Patents
Literature
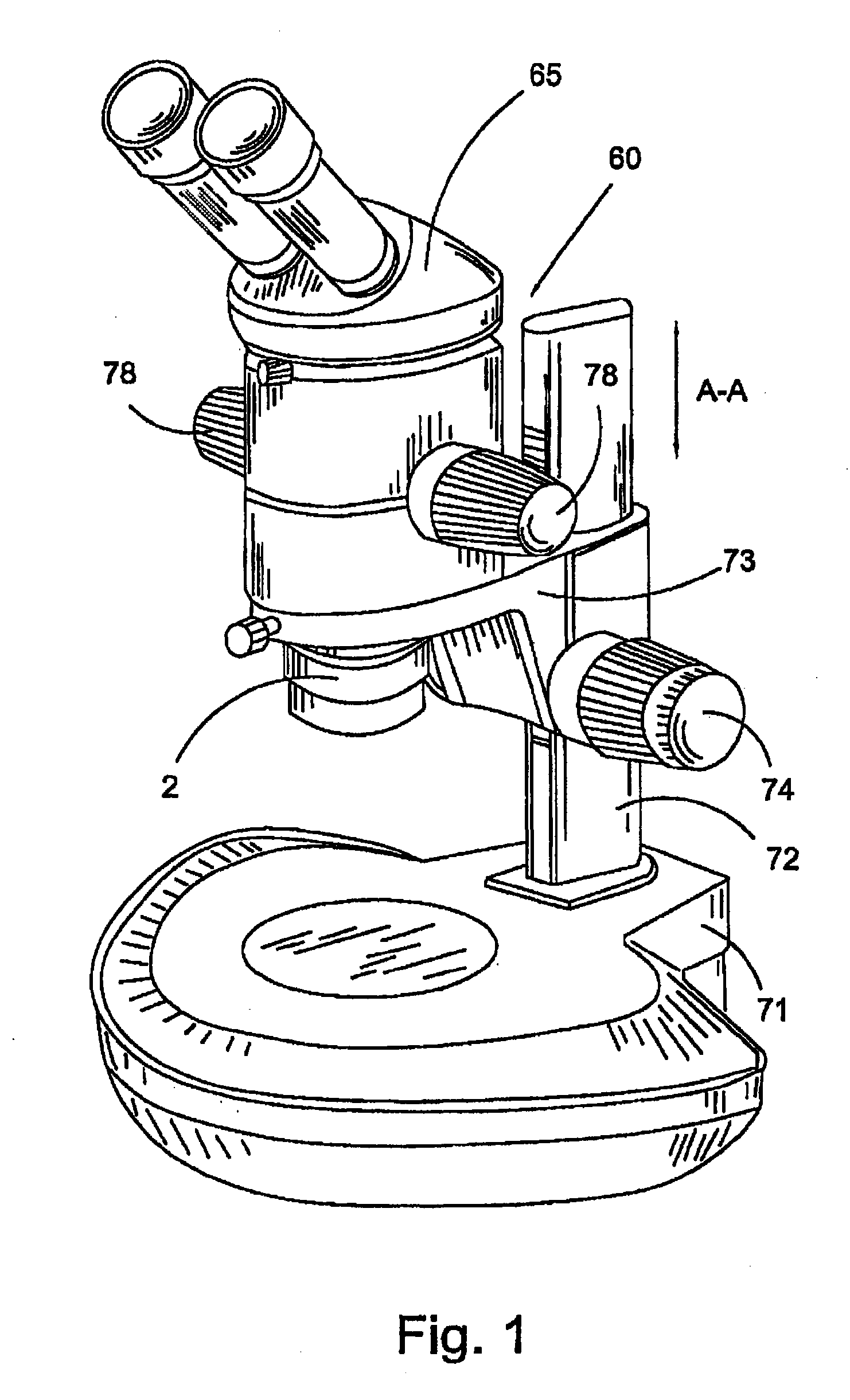
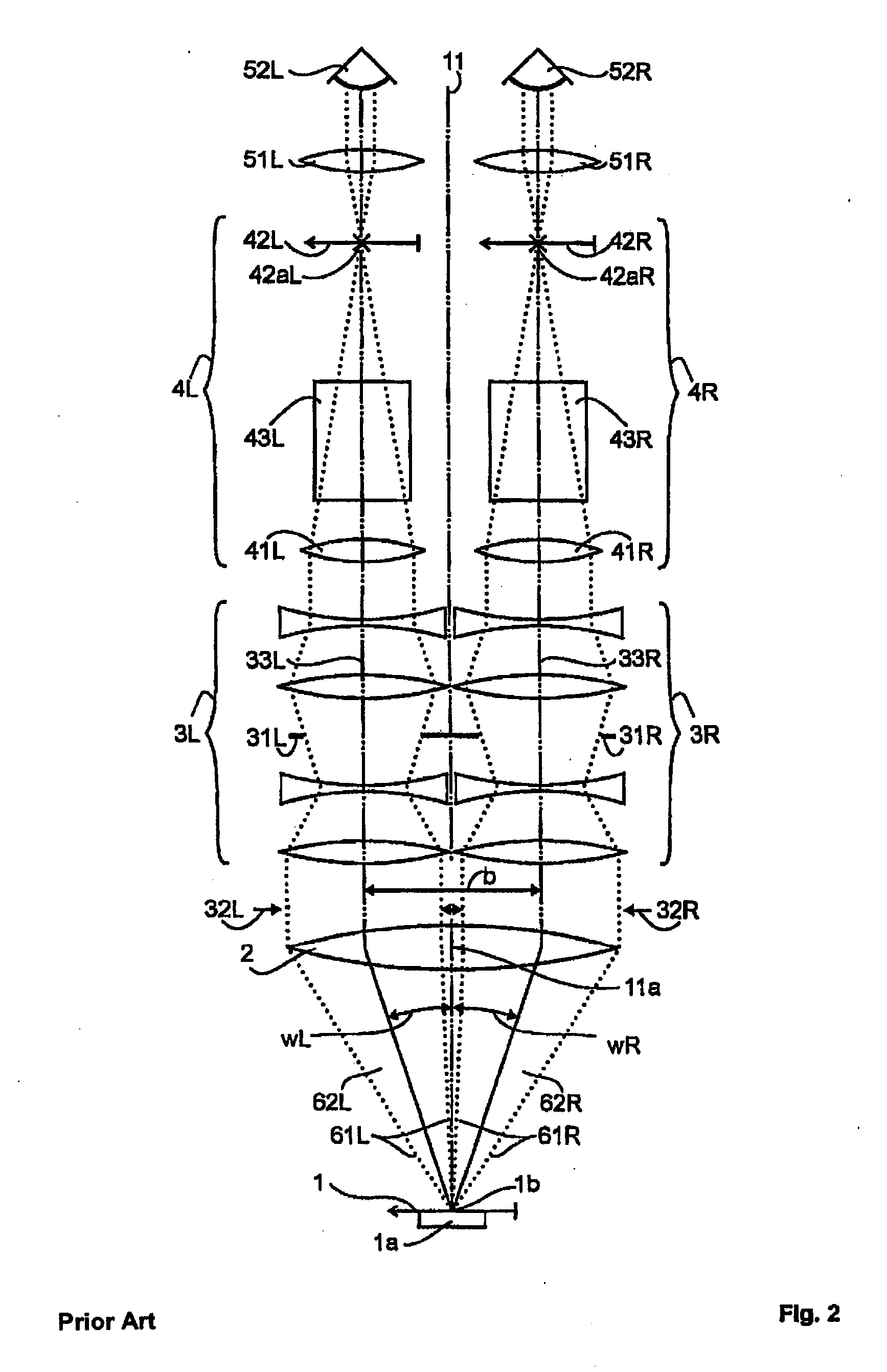
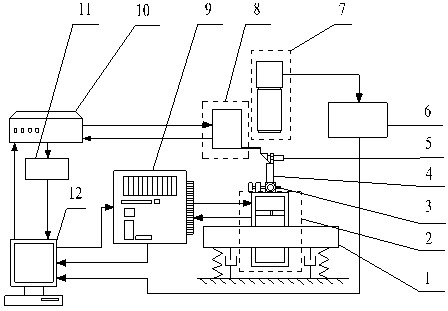
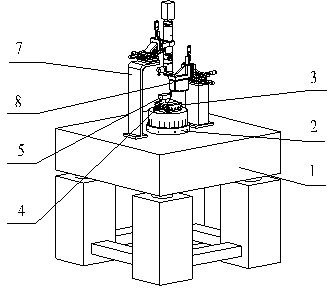
273 results about "Stereo microscope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
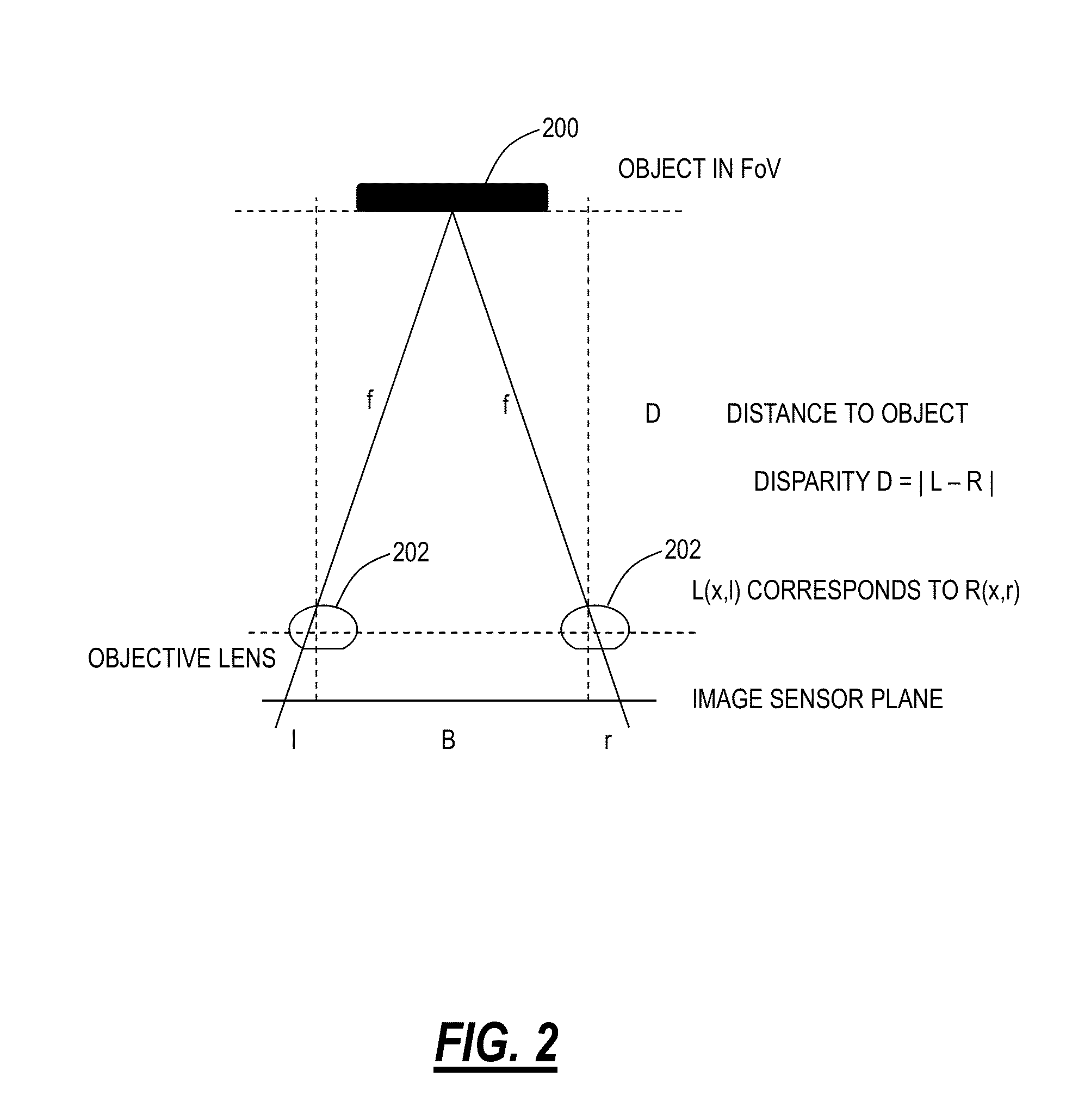
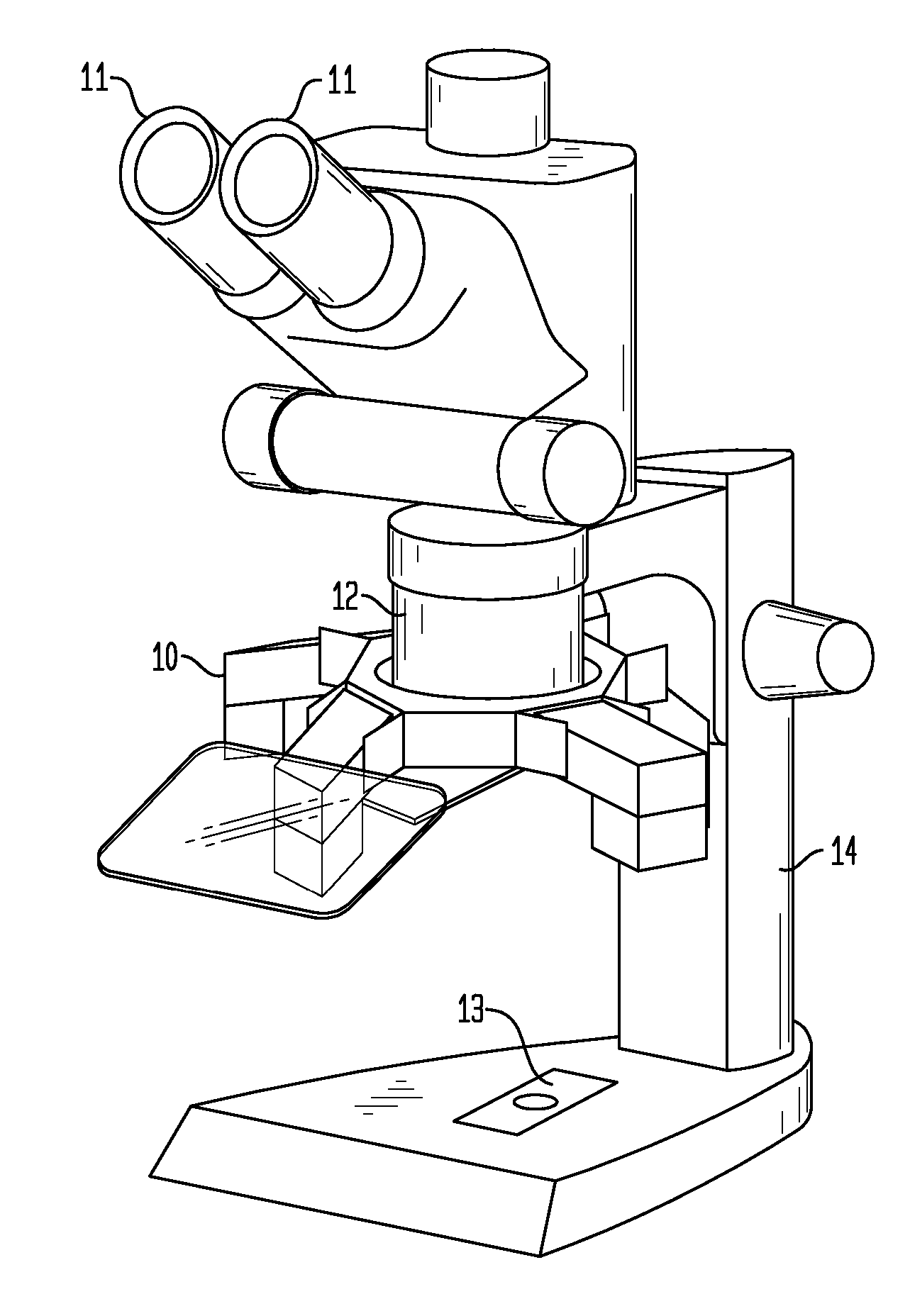
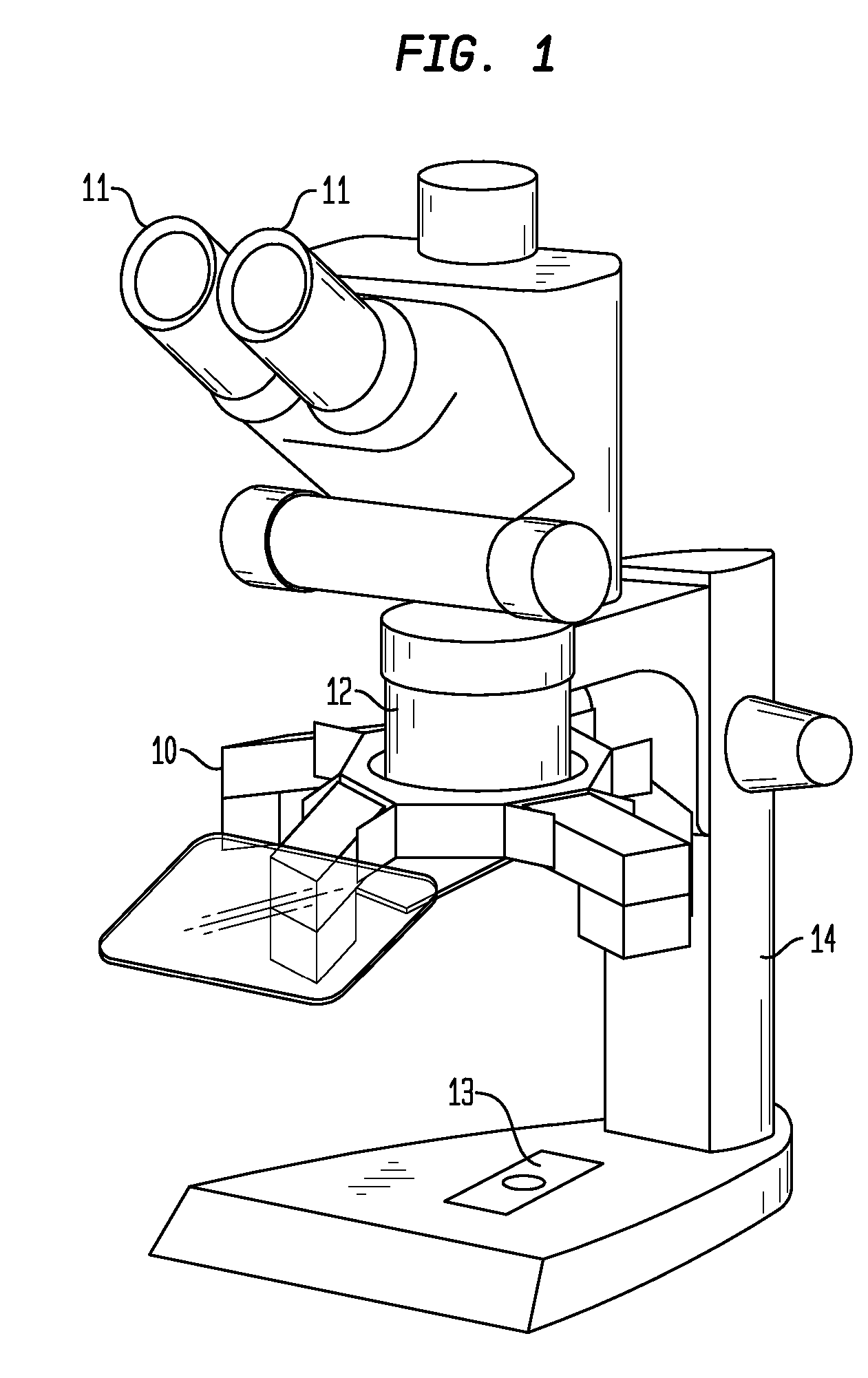
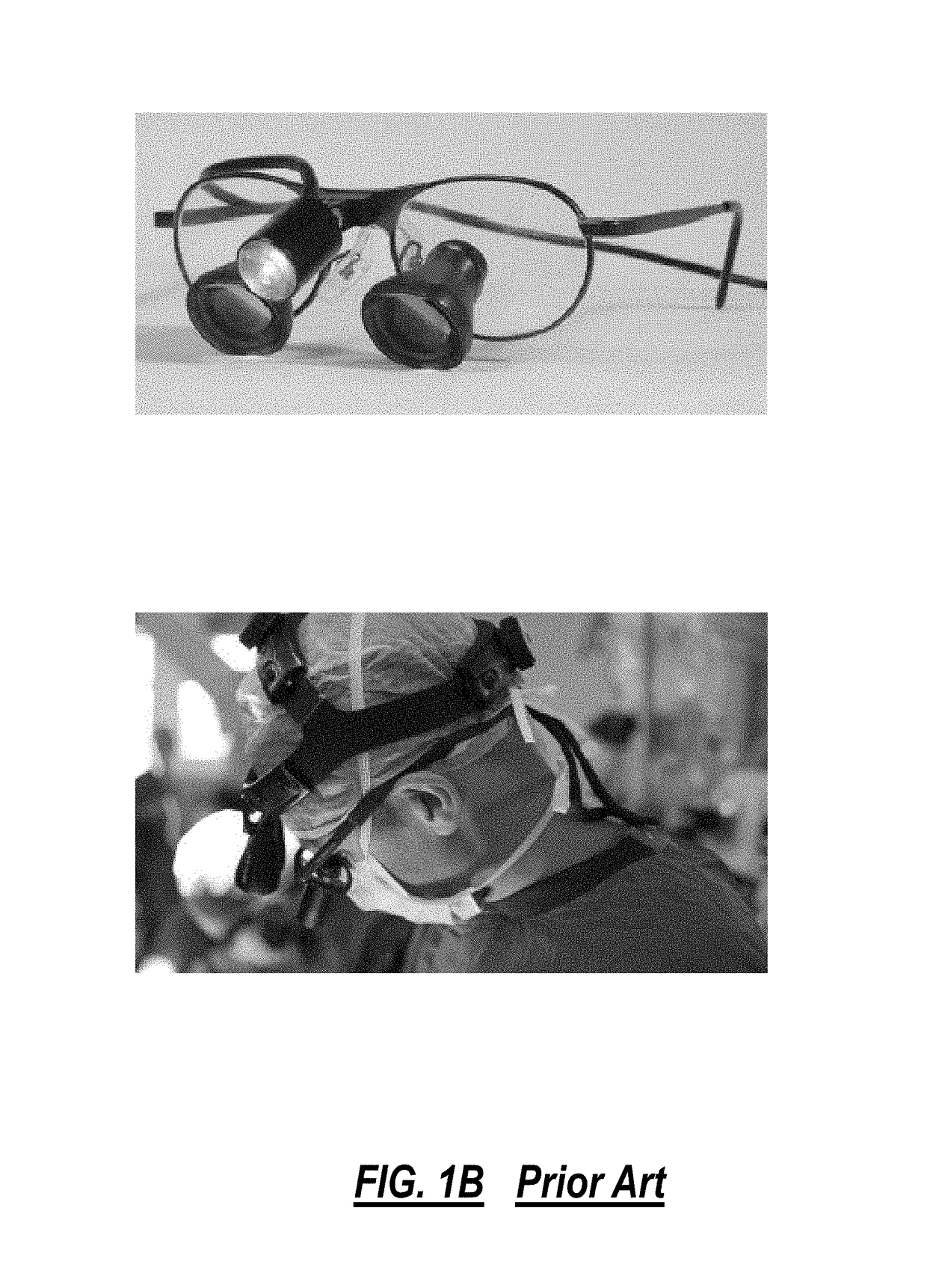
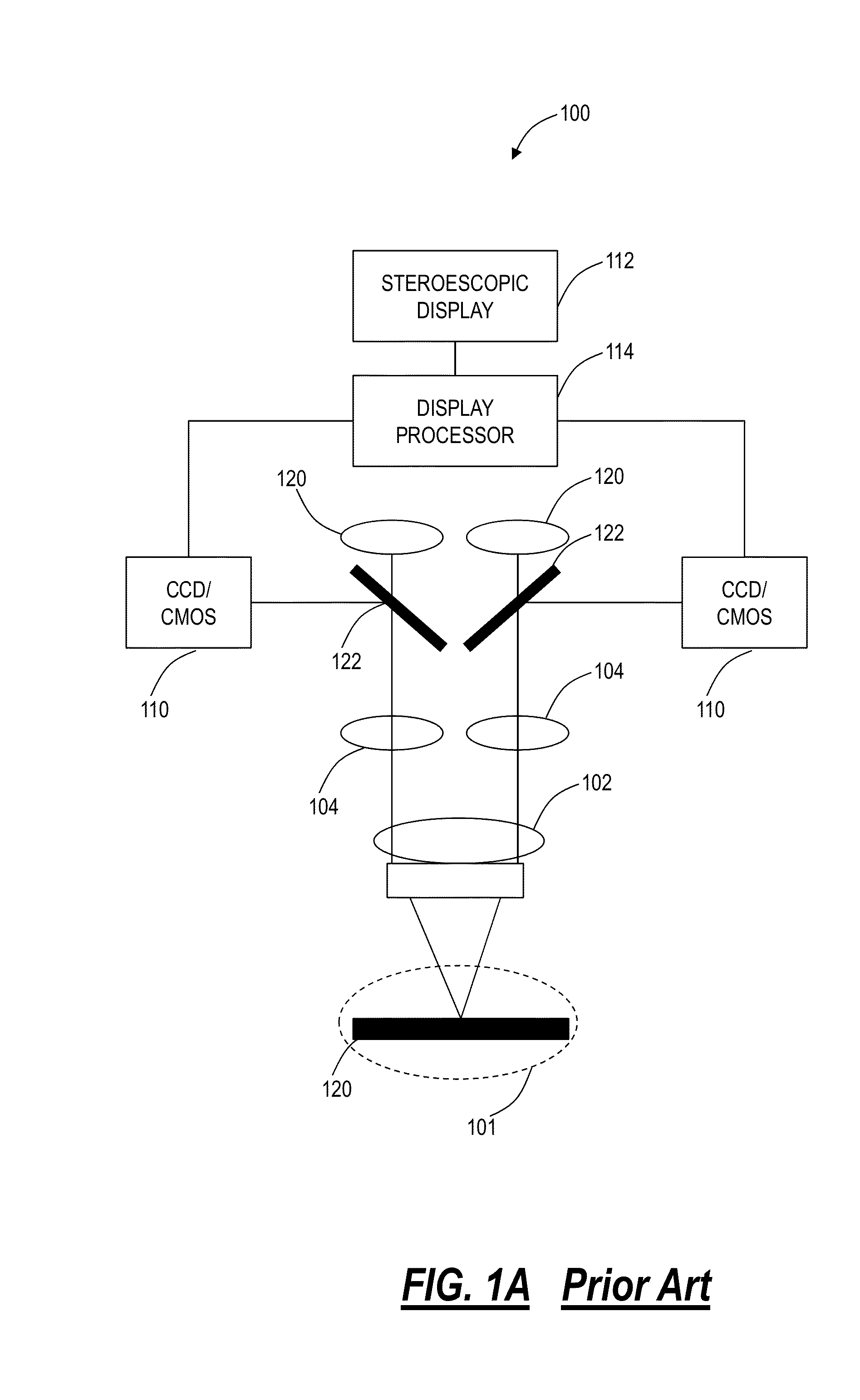
The stereo, stereoscopic or dissecting microscope is an optical microscope variant designed for low magnification observation of a sample, typically using light reflected from the surface of an object rather than transmitted through it. The instrument uses two separate optical paths with two objectives and eyepieces to provide slightly different viewing angles to the left and right eyes. This arrangement produces a three-dimensional visualization of the sample being examined. Stereomicroscopy overlaps macrophotography for recording and examining solid samples with complex surface topography, where a three-dimensional view is needed for analyzing the detail.
