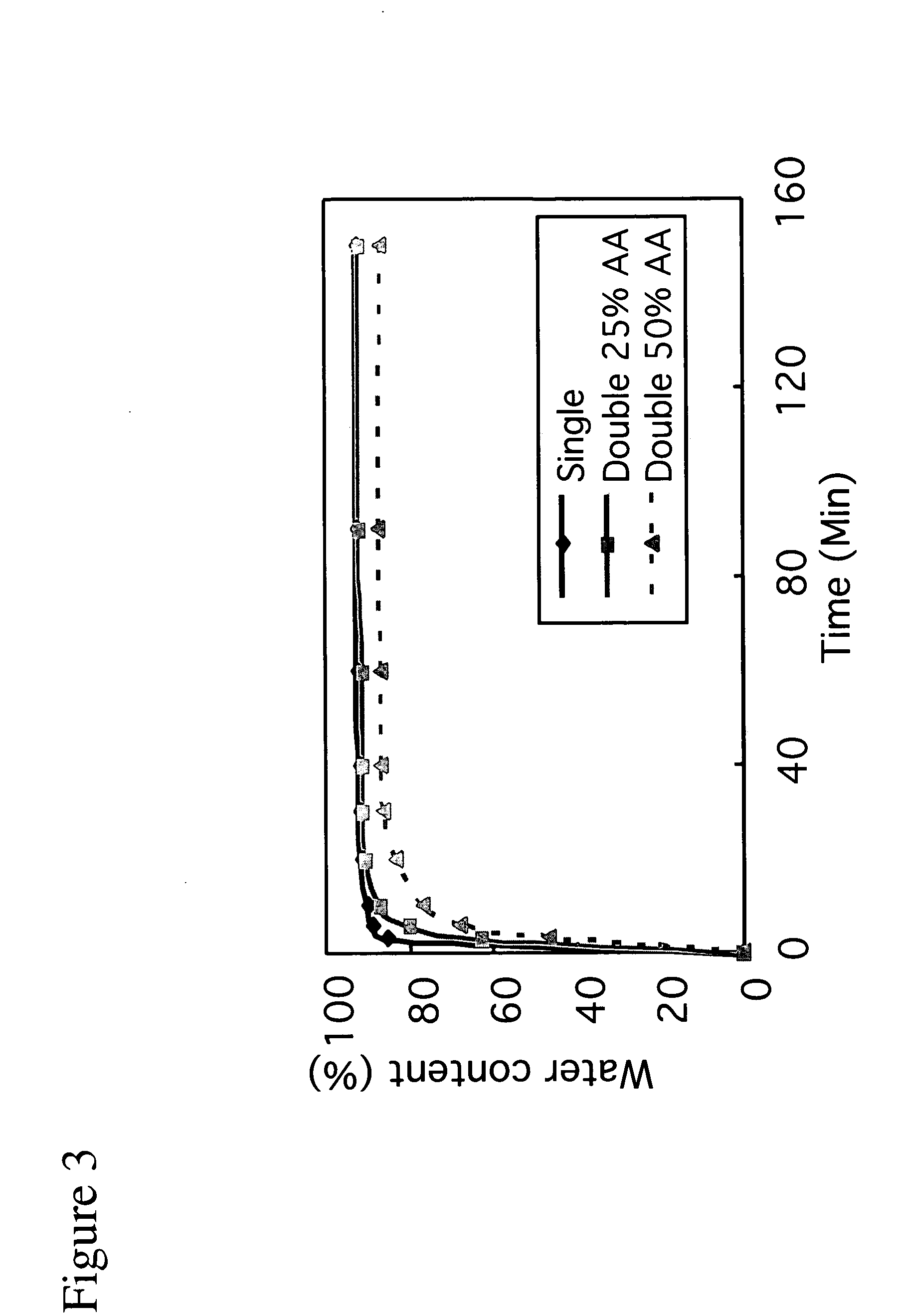
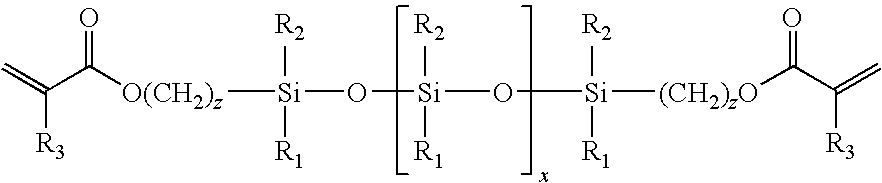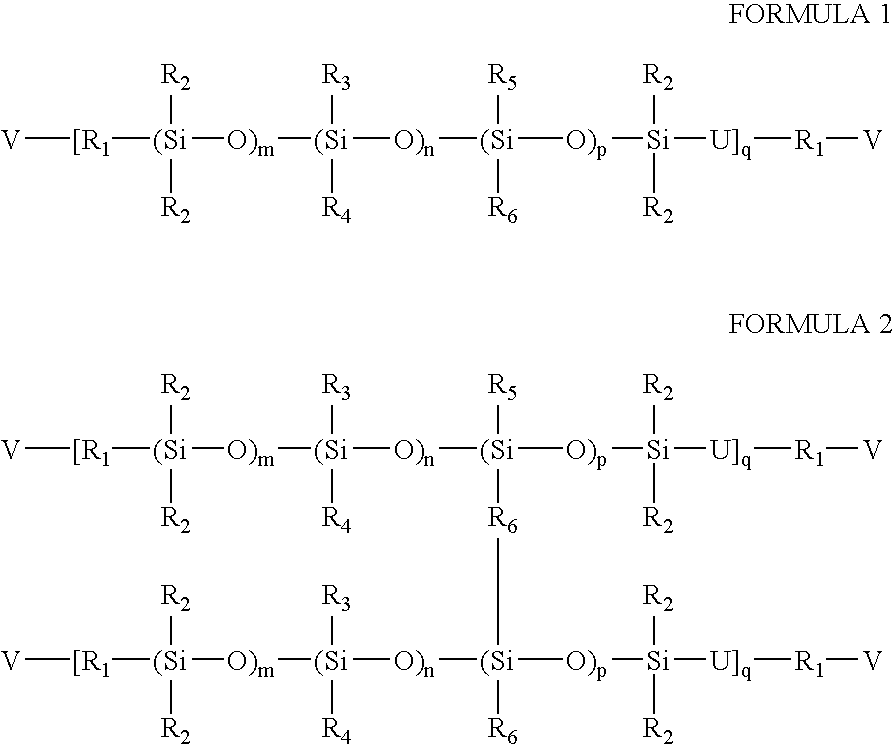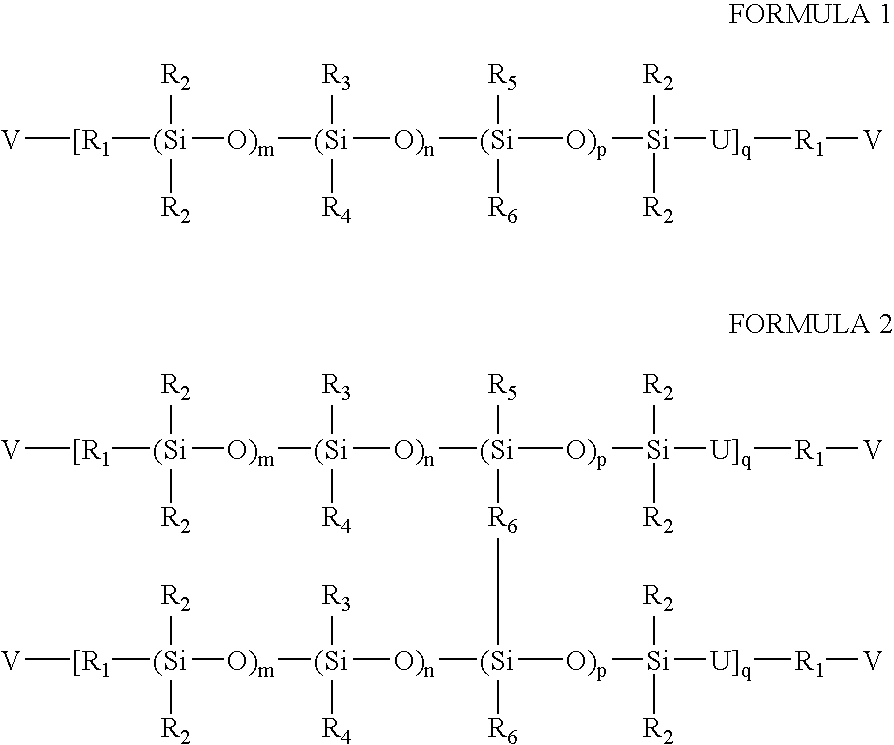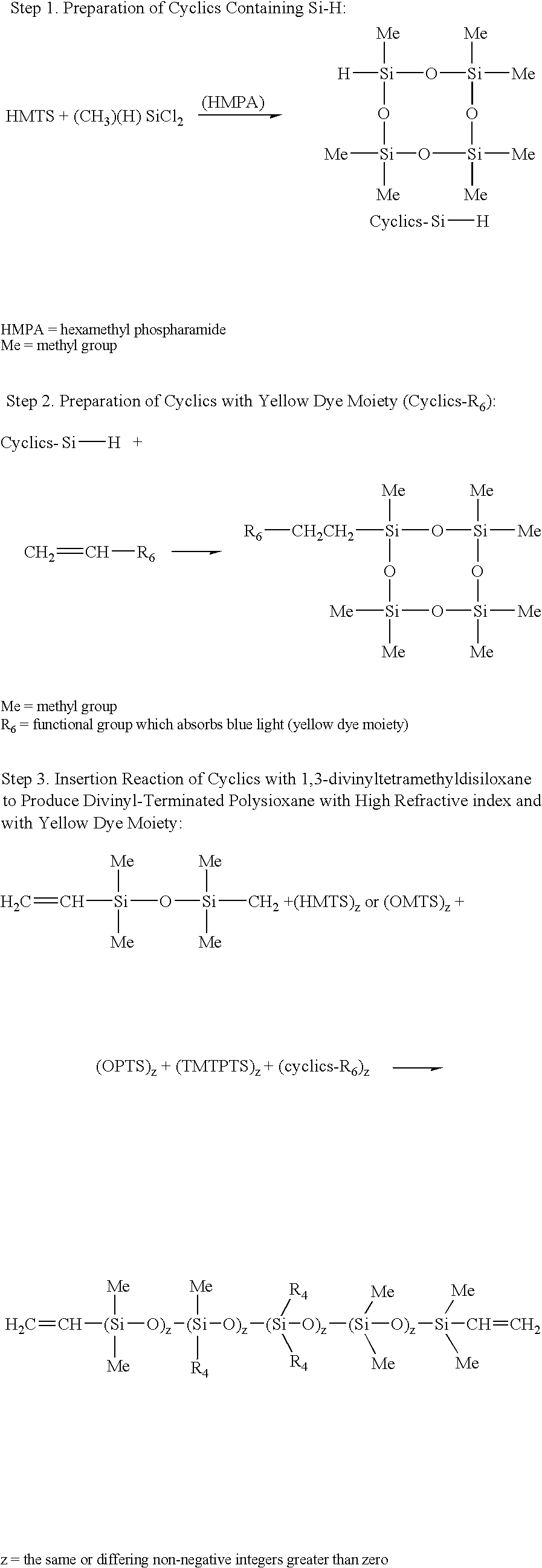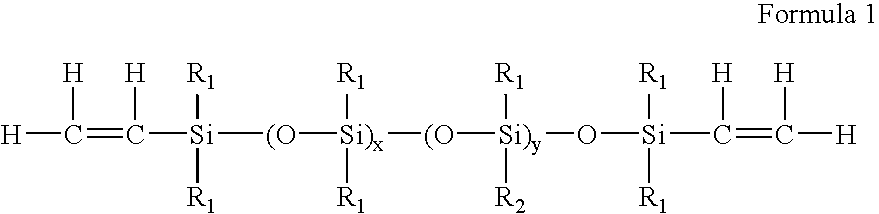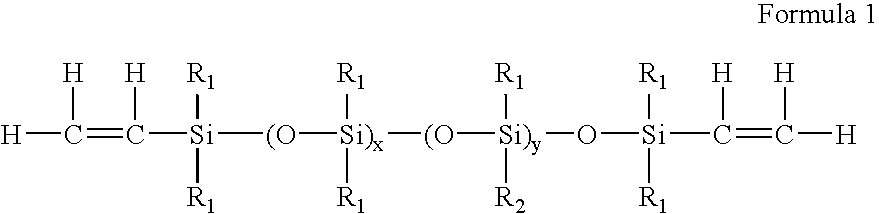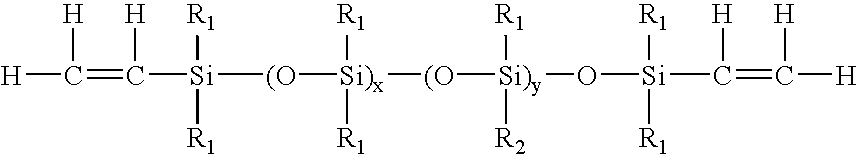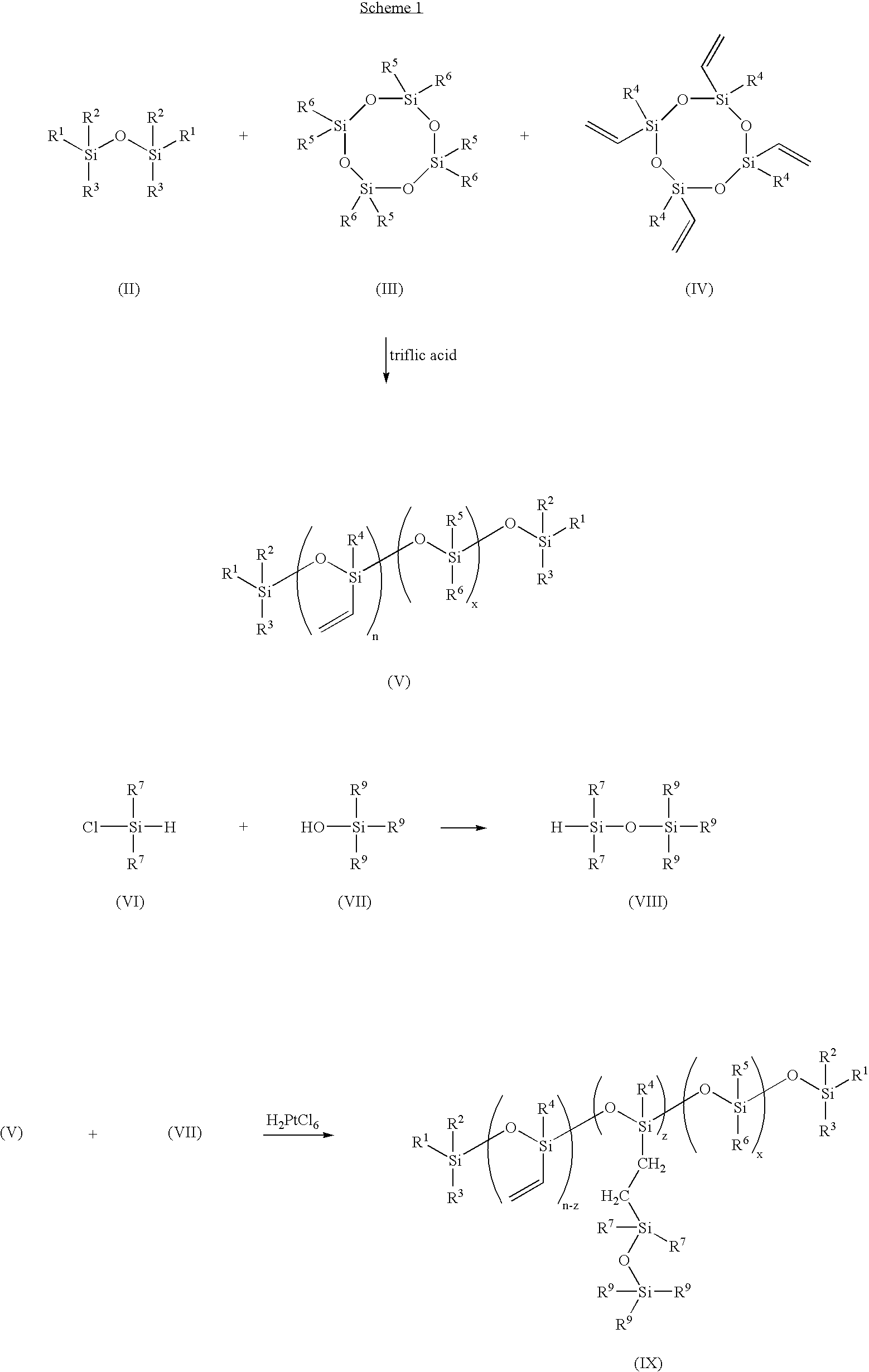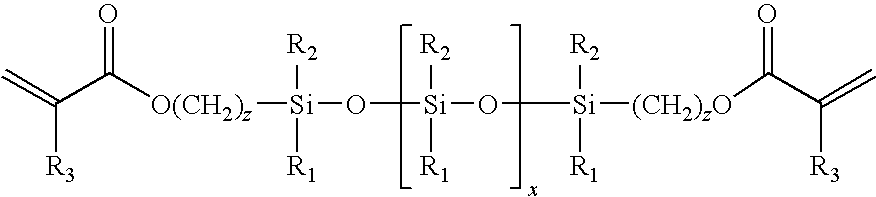Patents
Literature
65 results about "Corneal inlay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
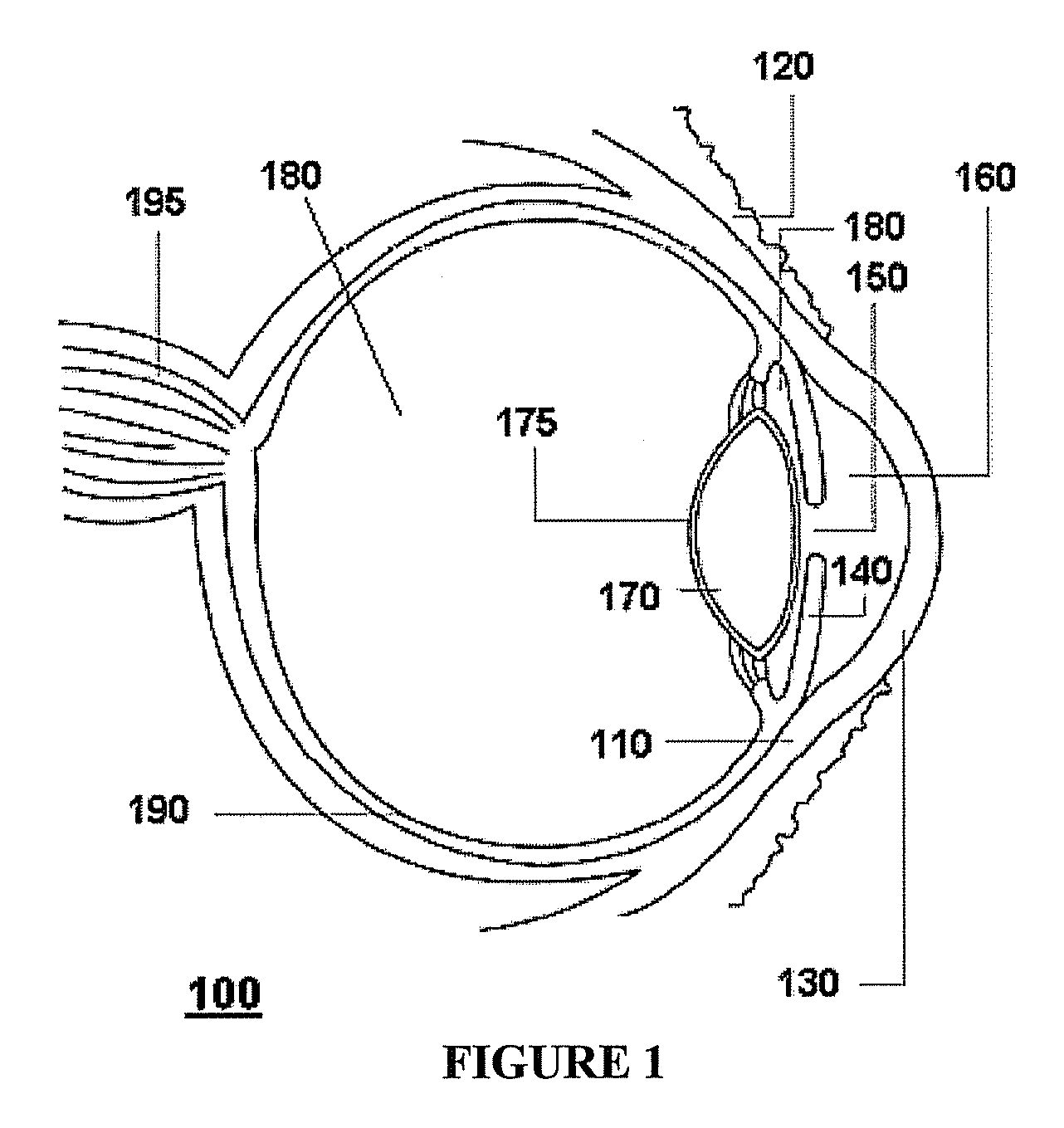
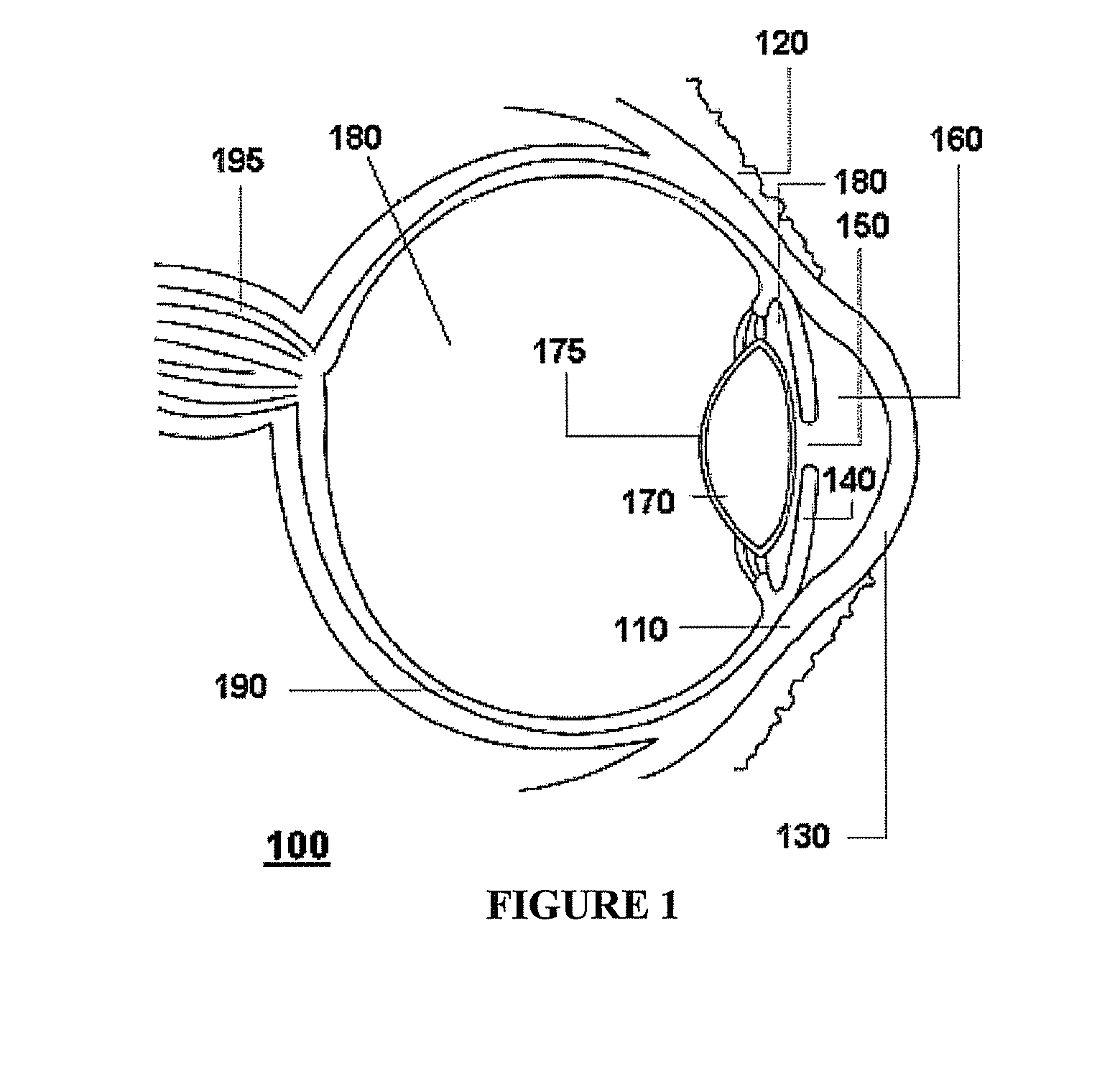
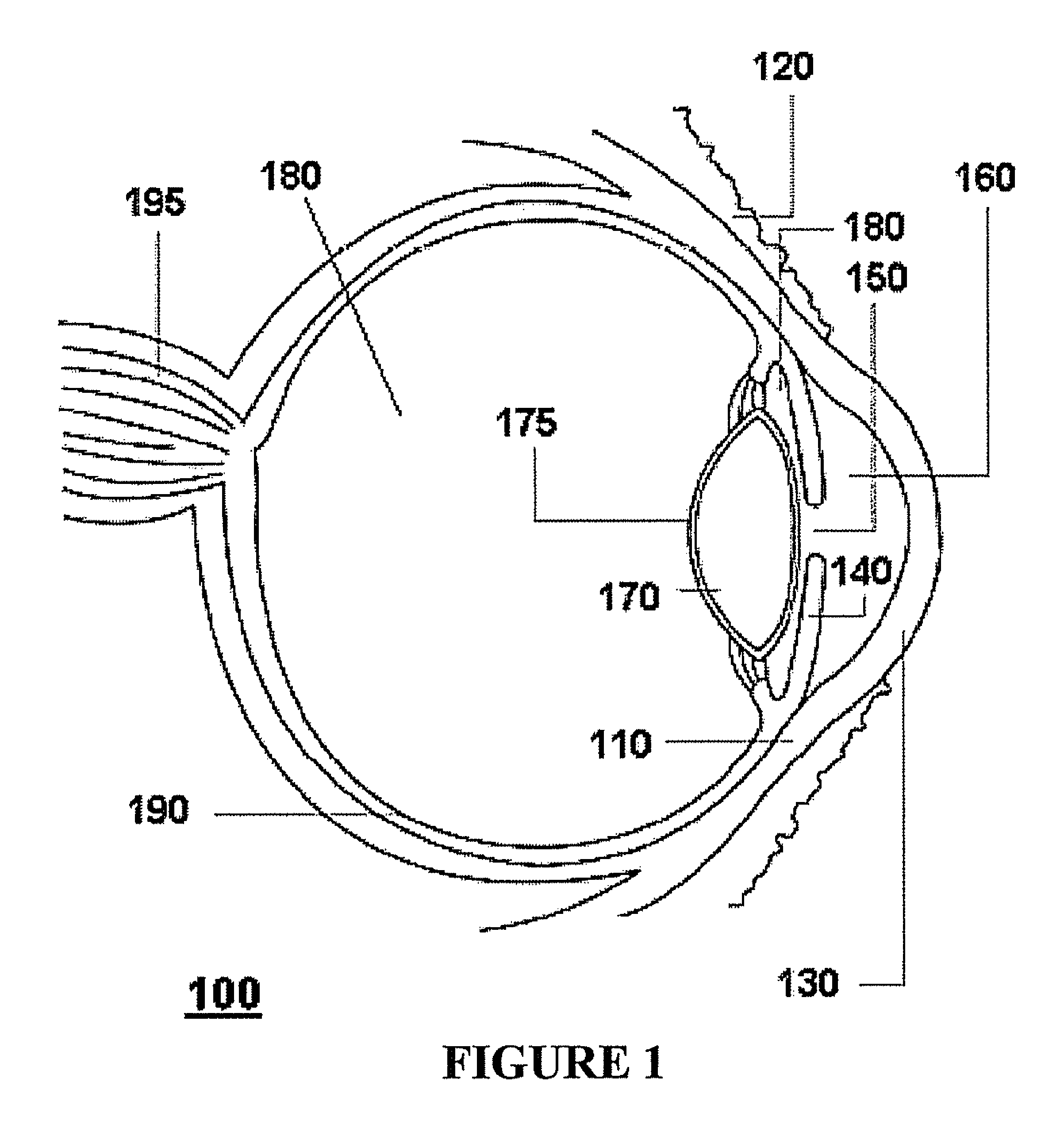
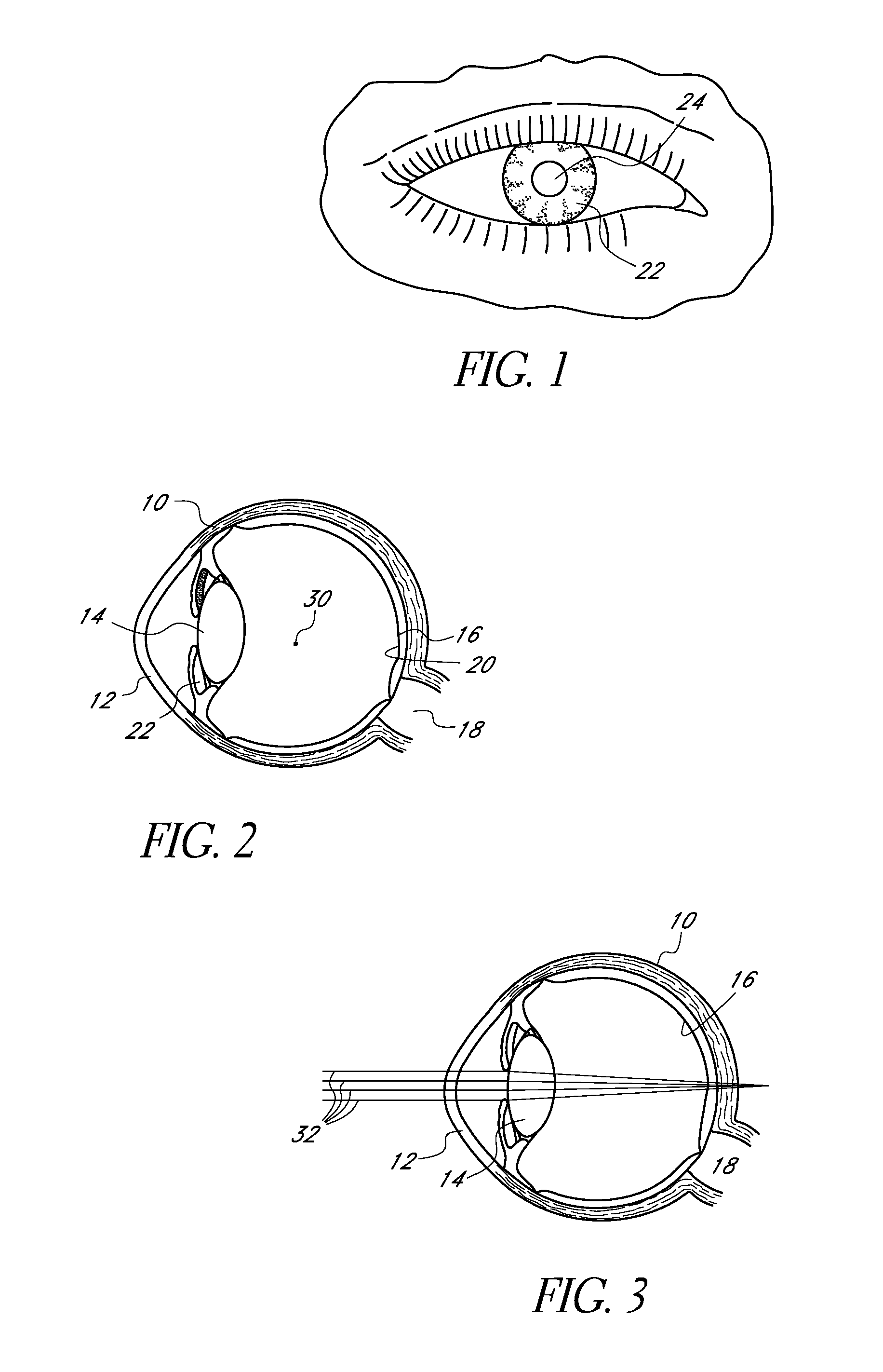
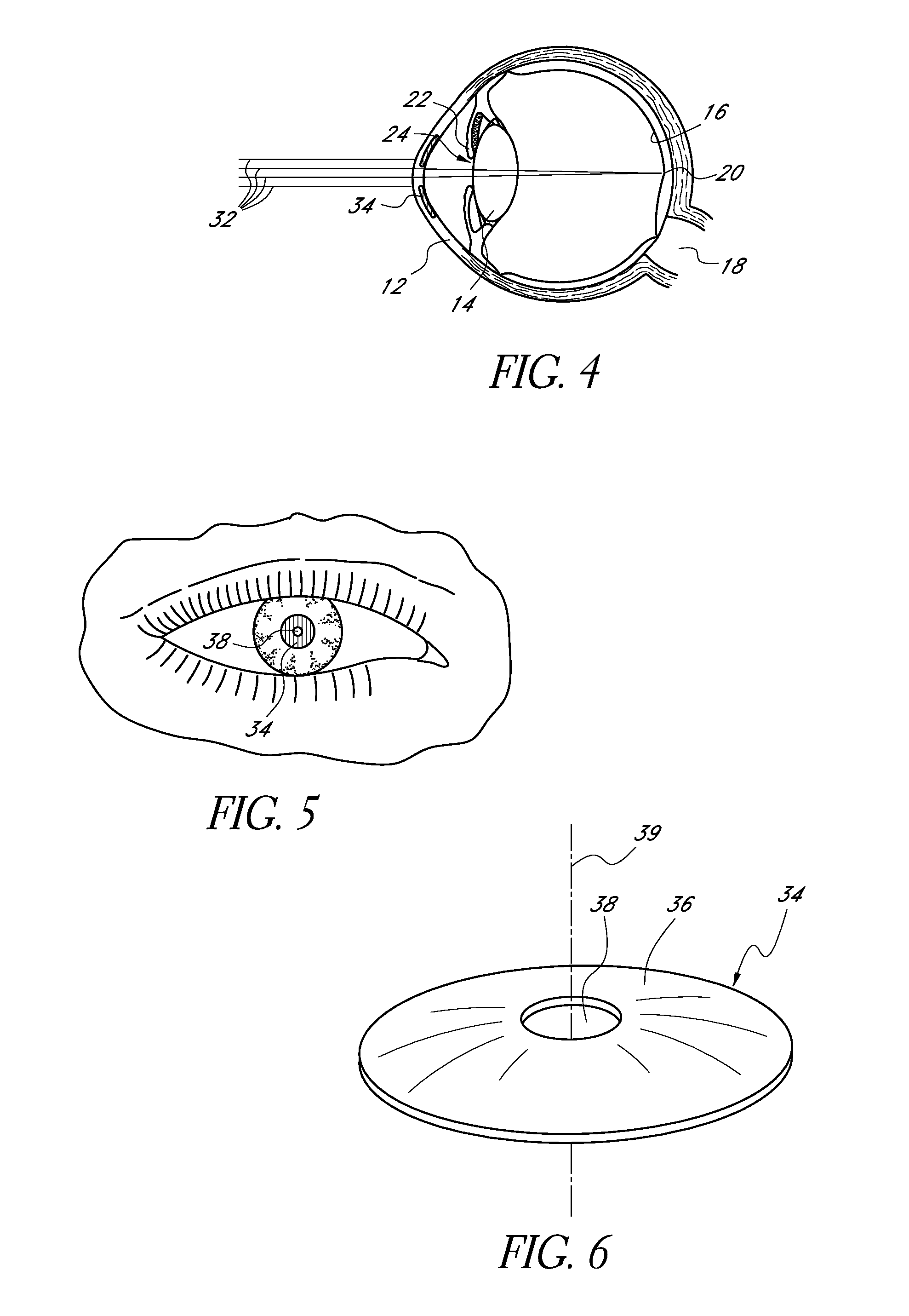
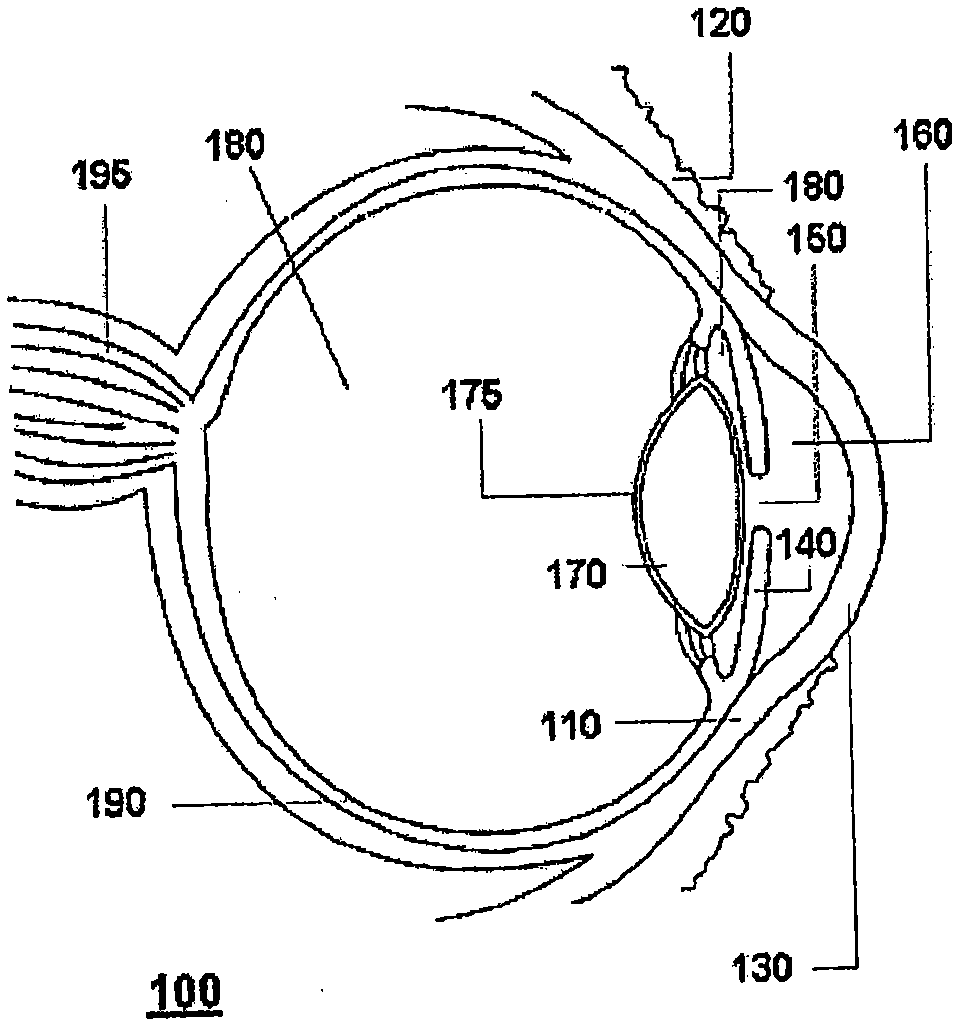
A corneal inlay (also called an intracorneal implant) is a device which is surgically implanted in the cornea of the eye as a treatment for presbyopia. Successful installation results in reducing dependence on reading glasses, so that the user can more easily engage in everyday tasks such as using a mobile phone, reading store shelf prices and working on a computer.
