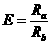Patents
Literature
96 results about "Corneal curvature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
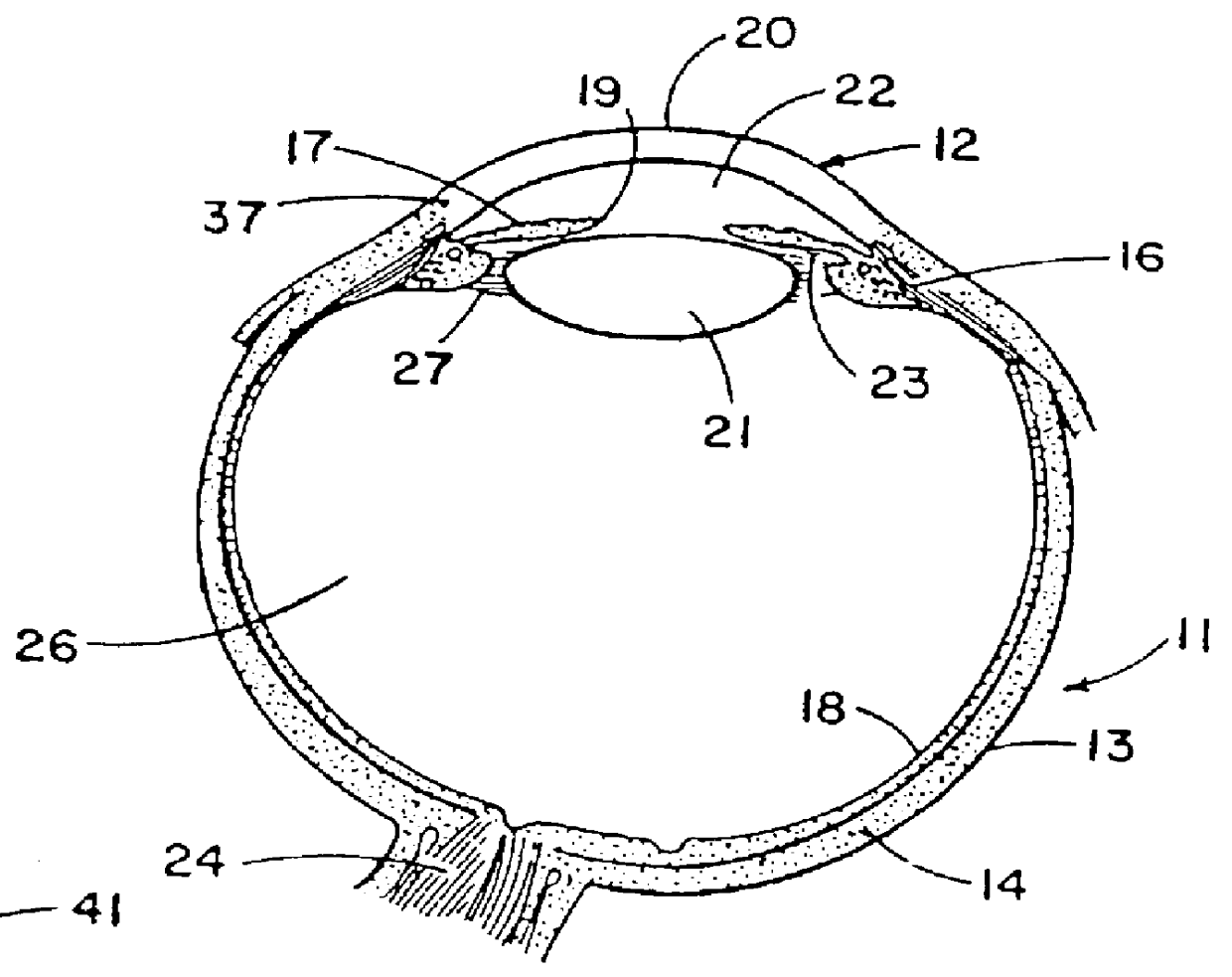
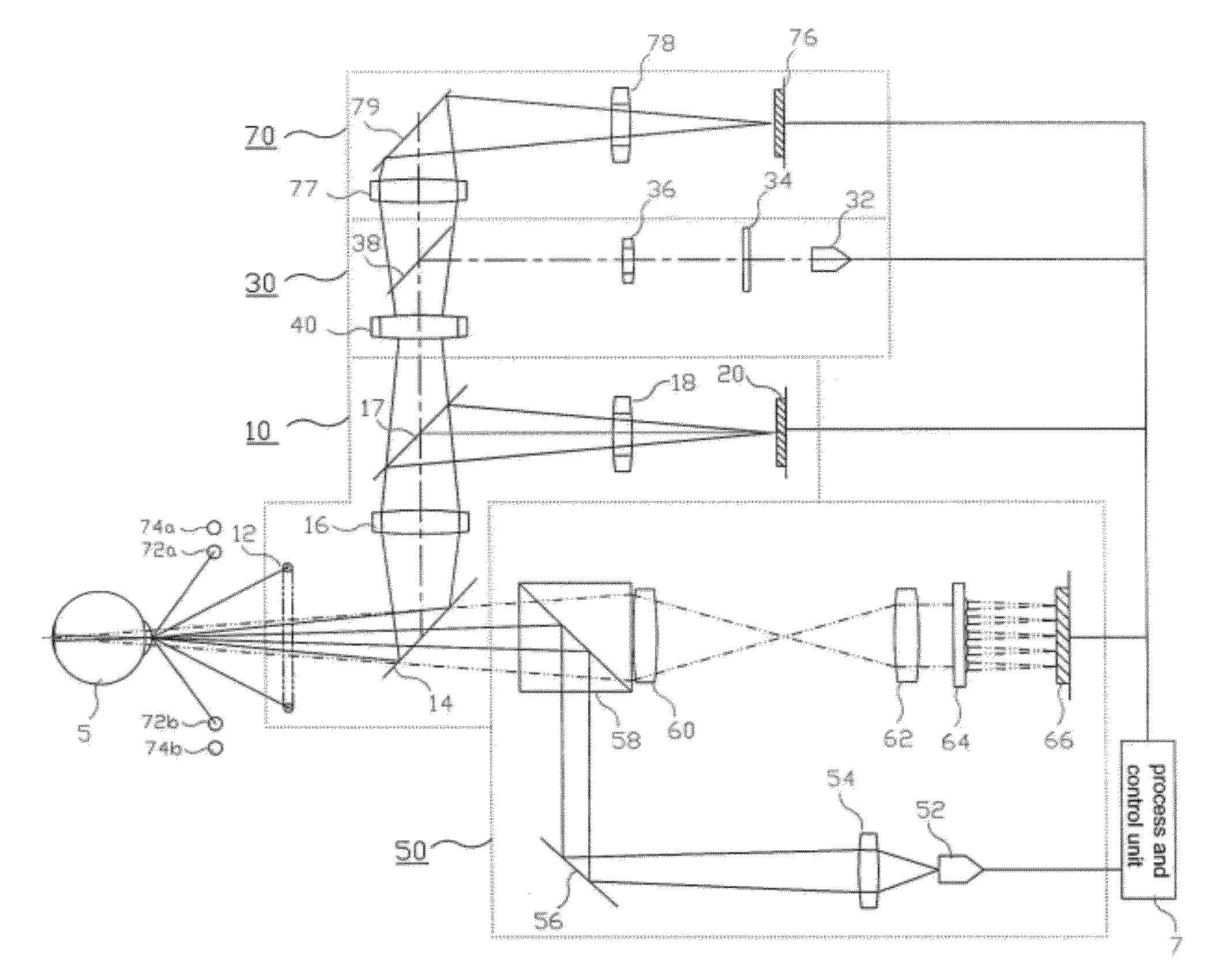
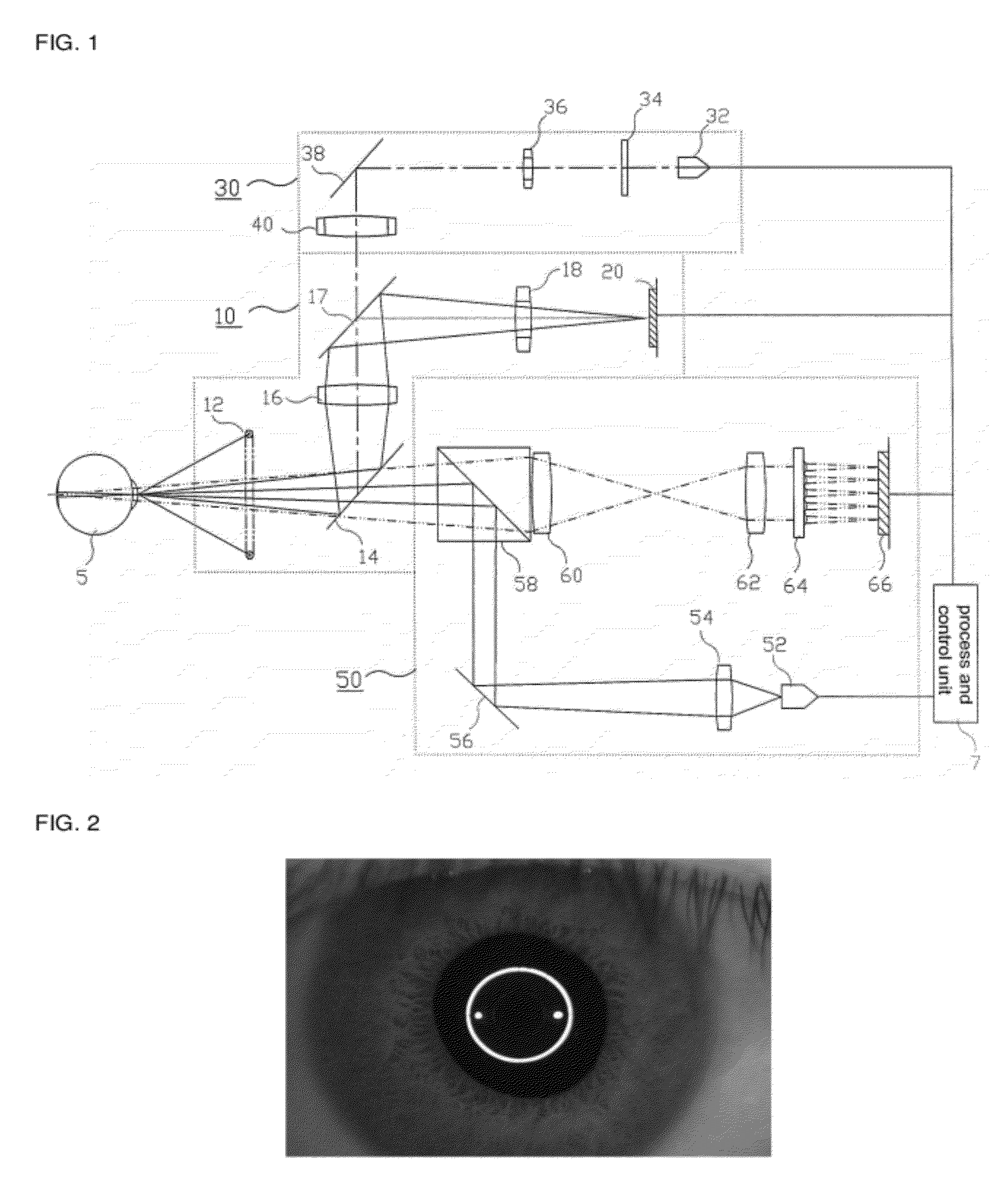
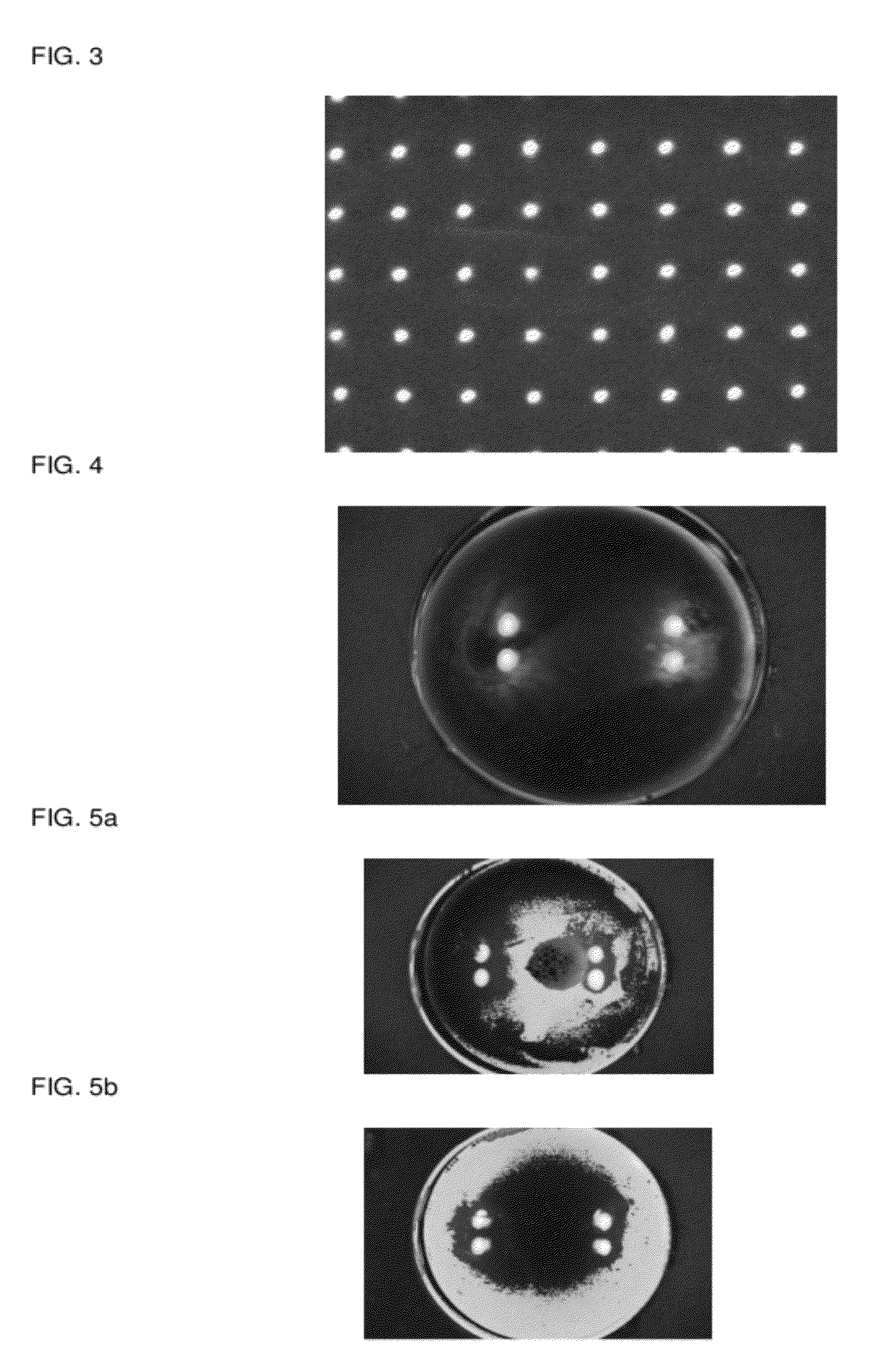
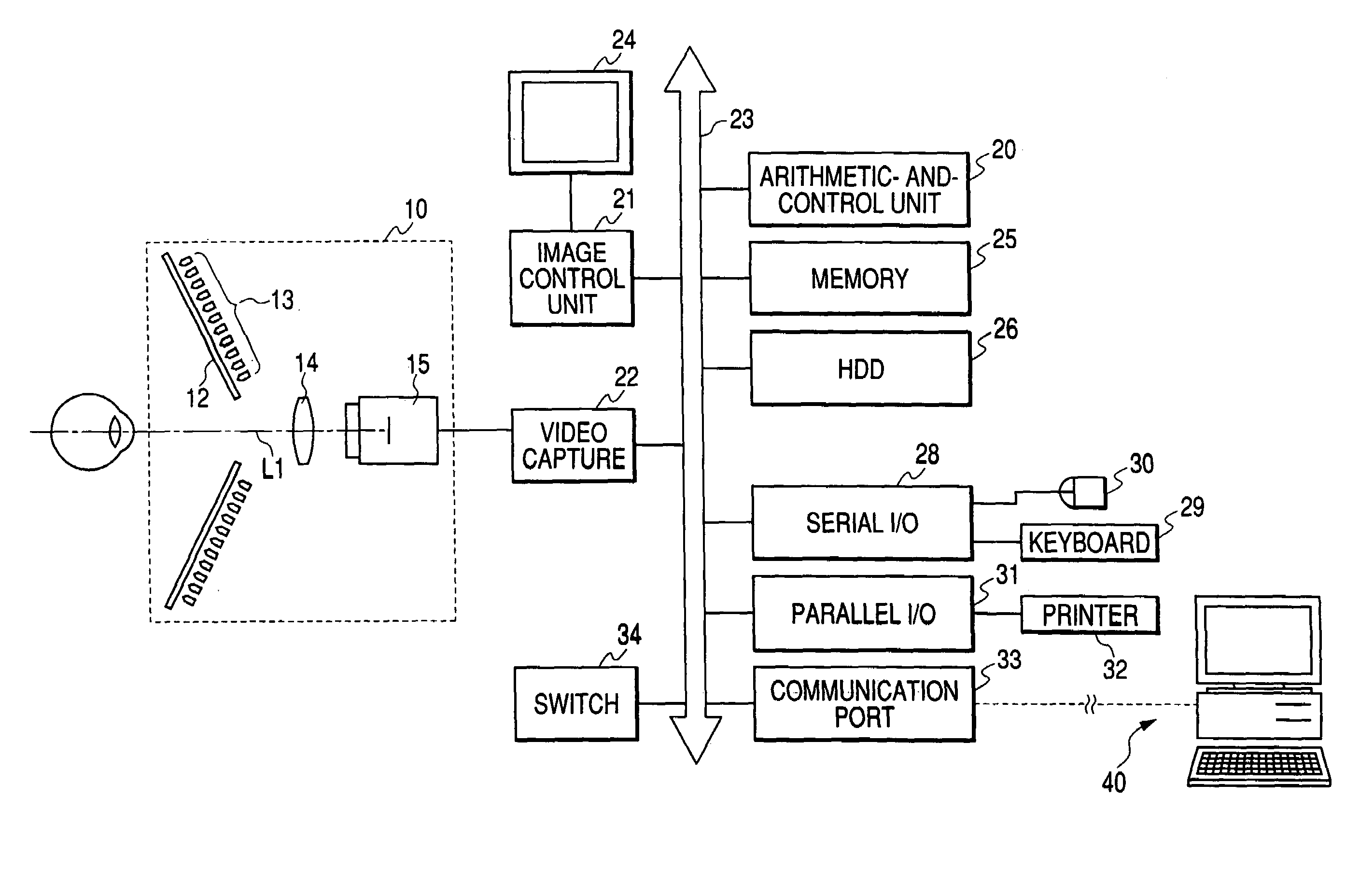
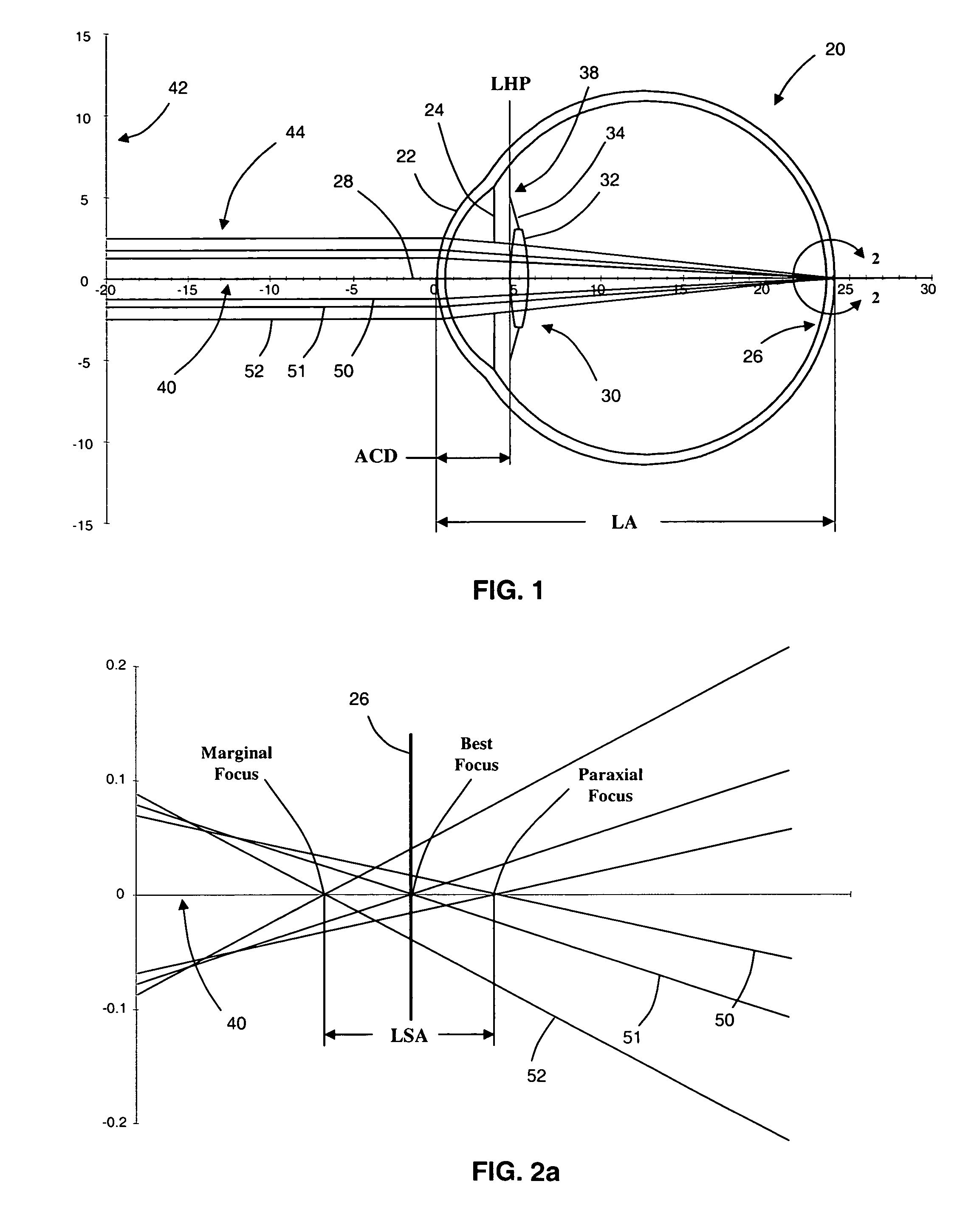
Corneal curvature is usually used for IOL calculations and corneal refractive surgery. It is also helpful for contact lens fitting and detecting irregular astigmatism. A keratometer measures the size of an image reflected from 2 paracentral points on the cornea.