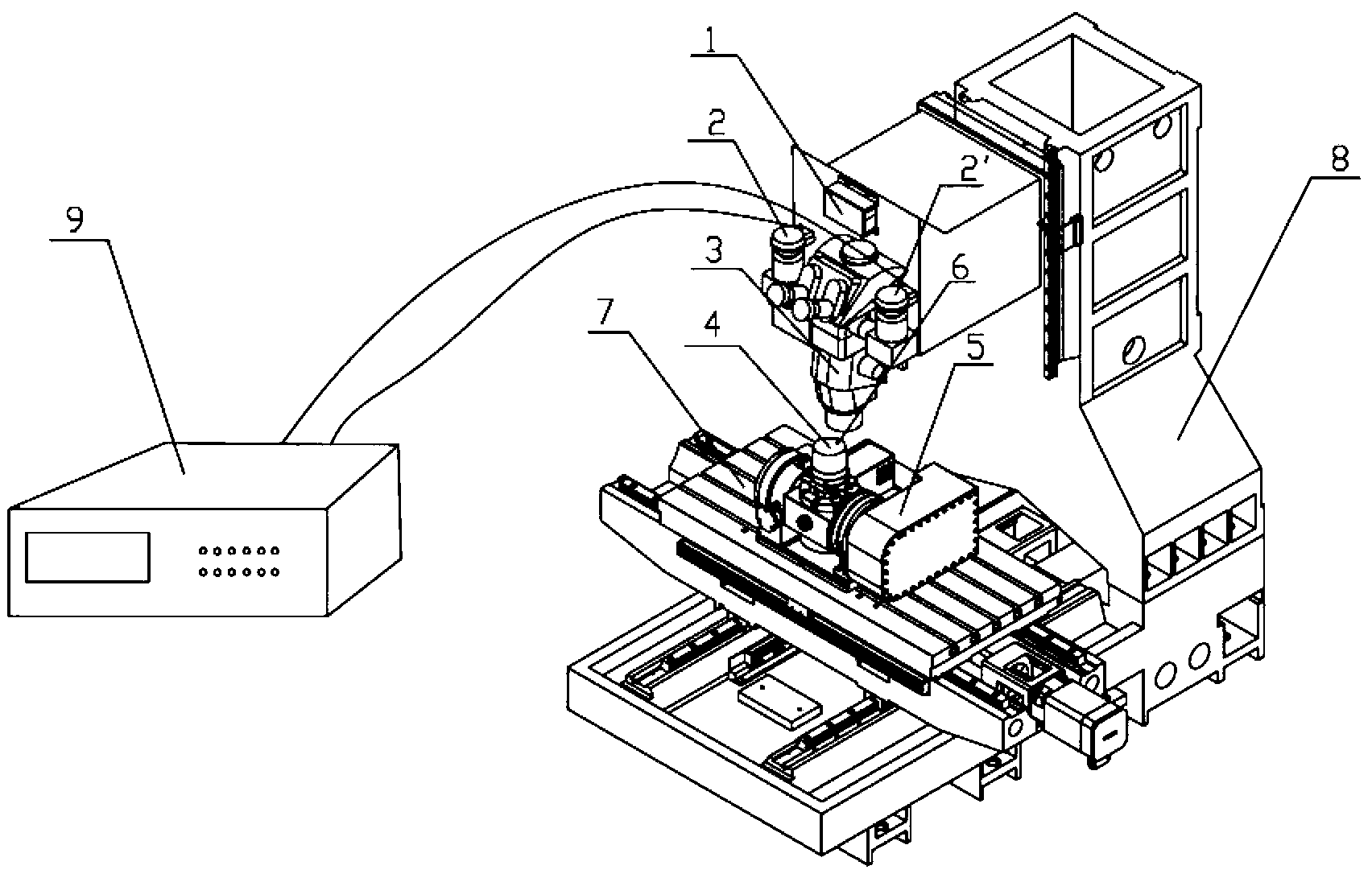
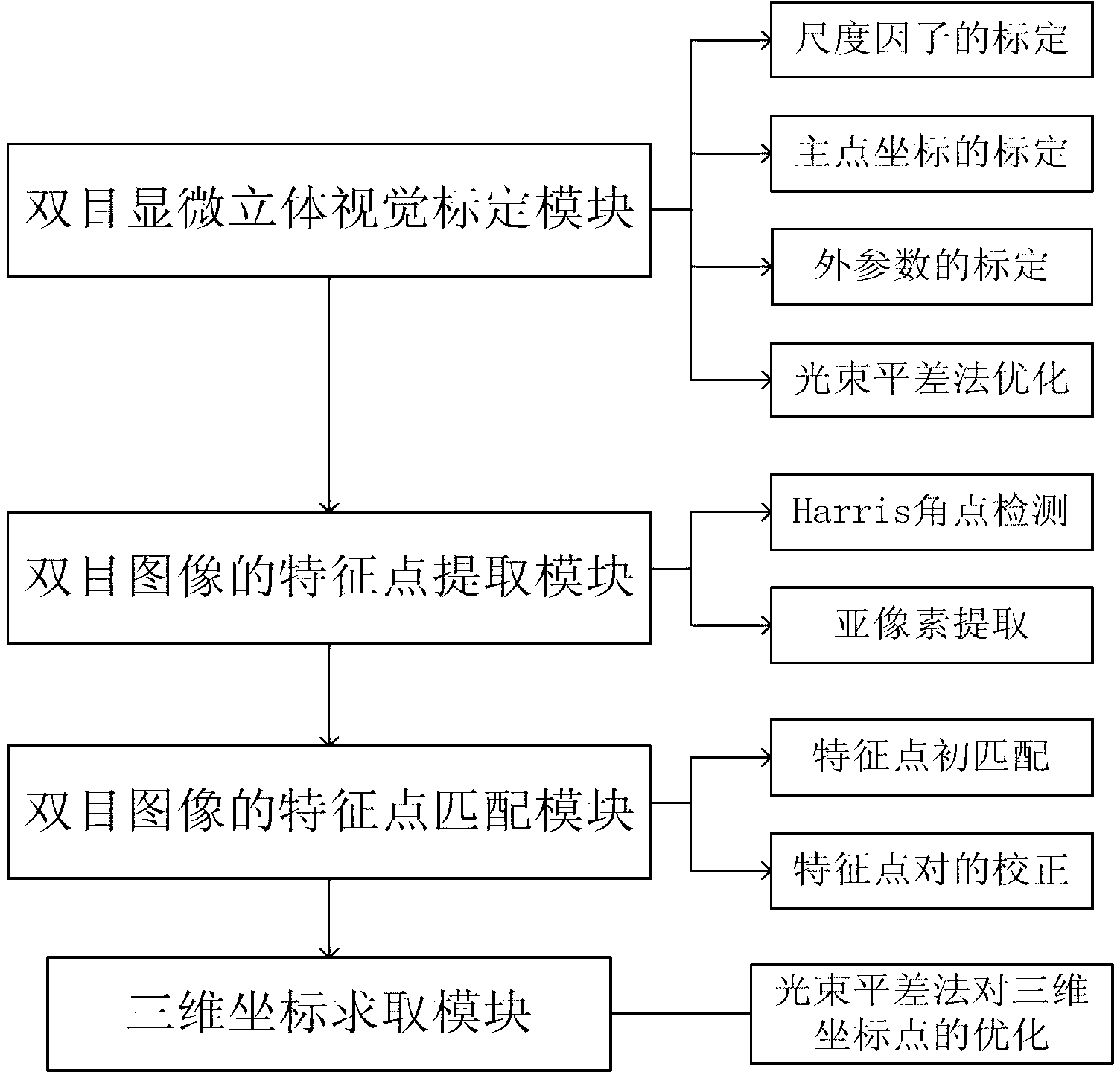
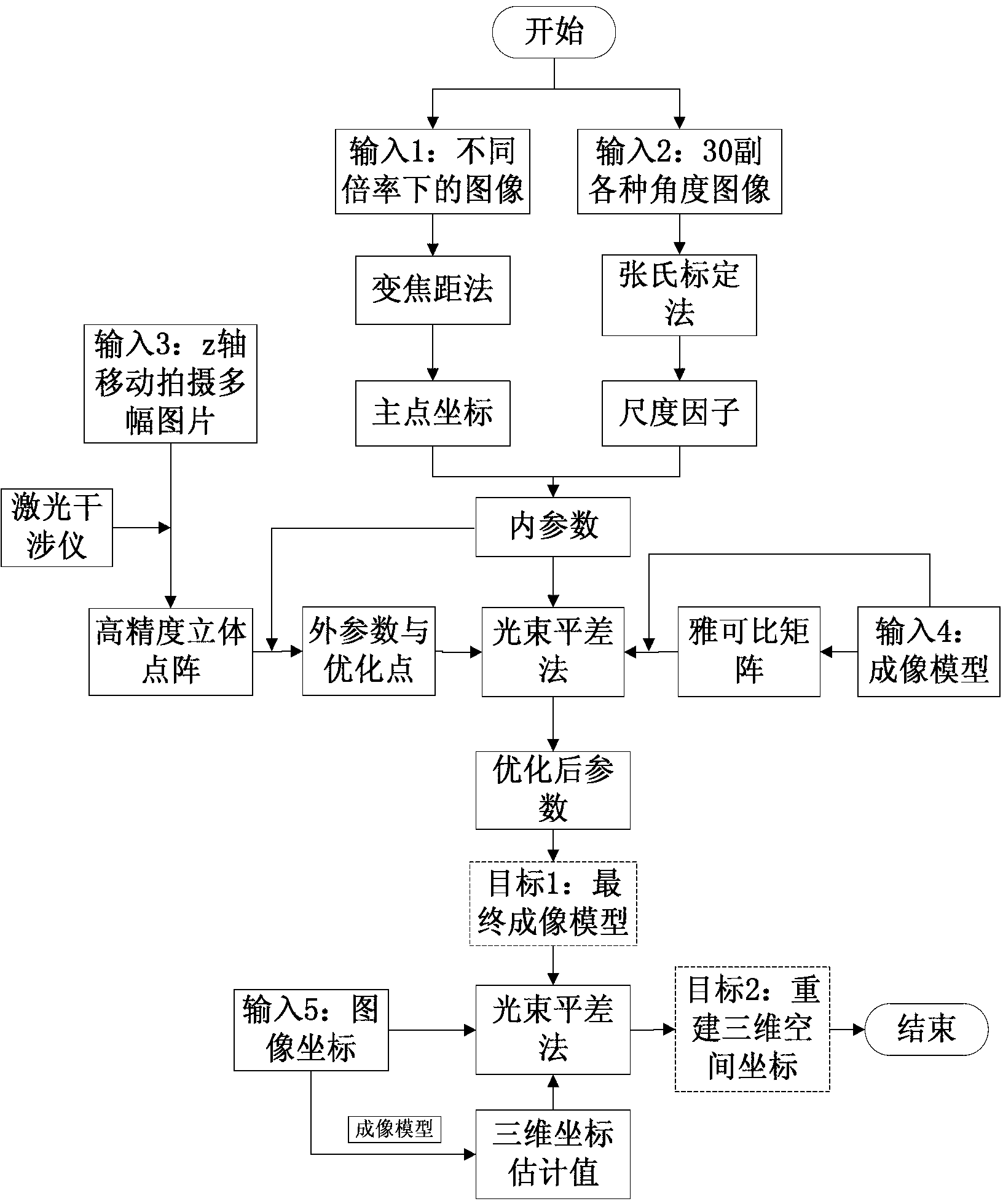
Accurate part positioning method based on binocular microscopy stereo vision
The invention discloses an accurate part positioning method based on binocular microscopy stereo vision, which belongs to the technical field of computer visual measuring and relates to an accurate precision part positioning method based on the binocular microscopy stereo vision. A binocular microscopy stereo vision system is adopted, two CCD (charge coupled device) cameras are adopted to acquire the images of the measured parts, the image information in the to-be-measured area on the measured part is amplified by a stereo microscope, a checkerboard calibrating board is adopted to calibrate the two CCD cameras, and a Harris corner point detecting algorithm and a sub-pixel extracting algorithm are adopted to extract feature points. The extracted feature points are subjected to the primary matching and correcting of matching point pairs, and the feature point image coordinates are inputted to a calibrated system to obtain the space actual coordinates of the feature points. The accurate part positioning method based on the binocular microscopy stereo vision solves the measuring difficult problems generated by the small size of the to-be-measured area, high positioning demand, non-contact and the like. The accurate positioning of the precision part is well finished by adopting the non-contact measuring method of the binocular microscopy stereo vision.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
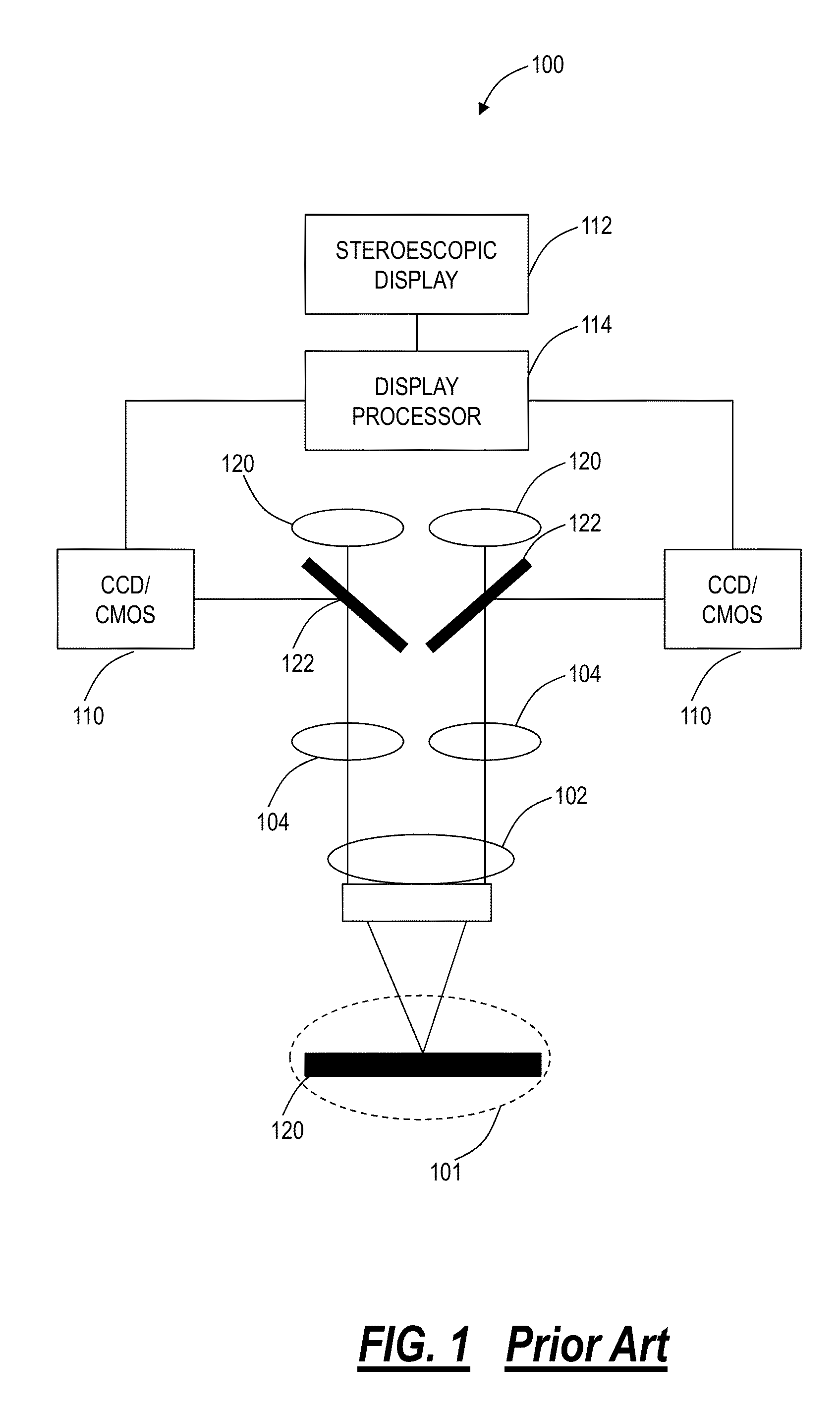
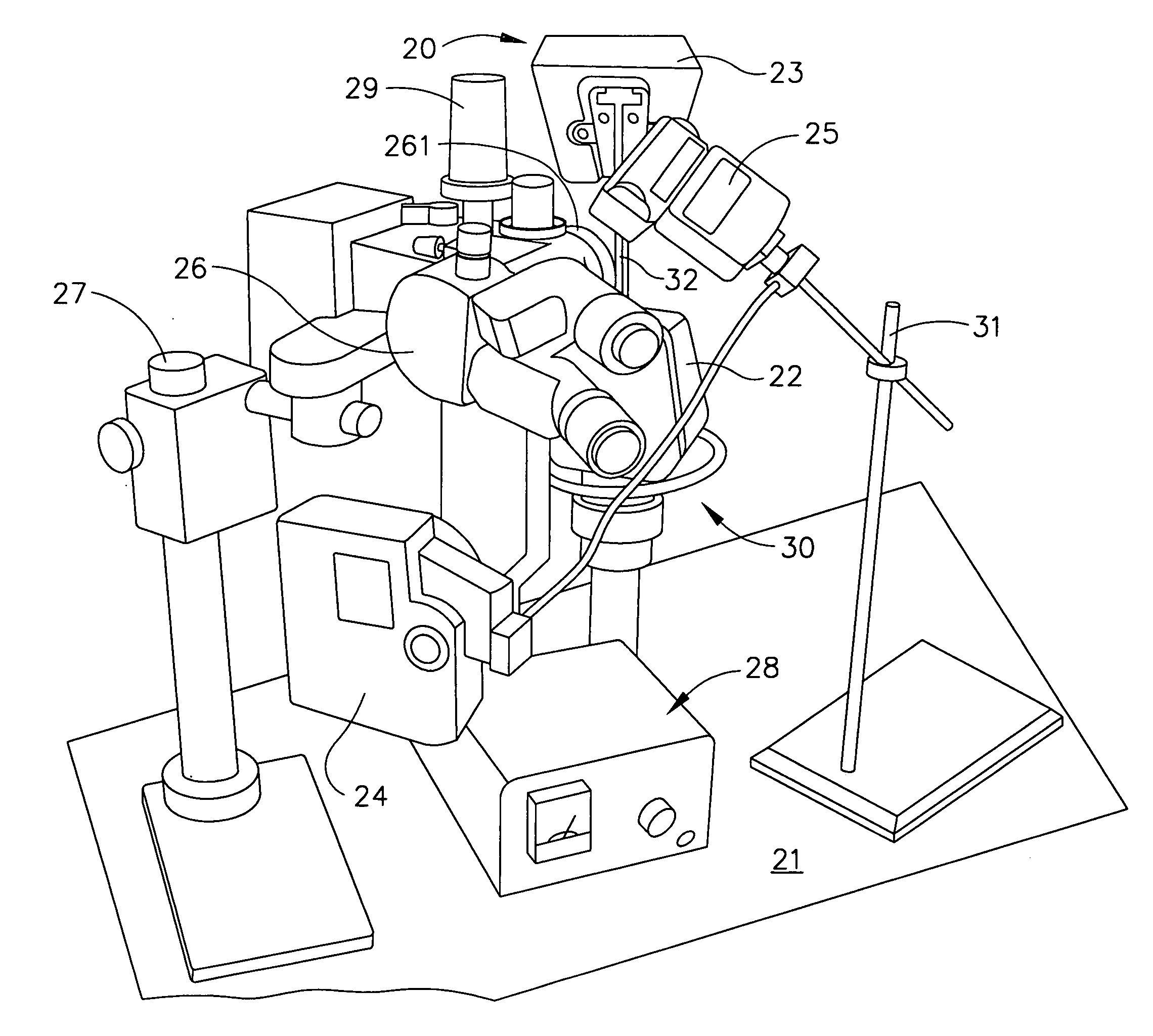
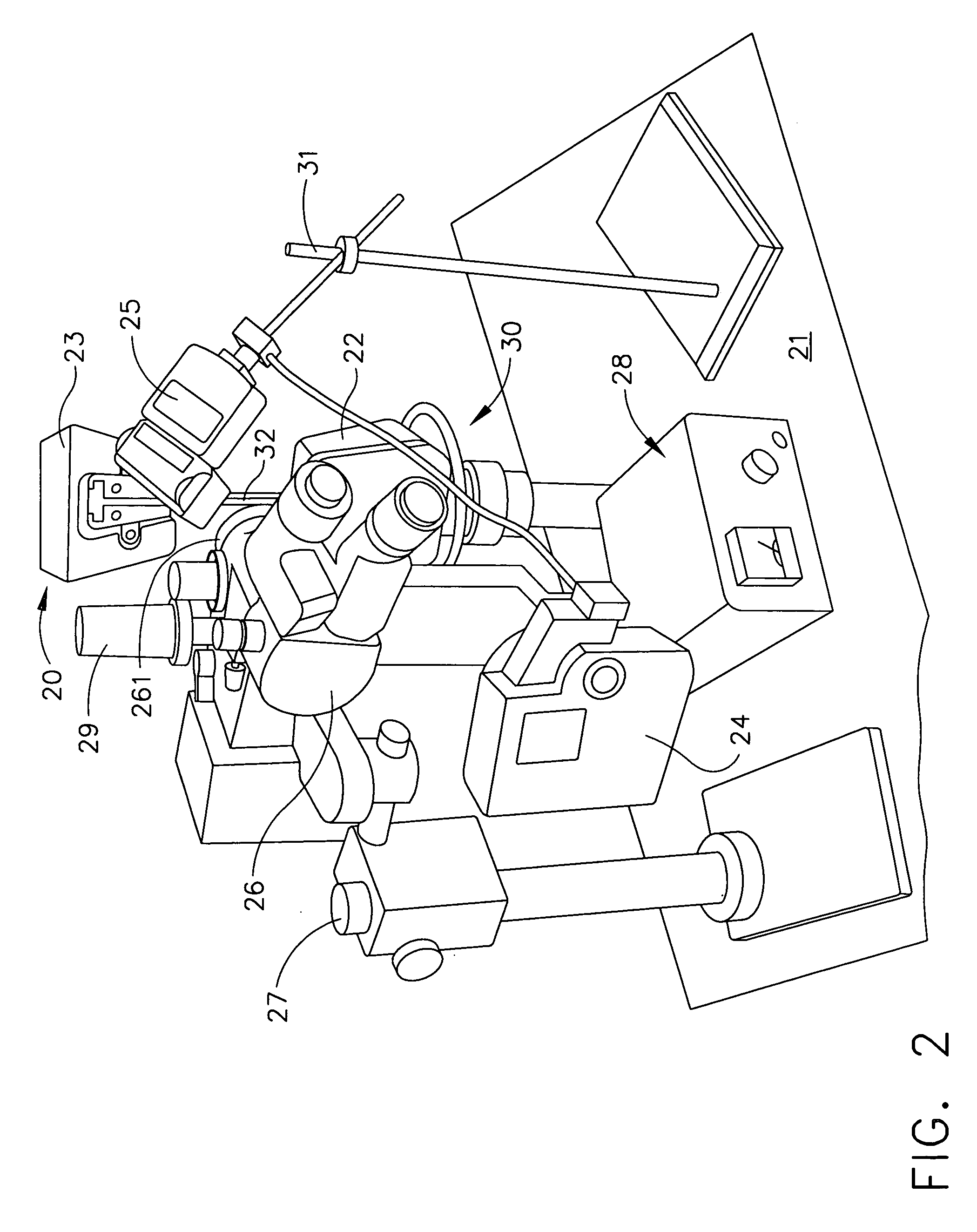
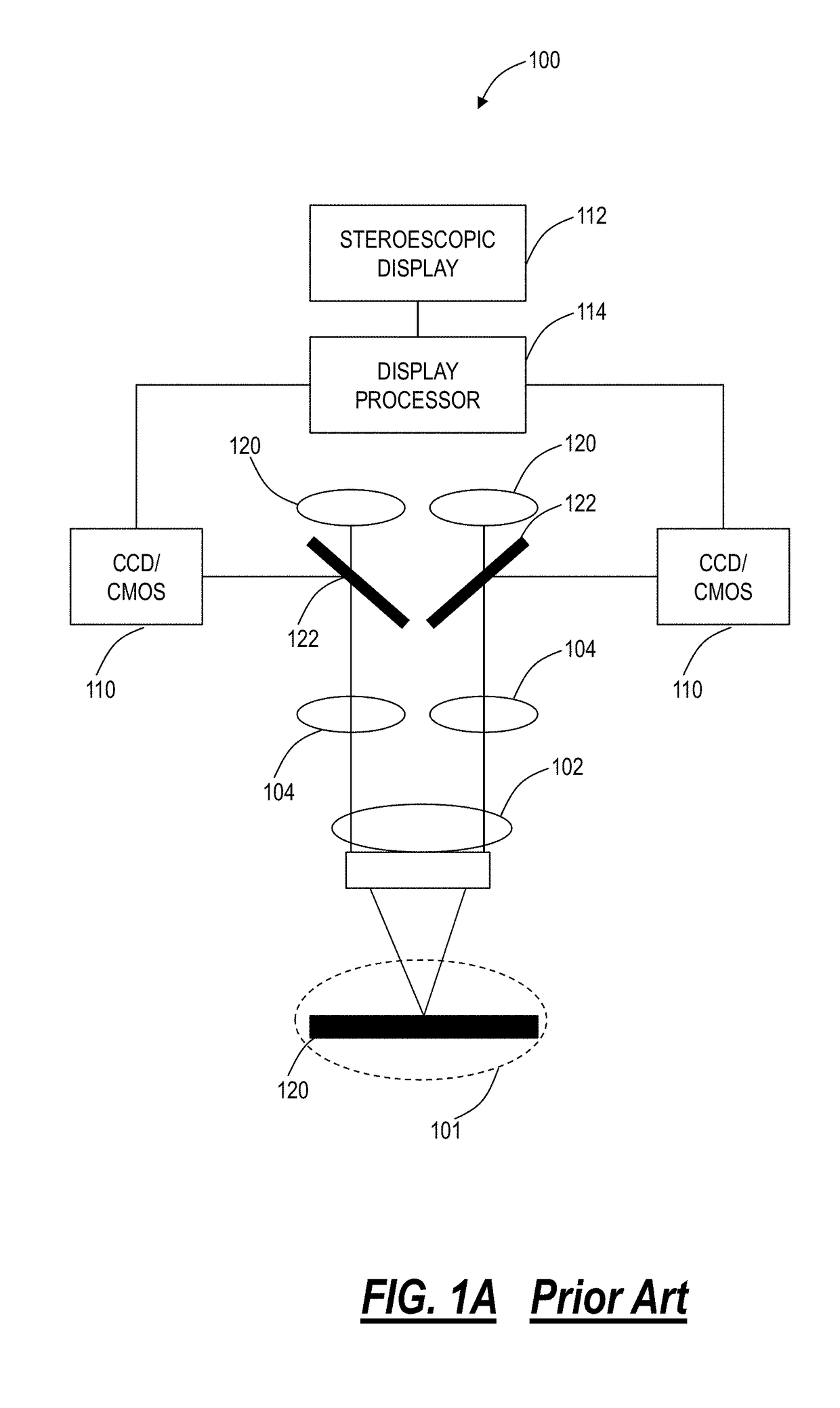
Surgical stereo vision systems and methods for microsurgery
ActiveUS20130076863A1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapies2D-image generationCollocationImage resolution
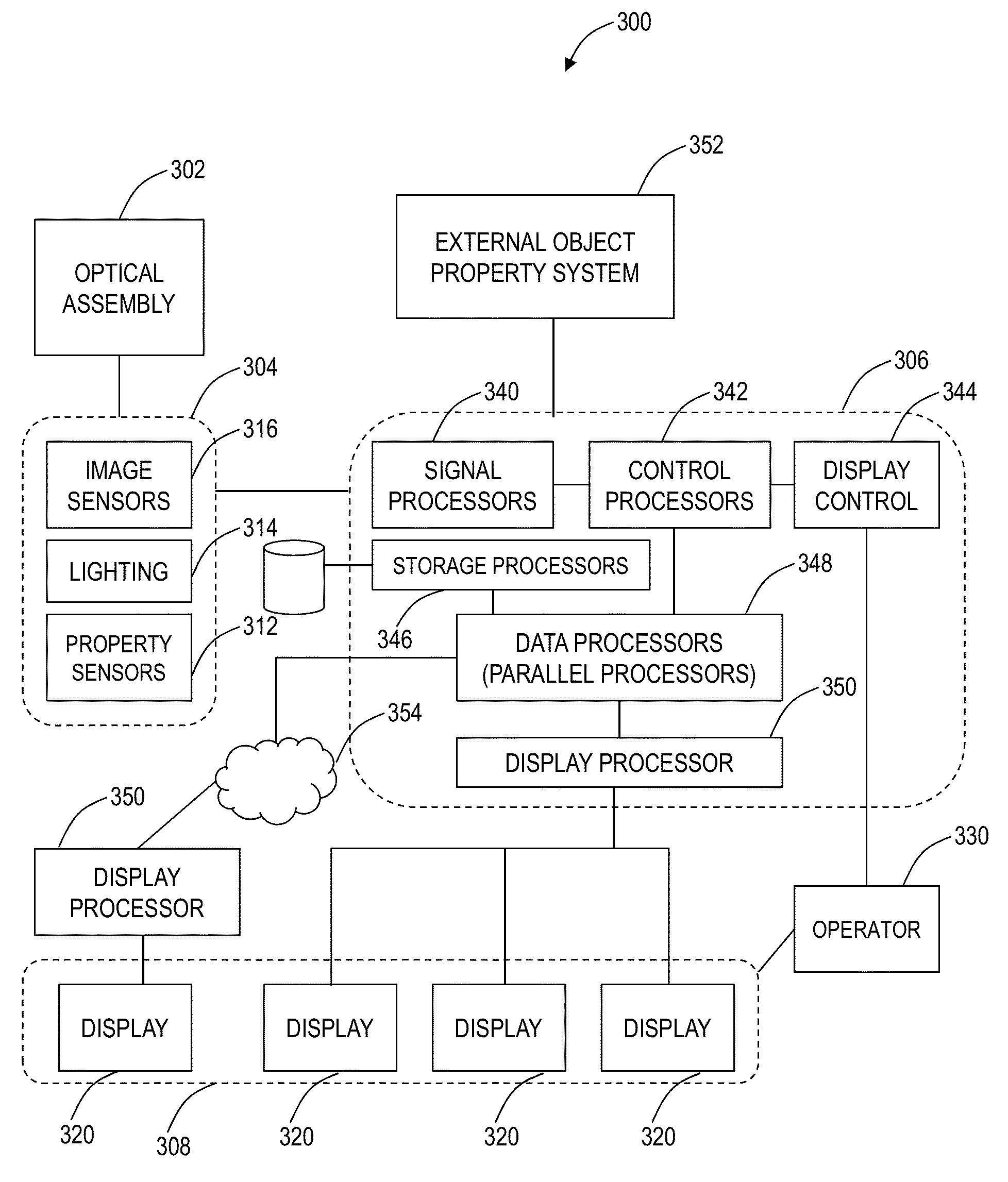
Surgical stereo vision systems and methods for microsurgery are described that enable hand-eye collocation, high resolution, and a large field of view. A digital stereo microscope apparatus, an operating system with a digital stereo microscope, and a method are described using a display unit located over an area of interest such that a human operator places hands, tools, or a combination thereof in the area of interest and views a magnified and augmented live stereo view of the area interest with eyes of the human operator substantially collocated with the hands of the human operator.
Owner:DIGITAL SURGICALS
Microscope camera
The invention is directed to a microscope camera which is suitable particularly for recording digital images in stereomicroscopy. The complete camera, including a deflecting element for one of the stereo beam paths, image recording chip, control unit and processing unit, monitor and data interfaces, is integrated in an intermediate tube.
Owner:CARL ZEISS JENA GMBH
Surgical stereo vision systems and methods for microsurgery
ActiveUS9330477B2Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapies2D-image generationCollocationImage resolution
Surgical stereo vision systems and methods for microsurgery are described that enable hand-eye collocation, high resolution, and a large field of view. A digital stereo microscope apparatus, an operating system with a digital stereo microscope, and a method are described using a display unit located over an area of interest such that a human operator places hands, tools, or a combination thereof in the area of interest and views a magnified and augmented live stereo view of the area interest with eyes of the human operator substantially collocated with the hands of the human operator.
