Patents
Literature
285results about "Color burst signal generation/insertion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
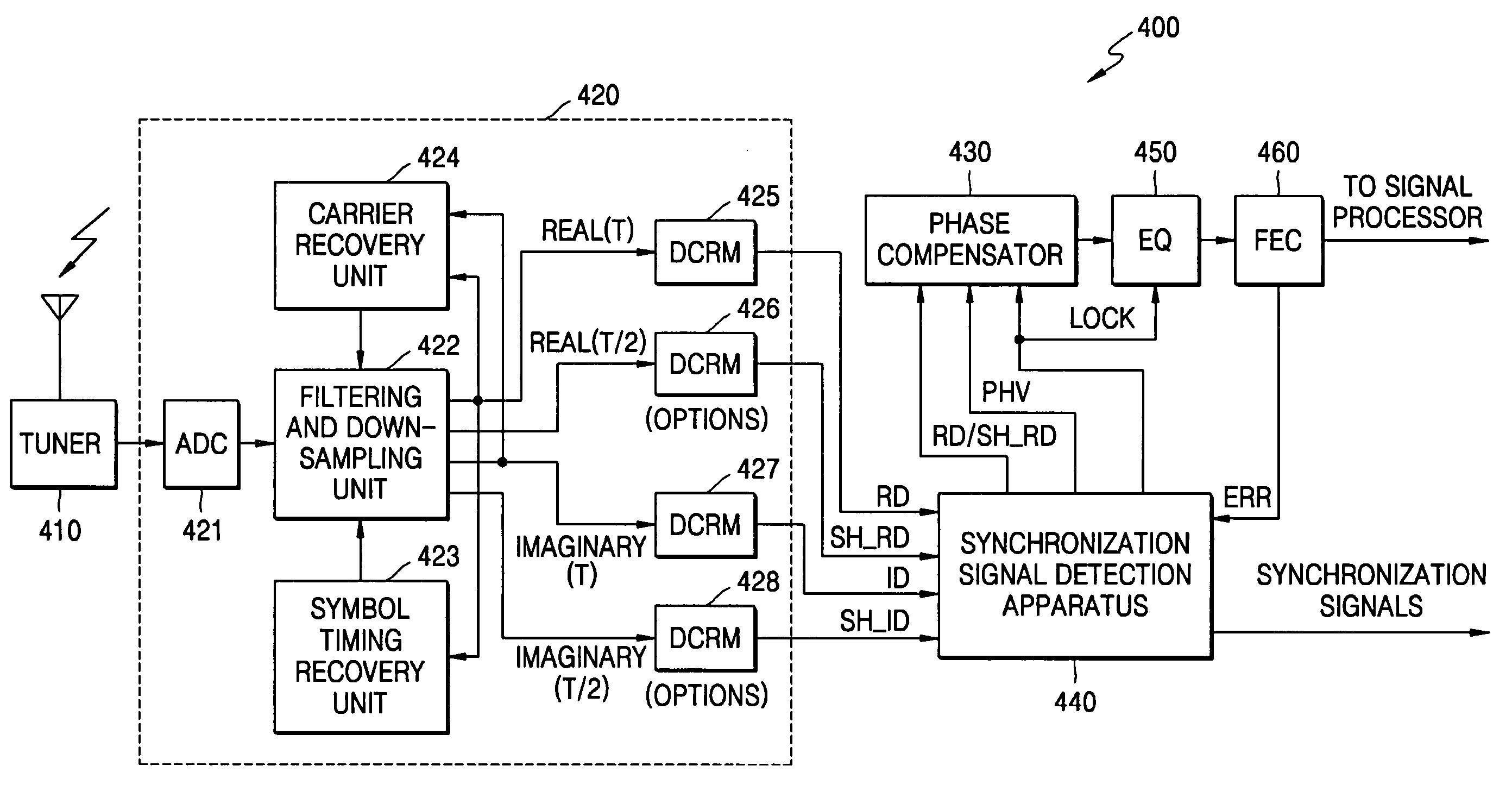
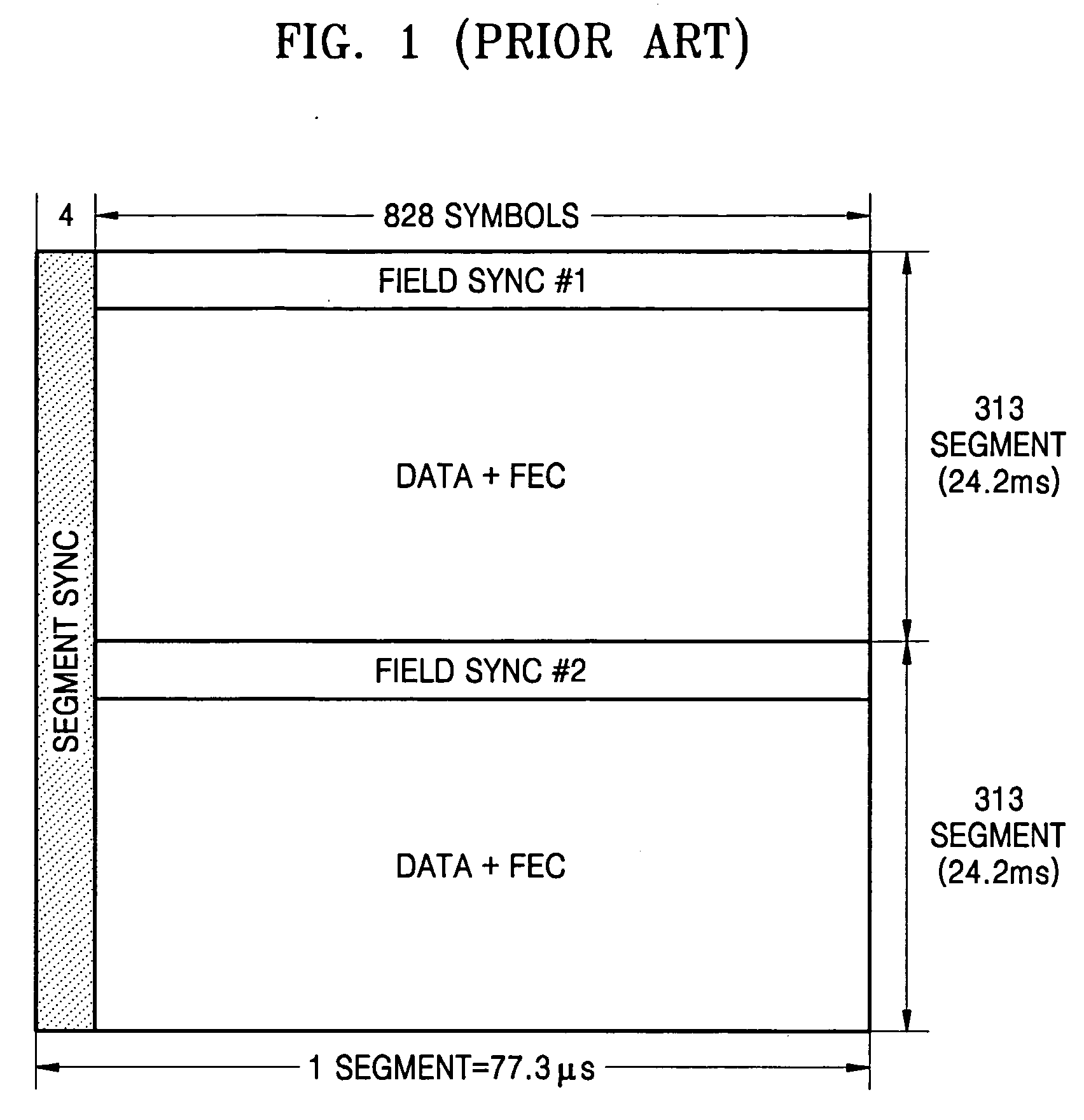
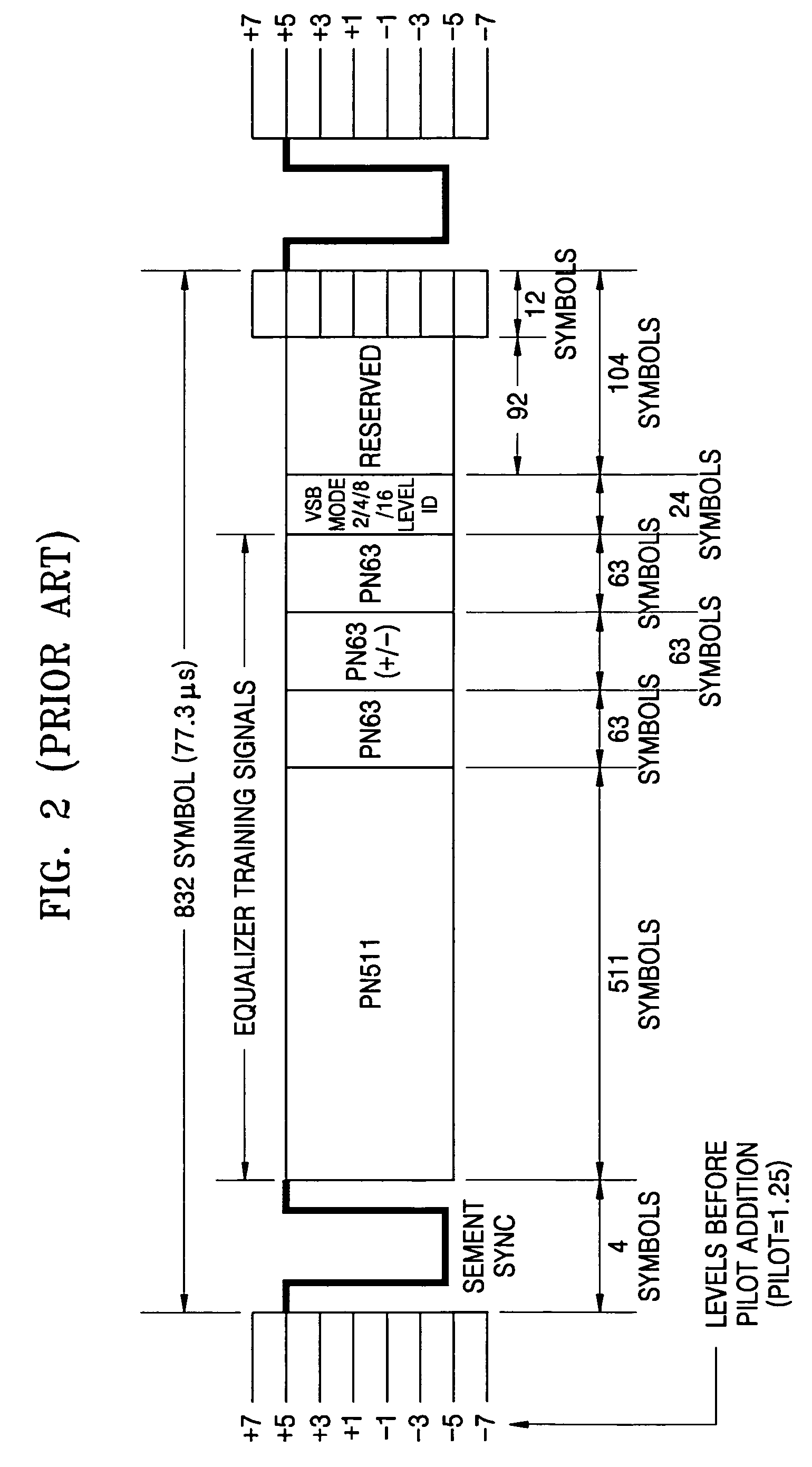
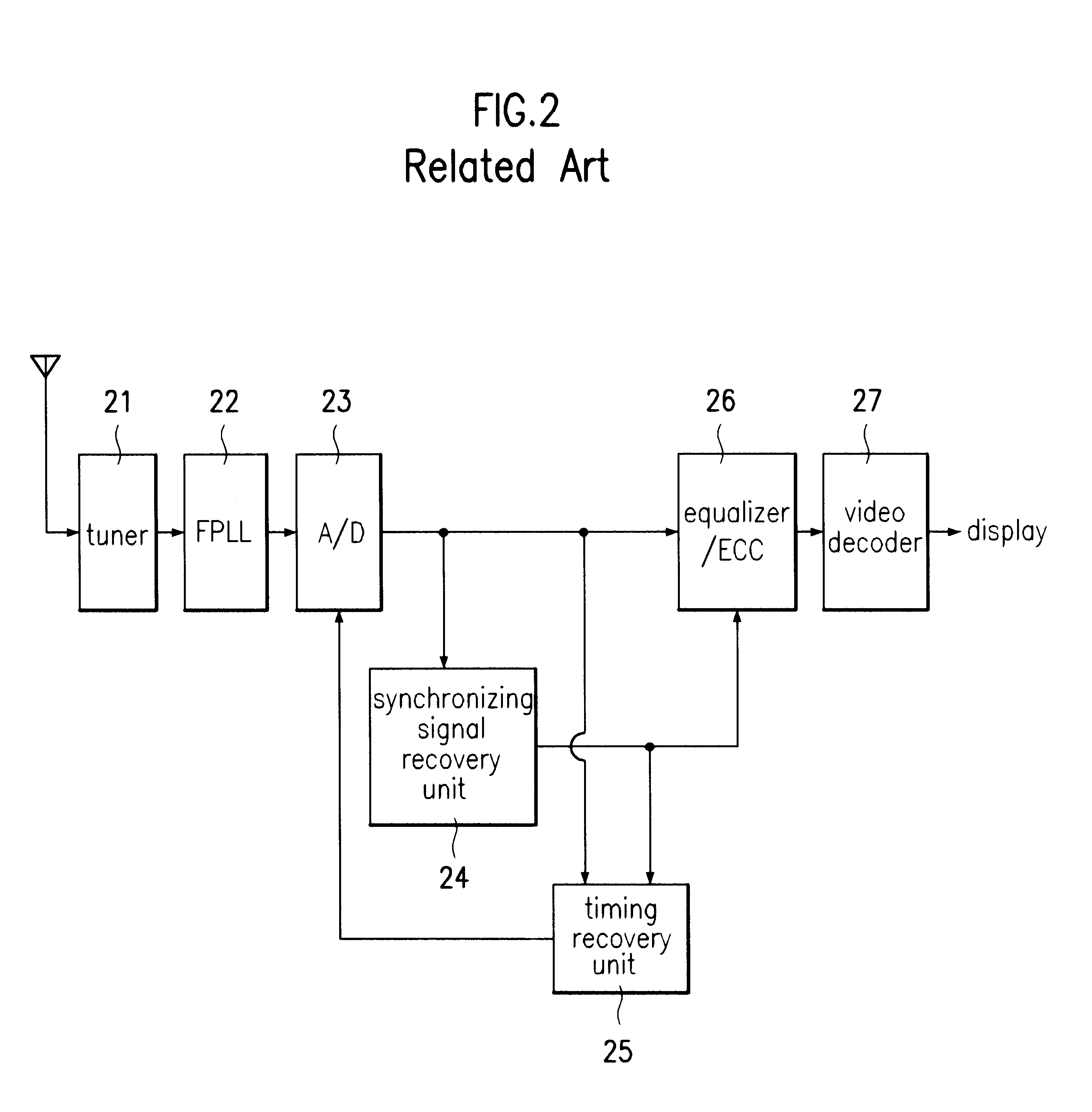
Synchronization signal detection circuit and method of digital television (DTV) receiver
InactiveUS20060078072A1Guaranteed uptimeStable operation can be assuredTelevision system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionControl signalDTV receiver
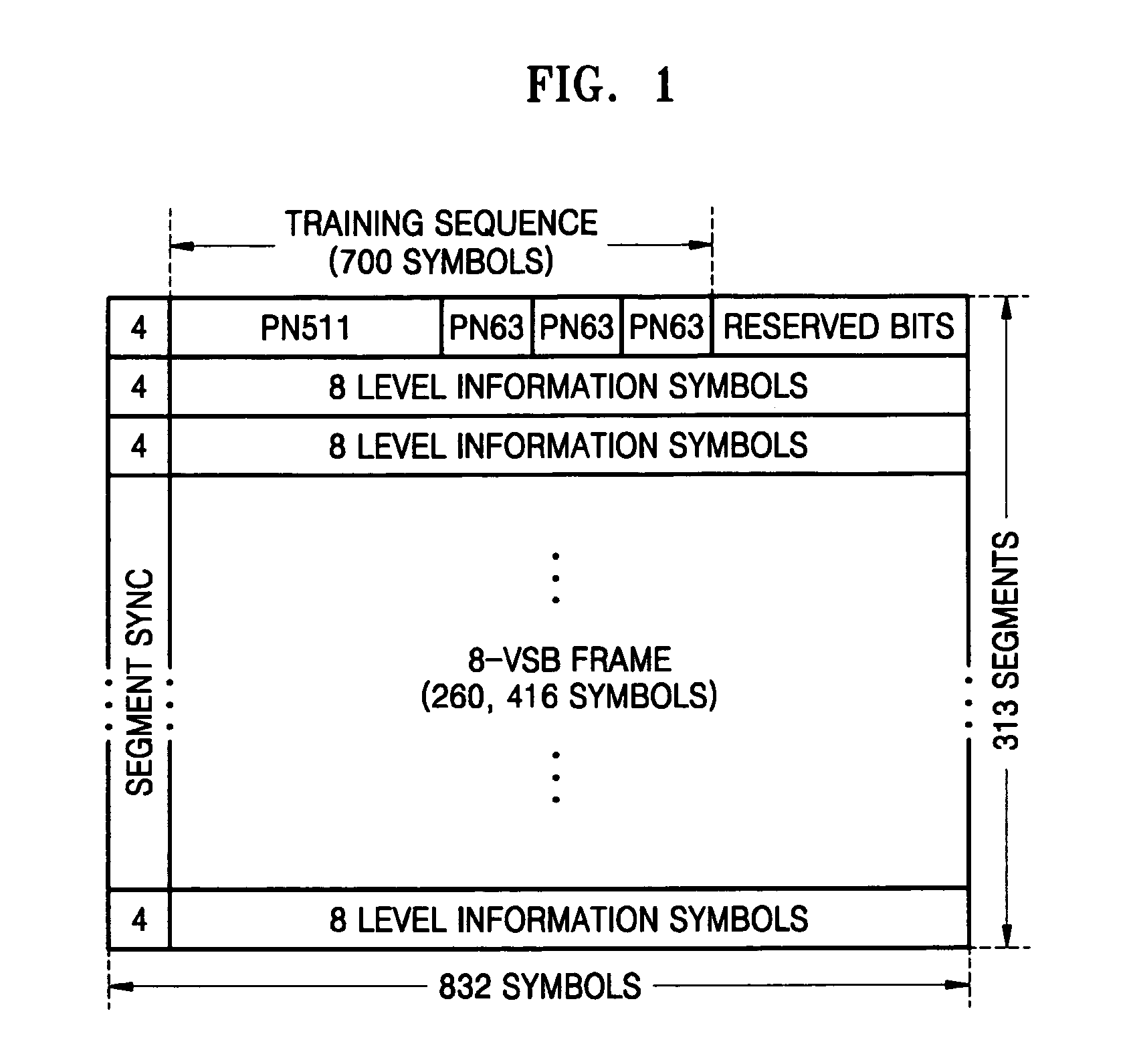
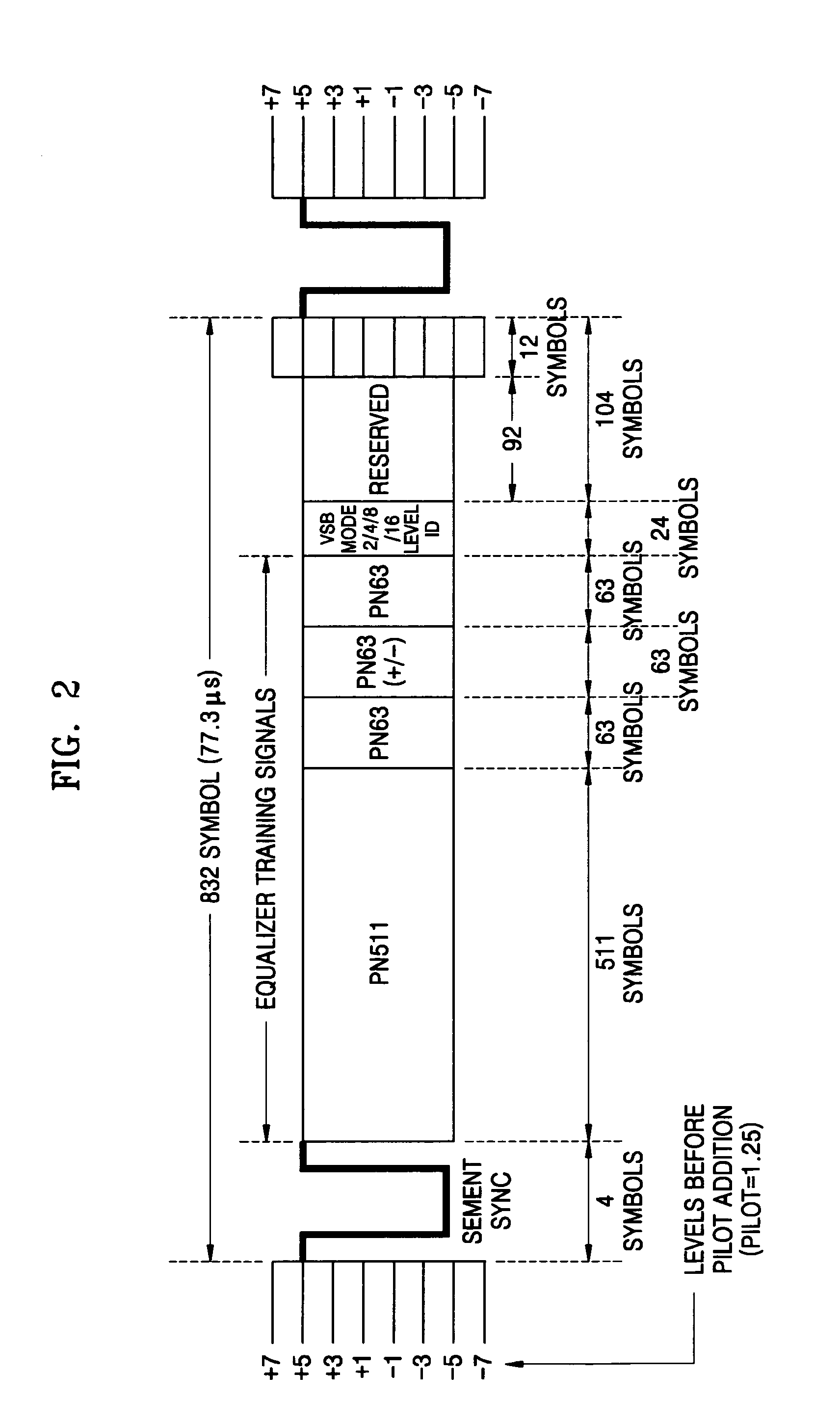
A synchronization signal detection circuit and method of a digital TV (DTV) receiver are provided. The synchronization signal detection circuit determines a precise main path by determining powers in consideration of the influence of multiple paths near signals located at a peak value location and guarantees a stable operation of an equalizer by using error values output from a decoder to generate a synchronization locking control signal. A power signal based on the correlation of the received signal with a PN511 sequence is filtered to compensate for a dynamic multipath distortion (e.g., due to other multipath signals near signals located at a peak value location). The magnitude of the filtered power signal is then compared (e.g., with a predetermined threshold value) to determine the position of the main path (e.g., at the peak value location, or at a pre or post multipath signal location).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
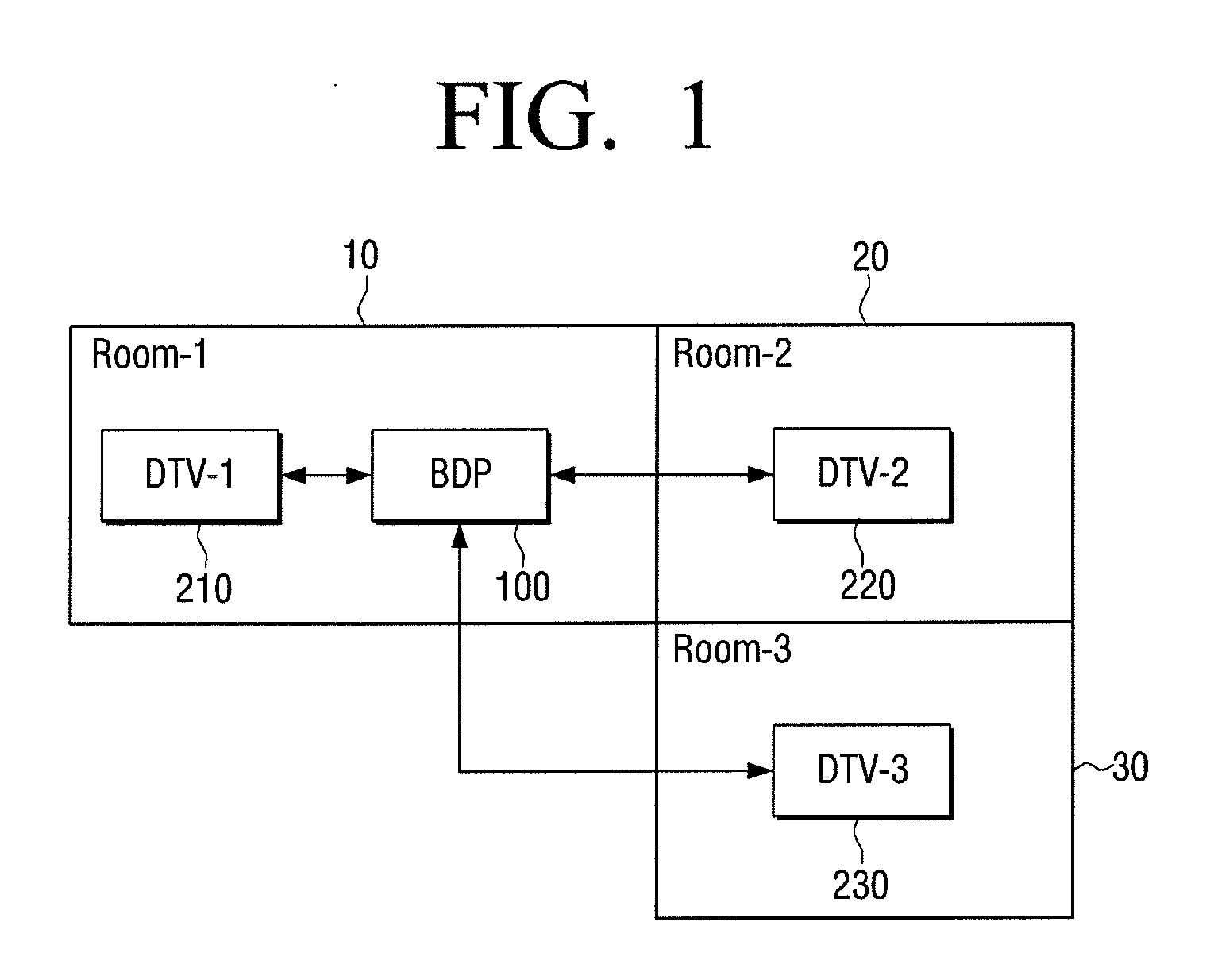
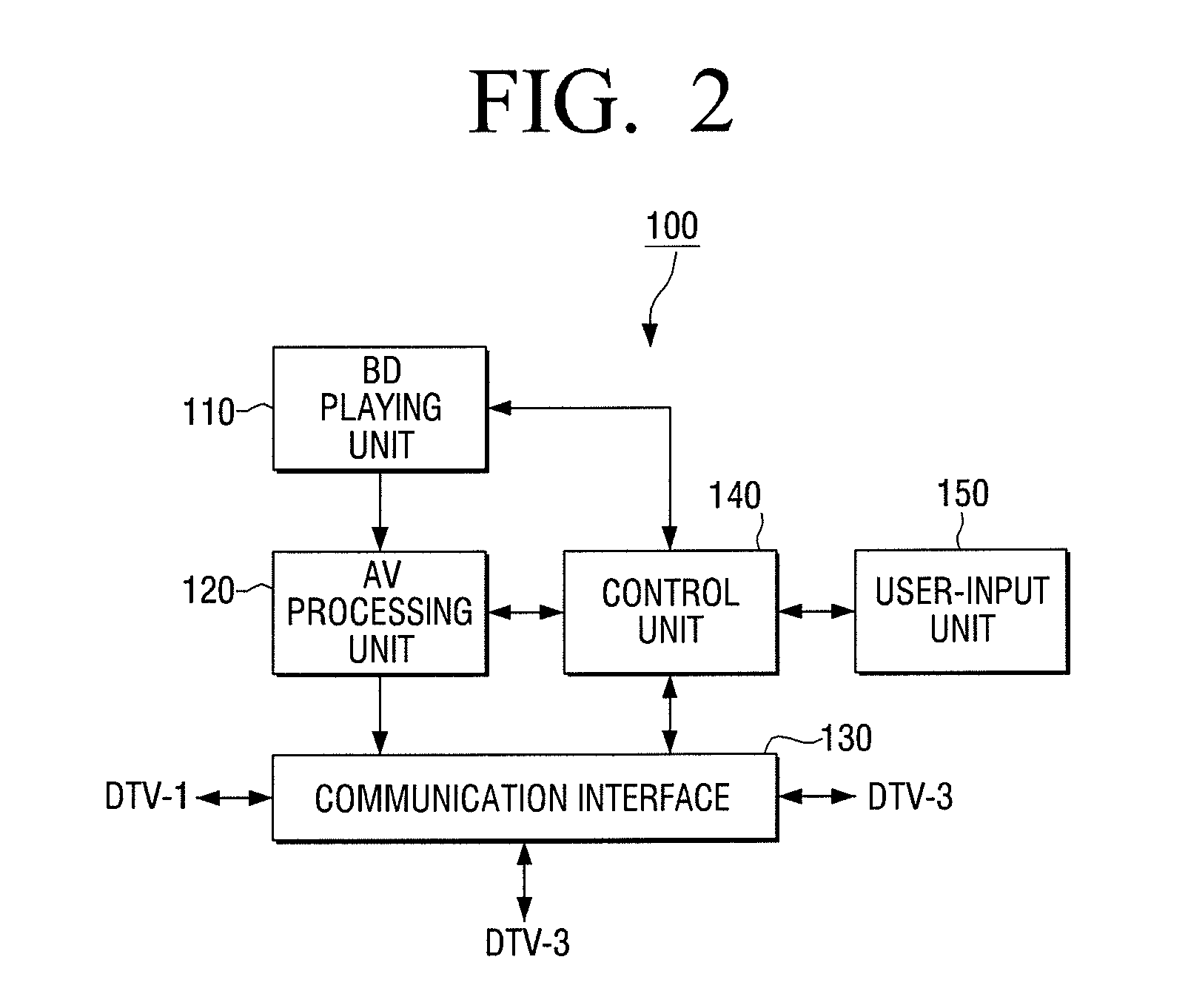
Method for converting sink device and apparatus for providing contents using the same
ActiveUS20110164180A1Television system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionComputer hardware
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
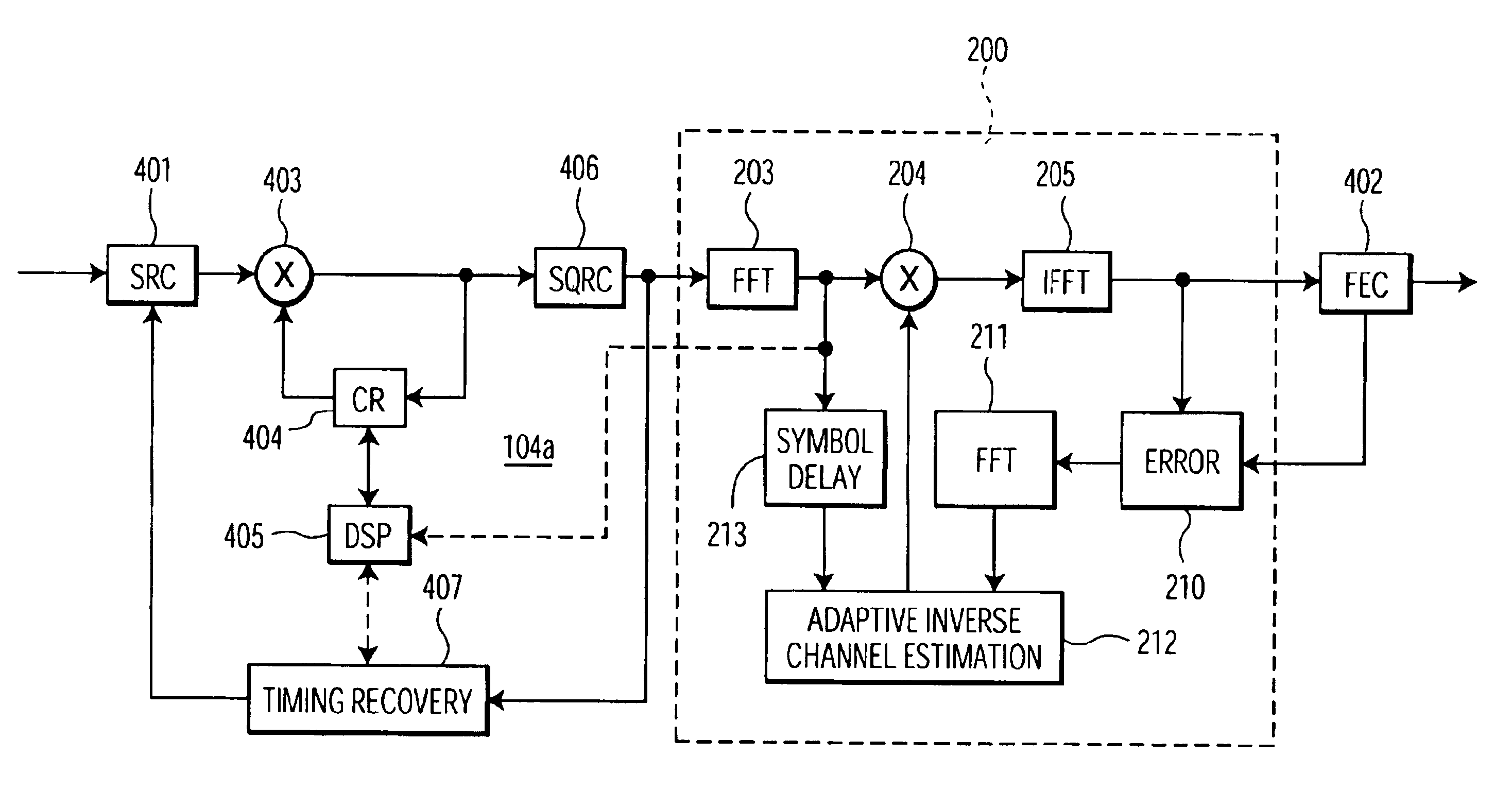
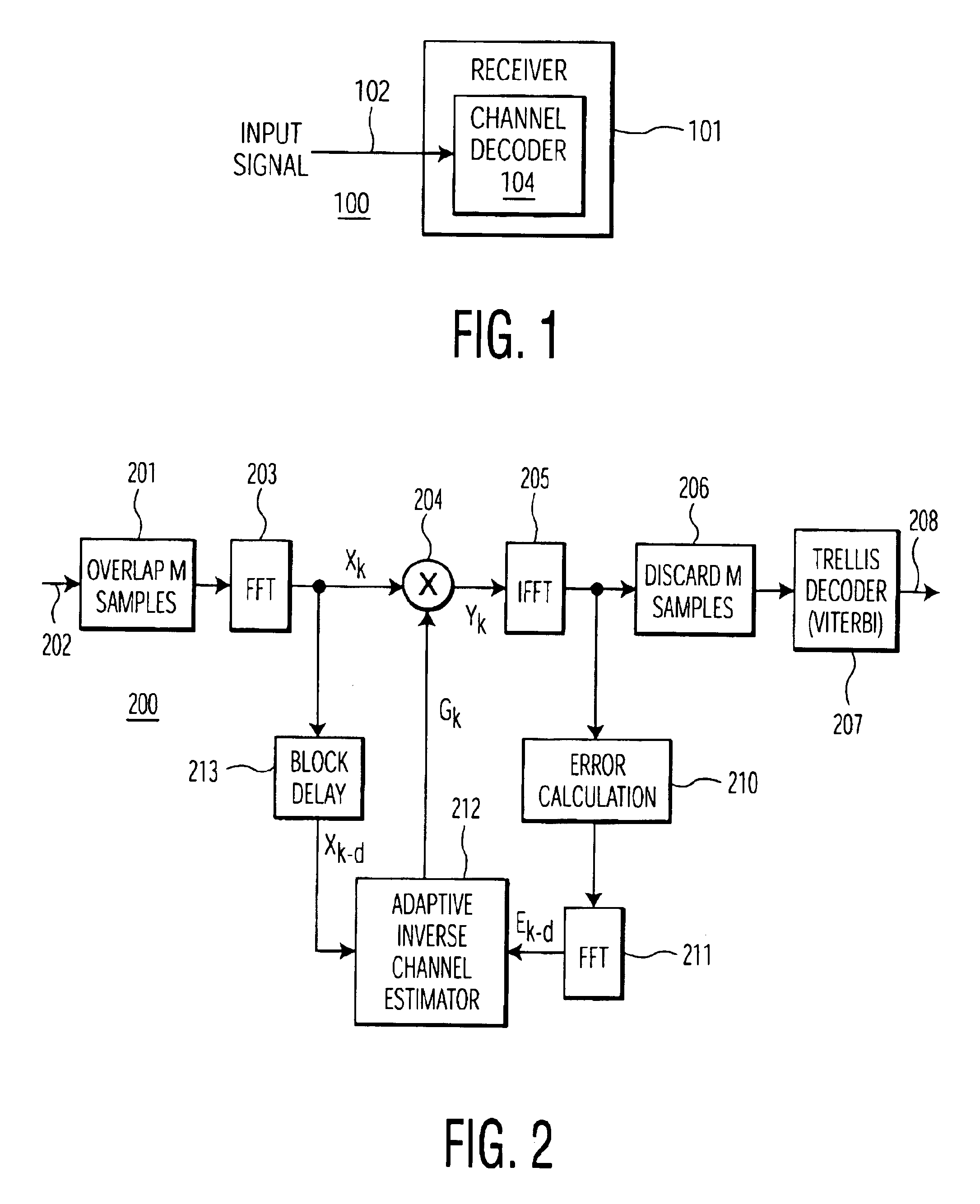
Frequency-domain equalizer for terrestrial digital TV reception
InactiveUS6912258B2Few computational resourceImproving integrated circuit cost-effectiveness of the multi-standard demodulatorTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksCost effectivenessSelf adaptive
