Patents
Literature
180results about How to "Efficient calibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
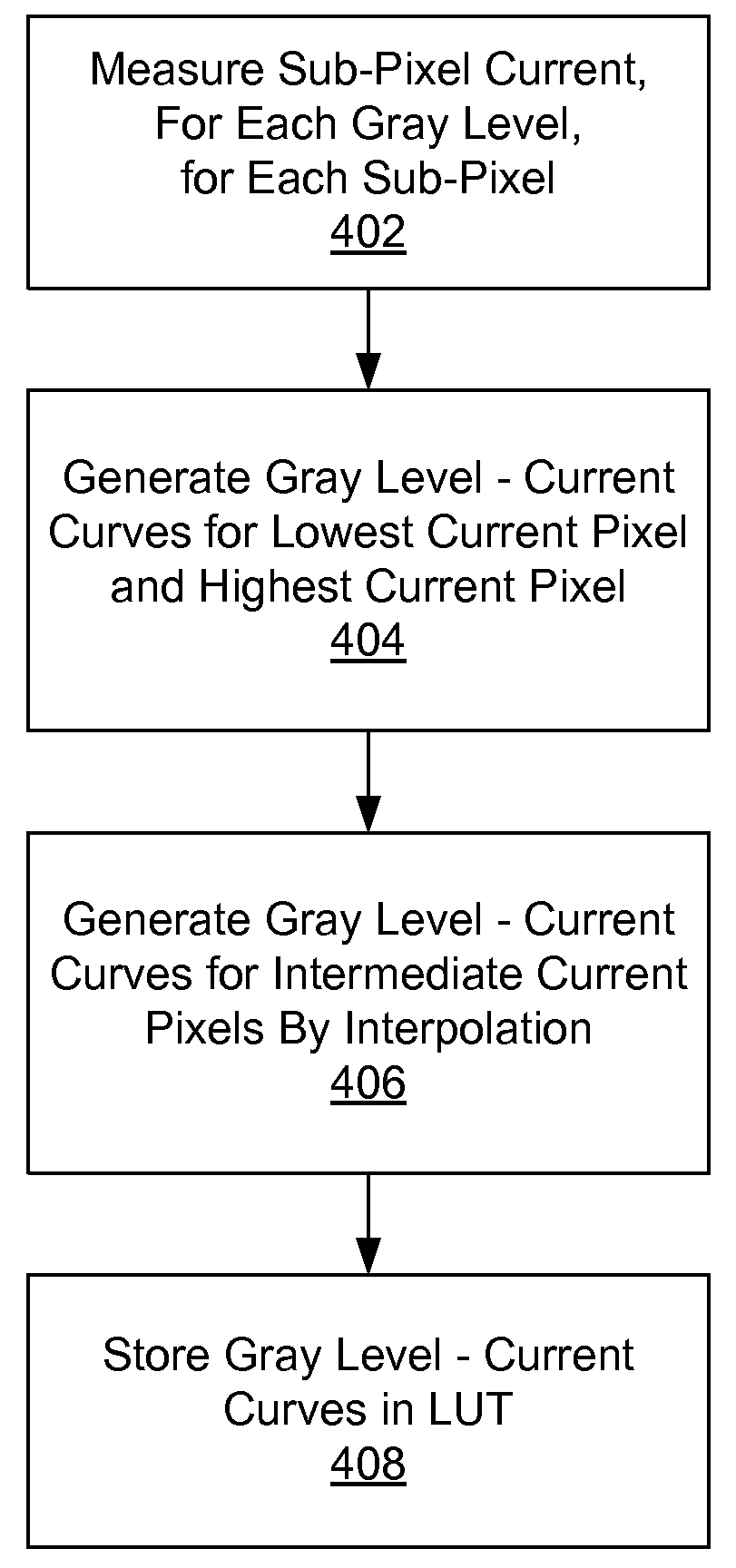
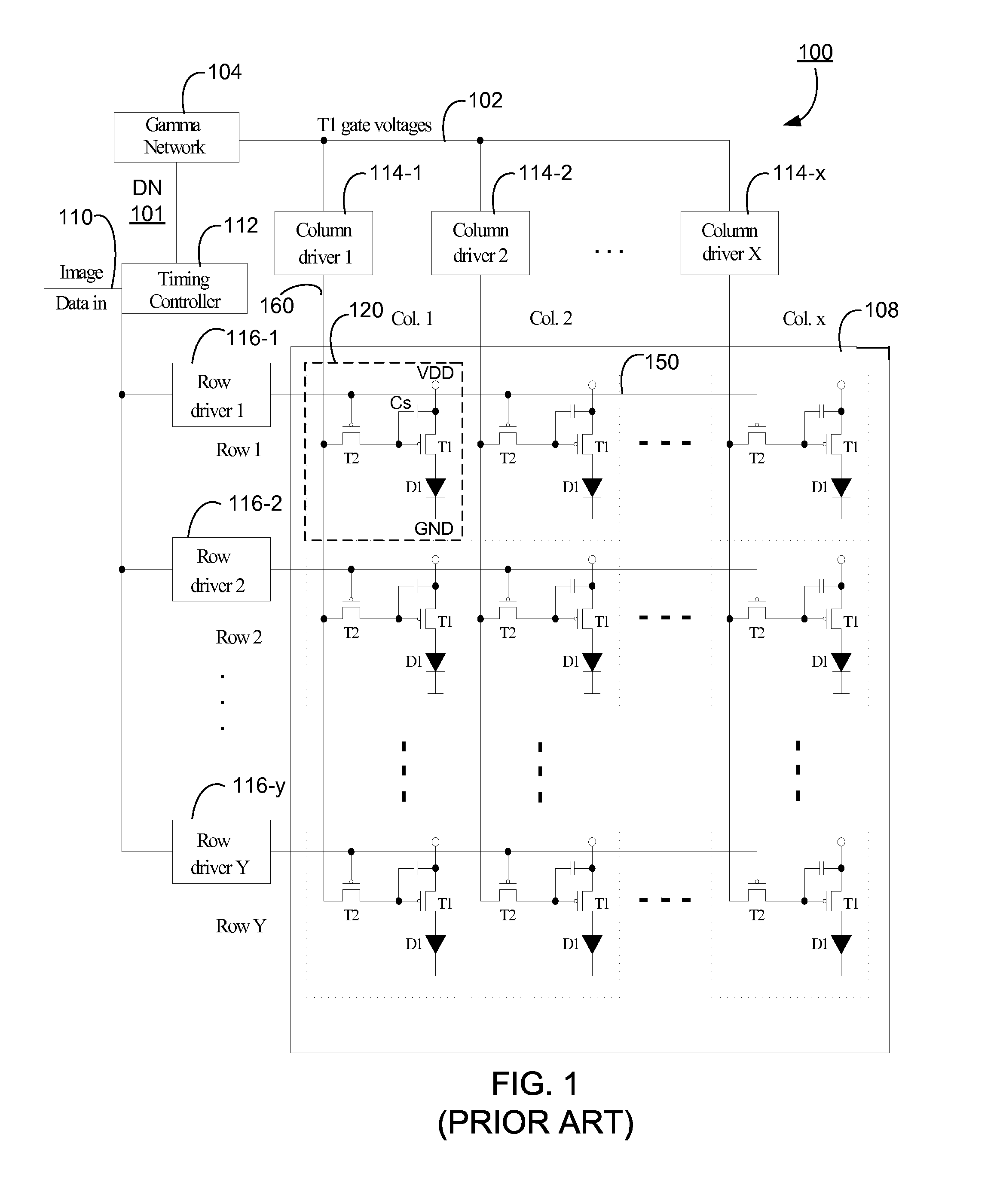
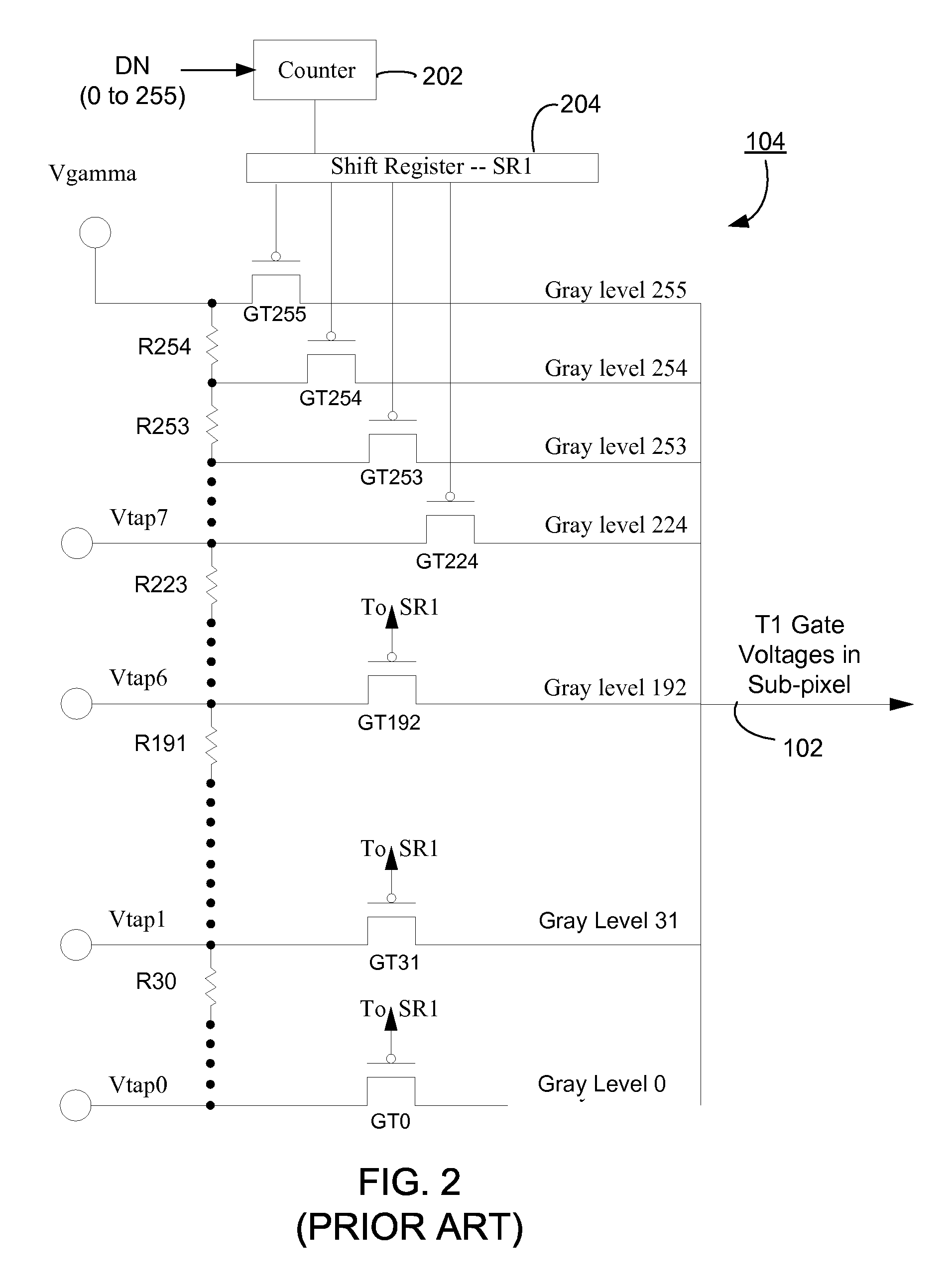
Using standard current curves to correct non-uniformity in active matrix emissive displays
InactiveUS20090195483A1Shorten timeEfficient calibrationStatic indicating devicesGray levelEngineering
A plurality of gray level versus OLED current curves are generated by measuring many OLED panels from a stable manufacturing process, and those curves are stored as standard gray level versus OLED current curves. When a new OLED display is manufactured from the process, each of its sub-pixels is characterized as having the characteristics of one of the pre-generated standard gray level versus OLED current curves, based on a gray level versus OLED current measurement at a single gray level. This drastically reduces the time it takes to determine the TFT gate voltage versus OLED current characteristics of the sub-pixels in the OLED display. The OLED display can use the selected one of the pre-generated standard gray level versus OLED current curves to correct non-uniformities of the sub-pixels in the OLED display caused by non-uniform TFTs in the active matrix.
Owner:LEADIS TECH
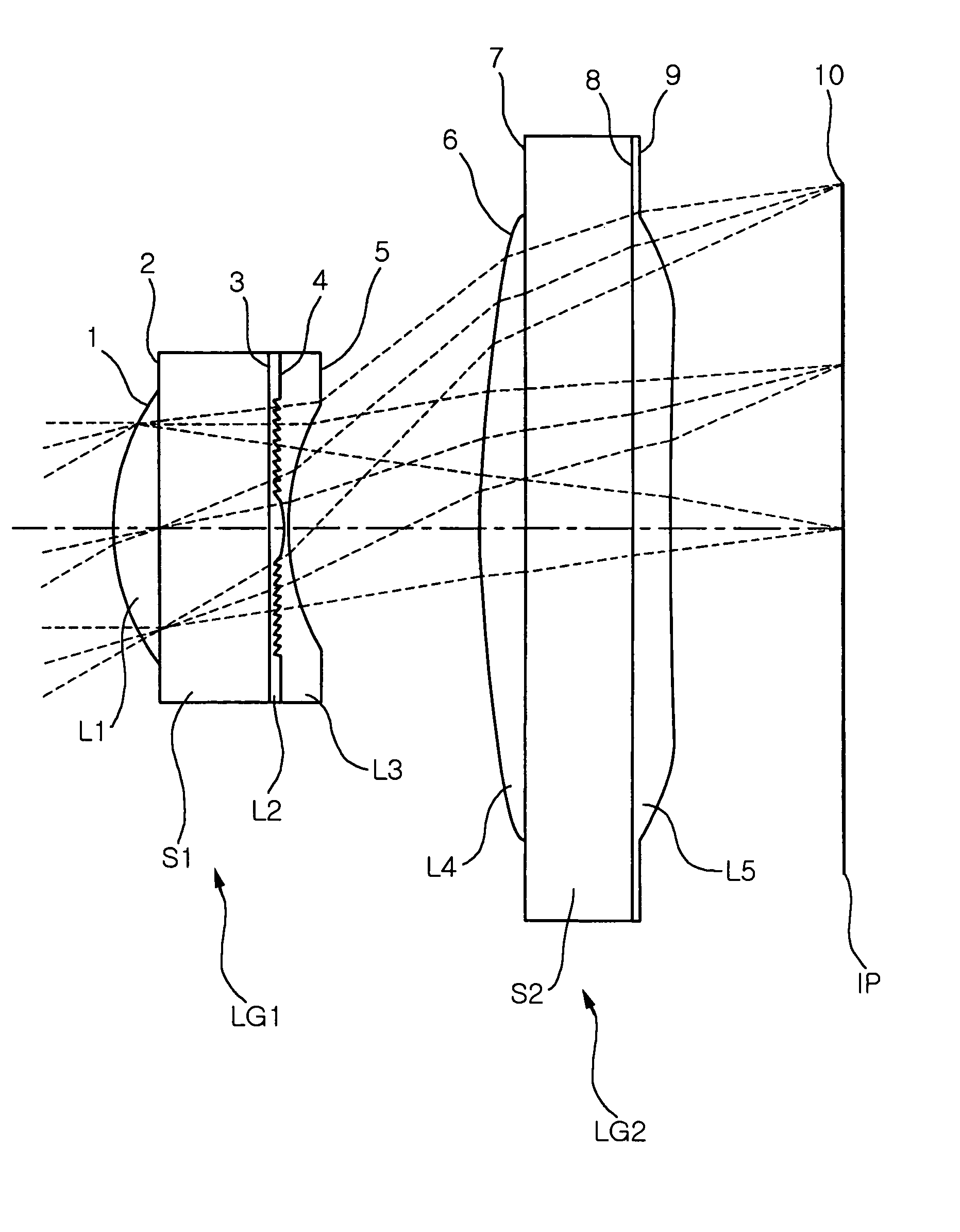
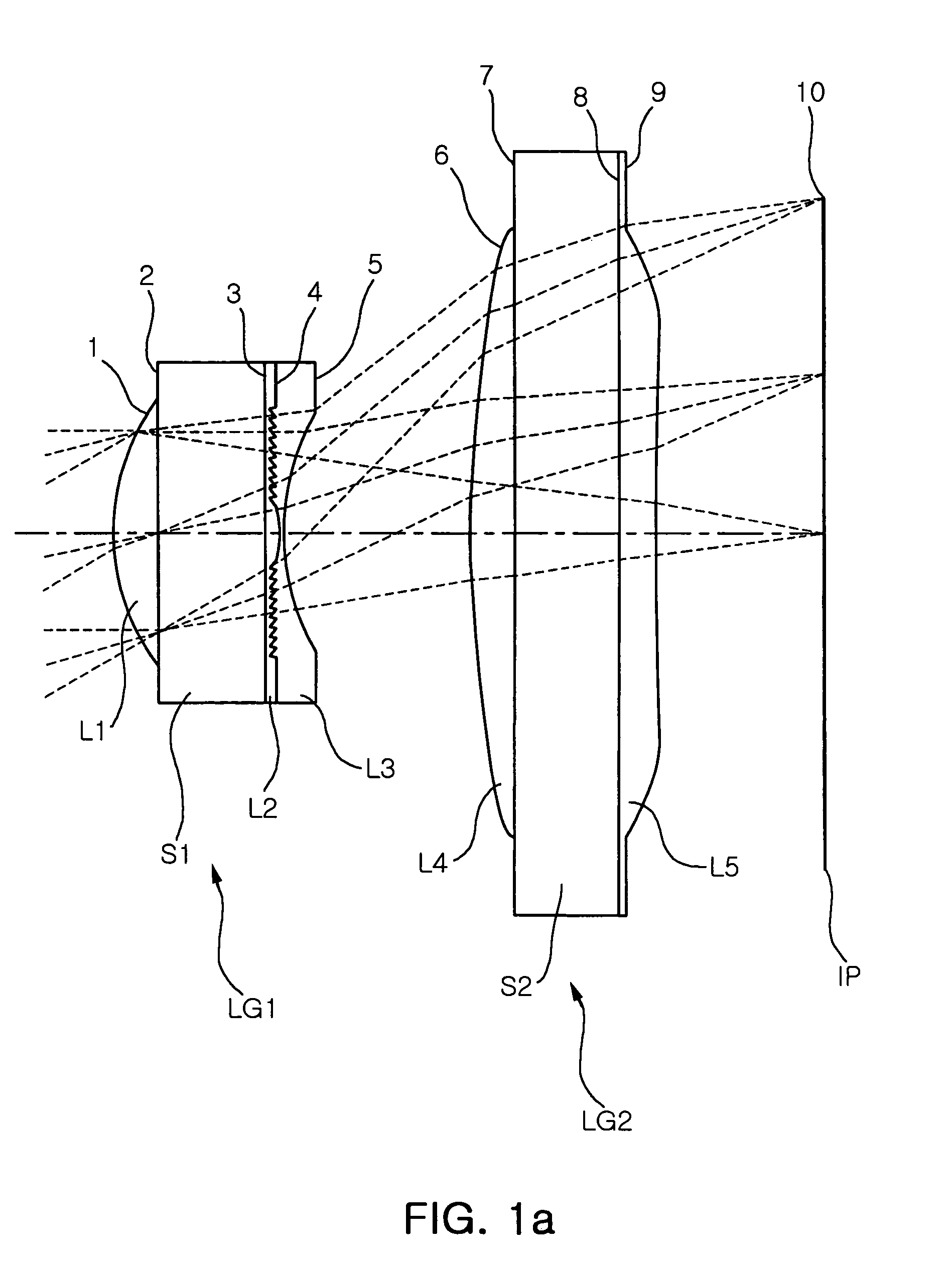
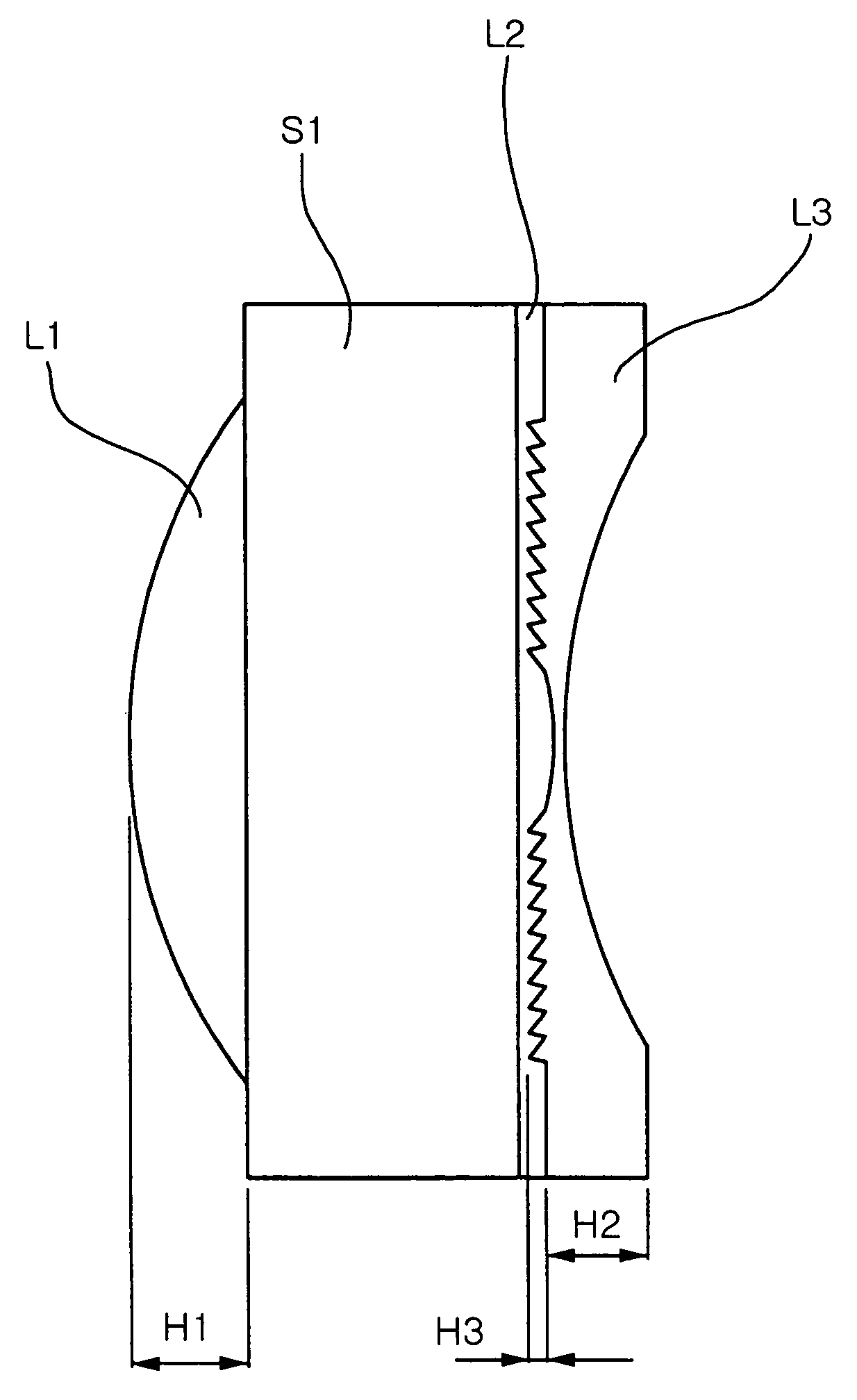
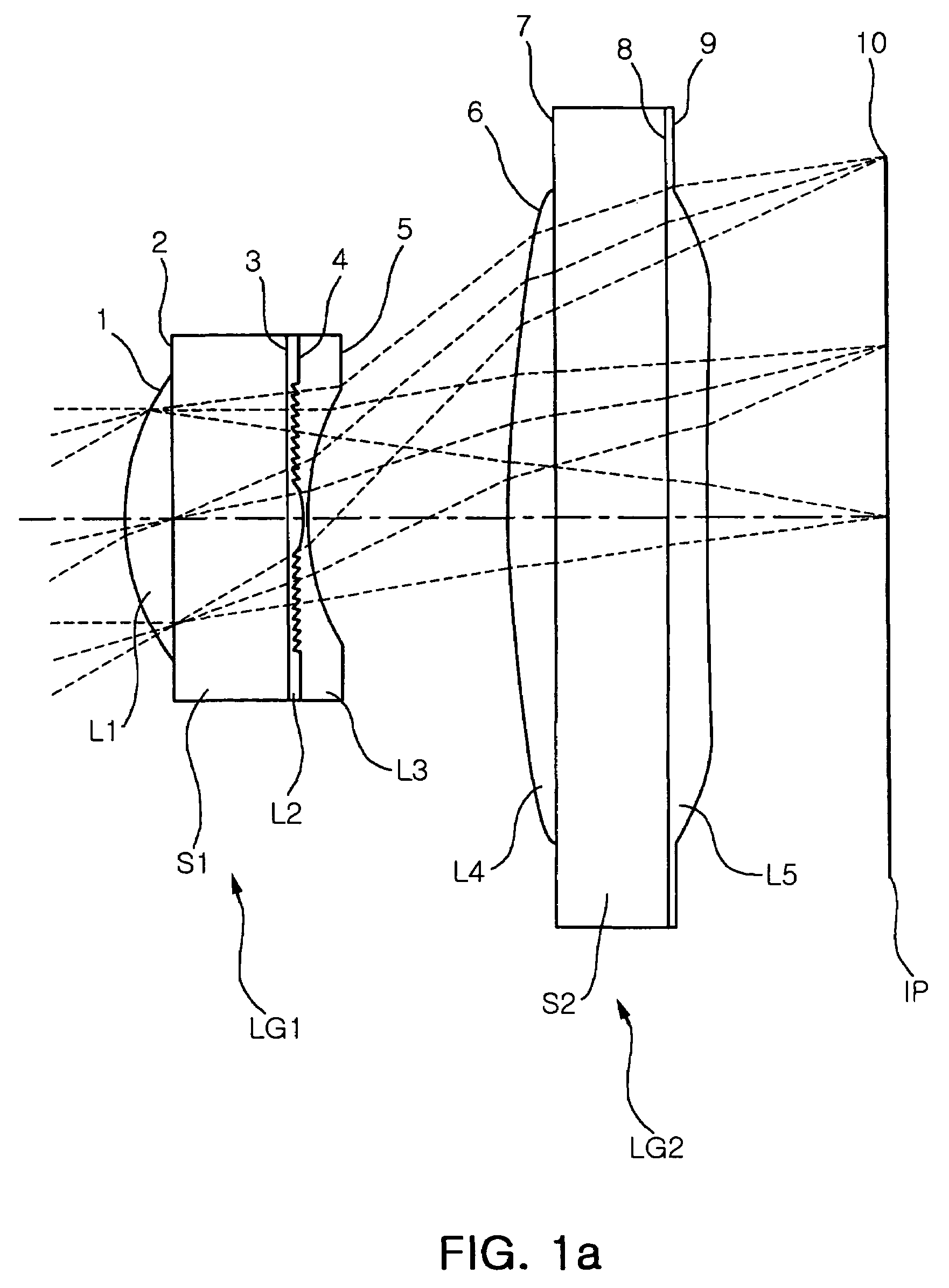
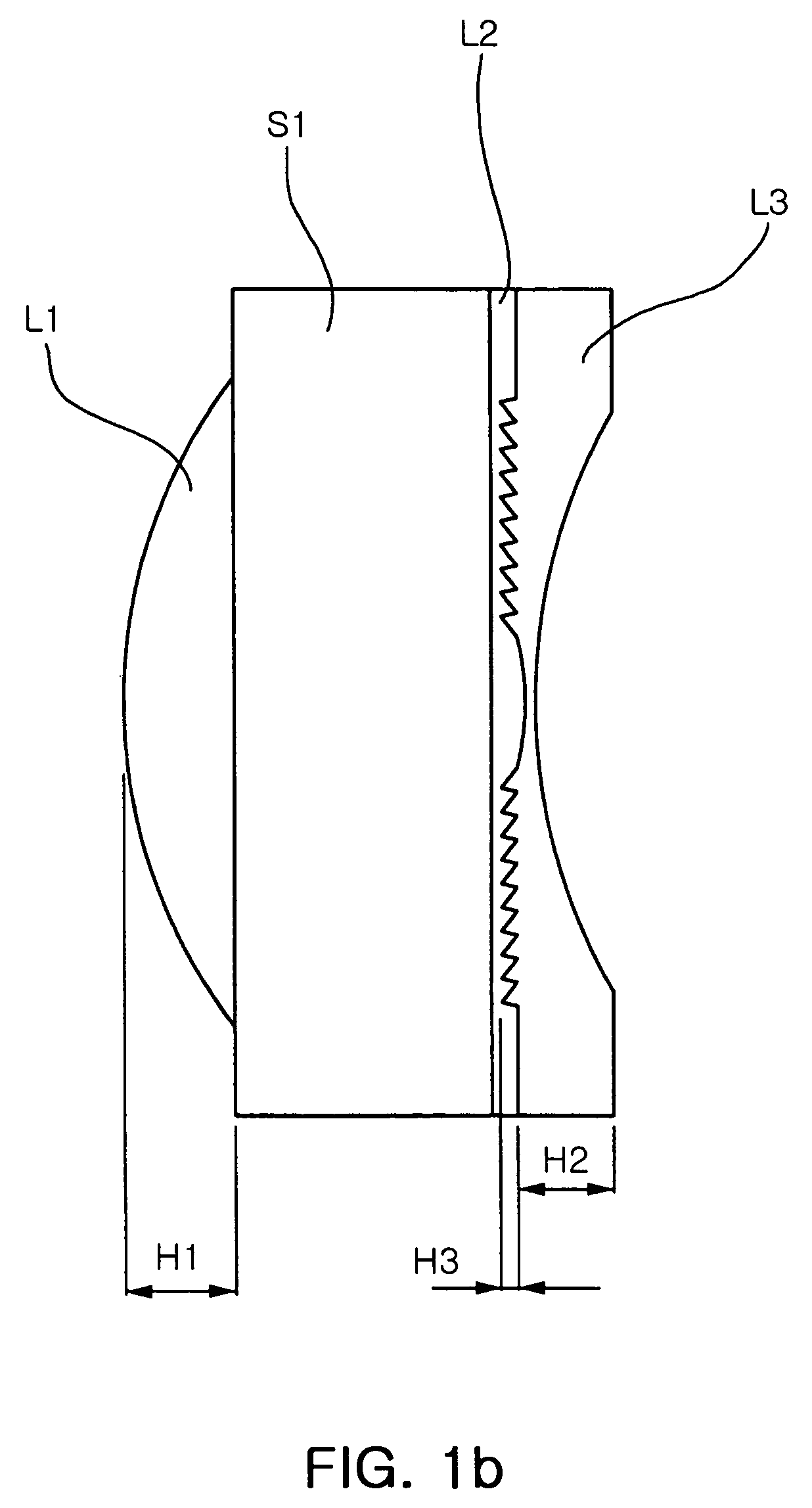
Wafer scale lens and optical system having the same
InactiveUS20060262416A1High diffraction efficiencyReducing angle of lightMountingsLensMiniaturizationOptoelectronics
