Patents
Literature
58results about How to "Improve productivity and efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
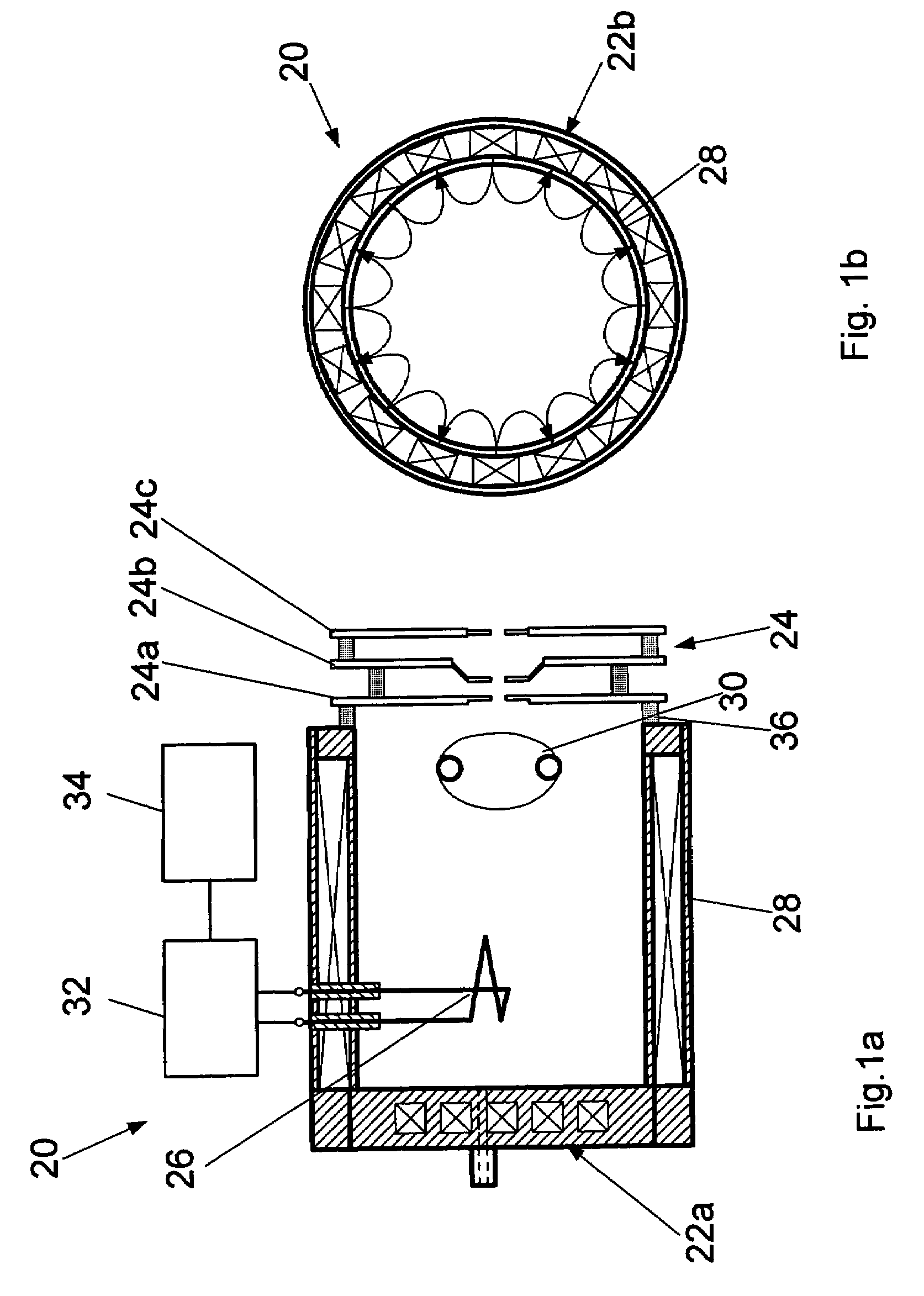
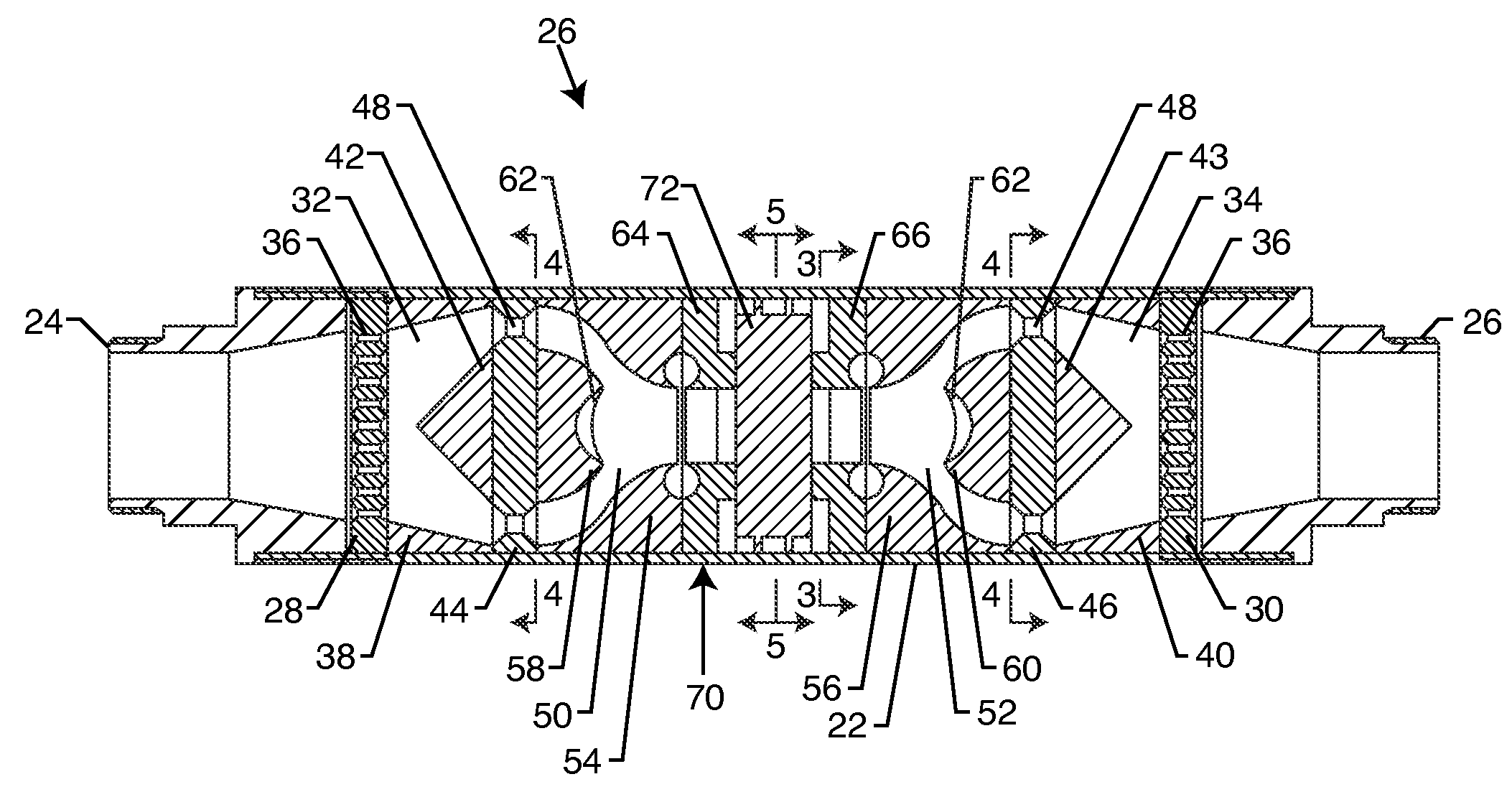
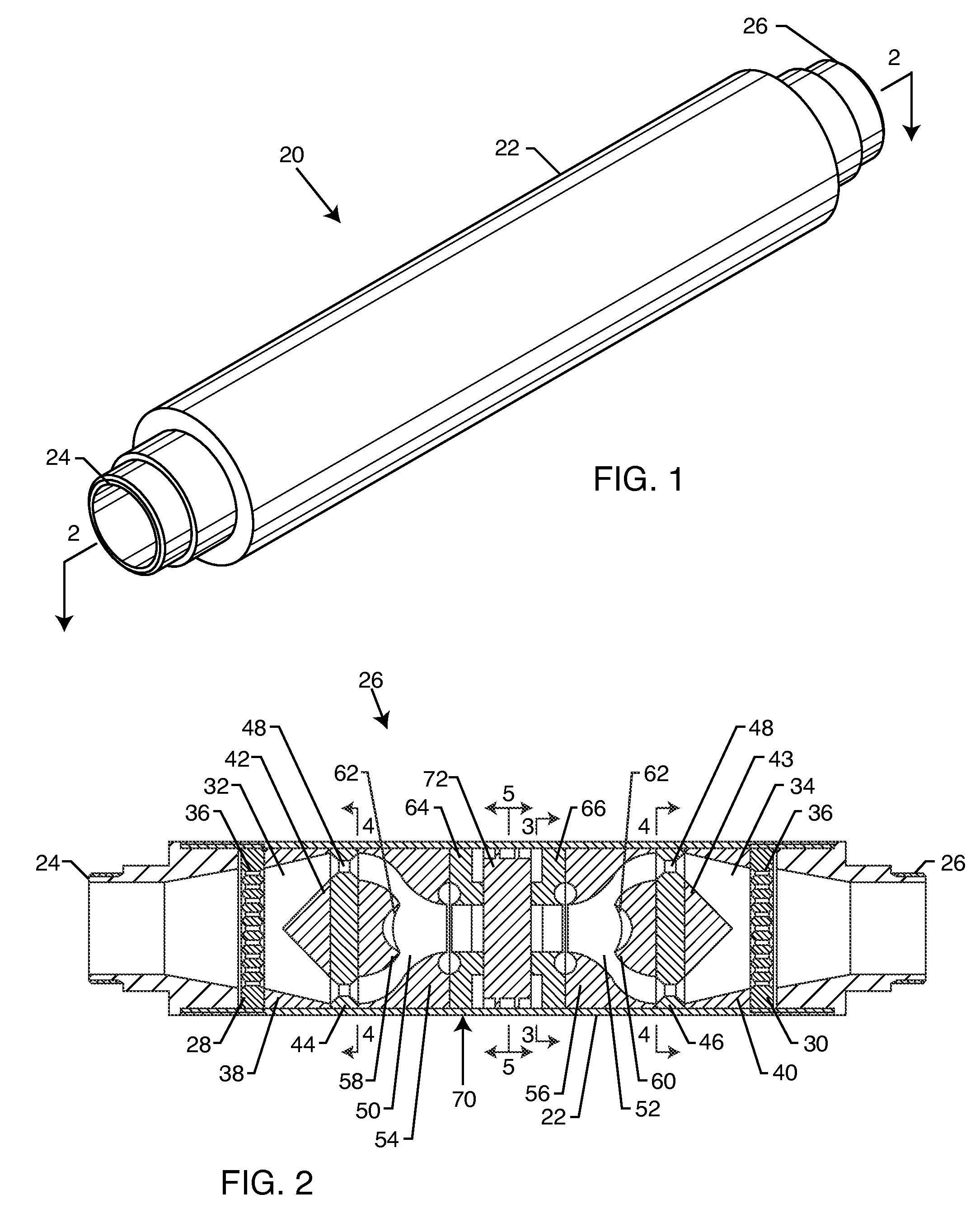
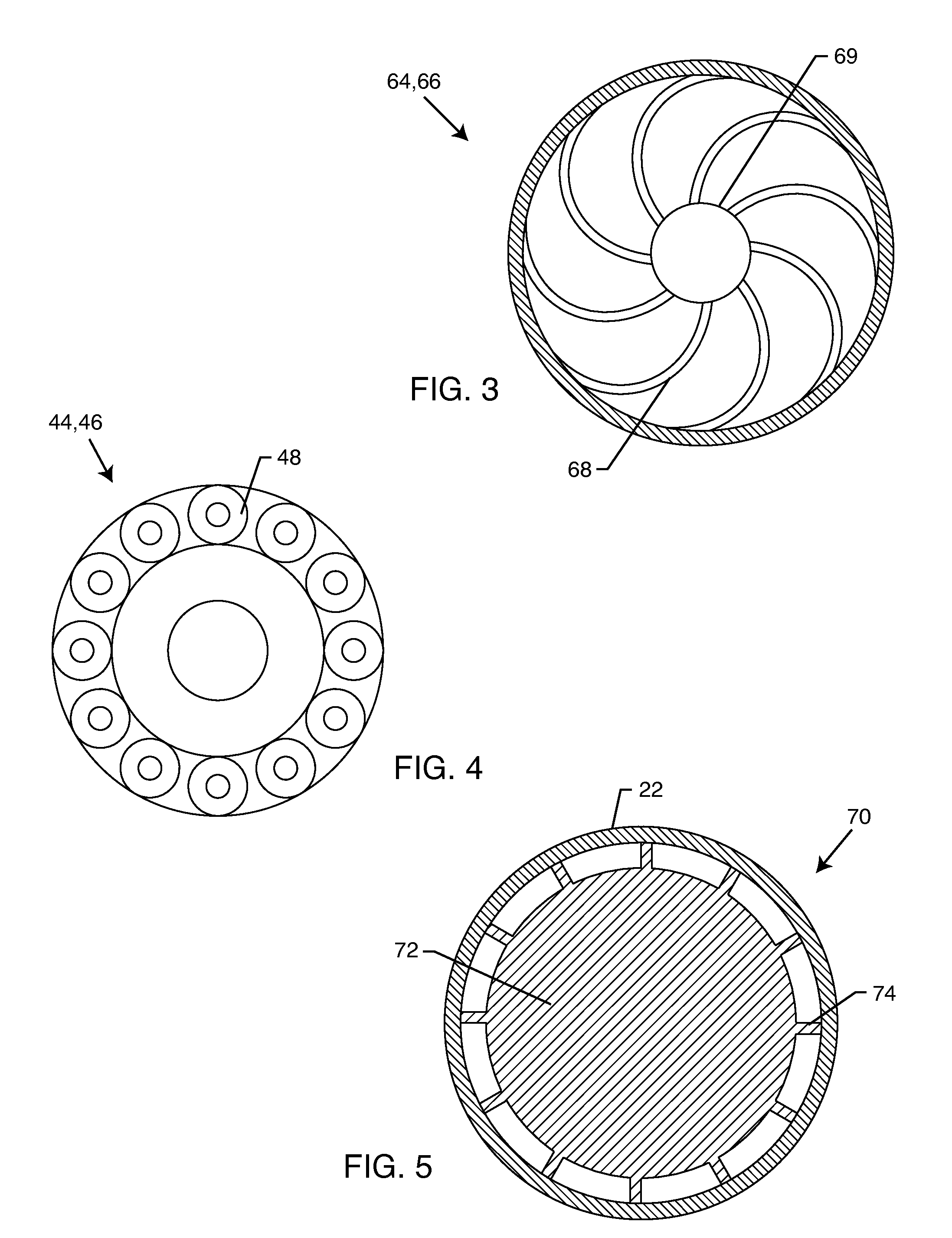
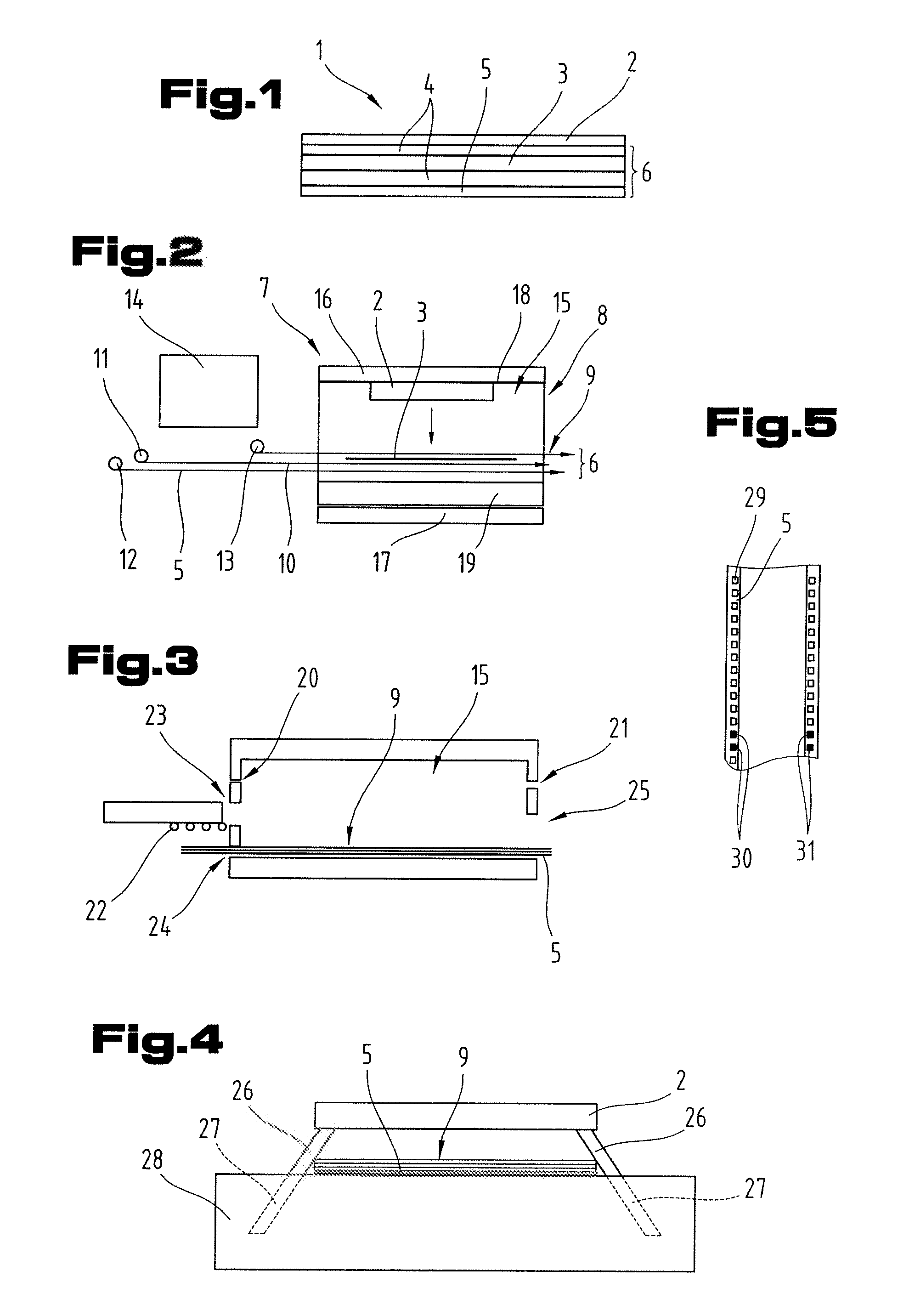
Multi-stage cavitation device
ActiveUS8042989B2Improve productivity and efficiencyWeaken energyThermal non-catalytic crackingFlow mixersSpray nozzleCavitation bubble
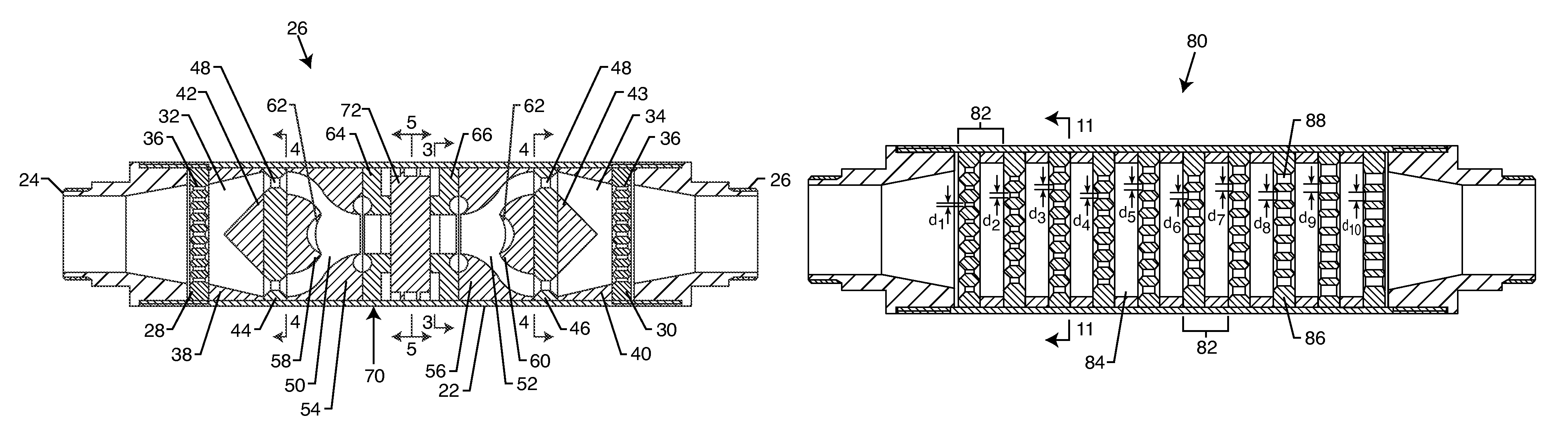
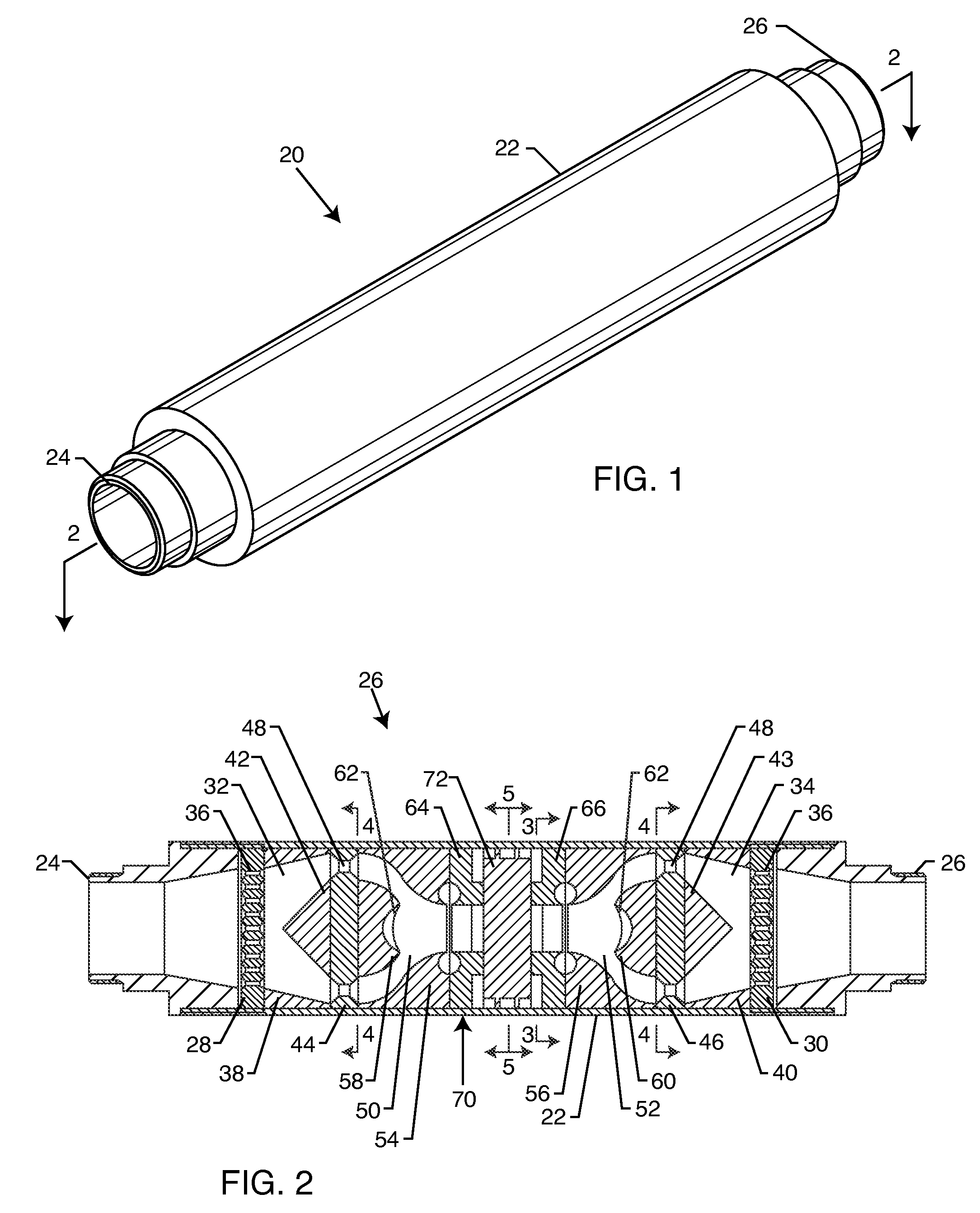
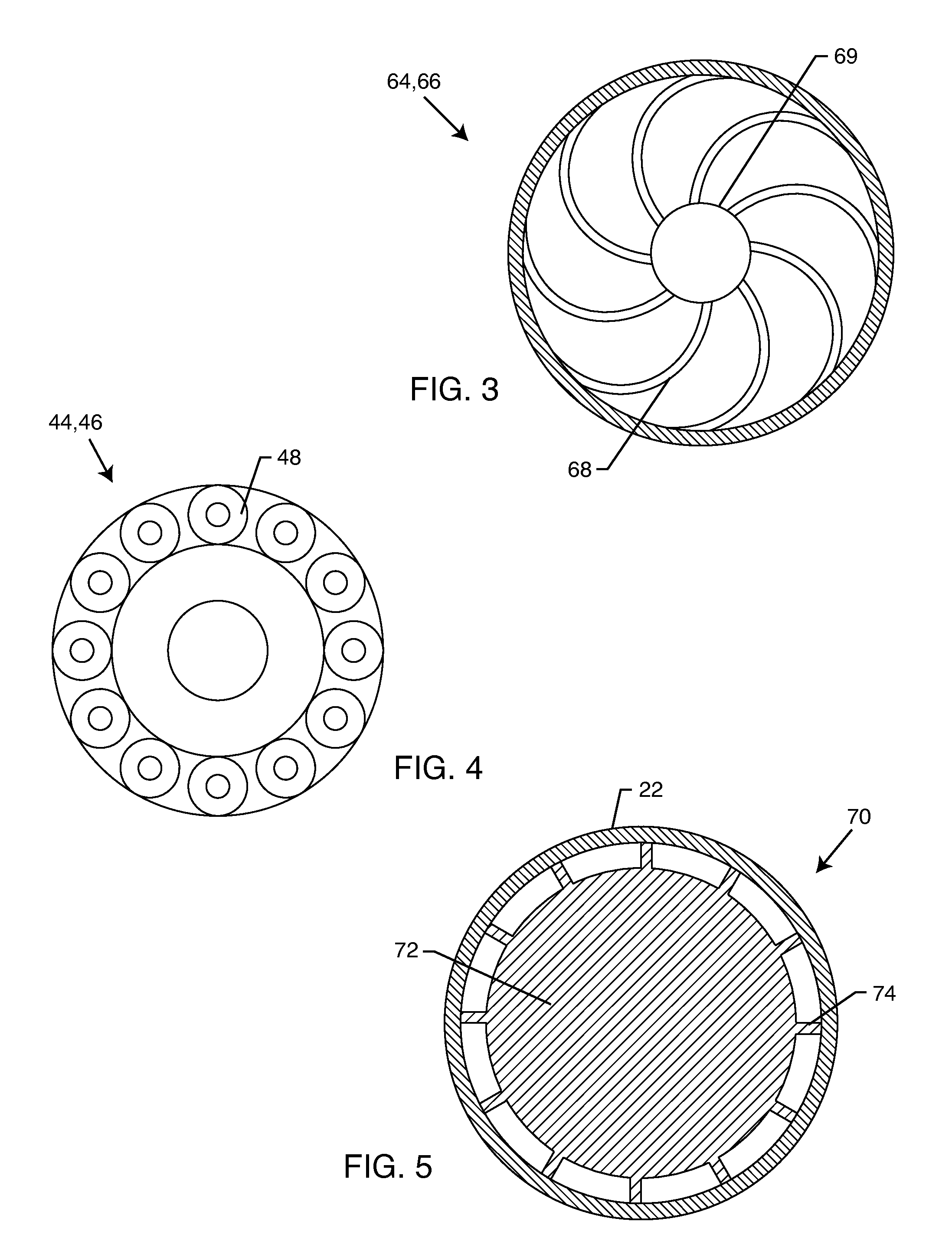
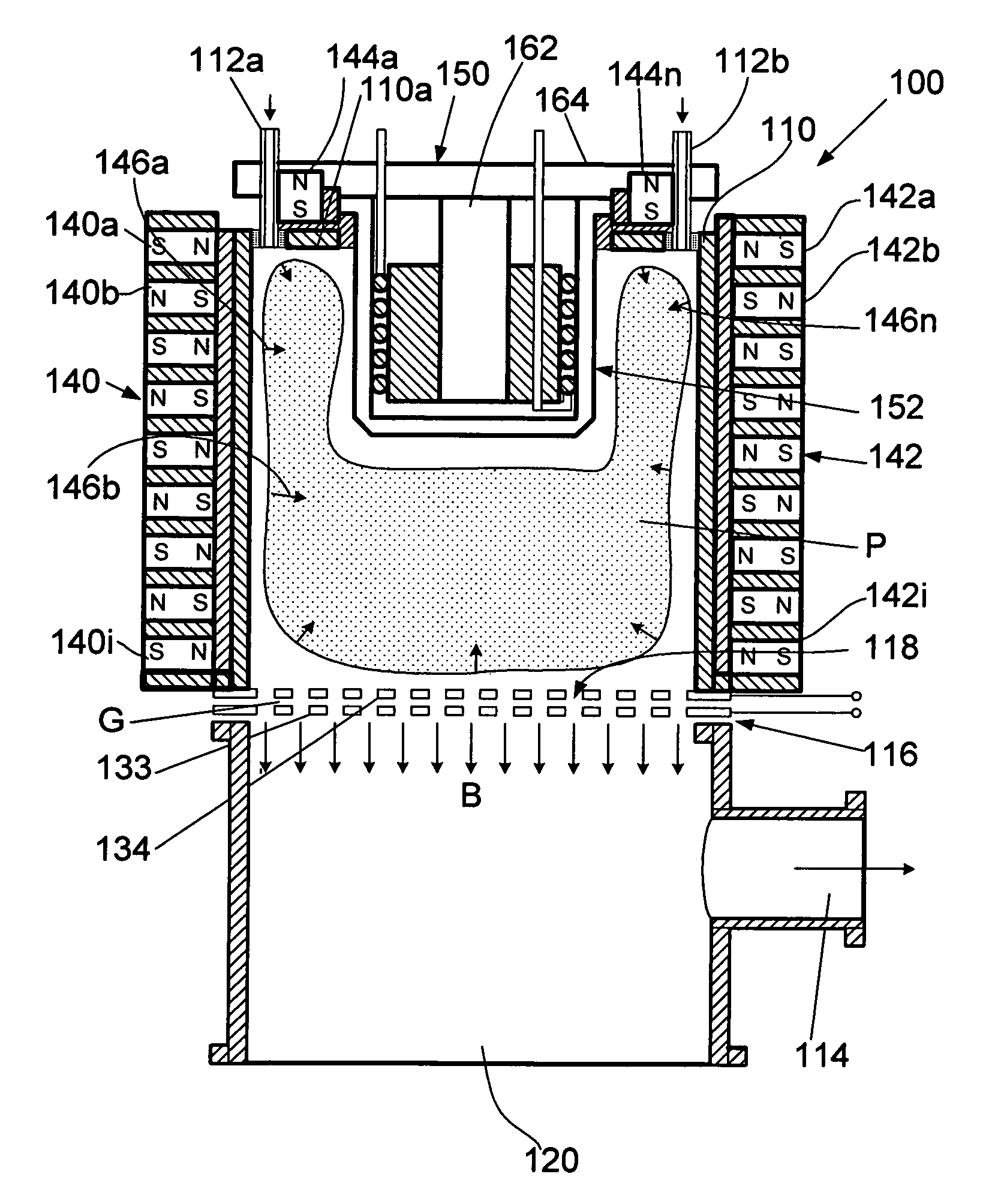
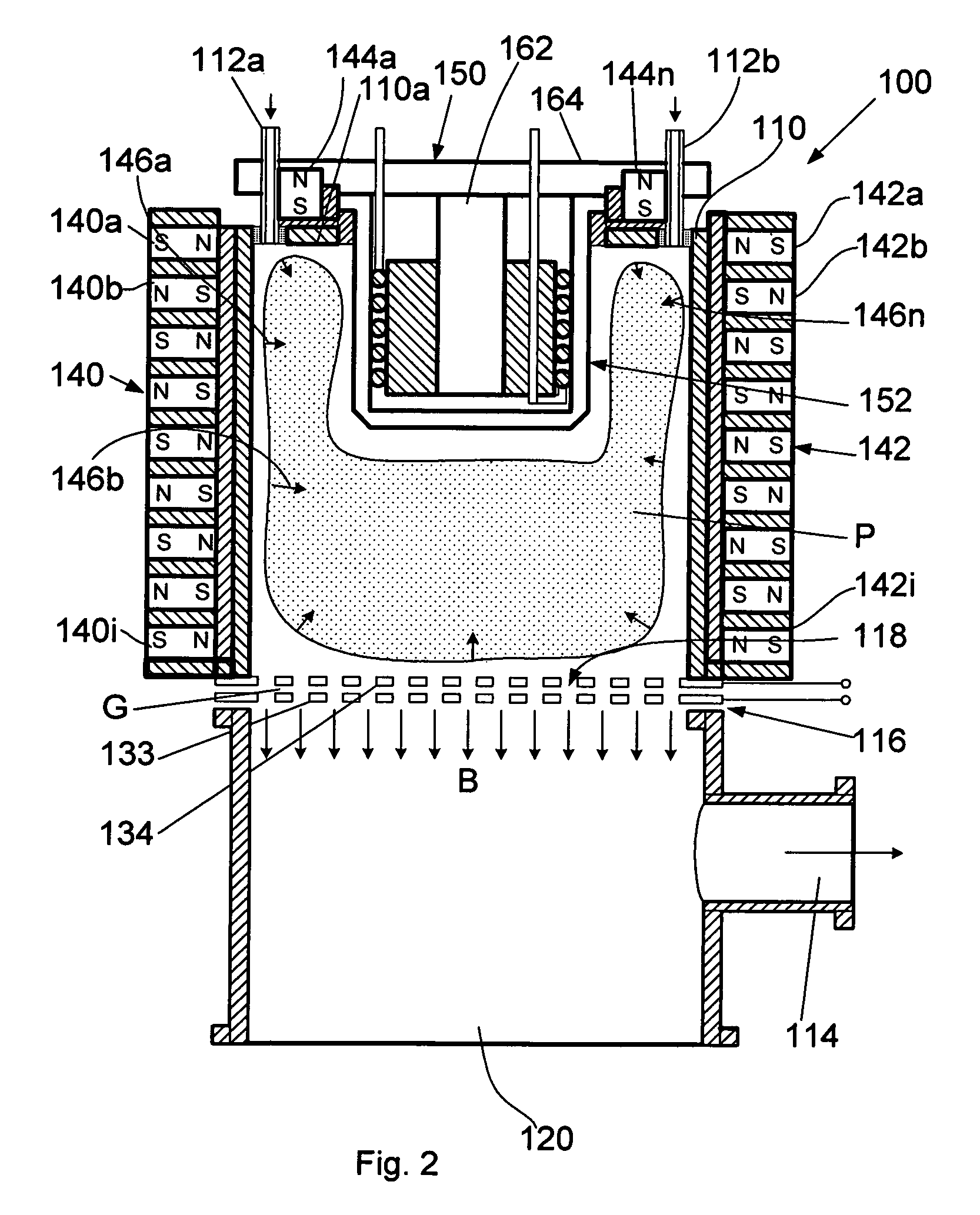
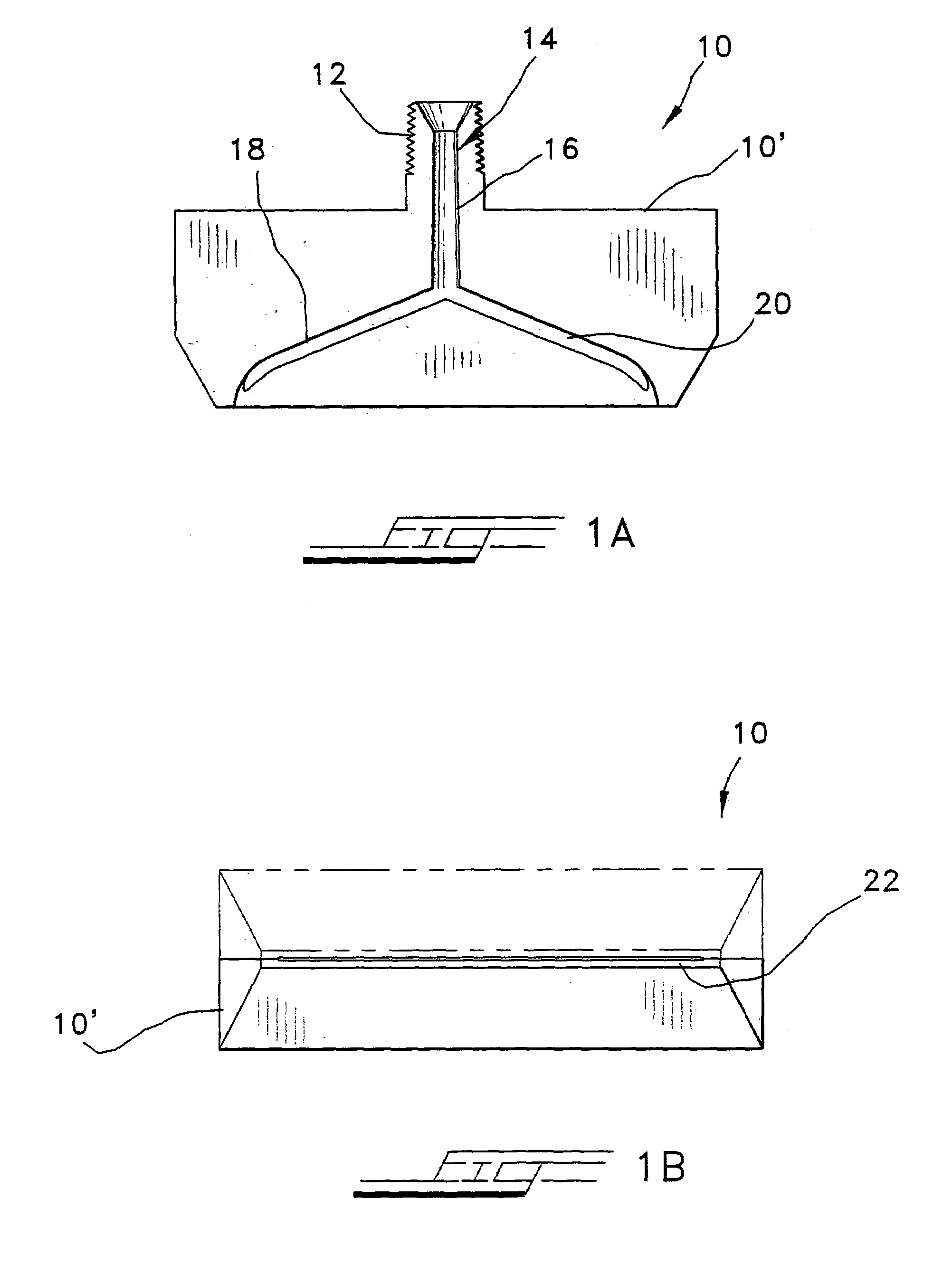
A method for processing a fluidic mixture in a multi-stage hydrodynamic cavitation device is disclosed. The fluidic mixture is introduced to an inlet and passed through a flowpath having at least ten cavitation zones. The fluidic mixture is exposed to cavitation inducing features in each of the at least ten cavitation zones to induce cavitation bubbles, which bubbles are then collapsed between every two adjacent of the at least ten cavitation zones. The multi-stage hydrodynamic cavitation device for processing the fluidic mixture has a generally