A single integrated circuit multi-standard demodulator includes an adaptive inverse channel estimator for frequency domain equalization which employs a recursive least square cost function in estimating the inverse channel from the received signal and an error estimate. Utilizing a diagonal correlation matrix, the solution to may be determined utilizing fewer computational resources than required by conventional frequency domain equalizers, shifting from a computational intensive to memory intensive implementation. The memory requirement is fully satisfied by memory available within conventional OFDM decoders, and the necessary computational resources may be readily mapped to the resources available within such decoders, improving integrated circuit cost-effectiveness of the multi-standard demodulator.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
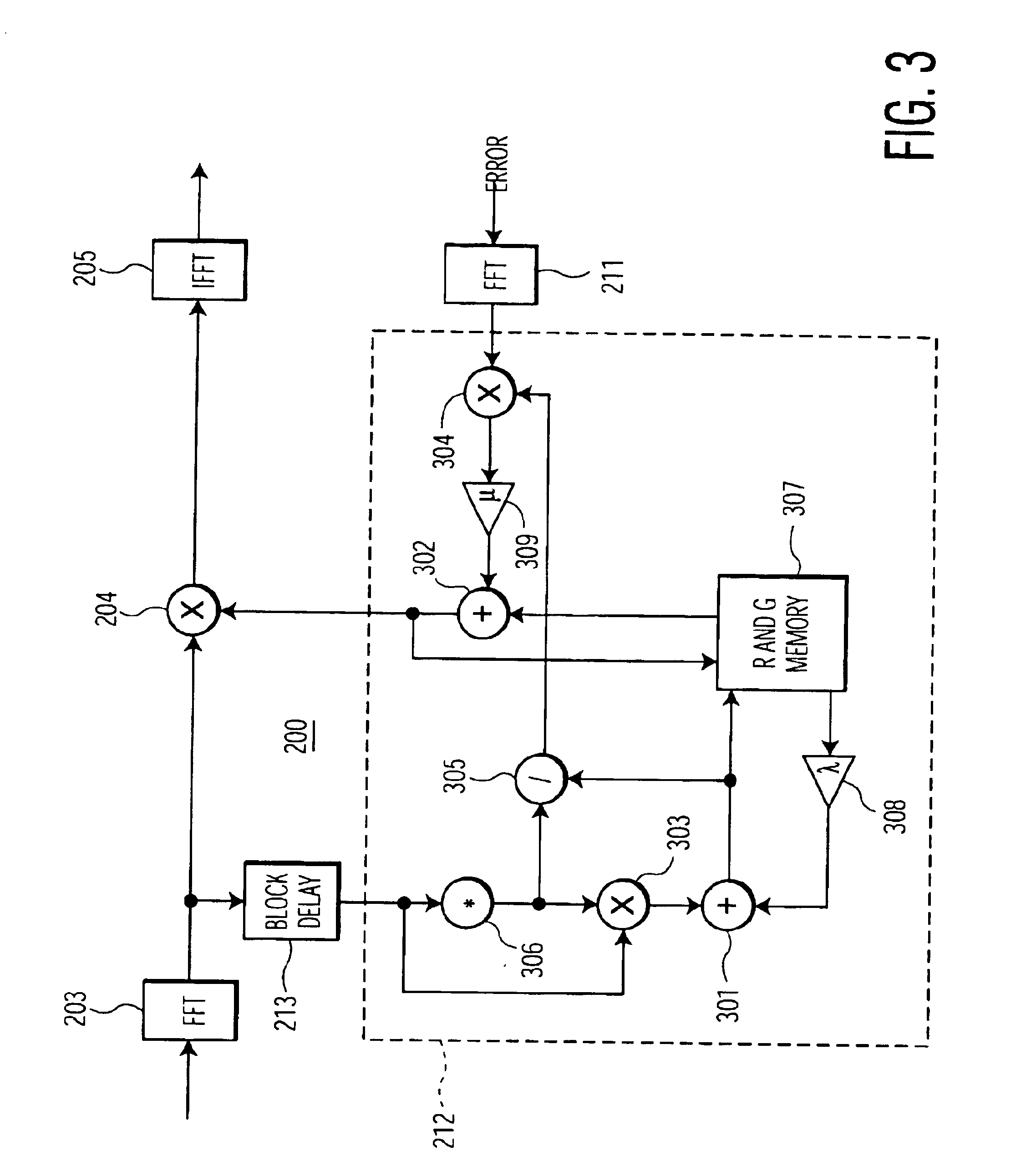
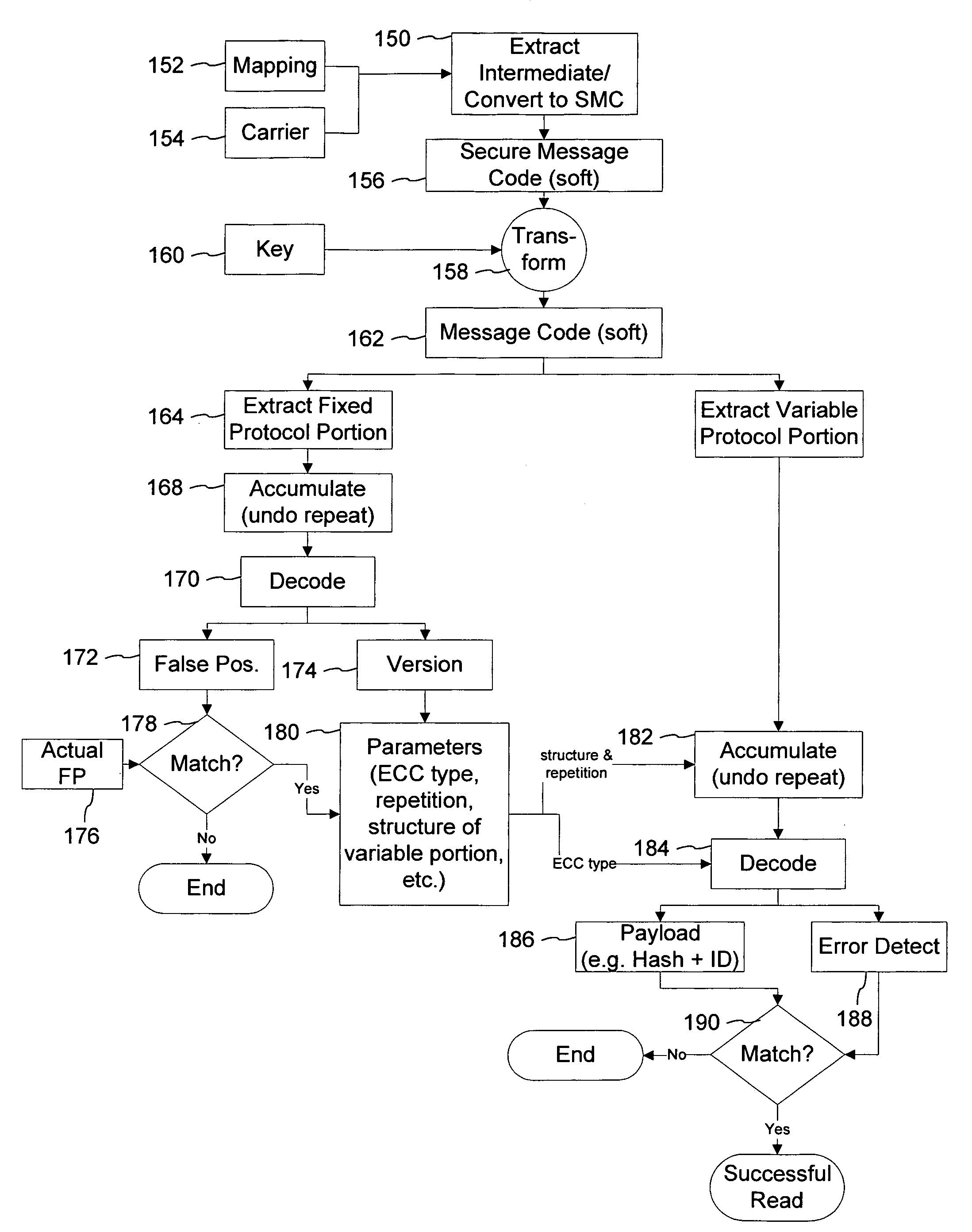
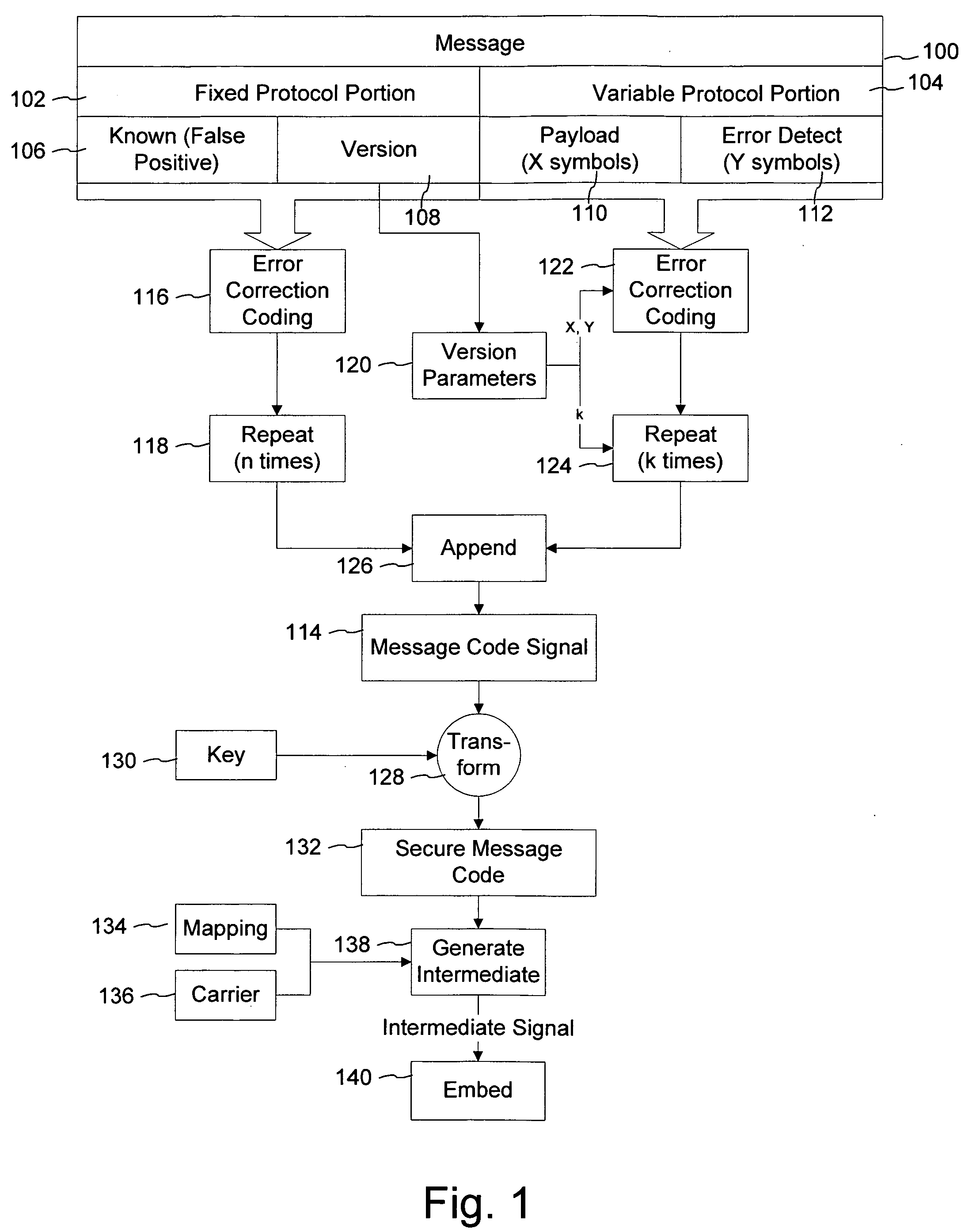
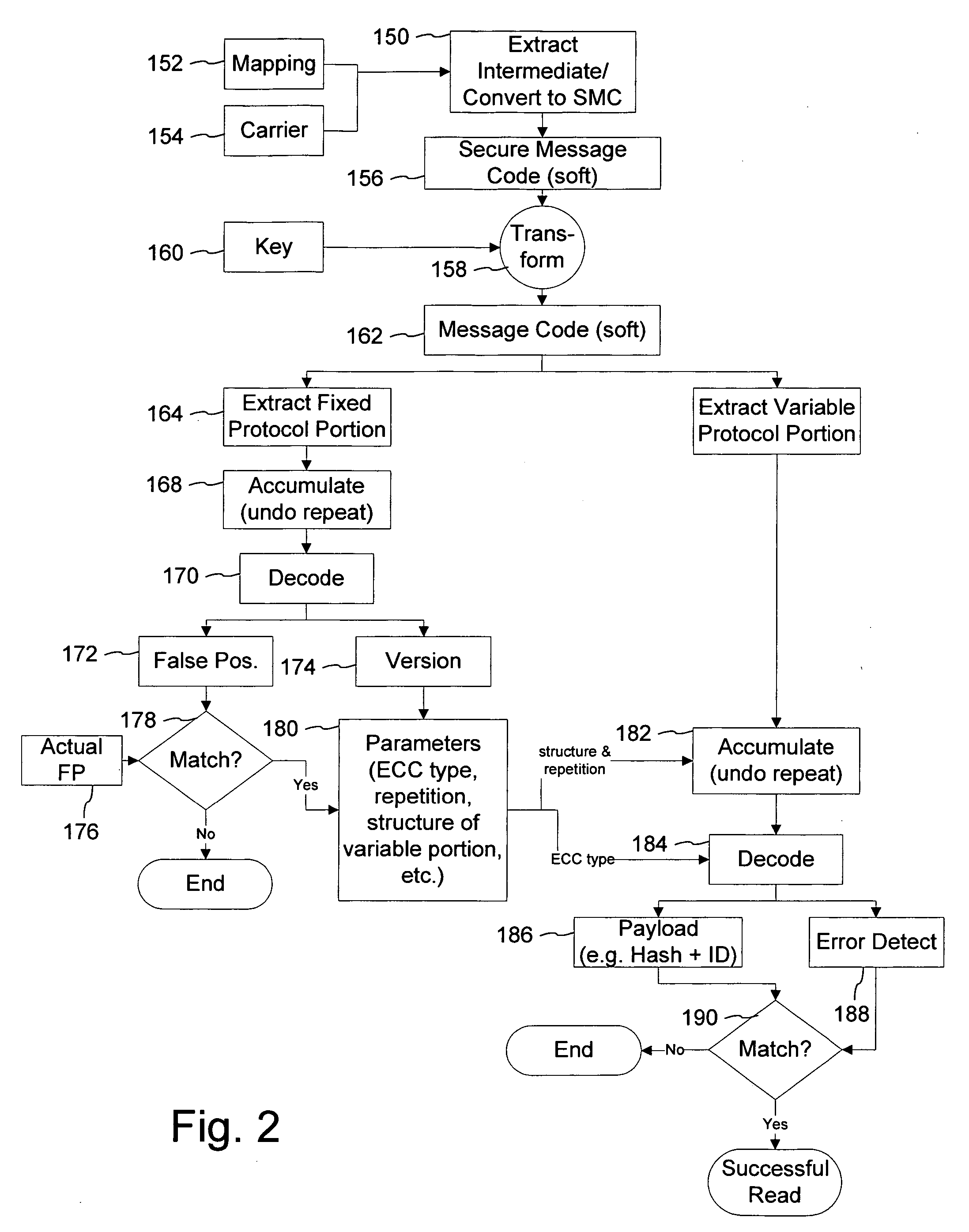
Watermark payload encryption for media including multiple watermarks
ActiveUS20050262351A1Key distribution for secure communicationColor burst signal generation/insertionRandomizationEncryption
The present invention provides encryption techniques useful with digital watermarking payloads. In a first implementation, we encrypt one of two different cooperating watermark payloads, but the encryption and payload data structure helps to authenticate both payloads. Another implementation provides a three encryption key pair system for managing messages and watermark embedding. Still another aspect of the invention is a watermark embedding process that uses encryption to whiten, randomize or spread a message, instead of convention spread-spectrum modulation.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Method and apparatus for generating a reference television signal
ActiveUS7764305B2Easy and accurate methodReduce operating costsTelevision system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionTelevision stationSignal generator
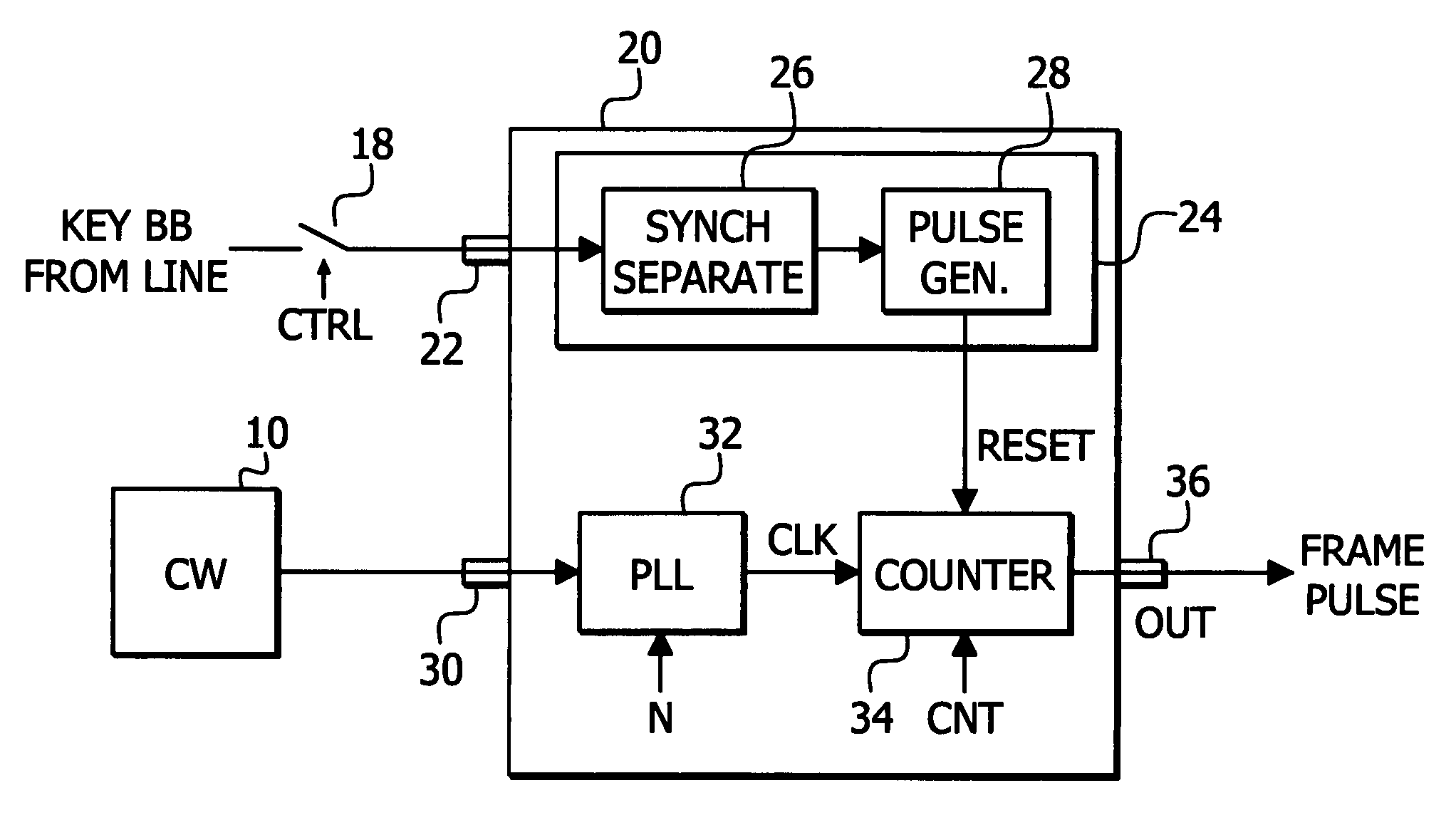
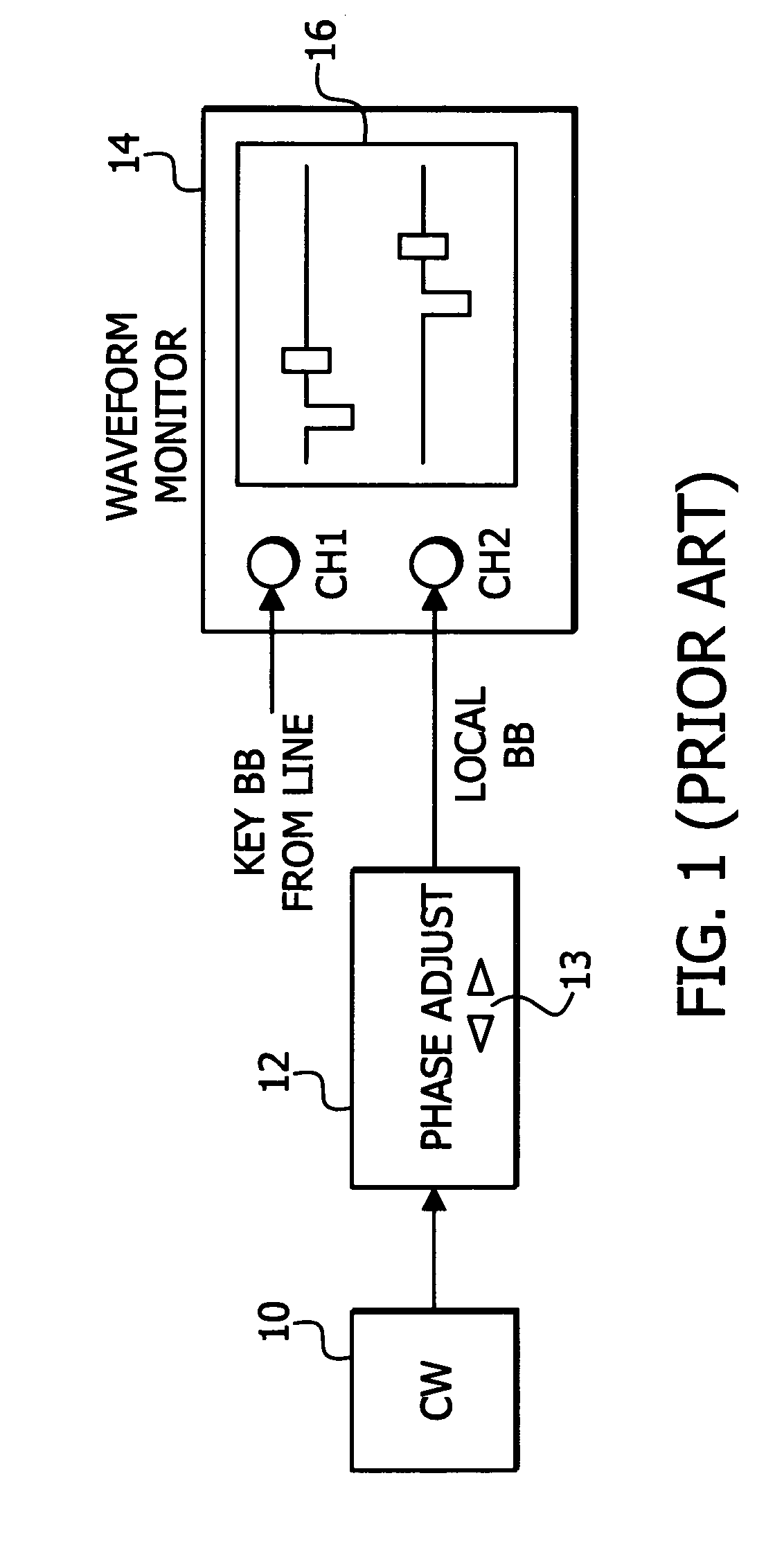
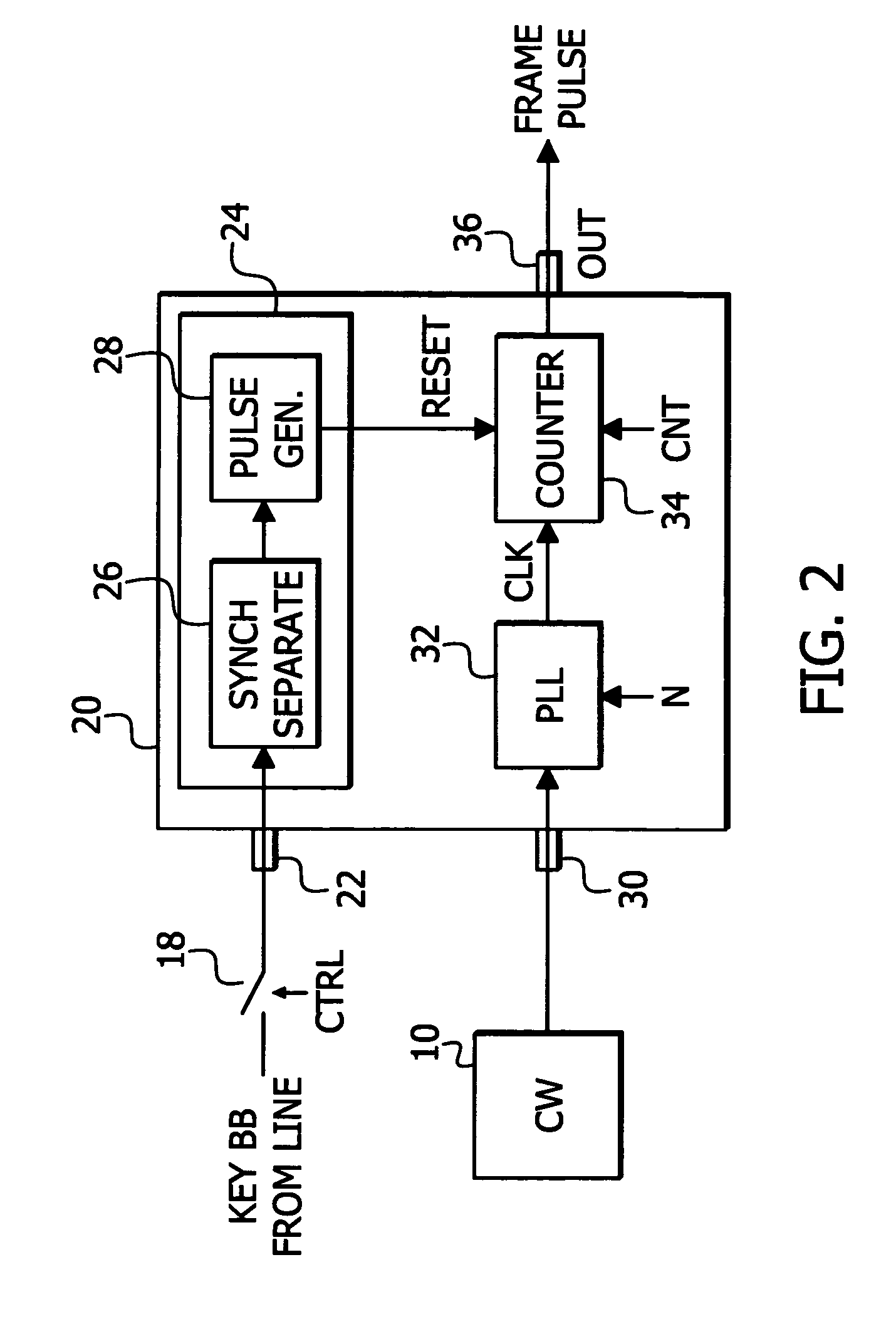
CW lock is conducted with less manual operation. A first input 22 receives a black burst (BB) signal from a key TV station. A second input 30 receives a continuous wave (CW) signal having an accurate, known frequency. A phase adjust signal generator 24 generates a reset signal having a known phase relationship with regard to the key TV station BB signal. The reset signal is used as a phase adjust signal. A PLL 32 receives the CW signal to provide clock. A counter 34 receives the clock and provides a frame pulse signal for synchronizing the key and local TV signals at a local TV station wherein the BB signal of the local station may be derived from the frame pulse signal. The counter 34 uses the reset signal to adjust the phase relationship between the key TV station BB signal and the frame pulse to a desired phase relationship based upon the key TV station BB signal.