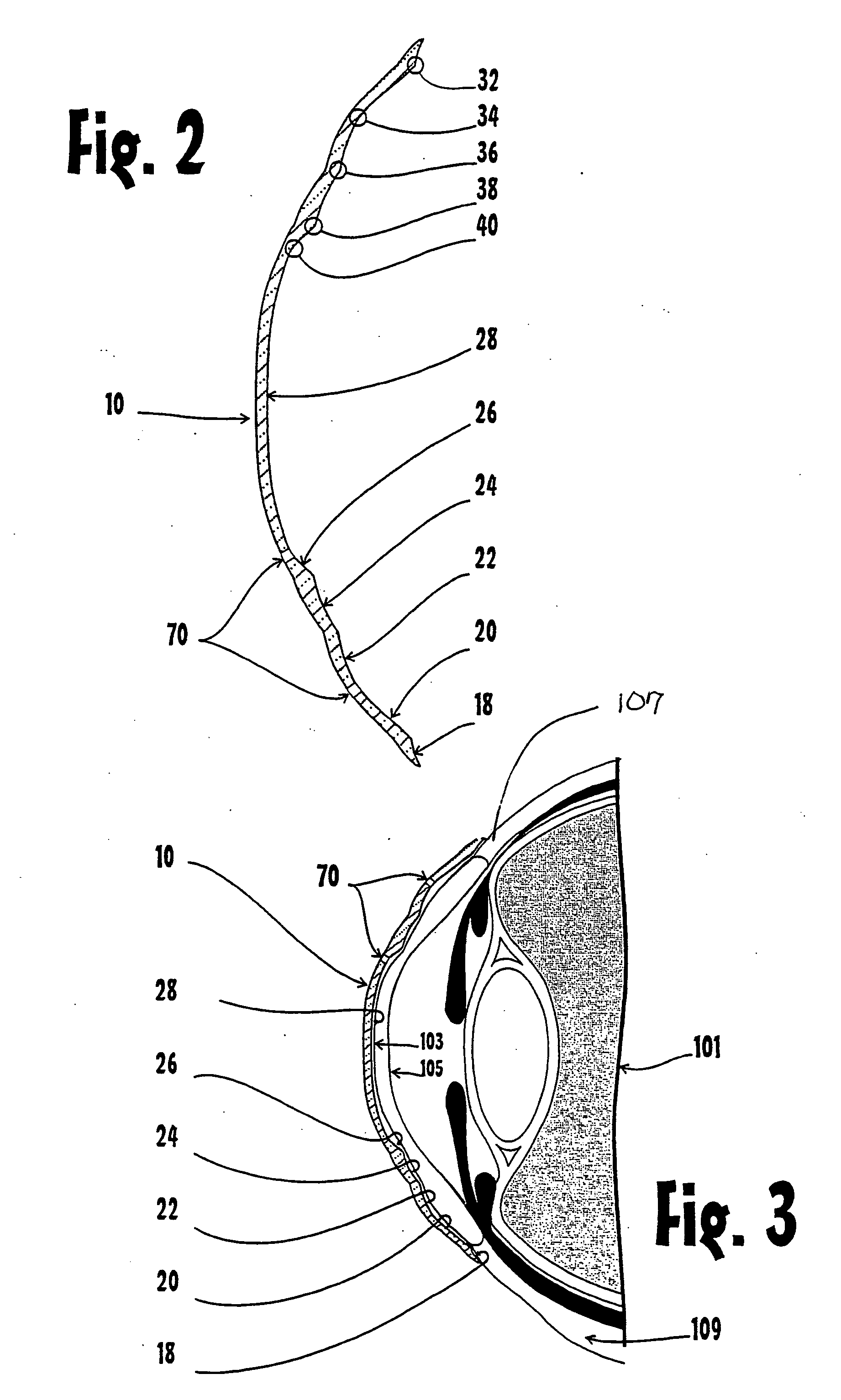
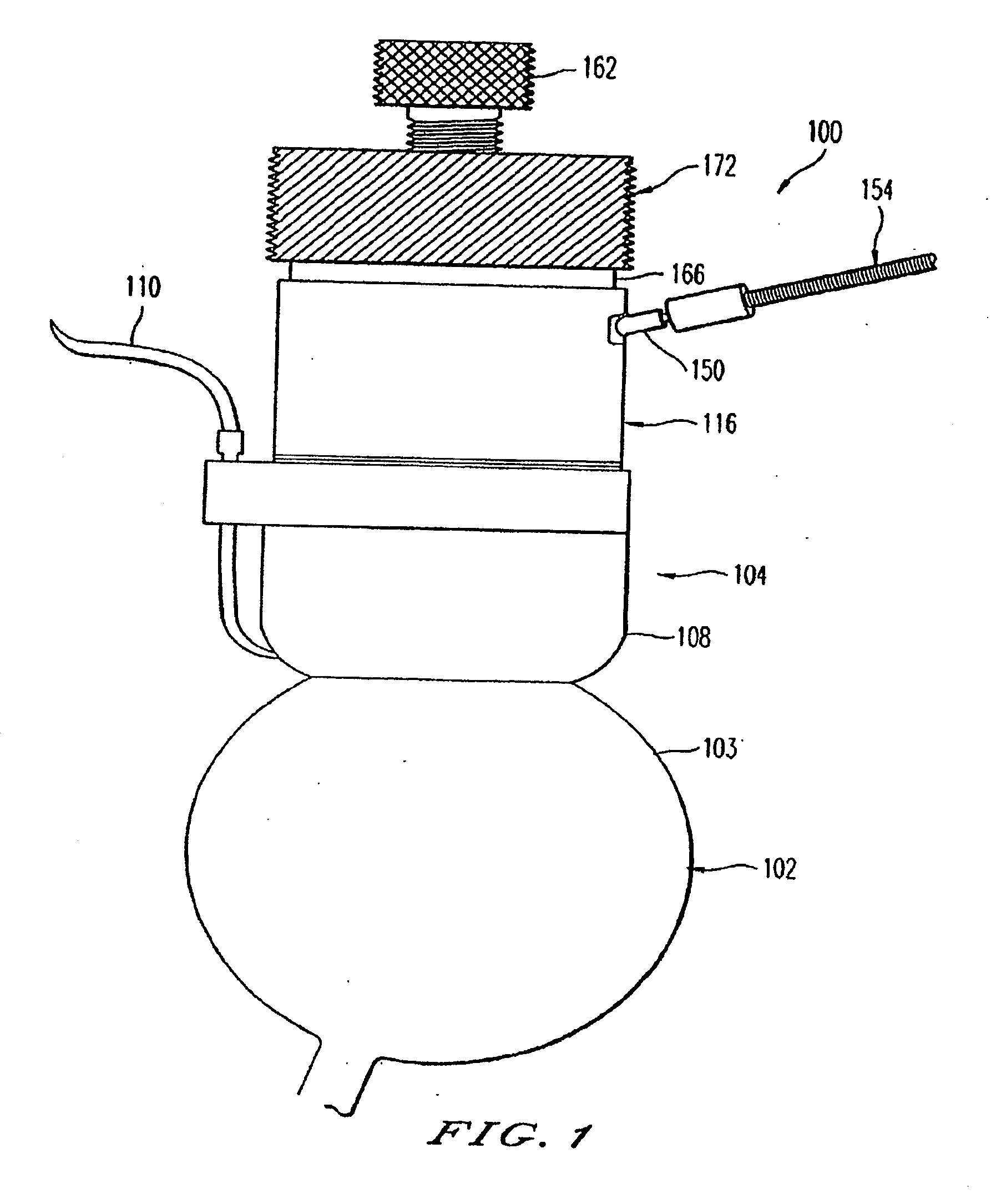
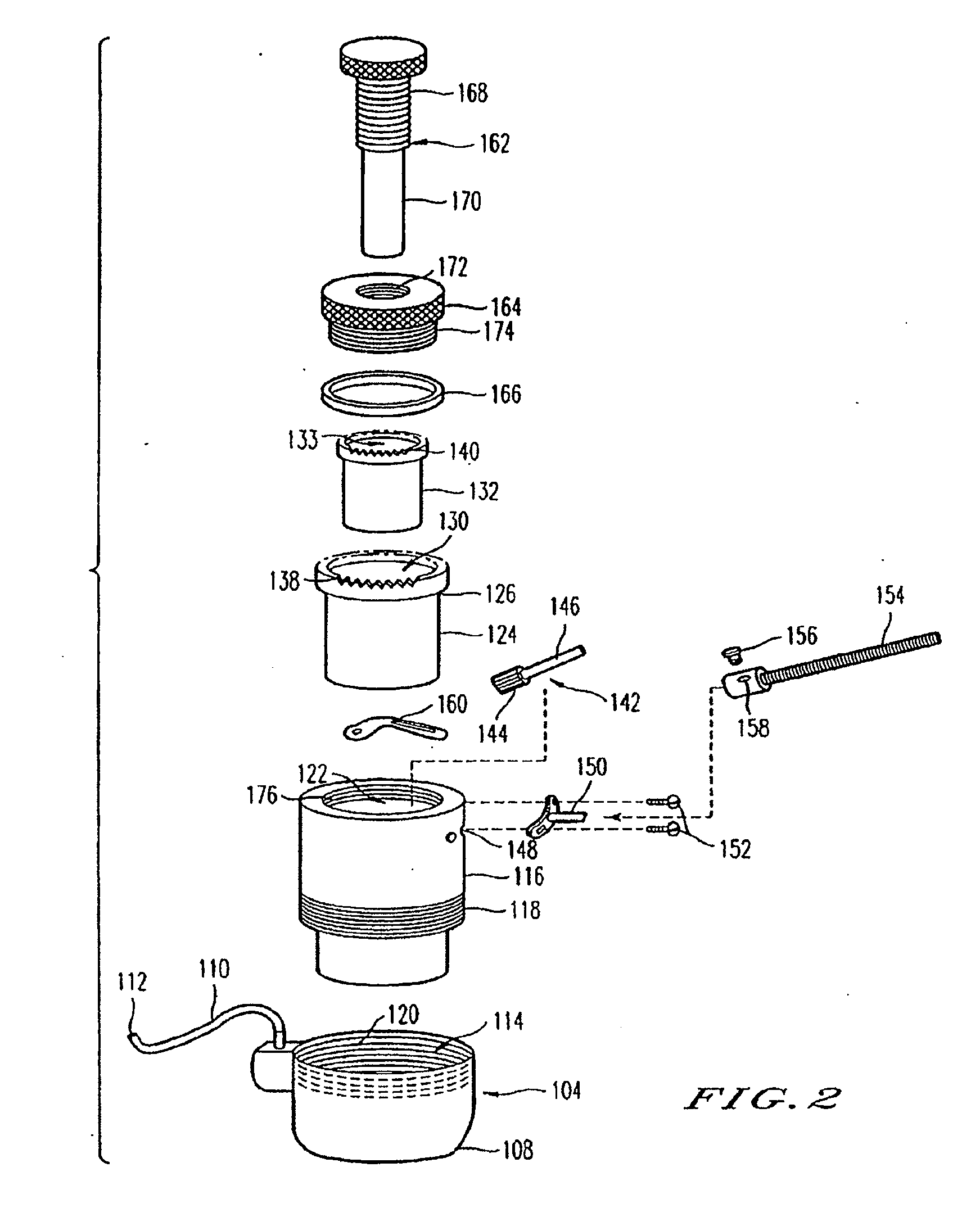
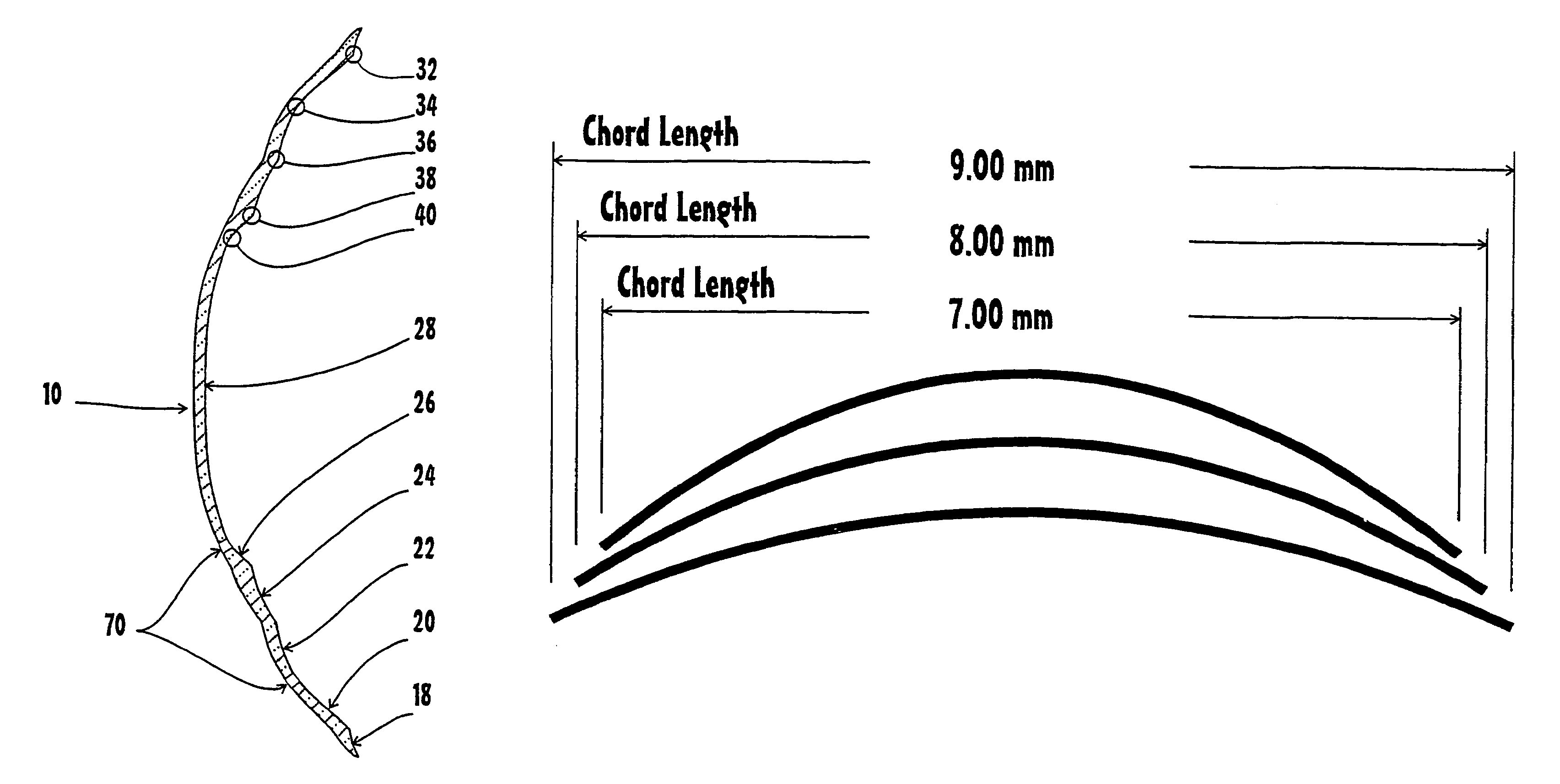
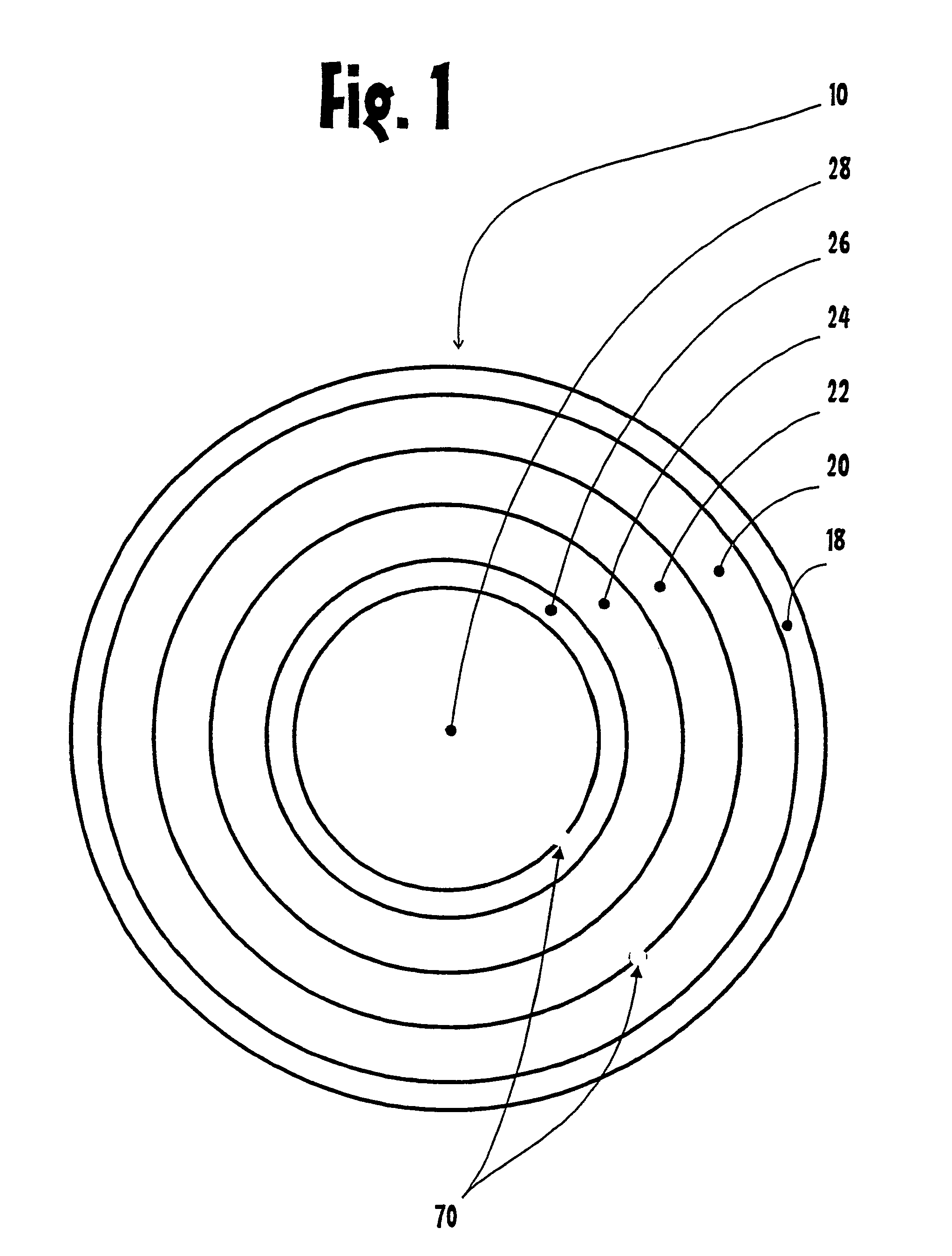
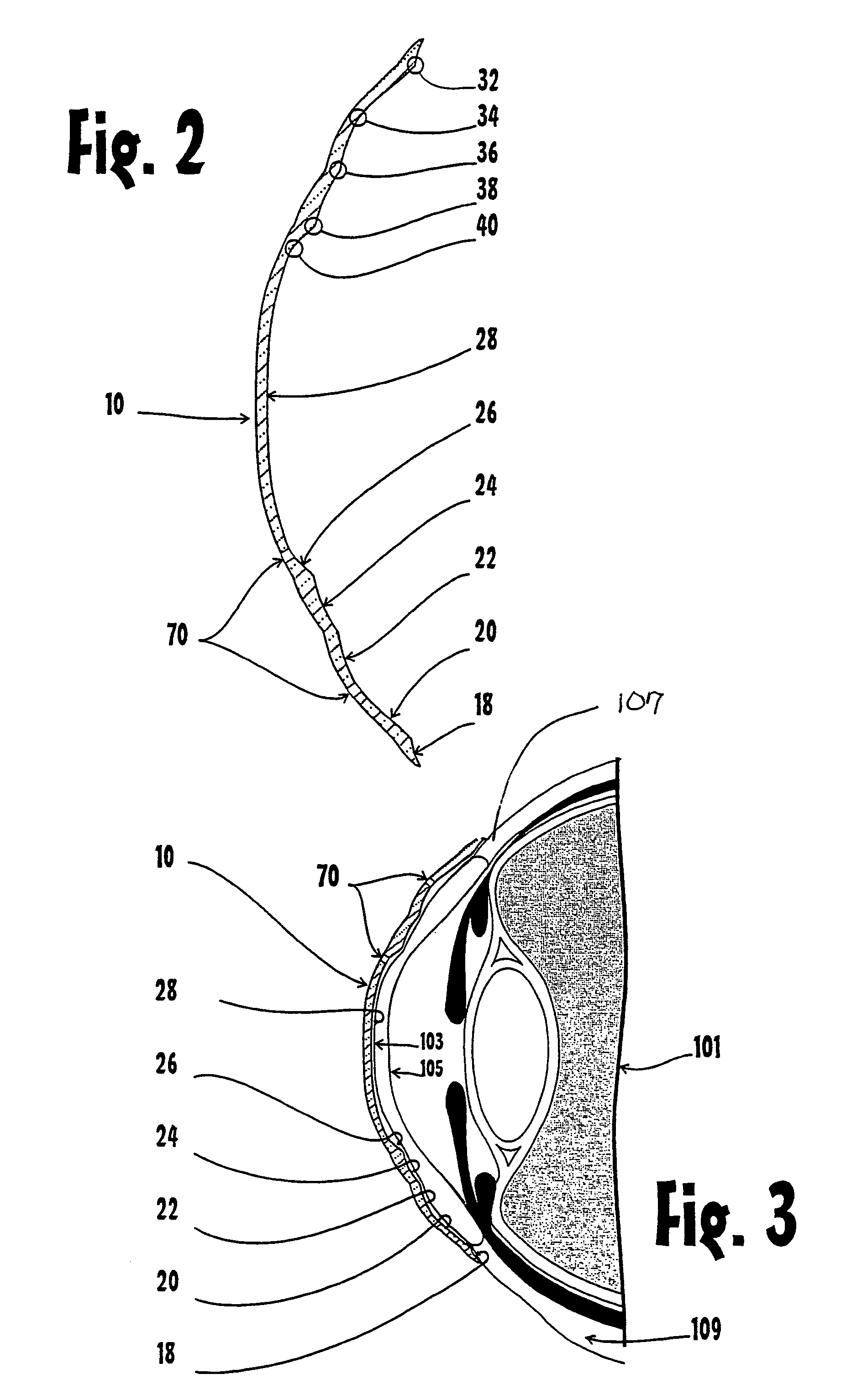
Adjustable universal implant blank for modifying corneal curvature and methods of modifying corneal curvature therewith
InactiveUS6949093B1Severe conditionImprove eyesightLaser surgeryEye implantsCorneal curvatureCorneal surface
A method for correcting the refractive error in a cornea of an eye, including the steps of positioning an inlay on the surface of the cornea, the inlay having a first surface and a second surface, and the second surface being adjacent the surface of the cornea. Energy is applied to the inlay to ablate a portion of the first surface of the inlay by an amount adapted to correct the refractive error in the eye. The inlay is removed from the surface of the cornea, and the cornea is separated into a first corneal surface and a second corneal surface, the first corneal surface facing in a posterior direction of the eye and the second corneal surface facing in an anterior surface of the eye. The inlay is then positioned adjacent at least one of the first corneal surface and the second corneal surface.
Owner:MINU
Devices and methods of selecting intraocular lenses
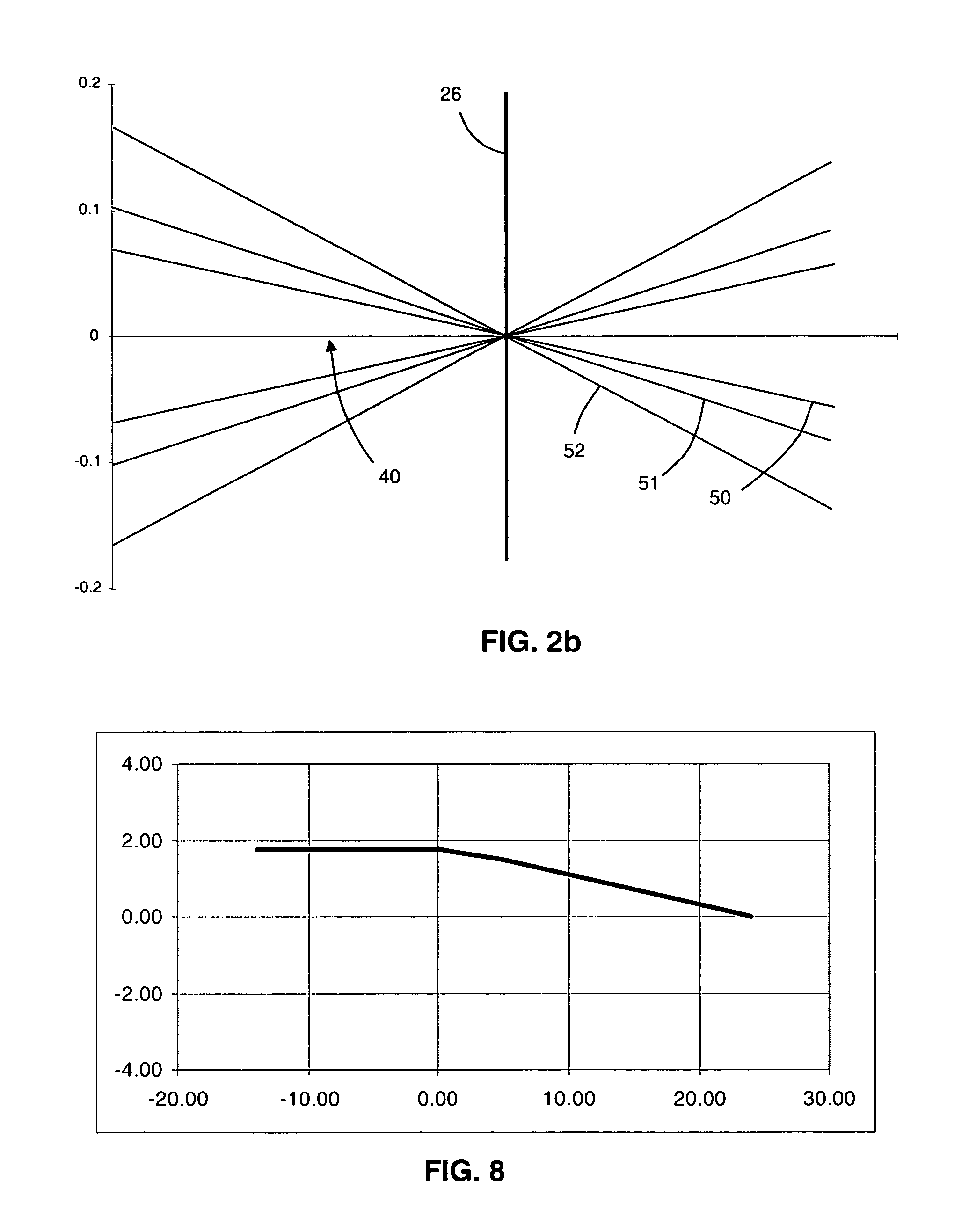
The invention relates to devices and methods for selecting IOLs for implantation and eye models useful with the methods. One method comprises the steps of determining the axial eye length, the pupil size at a desired light level; the desired postoperative refraction; determining an aspheric representation of the corneal curvature and determining the location of the plane of fixation of the IOL following implantation.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Corneal-scleral orthokeratology contact lens
ActiveUS20060152673A1Improve abilitiesFast and reliable and comfortable resultOptical partsCorneal curvatureRigid gas permeable lens
A corneal-scleral orthokeratology contact lens is formed of rigid gas permeable material with uniform arc lengths in the treatment area even when the corneal curvature varies and asymmetric blends or splines called minor zones, where the portion of the blend or spline is shorter toward the lens center and broader toward the lens edge, and relieve the treatment area of all centering responsibility, transferring it to the limbal-scleral region. The method of determining the total sagittal height of an eye at a given chord diameter to predetermine exact fitting parameters and predict unaided visual outcome trial lenses, with exact chord and sagittal height values used to match the sagittal height of an eye, the sagittal value may be obtained from some ocular topographers. A computer program can easily take the sagittal information and design an optimum lens.