cylindrical housing with an inlet, an outlet, a flowpath therebetween, and a plurality of cavitation zones along the flowpath. Two or more of the cavitation zones along the flowpath comprise a disk multi-jet nozzle having a plurality of through channels disposed across the surface thereof, wherein each channel includes expansions and contractions of its cross-sectional area along its length.
Owner:CAVITATION TECH
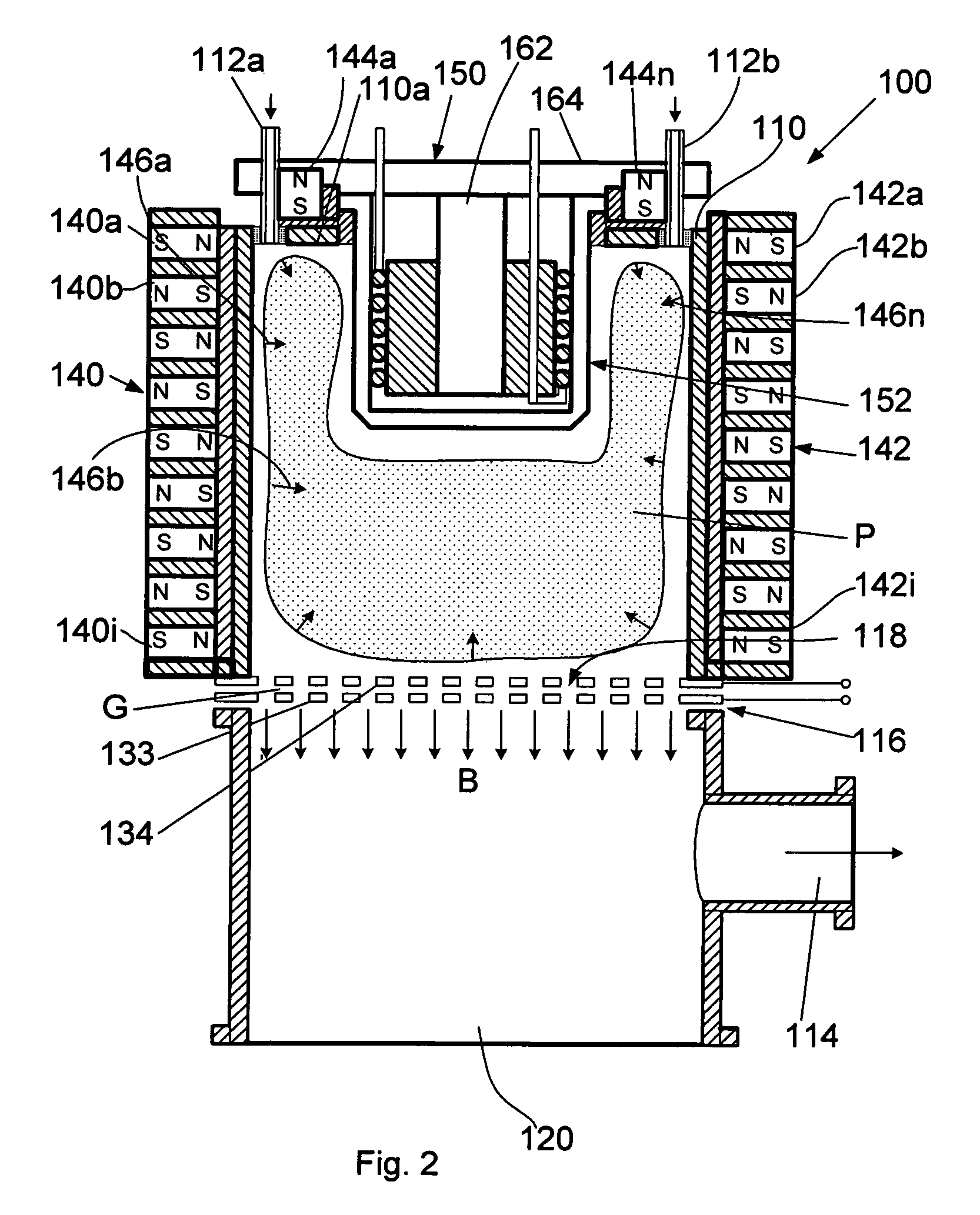
Ion-beam source
ActiveUS20090189083A1Enhanced couplingImprove efficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansIon beam tubesElectrical conductorIon beam
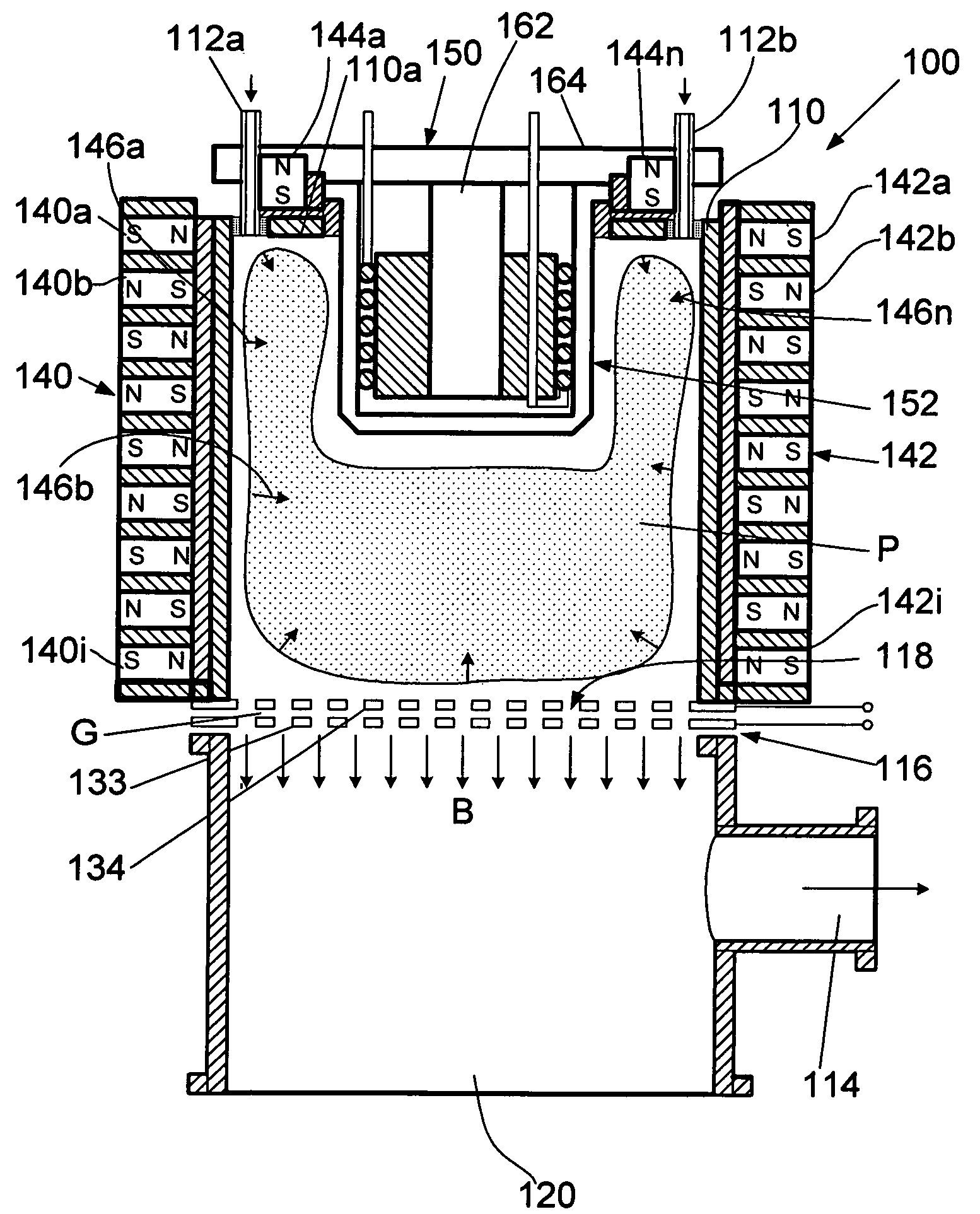
An ion-beam source comprising: a plasma-generation unit for generating plasma and an ion-extraction unit for extraction and acceleration of ions from the aforementioned plasma, where the ion-extraction unit is made in the form of at least one grid under a negative potential. The plasma generating unit consists of a working chamber having a deeply immersed antenna cell. The cell contains a ferromagnetic core, a heat conductor with a heat sink, at least one inductive coil wound onto the ferromagnetic core, and a cap made from a dielectric material that sealingly covers the ferromagnetic core and the inductive coil.
