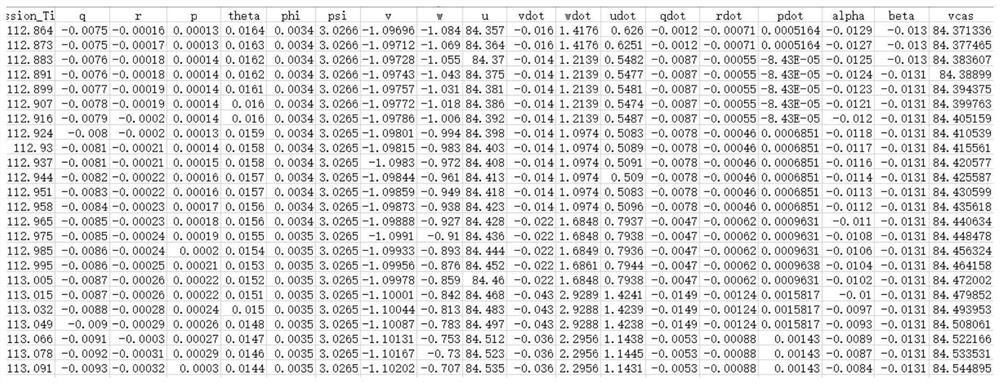
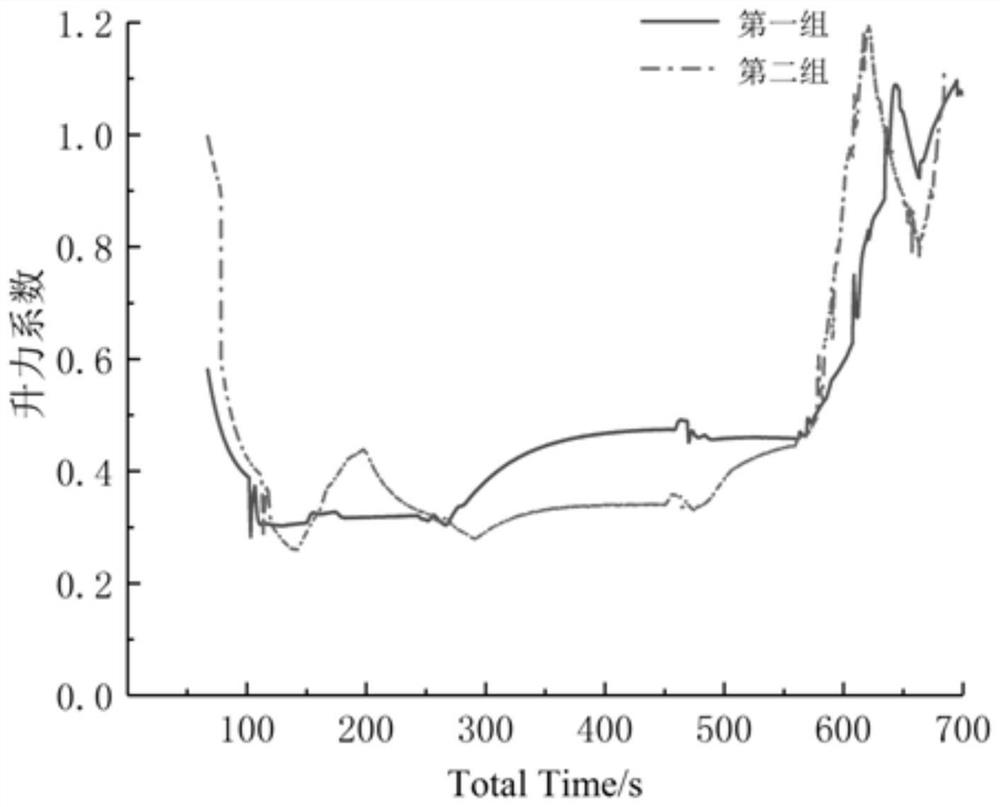
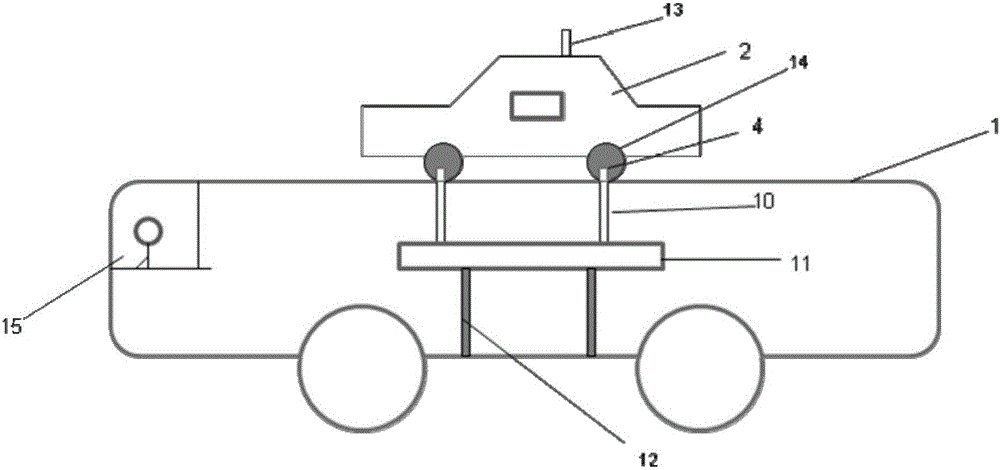
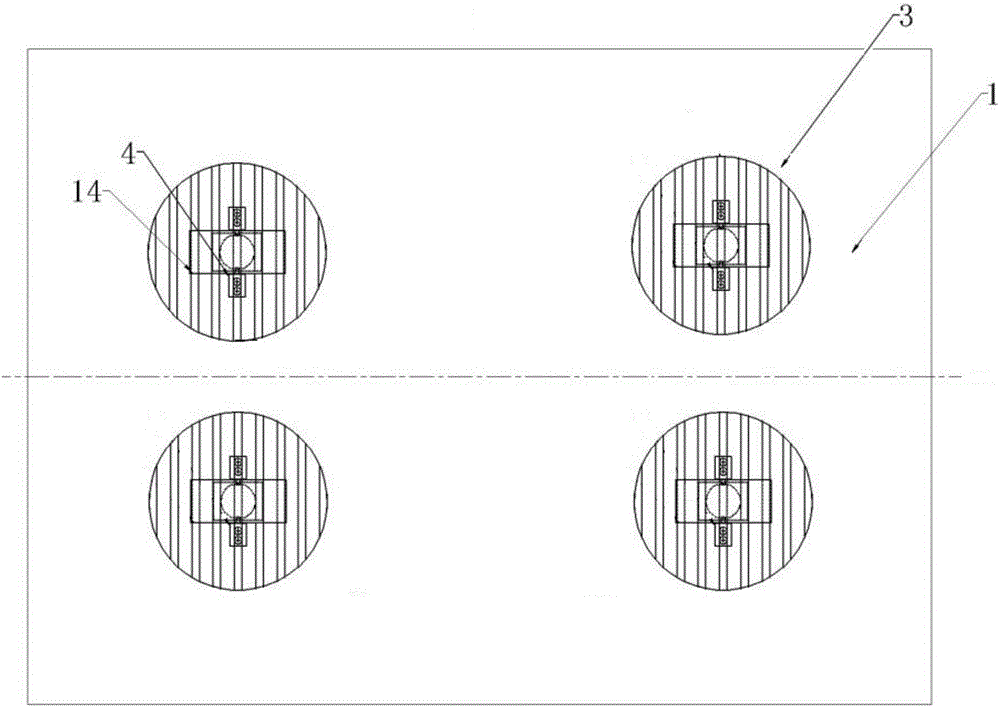
Patents
Literature
58 results about "Aerodynamic torque" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
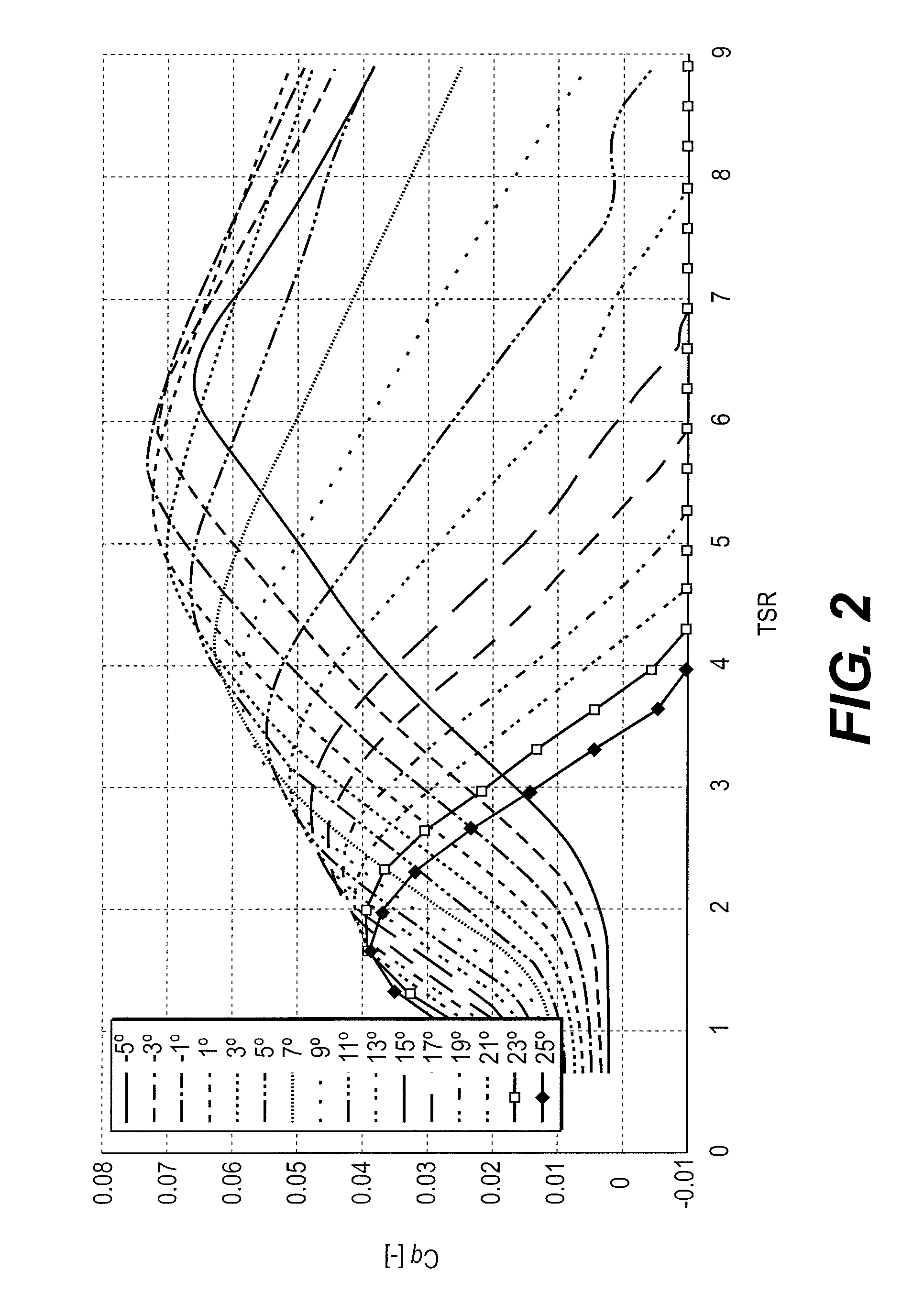
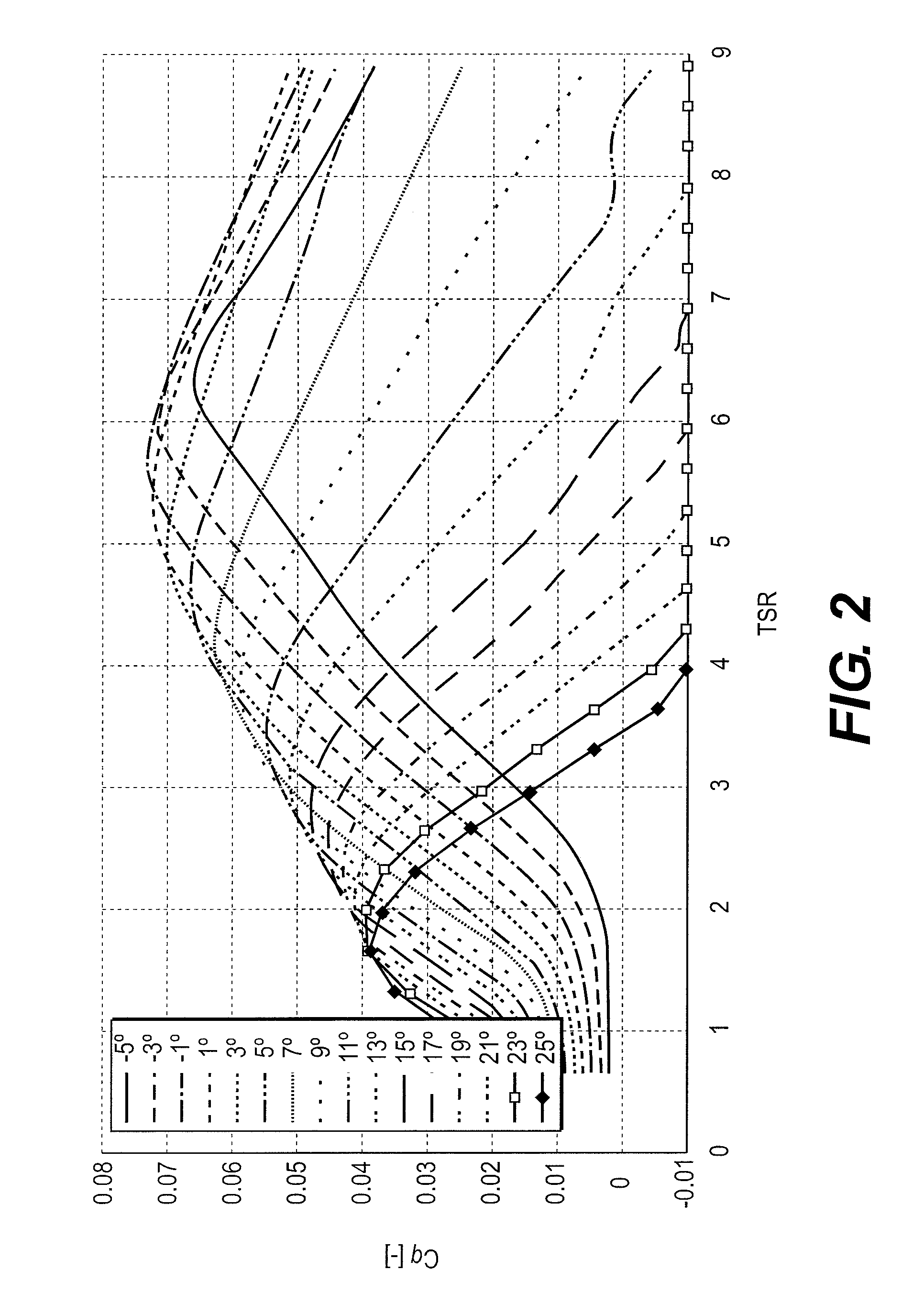
Aerodynamic torque is caused when non-uniform static pressure distribution from fluid flows past the ball. Dynamic torque study. MOGAS is investigating the impact of aerodynamic torque on an overall torque curve, with a goal to customize the torque curve to suit the user’s specific flow conditions.
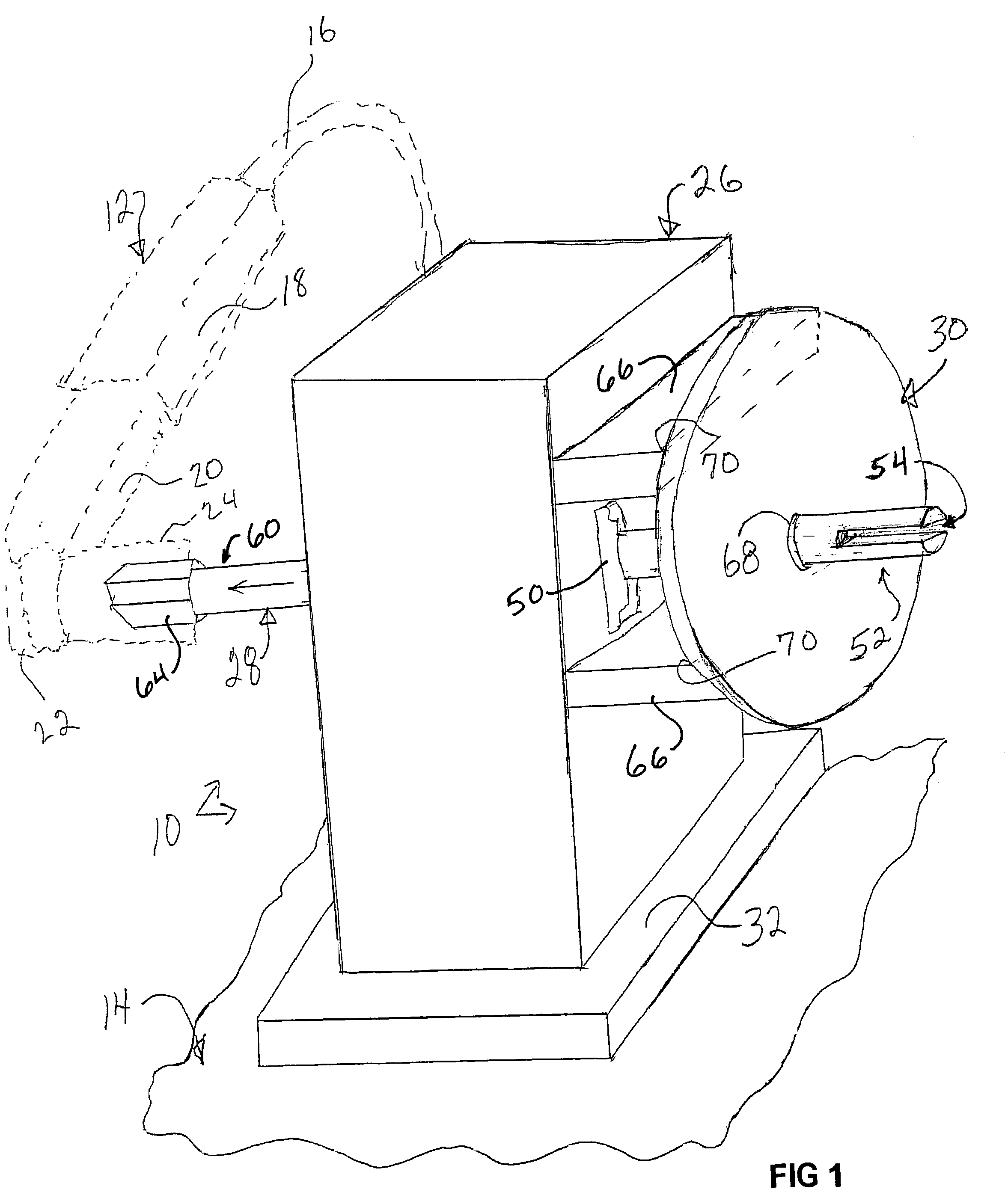
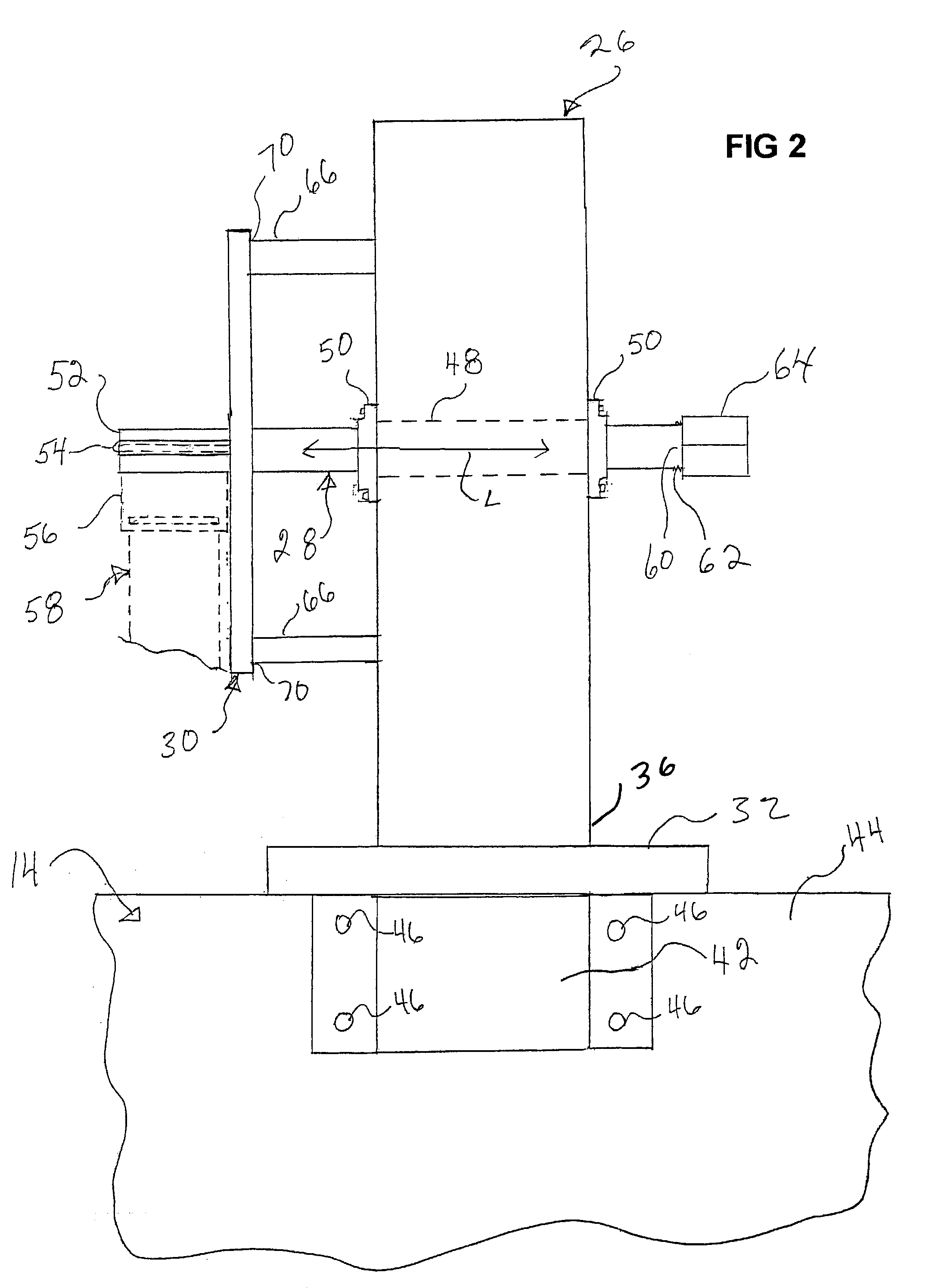
Powered strap winder
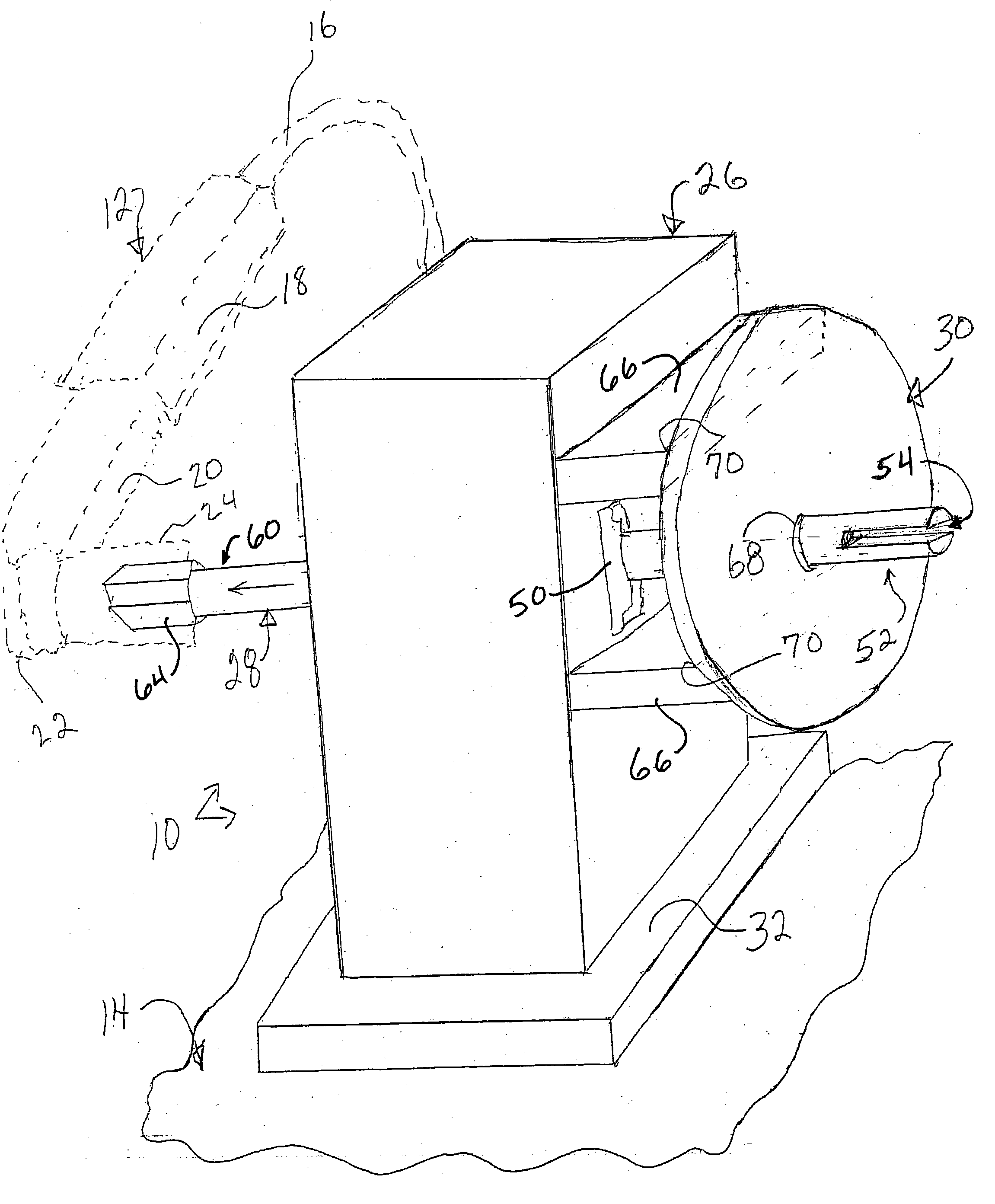
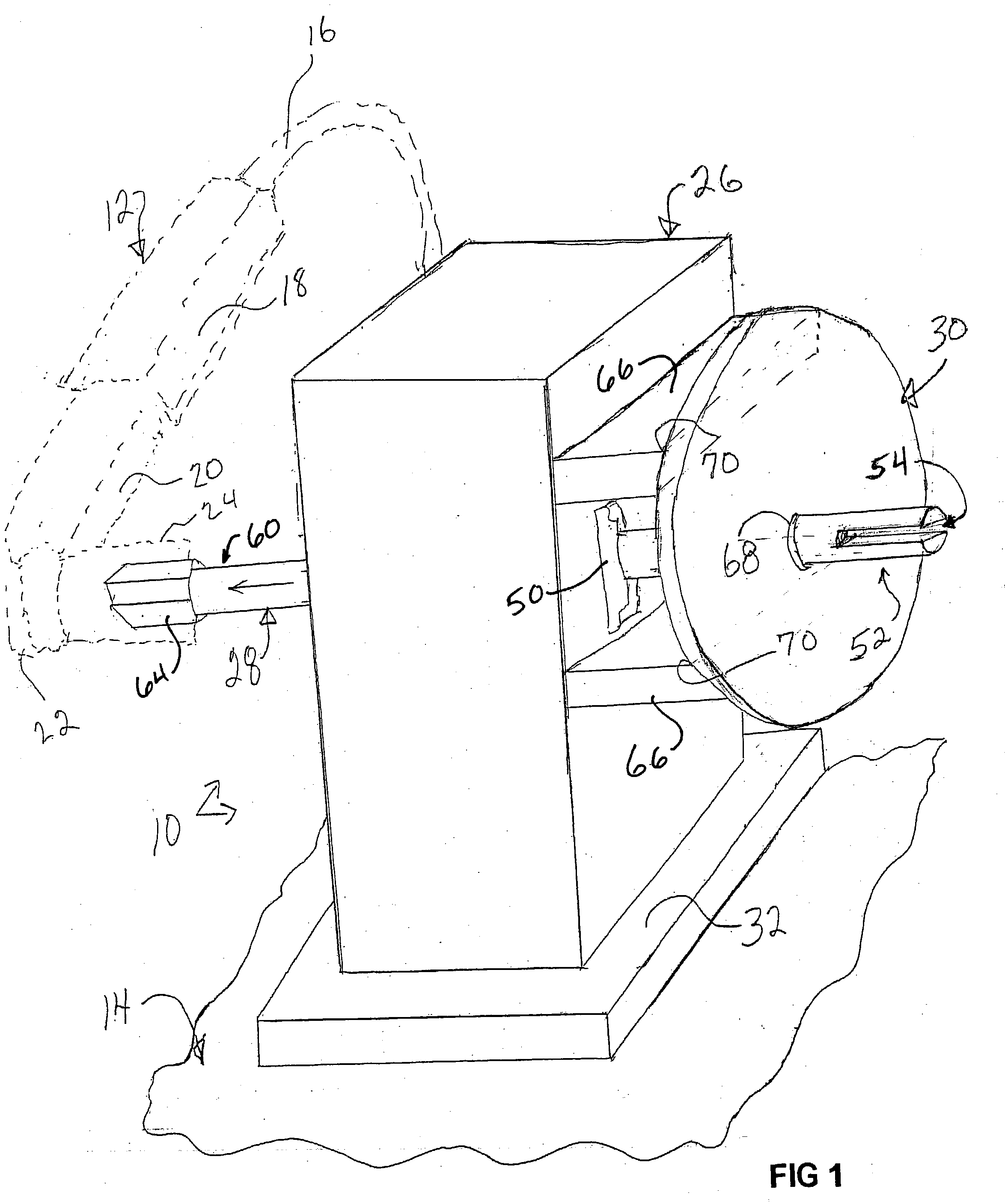
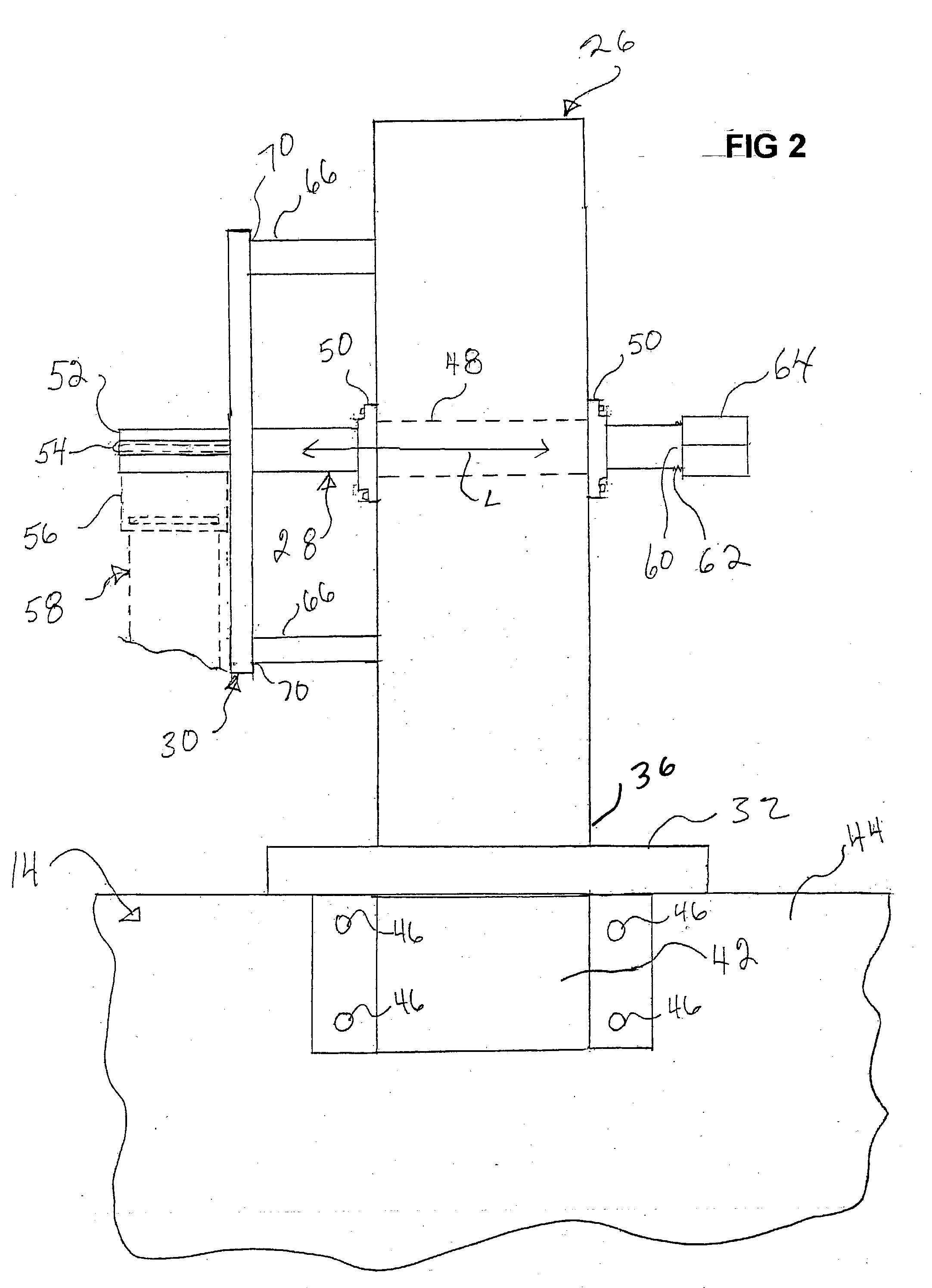
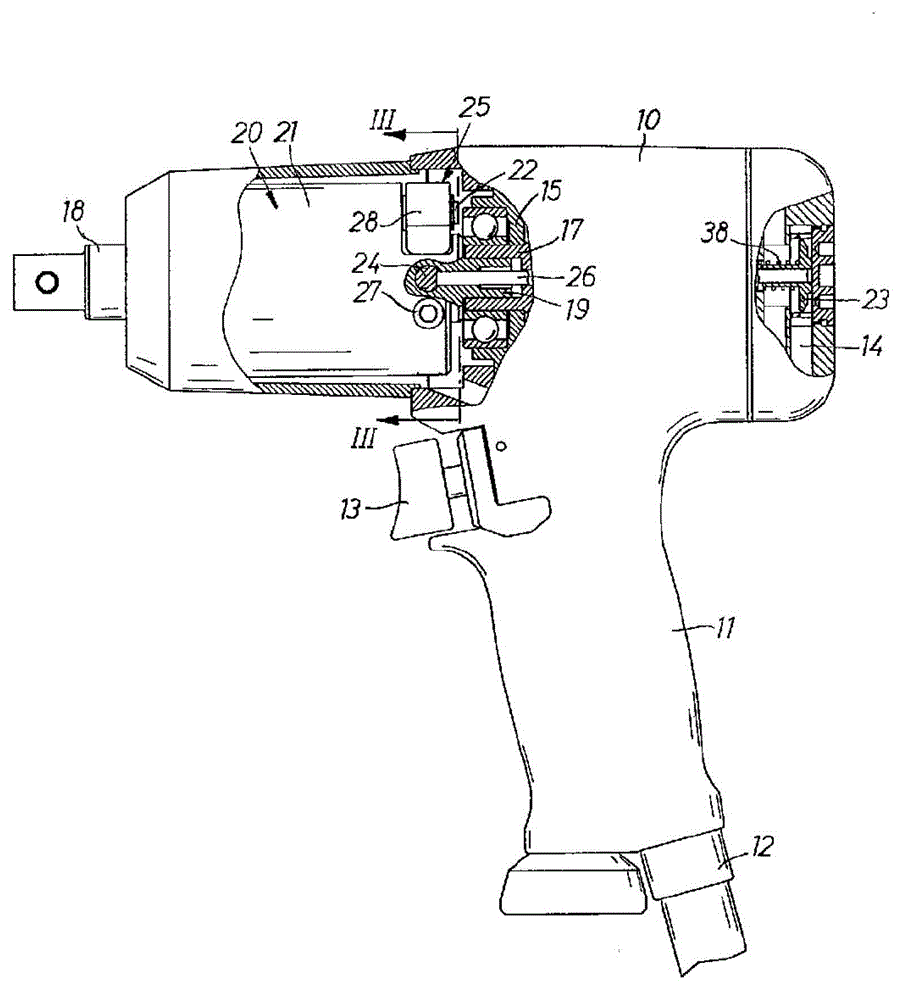
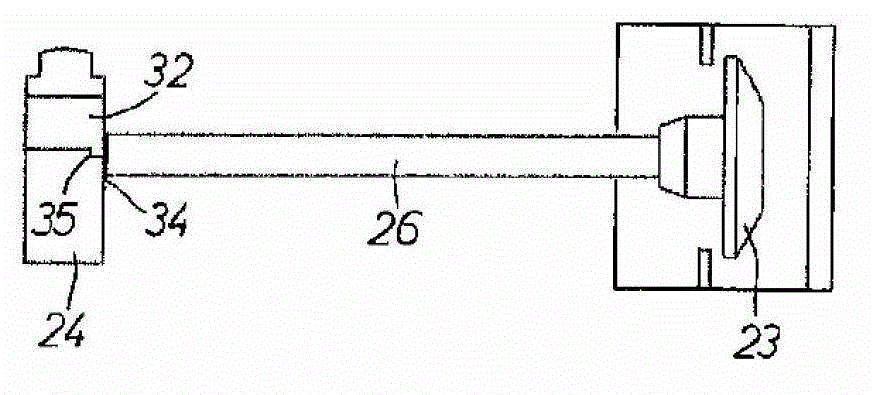
A strap winder (10) is provided for winding up an elongated strap (58). The strap winder (10) is actuated by a power-operated driver, e.g., a pneumatic torque or a wrench (12) or an electric, pneumatic or hydraulic motor (281) and includes a body (26) and a shaft (28) that is rotatably supported by the body (26). The shaft (28) has, at one end, a slot (52a) configured for receipt of a strap (58). The other end of the shaft (28) is configured to connect with the power-operated driver and a guide plate (30) is provided that is supported by the body (26) and extends is a direction that is generally perpendicular to a longitudinal axis of the shaft (28). An optional guard plate (286) is pivotably mounted in parallel relation to guide plate (30) to protect the user from inadvertent contact with the rotating shaft (28) or the strap thereon. When winding is done, the guard plate (286) can be pivoted out of the way so that the coiled strap (58) can be removed from the shaft (28).
Owner:HECT OR OLL
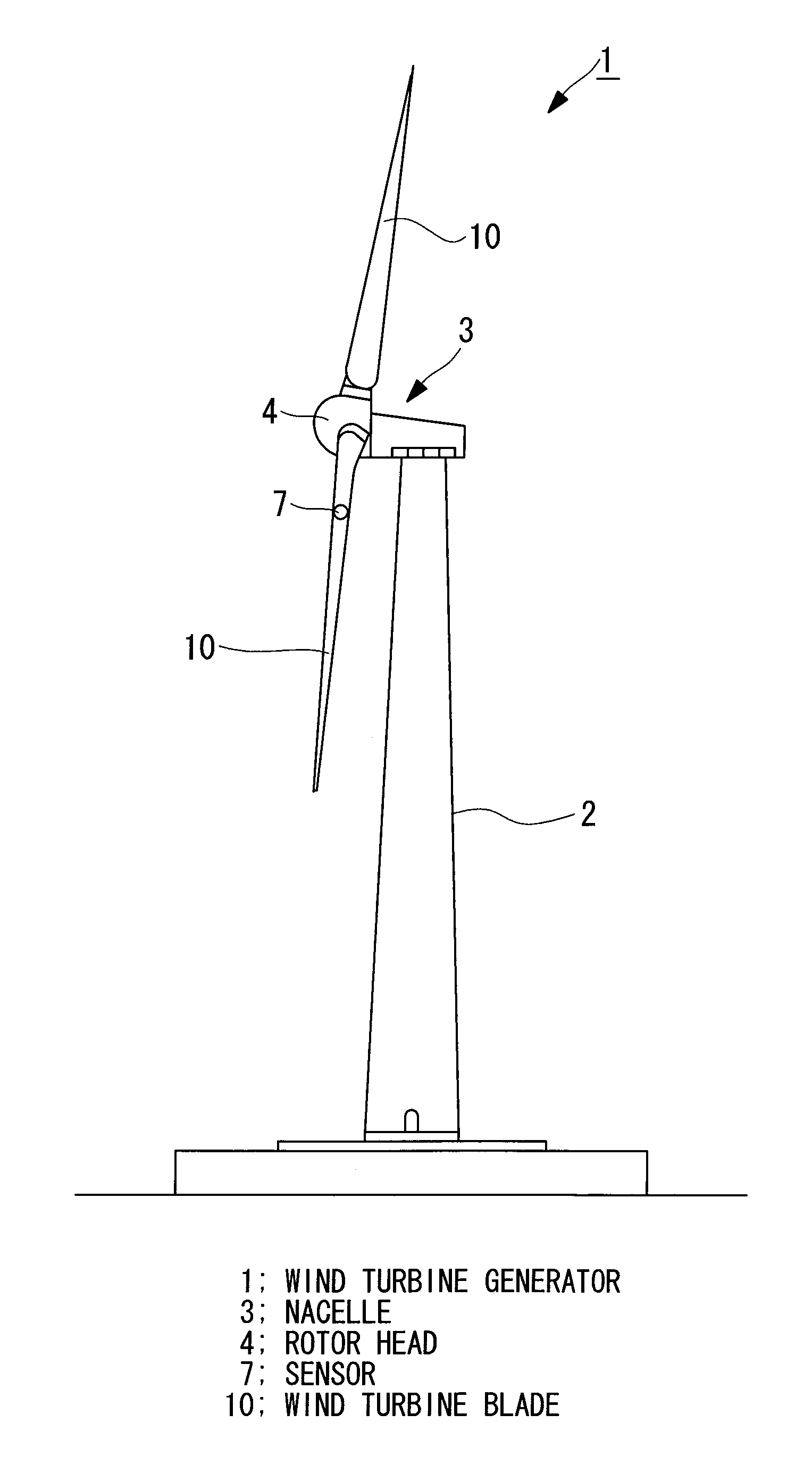
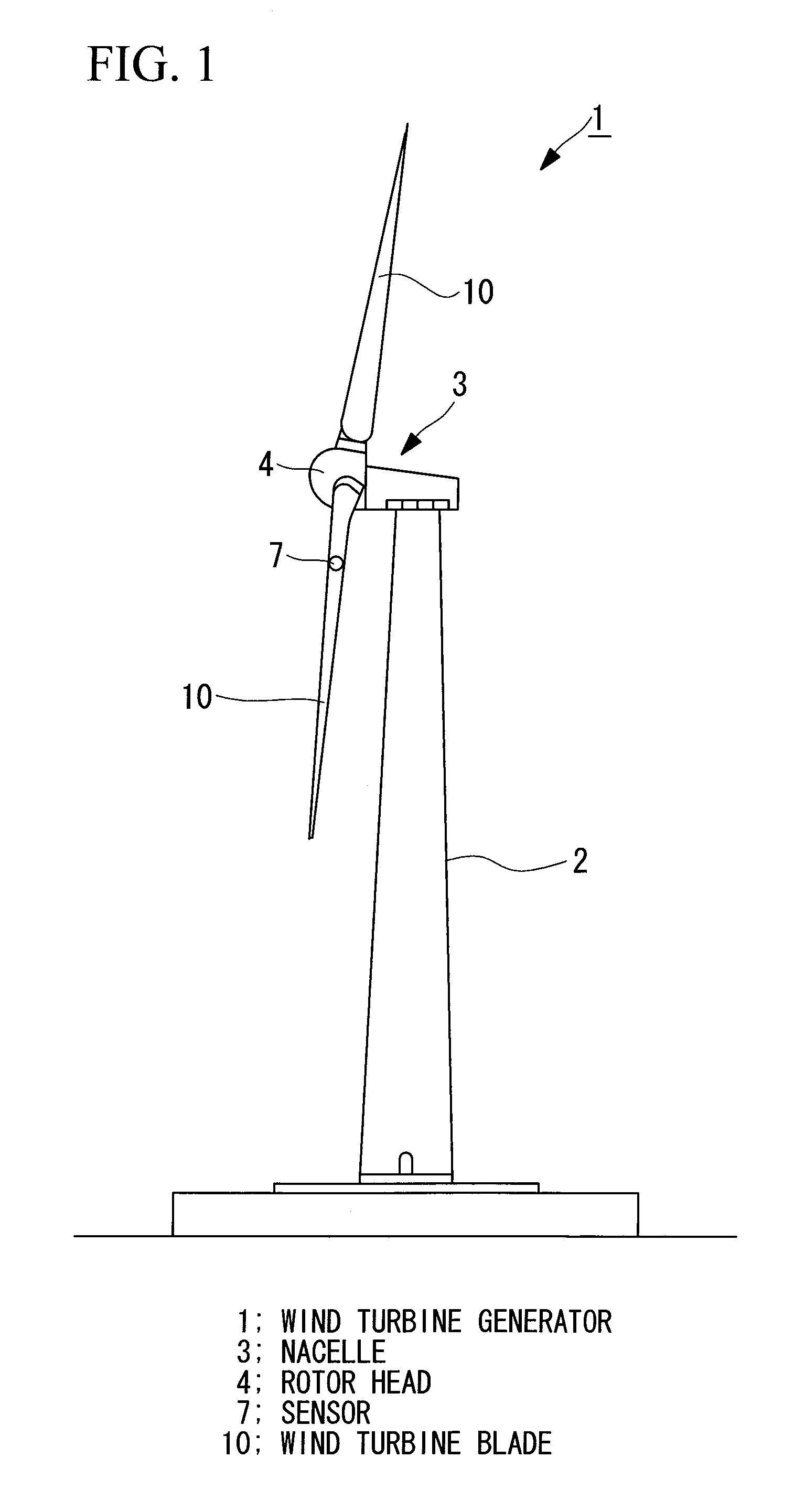
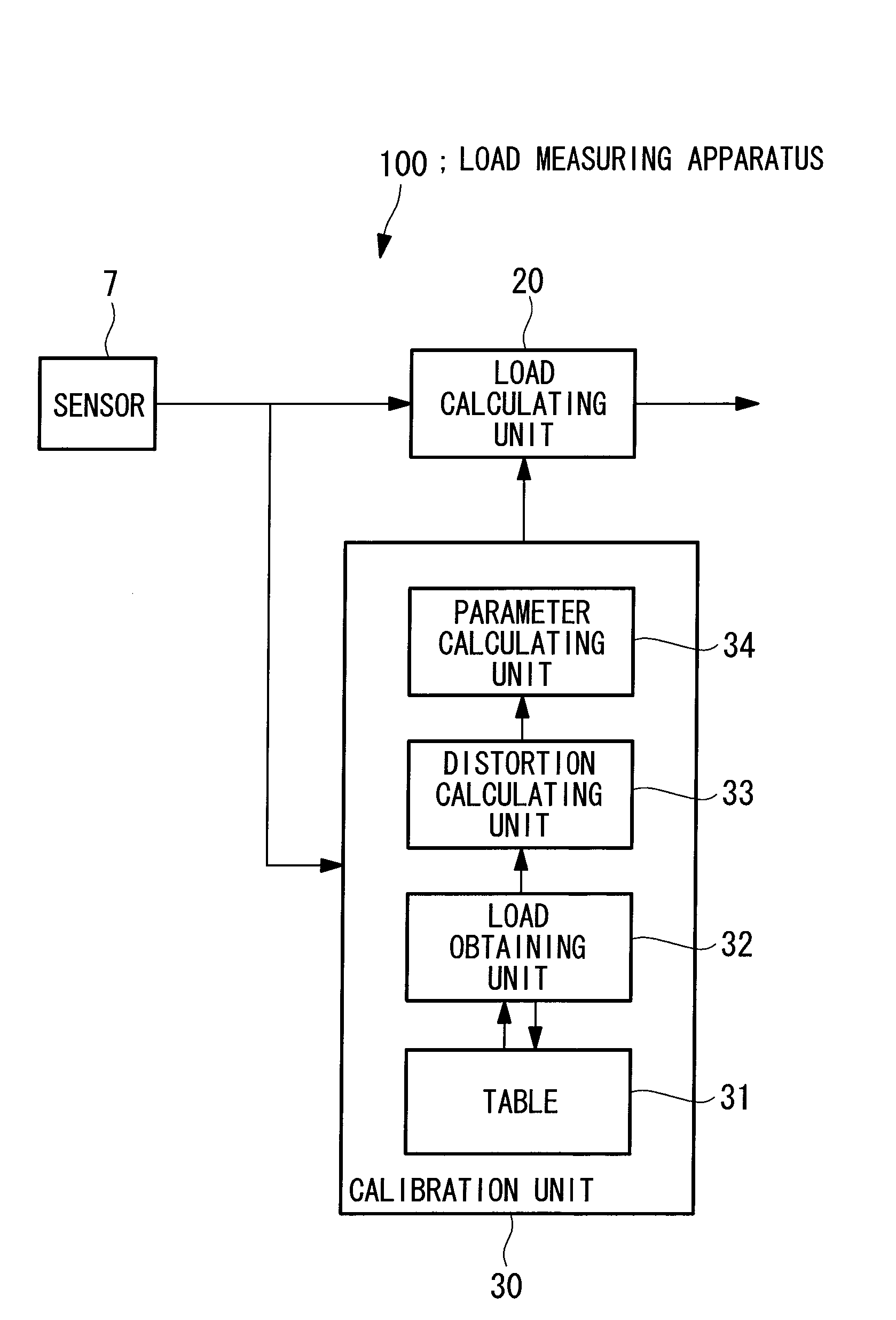
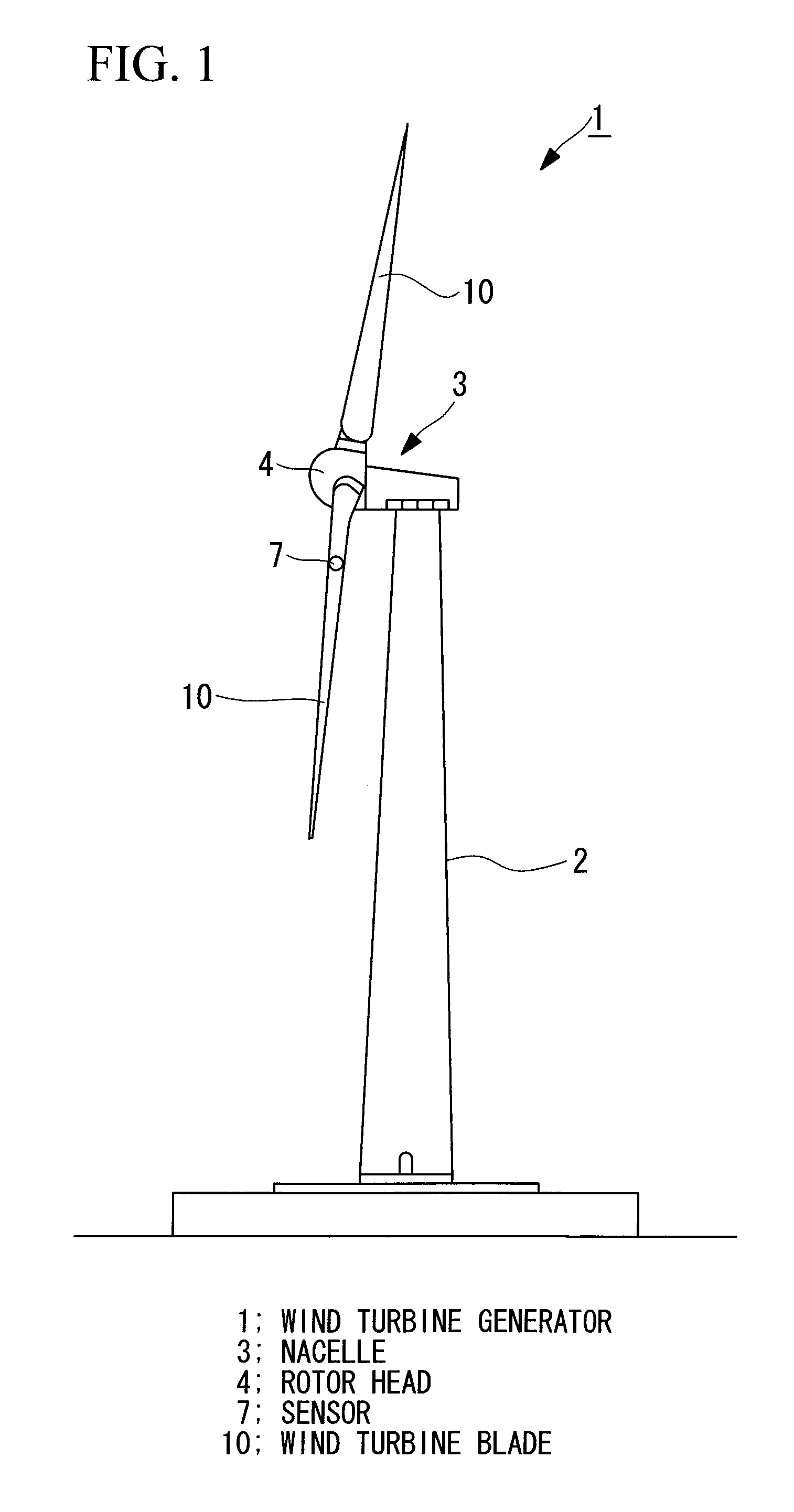
Load measuring apparatus, method, and program
ActiveUS20120035865A1Efficient calibrationImprove the situationEngine fuctionsForce measurementAerodynamic torqueTurbine blade
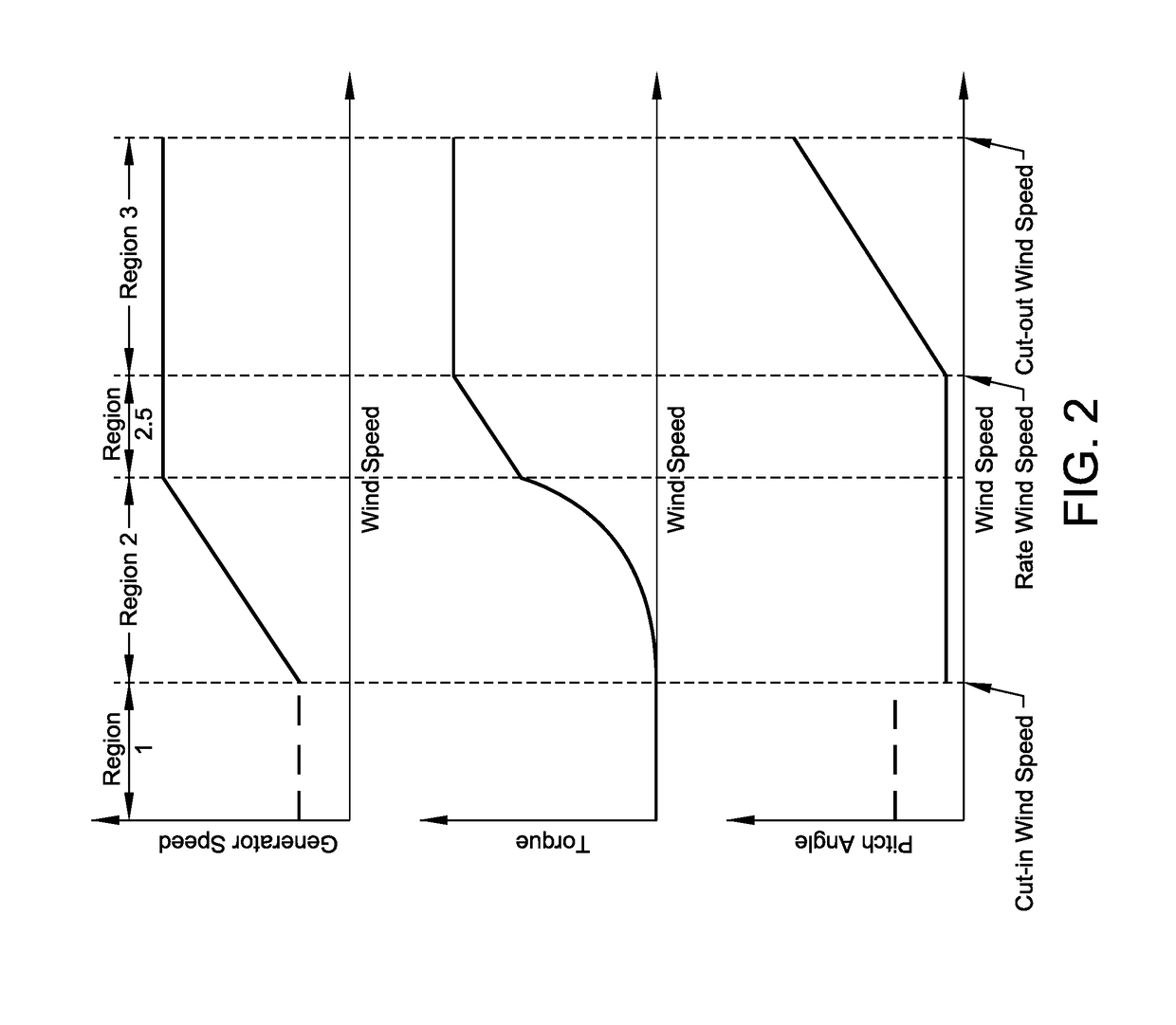
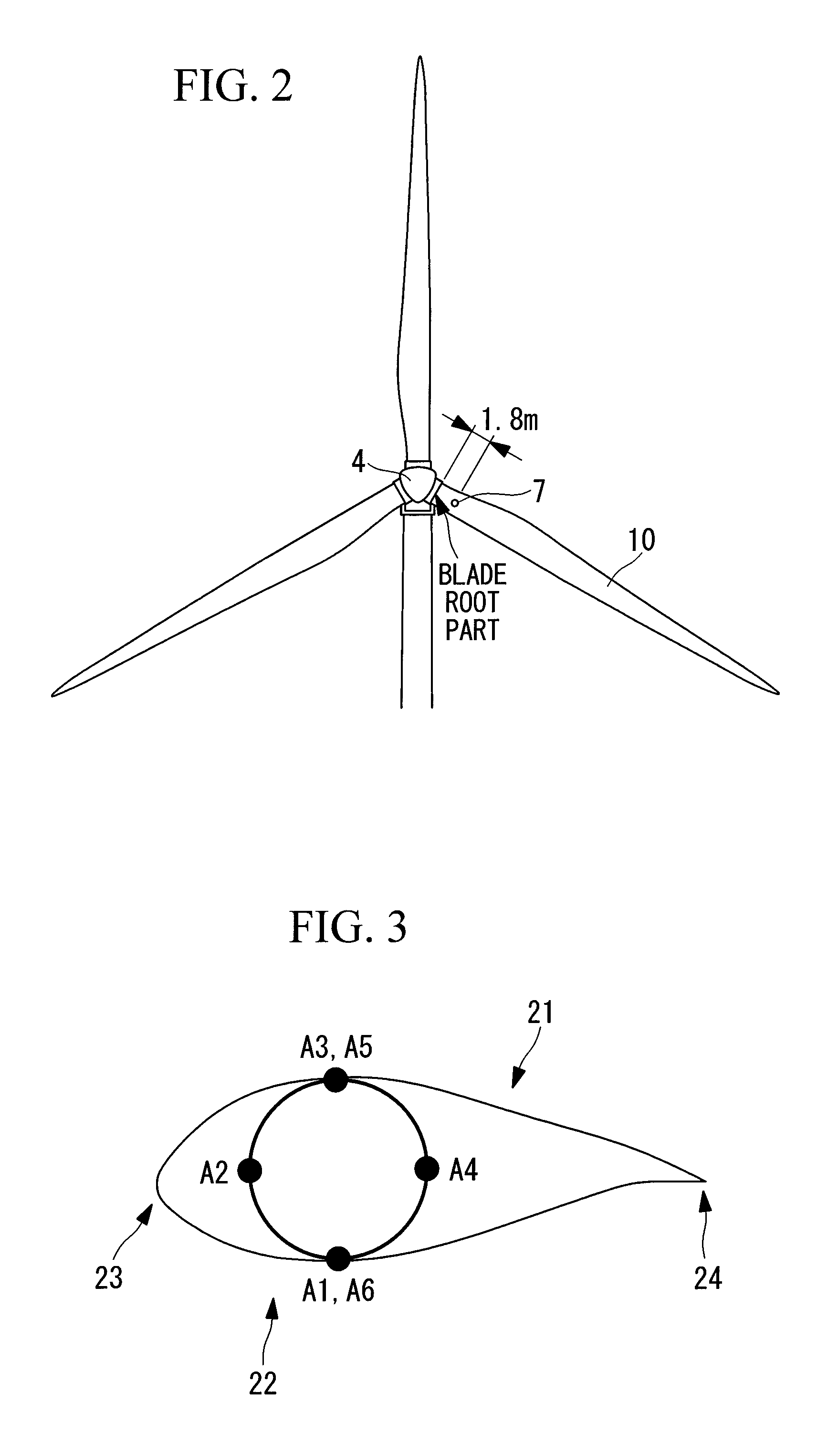
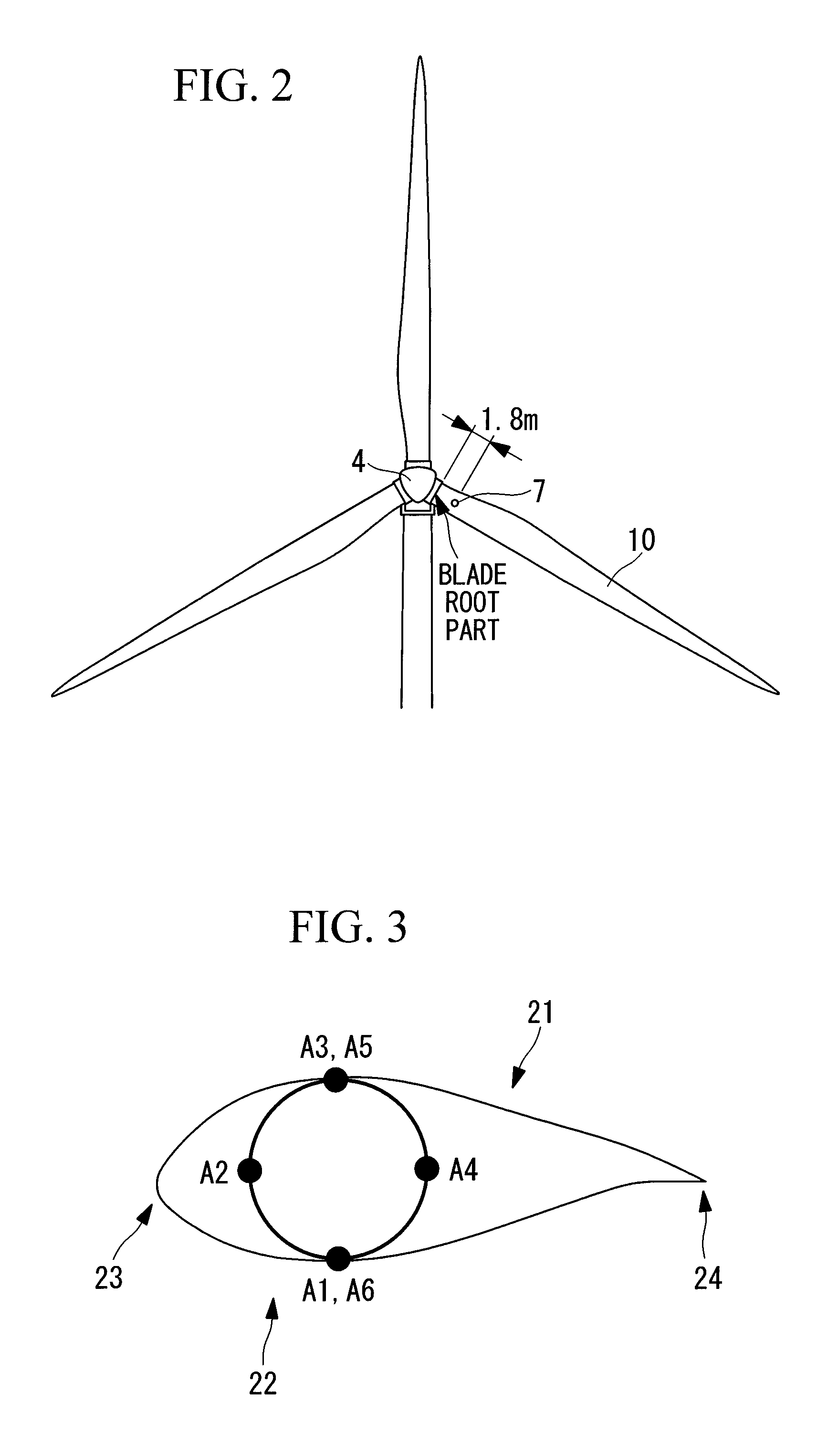
A load is based calibrate on data collected under wide observation conditions and promptly calibrate loads of a plurality of wind turbine blades. A load measuring apparatus is applied to a wind turbine in which a pitch angle of a wind turbine blade is variable. The apparatus includes a sensor for obtaining a distortion of the wind turbine blade; a load calculating unit having a function expressing a relation between the distortion of the wind turbine blade and a load on the wind turbine blade, for obtaining the load on the wind turbine blade by applying to the function the distortion based on measurement data of the sensor; and a calibration unit for calibrating the function based on the measurement data of the sensor obtained in a pitch angle range and a rotational speed range of the wind turbine blade in which a variation between maximum and minimum aerodynamic torques is equal to or less than a predetermined value.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Powered strap winder
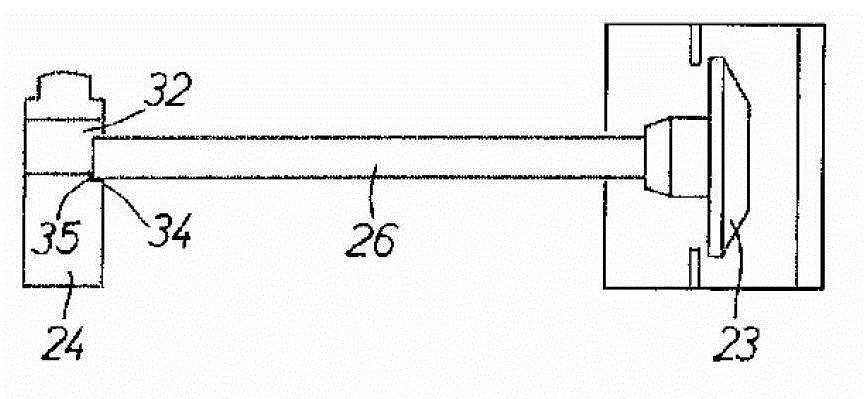
A strap winder (10) is provided for winding up an elongated strap (58). The strap winder (10) is actuated by a power-operated driver, e.g., a pneumatic torque or a wrench (12) or an electric, pneumatic or hydraulic motor (281) and includes a body (26) and a shaft (28) that is rotatably supported by the body (26). The shaft (28) has, at one end, a slot (52a) configured for receipt of a strap (58). The other end of the shaft (28) is configured to connect with the power-operated driver and a guide plate (30) is provided that is supported by the body (26) and extends is a direction that is generally perpendicular to a longitudinal axis of the shaft (28). An optional guard plate (286) is pivotably mounted in parallel relation to guide plate (30) to protect the user from inadvertent contact with the rotating shaft (28) or the strap thereon. When winding is done, the guard plate (286) can be pivoted out of the way so that the coiled strap (58) can be removed from the shaft (28).