Owner:DAKOTA SCI
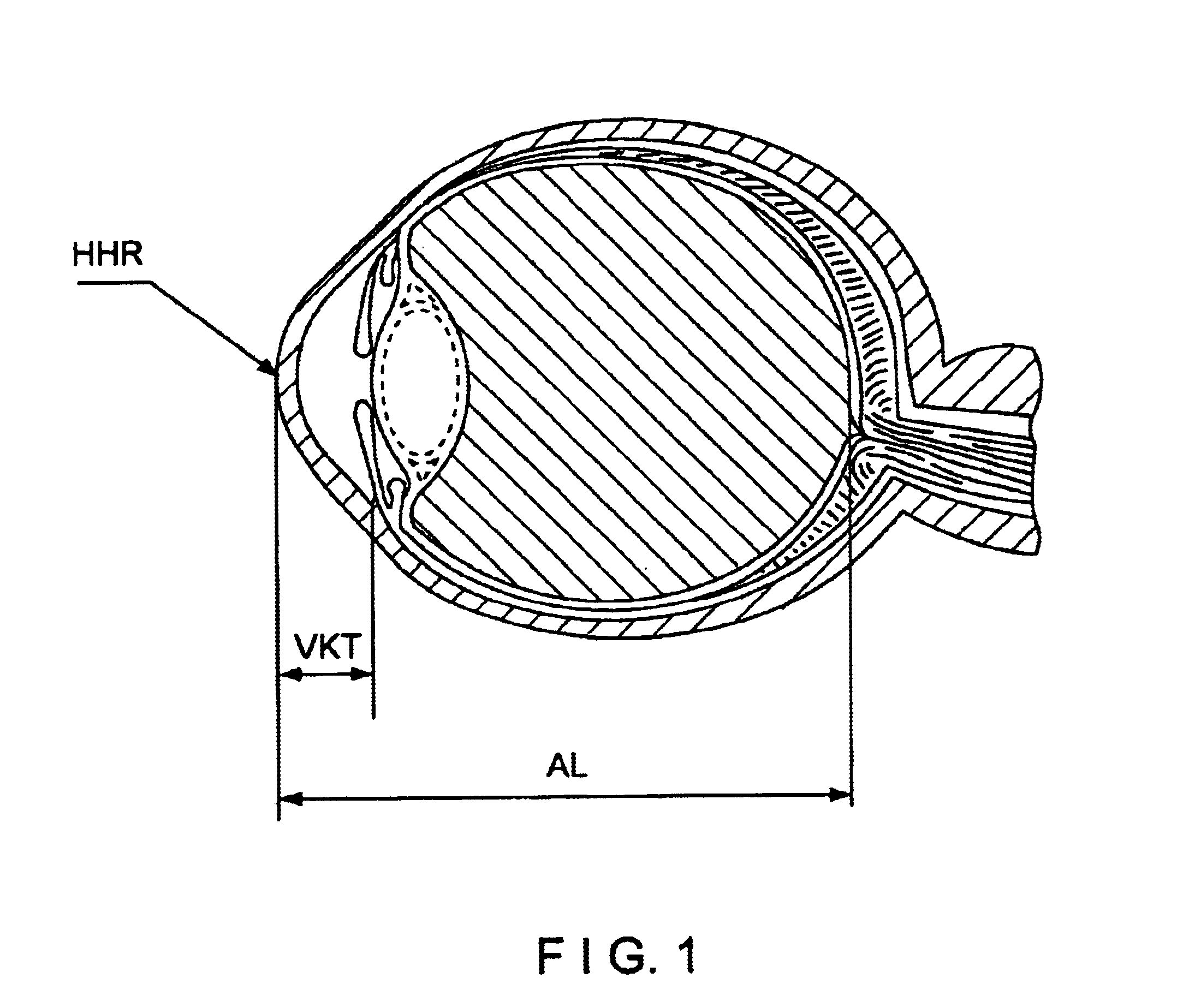
System and method for non-contacting measurement of the eye
InactiveUS6779891B1Reduce device-dependent measurement errorReduce measurement errorEye inspectionGonioscopesCorneal curvatureIntraocular lens
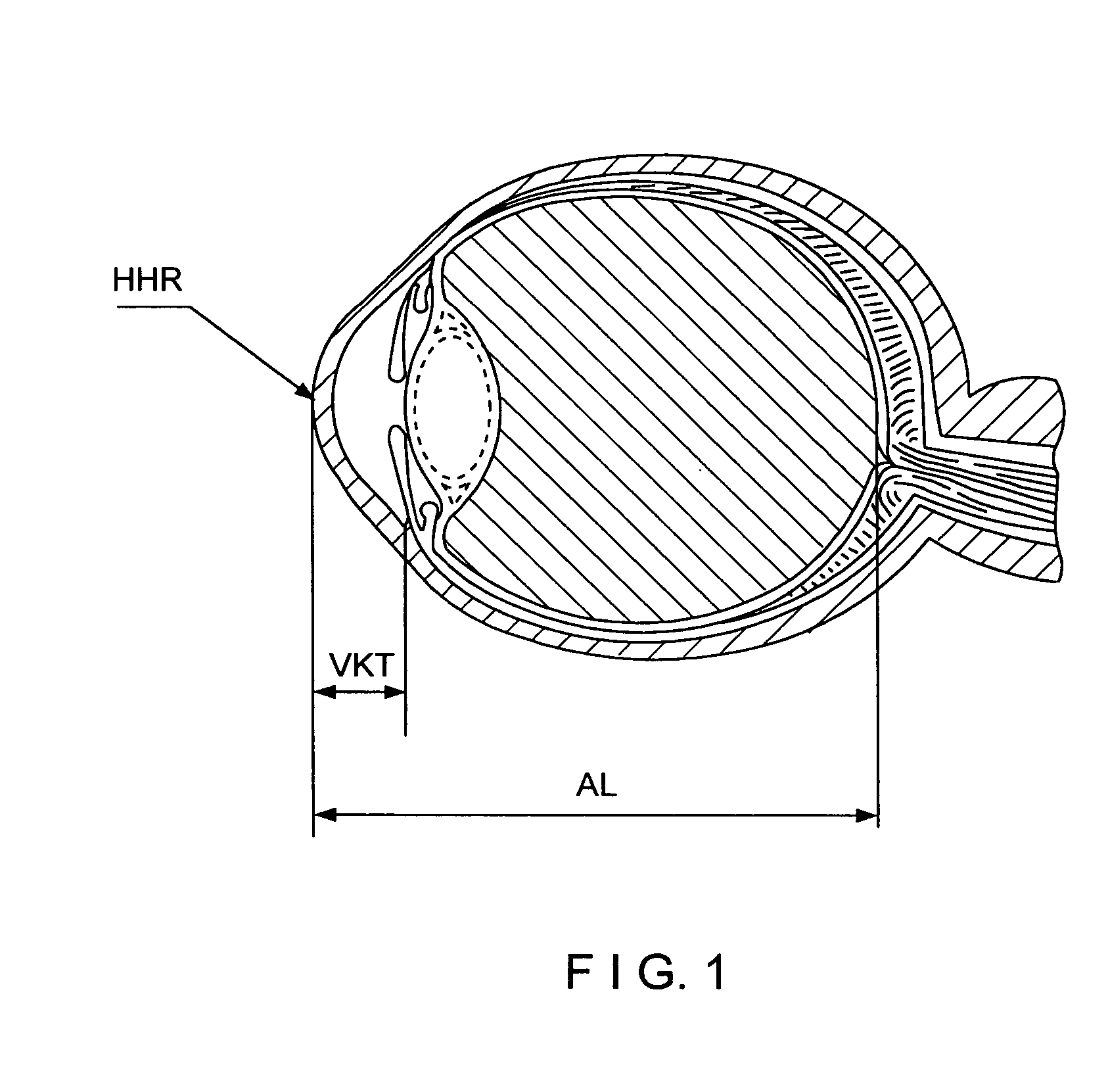
Combined equipment for non-contacting determination of axial length (AL), anterior chamber depth (VKT) and corneal curvature (HHK) of the eye are also important for the selection of the intraocular lens IOL to be implanted, particularly the selection of an intraocular lens IOL to be implanted, preferably with fixation of the eye by means of a fixating lamp and / or illumination through light sources grouped eccentrically about the observation axis.
Owner:CARL ZEISS JENA GMBH
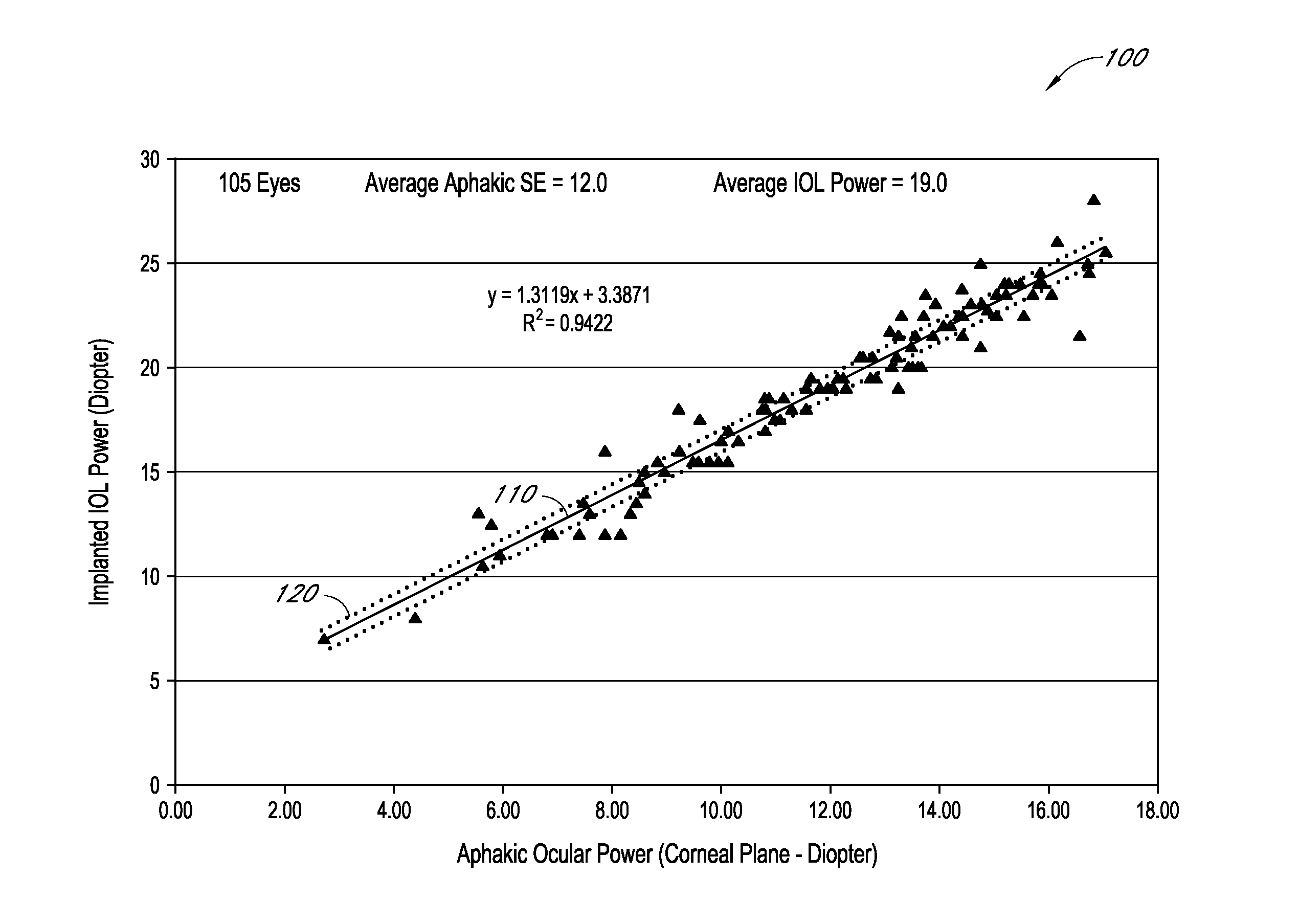
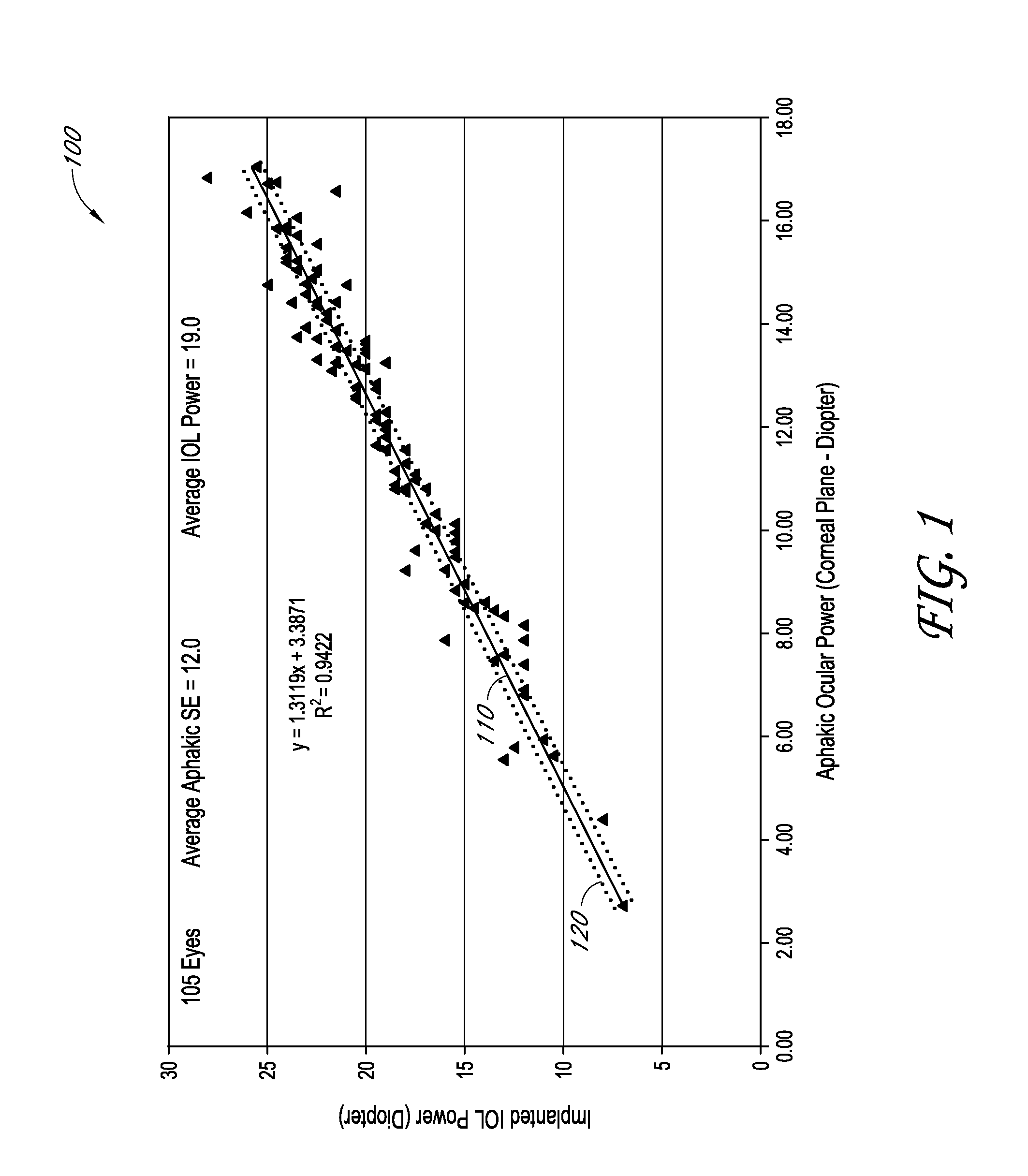
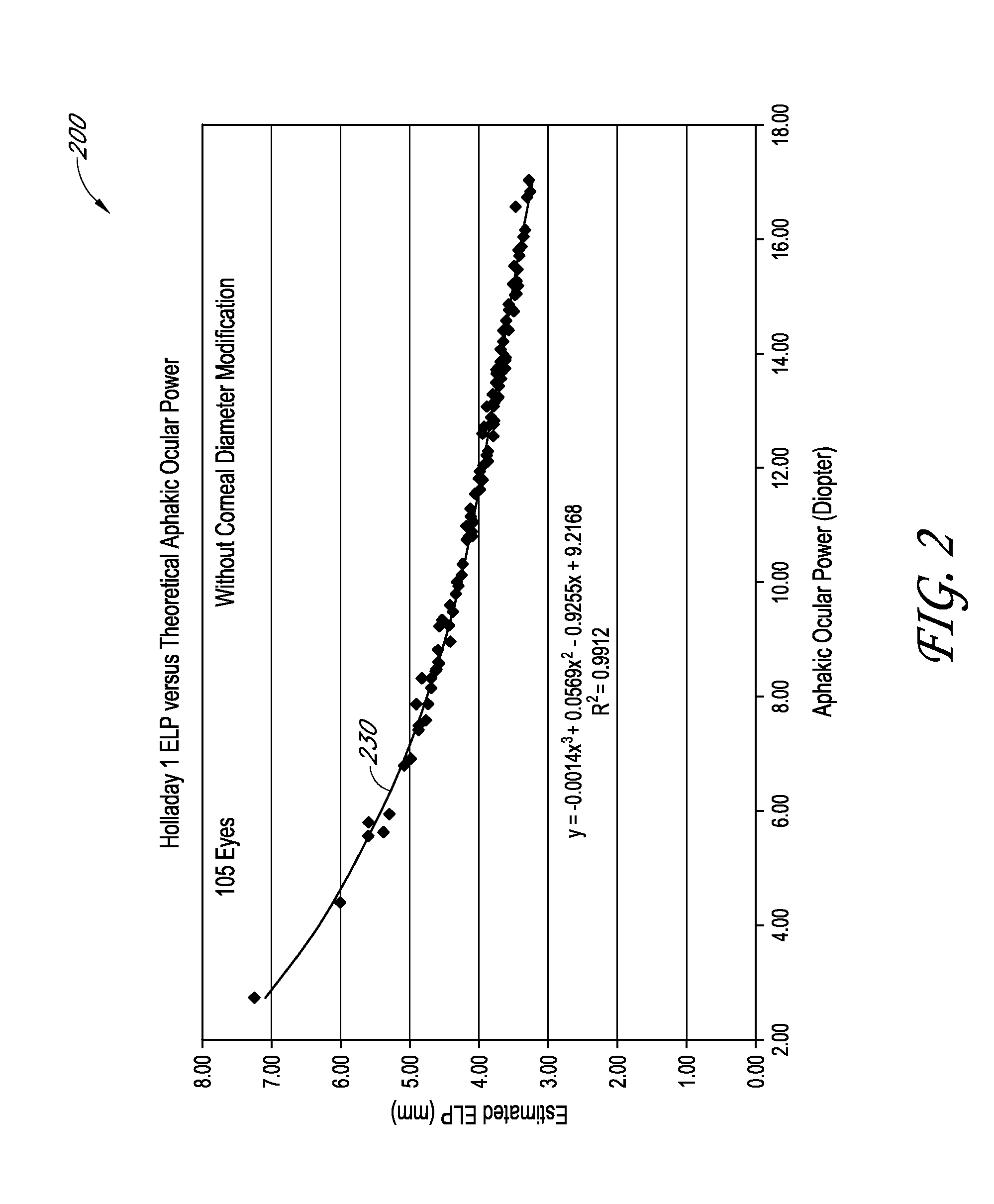
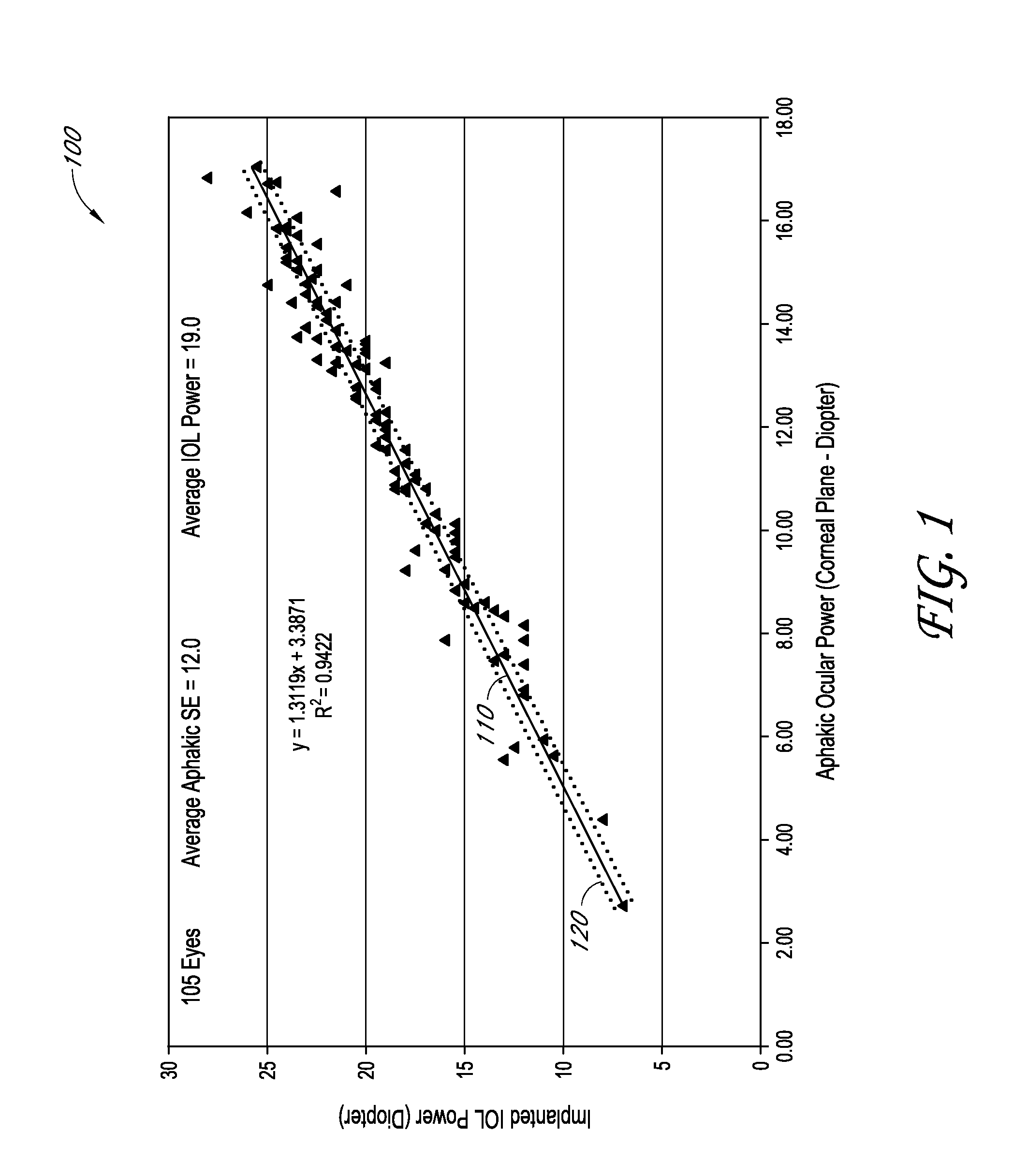
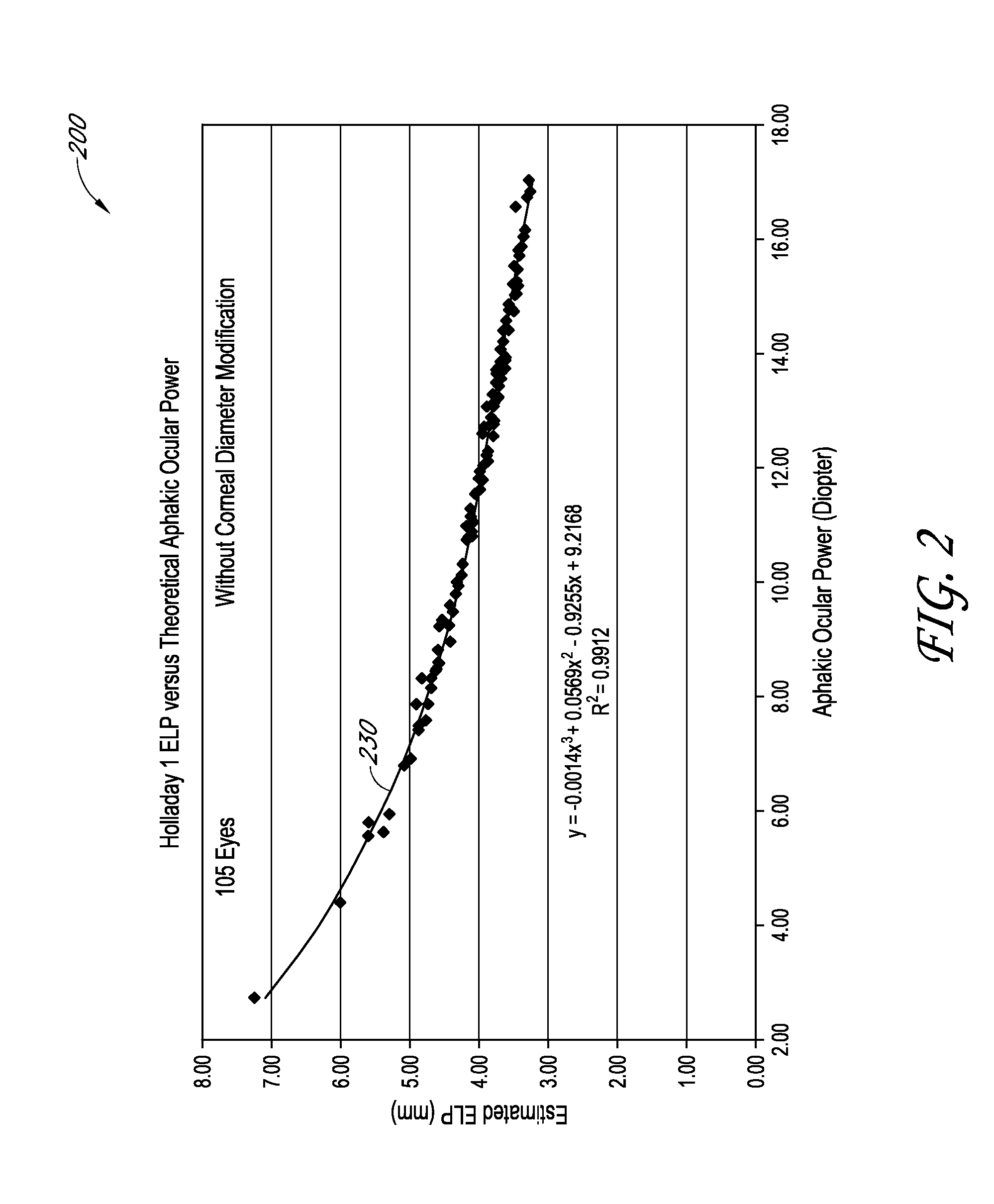
Determination of the effective lens position of an intraocular lens using aphakic refractive power
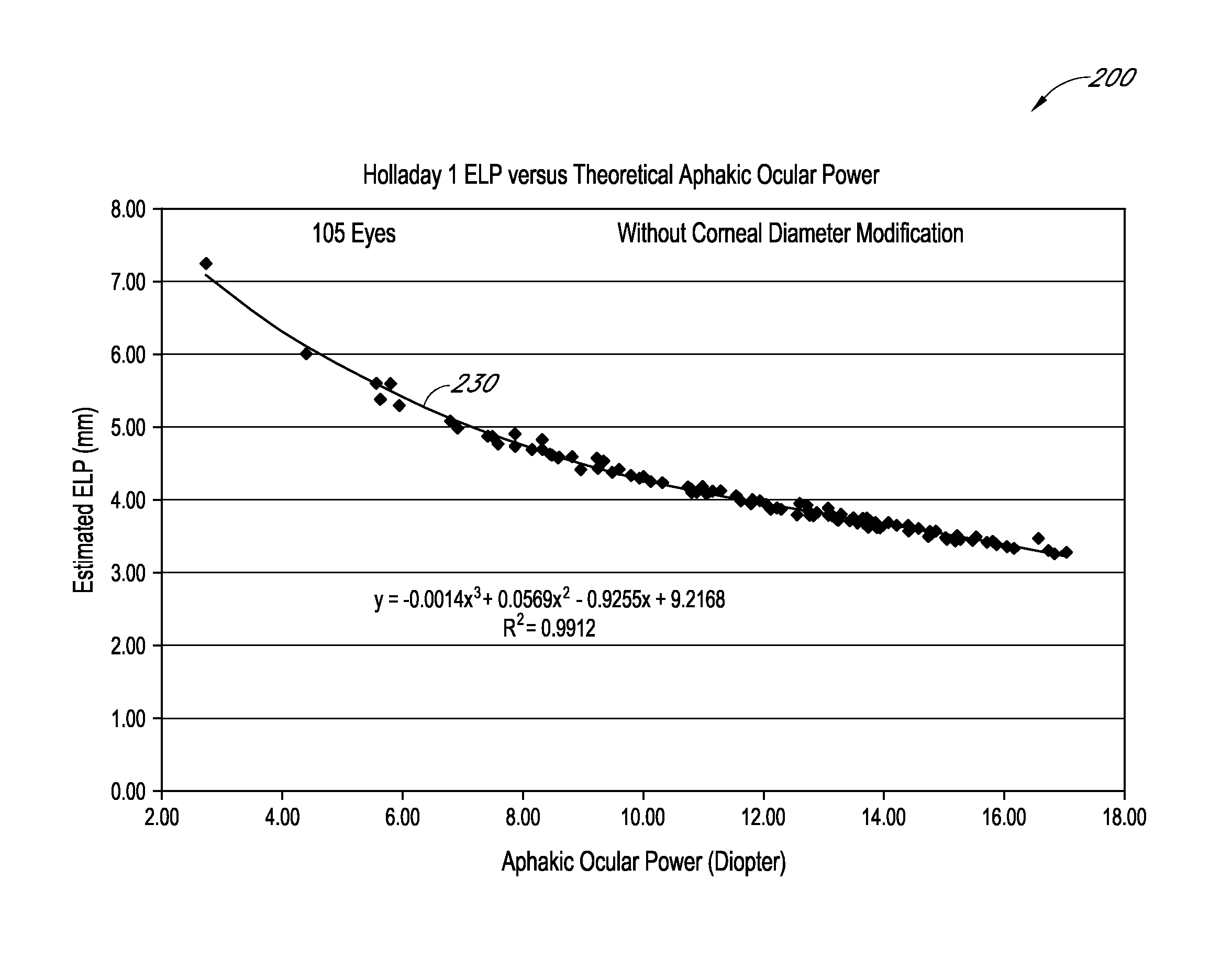
An ophthalmic method for determining a relationship between aphakic ocular power and estimated effective lens position (ELP) of an intraocular lens (IOL) to be implanted in a patient's eye. The method can be used to determine an estimate of the ELP of an IOL given the aphakic ocular power of the patient's eye, for example, without measurement of the corneal curvature or axial length of the patient's eye. The estimate of ELP can then be used to determine a suitable value of optical power for the IOL to be implanted in the patient's eye.
