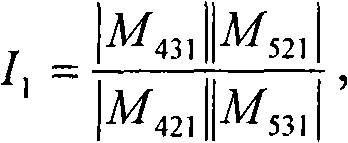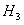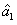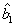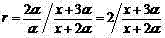Patents
Literature
68 results about "Cross-ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
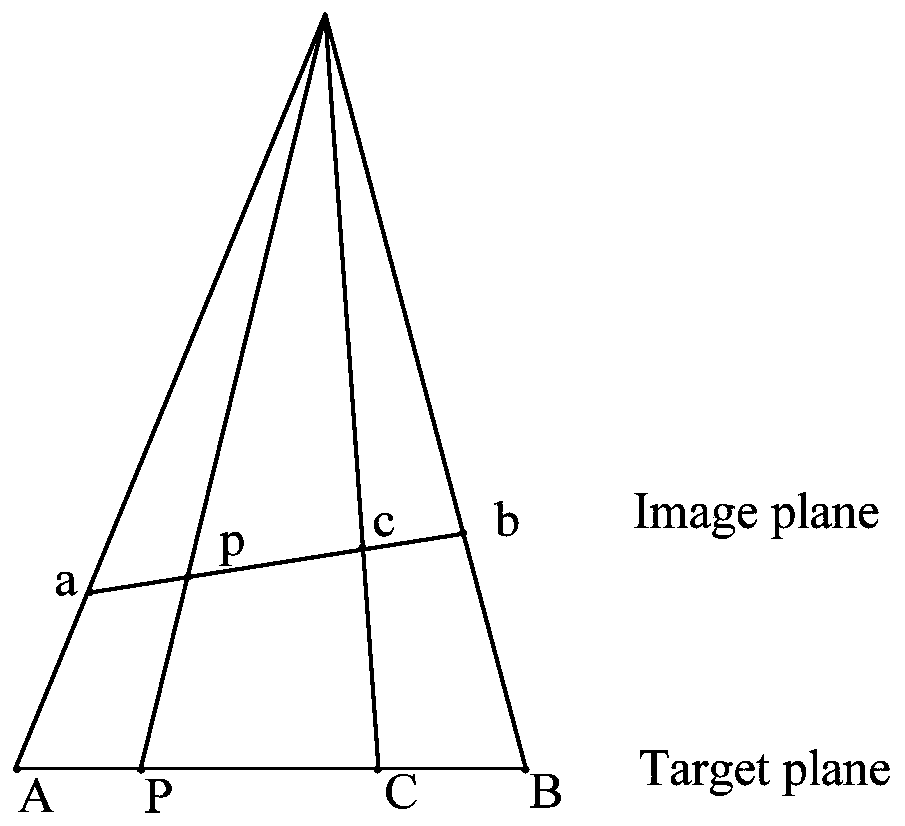
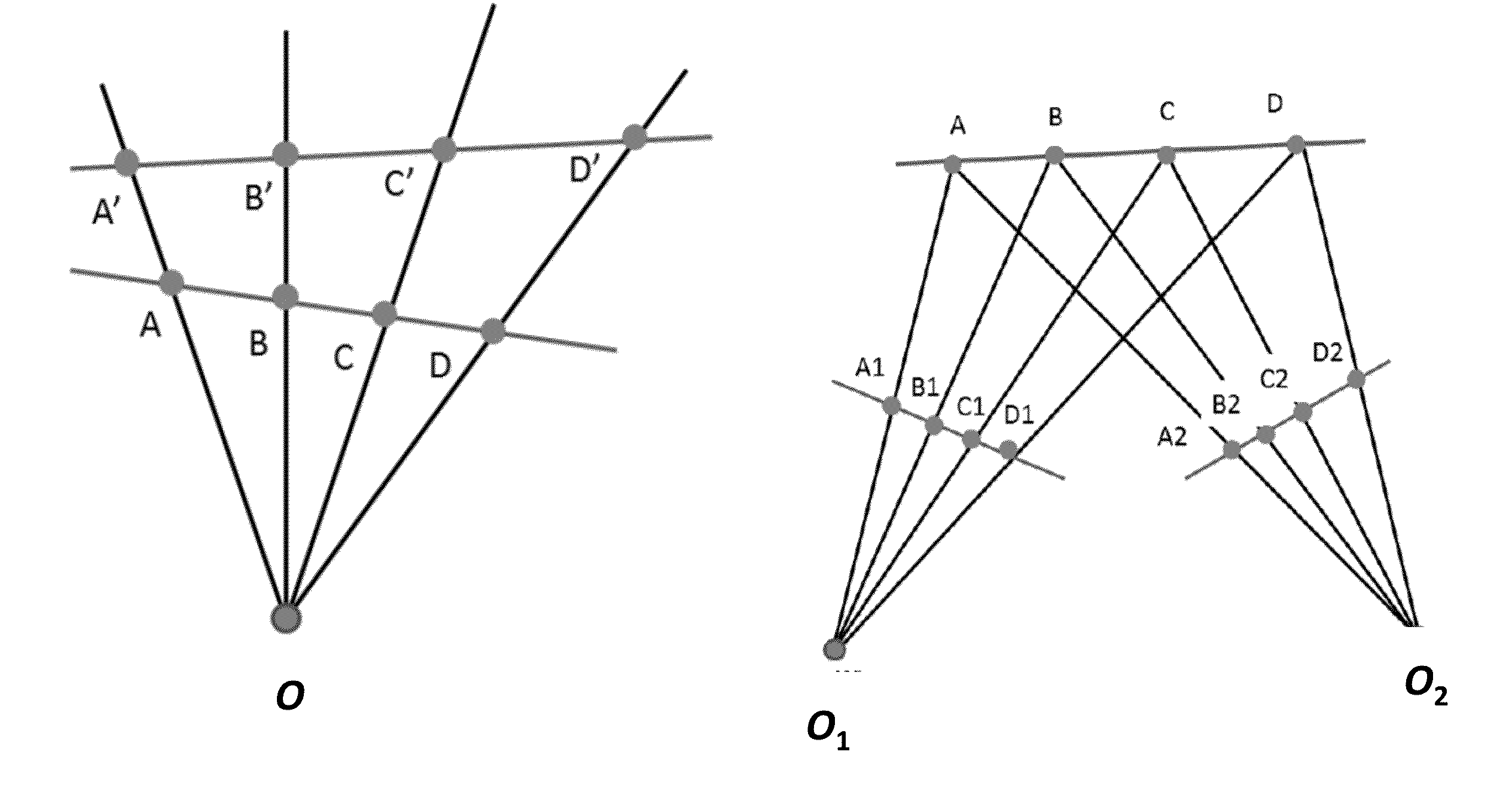
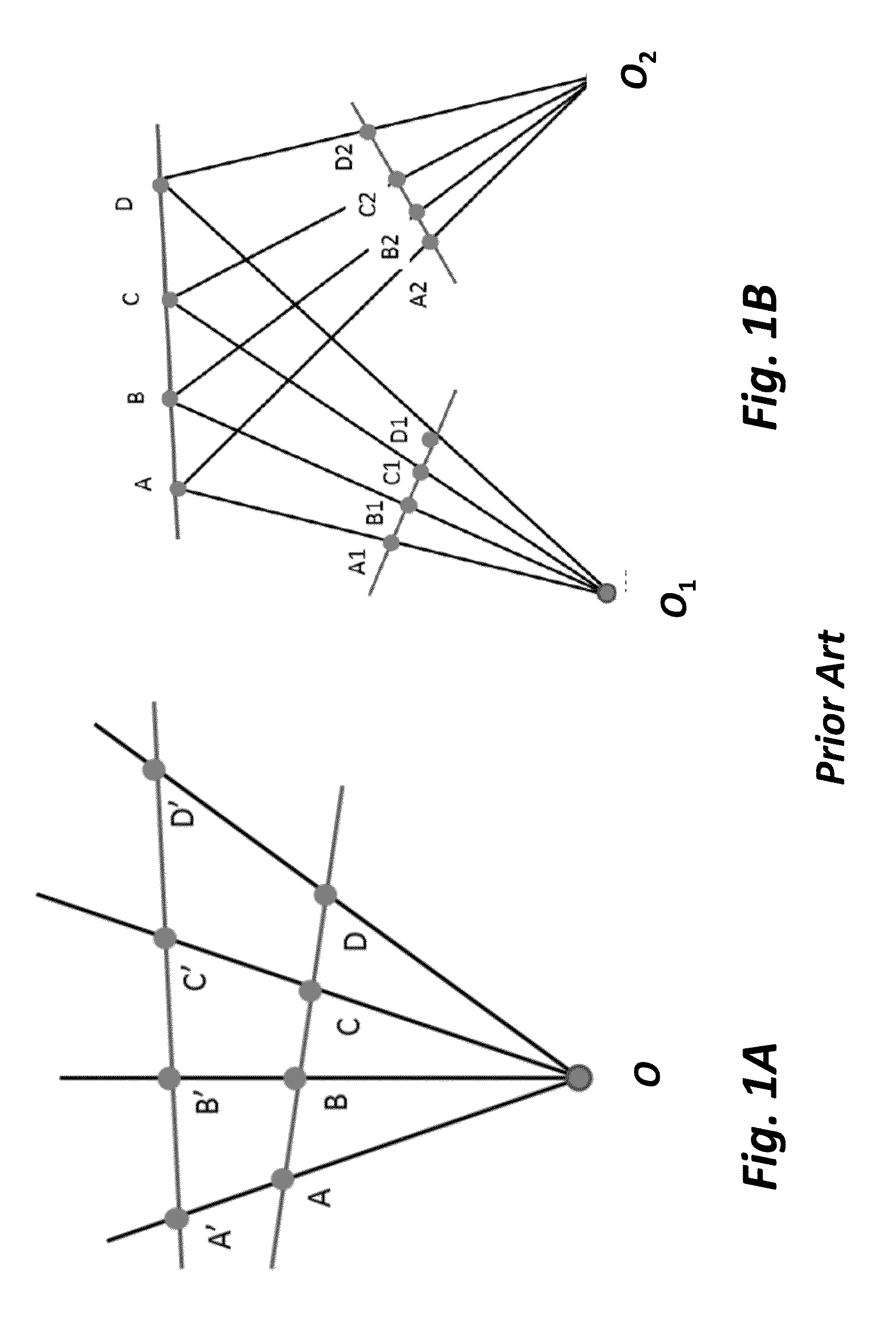
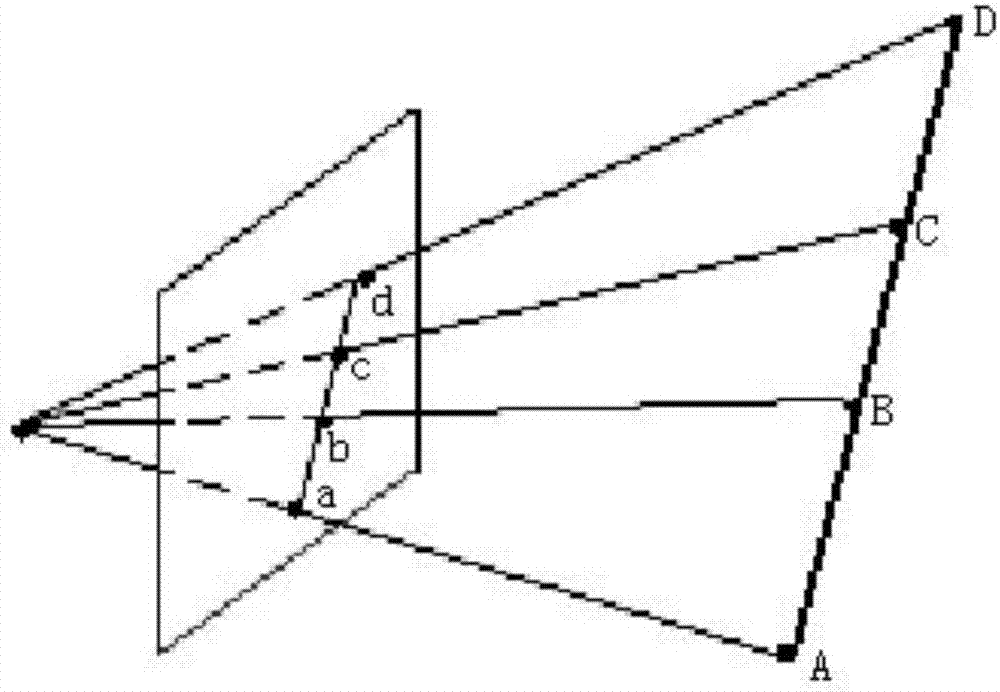
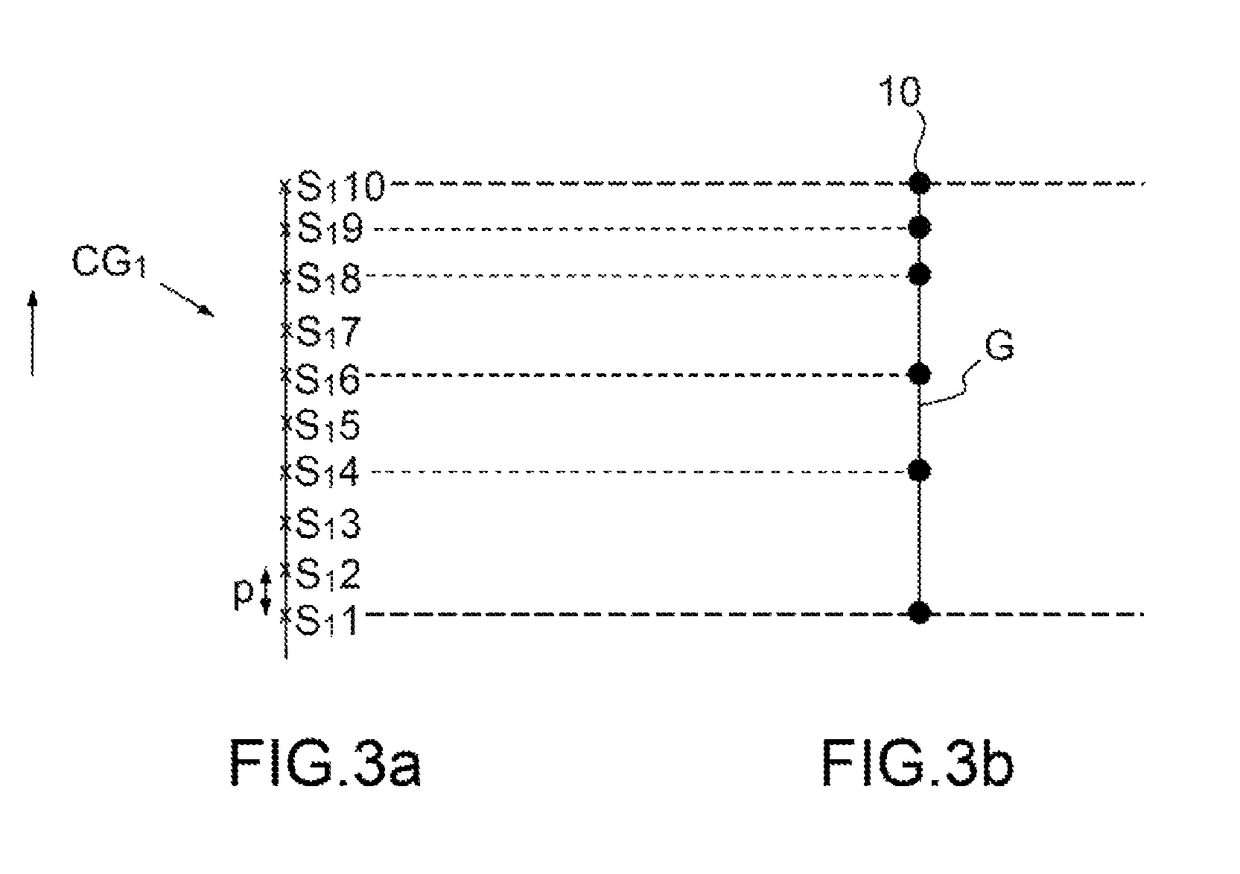
In geometry, the cross-ratio, also called the double ratio and anharmonic ratio, is a number associated with a list of four collinear points, particularly points on a projective line. Given four points A, B, C and D on a line, their cross ratio is defined as (A,B;C,D)=AC·BD/BC·AD where an orientation of the line determines the sign of each distance and the distance is measured as projected into Euclidean space.
