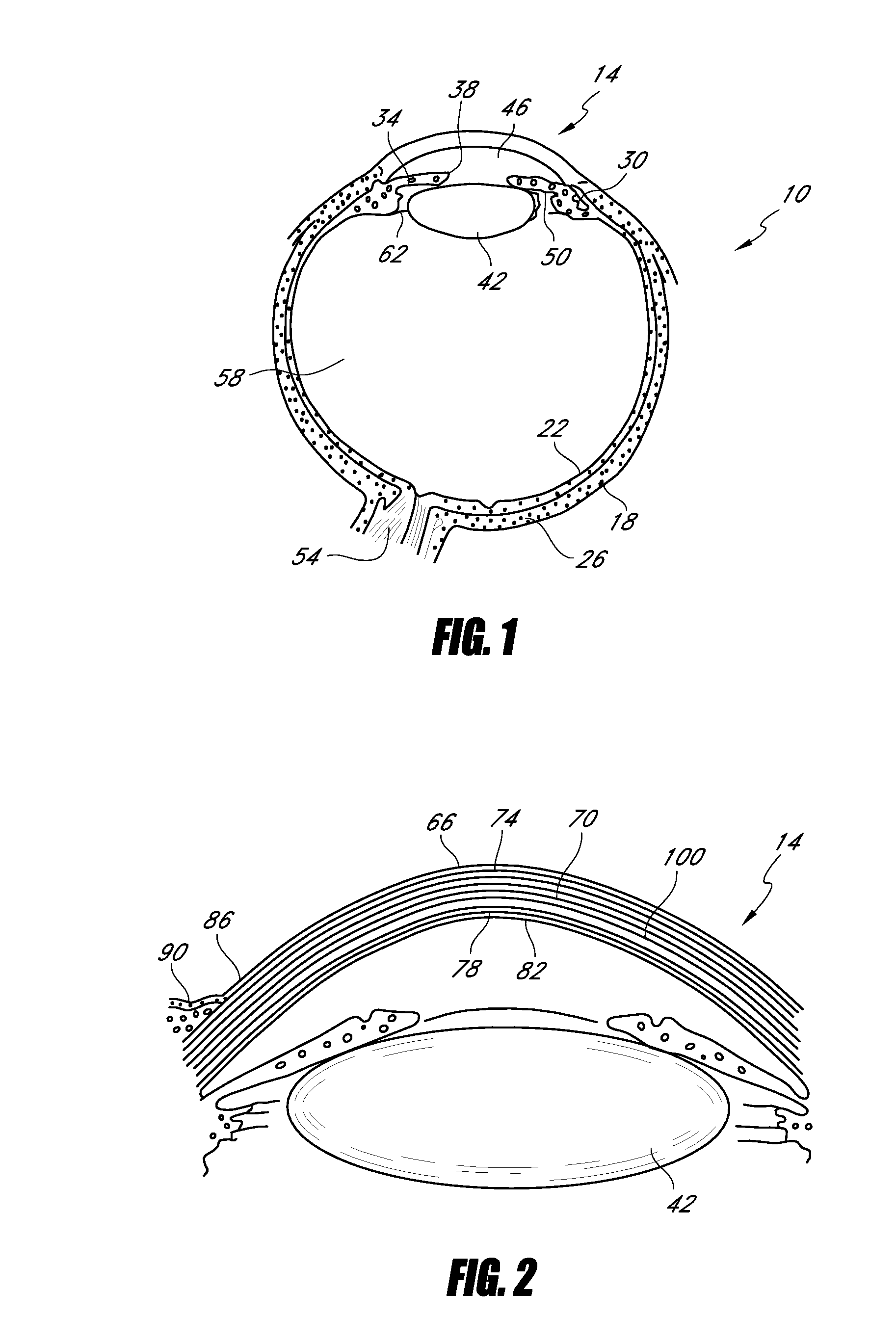
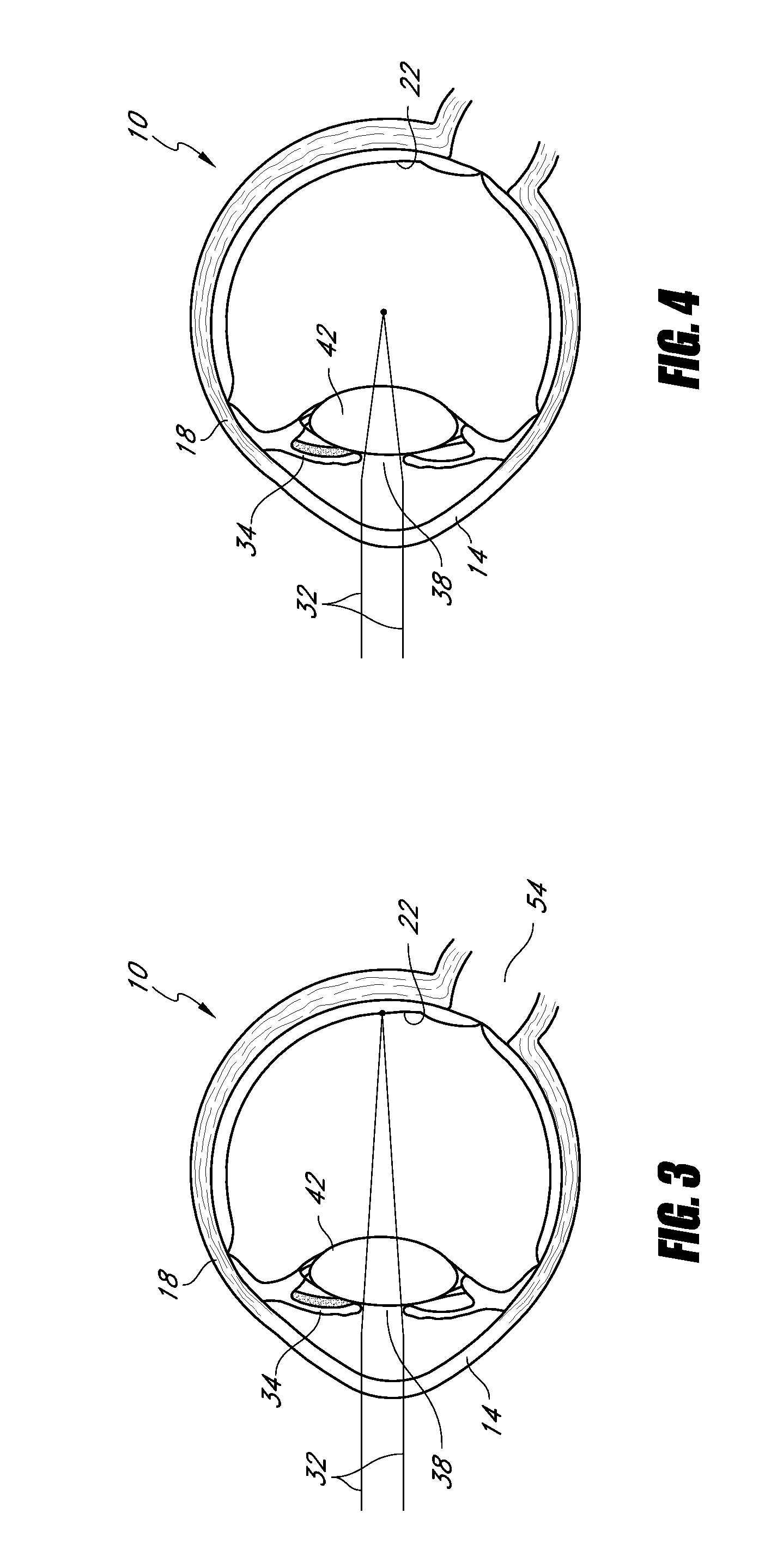
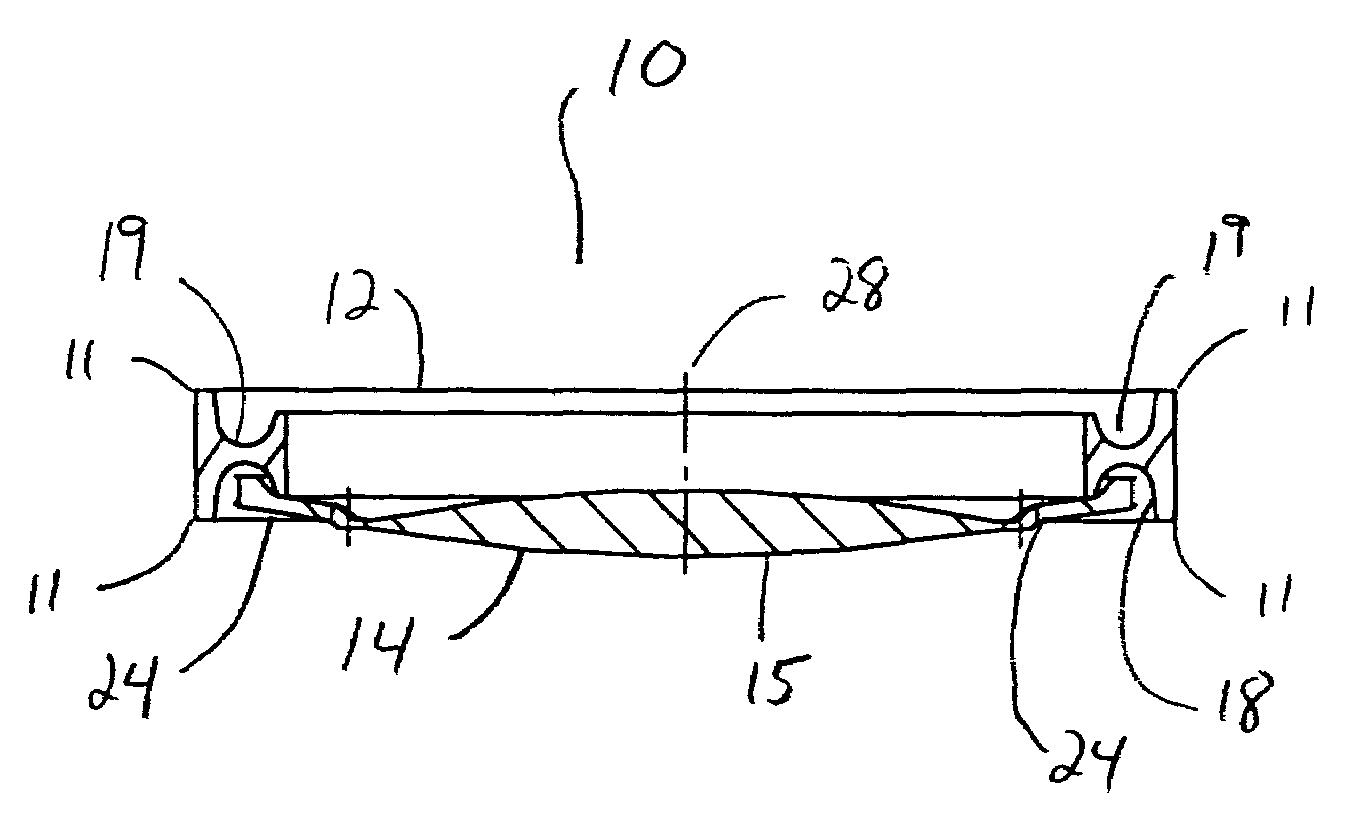
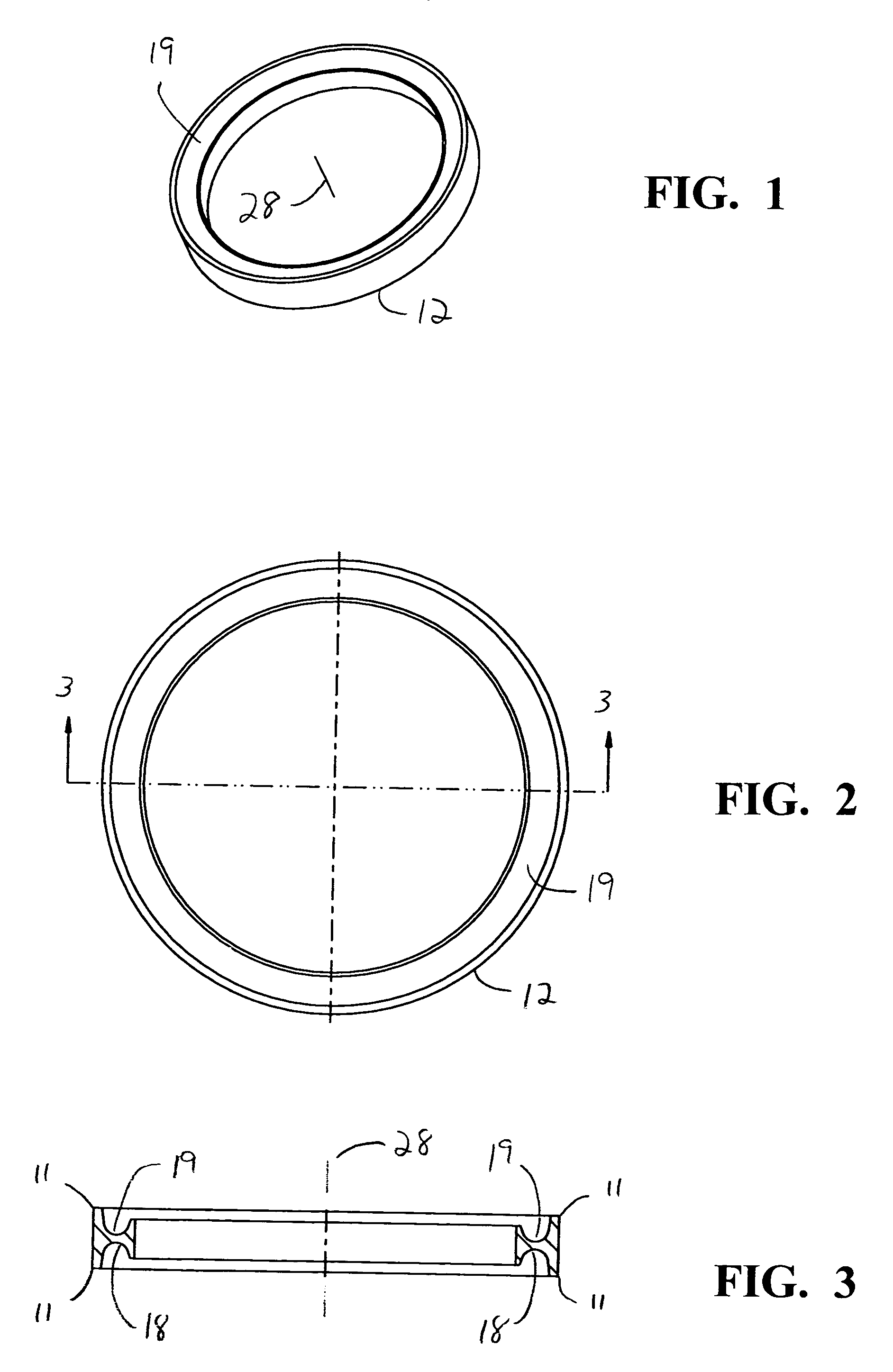
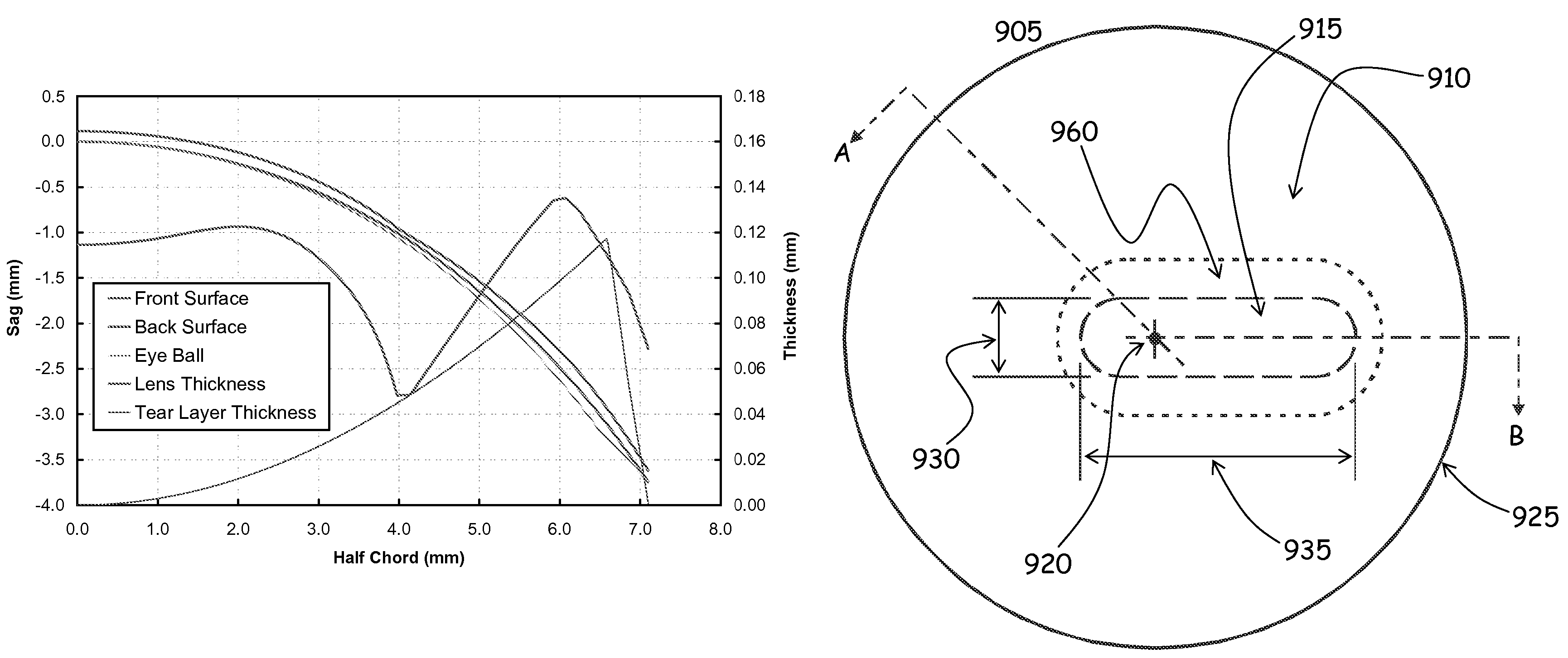
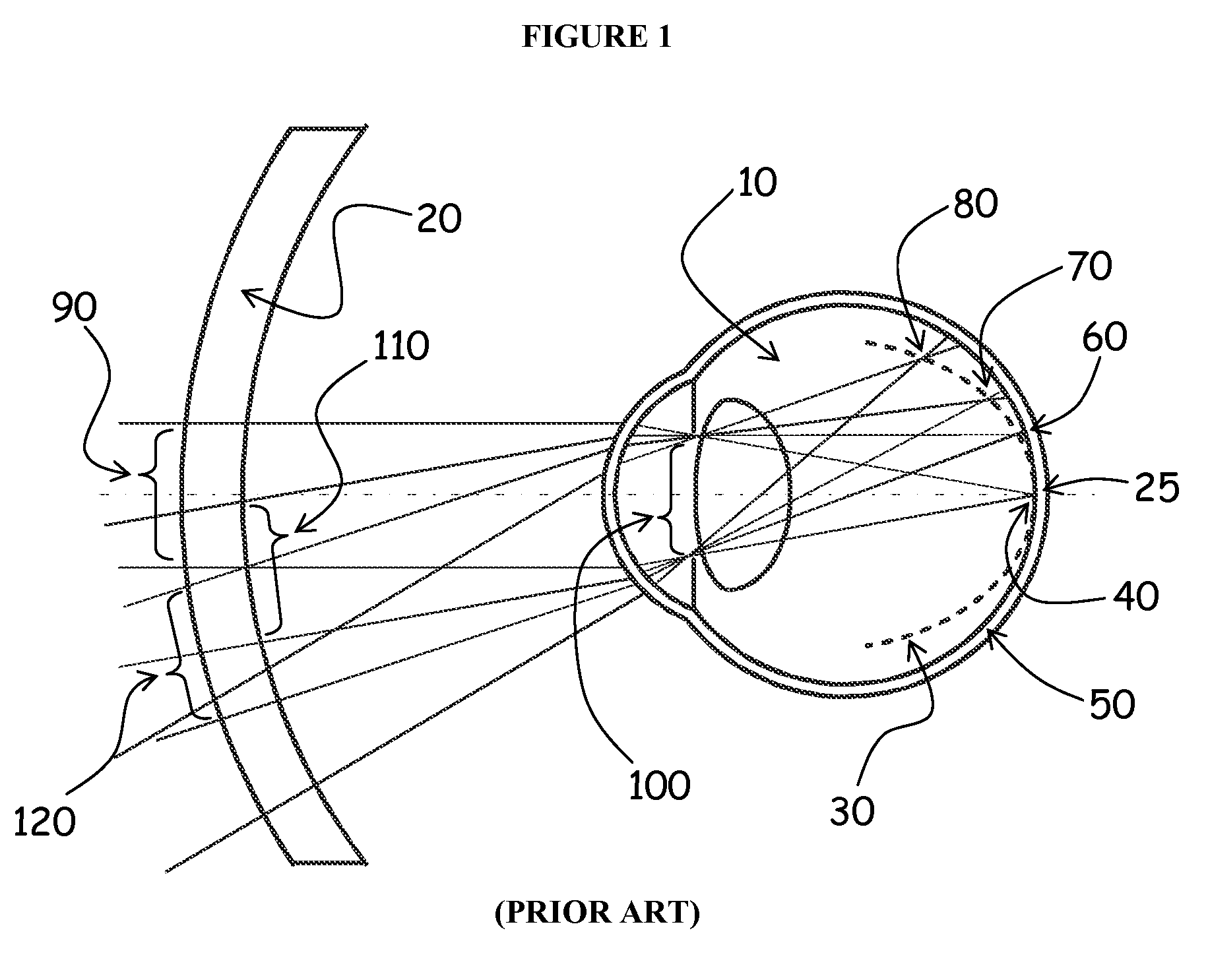
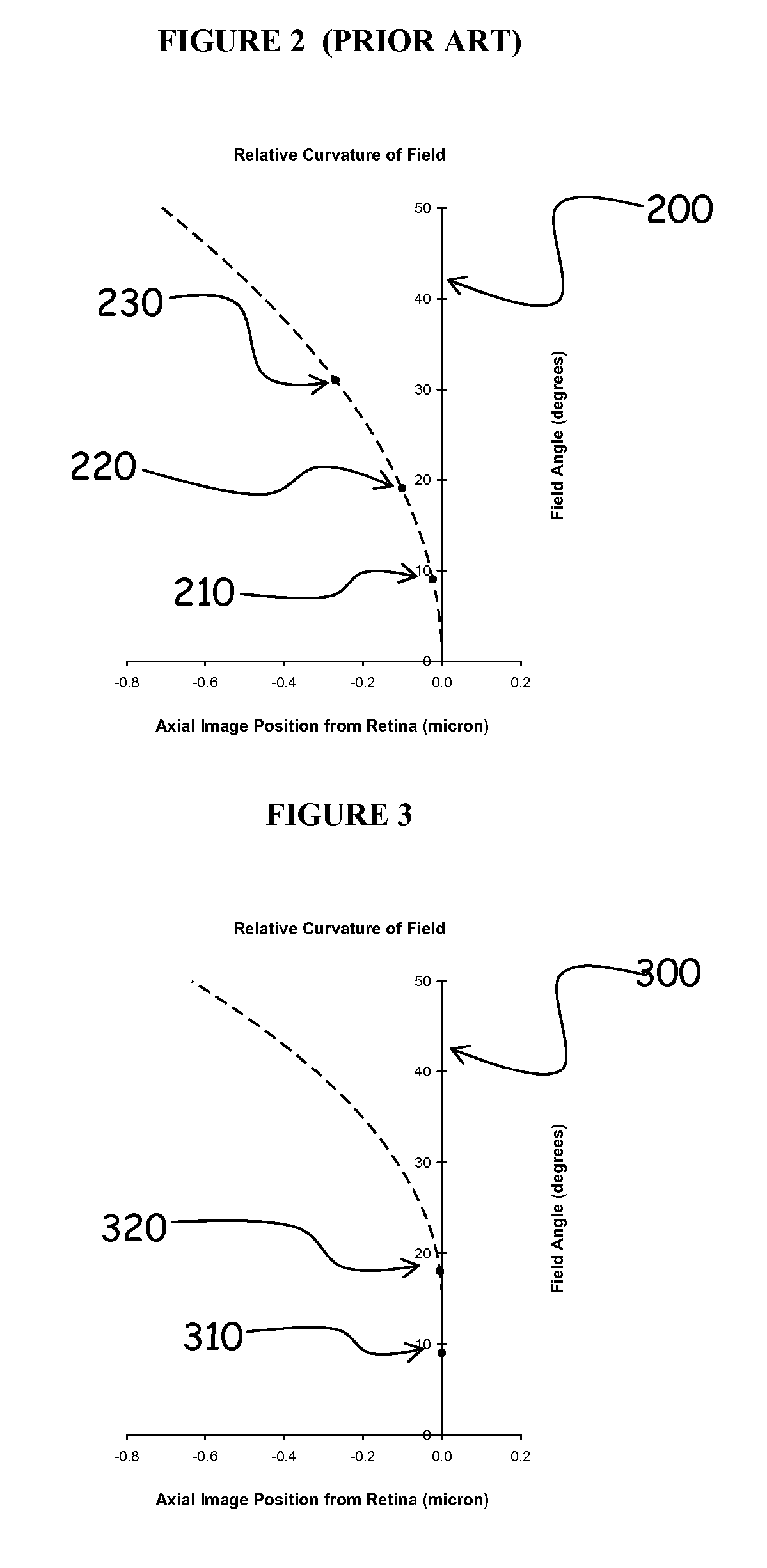
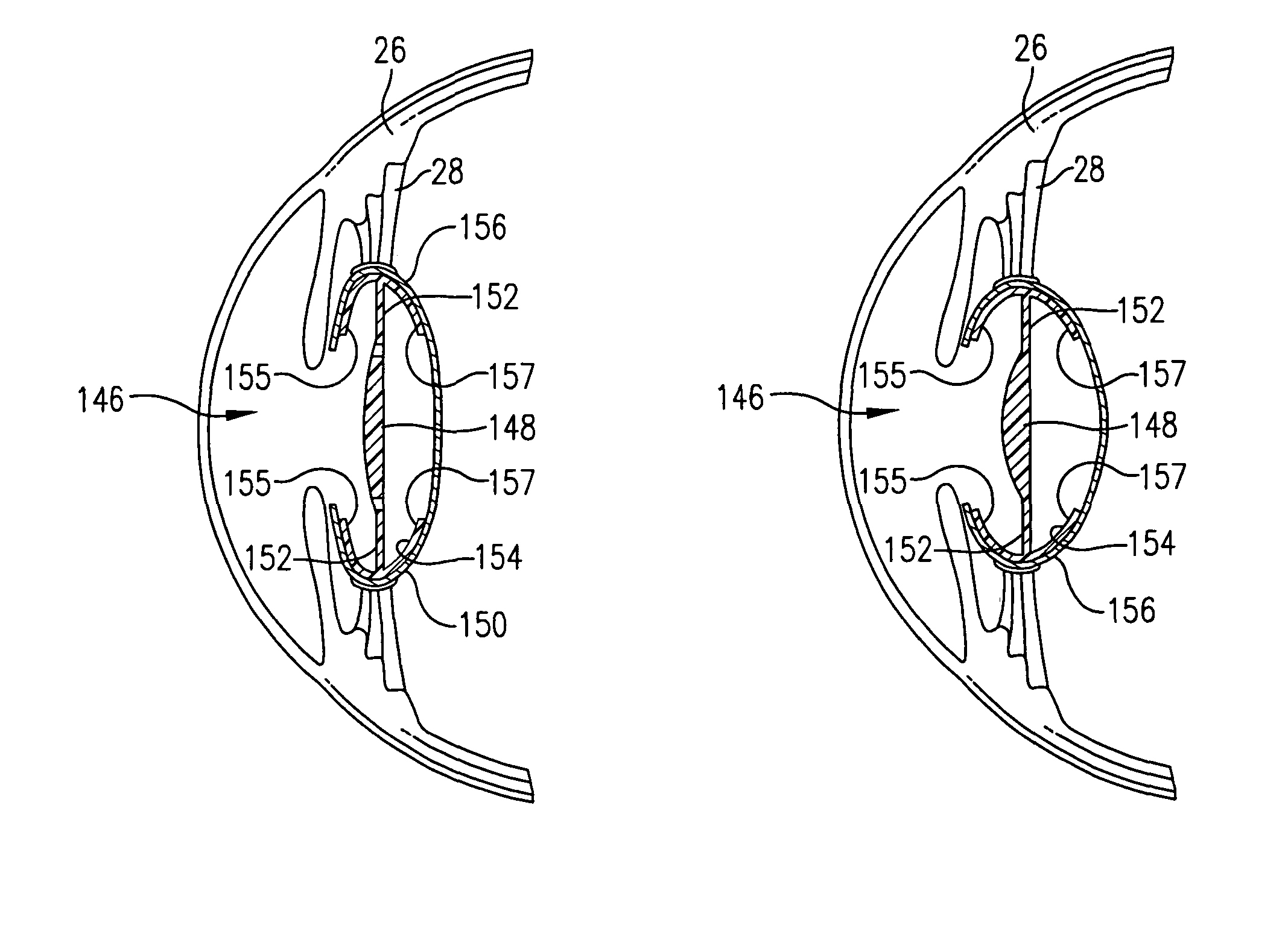
Patents
Literature
264 results about "Refraction errors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
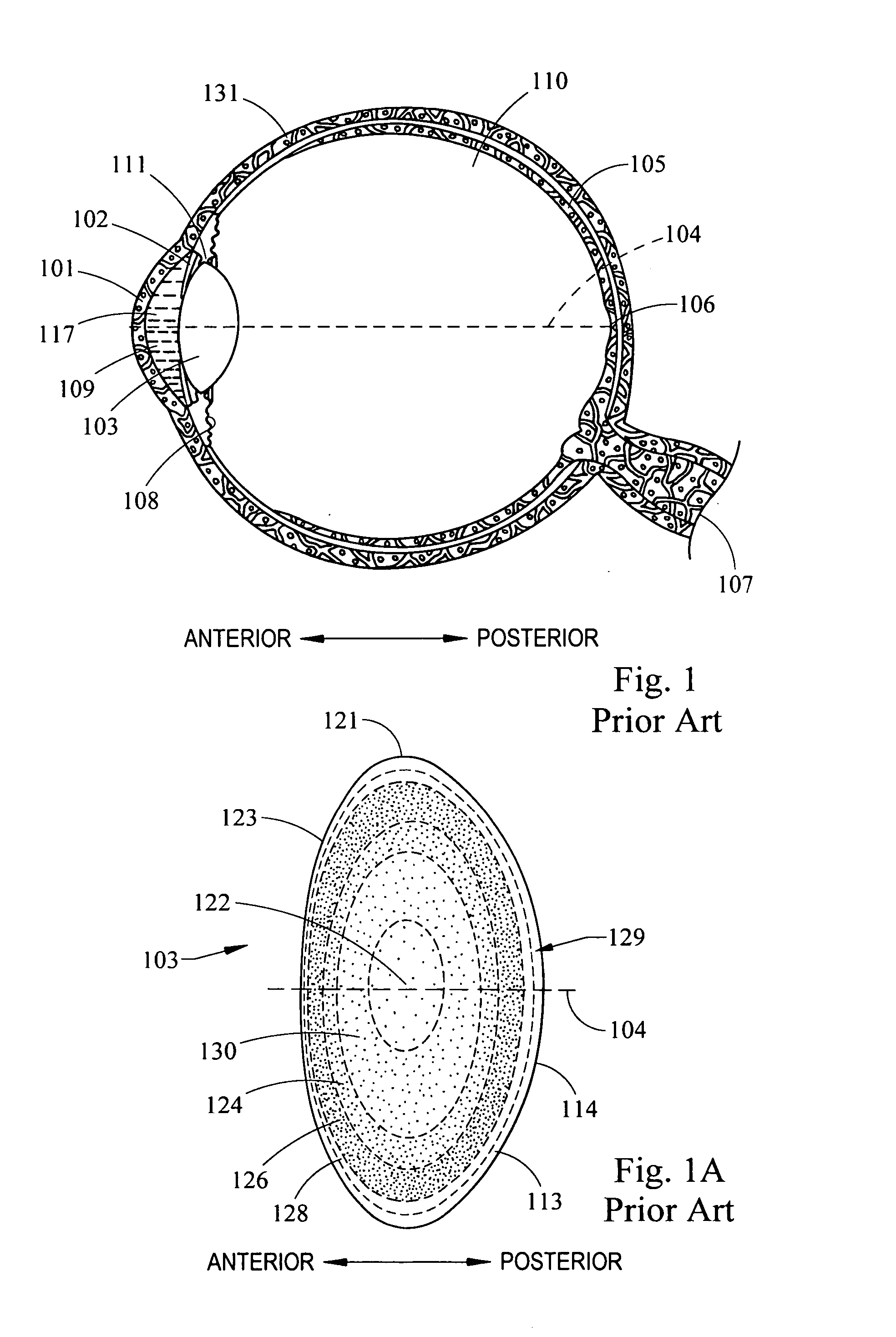
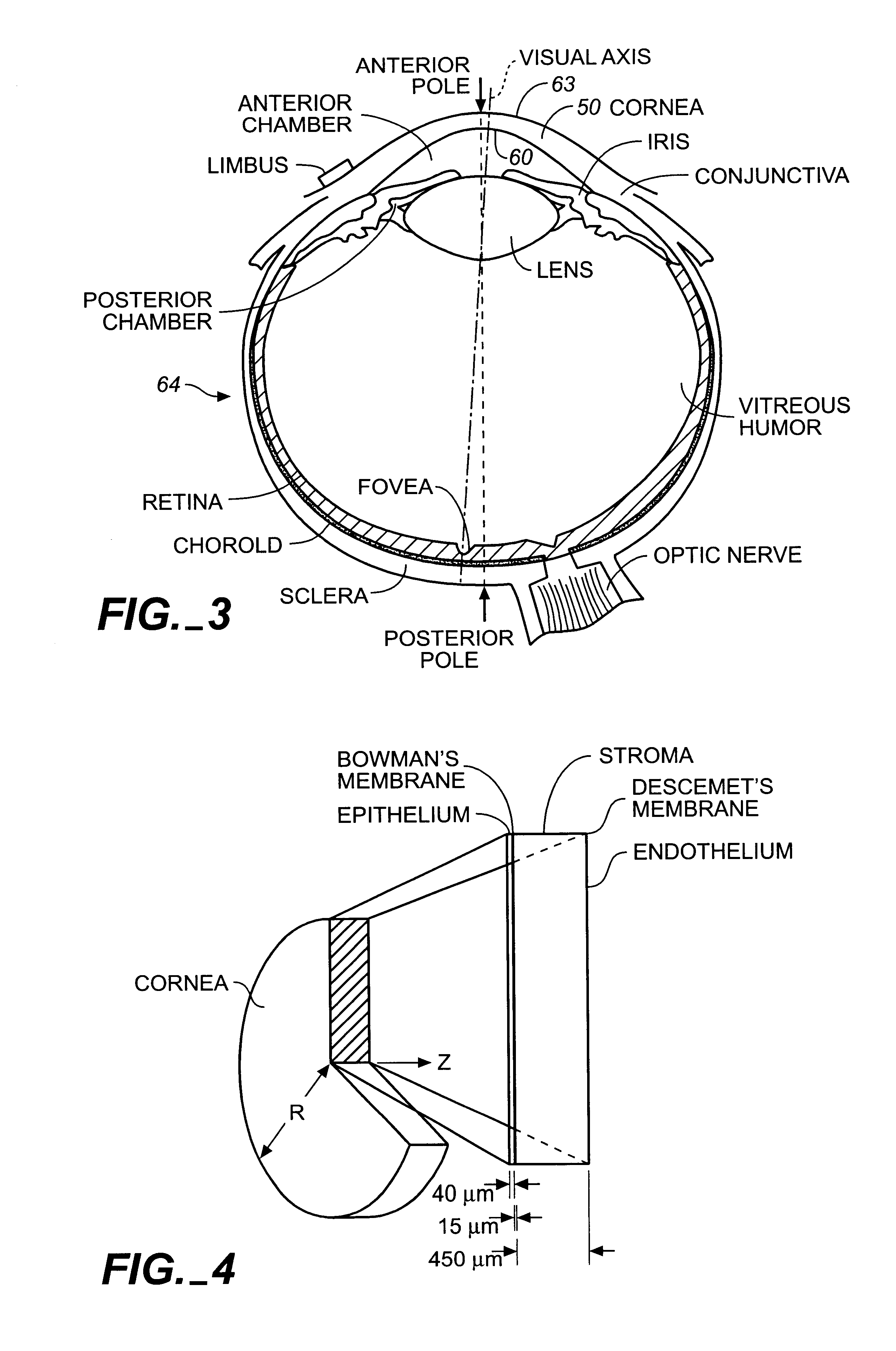
Refractive error, also known as refraction error, is a problem with focusing light accurately onto the retina due to the shape of the eye. The most common types of refractive error are near-sightedness, far-sightedness, astigmatism, and presbyopia.
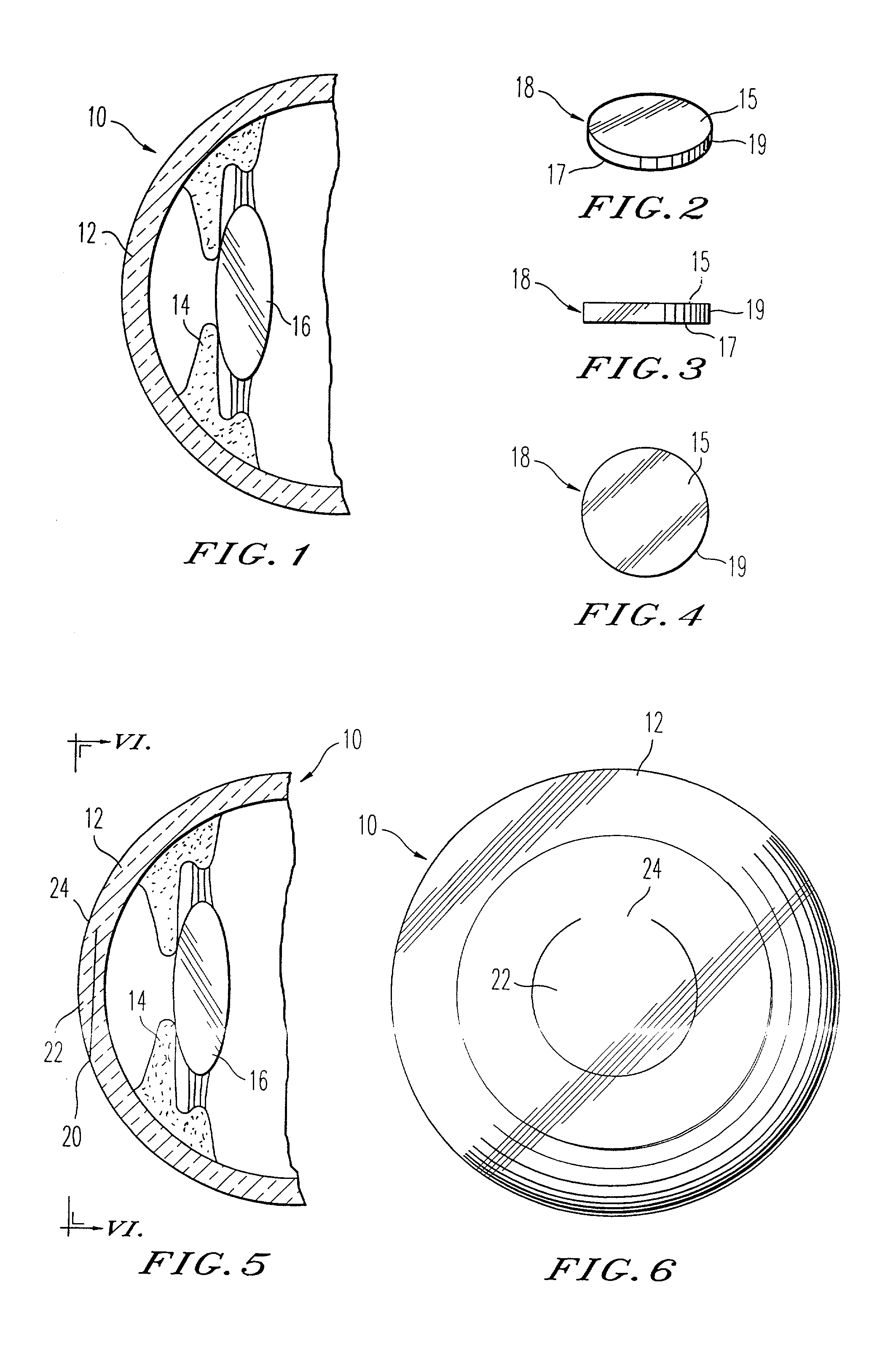
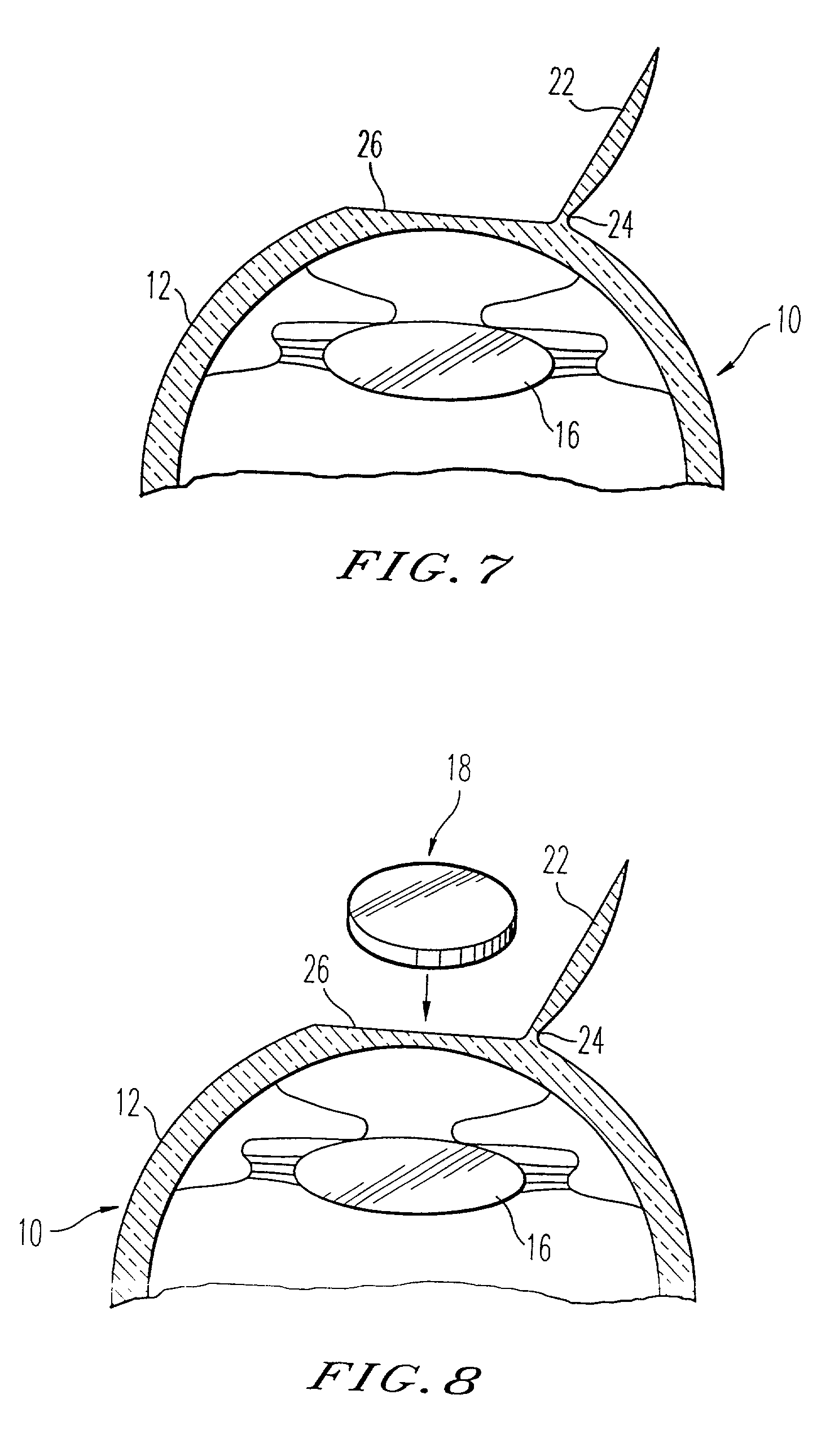
Lenticular refractive surgery of presbyopia, other refractive errors, and cataract retardation
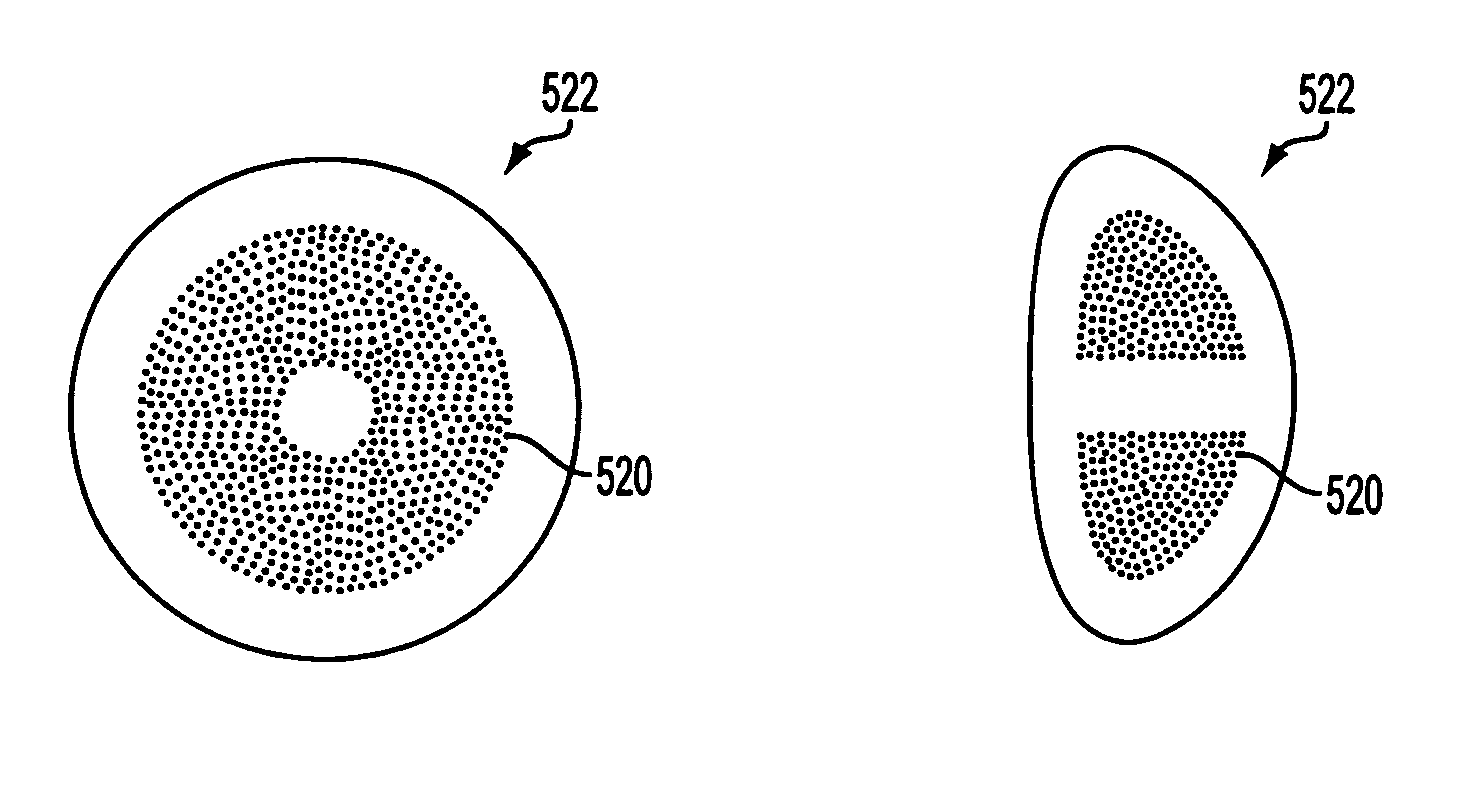
InactiveUS7655002B2Impaired growthReduce decreaseLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsFluid transportRefractive error
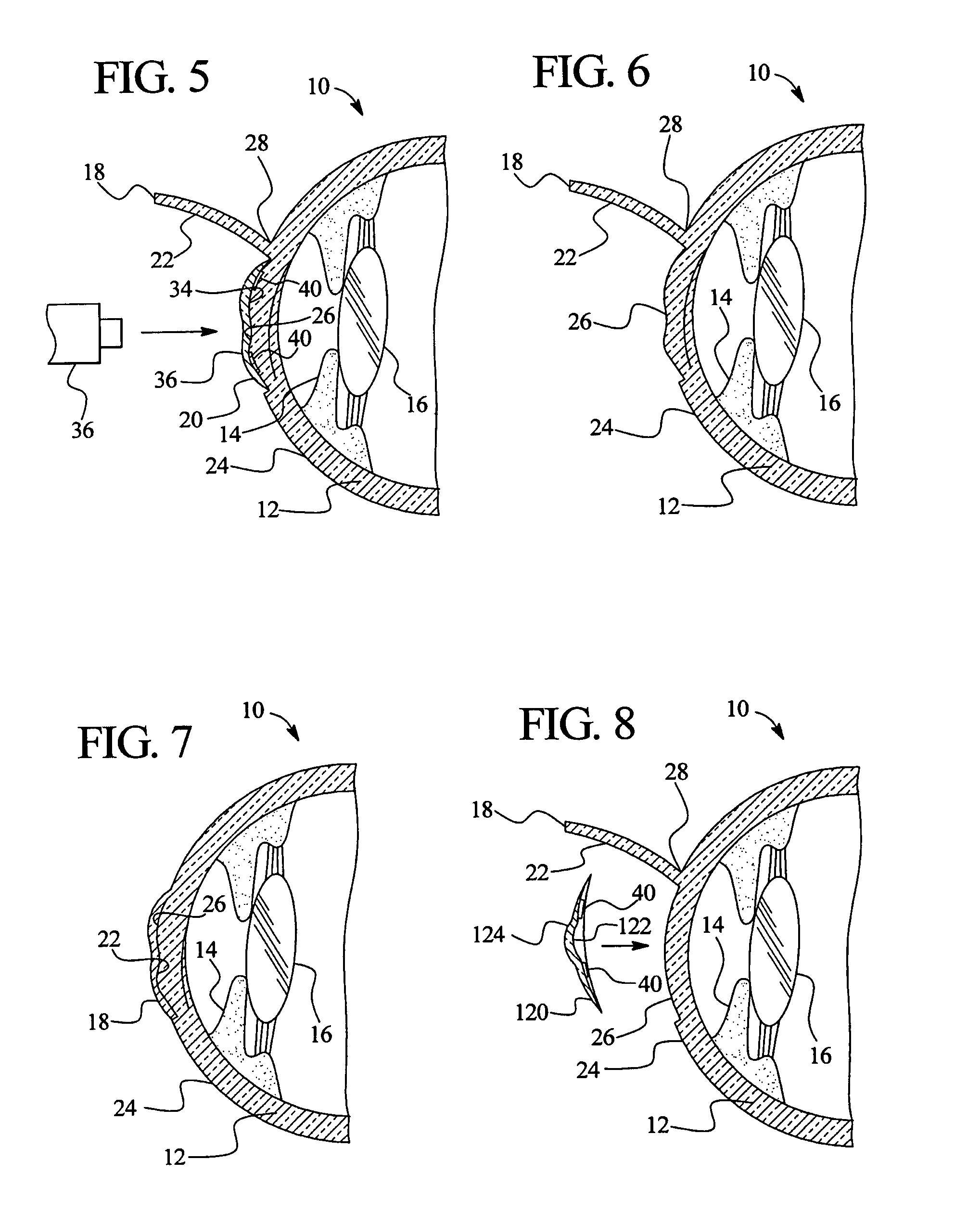
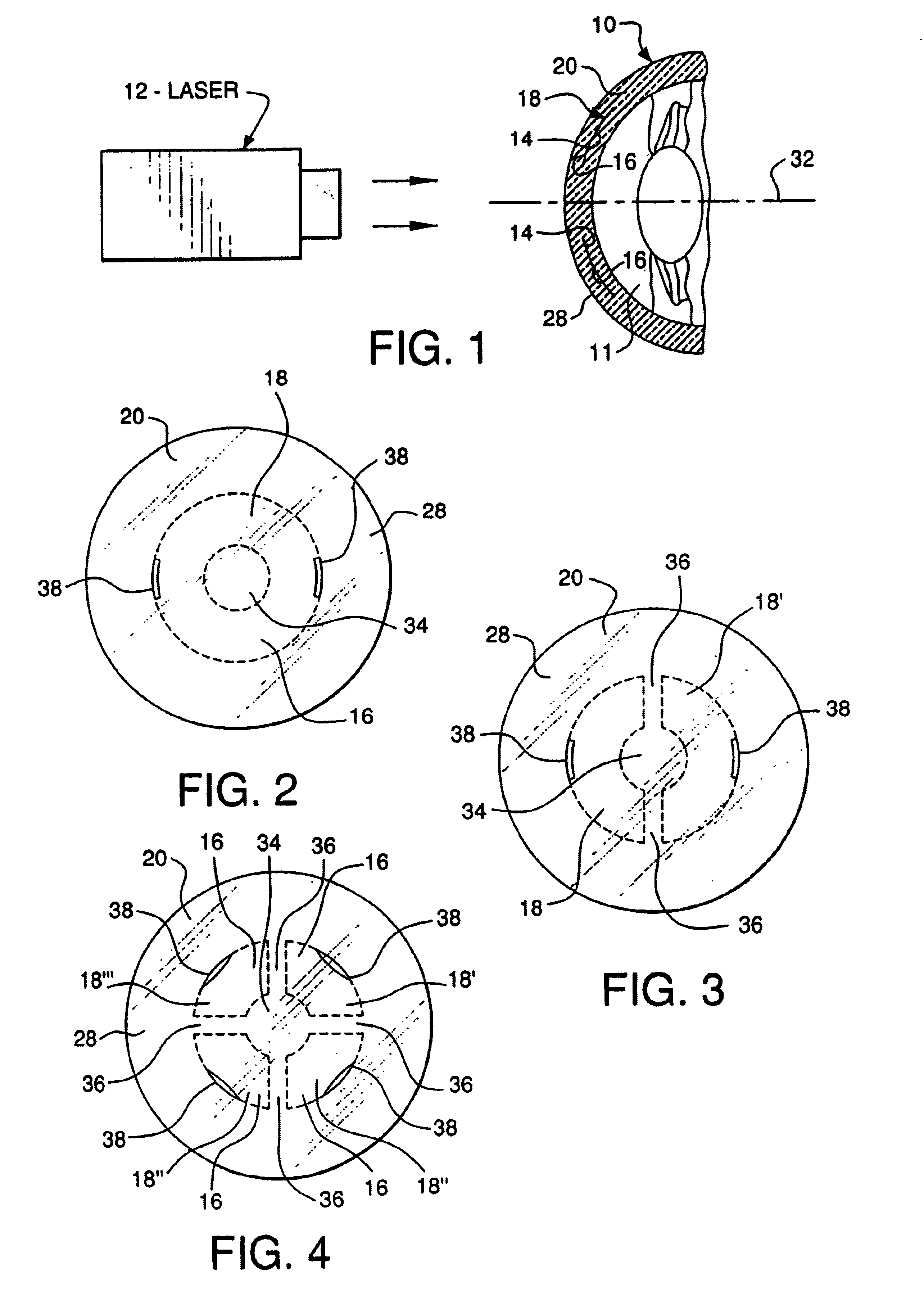
Methods for the creation of microspheres treat the clear, intact crystalline lens of the eye with energy pulses, such as from lasers, for the purpose of correcting presbyopia, other refractive errors, and for the retardation and prevention of cataracts. Microsphere formation in non-contiguous patterns or in contiguous volumes works to change the flexure, mass, or shape of the crystalline lens in order to maintain or reestablish the focus of light passing through the ocular lens onto the macular area, and to maintain or reestablish fluid transport within the ocular lens.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT LASER TECH