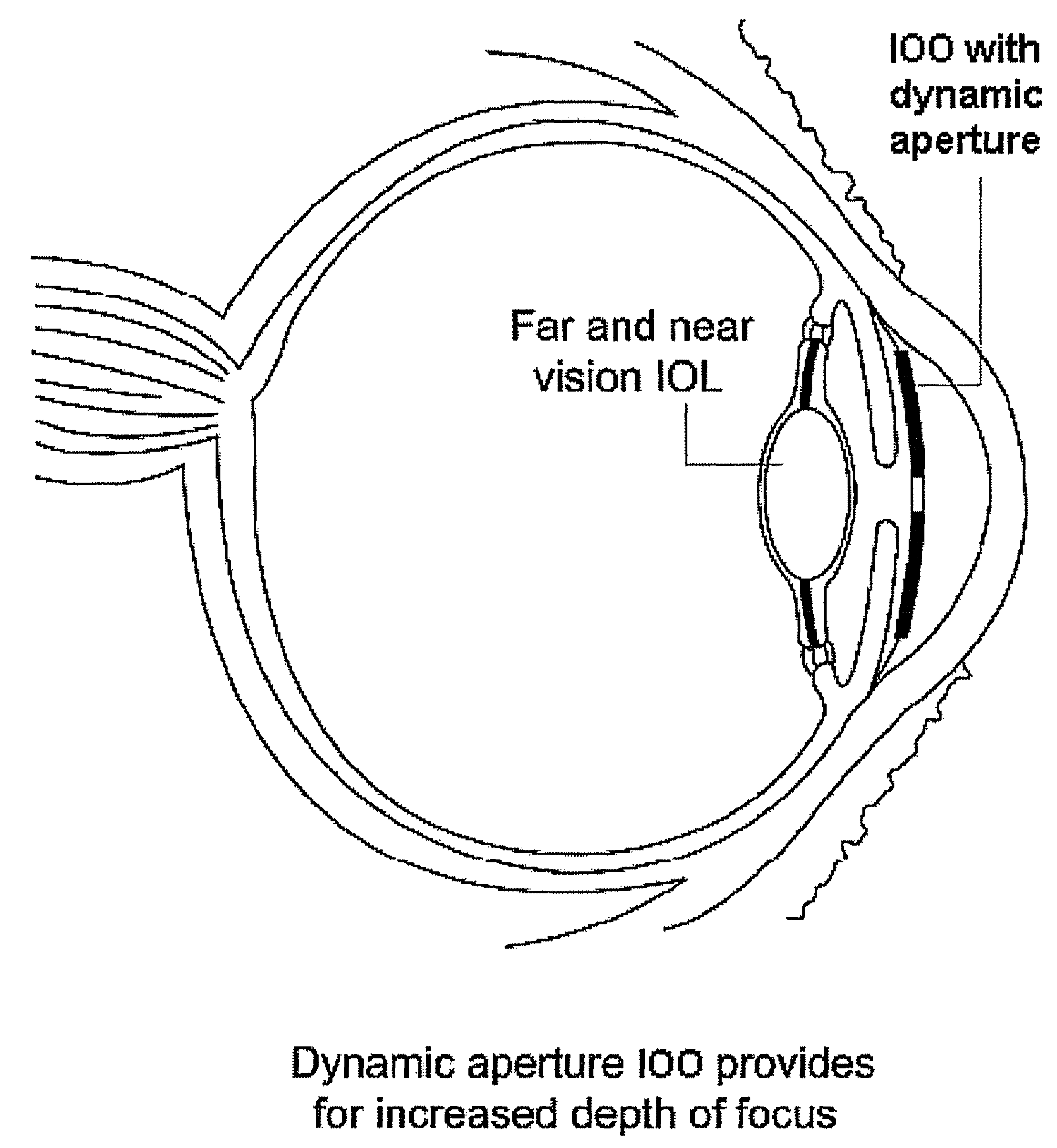
Ophthalmic dynamic aperture
ActiveUS20090033863A1Increase heightAdd depthSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensCorneal inlayDynamic aperture
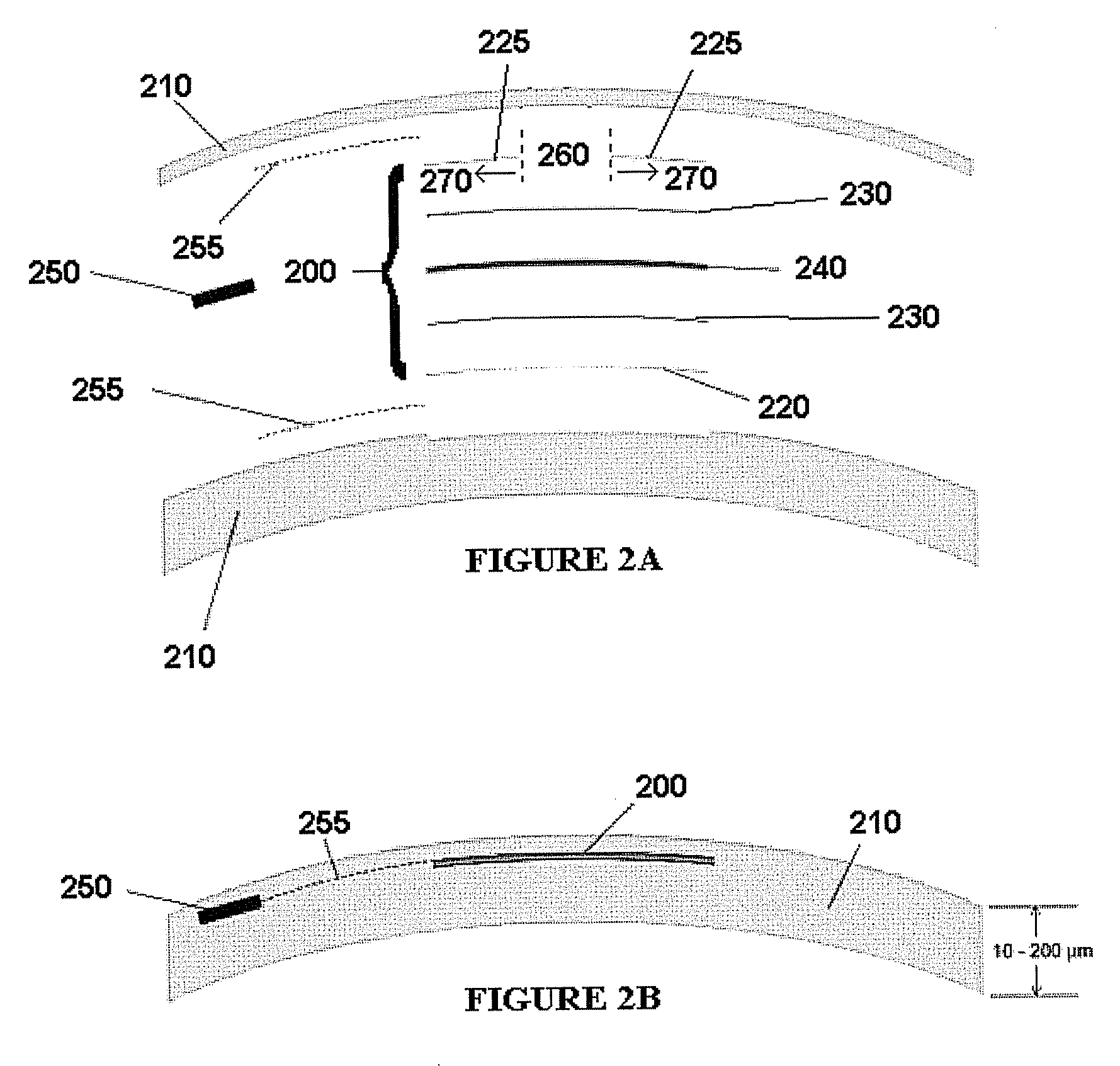
Embodiments of the present invention relate to an electro-active element having a dynamic aperture. The electro-active element provides increased depth of field and may be used in a non-focusing ophthalmic device that that is spaced apart from but in optical communication with an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, a contact lens, or a spectacle lens that provide an optical power. The electro-active element provides increased depth of field and may also be used in a focusing or non-focusing device such as an intraocular optic, an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, or a contact lens which may or may not have an optical power. By changing the diameter of dynamic aperture either increased depth of field or increased light reaching the retina may be achieved.
