Patents
Literature
233 results about "Phase tuning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
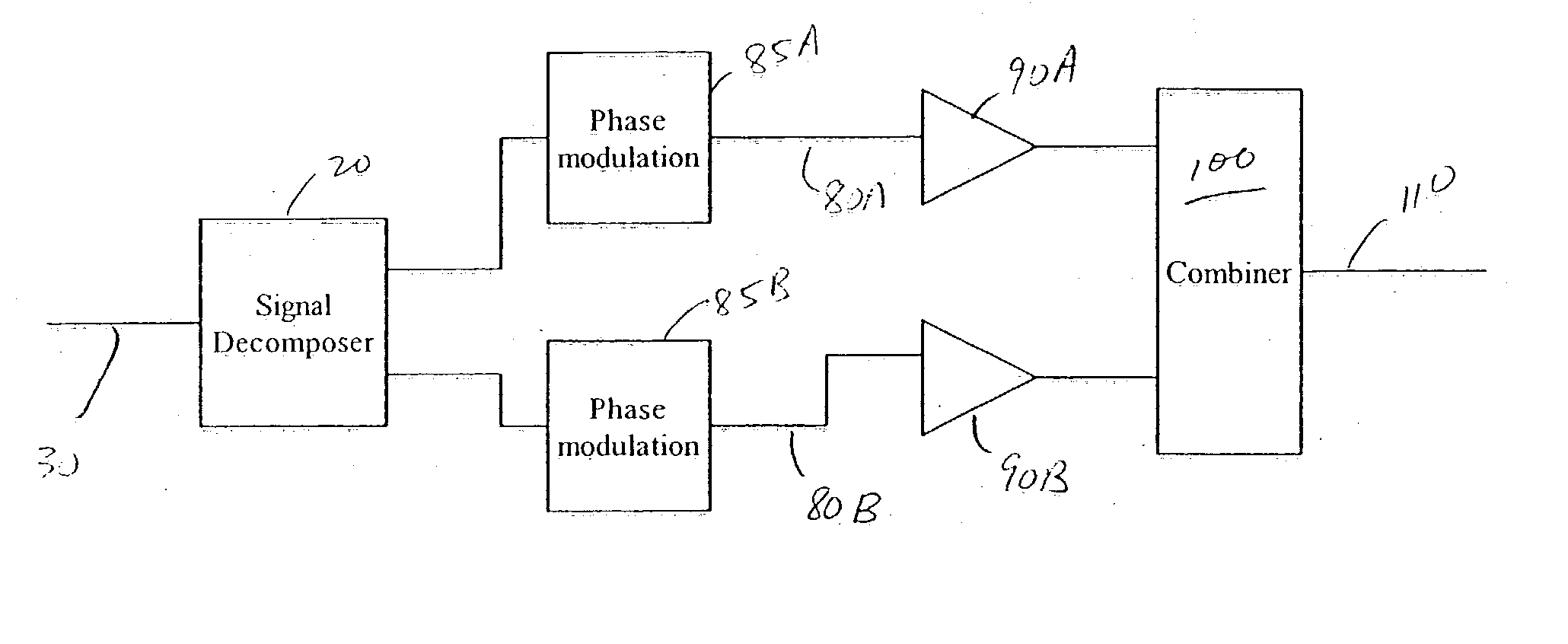
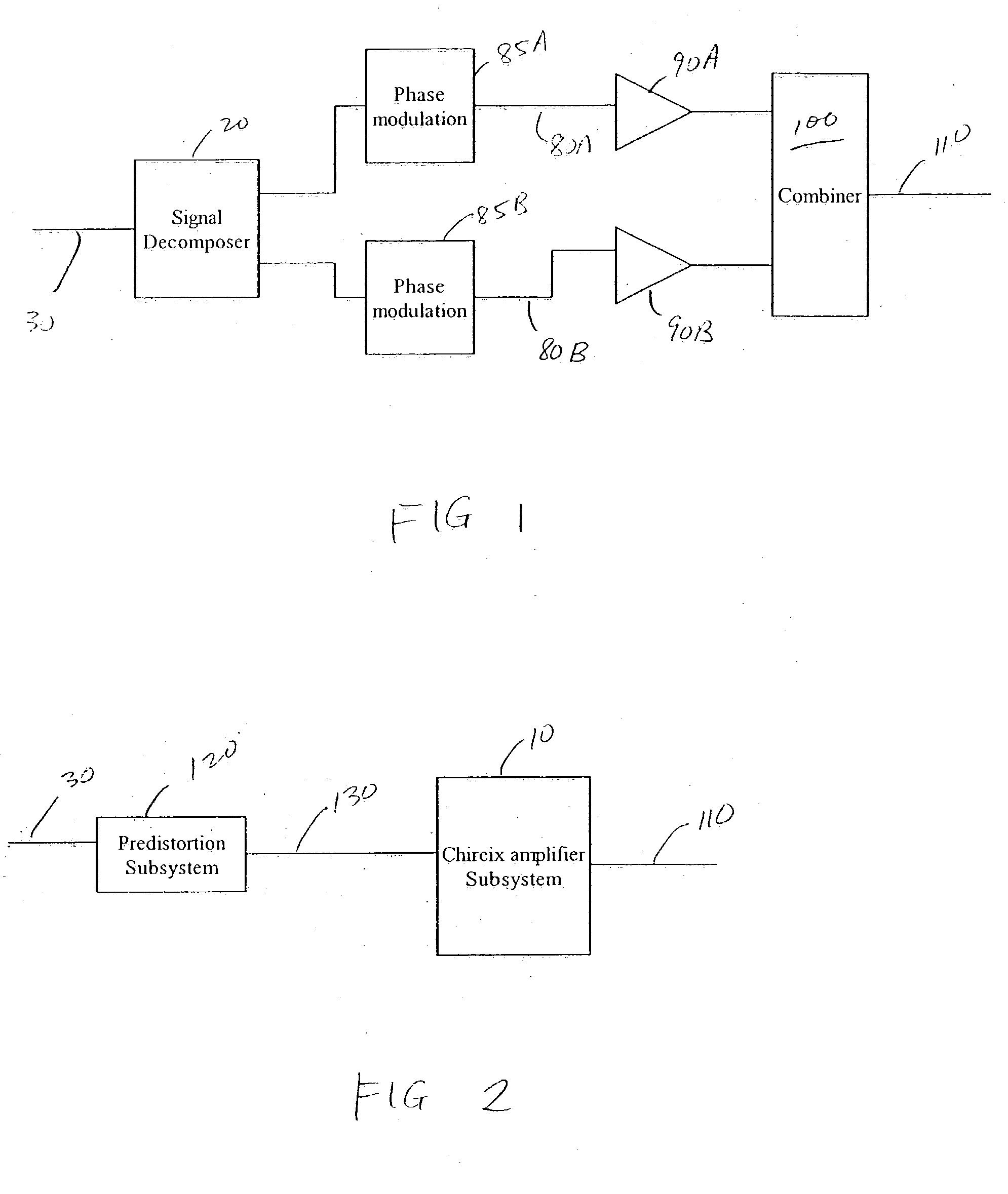
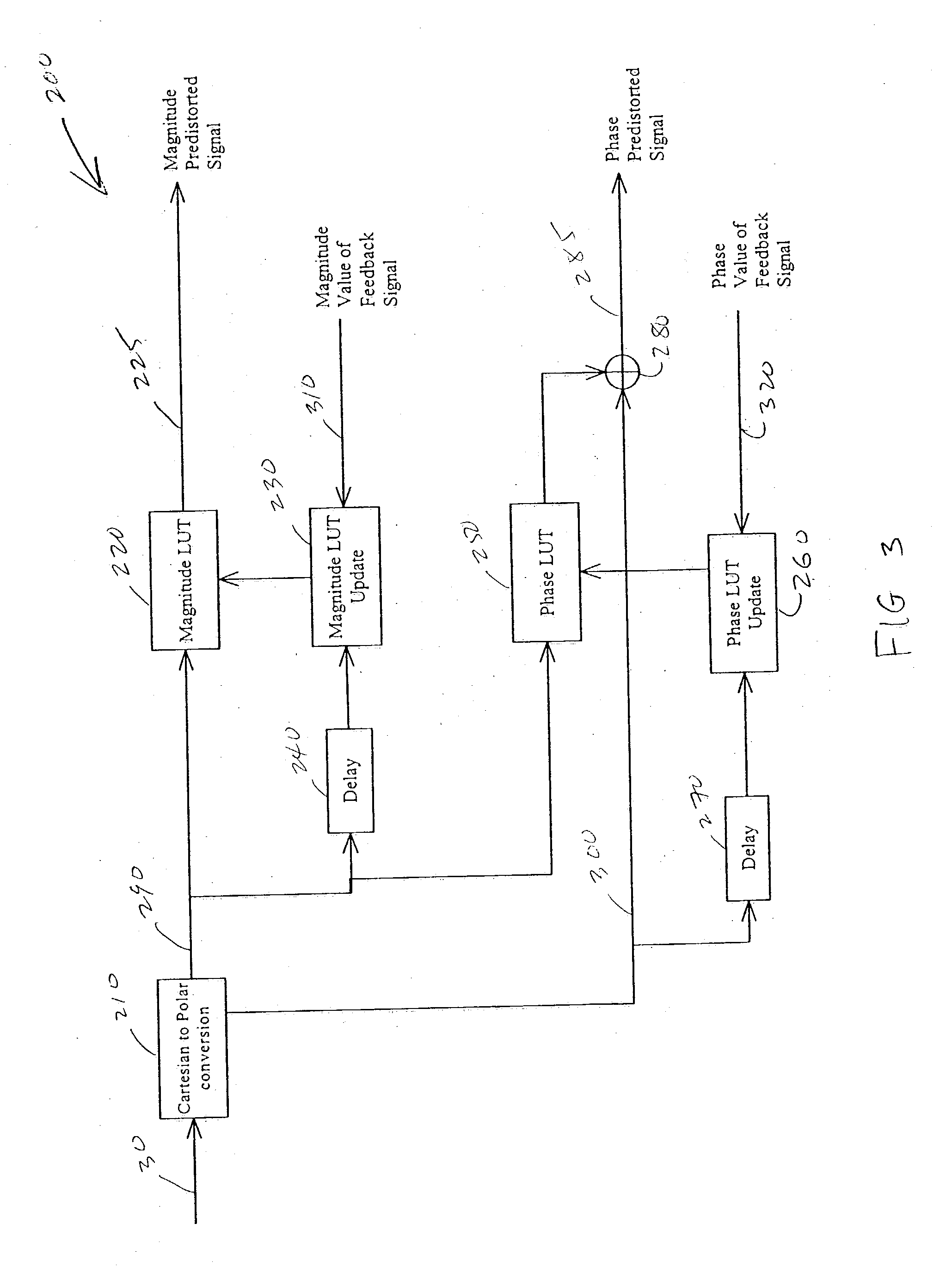
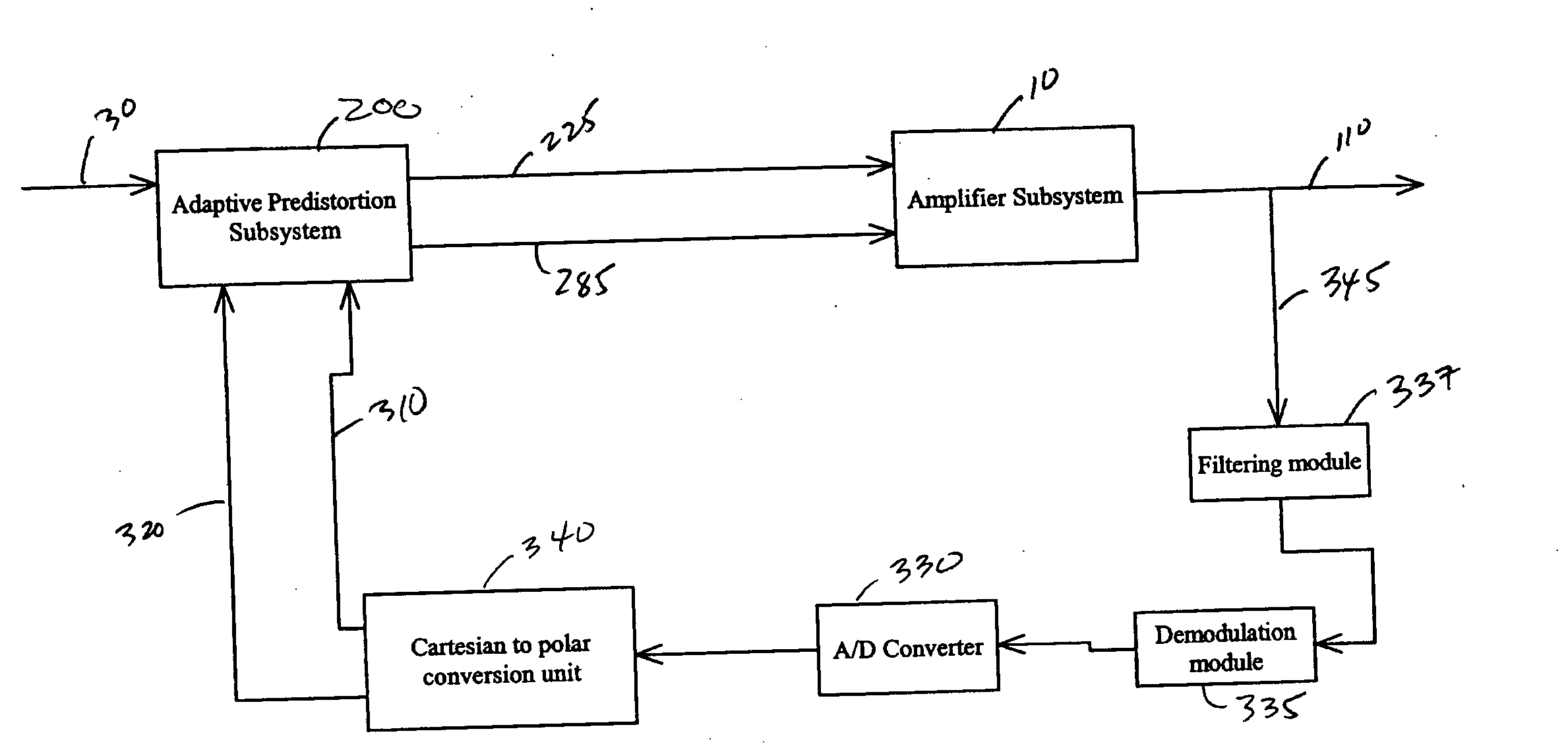
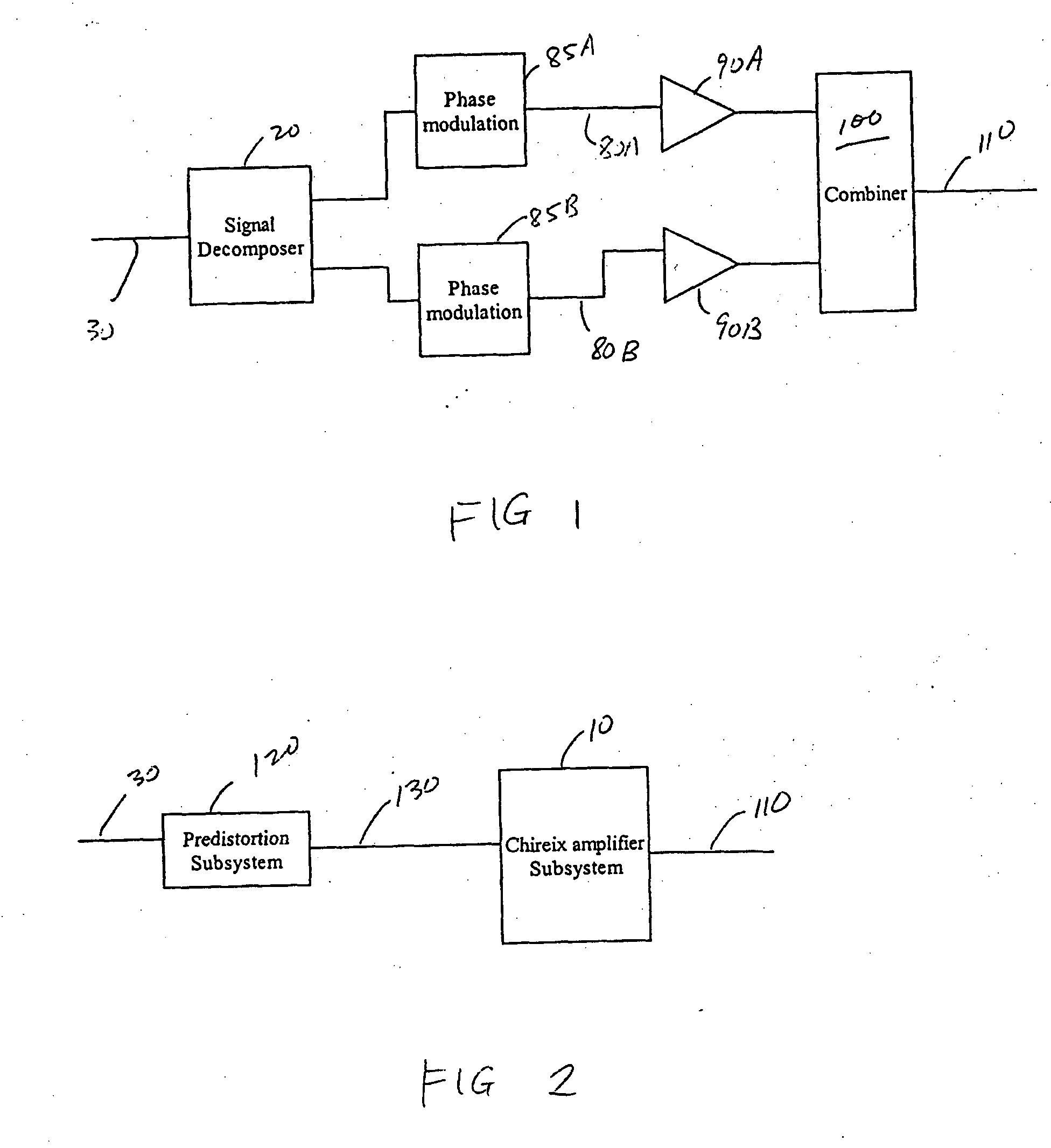
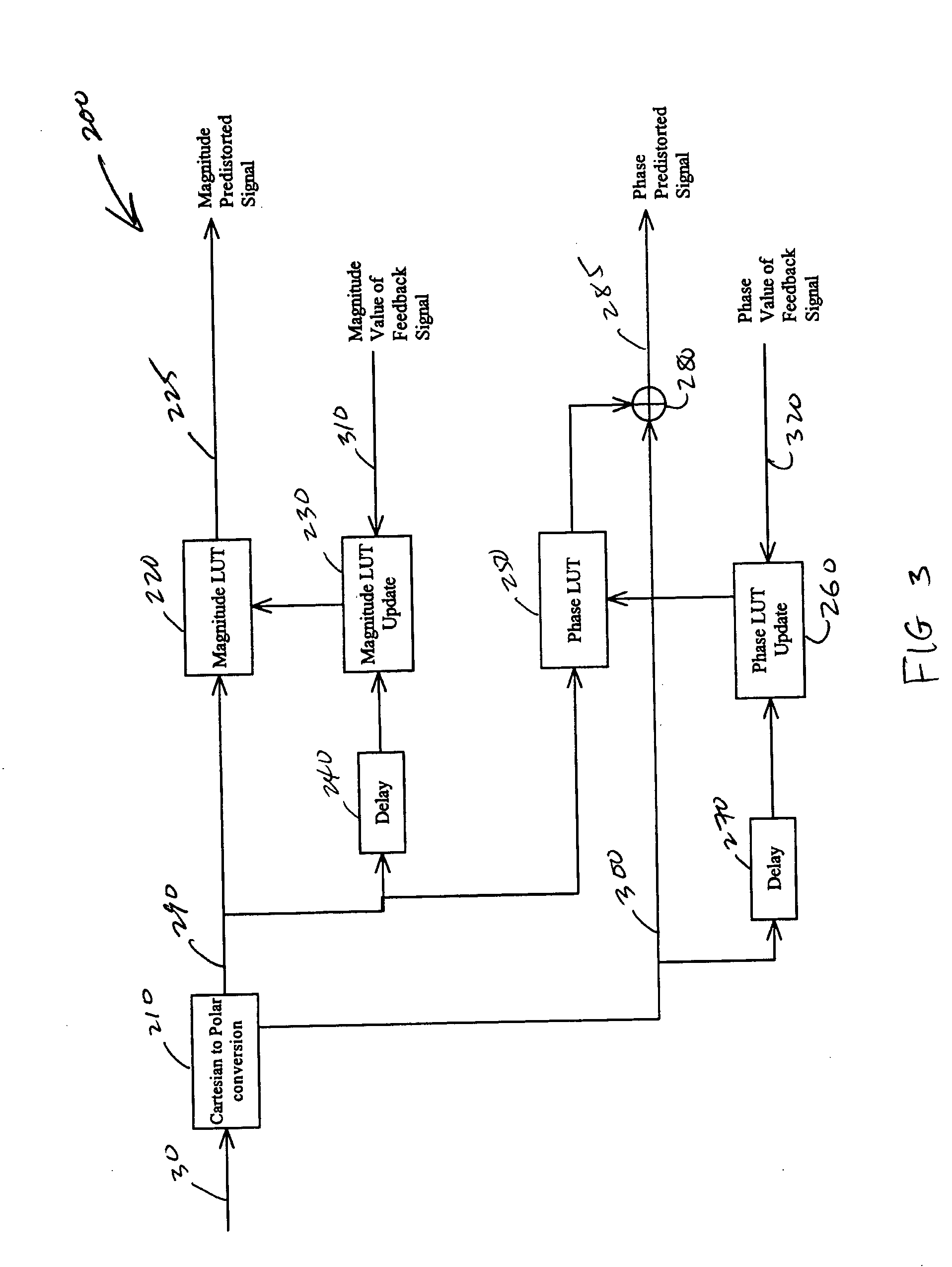
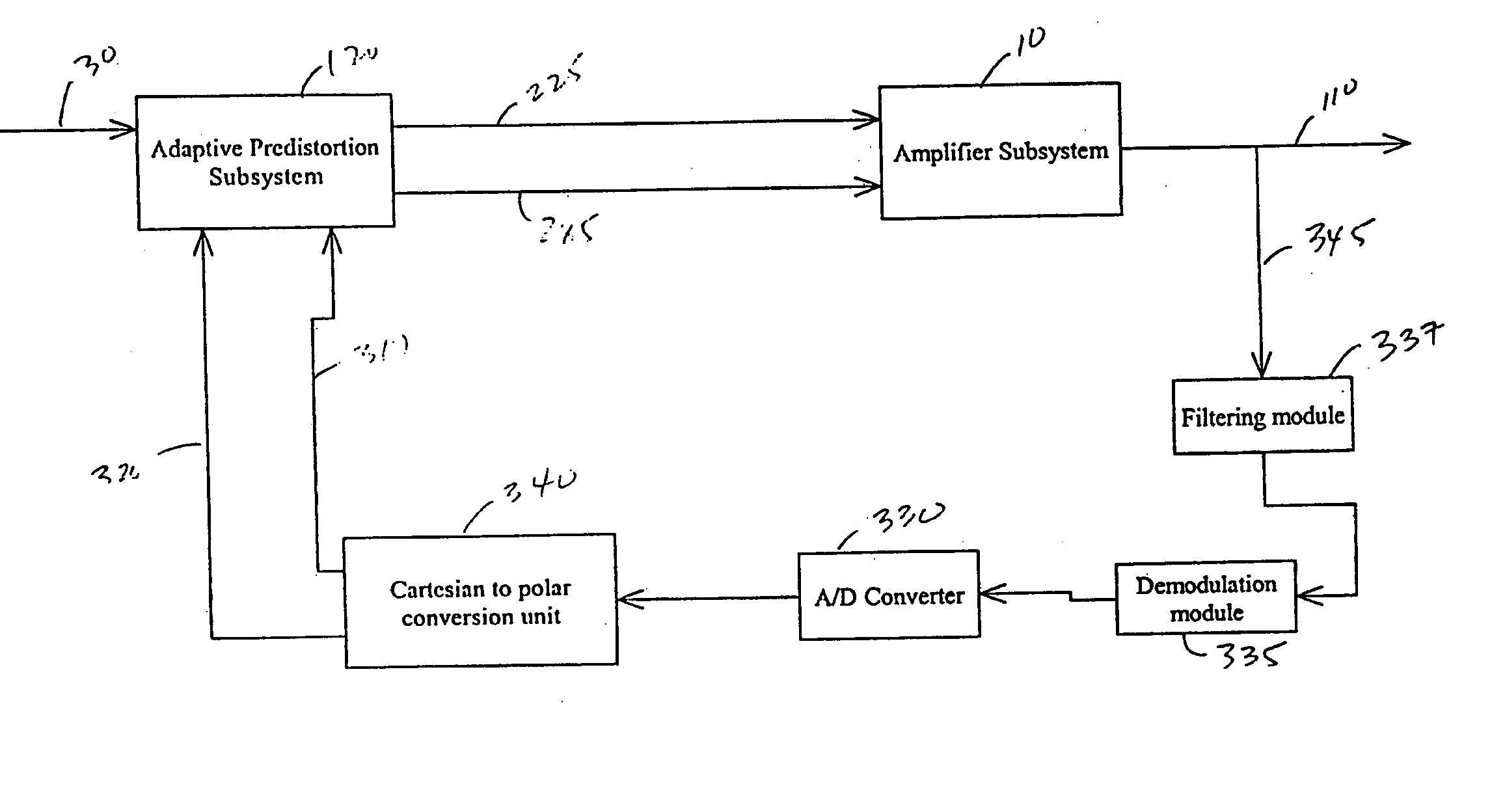
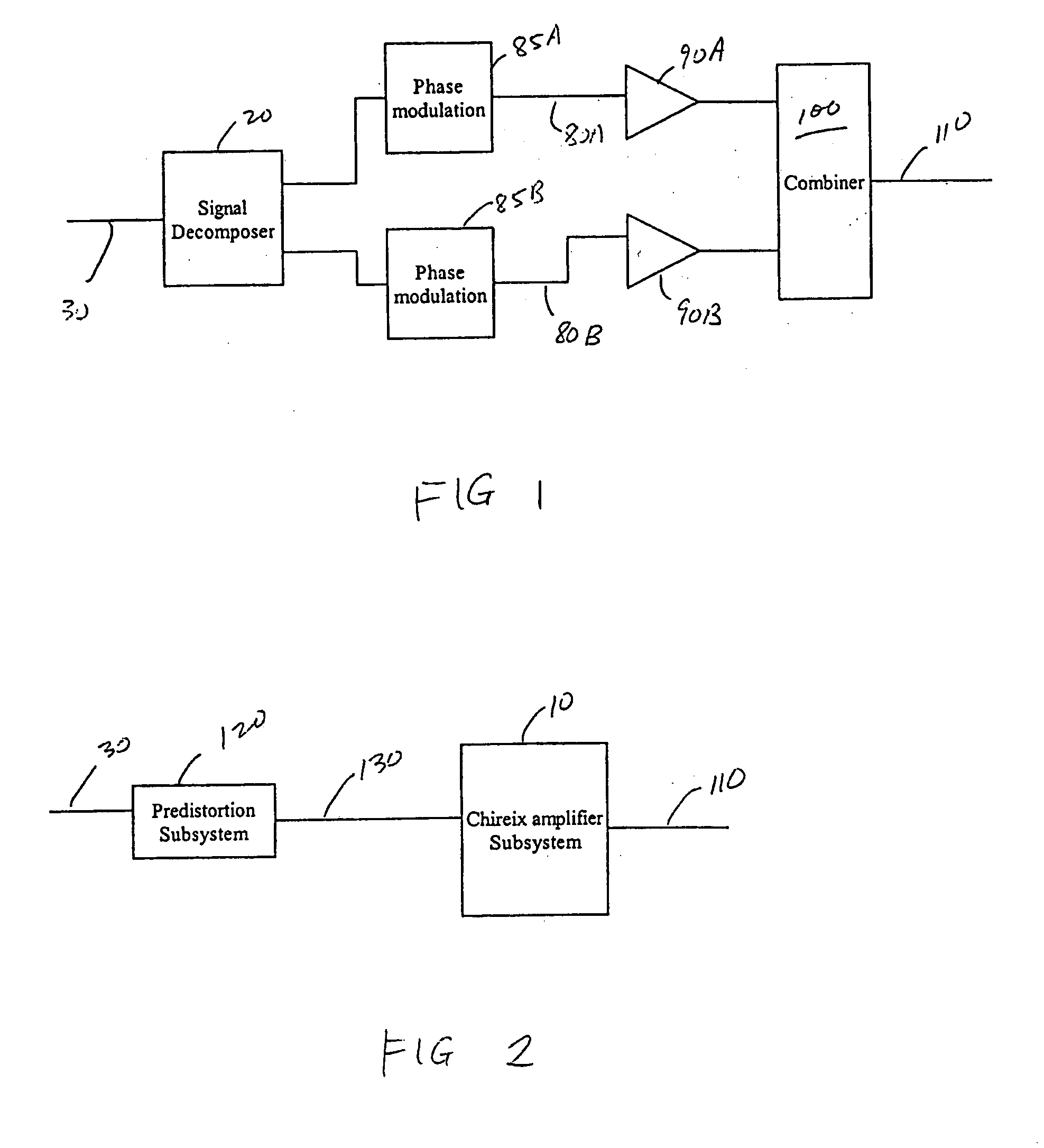
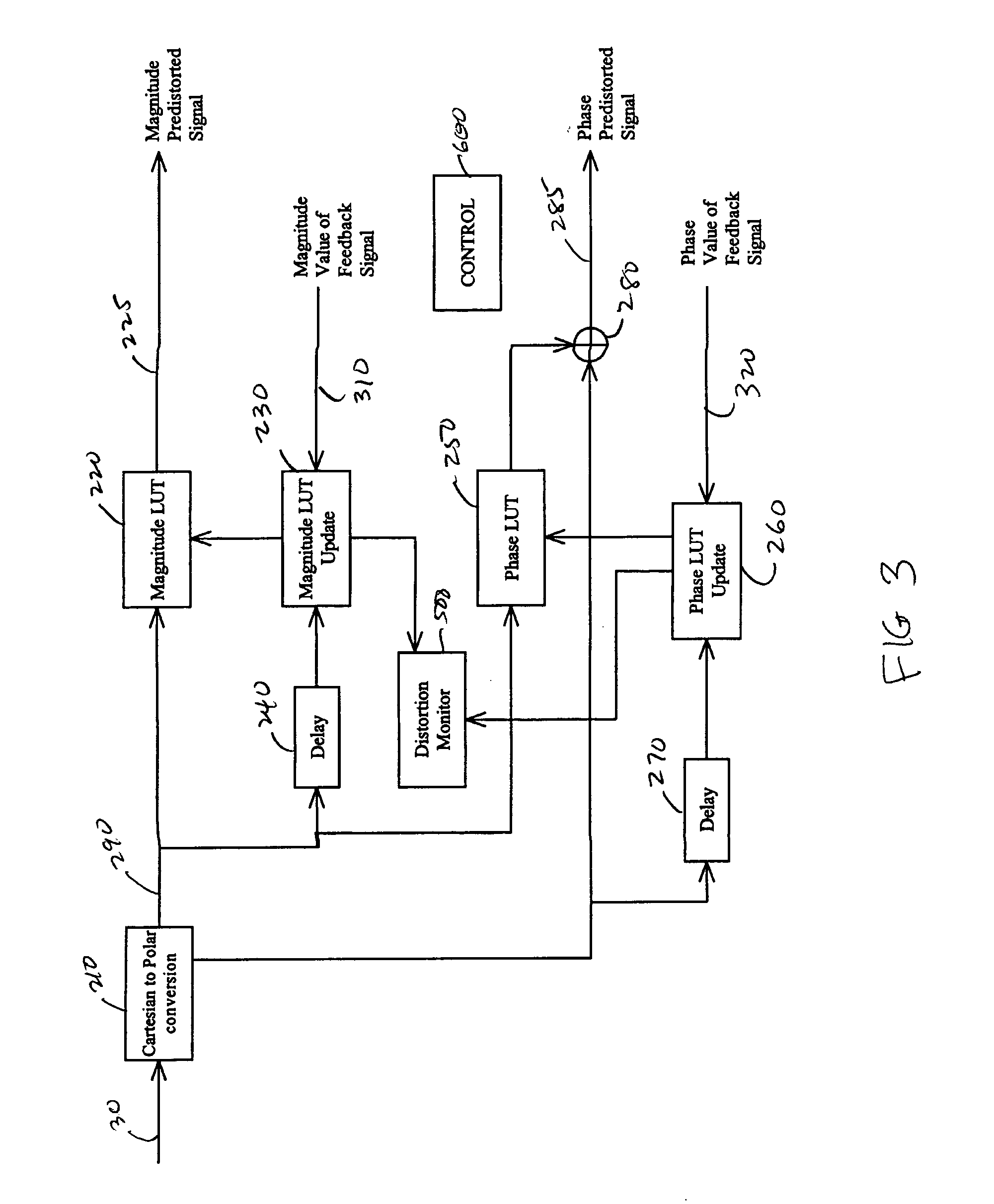
Adaptive predistortion for a transmit system with gain, phase and delay adjustments
ActiveUS20050001675A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsEngineeringSelf adaptive
Systems and methods relating to the provision of gain, phase and delay adjustments to signals to be used by a predistortion subsystem. A portion of an input signal is delayed by delay elements prior to being received by the predistortion subsystem. The delayed input signal portion is also received by a feedback signal processing subsystem that adjusts the gain and phase of the feedback signal based on the delayed input signal portion. The adjusted feedback signal is used, along with the delayed portion of the input signal, to determine an appropriate predistortion modification to be applied to the input signal.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
Adaptive predistortion for a transmit system with gain, phase and delay adjustments
InactiveUS20050001679A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsSelf adaptivePredistortion
Systems and methods relating to the provision of gain, phase and delay adjustments to signals to be used by a predistortion subsystem. A portion of an input signal is delayed by delay elements prior to being received by the predistortion subsystem. The delayed input signal portion is also received by a feedback signal processing subsystem that adjusts the gain and phase of the feedback signal based on the delayed input signal portion. The adjusted feedback signal is used, along with the delayed portion of the input signal, to determine an appropriate predistortion modification to be applied to the input signal.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
Adaptive predistortion for transmit system with gain, phase and delay adjustments
InactiveUS20050001676A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsEngineeringSelf adaptive
Systems and methods relating to the provision of gain, phase and delay adjustments to signals to be used by a predistortion subsystem. A portion of an input signal is delayed by delay elements prior to being received by the predistortion subsystem. The delayed input signal portion is also received by a feedback signal processing subsystem that adjusts the gain and phase of the feedback signal based on the delayed input signal portion. The adjusted feedback signal is used, along with the delayed portion of the input signal, to determine an appropriate predistortion modification to be applied to the input signal.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
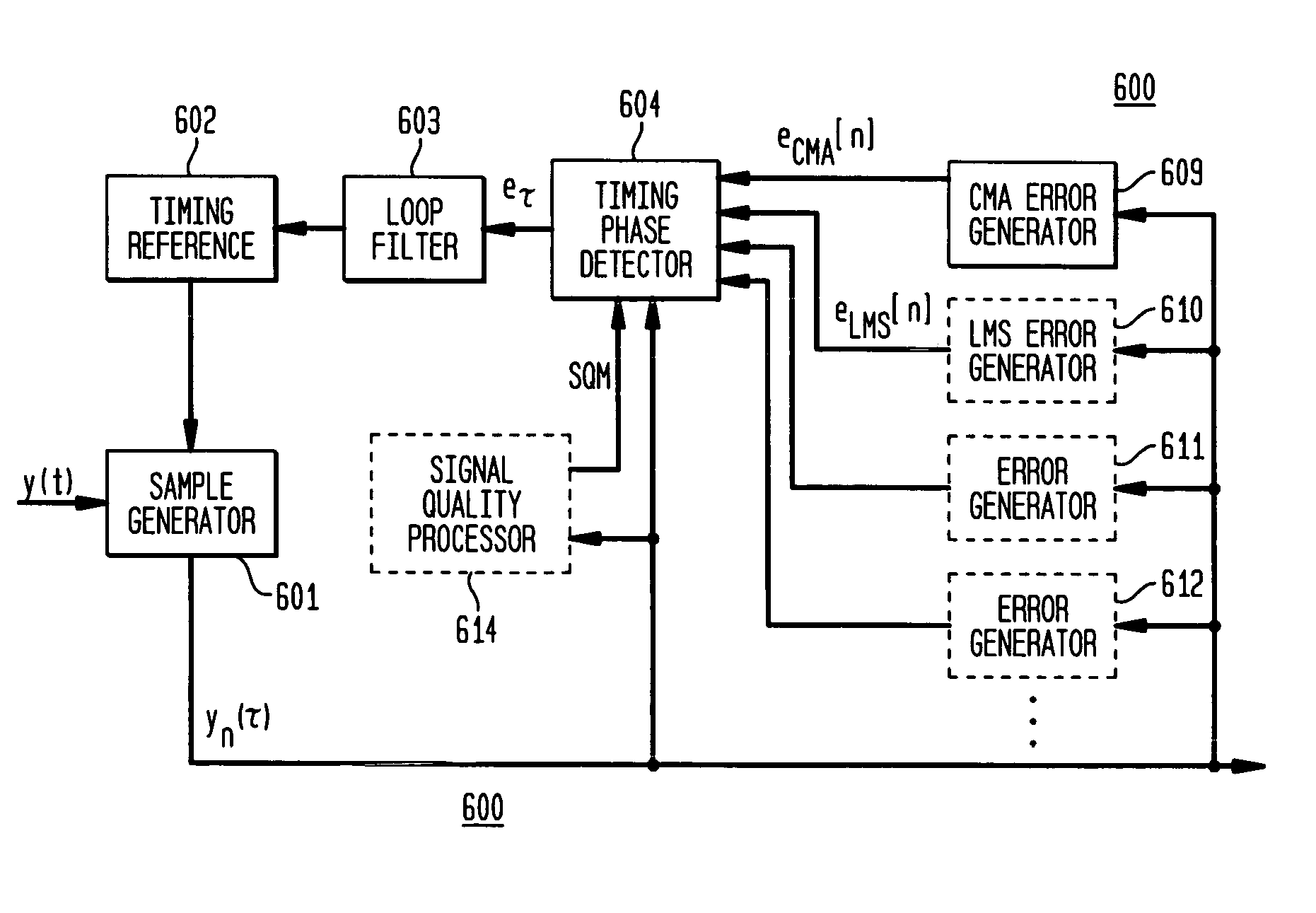
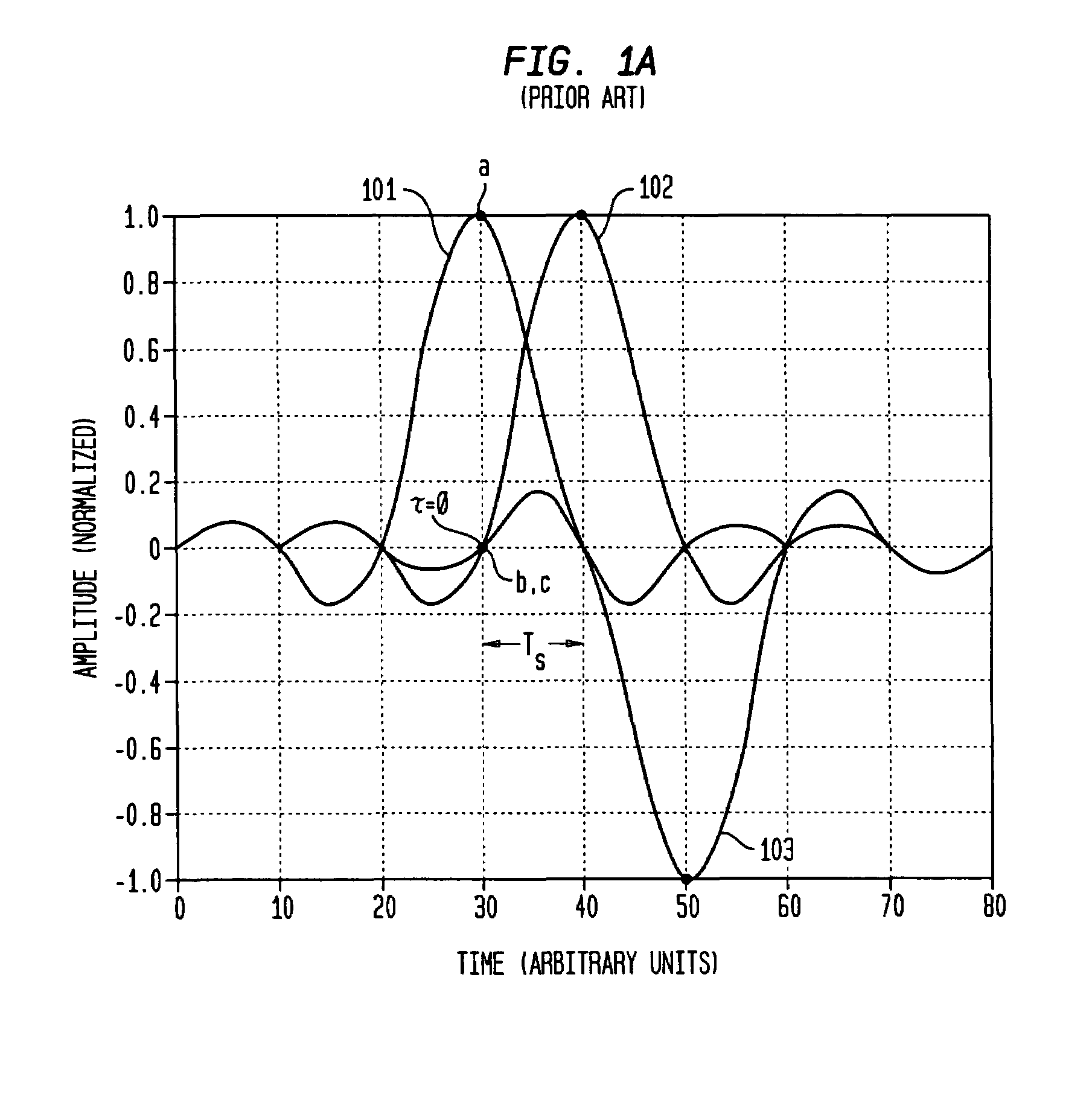
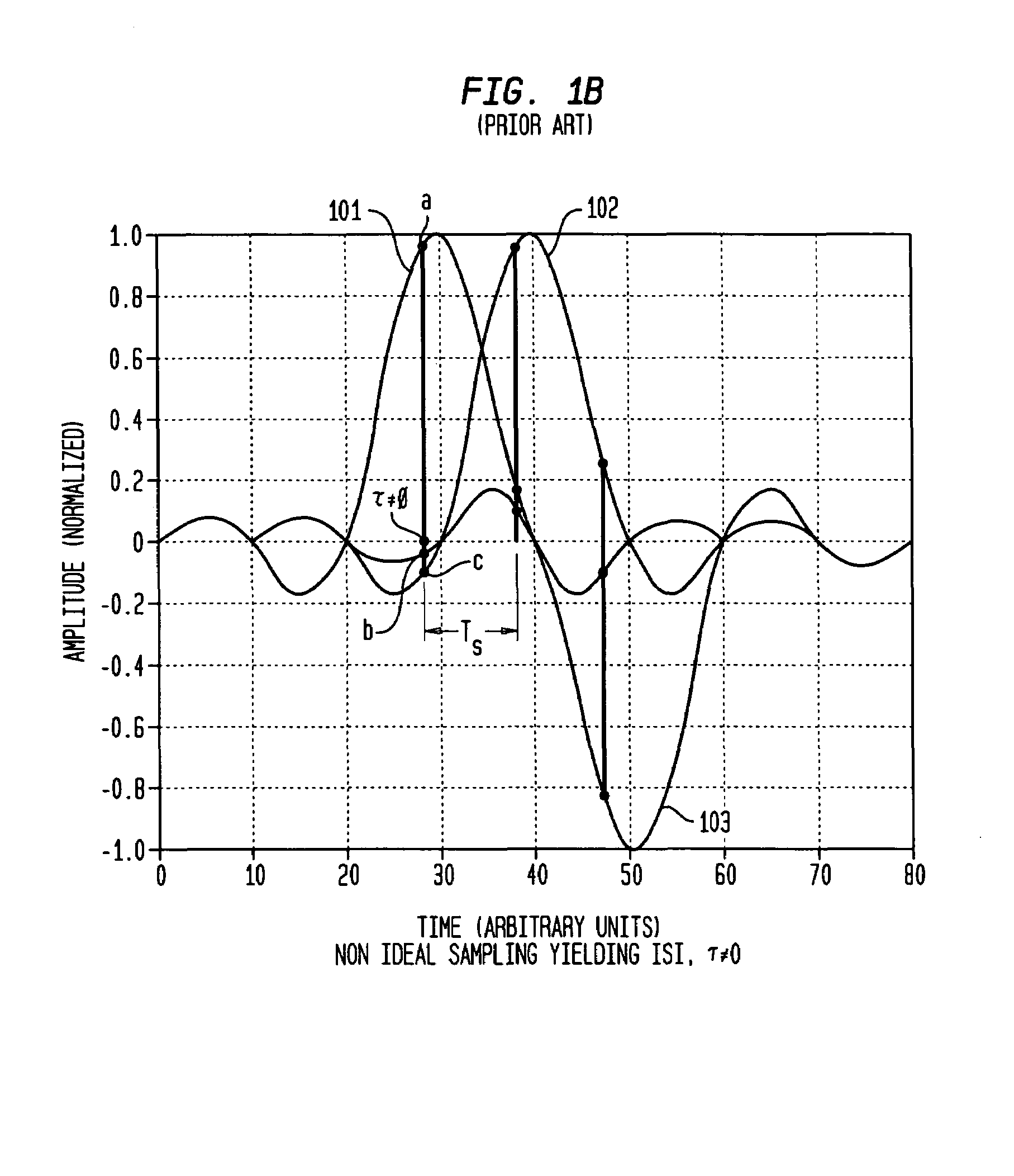
Blind cost criterion timing recovery
Symbol timing recovery employs a blind cost criterion from the Bussgang class of functions, and its stochastic gradient, to generate a timing phase error used to adjust sampling of received symbols. For one implementation, the estimate is derived in accordance with the Constant Modulus (CM) criterion and its gradient via the CM algorithm (CMA), and the estimate is calculated from a sequence of samples. This estimate is then used to adjust the period and phase of the sample sequence toward the period and phase of the transmitted symbols, driving the timing phase error to zero. The values used may be either i) samples themselves, ii) processed (e.g., interpolated) samples, or iii) equalized and processed samples. In addition, timing phase error estimates for other cost criteria, including the least mean squares algorithm, may be generated. These timing phase error estimates are selected either alone or in combination for deriving the timing phase error used to adjust the period and phase of the sample sequence.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Leakage power reduction apparatus