System and method for providing the shaped structural weakening of the human lens with a laser
ActiveUS20070185475A1Increase amplitudeImprove errorLaser surgeryDiagnosticsRefractive errorRefraction errors
A system and method for increasing the amplitude of accommodation and / or changing the refractive power of lens material of a natural crystalline lens is provided. Generally, there is provided methods and systems for delivering a laser beam to a lens of an eye in a plurality of sectional patterns results in the shaped structural weakening of the lens. There is also provided a method and system for determining adjustments to refractive errors in the lens of an eye relating to the treatment of presbyopia. The change to refractive error can be a predicted error or an actual error that has been determined.
Owner:LENSAR LLC
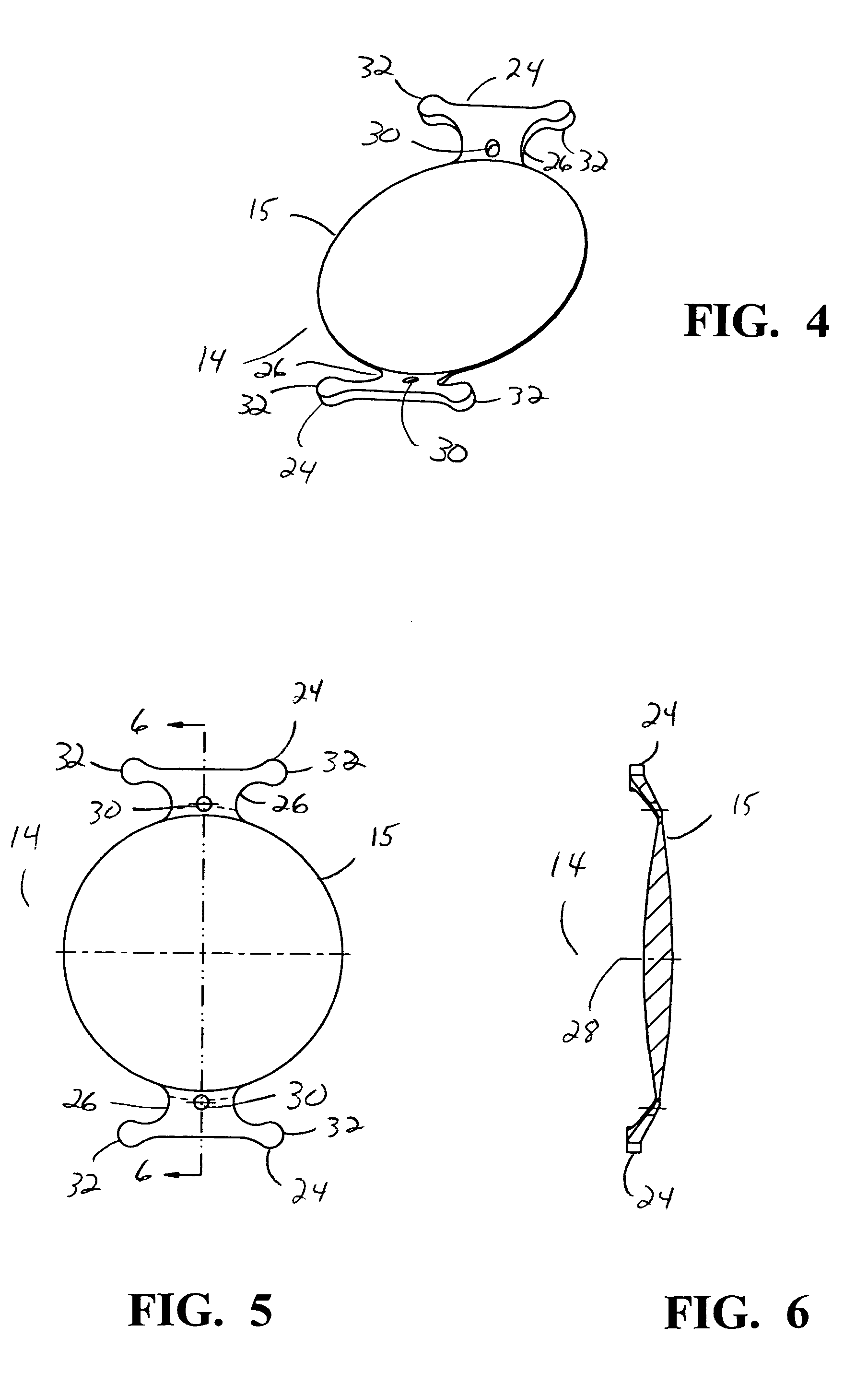
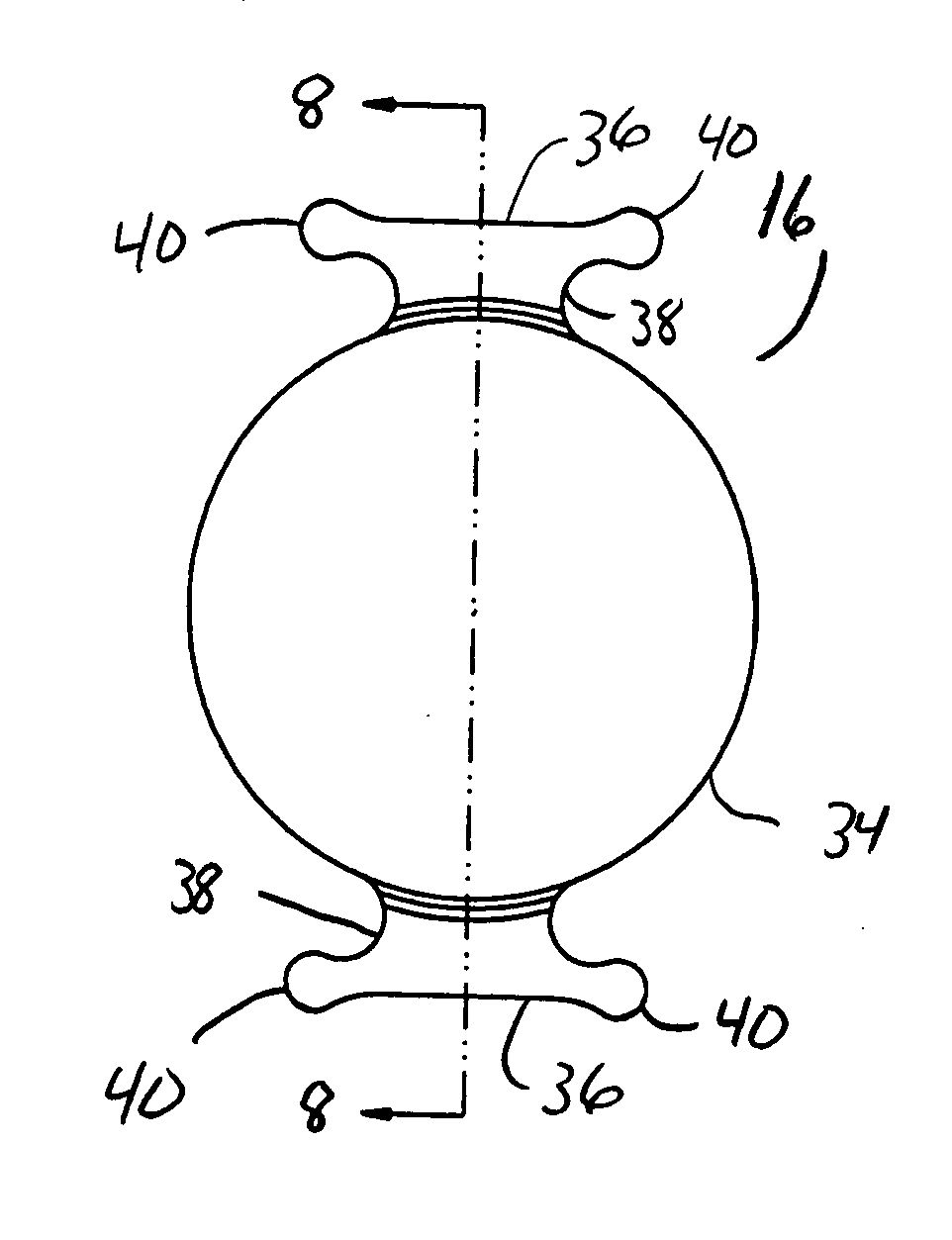
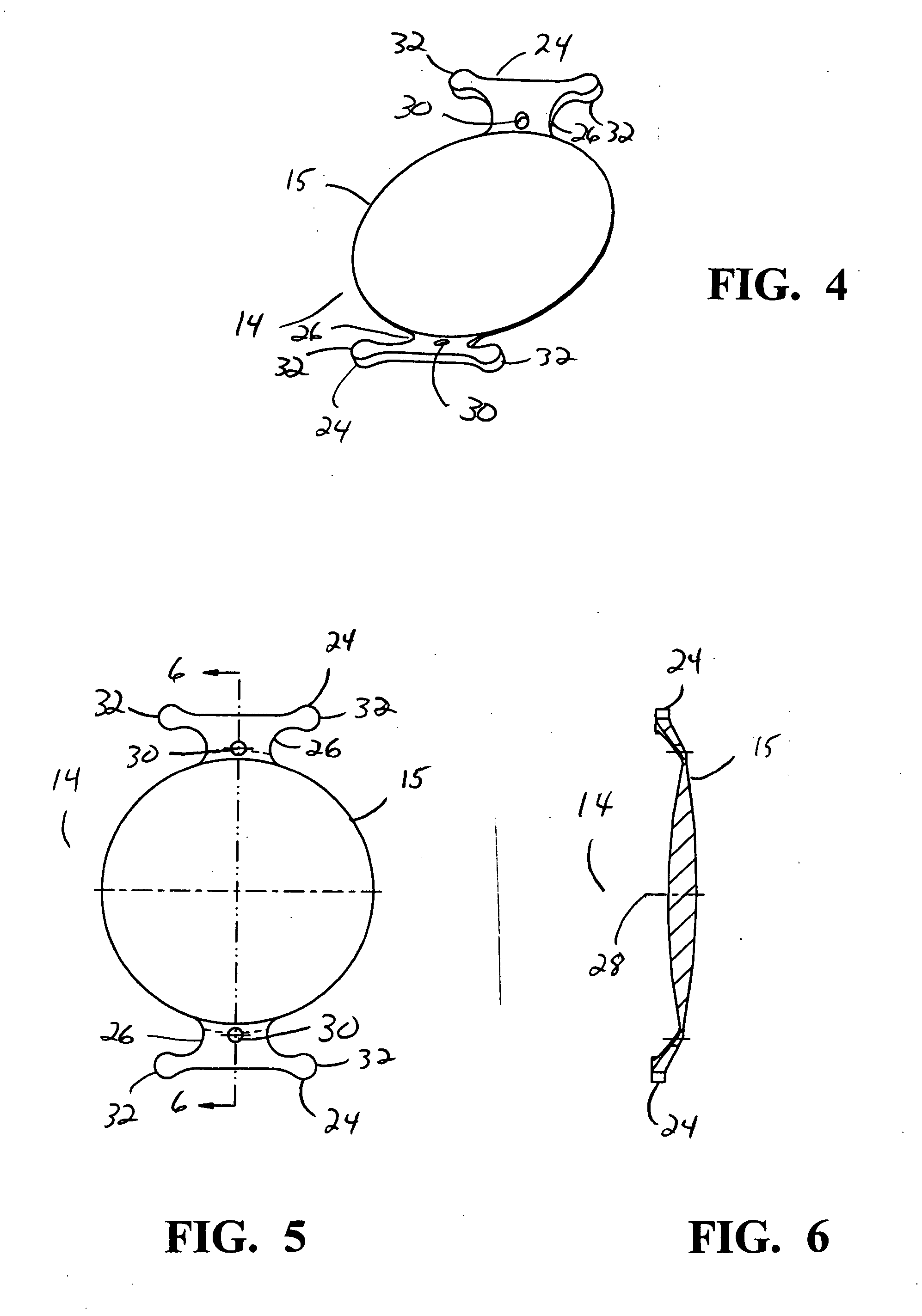
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors by active composite artificial muscle implants
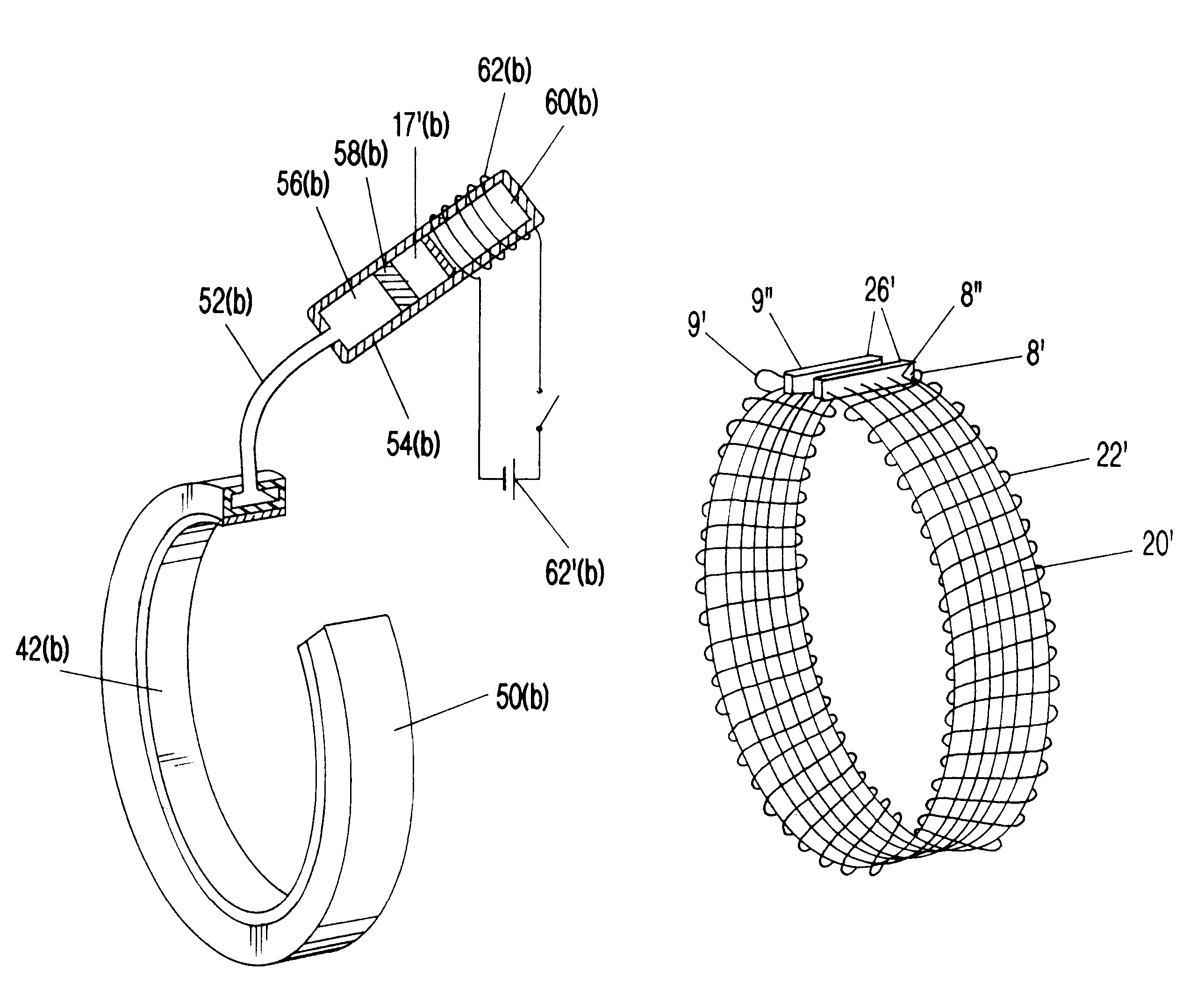
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors such as presbyopia, hyperopia, myopia, and stigmatism by using transcutaneously inductively energized artificial muscle implants to either actively change the axial length and the anterior curvatures of the eye globe. This brings the retina / macula region to coincide with the focal point. The implants use transcutaneously inductively energized scleral constrictor bands equipped with composite artificial muscle structures. The implants can induce enough accommodation of a few diopters, to correct presbyopia, hyperopia, and myopia on demand. In