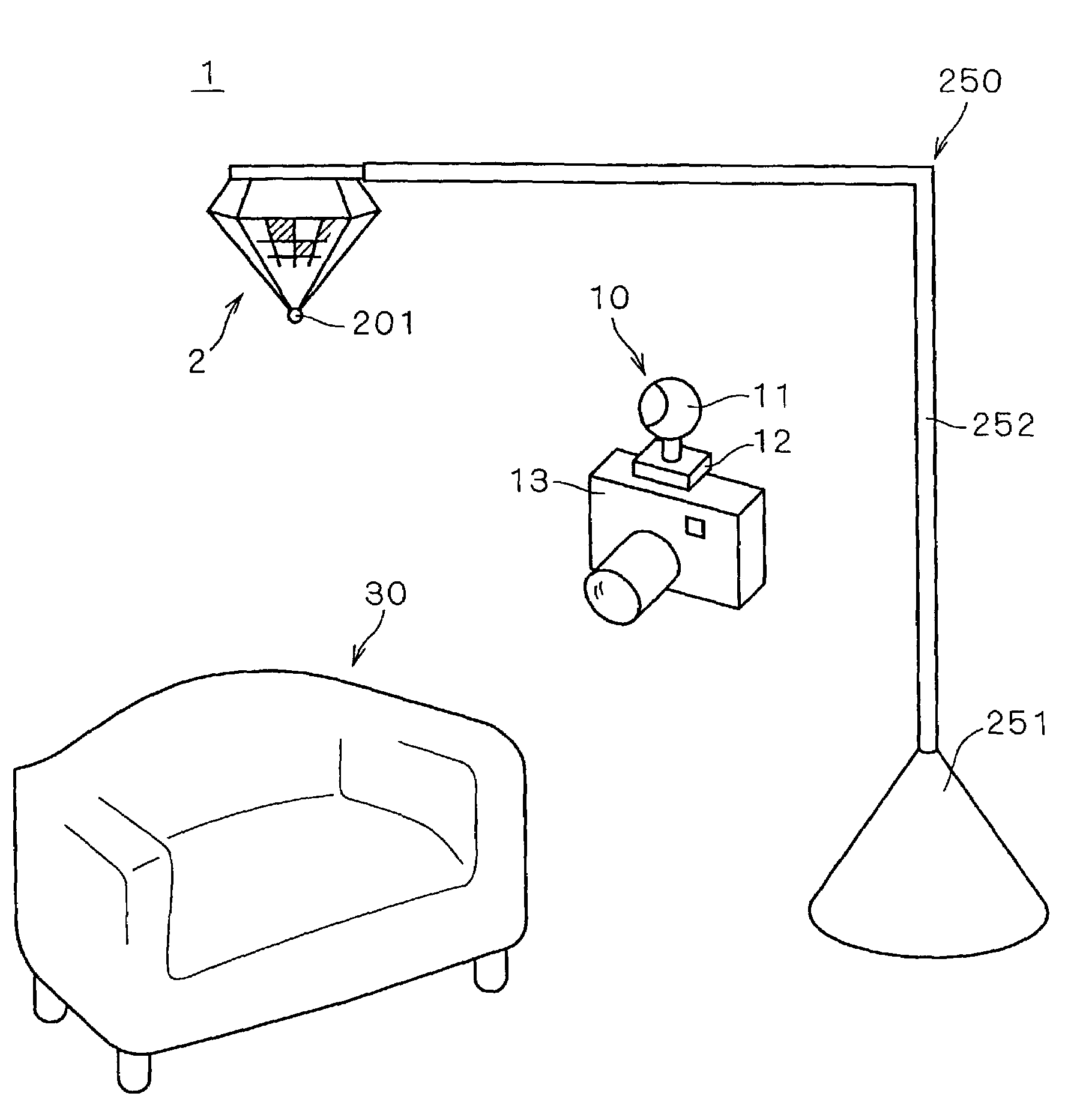
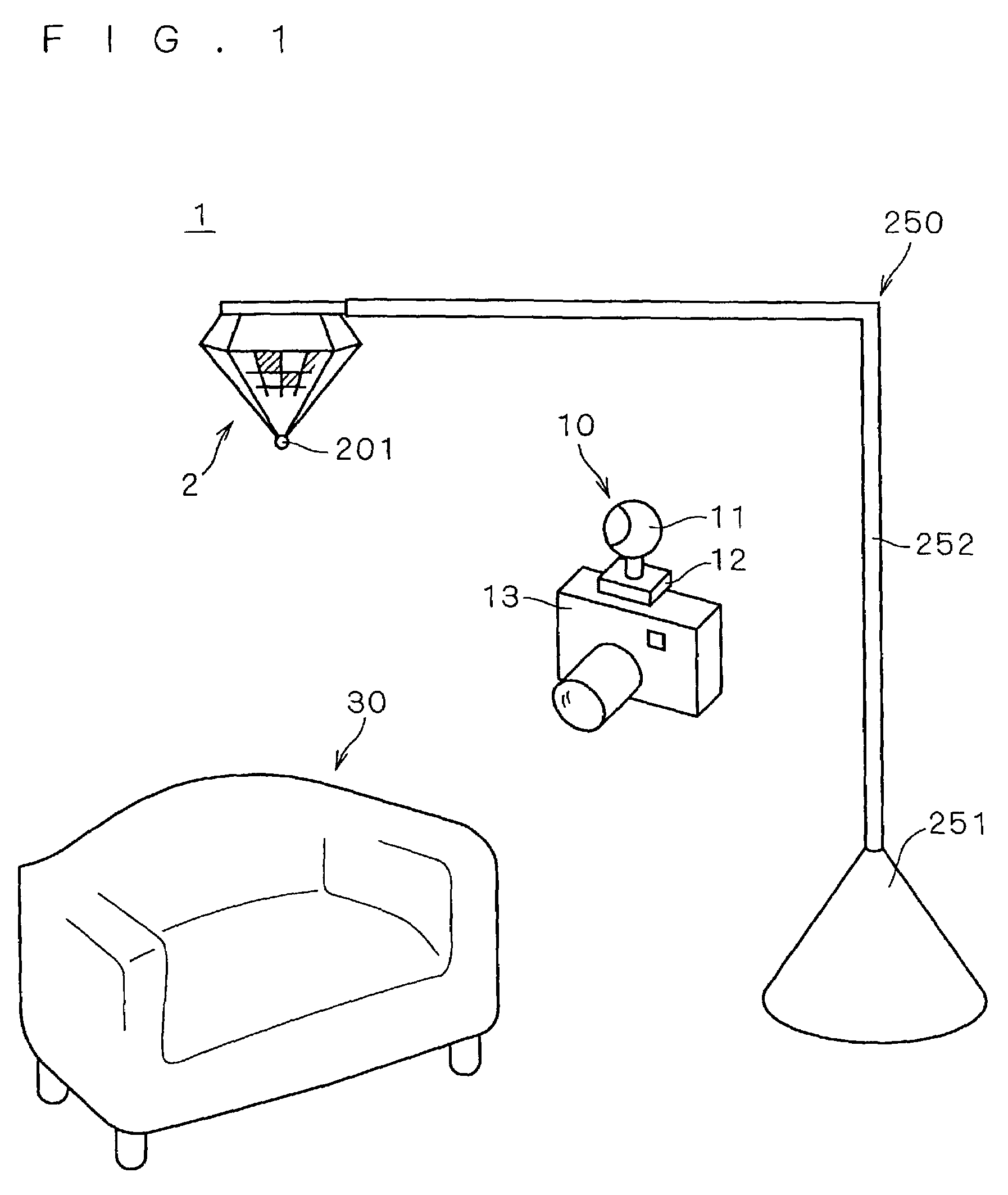
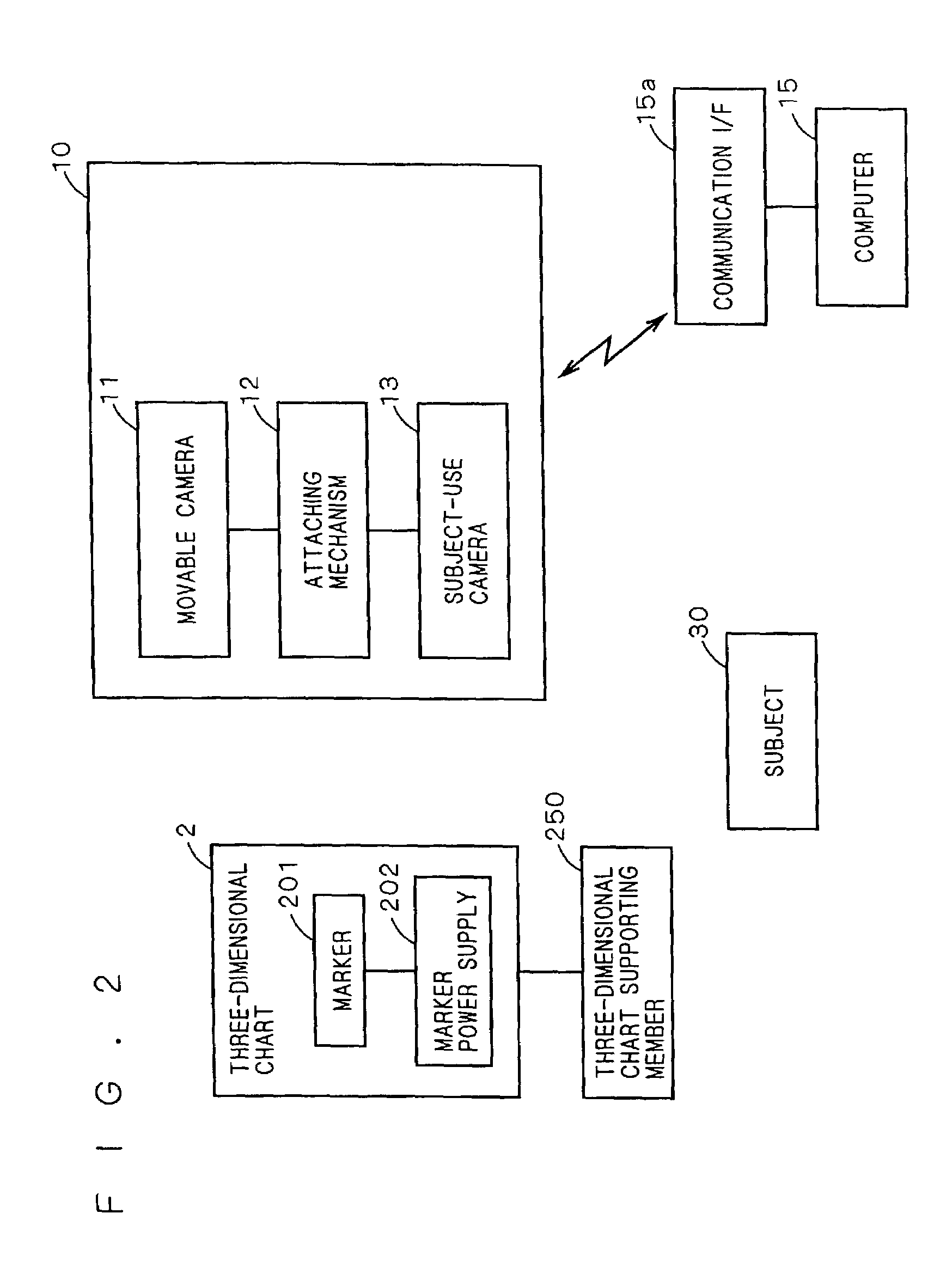
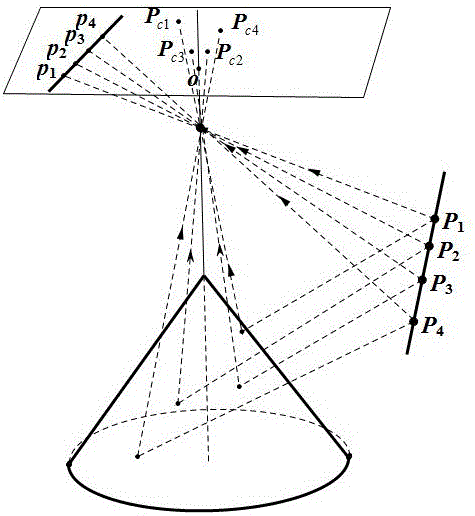
Image pickup system employing a three-dimensional reference object
InactiveUS7423666B2Easy to measureWide movable rangeInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementInformation processingGraphics
The present invention provides a three-dimensional chart, a parameter acquiring method and an information processing device that are used for carrying out camera calibration in a wide range with high precision. For this reason, a plurality of unit graphic forms the sizes of which are coded by using different cross-ratios are placed on side faces of a three-dimensional chart. The cross-ratios of unit graphic forms are calculated from a picked-up image of the three-dimensional chart, and by collating these with actual values, the position and orientation of the image-pickup point are determined. The shifting average of the heights of the unit graphic forms is made approximately proportional to the distance from the apex so that it is possible to reduce the limitation of image-pickup distances. A movable camera is attached to a subject-use camera, and upon picking up an image of the subject, an image of the three-dimensional chart is also picked up simultaneously. Based upon the position and orientation of the movable camera found out by the above-mentioned sequence of image-pickup processes and the relative position and orientation between the two cameras that have been preliminarily found, it is possible to determine the position and orientation of the subject-use camera.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
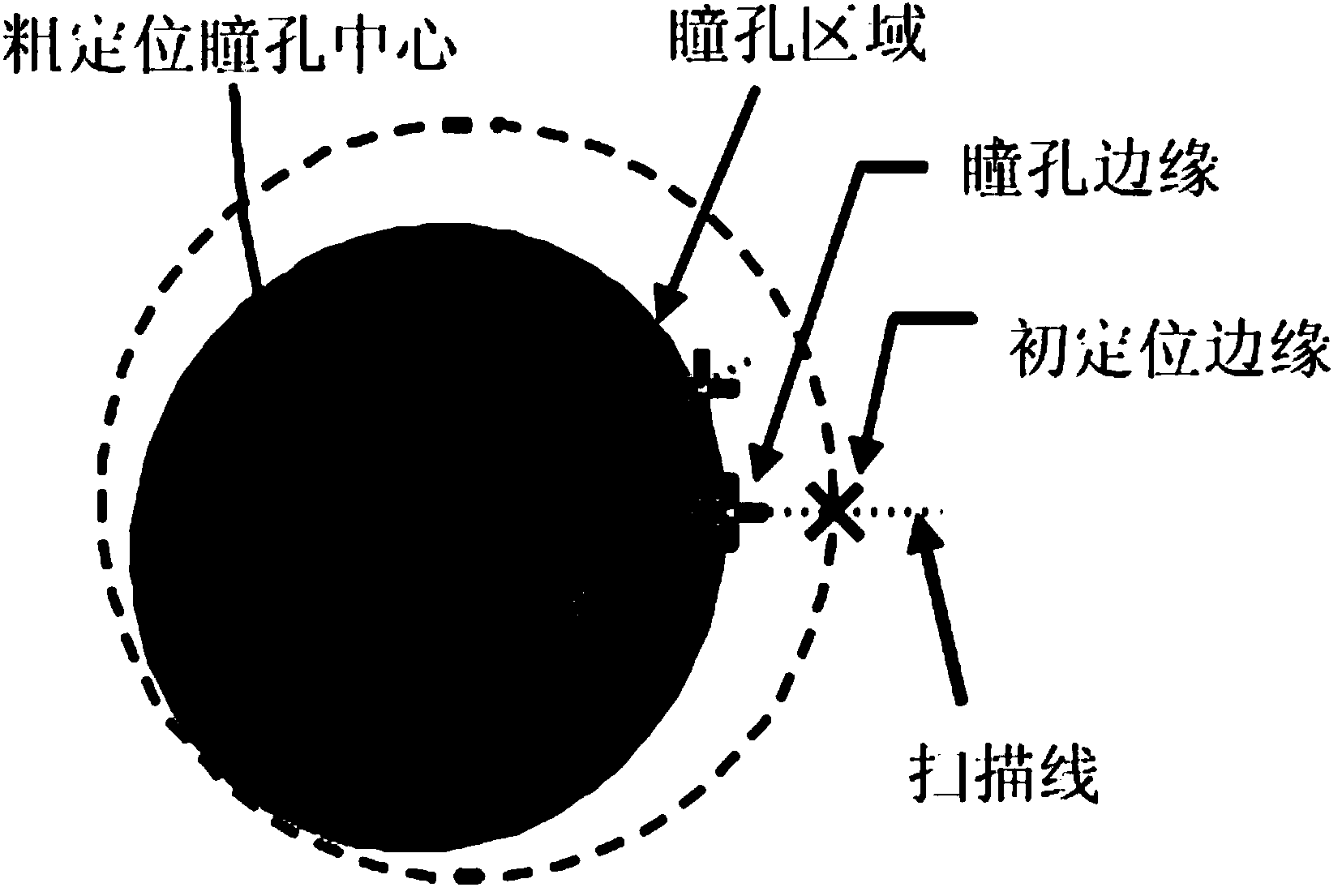
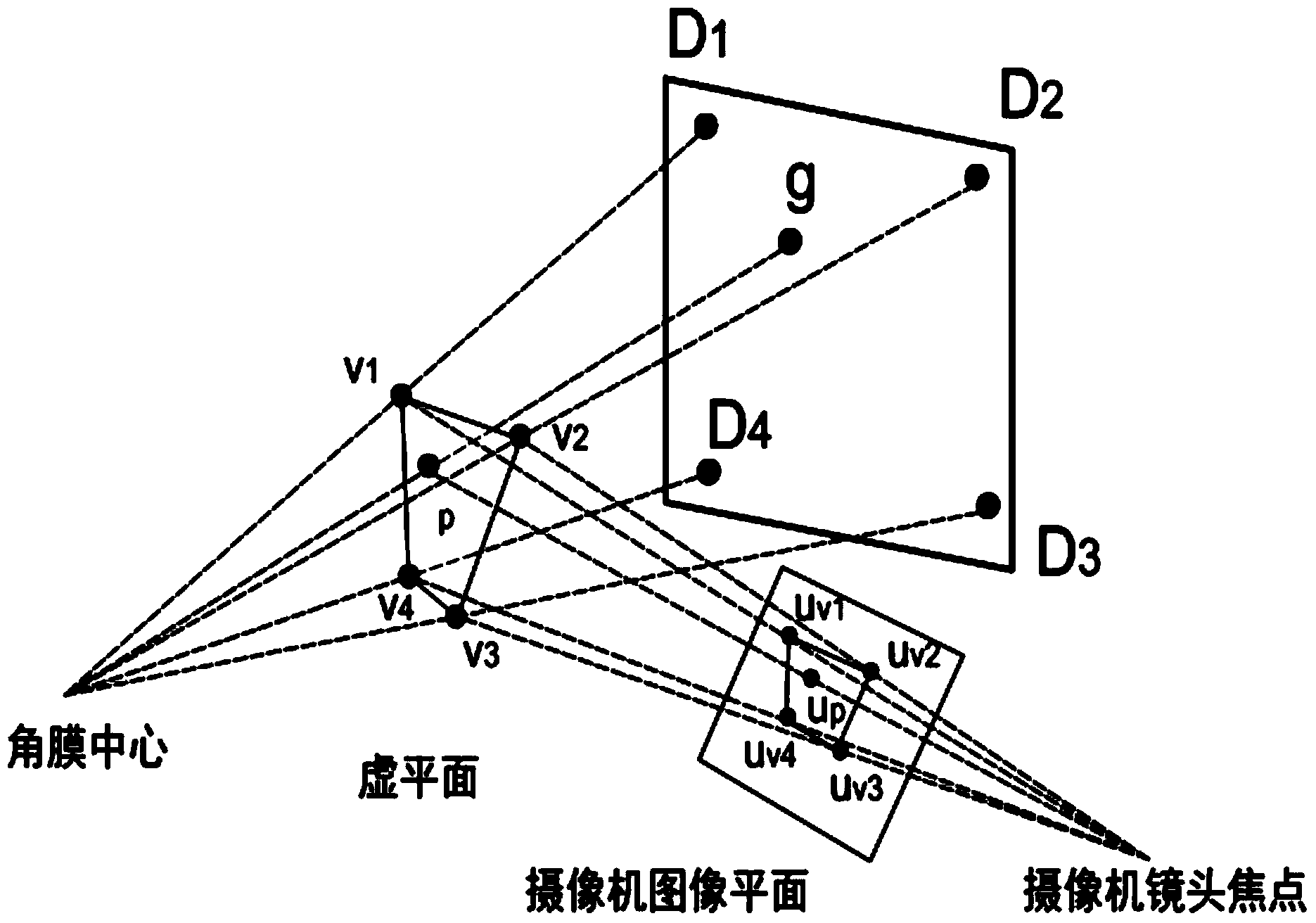
Non-contact sight tracking method based on corneal reflex
InactiveCN103530618AReduce restrictionsHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionCross-ratioLight spot
The invention provides a non-contact sight tracking method based on corneal reflex. The method comprises steps as follows: step one, positioning of human eyes; steps two, calculation of light spot coordinates; step three, accurate positioning of pupils; and step four, space mapping: mapping of space coordinates is performed according to the calculated coordinates of four light spots on a screen, the coordinates of the pupil centers and the invariant principle of a cross ratio in the projective geometry. According to the provided technical scheme, a user doesn't need to wear other devices, so that limitation to the user is reduced greatly; a new pupil edge fitting scheme is proposed and used for circularly fitting and rejecting ideal points, so that the accurate pupil center is obtained, and the mapping accuracy is improved; and compared with the conventional correlational research, the accuracy is improved greatly.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
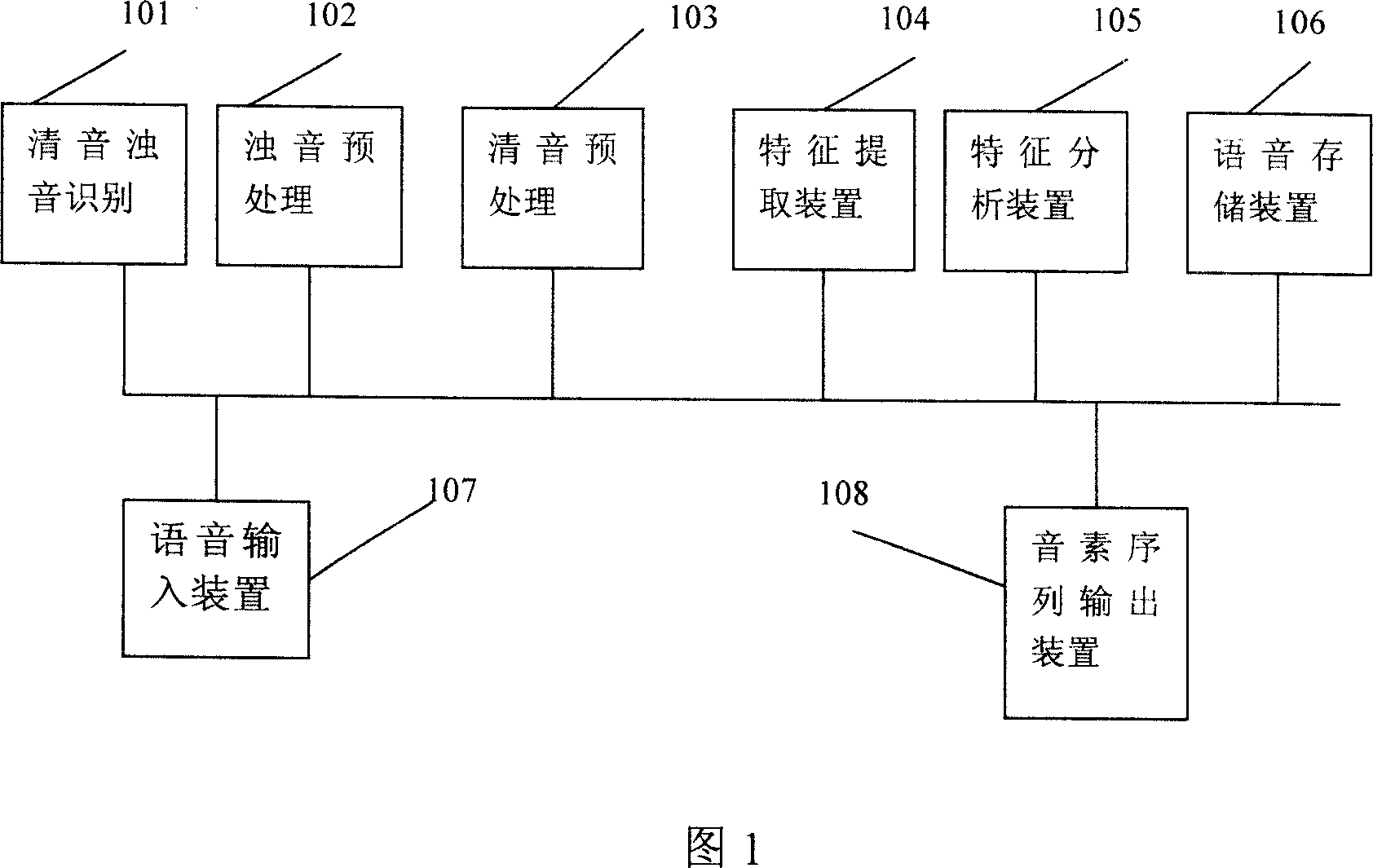
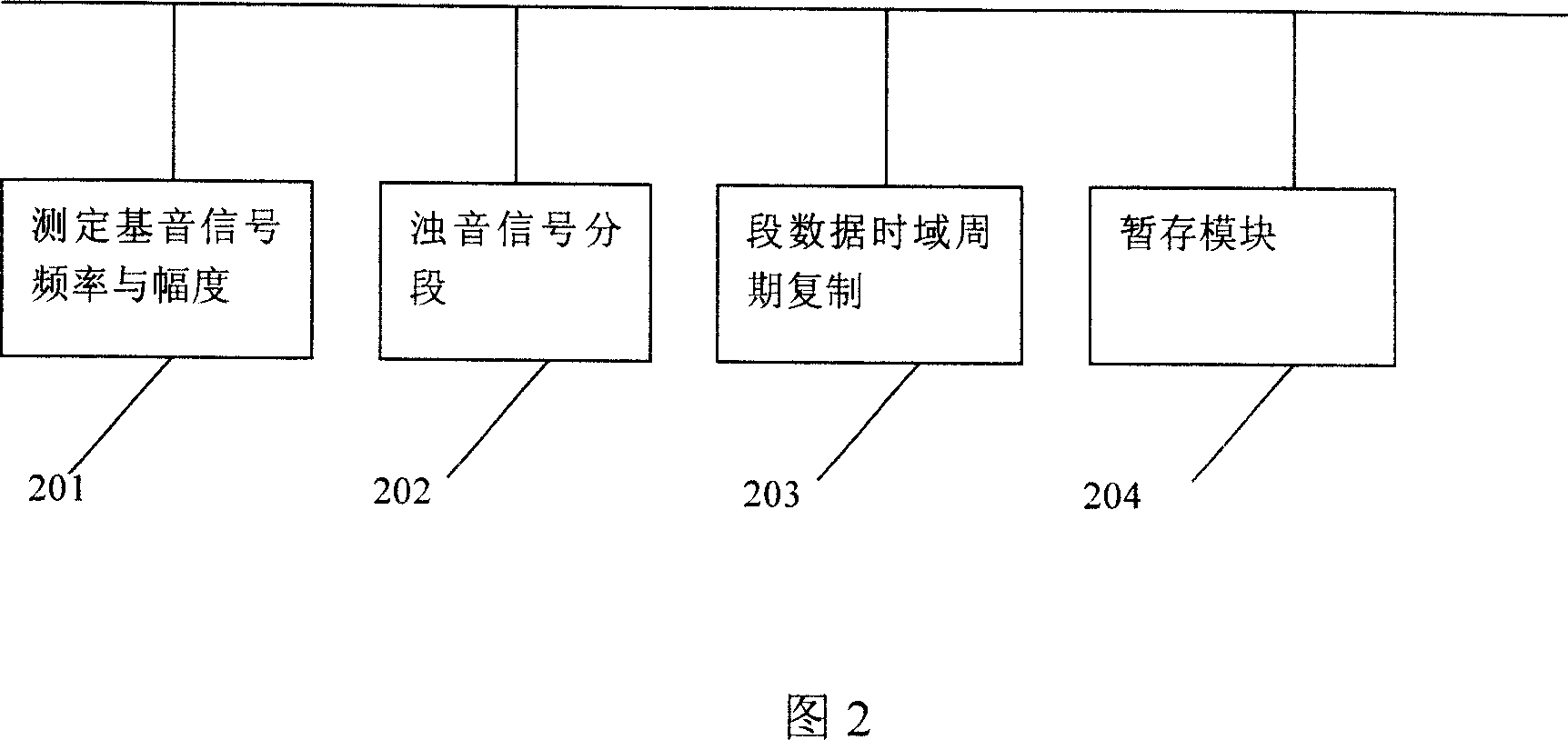
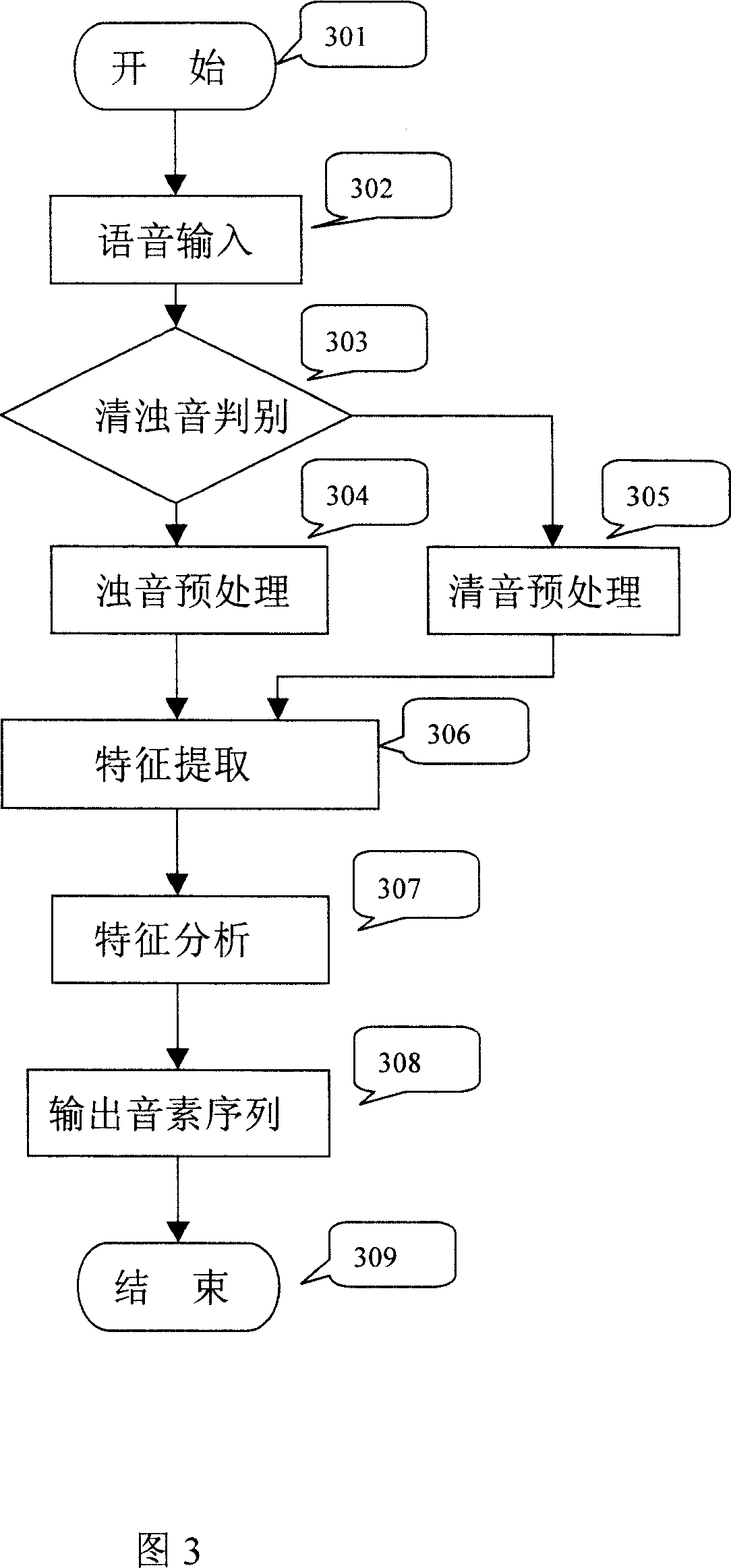
Phoneme based voice recognition method and system
InactiveCN1991976AOvercome deficienciesImprove recognition efficiencySpeech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsFrequency spectrumCross-ratio
A voice recognizing method and system based on the phoneme includes: A) the analog voice signal is transferred into digital voice signal; B) the short-time zero-crossing ratio is detected, if the short-time zero-crossing ratio is less than the preset value, it is judged to sonant to processed as sonant, if the short-time zero-crossing ratio is higher than the preset value, it is judged to surd to processed as surd; C) the data after pretreatment is spectrum transformed to pick up character; D) the character data is analyzed; E) the phoneme sequence is output according to the analyzed result. The voice recognizing method and system can introduce different process method to surd and sonant, specially the sonant phoneme is modeled based on the single keynote cycle spectrum; it resolves the defect of current voice input recognizing system. It possesses advantages of high recognizing efficiency, high accuracy and high stability.