Owner:E VISION LLC +1
Adaptive optic lens and method of making
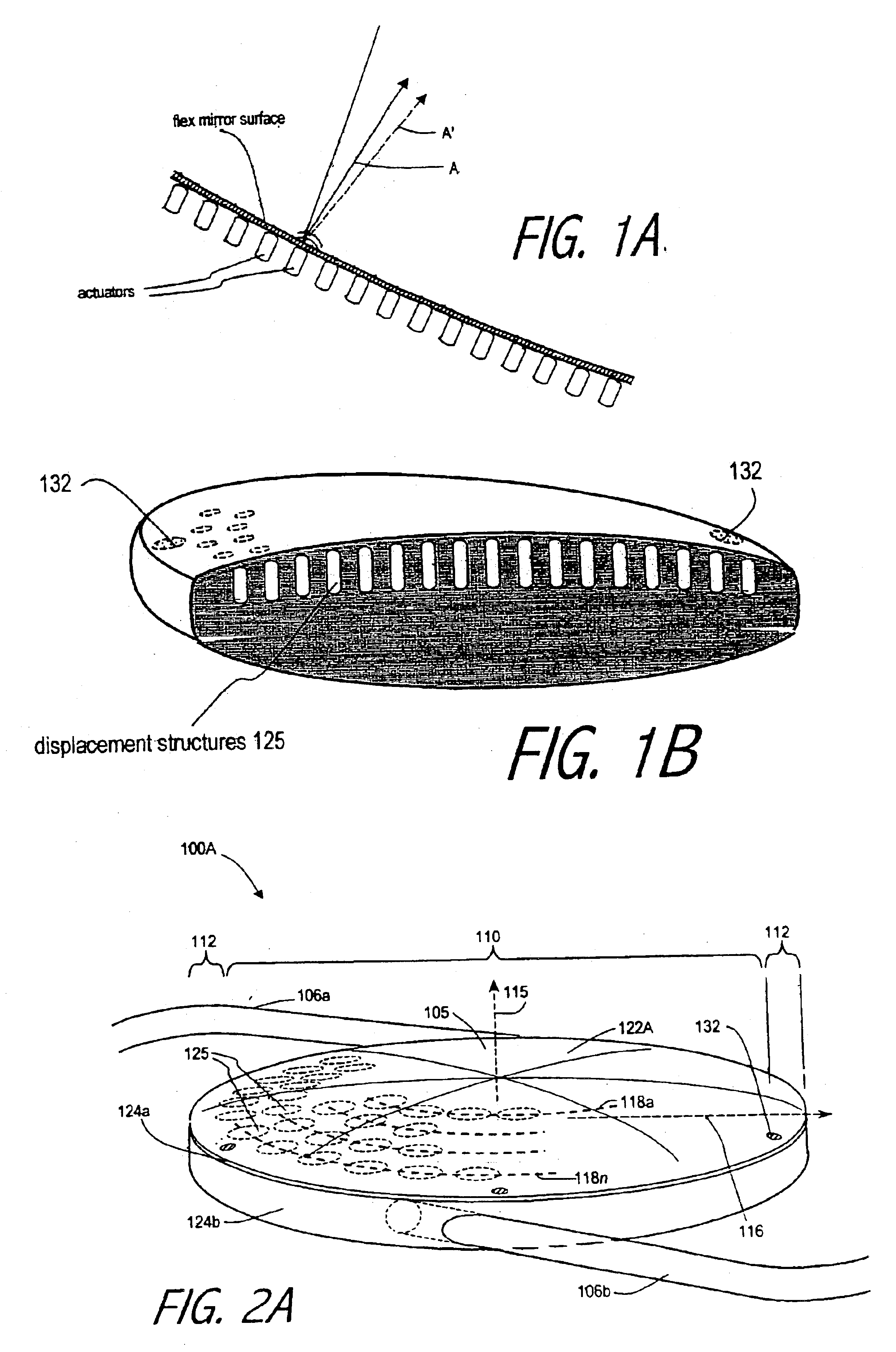
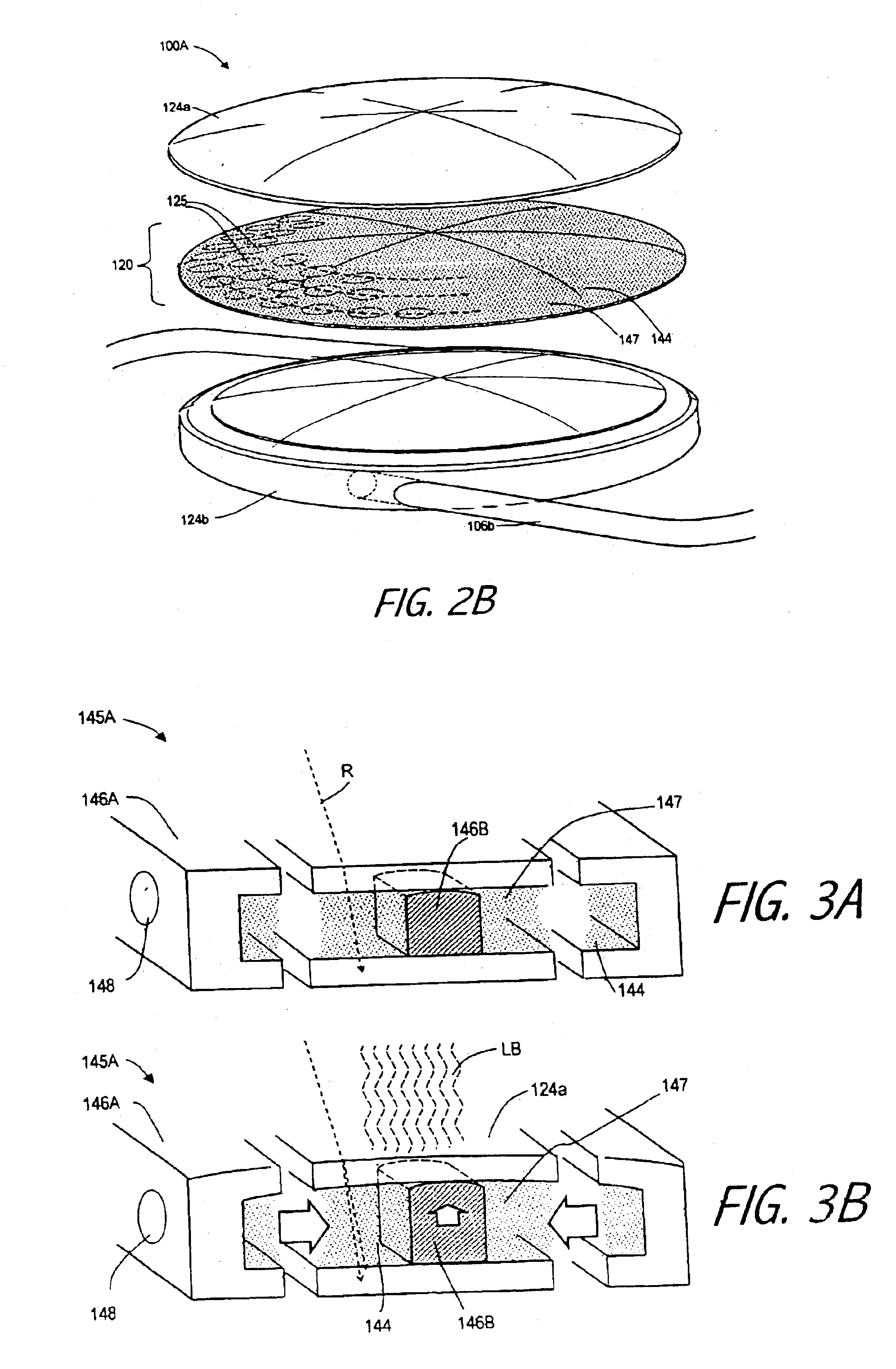
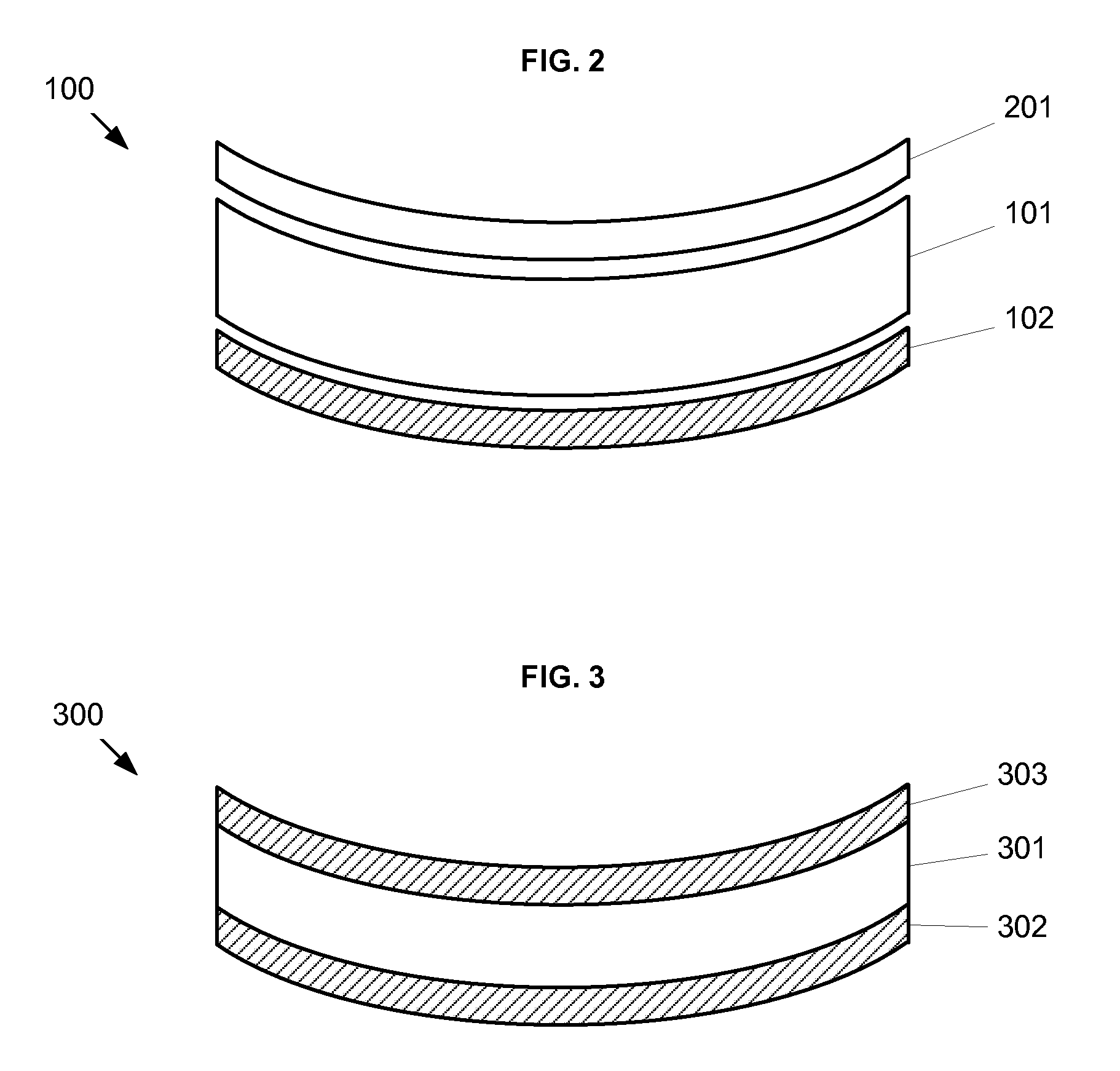
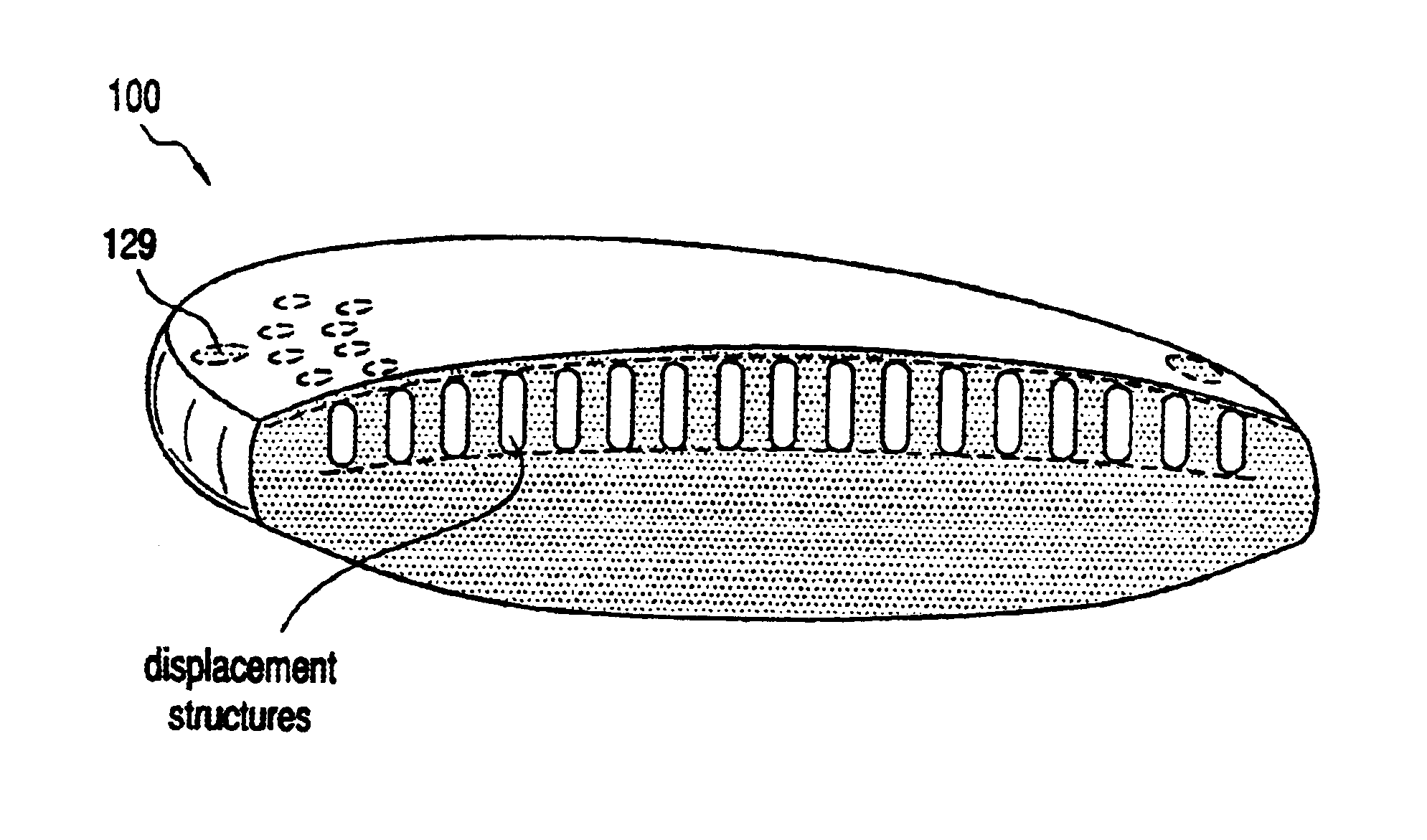
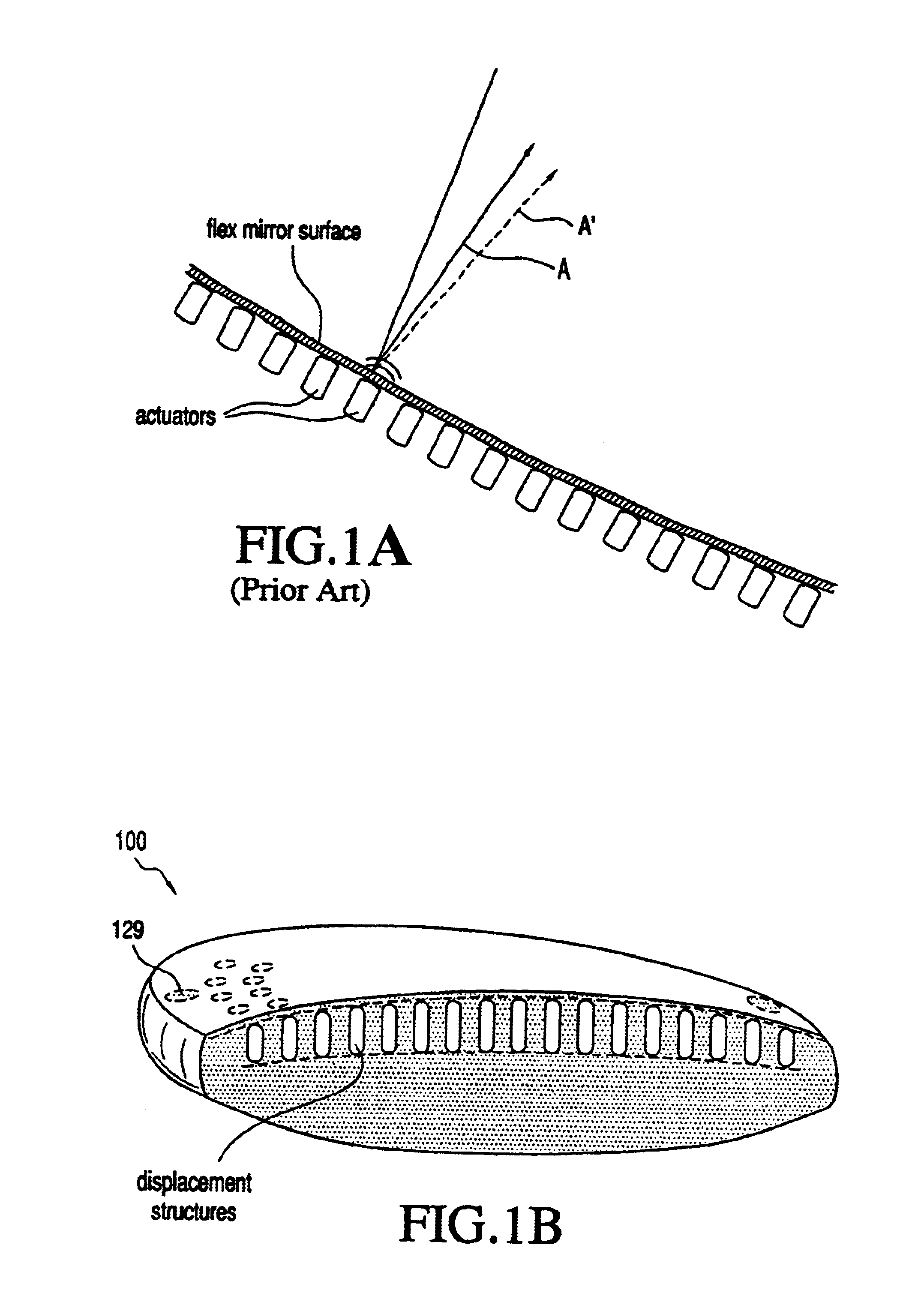
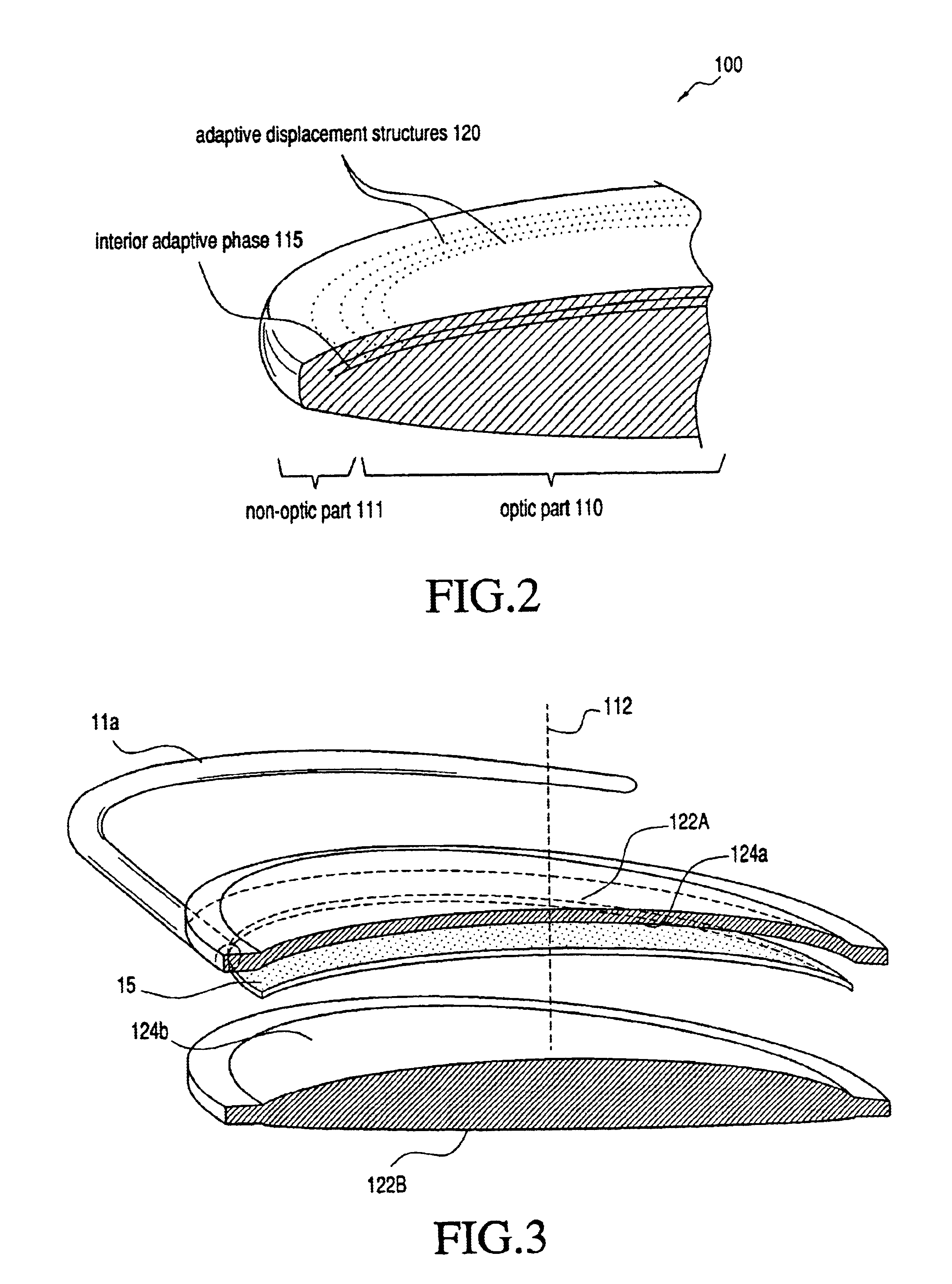
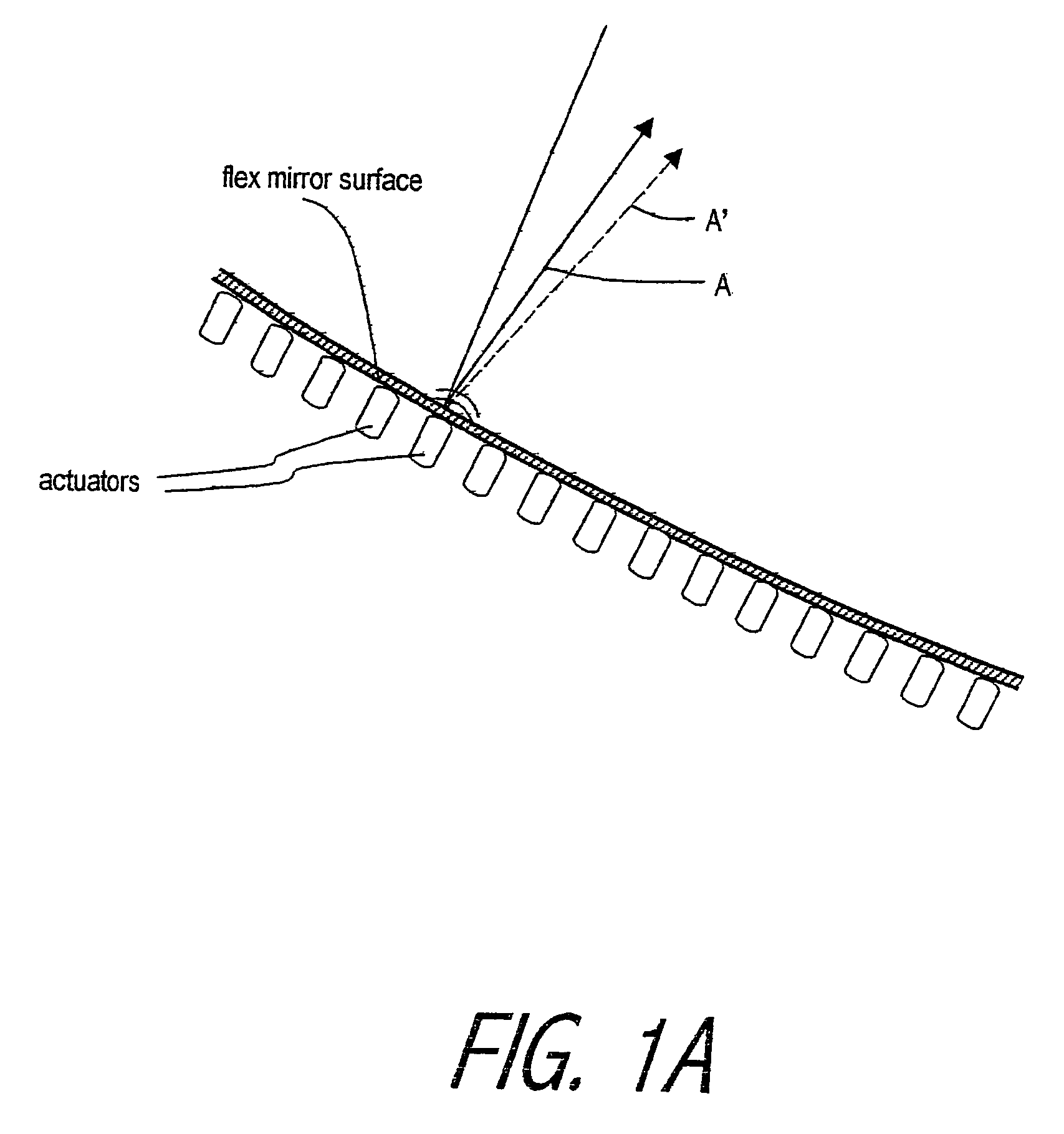
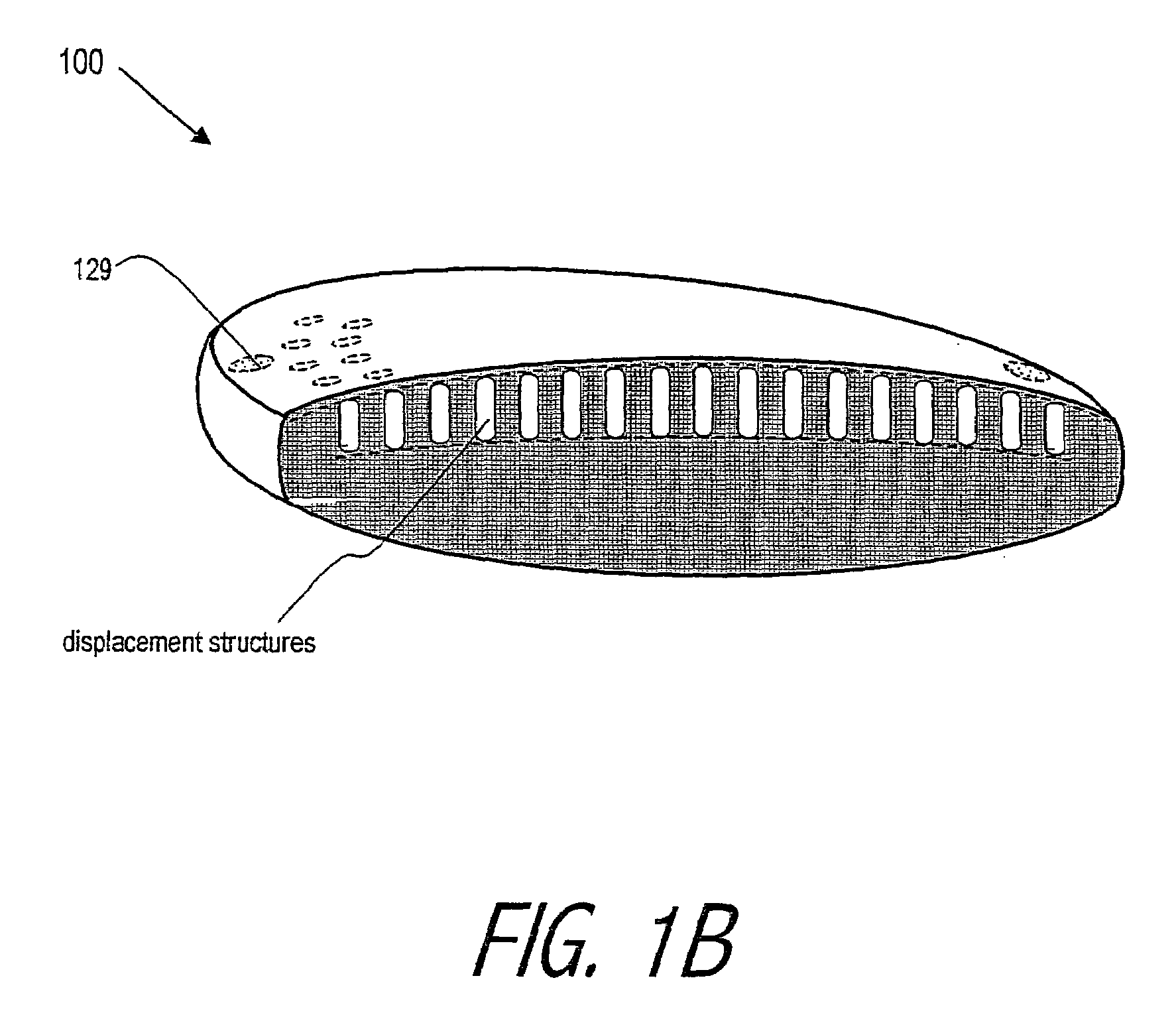
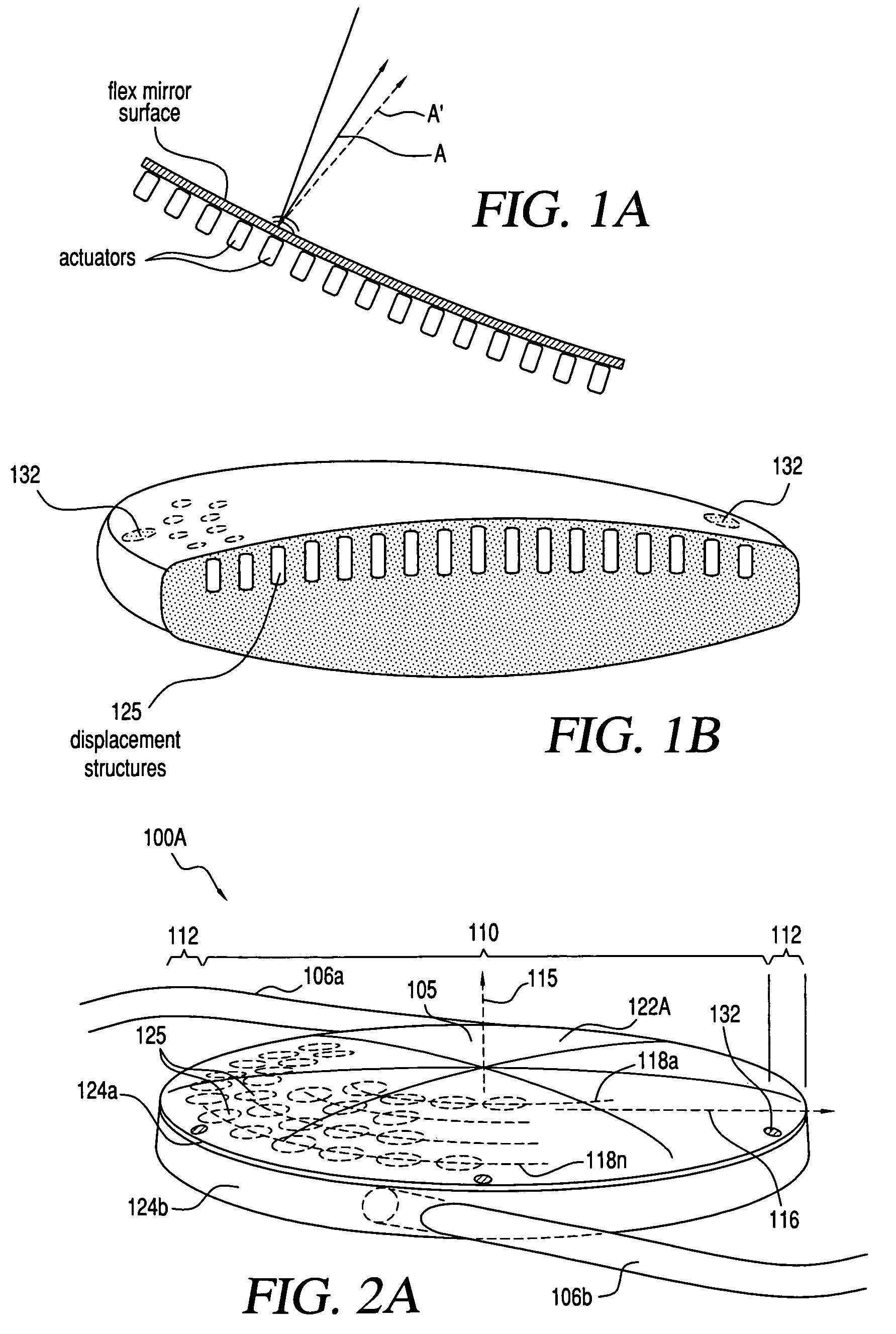
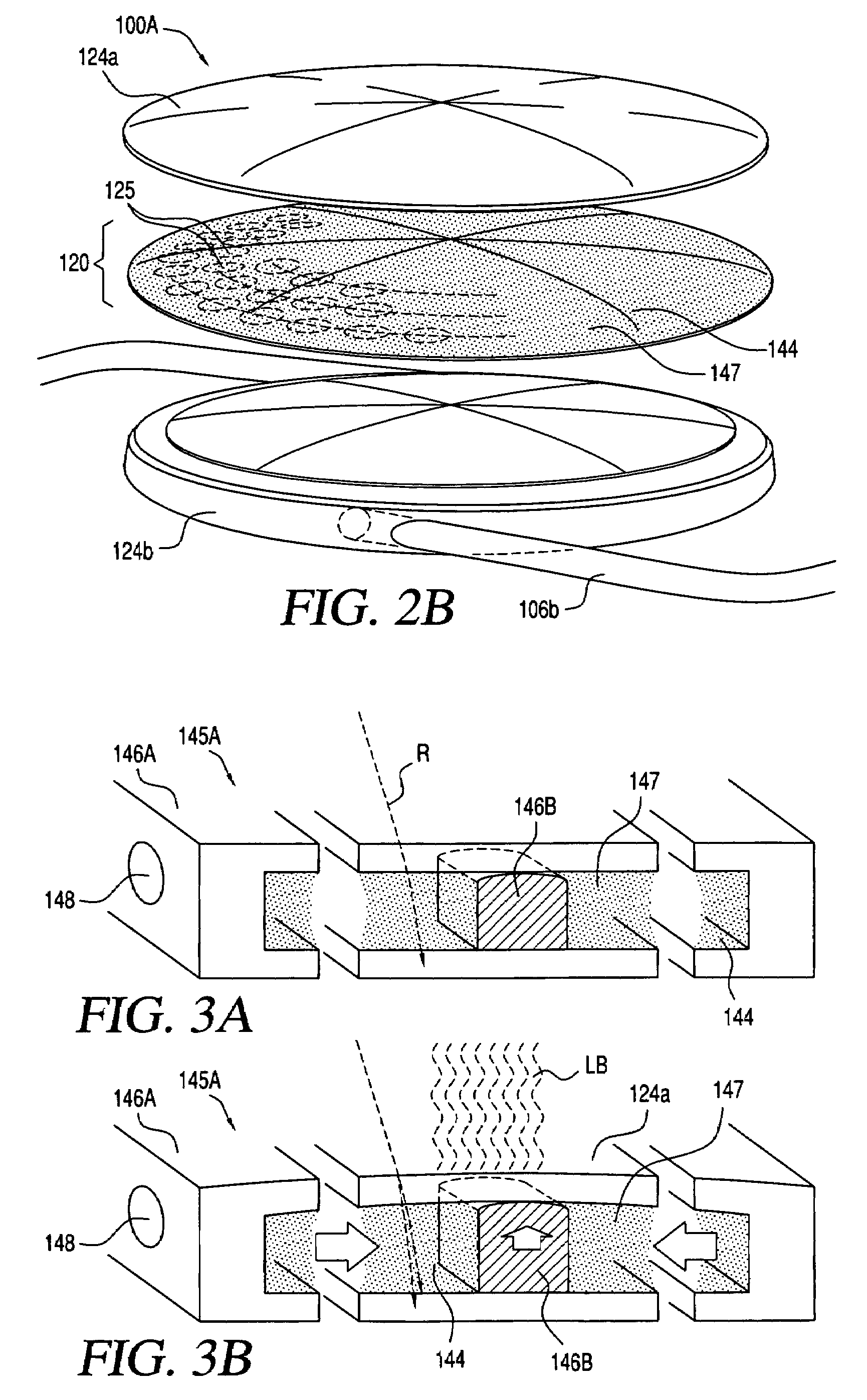
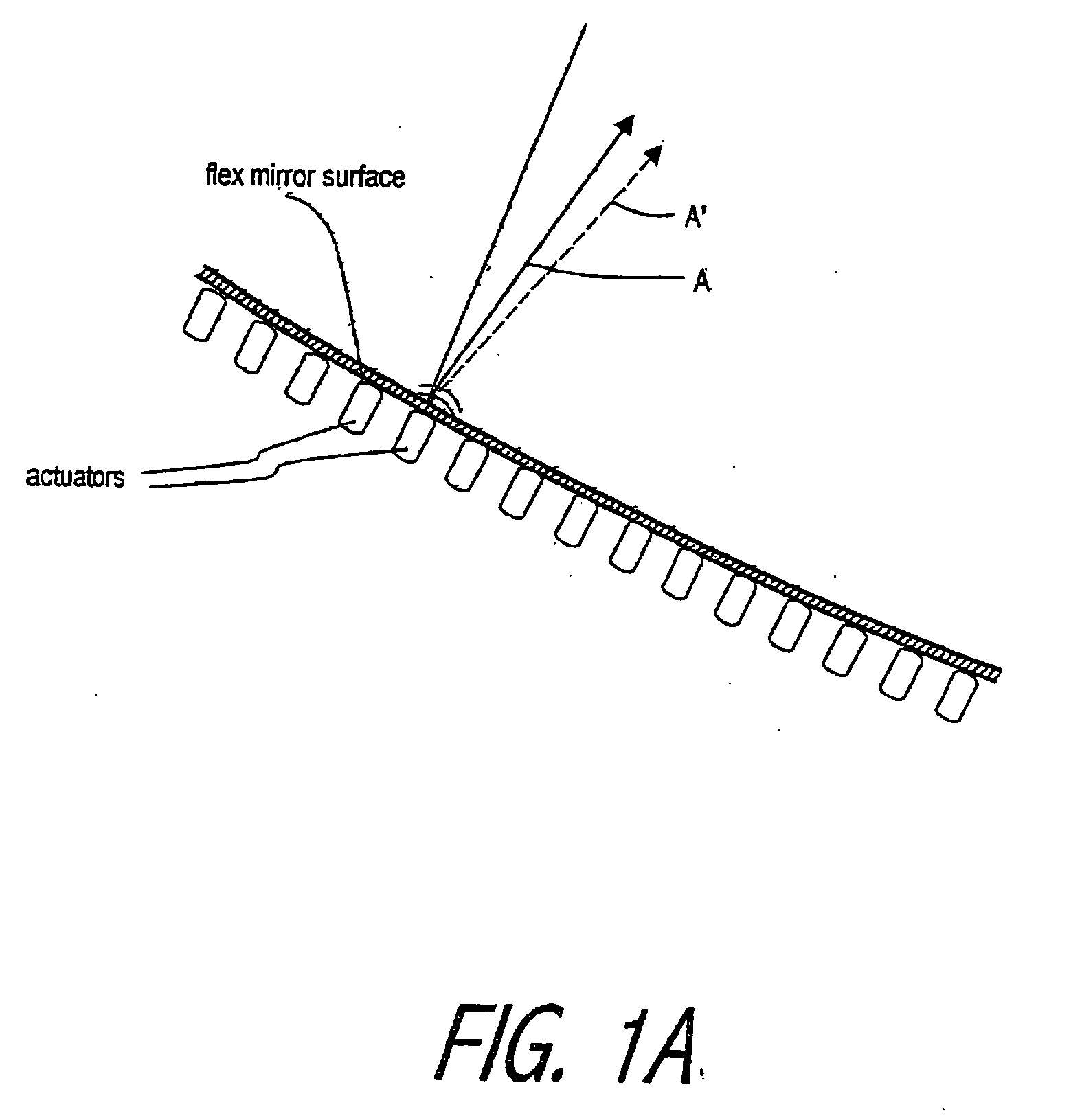
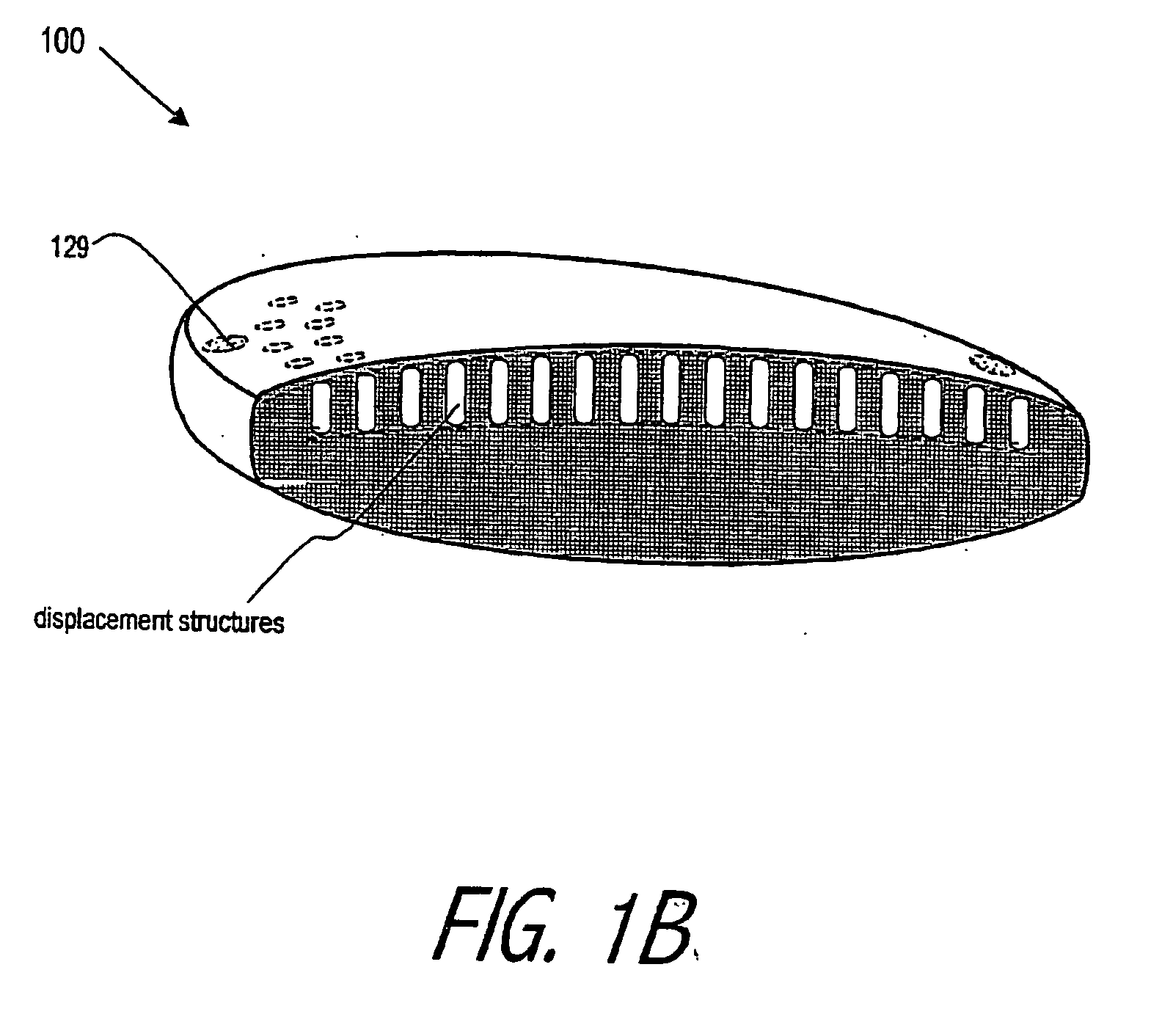
An lens for correcting human vision, for example an IOL, contact lens or corneal inlay or onlay, that carries and interior phase or layer comprising a pattern of individual transparent adaptive displacement structures. In the exemplary embodiments, the displacement structures are actuated by shape change polymer that adjusts a shape or other parameter in response to applied energy that in turn displaces a fluid media within the lens that actuates a flexible lens surface. The adaptive optic means of the invention can be used to create highly localized surface corrections in the lens to correct higher order aberrations-which types of surfaces cannot be fabricated into and IOL and then implanted. The system of displacement structures also can provide spherical corrections in the lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
High performance corneal inlay
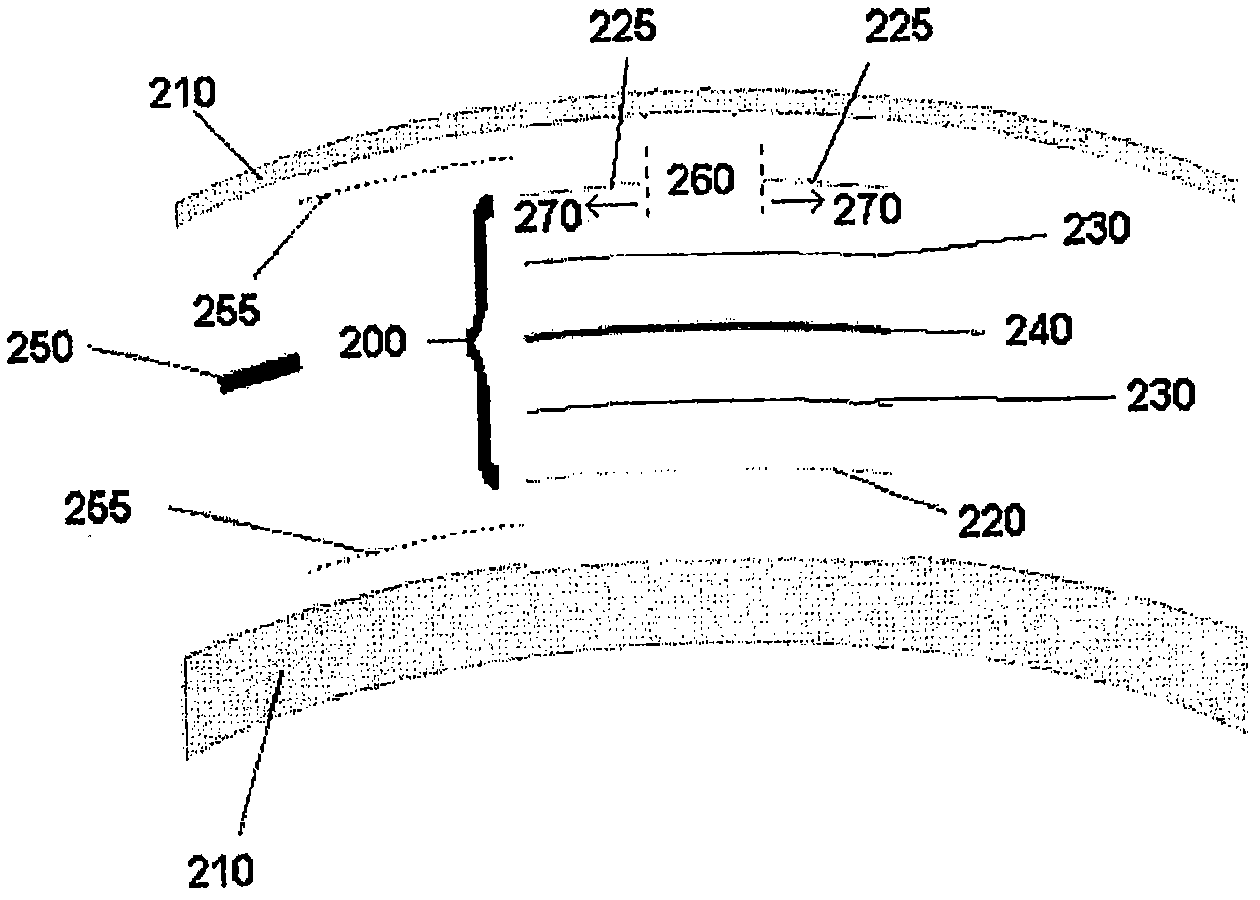
A corneal inlay protects ocular structures from harmful wavelengths of light while maintaining acceptable color cosmetics, color perception, overall light transmission, photopic vision, scotopic vision, color vision, and / or cirdadian rhythms. The corneal inlay can also include a pinhole effect to increase depth of focus. In some embodiments, the corneal inlay can also correct refractive errors including, but not limited to, higher order aberration, lower order aberration, myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and / or presbyopia.
Owner:HIGH PERFORMANCE OPTICS
Adaptive optic lens system and method of use
InactiveUS6860601B2Reduce aberrationHigh order aberrationSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsCamera lensCorneal inlay
An lens for correcting human vision, for example an IOL, contact lens or corneal inlay or onlay, that carries and interior phase or layer comprising a pattern of individual transparent adaptive displacement structures. In one embodiment, the displacement structures are actuated by a shape memory polymer (SMP) material or other polymer that is adjustable in shape in response to applied energy. The SMP can be designed to be selectively adjustable in volumetric dimension, modulus of elasticity and / or permeability. The adaptive optic means of the invention can be used to create highly localized surface corrections in the lens to correct higher order aberrations-which types of surfaces cannot be fabricated into and IOL and then implanted. The system of displacement structures also can provide spherical corrections in the lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
Advanced electro-active optic device
Optical devices having a dynamic aperture and / or an apodization mask are provided. The aperture and / or mask may be provided by one or more electro-active elements, and may be used in an ophthalmic device that that is spaced apart from but in optical communication with an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, or a spectacle lens that provide an optical power.
Owner:EA3TECH LLC +1
Adaptive optic lens system and method of use
InactiveUS6966649B2Reduce aberrationHigh order aberrationSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsCamera lensCorneal inlay