Owner:GODYAK VALERY
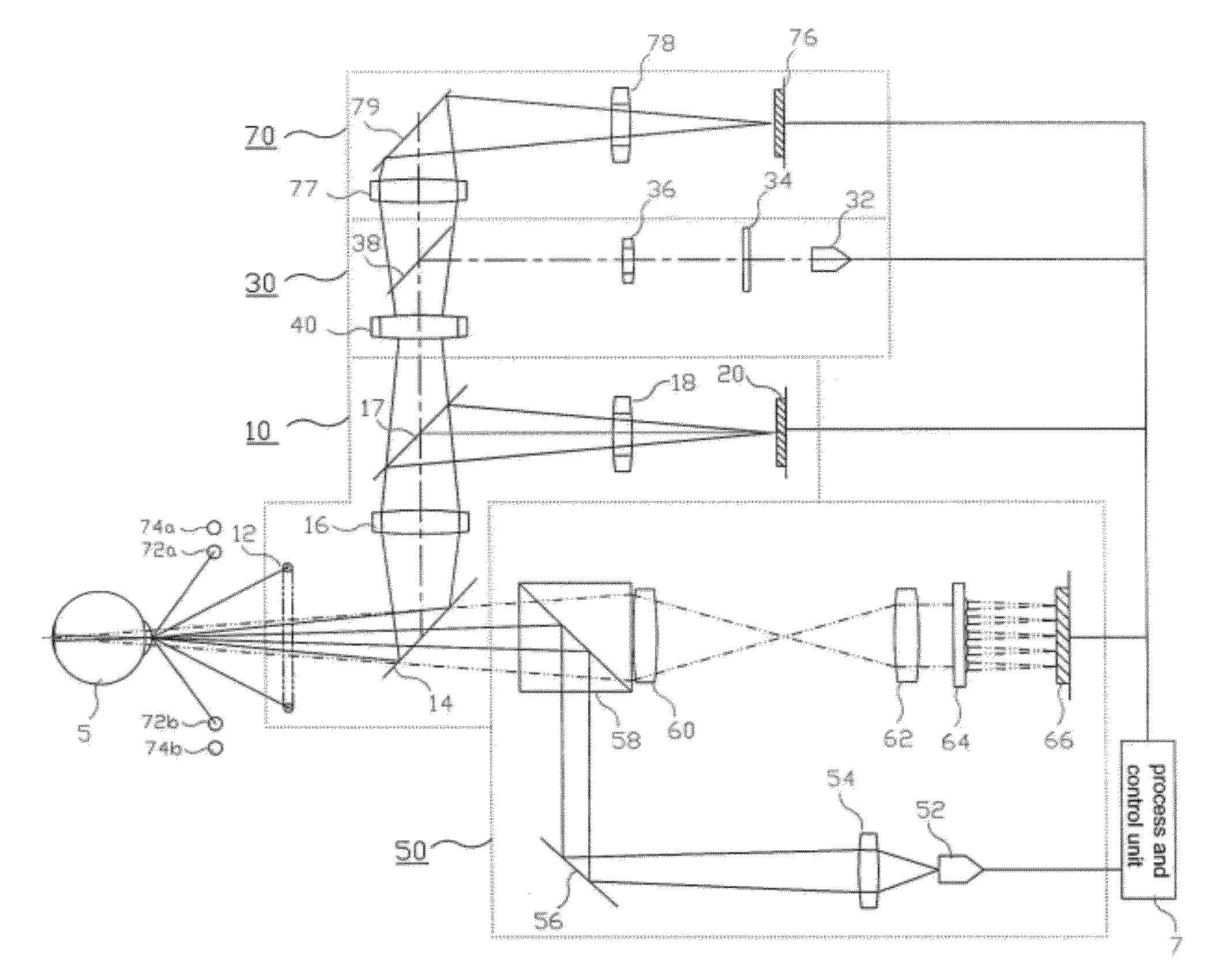
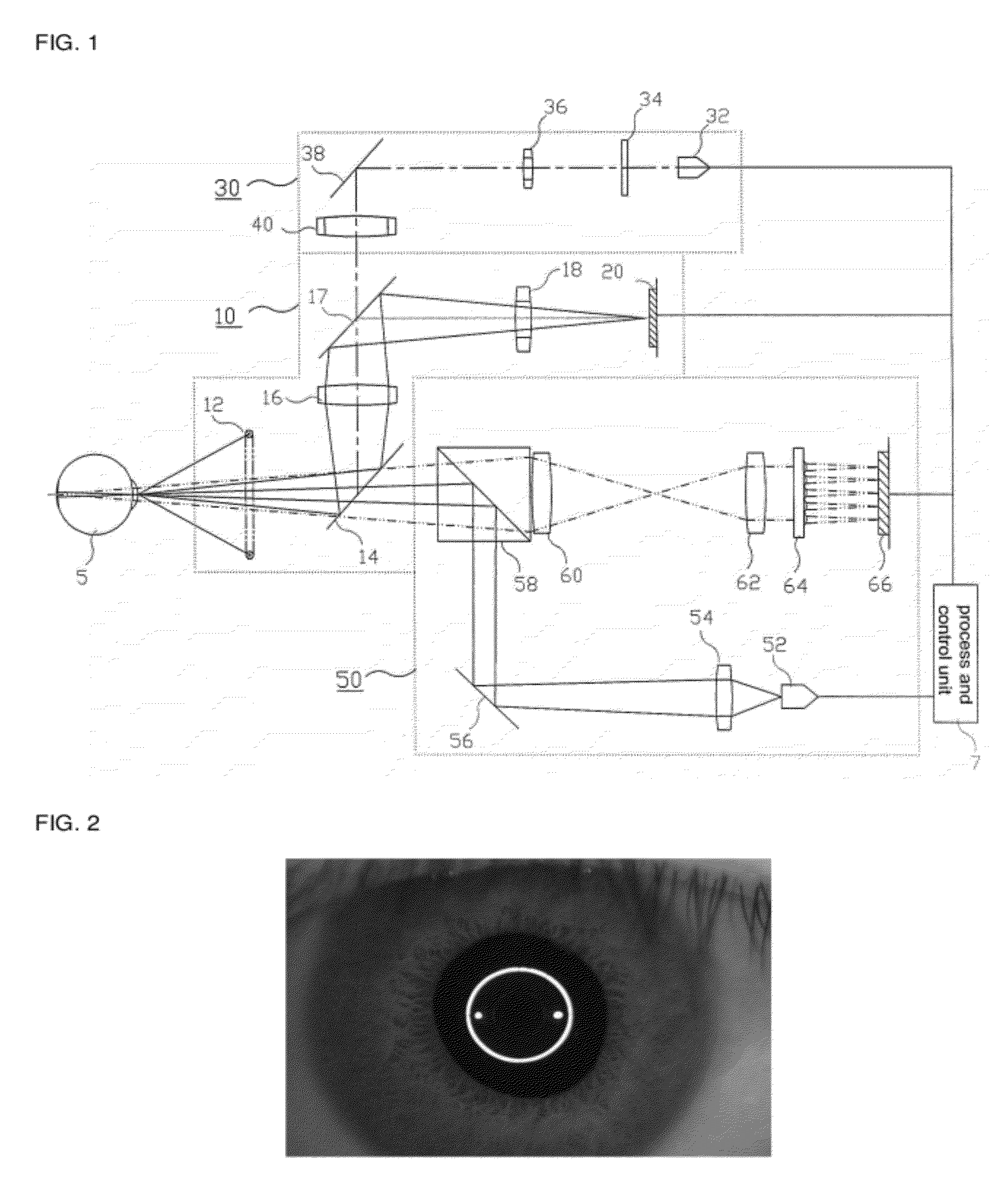
Automatic Refracto-Keratometer
ActiveUS20120188508A1Efficient executionImprove productivity and efficiencyRefractometersSkiascopesCorneal curvatureLuminosity
An auto refracto-keratometer not only produces a black-and-white image for observing the alignment of eyes to be examined using an infrared illumination light but also has a color observation optical system for observing a condition of eyes to be examined using color-illumination light. The auto refracto-keratometer comprises an infrared optical system for examining an alignment and corneal curvature of eyes to be examined; a fogging optical system for relaxing accommodation of the eyes; a measuring optical system for measuring refractive power of the eyes; and a color observation optical system having a visible light source for emitting at least one visible light to the eyes and a 2-dimensional imaging device for detecting image of visible light reflected by the eyes.
Owner:HUVITZ
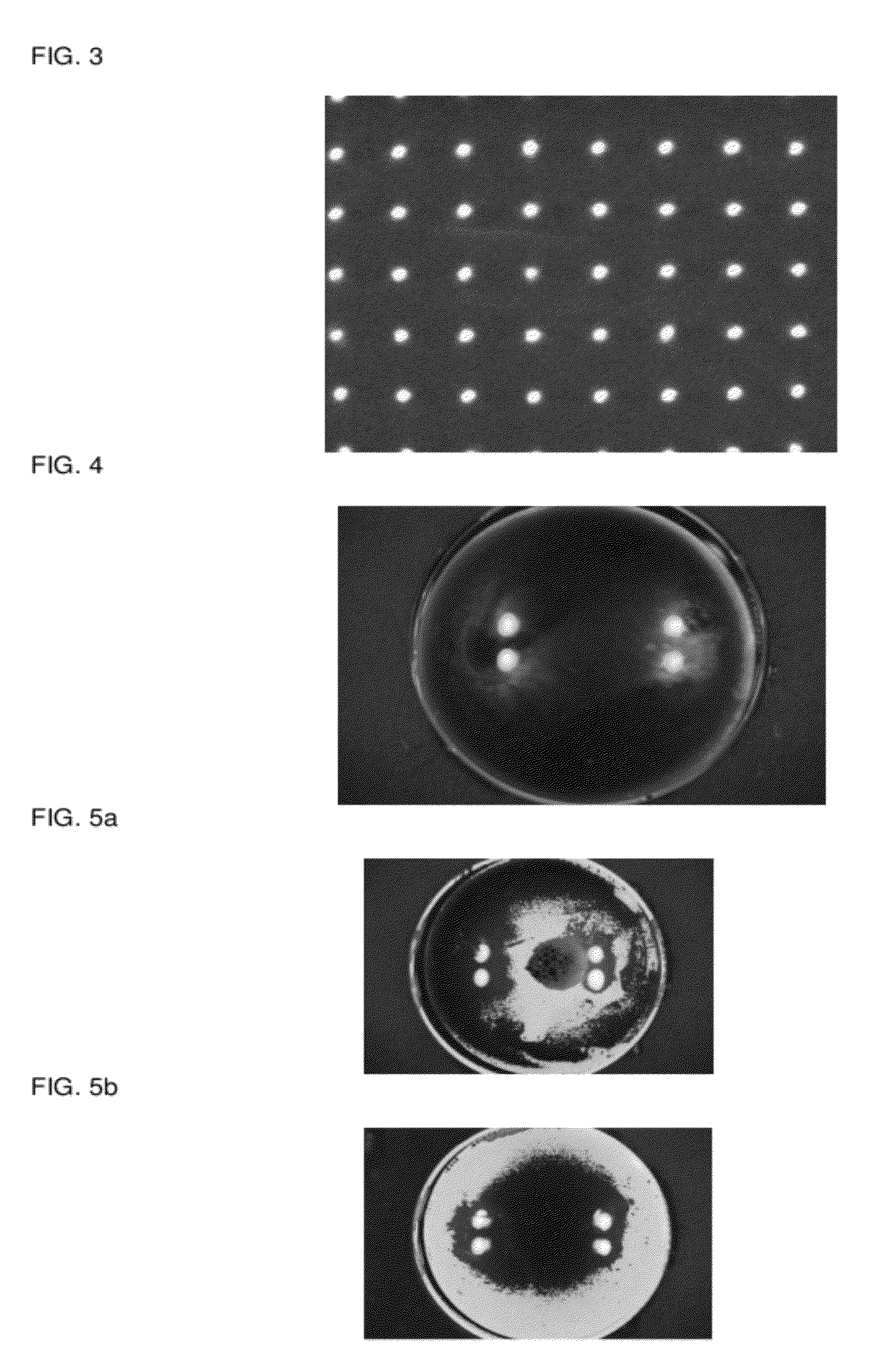
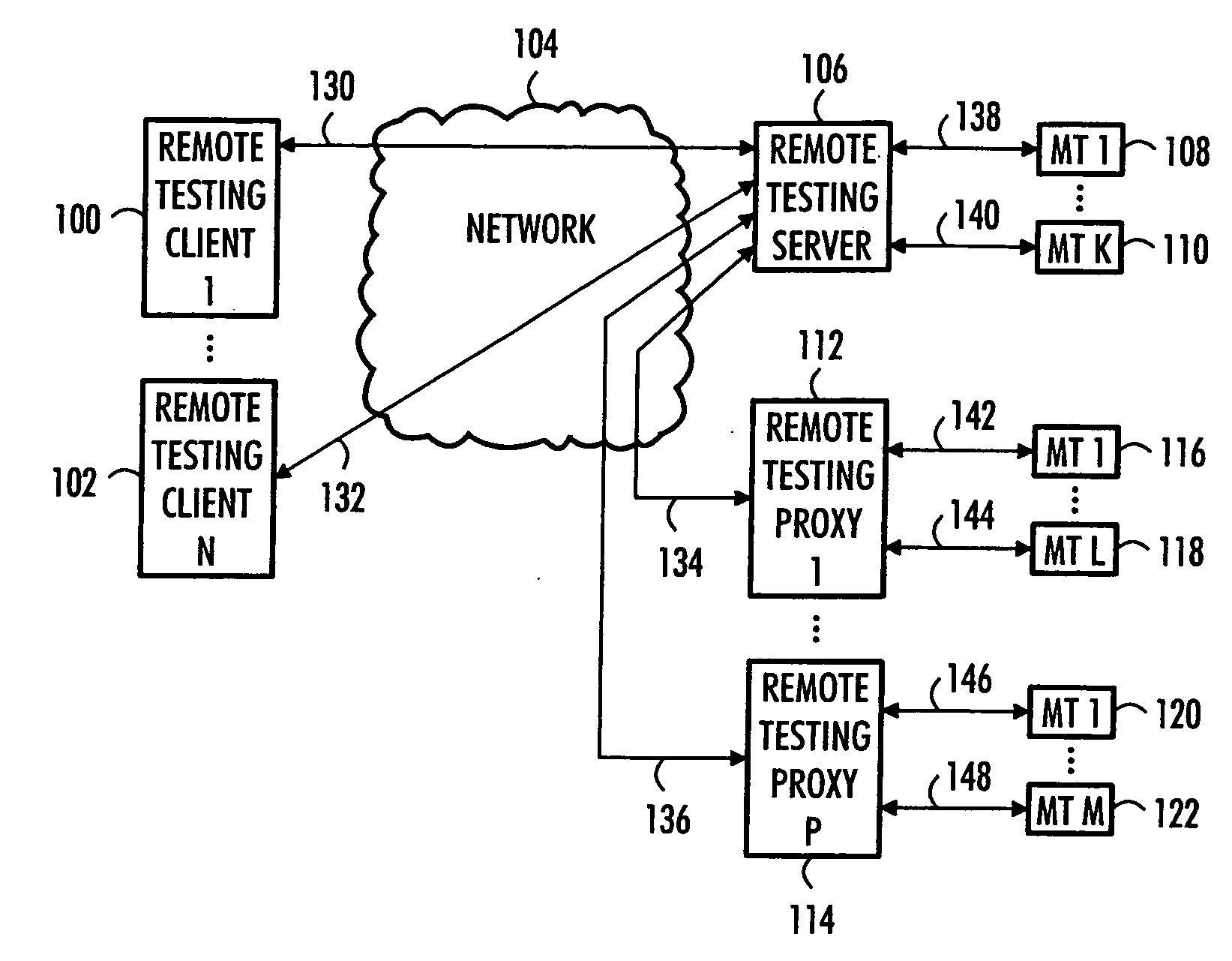
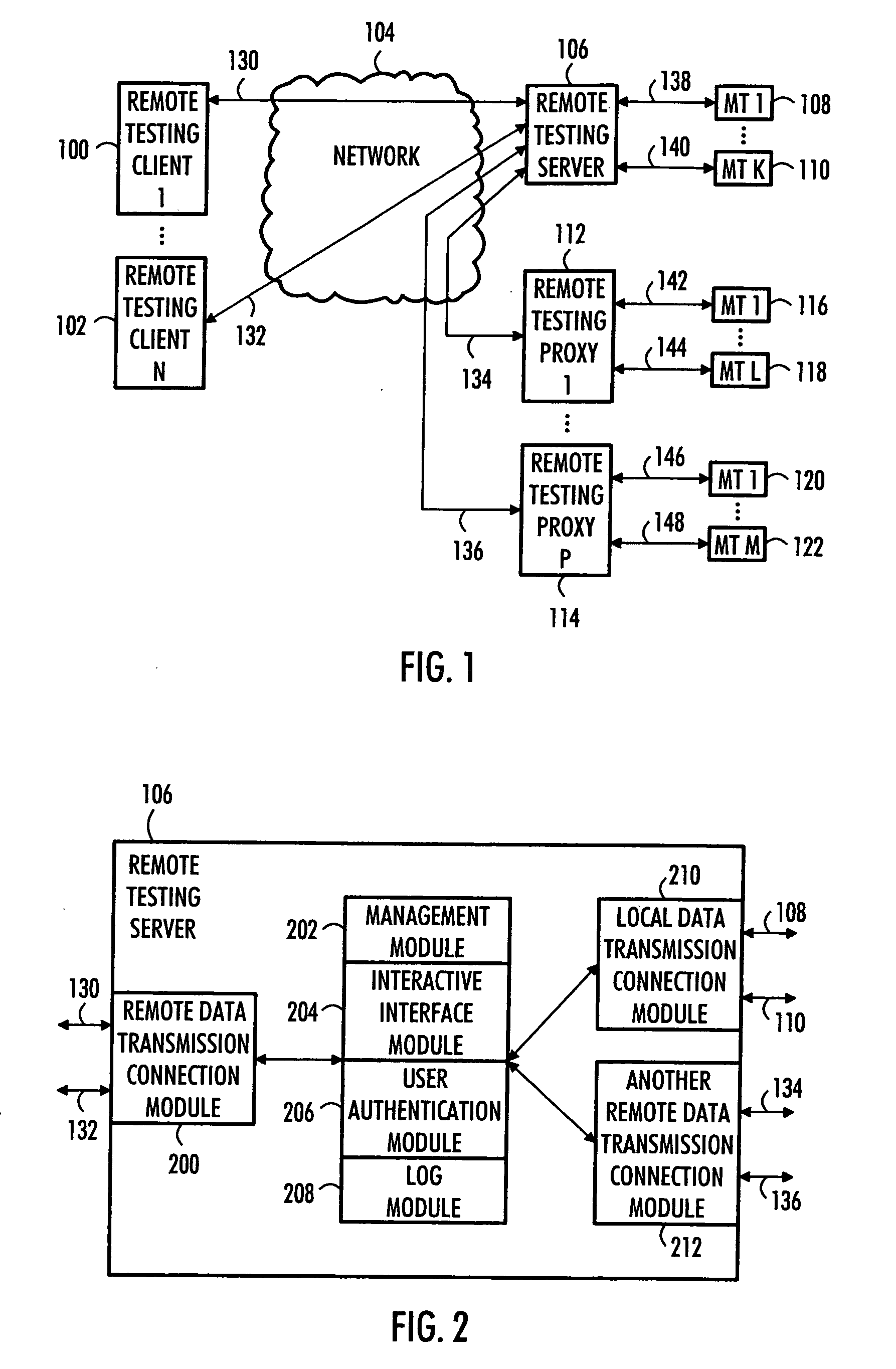
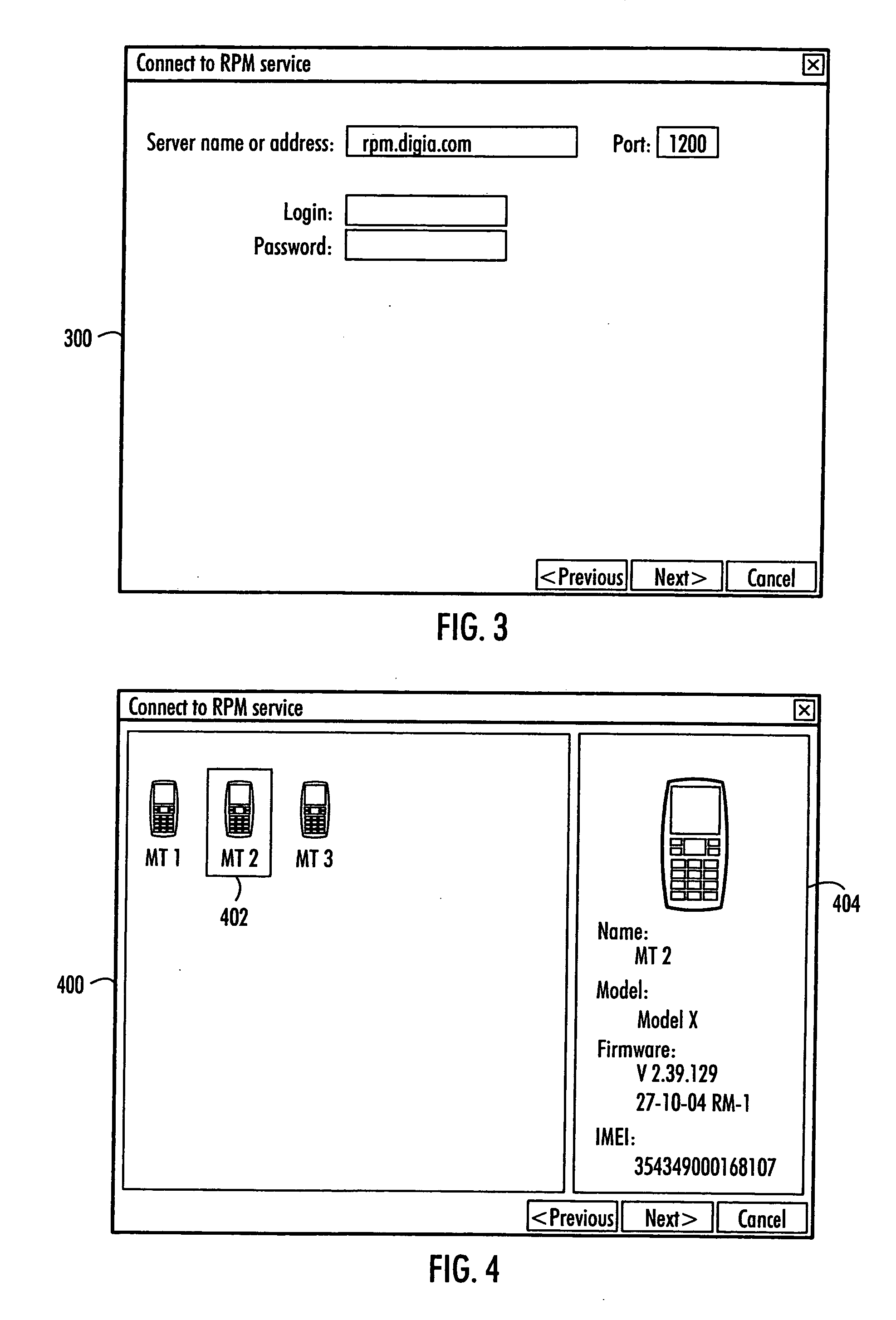
Remote testing of mobile terminals
InactiveUS20070117560A1Improve productivity and efficiencyRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationClient-sideRemote data transmission
Remote testing of mobile terminals is presented. A remote testing server includes: a local data transmission connection module to couple the remote testing server with a pool of mobile terminals; a remote data transmission connection module to couple the remote testing server with remote testing clients; a management module to manage a use of the mobile terminals by the remote testing clients; and an interactive interface module to convey information between a remote testing client and a mobile terminal during a testing session.