Owner:潘建强
Method for correcting circle center error of circular index point when translating camera perspective projection
InactiveCN101303768ACorrection of center deviationThe result is accurateImage analysisEllipseCross-ratio
The invention relates to a correction method for circle center deviation of a circular mark point when a video camera carries out perspective projection transformation, which is characterized in that the method for setting the circular mark point comprises a step of arranging concentric circles consisting of a large circle and a small circle; the method for acquiring the data of the circular mark point in the image comprises steps of acquiring the image, applying filtration, threshold segmentation, edge detection, contour extraction and least square method ellipse fitting to the image to derive a link of the circle centers of ellipses in the image corresponding to the large circle and the small circle of the concentric circles; the link is intersected with the edges of the ellipses to which the large circle and the small circle of the concentric circles correspond in the image to generate four intersection points; the invariance of cross ratio in projective transformation is hired to derive the real positions of the projection points of the circle centers of the large circle and the small circle of the concentric circles in the image.
Owner:HAIAN COUNTY SHENLING ELECTRICAL APPLIANCE MFG +1
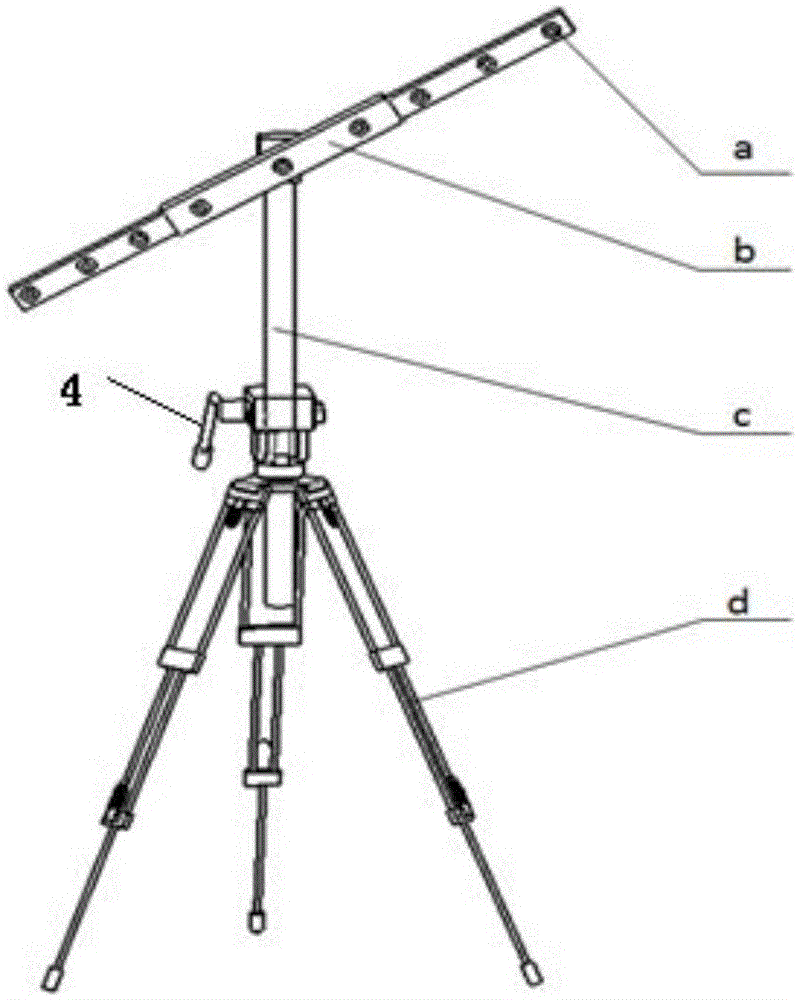
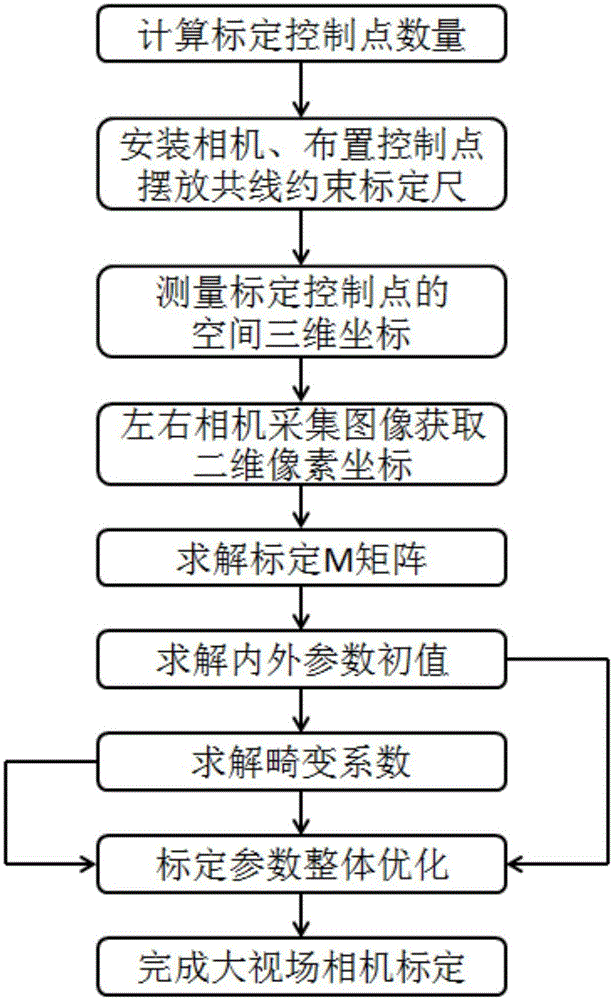
Large visual field camera calibration method based on four sets of collinear constraint calibration rulers
ActiveCN105139411AAchieve high-precision calibrationImprove defectsImage analysisVisual field lossCross-ratio
The invention discloses a large visual field camera calibration method based on four sets of collinear constraint calibration rulers and belongs to the field of optical measurement. The calibration method comprises steps of arranging four sets of collinear constraint calibration rulers in a large optical measurement field; solving distortion parameters by using unlimited characteristics of the cross ratio and straight line constrains; linearly solving the initial value of the calibrated parameter via the calibrated control point in the space; and at last by combining the distortion coefficients and the calibrated initial value and using the L-M optimization method, performing overall optimization with the goal of minimizing the re-projection error so as to get the calibrated precise result of the large visual field camera. According to the invention, by flexibly arranging the calibration control point in the large view field measurement space and combining the four sets of collinear constraint calibration rulers, overall optimization is performed on the calibrated results, high precision calibration for the large view field camera is achieved and the calibration method has a wide application prospect.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
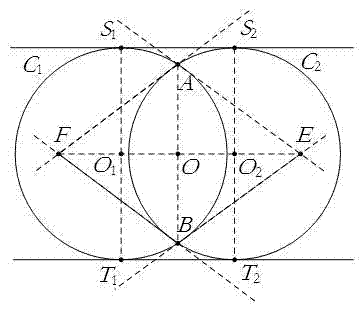
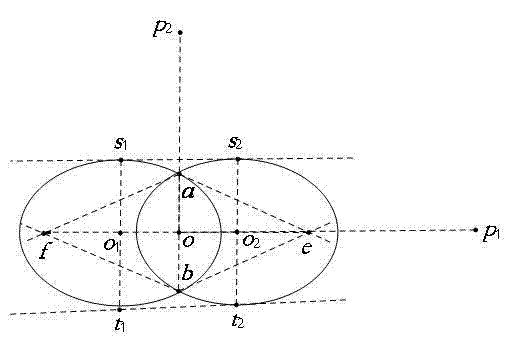
Linear solving of video camera internal parameters by utilizing two intersected same circles and common tangent
The invention relates to linear solving of video camera internal parameters by utilizing two intersected same circles and a common tangent, and the method is a drone composed of two intersected same circles and the common tangent and used for calibrating video cameras. The drone is shoot for six images from different directions; elliptic equations and characteristic points are extracted from the images, and intersection point of two ovals are solved; vanishing points on image planes at the orthogonal direction is obtained according to perpendicular bisector of circle center line segment connecting the two circles and the common tangent of the two intersected circles and cross ratio of collinear four points; and the video camera internal parameters are performed with linear solving by utilizing the vanishing points at the orthogonal direction and restraint of images of an absolute conic. By utilizing the drone, full-automatic calibration can be achieved, and error caused by measurement during the calibration process is reduced. Circle is an element which is more concise and global, and accordingly calibration accuracy is improved during the calibration process.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Pose measurement method of rotating target in approaching state
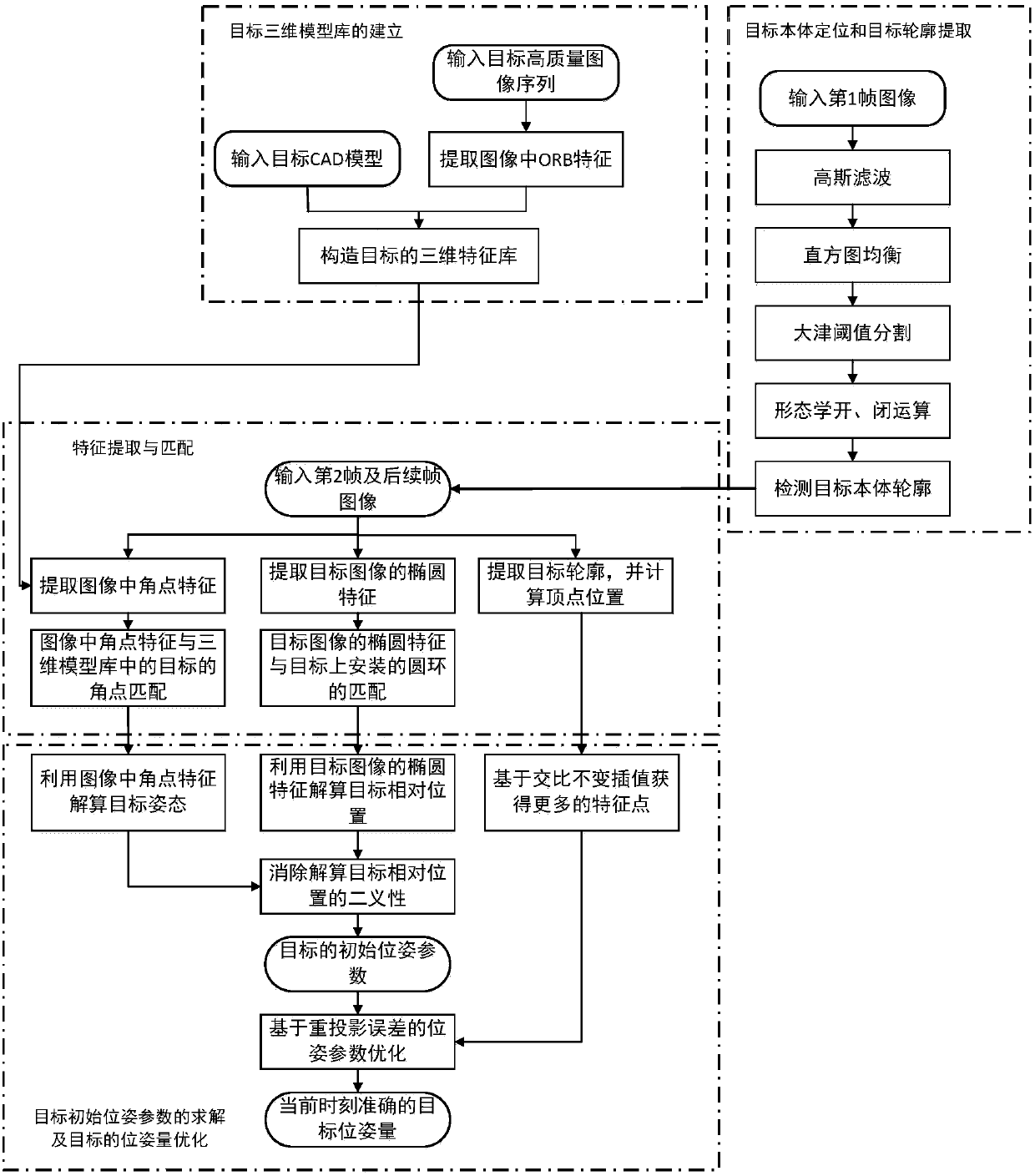
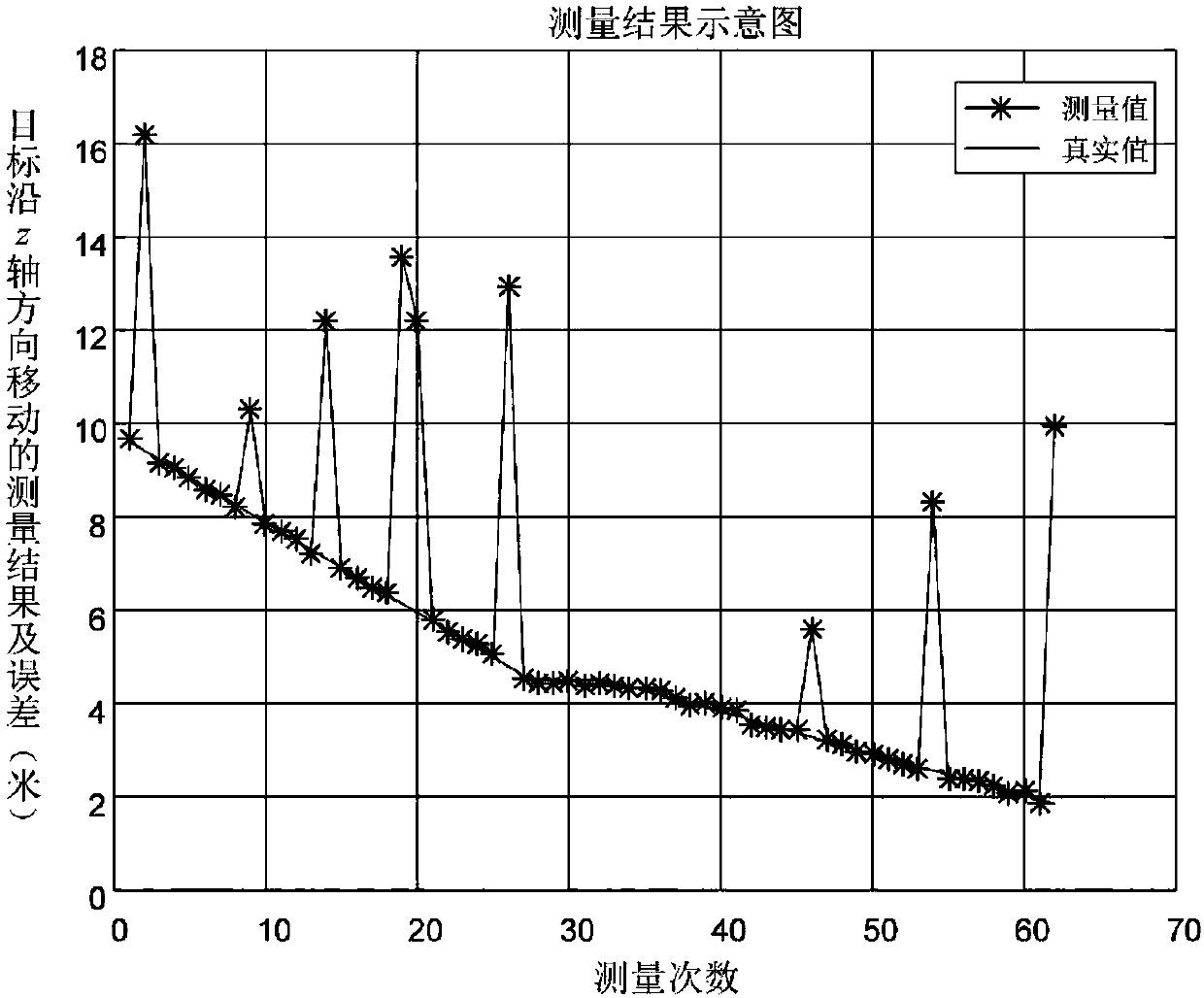
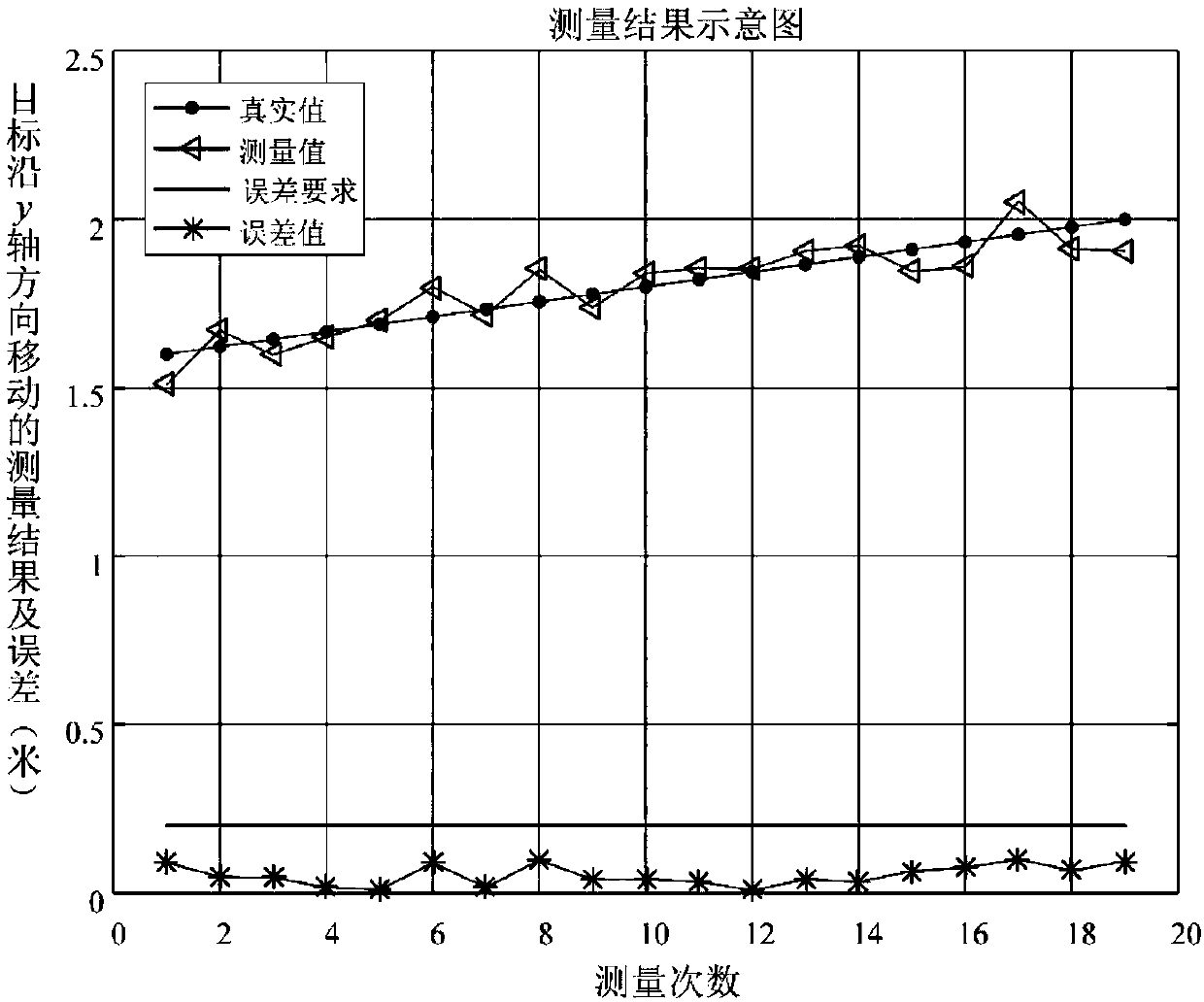
ActiveCN108122256AImplement featuresCorner matching to achieve the goalImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionCross-ratio
The invention discloses a pose measurement method of a rotating target in an approaching state. The method comprises the steps of constructing a three-dimensional feature library of the target according to known model data and a shot target image sequence of the target, denoising and enhancing an input initial frame image, performing target positioning and profile extraction via image erosion anddilation operation, extracting ring features and corner features of the target from the second frame of the input image sequence, achieving matching between two-dimensional image corner features and three-dimensional features of a target model, obtaining more feature point locations via cross-ratio invariance interpolation, calculating a pose parameter of the target via the ring features and the corner features, and performing parameter optimization. The method reduces the area of a region to be processed in the image and improves calculating efficiency via target positioning. The calculatingprecision of the pose parameter is ensured by using the scheme that the ring features, a profile and the corner features are combined for use and more feature points are obtained by the cross-ratio invariance interpolation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
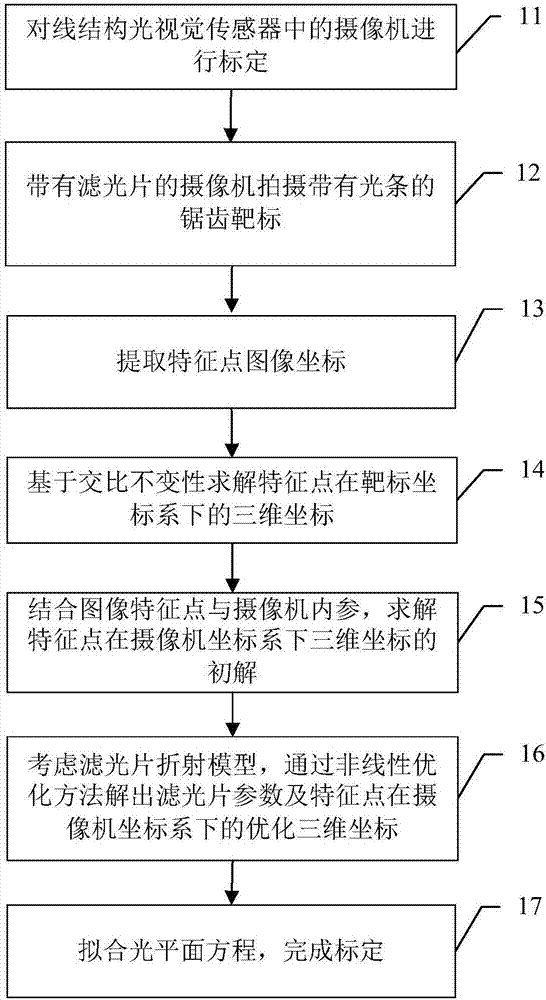
