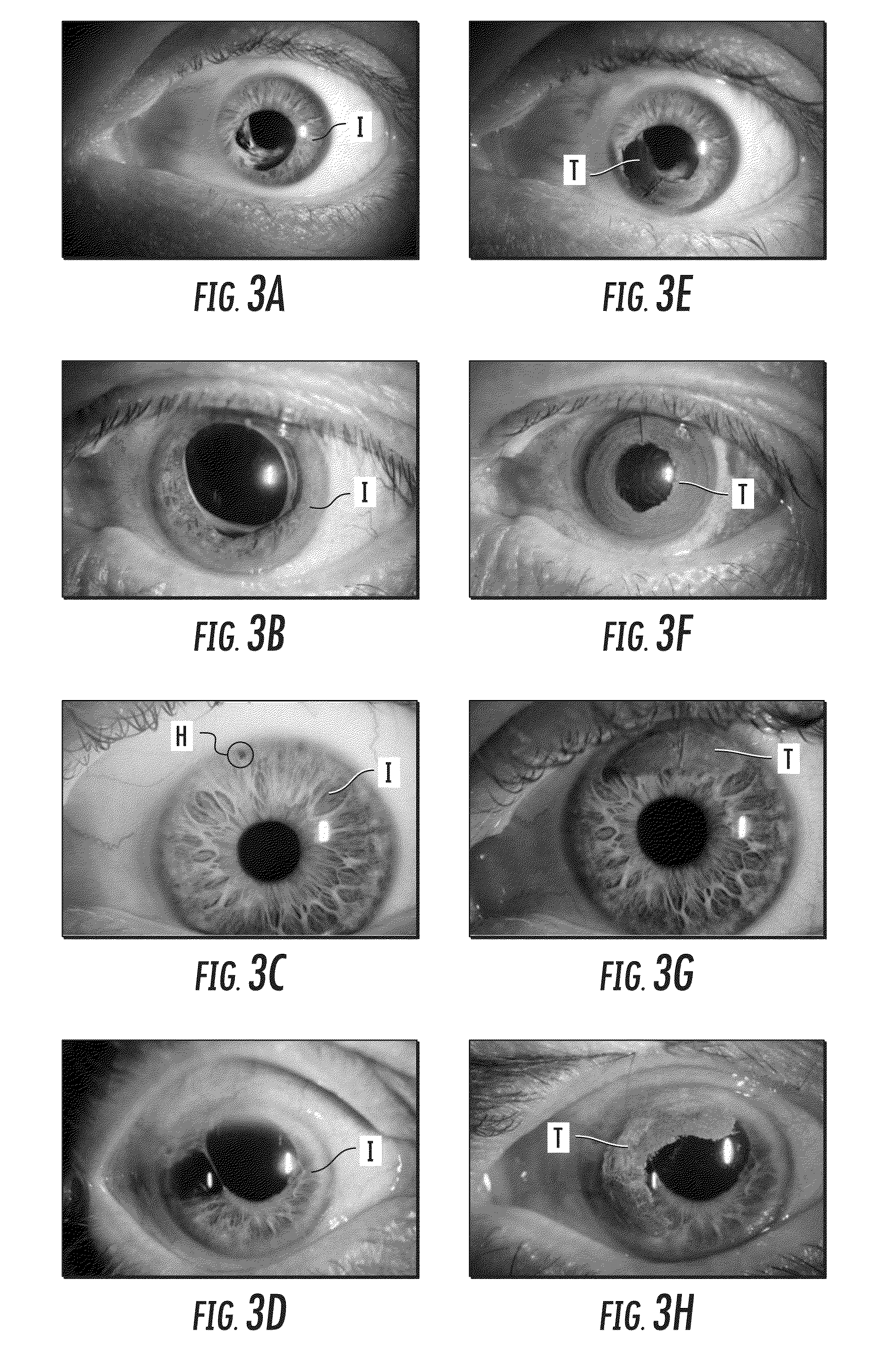
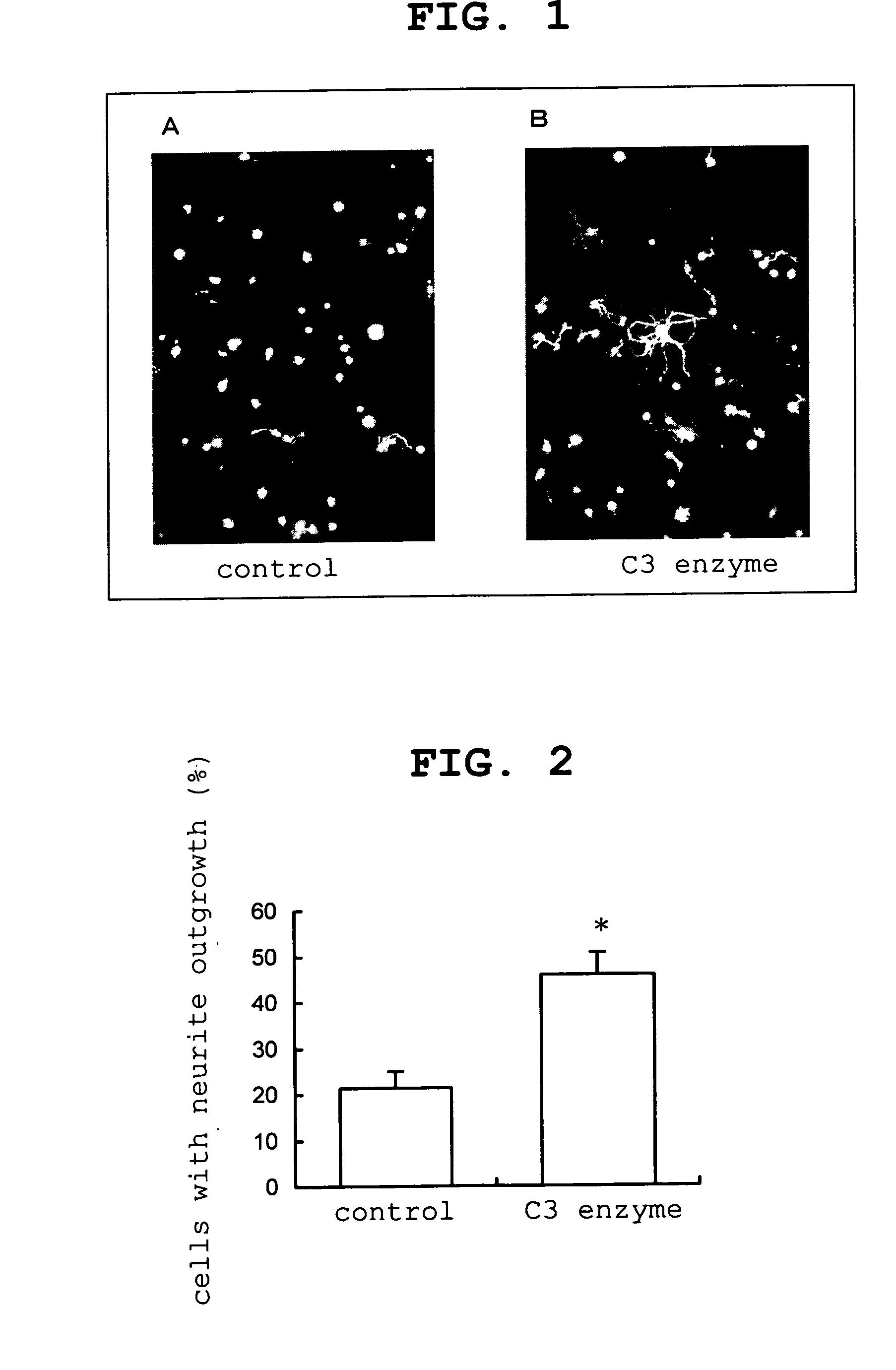
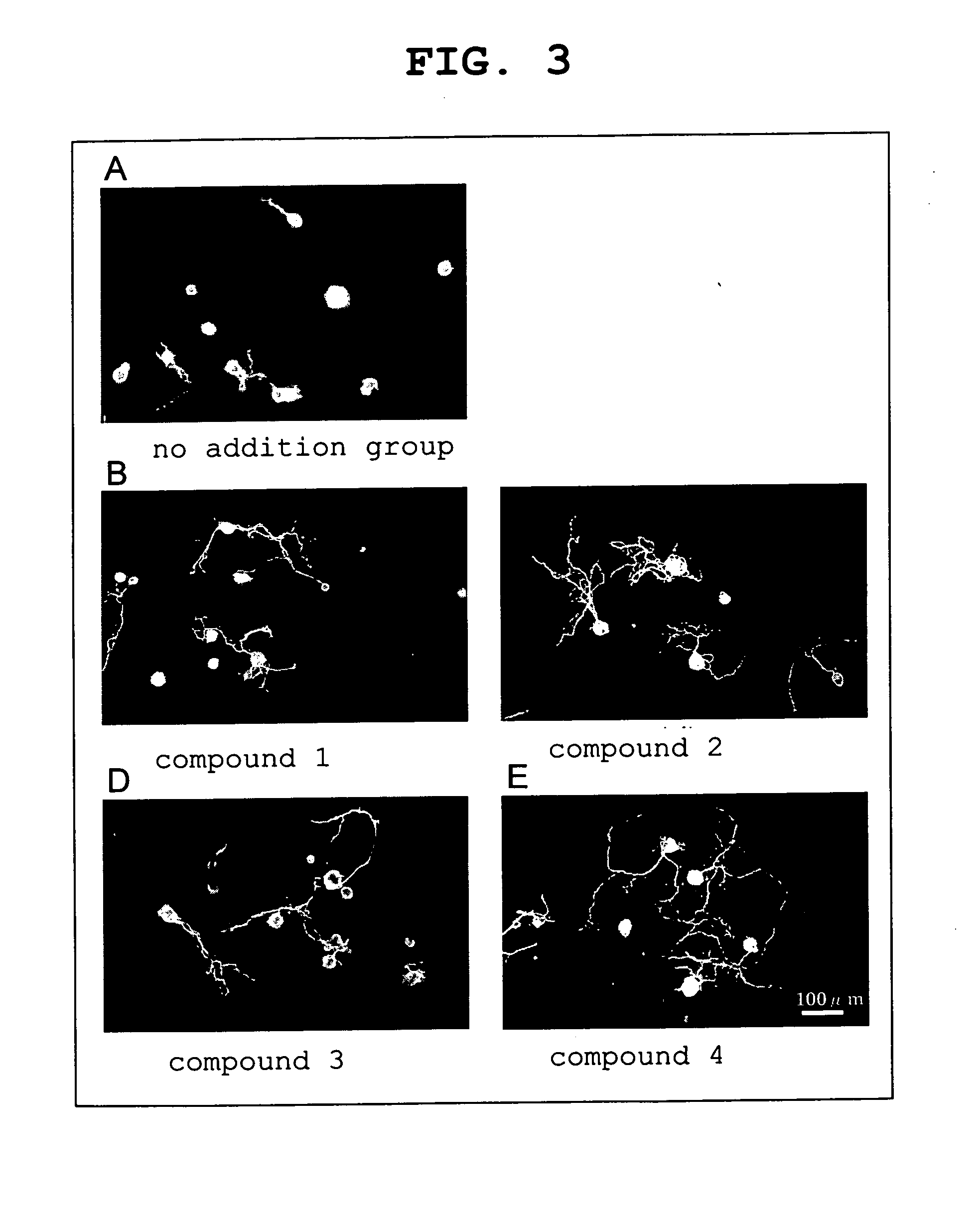
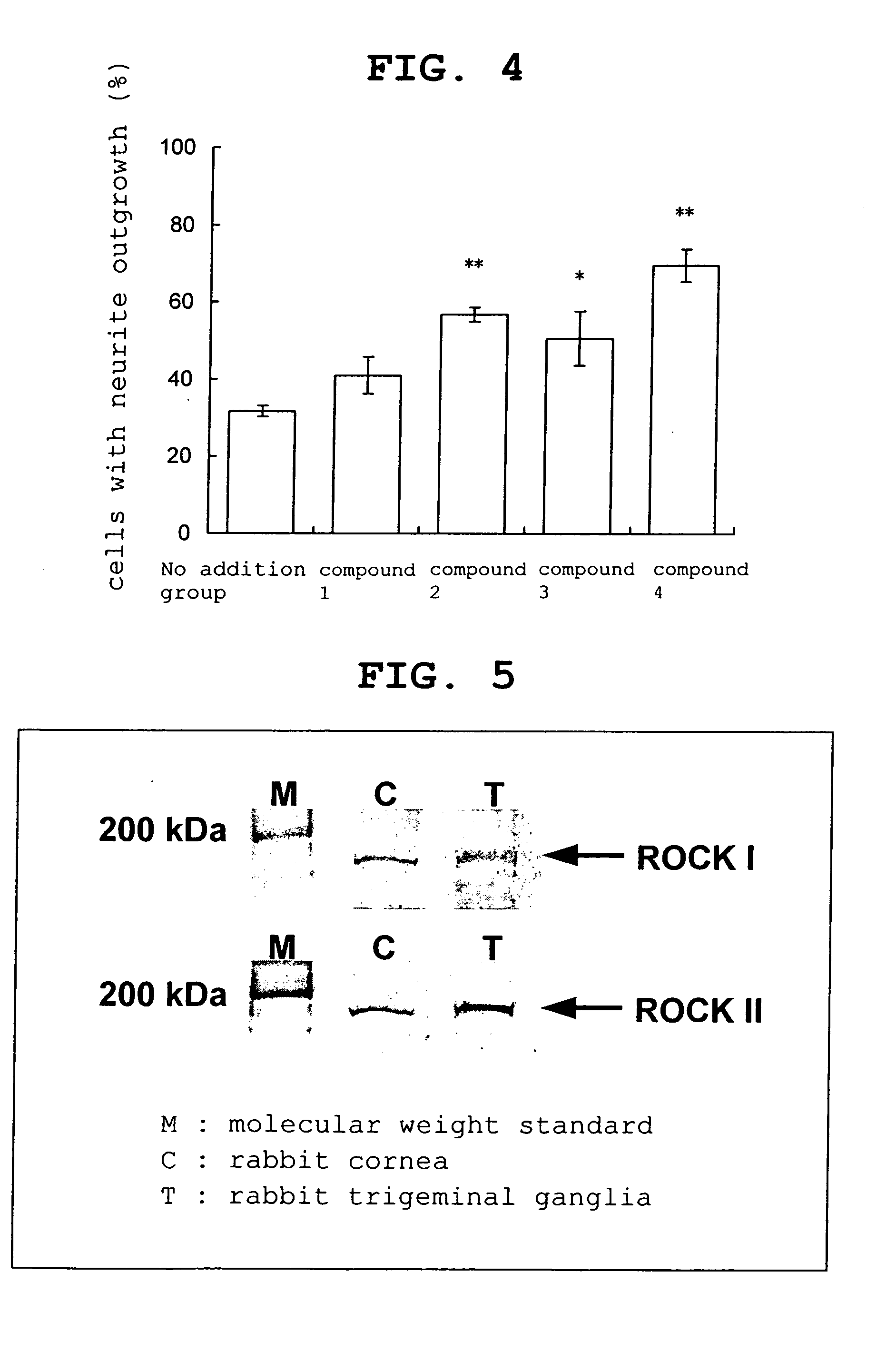
Patents
Literature
43 results about "Corneal surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
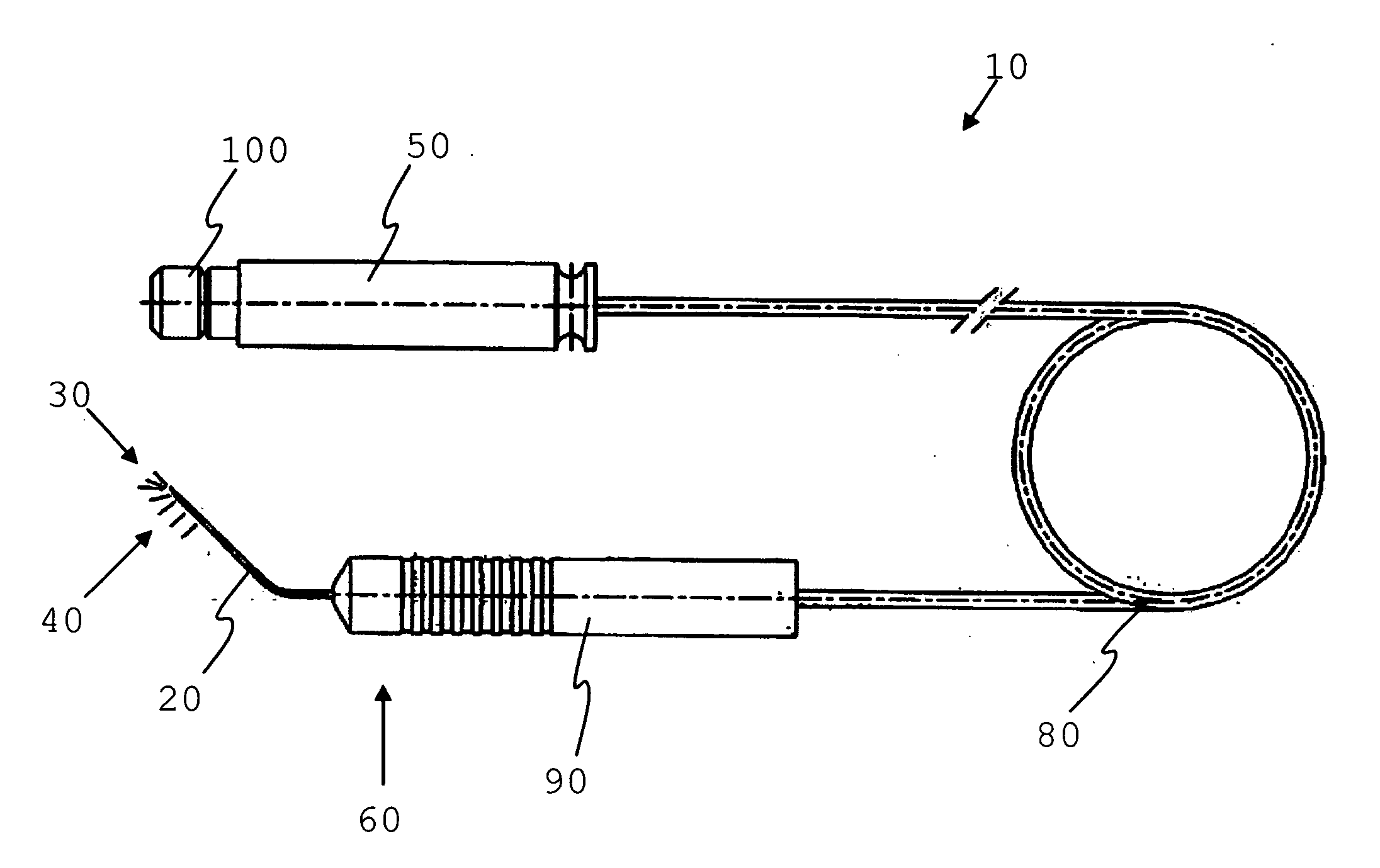
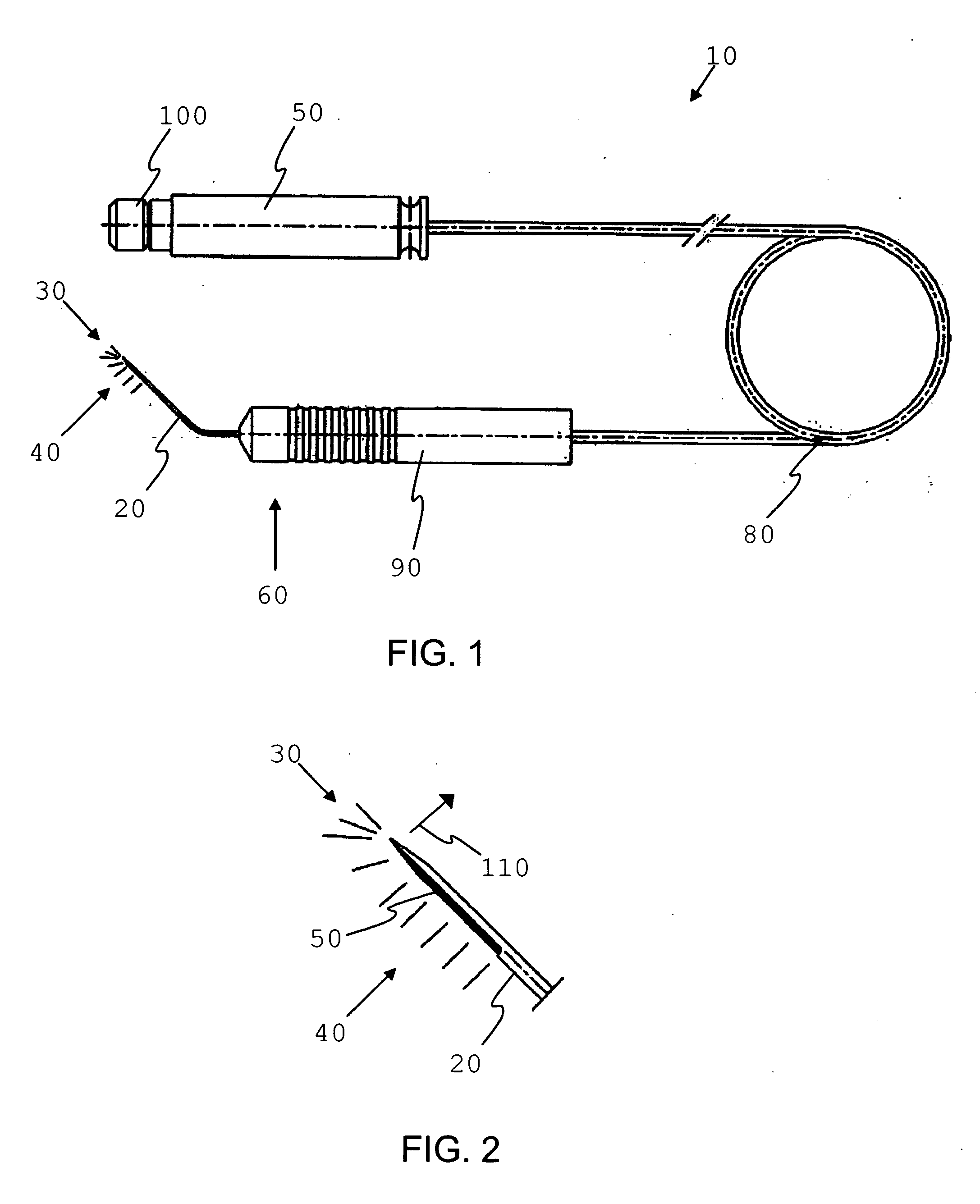
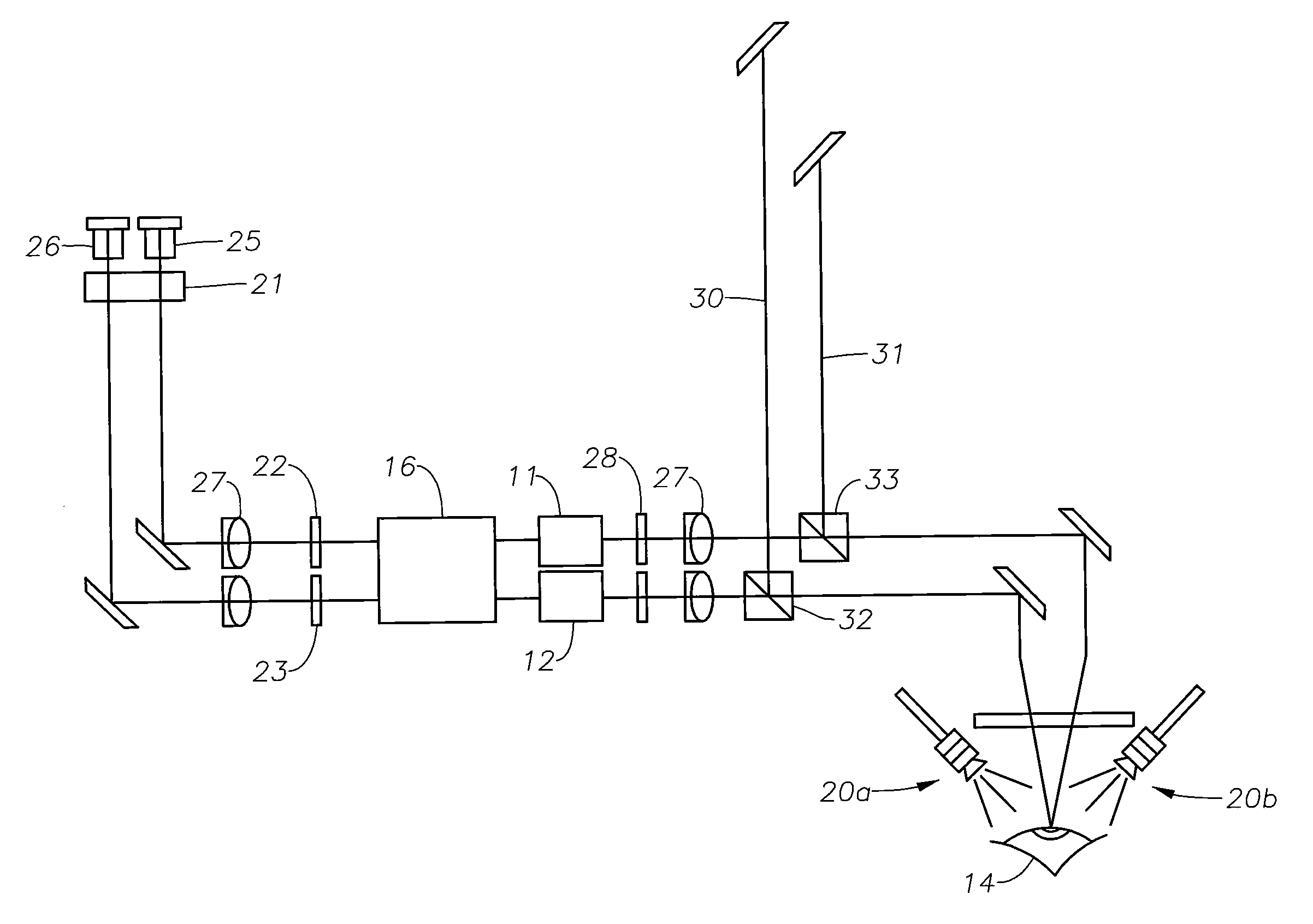
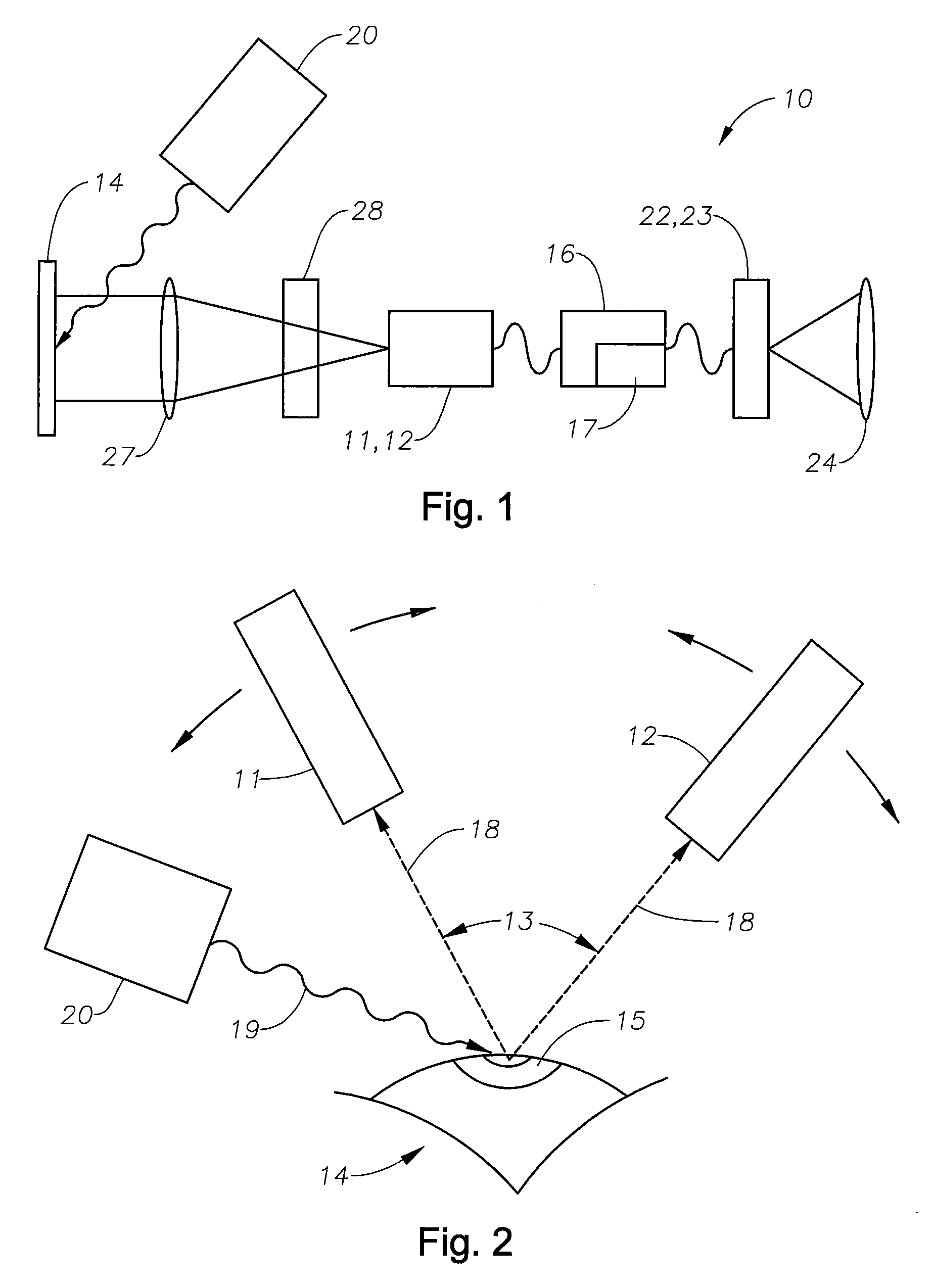
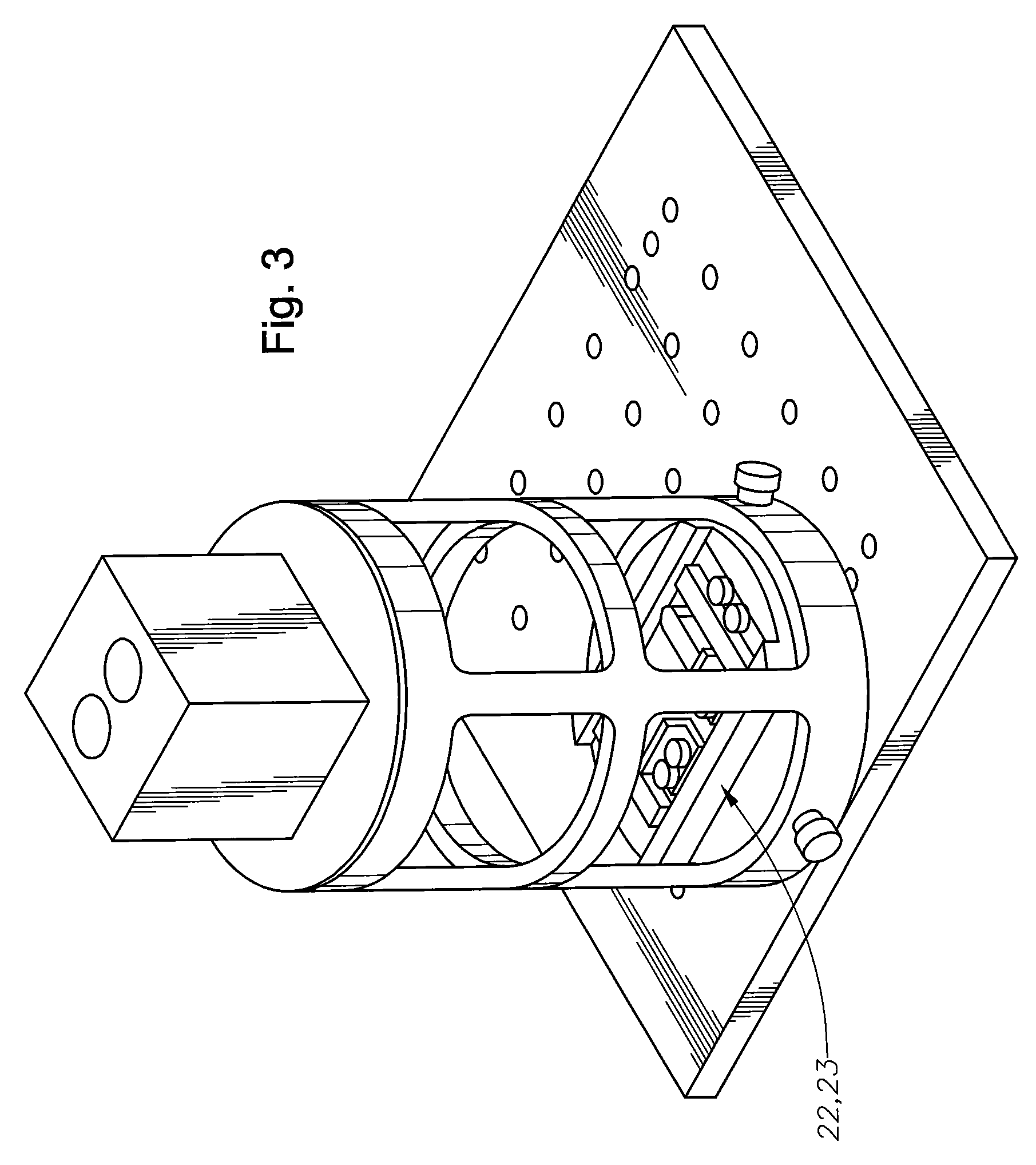
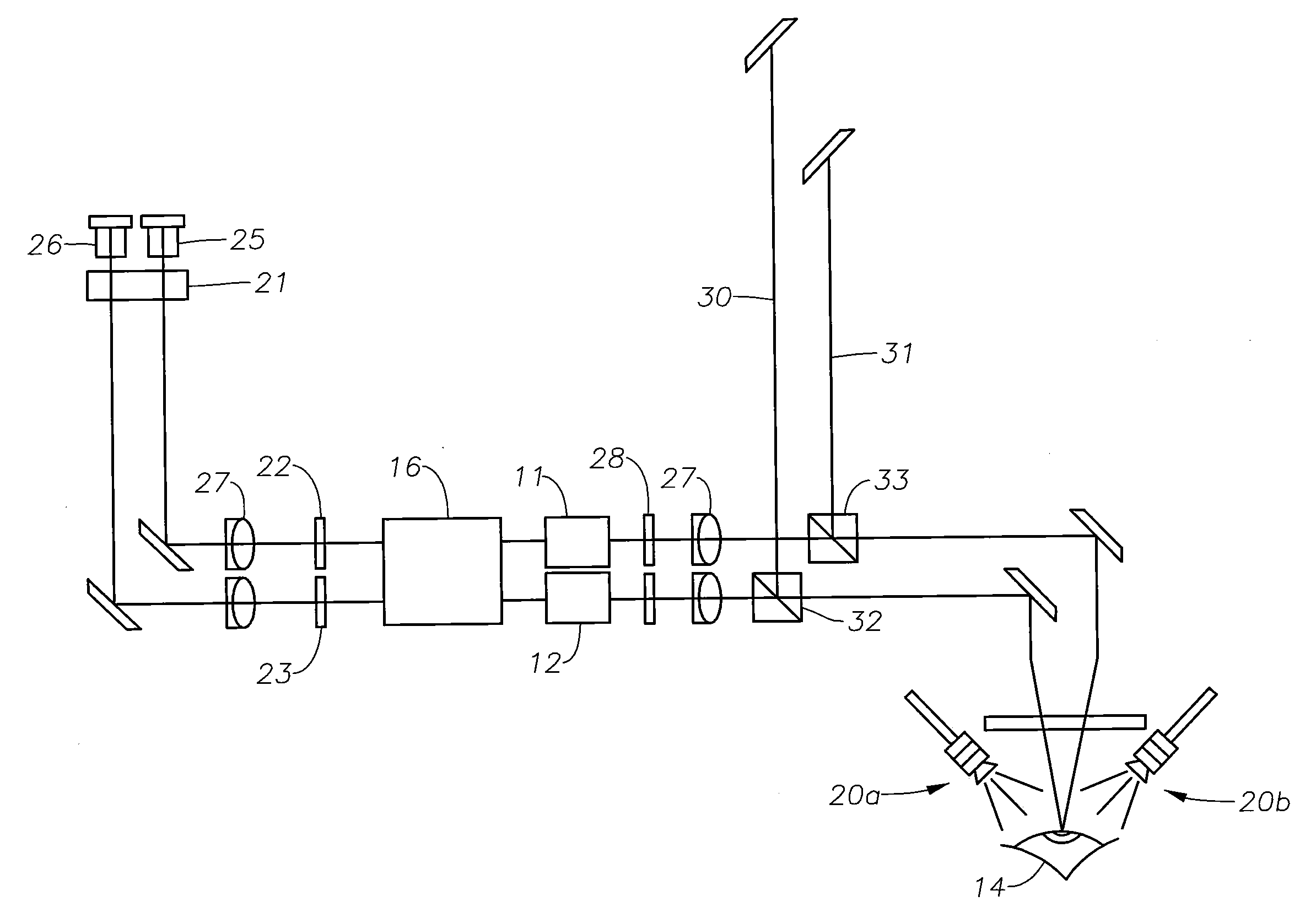
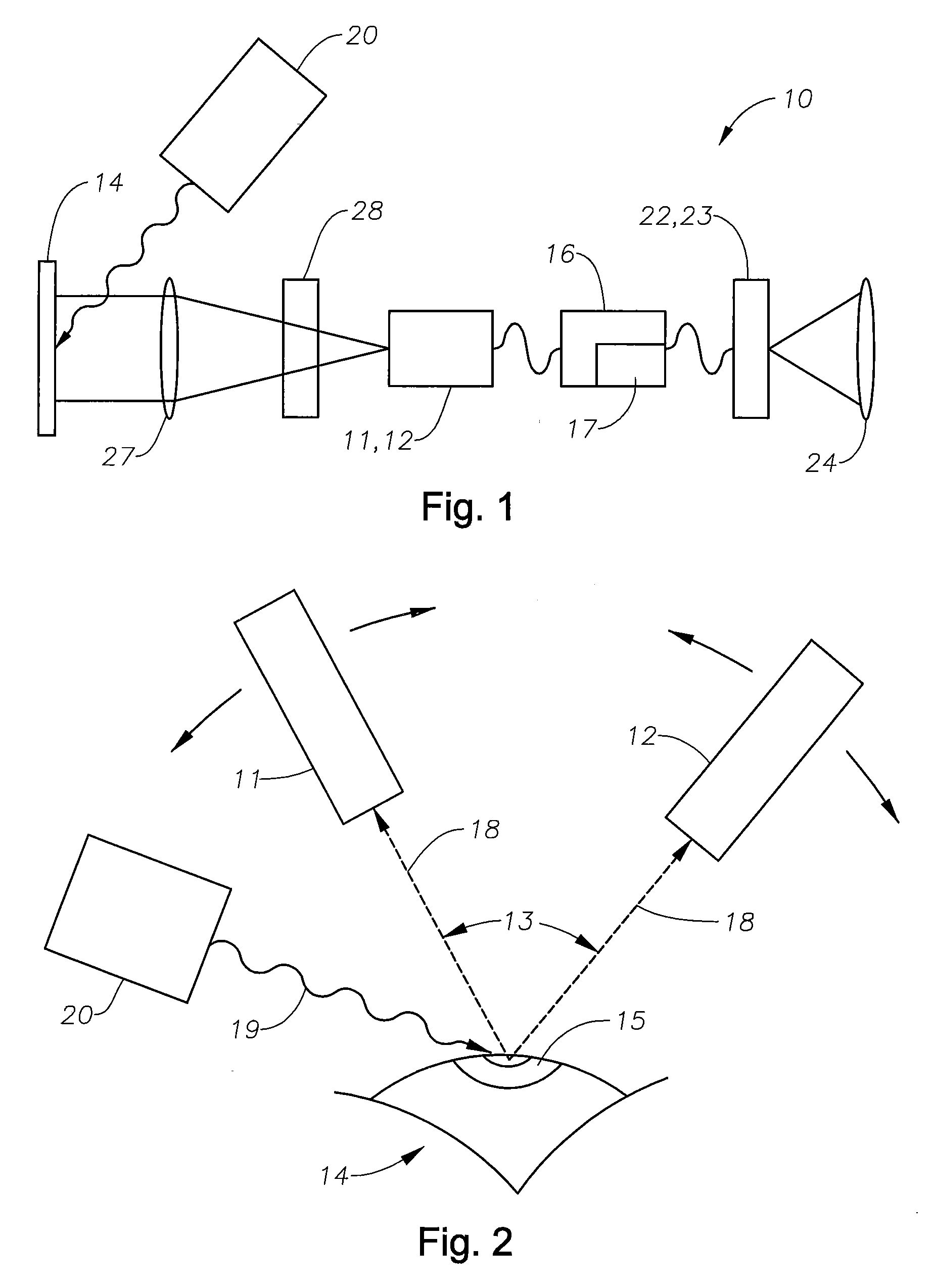
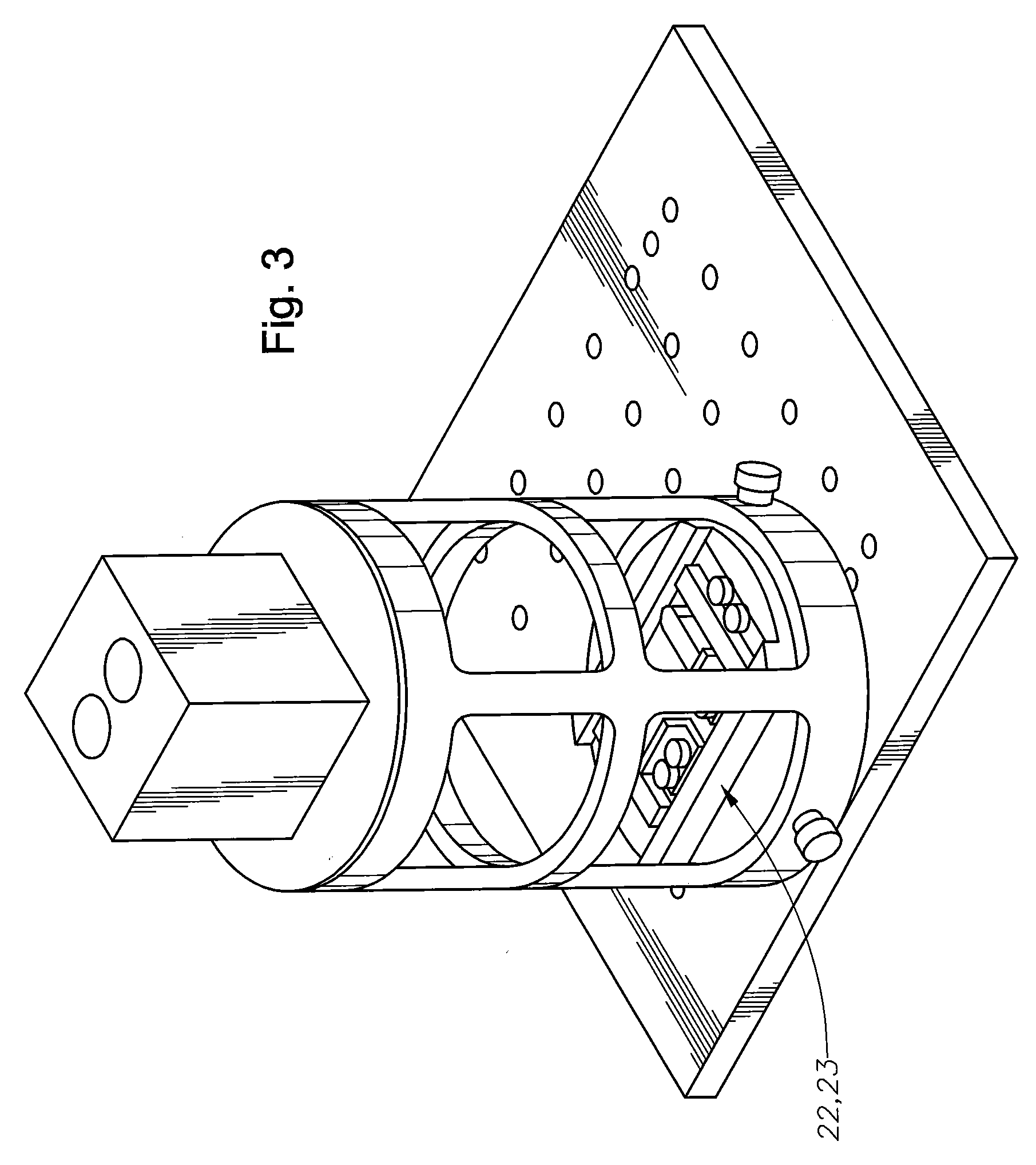
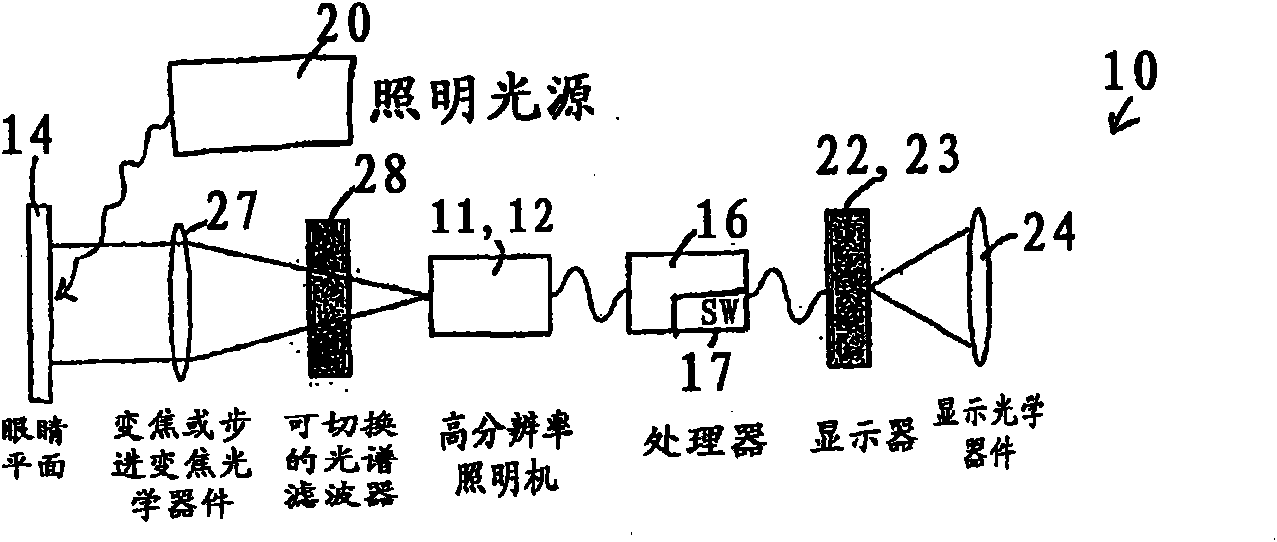
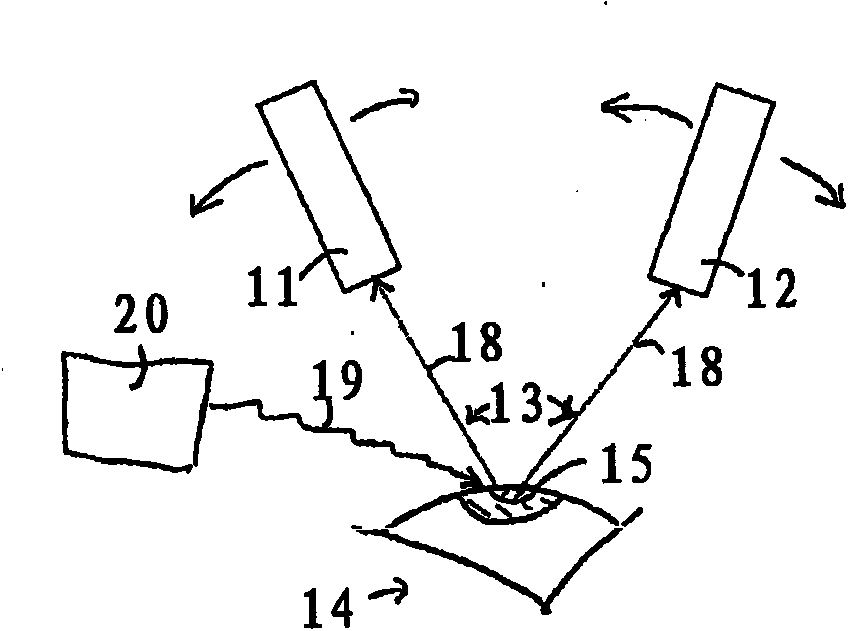
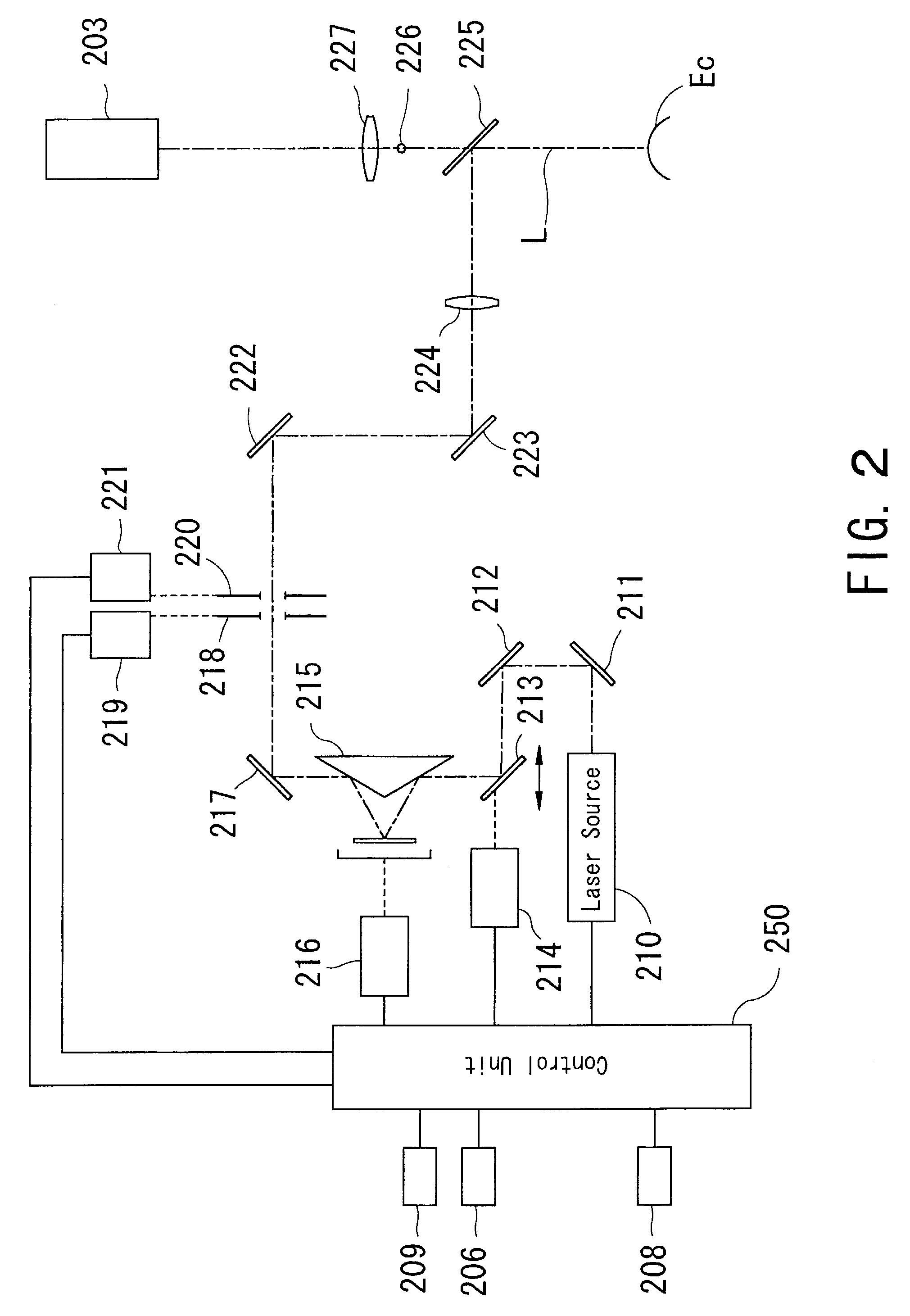
Method and apparatus to guide laser corneal surgery with optical measurement
InactiveUS20070282313A1Faster visual recoveryLess invasiveLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive errorPhototherapeutic keratectomy
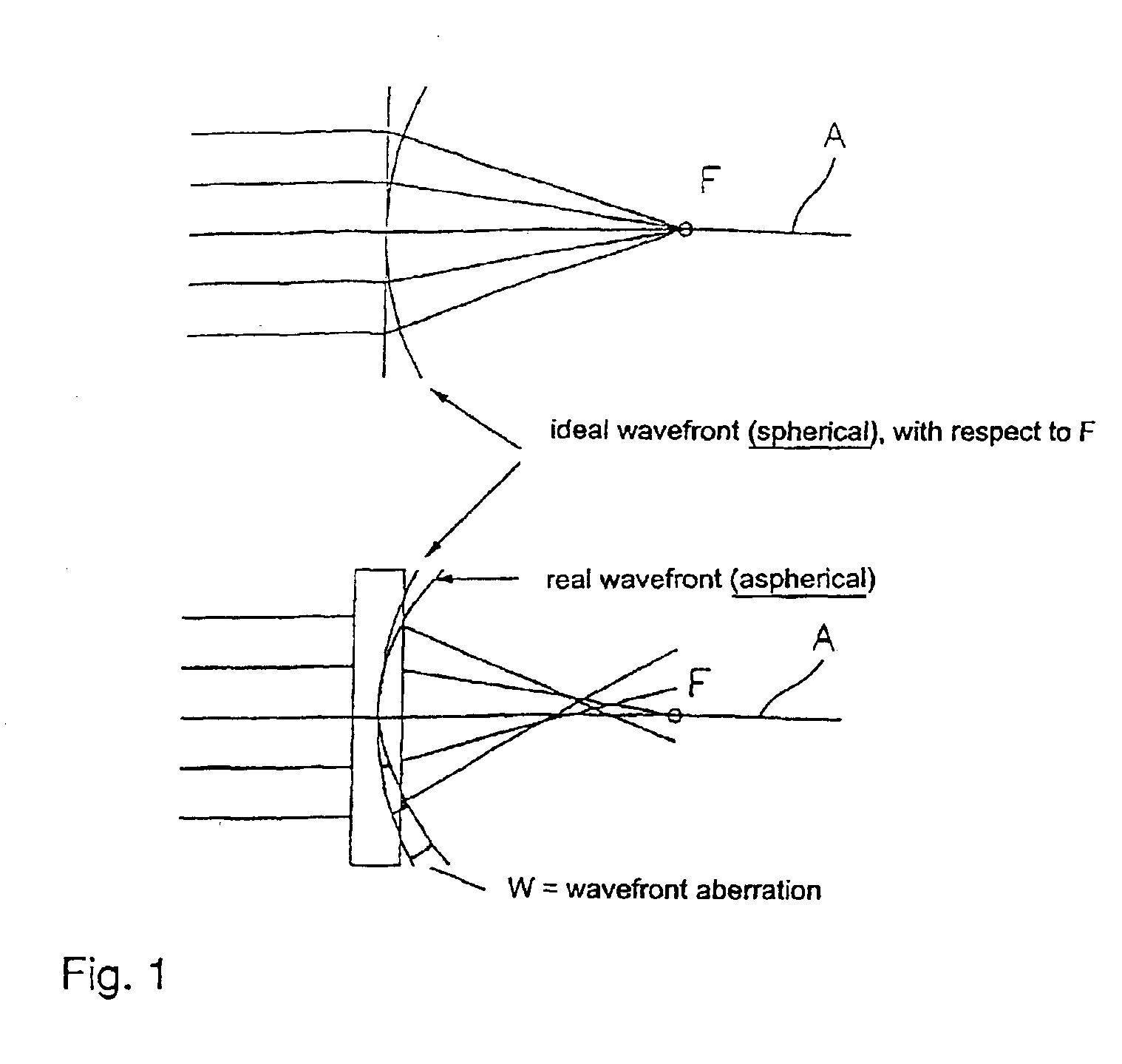
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is used to map the surface elevation and thickness of the cornea. The OCT maps are used to plan laser procedures for the treatment of an irregular, opacified or weakened cornea, and in the treatment of refractive errors. In the excimer laser phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK) procedure, the OCT data is used to plan a map of ablation