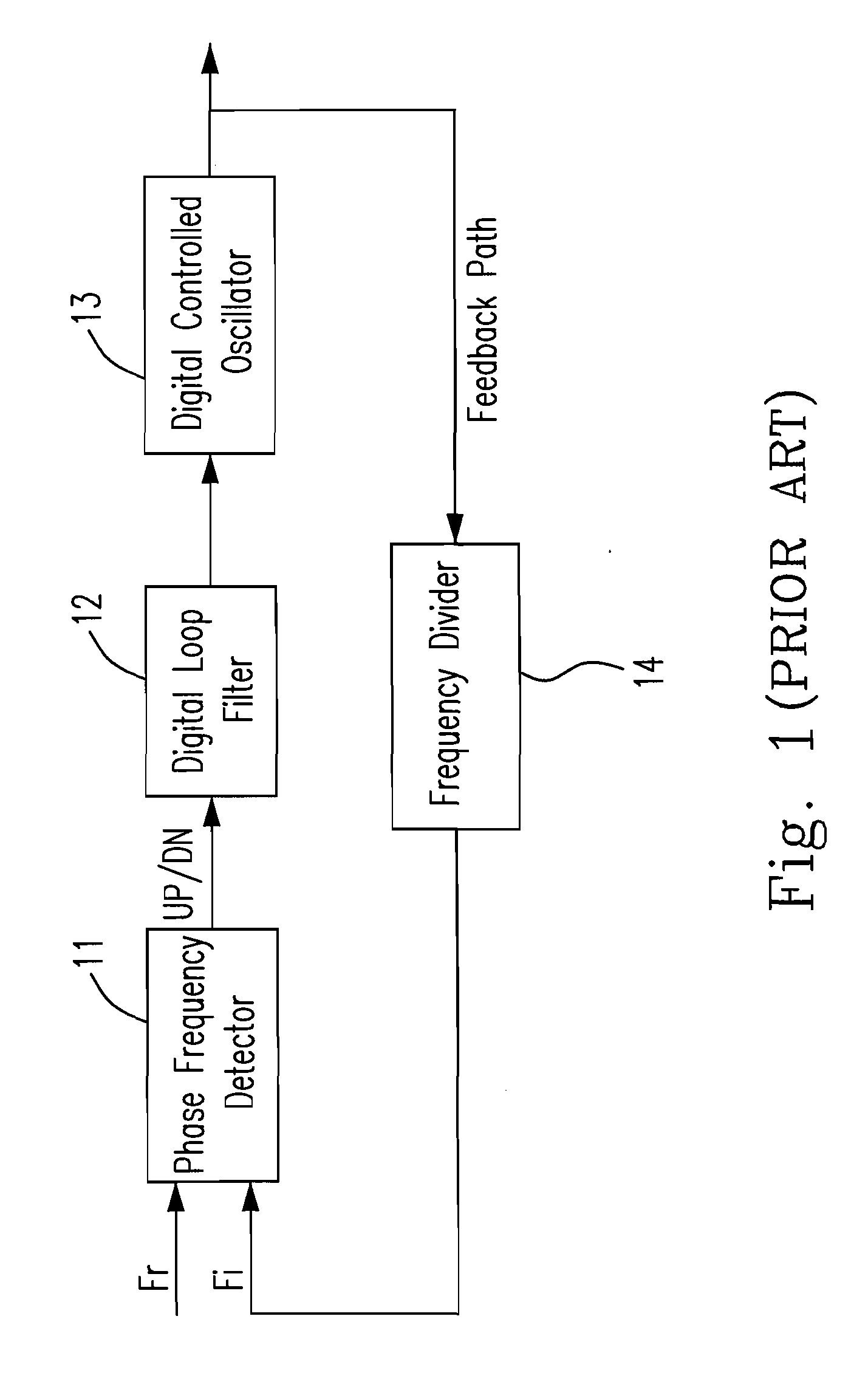
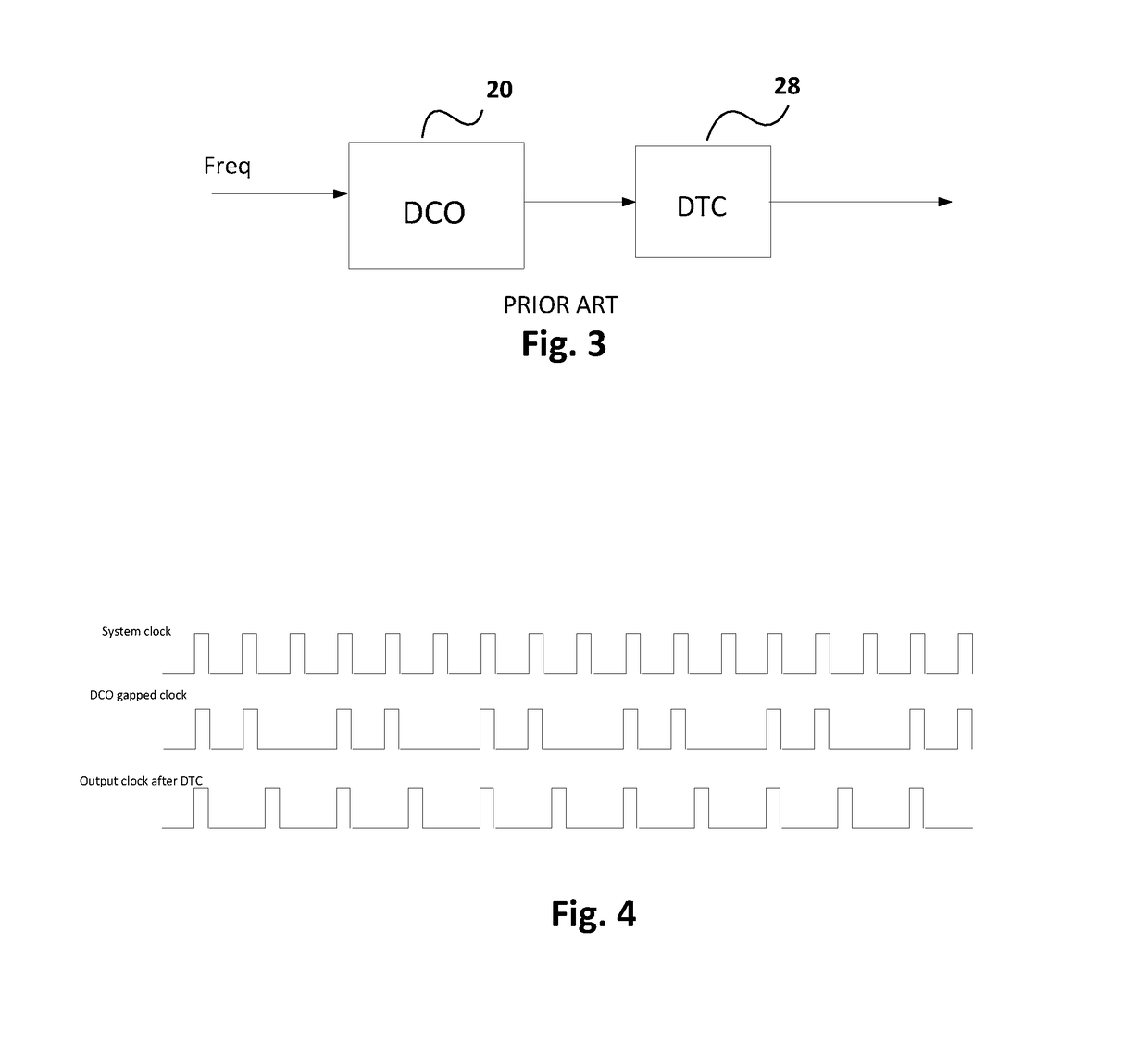
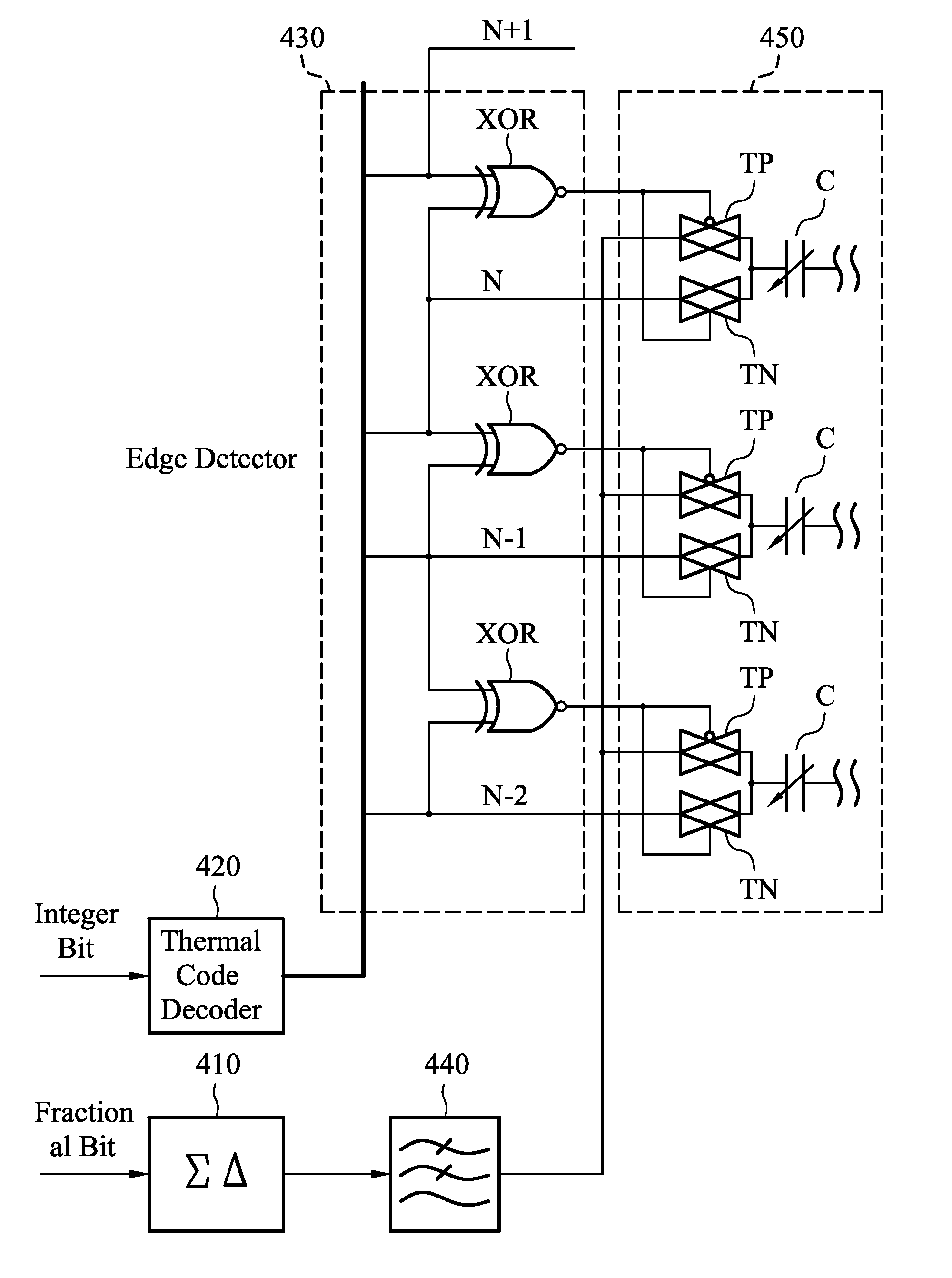
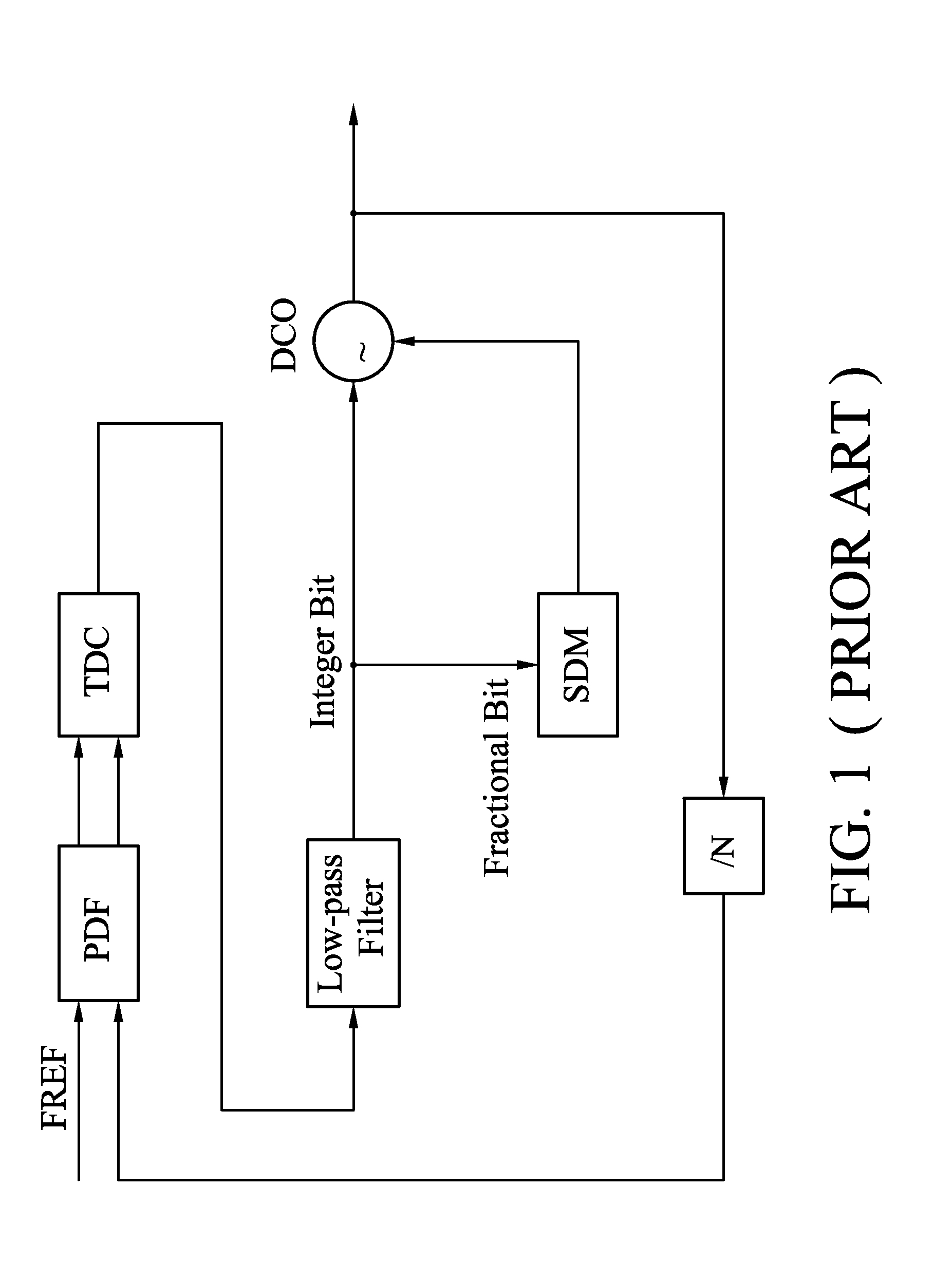
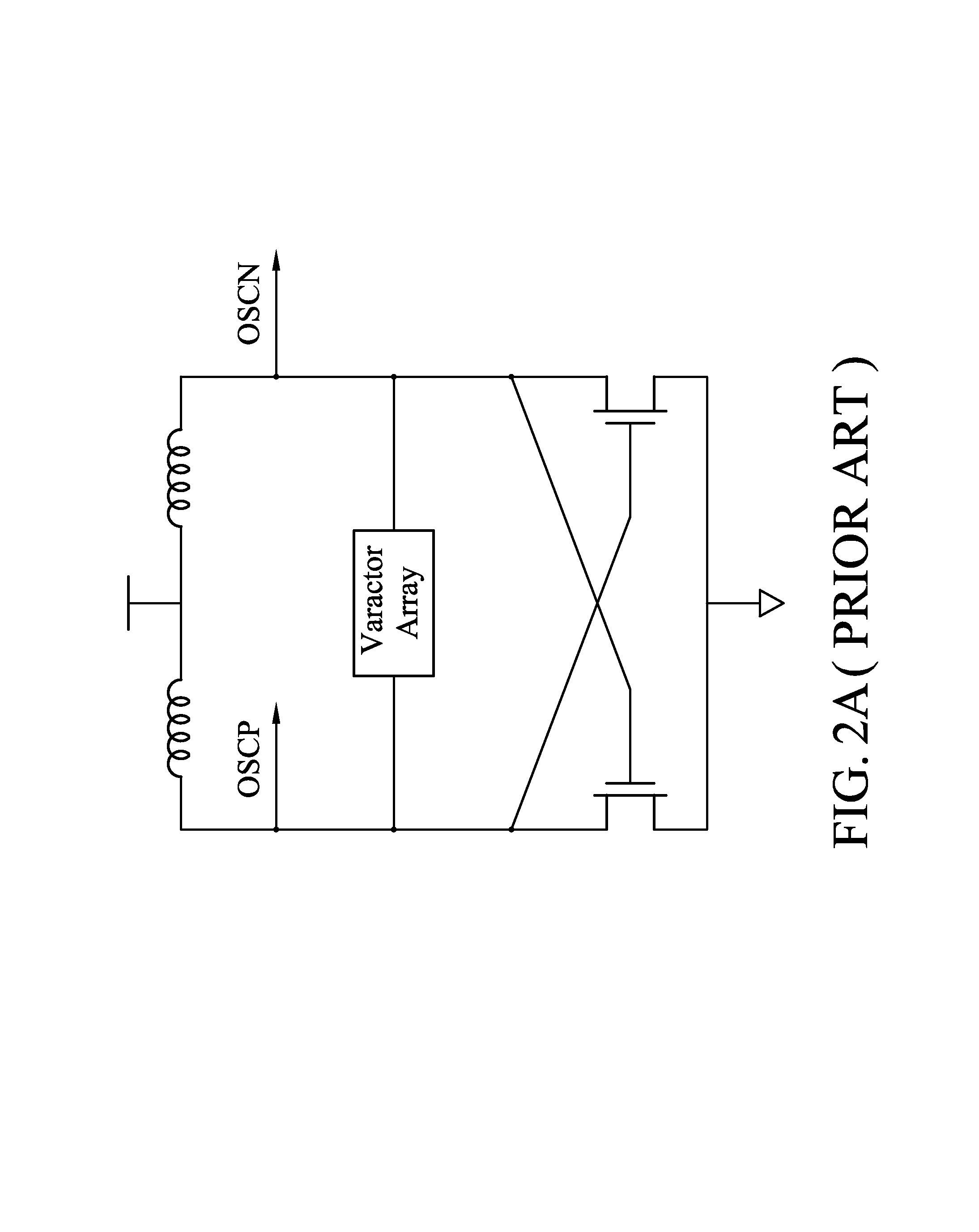
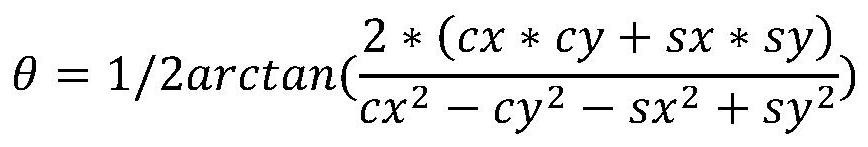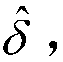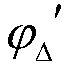Patents
Literature
83 results about "Digital control oscillator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
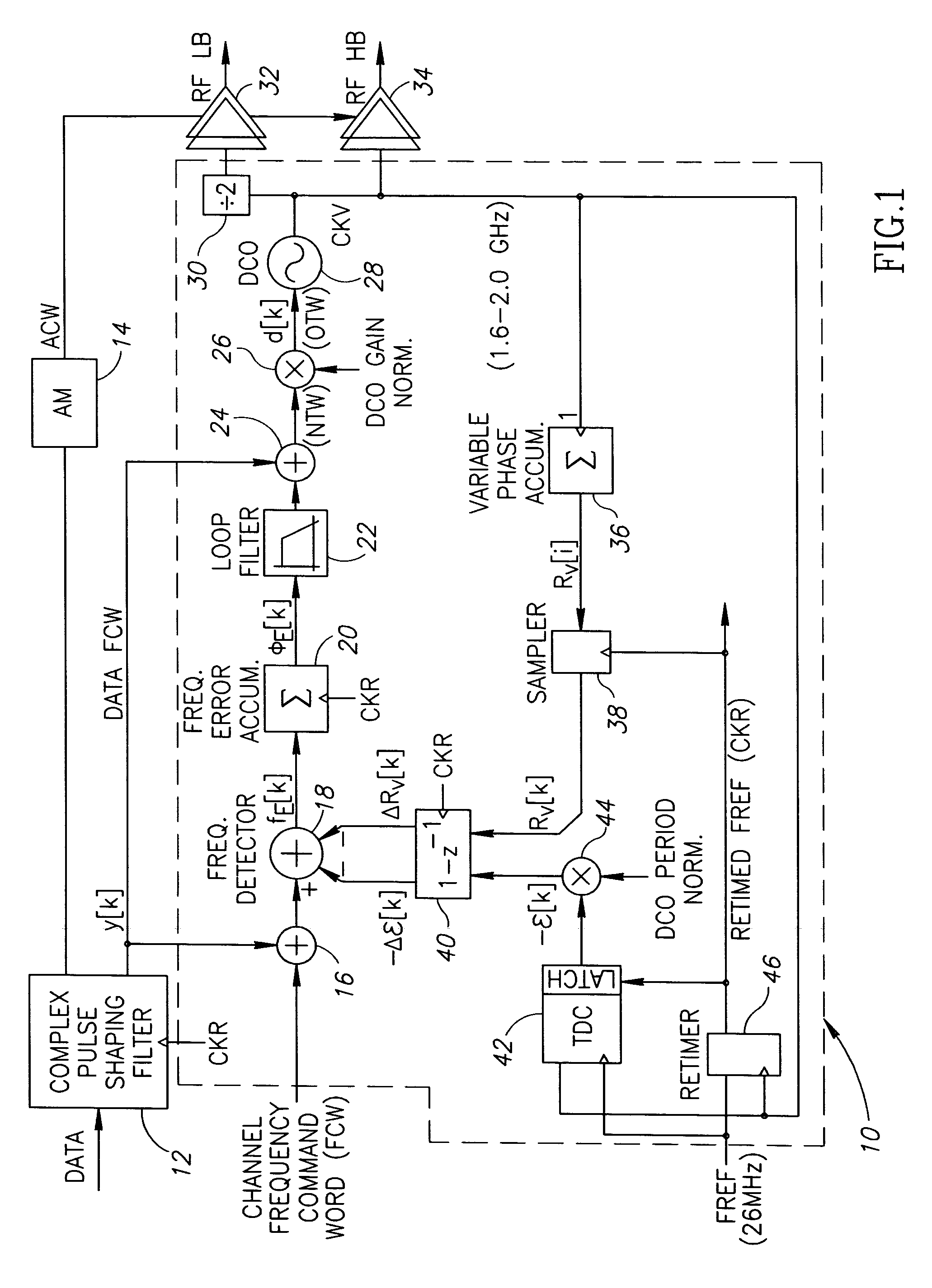
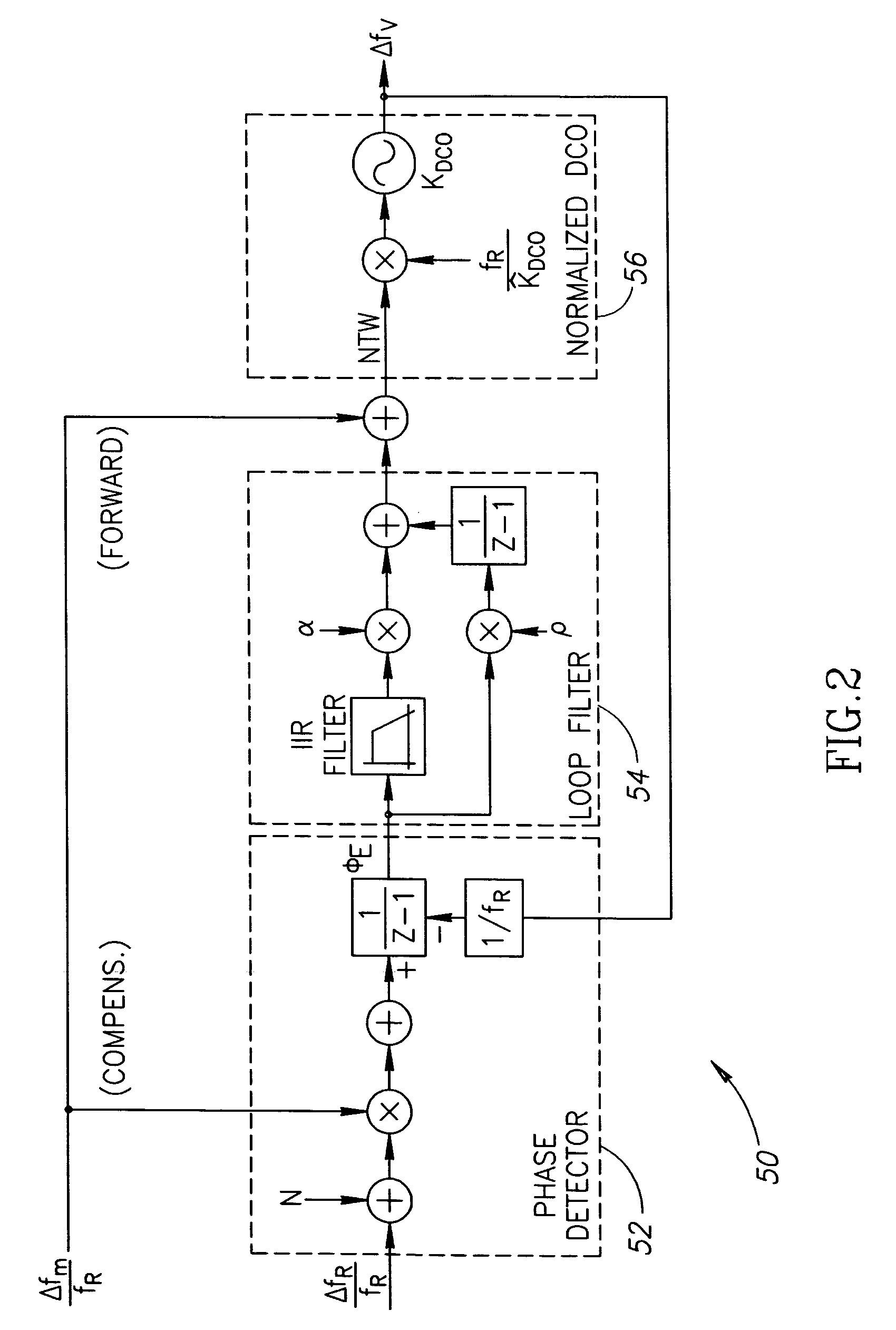
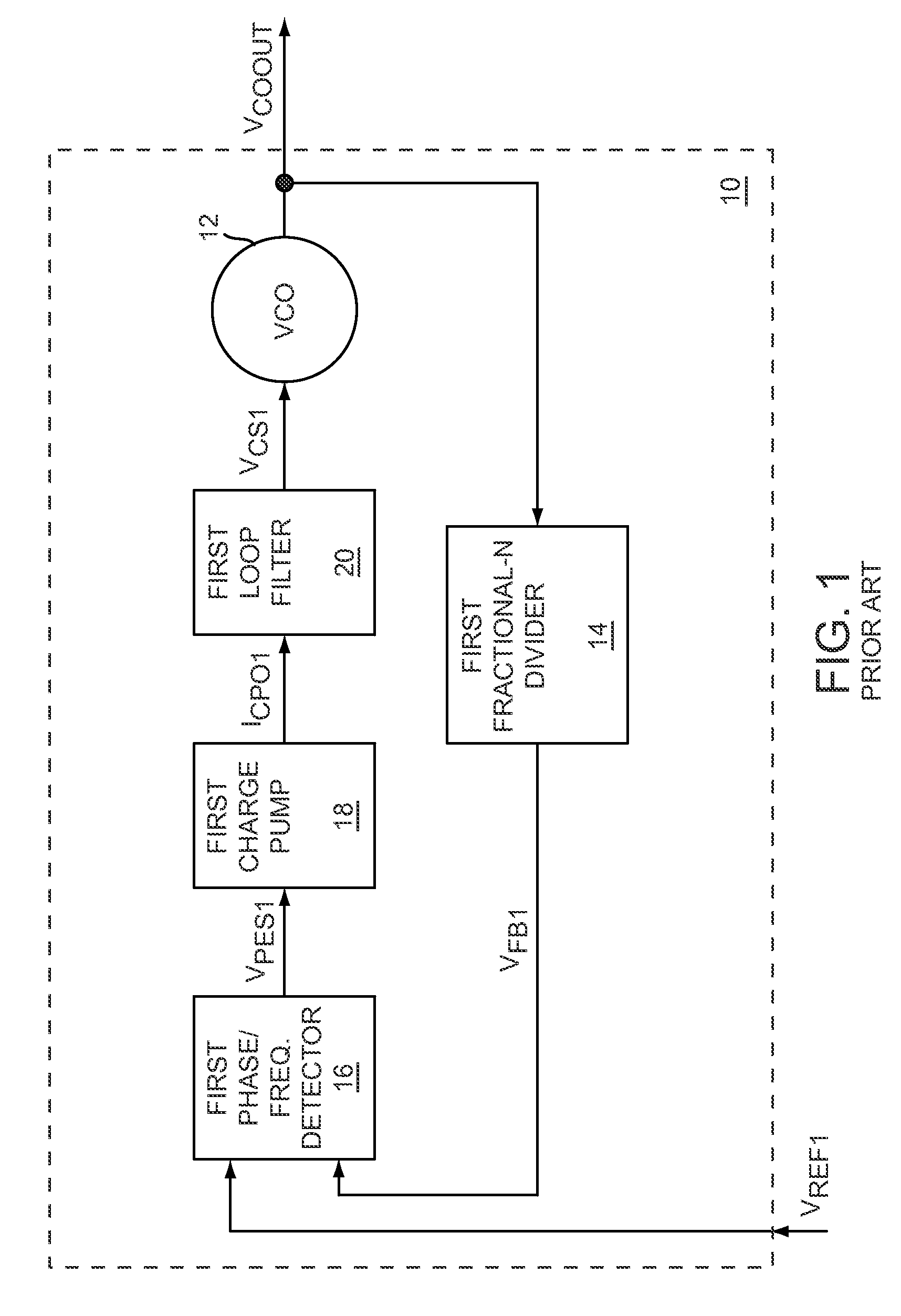
Gain calibration of a digital controlled oscillator
ActiveUS20060033582A1Good estimateImprove performancePulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsSteep descentDigital control oscillator
A novel apparatus for and a method of estimating, calibrating and tracking in real-time the gain of a radio frequency (RF) digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) in an all-digital phase locked loop (ADPLL). Precise setting of the inverse DCO gain in the ADPLL modulating path allows direct wideband frequency modulation that is independent of the ADPLL loop bandwidth. The gain calibration technique is based on a steepest descent iterative algorithm wherein the phase ADPLL error is sampled and correlated with the modulating data to generate a gradient. The gradient is then scaled and added to the current value of the DCO gain multiplier.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Gain calibration of a digital controlled oscillator
ActiveUS7183860B2Good estimatePulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsSteep descentDigital control oscillator
