi-agent; sending the motion sequence to every driven motor controller of the individual driven electromobile through the muli-agent, sending instructions to every driven motor to carry out received motion sequence, generating needed yawing moment and rectifying the posture of the electromobile. The yawing moment control method of the individual driven electromobile based on the multi-agent has the advantages of avoiding energy consumption during actuating process by utilizing driving force control, disposing non-linear elements existing in the system and guaranteeing the stability of turning.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Output power control of an RF amplifier
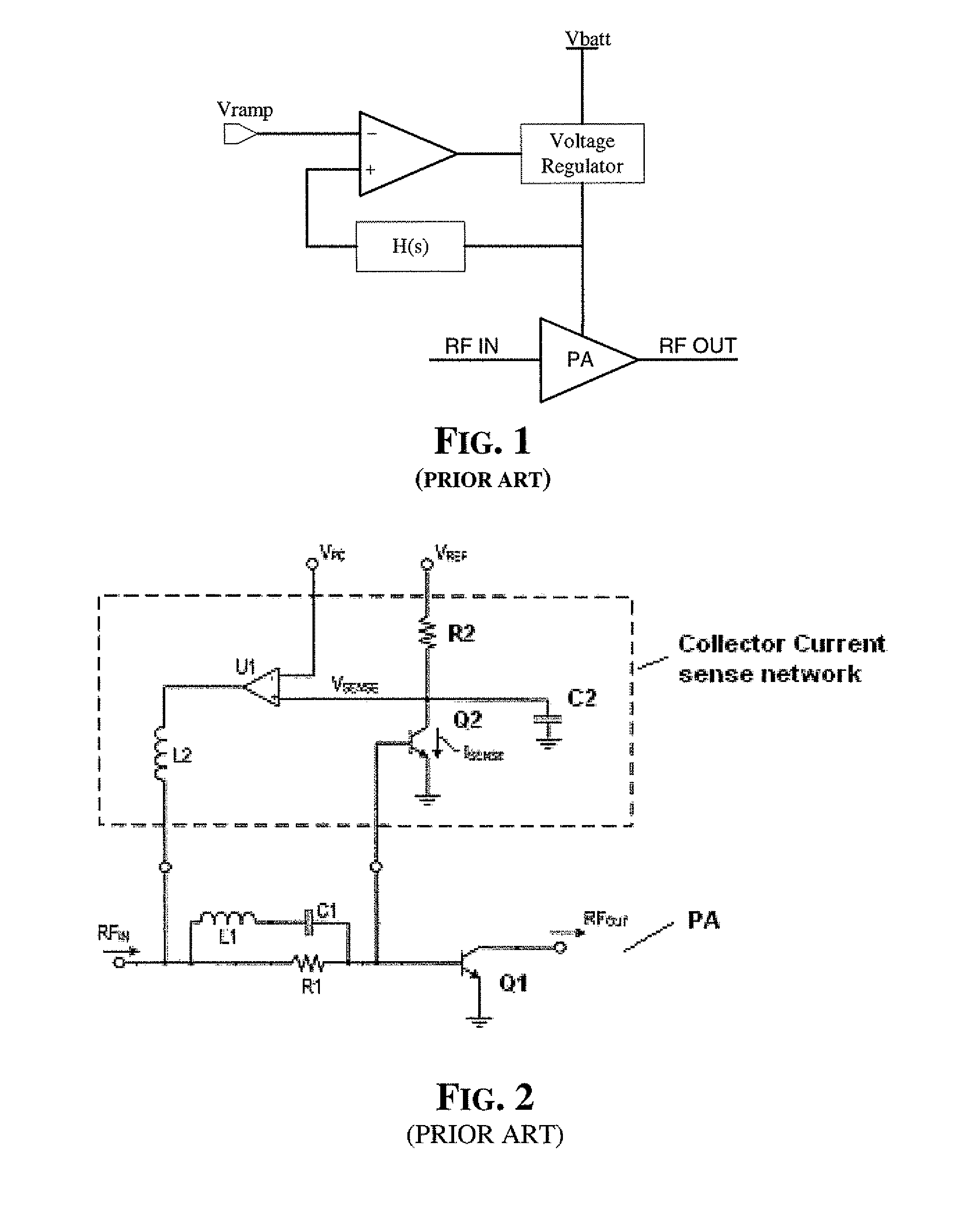
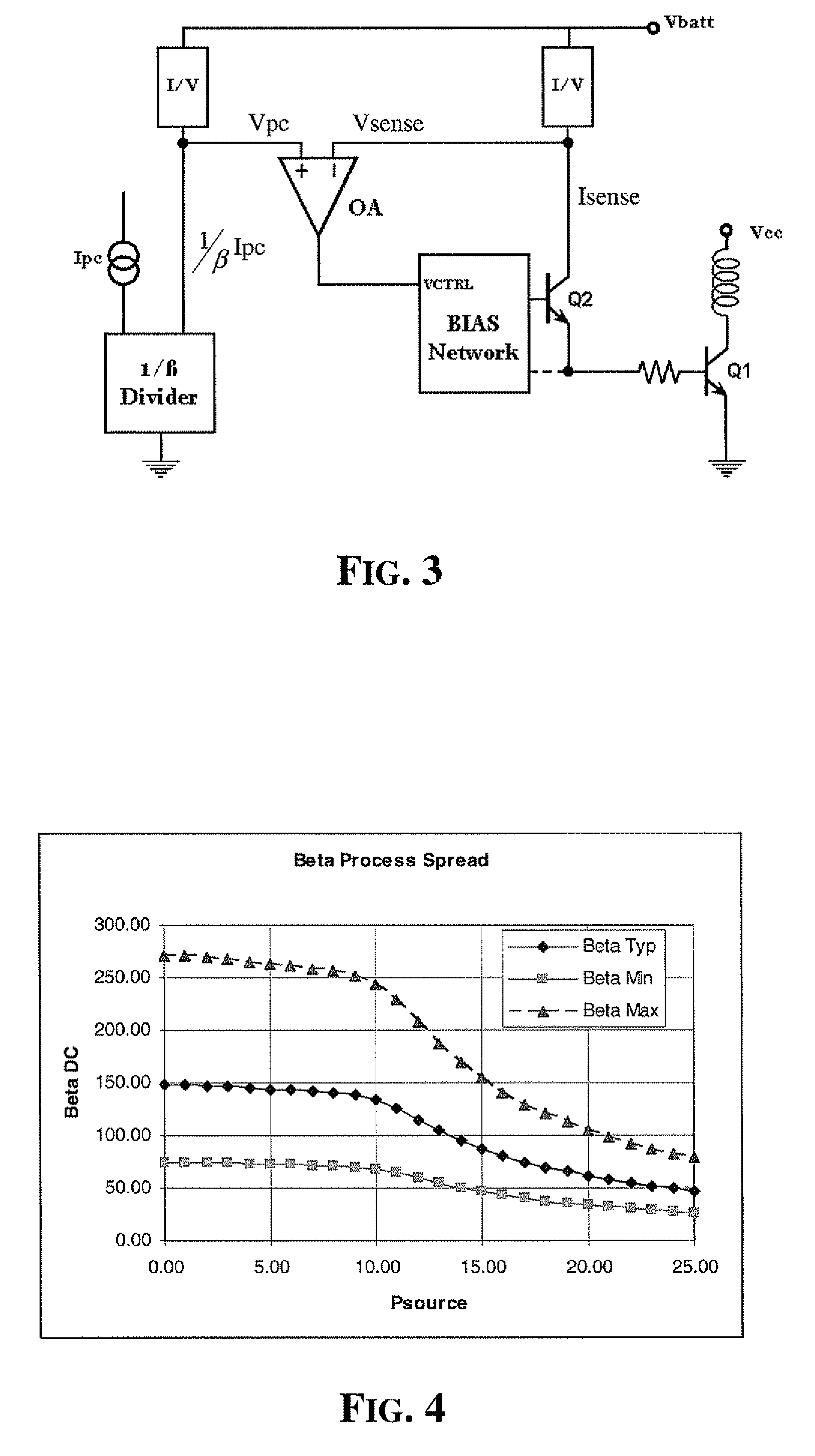
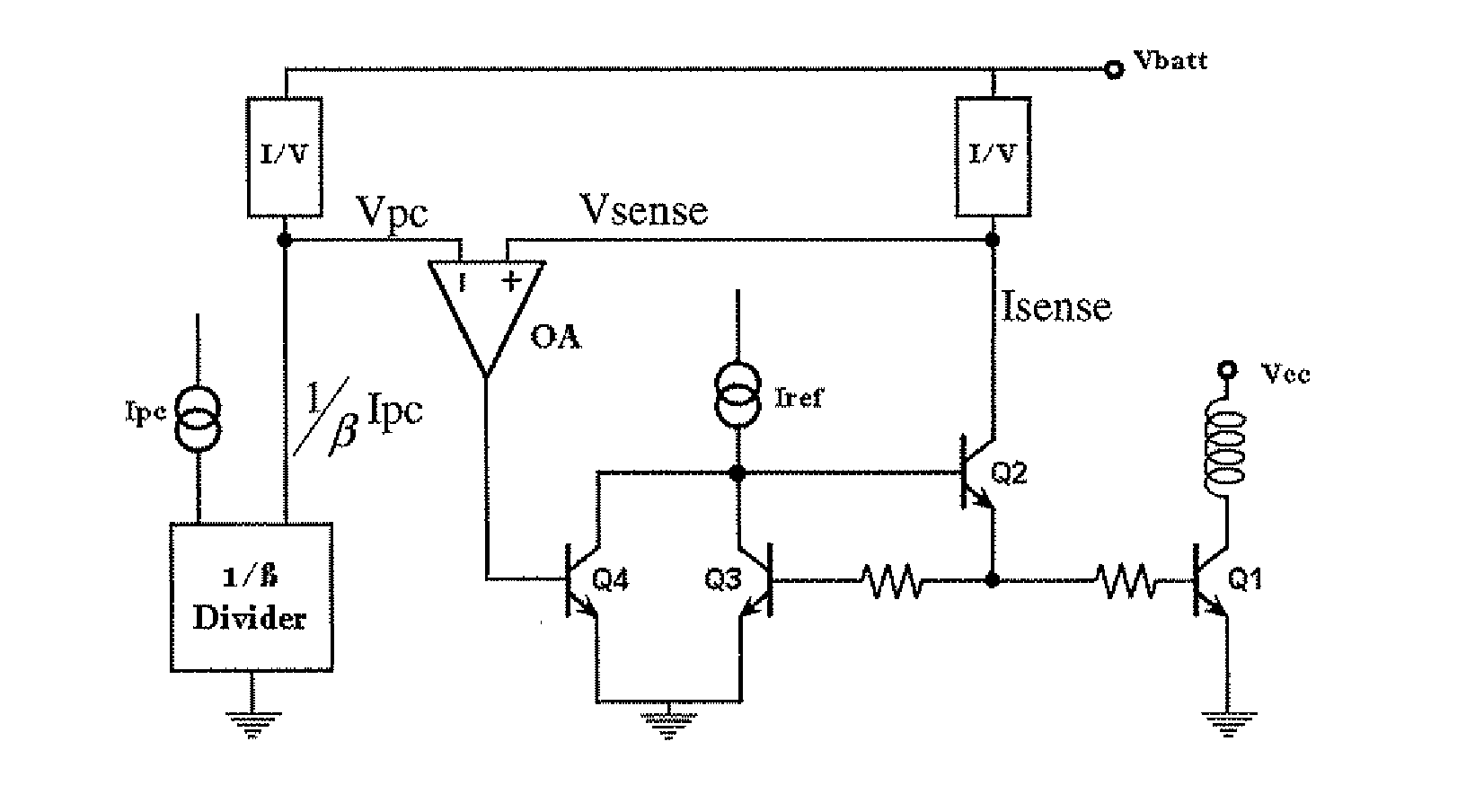
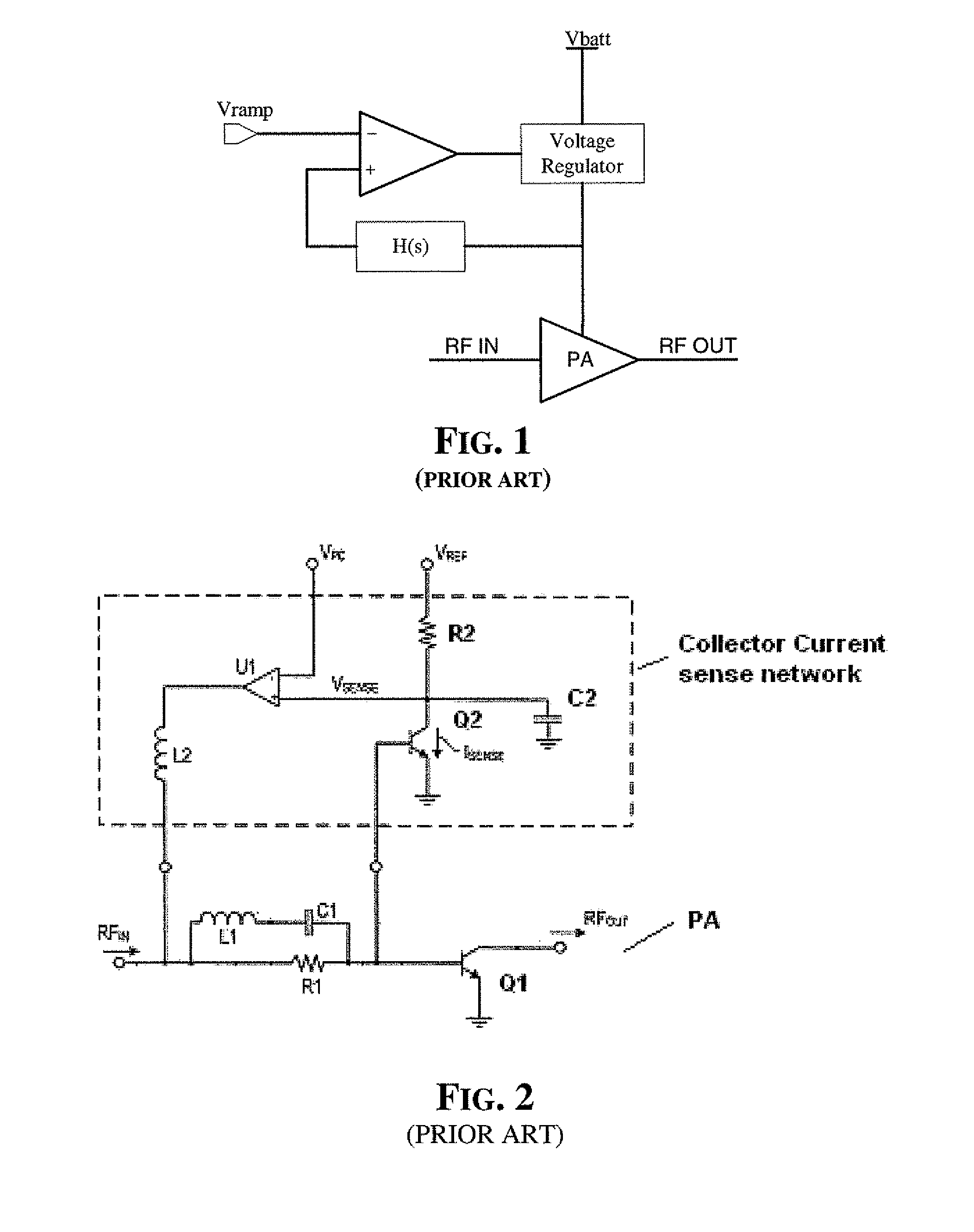
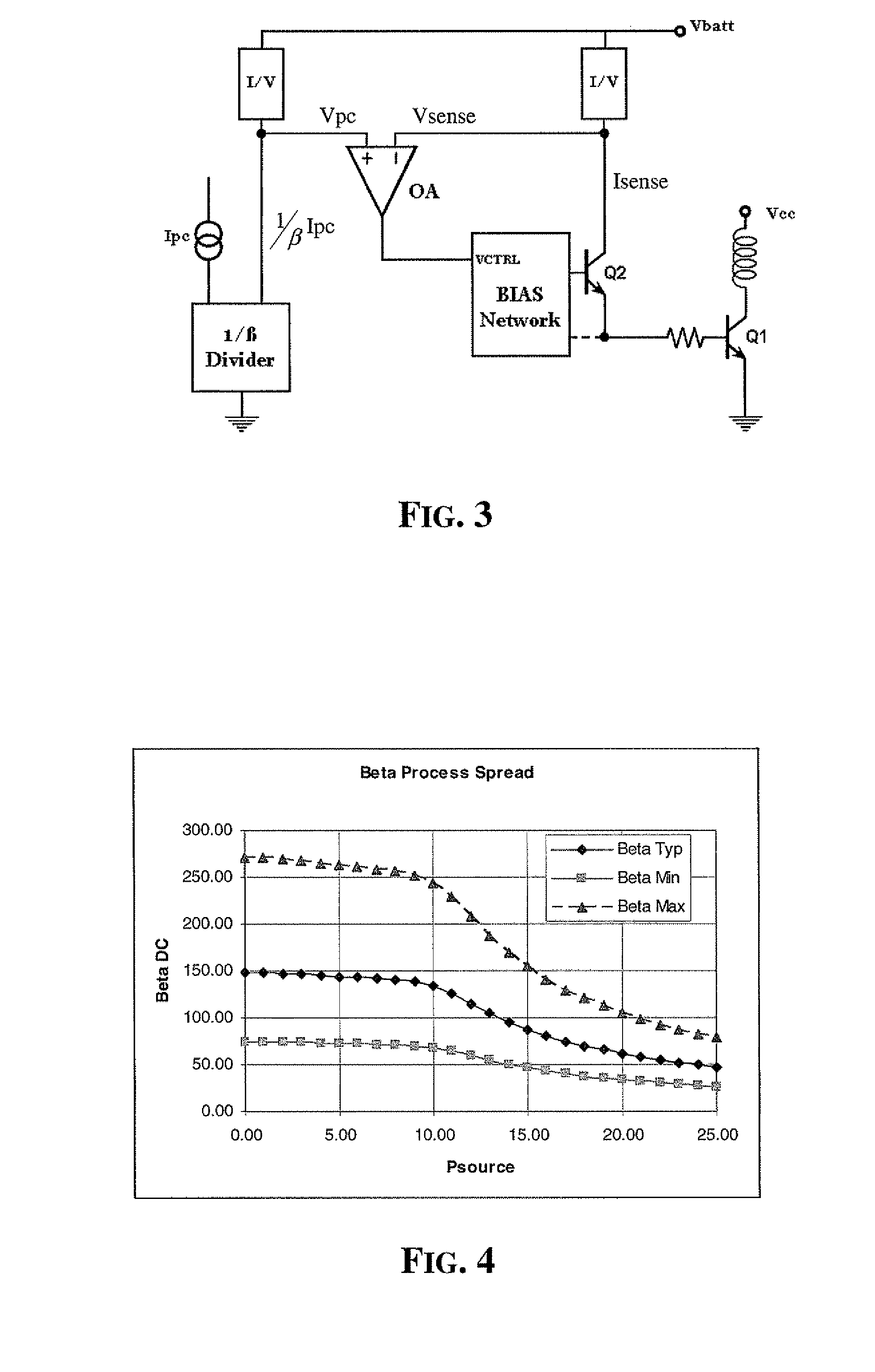
InactiveUS7489196B2Improve reliability and precisionWide power rangeGain controlAmplifier detailsCurrent limitingEngineering