Owner:PROJECT GIANTS LLC
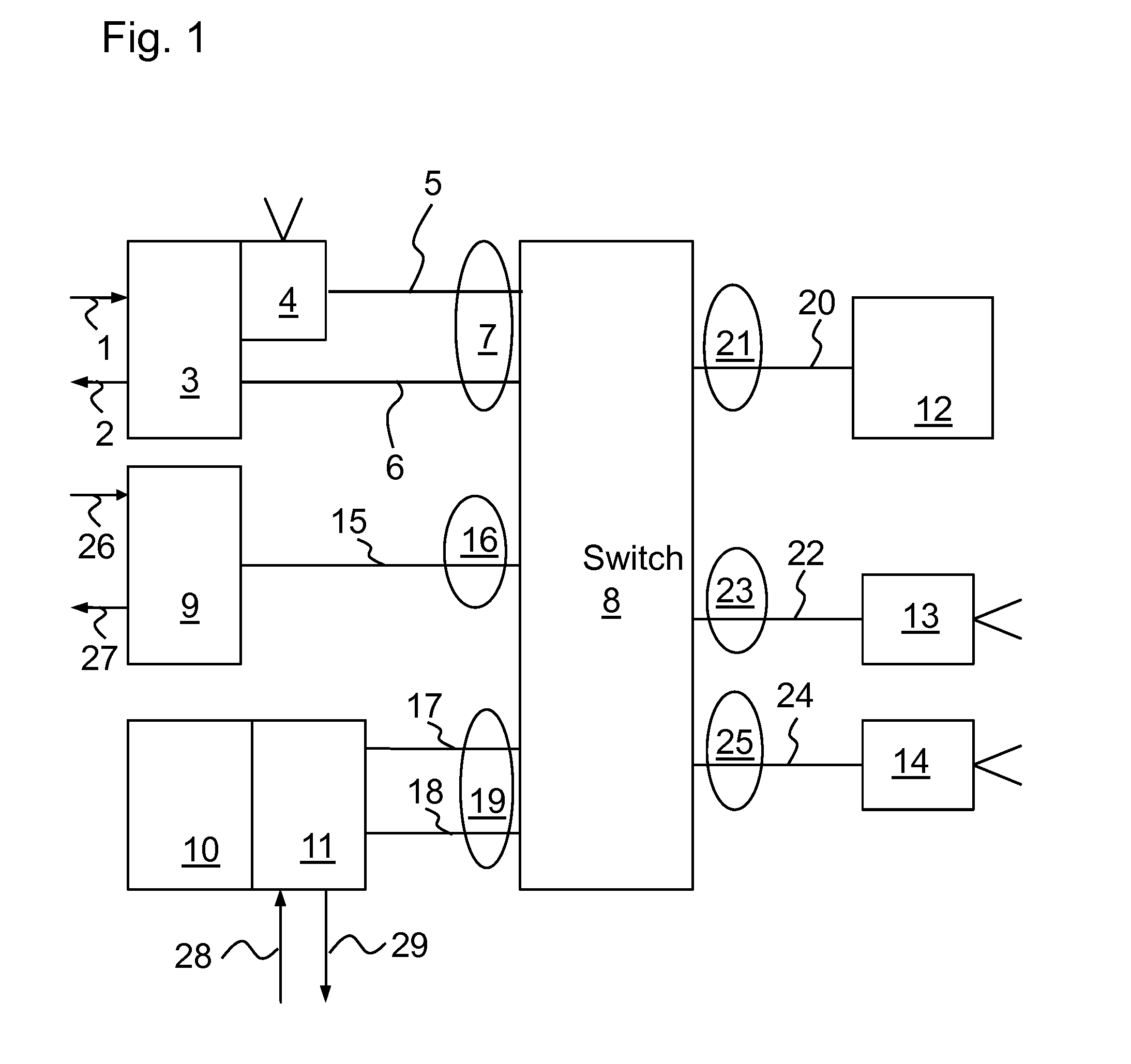
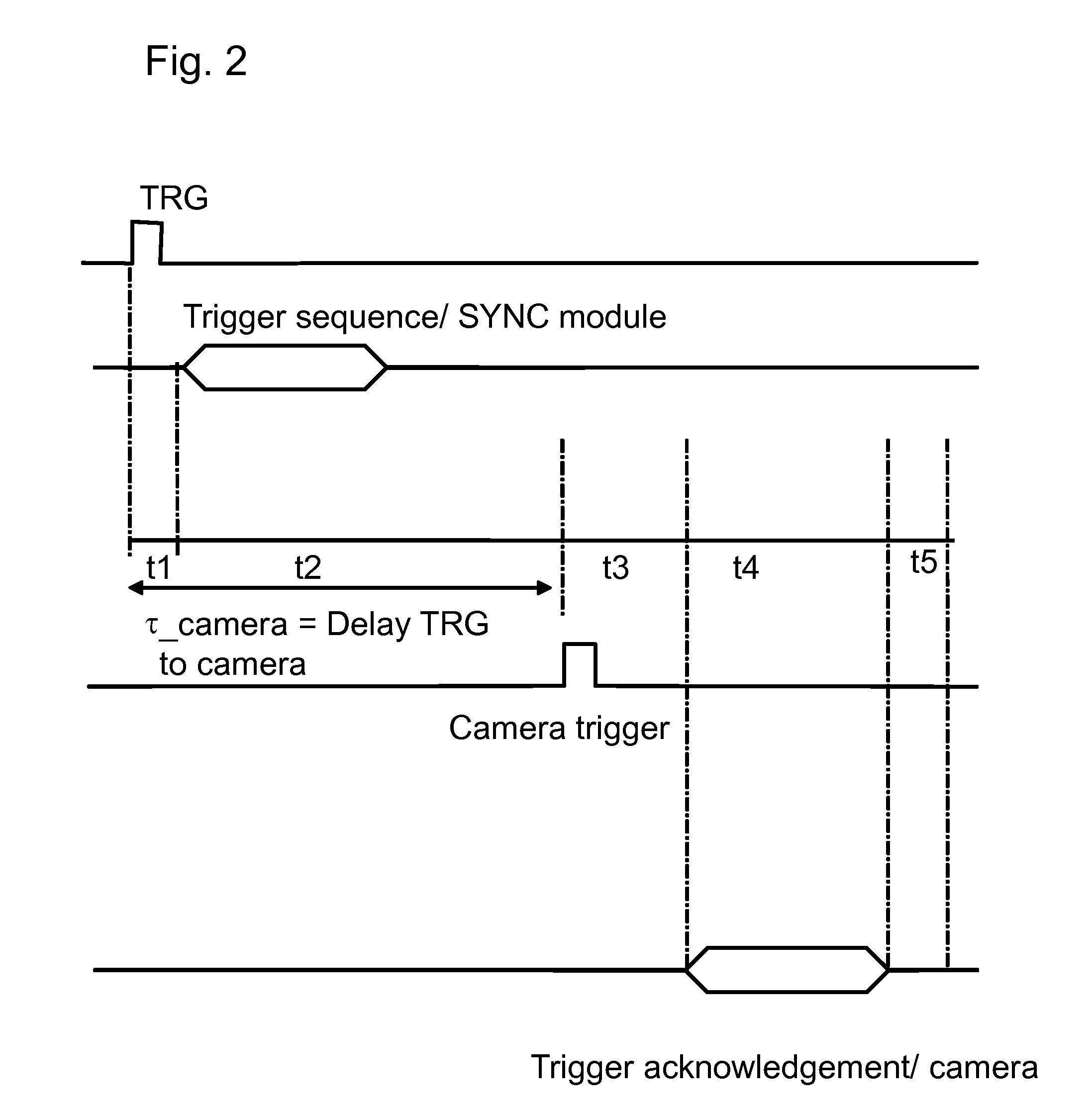
Method and device for synchronizing camera systems
InactiveUS20090251601A1Less jitter in the propagation times via the networkMinimal time differenceTelevision system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionComputer hardwareComputer science
The invention relates to a method and to a device for synchronizing the image capture by cameras. For this purpose, a duplex-capable network is provided. Within the network, one or more hardware-supported synchronization modules with a logical channel of a first type are provided, wherein the synchronization module or modules transmit, via the logical channel, image-capture signals that control the capture time of image sensors, wherein the image-capture signals are received by image-capture devices, and wherein the image-capture devices each capture an image as a response to the reception of an image-capture signal, and wherein the image data is then transmitted via the network by the image-capture devices via a logical channel of a second type.
Owner:BAUMER OPTRONIC
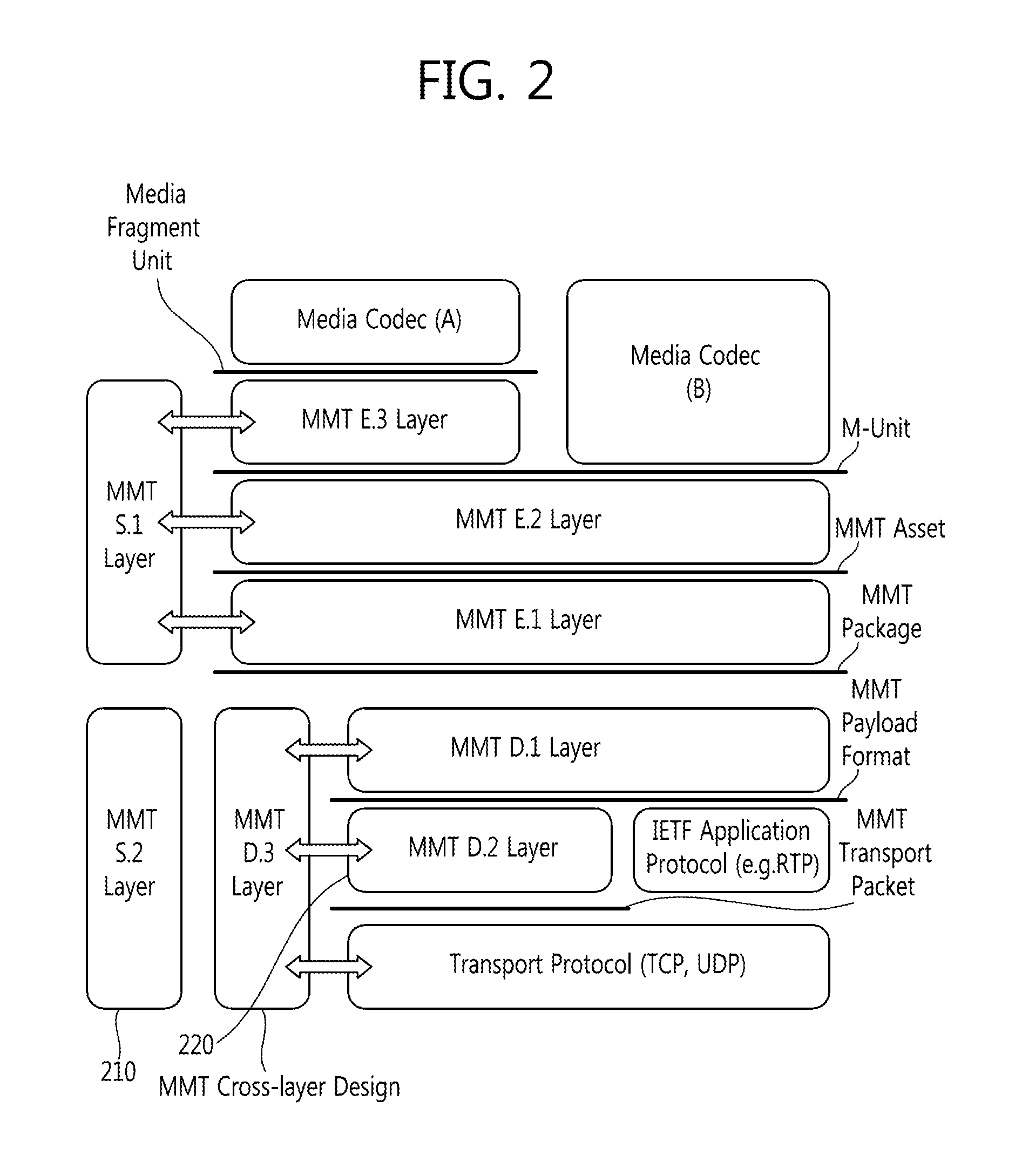
Method of providing timing information for synchronizing MMT packet stream in MMT hybrid delivery service and method of synchronizing MMT packet stream in MMT hybrid delivery service
InactiveUS20130016282A1Smoothly providedTelevision system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionComputer network
A method of providing timing information for synchronizing packet streams delivered from a first server and a second server, respectively, that are different from each other under hybrid delivery service environment is provided. The first server delivers a first media object and the second server delivers a second media object. The timing information for synchronizing a second packet including the second media object and a first packet including the first media object is generated in the second server. The timing information and the second packet including the second media object are provided from the second server to the client.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Device and method for synchronizing different parts of a digital service
ActiveUS20130242191A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionTelecommunications equipmentReproduction
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Satellite set-top box decoder for simultaneously servicing multiple independent programs for display on independent display devices
InactiveUS7533402B2Television system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionSignal onDisplay device
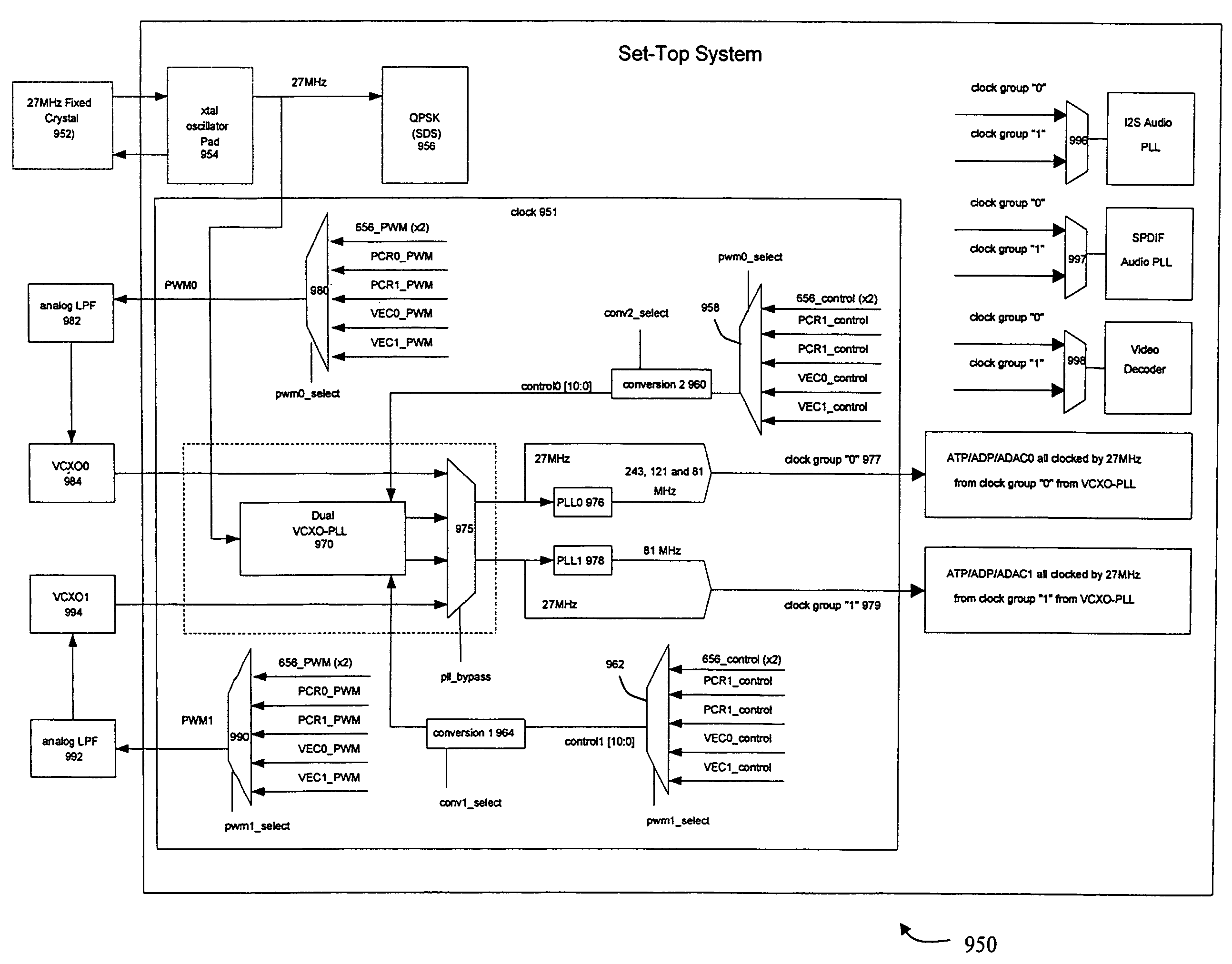
An integrated receiver with dual channel transport stream decoding and delivery substantially implemented on a single CMOS integrated circuit is described. A receiver front end provides multiple time-base clocks for two transport streams. Transport processor circuitry uses multiple PCRs to track transport streams through decoding, storage and or delivery of the decoded signals for display. Provision of a multiple time-base clock for decoding and delivering multiple transport streams allows display of the two decoded audio-video signals on independent monitors.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Synchronization signal detection in a digital television receiver
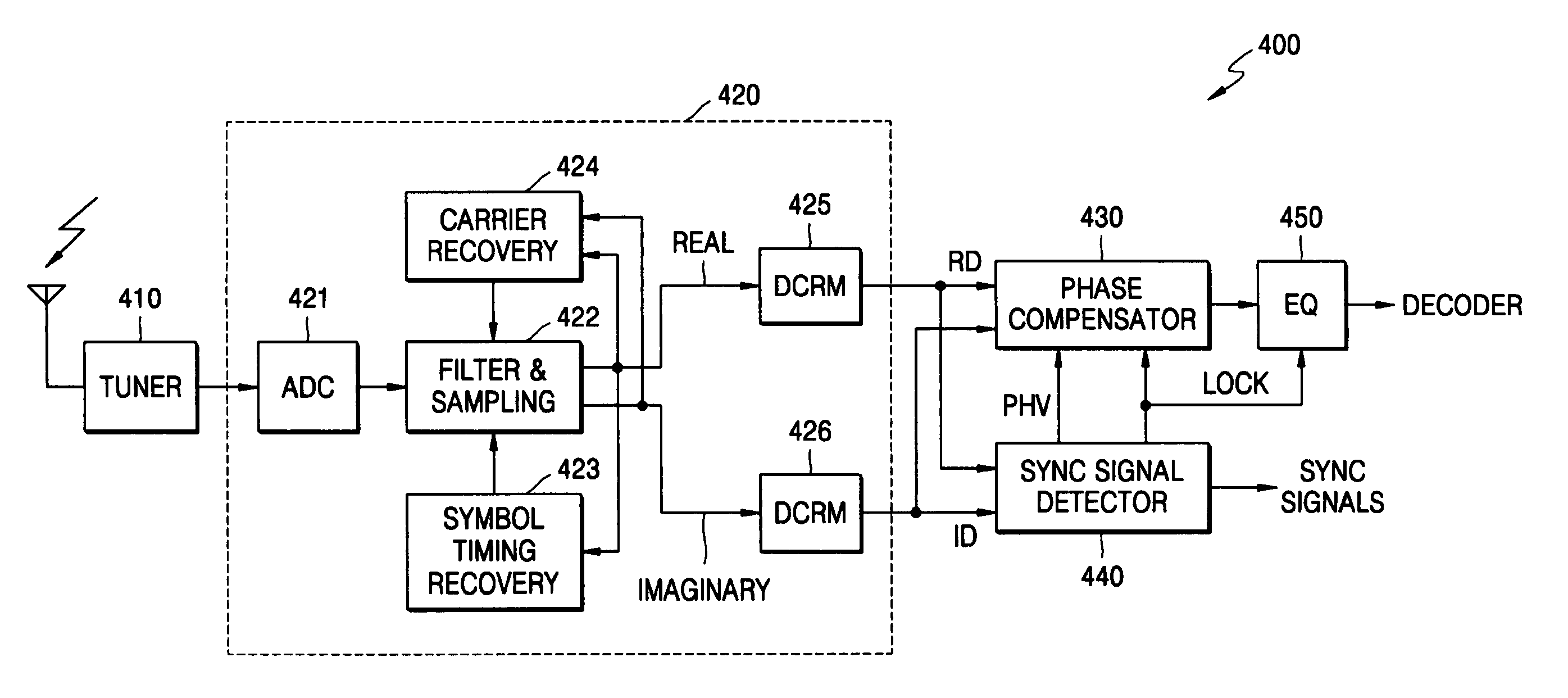
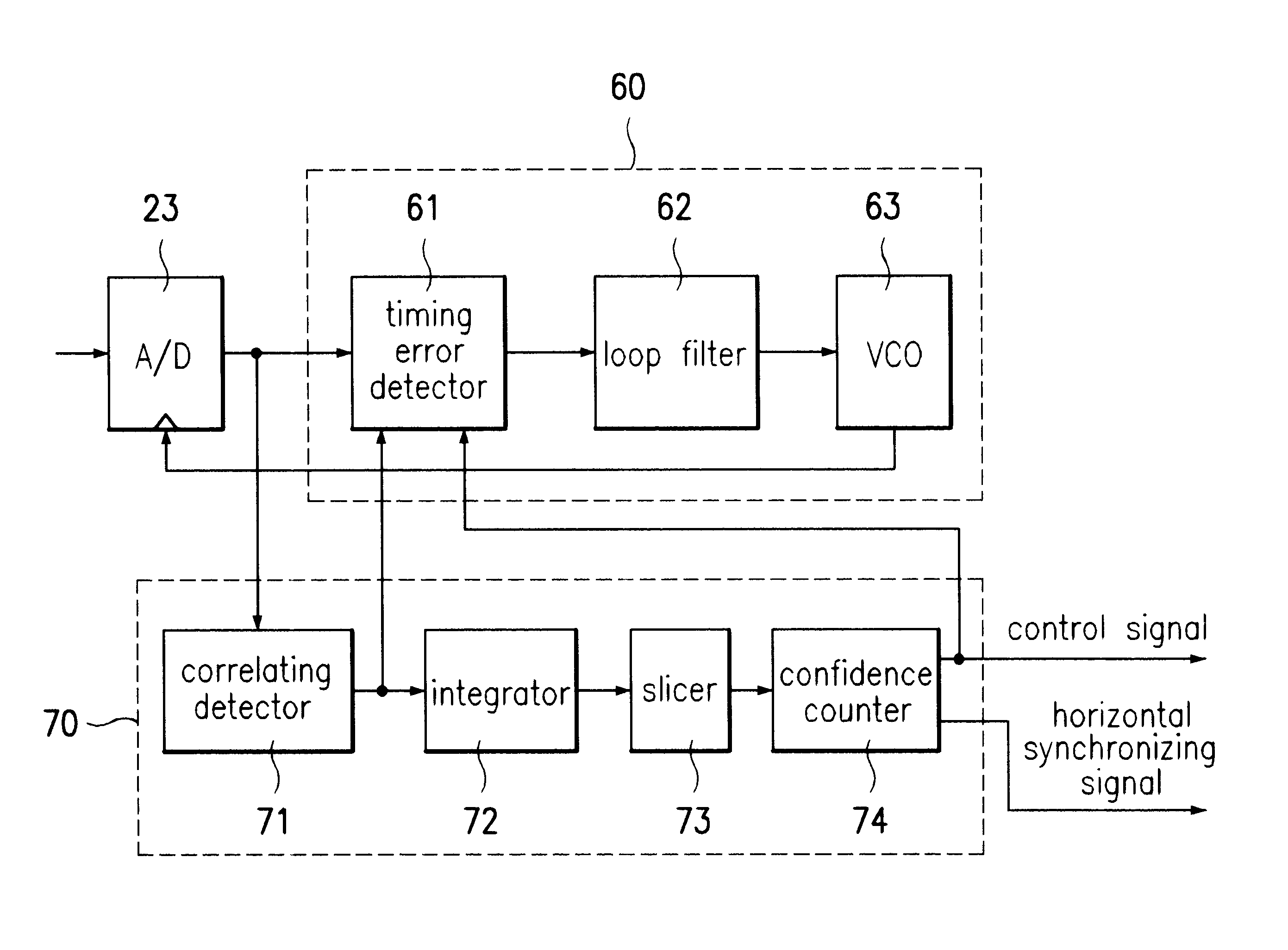
A digital television (DTV) receiver is provided, comprising: a demodulator that demodulates television signals and outputs equalizer training signals in the form of real (I) and imaginary (Q) data; a sync signal detector, and a phase compensator that offsets the phase of the I and Q data based on the phase offset signal and outputs phase adjusted I data under control of the lock control signal. The sync signal detector comprises: a correlator that correlates the equalizer training signals including the I and Q data; a power calculator that calculates the sum of the power of the correlated I and Q data; a comparator that compares (the sum) against a preset threshold and outputs a compare indication signal; a sync lock controller that monitors the compare indication signal and outputs a lock control signal; and a phase calculator that calculates a phase of the equalizer training signals based on the I and Q data and outputs a phase offset signal based on the compare indication signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