Owner:DIGITAL SURGICALS
Fine observation mechanical test system containing gas coal rock
InactiveCN101354355AEasy to installEasy to debugMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesMaterial analysis by optical meansGas cylinderCcd camera
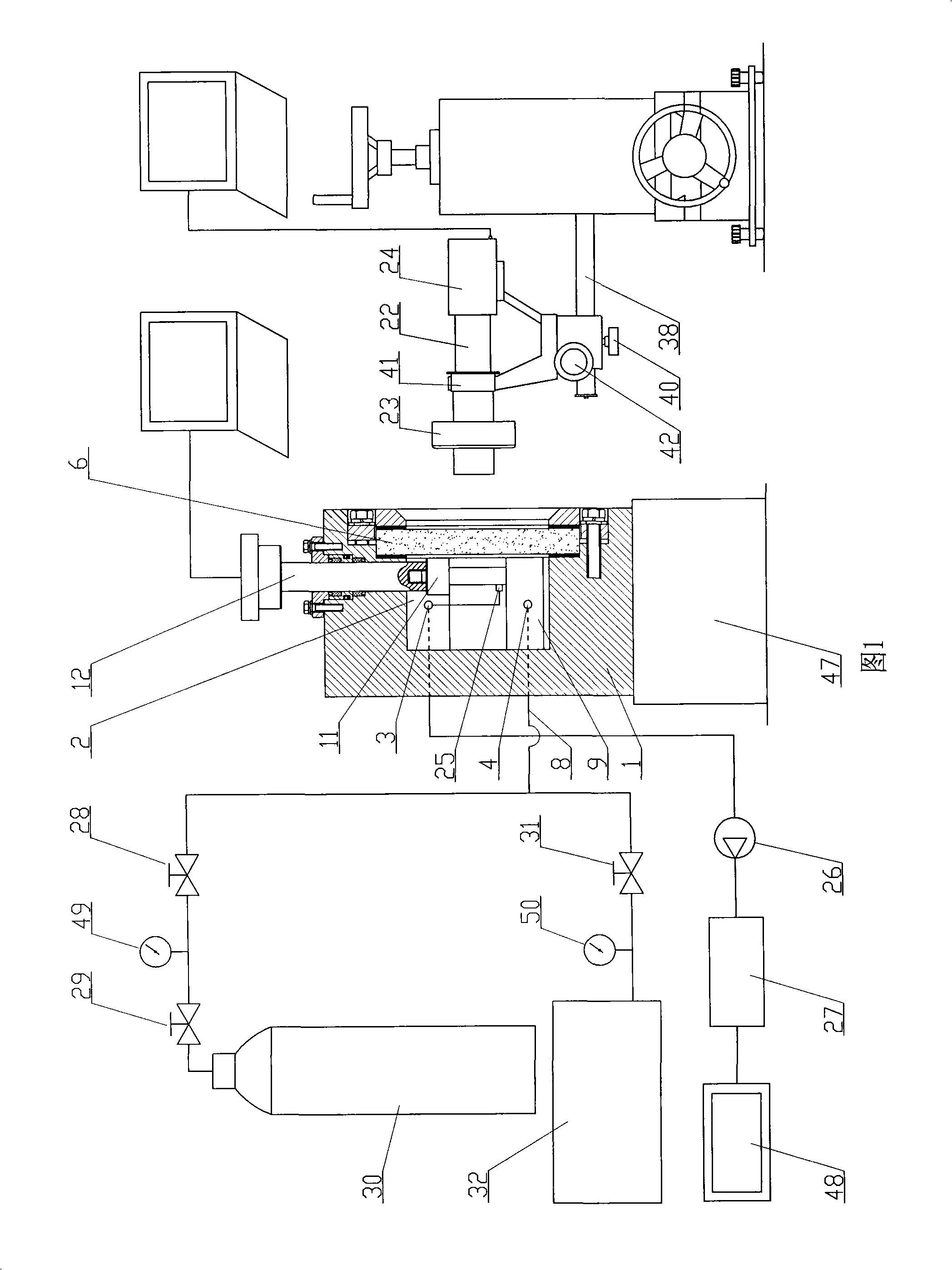
The invention discloses a mesomechanics testing system of gas-containing coal rocks, which comprises a transparent sight glass that is fixed at an opening position of a testing cavity, a three-dimensional moving microscopic observing frame that is arranged outside the transparent sight glass, and a stereoscopic microscope and a CCD camera that are arranged on the three-dimensional moving microscopic observing frame; an inner end of a measuring conducting wire is connected with an acoustic emission sensor, and an outer end of the measuring conducting wire is connected with an acoustic emission magnifier and an acoustic emission card; the testing cavity is communicated with a gas pipe through a multi-purpose air vent, and the gas pipe is divided into two paths with one path connected with a high-pressure gas bottle and the other path connected with a vacuum pump; a cushion block, a limit pressure head and a loading head are arranged inside the testing cavity, a vertical surface of an L-shaped nick of the cushion block is over against the limit pressure head, and a transverse surface of the L-shaped nick of the cushion block is over against the loading head. The mesomechanics testing system of the gas-containing coal rocks provides more complete and reliable test methods for revealing the micro-structural damage law of the coal rocks under the gas action, further and deeper finding out the physical and mechanical properties of the gas-containing coal rocks, scientifically revealing the occurrence mechanism of the dynamic phenomenon of the coal rocks, and developing corresponding disaster prevention techniques.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
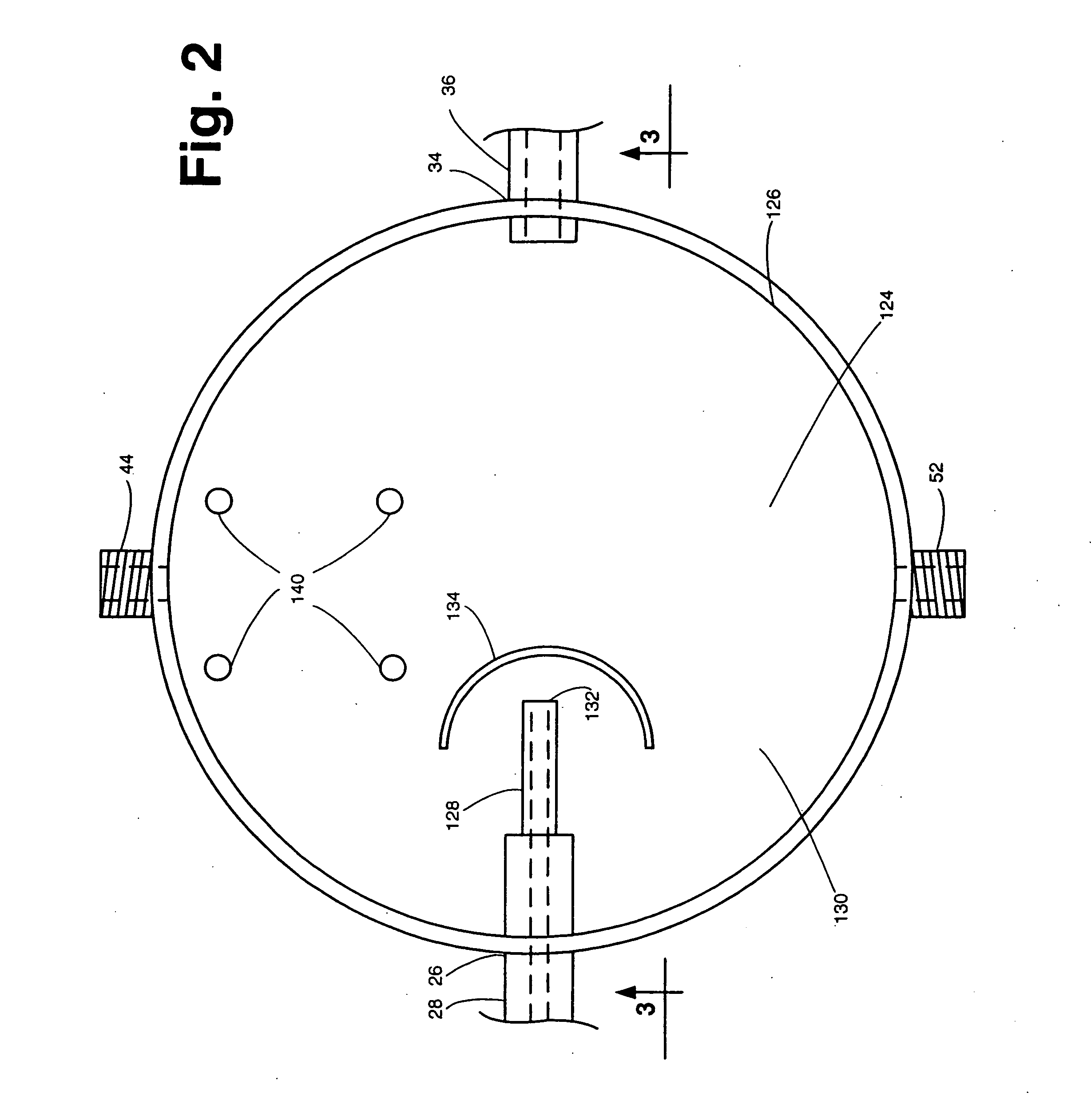
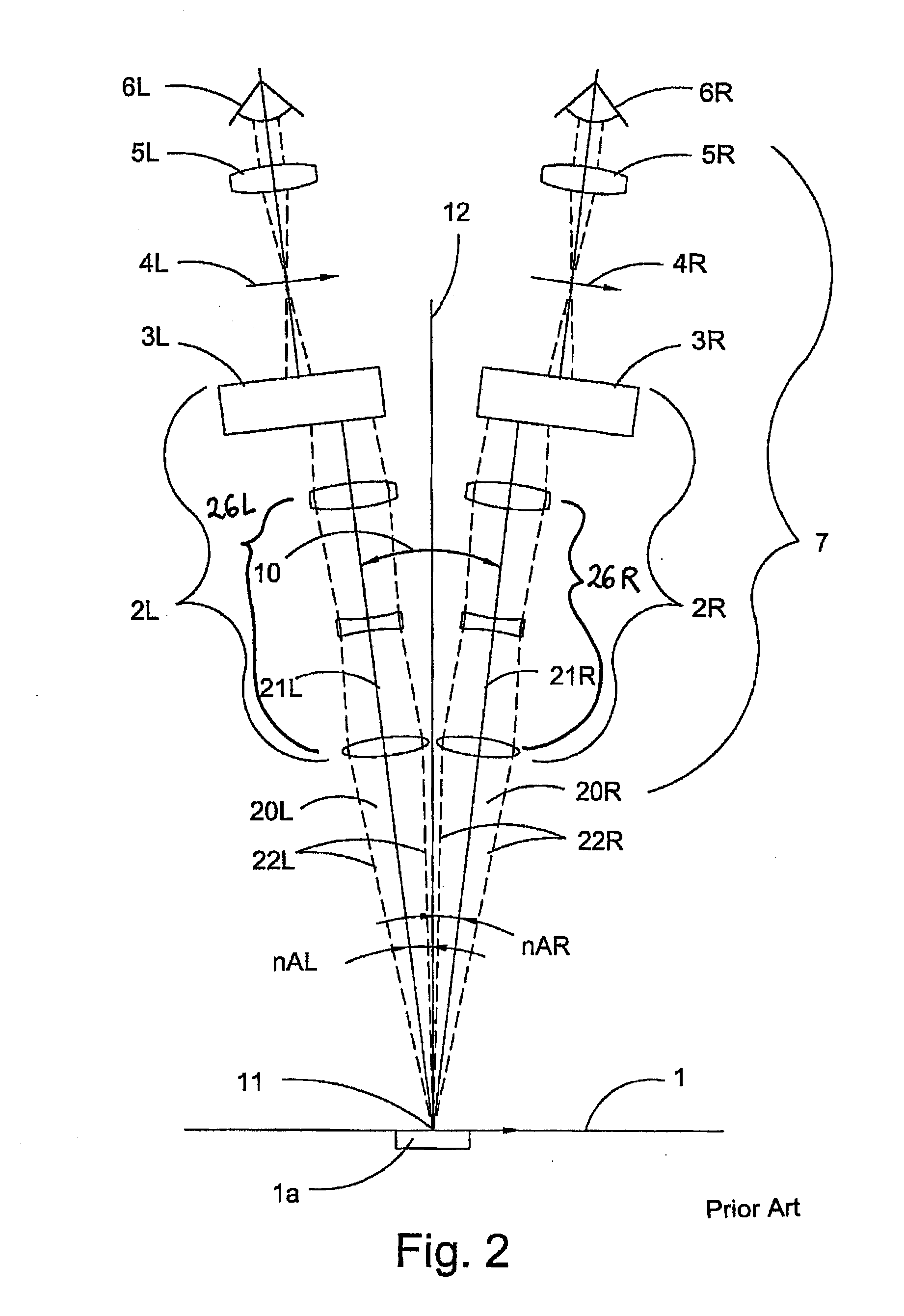
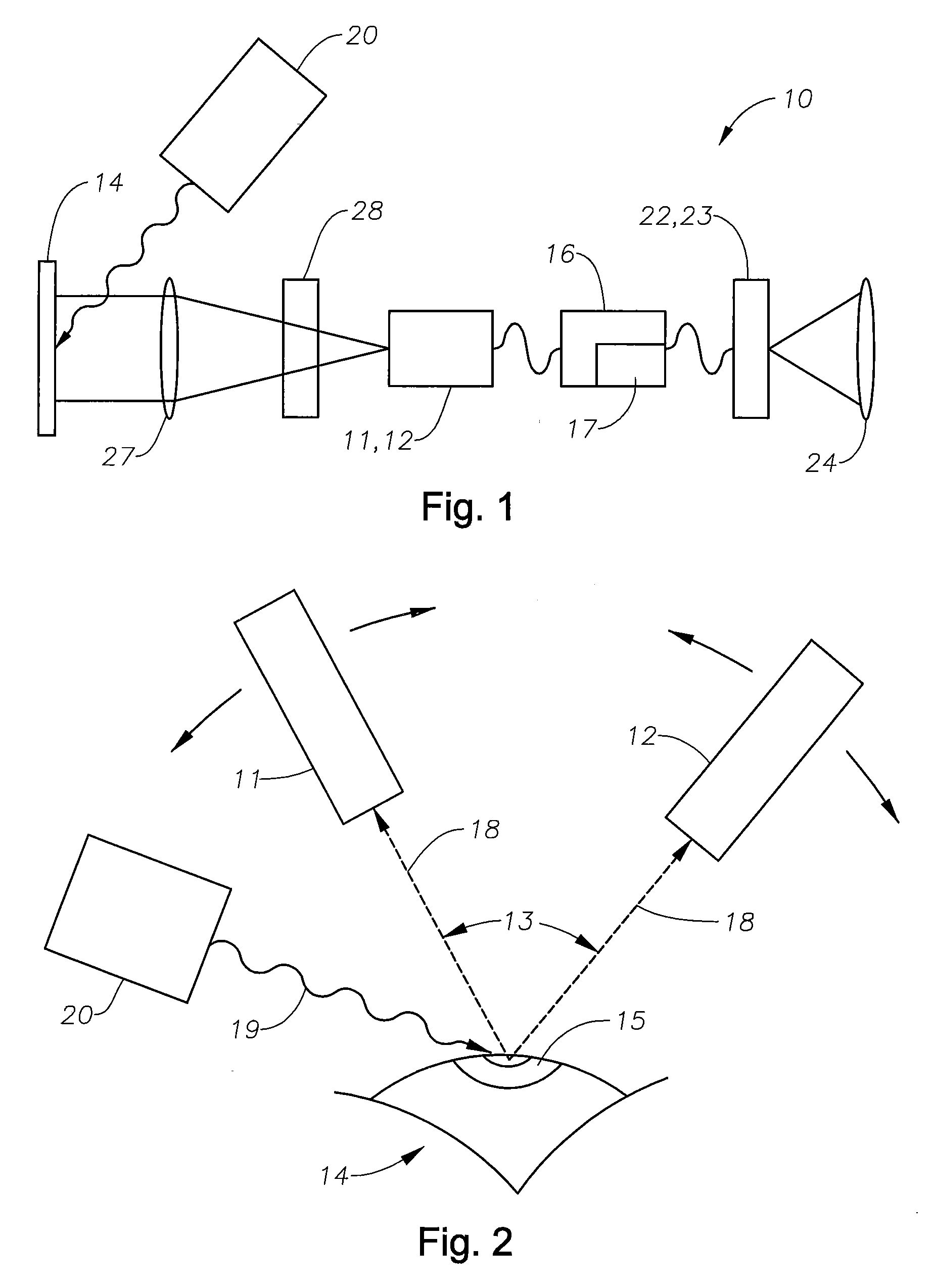
Stereomicroscope
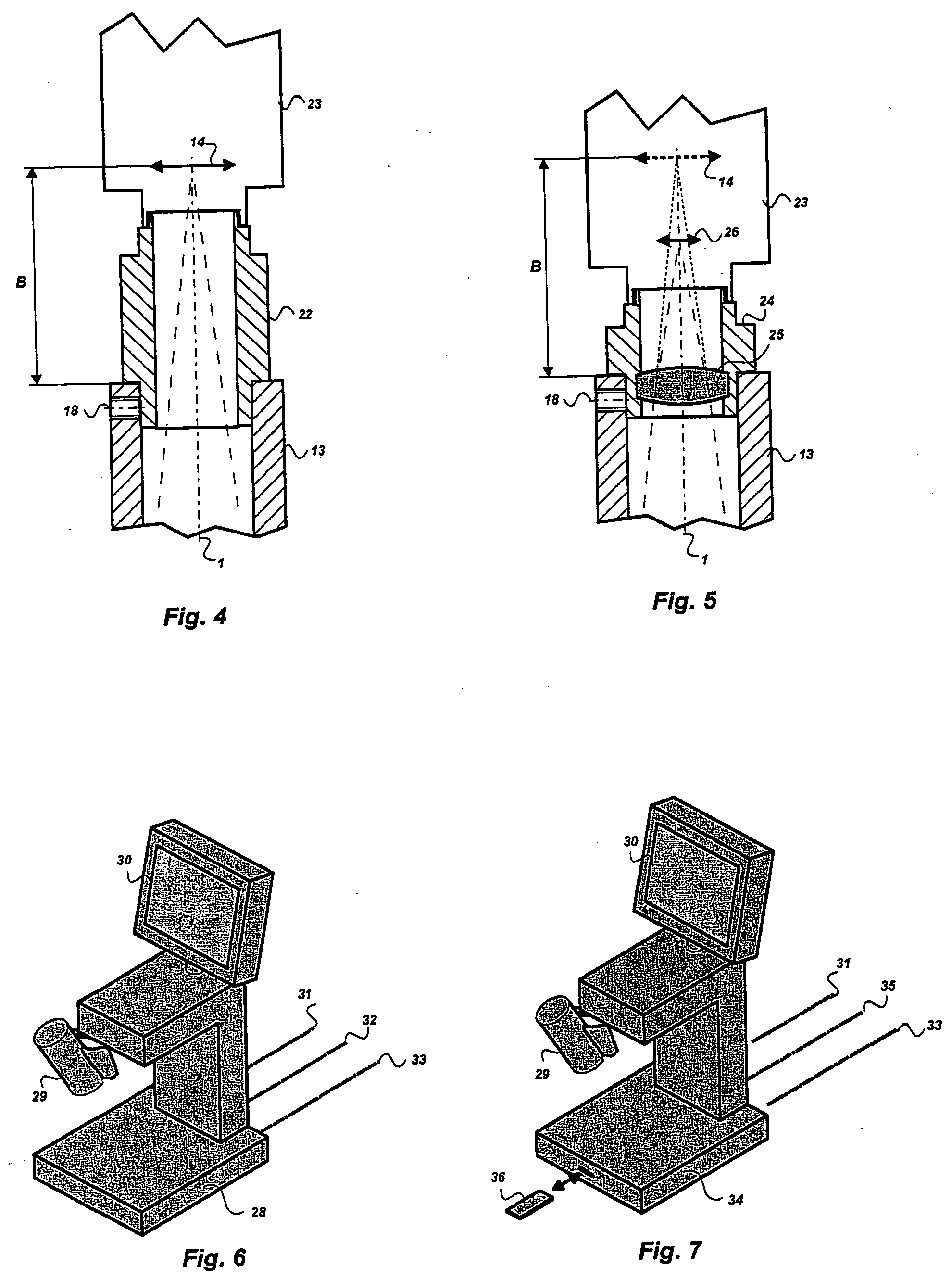
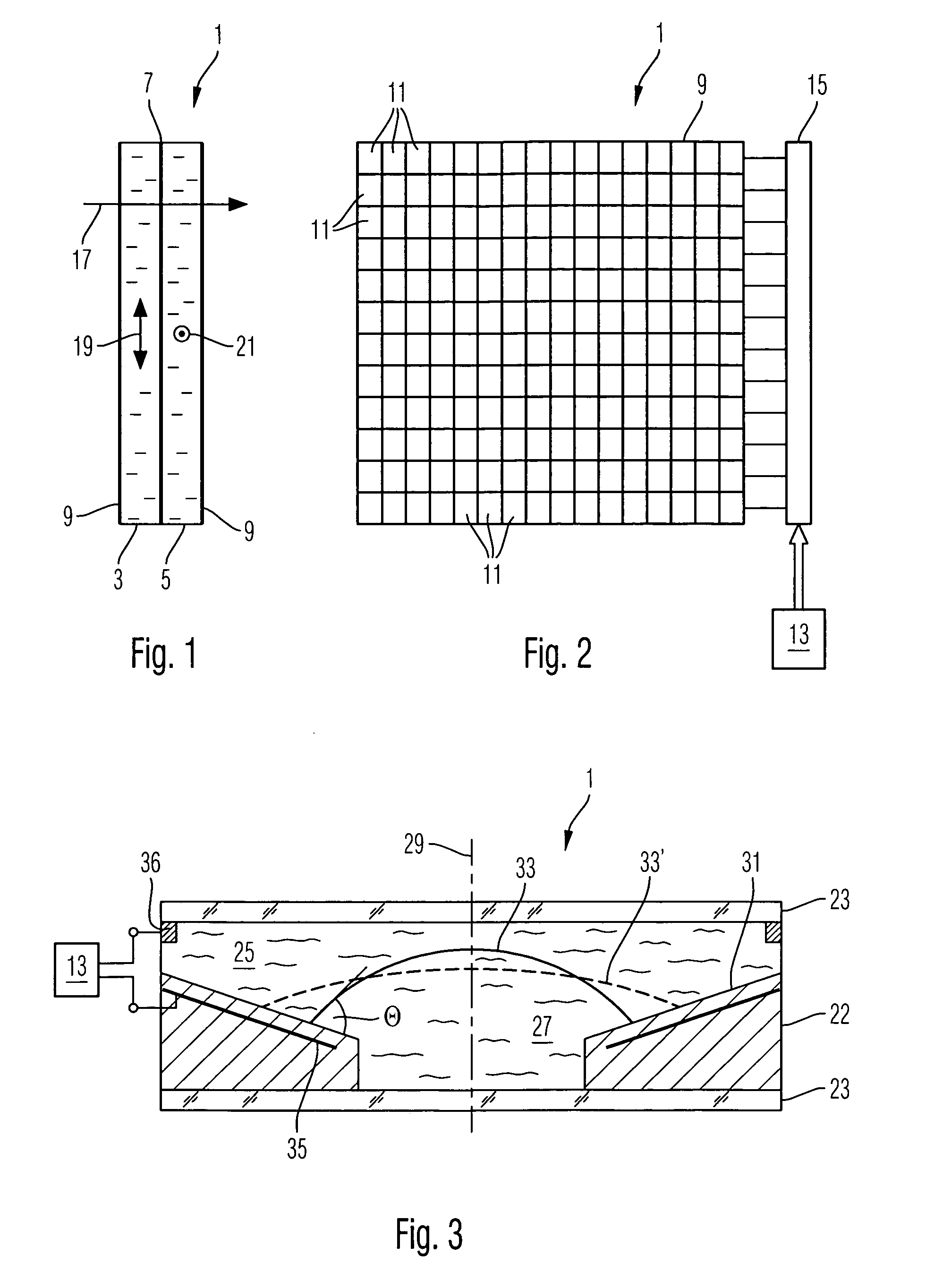
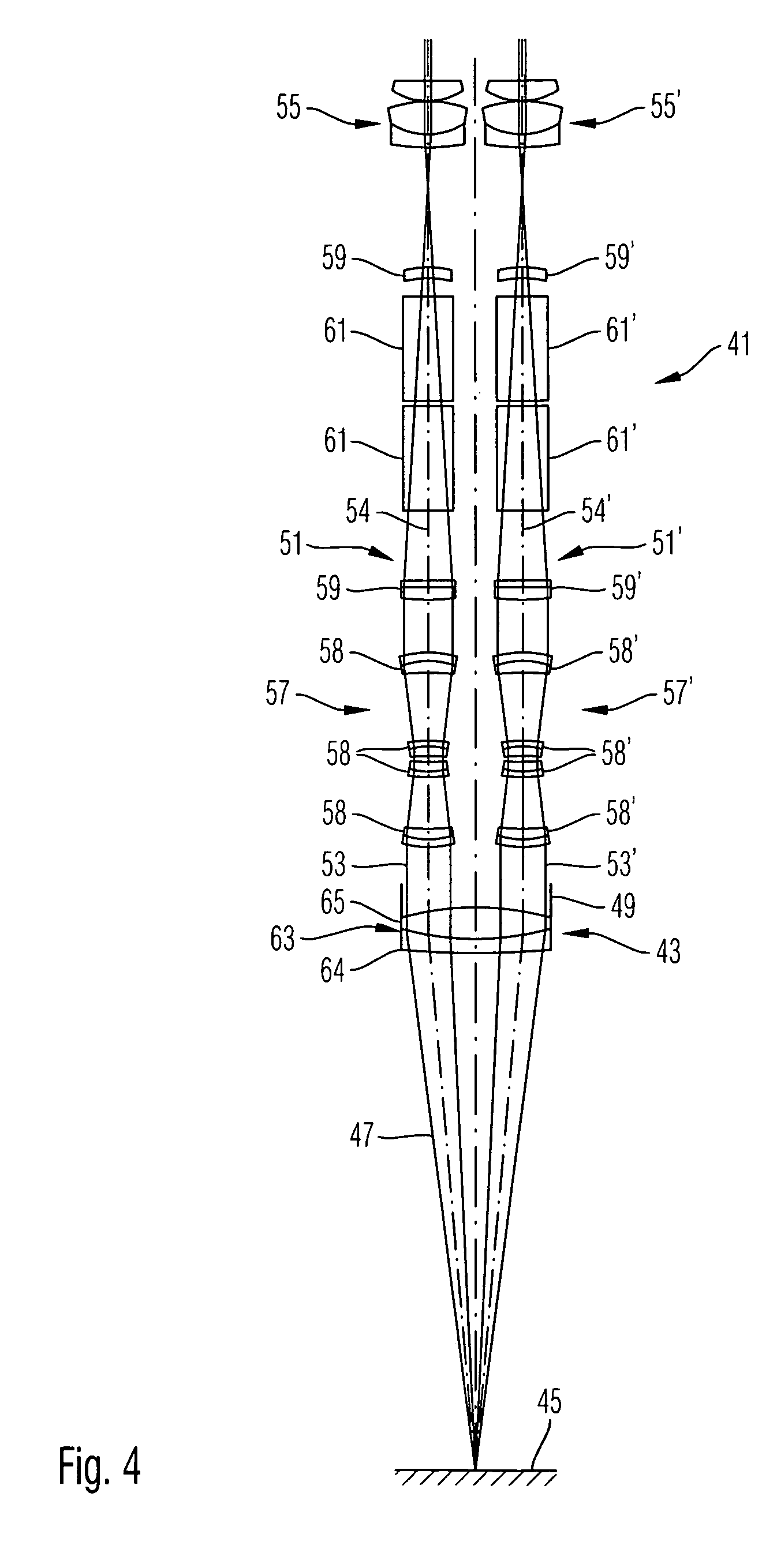
A stereomicroscope of the telescope type includes a first beam path and a second beam path, wherein in the first beam path a first telescope system and in the second beam path a second telescope system are provided, wherein the magnifications of both telescope systems are equal and can be changed synchronously to each other, and wherein a common main objective is allocated to both beam paths. In order to increase the resolution without loss in depth of field, it is proposed that at least one optical element of the first telescope system has, compared to at least one corresponding optical element of the second telescope system, a different optically effective diameter.
Owner:LEICA INSTR SINGAPORE PTE
High-efficiency and high-precision detection device for circular arc roundness of cutter point of diamond cutter