A novel apparatus for and a method of estimating, calibrating and tracking in real-time the gain of a radio frequency (RF) digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) in an all-digital phase locked loop (ADPLL). Precise setting of the inverse DCO gain in the ADPLL modulating path allows direct wideband frequency modulation that is independent of the ADPLL loop bandwidth. The gain calibration technique is based on a steepest descent iterative algorithm wherein the phase ADPLL error is sampled and correlated with the modulating data to generate a gradient. The gradient is then scaled and added to the current value of the DCO gain multiplier.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
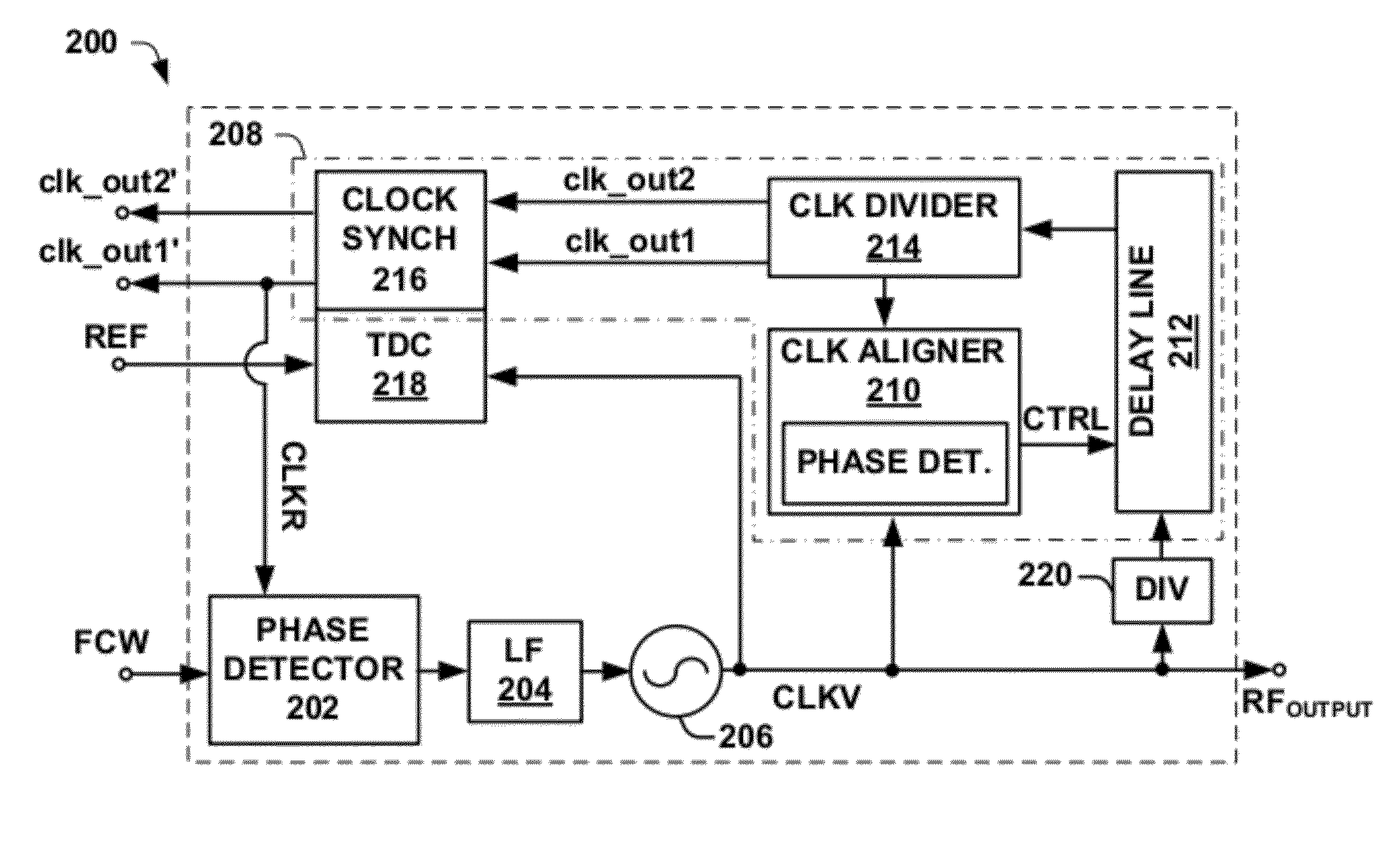
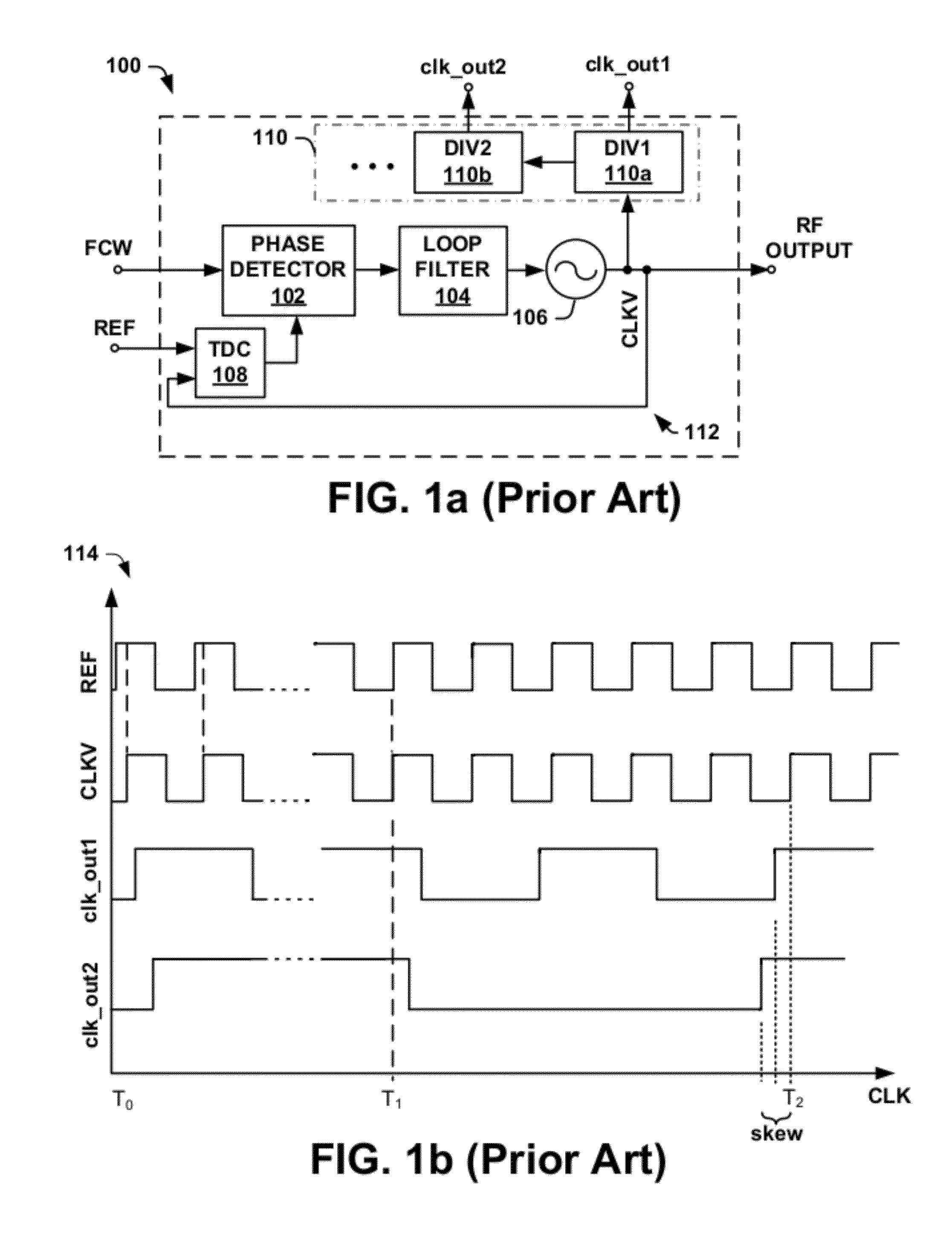
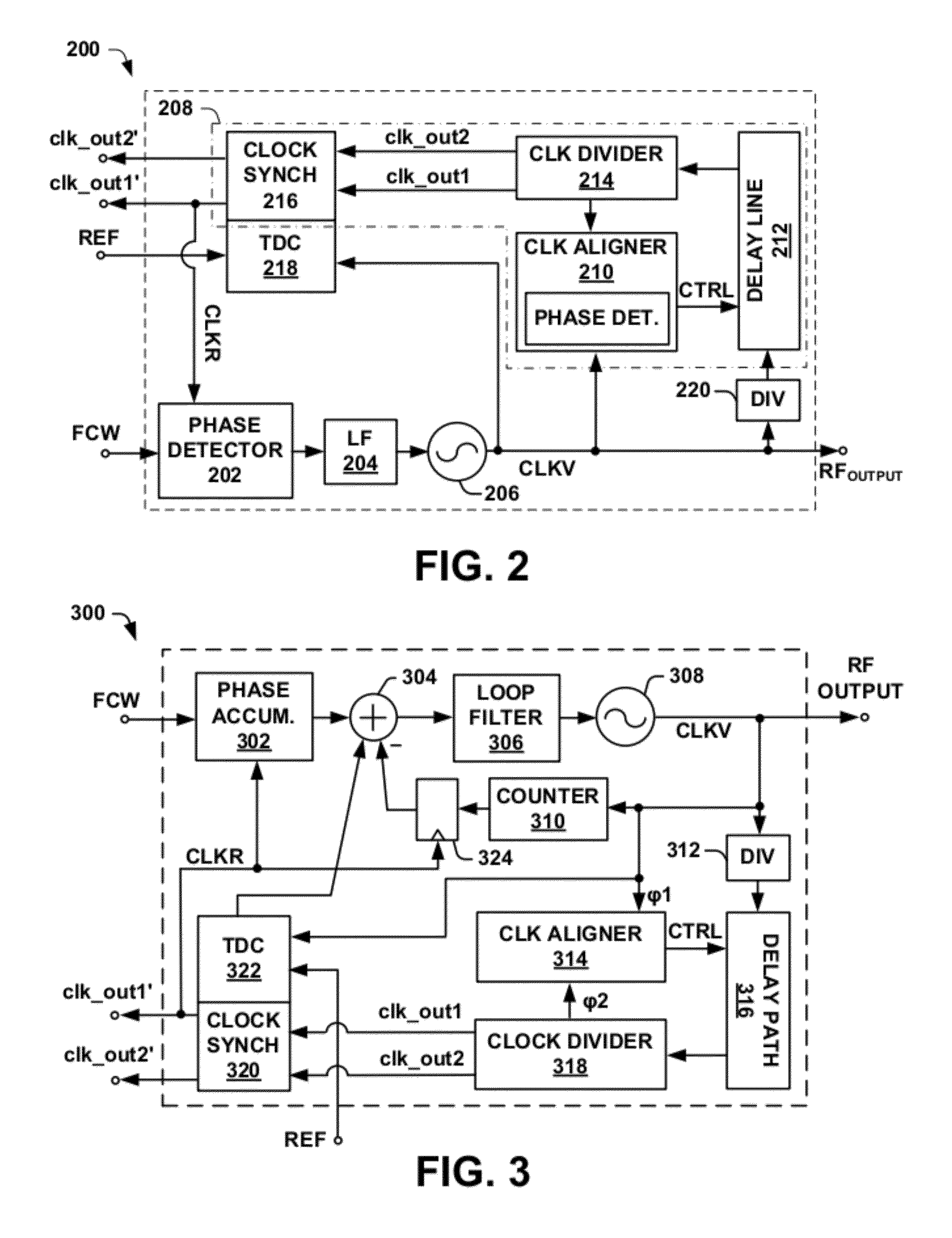
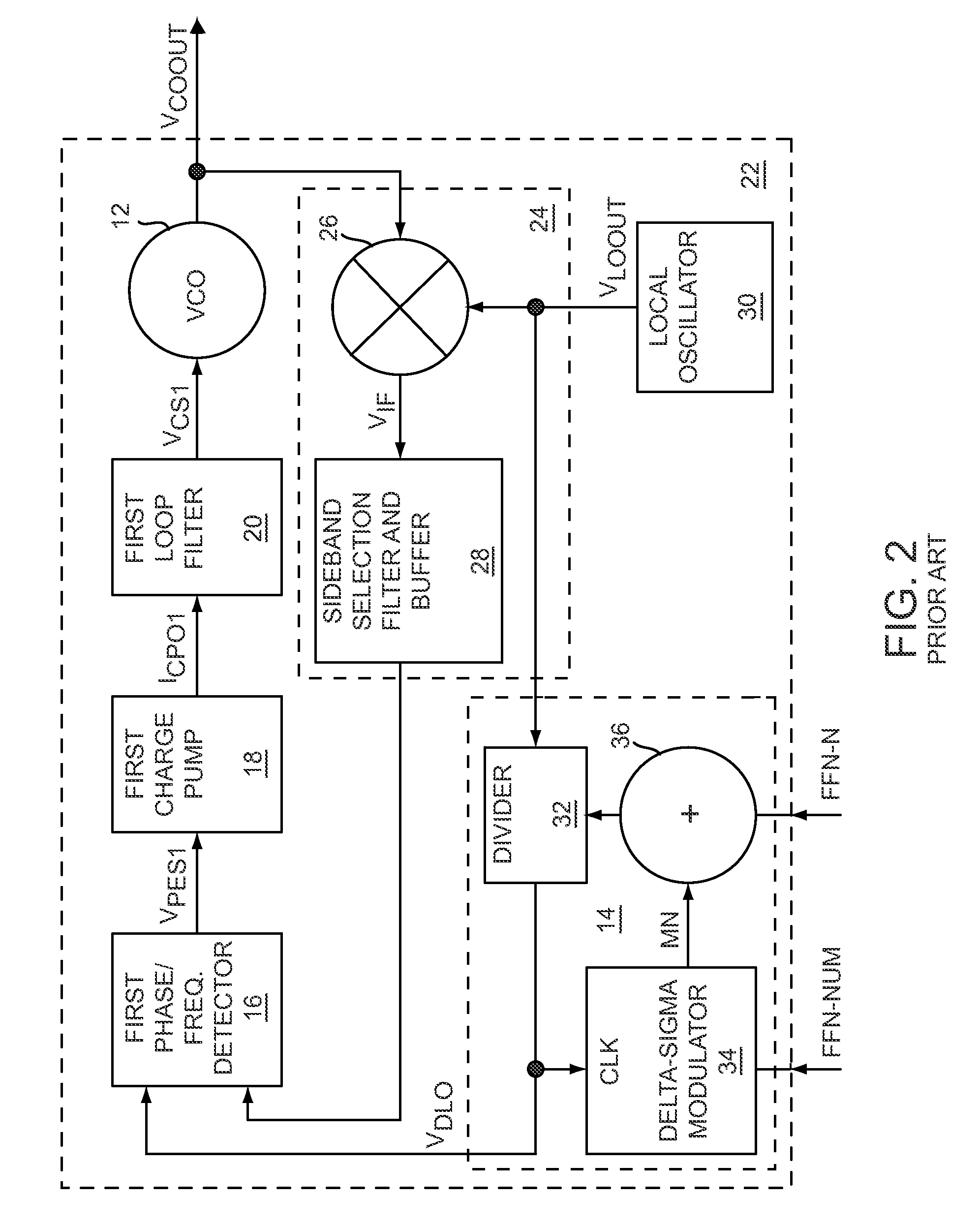
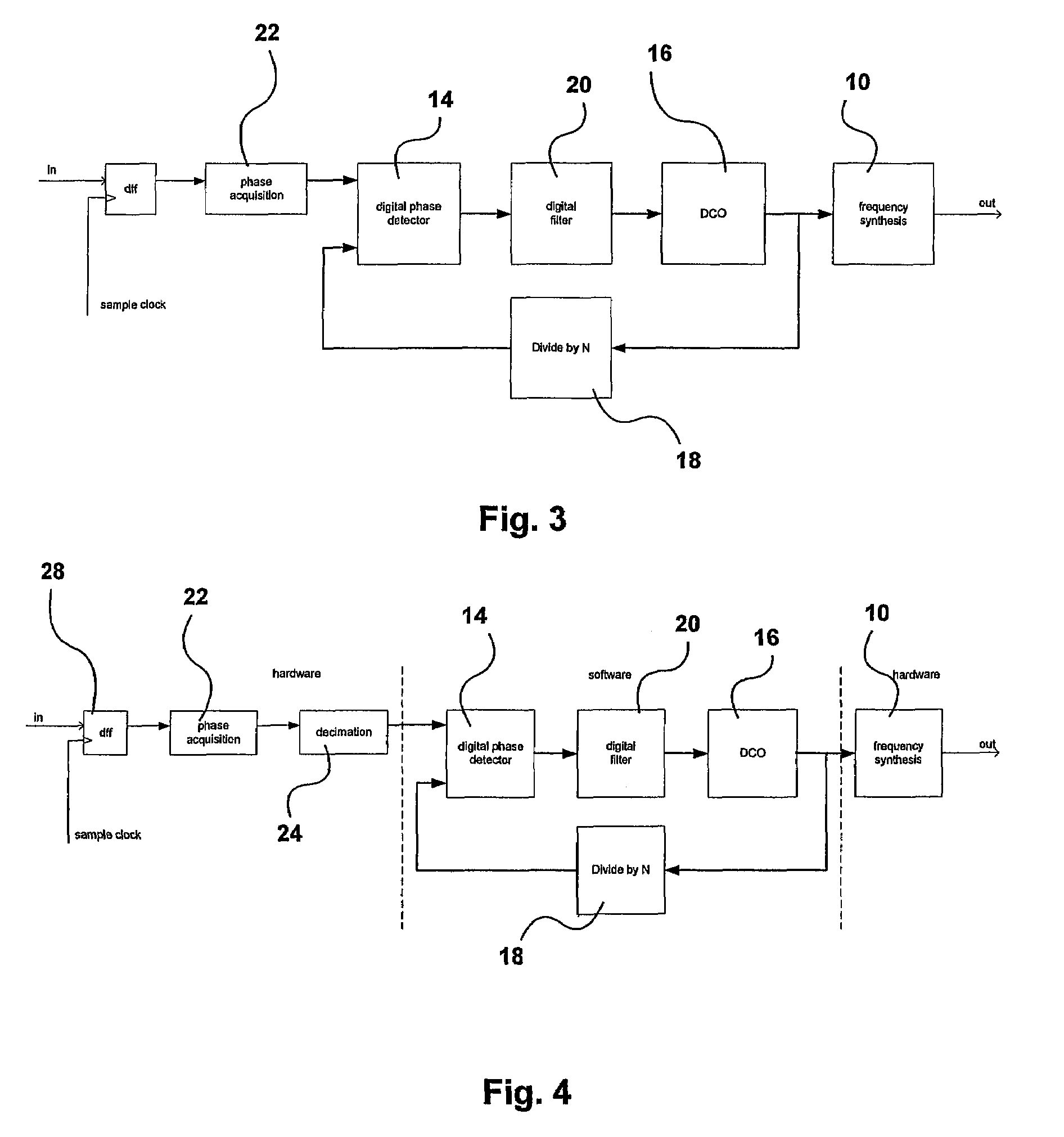
Digital pll with automatic clock alignment
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a digital phase locked loop (ADPLL) configured to generate a plurality of time-aligned output clock signals having different frequency values. The ADPLL comprises a digital controlled oscillator configured to generate a variable clock signal that is separated into two signal paths operating according to two separate clock domains. A first signal path is configured to generate a feedback signal that synchronizes the variable clock signal with a reference signal. A second signal path comprises a clock divider circuit configured to synchronously divide the variable clock signal to automatically generate a plurality of time-aligned output clock signals having different frequencies. A clock aligner monitors a phase difference between the variable clock signal and one of the plurality of time-aligned output clock signals and generates a control signal that causes a programmable delay line to automatically time-align the output clock signals with the variable clock signal.