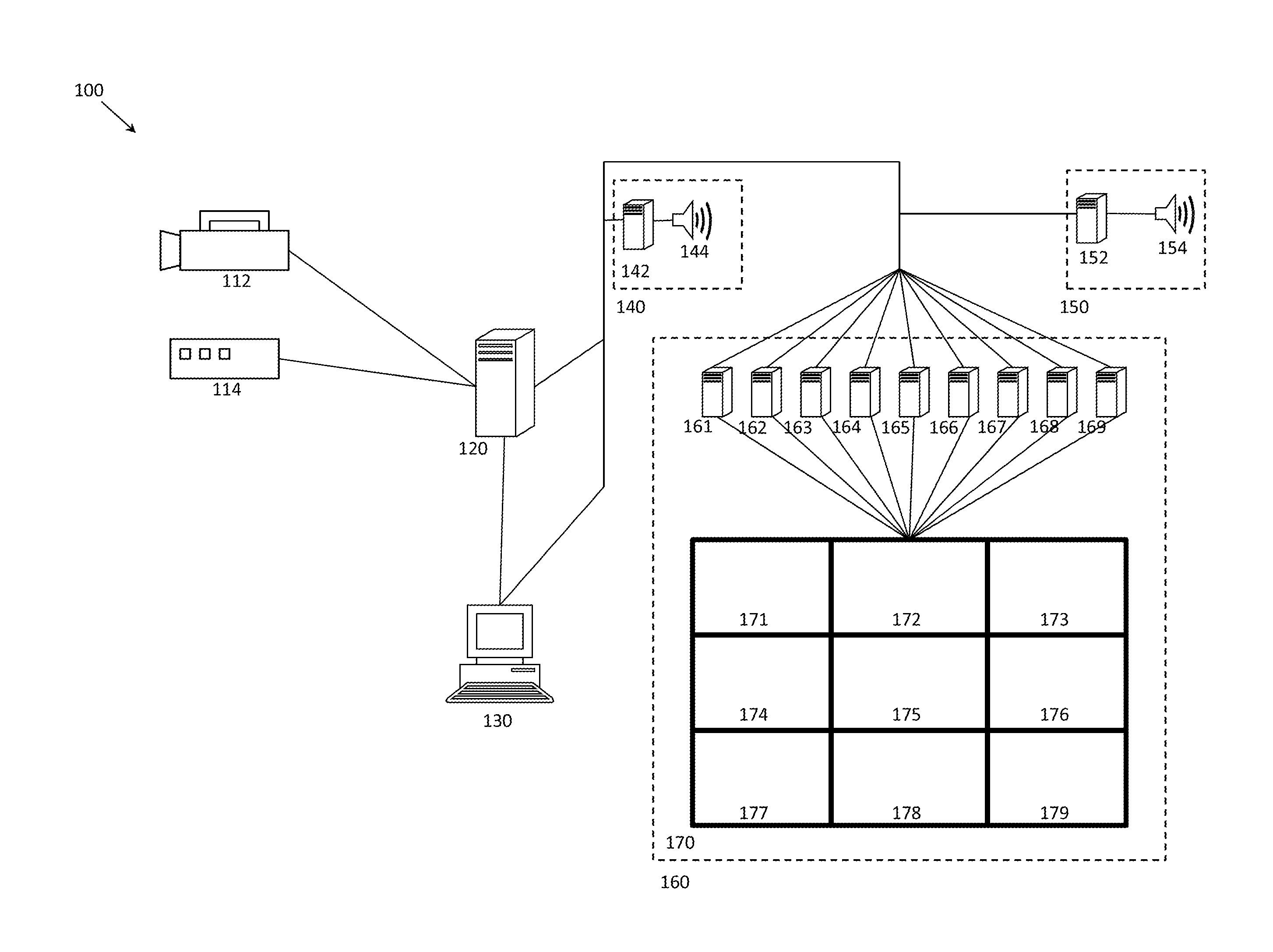
System and method of video capture for sports applications
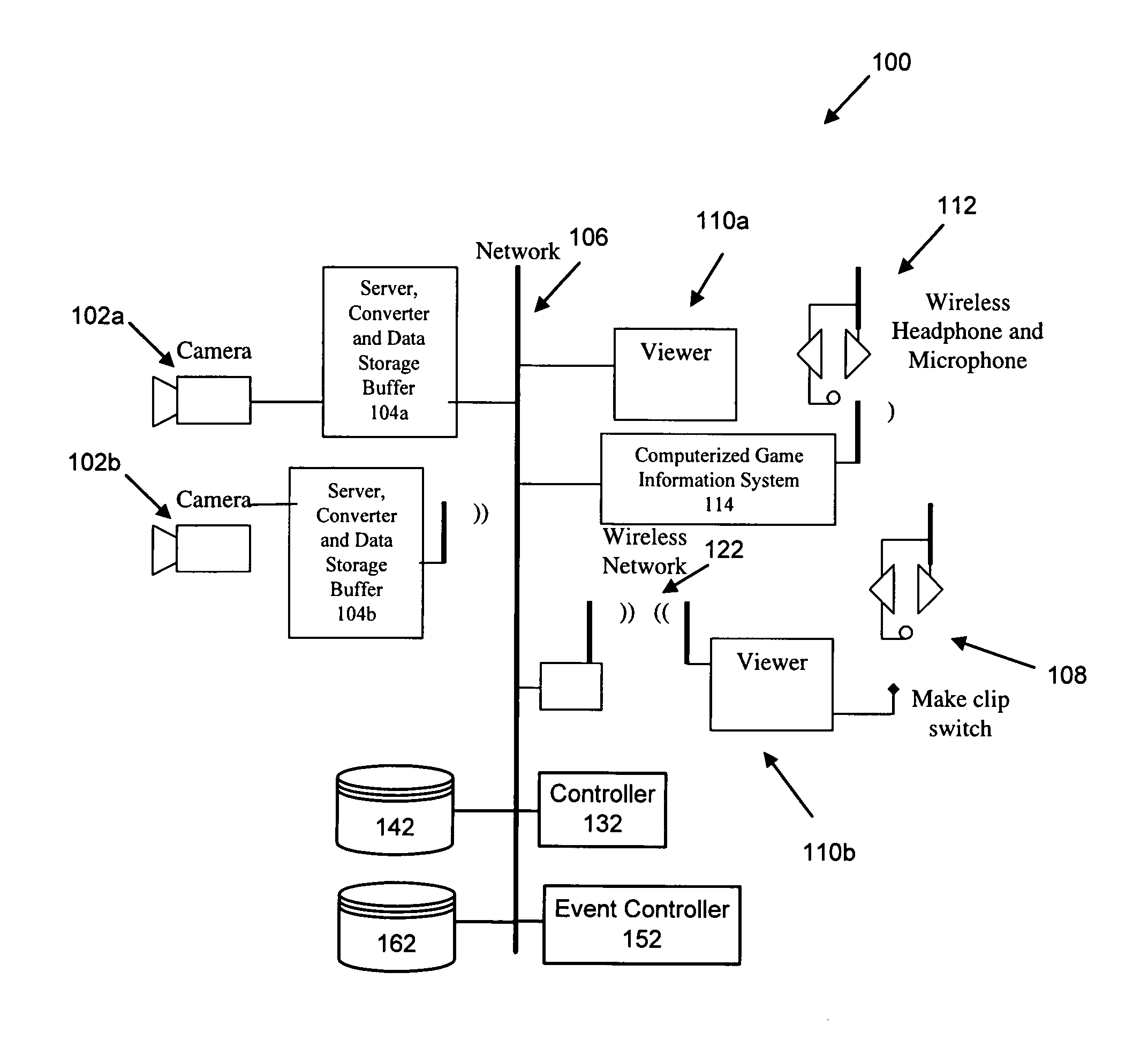
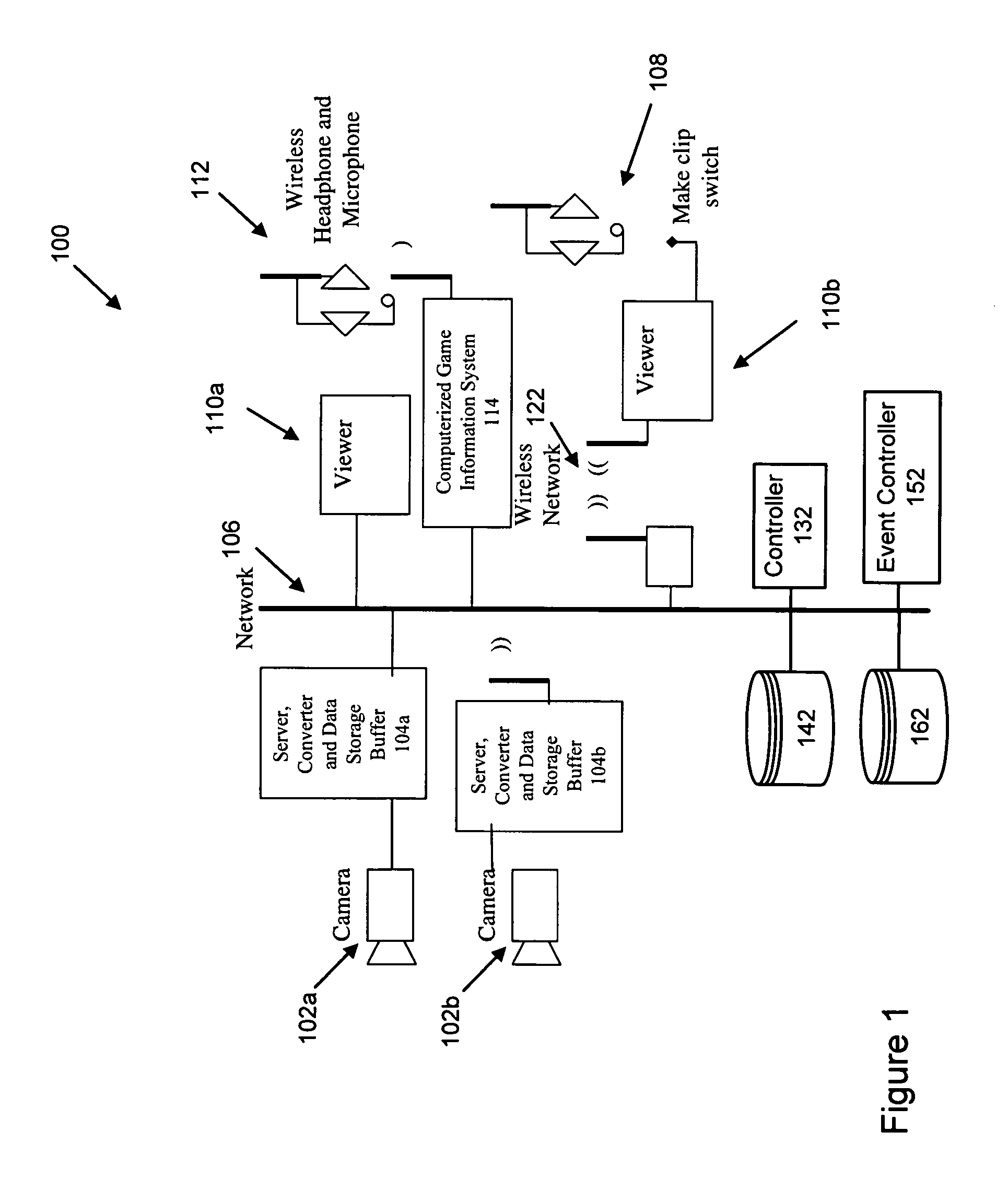
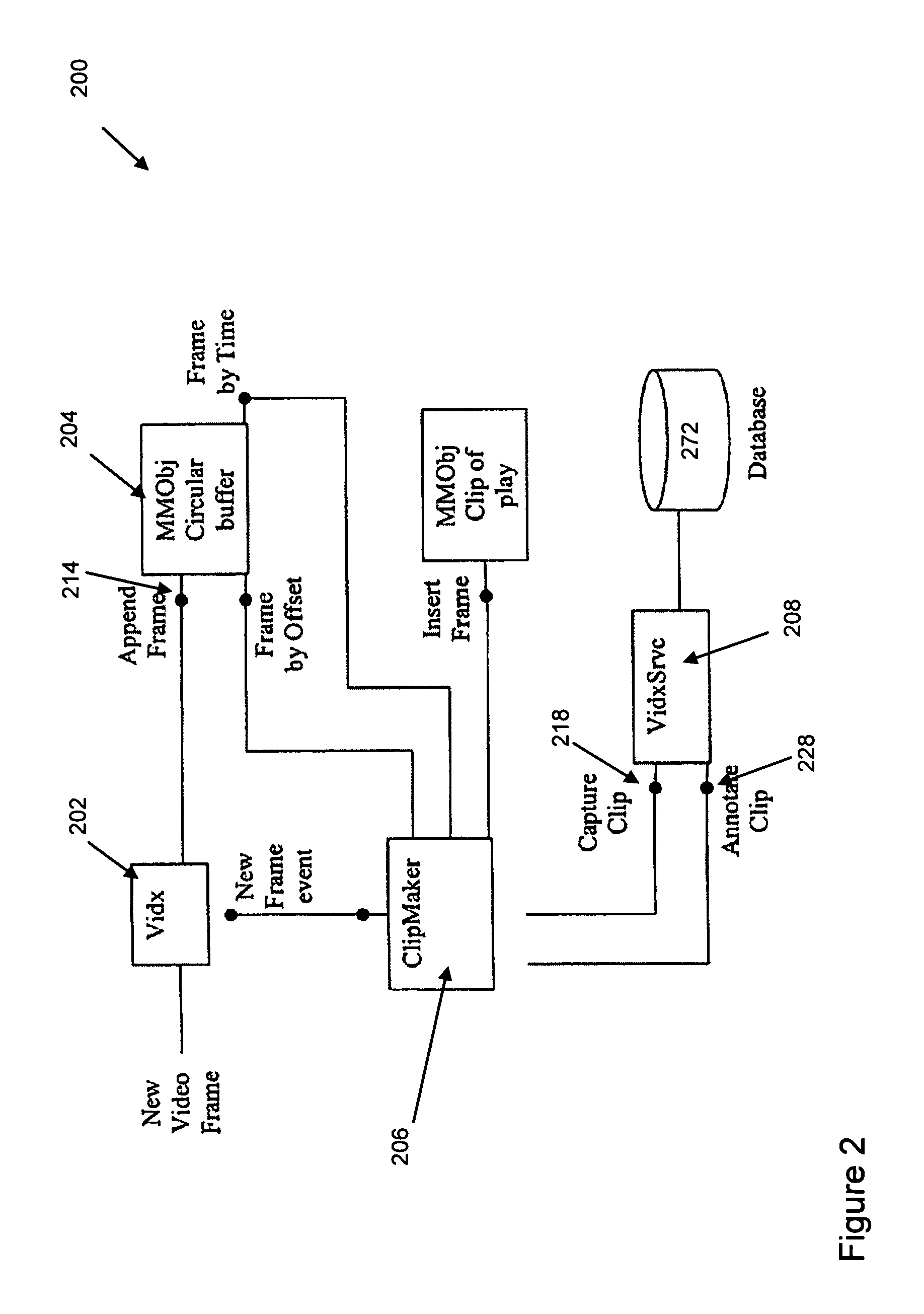
ActiveUS8358345B1Increase capacityAvoid problemsTelevision system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionData bufferMonitoring data
A system for monitoring a sporting event includes devices for monitoring characteristics of the event and collecting monitored data. Devices address different aspects of the event and monitor and collect real-time data. The devices process the data into digitized frames, and a digital storage device receives and stores the frames in a random access storage buffer as time-stamped digitized data frames with unique addresses. The storage device is capable of both time-shifting and relational association. The system includes a controller and devices for monitoring and extracting a digitized data frame according to a predetermined criterion. A viewer communicates with the storage device and controller and selects, manipulates, and extracts the digitized data frame. The system records and plays back the monitored data using a circular storage buffer with a memory mapped file and allows playback of stored data without interrupting simultaneous recording of new input data.
Owner:IM52
Video snychronisation
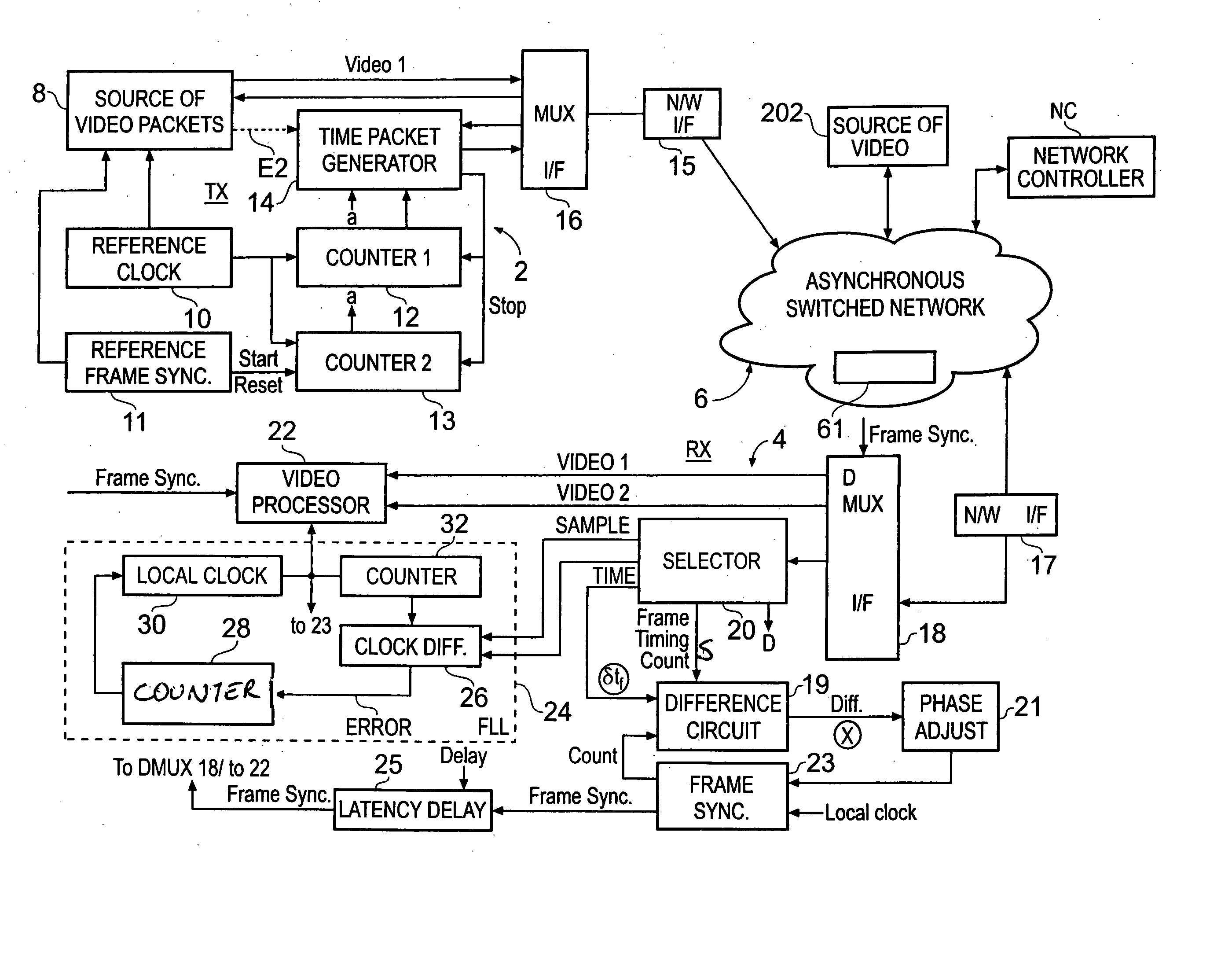
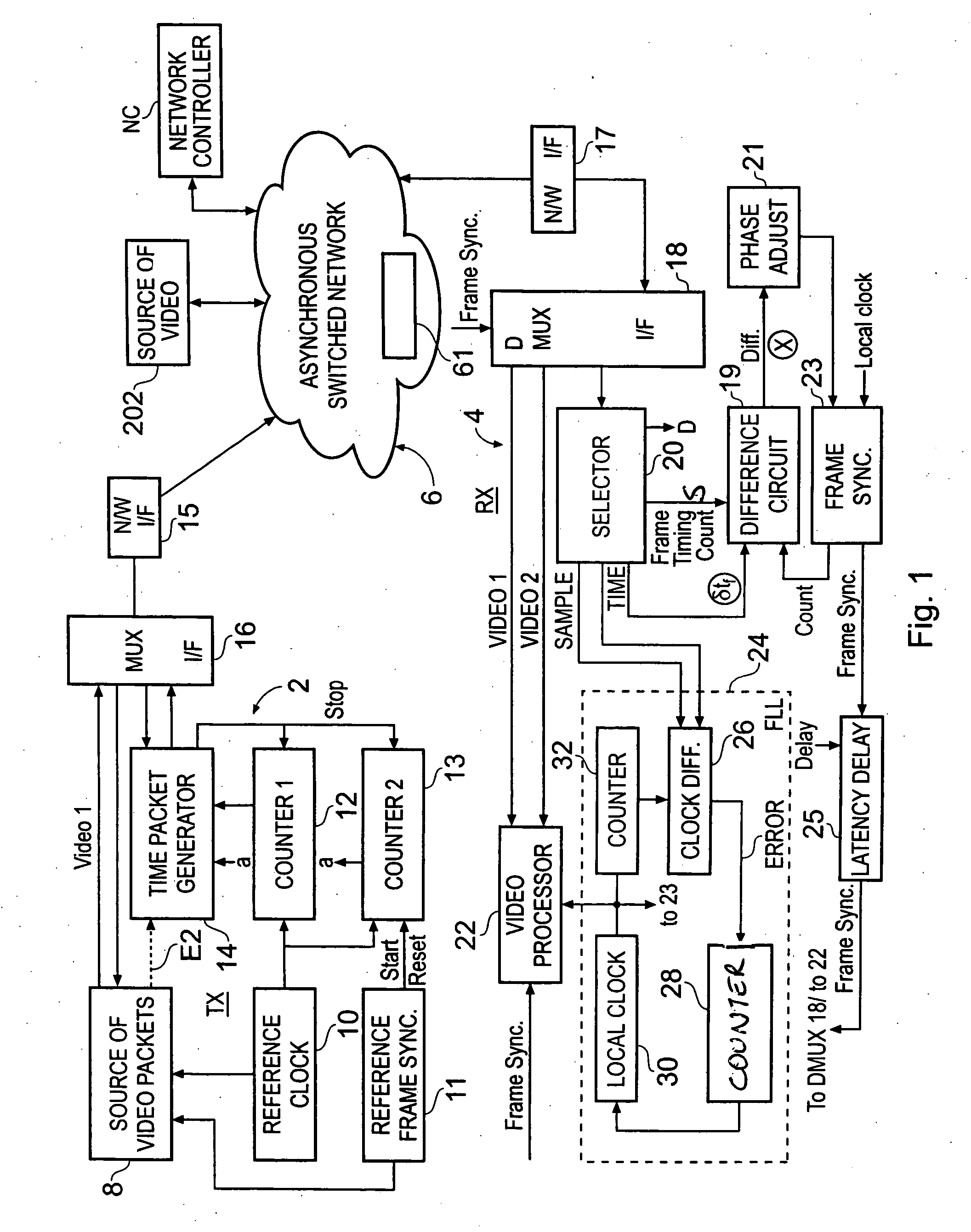
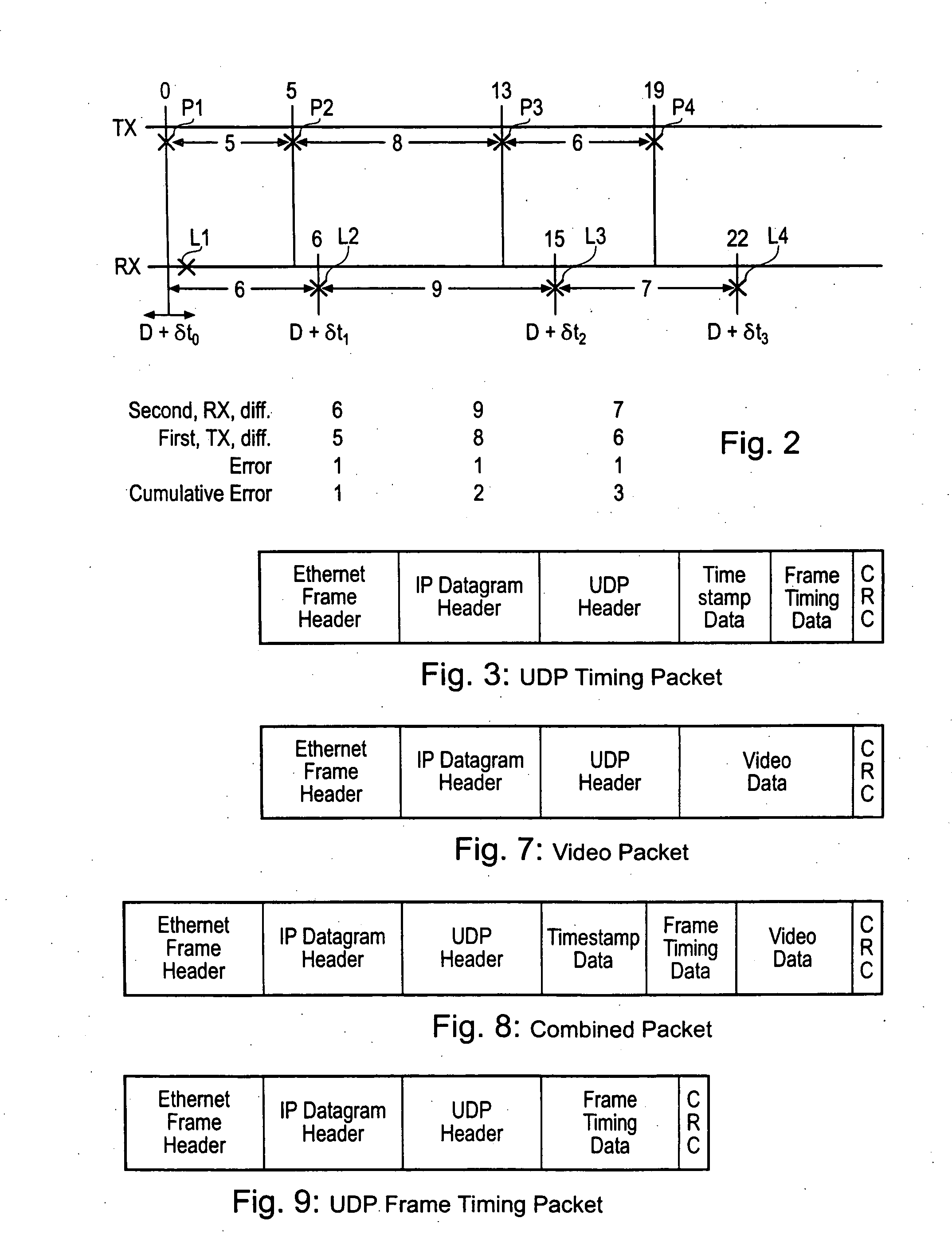
ActiveUS20040257469A1Reduce dataEliminate the effects ofTelevision system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionReference imageData treatment
A method of synchronising the phase of a local image synchronisation signal generator of a local video data processor in communication with an asynchronous switched packet network to the phase of a reference image synchronisation signal generator of a reference video data processor also coupled to the network, the local and reference processors having respective clocks, the reference and local image synchronisation signal generators generating periodic image synchronisation signals in synchronism with the reference and local clocks respectively comprises the steps of: frequency synchronising the local and reference clocks; the reference video data processor sending, via the network, to the local data processor an image timing packet providing reference image synchronisation data indicating the difference in timing, measured with respect to the reference processor's clock, between the time at which the image timing packet is launched onto the network and the time of production of a reference image synchronisation signal; and the local processor controlling the timing of the production of the local image synchronisation signal in dependence on the reference image synchronisation data and the time of arrival of the timing packet.
Owner:SONY EUROPE BV
Methods and systems for synchronizing media stream presentations
ActiveUS20150215497A1Quickly renderingNot alleviating taskTelevision system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionComputer monitorDisplay device
A system synchronizes one or more media streams, such as video stream or audio streams, by embedding frame identifiers in each compressed media stream, and then by using synchronizing signals to render each frame simultaneously by referencing the embedded frame identifier. Since the frame identifier is embedded in between encoded frames of the compressed media stream without altering any of the compressed, encoded data, the frame identifier information could be rapidly embedded without creating lag associated with manipulating existing data. This technique could be used, for example, to synchronize a single HD video on a plurality of display devices (e.g. a football game on a wall of video monitors), or to synchronize a plurality of HD video streams on a single display device (e.g. a plurality of live video feeds on a single computer monitor).