Owner:ALCON INC
Method and apparatus to correct refractive errors using adjustable corneal arcuate segments
InactiveUS6206919B1Steepening of corneal curvatureEasy to modifyEye implantsCorneal curvatureRefractive error
A method and apparatus for adjusting corneal curvature of the eye comprising an adjustable corneal arcuate segment or segments which is implantable into the cornea. The arcuate segment is a flexible hollow shell composed of a synthetic or a natural material, with an annular chamber that is filled with a predetermined amount of a biocompatible material. The corneal curvature is adjusted by removing or augmenting the predetermined amount of biocompatible material contained in the arcuate segment.
Owner:LEE JOSEPH Y
Method for determining the power of an intraocular lens used for the treatment of myopia
InactiveUS7044604B1Improve predictabilityCorrection of myopiaEye diagnosticsIntraocular lensCorneal curvatureIntraocular lens
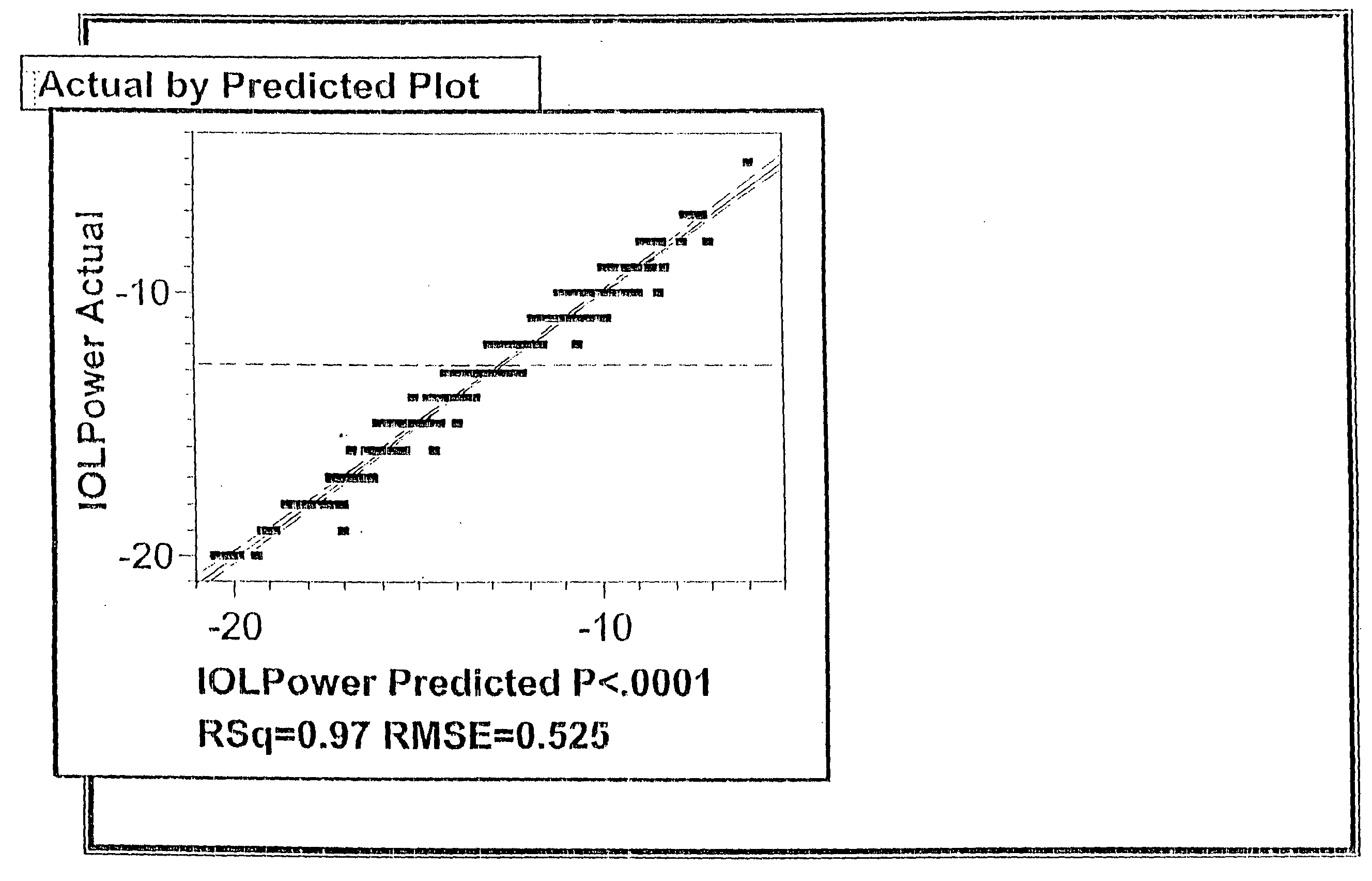
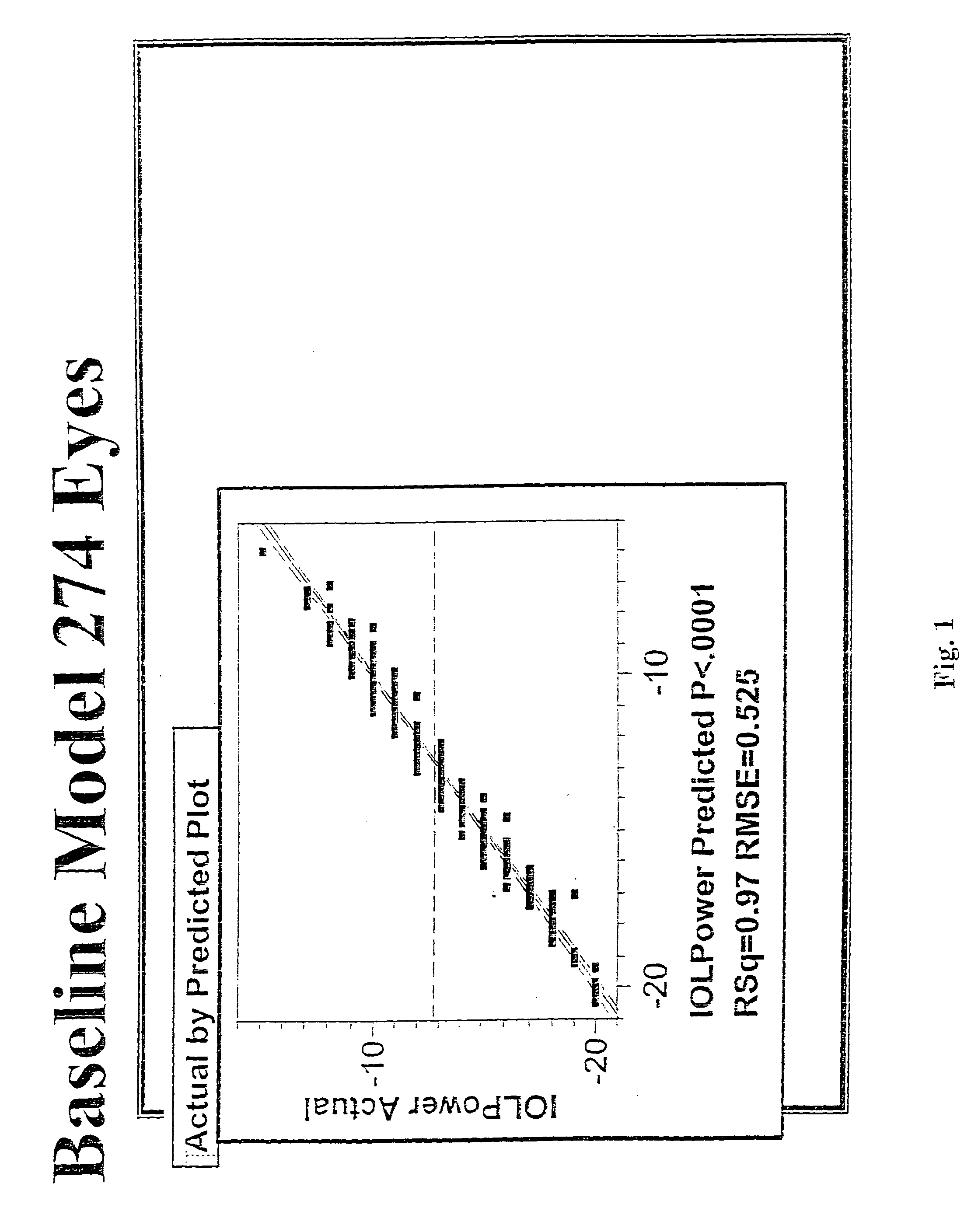
A method of deriving a prediction model and calculating a predicted lens power to provide a desired post-operative spherical equivalent to correct myopia in a phakic eye of a patient using an intraocular lens includes measuring and determining the predictive significance of certain pre-operative characteristics of the eye, including cycloplegic and manifest spherical equivalent, vertex distance, anterior chamber depth, axial length, and keratometry. The prediction model is derived using multiple regression analysis on the pre-operative and post operative data. Measured data corresponding to a particular patient is used in the lens power prediction model to calculate the predicted lens power for implantation in the patient.
Owner:ARROWSMITH PETER N
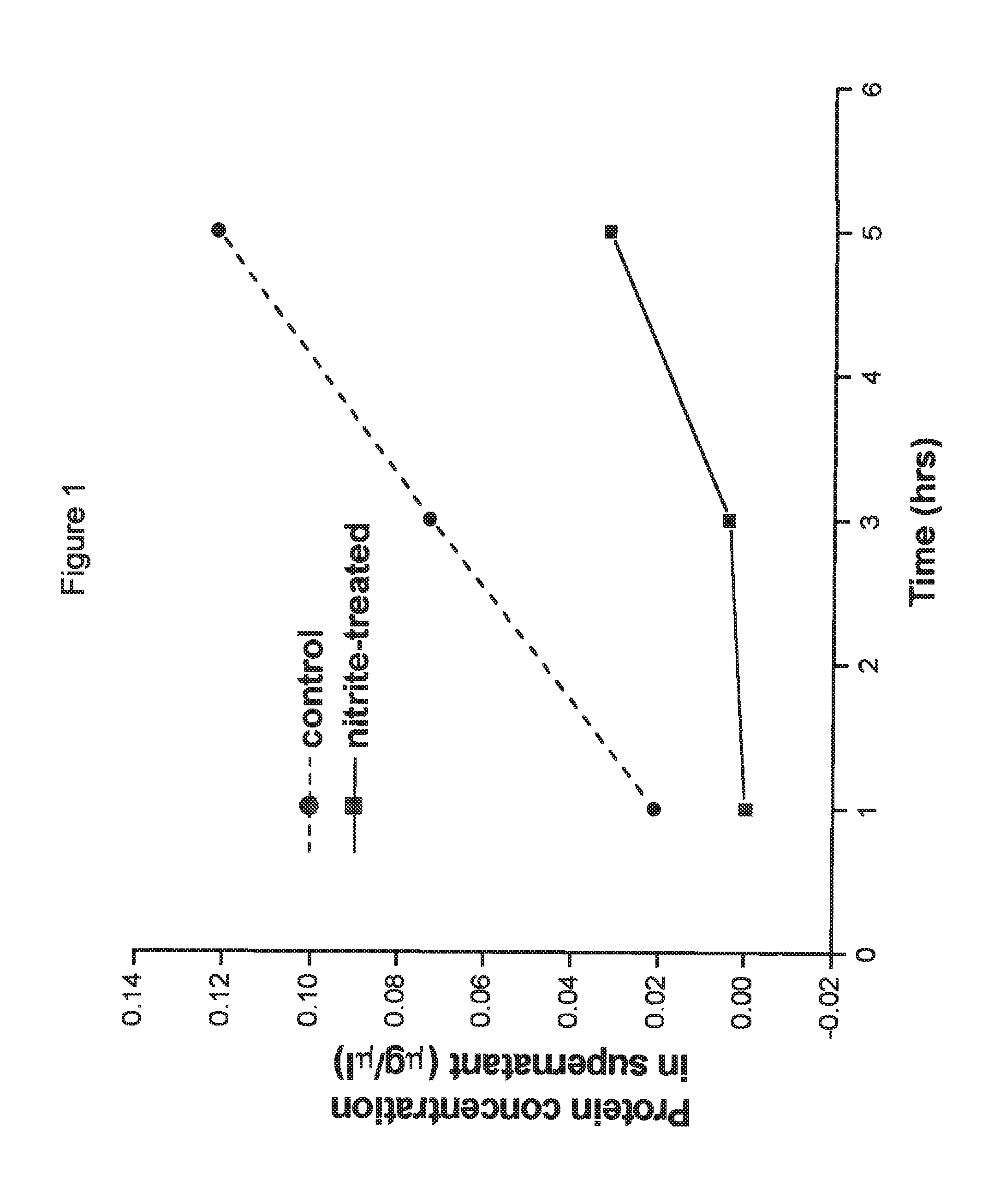
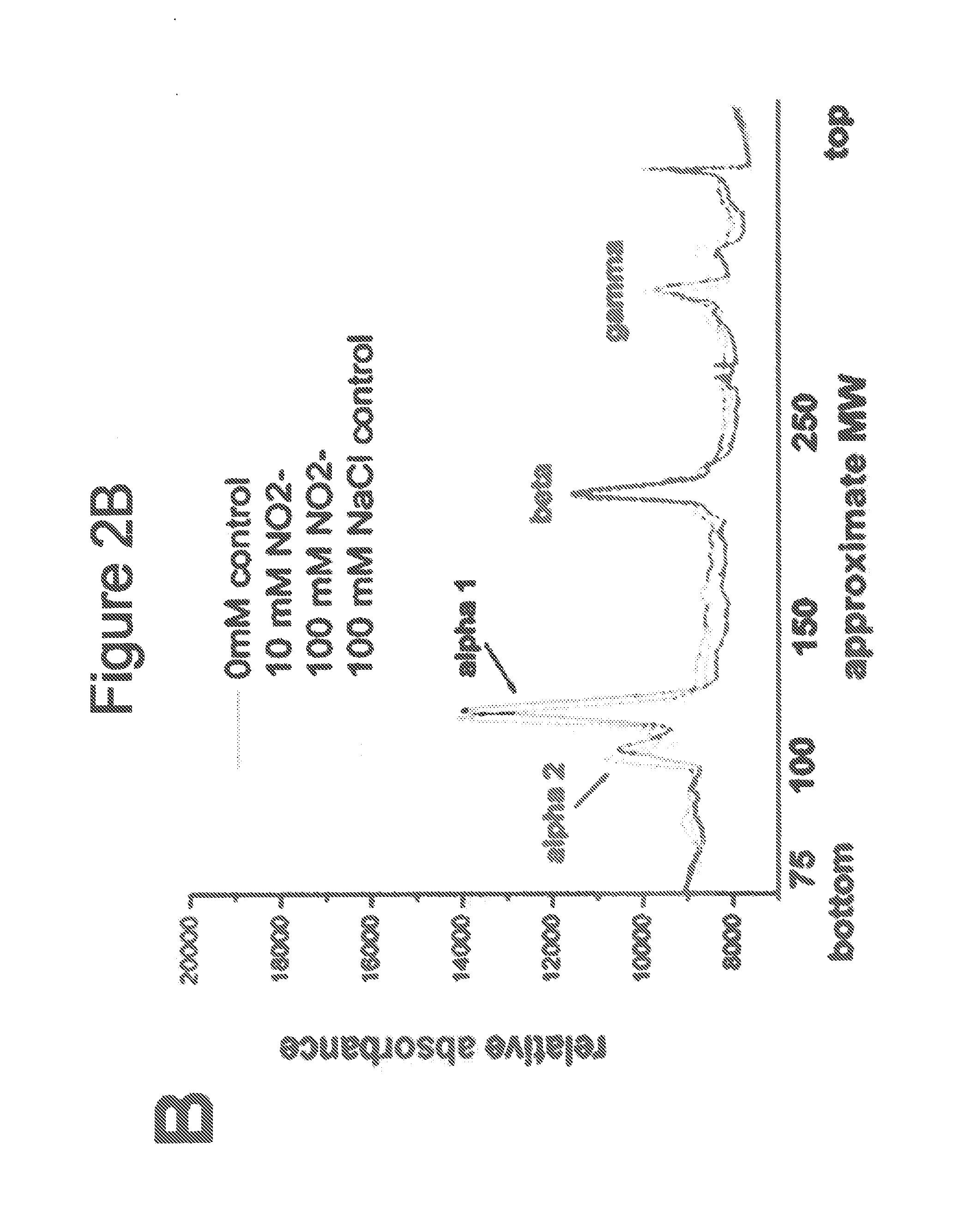
Method of stabilizing human eye tissue by reaction with nitrite and related agents such as nitro compounds
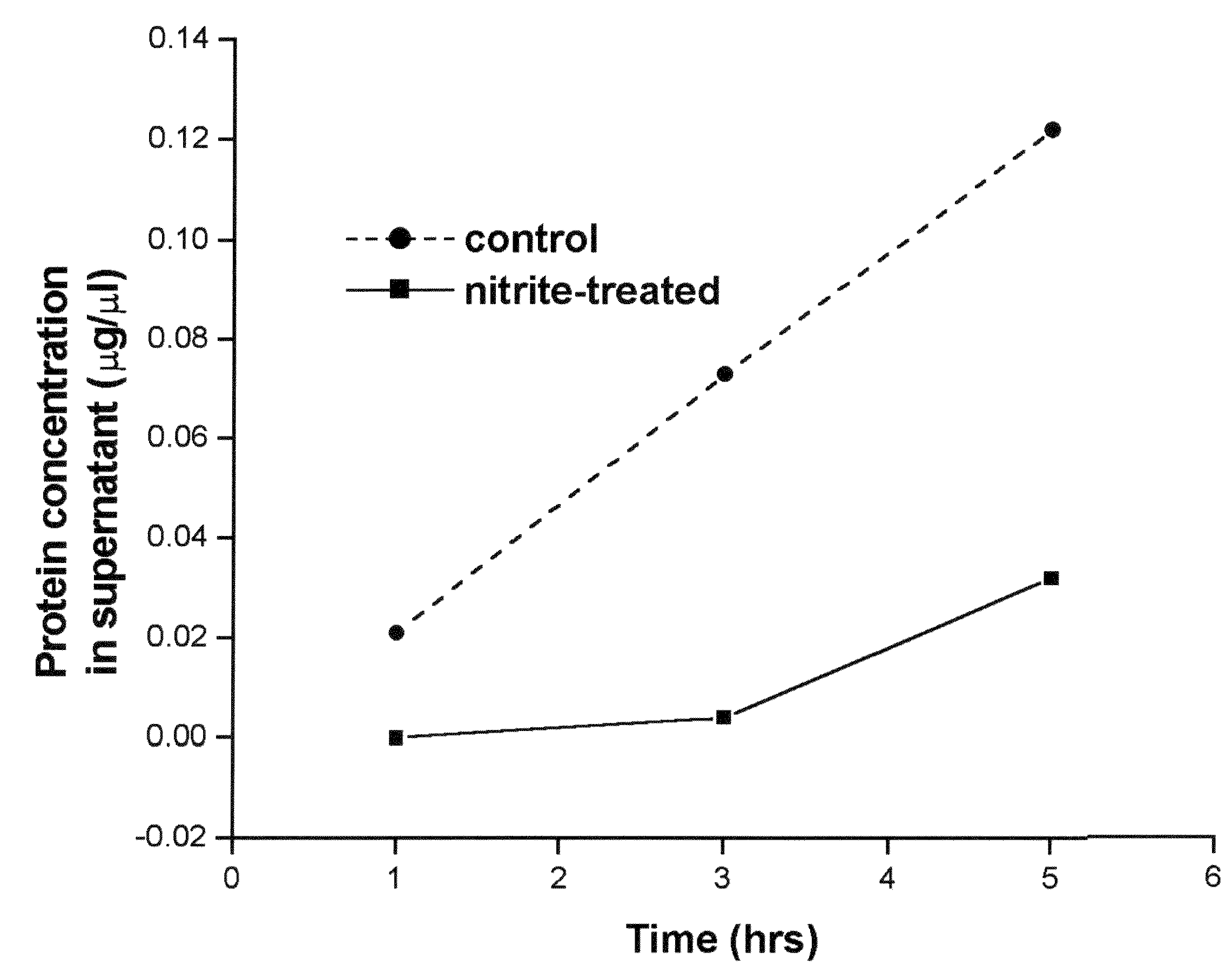
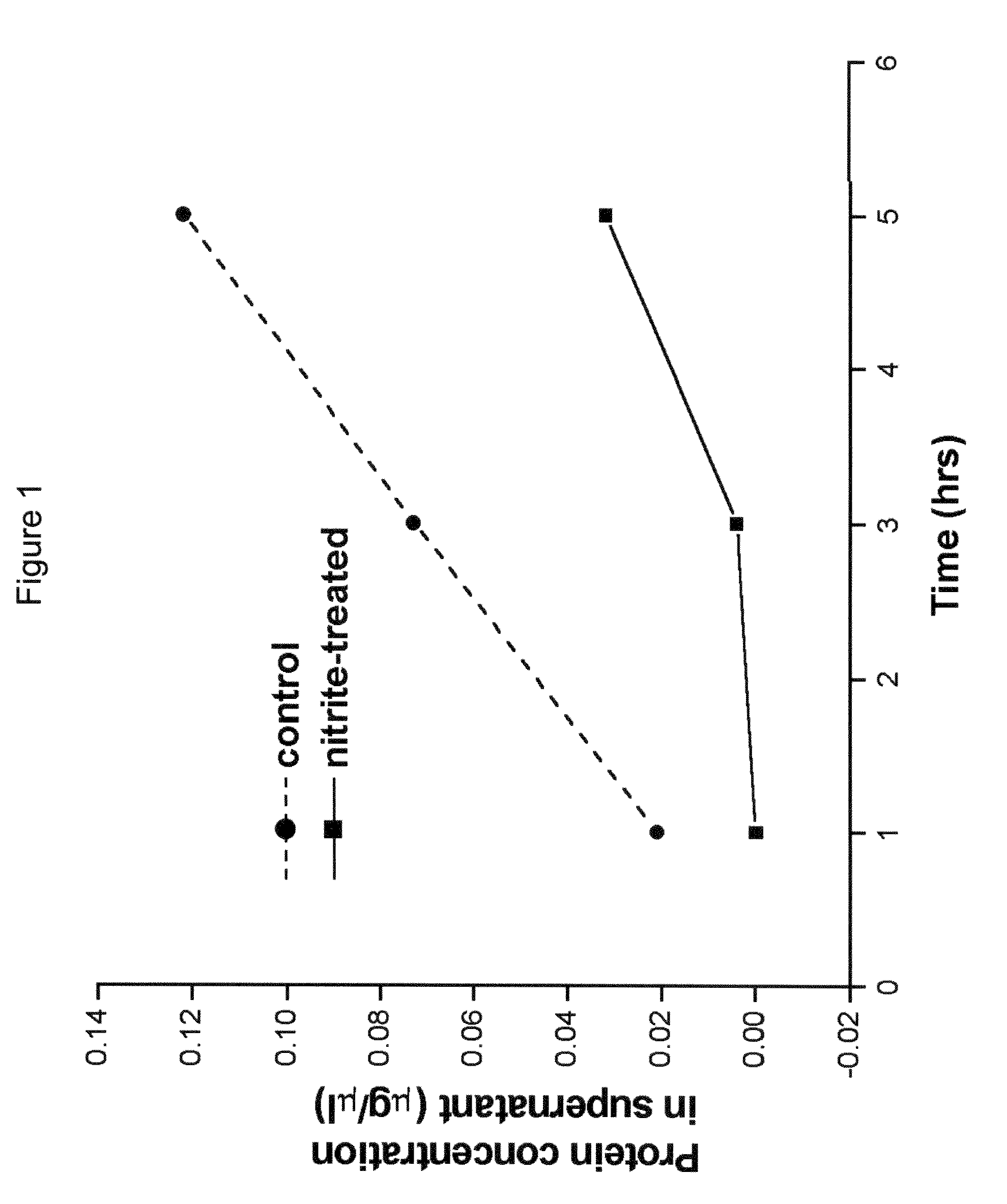
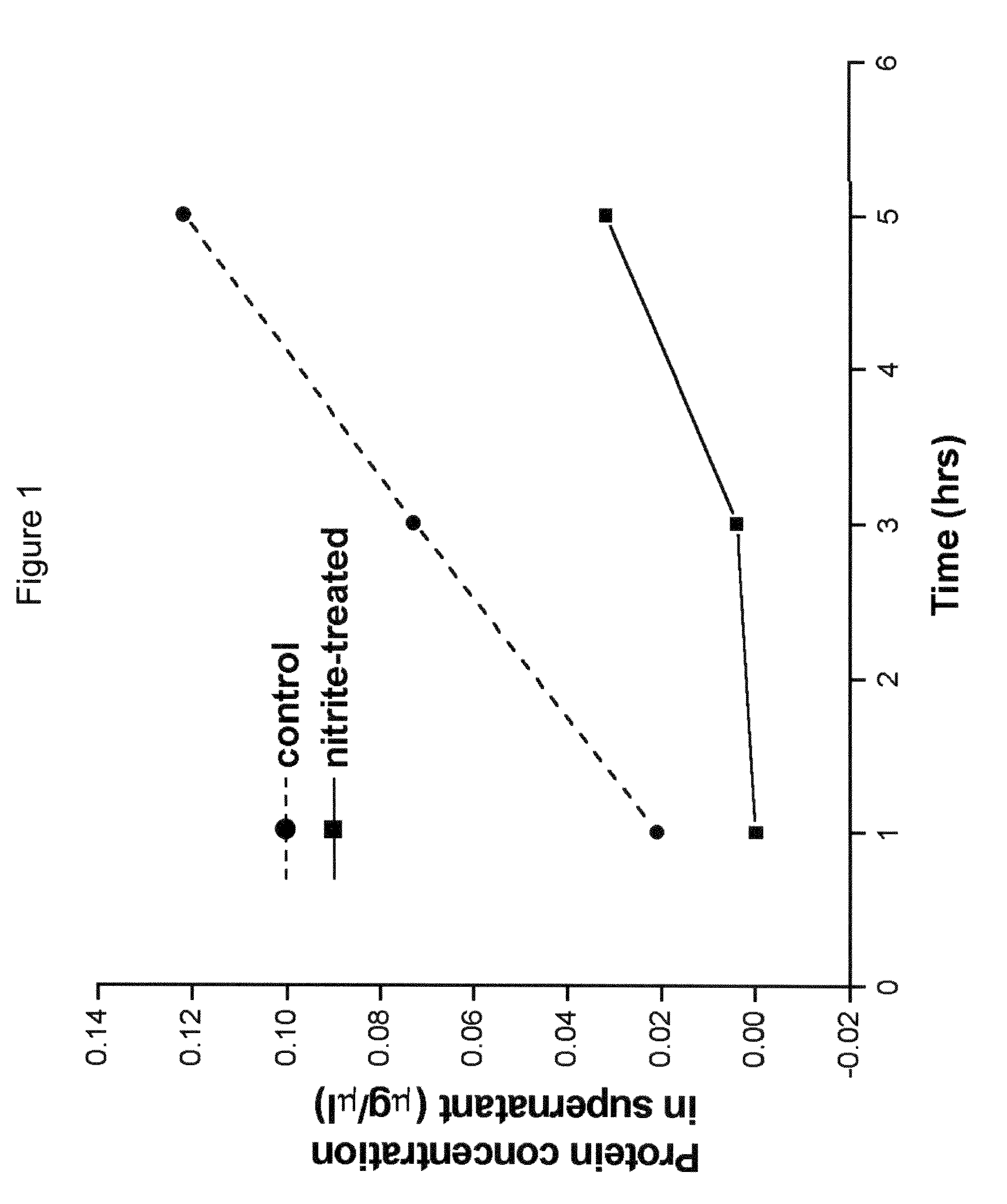
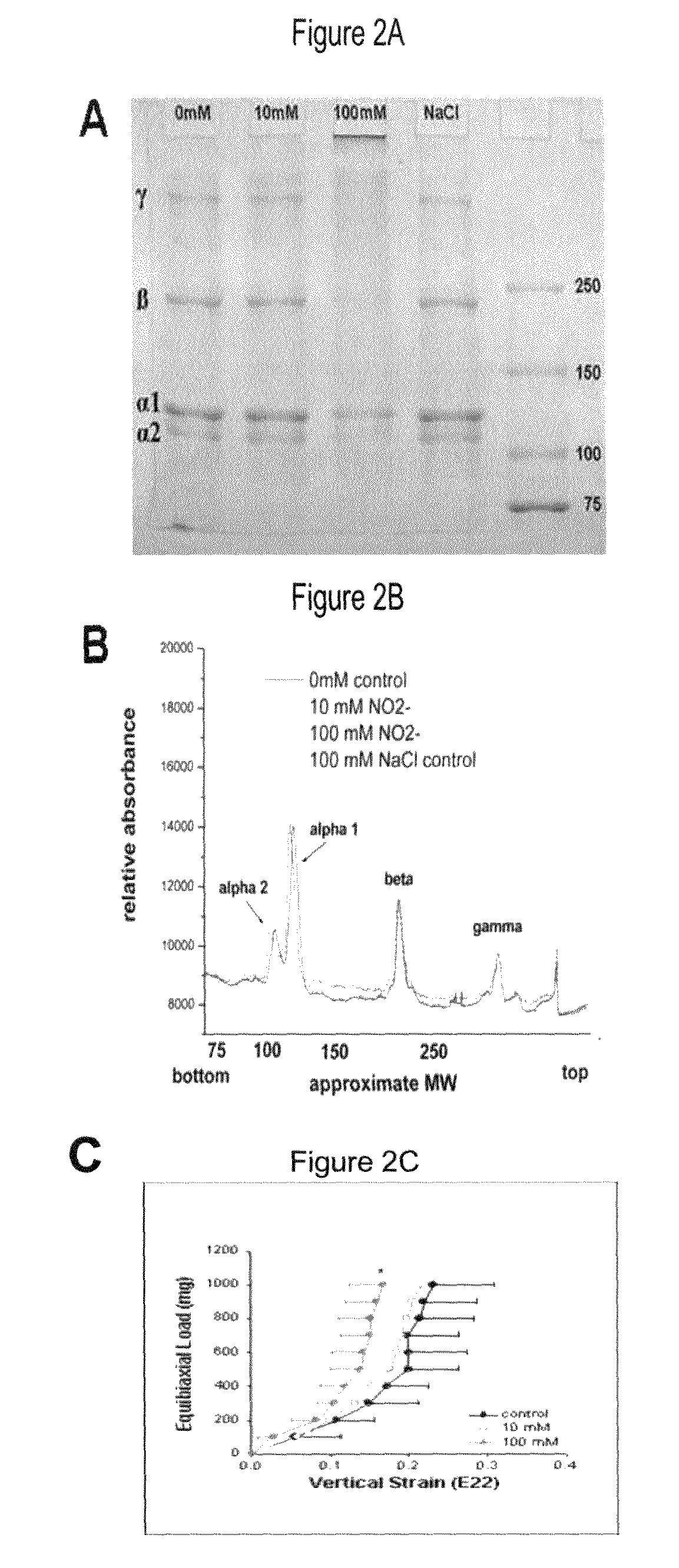
A method for stabilizing collagenous eye tissues by nitrite and nitroalcohol treatment. The topical stiffening agent contains sodium nitrite or a nitroalcohol in a buffered balanced salt solution and can be applied to the surface of the eye on a daily basis for a prolonged period. Application of the solution results in progressive stabilization of the corneal and scleral tissues through non-enzymatic cross-linking of collagen fibers. The compounds can penetrate into the corneal stroma without the need to remove the corneal epithelium. In addition, ultraviolet light is not needed to activate the cross-linking process. The resulting stabilization of corneal and scleral tissues can prevent future alterations in corneal curvature and has utility in diseases such as keratoconus, keratectasia, progressive myopia, and glaucoma.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
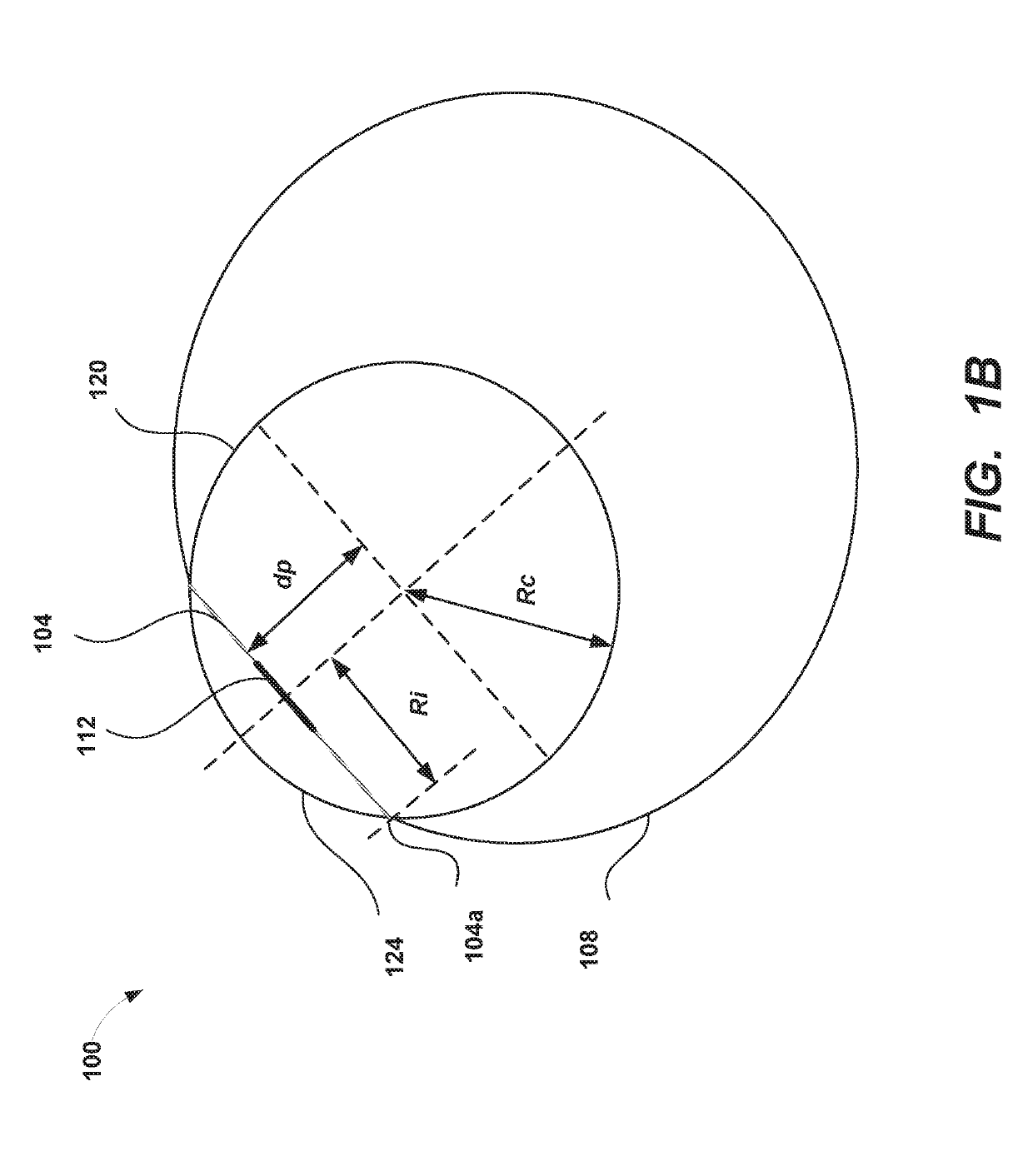
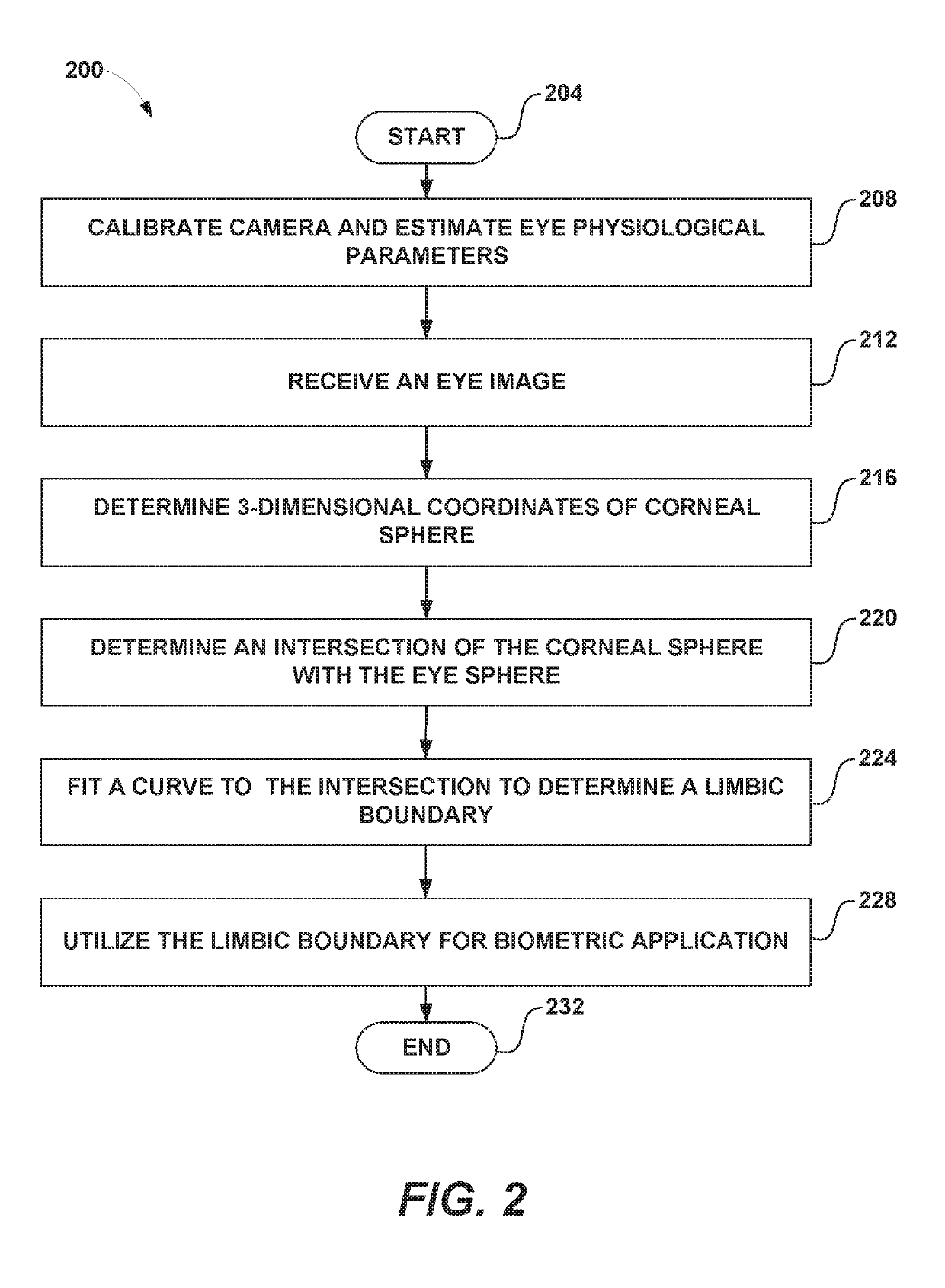
Iris boundary estimation using cornea curvature
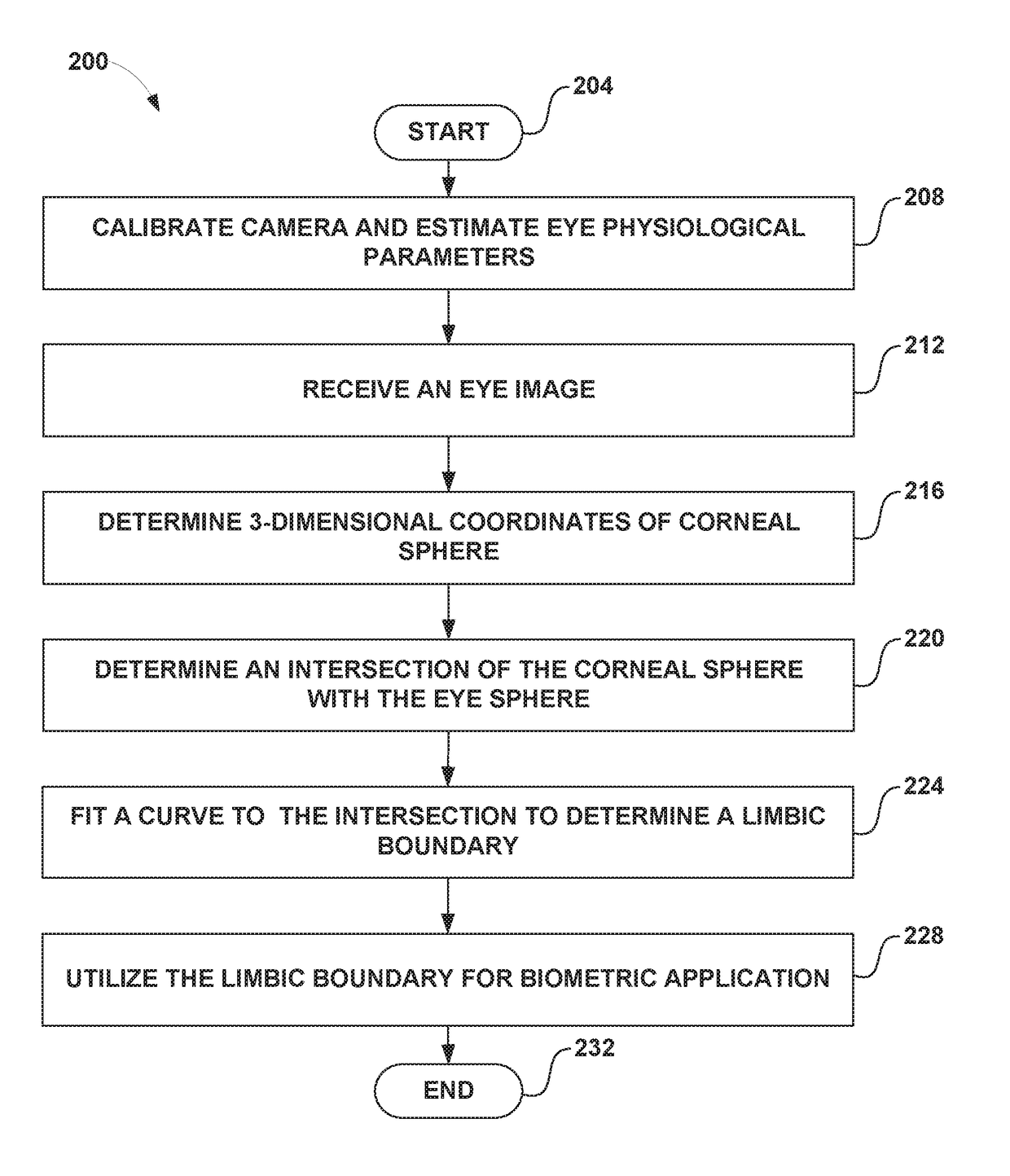
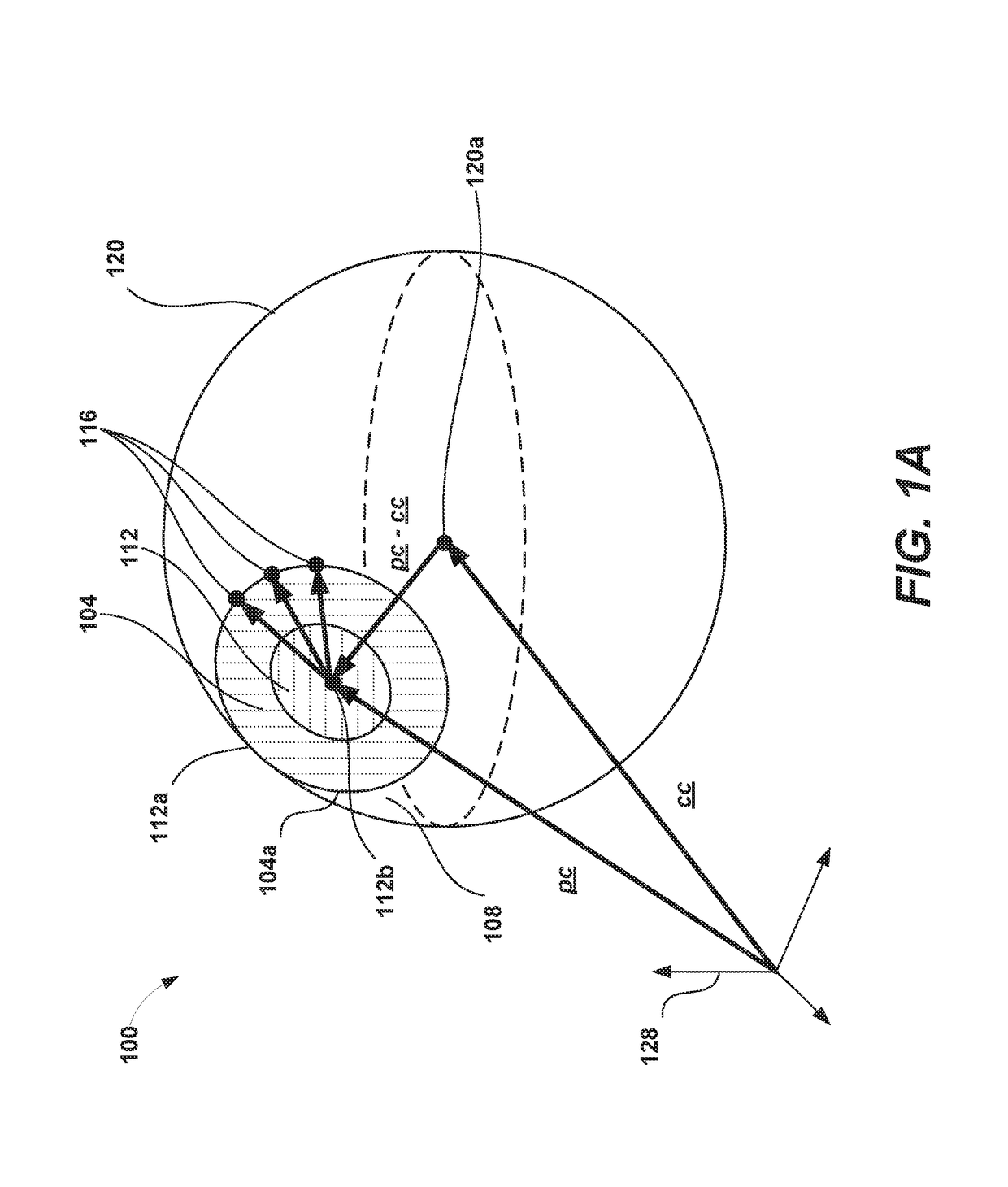
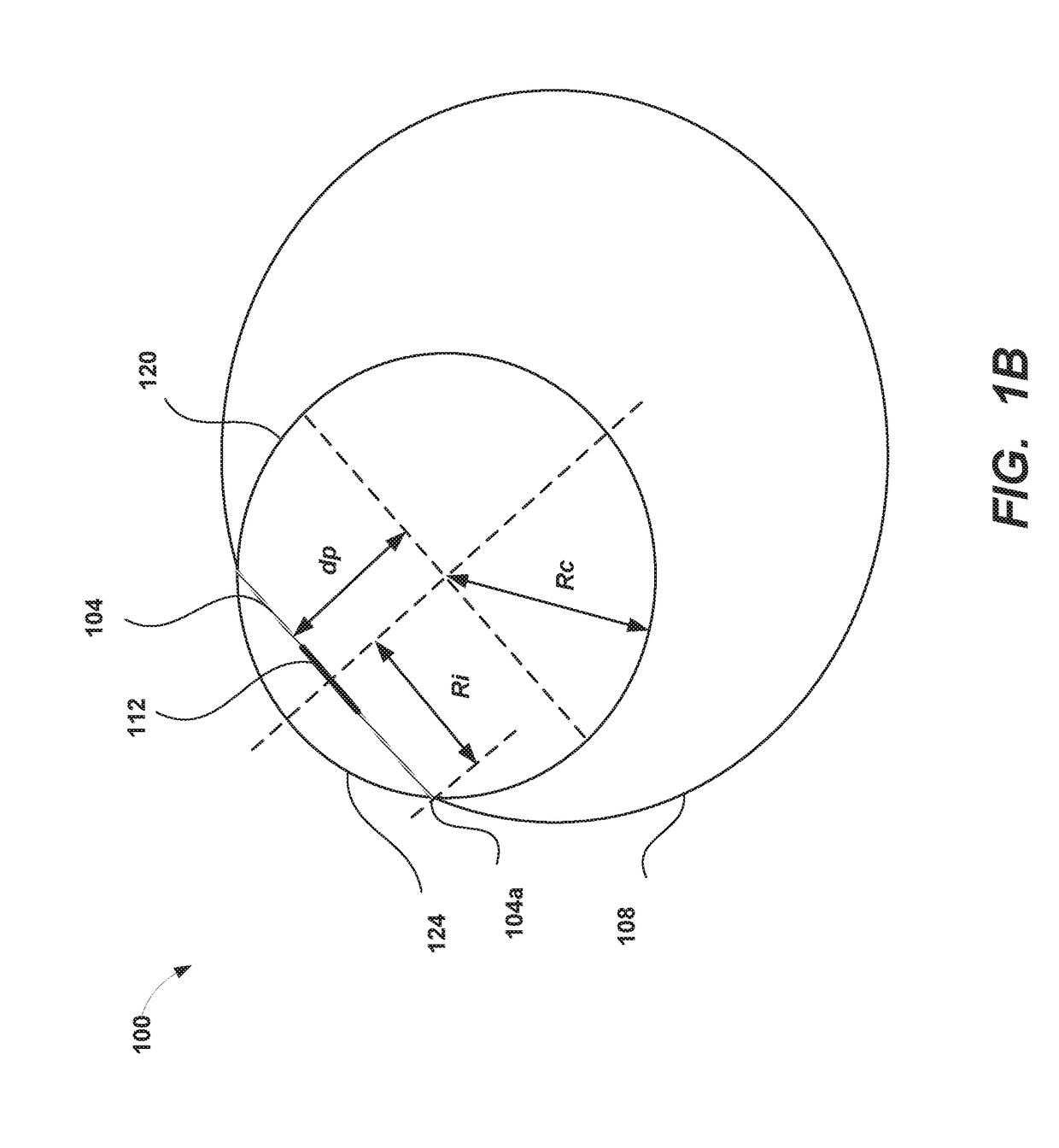