Owner:HECT OR OLL
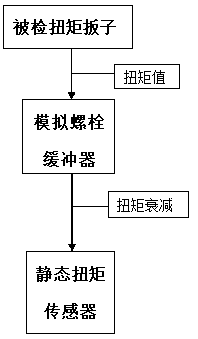
Dynamic torque detection system
PendingCN106768621AHigh measurement accuracyPrevent sideways movementForce/torque/work measurement apparatus calibration/testingAerodynamic torqueElectricity
The invention discloses a dynamic torque detection system, comprising a bench and a torque sensor; an electrical-pneumatic torque wrench is fixedly mounted on the bench; one end of the torque sensor is connected with an output shaft of the electrical-pneumatic torque wrench; the other end of the torque sensor is connected with a sleeve through a coupling; the sleeve is rotationally fixed on the bench and is connected with a torque brake device that may provide continuous braking for torque. By providing the torque brake device that may provide continuous braking for torque to detect a torque peak, measurement precision is improved; the torque brake device is arranged as a bolt, continuous braking is achieved by tightening the bolt; compared with simulated bolts, the dynamic torque detection system as a calibrator allows an actually used bolt to be sued in the detection process, and the actual condition can be simulated to maximum extent.
Owner:SICHUAN DONG TAI MACHINERY MFG CO LTD
Load measuring apparatus, method, and program
ActiveUS8255173B2Efficient calibrationImprove the situationWind motor controlEngine fuctionsAerodynamic torqueMeasurement device
A load is based calibrate on data collected under wide observation conditions and promptly calibrate loads of a plurality of wind turbine blades. A load measuring apparatus is applied to a wind turbine in which a pitch angle of a wind turbine blade is variable. The apparatus includes a sensor for obtaining a distortion of the wind turbine blade; a load calculating unit having a function expressing a relation between the distortion of the wind turbine blade and a load on the wind turbine blade, for obtaining the load on the wind turbine blade by applying to the function the distortion based on measurement data of the sensor; and a calibration unit for calibrating the function based on the measurement data of the sensor obtained in a pitch angle range and a rotational speed range of the wind turbine blade in which a variation between maximum and minimum aerodynamic torques is equal to or less than a predetermined value.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
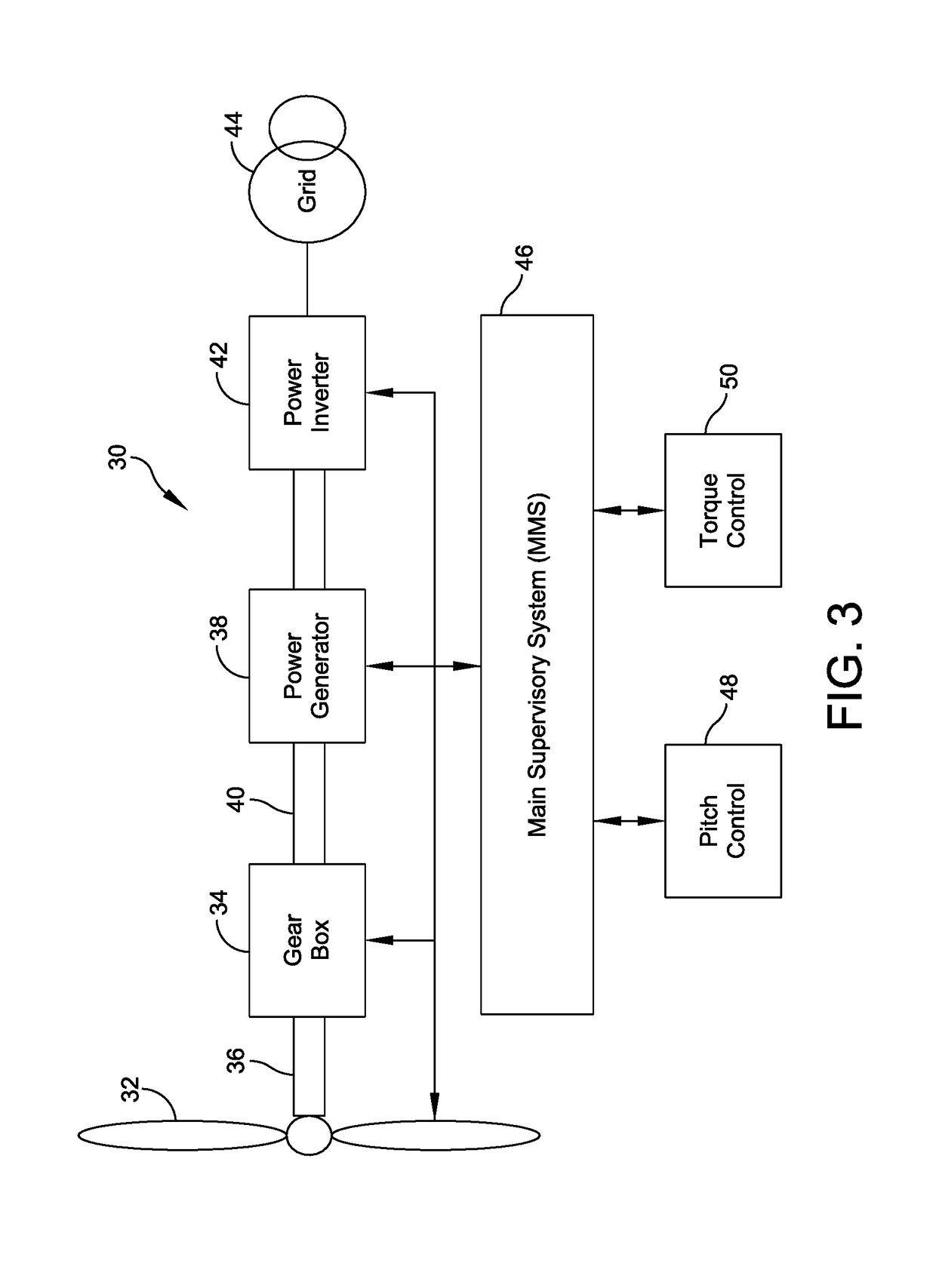
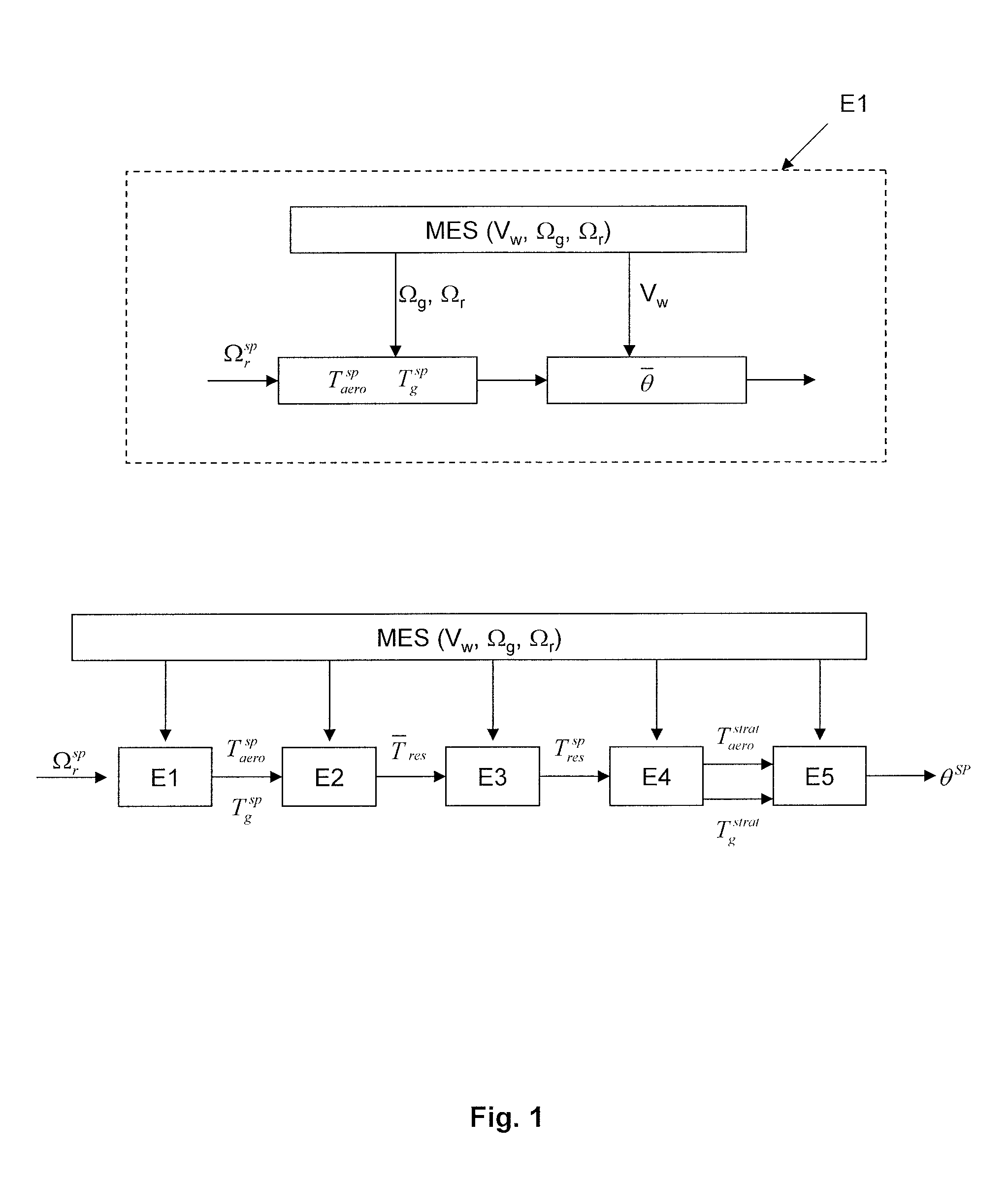
Wind turbine control methods and systems
ActiveUS20120193918A1Control speedRapid responseRotational speed controlWind motor controlAerodynamic torqueControl system
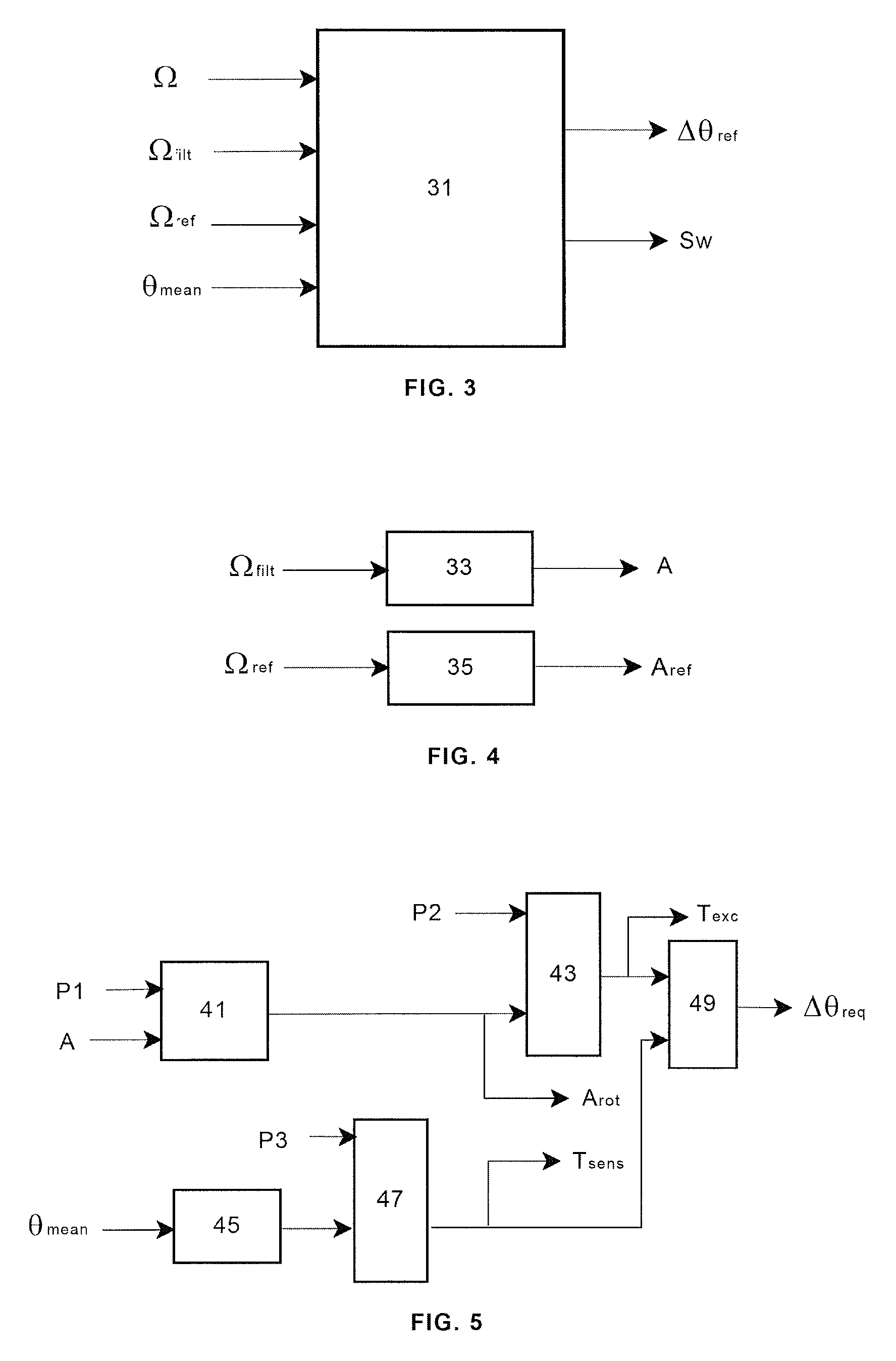
Improved wind turbine control methods and systems. The invention relates to a method for the operation of a variable speed wind turbine having pitch and torque control means that include additional steps for providing to the pitch control means in case of a wind gust a pitch angle reference increment Dθref in the amount needed for avoiding that the aerodynamic torque added by the wind gust exceeds a predetermined limit. The present invention also relates to a wind turbine comprising a control system arranged for performing an additional regulation in case of wind gust
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
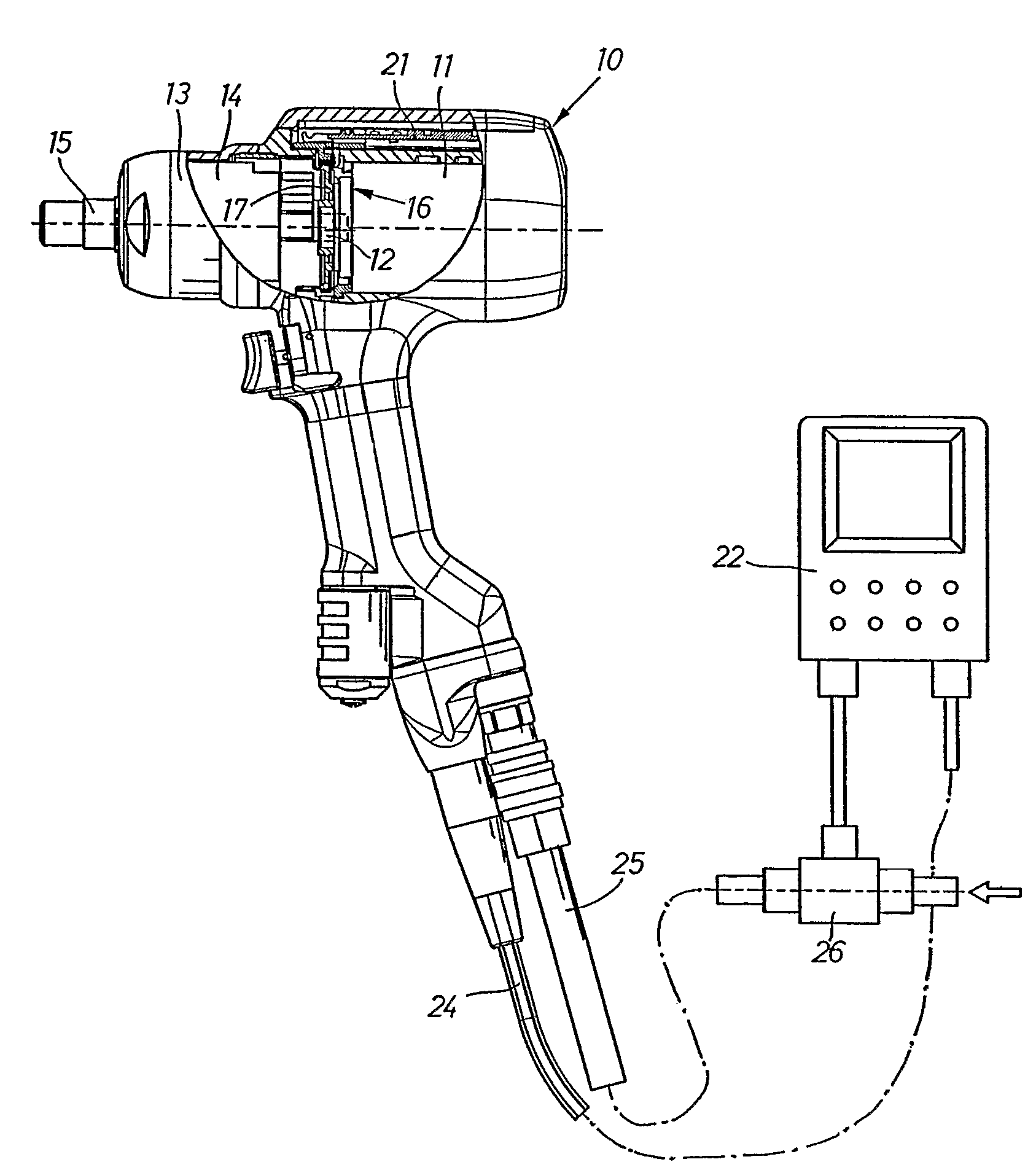
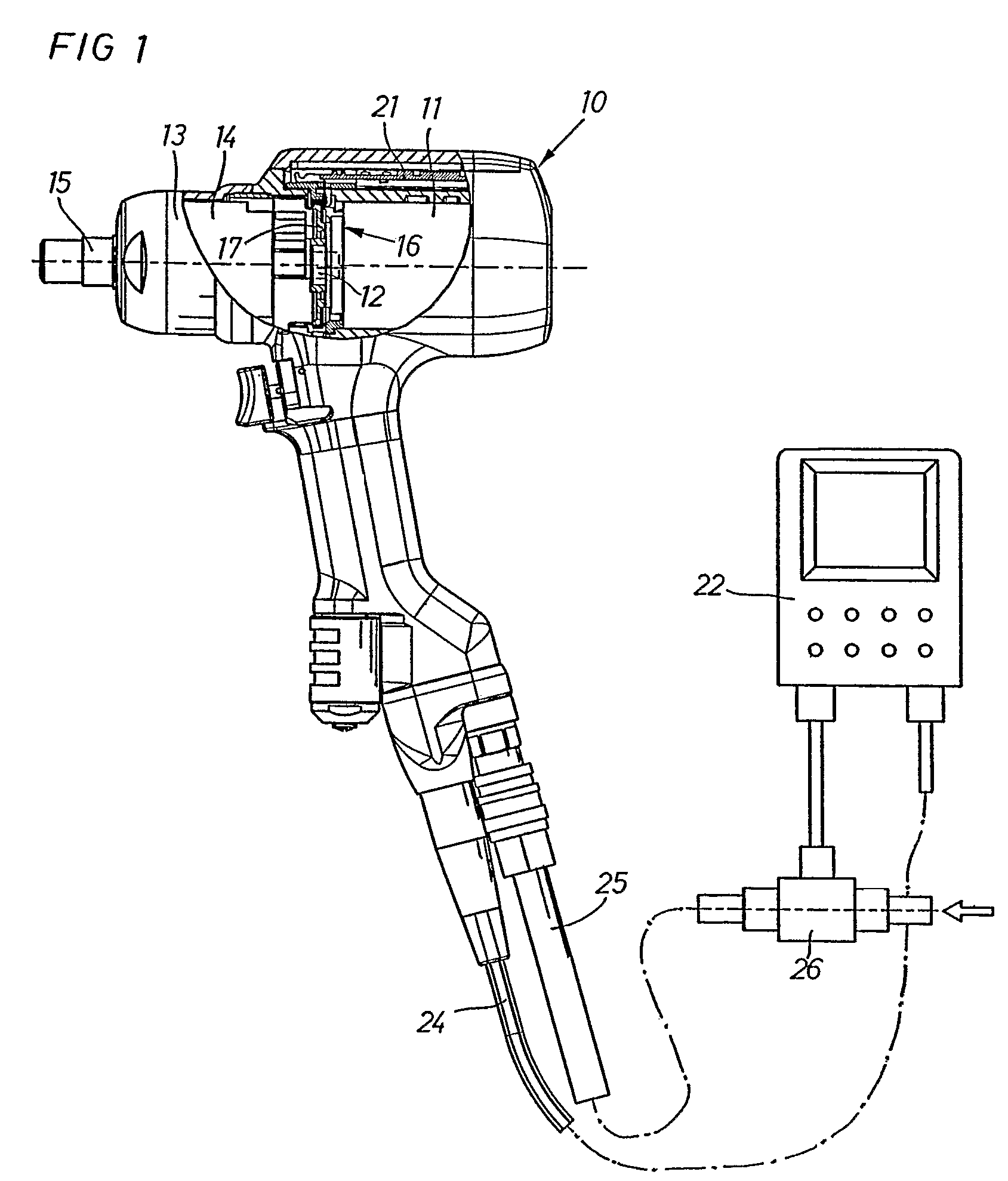
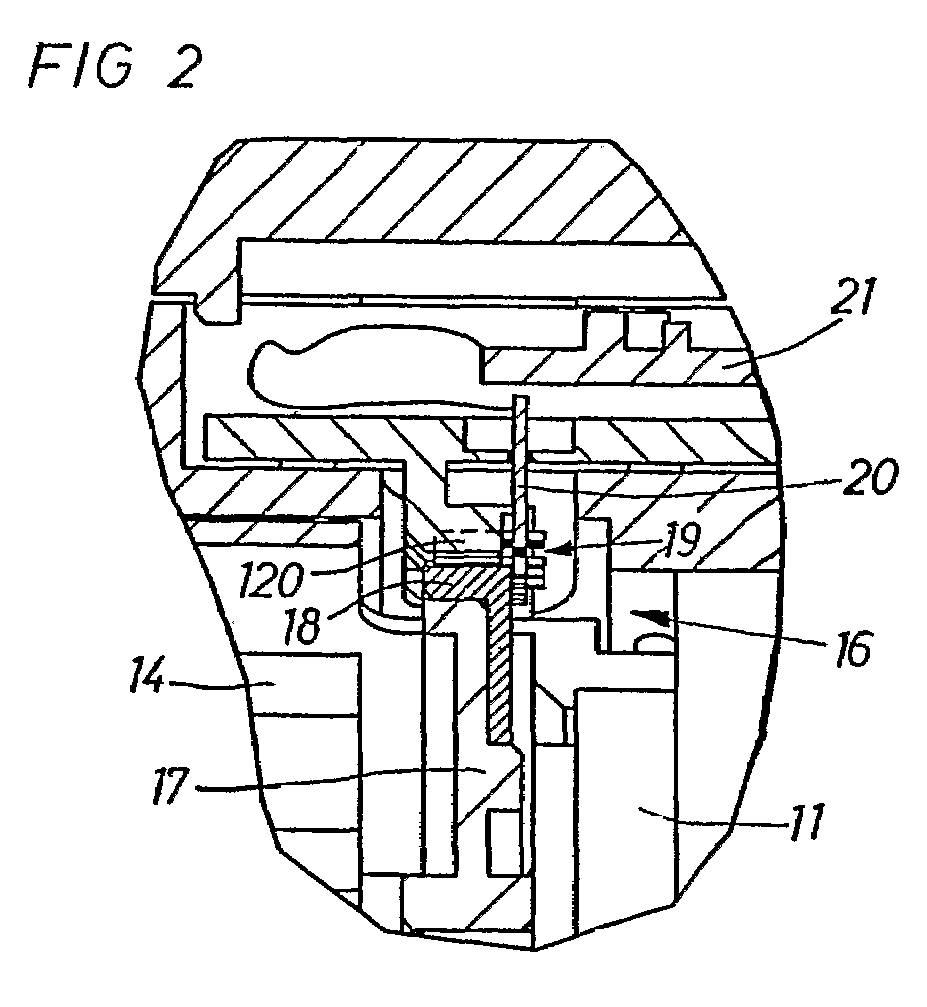
Method for governing the operation of a pneumatic impulse wrench and a power screw joint tightening tool system
A method and a power tool system are provided for performing screw joint tightening using a pneumatic torque impulse power tool that is controlled by a control unit. A torque magnitude and a torque growth are calculated based on signals delivered by an angle sensor, and pressurized air is supplied to the power tool via a flow regulating valve which is successively adjustable between zero and full power flow. The flow regulating valve is controlled by the control unit to deliver a reduced power air flow to the power tool before and during a first delivered impulse, and then to deliver full power flow until a certain torque magnitude or a percentage of a target torque level is reached, whereafter the air supply flow is again reduced until the target torque level is reached, and when the target torque level is reached the air flow is shut off.