Owner:HIPERWALL
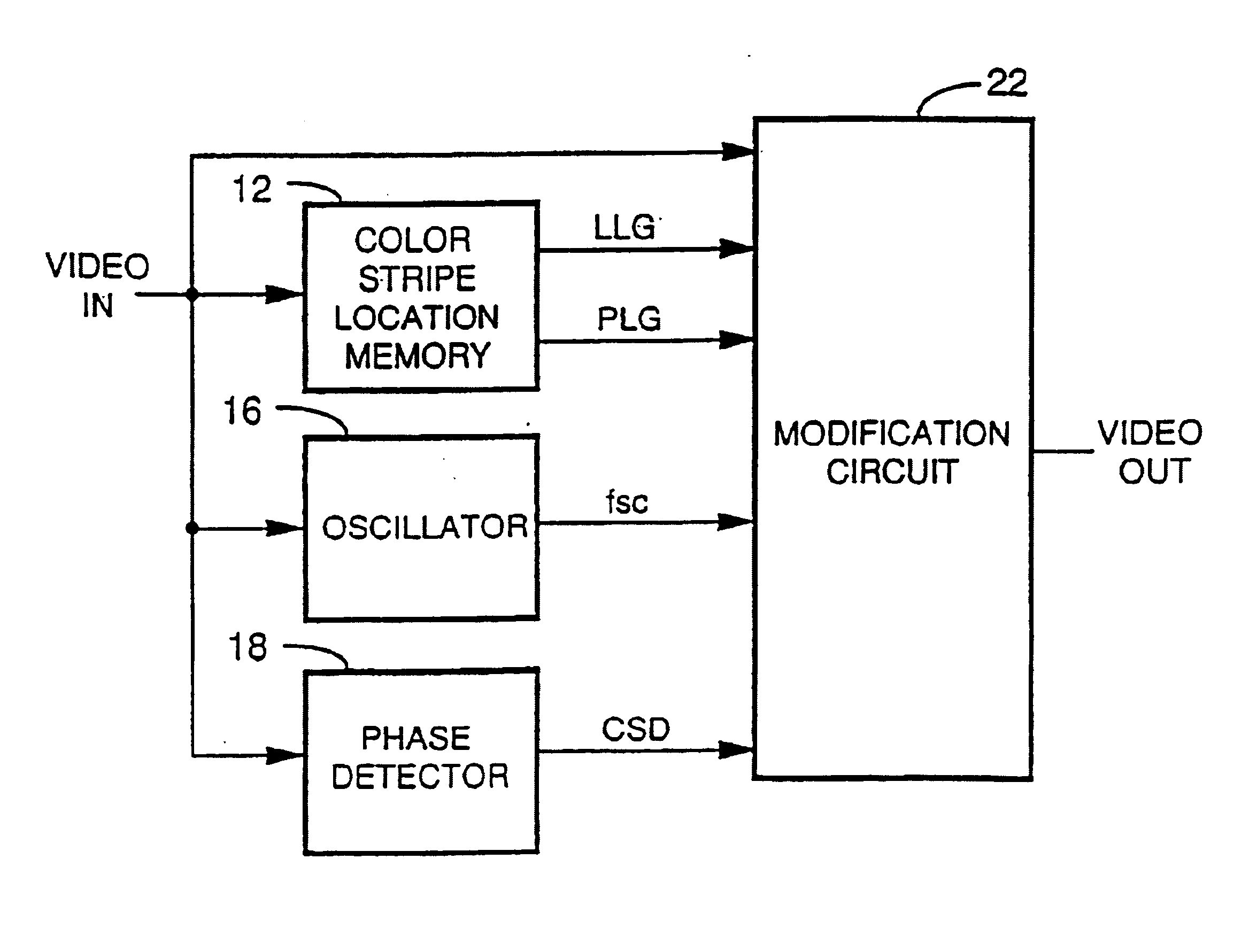
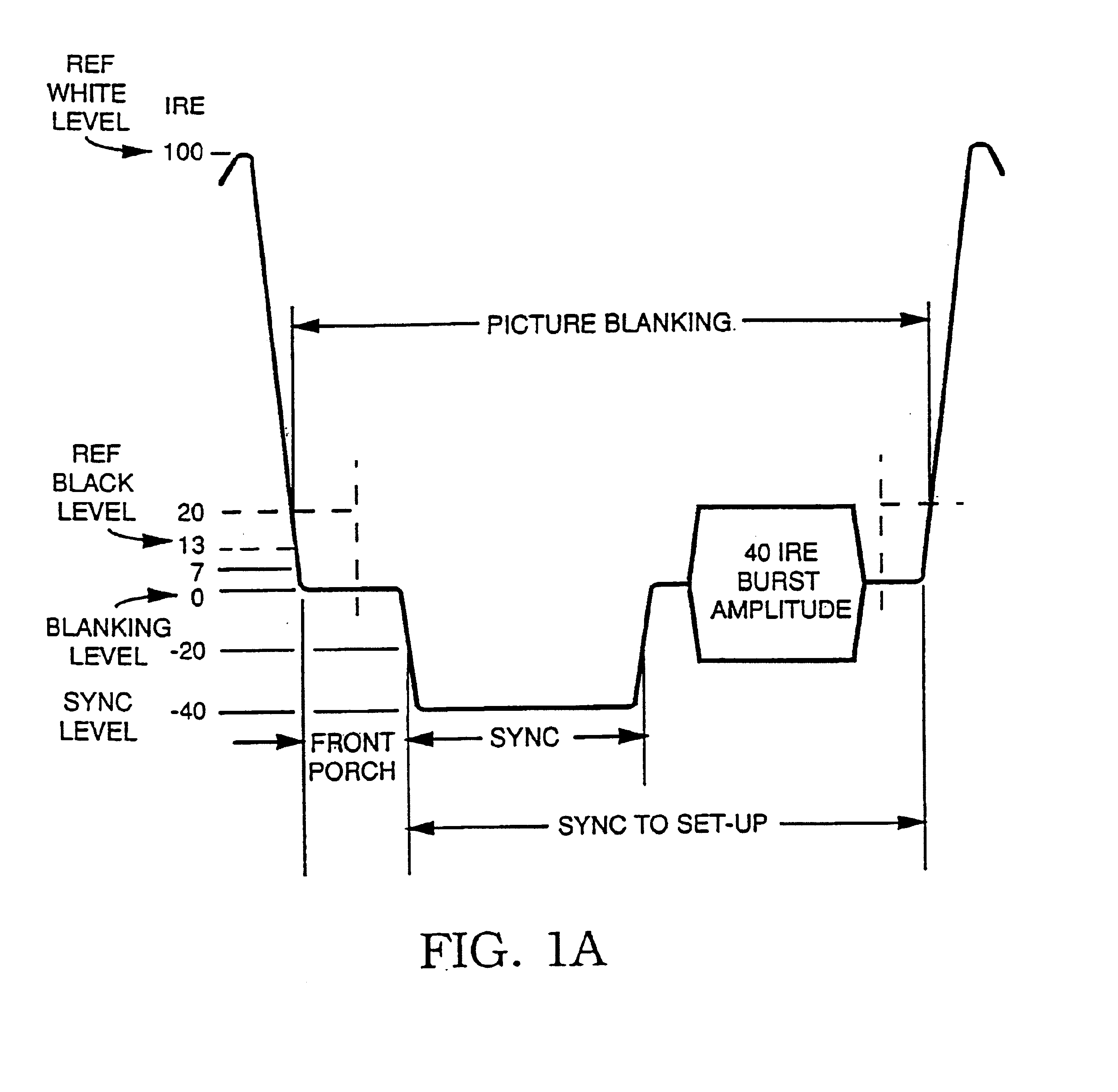
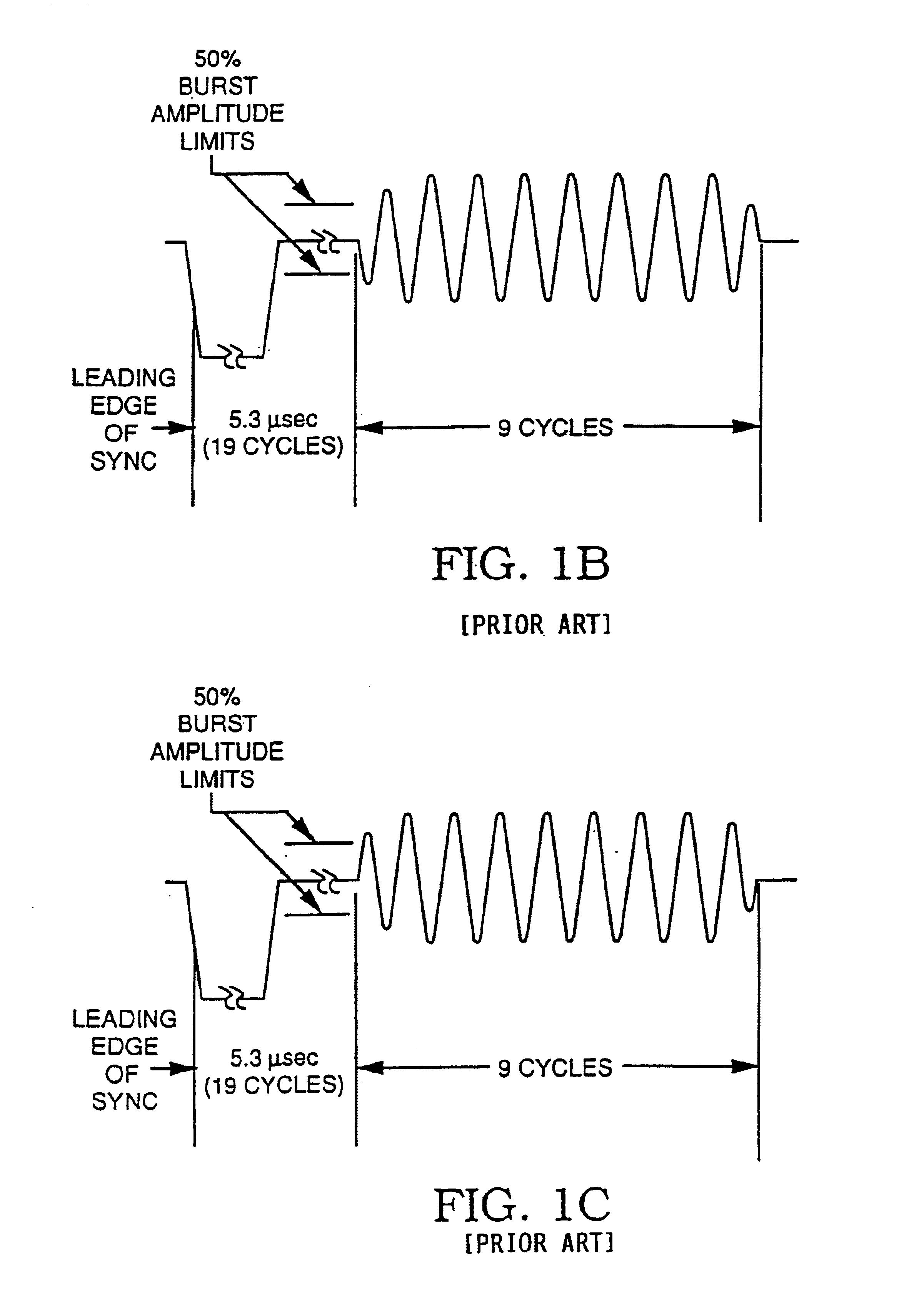
Method and apparatus for modifying the effects of color burst modifications to a video signal
InactiveUS7039294B2Effect of the color stripe process is attenuated or eliminatedAttenuate and eliminate effectTelevision system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionPhase shiftedComputer graphics (images)
In the known color stripe process for preventing recording of video signals, the color burst present on each line of active video is modified so that any subsequent video tape recording of the video signal shows variations in the color fidelity that appear as undesirable bands or stripes of color error. This color stripe process is defeated first by determining the location of the video lines including the color stripe process, either by prior experimentation or by on-line detection. Then some or all of the lines including the modified color bursts are modified so as to render the overall video signal recordable. The modification is accomplished in a number of ways, including phase shifting the color stripe burst into the correct phase, replacing some of the color stripe bursts or a portion of particular color stripe bursts so that they are no longer effective, and mixing the color stripe burst with color stripe signals of the correct phase so as to eliminate most or all of the phase error present. The modified color bursts are defeated, in other versions, by modifying the horizontal sync pulse signals immediately preceding the modified color bursts so that the modified color bursts are not detected by a VCR and hence have no effect.
Owner:ALL MEDIA GUIDE +10
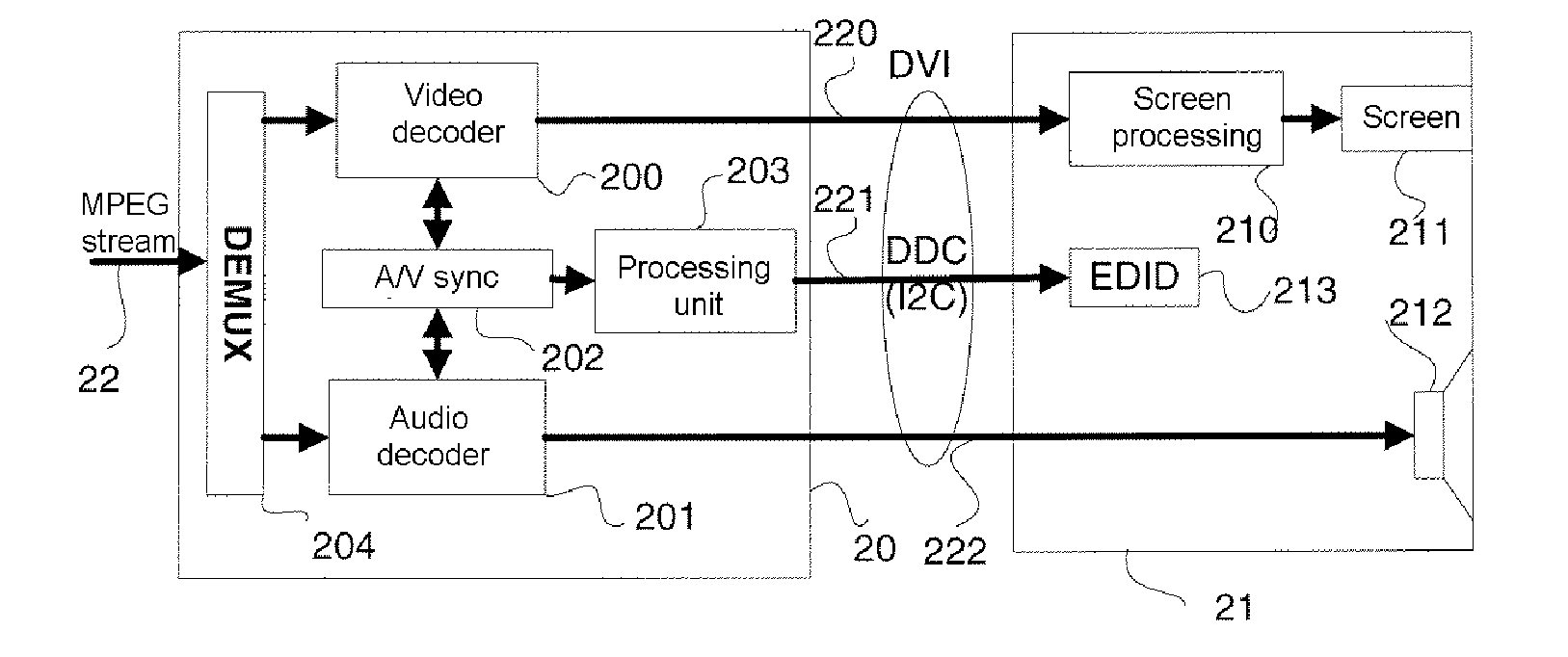
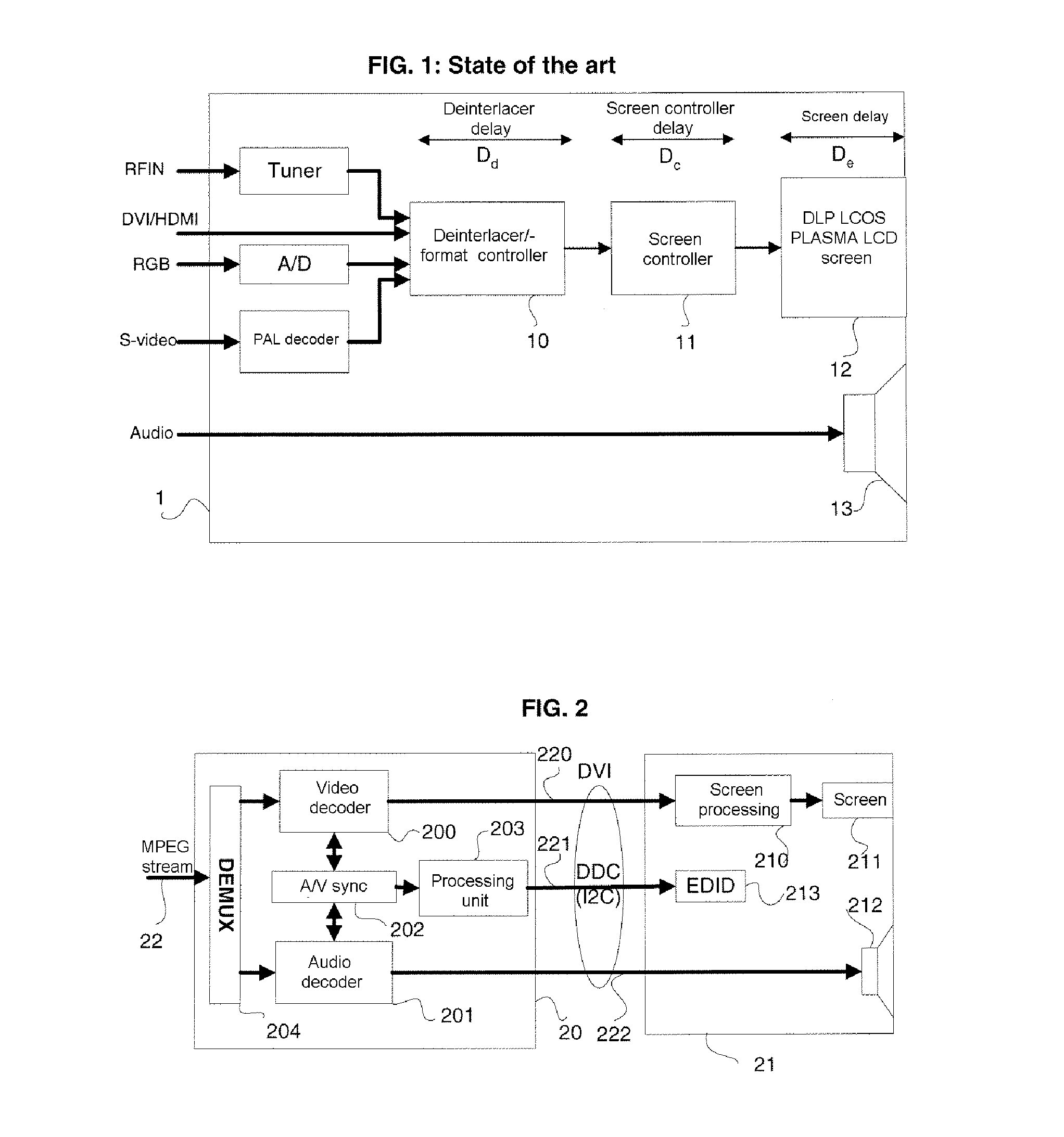
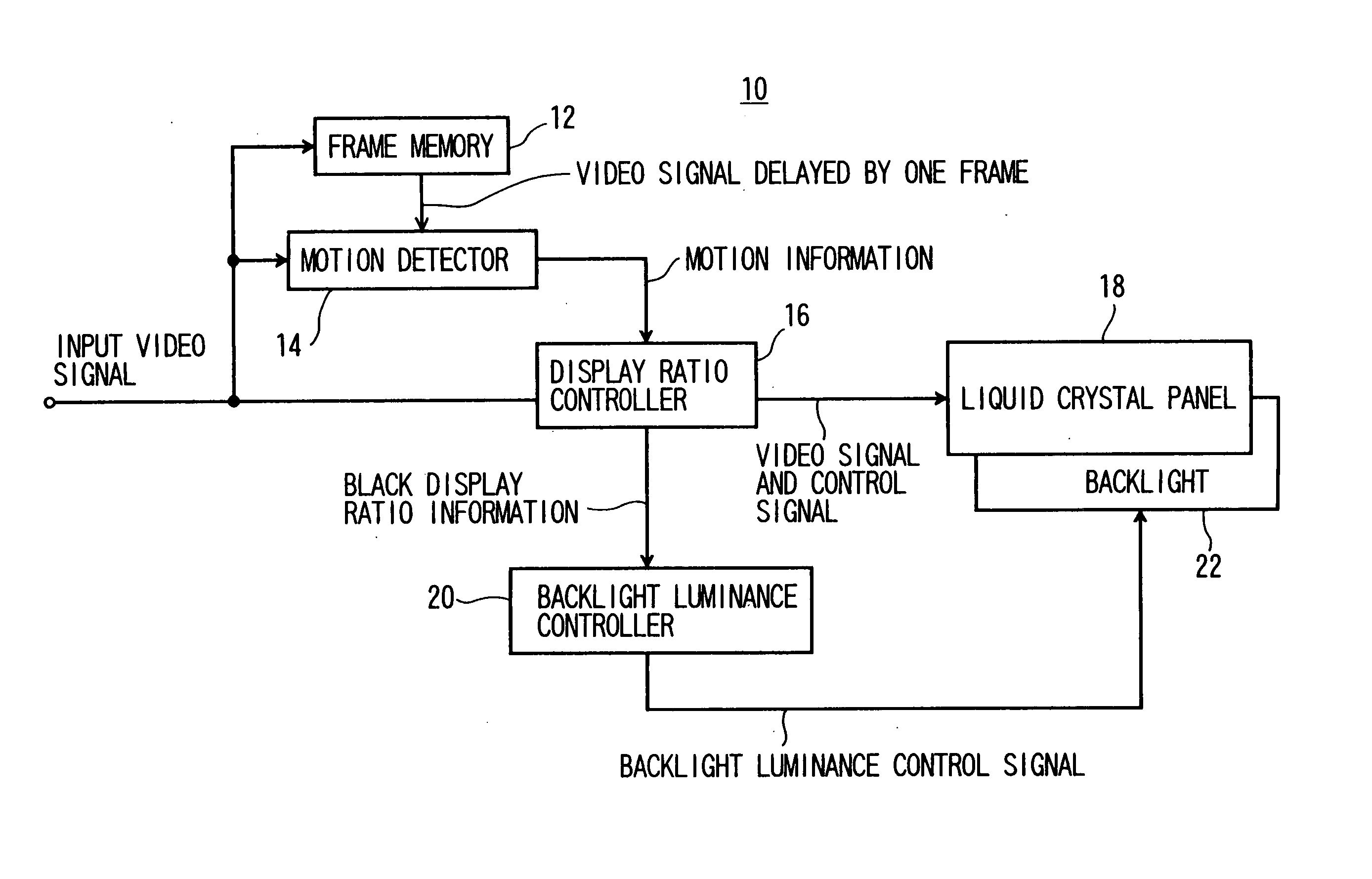
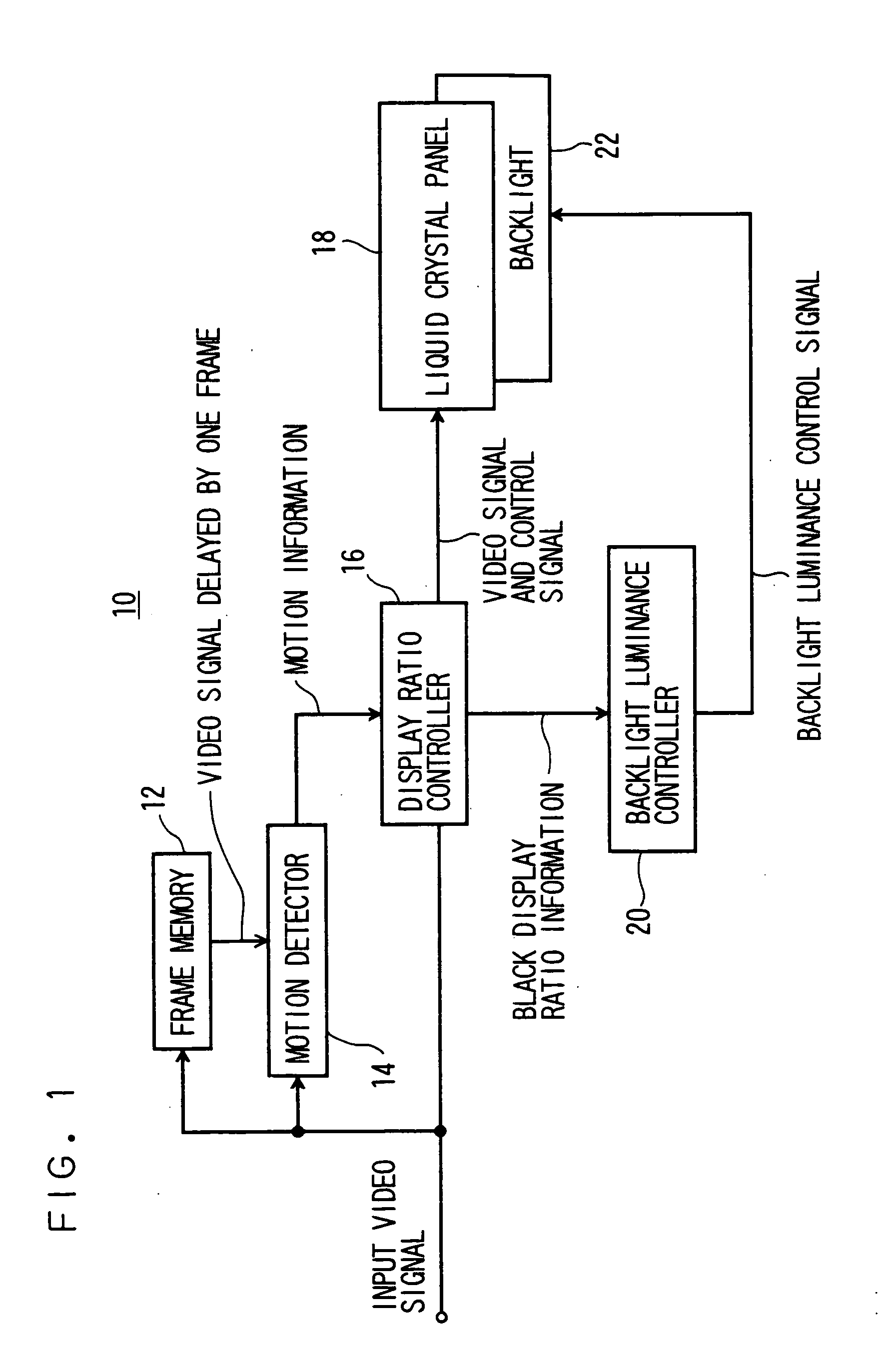
Image display device and image display method thereof
InactiveUS20060170822A1Improve picture qualitySuppressing increase in consumed powerTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesMotion detectorComputer graphics (images)
An image display device comprising: a display 18 to display an input image and a black image within one frame period; a motion detector 14 to detect a motion information from the input image; a display ratio controller 16 to set a black display time ratio as a ratio of a black period to said one frame period based on the motion information, the black period being a period for displaying the black image within said one frame period; and a display luminance controller 30 to suppress, within a predetermined range, a luminance fluctuation caused by a change in the black display time ratio, the luminance fluctuation corresponding to a fluctuation of a total luminance for said one frame period.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and apparatus for reducing channel change response times for IPTV
ActiveUS20110061084A1Improve channel change response timeChange timeTelevision system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionUser deviceChange request
The invention includes a method and apparatus for improving a channel change response time. A method includes propagating a plurality of media streams toward at least one user terminal using a respective plurality of multicast groups and propagating a meta channel toward the at least one user terminal for conveying information adapted for use in selecting one of the media streams in a manner tending to improve the channel change response time. The media streams include an original media stream conveying media content and at least one auxiliary media stream, generated from the original media stream, where each of the at least one auxiliary media stream conveys the media content of the original media stream, where each of the at least one auxiliary media stream is offset in time with respect to the original media stream. The information conveyed by the meta channel is associated with the media streams. A user device may receive the meta channel information and select one of the media streams using the meta channel information in response to a channel change request from the user terminal, or a network device may select one of the media streams for a user terminal in response to a channel change request from the user terminal.