An lens for correcting human vision, for example an IOL, contact lens or corneal inlay or onlay, that carries and interior phase or layer comprising a pattern of individual transparent adaptive displacement structures. In one embodiment, the displacement structures are actuated by a shape memory polymer (SMP) material or other polymer that is adjustable in shape in response to applied energy. The SMP can be designed to be selectively adjustable in volumetric dimension, modulus of elasticity and / or permeability. The adaptive optic means of the invention can be used to create highly localized surface corrections in the lens to correct higher order aberrations—which types of surfaces cannot be fabricated into and IOL and then implanted. The system of displacement structures also can provide spherical corrections in the lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
Artificial corneal implant
A material that can be applied as implants designed to artificially replace or augment the cornea, such as an artificial cornea, corneal onlay, or corneal inlay (intrastromal lens) is provided. The artificial corneal implant has a double network hydrogel with a first network interpenetrated with a second network. The first network and the second network are based on biocompatible polymers. At least one of the network polymers is based on a hydrophilic polymer. The artificial cornea or implant has epithelialization promoting biomolecules that are covalently linked to the surface of the double network hydrogel using an azide-active-ester chemical linker. Corneal epithelial cells or cornea-derived cells are adhered to the biomolecules. The double network has a physiologic diffusion coefficient to allow passage of nutrients to the adhered cells.
Owner:SANTA CLARA UNIVERSITY
Adaptive optic lens and method of making
An lens for correcting human vision, for example an IOL, contact lens or corneal inlay or onlay, that carries and interior phase or layer comprising a pattern of individual transparent adaptive displacement structures. In the exemplary embodiments, the displacement structures are actuated by shape change polymer that adjusts a shape or other parameter in response to applied energy that in turn displaces a fluid media within the lens that actuates a flexible lens surface. The adaptive optic means of the invention can be used to create highly localized surface corrections in the lens to correct higher order aberrations-which types of surfaces cannot be fabricated into and IOL and then implanted. The system of displacement structures also can provide spherical corrections in the lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
Vision enhancing ophthalmic devices and related methods and compositions
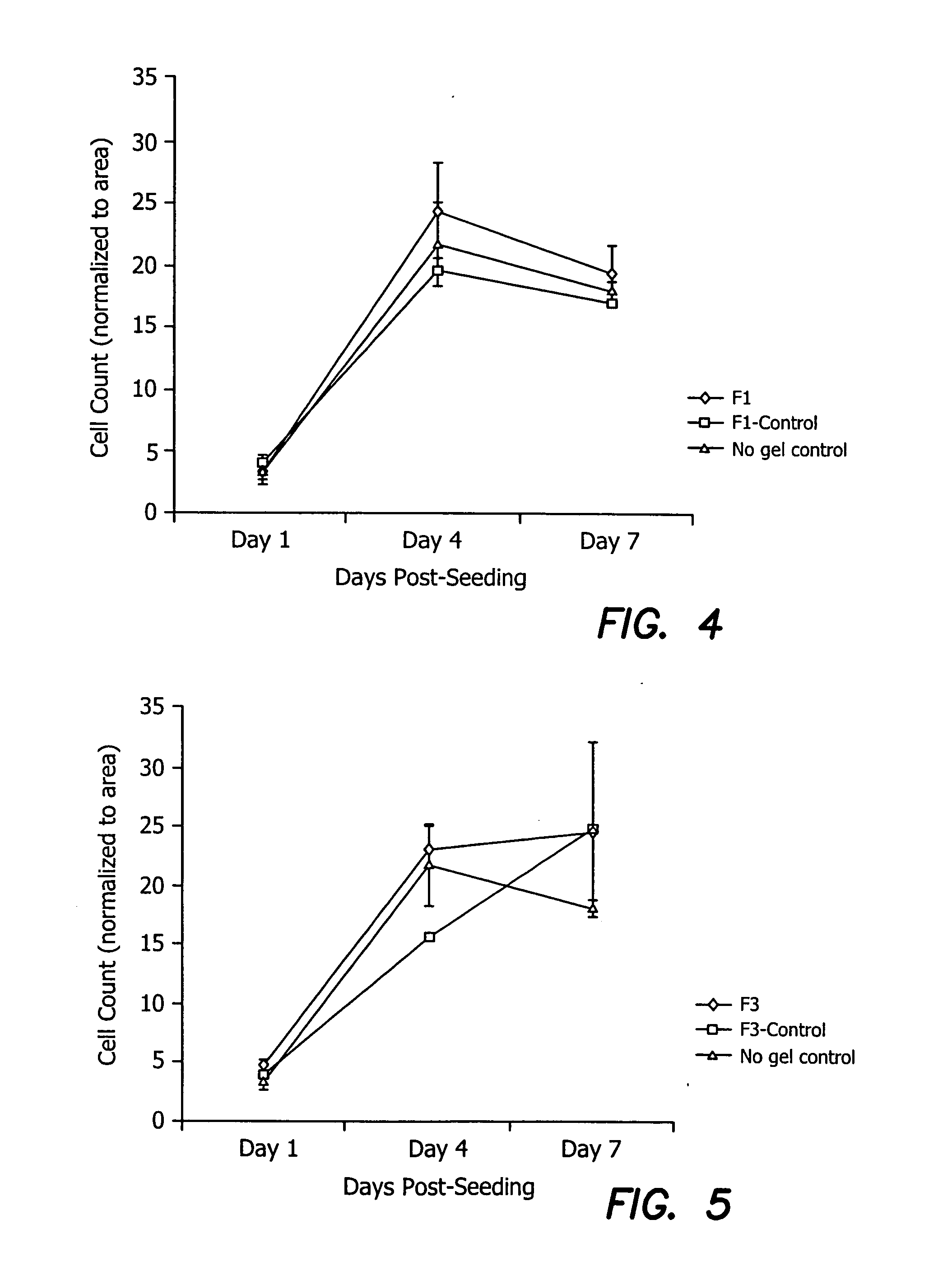
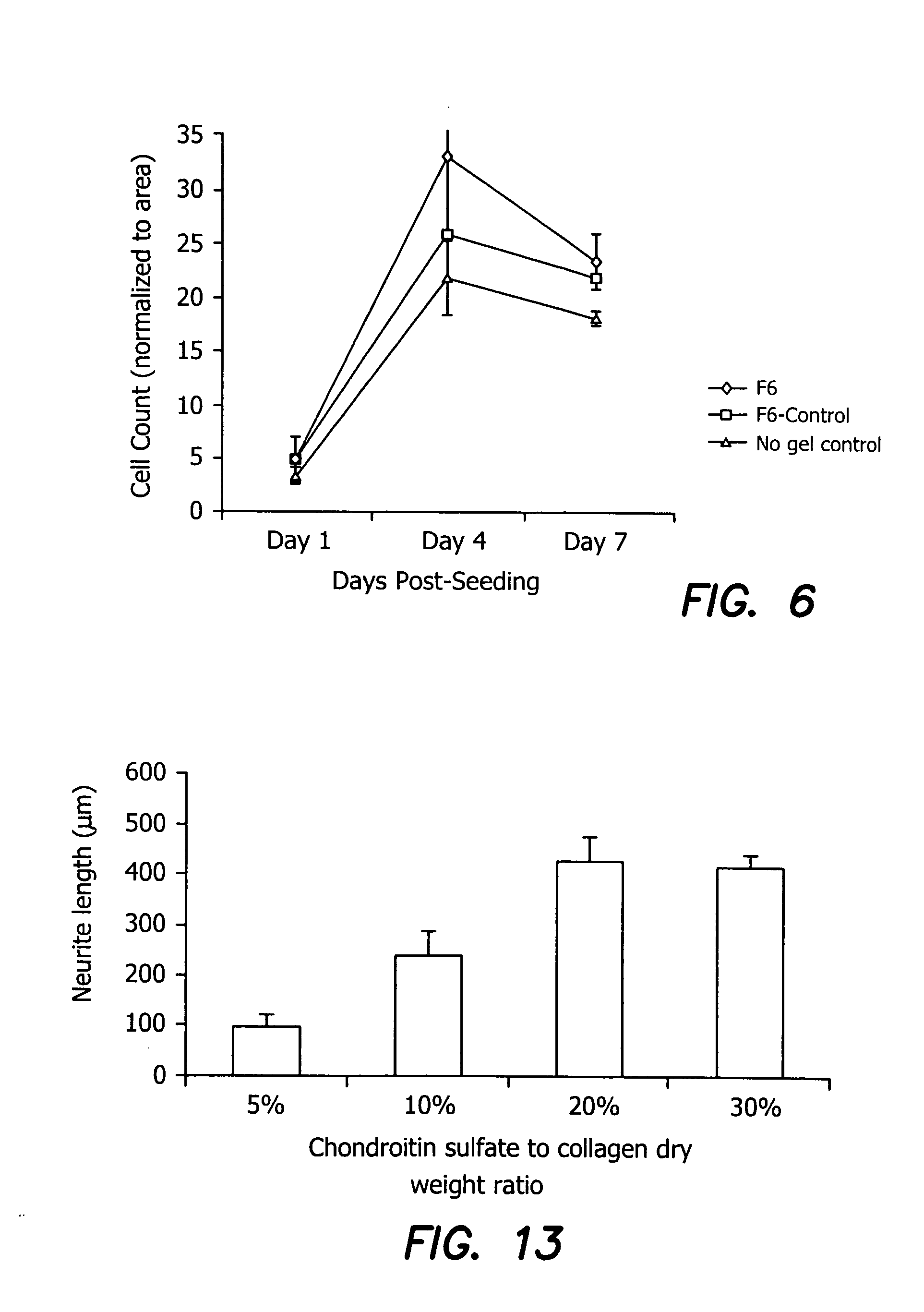
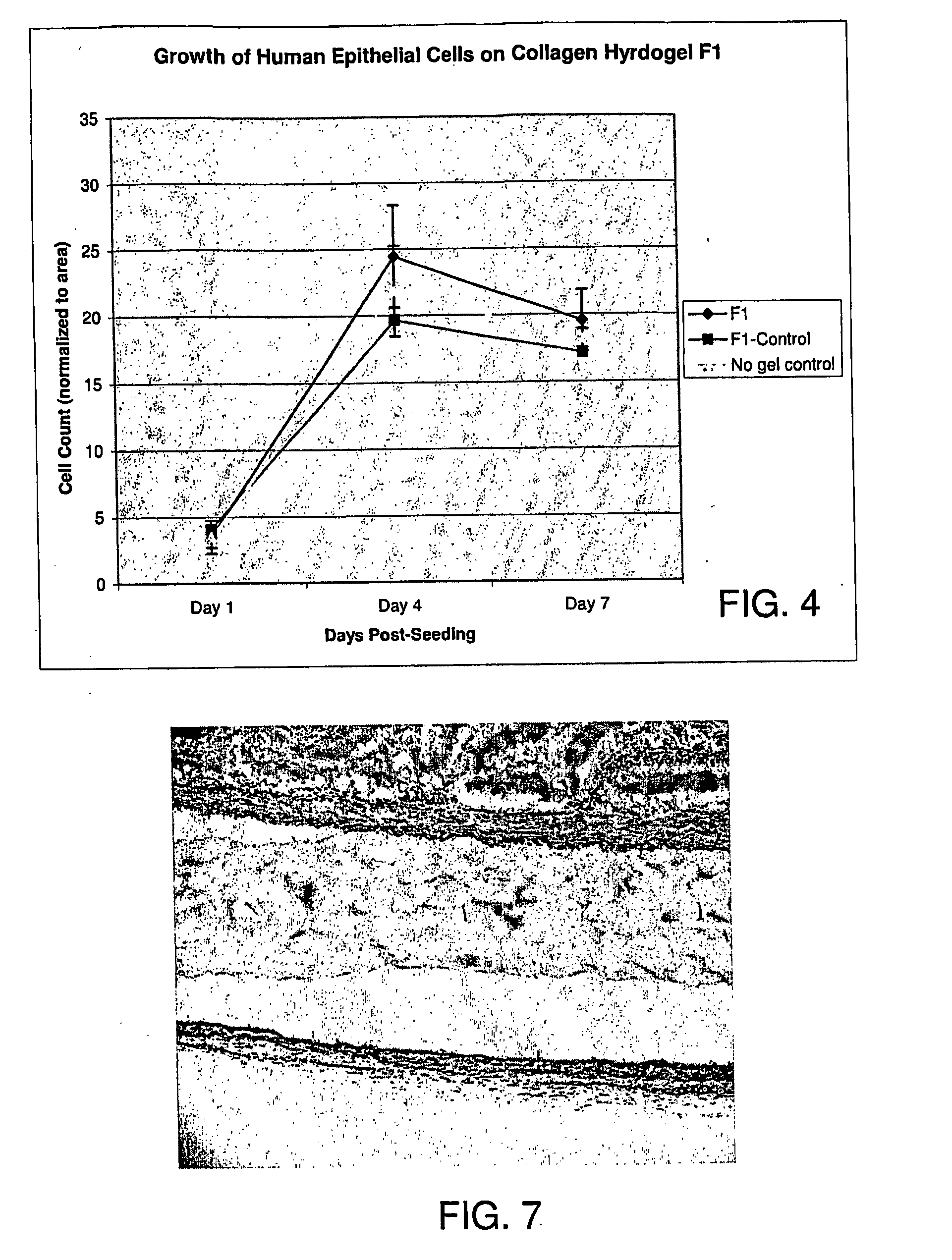
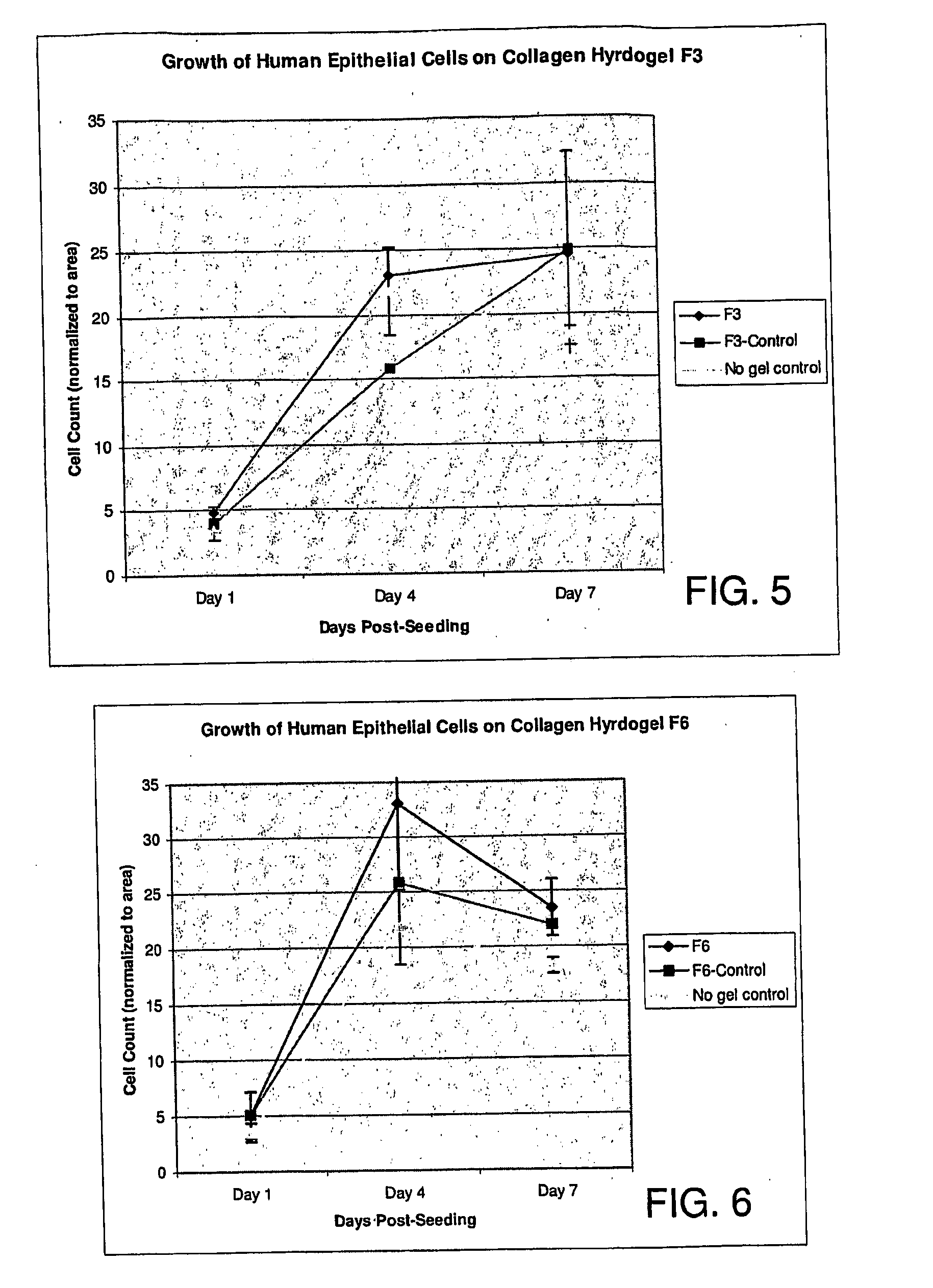
Devices, methods, and compositions for improving vision or treating diseases, disorders or injury of the eye are described. Ophthalmic devices, such as corneal onlays, corneal inlays, and full-thickness corneal implants, are made of a material that is effective in facilitating nerve growth through or over the device. The material may include an amount of collagen greater than 1% (w / w), such as between about 10% (w / w) and about 30% (w / w). The material may include collagen polymers and / or a second biopolymer or water-soluble synthetic polymer cross-linked using EDC / NHS chemistry. The material may additionally comprise a synthetic polymer. The devices are placed into an eye to correct or improve the vision of an individual or to treat a disease, disorder or injury of an eye of an individual.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA +3
Ophthalmic dynamic aperture
Embodiments of the present invention relate to an electro-active element having a dynamic aperture. The electro-active element provides increased depth of field and may be used in a non-focusing ophthalmic device that that is spaced apart from but in optical communication with an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, a contact lens, or a spectacle lens that provide an optical power. The electro-active element provides increased depth of field and may also be used in a focusing or non-focusing device such as an intraocular optic, an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, or a contact lens which may or may not have an optical power. By changing the diameter of dynamic aperture either increased depth of field or increased light reaching the retina may be achieved.