Owner:ATLAS COPCO TOOLS AB
Stator blade mounting structure
ActiveCN107725117AMeet the sealMeet the structureBlade accessoriesMachines/enginesAerodynamic torqueGas turbines
The invention relates to a stator blade mounting structure which can be applied to the fields of ground gas turbines, aero-engines and the like. The stator blade mounting structure comprises stator blades with a pressing plate, inner and outer ring light elastic parts, inner and outer ring casings and an outer ring pressing hoop. Through the parts, the single blade dismantling function of the stator blades can be achieved. As the light elastic parts are adopted, assembling and positioning of the whole-ring stator blades are achieved through the cold-state interference magnitude of the light elastic parts and the inner and outer ring blade profiles of the blades. Under an assembly state, the stator blade mounting structure has certain rigidity and can transfer aerodynamic torque of the stator blades to the corresponding position of a casing mounting edge. By means of the structure, the weight of the ground gas turbines and the aero-engines can be remarkably reduced. The maintainabilityof the stator blades is improved while the machining difficulty of the stator blades is lowered, and the single blade dismantling function of the blades is achieved. Through the structure, under the excitation action force of mainstream unsteady airflow in a channel, the risk of self-excited vibration of the stator blades can be reduced.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Variable speed control of wind turbine generator based on estimated torque
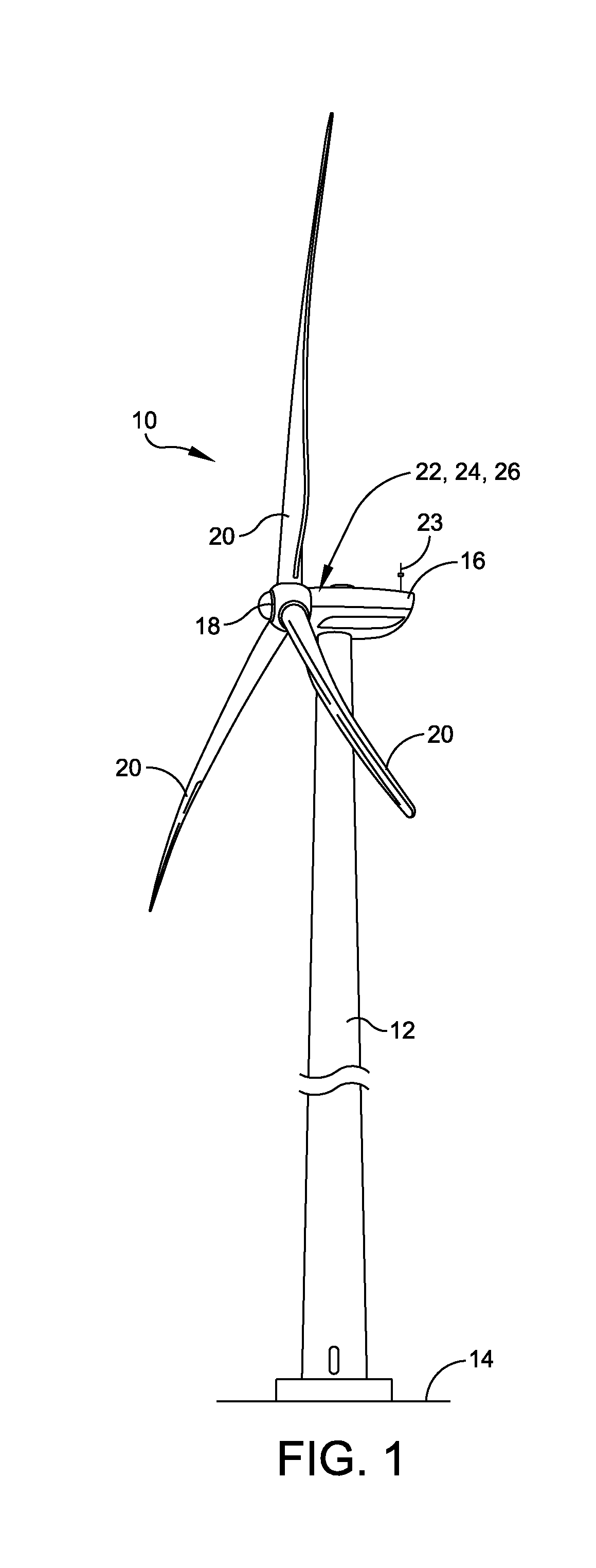
InactiveUS20190072072A1Minimal torque valueEasy to harvestWind motor controlWind motor combinationsAerodynamic torqueActuator
A system for controlling a wind turbine generator includes a rotor blade assembly having rotor blades and a pitch actuator to control a pitch of the rotor blades, a gear box coupled to the rotor blade assembly, a power generator coupled to the gear box, and a main controller. The main controller is configured to control the aerodynamic torque applied on the rotor blades based on pitch control commands, and separately configured to control a generator speed of the power generator based on torque control commands. The system further includes a pitch controller configured to receive pitch calculation information from the main controller, calculate the pitch control commands, and return the pitch control commands to the main controller. The system further includes a torque controller configured to receive torque calculation information from the main controller, calculate the torque control commands, and return torque control commands to the main controller.
Owner:ENVISION ENERGY USA LTD
Wind turbine control methods and systems
ActiveUS8810055B2Control speedRapid responseRotational speed controlWind motor controlAerodynamic torqueControl system
Improved wind turbine control methods and systems. The invention relates to a method for the operation of a variable speed wind turbine having pitch and torque control means that include additional steps for providing to the pitch control means in case of a wind gust a pitch angle reference increment Dθref in the amount needed for avoiding that the aerodynamic torque added by the wind gust exceeds a predetermined limit. The present invention also relates to a wind turbine comprising a control system arranged for performing an additional regulation in case of wind gust.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
Method for controlling a wind turbine by optimizing its production while minimizing the mechanical impact on the transmission
ActiveUS20130261819A1Optimizing energy productionMinimizing mechanical impactMechanical power/torque controlOptimise machine performanceAerodynamic torqueNacelle
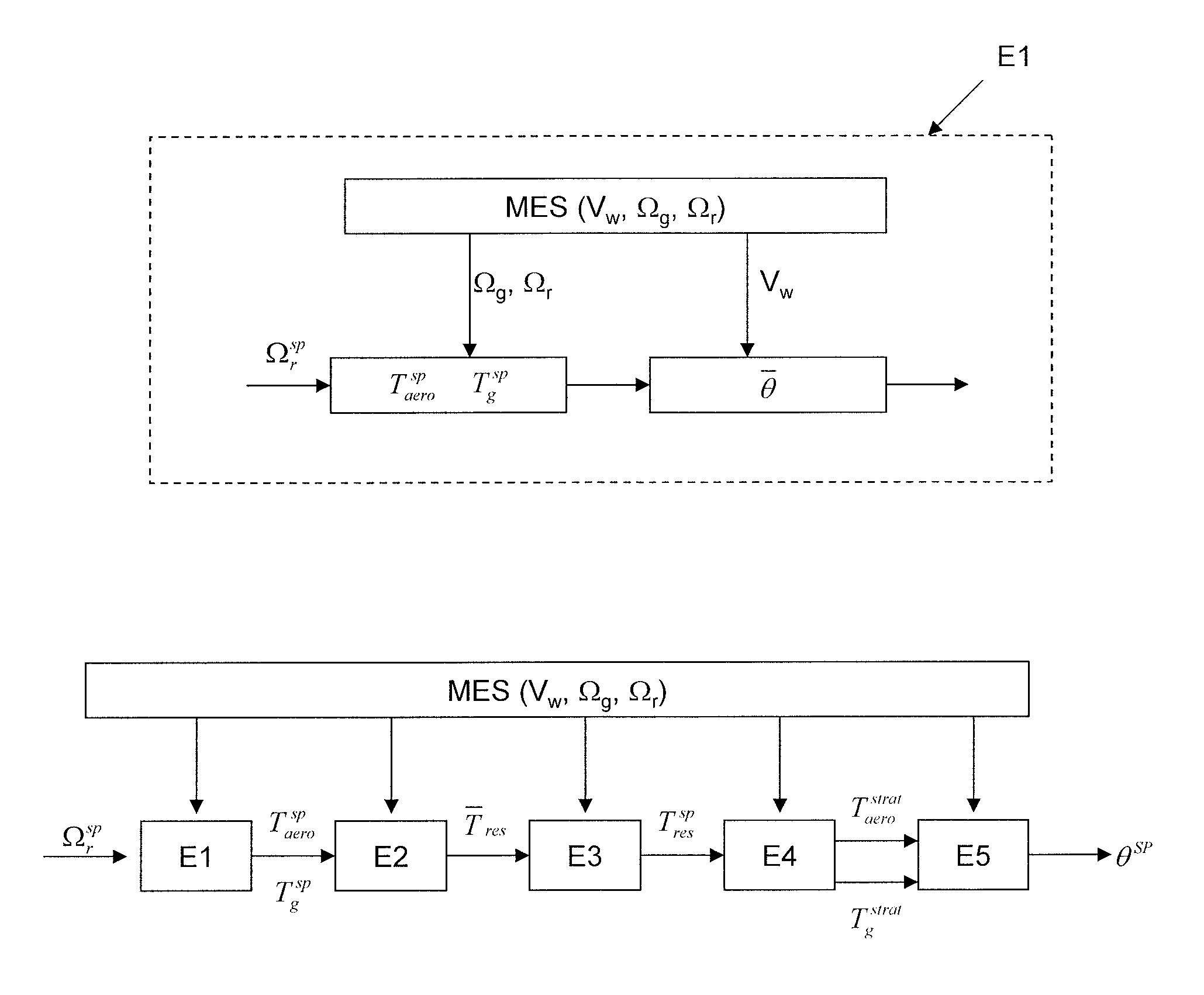
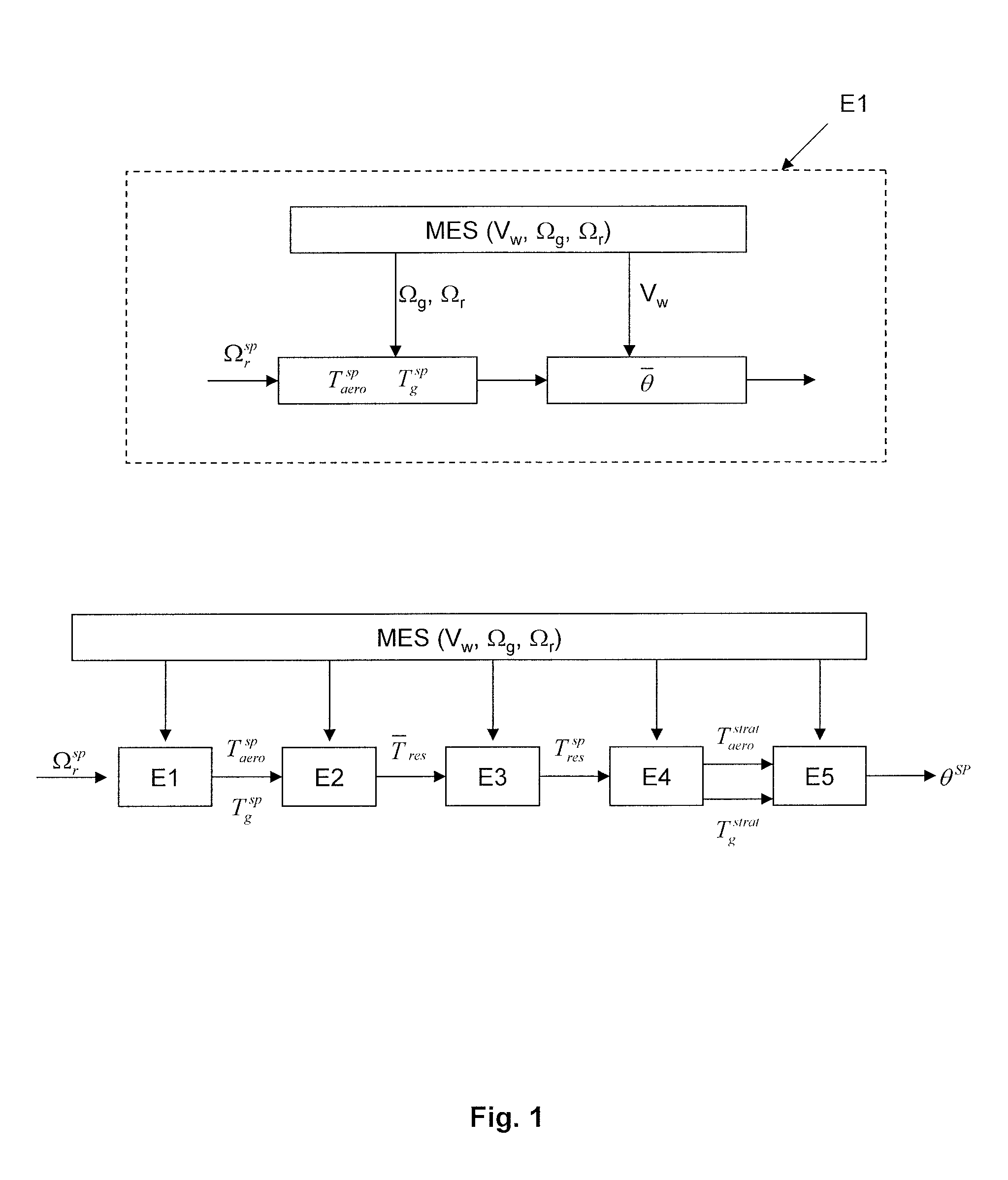