Owner:RPX CORP
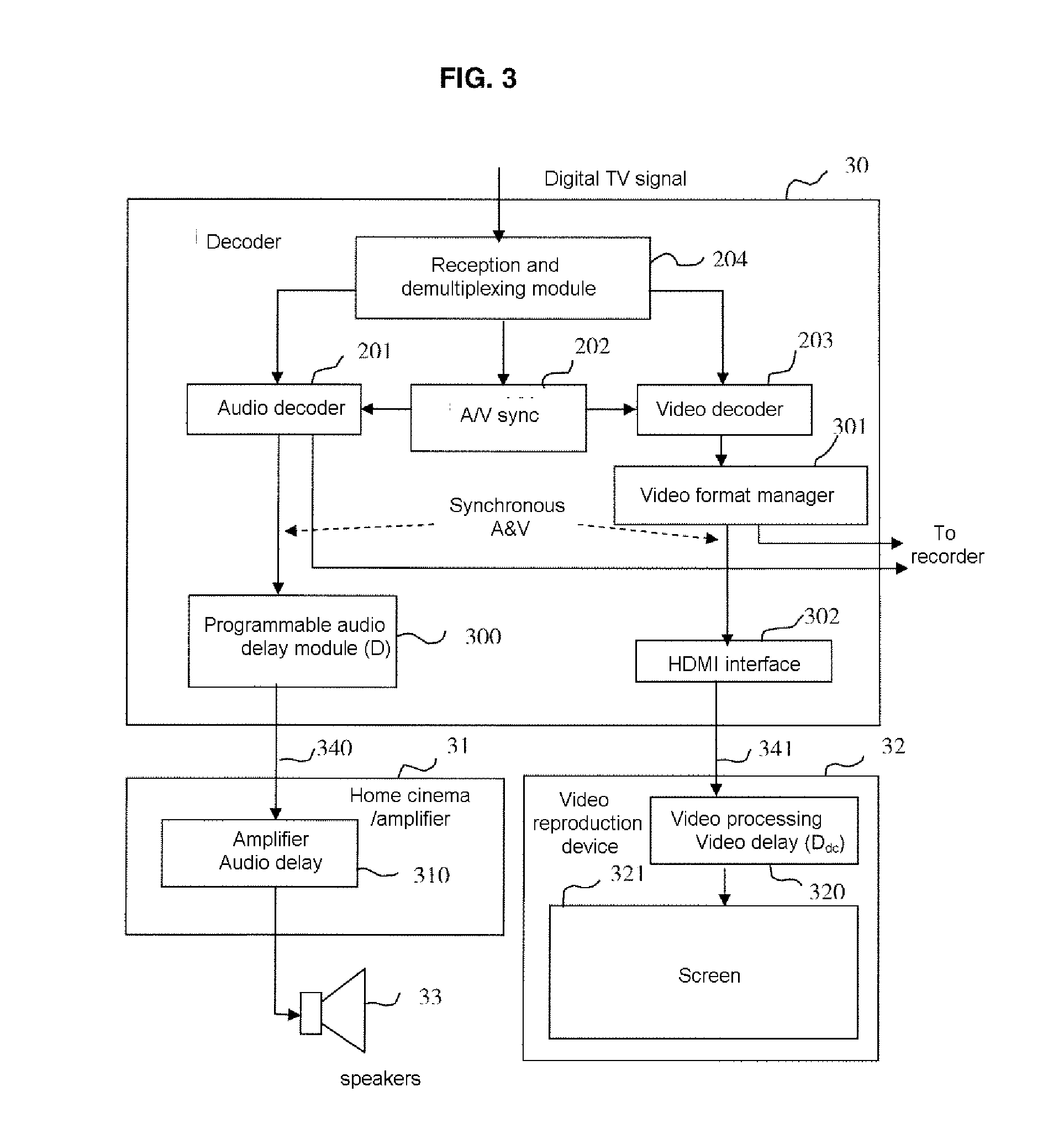
Sync signal generating apparatus and method for a video signal processor
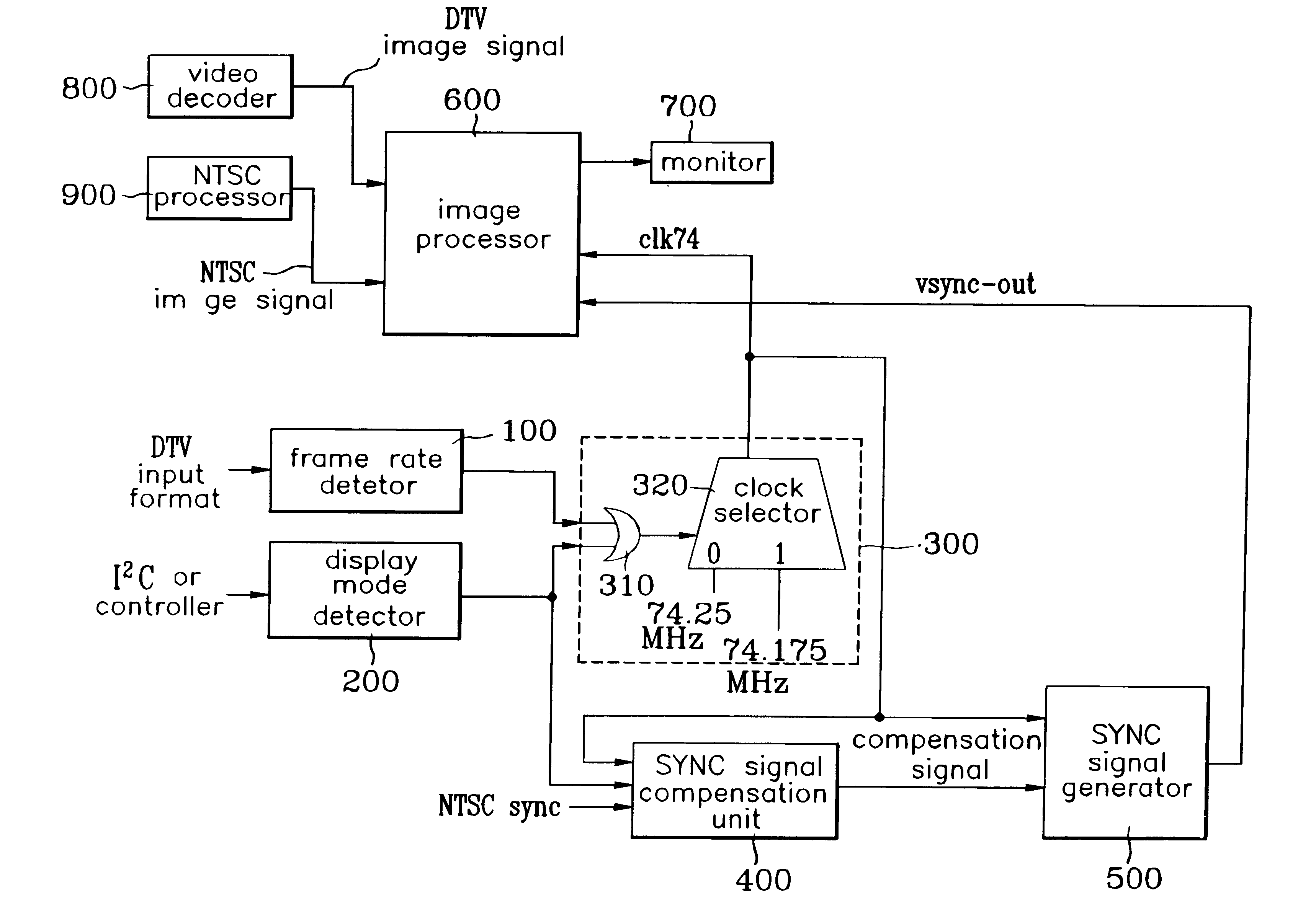
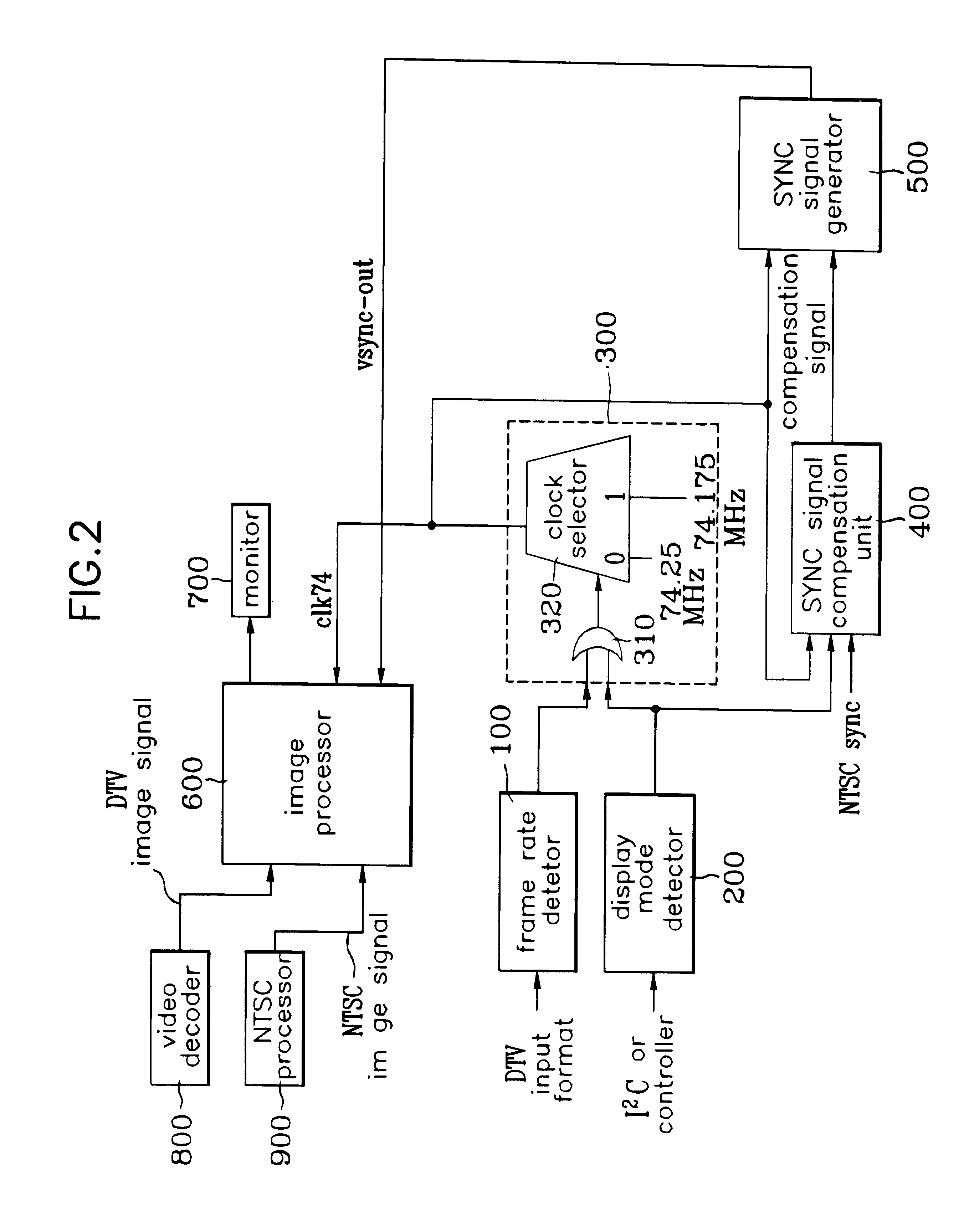
InactiveUS6297850B1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDigital videoSignal generator
A sync signal generating apparatus and method for video signal processor are disclosed comprising an image processor processing either an input digital television video signal or an input analog television video signal to display one of the signals; a display unit displaying an output signal of the image processor; a frame rate detector detecting a frame of the digital video signal and generating a frame rate signal; a display mode detector detecting whether an image to be currently displayed is a digital television image or an analog television image and generating a display mode signal; a clock generator generating a clock signal according to the display mode signal and the format signal to the image processor; a sync signal compensation unit generating a sync compensation signal based upon the display mode signal, the clock signal, and a vsync signal of the analog television video signal; and a sync signal generator resetting and compensating a sync signal based upon the sync compensation signal and the clock signal and sending the compensated sync signal to the image processor.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
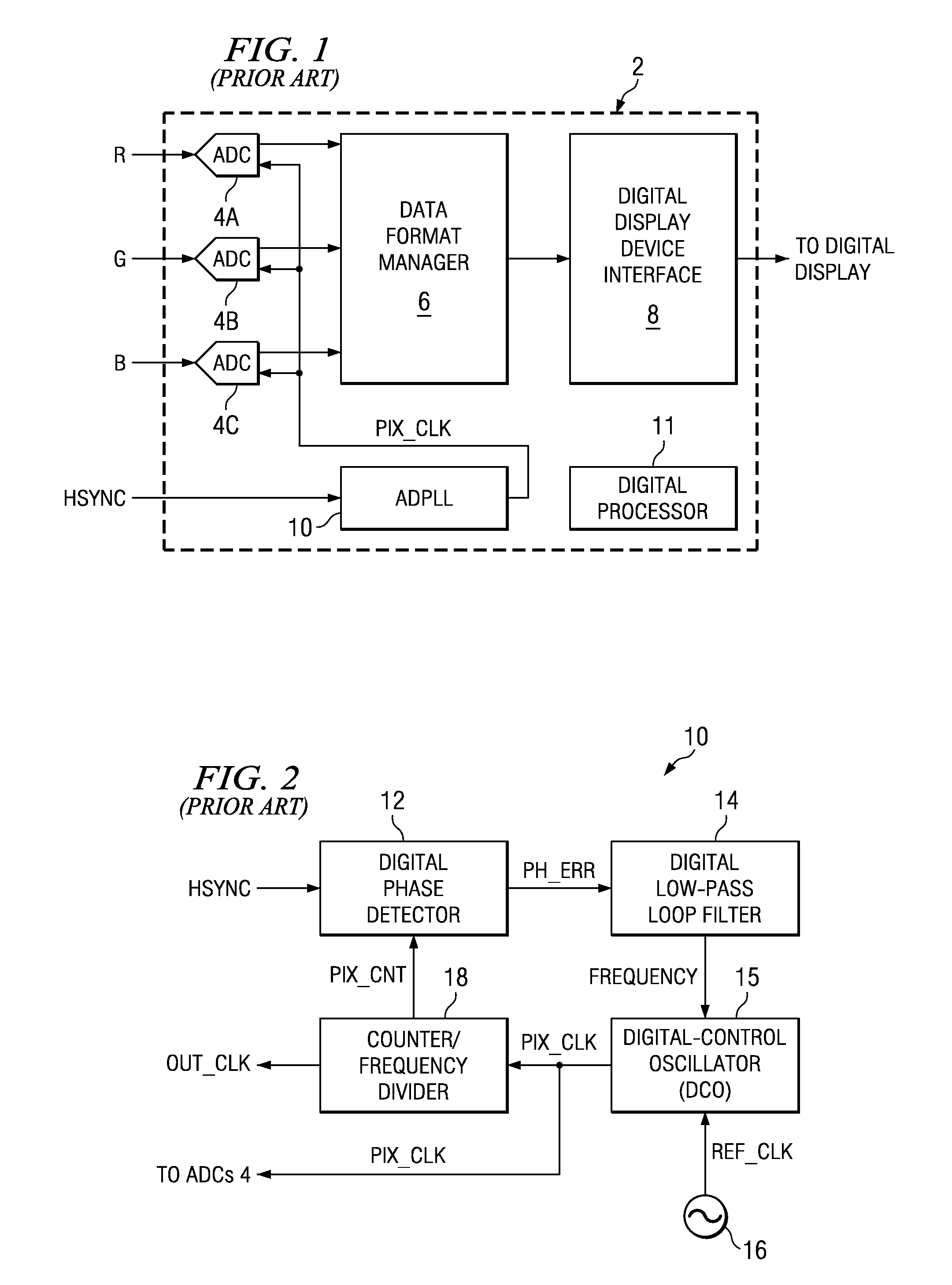
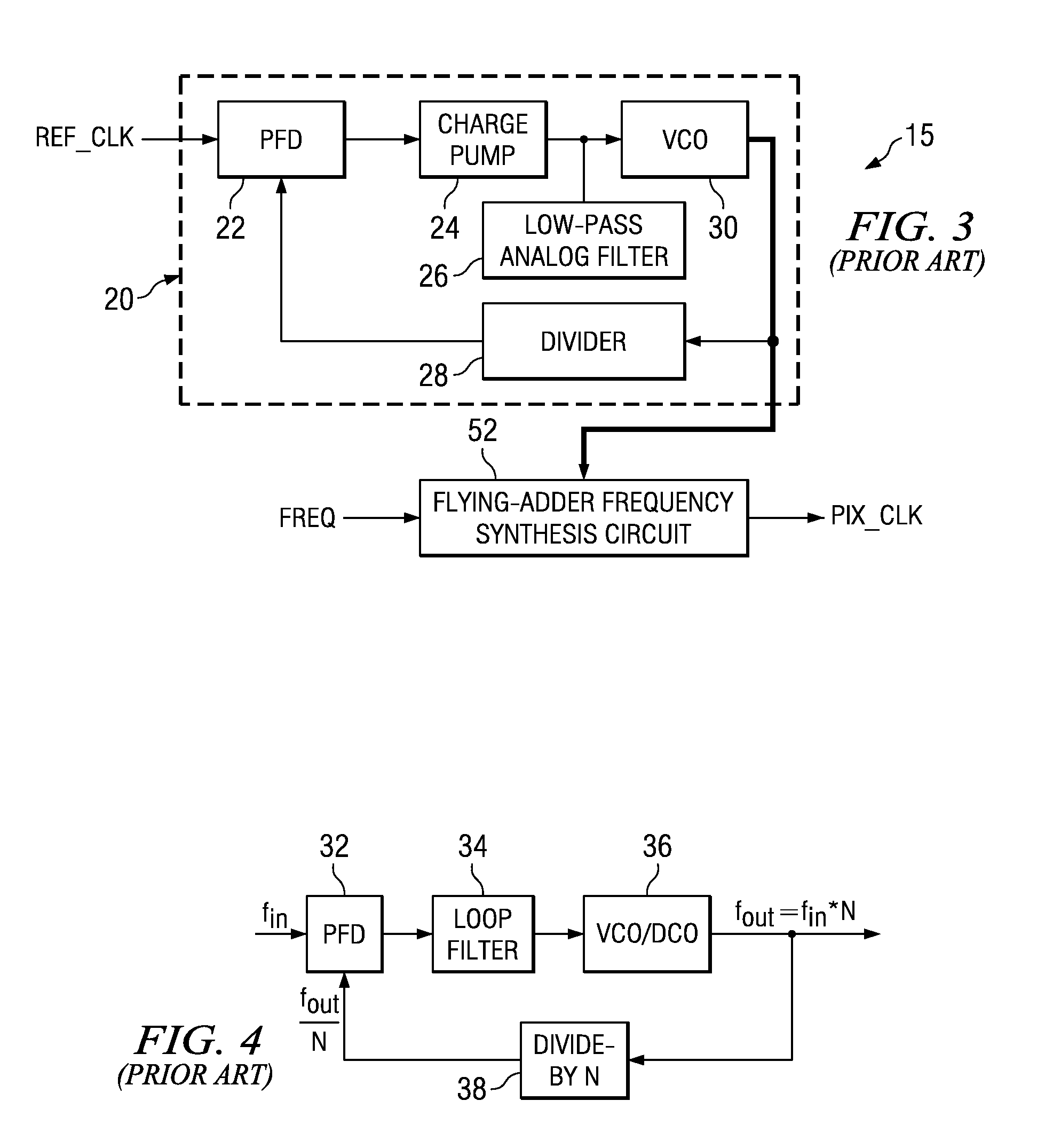
Flying-adder frequency synthesizer-based digital-controlled oscillator and video decoder including the same
ActiveUS7356107B2Large frequencyAccurate frequencyTelevision system detailsPulse automatic controlDigital control oscillatorMode control
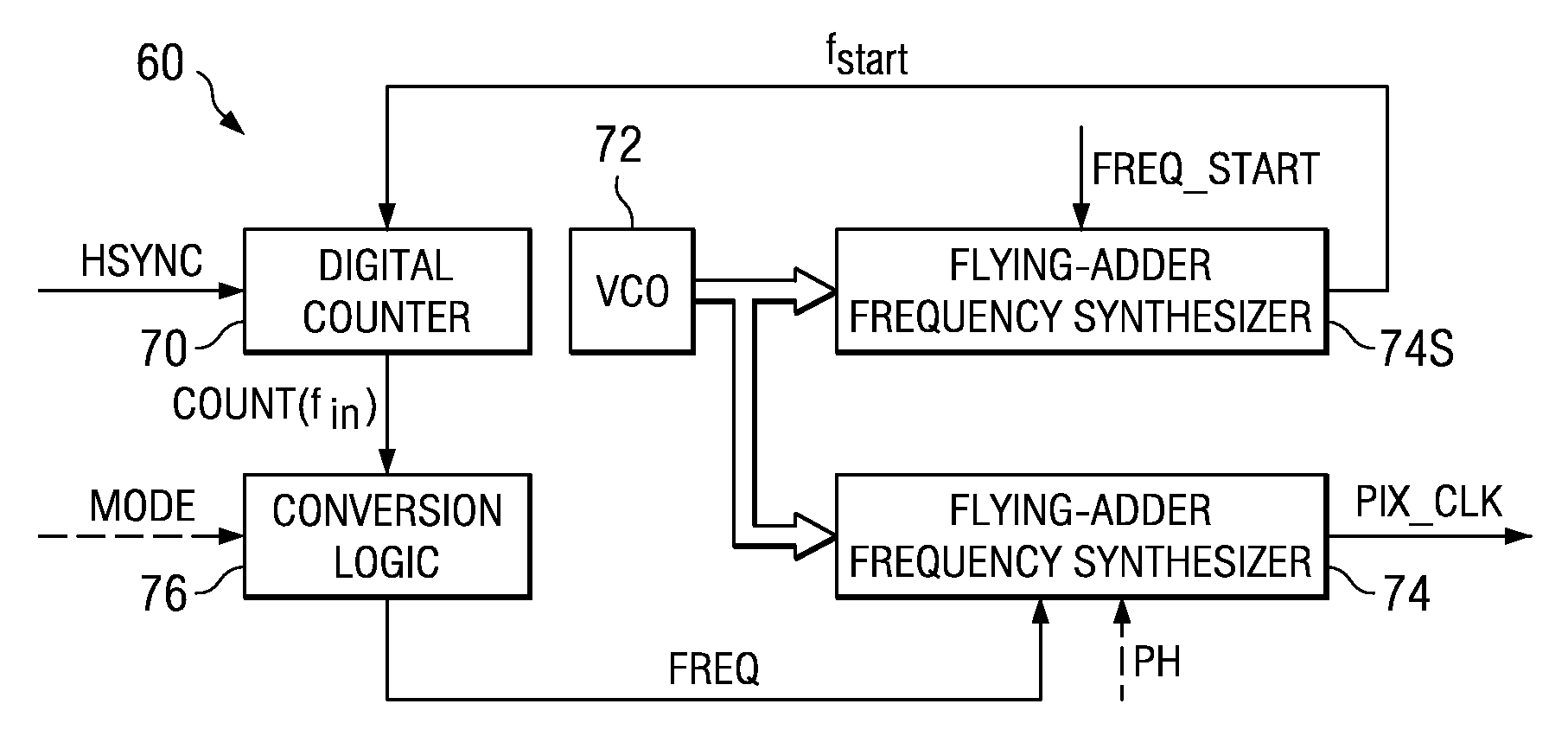
A video decoder (52, 152) including a digital-control oscillator (DCO) (60, 160) is disclosed. The DCO (60, 160) includes a first flying-adder frequency synthesis circuit (74S) that measures an input signal frequency, such as the horizontal sync frequency of an input video signal. A frequency control word (FREQ) is generated in response to this input signal frequency, and is applied to a second flying-adder frequency synthesis circuit (74), which in turn selects the appropriate phases for leading and trailing edges of the output clock signal (PIX_CLK). Phase tuning of the output clock signal (PIX_CLK) can be effected by using an alternate flying-adder frequency synthesis circuit (74′) architecture, in combination with a phase signal (PH) generated by a digital controller (61). Multiple phase-tuned sample clocks (PIX_CLK_A, PIX_CLK_B, PIX_CLK_C) can be similarly generated from multiple flying-adder frequency synthesis circuits (174A, 174B, 174C), each controlled by the frequency control word (FREQ) and a corresponding phase signal (PHA, PHB, PHC). Video mode control logic (65, 165) can also be implemented by way of a similar DCO architecture. The DCO (60) may be used to generate a clock signal at a large frequency multiple relative to the input signal, outside of the video decoder context.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
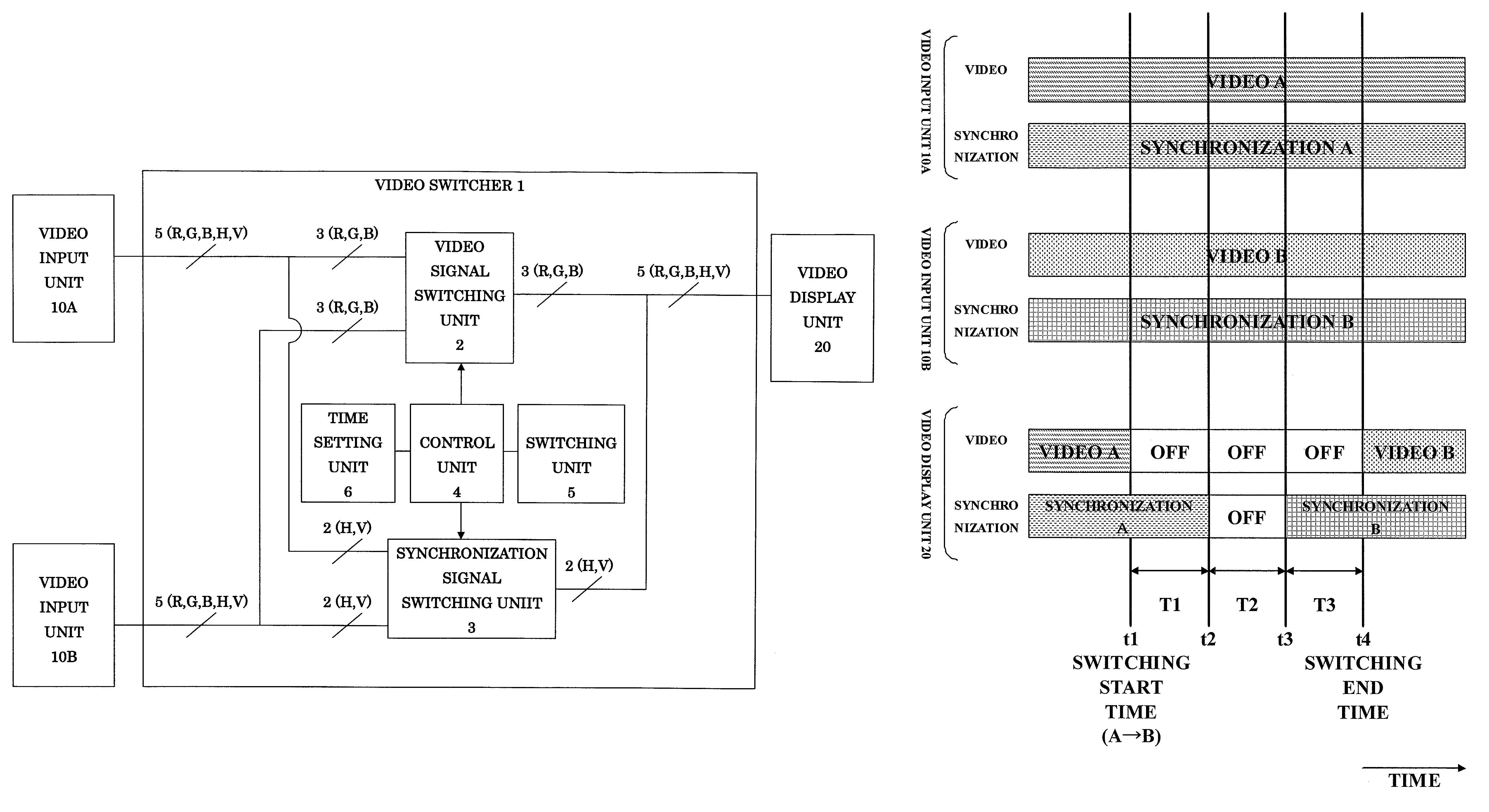
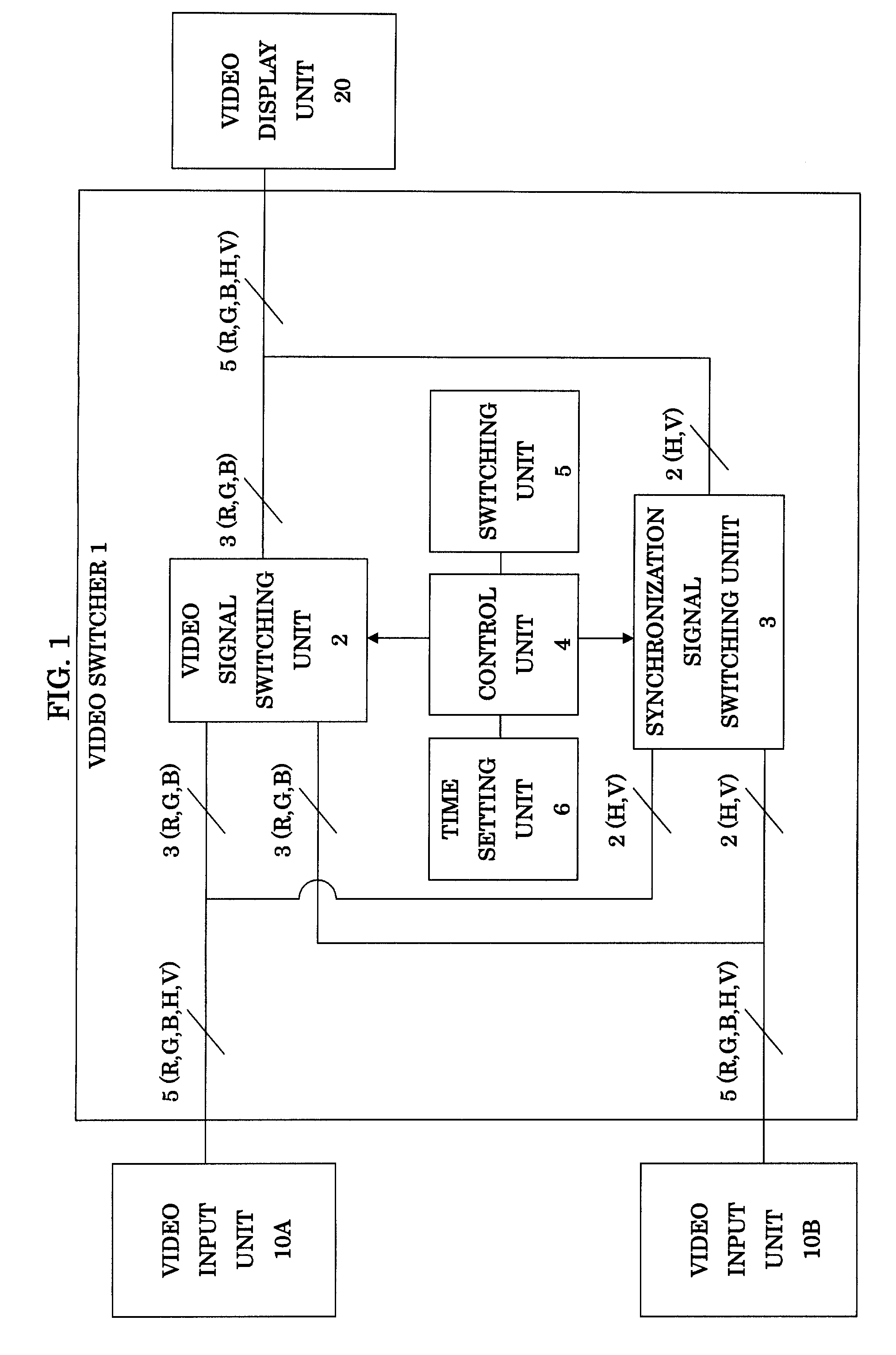
Video switcher and video switching method
InactiveUS7667774B2Reduce distortion problemsReduce displayTelevision system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionSignal transitionComputer engineering
A video switcher includes: a video signal switching device for switching a video signal to be transmitted to a video display unit from a first video signal supplied from a first video input unit into a second video signal supplied from a second video input unit; and a synchronization signal switching device for switching a synchronization signal to be transmitted to the video display unit from a first synchronization signal supplied from the first video input unit into a second synchronization signal supplied from the second video input unit. The synchronization signal switching device starts transmission of the second synchronization signal to the video display unit after stops transmission of the first synchronization signal to the video display unit. The video signal switching device starts transmission of the second video signal to the video display unit, after stop of transmission of the first video signal to the video display unit and start of transmission of the second synchronization signal to the video display unit.