depth needed to restore a smooth optical surface. In the excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy procedure, OCT mapping of epithelial thickness is used to achieve clean laser epithelial removal. In femtosecond laser anterior keratoplasty procedure, OCT data is used to plan the depth of femtosecond laser dissection to remove an anterior layer of the cornea, leaving a smooth recipient bed of uniform thickness to receive a disk of donated corneal tissue. The linkage of an OCT system to a precise laser surgical system enables the performance of new procedures that are safer, less invasive and produce faster visual recovery than conventional surgical procedures.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for laser surgery of the cornea
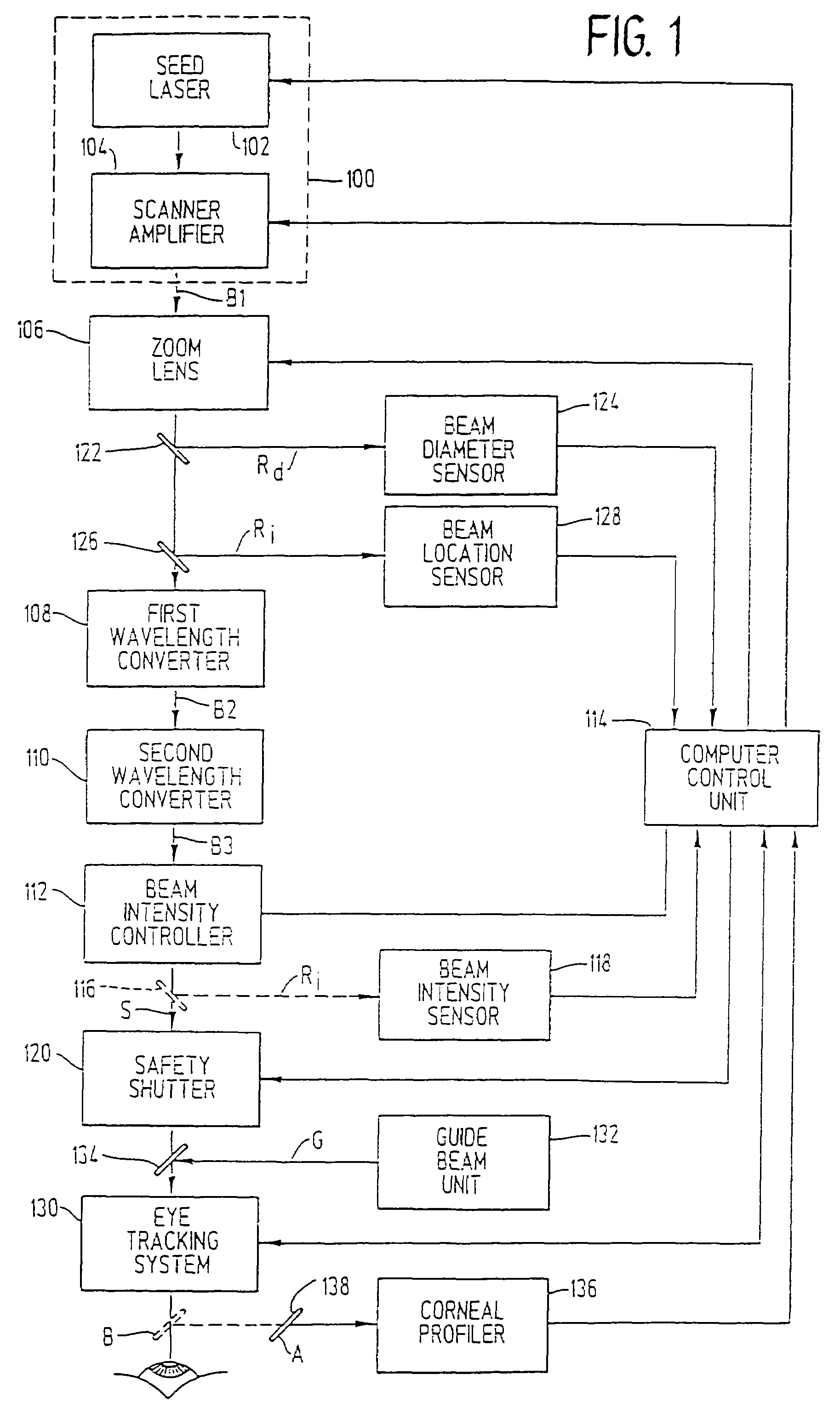
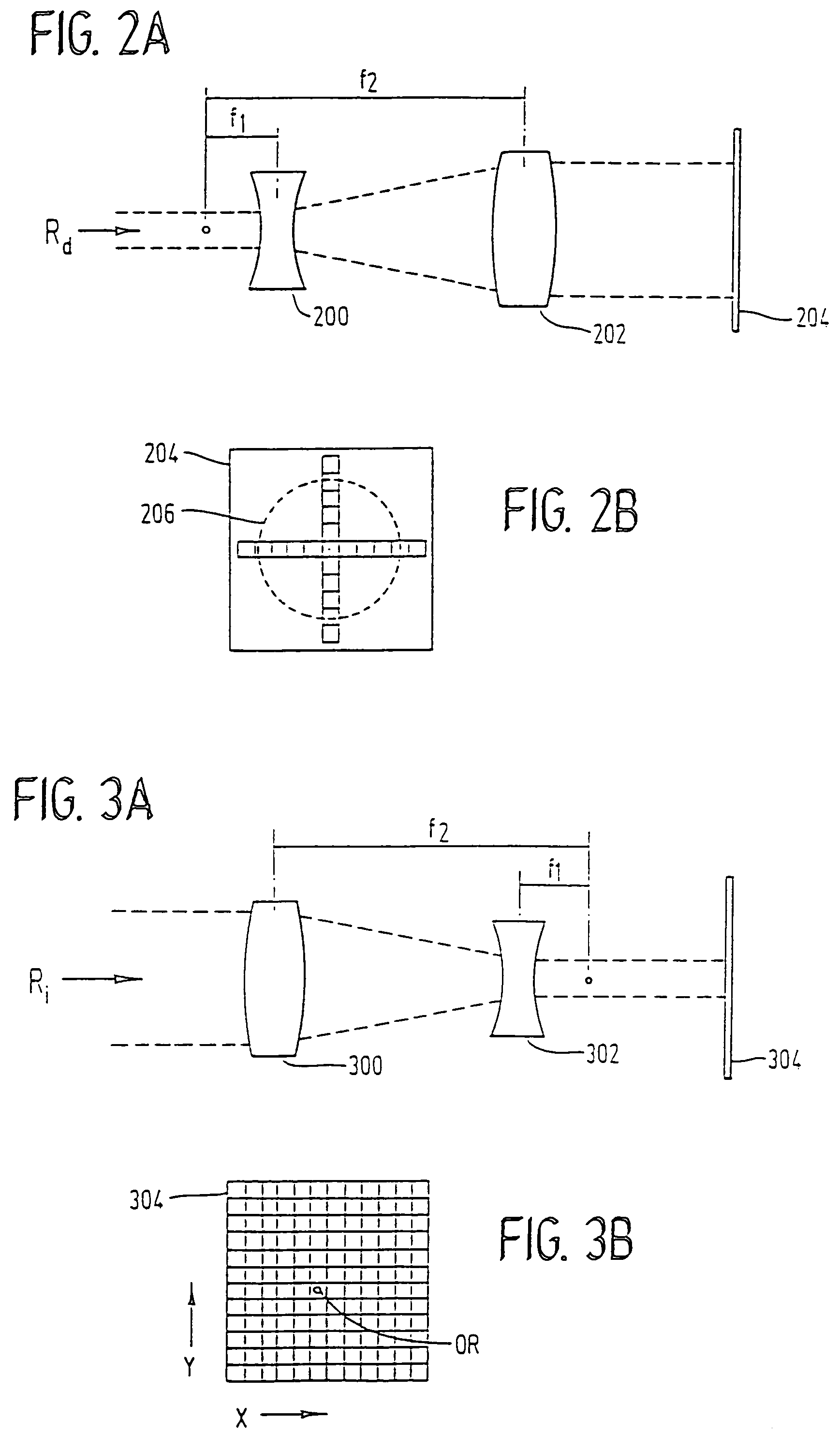
InactiveUS7220255B2Easy to controlIncrease powerLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCorneal ablationSurgical lasers
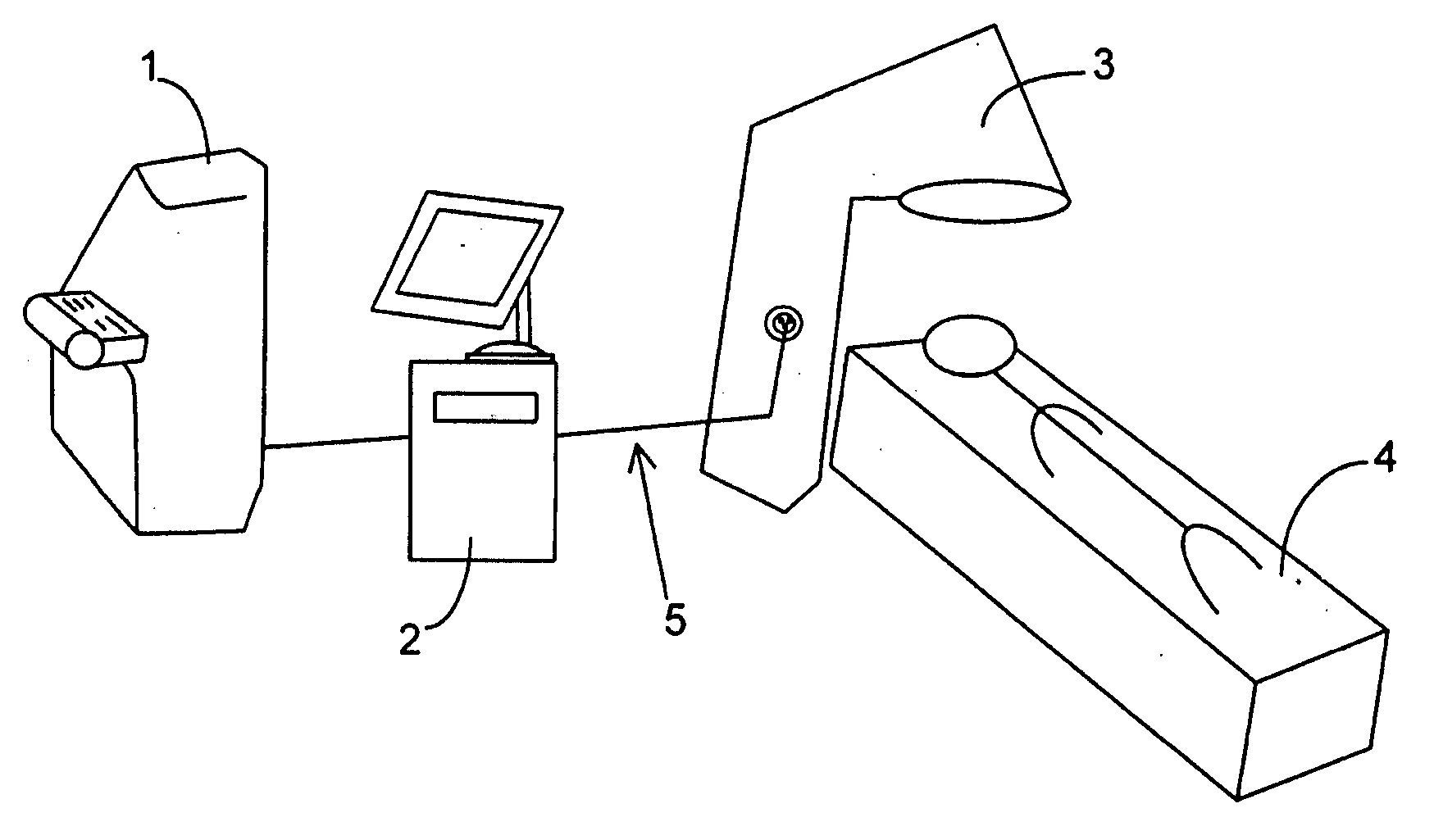
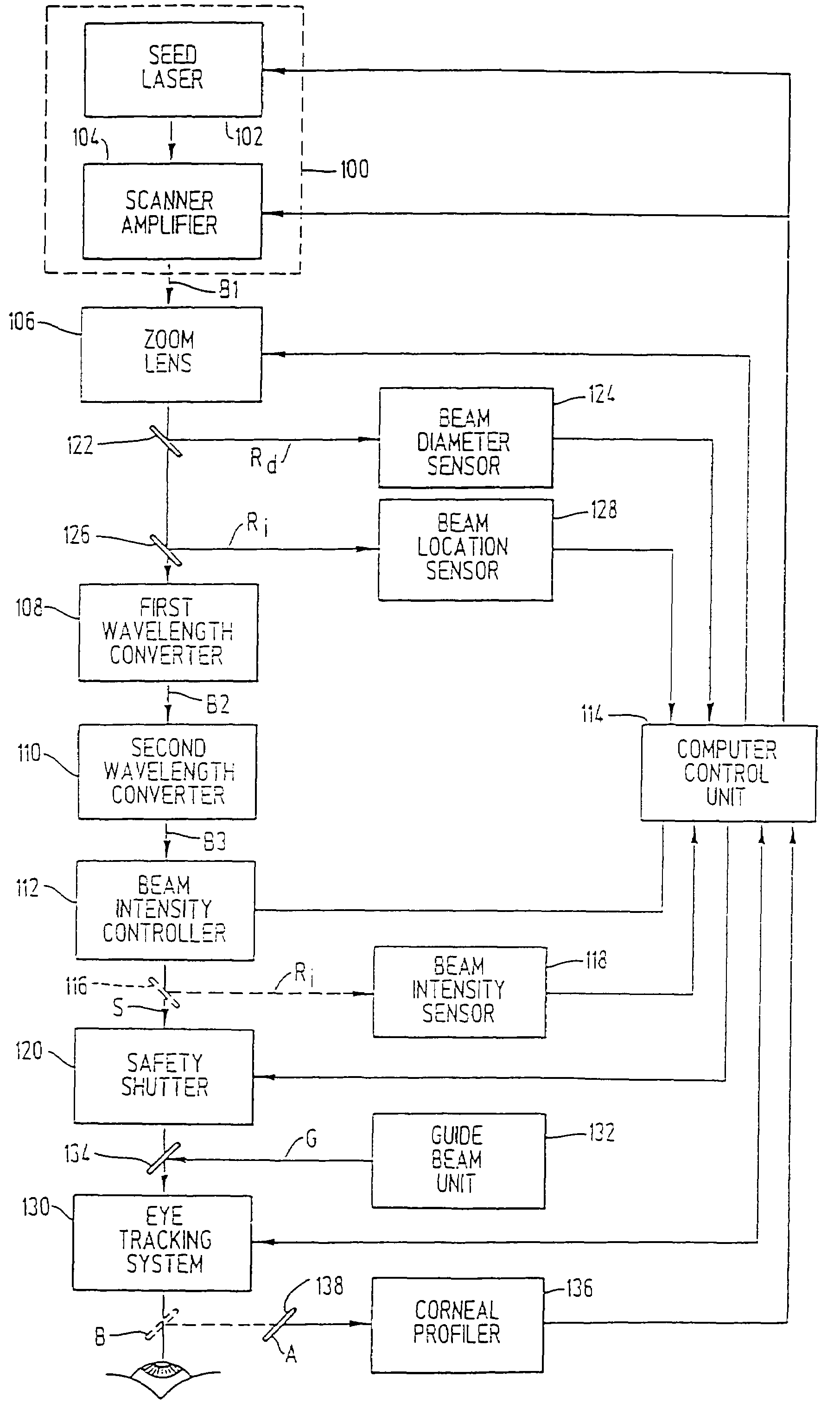
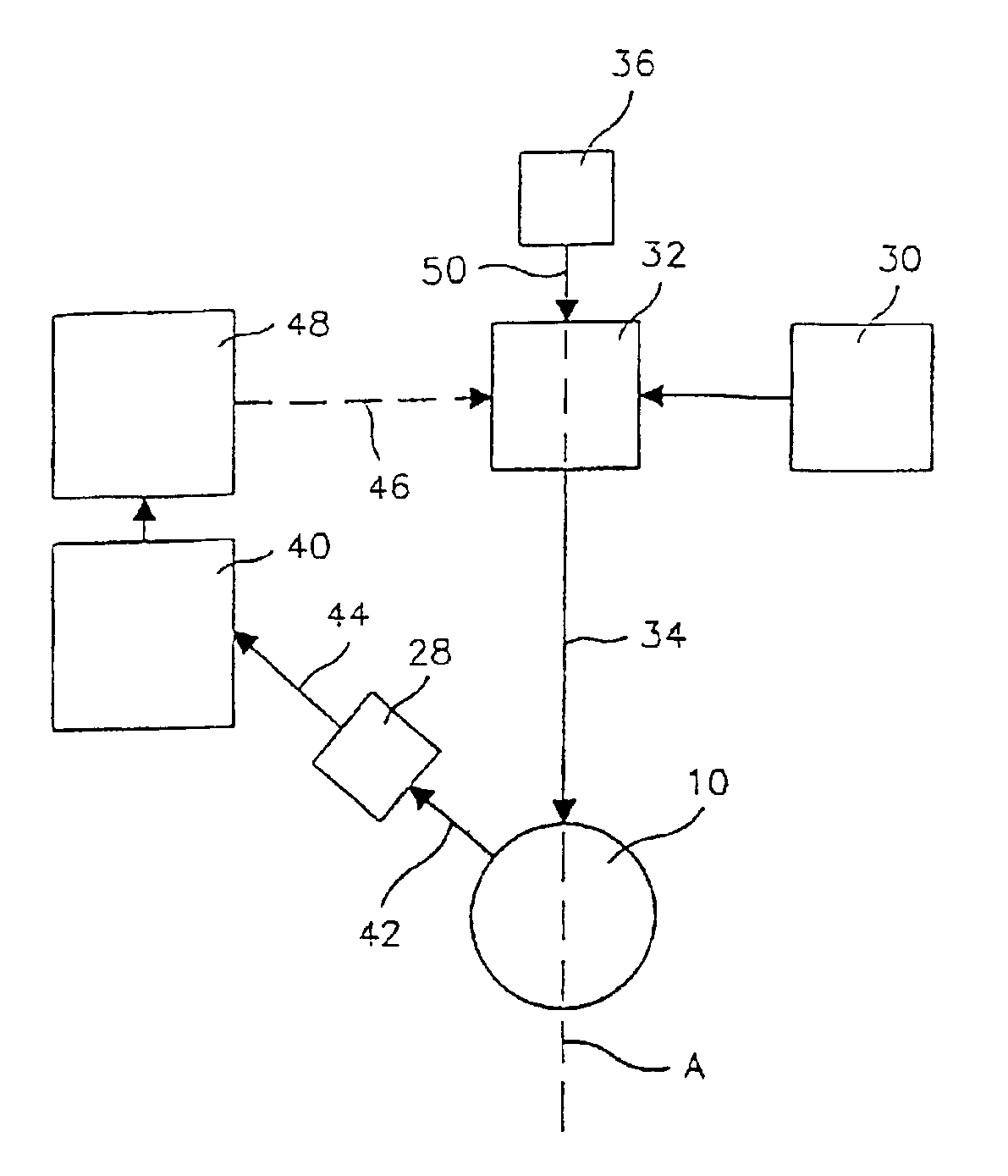
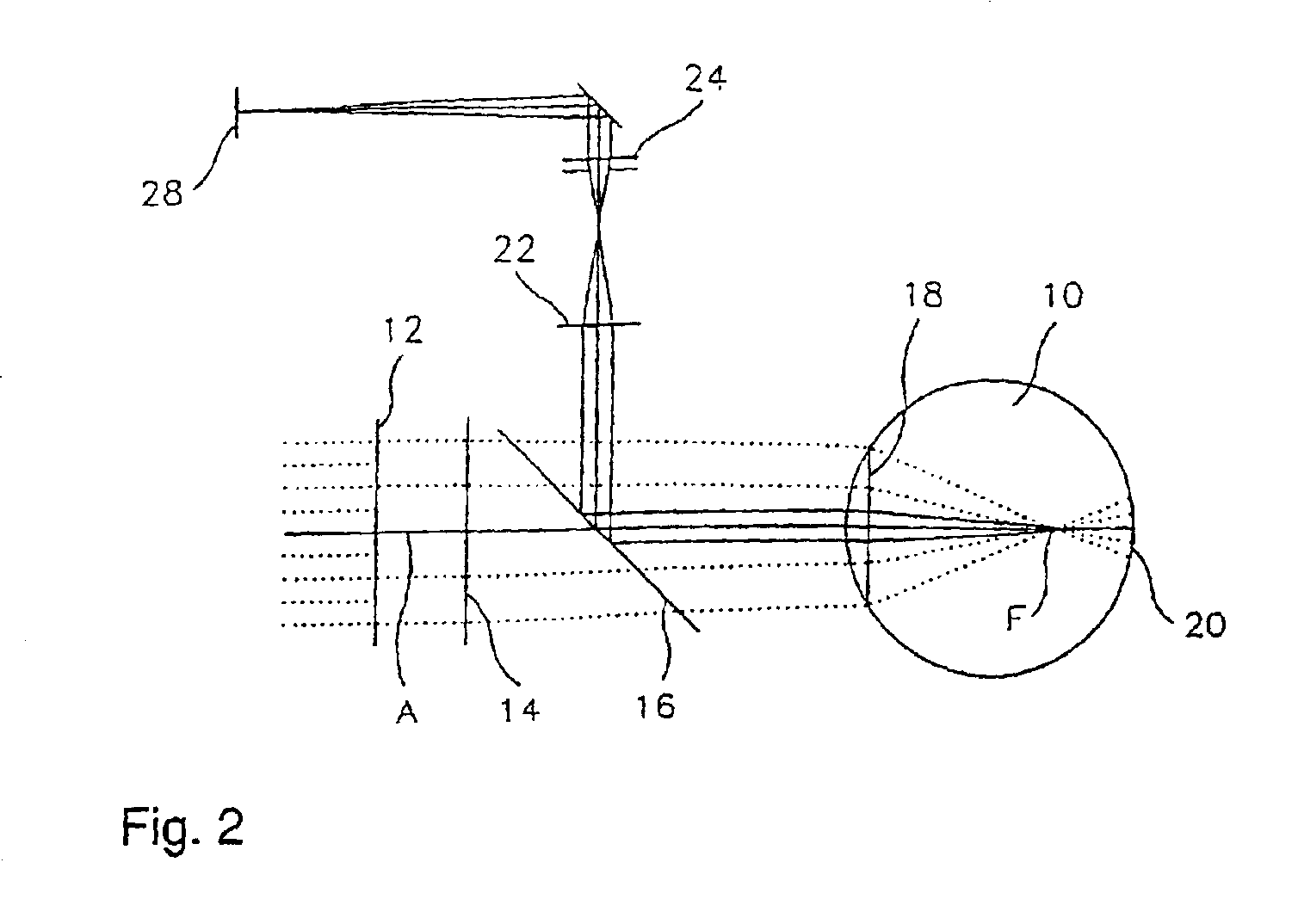
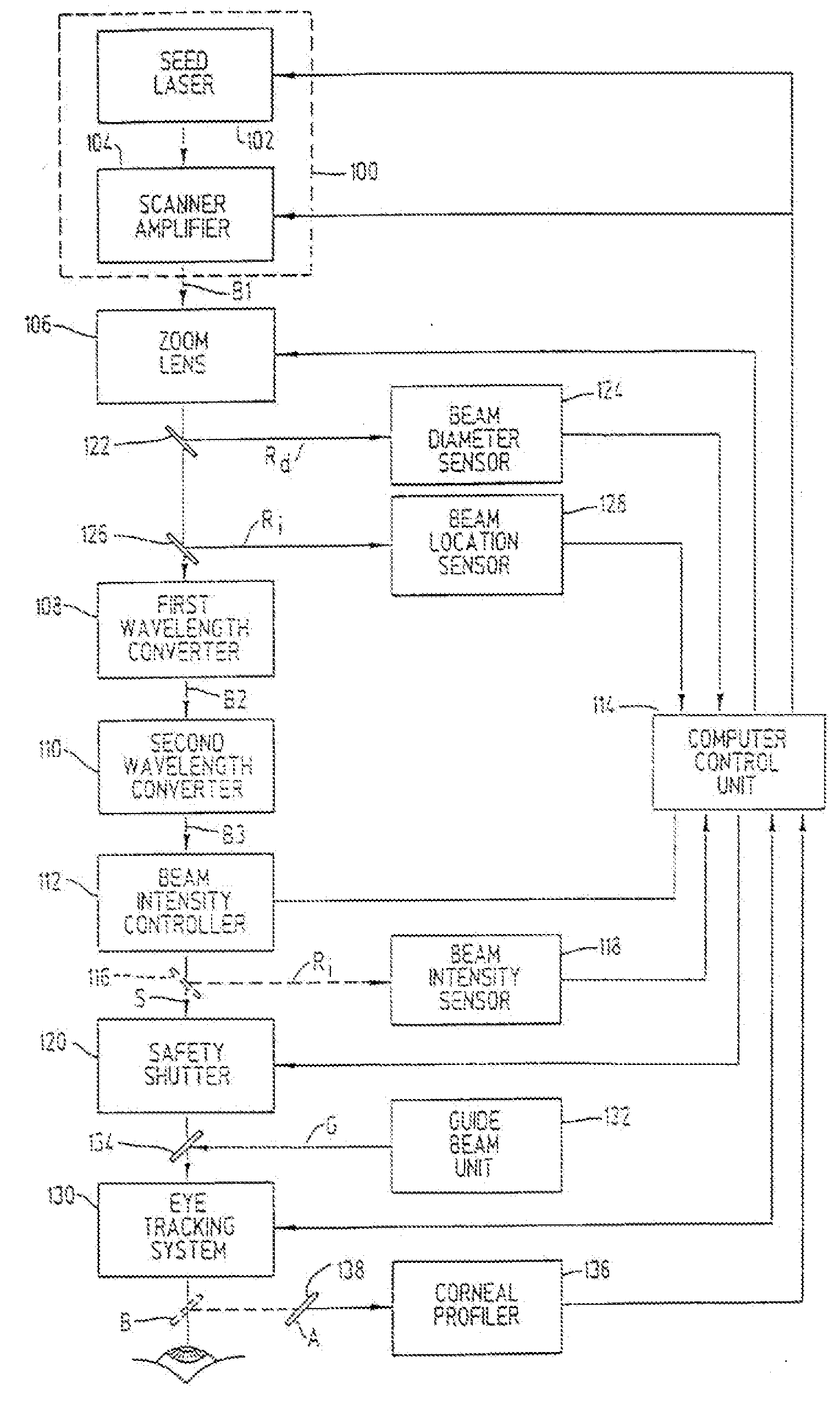
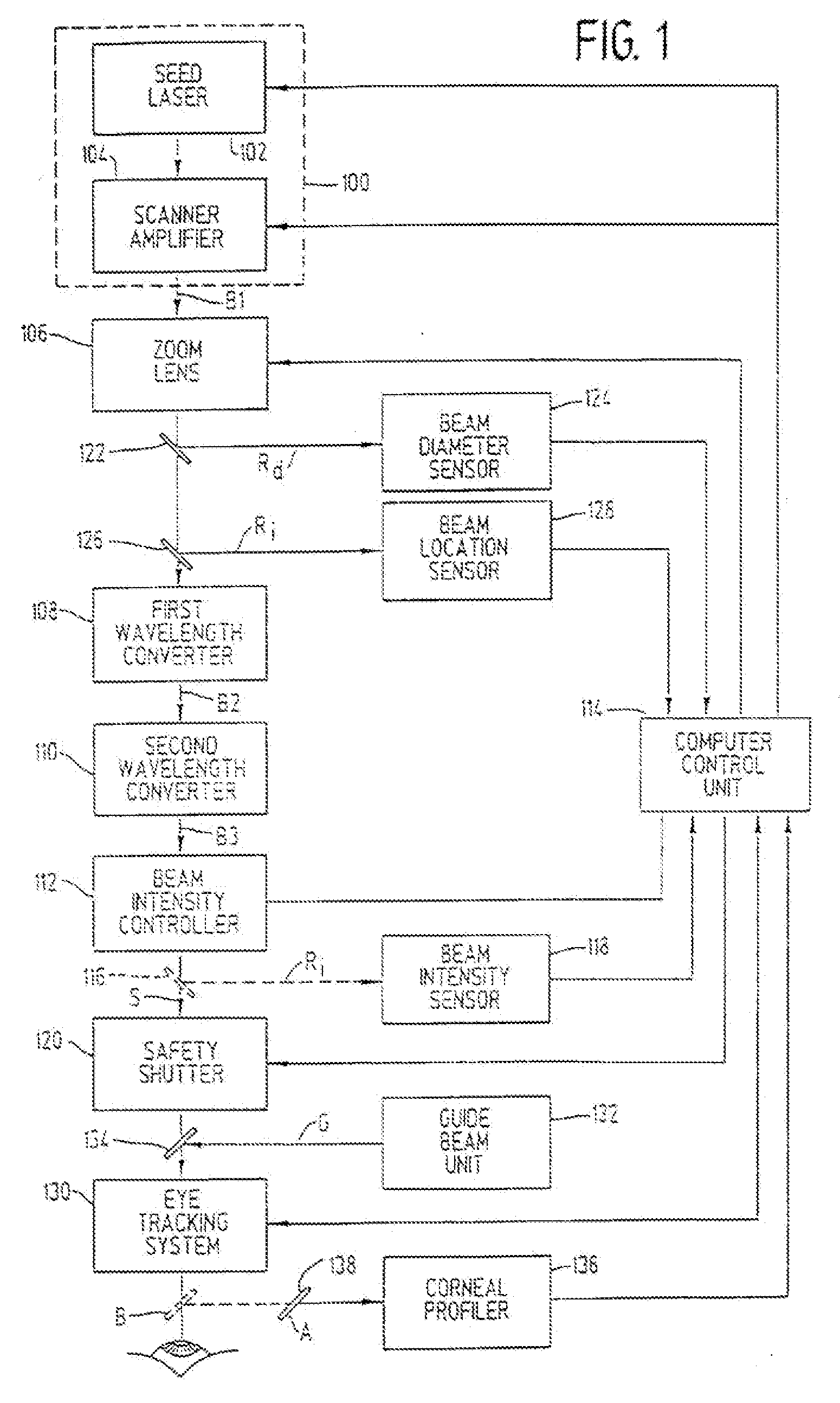
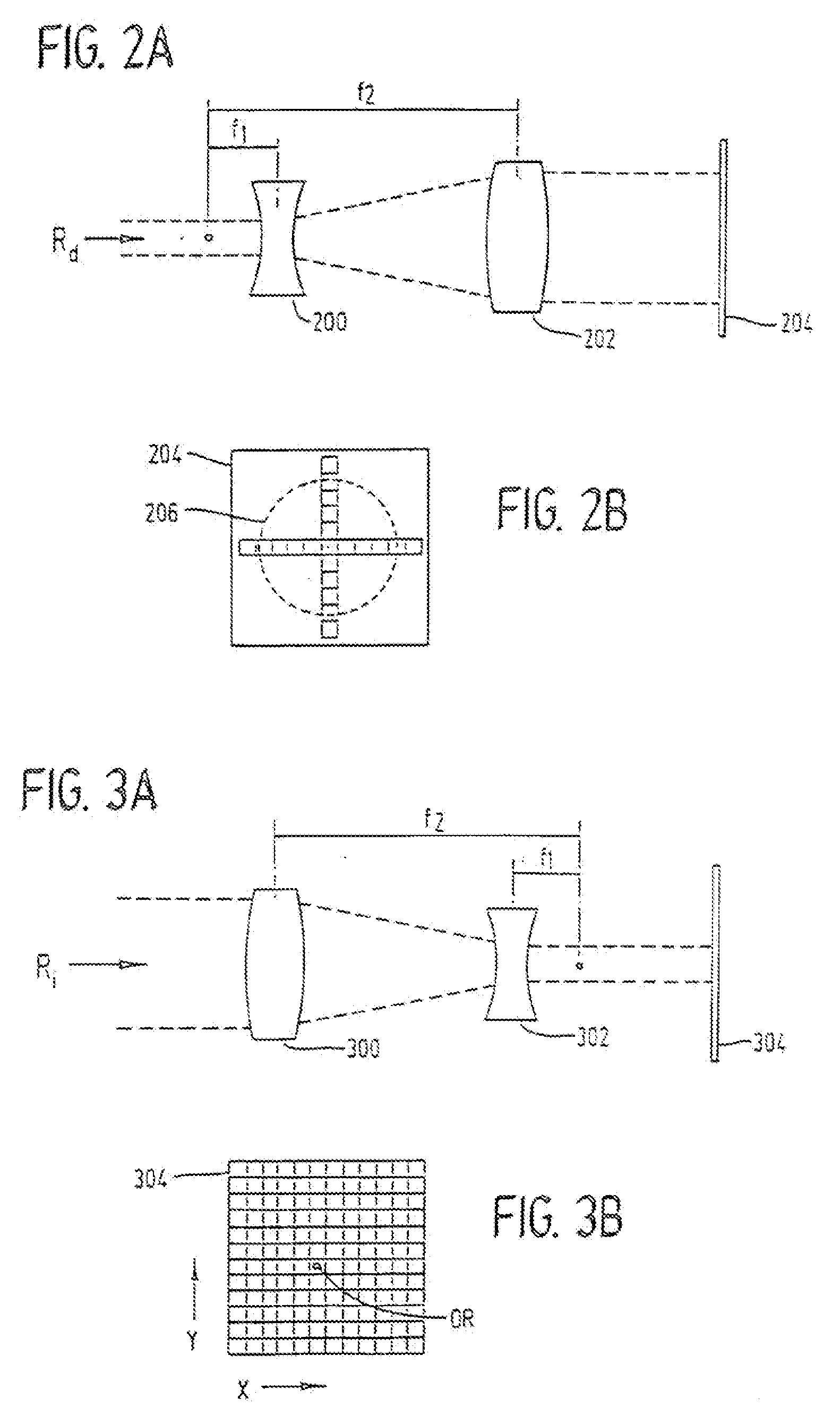
A laser-based method and apparatus for corneal surgery. The present invention is intended to be applied primarily to ablate organic materials, and human cornea in particular. The invention uses a laser source which has the characteristics of providing a shallow ablation depth (0.2 microns or less per laser pulse), and a low ablation energy density threshold (less than or equal to about 10 mJ / cm2), to achieve optically smooth ablated corneal surfaces. The preferred laser includes a laser emitting approximately 100–50,000 laser pulses per second, with a wavelength of about 198–300 nm and a pulse duration of about 1–5,000 picoseconds. Each laser pulse is directed by a highly controllable laser scanning system. Described is a method of distributing laser pulses and the energy deposited on a target surface such that surface roughness is controlled within a specific range. Included is a laser beam intensity monitor and a beam intensity adjustment means, such that constant energy level is maintained throughout an operation. Eye movement during an operation is corrected for by a corresponding compensation in the location of the surgical beam. Beam operation is terminated if the laser parameters or the eye positioning is outside of a predetermined tolerable range. The surgical system can be used to perform surgical procedures including removal of corneal scar, making incisions, cornea transplants, and to correct myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and other corneal surface profile defects.