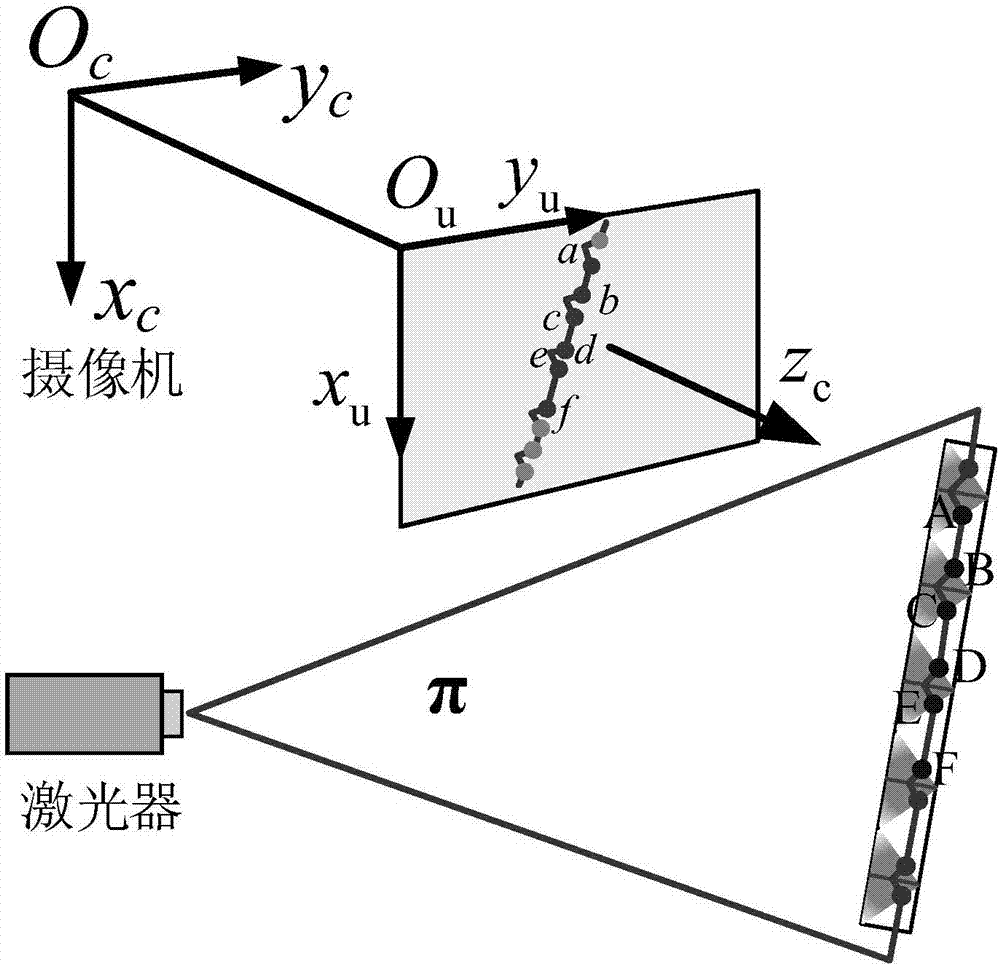
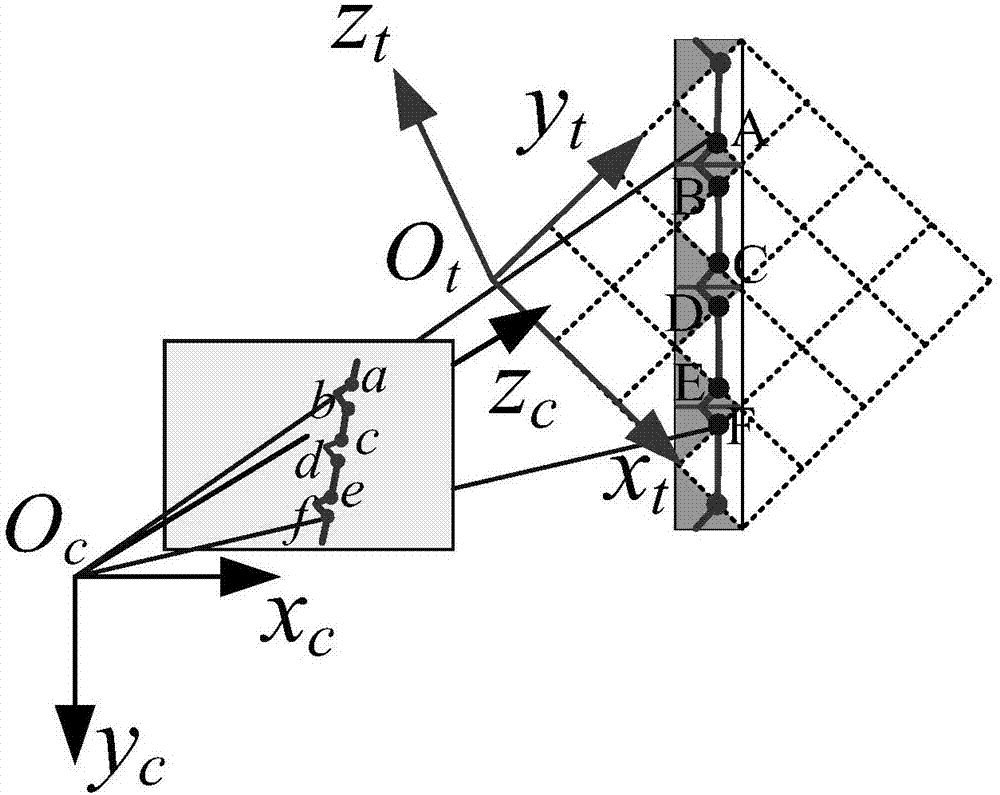
Line structured light visual sensor calibration method based on sawtooth target
The present invention discloses a line structured light visual sensor calibration method based on a sawtooth target. The method comprises: in the condition that a camera has no an optical filter, performing calibration of the camera in a line structured light visual sensor; installing an optical filter at the front portion of the camera lens, allowing the camera to shoot a sawtooth target image with a light bar, obtaining image coordinates of the intersection point of the light bar and the target tooth-shaped edge, namely the image coordinates of feature points, and solving the three-dimensional coordinates of the feature points in the camera coordinate system based on the principle of cross-ratio invariance; considering an optical filter refraction model, and solving the parameters of the optical fiber and the three-dimensional coordinates of the feature points after optimization in the camera coordinate system through the nonlinear optimization method; and moving the target for more than two times, obtaining the three-dimensional coordinates of all the position feature points of the target in the camera coordinate system, fitting the three-dimensional coordinate points to solve a light plane equation, and completing the calibration. The line structured light visual sensor calibration method based on the sawtooth target is suitable for a field complex light environment and even can complete line structured vision sensor calibration in the condition that the camera has the optical filter.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Novel mark point graph and its recognition, tracking and positioning algorithm based on visual sense constantmagnitude
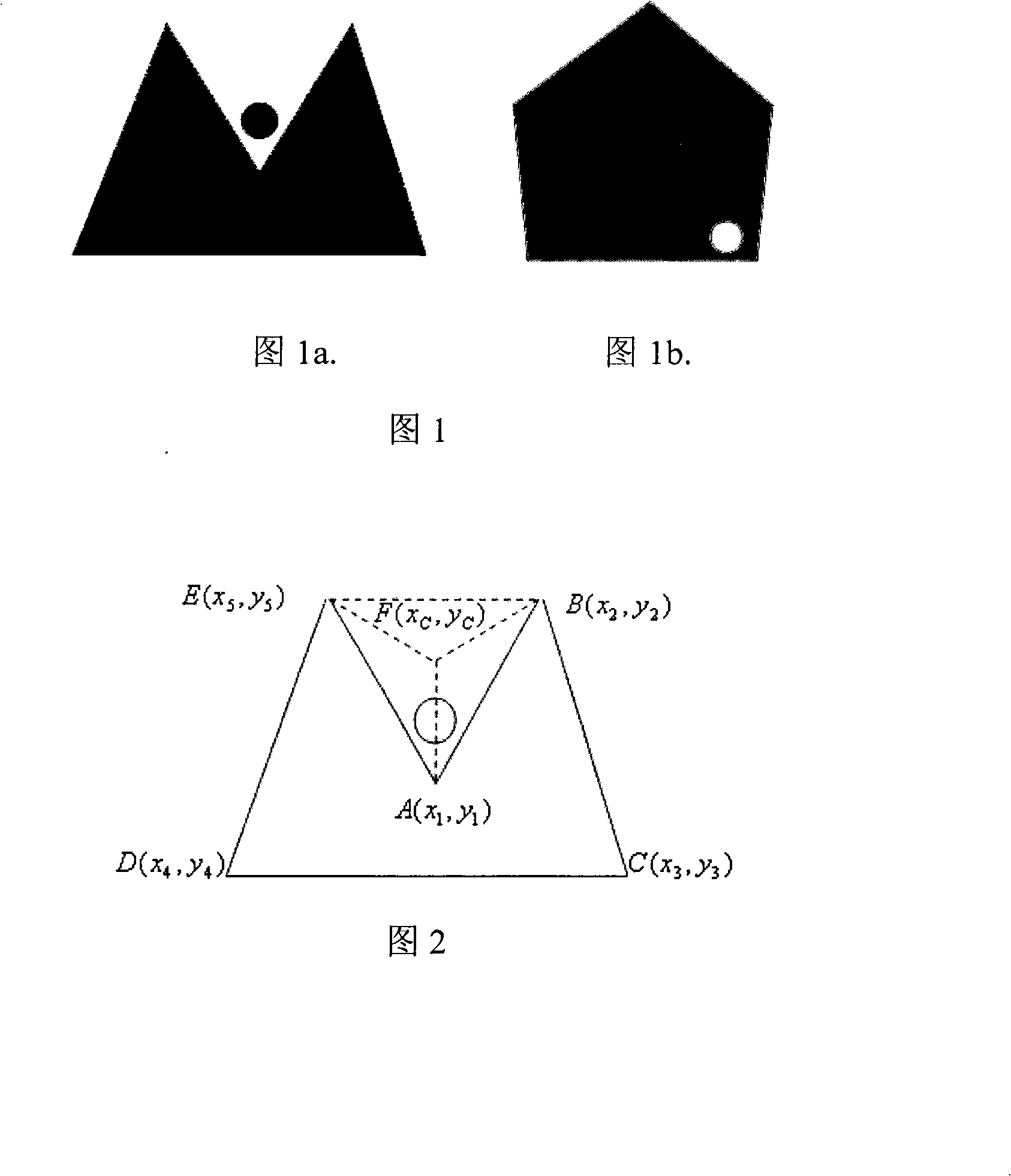
ActiveCN101339604ASmall space sizeReduce areaCharacter and pattern recognition3D-image renderingGraphicsCross-ratio
The invention relates to a novel marked point pattern based on vision invariants and identification and tracking positioning algorithm thereof. The invention comprises a design of novel marked point pattern based on vision invariants and identification and tracking positioning algorithm based on the novel marked point. The novel marked point pattern based on vision invariants is a black pentagon with a round mark. The marked point can be a convex pentagon or a concave pentagon. The round mark is used for identifying a first vertex of the pentagon. The pattern is coded using the cross-ratio invariant of the pentagon and combining the concavity and convexity of the vertex. The marked point pattern based on vision invariants can conduct attitude calculation using self-characteristics and realize the coding of the marked point, thus saving the area needed by coding patterns, reducing the pattern size of the marked point and improving the registration precision in unit area. The tracking registration algorithm can be used for identifying the marked point, tracking the head posture of the user and calculating the accurate position and posture of virtual scenes in true environmental space.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Shape matching method based on projective invariant
The invention belongs to the field of computer vision, and relates to a constructing and matching method of projective invariant contexts. According to the method, the hierarchical projective invariant contexts are constructed and used for achieving the shape recognition under the projective changes. According to the method, all sampling points are selected from coarseness to fineness to form the contexts of the sampling points, and therefore the overall geometrical information is ensured, and the contextual information of a contour is reserved. Five contexts based on the traditional projective invariant cross ratio and the newly found projective invariant features are further provided on the framework. The stability and noise immunity of the contexts are improved by introducing exterior points and the ratio in. Experiments show that the method not only has higher recognition rate on the shapes with severe projective deformation, but also has a very good distinguishing effect on the shapes with high similarity.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for solving parameters in parabolic catadioptric camera through three unparallel straight lines in checkerboard
InactiveCN103942784AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisGeometric propertyCross-ratio
The invention relates to a method for linearly solving parameters in a parabolic catadioptric camera through three unparallel straight lines in a checkerboard. The method is characterized in that only linear elements are utilized, and a template is composed of the three unparallel straight lines on the checkerboard; parabolic catadioptric images of the straight lines are quadratic curves, the parabolic catadioptric camera is used for taking an image of a target, image points of the target are extracted from the image first, fitting is conducted to obtain the curve equation, and the intersection points of every two curves are solved, six sets of orthogonal fading points on the image plane are then obtained according to the geometric properties of a circle and the cross ratio invariance property, and the parameters in the parabolic catadioptric camera are linearly solved for constraints on images of the absolute quadratic curves through the orthogonal fading points. According to the method, the target can be calibrated in a full-automatic mode, and errors caused by measurement in the calibration process are reduced. Due to the fact that the straight lines are the simpler and more comprehensive elements, calibration accuracy is improved in the calibration process of the camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Line structure cursor calibration method based on projection geometry