Owner:IMAGENICS
Apparatus and method for detecting vertical synchronizing signal of digital TV
InactiveUS6504578B1Television system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionComputer scienceDigital television
An apparatus and method for detecting a vertical synchronizing signal in a digital TV receiver using a VSB system is disclosed. The present invention includes a vertical obtaining the correlation between a received signal and a previously set vertical synchronizing signal, detecting the position of a symbol having a maximum correlation in every field to output the detected position, and checking the reliability of the output of the maximum value position detector.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Video signal processing device, method of the same and vehicle-mounted camera system
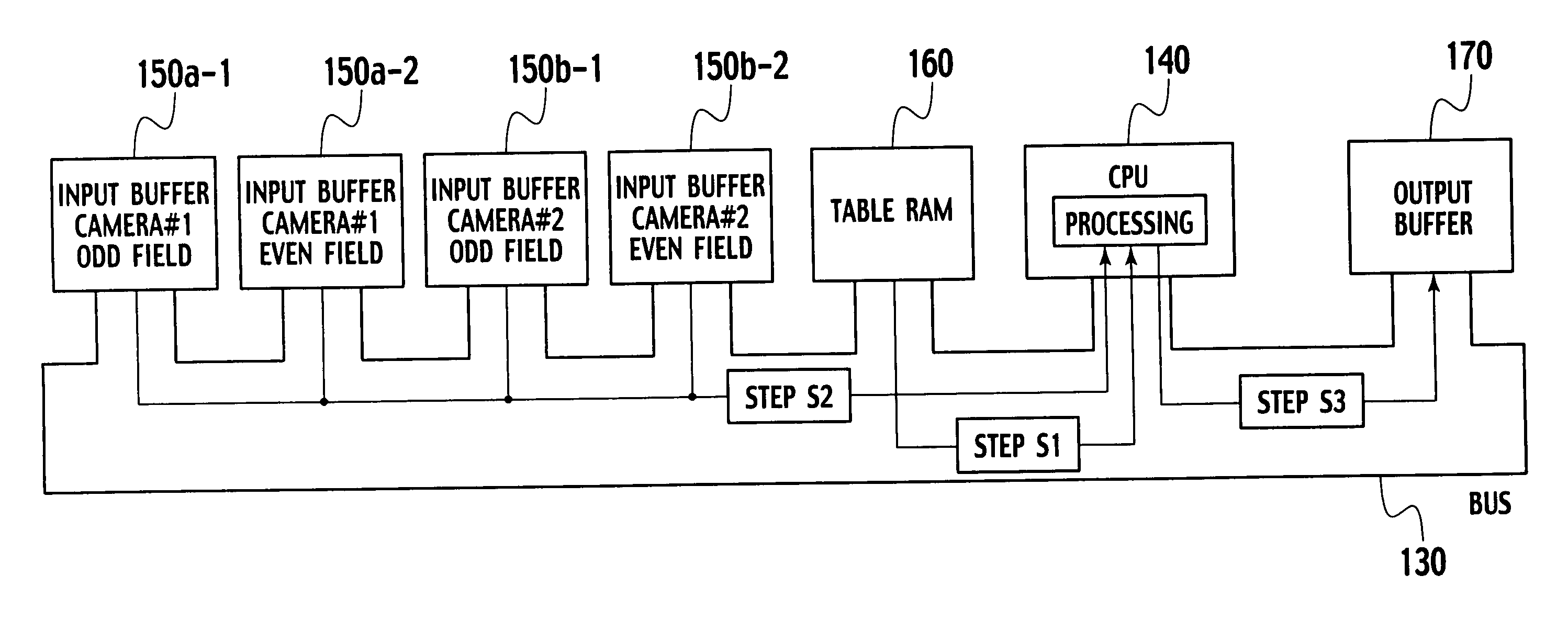
InactiveUS20060139488A1Reduce latencyReduce memory capacityTelevision system detailsTelevision with combined individual color signalComputer graphics (images)Imaging equipment
A video signal processing device, which includes: a plurality of imaging devices outputting mutually asynchronous interlace video signals; input buffers temporarily storing field by field the video signals outputted from the respective imaging devices; and an output image generating device generating field by field video signals of output target images from the video signals stored in the input buffers, wherein each of the video signals of the output target images is generated when all of the latest video signals to be components thereof are stored in the input buffers.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Digital photo album having a built-in scanner
InactiveUS7019871B2Reduce usageImprove viewing angleColor burst signal generation/insertionCathode-ray tube indicatorsHard disc driveDigital image
The present invention relates to a digital photo album having a hard drive and built-in scanner configured to scan photographic prints. The digital photo album allows a user to save the photographic prints as digital images on the hard drive, or another medium, and then view individual images or play photo album slideshows comprising a plurality of digital images. Additionally, a user may upload digital images from an external medium to the hard drive of the photo album, and then view those images and / or include them in a playlist. The digital photo album of the present invention advantageously allows a user to scan photographic prints, upload or download digital images, and view digital images individually or in an album format, in a substantially automated manner and without the need for complex peripheral devices.
Owner:TR MARKETING
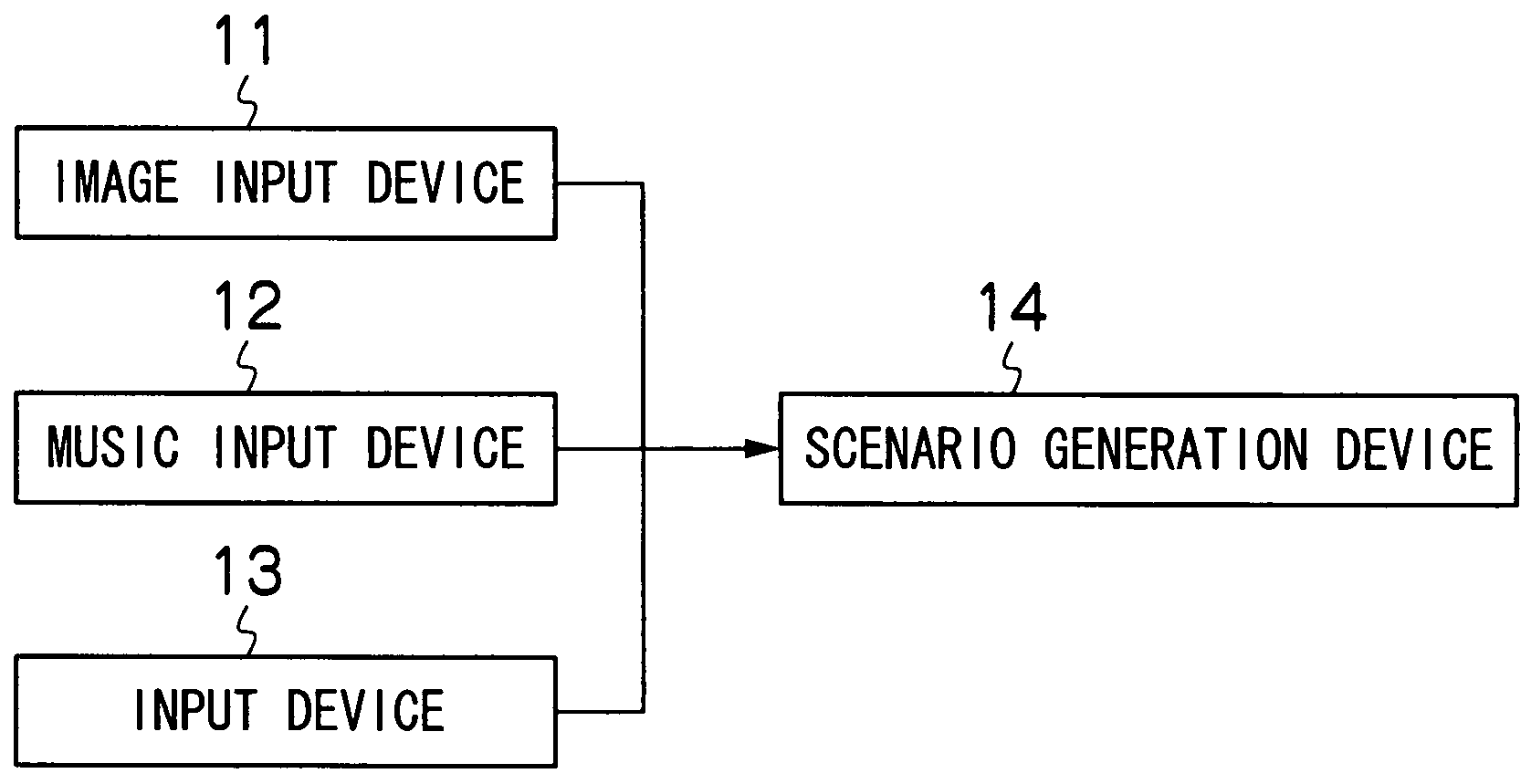
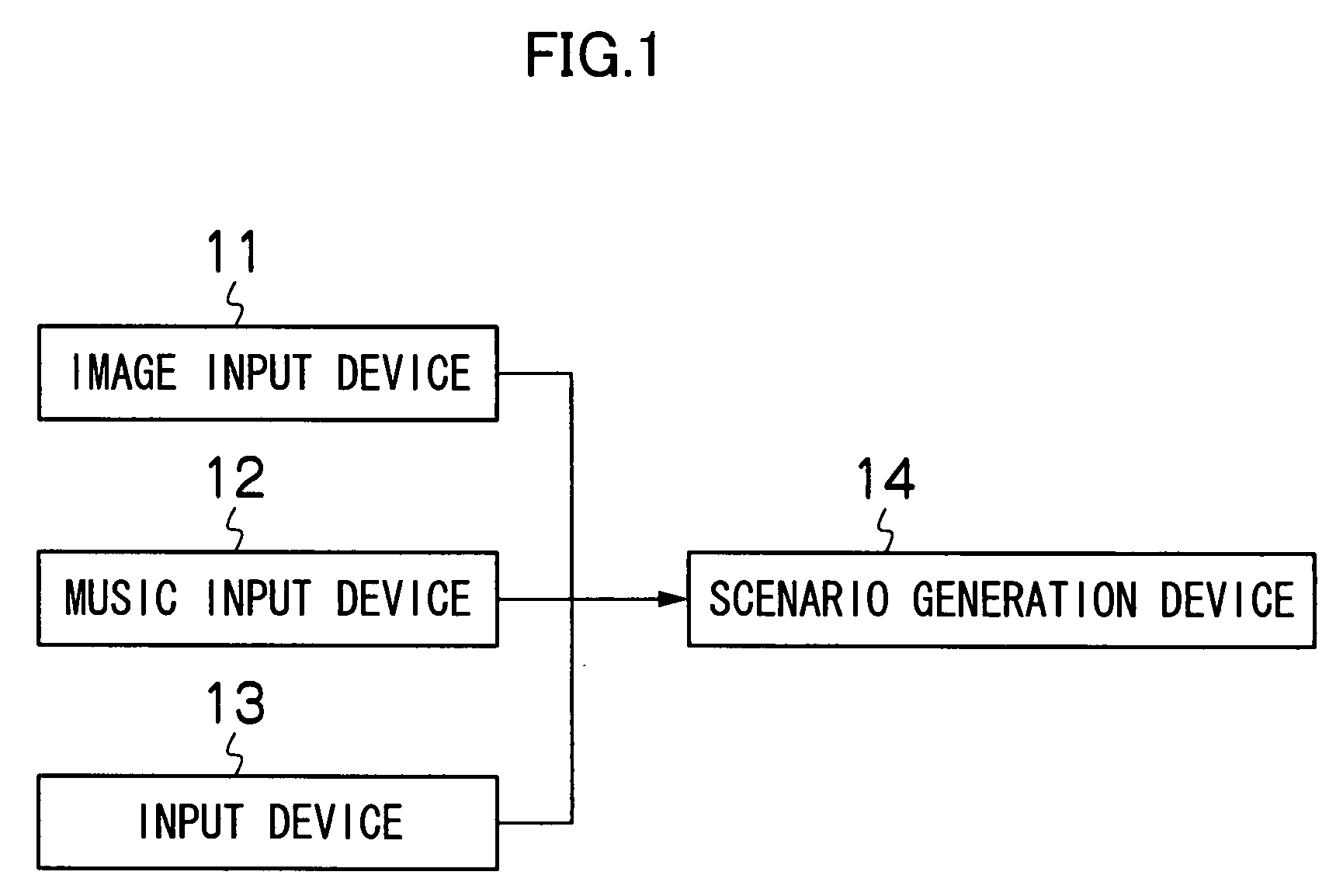
Method, program and apparatus for generating scenario for music-and-image-synchronized motion picture
InactiveUS20080055469A1Quality improvementTelevision system detailsElectrophonic musical instrumentsFeature extractionReproduction
The present invention provides a method for generating a scenario for a music-and-image-synchronized motion picture comprising the steps of: extracting characteristics of music; extracting structure of the music on the basis of the extracted characteristics of the music and dividing the music into multiple components on the basis of the result of the extraction; analyzing characteristics of images; associating the music and the images with each other according to the characteristics corresponding to the components of the music and the characteristics of the images; and generating a motion picture scenario that enables the associated music and images to be synchronously reproduced. According to the invention, since a component of music and images are associated with each other according to the characteristics of the images, it is possible to synchronously reproduce images that match the contents of music being reproduced, in comparison with the conventional synchronous reproduction.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Imaging system, imaging controller, and method and program for vertical synchronization
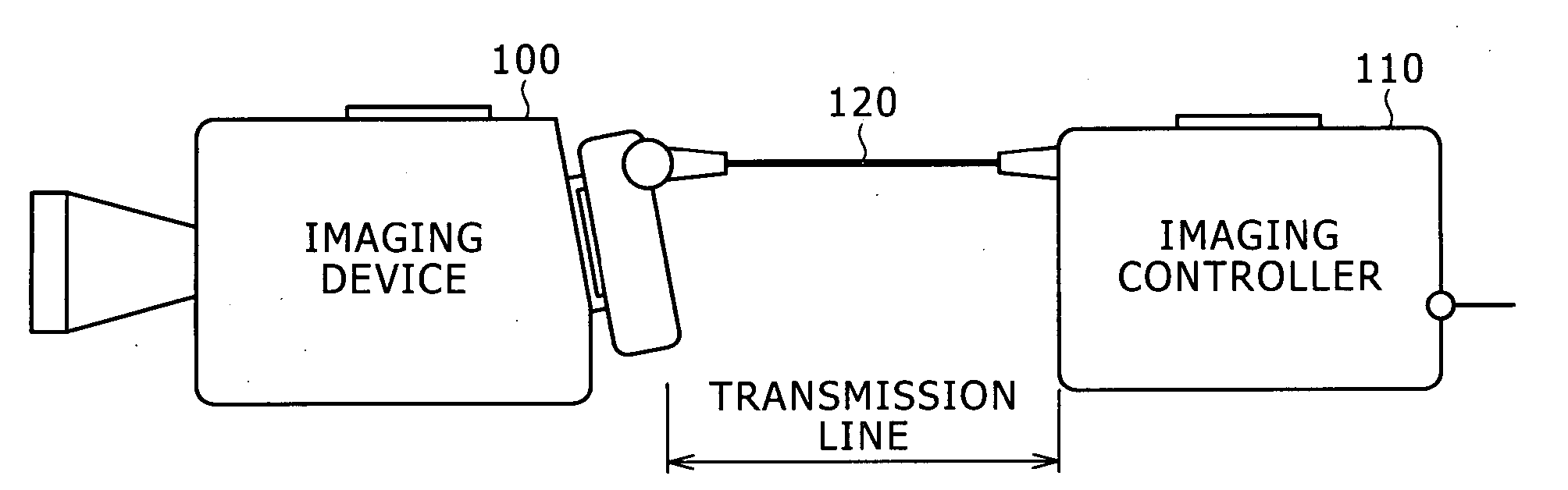
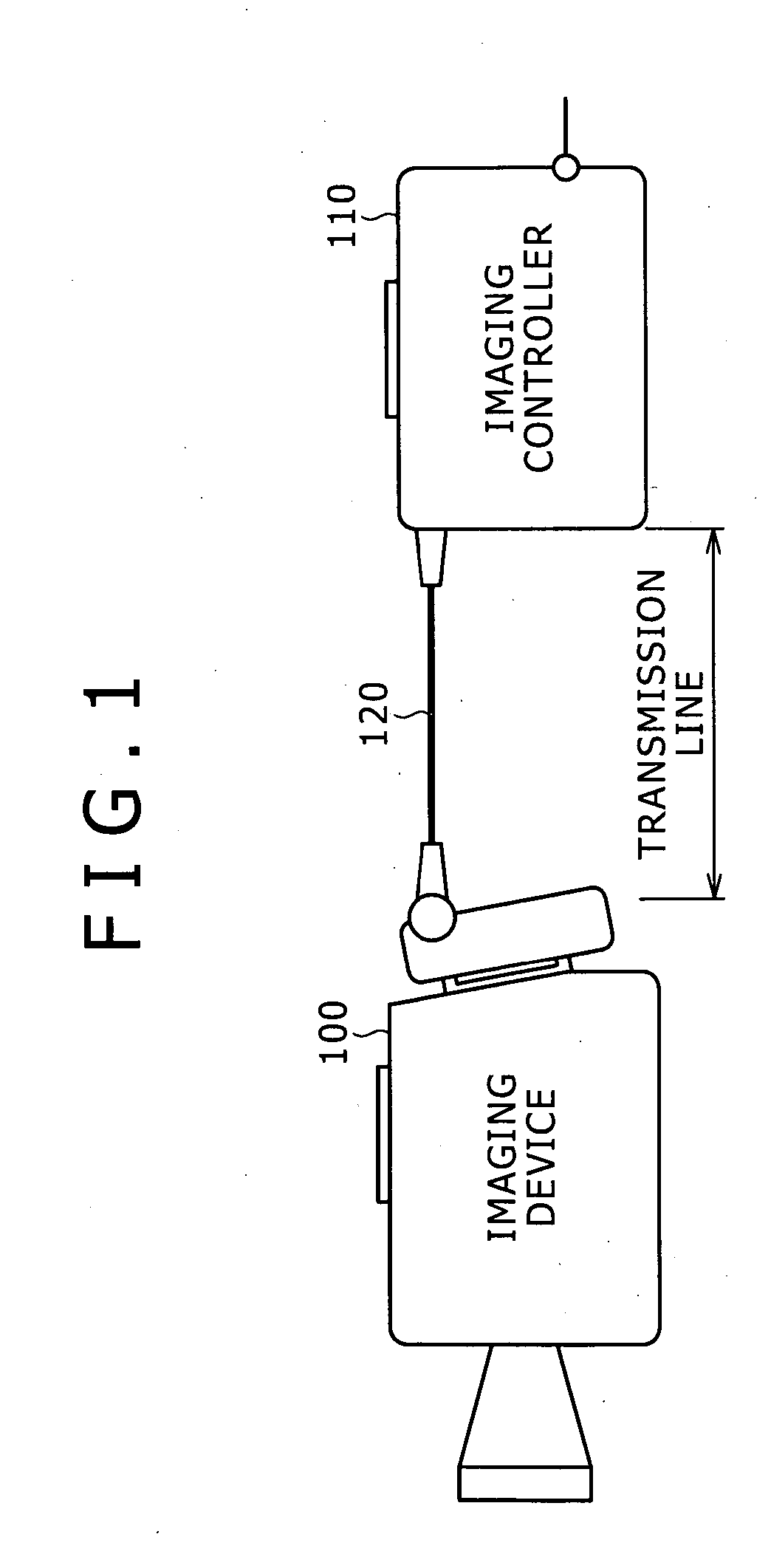
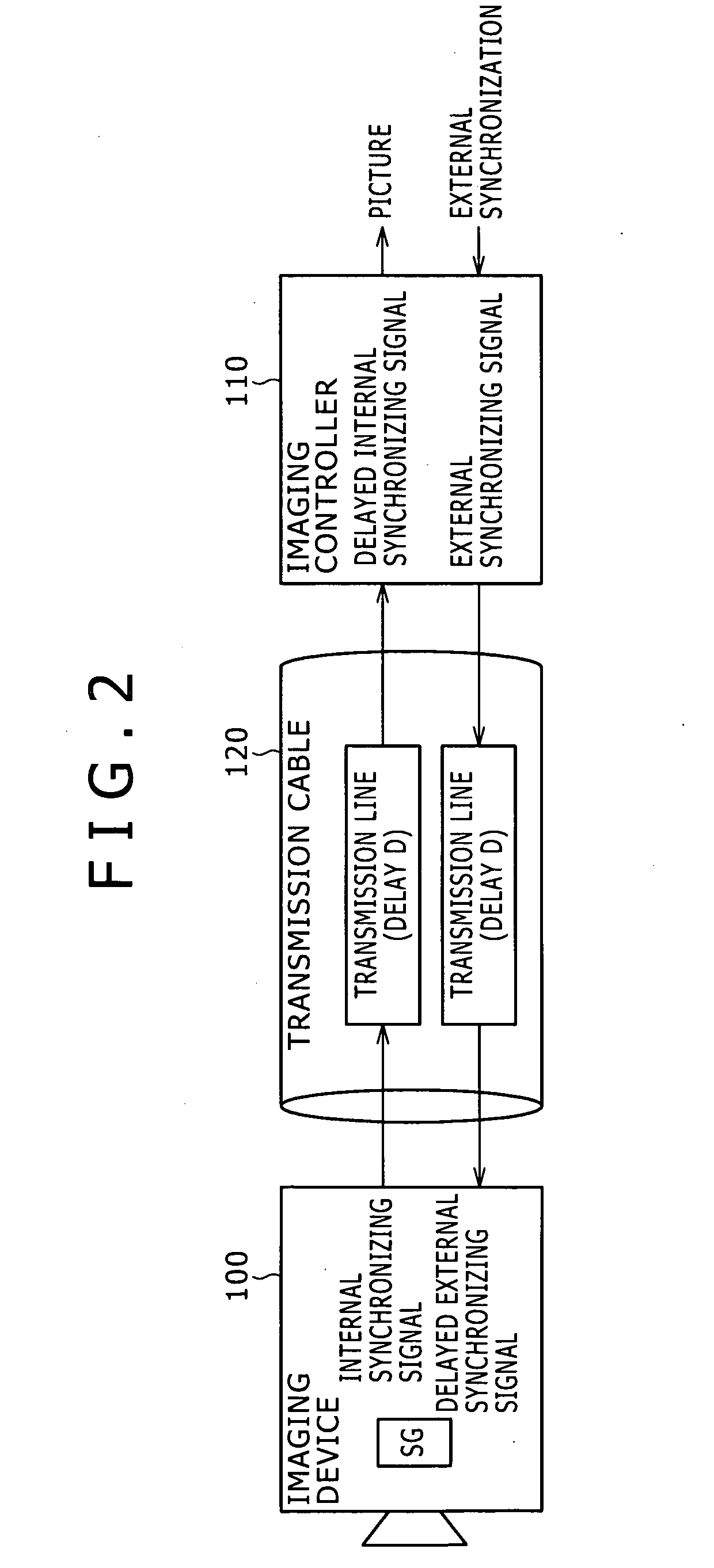
InactiveUS20060261282A1Reliable measurement resultsTelevision system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionImaging equipmentPhase advance
Disclosed is an imaging system having an imaging device for producing images of objects and picture signals and an imaging controller connected to the imaging device through a transmission line. The imaging device includes a vertical synchronizing signal-producing circuit to produce an internal vertical synchronizing signal for the production of images of objects. The imaging controller includes a delay-measuring circuit and a vertical-synchronization phase-advancing circuit. In the system: the imaging controller transmits a test signal to the imaging device and receives the test signal returned from the imaging device and the delay-measuring circuit measures a delay of a phase of the returned test signal relative to a phase of the original test signal; the vertical-synchronization phase-advancing circuit advances a phase of an external vertical synchronizing signal by the delay and transmits the external vertical synchronizing signal to the imaging device; and the vertical synchronizing signal-producing circuit is reset by a signal transmitted from the vertical-synchronization phase-advancing circuit.
Owner:SONY CORP
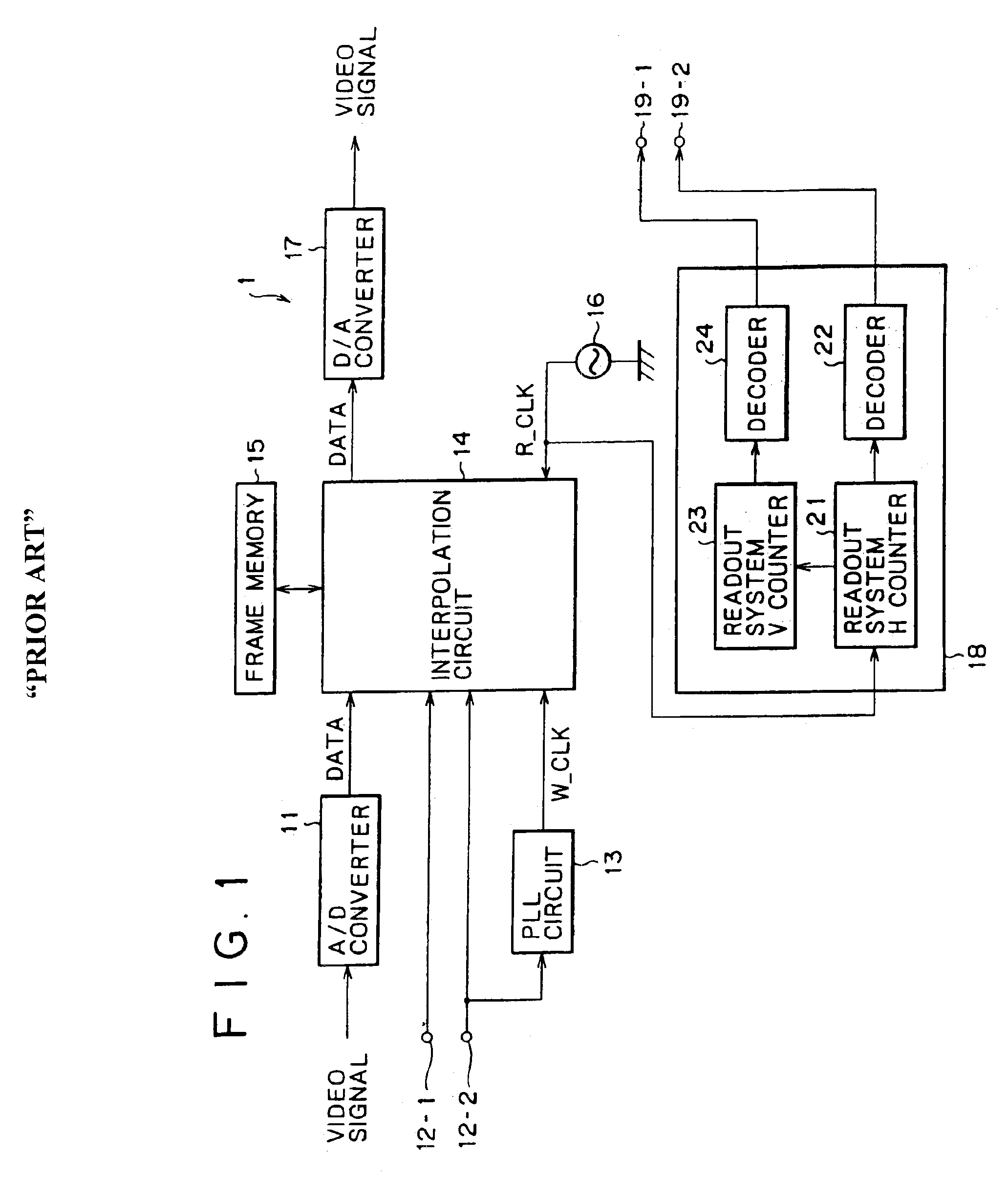
Video signal conversion processing apparatus and method
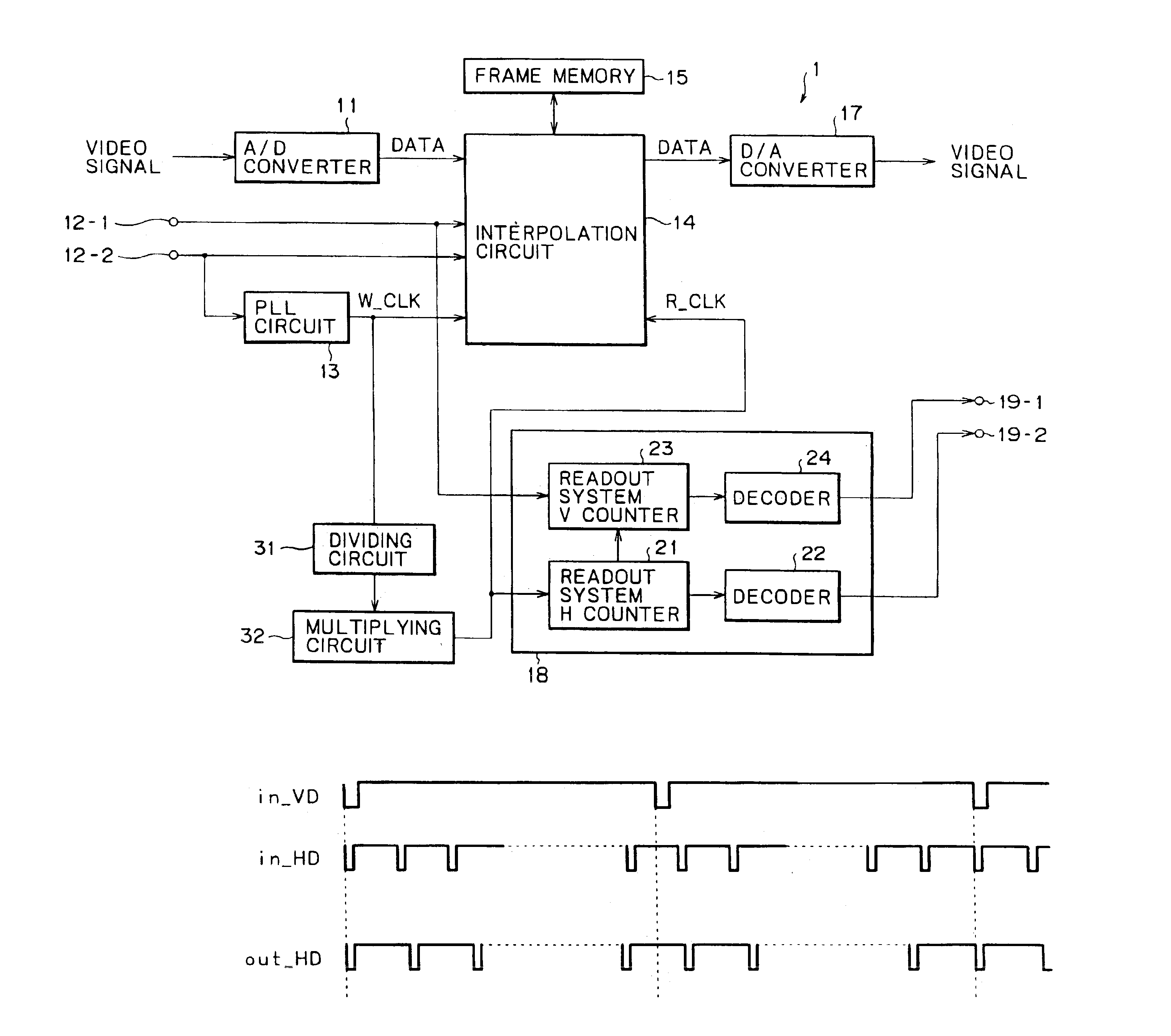
InactiveUS6891572B2High precisionImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsPulse automatic controlDividing circuitsComputer science
A signal processing apparatus and method for up or down conversion of an interlace signal with a high degree of accuracy. The frequency of a write system clock supplied from a PLL circuit is divided by N by a dividing circuit and then multiplied by M by a multiplying circuit to produce a readout system clock. An interpolation circuit writes a video signal into a frame memory in synchronism with the write system clock from the PLL circuit, and reads out the video signal in synchronism with the readout system clock from the multiplying circuit.