Owner:INTEL CORP
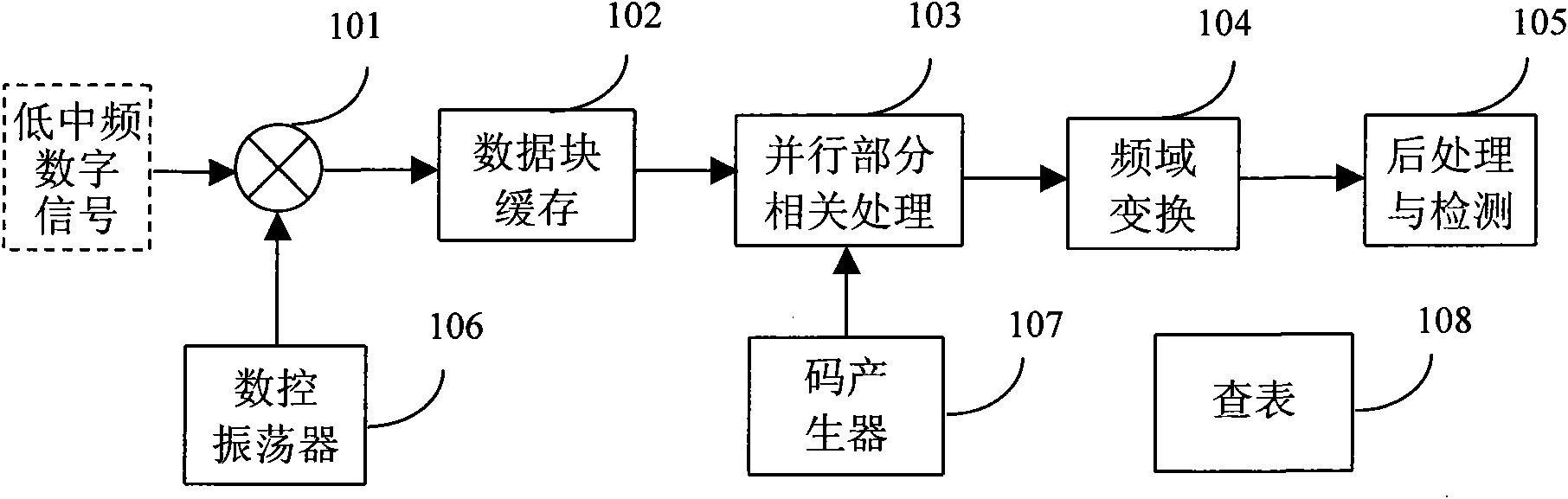
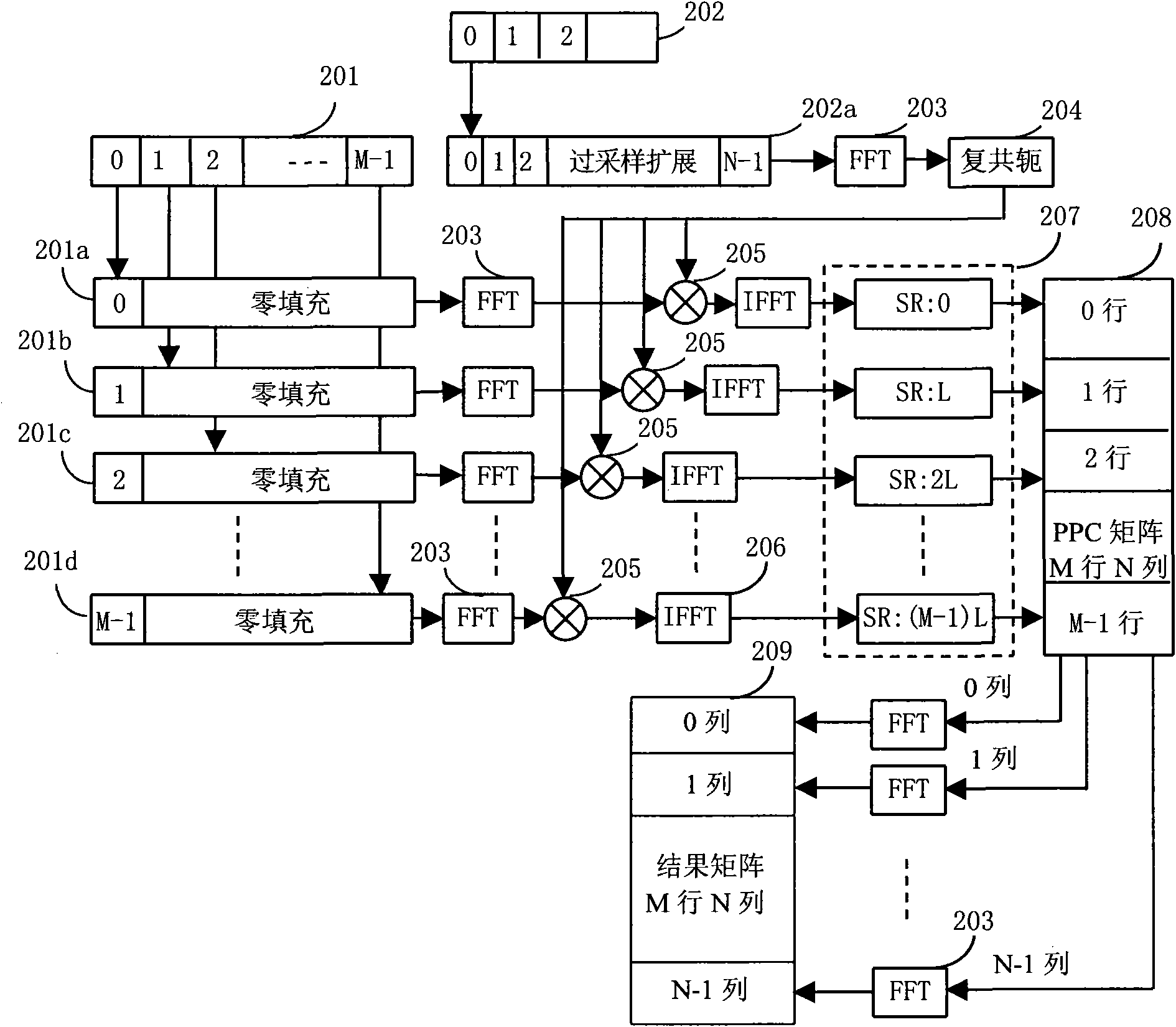
GPS signal large-scale parallel quick capturing method and module thereof
ActiveCN101625404ALow costCapture flexibleBeacon systemsTransmissionData segmentIntermediate frequency
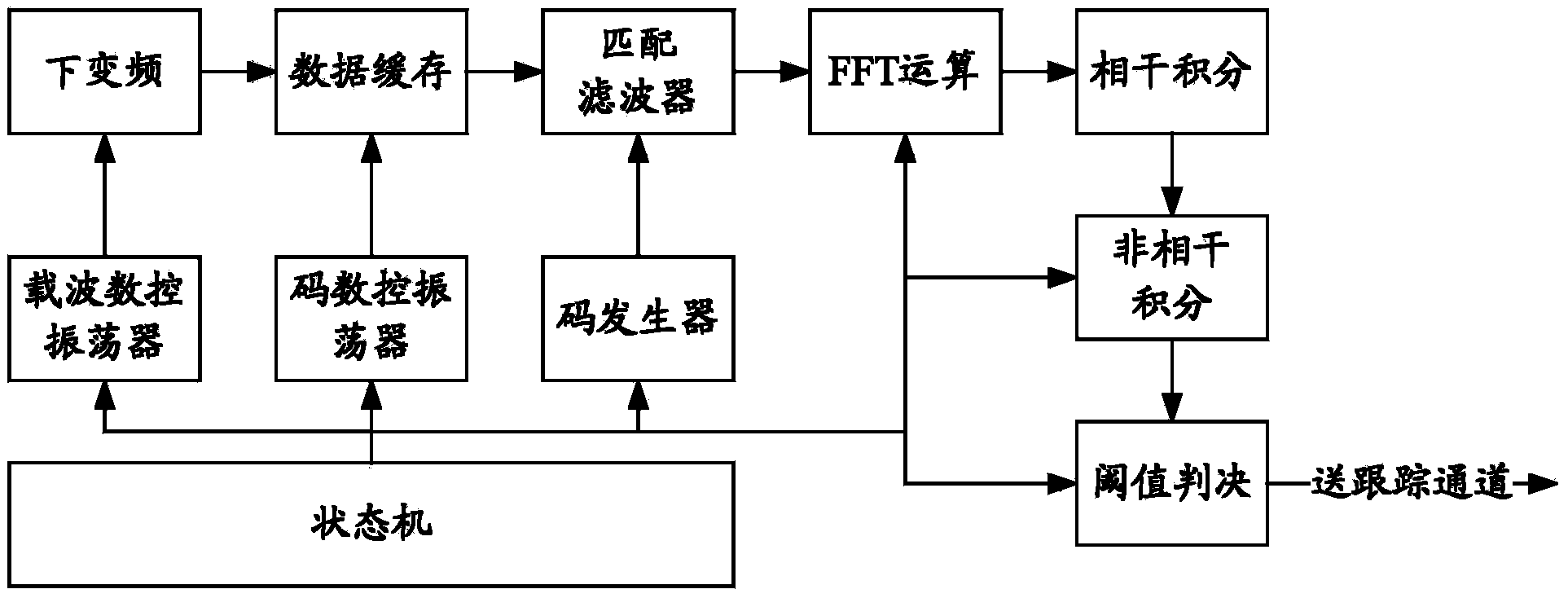
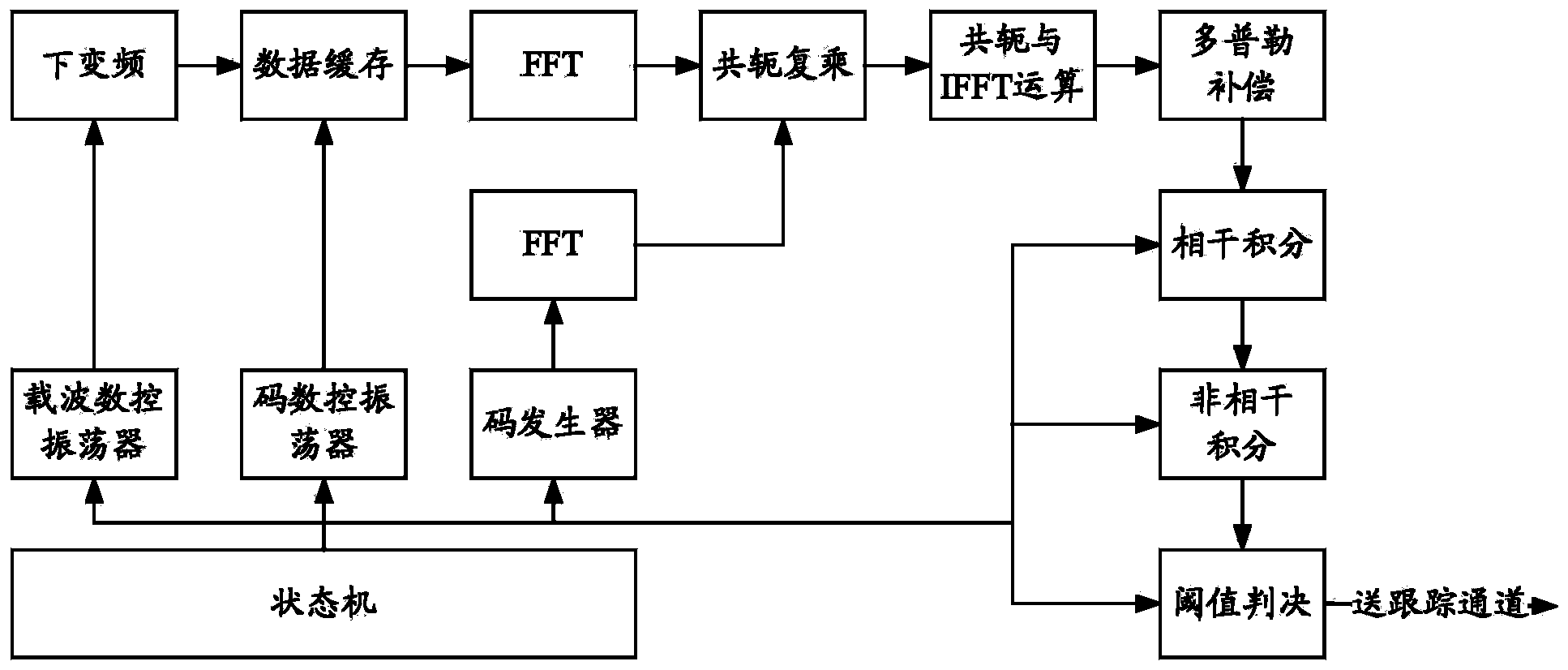
The invention discloses a GPS signal large-scale parallel quick capturing method, which comprises the following steps: configuring a large-scale parallel quick capturing module firmware comprising submodules of multiplier, data block cache, parallel part correlative processing, frequency domain transformation, postprocessing and digital controlled oscillator, code generator and the like in a system CPU; through the calling computation, converting low-medium frequency digital signals into baseband signals in a processing procedure to combine a data block; performing zeroing extension of the length and the data block on each equational data section in the data block; then based on FFT transformation computation, performing parallel part correlative PPC processing on each extended data section and local spreading codes, and performing FFT transformation on each line of a formed PPC matrix to obtain a result matrix; and performing coherent or incoherent integration on a plurality of result matrixes formed by processing a plurality of data blocks to increase the processing gain, improve the capturing sensitivity, roughly determine the code phase and the Doppler frequency of GPS signals, and achieve two-dimensional parallel quick capturing of the GPS signals. The method has high processing efficiency and high capturing speed, and can be applied to various GPS positioning navigation aids.
Owner:杭州中科微电子有限公司
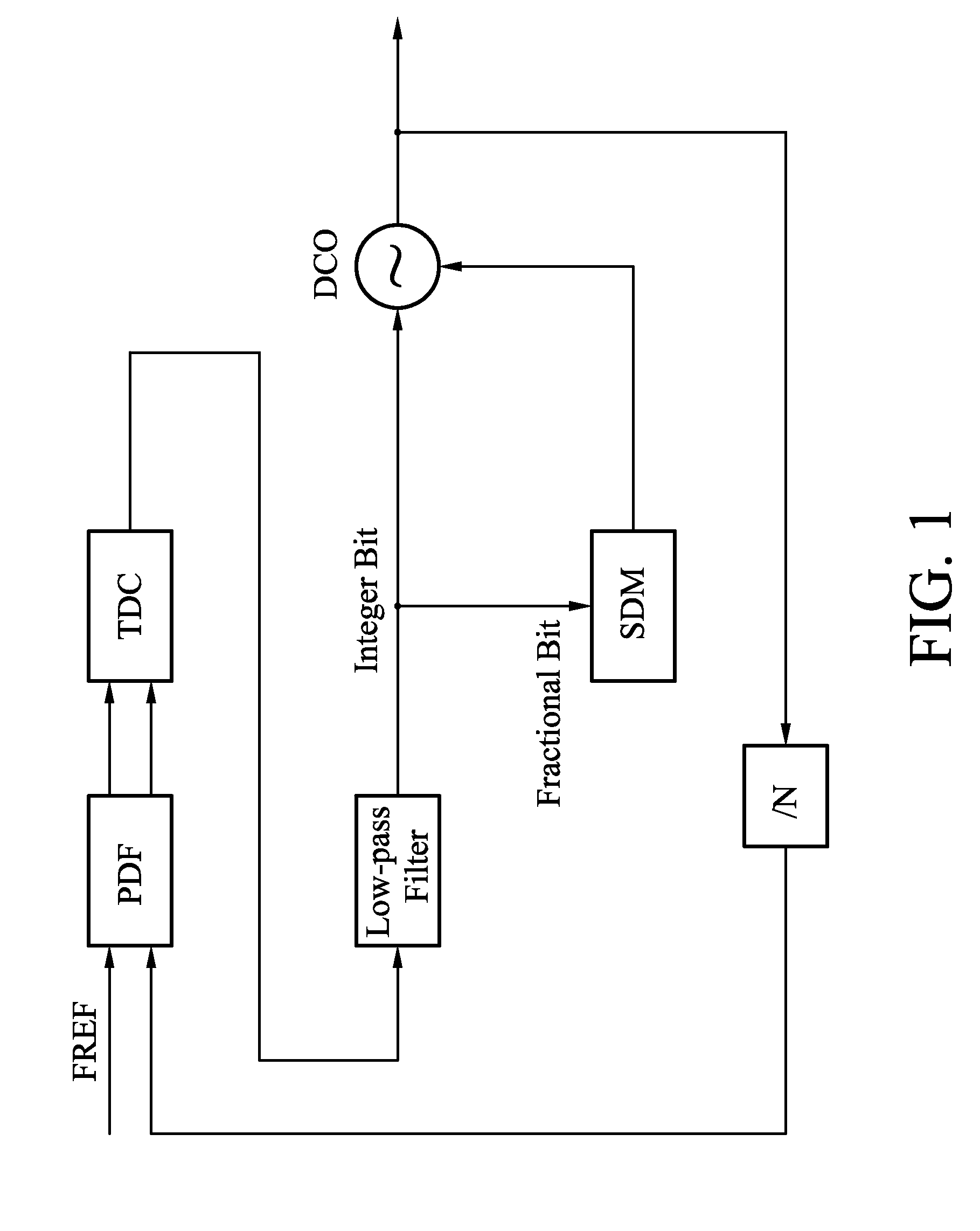
Error Compensation Method, Digital Phase Error Cancellation Module, and ADPLL thereof
InactiveUS20090097609A1Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionDigital control oscillatorReference Period
Phase error of a time-to-digital converter (TDC) within an all-digital phase-locked loop (ADPLL) is compensated by predicting possible phase error, which are predicted according to an estimated quantization error, a period of a digital-controlled oscillator (DCO), a gain of the TDC or a combination thereof. By appropriate inductions, the possible phase error may be further indicated by the quantization error, a code variance corresponding to a half of a reference period received by a TDC module having the TDC, a dividing ratio of a frequency divider of the ADPLL, a fractional number related to the quantization error o a combination thereof. A digital phase error cancellation module is also used for generating the possible phase error for compensating the phase error of the TDC.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
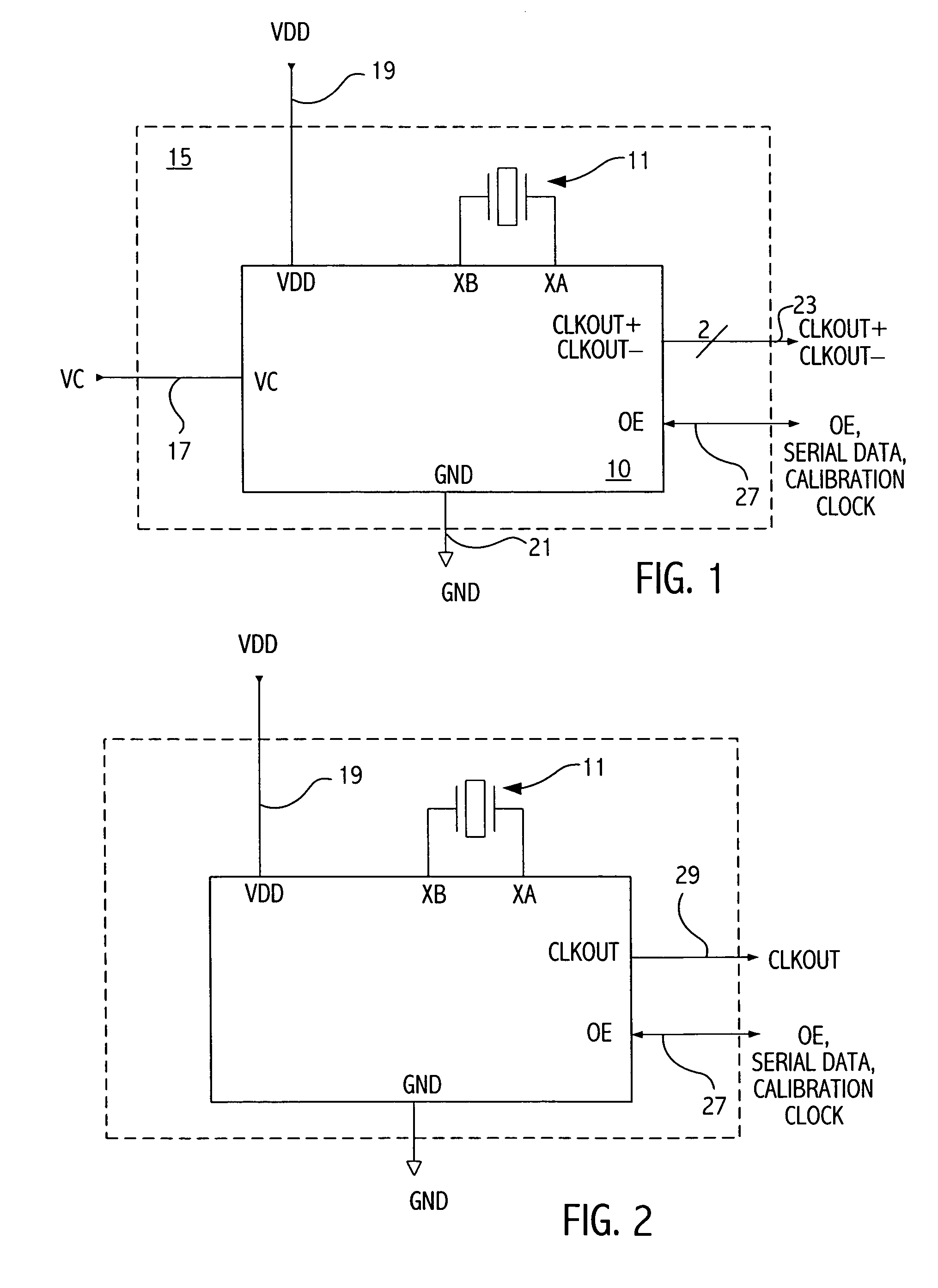
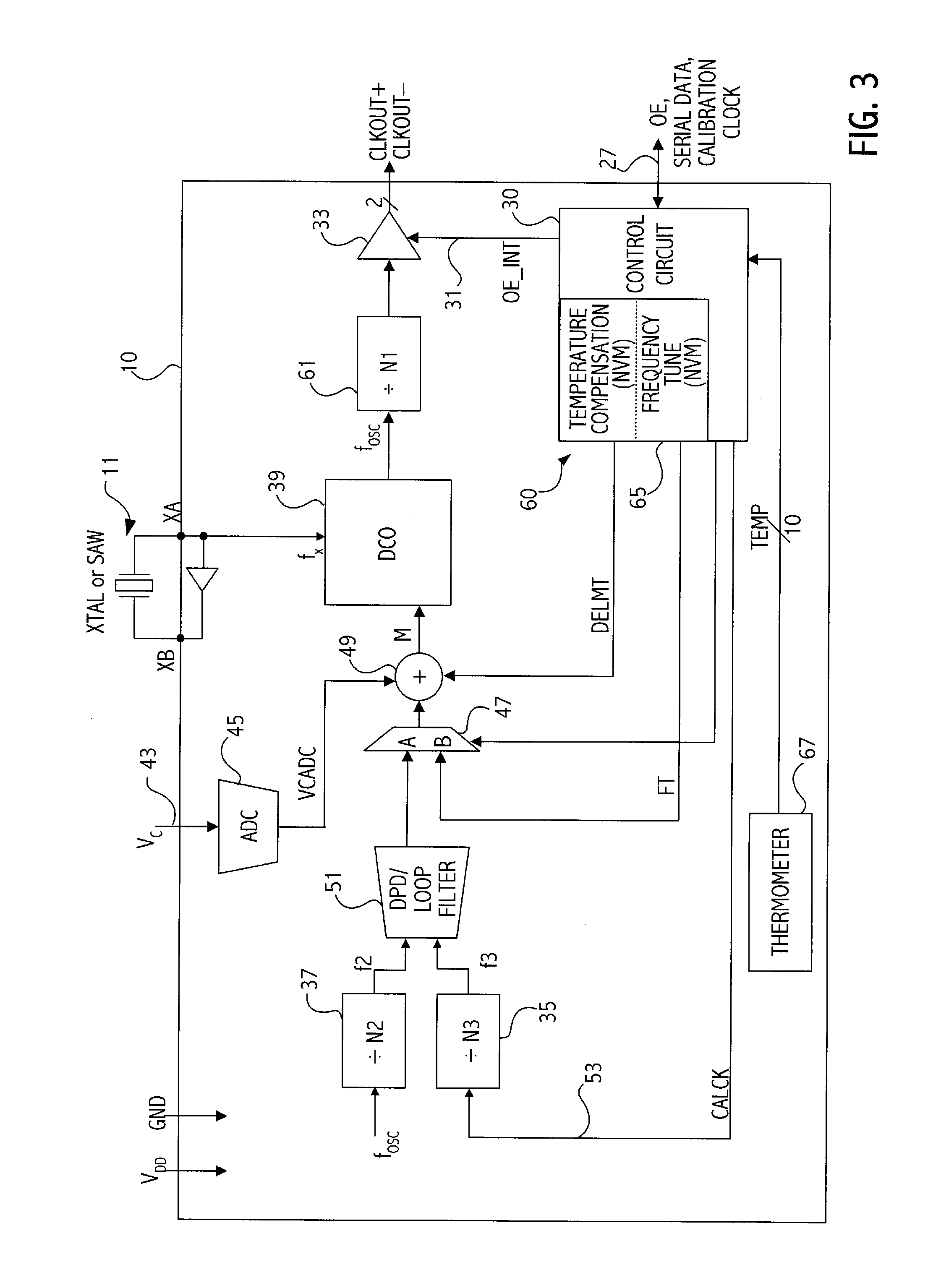
Calibration of oscillator devices
ActiveUS7187241B2Pulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationDigital controlled oscillatorNon-volatile memory
A clock device having a resonating device such as a crystal of SAW supplying a controllable oscillator such as a digitally controlled oscillator is calibrated by supplying a calibration clock. A phase-locked loop is utilized to generate one or more correction factors causing the PLL to lock to the calibration clock. The one or more correction factors are then stored in non-volatile memory.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
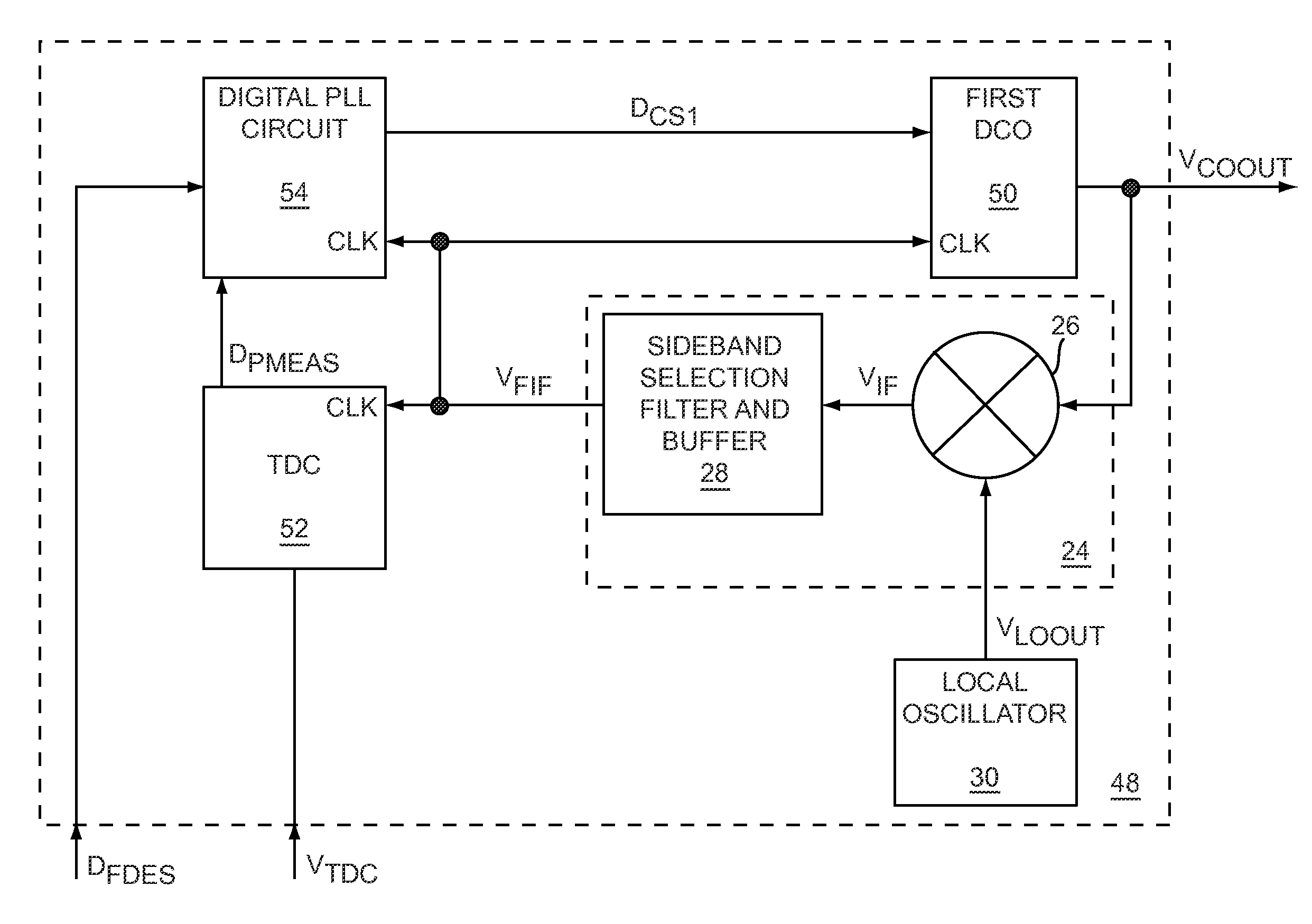
Digital offset phase-locked loop
ActiveUS7746178B1Reducing loop gainKeep linearPulse automatic controlDigital feedbackDigital control oscillator
The present invention relates to a digital offset phase-locked loop (DOPLL), which may have advantages of size, simplicity, performance, design portability, or any combination thereof, compared to analog-based phase-locked loops (PLLs). The DOPLL may include a digital controlled oscillator (DCO), which provides a controllable frequency output signal based on a digital control signal, a radio frequency (RF) mixer circuit, which provides a reduced-frequency feedback signal based on the controllable frequency output signal without reducing loop gain, a time-to-digital converter (TDC), which provides a digital feedback signal that is a time representation of the reduced-frequency feedback signal, and digital PLL circuitry, which provides the digital control signal based on the digital feedback signal and a digital setpoint signal.
