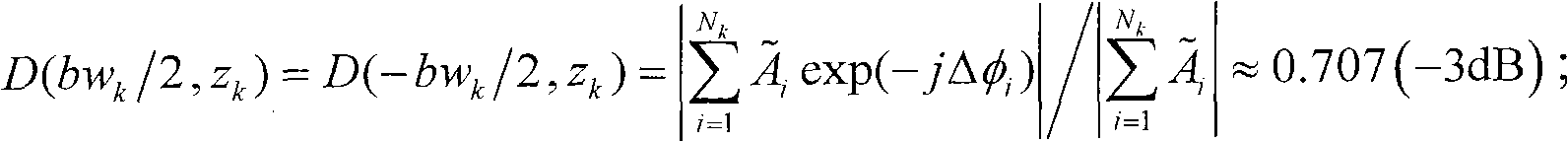Patents
Literature
48 results about "Dynamic aperture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In acoustics, dynamic aperture is analogous to aperture in photography. The arrays in side-scan sonar can be programmed to transmit just a few elements at a time or all the elements at once. The more elements transmitting, the narrower the beam and the better the resolution.
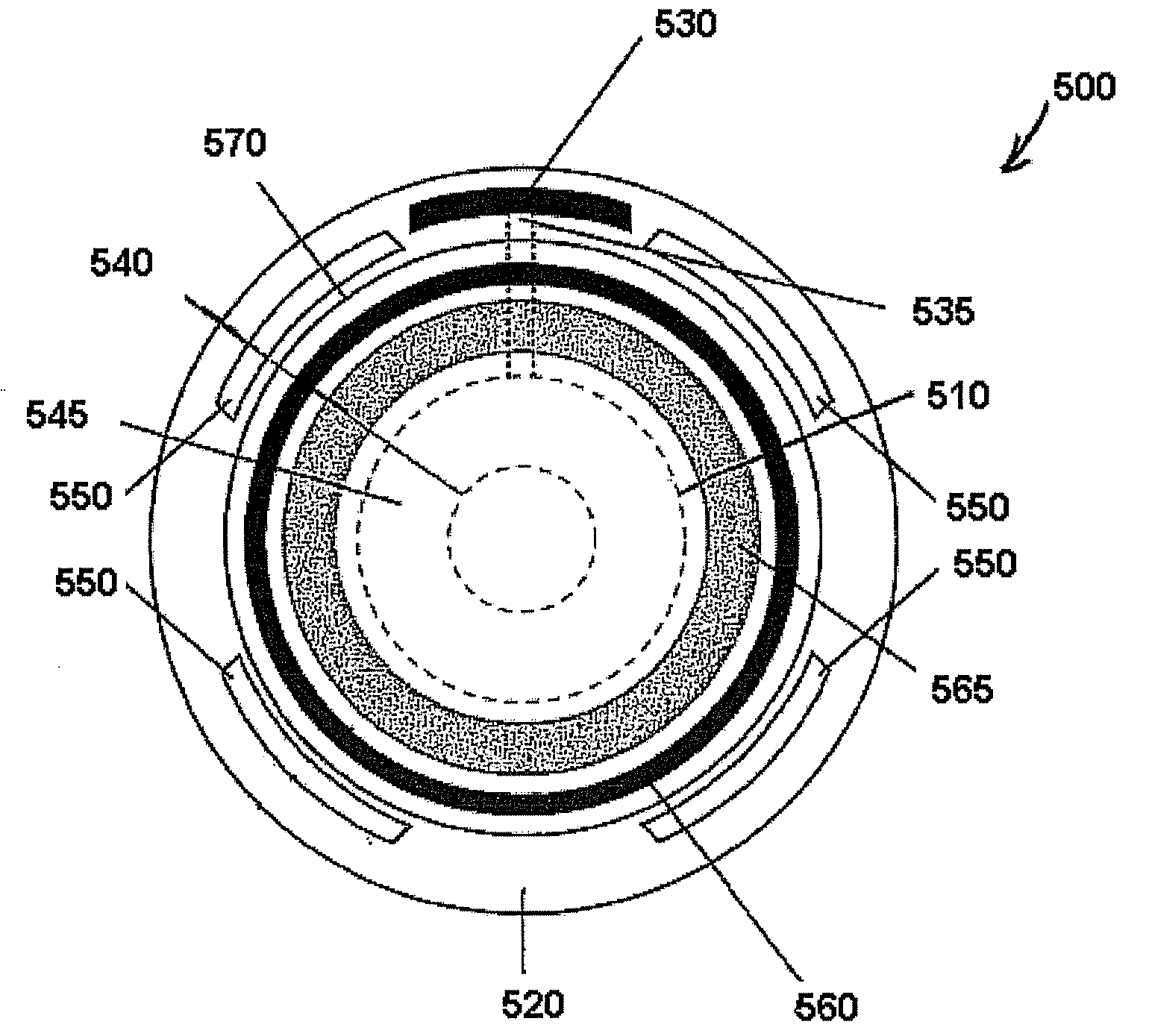
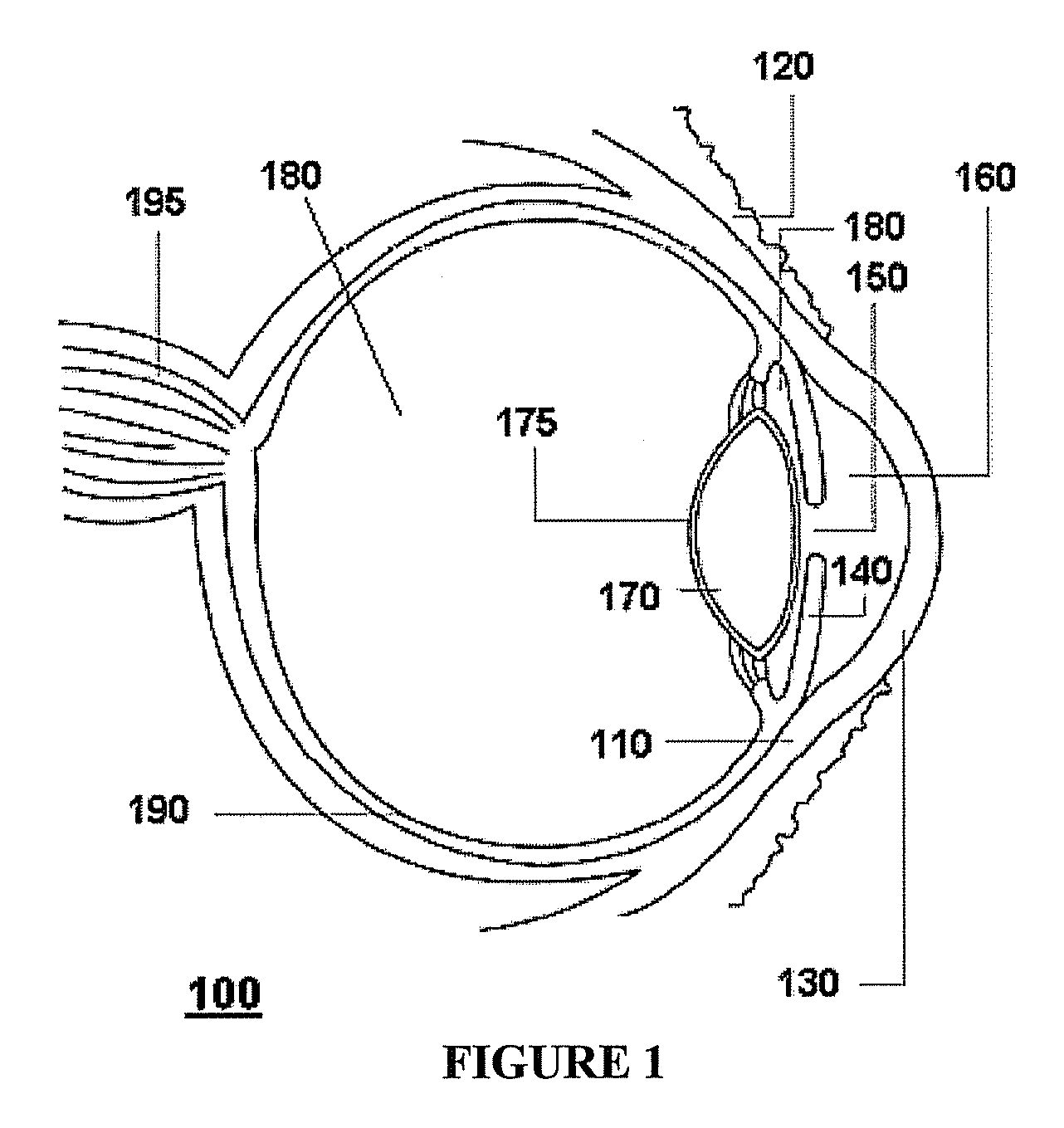
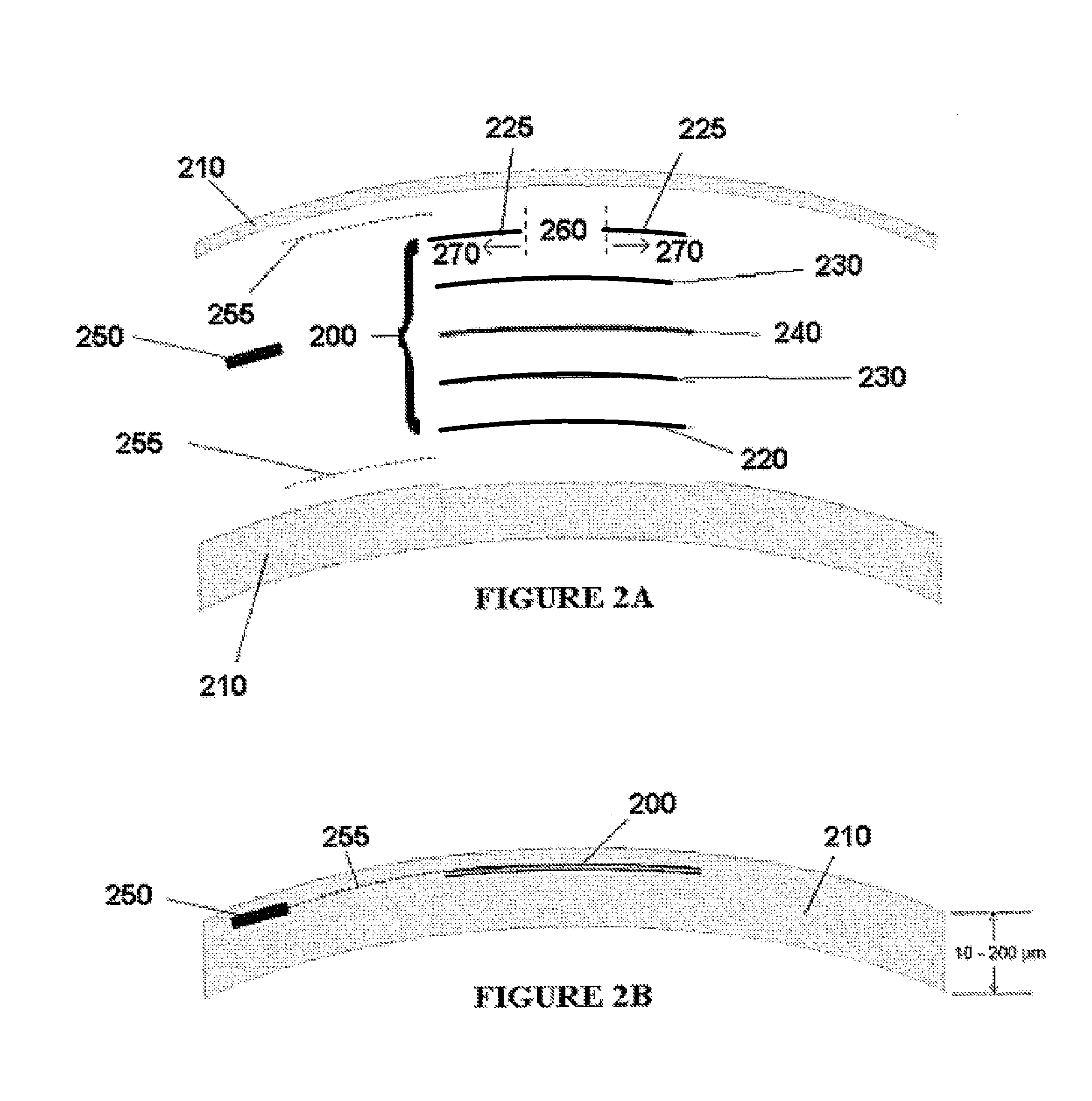
Ophthalmic dynamic aperture
ActiveUS20090033863A1Increase heightAdd depthSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensCorneal inlayDynamic aperture
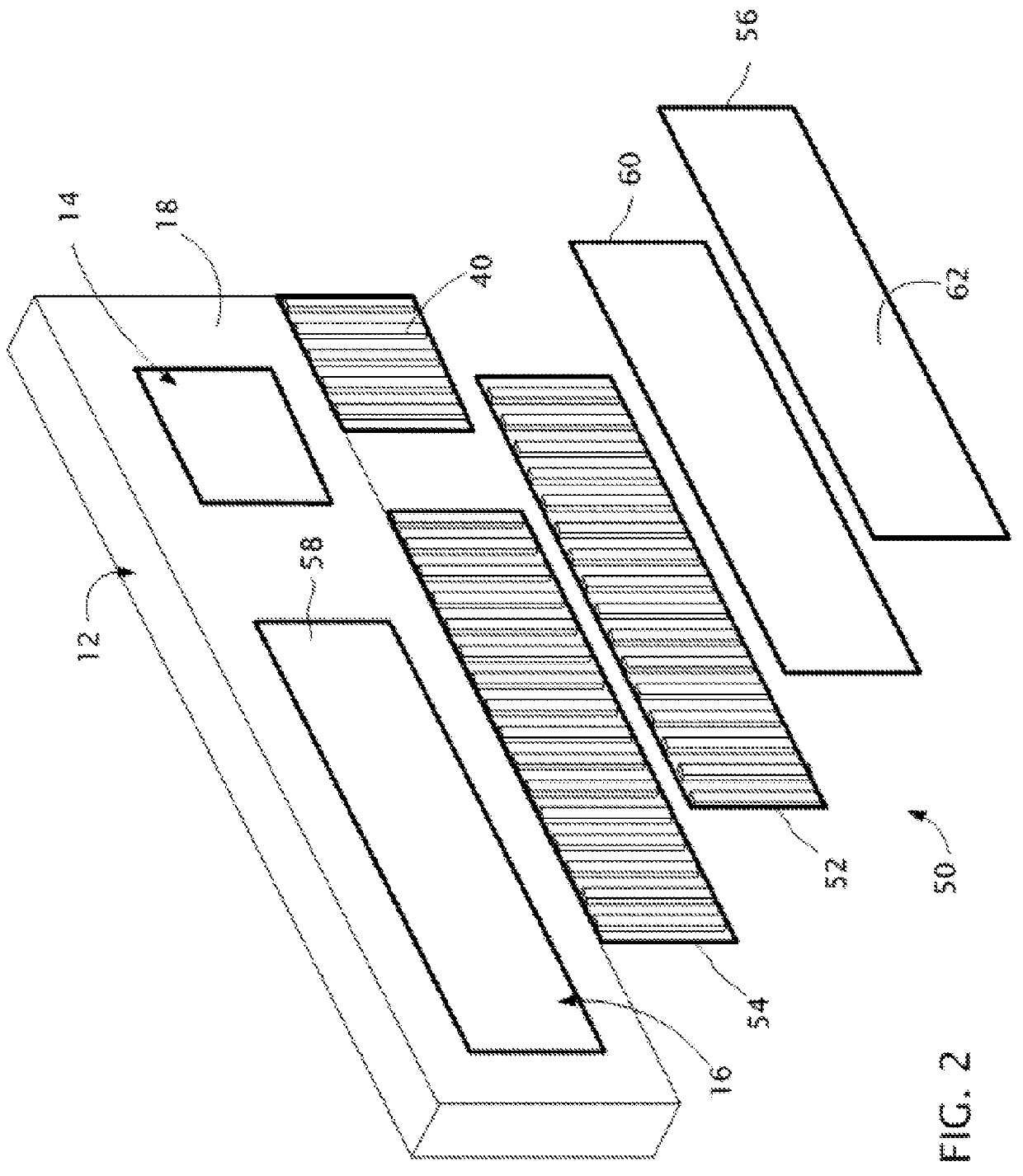
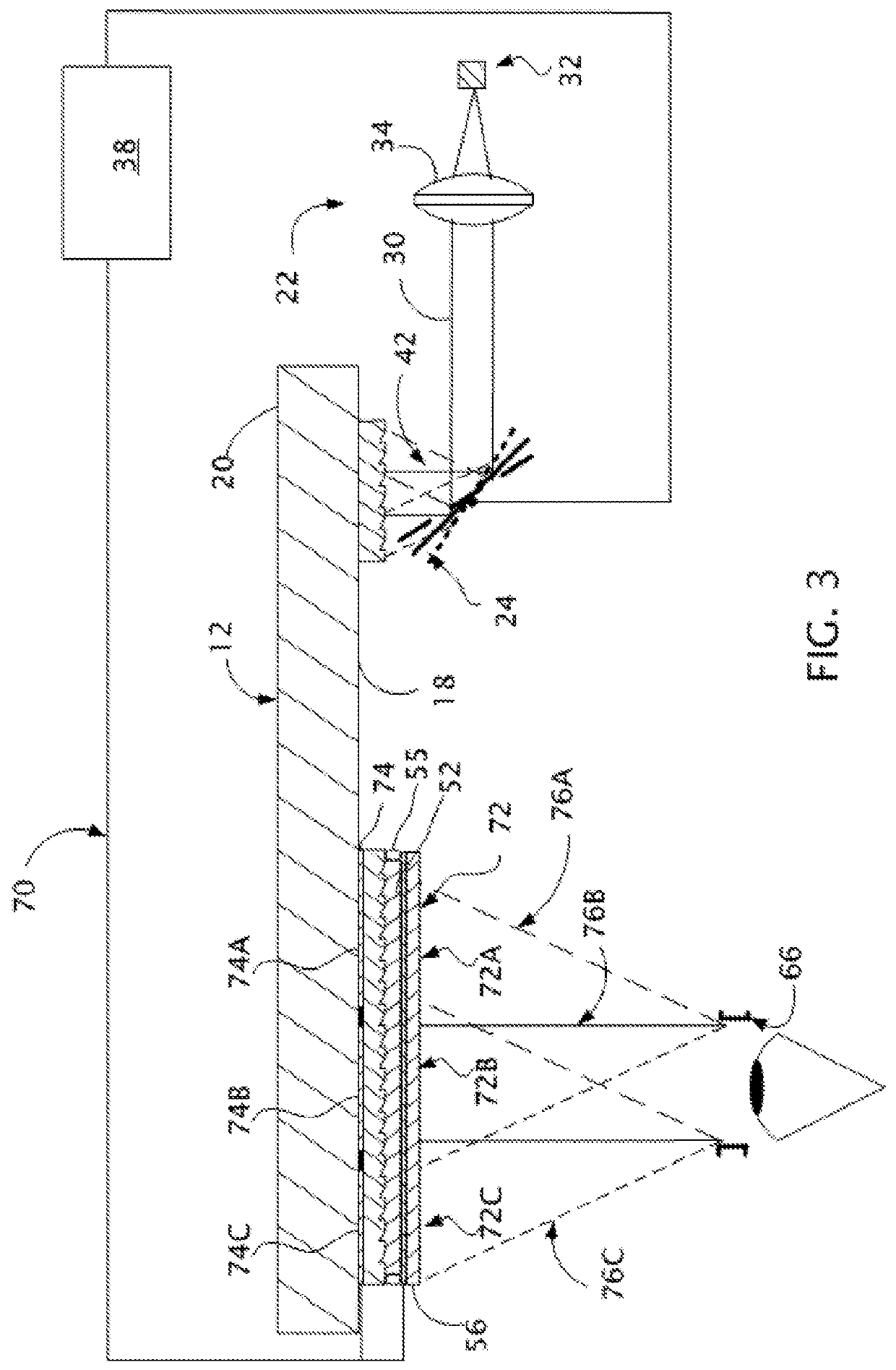
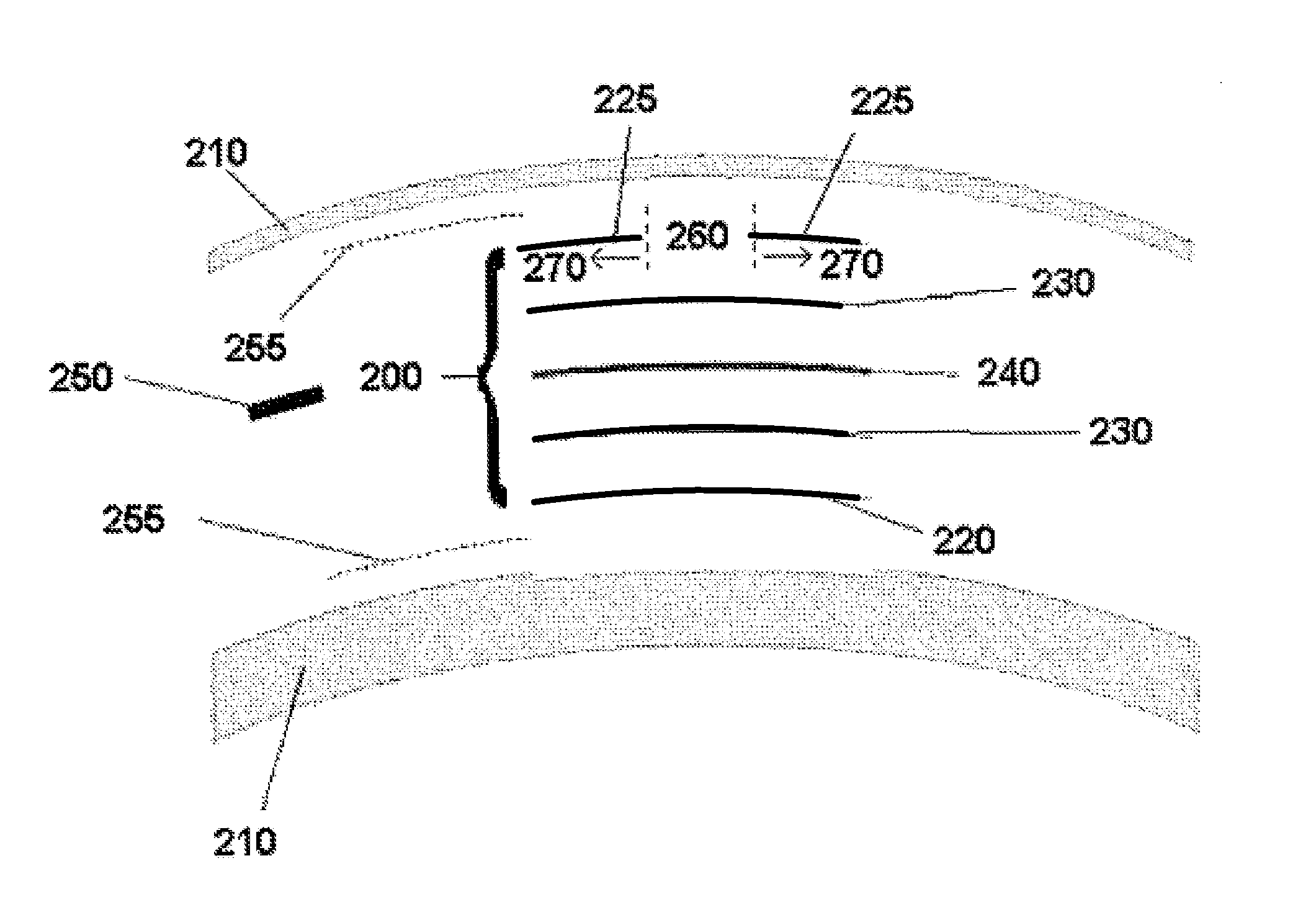
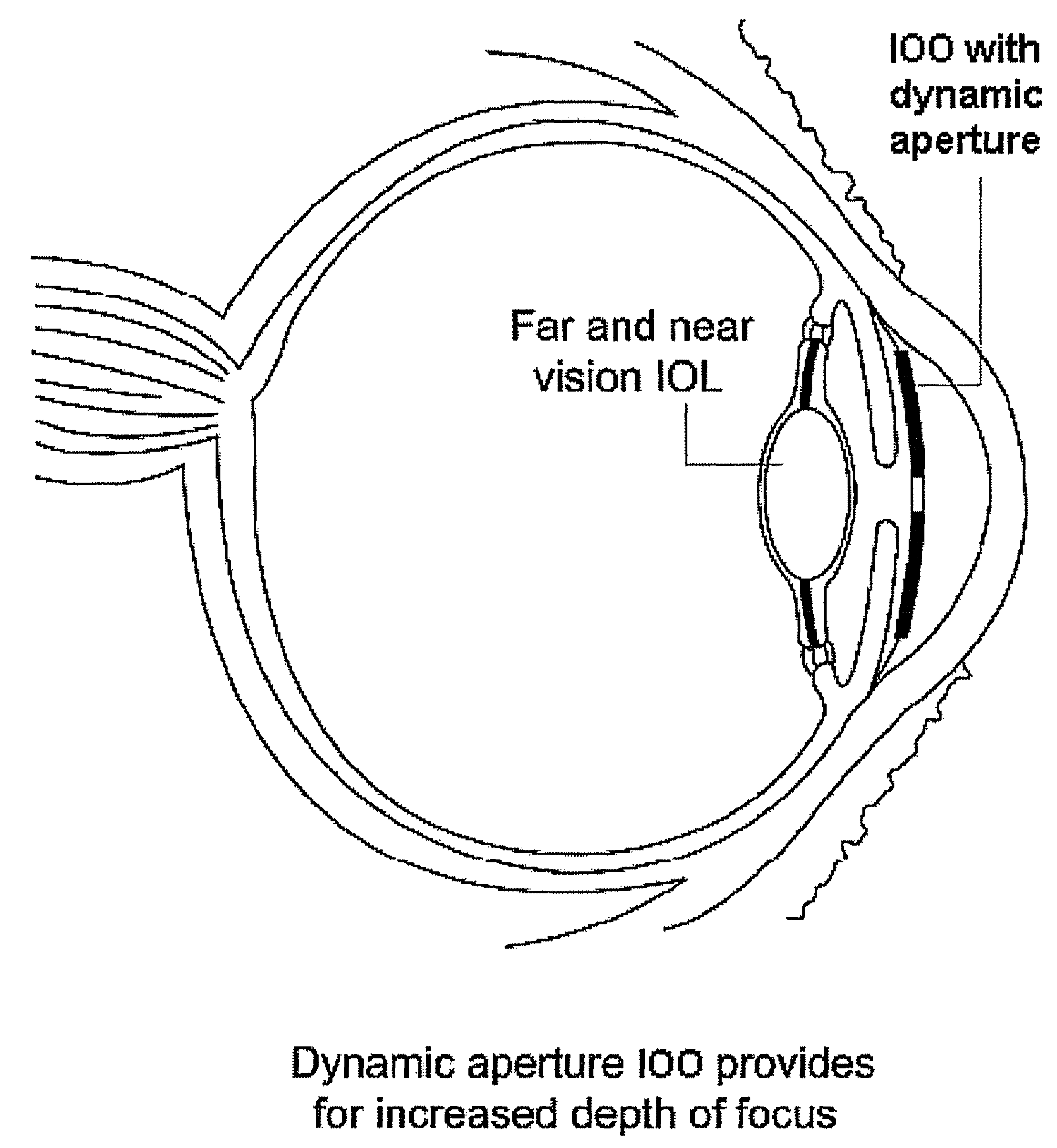
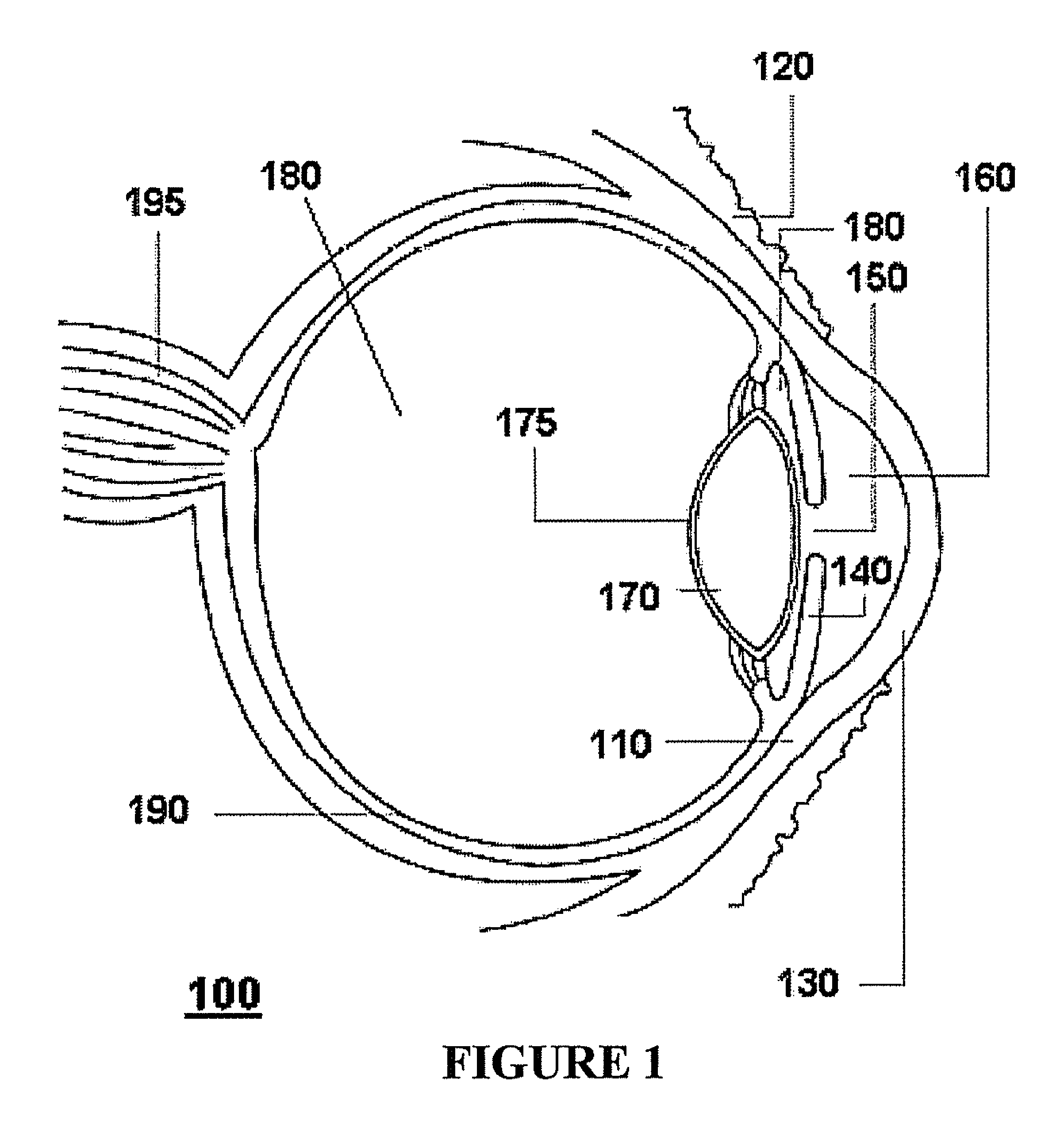
Embodiments of the present invention relate to an electro-active element having a dynamic aperture. The electro-active element provides increased depth of field and may be used in a non-focusing ophthalmic device that that is spaced apart from but in optical communication with an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, a contact lens, or a spectacle lens that provide an optical power. The electro-active element provides increased depth of field and may also be used in a focusing or non-focusing device such as an intraocular optic, an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, or a contact lens which may or may not have an optical power. By changing the diameter of dynamic aperture either increased depth of field or increased light reaching the retina may be achieved.