Owner:SYSOPEN DIGIA
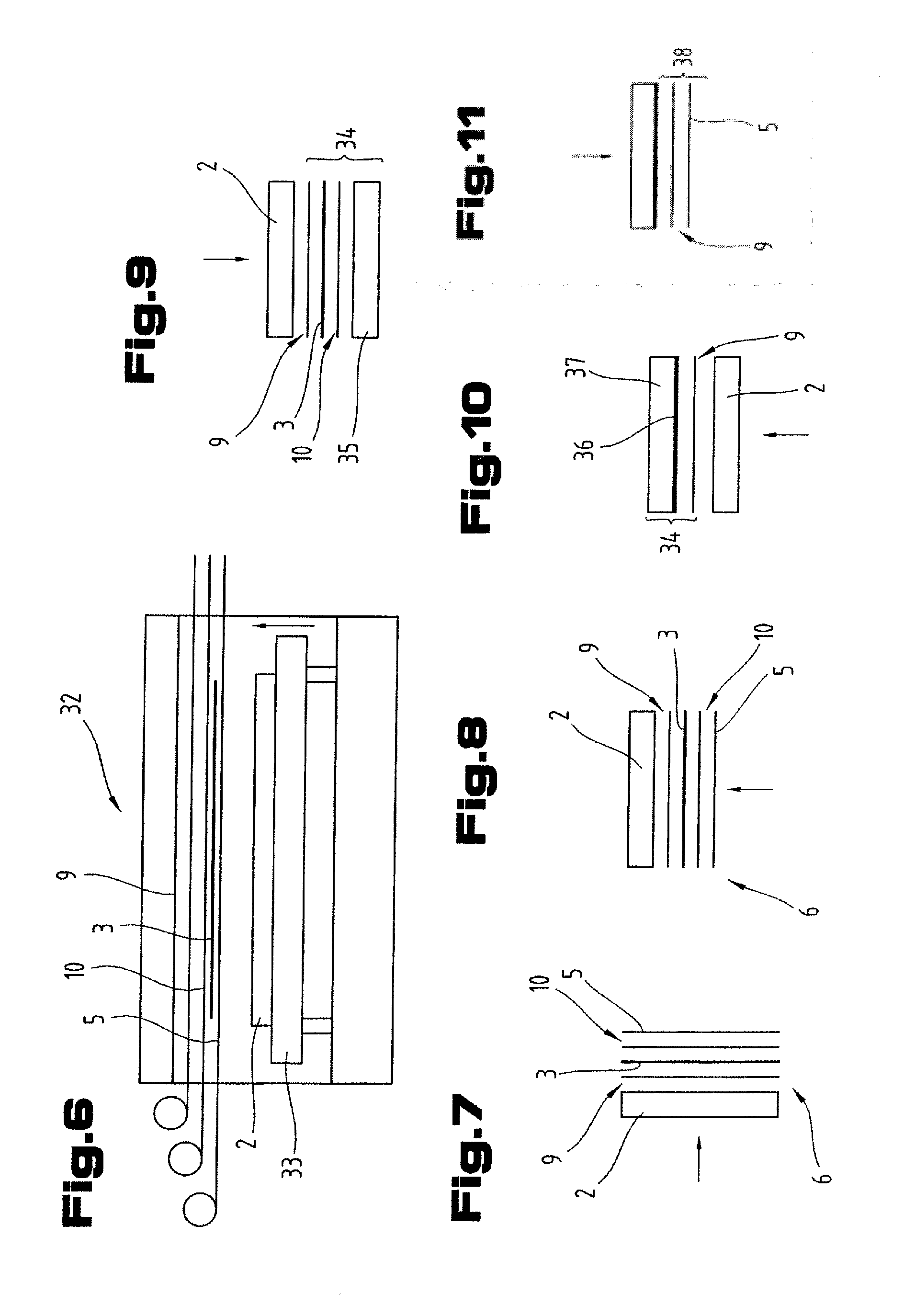
Multi-stage cavitation device
ActiveUS20100290307A1Low equipment , handling and energy costImprove efficiency and productivityThermal non-catalytic crackingFlow mixersCavitationMaterials science
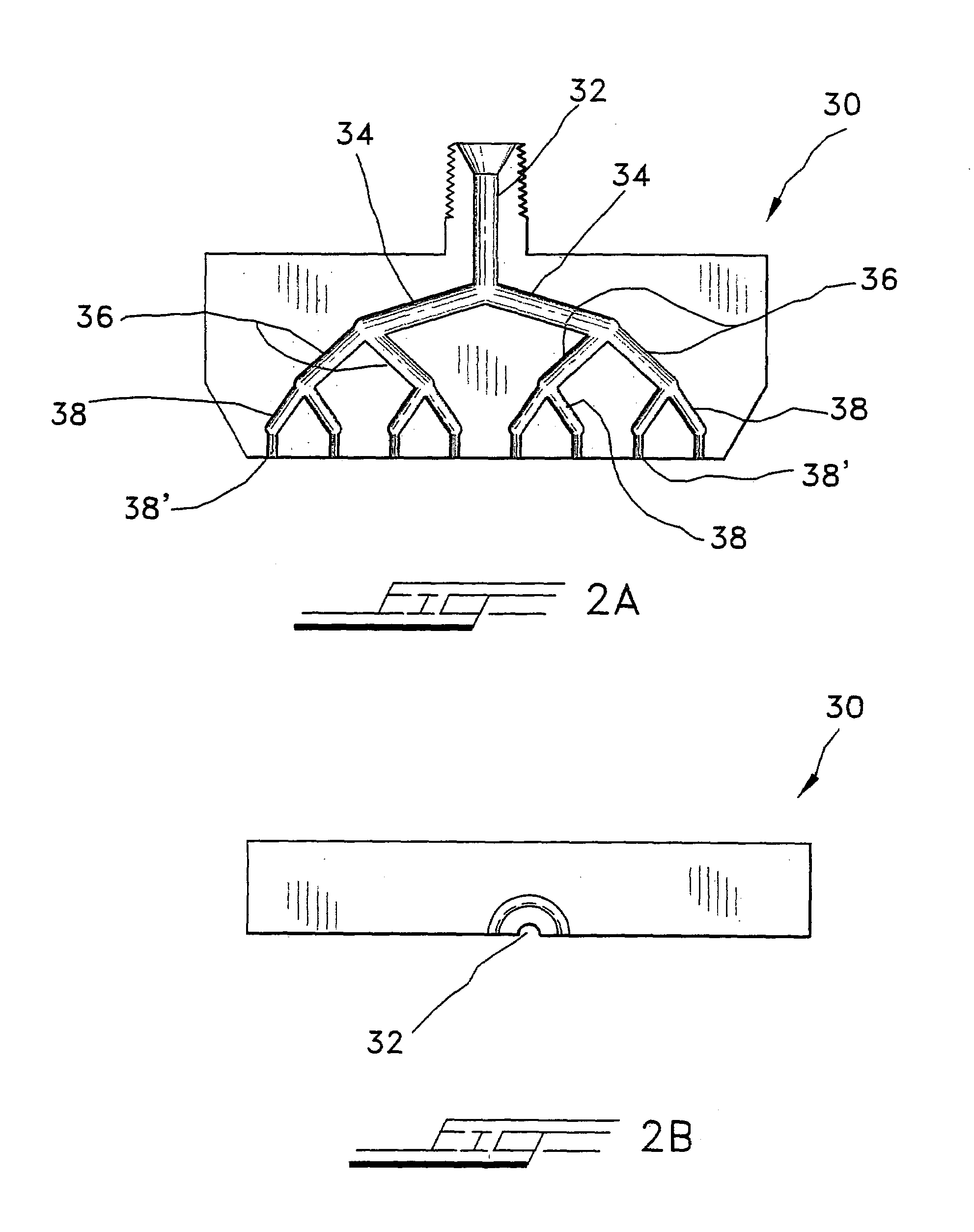
The flow-through cavitation device is provided for mixing and manipulating fluids that comprises feeding a fluidic mixture in a multi-stage flow-through hydrodynamic cavitation system, subjecting said fluid to a controlled multi-stage cavitation and continuing the treatment for a period of time sufficient for obtaining desirable changes in the physical and / or chemical properties and generating upgraded products.
Owner:CAVITATION TECH
Substrate cleaning apparatus
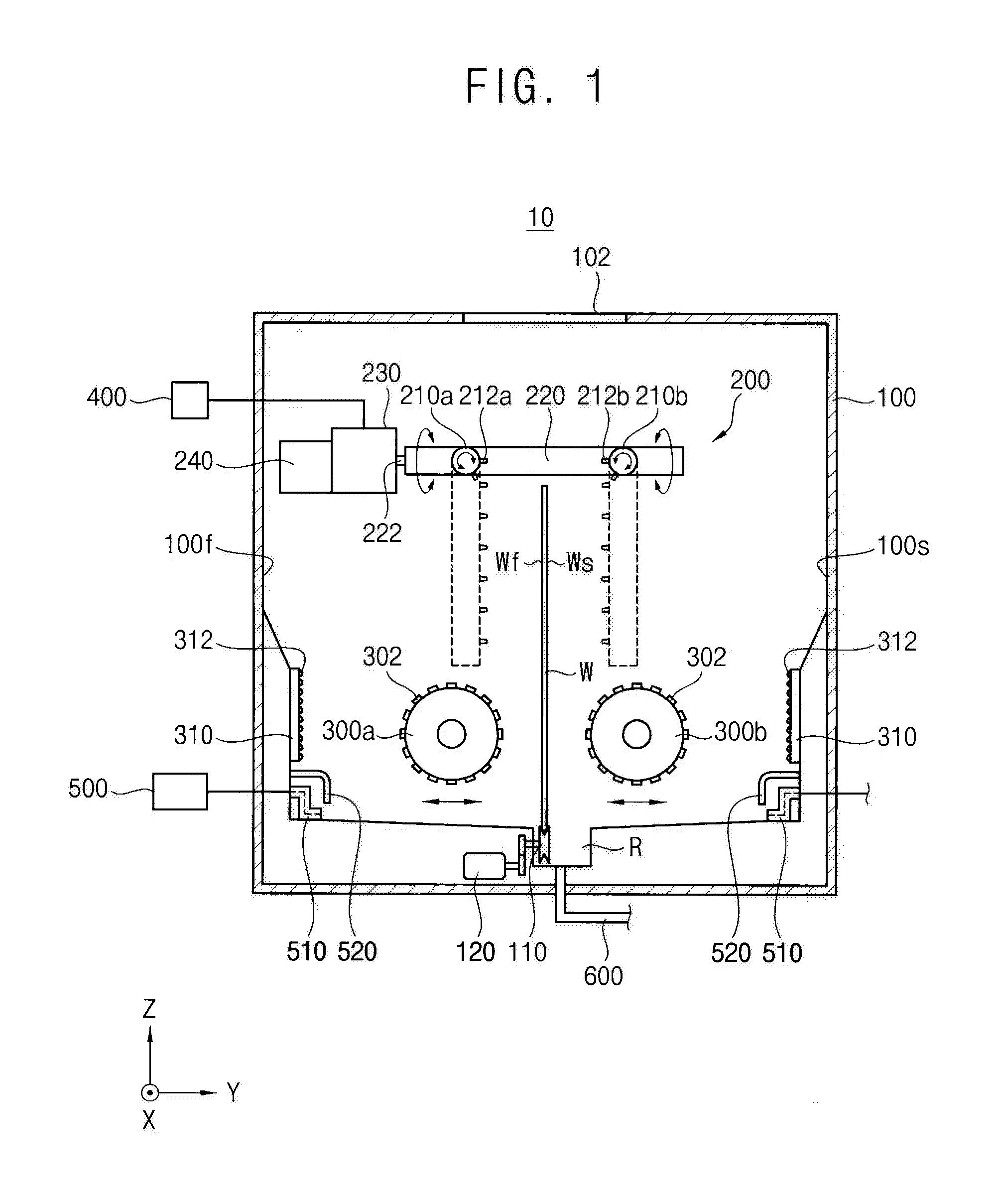
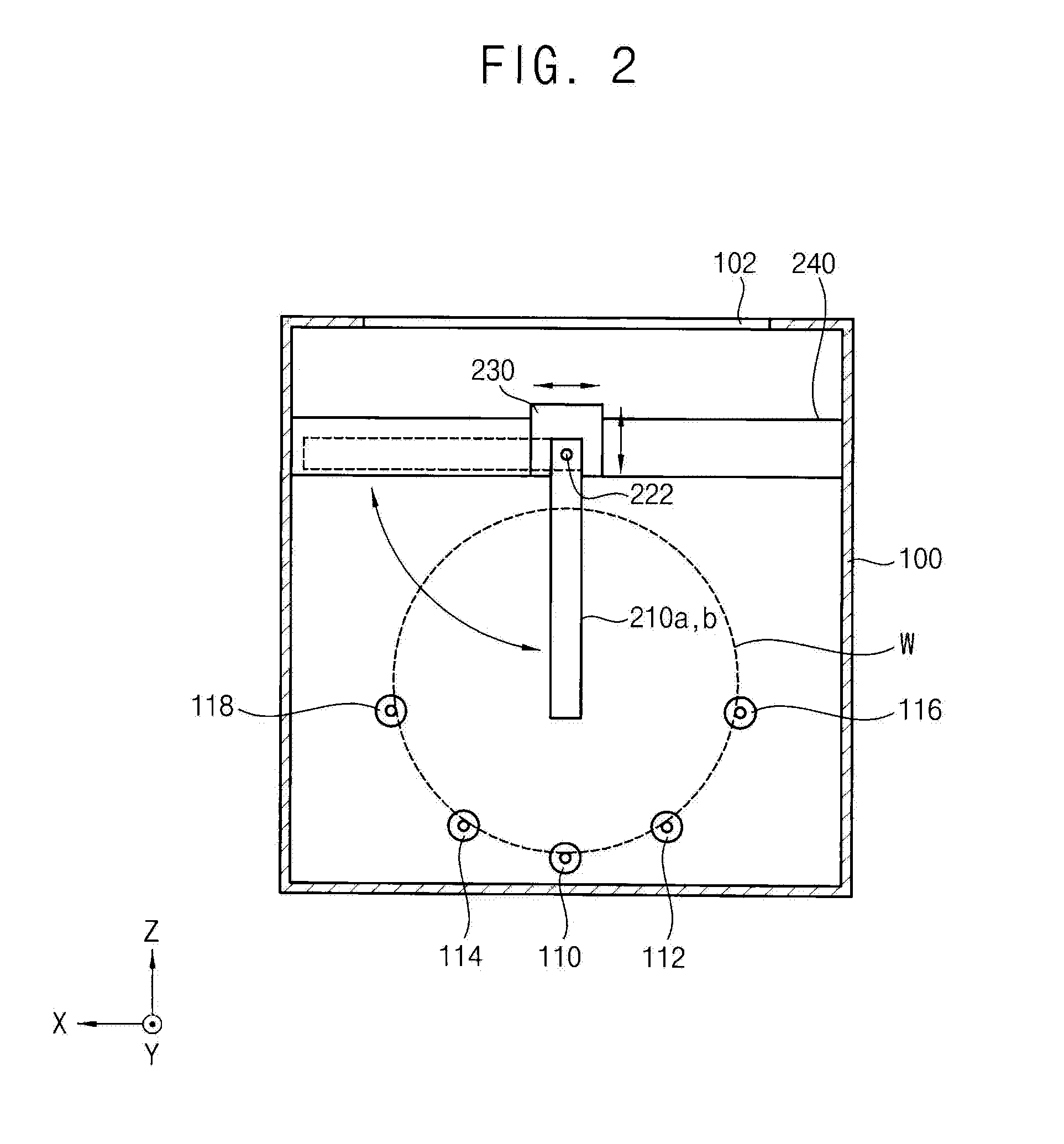
ActiveUS20160329219A1Improve efficiencyIncrease productivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpray nozzlesEngineeringPlane parallel
Provided is a substrate cleaning apparatus including: a cleaning bath configured to accommodate a substrate having a first surface and a second surface; a substrate support configured to support the substrate; first and second nozzle bars provided in the cleaning bath to be rotatable in a plane parallel with the substrate, each of the first and the second nozzle bars including a passage; a plurality of nozzles provided along a longitudinal direction of each of the first and the second nozzle bars and configured to spray the cleaning solution from the passage of each of the first and the second nozzle bars to the substrate; and first and second brushes, the first brush provided on a first side of the substrate and configured to clean the first surface and the second brush provided on a second side of the substrate and configured to clean the second surface of the substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
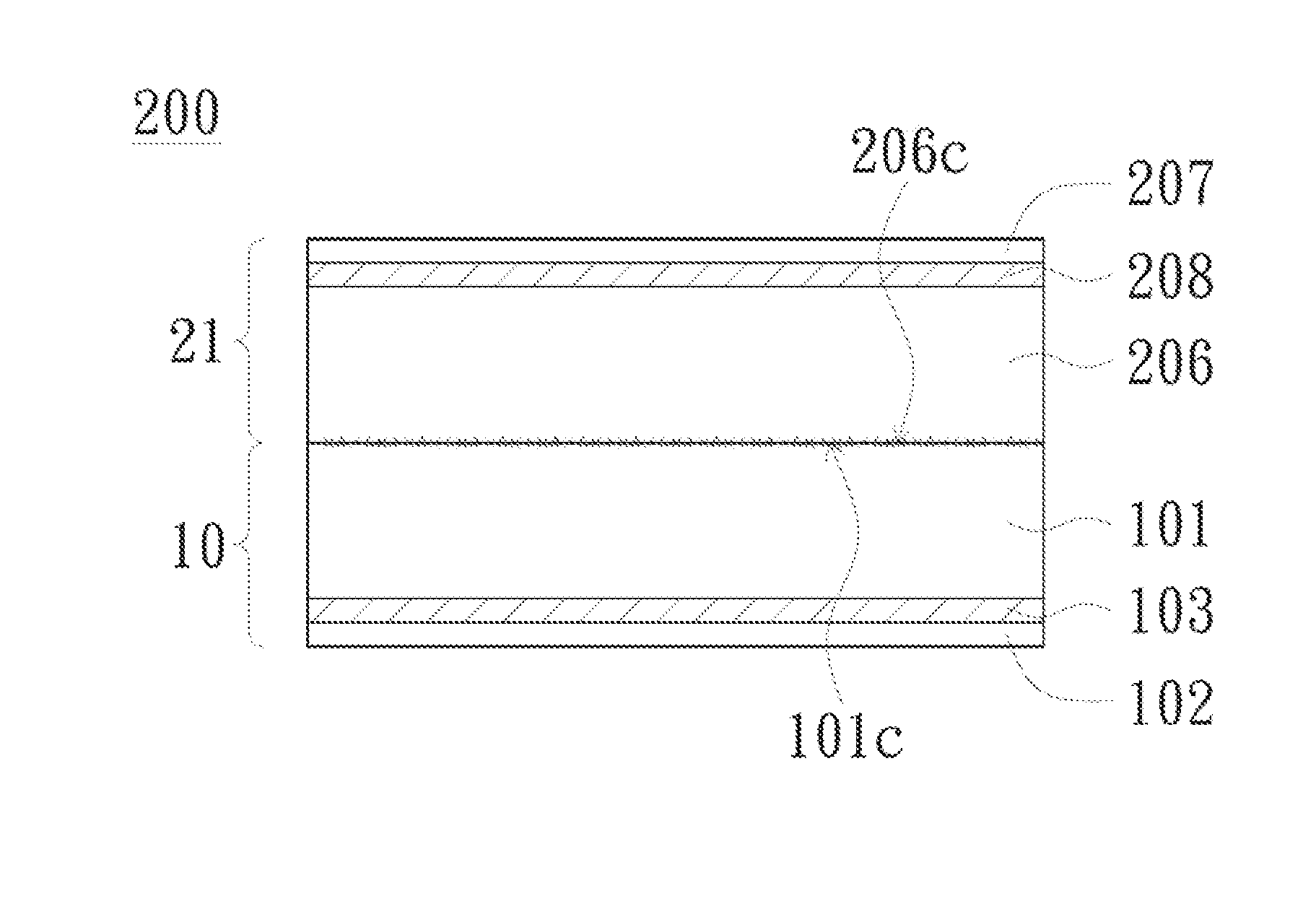
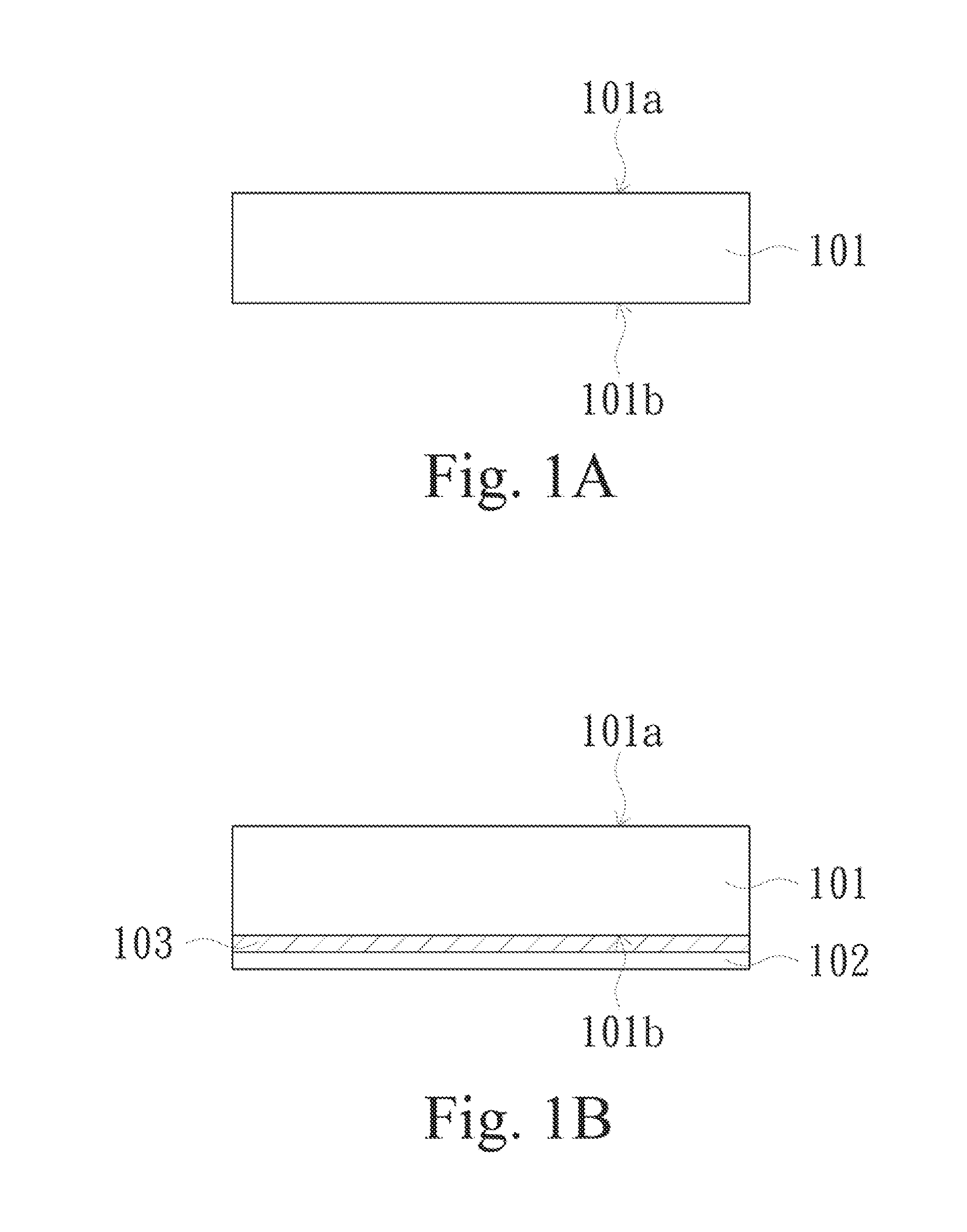
Metal substrate and method of manufacturing the same
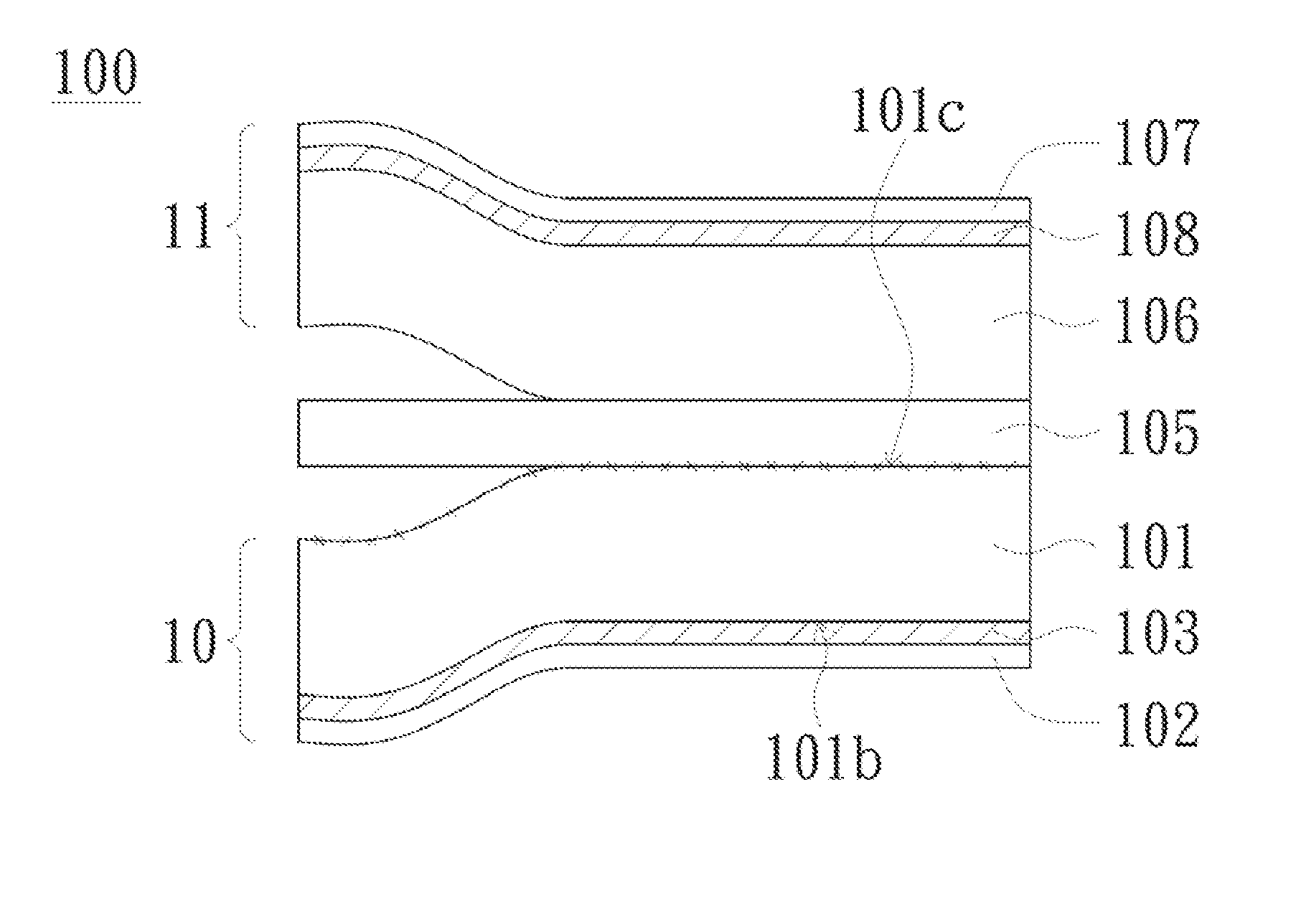
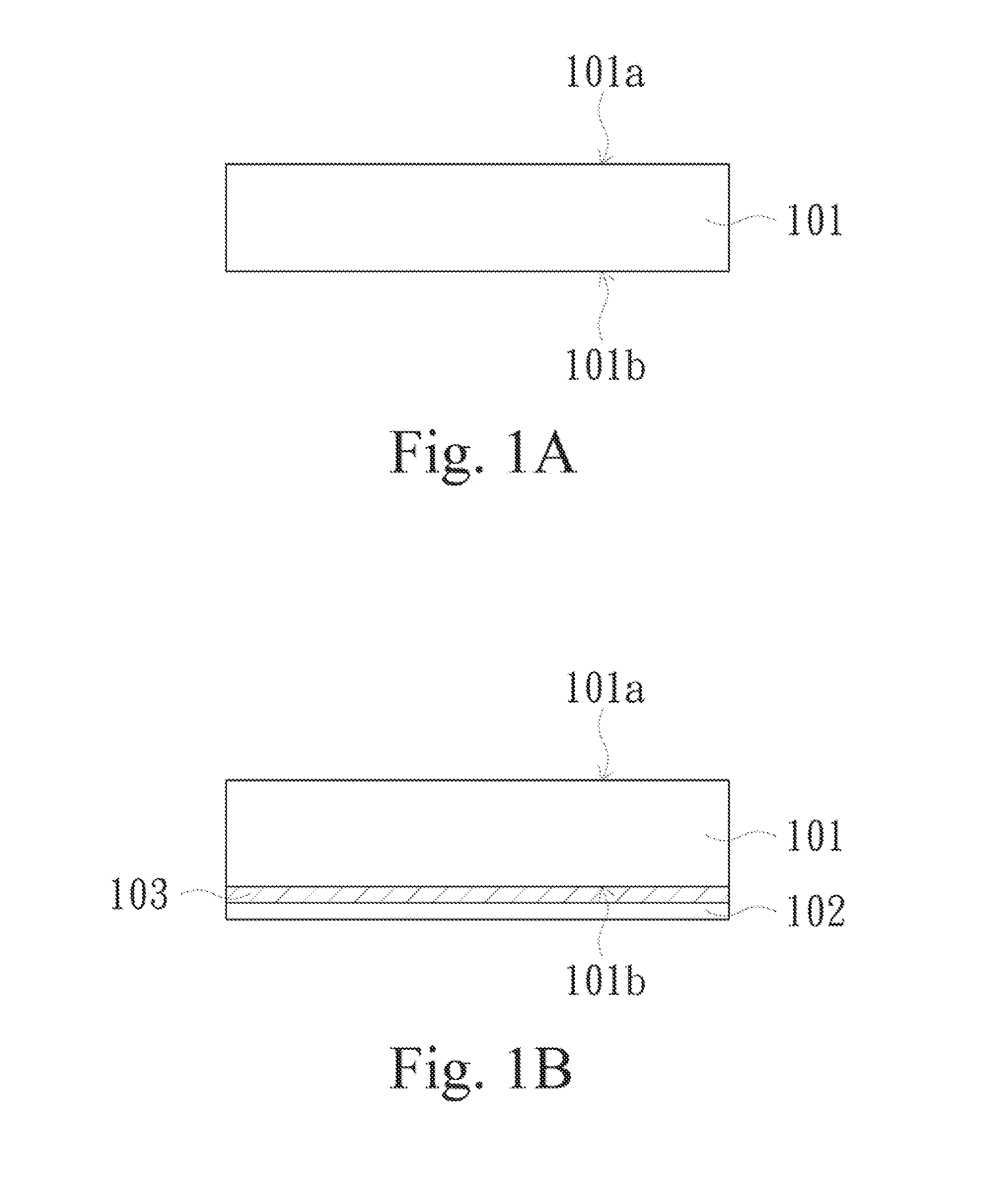
ActiveUS20150257253A1Increased yieldIncrease productivity and efficiencyRecord information storageMagnetic recordingMetal substrateOptoelectronics