Owner:QORVO US INC
All-digital fractional-N phase-locked loop structure
ActiveCN106209093ASmall coverageShorten the effective lengthPulse automatic controlDigital control oscillatorEngineering
The invention provides an all-digital fractional-N phase-locked loop structure comprising a time-digital converter TDC, a digital filter DLF, a digital-controlled oscillator DCO, a digital-controlled phase interpolator DPI, a sigmadelta modulator SDM, an integer frequency divider DIV and a feedforward correction module. Conversion from digital control signals to phase information is completed by using the digital-controlled phase interpolator DPI, and the nonlinearity brought by the DPI can be eliminated by using the feedforward correction means. According to the structure, the complexity of the circuit design can be reduced, and the problems of high power consumption, complex design and poor noise in the existing structure can also be solved so that the structure is suitable for the field of high-performance and low-power-consumption wireless communication.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
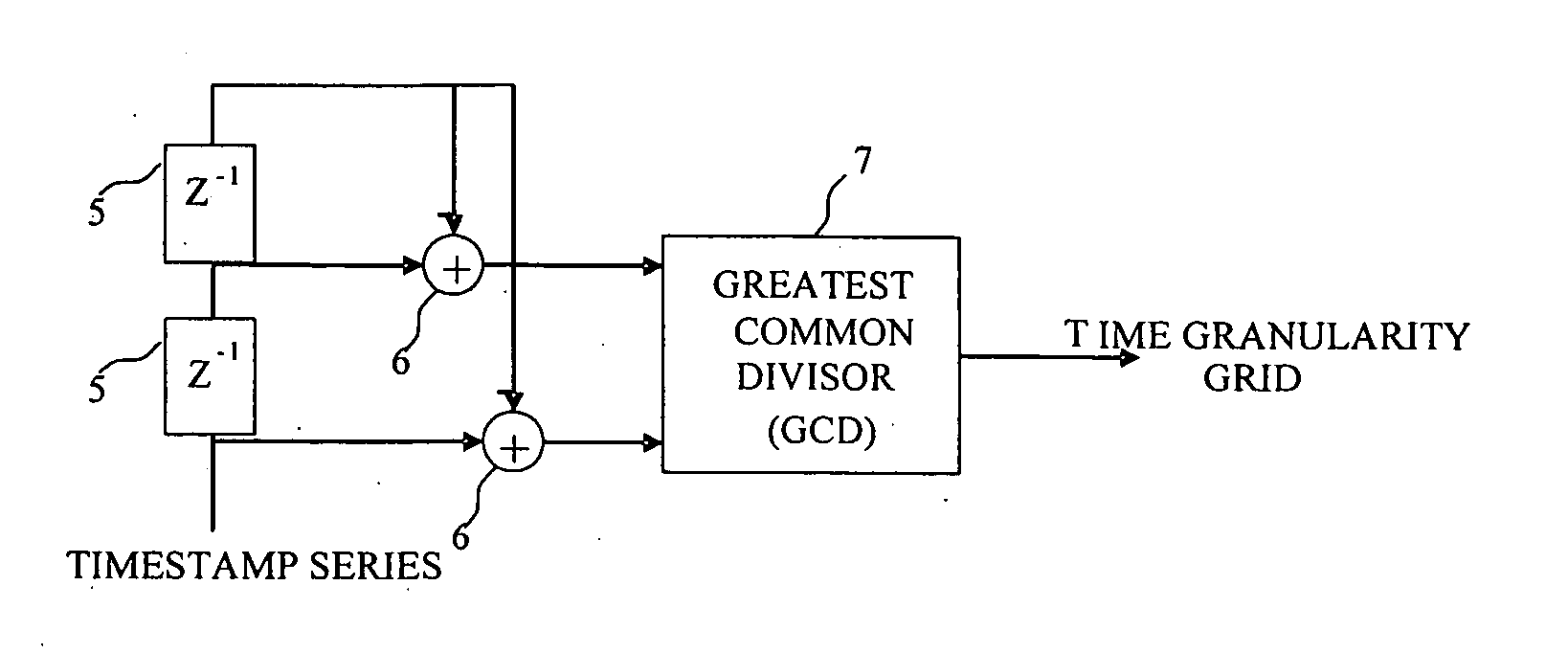
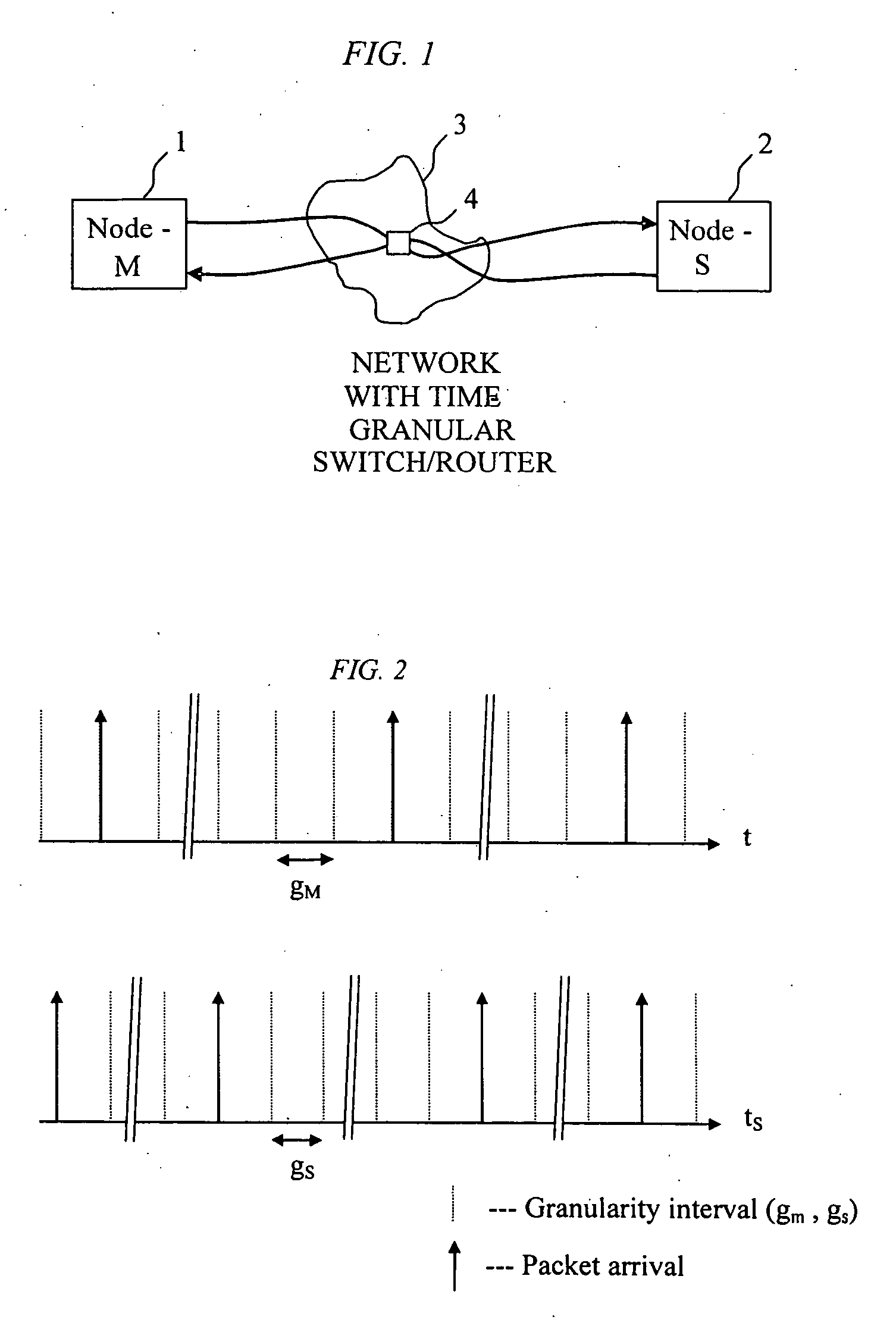
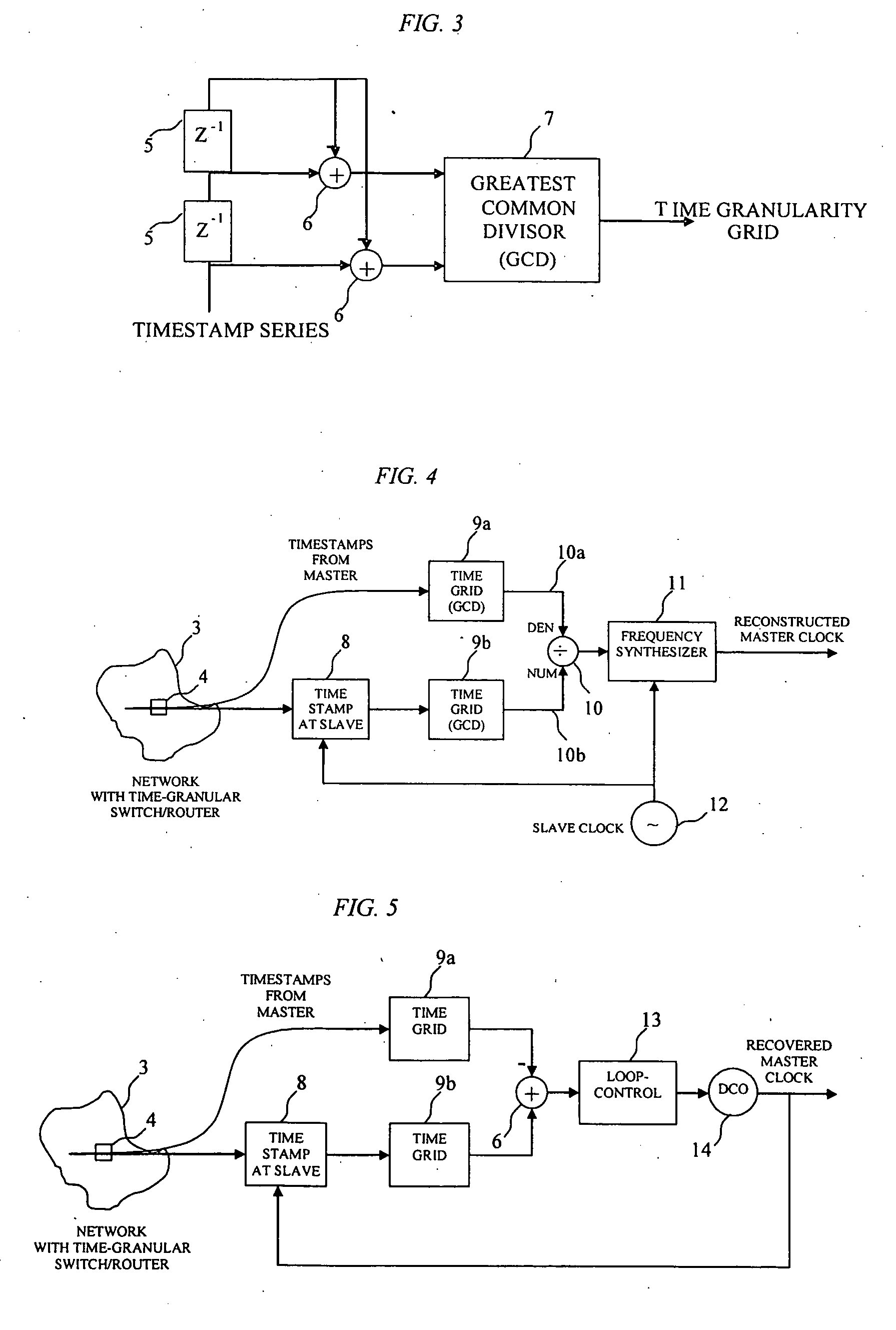
Method of recovering timing over a granular packet network
ActiveUS20060269029A1Overcome lossControl precisionTime-division multiplexSynchronising arrangementDigital control oscillatorSlave clock
A method is disclosed for recovering timing information between master and slave nodes interconnected over a packet network having an underlying time grid with a distinct granularity. A series timing packets are exchanged between said master and slave nodes to measure the time offset of the time grid relative to clocks at the master and slave clocks. This offset is then used to either adjust the local clock at the slave node, or generate the clock using a digital controlled oscillator.
Owner:ZARLINK SEMICON LTD
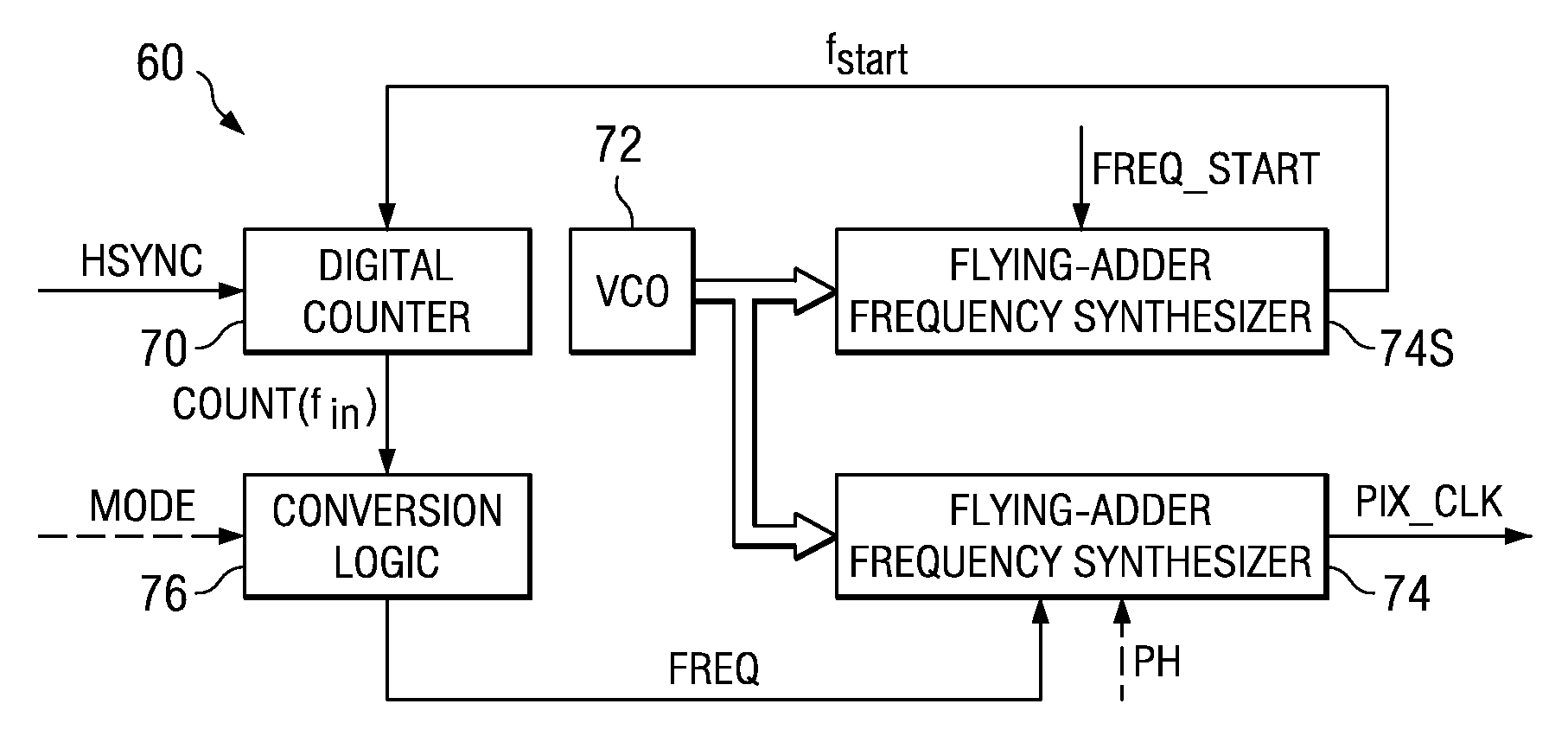
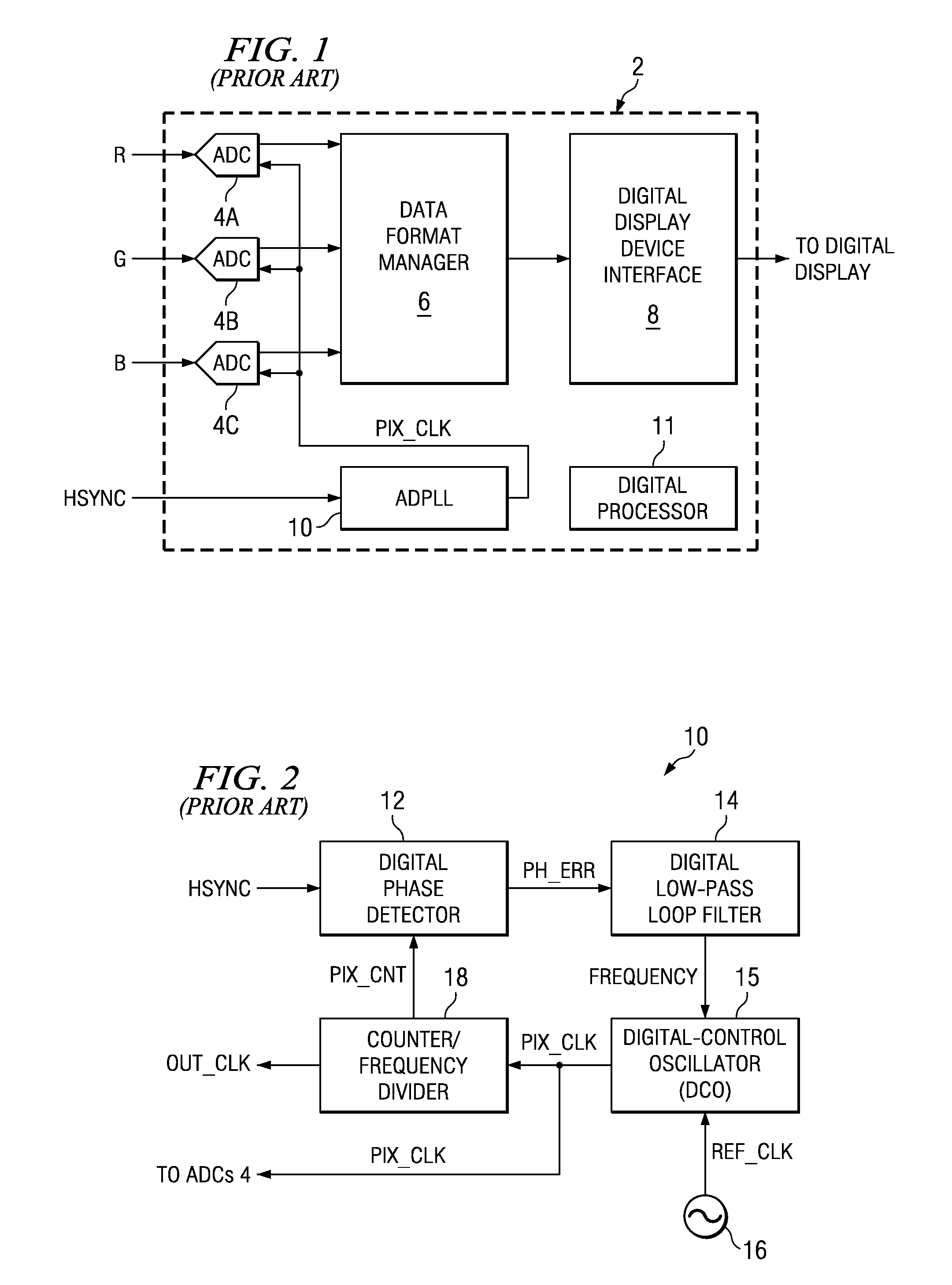
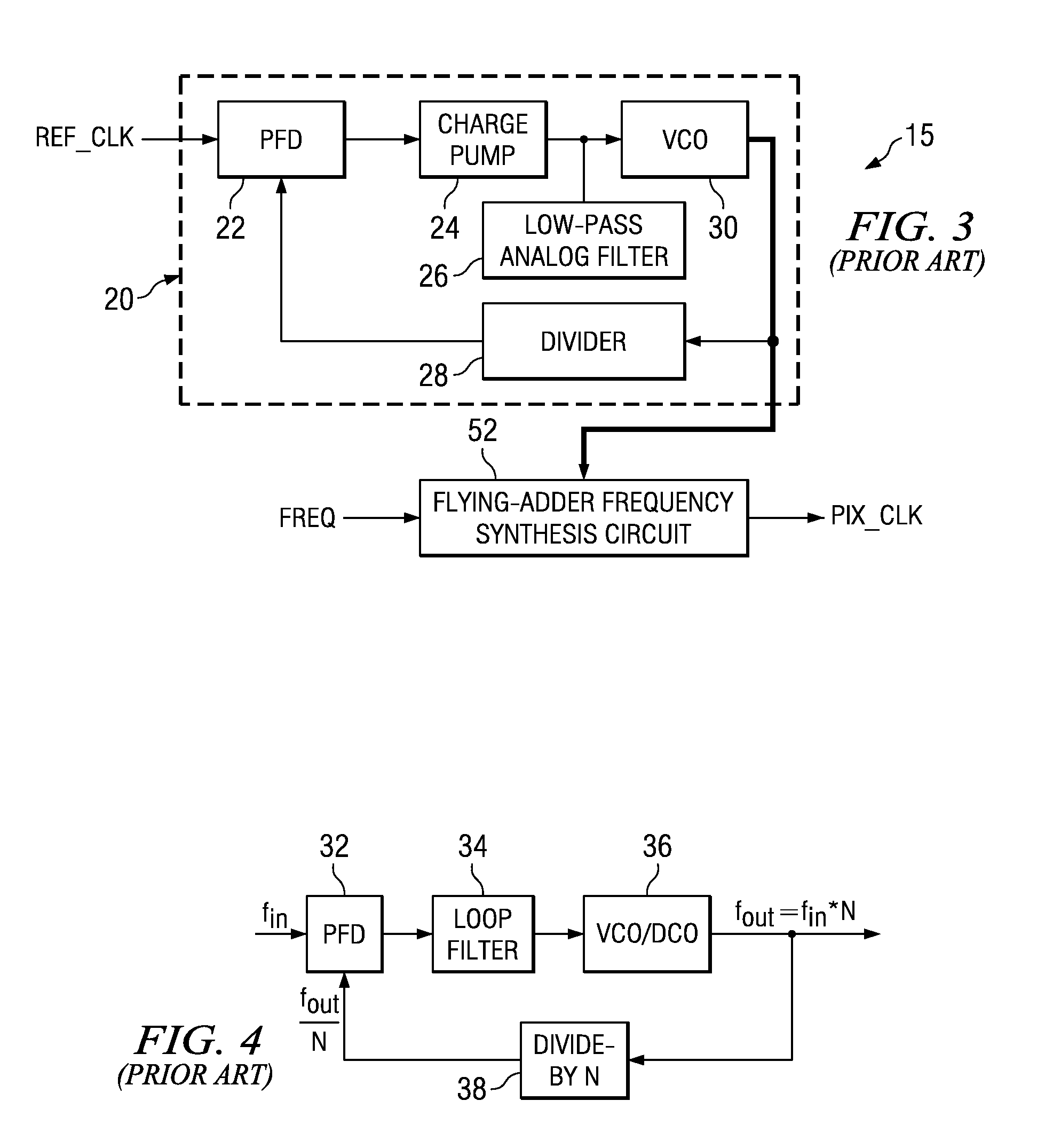
Flying-adder frequency synthesizer-based digital-controlled oscillator and video decoder including the same
ActiveUS7356107B2Large frequencyAccurate frequencyTelevision system detailsPulse automatic controlDigital control oscillatorMode control
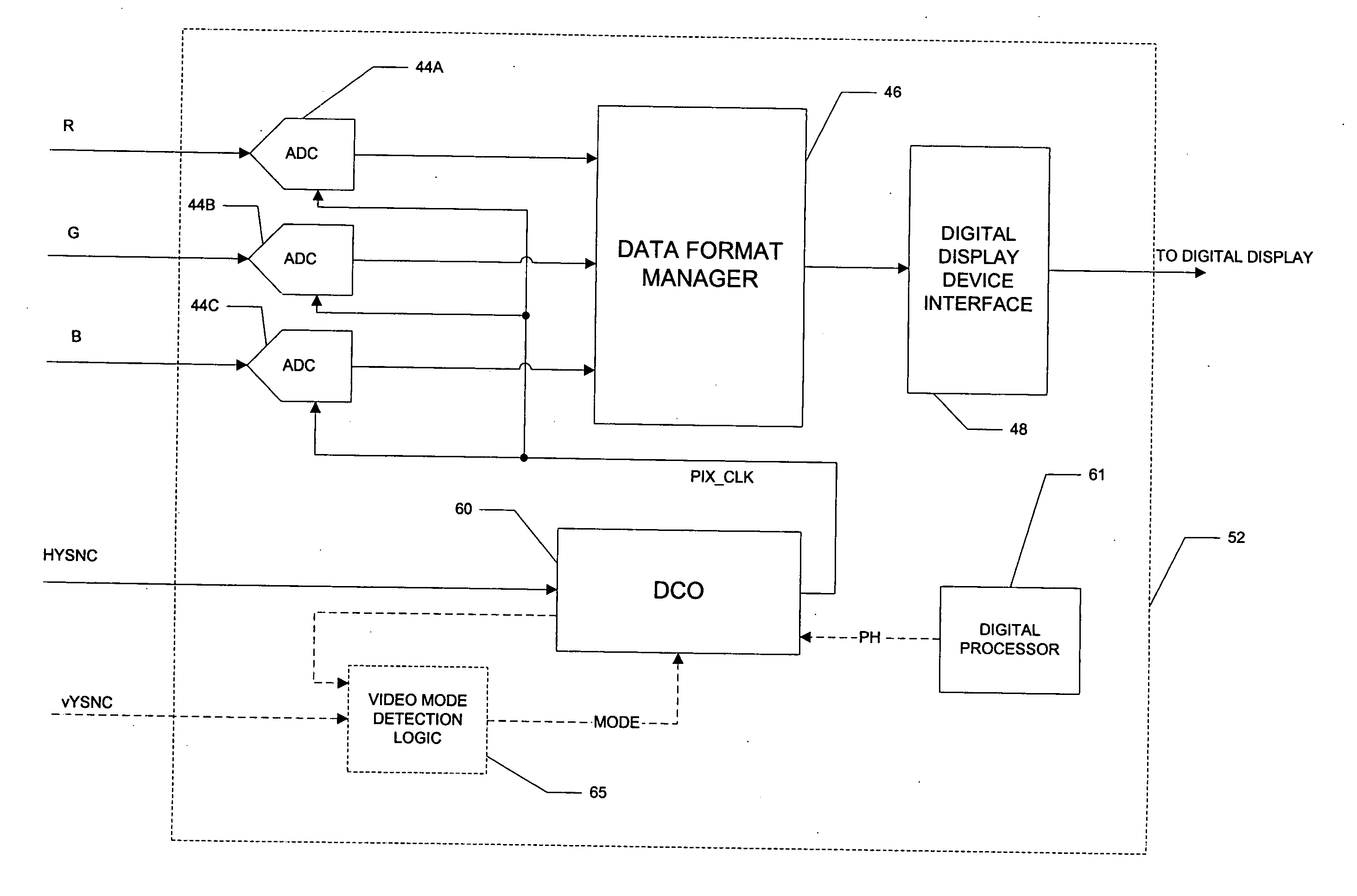
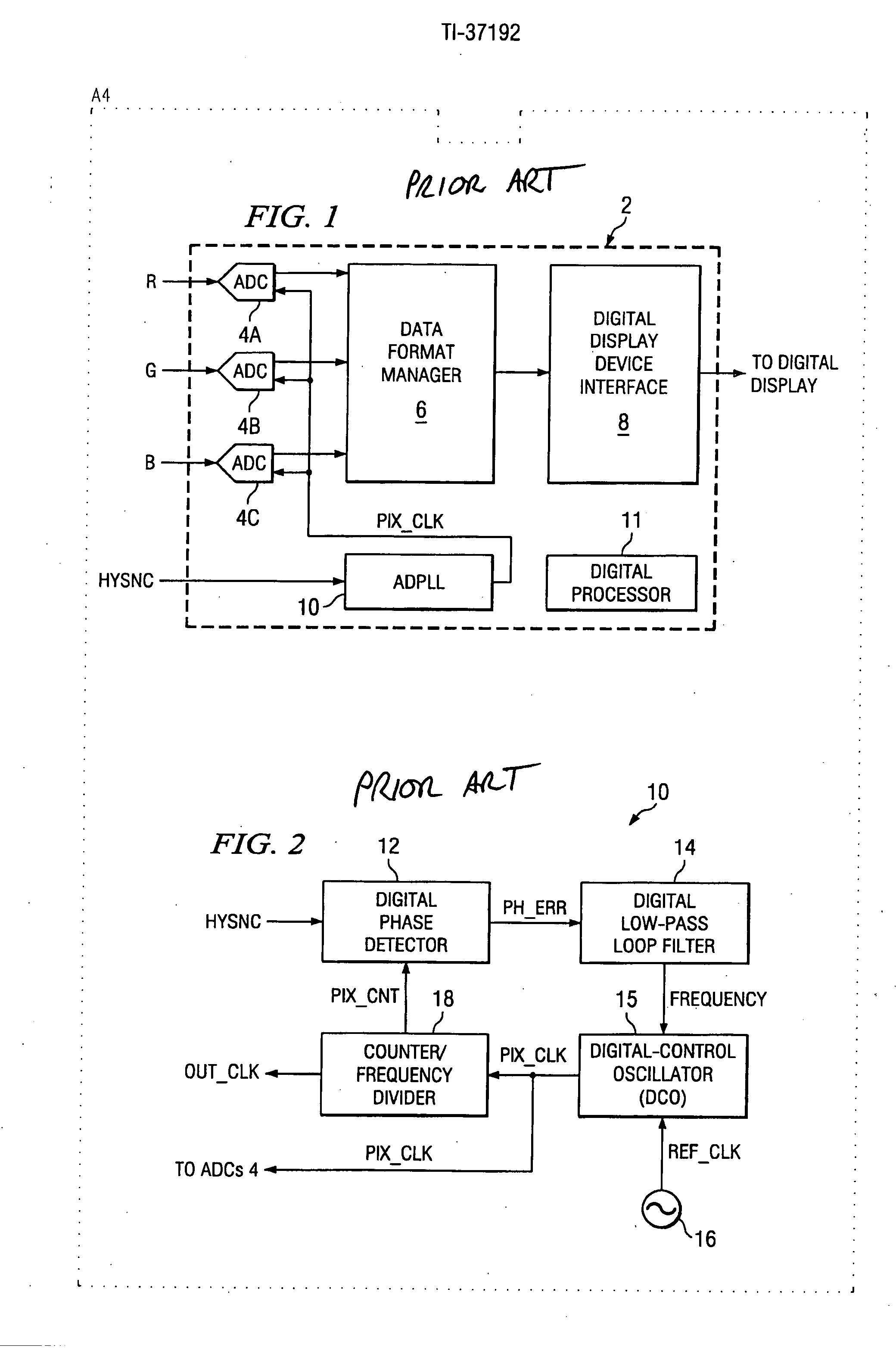
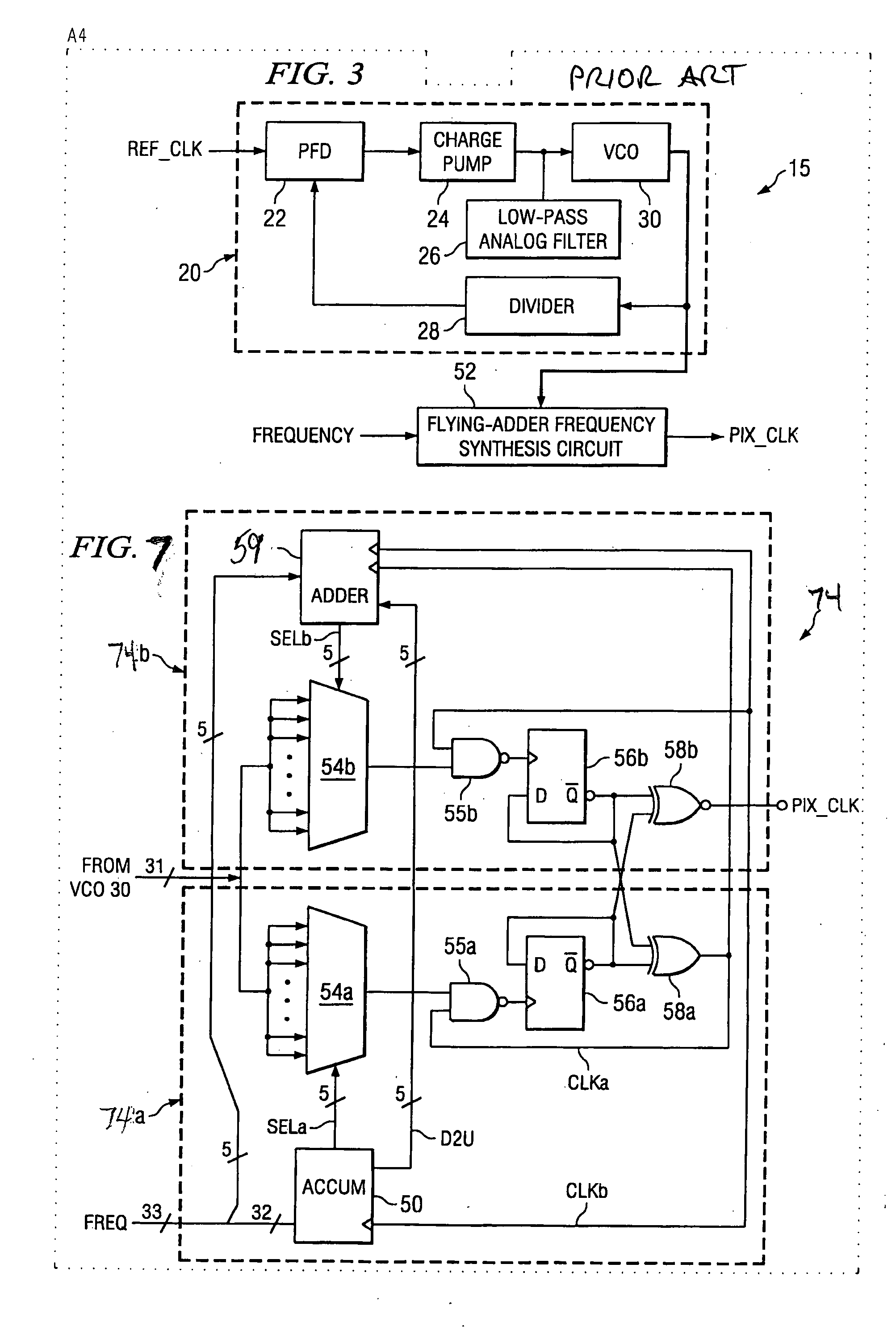
A video decoder (52, 152) including a digital-control oscillator (DCO) (60, 160) is disclosed. The DCO (60, 160) includes a first flying-adder frequency synthesis circuit (74S) that measures an input signal frequency, such as the horizontal sync frequency of an input video signal. A frequency control word (FREQ) is generated in response to this input signal frequency, and is applied to a second flying-adder frequency synthesis circuit (74), which in turn selects the appropriate phases for leading and trailing edges of the output clock signal (PIX_CLK). Phase tuning of the output clock signal (PIX_CLK) can be effected by using an alternate flying-adder frequency synthesis circuit (74′) architecture, in combination with a phase signal (PH) generated by a digital controller (61). Multiple phase-tuned sample clocks (PIX_CLK_A, PIX_CLK_B, PIX_CLK_C) can be similarly generated from multiple flying-adder frequency synthesis circuits (174A, 174B, 174C), each controlled by the frequency control word (FREQ) and a corresponding phase signal (PHA, PHB, PHC). Video mode control logic (65, 165) can also be implemented by way of a similar DCO architecture. The DCO (60) may be used to generate a clock signal at a large frequency multiple relative to the input signal, outside of the video decoder context.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Interpolation-based all-digital high-speed parallel timing synchronization method
InactiveCN103746790AReduce demandAccurate timing synchronizationSynchronising arrangementLoop filterDigital control oscillator
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
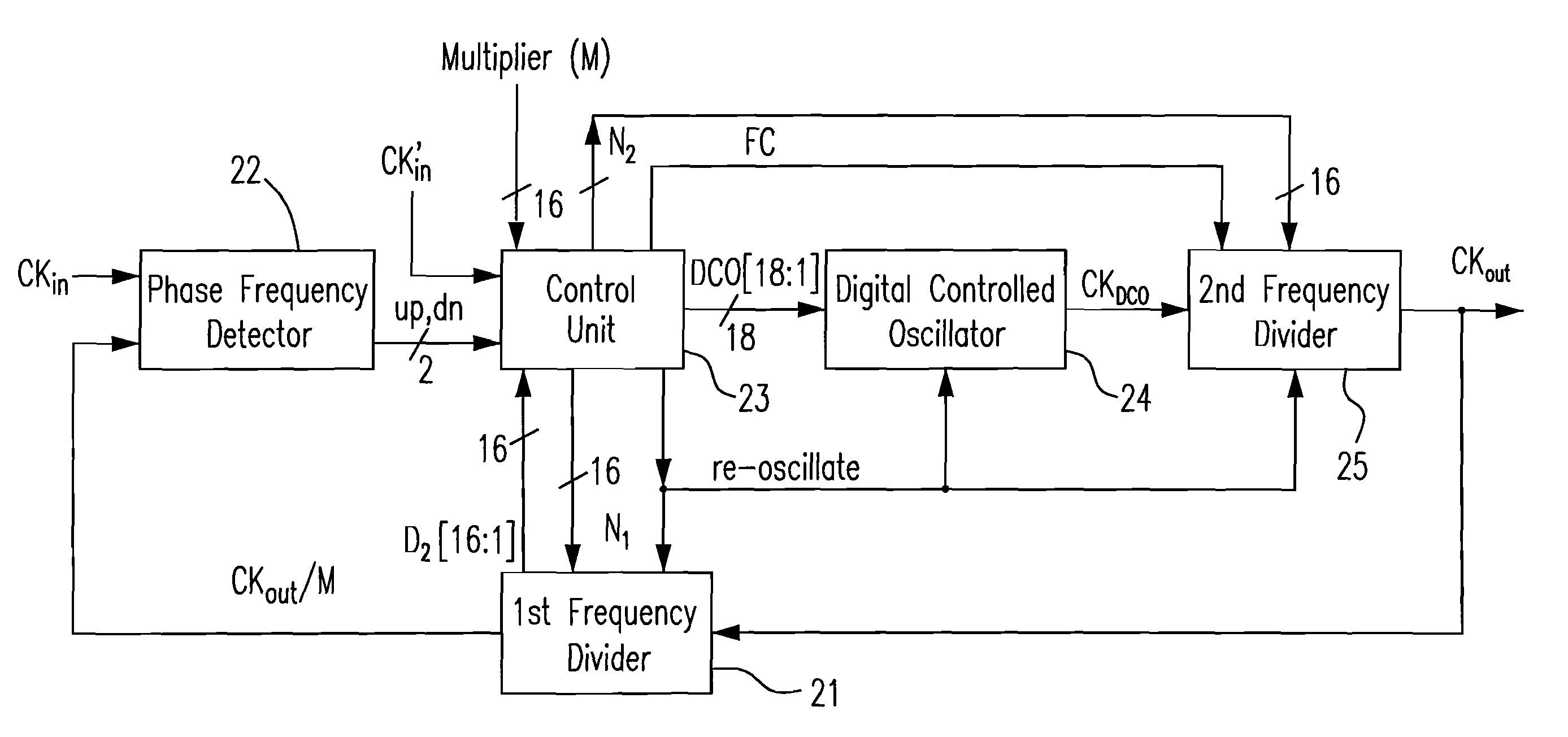
All digital phase-locked loop with widely locked frequency