InactiveUS8086191B2Suppress leakageWithout lowering power utilization efficiencyTransmission control/equalisingEngineeringLeakage power
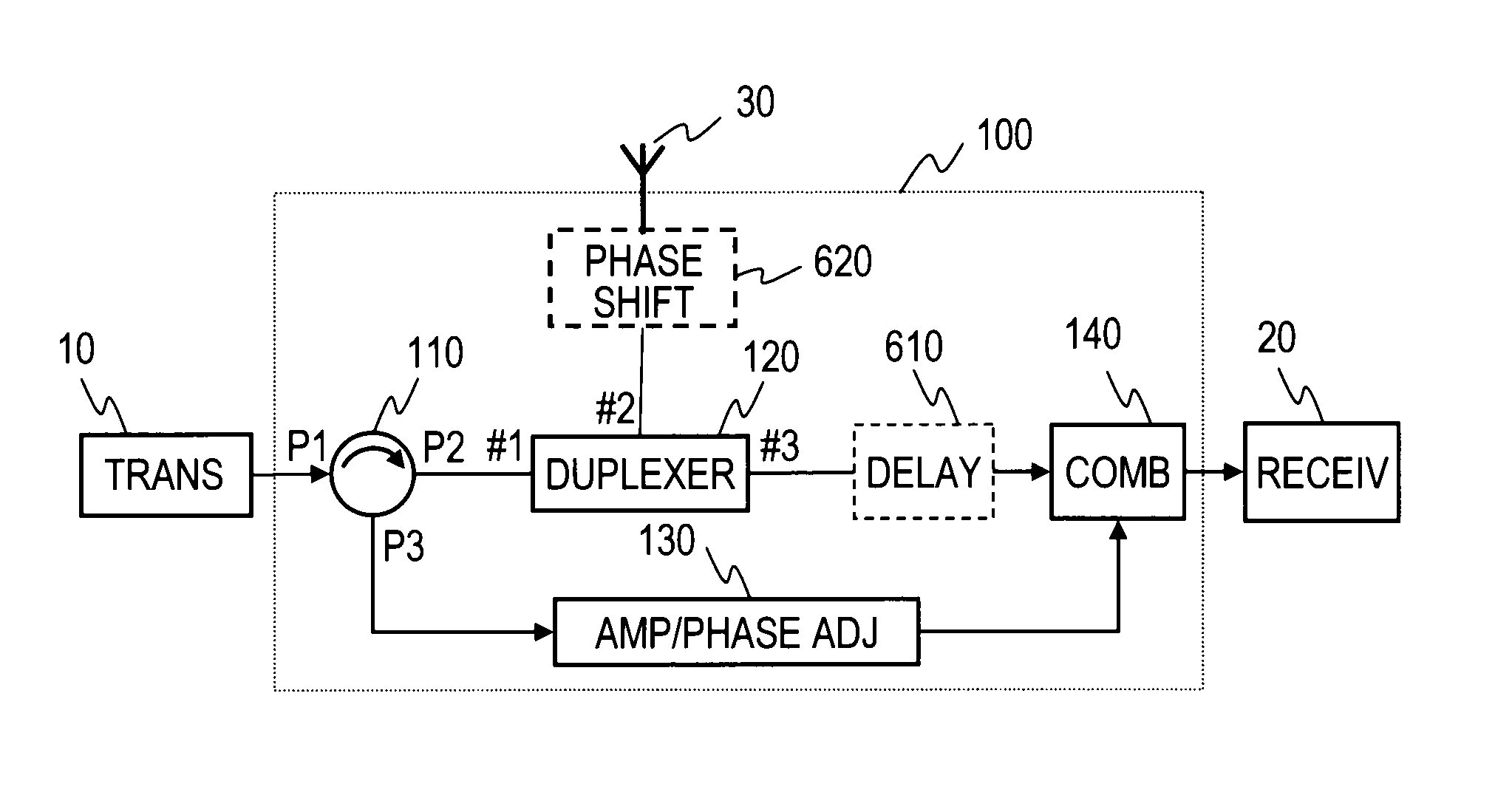
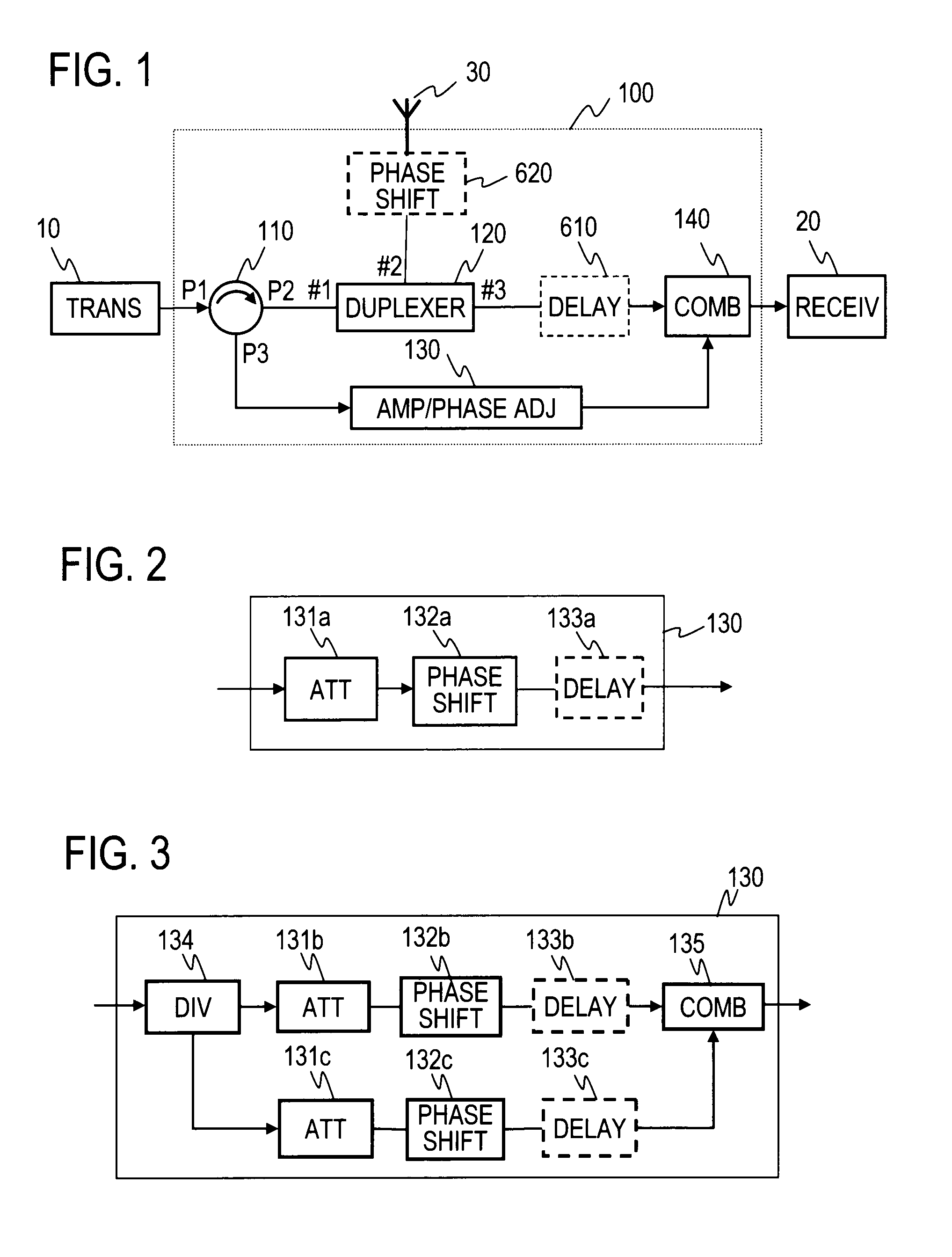
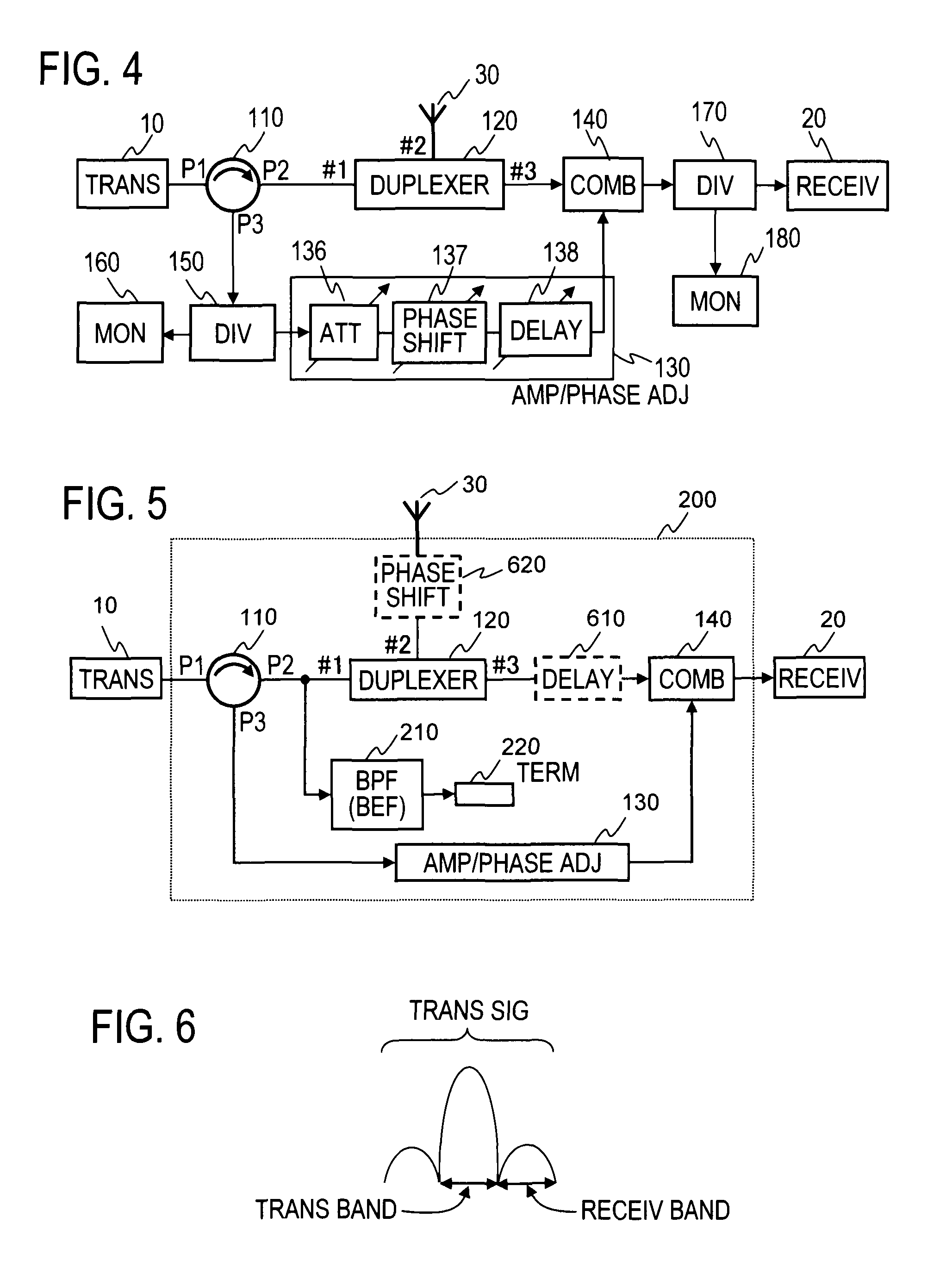
A circulator extracts a transmission signal sent from a transmitter to antenna via the circulator and a duplexer, reflected by an antenna, and returned via the duplexer to the transmitter side. The amplitude and phase of the extracted signal are adjusted by an amplitude-and-phase adjuster to generate an offset signal having the same amplitude and the opposite phase with respect to a leaking transmission signal included in a signal output from a third terminal of the duplexer when combined by a combiner. The offset signal is combined in the combiner with the leaking transmission signal included in the signal output from the third terminal of the duplexer to suppress the leaking transmission signal.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
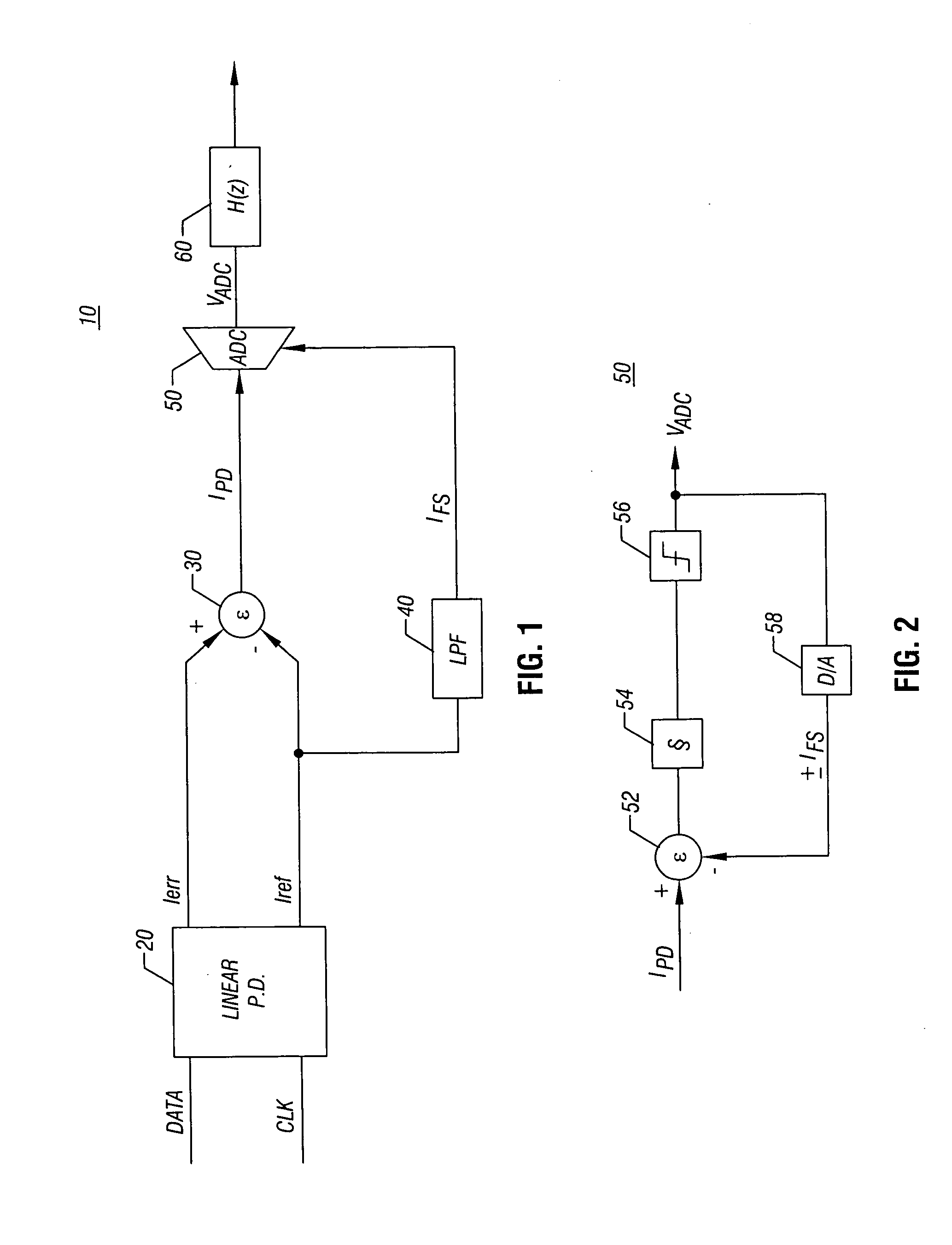
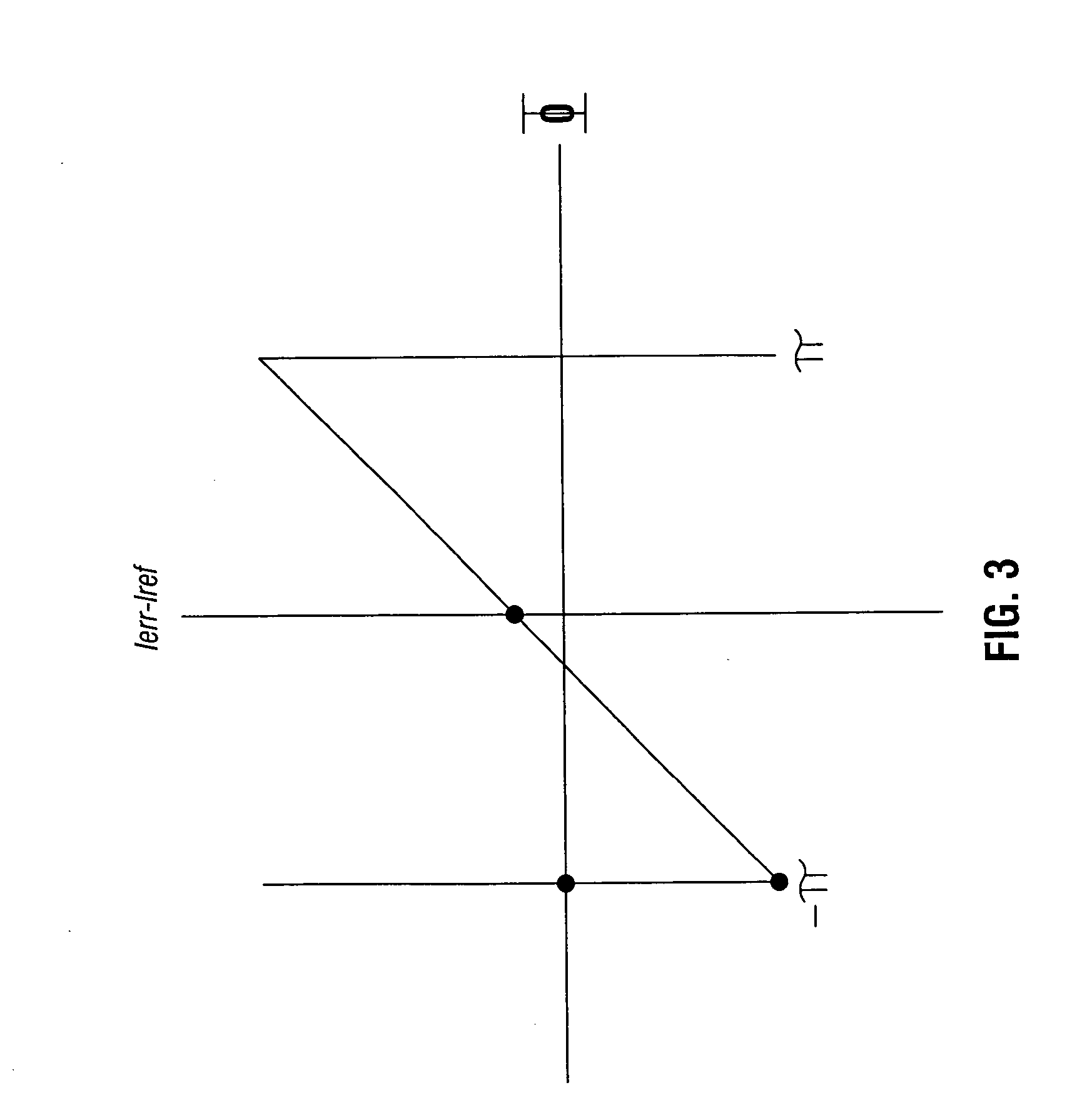
Calibrating a phase detector and analog-to-digital converter offset and gain
ActiveUS20060140319A1Reducing and eliminating offsetImprove errorReceiver initialisationAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionPhase detectorA d converter
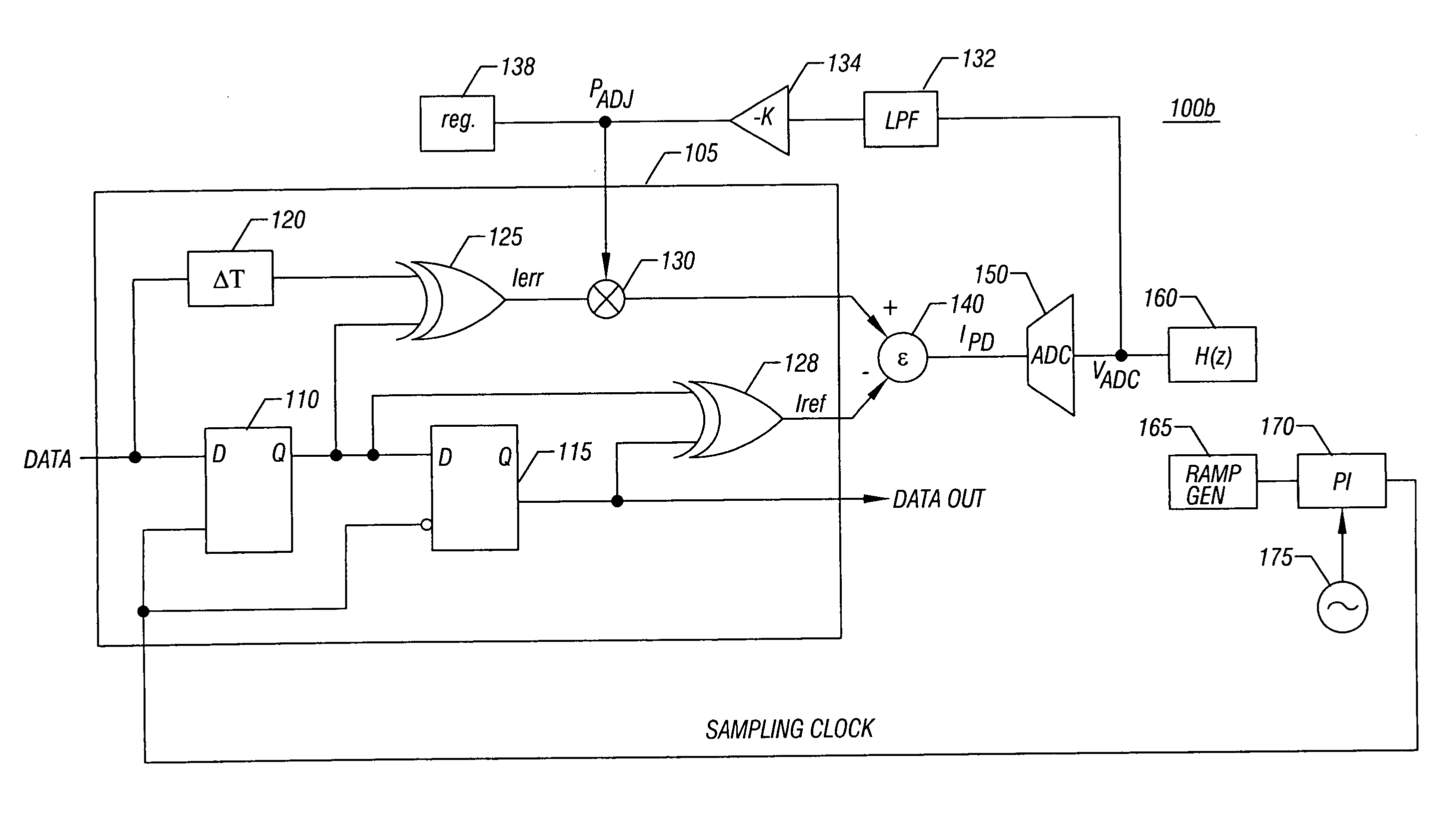
The present invention includes apparatus and methods to calibrate a phase detector and an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) offset and gain. In one such embodiment, an apparatus includes a phase detector to generate an error pulse and a reference pulse, a combiner to combine the pulses, and an ADC to receive the combined pulses, where the ADC has a full scale set by an average of the reference pulse. Still further, a calibration loop may be coupled between the output of the ADC and the phase detector to generate and provide a phase adjust signal to reduce or eliminate phase offsets. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
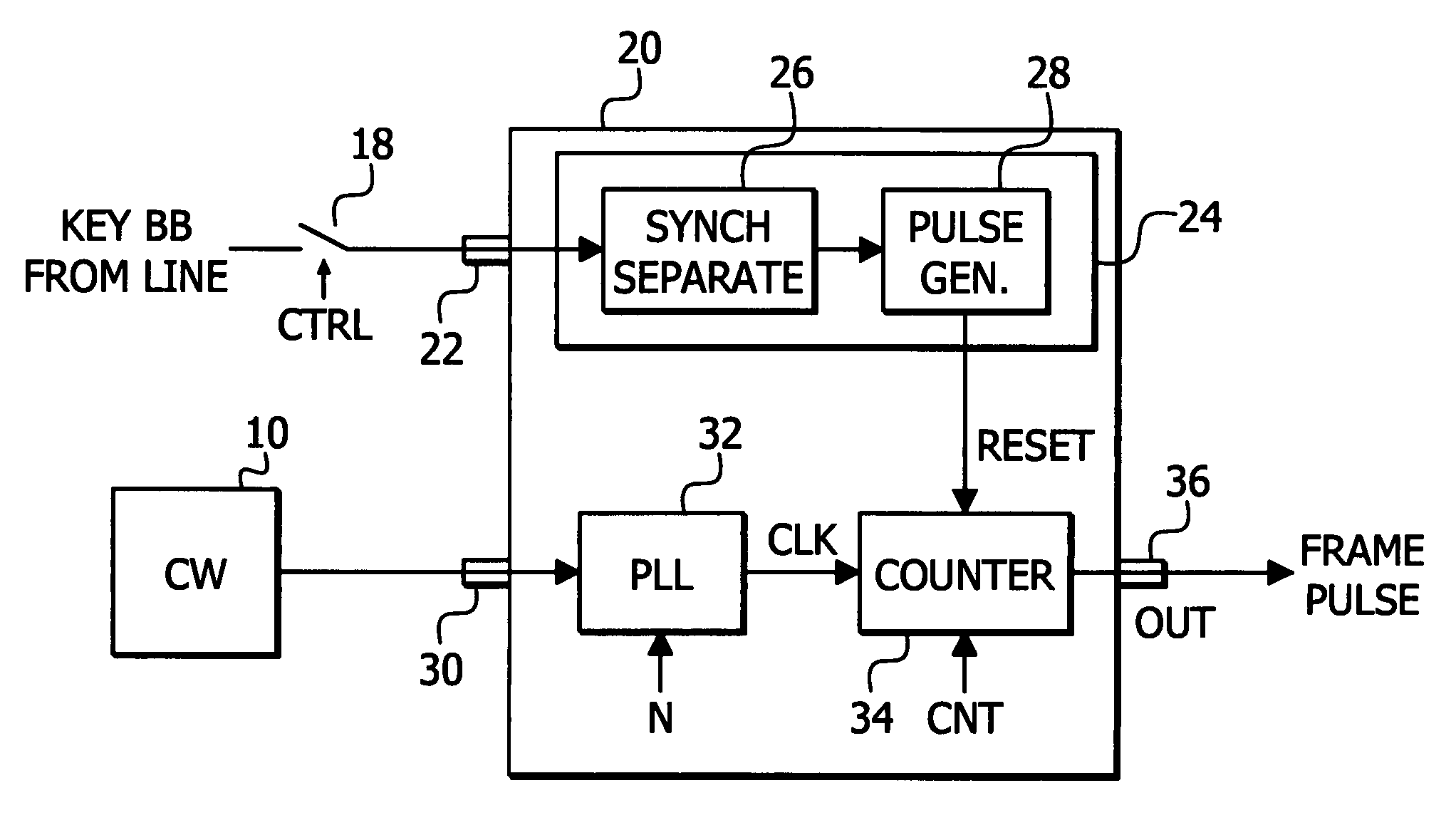
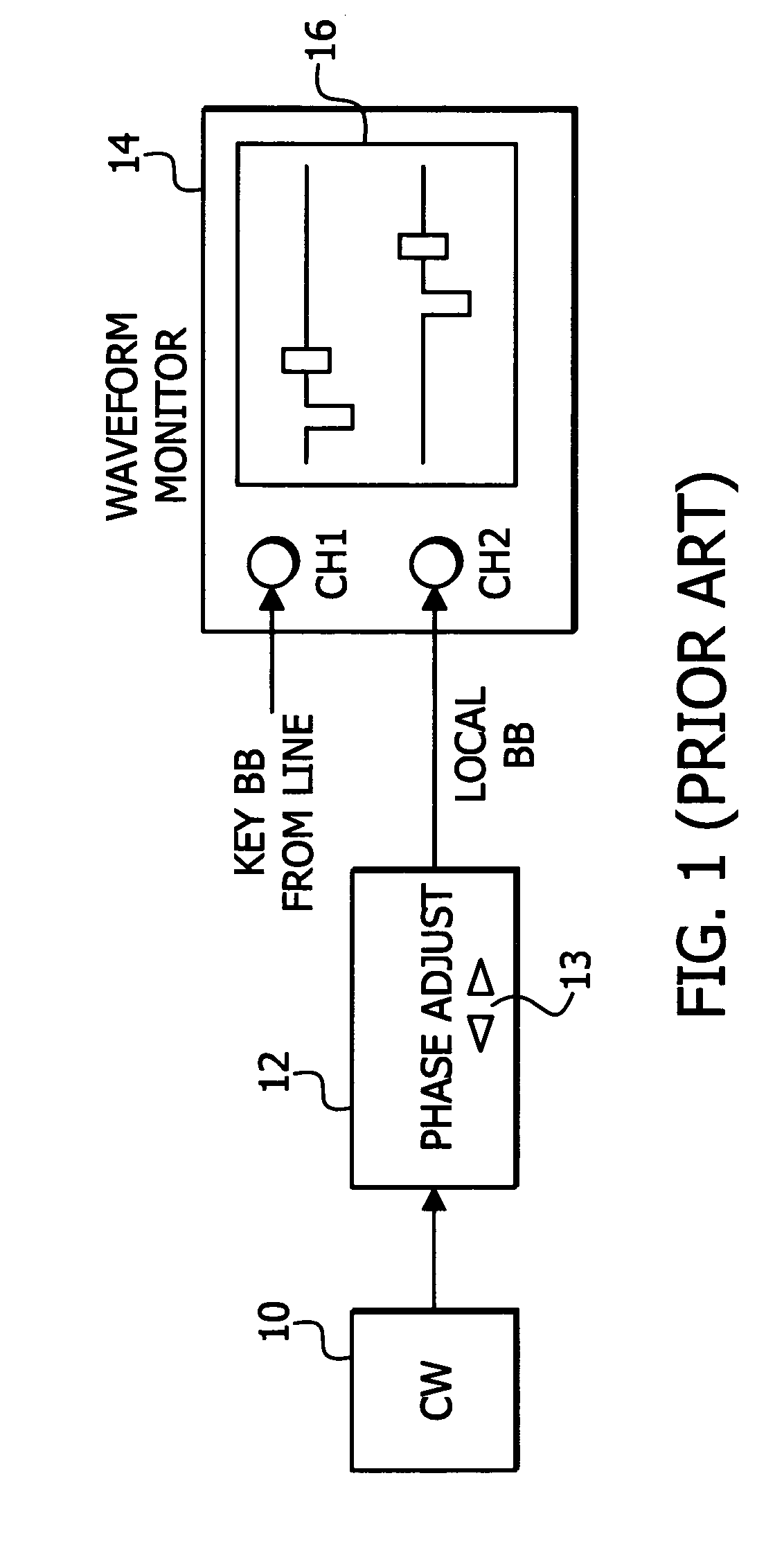
Method and apparatus for generating a reference television signal
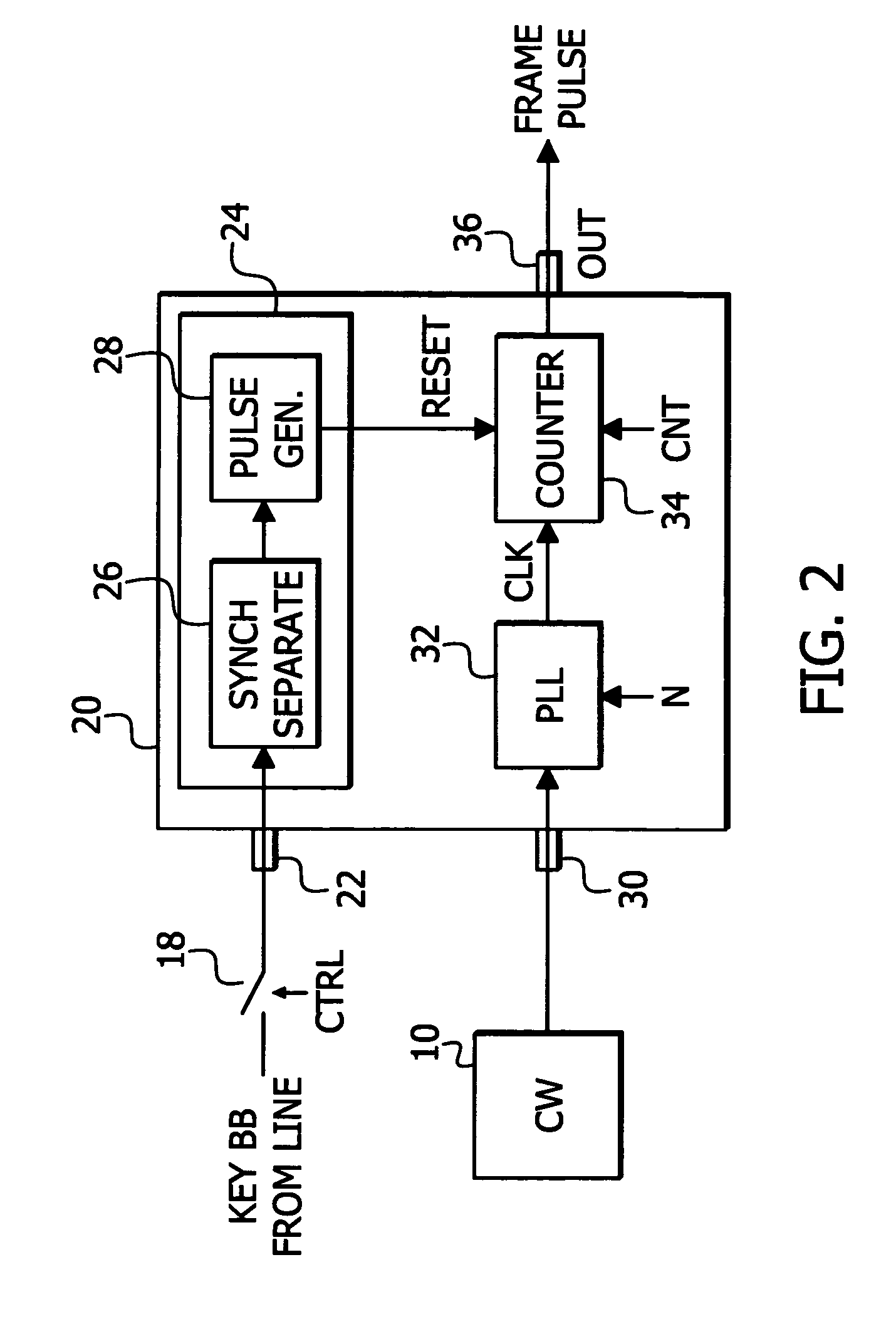
ActiveUS7764305B2Easy and accurate methodReduce operating costsTelevision system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionTelevision stationSignal generator
CW lock is conducted with less manual operation. A first input 22 receives a black burst (BB) signal from a key TV station. A second input 30 receives a continuous wave (CW) signal having an accurate, known frequency. A phase adjust signal generator 24 generates a reset signal having a known phase relationship with regard to the key TV station BB signal. The reset signal is used as a phase adjust signal. A PLL 32 receives the CW signal to provide clock. A counter 34 receives the clock and provides a frame pulse signal for synchronizing the key and local TV signals at a local TV station wherein the BB signal of the local station may be derived from the frame pulse signal. The counter 34 uses the reset signal to adjust the phase relationship between the key TV station BB signal and the frame pulse to a desired phase relationship based upon the key TV station BB signal.