the preferred embodiment, the implant comprises an active sphinctering smart band to encircle the sclera, preferably implanted under the conjunctiva and under the extraocular muscles to uniformly constrict the eye globe, similar to a scleral buckle band for surgical correction of retinal detachment, to induce active temporary myopia (hyperopia) by increasing (decreasing) the active length of the globe. In another embodiment, multiple and specially designed constrictor bands can be used to enable surgeons to correct stigmatism. The composite artificial muscles are either resilient composite shaped memory alloy-silicone rubber implants in the form of endless active scleral bands, electroactive ionic polymeric artificial muscle structures, electrochemically contractile endless bands of ionic polymers such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN), thermally contractile liquid crystal elastomer artificial muscle structures, magnetically deployable structures or solenoids or other deployable structures equipped with smart materials such as preferably piezocerams, piezopolymers, electroactive and eletrostrictive polymers, magnetostrictive materials, and electro or magnetorheological materials.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL ROBOTS
Adjustable inlay with multizone polymerization
The present invention relates to an inlay for correcting refractive error in an eye. The inlay includes a first portion having a first volume that remains substantially constant when exposed to an energy, and a second portion having a second volume that is adapted to change when exposed to the energy. This inlay results in a device that can correct severe ametropic conditions, without ablating any portion of the inlay itself or the cornea.