Owner:LAI SHUI T
Method of corneal surgery by laser incising a contoured corneal flap
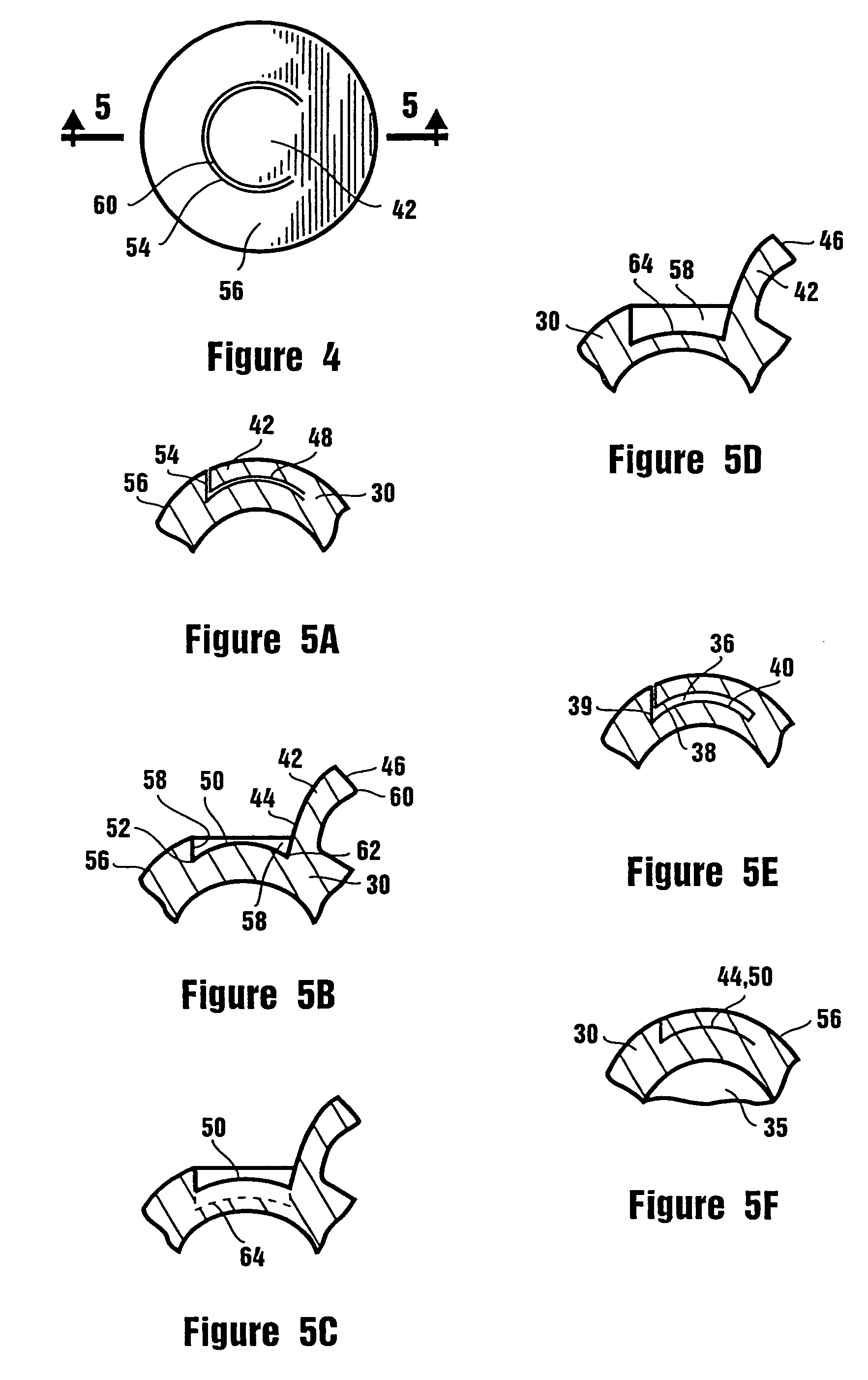
A method of corneal laser surgery is disclosed. A first periphery is defined at an anterior surface of the cornea. This first periphery bounds a first planar area. A second periphery is defined within stromal tissue of the cornea. This second periphery bounds a second planar area. The second planar area is sized differently than the first planar area. A layer of stromal tissue which is bounded by the second periphery is subsequently incised. Stromal tissue between substantial portions of the first periphery and the second periphery is also incised, such that at least some corneal tissue disposed between the first and second peripheries remains connected to corneal tissue outside of the first and second peripheries.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Shielded intraocular probe for improved illumination or therapeutic application of light
ActiveUS20050245916A1Diminishes unwanted glareLaser surgeryEndoscopesKeratorefractive surgeryForceps
An intraocular light probe has a mask or shield affixed at its distal end thereof which forms a directed light beam for intraocular illumination of target tissues or intraocular application of therapeutic light. The mask or shield serves to more fully focus, intensify and direct the beam toward the target tissues. The mask or shield also helps direct light away from other tissues and away from the eyes of the surgeon. This lessens unwanted glare. By placing a light probe beneath a surgical instrument such as a phacoemulsifier or vitrector, laser, cutting instrument (e.g., scissors or knife), forceps or probe / manipulator, whether as part of or separate from an infusion sleeve, a mask or shield effect is created. This has the same benefits of directing the beam toward target tissues, away from other tissues and away from the eyes of the surgeon. The mask or shield is opaque or semi-opaque and made of a soft, semi-rigid or rigid material. The shield can be rigid enough to serve as the shaft of an instrument with a probe or manipulator at its distal tip. It may also be reflective on the side adjacent to the fiber bundle to help direct, magnify, and intensify the beam of light. The shape of the shield can be flat, curved or circular with an opening along one side. The mask / shield can be removed from the fiberoptic light for sterilization. The device of the invention is preferably introduced into the eye via the primary or side-port incision to provide intraocular cross-lighting of tissues during surgical procedures such as cataract surgery, corneal surgery, vitrectomy, intraocular lens implantation, refractive surgery, glaucoma surgery and vitreo / retinal surgery.
Owner:CONNOR CHRISTOPHER S
Control program for a device for photorefractive corneal surgery of the eye
In a control program, according to which a laser-beam spot is guided, while being controlled with respect to position and time, over a cornea to be corrected photorefractively, so as to ablate a predetermined ablation profile therefrom, the effect of the angle between the laser earn and the corneal surface on the energy density of the laser-beam spot incident on the corneal surface and / or on the fraction of the laser-beam energy incident on the corneal surface which is reflected away, is taken into account when generating the control program.
Owner:WAVELIGHT LASER TECH
Method and Apparatus for Laser Surgery of the Cornea
InactiveUS20060217688A1Correction of myopiaCorrected astigmatismLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCorneal ablationSurgical lasers
A laser-based method and apparatus for corneal surgery. The present invention is intended to be applied primarily to ablate organic materials, and human cornea in particular. The invention uses a laser source which has the characteristics of providing a shallow ablation depth (0.2 microns or less per laser pulse), and a low ablation energy density threshold (less than or equal to about 10 mJ / cm.sup.2), to achieve optically smooth ablated corneal surfaces. The preferred laser includes a laser emitting approximately 100-50,000 laser pulses per second, with a wavelength of about 198-300 nm and a pulse duration of about 1-5,000 picoseconds. Each laser pulse is directed by a highly controllable laser scanning system. Described is a method of distributing laser pulses and the energy deposited on a target surface such that surface roughness is controlled within a specific range. Included is a laser beam intensity monitor and a beam intensity adjustment means, such that constant energy level is maintained throughout an operation. Eye movement during an operation is corrected for by a corresponding compensation in the location of the surgical beam. Beam operation is terminated if the laser parameters or the eye positioning is outside of a predetermined tolerable range. The surgical system can be used to perform surgical procedures including removal of corneal scar, making incisions, cornea transplants, and to correct myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and other corneal surface profile defects.
Owner:LAI SHUI T
Device and Method for Axial Length Measurement Having Expanded Measuring Function in the Anterior Eye Segment
InactiveUS20100271594A1Accurate calculationImprove accuracyUsing optical meansGonioscopesKeratorefractive surgeryCorneal surface
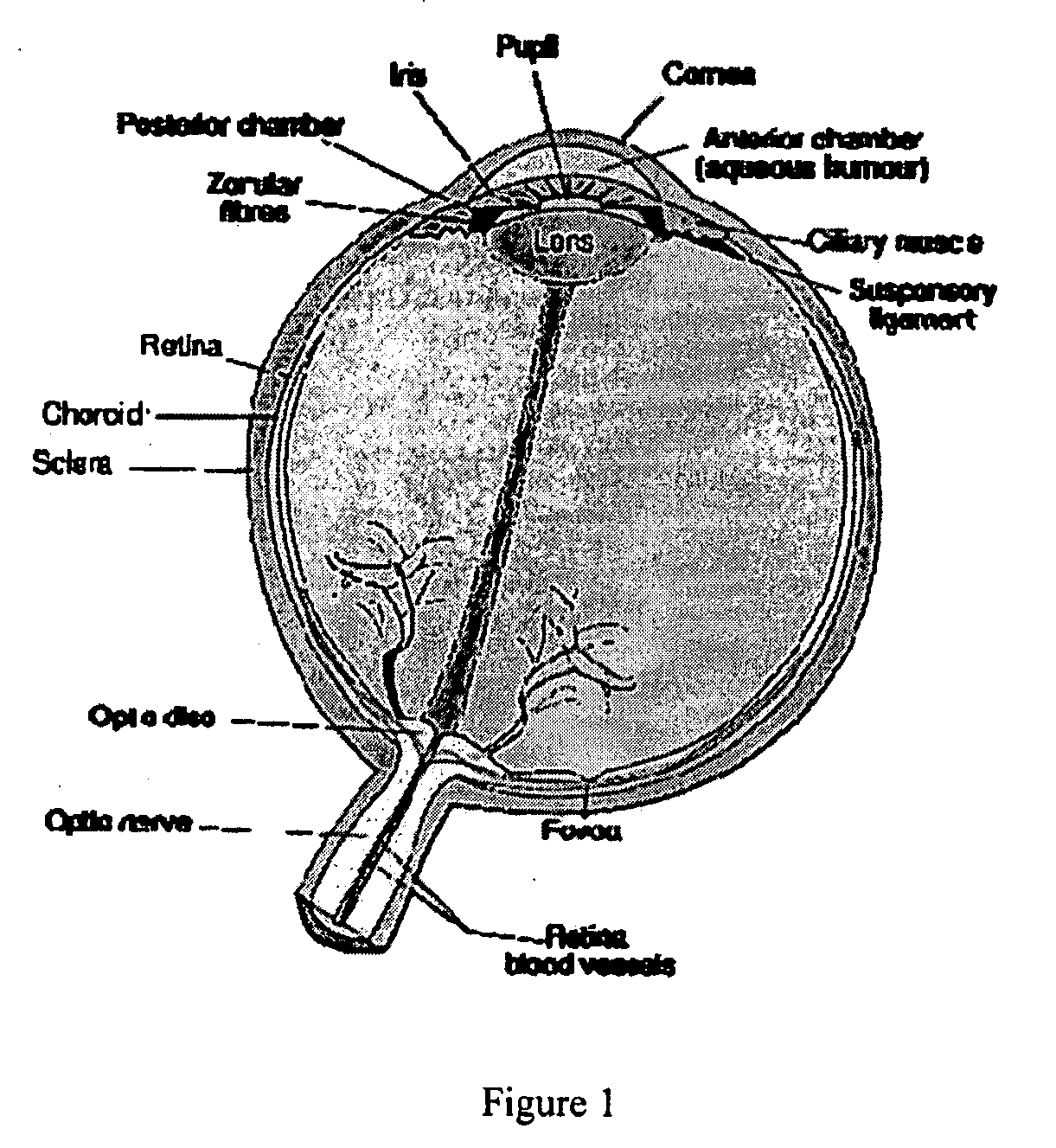
The present invention is directed to a solution for measuring geometric parameters in the eye which are required for calculating the refractive power of intraocular lenses. The device according to the invention for axial length measurement which acquires axial length, anterior corneal radii, anterior chamber depth, and other parameters in the anterior eye segment includes a control unit, a first measuring device for determining axial length, and an additional measuring device which acquires a plurality of structures in the anterior segment (such as the cornea, anterior chamber, and lens) and which has at least one illumination unit and at least one image recording unit. By determining additional partial-distance parameters of the anterior eye segments, the IOL can be calculated with high precision even after refractive surgery in which the natural relationship between the radii of the anterior and posterior corneal surfaces is extensively altered by corneal surgery.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
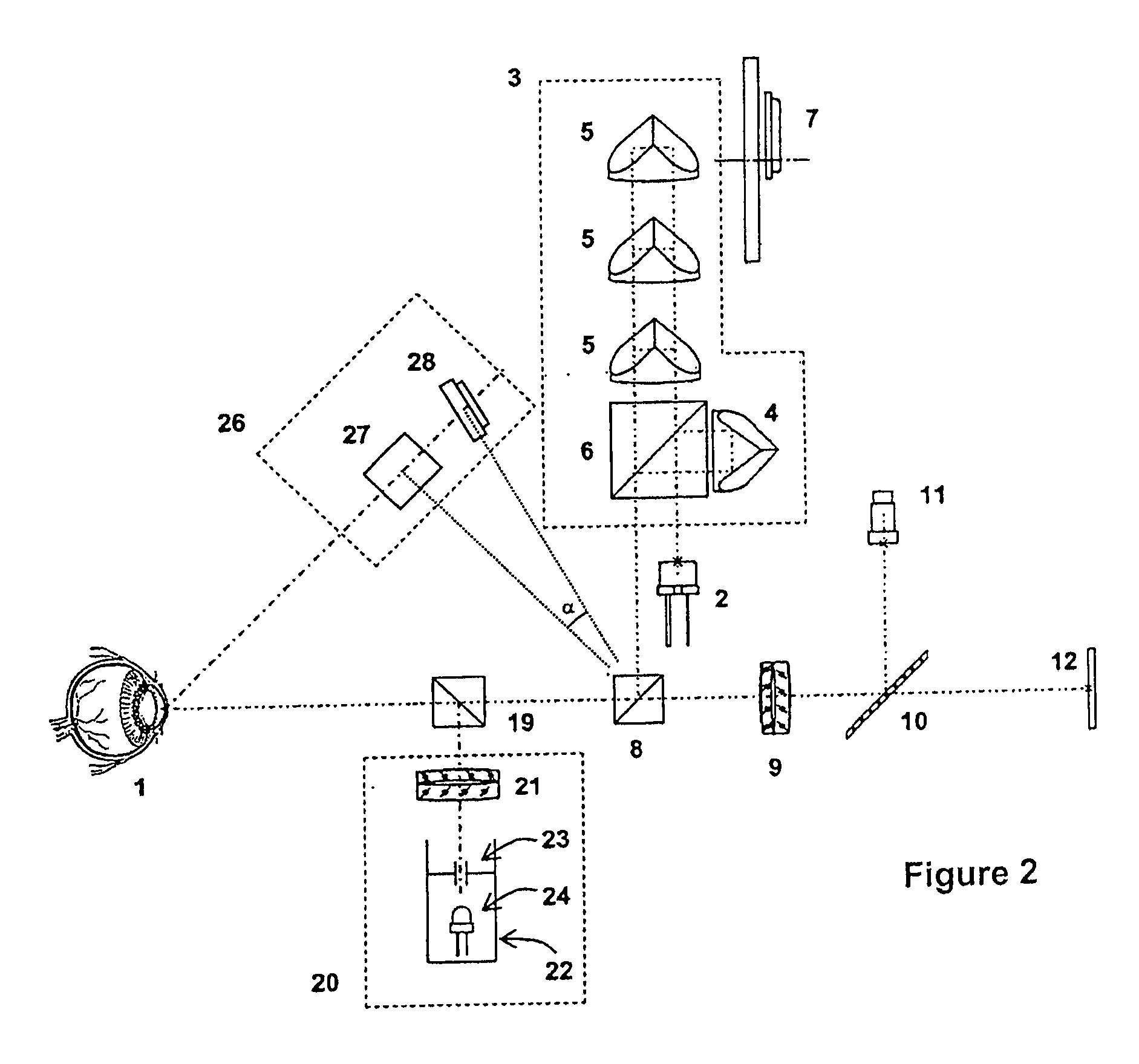
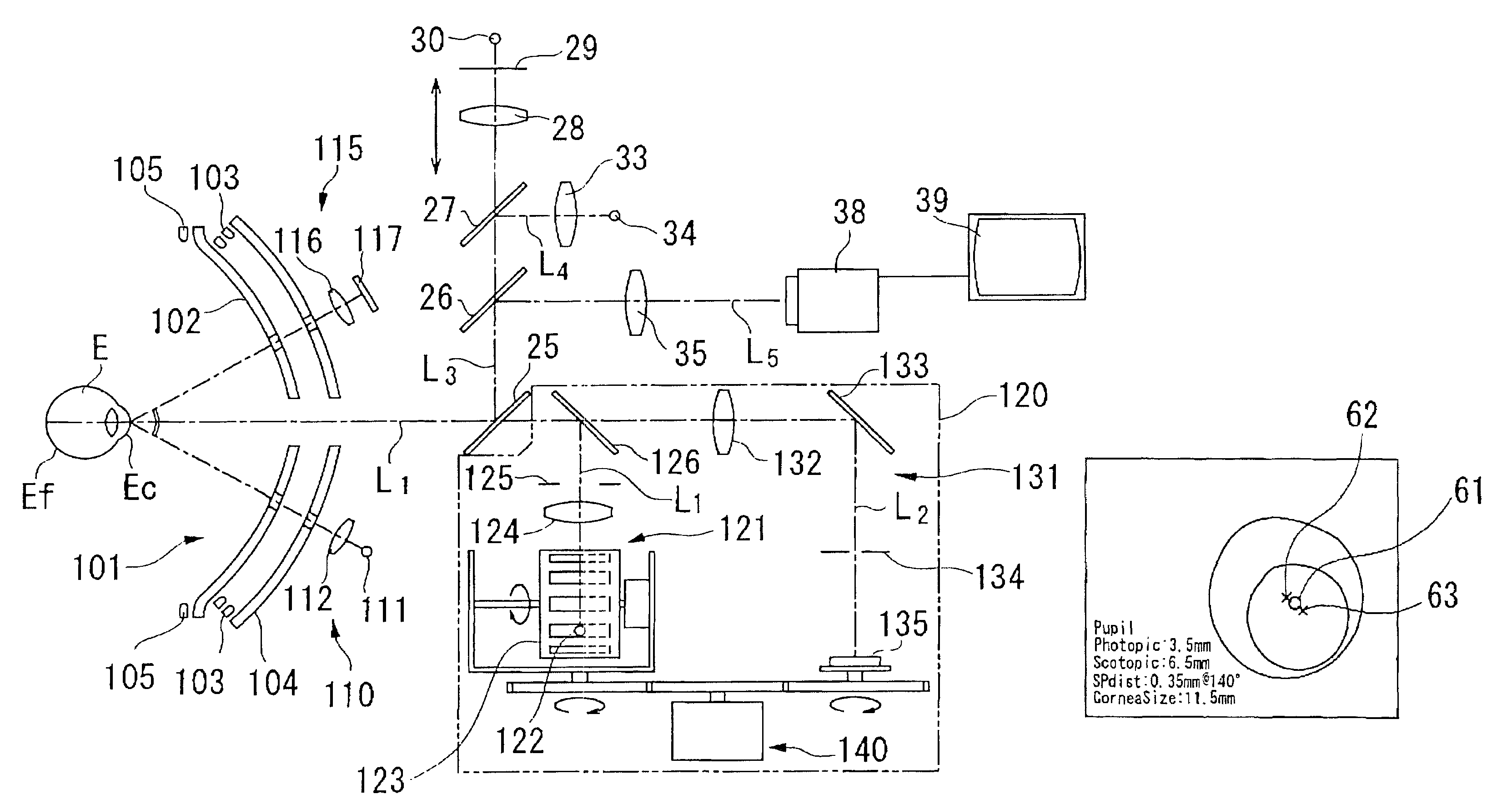
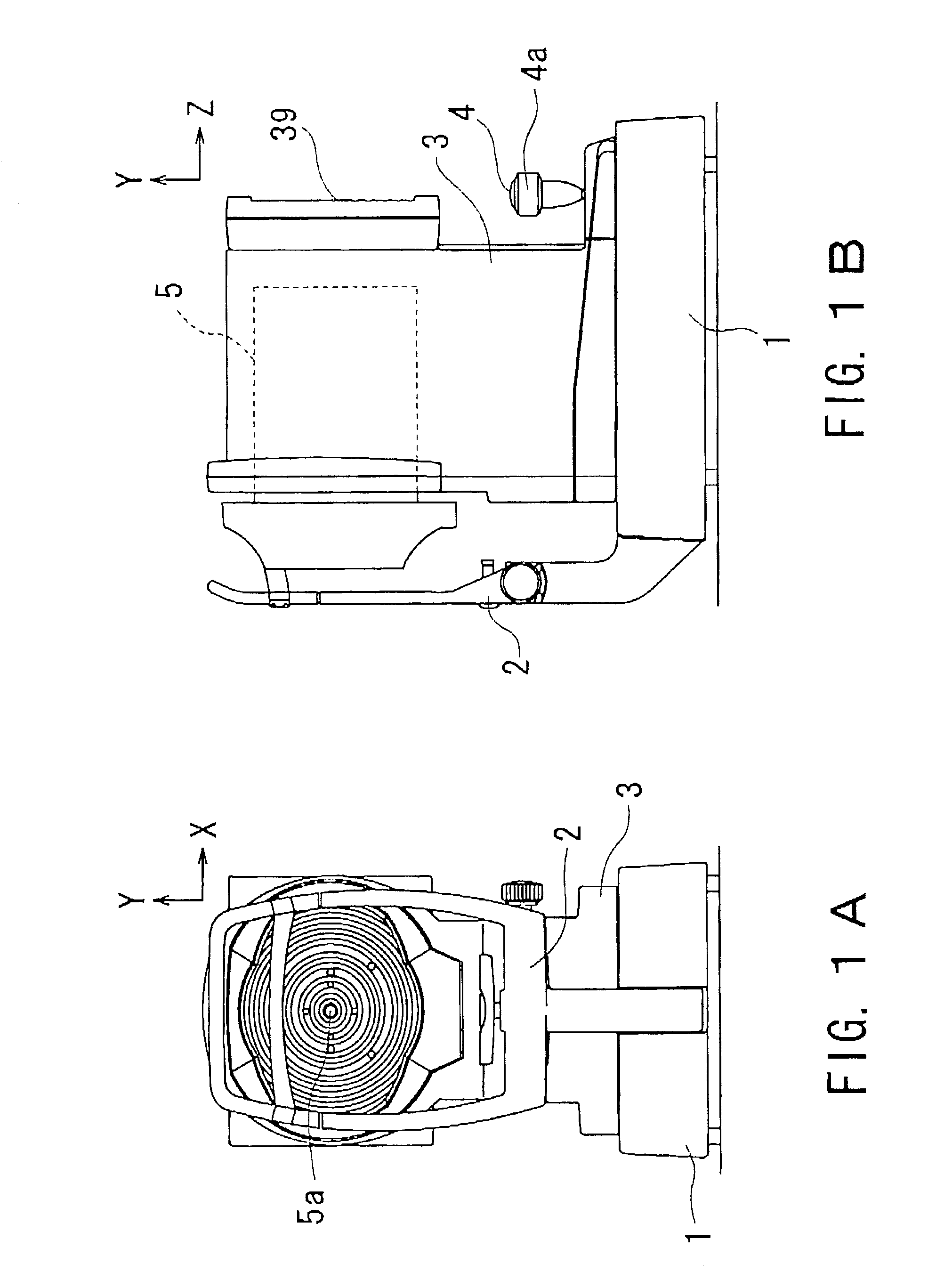
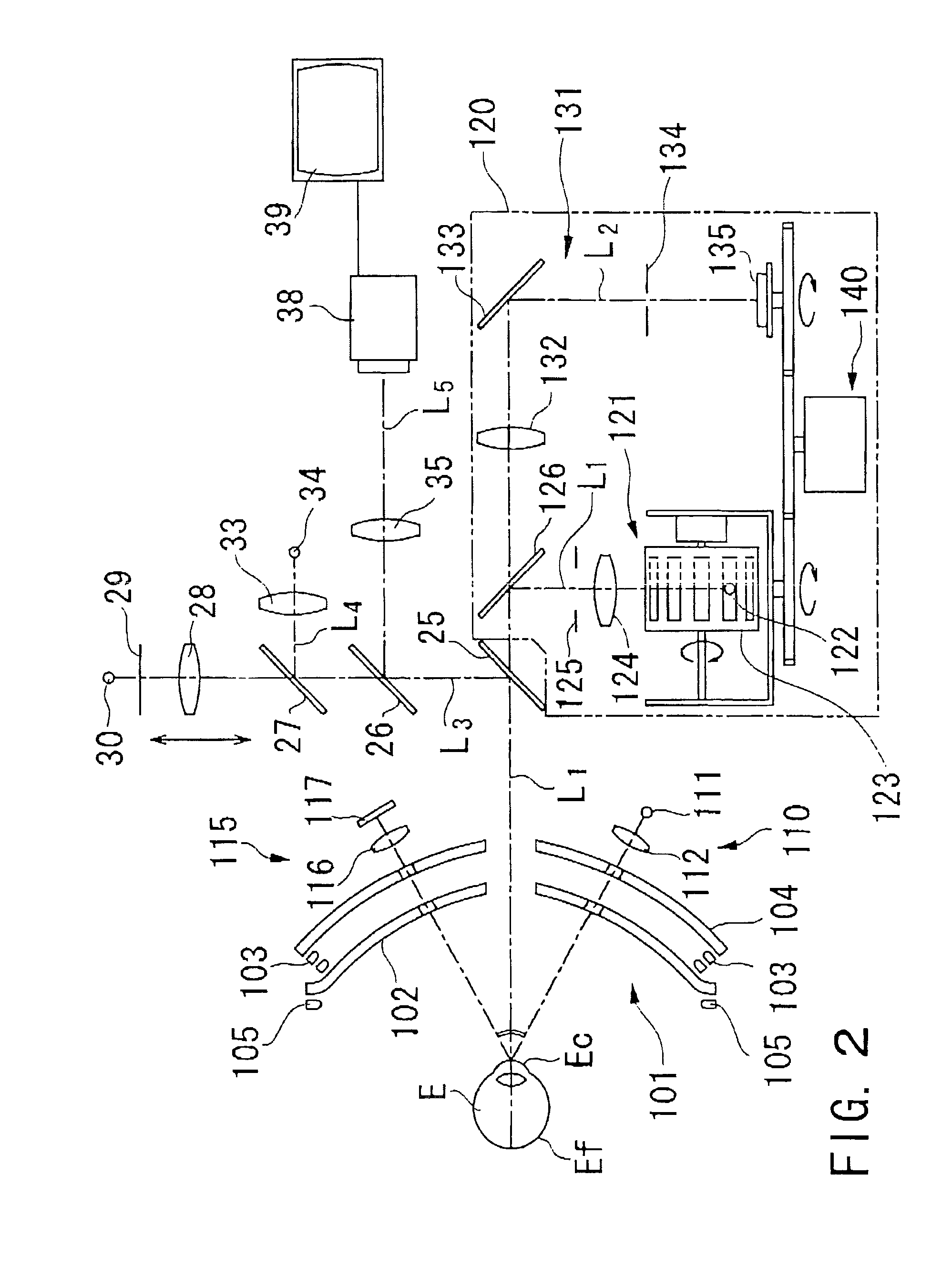
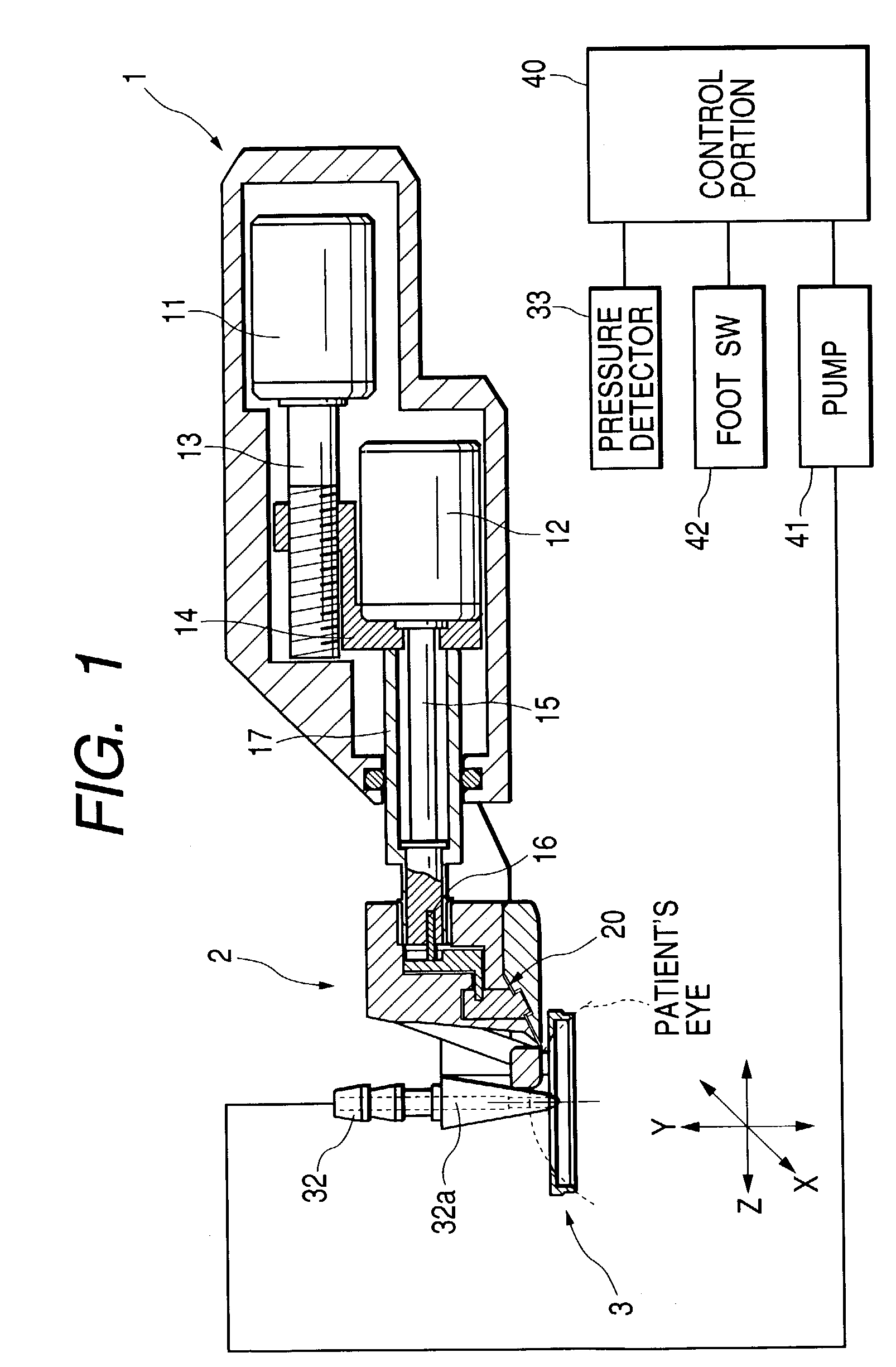
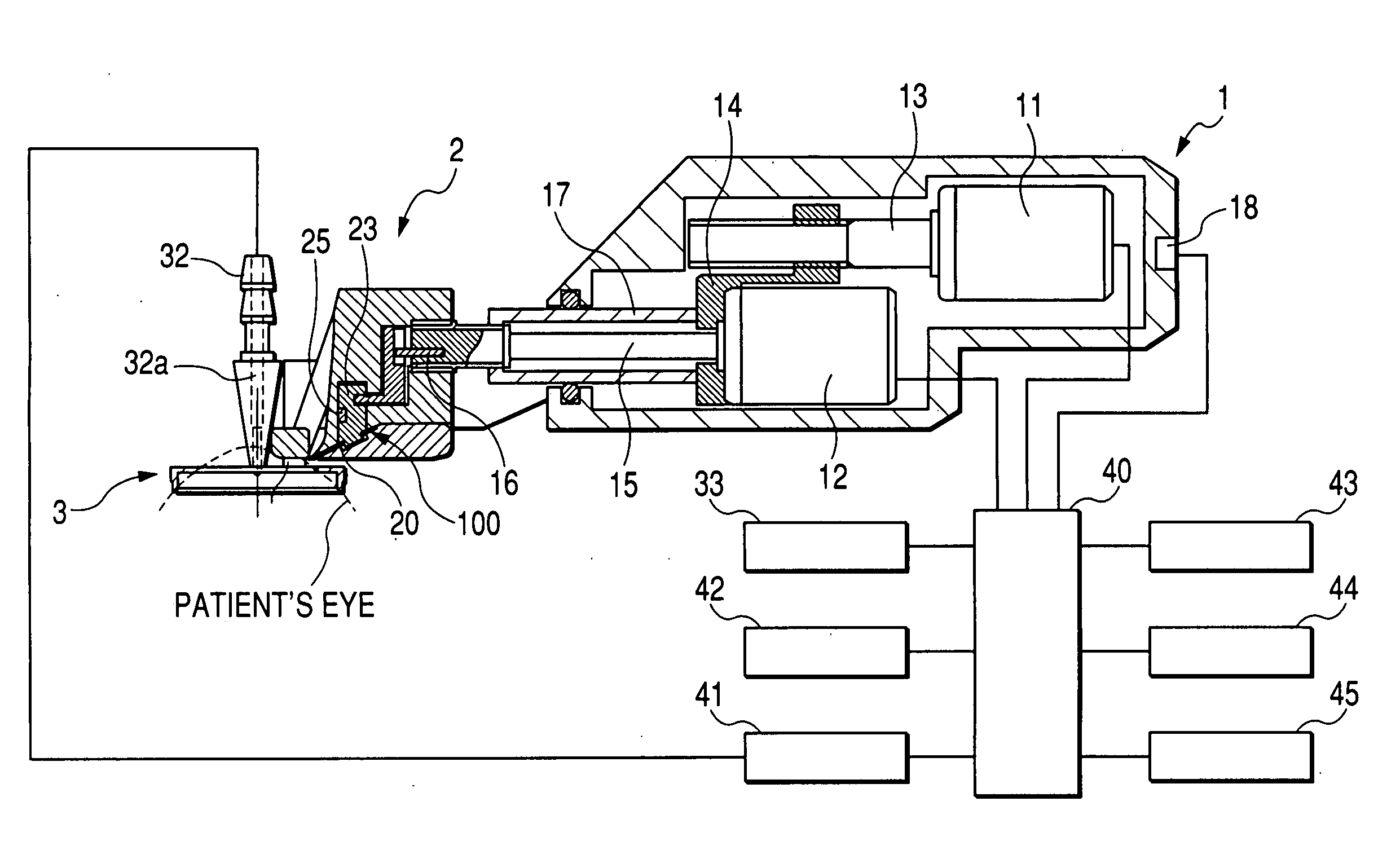
Ophthalmic apparatus and corneal surgery apparatus
An ophthalmic apparatus for obtaining differences between the pupil positions in photopia and scotopia accurately, and a corneal surgery apparatus for ablating a cornea of an eye by laser beam irradiation allowing for the differences. The ophthalmic apparatus has devices for inputting a first image of an anterior eye segment in photopia and a second one in scotopia, for obtaining pupil information in the images and differences between the pupil information in photopia and that in scotopia, and for outputting the differences. The corneal surgery apparatus has devices for irradiating the cornea with a laser beam, for aligning an irradiation position with the eye, for inputting differences between the pupil positions in photopia and scotopia, for detecting the photopic pupil position, for obtaining an alignment position of the laser beam based on the pupil position and the positional difference, and for controlling the alignment device based on the alignment position.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Virtual microscope system for monitoring the progress of corneal ablative surgery and associated methods
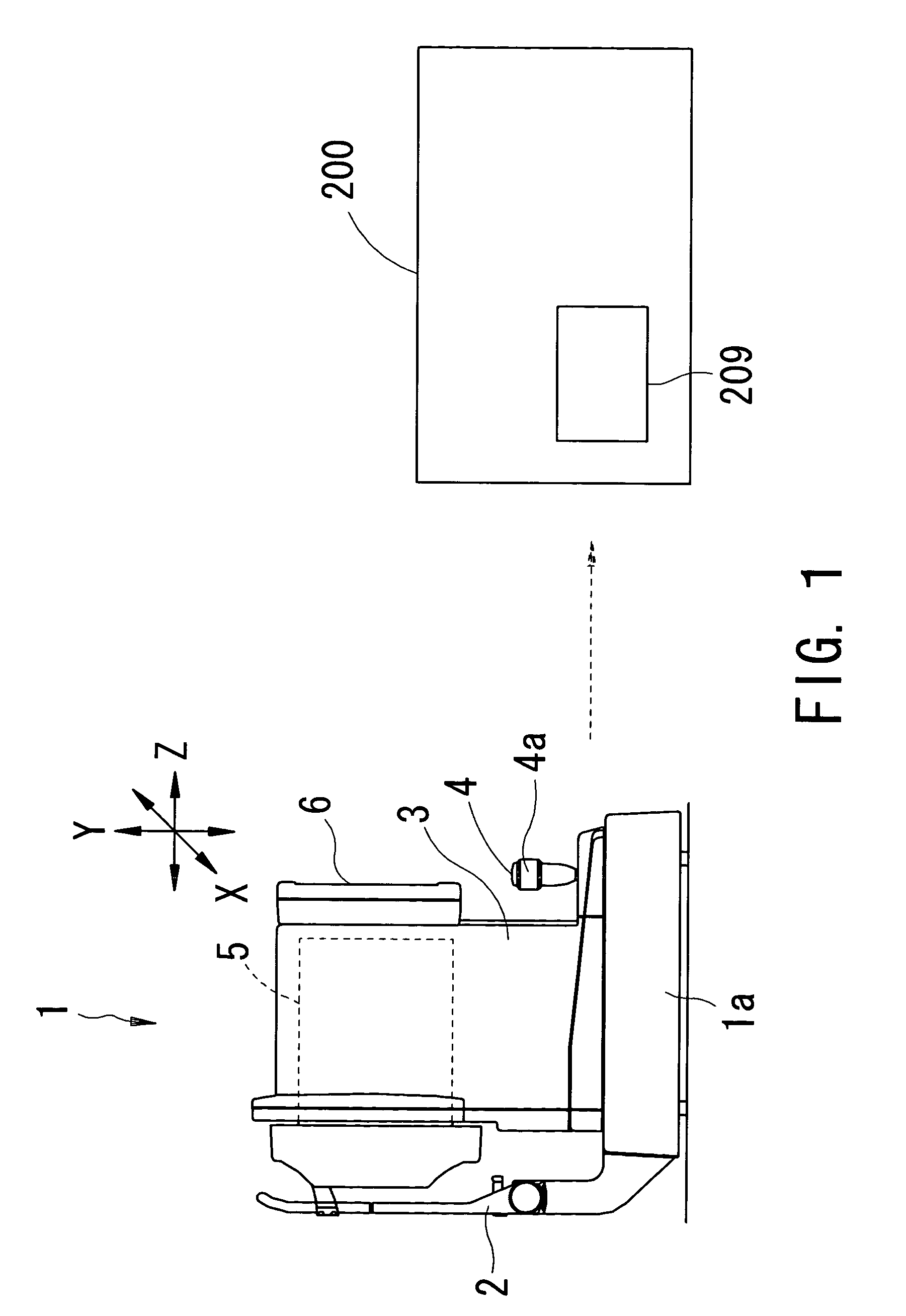
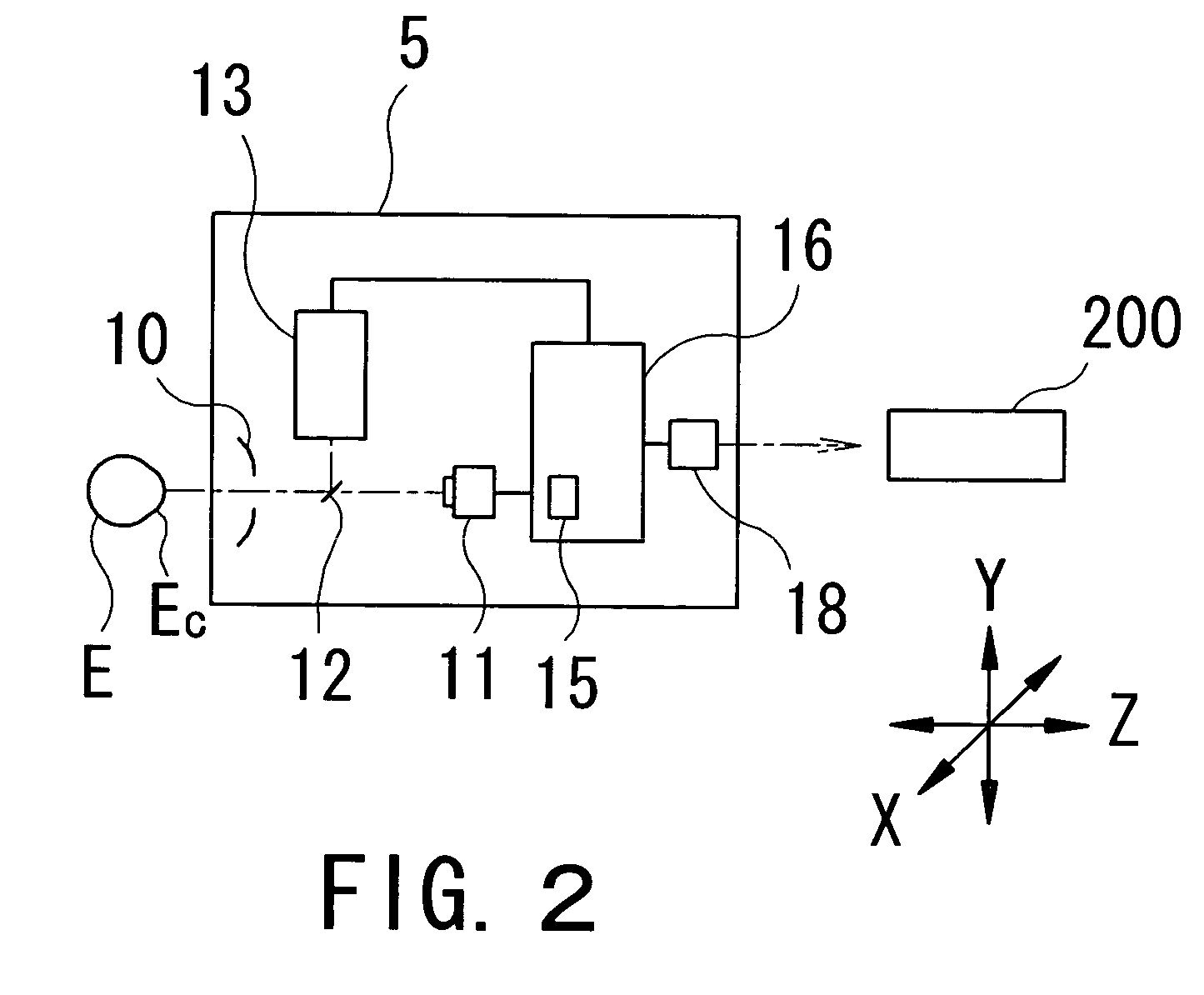
A system for visualizing an eye of a patient during corneal surgery includes a processor and a first and second camera in signal communication with the processor. The cameras are positionable for focusing on a cornea positioned for surgery. A first and a second display and optics therefor are in signal communication with the processor and are positionable for viewing through a first and a second eyepiece of a stereo microscope, respectively. Software is resident on the processor for receiving a first and second corneal image from the first and second cameras, for processing the received first and second images for display, and for transmitting the processed first and second images to the first and the second displays, respectively, via the display optics. The displays can then be viewed by a surgeon through the microscope at least during the surgery.