Examples of systems and methods for determining a limbic boundary of an iris of an eye are provided. Properties of the corneal bulge can be computed from eye images. An intersection of the corneal bulge with the eye surface (e.g., sclera) can be determined as the limbic boundary. The determined limbic boundary can be used for iris segmentation or biometric applications. A head mounted display can include a camera that images the eye and a processor that analyzes the eye images and determines the limbic boundary.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Intrastromal corneal modification
A method for modifying the curvature of a live cornea to correct a patient's vision. The live cornea is first separated into first and second opposed internal surfaces. Next, a laser beam or a mechanical cutting device can be directed onto one of the first and second internal surfaces, or both, if needed or desired. The laser beam or mechanical cutting device can be then used to incrementally and sequentially ablate or remove a three-dimensional portion of the cornea for making the cornea less curved. An ocular material is then introduced to the cornea to modify the curvature. The ocular material can be either a gel or a solid lens or a combination thereof. In one embodiment, a pocket is formed in the central portion of the cornea to receive an ocular material. In another embodiment, a plurality of internal tunnels are formed in the cornea to receive the ocular material. The ocular material can be either a fluid such as a gel or a solid member. In either case, the ocular material is transparent or translucent, and can have a refractive index substantially the same as the intrastromal tissue of the cornea or a different refractive index from the intrastromal tissue of the cornea.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
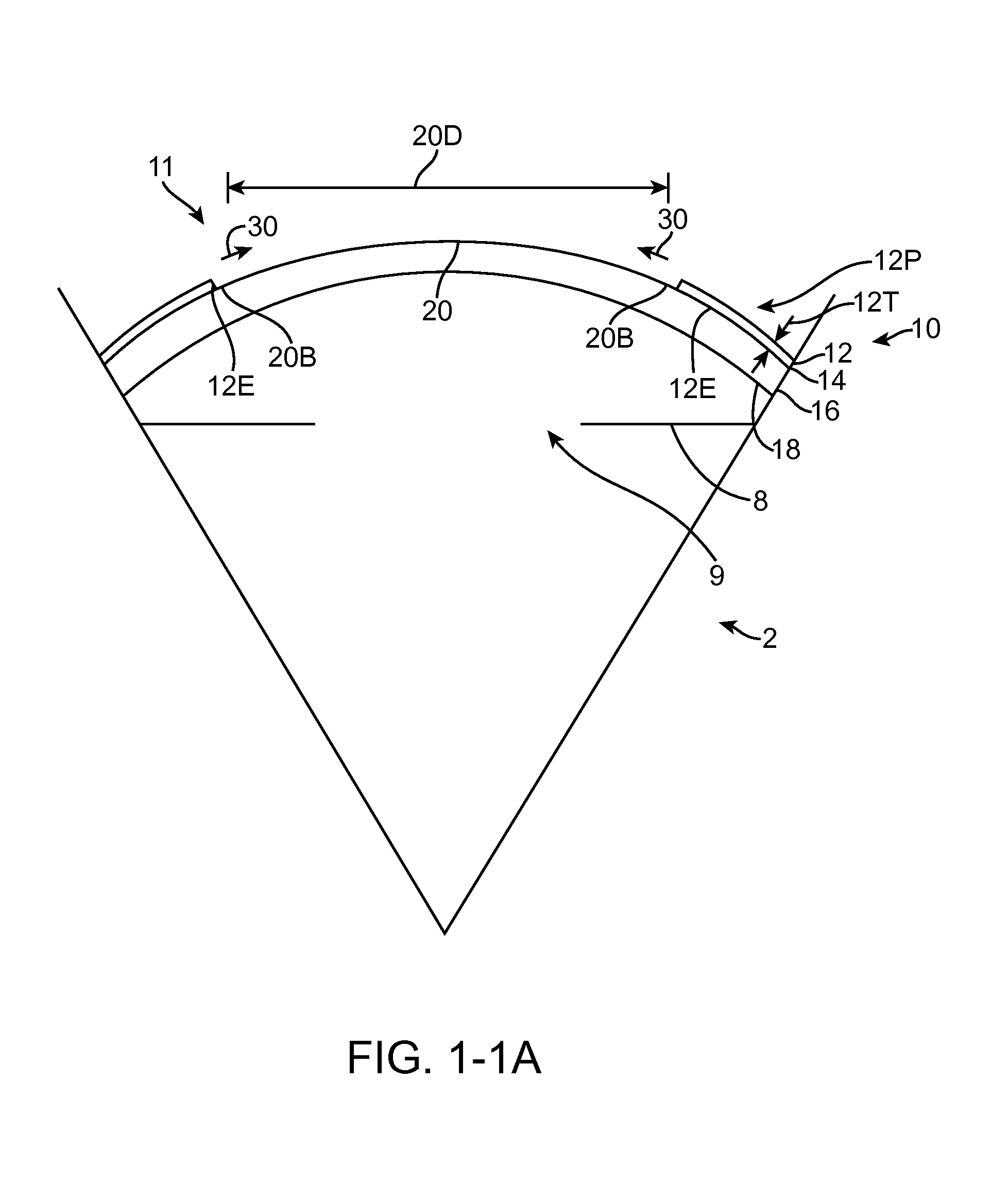
Corneal curvature adjustment ring and apparatus for making a cornea
Surgical apparatus for inserting a plastic, split end, adjusting ring into the stroma of the cornea of the eye wherein the adjusting ring includes, as a part thereof, a dissecting head to part the stroma and provide a pathway for the adjusting ring as the ring is rotated. The ends of the adjusting ring are moved to change the shape of the cornea to a desired shape in accordance with the desired visual correction after which the ends of the adjusting ring are fixably joined to maintain the desired shape.
Owner:ADDITION TECH INC
Methods and apparatus to identify eye coverings for vision
ActiveUS20140028979A1Speed up the flowPromote hydrationSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryCorneal curvatureConjunctiva
Methods and apparatus can fit coverings to treat eyes. The covering can be identified so as to provide improved flow of tear liquid under the covering. The covering can be identified based on an inner corneal curvature and an outer corneal curvature and one or more of a limbus sag height or a conjunctival sag height. The covering may form a chamber when placed on the eye to pump tear liquid under at least a portion of the covering. The covering may comprise an outer portion with rigidity to resist movement on the cornea and an inner portion to contact the cornea and provide an environment for epithelial regeneration. The covering may comprise a material having high oxygen permeability, for example silicone, with a wettable coating disposed on at least an upper surface of the coating.