A method is disclosed for controlling a wind turbine by optimizing its production while minimizing the mechanical impact on the transmission. The wind turbine comprises a nacelle provided with a rotor on which blades are fastened, and an electrical machine linked to the rotor by a transmission, in which an pitch angle of the blades is controlled, comprising: An aerodynamic torque setpoint and an electrical machine torque setpoint making possible maximizing the recovered power are determined, from measurements of wind speed, of rotor speed and of electric machine speed. At least one of the setpoints is modified by subtracting from it a term proportional to a difference between the measured speed of the rotor and the measured speed of the electric machine. A pitch angle of the blades making possible production of the aerodynamic torque setpoint is determined. The blades are oriented according to the angle of inclination.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Torque ripple suppression method for direct-drive wind turbine generator
ActiveCN111987956AReduce speed fluctuationHarmonic reductionElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlMathematical modelLow-pass filter
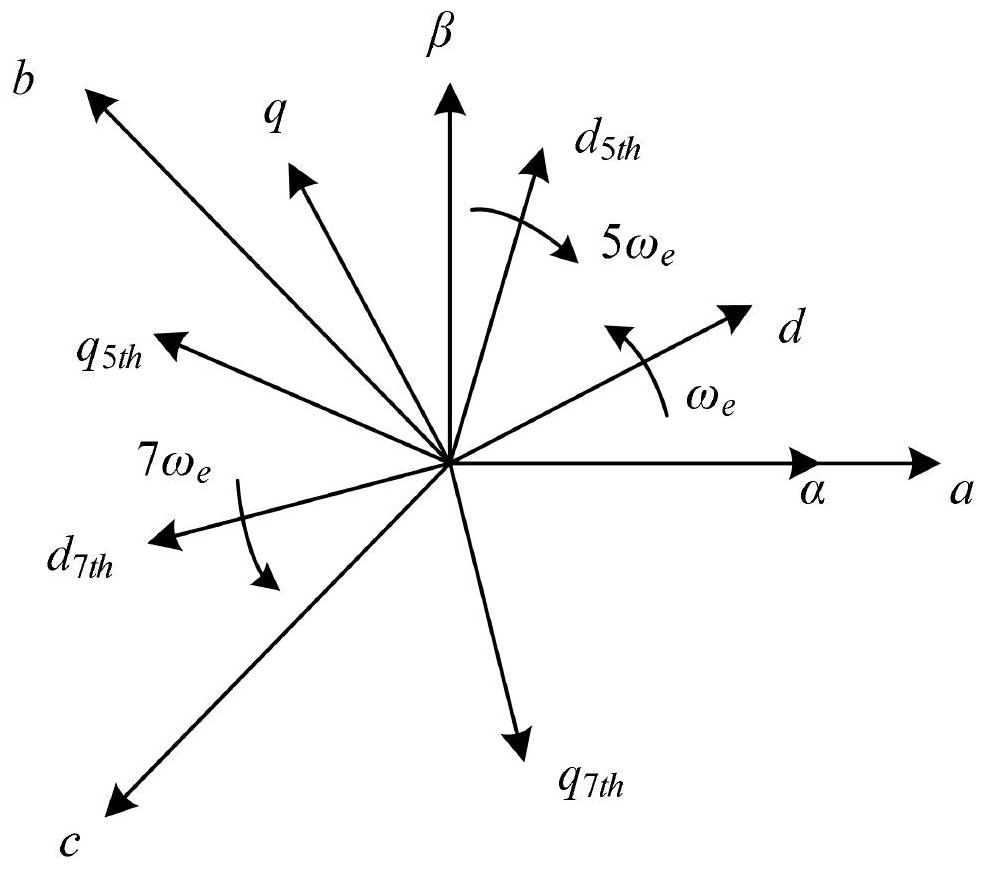
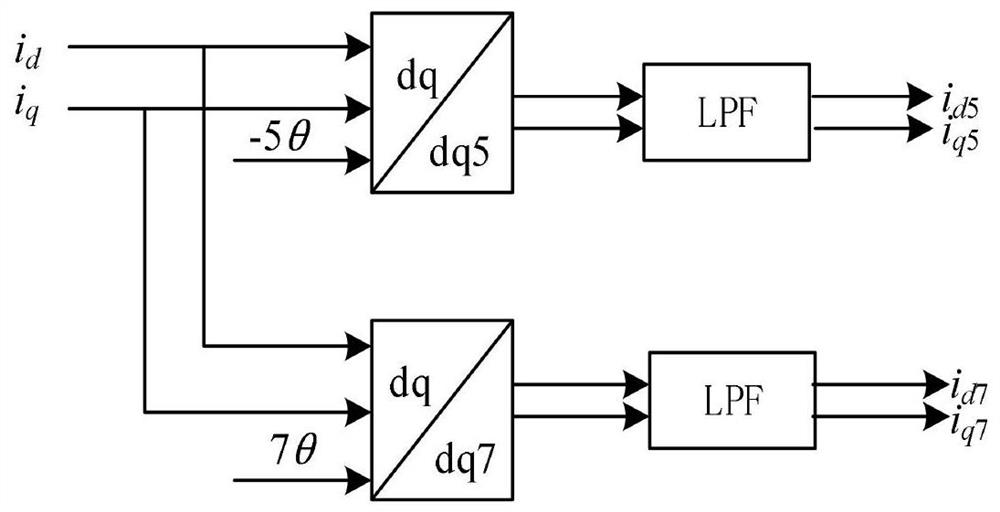
The invention provides a torque ripple suppression method for a direct-drive wind turbine generator, and relates to the technical field of wind power generation. The method comprises: for electromagnetic torque pulsation, using a harmonic voltage compensation suppression method: using a low-pass filter to extract a higher harmonic current component, calculating and superposing a harmonic voltage compensation value to a reference voltage, and the harmonic component being offset; for aerodynamic torque pulsation, using an independent variable pitch control method, establishing a weight coefficient distributor, calculating pitch angles corresponding to different blades through a mathematical model of weight coefficient distribution and acting on a variable pitch mechanism, and aerodynamic torque pulsation caused by pitch angle pulsation being reduced; and finally, on the basis of a harmonic voltage compensation method, arranging a rotating speed controller, the difference value between the actual rotating speed and the rated rotating speed of a generator serving as a deviation value and being introduced into the input end of the rotating speed controller, the output end of the rotating speed controller being a unified pitch angle reference value, and then achieving the cooperative suppression of pneumatic torque pulsation and electromagnetic torque pulsation in combination with anindependent variable pitch control method.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method for controlling a wind turbine by optimizing its production while minimizing the mechanical impact on the transmission
ActiveUS9458826B2Promote productionMinimize impactMechanical power/torque controlOptimise machine performanceAerodynamic torqueNacelle
A method is disclosed for controlling a wind turbine by optimizing its production while minimizing the mechanical impact on the transmission. The wind turbine comprises a nacelle provided with a rotor on which blades are fastened and an electrical machine linked to the rotor by a transmission in which pitch angle of the blades is controlled, comprising An aerodynamic torque setpoint and an electrical machine torque setpoint making possible maximizing the recovered power are determined from measurements of wind speed, of rotor speed and of electrical machine speed. At least one of the setpoints is modified by subtracting from it a term proportional to a difference between the measured speed of the rotor and the measured speed of the electrical machine. A pitch angle of the blades making possible production of the aerodynamic torque setpoint is determined. The blades are oriented according to the angle of inclination.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
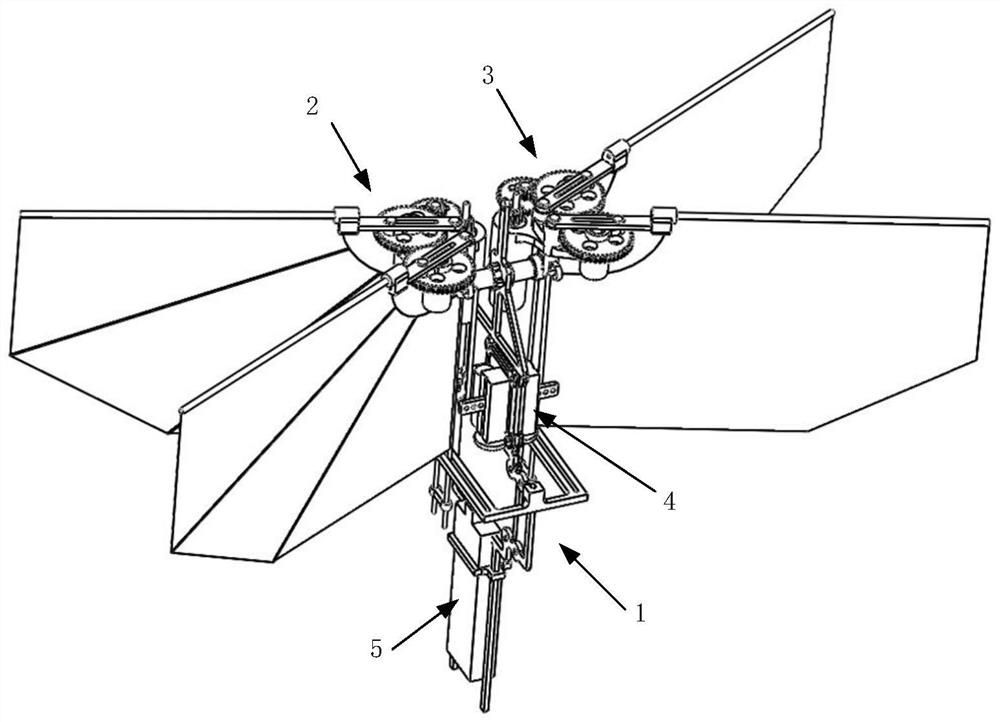
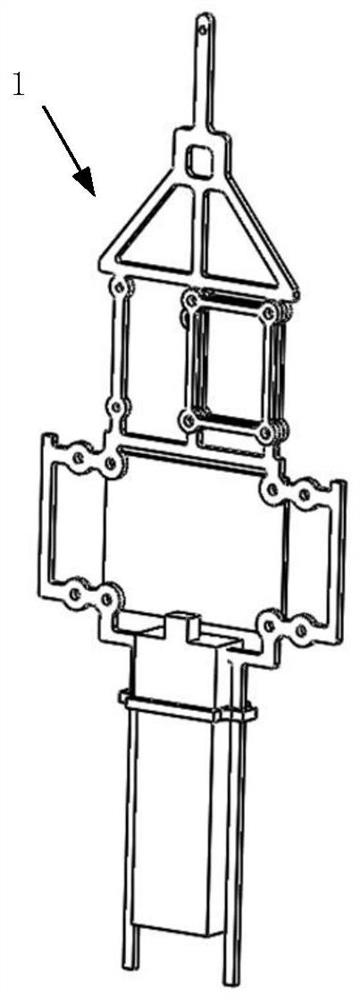
Hovering type miniature bionic double-flapping-wing flying robot