A metal substrate includes a first insulating substrate, a second insulating substrate, a first metal layer, a second metal layer and a release layer. The first insulating substrate has a first modified surface and a second surface opposite to the first modified surface. The first metal layer faces the second surface. The release layer is bonded on the first modified surface. The second insulating substrate is bonded on a side of the release layer, such that the release layer is between the first modified surface and the second insulating substrate. The second metal layer is disposed on a side of the second insulating substrate, such that the second insulating substrate is between the release layer and the second metal layer. An original surface roughness of the first modified surface has a variation substantially less than 10% after the first modified surface is released from the release layer.
Owner:AZOTEK
Ion-beam source
ActiveUS7863582B2Generated reliablyImprove productivity and efficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansIon beam tubesElectricityElectrical conductor
An ion-beam source comprising: a plasma-generation unit for generating plasma and an ion-extraction unit for extraction and acceleration of ions from the aforementioned plasma, where the ion-extraction unit is made in the form of at least one grid under a negative potential. The plasma generating unit consists of a working chamber having a deeply immersed antenna cell. The cell contains a ferromagnetic core, a heat conductor with a heat sink, at least one inductive coil wound onto the ferromagnetic core, and a cap made from a dielectric material that sealingly covers the ferromagnetic core and the inductive coil.
Owner:GODYAK VALERY
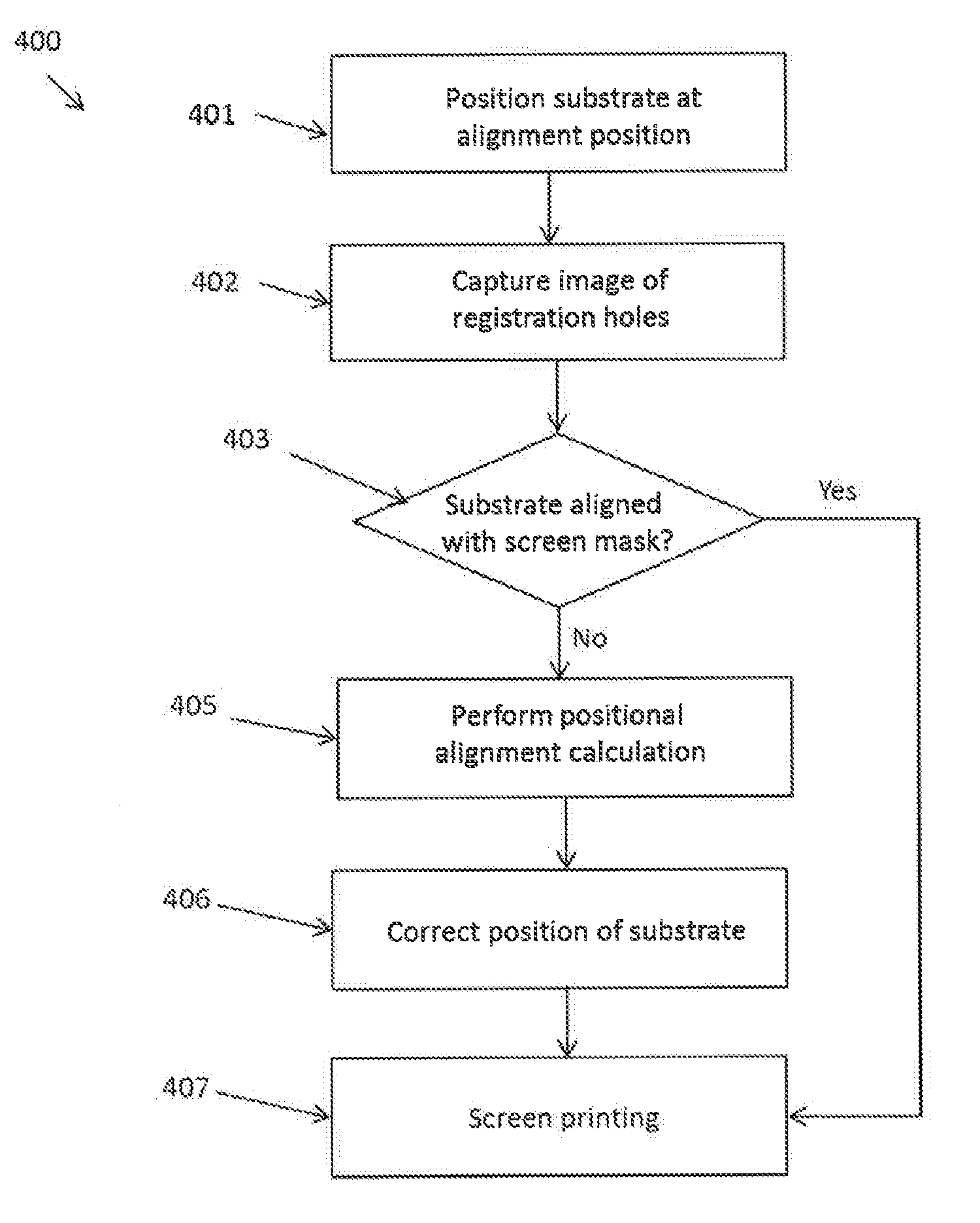
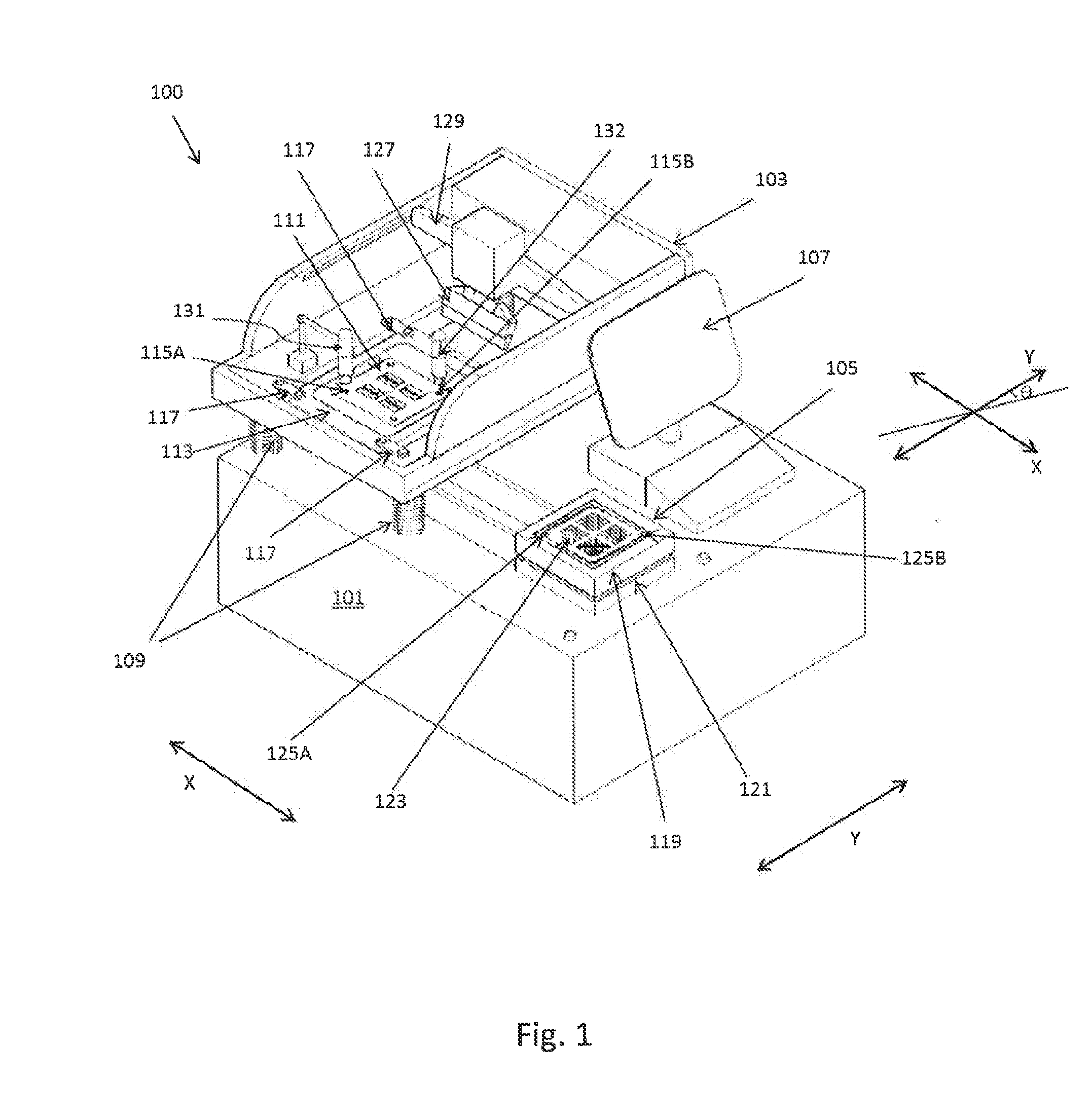
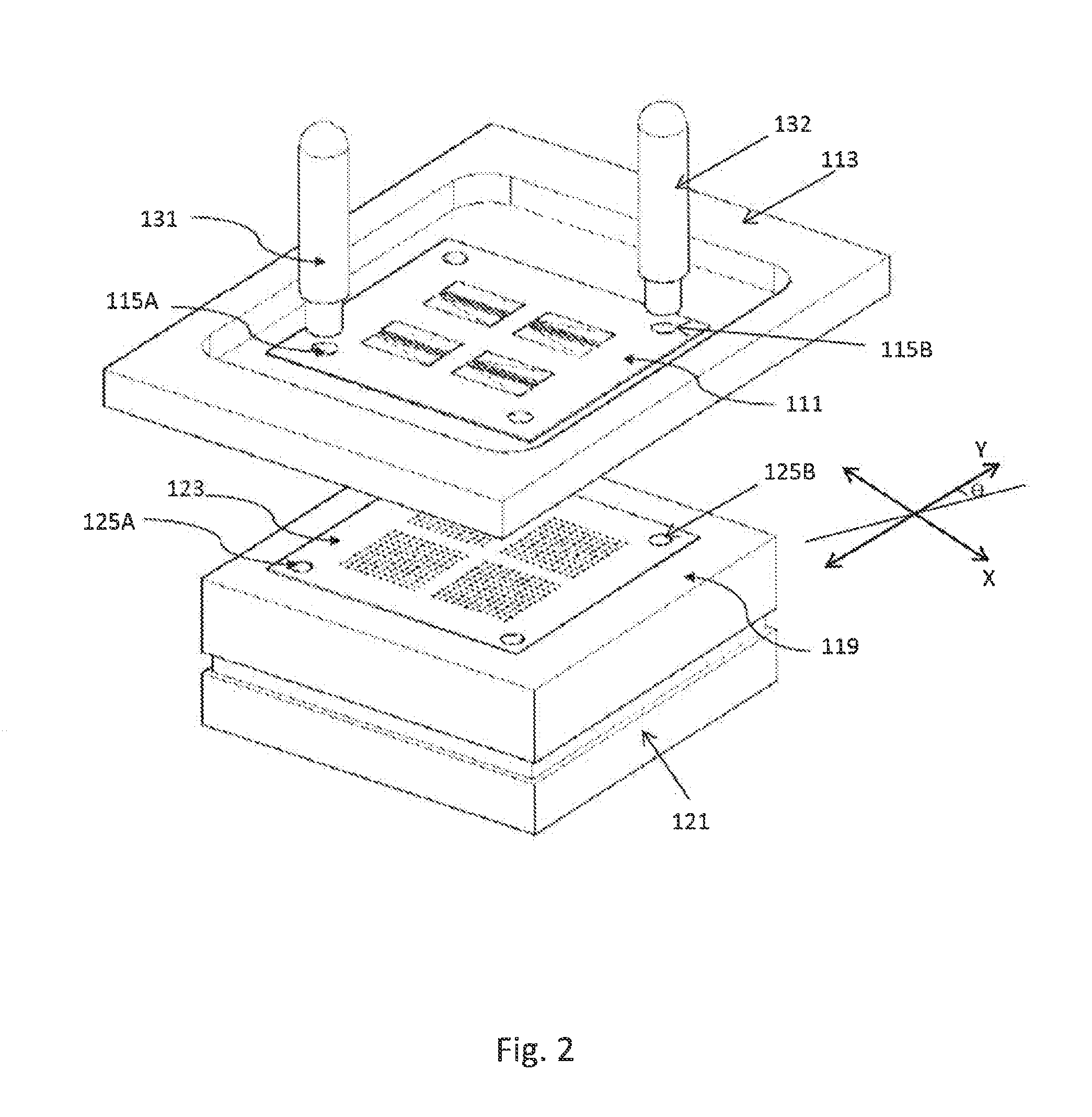
Screen printing system with positional alignment
ActiveUS20140261027A1Reduce setup timeImprove productivity and efficiencyLiquid surface applicatorsScreen printersScreen printingEngineering
Screen printing system with positional alignment for aligning a substrate with a screen mask. The substrate and the screen mask have two registration holes for facilitating the positional alignment. The positional alignment method includes calculating alignment values for correcting the position of the substrate based on the determined offsets between the registration holes of the substrate and the screen mask. The position of the substrate is corrected based on the calculated alignment values so that registration holes of the substrate are vertically aligned with the registration holes of the screen mask.