ActiveCN103234481AOvercome the defect of small measurement rangeSolving Precision Measurement ProblemsUsing optical meansDiamond turningThree dimensional measurement
The invention provides a high-efficiency and high-precision detection device for circular arc roundness of a cutter point of a diamond cutter and belongs to the technical field of cutter detection devices. A precision air flotation shafting is vertically arranged at the center of a vibration isolation platform; a fine-aligning device is fixedly arranged at the upper end part of the precision air flotation shafting; a cutter fixture is fixedly arranged at the upper part of the fine-aligning device; a stereoscopic microscope system is arranged above the cutter fixture; and an atomic force microscope (AFM) system is arranged above one side of the cutter fixture. According to the high-efficiency and high-precision detection device disclosed by the invention, the stereoscopic microscope system assists the fine-aligning device in aligning, so that the aligning precision is increased, the defect that the measurement range of the AFM is narrow is overcome, and three-dimensional measurement with high measurement precision is realized; the problem of precision measurement of the circular arc roundness of the cutter point of the diamond cutter with a circular arc edge can be solved; and measurement data of the circular arc roundness can be used for reflecting dynamic characteristic of a cutter grinding machine, evaluating the cutter grinding quality of the cutter and providing data support for cutter compensation in the numeric control single-point diamond turning.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
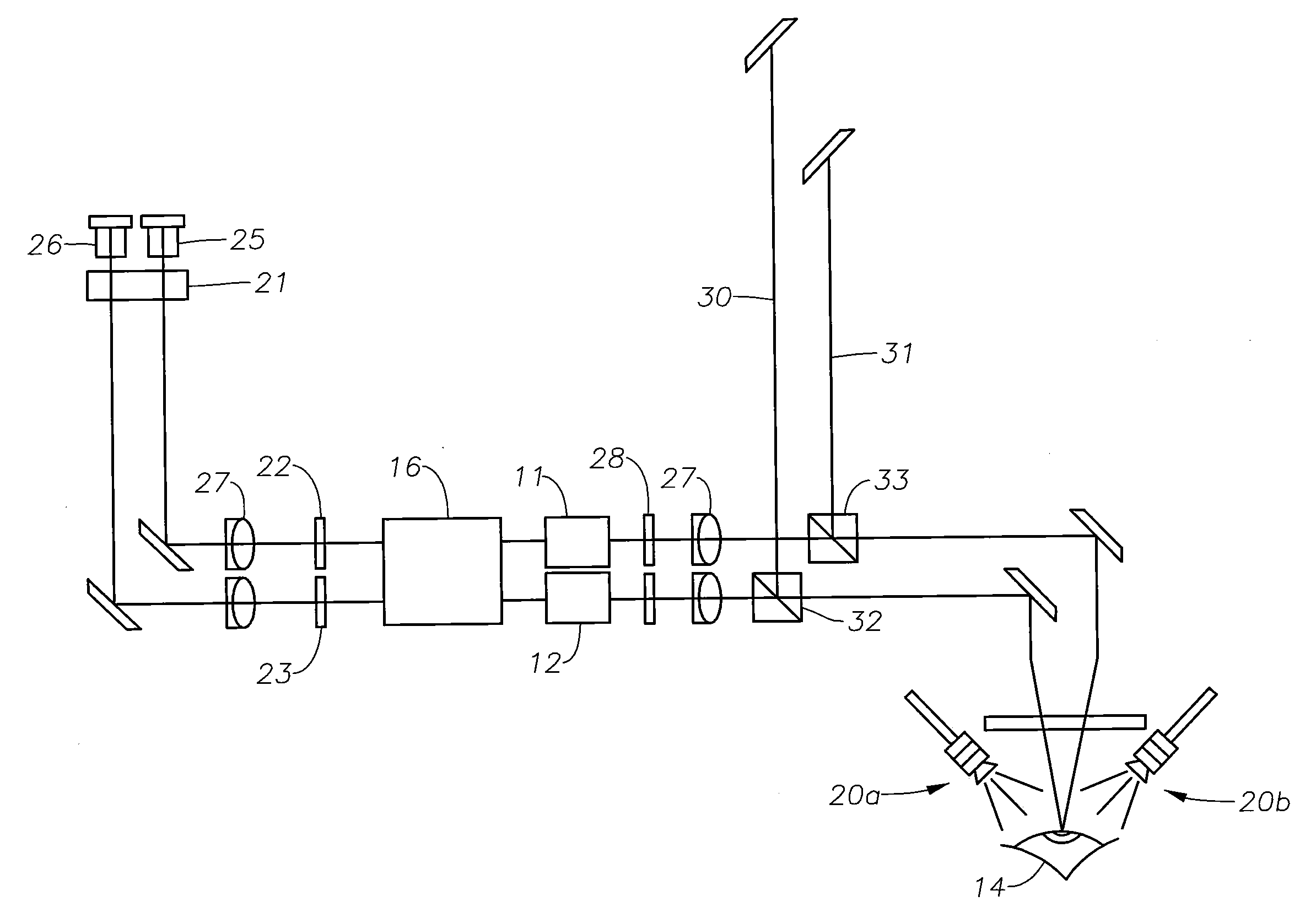
Special-illumination surgical video stereomicroscope
InactiveUS20120056996A1High light efficiencyReduce resolutionDiagnosticsMicroscopesFluorescenceLength wave
A special-illumination surgical video stereomicroscope having at least one light source for illuminating an in-situ specimen, at least one video imaging unit (104a) being provided for acquiring a fluorescence image of the specimen, the spectral sensitivity of the at least one video imaging unit (104a) exhibiting a higher spectral sensitivity in at least one light wavelength region of a special light radiation to be expected, e.g. fluorescence radiation, than in another light wavelength regions.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS (SCHWEIZ) AG
Hot fatigue performance test and analysis method for steel
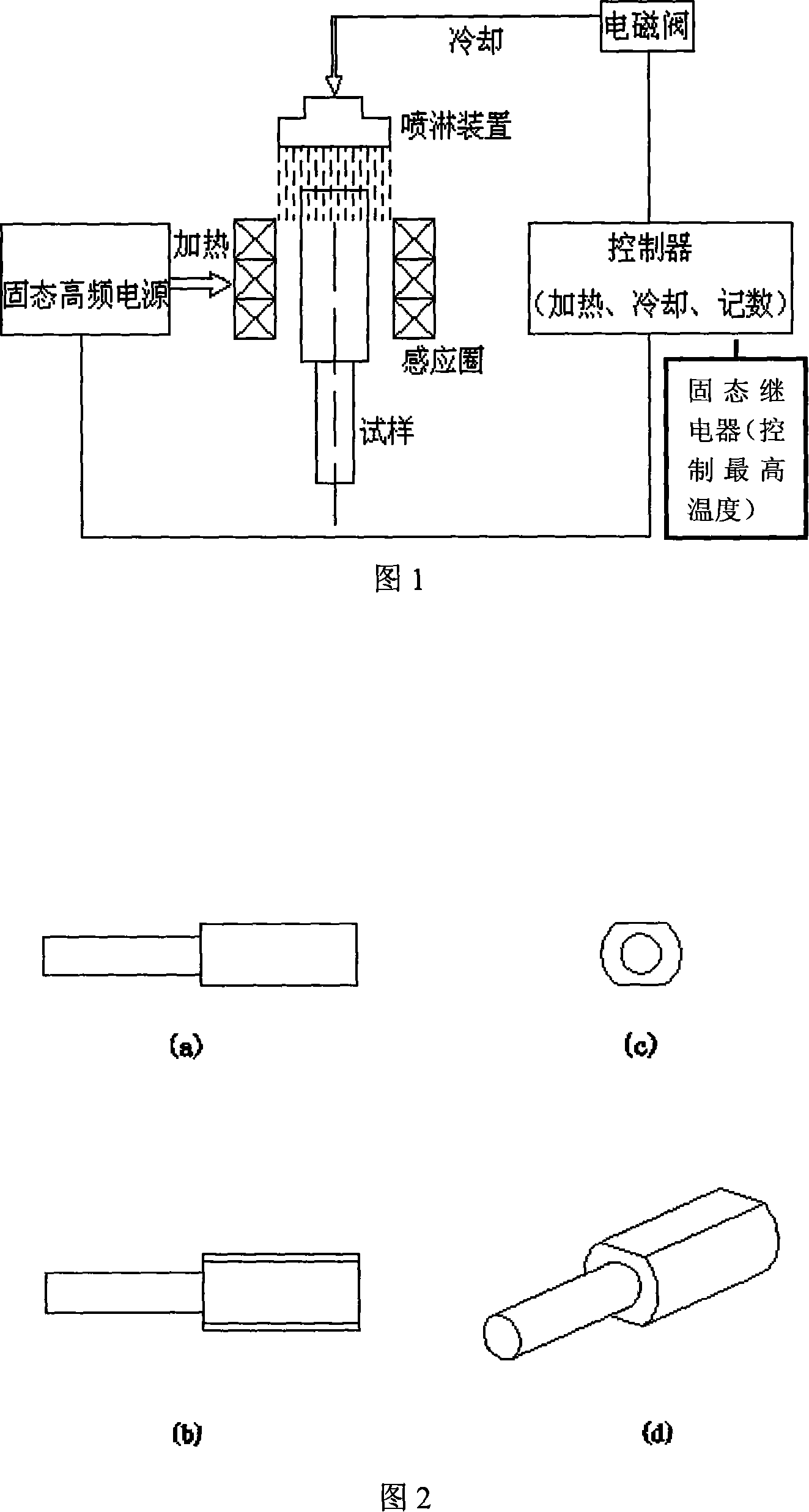
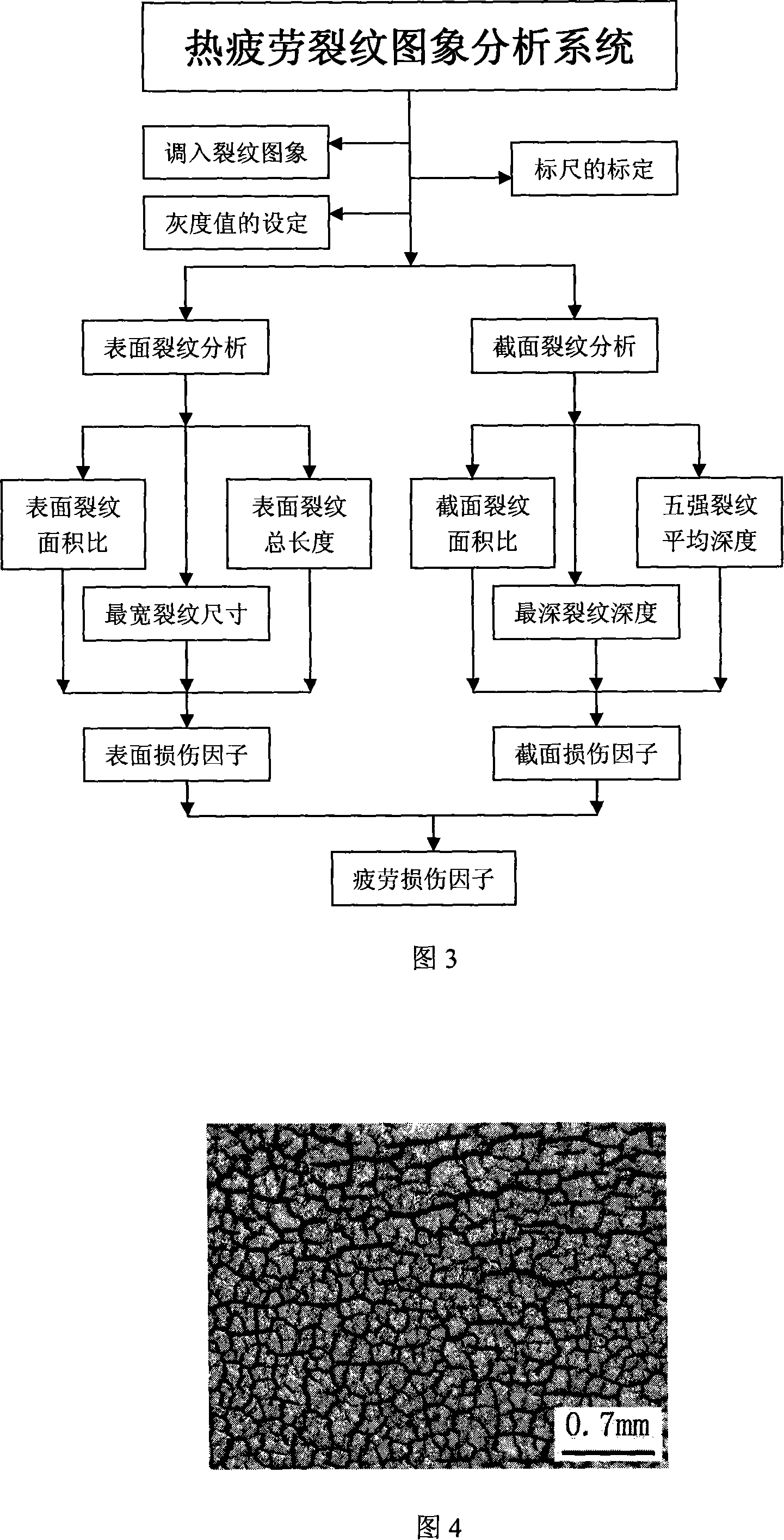
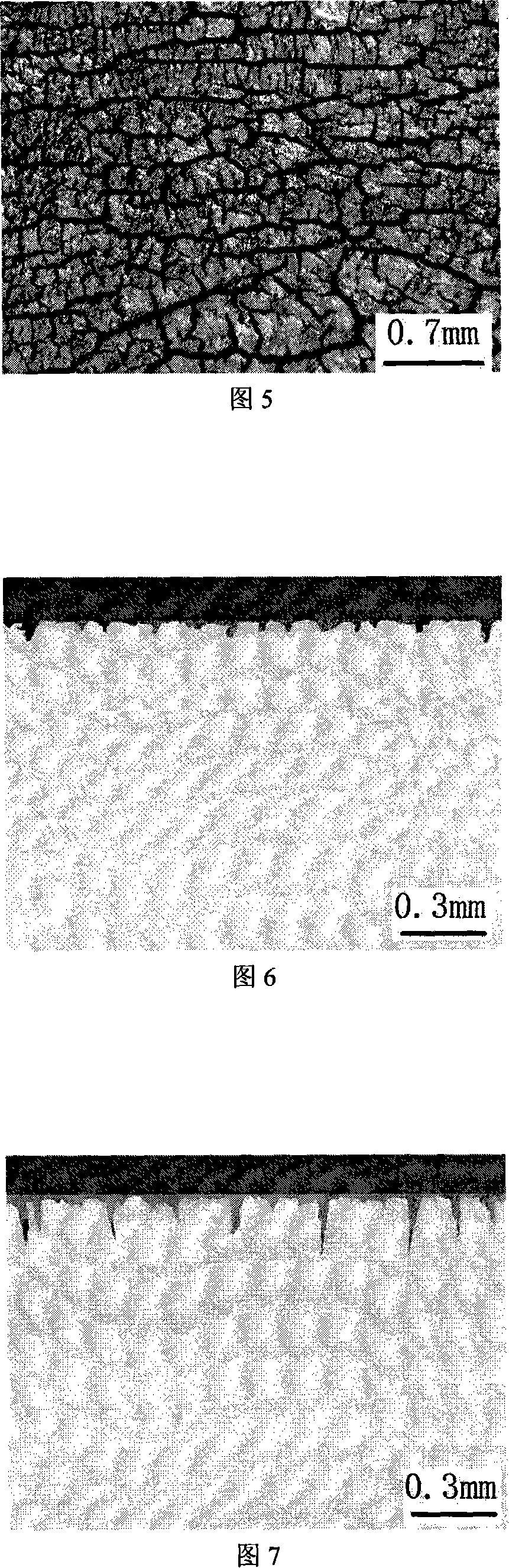
InactiveCN101105436ASimulate thermal fatigue working conditionsAvoid human errorsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationStrength propertiesMetallic materialsStereo microscope
