Therapeutic agent for corneal sensory nerve damage containing semaphorin inhibitor as active ingredient
An active ingredient, sensory nerve technology, applied in the field of therapeutic agents, can solve problems such as no inhibitory experiments, no description of sensory nerve function, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
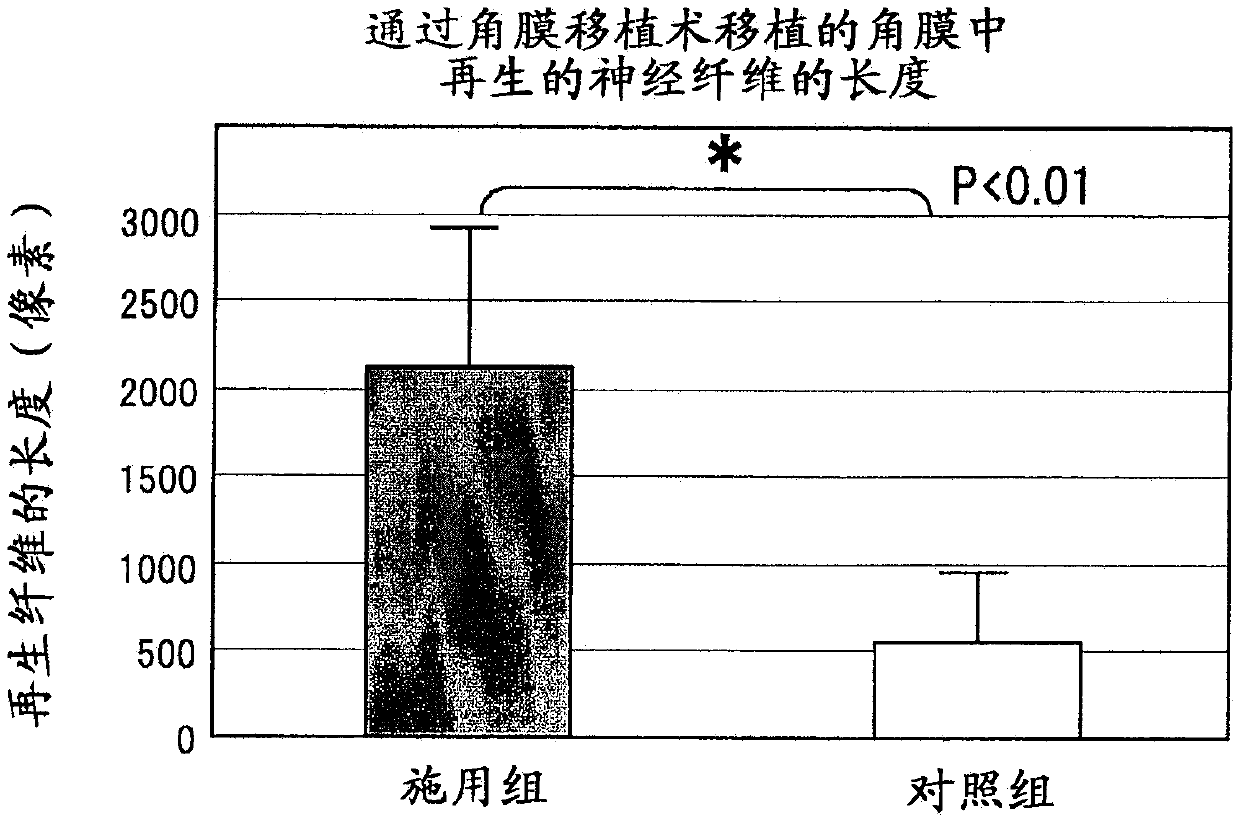
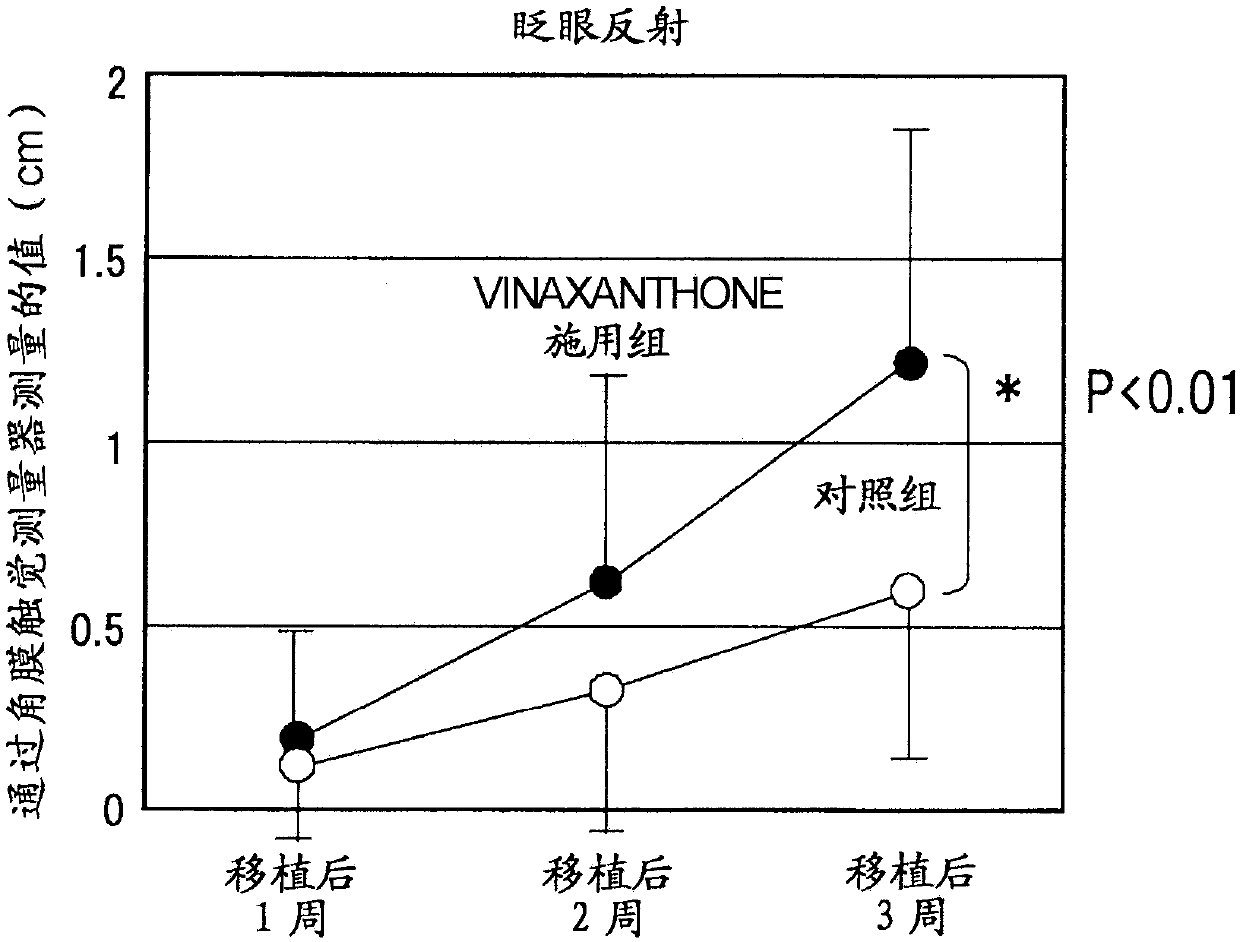
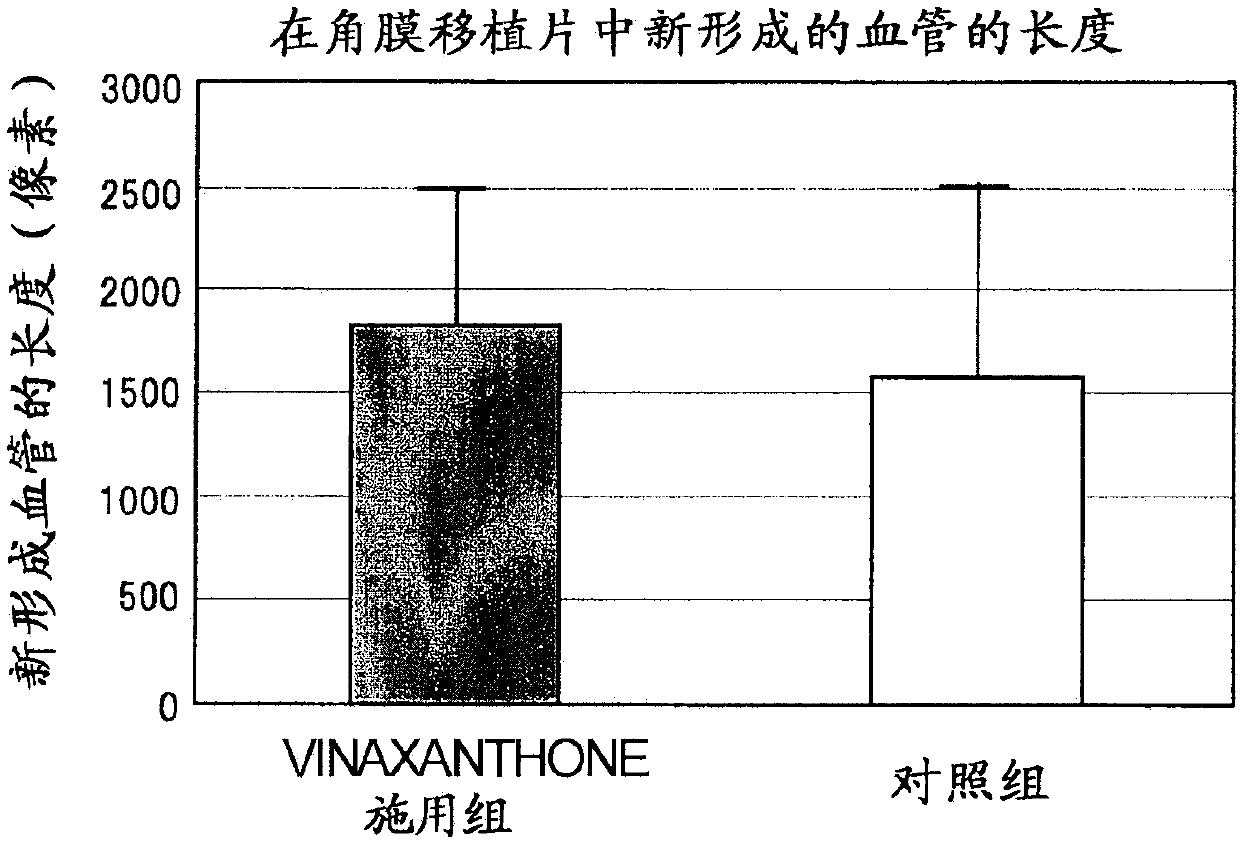
[0160] Vinaxanthone promotes corneal sensory nerve regeneration in keratoplasty in a mouse keratoplasty model role in life
[0161] In this experiment, genetically modified mice (P0-Cre / Floxed-EGFP mice) in which corneal parenchymal cells, corneal endothelial cells, and nerves express green fluorescent protein (GFP), a type of fluorescent protein in the cornea, were used. Using these mice, corneal sensory nerve fibers traveling in the cornea can be easily visualized by removing a layer of corneal endothelial cells.
[0162] Corneas derived from syngeneic wild-type mice were implanted into each of the mice listed above. Thereafter, 50 ul of vinaxanthone (which had been dissolved in Rinderon (1 mg / ml