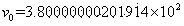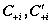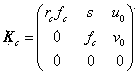Method of determining intrinsic parameters of parabolic catadioptric camera through linearity of two mutually-shielded spheres
A camera internal parameter, catadioptric technology, applied in the field of computer vision, can solve the problem of complex ring point selection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0035] The present invention proposes to linearly determine the internal parameters of the parabolic catadioptric camera by using two mutually occluded spheres in space as targets. The experimental module structure diagram that the present invention adopts is as figure 1 shown. The implementation of the present invention will be described in more detail with an example below.
[0036] The experimental template used in the parabolic catadioptric camera calibration method based on two mutually occluded spheres in space is two mutually occluded spheres, such as figure 1 shown. The two balls are and , using the method in the present invention to calibrate the parabolic catadioptric camera for implementation, the specific steps are as follows:
[0037] 1. Fit image boundary and target curve equation
[0038] The image resolution adopted by the present invention is pixels, take 5 experimental pictures with a parabolic catadioptric camera, read in the images, use the funct...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com