The invention relates to a test and analysis method of the heat weary performance of steel, which belongs to the field of the performance and test analysis of metal material. The invention is characterized in that the quantitative research and analysis of the heat weary performance is realized. And the invention has following technological processes and steps: (1) the specimen is processed into a shape which has two side surfaces, one of the two surfaces is connected with temperature controlling equipment through a thermo-element, and the highest heating temperature of the specimen can be controlled. The two surfaces are both grinded into the state of polishing. (2) The specimen is put in the center of the induction coil of the heat weary performance testing machine, and then is cooled by circulation cooling water; the highest heating temperature is set, and the cooling time is set. After the heat weary performance testing, the specimen is processed with etch cleaning, and the oxide skin on the surface of the specimen is removed; cracks on the surface of the specimen is given a photo by zoom stereo microscope; the specimen is cut crosswise along the closest packed cracks, and then is grinded and polished and is again given a photo of the sectional plane. (3) The photo is input into the computer, and the cracks are quantitatively analyzed by heat weary performance cracking image analysis system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
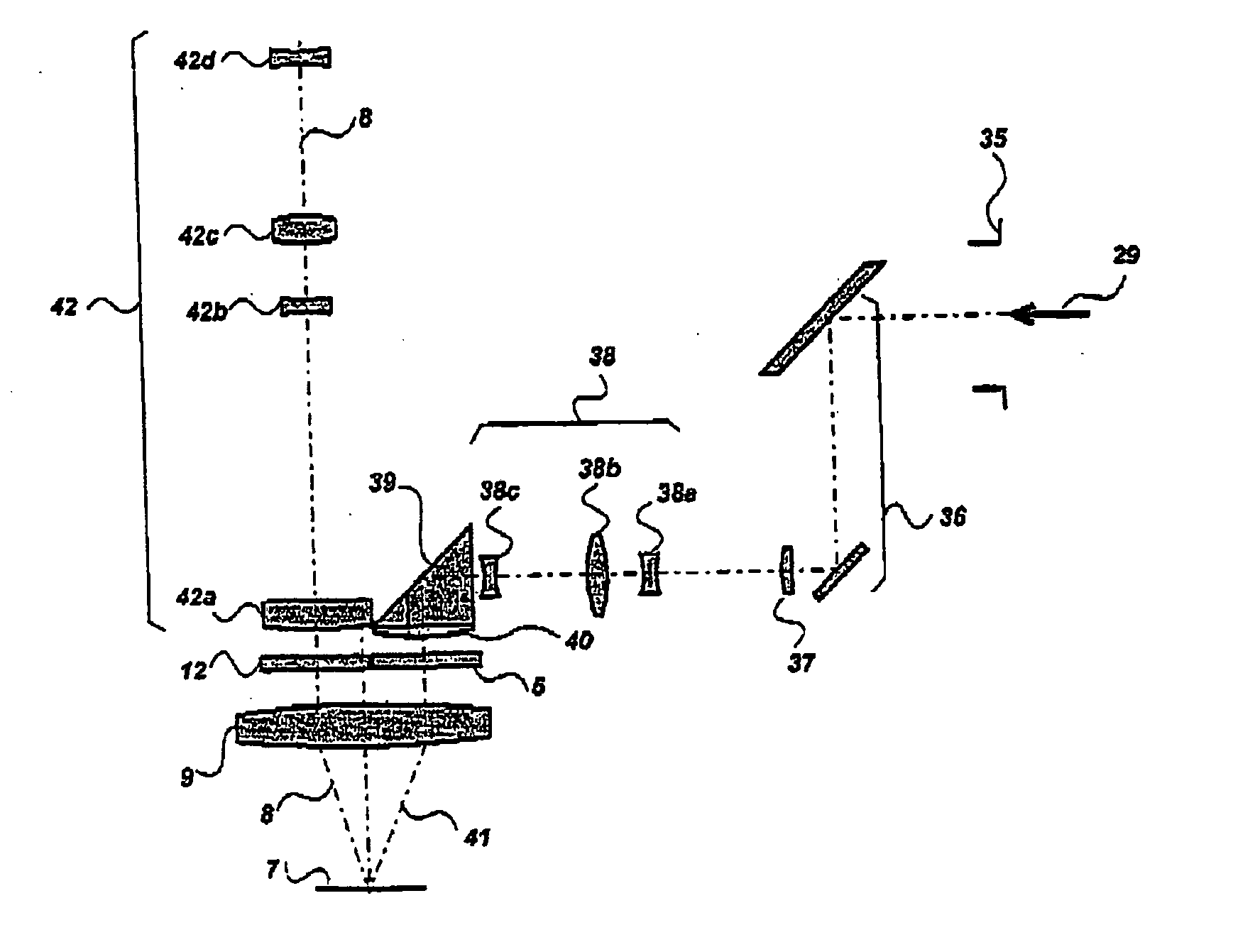
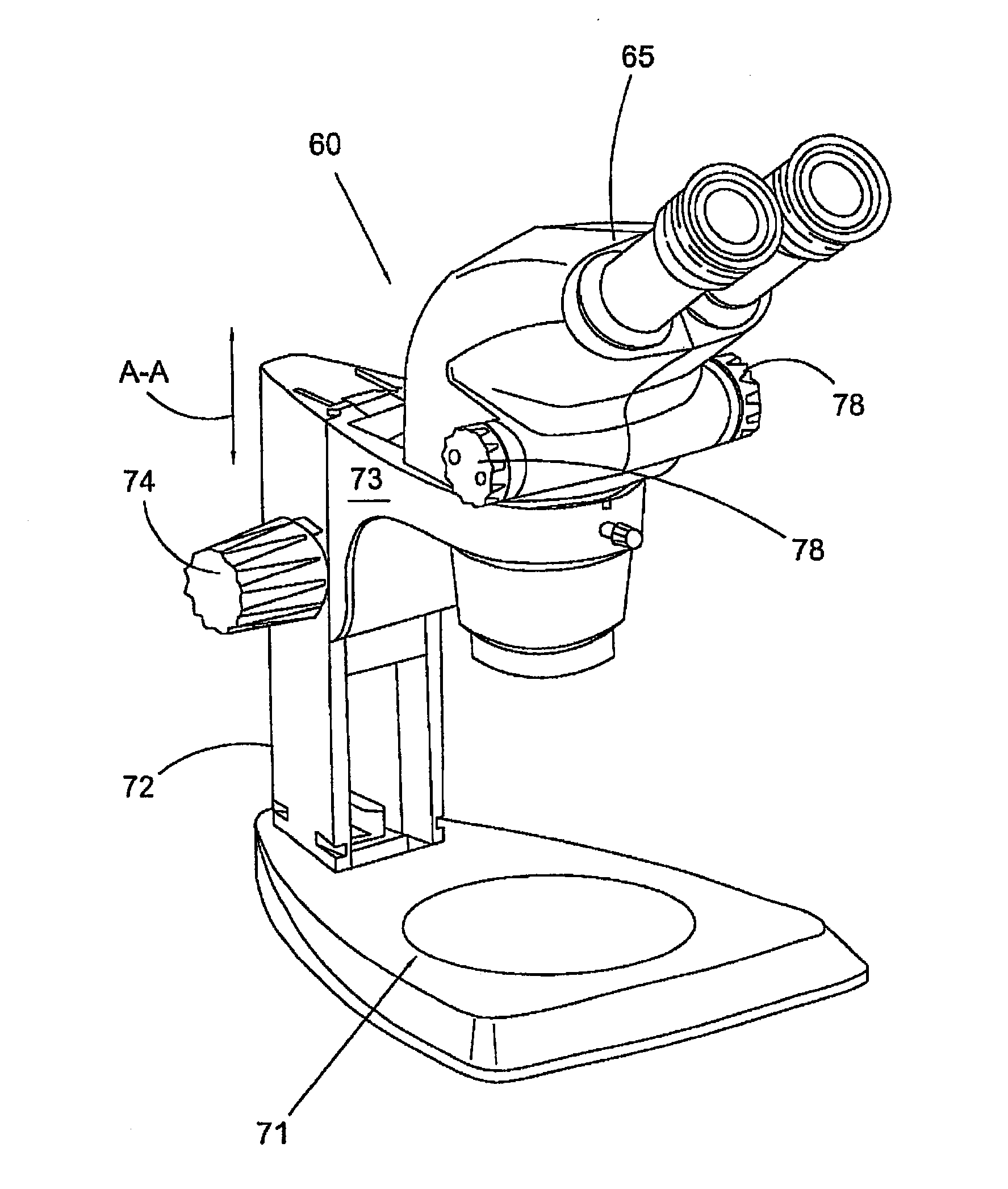
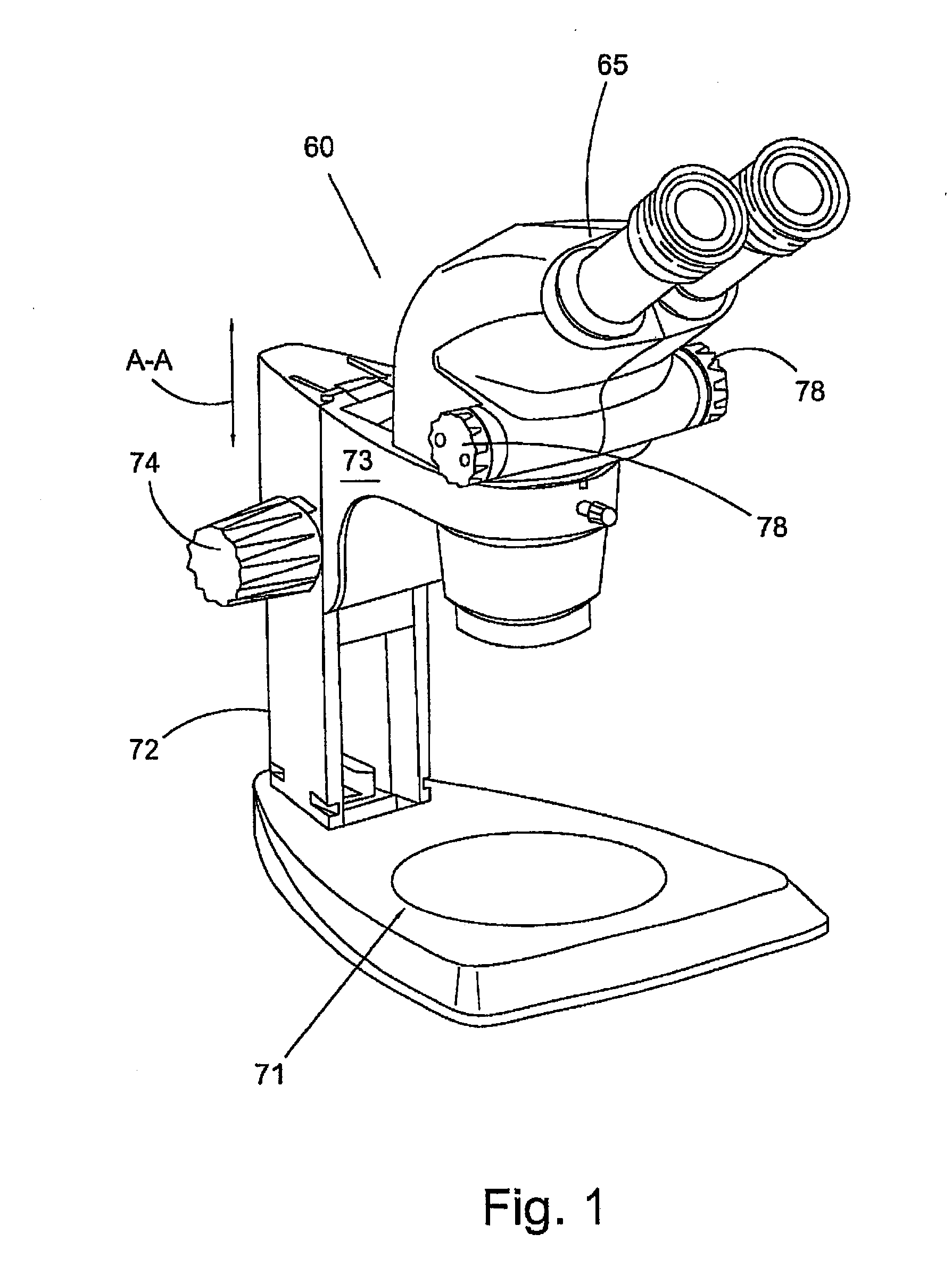
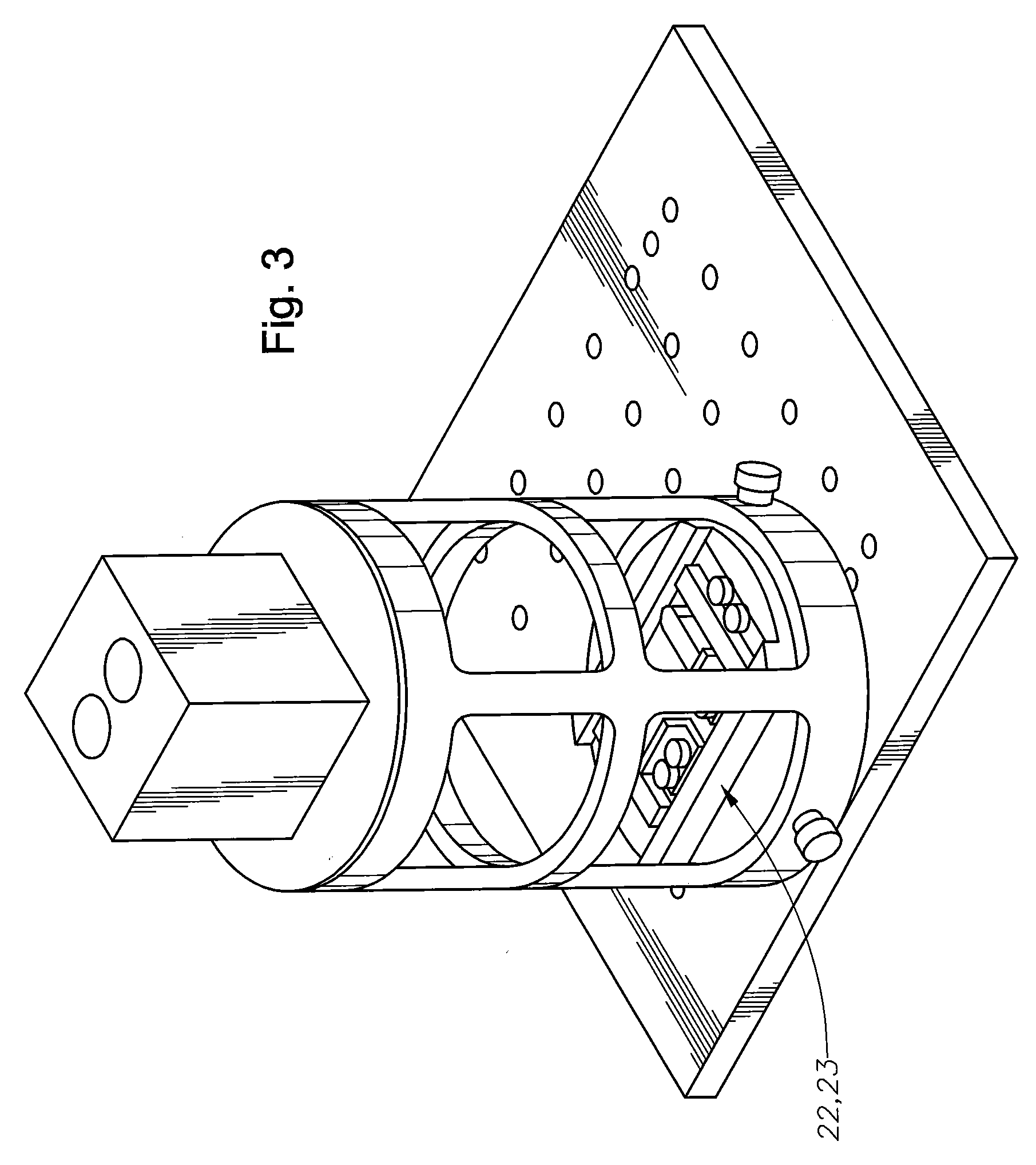
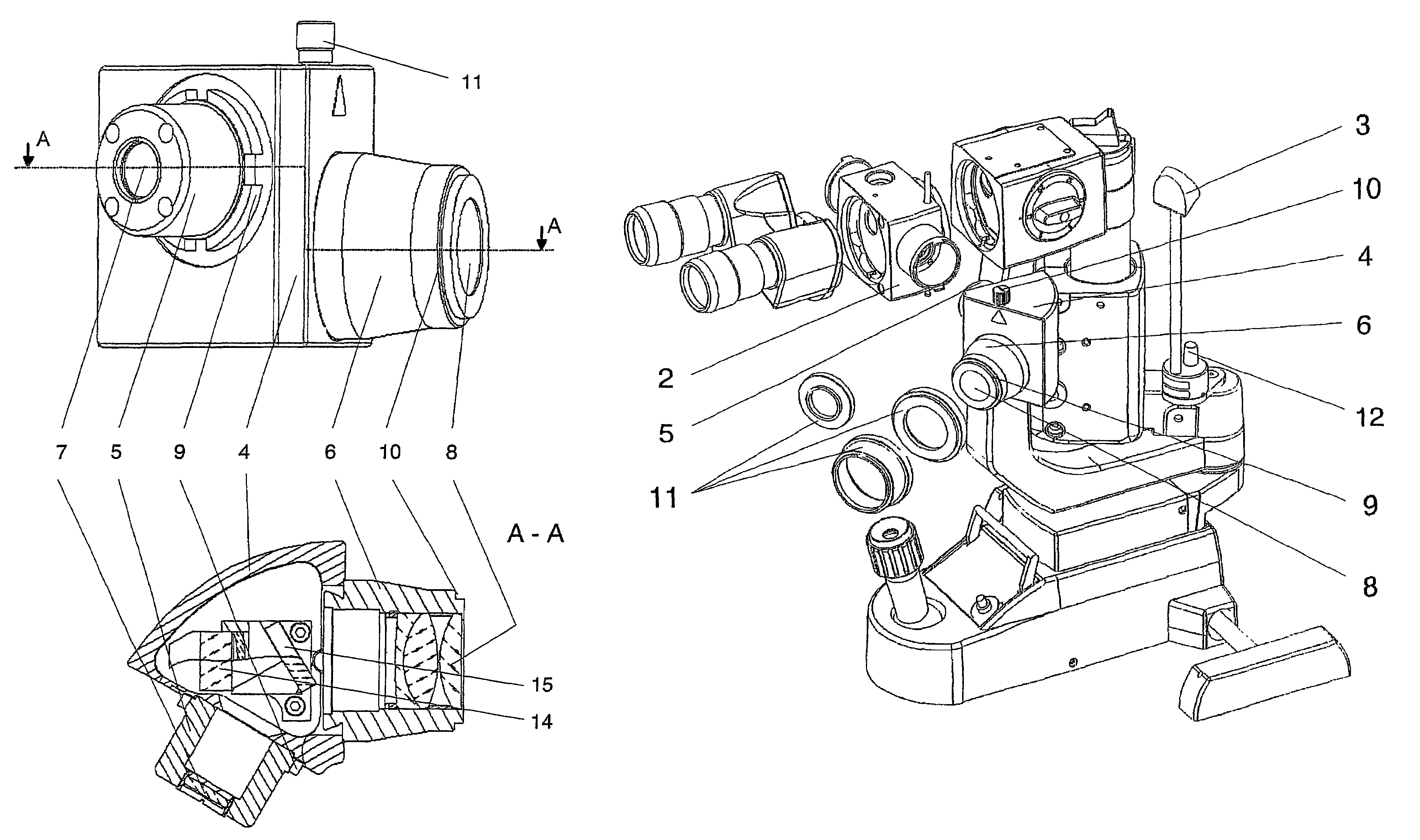
Stereomicroscope or additional element for a stereomicroscope
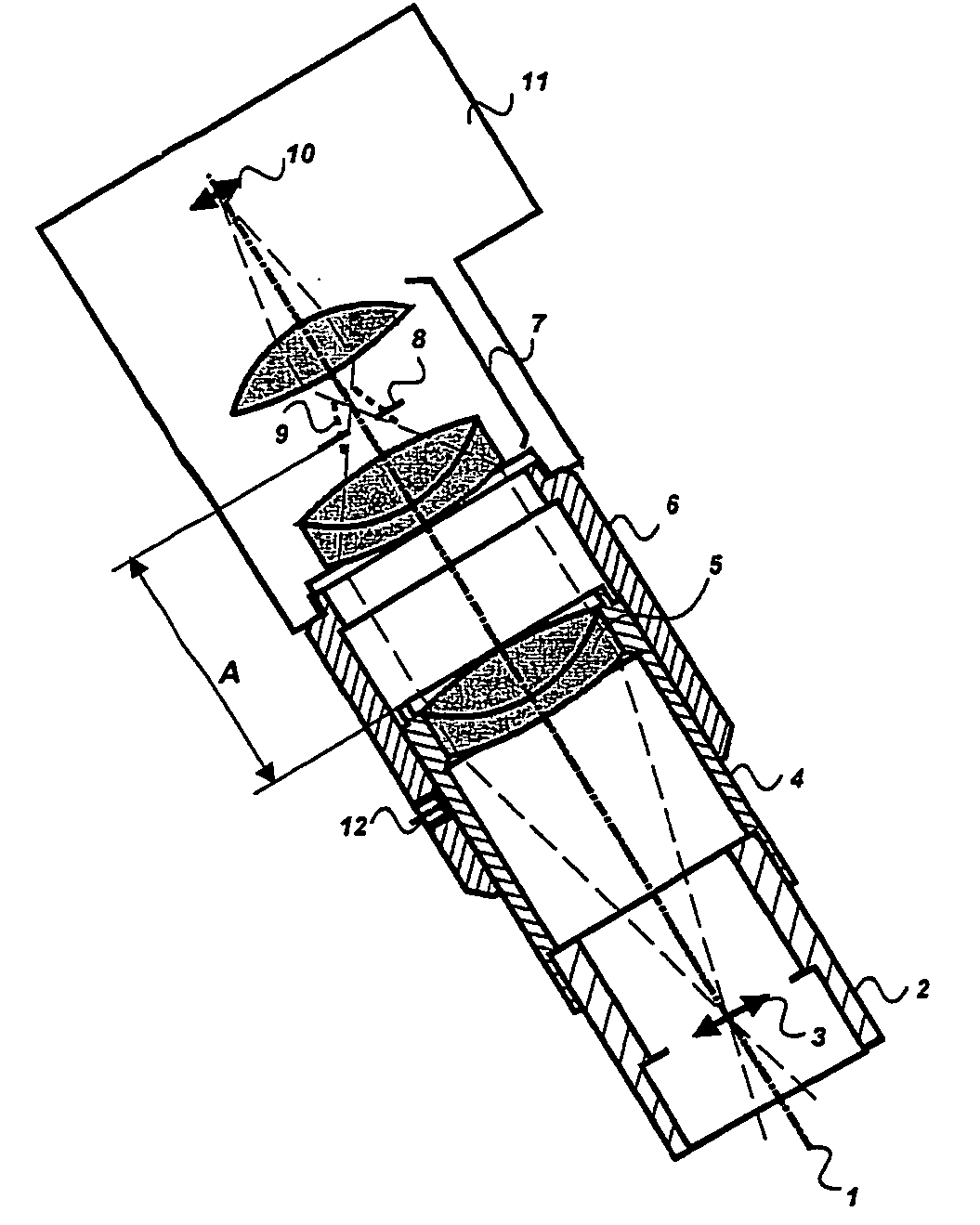
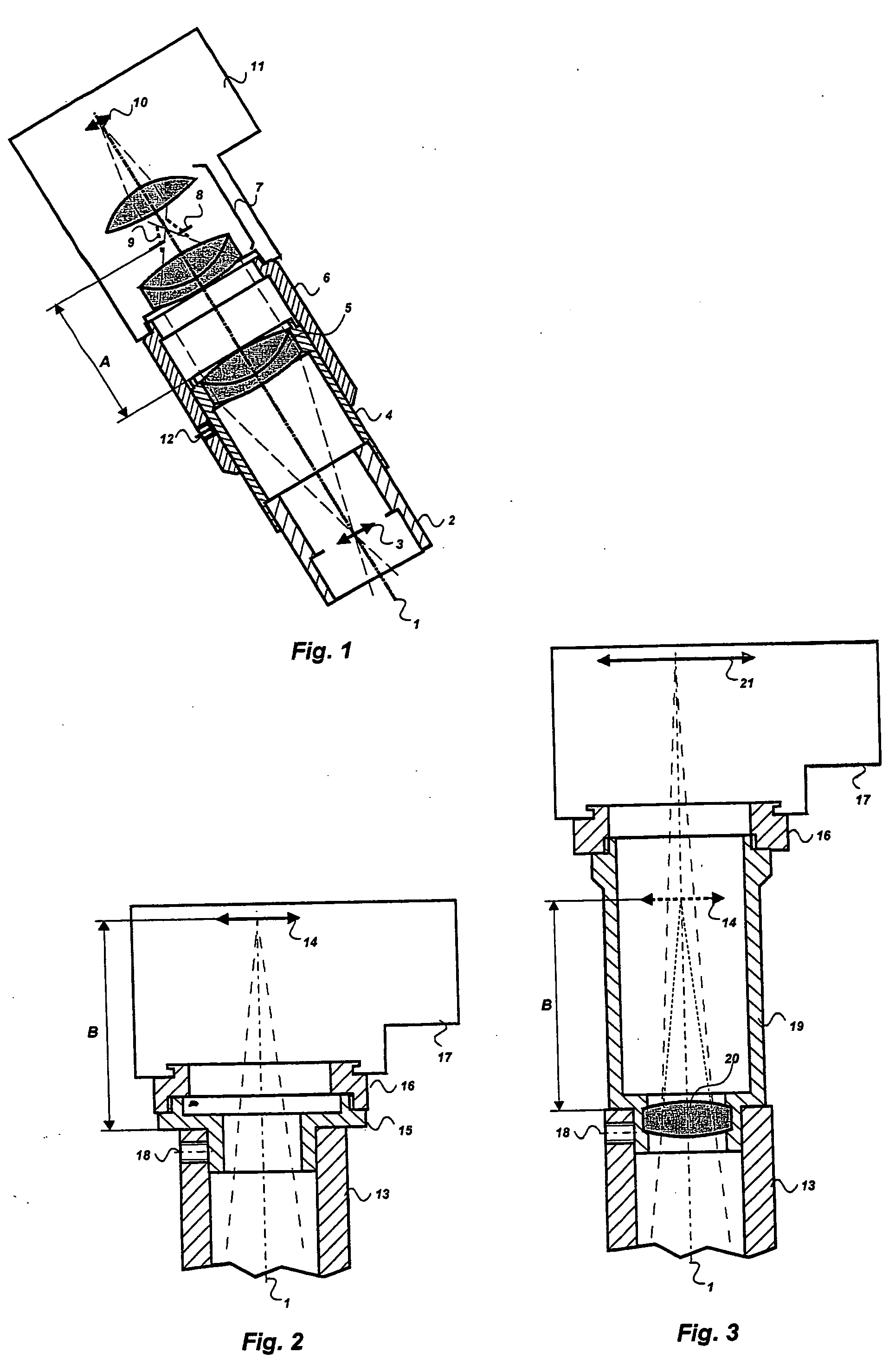
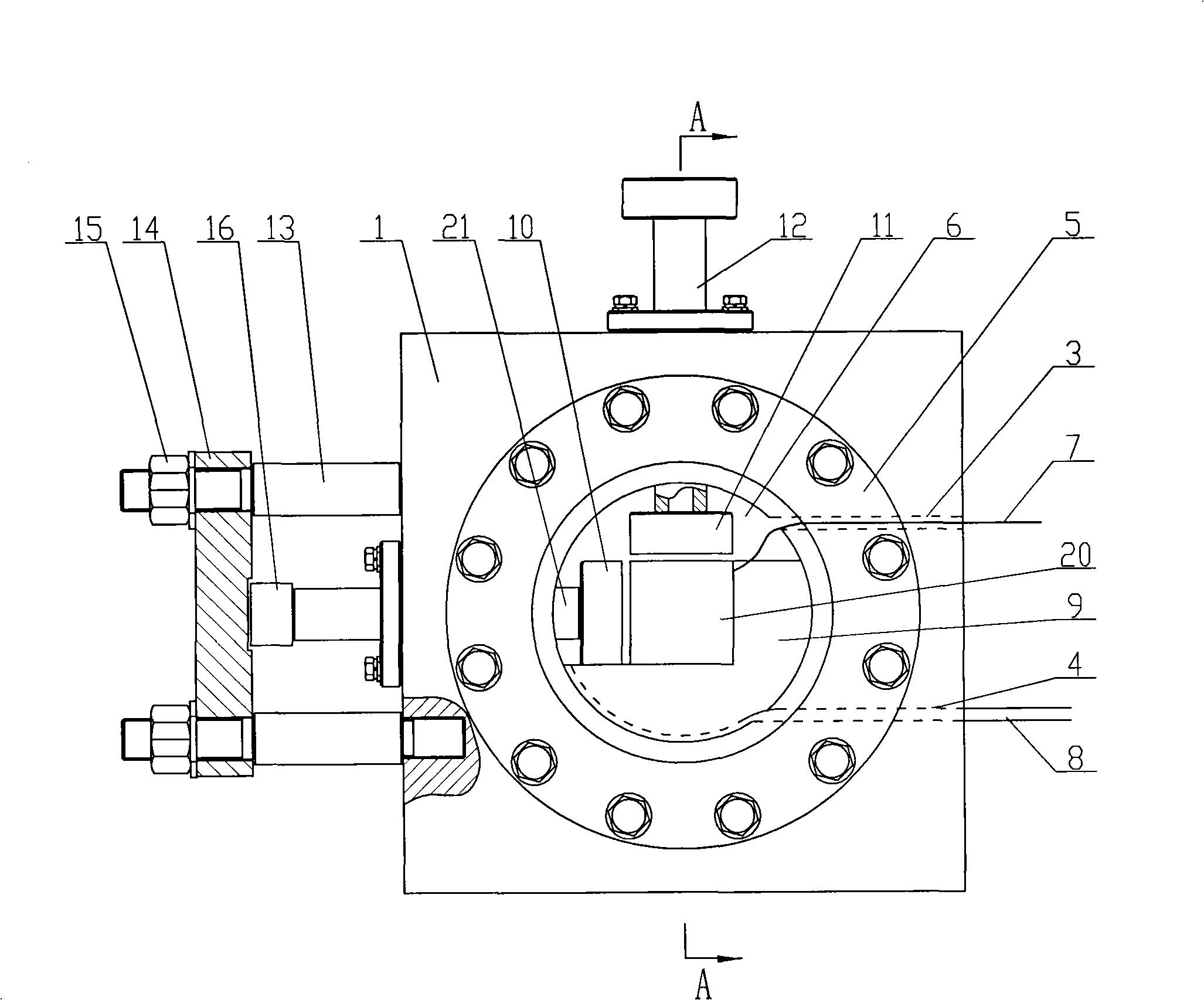
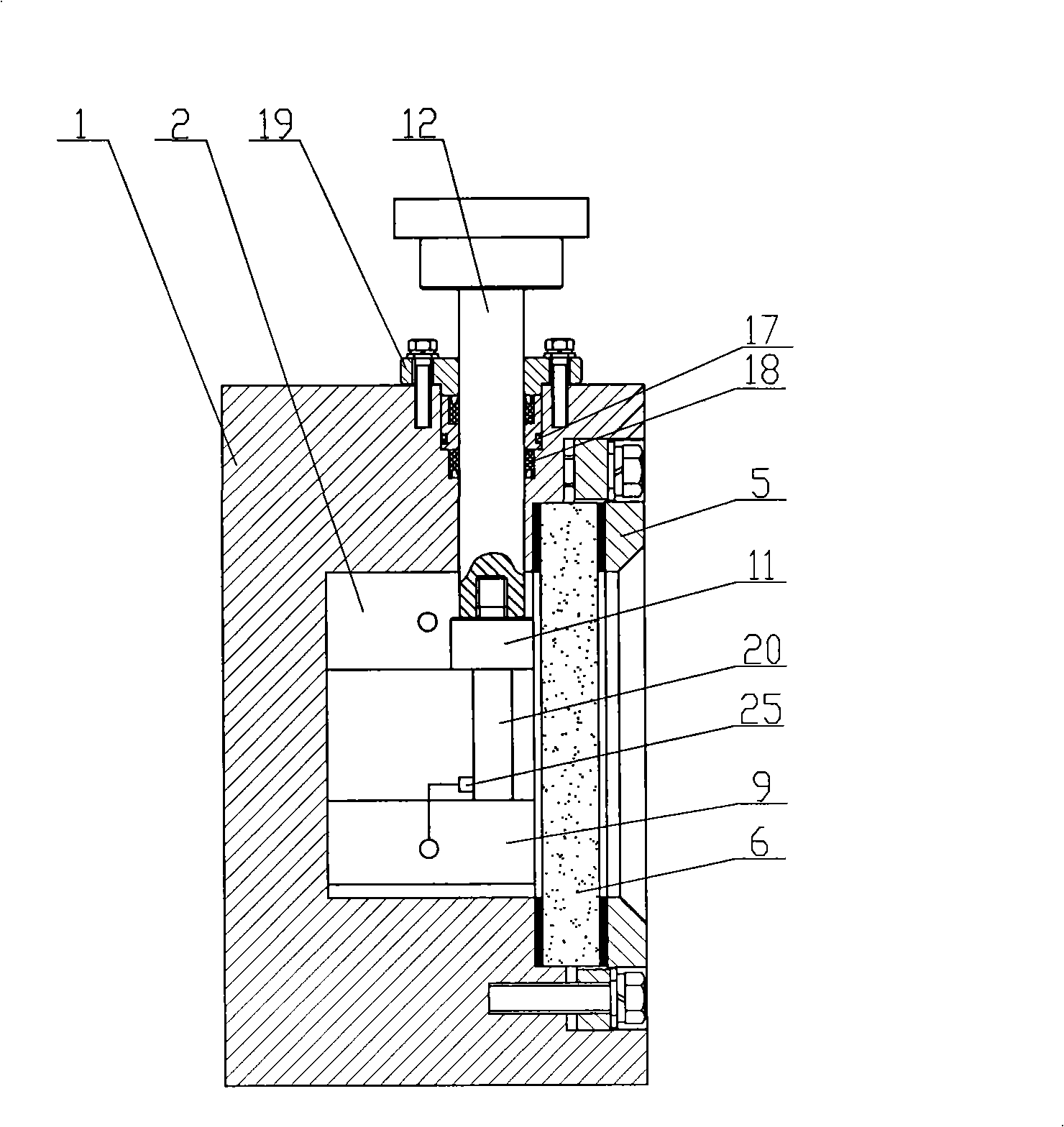
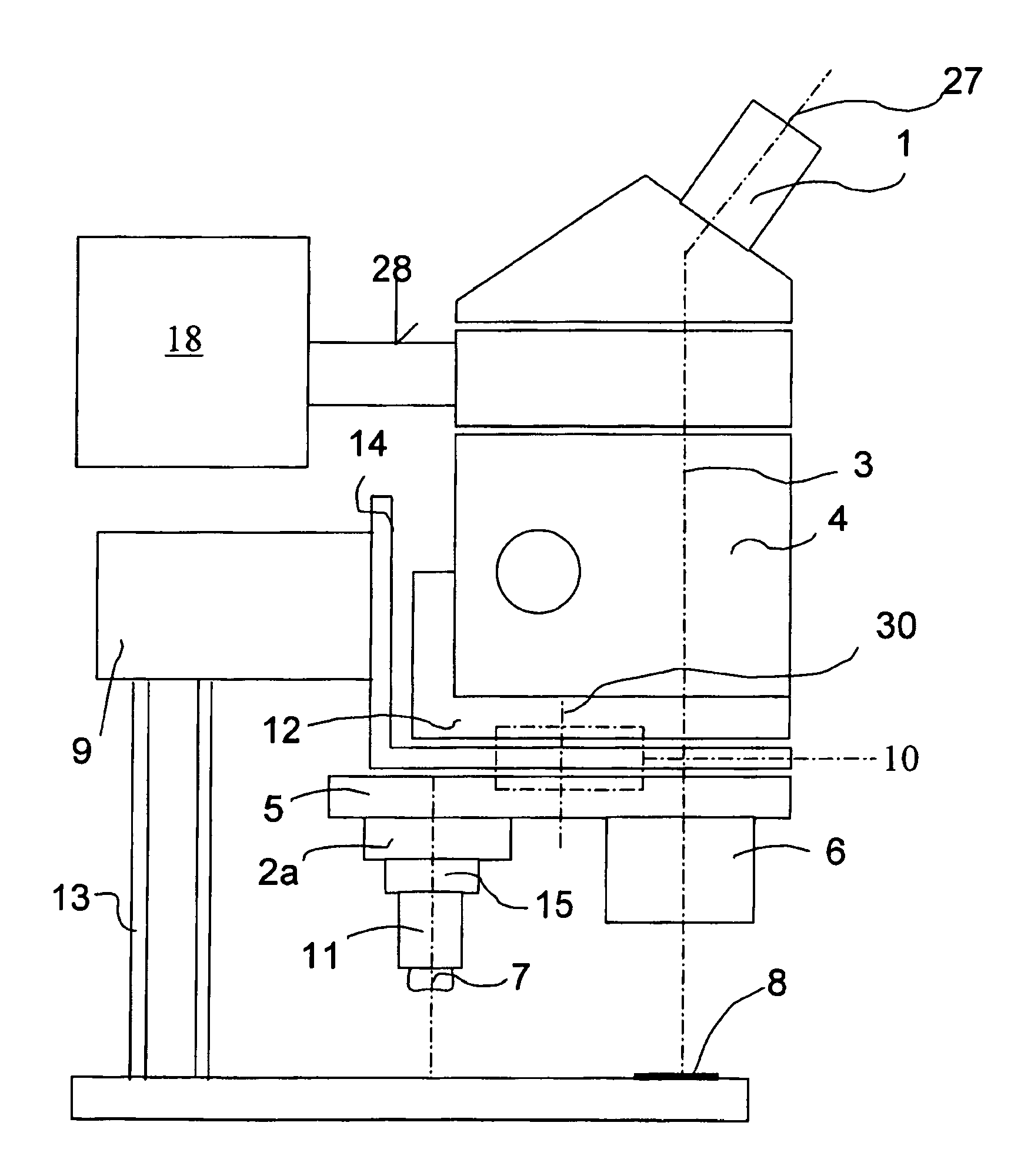
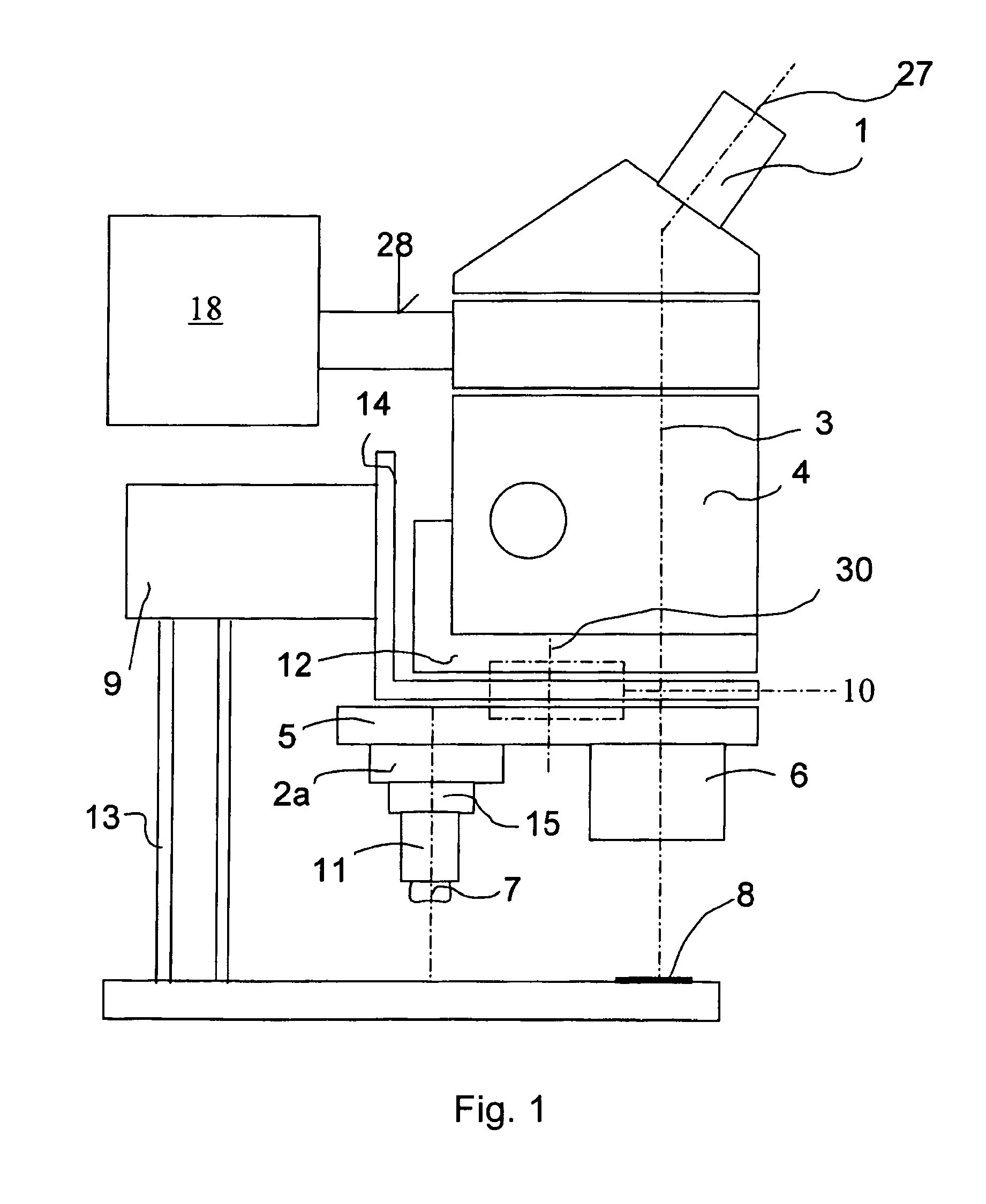
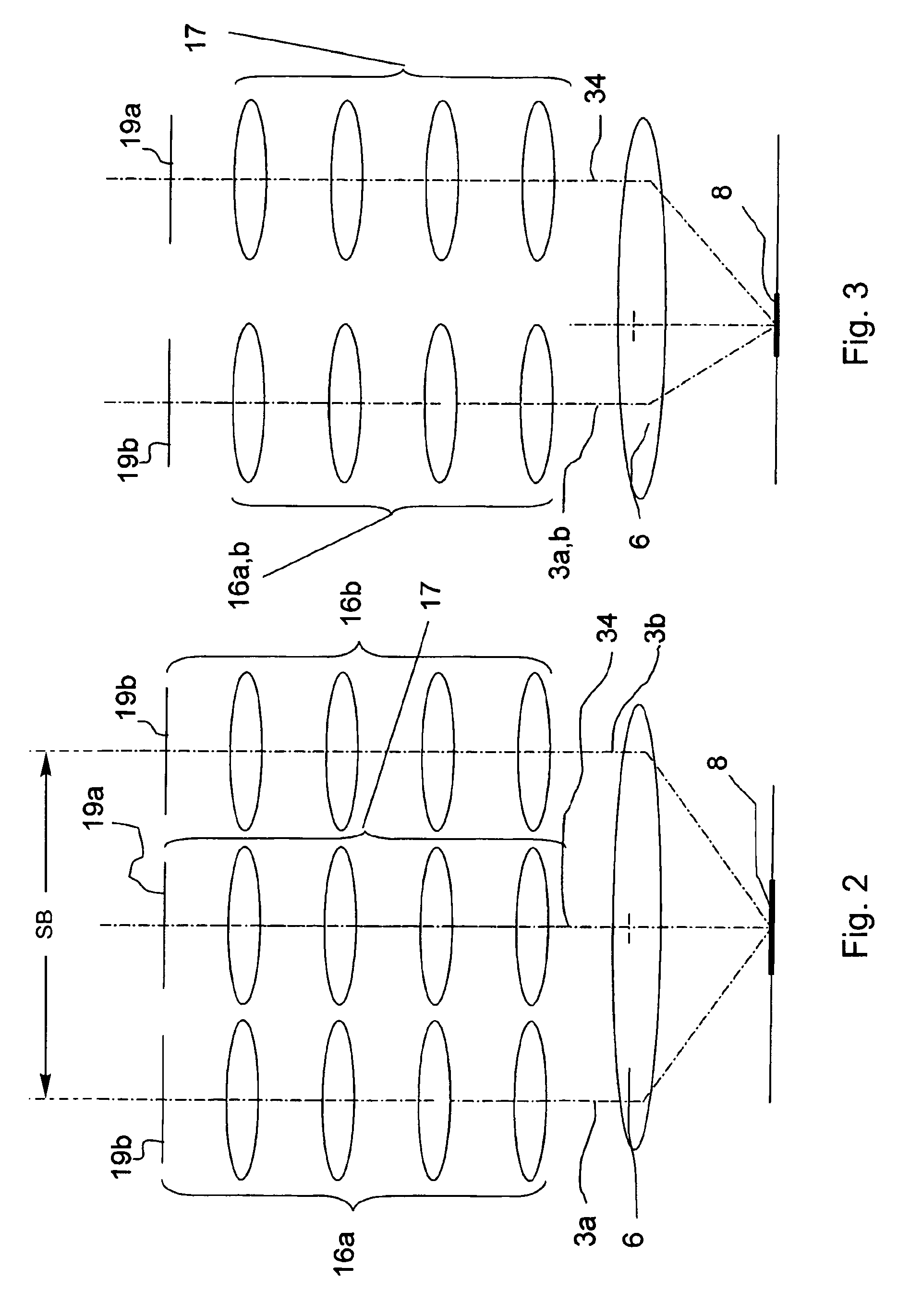
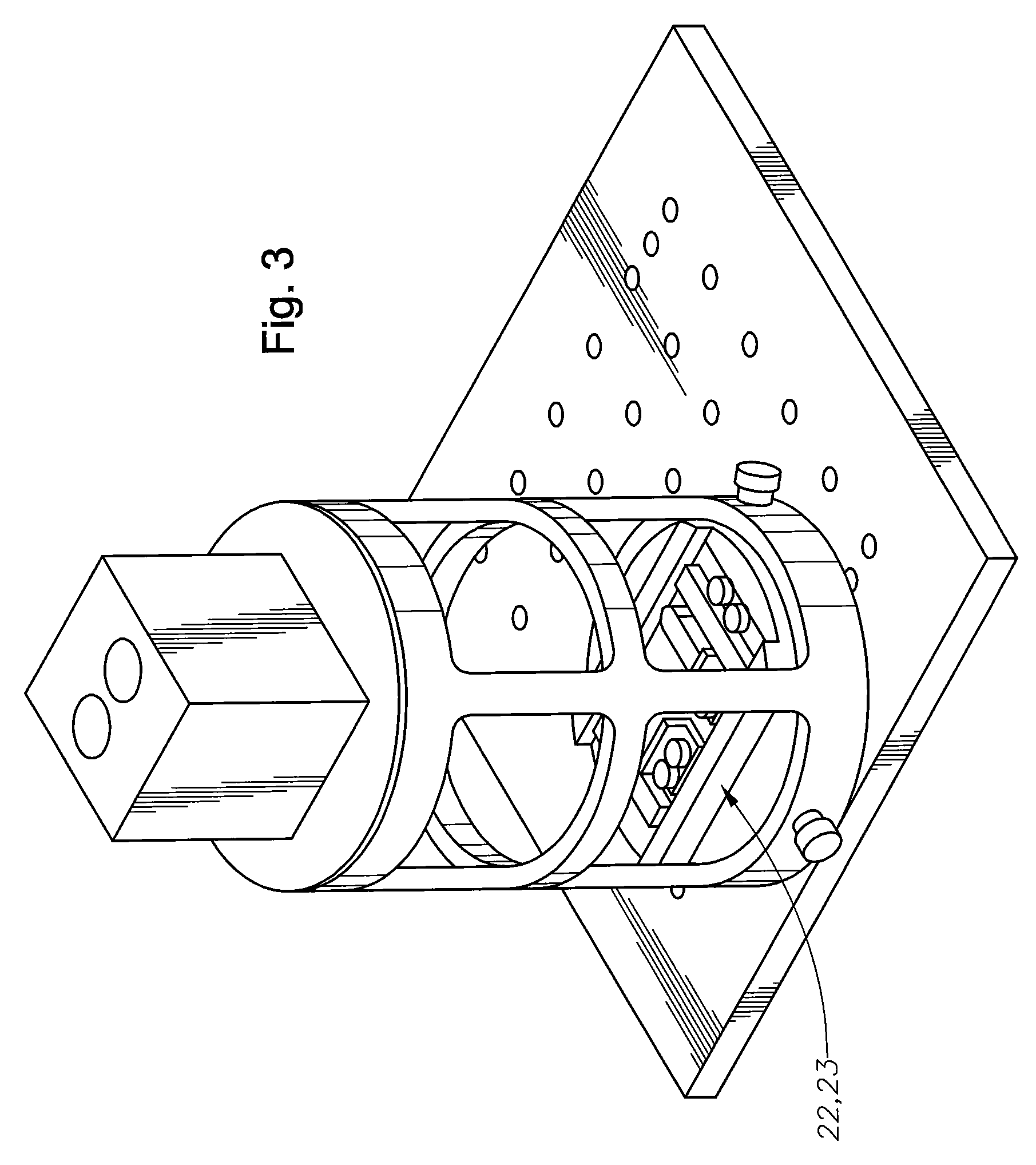
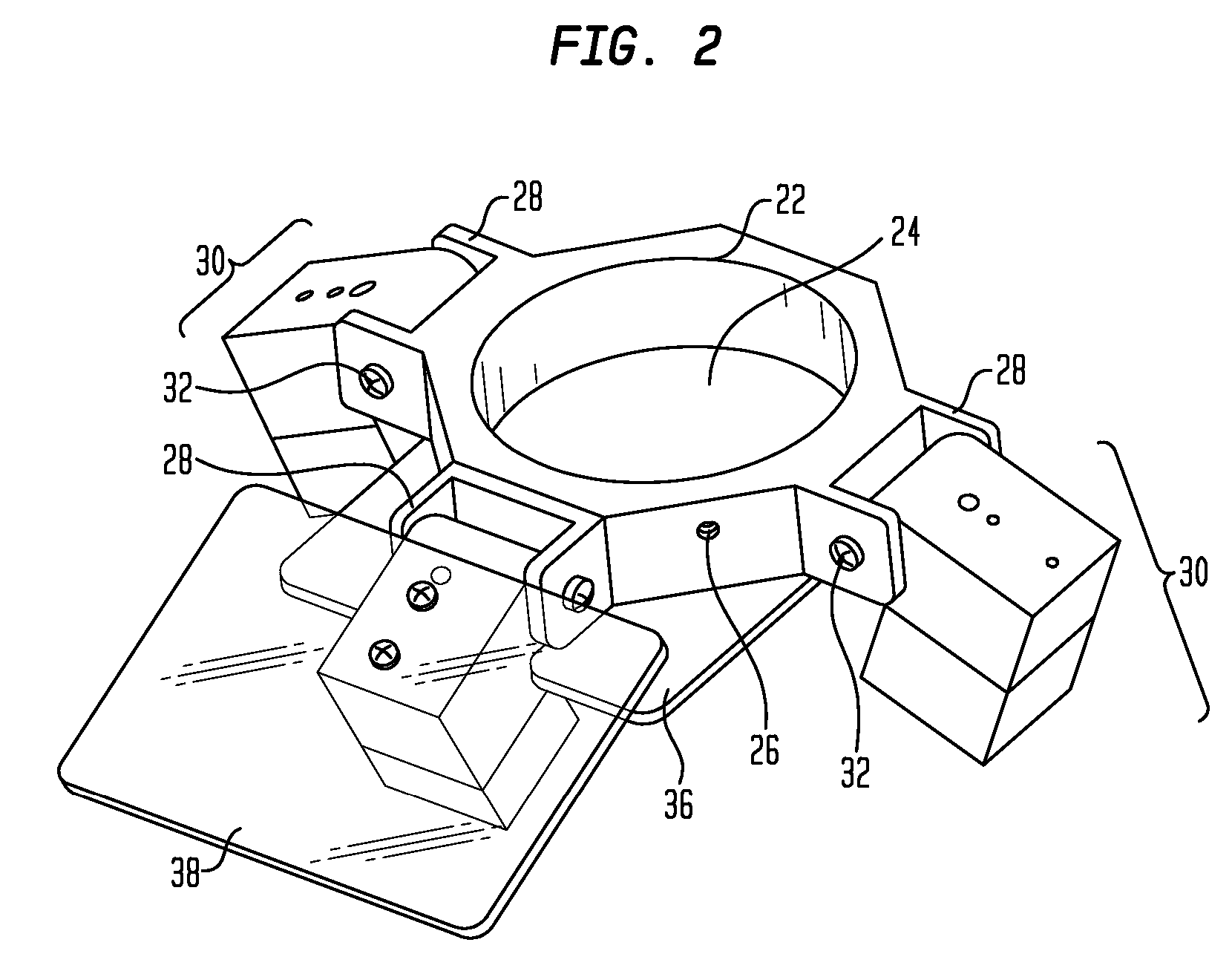
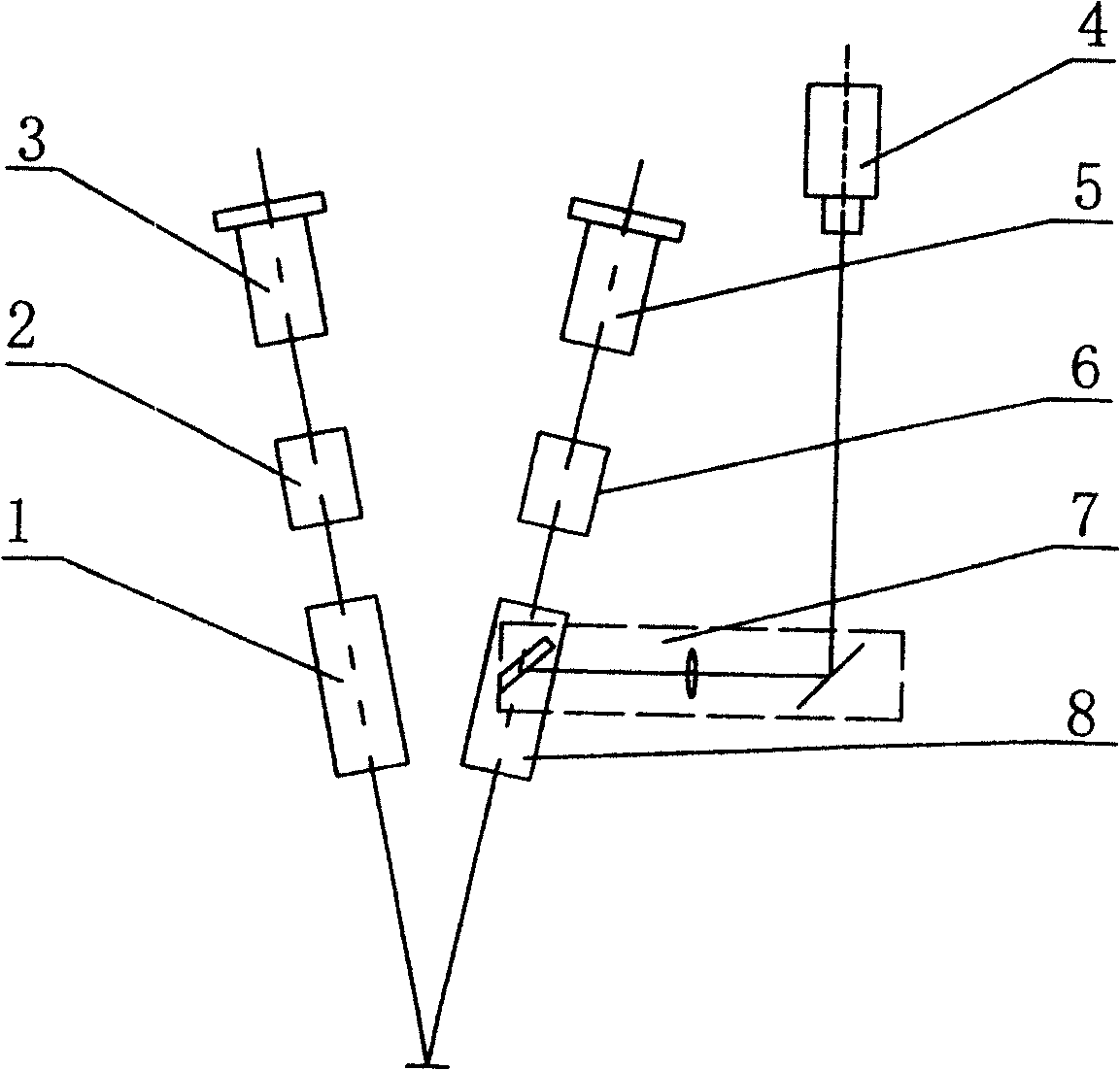
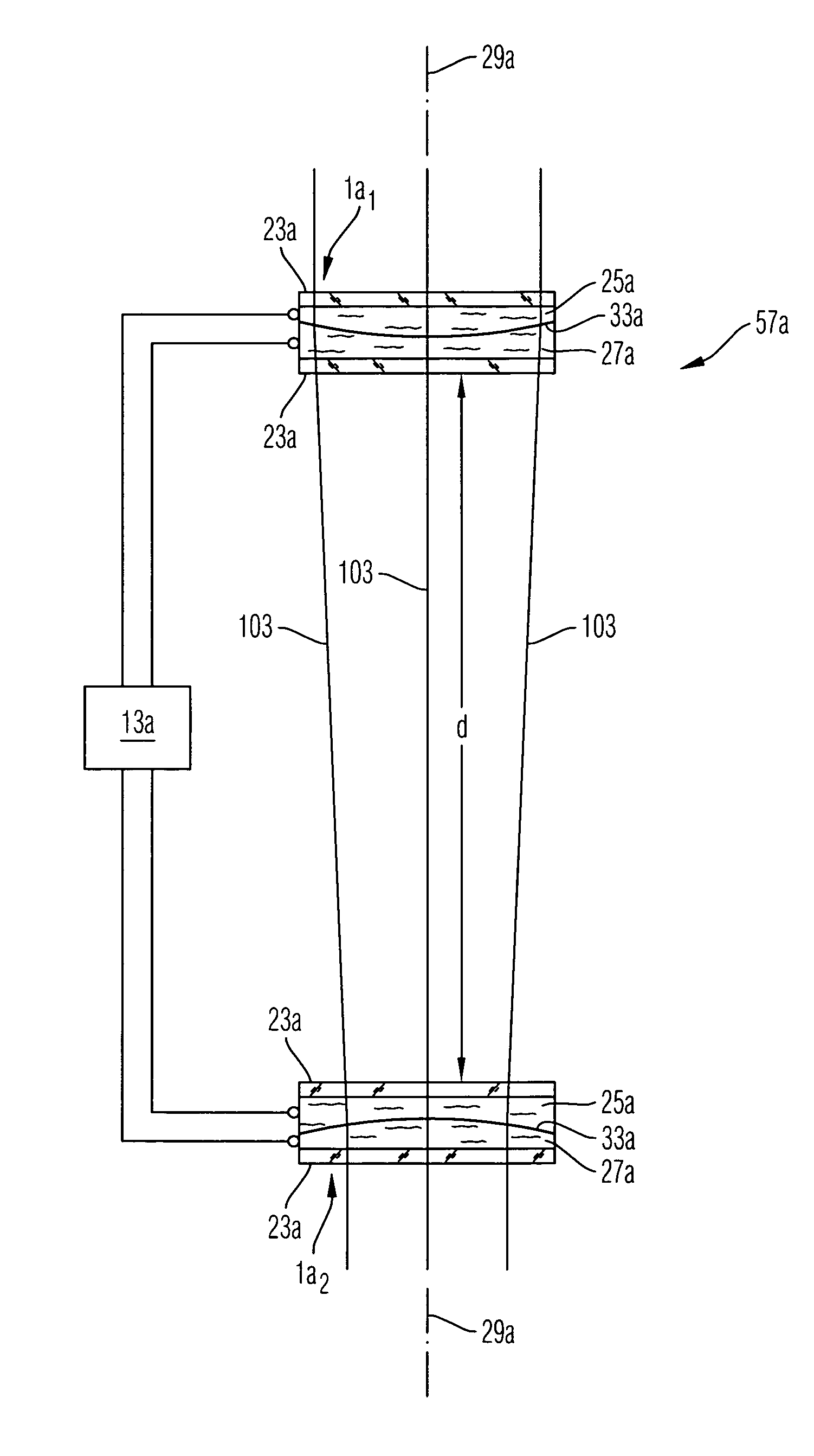
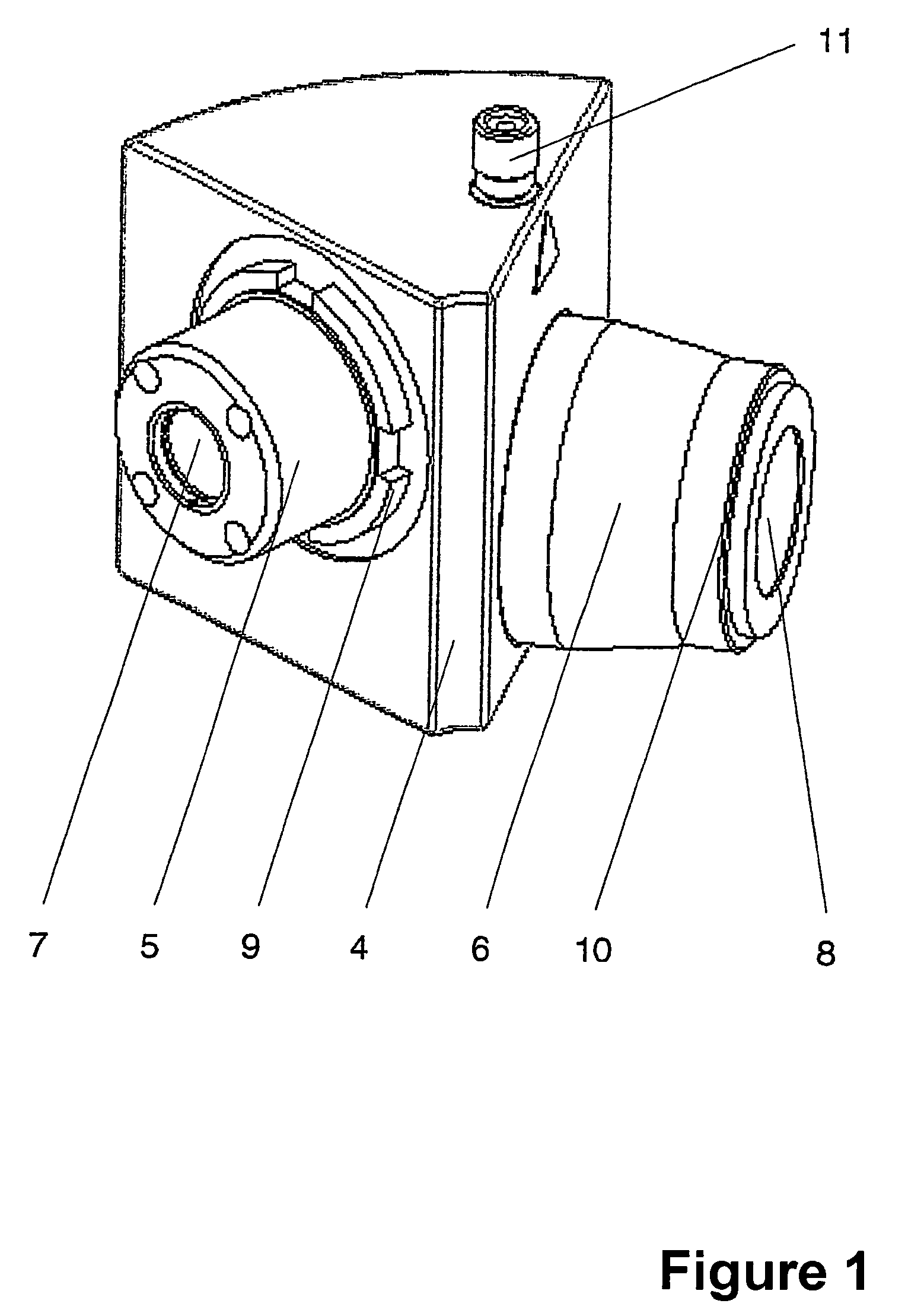
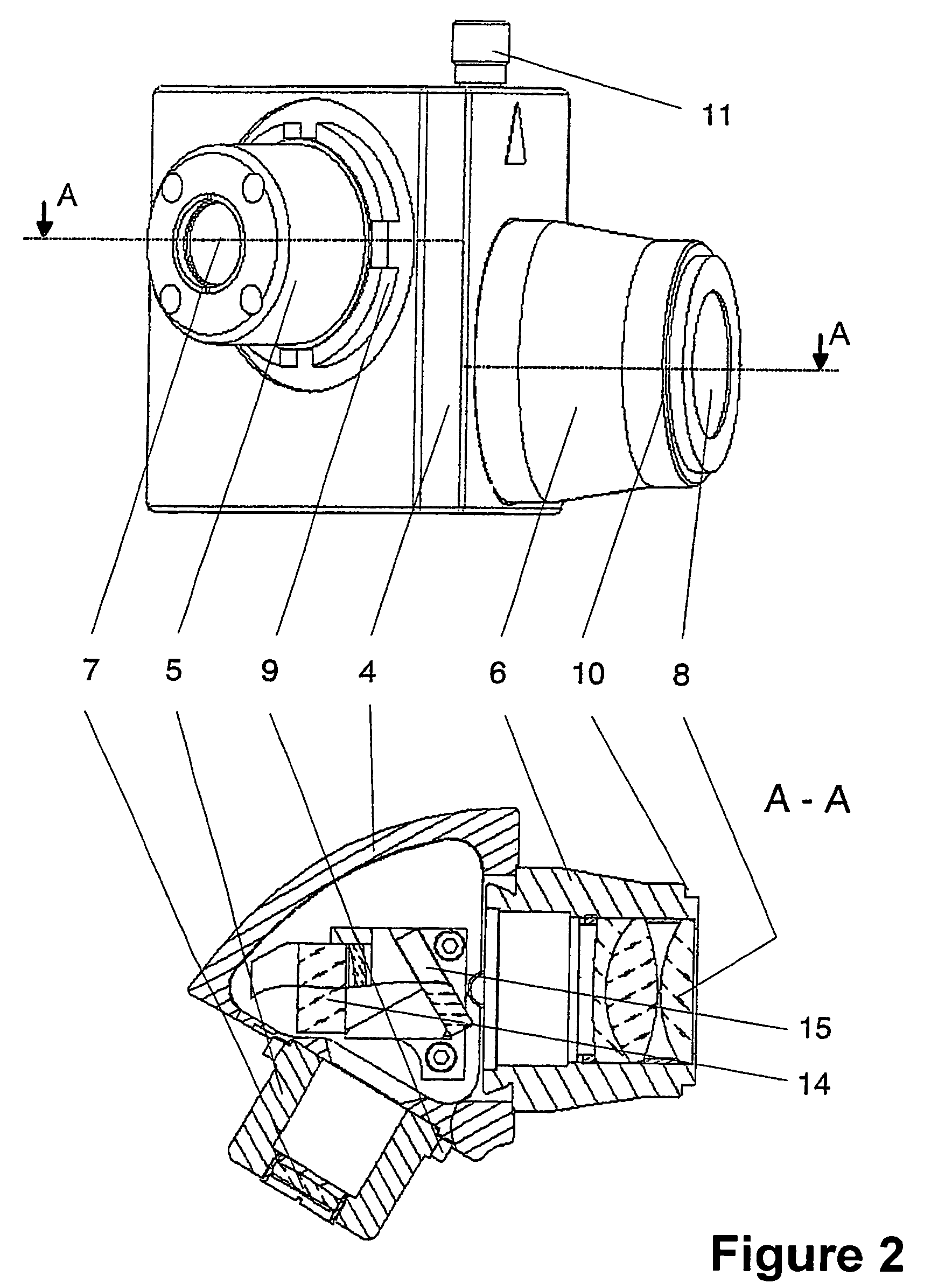
A stereomicroscope having a carrier (12) bearing a microscope body (4) displaceable obliquely relative to a displacement direction of a focus-adjusting mechanism (9). A binocular beam splitter (2a) is used to combine two stereoscopic observation beam paths (3a, 3b) into a common beam path (3c), wherein the axes of the two observation beam paths (3a, 3b) entering into the binocular beam splitter (2a) and the axis of the beam path (3c) emerging from the binocular beam splitter (2a) are parallel to each other, and the axis of the emerging beam path (3c) is disposed at displacement (Vs) from a symmetry axis of the two entering observation beam paths (3a, 3b). Displacement of the carrier being able to compensate for displacement (Vs). A switching device (5) is provided that can be activated to bring lenses (6, 7) over an object (8) parfocally and parcentrically.