Owner:PROJECT GIANTS LLC
Rugate induced transmission filter
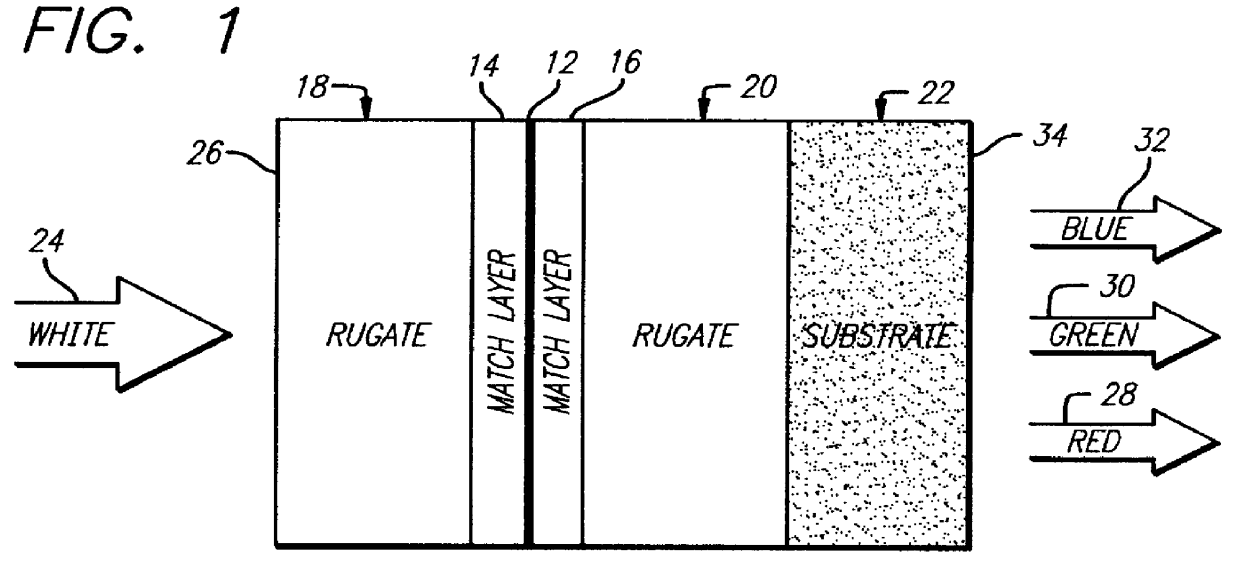
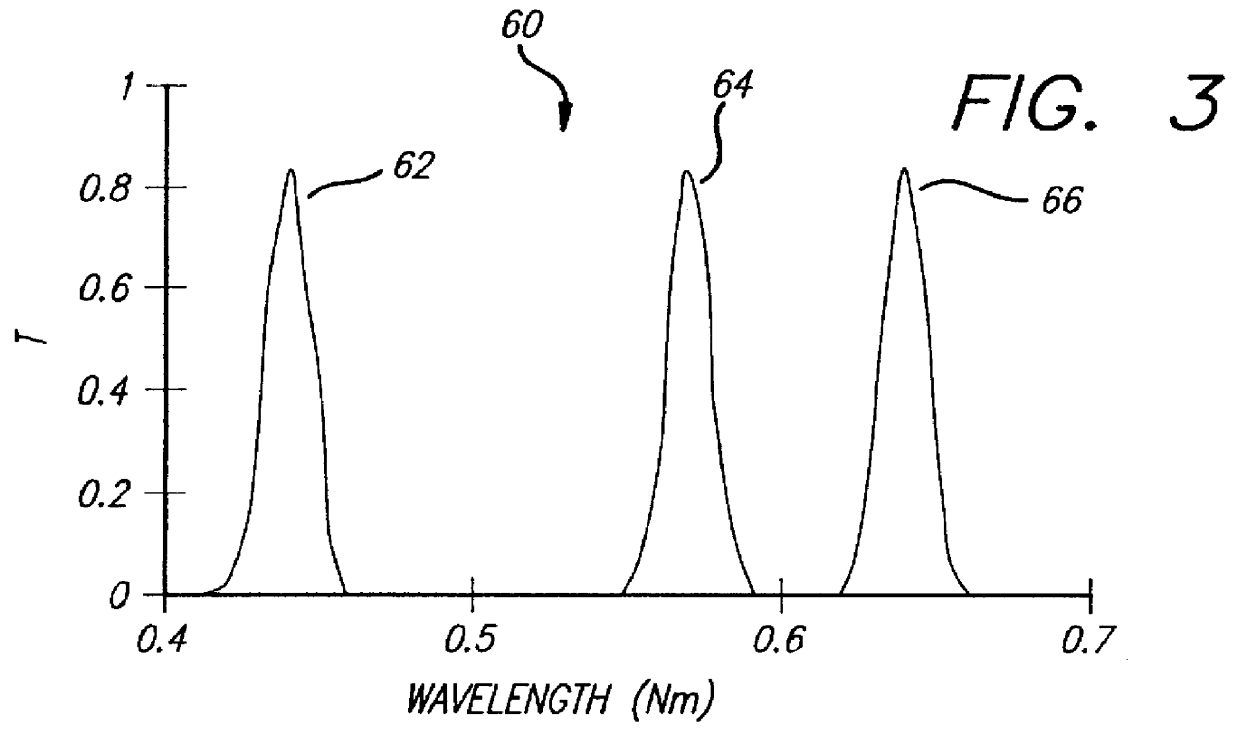
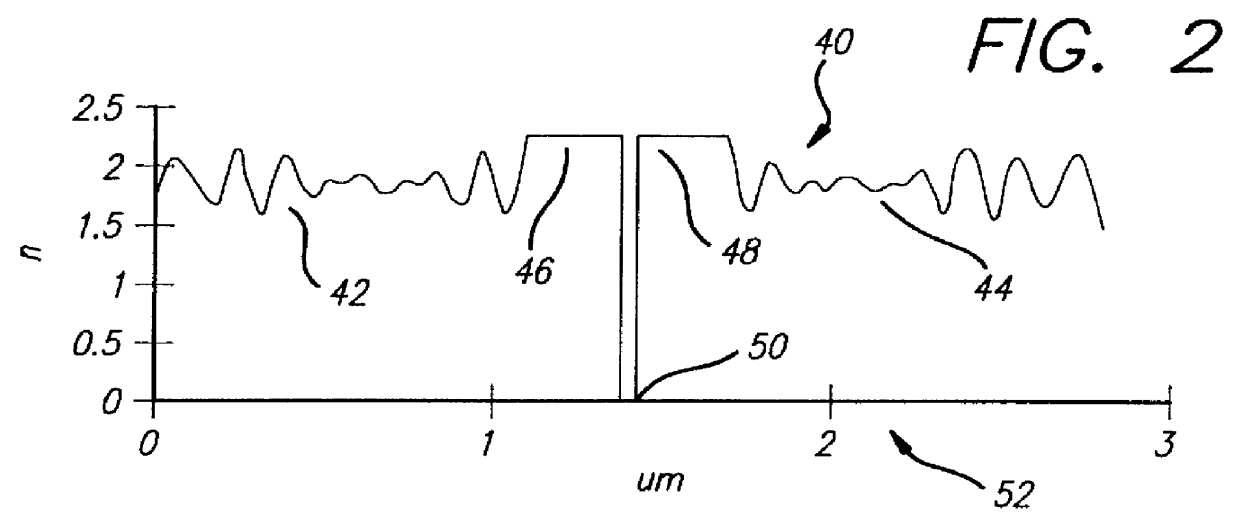
A filter (10) for selectively transmitting electromagnetic energy over a range of frequencies (28, 30, 32) adapted for use with white light (24). The filter (10) includes rugate layers (18, 20) for creating a resonant cavity that resonates at desired bandpass frequencies (28, 30, 32). An absorptive layer (12) absorbs frequencies near the bandpass frequencies (28, 30, 32) and reflects frequencies outside the bandpass frequencies (28, 30, 32). Phase matching layers (14, 16) allow the transmission of electromagnetic energy within the transmission bands (28, 30, 32) through the absorption layer 12. In an illustrative embodiment, the bandpass frequencies (28, 30, 32) comprise the three tristimulus frequencies, i.e., red (28), green (30) and blue (32) frequencies. The rugate layers (18, 20) include first (18) and second (20) rugate layers made of SiO2 and Ta2O5, respectively. Located between the first (18) and second (20) rugate layers is the absorption layer (12) that is surrounded by the first (14) and second (16) phase matching layers. The absorption layer (12) is a silver layer that is approximately 500 angstroms thick. The first rugate layer (18) has a first index of refraction versus layer thickness profile representing a superposition of sinusoids. Each sinusoid has a frequency directly corresponding to tristimulus band frequency. The second rugate layer (20) has a second index of refraction versus layer thickness profile that is a phase-adjusted version of the first index of refraction versus layer thickness profile. Both rugate layers (18, 20) have index or refraction versus layer thickness profiles have several cycles.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
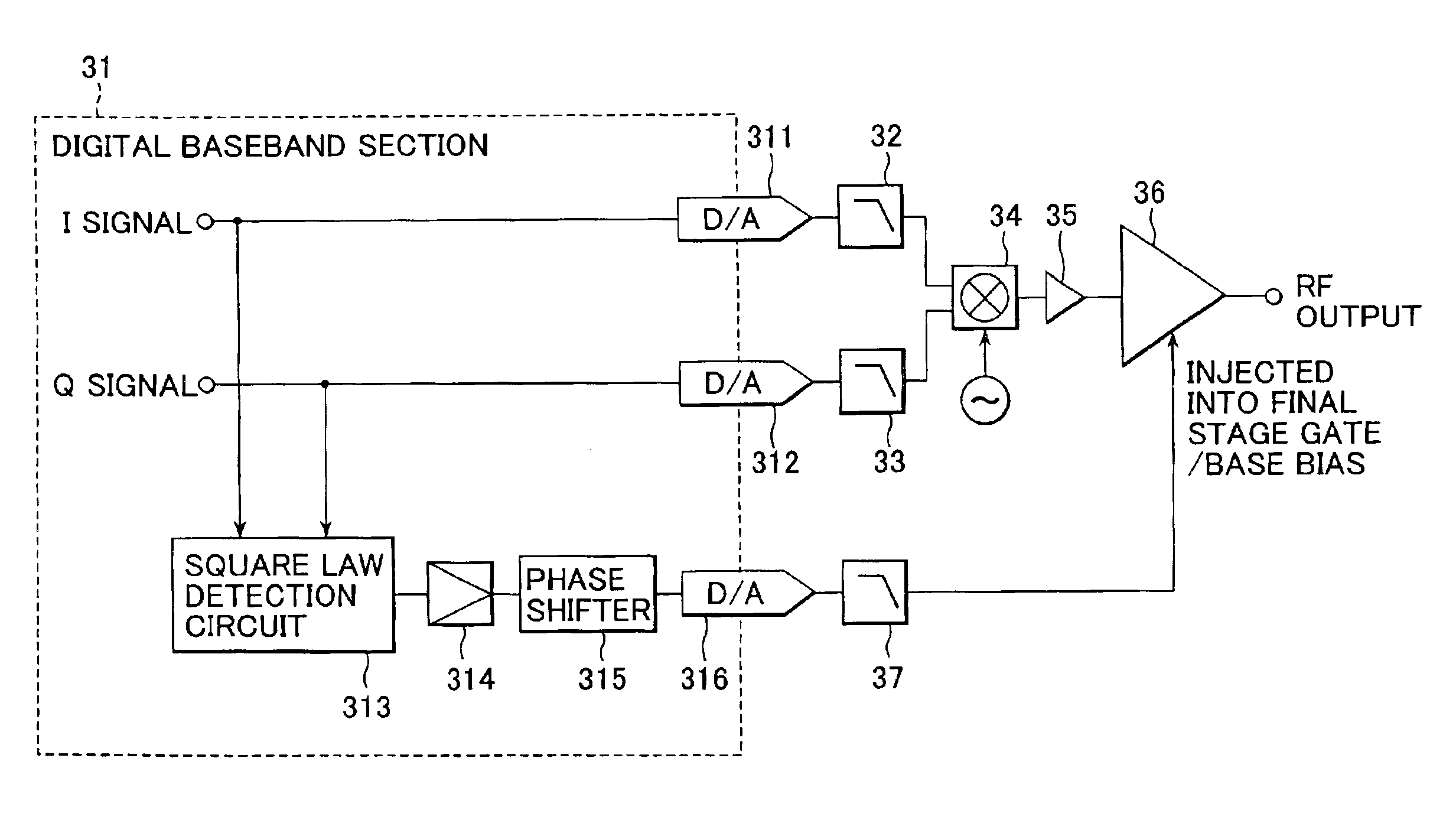
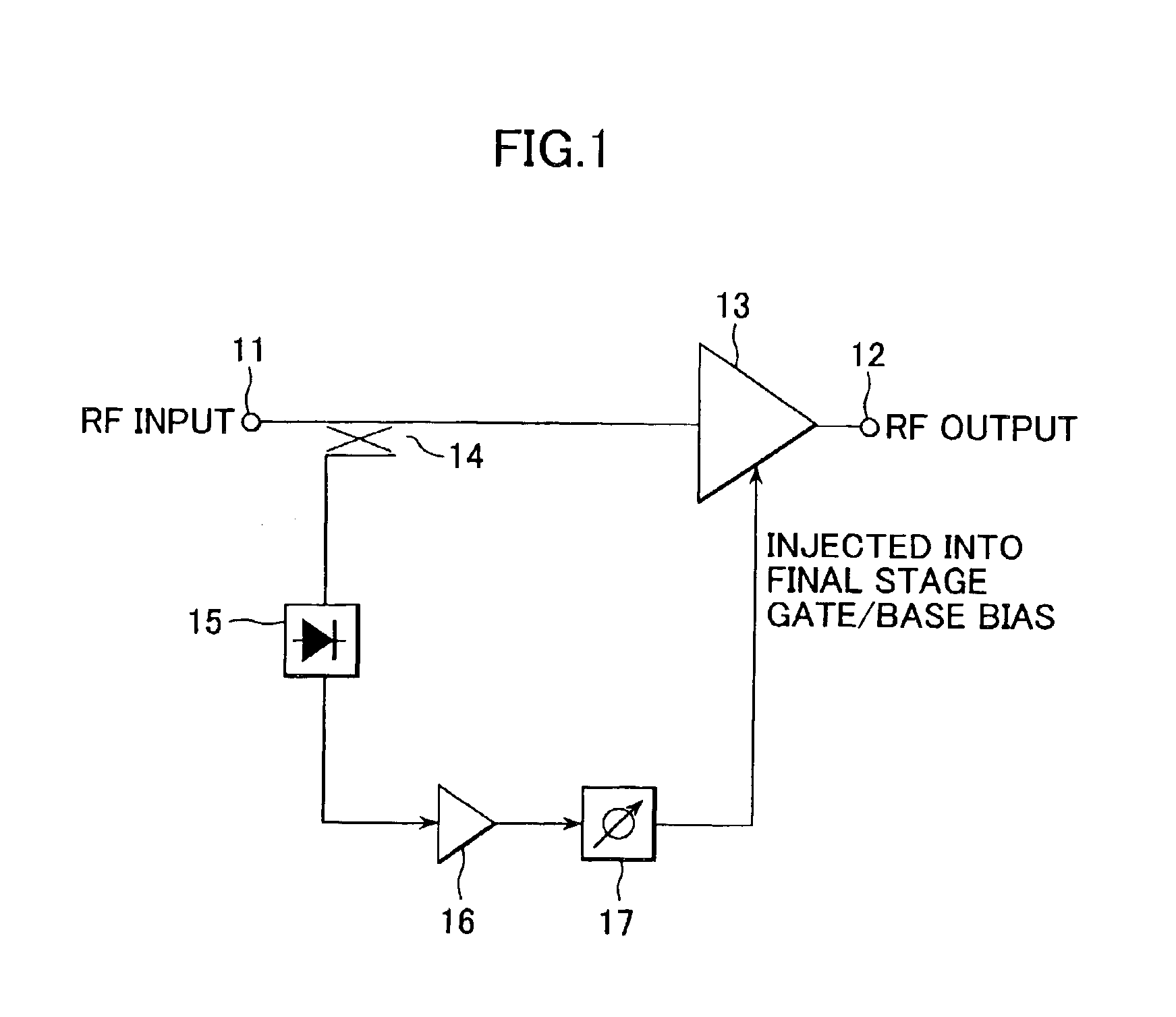
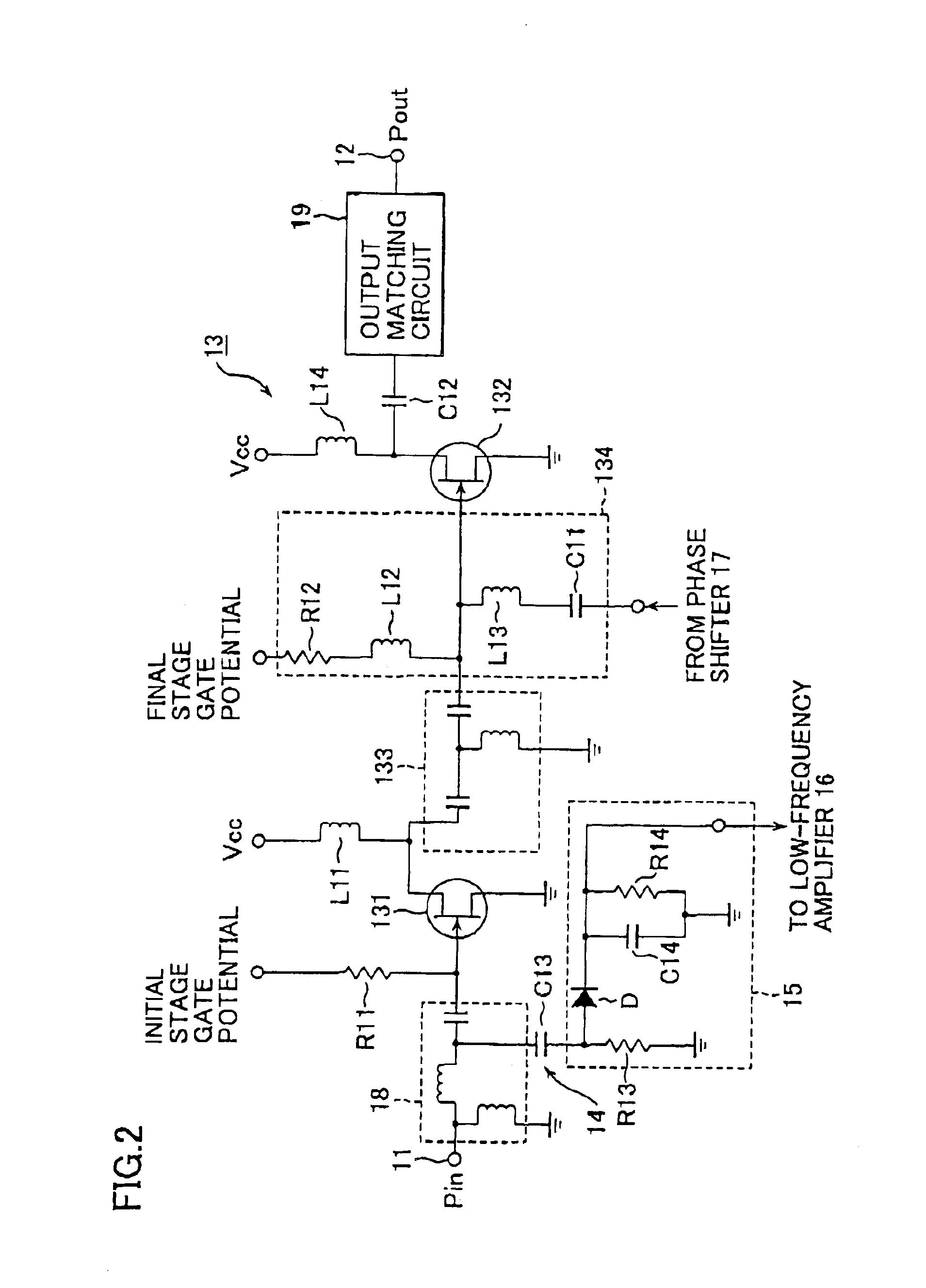
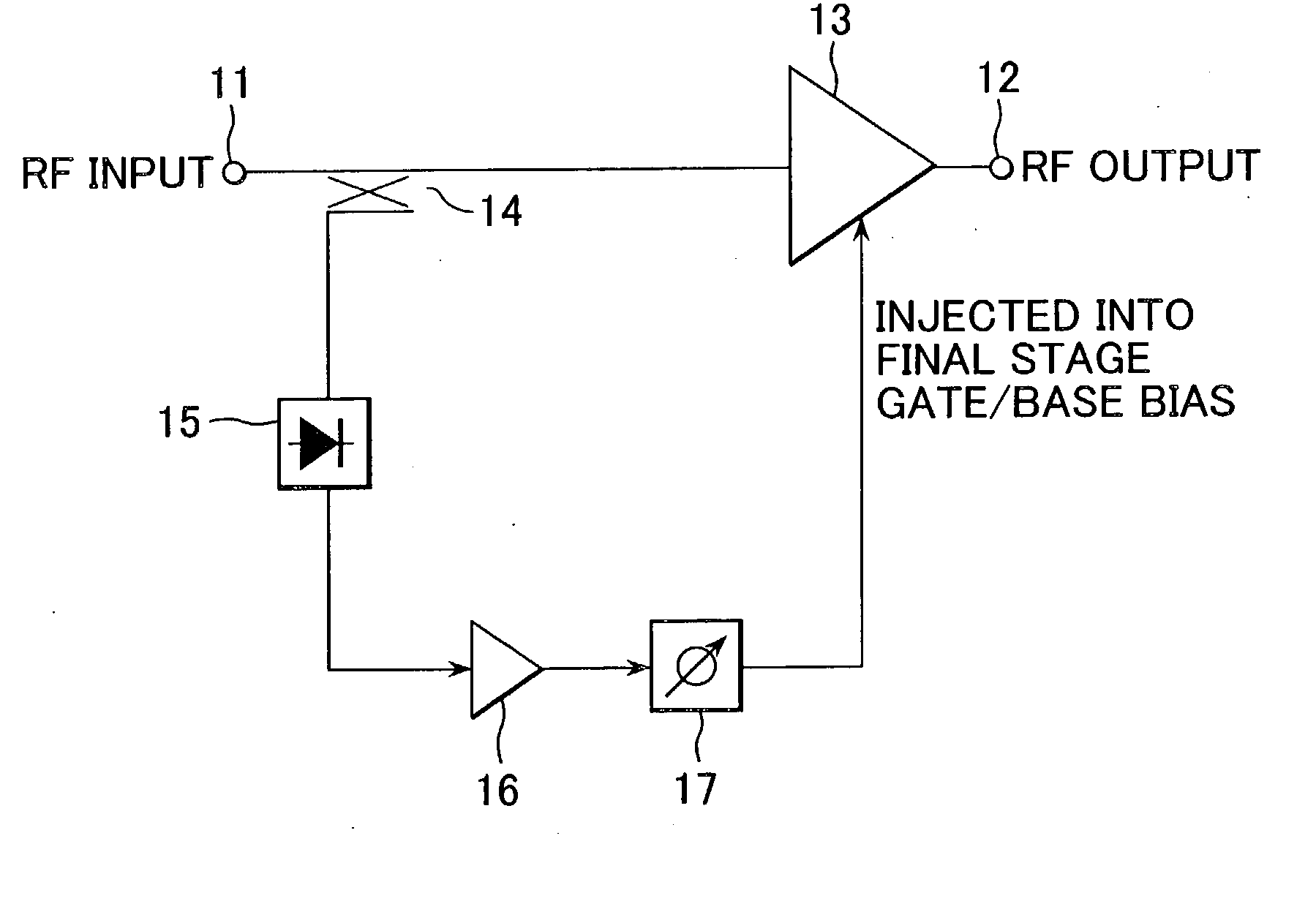
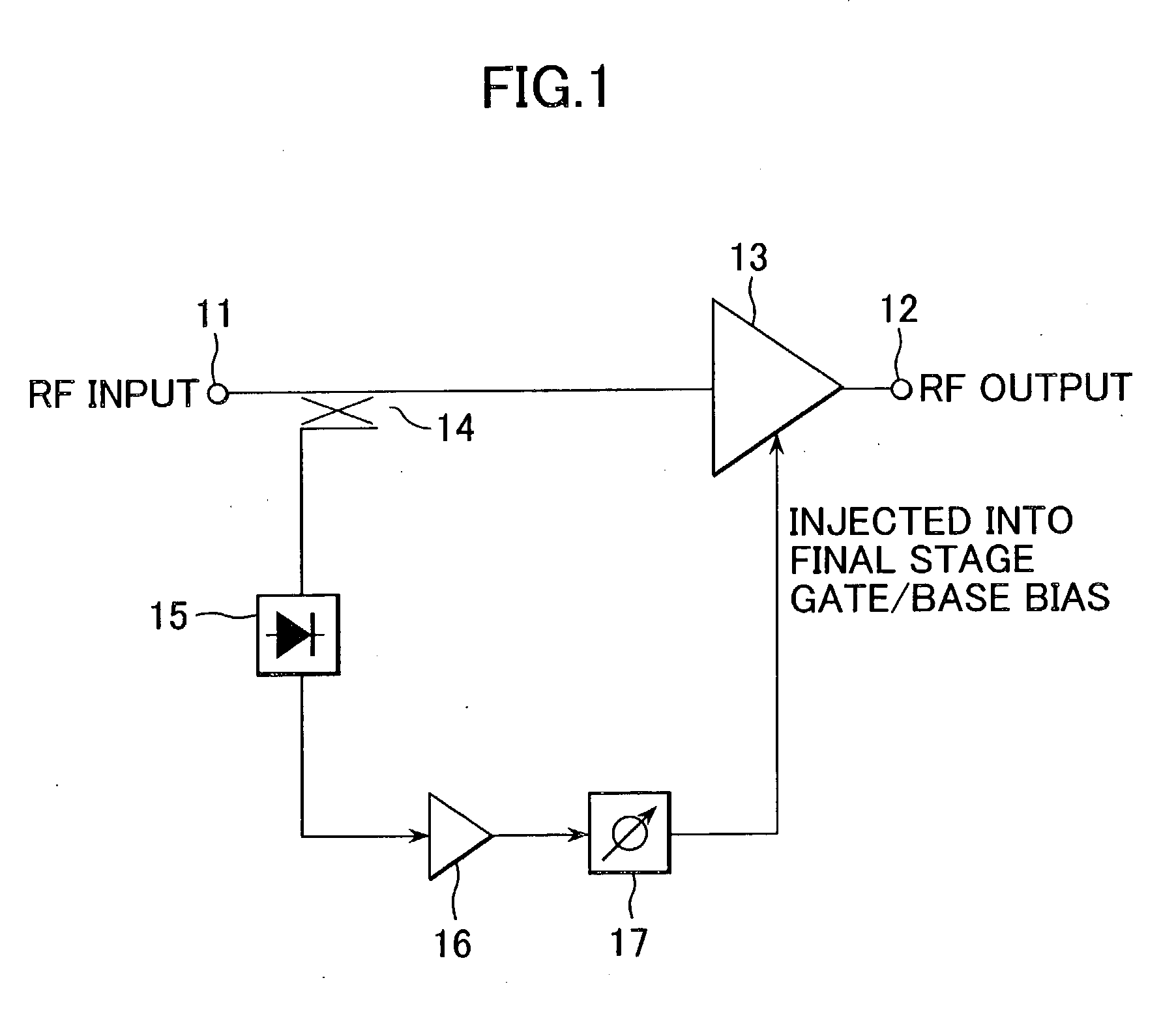
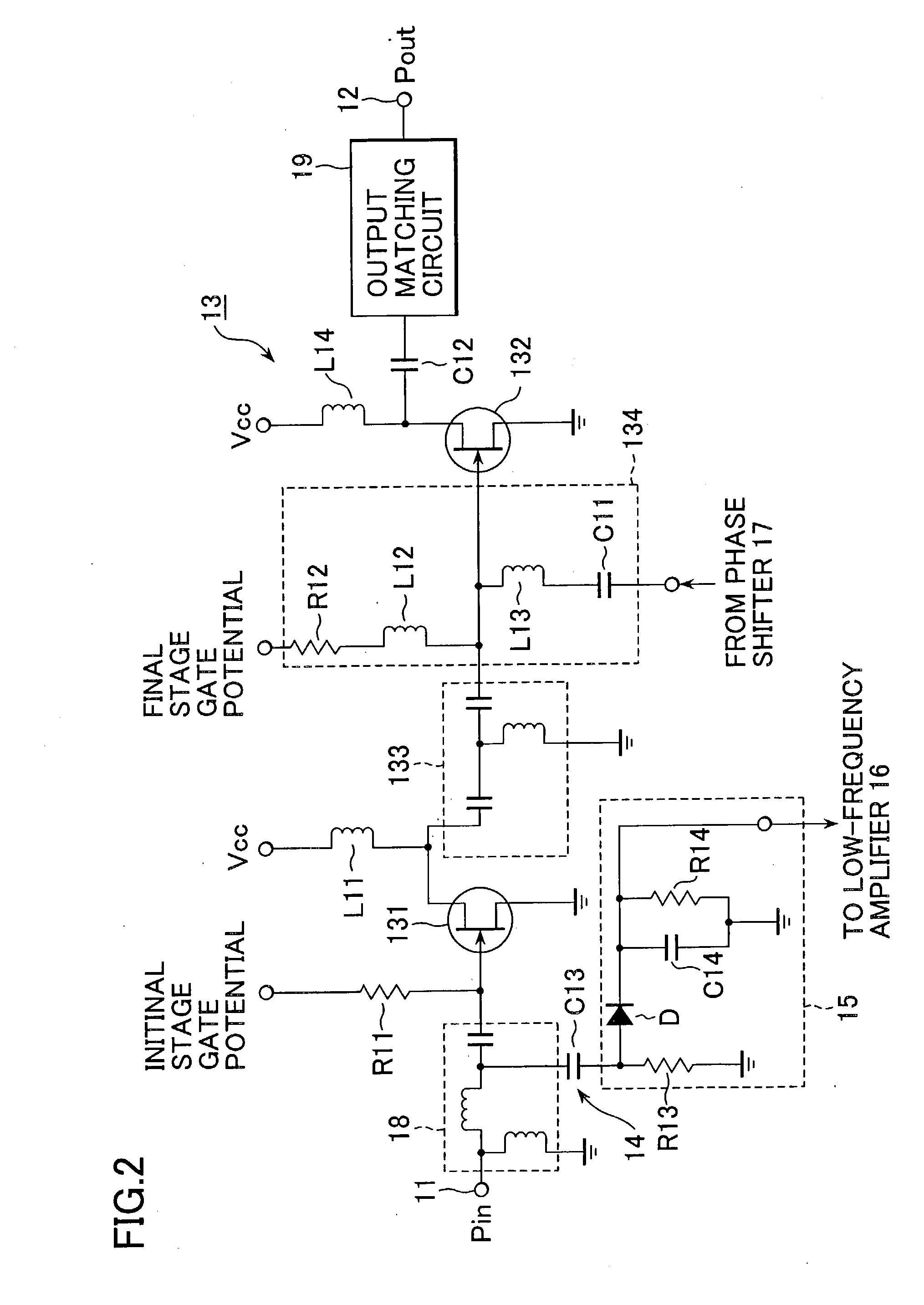
Power amplifying apparatus and radio communications apparatus using same
InactiveUS6900693B2Sufficient powerLow costAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlAudio power amplifierThird harmonic
By extracting a portion of RF signals from an input side of a multistage RF amplifier with a detector, and converting extracted signals into envelope signals, low-frequency second-harmonic distortion components are efficiently extracted. Then, the extracted low-frequency second-harmonic distortion components are amplified with a low-frequency amplifier, and phase adjusted with a phase shifter, after which they are injected into a gate or base bias of the final stage of the multistage RF amplifier. As a result, the low-frequency second-harmonic distortion components are converted into third-harmonic distortion due to the non-linearity of transistors, and the third-harmonic distortion thus obtained cancels out the third-harmonic distortion originally present in the multistage RF amplifier.