Owner:JOURNEY1 INC
Corneal-scleral orthokeratology contact lens
ActiveUS7559649B2Fast and reliable and comfortable resultAccurately determineOptical partsCamera lensCorneal curvature
A corneal-scleral orthokeratology contact lens is formed of rigid gas permeable material with uniform arc lengths in the treatment area even when the corneal curvature varies and asymmetric blends or splines called minor zones, where the portion of the blend or spline is shorter toward the lens center and broader toward the lens edge, and relieve the treatment area of all centering responsibility, transferring it to the limbal-scleral region. The method of determining the total sagittal height of an eye at a given chord diameter to predetermine exact fitting parameters and predict unaided visual outcome trial lenses, with exact chord and sagittal height values used to match the sagittal height of an eye, the sagittal value may be obtained from some ocular topographers. A computer program can easily take the sagittal information and design an optimum lens.
Owner:DAKOTA SCI
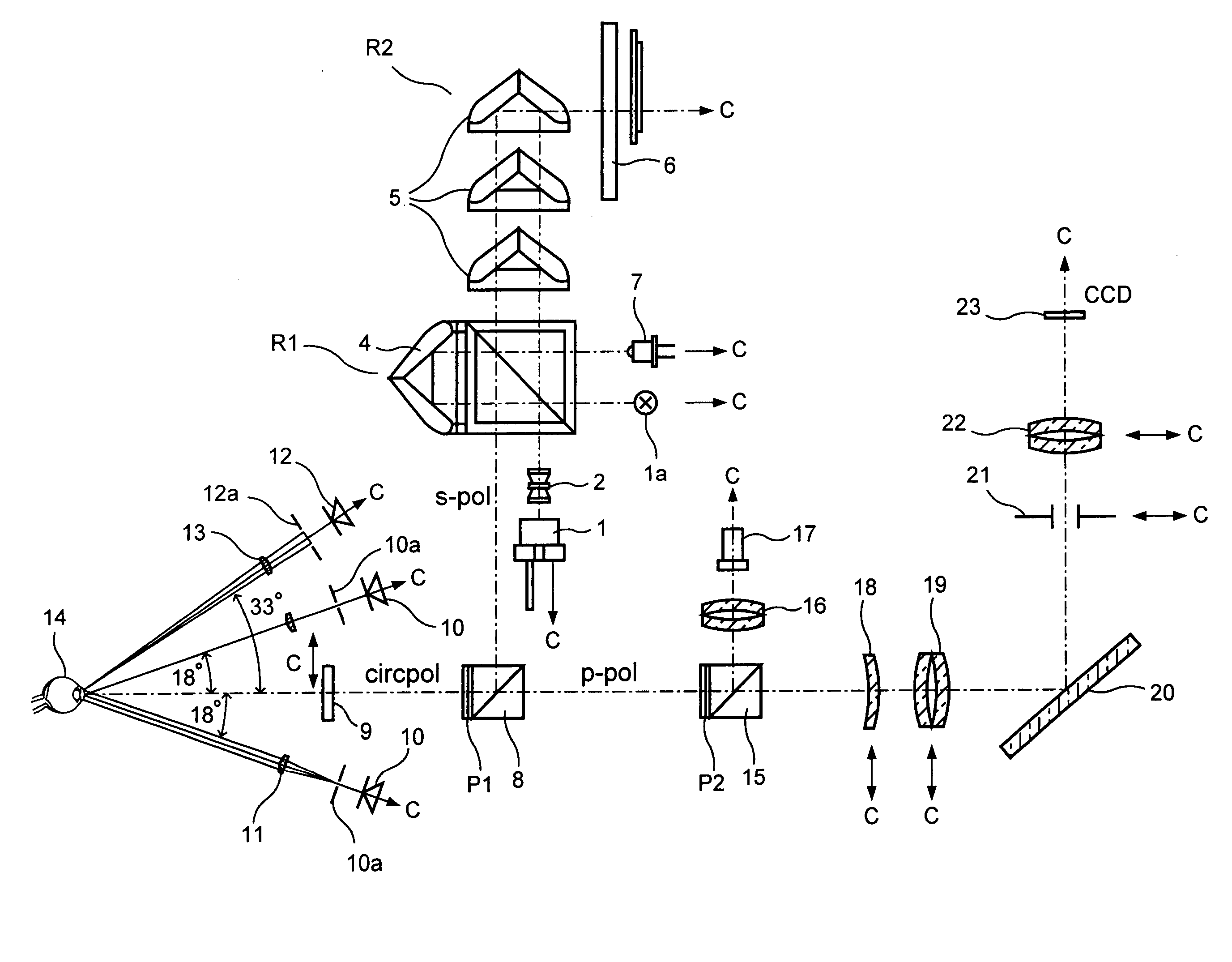
System and method for the non-contacting measurement of the axis length and/or cornea curvature and/or anterior chamber depth of the eye, preferably for intraocular lens calculation
InactiveUS20050018137A1Reduce measurement errorEye inspectionGonioscopesCorneal curvatureIntraocular lenses
Combined equipment for non-contacting determination of axial length (AL), anterior chamber depth (VKT) and corneal curvature (HHK) of the eye, are also important for the selection of the intraocular lens IOL to be implanted, particularly the selection of an intraocular lens (IOL) to be implanted, preferably with fixation of the eye by means of a fixating lamp and / or illumination through light sources grouped eccentrically about the observation axis.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Adapter for coupling a laser processing device to an object
ActiveUS20100228236A1Quality improvementEasy to gatherLaser surgeryDiagnosticsCorneal curvatureCorneal surface
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
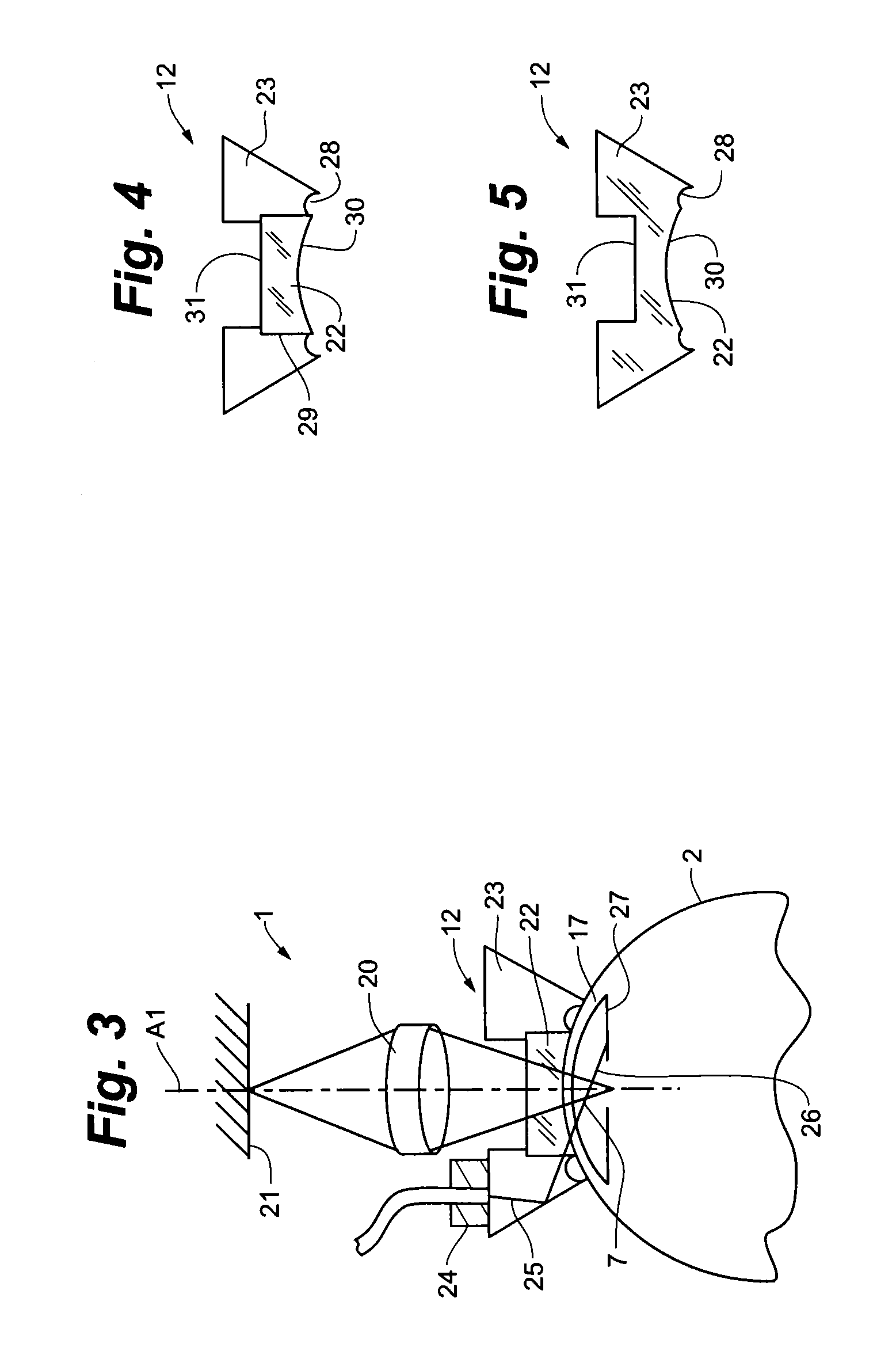
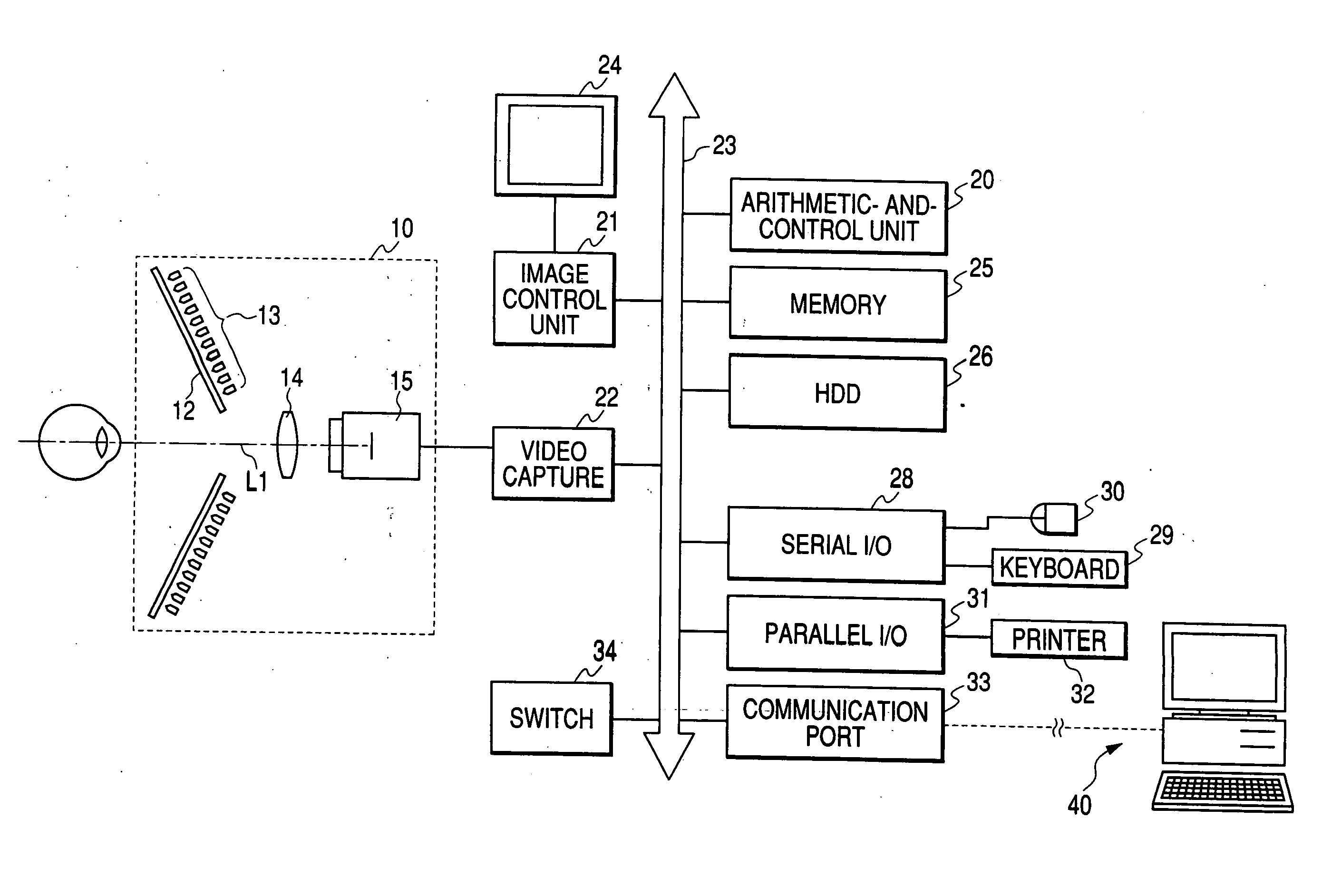
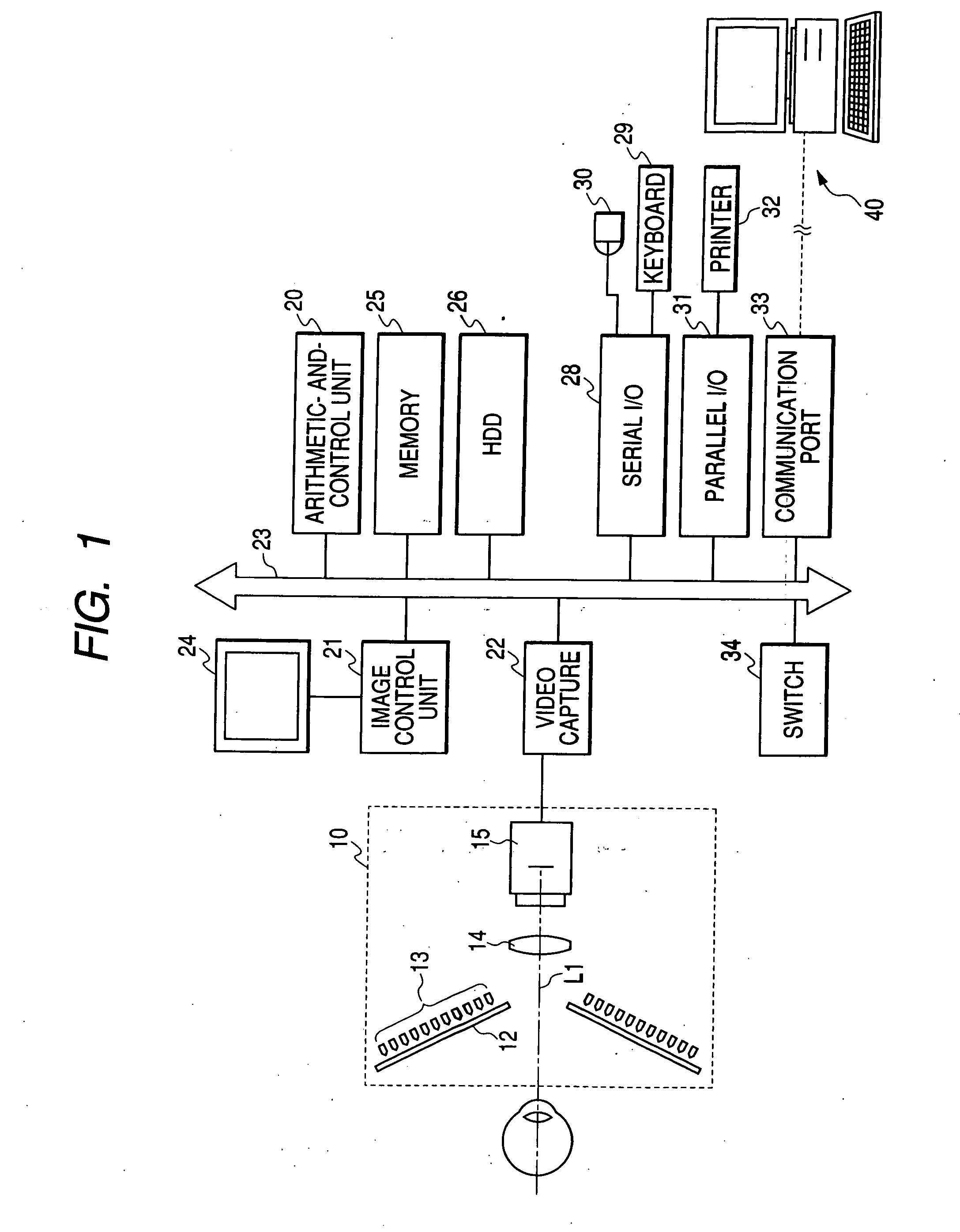
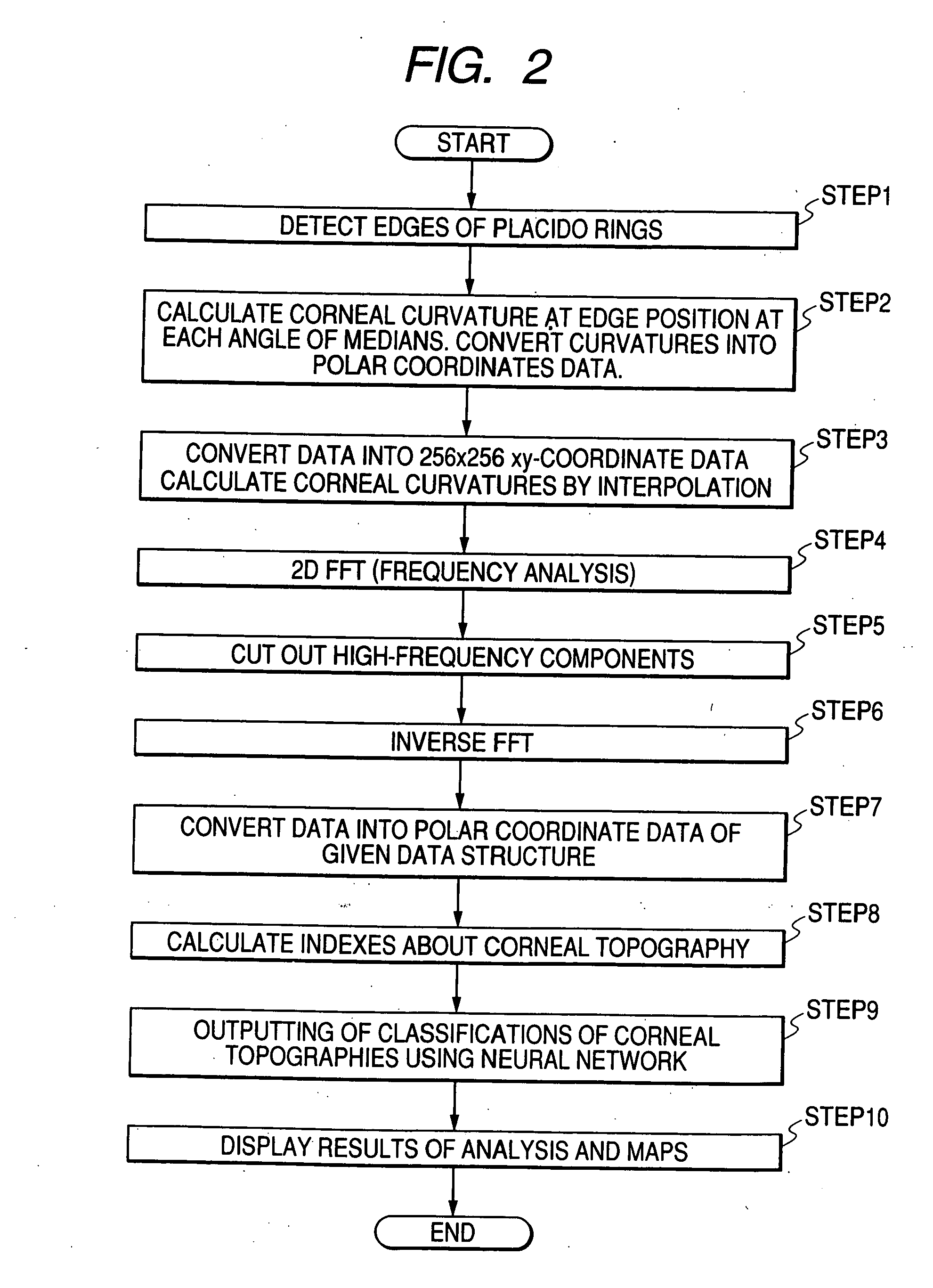
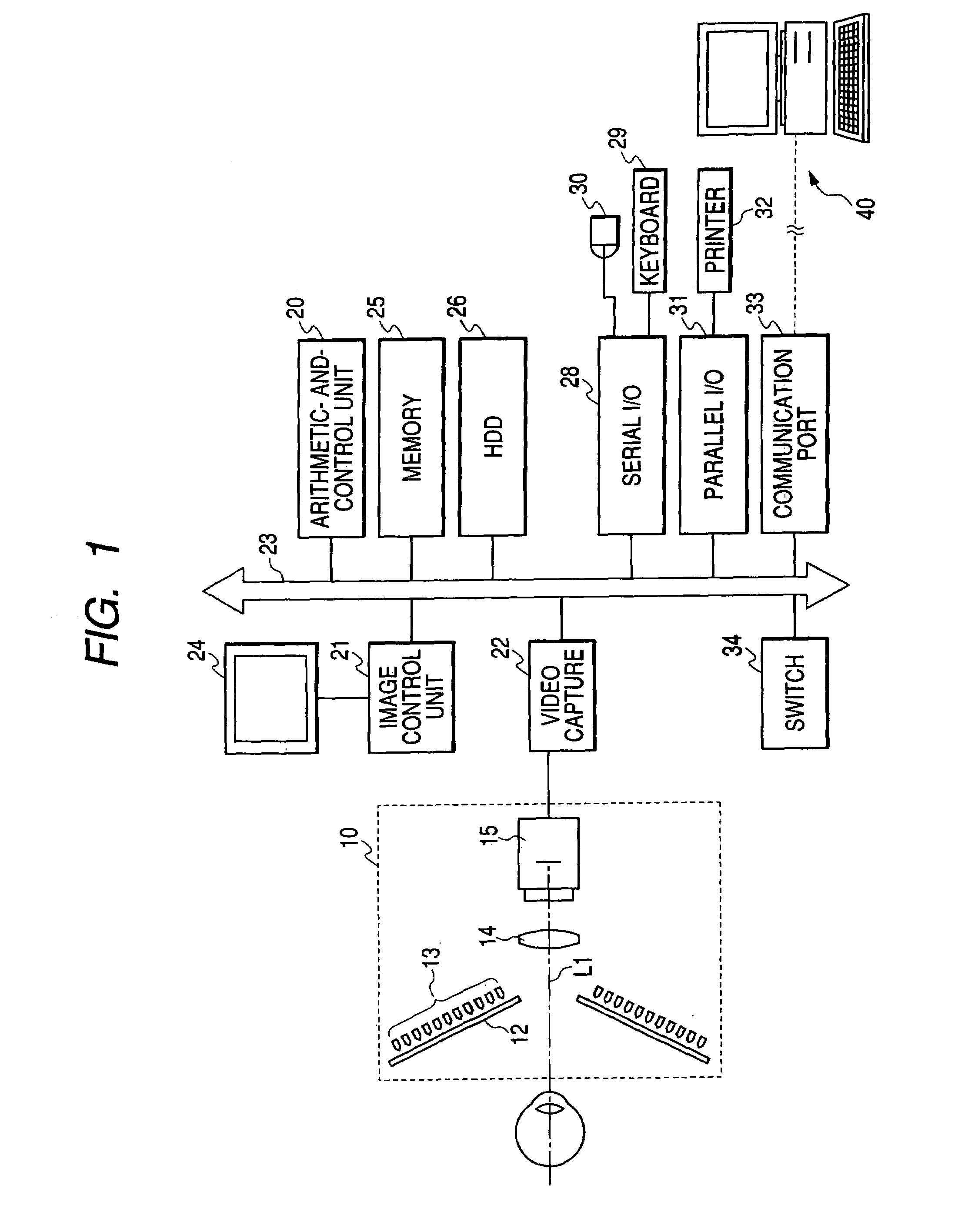
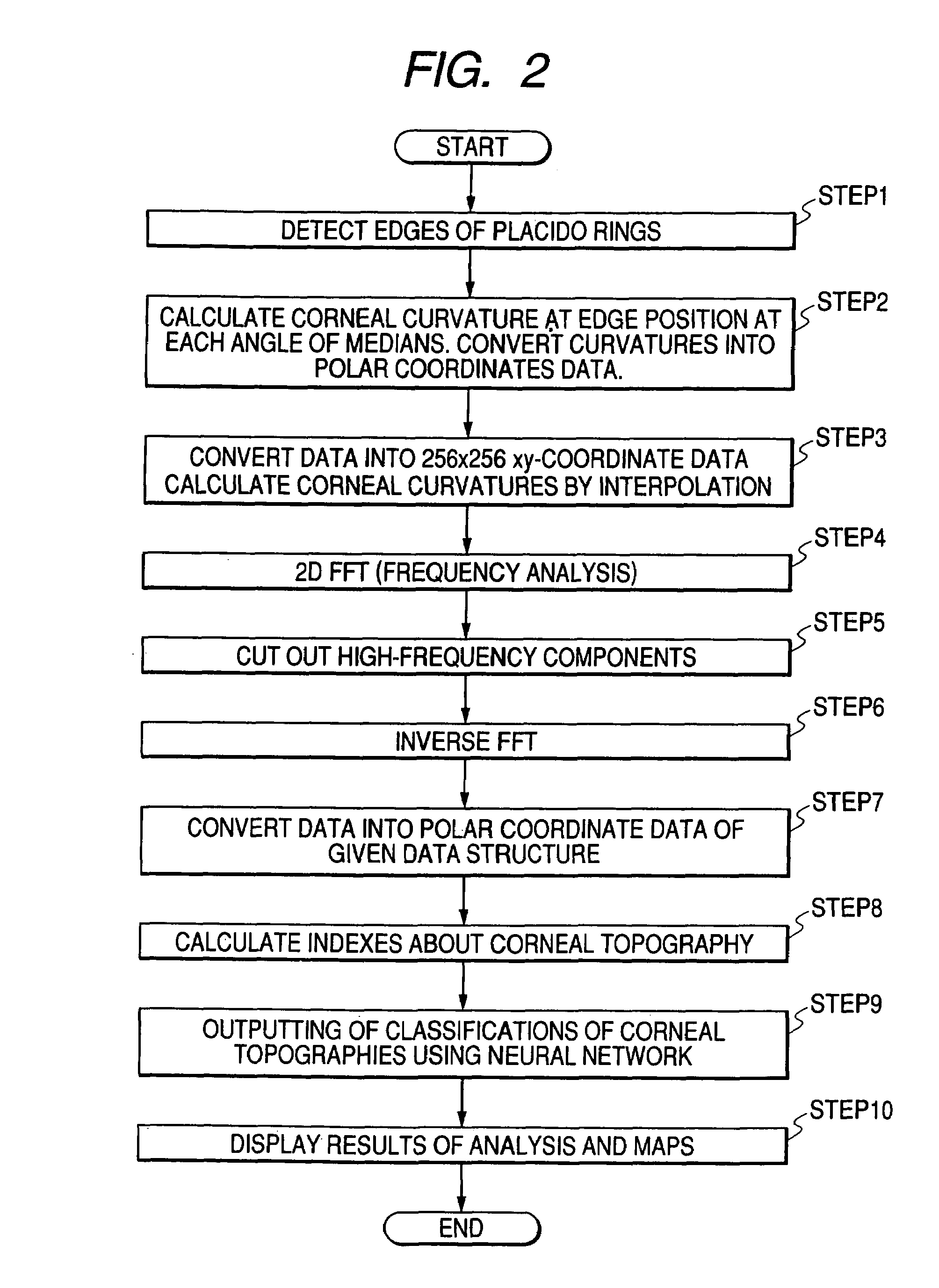
Corneal topography analysis system
ActiveUS20050225724A1Easy to classifyAccurate diagnosisPerson identificationSensorsCorneal curvaturePellucid marginal degeneration
A corneal topography analysis system includes: an input unit for inputting corneal curvature data; and an analysis unit that determines plural indexes characterizing topography of the cornea based on the input corneal curvature data, the analysis unit further judges corneal topography from features inherent in predetermined classifications of corneal topography using the determined indexes and a neural network so as to judge at least one of normal cornea, myopic refractive surgery, hyperopic refractive surgery, corneal astigmatism, penetrating keratoplasty, keratoconus, keratoconus suspect, pellucid marginal degeneration, or other classification of corneal topography.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