Owner:E VISION LLC +1
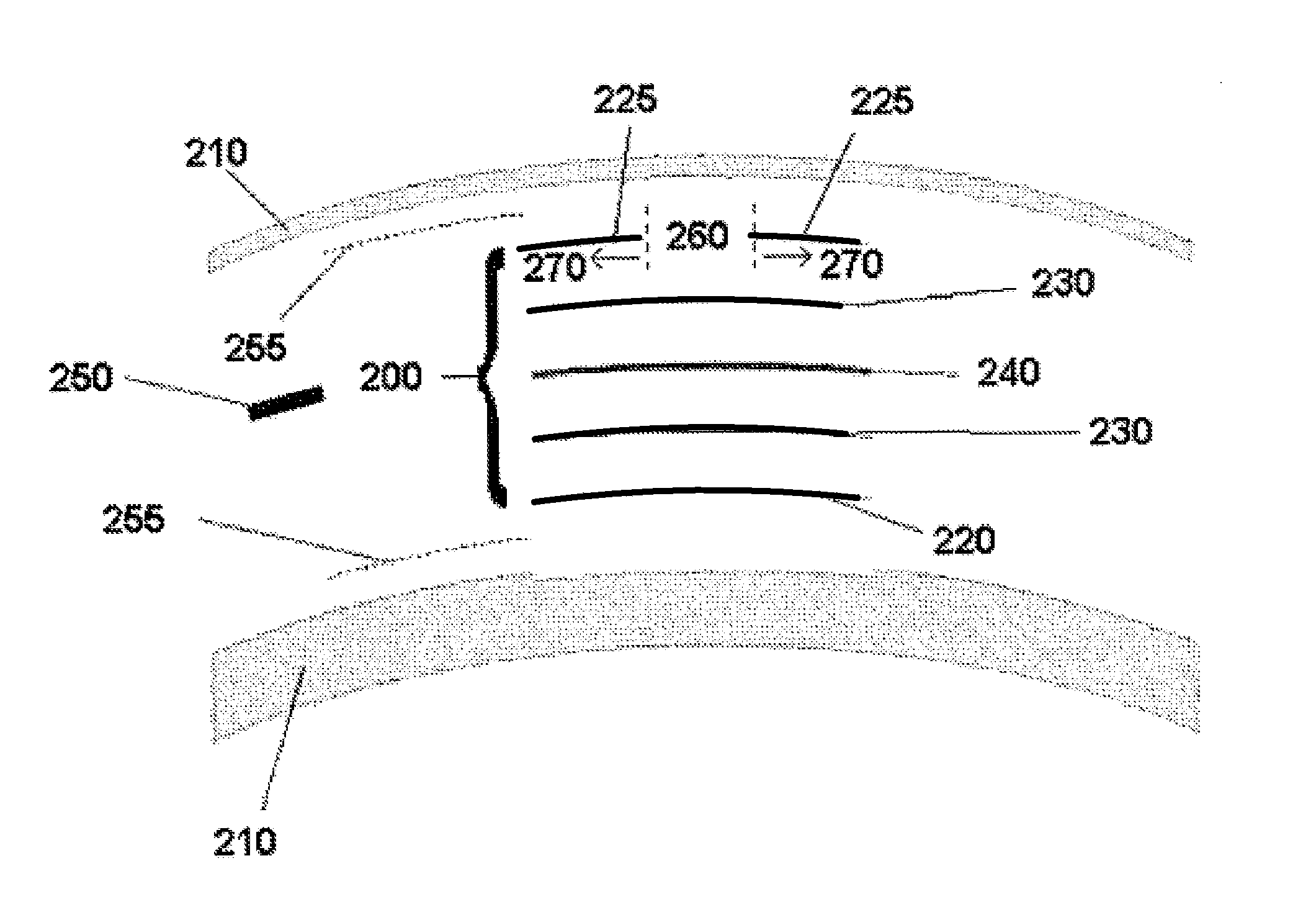
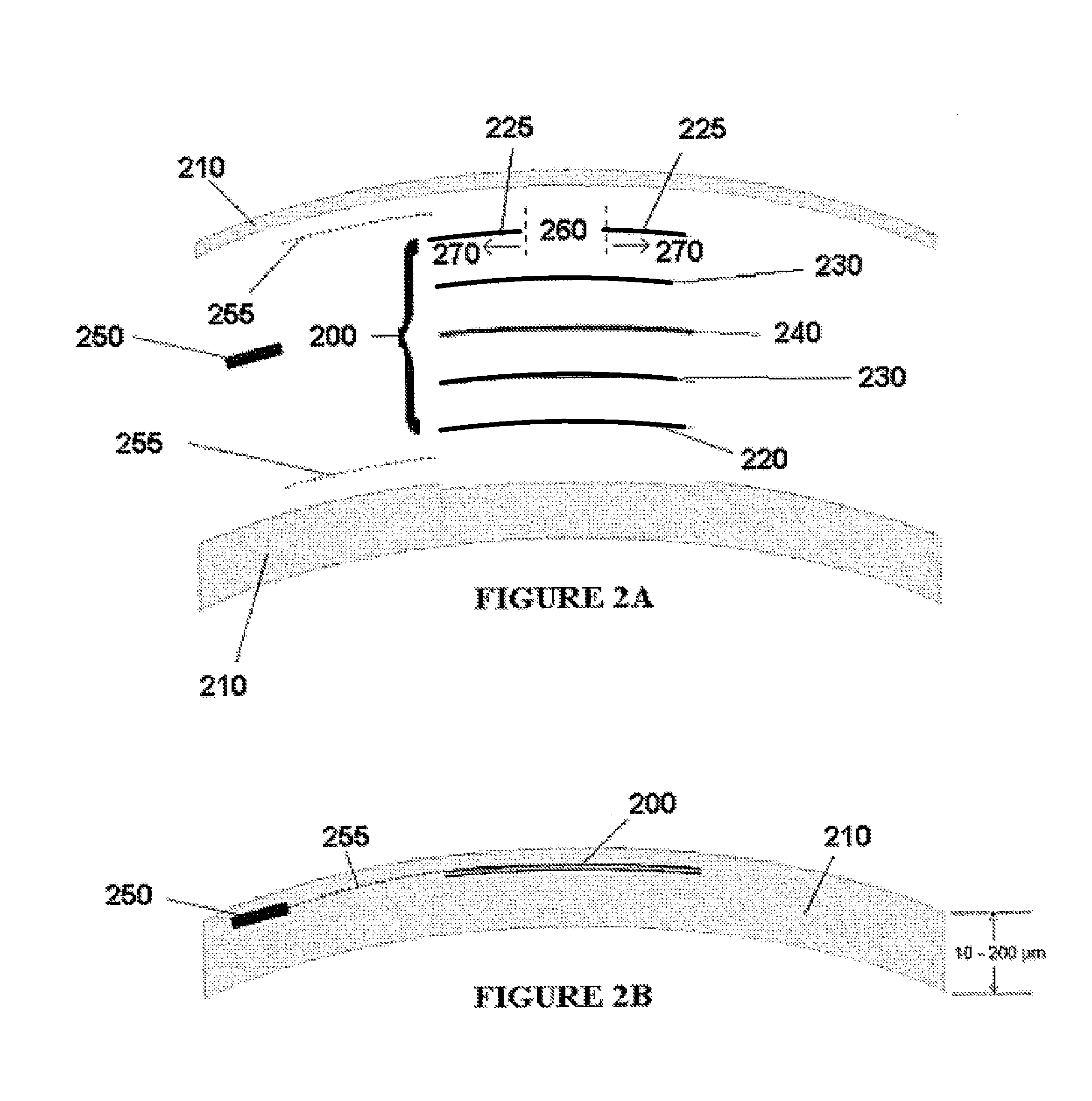
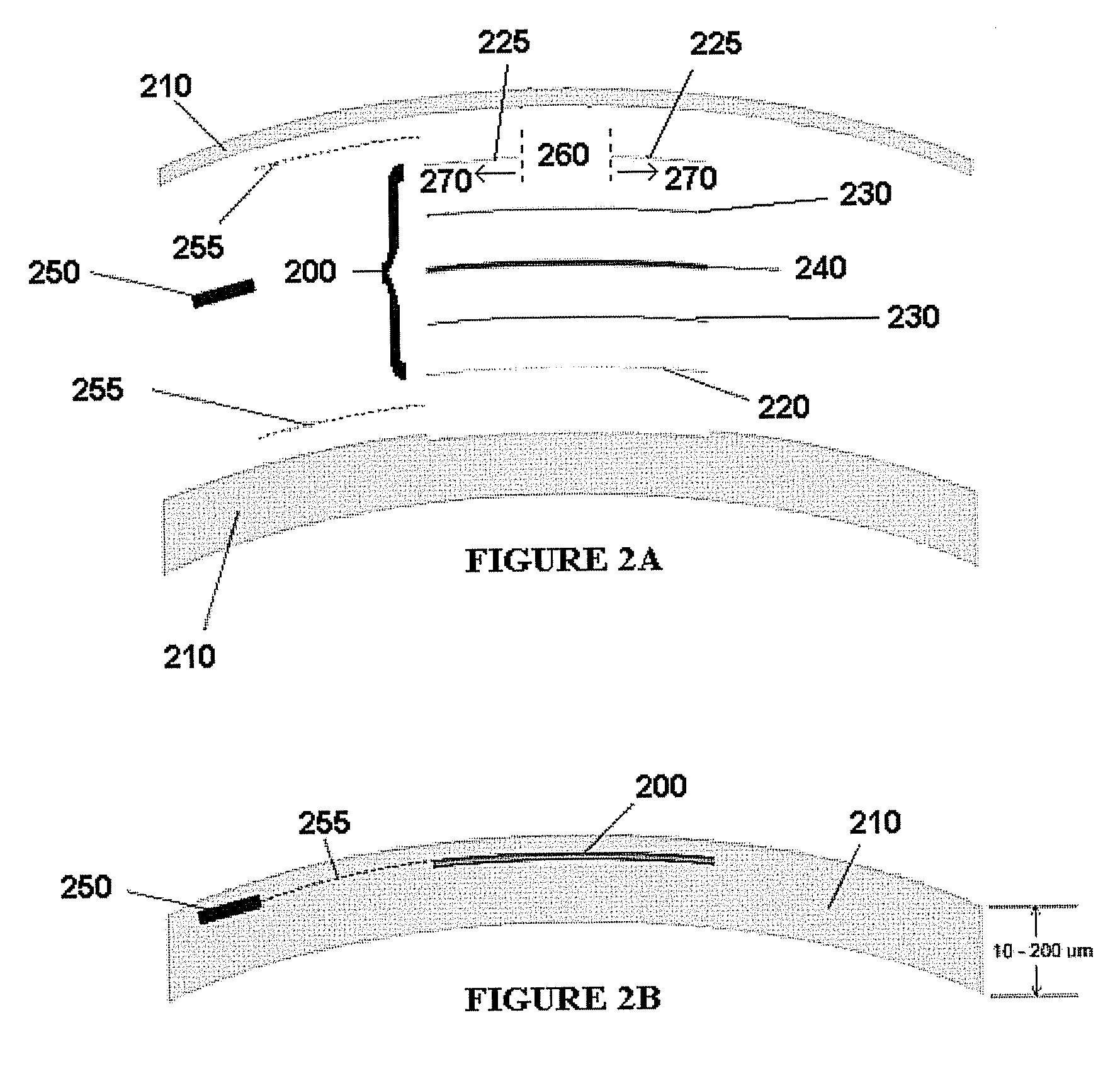
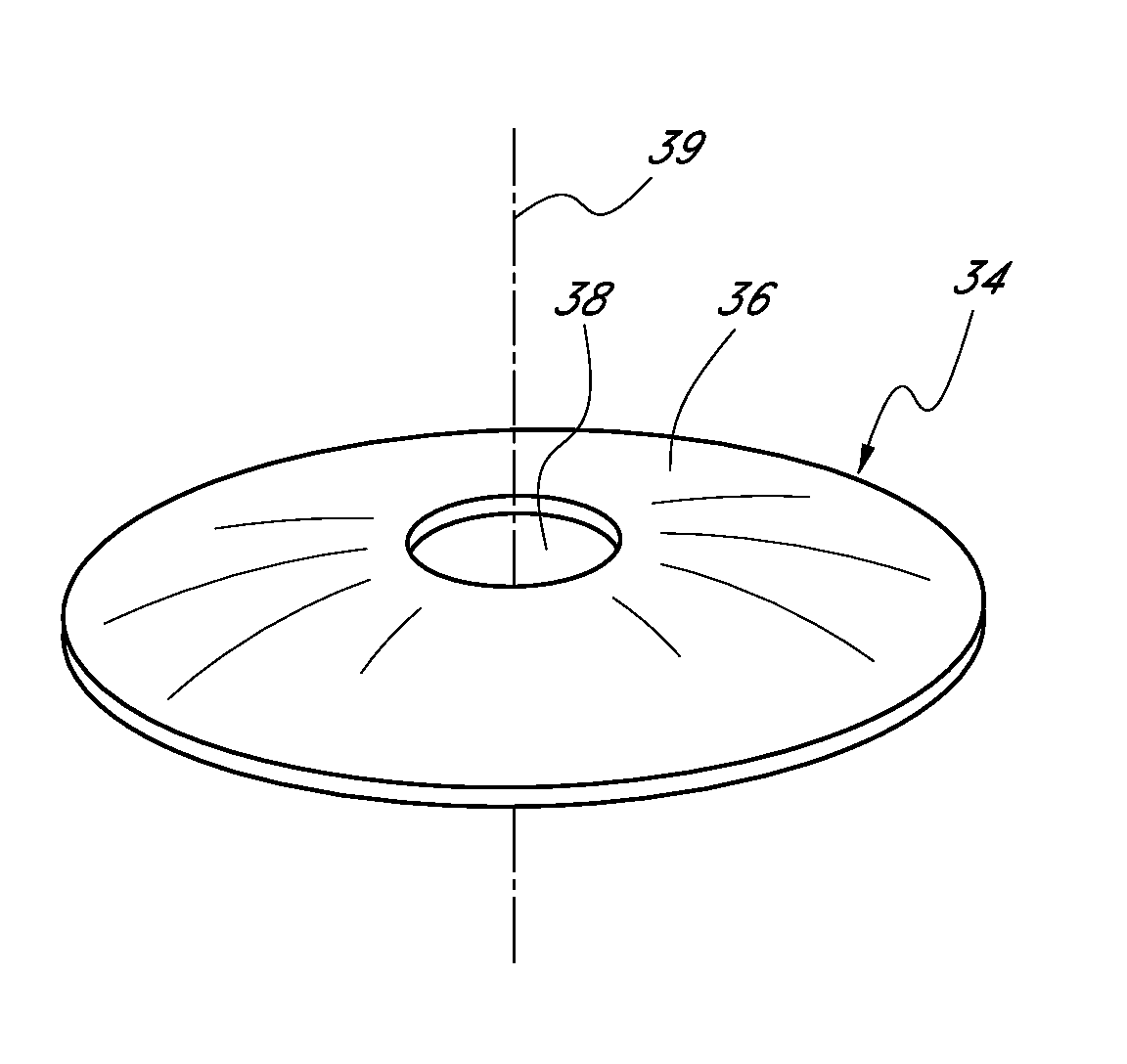
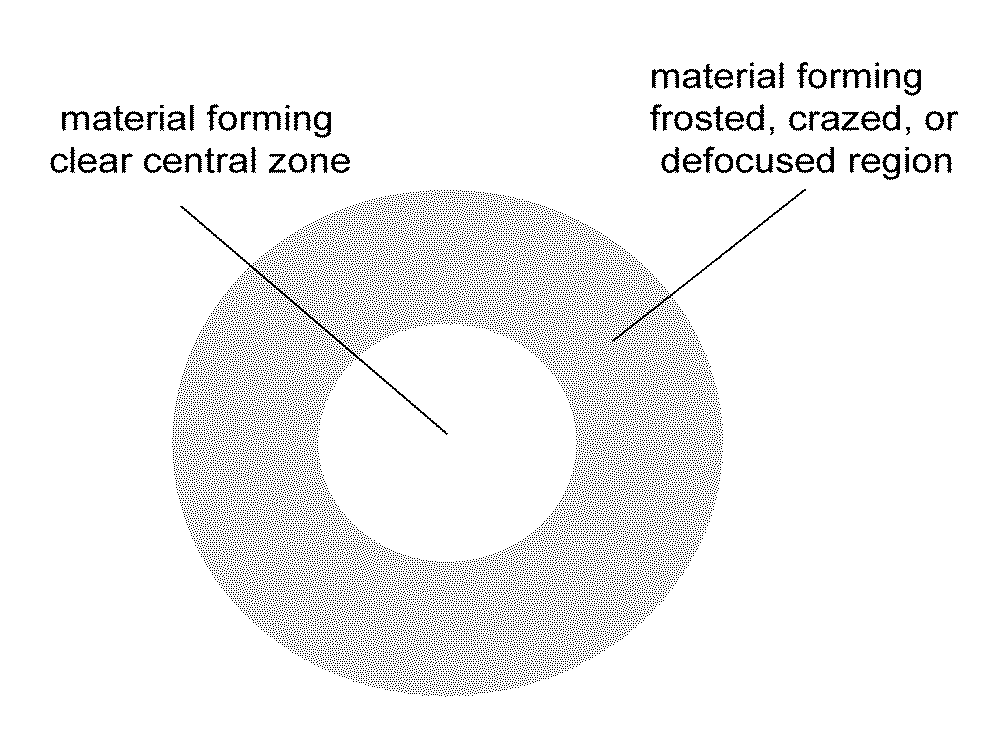
Corneal inlay with nutrient transport structures
ActiveUS20120143325A1Improve eyesightEnhanced nutrient flowEye implantsOptical partsCorneal inlayNutrient flow
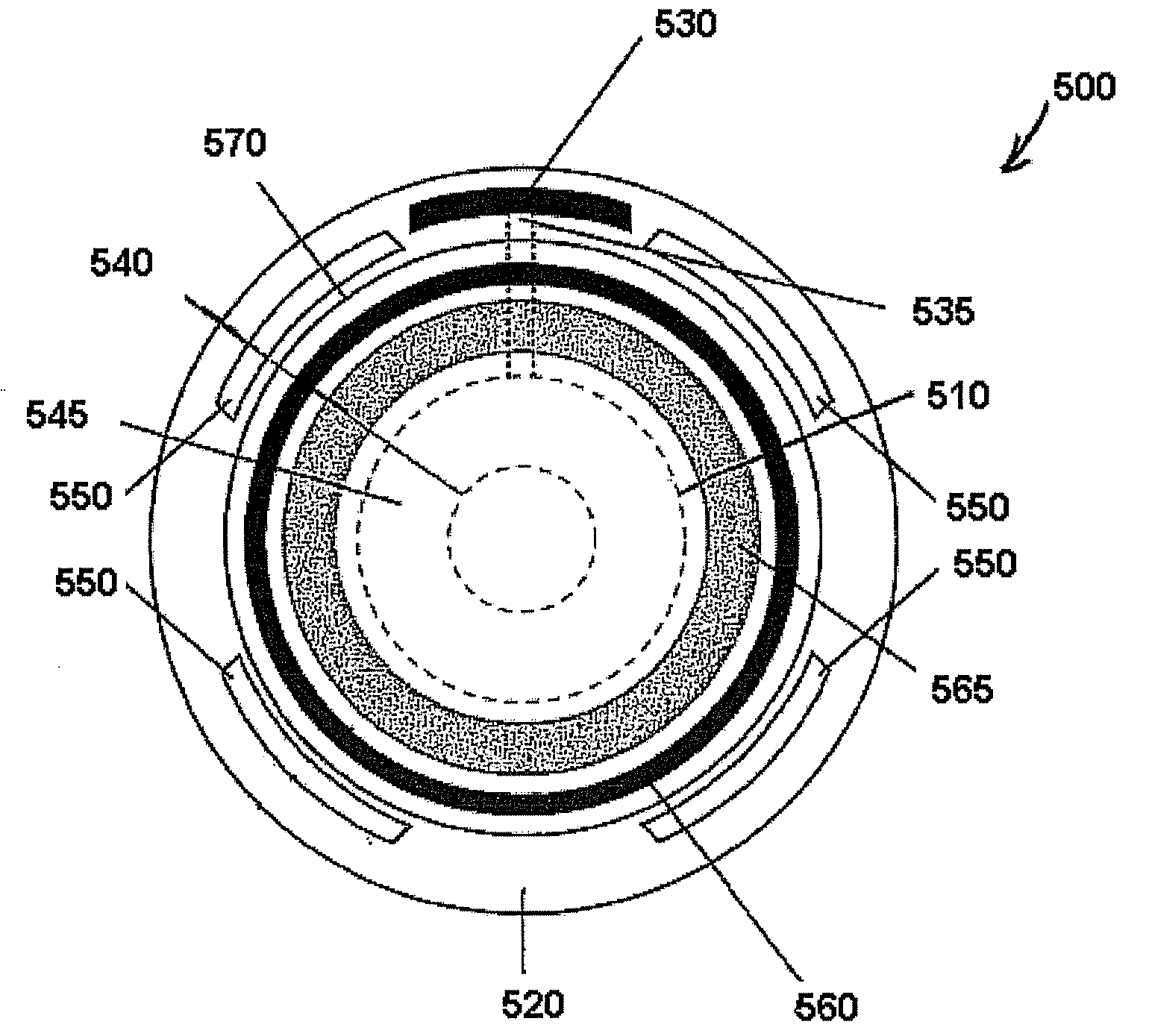
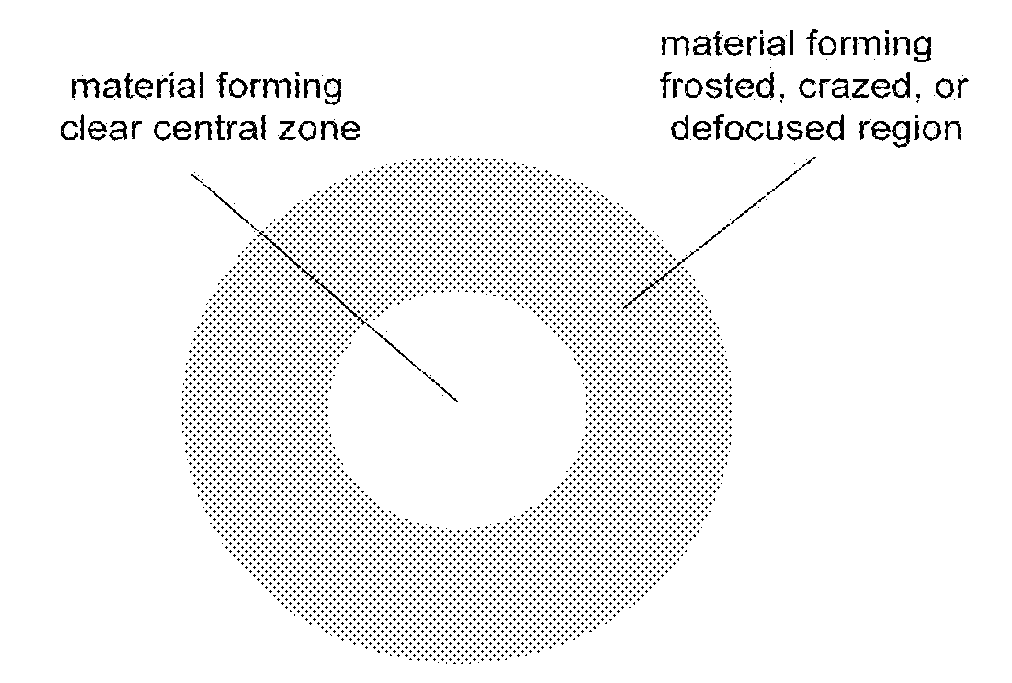
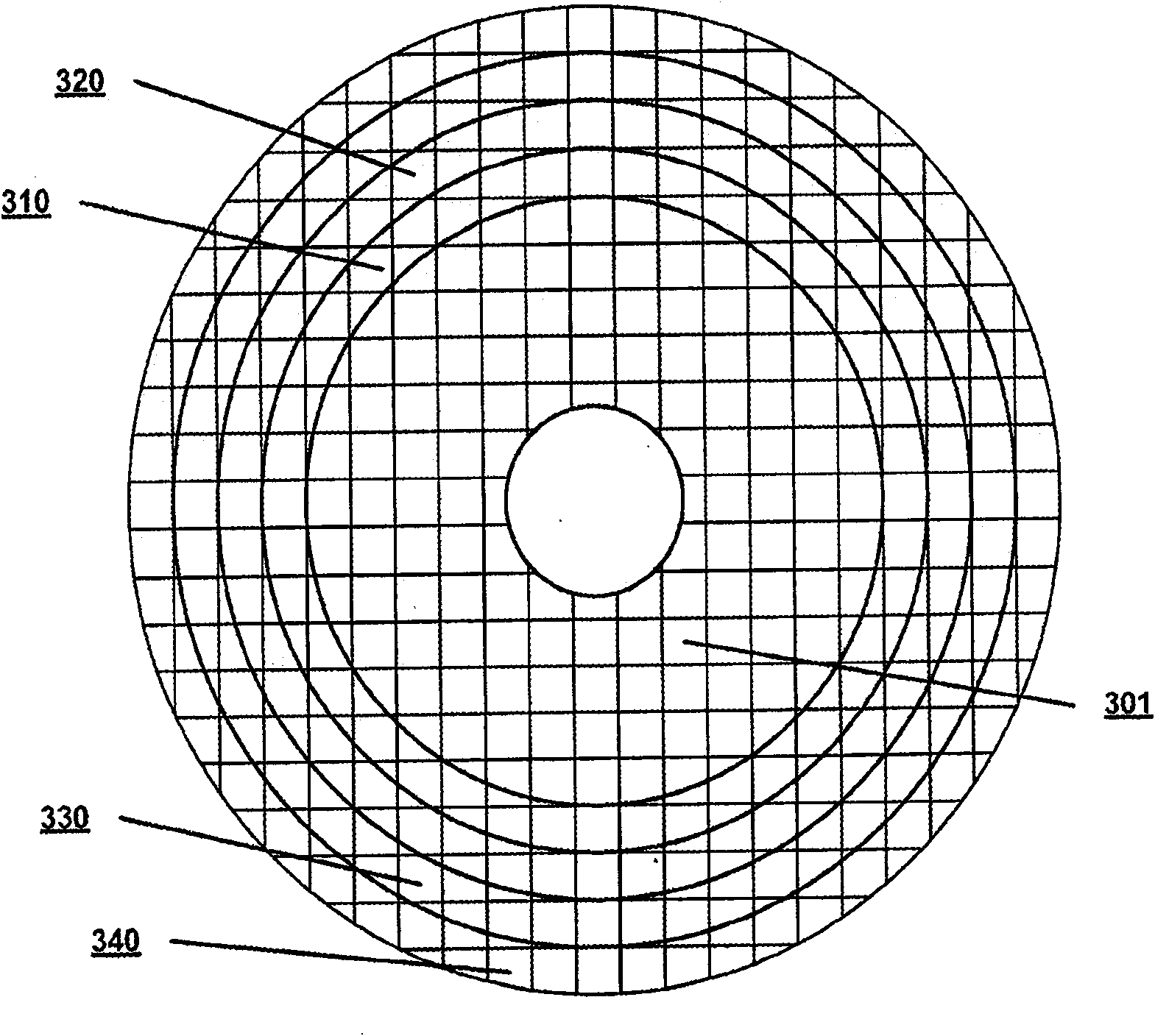
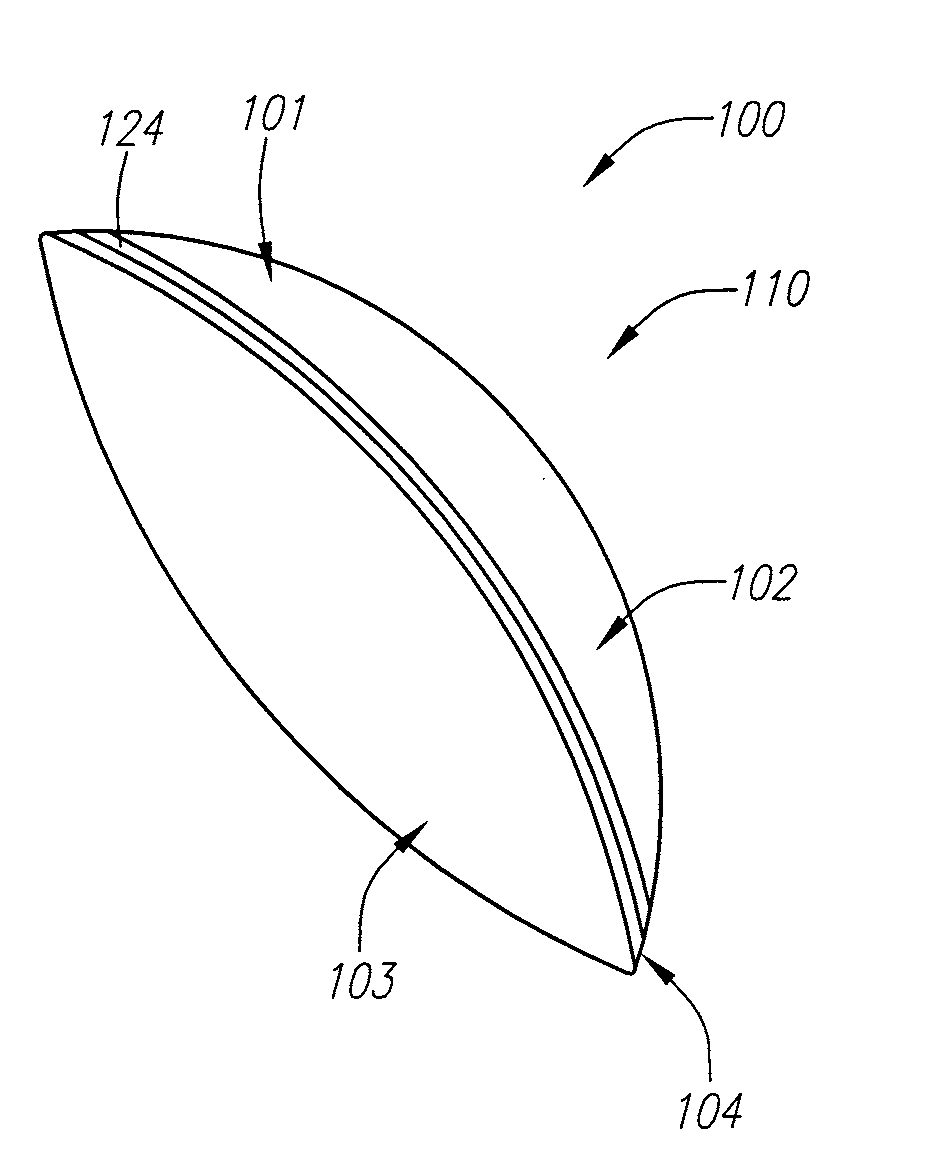
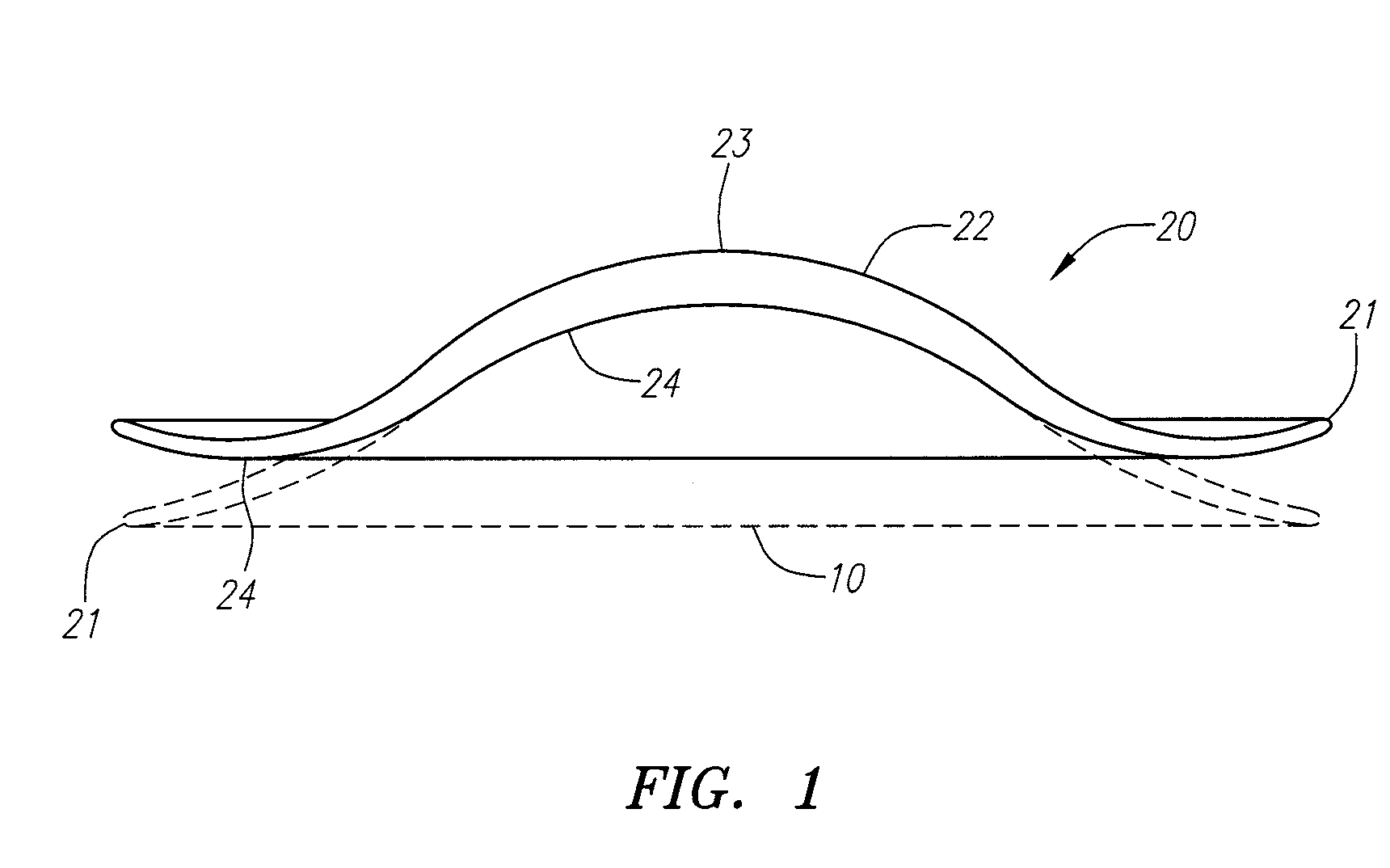
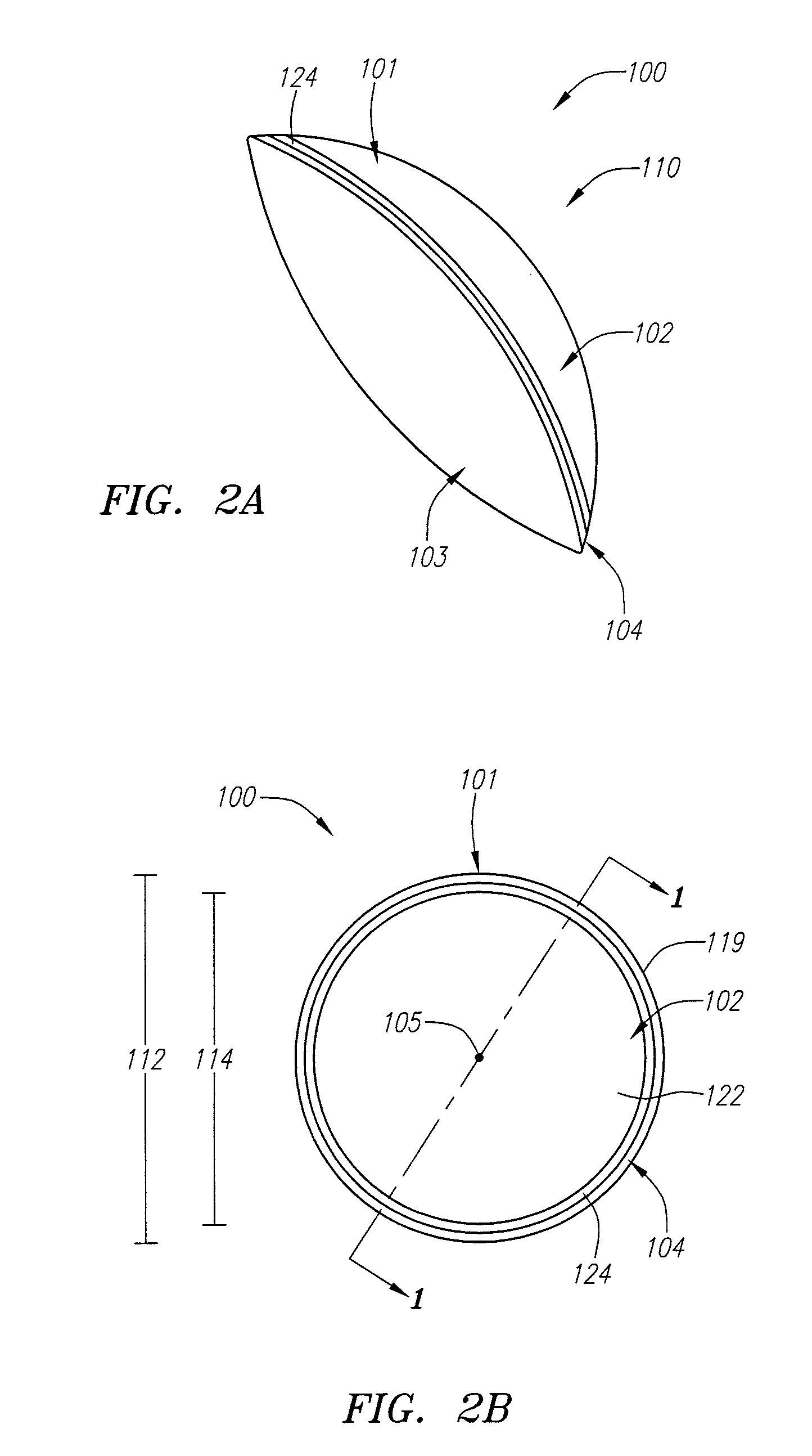
Corneal inlays and masks and methods of improving vision of a patient with corneal inlays and masks are provided. Masks with an aperture can improve the vision of a patient, such as by increasing the depth of focus of an eye of a patient. For example, a mask can have an annular portion with a relatively low visible light transmission surrounding a relatively high transmission central portion, such as a clear lens or aperture. This provides an annular mask with a small aperture for light to pass