Owner:SONY CORP
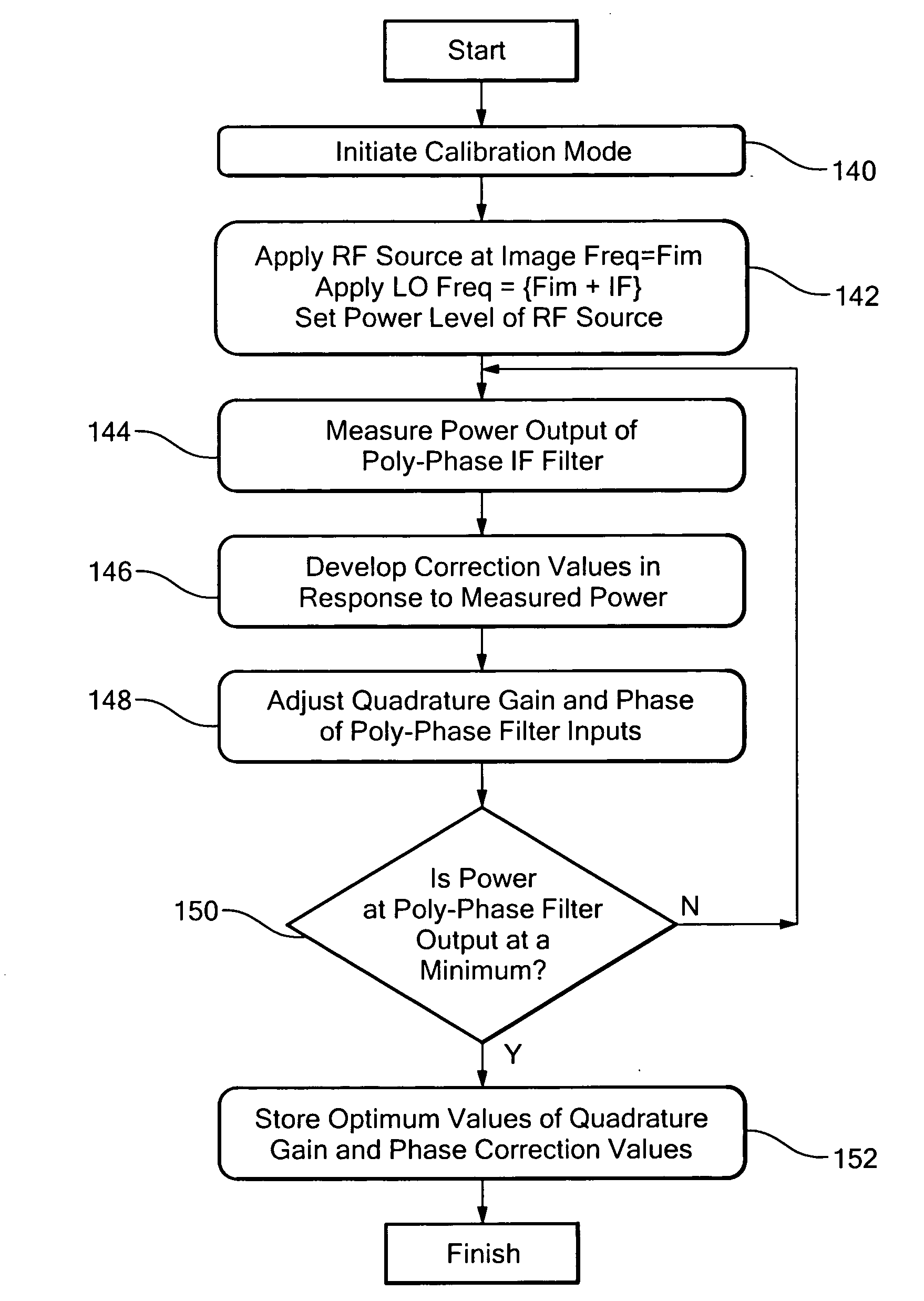
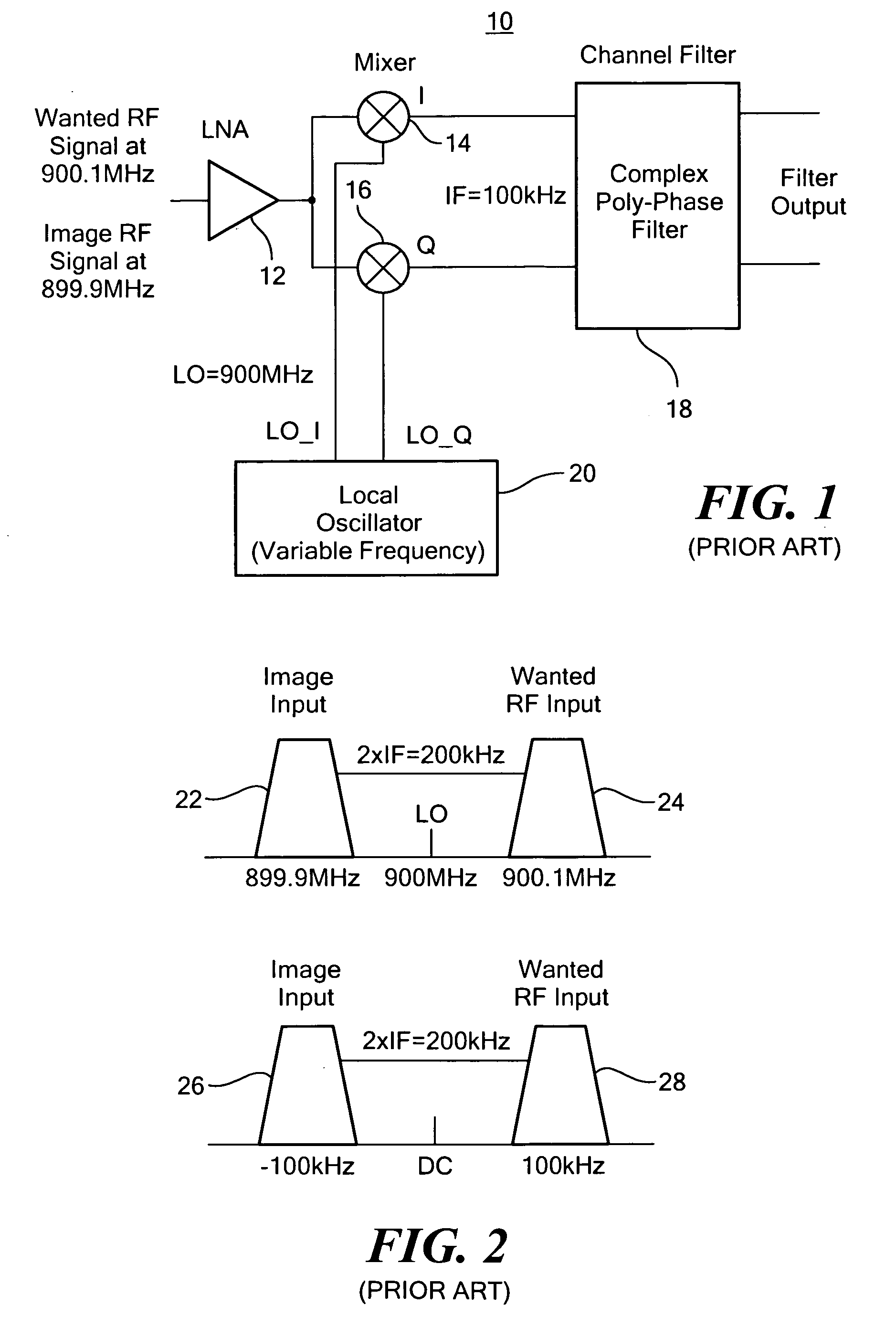
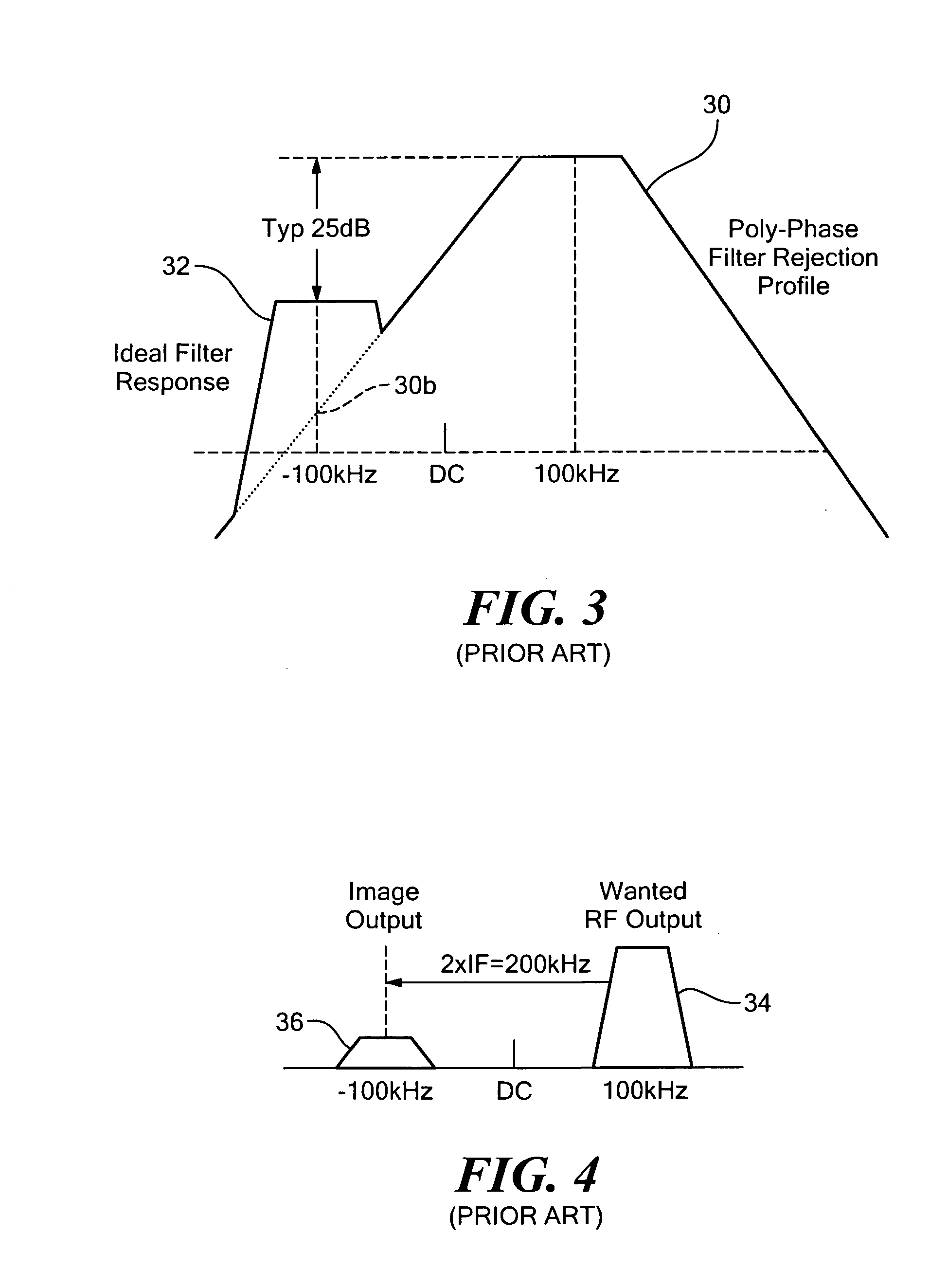
Image rejection calibration system
ActiveUS20080132191A1Improved image rejectionRadio transmissionFrequency-changer modificationsPhase filterLocal oscillator
Image rejection calibration includes initializing the calibration mode by applying to quadrature mixers, in place of the wanted RF input, an RF source in the frequency range of the wanted RF input, sensing the power output from the poly-phase filter, developing gain adjust and phase adjust correction values in response to the power output and adjusting in accordance with the correction values the gain of the quadrature signals from the quadrature mixers to the poly-phase filter and the phase of local oscillator quadrature signals from the local oscillator to the quadrature mixers to reduce the power output.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
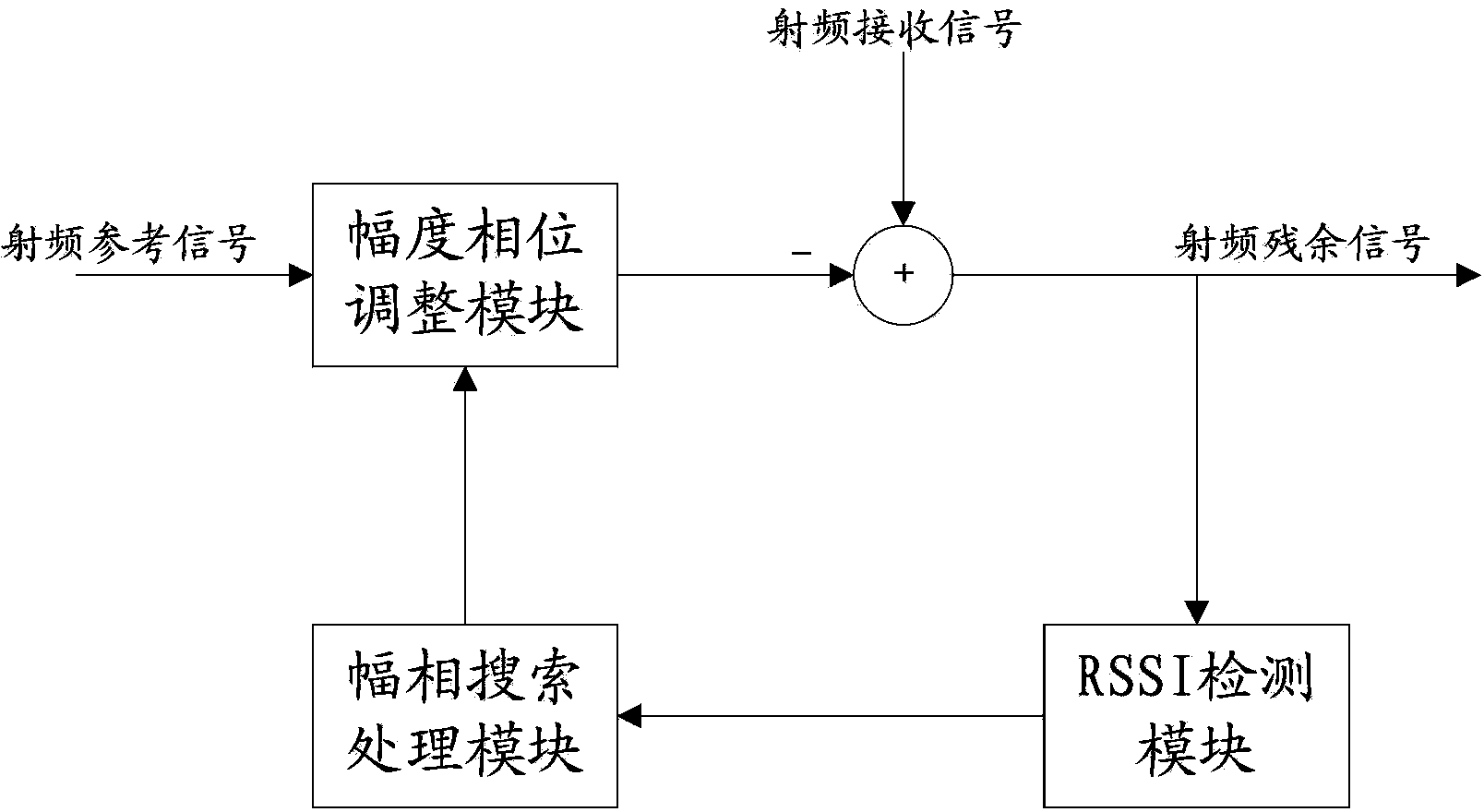
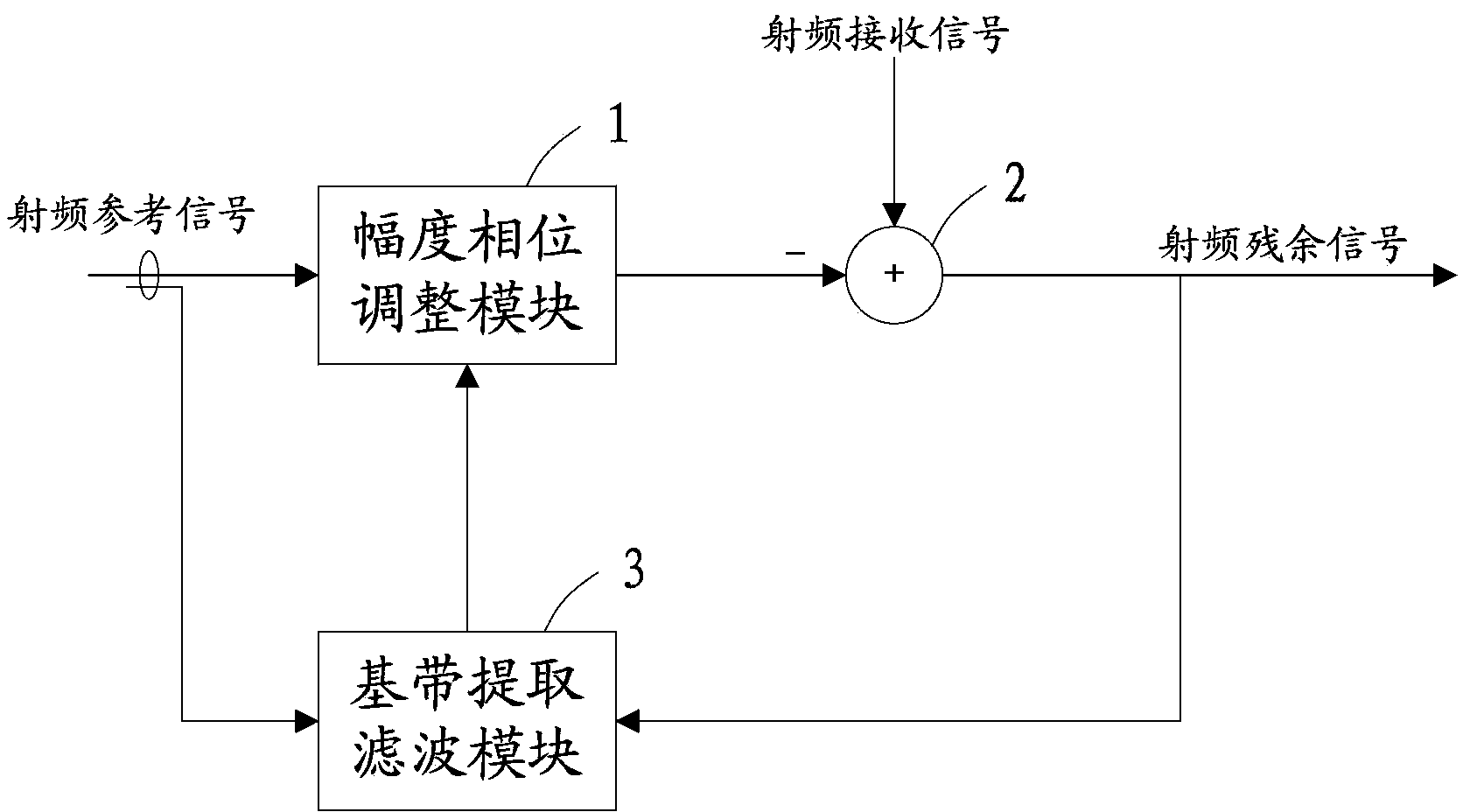
Self-adaption radio frequency interference offsetting device, method and receiver
ActiveCN103916148AFast convergenceEstimates are accurateTransmissionSelf interferenceFilter algorithm
The invention relates to the technical field of mobile communication and provides a self-adaption radio frequency interference offsetting device, method and receiver and a wireless full-duplex communication system. The device comprises an amplitude and phase adjusting module, a subtractor and a baseband extracting and filtering module. The amplitude and phase adjusting module is used for adjusting the amplitude and the phase of radio frequency reference signals and outputting radio frequency adjusting signals to enable the radio frequency adjusting signals to be collected in self-interference signals of radio frequency receiving signals. The subtractor is used for outputting radio frequency residue signals which are the difference value signals between the radio frequency receiving signals and the radio frequency reference signals. The baseband extracting and filtering module is used for receiving the radio frequency reference signals and radio frequency residue signals outputted from the subtractor and extracting the baseband signals. The baseband signals are processed in a minimum mean square self-adaption filtering mode to obtain amplitude phase control signals which are outputted to the amplitude and phase adjusting module. The self-adaption radio frequency interference offsetting device, method and receiver adopt an LMS self-adaption filtering algorithm, so that the convergence rate is higher and the estimation results are more accurate.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
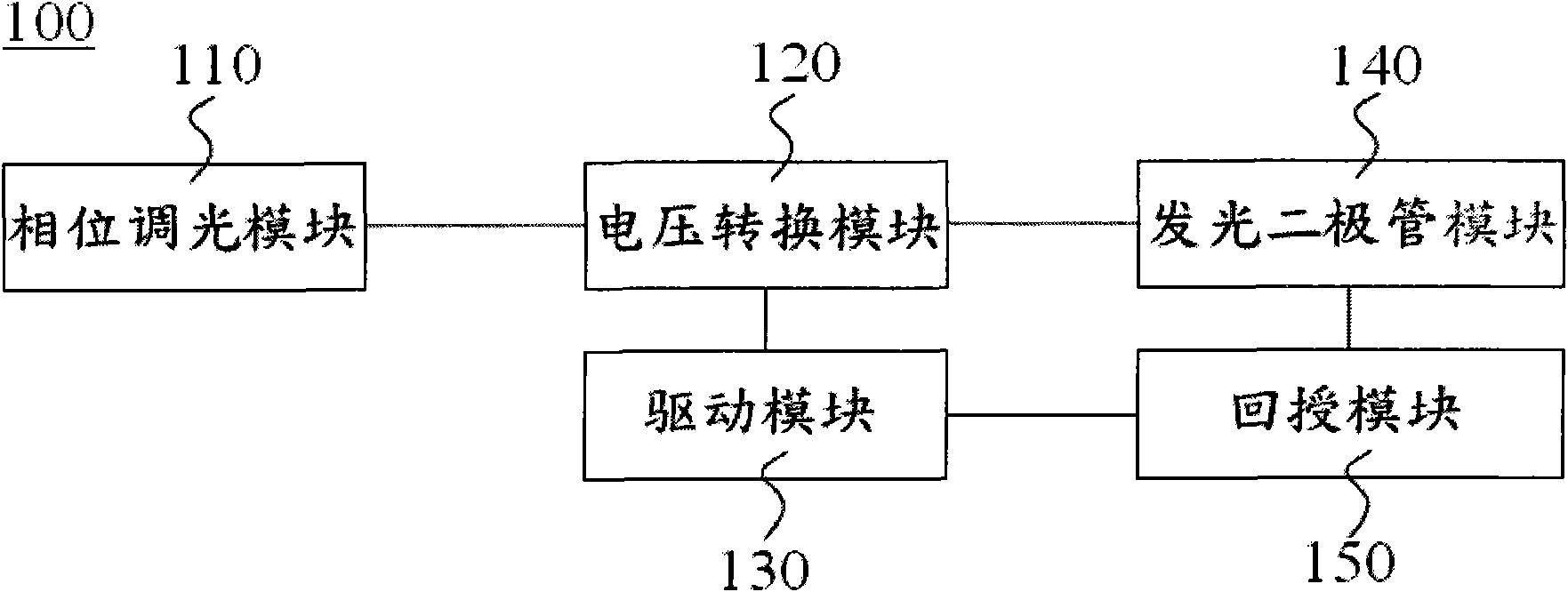
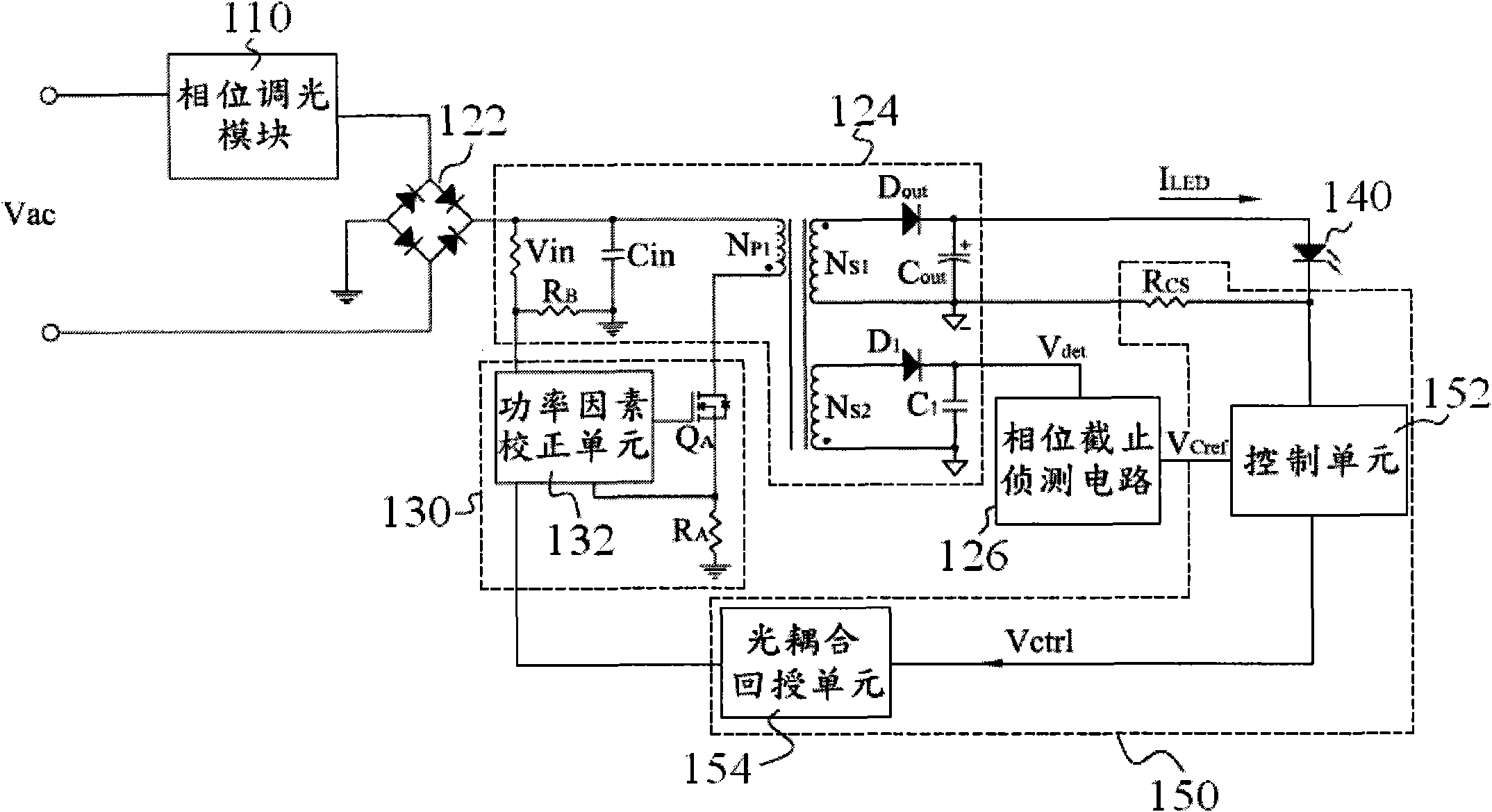
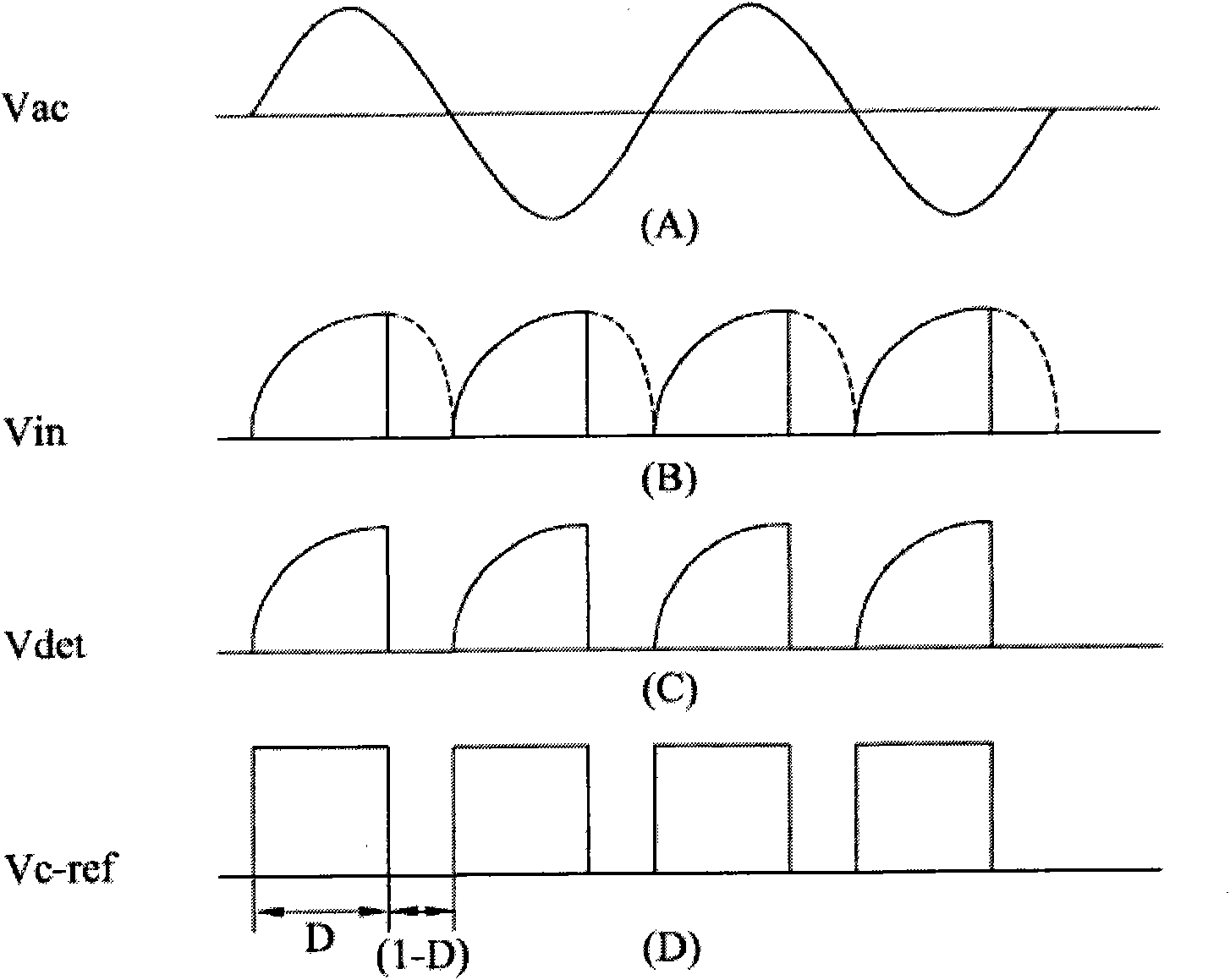
Dimmable light-emitting diode device used for reducing output ripple current and driving circuit thereof
InactiveCN101938865AReduce Ripple ComponentsStable light outputElectric light circuit arrangementPower conversion systemsEngineeringConductor Coil
The invention discloses a dimmable light-emitting diode device used for reducing output ripple current, which comprises a light-emitting diode module, a phase tuning module, a voltage conversion module, a driver module and a feedback module. A flyback converter in the voltage conversion module is provided with a secondary clockwise winding and a phase cutoff sensing circuit so as to provide sensing voltage serving as an output current reference standard of the light-emitting diode module. The dimmable light-emitting diode device can make the flayback converter with the phase dimming function greatly increase output capacity and reduce the output ripple current, so that the light-emitting diode has stable light output. Therefore, the dimmable light-emitting diode device can prolong the service life of the dimmable light-emitting diode and prevent a light source flicker index from changing low.