Owner:E VISION LLC +1
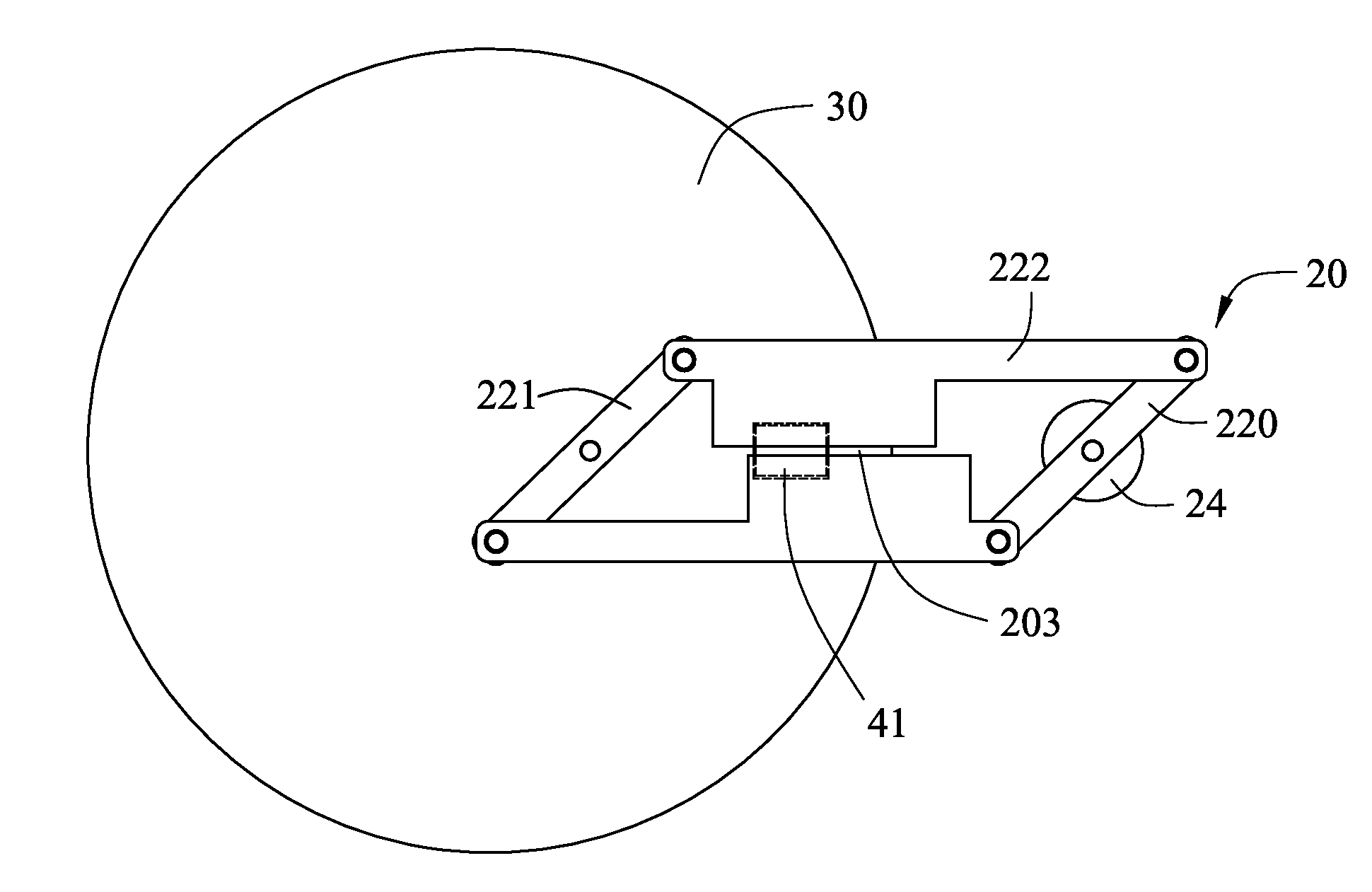
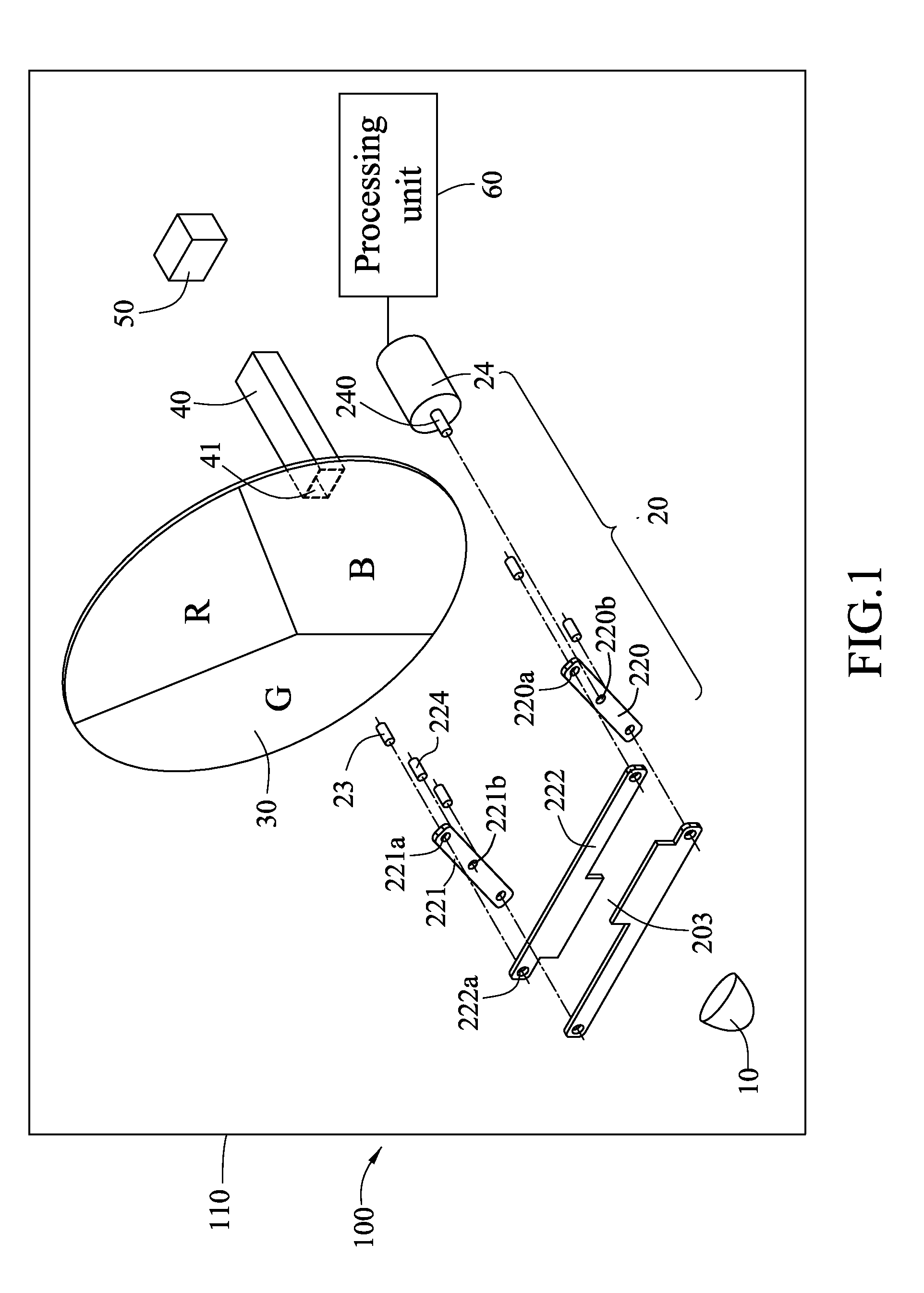
Dynamic apertured waveguide for near-eye display
ActiveUS20130051730A1Diffraction efficiencyGood image uniformityDiffraction gratingsCoupling light guidesDynamic apertureLight beam
A near-eye display of a type having an image generator for generating a succession of angularly related beams and waveguide for propagating the angularly related beams to an eyebox within which a virtual image is visible includes a controllable output aperture for such purposes as reconstructing a better defined pupil within the eyebox while also preserving the possibility for viewing the ambient environment from the eyebox through the controllable output aperture.
Owner:VUZIX
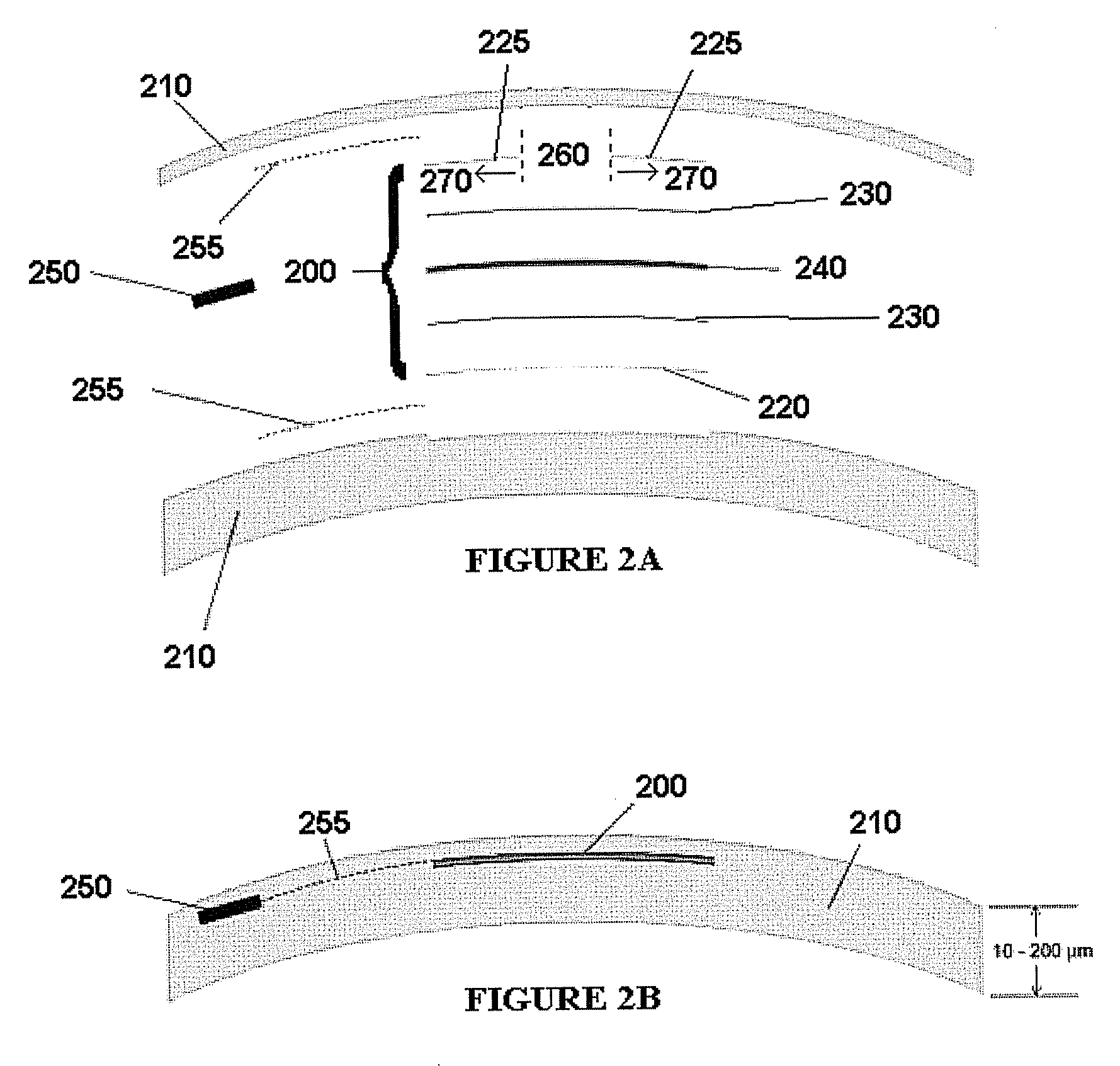
Advanced electro-active optic device
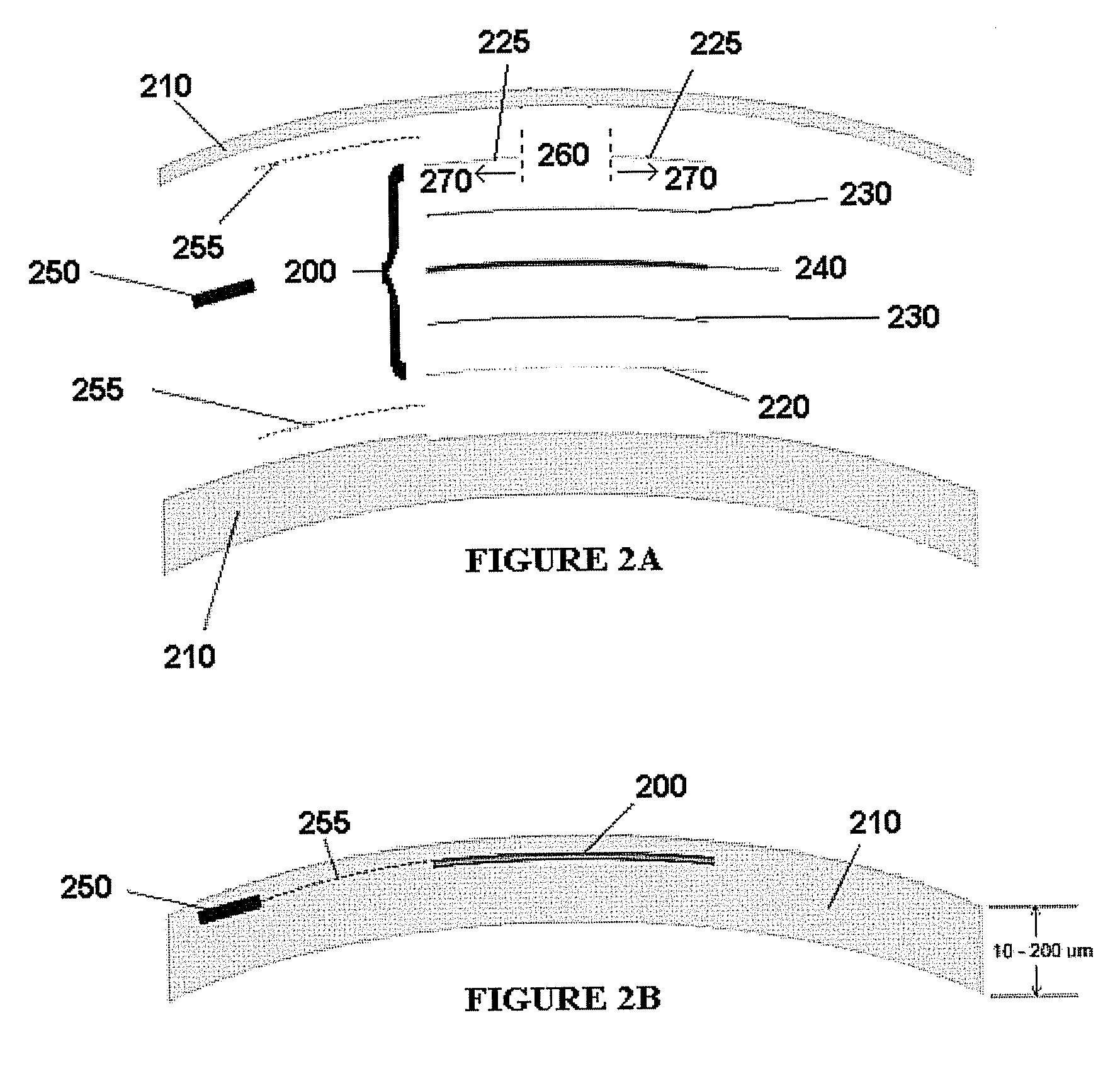
Optical devices having a dynamic aperture and / or an apodization mask are provided. The aperture and / or mask may be provided by one or more electro-active elements, and may be used in an ophthalmic device that that is spaced apart from but in optical communication with an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, or a spectacle lens that provide an optical power.
Owner:EA3TECH LLC +1
Dynamic apertured waveguide for near-eye display
A near-eye display of a type having an image generator for generating a succession of angularly related beams and waveguide for propagating the angularly related beams to an eyebox within which a virtual image is visible includes a controllable output aperture for such purposes as reconstructing a better defined pupil within the eyebox while also preserving the possibility for viewing the ambient environment from the eyebox through the controllable output aperture.
Owner:VUZIX
Ophthalmic dynamic aperture
Embodiments of the present invention relate to an electro-active element having a dynamic aperture. The electro-active element provides increased depth of field and may be used in a non-focusing ophthalmic device that that is spaced apart from but in optical communication with an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, a contact lens, or a spectacle lens that provide an optical power. The electro-active element provides increased depth of field and may also be used in a focusing or non-focusing device such as an intraocular optic, an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, or a contact lens which may or may not have an optical power. By changing the diameter of dynamic aperture either increased depth of field or increased light reaching the retina may be achieved.
Owner:E VISION LLC +1
Small Spot Size Spectroscopic Ellipsometer
ActiveUS20130321810A1High measurement sensitivityIncrease the number ofPolarisation-affecting propertiesPhotomechanical apparatusAngle of incidenceMetrology
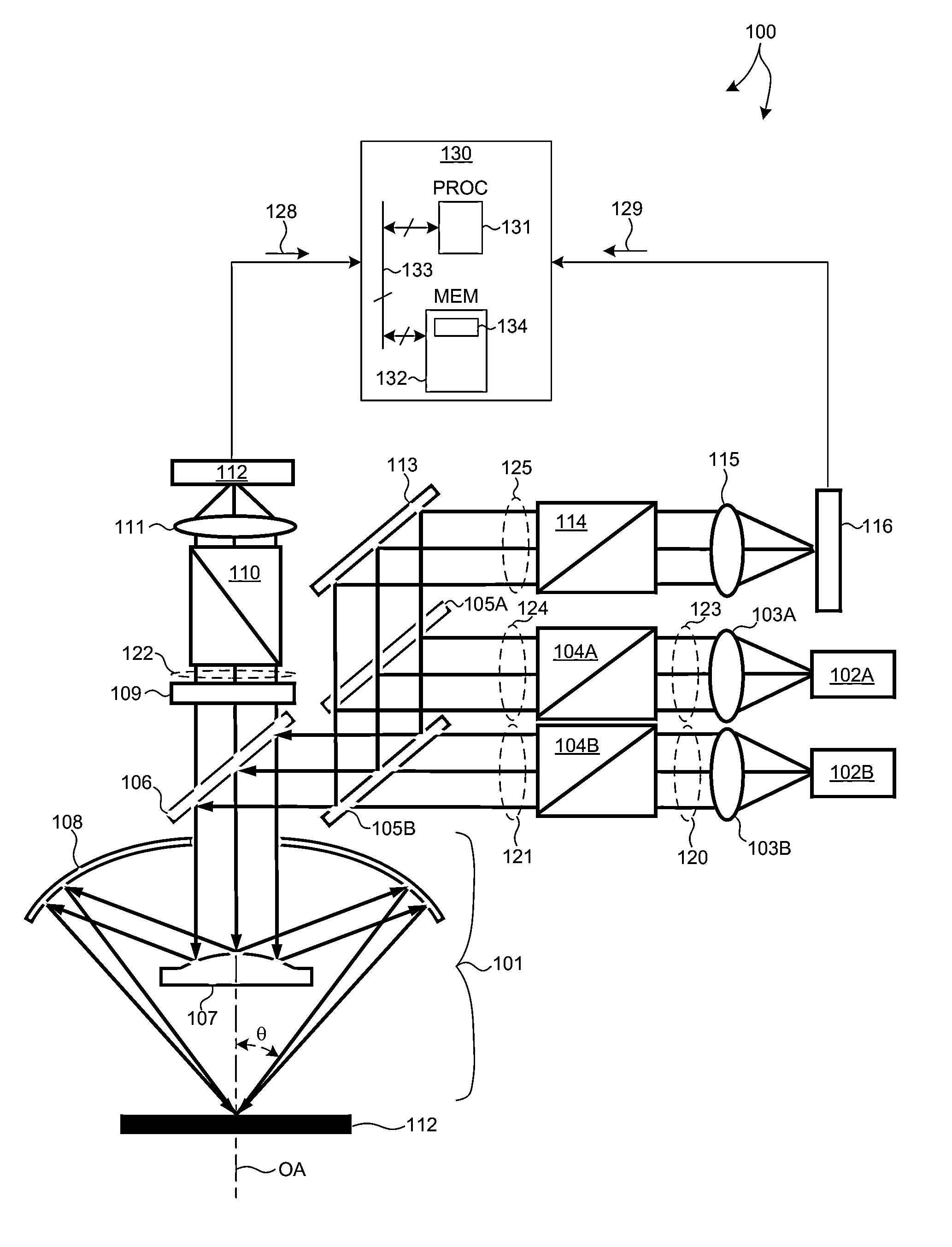
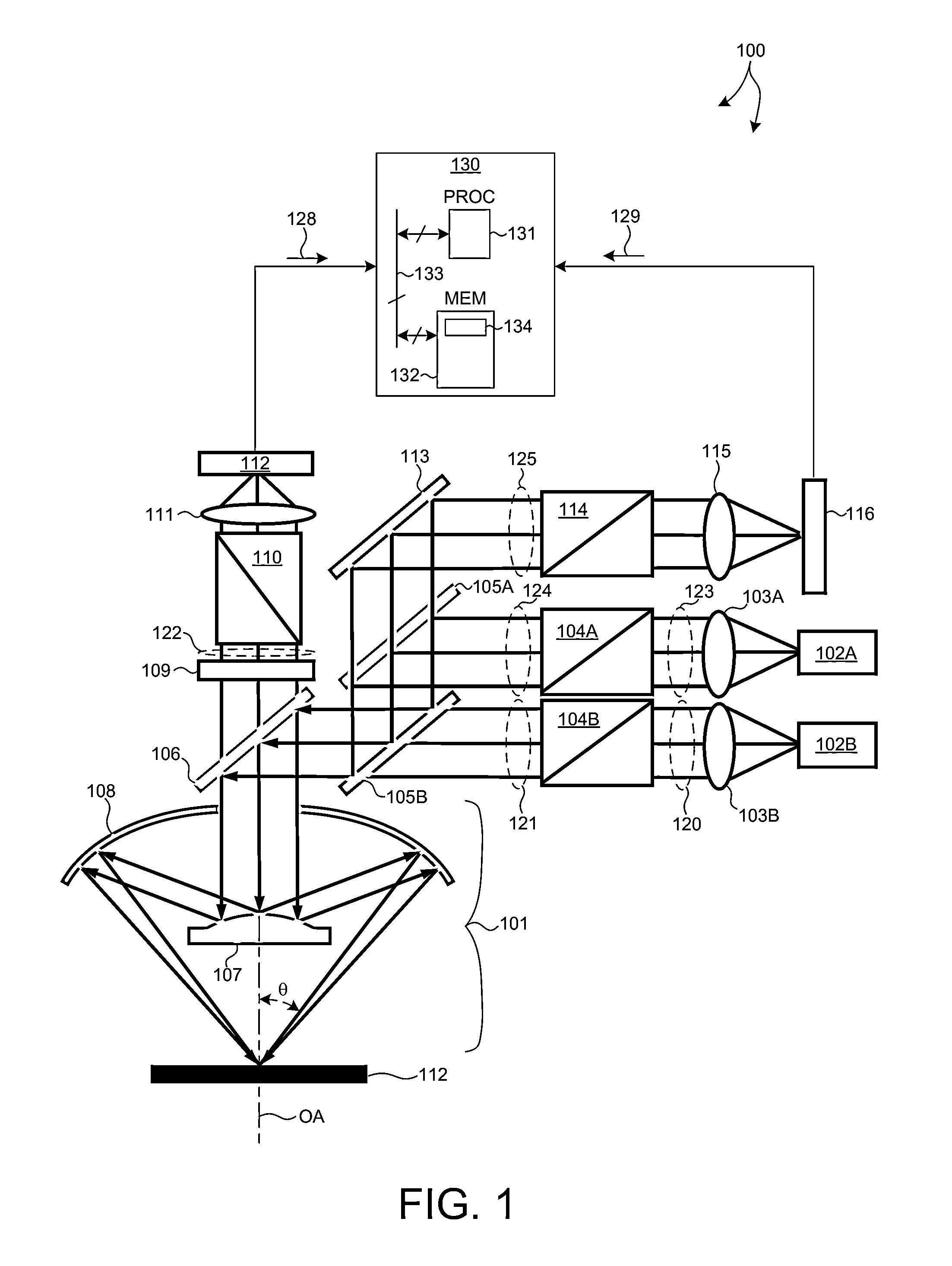
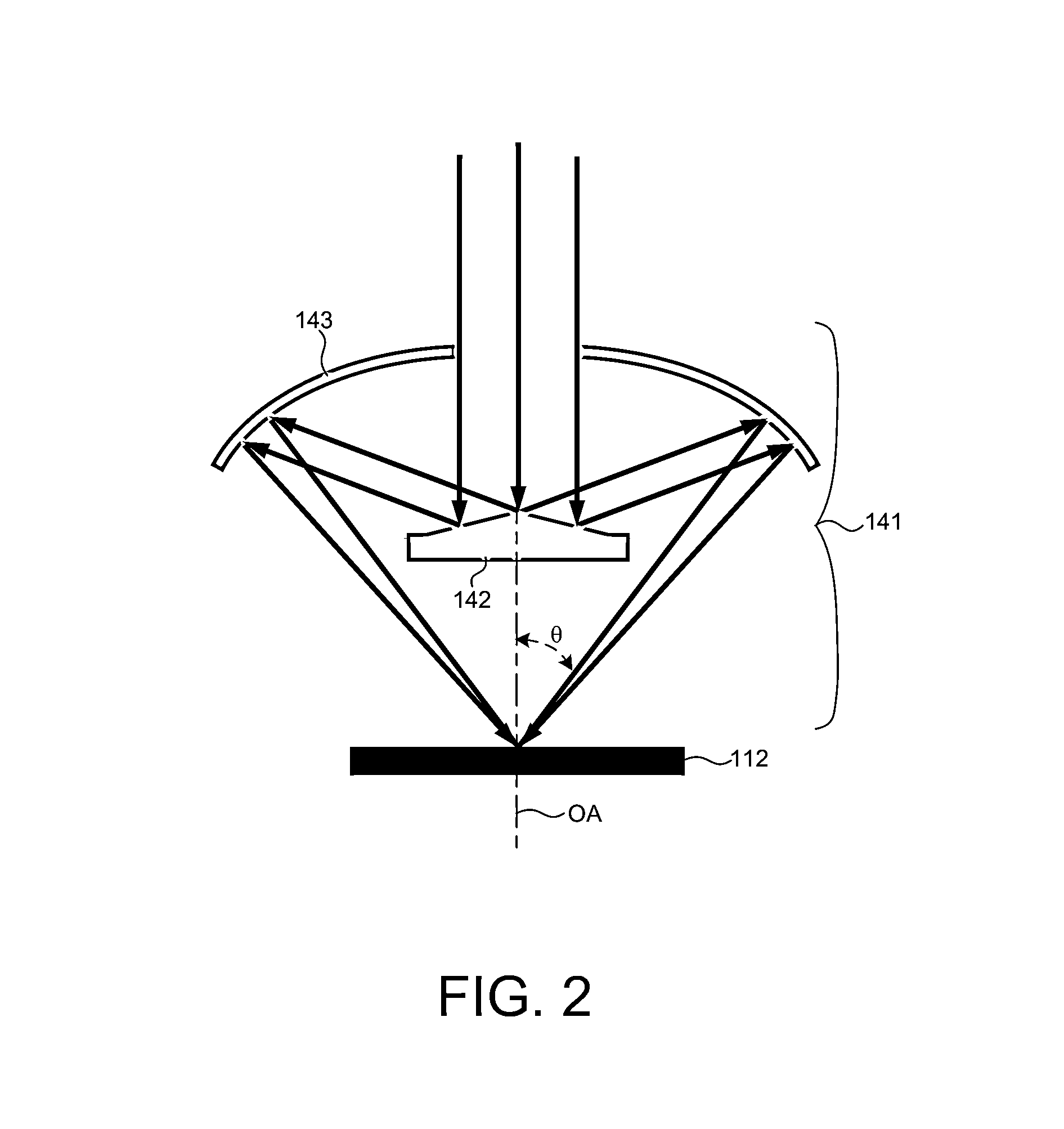
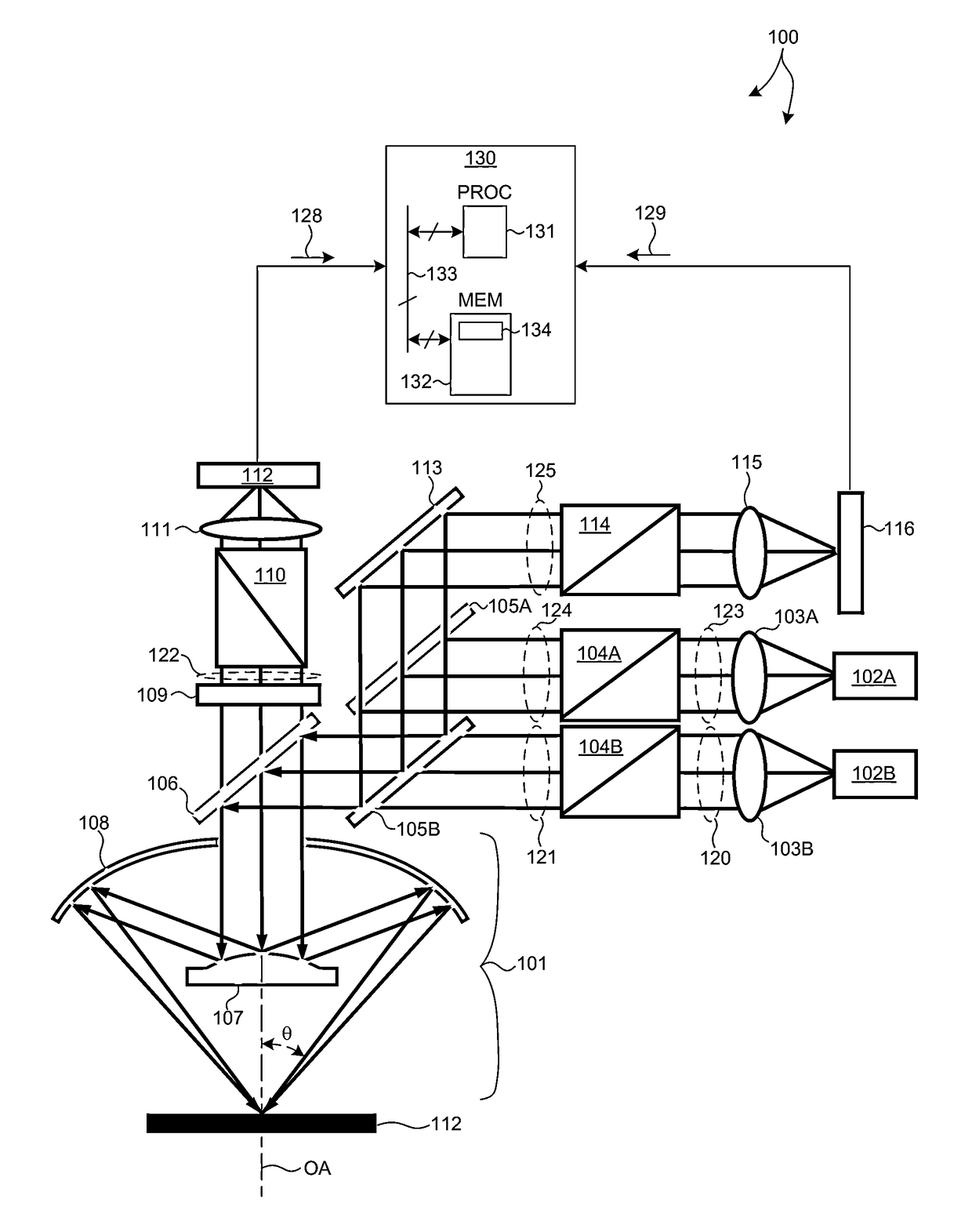
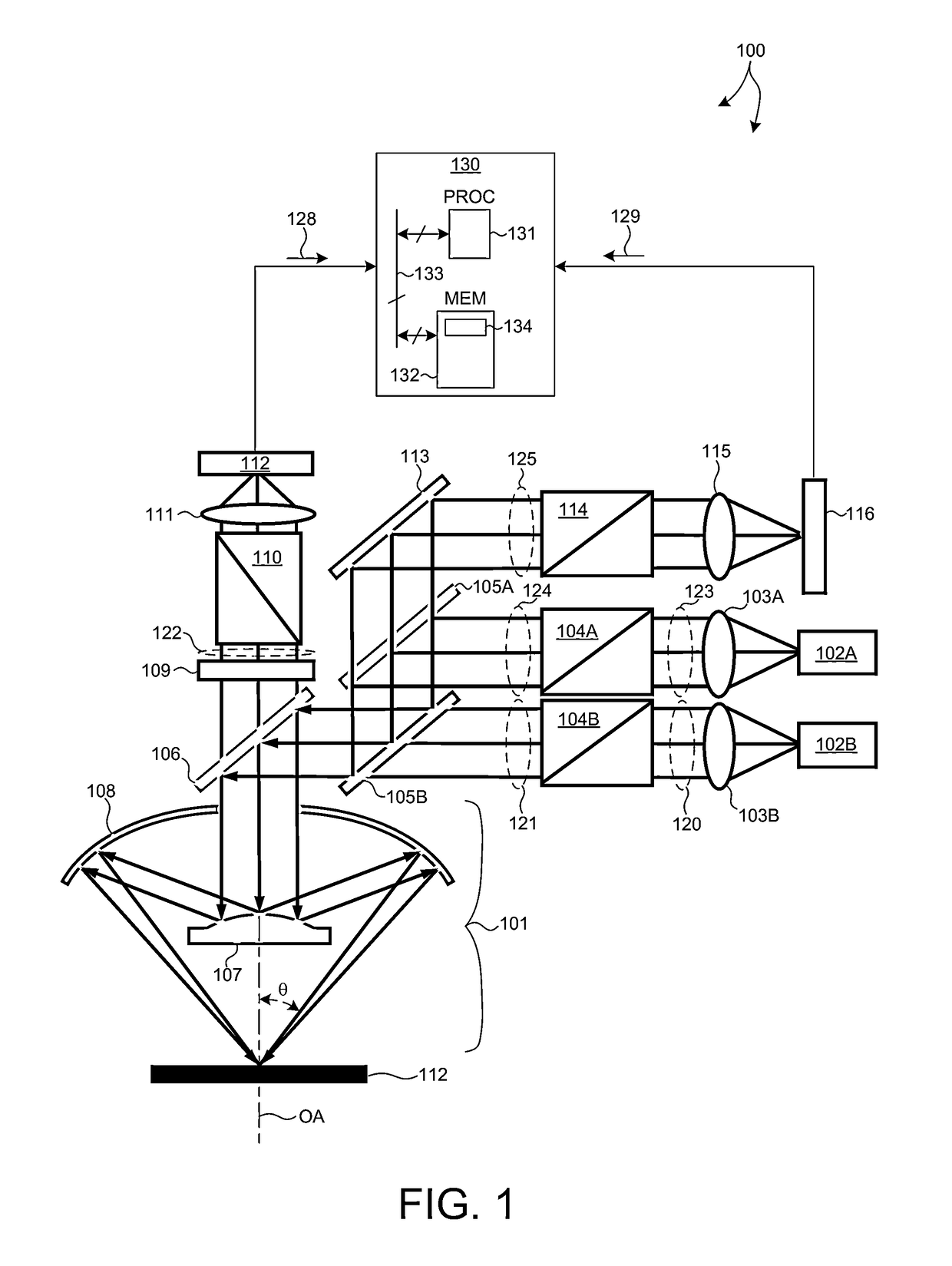
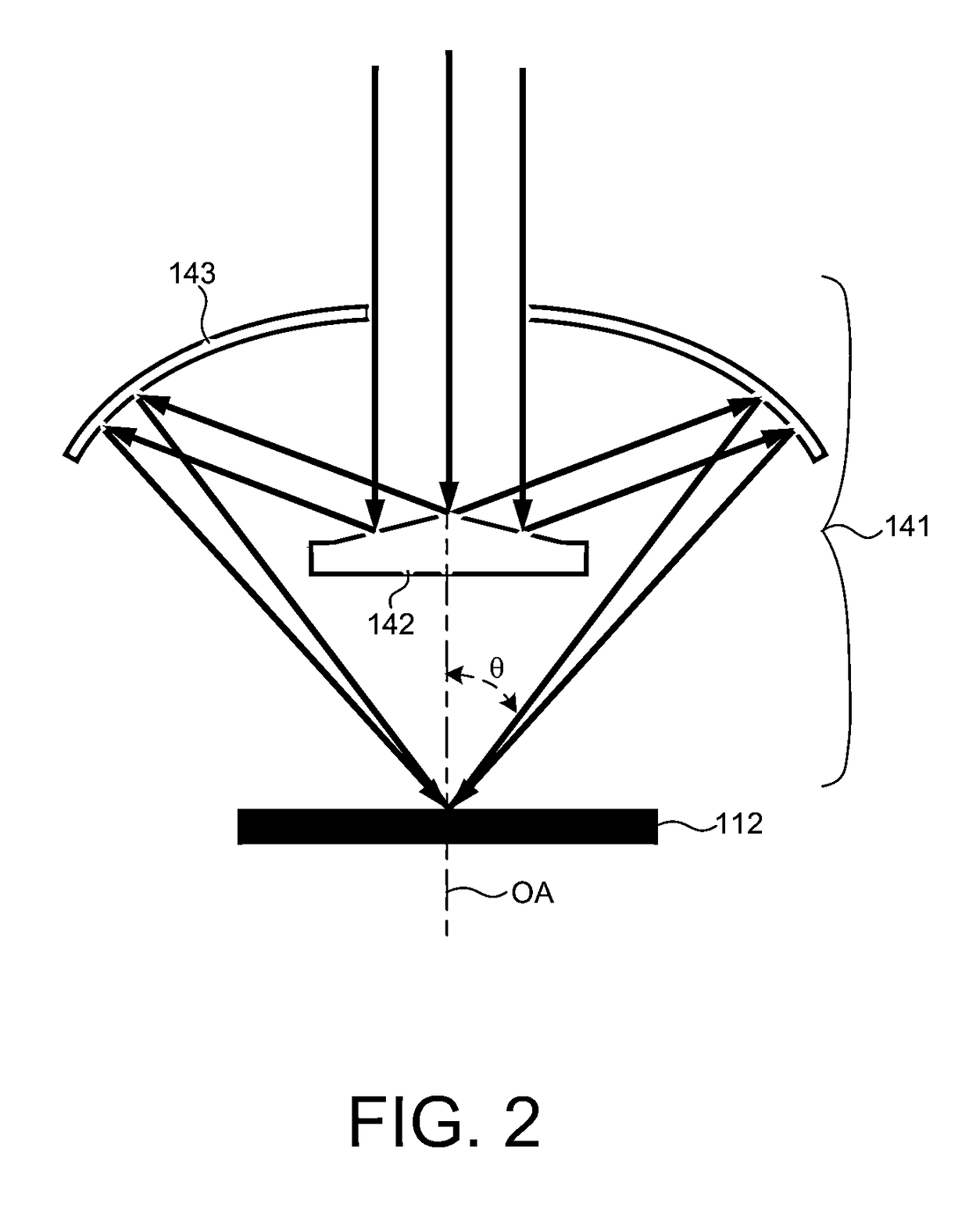
