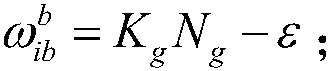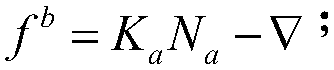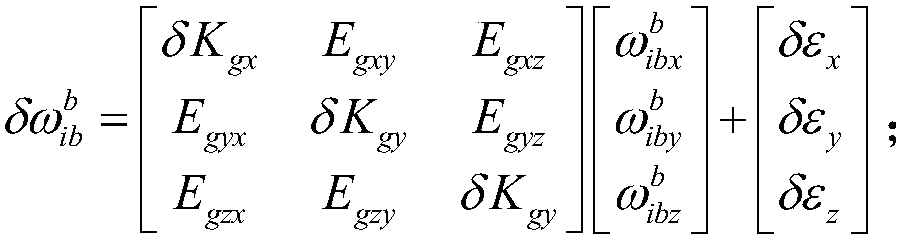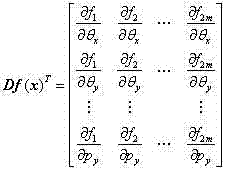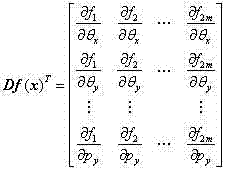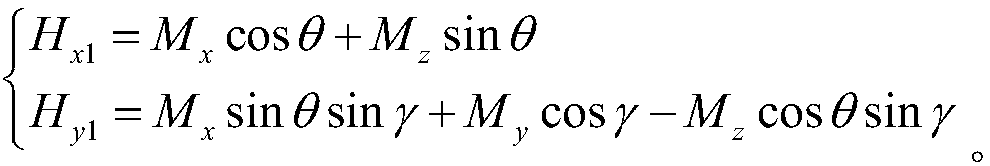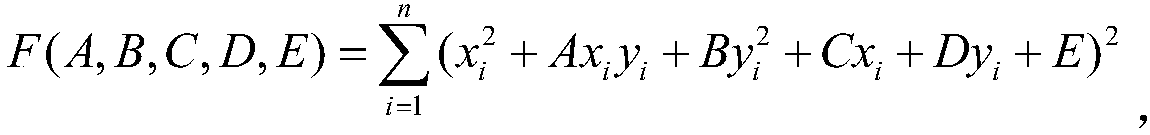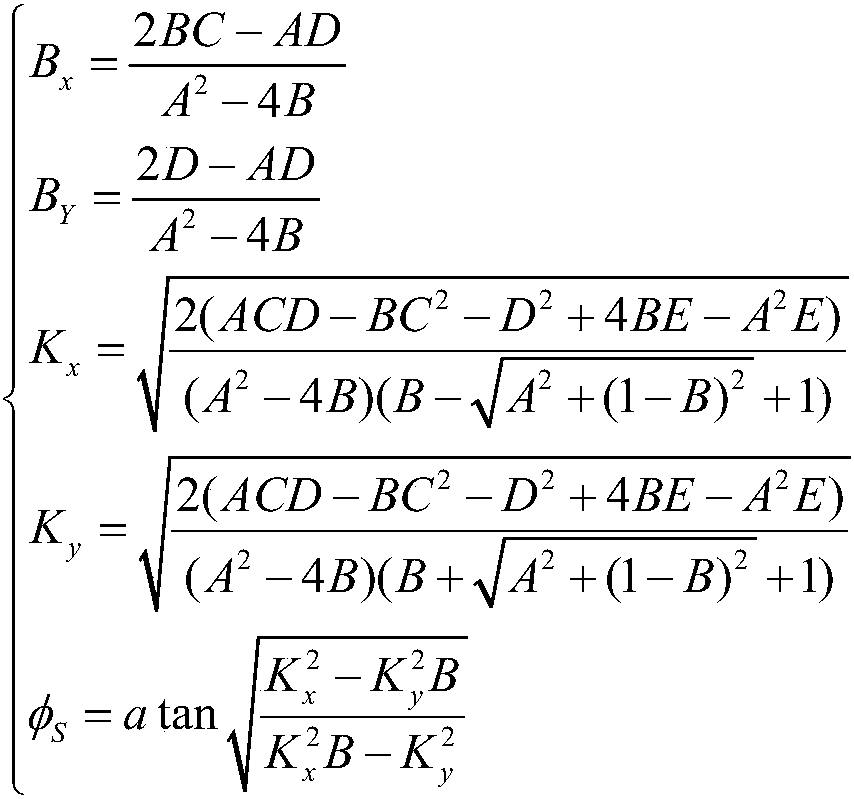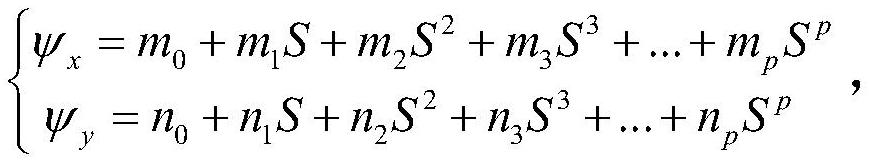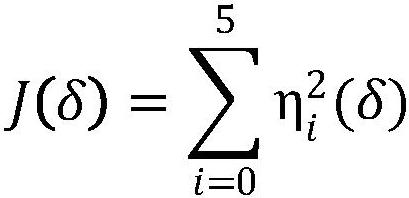Patents
Literature
36results about How to "Achieve high-precision calibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
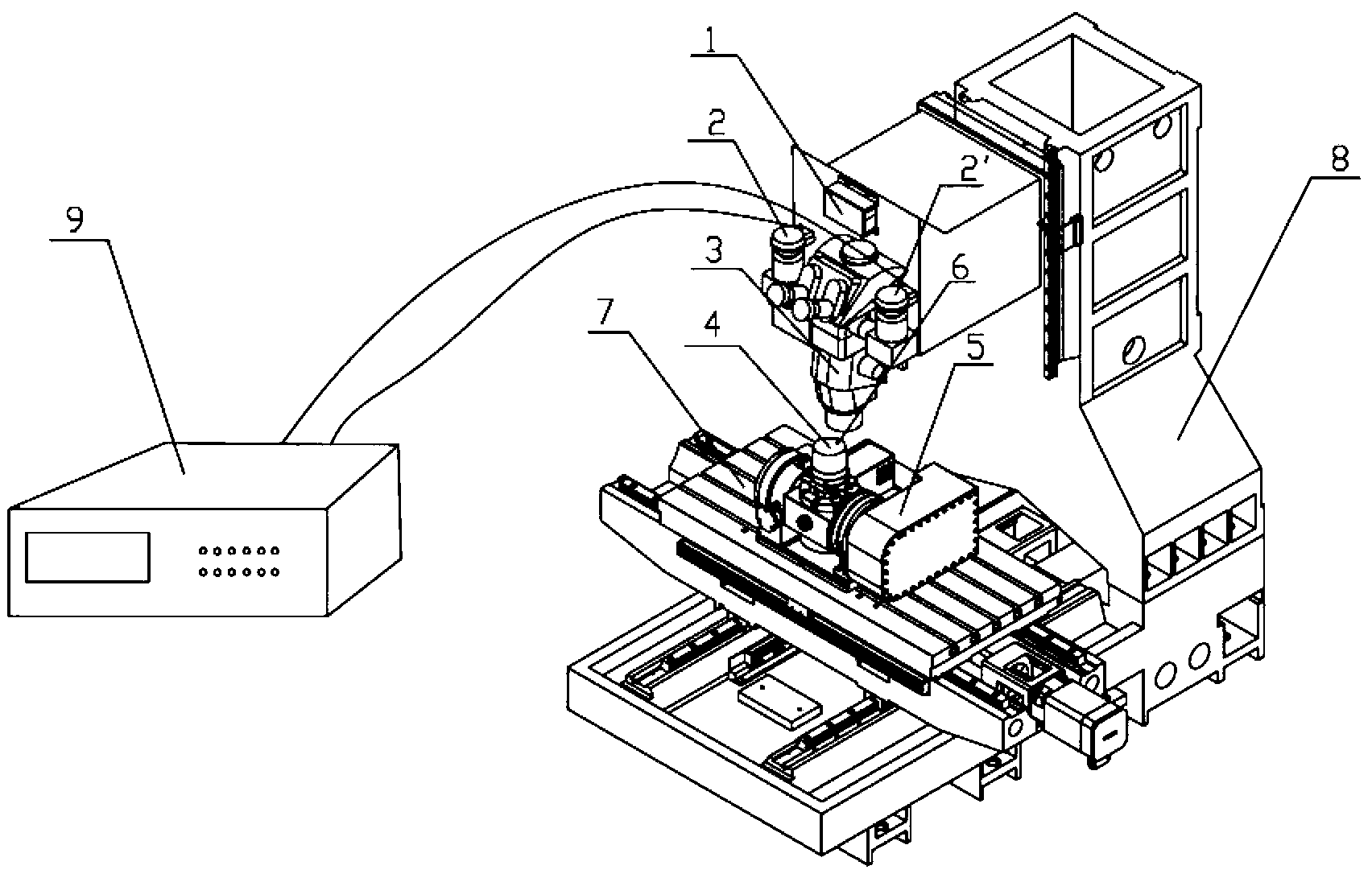
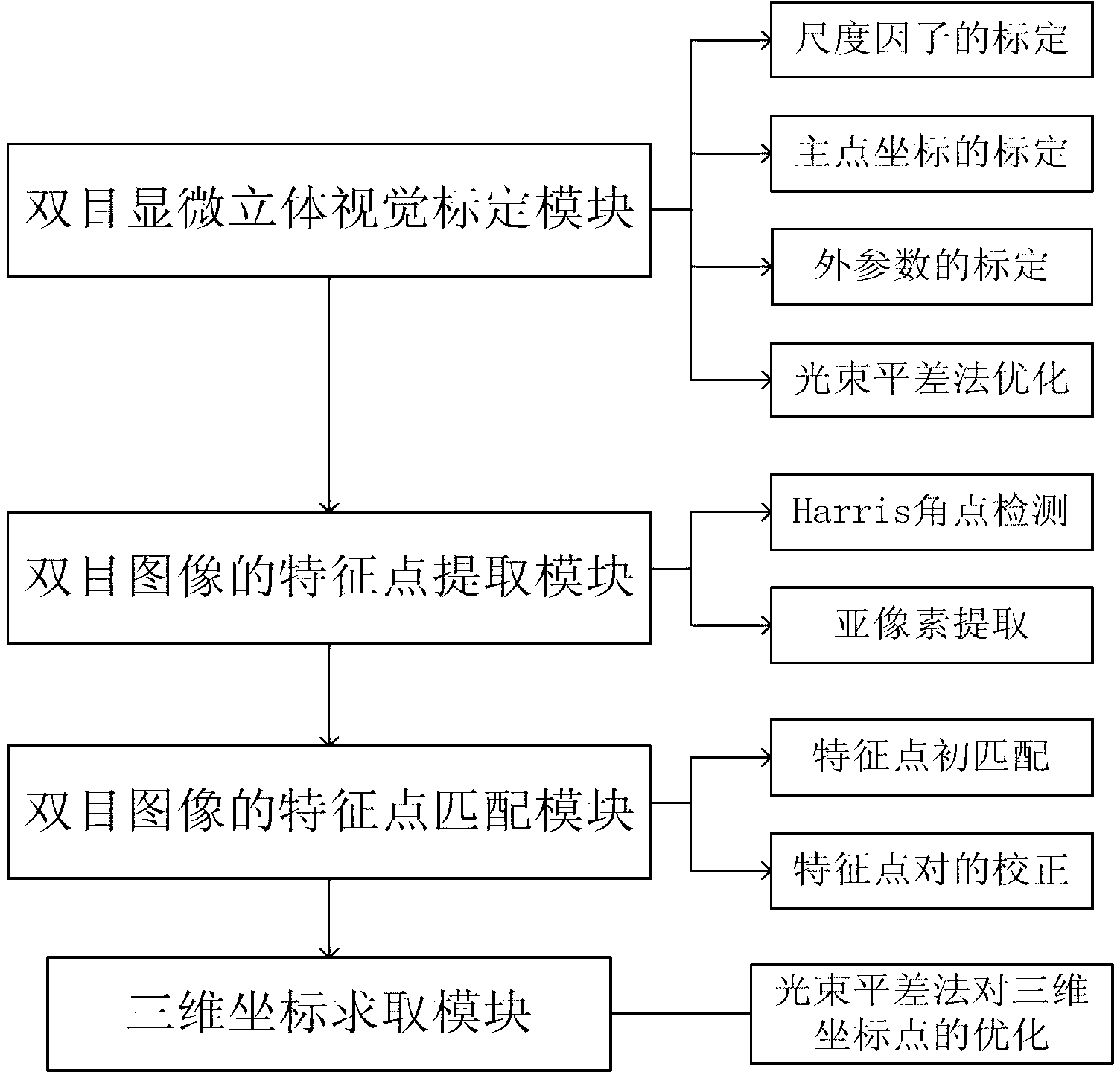
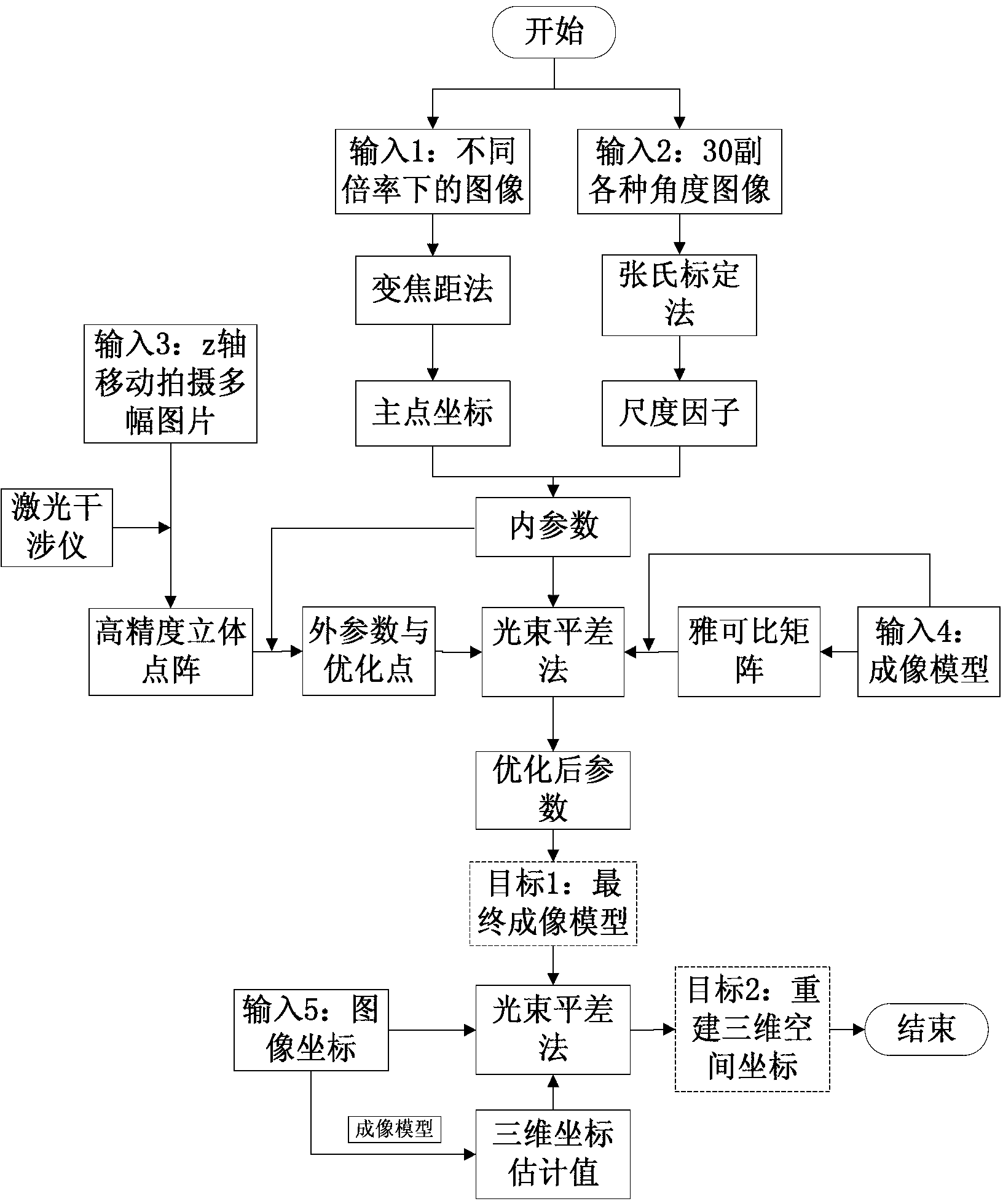
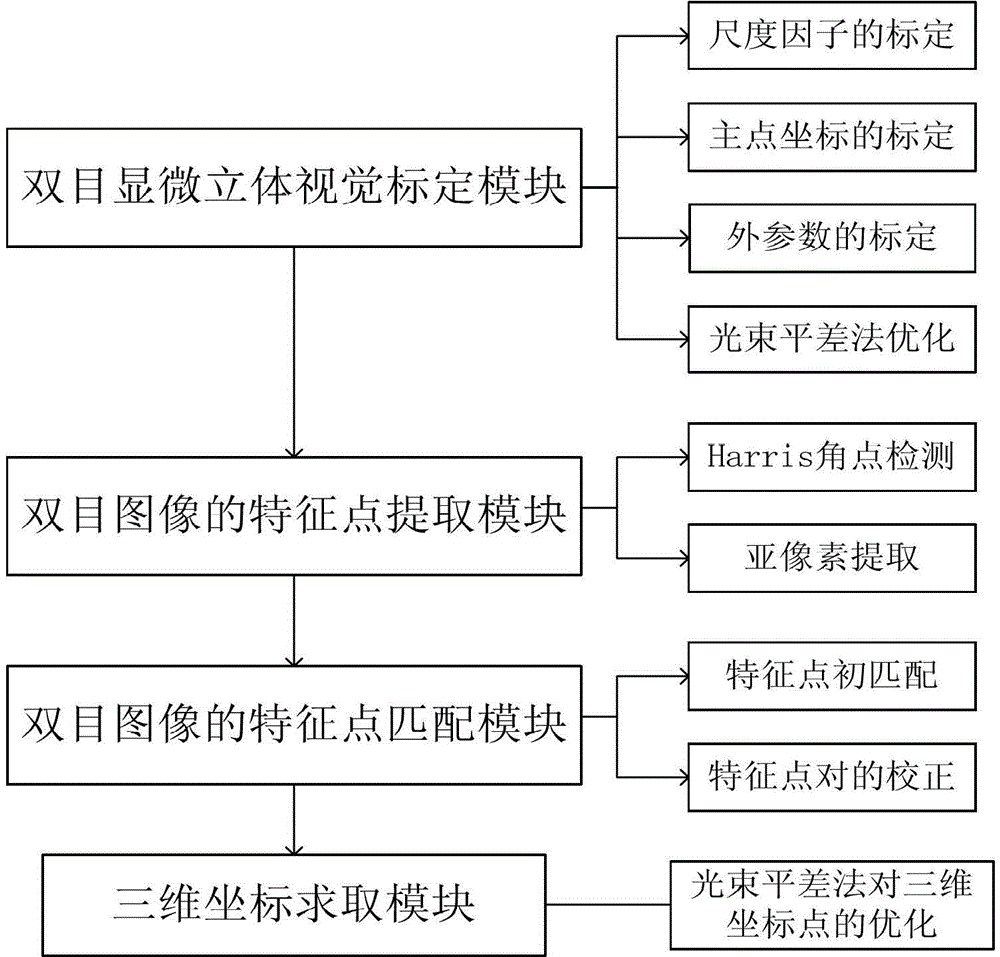
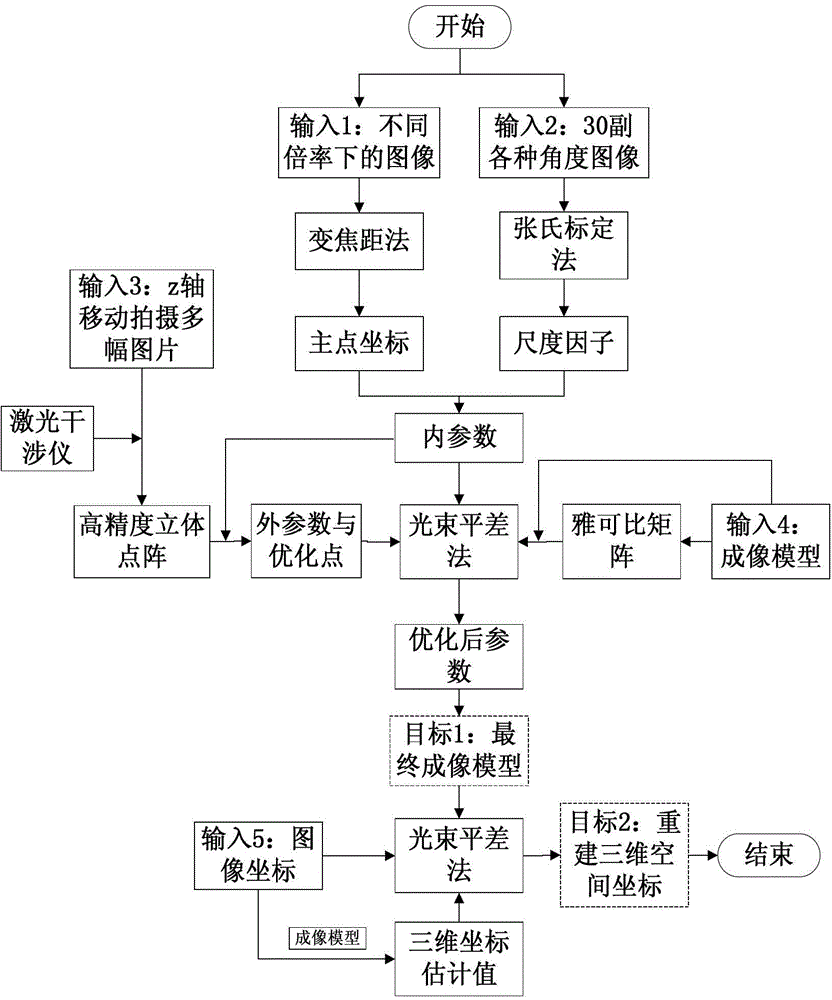
Accurate part positioning method based on binocular microscopy stereo vision
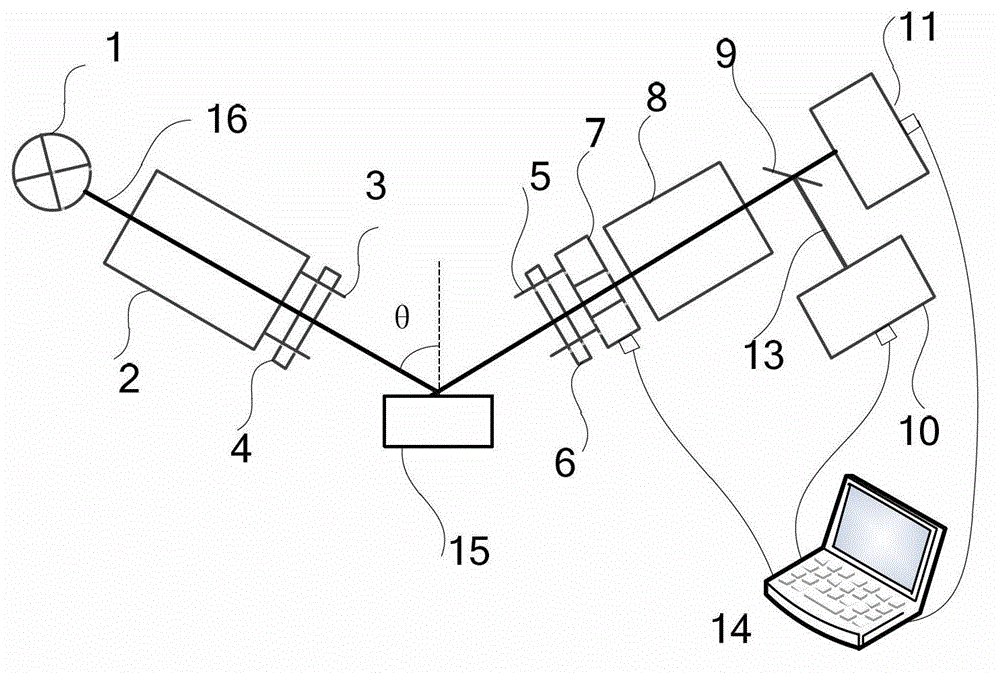
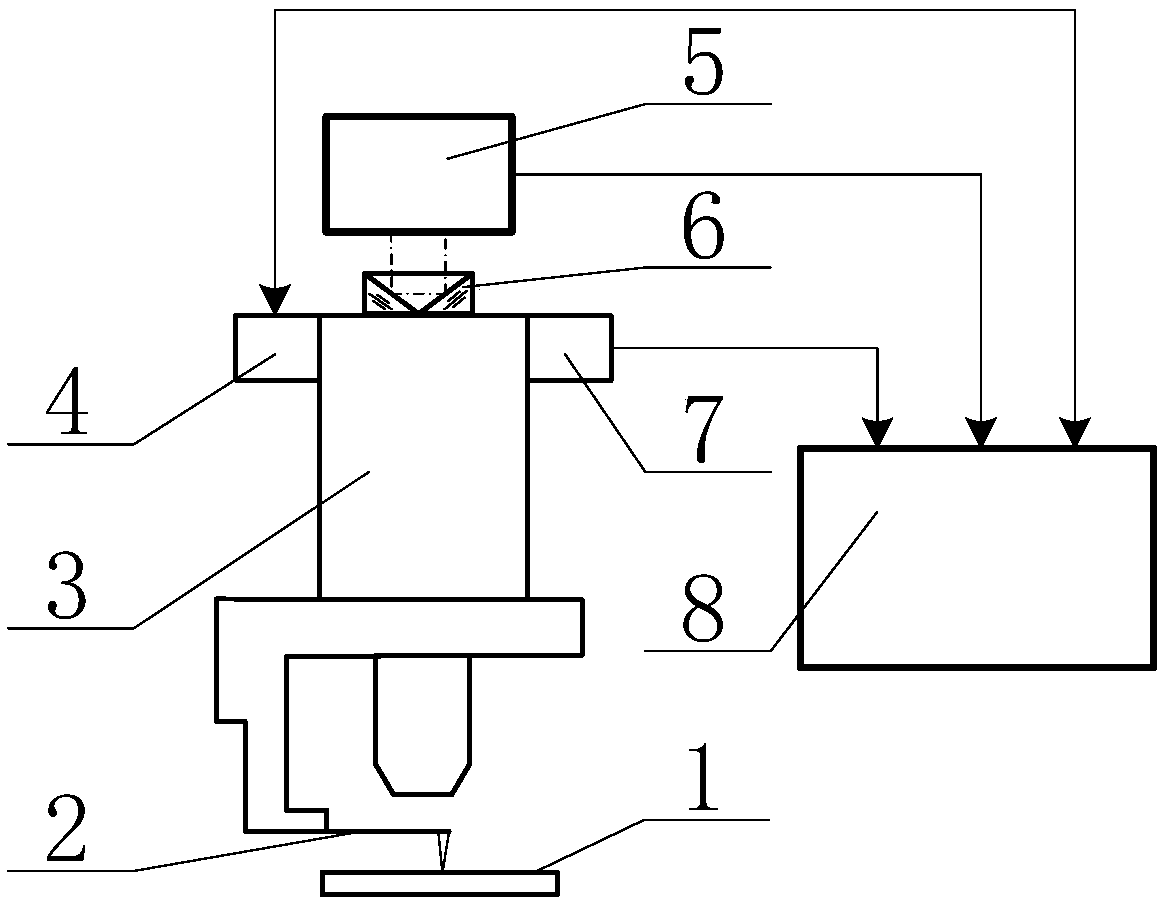
The invention discloses an accurate part positioning method based on binocular microscopy stereo vision, which belongs to the technical field of computer visual measuring and relates to an accurate precision part positioning method based on the binocular microscopy stereo vision. A binocular microscopy stereo vision system is adopted, two CCD (charge coupled device) cameras are adopted to acquire the images of the measured parts, the image information in the to-be-measured area on the measured part is amplified by a stereo microscope, a checkerboard calibrating board is adopted to calibrate the two CCD cameras, and a Harris corner point detecting algorithm and a sub-pixel extracting algorithm are adopted to extract feature points. The extracted feature points are subjected to the primary matching and correcting of matching point pairs, and the feature point image coordinates are inputted to a calibrated system to obtain the space actual coordinates of the feature points. The accurate part positioning method based on the binocular microscopy stereo vision solves the measuring difficult problems generated by the small size of the to-be-measured area, high positioning demand, non-contact and the like. The accurate positioning of the precision part is well finished by adopting the non-contact measuring method of the binocular microscopy stereo vision.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
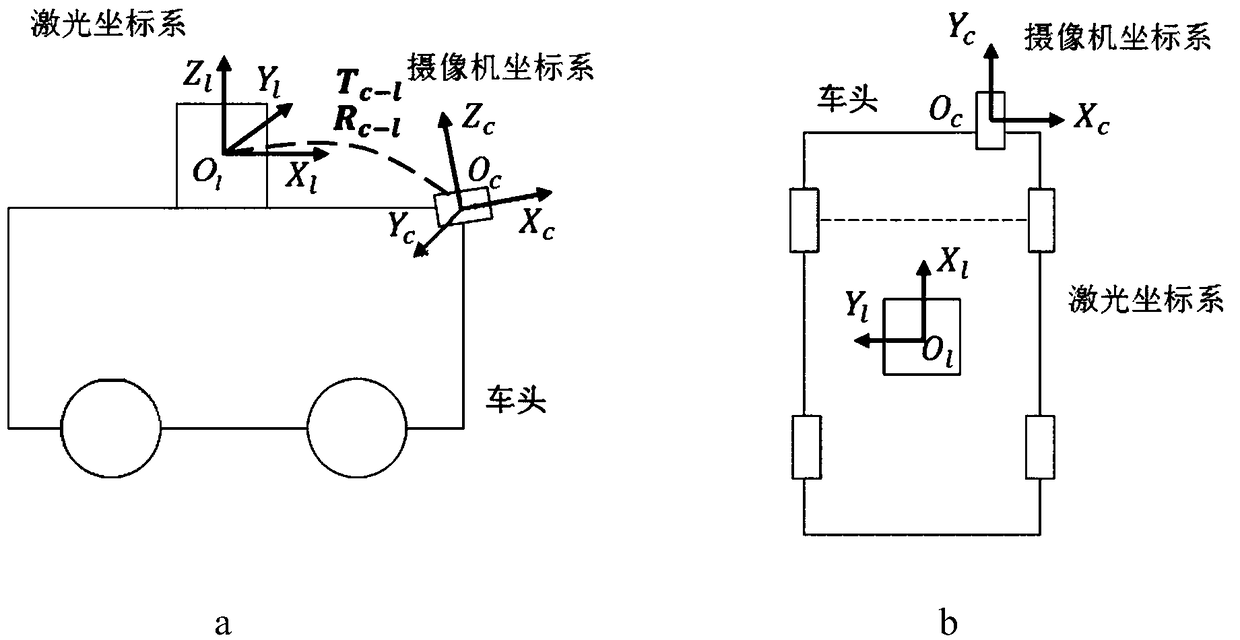
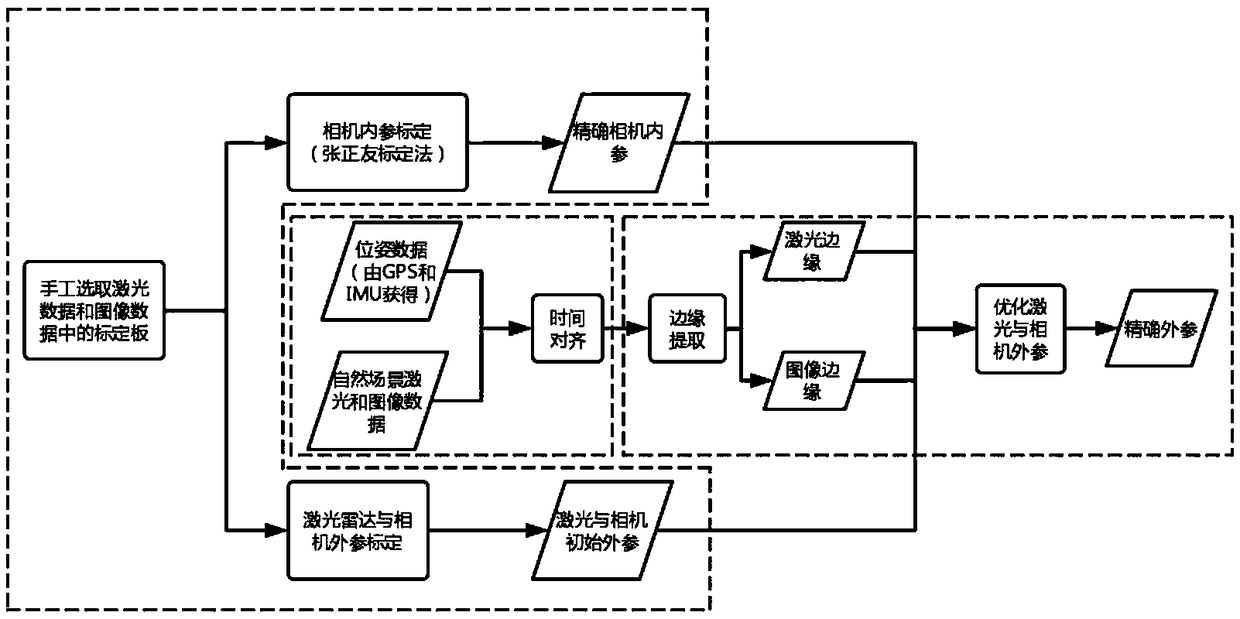
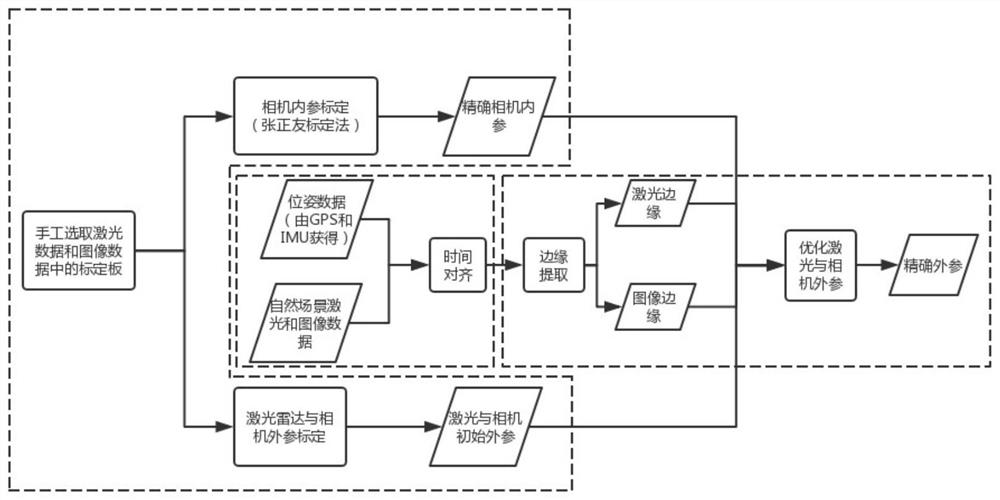
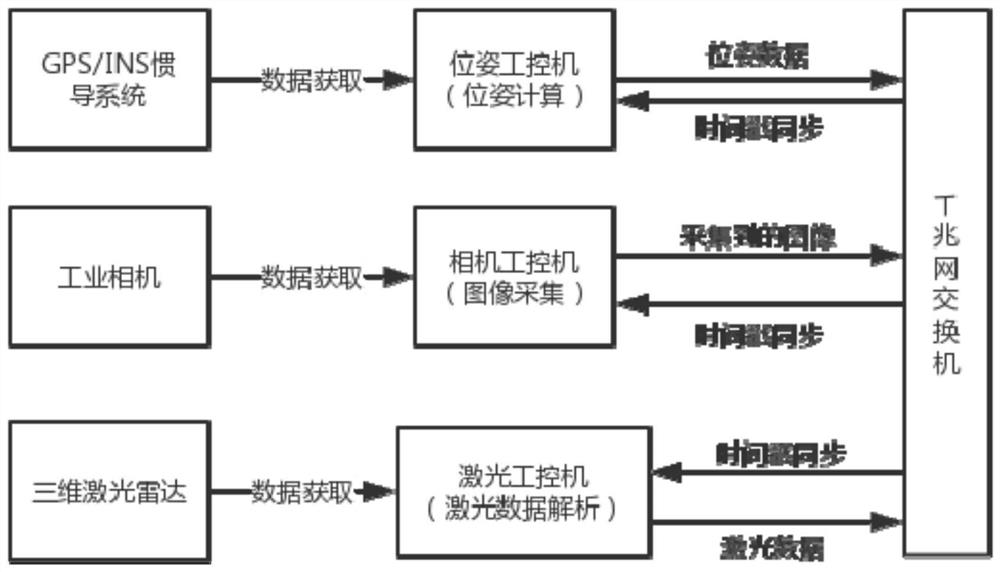
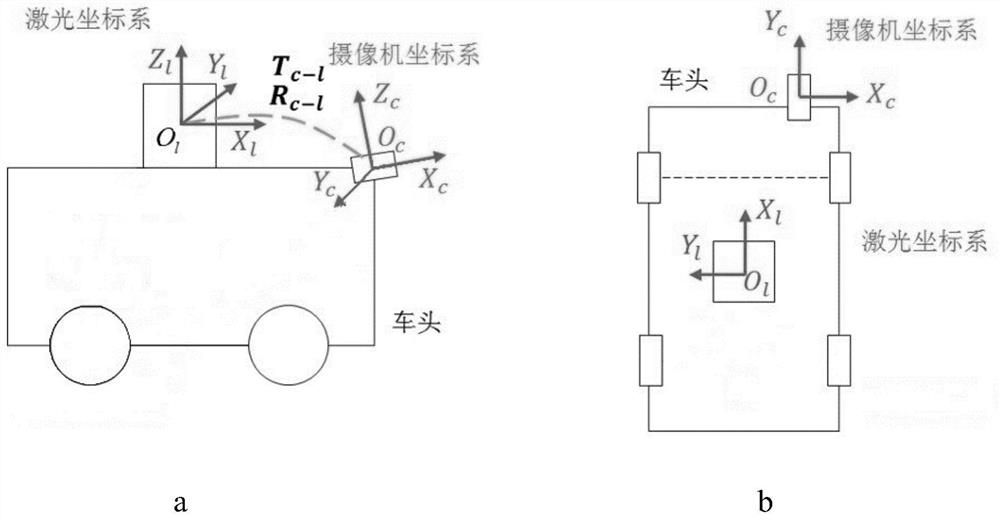
Intelligent vehicle laser sensor and online camera calibration method
ActiveCN109270534AAchieve high-precision calibrationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLaser dataTime alignment
The invention discloses an intelligent vehicle laser sensor and an online camera calibration method. Laser data and image data are accurately calibrated via the steps of camera calibration, offline calibration of a three-dimensional laser sensor and an image sensor, time alignment of laser data and image data, and online alignment of the laser sensor and the image sensor. The calibration system can be applied to multiple different road conditions and scene, to achieve online high precision calibration of laser and an image. After the laser and the image are calibrated, the information of the two sensors can be used for comprehensively analyzing a barrier and making an accurate decision, so that the method has is significant in sensing technology of an intelligent vehicle. Therefore, the technology can be widely applied to the fields of driverless vehicle visual navigation and intelligent vehicle visual assistance driving.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
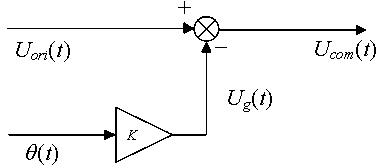
Unsmooth dynamic compensation method for ultralow-frequency horizontal vibration table guide rail
ActiveCN103822703ALittle impact on accuracyReduced precision requirementsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementCalibration resultEngineering