Owner:TELEKOM MALAYSIA BERHAD
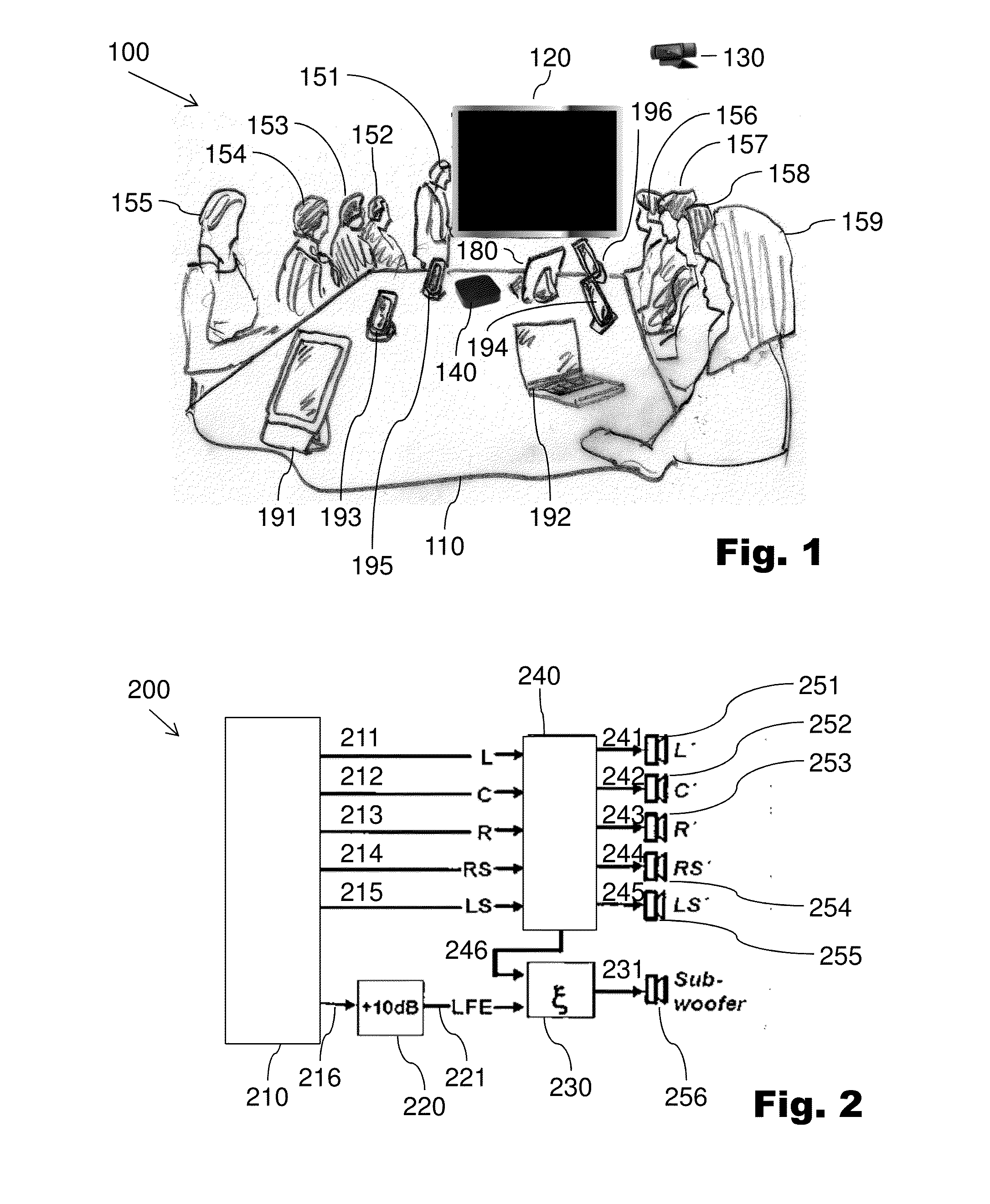
Method, device, and system for managing a conference
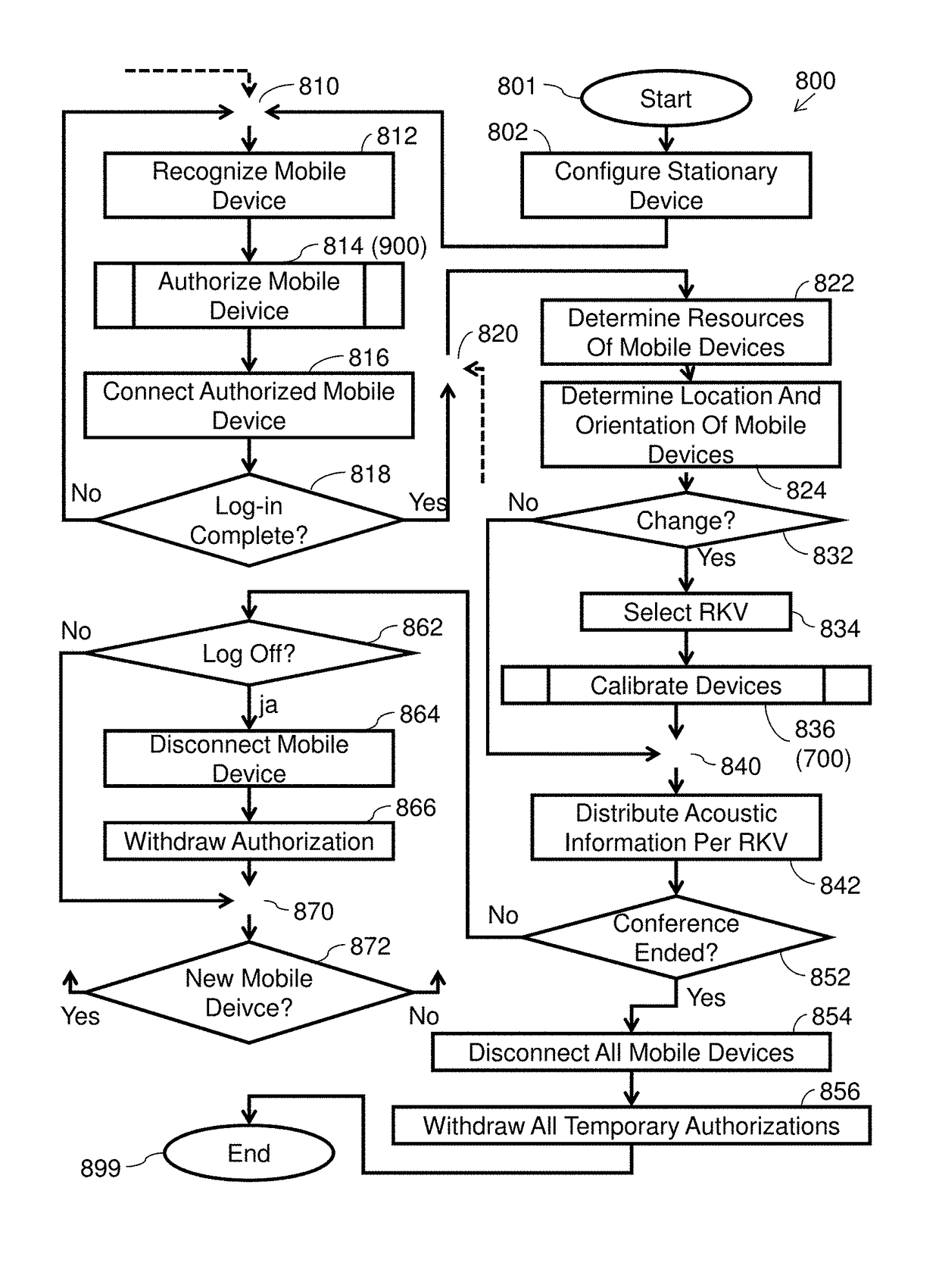
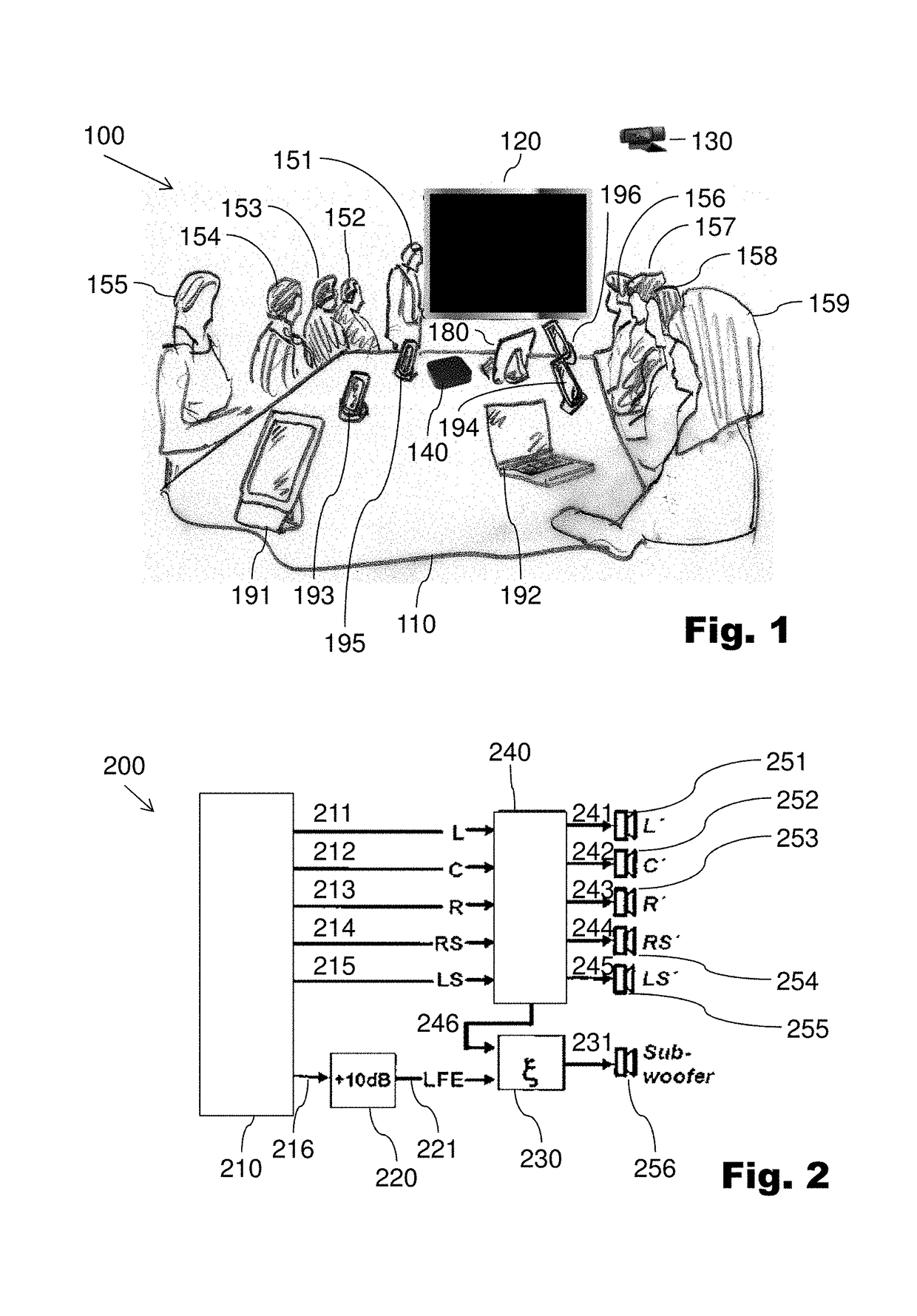
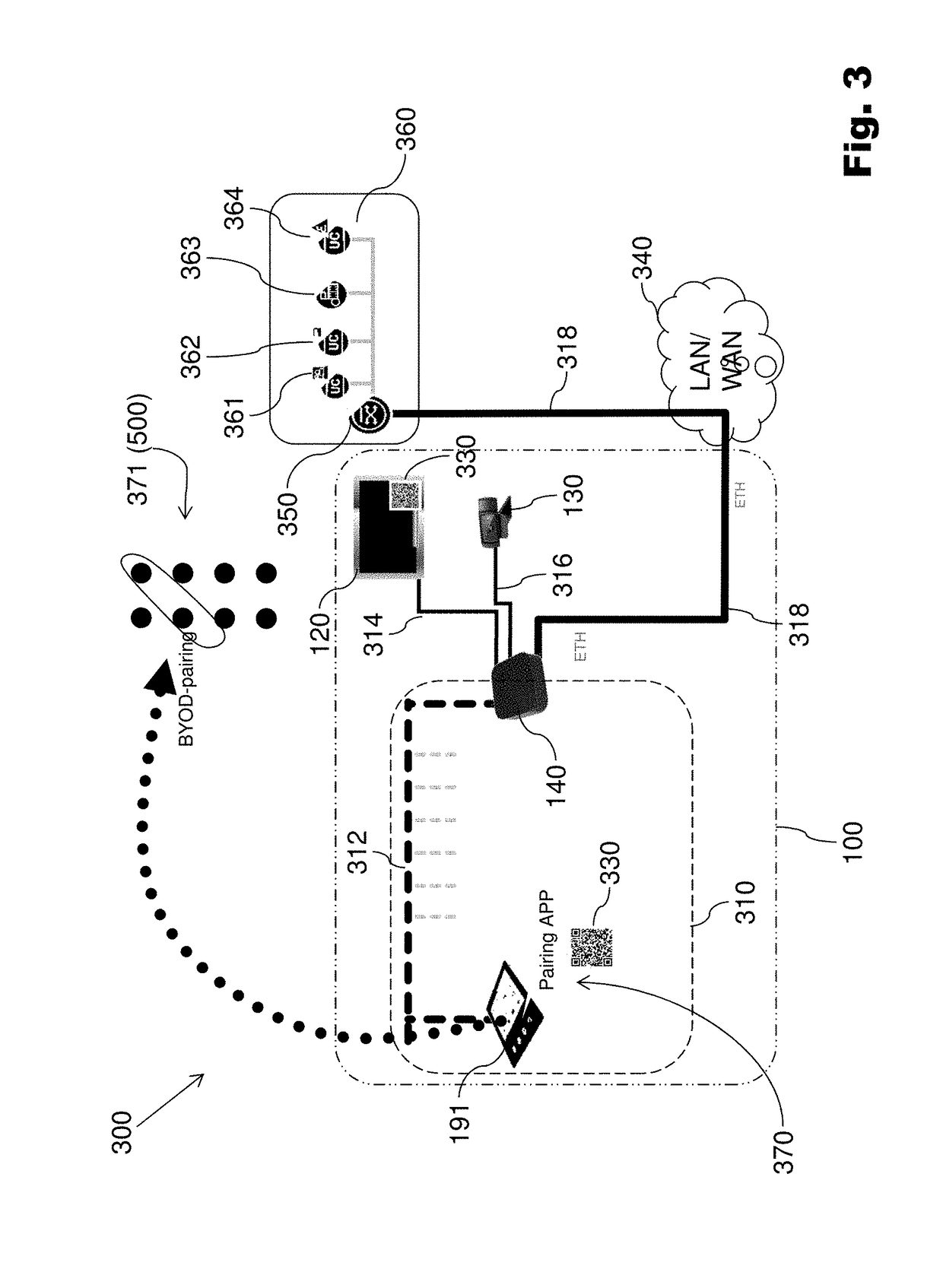
ActiveUS20150271341A1Promote reproductionImprove productivity and efficiencyUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsCommunications systemUser device
A method can include the steps of logging in of mobile devices of participants when they are located in the same physical conference environment and managing the resources of these devices such that the resources of the logged-in devices are combined into an audio system to output audio conference information using a sound output process in the conference environment. The conference environment may be a conference room. The audio conference information may be audio to be output to the participants at the conference environment. The formed audio system can include speakers of the user devices for outputting such audio. The microphones of the user devices may also be used to form an audio input system for the conference for allowing audio of the participants to be received and transmitted during the conference. A communication system can be configured to implement embodiments of the method.