Owner:MINU
High performance corneal inlay
A corneal inlay protects ocular structures from harmful wavelengths of light while maintaining acceptable color cosmetics, color perception, overall light transmission, photopic vision, scotopic vision, color vision, and / or cirdadian rhythms. The corneal inlay can also include a pinhole effect to increase depth of focus. In some embodiments, the corneal inlay can also correct refractive errors including, but not limited to, higher order aberration, lower order aberration, myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and / or presbyopia.
Owner:HIGH PERFORMANCE OPTICS
Method and apparatus to guide laser corneal surgery with optical measurement
InactiveUS20070282313A1Faster visual recoveryLess invasiveLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive errorPhototherapeutic keratectomy
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is used to map the surface elevation and thickness of the cornea. The OCT maps are used to plan laser procedures for the treatment of an irregular, opacified or weakened cornea, and in the treatment of refractive errors. In the excimer laser phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK) procedure, the OCT data is used to plan a map of ablation depth needed to restore a smooth optical surface. In the excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy procedure, OCT mapping of epithelial thickness is used to achieve clean laser epithelial removal. In femtosecond laser anterior keratoplasty procedure, OCT data is used to plan the depth of femtosecond laser dissection to remove an anterior layer of the cornea, leaving a smooth recipient bed of uniform thickness to receive a disk of donated corneal tissue. The linkage of an OCT system to a precise laser surgical system enables the performance of new procedures that are safer, less invasive and produce faster visual recovery than conventional surgical procedures.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Optical adapter for ophthalmological imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20130083185A1Reduce intensityConvenient lightingColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsCamera lensEngineering
An optical adapter system for a smart-phone has a lens and a light transmission guide within a housing. The adapter lens is located at the distal end of the housing in optical alignment with the smart-phone's camera lens, and the light transmission guide extends from one end that is adjacent to the smart-phone's light source toward the distal end of the housing and directs light outside of the housing to the subject being imaged. The optical adapter is preferably used in combination with the smart-phone as an ophthalmic examination tool and can be used with a computer program that runs on the smart-phone's processor. The computer program can be calibrated for use with the particular optical adapter and can be used to control the smart-phone's imaging system, such as varying the intensity of the light source, and can determine a refractive error in a patient's eye.
Owner:INTUITIVE MEDICAL TECH
Method and apparatus for controlling ablation in refractive surgery
InactiveUS20050107775A1Minimize spatial overlapThe result is accurateLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive errorFarsightedness
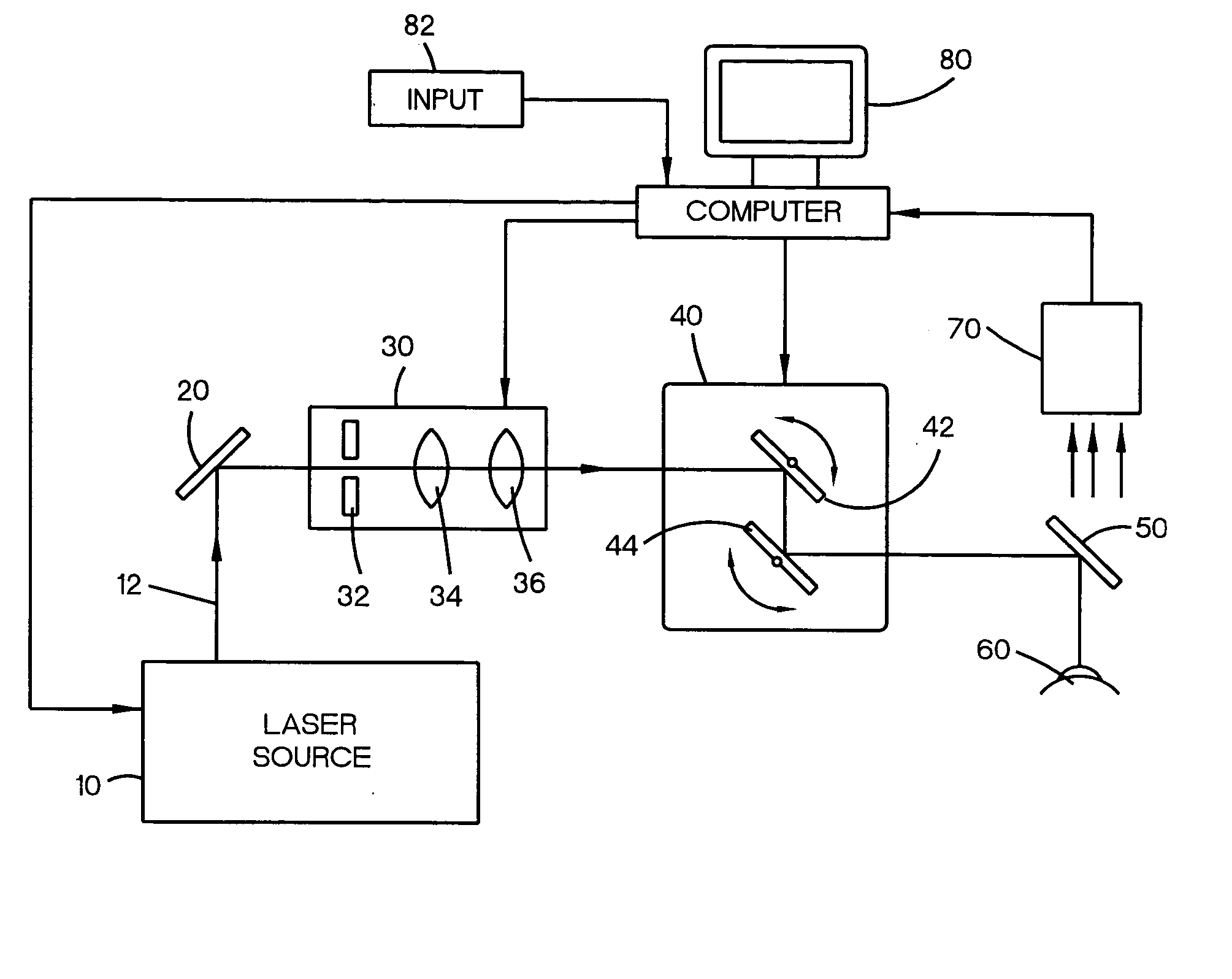
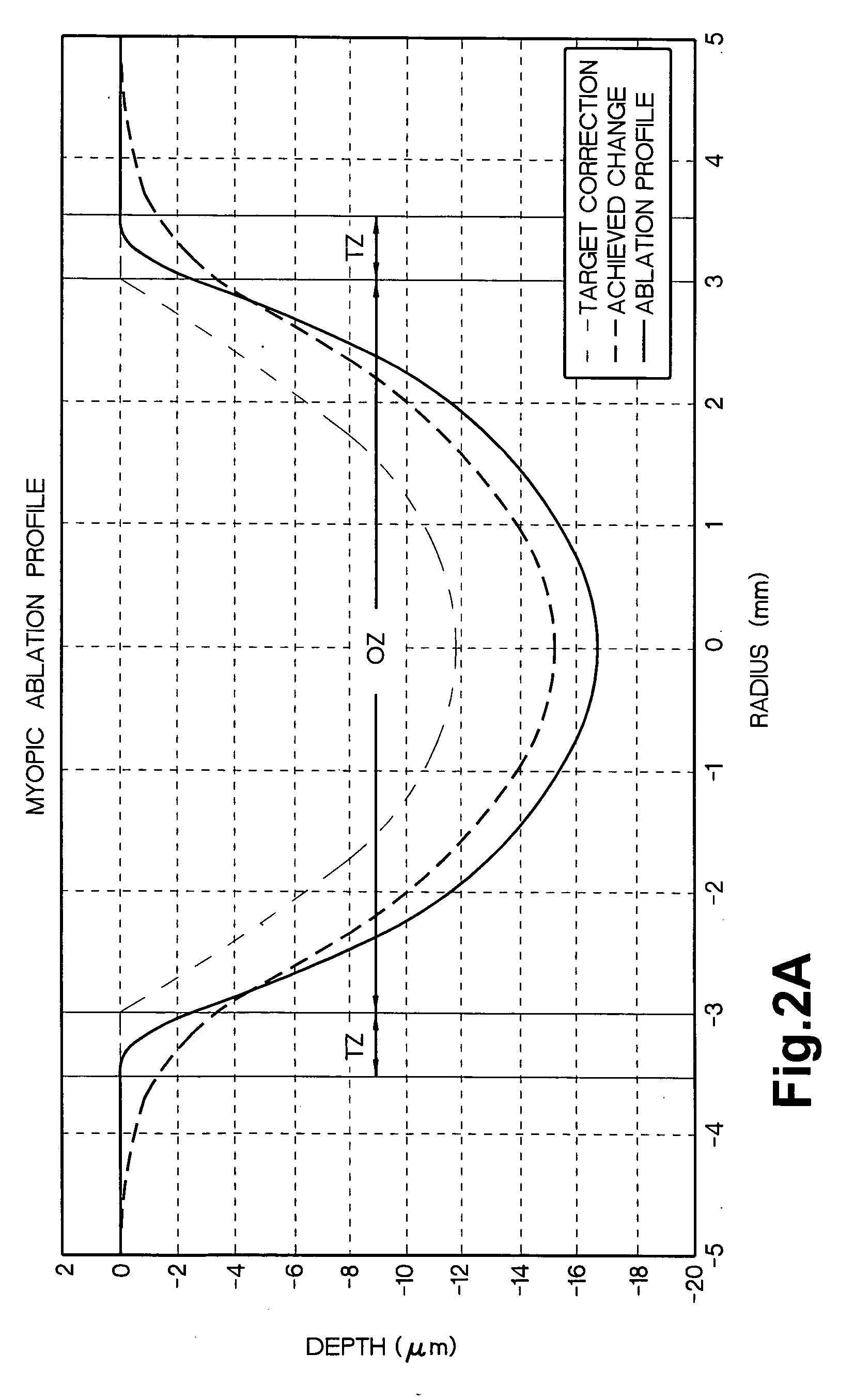
The present invention relates to laser ablation patterns to correct refractive errors of the eye (60) such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism, and higher order aberrations of the eye (60). The laser ablation patterns used to control the laser (10) prevent induced aberrations by compensating for post-procedure epithelial smoothing. The position of laser pulses (12) is also controlled to optimize the achievement of the intended ablation pattern.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Apparatus for cornea reshaping
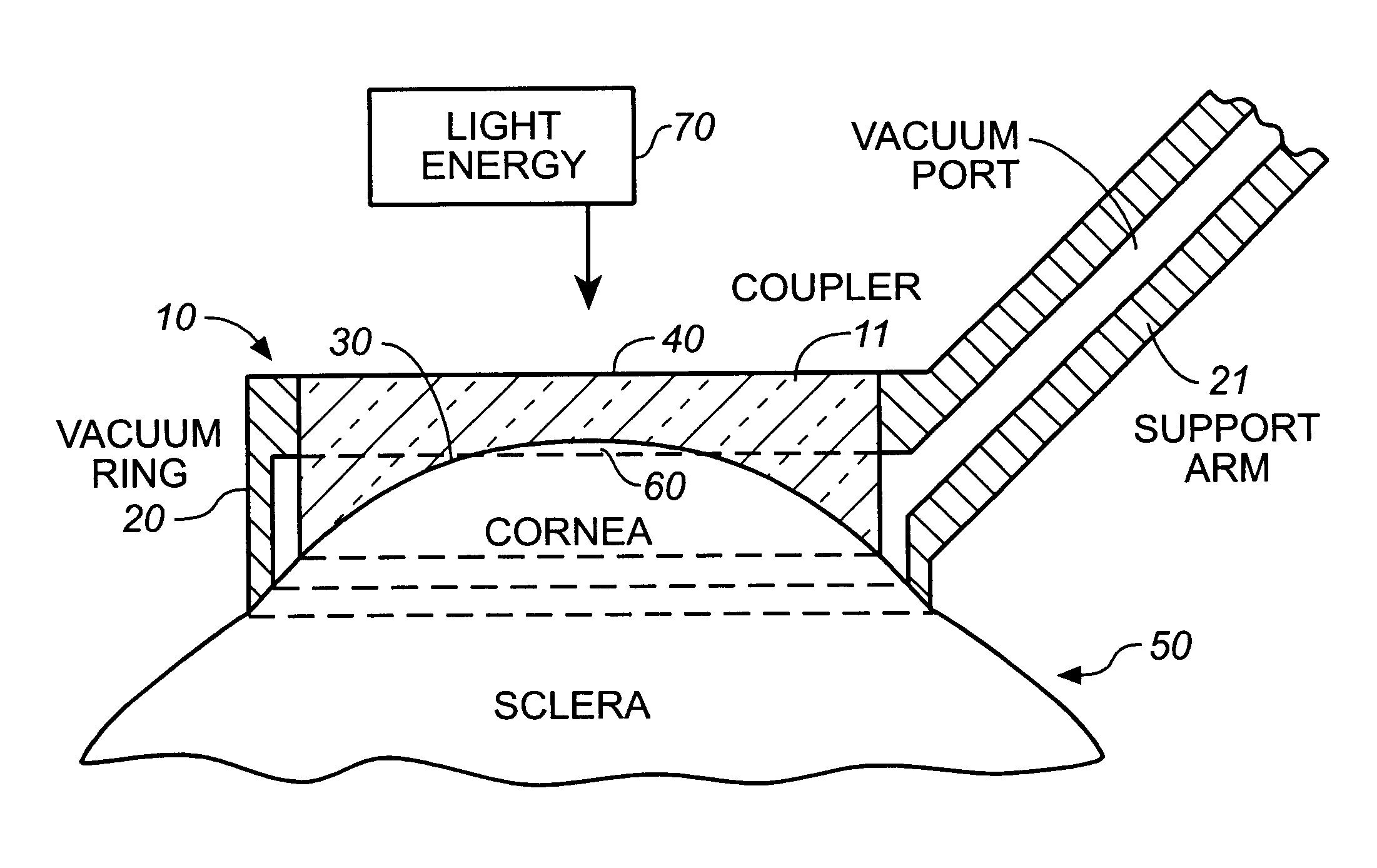
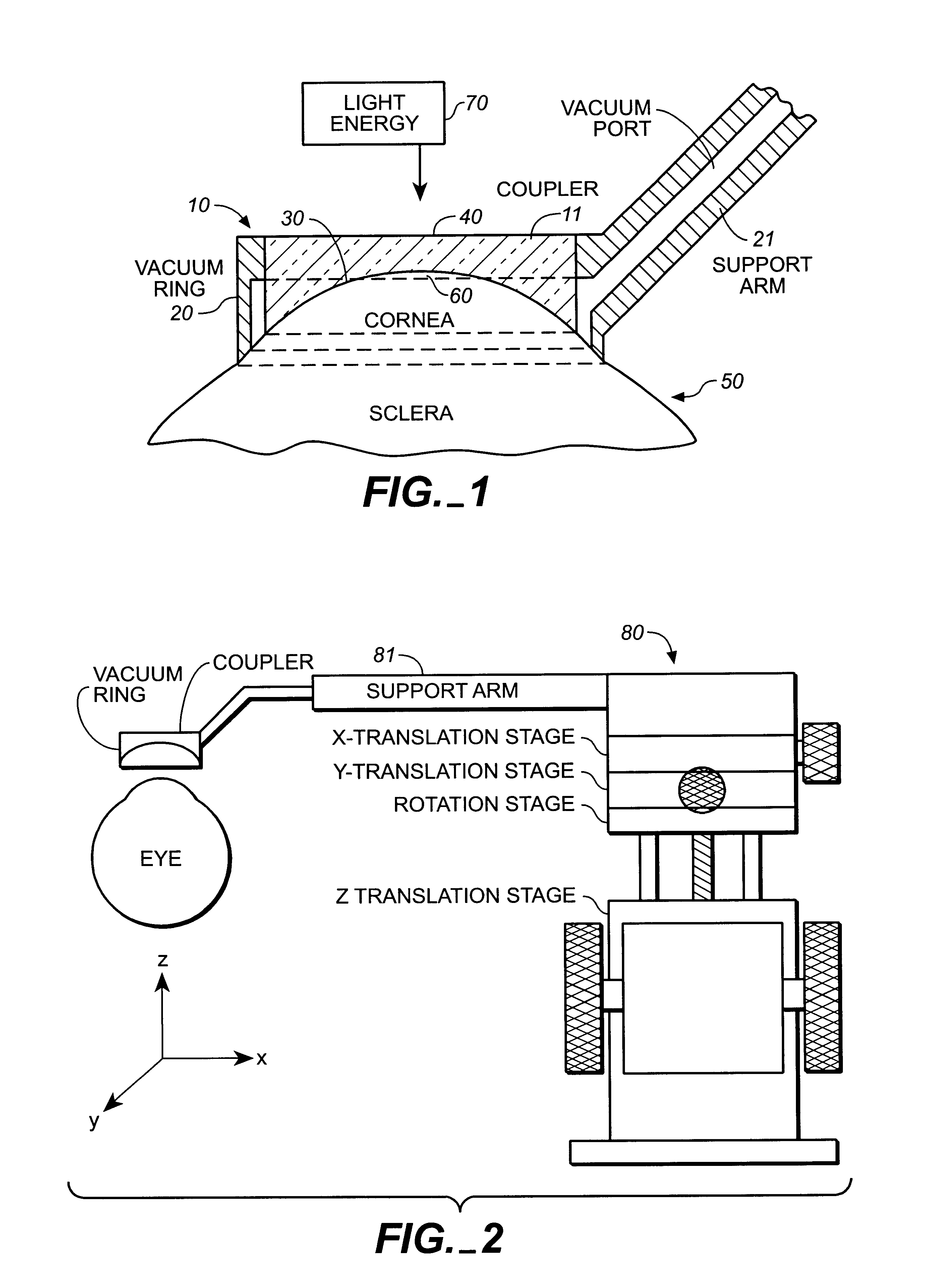
InactiveUS6342053B1Prevent accidental contactImprove protectionLaser surgerySurgical instruments for heatingOcular refractionOptical energy
An apparatus is described for use in combination with a noninvasive ophthalmological method for cornea reshaping in order to correct ocular refractive errors such as myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), and astigmatism. This apparatus is called a coupler and it is made of a material which is substantially transparent to the light energy used to reshape the cornea. The coupler conducts heat from the anterior portion of the cornea during the heating of the stroma by the light energy. The reshaping is enhanced by the coupler as it has a corneal engaging surface with a radius of curvature which approximates the desired emmetropic shape of the cornea. In addition to being a heat sink and template for the eye, the coupler also acts as a positioner and restrainer of the eye by attaching itself to the eye via an annular suction ring. Finally, the coupler also acts as a mask to prevent accidental exposure of the central optic zone to any light energy during the cornea reshaping procedure.