Methods and systems for small angle CD metrology with a small spot size are introduced to increase measurement sensitivity while maintaining adequate throughput necessary for modern semiconductor manufacture. A small angle CD metrology system includes a small angle spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE) subsystem combined with a small angle spectroscopic reflectometry system, both operated at small angles of incidence. The small angle SE subsystem is configured to operate in a complete Mueller Matrix mode to further improve measurement sensitivity. The small angle CD metrology system includes an objective having all reflective surfaces in the light path. In some embodiments, the all-reflective objective is a Schwartzschild objective having an axicon mirror element to further reduce measurement spot size. In some embodiments, the small angle CD metrology system includes a dynamic aperture subsystem to isolate specific ranges of angles of incidence and azimuth for improved measurement sensitivity.
Owner:KLA CORP
Advanced electro-active optic device
Optical devices having a dynamic aperture and / or an apodization mask are provided. The aperture and / or mask may be provided by one or more electro-active elements, and may be used in an ophthalmic device that that is spaced apart from but in optical communication with an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, or a spectacle lens that provide an optical power.
Owner:PIXELOPTICS
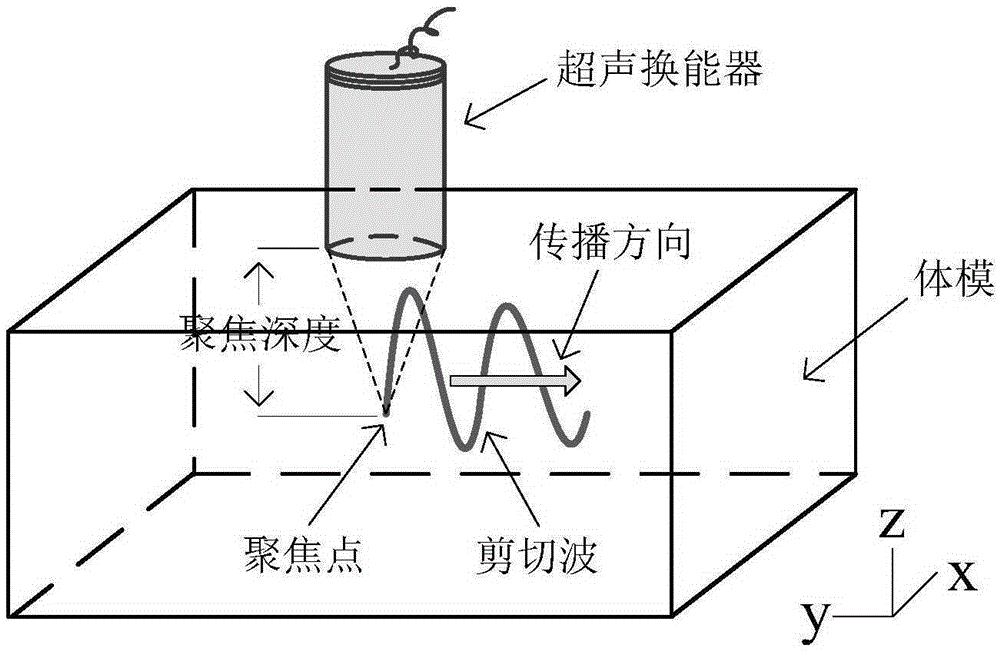
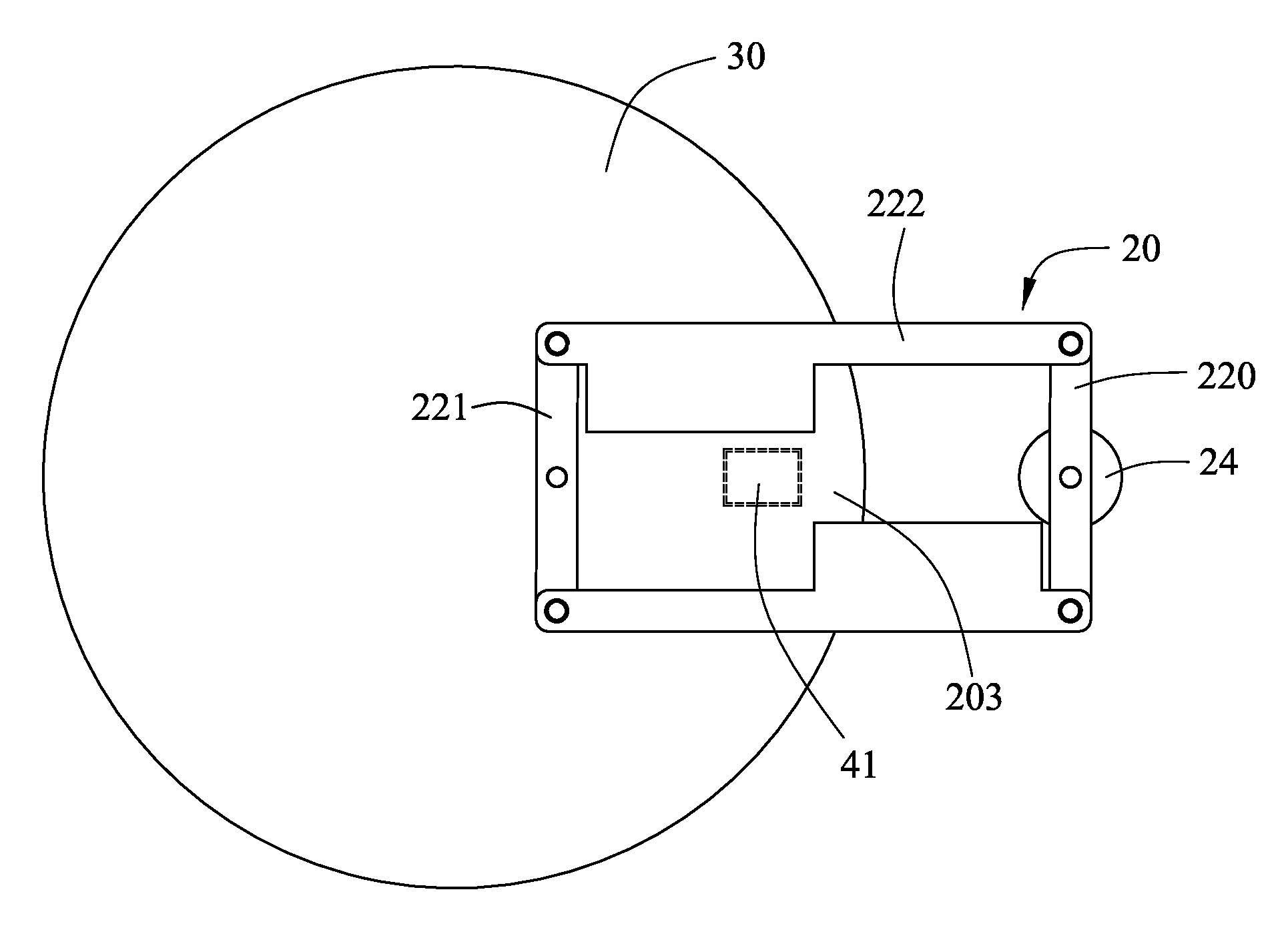
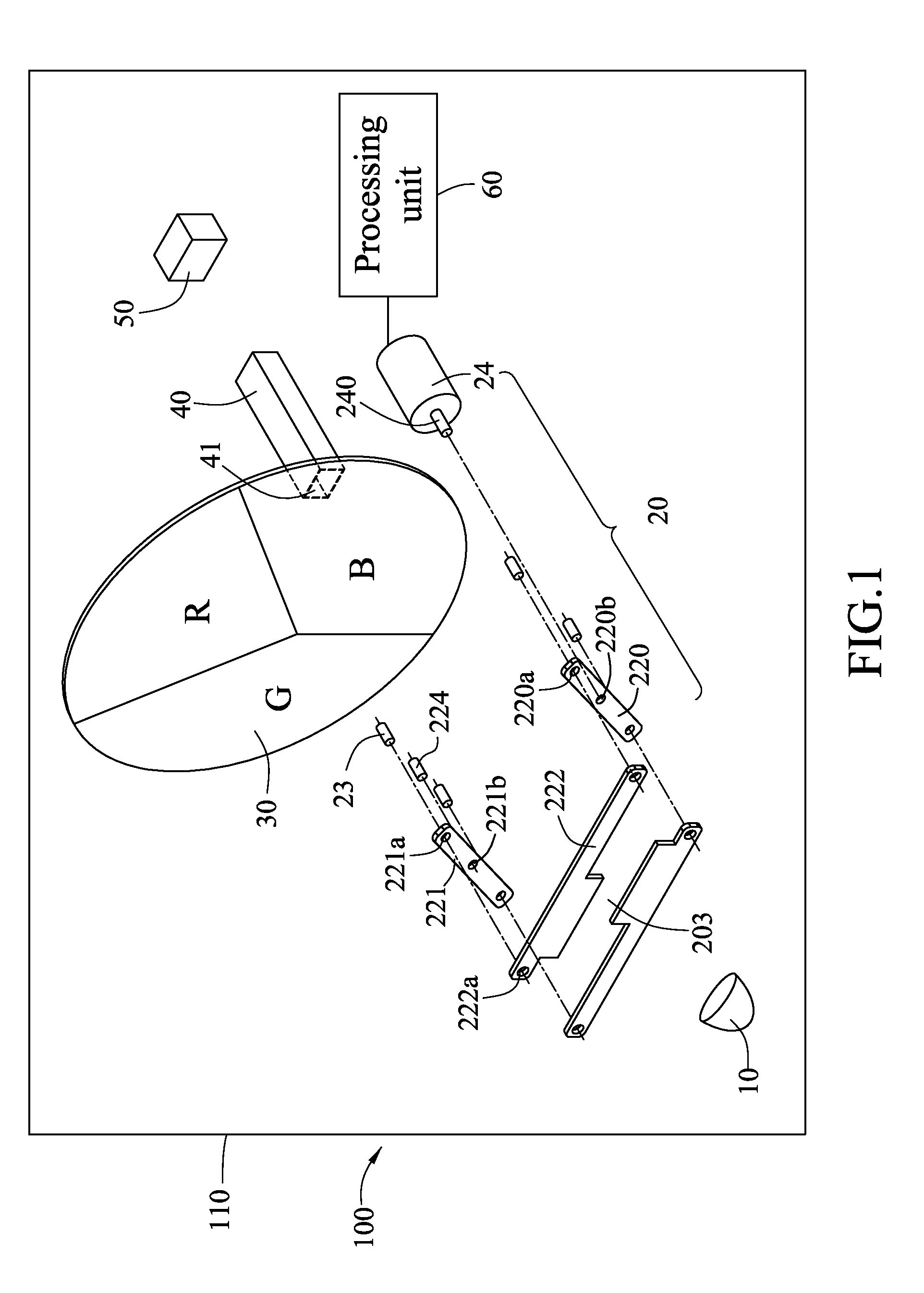
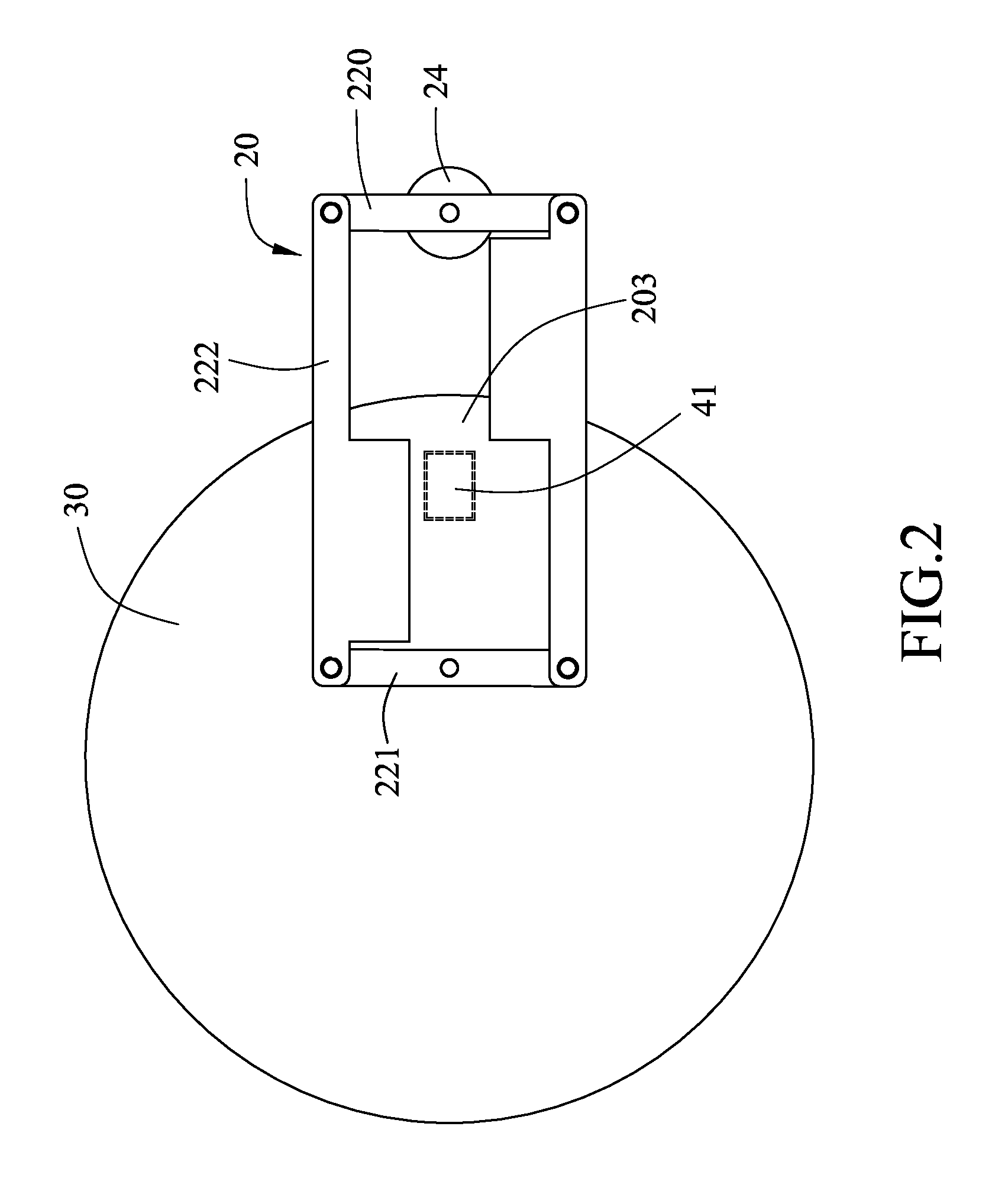
Ultrasonic shearing wave elastic imaging method based on dynamic aperture control
InactiveCN105232085AEliminate spurious displacementsImprove measurement accuracyOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsElastographyAcoustic radiation force
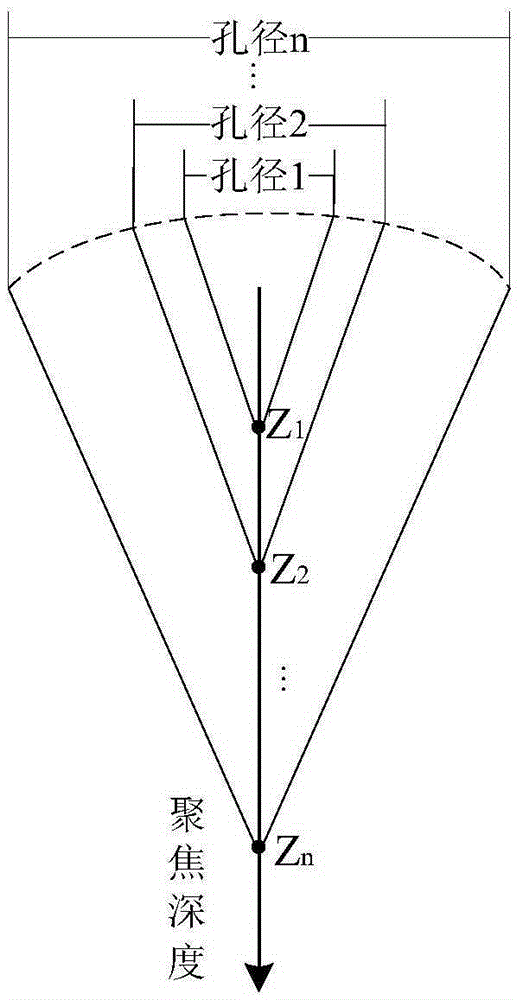
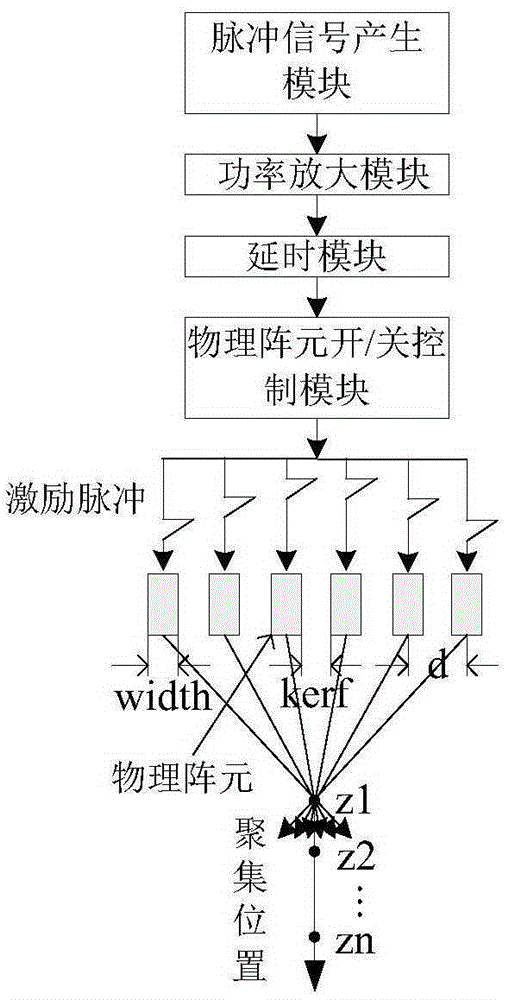
The invention provides an ultrasonic shearing wave elastic imaging method based on dynamic aperture control. Array elements of which the number corresponds to different focus depths are started, the aperture is set up, grating lobe phenomena and false displacement in a displacement field can be effectively eliminated, an obtained mass point displacement-time curve relatively well meets the rule that a single point triggered shearing wave is attenuated along with time, and the shearing wave transmission speed measurement accuracy can be improved. By using the ultrasonic shearing wave elastic imaging method, the technical problems that in the prior art in shallow focus depth, because of the influence of acoustic radiation force grating lobe, a mark point displacement-time curve is deformed and the shearing wave transmission speed measurement accuracy is degraded can be solved.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
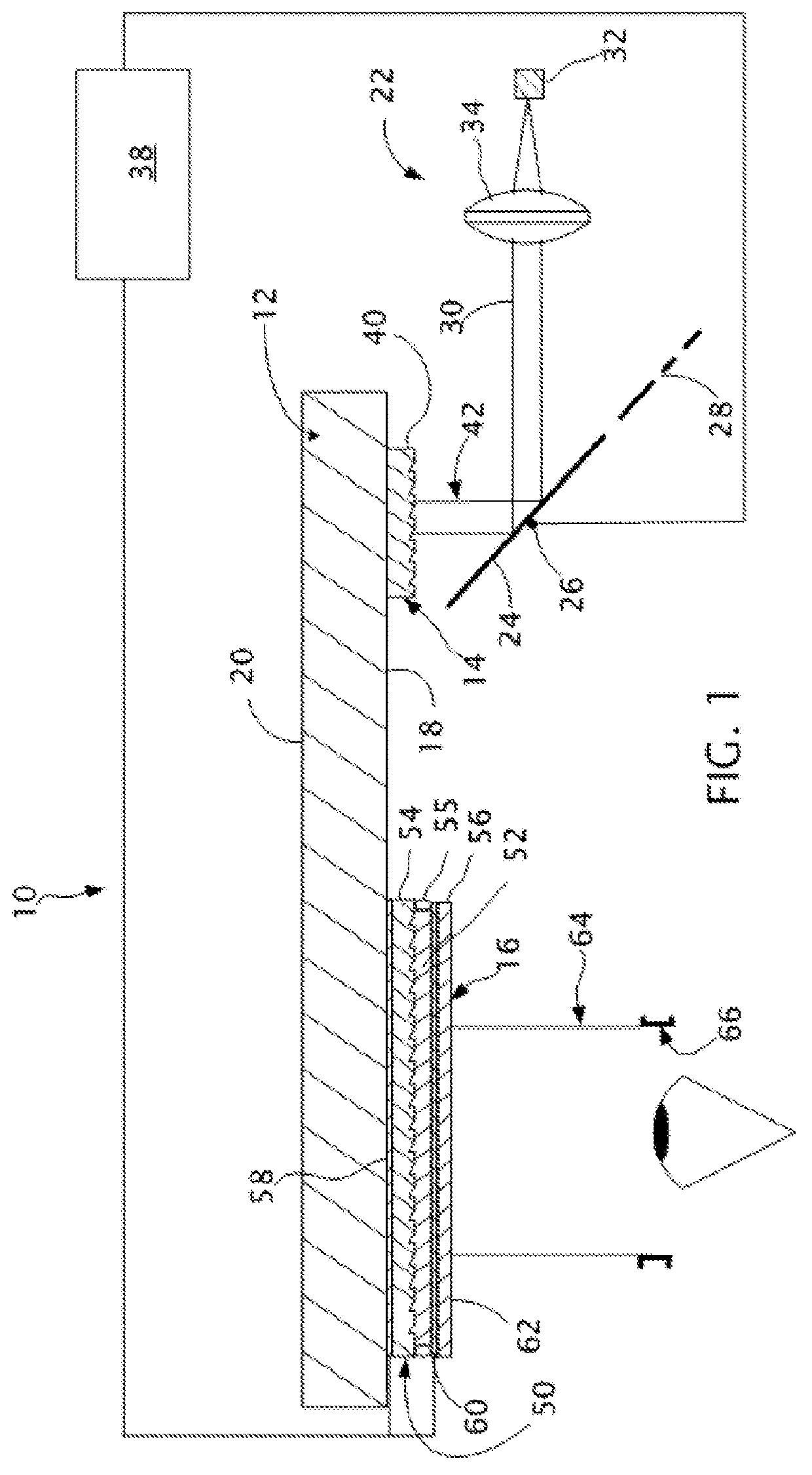
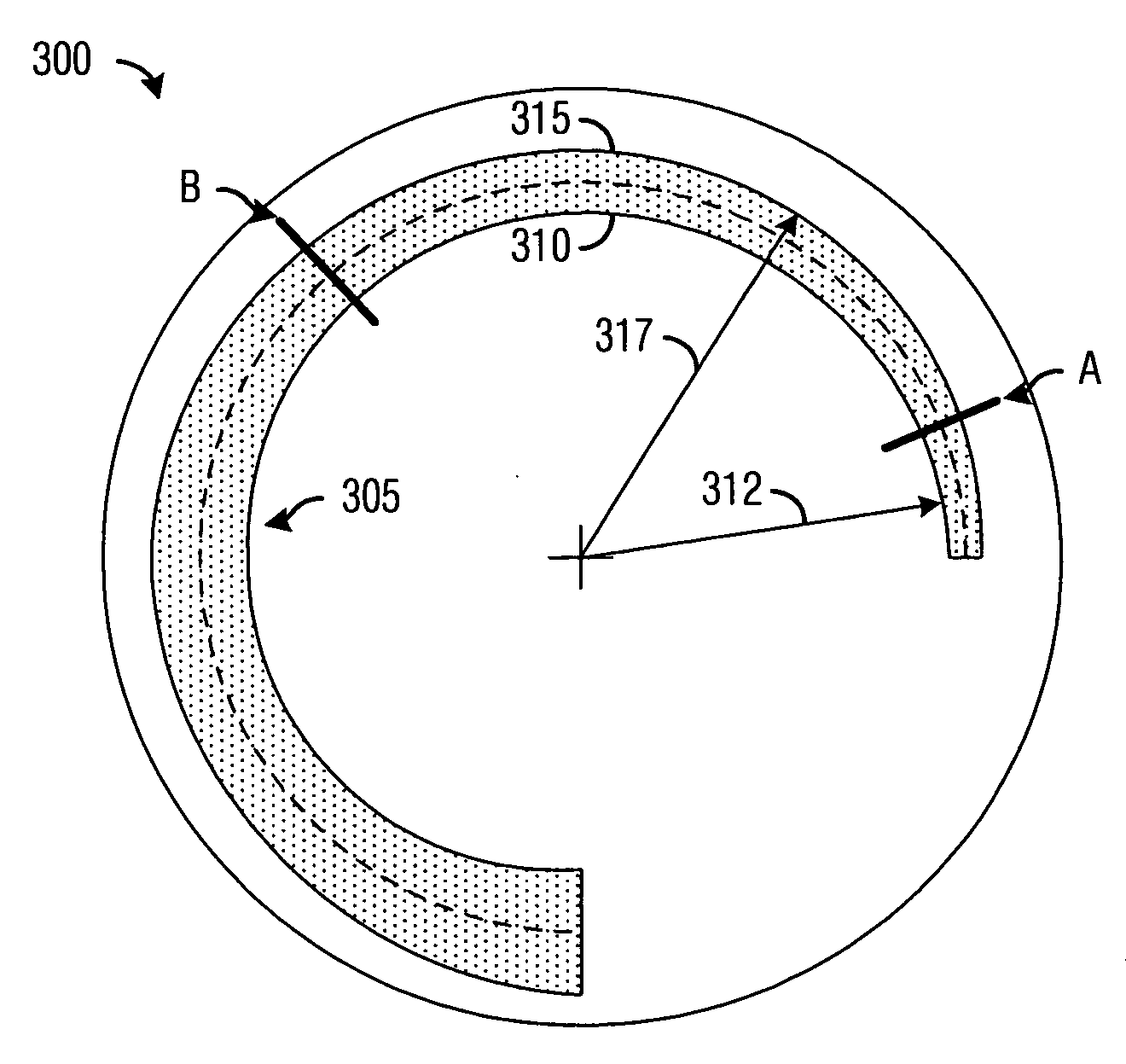
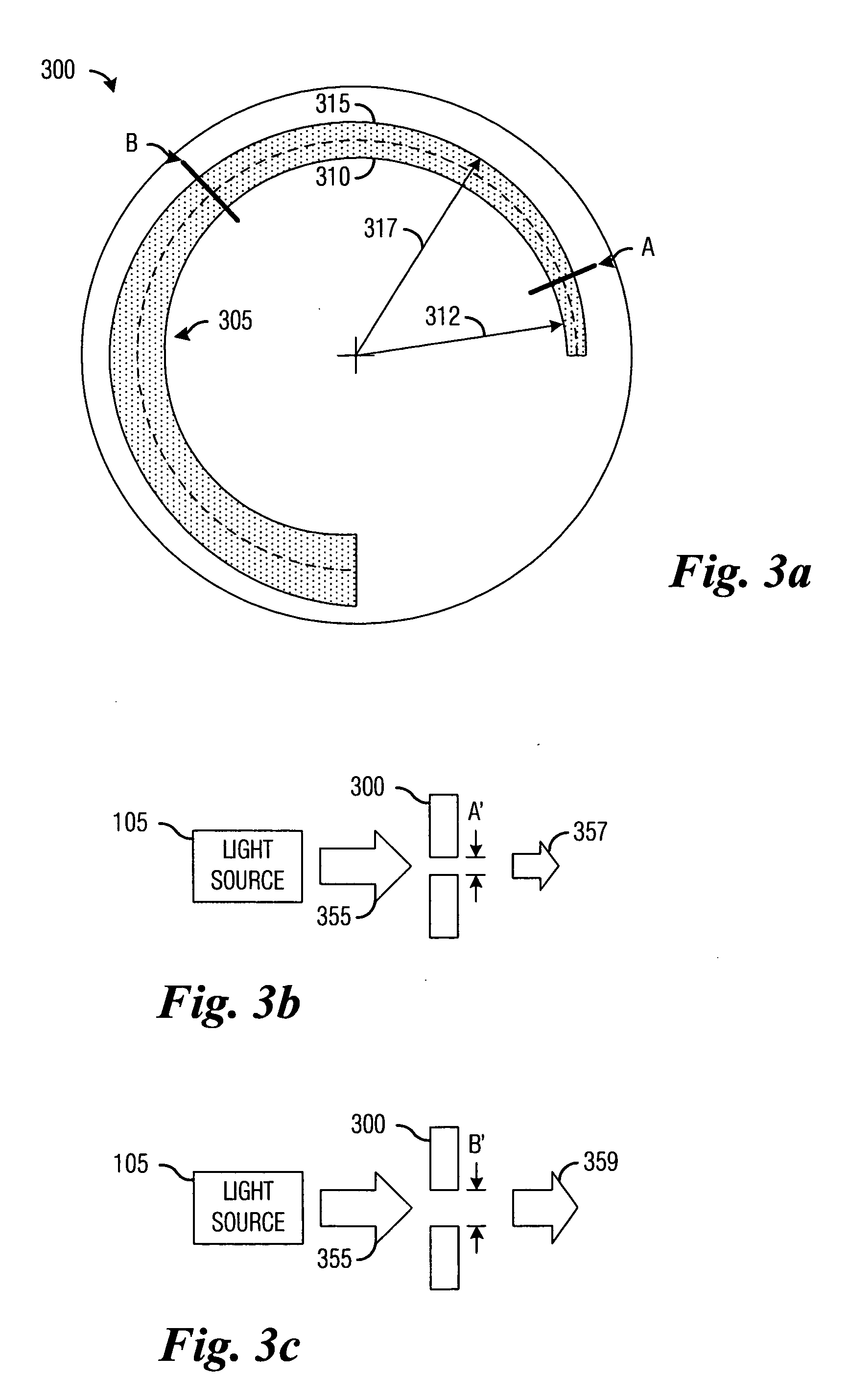
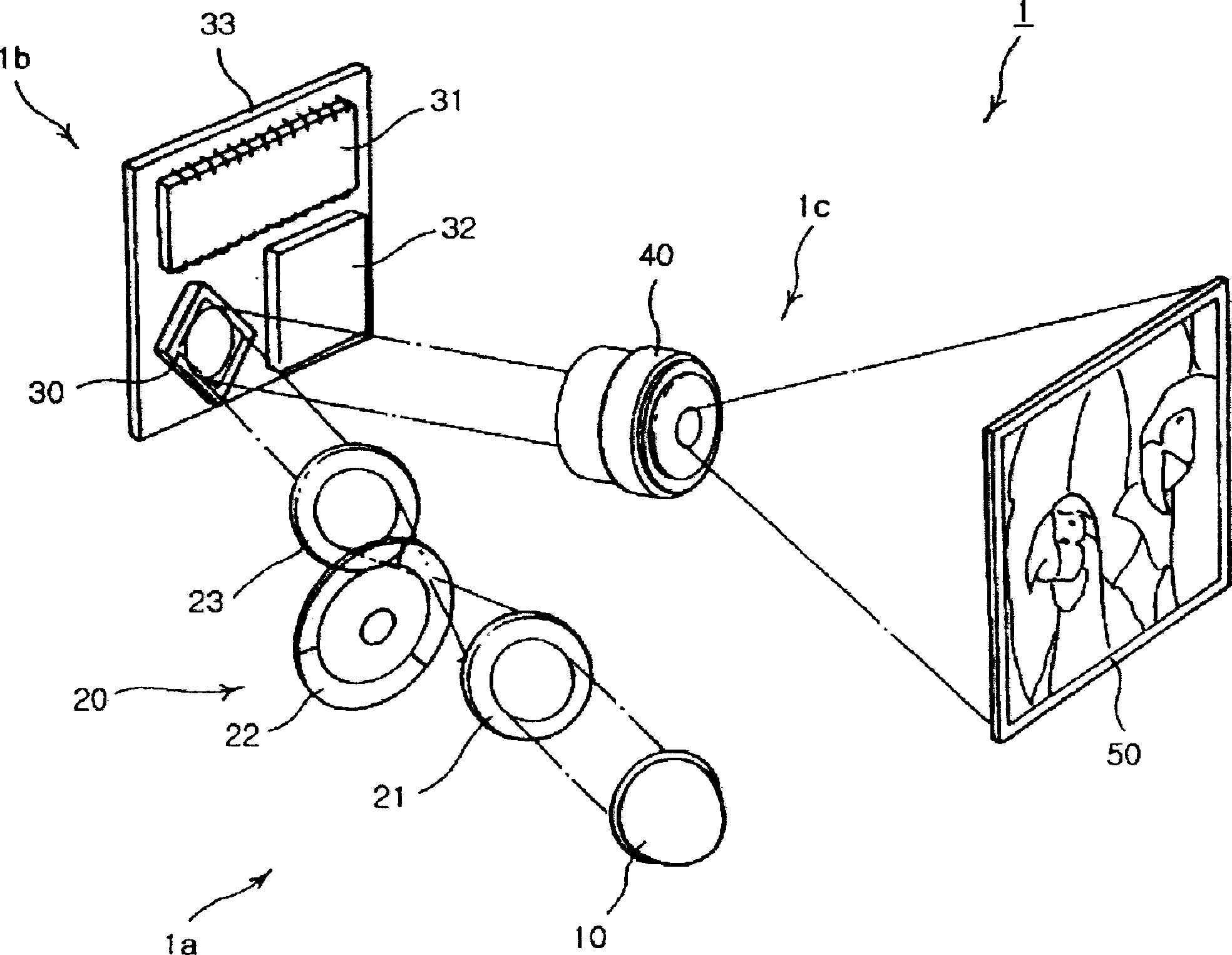
Dynamic aperture for display systems
InactiveUS20070133208A1Improve image qualityCost advantageProjectorsColor photographyBrushless motorsDynamic aperture
System and apparatus for improving the display quality of display systems. A preferred embodiment comprises a planar object configured to variably pass light produced by a light source located on a first side of the planar object to a second side of the planar object, and a motor coupled to the planar object, the motor to rotate the planar object and change the amount of light passed by the planar object. The planar object includes a semi-circular beveled portion formed on a first side of the planar object. A slot with monotonically increasing width is cut along a spine of the semi-circular beveled portion and through the planar object and depending upon a width of the slot that is in front of the light source, the planar object passes a different amount of light. The motor is a DC brushless motor or a limited angular torque motor.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Ultrasonic water immersion automatic detection device and method for complex ring forgings