Owner:PHIHONG TECH CO LTD
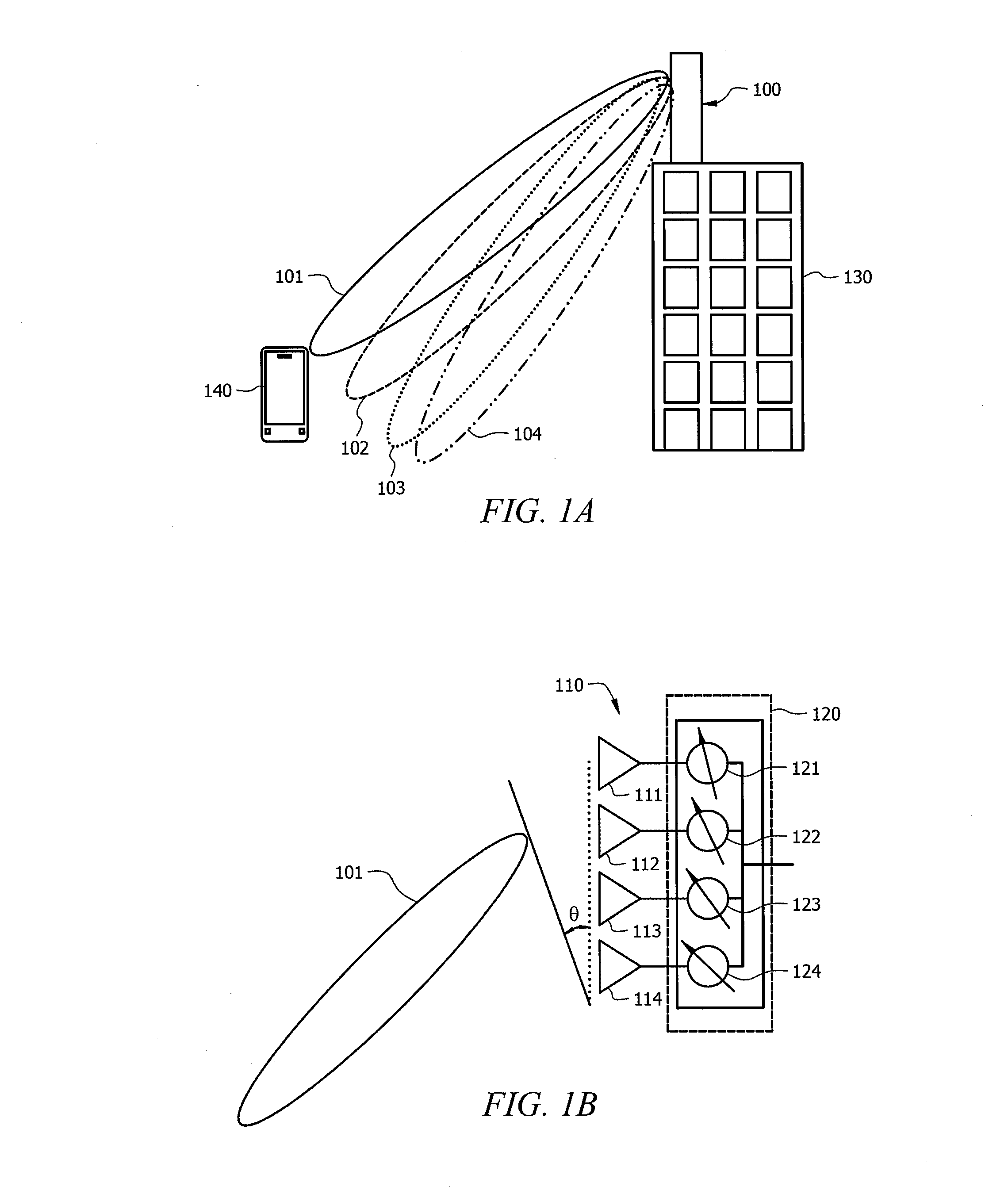
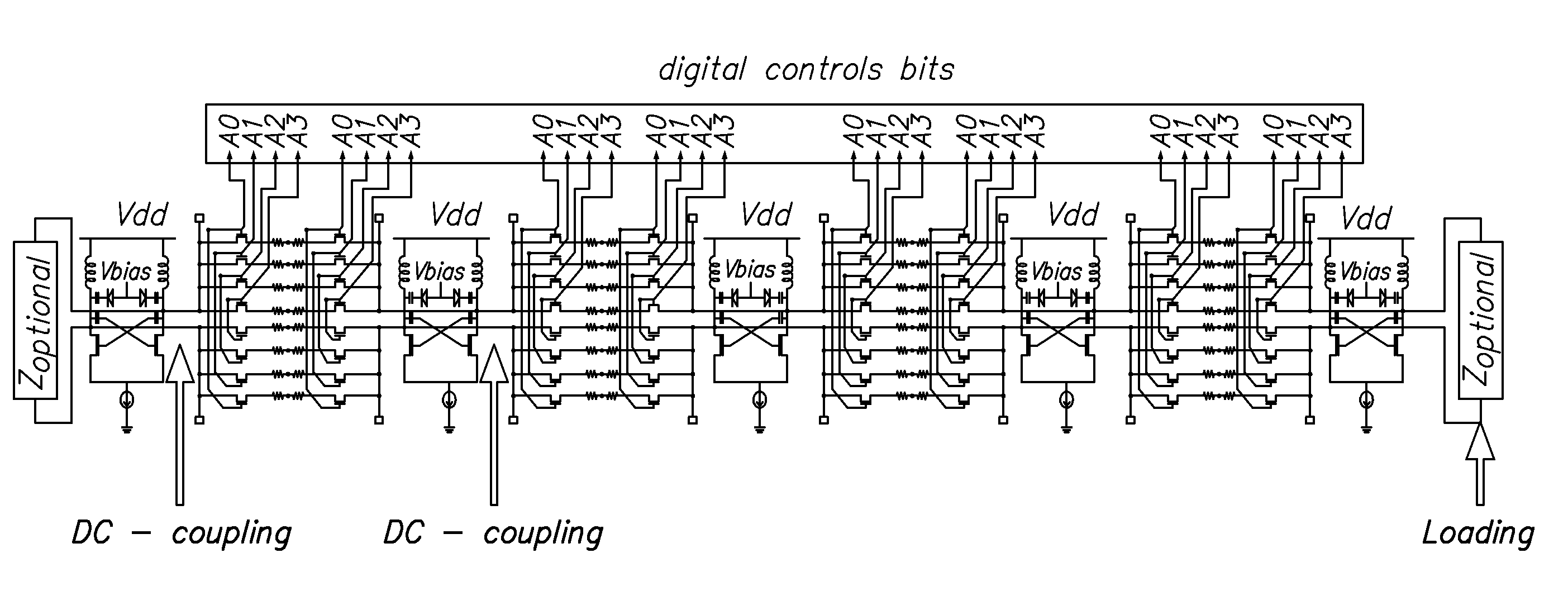
Cellular base station antenna
InactiveUS20020126059A1Antenna supports/mountingsAntenna equipments with additional functionsElectrical and Electronics engineeringPhase tuning
An antenna assembly for emitting a signal. The antenna assembly includes at least two antennas which are separated into a first group and a second group. Both groups of antennas are mounted on a panel. A first phase adjuster is coupled to the first antenna group. The first phase adjuster is also coupled to a second phase adjuster, which is also coupled to said second antenna group. The first phase adjuster is coupled to the second phase adjuster, such that an adjustment of the first phase adjuster causes an adjustment of the second phase adjuster. The first phase adjuster is adapted to adjust a phase angle of the signal of the first antenna group, while the second phase adjuster is adapted to adjust a phase angle of the signal of said second antenna group.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
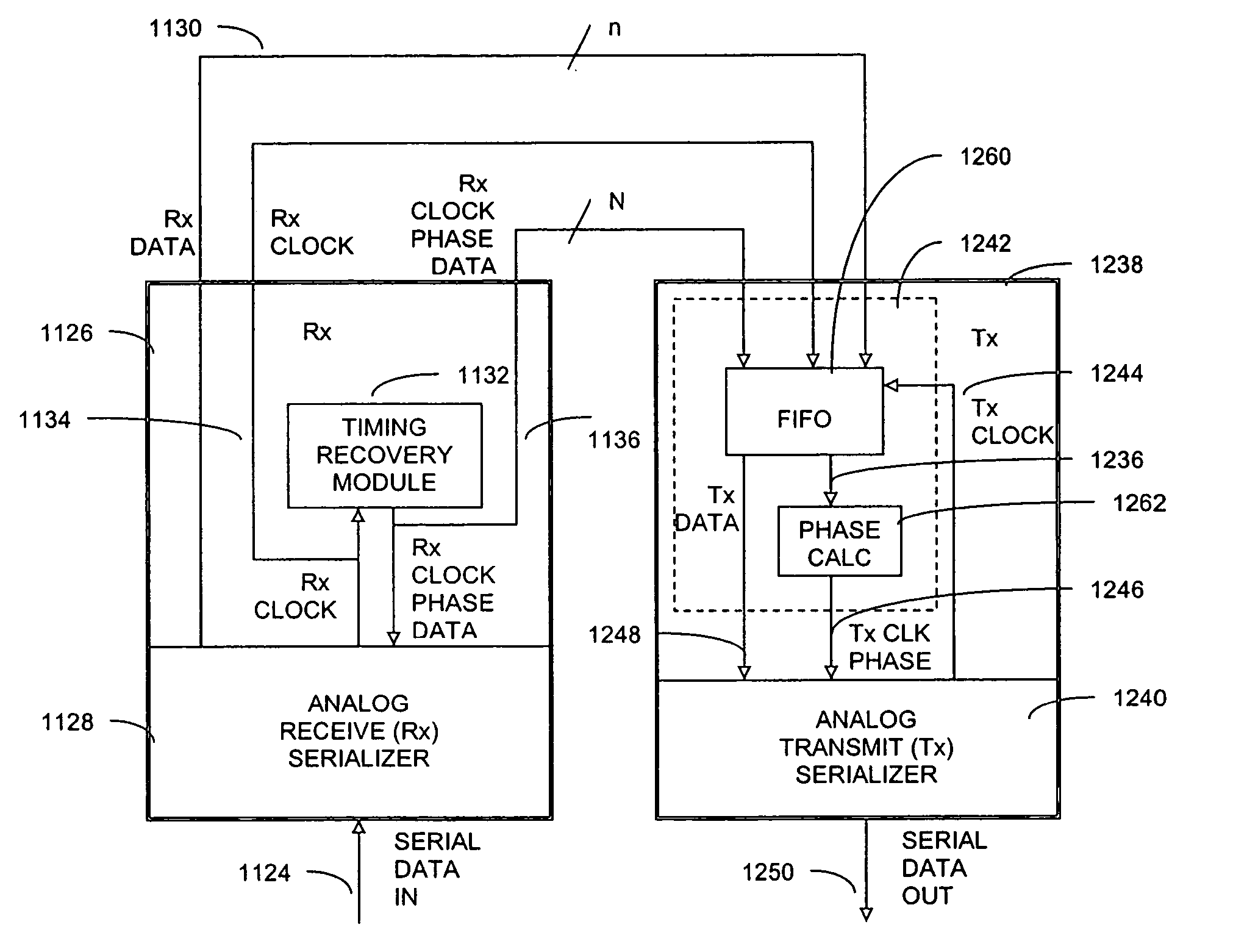
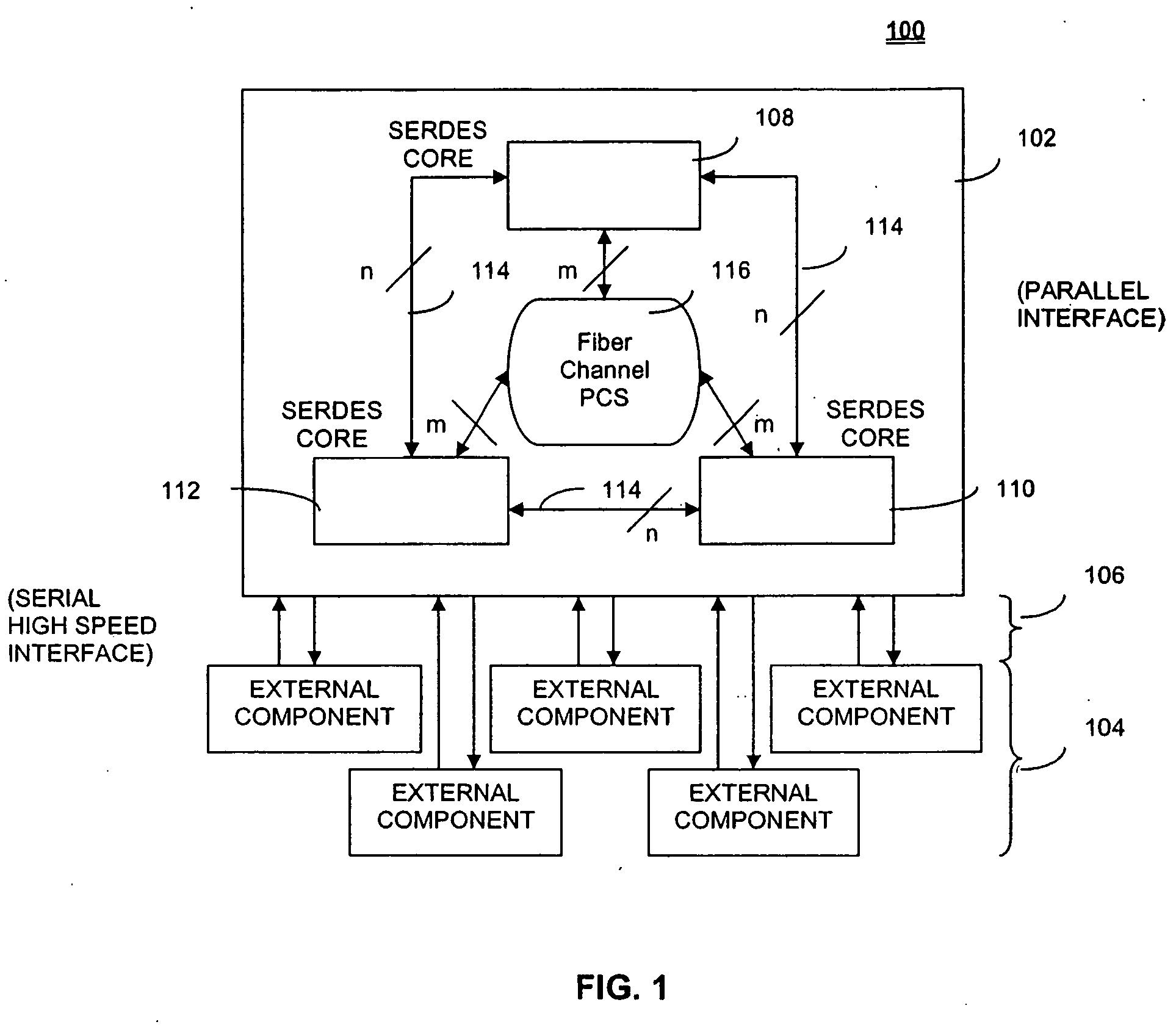
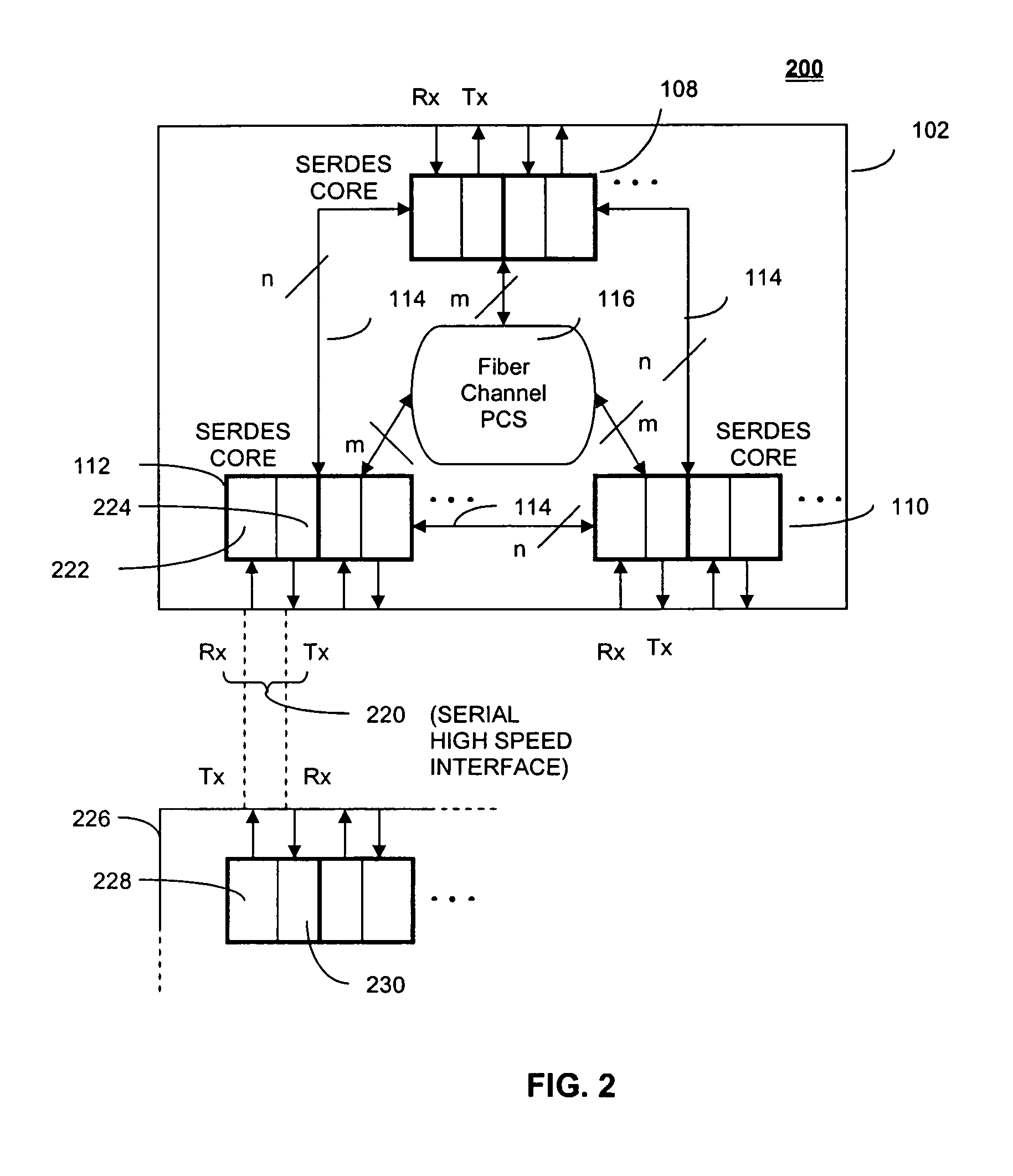
System and method of phase-locking a transmit clock signal phase with a receive clock signal phase
ActiveUS20050169417A1Parallel/series conversionSynchronisation information channelsPhase differenceTransmission channel
Systems and methods for synchronizing a receive clock signal phase with a transmit clock signal phase are presented. A system includes a receiving channel and a transmitting channel, wherein the transmitting channel synchronizes a transmit clock signal phase with a receive clock signal phase based on receive clock signal phase data. A method includes storing a previous receive clock signal phase of a receiving channel and identifying a current receive clock signal phase of the receiving channel. The method further includes determining a phase difference between the previous receive clock signal phase and the current receive clock signal phase, and identifying a direction of the phase difference between the previous receive clock signal phase and the current receive clock signal phase. The method further includes adjusting a previous transmit clock signal phase of the transmitting channel to a current transmit clock signal phase of the transmitting channel based on the phase difference and direction.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
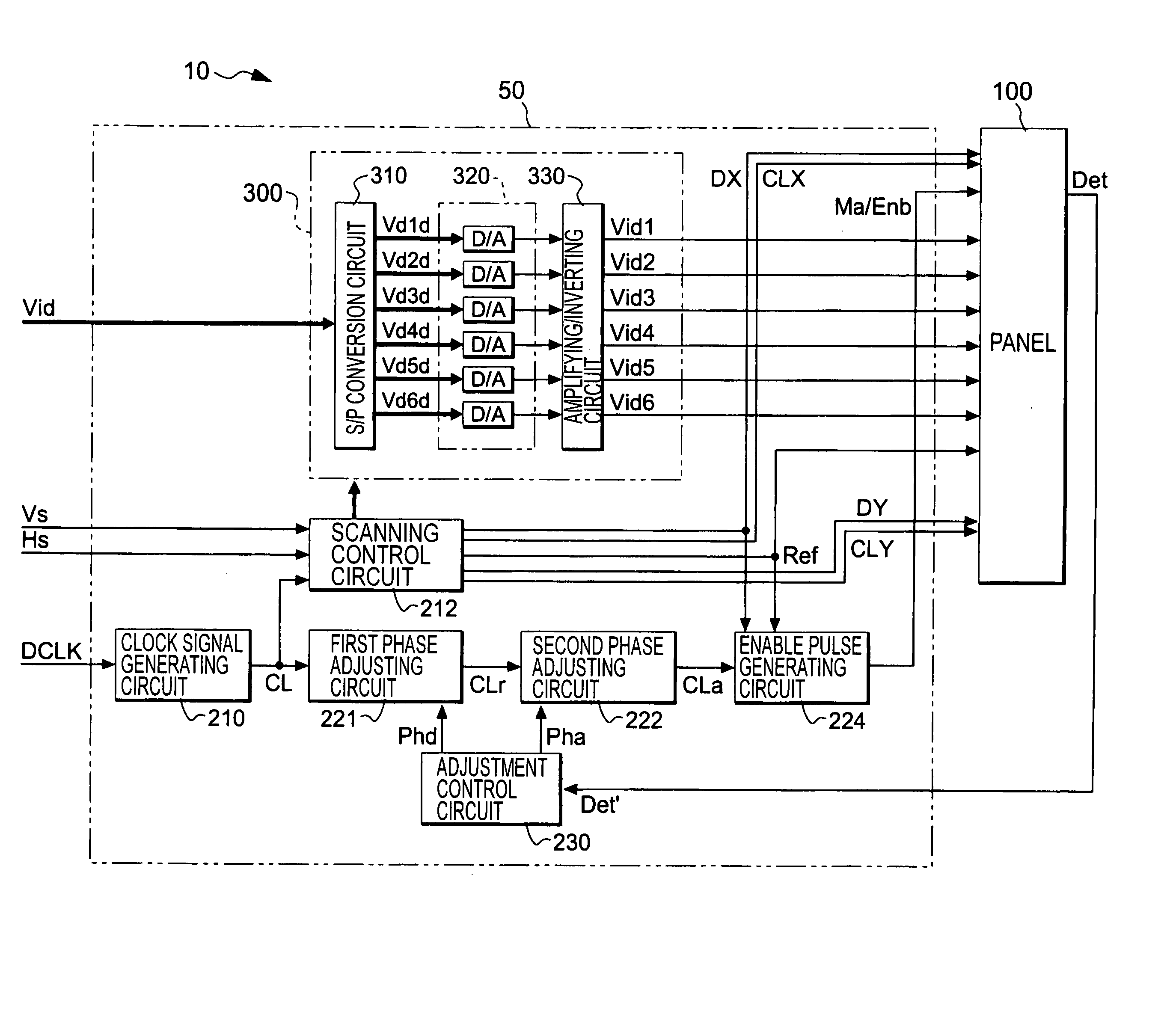
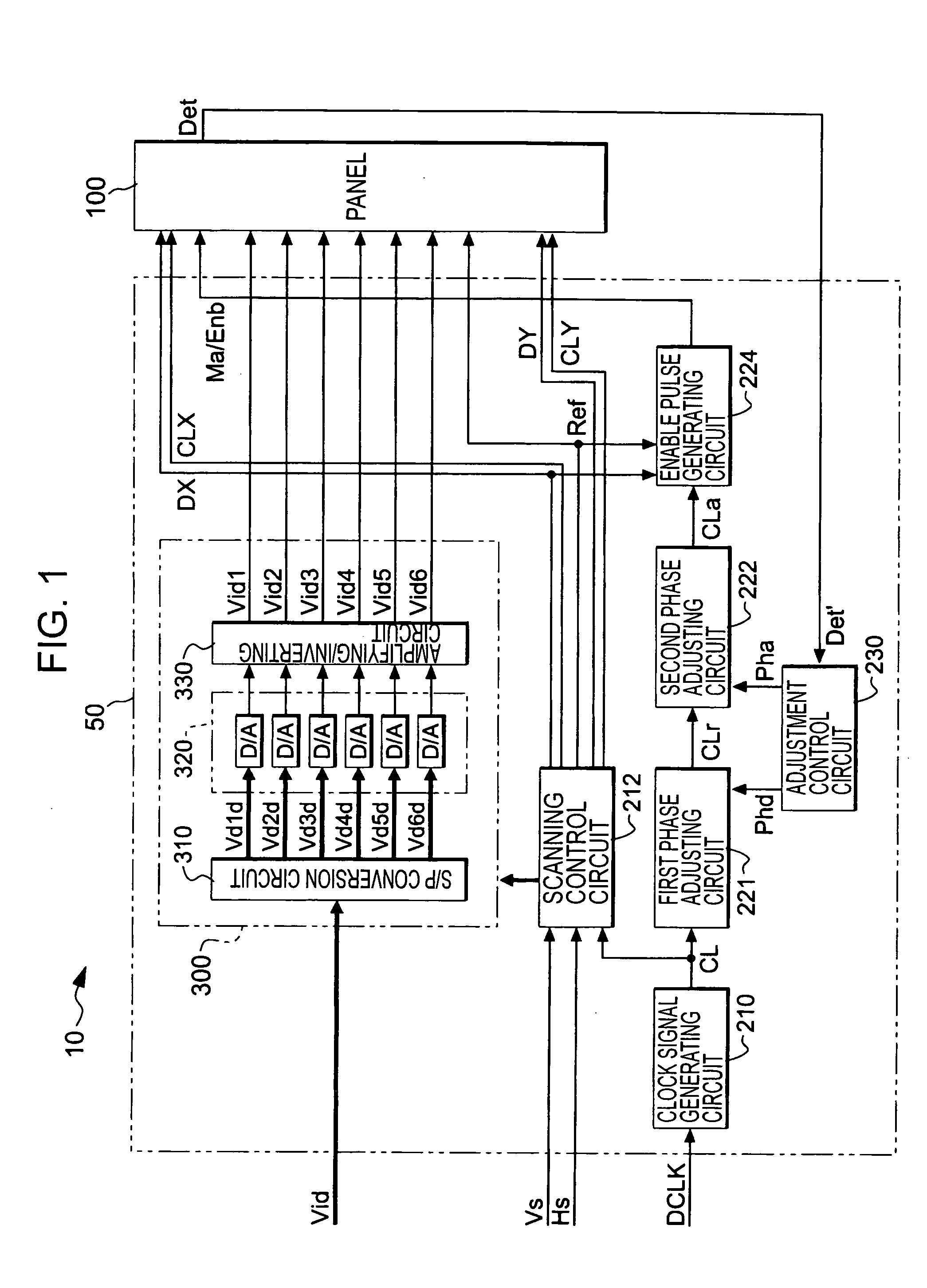
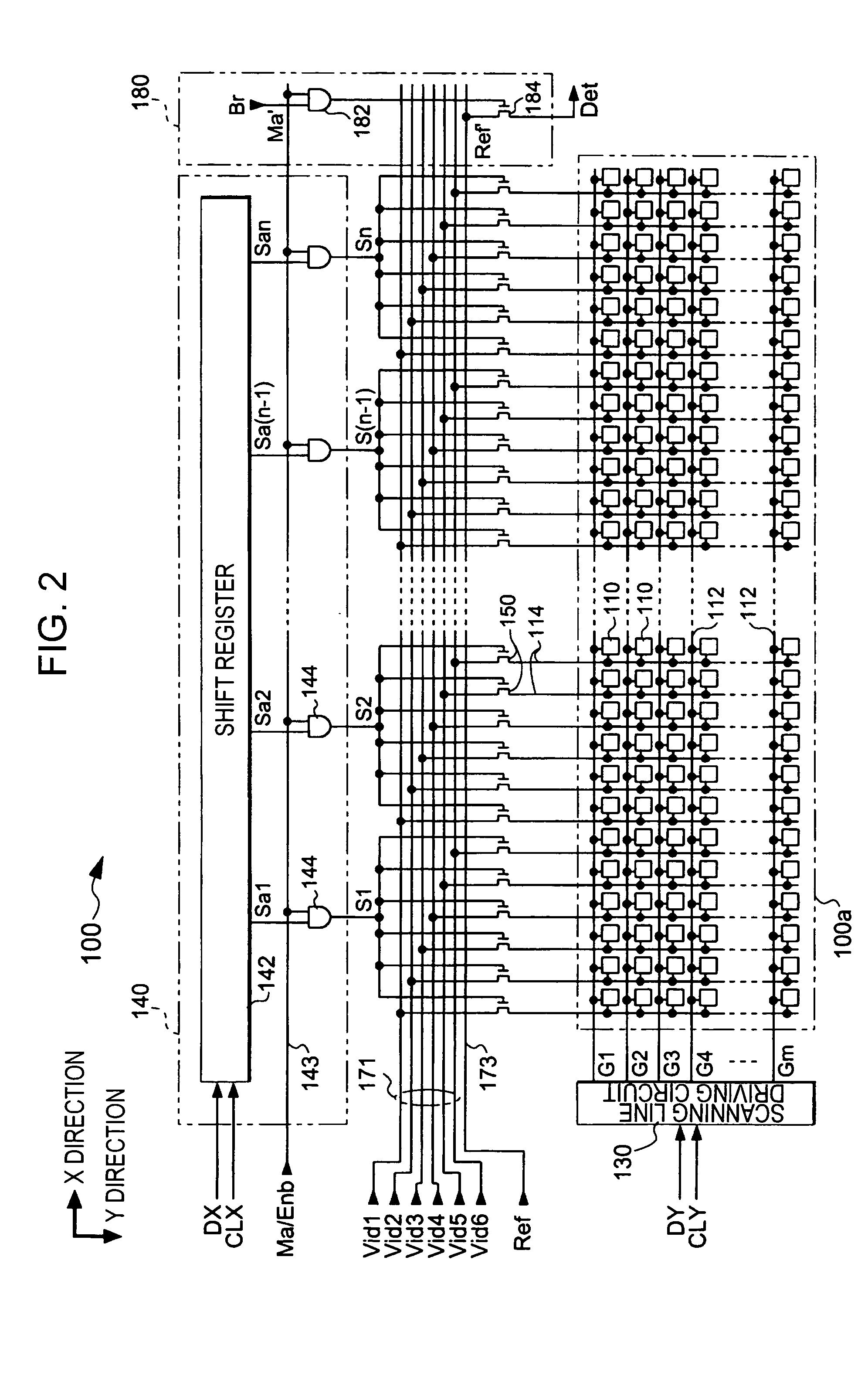
Electro-optical device, driving circuit of the same, driving method of the same, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20060007208A1Inhibit deteriorationSimple structureElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesShift registerPhase difference
The electro-optical device includes a plurality of pixels which are provided to correspond to intersections of a plurality of scanning lines and a plurality of data lines and which display the gray-scale levels corresponding to data signals sampled to the data lines when the scanning lines and the data lines are selected; a scanning line driving circuit which selects the scanning lines; shift registers which generate pulse signals for selecting the data lines for a period of time when the scanning lines are selected; a logical circuit which restricts the pulse signals respectively generated by the shift registers to the pulse width of an enable pulse to output them as sampling signals; and a sampling circuit which samples the data signals to the data lines according to the sampling signals. The driving circuit includes a phase difference detecting circuit which detects the phase difference between a monitoring signal supplied in synchronization with the data signal and a reference pulse supplied in synchronization with the enable pulse and which outputs the detected result as a phase difference signal; a first phase adjusting circuit which roughly adjusts the phase of the enable pulse supplied to the logical circuit; a second phase adjusting circuit which minutely adjusts the phase of the enable pulse supplied to the logical circuit with higher precision than the first phase adjusting circuit; and an adjustment control circuit which, when the phase difference signal indicates that the phase of the monitoring signal is delayed with respect to the reference pulse, controls the first phase adjusting circuit to advance the phase of the enable pulse and then controls the second phase adjusting circuit to minutely adjust the phase of the enable pulse such that the phase difference indicated by the phase difference signal is minimum, and which, when the phase difference signal indicates that the phase of the monitor signal precedes that of the reference pulse, controls the first phase adjusting circuit to delay the phase of the enable pulse and then controls the second phase adjusting circuit to minutely adjust the phase of the enable pulse such that the phase difference indicated by the phase difference signal is minimum.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
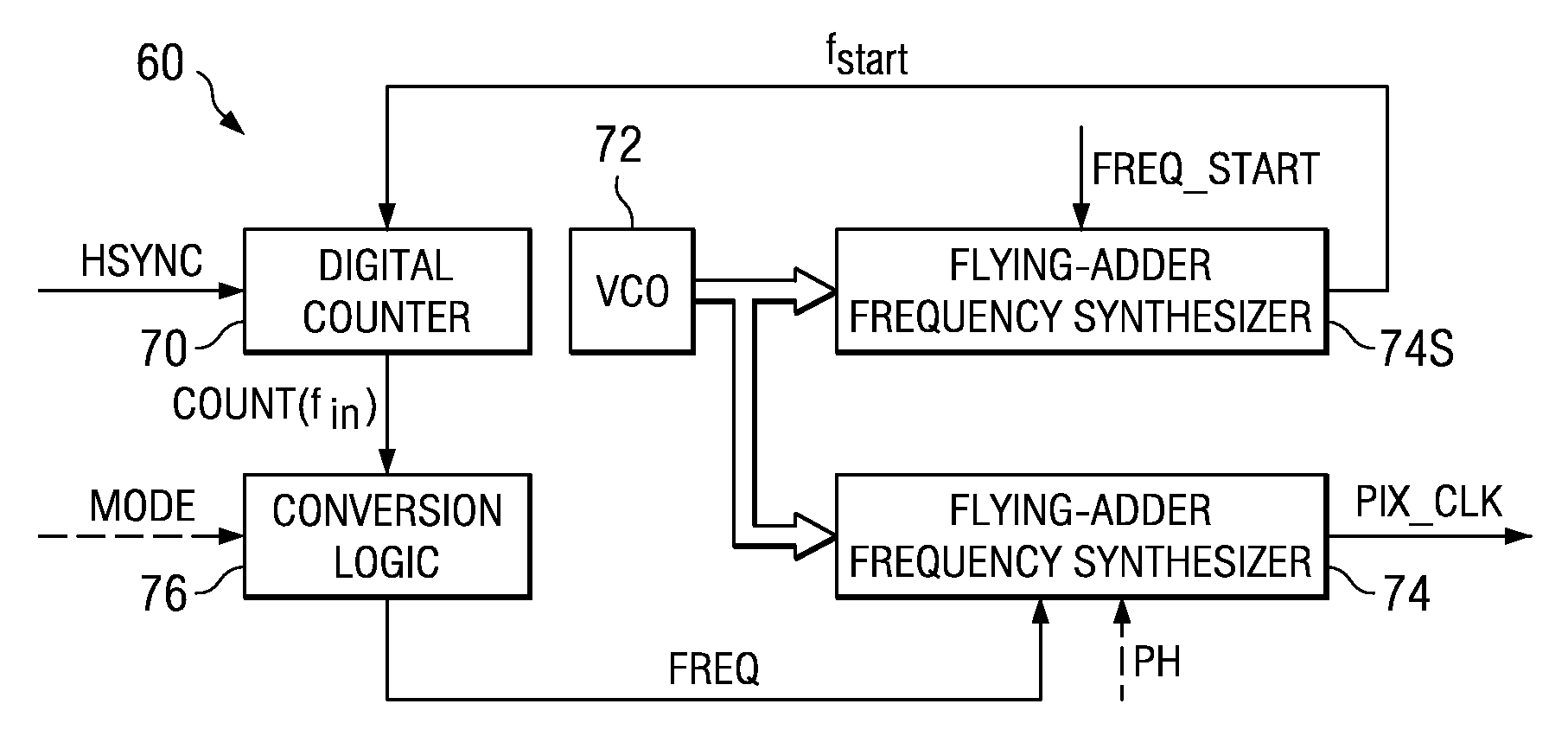
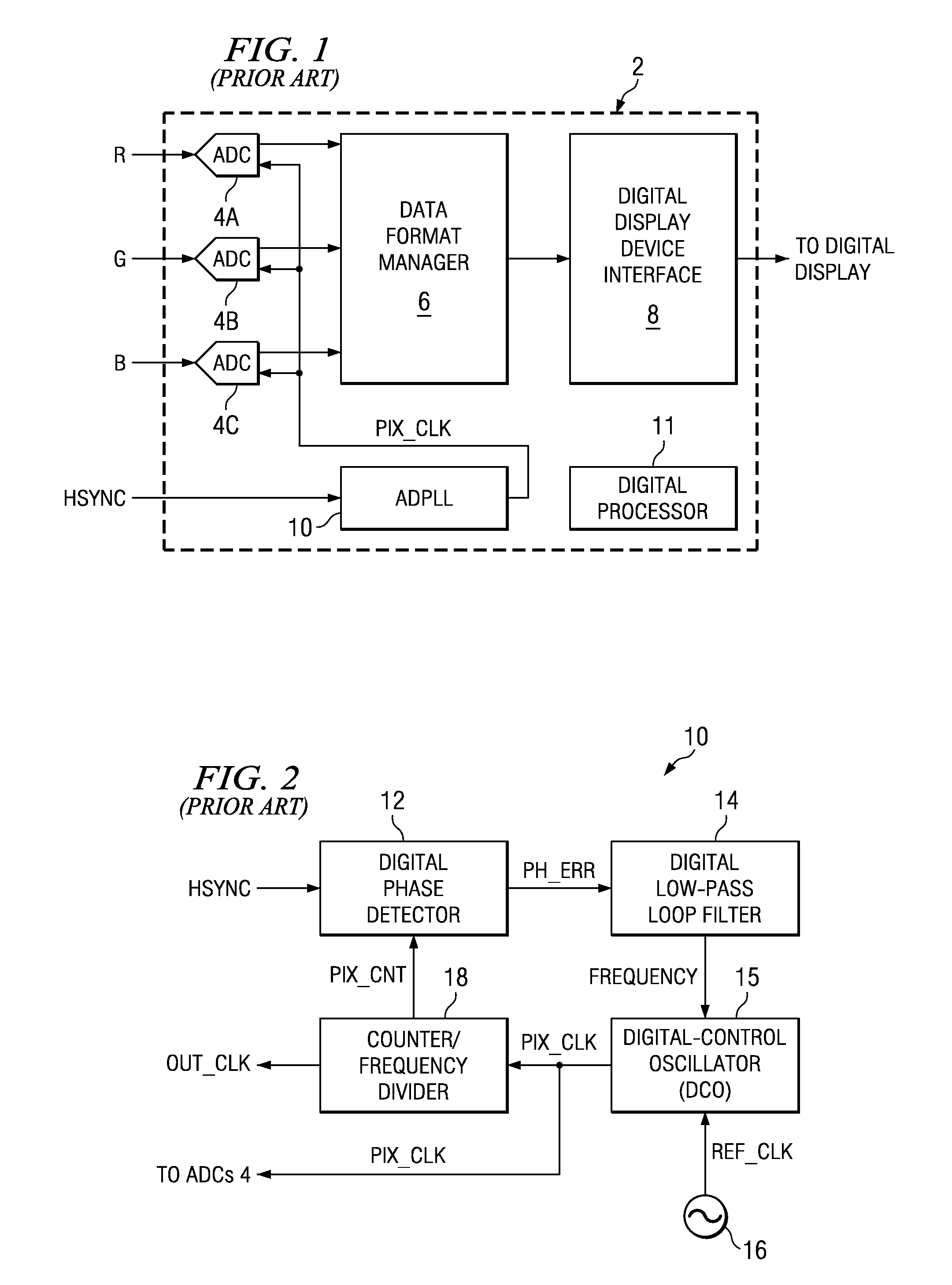
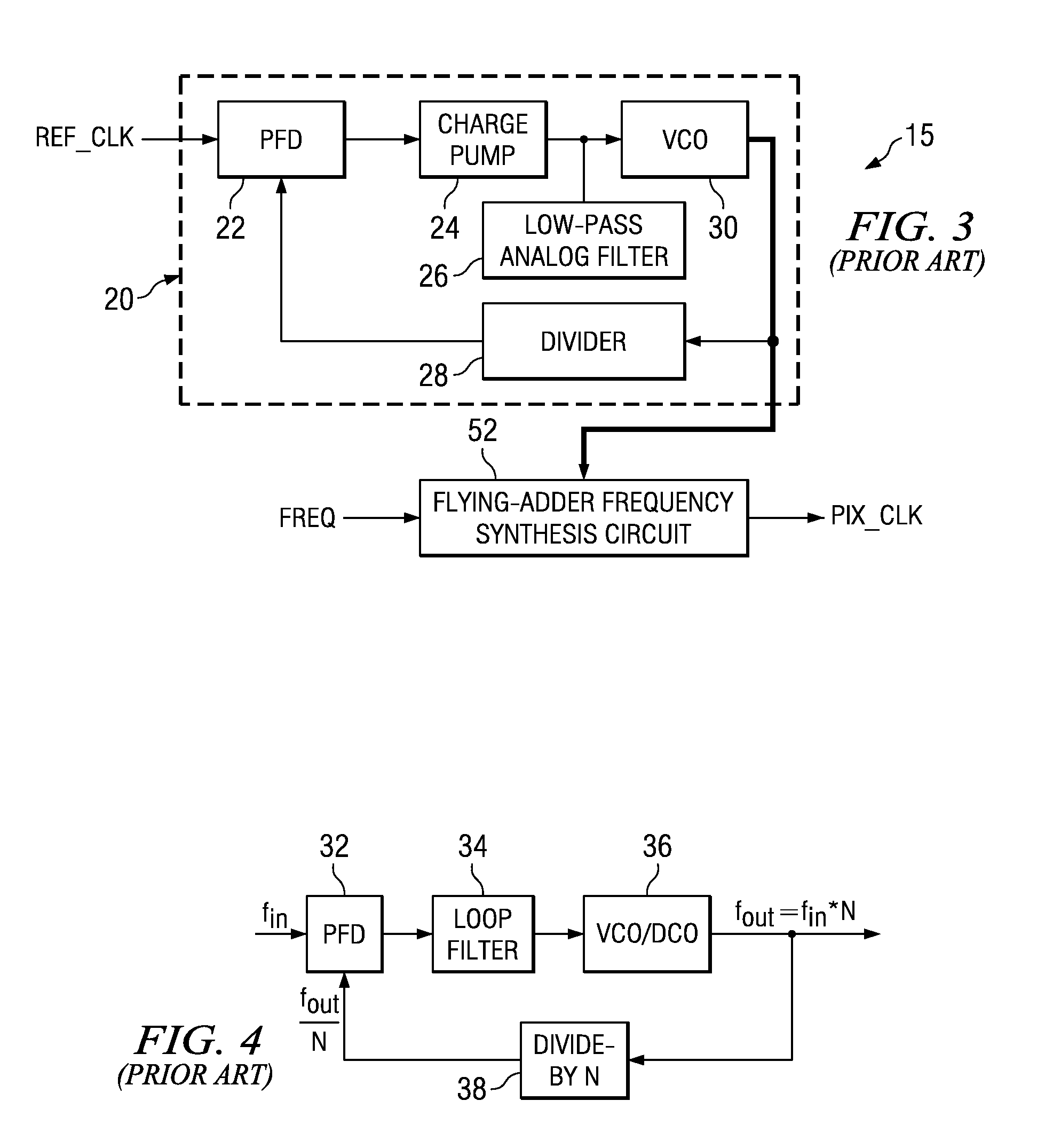
Flying-adder frequency synthesizer-based digital-controlled oscillator and video decoder including the same
ActiveUS7356107B2Large frequencyAccurate frequencyTelevision system detailsPulse automatic controlDigital control oscillatorMode control
A video decoder (52, 152) including a digital-control oscillator (DCO) (60, 160) is disclosed. The DCO (60, 160) includes a first flying-adder frequency synthesis circuit (74S) that measures an input signal frequency, such as the horizontal sync frequency of an input video signal. A frequency control word (FREQ) is generated in response to this input signal frequency, and is applied to a second flying-adder frequency synthesis circuit (74), which in turn selects the appropriate phases for leading and trailing edges of the output clock signal (PIX_CLK). Phase tuning of the output clock signal (PIX_CLK) can be effected by using an alternate flying-adder frequency synthesis circuit (74′) architecture, in combination with a phase signal (PH) generated by a digital controller (61). Multiple phase-tuned sample clocks (PIX_CLK_A, PIX_CLK_B, PIX_CLK_C) can be similarly generated from multiple flying-adder frequency synthesis circuits (174A, 174B, 174C), each controlled by the frequency control word (FREQ) and a corresponding phase signal (PHA, PHB, PHC). Video mode control logic (65, 165) can also be implemented by way of a similar DCO architecture. The DCO (60) may be used to generate a clock signal at a large frequency multiple relative to the input signal, outside of the video decoder context.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