The invention discloses an unsmooth dynamic compensation method for an ultralow-frequency horizontal vibration table guide rail. The unsmooth dynamic compensation method comprises the following steps: measuring unsmooth dynamic characteristics of the ultralow-frequency horizontal vibration table guide rail and output uori t of a calibrated acceleration sensor in real time by taking a horizontal direction as reference; constructing a guide rail unsmoothness dynamic compensation system, and removing a gravitational acceleration component in the output of the calibrated sensor generated by pitching of a sliding table from the original output of the calibrated sensor in real time in the vibration calibration process; calibrating a calibrated acceleration sensor by adopting the compensated output ucomt of the calibrated sensor, calculating to obtain a compensated amplitude-frequency curve, and finishing vibration calibration of the calibrated sensor. The unsmooth dynamic compensation method has the advantages that the calibration result deviation of the acceleration sensor with zero frequency response caused by guide rail unsmoothness based on the ultralow-frequency horizontal vibration table can be compensated in real time in the vibration calibration process, so that the precision of ultralow-frequency vibration calibration is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
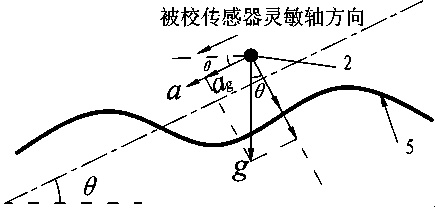
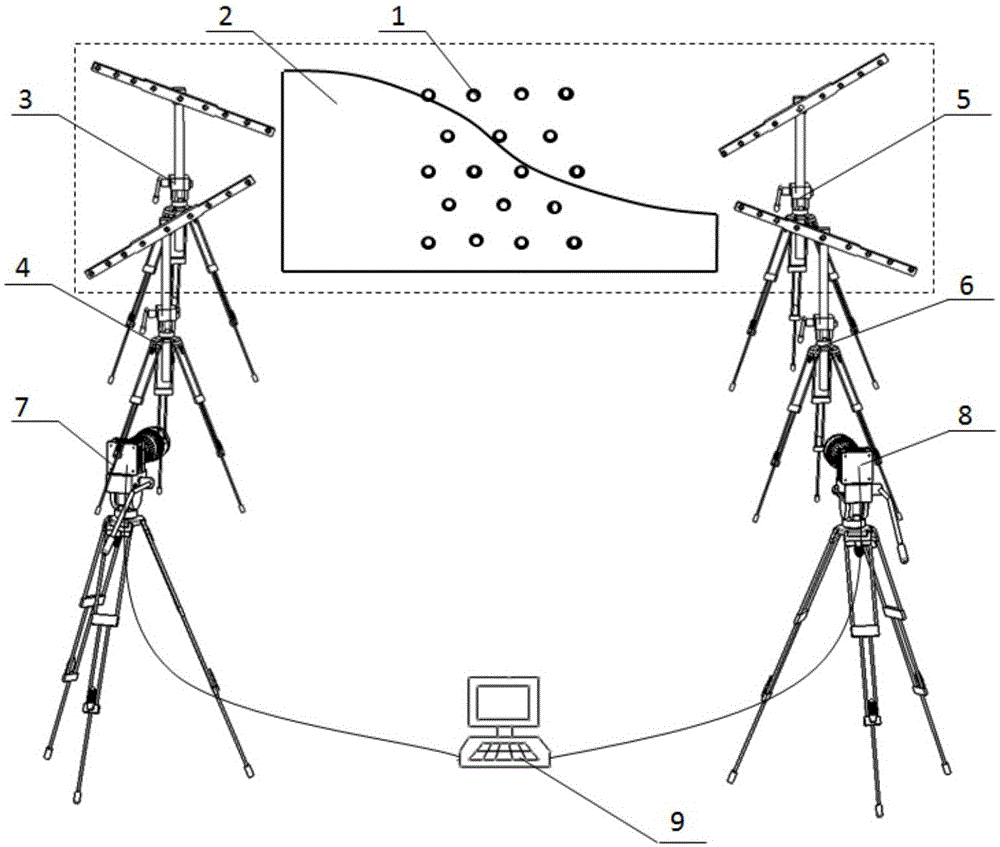
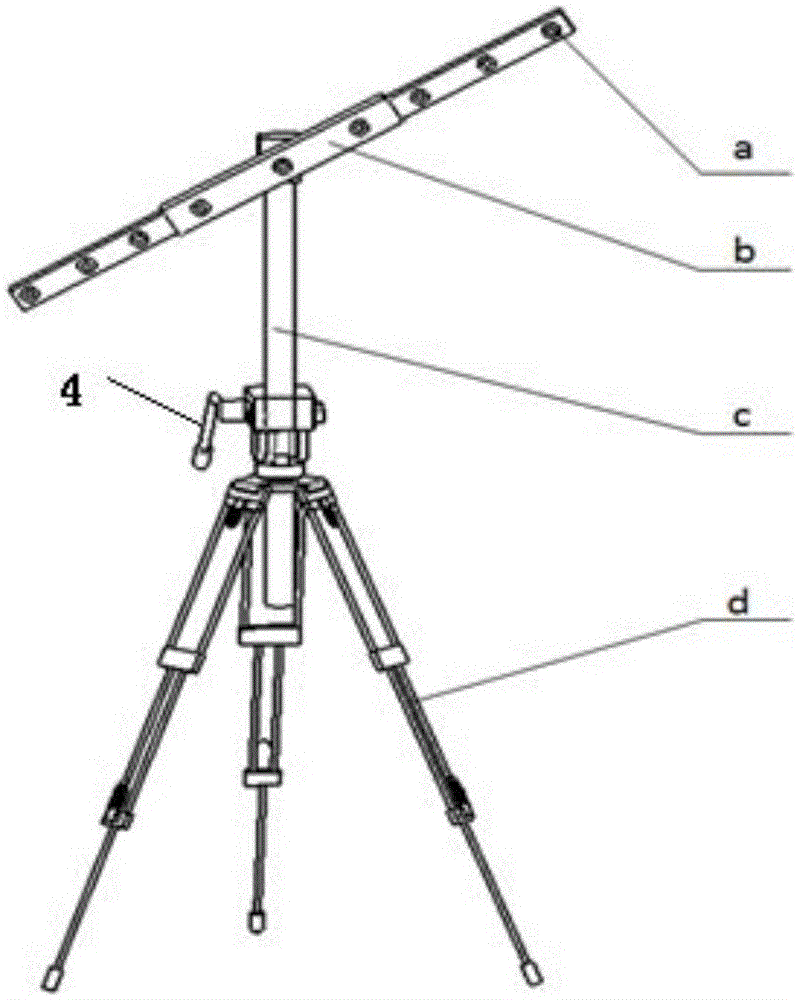
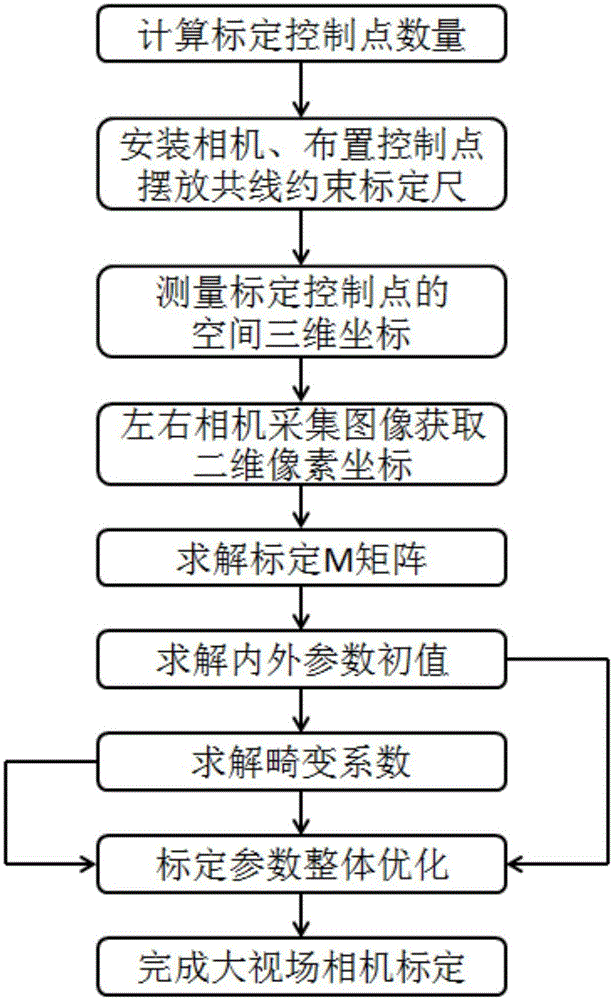
Large visual field camera calibration method based on four sets of collinear constraint calibration rulers
ActiveCN105139411AAchieve high-precision calibrationImprove defectsImage analysisVisual field lossCross-ratio
The invention discloses a large visual field camera calibration method based on four sets of collinear constraint calibration rulers and belongs to the field of optical measurement. The calibration method comprises steps of arranging four sets of collinear constraint calibration rulers in a large optical measurement field; solving distortion parameters by using unlimited characteristics of the cross ratio and straight line constrains; linearly solving the initial value of the calibrated parameter via the calibrated control point in the space; and at last by combining the distortion coefficients and the calibrated initial value and using the L-M optimization method, performing overall optimization with the goal of minimizing the re-projection error so as to get the calibrated precise result of the large visual field camera. According to the invention, by flexibly arranging the calibration control point in the large view field measurement space and combining the four sets of collinear constraint calibration rulers, overall optimization is performed on the calibrated results, high precision calibration for the large view field camera is achieved and the calibration method has a wide application prospect.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Strapdown inertial navigation system shaking pedestal systematic calibration method
The invention discloses a strapdown inertial navigation system shaking pedestal systematic calibration method. The strapdown inertial navigation system shaking pedestal systematic calibration method comprises following steps: 1, an inertial navigation calibration compensation model is established; 2, an inertial navigation calibration compensation error model is established; 3, calibration sequence conversion arrangement and data acquisition are carried out; 4, calibration error calculating and correction are carried out, wherein the step 4 comprises following sub-steps: a, a northeast sky coordinate system of a location for calibration is taken as a navigation coordinate system; b, in overturning process time, attitude updating is carried out; c, in T1 time of a second location after overturning, open loop navigation attitude, position, and speed calculating are carried out; d, calculating of related matrix and error parameters is carried out; e, the overturning data from a second time to a 18th time is obtained through the sub-steps from a to d; f, calculating of calibration compensation error parameters is carried out; and h, iterative computation is carried out so as to obtainthe strapdown inertial navigation system shaking pedestal systematic calibration results. The strapdown inertial navigation system shaking pedestal systematic calibration method is invented based on least square identification method disadvantages, and is capable of realizing high precision calibration of inertial navigation at different initial attitudes and different overturning orders under baseless conditions.