ActiveCN111796028AEnables high-resolution detectionEnhanced couplingAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWater immersionDynamic aperture
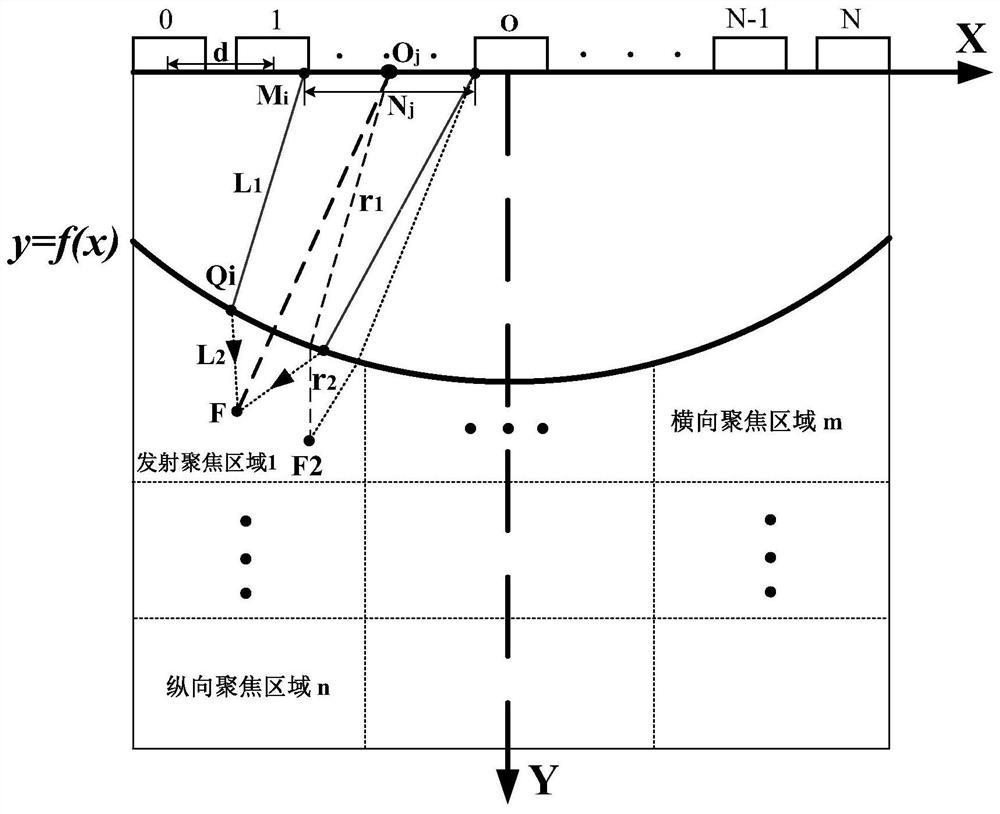
The invention discloses an ultrasonic water immersion automatic detection device and method for complex ring forgings. The method comprises the steps of: placing a to-be-detected complex ring forgingin a water tank, carrying out the single detection of a complex curved surface through an ultrasonic phased array, and carrying out the regional detection of a flat end surface through a multi-frequency array water immersion probe according to the detection depth; during detection of complex curved surfaces, determining the optimal emission dynamic aperture array center and the array element number of each detection region according to a dynamic aperture emission focusing method; determining array emission delay time of each region according to a curved surface multi-medium emission focusing delay time calculation method, and calculating delay superposition time of all sampling points of each region according to a dynamic received beam synthesizer delay algorithm; during detection of the flat end face, selecting array water immersion probes of various different frequency models, and achieving full-coverage detection of the end face of the ring forging. A complete water immersion methodis adopted, the problem of poor coupling is solved, and full-coverage ultrasonic nondestructive testing can be achieved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
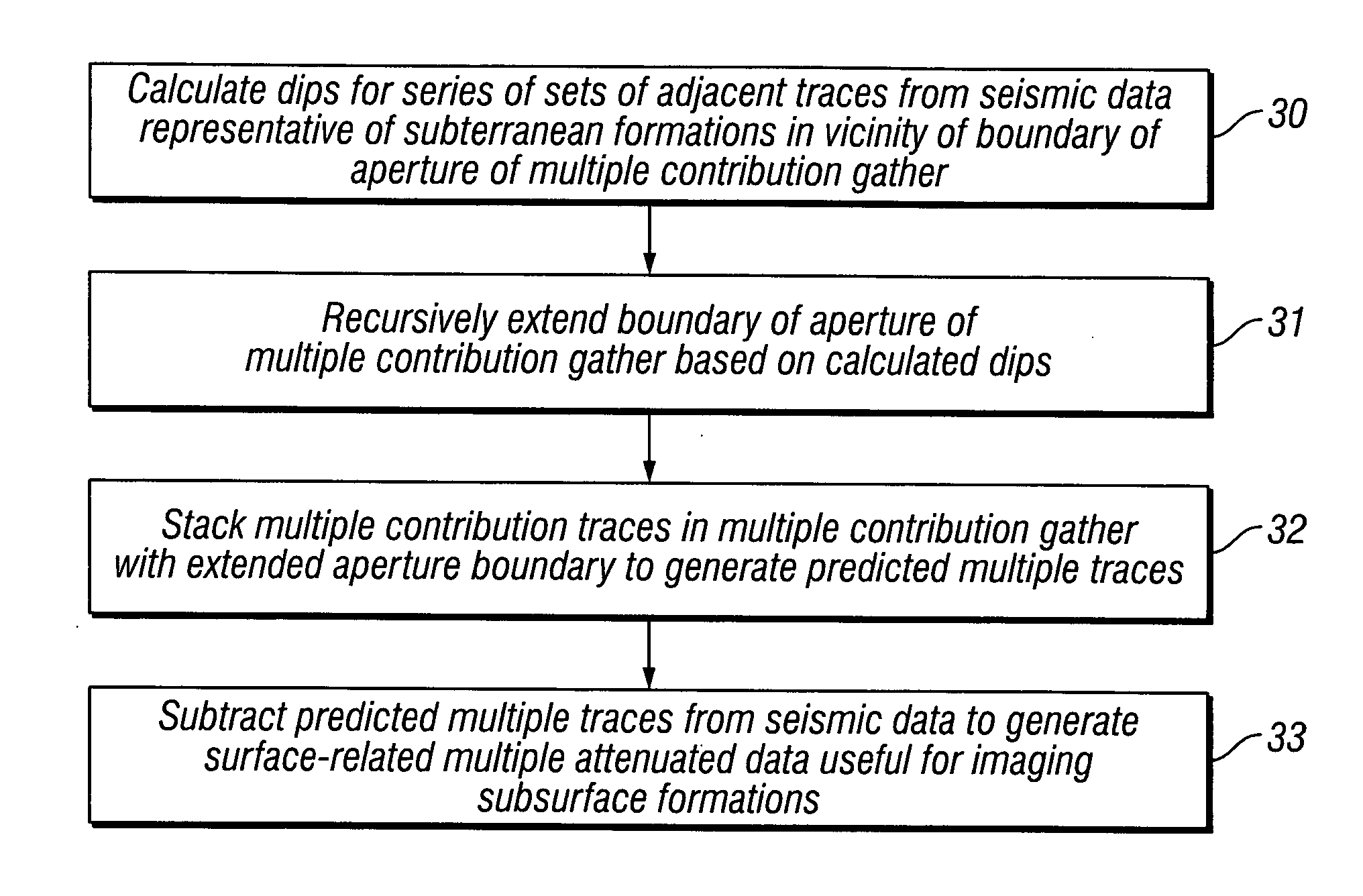
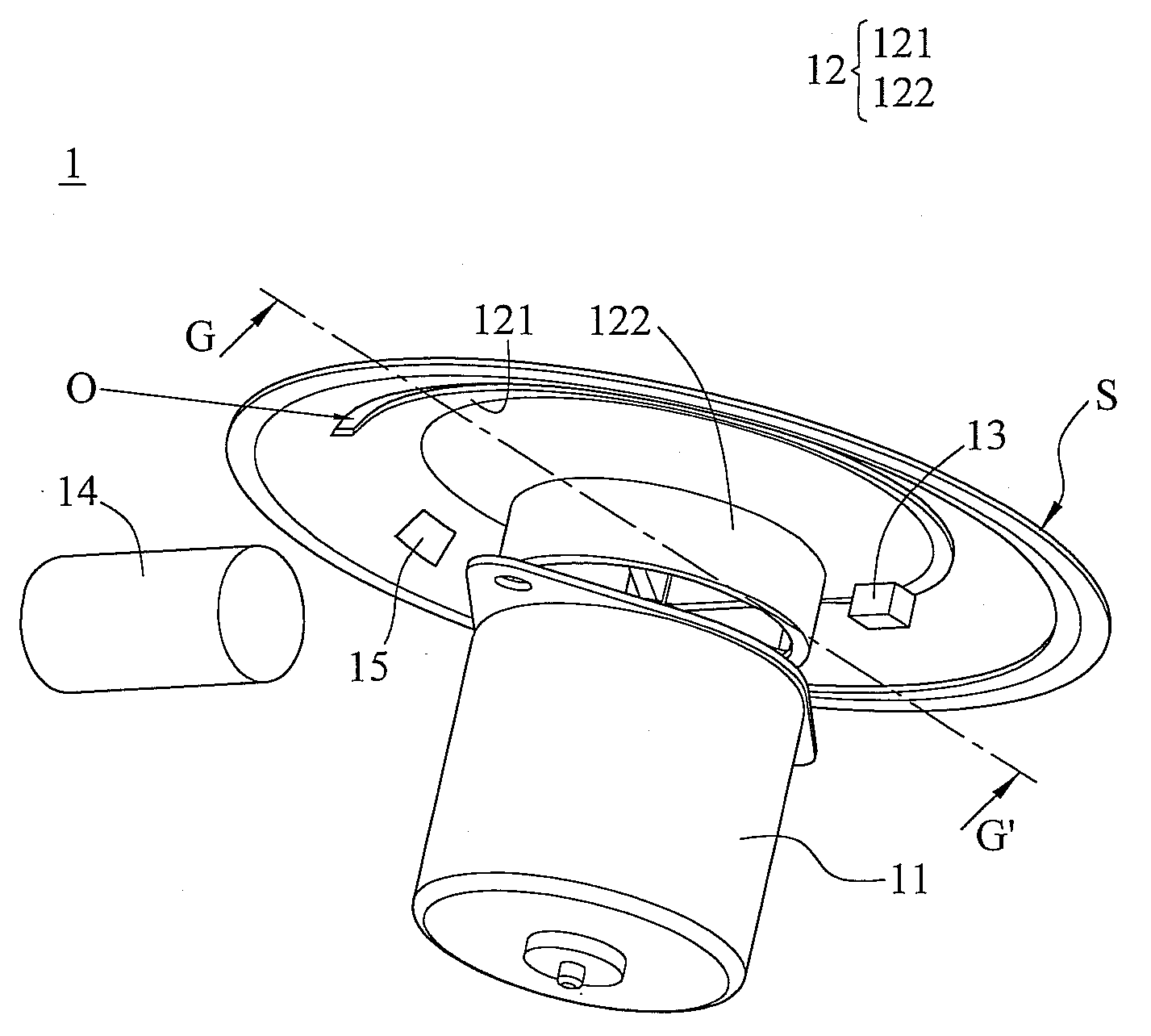
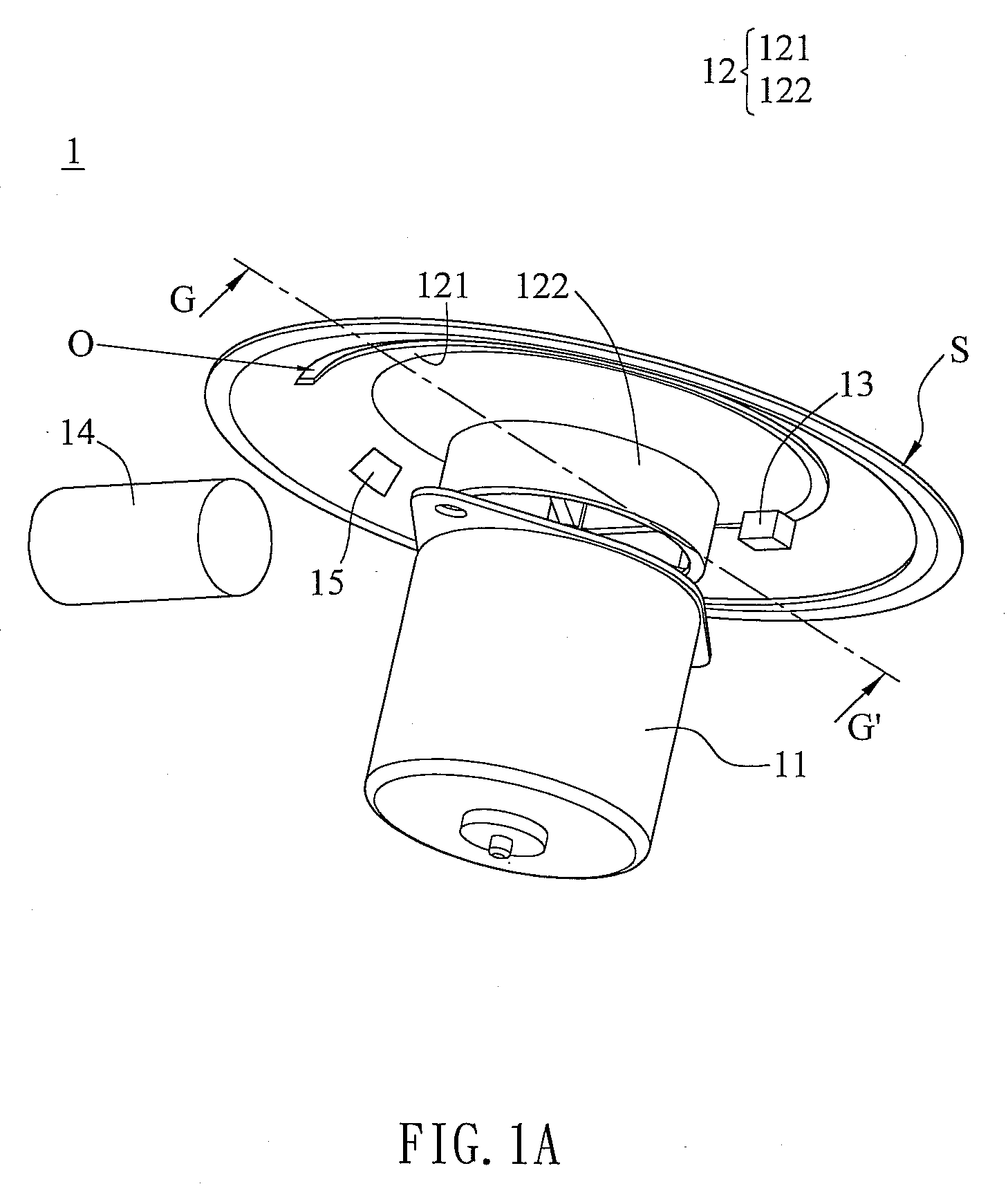
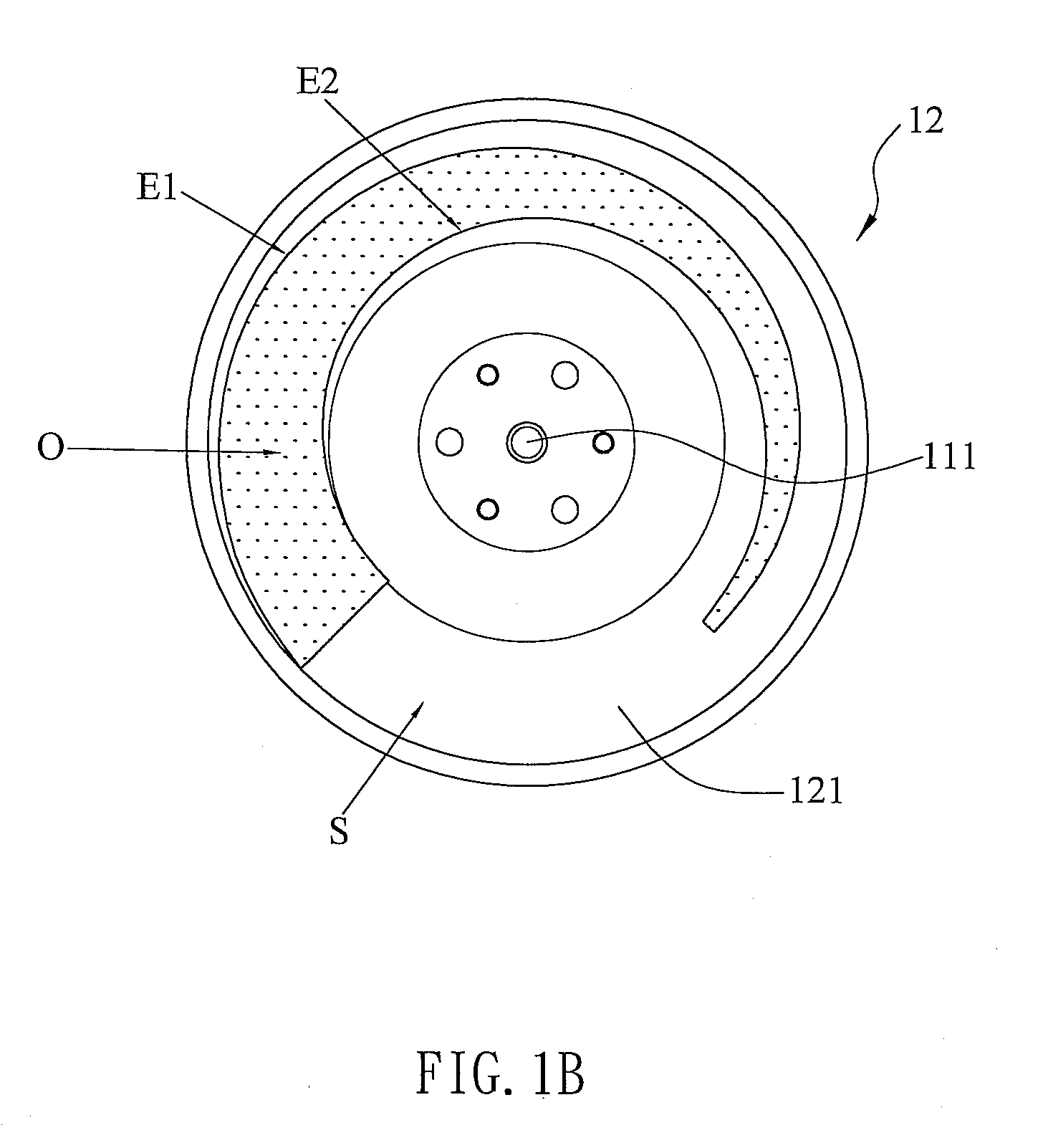
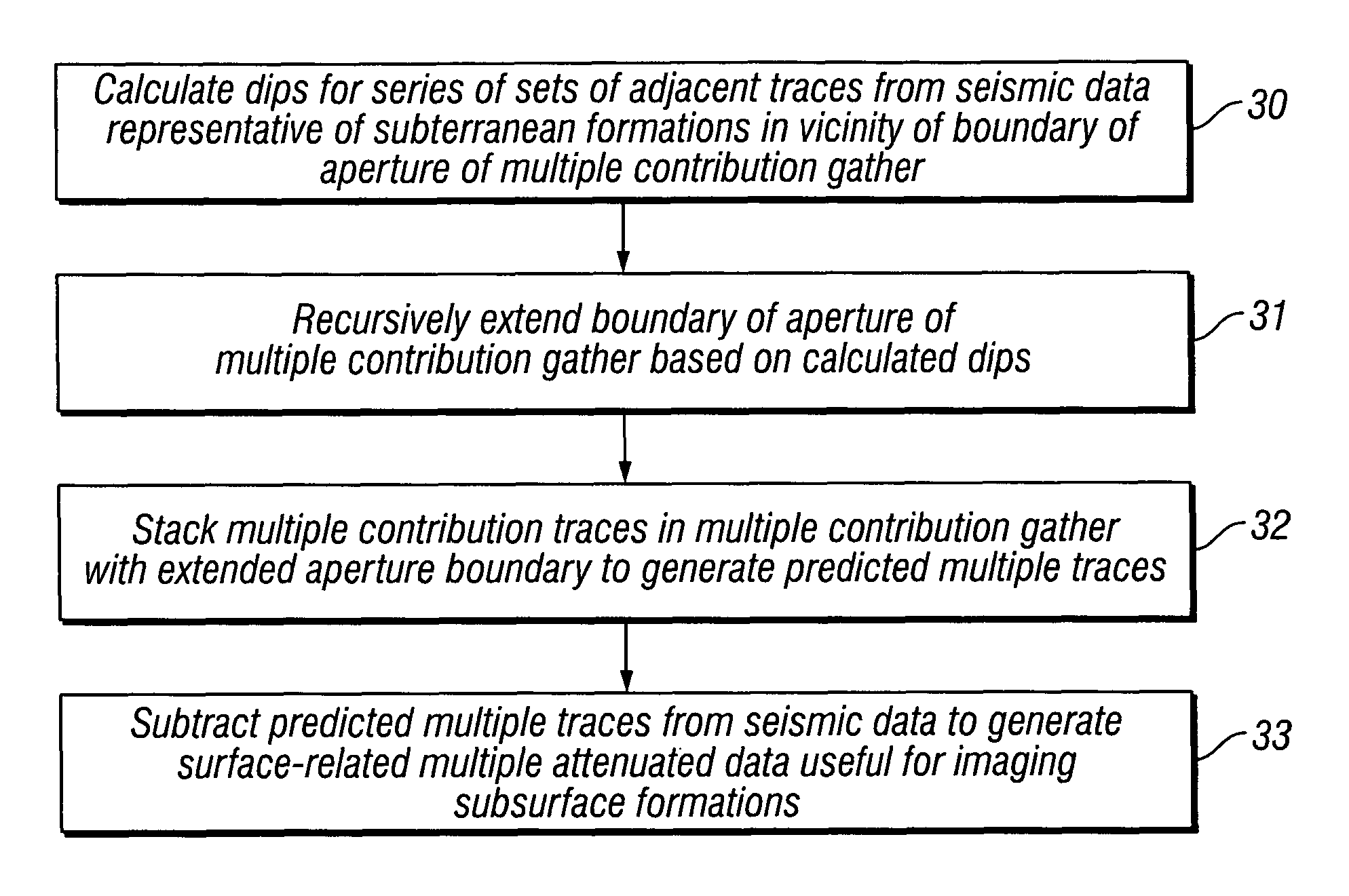
Method for dynamic aperture determination for three-dimensional surface-related multiple elimination
Dips are calculated for a series of sets of adjacent multiple contribution traces, from seismic data representative of subsurface formations, in the vicinity of a boundary of an aperture of a multiple contribution gather, the seismic data acquired by deploying a plurality of seismic sensors proximate an area of the earth's subsurface to be evaluated, the seismic sensors generating at least one of an electrical and optical signal in response to seismic energy. The boundary of the aperture of the multiple contribution gather is recursively extended, based on the calculated dips. Multiple contribution traces in the multiple contribution gather with the extended aperture boundary are stacked to generate predicted multiple traces. The predicted multiple traces are subtracted from the seismic data to generate surface-related multiple attenuated data useful for imaging the subsurface formations.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
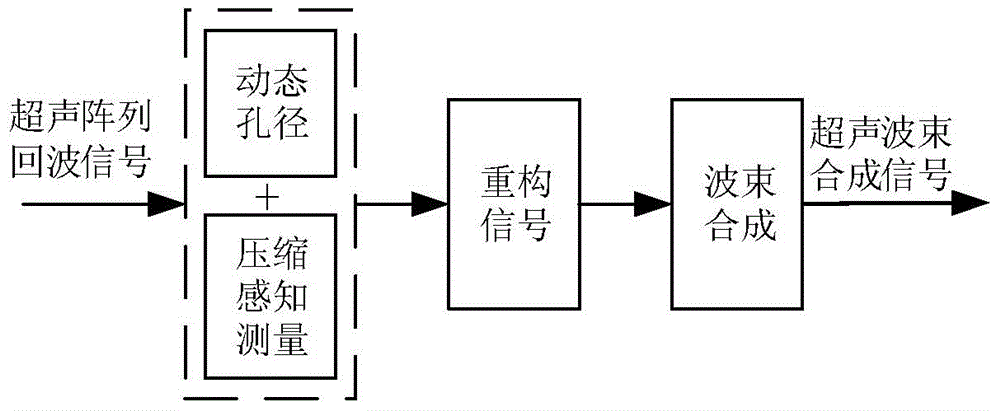
Dynamic aperture integrating compressive sensing ultrasonic beam forming method
InactiveCN104914440AReduce the burden onImprove sparsityAcoustic wave reradiationUltrasound imagingSonification