The invention discloses a hovering type miniature bionic double-flapping-wing flying robot which is composed of flapping mechanisms, a control mechanism and a power supply and control system, wherein the flapping mechanisms and the control mechanism are arranged on the two sides of a main machine frame. The flapping mechanism can rotate around the connecting shaft, power is output through the hollow cup motor, flapping motion of the bionic wings is achieved, then aerodynamic force and aerodynamic torque (rolling torque) are generated, when the bionic wings move, high lift force is generated through a clap-fling mechanism similar to insect flapping, and high aerodynamic efficiency is achieved. The control mechanism drives the whole flapping mechanism rack to rotate by virtue of a linear steering engine, so that the flapping plane of the bionic wing is changed, the aerodynamic force / moment direction is changed, and pitching and yawing torques are generated; The power supply and control system is realized by a control circuit board, and the whole system is powered by a battery. The parts are made of carbon fiber plates or 3D printing materials, so that the robot is light and small, the flight efficiency is improved, and the robot has ultrahigh maneuverability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Detection equipment and detection method for torque spanners
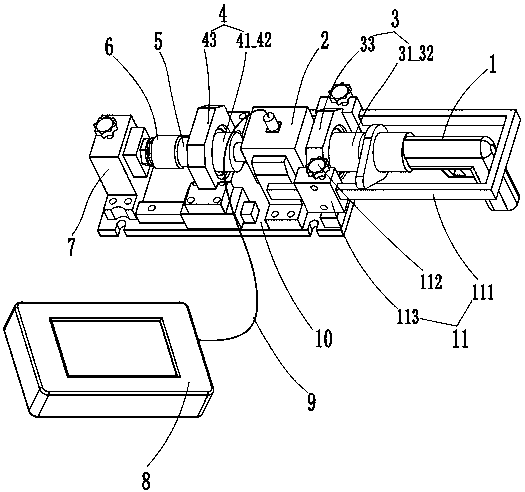
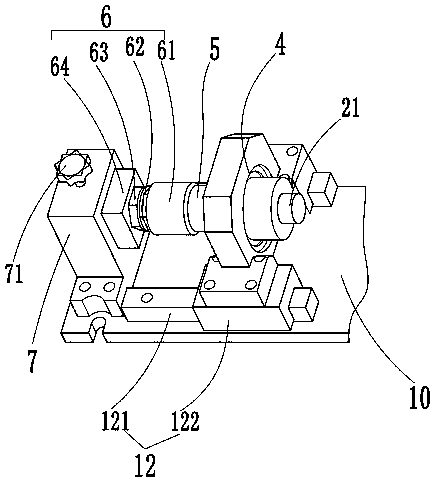
PendingCN107588881AHigh sampling frequencyImprove measurement accuracyMachine part testingMeasurement of torque/twisting force while tighteningAerodynamic torquePeak value
The invention discloses a detection technology for torque spanners. Detection equipment for the torque spanners comprises a rack, a dynamic torque sensor and a bolt clamping part, wherein one end of arotary shaft of the dynamic torque sensor is used for installing the torque spanner, and the other end of the rotary shaft of the dynamic torque sensor is connected with the bolt clamping part; the rack is provided with a positioning bracket for installing the dynamic torque sensor; a shell of the dynamic torque sensor is arranged on the positioning bracket in a supporting manner, so that a rotary shaft of the dynamic torque sensor can rotate along the torque spanners. According to the detection equipment disclosed by the invention, the dynamic torque sensor is adopted, the rotary shaft of the dynamic torque sensor rotates along the torque spanners, so that no impact is caused to the torque sensor, the actual state when a bolt is screwed can be simulated, the torque in the screwing process of the bolt can be dynamically detected, and the detection equipment can be used for verification, calibration and test of electric and pneumatic torque spanners; the sampling frequency is very high; an instantaneous peak value output by the detected torque spanners can be acquired, so that higher measurement accuracy can be guaranteed.
Owner:中国测试技术研究院力学研究所
Aircraft attitude control method and system under high-altitude condition based on numerical simulation
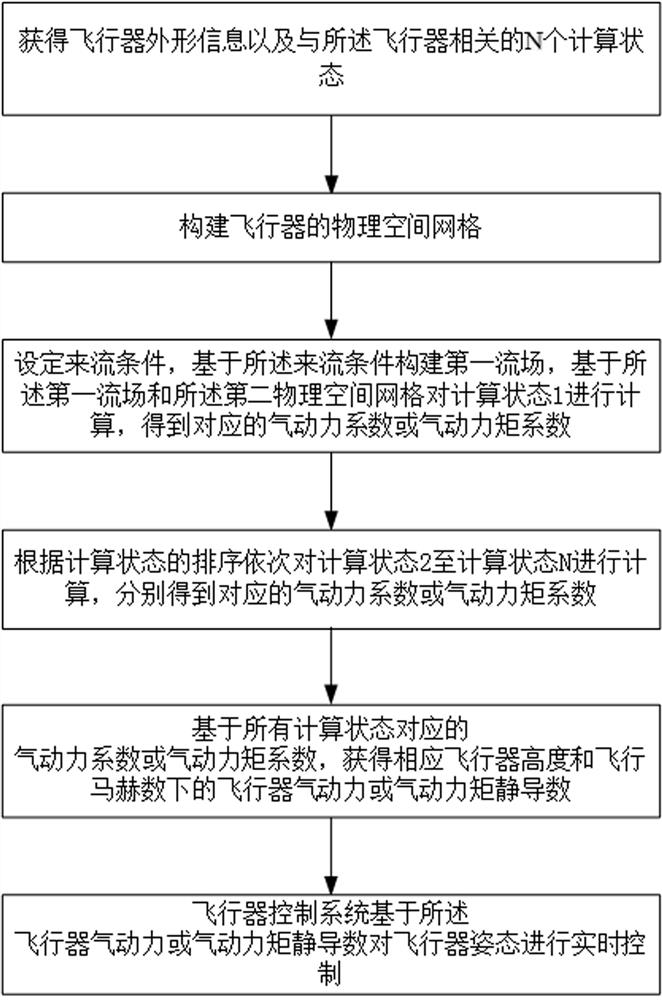
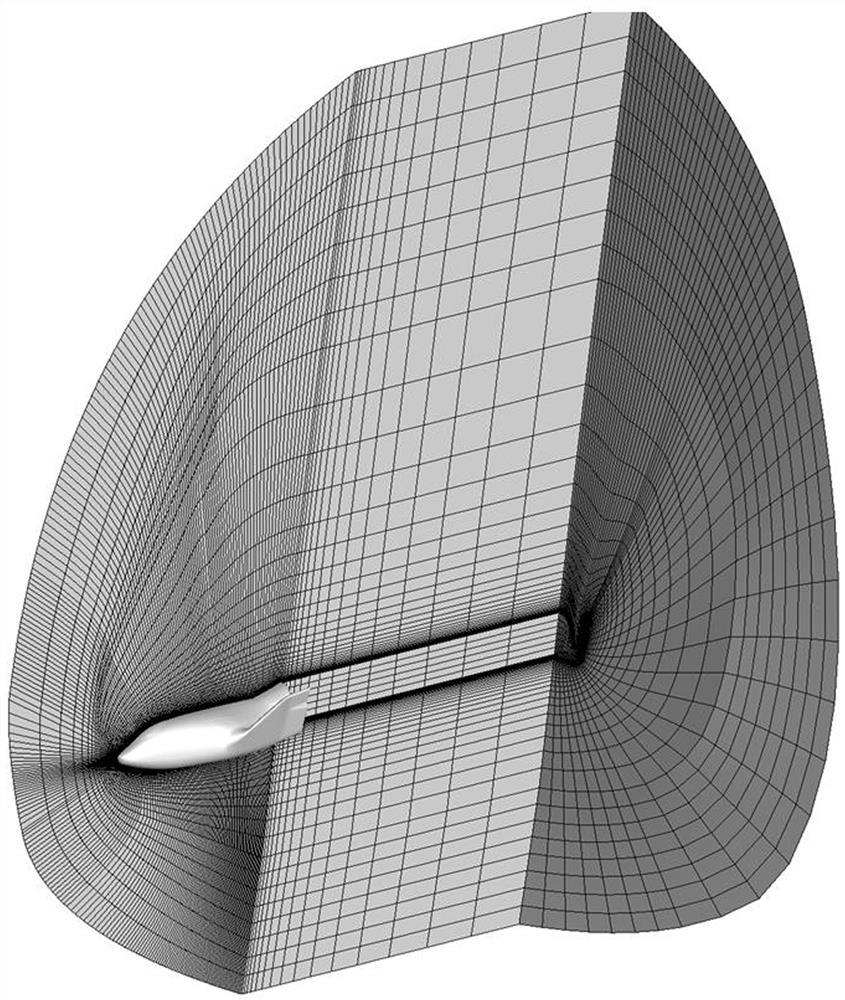
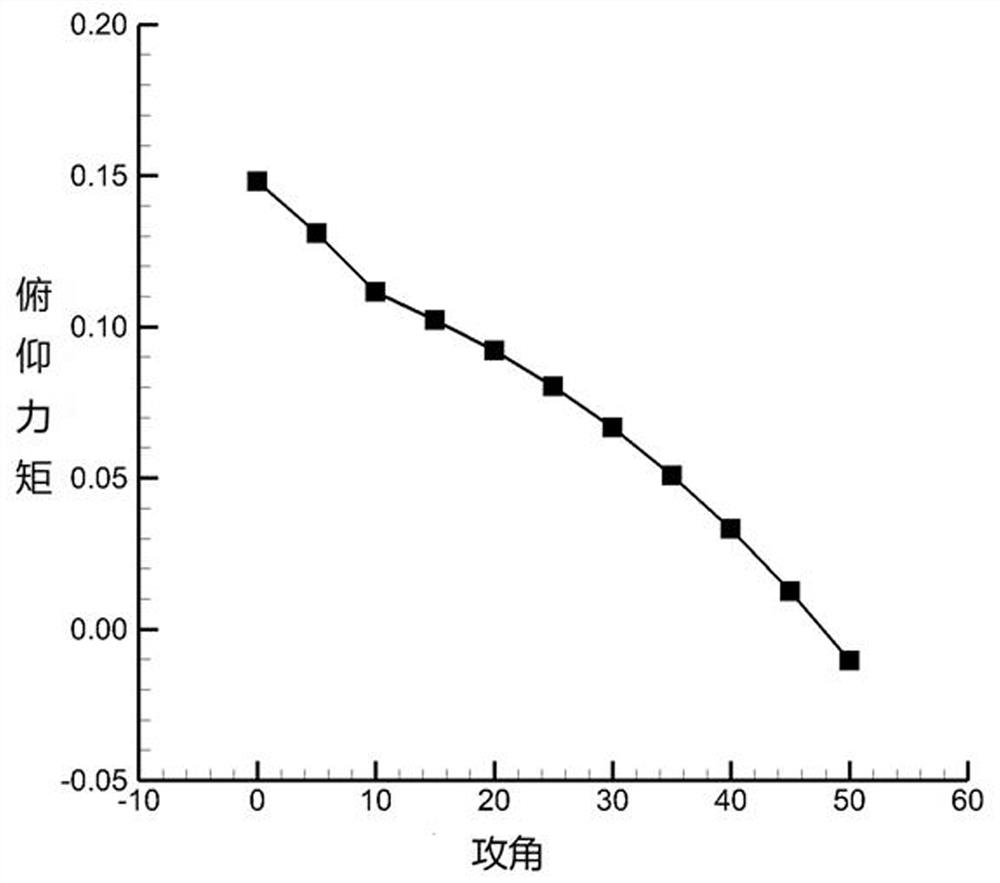
ActiveCN114444216AEffective controlEfficiently obtain static derivativesGeometric CADSustainable transportationAerodynamic torquePhysical space
The invention discloses an aircraft attitude control method and system under a high-altitude condition based on numerical simulation, and relates to the field of aircraft control, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining the shape information of an aircraft and N calculation states related to the aircraft, and obtaining a physical space grid of the aircraft; constructing a first flow field based on the incoming flow condition, and calculating the calculation state 1 based on the first flow field and the physical space grid to obtain a corresponding aerodynamic coefficient or aerodynamic torque coefficient; according to the sequence of the calculation states, calculating the calculation state 2 to the calculation state N in sequence to obtain corresponding aerodynamic coefficients or aerodynamic moment coefficients, and based on the aerodynamic coefficients or aerodynamic moment coefficients corresponding to all the calculation states, obtaining aircraft aerodynamic or aerodynamic moment static derivatives under corresponding aircraft heights and flight Mach numbers; the aircraft control system performs real-time control on the aircraft attitude based on the aircraft aerodynamic force or aerodynamic moment static derivative. According to the method, the calculation cost of numerical simulation in aircraft attitude control is reduced.