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF COMP TECH & APPL
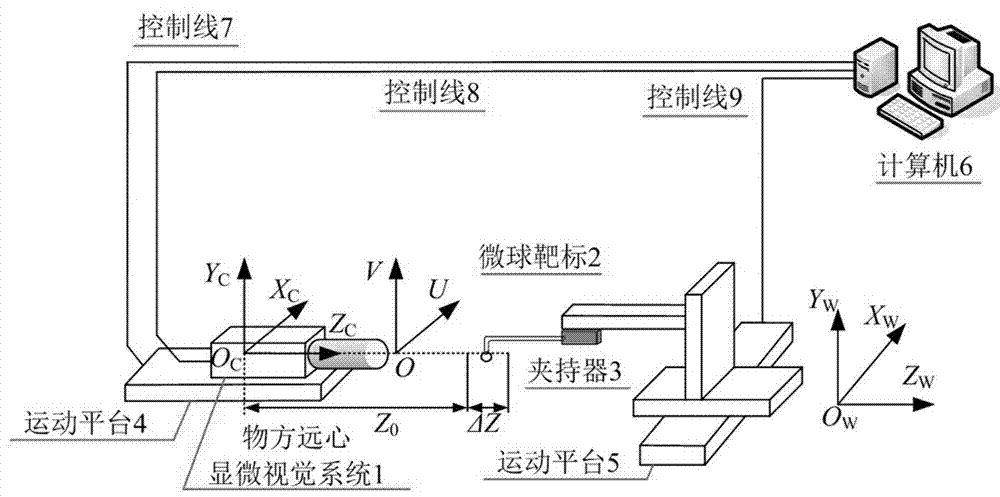
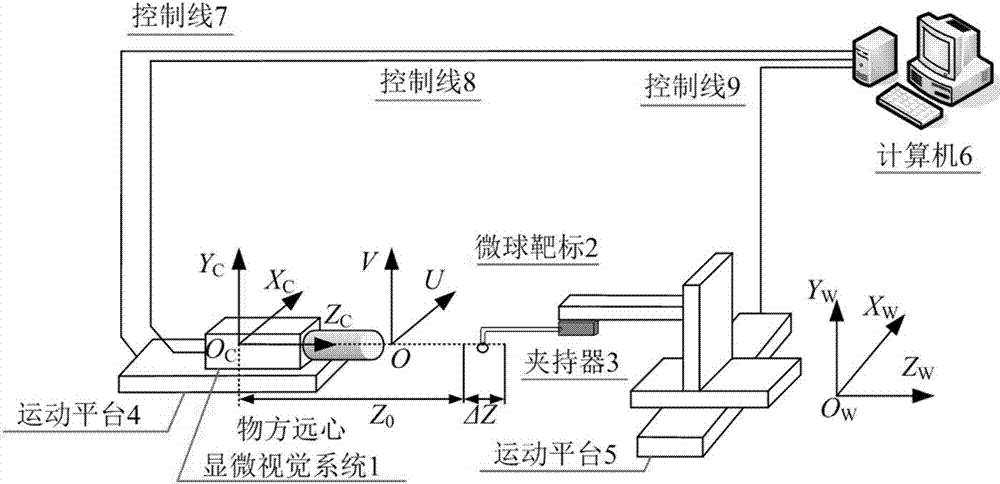
Microsphere-target-based objective image space telecentric microscopic vision system calibration method
ActiveCN103778640AAchieve high-precision calibrationImprove calibration accuracyImage analysisMicrosphereTelecentric lens
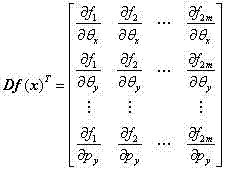
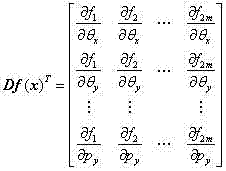
The invention provides a microsphere-target-based objective image space telecentric microscopic vision system calibration method. First, obtaining a camera model of a objective image space telecentric microscopic vision system on the basis of a telecentric imaging principle of an objective image space telecentric lens; second, obtaining an iteration calculation formula of the camera model of the objective image space telecentric microscopic vision system on the basis of a nonlinear damped least squares method; Finally, achieving objective image space telecentric microscopic vision system calibration by using a microsphere target performing relative motion in the telecentric depth range of the microscopic vision system for m times as well as the iterative calculation formula. The microsphere-target-based objective image space telecentric microscopic vision system calibration method has the advantages of being easy to operate and high accuracy in calibration and has good application prospect.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Unsmooth static compensation method for ultralow-frequency horizontal vibration table guide rail
ActiveCN103822768AAchieve high-precision calibrationLittle impact on accuracyVibration testingEngineeringCalibration result
The invention discloses an unsmooth static compensation method for an ultralow-frequency horizontal vibration table guide rail. The method comprises the following steps: measuring the unsmooth static performance of the ultralow-frequency horizontal vibration table guide rail, wherein unsmooth static performance is represented in a formula I as shown in the specification, and in the formula I, a formula II is represented as an output signal of a displacement sensor, x refers to different positions in which a sliding table is positioned along the vibration direction, Sgra is the sensitivity of the displacement sensor, and theta is an inclination angle of the sliding table at the position x; performing static compensation on the unsmooth ultralow-frequency horizontal vibration table guide rail as a sampling time point, wherein ti serves as a sampling time point, uati serves as the output voltage of the calibrated sensor at the moment ti after compensation, uatti serves as the output voltage of the calibrated sensor before compensation, ugti is output voltage which is superposed on the calibrated sensor due to the unsmooth guide rail and is caused by a gravitational acceleration component, a formula II as shown in the specification is a sampling value of a formula III as shown in the specification at the moment ti, and SaH is a theoretical value of the sensitivity of the calibrated sensor. The method has the advantages that the calibration result deviation caused by the unsmooth guide rail can be corrected, and the precision of ultralow-frequency vibration and calibration is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Online calibration method of magnetic sensor for unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN108458728ATroubleshoot calibration issuesAchieve high-precision calibrationNavigation by terrestrial meansUncrewed vehicleComputer science