ActiveCN110163918AEasy to operateReduce accumulationImage enhancementImage analysisCross-ratioImaging processing
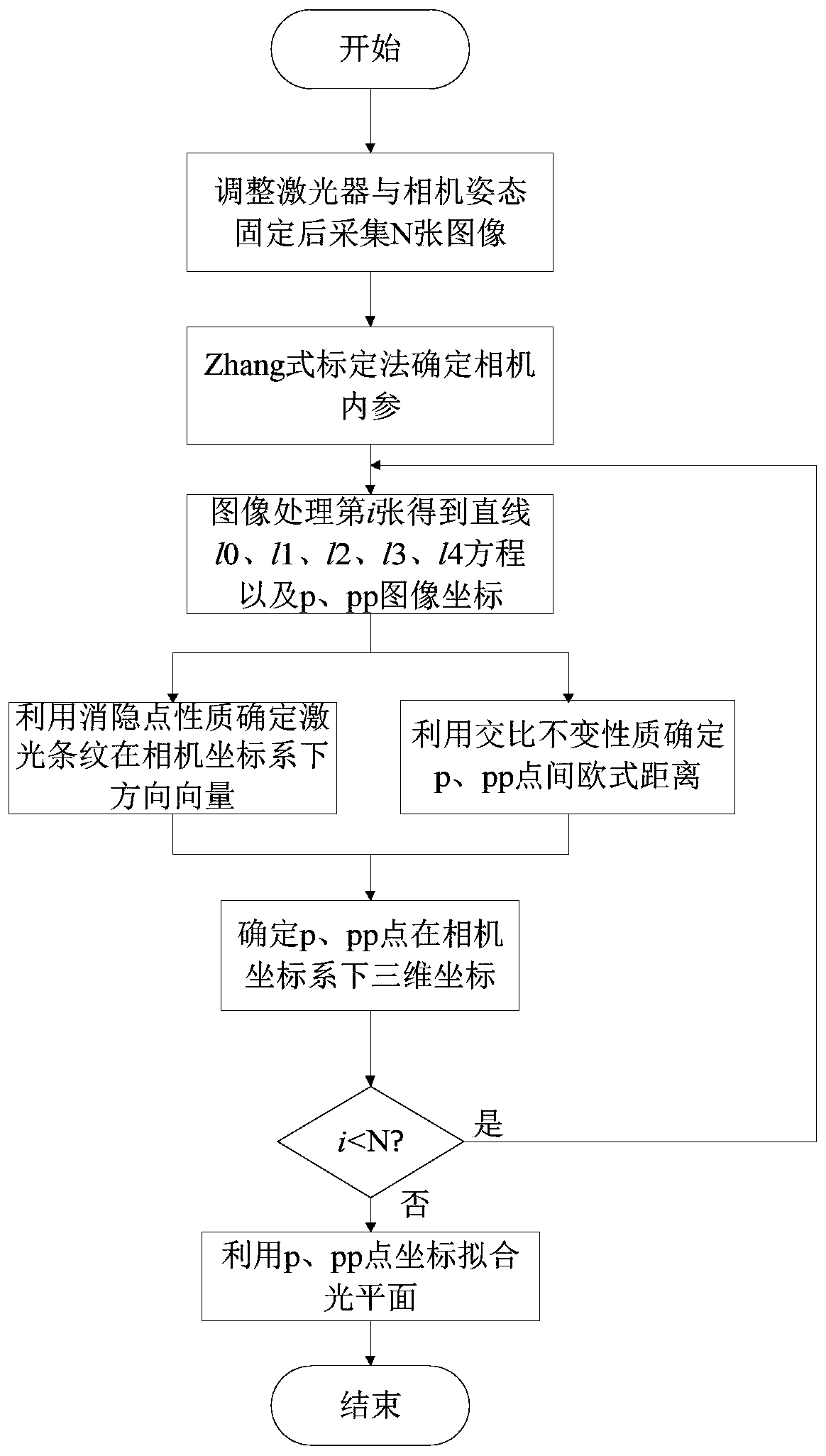
The invention discloses a line structure cursor calibration method based on projection geometry, which comprises the following steps of: acquiring a fringe image which comprises a laser and is projected on a calibration plate, and solving a camera internal parameter by utilizing a tensor calibration method. Information of related straight lines and intersection points is obtained through image processing, a blanking line equation corresponding to a target plane is obtained through homogeneous coordinate expression of parallel straight lines, then blanking point coordinates corresponding to laser stripes are obtained, and a direction vector of the laser stripes in a camera coordinate system is obtained through further conversion; the Euclidean distance between two feature points on a laserstripe is obtained by using a projection property with an invariable cross ratio, three-dimensional coordinates of the feature points in a camera coordinate system are obtained by combining a direction vector and imaging model information and combining an equation set, plane fitting is performed on the coordinates of all the image feature points by using a least square method to obtain a light plane equation, and line structure cursor calibration is completed. According to the method, the characteristics and properties of projection geometry are used for calibration, other measurement devicesare not needed, the precision is high, and the method is simple and feasible.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Homography matrix H computing method of single line array camera
InactiveCN104123725ASolve the problem that the homography matrix H cannot be calculatedThe method system is simpleImage analysisCross-ratioAlgorithm
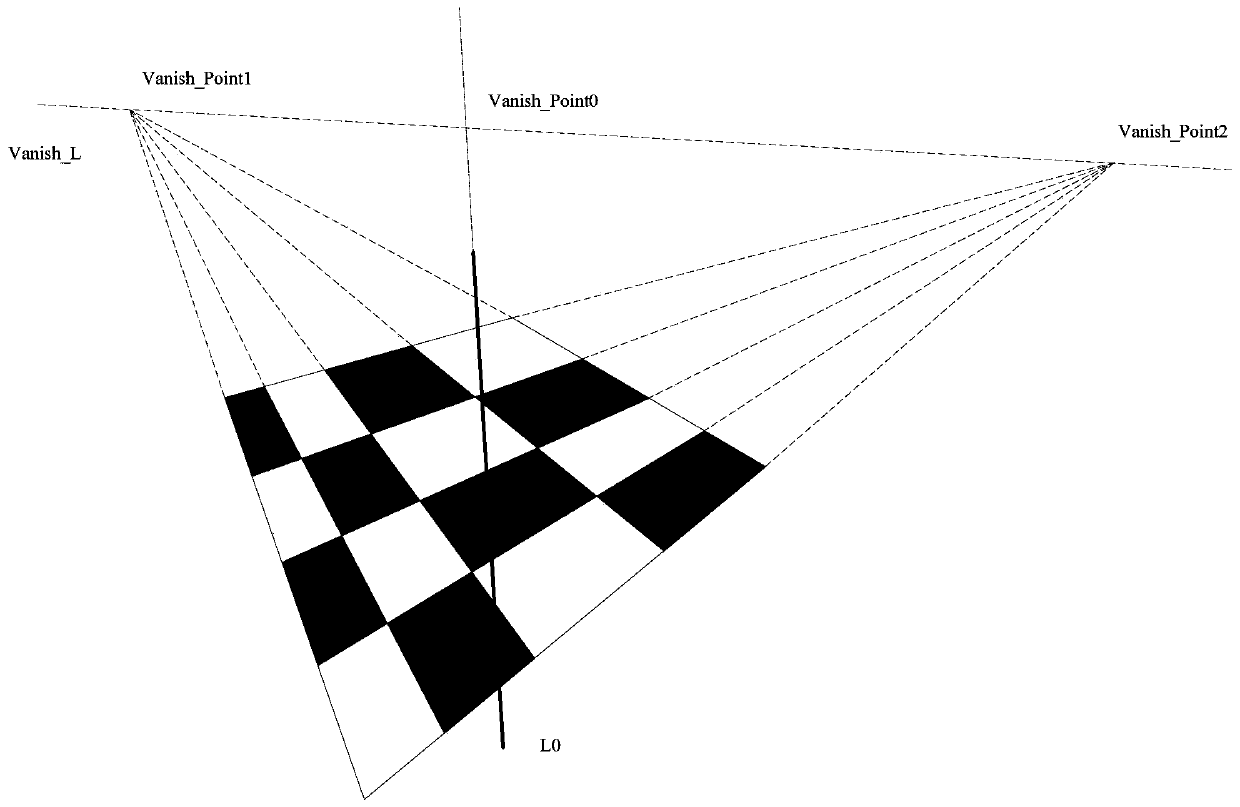
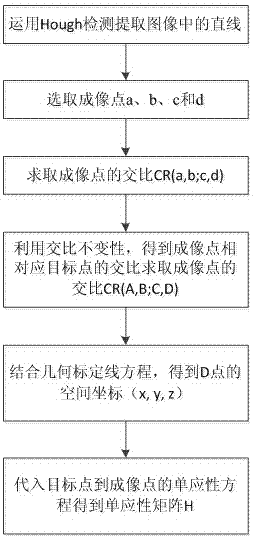
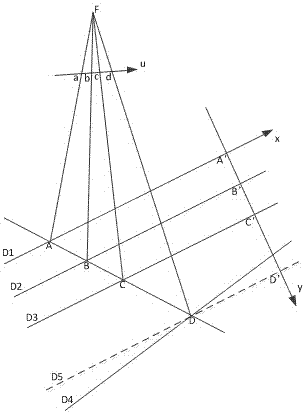
A homography matrix H computing method of a single line array camera applies a cross-ratio invariance principle and given four line calibration plates, wherein four lines meet the following rules (shown in the description), a (x, y, z) coordinate on a D4 line is calculated according to a line array camera imaging characteristic, the cross ratio of four collinear points in an image plane and application of the cross-ratio invariance, and a homography matrix H is further calculated.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
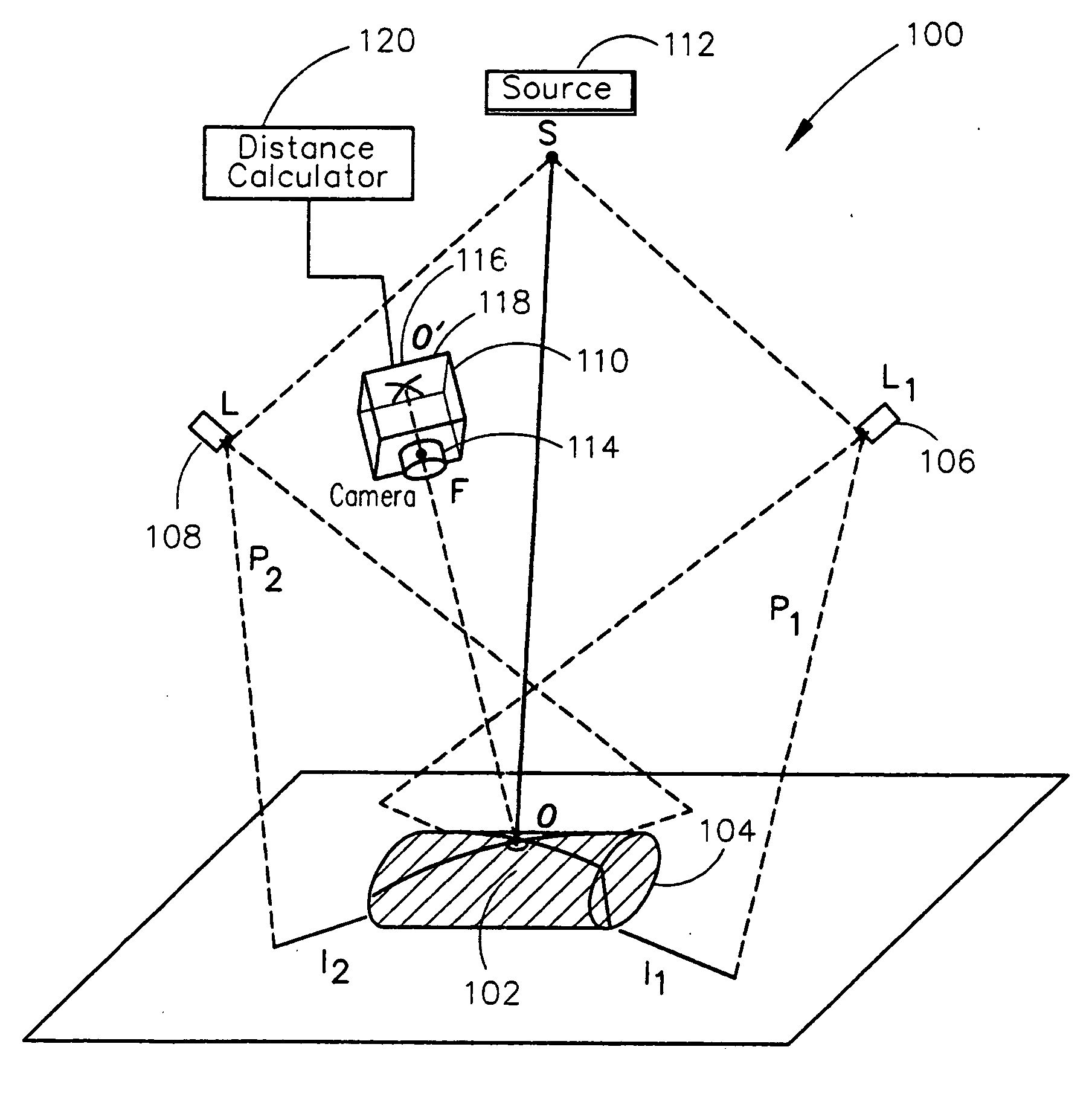
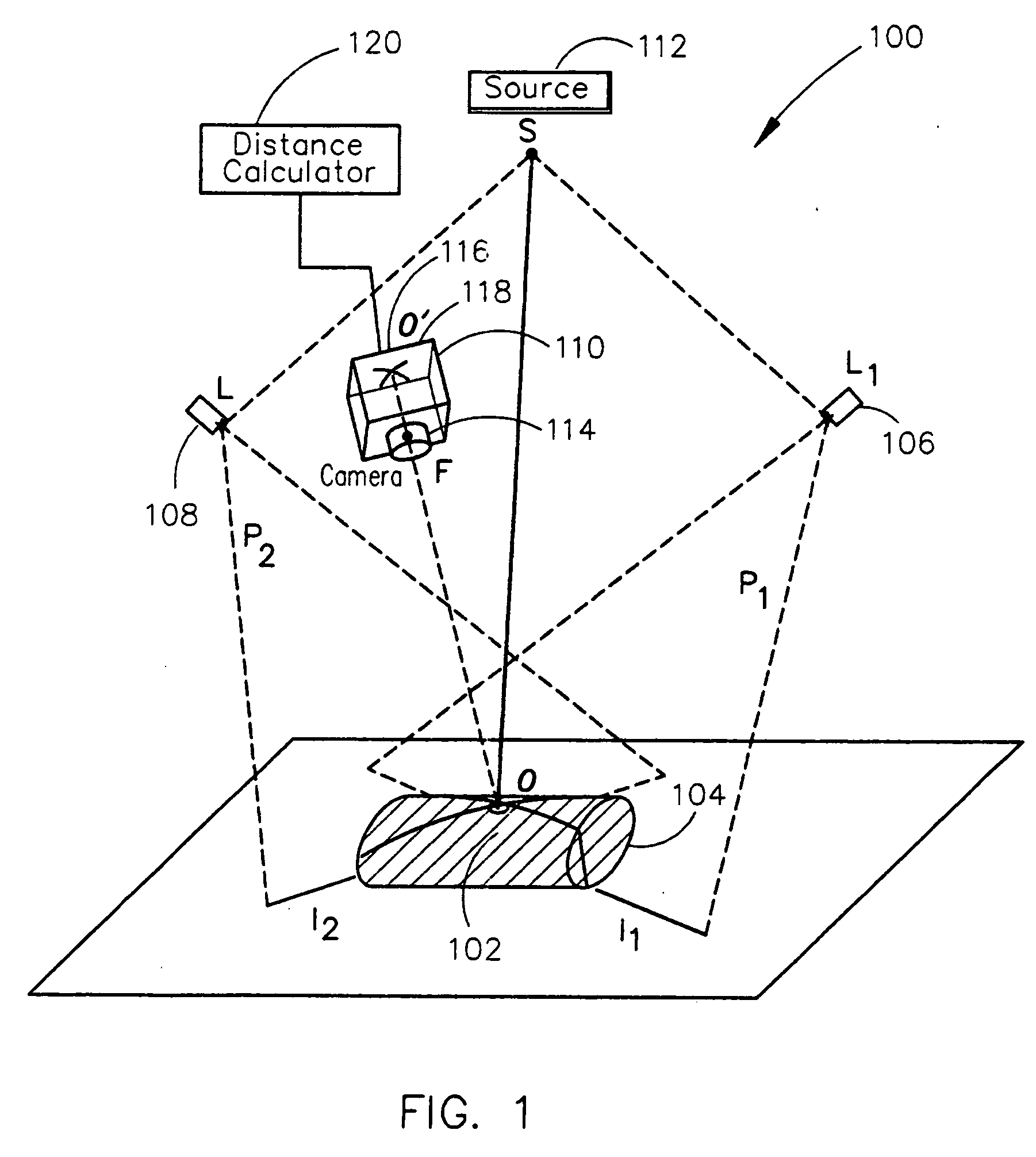
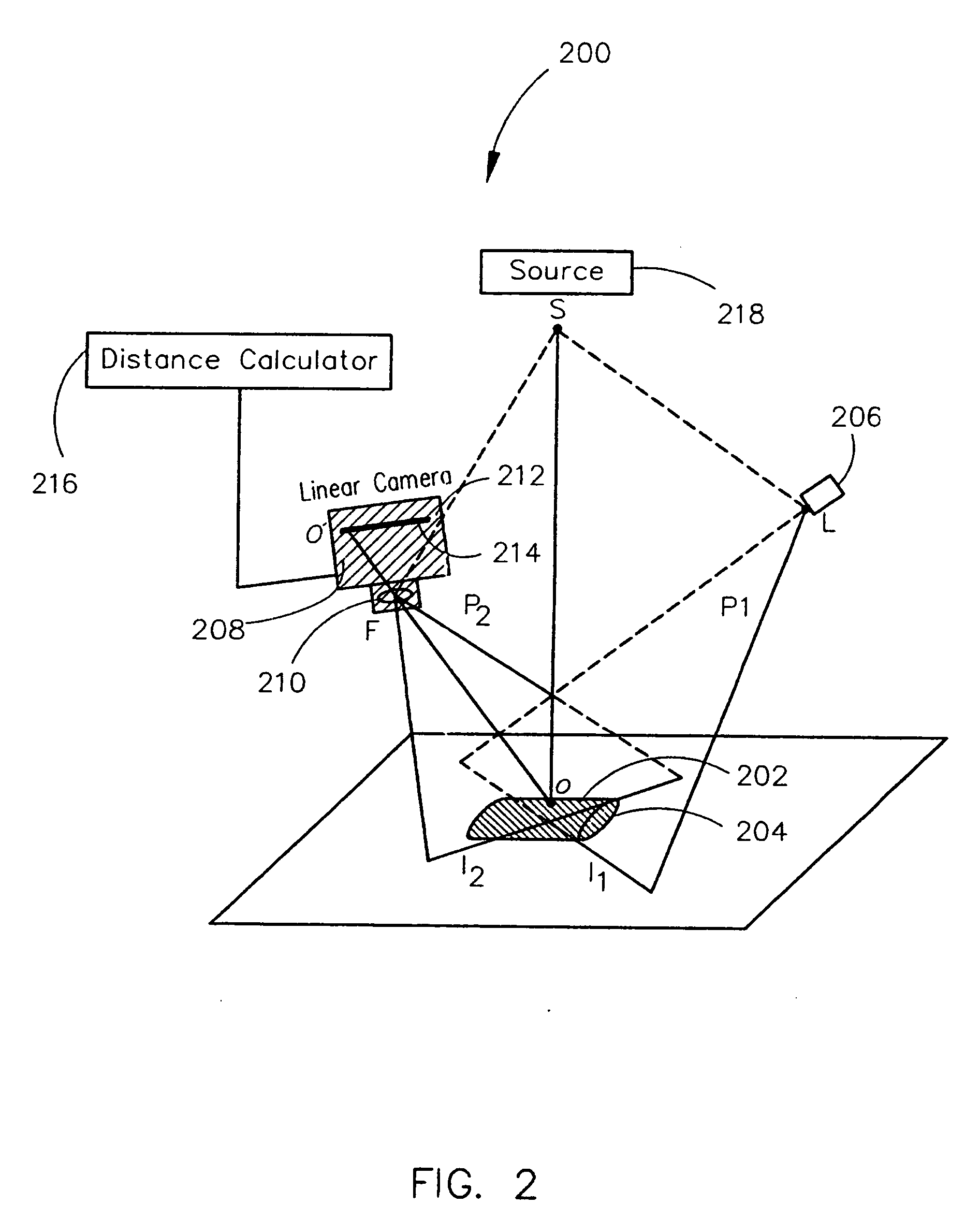
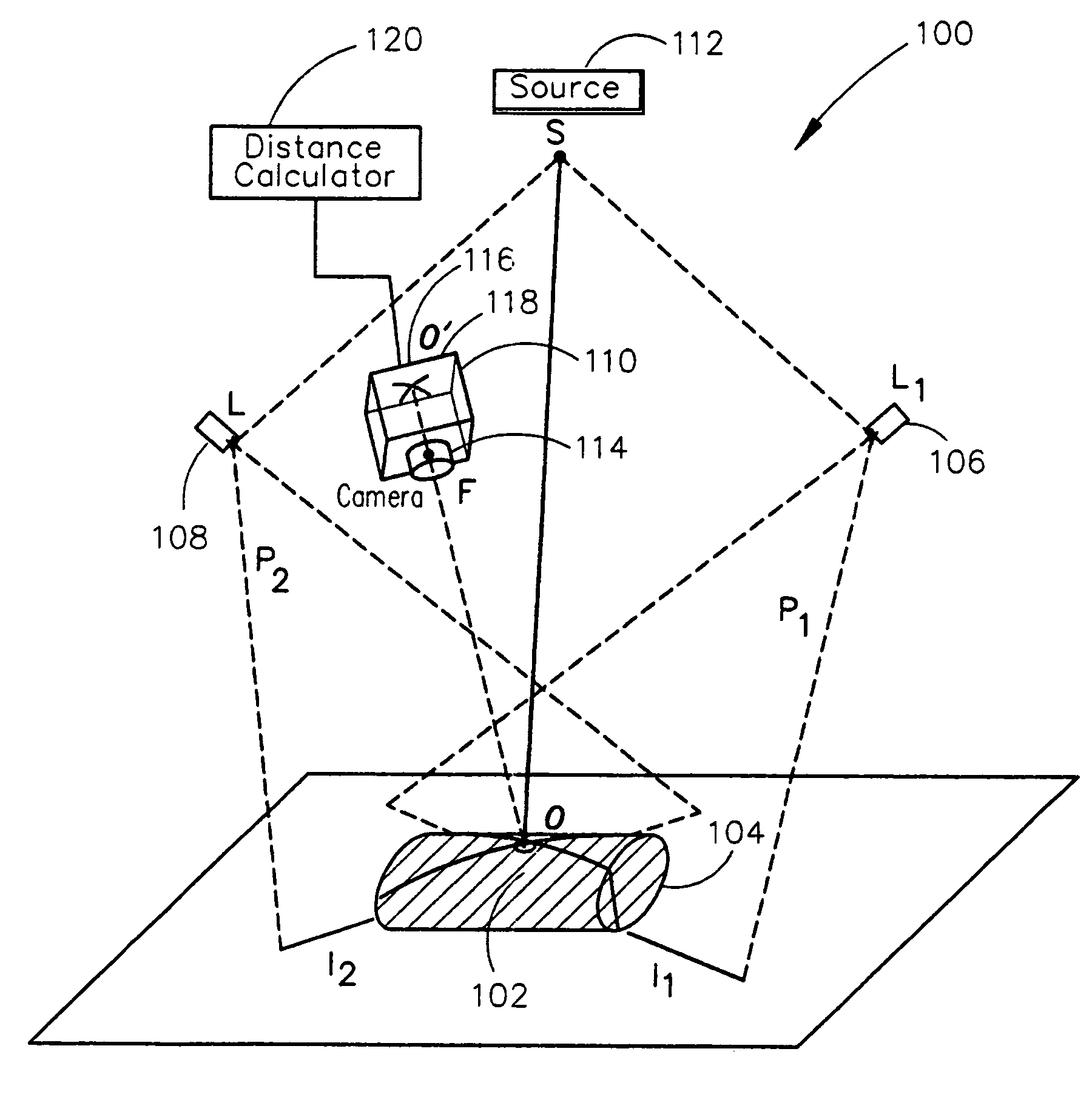
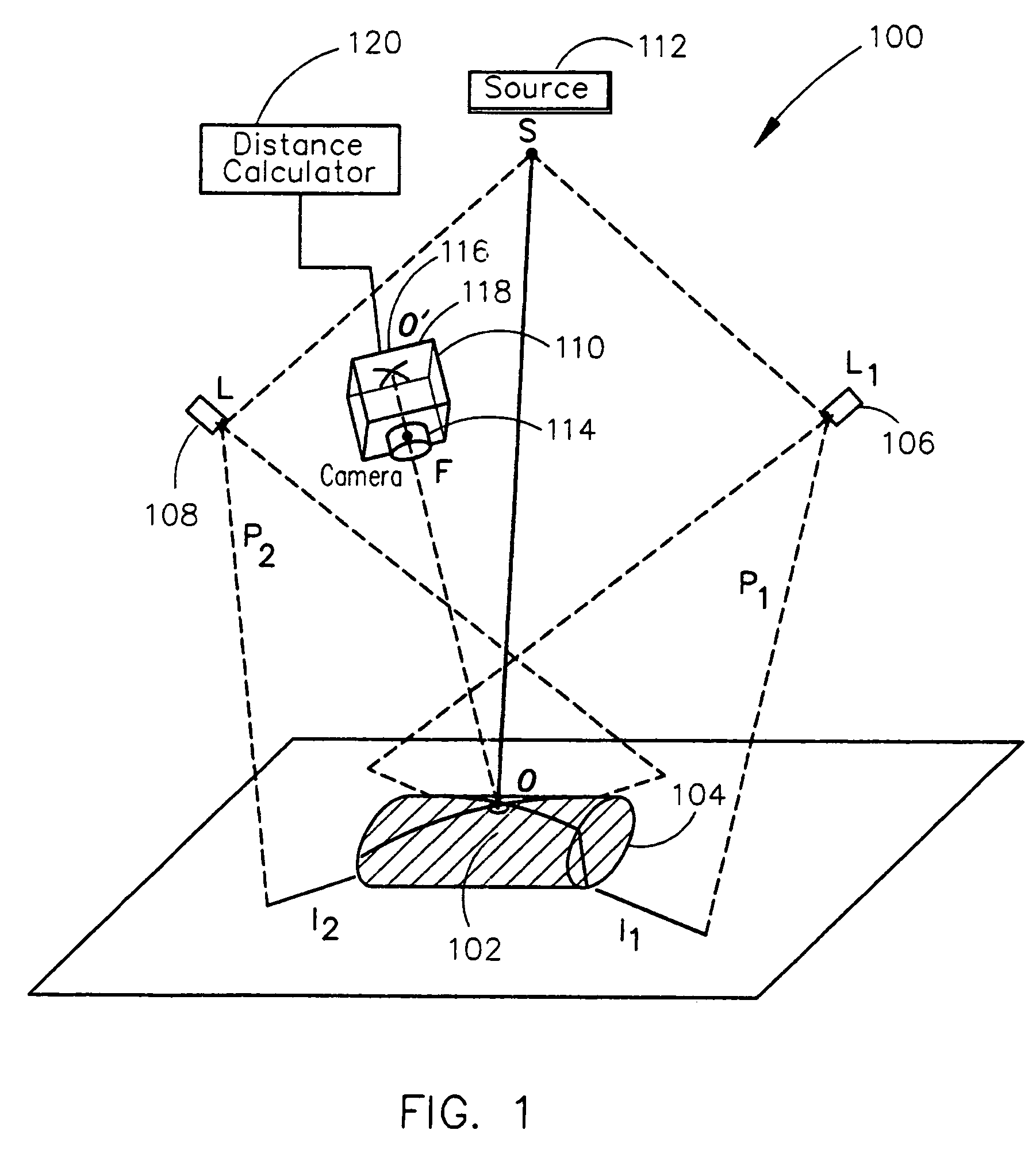
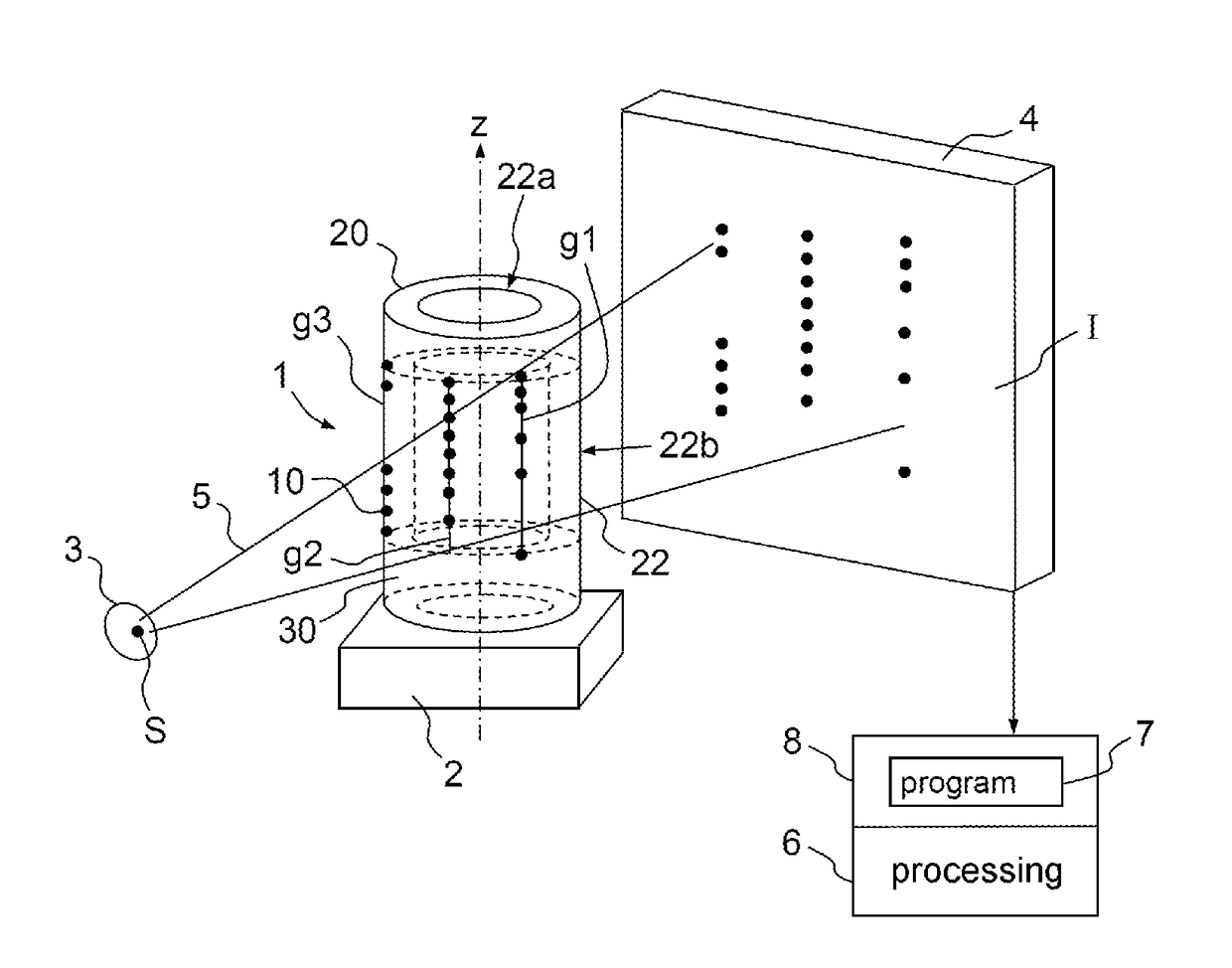
Remote center range finder
ActiveUS20060152704A1Highly accurate distance measurementEfficient calibrationOptical rangefindersRecord information storageCross-ratioCalculator
A system for measuring the distance from a first point spaced away from a surface of an object to a second point on a surface of the object along an axis extending through the first and second points includes one or more light projection assemblies for projecting light stripes onto the surface of the object so that the light stripes pass though the second point. An imaging device detects the position of the second point by sensing the light stripes at the second point. A distance calculator may then calculate the distance between the first point and the second point using the position of the second point detected by the imaging device. The system is calibrated using the cross-ratio of points detected along the axis by the imaging device.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Method for inferring intrinsic parameters of camera by utilizing bimirror device and Laguerre theorem
The invention discloses a method used for camera self-calibration by utilizing two rectangular plane mirrors, wherein the two plane mirrors are vertical to a plane formed by bottom edges of the two plane mirrors. The method comprises the following specific steps of shooting three images including an object and four images of the object, formed in the plane mirrors; extracting feature points from the images; acquiring end points of the plane mirrors in a normal direction by utilizing the plane mirror imaging principle; acquiring end points of the two plane mirrors in a mirror plane direction by utilizing the property of cross ratio; finally, acquiring images of circular points according to the deduction of the Laguerre theorem; establishing six groups of constraint equations of the images of the circular points to absolute conic images by utilizing the three images; and linearly solving the intrinsic parameters of a camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for calibrating conic refraction and reflection camera of non-center axial symmetrical system
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a conic refraction and reflection camera of a non-center axial symmetrical system. The method includes: a calibration block image is shot by employing the conic refraction and reflection camera, principal point locus curves are constrained through image points of the refraction and reflection image, and the coordinate of a principal point is determined by multiple loci; the polar line of the principal point is solved by employing a contour circle formed by a certain image point, wherein the intersection point of the polar line and a tangent passing the image point and the intersection point of the principal point and a connecting line of the image points are a group of vanishing points in the orthogonal direction; and two groups of vanishing points in the orthogonal direction are calculated by employing two image points so that the scale factor and the distortion factor of the conic mirror refraction and reflection camera are solved. By employing the method, the cross ratio is determined by directly employing the distances between the points on lines of the spatial calibration block, and point selection on the lines of the spatial calibration block is easy, convenient and accurate so that the accuracy of calibration results is improved.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