betamethasone sodium phosphate injection) to a concentration of 0.1 mg / mL) was administered to the mice by subconjunctival injection immediately after completion of the operation, followed by administration of 1 times, a total of 11 times. Only the drug-free solvent was admini...
Embodiment 2
[0169] Evaluation of retention of vinaxanthone formulations in corneal tissue
[0170] Apply 50 μL of vinaxanthone (0.5, 1.5 and 5.0 mg / mL) in PBS solution (0.12 M phosphate buffer saline (pH7.4)), and then closed his eyes for 30 seconds. Thereafter, at 0.5, 2 and 6 hours after administration, the rabbits were euthanized, and then the excised eyeballs were washed with physiological saline. Thereafter, corneas were harvested from each eyeball. Homogenize the cornea, then extract vinaxanthone from it. Use HPLC to examine the content and concentration of vinaxanthone in corneal tissue over time.
[0171] From Figure 4 , 5 As demonstrated in the results shown in 6 and 6, vinaxanthone was transferred into corneal tissue in an applied concentration / dose dependent manner. In the 5.0 mg / mL vinaxanthone solution administration group, it was confirmed that even 6 hours after the completion of the operation, the retention of vinaxanthone in the cornea was greater than the IC obt...
Embodiment 3
[0174] Production of xanthone compound represented by formula (1)
[0175] The xanthone compound represented by the formula (1) of the present invention is a well-known compound and is disclosed in International Publication No. WO02 / 09756 (Patent Document 1 cited above), International Publication No. WO03 / 062243 (Patent Document 2 cited above) , International Publication No. WO03 / 062440 (Patent Document 3 cited above), JP2006-335683A and JP2008-13530A. The xanthone compound of the present invention can be produced by culturing, chemical general synthesis or chemical transformation of the SPF-3059 strain. In addition to the production method, the physicochemical properties of the compound are also disclosed in the patent documents cited above. The details of the production method and the like are as follows.
[0176] Already adjusted containing 2% glucose, 5% sucrose, 2% cottonseed meal, 0.1% sodium nitrate, 0.1% L-histidine, 0.05% dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.07% pota...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com