The invention provides an online calibration method of a magnetic sensor for an unmanned aerial vehicle, which can solve the calibration problem of the magnetic sensor in a complicated magnetic ring environment. After being installed, a product makes one-time horizontal circular motion on an application device without being disassembled to realize the high-accuracy calibration of magnetic course parameters. The online calibration method has the beneficial effects that the operation and maintenance cost of a navigation device in the fields such as the unmanned aerial vehicle and an unmanned boat can be greatly decreased.
Owner:北京扬舟科技有限公司
REVO measuring head B-axis zero error calibration method
ActiveCN110017803AAvoiding Situations That Introduce Additional Calibration ErrorsRealize high-precision calibration of zero errorMeasurement devicesAngular degreesNon orthogonal
The invention discloses an REVO measuring head B-axis zero error calibration method applied to a non-orthogonal coordinate measurement system and belongs to the field of precision test technologies and instruments. The method comprises the steps that a square ruler is placed on a flat plate which is placed horizontally, and one working face M of the square ruler is fixed after being adjusted to beparallel to the X-direction of a measuring machine; a flat ruler is fixed after being closely attached to a working face N perpendicular to the working face M of the square ruler; three principal axes of the measuring machine are kept static, an A-axis of an REVO measuring head is placed at an appropriate position, and a B-axis of the REVO measuring head rotates to detect two symmetric points onthe flat ruler; and according to calculation of B-axis angles of the two detection points, a zero error of the B-axis of the measuring head can be calibrated. According to the method, under the statethat the three principal axes of the measuring machine are static, the situation that the angle of a joint arm is changed due to measuring force generated in the calibration process, and consequentlyan additional calibration error is introduced is avoided, high-precision calibration of the zero error of the B-axis of the REVO measuring head is realized, and the method can be applied to precisionmeasurement.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
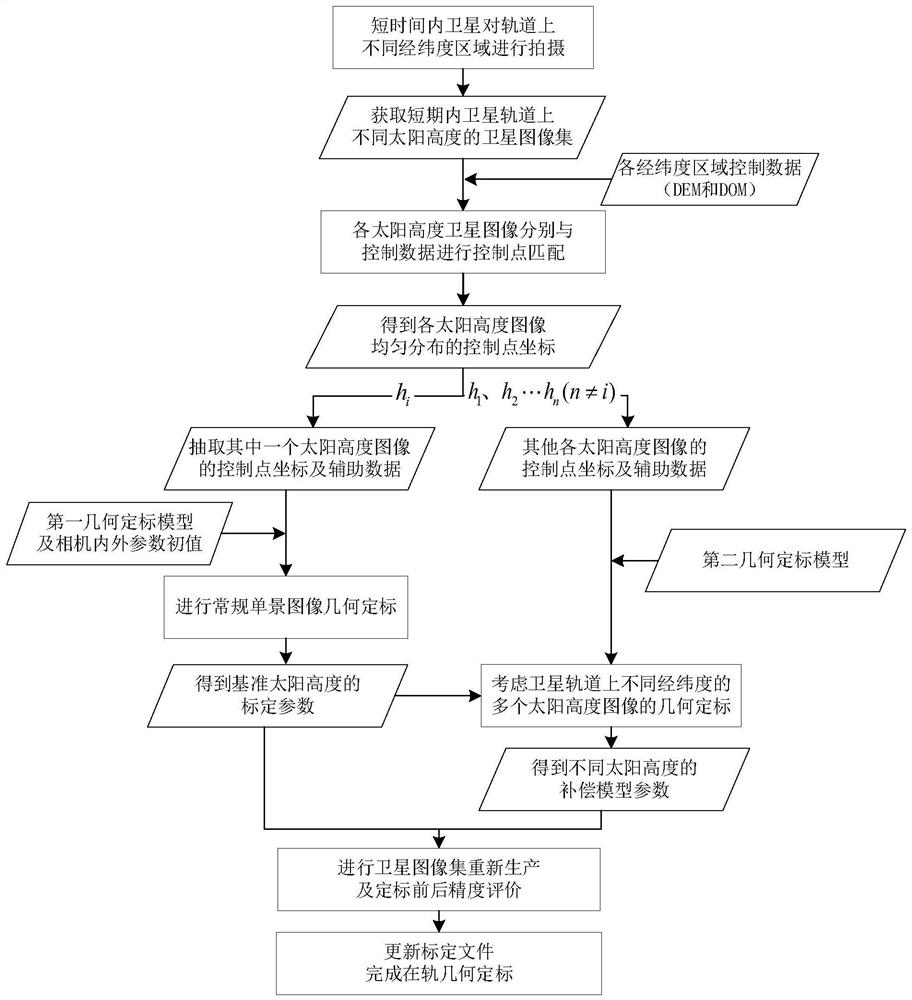
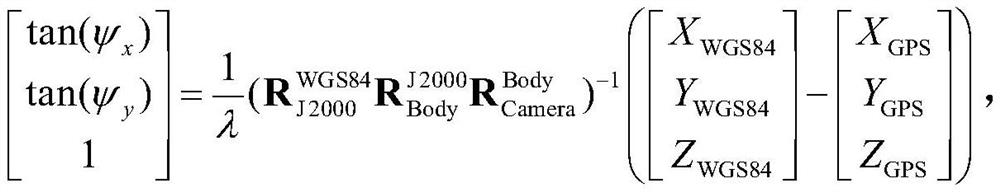
Satellite image geometric calibration method considering regions with different longitudes and latitudes
PendingCN114838740AAchieve high-precision calibrationImage analysisMeasurement devicesSatellite imageLongitude
The invention discloses a satellite image geometric calibration method considering different longitude and latitude areas. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a satellite image set with different sun heights in each longitude and latitude area in the same orbit; acquiring a control point in the satellite image set based on the control data of each longitude and latitude area; selecting a control point in one of the reference sun altitude images, and obtaining camera calibration parameters of the sun altitude based on a first geometric calibration model; constructing attitude error compensation models of different sun altitudes, and establishing a second geometric calibration model considering different latitude and longitude regions; using control points in other sun altitude images to obtain attitude compensation parameters; and updating the calibration file based on a second geometric calibration model according to the camera calibration parameters of the reference sun altitude and the attitude compensation parameters of different sun altitudes. According to the invention, unified calibration of satellite images of different longitude and latitude areas can be considered, and accurate calibration of satellite images of different sun heights on the whole satellite orbit is realized.