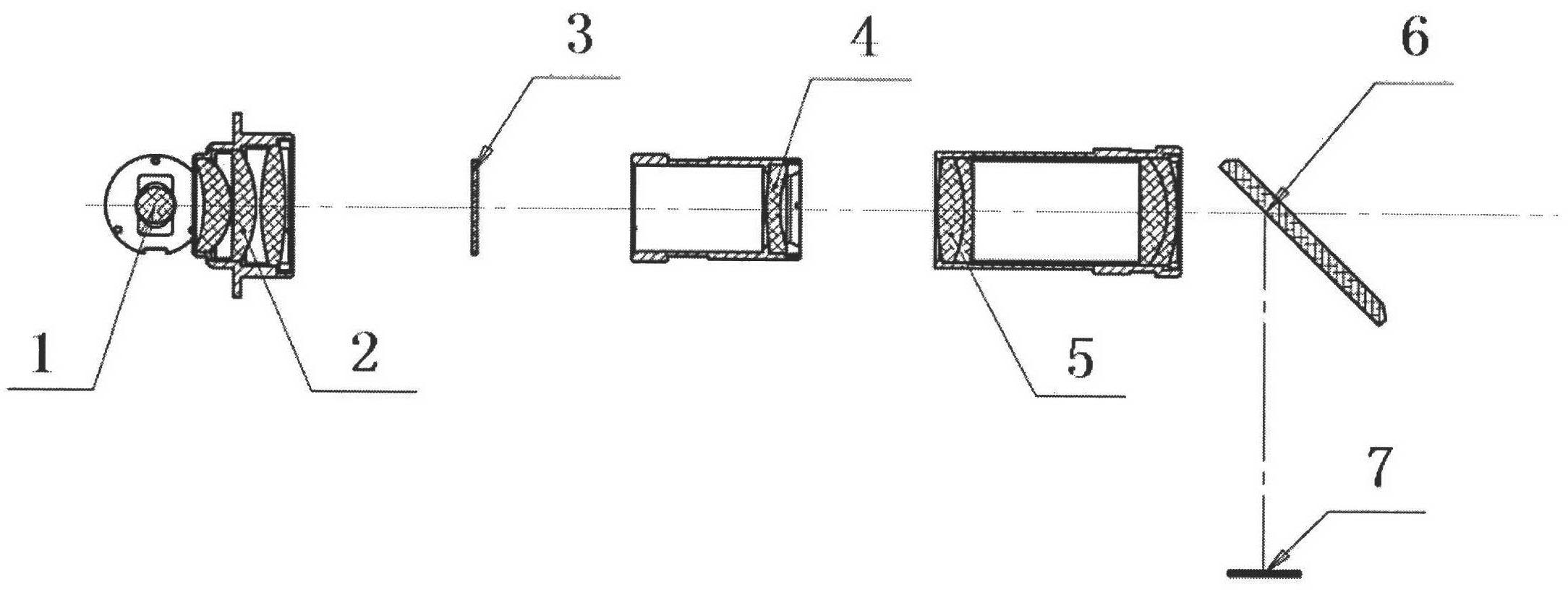
Automatic Refracto-Keratometer
ActiveUS20120188508A1Efficient executionImprove productivity and efficiencyRefractometersSkiascopesCorneal curvatureLuminosity
An auto refracto-keratometer not only produces a black-and-white image for observing the alignment of eyes to be examined using an infrared illumination light but also has a color observation optical system for observing a condition of eyes to be examined using color-illumination light. The auto refracto-keratometer comprises an infrared optical system for examining an alignment and corneal curvature of eyes to be examined; a fogging optical system for relaxing accommodation of the eyes; a measuring optical system for measuring refractive power of the eyes; and a color observation optical system having a visible light source for emitting at least one visible light to the eyes and a 2-dimensional imaging device for detecting image of visible light reflected by the eyes.
Owner:HUVITZ
Corneal topography analysis system
ActiveUS7370969B2Easy to classifyDiagnose them more preciselyPerson identificationEye diagnosticsPellucid marginal degenerationCorneal curvature
A corneal topography analysis system includes: an input unit for inputting corneal curvature data; and an analysis unit that determines plural indexes characterizing topography of the cornea based on the input corneal curvature data, the analysis unit further judges corneal topography from features inherent in predetermined classifications of corneal topography using the determined indexes and a neural network so as to judge at least one of normal cornea, myopic refractive surgery, hyperopic refractive surgery, corneal astigmatism, penetrating keratoplasty, keratoconus, keratoconus suspect, pellucid marginal degeneration, or other classification of corneal topography.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Handheld independent vision measurement device and method
ActiveCN104887176AEasy to measure visual acuityRefractometersSkiascopesKeratometry measurementCorneal curvature
The invention provides a handheld independent vision measurement device and method. The handheld independent vision measurement device comprises a corneal curvature measurement module which comprises a first light source, a first image collector and a motor; first light beams are emitted from the first light source; the first image collector is used for collecting images formed by the first light beams after reflection through a cornea; the motor is used for driving the first image collector; the first image collector is driven by the motor to move along a corneal curvature measurement light path. The first image collector is driven by the motor to automatically focus and accordingly the focusing is achieved without the help of a second person and an examinee can achieve the version measurement independently. According to the handheld independent vision measurement device and method, the single-person operation of the examinee is implemented, the vision measurement is convenient, and the miniaturization and the portability of an optometry system can be effectively implemented.