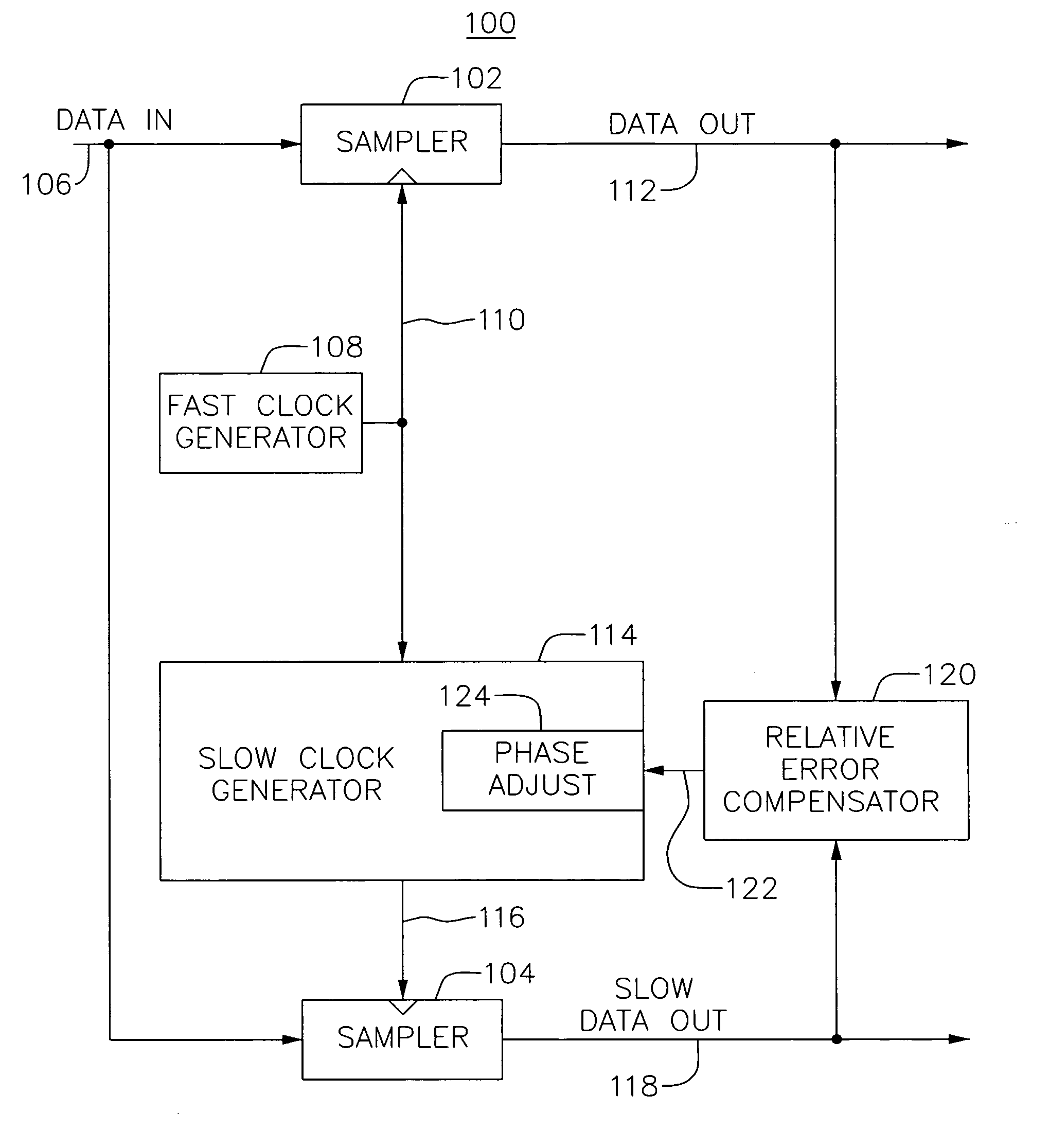
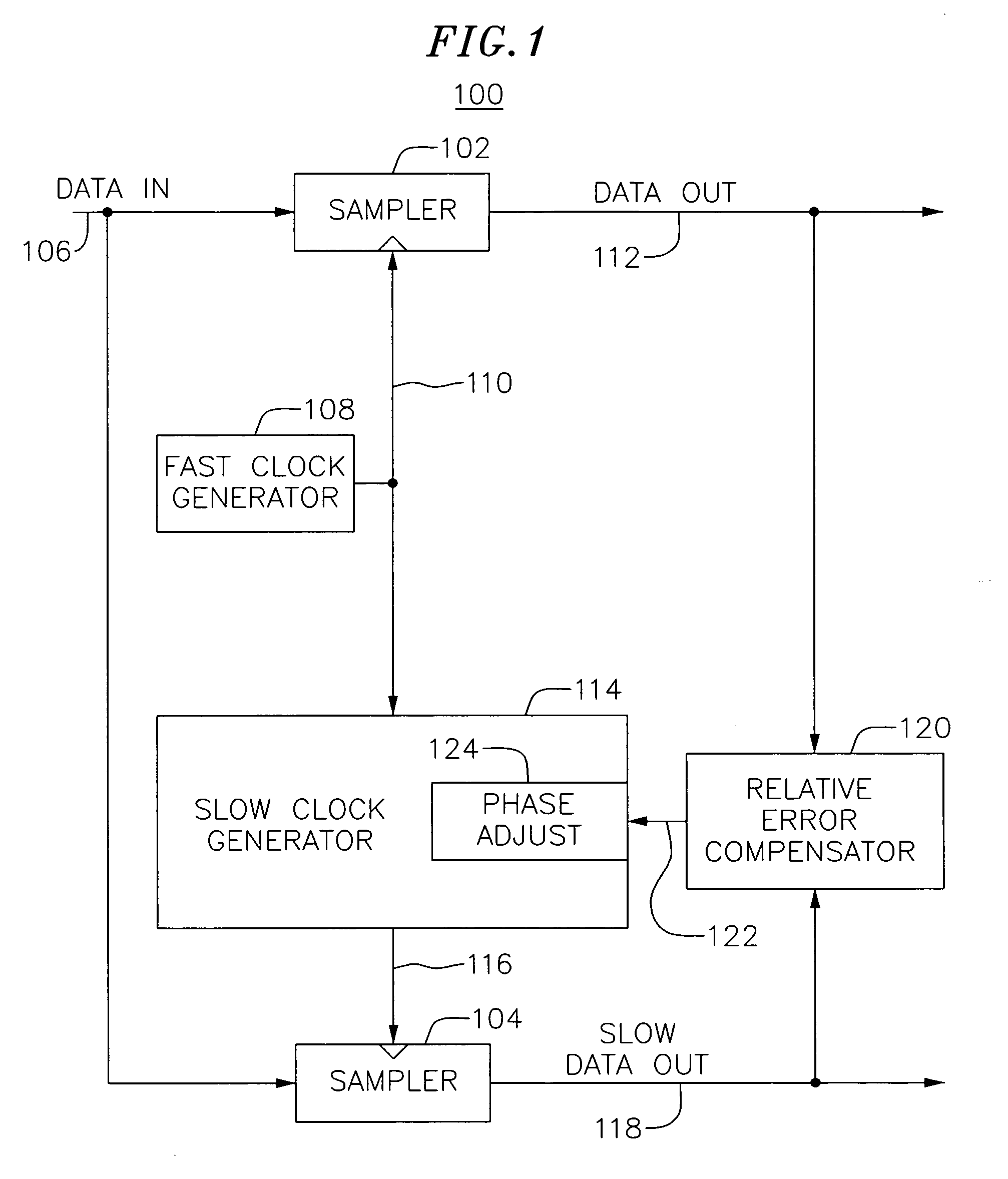
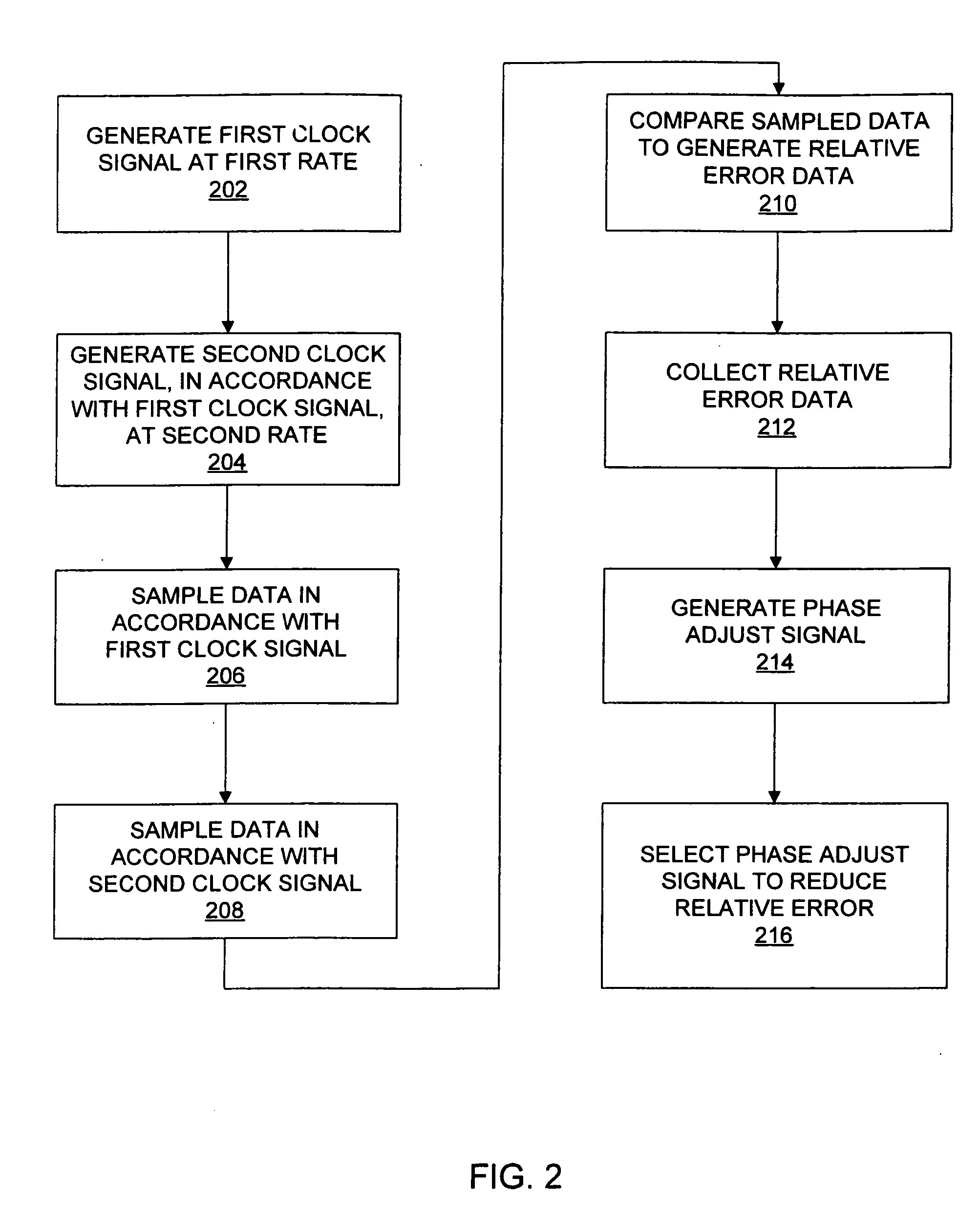
Phase adjust using relative error
InactiveUS20060253746A1Analogue/digital conversionPulse automatic controlDigital down converterLow data rate
A system may adjust the times at which data is sampled by separate sampling mechanisms. Here, it may be desirable to ensure that one sampler samples data at substantially the same time as the other sampler. For example, output data from a high speed sampler that samples received data may be compared with an output of an analog to digital converter that samples the received data at a lower data rate. This difference or relative error may be accumulated over a period of time for given values of delay applied to the clock for the analog to digital converter. In this way, a delay value that minimizes the relative error may be selected as a desired delay value.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Weld analysis using laser generated narrowband lamb waves
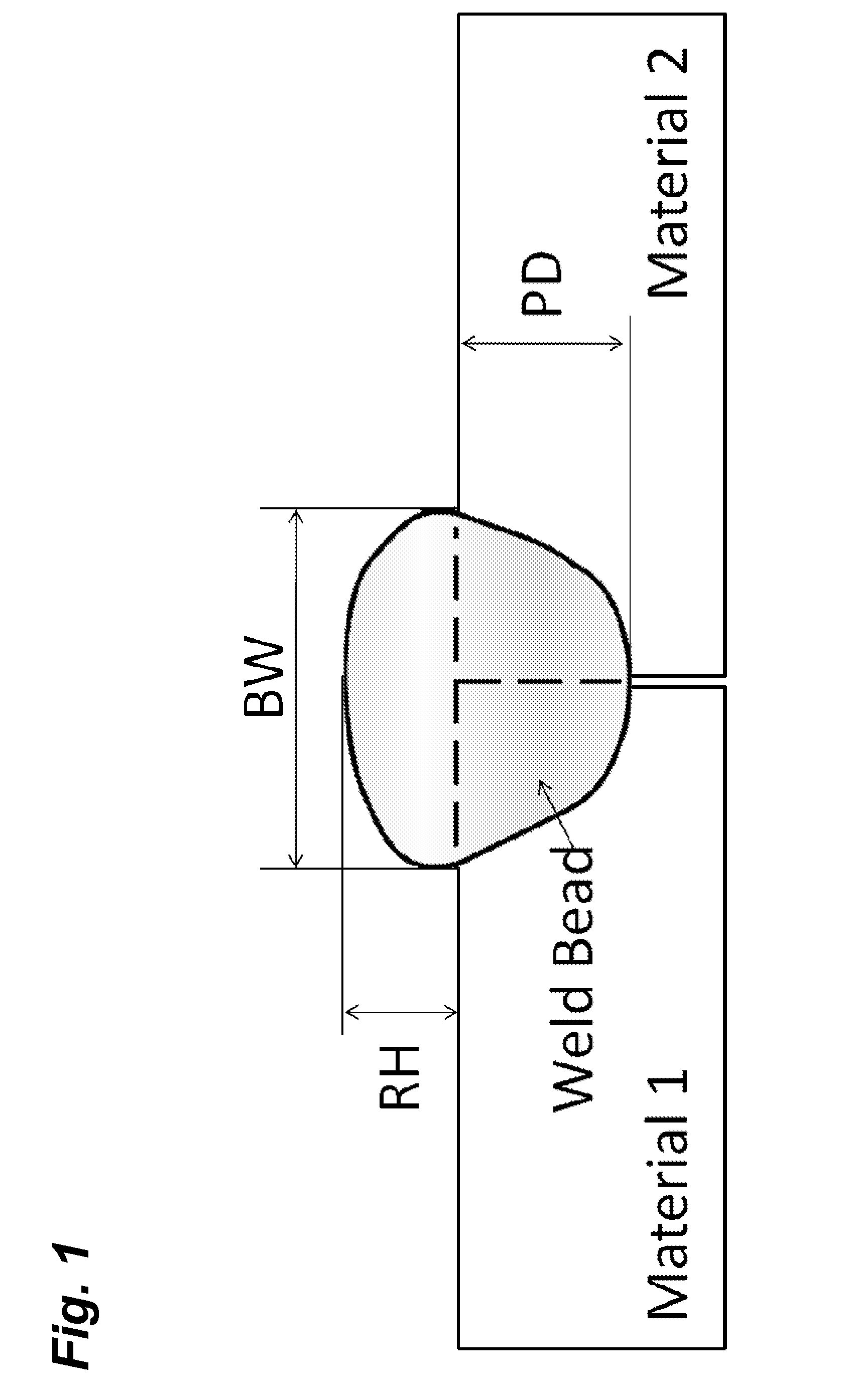
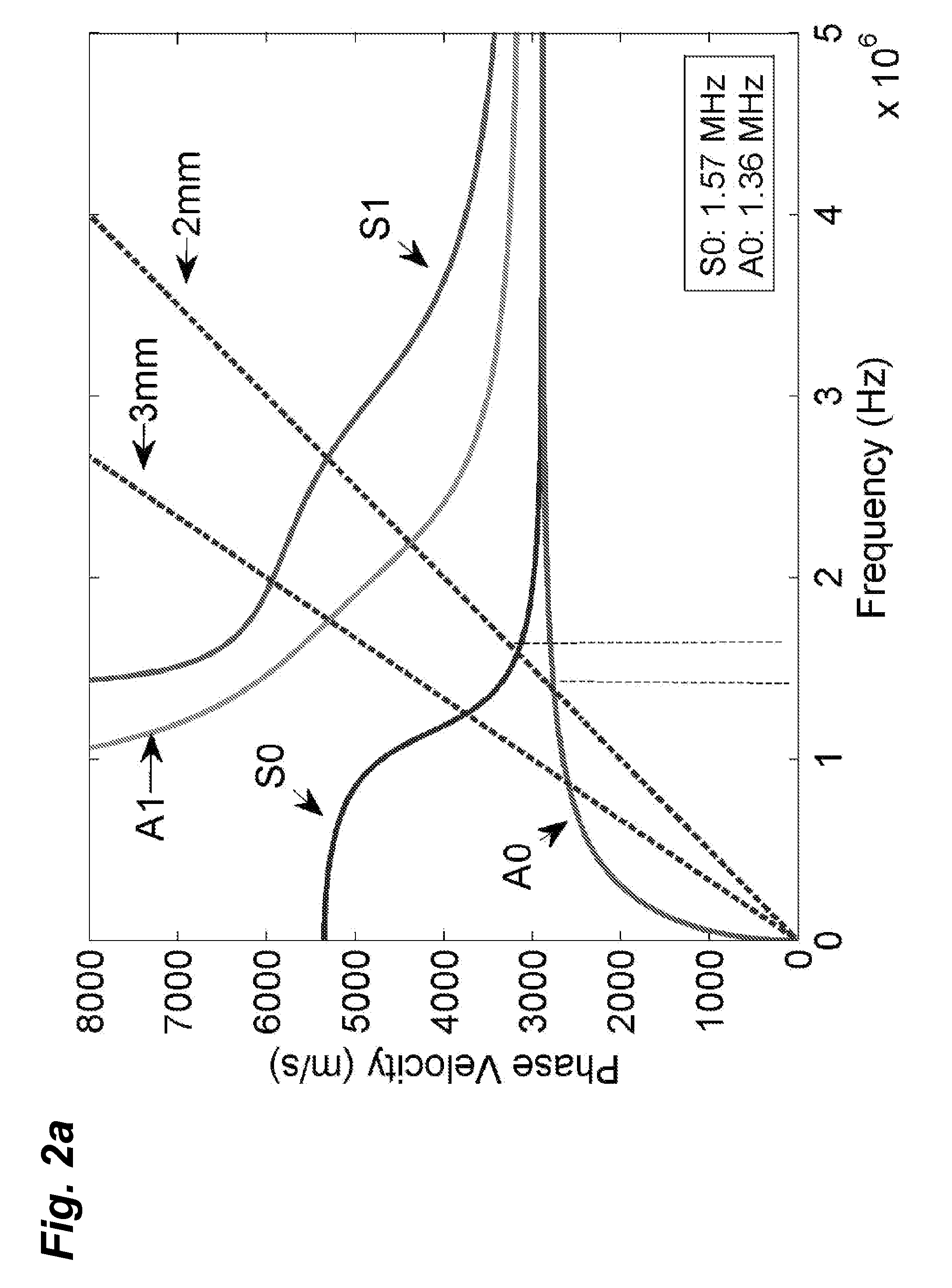
ActiveUS20140172399A1Allow flexibilityReduce signal complexityAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalogue computers for electric apparatusRegression analysisPenetration depth
A system and method for measuring various weld characteristics is presented. The system and method can comprise a means to measure penetration depth of butt welds in thin plates, for example, using laser generated ultrasounds. Superimposed line sources (SLS) can be used to generate narrowband ultrasounds. A signal processing procedure that combines wavenumber-frequency (k-ω) domain filtering and synthetic phase tuning (SPT) is used to reduce the complexity of Lamb wave signals. The reflection coefficients for different wavelengths corresponding to each wave mode can be calculated. Regression analysis that can include stepwise regression and corrected Akaike's information criterion (AIC) can be performed to build prediction models that use the reflection coefficients as predictors.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
PLL circuit
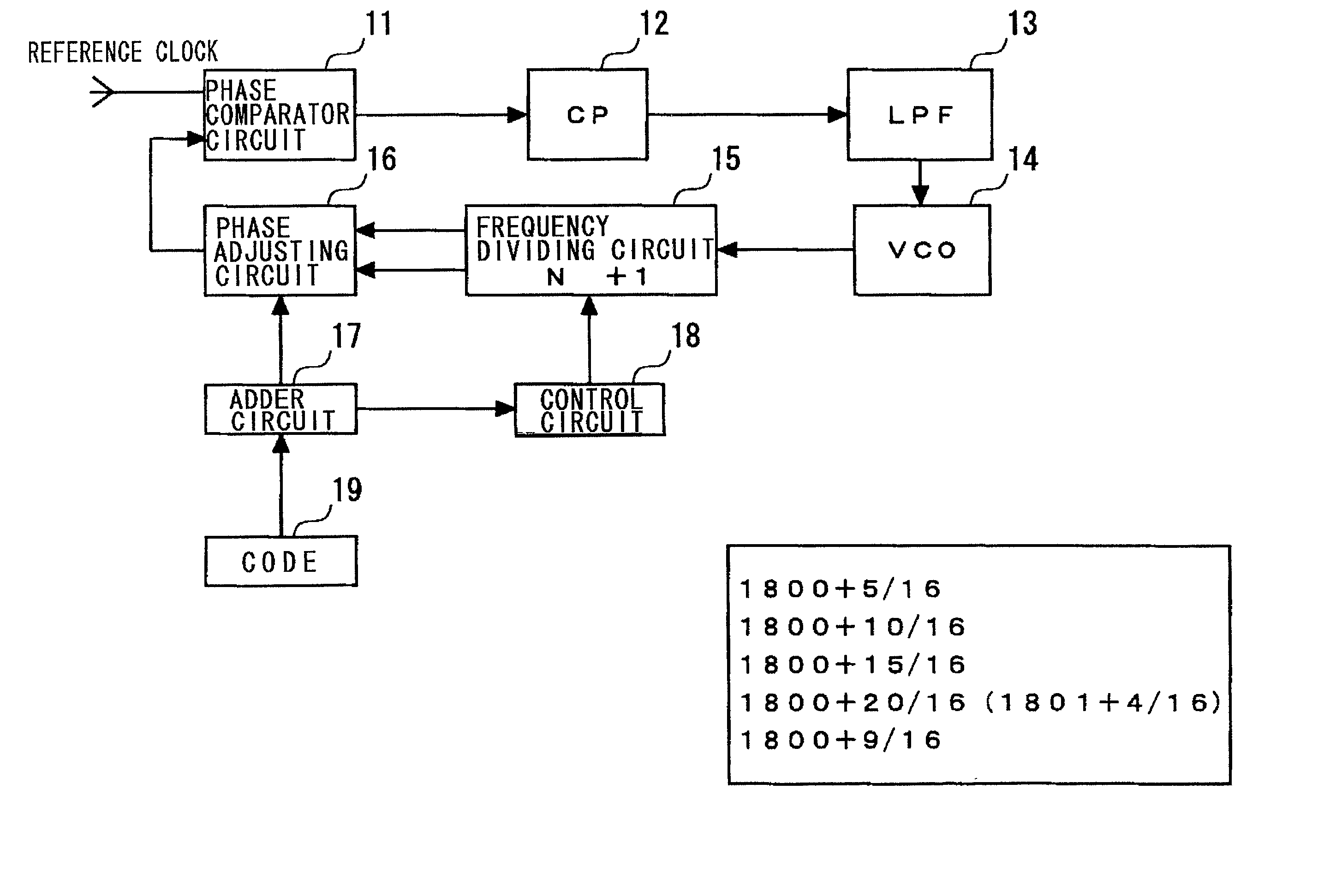
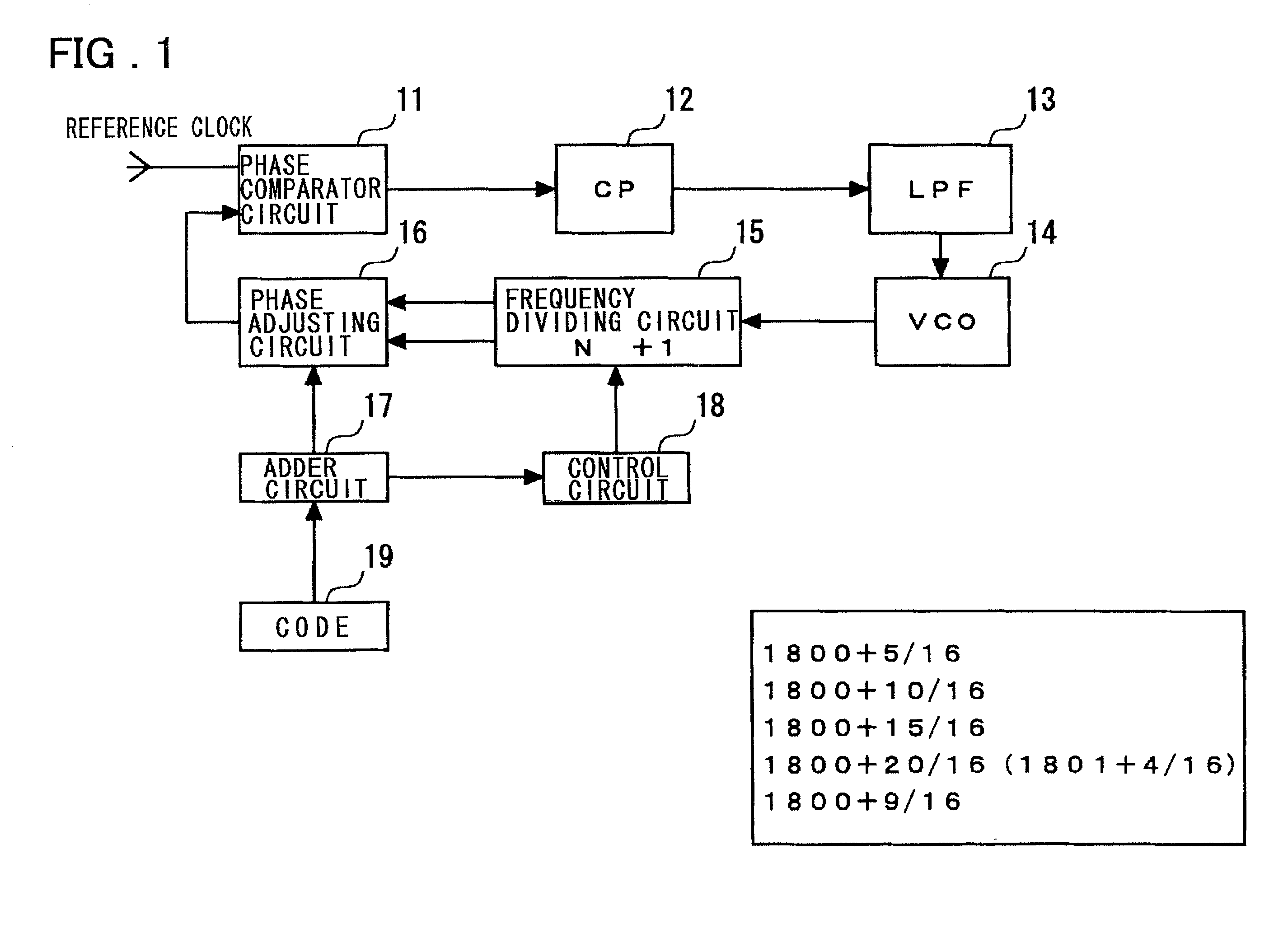
InactiveUS20020033738A1Pulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersLoop filterDividing circuits
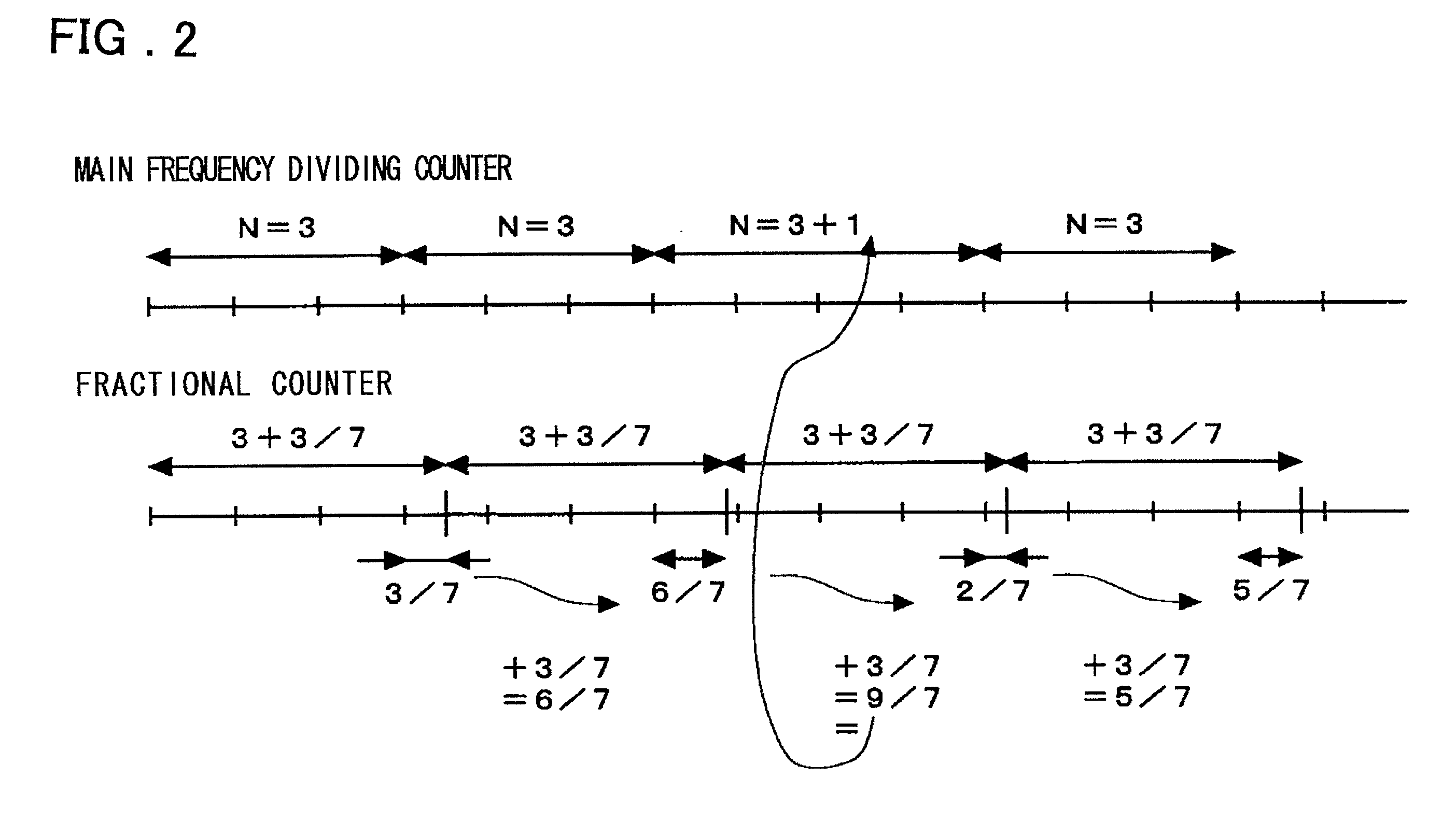
Disclosed is a PLL circuit that makes fractional frequency division possible without causing spurious components to be produced in the output of a VCO. The PLL circuit comprises a frequency dividing circuit for frequency-dividing the output of a VCO; a phase adjusting circuit, to which are input two clocks of different phases obtained by frequency division performed by the frequency dividing circuit, for producing an output signal having a delay time defined by a time that is the result of internally dividing a timing difference between the two clocks; a charge pump for generating a voltage conforming to a phase difference output from the phase comparator circuit; and a loop filter for smoothing the voltage conforming to the phase difference and applying the voltage to the VCO, wherein the dividing value of the timing difference in the phase adjusting circuit is represented by MF / MD, and an accumulation operation is performed in units of MF every frequency-divided clock. If the cumulative result by MF is equal to or greater than MD, then a remainder obtained by dividing the cumulative result by MD is adopted as the cumulative result and the dividing ratio of the frequency dividing circuit is set to N+1. A control signal for setting the dividing ratio of the timing difference in the phase adjusting circuit is output to the phase adjusting circuit, and a clock obtained by frequency-dividing the output of the VCO in accordance with a dividing ratio N+MF / MD is input to a phase comparator.
Owner:NEC CORP
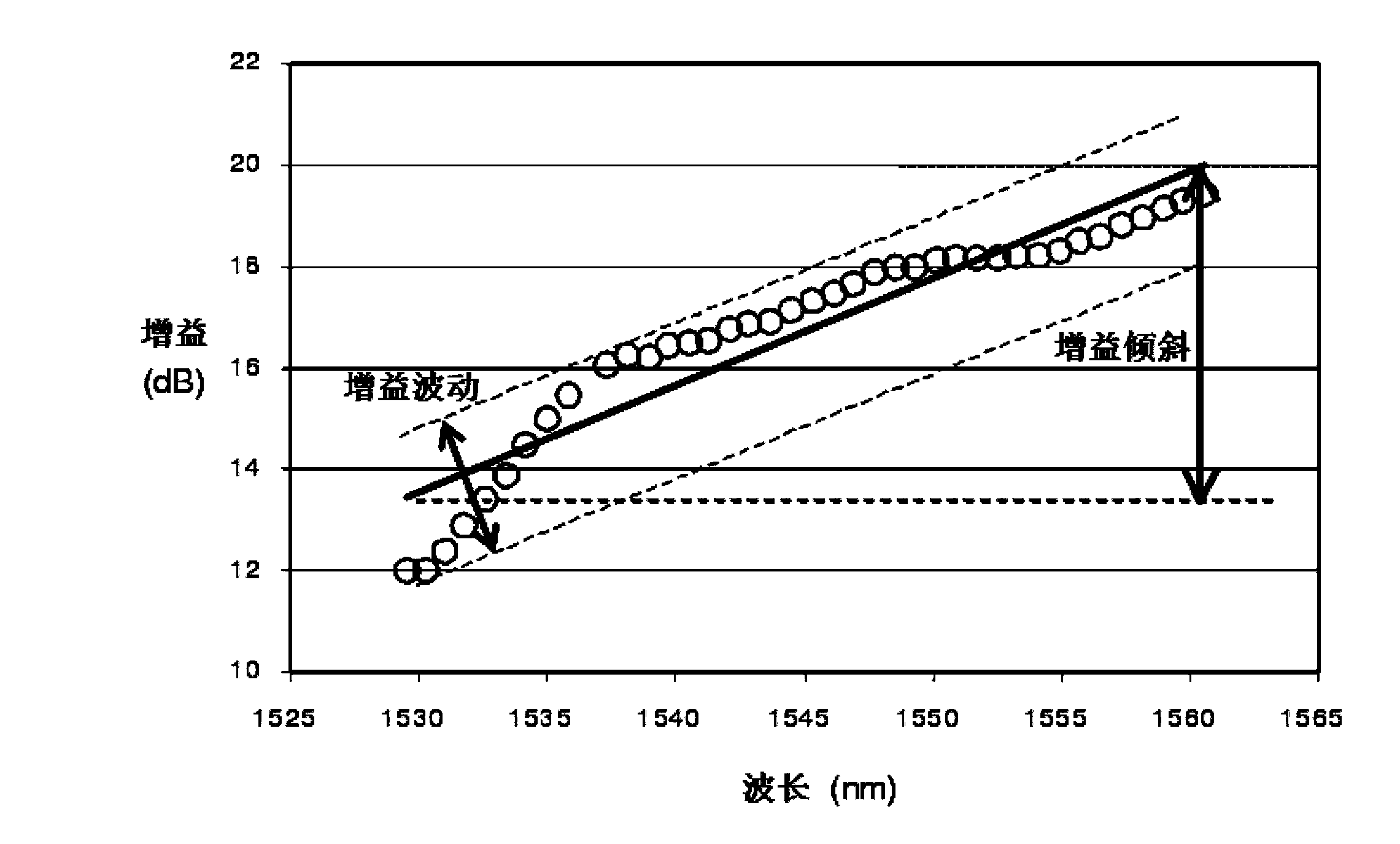
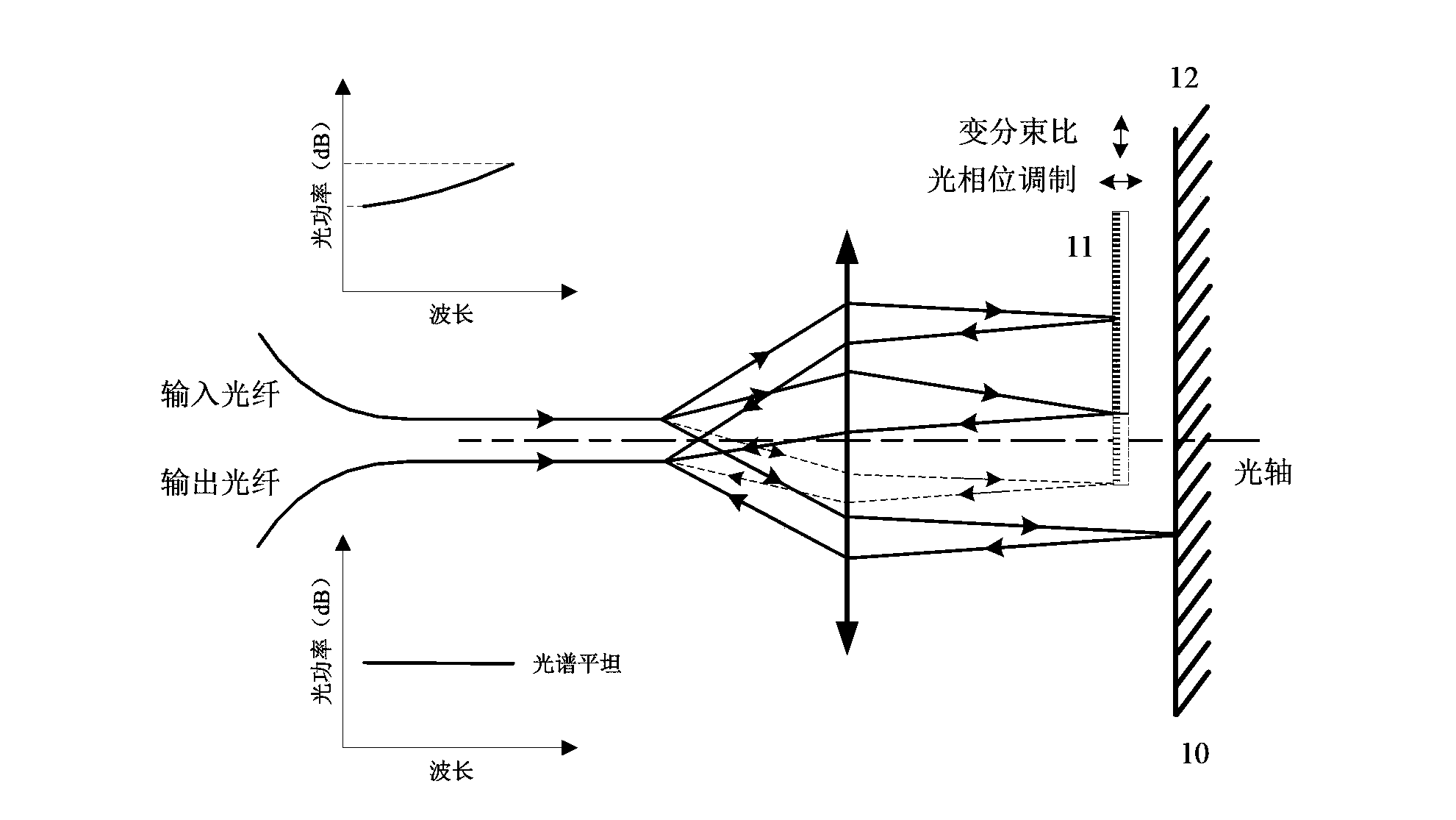
Optical fiber amplifier dynamic gain slope equalizer and manufacturing technology thereof
ActiveCN103885177AMature technologyImprove yieldElectromagnetic transmissionOptical elementsManufacturing technologyFiber chromatic dispersion
The invention discloses an optical fiber amplifier dynamic gain slope equalizer and a manufacturing technology thereof. The equalizer comprises an MEMS optical micro mirror driver chip and a double-optical fiber collimator through optical package; the MEMS optical micro mirror driver chip comprises an first optical micro reflecting mirror, a second optical micro reflecting mirror and a micro displacement regulating unit; the micro displacement regulating unit is used for controlling micro displacement motion of the first optical micro reflecting mirror and / or the second optical micro reflecting mirror in the horizontal direction or / and vertical direction, MZI splitting ratio and interference arm phase tuning can be realized, and spectral slope with inputted WDM optical signals can be dynamically controlled. The dynamic gain slope equalizer provided by the invention is manufactured by adopting the MEMS technology, has the advantages of low insertion loss, wide equalized range, small size, quick tuning speed, micro driving power and the like, can be directly integrated in the EDFA for realizing dynamic gain slope equalization, and can also be applied to the problem that signal power in the DWDM channel is not equalized due to transmission optical fiber, an optical fiber dispersion compensation module, optical fiber SRS effect and the like.