The invention discloses a dynamic aperture integrating compressive sensing ultrasonic beam forming method. The method comprises the steps of firstly adopting a delta matrix to act as a measurement matrix of a compressive sensing theory in an ultrasonic beam forming system, then selecting a cosine transformation matrix to act as a sparse matrix of the compressive sensing theory, and carrying out organic integration on a dynamic aperture technology and the measurement matrix of the compressive sensing technology, thereby realizing the dynamic aperture integrating compressive sensing ultrasonic beam forming method. The method disclosed by the invention can reduce a burden brought about by a high sampling rate for data sampling, transmission and storage of an ultrasonic imaging system, and enables acquisition of ultrasonic images with high longitudinal resolution to become possible. In addition, introduction of the dynamic aperture technology also further increases the sparseness of ultrasonic echo signals, the sampling data volume is reduced, and the transverse resolution of near-field ultrasonic images is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
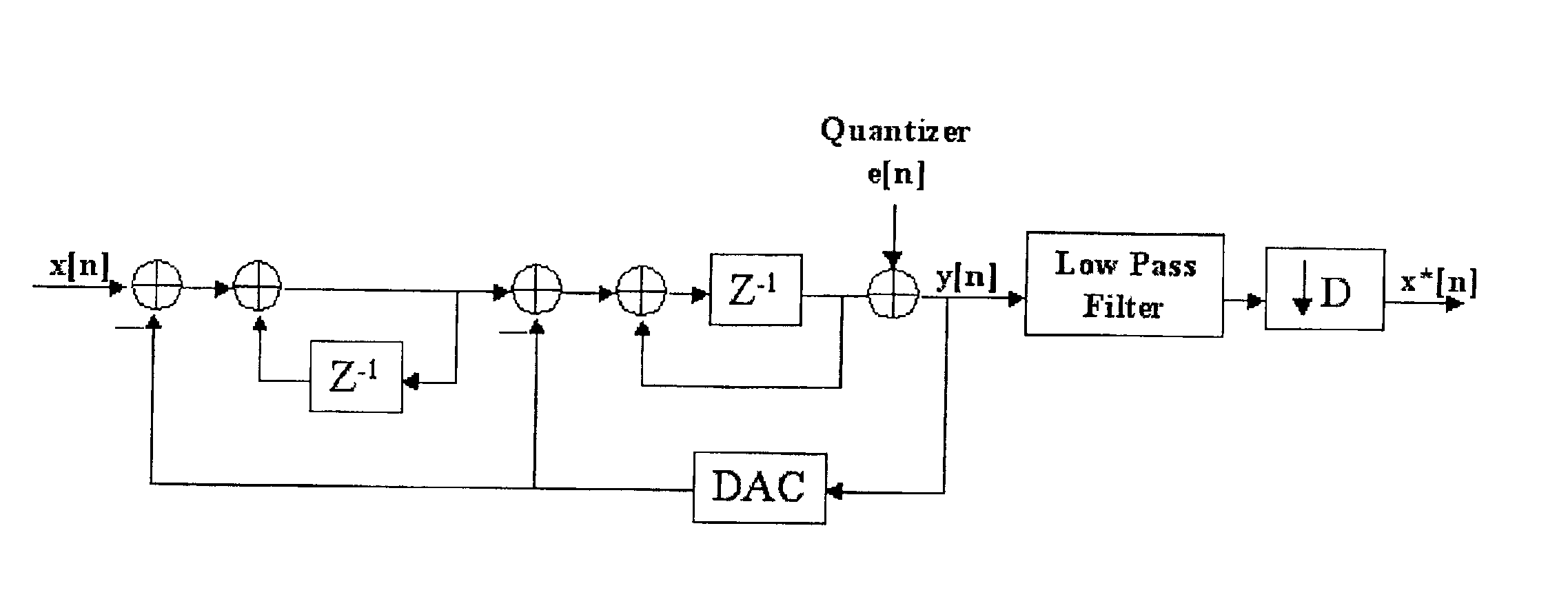
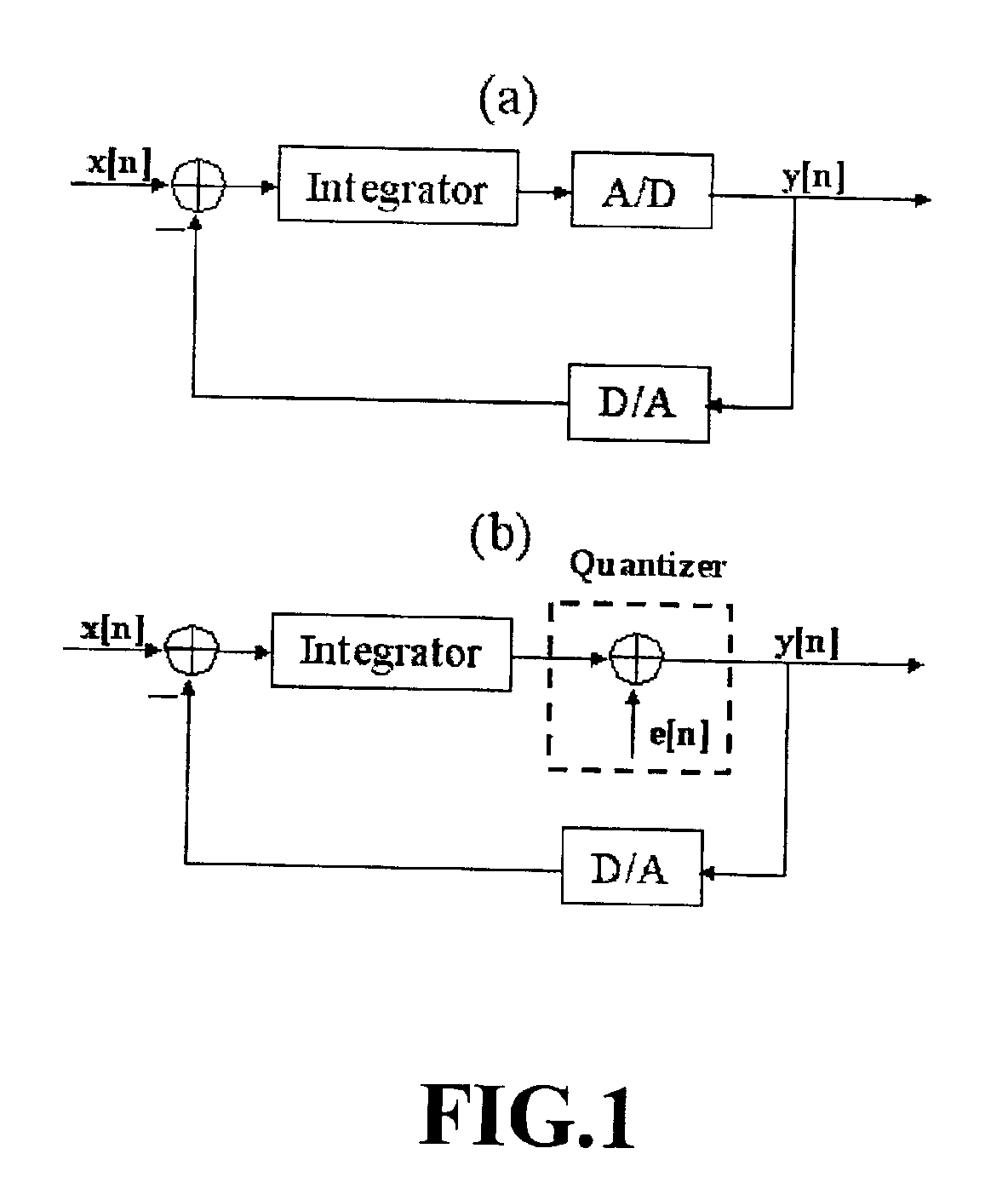
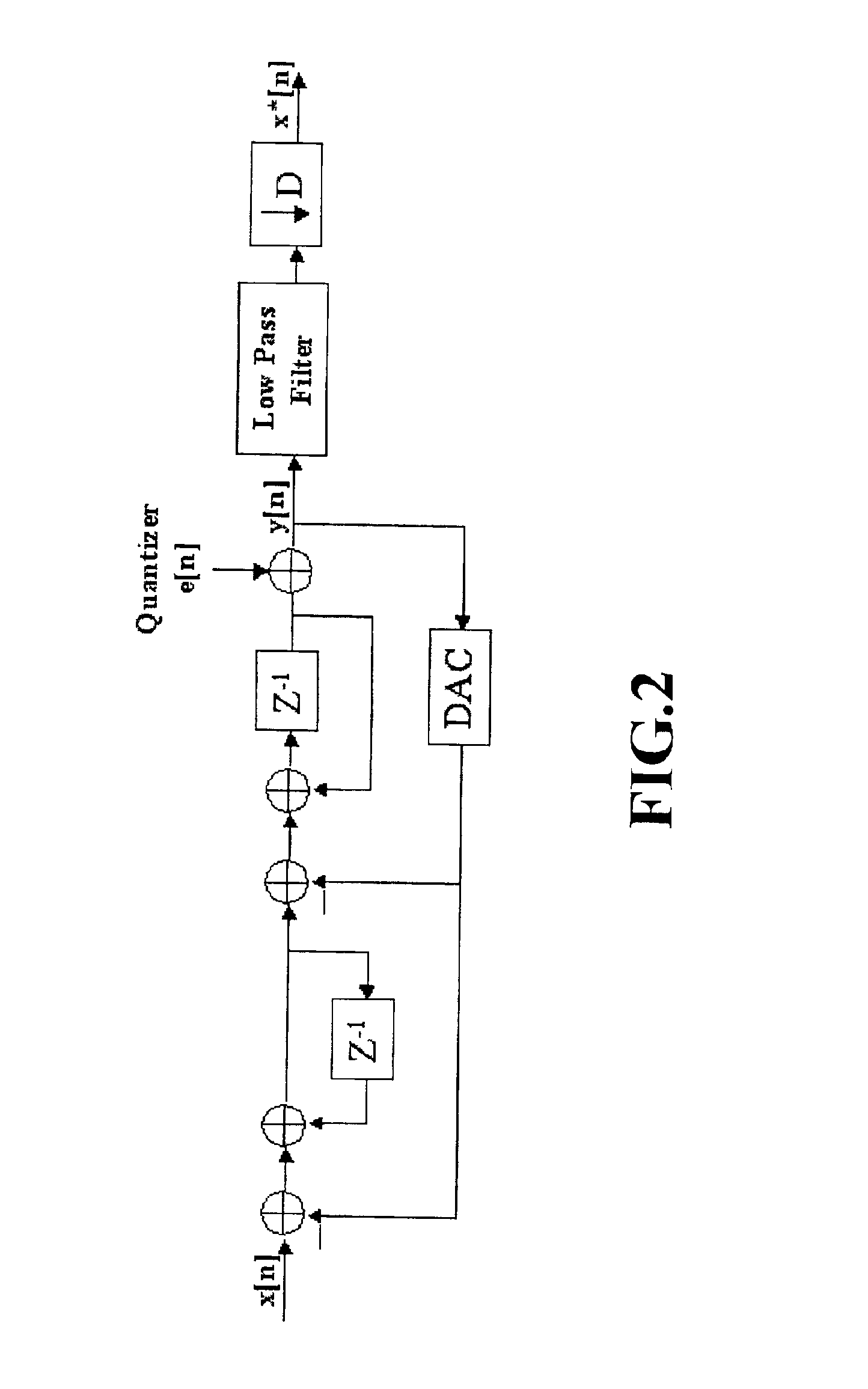
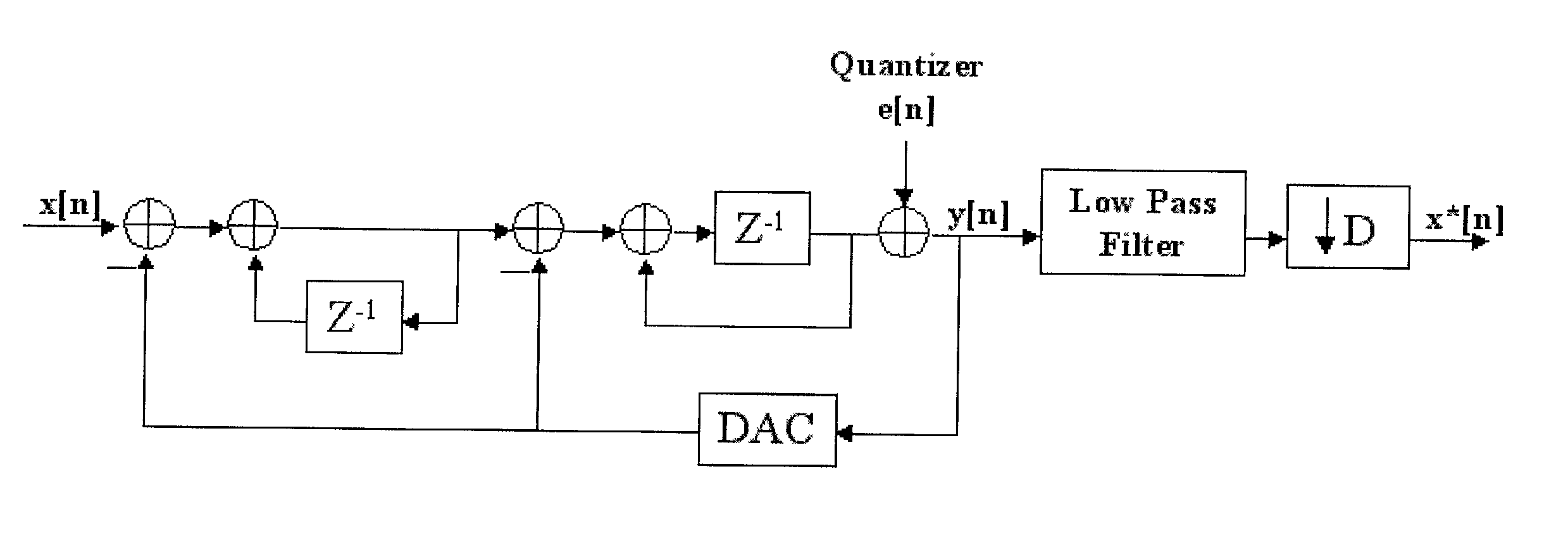
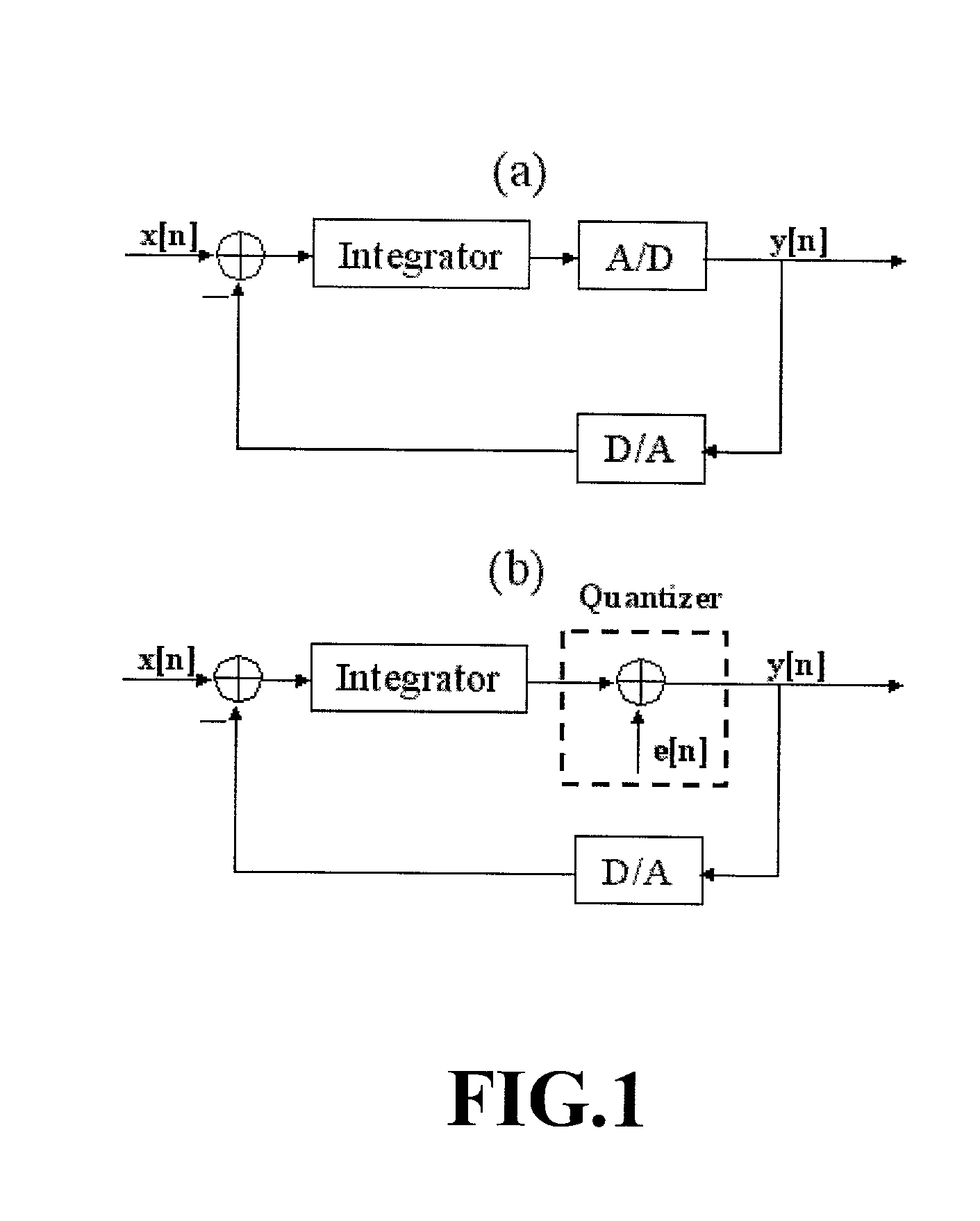
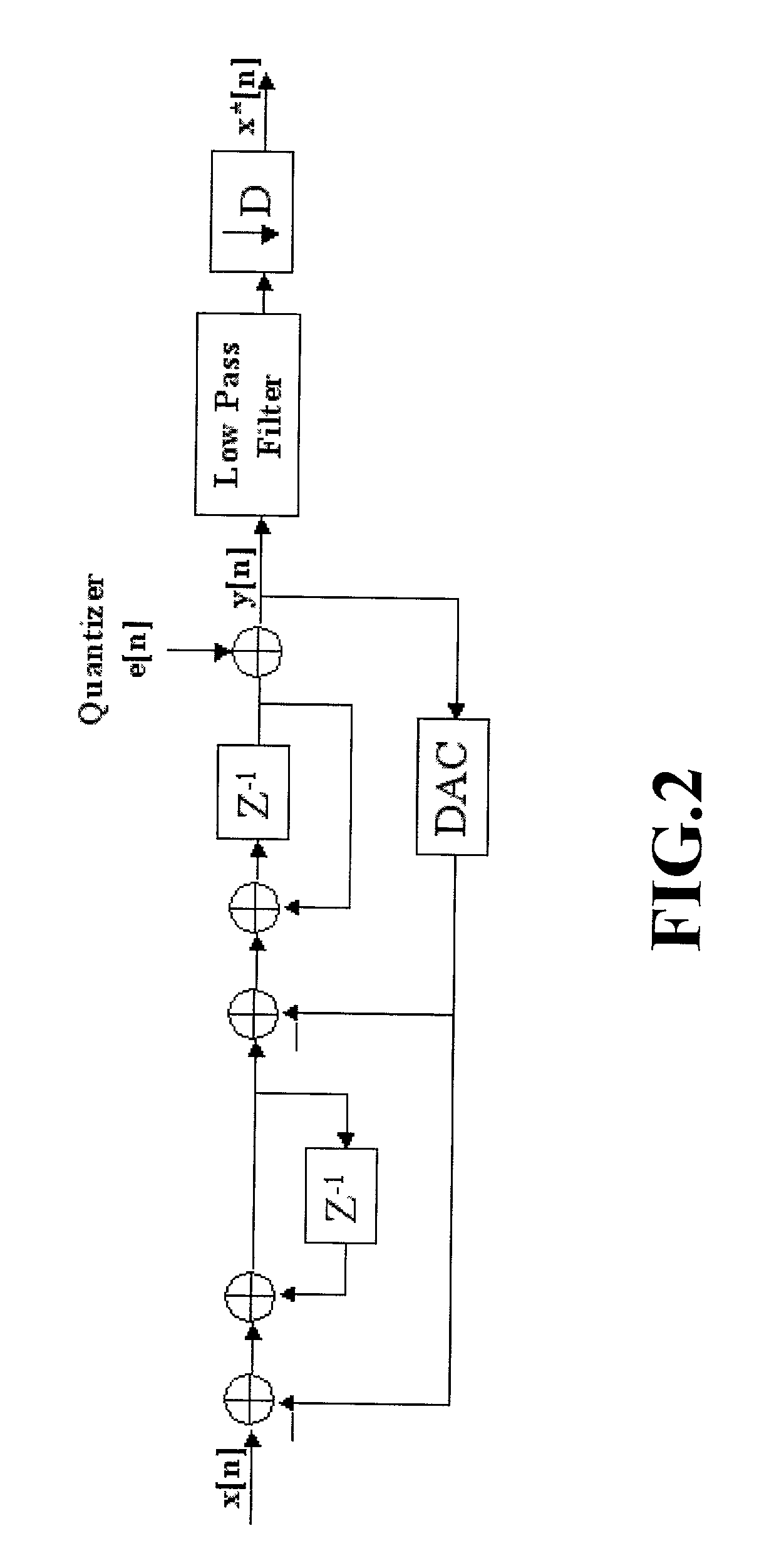
Focus control method for Delta-Sigma based image formation device
InactiveUS6895123B2Lot of noiseWave based measurement systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionDynamic apertureImage formation
Owner:NAT CHUNG SHAN INST SCI & TECH
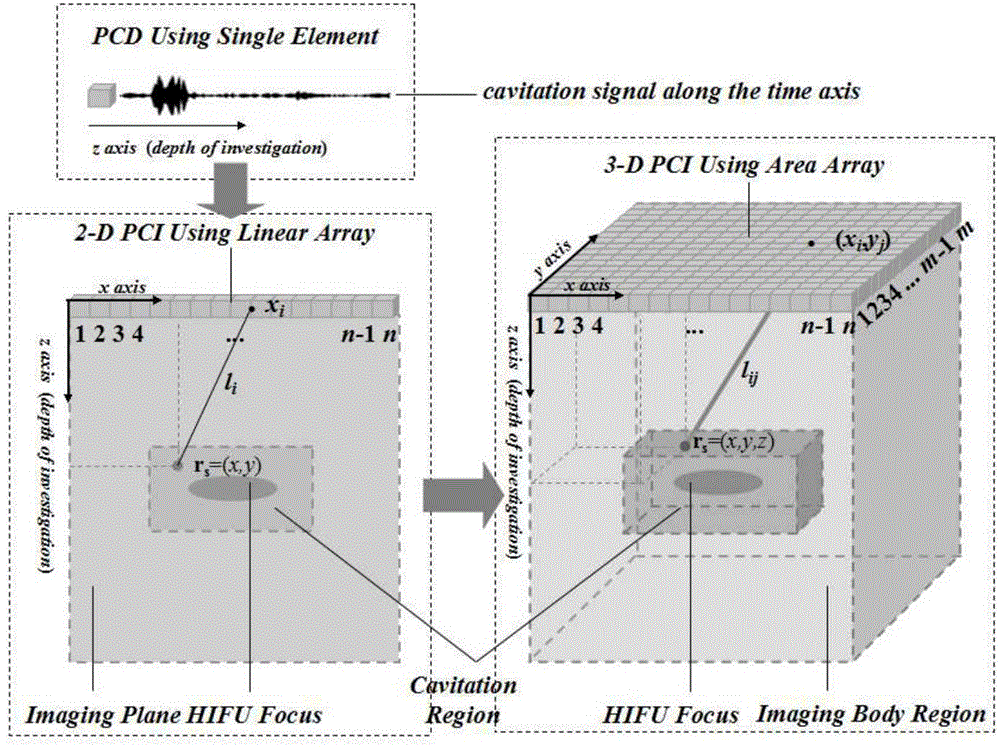
Method for small-area three-dimensional passive cavitation imaging and three-dimensional composite imaging based on area array
ActiveCN104887266AImprove signal-to-noise ratioHigh resolutionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonic diagnosticsCavitationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention provides a method for small-area three-dimensional passive cavitation imaging and three-dimensional composite imaging based on an area array, wherein a two-dimensional passive cavitation imaging algorithm is expanded to a three-dimensional algorithm and a multi-stage continuous self-adaption trapped wave system is designed to research a mechanism of inertial oscillation of a cavitation micro bubble in a sound field, and a dynamic aperture receiving technique is used for further processing of three-dimensional data. Delayed array element receiving of the area array is then disposed to adjust an angle of a passive receiving plane, three-dimensional conversion is carried out on the three-dimensional data and then three-dimensional recombination is carried out on the data in order to realize the three-dimensional passive cavitation imaging. By the method for the small-area three-dimensional passive cavitation imaging and the three-dimensional composite imaging based on the area array provided by the invention, three-dimensional passive cavitation multi-angle compound imaging with high resolution, high signal-to-noise ratio and high efficiency can be obtained, and a selective monitoring manner can be provided for clinical operations by combing the passive cavitation imaging with other techniques.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
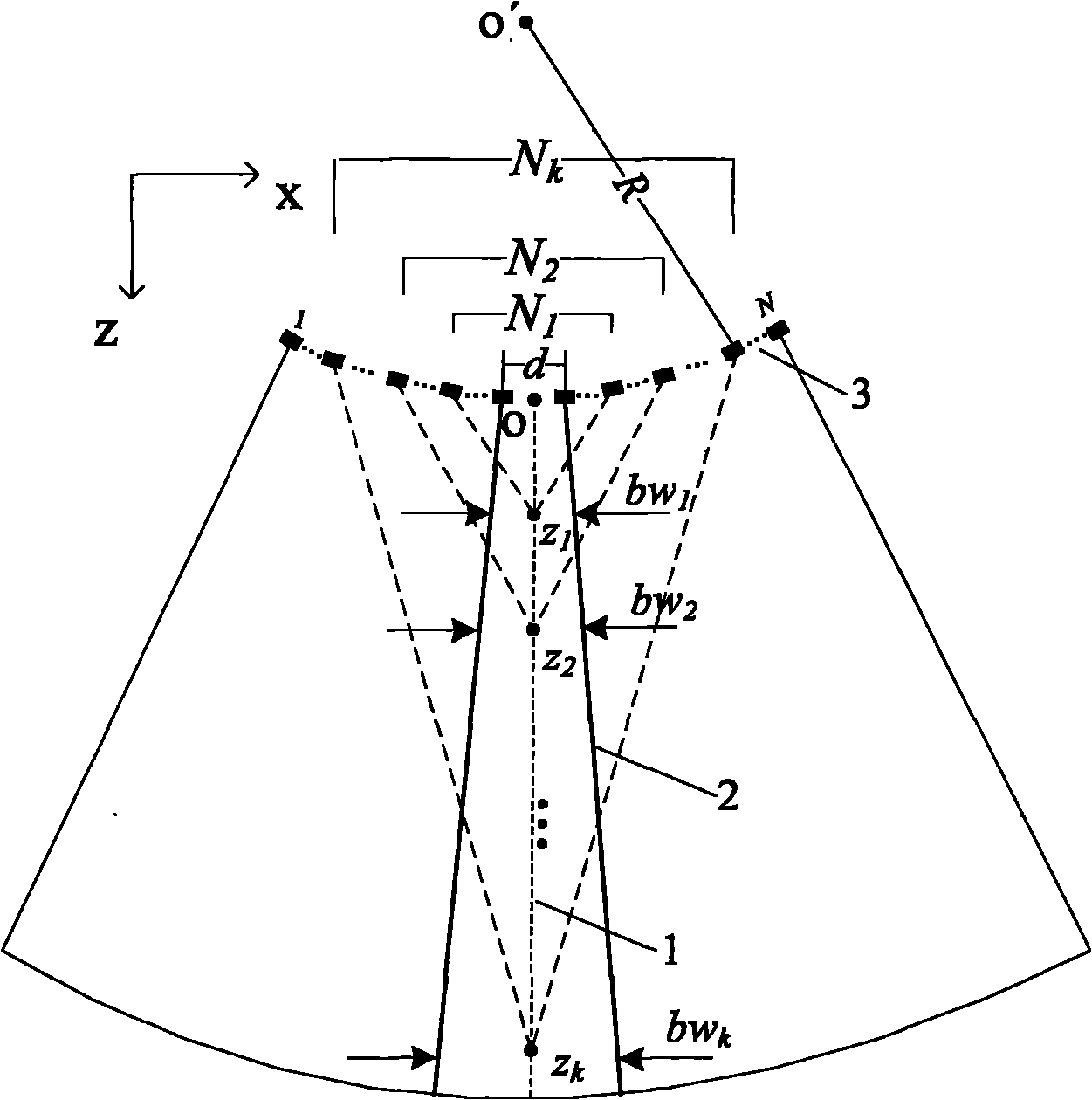