Precision and reliability of a current limited mode output power control of an RF amplifier is enhanced by sensing the base current of the current controlled output power transistor. The base current is compared to a control current that is normalized by scaling it as a function of the current gain of a bipolar junction transistor of similar characteristics as the output power transistor. Fabrication process spread of current gain figures of bipolar junction transistors is effectively compensated. Moreover, by using a band-gap temperature compensation control current that is eventually β-scaled before comparing it with the sensed base current of the output power transistor, the output power may be effectively controlled and maintained constant over temperature as well as process spread variations.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
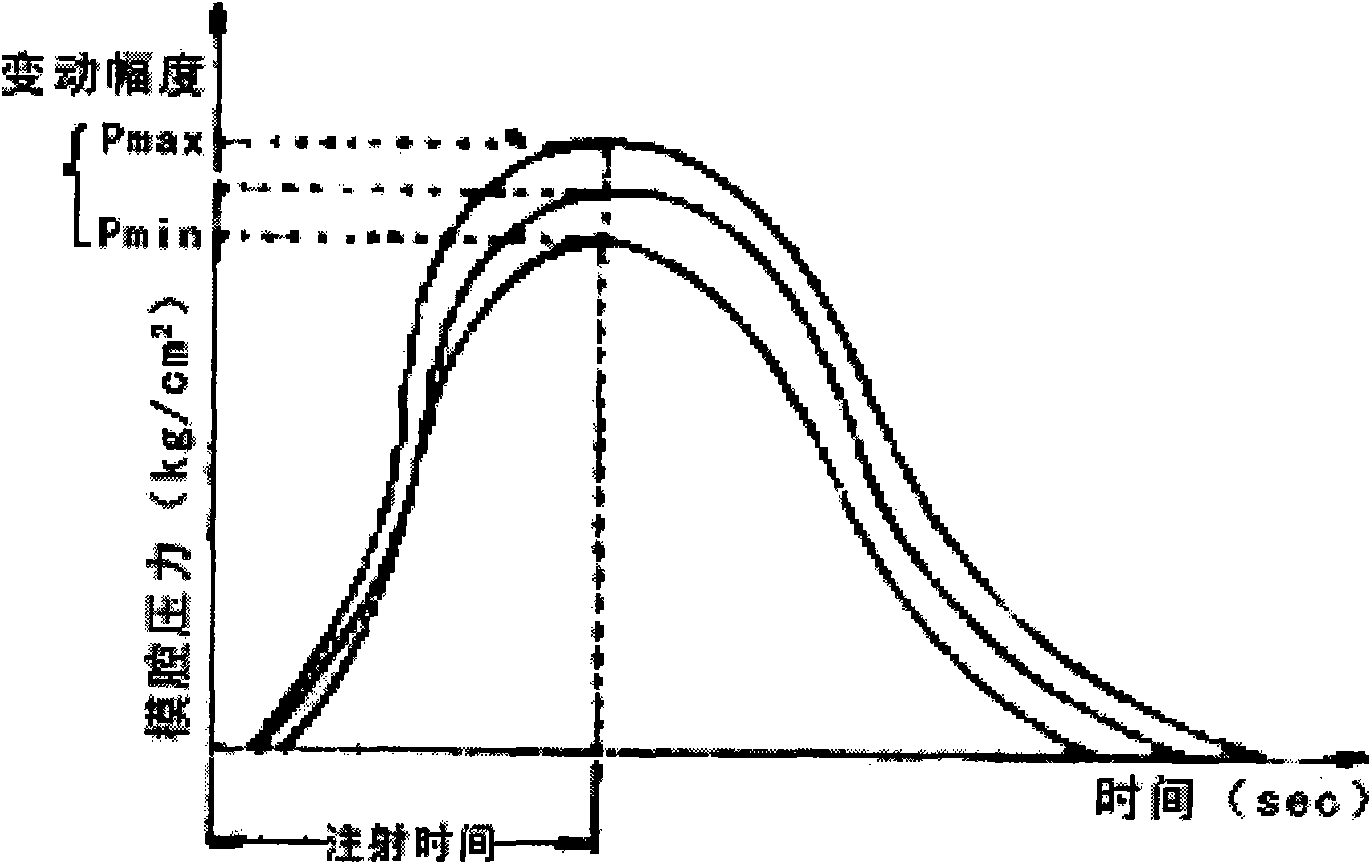
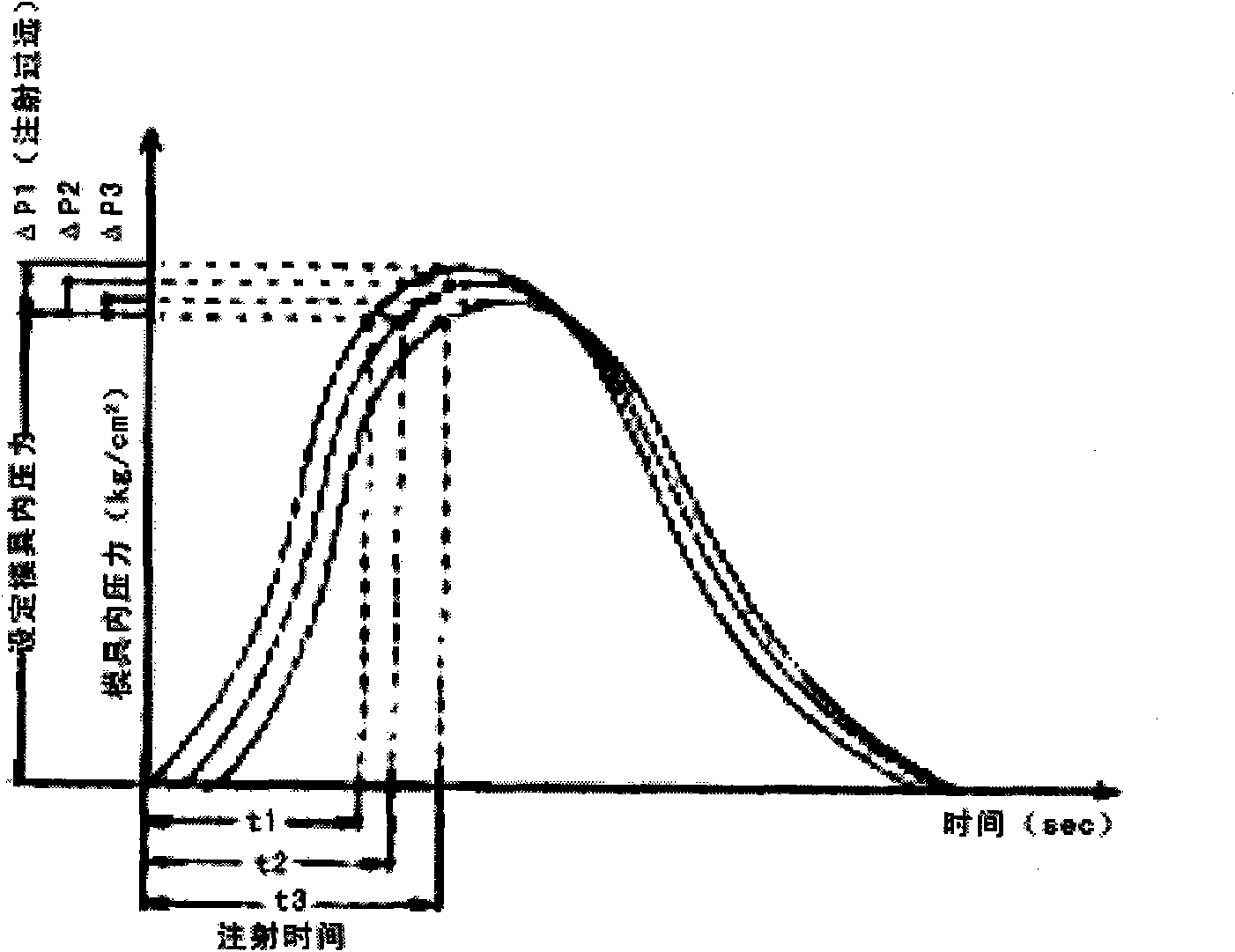
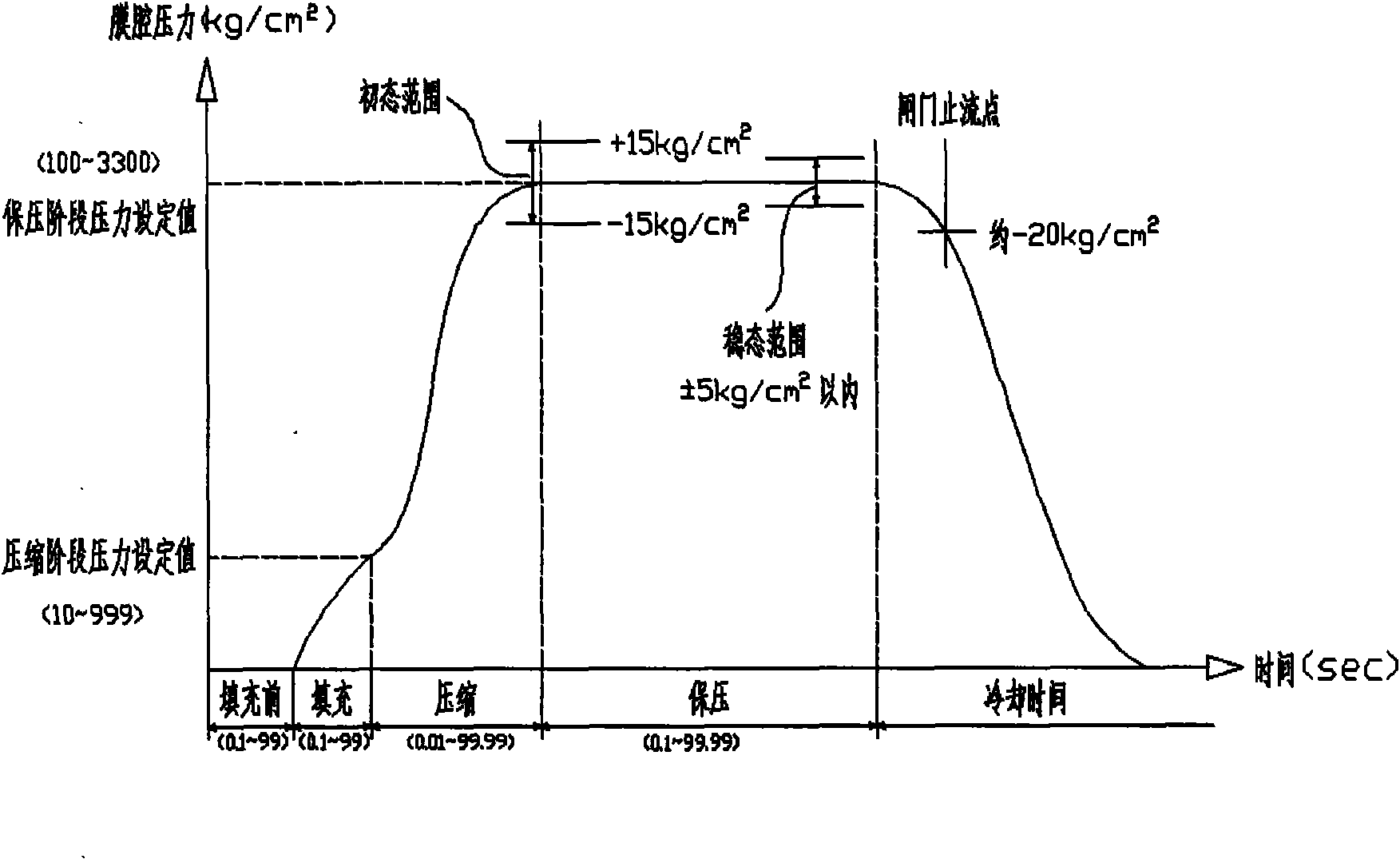
Method for controlling mold cavity resin pressure of injection molding machine
The invention relates to a principle and a method for controlling the mold cavity resin pressure of an injection molding machine. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the method for controlling the mold cavity resin pressure of an injection molding machine comprises the following steps: firstly, setting the detection position of a pressure sensor, wherein during setting, the detection position of the pressure sensor is arranged close to a main flow passage of the cavity when a mold cavity is directly arranged below a sprue gate, and the detection position of the pressure sensor is arranged close to a branch flow passage when the mold cavity is arranged at both sides of the sprue gate; and secondly, during the injection molding control, the pressure in the mold cavity gradually rises along with materials constantly entering into the mold cavity; in the whole entering process of the materials, the pressure sensor is utilized to instantly detect the actual pressure in the mold cavity before the pressure in the mold cavity reaches the set value of the pressure in the mold cavity and to instantly send the pressure value to a controller which controls the pressure in the mold cavity by calculating the approaching speed of the actual pressure in the mold cavity to the set value of the pressure in the mold cavity. The method can effectively enhance the quality and the precision of produced products and lower the cost.