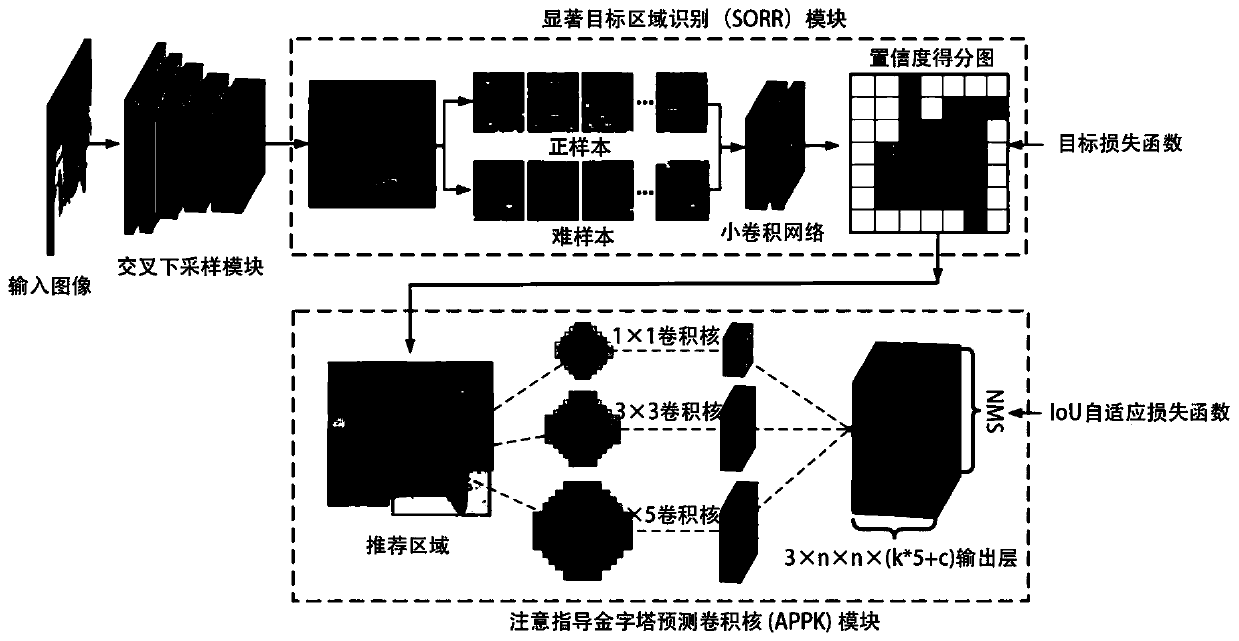
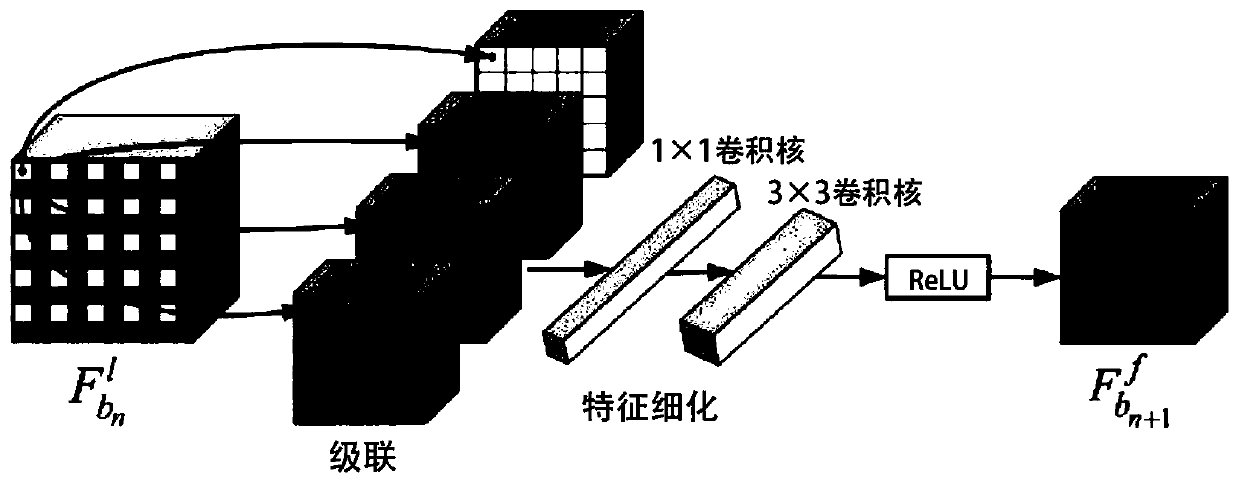
General target detection method of adaptive attention guidance mechanism
ActiveCN111259930AImprove efficiencyImprove detection accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesCross-ratioEngineering
The invention discloses a general target detection method of an adaptive attention guidance mechanism, and belongs to the field of computer vision target detection. The method comprises the steps of cross downsampling, target region recognition (SORR), pyramid prediction convolution (APPK) of an attention guidance mechanism and parallel-to-cross ratio (Ioff) adaptive loss optimization. Overall fine texture features in the multi-scale feature map can be reserved through cross downsampling, and loss of spatial information in the image downsampling process is reduced. The SORR module divides thefeature map into n * n grids and obtains an attention score map, so that the target detection efficiency is improved; the APPK module can select a recommendation area to solve the problem of mismatching between the prediction module and the multi-scale target; wherein the IOU adaptive loss function is used for processing the problem that a sample (Hard example) is difficult to process in training.The target detection method is superior to an existing general target detection method in the aspects of accuracy and detection speed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
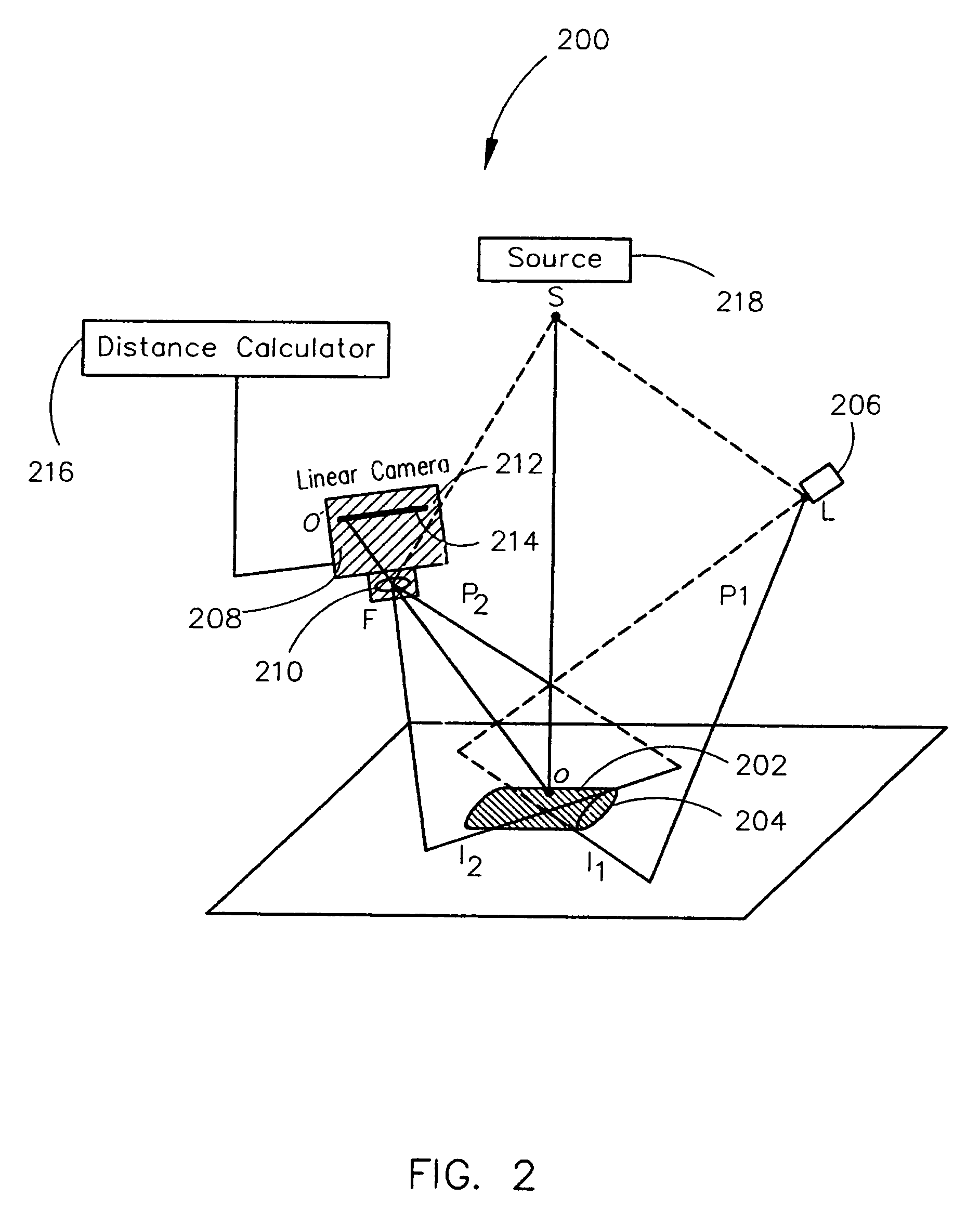
Remote center range finder
ActiveUS7355682B2Efficient calibrationAccurate distance measurementOptical rangefindersHeight/levelling measurementCross-ratioCalculator
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Method of solving intrinsic parameters of camera with regular pentagonal prismatic table
The invention discloses a target used for self-calibrating of a camera and consisting of a regular prismatic table with regular pentagonal bottom surfaces. A method comprises the particular steps as follows: characteristic points on the upper bottom surface and the two side faces of the regular positive pentagonal prismatic table are extracted from an image; coordinates of vanishing points on a plane of the image are solved according to attributes that an intersection point of two parallel straight lines is an infinite point, and a simulacrum of the infinite point is the vanishing point, and according to the attribute of a cross ratio of four collinear points; intrinsic parameters of the camera are solved linearly according to constraint of the orthogonal vanishing points on an absolute conic; two images of the target are shot in different directions; the coordinates of the characteristic points on the images are extracted; the orthogonal vanishing points on the upper bottom surface and the two side faces of the regular positive pentagonal prismatic table are calculated; constraint equations of the orthogonal vanishing points relevant to the intrinsic parameters of the camera are established; and matrixes of the intrinsic parameters of the camera are solved linearly. With the adoption of the target, full automatic calibration can be realized, and errors due to measuring in a calibrating process are reduced. The vanishing points are more concise and global elements, and the accuracy is improved in the calibrating process.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
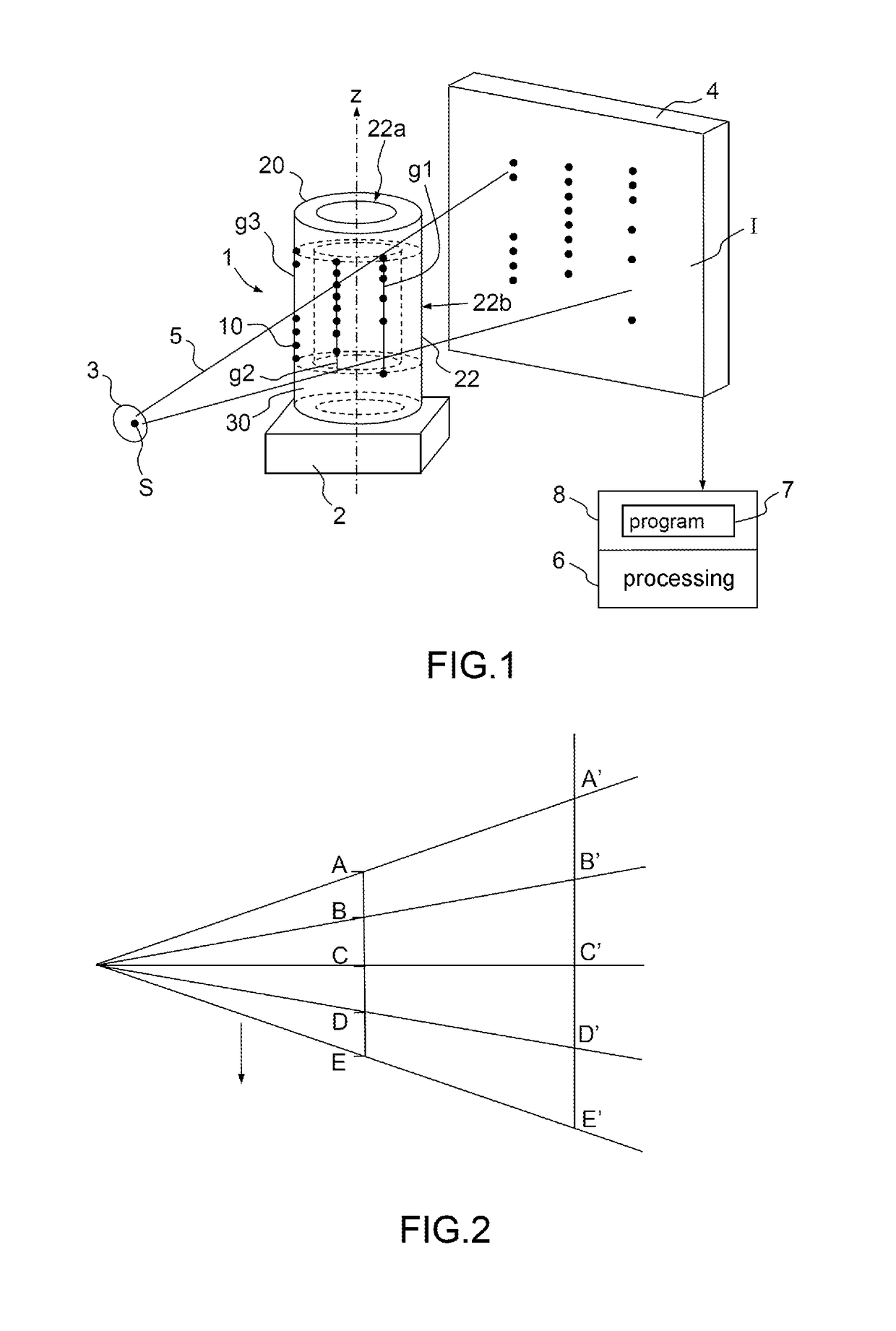
Test pattern and method for calibrating an x-ray imaging device
ActiveUS20170074808A1Robust and simple and reliable calibrating methodReliable detectionTomographyMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationSoft x rayCross-ratio
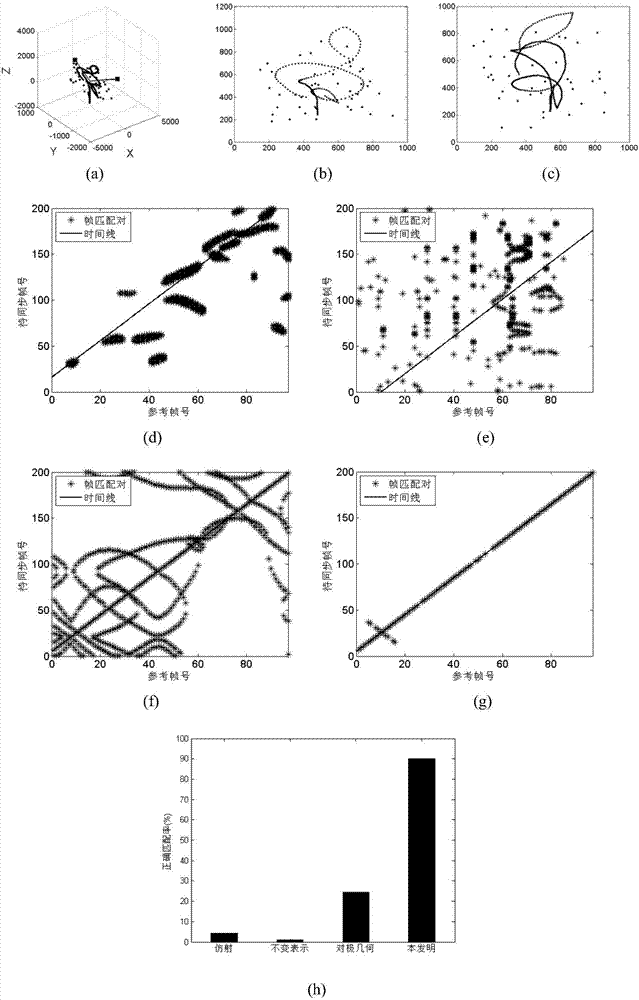
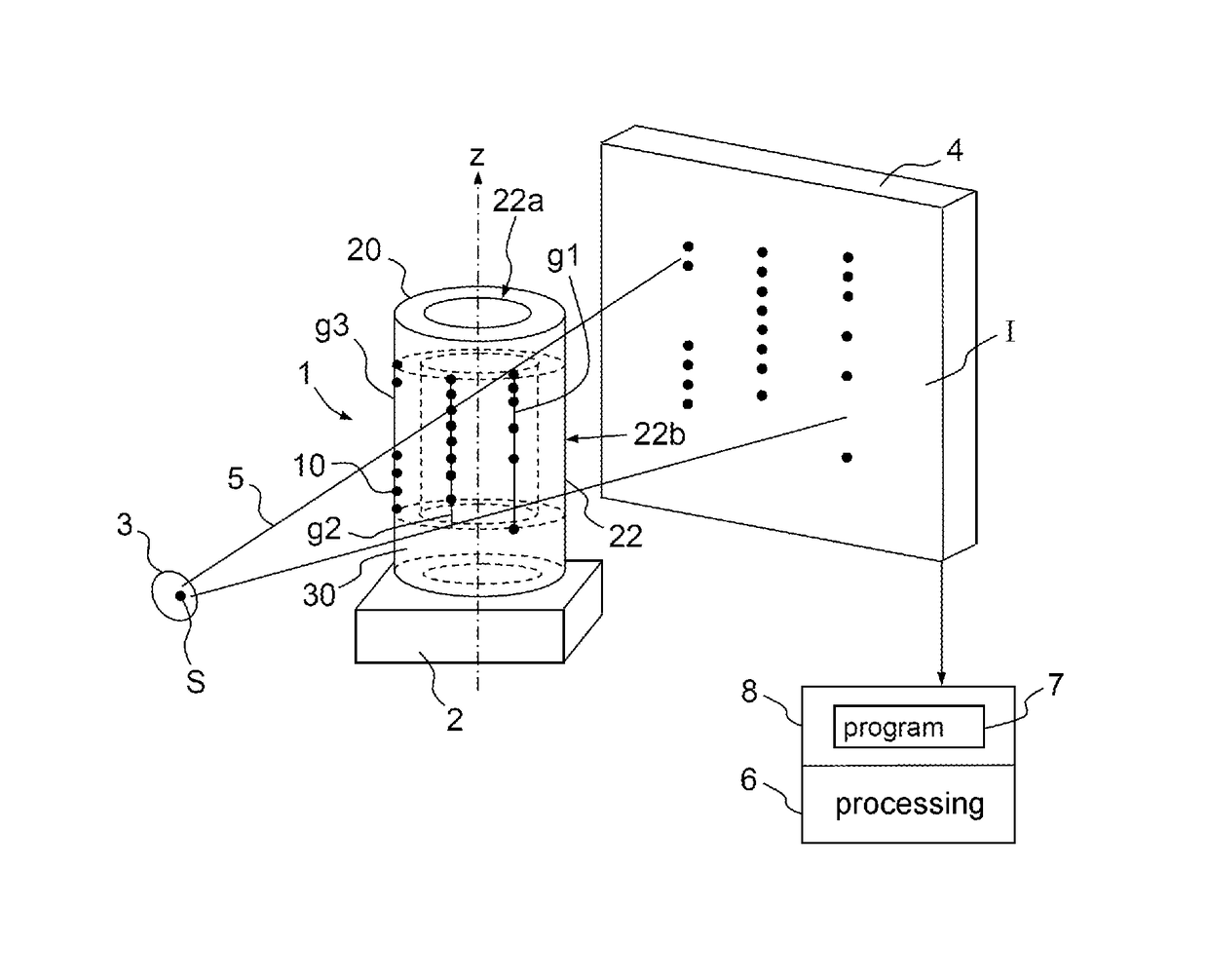
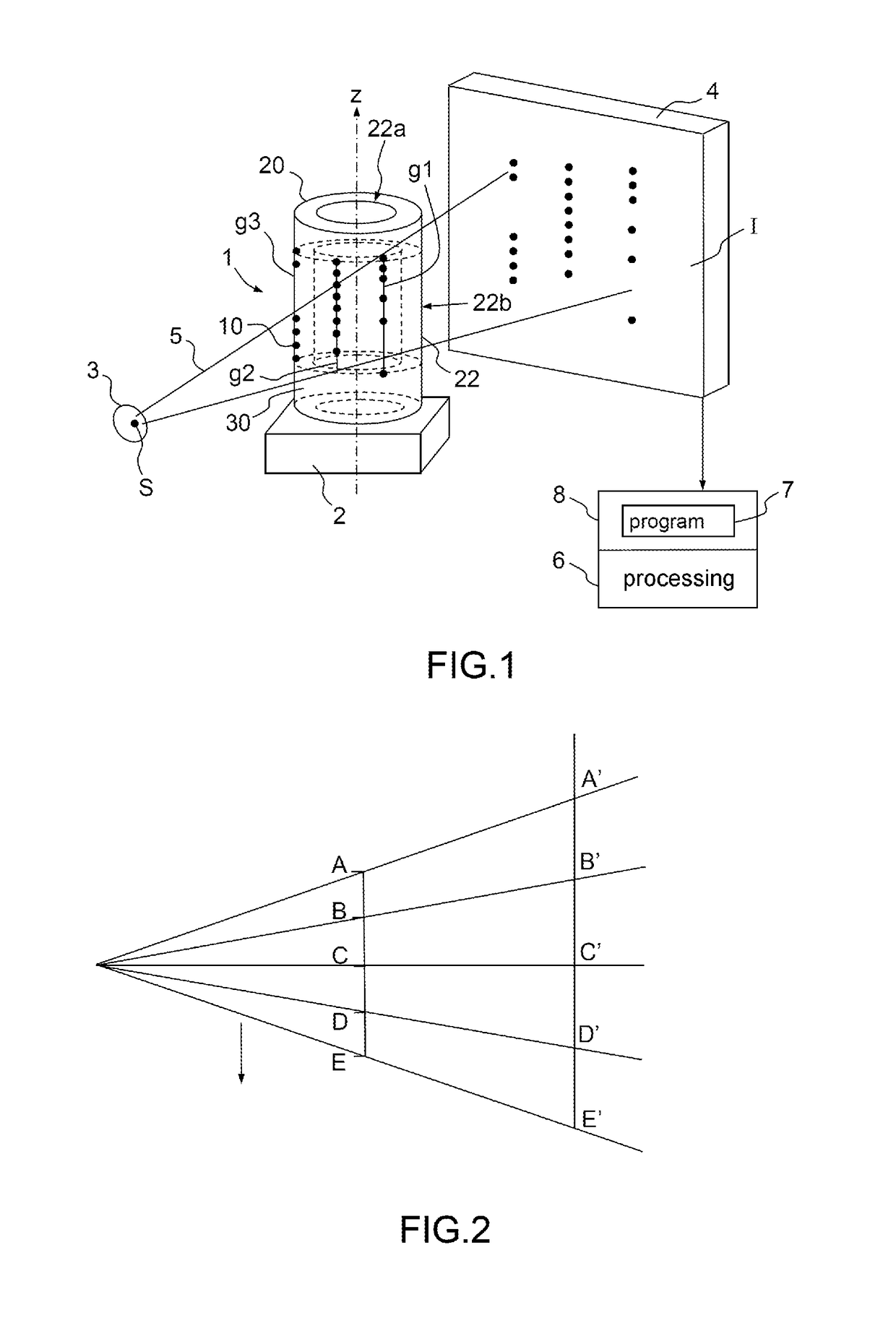
A test pattern geometrically calibrates an x-ray imaging device to generate three-dimensional images of an object by reconstruction based on two-dimensional projections of the object, the calibrating test pattern comprising a volume support with markers having a radiological absorbance providing contrast to the volume support, the markers distributed in a three-dimensional pattern, in subsets substantially in parallel respective straight lines wherein sequences of cross-ratios are constructed from the respective subsets of markers. Each sequence of cross-ratios comprises a single cross-ratio for each quadruplet of markers in which quadruplet the markers are ordered depending on rank number of respective markers along the straight line they are aligned in a predefined first direction, the order being common to all cross-ratios. When a subset of markers comprises at least five markers, the order of the cross-ratios in the respective sequences of cross-ratios is defined by a rule common to all sequences of cross-ratios.
Owner:THALES SA
A stumpage height extraction method under a plane constraint
InactiveCN109448043AReduce cumbersomeReduce mistakesImage enhancementImage analysisCross-ratioExtinction
The invention discloses a stumpage height extraction method under a plane constraint, which is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps of step 1 selecting a reference object; 2obtaining a standing wood image of that height to be measured; 3 identifying that outline of the reference object; 4 detecting that coordinates of the extinction point; 5 constructing cross ratio information, setting MN as a reference object of a known height, so that that height of the object to be measure MQ can be calculated through the ratio of the two, the height of the tree to be measured isset as T2, and the height of the tree to be measured can be obtain according to the proportional relationship between pixels when the height of the tree to be measured is known T2=MQ. The method of the invention can complete the height measurement of the standing timber without obtaining the internal and external parameters of the camera, simplifies the tedious process in the computer operation process, reduces the error of the straight line detection result, improves the flexibility of the line segment calculation in the plane, and is particularly suitable for the geometric information extraction of the standing timber scene object under the structured condition.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for 3D Scene Reconstruction with Cross-Constrained Line Matching