Owner:LEICA INSTR SINGAPORE PTE
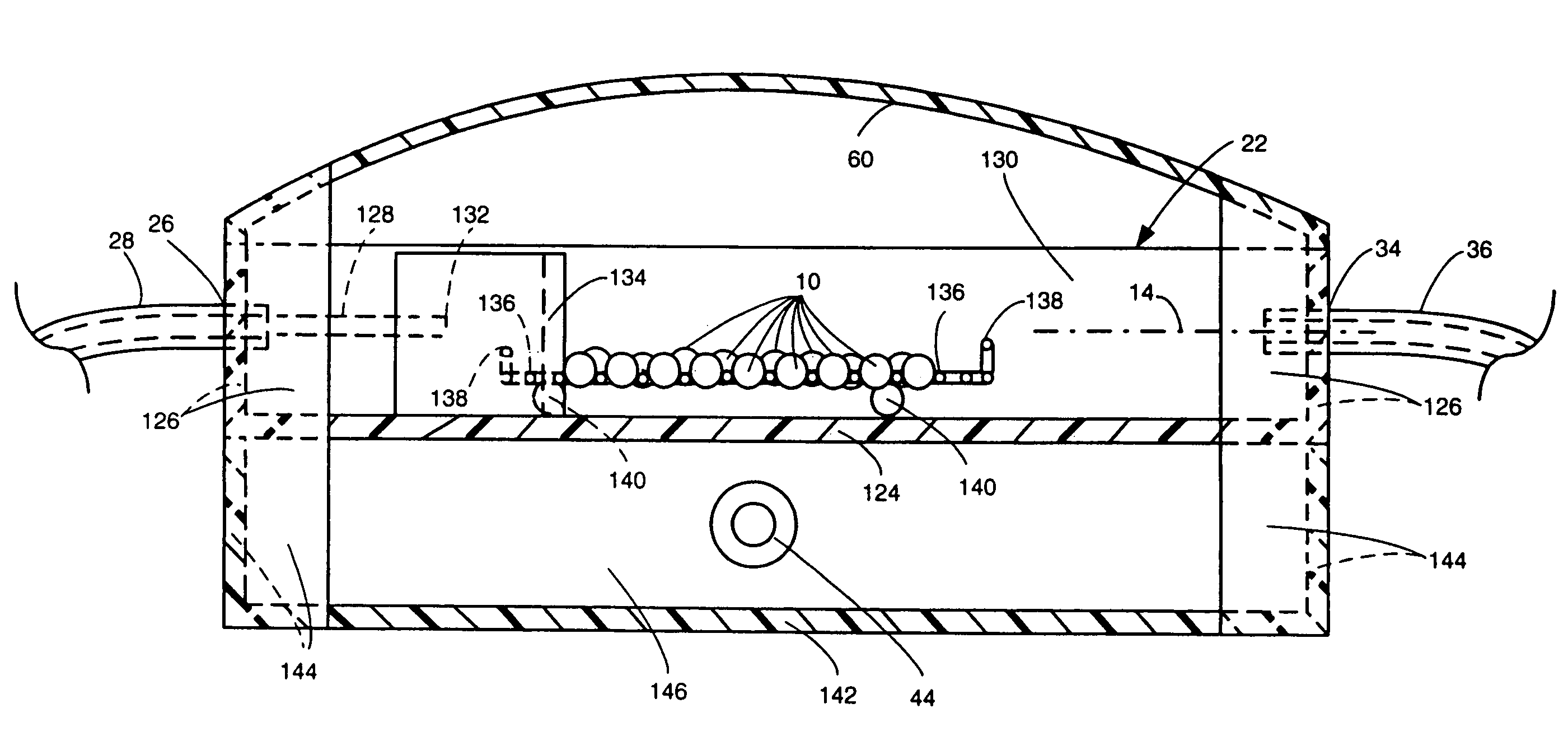
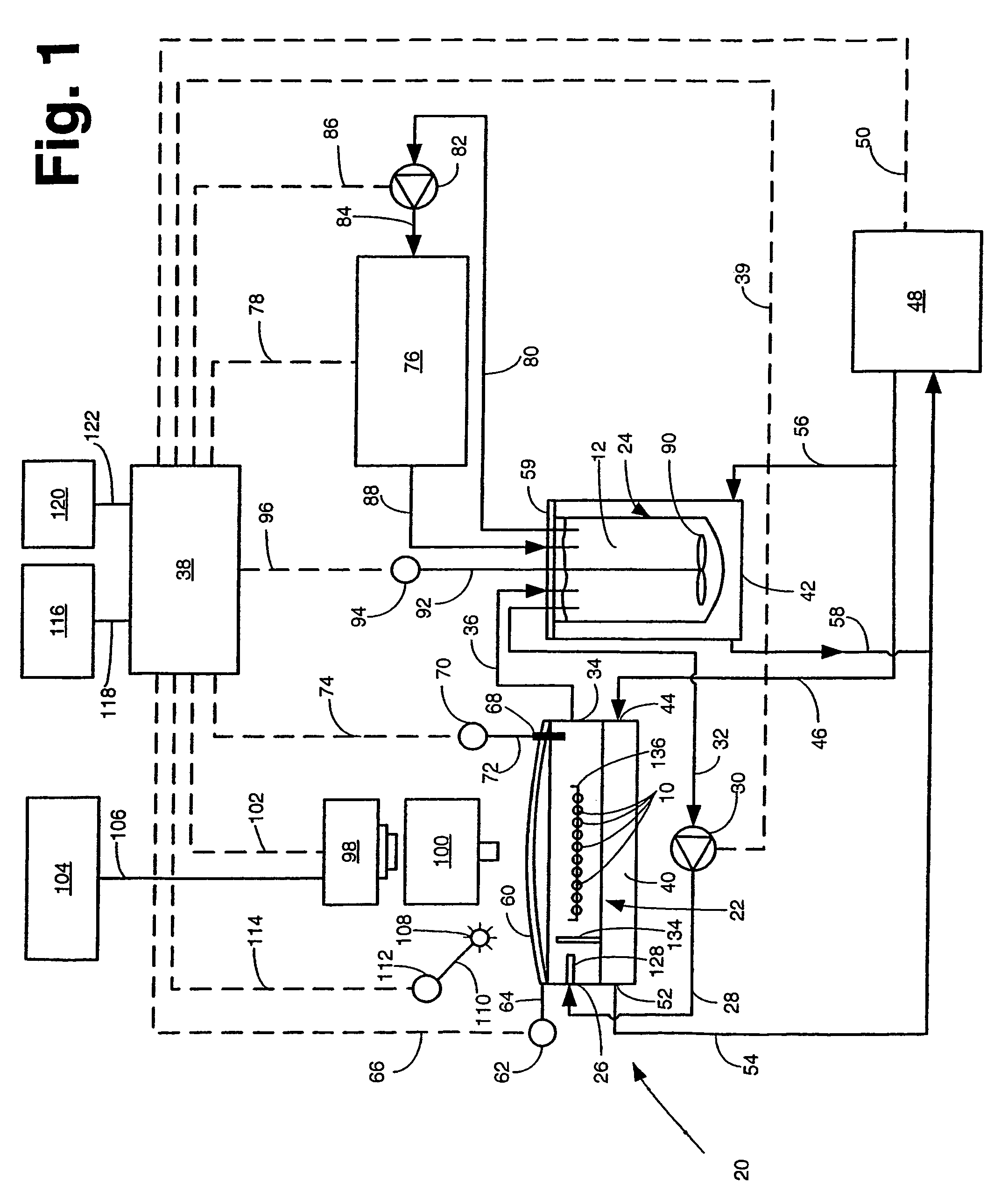
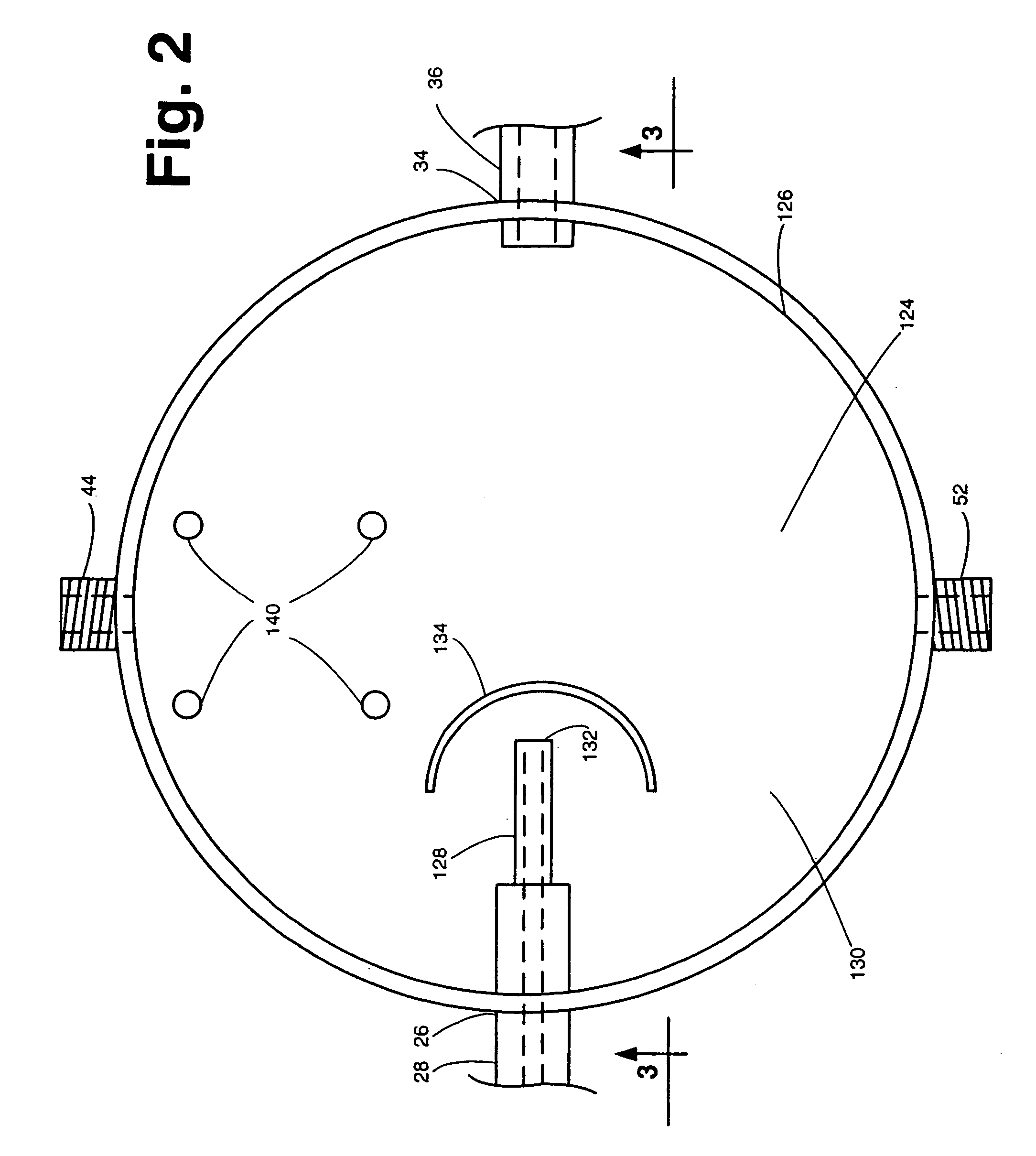
Apparatus and method for concurrently monitoring active release and physical appearance of solid dosage form pharmaceuticals
InactiveUS20050003550A1Quality improvementAvoid displacementComponent separationMaterial analysis by optical meansVideo monitoringCompound (substance)
An apparatus and method for monitoring the dissolution properties of a solid dosage form pharmaceutical or other material. The apparatus includes a hollow dissolution chamber for supporting the dosage form and subjecting it to a dissolution liquid so that the dosage form dissolves in the liquid. A dissolution liquid analyzing device (e.g., a spectrophotometer) analyzes the properties of the dissolution liquid as the dosage form dissolves. A video monitoring means (e.g., a stereo-microscope and video camera) provides a series of images of the dosage form as it dissolves. The series of images and data resulting from the analysis are recorded and correlated. The temperature, flow rate and chemical parameters of the dissolution liquid can be controlled (e.g., held constant or altered), if desired.
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
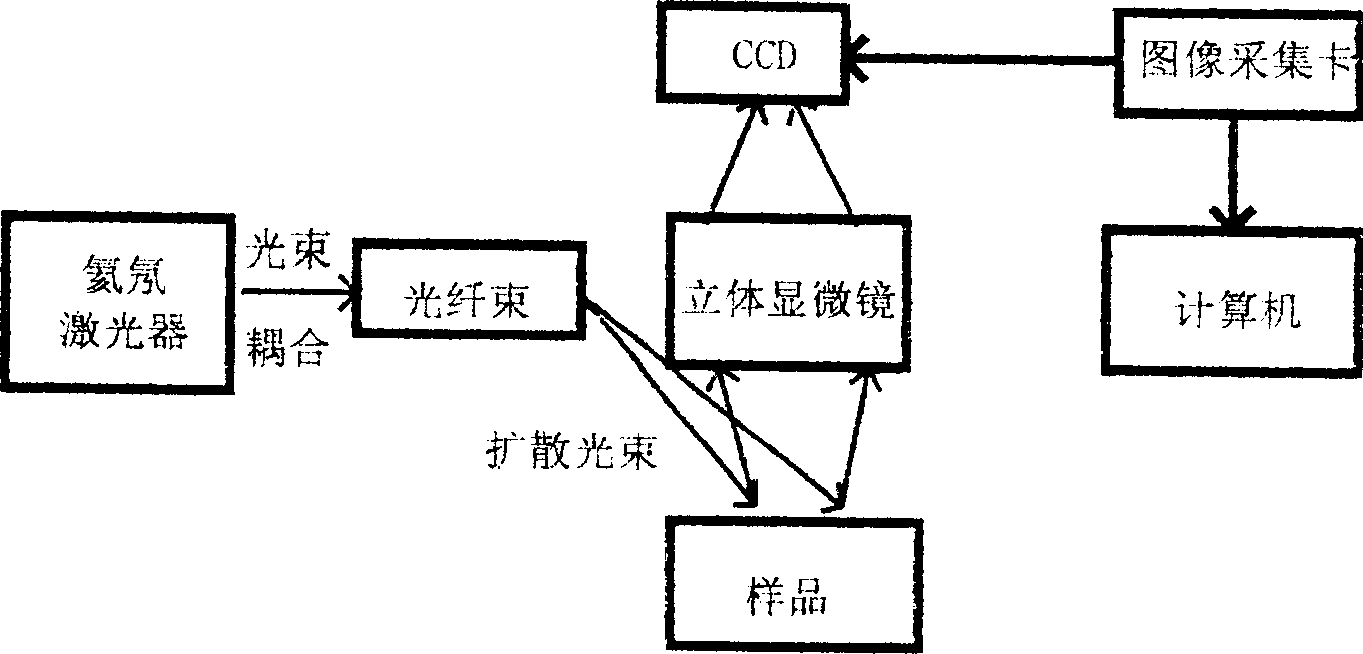
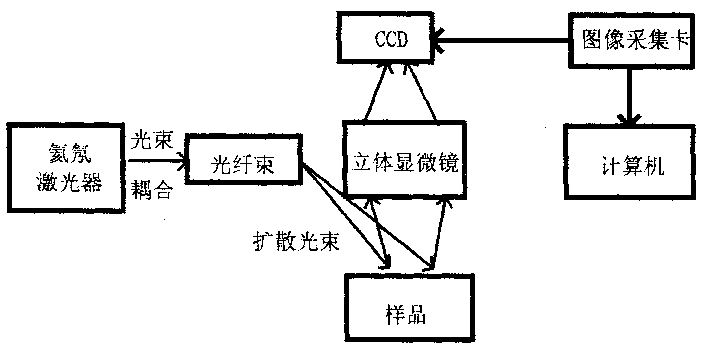
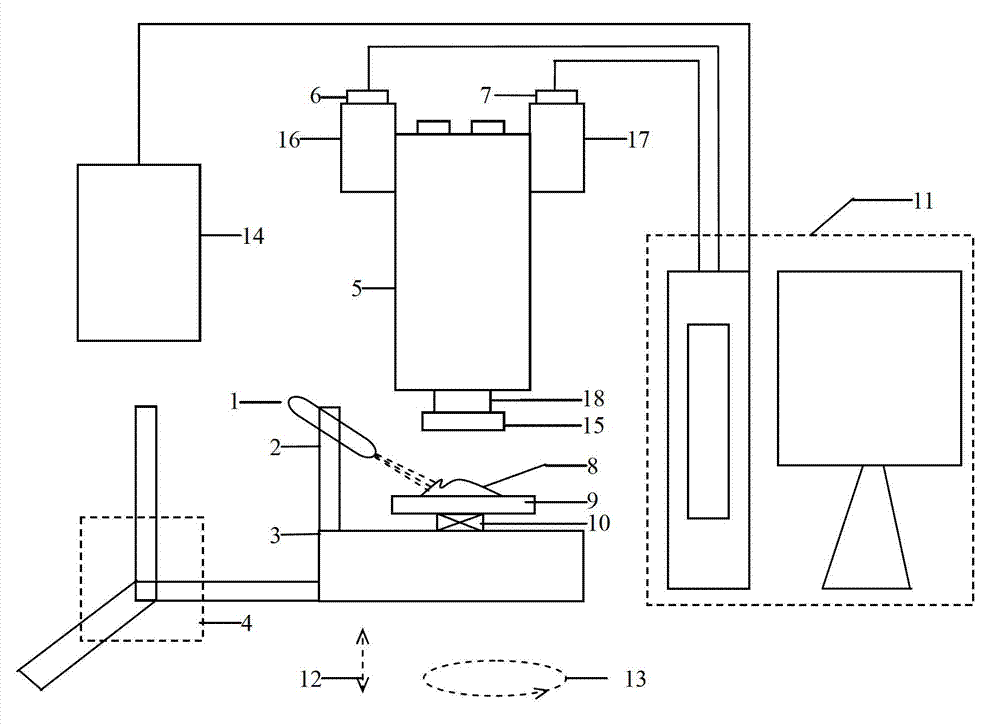
Method for monitoring micro circulation blood flow time-space response characteristic on mesentery by using laser speckle imaging instrument
InactiveCN1391869AMonitor blood flow velocitySimple structureMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterCcd cameraStereo microscope
The equipment for monitoring micro circulation body flow time-space response characteristic on mesentery includes an optical path and an imaging system. In the optial path, the laser bean from helium neon laser is coupled to fiber bundle to form homogeneous diffused beam; and the imaging system consists of stereo microscope with CCD camera, image collecting card with image collecting and controlling software. The CCD signal is output to the image collecting card connected to PC, the collection parameters are set via the image collecting and controlling software and local blood flow information are obtained with the image signal and via the signal analysis software. The equipment provides one new way to the research of influence of medicine and other stimulation to the micro circulation blood flow on mesentery.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Incident light fluorescence stereo microscope
InactiveUS20050111090A1High illumination apertureIncrease valueDiffraction gratingsMicroscopesFluorescenceLight beam
The invention is directed to a stereo microscope which is suitable particularly for observing fluorescence with incident light. Particularly advantageous fluorescence excitation is achieved when the illumination beam path has a zoom system by which an illumination is achieved that is adapted to the zoom factor of the observation beam path.
Owner:CARL ZEISS JENA GMBH
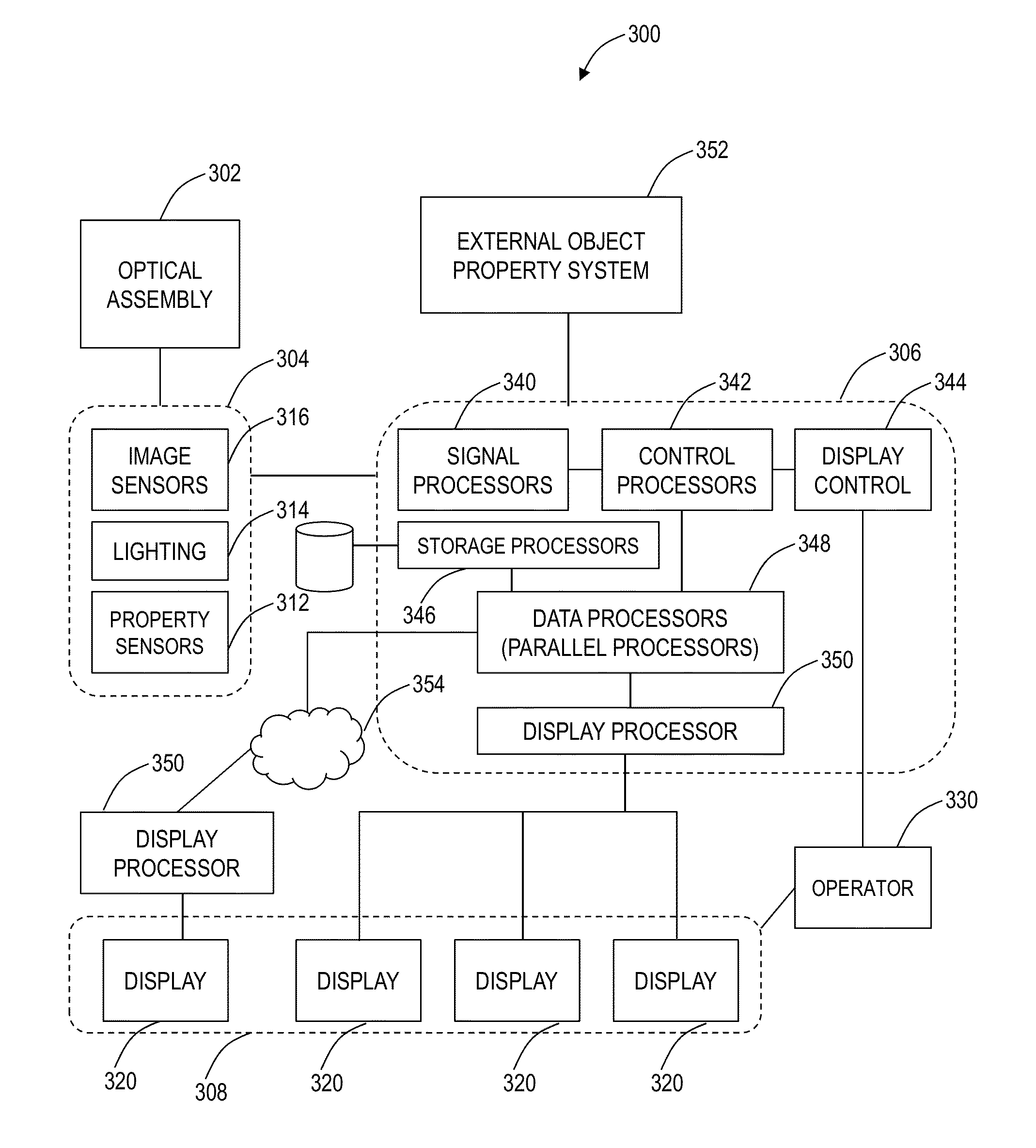
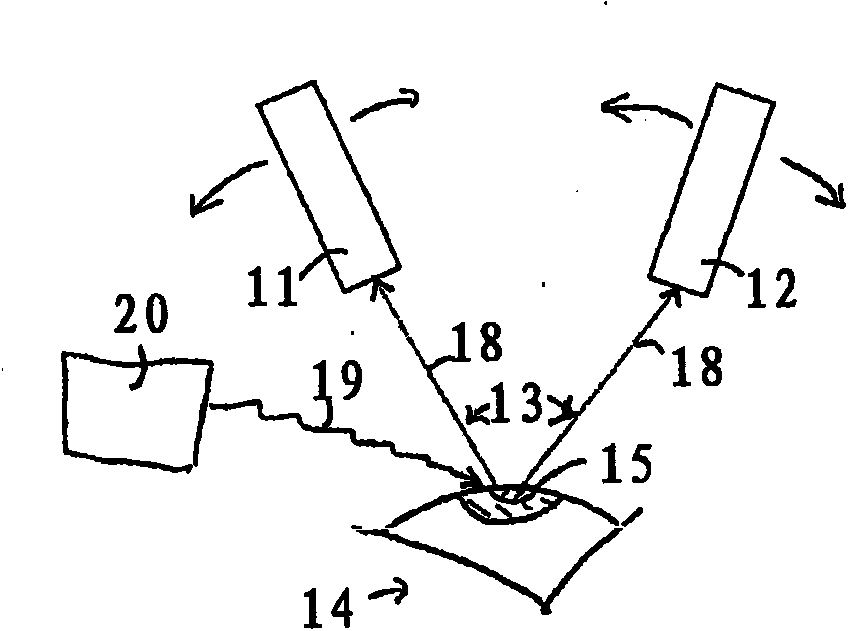
Virtual microscope system for monitoring the progress of corneal ablative surgery and associated methods
A system for visualizing an eye of a patient during corneal surgery includes a processor and a first and second camera in signal communication with the processor. The cameras are positionable for focusing on a cornea positioned for surgery. A first and a second display and optics therefor are in signal communication with the processor and are positionable for viewing through a first and a second eyepiece of a stereo microscope, respectively. Software is resident on the processor for receiving a first and second corneal image from the first and second cameras, for processing the received first and second images for display, and for transmitting the processed first and second images to the first and the second displays, respectively, via the display optics. The displays can then be viewed by a surgeon through the microscope at least during the surgery.
Owner:ALCON INC
Fluorescence illumination method and apparatus for stereomicroscopes
The invention provides a fluorescence illumination adapter capable of being fitted to a wide range of existing stereomicroscopes. The fluorescence illumination adapter attaches to the stereomicroscope barrel that contains the imaging optics, and has high intensity light-emitting diodes that stimulate fluorescence in a specimen. A removable barrier filter is positioned in the optical path underneath the stereomicroscope barrel to prevent the fluorescence stimulating light entering the imaging optics. The light-emitting diodes are mounted on pivoting elements so that the location of the illumination spot on the specimen can be easily adjusted. The adapter also incorporates a white light-emitting diode source that can be used either for white-light viewing or for selective mixing with the fluorescence excitation illumination. The barrier filter is easily removed to facilitate rapid switching between fluorescence and white-light viewing.
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
Greenough-type stereomicroscope
ActiveUS20070047072A1Improved detail recognitionIncrease in convergence angleMicroscopesTelescopesLight beamMagnification
A stereomicroscope of the Greenough type includes a first monocular microscope and a second monocular microscope, which define a first beam path and a second beam path, respectively, wherein the first and second microscopes are arranged at a convergence angle to one another and comprise magnification systems for producing equal magnifications which can be varied synchronously with one another. At least one optical element in the first microscope has a different optically effective diameter compared to at least one corresponding optical element in the second microscope.