through to the retina to increase depth of focus. The mask may also include nutrient transport structures that provide nutrient flow through mask to prevent nutrient depletion. These nutrient transport structures can be configured to concentrate nutrient transmission near a center region of the mask to provide more nutrient flow near the center region.
Owner:CORNEAGEN INC
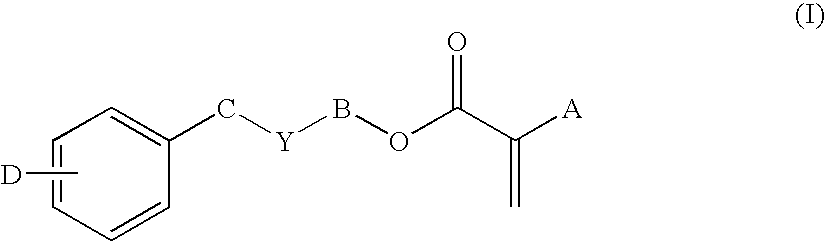
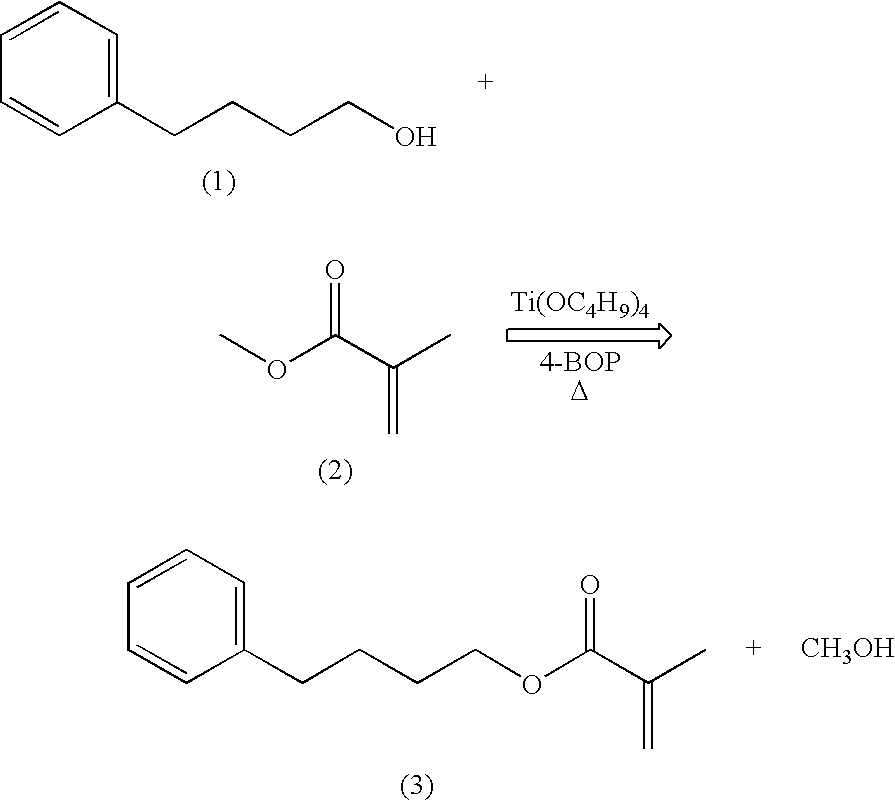
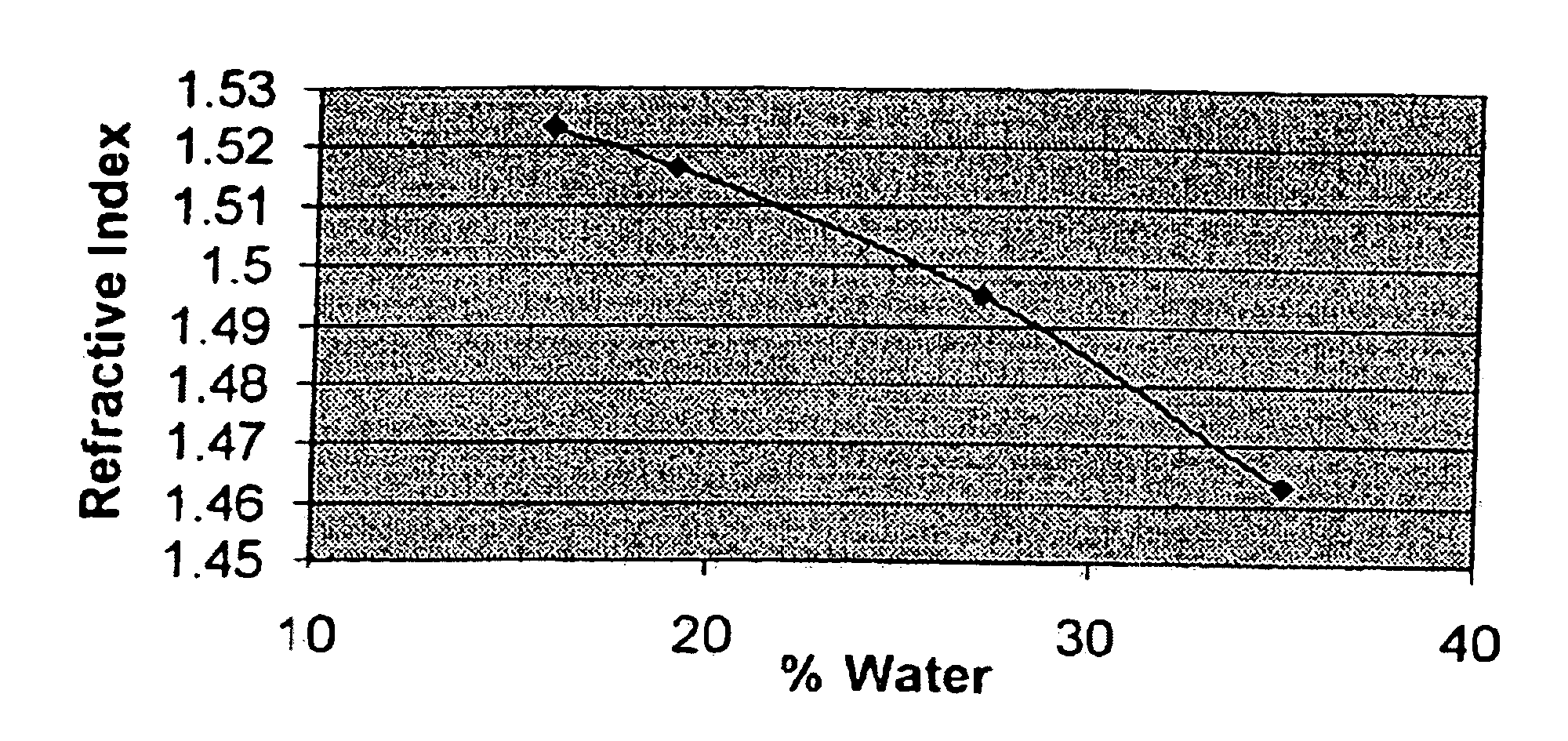
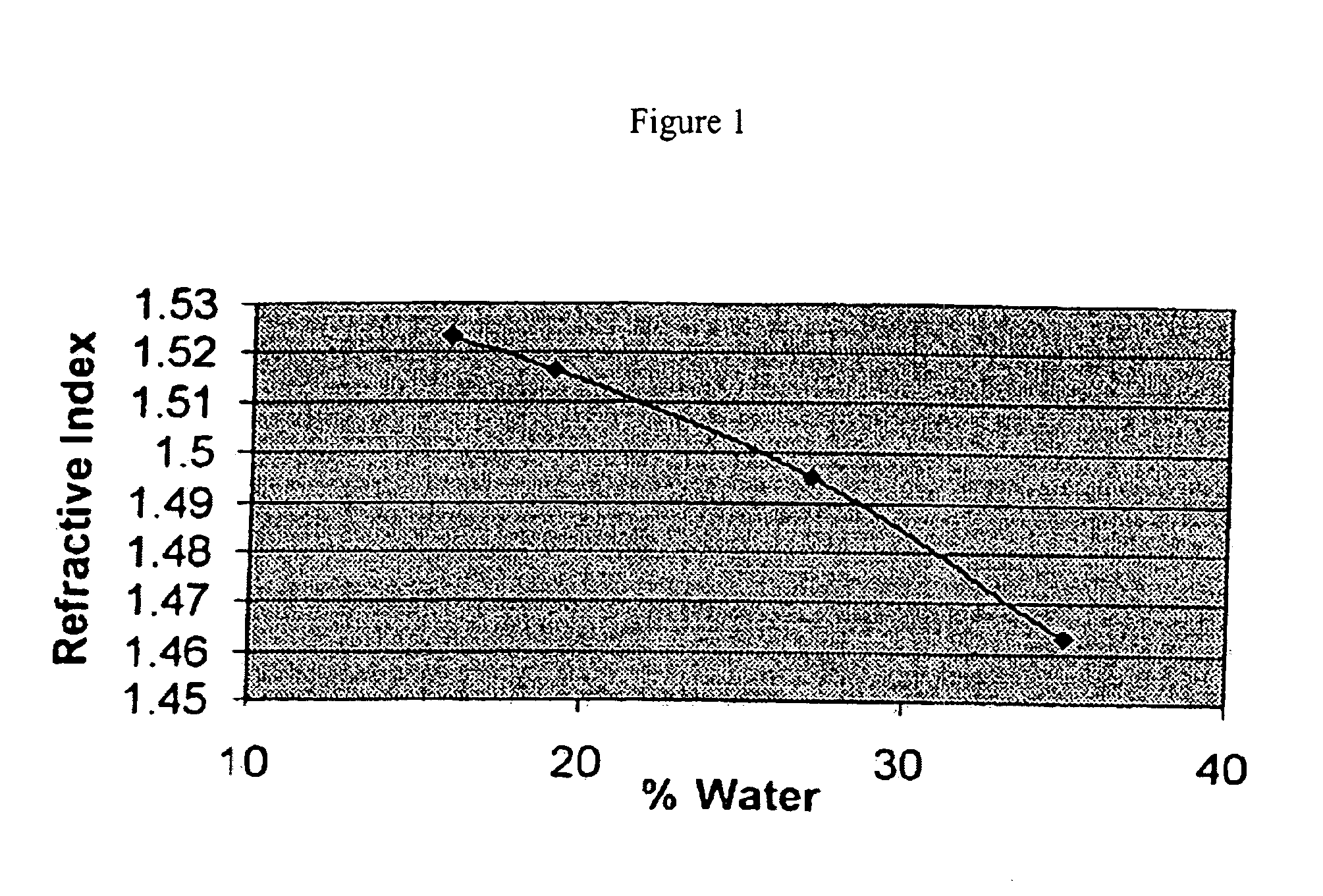
Low-tack ophthalmic and otorhinolaryngological device materials
Disclosed are soft, high refractive index, acrylic materials. These materials, especially useful as intraocular lens materials, contain an aryl acrylic hydrophobic monomer as the single principal device-forming monomer and a tack-reducing macromer additive. In addition to their use as intraocular lens materials, the present materials are also suitable for use in other ophthalmic or otorhinolaryngological devices, such as contact lenses, keratoprostheses, corneal inlays or rings; otological ventilation tubes and nasal implants.