Owner:RINGCENTRAL INC
Method and device for replacing the printing roller of a printing unit of a printing machine
ActiveUS20170043570A1Improve efficiencyIncrease productivityPrinting platesOther printing apparatusEngineeringPrinting press
Owner:BOBST FIRENZE
Cells and connecting channels for centrifugal partition chromatography devices
ActiveUS20100200488A1Improve efficiencyIncrease productivityIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationCircular discEngineering
The present invention relates to cells (1) for a centrifugal partition chromatography column, consisting of stacked discs and comprising a network of three-dimensional cells interconnected in series and communicating with liquid phase circulation channels, said cells being distributed over the periphery of at least one disc driven into rotation about a main axis (8); the cells have a geometric shape of revolution about a substantially radial axis with respect to said disc and they are connected by channels (2, 4) of substantially circular, elliptical or parallelepipedic section, the main two dimensions of which are smaller than the largest cross-section of the cell.The invention also relates to methods of manufacturing these cells.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE +1
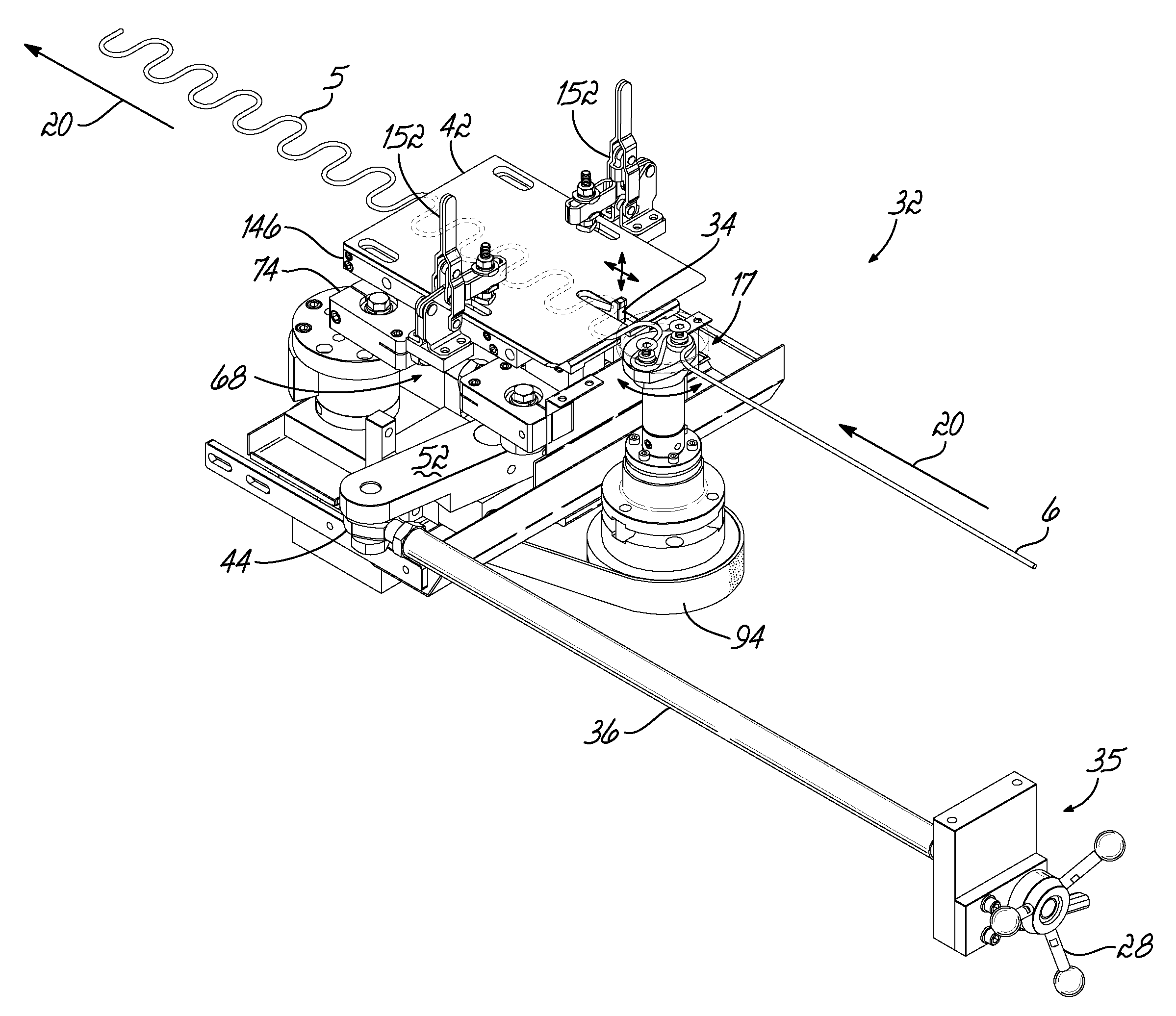
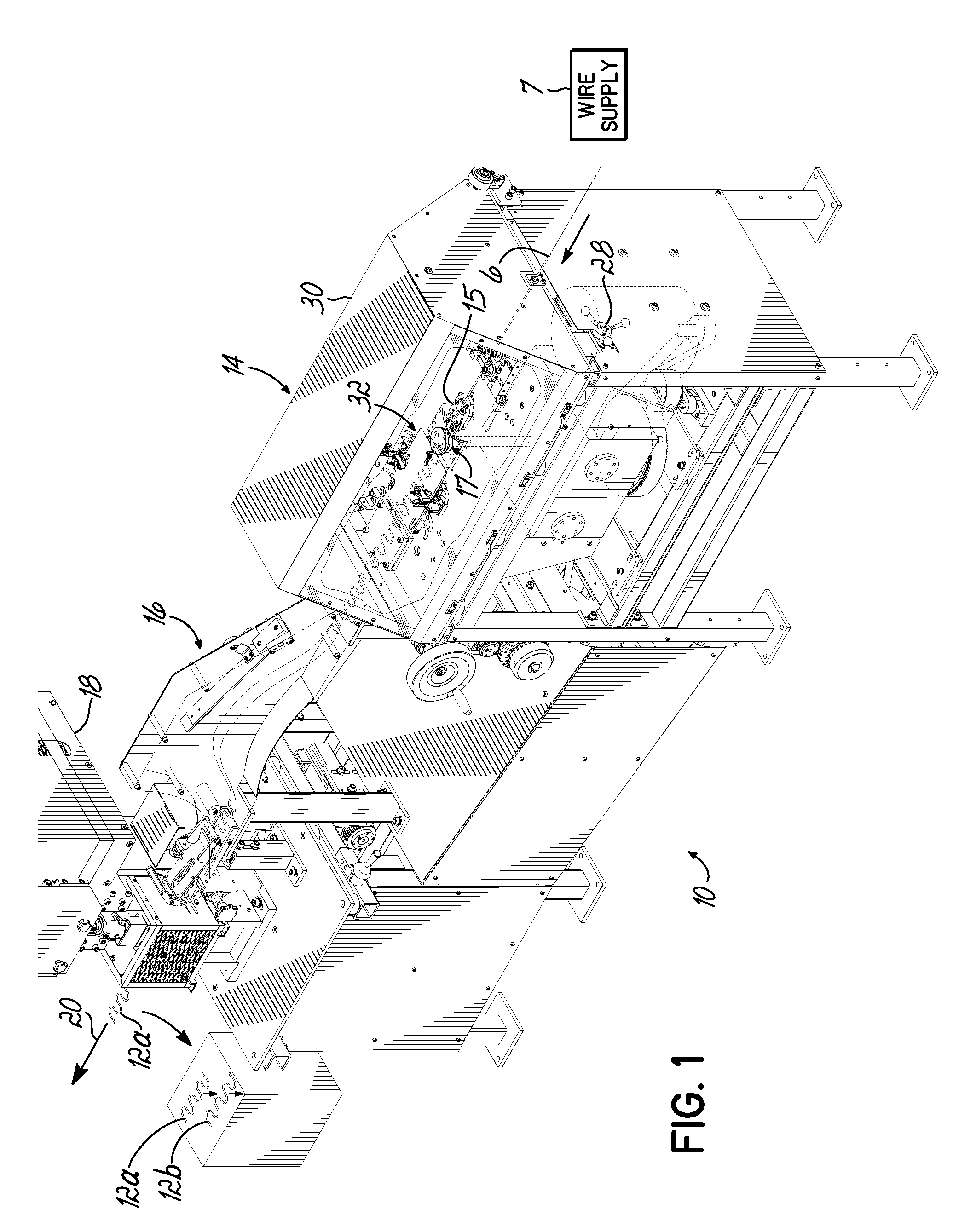
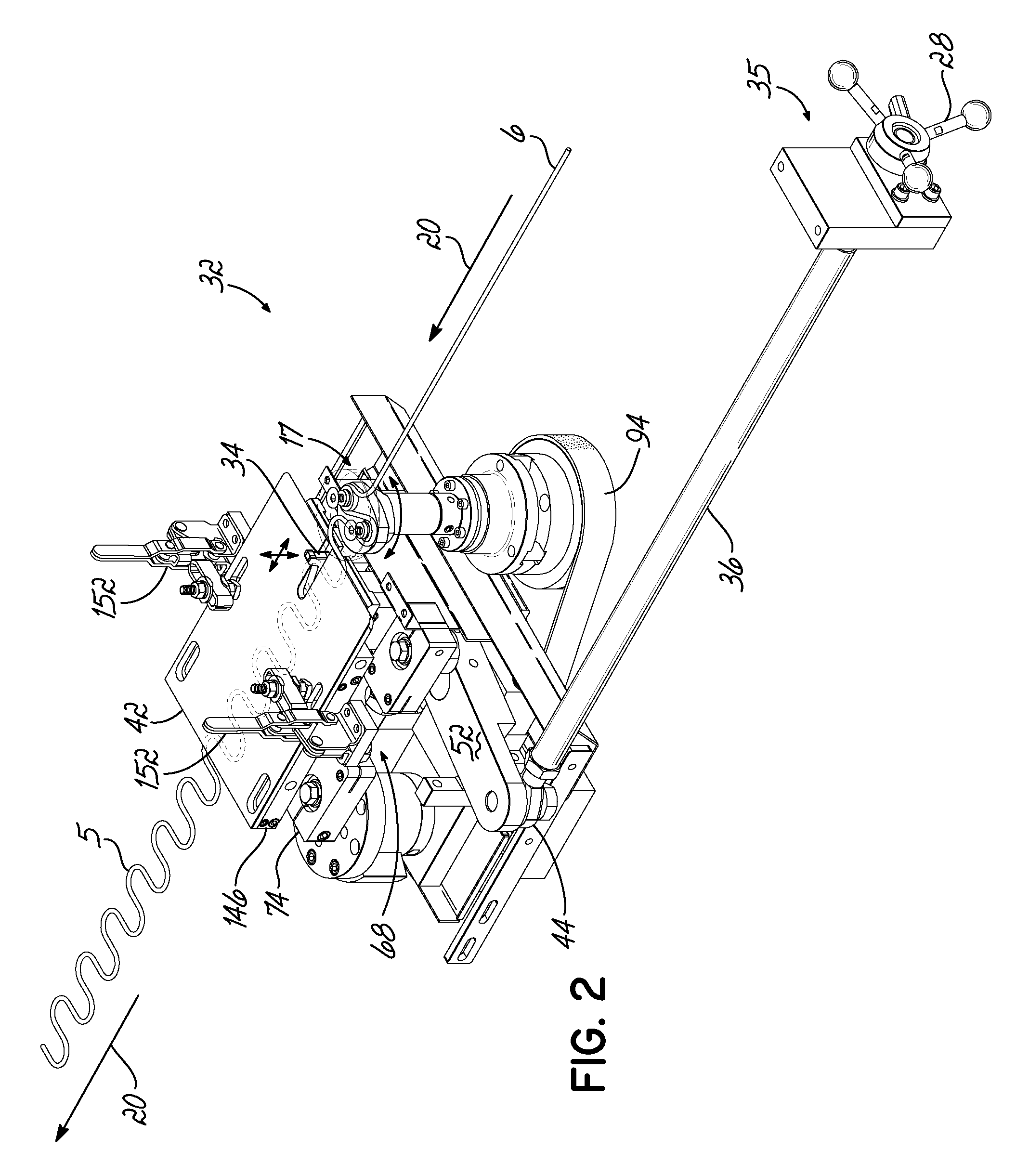
Method and Apparatus For Automating Production of Sinuous Springs
ActiveUS20090260411A1Improve productivity and efficiencyEfficiency and productivity be reduceEngineeringMechanical engineering
A method and apparatus is disclosed for manufacturing sinuous springs wherein each spring comprises a discrete length of sinuous spring wire having parallel straight bar segments interconnected at their opposite ends by oppositely directed curved connecting segments. This apparatus is operable to adjust the length of the sinuous spring wires exiting the machine without turning off or stopping the machine. An operator need only rotate a handle outside a housing of the machine to increase or decrease the length of the sinuous spring wires exiting the machine.
Owner:L & P PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO
Method for producing a solar panel
InactiveUS20120073746A1Improved combination of convenienceImproved combination of utilityLamination ancillary operationsLayered product treatmentThermal energyEngineering
Processes and apparatus for producing laminated solar panels built up of a plurality of layers, wherein at least one layer is preheated and stores thermal energy. The at least one layer is laminated, under vacuum or in controlled gas atmosphere, with at least one other layer.
Owner:3S SWISS SOLAR SYST
Metal substrate and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20150251397A1Improve structural strengthPrevent fold injury injuryRecord information storageMagnetic recordingSurface roughnessOptoelectronics
A metal substrate includes a first insulating substrate, a second insulating substrate, a first metal layer and a second metal layer. The first insulating substrate has a first modified surface and a second surface opposite to the first modified surface. The first metal layer faces the second surface. The second insulating substrate is bonded on the first modified surface, such that the first insulating substrate is between the second insulating substrate and the first metal layer. The second metal layer is disposed on a side of the second insulating substrate, such that the second insulating substrate is between the first modified surface and the second metal layer. An original surface roughness of the first modified surface has a variation substantially less than 10% after the first modified surface is released from the second insulating substrate.
Owner:AZOTEK
Nozzle for use in rotational casting apparatus
InactiveUS6989061B2Improve productivity and efficiencyEfficient coatingPretreated surfacesSpray nozzlesElastomerSpin casting
For use in a rotational casting machine used for coating a rotating body with elastomer, such as polyurethane, there is provided a nozzle used for dispensing the liquid polyurethane onto the rotating body to be coated. The outlet of the nozzle is a narrow, elongated slit or opening. However, the interior passageway of the nozzle continually changes shape from the inlet to the outlet thereof, in order to ensure a constant cross-sectional area of the interior passageway along the length thereof, and in order to arrive at the desired narrow, elongated outlet-opening, whereby laminar flow of the liquid polyurethane is achieved with the concomitant reduced dwell-time of the liquid polyurethane therein, in order to reduce build up and clogging of the nozzle.
Owner:KASTALON
Method, device, and system for managing a conference
ActiveUS9866699B2Promote reproductionImprove productivity and efficiencySpecial service provision for substationSpecial service for subscribersCommunications systemUser device
A method can include the steps of logging in of mobile devices of participants when they are located in the same physical conference environment and managing the resources of these devices such that the resources of the logged-in devices are combined into an audio system to output audio conference information using a sound output process in the conference environment. The conference environment may be a conference room. The audio conference information may be audio to be output to the participants at the conference environment. The formed audio system can include speakers of the user devices for outputting such audio. The microphones of the user devices may also be used to form an audio input system for the conference for allowing audio of the participants to be received and transmitted during the conference. A communication system can be configured to implement embodiments of the method.
Owner:RINGCENTRAL INC
Assembly line quality control cart and method
InactiveUS20150128719A1Insufficient improvementReduce buildAssembly machinesElectrode supporting devicesTest couponQuality control
Disclosed are assembly line equipment maintenance devices and methods. A maintenance cart is selectively engaged to a transport conveyor and integrated into a moving assembly line. The cart can include maintenance tools to refurbish robot end effector tools or replacement tools engageable by robot wrists. The maintenance or replacement tools can include a variety of maintenance equipment including weld tip dressing tools, weld force gauges, replacement weld guns, and test coupon disks.
Owner:COMAU LLC
Methods of producing printed packaging
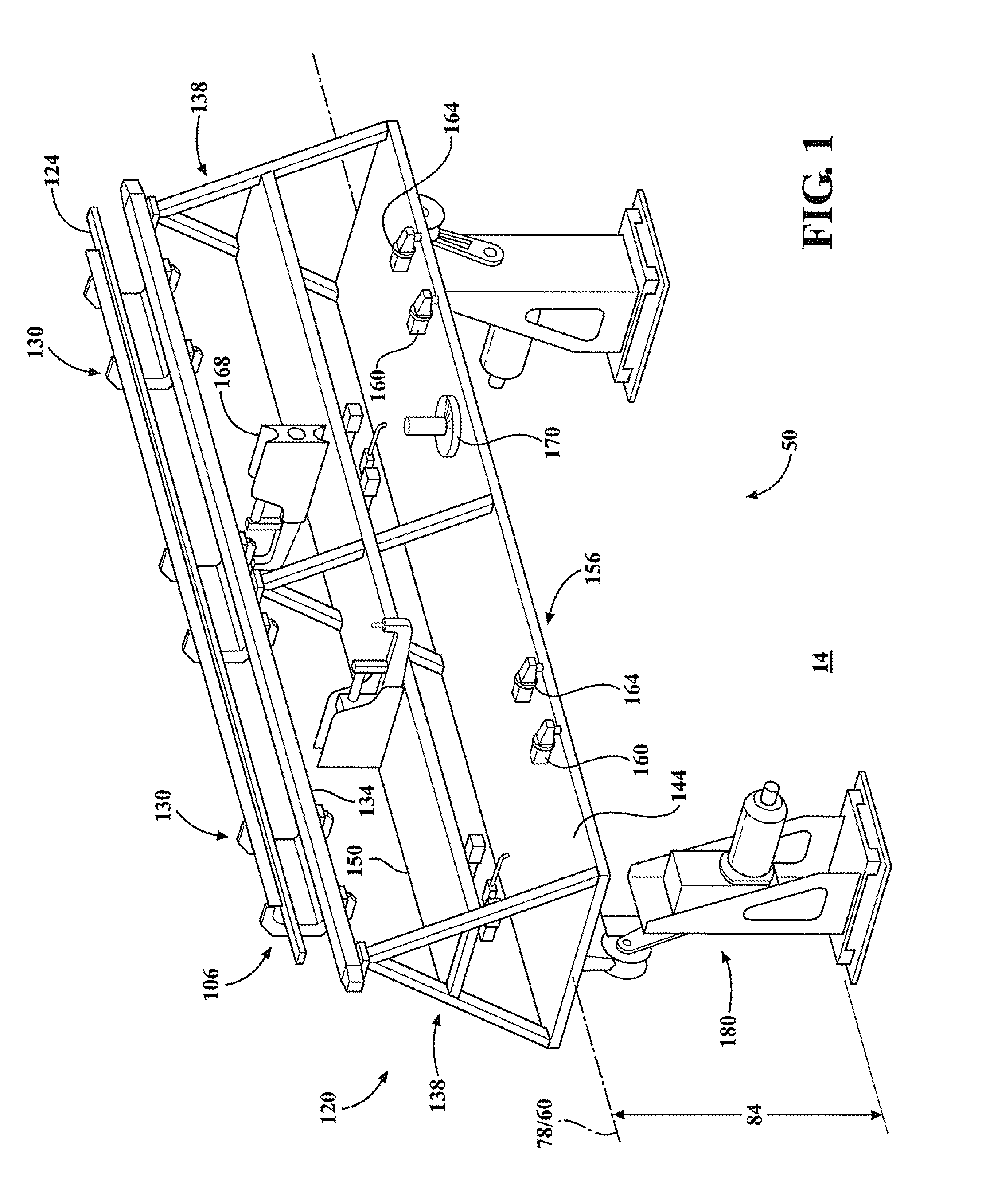
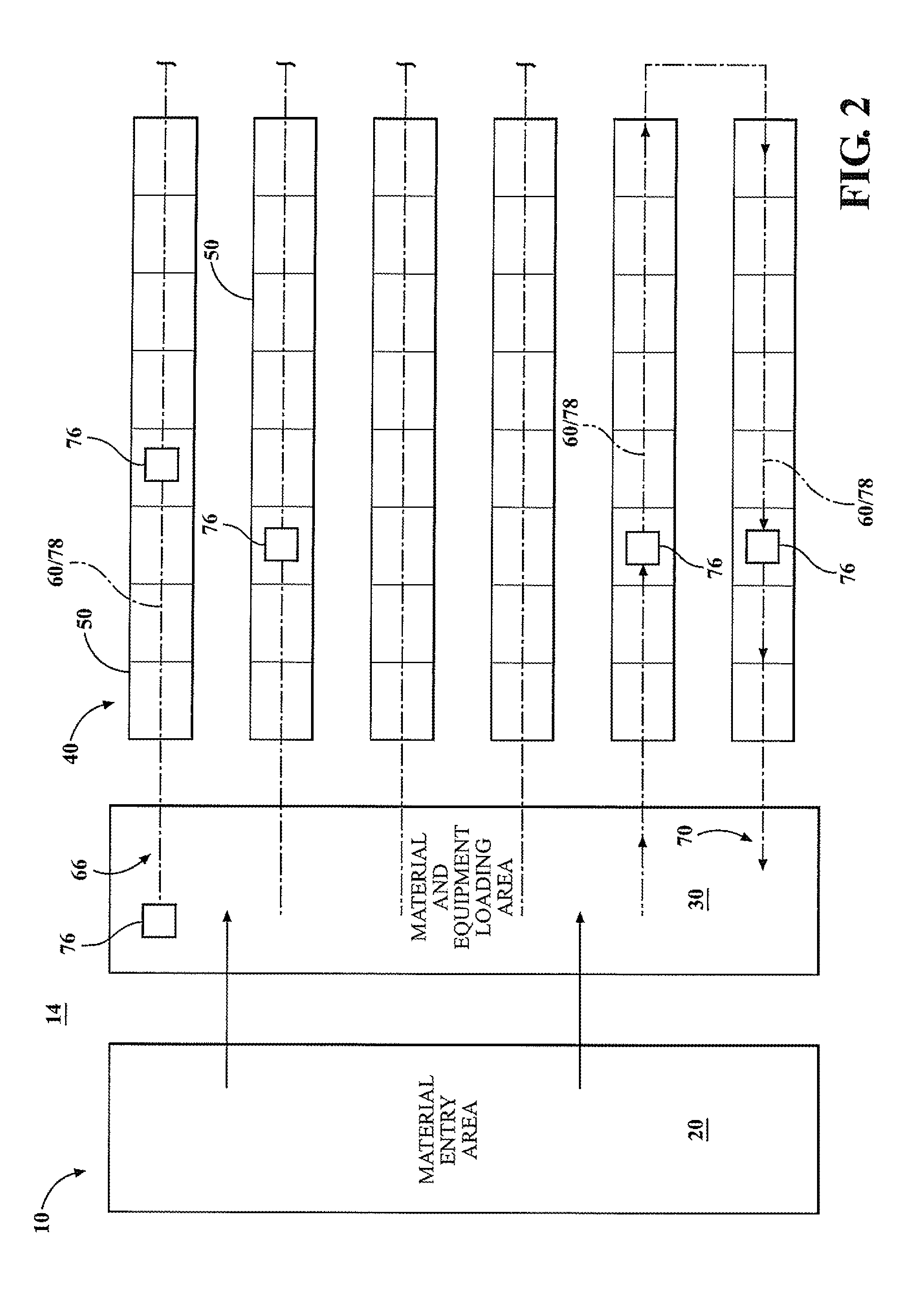
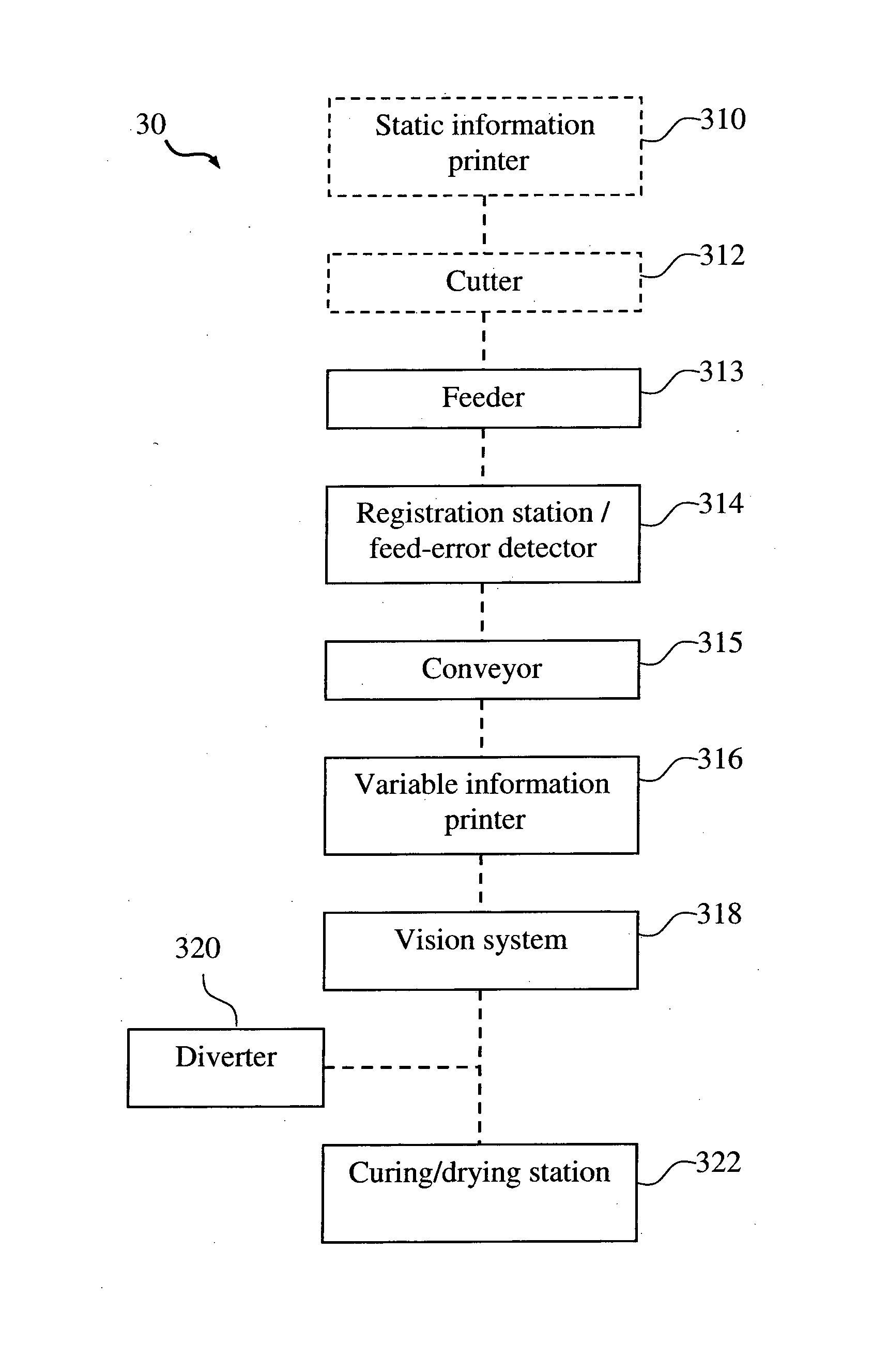
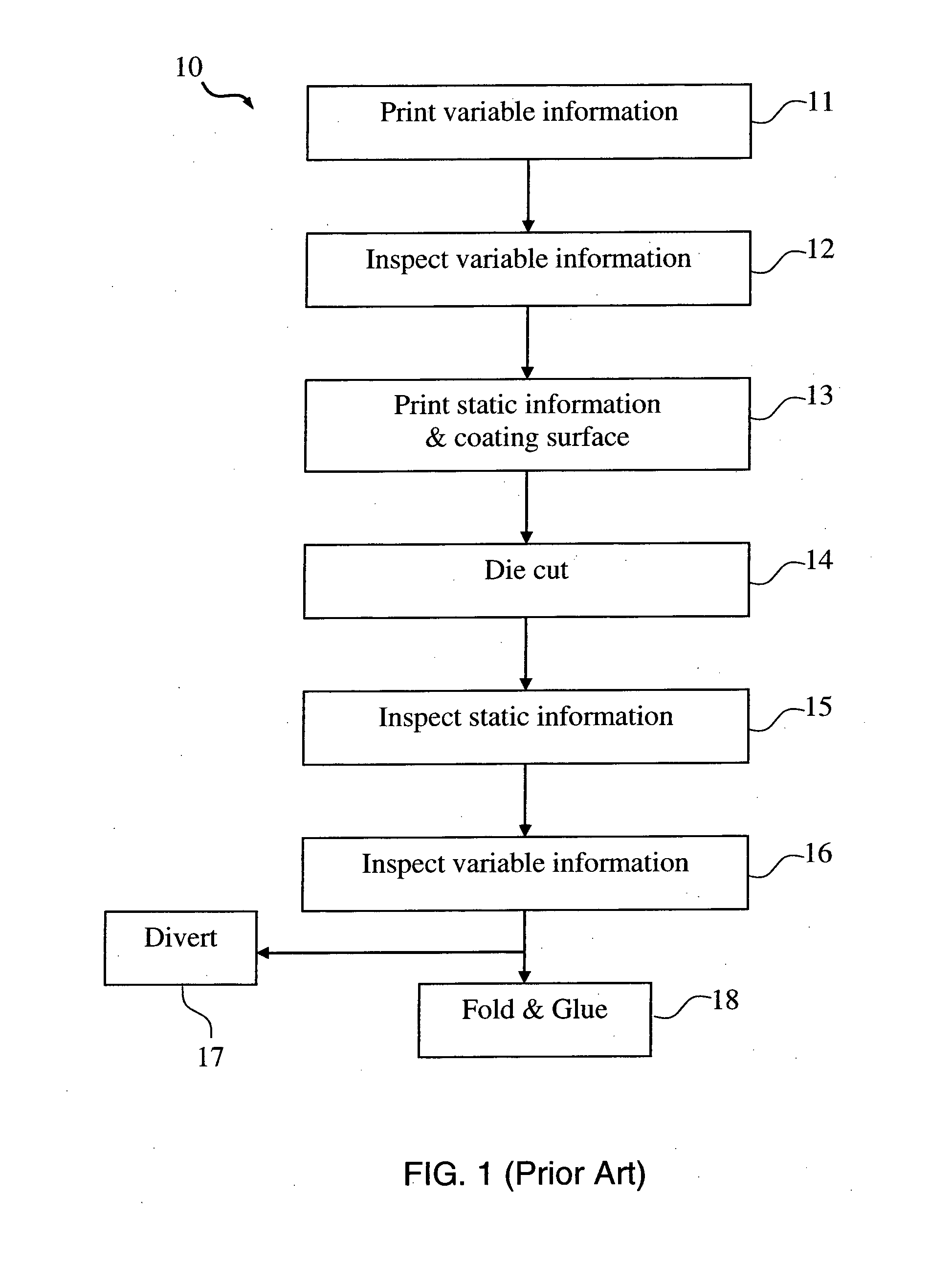
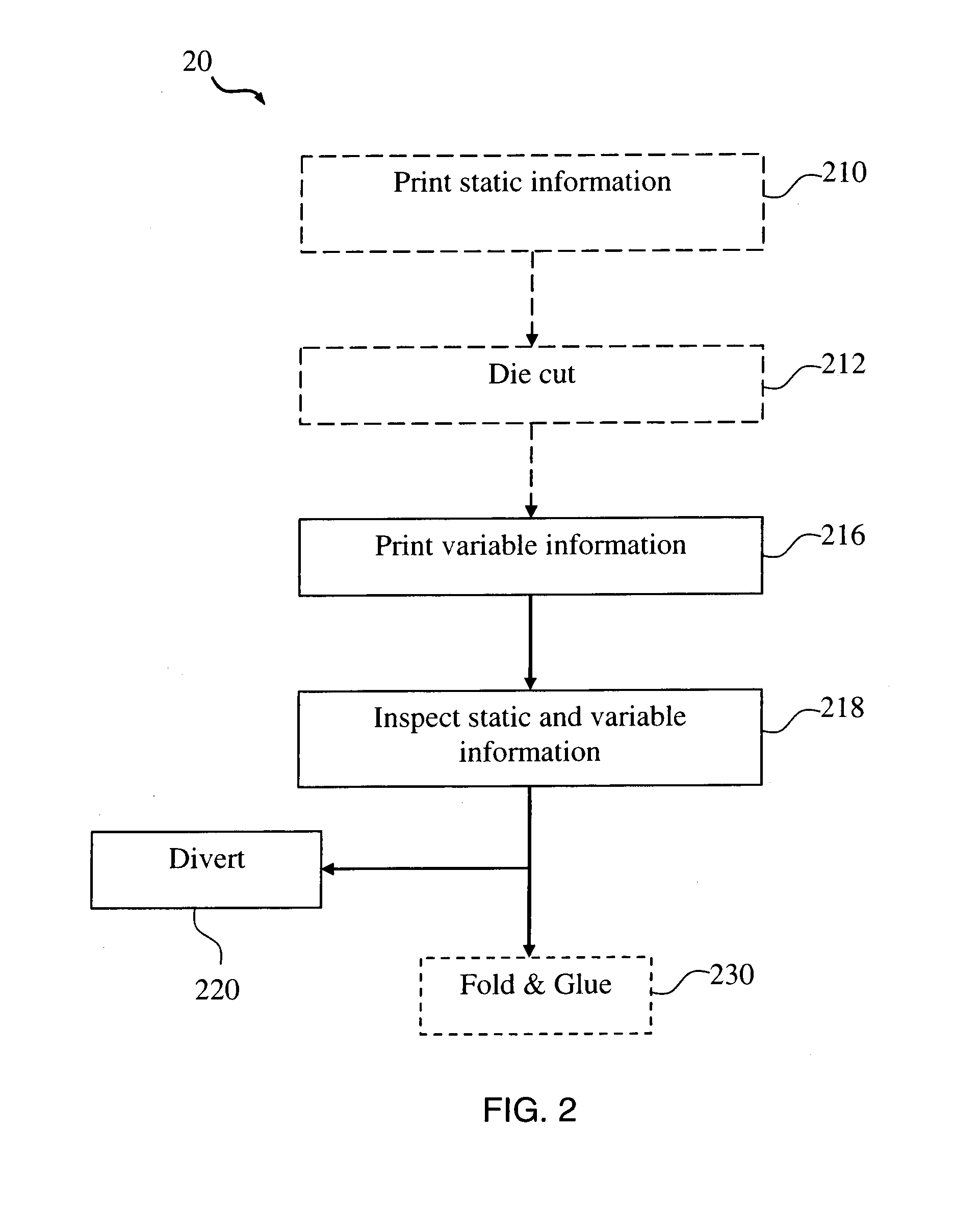
InactiveUS20150291382A1Improve productivity and efficiencyReduce wastageBox making operationsPaper-makingEngineering