Owner:无锡威锐科智能测控技术有限公司
Output power control of an RF amplifier
InactiveUS20070273448A1Improve precisionImprove reliabilityGain controlAmplifier detailsCurrent limitingAudio power amplifier
Precision and reliability of a current limited mode output power control of an RF amplifier is enhanced by sensing the base current of the current controlled output power transistor. The base current is compared to a control current that is normalized by scaling it as a function of the current gain of a bipolar junction transistor of similar characteristics as the output power transistor. Fabrication process spread of current gain figures of bipolar junction transistors is effectively compensated. Moreover, by using a band-gap temperature compensation control current that is eventually β-scaled before comparing it with the sensed base current of the output power transistor, the output power may be effectively controlled and maintained constant over temperature as well as process spread variations.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Calibrating an optical FMCW backscattering measurement system
ActiveUS7742892B2High precisionSuitable for automationRadiation pyrometryTesting/calibration apparatusMeasurement precisionElectric signal
The object of the invention is to provide a method of calibrating an optical FMCW backscattering measurement system that improves the precision of the measurement. The problem is solved by a method comprising the steps of A. Converting said received sensor signal to a complex received electrical signal as a function of said modulation frequency fm, said complex received electrical signal being represented by a magnitude part and a phase angle part as a function of said modulation frequency fm; B. Performing a transformation of said received electrical signal to provide a backscattering signal as a function of location between said first and second ends of said sensor and beyond said second end; C. From said backscattering signal as a function of location determining characteristics of a curve representative of said backscattering signal beyond said second end; D. Correcting said magnitude part of said received electrical signal and said phase angle part of said received electrical signal in a predetermined dependence of said curve; and E. Repeating step B) on the basis of the corrected received electrical signal.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS GMBH
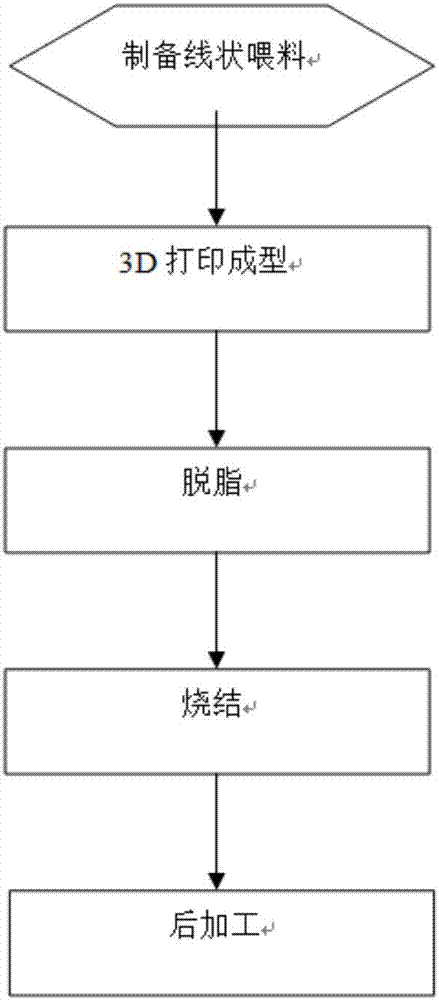
Feed for 3D printing as well as preparation method thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN106984805AAvoid wastingControl precisionAdditive manufacturing apparatusTransportation and packagingEconomic benefitsEngineering
The invention relates to feed for 3D printing as well as a preparation method thereof and an application thereof. The feed is metal powder packaged by a high-molecular binder, and is linear. After being printed into raw blank with a preset shape through a 3D printer, the linear feed is sequentially degreased and sintered, so that a metal product with a complex structure and high precision can be obtained. Compared with the prior art, the linear feed is applied to 3D printing, so that waste of raw materials can be avoided; precision of a product surface is controlled and quality of a product is improved by selecting different linear diameters of the feed and controlling a heating temperature; and melting treatment can be performed by a simple thermocouple, and complex and dear laser heating equipment does not need, so that production cost is reduced. A powder injection molding technology and a 3D printing technology are combined, so that the complex product can be quickly printed and manufactured, development flow is shortened, and mass production popularization is realized. The feed has good economic benefits and a wide application prospect.