Owner:北京市遥感信息研究所
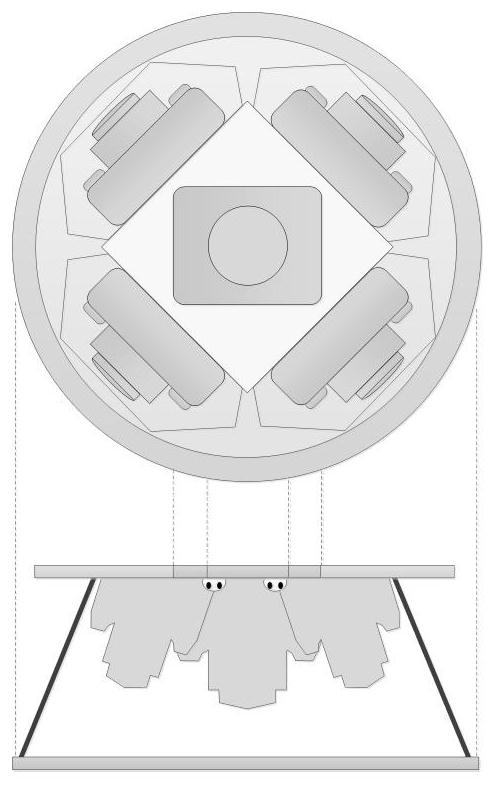
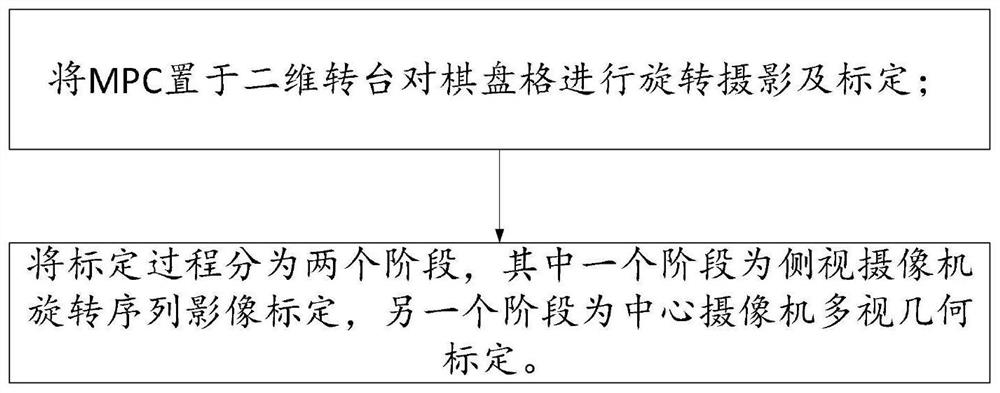
Multi-head panoramic camera combined calibration method
PendingCN113763480AGet rid of dependenceAchieve high-precision calibrationImage analysisNumerical controlView camera
The invention relates to the technical field of computer vision, and particularly discloses a multi-head panoramic camera combined calibration method. The method comprises the following steps: placing MPCs on a two-dimensional turntable to carry out rotary photographing and calibration on a checkerboard; and dividing a calibration process into two successive stages, wherein the previous stage is rotation sequence image calibration of side-view cameras, and the latter stage is multi-view geometric calibration of a center camera. According to the method, high-precision calibration of external parameters of an MPC can be realized only by using a common two-dimensional numerical control turntable and a single checkerboard, the cost is low, the operation is simple, the requirement on a real-time environment is low, the dependence on a 3D calibration field is successfully eliminated, and the method has a good application value.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
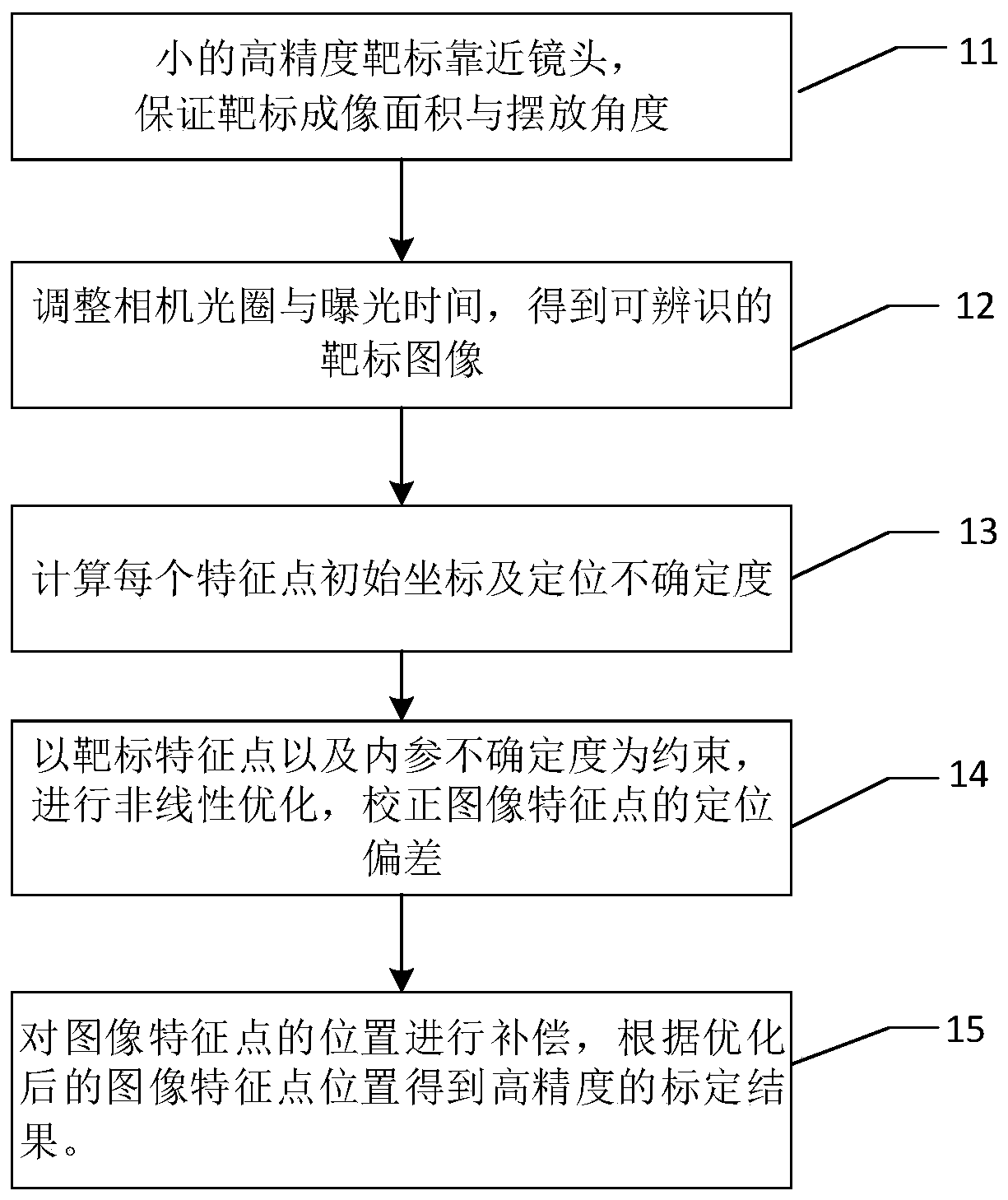
Camera online calibration method based on small target blurred image
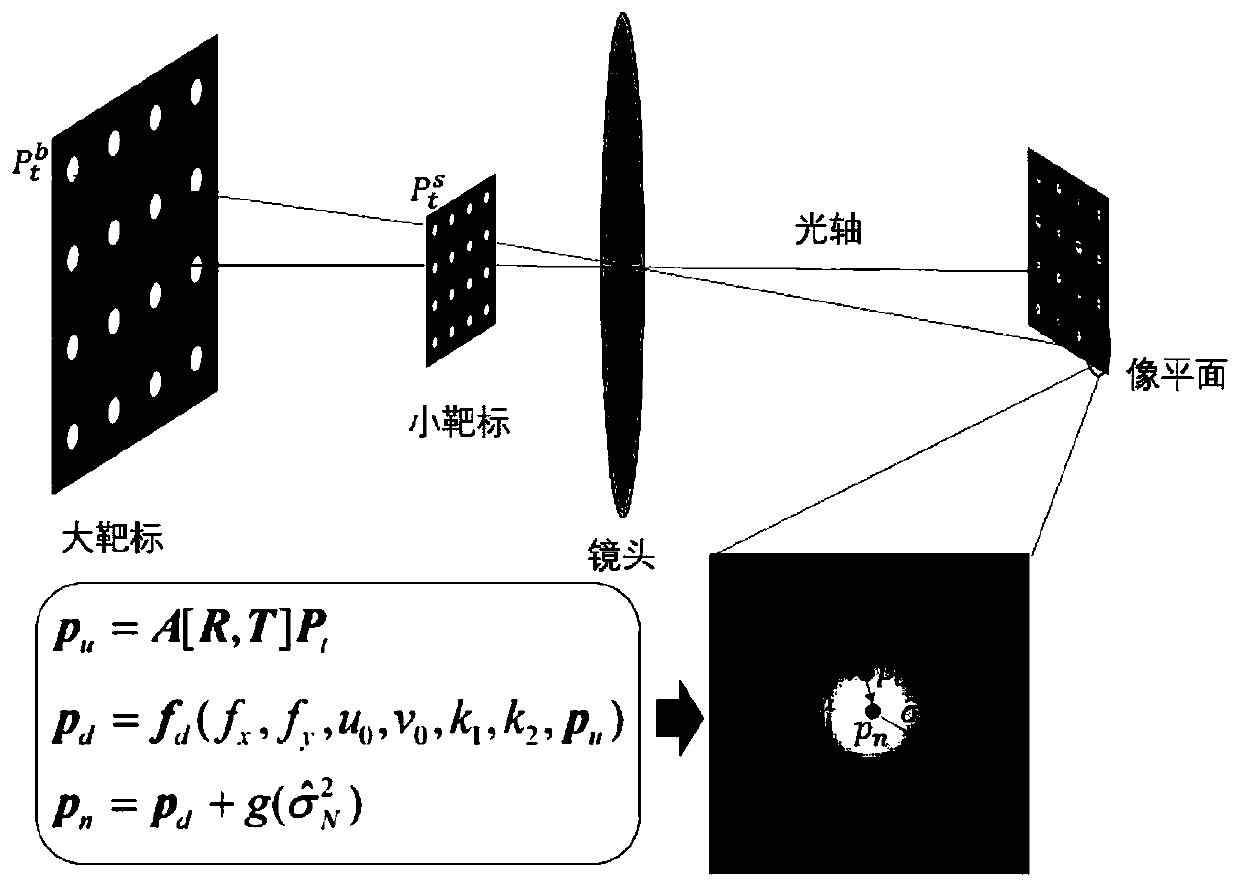
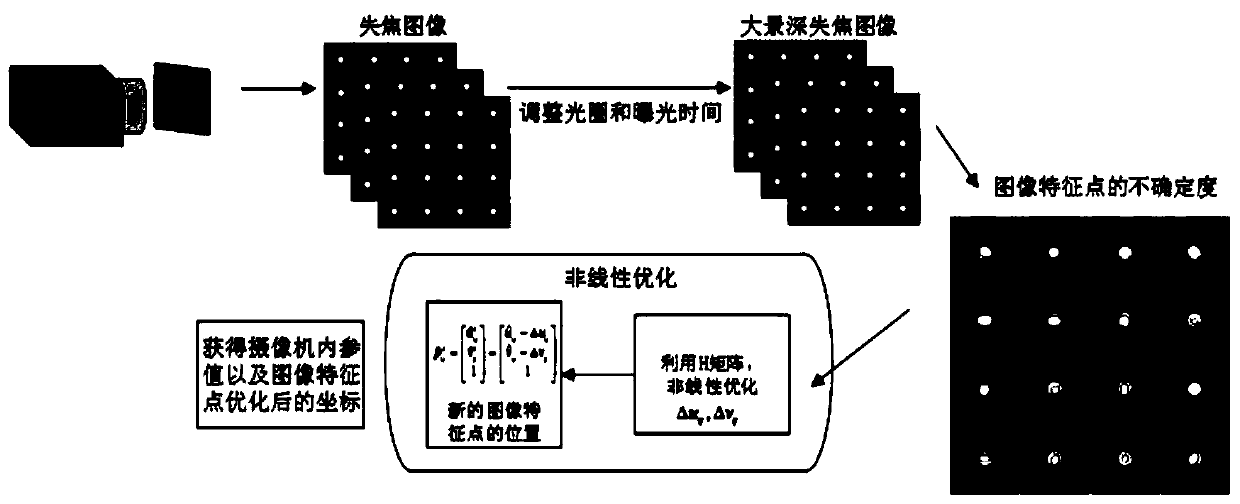
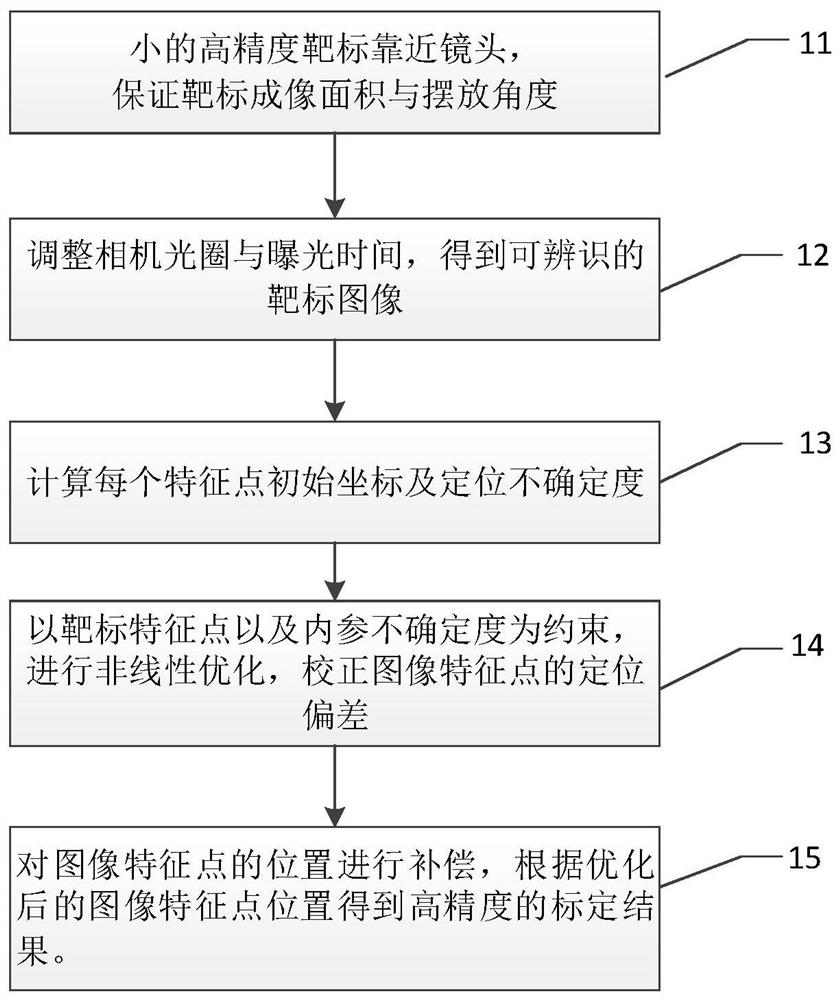
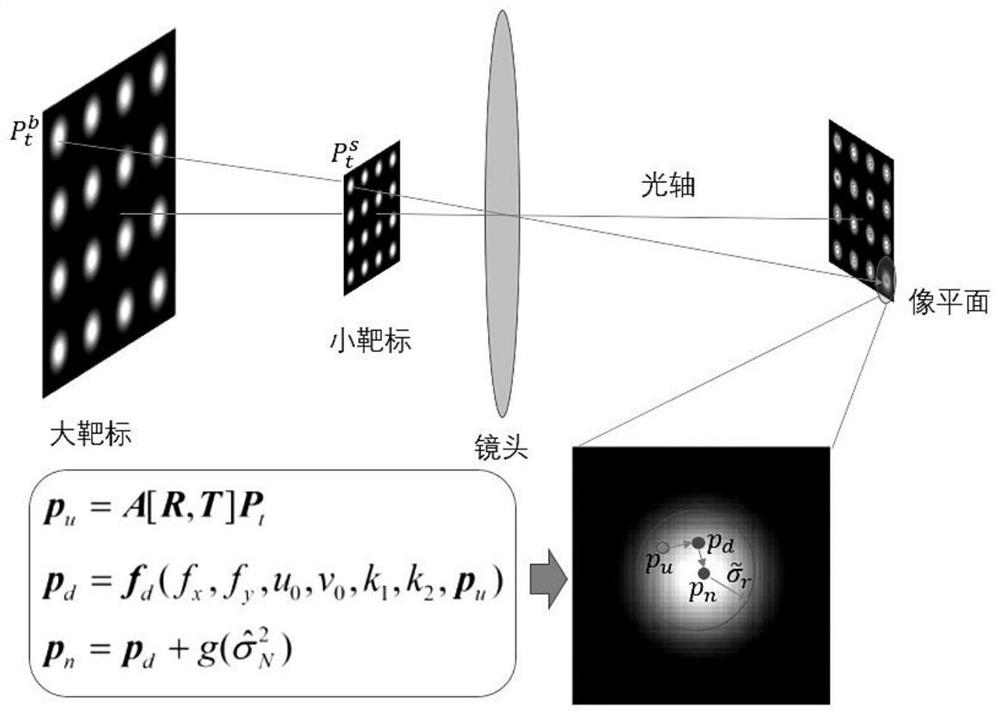
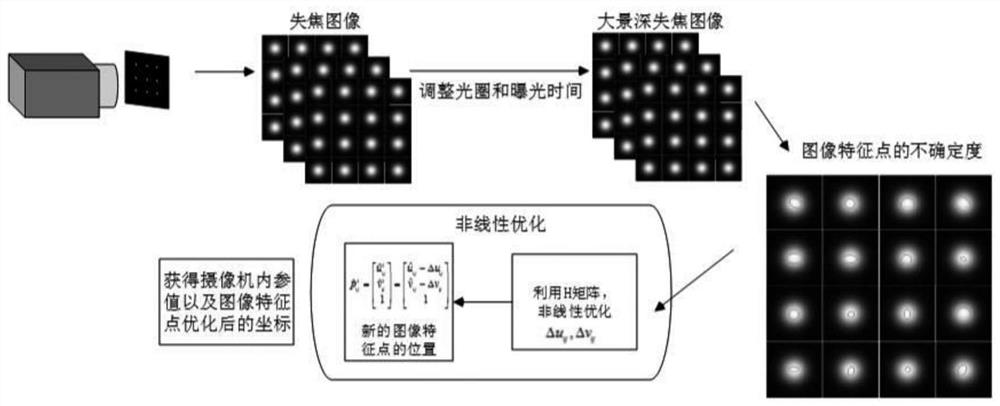
ActiveCN109754435AAchieve high-precision calibrationBreak the traditional calibration modeImage analysisCamera lensMathematical model
The invention relates to a camera online calibration method based on a small target blurred image, which comprises the following steps: enabling a high-precision small circular light-emitting point target to be close to a lens as much as possible, and ensuring that the target obtains a large image proportion and a placement angle; adjusting a camera aperture and exposure time to obtain an identifiable target image; establishing a target feature point positioning uncertainty mathematical model, and solving the positioning uncertainty of each feature point; By taking target feature point positioning and parameter uncertainty as constraints, solving high-precision solutions of internal and external parameters of the camera through a nonlinear optimization method; according to the method, thefocusing space and the target size of the camera do not need to be considered, and the ultrahigh-precision calibration of the camera can be realized under the conditions of large image blurring and noise only by placing a very small high-precision target at a position close to a lens. The method is suitable for online calibration of large-view-field and shallow-depth-of-field cameras and even cameras in use, and has great flexibility and adaptability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Multi-parameter model of articulated arm coordinate measuring machine and calibration method
ActiveCN112344895AHigh precisionAchieve high-precision calibrationMeasurement devicesControl engineeringCoordinate-measuring machine
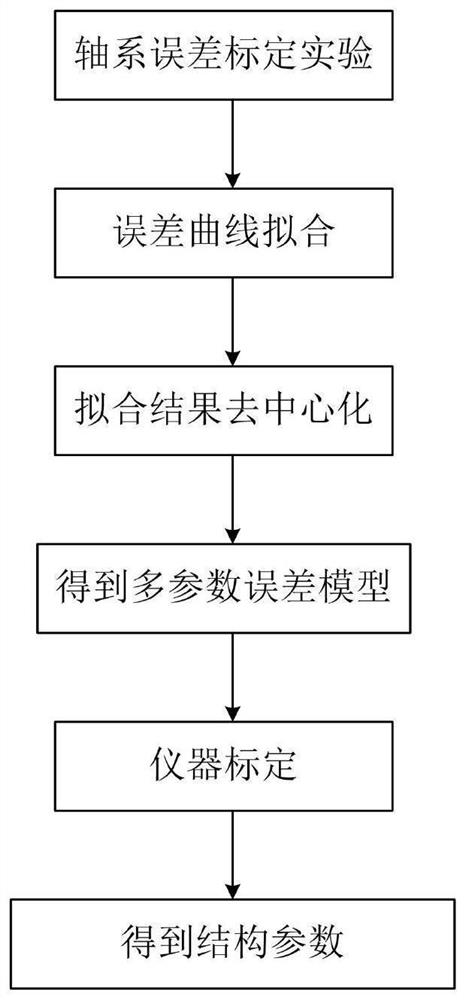
The invention discloses a multi-parameter model of an articulated arm coordinate measuring machine and a calibration method, relates to the technical field of precision measurement, expands a 23-itemerror model of an original articulated arm coordinate measuring machine into a 59-item error model, greatly increases the number of structural parameters of the error models of the articulated arm coordinate measuring machine, and improves the precision of the articulated arm coordinate measuring machine. According to the articulated arm coordinate measuring machine multi-parameter model and the calibration method provided by the invention, the shafting shaking error term is added on the basis of the original articulated arm measuring machine error model, the articulated arm coordinate measuring machine multi-parameter error model is established, and high-precision calibration of the articulated arm coordinate measuring machine is realized.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