Provided are wafer scale lenses having a diffraction surface as well as a refractive surface, and an optical system having the same. The wafer scale lens includes a lens substrate, a first lens element formed on the object side of the lens substrate, having a positive refractive power, a second lens element formed on the image side of the lens substrate, having a diffraction surface, and a third lens element deposited on the diffraction surface of the second lens element, having a negative refractive power. The invention allows miniaturized optical system and efficient calibration of angle of view, reducing the angle of light incident onto the diffractive surface, thereby increasing diffraction efficiency and eliminating high order diffraction light to improve picture quality.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
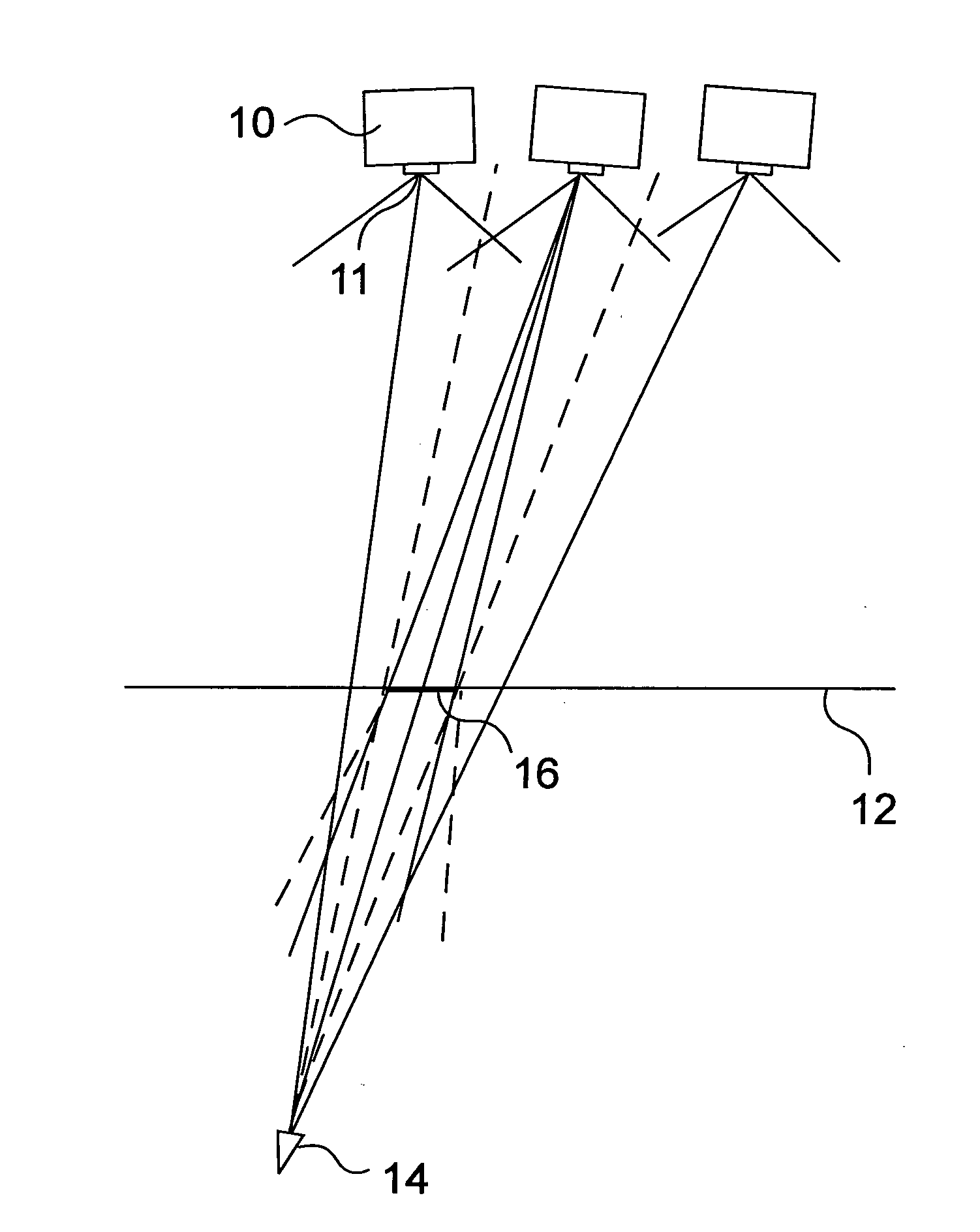
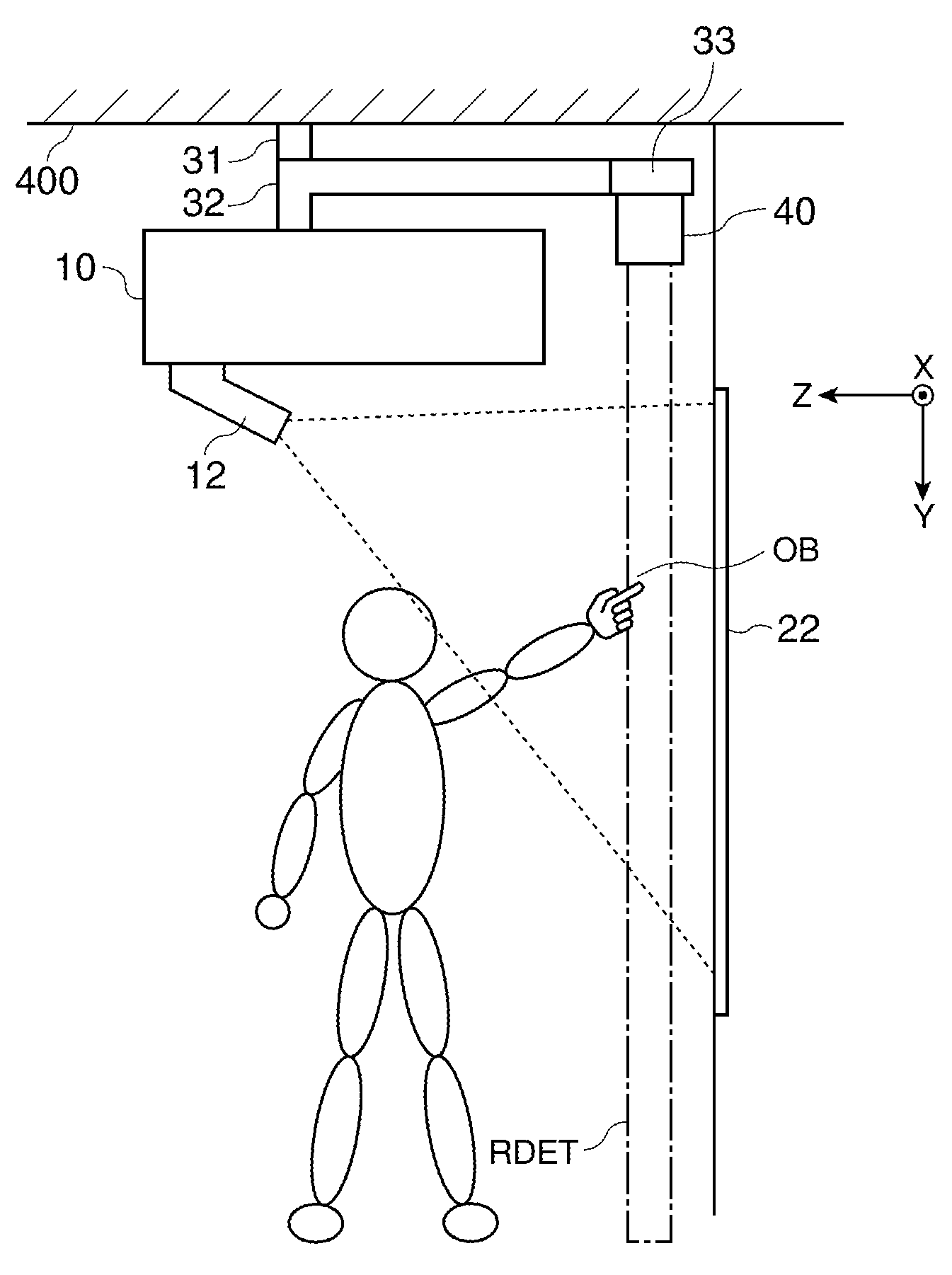
Method And Apparatus For Displaying 3D Images
ActiveUS20120127320A1Less complexEfficient calibrationProjectorsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDiffusionComputer graphics (images)
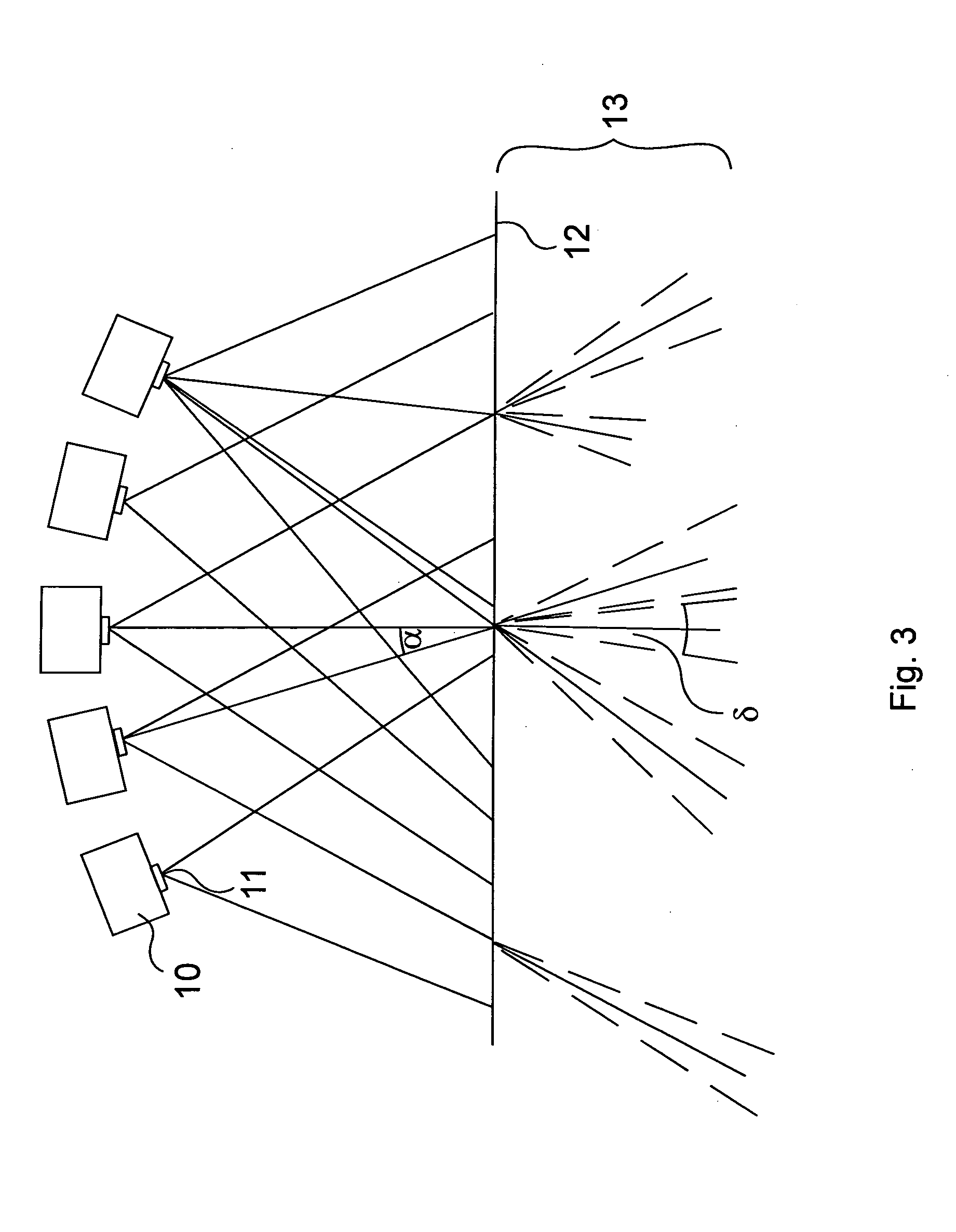
A method and an apparatus for displaying 3D images are disclosed. 2D images are projected from multiple points to a surface with narrow diffusion characteristics, thus it is possible to get a 3D light field with arbitrary angular dependence. According to the invention, the projectors (10) do not target particular screen (12) points. The projectors (10) are directed to the screen (12) with no special positioning, however from the bunch of light beams present, pertaining to the large number of pixels in the projected images, it is possible to select and define a pixel-wise precise 3D light-field through a calibration process. A novel calibration method and device are also described for calibrating 3D display systems, the device being equipped with proper image sensor(s) and a control system.