Owner:QST CORP
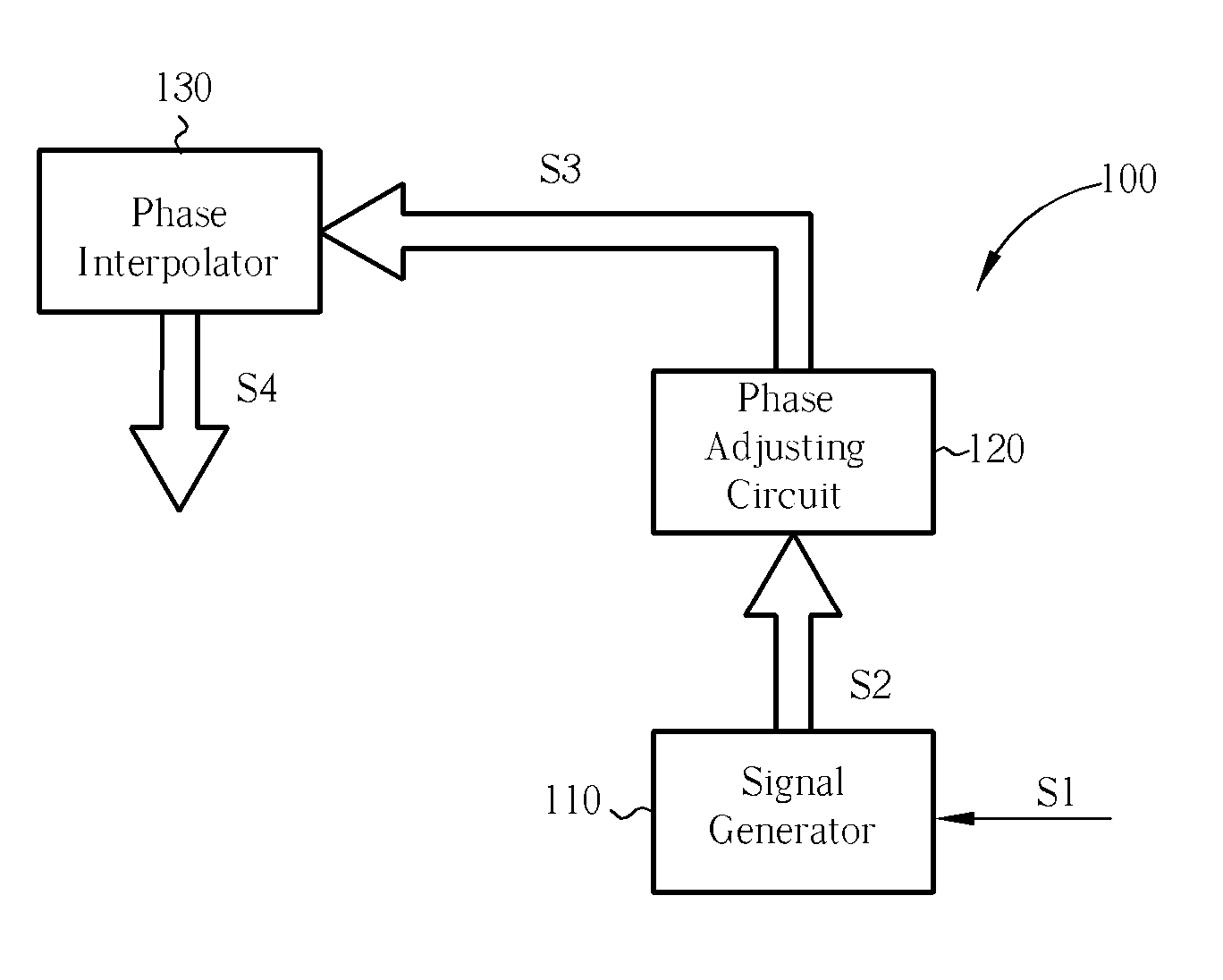
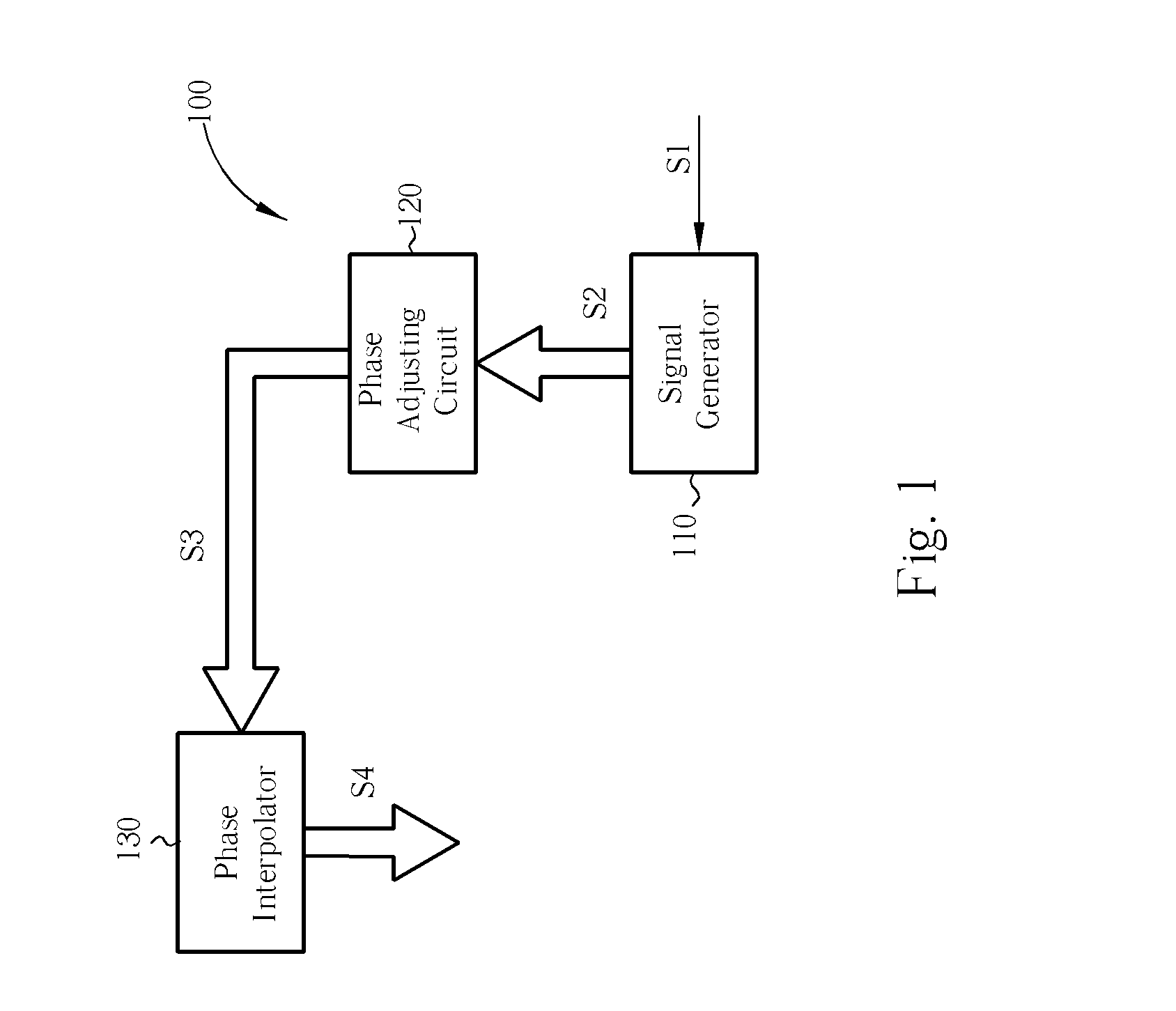
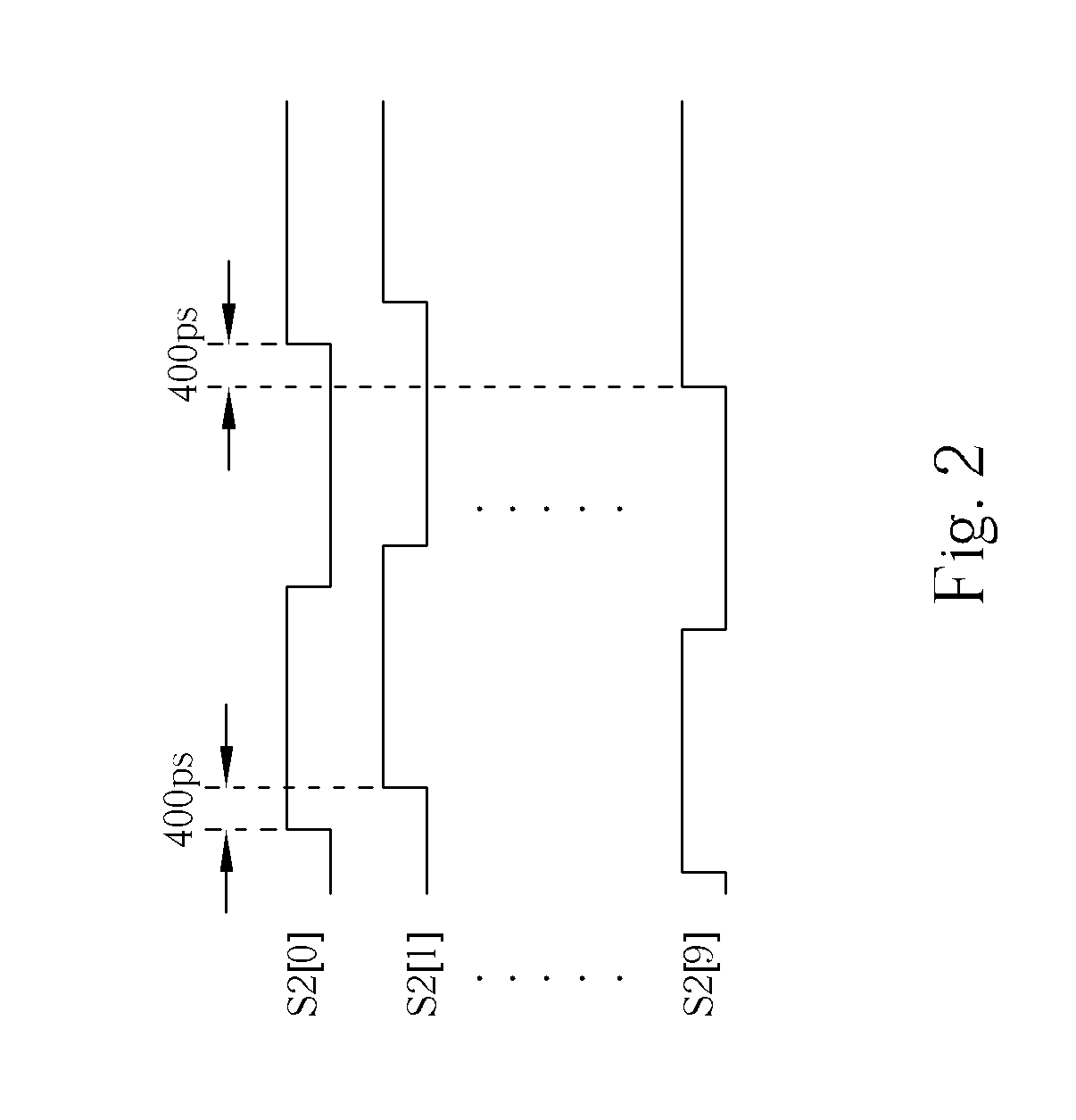
Multi-phase clock generator and method thereof
A multi-phase clock generator for generating a set of multi-phase clock signals is disclosed. The multi-phase clock generator includes a signal generator, a phase adjusting circuit, and a phase interpolator. The signal generator generates a plurality of first clock signals according to a reference clock signal. The phase adjusting circuit, which is a phase rotator or a phase selecting circuit and coupled to the signal generator receives the first clock signals and adjusts the phases of the first clock signals according to a control signal to generate a plurality of second clock signals. The phase interpolator, which is coupled to the phase adjusting circuit, interpolates the second clock signals to generate the set of multi-phase clock signals.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
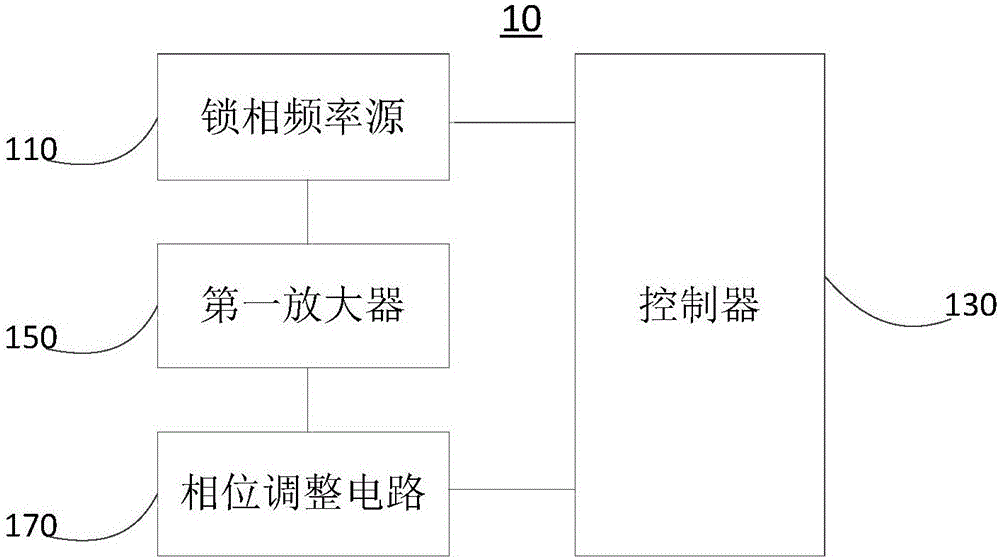
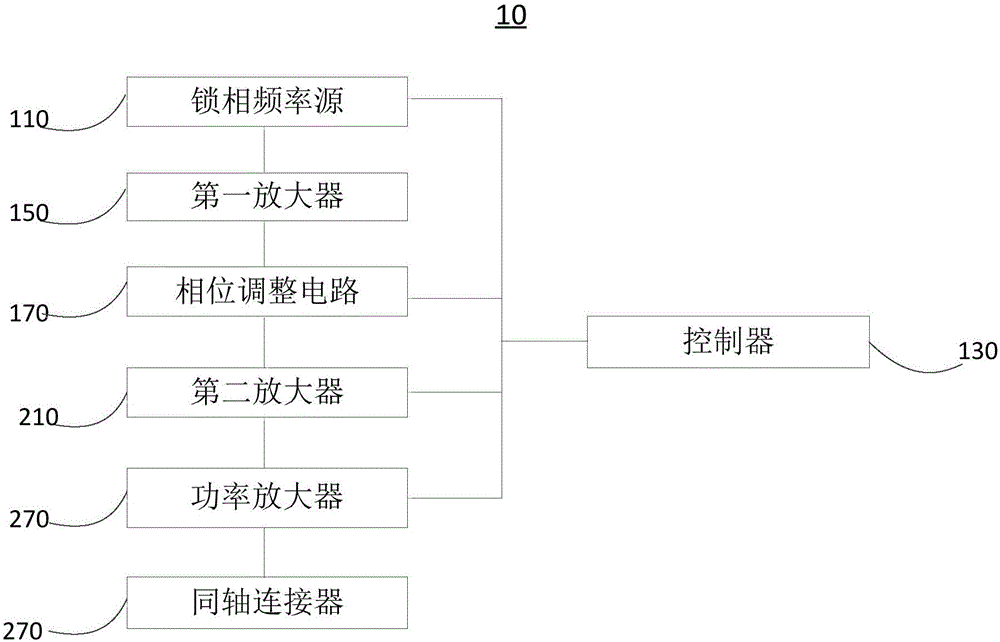
Radio frequency power source and radio frequency unfreezing device
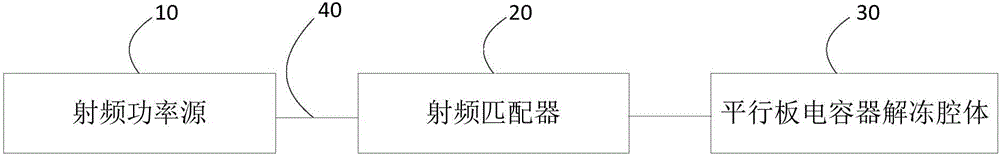
PendingCN106234557AImprove temperature unevennessMeat/fish preservation by freezing/coolingFood electrical treatmentAudio power amplifierEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of radio frequency unfreezing, in particular to a radio frequency power source and a radio frequency unfreezing device. The radio frequency unfreezing device comprises the radio frequency power source. The radio frequency power source comprises a phase-locked frequency source, a controller, a first amplifier and a phase regulating circuit, wherein the first amplifier is connected between the phase-locked frequency source and the phase regulating circuit, and the controller is respectively connected with the phase-locked frequency source and the phase regulating circuit. The controller controls the frequency and on and off of the phase-locked frequency source. The phase-locked frequency source generates a first signal under the control of the controller and transmits the first signal to the first amplifier. The first amplifier amplifies the first signal, then generates a second signal and transmits the second signal to the phase regulating circuit. The phase regulating circuit regulates the phase of the second signal and generates and outputs a third signal. By the arrangement, the frequency and power of the third signal output by the radio frequency power source can be controlled, and the problem that temperature in frozen meat is uneven when the unfreezing device is used to unfreeze the frozen meat is improved.
Owner:成都沃特塞恩电子技术有限公司
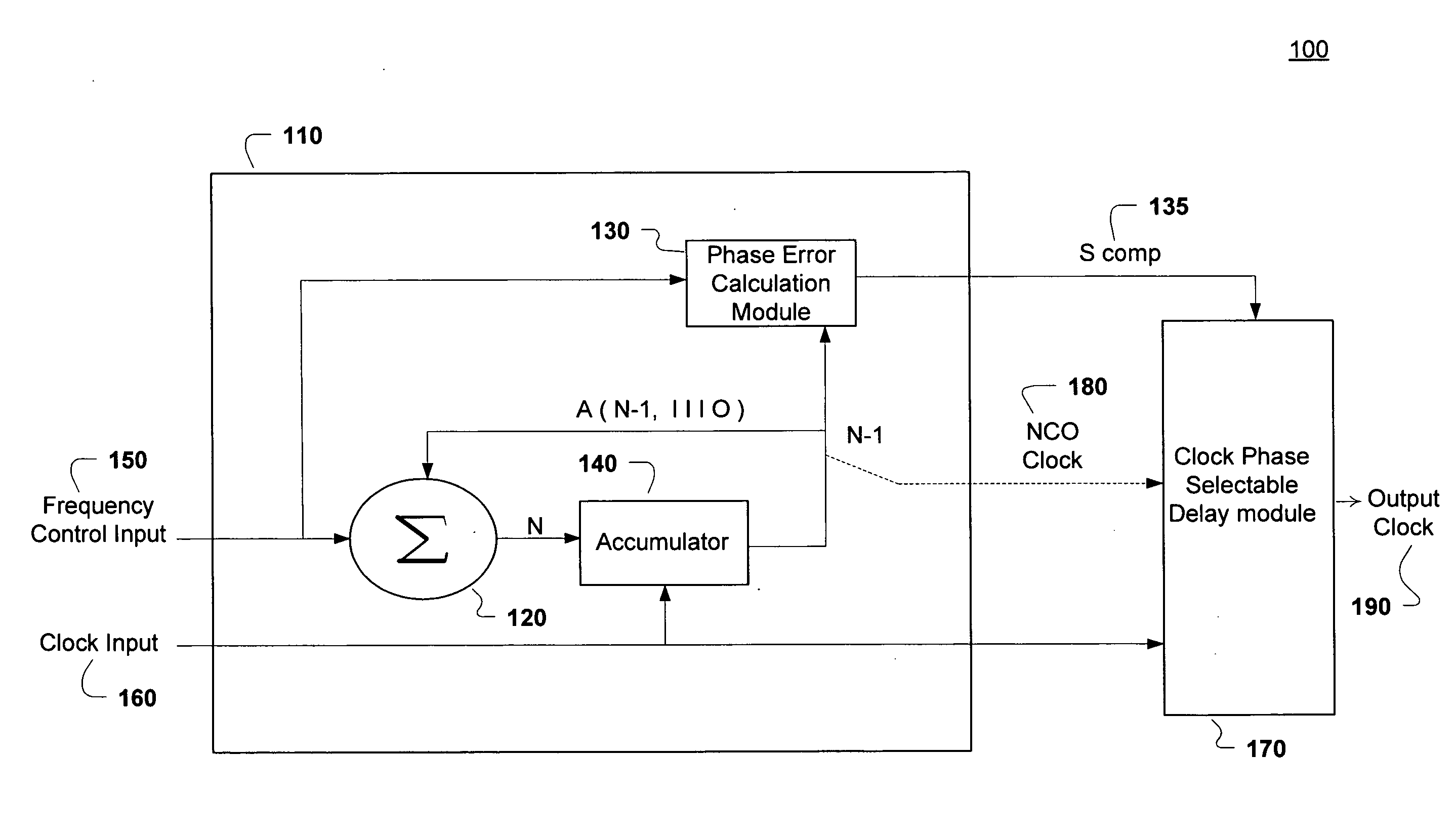
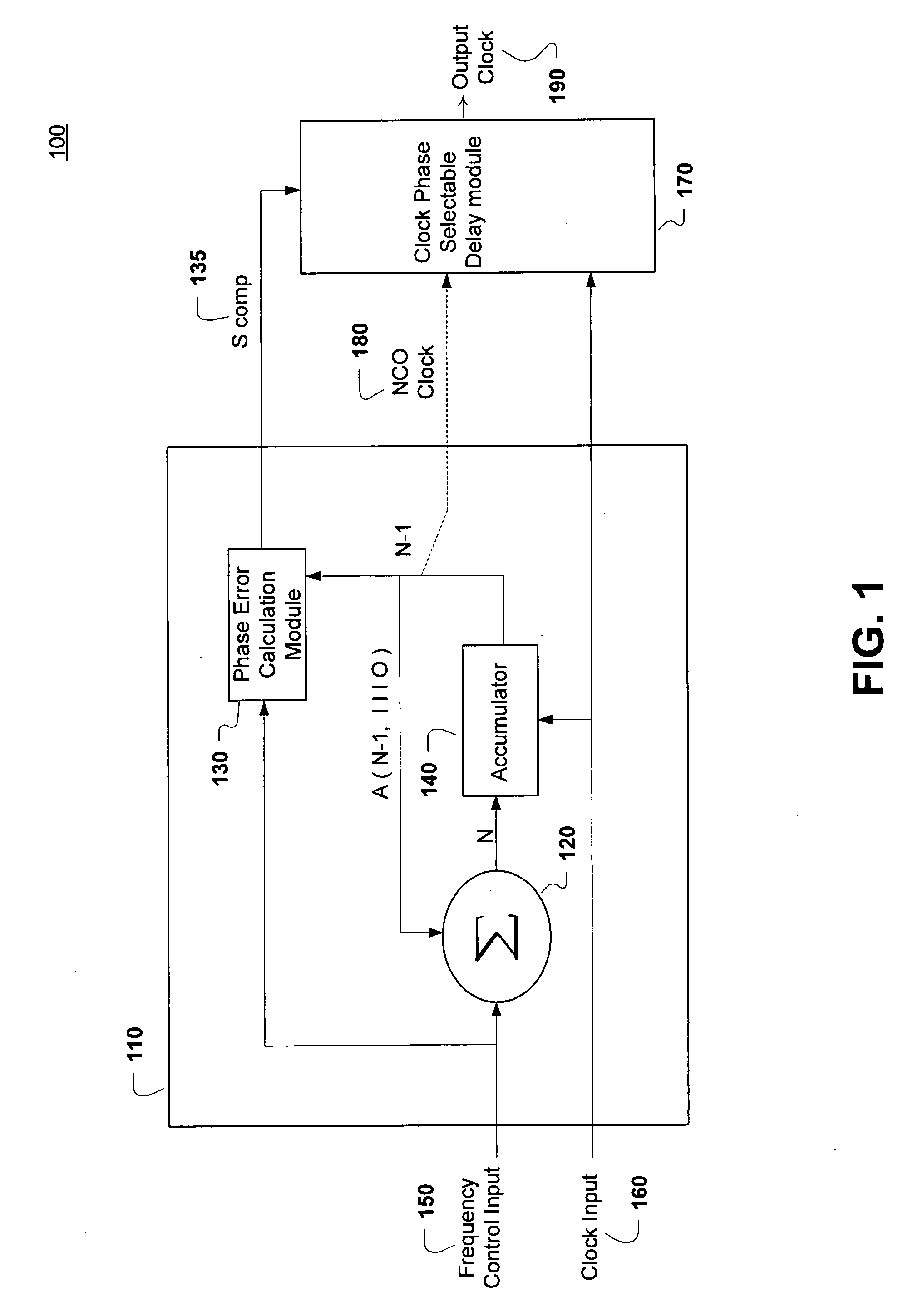
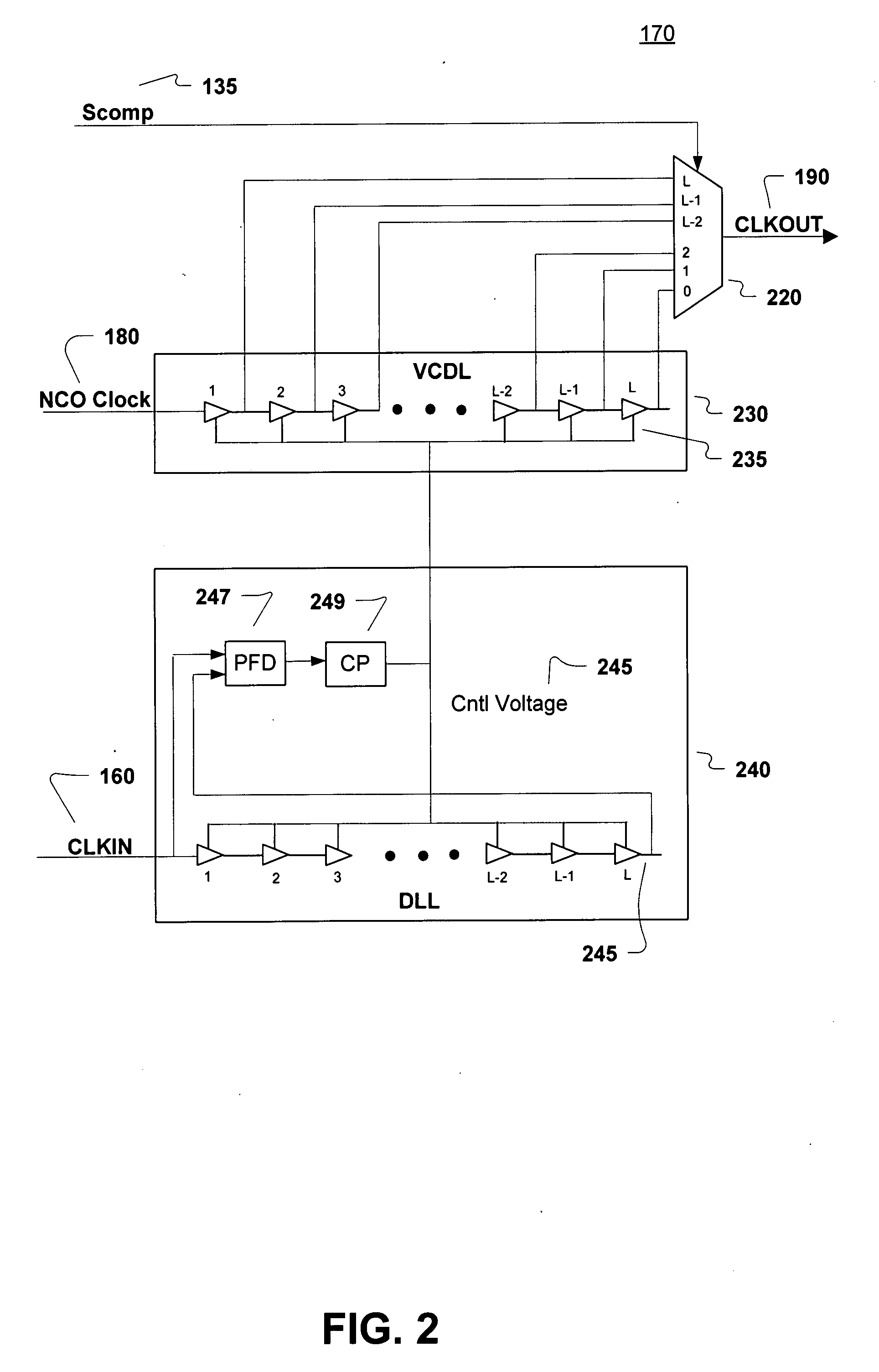
Numerically controlled oscillator (NCO) output clock phase smoothing
ActiveUS20080069284A1Pulse automatic controlDigital data processing detailsDigital controlled oscillatorEngineering
A system and method for performing output clock phase smoothing. A phase smoothing circuit is described and includes a numerically-controlled oscillator (NCO) configured to produce a plurality of NCO clock pulses at a selectable frequency that is based on an input clock. Edges of the plurality of NCO clock pulses are aligned to edges of the input clock. A phase error calculation module is coupled to the NCO and is configured to generate a corresponding phase error for each of the plurality of NCO clock pulses. A clock phase selectable delay is coupled to the phase error calculation module and is configured to adjust each of the plurality of NCO clock pulses according to the corresponding phase error to generate an output clock at the selectable frequency that are phase-adjusted to more closely match an ideal output clock phase. Edges of the output clock need not necessarily align to the edges of the input clock.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
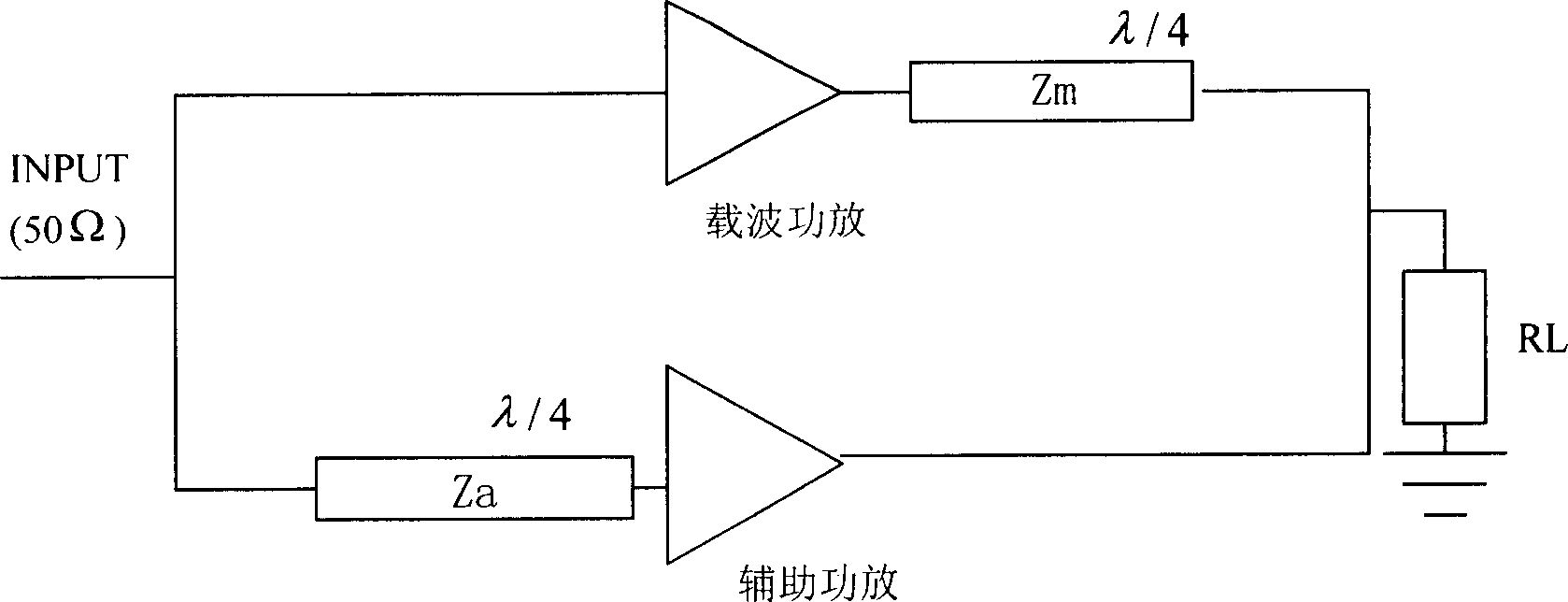
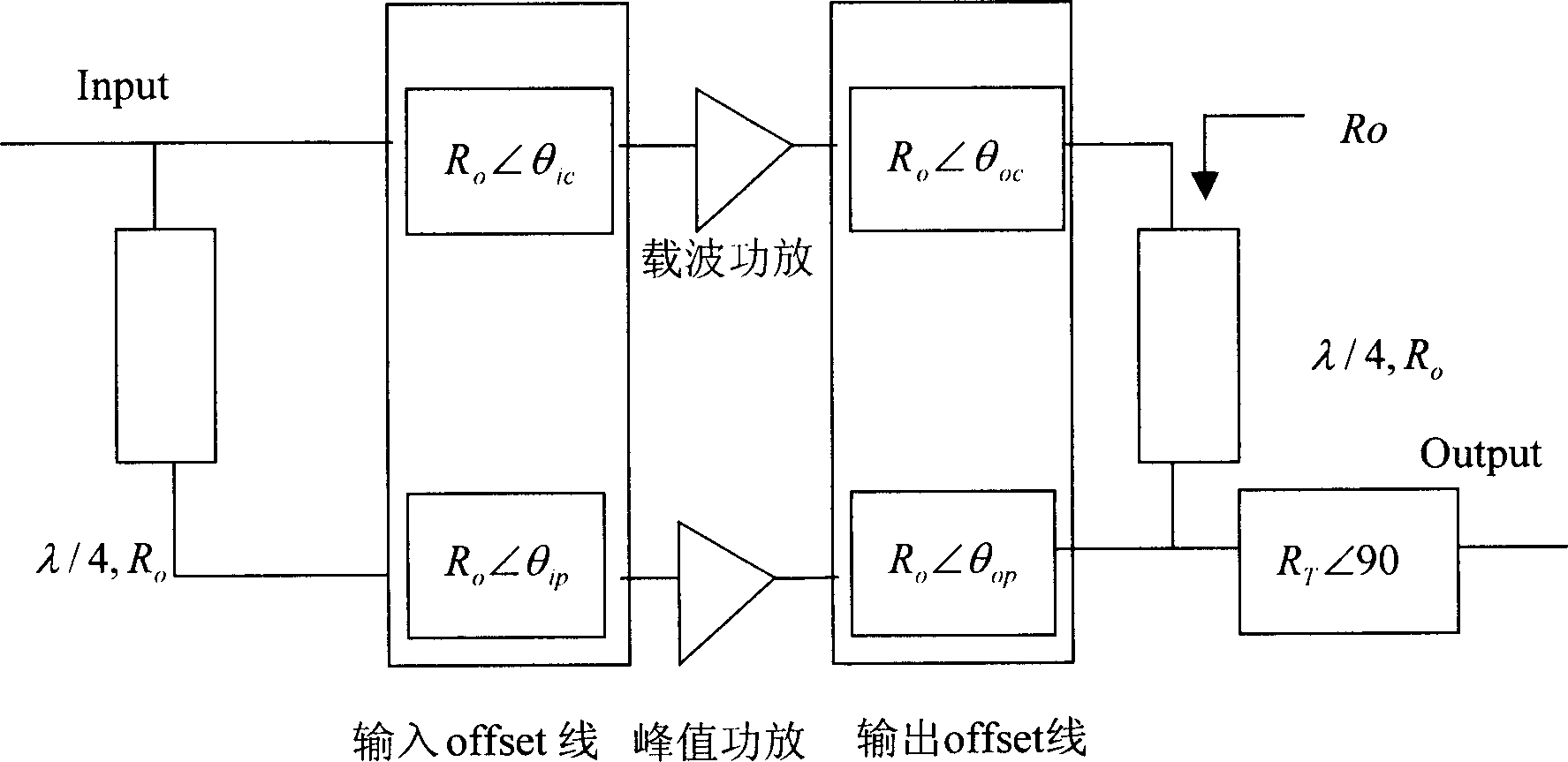
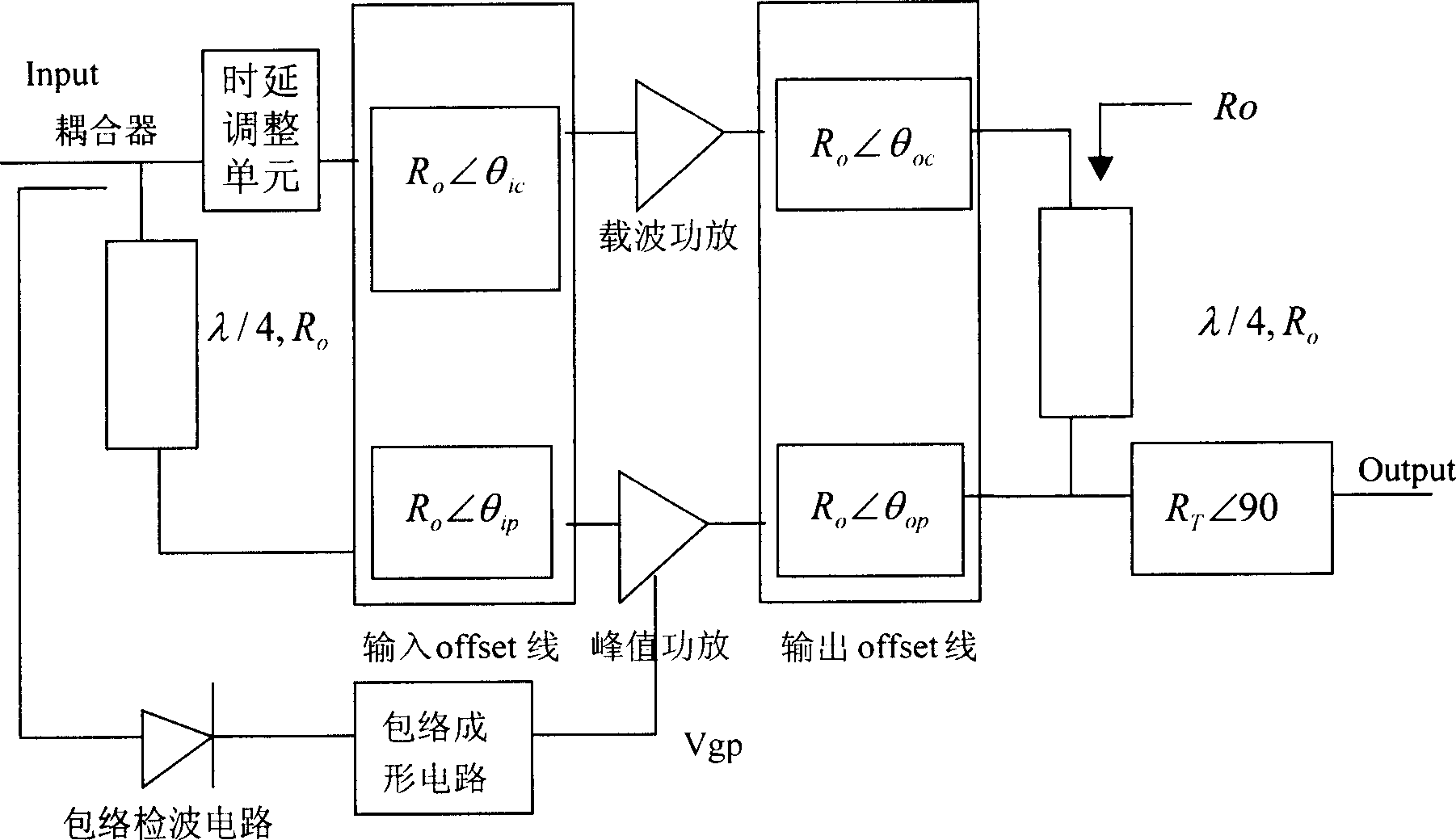
Power amplifier
The invention discloses a power amplifier device, which is characterized by the following: the signal amplitude and signal phase of crest value power amplifier route or carrier power amplifier route are adjusted by phase-adjusting unit; the invention realizes active load drag and improves the overall efficiency of Doherty power amplifier; the system adjustment phase shifter and attenuator control voltage to adjust the amplitude and phase, so the problem of Doherty output measure is reduced; the flexibility of Doherty power amplifier design is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
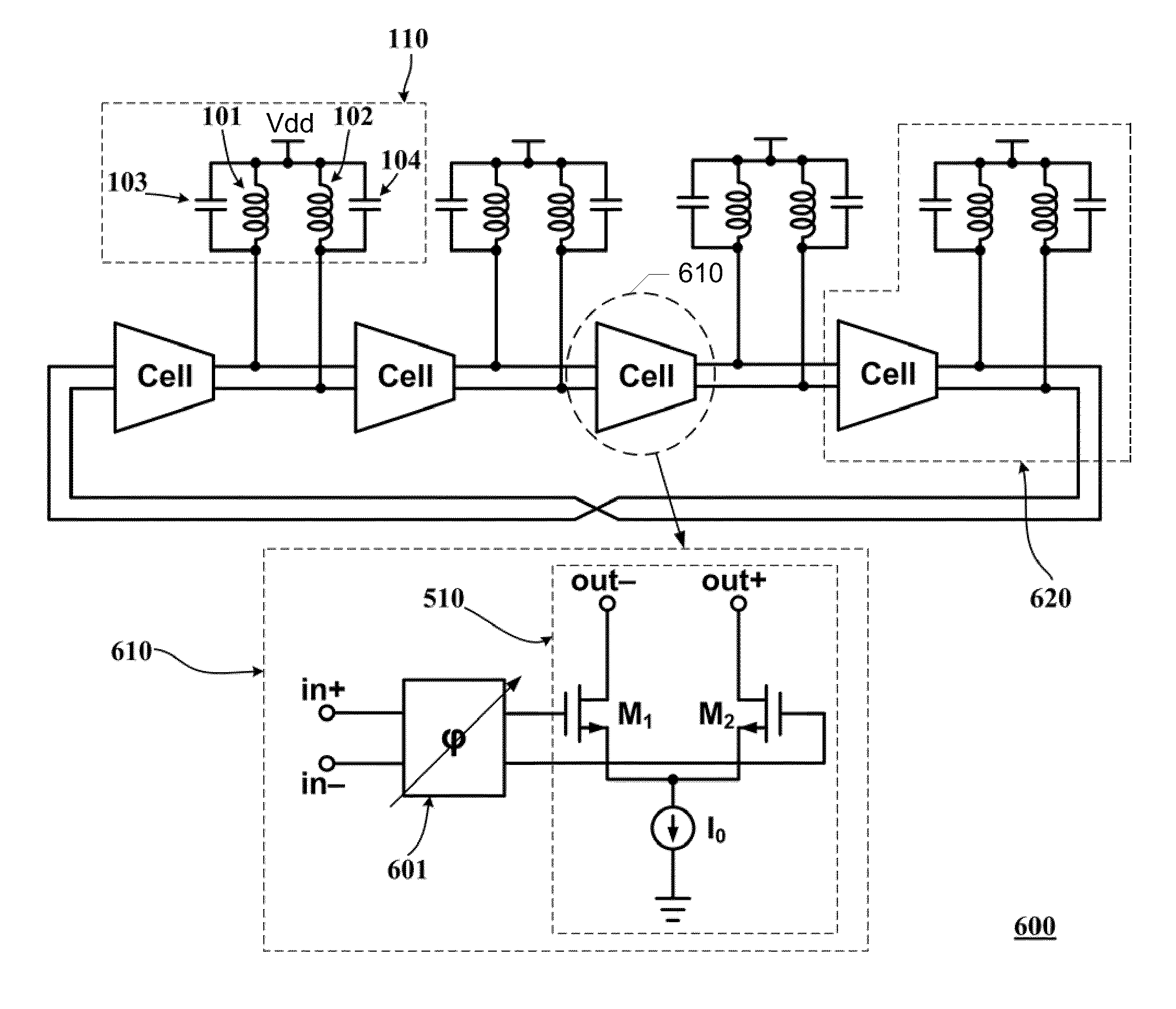
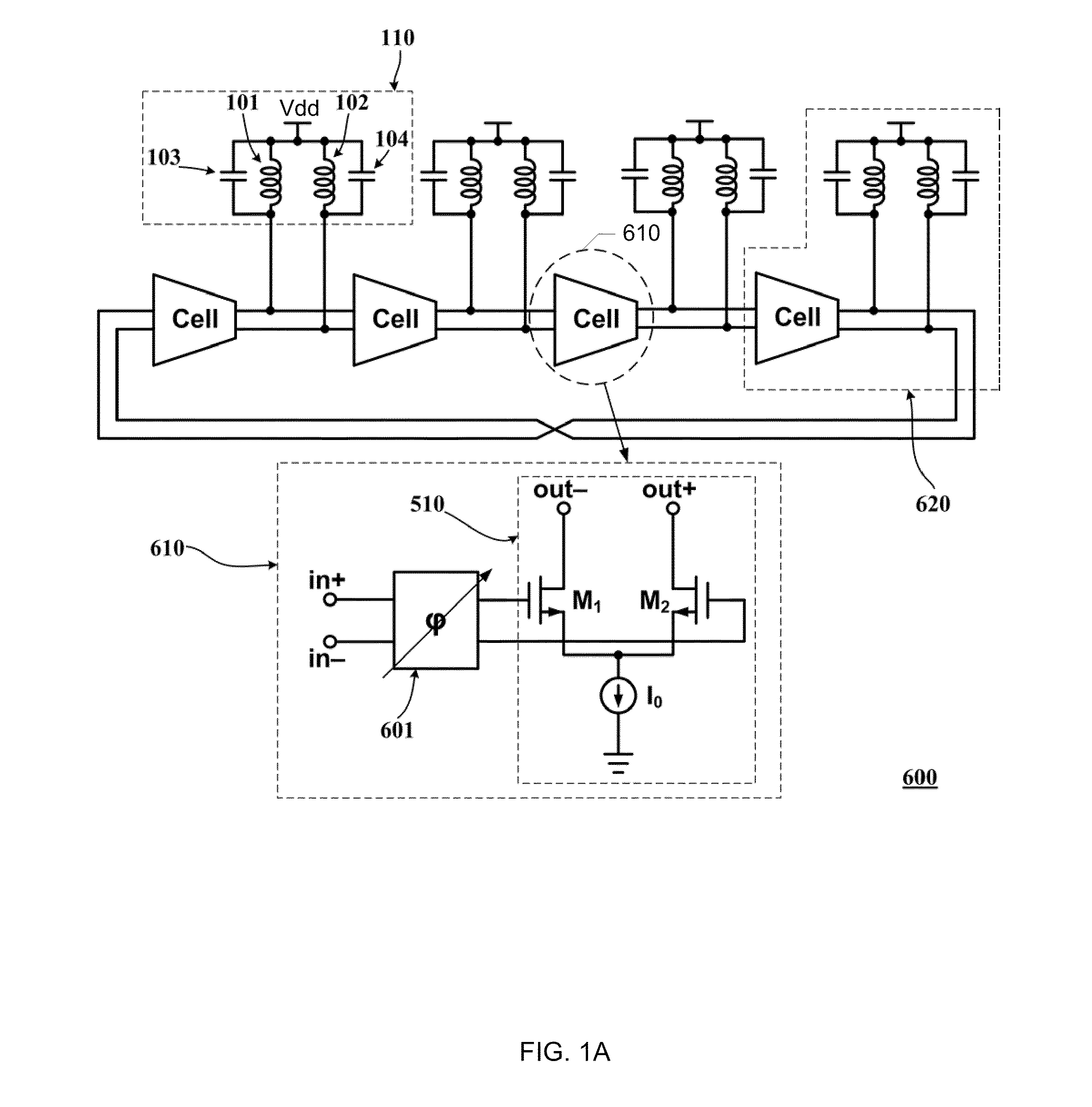
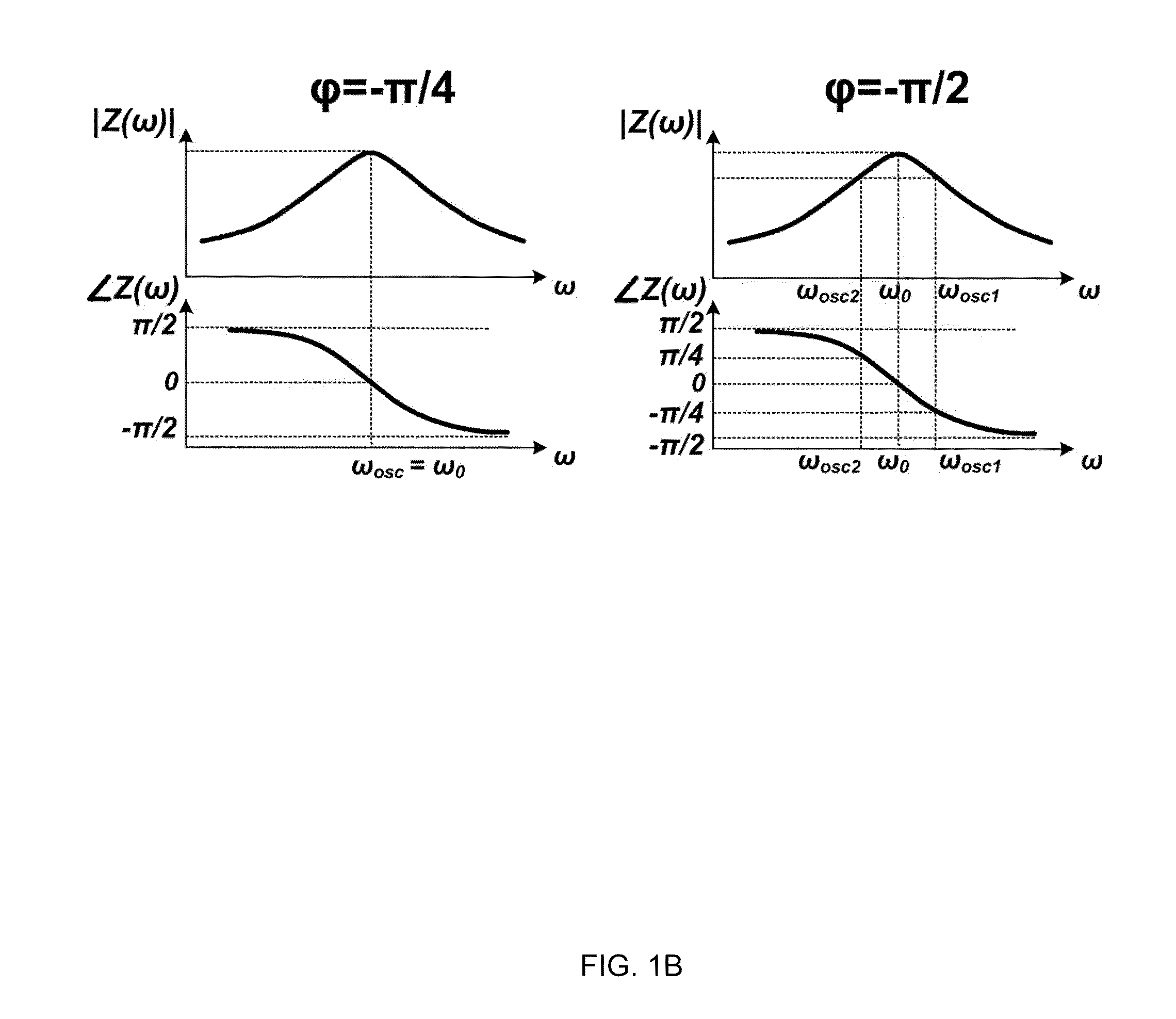
Method and apparatus for tuning frequency of LC-oscillators based on phase-tuning technique
ActiveUS8339208B2Limited rangeReduce power supply voltagePulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsPhase shiftedPhase shift module
A tunable multiphase ring oscillator includes a plurality of stages connected in series in a ring structure, where each stage generating a stage output from a stage input. Each stage of the tunable multiphase ring oscillator includes a plurality of trans-conductance cells, each generating an output from at least one portion of the stage input. Each stage further includes at least one phase shifting module for imparting at least one phase shift to the at least one portion of the stage input, an oscillator unit for generating the stage output from a combination of the plurality of outputs, and means for varying at least one of the plurality outputs so as to adjust a phase of the stage output.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