A method reconstructs a three-dimensional (3D) scene using a pair of 2D images acquired from two different viewpoints by first detecting real lines in the pair of images, and then matching points in the pair of images to detect matched points. Virtual lines in the pair of images are generated using pairs of the matched points, and then detecting additional matched points on the virtual lines using a cross-ratio constraint. Line matching is performed using all matching points to detect matched lines, and then a line-based 3D reconstruction of the scene, from the matched lines.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
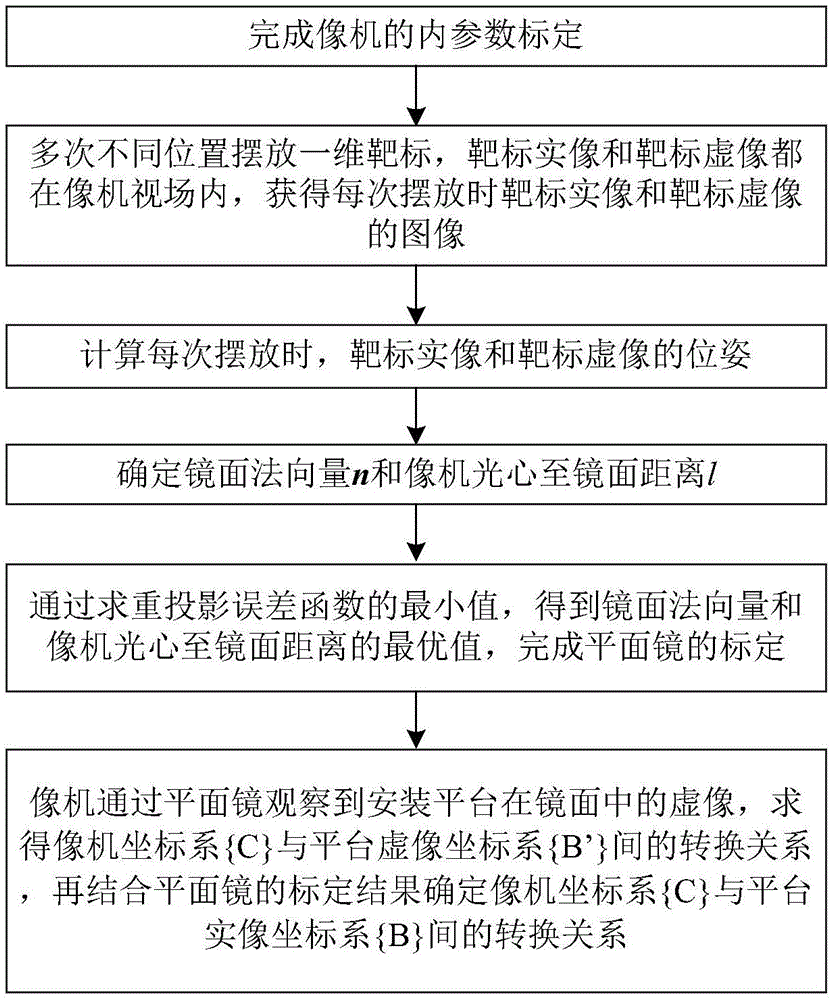
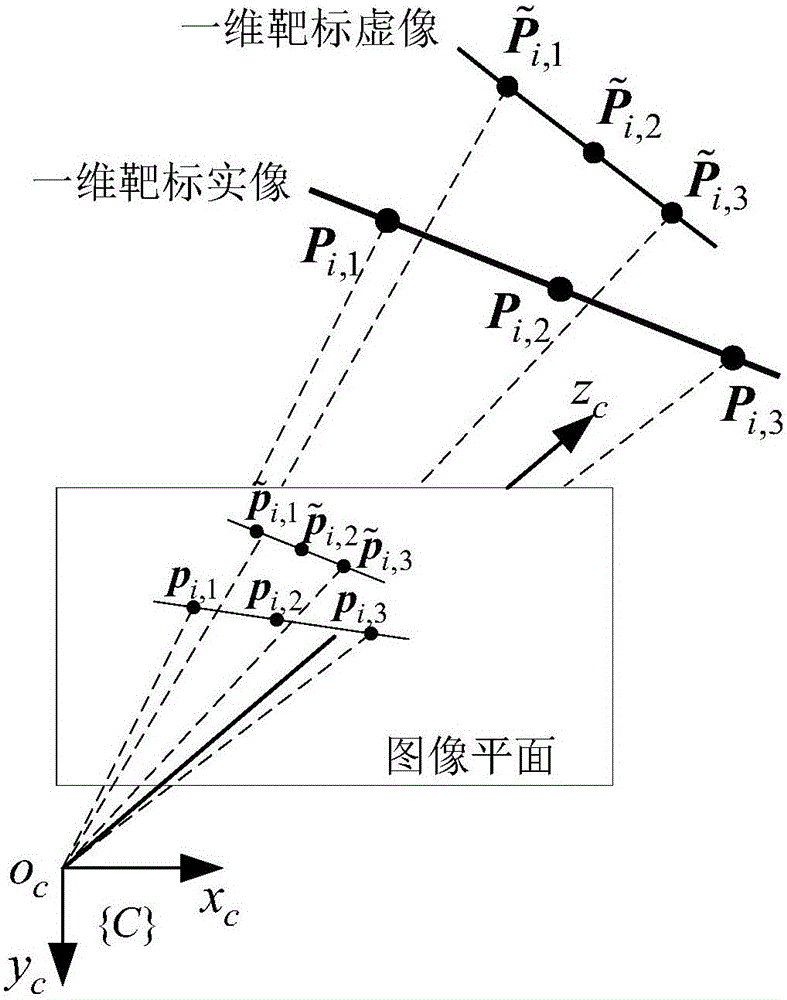
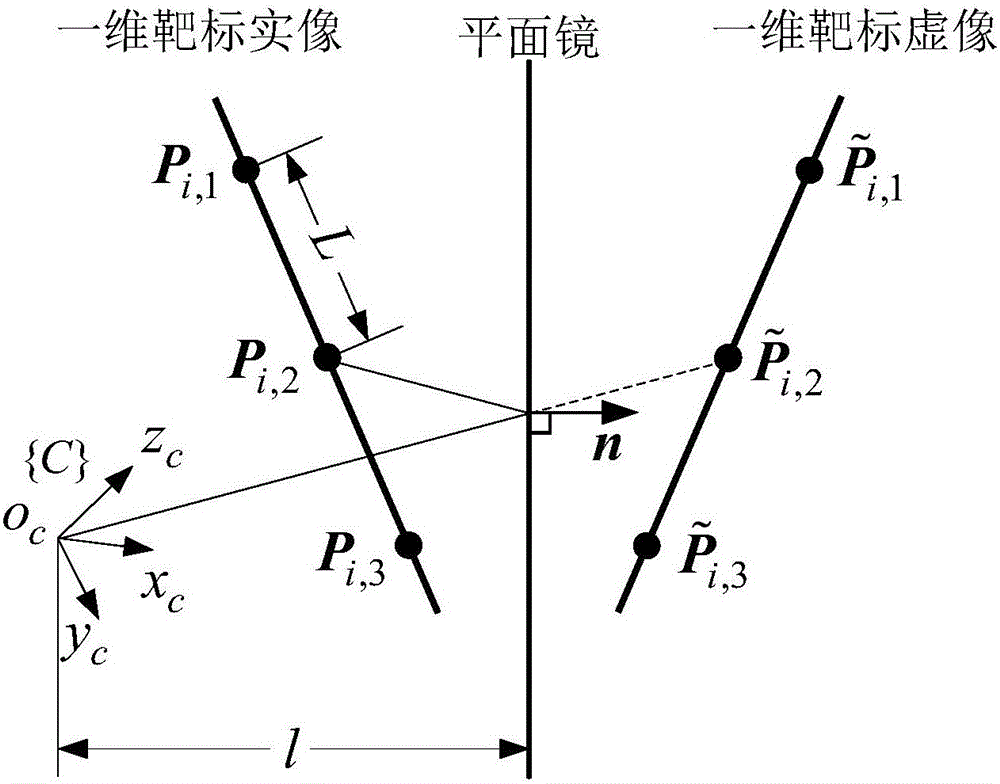
Camera mounting position calibration method based on plane mirror
The invention discloses a camera installation position calibration method based on a plane mirror, and belongs to the technical field of photogrammetry of optical systems. The present invention includes the following steps: placing the one-dimensional target in front of the camera for several times, calculating the initial value of the pose of the one-dimensional target in the camera coordinate system according to the cross-ratio invariance, and obtaining the target position by minimizing the reprojection error The optimal solution of the pose of the plane mirror; the closed-form solution method is used to calculate the mirror normal vector and the distance from the optical center of the camera to the mirror; then the optimal solution of the plane mirror pose is obtained by minimizing the reflection and reprojection error; when the mirror pose is determined, combined with the camera The conversion relationship between the coordinate system and the platform virtual image coordinate system is obtained, and the conversion relationship between the camera coordinate system and the platform real image coordinate system is obtained, and the calibration of the camera installation parameters is completed. The present invention does not need to know the target motion and the attitude information of the camera in advance, and the attitude of the mirror surface can be obtained by placing the position at least twice, which is simple and convenient to realize, and is especially suitable for the occasion where the camera and the mirror surface are in fixed positions.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for measuring tailings pond dry beach length by utilizing machine vision
The invention relates to a method for measuring tailings pond dry beach length by utilizing machine vision. The method comprises the steps of setting three marker posts on a tailings dry beach, wherein the three marker posts are in one straight line, which is perpendicular to a dam body; respectively measuring the distance between each two adjacent marker posts, and the distance from each marker post to the dam body; utilizing a color high-definition digital video camera for shooting a digital image, and extracting positions of the three marker posts in the digital image; dividing the digital image into a dry beach area and a water area; fitting position coordinates of the three marker posts in the digital image into a straight line, and calculating position points of the marker posts on the fitted straight line and cross ratio of boundary intersection points; utilizing the property of constant cross ratio for calculating the distance of the dry beach. By utilizing the machine vision for automatically measuring the dry beach length, no other factors such as dry beach slope and dam water level height needed to be referred, so that the method has the characteristics of convenience in implementation, low measuring system cost and small measurement error, and has a higher application value.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH LIAONING
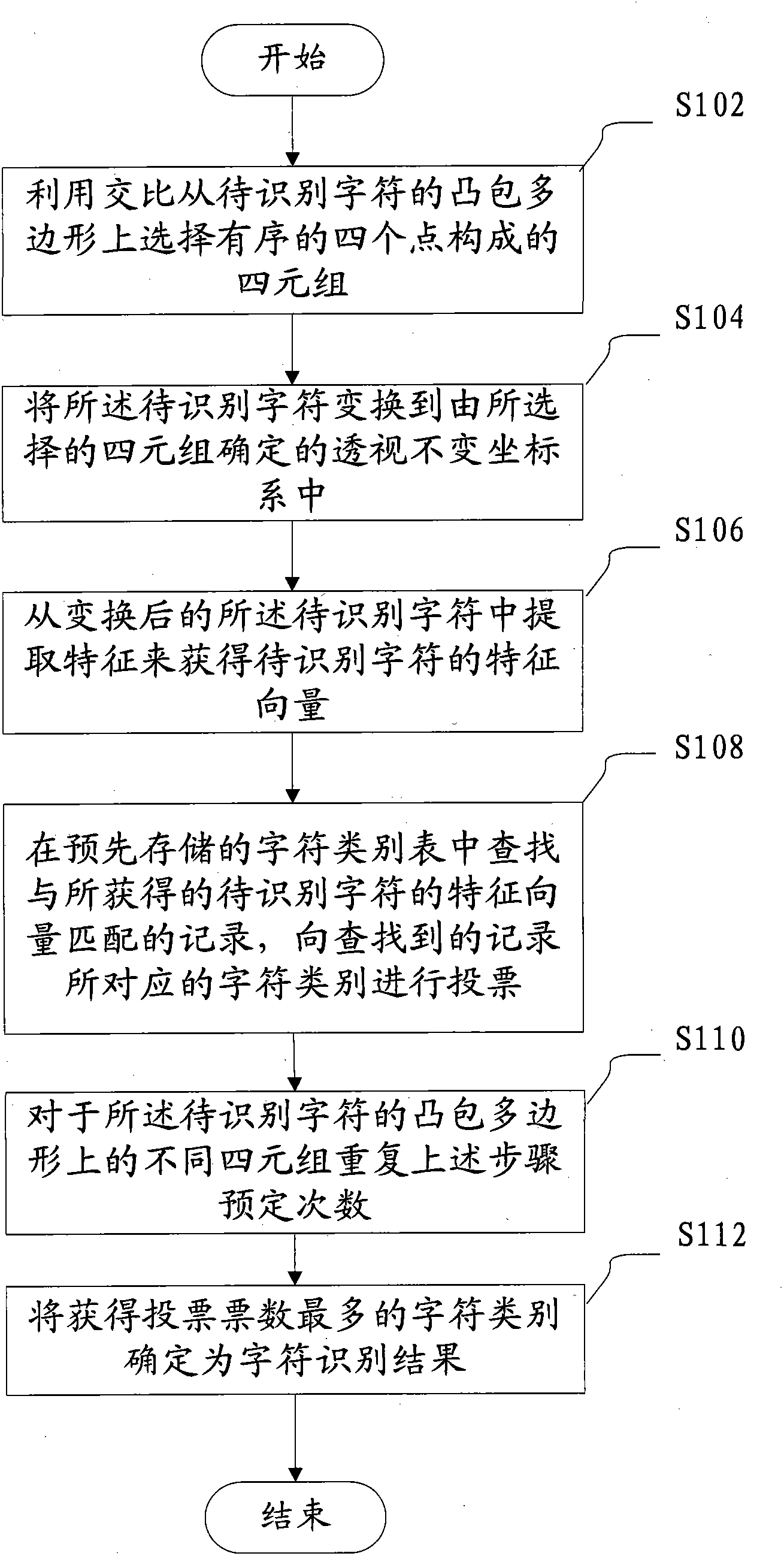
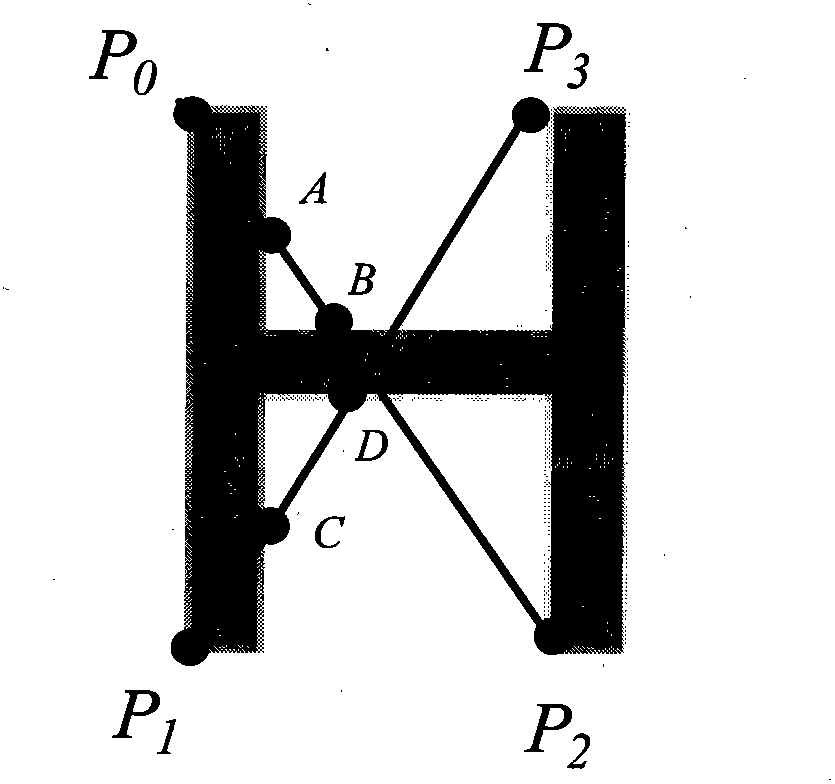
Character recognition method and device
ActiveCN102855498AImprove recognition rateIdentifyCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorCross-ratio
The invention relates to a character recognition method and device. The character recognition method comprises the following steps of: selecting a tetrad formed by four points in sequence from a convex hull polygon of a character to be recognized by a cross-ratio; converting the character to be recognized into a perspective invariant coordinate system which is defined by the tetrad; extracting features from the converted character to be recognized so as to obtain feature vectors of the character to be recognized; checking records which are matched with the obtained feature vectors of the character to be recognized in a character class table which is stored in advance, and voting character classes corresponding to the checked records; and repeating the steps on different tetrads on the convex hull polygon of the character to be recognized for preset times, thereby determining the character class having the most votes as a character recognition result.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
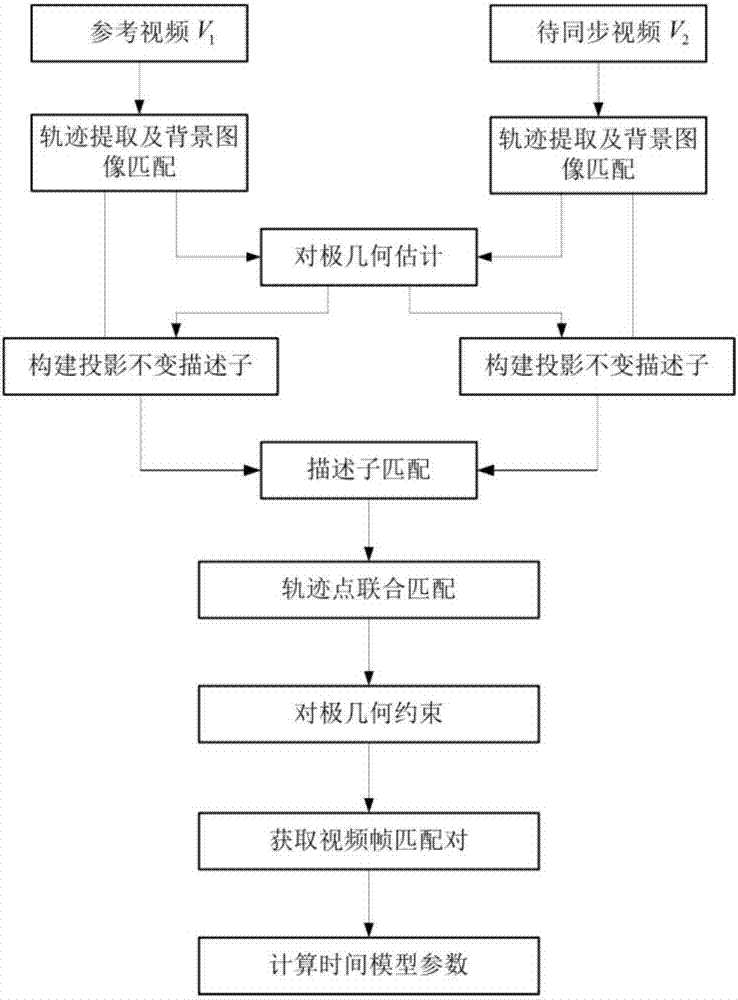
Video synchronization method based on projection unchangeable descriptor
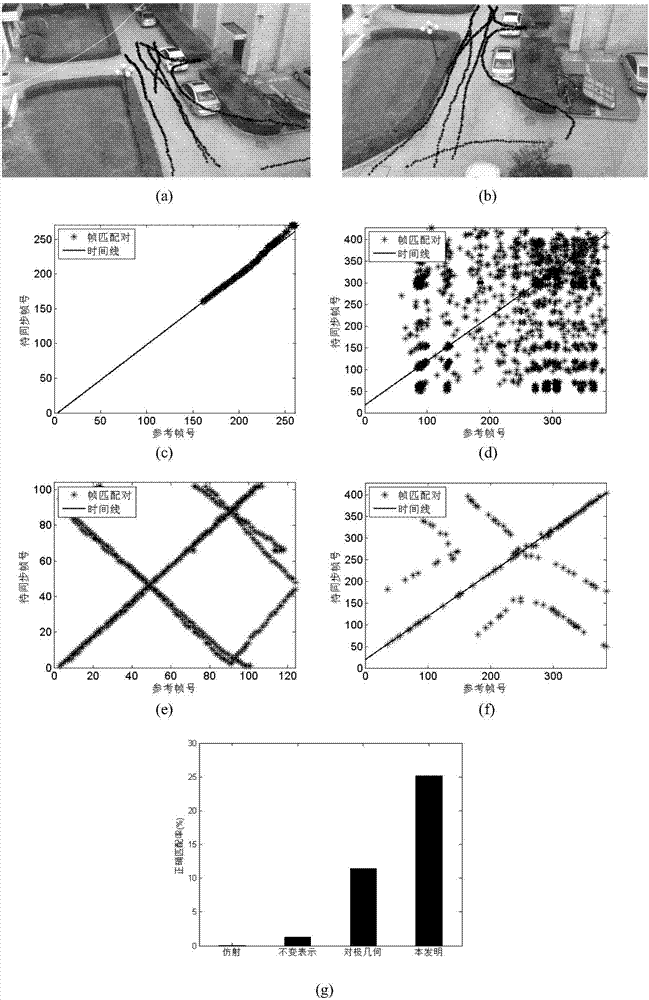
ActiveCN107316008AImprove robustnessImprove the ability to distinguishCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionData synchronization