Owner:BALOGH
Three-dimensional target devices, assemblies and methods for calibrating an endoscopic camera
The present disclosure relates to calibration target devices, assemblies and methods for use with imaging systems, such as a stereoscopic endoscope. A calibration assembly includes: a target surface extends in three dimensions with calibration markers and a body with an interface that engages an endoscope so the markers are within the field of view. A first calibration marker extends along a first plane of the target surface and a second marker extends along a second plane of the target surface. The planes are different and asymmetric relative to the field of view as seen through the endoscope. Three-dimensional targets, in particular, enable endoscopic calibration using a single image (or pair of images for a stereoscopic endoscope) to reduce the calibration process complexity, calibration time and chance of error as well as allow the efficient calibration of cameras at different focus positions.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
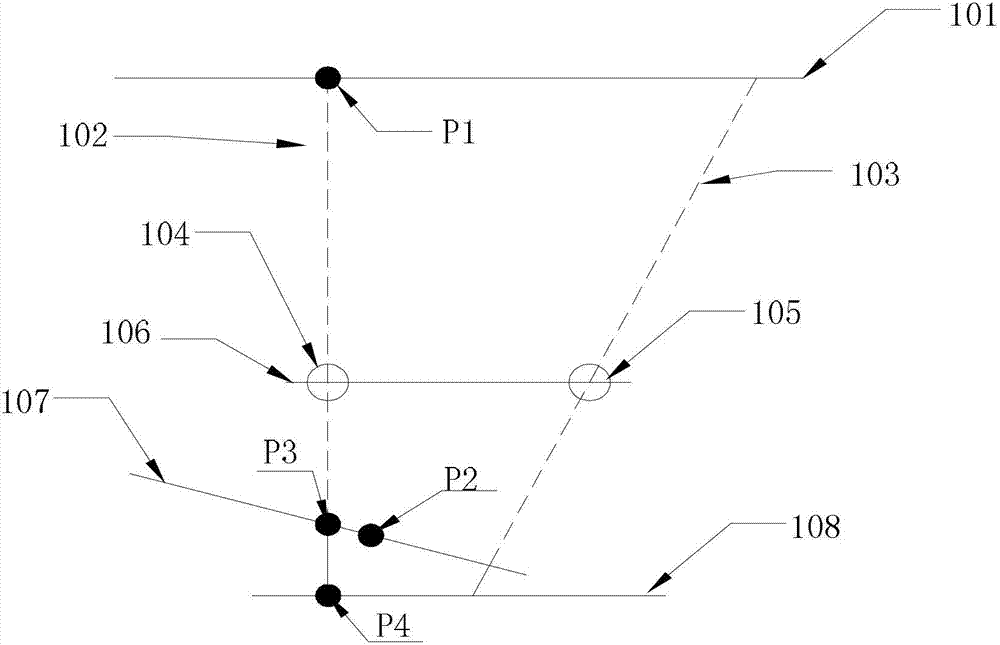
Calibrating apparatus and method
ActiveUS20100079412A1Precise positioningImprove precisionInput/output processes for data processingImaging processingReference line
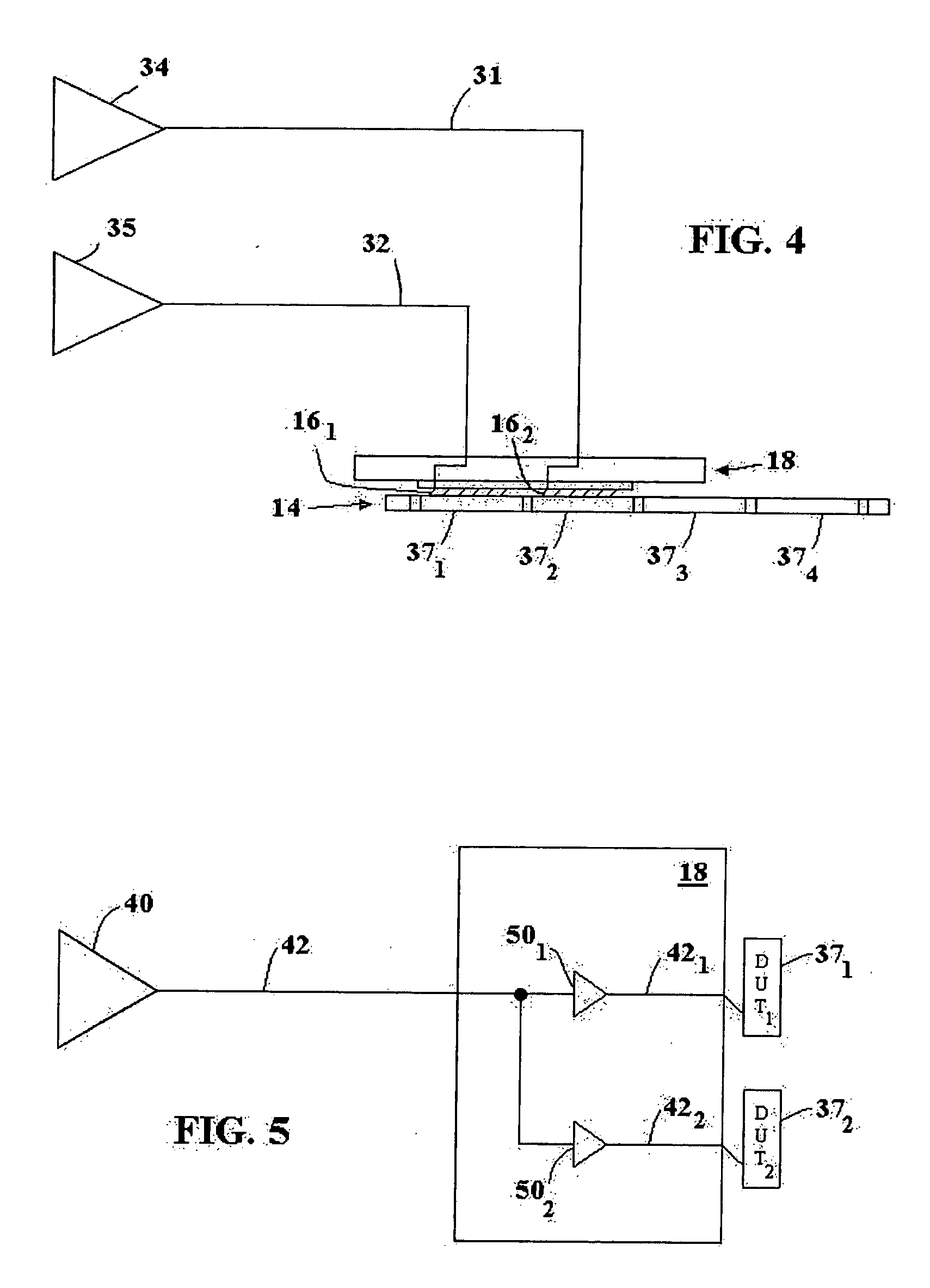
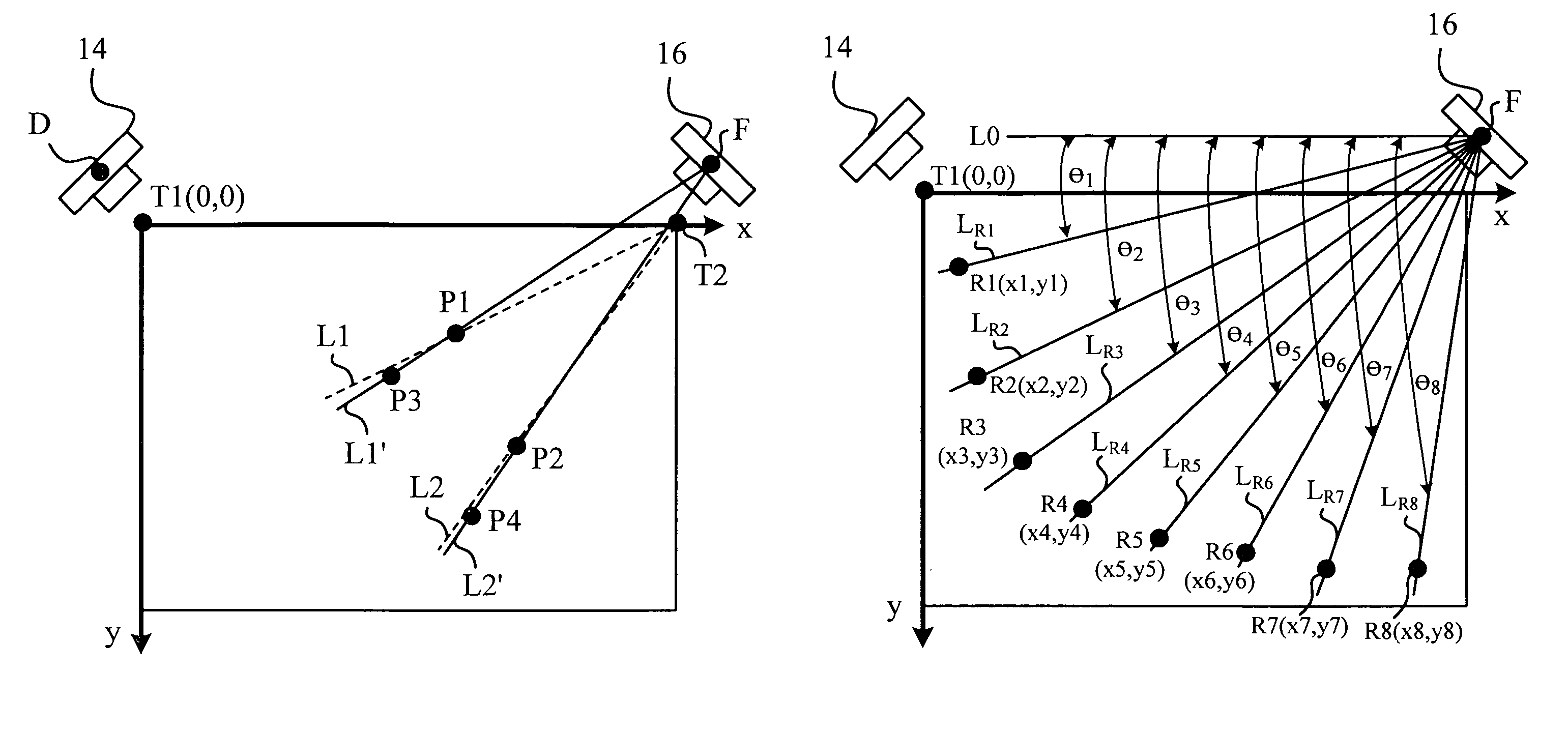
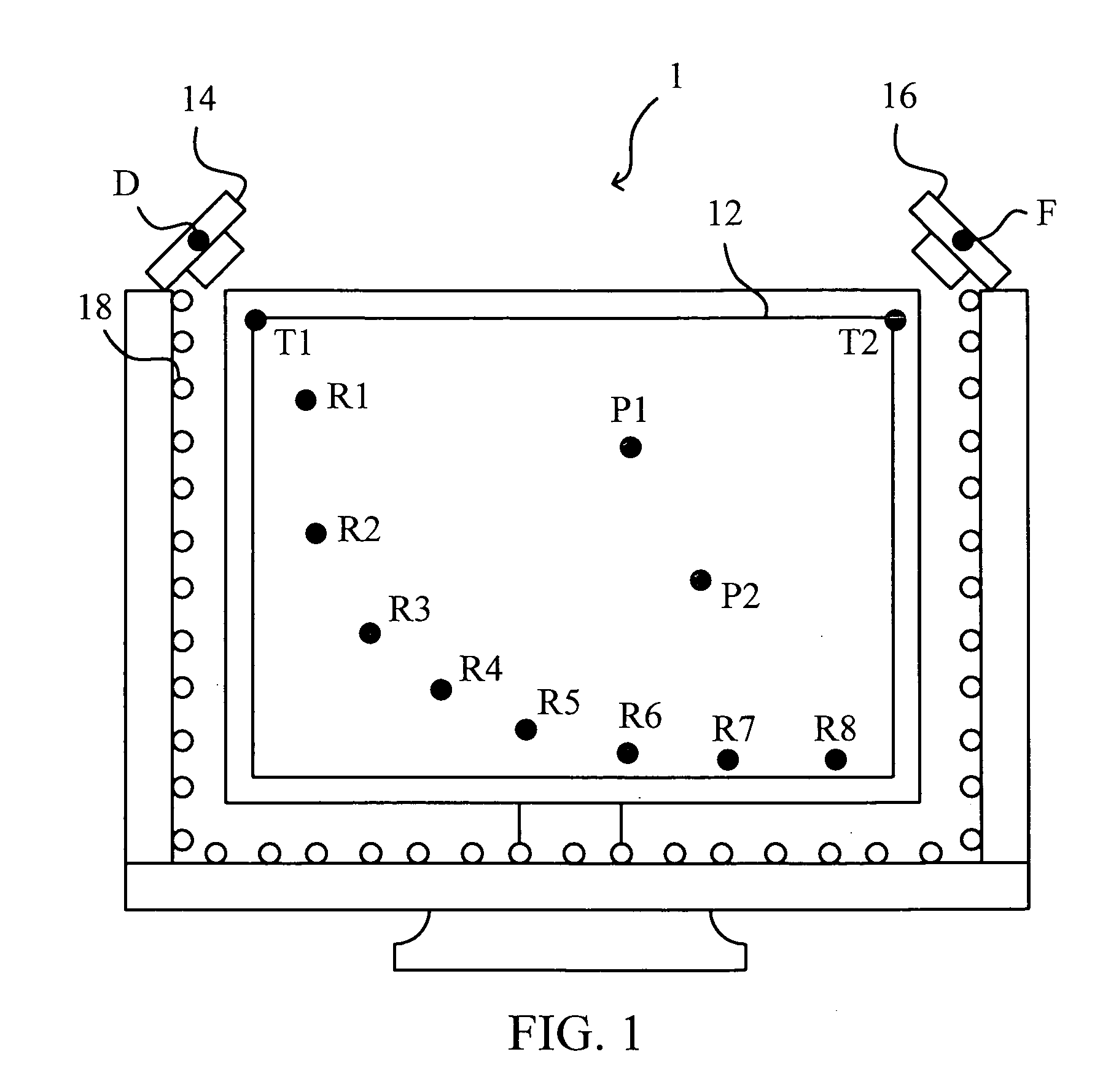
A calibrating apparatus for an image processing apparatus is disclosed. The calibrating apparatus comprises a first operating module and a second operating module. The first operating module determines a third indicating point and a fourth indicating point according to a first indicating point, a second indicating point, and a specific point, and determines a calibration point (i.e. the predetermined position of a sensor) according to a first line through the first indicating point and third indicating point and a second line through the second indicating point and fourth indicating point. The second operating module forms reference lines according to reference points and the calibration point, forms reference angles according to the reference lines and a parallel line, generates reference coordinates of the reference points in an image and generates a calibration function according to the reference coordinates of the reference points and the reference angles.
Owner:QUANTA COMPUTER INC
System and method for image based control using inline sensors
InactiveUS20070139734A1Promote sharingImprove image qualityDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImage basedComputer graphics (images)
Disclosed are a system and method are directed to efficient image based color calibration and improving color consistency performance, and more particularly to the use of continuous or dynamic calibration performed during printing and enabling adjustment on a page by page basis.
Owner:XEROX CORP
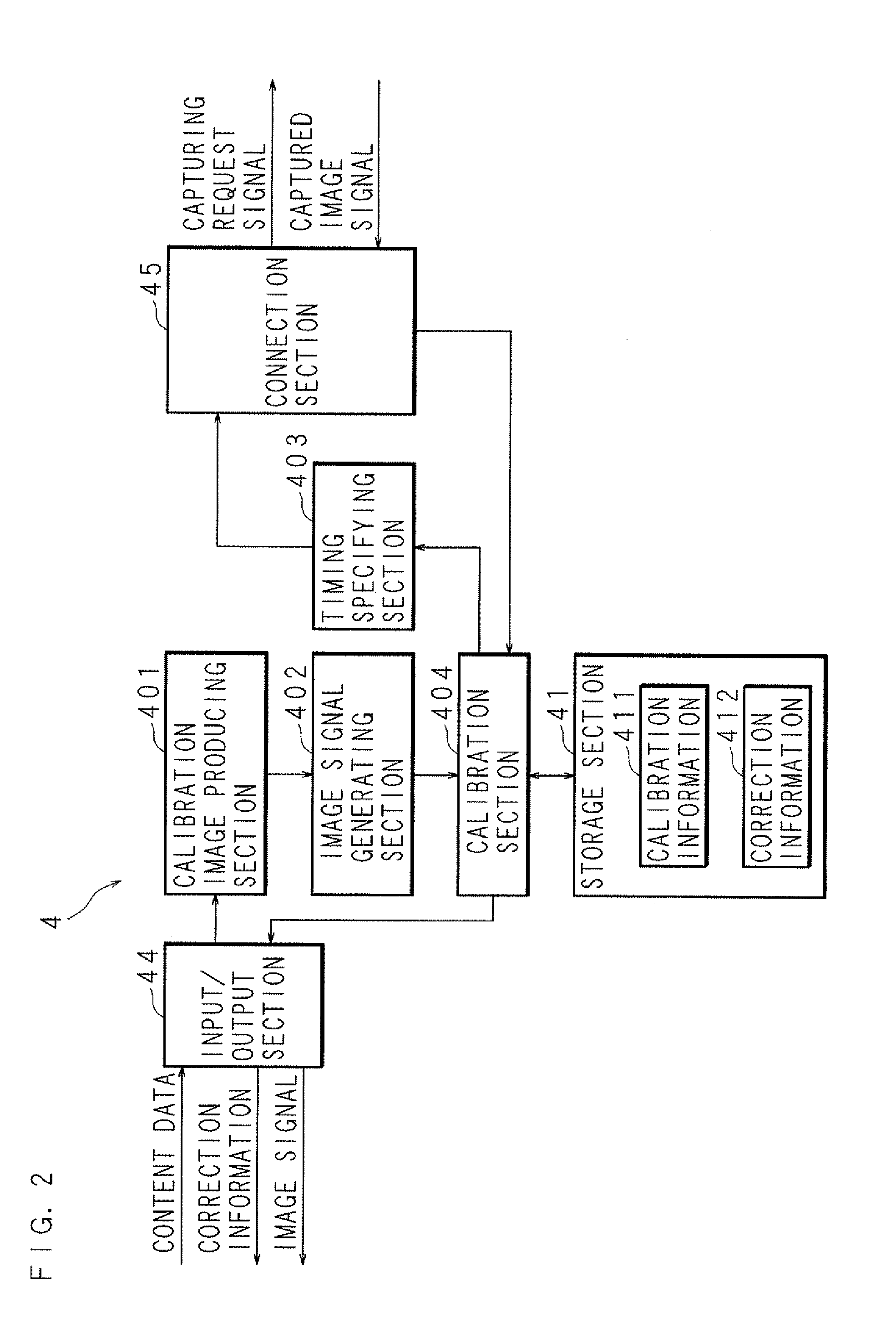
Display system and computer-readable medium
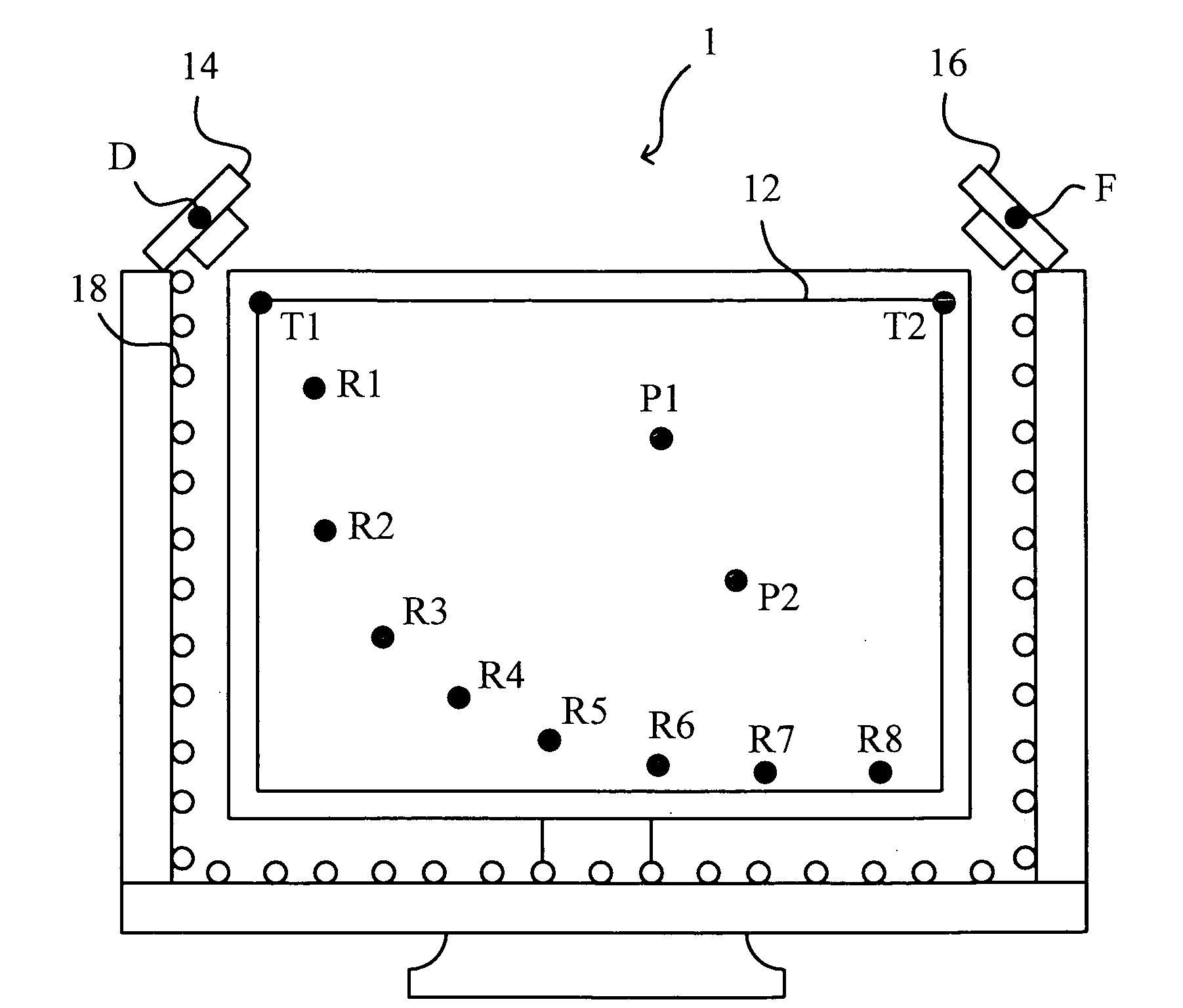
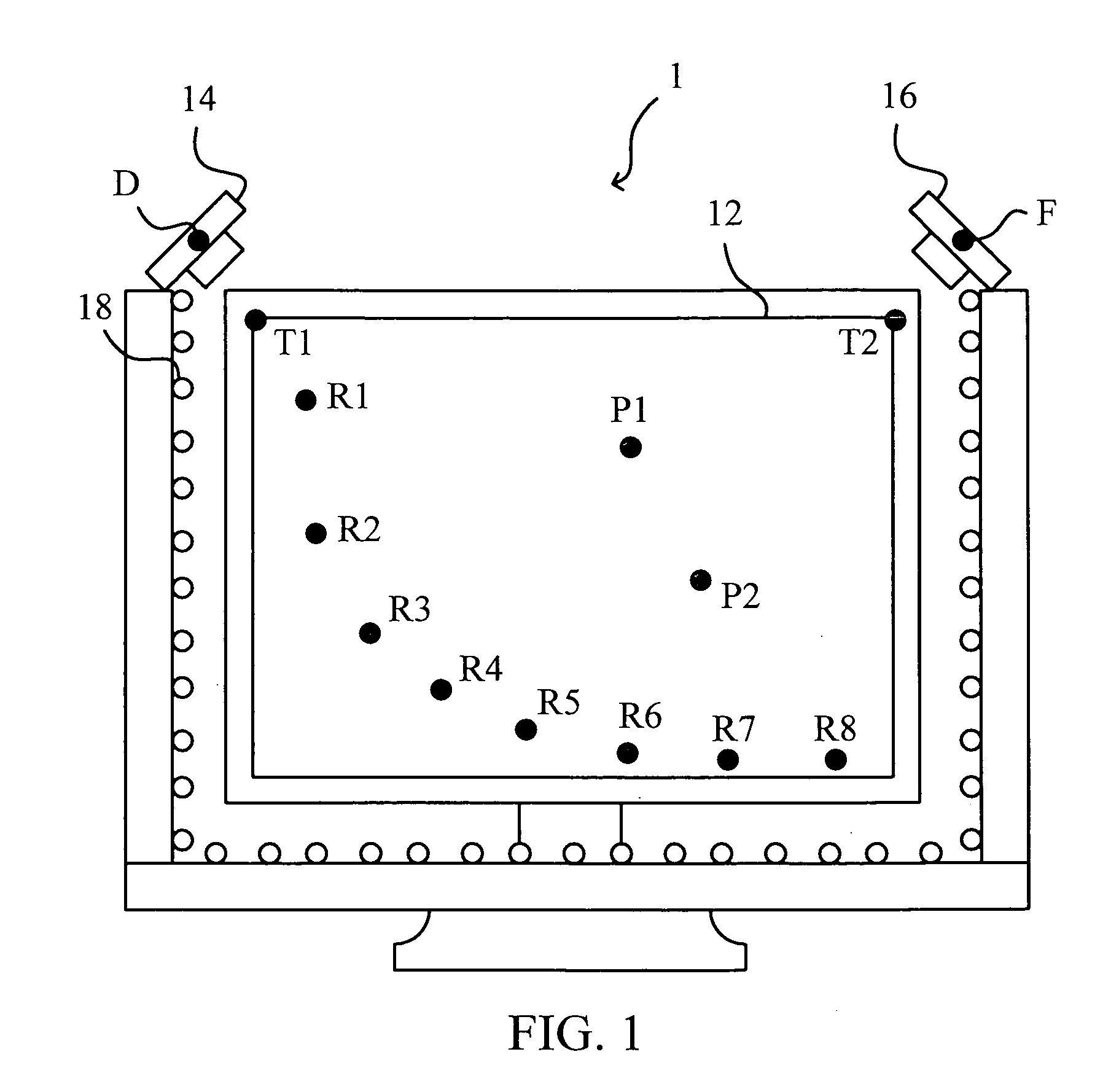
ActiveUS20130147860A1Efficient calibrationLow costCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingComputer graphics (images)Radiology
The present invention provides a display system capable of efficiently calibrating image content even when the image is displayed and thereby capable of reducing the time and cost required for calibration, and also provides a computer-readable recording medium. The control device thereof processes an image to be displayed on a display section beforehand so as to be usable for calibration. While the image is actually being displayed on the display section, the control device captures an image displayed on the display section using a capturing device at the timing at which a calibration image is displayed, compares the luminance or color in the calibration image with the luminance or color in the image obtained by capturing the calibration image, and creates correction information for correcting an image signal to be output to the display section on the basis of the result of the comparison.