Owner:CALCULATION AERODYNAMICS INST CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Method of torque control and apparatus thereof
ActiveUS10564657B2Accurate outputAccurate tightening torqueMechanical power/torque controlSpannersMaximum torqueAerodynamic torque
Owner:CHINA PNEUMATIC CORP
Improved observation method suitable for equivalent wind speed of impeller surface of wind driven generator
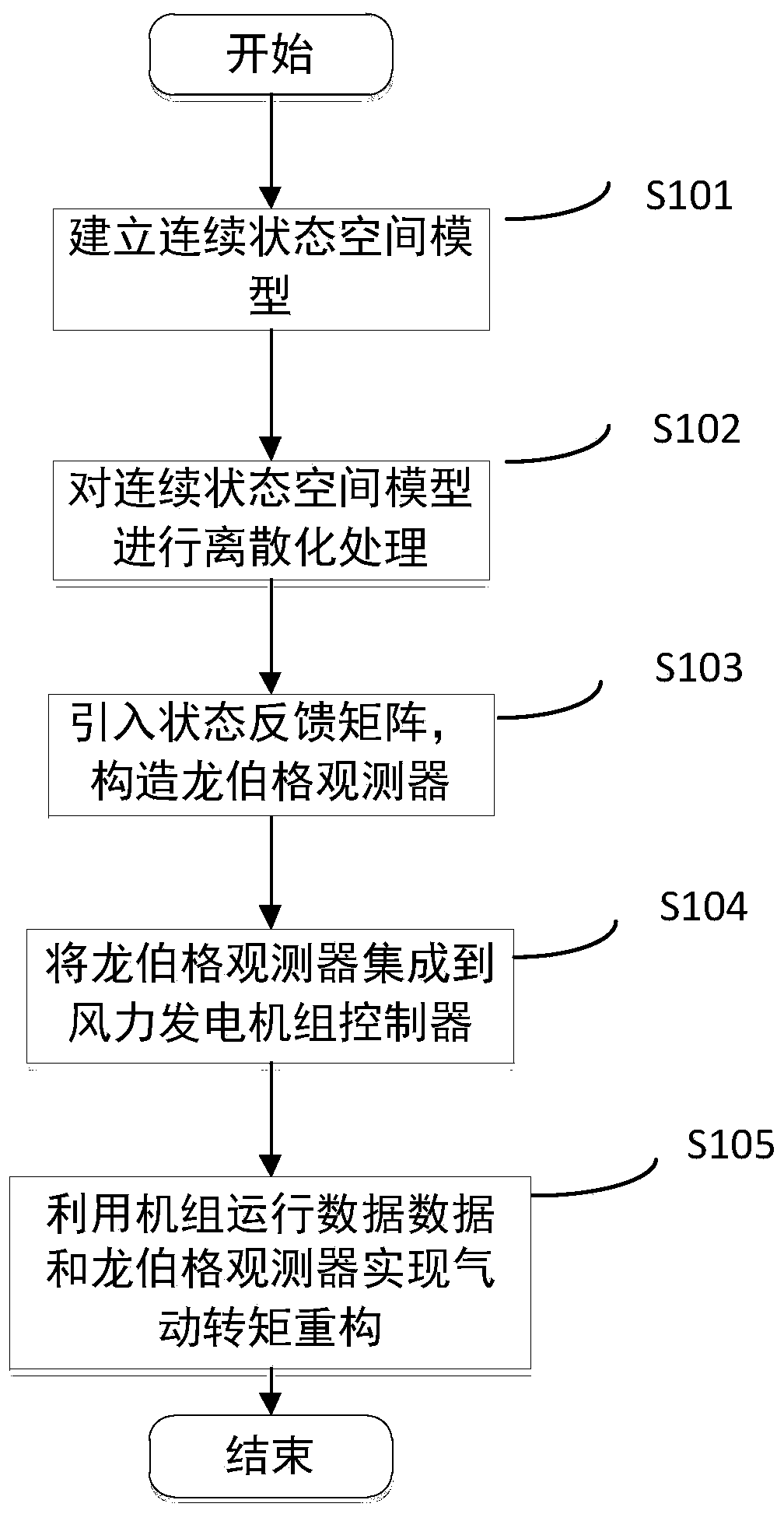
PendingCN111027169AAvoid excessive dependenceAchieve observationWind motor controlMachines/enginesLearning machineWind driven
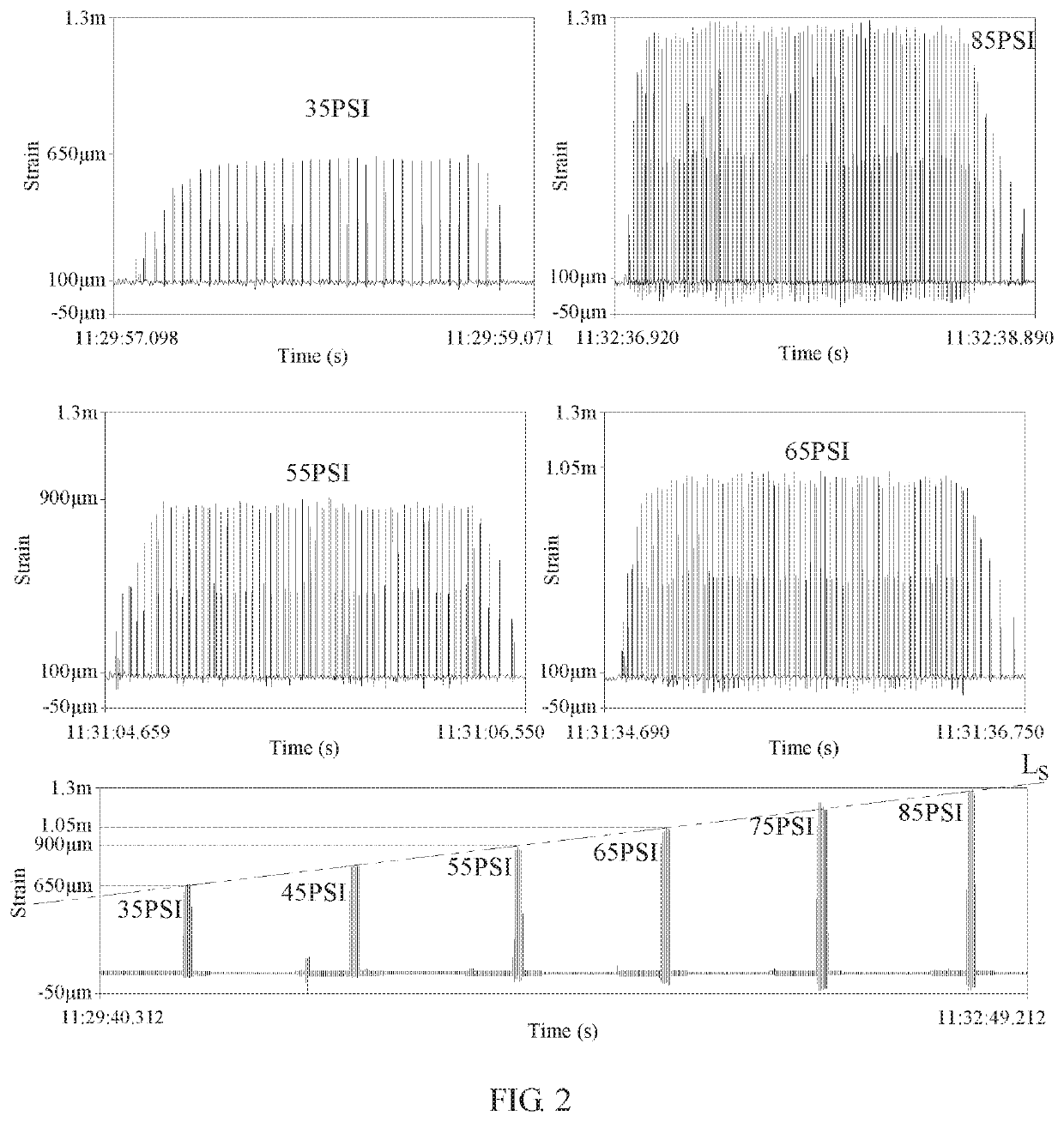
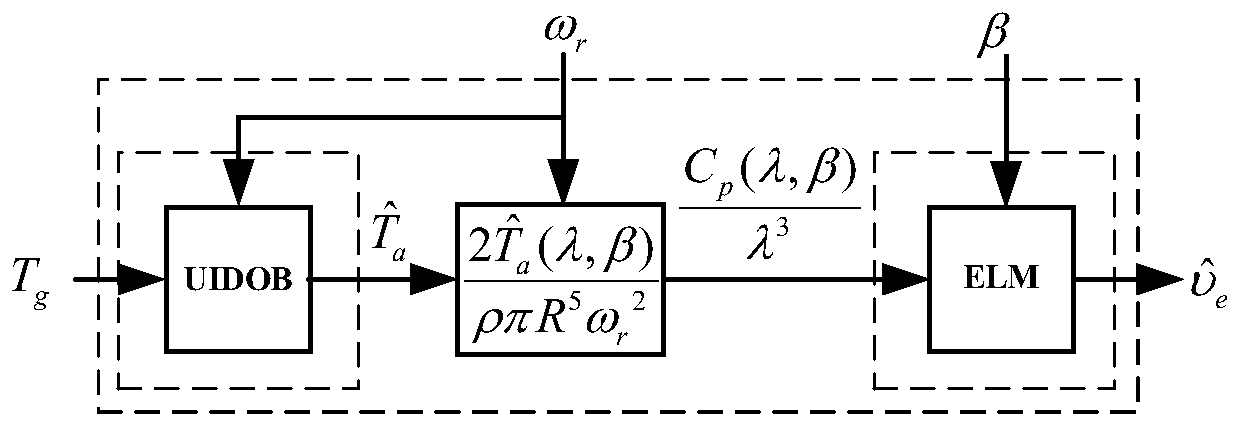
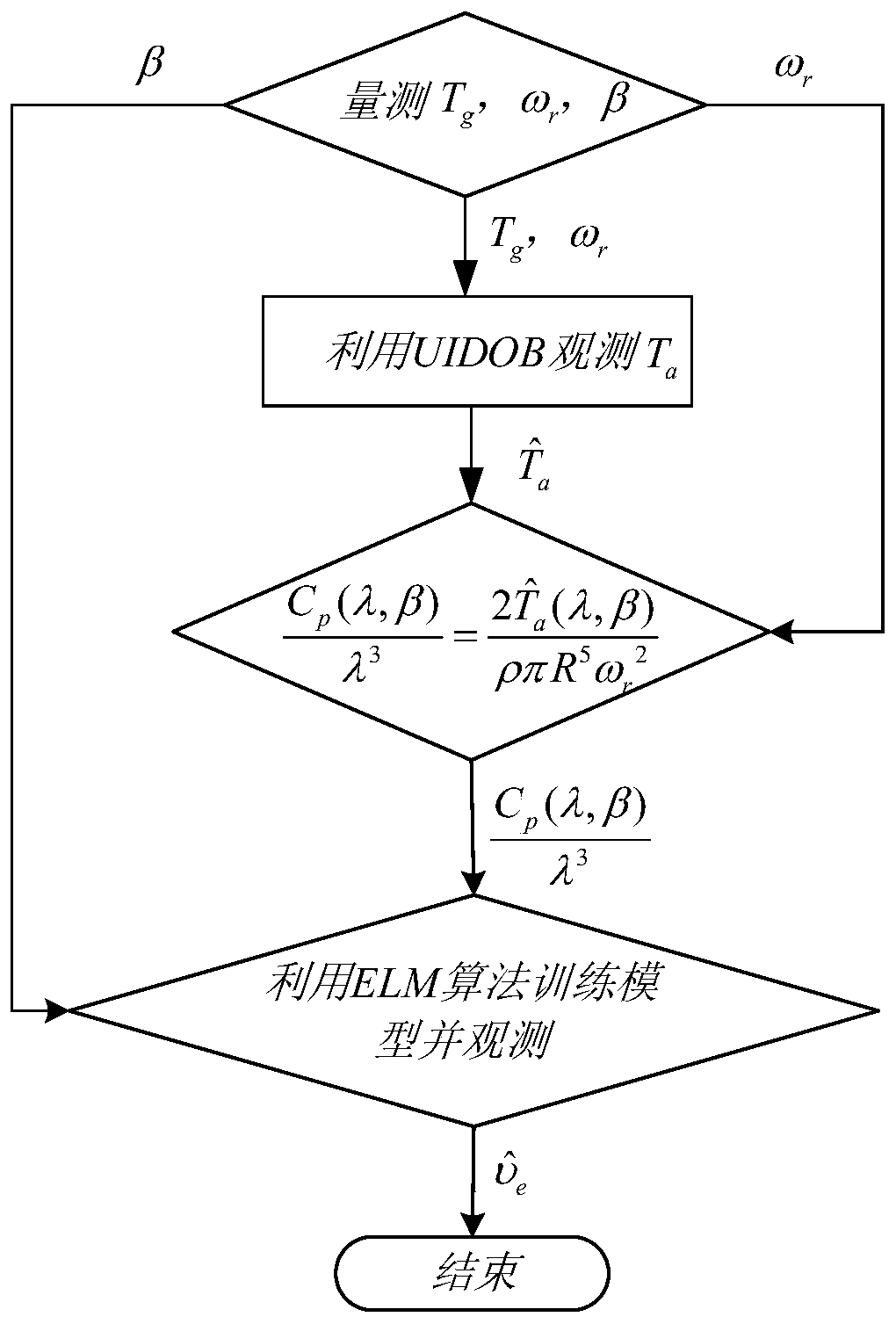
The invention provides an improved observation method for equivalent wind speed of an impeller surface of a wind driven generator. Aiming at the defects that an observation method based on a wind turbine generator mechanism model is high in dependence on model parameters and a method based on a neural network model is large in data volume, large in calculated amount, complex in model and the like,targeted improved modeling is carried out. Firstly, an unknown input disturbance observer is used for accurately observing unknown input aerodynamic torque of a fan transmission chain model; and thenan extreme learning machine model based on nonlinear input-output mapping is utilized to approach the aerodynamic characteristics of the wind turbine, so that the complexity of the model is reduced,meanwhile, the observation precision of the equivalent wind speed of the impeller surface is improved, and the observation speed is greatly increased.
Owner:JISHOU UNIVERSITY
Laser radar auxiliary control method based on impeller equivalent wind speed correction
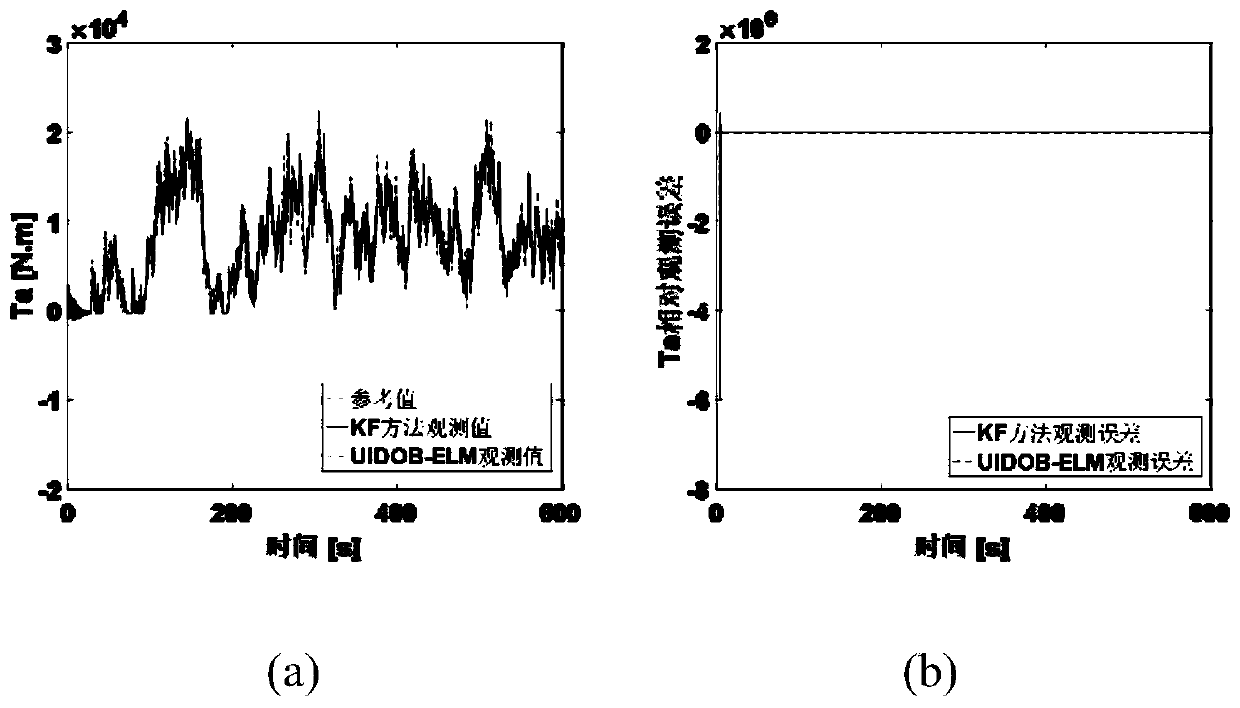
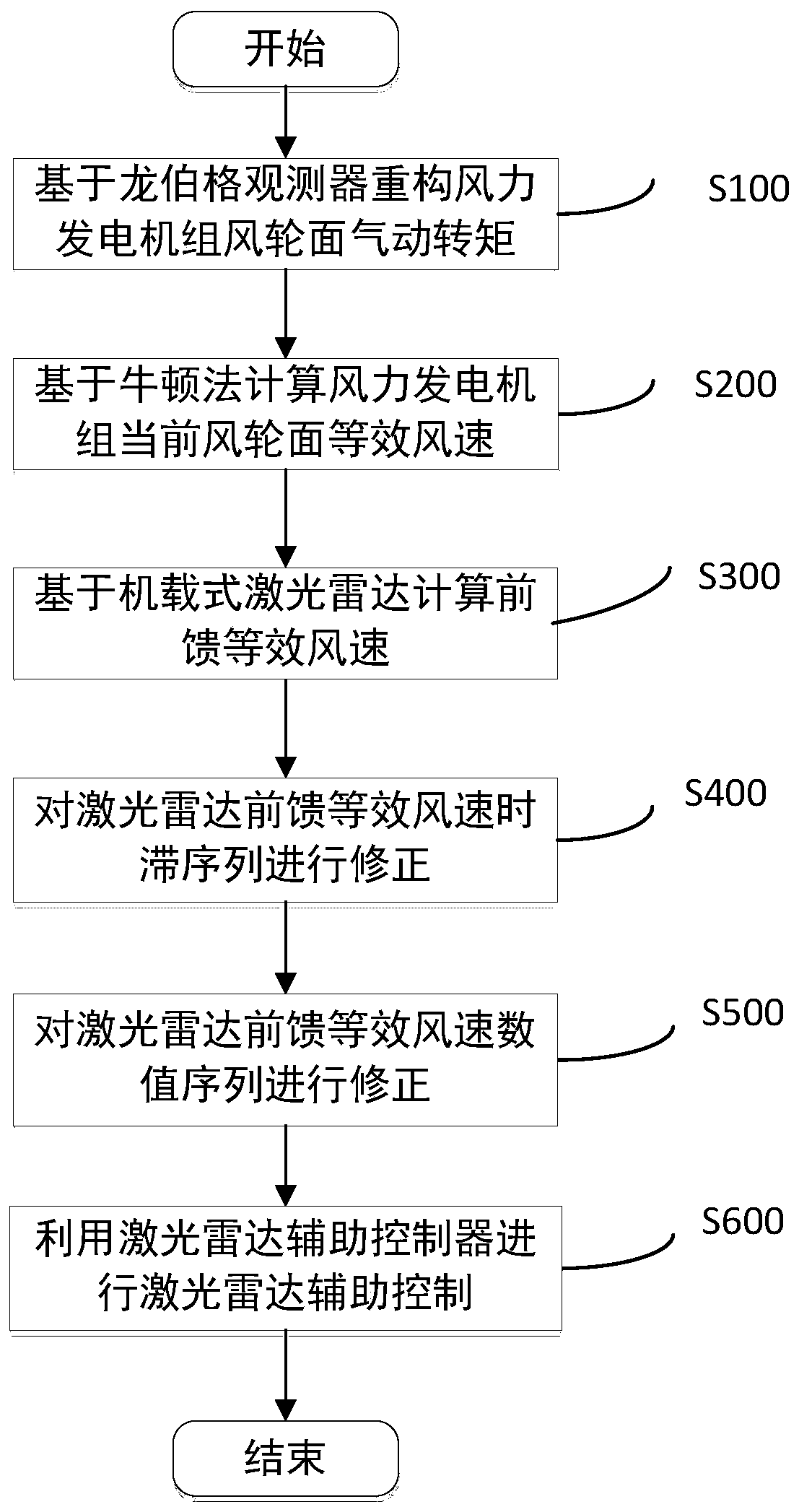
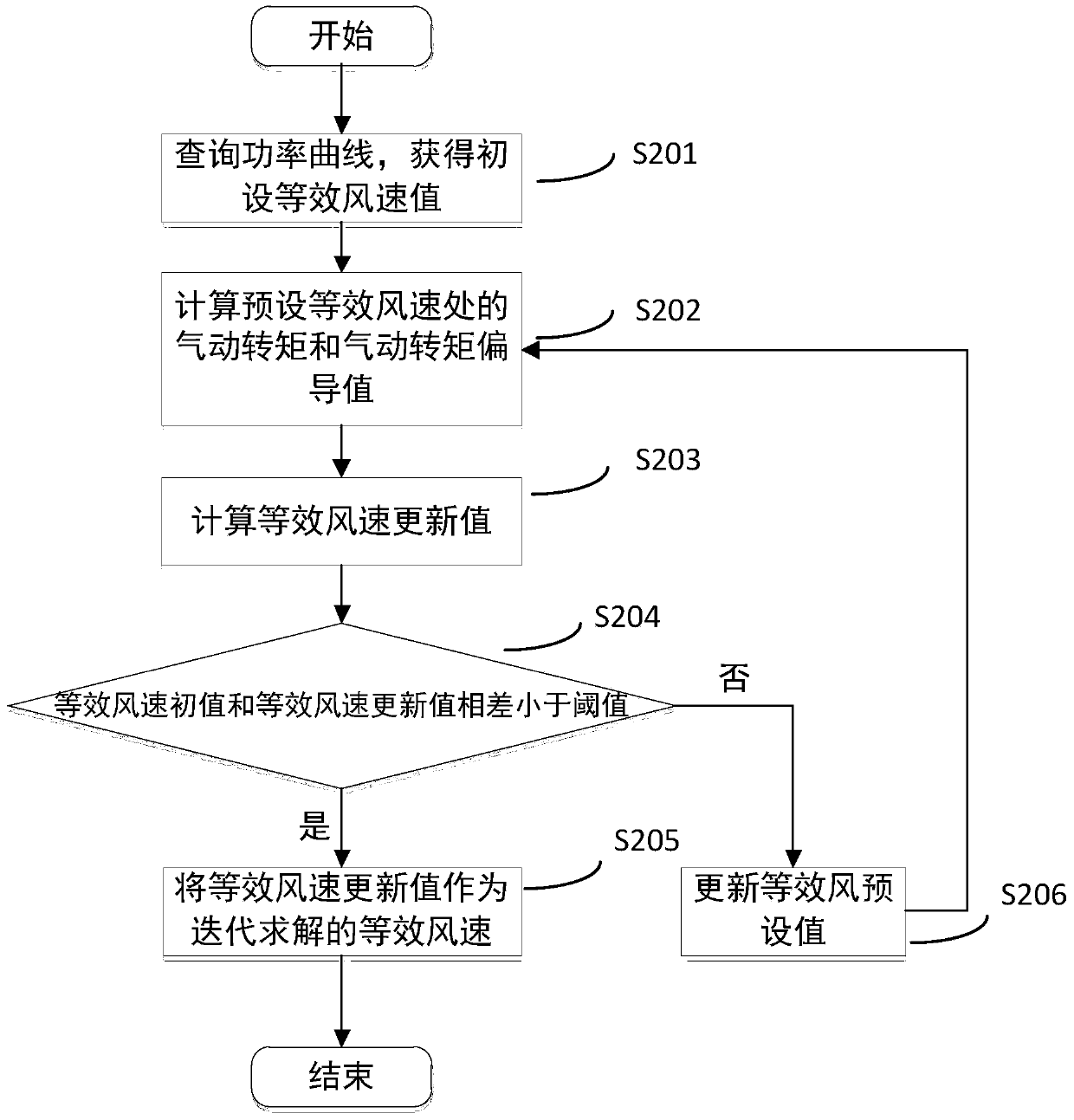
ActiveCN111396246AAuxiliary control implementationReduce the deviation of the actual equivalent wind speed valueWind motor controlMachines/enginesAerodynamic torqueRadar
The invention discloses a laser radar auxiliary control method based on impeller equivalent wind speed correction. The method comprises the following steps of reconstructing wind wheel surface aerodynamic torque of a wind generating set based on a luenberger observer; calculating current wind wheel surface equivalent wind speed of the wind generating set based on a newton method; calculating feedforward equivalent wind speed based on airborne laser radar; correcting laser radar feedforward equivalent wind speed time lag sequence; correcting laser radar feedforward equivalent wind speed numbersequence; and carrying out laser radar auxiliary control by using a laser radar auxiliary controller. The method has the following beneficial effects that the number deviation between the feedforwardequivalent wind speed provided by the airborne laser radar and the actual equivalent wind speed of a wind wheel of the wind generating set can be reduced, the actual time precision of the wind wheel of the wind generating set is improved, and the radar auxiliary control effect is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WINDEY
UAV(unmanned aerial vehicle) stability augmentation control method and device and UAV
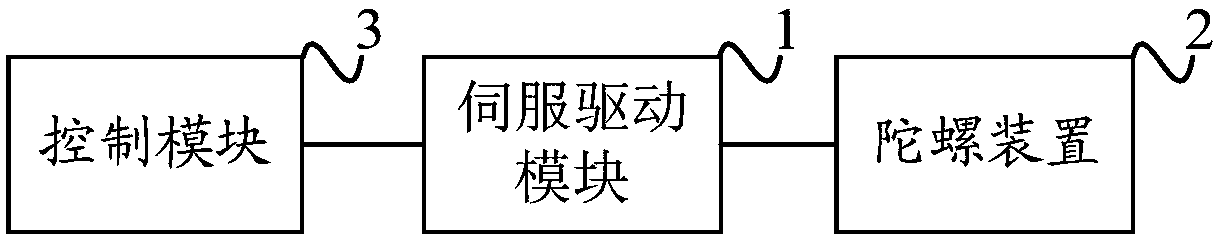
InactiveCN107894776ASolve instabilityImprove impact resistanceAttitude controlAerodynamic torqueComputer module
The invention discloses an UAV(unmanned aerial vehicle) stability augmentation control method and device. A control module obtains a current disturbance moment of an UAV platform, determines precession angle velocity of a gyro device needing for suppressing disturbance according to the current disturbance moment and generates a driving instruction for driving the gyro device to generate a corresponding control moment, and sends the driving instruction to a servo-driven module; and the servo-driven module receives the driving instruction, drives the gyro device to deflect to provide the corresponding control moment so as to suppress the interference of the current transient disturbance on UAV attitudes. The control method and device can increase additional mechanical torque control quantityunder the condition of not changing an original aerodynamic moment control structure, and quickly provide the control moment which is far greater than that capable of being provided by the aerodynamic torque of an UAV body, thereby solving the problem of easy instability of the UAV when the UAV is subjected to the impact load, and greatly improving disturbance resistance and impact resistance capability of the UAV. Besides, the invention also provides the UAV having the technical advantages above.