The invention provides a video synchronization method based on a projection unchangeable descriptor. The objective of the invention is to solve a technical problem of the quite narrow applicable range caused by the fact that the existing method fails to be applicable to video synchronization of different scenes. The method comprises steps of carrying out moving target track extraction and background image matching on an input video; estimating epipolar geometries between background images; based on the cross ratio of five coplane points, constructing a projection unchangeable descriptor for each track point; by use of the principle that the nearest-neighbor next nearest neighbor is smaller than a designated threshold value, establishing initial track point matching pairs; by combining the track points, the matching and the epipolar geometries, restraining track point matching pairs without errors; by use of the repeated sampling for many times, constructing scoring matrixes and a thresholding method, and acquiring final frame matching pairs; and finally, using the random sampling consistency algorithm, calculating time model parameters between input videos. According to the invention, the method is suitable for video synchronization of multiple complex scenes; and quite average time synchronization errors and quite high correct matching rate can be acquired.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Test pattern and method for calibrating an X-ray imaging device
ActiveUS10119922B2Robust and simple and reliable methodReliable detectionComputerised tomographsTomographySoft x rayCross-ratio
Owner:THALES SA
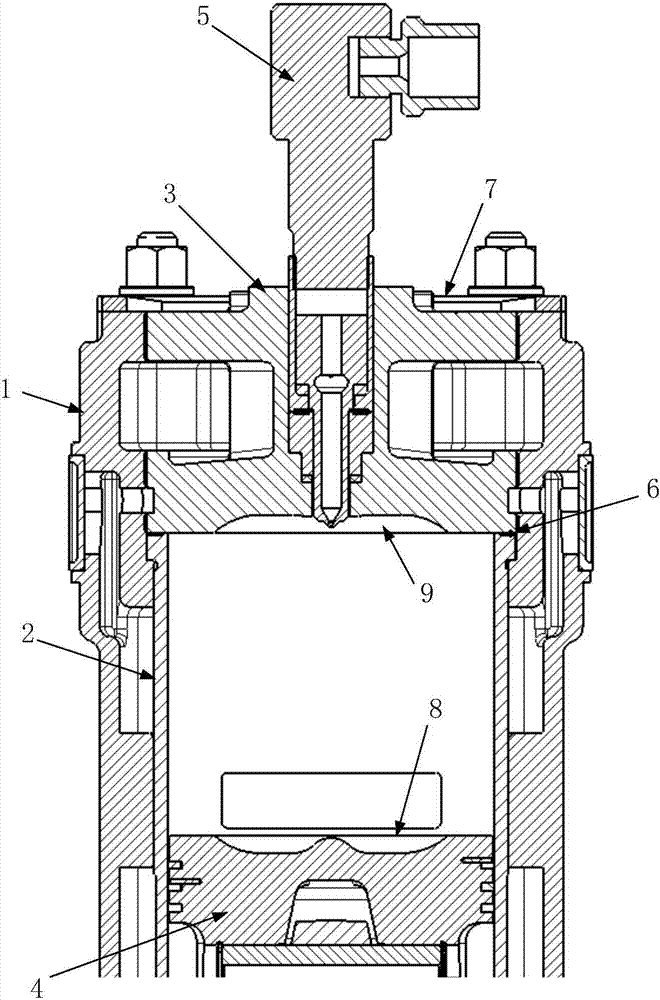
Combined type combustion chamber for two-stroke aviation heavy oil plunger engine
InactiveCN107060986ACompact structureReduce weightInternal combustion piston enginesCylinder headsAviationCross-ratio
The invention discloses a combined type combustion chamber for a two-stroke high-power cross-ratio aviation heavy oil plunger engine. The combined type combustion chamber comprises a cylinder body, a cylinder sleeve, a cylinder head, a plunger and a mono-block pump; the cylinder head is fixed to the top of the cylinder body, the cylinder sleeve is fixed in the cylinder body, and the plunger is arranged inside the cylinder sleeve; a concave pit A is designed in the middle of the top surface of the plunger, a concave pit B is designed in the middle of the bottom surface of the cylinder head, and the concave pit A and the concave pit B are all shallow pits; the concave pit A, the concave pit B and the cylinder sleeve are combined together to form the combined type combustion chamber; and the mono-block pump is fixed to the cylinder head, a nozzle of the mono-block pump extends into the combined type combustion chamber, and nozzle holes of the nozzle are located in the concave pit B. Two air inlets and one air outlet which are opposite to each other are designed and formed in the side wall of the lower portion of the cylinder body. According to the combined type combustion chamber, the structure is compact, the power to weight ratio is big, the combustion speed is high, and the maximum combustion pressure is small; the combustion temperature is low, and the air-exhausting quality is good; and the scavenging form is rotational flow scavenging, the charging loss is effectively lowered, and the volume efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
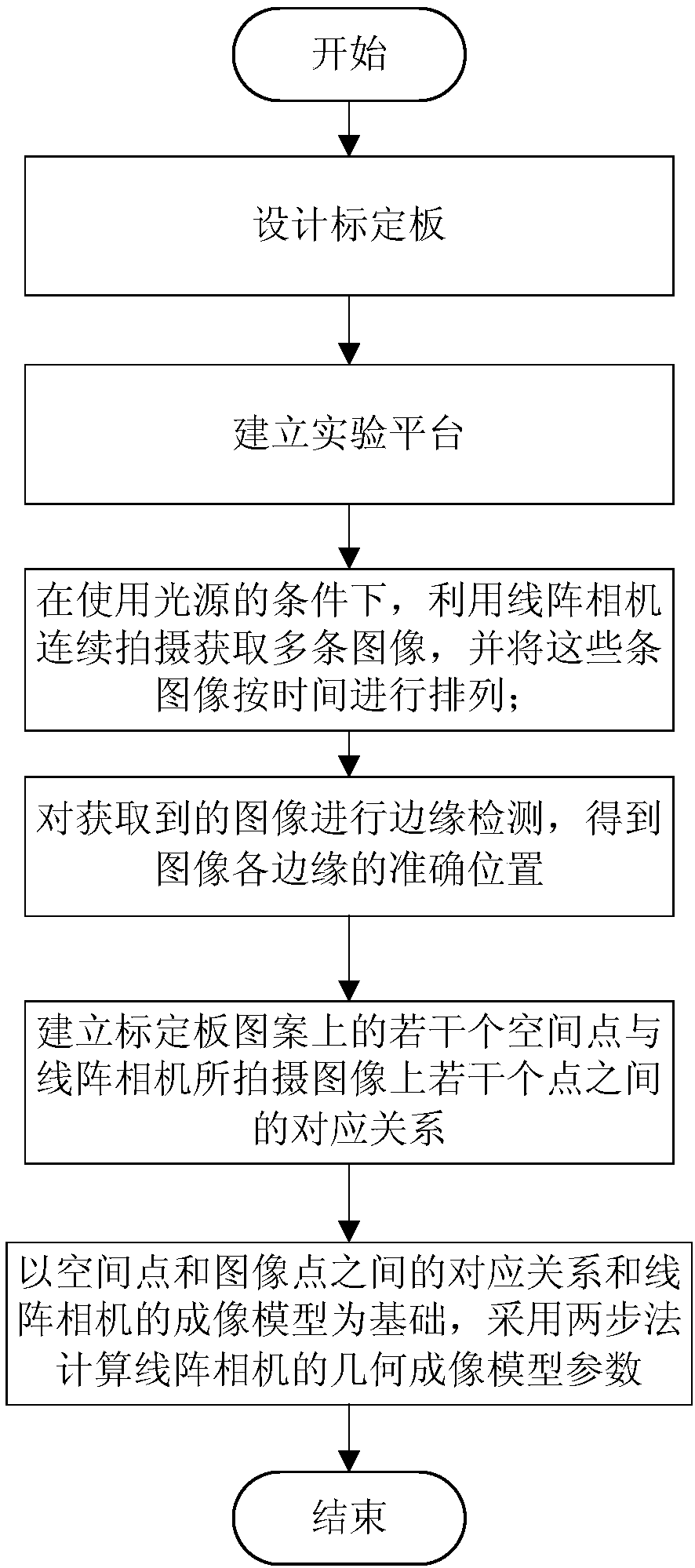
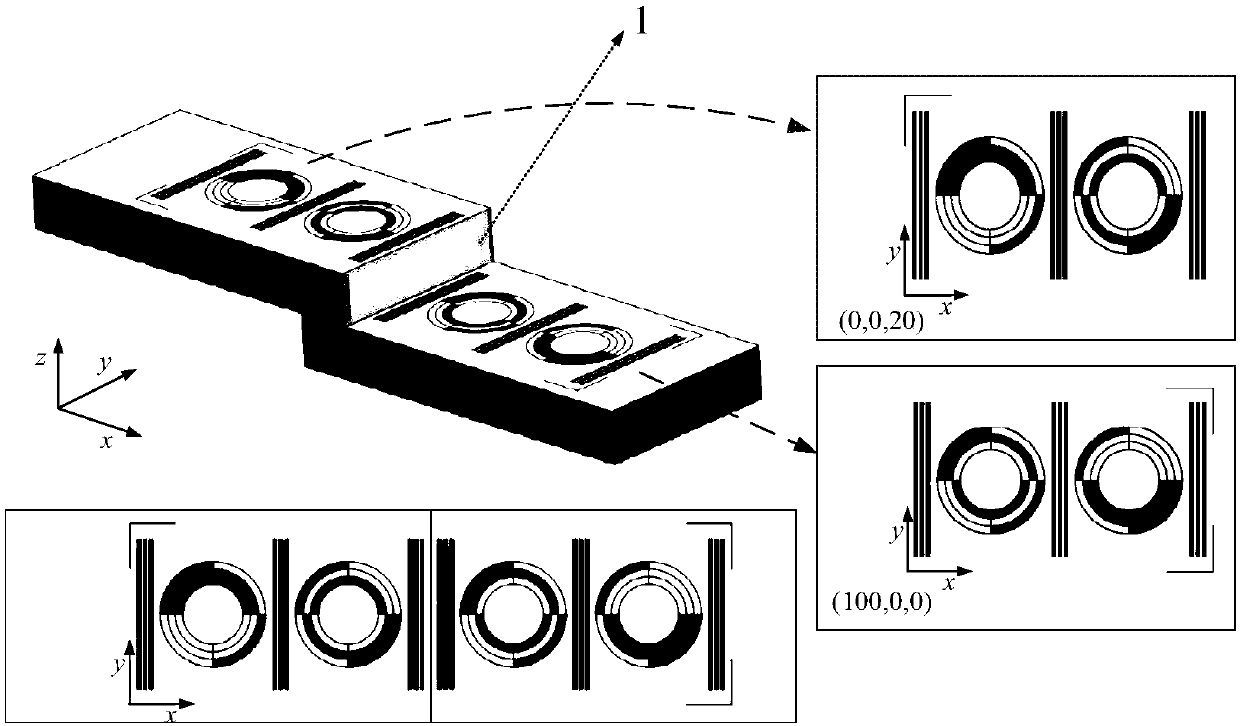
Cross-ratio-invariance-based linear-array camera calibration method containing eight-diagram coding information
The invention, which relates to the technical field of camera calibration, provides a cross-ratio-invariance-based linear-array camera calibration method containing eight-diagram coding information. According to the method, the eight-diagram theory is applied to the design of a linear-array camera calibration plate, so that a pattern of the calibration plate contains the coding information; on thebasis of cross-ratio invariance of projection, intersection points of the pattern on the calibration plate and the view plane of the camera are obtained; calculation is carried out by using the intersection points and corresponding pixel values to obtain internal and external parameters of the linear-array camera and the obtained internal and external parameters of the linear-array camera are used as initial values; and a final calibration result is obtained by using a nonlinear optimization method under an actual imaging model. According to method provided by the invention, the position of the view field line is distinguished clearly without moving the calibration plate; the calibration plate is made simply and the cost is low; and calibration of the linear-array camera is carried out simply and quickly.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
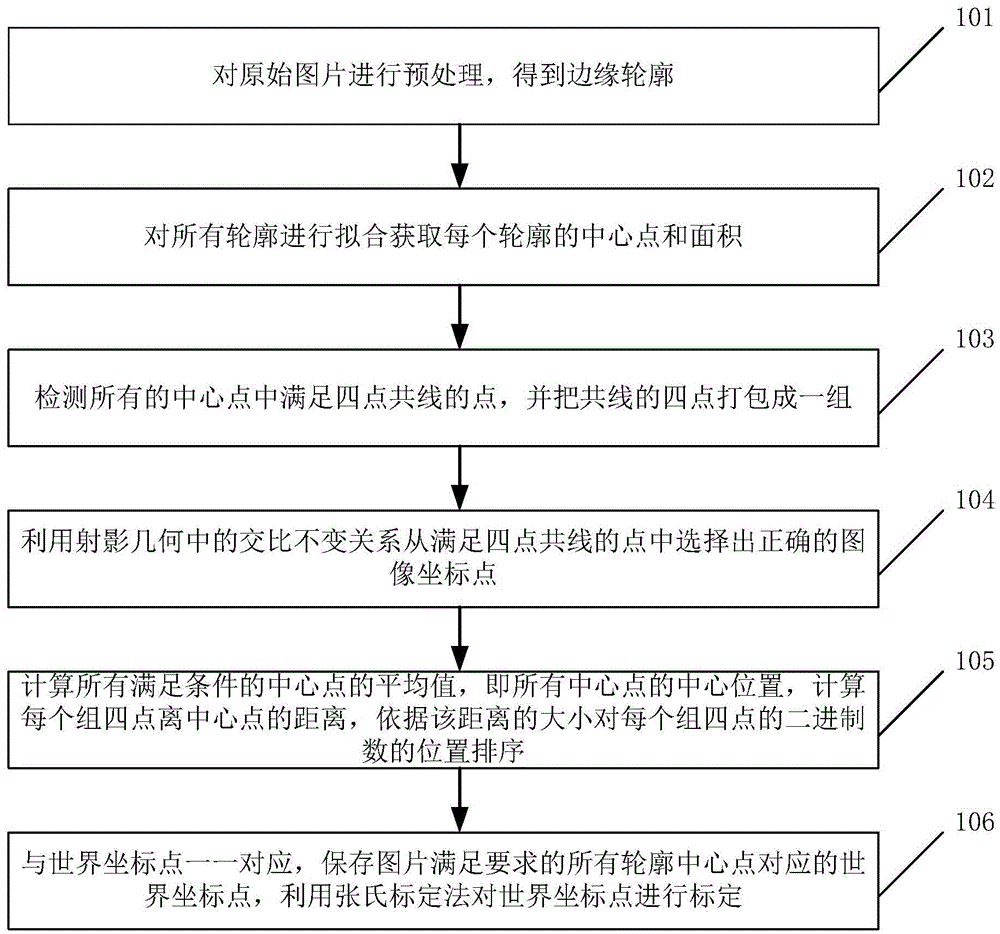
High-precision calibration method of handheld multi-lens camera
InactiveCN105574886AIncrease flexibilityGood precisionImage analysisCross-ratioIterative reconstruction
The invention belongs to the field of images, and provides a high-precision calibration method of a handheld multi-lens camera. The high-precision calibration method comprises the steps of performing preprocessing on an original picture, thereby obtaining an edge contour; fitting all contours for obtaining the central point and area of each contour; detecting the points which satisfy a collinear relationship in all central points, and packing four collinear points to one set; selecting correct image coordinate points from the points which satisfy the collinear relationship according to a cross ratio invariance relationship in projective geometry; and calibrating world coordinate points according to a Zhang's camera calibration method. The high-precision calibration method has advantages of accurate three-dimensional reconstruction and accurate measurement.
Owner:深圳创客帝国教育技术有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com