Owner:ALCON INC
Virtual Microscope System for Monitoring the Progress of Corneal Ablative Surgery and Associated Methods
A system for visualizing an eye of a patient during corneal surgery includes a processor and a first and second camera in signal communication with the processor. The cameras are positionable for focusing on a cornea positioned for surgery. A first and a second display and optics therefor are in signal communication with the processor and are positionable for viewing through a first and a second eyepiece of a stereo microscope, respectively. Software is resident on the processor for receiving a first and second corneal image from the first and second cameras, for processing the received first and second images for display, and for transmitting the processed first and second images to the first and the second displays, respectively, via the display optics. The displays can then be viewed by a surgeon through the microscope at least during the surgery.
Owner:ALCON INC
Virtual microscope system for monitoring the progress of corneal ablative surgery and associated methods
A system for visualizing an eye of a patient during corneal surgery includes a processor and a first and second camera in signal communication with the processor. The cameras are positionable for focusing on a cornea positioned for surgery. A first and a second display and optics therefor are in signal communication with the processor and are positionable for viewing through a first and a second eyepiece of a stereo microscope, respectively. Software is resident on the processor for receiving a first and second corneal image from the first and second cameras, for processing the received first and second images for display, and for transmitting the processed first and second images to the first and the second displays, respectively, via the display optics. The displays can then be viewed by a surgeon through the microscope at least during the surgery.
Owner:ALCON REFRACTIVEHORIZONS
Method and apparatus for universal improvement of vision
InactiveUS20090048670A1Efficient changeImprove eyesightLaser surgeryIntraocular lensAnterior surfaceCorneal surgery
“Universal improvement” of vision is achieved by effectively changing the shape of the anterior refracting surface of the cornea to an ideal “turtleback” shape, on which is imposed the necessary curvature adjustment to achieve correction of distance vision. In accordance with one embodiment, the cornea is actually formed to the turtleback shape through corneal surgery, preferably laser ablation surgery. In accordance with a second embodiment, a contact lens with the desired distance corrected ideal turtleback shape on its anterior surface is positioned over the cornea.
Owner:SCI OPTICS INC
Laser-based methods and systems for corneal surgery
InactiveUS20110295243A1Minimal risk of damageMinimal damageLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCorneal surgeryLaser source
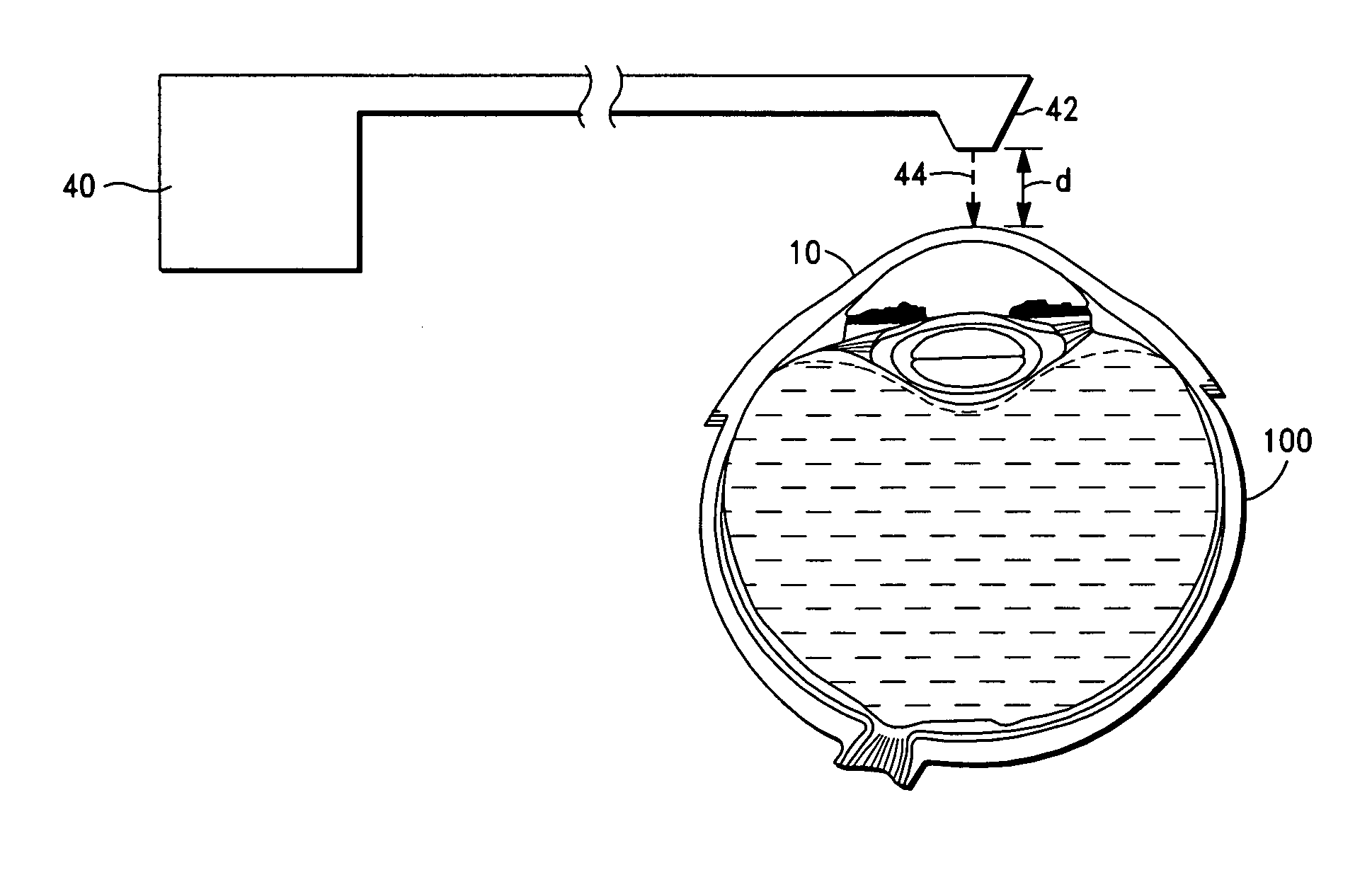
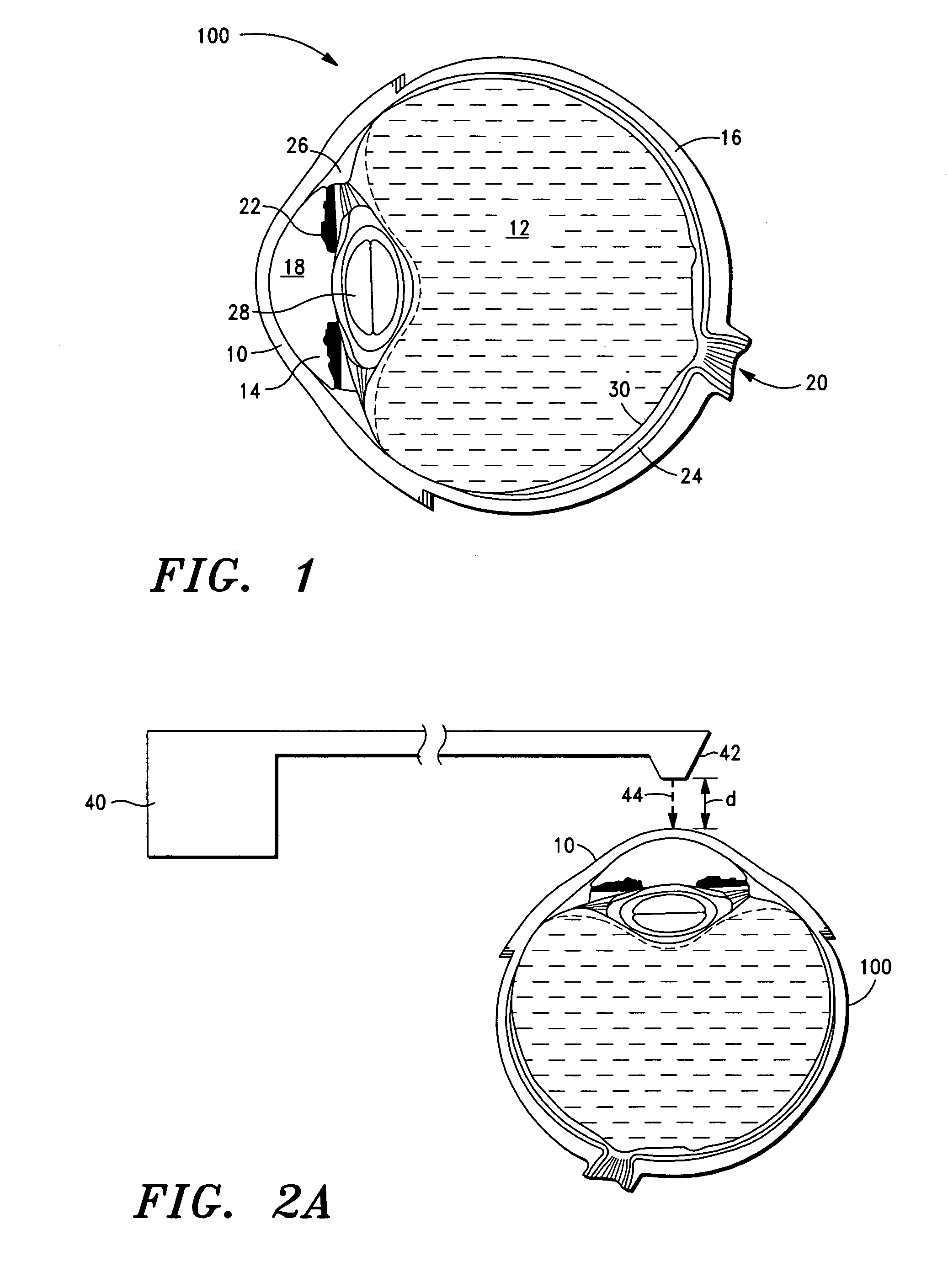
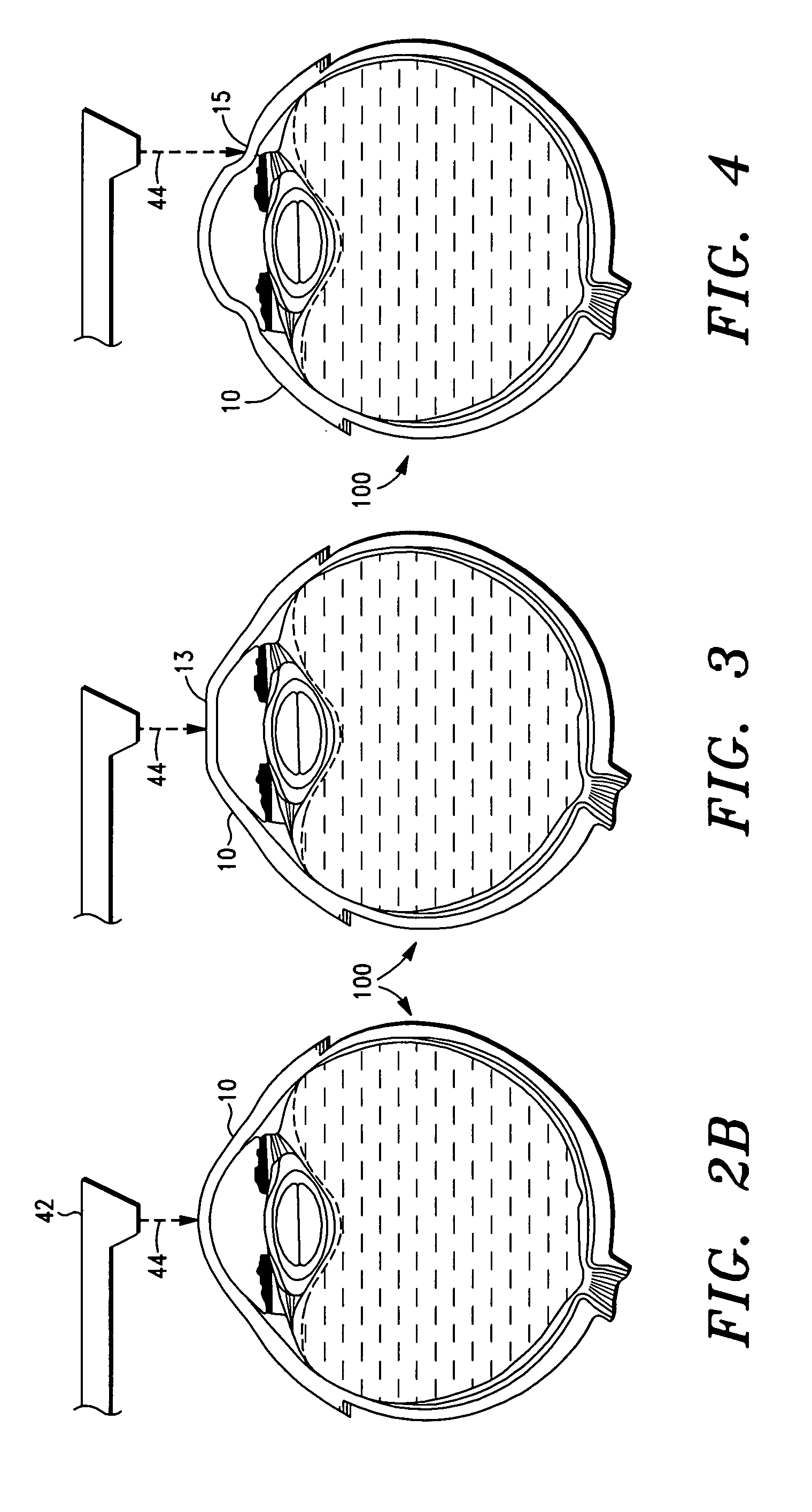
A method for surface ablation of cornea tissue comprising the steps of (i) providing a laser source that is adapted to generate and transmit focused pulsed laser energy, the laser source including a delivery head that is adapted to direct the laser energy to a target structure of an eye, (ii) disposing the delivery head a spaced distance from the target eye structure, and (iii) transmitting the laser energy to the target eye structure, whereby the surface of the eye structure tissue is primarily, more preferably, solely ablated.
Owner:PEYMAN GHOLAM A
Method and apparatus for reducing outbreaks of diffuse lamellar keratitis
Diffuse lamellar keratitis or DLK is a recently recognised post-surgical condition involving an inflammation that occurs in laser corneal surgery patients. This condition is typically associated with the LASIK surgical procedure (Laser Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis). The cause is presently unknown. the present invention provides a sterilization apparatus, which may be a retrofitting of the existing sterilizer, which reduces the occurrence of DLK and also methods for maintaining the sterilizer to reduce the occurrence of DLK.
Owner:MORCK DOUGLAS W +1
Surgical tools and systems for corneal tattooing and related methods
InactiveUS20150305927A1Reduced aperture areaLaser surgerySurgical needlesCorneal surgeryLaser assisted
Devices, systems, surgical kits and methods for corneal surgery, preferably using femto-laser assisted, corneal tattooing. The corneal tattoos are formed with one or more viscous opaque substances such as pasty substances of different colors to match eye colors of different patients.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Agent for repairing corneal perception
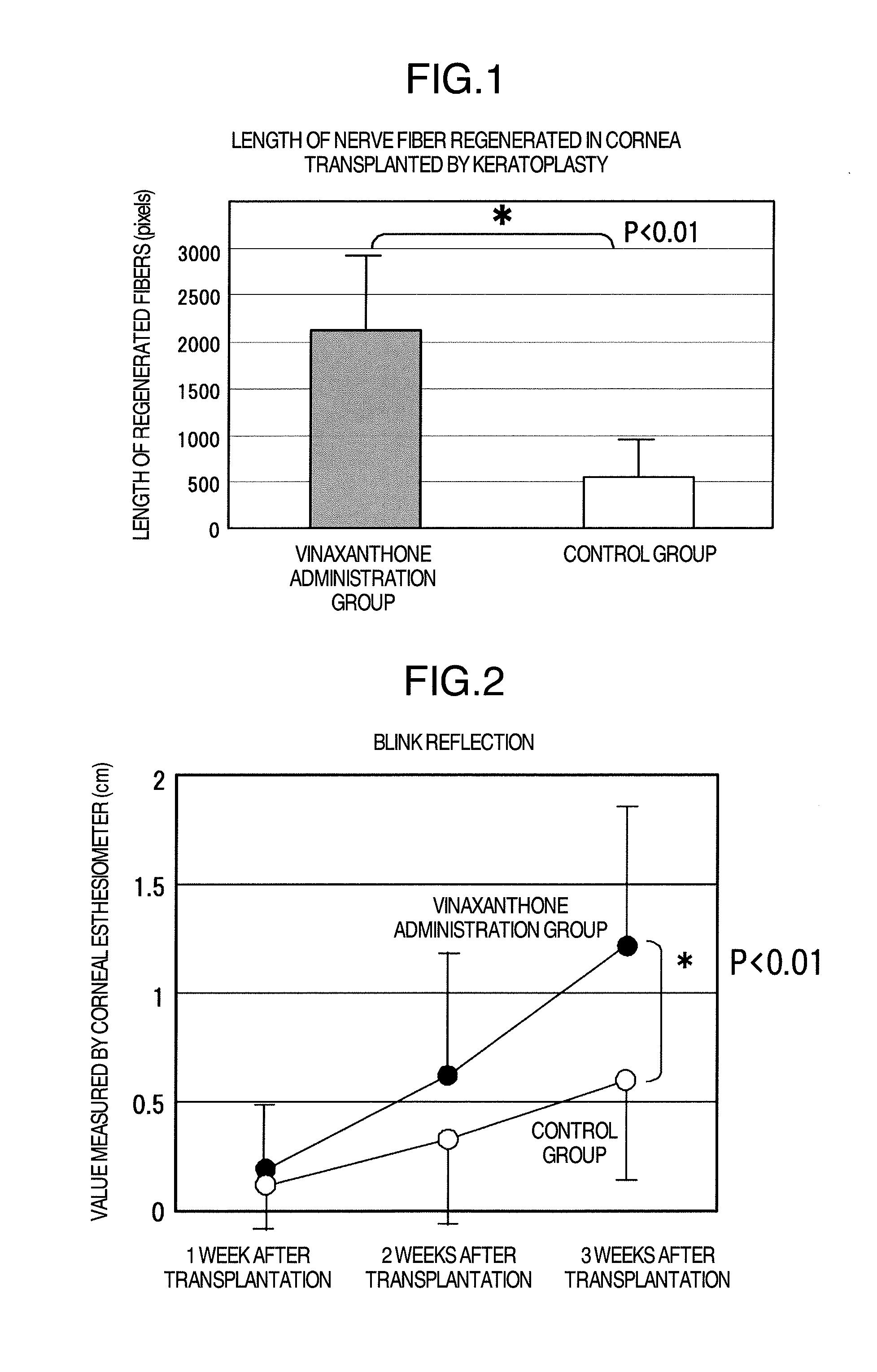
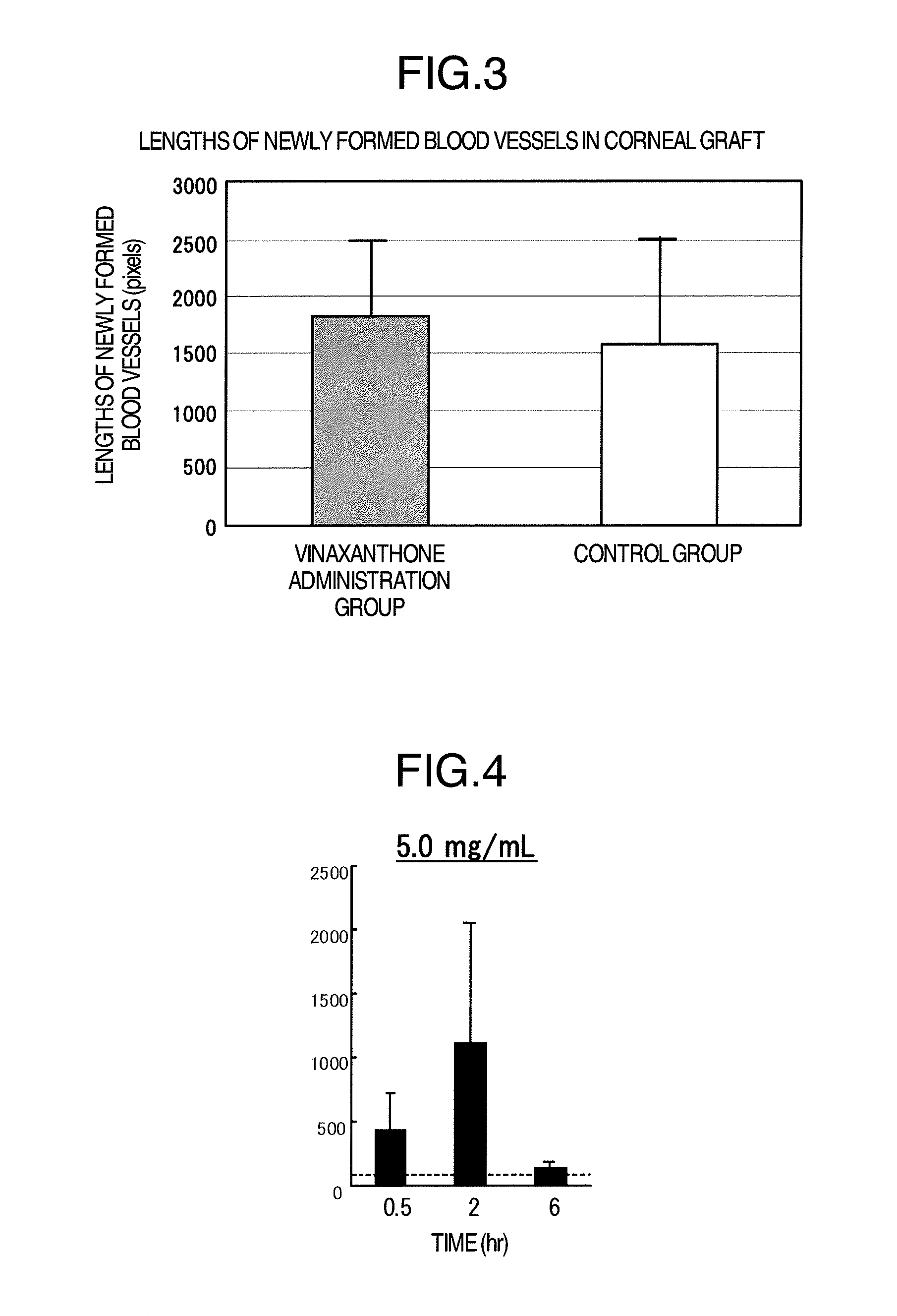
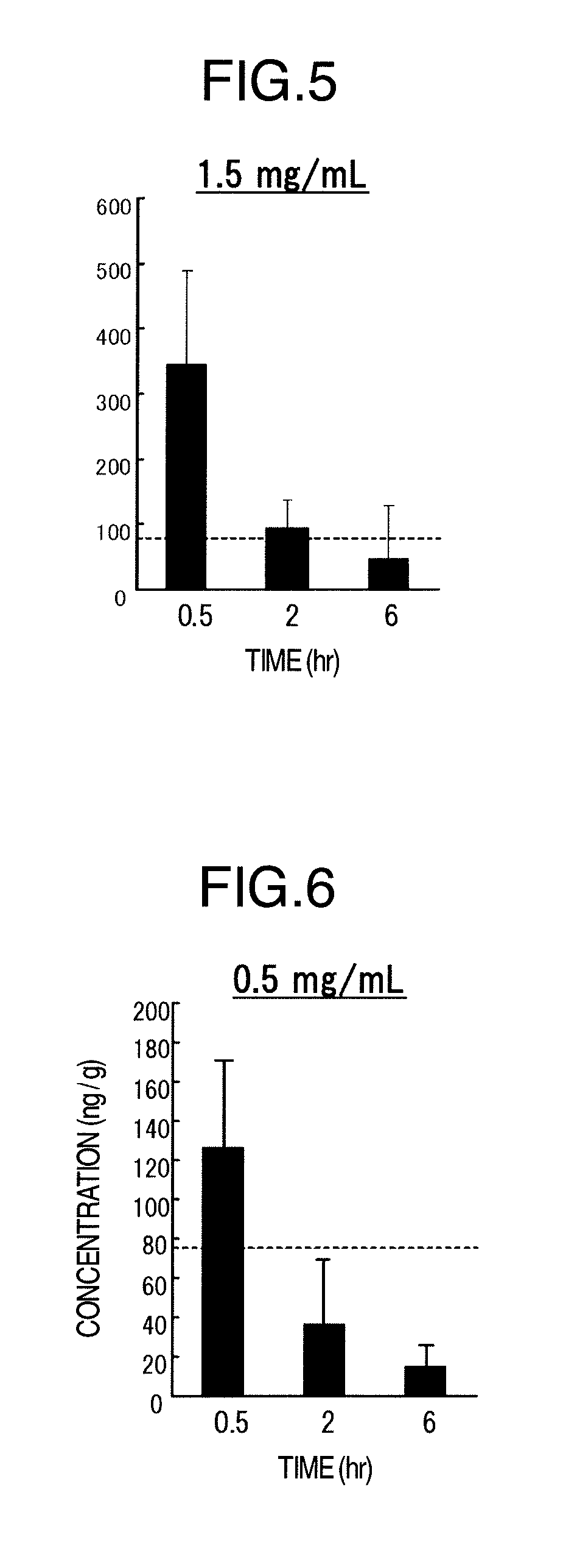
InactiveUS20070093513A1Recovers corneal sensitivityImprove the situationBiocideSenses disorderNeuroparalytic keratopathyCataract surgery
The present invention provides a novel pharmaceutical agent for recovering corneal sensitivity after corneal surgery and improving symptoms of dry eye. This pharmaceutical agent is useful for improving decreased corneal sensitivity and dry eye associated with corneal neurodegeneration such as post-cataract operation, post-LASIK operation, post-PRK operation, postkeratoplasty operation, neuroparalytic keratopathy, corneal ulcer, diabetic keratopathy and the like, since it contains a Rho protein inhibitor.