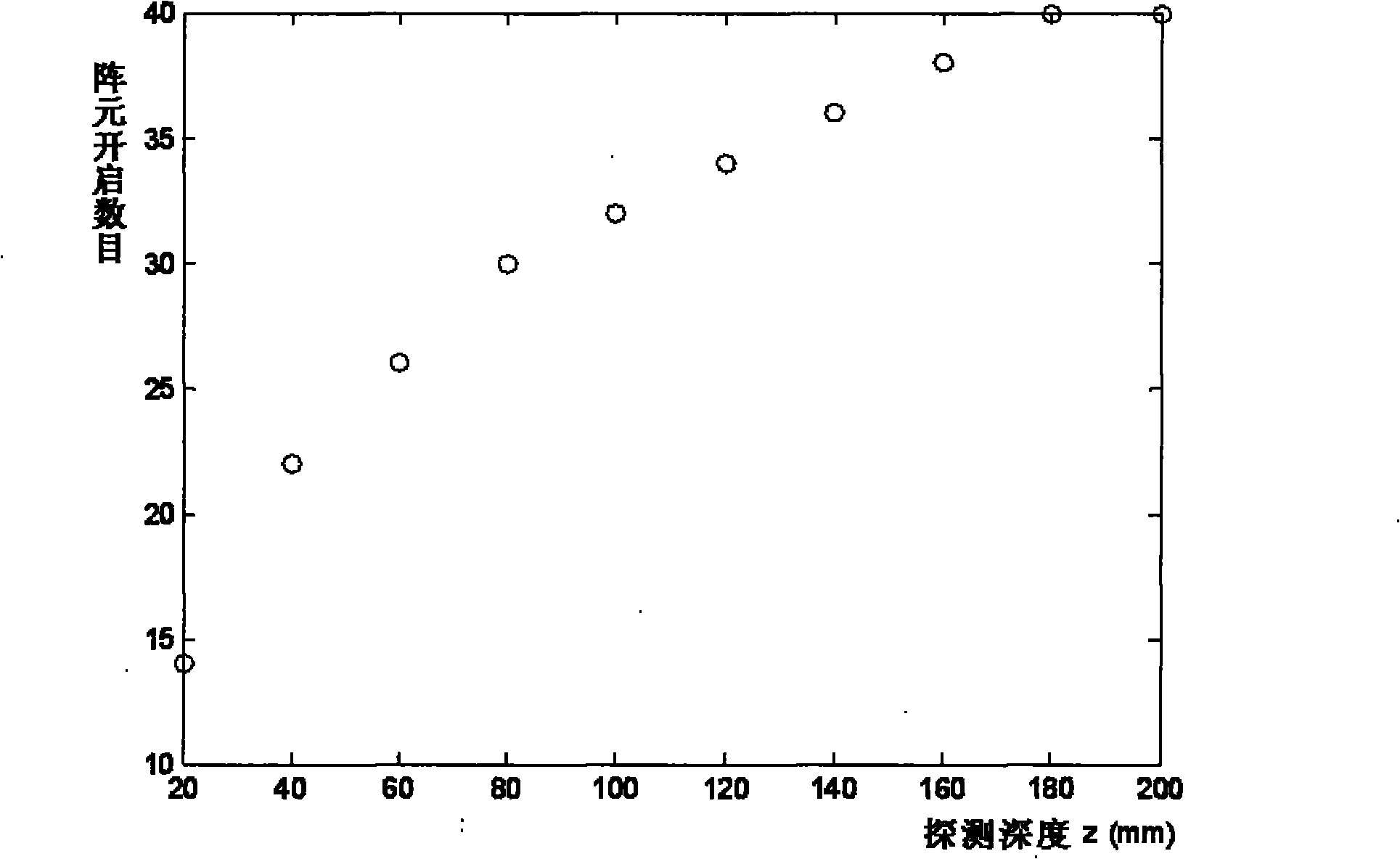
Control method of dynamic aperture based on ultrasonic imaging system
InactiveCN101893705AImprove imaging effectImprove image qualityAcoustic wave reradiationSonificationUltrasonic imaging
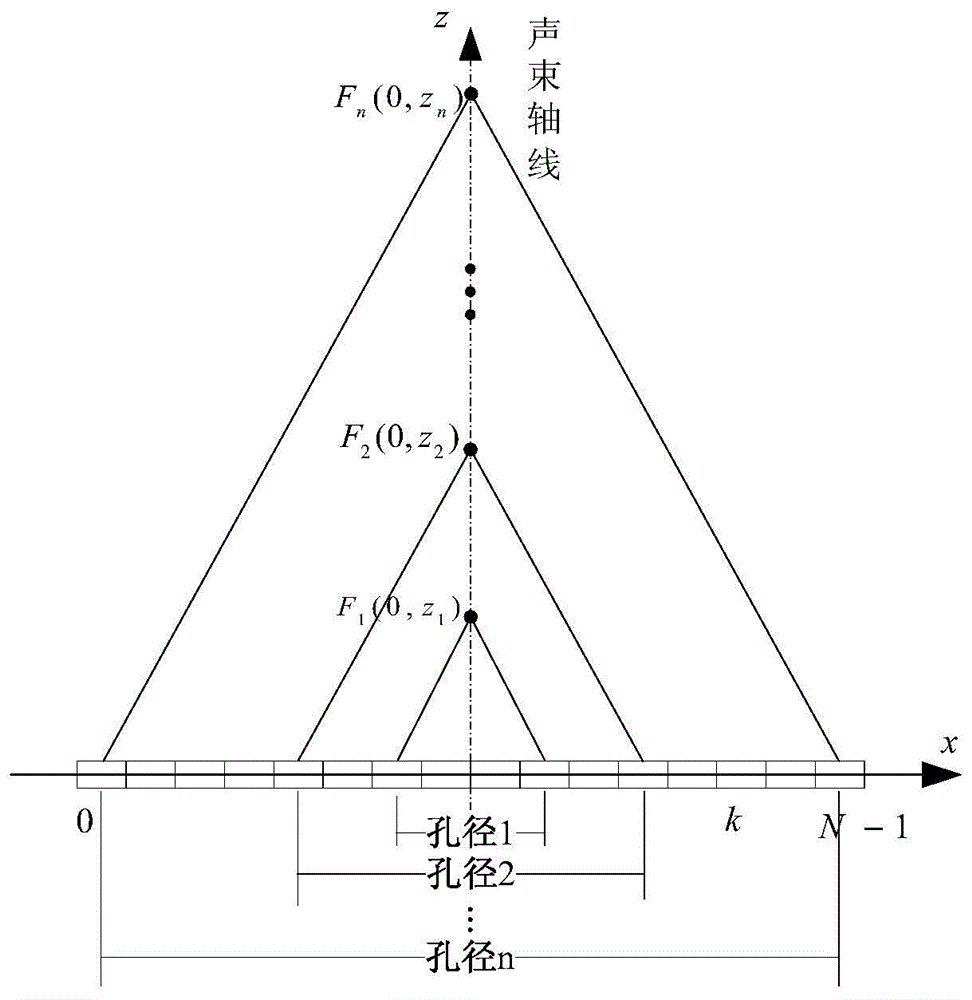
The invention belongs to the ultrasonic imaging technical field, and in particular relates to a control method of a dynamic aperture based on an ultrasonic imaging system, which aims at ultrasonic imaging in a sequential scanning mode by virtue of a convex lens probe. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly segmenting depths of investigation and then calculating beam width which can fully cover the area between two adjacent scanning lines under different depths according to known probe parameters such as curvature radius and array element spacing of the probe; and reversely calculating the number of array elements which need to be started by the probe under the corresponding depths according to the beam width value with different depths of investigation and a probe normalized directivity function with a discrete array. In the control method of the dynamic aperture, the beam width which can fully cover the area between the two adjacent scanning lines can be obtained throughcalculation to eliminate parts of dead zones which can not be imaged and improve imaging capability of the system on the area among the scanning lines, thus effectively enhancing the overall imaging quality of the ultrasonic system.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
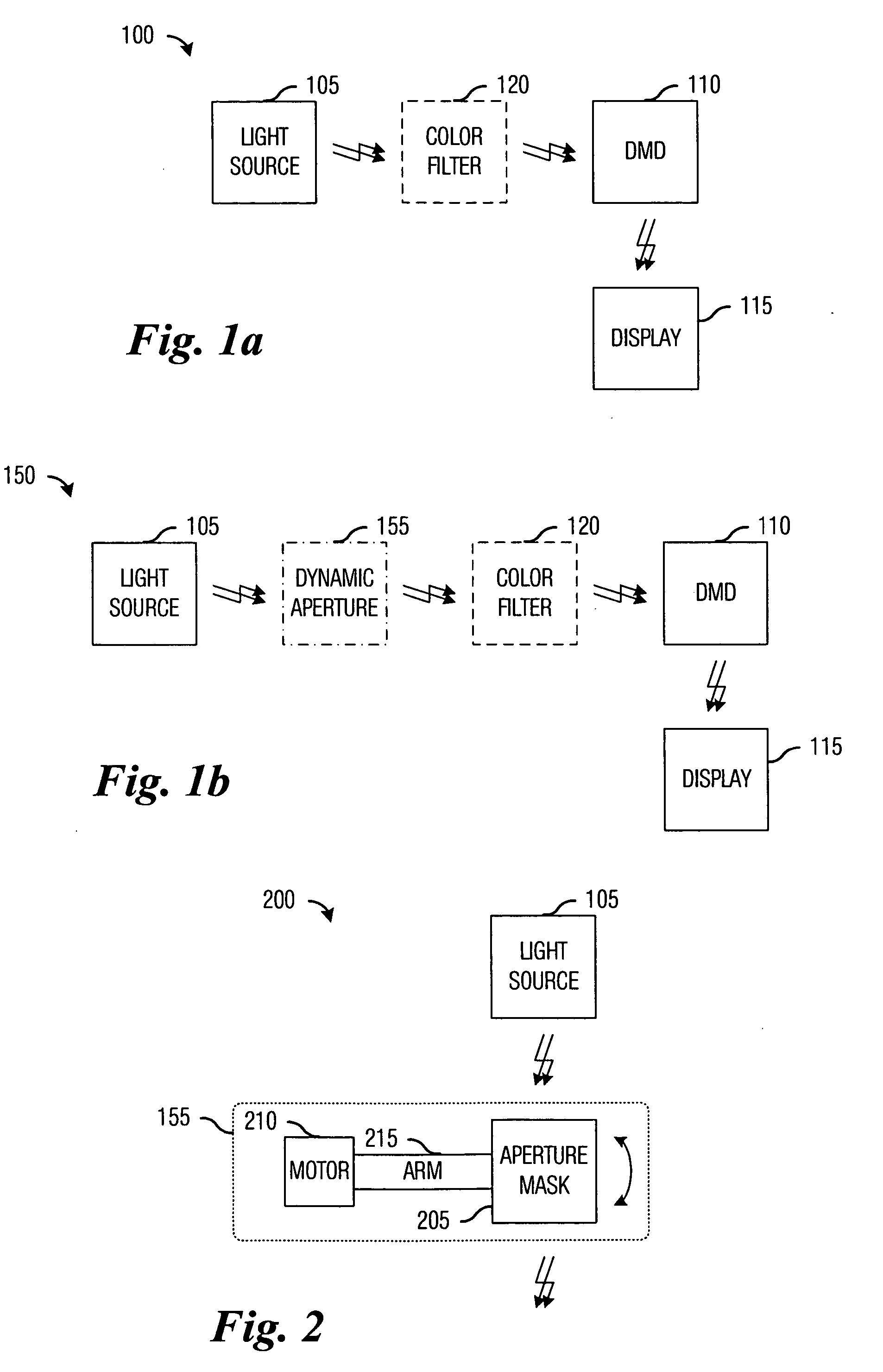
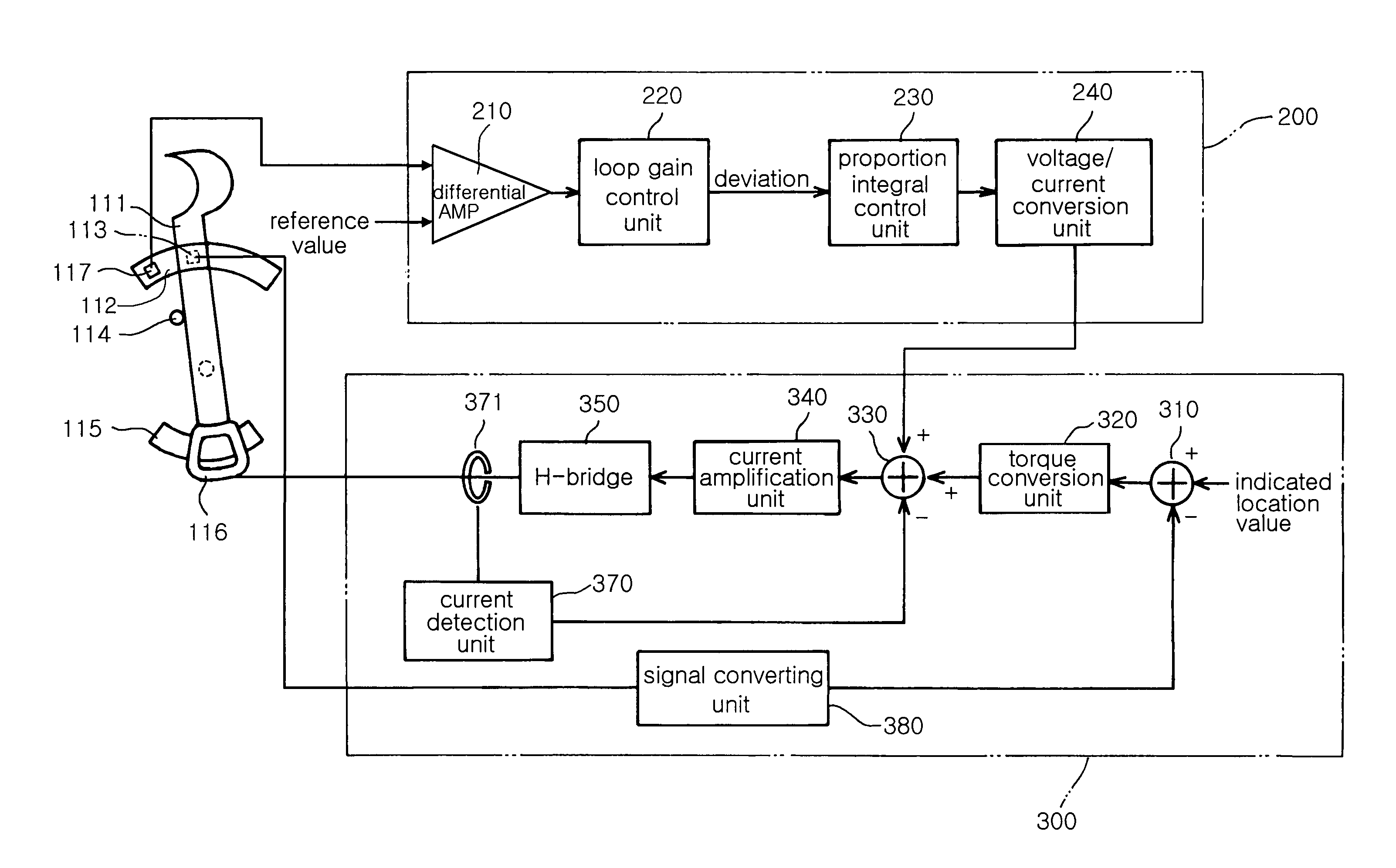
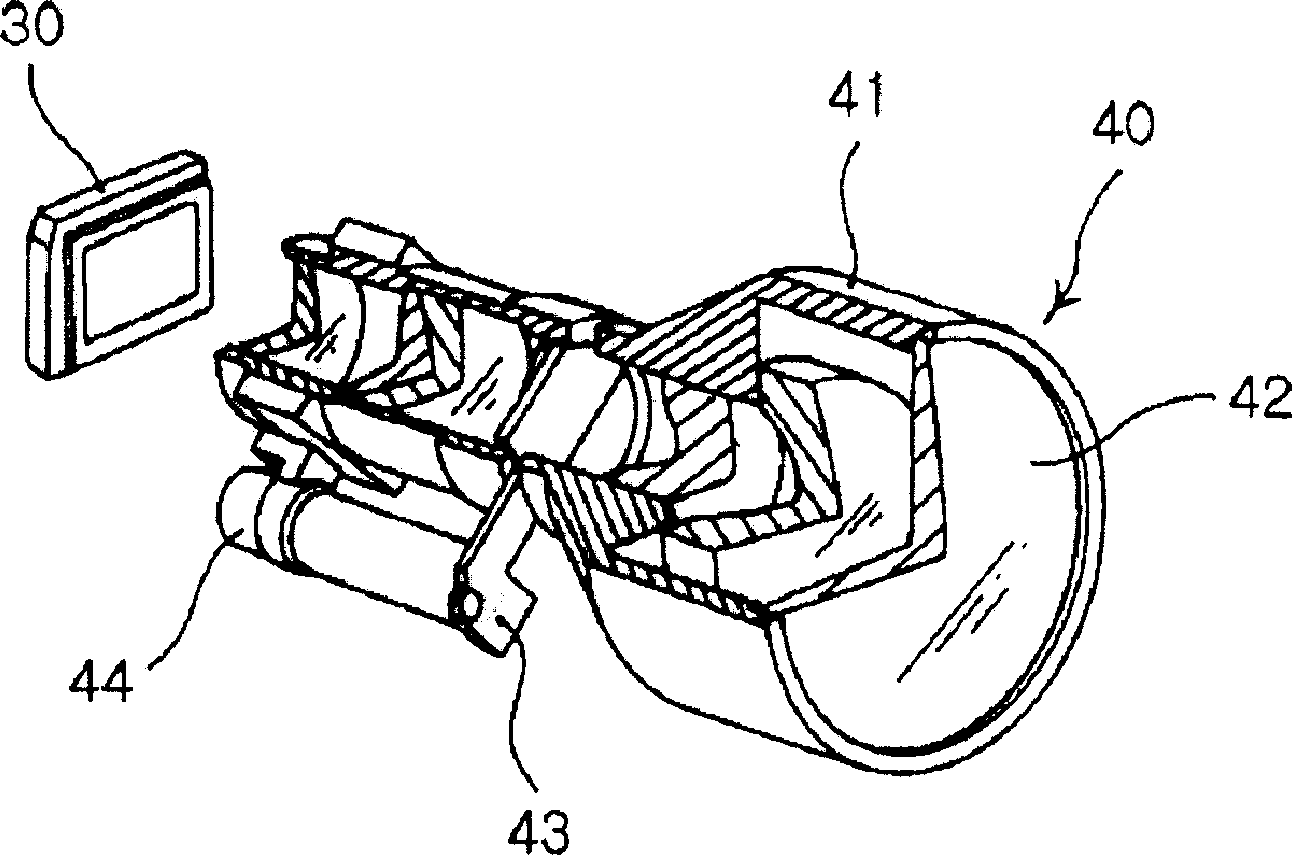
Apparatus for driving dynamic aperture and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS6999245B1Simple configurationPrecise position controlTelevision system detailsProjectorsDynamic apertureEngineering
Disclosed herein is a dynamic aperture driving apparatus for adjusting the amount of light of a projection optical system and a method of controlling the same. The system includes a rotation means, a driving means, a first detection means and a first detection means. The rotation means is connected at the upper end thereof to the dynamic aperture to be rotated to the right and left within a range of rotating angles. The driving means rotates the rotation means to the right and left according to a predetermined electric signal. The first detection means detects the position of the rotation means using a Hall effect. The second detection means detects the operational error of the first detection means due to variation in temperature.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
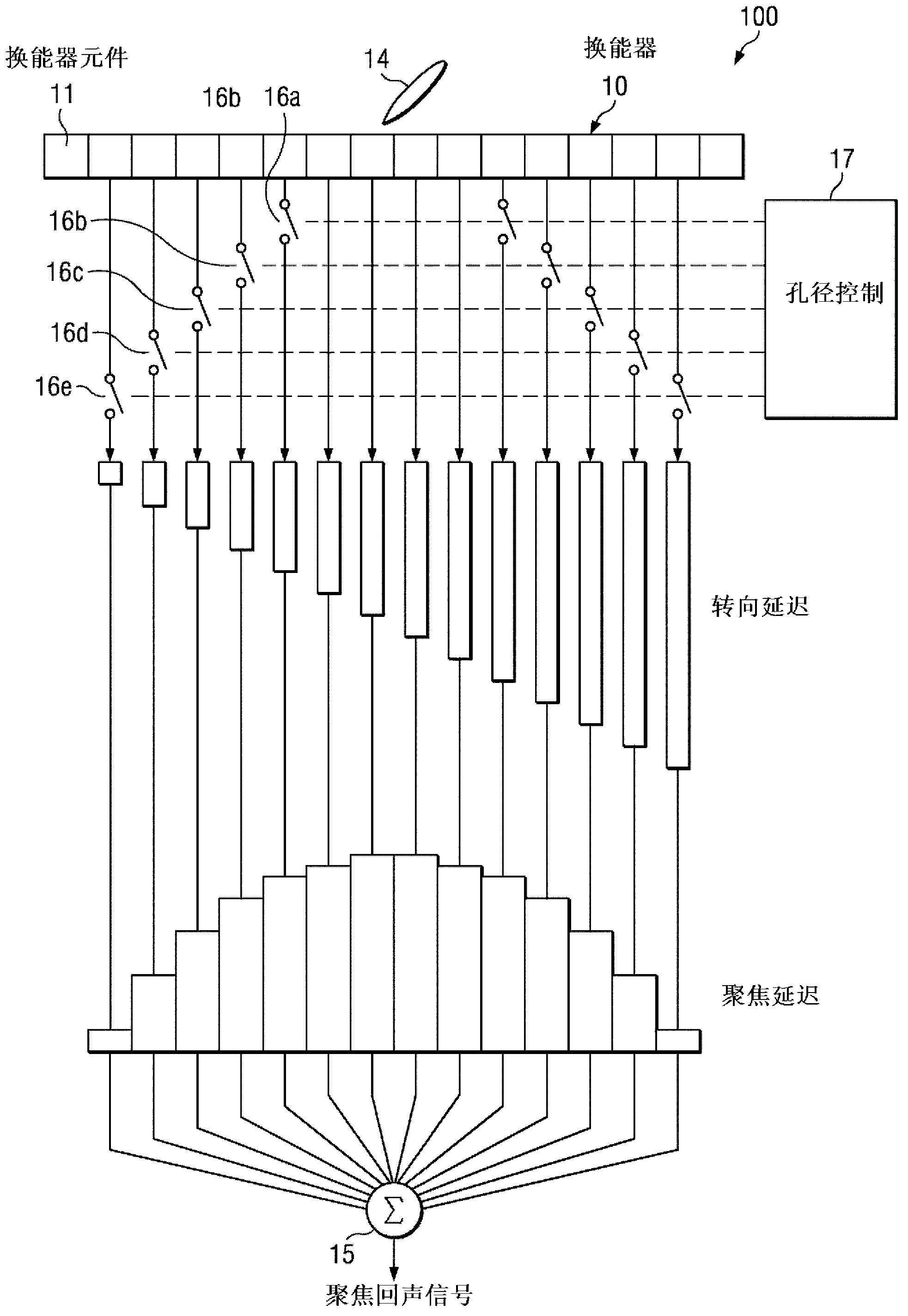
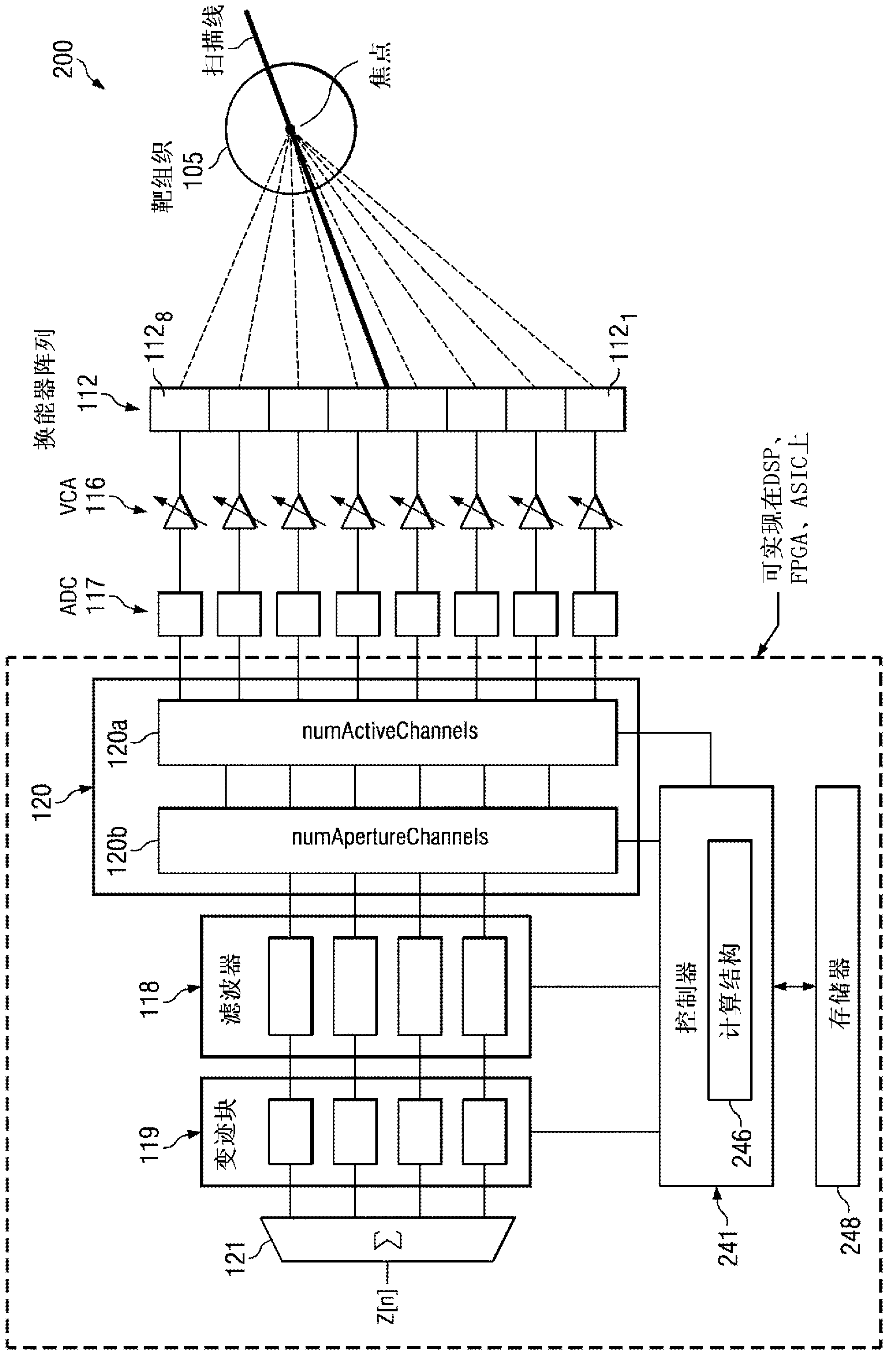
Dynamic aperture control and normalization for apodization in beamforming
ActiveCN103237500AAvoid the need to switchAccurate timingMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationDynamic aperture