Owner:SUZHOU SIHAITONG INSTR
Method of stabilizing human eye tissue
InactiveUS9125856B1Low toxicityFacilitate the cross-linking of collagenHydroxy compound active ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsDiseaseCross-link
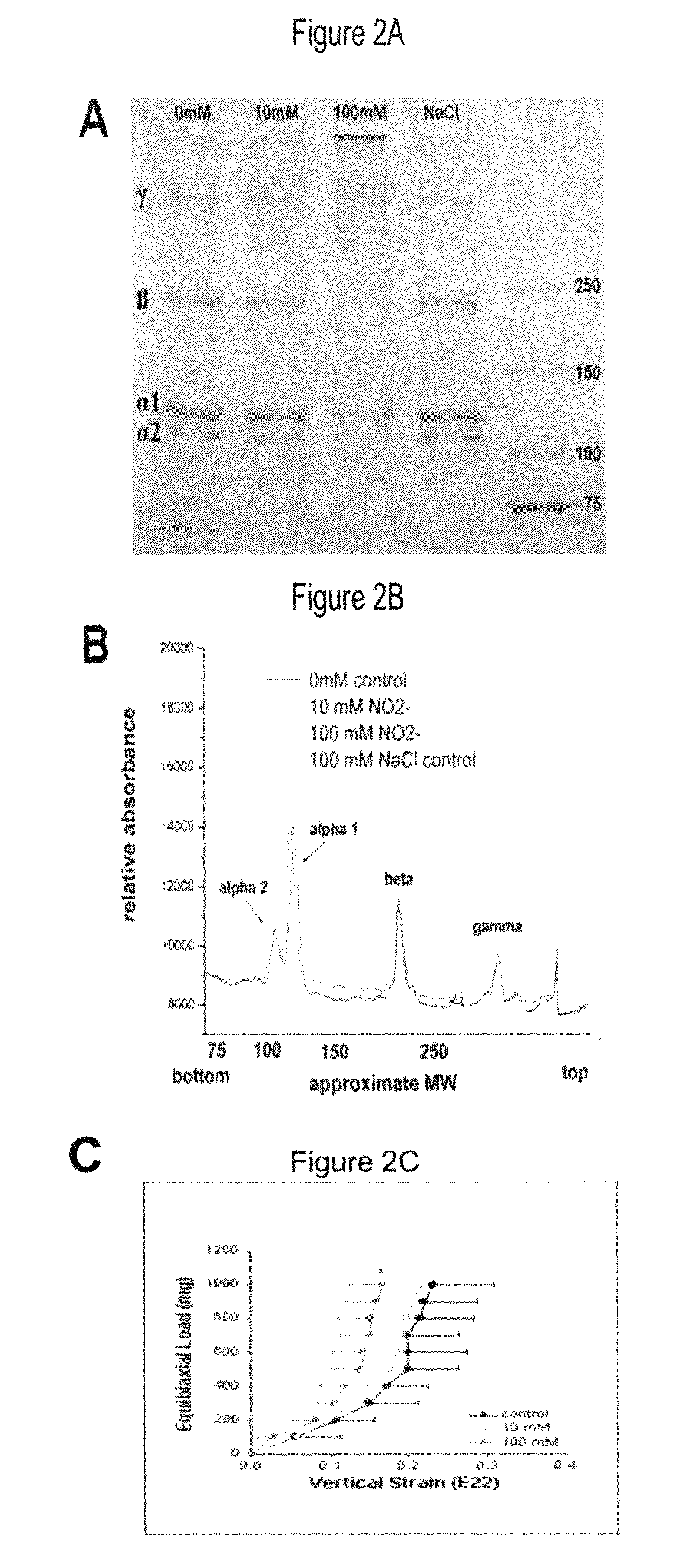
Disclosed are compounds and related methods useful for cross-linking collagen and stabilizing collagenous tissues using formaldehyde-donating compounds or nitrogen oxide-containing compounds such as β-Nitro Alcohols. Also disclosed are compounds and related methods for modulating the rate or degree of collagen cross-linking using nitrogen oxide-containing compounds such as β-Nitro Alcohols. The formaldehyde-donating, nitrogen oxide-containing and / or β-Nitro Alcohol compounds disclosed are capable of stabilizing collagenous tissues such as the corneal and scleral tissues and are useful in the treatment or prevention of diseases such as alterations in corneal curvature, keratoconus, keratectasia, progressive myopia and glaucoma.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Keratometric to apical radius conversion
InactiveUS20020115988A1Laser surgerySurgical instrument detailsKeratometry measurementCorneal curvature
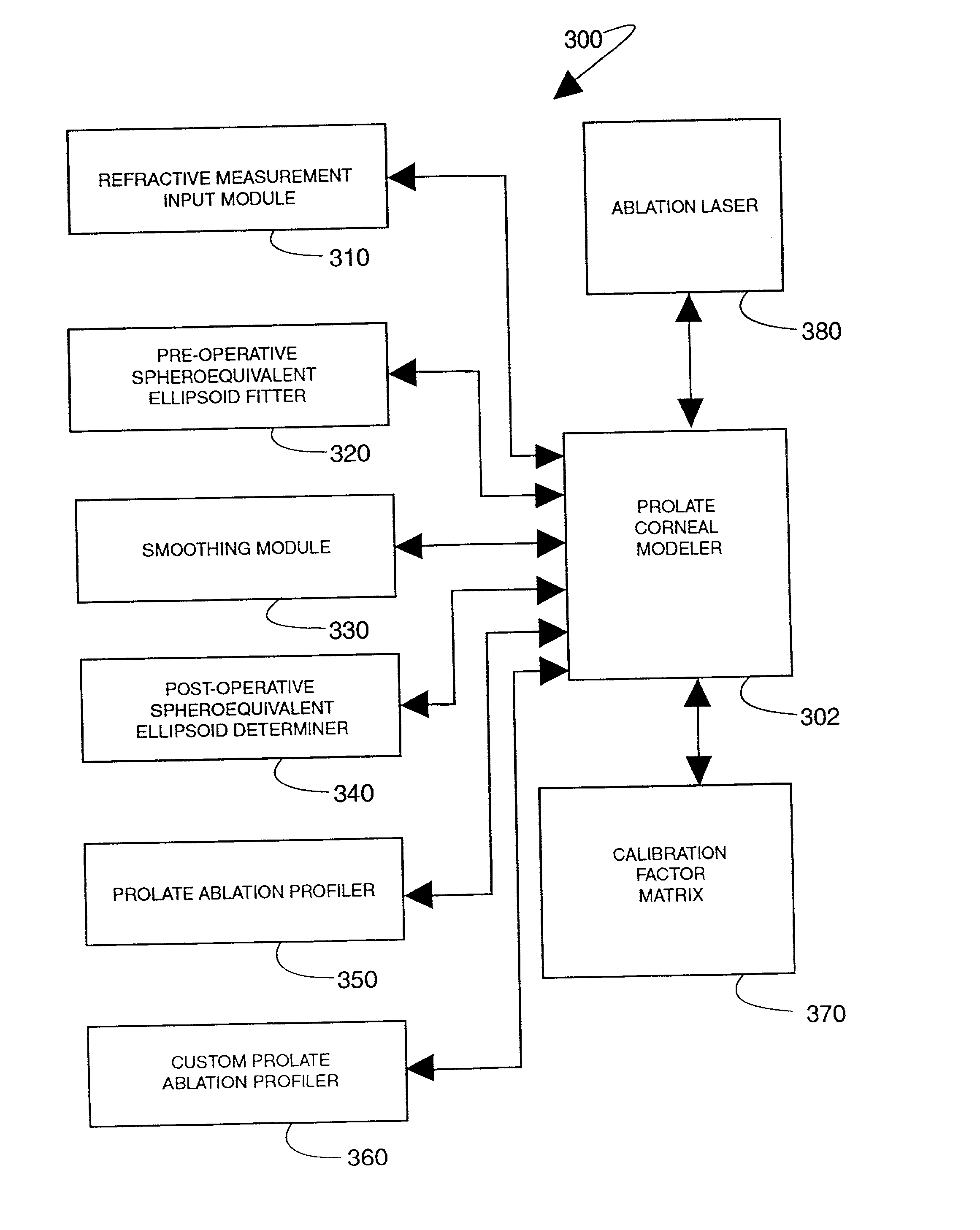
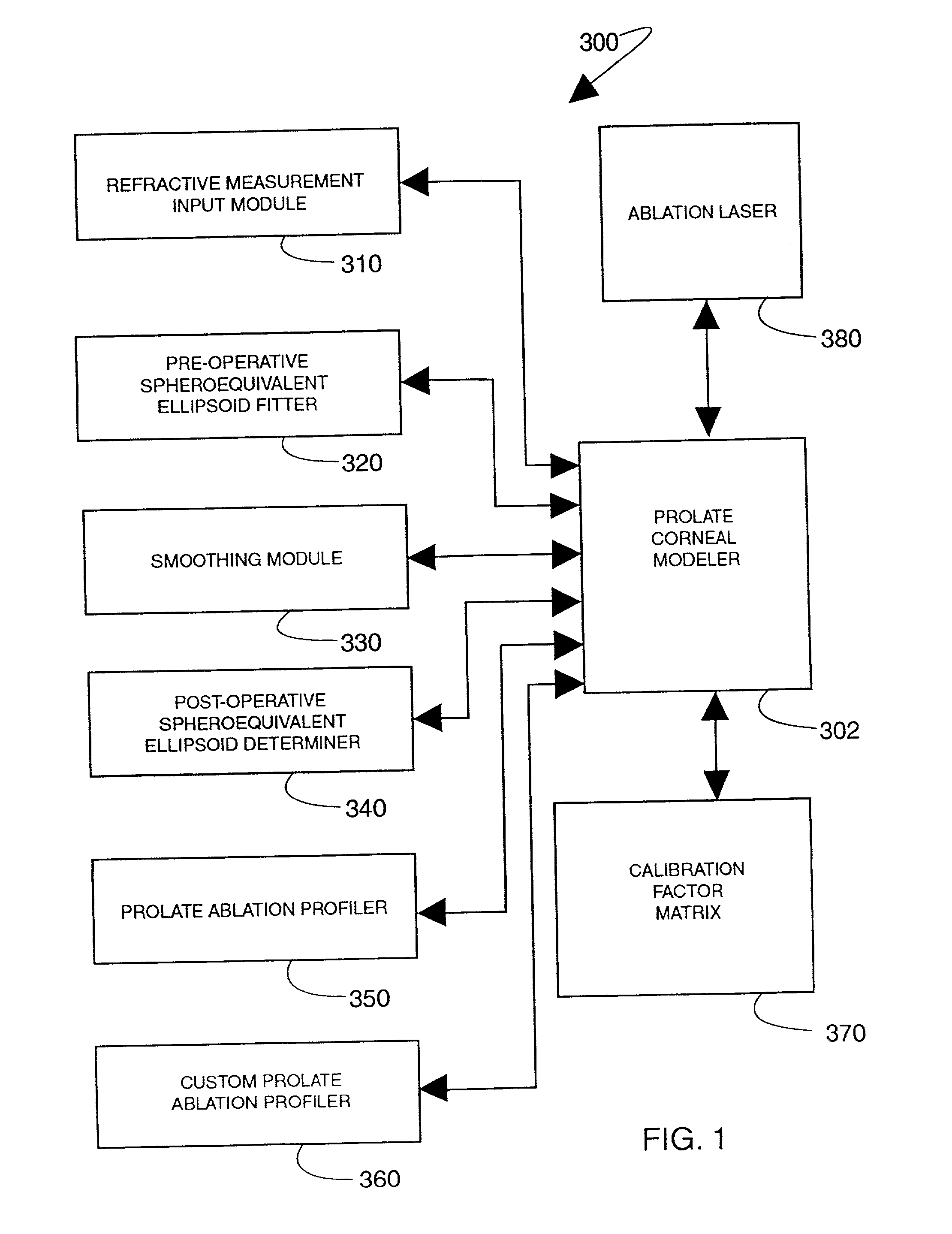
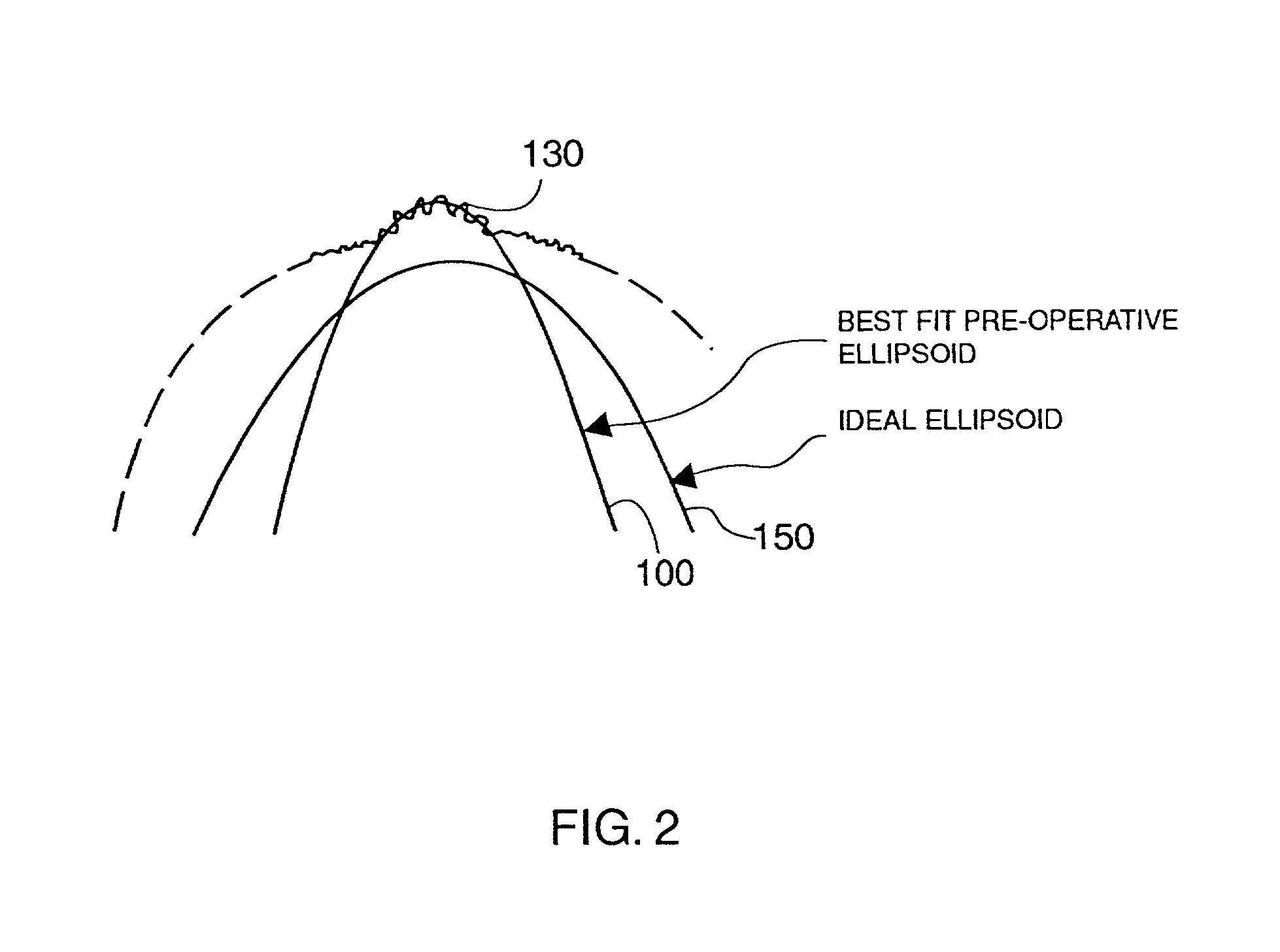
The present invention provides apparatus and techniques for performing prolate shaped corneal reshaping using an ellipsoid corneal modeler. In accordance with the principles of the present invention, an ellipsoid corneal modeler is implemented with the well behaved conicoid, combined with a modeled surface which can be used for astigmatic treatments. An ellipsoid corneal modeler includes an ellipsoid fitter which utilizes two radii of curvature, asphericity (Q), and a surface rotation about the pupil center (roation of theta), yielding the equation: <math-cwu id="MATH-US-00001"> <number>1< / number> x 2 R x + y 2 R y + z z ( 2 R x R y ( 1 + Q ) R x + R y ) = 2 R x R y ( 1 + Q ) R x + R y ( 5 ) <mathematica-file id="MATHEMATICA-00001" file="US20020115988A1-20020822-M00001.NB" / > <image id="EMI-M00001" wi="216.027" he="30.9582" file="US20020115988A1-20020822-M00001.TIF" imf="TIFF" ti="MF" / > < / math-cwu> Moreover, a conversion is provided to convert between measurements obtained by a keratometer, and apical radii. In a further embodiment provided by the present invention, conversion is made possible between radii measurements obtained clinically (e.g., using a keratometer) and radii measurements at the apex, i.e., keratometric to apical radius conversion.
Owner:LASERSIGHT TECH
Determination of the effective lens position of an intraocular lens using aphakic refractive power
An ophthalmic method for determining a relationship between aphakic ocular power and estimated effective lens position (ELP) of an intraocular lens (IOL) to be implanted in a patient's eye. The method can be used to determine an estimate of the ELP of an IOL given the aphakic ocular power of the patient's eye, for example, without measurement of the corneal curvature or axial length of the patient's eye. The estimate of ELP can then be used to determine a suitable value of optical power for the IOL to be implanted in the patient's eye.
Owner:ALCON INC
Methods and apparatus to identify eye coverings for vision
Methods and apparatus can fit coverings to treat eyes. The covering can be identified so as to provide improved flow of tear liquid under the covering. The covering can be identified based on an inner corneal curvature and an outer corneal curvature and one or more of a limbus sag height or a conjunctival sag height. The covering may form a chamber when placed on the eye to pump tear liquid under at least a portion of the covering. The covering may comprise an outer portion with rigidity to resist movement on the cornea and an inner portion to contact the cornea and provide an environment for epithelial regeneration. The covering may comprise a material having high oxygen permeability, for example silicone, with a wettable coating disposed on at least an upper surface of the coating.
Owner:JOURNEY1 INC
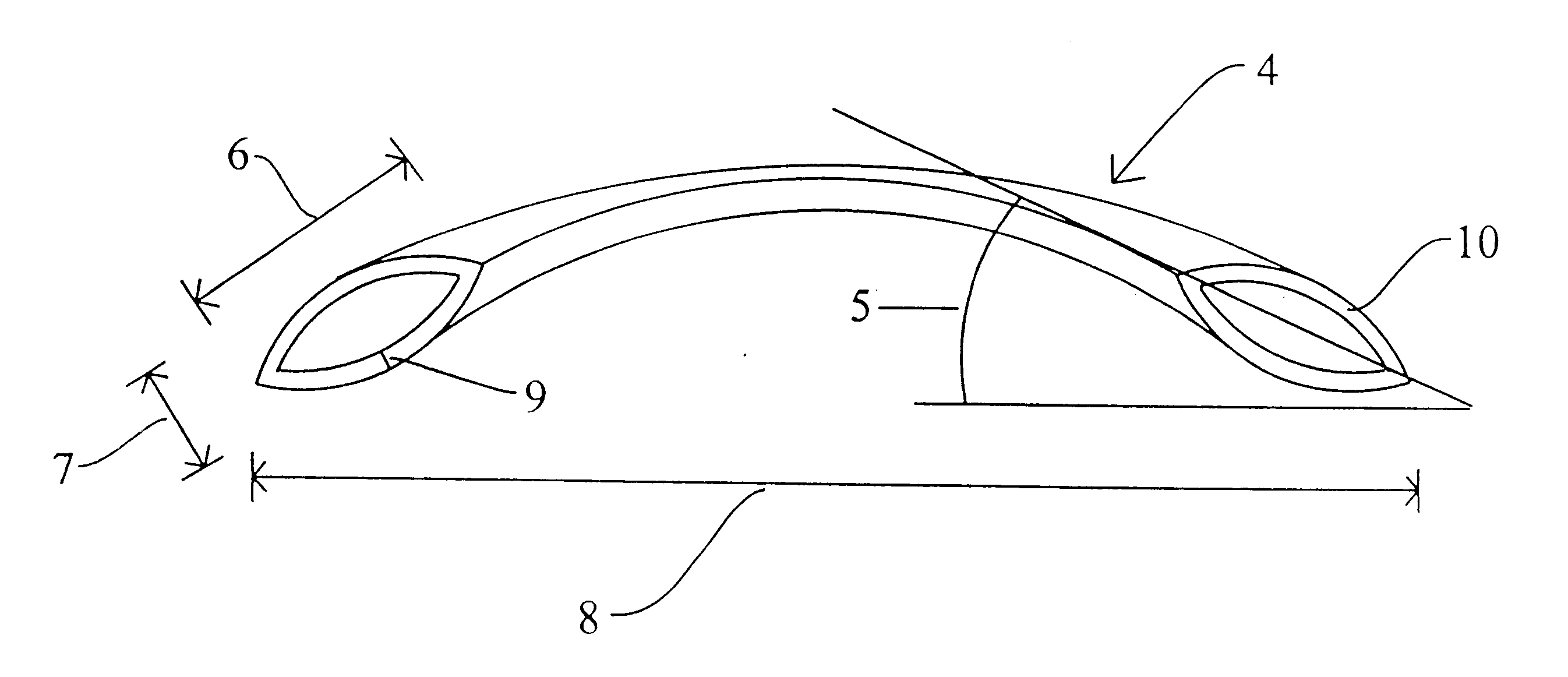
Implantable device for molding the curvature of the cornea
InactiveUS20140074232A1Reduction in negative visual effectPromoting remodeling of the corneaEye implantsCorneal curvatureConvex side
The present invention relates to an intrastromal corneal device for reshaping the curvature of the cornea comprising a substantially circular structure having a convex surface provided with openings for biological exchange between the layers of the cornea, said substantially circular structure comprising the shape of a circular segment or of a spherical / aspheric cap provided or not with a central opening. Said device further comprises means for promoting the reshaping of the cornea, so that it assumes a curvature closer to the intended curvature, thus providing a significant reduction of visual disturbances caused by corneal ectatic conditions such as keratoconus.
Owner:MEDIPHACOS IND MEDICAS
Device and method for measuring corneal curvature
ActiveCN103340596ARealize automatic measurementEasy to useEye diagnosticsCorneal curvatureGray level
The invention relates to a device for measuring corneal curvature. The device for measuring the corneal curvature comprises a double ring measurement light source, an image acquisition system and an image process and control system. The double ring measurement light source comprises an inner ring point light source and an outer ring measurement light source, wherein the inner ring point light source emits point-shaped focus light spots to the cornea of an eye, and the outer ring measurement light source emits ring-shaped measurement light to the cornea of the eye. The image acquisition system collects and detects the point-shaped focus light spot image and ring-shaped image reflected by the cornea. The image process and control system obtains the gray level change rate K of different point-shaped light spots of the point-shaped focus light spot image detected by the image acquisition system, confirms whether the detected eye is measured within an allowable range, compensates the ring-shaped image and guides the compensation direction if the eye is not measured within the allowable range and computes the corneal curvature of the detected eye according to the radius R of the compensated ring-shaped image. The invention further provides a method for measuring the corneal curvature with the device. The method for measuring the corneal curvature is simple, and an operator can find the best measurement position quickly as long as the operator follows the guide of an instrument output device.
Owner:TAIYUAN XINYUAN HIGH-TECH CENT NORTH UNIV OF CHINA
Devices and methods of selecting intraocular lenses
The invention relates to devices and methods for selecting IOLs for implantation and eye models useful with the methods. One method comprises the steps of determining the axial eye length, the pupil size at a desired light level; the desired postoperative refraction; determining an aspheric representation of the corneal curvature and determining the location of the plane of fixation of the IOL following implantation.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Ocular anterior segment detection and illumination system
InactiveCN102499632AAchieve regulationTo achieve the effect of observation lightingLighting device detailsOthalmoscopesCorneal curvatureImaging quality
The invention discloses an ocular anterior segment detection and illumination system, comprising a light source as well as a light condensing mirror, a R, G and B (red, green and blue) three-color liquid crystal sheet unit or a digital light processor (DLP), a lower projecting mirror group and a reflecting mirror, which are sequentially distributed in an emerging direction of light rays of a light source, wherein the light condensing mirror and the lower projecting mirror group are coaxially arranged, and a liquid crystal sheet or a digital micromirror unit is connected with a control unit. The control unit comprises a computer system, preferentially, the computer system is also connected with at least one control device of a game control rod, a mouse and a keyboard. The ocular anterior segment illumination system is simple in structure, easy to control, has high stable property and high image quality and can achieve new functions for data measurement such as measurement of corneal topography, corneal curvature and the like.
Owner:沈激
Method of stabilizing human eye tissue by reaction with nitrite and related agents such as nitro compounds
InactiveUS8466203B2Impede structural integrityAvoid structureBiocideSenses disorderNitro compoundDisease
A method for stabilizing collagenous eye tissues by nitrite and nitroalcohol treatment. The topical stiffening agent contains sodium nitrite or a nitroalcohol in a buffered balanced salt solution and can be applied to the surface of the eye on a daily basis for a prolonged period. Application of the solution results in progressive stabilization of the corneal and scleral tissues through non-enzymatic cross-linking of collagen fibers. The compounds can penetrate into the corneal stroma without the need to remove the corneal epithelium. In addition, ultraviolet light is not needed to activate the cross-linking process. The resulting stabilization of corneal and scleral tissues can prevent future alterations in corneal curvature and has utility in diseases such as keratoconus, keratectasia, progressive myopia, and glaucoma.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Iris boundary estimation using cornea curvature
Examples of systems and methods for determining a limbic boundary of an iris of an eye are provided. Properties of the corneal bulge can be computed from eye images. An intersection of the corneal bulge with the eye surface (e.g., sclera) can be determined as the limbic boundary. The determined limbic boundary can be used for iris segmentation or biometric applications. A head mounted display can include a camera that images the eye and a processor that analyzes the eye images and determines the limbic boundary.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Methods and apparatus to identify eye coverings for vision
InactiveUS20170131566A1Prevent movementSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryRefractive errorCorneal curvature
Methods and apparatus can fit coverings to treat eyes. The treated eye may comprise a natural eye, for example an eye treated for refractive error with a contact lens, or an eye having an epithelial defect of the eye, such as an eye ablated with PRK refractive surgery. In many embodiments, the covering can be identified so as to provide improved flow of tear liquid under the covering. The covering can be identified based on an inner corneal curvature and an outer corneal curvature and one or more of a limbus sag height or a conjunctival sag height. The covering may form a chamber when placed on the eye to pump tear liquid under at least a portion of the covering. The covering may comprise an outer portion with rigidity to resist movement on the cornea and an inner portion to contact the cornea and provide an environment for epithelial regeneration. The covering may comprise a material having high oxygen permeability, for example silicone, with a wettable coating disposed on at least an upper surface of the coating.
Owner:JOURNEY1 INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com