Owner:KUNSHAN KADAM NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Vertical-type heat processing apparatus and method of controlling transfer mechanism in vertical-type heat processing apparatus
InactiveUS20070238062A1Avoid damageDetection of limitedCharge supportsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringTransfer mechanism
The present invention is a vertical-type heat processing apparatus comprising: a heat processing furnace; a holder capable of being loaded into the heat processing furnace and unloaded therefrom, with holding therein a plurality of objects to be processed at predetermined vertical intervals in a tier-like manner; a transfer mechanism including a base table capable of vertically moving and rotating, and a substrate supporter capable of horizontally moving on the base table; and a controller for controlling the transfer mechanism; wherein the transfer mechanism is adapted to transfer an object to be processed between a container containing a plurality of objects to be processed at predetermined intervals, and the holder; the substrate supporter includes a to-and-fro driving part for driving the substrate supporter in the horizontal direction, and a pitch-change driving part for changing a pitch at which the objects to be processed are supported; the controller is adapted to monitor an encoder value outputted from an encoder of the pitch-change driving part during an operation of the to-and-fro driving part of the substrate supporter; and the controller is adapted to judge upon a change of the encoder value that the transfer mechanism is abnormally driven, and then is adapted to stop the drive of the transfer mechanism.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
System and method for non-linear modeling
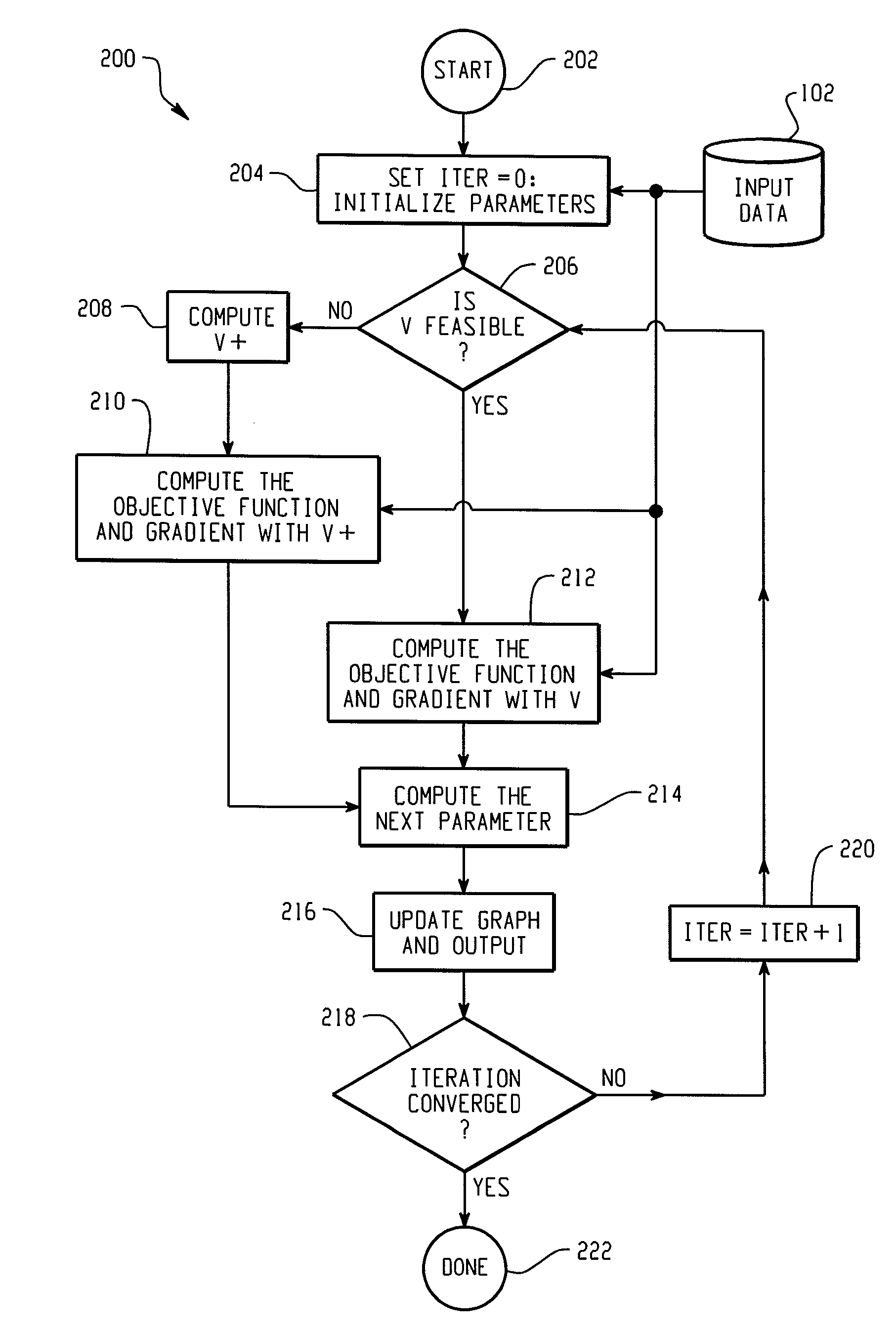
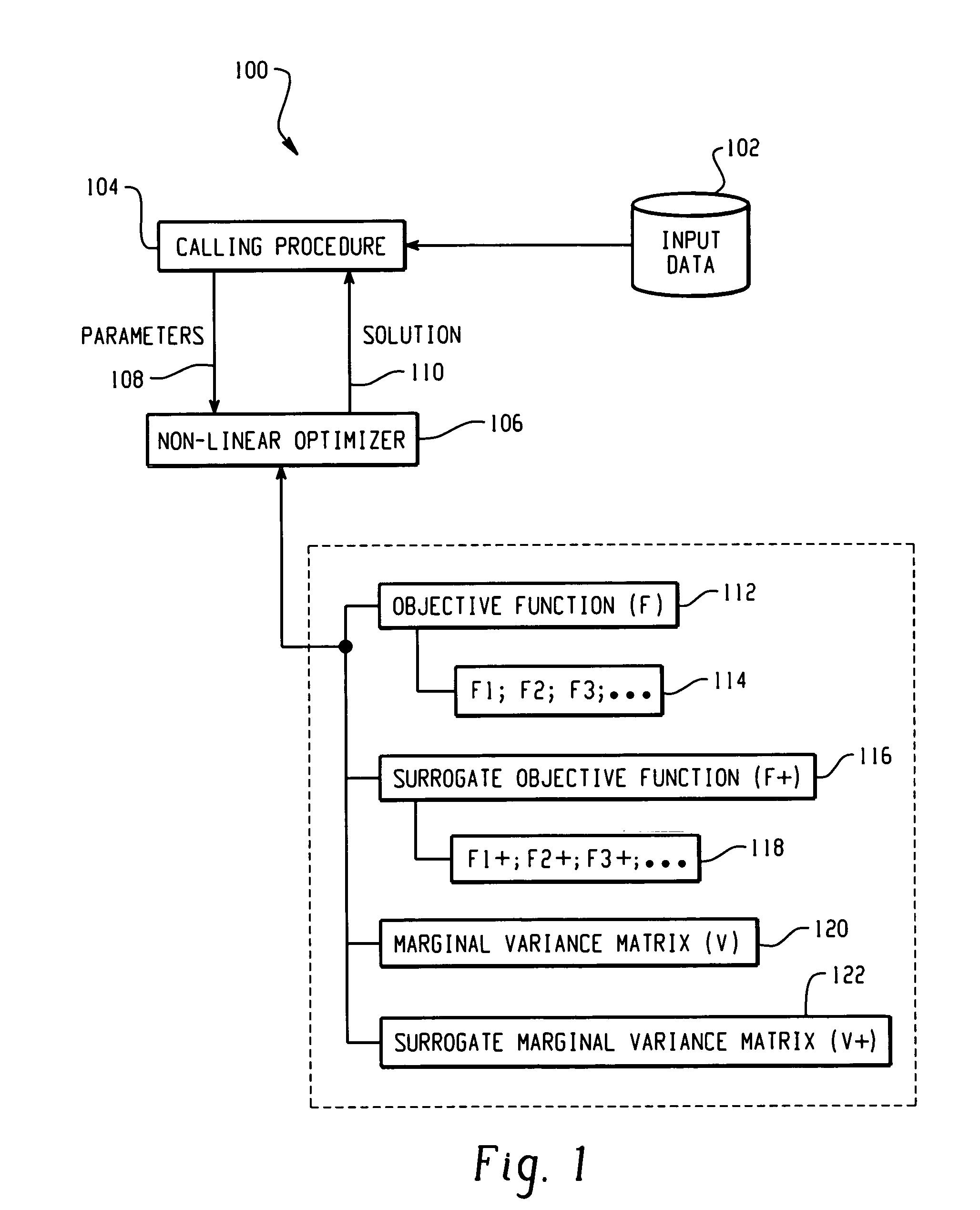
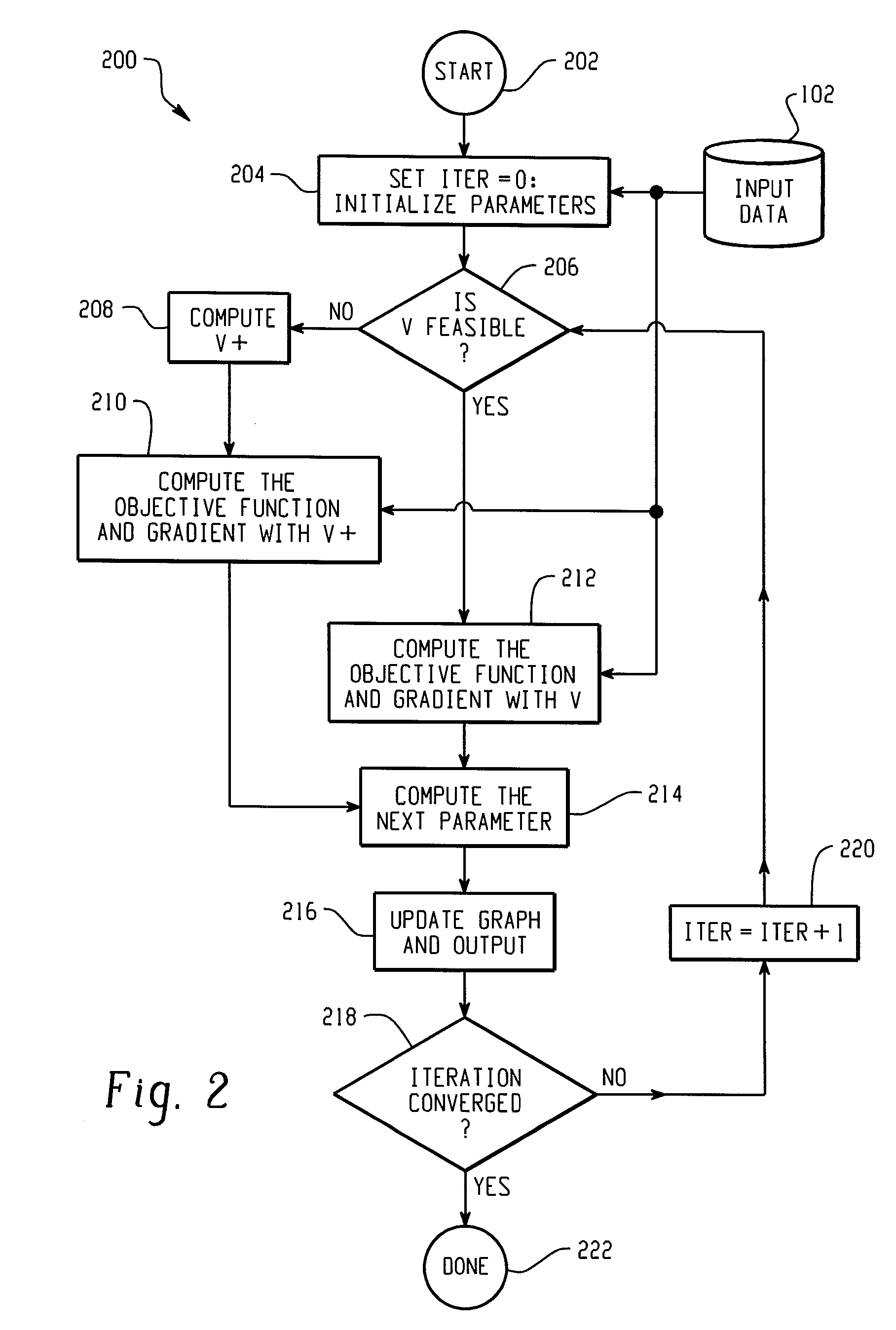
ActiveUS7433809B1Control precisionComputation using non-denominational number representationComplex mathematical operationsNonlinear modellingComputerized system
A computer-implemented system and method of non-linear modeling in a computer system having a limited precision processor is provided. A non-linear model is initialized by forming an objective function having one or more functional components and a marginal variance matrix. The model is then iteratively solved using the computer processor until it has converged to a feasible solution. In doing so, the feasibility of computing the objective function is evaluated by determining if the marginal variance matrix is positive definite, thereby indicating whether or not the computer processor is capable of calculating a feasible solution to the non-linear model. If the marginal variance matrix is positive definite, then the objective function and its gradient are computed using the marginal variance matrix. If the marginal variance matrix is not positive definite, then a surrogate marginal variance matrix is constructed that is positive definite and a surrogate objective function is constructed having components continuous first derivatives. The surrogate objective function and its gradient are then computed using the surrogate marginal variance matrix.