Owner:COOL HIGH TECH BEIJING CO LTD +1
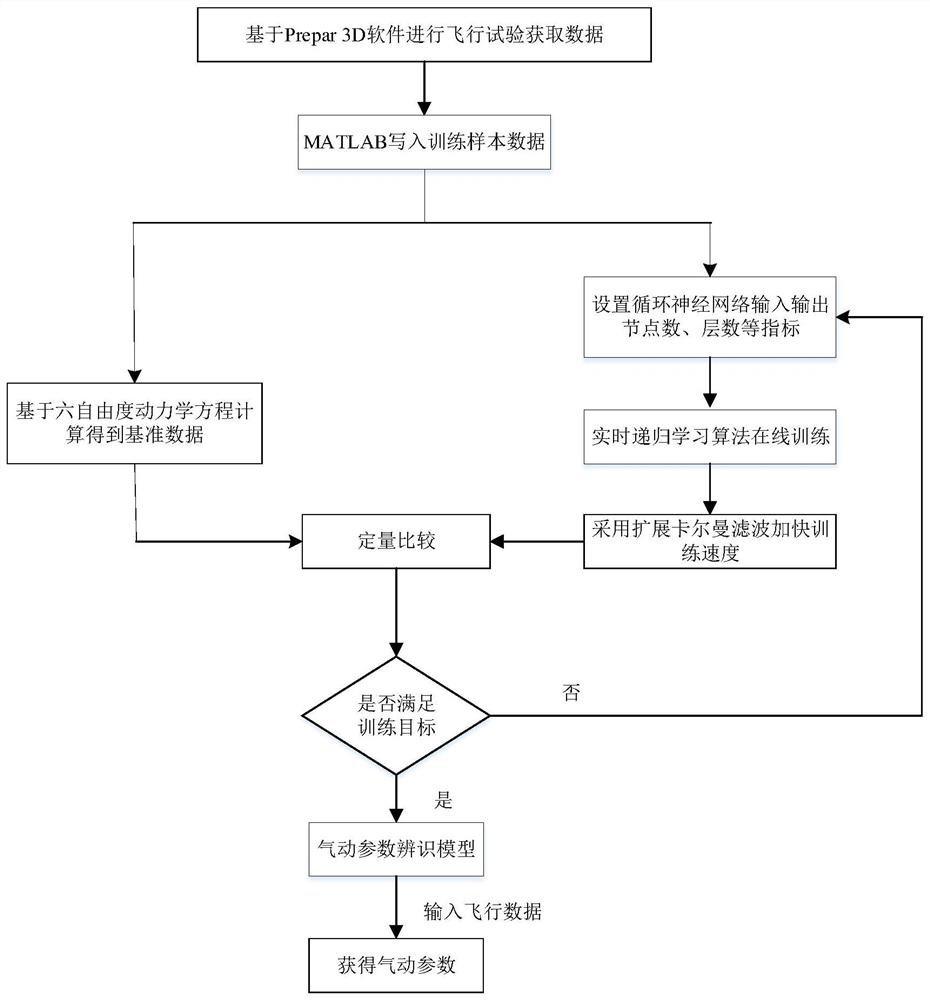
Aircraft aerodynamic parameter identification method based on recurrent neural network
PendingCN114004023ASolve nonlinear problemsFast operationGeometric CADSustainable transportationDynamic equationFlight experiment
The invention discloses an aircraft aerodynamic parameter identification method based on a recurrent neural network. The method comprises the following steps: 1) performing a simulated flight test by using a training-level simulator in combination with flight simulation software to obtain flight data; 2) taking the six-degree-of-freedom dynamic equation set of the aircraft rigid body as a state equation of the system, and calculating to obtain corresponding aerodynamic force and aerodynamic torque according to data obtained by the test; 3) taking flight data such as an attack angle and a sideslip angle as input, taking the aerodynamic parameters calculated in the step 2 as reference data, and training by utilizing a recurrent neural network combined with a real-time recurrent learning algorithm to obtain an aerodynamic parameter identification model; 4, selecting and loading flight data which do not participate in model training into the aerodynamic parameter identification model of the recurrent neural network obtained in the third step for parameter identification, and corresponding aerodynamic force and aerodynamic moment. The parameter identification model established through the method has good applicability, accurate modeling can be completed for aerodynamic force, and application and popularization can be achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Device for testing pneumatic performance of automobile
The invention discloses a device for testing the pneumatic performance of an automobile. The device is used for testing the pneumatic performance of the automobile. According to the technical scheme of the invention, each tray of the device is provided with a wheel fixing assembly and the lower surface of each tray is fixedly connected with a supporting rod. The lower end of the supporting rod is fixedly connected with a force measuring balance and the force measuring balance is arranged on a force measuring balance installation frame. The force measuring balance installation frame is fixedly installed in a carrying device. An ultrasonic anemometer is installed on the roof of a testing automobile, and is used for measuring the wind speed. The ultrasonic anemometer and the force measuring balance are both connected with a controller. An automobile speed detection device on the carrying device is connected with the controller. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the device can be used for testing the pneumatic performance of the automobile directly on the road and can simulate an acting force and an acting torque basically similar to the acting force and the acting torque of the automobile when the automobile runs normally on the road. Therefore, compared with an automobile air tunnel, measured experimental data are closer to the aerodynamic force and the aerodynamic torque of the automobile during the actual running process.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
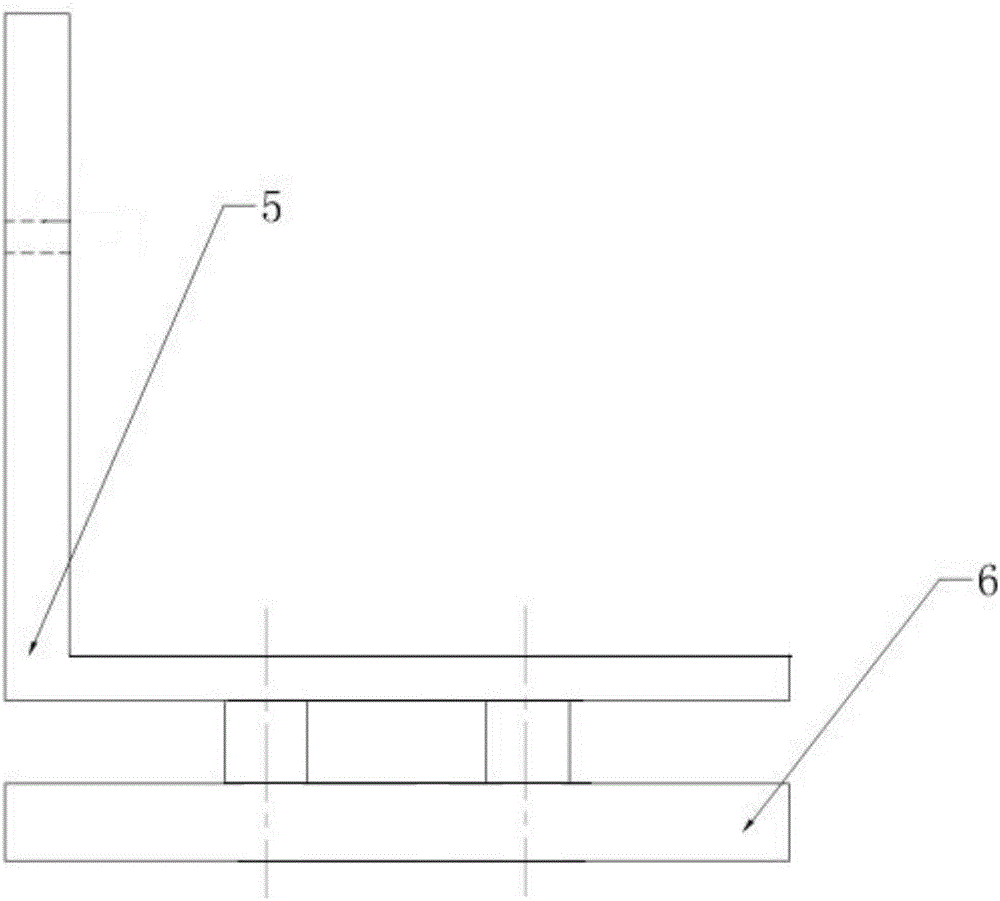
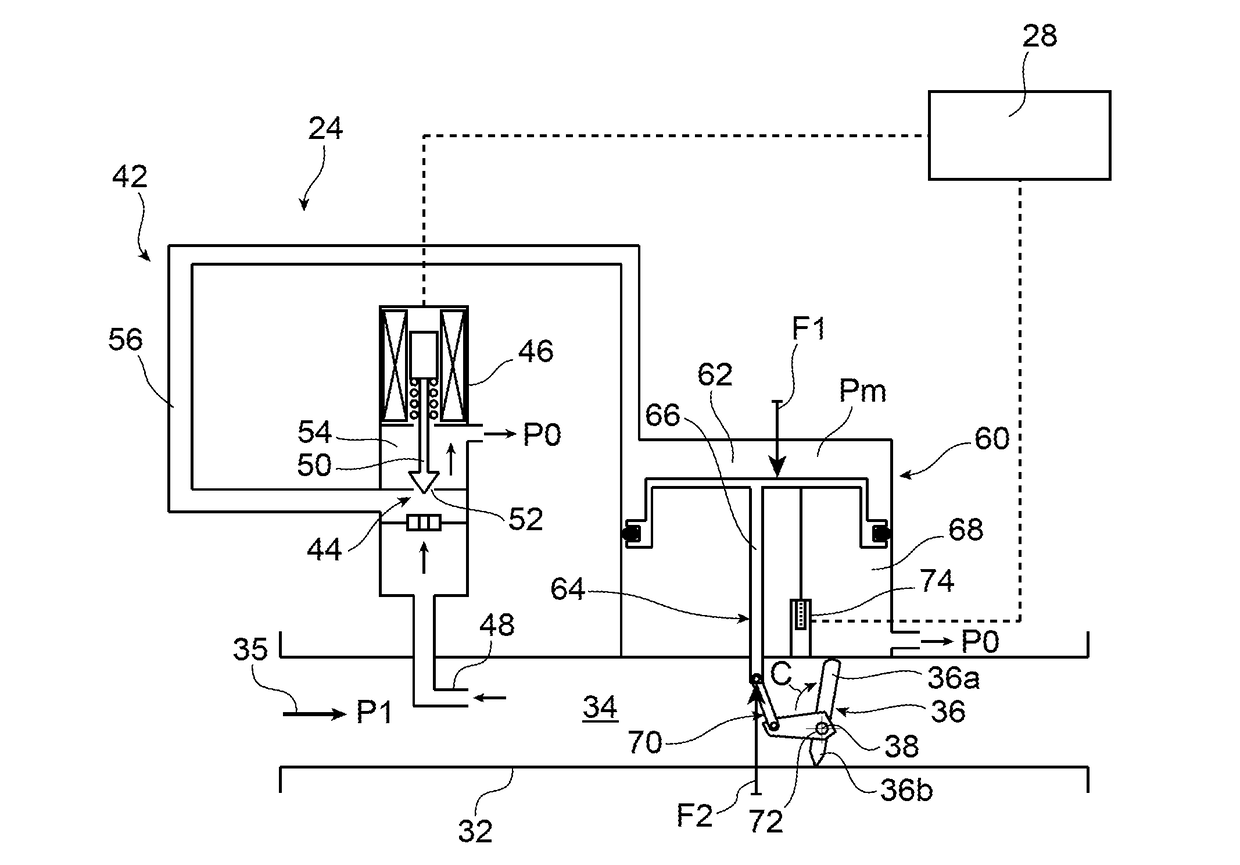
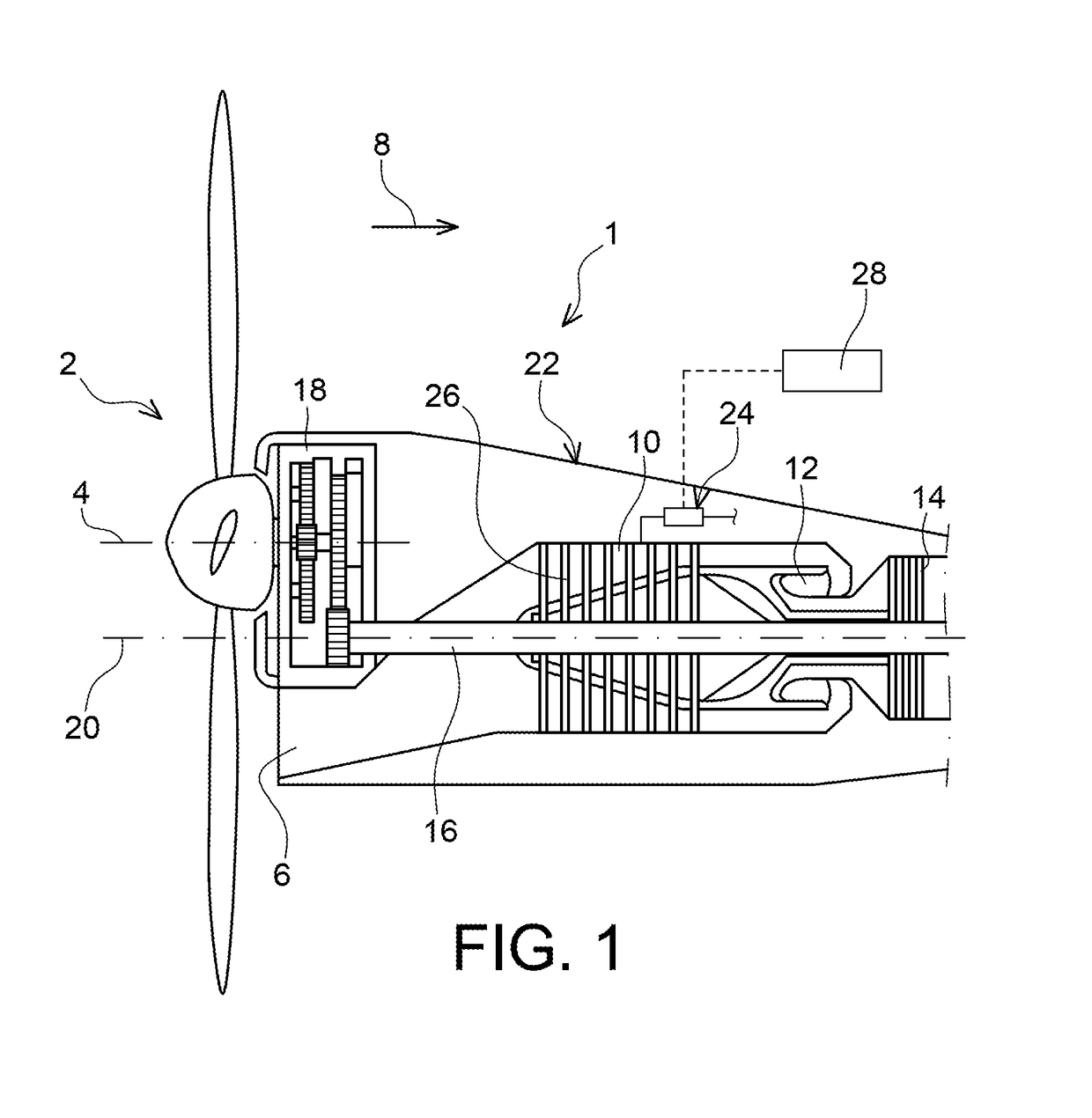
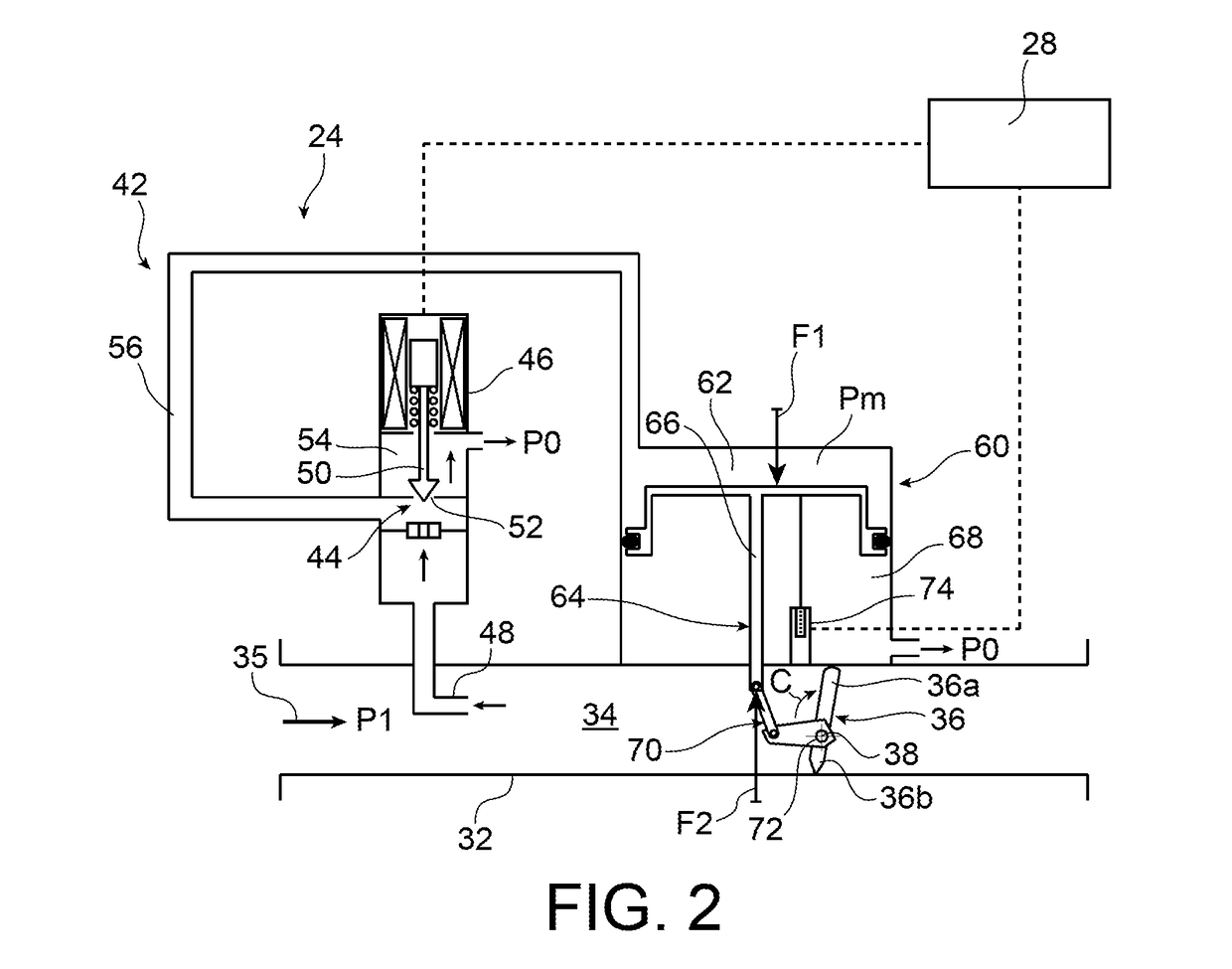
Butterfly valve for bleeding a compressor for an aircraft turbine engine
ActiveUS20180142626A1Increase speedShort response timeGas turbine plantsEngine controlAerodynamic torqueEngineering
The invention relates to a butterfly valve (24) for bleeding a compressor for an aircraft turbine engine, the valve including a valve body (32), a butterfly (36), and a device (42) for controlling the angular position of the butterfly, the device (42) including a mobile actuation member (64) connected to the butterfly by a link (70), the member (64) being subjected: to a first adjustable pressure force (F1) applied by air from the compressor, the first force (F1) returning the butterfly (36) to a closed position; and to a second mechanical force (F2) returning the butterfly (36) to an open position, and coming from an aerodynamic torque (C) applied by the air to the butterfly (36), of which the axis of rotation (38) is off-centre relative to the butterfly.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Load shedding control method for wind generating set and wind generating set
ActiveCN110374806AImprove reliabilityExtended service lifeWind motor controlMachines/enginesLoad SheddingAerodynamic torque
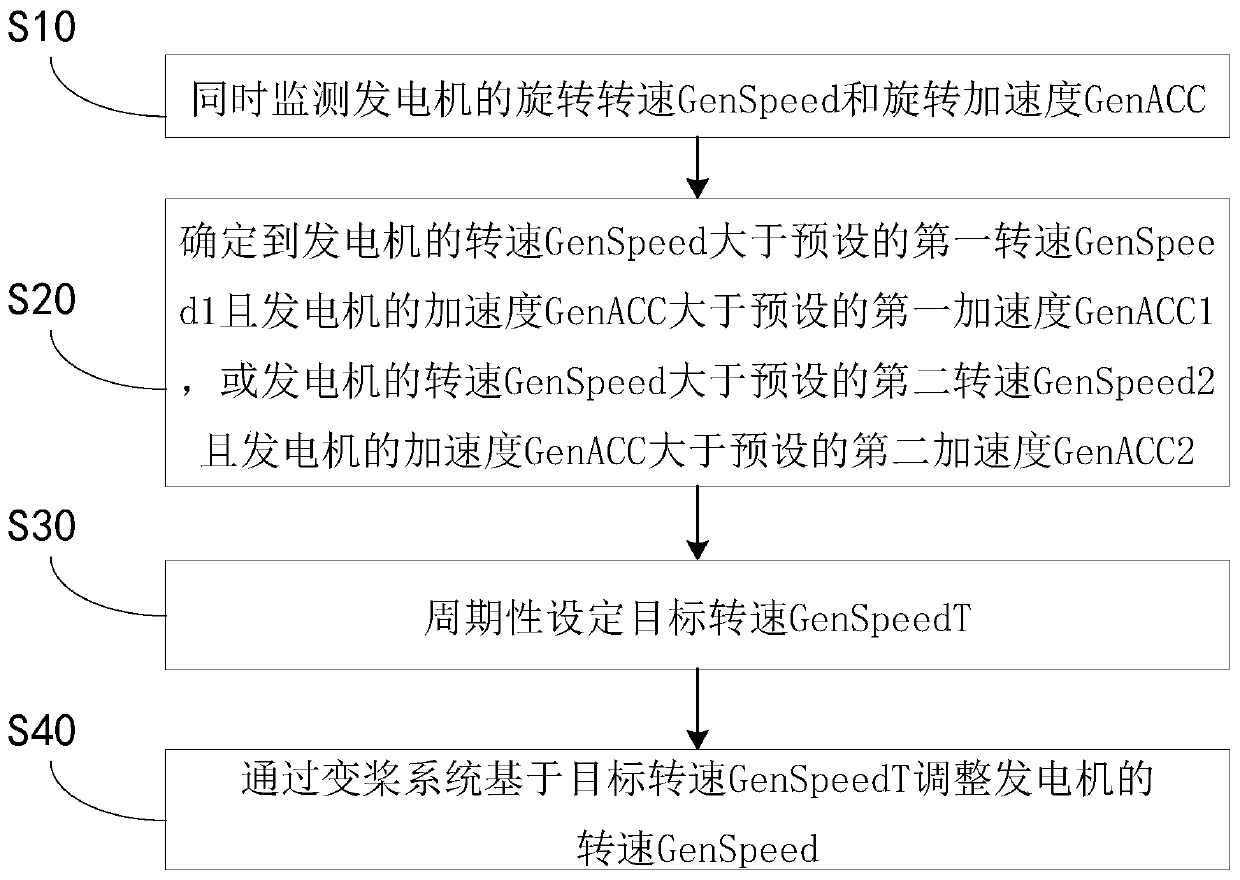
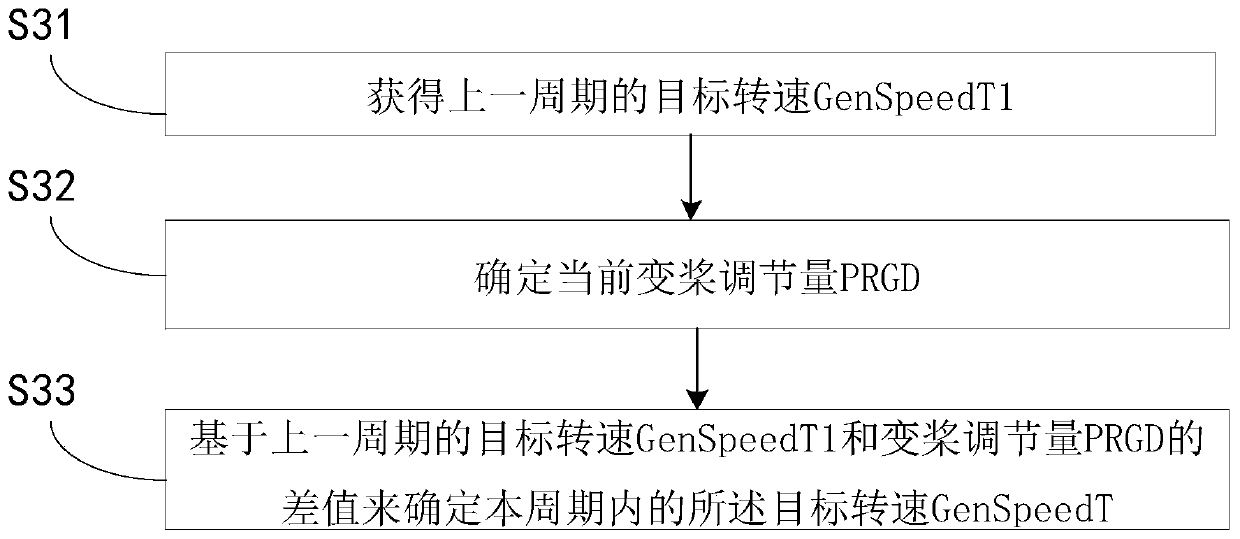
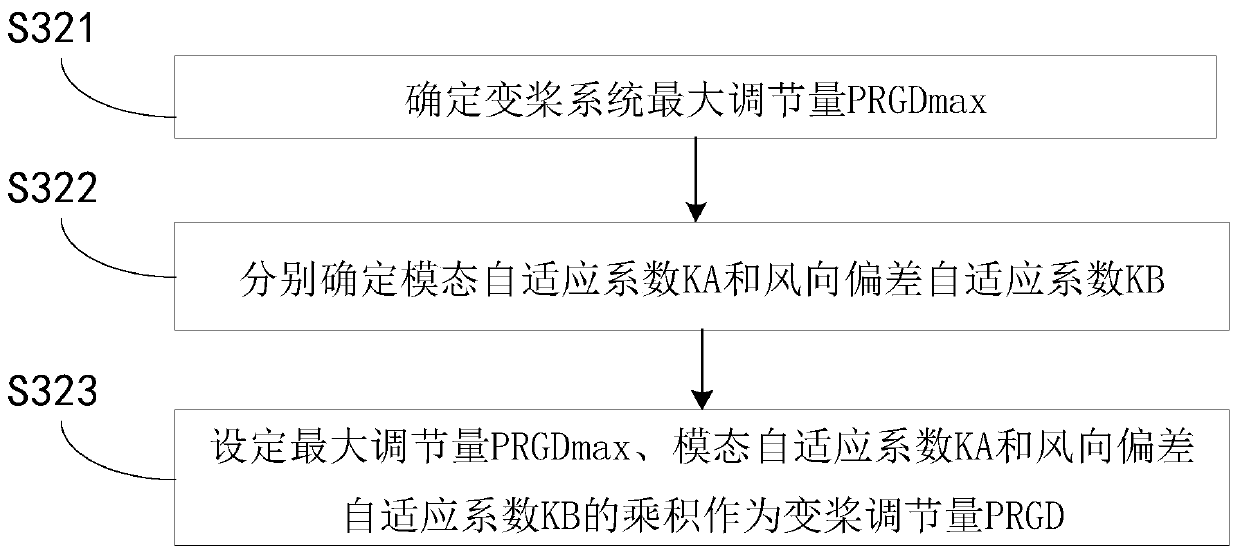
The invention provides a load shedding control method for a wind generating set, and the method is characterized in that the rotating speed and the rotating acceleration of a generator are monitored simultaneously, when the rotating speed is determined to be greater than a preset first rotating speed and the acceleration is greater than a preset first acceleration, or the rotating speed is determined to be greater than a preset second rotating speed and the acceleration is determined to be greater than a preset second acceleration, the stage of periodically setting a target rotating speed is entered, and the rotating speed of the generator is adjusted through a variable pitch system based on the target rotating speed. Since the running state of the generator is monitored based on the rotating speed and the rotating acceleration of the generator, the rotating speed of the generator can be controlled more stably under the working condition of high rotating speed and high acceleration, and the phenomena that the rotating speed is overhigh and the machine is shut down due to overhigh pneumatic torque and the parts of the wind generating set are damaged are avoided.
Owner:CSIC CHONGQING HAIZHUANG WINDPOWER EQUIP
Pneumatic torque pulse wrench with step-by-step shutoff
ActiveCN103167934BMeasurement of torque/twisting force while tighteningSpannersAerodynamic torqueScrew thread
A pneumatic torque impulse wrench comprises a housing (10), a motor (15), a hydraulic impulse unit (20) including an inertia drive member (21) and intermittently coupling the motor (15) to an output shaft (18), a shut-off valve (23) controlling the pressure air supply to the motor (15), and an activating mechanism (25) arranged to shift the shut-off valve (23) from a fully open position to a closed position via one or more partly closed positions. An activating mechanism (25) for shifting the shut-off valve (23) comprises a retardation responsive inertia element (28) movably supported on the inertia drive member (21), and a trip element (24) displaceable by the inertia element (28) and arranged to initially support the shut-off valve (23) in a fully open position during a screw joint tightening process and in succeeding one or more partly open positions for obtaining a power reduction of the motor (15) when approaching a target torque level.