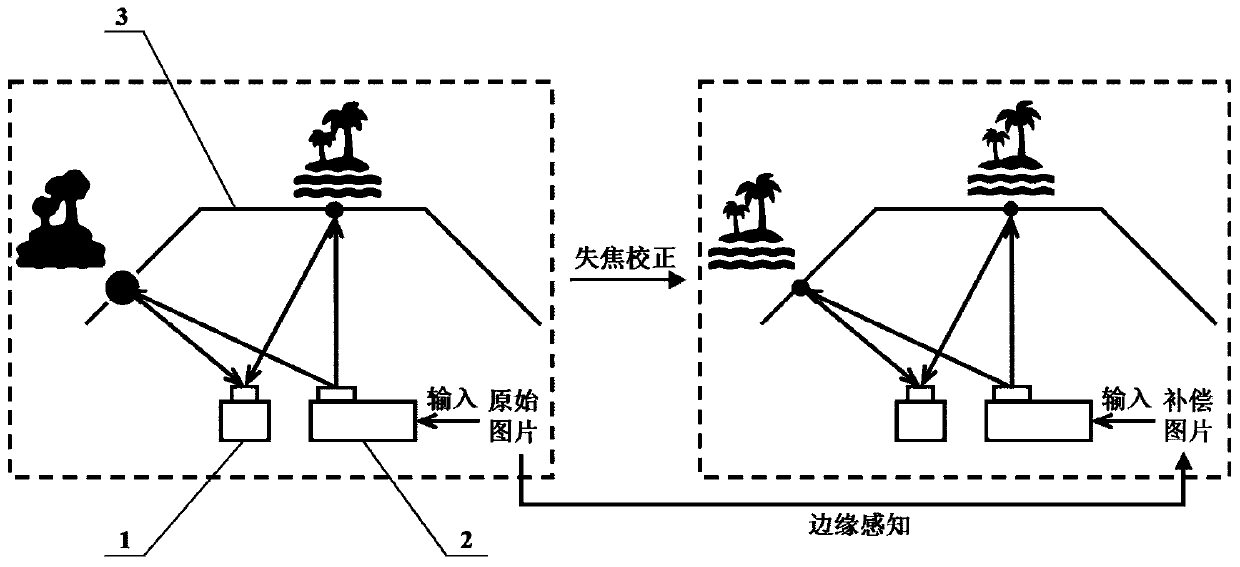
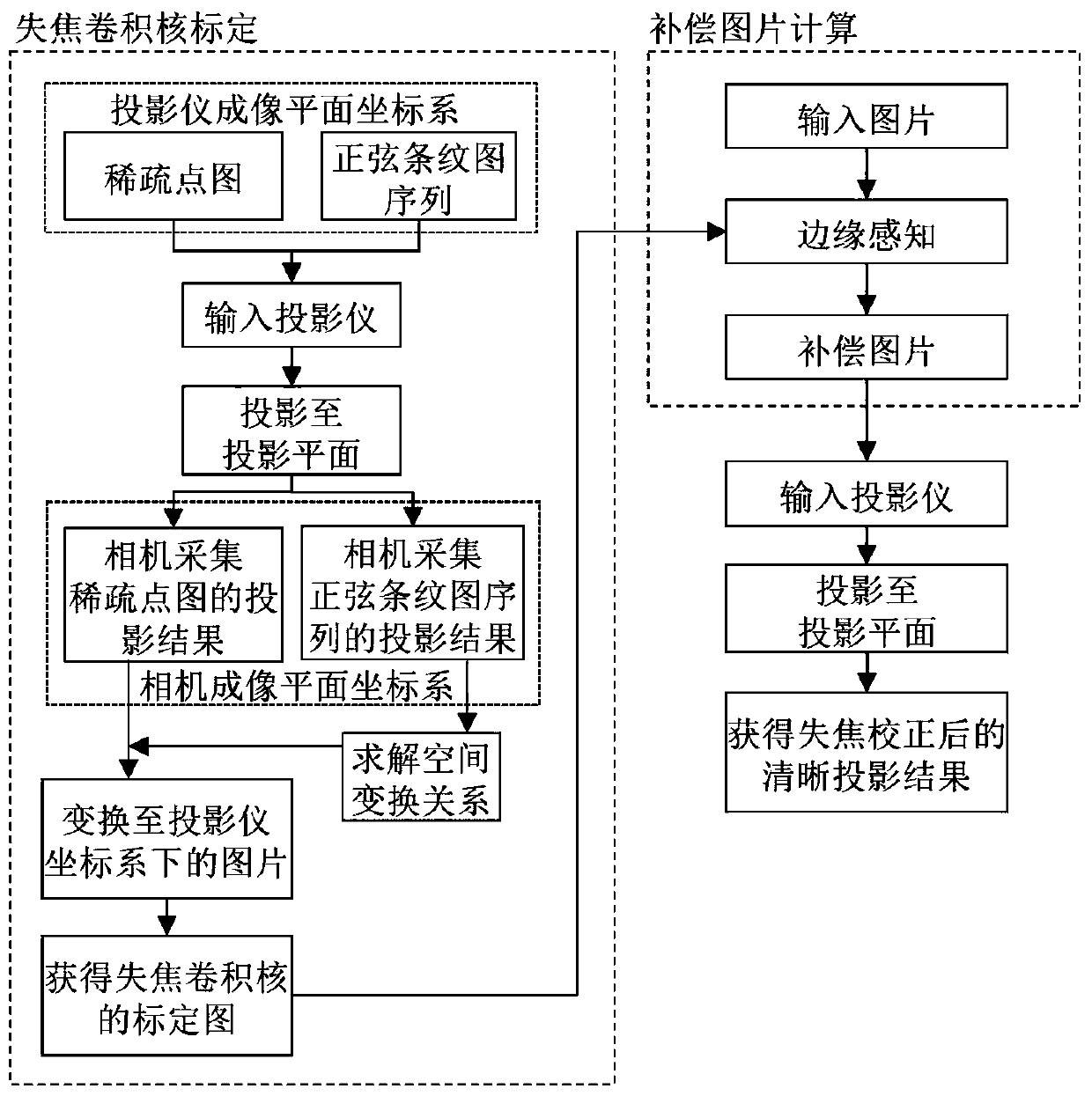
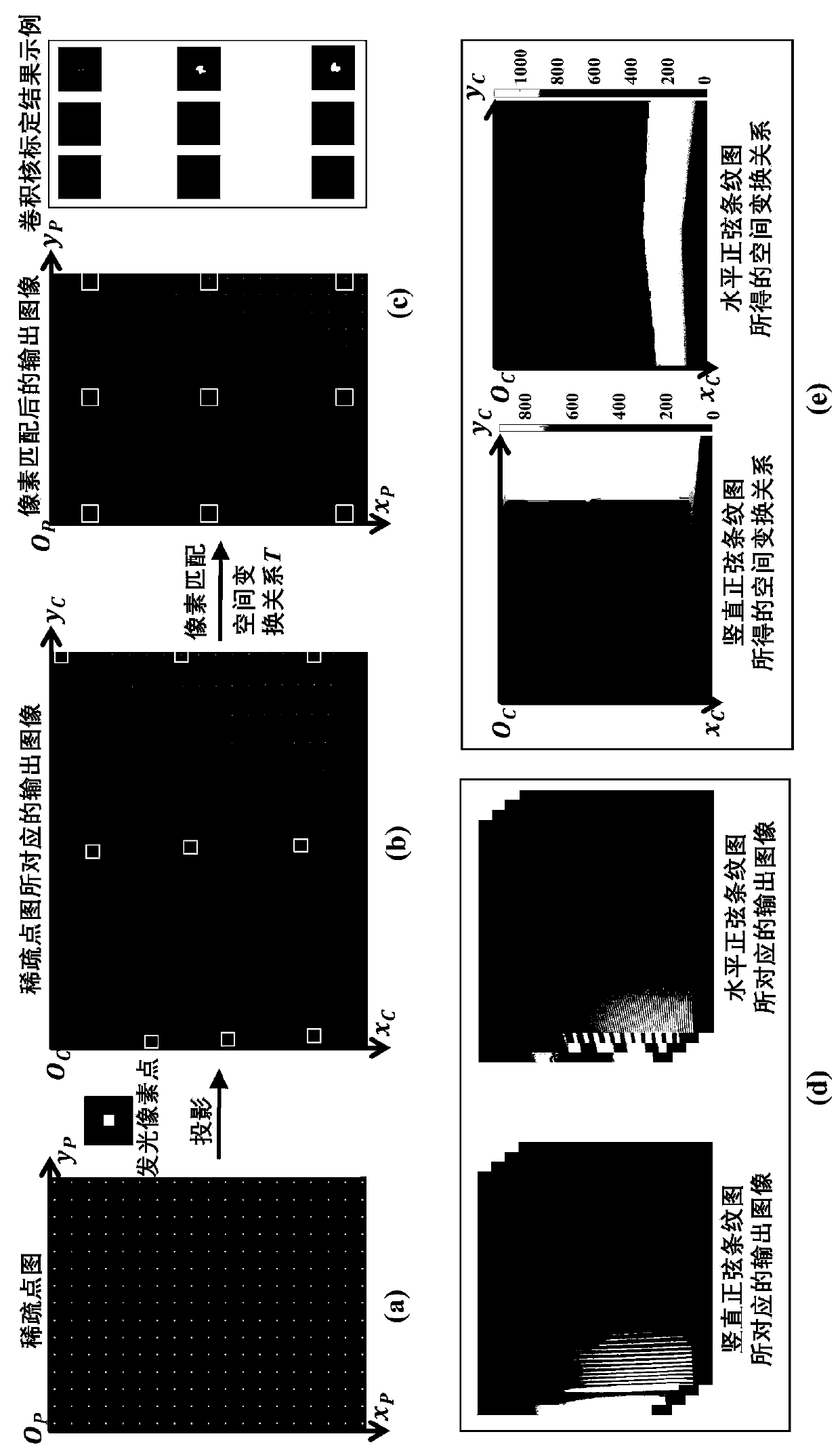
Projector out-of-focus correction method based on edge perception
ActiveCN111311686AAchieving out-of-focus correctionLow hardware requirementsImage analysisProjectorsProjector camera systemsComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a projector out-of-focus correction method based on edge perception. According to the method, a projector-camera system is adopted, and a lens of a projector and a lens of a camera face the projection surface; inputting the special input image into a projector, projecting and irradiating the special input image onto a projection surface, and acquiring a projection result projected and irradiated onto the projection surface by the projector as an output image by a camera; and performing out-of-focus convolution kernel calibration by using the special input image and theoutput image to obtain a compensation picture, and performing correction compensation on the to-be-projected picture of the projector by taking the compensation picture as the input of the projector to obtain a clear projection result after out-of-focus compensation. The physical focal length of the projector does not need to be adjusted; according to the technical scheme, the clearness of the out-of-focus projection result of the projector can be realized only by processing the original picture input into the projector, the requirements of using the projector in complex application scenes such as thermal out-of-focus and large-amplitude height change of the projection surface of the projector can be met, and the applicability of the projector equipment is expanded to a certain extent.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
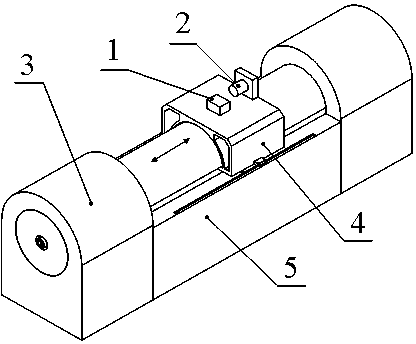
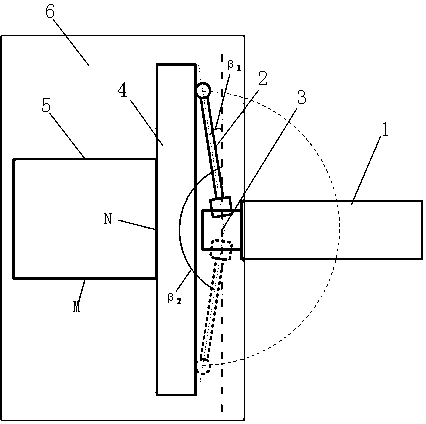
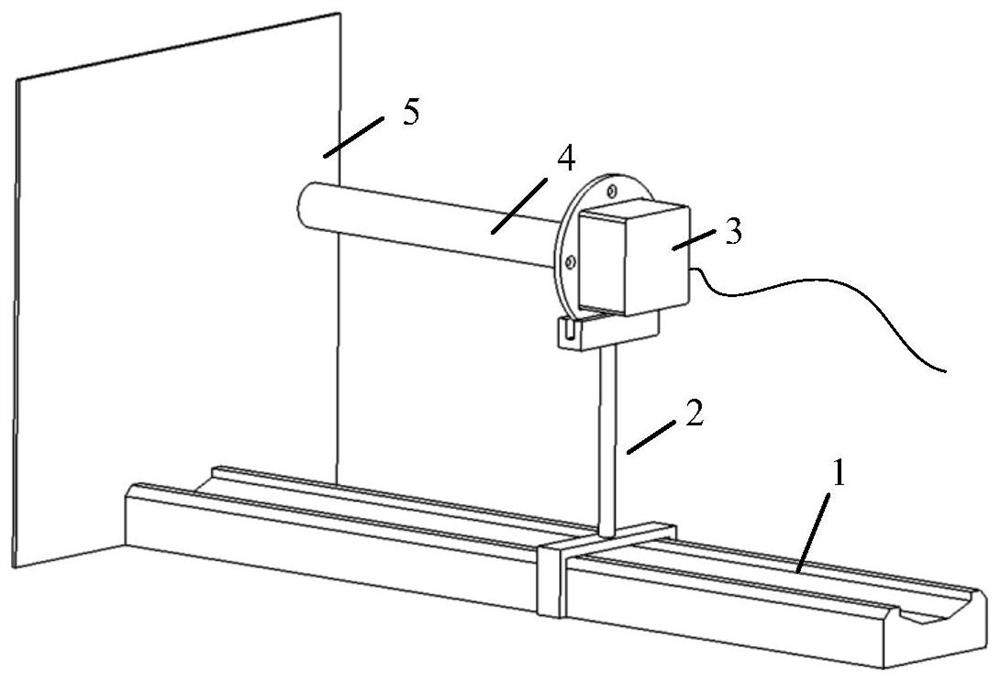
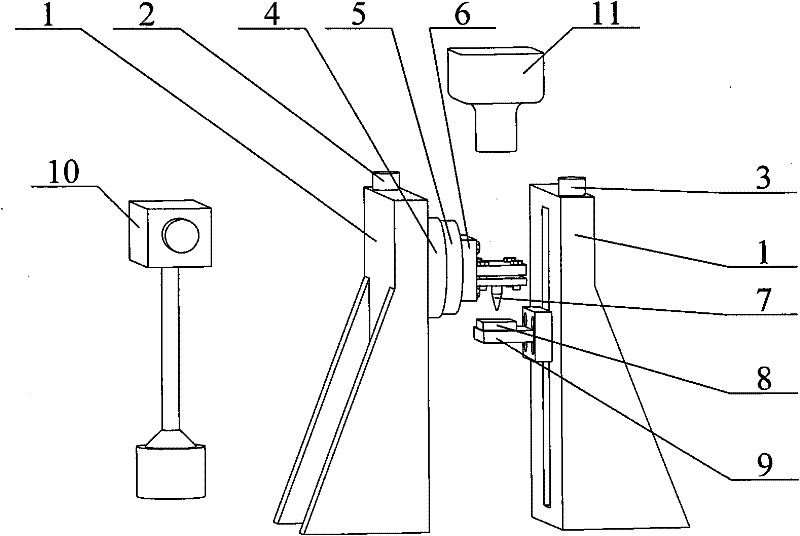
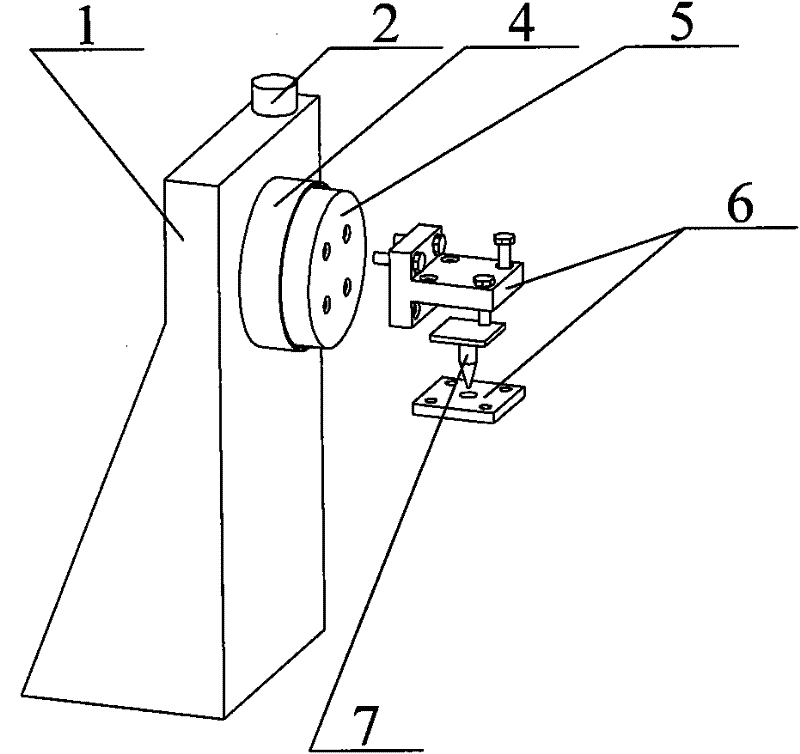
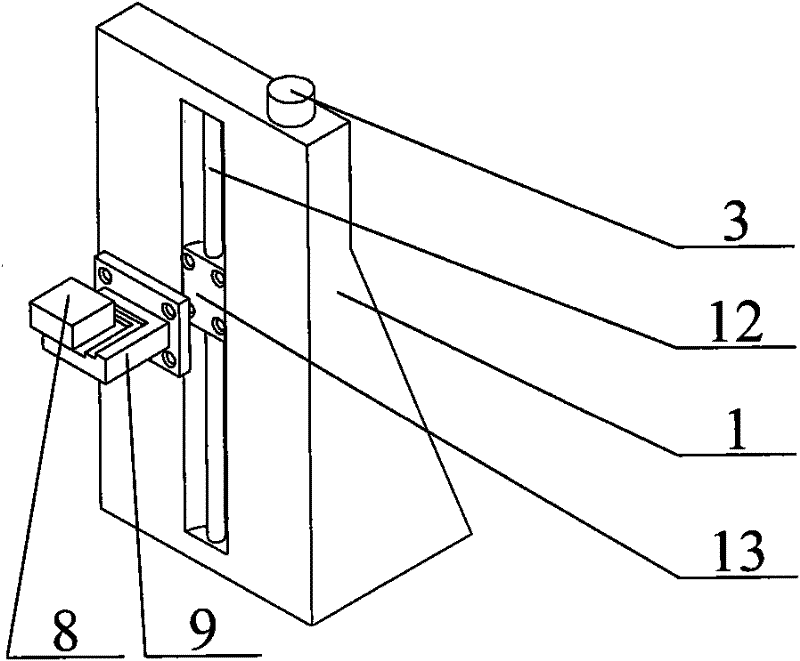
Solid-state area array laser radar calibration device and method based on dynamic simulation
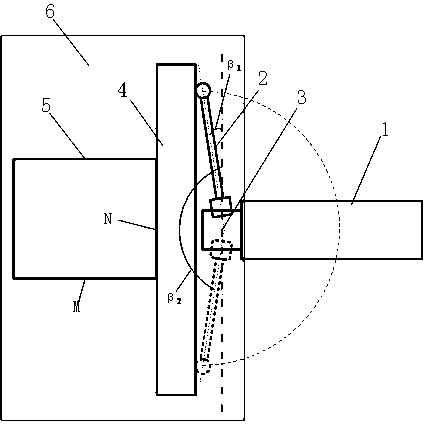
PendingCN112346035AImprove adaptabilityReduce the impact of environmental errorsWave based measurement systemsEngineeringTranslation table
The invention discloses a solid-state area array laser radar calibration device and method based on dynamic simulation, and the device and method can meet the calibration demands of different application scenes, and achieve the multi-angle and variable-reflectivity multi-mode high-precision calibration. The solid-state area array laser radar calibration device based on dynamic simulation comprisesa high-precision scale translation table (1), a fixing frame (2), a solid-state area array laser radar (3), a calibration cylinder (4) and a calibration plate (5), the fixing frame (2) is hinged to the calibration cylinder (4) through a universal joint, and the fixing frame (2) slides on the high-precision scale translation table (1), so that the distance and the axial angle between the calibration cylinder (4) and the calibration plate (5) are changed; the solid-state area array laser radar (3) and the calibration cylinder (4) are installed and fixed in an embedded installation mode so thatthe optical path of an emitter of the solid-state area array laser radar (3) is enabled to be parallel to the axis of the calibration cylinder (4).