Owner:SAS INSTITUTE
Press-in type slide-vane sampler for acquiring soft mud sample and sampling method
The invention provides a press-in slide-vane sampler structure for acquiring a soft soil, sludge or sewage sludge undisturbed sample with high water content in a sludge storage field, dredger fill field and landfill field and an installation and using method. The press-in slide-vane sampler structure can sample according to the conditions of soft flow state soil in the depth direction of sludge storage yards and dredge fill fields, and the acquired mud sample retains in-situ physical and chemical properties in the sampler. The whole structure comprises a three-sided square cylinder, a slide soft vane, a trabecula slot baffle plate and a trabecula. The sampler adopts a modular design, can control the length of sample separation length as well as the size of a sampling region and sampling precision. The sampler is simple, light, simple and convenient in operation, high in efficiency and low in sampling cost.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
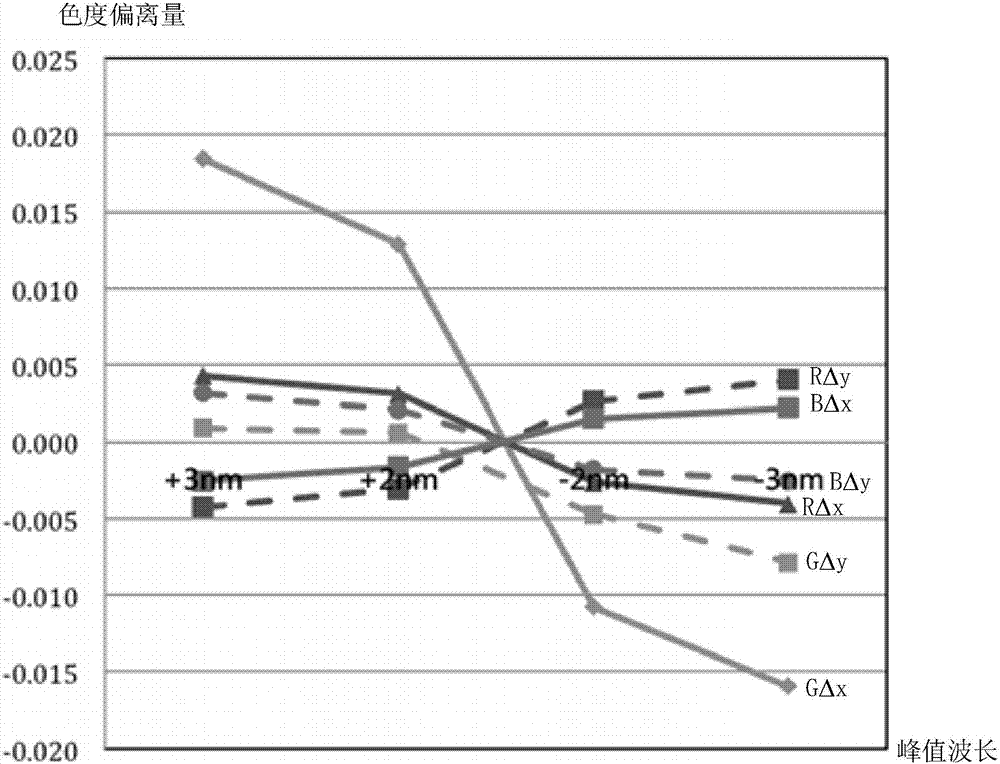
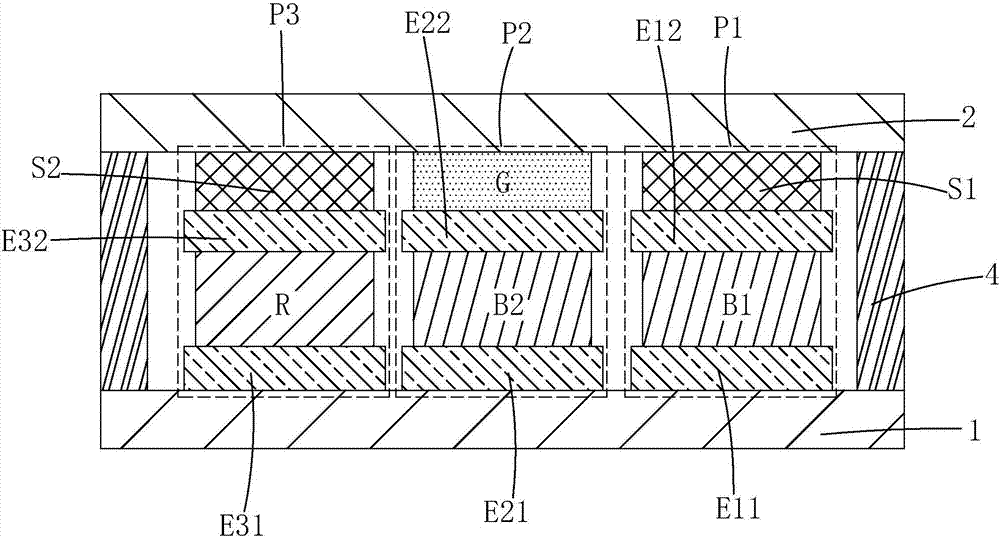
Micro LED color display device
InactiveCN107068707AControl precisionGood precisionStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceLength wave
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
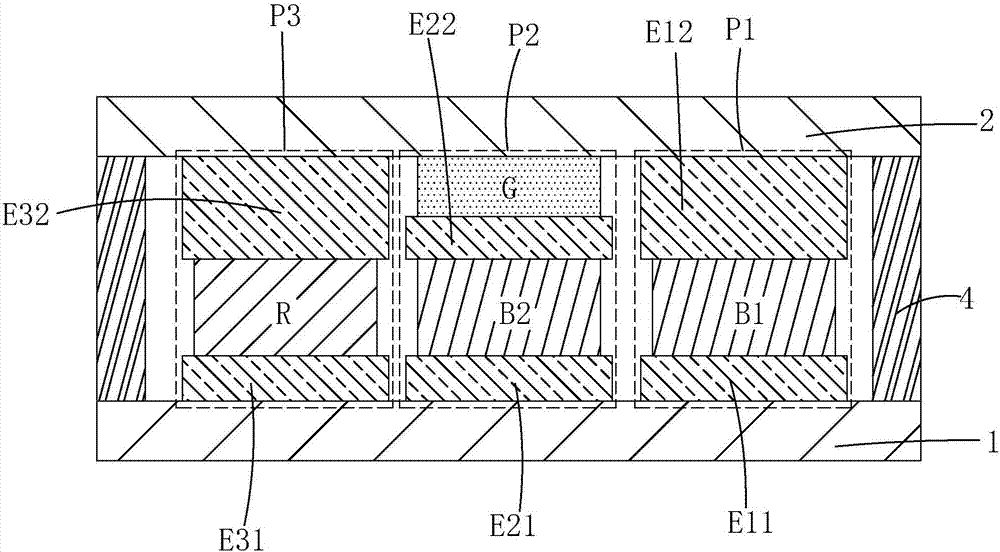
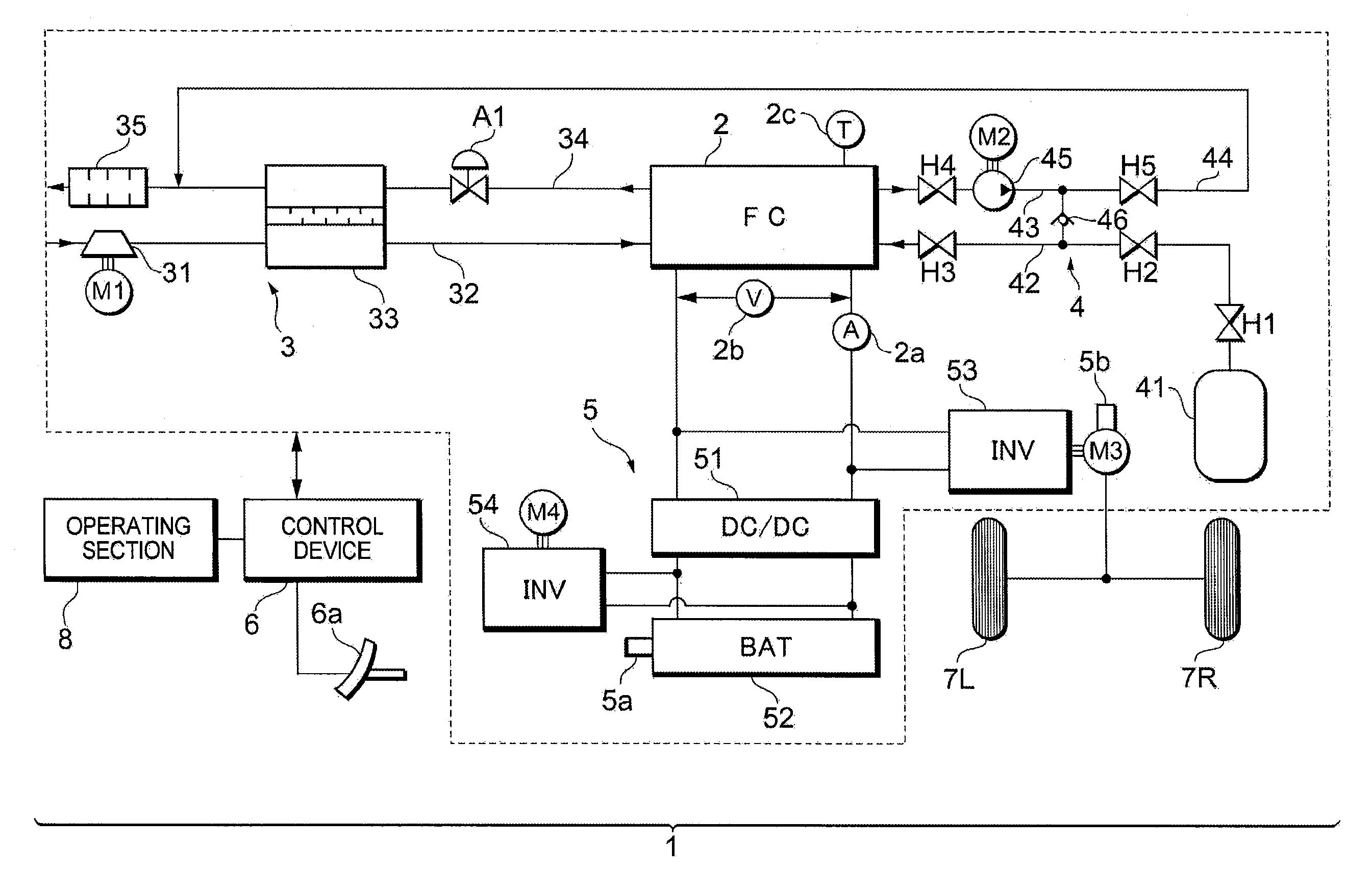
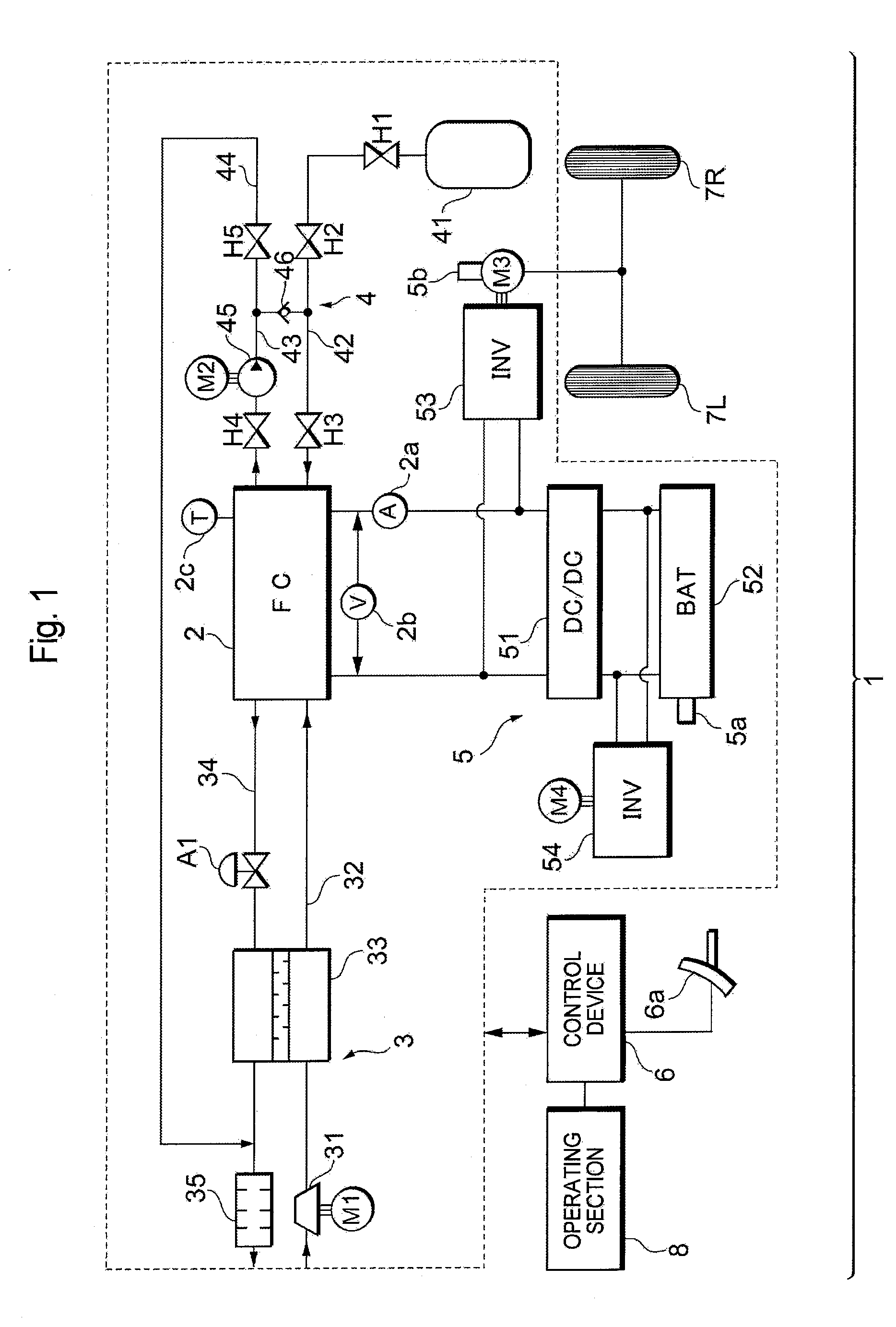
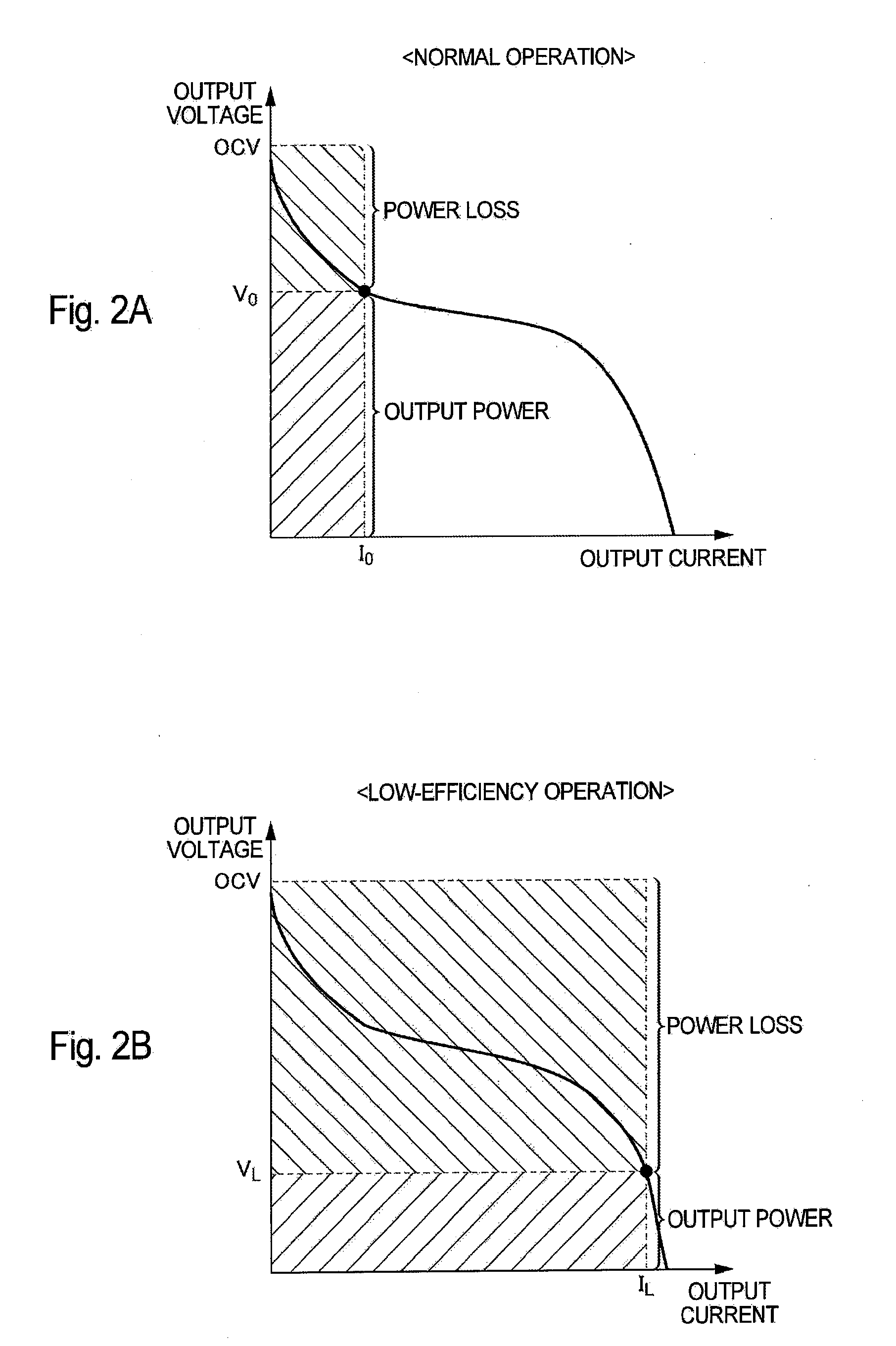
Fuel cell system and its operation method
ActiveUS20100047630A1Constant output voltageControl precisionFuel cell auxillariesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsElectricityFuel cells
A fuel cell system includes: a fuel cell which generates electricity; and control means which supplies an output power from the fuel cell to a predetermined load power source while realizing a low-efficiency operation of the fuel cell, thereby driving and controlling the load power source. The control means sets the output voltage of the fuel cell during the low-efficiency operation to a value not smaller than the minimum drive voltage of the load power source.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