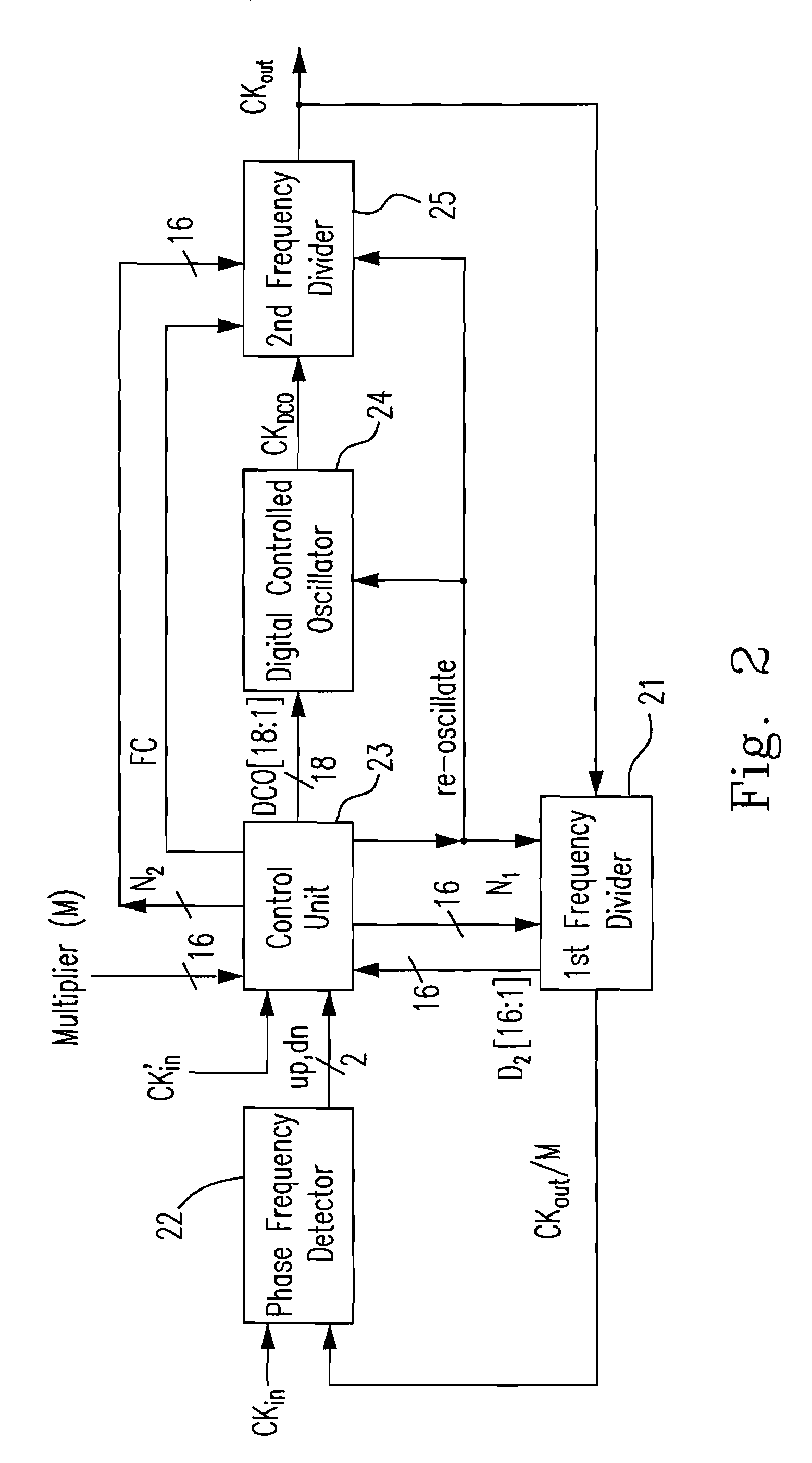
ActiveUS20090147902A1Short lock timeLess process dependencyPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionDigital control oscillatorPhase difference
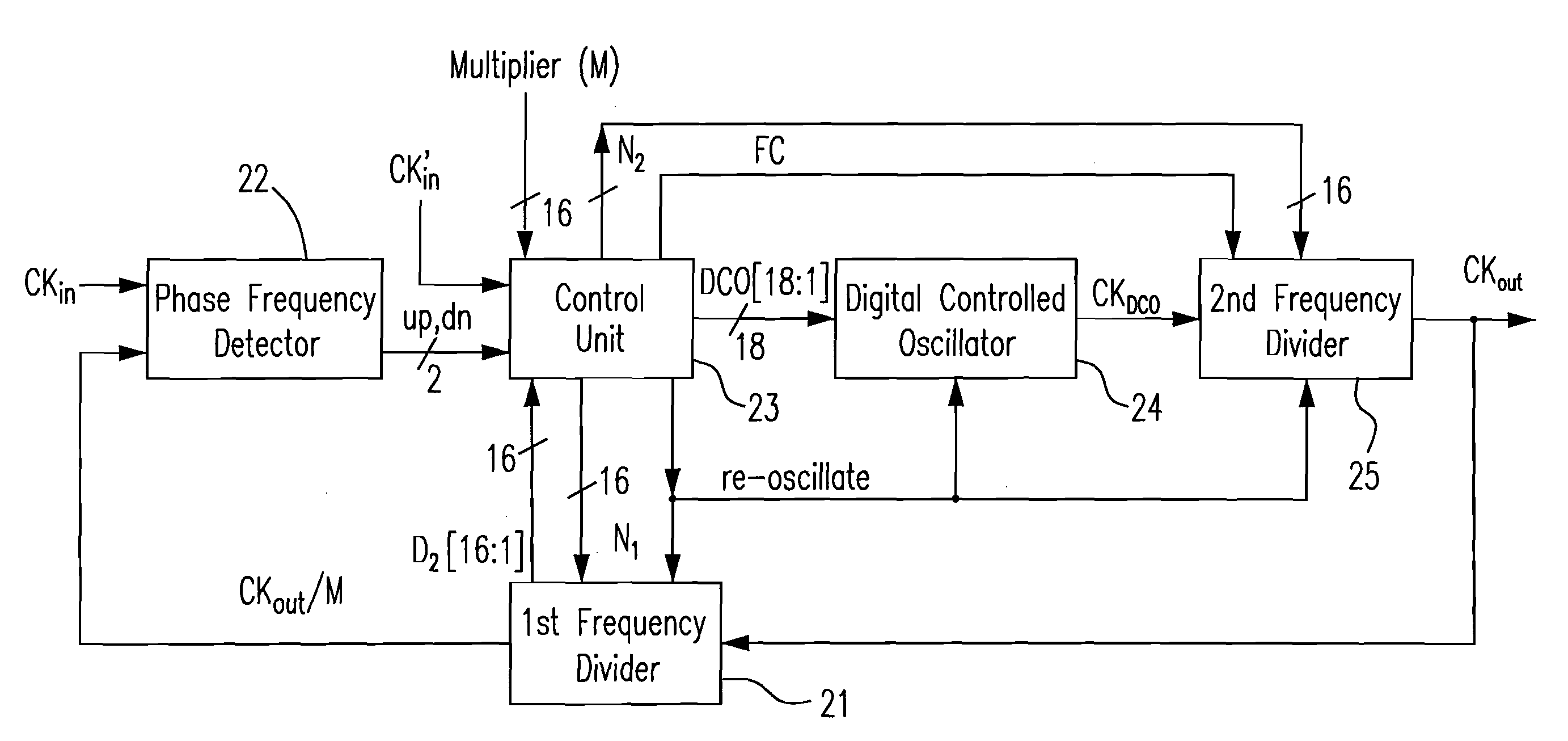
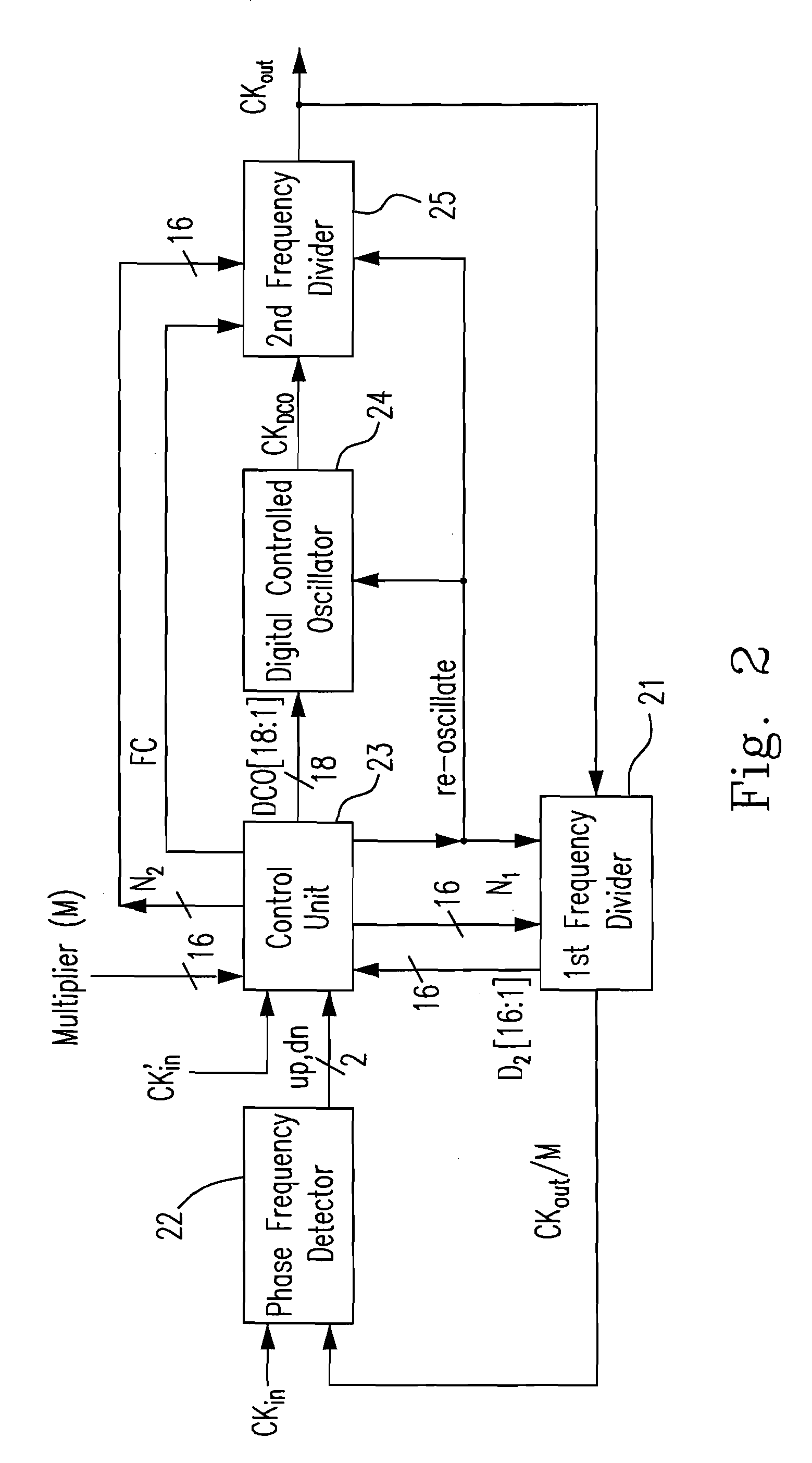
An all-digital phase-locked loop (ADPLL) composed of digital circuits is provided. The ADPLL includes a phase-frequency detector (PFD), a control unit, a digital controlled oscillator (DCO), and a plurality of frequency dividers. A first frequency divider divides a frequency of a feedback signal CKOUT by a natural number M to generate a first output signal CKOUT / M. The PFD generates a decrement signal dn and an increment signal up, based on a phase difference and a frequency between a first reference clock signal CKIN and the first output signal CKOUT / M. The DCO generates a clock signal CKDCO based on the digital control signals. A second frequency divider receives the digital control signals from the control unit and the CKDCO from the DCO and divides the frequency of the CKDCO by a bit number of the digital control signals to generate a feedback signal CKOUT to the first frequency divider.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Flying-adder frequency synthesizer-based digital-controlled oscillator and video decoder including the same
ActiveUS20050162552A1Accurate frequencyEasy to controlTelevision system detailsPulse automatic controlDigital control oscillatorMode control
A video decoder (52, 152) including a digital-control oscillator (DCO) (60, 160) is disclosed. The DCO (60, 160) includes a first flying-adder frequency synthesis circuit (74S) that measures an input signal frequency, such as the horizontal sync frequency of an input video signal. A frequency control word (FREQ) is generated in response to this input signal frequency, and is applied to a second flying-adder frequency synthesis circuit (74), which in turn selects the appropriate phases for leading and trailing edges of the output clock signal (PIX_CLK). Phase tuning of the output clock signal (PIX_CLK) can be effected by using an alternate flying-adder frequency synthesis circuit (74′) architecture, in combination with a phase signal (PH) generated by a digital controller (61). Multiple phase-tuned sample clocks (PIX_CLK_A, PIX_CLK_B, PIX_CLK_C) can be similarly generated from multiple flying-adder frequency synthesis circuits (174A, 174B, 174C), each controlled by the frequency control word (FREQ) and a corresponding phase signal (PHA, PHB, PHC). Video mode control logic (65, 165) can also be implemented by way of a similar DCO architecture. The DCO (60) may be used to generate a clock signal at a large frequency multiple relative to the input signal, outside of the video decoder context.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Array type channel, GNSS receiver and signal processing method
ActiveCN103472467AImplement searchAchieve stabilizationSatellite radio beaconingShift registerDiscriminator
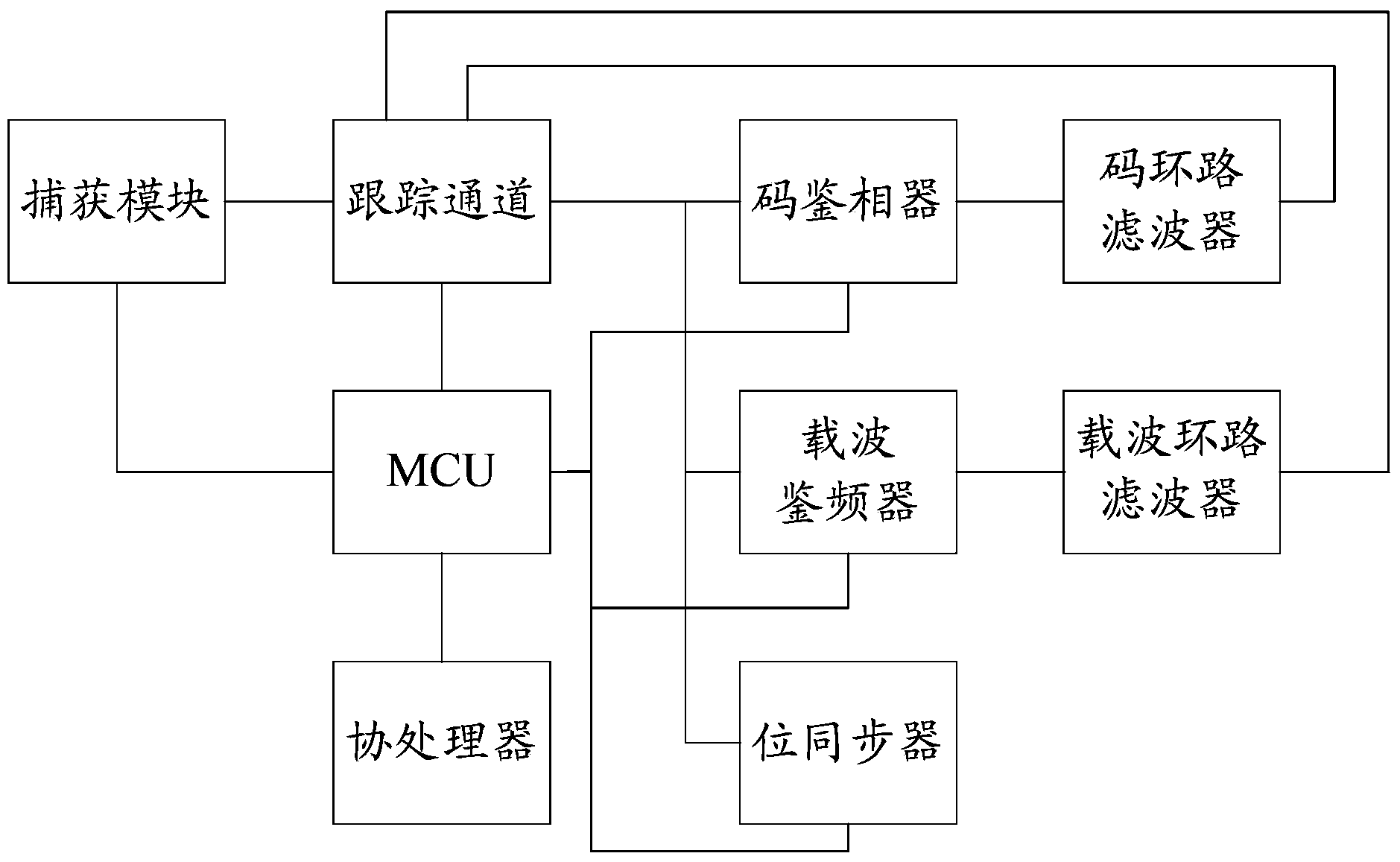
Provided are an array type channel, a GNSS receiver and a signal processing method. The GNSS receiver comprises a control unit, at least one array type channel, a code phase discriminator, a code loop filter, a carrier frequency discriminator, a carrier loop filter and a bit synchronizer. The code phase discriminator, the code loop filter, the carrier frequency discriminator, the carrier loop filter and the bit synchronizer respectively correspond to the array type channels which comprise a carrier digital-controlled oscillator, a plurality of digital down converter, a spread spectrum code digital-controlled oscillator, a spread spectrum code generator, a spread spectrum code shifting register set, a plurality of correlator sets, a plurality of incoherent accumulator sets and a preprocessing unit. According to the technical scheme, the GNSS receiver is simple in structure, capturing and tracking resource multiplexing can be achieved through the array type channels, the system operation state is simplified, and ideal capturing and tracking performance is achieved.