Owner:LASER BIOTECH +1
Adjustable universal implant blank for modifying corneal curvature and methods of modifying corneal curvature therewith
InactiveUS6949093B1Severe conditionImprove eyesightLaser surgeryEye implantsCorneal curvatureCorneal surface
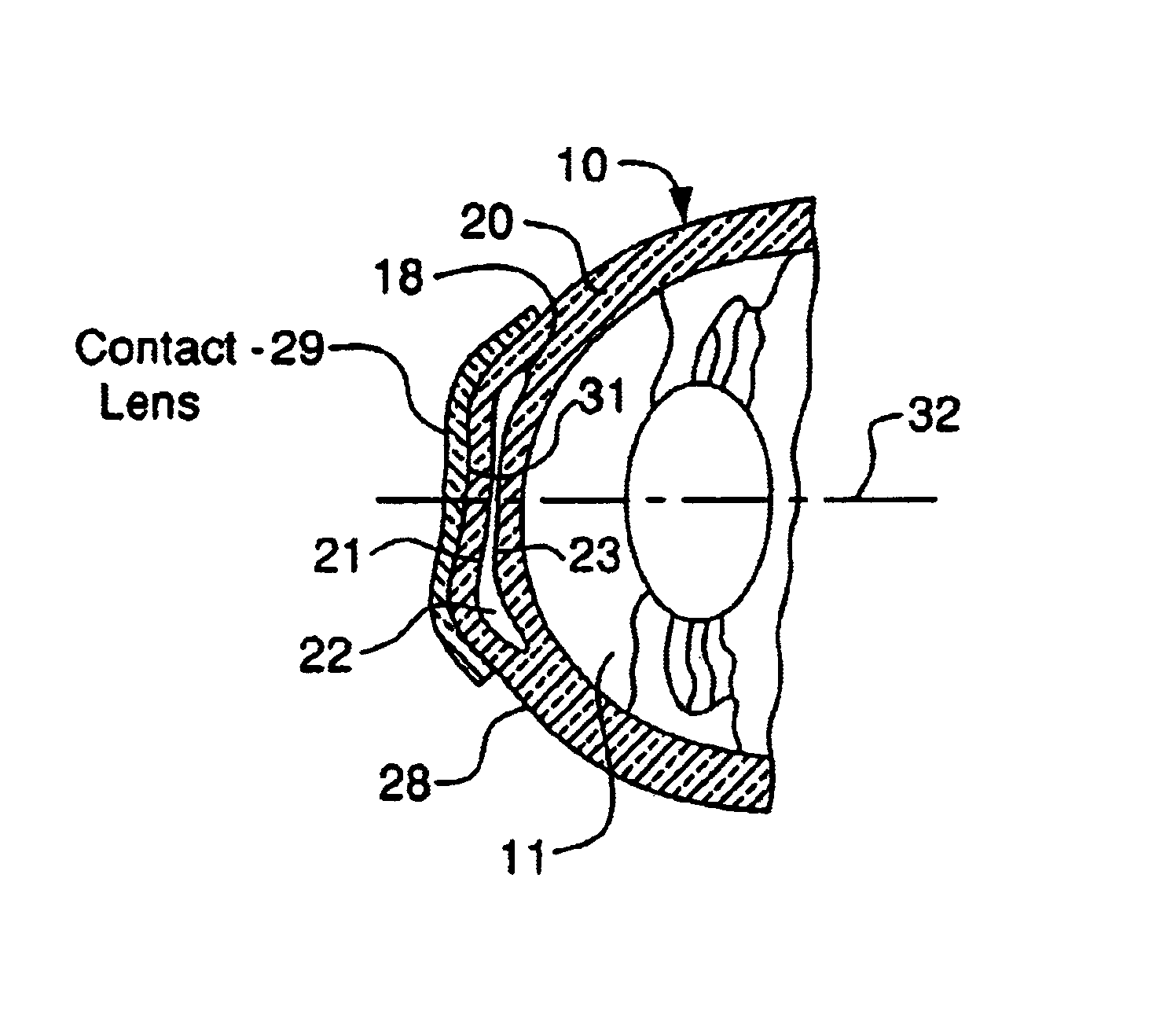
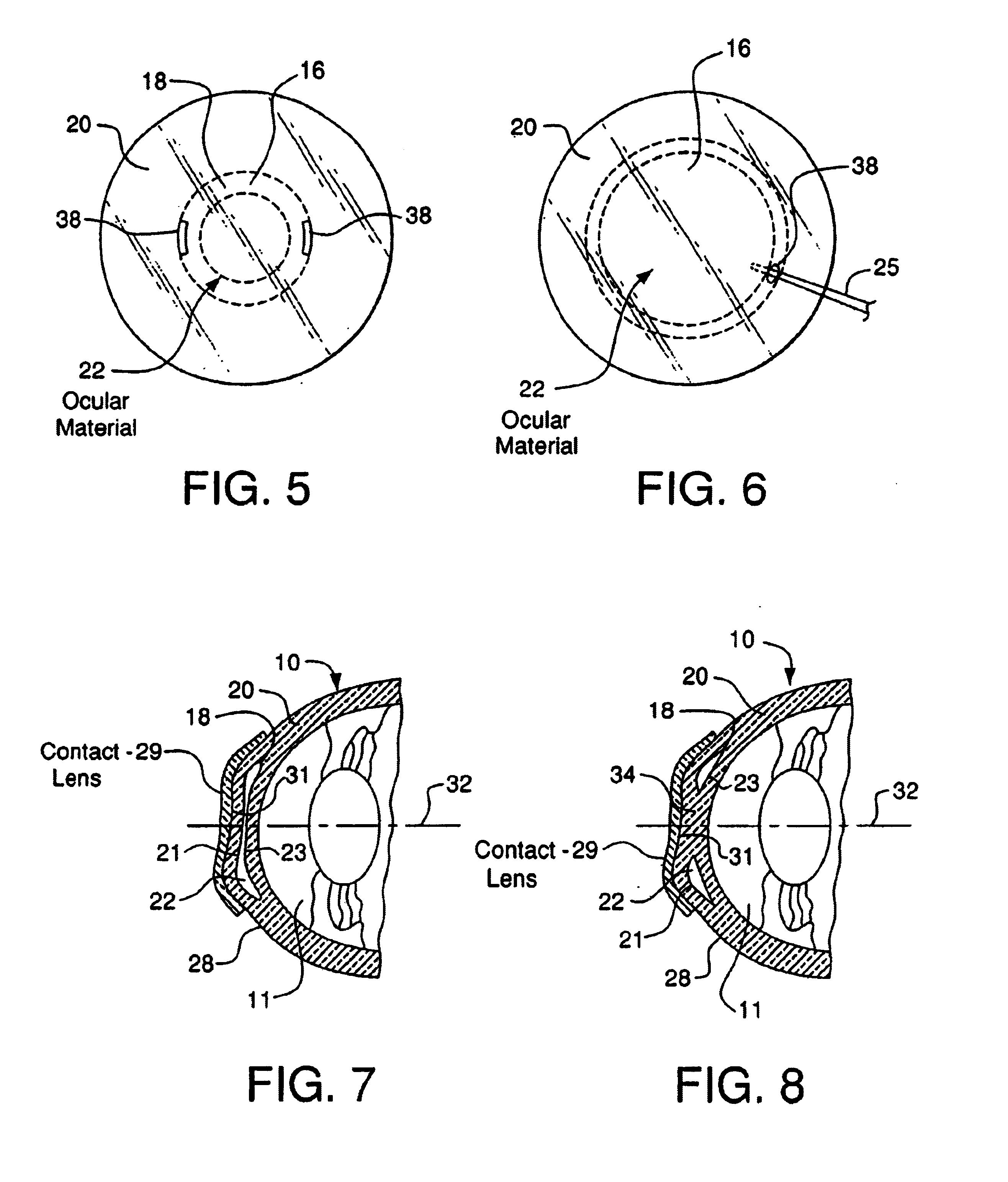
A method for correcting the refractive error in a cornea of an eye, including the steps of positioning an inlay on the surface of the cornea, the inlay having a first surface and a second surface, and the second surface being adjacent the surface of the cornea. Energy is applied to the inlay to ablate a portion of the first surface of the inlay by an amount adapted to correct the refractive error in the eye. The inlay is removed from the surface of the cornea, and the cornea is separated into a first corneal surface and a second corneal surface, the first corneal surface facing in a posterior direction of the eye and the second corneal surface facing in an anterior surface of the eye. The inlay is then positioned adjacent at least one of the first corneal surface and the second corneal surface.
Owner:MINU
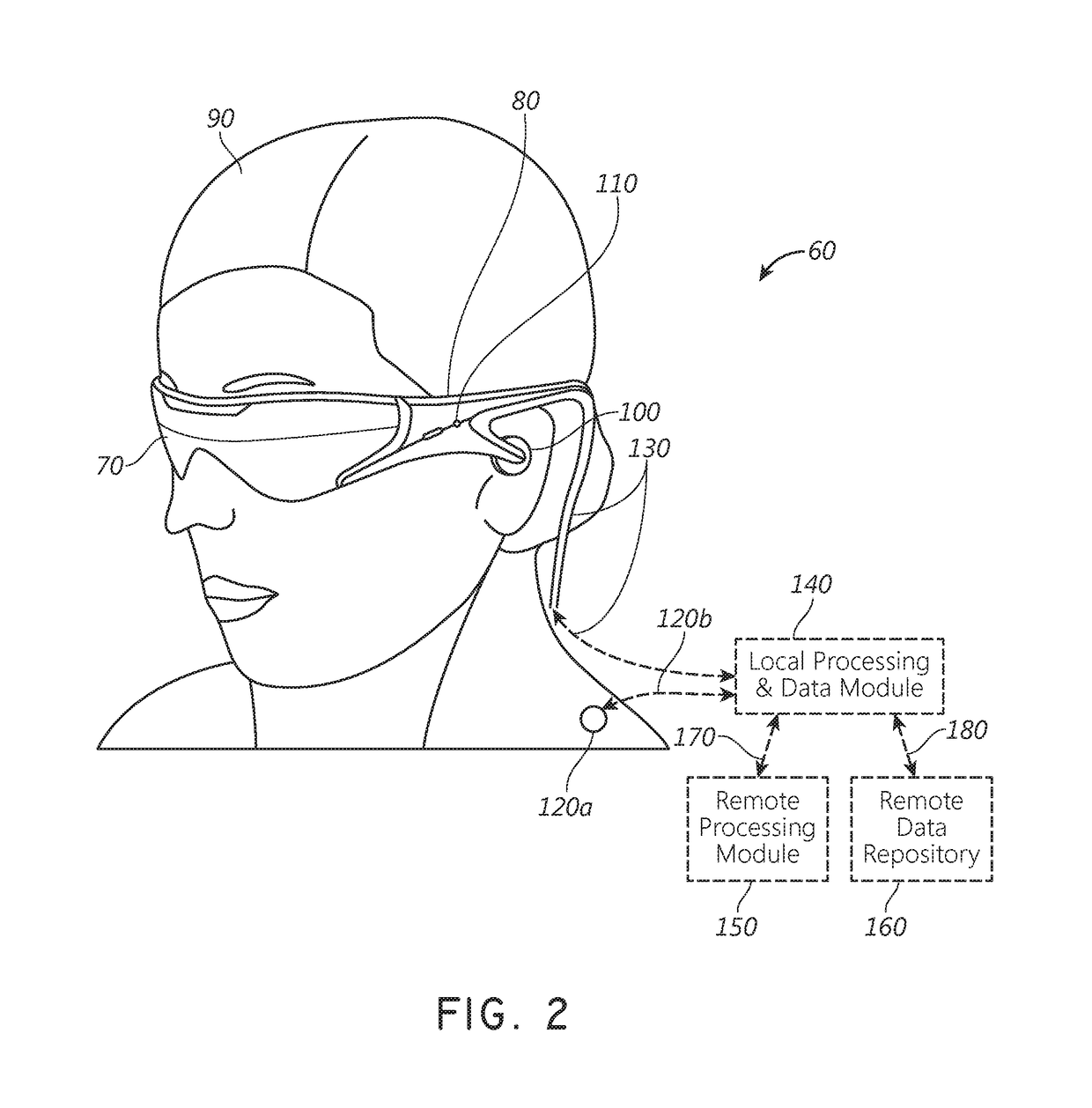
Augmented reality systems and methods with variable focus lens elements
ActiveUS20170293145A1Input/output for user-computer interactionNon-optical adjunctsRefractive errorOphthalmology
An augmented reality display system includes a pair of variable focus lens elements that sandwich a waveguide stack. One of the lens elements is positioned between the waveguide stack and a user's eye to correct for refractive errors in the focusing of light projected from the waveguide stack to that eye. The lens elements may also be configured to provide appropriate optical power to place displayed virtual content on a desired depth plane. The other lens element is between the ambient environment and the waveguide stack, and is configured to provide optical power to compensate for aberrations in the transmission of ambient light through the waveguide stack and the lens element closest to the eye. In addition, an eye-tracking system monitors the vergence of the user's eyes and automatically and continuously adjusts the optical powers of the pair of lens elements based on the determined vergence of those eyes.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
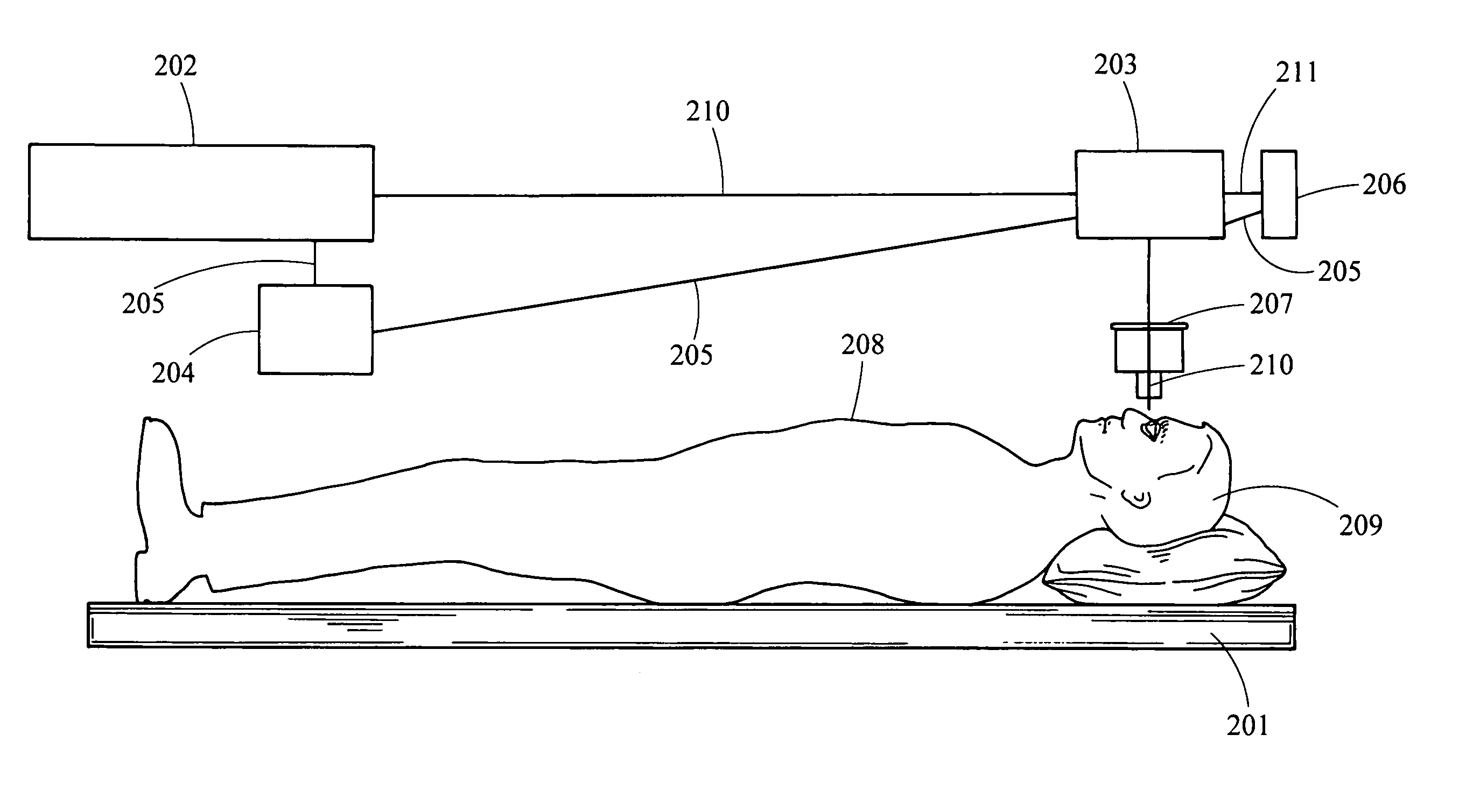
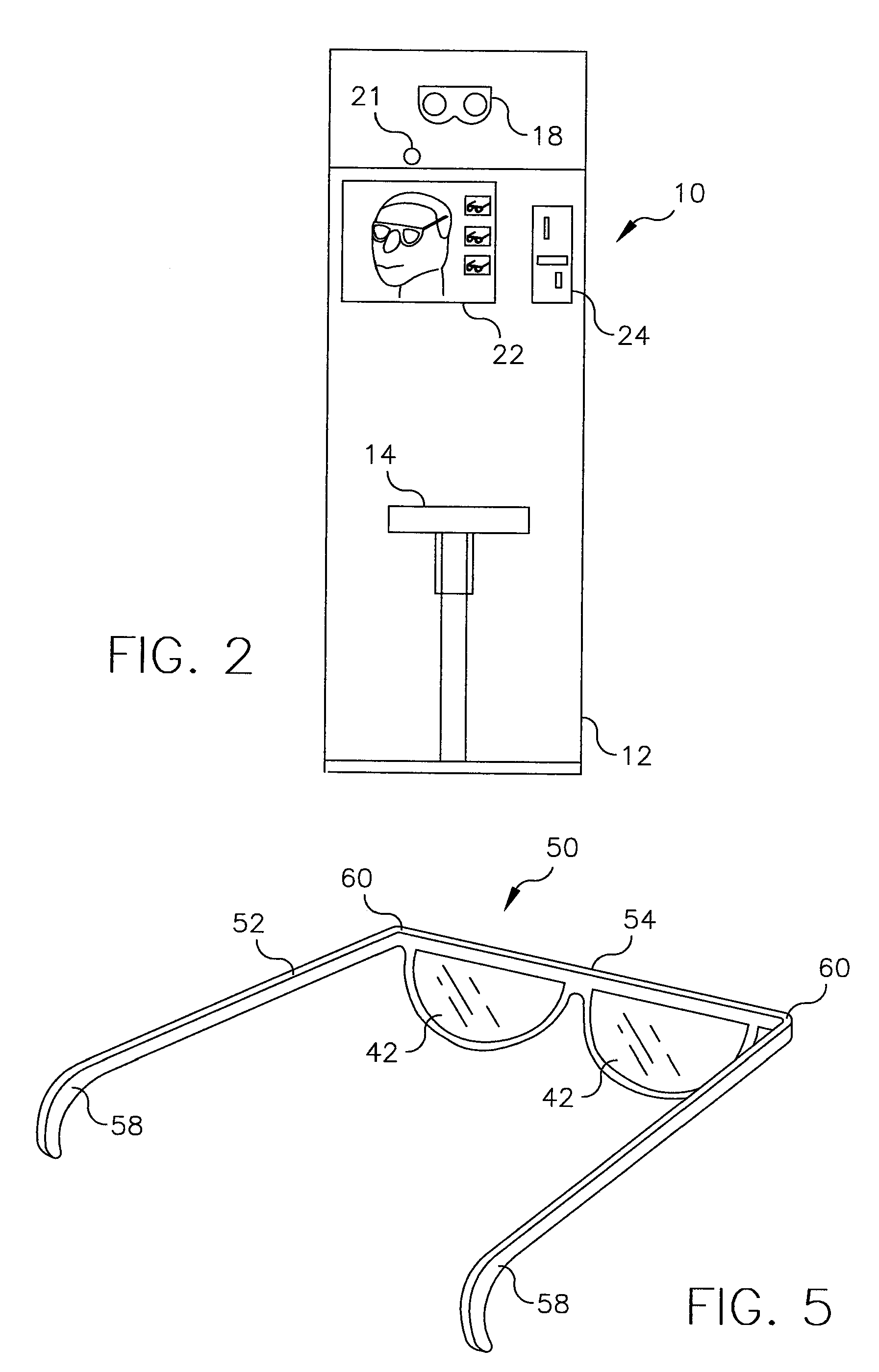
Health care kiosk having automated diagnostic eye examination and a fulfillment remedy based thereon
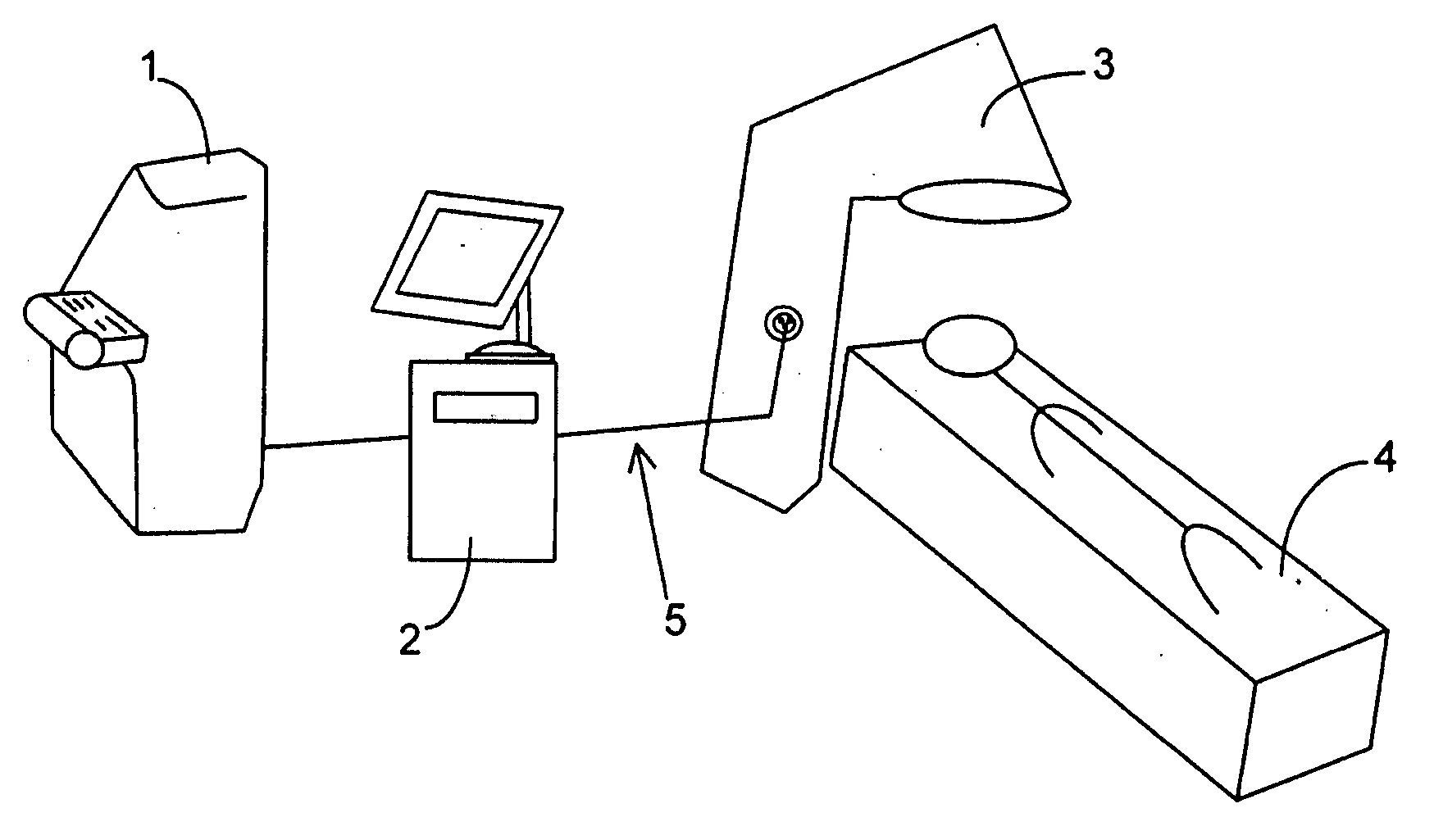
A stand-alone station such as a kiosk (10) includes automated equipment for performing eye examination procedures on a user positioned in the station (11). Information derived from the examination determines possible existence of a correctable medical condition. The station includes a user interface (22) and a fulfillment remedy section (30) that addresses the medical condition, as by fabrication of eyeglasses (32) for correction of refraction error, or by communicating treatments through the user interface to the user for treating such conditions as age-related macula degeneration, Alzheimer's disease, or visual field impairment. The station also includes a payment device (24) allowing the user to directly pay for the procedure and to indirectly pay using identified health insurance coverage.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Optimizing vision correction procedures