Owner:SHARP KK
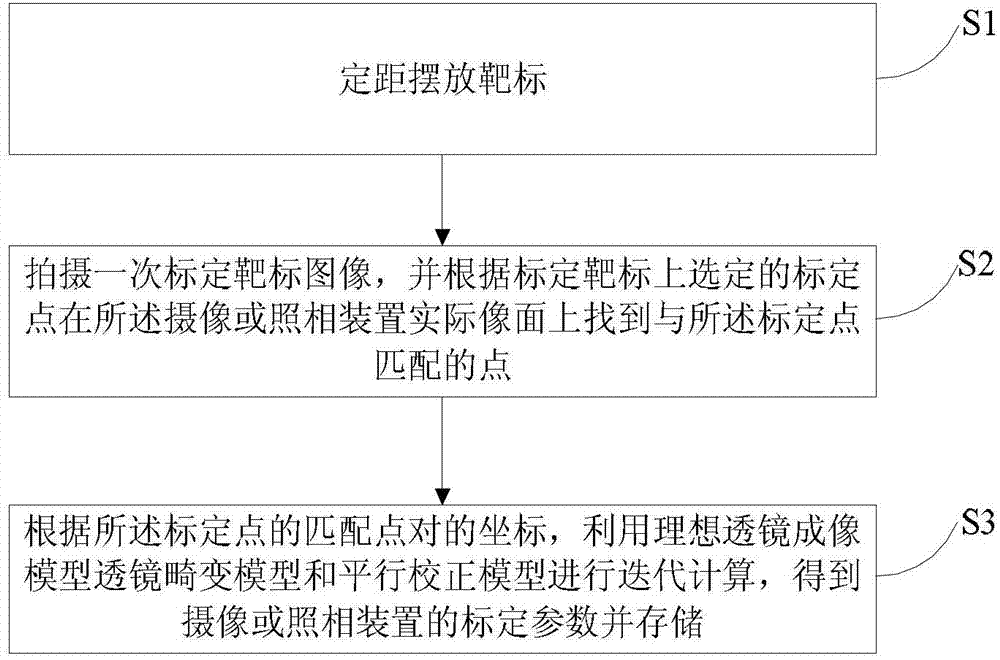
Method for calibrating camera shooting or photographing device
The invention discloses a method for calibrating a camera shooting or photographing device, and belongs to the technical field of measurements. The method comprises the following steps of: presetting a position relationship between a calibration target and the camera shooting or photographing device; performing iterative computations according to coordinates of a preselected calibration point on the calibration target and a matching point of the calibration point on an actual image plane of the camera shooting or photographing device by utilizing an ideal lens imaging model, a lens distortion model and a collimation model; and calibrating the parameters of the camera shooting or photographing device. By the method, the position relationship between the calibration target and the camera shooting or photographing device is preset, the displacement calculation process of the optical center of the lens of the camera shooting or photographing device relative to the origin of coordinates of the plane of the calibration target is simplified, so that the whole calibration process is high-efficiency; and moreover, by the method, the problem that the parameters of the device are calibrated when the focusing is inaccurate can be effectively solved, the target pattern is only required to be photographed at one time, and the calibration efficiency is improved. In addition, the three-dimensional distance under the out-of-focus condition can be effectively measured.
Owner:SHENZHEN TAISHAN SPORTS TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for displaying 3D images
ActiveUS9383587B2Less complexEfficient calibrationDiffusing elementsSteroscopic systemsDiffusionComputer graphics (images)
A method and an apparatus for displaying 3D images are disclosed. 2D images are projected from multiple points to a surface with narrow diffusion characteristics, thus it is possible to get a 3D light field with arbitrary angular dependence. According to the invention, the projectors (10) do not target particular screen (12) points. The projectors (10) are directed to the screen (12) with no special positioning, however from the bunch of light beams present, pertaining to the large number of pixels in the projected images, it is possible to select and define a pixel-wise precise 3D light-field through a calibration process. A novel calibration method and device are also described for calibrating 3D display systems, the device being equipped with proper image sensor(s) and a control system.
Owner:BALOGH
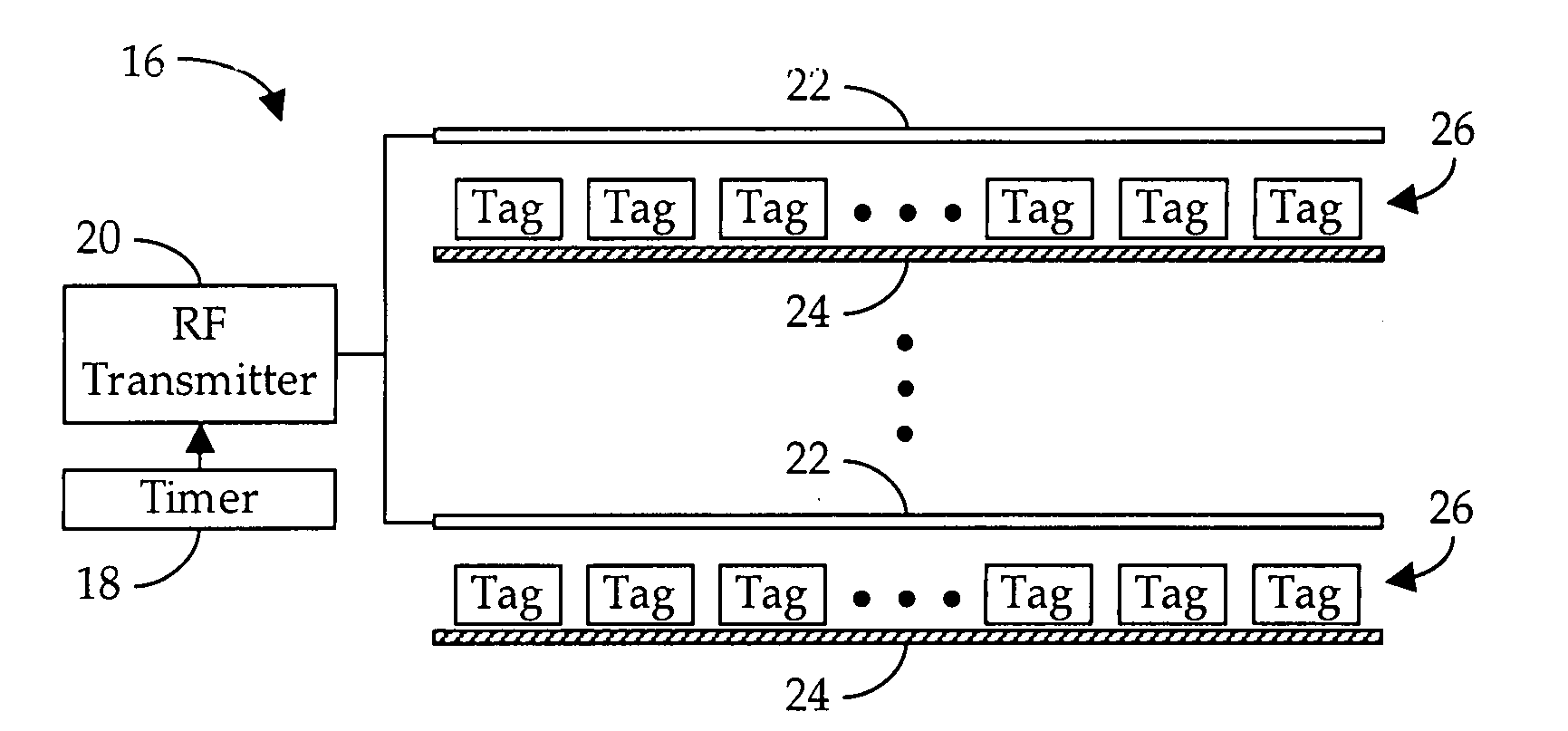
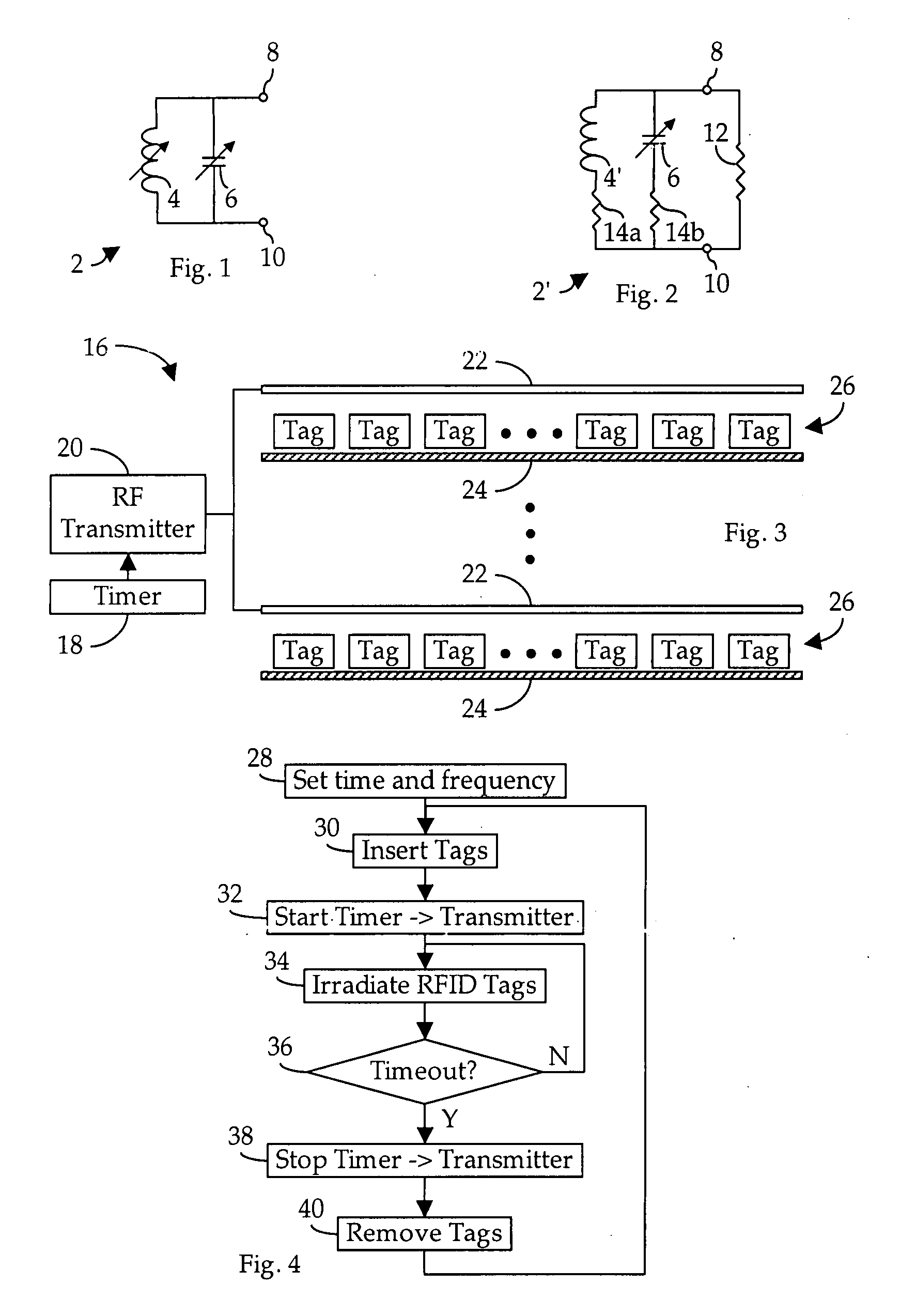
Method and apparatus for bulk calibrating RFID tags
InactiveUS20090160648A1Efficient calibrationRecord carriers used with machinesBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalSelf-tuningSufficient time
A method and apparatus for bulk calibrating self-tuning radio frequency identification (“RFID”) tags wherein a plurality of the tags are simultaneously exposed to a broadcast RF signal of sufficient strength and for a sufficient period of time to assure self-calibration of all tags.
Owner:RFMICRON
Digital measurement system
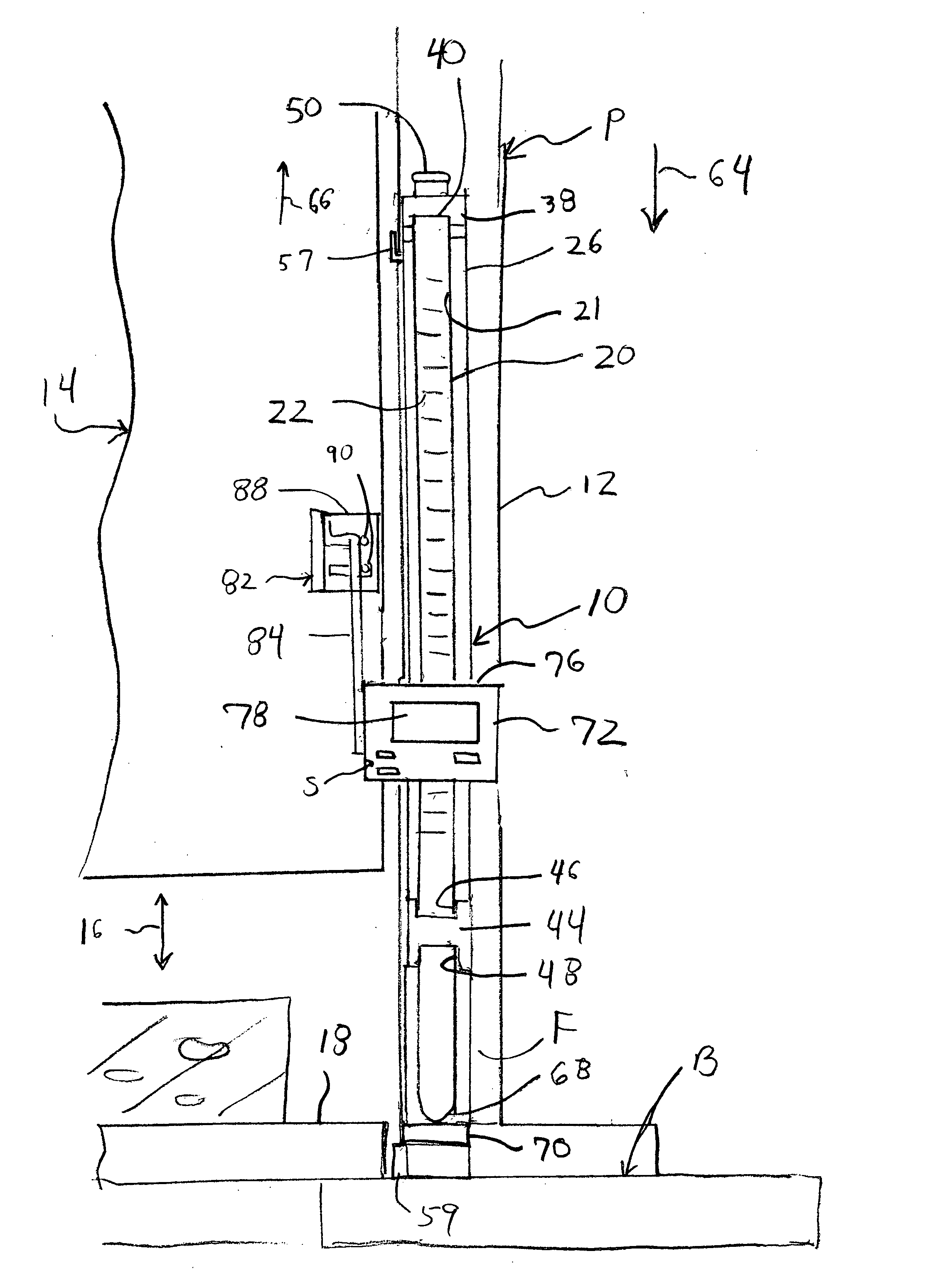
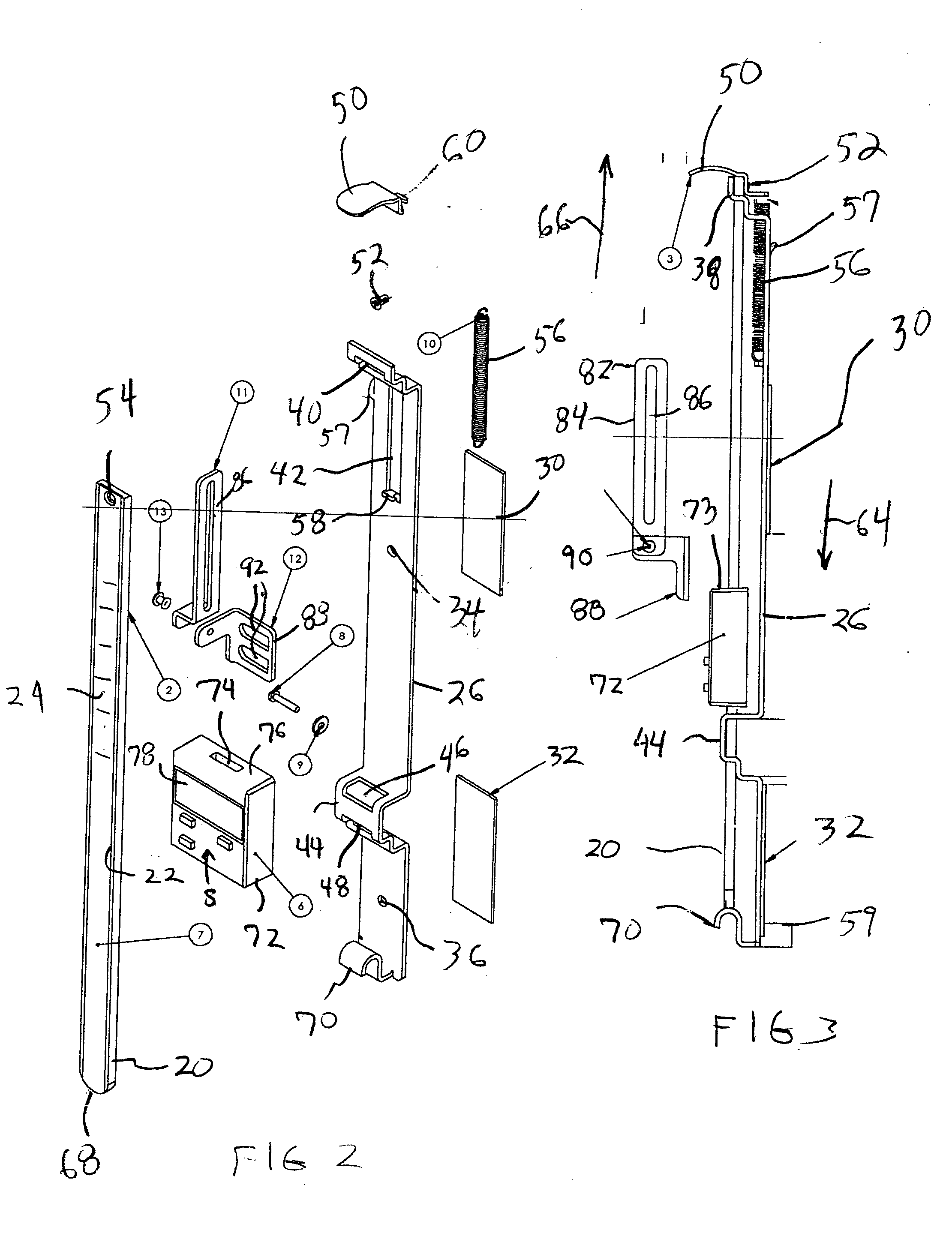
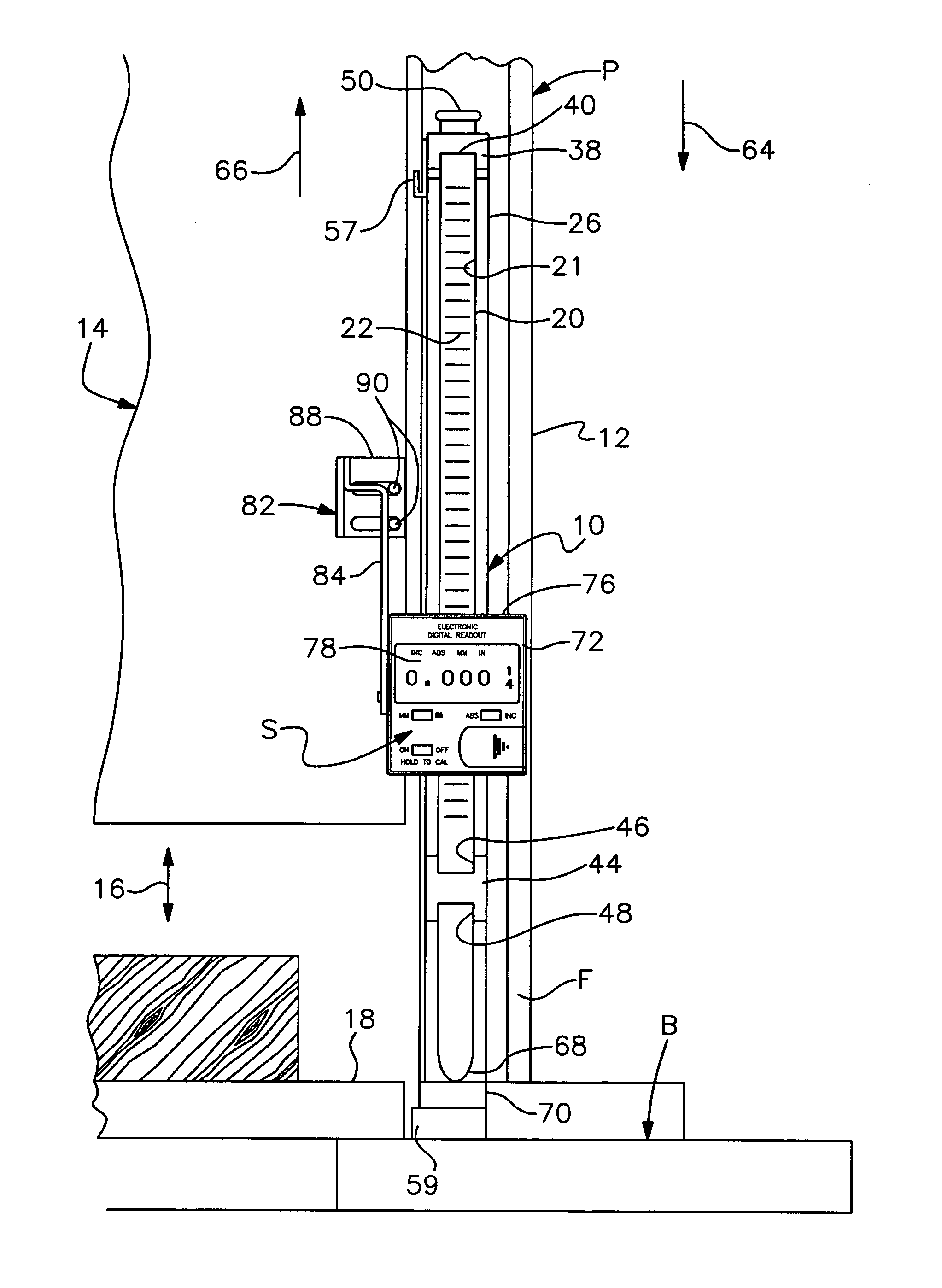
ActiveUS20050005468A1Highly accurate and calibrated measurementAccurate measurementDrilling/boring measurement devicesMeasurement/indication equipmentsEngineeringHead parts
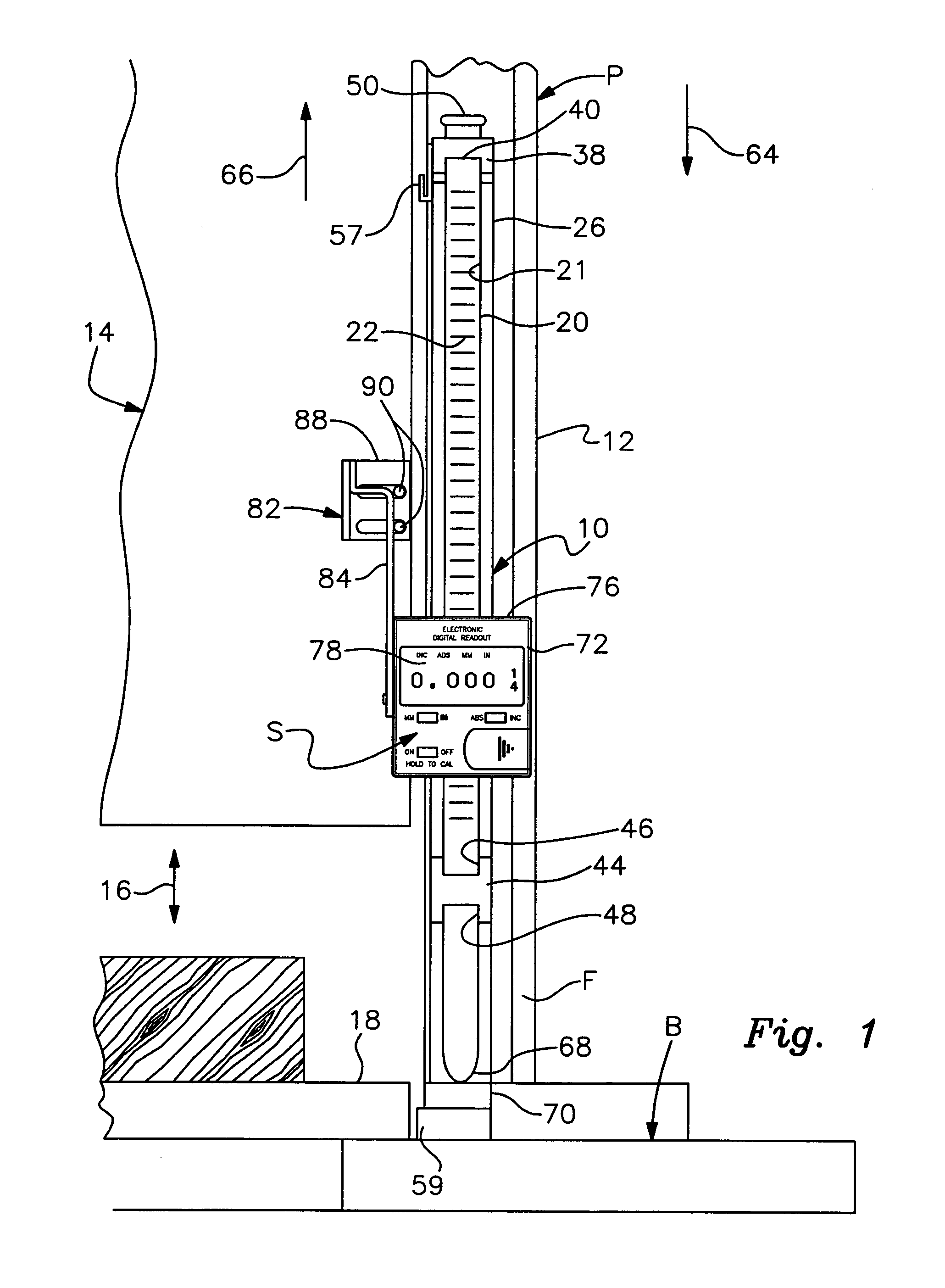
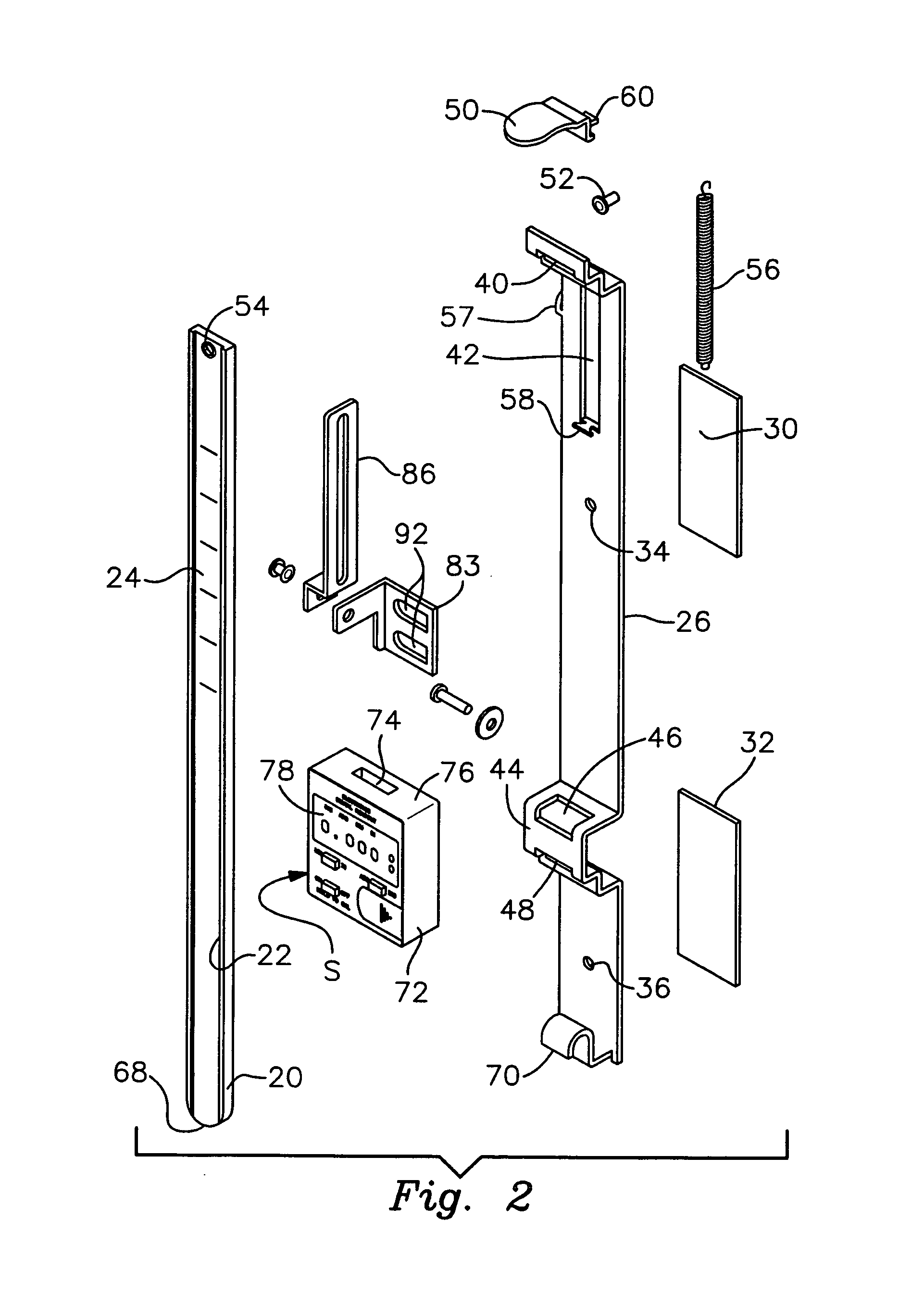
A digital measurement system is provided for an apparatus including first and second parts that are positionally adjustable relative to one another, the first part having a base surface and the second part being selectively adjustable toward and away from the base surface. The measurement system includes an elongate reference element mounted for longitudinal movement on the first part such that a first end of the reference element is positionable to be substantially even with the base surface of the first part. A digital reader head is attachable to the second part. The reader head is operable is operably engaged with and moveable along the reference element for measuring relative movement of the reader head along the reference element. The readout further includes a digital display for indicating a measurement corresponding to the relative movement of the reader head along the reference element.