Owner:LEICA INSTR SINGAPORE PTE
Multi-visual-angle great-depth micro stereo visual-features fusion-measuring method
InactiveCN103075960ASolving Precision Measurement ProblemsOvercome mismatchUsing optical meansStereo microscopeVisual perception
The invention relates to a multi-visual-angle great-depth micro stereo visual-features fusion-measuring method, which comprises the following steps of: acquiring an original stereo-image pair through a barrel-type node structure by using a compound stereomicroscope visual system, and providing accurate matching-parallax data through the image registration and the stripe registration at different node positions on the same depth surface, the fusion of original composite-image sequences on different depth surfaces and the local matching of original images, so that high-precision three-dimensional figures can be reconstructed. The method can be used for solving the problems of sheltering in micro stereo measurement and precise visual measurement of large-scale microscopic objects, and technical bottlenecks existing in an existing stereomicroscope visual-measuring method are essentially overcome.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Mending hair damage with polyelectrolyte complexes
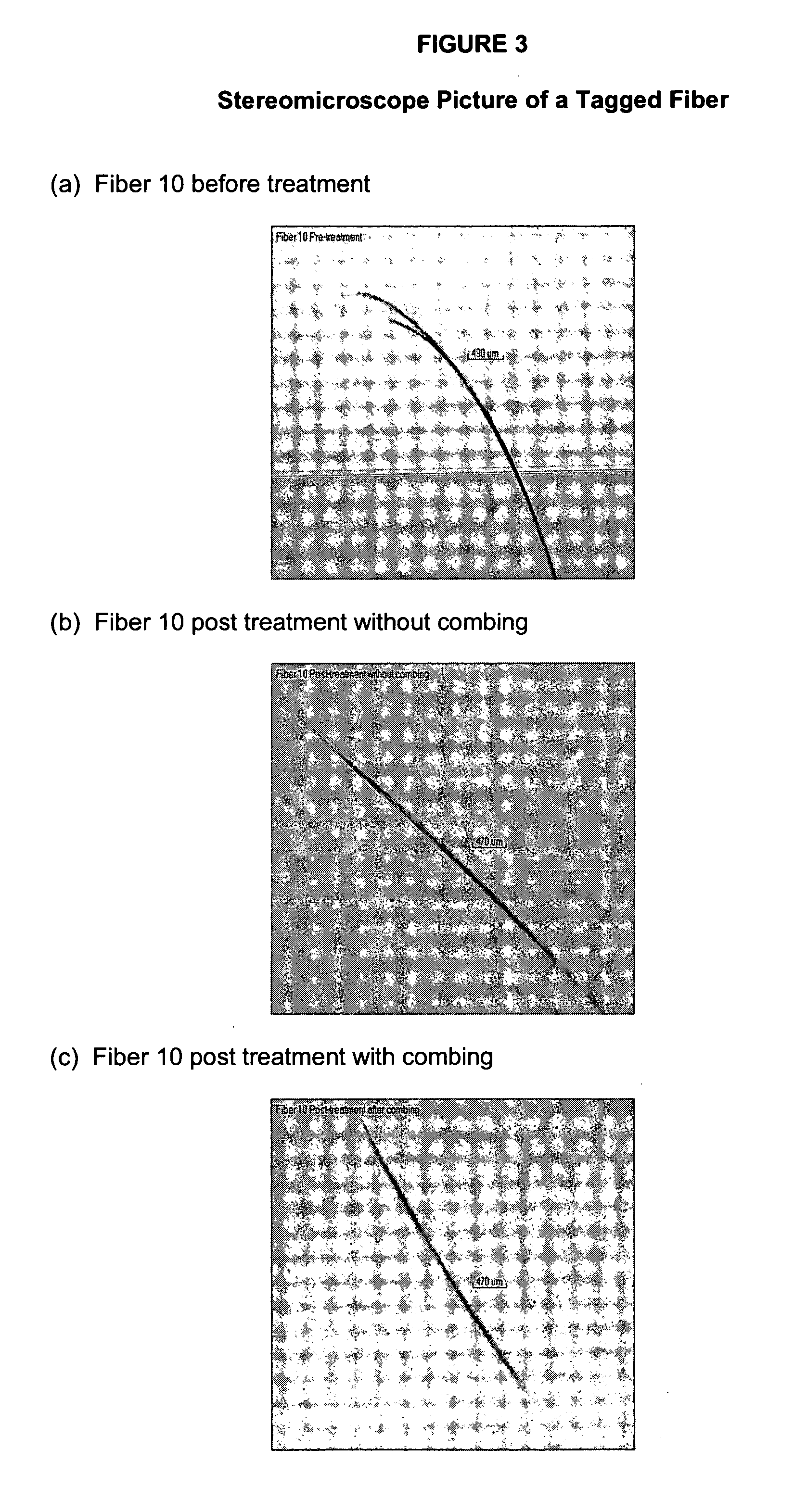
Polyelectrolyte complexes between anionic and cationic polymers are used to mend damaged hair fibers, especially damage exhibited by split ends. An improved test method designed for the assessment of the degree of split end repair is described which consists of tagging hair fibers and observing the repair process by stereomicroscopy.
Owner:ISP INVESTMENTS INC
Virtual Microscope System for Monitoring the Progress of Corneal Ablative Surgery and Associated Methods
A system for visualizing an eye of a patient during corneal surgery includes a processor and a first and second camera in signal communication with the processor. The cameras are positionable for focusing on a cornea positioned for surgery. A first and a second display and optics therefor are in signal communication with the processor and are positionable for viewing through a first and a second eyepiece of a stereo microscope, respectively. Software is resident on the processor for receiving a first and second corneal image from the first and second cameras, for processing the received first and second images for display, and for transmitting the processed first and second images to the first and the second displays, respectively, via the display optics. The displays can then be viewed by a surgeon through the microscope at least during the surgery.
Owner:ALCON INC
Visual documentation of micro-cracks during tensile coupon testing
ActiveUS20060070452A1Avoid fatigue failureForce measurement by measuring optical property variationMaterial analysis by optical meansAviationDocumentation procedure
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Surgical stereo vision systems and methods for microsurgery
Surgical stereo vision systems and methods for microsurgery are described that enable hand-eye collocation, high resolution, and a large field of view. A digital stereo microscope apparatus, an operating system with a digital stereo microscope, and a method are described using a display unit located over an area of interest such that a human operator places hands, tools, or a combination thereof in the area of interest and views a magnified and augmented live stereo view of the area interest with eyes of the human operator substantially collocated with the hands of the human operator.
Owner:DIGITAL SURGICALS
Electrochemical detection method and device of integrated in chip capillary electrophoresis
InactiveCN1563972AAvoid alignment problemsGuaranteed reproducibilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCircular discFiber
The method includes following steps: using high voltage power supply dedicated to capillary in chip monitors whether separator tube and sample adding tube are unblocked; high voltage is applied to separator tube for a longer time to activate working electrode; if tubes are unblocked and electrode is activated, electrode holder is clamped on optical fiber clip matching to 3D adjuster; under stereomicroscope, front end of working electrode is put into micro tube; working electrode made from ultramicro disc carbon fiber is put inside micro tube through fine 3D adjuster. The invented device can detect electric active substance as well as non-electric active substance. Separating and detecting nonorganic as well as organic sample are realized through controlling electric potential on specific position and position of working electrode.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Microscope camera ocular glass free stereomicroscope with display
InactiveCN101266333AExpand the scope of activitiesEasy for fine processingMicroscopesDisplay devicePrism
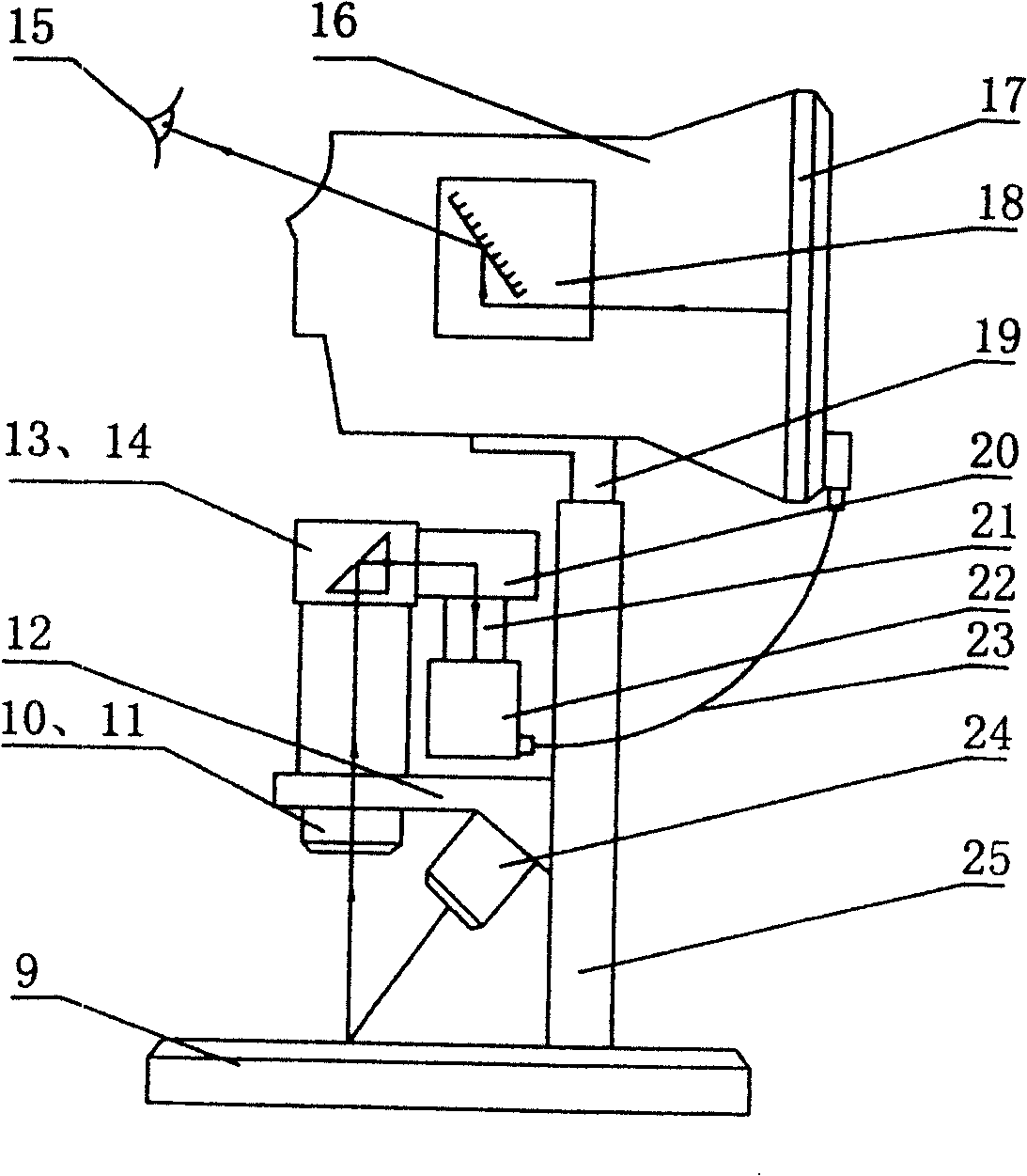
A stereomicroscope without eyepiece with display using microscope camera belongs to a photoelectric instrument technical field. The invention provides a stereomicroscope without eyepiece with display using microscope camera. The stereomicroscope without eyepiece with display using microscope camera comprises a platform, a left and right light path system, a split-image prism group, a pick-up head, an overviewing and displaying device and the like. The object planes of the left and right object lens are on the platform and the micro object is amplified by the left and right object lens and imaged by the split-image prism group and then the image is picked up by the pick-up head and the amplified stereo image is seen by the human eyes by overviewing the display and reflecting by the turning lens. When the eyes relief of the operating state of close clinging to the eye lens and visual sense being high tired, therefore the eyes have a wider motion range.
Owner:张吉鹏
Surgical stereo vision systems and methods for microsurgery
Surgical stereo vision systems and methods for microsurgery are described that enable hand-eye collocation, high resolution, and a large field of view. A digital stereo microscope apparatus, an operating system with a digital stereo microscope, and a method are described using a display unit located over an area of interest such that a human operator places hands, tools, or a combination thereof in the area of interest and views a magnified and augmented live stereo view of the area interest with eyes of the human operator substantially collocated with the hands of the human operator.
Owner:DIGITAL SURGICALS
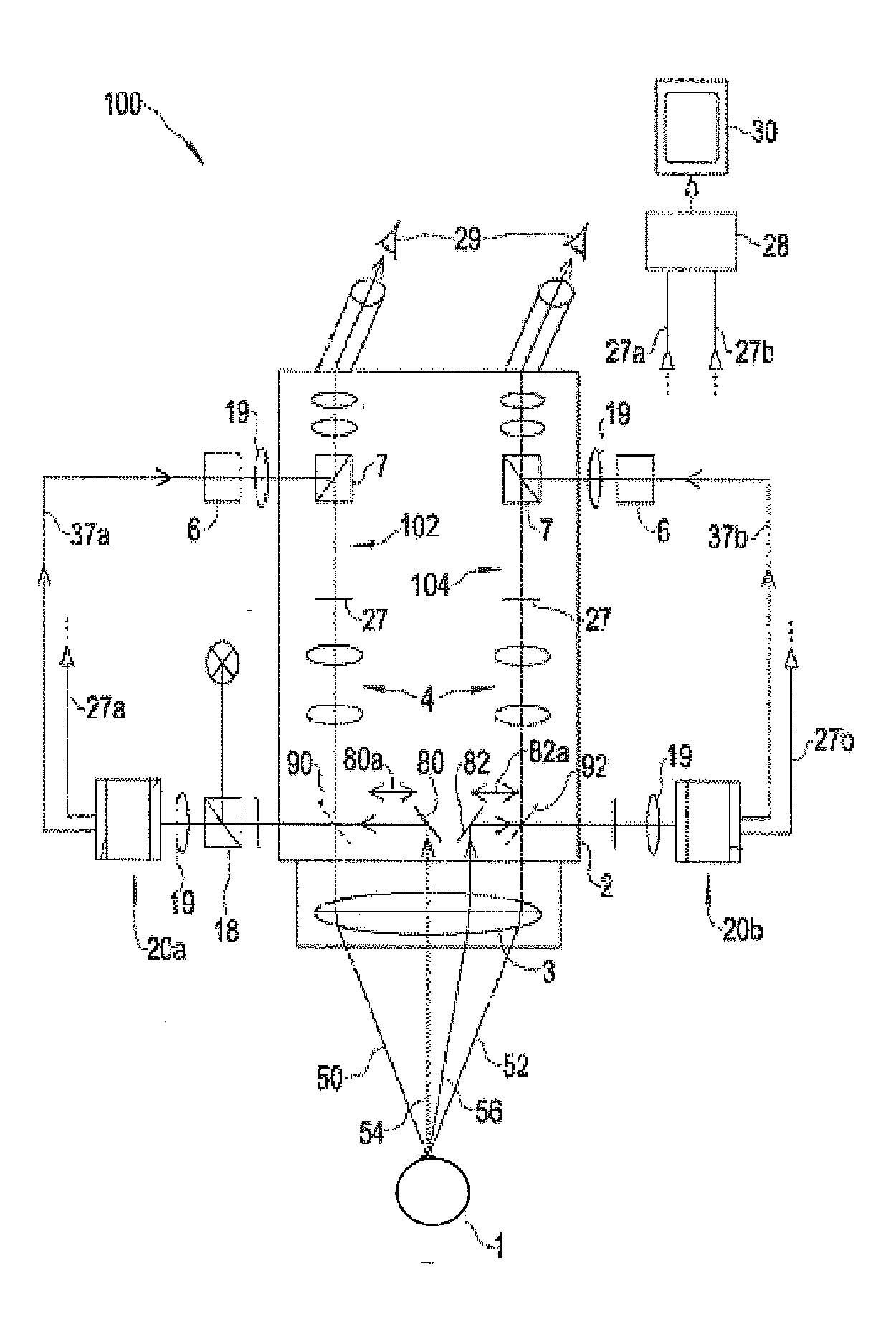
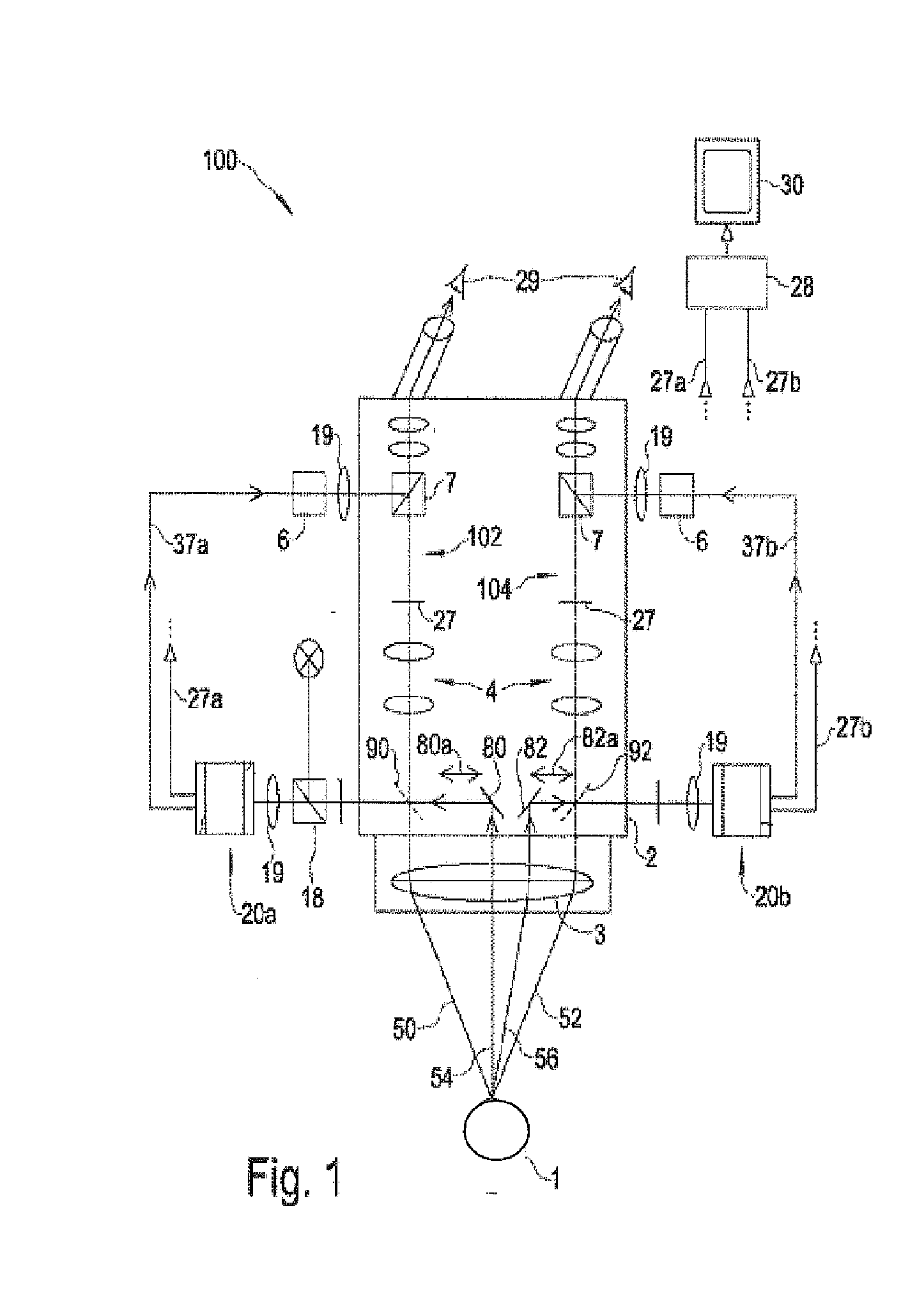
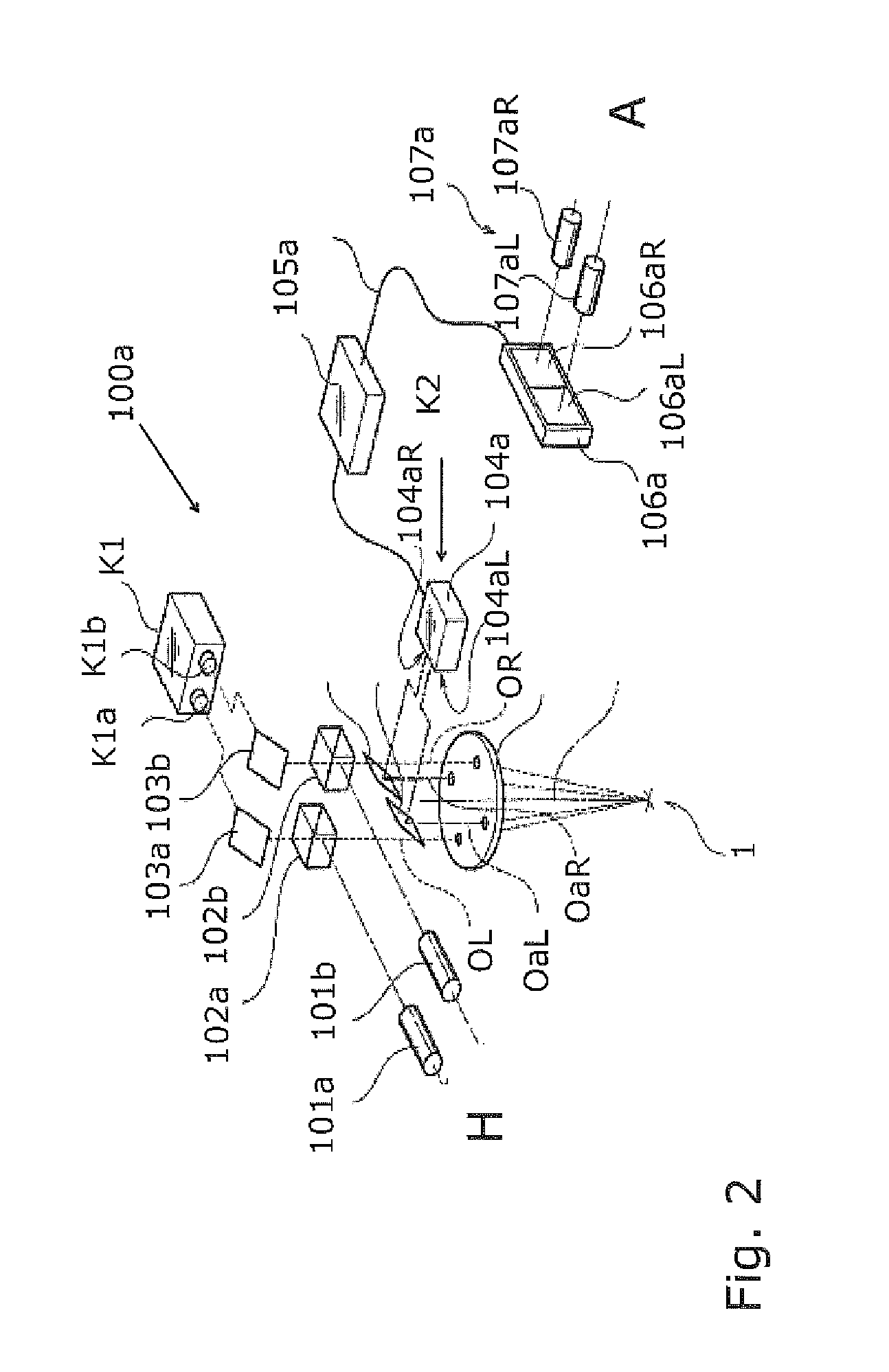
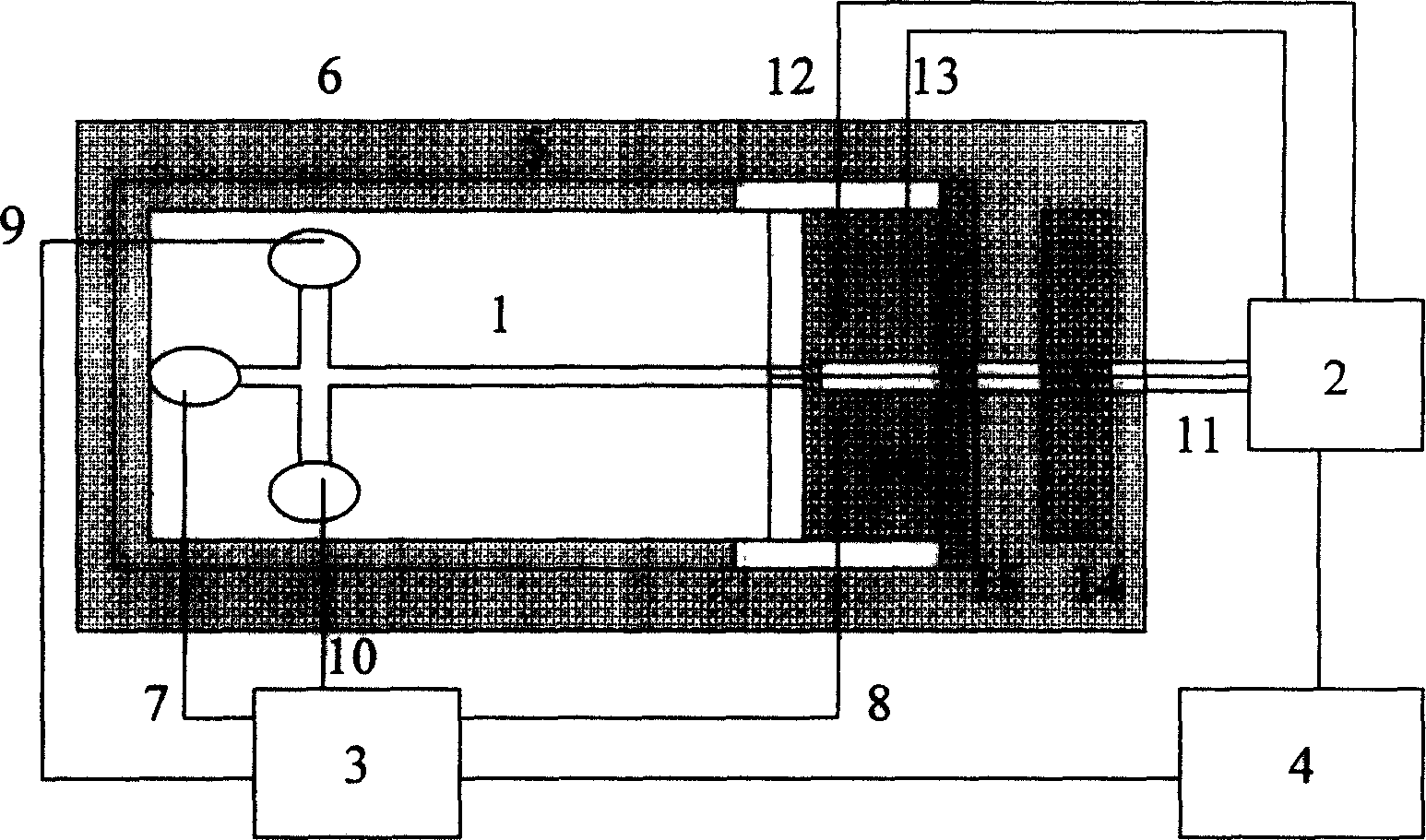
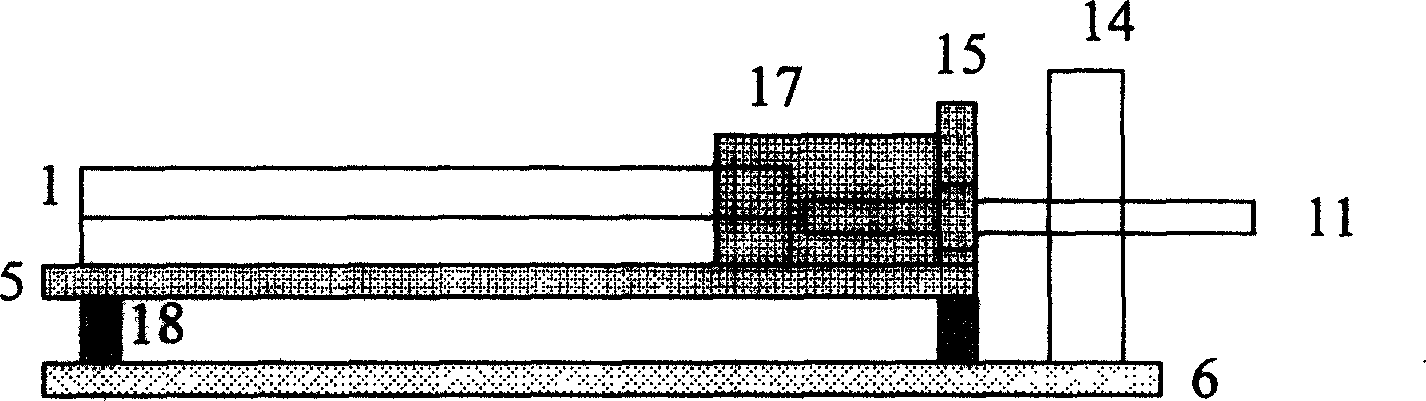
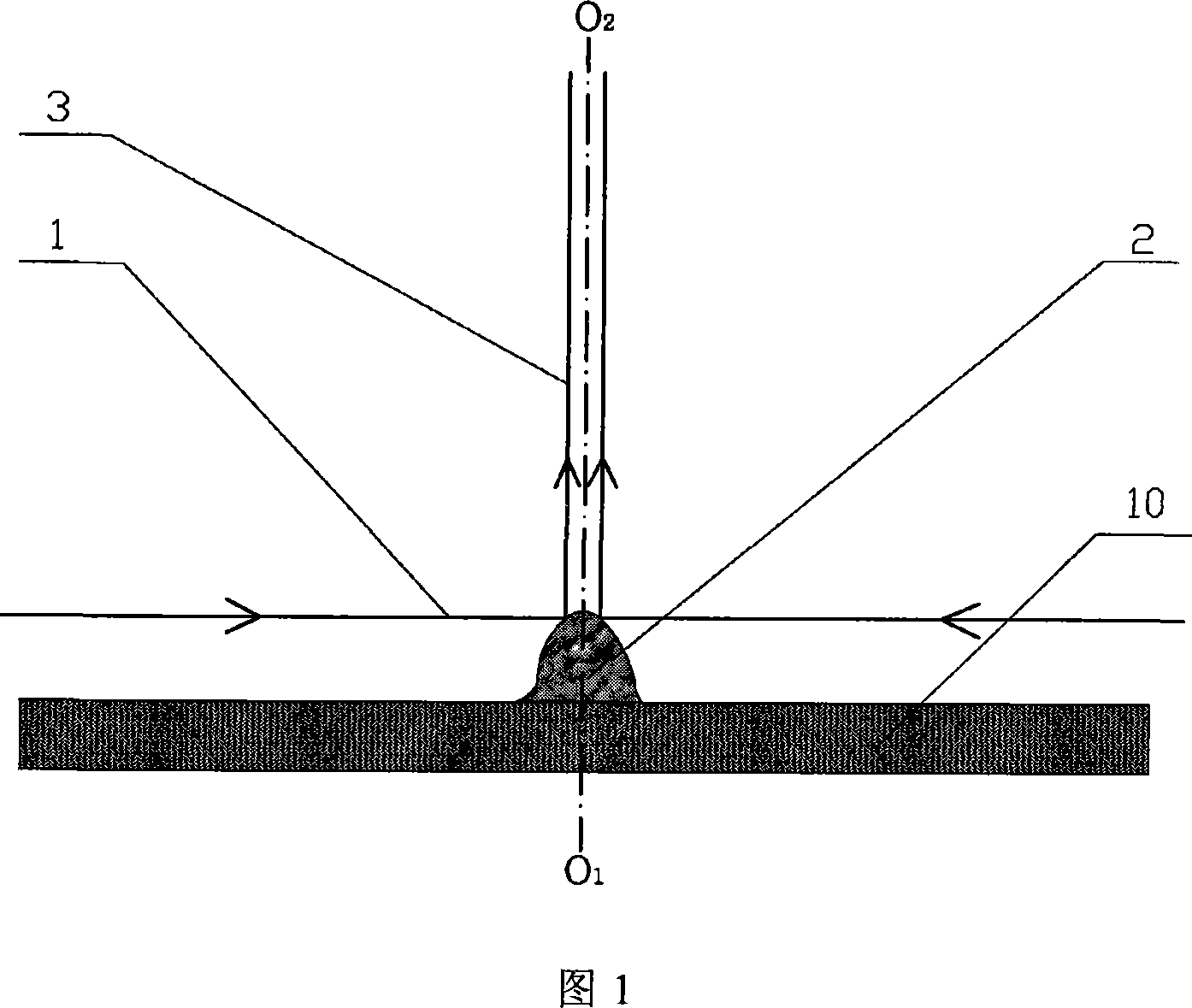
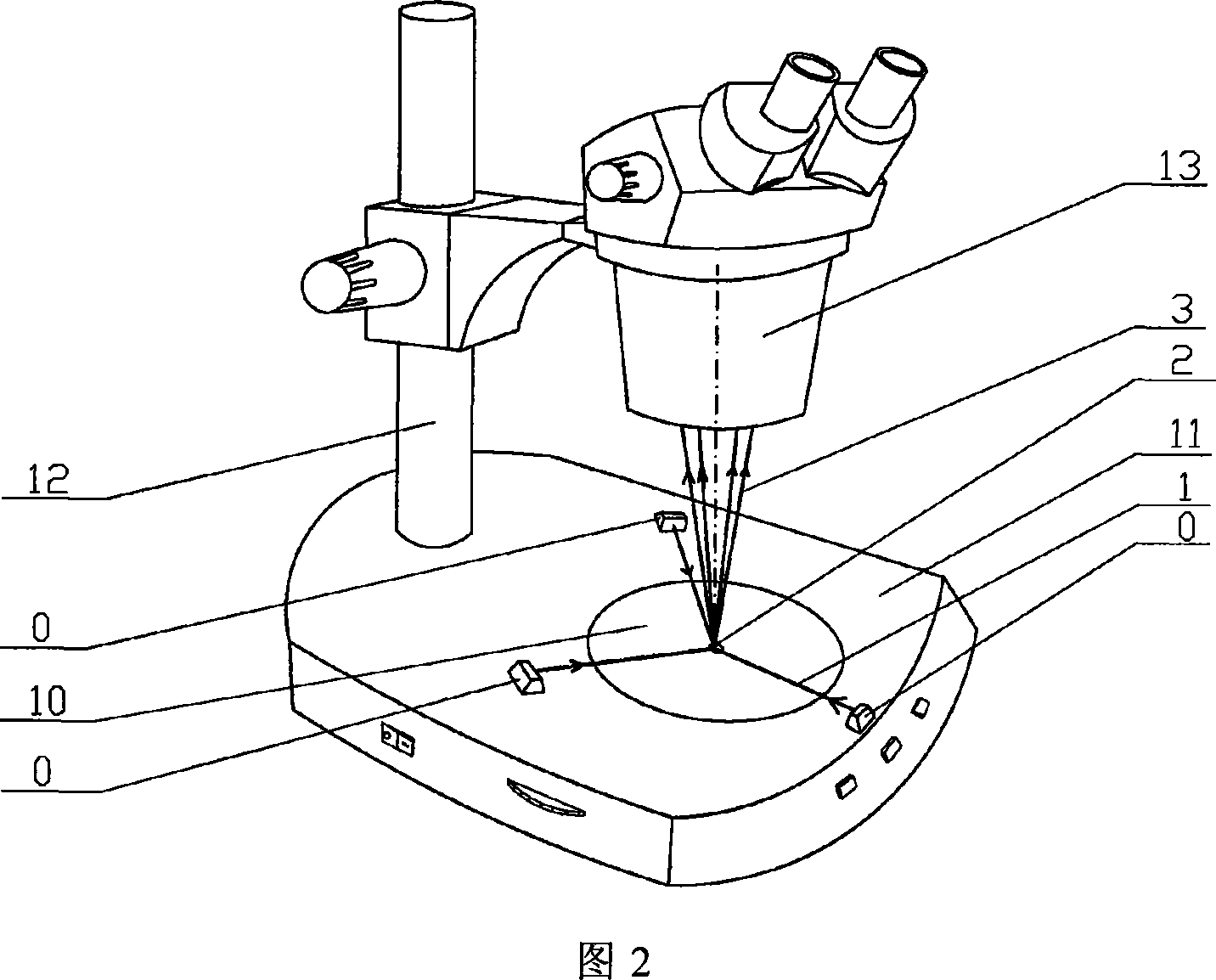
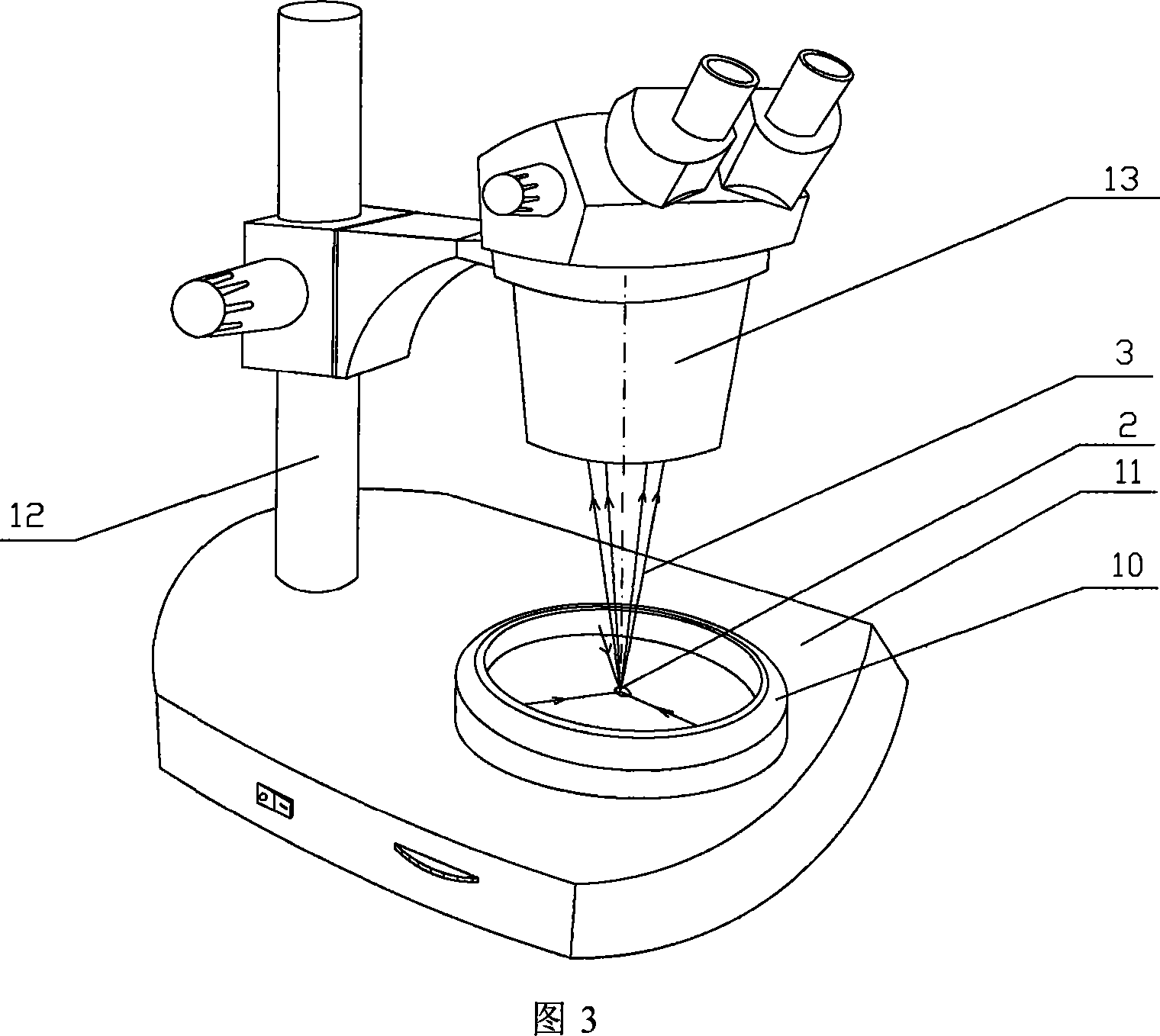
Stereomicroscope side-irradiation type lighting method and its dark view stereomicroscope
The invention relates to a stereomicroscope side lighting method and the dark-field stereomicroscope thereof. The method uses the beam emitted from the light source to lighting the observed sample from the side of the stereomicroscope stage, and the beam is satisfied the following characteristic: firstly,the beam and the observed sample are in a same plane spatial limit, secondly, the included angle between the beam and the symmetrical line O1O2 of the two object lens primary optic axis of the stereomicroscope is 80 to 100 degrees. The design consideration of the dark-field stereomicroscope which is an improvement for the traditional stereomicroscope, is enable the last light part directly emitted from the light source or through the optical instrument to change the direction to horizontally locate the observed sample stage, so that the symmetrical line O1O2 of the stage and the two object lens primary optic axis is arranged vertically. By using the method and the dark-field stereomicroscope thereof can effectively lighten the interference of the background light, greatly improve the contrast and the signal to noise ratio of the observed sample, especially fit for the liquid phase dissection observation.