A method of apodizing for ultrasound beamforming includes providing filtered digital channel data representing echo data from target tissue in a plurality (k) of data channels and a predefined number of active channels (Nact). A software-based integrated apodization algorithm dynamically apodizes the digital channel data using a selected apodizing function h[n,k], n being the sample number. The integrated apodization algorithm applies dynamic aperture control to create an effective aperture by generating a parameter numApertureChannels (Nap[n]), where Nap[n]@Nact, and selecting Nap[n] particular data channels based on a dynamic beam focusing location for beamforming. Applied dynamic data scaling provides data normalization using a vector inner product between h[n,k] and a scale factor to generate normalized apodization factors hnorm [n,k]. The normalized apodization factors are applied to the digital channel data in the Nap[n] particular data channels to generate apodized and normalized digital channel data.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
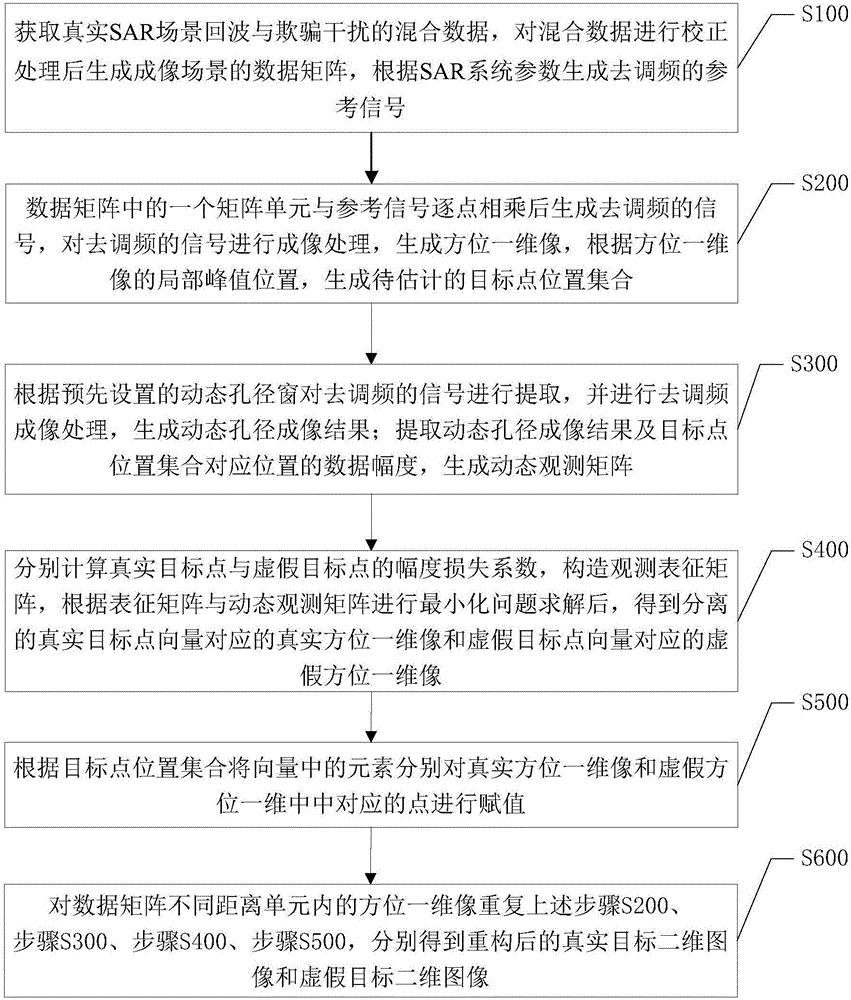
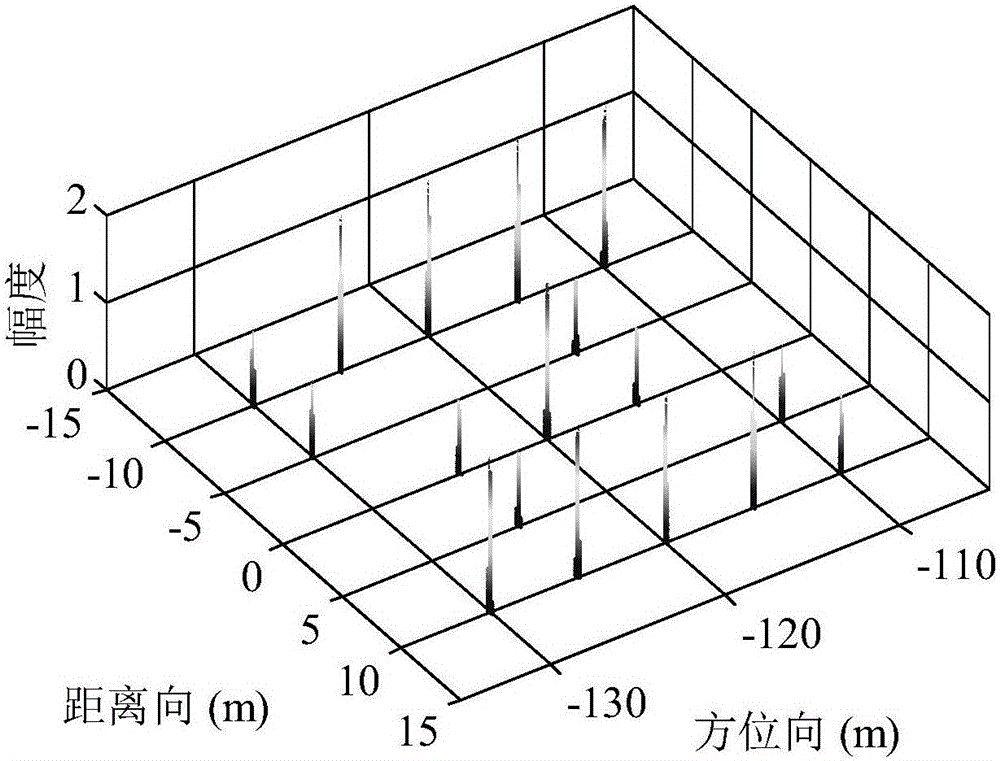
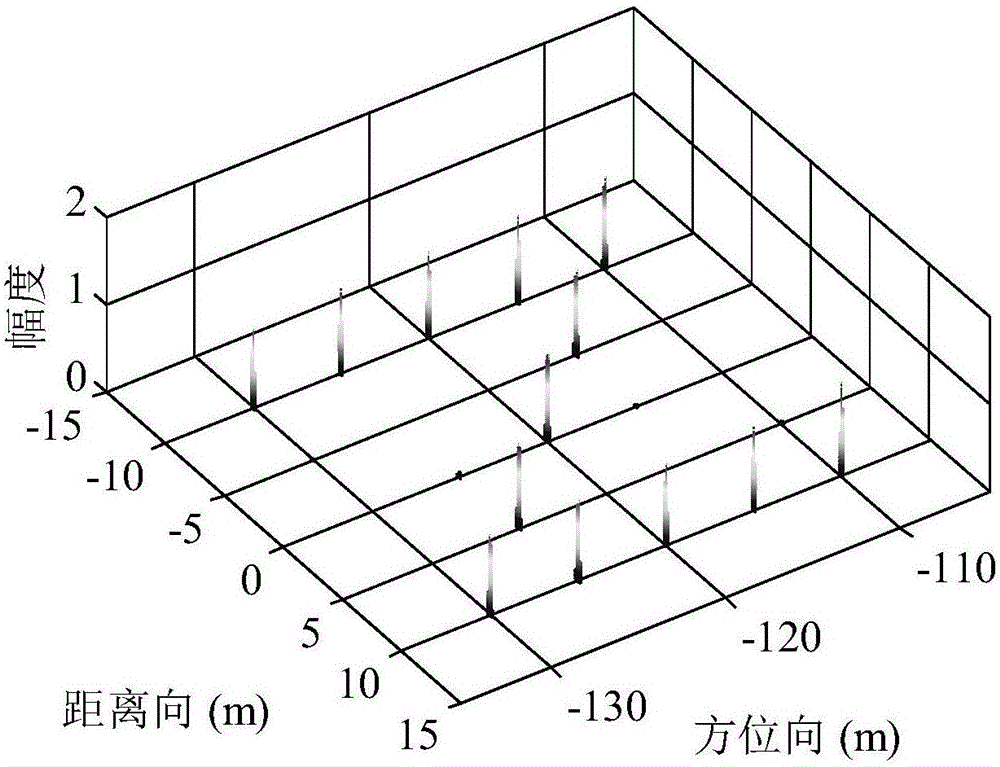
SAR false target interference suppression method and system based on dynamic aperture
The invention provides an SAR false target interference suppression method and system based on dynamic aperture. The method comprises the steps that a data matrix and a reference signal are generated based on mixed data; the data matrix and the reference signal are subjected to imaging processing to generate an azimuth one-dimensional image, and a target point position set to be estimated is generated according to the azimuth one-dimensional image; a dynamic observation matrix is generated according to a preset dynamic aperture window and the target point position set; a constructed observation representation matrix and the dynamic observation matrix are used to carry out minimized solving to acquire the true azimuth one-dimensional image corresponding to a separated true target point vector and a false azimuth one-dimensional image corresponding to a false target point vector; and the steps are repeated to acquire a reconstructed true target two-dimensional image and false target two-dimensional image. According to the invention, without improving the complexity of the existing radar system, the interference of a false target is effectively suppressed and the high cost of system upgrade is reduced by constructing the objective function of a deception interference separation problem and through optimization solving.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
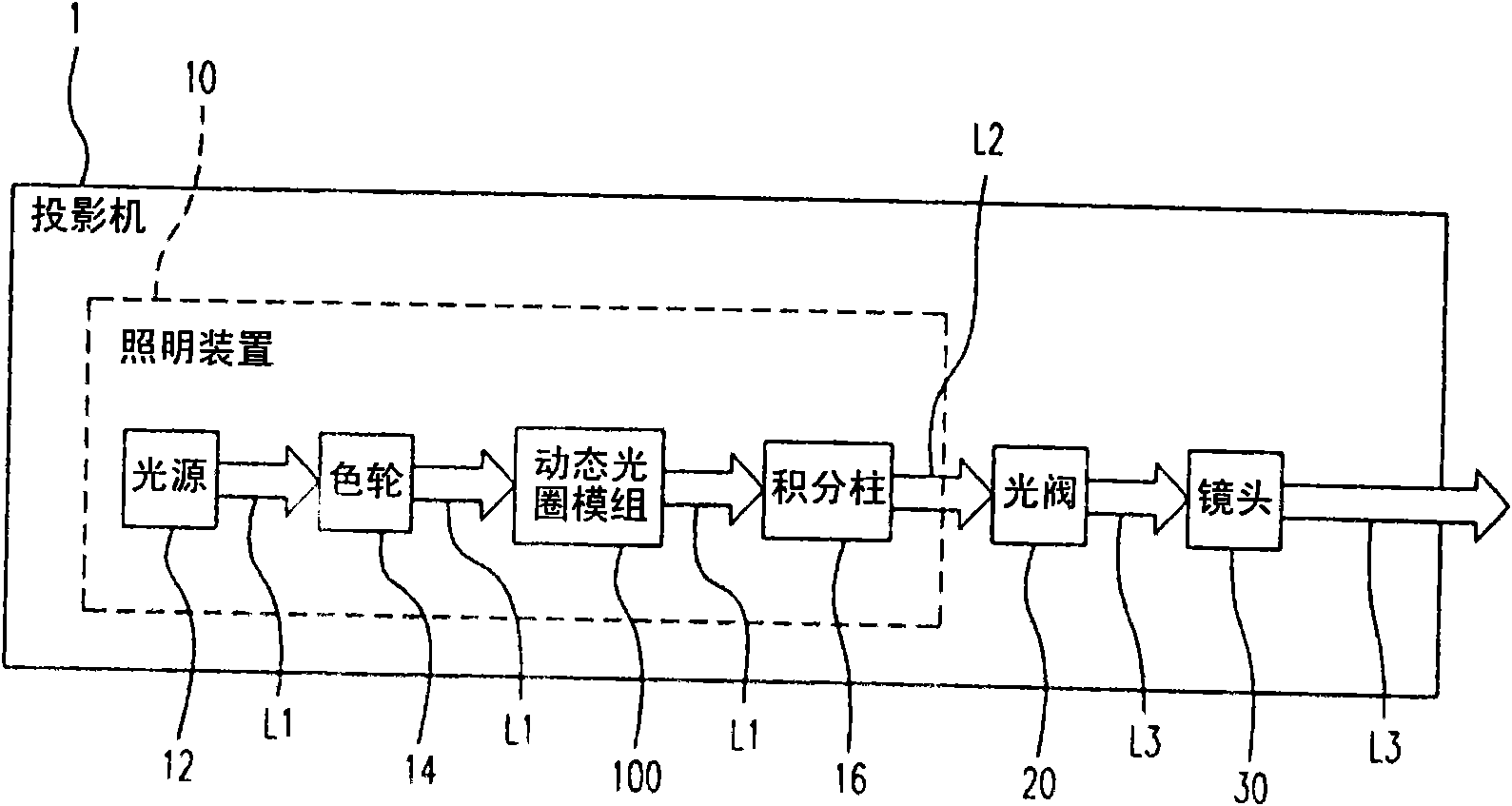
Dynamic aperture module, lighting device and projector
InactiveCN102141715AImprove reliabilityCause out of step situationProjectorsCamera diaphragmsLight beamDynamic aperture
The invention relates to a dynamic aperture module, a lighting device and a projector. The projector comprises a lighting device, a light valve and a lens, wherein the lighting device comprises a light source for providing a beam, an integration rod, a color wheel and a dynamic aperture module, the dynamic aperture module is arranged between the integration rod and the color wheel and comprises a fixed seat, a first airflap, a second airflap and a driver; the first airflap and the second airflap are mutually coupled and respectively pivoted on the fixed seat; the driver is coupled to the first airflap; the driver drives the first airflap to rotate relative to the fixed seat so that the first airflap drives the second airflap to rotate; and the first airflap and the second airflap respectively rotate in opposite clockwise directions relative to the fixed seat to control the width of a gap between the first airflap and the second airflap and further adjust the luminous flux of a light beam passing through the gap.