Owner:SENJU PHARMA CO LTD
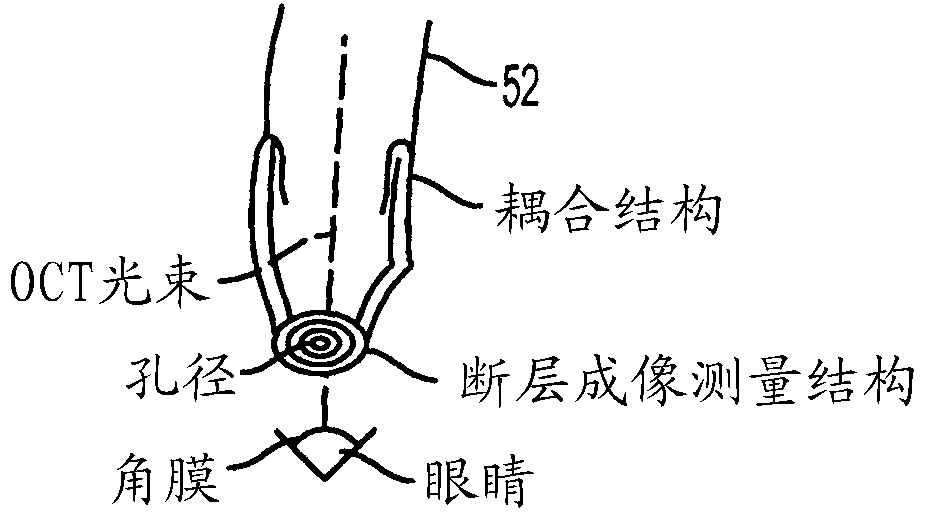
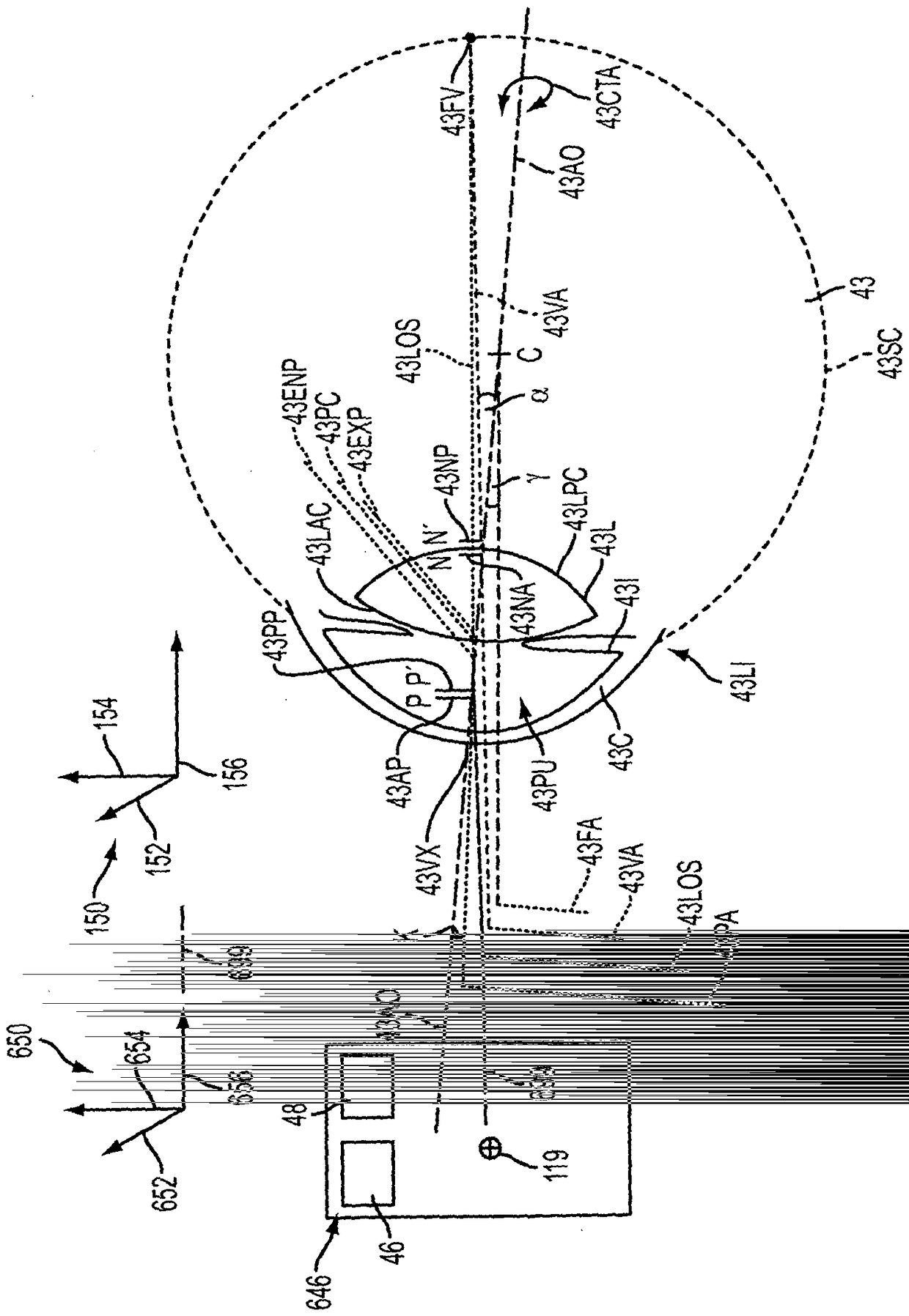
Corneal topography measurement and alignment of corneal surgical procedures
Methods and apparatus are configures to measure an eye without contacting the eye with a patient interface, and these measurements are used to determine alignment and placement of the incisions when the patient interface contacts the eye. The pre-contact locations of one or more structures of the eye can be used to determine corresponding post-contact locations of the one or more optical structures of the eye when the patient interface has contacted the eye, such that the laser incisions are placed at locations that promote normal vision of the eye. The incisions are positioned in relation to the pre-contact optical structures of the eye, such as an astigmatic treatment axis, nodal points of the eye, and visual axis of the eye.
Owner:眼力健发展有限责任公司
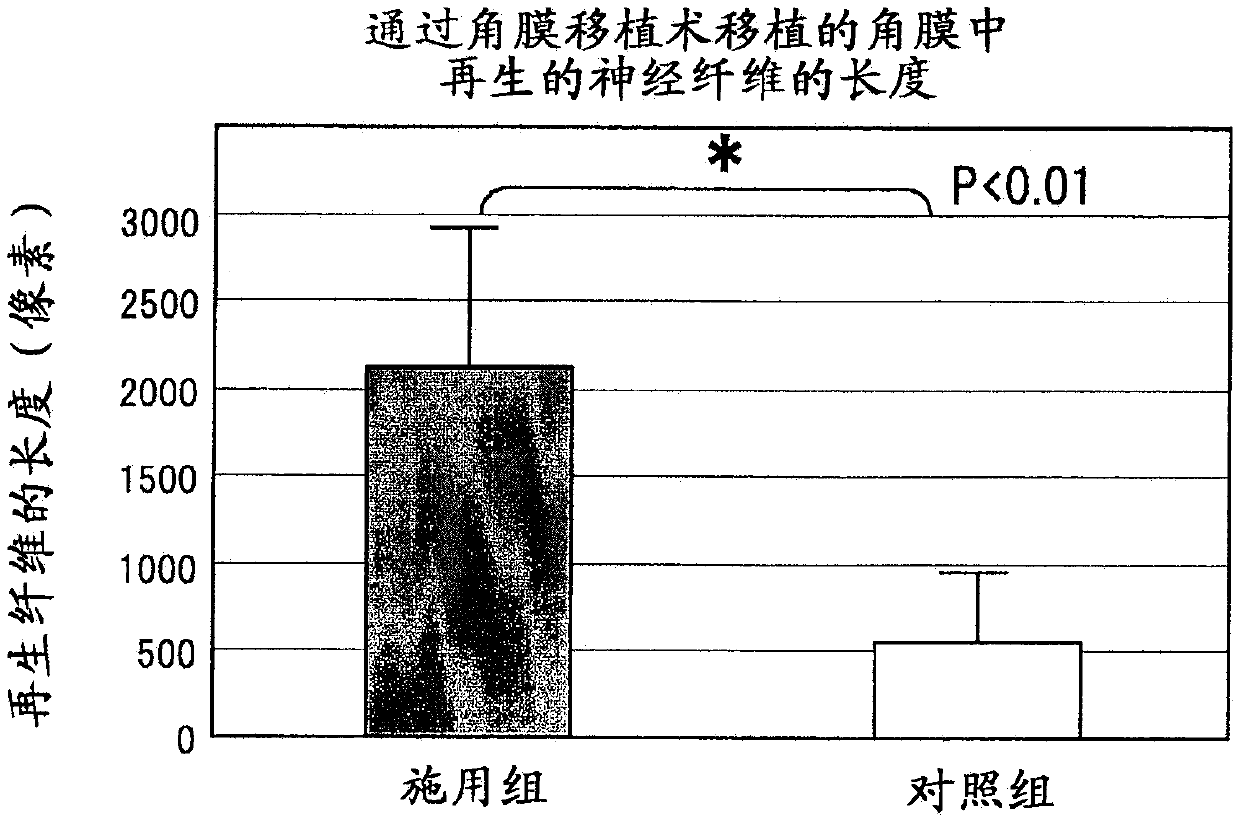
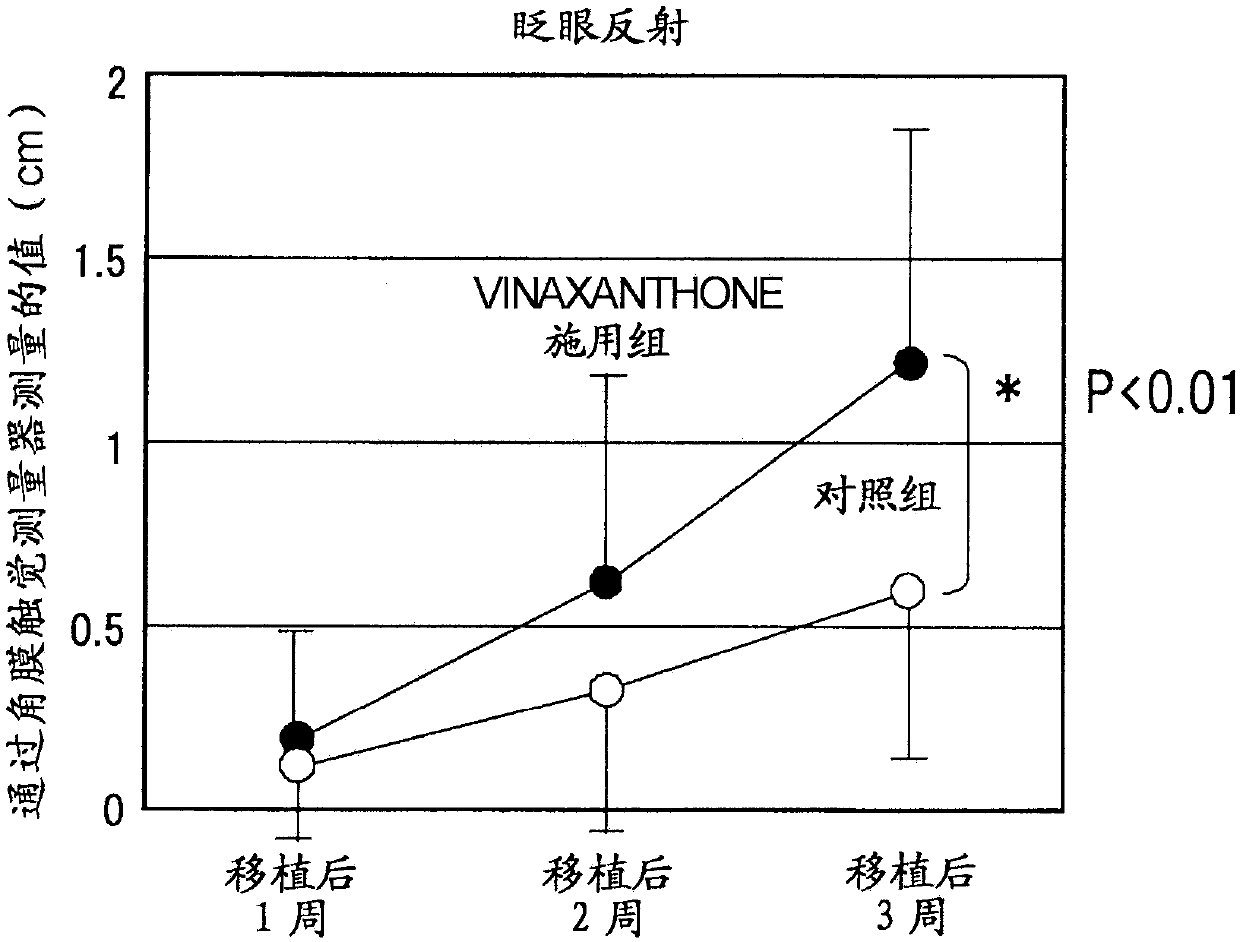
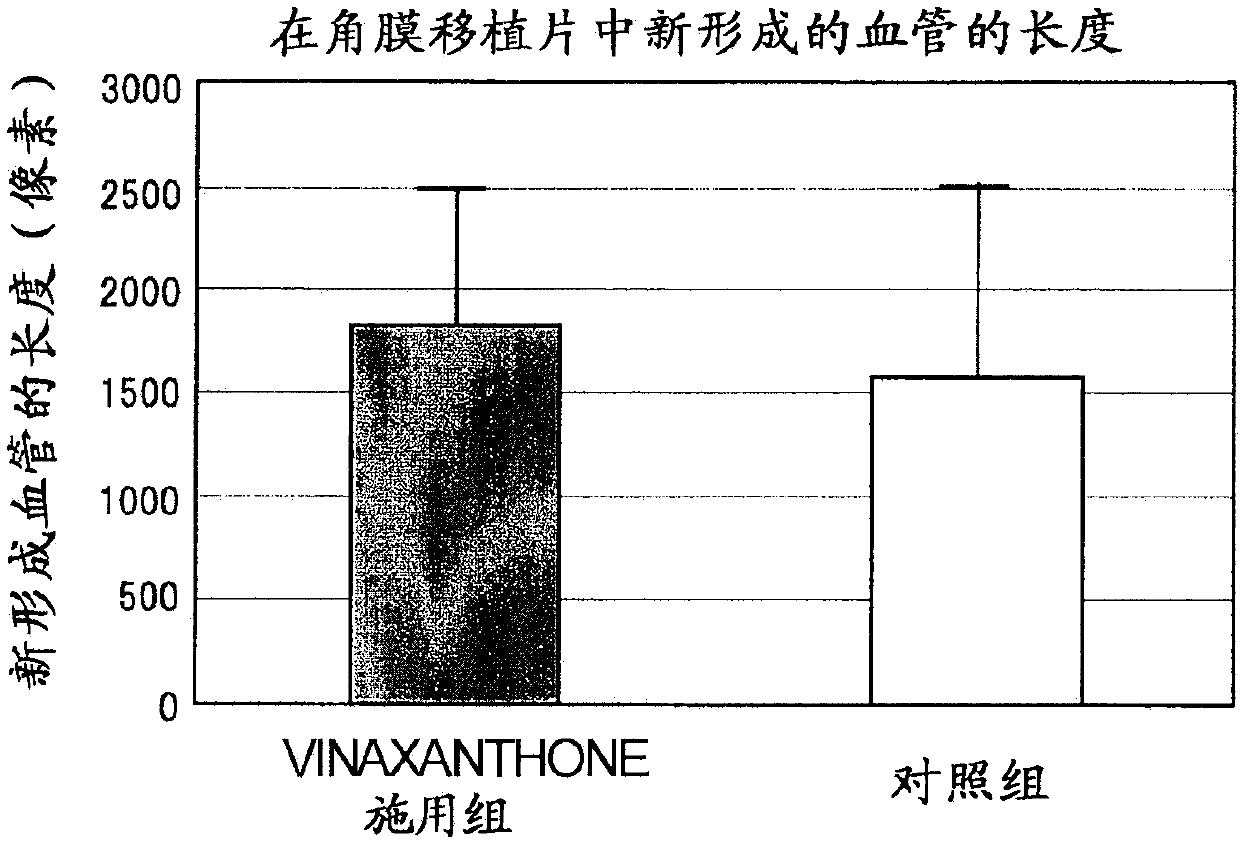
Therapeutic agent for corneal sensory nerve damage containing semaphorin inhibitor as active ingredient
InactiveUS20140018416A1Treat and prevent sensory neuropathyEasy to useBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseHydrogen atom
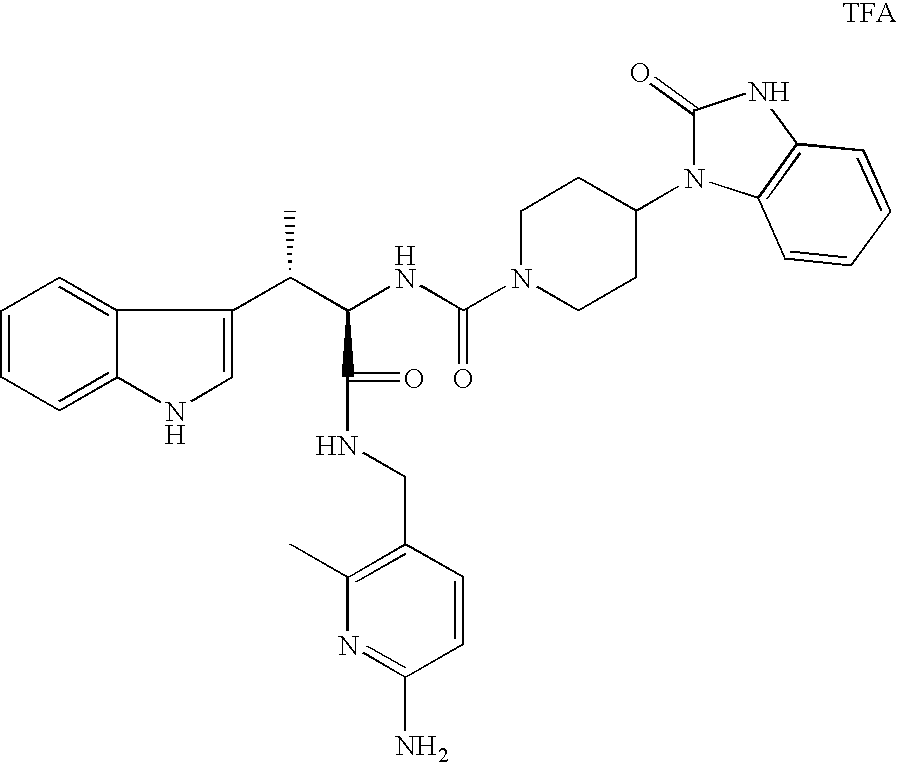
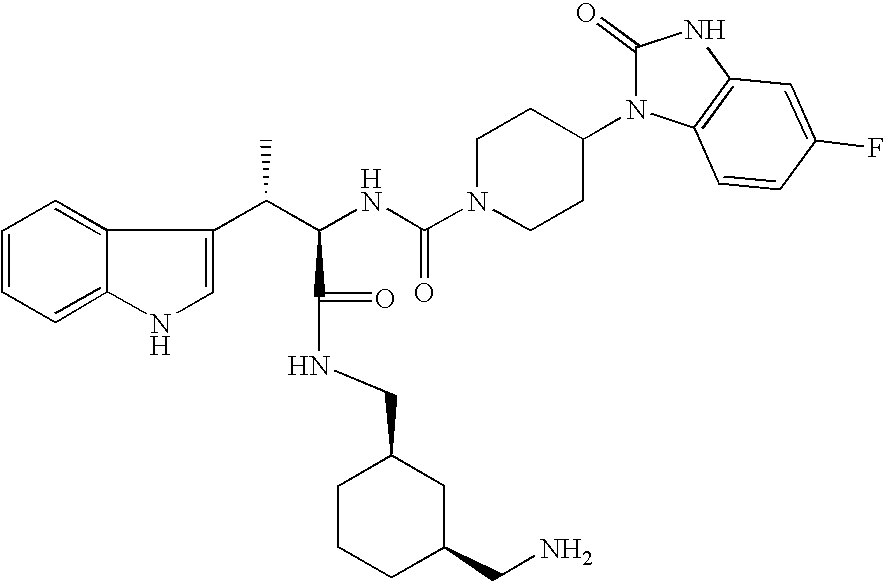
A compound represented by formula (1), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof is effective as a therapeutic agent or a prophylactic agent for a corneal disease or sensory nerve damage due to corneal surgery, and as a regeneration accelerator for corneal sensory nerves:wherein R1 represents a hydrogen atom or a carboxyl group, R2 represents a hydrogen atom or a hydroxy group, R3 represents a hydrogen atom or a carboxyl group, and R4 represents a hydrogen atom or a hydroxy group.
Owner:KEIO UNIV +1
Remedy for corneal failure
InactiveUS20060234922A1Recovers corneal sensitivityImproves condition of dry eyeBiocideSenses disorderNeuroparalytic keratopathyCorneal surgery
The present invention provides a new type of pharmaceutical agent that recovers corneal sensitivity after corneal surgery or improves the condition of dry eye. Application of a somatostatin receptor agonist is expected to provide an improvement effect on decreased corneal sensitivity after cataract surgery or LASIK surgery, decreased corneal sensitivity and dry eye associated with corneal neurodegeneration such as neuroparalytic keratopathy, corneal ulcer, diabetic keratopathy and the like.