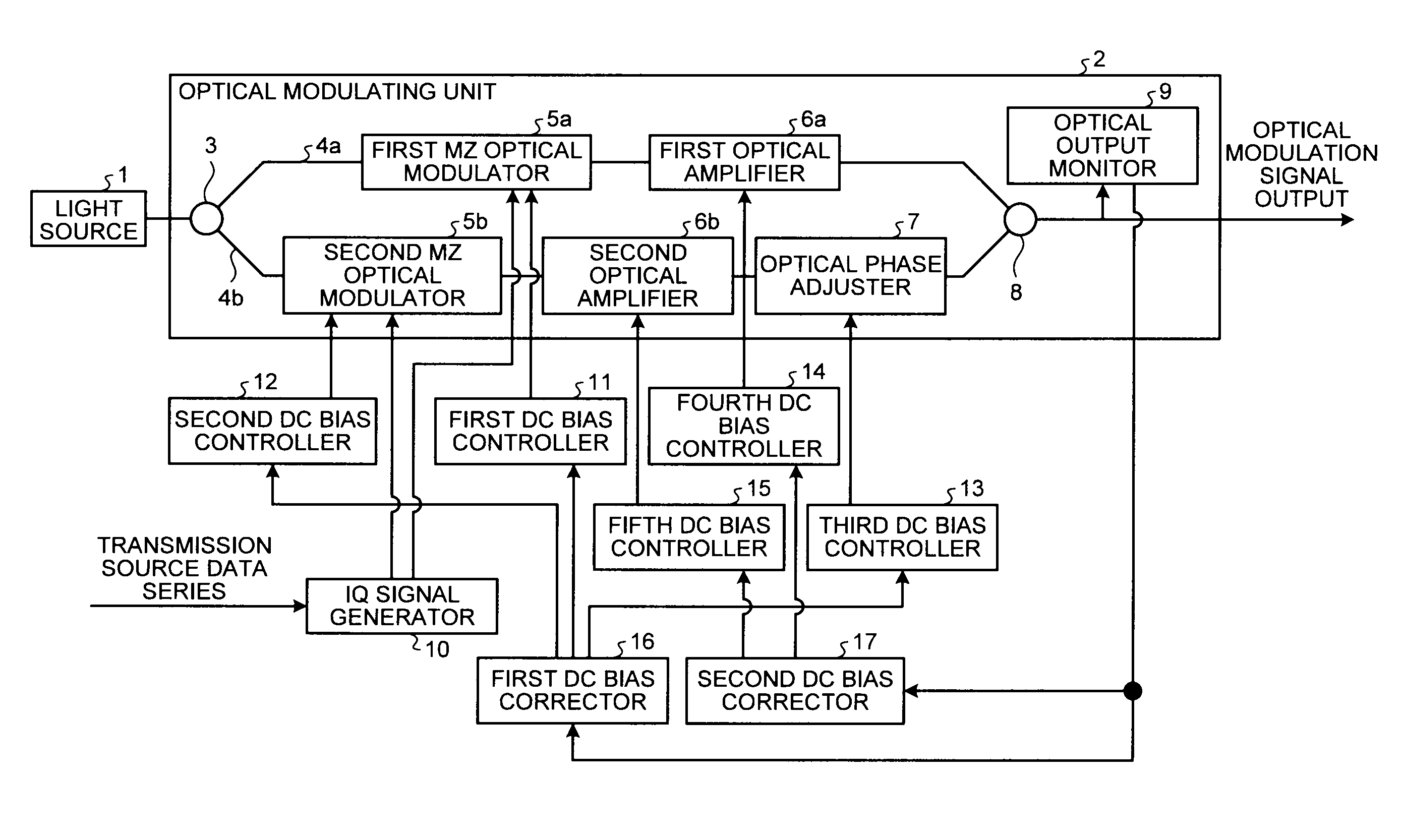
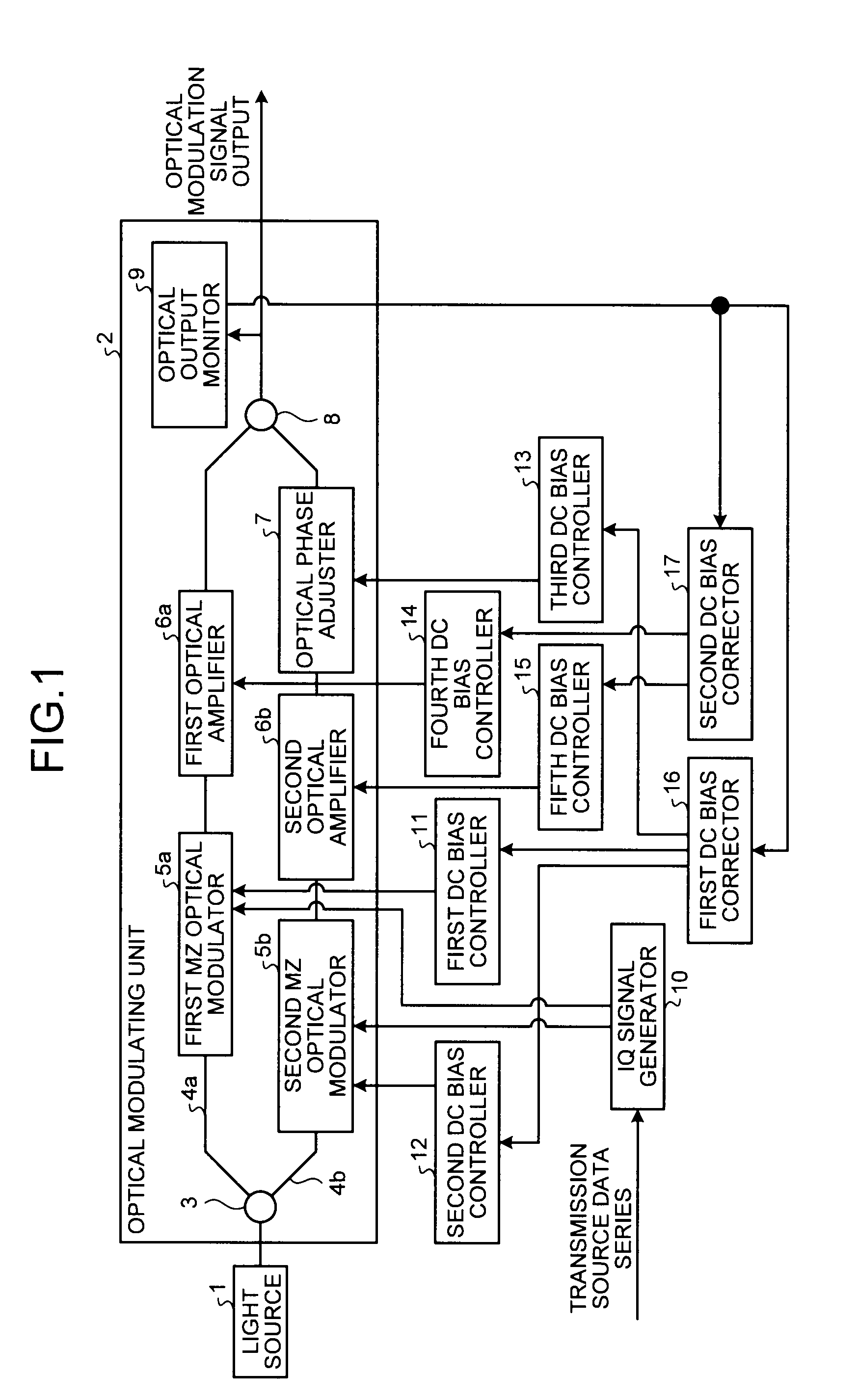
Optical modulator, optical transmission device, and bias adjusting method
ActiveUS20120008963A1Solve problemsElectromagnetic transmittersElectromagnetic receiversMultiplexingAudio power amplifier
Included are a first modulator, a second modulator, a first optical amplifier that amplifies an output of the first modulator at an amplification factor based on a first bias signal, a second optical amplifier that amplifies an output of the second modulator at an amplification factor based on a second bias signal, an optical phase adjuster that phase-rotates an output of the second optical amplifier, an optical multiplexer that multiplexes an output of the first optical amplifier with an output of the optical phase adjuster, and a second bias corrector that generates a first pulse signal and a second pulse signal, which are complementary to each other, and obtains a first bias value and a second bias value based on a change of strength of an output signal of the optical multiplexer. The first and second pulse signals are superimposed on the first and second bias signals, respectively.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Power amplifying apparatus and radio communications apparatus using same
InactiveUS20030214359A1Reduce total powerLow costAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlAudio power amplifierThird harmonic
By extracting a portion of RF signals from an input side of a multistage RF amplifier with a detector, and converting extracted signals into envelope signals, low-frequency second-harmonic distortion components are efficiently extracted. Then, the extracted low-frequency second-harmonic distortion components are amplified with a low-frequency amplifier, and phase adjusted with a phase shifter, after which they are injected into a gate or base bias of the final stage of the multistage RF amplifier. As a result, the low-frequency second-harmonic distortion components are converted into third-harmonic distortion due to the non-linearity of transistors, and the third-harmonic distortion thus obtained cancels out the third-harmonic distortion originally present in the multistage RF amplifier.
Owner:SONY CORP
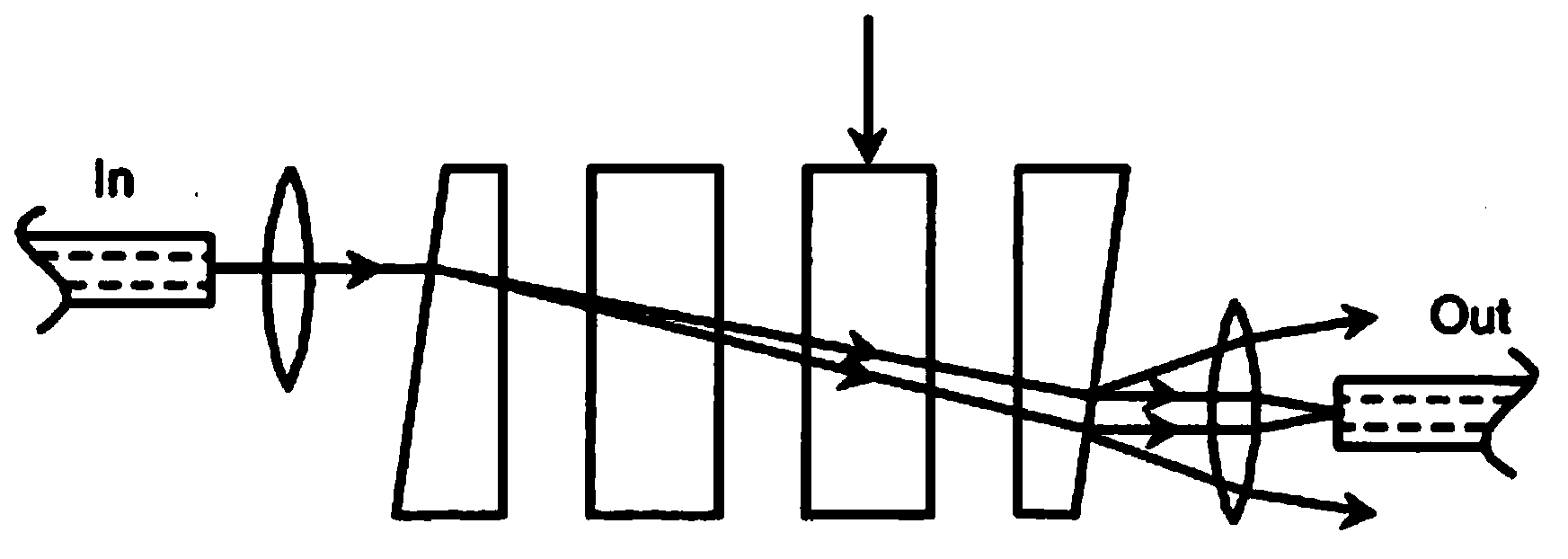
Stub array microstrip line phase shifter
Systems and methods which utilizes a stub array microstrip line for providing a phase shifter configuration are shown. A stub array microstrip line phase shifter of embodiments may comprises a microstrip line structure, an isolation structure, and a phase tuning structure cooperative to provide phase shifting of signals passed through the microstrip line structure. A microstrip line structure comprises a stub array microstrip line having a plurality of microstrip stubs provided in association with a slotted ground plane having a plurality of slots. The stub array microstrip line is adapted to provide compensation for capacitance and / or inductance associated with the slots of the slotted ground plane. A phase tuning structure provides coupling of signals transmitted by the stub array microstrip line to the slots of the slotted ground plane for signal phase shifting.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Frequency tuning and phase shifting techniques using 1-dimensional coupled voltage-controlled-oscillator arrays for active antennas
InactiveUS8558625B1Reduce phase noiseLarge tuning rangePulse generation by logic circuitsOscillations generatorsPhase noiseBeam steering
A technique for enhancing the frequency tuning range for monolithic RF source generation using fully-integrated coupled Voltage-Controlled-Oscillator (VCO) arrays that contain an odd number of VCOs. Fully-monolithic SiGe VCO arrays using on-chip inductor and varactor with on-chip bias current sources have been carefully designed and simulated in IBM 7HP 0.18 μm BiCMOS technology and taped out for fabrication. The SPICE simulated frequency and phase tuning of the 1-D VCO×5 array is dependent on the edge VCOs termination impedance, the tuning voltages, and the VCO coupling strength. The simulated data suggests that the enhanced tuning range and beam steering can be accomplished using coupled-VCO arrays without needing complex and bulky phase shifters. This design technique imposes no apparent phase noise penalty but can provide simulated RF frequency tuning range of ˜40% and also ˜+ / −25° beam steering for active antennas applications.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
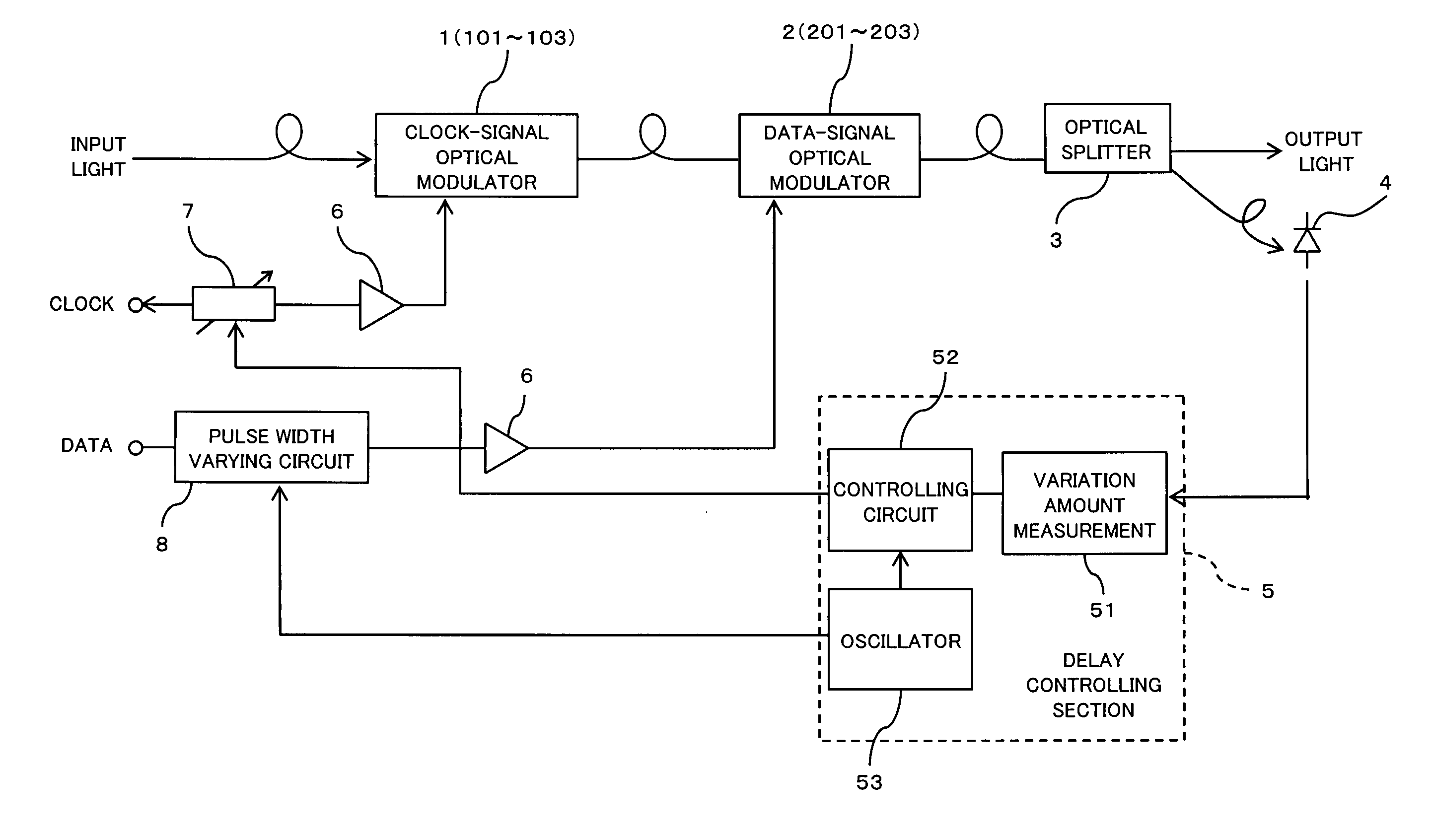
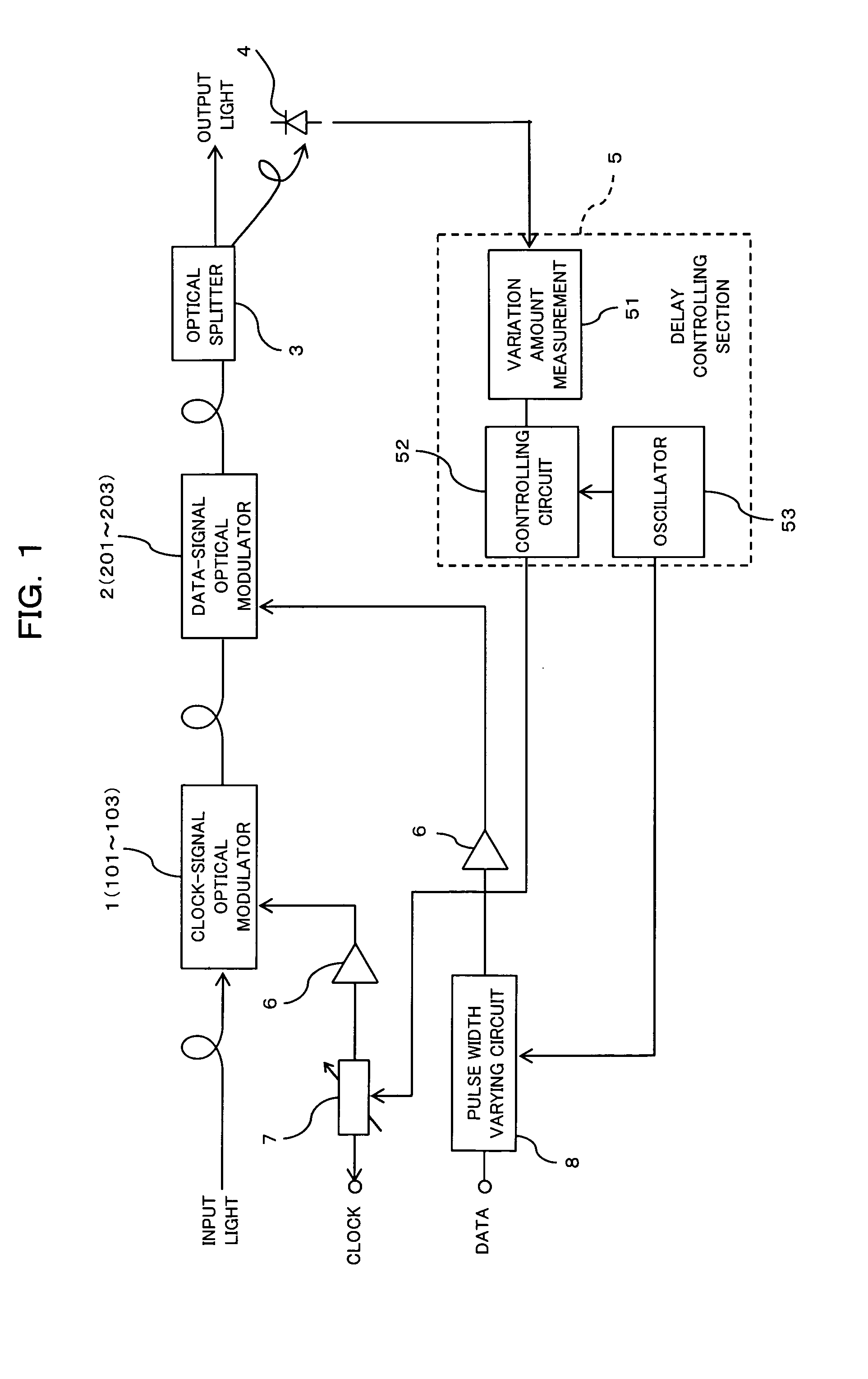
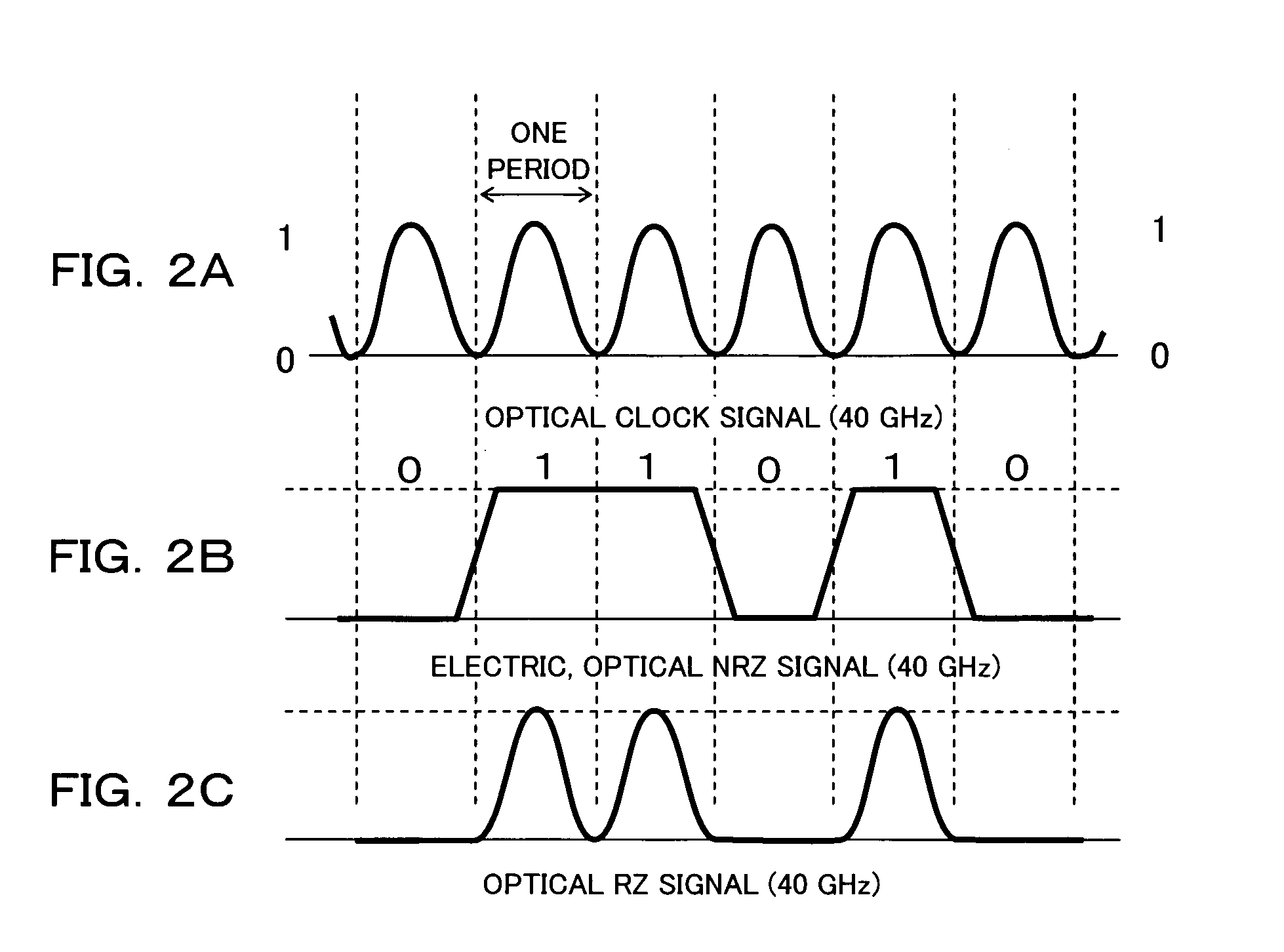
Driving circuit for optical modulator and method for driving optical modulator
InactiveUS20050238368A1Electromagnetic transmittersTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsPhase differenceData signal
For an optical modulator for modulating input light using a clock signal and a data signal respectively, a pulse width varying circuit varies the pulse width of the data signal that is used for modulating the input light, and a delay control section carries out controls based on the light output power of the optical modulator in this state in such a manner that the phase difference between the clock signal and the data signal becomes minimum. As a result, it is possible to always adjust phases of the clock signal and the data signal to optimum phases and to stably obtain a fine light output waveform.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com