Owner:CORETRONIC
3D printing with variable voxel sizes
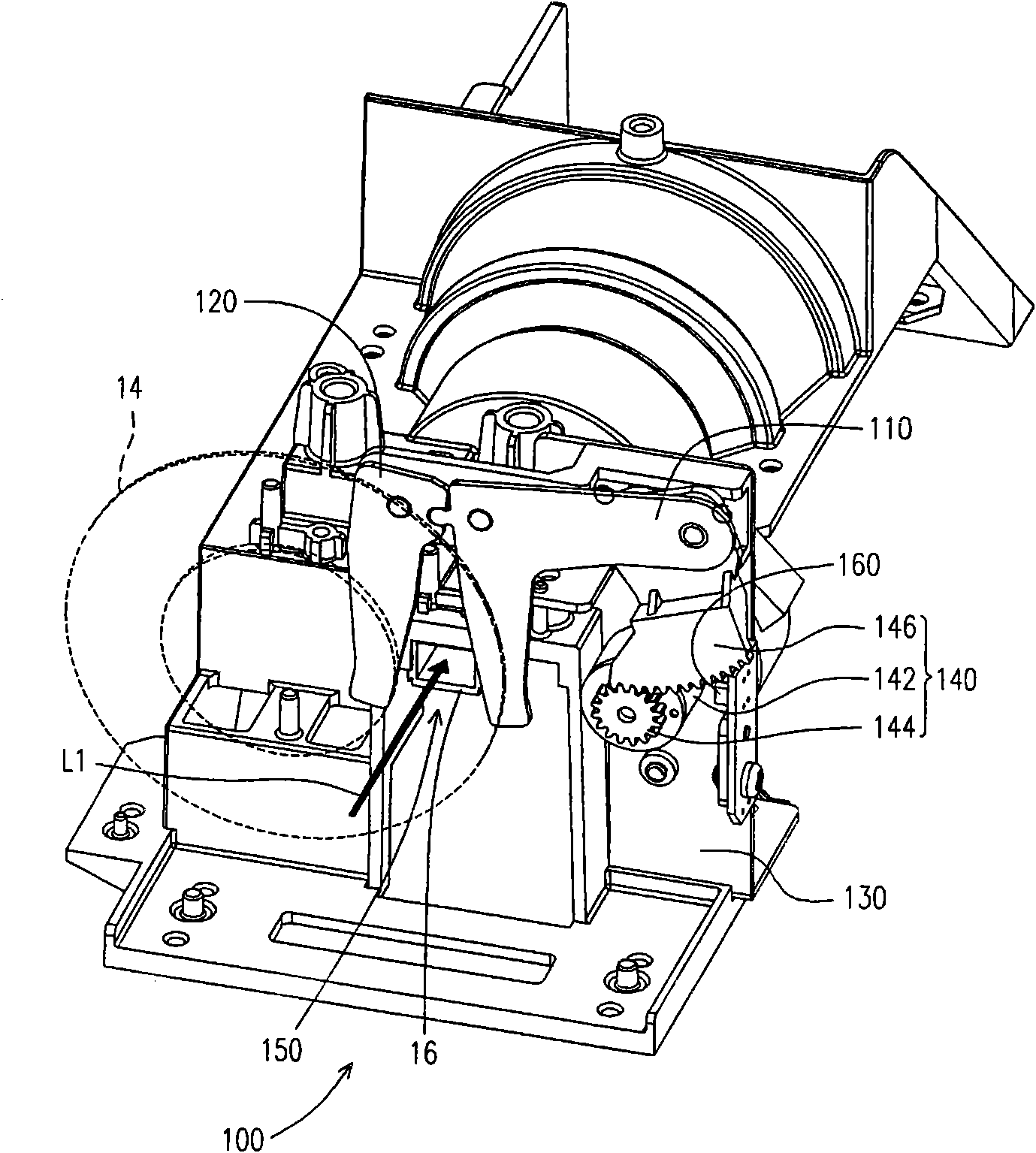
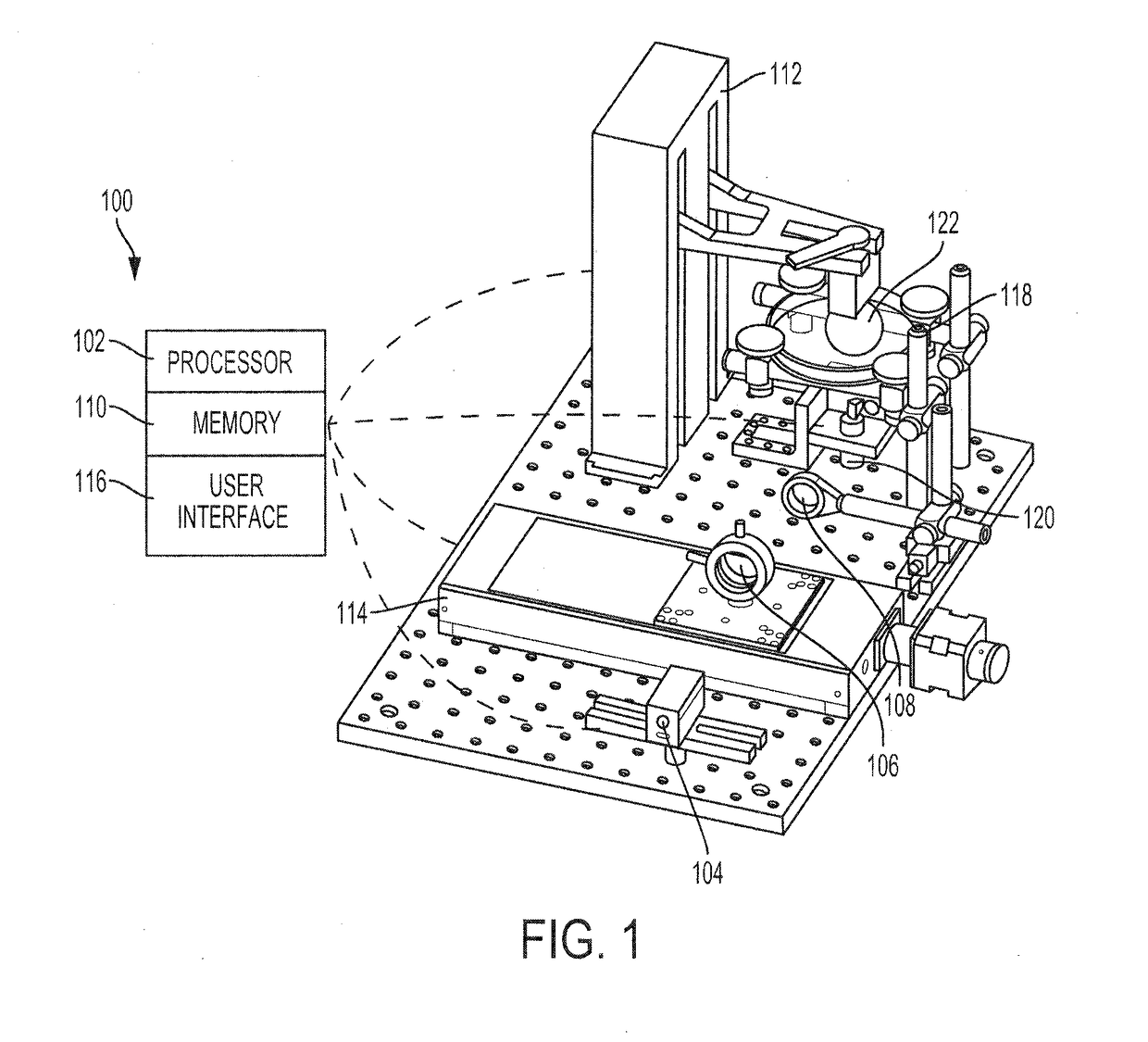
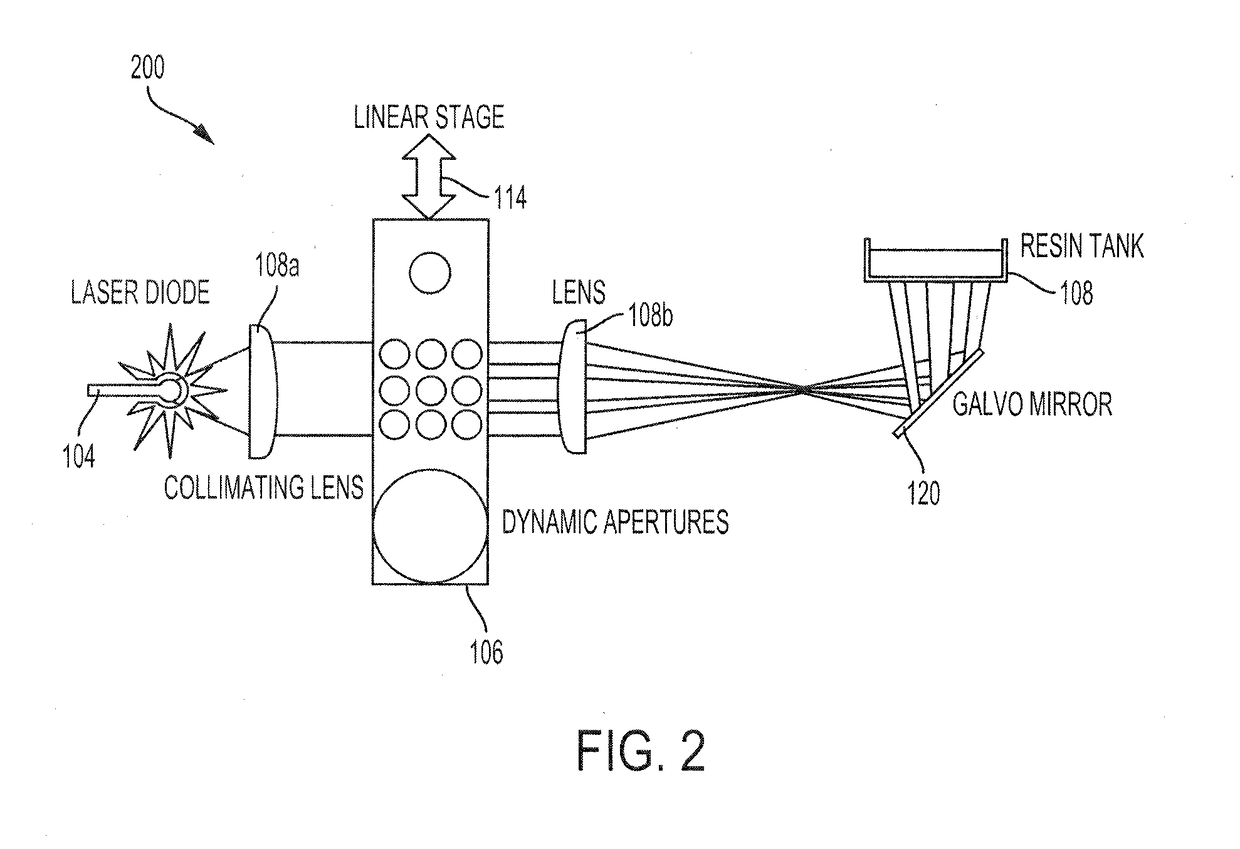
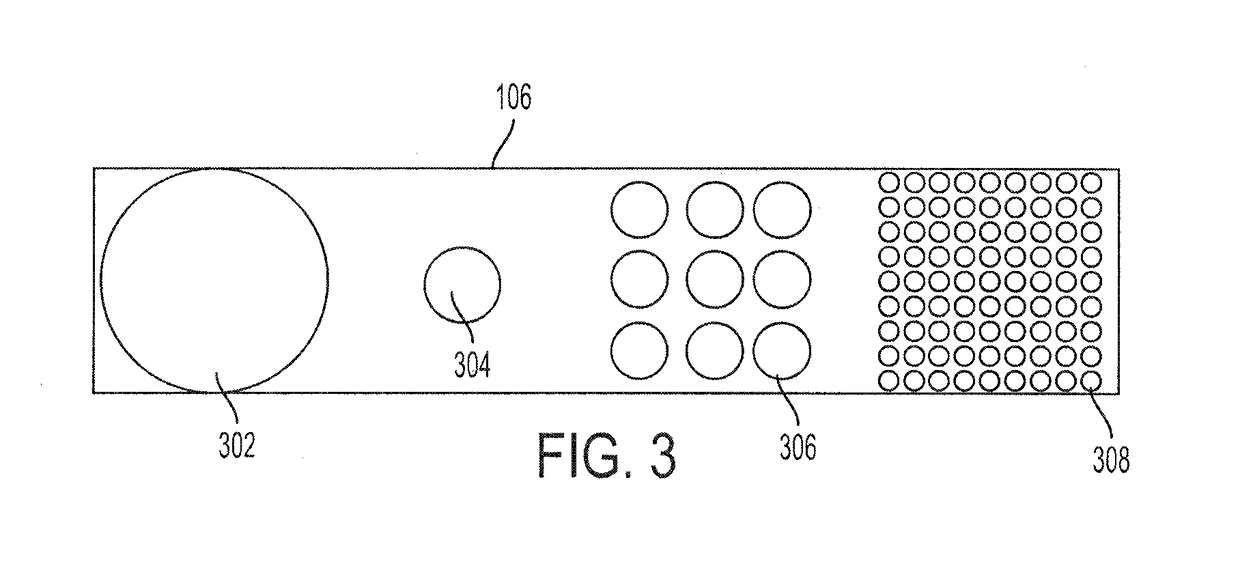
ActiveUS20180345580A1Manufacturing platforms/substrates3D object support structuresDynamic apertureVoxel size
Methods, systems, and apparatus for multi-scale stereolithography. The apparatus includes a light source for providing a laser beam having a first shape and a first size. The apparatus includes a dynamic aperture having multiple apertures that are of the same or different sizes or shapes. The dynamic aperture is configured to receive the laser beam and modify at least one of the shape or the size of the laser beam. The apparatus includes a platform for holding an object to be printed. The apparatus includes a processor connected to at least one of the light source, the dynamic aperture or the platform. The processor is configured to move the platform to direct the laser beam or direct the laser beam to cure resin onto the object to be printed using a first aperture of the multiple apertures to form the object.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Dynamic aperture driving apparatus and method for reducing vibration
InactiveCN1834766ANo vibrationReduce noiseTelevision system detailsProjectorsFall timeControl signal
The present invention generally relates to a dynamic aperture for controlling the intensity of light of projection lens, more particularly to a dynamic aperture driving apparatus and method for reducing vibration by which vibrations are minimized in spite of command for sudden location change. The dynamic aperture driving apparatus comprises rotating means, driving means, sensing means and driving control means, whereas a location control signal is characterized by minimizing vibration when the rotating means arrives at a commanded location by an increase in rising time and / or falling time of a target location signal through an RC integral circuit within the driving control means.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
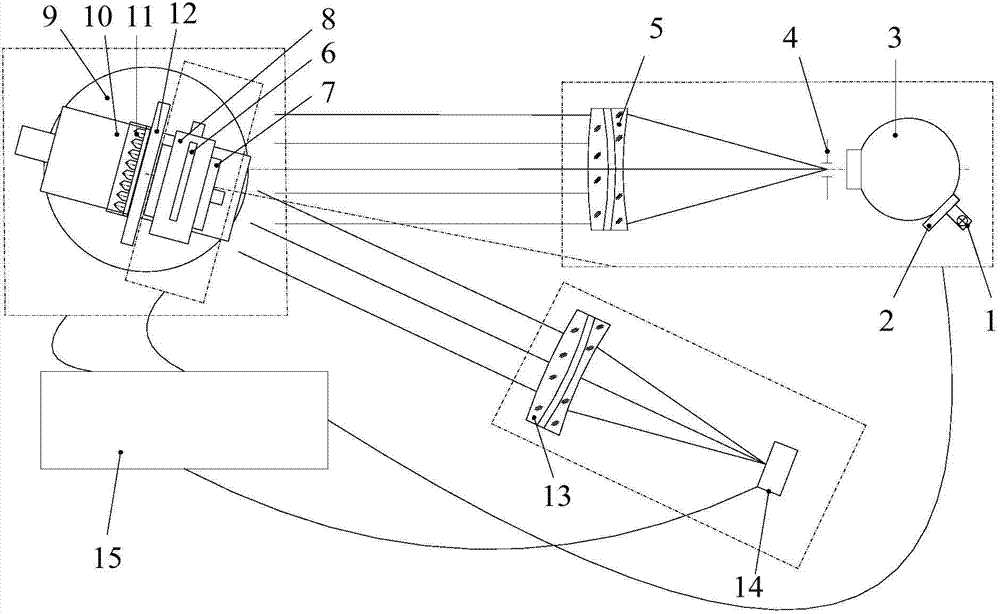
Optical axis orientation consistency detection system and method of corner reflector or corner reflector array
InactiveCN104748945ASolve the resultSolve the problem corresponding to the sub-corner reflectorTesting optical propertiesLiquid crystal light valveOptical axis
The invention discloses an optical axis orientation consistency detection system and method of a corner reflector or a corner reflector array. The optical axis orientation consistency detection system includes a collimated light source unit, an LCLV (liquid crystal light valve) dynamic aperture unit, a corner reflector attitude adjustment unit, a CCD (charge coupled device) measurement unit and a control unit. The LCLV dynamic aperture unit is arranged on an emergent light path of the collimated light source unit. The corner reflector attitude adjustment unit is arranged on an emergent light path of the LCLV dynamic aperture unit. The corner reflector or corner reflector array to be measured is arranged on the corner reflector attitude adjustment unit. The CCD measurement unit is arranged on a light path in which the reflected light, reflected by the corner reflector or corner reflector array to be measured, exists. The control unit is respectively connected with the collimated light source unit, the LCLV dynamic aperture unit, the corner reflector attitude adjustment unit and the CCD measurement unit. By the use of the optical axis orientation consistency detection system and method, quickly and accurately measured is an included angles between a corner reflector mounting datum plane and the optical axis orientation of the corner reflector or the sub-corner reflectors of the corner reflector array.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
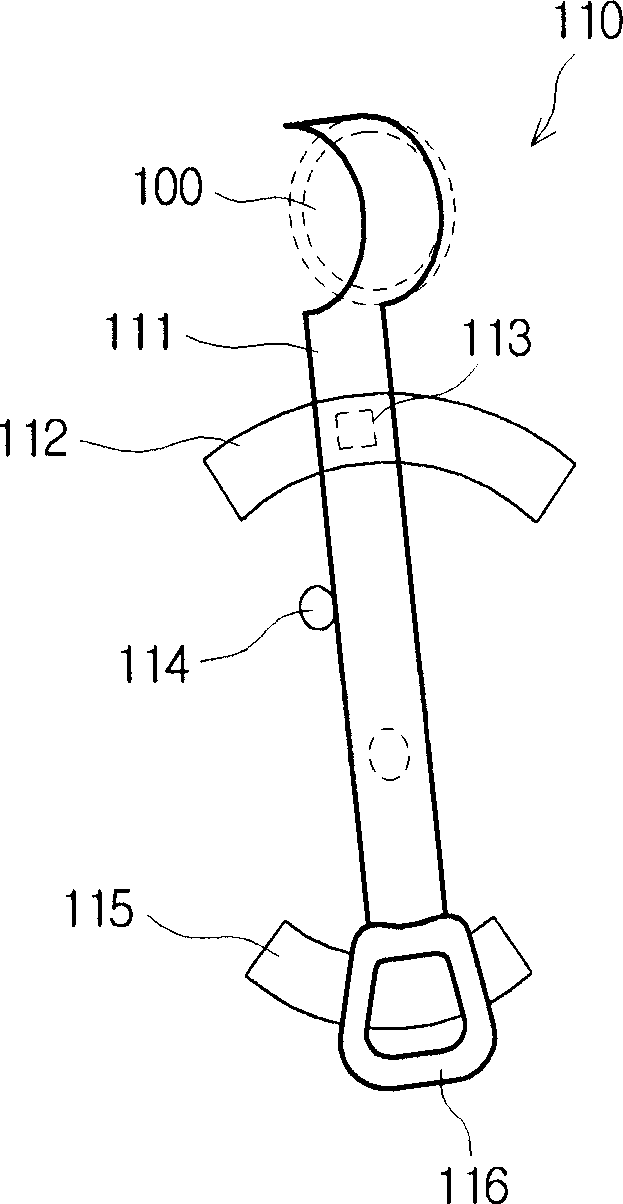
Dynamic aperture and projection device having same
InactiveUS20100097577A1Easily brokenShorten service timeProjectorsRecord information storageDynamic apertureEngineering
A dynamic aperture, positioned in the path of light, includes a pair of parallel blades, a connecting member, a driving member, and a motor. The projection device includes a light source configured for generating light. The connecting member is fixed to the projection device and rotatably interconnects a same side of the blades. The driving member rotatably interconnects the opposite side of the blades so that the blades, the connecting member, and the driving member constituting a variable quadrangular frame. The motor is coupled to the driving member and is configured for rotating the driving member. Rotation of the driving member and restriction of the projection device to the connection member alter dimensions of the variable quadrangular frame and accordingly adjust a gap between the blades through which the generated light passes.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Dynamic aperture holography
InactiveUS9760061B2High densityInformation arrangementRecord information storageMultiplexingDynamic aperture
Methods and systems for performing dynamic aperture holography are described. Examples include a method of recording multiple holograms in a photosensitive recording medium, where multiple signal beam angular apertures used to record the multiple holograms differ from each other. The multiple signal beam angular apertures can facilitate using a larger range of reference beam angular apertures. The multiple holograms are typically multiplexed, and examples of dynamic aperture holography enable packing the multiplexed holograms more densely in the recording medium. Some dynamic aperture holography systems include monocular objective lens architecture.
Owner:AKONIA HOLOGRAPHICS
Dynamic aperture device and projector with the same
InactiveUS20090109514A1Reduce vibrationAccurate rotation positioningMountingsDynamic apertureEngineering
A dynamic aperture device includes a motor, a light shielding element and a balancer. The motor has a shaft. The light shielding element has a light shielding portion and a hub connected to the light shielding portion. The hub is coupled to the shaft. The balancer is disposed on the light shielding element, the hub or the shaft.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Method for dynamic aperture determination for three-dimensional surface-related multiple elimination
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
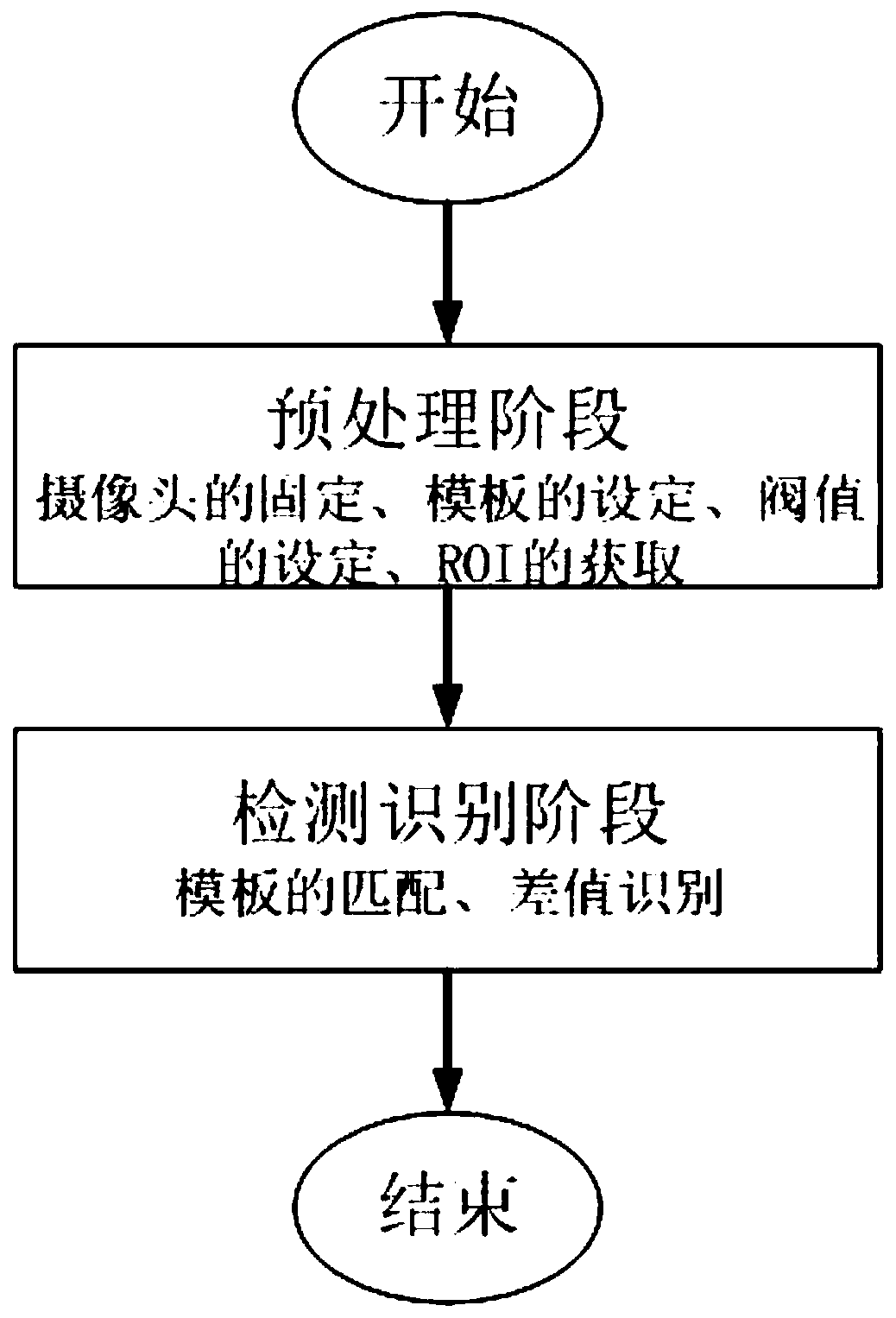
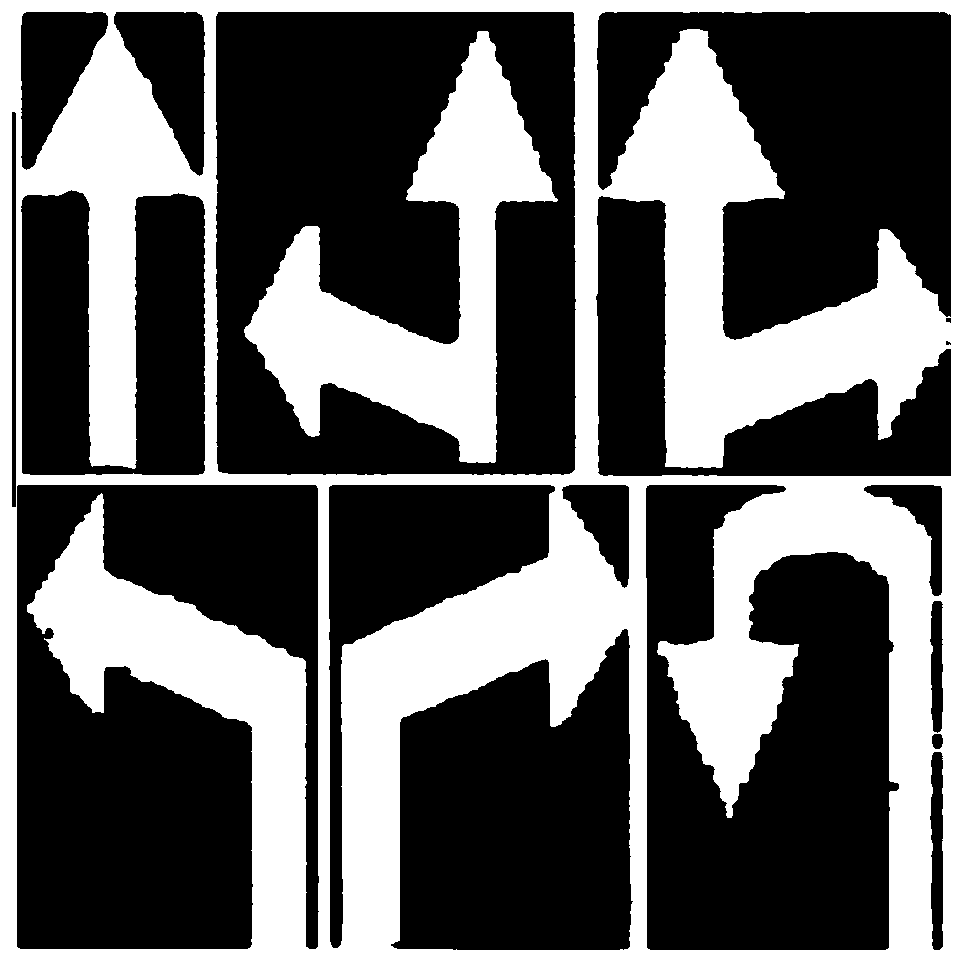
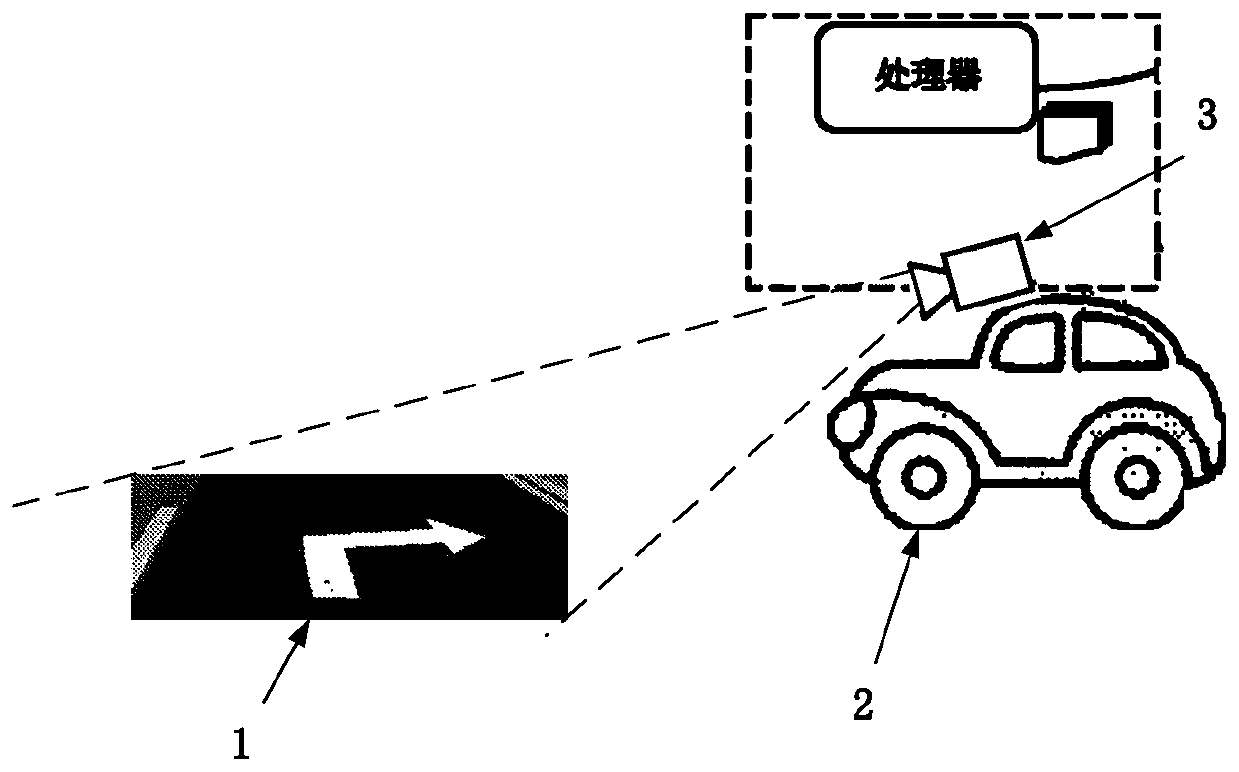
An urban road pavement guide arrow detection and identification method
PendingCN109815836AAccurate identificationImprove anti-interference abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionTemplate matchingDynamic aperture
The invention discloses an urban road pavement guiding arrow detection and recognition method, belongs to the technical field of unmanned driving recognition, and detects and recognizes an indicatingarrow of an urban road by fixing a camera with a high-definition dynamic aperture on an unmanned vehicle and adopting an improved template matching mode. The method can effectively improve the accuracy and robustness of identifying the urban road arrows, reduces the influence of illumination, geometric deformation, rotation and other factors, has higher anti-interference capability, and enables the intelligent unmanned vehicle to safely advance and steer according to the meaning of the road arrows.
Owner:INST OF INTELLIGENT MFG TECH JITRI
Dynamic aperture and projection device having same
InactiveUS7753536B2Easily brokenShorten service timeProjectorsRecord information storageDynamic apertureEngineering
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Small spot size spectroscopic ellipsometer
ActiveUS9952140B2High measurement sensitivityIncrease the number ofPolarisation-affecting propertiesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusAngle of incidenceMetrology
Owner:KLA CORP
Focus control method for Delta-Sigma based image formation
ActiveUS20030128868A1Wave based measurement systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage formationDynamic aperture
Disclosed is focus control method for Delta-Sigma based image formation devices in which a steering term and a focusing term of a delay formula are respectively quantized, and corresponding two channels at both sides of the probe are synchronized by a delay produced during dynamic focusing. During synchronizing the two channels, two numeral values with equal absolute value but with opposite signs are respectively inserted so as to eliminate extra noise the signals are after summing up, and controlling common delay of the two channels is performed by same one controller. After summing up the inserted two values, the dynamic aperture control of the Delta-Sigma based image formation device can be effectively realized and noise during dynamic focusing also is eliminated thereby achieving an ideal single bit output.
Owner:NAT CHUNG SHAN INST SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com