Owner:SENJU PHARMA CO LTD
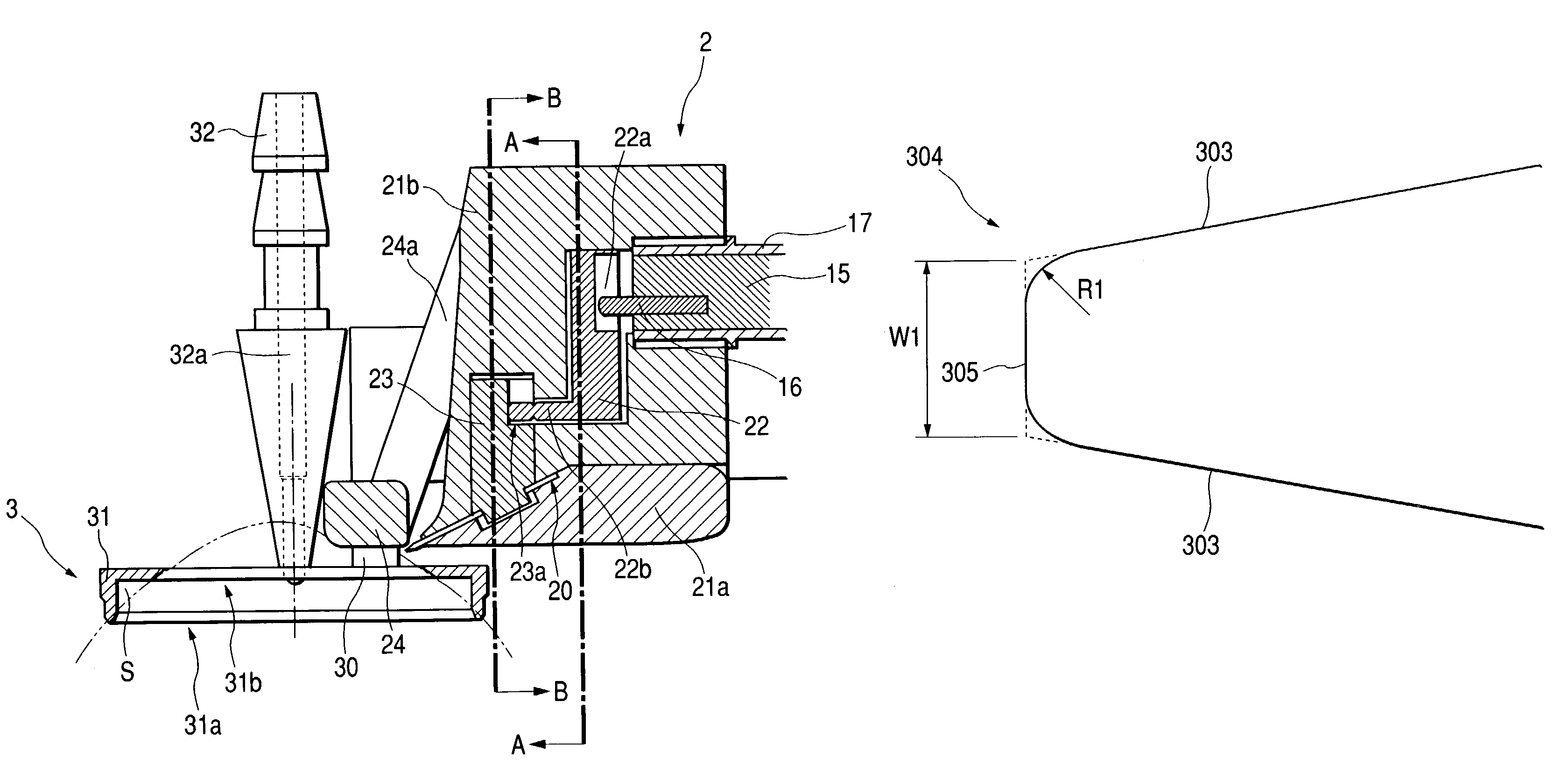
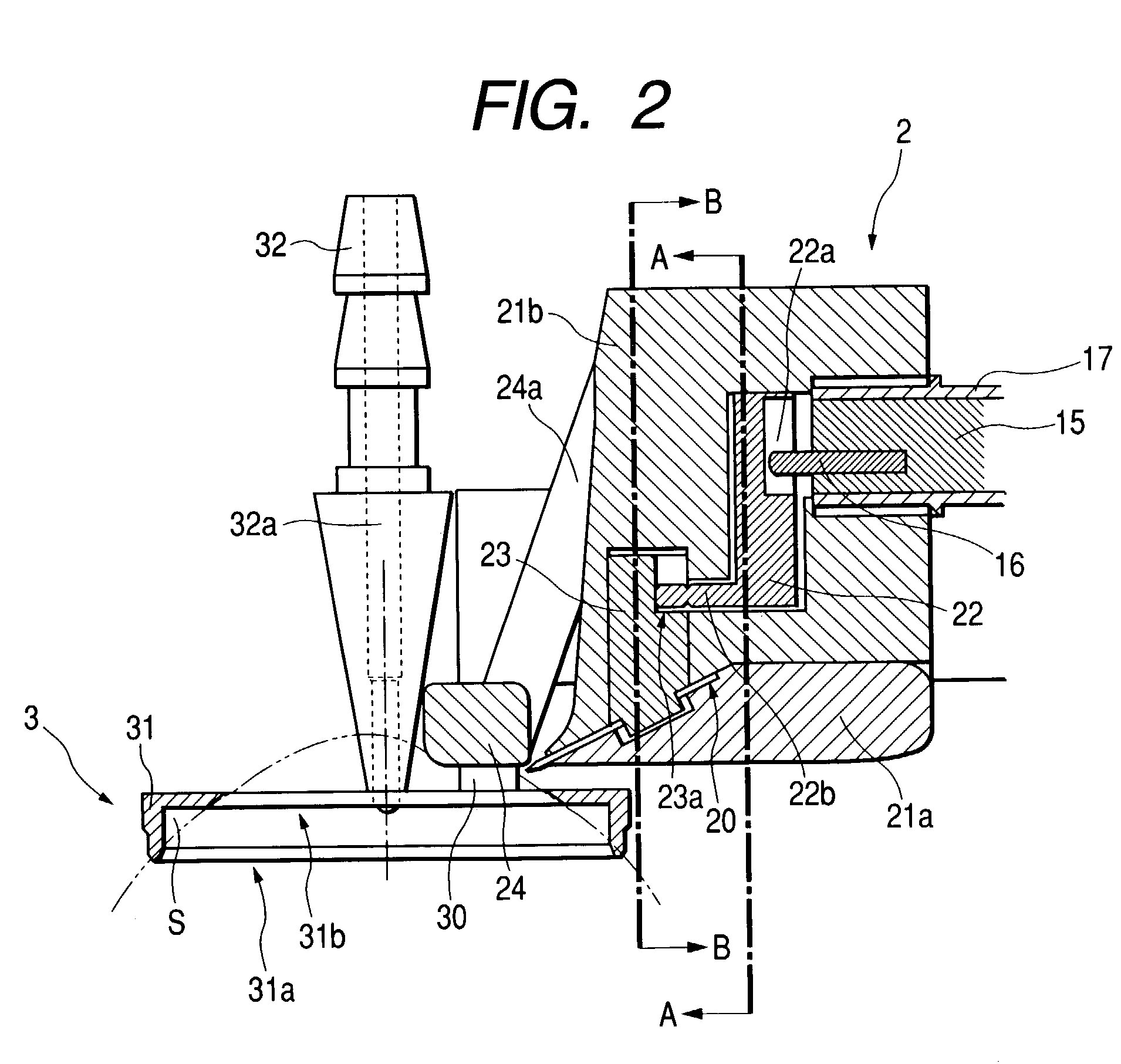
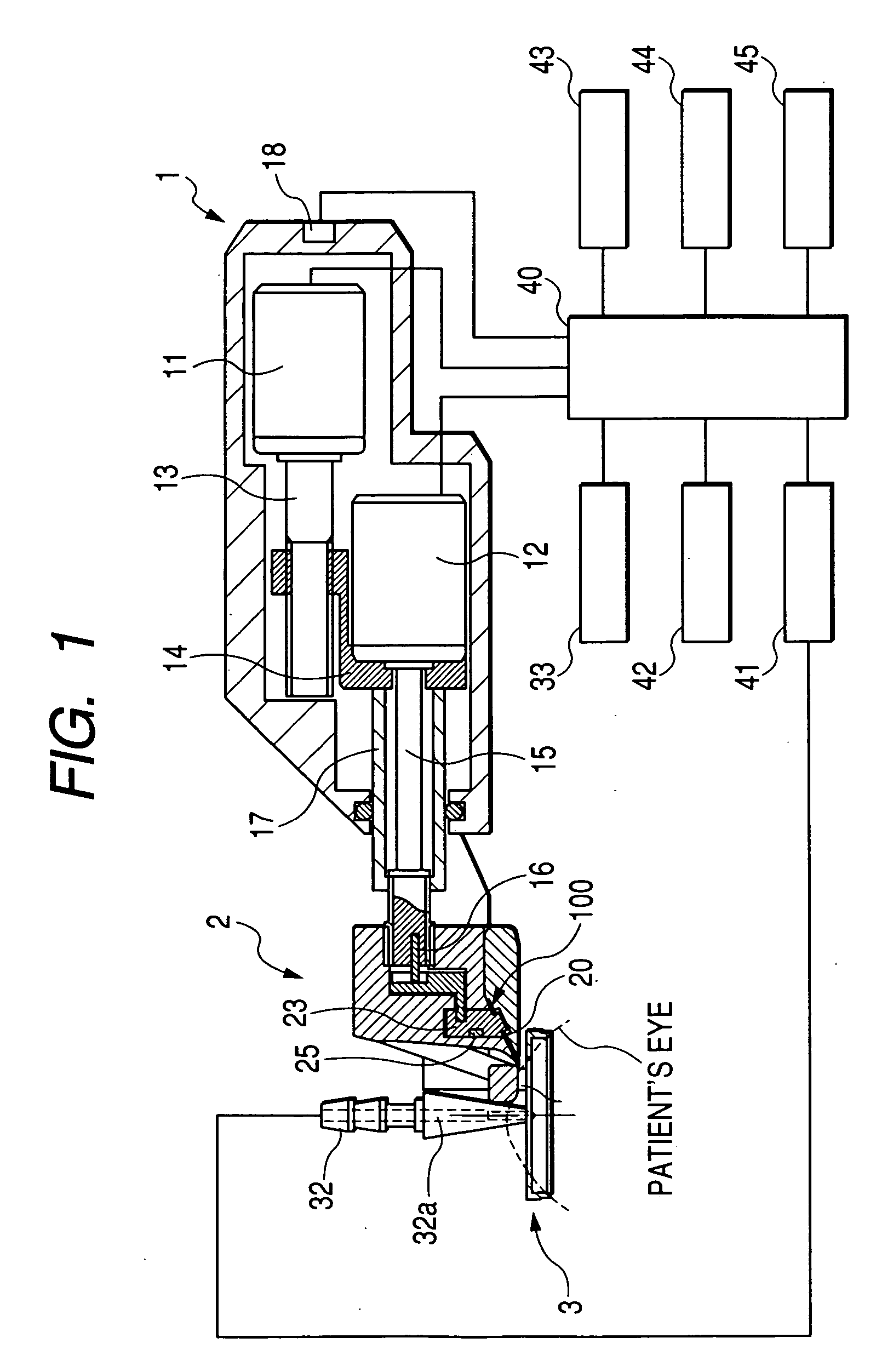
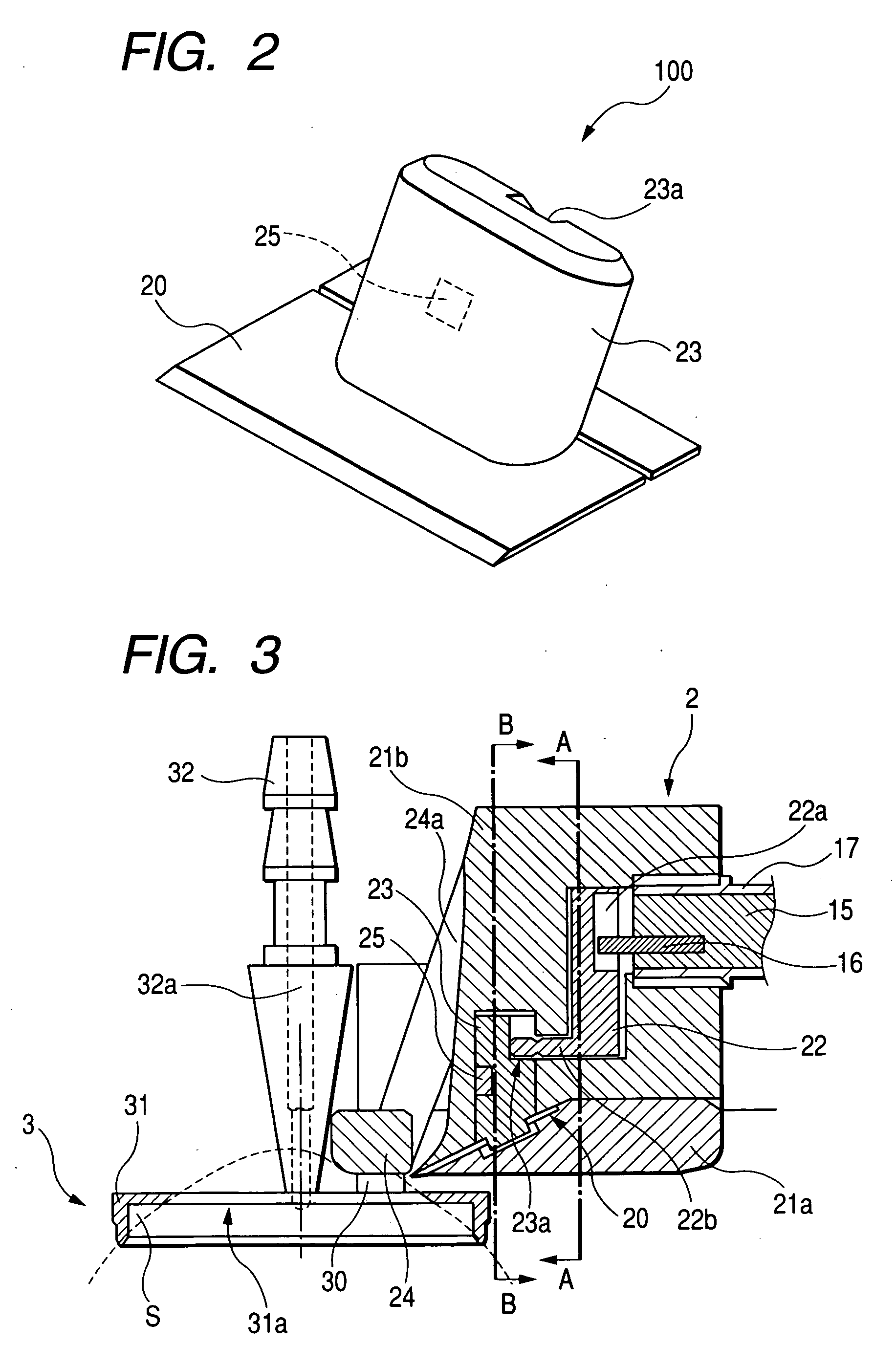
Corneal surgery apparatus
InactiveUS7118561B2Information obtainedEnsure correct executionLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCorneal surgeryIrradiation
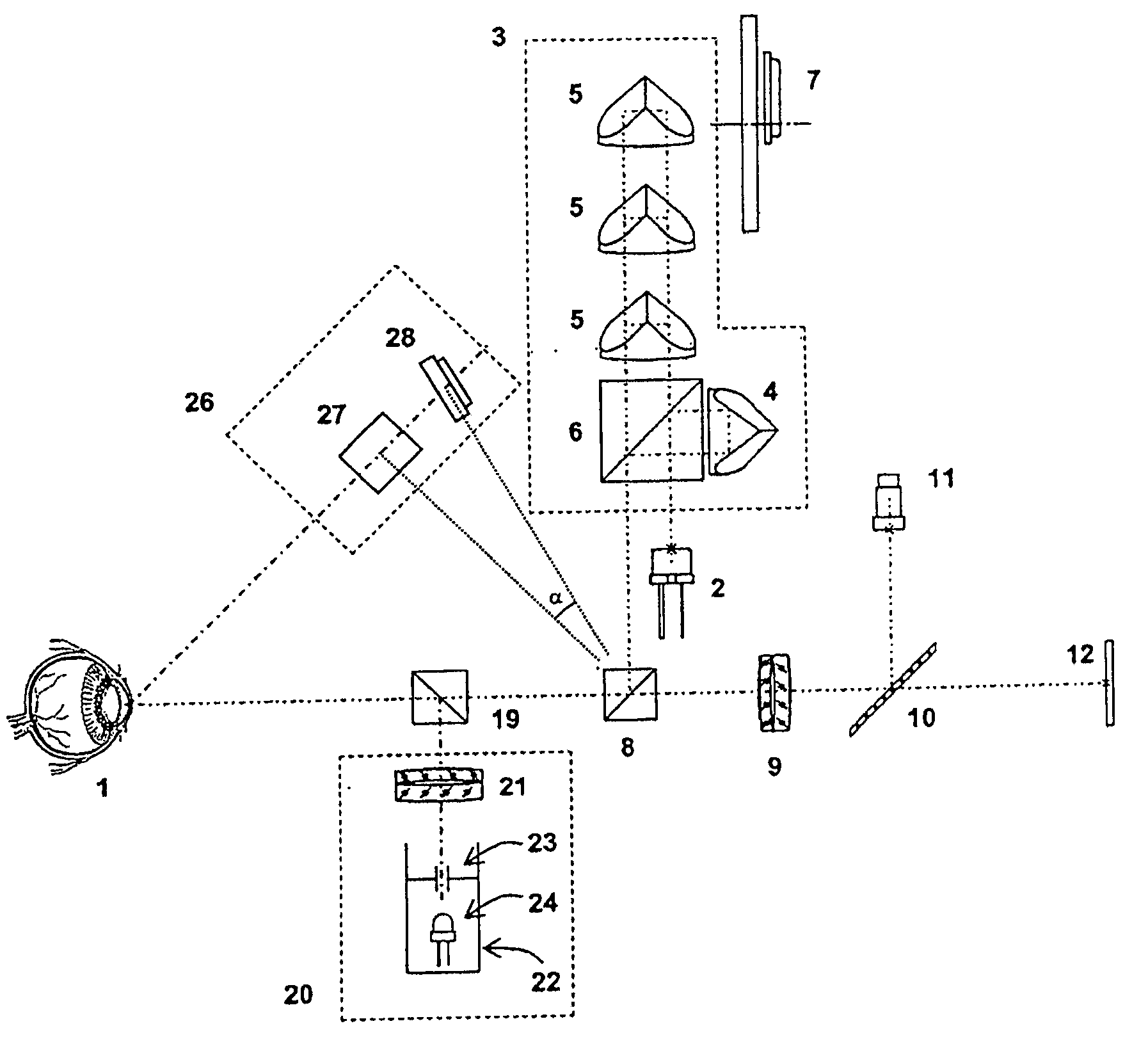
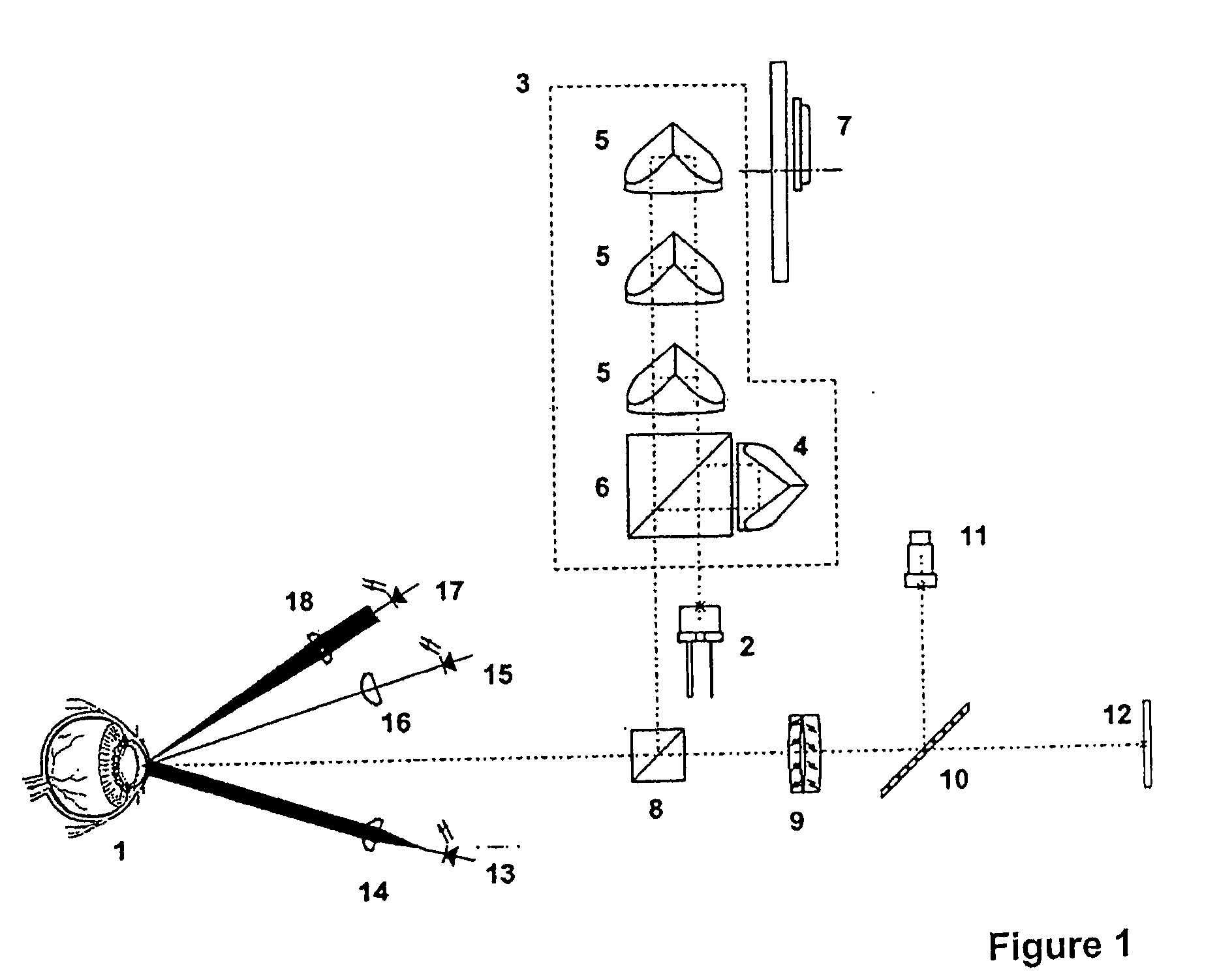
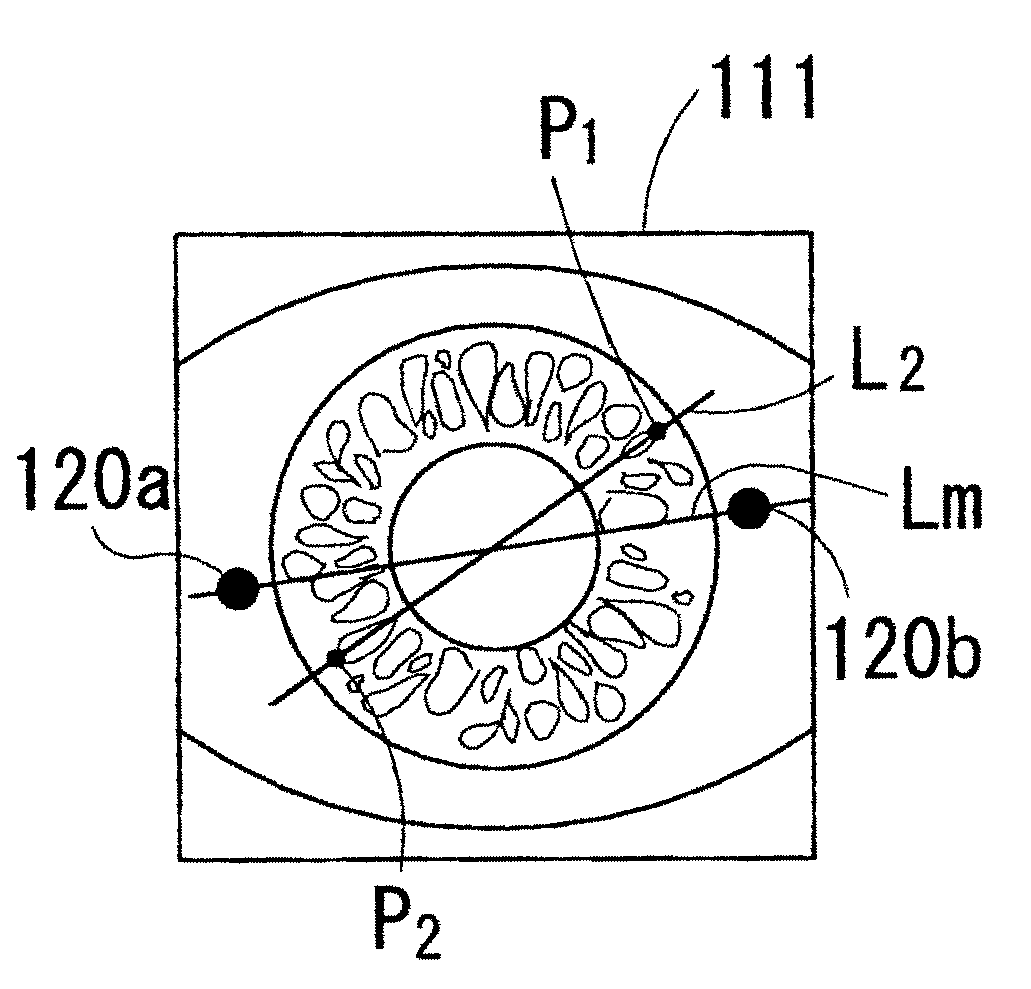
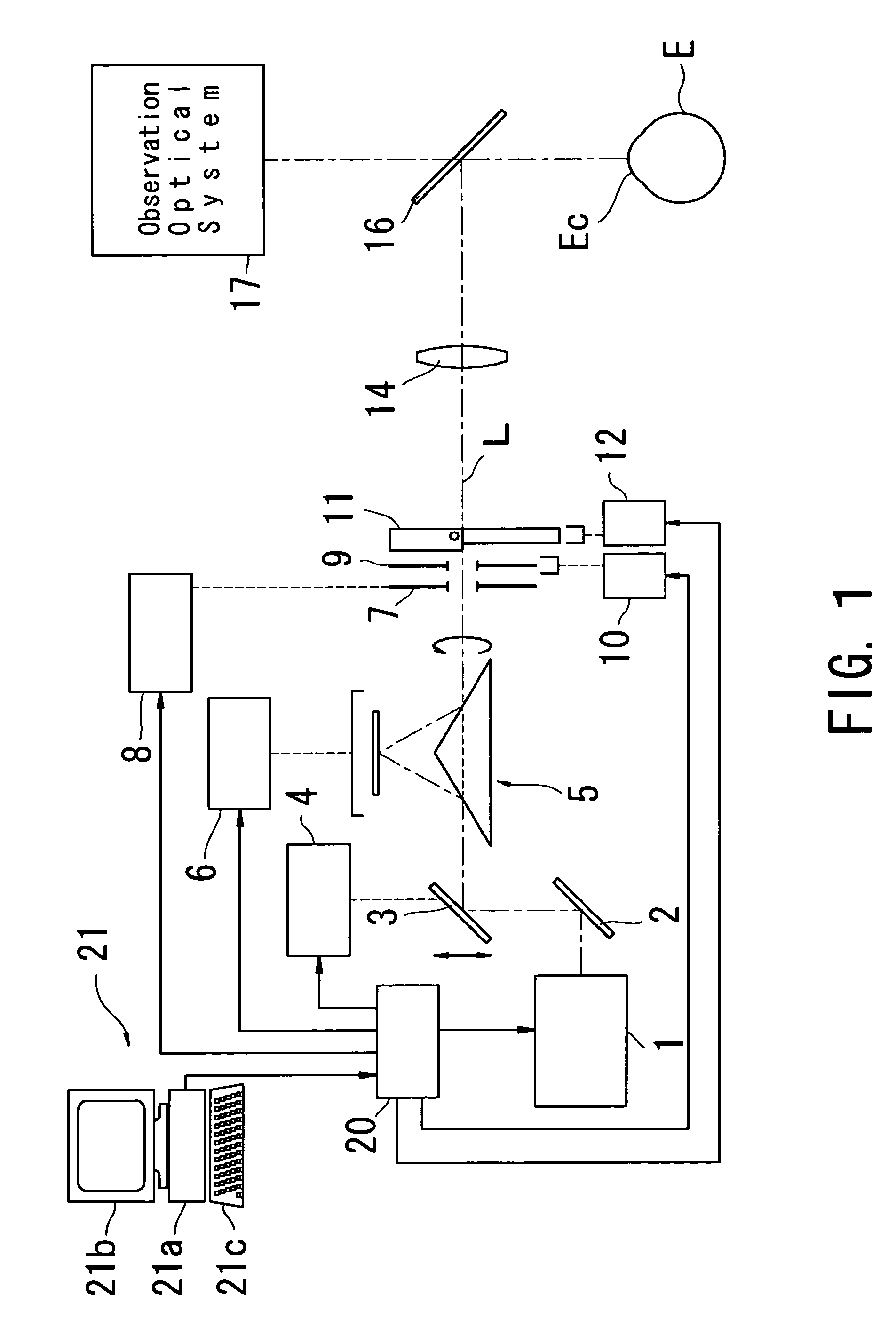
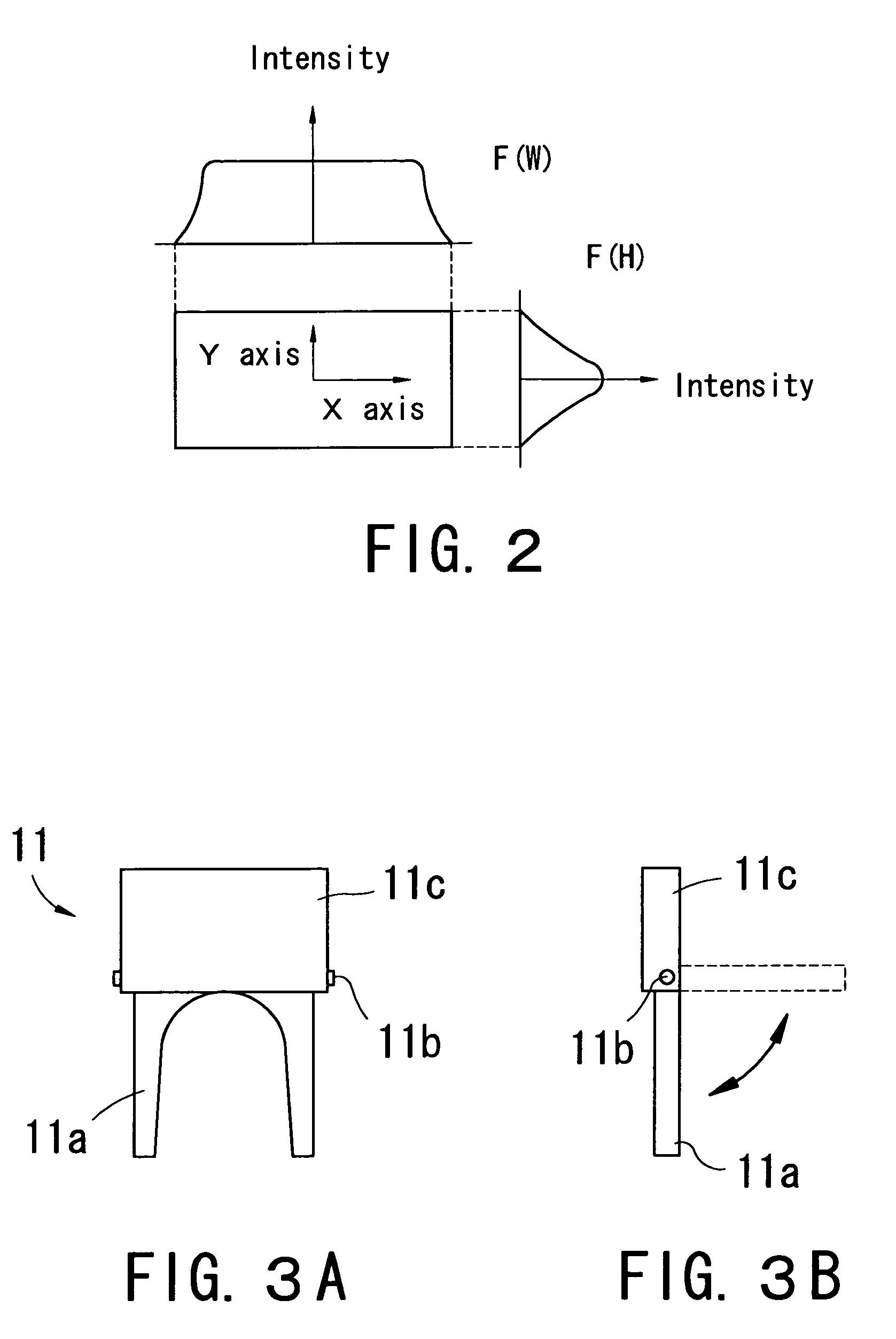
A corneal surgery apparatus capable of accurately obtaining torsion information on an eyeball or positional information on an eye even during laser irradiation or after a cornea is incised into a layer, and of accurately performing corneal surgery with a laser beam. The apparatus, for ablating a cornea of a patient's eye by irradiation of a laser beam, includes an irradiation optical system for irradiating the laser beam onto the cornea, an image-pickup device for picking up an image of an anterior-segment of the eye, a mark detection device for processing the obtained image of the anterior-segment and detecting a mark provided to the eye, a reference position setting device for setting a reference position in which the mark being detected is to be positioned, and a torsion detection device for obtaining torsion information on the eye based on the detected mark and the set reference position.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
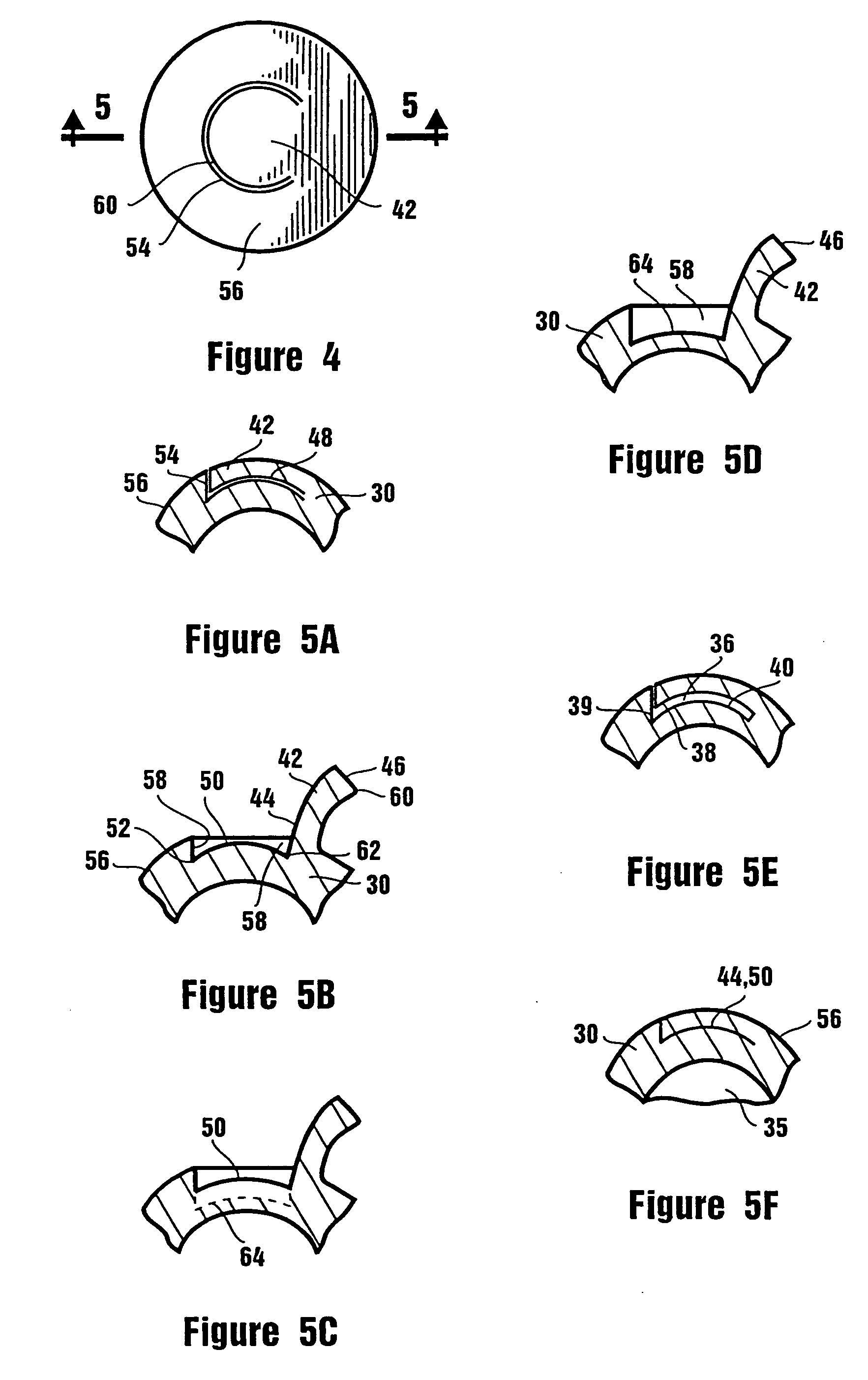
Blade for corneal surgery and corneal surgical apparatus comprising the same
A blade for corneal surgery for separating a corneal epithelium in a flap shape, includes: upper and lower blade surfaces; and an edge surface connecting the upper and lower blade surfaces, the edge surface having a height of 1 to 70 μm and a connecting portion with each of the upper and lower blade surfaces having a curved surface.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Corneal surgical apparatus and blade unit attached to corneal surgical apparatus for use in corneal surgery
A corneal surgical apparatus for forming a flap in a cornea, includes: a blade unit including a blade, and an identification information communicating portion that transmits identification information; a head portion that holds the blade unit detachably; an oscillation mechanism portion that oscillates the blade unit, which is held by the head portion, in a direction of a width of the blade; a receiving portion that receives the identification information transmitted from the identification information communicating portion; a storage portion that stores the identification information; and a control portion that collates the identification information received by the receiving portion with the identification information stored in the storage portion, and controls the driving of the oscillation mechanism portion based on a result of collation.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
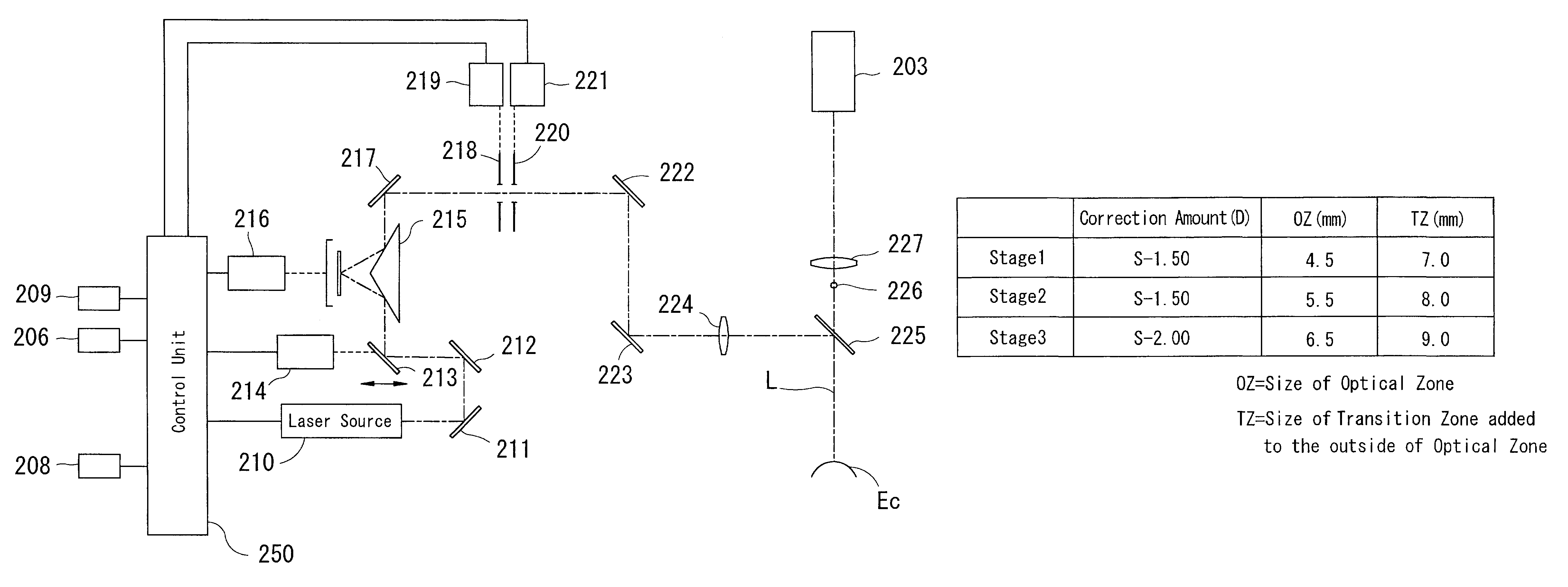
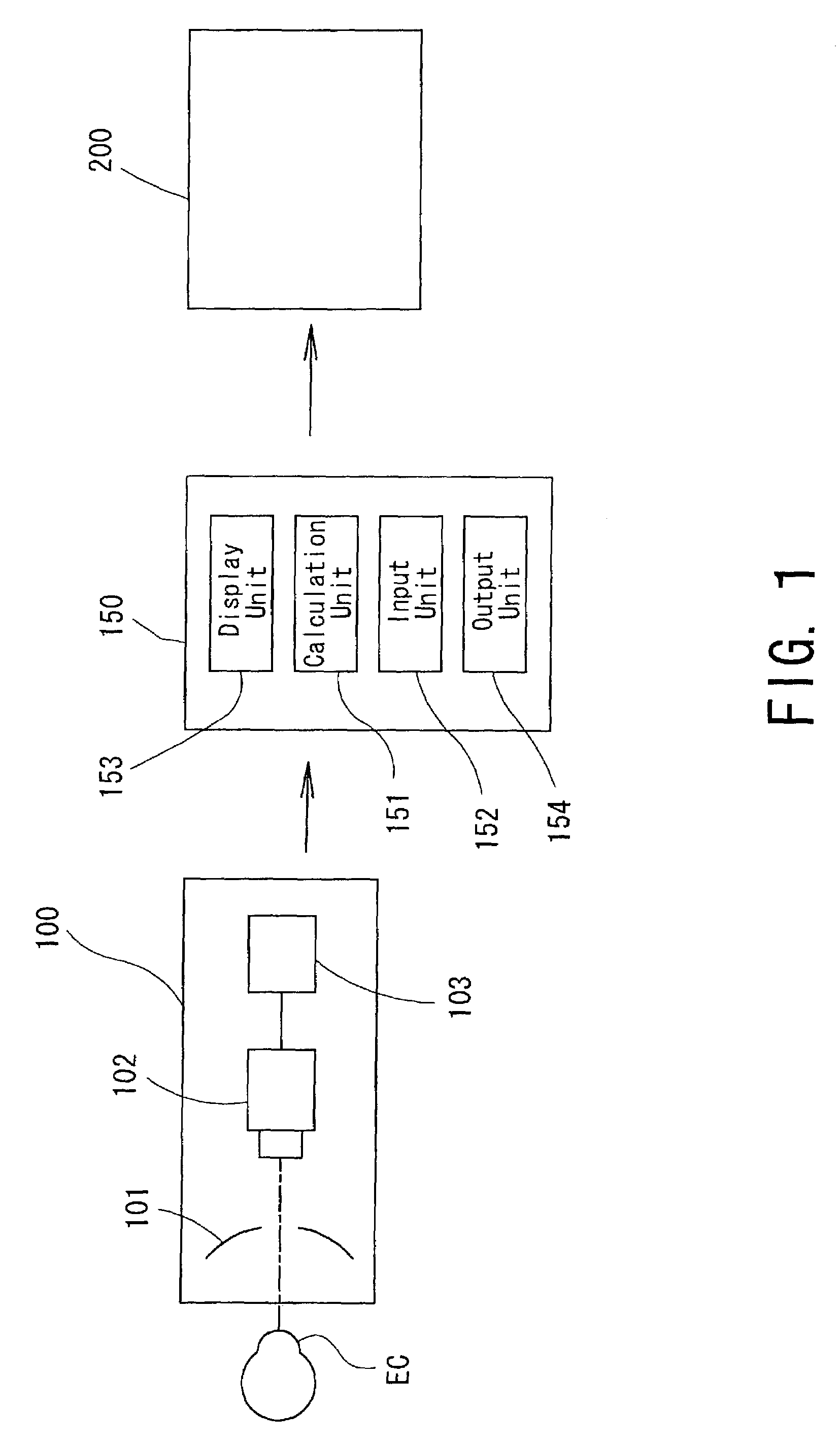
Corneal-ablation-amount determining apparatus and a corneal surgery apparatus
InactiveUS6994701B2Reduce partSimple methodLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCorneal curvatureCorneal surgery
A corneal surgery apparatus capable of reducing parts where a corneal curvature suddenly varies, and an apparatus for determining a corneal ablation amount. The corneal-ablation-amount determining apparatus includes a data input unit which inputs data on a correction amount of a patient's eye and data on a size of a second ablation zone for connecting a first ablation zone for securing the correction amount with a non-ablation area, a calculation unit which divides the inputted correction amount into at least ten, obtains an ablation amount for each divided correction amount as a lens component is ablated according to a size gradually enlarged from the first ablation zone to an outer diameter of the second ablation zone for each divided correction amount, and determines a total ablation amount by summing each obtained ablation amount, and an output unit which outputs data on the determined ablation amount.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Method and apparatus for universal improvement of vision
InactiveUS20100114078A1Improve eyesightLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsAnterior surfaceCorneal surgery
Owner:SCI OPTICS INC
Therapeutic agent for corneal sensory nerve damage containing semaphorin inhibitor as active ingredient
ActiveCN103379906APrevention of sensory neuropathySenses disorderNervous disorderCorneal diseaseHydrogen atom
A compound represented by formula (1) (wherein R1 represents a hydrogen atom or a carboxyl group, R2 represents a hydrogen atom or a hydroxy group, R3 represents a hydrogen atom or a carboxyl group, and R4 represents a hydrogen atom or a hydroxy group) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof is effective as a therapeutic agent or a prophylactic agent for a corneal disease or sensory nerve damage due to corneal surgery, and as a regeneration accelerator for corneal sensory nerves.