Owner:WIXEY BARRY
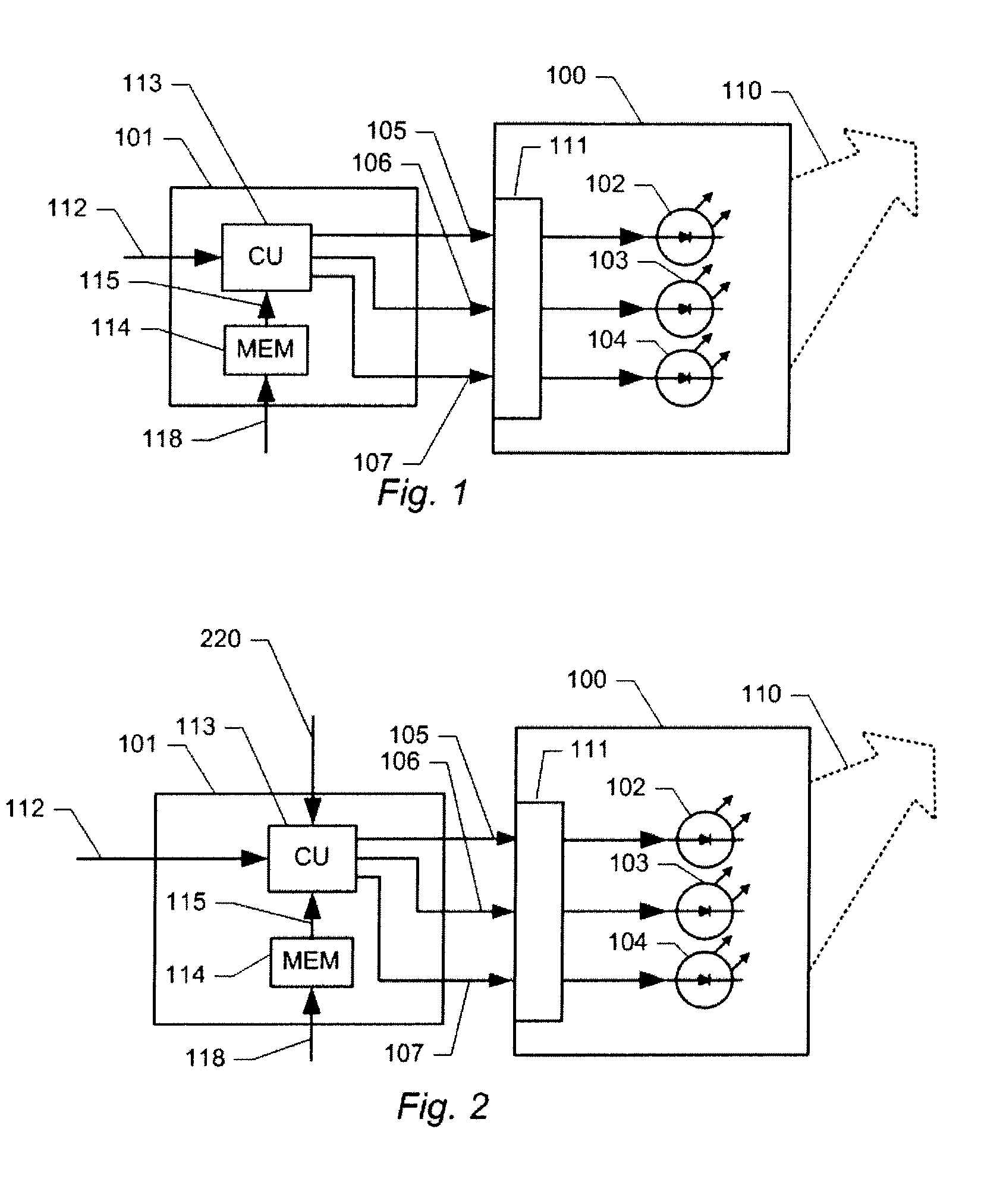
Method and apparatus for controlling a variable-colour light source
ActiveUS7893633B2Accurate colour controlAccurately reproduce desired colourElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesBiological activationBrightness perception
Disclosed is a control device for controlling a variable-color light source, the variable-color light source comprising a plurality of individually controllable color light sources. The control device comprises a control unit for generating, responsive to an input signal indicative of a color and a brightness, respective activation signals for each of the individually controllable color light sources. The control unit is configured to generate the activation signals from the input signal and from predetermined calibration data indicative of at least one set of color values for each of the individually controllable light sources.
Owner:MARTIN PROFESSIONAL
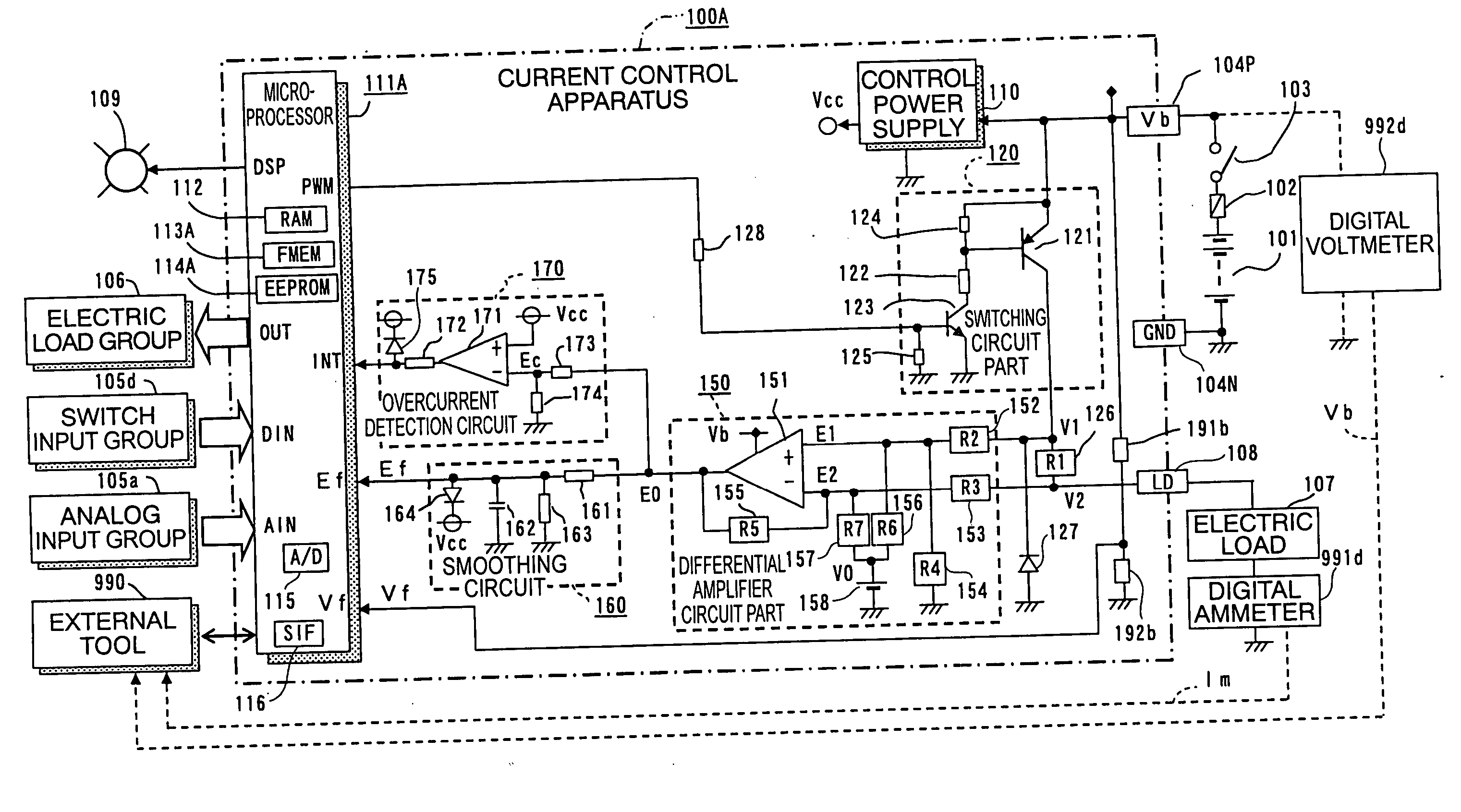
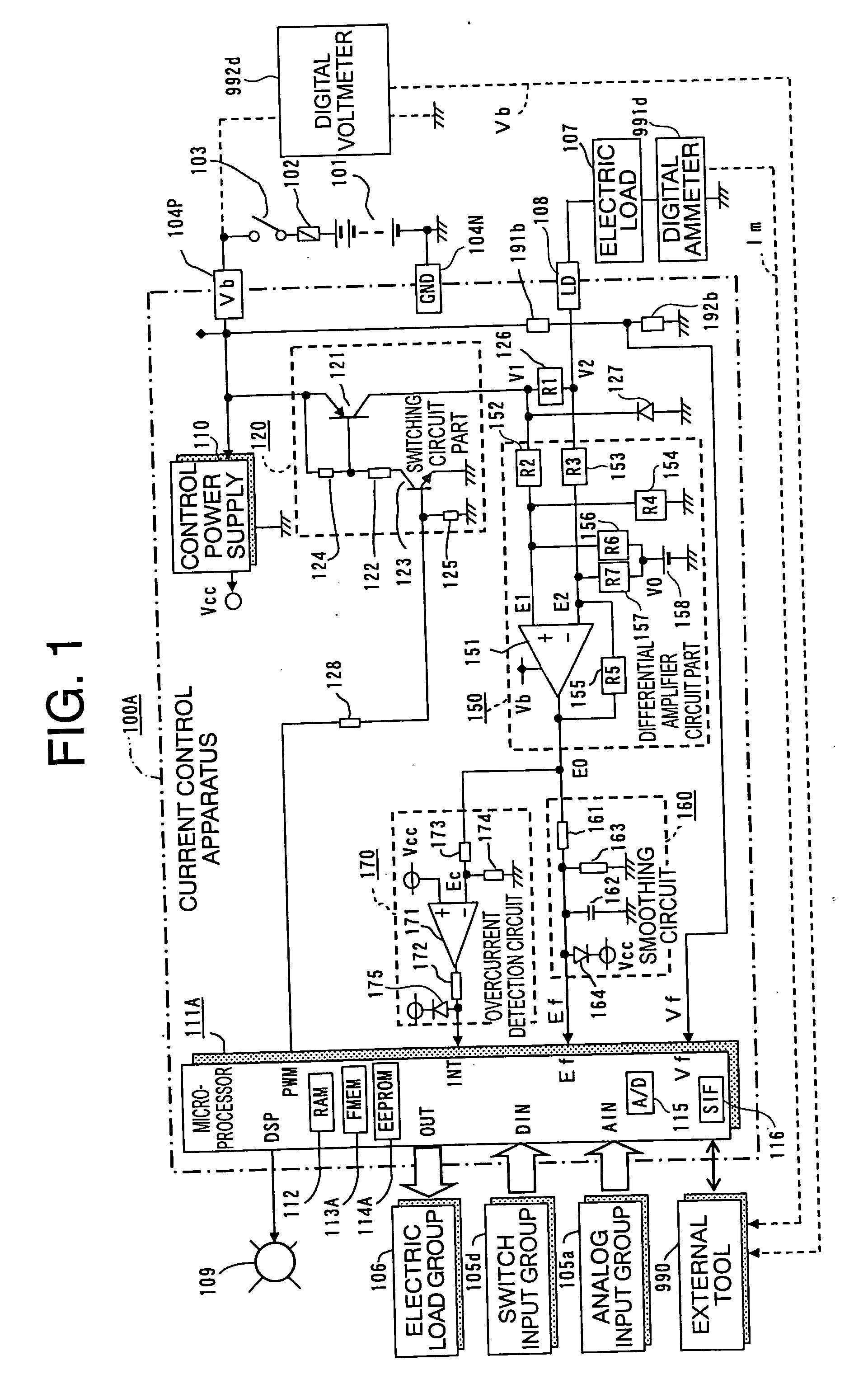
Current control apparatus for electric load
ActiveUS20060197508A1Easy to measureEfficient calibrationTransistorAC motor controlElectric forceElectrical resistance and conductance
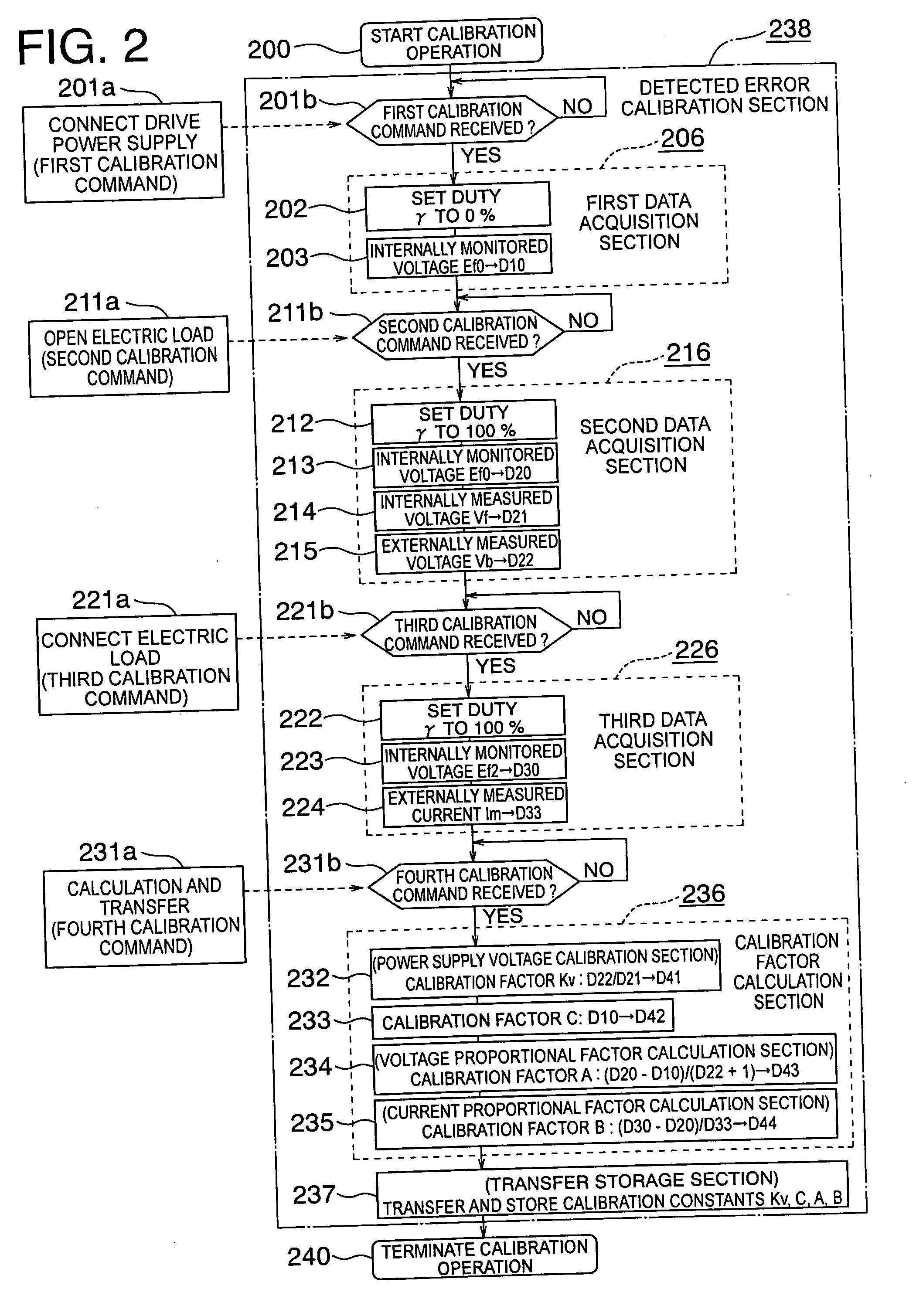
A current control apparatus for an electric load can prevent burnout at a short-circuit accident with high control precision. A switching element is interrupted by an overcurrent detection circuit upon occurrence of a load short circuit, but is transitionally limited in current by a current detection resistor. A differential amplifier amplifies a difference voltage between voltages at opposite ends of the current detection resistor to generate a monitored voltage Ef corresponding to a load current. A microprocessor controls the energization rate of the switching element so as to make an estimated load current Ime calculated from the monitored voltage Ef coincide with a target load current Is, and it calculates, upon calibration operation, calibration constants and estimates, during actual operation, a load current Ime from the monitored voltage Ef using the calibration constants.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
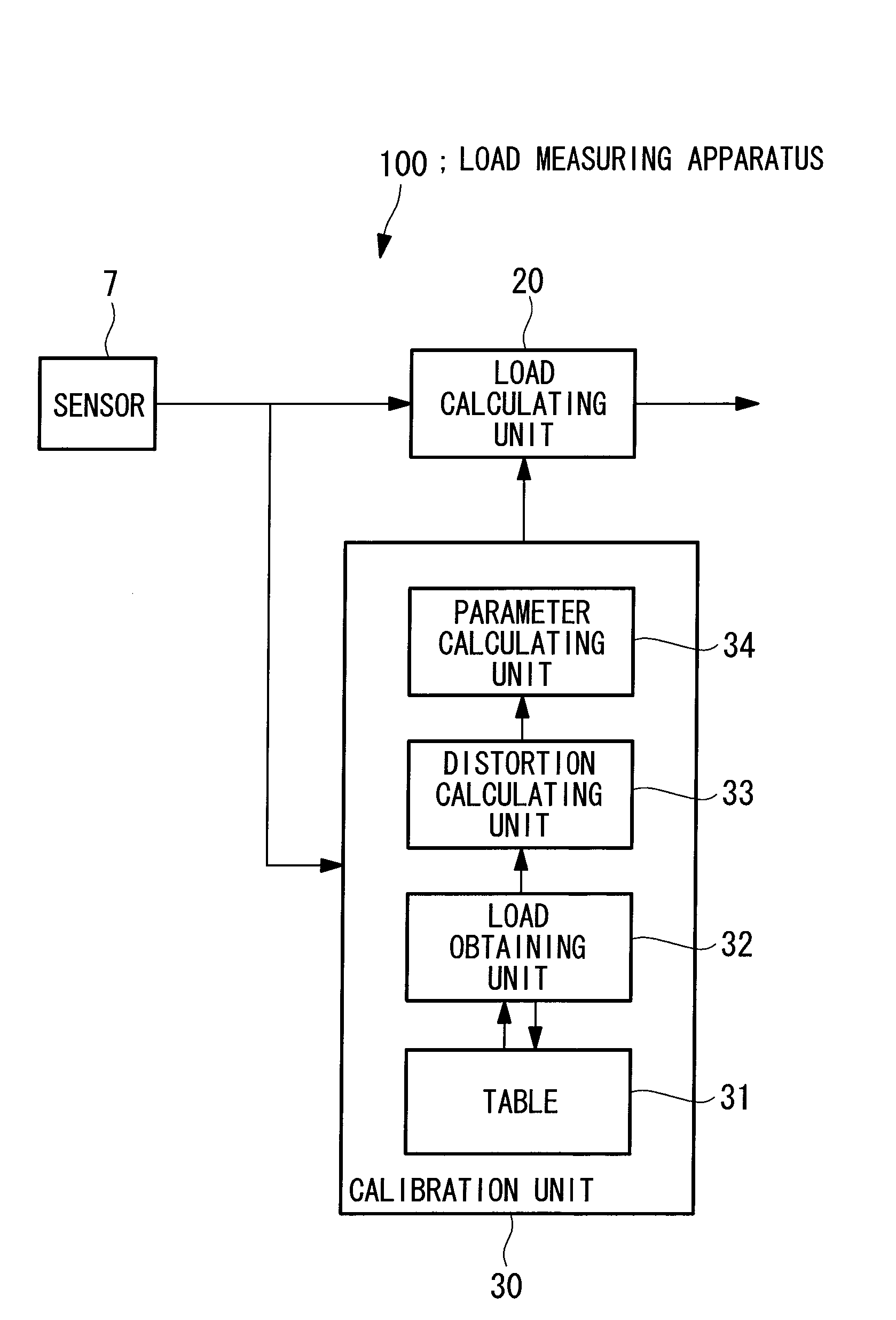
Load measuring apparatus, method, and program
ActiveUS20120035865A1Efficient calibrationImprove the situationEngine fuctionsForce measurementAerodynamic torqueTurbine blade
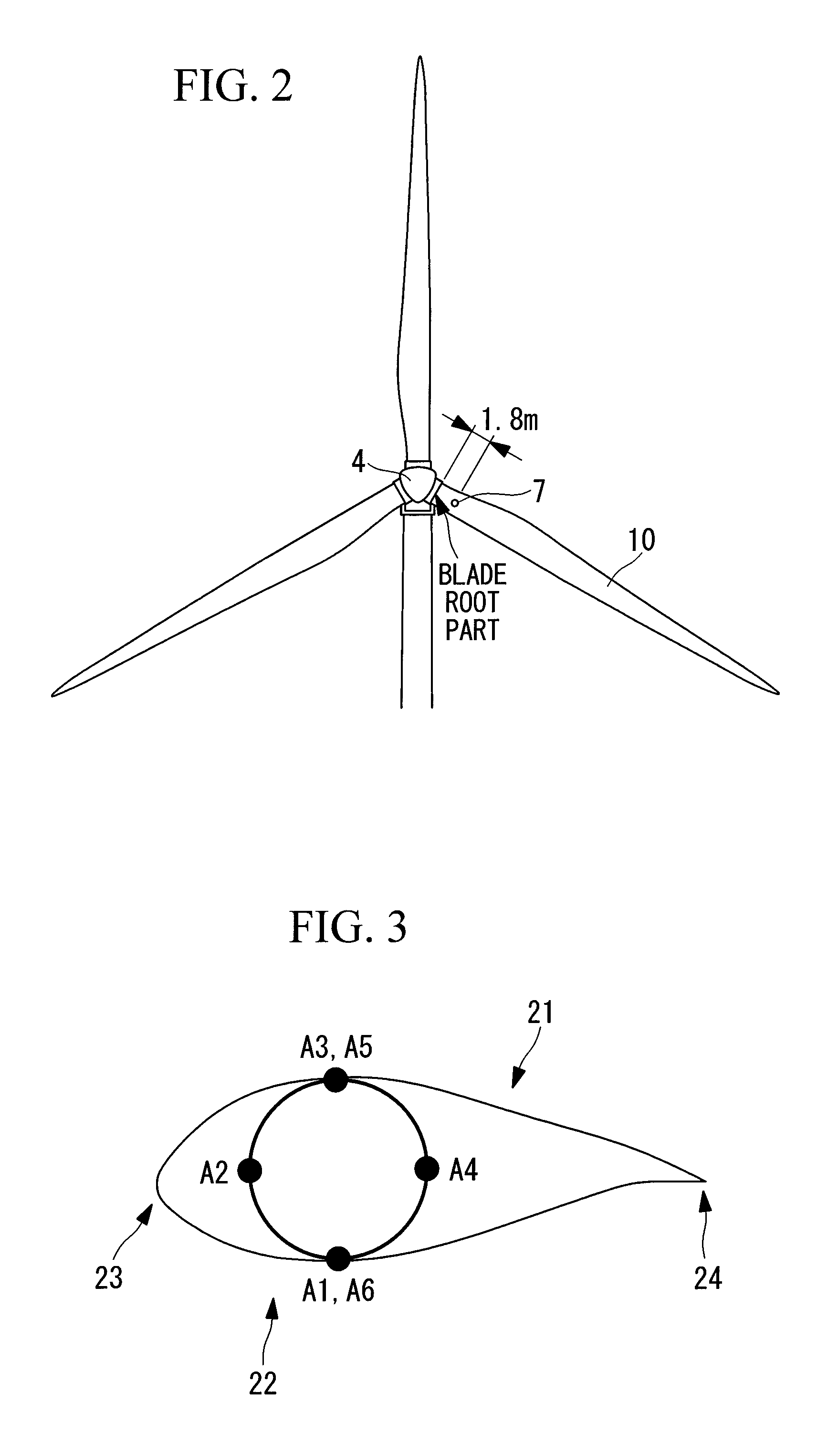
A load is based calibrate on data collected under wide observation conditions and promptly calibrate loads of a plurality of wind turbine blades. A load measuring apparatus is applied to a wind turbine in which a pitch angle of a wind turbine blade is variable. The apparatus includes a sensor for obtaining a distortion of the wind turbine blade; a load calculating unit having a function expressing a relation between the distortion of the wind turbine blade and a load on the wind turbine blade, for obtaining the load on the wind turbine blade by applying to the function the distortion based on measurement data of the sensor; and a calibration unit for calibrating the function based on the measurement data of the sensor obtained in a pitch angle range and a rotational speed range of the wind turbine blade in which a variation between maximum and minimum aerodynamic torques is equal to or less than a predetermined value.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Wafer scale lens and optical system having the same
InactiveUS7342731B2Efficient calibrationHigh diffraction efficiencyMountingsLensMiniaturizationOptoelectronics
Provided are wafer scale lenses having a diffraction surface as well as a refractive surface, and an optical system having the same. The wafer scale lens includes a lens substrate, a first lens element formed on the object side of the lens substrate, having a positive refractive power, a second lens element formed on the image side of the lens substrate, having a diffraction surface, and a third lens element deposited on the diffraction surface of the second lens element, having a negative refractive power. The invention allows miniaturized optical system and efficient calibration of angle of view, reducing the angle of light incident onto the diffractive surface, thereby increasing diffraction efficiency and eliminating high order diffraction light to improve picture quality.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Projection display system and attaching device
InactiveUS20110291990A1Easy to guaranteeEfficient calibrationMachine supportsProjectorsObject basedIrradiation