Owner:ATLAS COPCO INDAL TECHN AB
Method for simulating dynamic characteristics of wind turbine system
ActiveCN111310352AEasy to controlReproduce dynamic characteristicsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationAerodynamic torqueLoop control
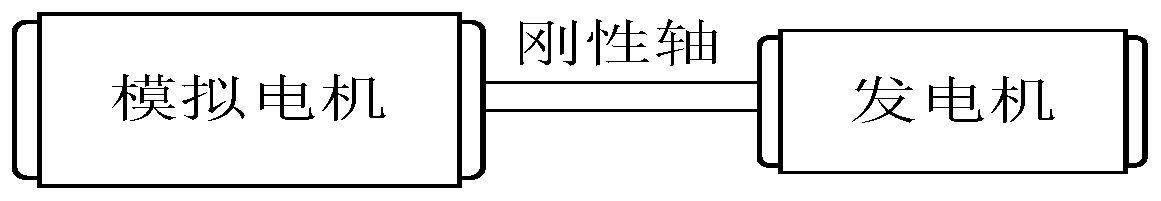
The invention discloses a method for simulating dynamic characteristics of a wind turbine system. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing time domain motion equations of an actual wind turbine system and a wind turbine simulation system; (2) simultaneously establishing a motion equation of the wind turbine system and the simulation system to obtain a simulation motor electromagnetic torque; (3) substituting the generator electromagnetic torque at the previous moment into a simulated motor electromagnetic torque calculation formula to obtain a simulated motor electromagnetictorque value at the current moment; and (4) carrying out torque closed-loop control on the simulation system according to the torque reference value of the simulation motor, so that the output torqueof the simulation motor follows a given value, and the simulation of the mechanical characteristics of the actual wind turbine system is completed. Compared with a traditional wind turbine simulationsystem, one-step delay introduced by an acceleration term can be eliminated, the dynamic characteristics of the wind turbine can be more accurately reproduced, and meanwhile the influence of sudden change of the aerodynamic torque of the wind turbine on the torque of the simulation motor can be reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Composite material adjustable stator blade
ActiveCN112460075ASolution feasibilitySolve engineering problemsPump componentsPumpsAerodynamic torqueCentral layer
The invention belongs to the technical field of engine maintenance equipment design, and particularly relates to a composite material adjustable stator blade which comprises an upper shaft neck, a lower shaft neck, an upper marginal plate, a lower marginal plate, and a blade body; besides, the blade is divided into a central layer plate area, a central filling area, a reinforced layer plate area and a molded surface structure area, the central layer plate area and the reinforced layer plate area are composed of laminated plates formed by laying composite material prepregs, the central fillingarea is composed of composite material prepregs, and the molded surface structure area is composed of resin or single-layer prepregs covering the surface of the molded surface structure area; and thecentral layer plate area and the central filling area form a core bearing area of the blade, the reinforced layer plate area is located on the two sides of the core bearing area, and the molded surface structure area is used for ensuring that the composite material adjustable stator blade is smooth in appearance. According to the composite material adjustable stator blade, the design feasibility and engineering problems of the composite material adjustable stator blade are effectively solved, the problems that the blade configuration is complex, and layering is difficult to achieve are effectively solved, and the pneumatic bending moment and pneumatic torque resistance of the composite material adjustable stator blade is improved.
Owner:AECC SHENYANG ENGINE RES INST
Aircraft attitude control method and device and electronic equipment
PendingCN114035599AShorten convergence timeImprove speedAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsAerodynamic torqueMathematical model
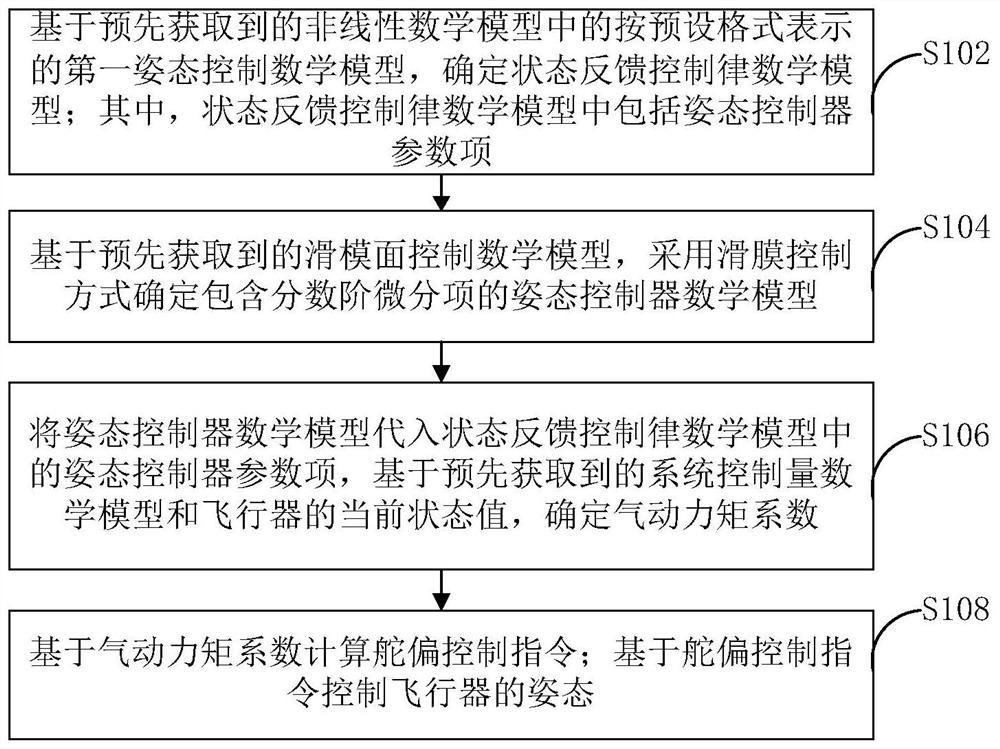
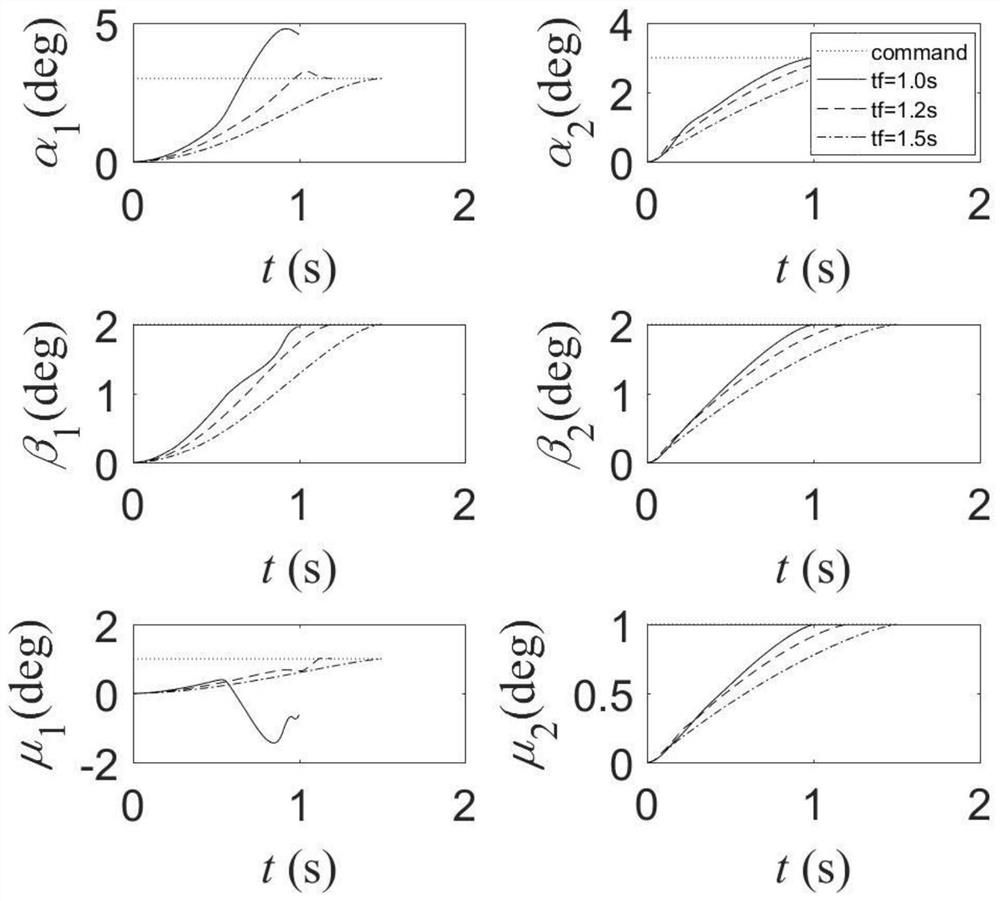
The invention provides an aircraft attitude control method and device and electronic equipment, and the method comprises the steps: determining a state feedback control law mathematical model based on a first attitude control mathematical model represented according to a preset format in a pre-obtained nonlinear mathematical model; determining an attitude controller mathematical model containing a fractional order differential item by adopting a sliding mode control mode based on a pre-obtained sliding mode surface control mathematical model; substituting attitude controller parameter items in the state feedback control law mathematical model, and determining an aerodynamic torque coefficient based on a pre-acquired system control quantity mathematical model and a current state value of the aircraft; calculating a rudder deflection control instruction based on the aerodynamic torque coefficient; and controlling the attitude of the aircraft based on the rudder deflection control instruction. The attitude controller mathematical model determined by the method comprises a fractional order differential item, so that the rudder can provide a large control quantity at the beginning, the rapidity and accuracy of an aircraft attitude control system are improved, and the convergence time of the aircraft attitude is shortened.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Aircraft attitude control method and aircraft
ActiveCN114489098AImprove stealth performanceAvoid inefficiencyAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsAerodynamic torqueFlight vehicle
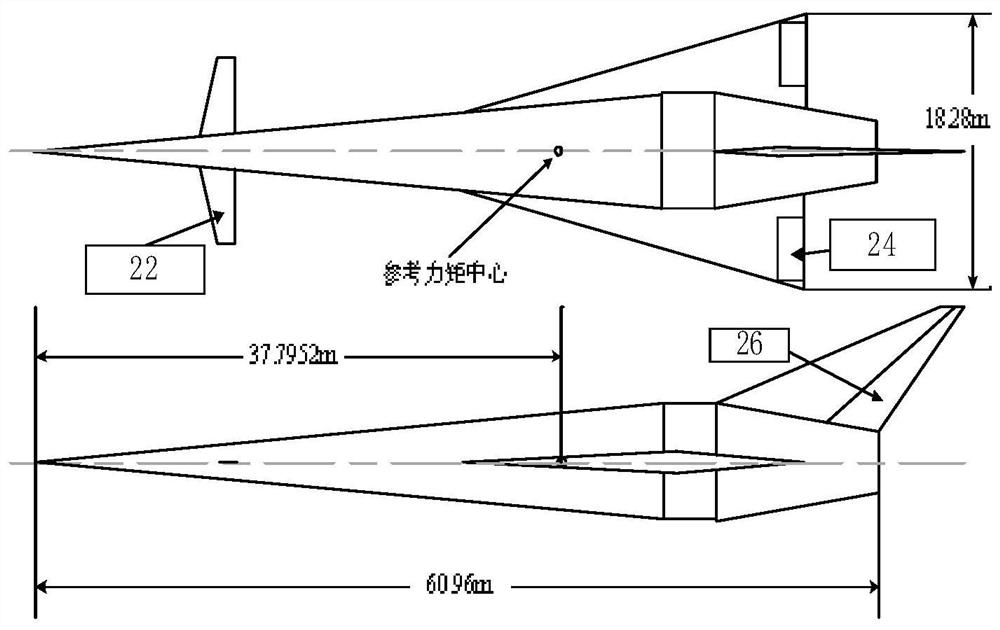
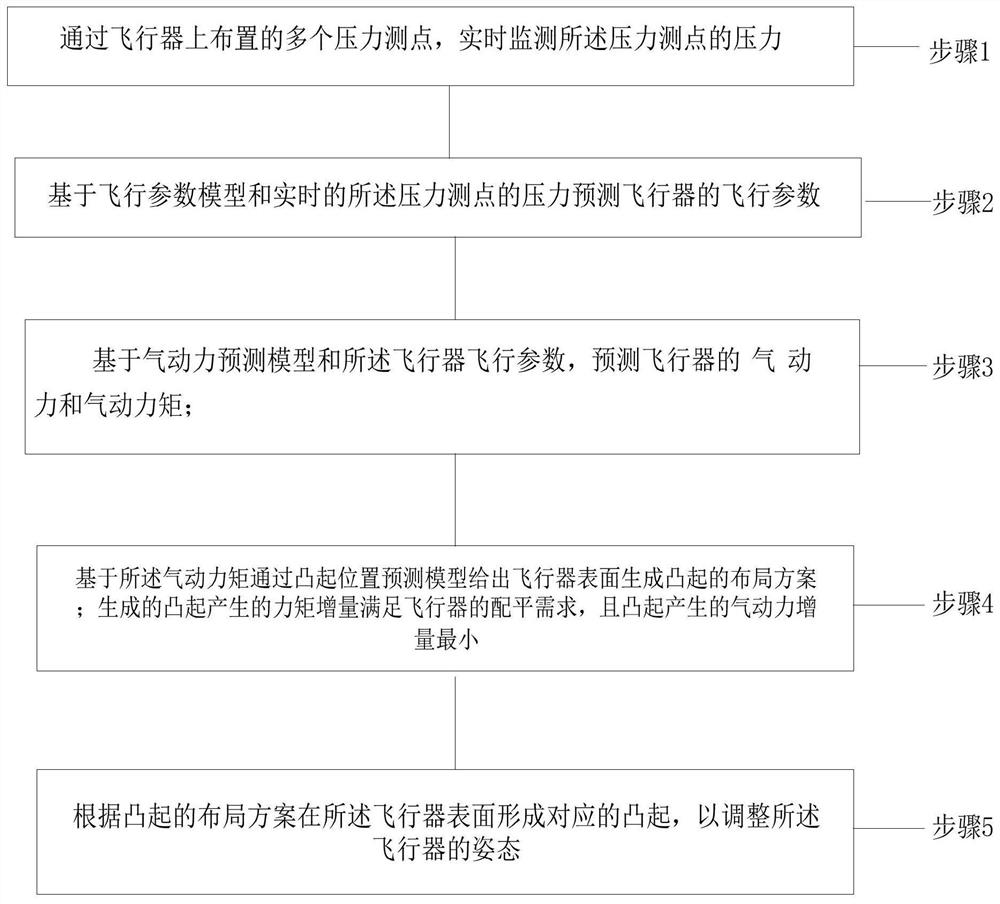
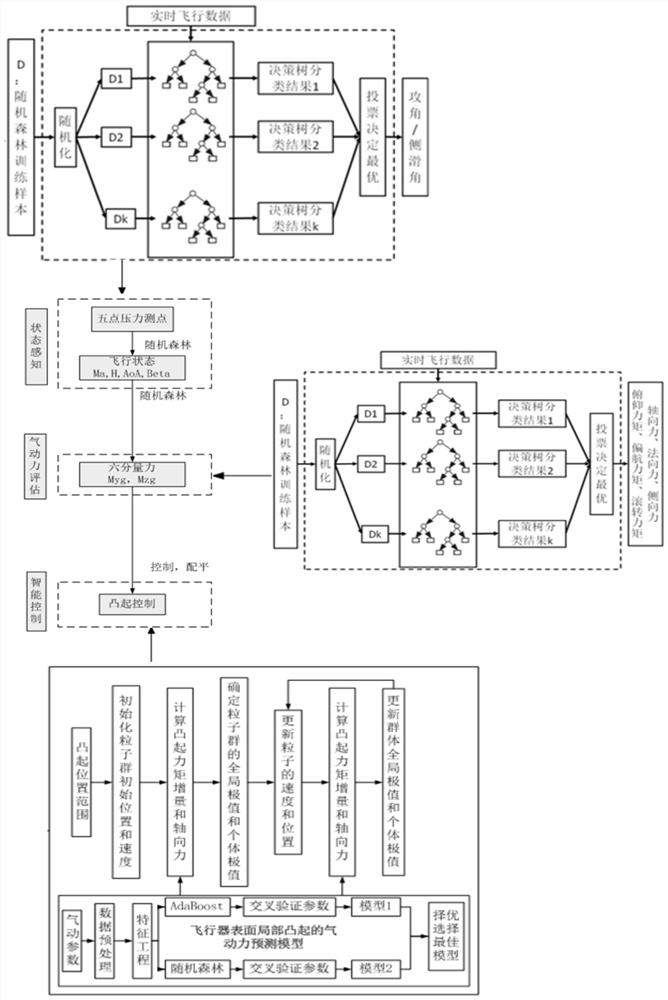
The invention discloses an aircraft attitude control method and an aircraft, and the control method comprises the steps: monitoring the pressure of pressure measurement points in real time through a plurality of pressure measurement points arranged on the aircraft; predicting flight parameters of the aircraft based on a flight parameter model and the real-time pressure of the pressure measuring point; predicting aerodynamic force and aerodynamic moment of the aircraft based on an aerodynamic force prediction model and the aircraft flight parameters; based on the aerodynamic torque, a layout scheme for generating protrusions on the surface of the aircraft is given through a protrusion position prediction model; the moment increment generated by the generated bulge meets the balancing requirement of the aircraft, and the aerodynamic force increment generated by the bulge is minimum; and forming corresponding bulges on the surface of the aircraft according to the layout scheme of the bulges so as to adjust the attitude of the aircraft. The attitude of the aircraft can be well controlled, the stealth performance of the aircraft is improved, and the influence on the aerodynamic performance is small.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
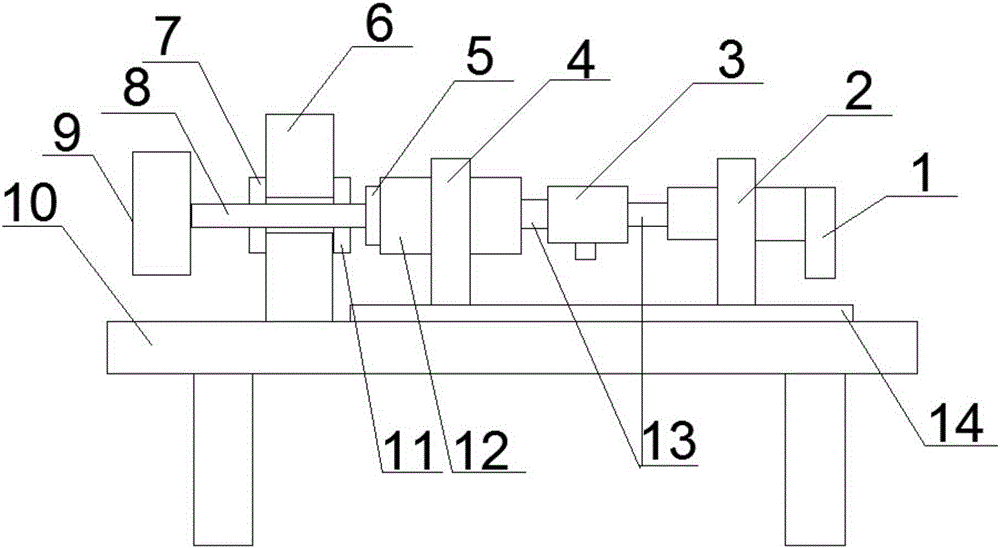
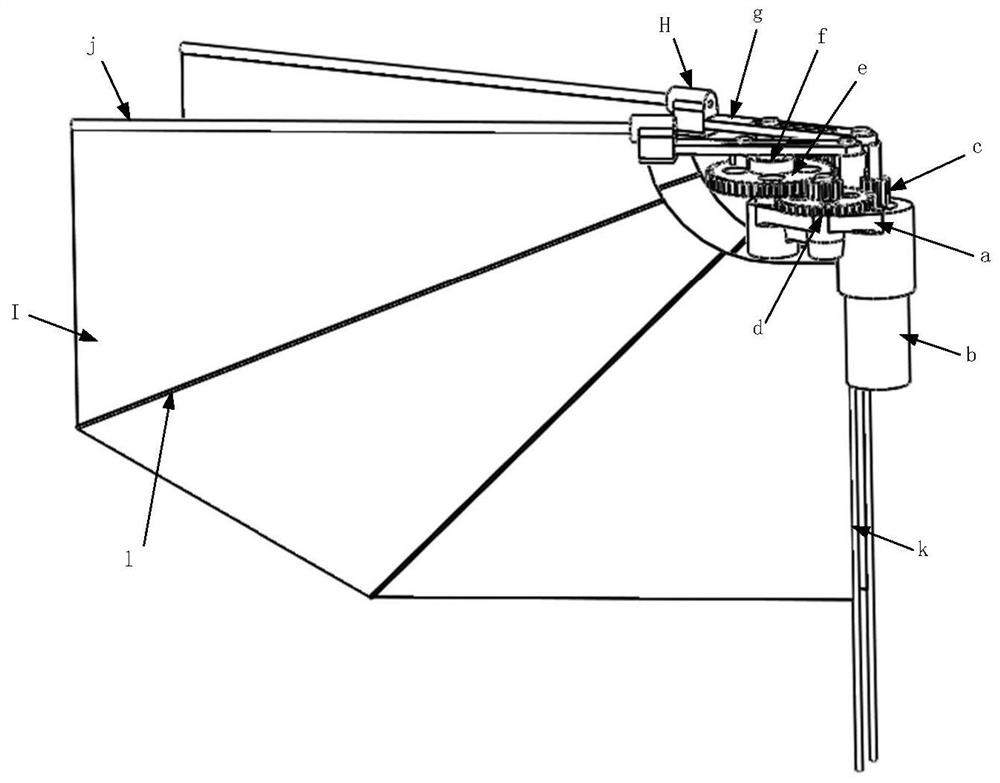
System and method for measuring aerodynamic torque in wind tunnel test of aircraft
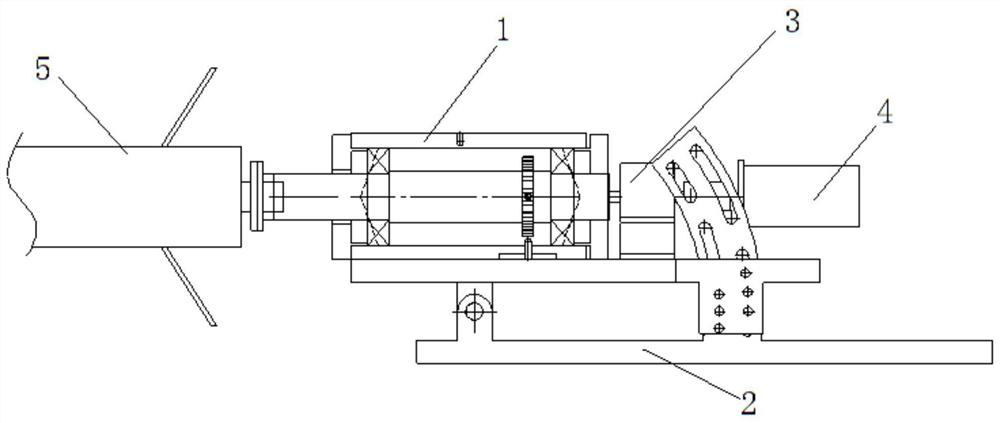
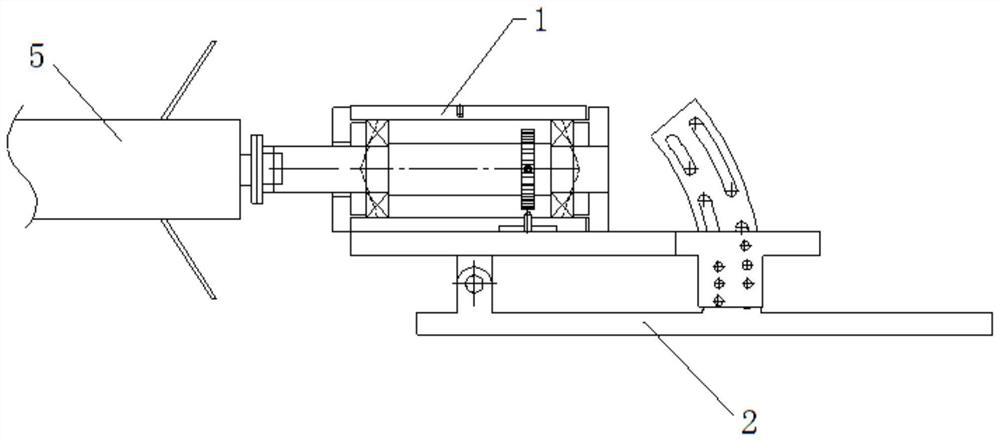
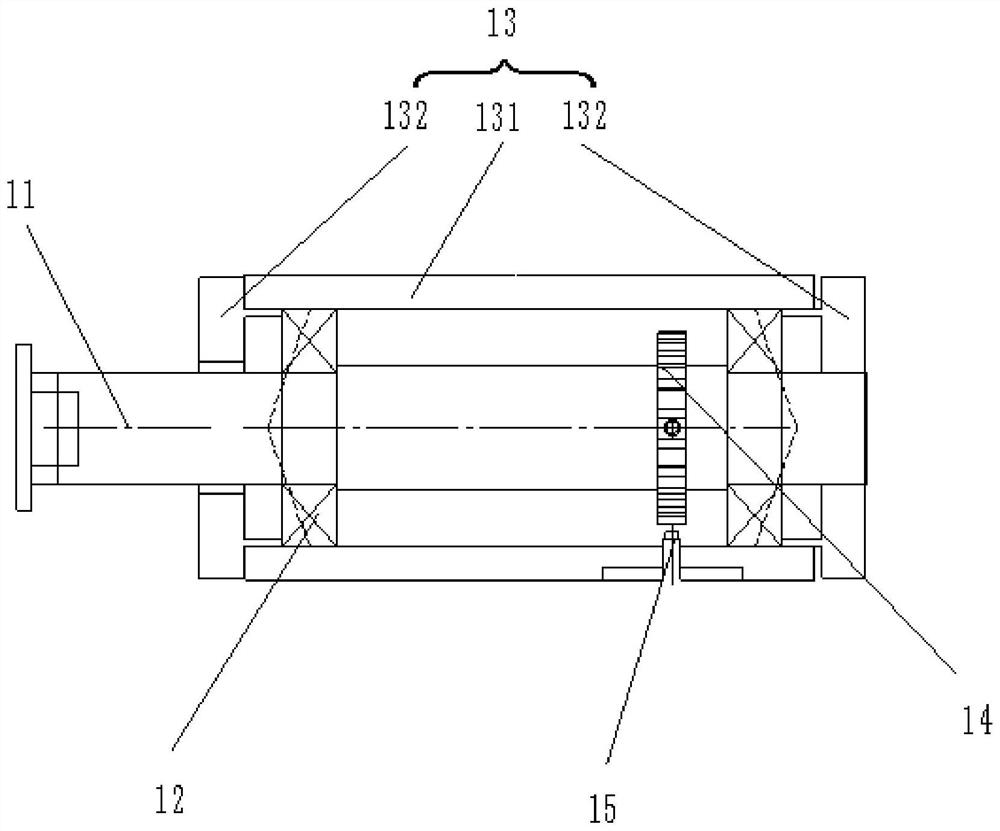
PendingCN114018536AAccurate measurementUndamagedAerodynamic testingAircraft components testingMotor speedAerodynamic torque
The invention provides a system and a method for measuring the aerodynamic torque in a wind tunnel test of an aircraft, and solves the problem that in an existing ground wind tunnel test, the frictional resistance characteristic of measurement equipment affects the free rolling speed rate of the aircraft. The system comprises a rotating speed measuring device, a torque sensor and a motor. The rotating speed measuring device comprises a rotating shaft mechanism and a rotating speed sensor. The rotating shaft mechanism comprises a rotating shaft mounting seat and a rotating shaft, the rotating shaft penetrates the rotating shaft mounting seat through a bearing, and the front end of the rotating shaft extends out of the rotating shaft mounting seat and is coaxially connected with a test piece; the rotating speed sensor comprises a gear coaxially arranged on the rotating shaft and a proximity switch arranged in the mounting seat and matched with the gear, and the proximity switch measures the number of teeth passed by the gear to obtain the rotating speed of the rotating shaft. The torque sensor and the motor are sequentially and coaxially arranged at the rear end of the rotating shaft, the torque sensor is close to the rotating shaft, and the motor is used for driving the rotating shaft to rotate.
Owner:XIAN AEROSPACE PROPULSION TESTING TECHN INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com