Owner:ALCON INC
High refractive index silicone-containing prepolymers with blue light absorption capability
InactiveUS7033391B2Desirable physical characteristicHigh refractive indexGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsIntraocular lensRefractive indexCorneal inlay
A process for producing silicone-containing prepolymers capable of absorbing blue light for use in the production of relatively high refractive index polymeric compositions is described herein. Polymeric compositions so produced are useful in the production of ophthalmic devices such as for example intraocular lenses and corneal inlays.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
High performance corneal inlay
A corneal inlay protects ocular structures from harmful wavelengths of light while maintaining acceptable color cosmetics, color perception, overall light transmission, photopic vision, scotopic vision, color vision, and / or cirdadian rhythms. The corneal inlay can also include a pinhole effect to increase depth of focus. In some embodiments, the corneal inlay can also correct refractive errors including, but not limited to, higher order aberration, lower order aberration, myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and / or presbyopia.
Owner:HIGH PERFORMANCE OPTICS
Radiation-absorbing polymeric materials and ophthalmic devices comprising same
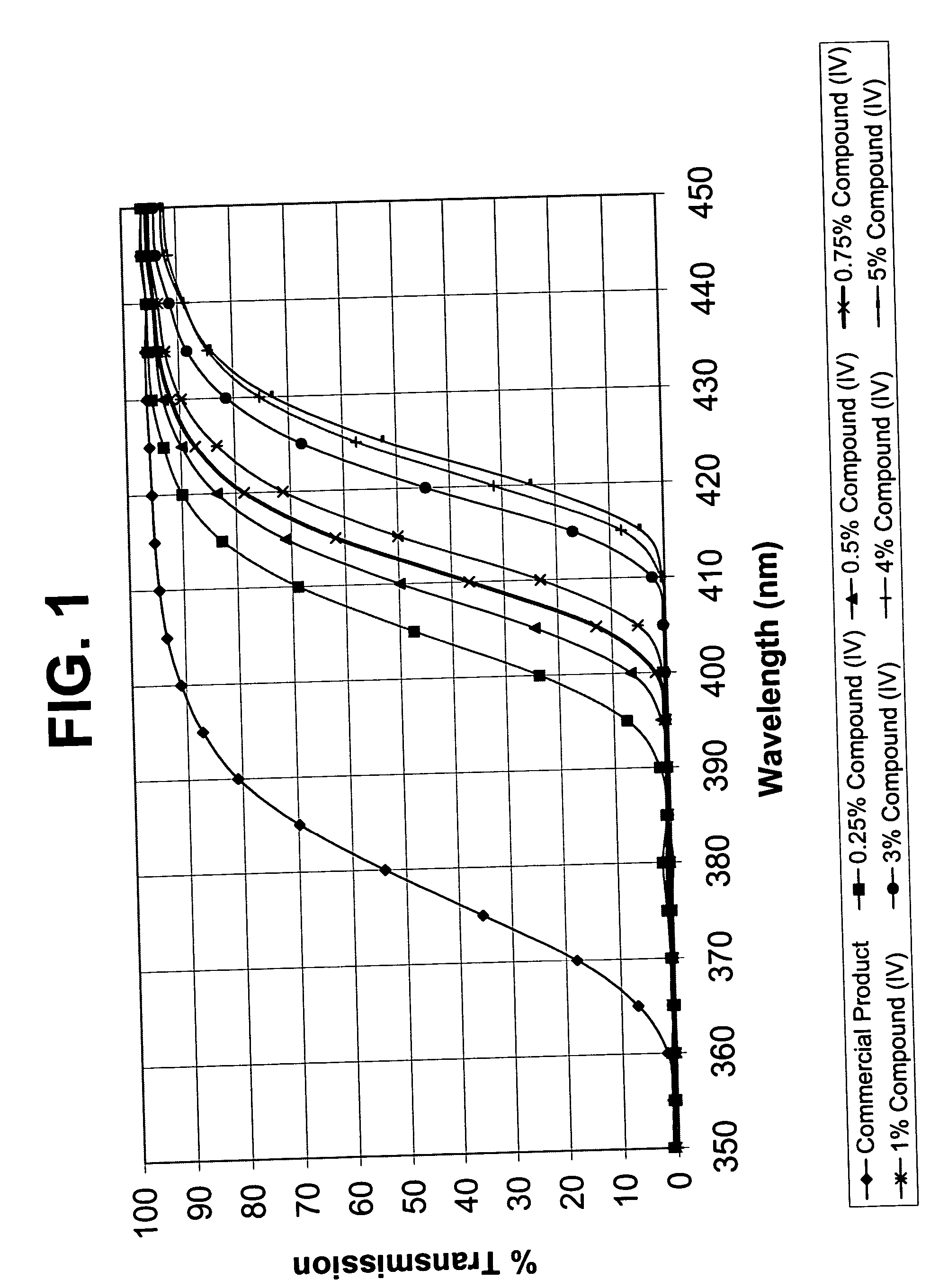
A radiation-absorbing polymeric material comprises units of a polymerizable UV-absorbing compound and a monomer, and is capable of absorbing UV radiation, and at least about 50 percent of light having wavelengths in the range from about 400 nm to about 425 nm. The radiation-absorbing polymeric material can further comprise units of a crosslinking agent. Ophthalmic devices, such as contact lenses, corneal rings, corneal inlays, keratoprostheses, and intraocular lenses, are made from such polymeric material.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Method of treatment of refractive errors using subepithelial or intrastromal corneal inlay with bonding coating
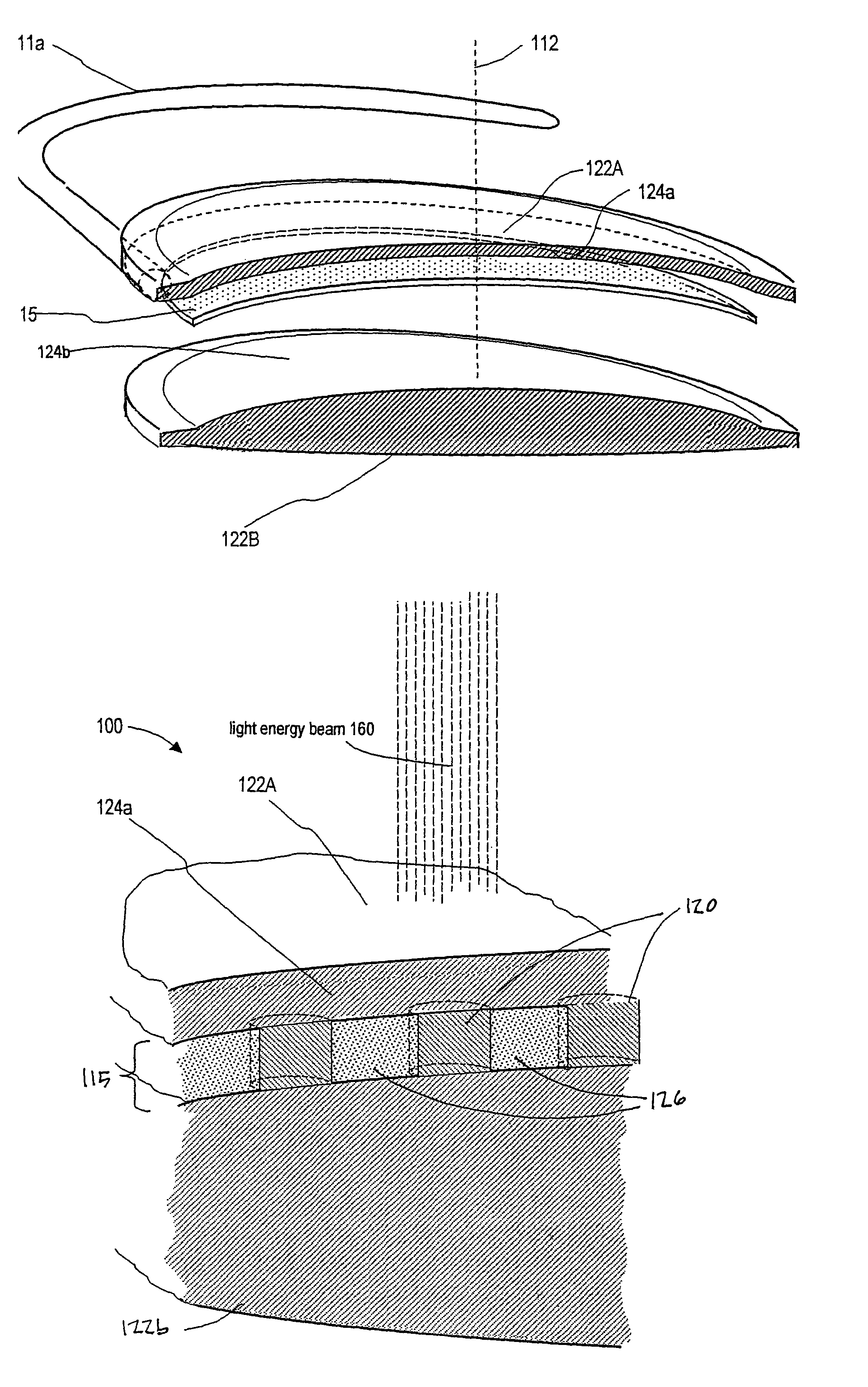
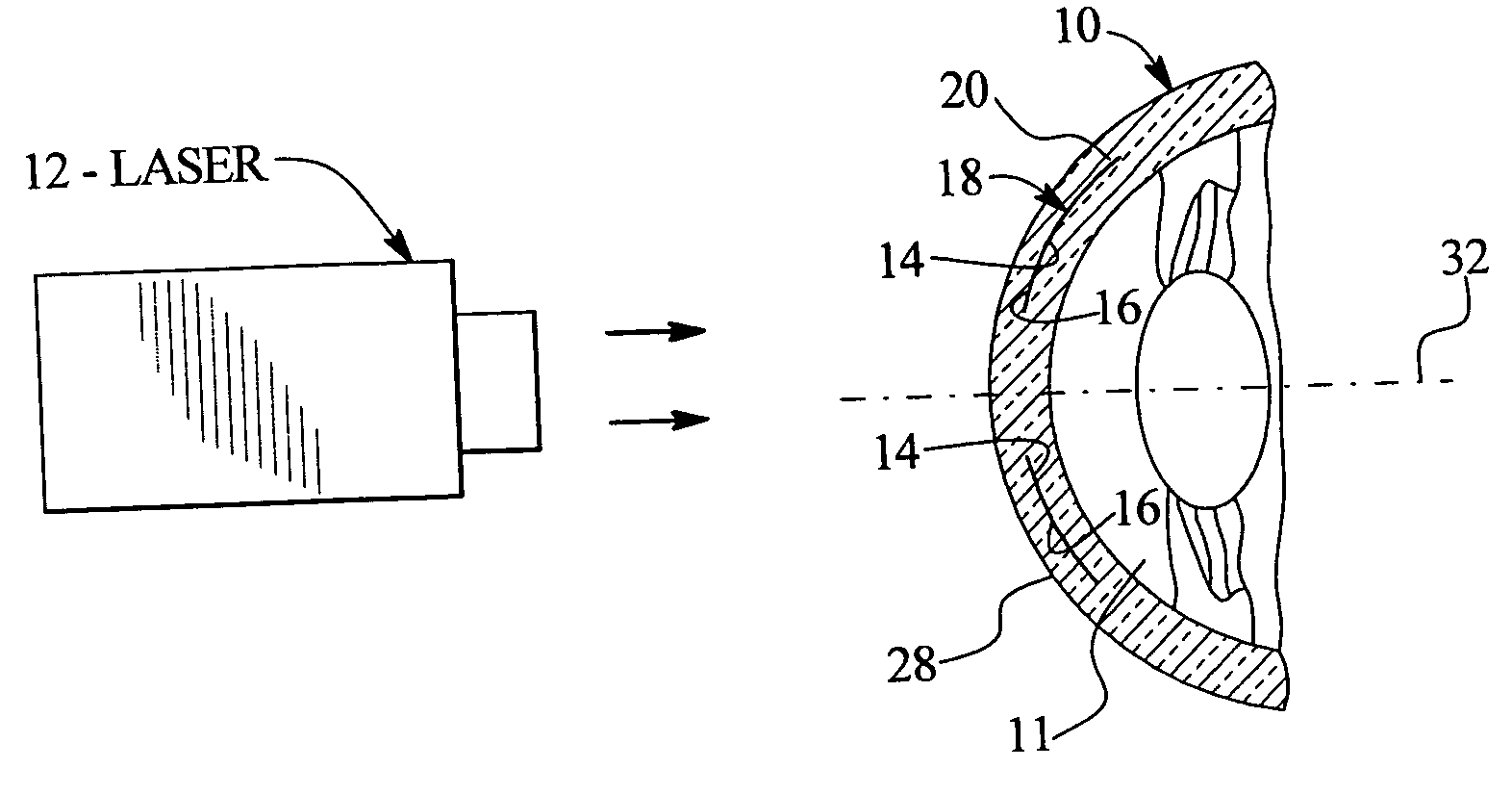
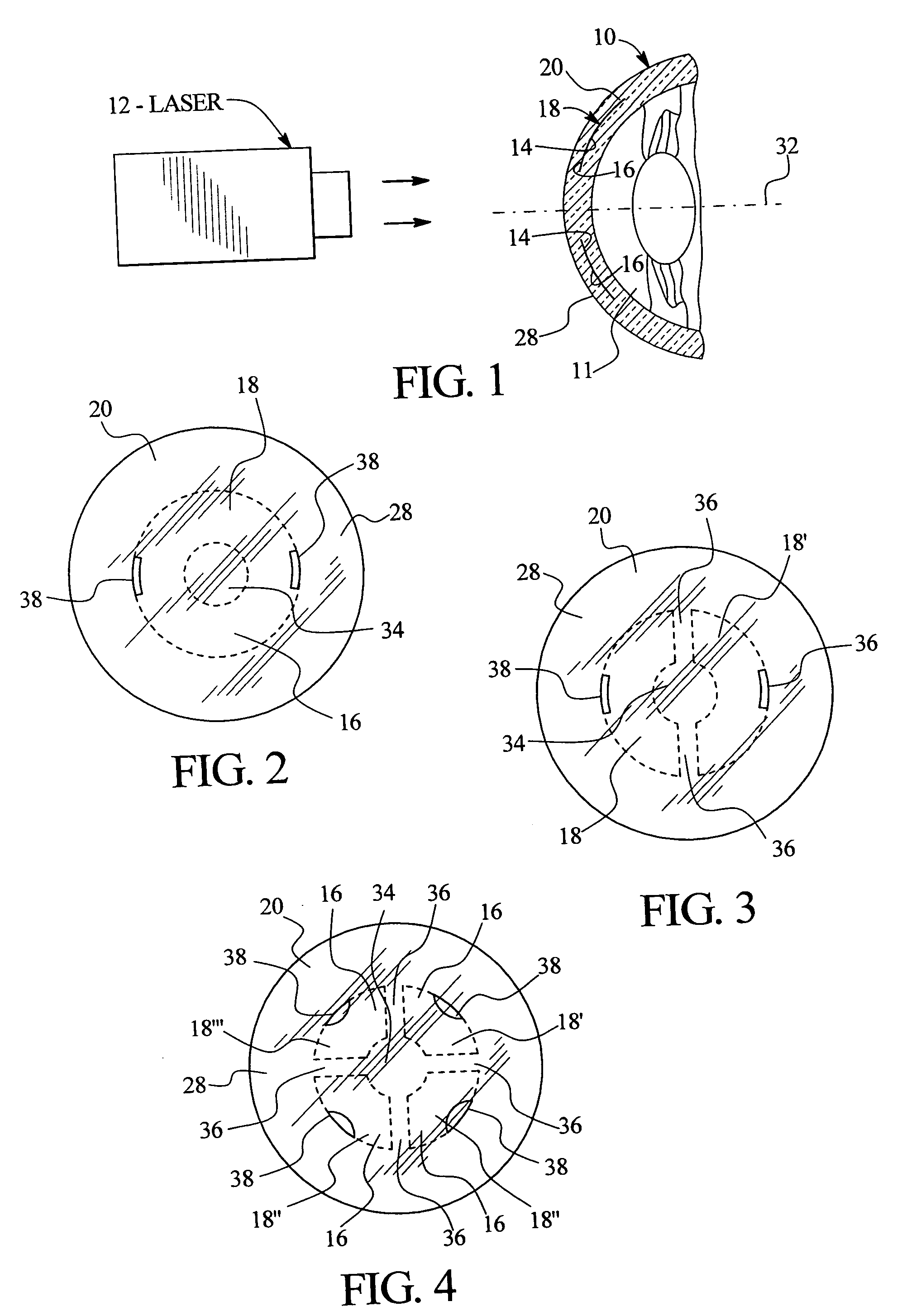
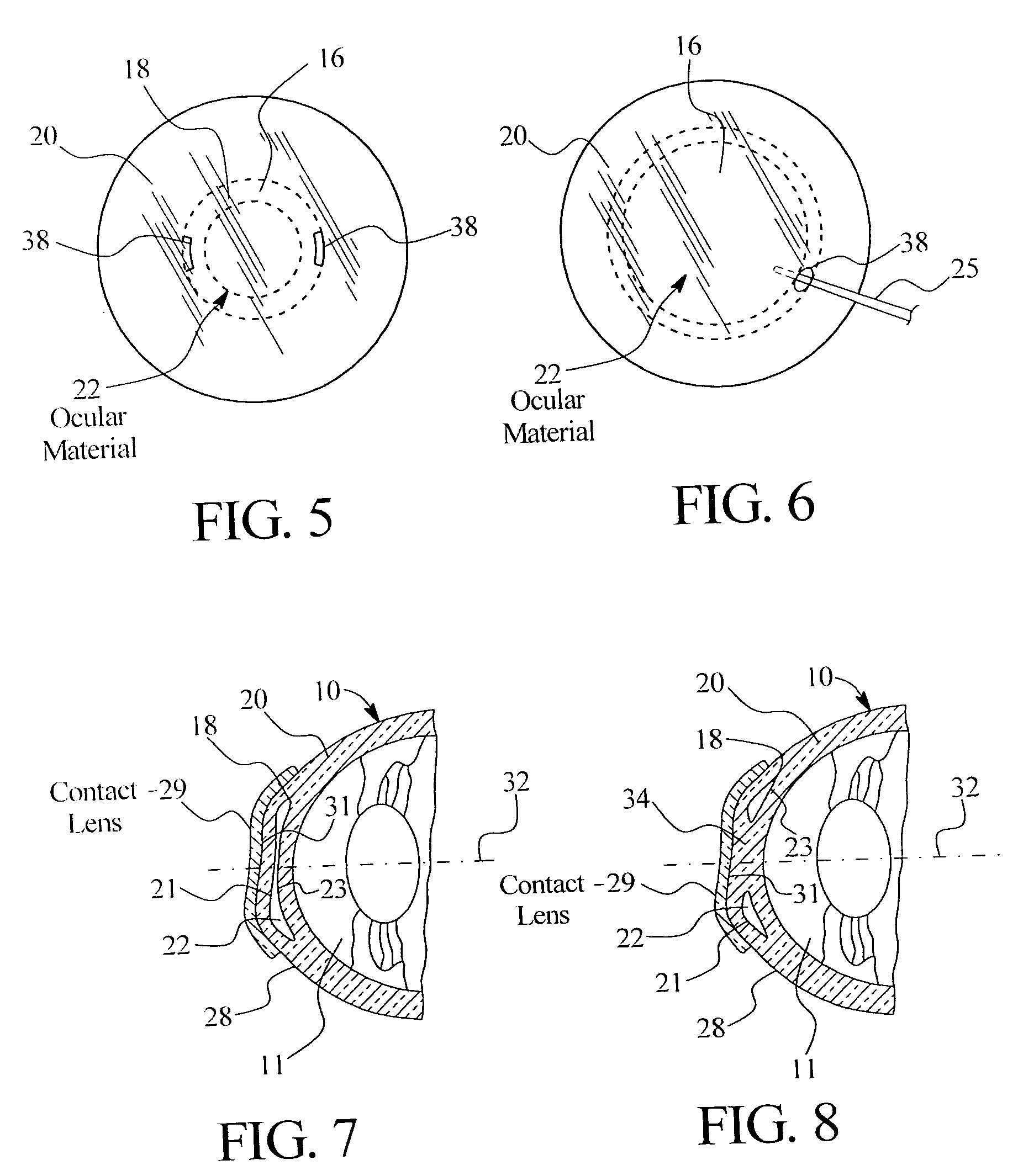
InactiveUS20050143717A1Simple methodAccurate separationLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive errorCorneal inlay
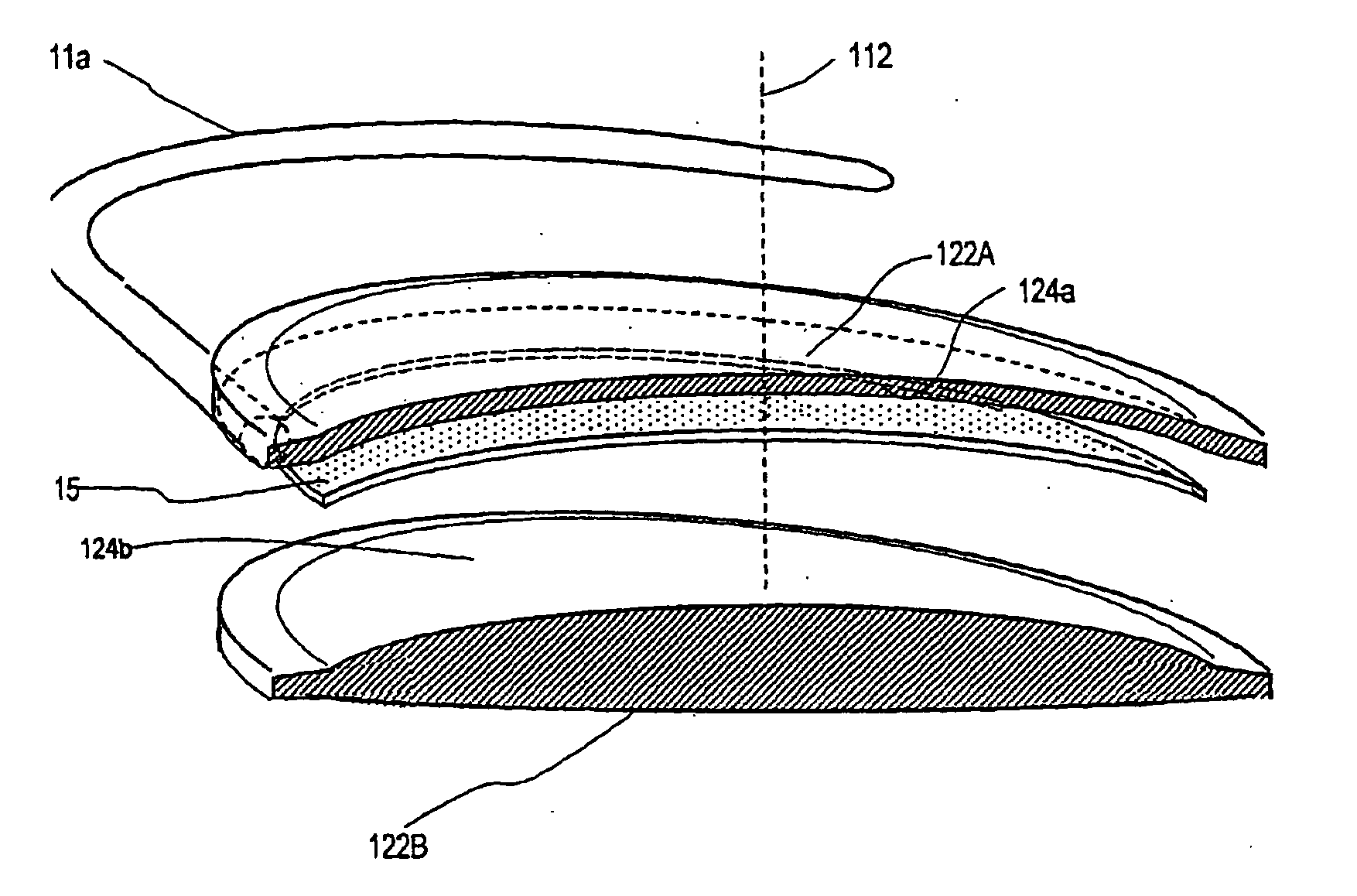
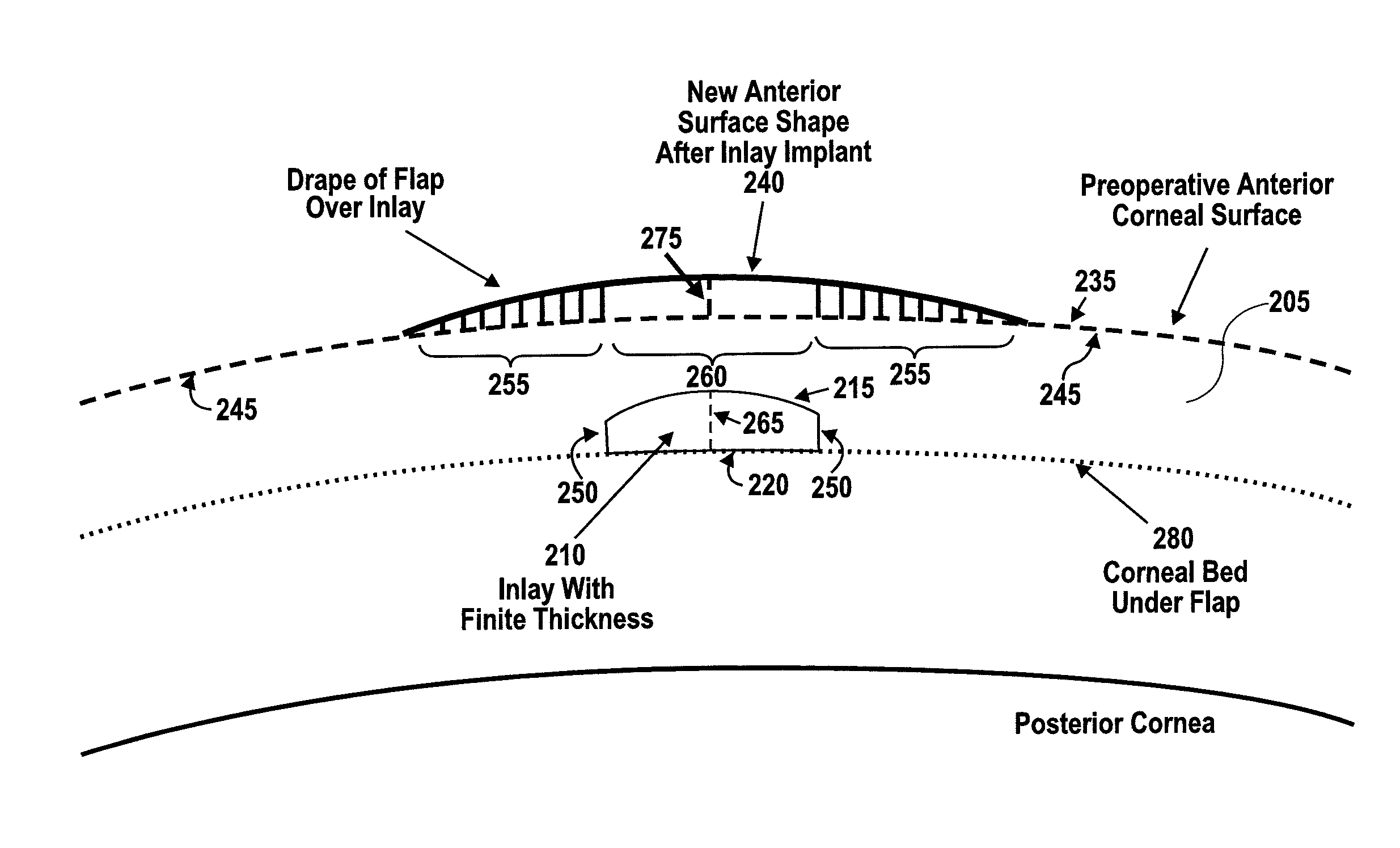
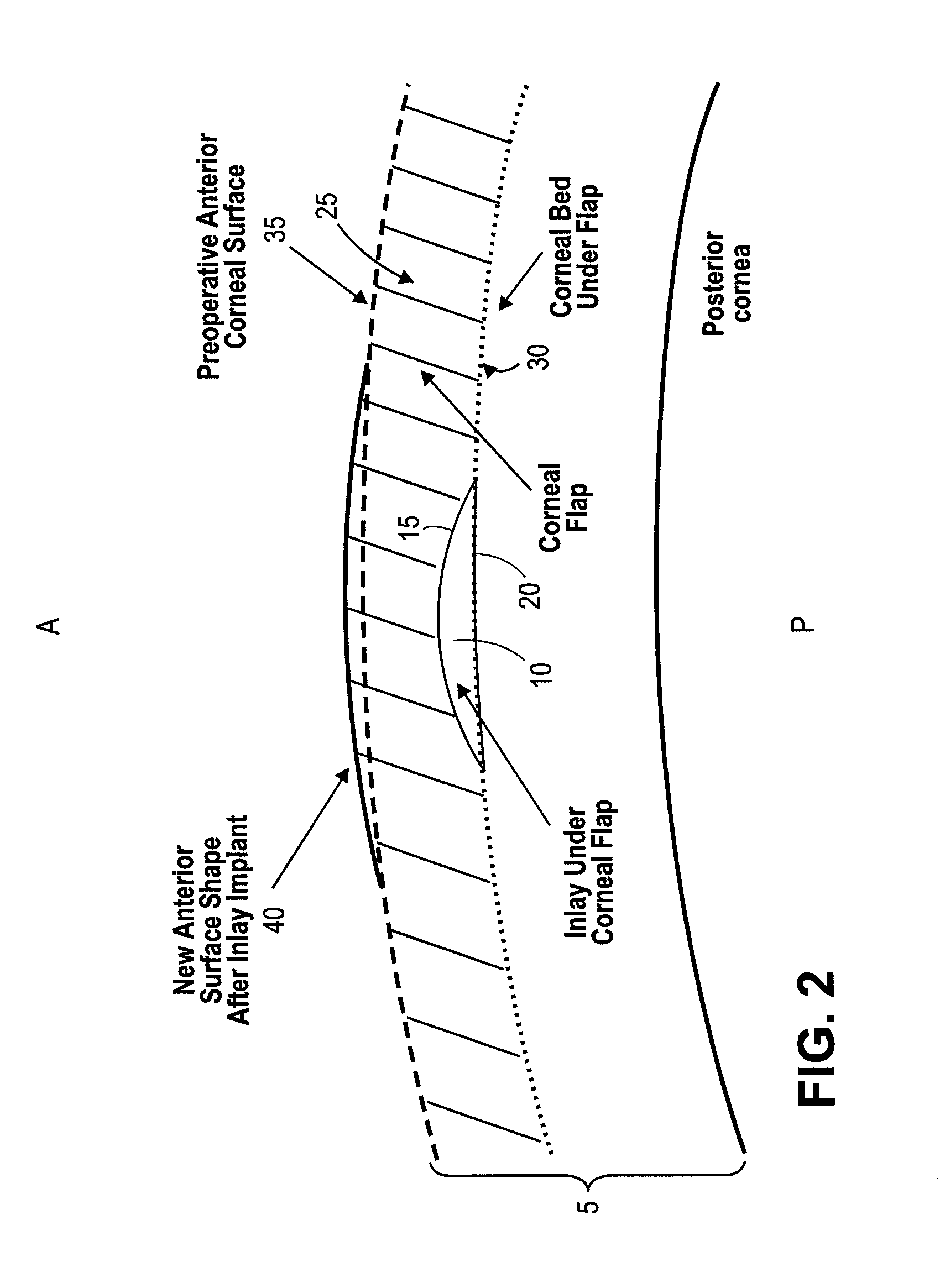
A method of treatment of refractive errors of an eye, the eye including a central visual axis and a cornea with a first corneal layer overlying a second corneal layer, comprising the steps of separating a first surface of the first corneal layer from a second surface of the second corneal layer, thereby forming a flap and exposing the second surface, implanting on the second surface an inlay adapted to correct a refractive error of the eye, coating a surface of the inlay with a compound that promotes bonding with the cornea, and replacing the flap over the inlay.