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Parts Precise Positioning Method Based on Binocular Microscopic Stereo Vision
The invention discloses an accurate part positioning method based on binocular microscopy stereo vision, which belongs to the technical field of computer visual measuring and relates to an accurate precision part positioning method based on the binocular microscopy stereo vision. A binocular microscopy stereo vision system is adopted, two CCD (charge coupled device) cameras are adopted to acquire the images of the measured parts, the image information in the to-be-measured area on the measured part is amplified by a stereo microscope, a checkerboard calibrating board is adopted to calibrate the two CCD cameras, and a Harris corner point detecting algorithm and a sub-pixel extracting algorithm are adopted to extract feature points. The extracted feature points are subjected to the primary matching and correcting of matching point pairs, and the feature point image coordinates are inputted to a calibrated system to obtain the space actual coordinates of the feature points. The accurate part positioning method based on the binocular microscopy stereo vision solves the measuring difficult problems generated by the small size of the to-be-measured area, high positioning demand, non-contact and the like. The accurate positioning of the precision part is well finished by adopting the non-contact measuring method of the binocular microscopy stereo vision.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
A smart car laser sensor and camera online calibration method
ActiveCN109270534BAchieve high-precision calibrationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationImage calibrationComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses an intelligent vehicle laser sensor and an online camera calibration method. Laser data and image data are accurately calibrated via the steps of camera calibration, offline calibration of a three-dimensional laser sensor and an image sensor, time alignment of laser data and image data, and online alignment of the laser sensor and the image sensor. The calibration system can be applied to multiple different road conditions and scene, to achieve online high precision calibration of laser and an image. After the laser and the image are calibrated, the information of the two sensors can be used for comprehensively analyzing a barrier and making an accurate decision, so that the method has is significant in sensing technology of an intelligent vehicle. Therefore, the technology can be widely applied to the fields of driverless vehicle visual navigation and intelligent vehicle visual assistance driving.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method and device for calibrating three-dimensional micro tactile sensor
InactiveCN101813499BAchieve high-precision calibrationEffective comparisonUsing electrical meansElectric/magnetic roughness/irregularity measurementsEngineeringCcd camera
The invention discloses a method and a device for calibrating a three-dimensional micro tactile sensor. The method and the device are characterized in that: a three-dimensional micro tactile sensor fixing device, a micromovement input device, a CCD camera and a laser interferometer are arranged in a vibration isolation chamber; the three-dimensional micro tactile sensor is put on a rotary table through different clamping mechanisms; the micromovement input device realizes Z-axis coarse movement positioning of the three-dimensional micro tactile sensor and zero contact of the sensor and piezoelectric ceramics through a control device; the piezoelectric ceramics output amplitude signals to apply displacement constraint signals to the three-dimensional micro tactile sensor through a control system; an input-output relational graph is established through a signal acquisition system and computer software; and a calibration system of the laser interferometer tracks and measures the displacement constraint quantity of the piezoelectric ceramics so as to test and calibrate performance parameters of the three-dimensional micro tactile sensor. The method and the device calibrate performanceof the three-dimensional micro tactile sensor with multiple sensing modes, such as linearity, measuring range and precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MEASUREMENT & TESTING TECH
A Calibration Method for Object Space Telecentric Microvision System Based on Microsphere Target
ActiveCN103778640BAchieve high-precision calibrationImprove calibration accuracyImage analysisMicroscope cameraCamera lens
The invention provides a method for calibrating an object-space telecentric microscopic vision system based on a microsphere target. Firstly, the camera model of the object-space telecentric microscopic vision system is obtained based on the telecentric imaging principle of the object-space telecentric lens; then, the iterative calculation formula of the camera model of the object-space telecentric microscopic vision system is obtained based on the nonlinear damped least square method; Finally, the microsphere target is used to perform m relative movements within the telecentric depth range of the microscopic vision system, and the iterative calculation formula is used to realize the calibration of the object-space telecentric microscopic vision system. The method of the invention has the characteristics of convenient operation and high calibration precision, and has good application prospects.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
System and method for optical gauge sample stage calibration
ActiveCN103063412BAchieve high-precision calibrationTesting optical propertiesFour quadrantsAngular degrees
The invention discloses a system and a method for optical gauge sample stage calibration. Alignment of an optical path system is carried out under the condition that an ellipsometer is of a straight-through type. The method for the optical gauge sample stage calibration includes calibration of a front optical path and a back optical path. Due to a knob on an oblique incidence type crude regulation the sample stage of the ellipsometer, a polarization detection arm optical receiver hole can receive a part of light beams; the knob on the sample stage is finely regulated so that a cross cursor indicating the light beams can appear at the central position; and a system front portion and system back portion scan in the Z-axis direction with a step length 1, overall light intensity received by a detector at each height position is recorded, a light intensity curve is drawn, and the system automatically selects the position where the maximum light intensity value is located as the optimal relative height position of the sample stage. The system for the optical gauge sample stage calibration mainly comprises a light source, a polarizing arm, a front-arranged four-quadrant detector, a polarization detection arm, a spectroscope, an internally-arranged four-quadrant detector, a charge coupled device (CCD) detector and a computer. By means of the method for the optical gauge sample stage calibration, inclination angles and heights of the sample stage can be calibrated with high precision, besides, response is fast, and operation is simple.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
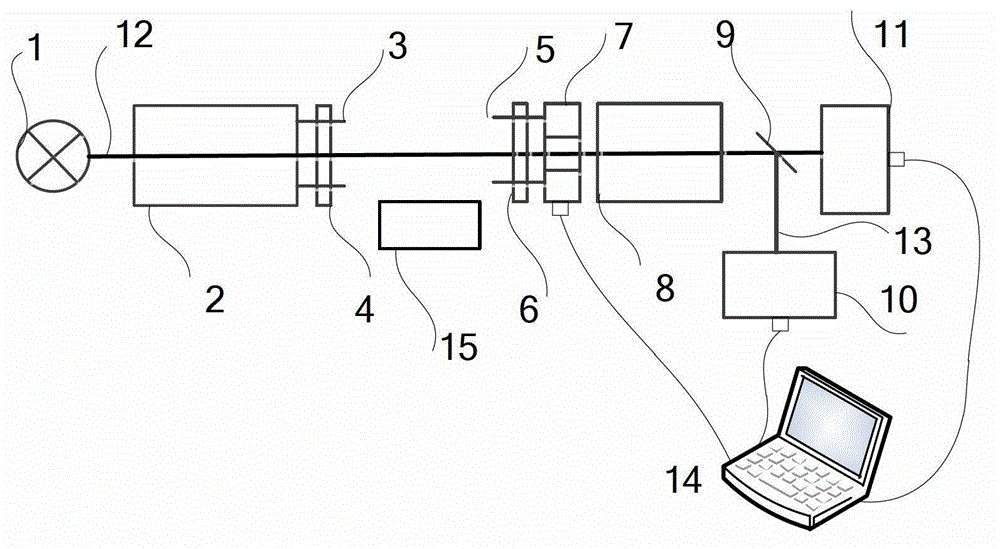
A super-resolution traceable white light interference atomic force probe calibration device and calibration method
ActiveCN106940389BHigh measurement accuracyImprove accuracyScanning probe techniquesVertical displacementCantilever
The present invention discloses a calibration device and a calibration method for a super-resolution and traceable type white-light interference atomic force probe. The calibration device is used for conducting the calibration method. The core technologies of the device and the method are composed of a traceable super-resolution displacement measurement system, a white-light interference zero-level fringe positioning algorithm, an atomic force probe bending model and a calibration process. The calibration device is used for generating the deformation of the probe. The traceable super-resolution displacement measurement system is used for accurately acquiring the vertical displacement generated during the probe deformation process. The white-light interference zero-level fringe positioning algorithm is used for accurately acquiring the position of an interference fringe on the cantilever of the probe. The atomic force probe bending model is used for fitting the relationship between the vertical displacement and the position of the fringe. The calibration process comprises specific implementation steps. According to the technical scheme of the calibration device and the calibration method, the relationship between the vertical displacement and the position of the fringe can be accurately and quickly acquired. Therefore, the accurate measurement of a white-light interference atomic force probe scanning microscope is realized.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
An in-situ calibration device for solid rocket motor ground rotation test
ActiveCN106546432BSimple structureAchieve high-precision calibrationEngine testingRotation testIn situ calibration
The invention relates to a solid rocket engine ground rotation test in-situ calibration device. The solid rocket motor ground rotation test in-situ calibration device comprises a switching device, a universal flexible component, a standard sensor, a force source loading device and a load bearing pier, wherein the switching device, the universal flexible component, the standard sensor, the force source loading device and the load bearing pier are coaxially and sequentially connected with one another; a standard simulation thrust is provided through the force source loading device; the standard sensor is used for reading the value of the standard simulation thrust; the standard simulation thrust is transmitted to a solid rocket engine through the universal flexible component and the switching device; and the value of the standard simulation thrust is compared with the measurement value of the working sensor of a solid rocket engine rotation test device, so that calibration can be carried out. Compared with an existing calibration device, the solid rocket engine ground rotation test in-situ calibration device is simple in structure, can effectively transmit the standard simulation thrust to the solid rocket engine under a condition that the solid rocket engine is rotating, and can achieve high-precision calibration of the solid rocket engine rotation test device.
Owner:中国航天科工动力技术研究院 +1
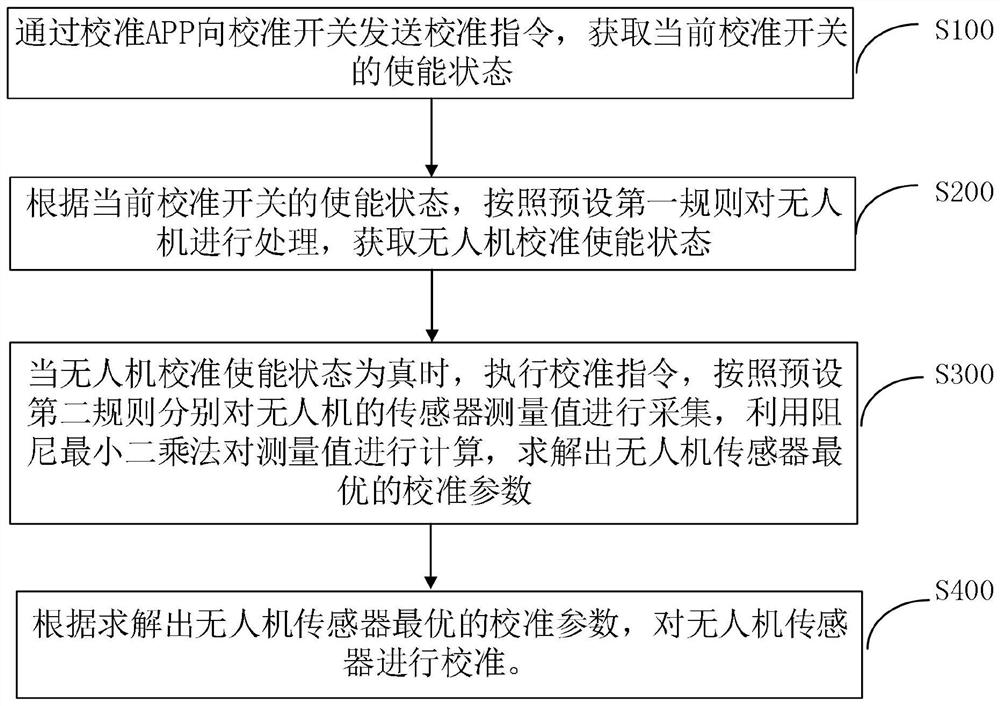
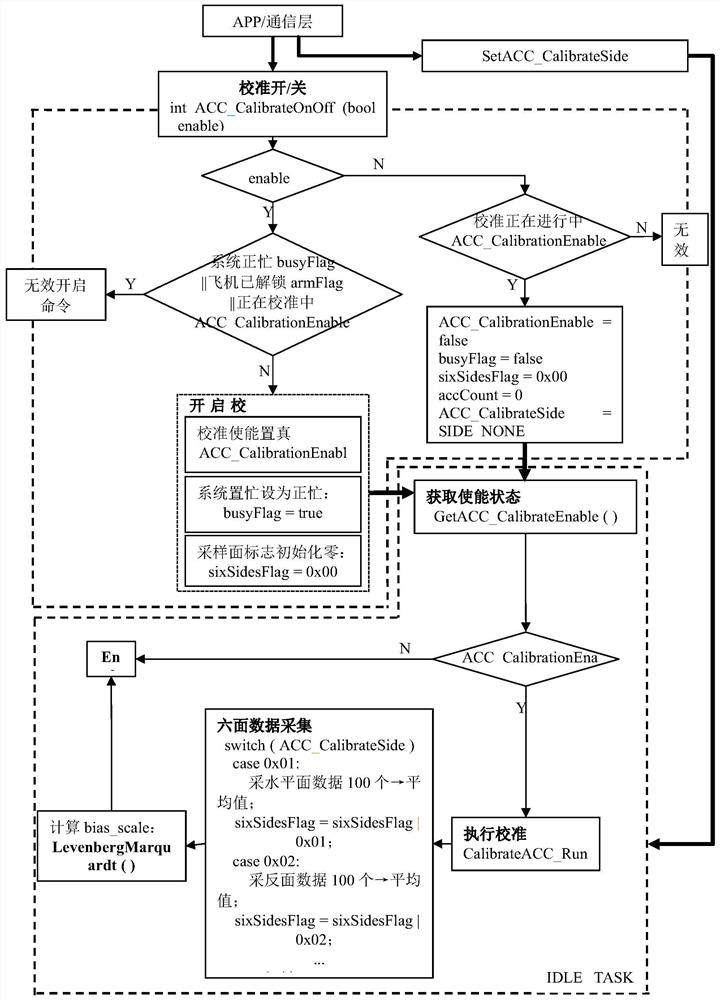
Calibration method of unmanned aerial vehicle sensor
PendingCN112781613AInteractive harmonyAchieve high-precision calibrationMeasurement devicesAircraft components testingUncrewed vehicleEngineering
The invention provides a calibration method of an unmanned aerial vehicle sensor, which comprises the steps that a calibration instruction is sent through an APP, and a system obtains the enabling state of a current calibration switch; according to the enabling state of the current calibration switch, the unmanned aerial vehicle is processed according to a preset first rule, and the calibration enabling state of the unmanned aerial vehicle is obtained; when the calibration enabling state of the unmanned aerial vehicle is true, a calibration instruction is exeucted, sensor measurement values of the unmanned aerial vehicle are collected according to a preset second rule, the measurement values are calculated by using a damping least square method, and an optimal calibration parameter of the unmanned aerial vehicle sensor is solved; and the unmanned aerial vehicle sensor is calibrated according to the solved optimal calibration parameter of the unmanned aerial vehicle sensor. The problems are solved that an unmanned aerial vehicle sensor calibration method in the prior art is high in dependence on a calibration environment and low in precision.