Owner:HERONAV BEIJING TECH DEV
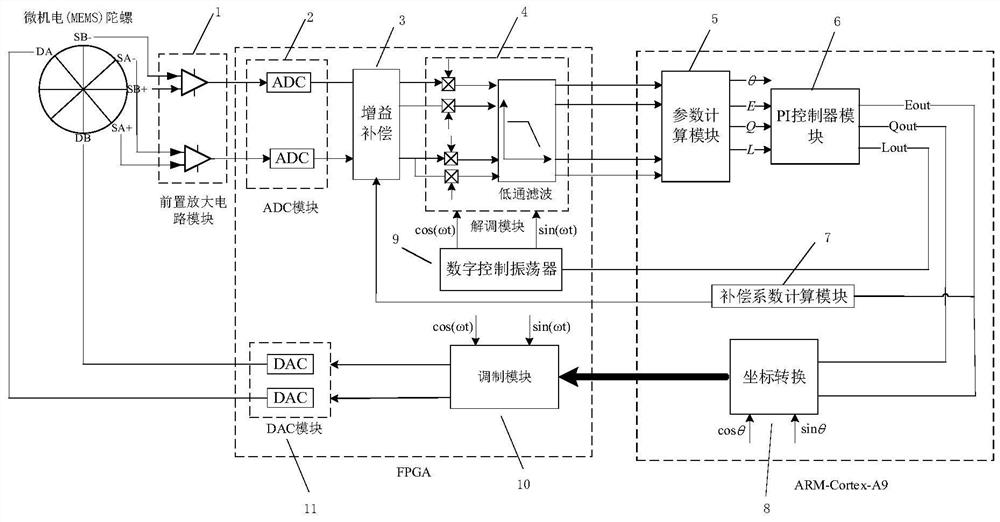
Full-angle mode circuit gain error self-compensation system of micro-electro-mechanical gyroscope
ActiveCN112146637AHigh precisionHigh control precisionSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTurn-sensitive devicesDigital control oscillatorGyroscope
The invention discloses a full-angle mode circuit gain error self-compensation system of a micro-electro-mechanical system gyroscope. The full-angle mode circuit gain error self-compensation system comprises a gyroscope pre-amplification circuit, an ADC module, a gain compensation module, a demodulation module, a parameter calculation module, a PI controller module, a coordinate conversion module,a compensation coefficient calculation module, a modulation module and a DAC module. The pre-amplification circuit module is connected to a detection electrode of the micro-electro-mechanical multi-ring gyroscope, the ADC module is connected to the pre-amplification circuit, the gain compensation module is connected to the ADC module, the demodulation module is connected to the gain compensationmodule, the PI controller module is connected to the parameter calculation module, the compensation coefficient calculation module is connected to the PI controller module, the coordinate conversion module is connected to the PI controller module, the modulation module is connected to the coordinate conversion module, the DAC module is connected to the modulation module, and the digital control oscillator module is connected to a PI controller. According to the system, real-time circuit gain error self-compensation in a full-angle mode of the micro-electro-mechanical gyroscope can be realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Apparatus for generating simulation navigational satellite reflected signal
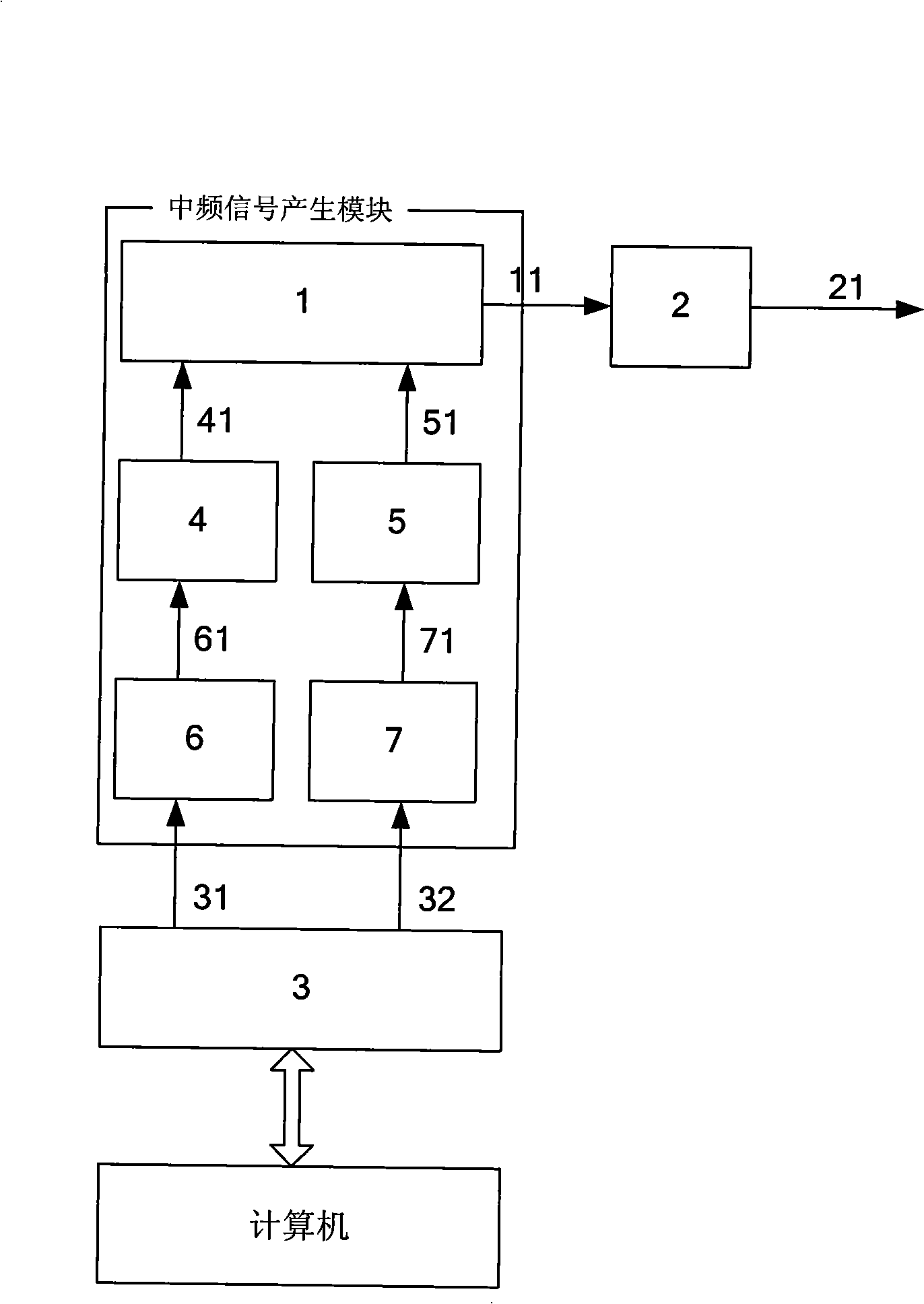
InactiveCN101349749ASolve debuggingSolve test problemsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTransmission time delayIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a generator for simulating navigation satellite reflected signals, comprising a common computer, an antenna, a navigation information module (3), an intermediate frequency signal generating module and a radio frequency module (2), wherein the navigation information module (3) and the intermediate frequency signal generating module are stored in the memory of the computer, the intermediate frequency signal generating module comprises a frequency spread modulator (1), a code digital control oscillator (4), a carrier digital control oscillator (5), a code delay generator (6) and a Doppler shift generator (7). The invention simulates the change of navigation satellite signals at a reflector surface or a reflector and generates the transmission time delay and Doppler shift of the reflected signals according to the change of the track of the receiver. The generator can test delay mapping receivers, to provide a new test method for the development of marine remote sensors and the utilization of reflected signals of global navigation satellite systems.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
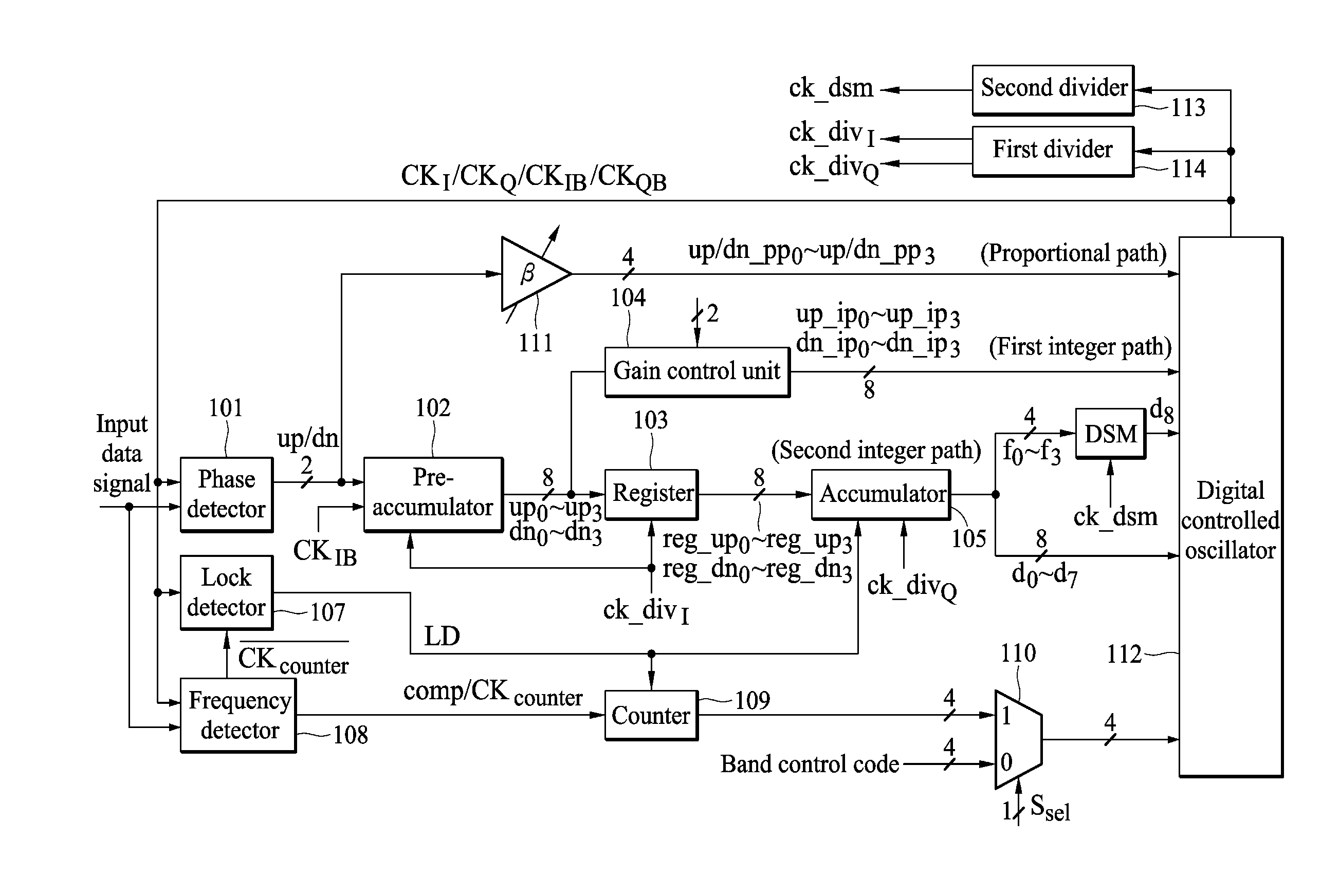
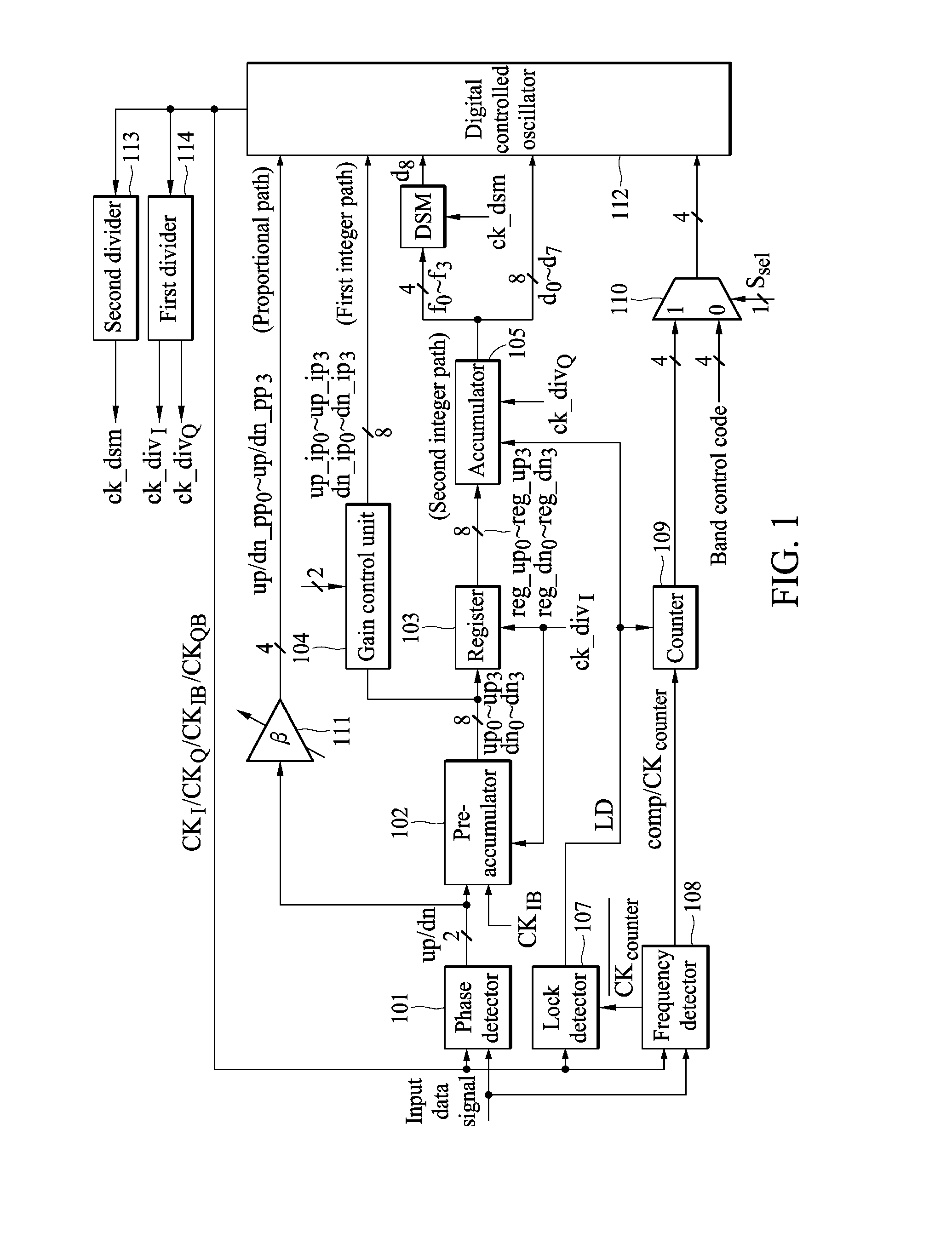
Clock and data recovery circuit
InactiveUS20100289593A1Pulse automatic controlRadio transmissionPhase detectorDigital control oscillator
An embodiment of the invention provides a clock and data recovery circuit. The clock and data recovery circuit comprises a phase detector, a pre-accumulator, a register, an accumulator and a digital controlled oscillator. By using the transmission path formed by the pre-accumulator, the output of the phase detector can be transmitted to the digital controlled oscillator in advance to adjust the frequency of its output clock signal and the latency due to the accumulator can be reduced.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
All digital phase-locked loop with widely locked frequency
ActiveUS8050376B2Efficient transferReduce time consumptionPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionDigital control oscillatorPhase difference
An all-digital phase-locked loop (ADPLL) composed of digital circuits is provided. The ADPLL includes a phase-frequency detector (PFD), a control unit, a digital controlled oscillator (DCO), and a plurality of frequency dividers. A first frequency divider divides a frequency of a feedback signal CKOUT by a natural number M to generate a first output signal CKOUT / M. The PFD generates a decrement signal dn and an increment signal up, based on a phase difference and a frequency between a first reference clock signal CKIN and the first output signal CKOUT / M. The DCO generates a clock signal CKDCO based on the digital control signals. A second frequency divider receives the digital control signals from the control unit and the CKDCO from the DCO and divides the frequency of the CKDCO by a bit number of the digital control signals to generate a feedback signal CKOUT to the first frequency divider.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Broadband up-converter and up-conversion method
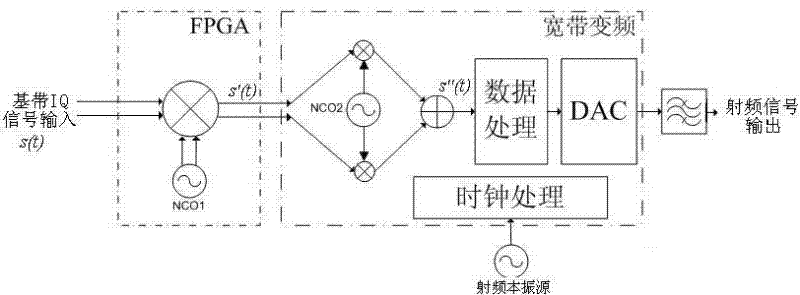
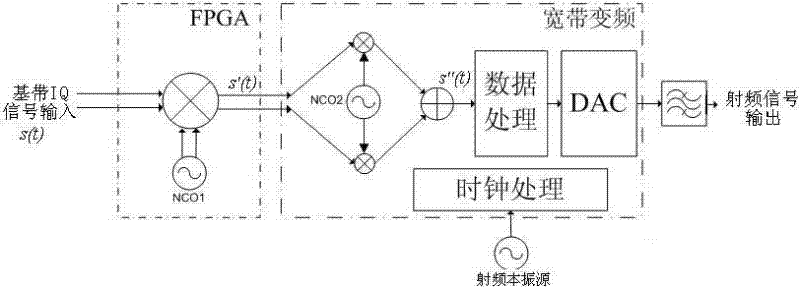
ActiveCN102176656AMeet the requirements of frequency conversionReduce in quantityMulti-frequency-changing modulation transferenceFrequency changerFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a broadband up-converter and an up-conversion method. The invention relates to the technical field of communication, in particular to a digital broadband up-converter and a digital up-conversion method in a digital wireless broadcast technology. The up-conversion method is mainly characterized by comprising the following steps of: carrying out first up-conversion on a digital baseband I / Q (In-phase / Quadrature) signal by adopting a complex multiplier and a digital controlled oscillator I, namely a frequency spectrum shift with small step; then carrying out secondary up-conversion on the digital signal subjected to the frequency spectrum shift with small step to shift the signal frequency spectrum to the needed high frequency section; finally, further processing the signal and then converting the signal into a simulated radio-frequency signal, and wirelessly transmitting the simulated radio-frequency signal to a receiving end by an emitter. In the invention, the up-conversion method can realize broadband up-conversion of with small step adjustment and the broadband up-converter has the advantages of simple structure and good reliability.