Owner:SONY CORP
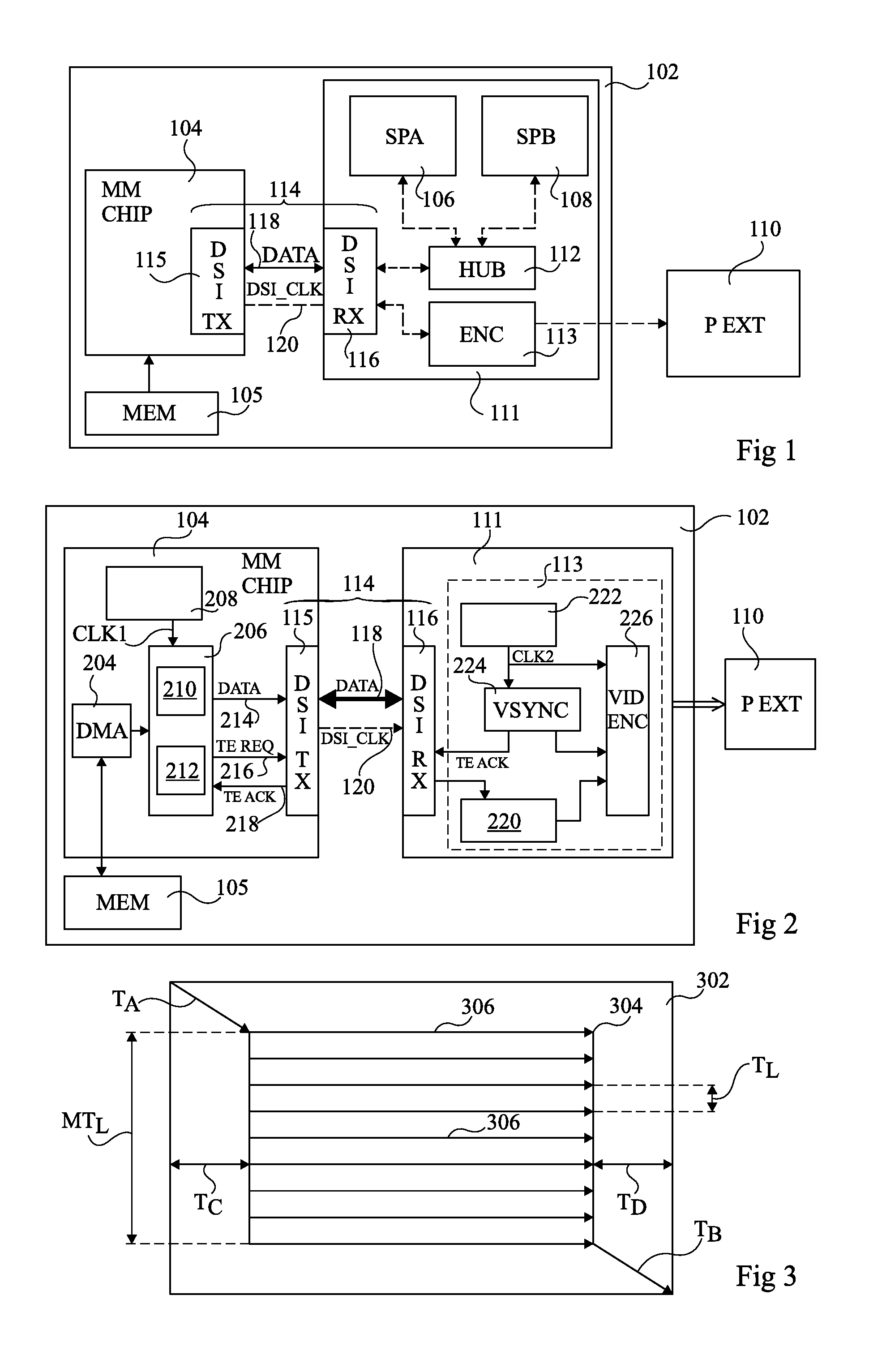
Video Transmission On A Serial Interface
InactiveUS20120147976A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionPacket generatorVideo transmission
A video transmission circuit for transmitting video data on a digital serial interface to a receive circuit arranged to process the video data at a constant rate, the circuit including a transmission block comprising: a packet generator arranged to generate, for each image of the video data, a plurality of packets, each containing a pixel group of the image; a transmit circuit arranged to transmit the packets of each image on a digital serial interface at time intervals based on the constant rate; and a synchronization circuit arranged to receive from the receive circuit, after transmission of a plurality of packets, a synchronization signal for synchronizing the beginning of the transmission of a next packet.
Owner:OPTIS CIRCUIT TECH LLC
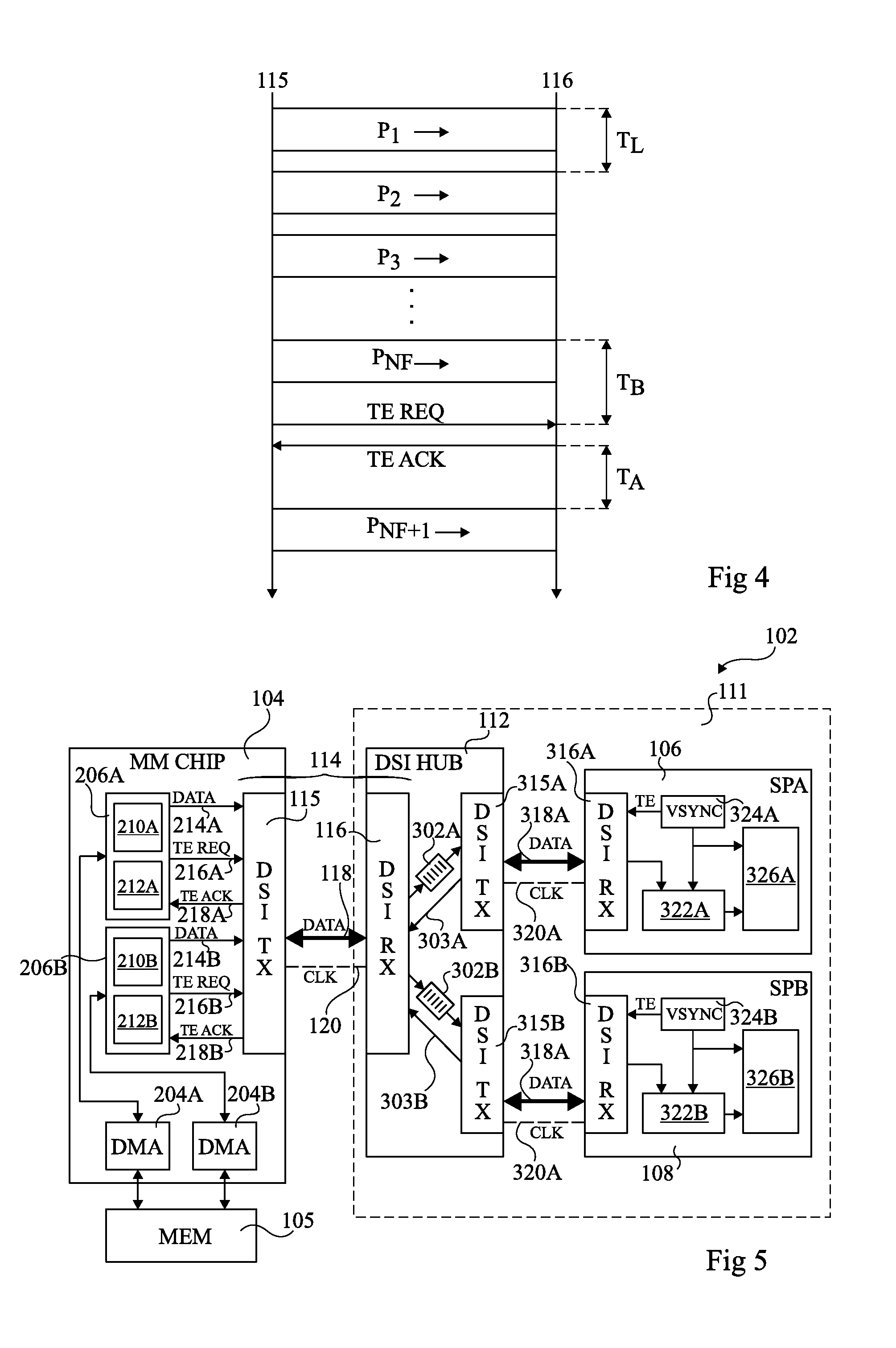
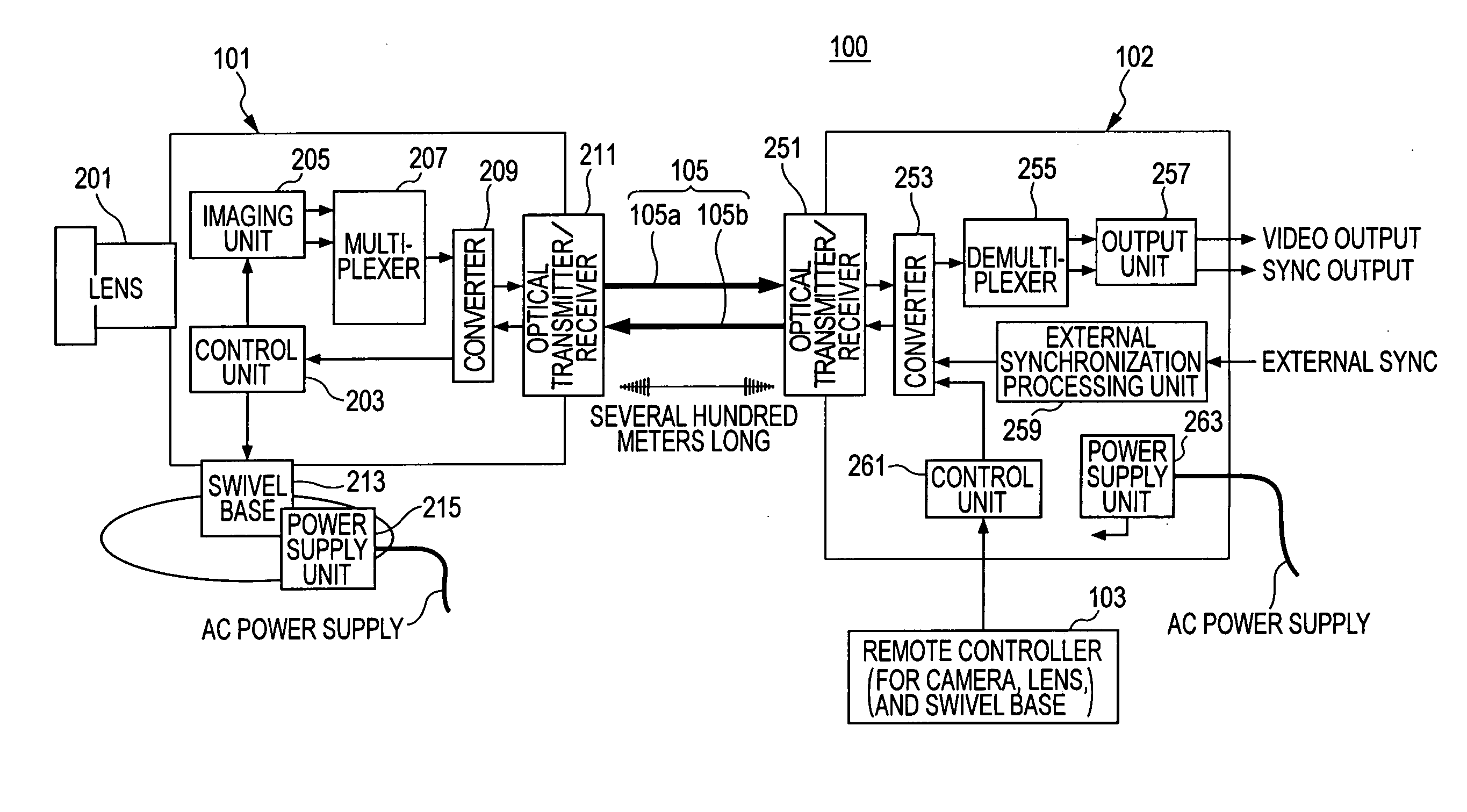
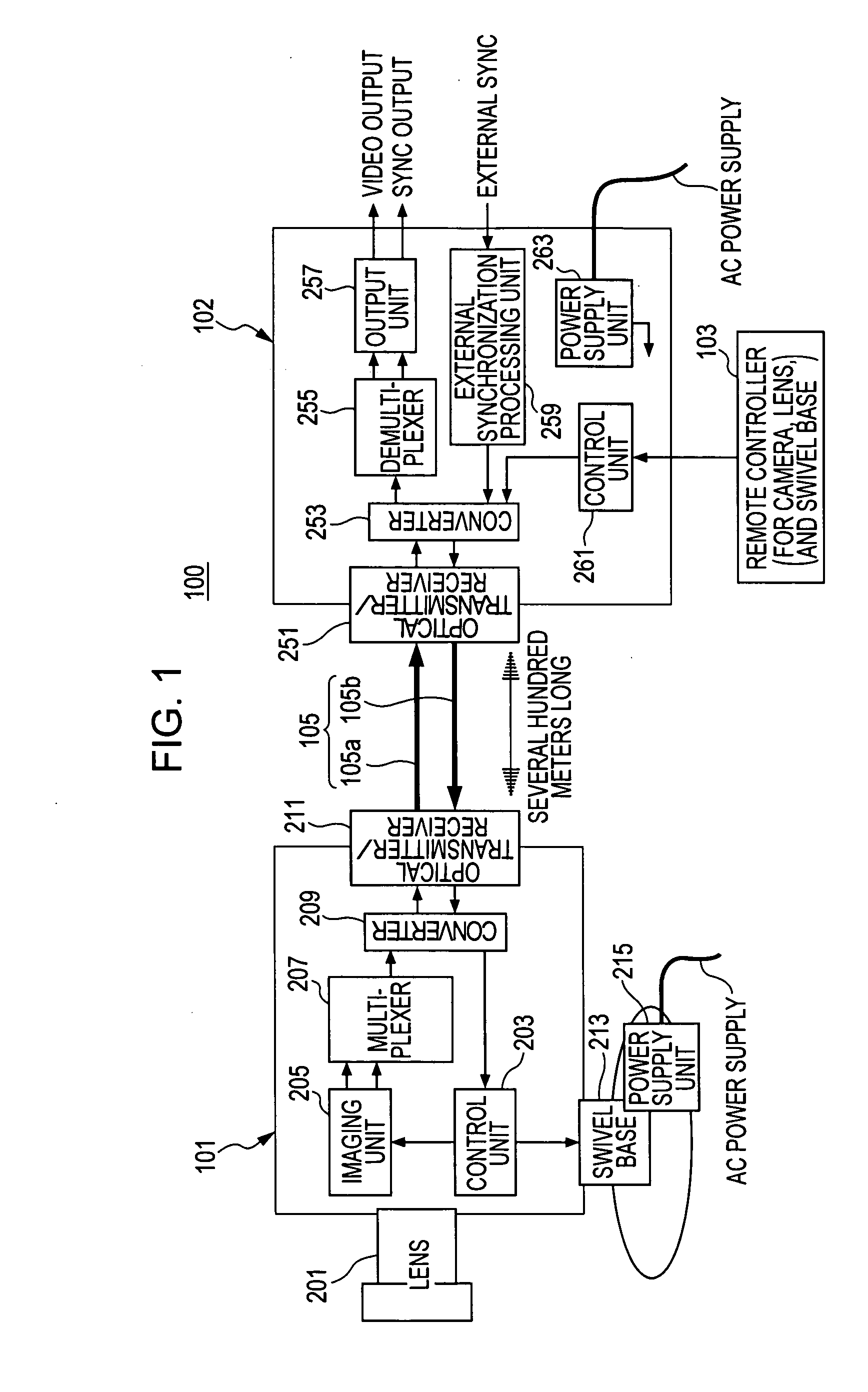
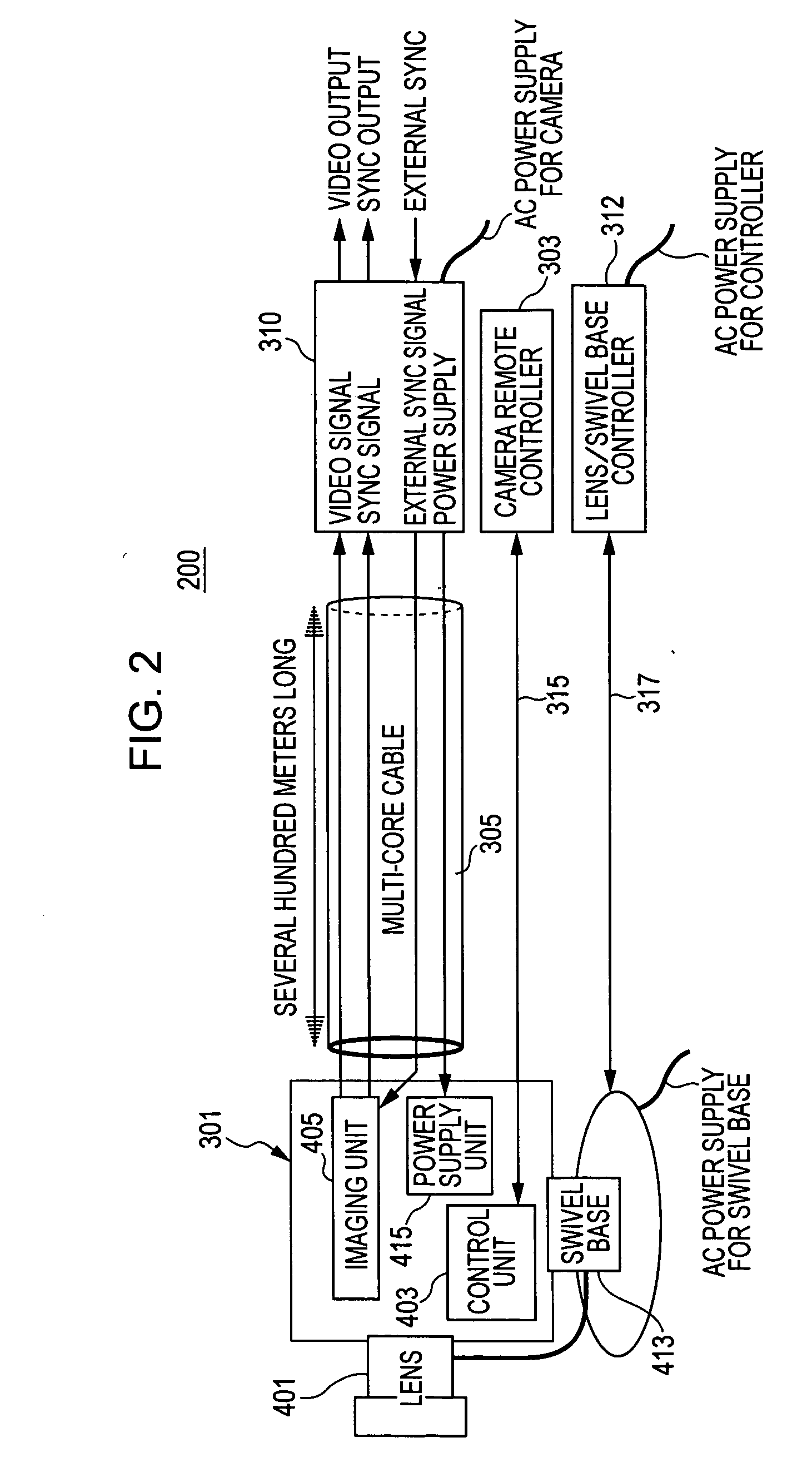
Imaging apparatus, phase control method, and synchronization method
ActiveUS20050174435A1Increase chanceTelevision system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionPhase controlImaging equipment
An imaging apparatus includes a camera device, a signal processor that receives a video signal from the camera, and a connection cable connecting the camera device and the signal processor. The camera device includes a first phase controller that compares the phase of a synchronization signal transmitted from the signal processor with the phase of an internal signal generated by the camera device, and that synchronizes the phase of the internal signal with the phase of the synchronization signal, a video synchronization signal generator that generates a video synchronization signal for the video signal based on the internal signal, and a signal transmitter that transmits the video signal. The signal processor includes a second phase controller that compares the phase of the video synchronization signal with the phase of the synchronization signal, and that synchronizes the phase of the video synchronization signal with the phase of the synchronization signal.
Owner:SONY CORP
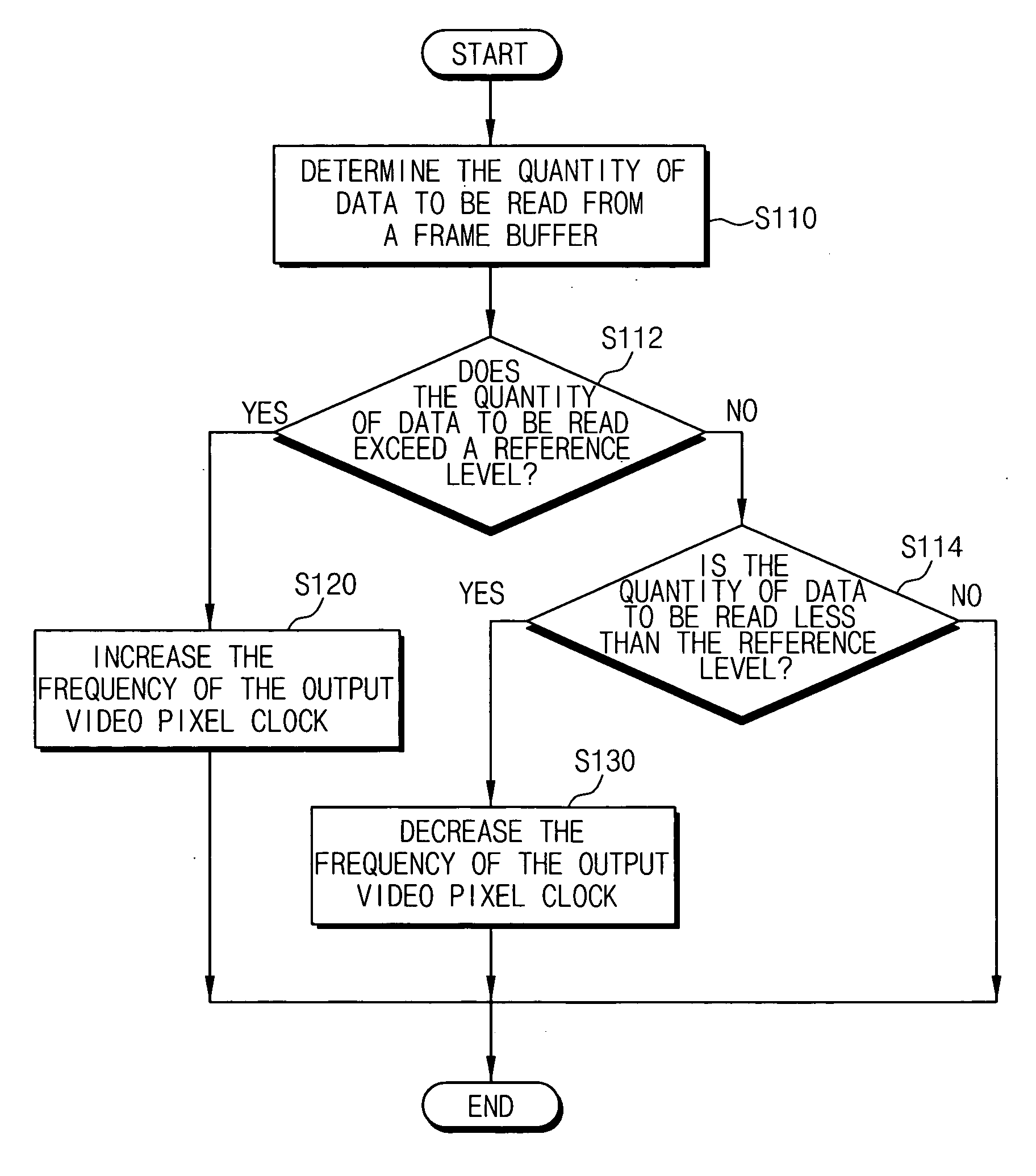
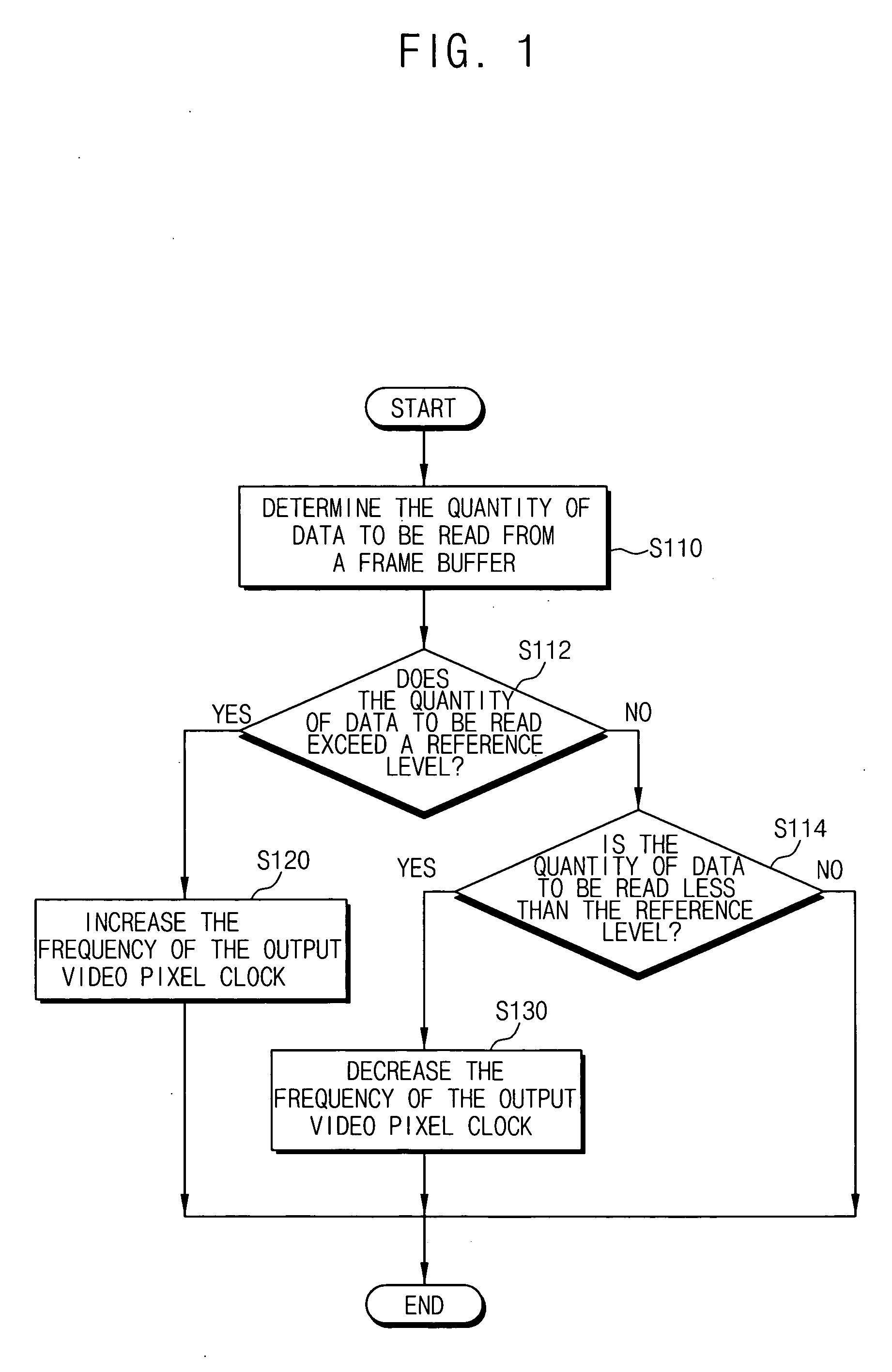
Method for generating a video pixel clock and apparatus for performing the same
InactiveUS20060158554A1Reduce imbalanceHigh frequencyTelevision system detailsPulse automatic controlComputer scienceImage signal
In a method of generating a video pixel clock, a frequency of an output video pixel clock is increased to a first frequency setting when a quantity of data read from a frame buffer storing video data is greater than a reference level. The frequency of the output video pixel clock is decreased to a second frequency setting when the quantity of data read from the frame buffer is less than the reference level. Accordingly, an imbalance between frame rates of input and output image signals may be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Pixel skew compensation apparatus and method
InactiveUS20060262226A1Eliminate skewTelevision system detailsChannel dividing arrangementsDigital videoComputer science
A two-stage pixel skew compensation circuit for use with digital display monitors. The first stage of the compensation circuit aligns the edges of the pixels received on the color component signal lines of an analog video signal. The second stage of the de-skew compensation circuit realigns the pixels themselves so that no skew exists between the digitized video color components. The digitized video signals drive a digital video monitor.
Owner:AVOCENT HUNTSVILLE CORPORATION
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com