Owner:PRODRONE TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Camera Calibration Method for Large Field of View Based on Four Sets of Collinear Constrained Calibration Rulers
ActiveCN105139411BAchieve high-precision calibrationImprove defectsImage analysisView cameraCalibration result
The invention relates to a large-field-of-view camera calibration method based on four sets of collinear constraint calibration rulers, belonging to the field of visual measurement, and relates to a large-field-of-view camera calibration method based on four sets of collinear constraint calibration rulers. The calibration method arranges four sets of collinear constraint calibration rulers in the large-scale visual measurement field of view, uses the cross-ratio unlimited nature and linear constraints to solve the distortion parameters, and uses the spatial calibration control points to linearly solve the initial value of the calibration parameters, and finally combines the distortion Coefficients and calibration initial values are optimized using the L-M optimization method, and the objective function is to minimize the reprojection error to obtain accurate results of camera calibration with a large field of view. The invention optimizes the calibration results as a whole by flexibly arranging the calibration control points in the large field of view measurement space and combining four sets of collinear constraint calibration rulers, and realizes the high-precision calibration of the large field of view camera, which has wide application prospects.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
A method for calibrating the probe length of a revo measuring head
ActiveCN110030963BAvoid the impact of length calibration accuracyAvoid situations that introduce additional calibration errorMeasurement devicesMechanical engineeringPrecision testing
The invention relates to a method for calibrating the probe length of a REVO measuring head, and belongs to the field of precision testing technology and instruments. The method comprises the following steps that a ring gauge is fixed on a horizontally placed flat plate; the main axes of a measuring machine are moved so that the A axis of the measuring head is located in the zero position state, and the measuring ball center of the measuring head coincides with the central axis of the ring gauge; and the three main axes of the measuring machine are kept stationary, the measuring head A axis and the measuring head B axis are moved, two symmetrical points on the same section of the ring gauge are detected, data are returned according to the two detected points, and the probe length of the REVO measuring head is calibrated through projection calculation. According to the method, calibration is carried out in a state that the three main axes of the measuring machine are stationary, so thatprobe length calibration errors caused by movement errors of the three main axes of the measuring machine and probe length calibration errors caused by misalignment between the axis of the B axis ofthe REVO measuring head and the axis of the ring gauge can be avoided, high-precision calibration of the probe length of the REVO measuring head can be realized, and the method can be applied to measurement.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
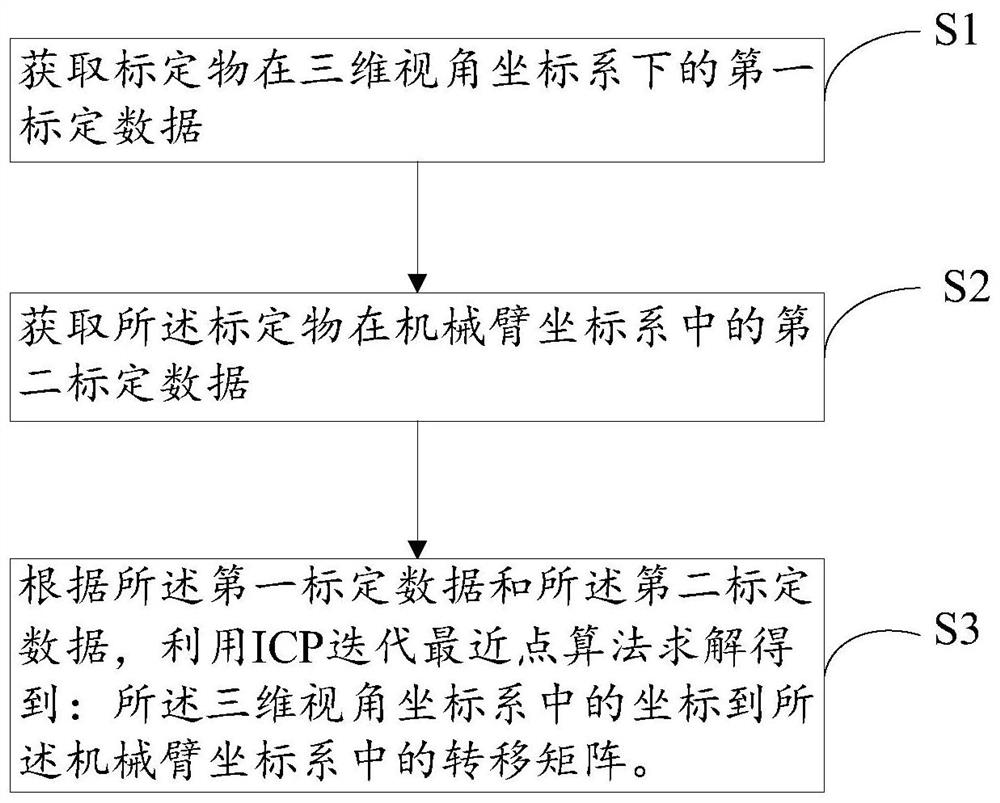
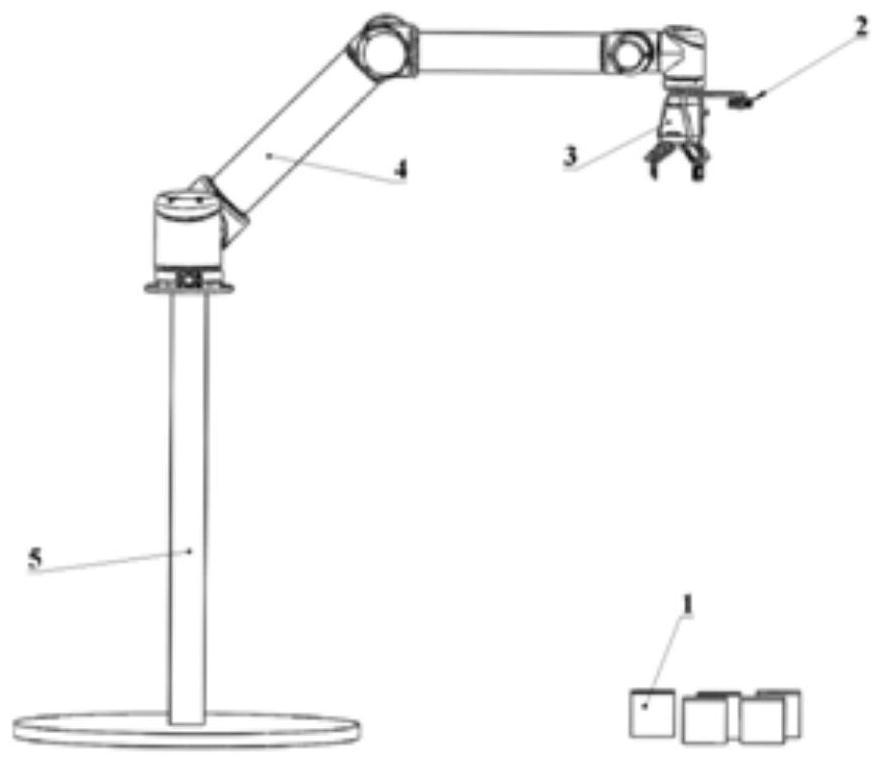
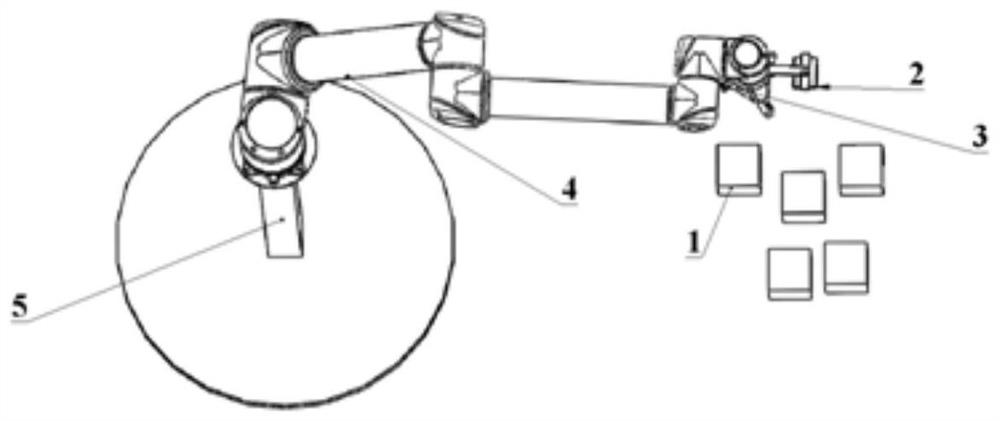
A method and device for hand-eye calibration of a robotic arm based on three-dimensional object recognition
ActiveCN109702738BEasy to operateAchieve high-precision calibrationProgramme-controlled manipulatorPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a method and device for hand-eye calibration of a manipulator based on three-dimensional object recognition, wherein the calibration method includes: step S1, obtaining the first calibration data of the calibration object in the three-dimensional viewing angle coordinate system; step S2, obtaining the calibration The second calibration data of the object in the mechanical arm coordinate system; step S3, according to the first calibration data and the second calibration data, using the ICP iterative closest point algorithm to solve: the coordinates in the three-dimensional viewing angle coordinate system to The transfer matrix in the robot coordinate system. This calibration method can still achieve high-precision calibration in an environment with weak light intensity, and has simple steps and strong operability, which overcomes the shortcomings of existing calibration methods such as low precision, complicated steps, poor operability, and large impact of light.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
A calibration method for b-axis zero error of revo probe
ActiveCN110017803BAvoiding Situations That Introduce Additional Calibration ErrorsRealize high-precision calibration of zero errorMeasurement devicesOrthogonal coordinatesEngineering
The invention discloses a method for calibrating the B-axis zero error of a REVO probe, which is applied to a non-orthogonal coordinate measurement system and belongs to the field of precision testing technology and instruments; the invention comprises the following steps: placing a square ruler on a flat plate placed horizontally, placing Adjust the working surface M of the square ruler to be parallel to the X direction of the measuring machine and then fix it; fix the square ruler close to the working surface N perpendicular to the working surface M of the square ruler; keep the three main axes of the measuring machine stationary, so that the A axis of the REVO probe is in a suitable position , Use the B-axis rotation of the REVO probe to detect two symmetrical points on the ruler; according to the calculation of the B-axis angle of the two detection points, the zero error of the B-axis of the probe can be calibrated. When the three main axes of the measuring machine are stationary, the present invention avoids the situation that the angle of the articulated arm changes due to the measurement force during the calibration process and introduces additional calibration errors, and realizes high-precision calibration of the B-axis zero error of the REVO probe, which can Used in precision measurement.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
An Online Camera Calibration Method Based on Blurred Images of Small Targets
ActiveCN109754435BAchieve high-precision calibrationBreak the traditional calibration modeImage analysisMathematical modelRadiology
The present invention relates to an on-line camera calibration method based on the fuzzy image of a small target. Obtain an identifiable target image; establish a mathematical model of target feature point positioning uncertainty, and solve the positioning uncertainty of each feature point; take the target feature point positioning and parameter uncertainty as constraints, and use nonlinear optimization methods to solve the camera High-precision solution of internal and external parameters; this method does not need to consider the camera focus space and target size, and only needs a small high-precision target to be placed close to the lens to achieve ultra-high-precision camera calibration under conditions of large image blur and noise . The invention is suitable for on-line calibration of a camera with a large field of view and a shallow depth of field or even a camera in use, and has great flexibility and adaptability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Establishment and calibration method of a multi-parameter model of an articulated arm coordinate measuring machine
ActiveCN112344895BHigh precisionAchieve high-precision calibrationMeasurement devicesControl engineeringCoordinate-measuring machine
The invention discloses a method for establishing and calibrating a multi-parameter model of an articulated arm coordinate measuring machine, relates to the technical field of precision measurement, expands the original 23-item error model of an articulated arm coordinate measuring machine into a 59-item error model, and greatly increases the number of joints The number of structural parameters of the arm coordinate measuring machine error model improves the accuracy of the joint arm coordinate measuring machine. The establishment and calibration method of a multi-parameter model of an articulated arm coordinate measuring machine provided by this application adds the shaft shaking error term to the original articulated arm coordinate measuring machine error model, and establishes a multi-parameter error model of an articulated arm coordinate measuring machine to realize High-precision calibration of an articulated arm coordinate measuring machine.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
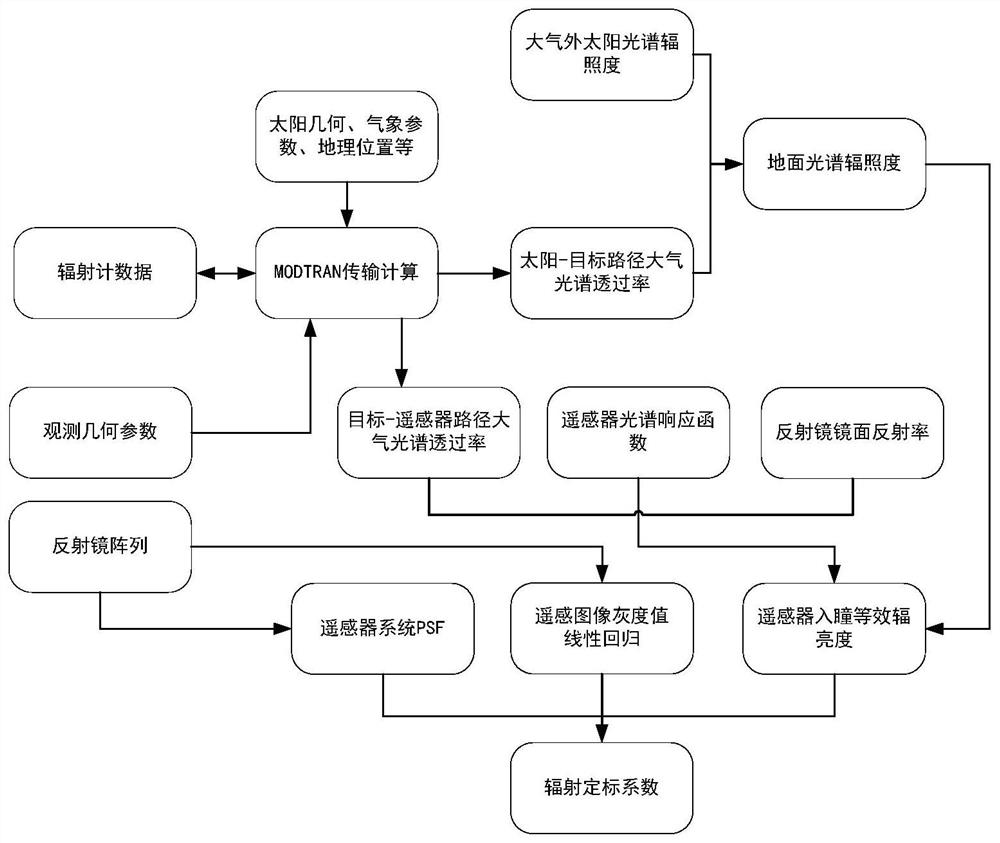
An On-orbit Absolute Radiometric Calibration Method Based on Mirror Array for Optical Remote Sensor
ActiveCN108120510BEvenly laid outLay out the ground evenlyRadiation pyrometryMiddle infraredMirror reflection
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com