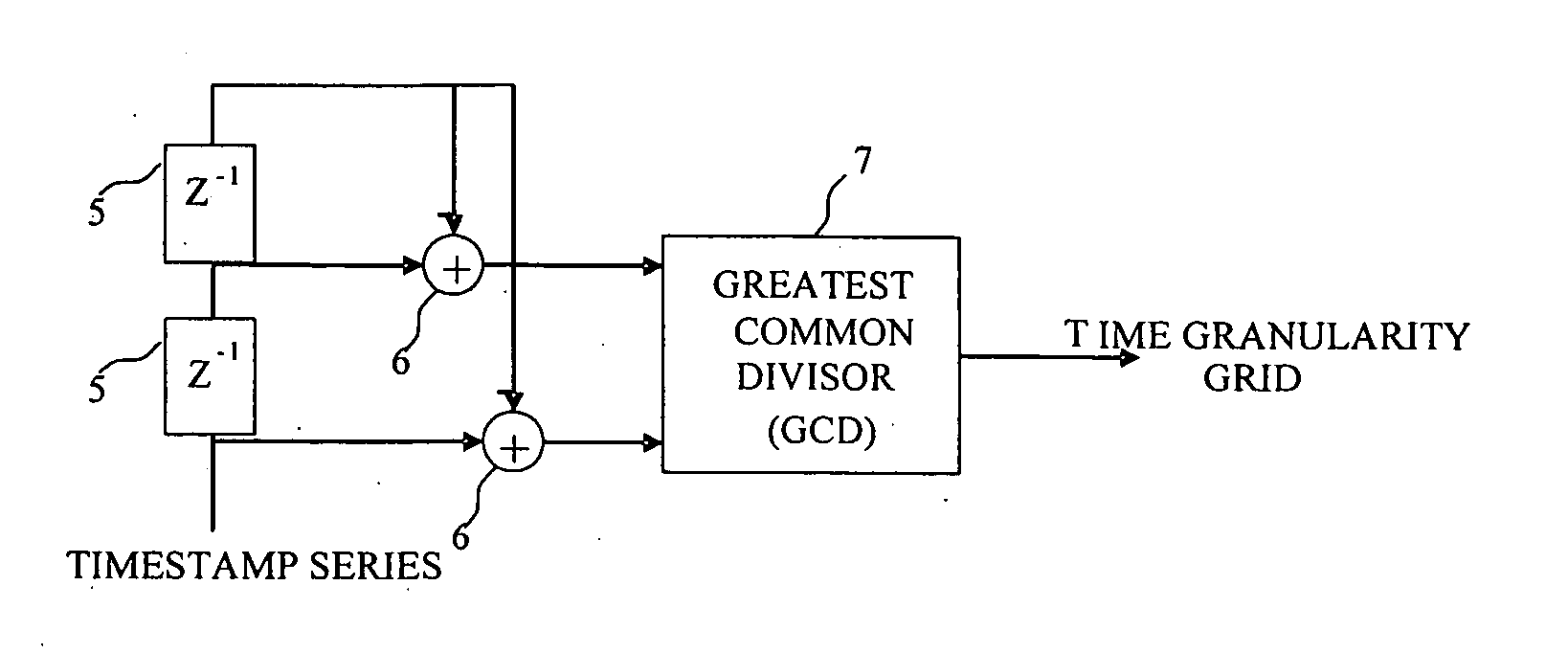
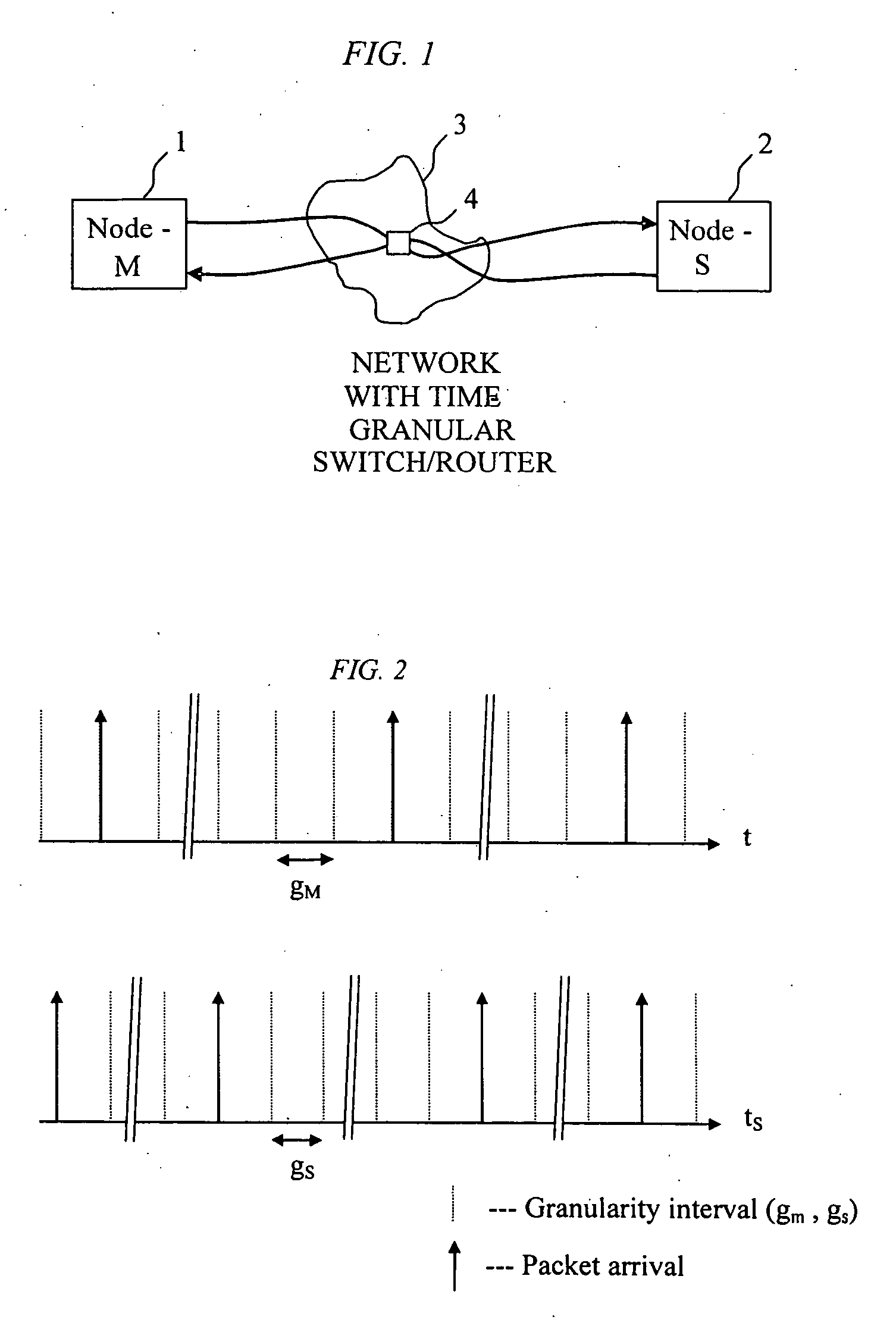
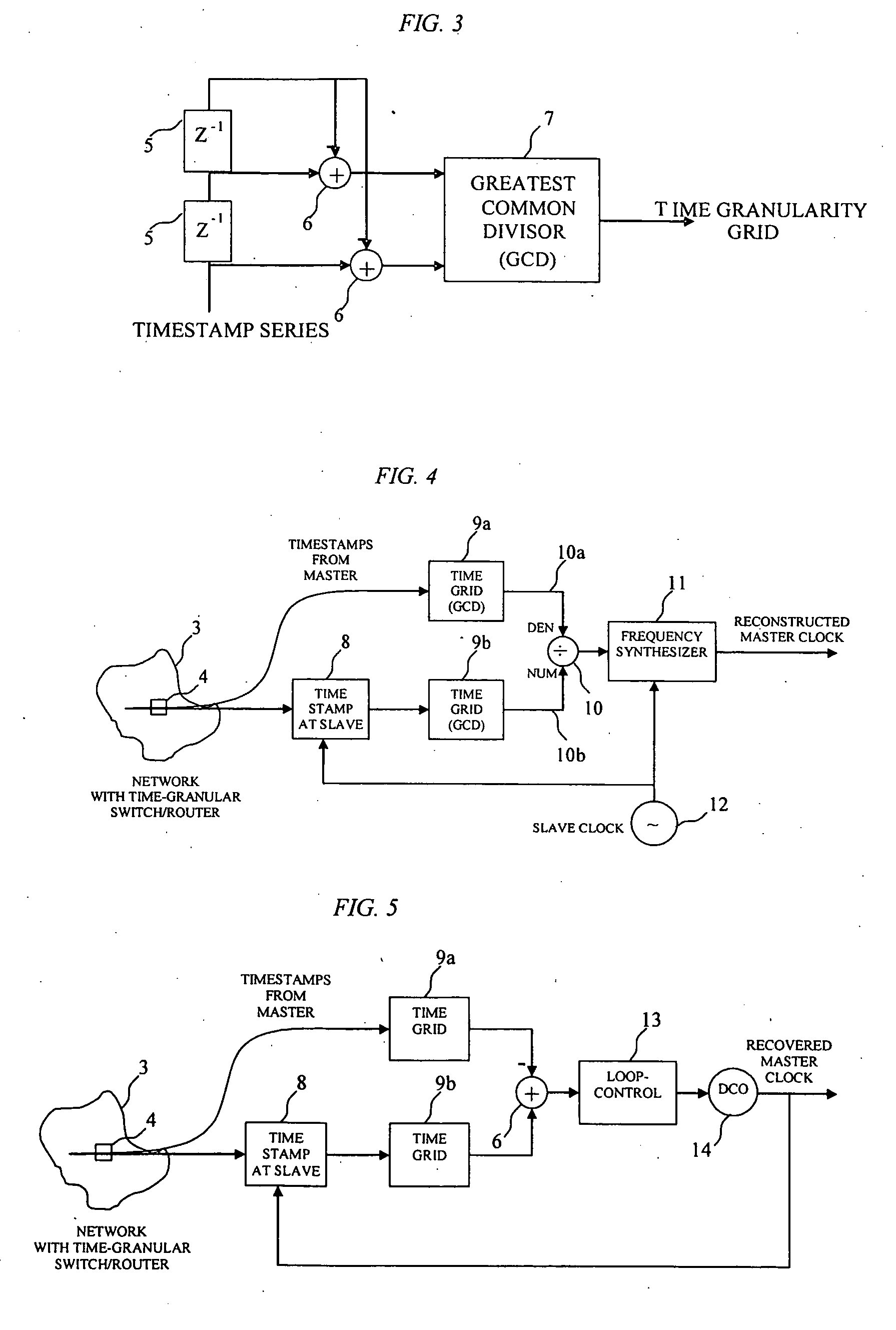
Method of recovering timing over a granular packet network
ActiveUS20060269029A1Overcome lossControl precisionTime-division multiplexSynchronising arrangementDigital control oscillatorSlave clock
A method is disclosed for recovering timing information between master and slave nodes interconnected over a packet network having an underlying time grid with a distinct granularity. A series timing packets are exchanged between said master and slave nodes to measure the time offset of the time grid relative to clocks at the master and slave clocks. This offset is then used to either adjust the local clock at the slave node, or generate the clock using a digital controlled oscillator.
Owner:ZARLINK SEMICON LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com