InactiveUS20100110379A1Easy to measureOut noiseOptical measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringWavefront sensorCylindroma
In one embodiment, an apparatus for optimizing vision correction procedures comprising: a narrow beam of light directed to a patient's retina; a dynamic defocus and compensation offsetting device configured to offset the defocus of a wavefront from an eye, a wavefront sensor configured to measure the local tilt of a number of subwavefronts sampled around an annular ring (the diameter of which can be dynamically changed) over the wavefront with the defocus offset; and a display device configured to display a two dimensional (2D) data points pattern in real time with each data point location representing a corresponding local tilt of the sampled subwavefronts. A proper defocus offset, not passive compensation, can reveal the predominant feature(s) of other wavefront aberration component(s), thus enabling a refractive surgeon to fine tune the vision correction procedure and minimize the remaining wavefront aberration(s) in real time. Meanwhile, by sampling the wavefront around annular rings and displaying the local tilt of the sampled subwavefronts on a monitor in the form of a 2D data points pattern, a refractive ophthalmic surgeon can easily correlate the measurement result to the two major refractive errors, namely spherical and cylinder refractive errors, including the axis of astigmatism.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
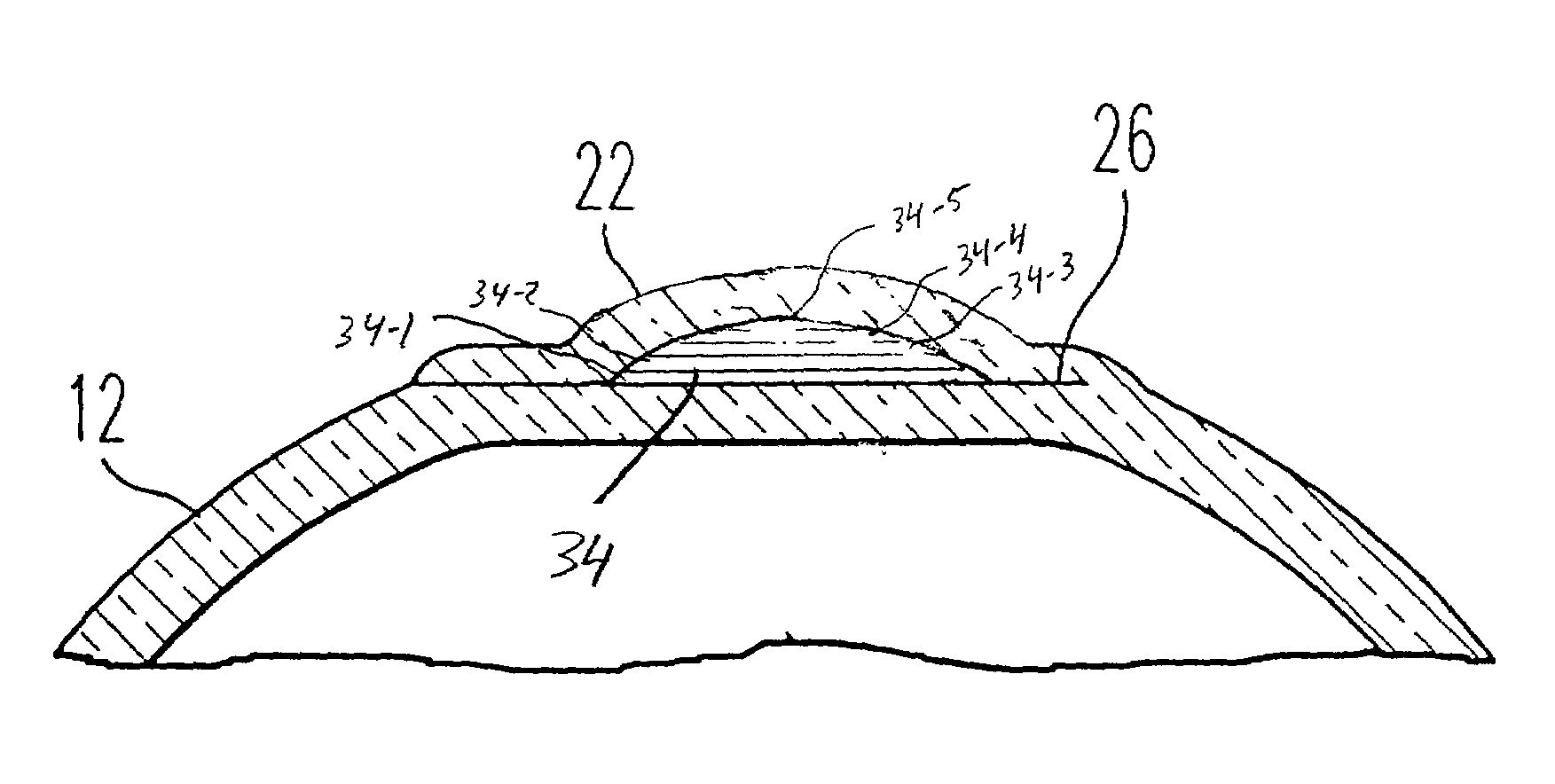
Corneal implant for refractive correction
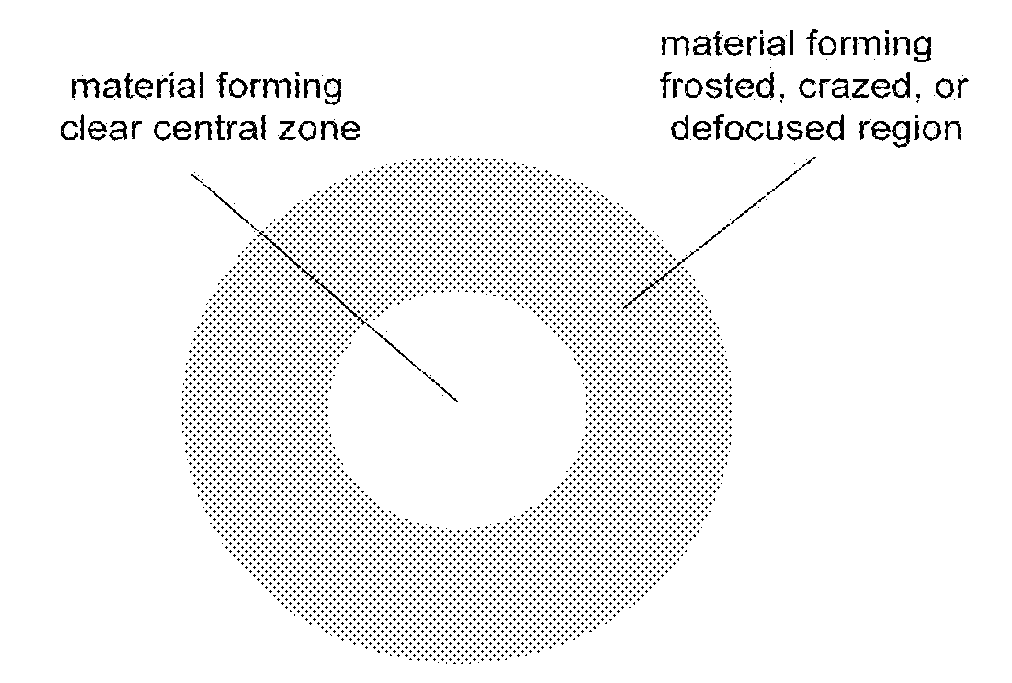
A corneal implant adapted for implantation between layers of a cornea to focus an image on a retina of an eye includes an inlay, an outer perimeter, and a clear central region capable of refracting light to compensate for a refractive error of an eye. The inlay also has an annular opaque region comprising a plurality of holes or otherwise being adapted to transport nutrients. The annular opaque region extends from the outer circumference of the inlay to the clear central portion. The opaque region extends over a minority of the surface area of the implant. The anterior and posterior surfaces of the inlay are configured to abut adjacent layers of the cornea.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
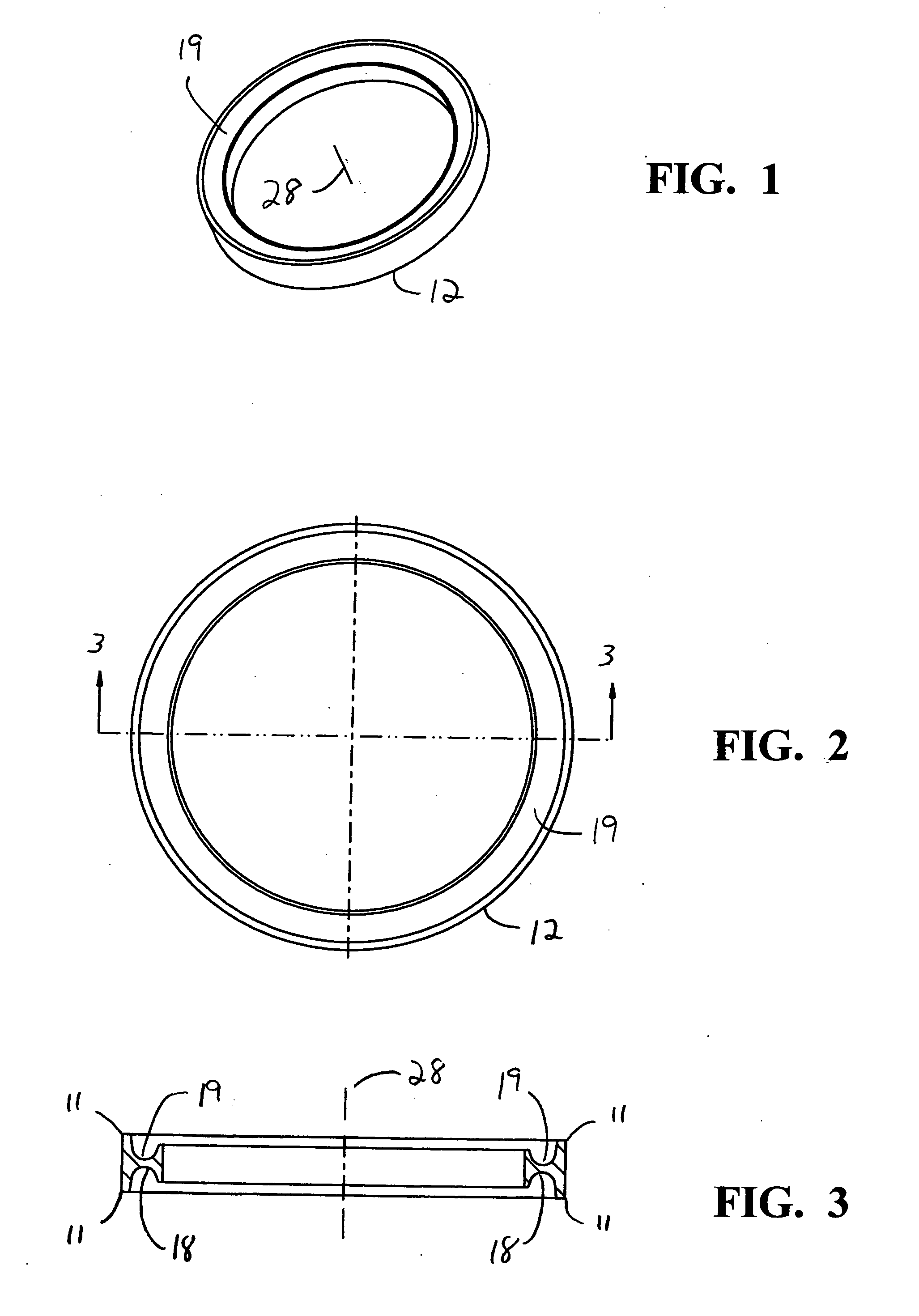
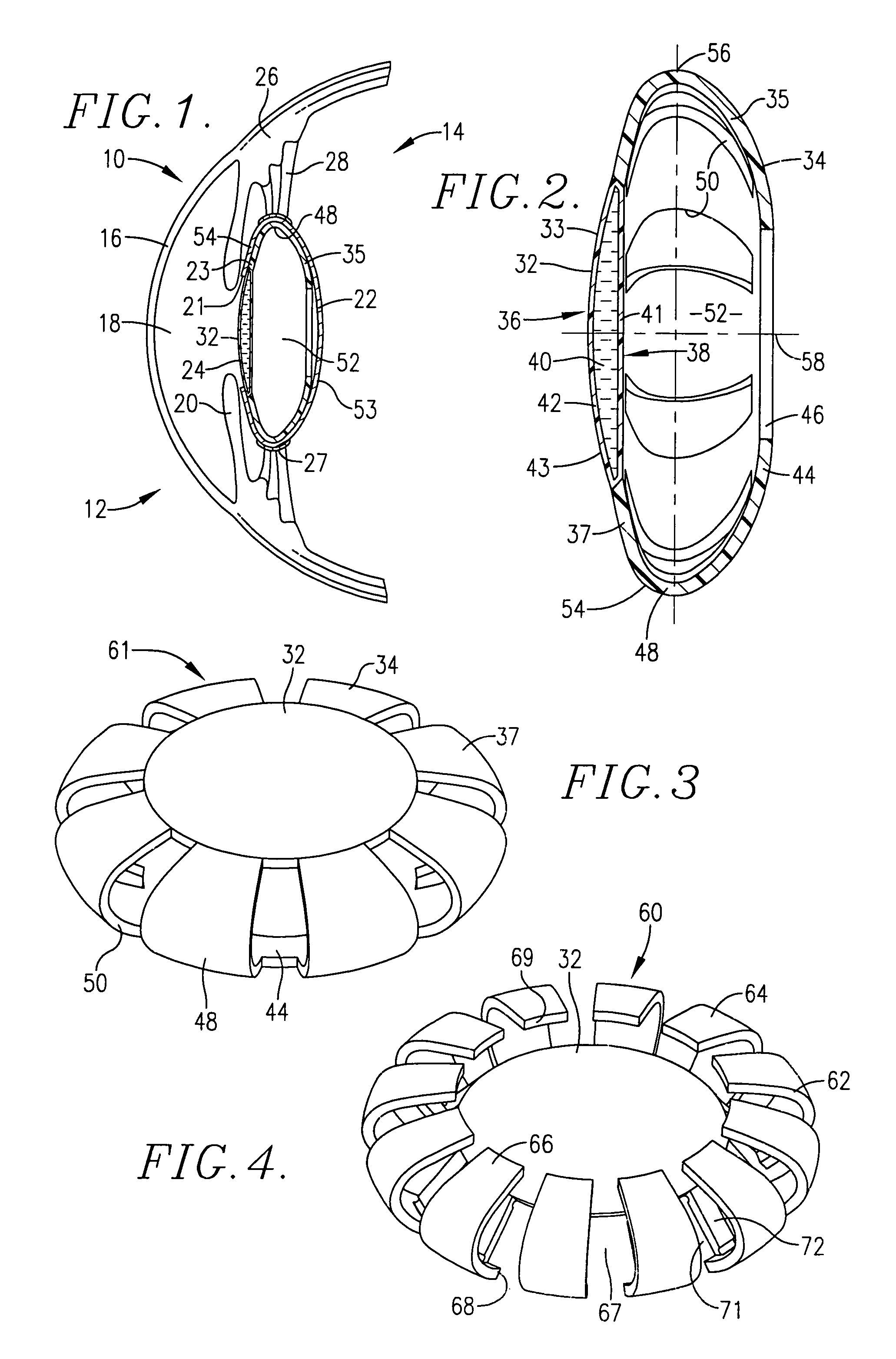
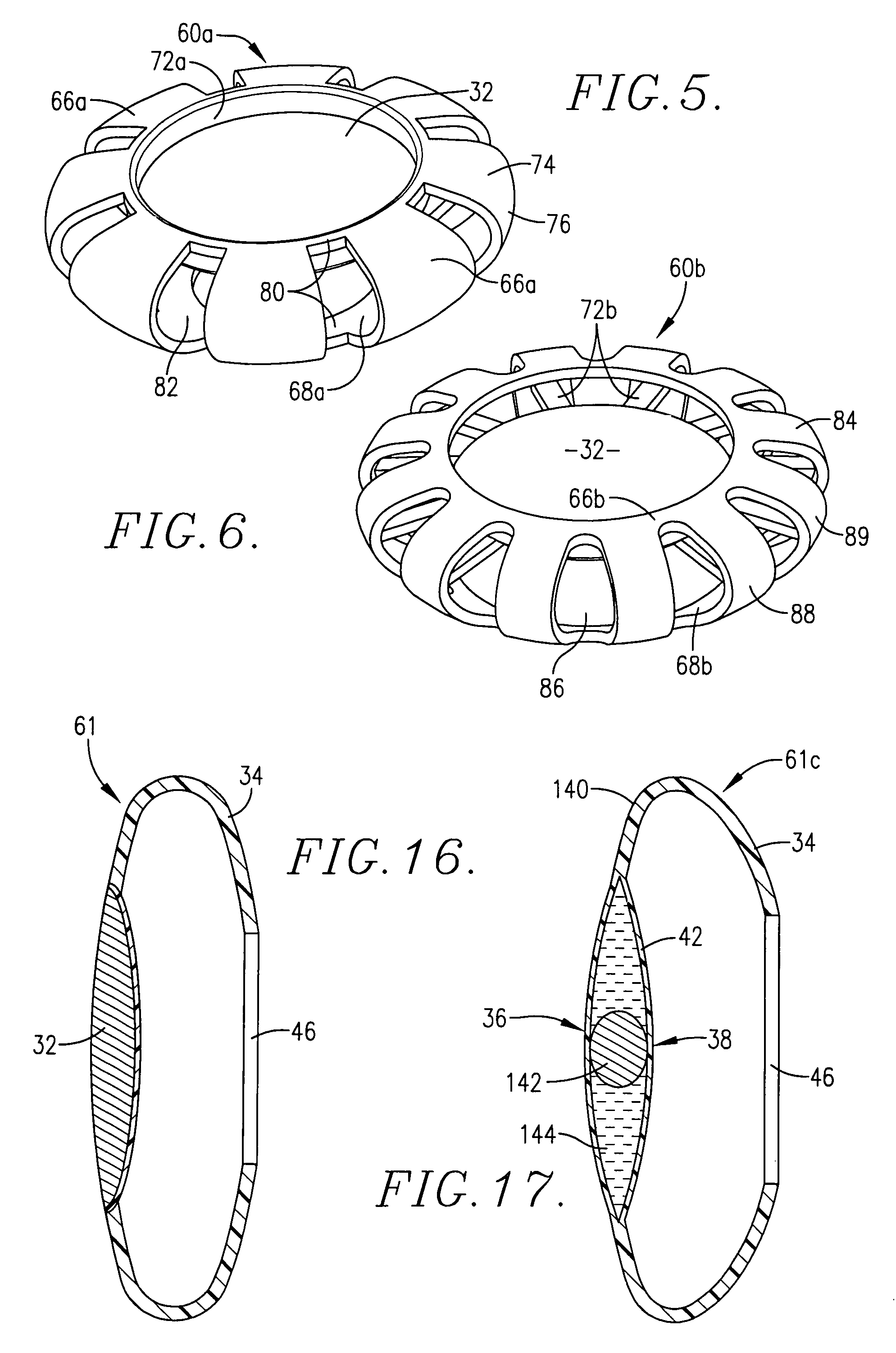
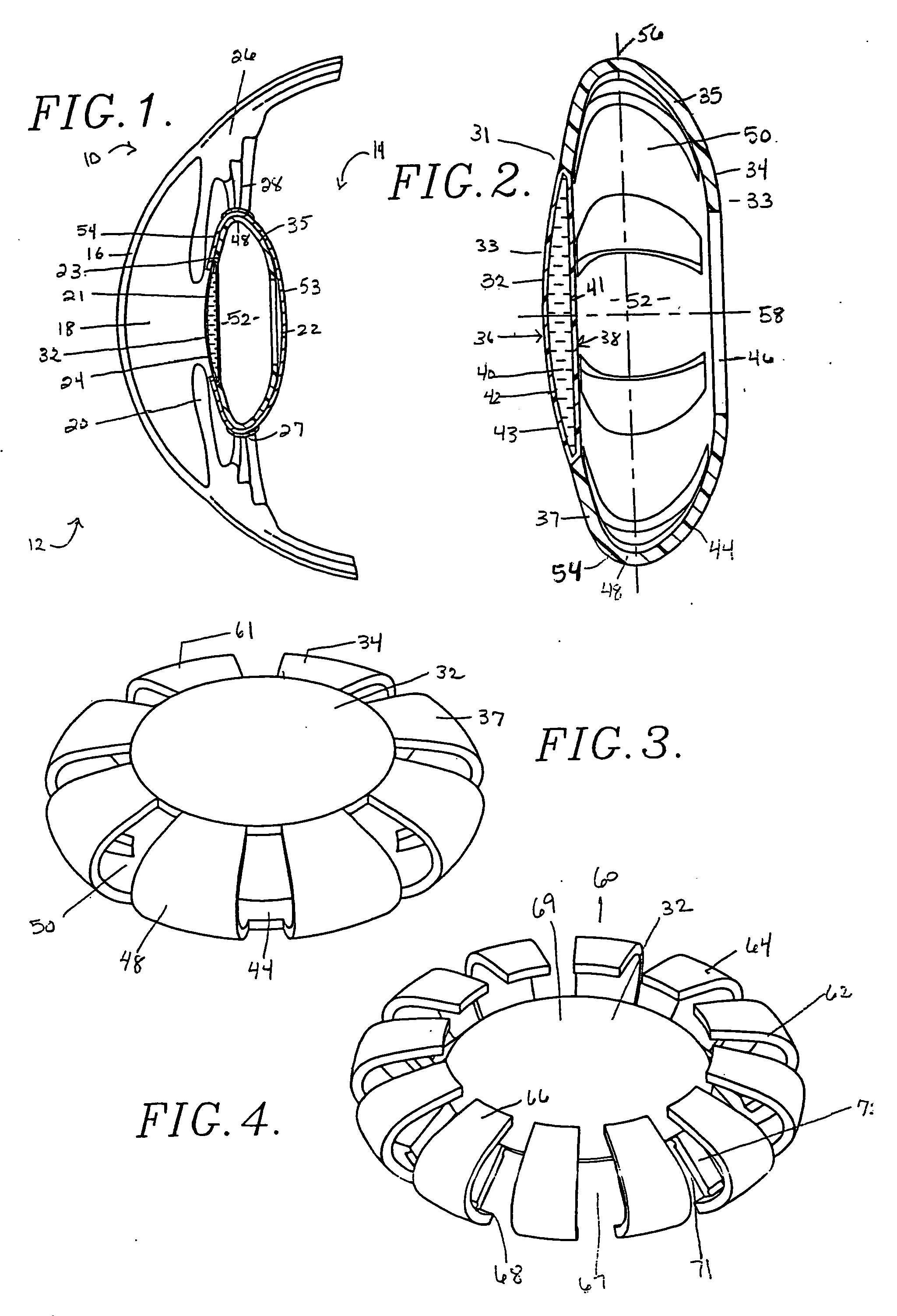
Intraocular lens
A two or three component lens system. The first component is a ring-like supporting component that is implanted in the capsular bag following cataract surgery. The first component is a non-optical component and does not correct for any refractive errors. The first component may contains features to help reduce or eliminate PCO. The second component is an optical component that may contain all of the corrective optical power of the lens system. The second component has a pair of tabs for locking the second component within the first component. The third component is optional and is similar to second component and contains some optical power to correct for any residual optical error not corrected by the second component. The second and third components may also be implanted so as to move relative to one another, thereby providing some accommodation.