Owner:MINU
Advanced electro-active optic device
Optical devices having a dynamic aperture and / or an apodization mask are provided. The aperture and / or mask may be provided by one or more electro-active elements, and may be used in an ophthalmic device that that is spaced apart from but in optical communication with an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, or a spectacle lens that provide an optical power.
Owner:PIXELOPTICS
Adaptive optic lens system and method of use
Owner:ALCON INC
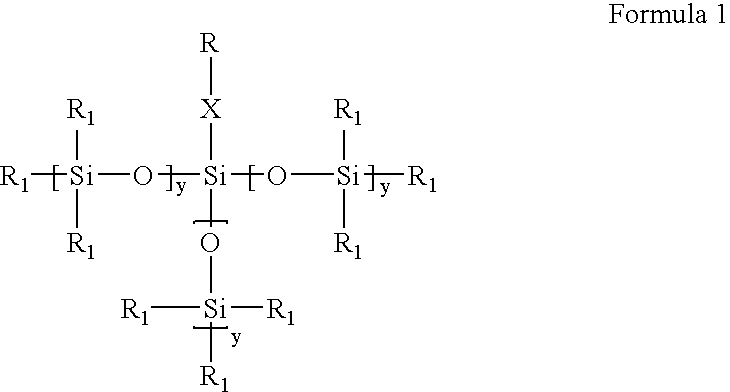
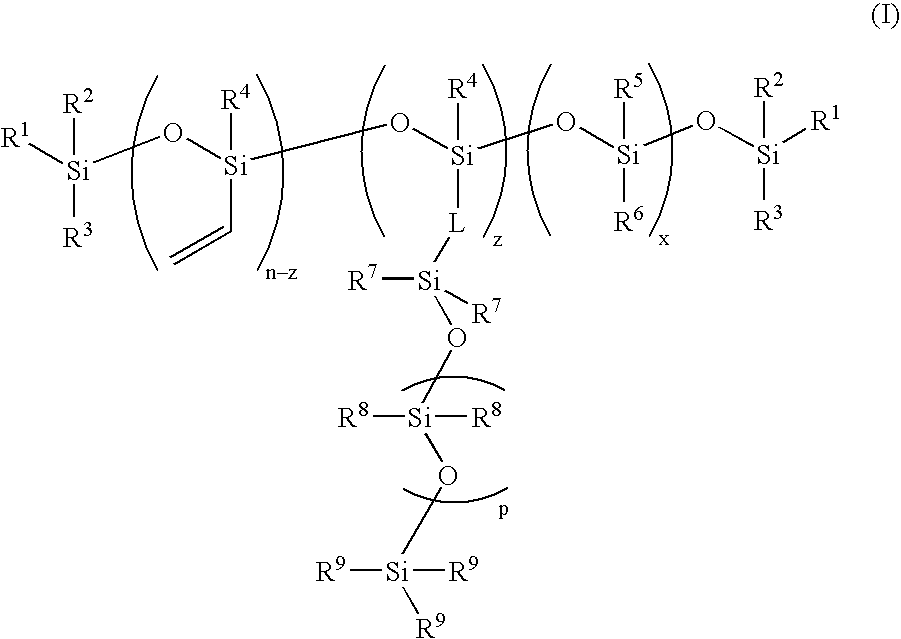
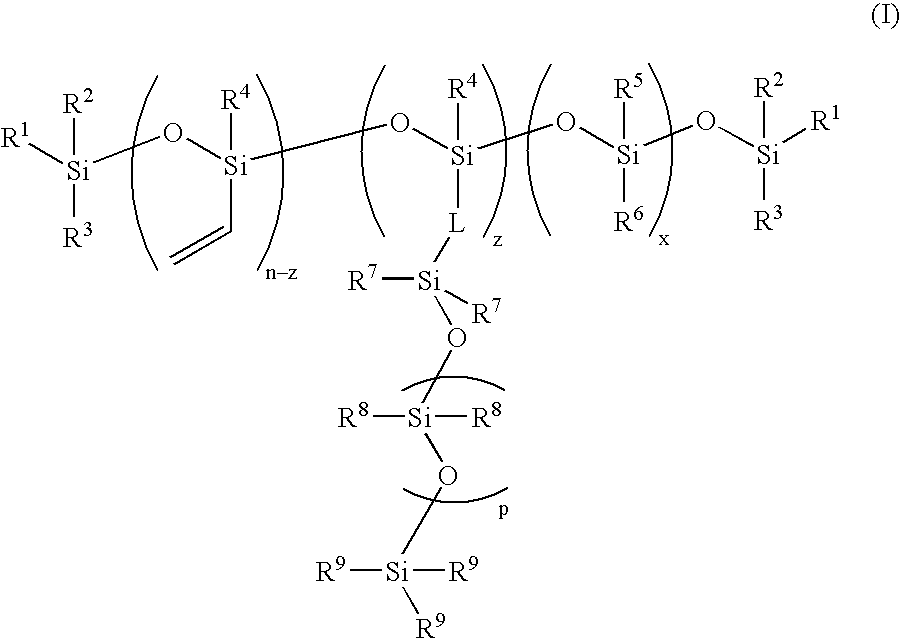
Process for the production of high refractive index polysiloxane-based polymeric compositions for use in medical devices
InactiveUS20050038219A1High refractive indexImprove homogeneityProsthesisOptical elementsPolymer scienceCorneal inlay
A process for producing polysiloxane prepolymers of improved homogeneity for use in the production of relatively high refractive index polymeric compositions is described herein. Polymeric compositions so produced are useful in the production of ophthalmic devices such as for example intraocular lenses and corneal inlays. The preferred polymeric compositions are produced through the copolymerization of one or more polysiloxane prepolymers with hydrosilane-containing polysiloxanes.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Prepolymers with yellow dye moiety
ActiveUS6918931B2Desirable physical characteristicHigh refractive indexGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOptical articlesYELLOW DYERefractive index
Yellow dye moiety-containing prepolymers with blue light absorbing priorities and methods for producing the same for use in the production of relatively high refractive index polymeric compositions are described herein. Polymeric compositions so produced are useful in the production of ophthalmic devices such as for example intraocular lenses and corneal inlays.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
High refractive index polysiloxane prepolymers
InactiveUS6956087B2Quality improvementImprove reliabilityOptical articlesSkin careCorneal inlayHigh-refractive-index polymer
A process for producing polysiloxane prepolymers of improved homogeneity for use in the production of relatively high refractive index polymeric compositions is described herein. Polymeric compositions so produced are useful in the production of ophthalmic devices such as for example intraocular lenses and corneal inlays.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Low-tack ophthalmic and otorhinolaryngological device materials
Disclosed are soft, high refractive index, acrylic materials. These materials, especially useful as intraocular lens materials, contain one or more aryl acrylic hydrophobic monomers as principal device-forming monomers and a tack-reducing macromer additive. In addition to their use as intraocular lens materials, the present materials are also suitable for use in other ophthalmic or otorhinolaryngological devices, such as contact lenses, keratoprostheses, corneal inlays or rings; otological ventilation tubes and nasal implants.
Owner:ALCON INC
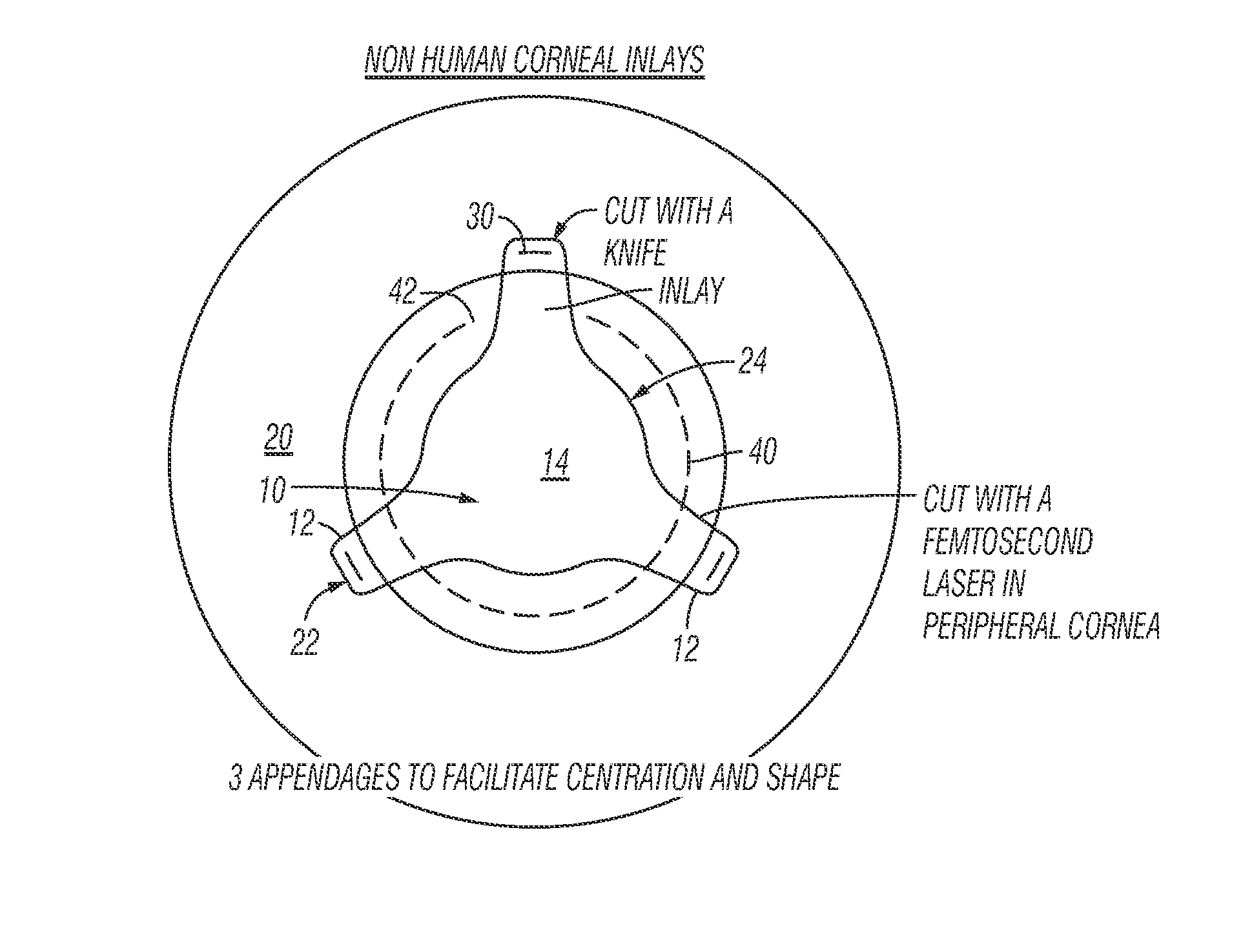
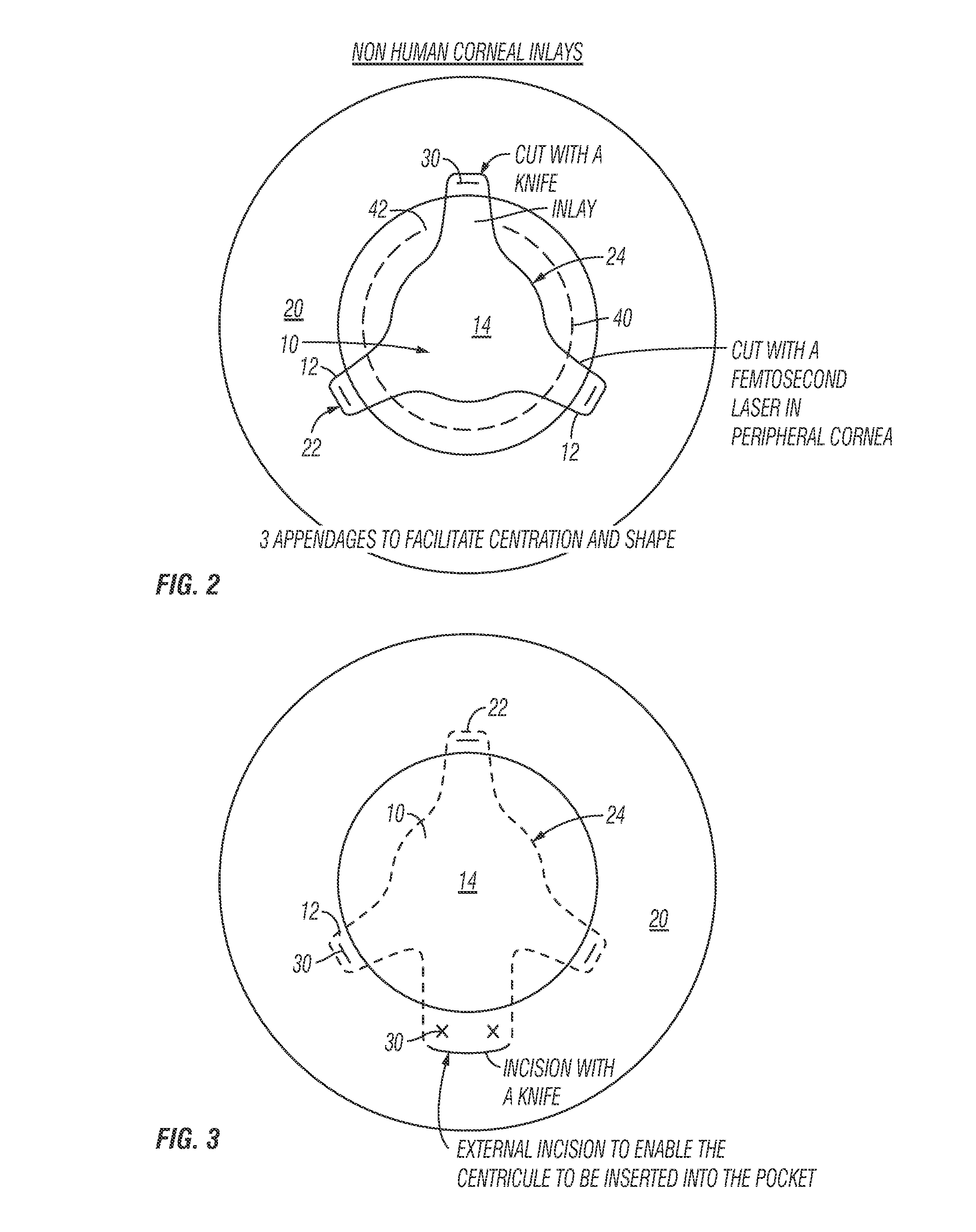
Method for preparing corneal donor tissue for refractive eye surgery utilizing the femtosecond laser
InactiveUS20140155871A1High precisionKeep clearLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsFiberCross-link
A method of accurately fabricating a non-human donor corneal tissue for implantation into a recipient human cornea, the method comprising the steps of: removing corneal tissue from a donor with a femtosecond laser; placing the corneal tissue in a fixative solution for a selected time interval to cross-link the collagen fibrils in the tissue and prevent swelling of the corneal tissue; and shaping the tissue to provide a conical inlay of a selected shape and thickness having one or more radial extensions. The method is such that the corneal inlay may be attached to the peripheral corneal and / or the sclera. The method is such that the corneal inlay may be stored for a period of up to two years prior to attachment.
Owner:CUMMING JAMES STUART
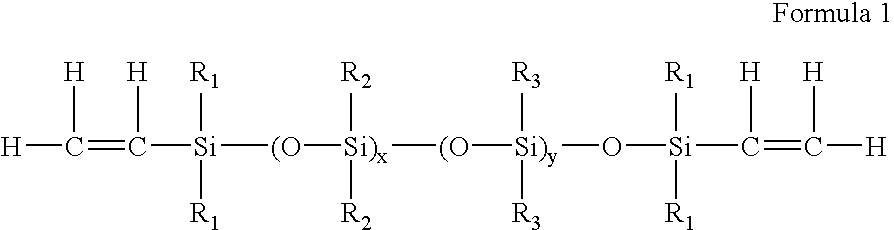
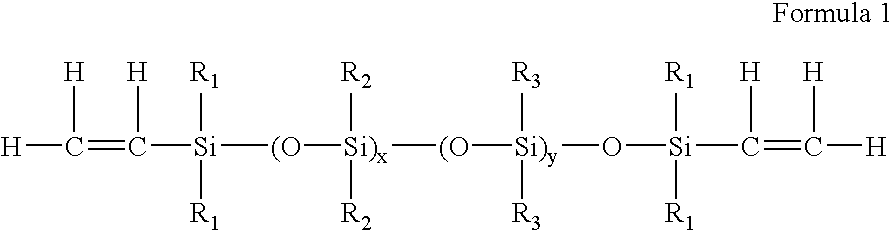
High refractive index polymeric siloxysilane compositions
InactiveUS6908978B2Improve clarityEasy to produceSilicon organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationHydrophilic monomerHydrophilic polymers
Optically transparent, relatively high refractive index polymeric compositions and ophthalmic devices such as intraocular lenses, contact lenses and corneal inlays made therefrom are described herein. The preferred polymeric compositions are produced through the polymerization of one or more siloxysilane monomers or the copolymerization of one or more siloxysilane monomers with one or more aromatic or non-aromatic non-siloxy monomers, hydrophobic monomers or hydrophilic monomers.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Ophthalmic Device and Related Methods and Compositions
Devices, methods, and compositions for improving vision or treating diseases, disorders or injury of the eye are described. Ophthalmic devices, such as corneal onlays, corneal inlays, and full-thickness corneal implants, are made of a material that is effective in facilitating nerve growth through or over the device. The material may include an amount of collagen greater than 1% (w / w), such as between about 10% (w / w) and about 30% (w / w). The material may include collagen polymers and / or a second biopolymer or water-soluble synthetic polymer cross-linked using EDC / NHS chemistry. The material may additionally comprise a synthetic polymer. The devices are placed into an eye to correct or improve the vision of an individual or to treat a disease, disorder or injury of an eye of an individual.
Owner:OTTAWA HOSPITAL RES INST +2
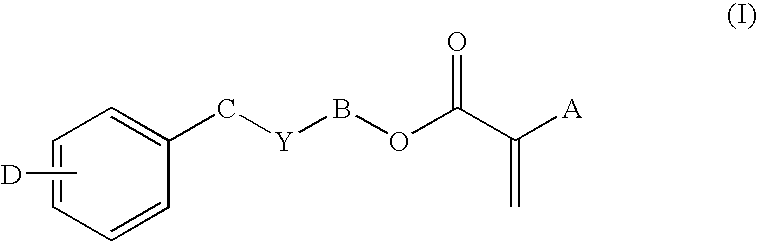
Optical Hydrogel Material with Photosensitizer and Method for Modifying the Refractive Index
ActiveUS20130268072A1Promote formationImprove visual effectsSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryPhotosensitizerOptical polymers
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Corneal inlay design and methods of correcting vision
Methods of designing corneal implants, such as inlays, to compensate for a corneal response, such as epithelial remodeling of the epithelial layer, to the presence of the implant. Additionally, methods of performing alternative corneal vision correction procedures to compensate for an epithelial response to the procedure. Methods of compensating for a corneal response when performing a vision correction procedure to create a center near region of the cornea for near vision while providing distance vision peripheral to the central near zone.
Owner:RVO 2 0 INC D B A OPTICS MEDICAL
Small Diameter Inlays
Small diameter corneal inlays adapted to change the corneal surface curvature to provide central near vision and peripheral distance vision.
Owner:REVISION OPTICS
High refractive-index siloxy-containing monomers and polymers, and ophthalmic devices comprising such polymers
ActiveUS20070142551A1High compositionHigh refractive indexCosmetic preparationsImpression capsCorneal ringRefractive index
Siloxy-containing monomers, macromonomers, or polymers have at least a siloxy-containing side group that comprises a refractive-index increasing substituent. Polymeric compositions comprising such siloxy-containing monomers, macromonomers, or polymers are advantageously used for making ophthalmic devices, such as intraocular lenses, contact lenses, corneal rings, corneal inlays, and keratoprostheses.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Low-tack ophthalmic and otorhinolaryngological device materials
Disclosed are soft, high refractive index, acrylic materials. These materials, especially useful as intraocular lens materials, contain one or more aryl acrylic hydrophobic monomers as principal device-forming monomers and a tack-reducing macromer additive. In addition to their use as intraocular lens materials, the present materials are also suitable for use in other ophthalmic or otorhinolaryngological devices, such as contact lenses, keratoprostheses, corneal inlays or rings; otological ventilation tubes and nasal implants.
Owner:ALCON INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com