A projection display system includes: an image projection device projecting an image on a projection surface; an optical detecting device; and an attaching device, wherein the optical detecting device includes an irradiating section emitting an irradiation light toward a detection region which is set along the projection surface, a light receiving section receiving a reflected light generated as a result of the irradiation light being reflected from the object, and a detecting section detecting position information of the object based on the result of the light received by the light receiving section, and the attaching device includes a first attaching section attached to a support supporting the attaching device, a second attaching section attached to the image projection device, and a third attaching section attached to the optical detecting device.
Owner:COLUMBIA PEAK VENTURES LLC
Method and apparatus for remotely buffering test channels
InactiveUS20060049820A1Keep the delay through multiple isolation buffers constantEfficient and cost-effective systemElectrical measurement instrument detailsMarginal circuit testingTest channelTransmission gate
A system is provided to enable leakage current measurement or parametric tests to be performed with an isolation buffer provided in a channel line. Multiple such isolation buffers are used to connect a single signal channel to multiple lines. Leakage current measurement is provided by providing a buffer bypass element, such as a resistor or transmission gate, between the input and output of each buffer. The buffer bypass element can be used to calibrate buffer delay out of the test system by using TDR measurements to determine the buffer delay based on reflected pulses through the buffer bypass element. Buffer delay can likewise be calibrated out by comparing measurements of a buffered and non-buffered channel line, or by measuring a device having a known delay.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
Calibrating apparatus and method
ActiveUS8243047B2Improve precisionEasy to identifyInput/output processes for data processingImaging processingReference line
A calibrating apparatus for an image processing apparatus is disclosed. The calibrating apparatus comprises a first operating module and a second operating module. The first operating module determines a third indicating point and a fourth indicating point according to a first indicating point, a second indicating point, and a specific point, and determines a calibration point (i.e. the predetermined position of a sensor) according to a first line through the first indicating point and third indicating point and a second line through the second indicating point and fourth indicating point. The second operating module forms reference lines according to reference points and the calibration point, forms reference angles according to the reference lines and a parallel line, generates reference coordinates of the reference points in an image and generates a calibration function according to the reference coordinates of the reference points and the reference angles.
Owner:QUANTA COMPUTER INC
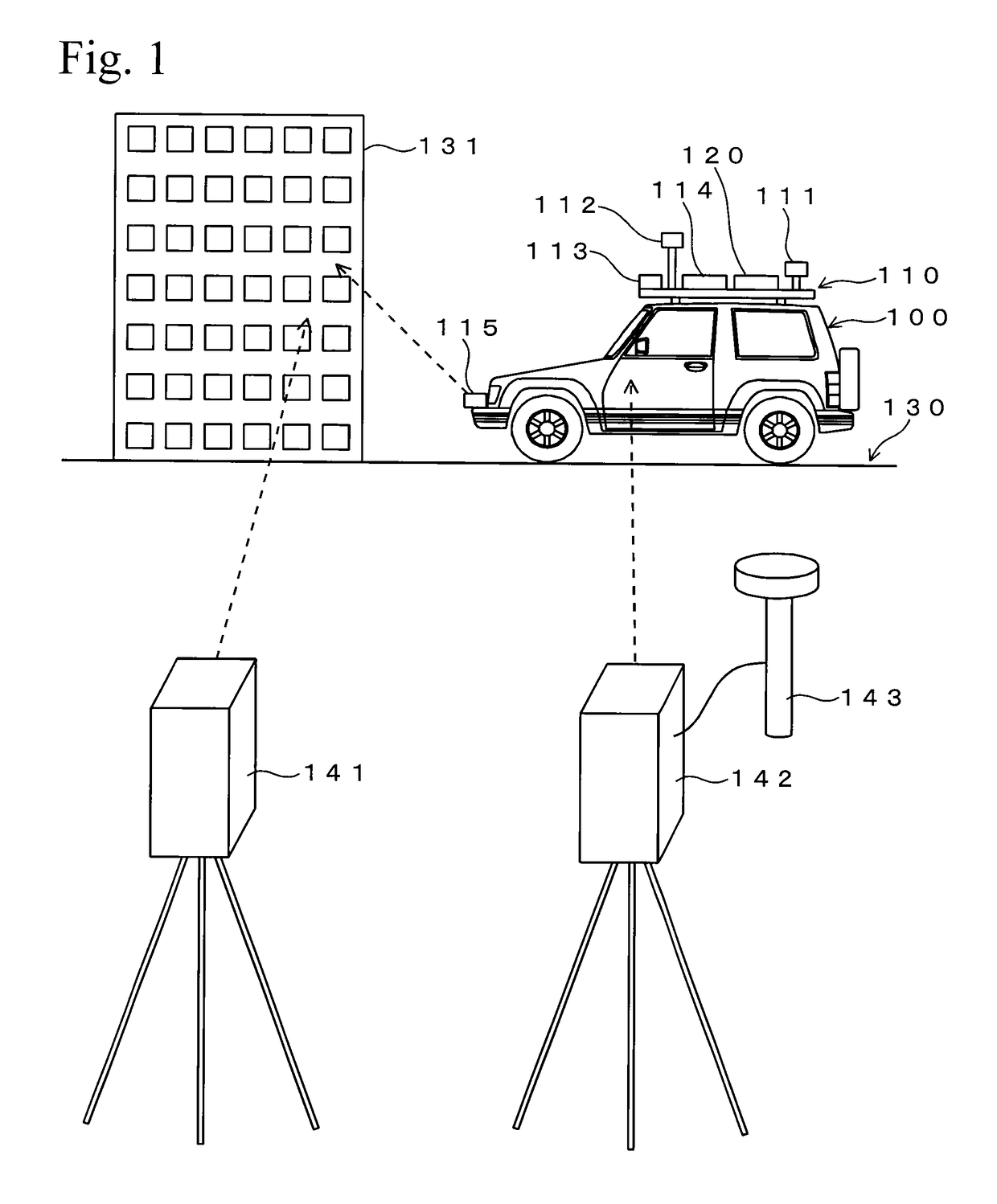
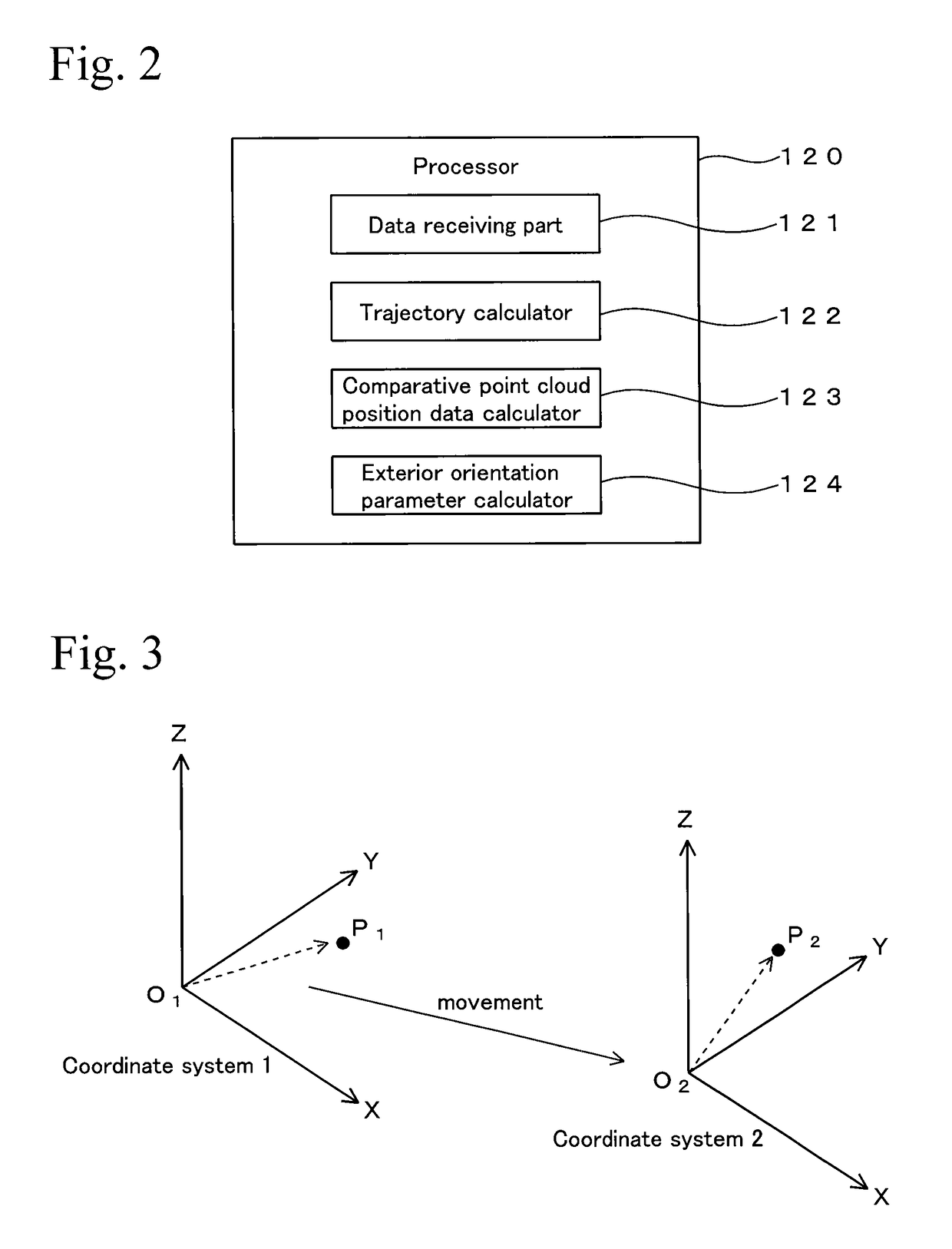
Point cloud position data processing device, point cloud position data processing system, point cloud position data processing method, and program therefor
ActiveUS20160063717A1Efficient executionEfficient calibrationImage enhancementImage analysisData processing systemPoint cloud
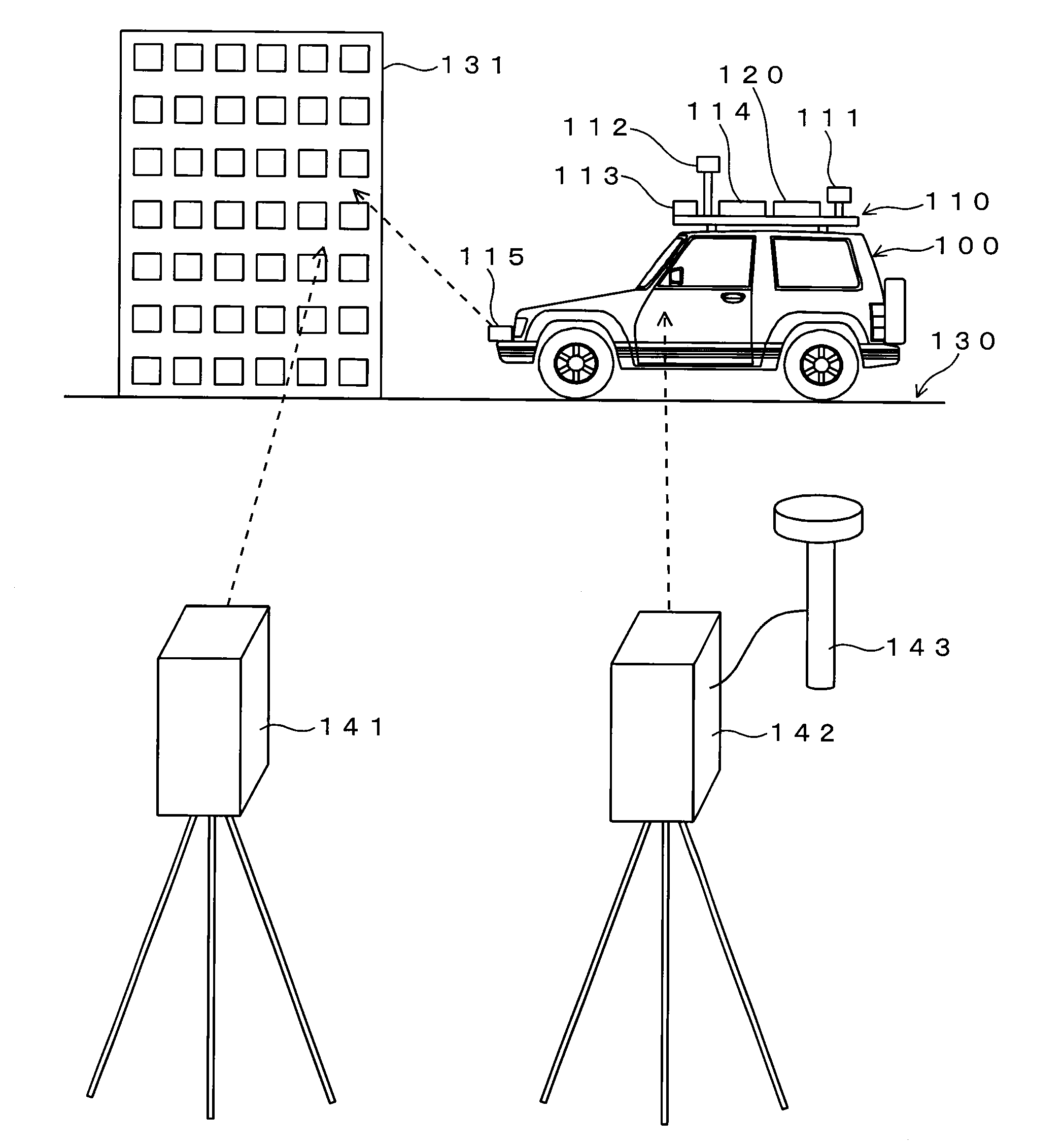
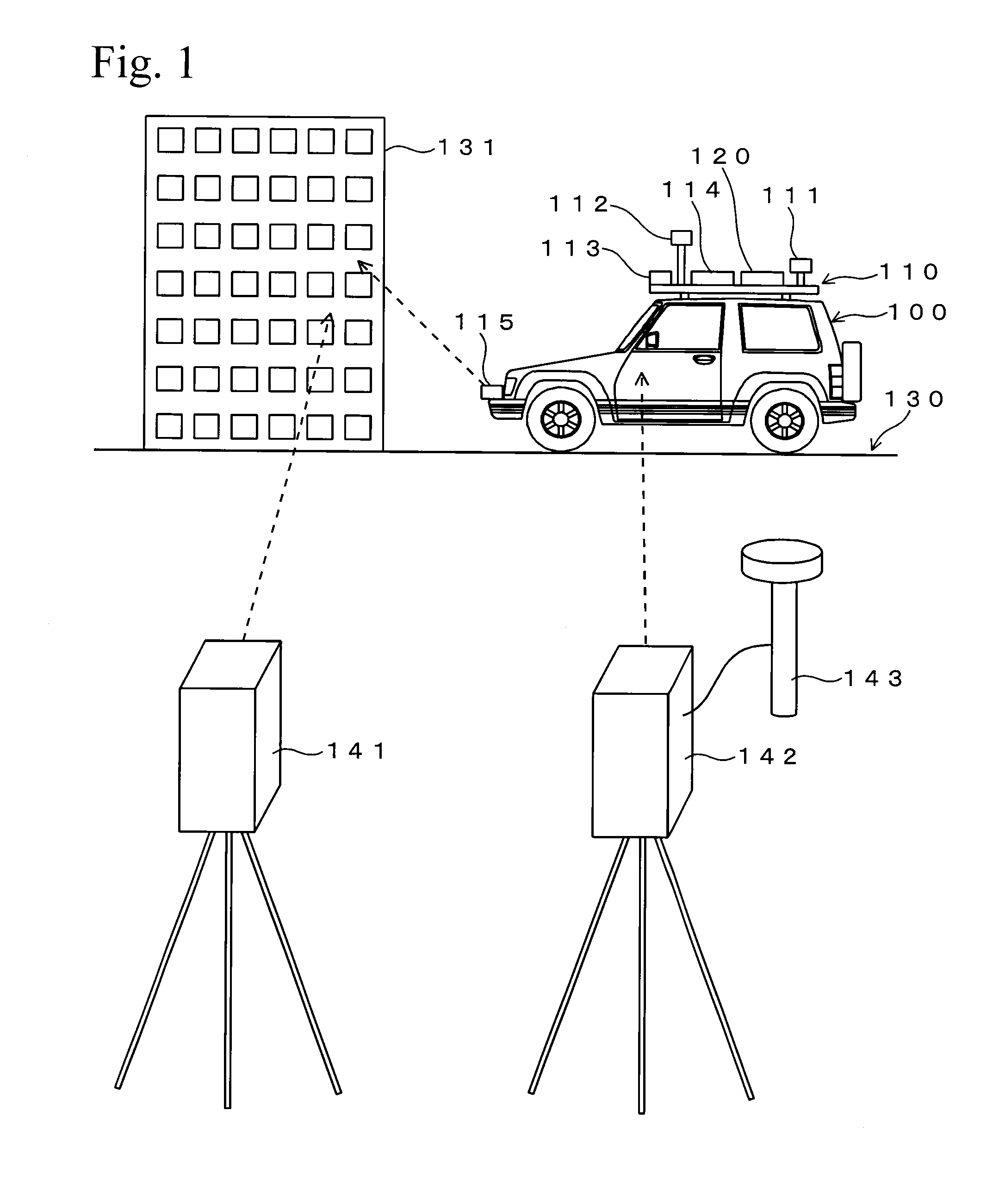
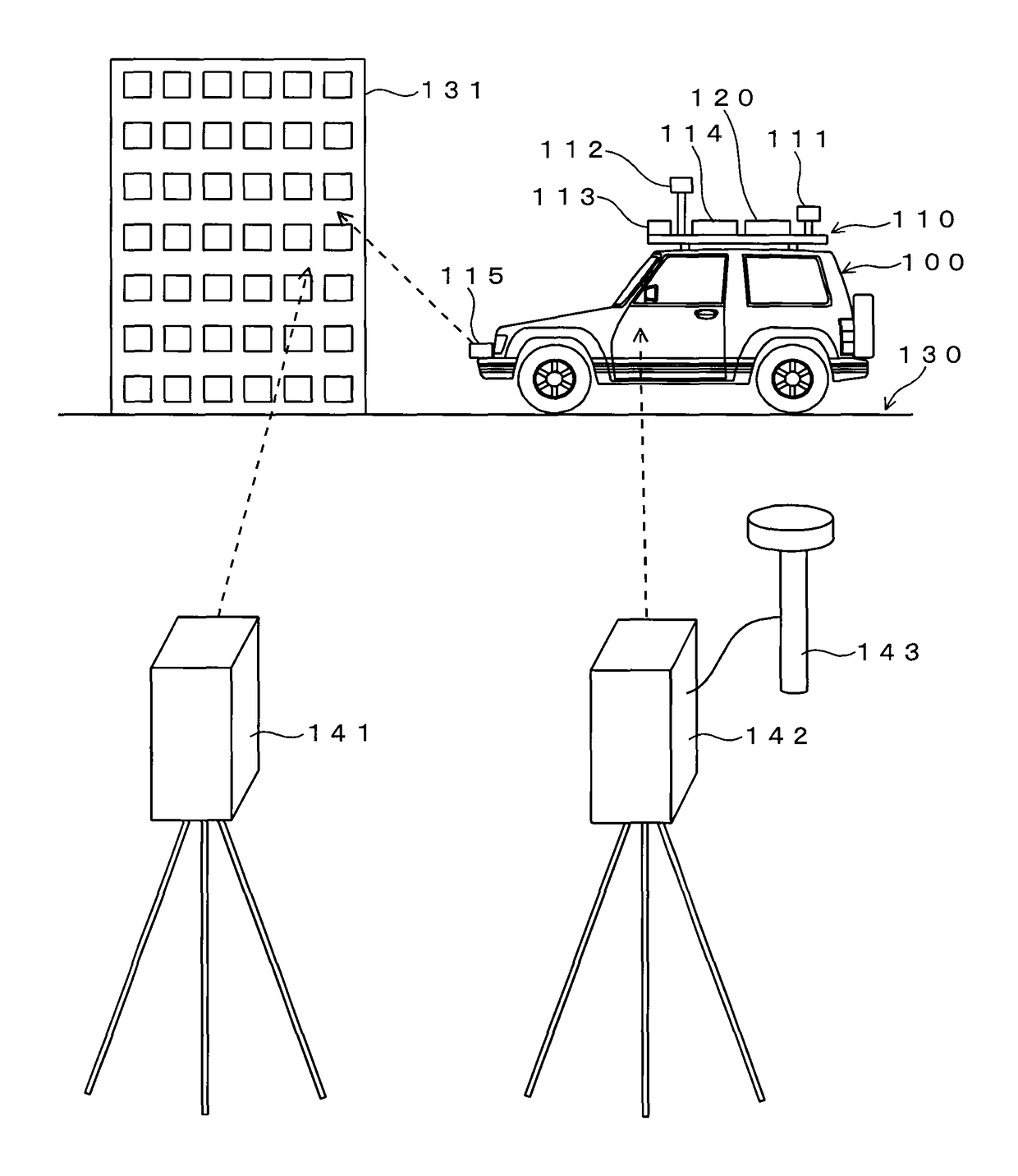
A technique for performing calibration of a laser scanner efficiently is provided. Point cloud position data of a building 131 is obtained by a laser scanner 141 in which exterior orientation parameters are already known. On the other hand, the building 131 is scanned by a laser scanner 115 while a vehicle 100 travels, and point cloud position data of the building 131 measured by the laser scanner 115 is obtained based on a trajectory the vehicle 100 has traveled. Then, exterior orientation parameters of the laser scanner 115 are calculated based on a correspondence relationship between these two point cloud position data.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Point cloud position data processing device, point cloud position data processing system, point cloud position data processing method, and program therefor
ActiveUS9659378B2Simple wayImprove performanceImage enhancementImage analysisData processing systemPoint cloud
A technique for performing calibration of a laser scanner efficiently is provided. Point cloud position data of a building 131 is obtained by a laser scanner 141 in which exterior orientation parameters are already known. On the other hand, the building 131 is scanned by a laser scanner 115 while a vehicle 100 travels, and point cloud position data of the building 131 measured by the laser scanner 115 is obtained based on a trajectory the vehicle 100 has traveled. Then, exterior orientation parameters of the laser scanner 115 are calculated based on a correspondence relationship between these two point cloud position data.