Owner:ALCON INC
Intraocular lens system
A two or three component lens system. The first component is a ring-like supporting component that is implanted in the capsular bag following cataract surgery. The first component is a non-optical component and does not correct for any refractive errors. The first component may contain features to help reduce or eliminate PCO. The second component is an optical component that may contain all of the corrective optical power of the lens system. The second component has a pair of tabs for locking the second component within the first component. The first component includes a feature that allows the surgeon to change the position of the second component along the optical axis of the lens system. The third component is optional and is similar to second component and contains some optical power to correct for any residual optical error not corrected by the second component. The second and third components may also be implanted so as to move relative to one another, thereby providing some accommodation.
Owner:ALCON INC
Method and apparatus for controlling peripheral image position for reducing progression of myopia
ActiveUS7665842B2Improve visual effectsGood and useful visionSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryRefractive errorCentral vision
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
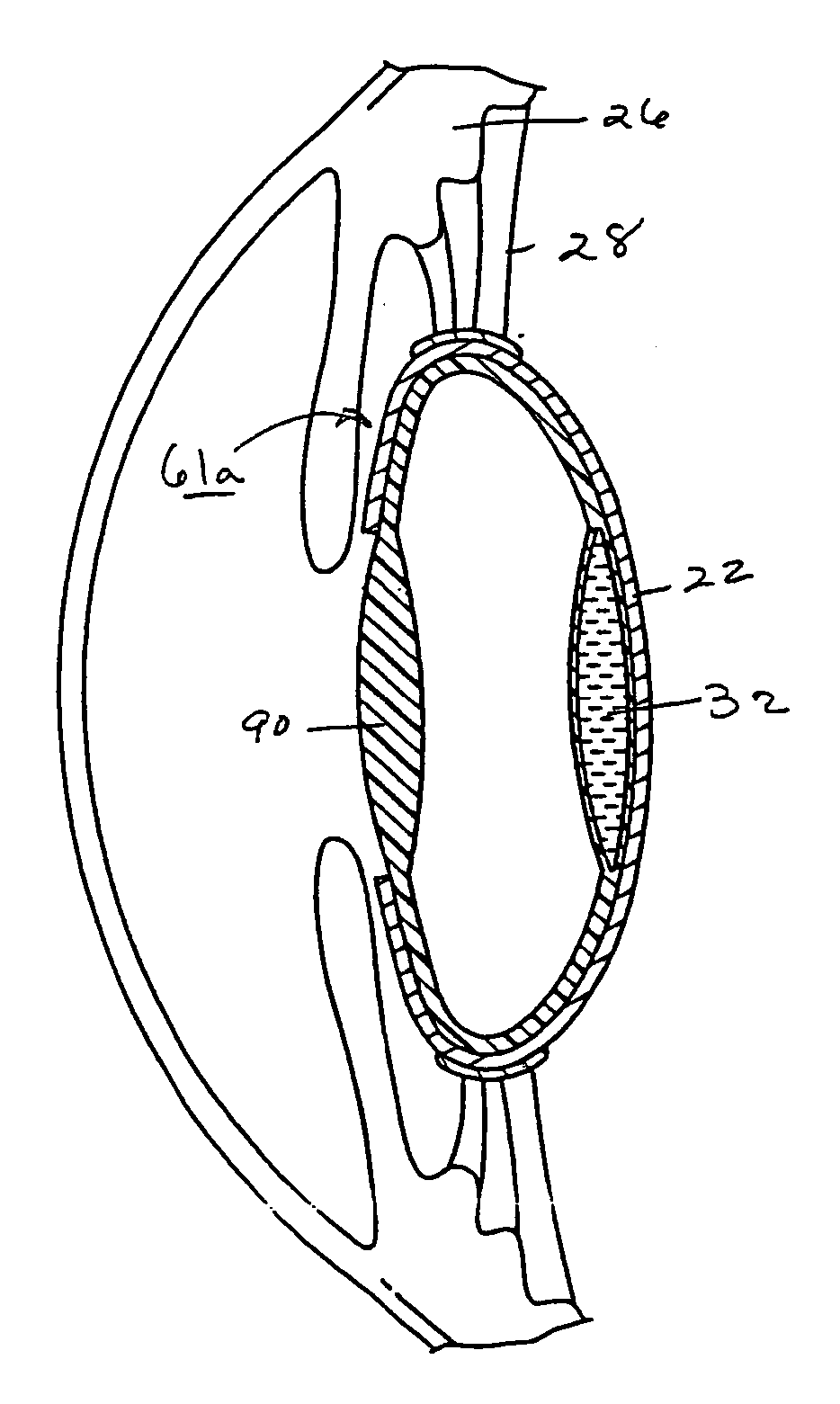
Capsular intraocular lens implant having a refractive liquid therein
InactiveUS8052752B2Long-term use safetyTreatment safetyIntraocular lensRefractive errorRefractive index
Owner:ABBOTT MEDICAL OPTICS INC
Capsular intraocular lens implant having a refractive liquid therein
An intraocular lens having a light-transmitting optic (32, 94a, 94b, 142, 216) comprised of a synthetic light-refractive material (40, 102) operably coupled with a flexible optic positioning member (34, 62, 74, 84, 100, 210) to refract light onto the retina in order to correct refractive errors in the eye (10). The refractive material has an index of refraction of from about 1.36 to 1.5 or higher. The optic positioning member (34, 62, 74, 84, 100, 210) is constructed of a flexible synthetic resin material such as polymethylmethacrylate and permits focusing upon objects located near to and far from the viewer. The optic (32, 94a, 94b, 142, 216) of the present invention possess greater refractive capability than optics conventionally used in IOL construction, and permits retinal receipt of the image being viewed in order to correct refractive errors.
Owner:ADVANCED MEDICAL OPTICS
Method and apparatus to correct refractive errors using adjustable corneal arcuate segments
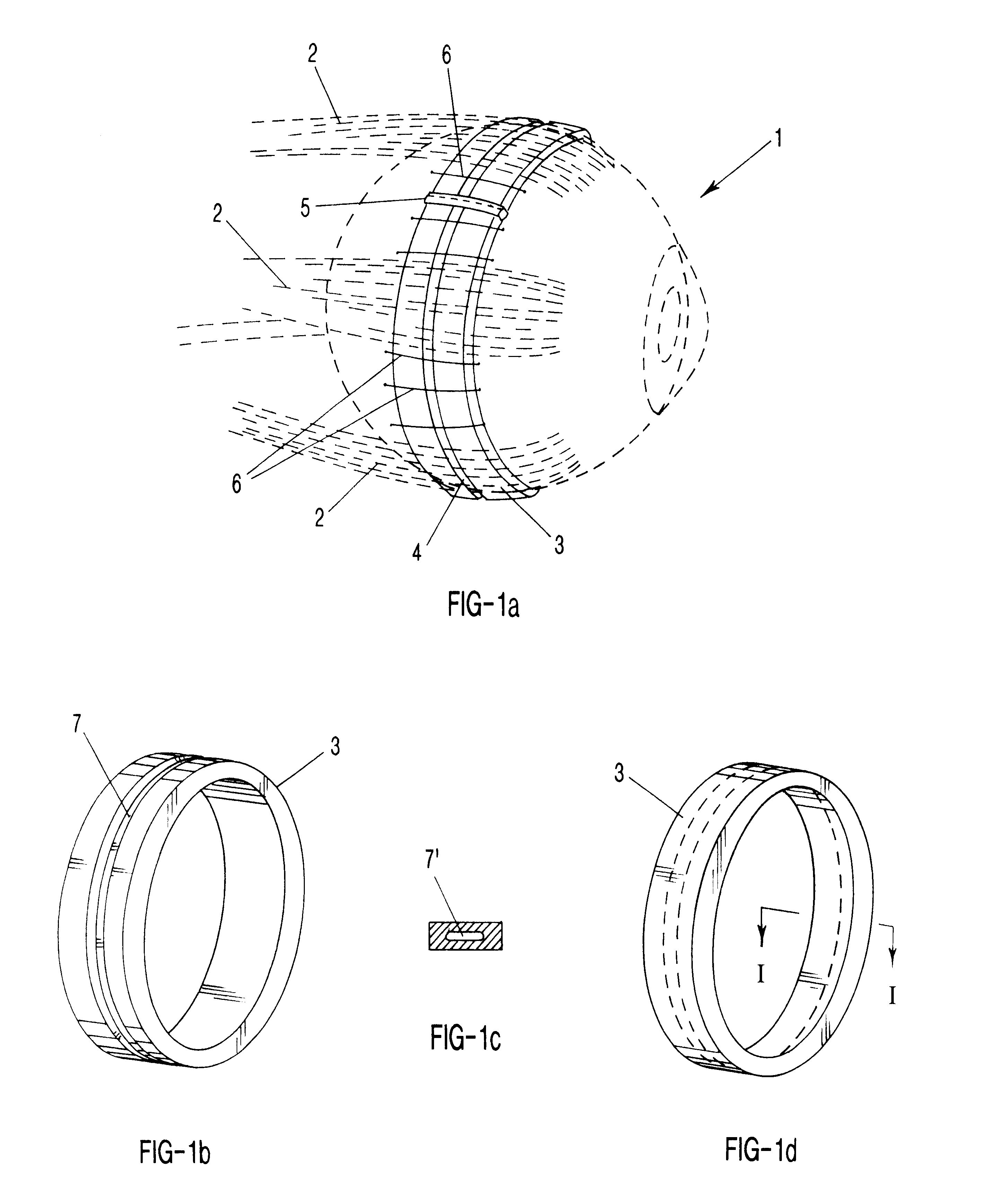
InactiveUS6206919B1Steepening of corneal curvatureEasy to modifyEye implantsCorneal curvatureRefractive error
A method and apparatus for adjusting corneal curvature of the eye comprising an adjustable corneal arcuate segment or segments which is implantable into the cornea. The arcuate segment is a flexible hollow shell composed of a synthetic or a natural material, with an annular chamber that is filled with a predetermined amount of a biocompatible material. The corneal curvature is adjusted by removing or augmenting the predetermined amount of biocompatible material contained in the arcuate segment.
Owner:LEE JOSEPH Y
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors by active composite artificial muscle implants
Correction of eye refractive errors such as presbyopia, hyperopia, myopia, and astigmatism by using either pre-tensioned or transcutaneously energized artificial muscle implants to change the axial length and the anterior curvatures of the eye globe by bringing the retina / macula region to coincide with the focal point. The implants are scleral constrictor bands, segments or ribs for inducing accommodation of a few diopters, to correct the refractive errors on demand or automatically. The implant comprises an active sphinctering band encircling the sclera, implanted under the conjunctiva and under the extraocular muscles to uniformly constrict the eye globe, to induce active temporary myopia (hyperopia) by increasing(decreasing) the length and curvature of the globe. Multiple and specially designed constrictor bands enable surgeons to correct astigmatism. The artificial muscles comprise materials such as composite magnetic shape memory (MSM), heat shrink, shape memory alloy-silicone rubber, electroactive ionic polymeric artificial muscles or electrochemically contractile ionic polymers bands.
Owner:OPHTHALMOTRONICS
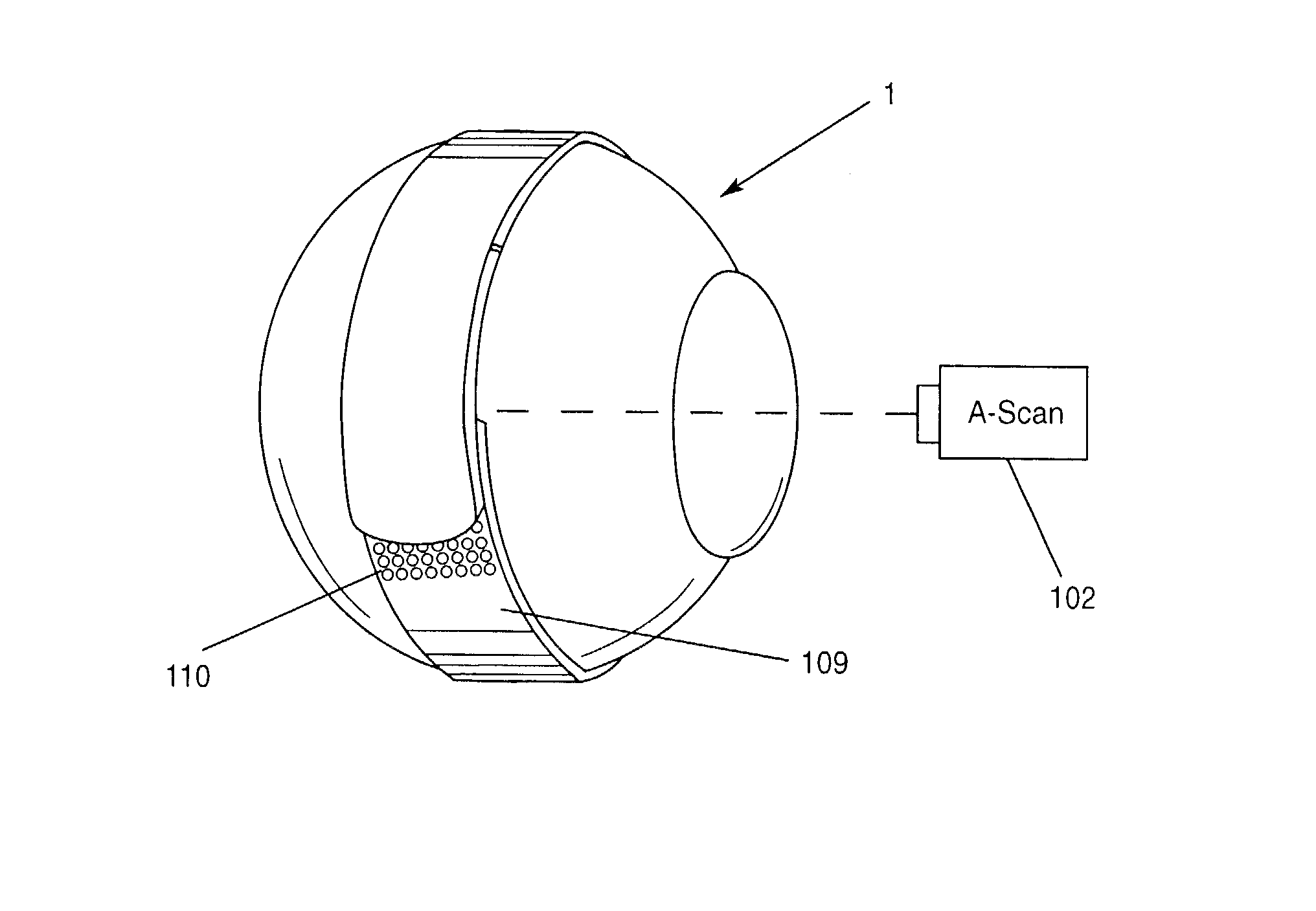
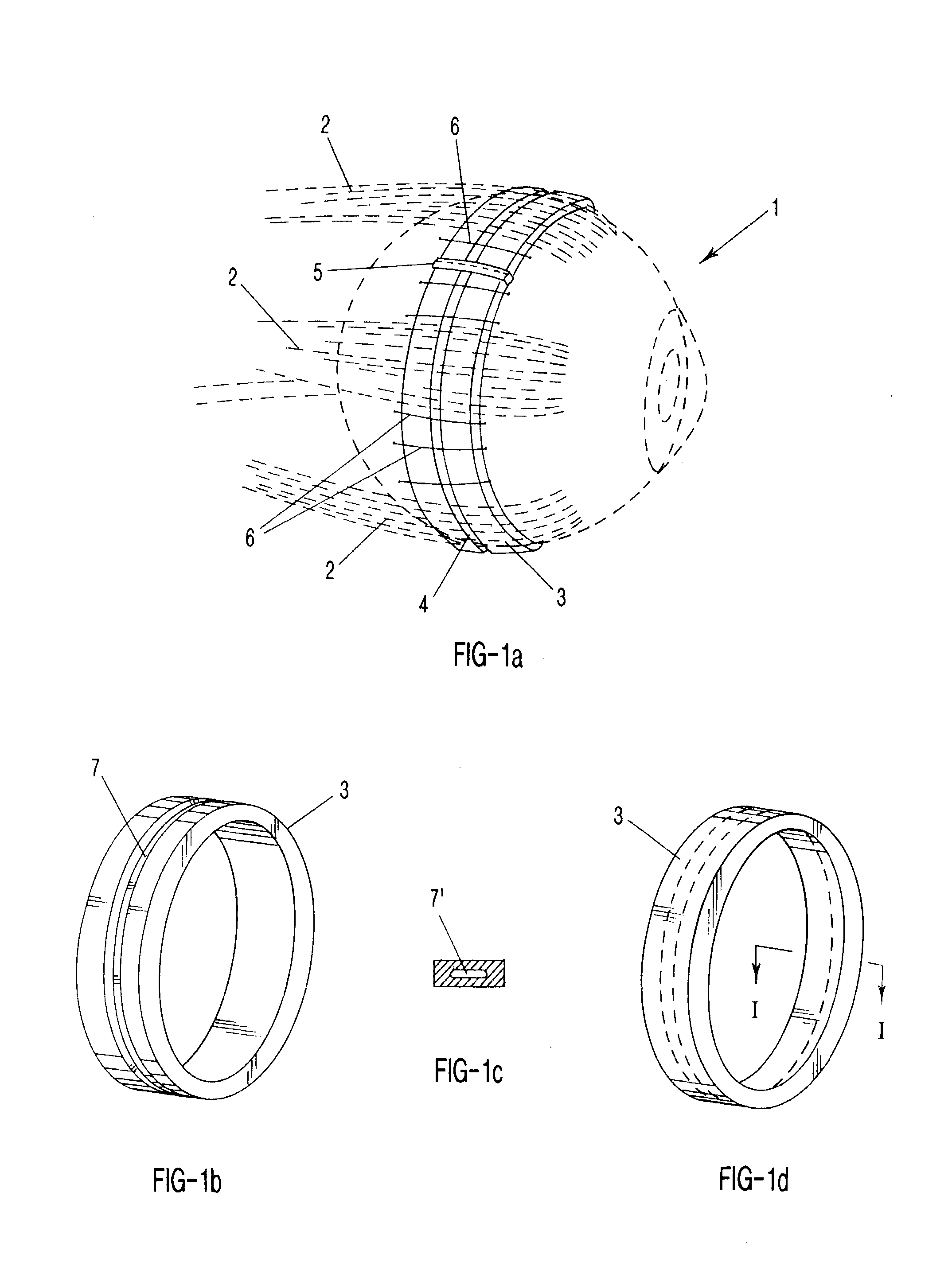
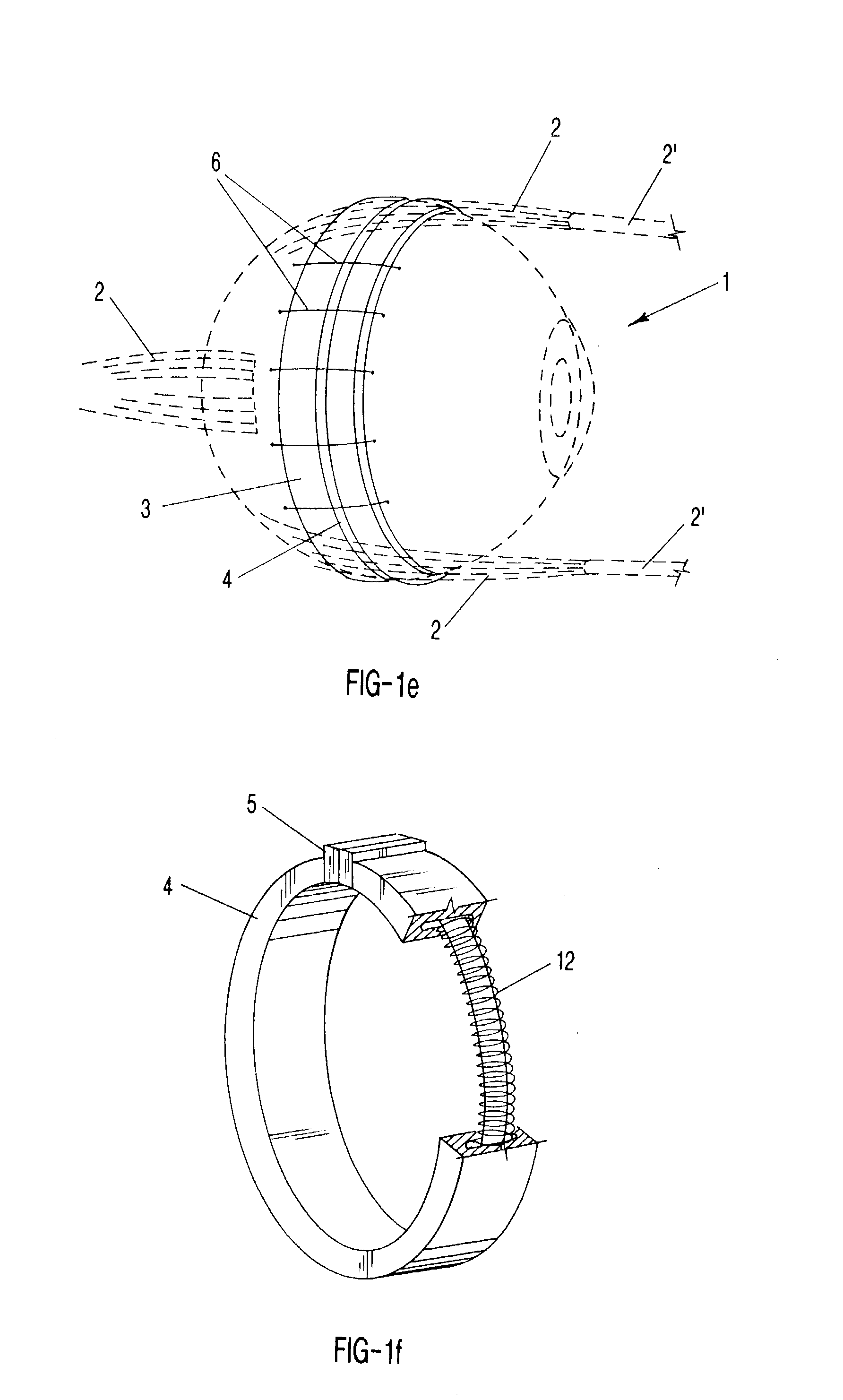
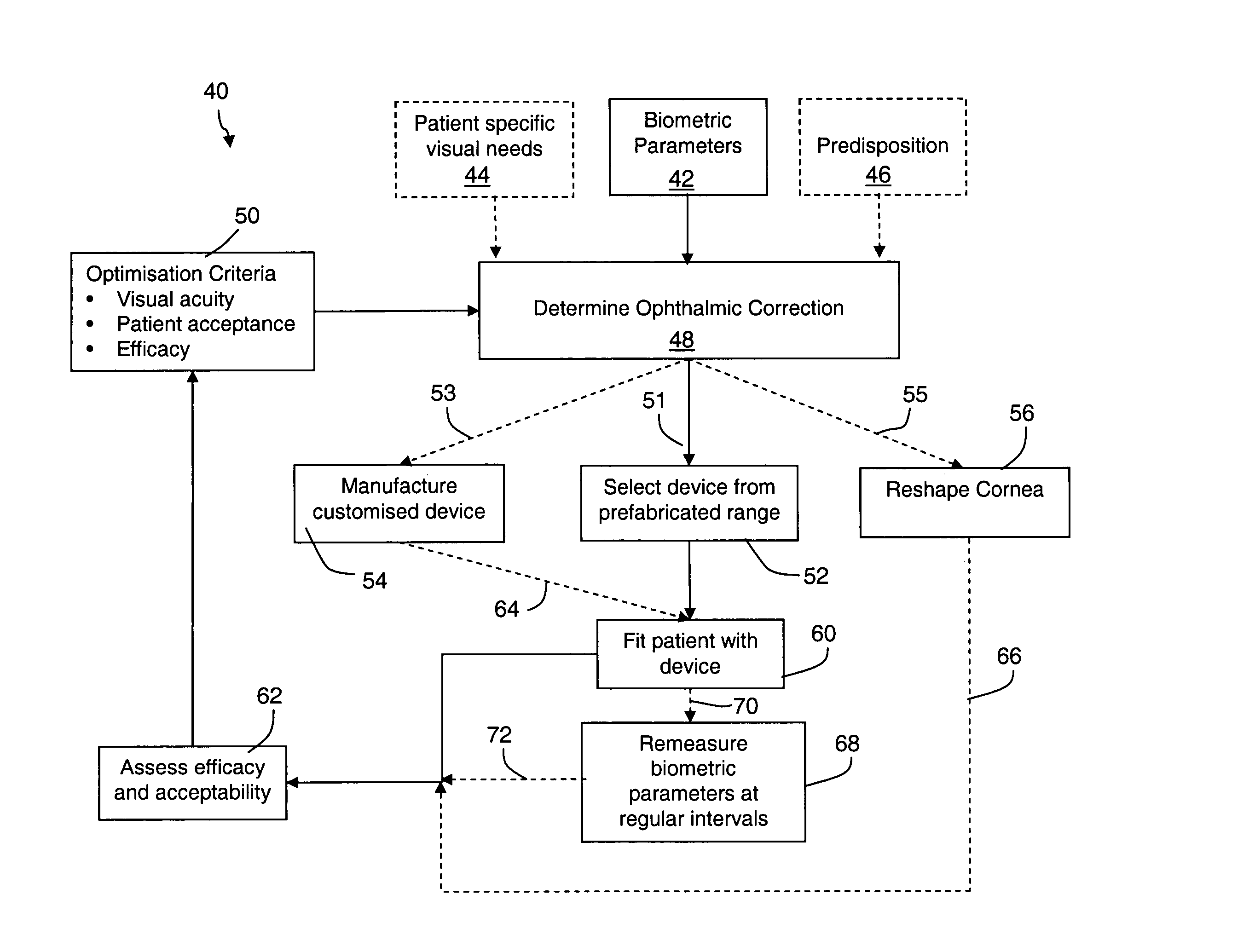
Determination of optical adjustments for retarding myopia progression
A method or process for providing an anti-myopia lens or treatment for a patient's eye with progressive myopia, which involves (in one form) generating biometric data relating to the central and peripheral refractive errors of the eye, optionally together with data relating to the patient's visual or lifestyle needs and the patient's predisposition to progressive myopia. This data is input to a processor or algorithm that generates a basic lens design, a customised design or a program for reshaping the cornea of the eye. The selected modality is applied to the patient and its suitability is assessed with the result of the assessment feedback to the algorithm to generate a refined output design, which is applied to the patient. The process is repeated at intervals to check continued myopia progression and adjust the design of the selected modality after further measurement.