Owner:TONGJI HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI TECH
Virtual microscope system for monitoring the progress of corneal ablative surgery and associated methods
A system for visualizing an eye of a patient during corneal surgery includes a processor and a first and second camera in signal communication with the processor. The cameras are positionable for focusing on a cornea positioned for surgery. A first and a second display and optics therefor are in signal communication with the processor and are positionable for viewing through a first and a second eyepiece of a stereo microscope, respectively. Software is resident on the processor for receiving a first and second corneal image from the first and second cameras, for processing the received first and second images for display, and for transmitting the processed first and second images to the first and the second displays, respectively, via the display optics. The displays can then be viewed by a surgeon through the microscope at least during the surgery.
Owner:ALCON REFRACTIVEHORIZONS
Imaging optics with adjustable optical power and method of adjusting an optical power of an optics
InactiveUS7411739B2Simplified zoom systemsChange intensityMicroscopesNon-linear opticsOptical powerStereo microscope
Owner:OBREBSKI ANDREAS
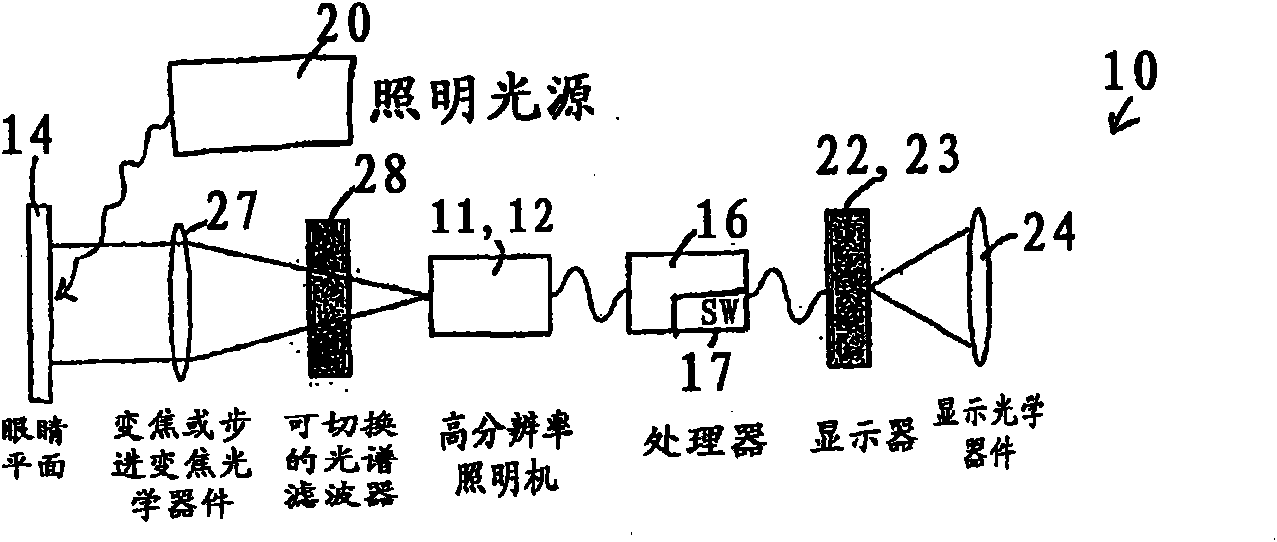
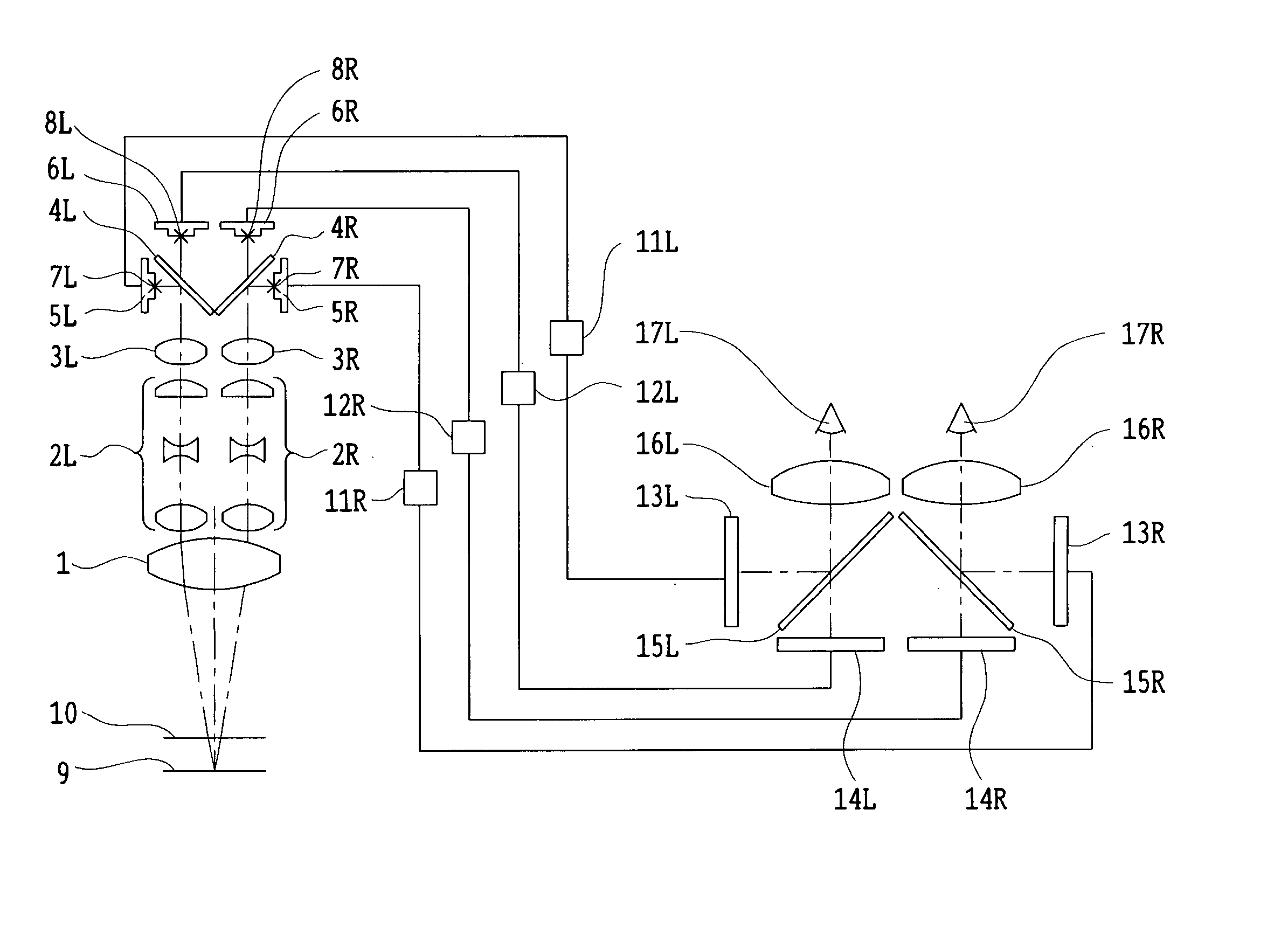
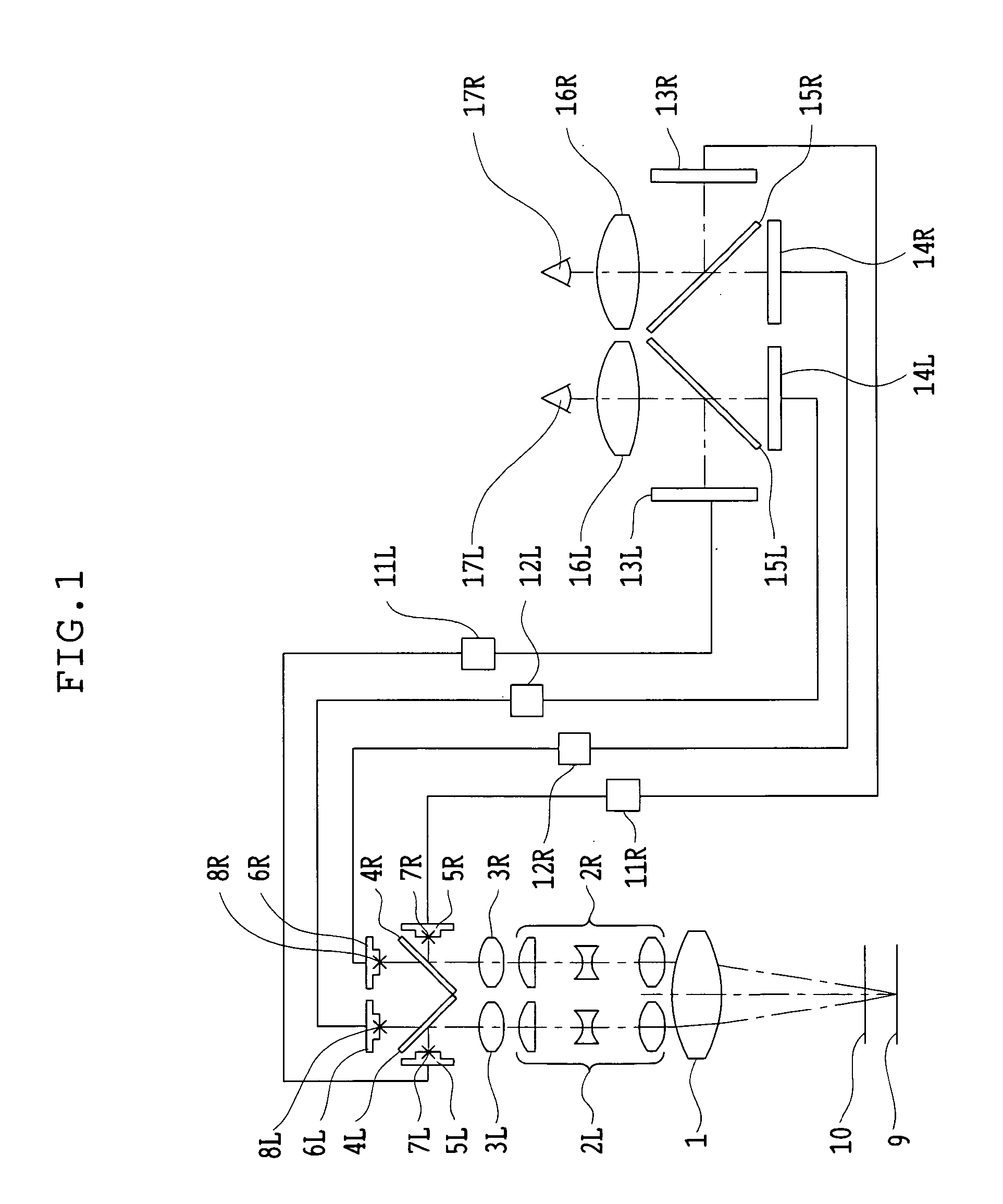
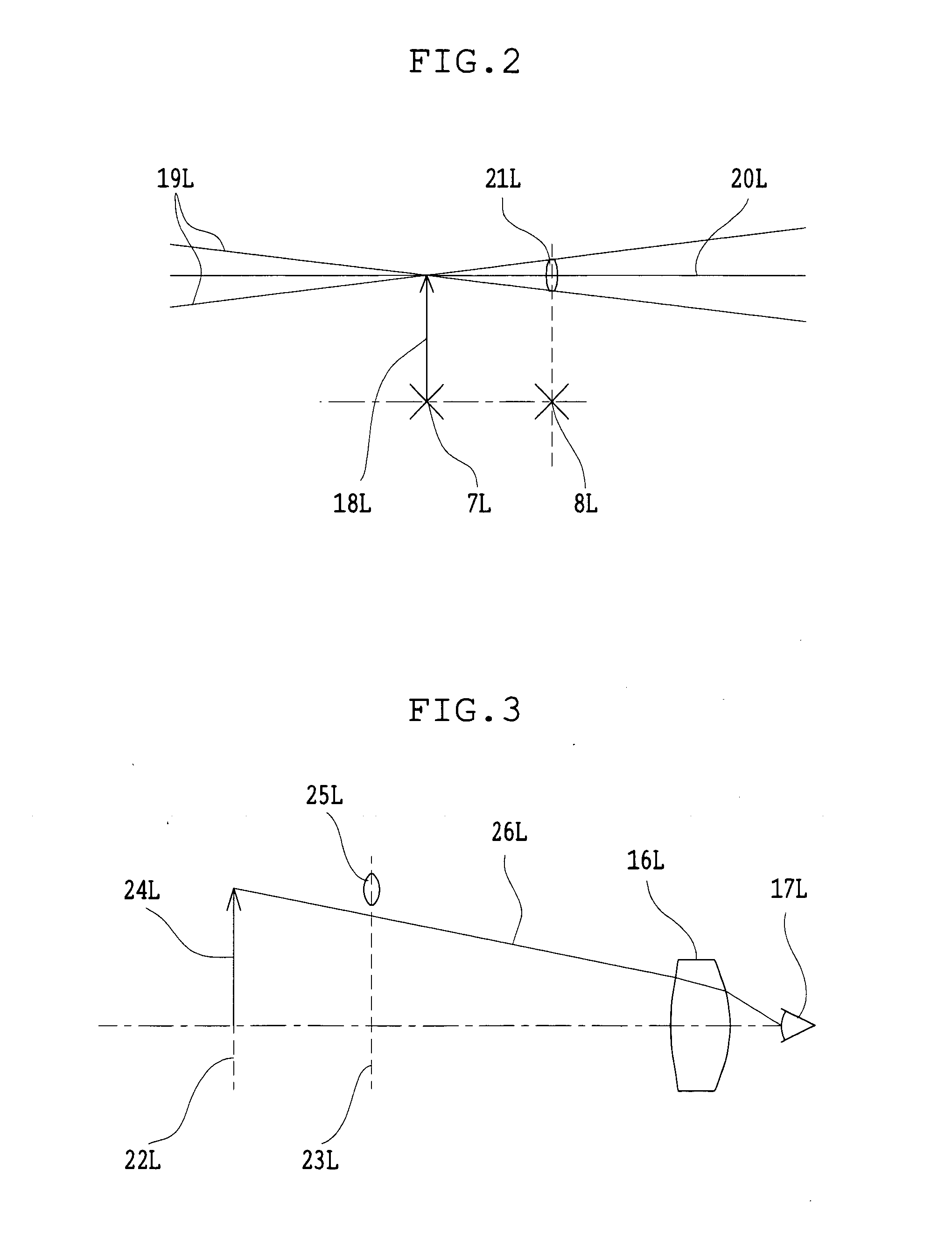
Binocular stereoscopic observation apparatus, electronic image stereomicroscope, electronic image stereoscopic observation apparatus, and electronic image observation apparatus
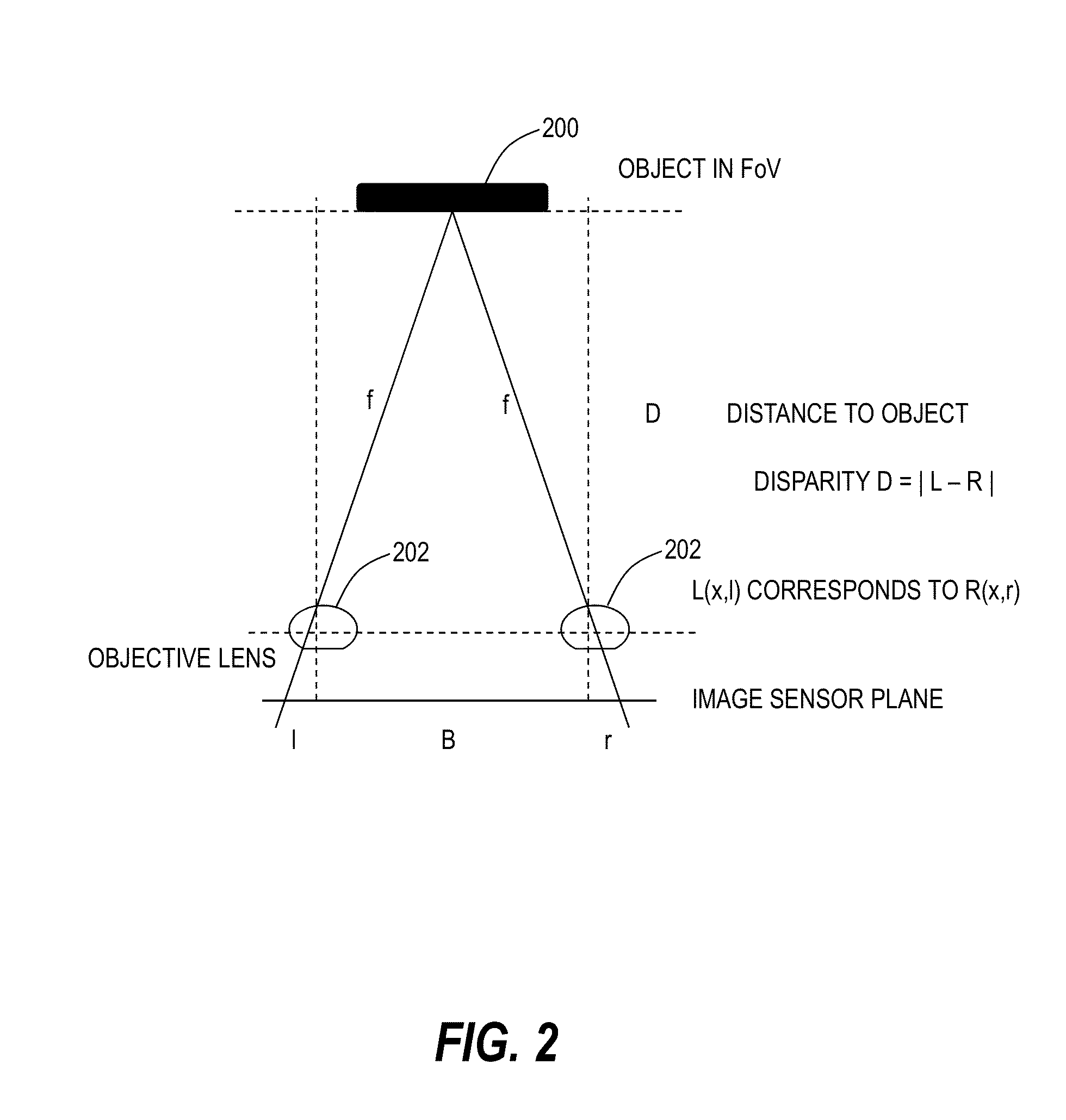
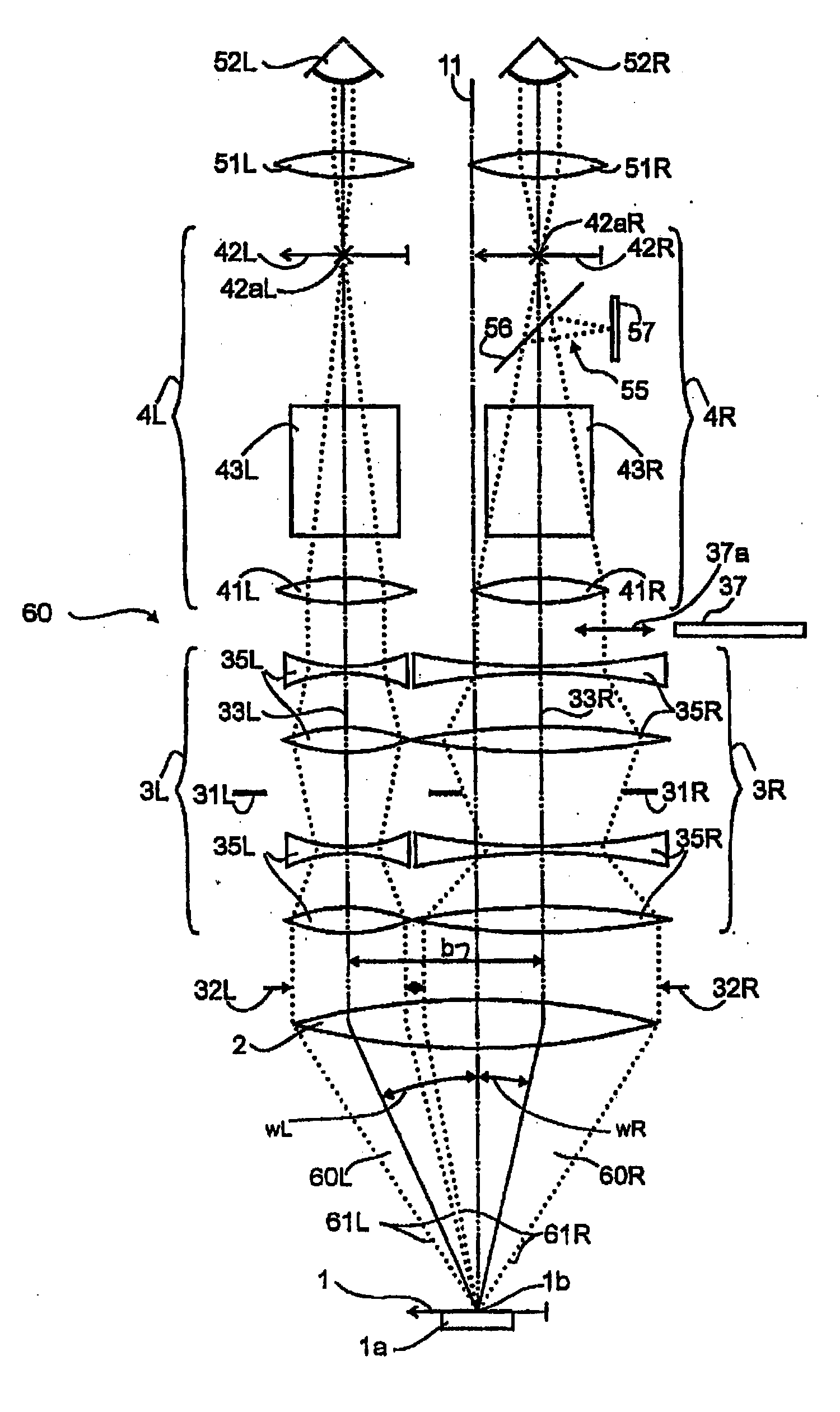
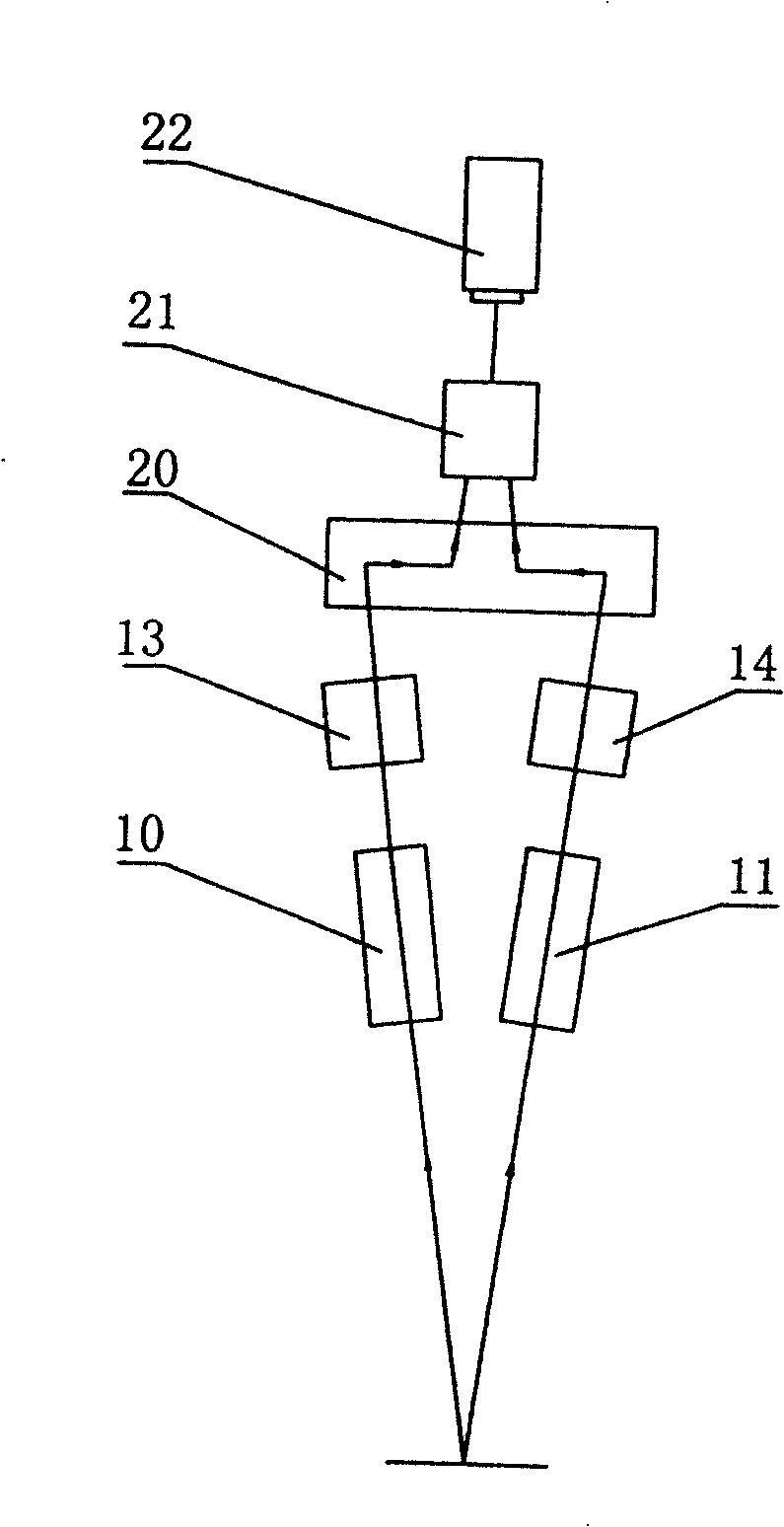
A binocular stereoscopic observation apparatus includes an imaging section forming left and right images with parallax in at least two directions and an observing section in which the images with parallax are stereoscopically observed with a viewer's eyes. In this case, the imaging section has an imaging lens forming images of an object at imaging positions on each of left and right optical paths and i imaging positions on the optical axis of the imaging lens, satisfying the following conditions: L(j−1)<Lj Ek=Lj−L(j−1) Dd<Ek where Lj is a distance, measured along the optical axis, from the imaging lens to the jth imaging position, Ek is a difference between distances, measured along the optical axis, from adjacent imaging positions to the imaging lens, and Dd is an image-side depth of an optical system of the imaging section. The observing section has an eyepiece optical system and i display devices on each of the left and right optical paths so that an image formed at the jth imaging position from the imaging lens on each optical path of the imaging section is displayed on the jth display device from the eyepiece optical system on a corresponding optical path, satisfying the following condition: Mj<M(j−1) where Mj is a distance, measured along the optical axis, from the eyepiece optical system to the jth display device. The observing section further has means for superimposing i displayed images on a viewer's pupil. Here, i is an integer of 2 or more and j is an integer satisfying conditions, 1≦j≦i and j≧2.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Apparatus and method for concurrently monitoring active release and physical appearance of solid dosage form pharmaceuticals
InactiveUS7021163B2Quality improvementAvoid displacementComponent separationMaterial analysis by optical meansVideo monitoringCompound (substance)
An apparatus and method for monitoring the dissolution properties of a solid dosage form pharmaceutical or other material. The apparatus includes a hollow dissolution chamber for supporting the dosage form and subjecting it to a dissolution liquid so that the dosage form dissolves in the liquid. A dissolution liquid analyzing device (e.g., a spectrophotometer) analyzes the properties of the dissolution liquid as the dosage form dissolves. A video monitoring means (e.g., a stereo-microscope and video camera) provides a series of images of the dosage form as it dissolves. The series of images and data resulting from the analysis are recorded and correlated. The temperature, flow rate and chemical parameters of the dissolution liquid can be controlled (e.g., held constant or altered), if desired.
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
Camera adapter for optical devices, in particular microscopes
InactiveUS7394979B2Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsPhotographic cameraEyepiece
A camera adapter for optical devices, in particular microscopes. The present solution includes a camera adapter which enables any video cameras and photographic cameras to connect to an existing image out-coupling system, e.g., the beam splitter of a microscope. The adapter can also be used for stereo microscopes. The camera adapter is arranged between the image out-coupling element and the camera. Its housing has two connection pieces. The microscope-side connection piece has a quick-change device and the camera-side connection piece has a filter thread. The technical solution provides a camera adapter for connecting digital cameras to a microscope. By using intermediate rings, the camera adapter is suitable for different cameras and facilitates exchange of cameras. The camera can be positioned in such a way that the observer can view the object through the eyepiece as well as on the camera monitor without substantially changing his / her sitting position.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com