Owner:KK TOPCON
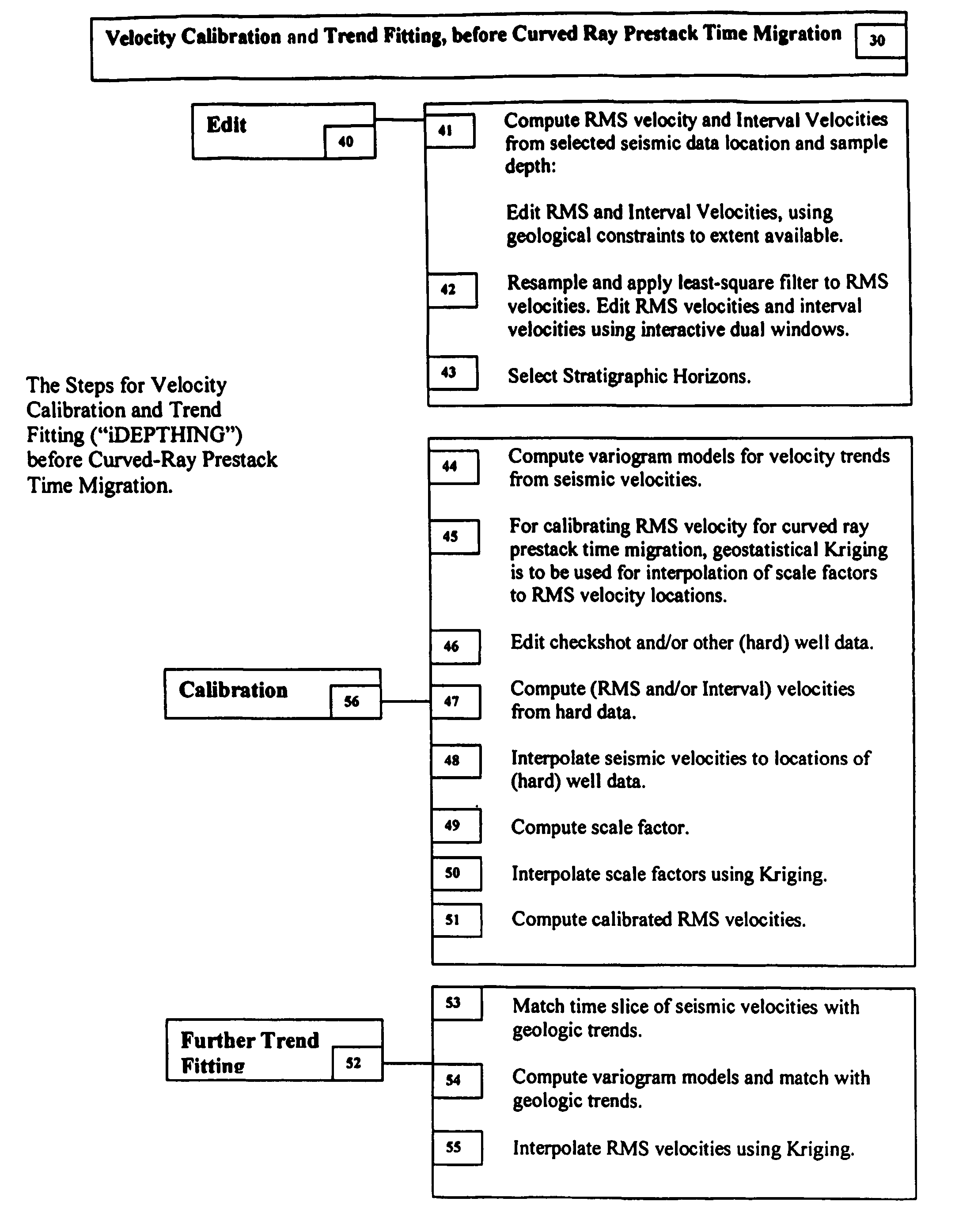
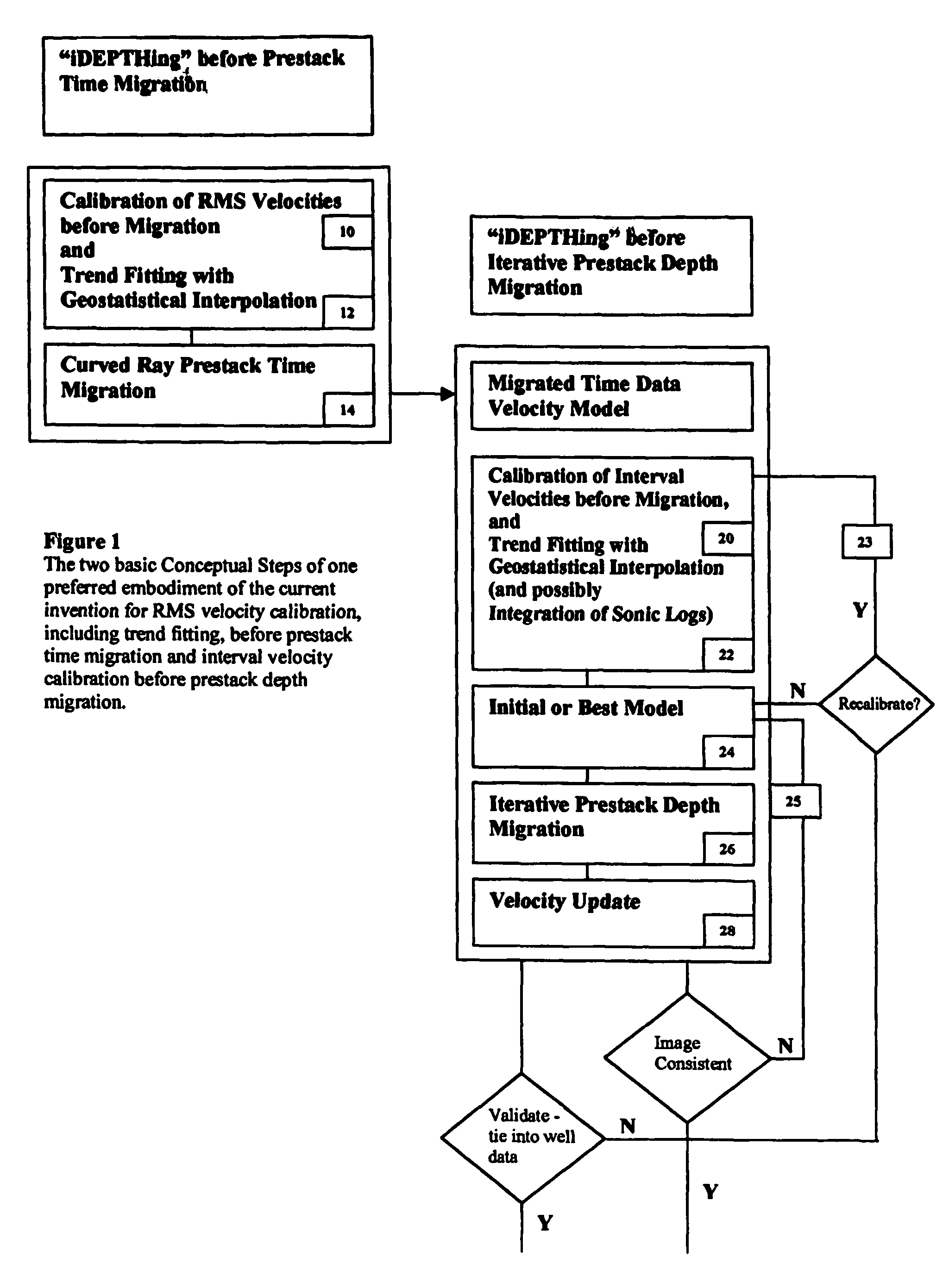
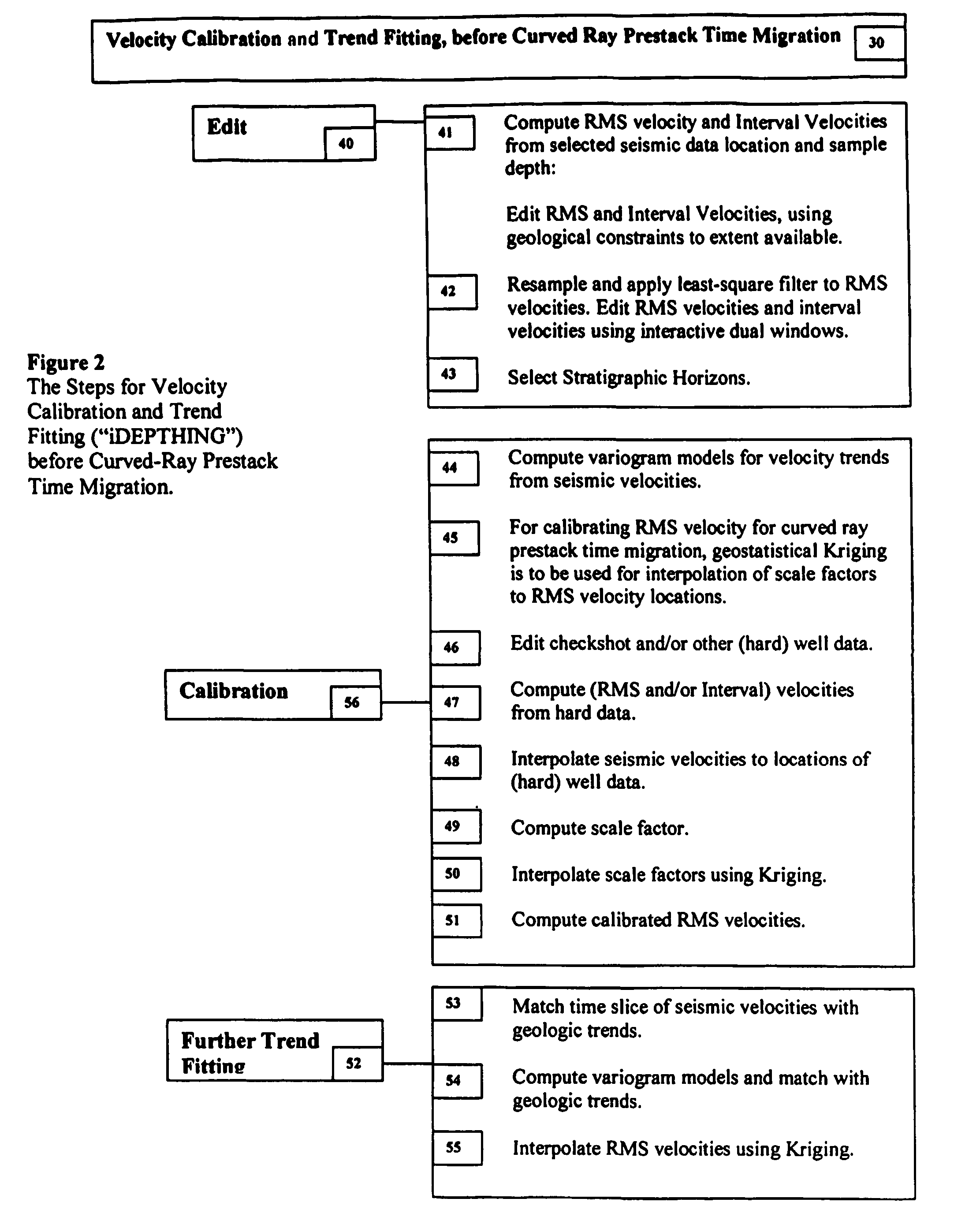
3D velocity modeling, with calibration and trend fitting using geostatistical techniques, particularly advantageous for curved for curved-ray prestack time migration and for such migration followed by prestack depth migration
InactiveUS7493241B2Advanced technologyImprove methodComputation using non-denominational number representationSeismic signal processingSeismic attributeRay
Owner:LEE WOOK B
Load measuring apparatus, method, and program
ActiveUS8255173B2Efficient calibrationImprove the situationWind motor controlEngine fuctionsAerodynamic torqueMeasurement device
A load is based calibrate on data collected under wide observation conditions and promptly calibrate loads of a plurality of wind turbine blades. A load measuring apparatus is applied to a wind turbine in which a pitch angle of a wind turbine blade is variable. The apparatus includes a sensor for obtaining a distortion of the wind turbine blade; a load calculating unit having a function expressing a relation between the distortion of the wind turbine blade and a load on the wind turbine blade, for obtaining the load on the wind turbine blade by applying to the function the distortion based on measurement data of the sensor; and a calibration unit for calibrating the function based on the measurement data of the sensor obtained in a pitch angle range and a rotational speed range of the wind turbine blade in which a variation between maximum and minimum aerodynamic torques is equal to or less than a predetermined value.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
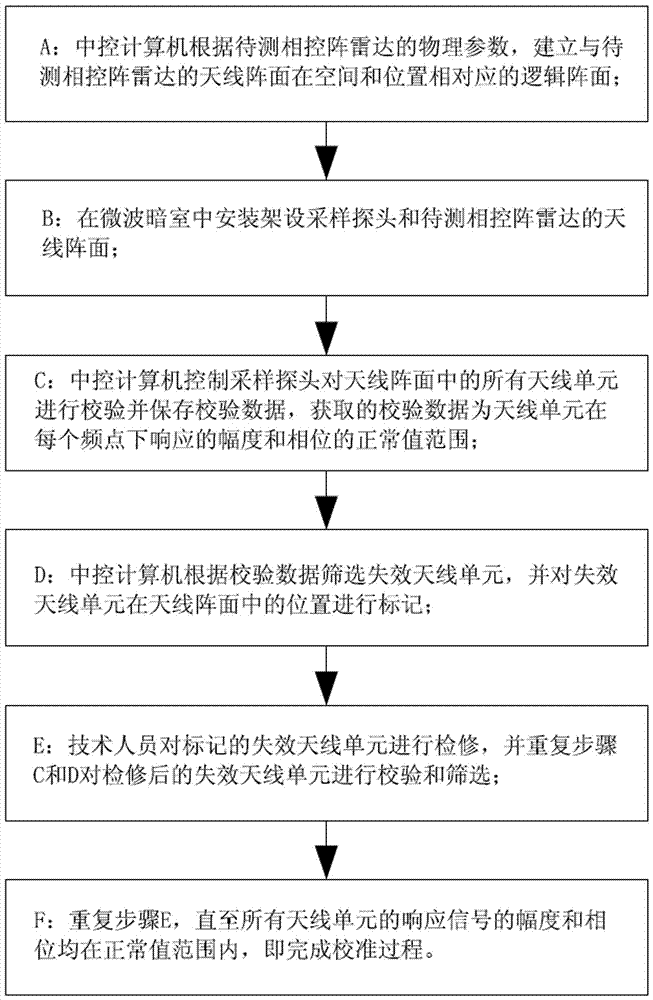
Amplitude-phase calibration method for antenna unit in planar or cylindrical phased array radar
ActiveCN106990394AReduce workloadReduce professional requirementsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarControl signal
The invention discloses an amplitude-phase calibration method for an antenna unit in a planar or cylindrical phased array radar. The replacement of human operation with a program-controlled machine is realized by way of replacing an array plane of a phased array radar with a logic array plane and cooperating with a center control computer in the control of a sampling probe and a rotary table, the workload of technical staff and the professional requirement for the technical staff are reduced, the operation is easy, and the precision and efficiency of calibration are greatly improved. Meanwhile, the center control computer is used to control the reception and transmission of a signal source and comparison and screening of response signals, the amplitude and phase information of each antenna unit are automatically recorded and compared, the manual recording is replaced, the influence of manual operation errors is substantially eliminated, the precision and efficiency of the calibration are improved, the whole calibration process is highly efficient and simple without additional interference of operation staff, the professional requirement and workload of the operation staff are greatly reduced, and the working efficiency is improved.
Owner:NO 27 RES INST CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Motorized blend alignment tool
ActiveUS20060227301A1Efficient calibrationEffective regulationMetal-working feeding devicesProjectorsRemote controlProjection system
A blending tool is described for blending sub-images of a multi-channel projection system comprising a plurality of projectors. The blending device typically has a number of adjustable optical blending means which each are adapted to be mounted on a projector of said multi-channel projection system. Using a removable controlling means allows automated controlling of at least one of the adjustable optical blending means, or a blending component thereof. The removable controlling means therefore has engaging means for temporary engaging the removable controlling means to the adjustable blending means. In a preferred version, the blending tool allows remote control of the adjustable blending means such that blending can be performed from the viewing side of the projection system, even for rear-projection systems. Furthermore a method for blending and projection systems adapted for being blended using the blending tool are provided.