Owner:CHENGDU KAITENG SIFANG DIGITAL RADIO & TELEVISION EQUIP CO LTD
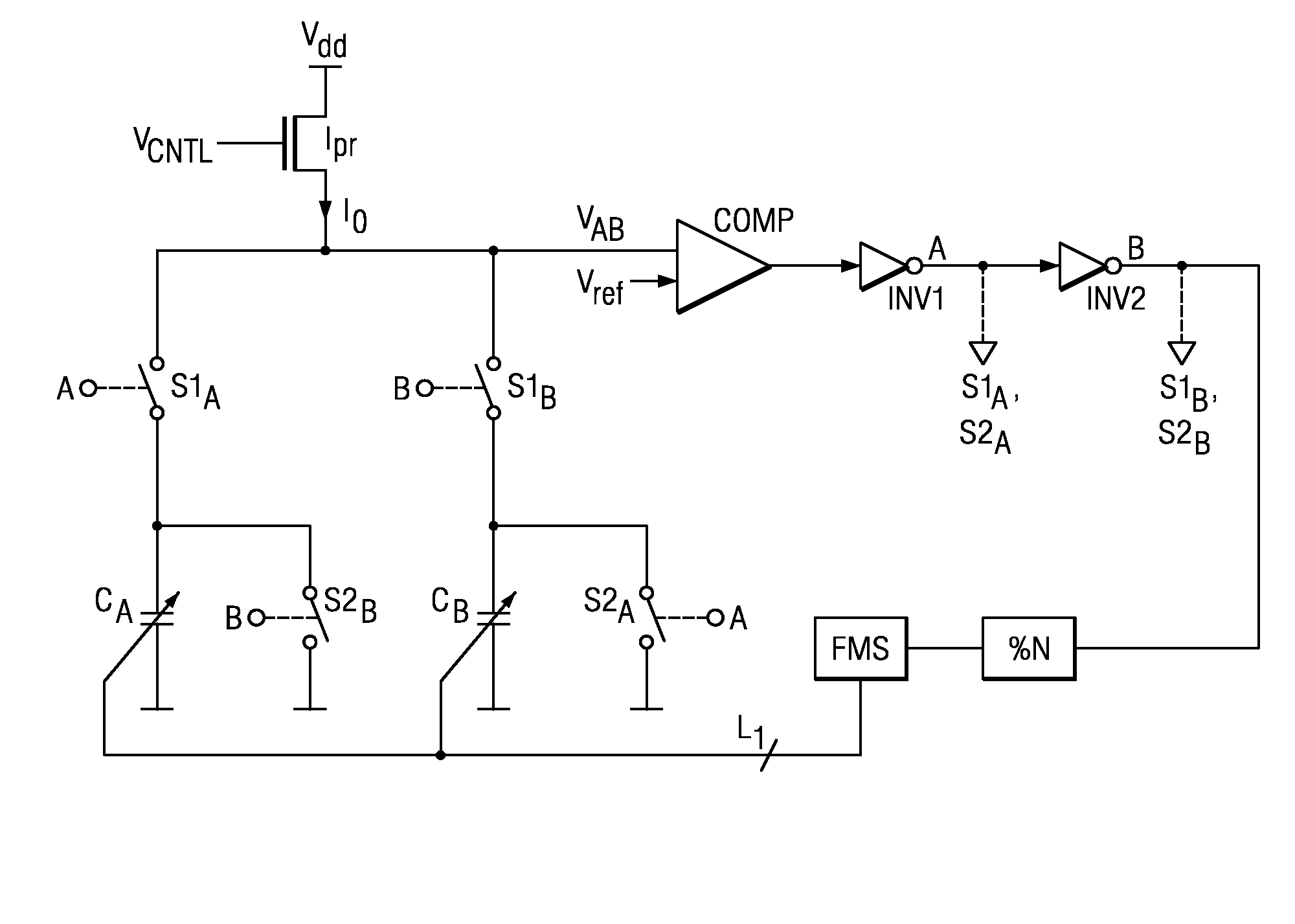
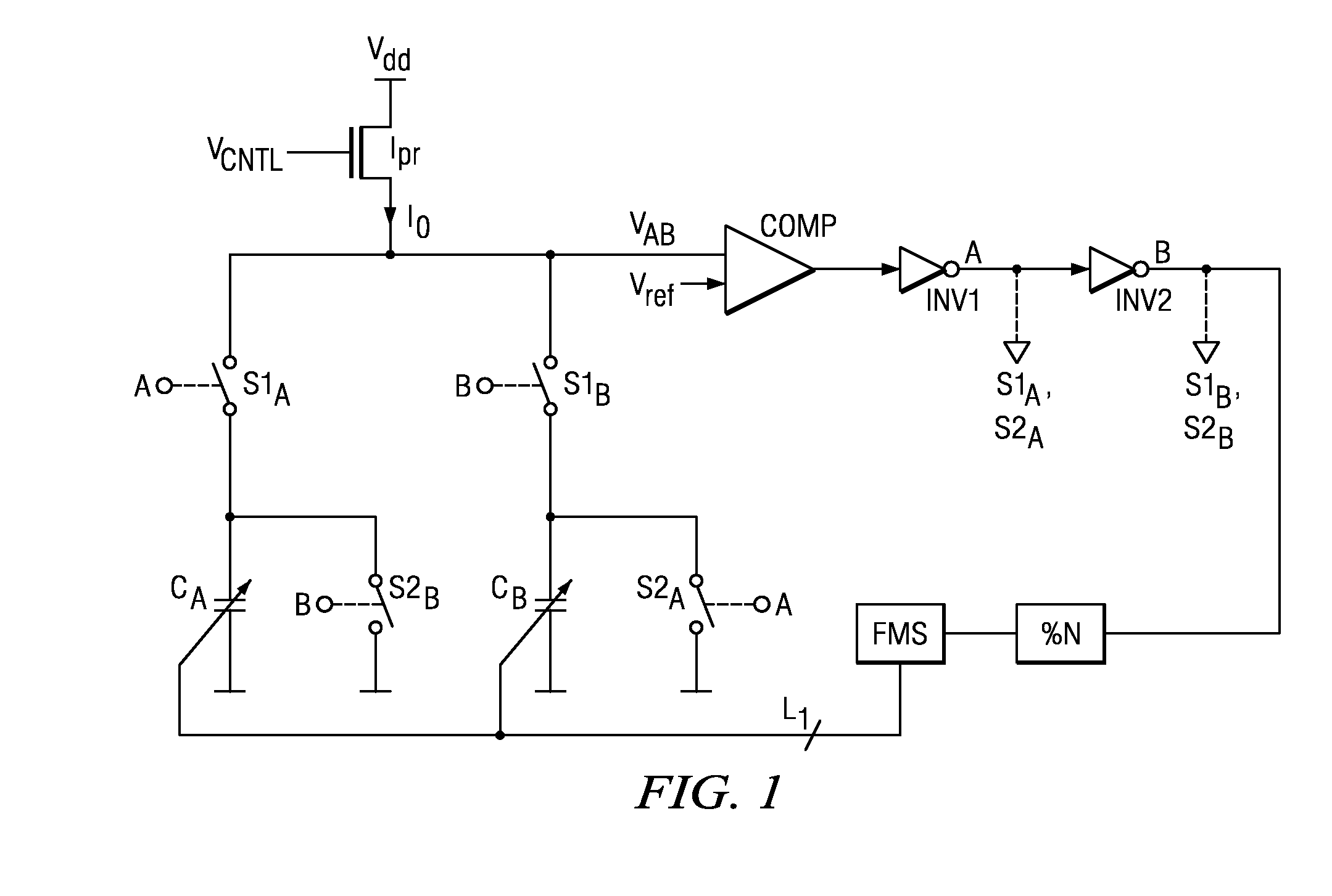
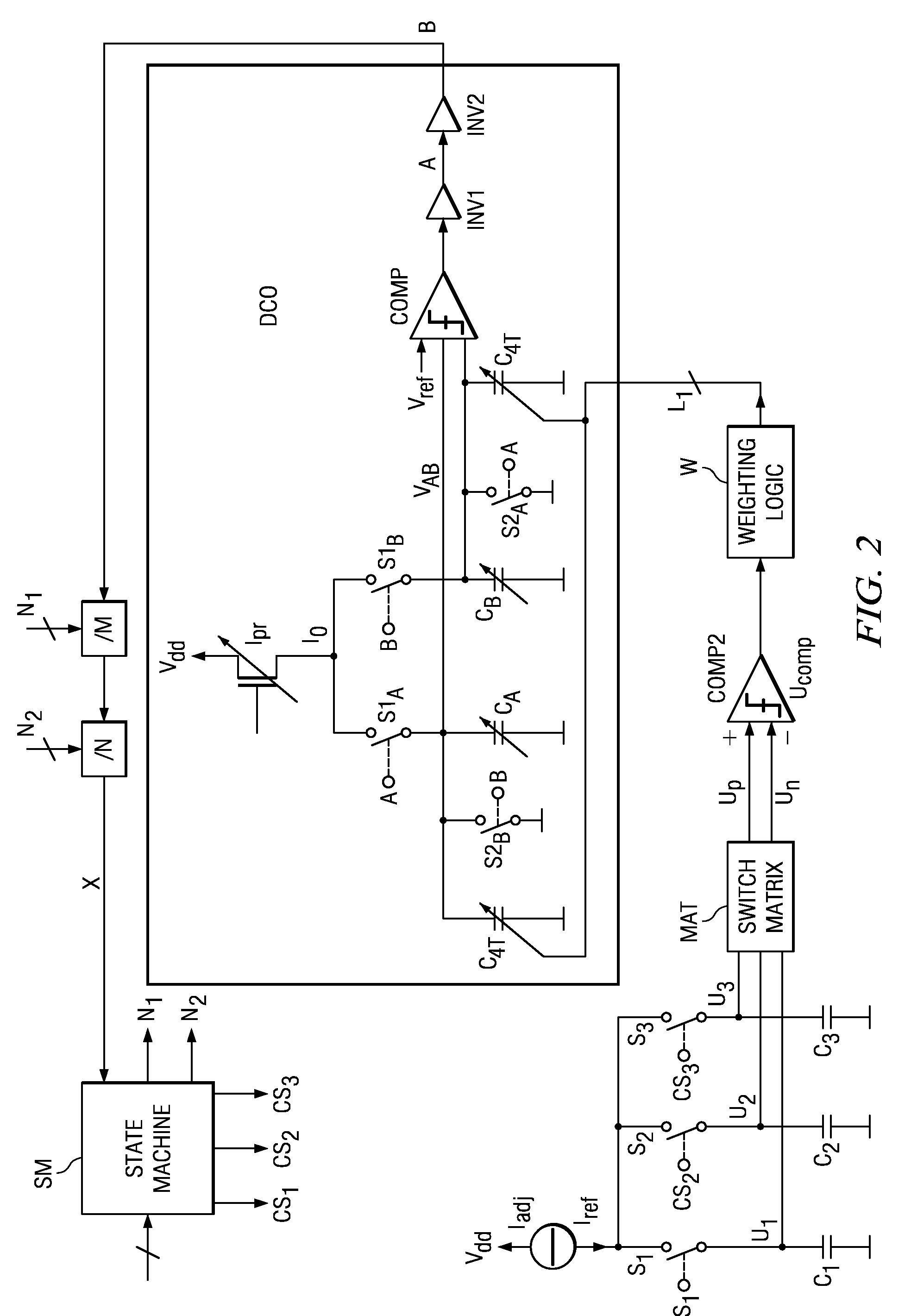
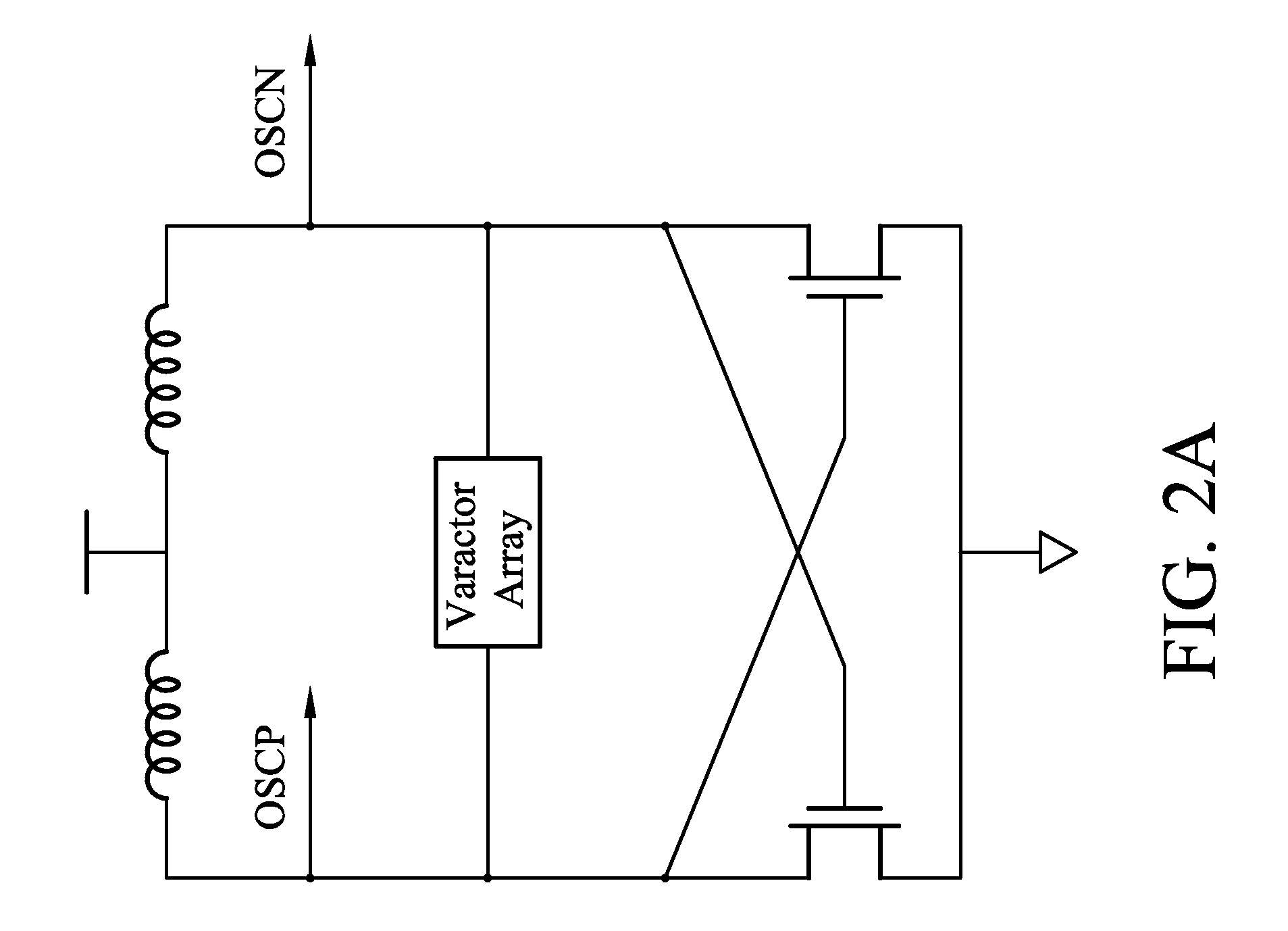
Digital Controlled Oscillator
ActiveUS20090045880A1Reduce errorsSimple and area-efficient implementationPulse generation by bipolar transistorsPulse automatic controlDigital control oscillatorVoltage reference
A digital controlled oscillator including a programmable current source, a first variable capacitor and a second variable capacitor. A comparator compares the voltage across the variable capacitors with a reference voltage level and generates a DCO output clock signal. A switching means alternately switches the variable capacitors to either charge from a programmable current source or discharge in response to an output signal of the comparator. A clock divider divides the DCO output clock signal by a factor N substantially greater than 1. A frequency monitor receives the divided clock signal, determines the time difference of successive clock periods of the divided clock signal and generates a feedback signal to adapt the frequency of the DCO output clock signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Phase-locked loop circuit and communication apparatus
InactiveUS8331520B2Reduce power consumptionReduce areaPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionPhase locked loop circuitPhase difference
A PLL circuit of which low power consumption and miniaturization are satisfied at the same time is provided. A phase comparator of the PLL circuit includes a counter and a time-to-digital converter. The counter receives a reference clock signal and a low frequency clock signal obtained by dividing an output of a digital controlled oscillator, and a high frequency clock signal. The counter detects a phase difference between the reference clock signal and the low frequency clock signal by counting the clock number of the high frequency clock signal. The time-to-digital converter receives the reference clock signal and the low frequency clock signal. The time-to-digital converter detects the phase difference between the reference clock signal and the low frequency clock signal to the accuracy of a time period shorter than a cycle of the high frequency clock signal, after the output of counter reaches a predetermined range.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Digital phase locked loop and method of driving the same
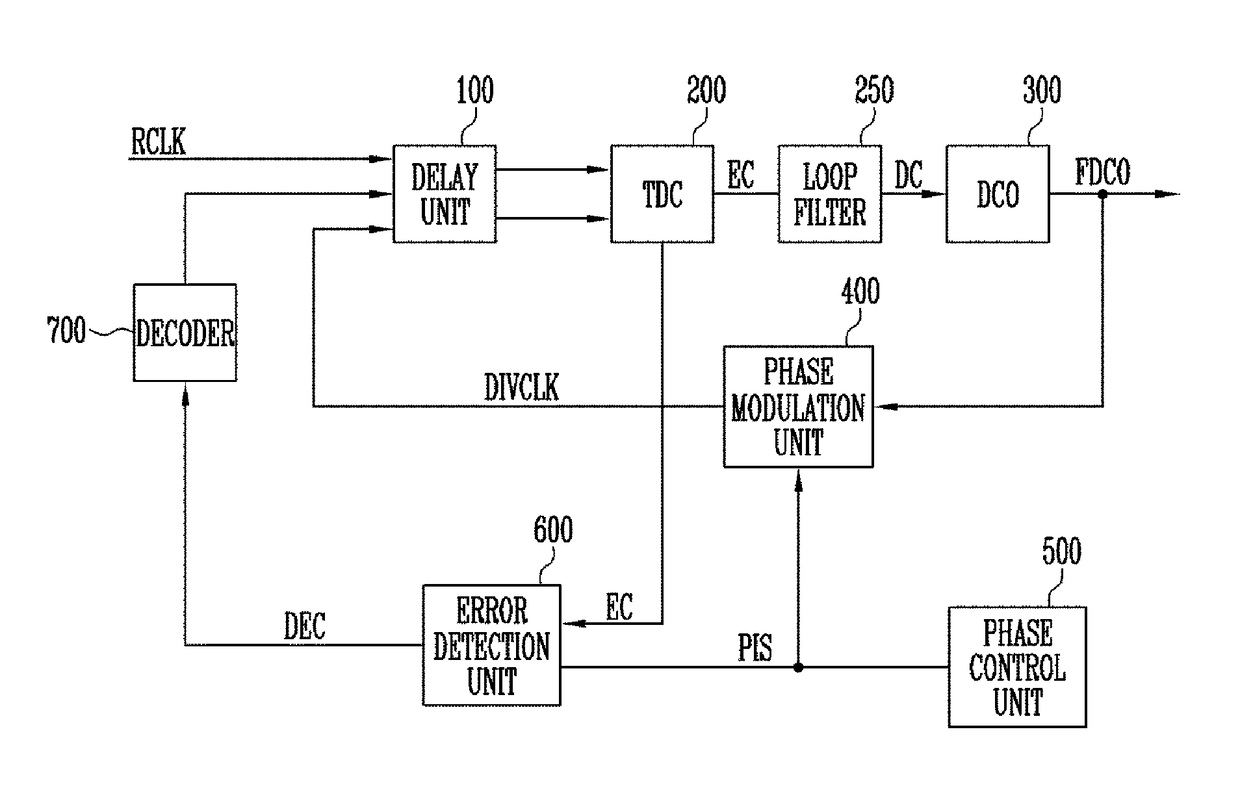
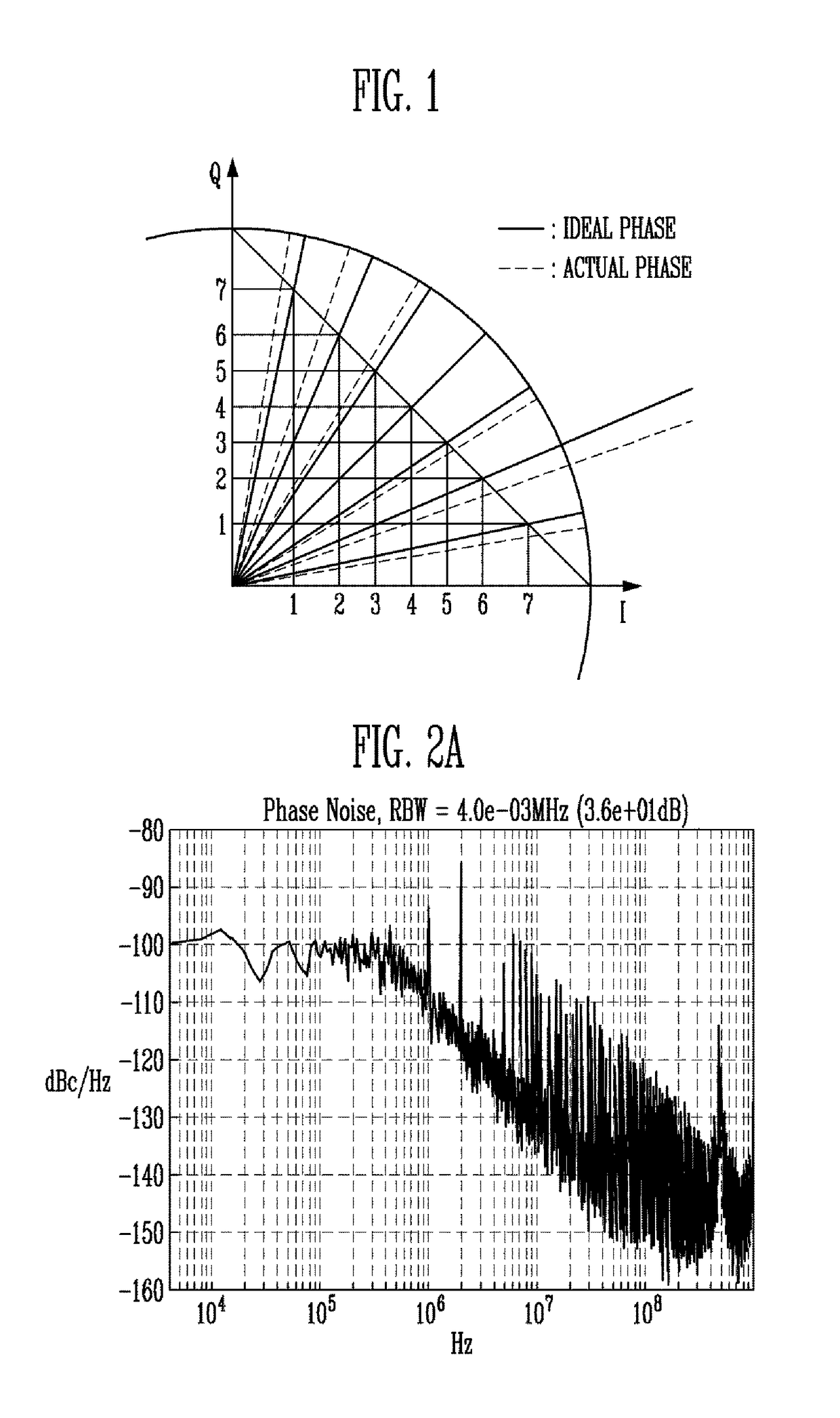
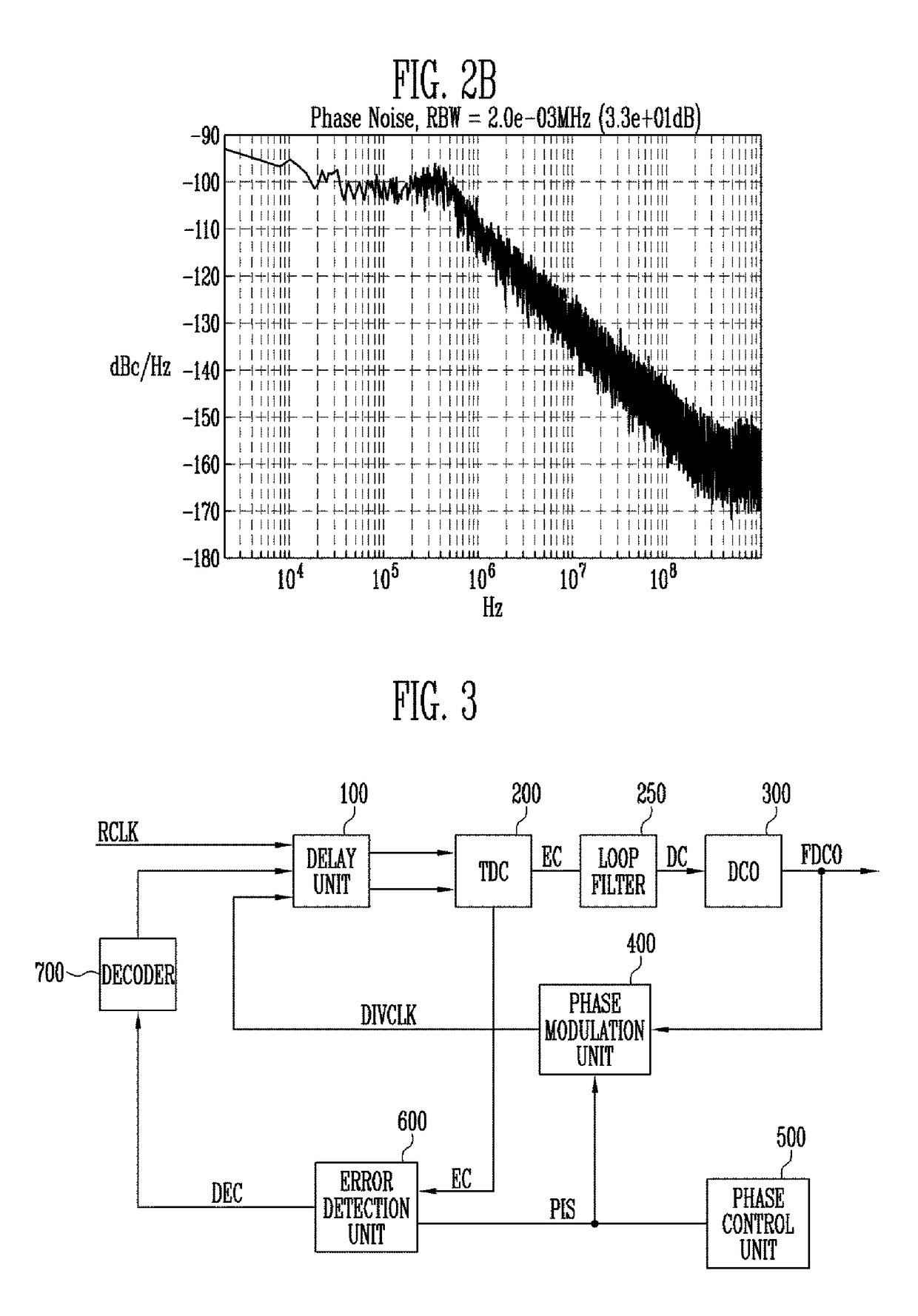
InactiveUS9705515B1Minimize spurious noiseNoise minimizationPulse automatic controlPhase shiftedDigital control oscillator
Provided herein is a digital PLL, which can minimize spurious noise. The digital PLL includes a digital controlled oscillator configured to generate an output oscillation signal in response to a digital code, a phase modulation unit configured to perform phase interpolation on the output oscillation signal in response to a phase control code, a TDC configured to generate an error code using a time difference between a reference clock signal and a modulated clock signal, an error detection unit configured to generate a delay code required to compensate for a phase shift error in response to the phase control code and the error code, a delay unit configured to delay at least one of the reference clock signal and the modulated clock signal and provide a delayed clock signal, and a first decoder configured to control the delay unit in response to the delay code.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Digital phase locked loop
Owner:ZARLINK SEMICON LTD
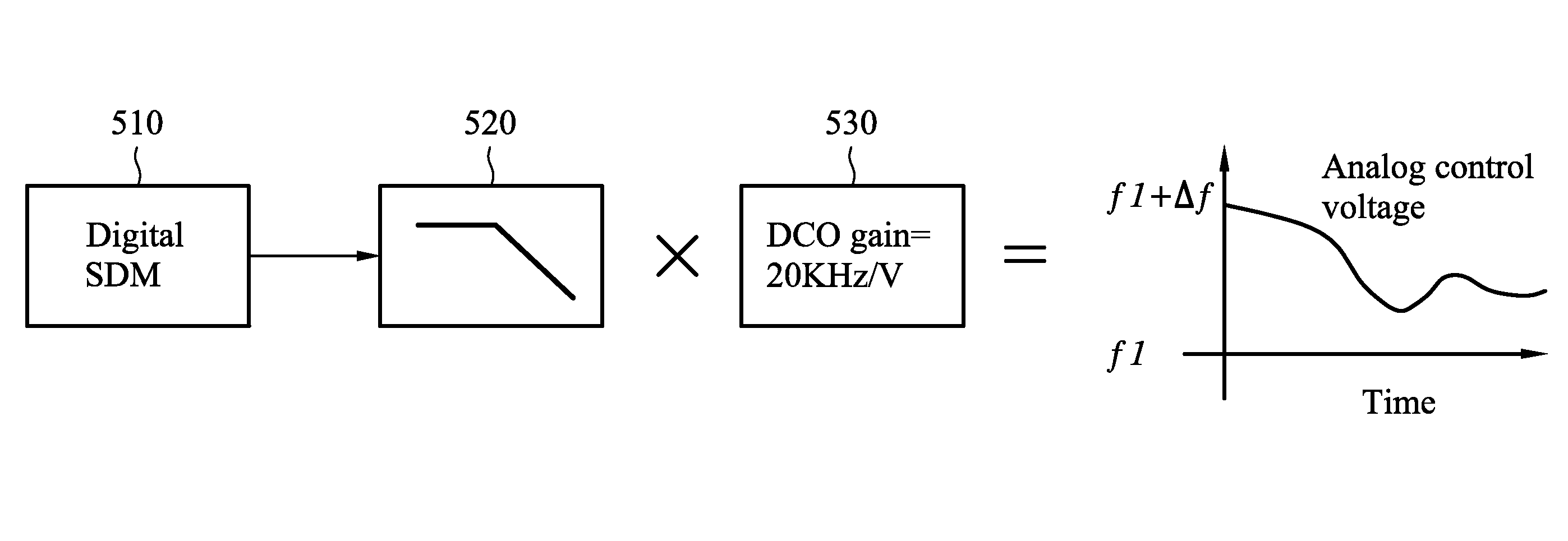
Mixed-mode pll
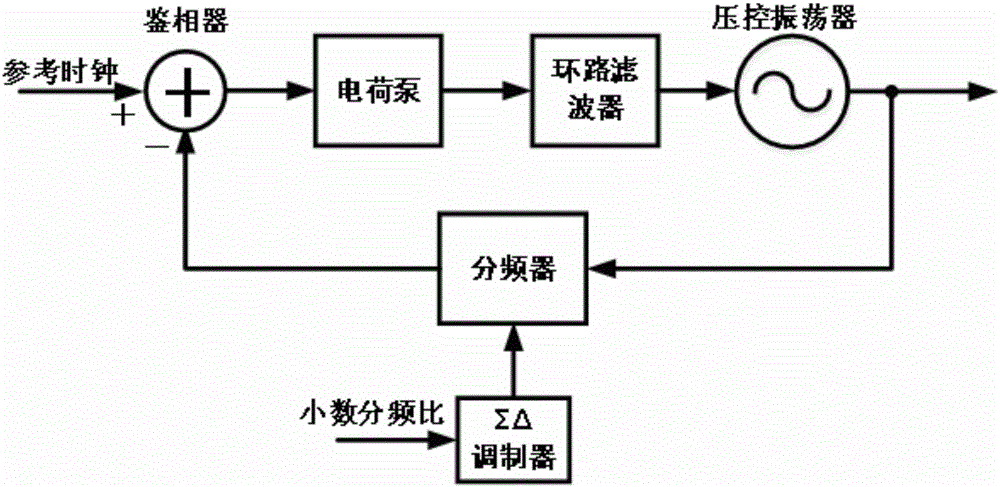
ActiveUS20100231310A1High frequency resolutionPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionDigital control oscillatorLow-pass filter
A mixed-mode PLL is disclosed. The mixed-mode PLL comprises a digital sigma-delta modulator, a low pass filter, and a digital controlled oscillator. The digital sigma-delta modulator receives a fractional bit signal. The low pass filter is coupled to the digital sigma-delta modulator. The low pass filter receives an output signal of the digital sigma-delta modulator and converts the output signal to an analog control signal. The digital controlled oscillator comprises a varactor dynamically coupled to the low pass filter and receiving the analog control signal.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Amplitude and phase correction and compensation method of multichannel receiver
InactiveCN109660305AEfficient and convenient calibrationEasy to correctWave based measurement systemsReceivers monitoringDigitally controlled oscillatorPhysics
The invention provides an amplitude and phase correction and compensation method of a multichannel receiver. A digital receiver controls to feed a calibration signal into a receiving channel through asum and difference instrument; a sum and difference signal is converted into an intermediate frequency signal through an analog front end; an intermediate frequency calibration signal is sampled by adigital intermediate frequency receiver, orthogonal demodulation is performed by digital down-conversion to obtain orthogonal sum and difference signals; the phase of a digital-controlled oscillatorof a receiver difference channel is controlled to linearly increase from -180 degrees to +180 degrees with 1 degree as an interval; an angle error corresponding to each phase is calculated according to the orthogonal sum and difference signals obtained by the orthogonal demodulation; a phase compensation value is obtained according to a phase and angle error relationship; the calibration signal iscontrolled to be fed into a sum and difference channel, the obtained corrected phase is applied to a difference channel NCO, a 16-point angle error is collected, an average value is calculated to serve as an estimated value of a measurement angle error, an ideal value is known, and an amplitude compensation factor is calculated. A working frequency point is replaced, and the above steps are repeated to complete the phase and amplitude calibration work of all working frequency points of the multichannel receiver.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
Clock synthesizer with integral non-linear interpolation (INL) distortion compensation
ActiveUS10128826B2Accurate methodQuickly and adaptively adjust the non-linear distortionPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsDigital control oscillatorComputer module
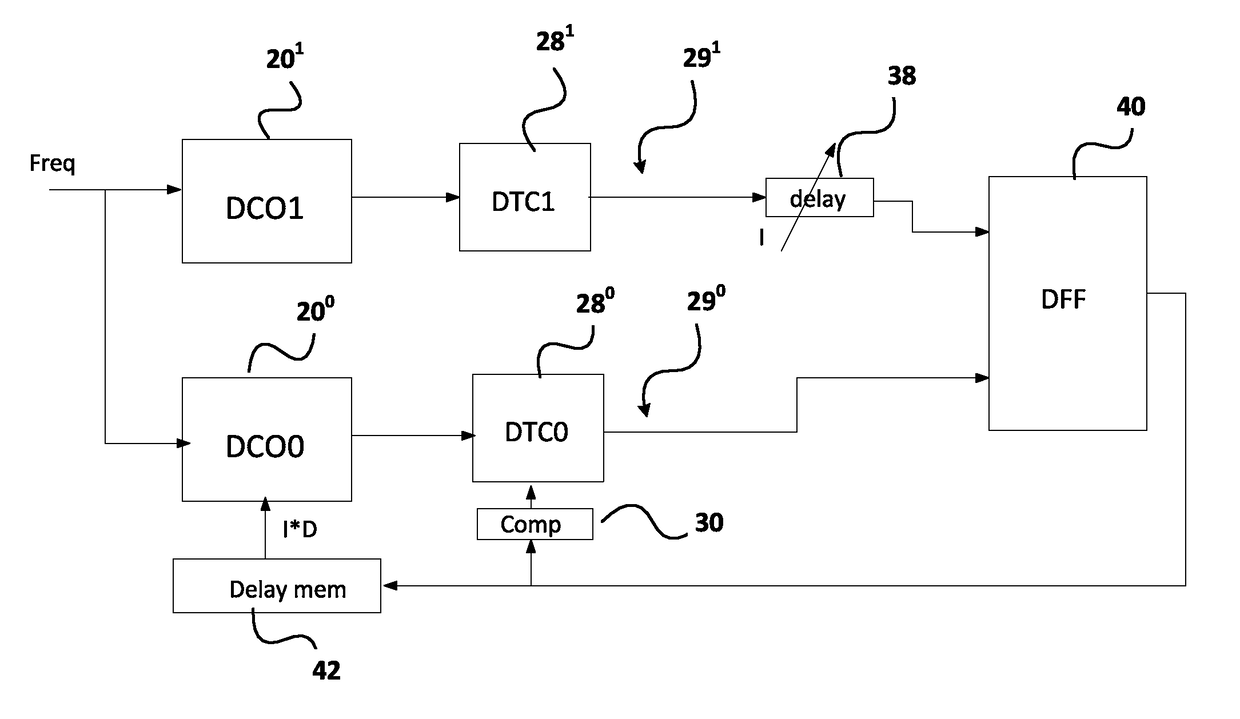