Owner:KEIO UNIV +1
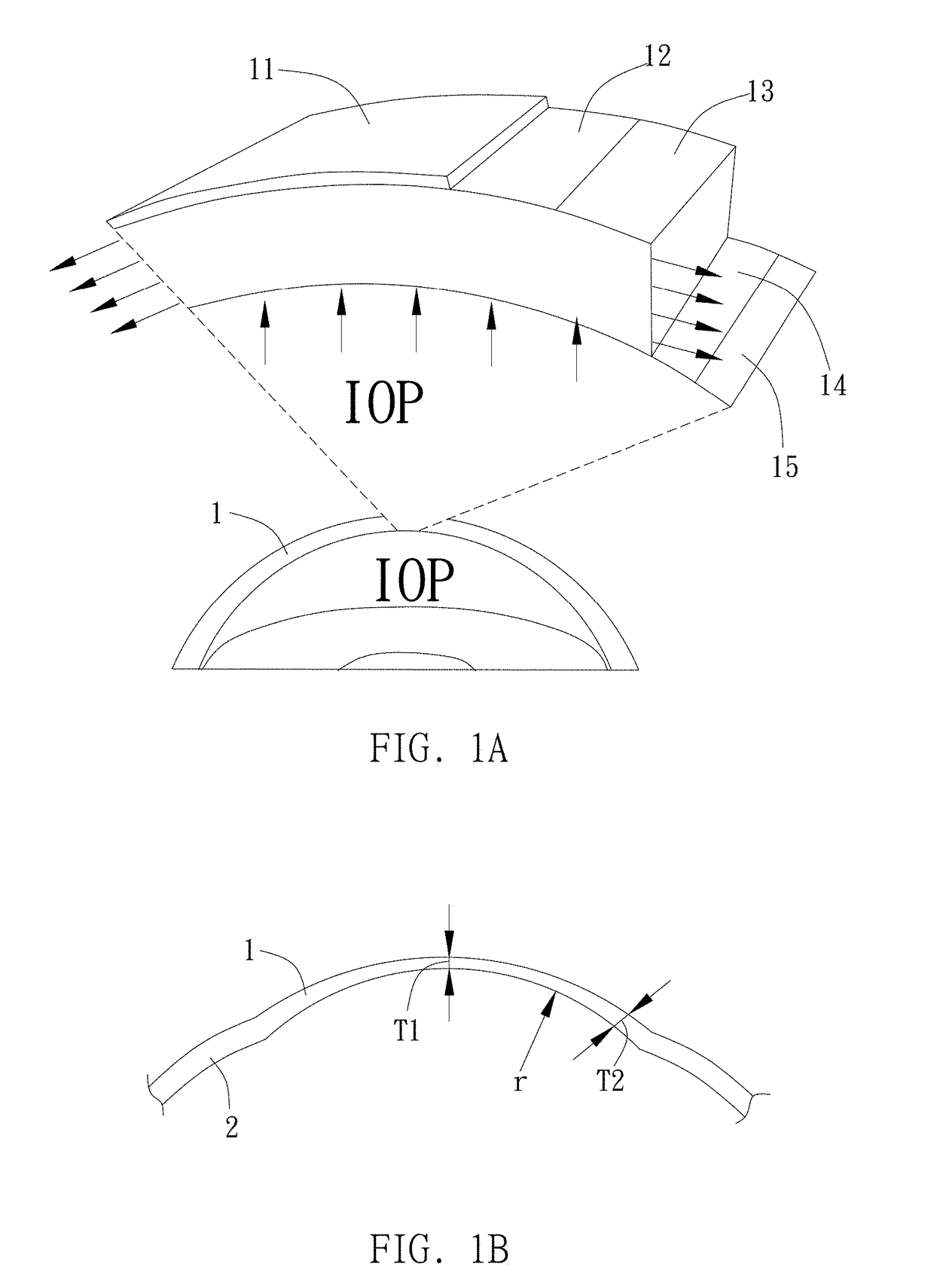
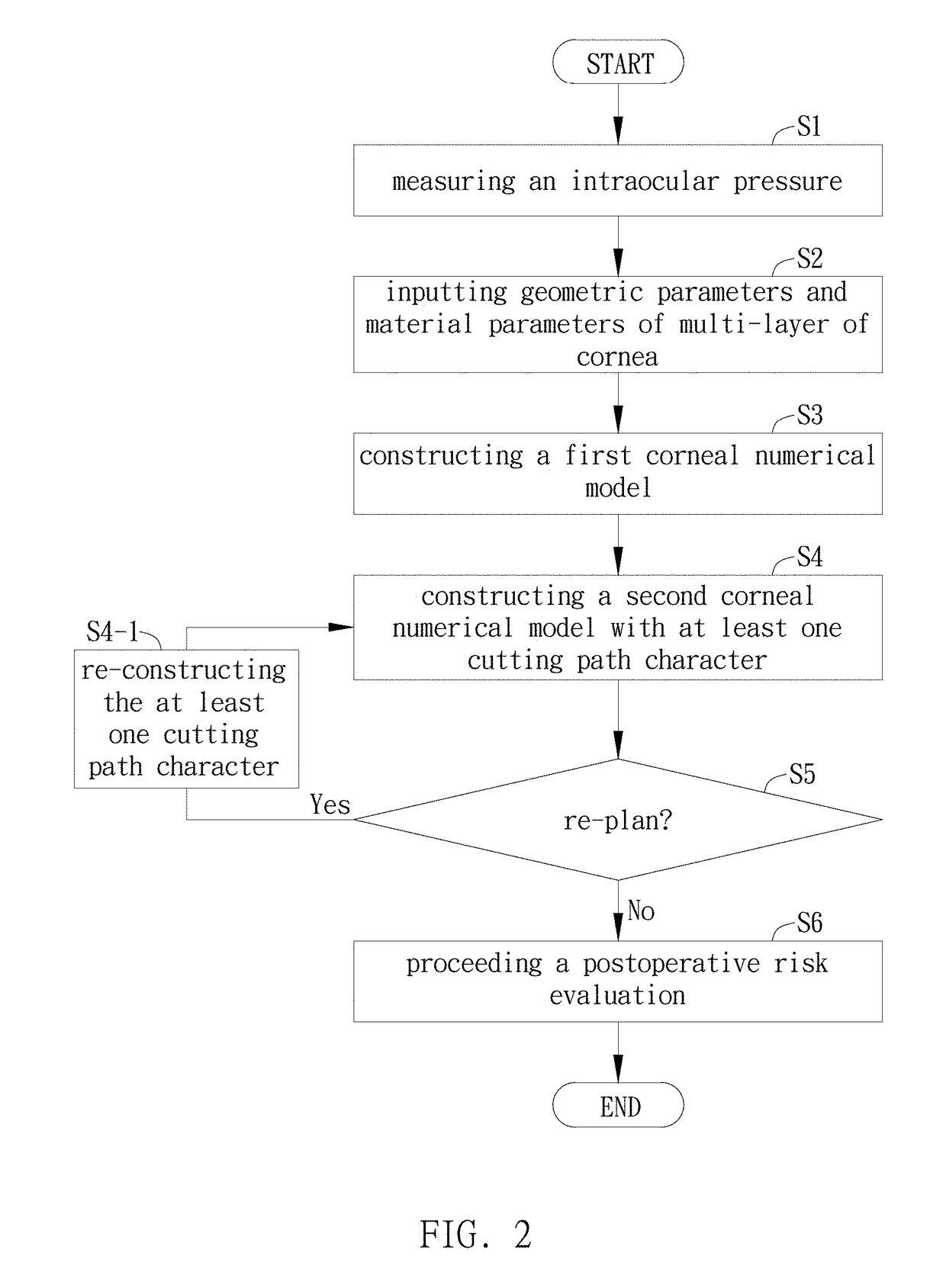
Corneal surgery risk evaluation method and system thereof
InactiveUS20180125582A1Safer and accurate evaluation wayWay accurateEye surgeryComputer-aided planning/modellingIntraocular pressureCorneal surgery
This invention provides a corneal surgery risk evaluation method and system thereof. Utilizing a mechanical numerical model to evaluate stress differences before corneal surgery and after, and further providing a suggested surgical path and risk after surgery. The evaluation method, comprising: measuring Intraocular pressure (IOP); inputting geometric parameters and material parameters of multi-layer of corneal; constructing a first corneal numerical model; constructing a second corneal numerical model with at least one cutting path character; evaluating whether the cutting path character should be re-constructed or not.
Owner:CHEN WEN CHIN
Method of corneal surgery by laser incising a contoured corneal flap
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Cornea surface optical path difference measuring device and method of measuring cornea thickness and refractivity
PendingCN109691972AAccurate thickness measurementHigh precisionEye diagnosticsKeratorefractive surgeryHigh resolution imaging
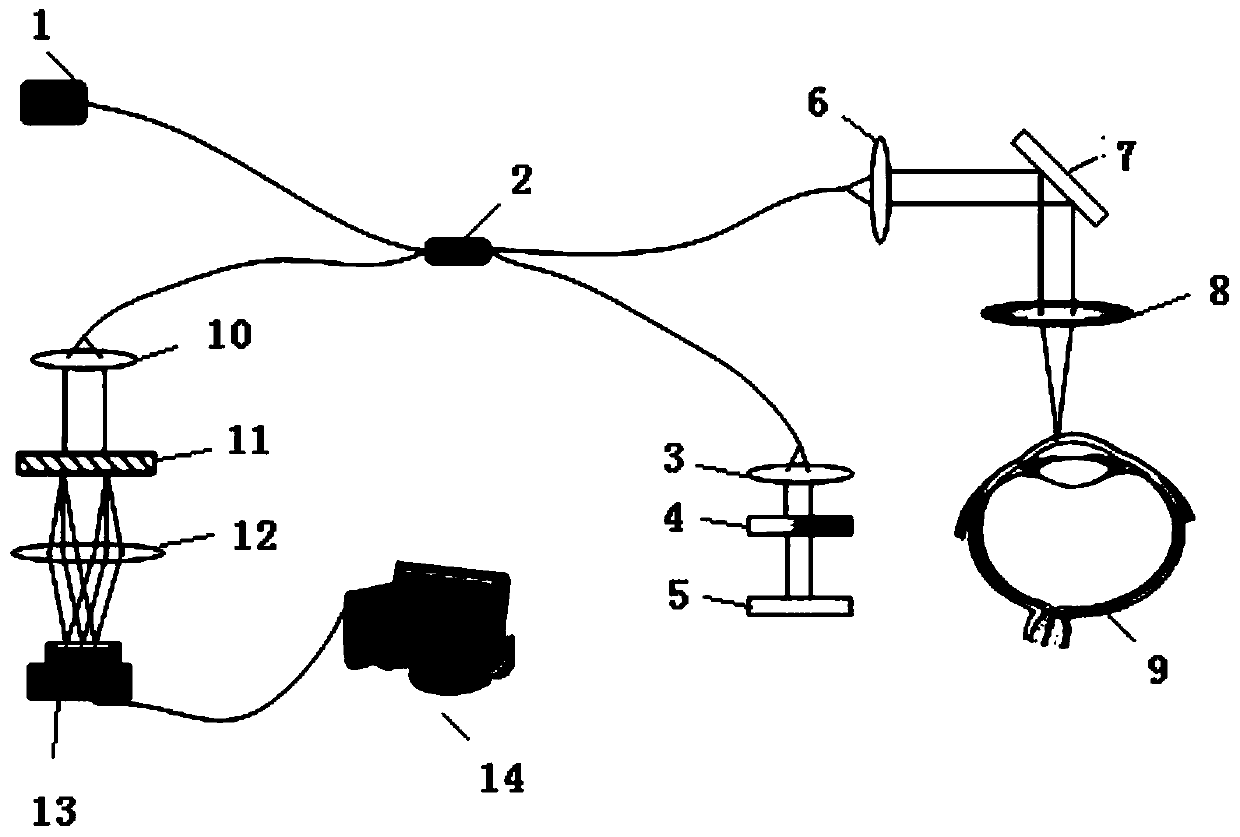
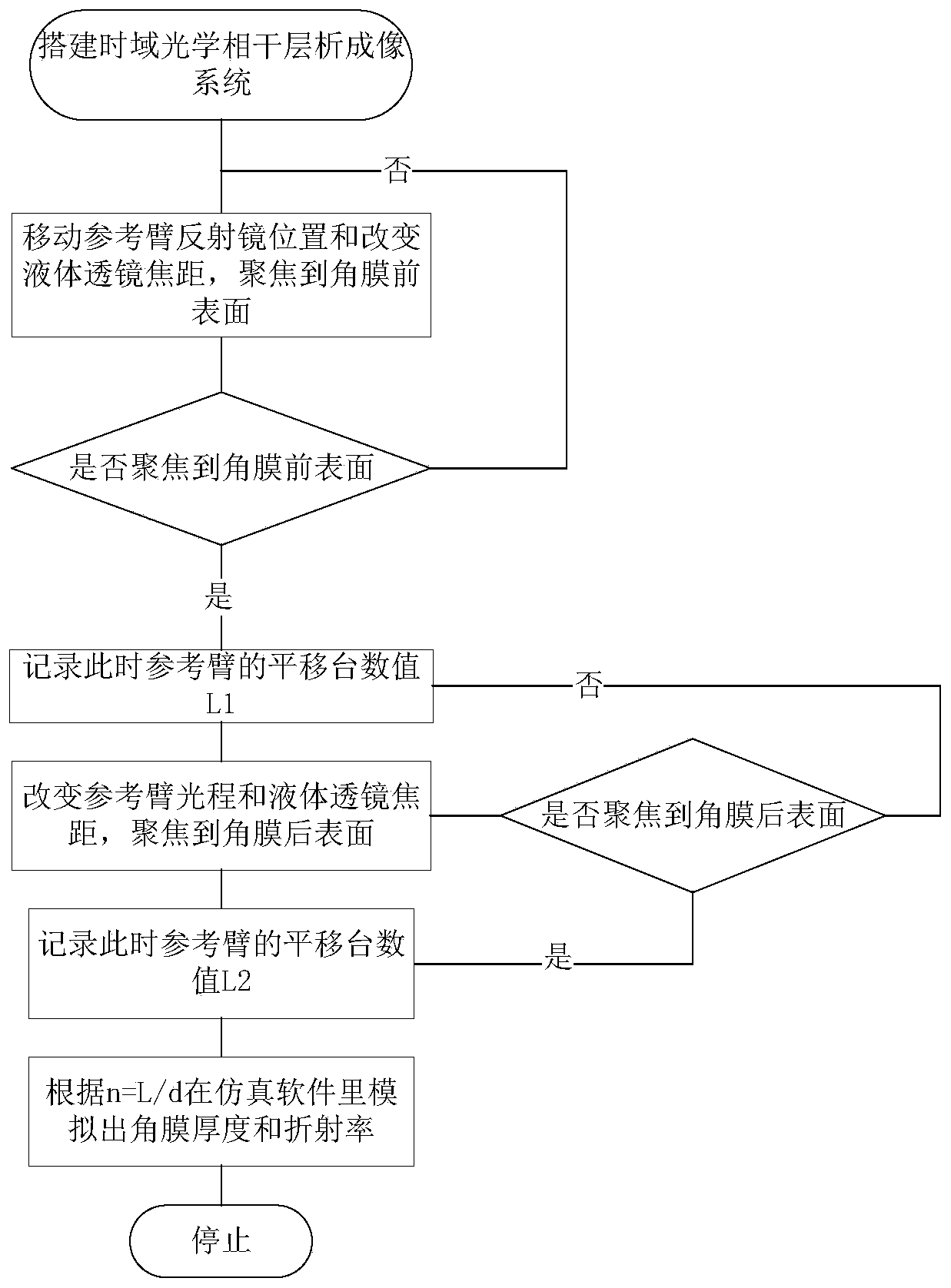
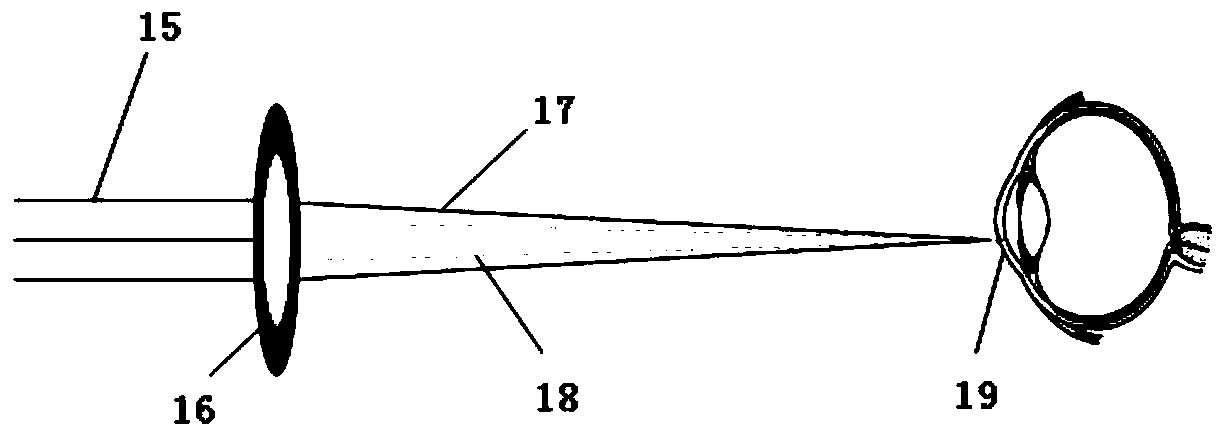
A time domain-optical coherence tomography (TD-OCT) technology is adopted to carry out high resolution imaging on a human cornea; the thickness of the human cornea can be accurately measured by usinga quick zoom lens; through the moving distance of a reference arm, the optical path difference between the front surface and the rear surface of a cornea can be calculated, thus the refractivity of the cornea can be calculated by ZEMAX optical simulation software; and the method is noncontact and is used to measure the thickness and refractivity of a cornea. The method can measure the thickness and refractivity of a cornea in a human body, the measurement is noncontact, high precision, and nondestructive; moreover, after a corneal surgery, the thickness and refractivity of corneas can be tracked, and at the same time, a preoperative detection device and method are provided for a refractive surgery.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
Corneal Topography and Alignment for Corneal Surgical Procedures
The methods and apparatus are configured to measure the eye without the eye contacting the patient interface, and use these measurements to determine the alignment and placement of the incision when the patient interface contacts the eye. The pre-contact position of one or more structures of the eye may be used to determine a corresponding post-contact position of one or more optical structures of the eye when the patient interface has contacted the eye such that the laser incision is placed at a location that promotes normal vision of the eye . The incisions are positioned relative to the pre-contact optics of the eye, such as the astigmatic axis, the nodes of the eye, and the visual axis of the eye.
Owner:眼力健发展有限责任公司
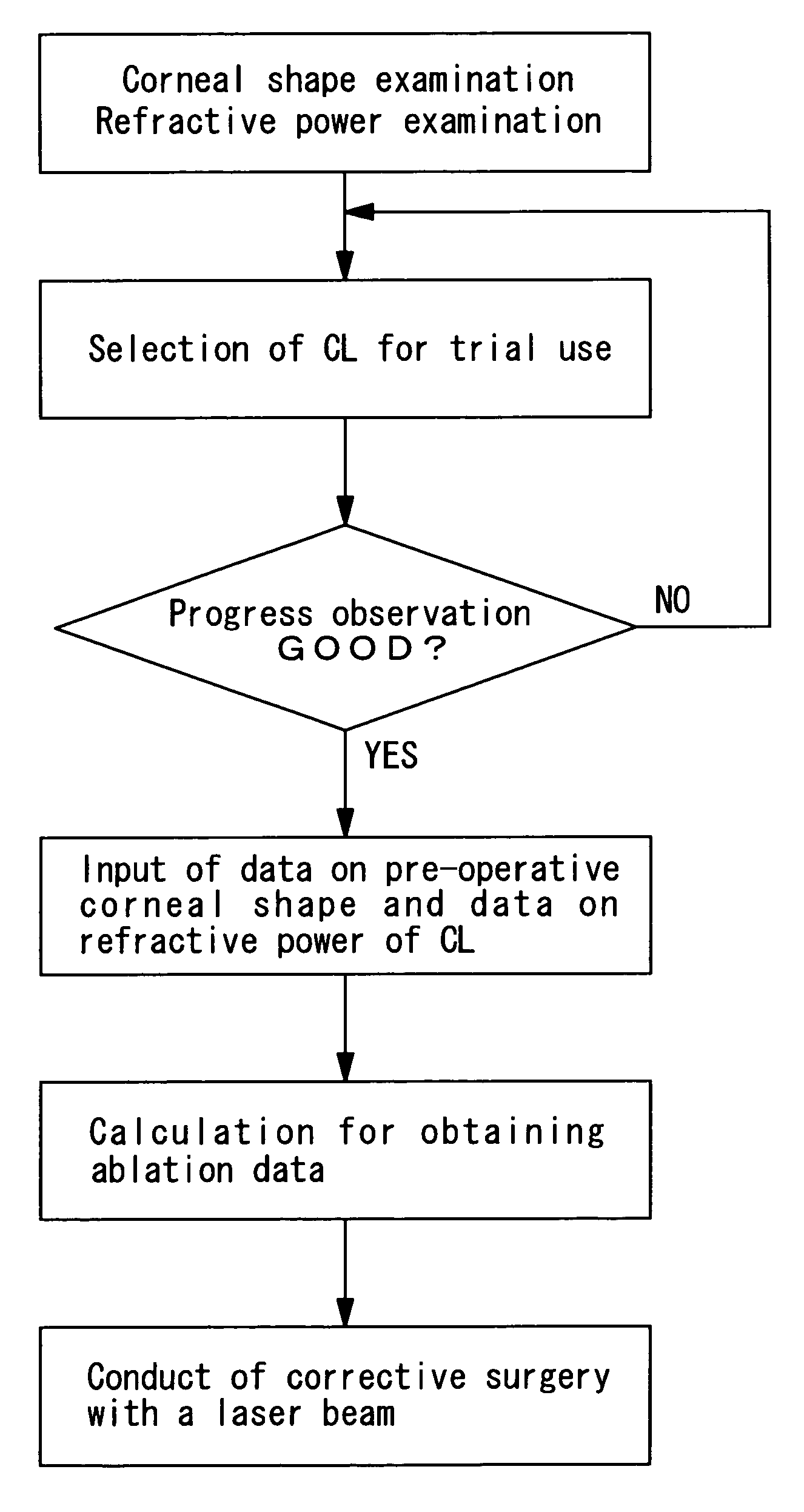
Corneal surgery apparatus and correction data determining methods
InactiveUS7052490B2Accurate correctionLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive errorCorneal surgery
A corneal surgery apparatus for correcting a refractive error by ablating corneal tissue with a laser beam, being capable of finding a correction pattern optimum for a patient to ensure precise correction, and a method of determining correction data. The apparatus includes units for inputting refractive power data on a trial contact lens, converting the refractive power data to obtain ablation data, controlling an ablation amount of the corneal tissue based on the ablation data, storing the refractive power data corresponding to each contact lens, and revising the refractive power data. The method includes processes for obtaining a correction value made with a contact lens based on of an ophthalmic examination, selecting a contact lens based on the value and converting the refractive power data on the selected contact lens into the ablation data for correcting the refractive error if the trial use of the contact lens results favorably.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com