Owner:BARCO NV
Methods and systems for lithography calibration using a mathematical model for a lithographic process
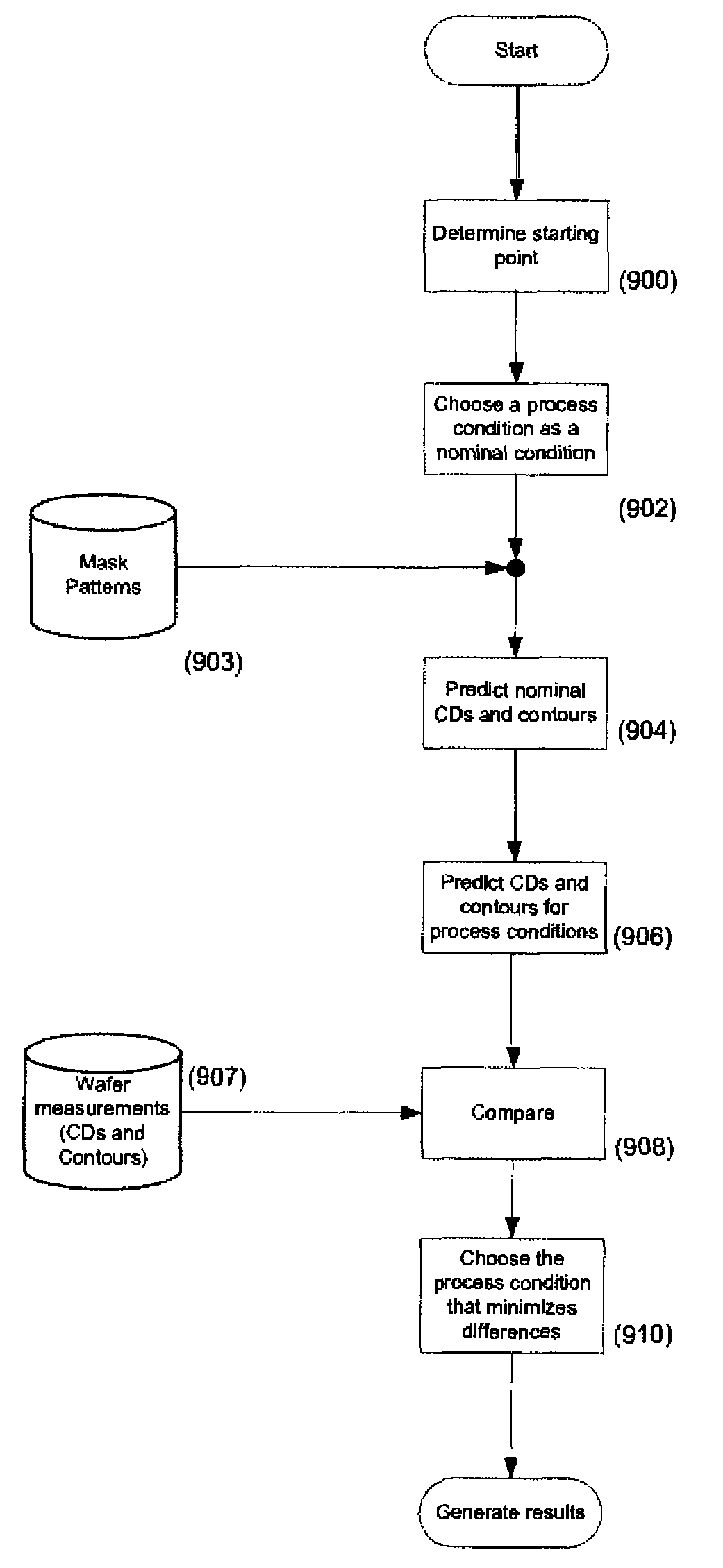
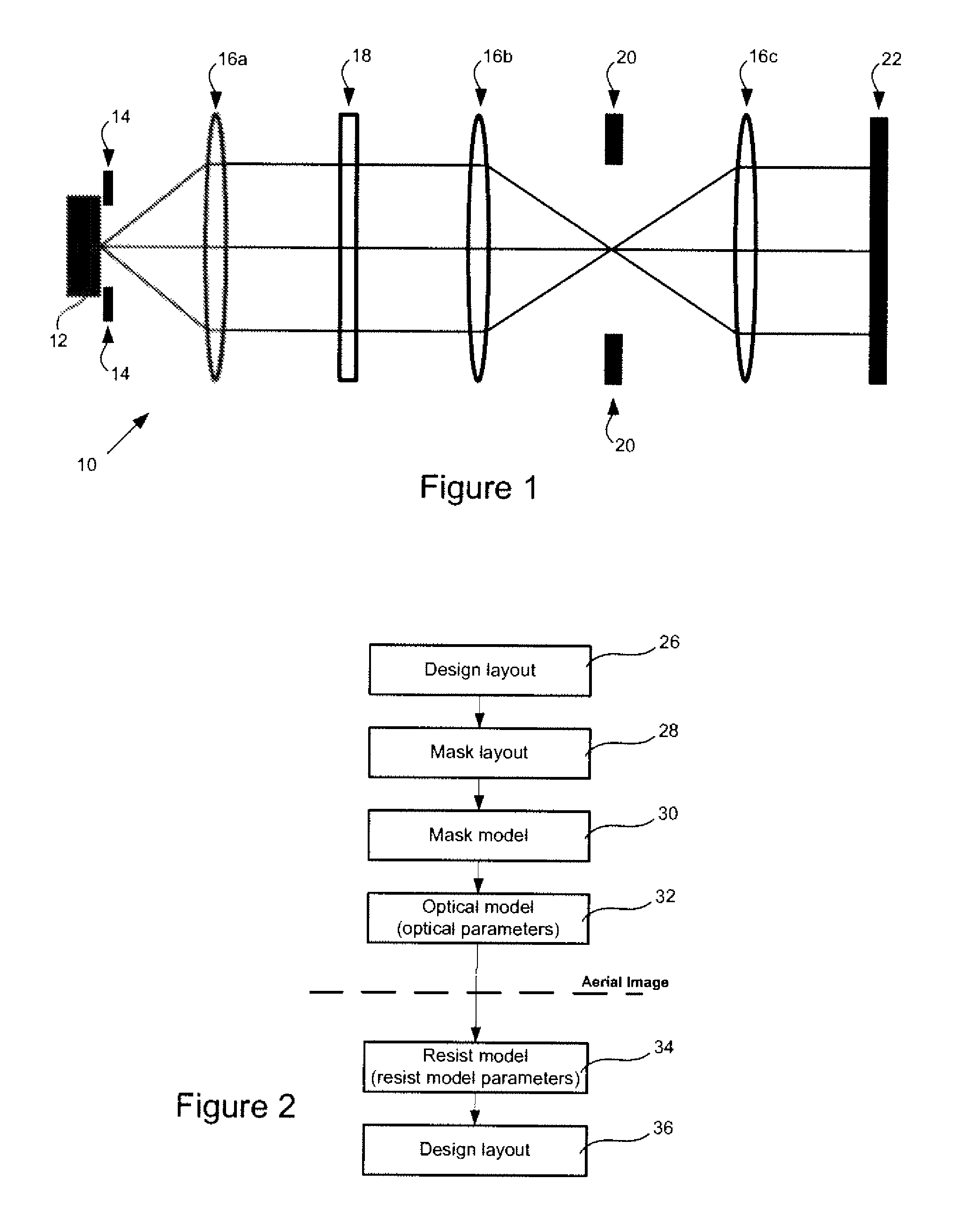
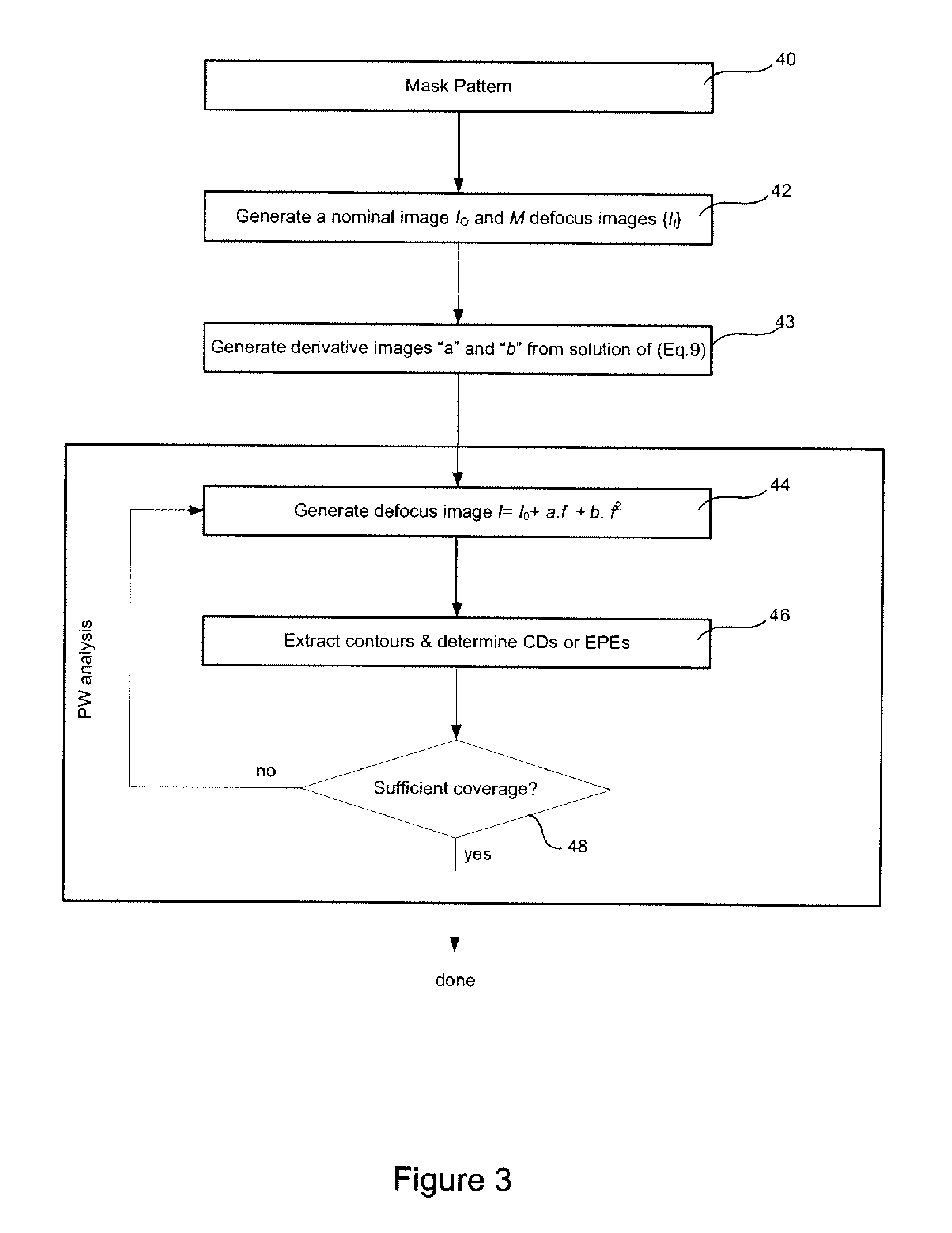
InactiveUS9009647B2Efficient calibrationComputationally efficientPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLithographic artistLithography process
A method of efficient optical and resist parameters calibration based on simulating imaging performance of a lithographic process utilized to image a target design having a plurality of features. The method includes the steps of determining a function for generating a simulated image, where the function accounts for process variations associated with the lithographic process; and generating the simulated image utilizing the function, where the simulated image represents the imaging result of the target design for the lithographic process. Systems and methods for calibration of lithographic processes whereby a polynomial fit is calculated for a nominal configuration of the optical system and which can be used to estimate critical dimensions for other configurations.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Digital measurement system
ActiveUS7207121B2Accurate measurementEfficient calibrationDrilling/boring measurement devicesMeasurement/indication equipmentsEngineeringRelative motion
A digital measurement system is provided for an apparatus including first and second parts that are positionally adjustable relative to one another, the first part having a base surface and the second part being selectively adjustable toward and away from the base surface. The measurement system includes an elongate reference element mounted for longitudinal movement on the first part such that a first end of the reference element is positionable to be substantially even with the base surface of the first part. A digital reader head is attachable to the second part. The reader head is operable is operably engaged with and moveable along the reference element for measuring relative movement of the reader head along the reference element. The readout further includes a digital display for indicating a measurement corresponding to the relative movement of the reader head along the reference element.
Owner:WIXEY BARRY
Input device and control method using input device
ActiveUS20150160783A1Efficient executionEfficient calibrationInput/output processes for data processingLocation detectionOffset calibration
An input device includes a position detection sensor capable of detecting an input operation position of an operation body on an operation surface, a load detection sensor capable of detecting a load in the input operation position, and a control unit capable of executing offset calibration to correct an offset of an output of the load detection sensor based on input operation information resulting from an output of the position detection sensor.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Luminescence lifetime based analyte sensing instruments and calibration technique
InactiveUS20130005047A1Efficient calibrationWave based measurement systemsCalibration apparatusAnalyteStart time
A method of calibrating a luminescence lifetime sensing instrument 20 and of interrogating a target-analyte long-decay luminescence probe 120 includes measuring and reporting luminescence lifetime of the probe 120 employing excitation radiation filtered to remove emission radiation, or a starting time tstart delayed by a predetermined decay delay time, or delayed by a predetermined growth delay time, or an ending time comprising the time at which luminescence intensity has decayed or risen a predetermined percentage.
Owner:MODERN CONTROLS
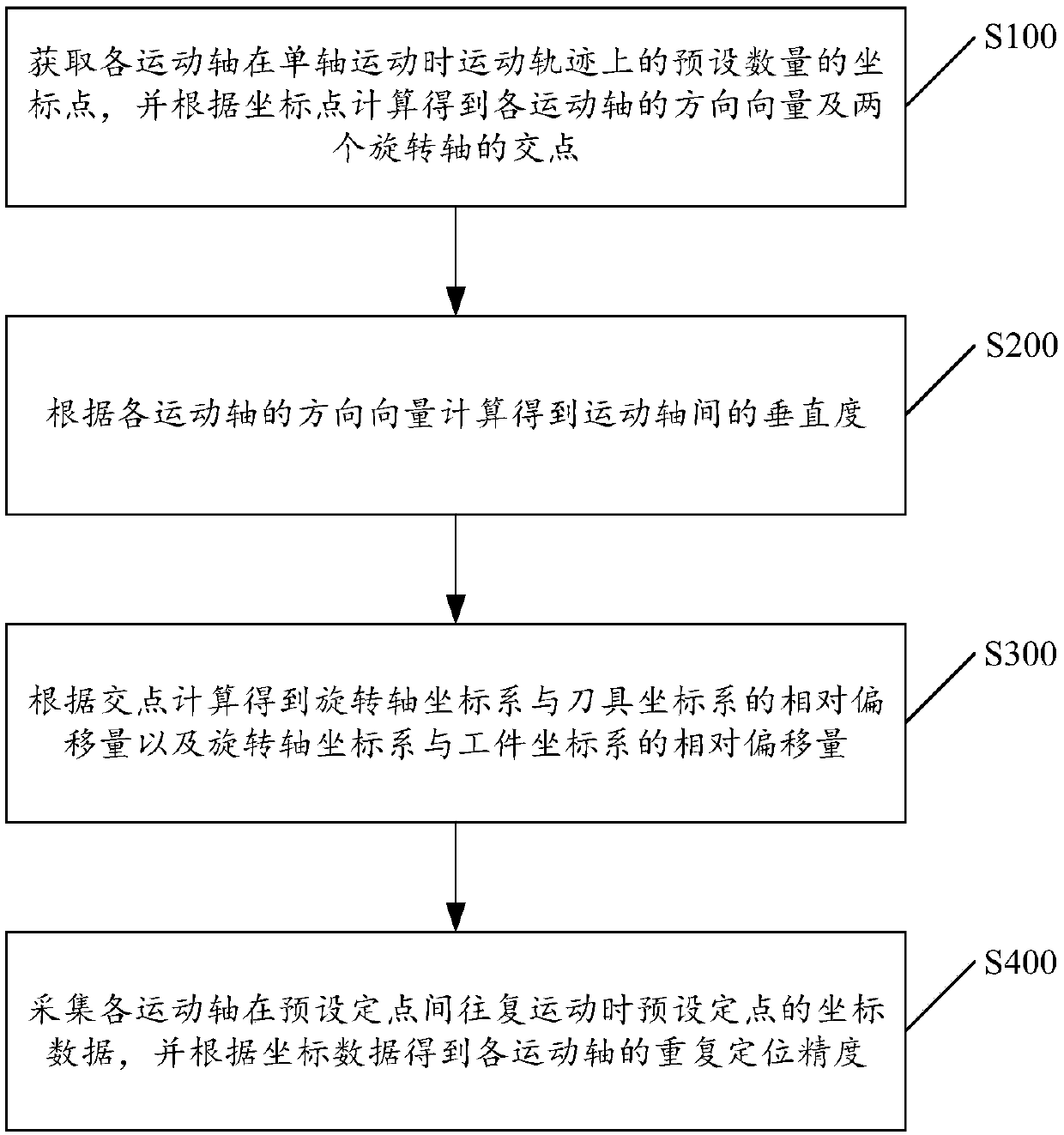
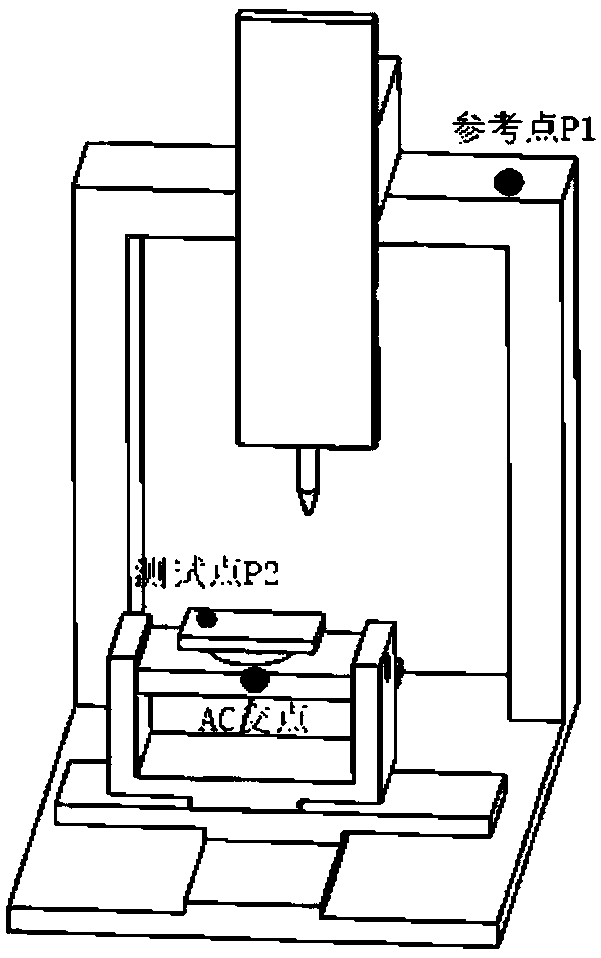
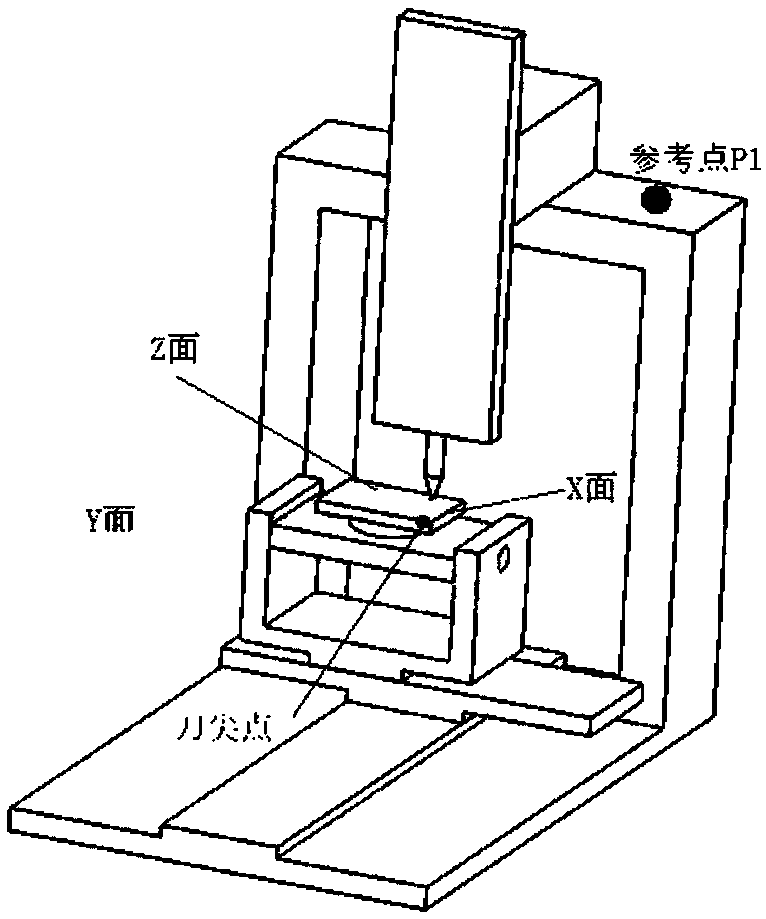
Calibration method of five-axis machine tool
ActiveCN109514351AEfficient calibrationImprove scale accuracyMeasurement/indication equipmentsDirection vectorMachine tool
The invention discloses a calibration method of a five-axis machine tool. The calibration method comprises the steps of obtaining a preset number of coordinate points on the movement trajectory when each movement axis conducts uniaxial motion and calculating the direction vectors of the movement axes and the intersection point of two rotation axes according to the coordinate points; figuring out the perpendicularity between the movement axes according to the direction vectors of the movement axes; calculating the relative offset between a rotation axis coordinate system and a tool coordinate system and the relative offset between the rotation axis coordinate system and a workpiece coordinate system according to the intersection point; and collecting coordinate data of preset fixed points when the movement axes reciprocate between the preset fixed points, and obtaining the repeated positioning accuracy of the movement axes according to the coordinate data. Simple and efficient calibration of the five-axis machine tool can be realized, and the calibration precision can be improved. The invention further discloses a calibration system of the five-axis machine tool, a calibration device and a computer readable storage medium, all of which have the above beneficial effects.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
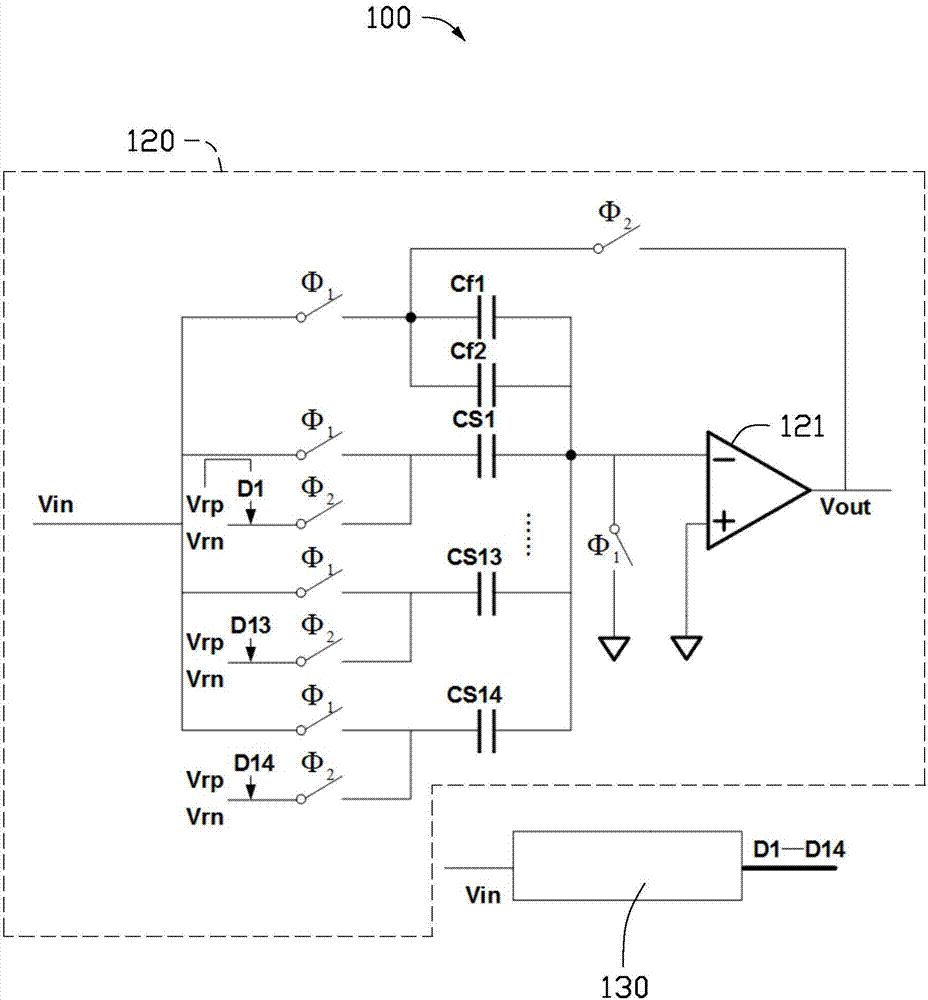
Method for improving output precision of assembly line analog-digital converter and analog-digital converter
ActiveCN107579740AImprove output accuracyReduce complexityAnalogue-digital convertersCapacitanceAssembly line
The invention provides a method for improving output precision of an assembly analog-digital converter and the assembly line analog-digital converter. The assembly analog-digital converter comprises multiple serially connected polar circuits, a residual error amplifying circuit and a sub analog-digital converter are arranged at each polar circuit; the method comprises the following steps: S1, adding a calibration module in a first stage polar circuit, wherein the calibration module comprises a switch capacitor array, and the switch capacitor array comprises at least one jittering capacitor; S2, measuring and storing each sampling capacitor in the residual error amplifying capacitor and an initial weight value of each jittering capacitor when the input signal of the polar circuit is zero; and S3, calibrating a digital signal output by the polar circuit by using the initial weight value of each sampling capacitor, and finishing the jittering-elimination processing at a digital domain byusing the initial weight value of each jittering capacitor so as to finish the foreground calibration process.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com