Owner:INST FOR EYE RES
Image display device and image display method
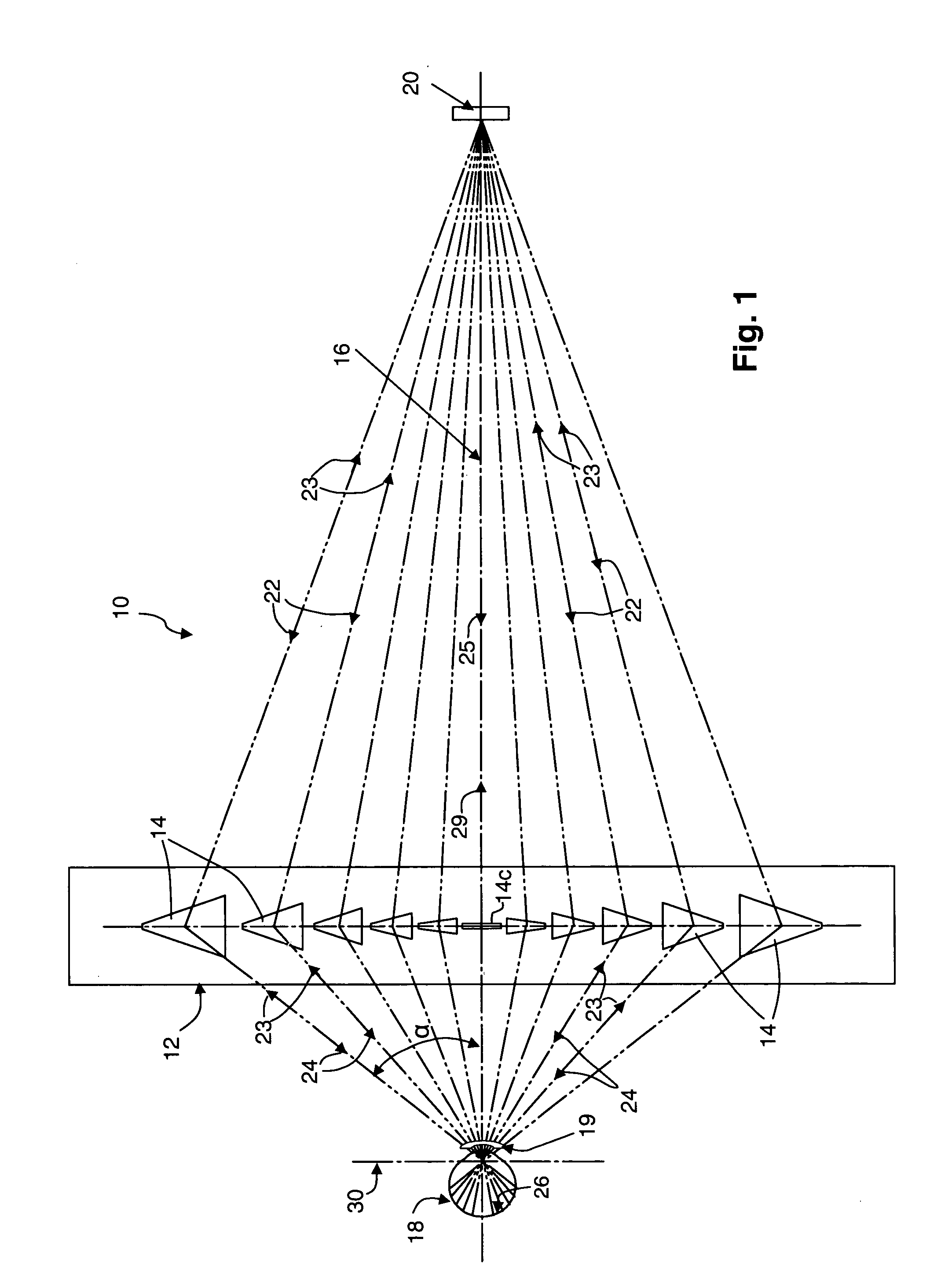
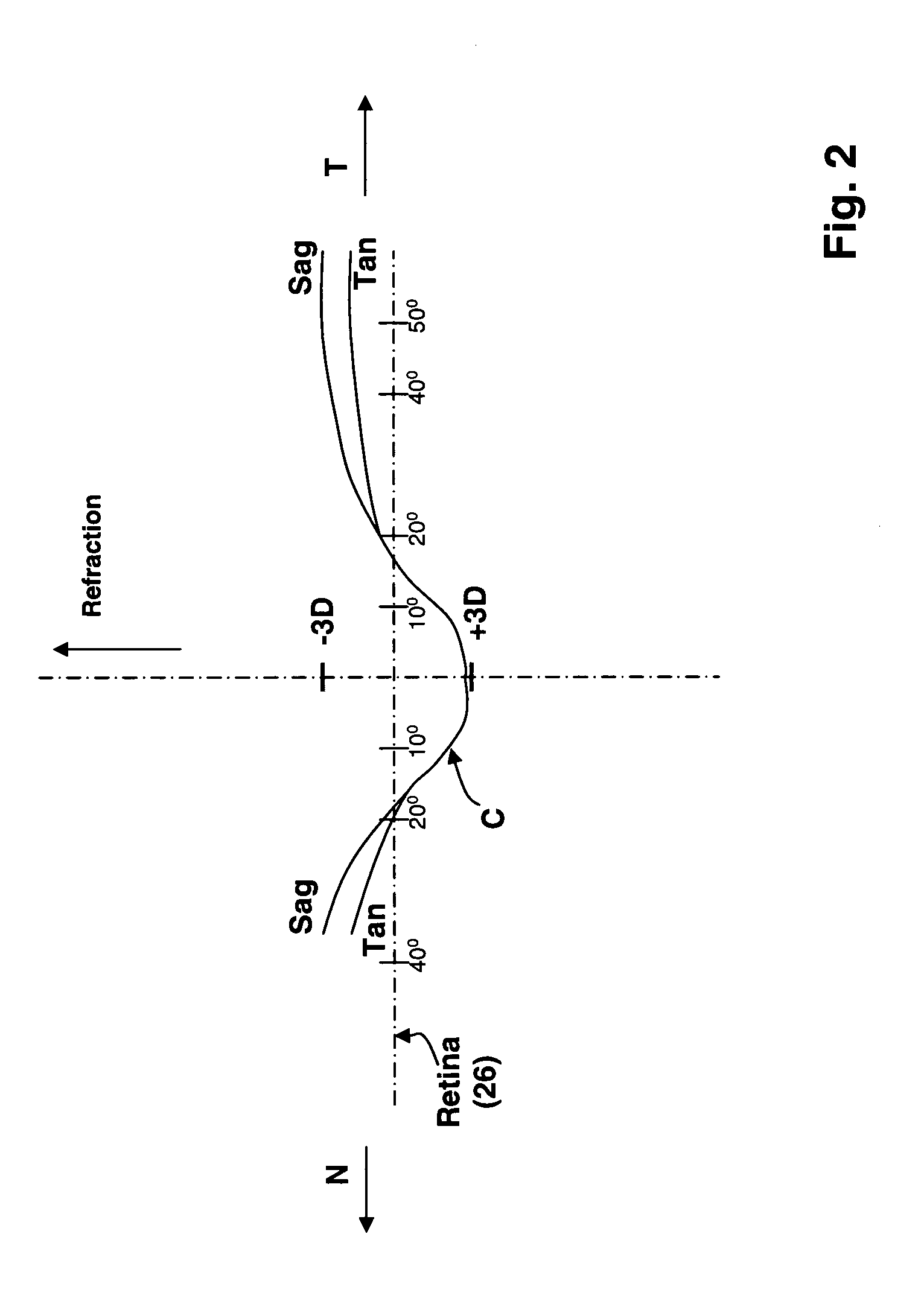
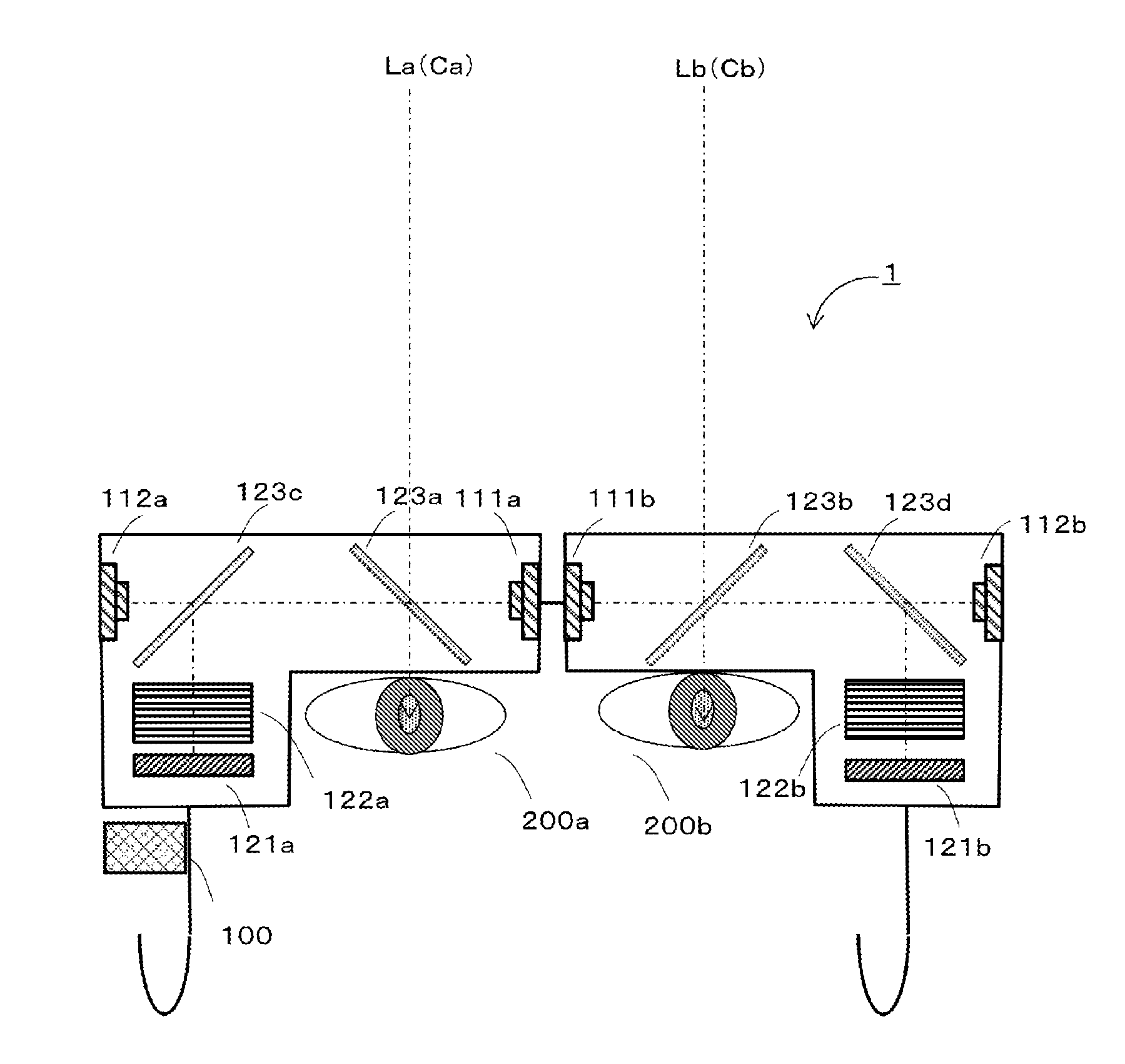
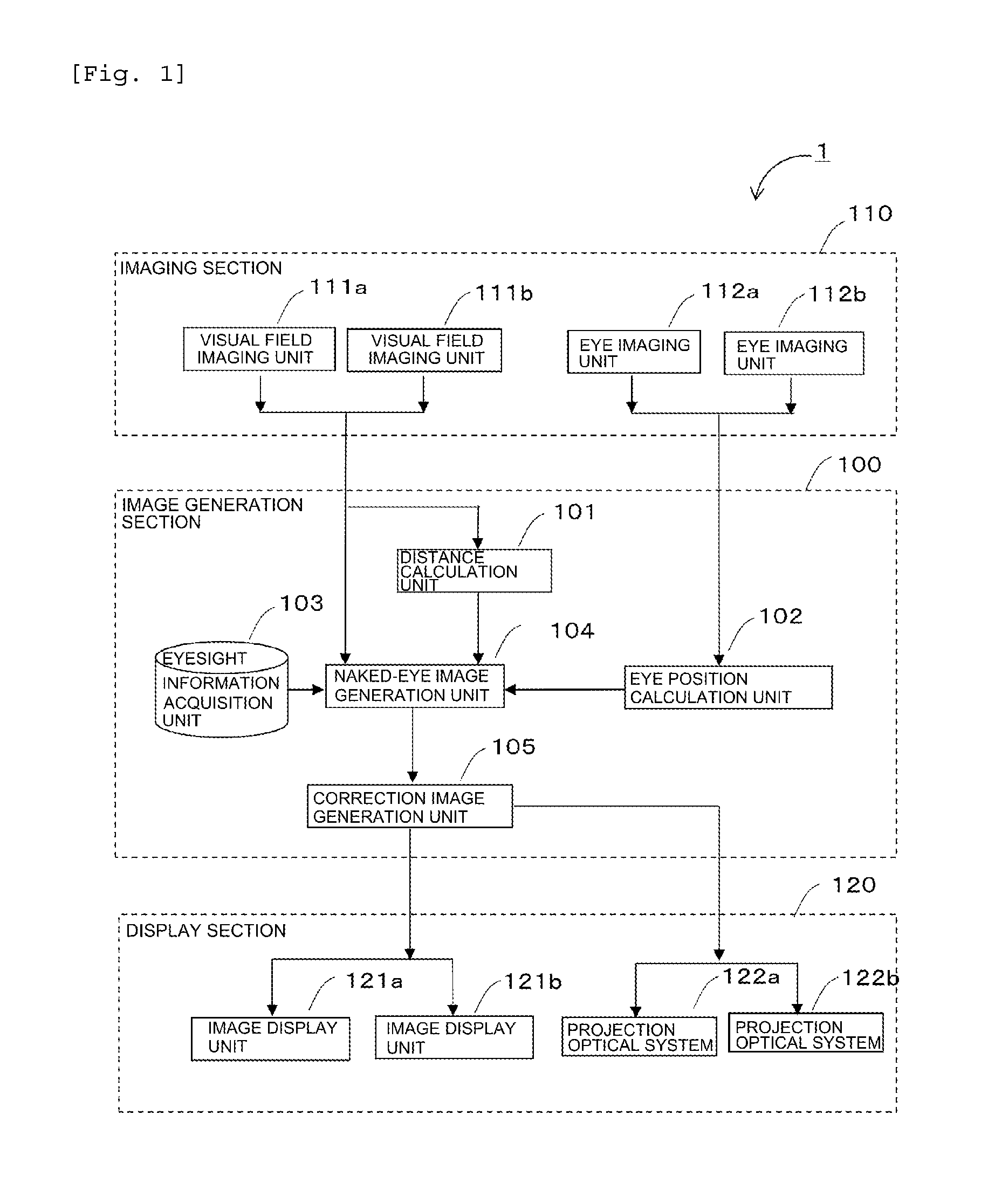
This invention solves the problem that objects in the field of view of reading glasses using multifocal lenses for correcting ocular refractive errors such as presbyopia appear distorted. This image display device is provided with the following: a distance computation unit that computes the distance to a subject in a field-of-view image; a visual-acuity-information acquisition unit that stores visual-acuity information for the user in advance; a corrected-image generation unit that generates and outputs a corrected image on the basis of the field-of-view image and an eye image generated from the field-of-view image, the distance information, and the visual-acuity information; and a display unit that displays the corrected image by superimposing same onto the user's field of view. Since the corrected image is superimposed without the use of lenses, lenses being the cause of the abovementioned distortion, the user can see close objects clearly.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Method of preventing the induction of aberrations in laser refractive surgery systems
InactiveUS20070038202A1Simple technologyImprove optical qualityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsNear sightednessVisual perception
The invention relates to a method of preventing the induction of aberrations in laser refractive surgery systems. Standard laser refractive surgery systems successfully correct low-order refractive errors (myopia, hypermetropia and astigmatism), but induce spherical aberration and, by extension, other high-order aberrations, which result in a worsening of vision quality. Said increase in spherical aberration is due to the shape of the cornea, and not inherent in the theoretical ablation profile, and, as a result, the problem is, in principle, common to all laser systems. The invention relates to a systematic method which can be used with any system and ablation profile in order to obtain a profile correction factor. The correction factor, which is specific to each system, can be applied in order to prevent the induction of spherical aberration and, in this way, improve the optical and visual quality of patients following surgery compared to surgery performed with standard systems. Moreover, the inventive method can be used to improve the production of lenses with controlled high-order aberrations using laser systems.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC)
Corneal remodelling contact lenses and methods of treating refractive error using corneal remodelling
InactiveUS20120320334A1Enhanced ability to affect progression of myopiaConvenient treatmentSpectales/gogglesEye treatmentRefractive errorRefraction errors
Contact lenses are described with a corneal remodelling effect. This corneal remodelling effect is one or both of broad-area corneal remodelling and localised remodelling. The contact lenses may also have a refractive power. The refractive power may vary across the lens and for myopia may have increased power centrally. The increased power may be provided over a lens area that has increased thickness due to localised remodelling.
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
High performance corneal inlay
A corneal inlay protects ocular structures from harmful wavelengths of light while maintaining acceptable color cosmetics, color perception, overall light transmission, photopic vision, scotopic vision, color vision, and / or cirdadian rhythms. The corneal inlay can also include a pinhole effect to increase depth of focus. In some embodiments, the corneal inlay can also correct refractive errors including, but not limited to, higher order aberration, lower order aberration, myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and / or presbyopia.
Owner:HIGH PERFORMANCE OPTICS
Method of reshaping the cornea by controlled thermal delivery
InactiveUS6918904B1Avoid and eliminate outwardbulgingAvoid and eliminate and instabilityLaser surgerySurgical instruments for heatingRefractive errorMedicine
A method of correcting the refractive error in the cornea of an eye. The cornea is heated, to loosen the molecules therein, thereby softening the cornea into a gelatinous material. The gelatinous material is then reshaped, so that it substantially conforms to a predetermined pattern, and cooled to maintain it in the predetermined pattern. This results in modification of the cornea without a gray to white response in the cornea and corneal tissue shrinkage.
Owner:MINU
Adjustable ablatable inlay
InactiveUS6989008B2Accurate separationAvoid and eliminate outbulgingLaser surgeryEye implantsRefractive errorOptical axis
A method of modifying a cornea of an eye to reduce refractive error, the cornea having a surface and a main optical axis, including the steps of aiming and firing a laser at the cornea of the eye. The laser first separates an internal portion of the cornea forming a first internal surface and a second internal surface, the first internal surface facing in a posterior direction of the cornea and the second internal surface facing in an anterior direction of the cornea, with the first and second internal surfaces forming an internal pocket therebetween. An incision is then made from the surface of the cornea to the internal pocket, and an ocular implant is introduced through the incision and into the internal pocket of the cornea.
Owner:ACUFOCUS +1
Optical diagnosis using measurement sequence
Devices, systems, and methods that facilitate optical analysis, particularly for the diagnosis and treatment of refractive errors of the eye. An optical diagnostic method for an eye includes obtaining a sequence of aberration measurements of the eye, identifying an outlier aberration measurement of the sequence of aberration measurements, and excluding the outlier aberration measurement from the sequence of aberration measurements to produce a qualified sequence of aberration measurements. The sequence of aberrations measurements can be obtained by using a wavefront sensor. An optical correction for the eye can be formulated in response to the qualified sequence of aberration measurements.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Eye treatment
The present invention relates to a method of determining the IOL refractive index for an ocular replacement material for replacing tissue in the capsular bag comprising combining a neutral (non-correcting) reference refractive index (“NRRI”) of between 1.421 and 1.450 with a refractive index correction factor (“RICF”) ascertained by reference to the refractive power required to correct the patient's refractive error. The present invention also relates to methods of treating presbyopia, myopia and hyperopia using the above method.
Owner:THE VISION CRC LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com