A method of compensating for integral nonlinear interpolation (INL) distortion in a clock synthesizer driven by a system clock running at a frequency fsys, involves introducing a selected nominal analog delay I*dt with an actual delay of I*dt+δ at the output of the a first path with a digital controlled oscillator (DCO) and a digital-to-time converter (DTC) and a nominal digital delay I*D with an actual delay of I*D+Δ at the input of a second path with a DCO and a DTC that offsets the actual analog delay in the first path, adjusting the contents x(k) of a compensation module in the second path to align the output pulses of the first and second paths for different values of k, where k represents an interpolation point, iteratively repeating the two preceding steps for all N values of I, and averaging the contents x(k) of the compensation module to derive the compensation values to be applied to a one of the DTCs to correct for INL distortion.
Owner:MICROSEMI SEMICON
Mixed-mode PLL
ActiveUS8031025B2High frequency resolutionAngle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlDigital control oscillatorLow-pass filter
A mixed-mode PLL is disclosed. The mixed-mode PLL comprises a digital sigma-delta modulator, a low pass filter, and a digital controlled oscillator. The digital sigma-delta modulator receives a fractional bit signal. The low pass filter is coupled to the digital sigma-delta modulator. The low pass filter receives an output signal of the digital sigma-delta modulator and converts the output signal to an analog control signal. The digital controlled oscillator comprises a varactor dynamically coupled to the low pass filter and receiving the analog control signal.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
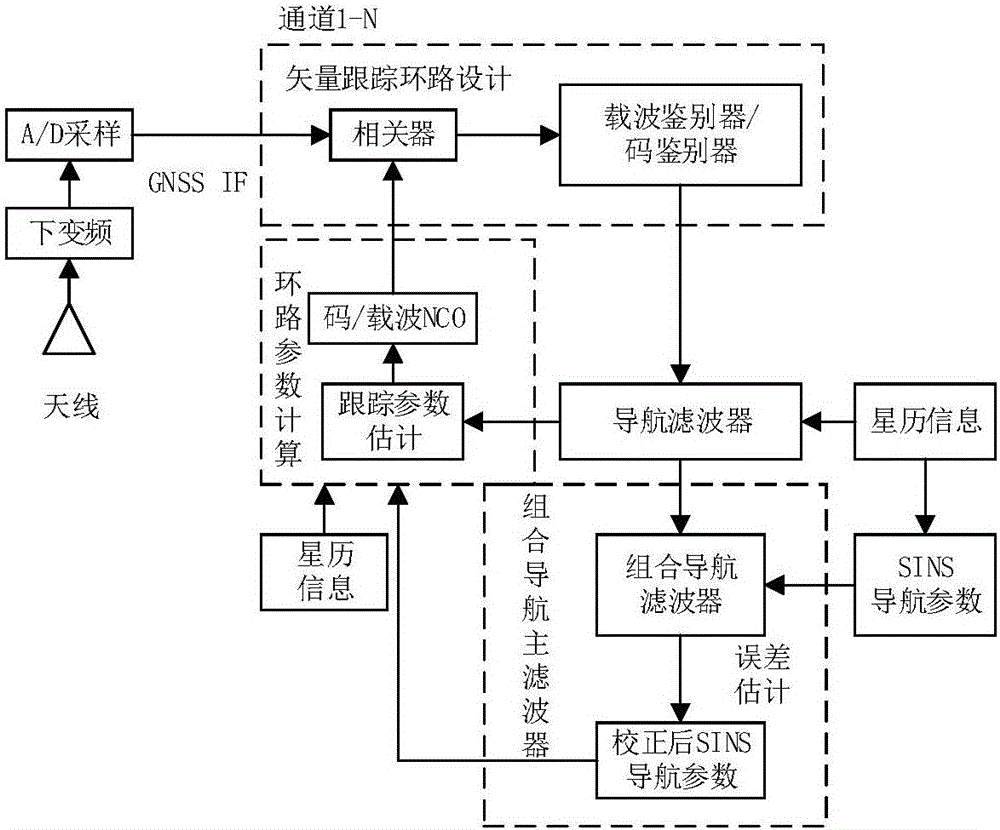
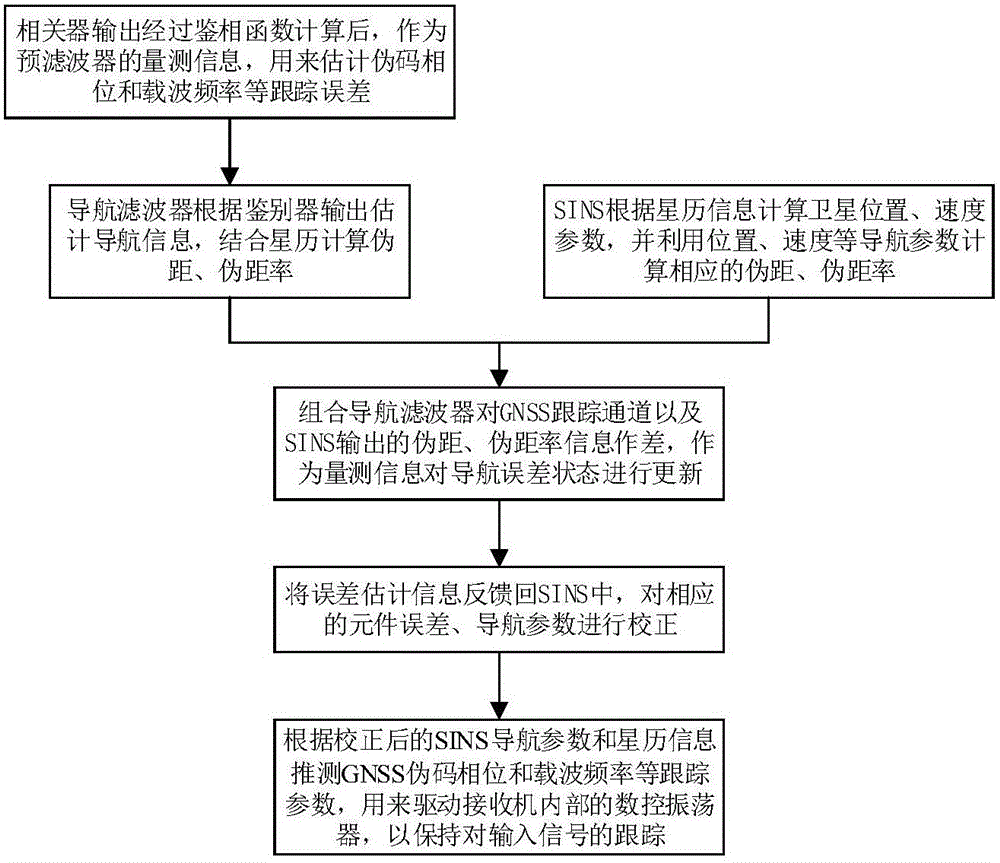
Cascaded GNSS/SINS deep integrated navigation method
InactiveCN106199668ARealize assistanceImprove tracking performanceNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingDiscriminatorClock drift
The invention discloses a cascaded GNSS / SINS deep integrated navigation method. The method comprises a step of designing a vector tracking loop: a carrier discriminator and a code discriminator output measurement information for a guide filter and are used for estimating receiver position, speed, clock error and clock drift, and the estimated information is used for calculating a receiver loop parameter, a step of building an integrated guide main filter model: the integrated guide main filter receives the measurement information outputted by a GNSS tracking channel and an SINS, and updates a state variable and feeds a navigation error parameters back to an SINS system to correct an SINS system error, a step of calculating a loop parameter by using inertial information: an integrated system calculates a tracking loop parameter by using the corrected SINS navigation information and ephemeris information and is used for controlling the local pseudo code of the receiver and a carrier digital controlled oscillator so as to maintain the stable tracking of an input signal. The method has good anti-interference performance and instantaneous signal bridge connection ability, a good positioning effect can be obtained in a high dynamic environment and a weak signal environment, and prospect of application is wide.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
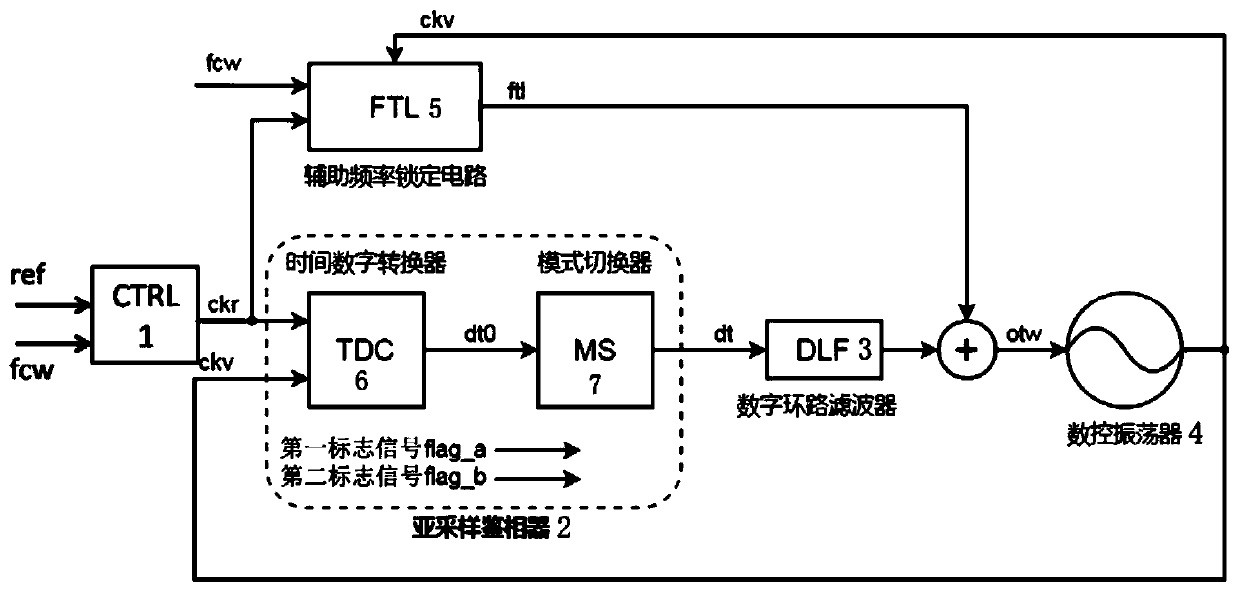
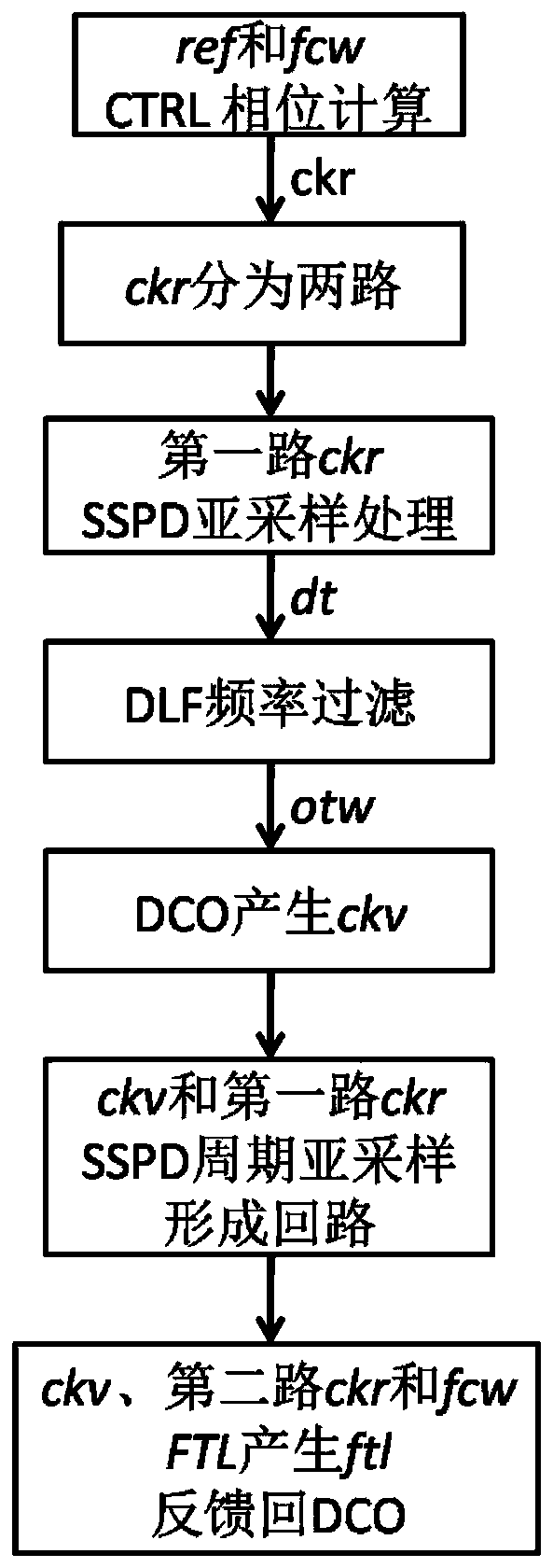
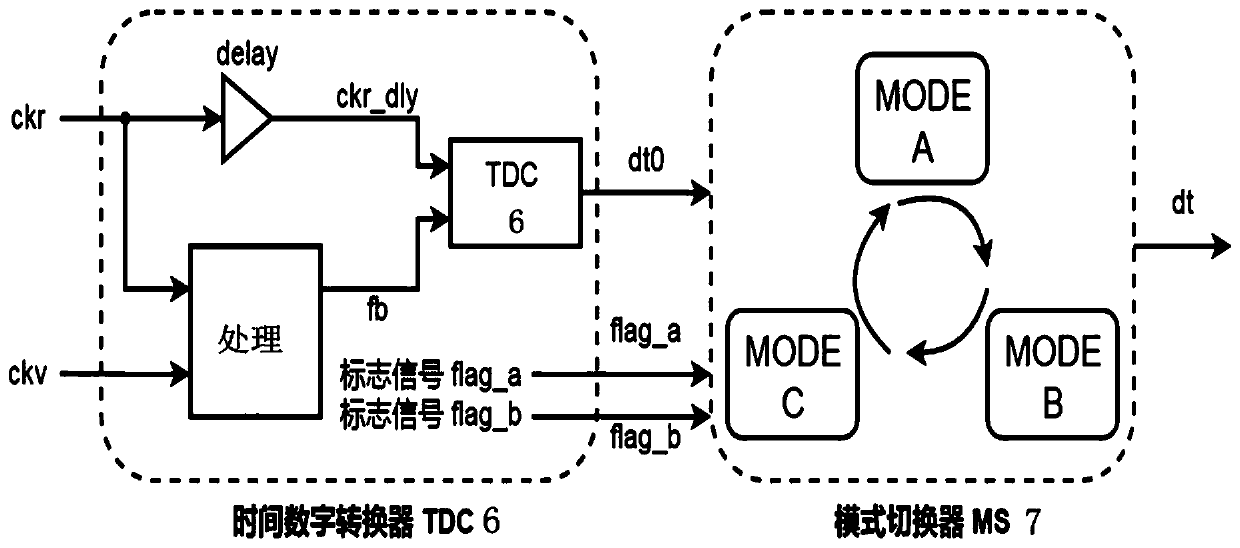
All-digital sub-sampling phase-locked loop and frequency range locking method thereof
ActiveCN110708061ASolve the problem of high power consumptionIncrease frequency lock rangePulse automatic controlNumerical controlLoop filter
The invention discloses an all-digital sub-sampling phase-locked loop and a frequency range locking method thereof. The all-digital sub-sampling phase-locked loop comprises a clock generation and control circuit; a sub-sampling phase discriminator the first input end of whichis connected with the first output end of the clock generation and control circuit; a digital loop filter the input end of whichis connected with the output end of the sub-sampling phase discriminator; a numerical control oscillator the first input end of whichis connected with the output end of the digital loop filter, and the first output end of which is connected with the second input end of the sub-sampling phase discriminator; and the first input end of the auxiliary frequency locking circuit is connected with thesecond output end of the clock generation and control circuit, the second input end is connected with the second output end of the numerical control oscillator, and the output end is connected with the second input end of the numerical control oscillator. The problems that a traditional sub-sampling phase-locked loop is small in frequency locking range and a frequency locking auxiliary circuit islarge in power consumption are solved, the output mode of the sub-sampling phase discriminator is judged and switched through the all-digital mode switcher, and the frequency locking range is expanded.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
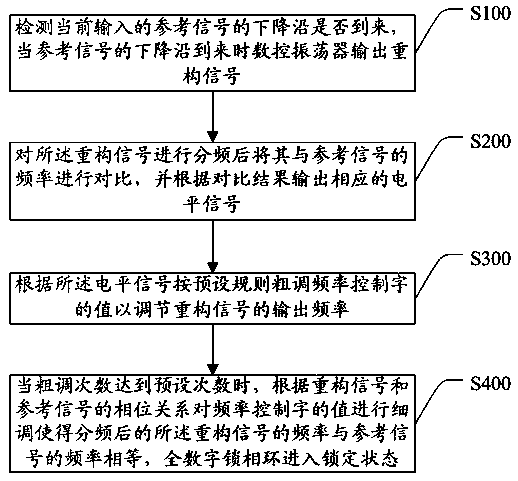
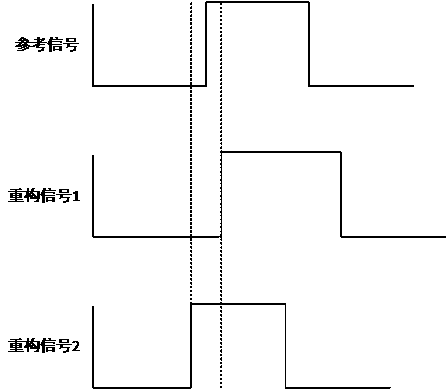
All-digital phase locked loop and fast phase locking method thereof
ActiveCN108923782APhase lock fastFewer searchesPulse automatic controlNumerically controlled oscillatorEngineering
The invention discloses an all-digital phase locked loop and a fast phase locking method thereof, wherein the fast phase locking method comprises the following steps: detecting whether a falling edgeof a currently input reference signal arrives, when the falling edge of the reference signal arrives, outputting a reconstructed signal by a digital-controlled oscillator; performing frequency division for the reconstructed signal and then comparing the reconstructed signal with the frequency of the reference signal, and outputting a corresponding level signal according to a comparison result; according to the level signal, coarsely regulating a value of a frequency control word according to a preset rule to adjust output frequency of the reconstructed signal; when times of coarse regulation reaches preset times, finely regulating the value of the frequency control word according to a phase relation of the reconstructed signal and the reference signal, thereby enabling the frequency of thereconstructed signal subjected to frequency division to be equal to the frequency of the reference signal, and enabling the all-digital phase locked loop to enter into a locked state. By the method,locking time of the phase locked loop is only related to frequency range and precision of output, moreover, times of search is reduced effectively through coarse regulation and fine regulation with different step sizes, the locking time is reduced and fast phase locking is realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com