The present invention provides methods of producing packaging for use in consumer goods packaging. In one embodiment, the method includes providing a plurality of printable substrates having pre-printed static information thereon; printing variable information on the plurality of printable substrates, inspecting the static information of each of the plurality of printable substrates; and inspecting the variable information of each of the plurality of printable substrates. The present invention is advantageous in that inspecting the static information and inspecting variable information are carried out at a same time therefore production efficiency is improved. In addition, inspection is done against separated individual printable substrates hence if any defect is detected, only the defected substrate needs to be discarded hence wastage rate is reduced.
Owner:WIN WIN DIGITAL SECURITY
Efficient camera accessory assembling and welding device
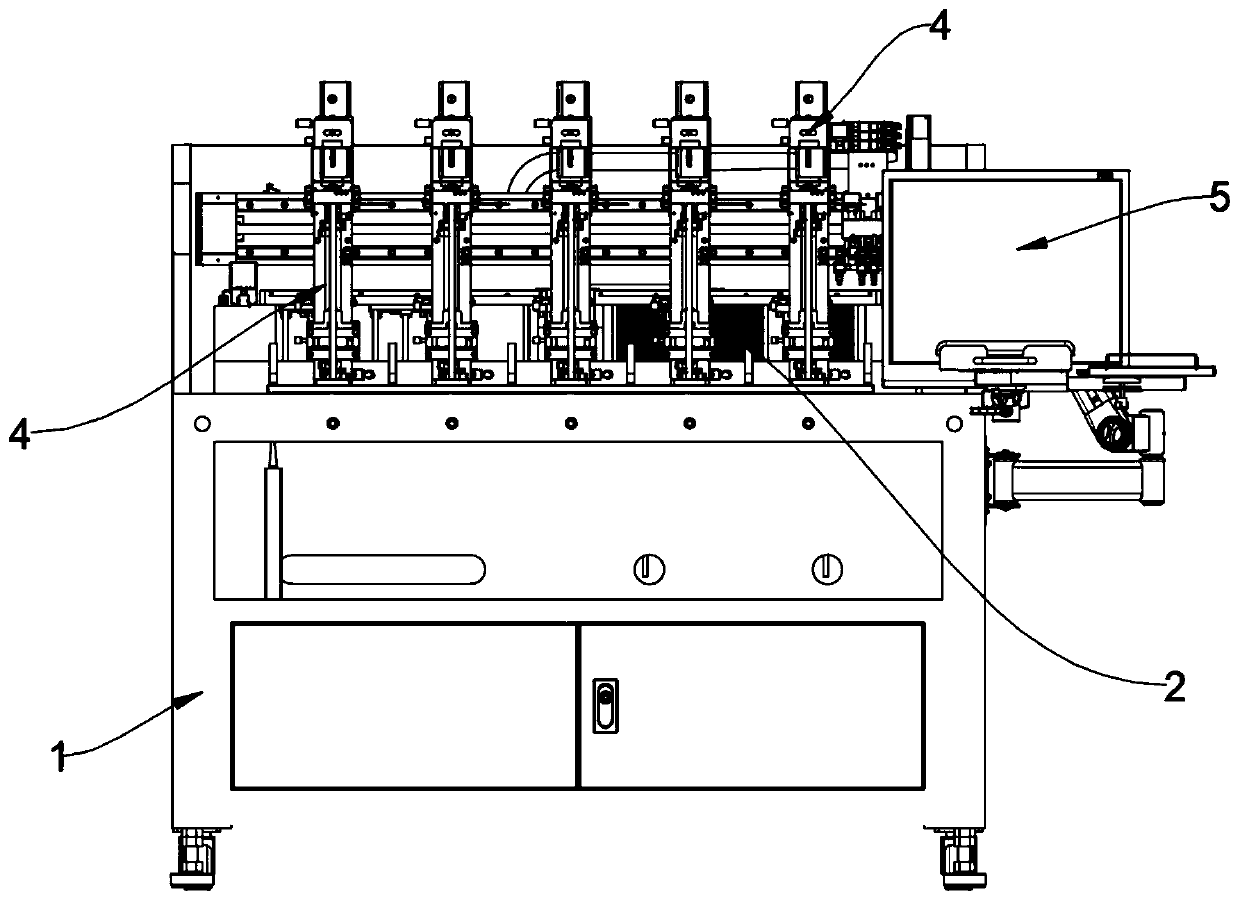
ActiveCN110695518AImprove productivity and efficiencyGuaranteed welding accuracyLaser beam welding apparatusPhysicsEngineering
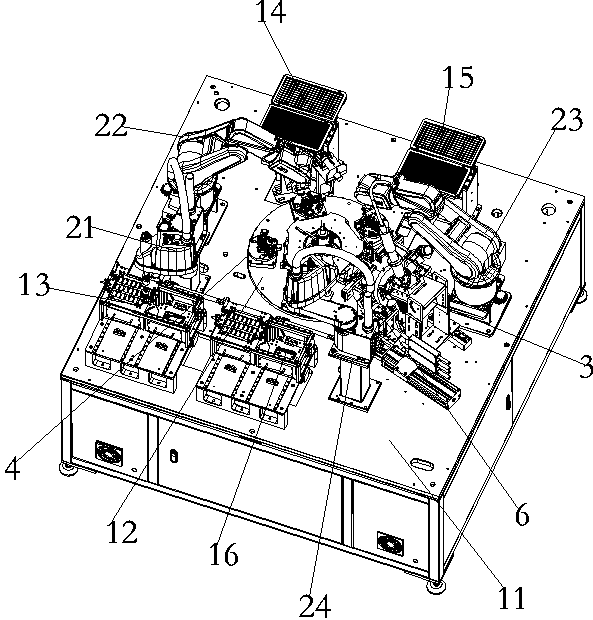
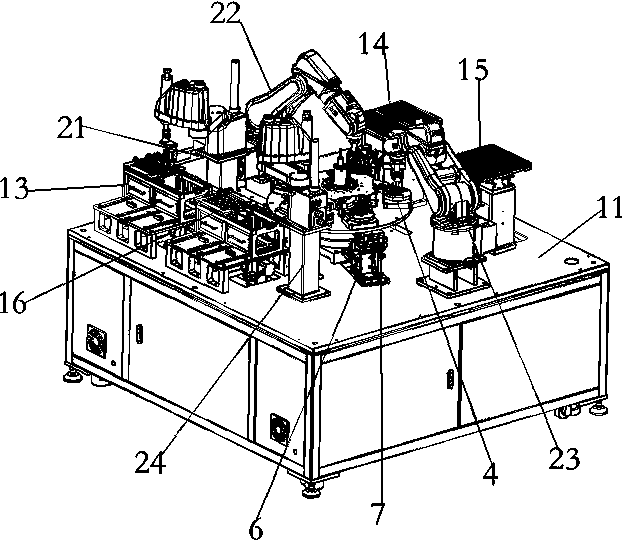
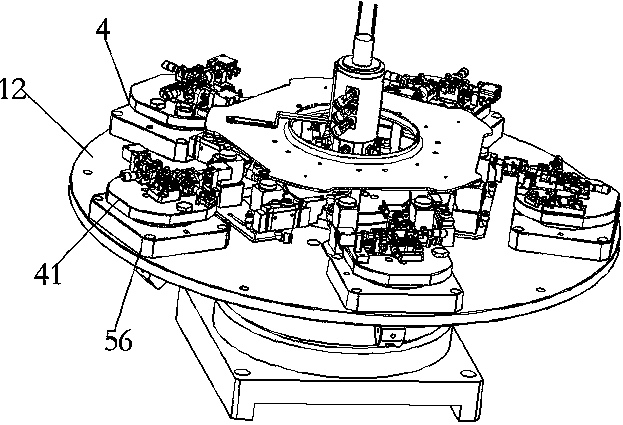
The invention relates to an efficient camera accessory assembling and welding device. The efficient camera accessory assembling and welding device comprises a placing assembly, a taking assembly, a welding assembly, an assembling assembly and a rotating assembly, wherein the placing assembly comprises a workbench, a rotating disc arranged above the workbench, a large part feeding disc, a first small part feeding disc, a second small part feeding disc and a discharging disc; the large part feeding disc, the first small part feeding disc, the second small part feeding disc and the discharging disc are sequentially arranged around the rotating disc; the taking assembly comprises a large part feeding mechanical arm, a first small part feeding mechanical arm, a second small part feeding mechanical arm and a discharging mechanical arm; the first small part feeding mechanical arm and the second small part feeding mechanical arm are connected with rotatable first cameras; the welding assemblycomprises a laser welding machine arranged between the second small part feeding mechanical arm and the discharging mechanical arm; the laser welding machine is connected with a rotatable second camera; the assembling assembly comprises a plurality of jig mechanisms distributed above the rotating disc in the circumferential direction; each jig mechanism is used for placing a large part and two small parts; the rotating assembly comprises a rotating mechanism; and the rotating mechanism is used for rotating the jig mechanisms.
Owner:苏州润弘安创自动化科技有限公司
System and method for constructing flexible ordering to improve productivity and efficiency in process flows
ActiveUS20100010791A1Increase productivityImprove efficiencyResourcesAnalogue processes for specific applicationsProduction rateOrder form
Owner:IBM CORP
Compressor exhaust temperature control device and its control method and applications
InactiveCN101338753AImprove productivity and efficiencyReduce startup timeMachines/enginesWorking capacityRefrigerant
The present invention relates to an exhaust temperature controller of a compressor and a control method and an application thereof. A compressing cavity is arranged in the compressor; a high-pressure gas circuit is arranged outside the compressor; one end of the high-pressure gas circuit is communicated with the high pressure side of the compressor or a system, and the other end is communicated with the compressing cavity. A gas valve and flow-regulating valves are arranged in the high-pressure gas circuit. The high-pressure gas circuit is communicated with a liquid refrigerant circuit connected between the condenser and the expansion valve of the system; control valves, which can realize the communication of only the high-pressure gas circuit, the communication of only the liquid refrigerant circuit or the simultaneous communications of the high-pressure gas circuit and the liquid refrigerant circuit, are arranged in the high-pressure gas circuit and / or the liquid refrigerant circuit. The controller injects the high-pressure gas in a housing into the compressing cavity of an air cylinder to rapidly increase the exhaust temperature and pressure of the compressor in order to improve the working capability and efficiency of a greenhouse. When the outside temperature is low, the startup time and defrosting operation time of the greenhouse can be greatly shortened in the process of startup, operation, defrosting, etc.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEIZHI COMPRESSOR
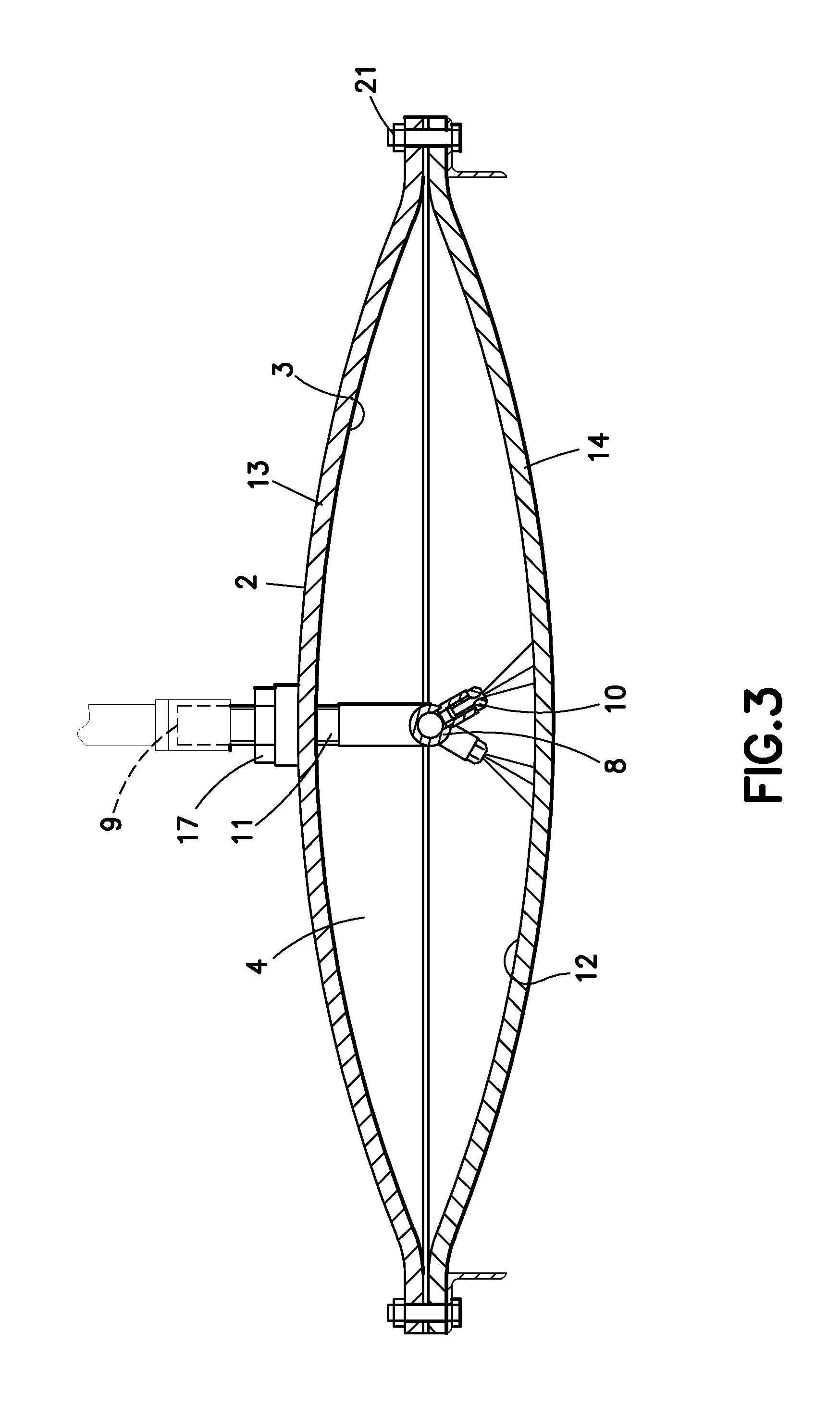
Solar radiation collection system and method
ActiveUS20110139888A1Improving efficiency and reliability and productivityImprove productivity and efficiencySolar heating energySolar heat devicesCollection systemRadiant energy
The invention relates to a radiant energy powered water heating methods and apparatus, particularly, to the open-loop solar radiation collection systems. At least one nozzle is directed against a reflection surface facing an evaporation surface to spray at least one jet with reflection to diffuse the fluid within the inner cavity in an atomized plume having the evaporation surface been moisturized by a part of the sprayed fluid and said moisturizing part of the sprayed fluid been sufficiently vaporized or evaporated (see FIG. 3).
Owner:VAPOSUN
Method and apparatus for implementing an end-to-end api design and development module integrating with firmwide tools and processes
PendingUS20220057999A1Improve productivity and efficiencyError detection/correctionComputer security arrangementsContinuous integrationLogisim
Various methods, apparatuses / systems, and media for implementing an API design and development module are disclosed. A receiver receives inputs for designing a specification. Codes are generated from the API specification and necessary business logic is added. A processor pushes the specification along with the code to a source control which automatically triggers a continuous integration / continuous deployment (CI / CD) pipeline in response to pushing of the specification along with the code to the source control. The CI / CD pipeline automatically executes, through pre-defined configuration, each phase of an API development life cycle to develop the API based on the designed specification.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
System and method for colorimetrically and geometrically parametrizing procedural textures on an object
ActiveUS20170249756A1Improve efficiency and productivityImprove productivity and efficiencyTexturing/coloringImage renderingProcedural textureMixture rule
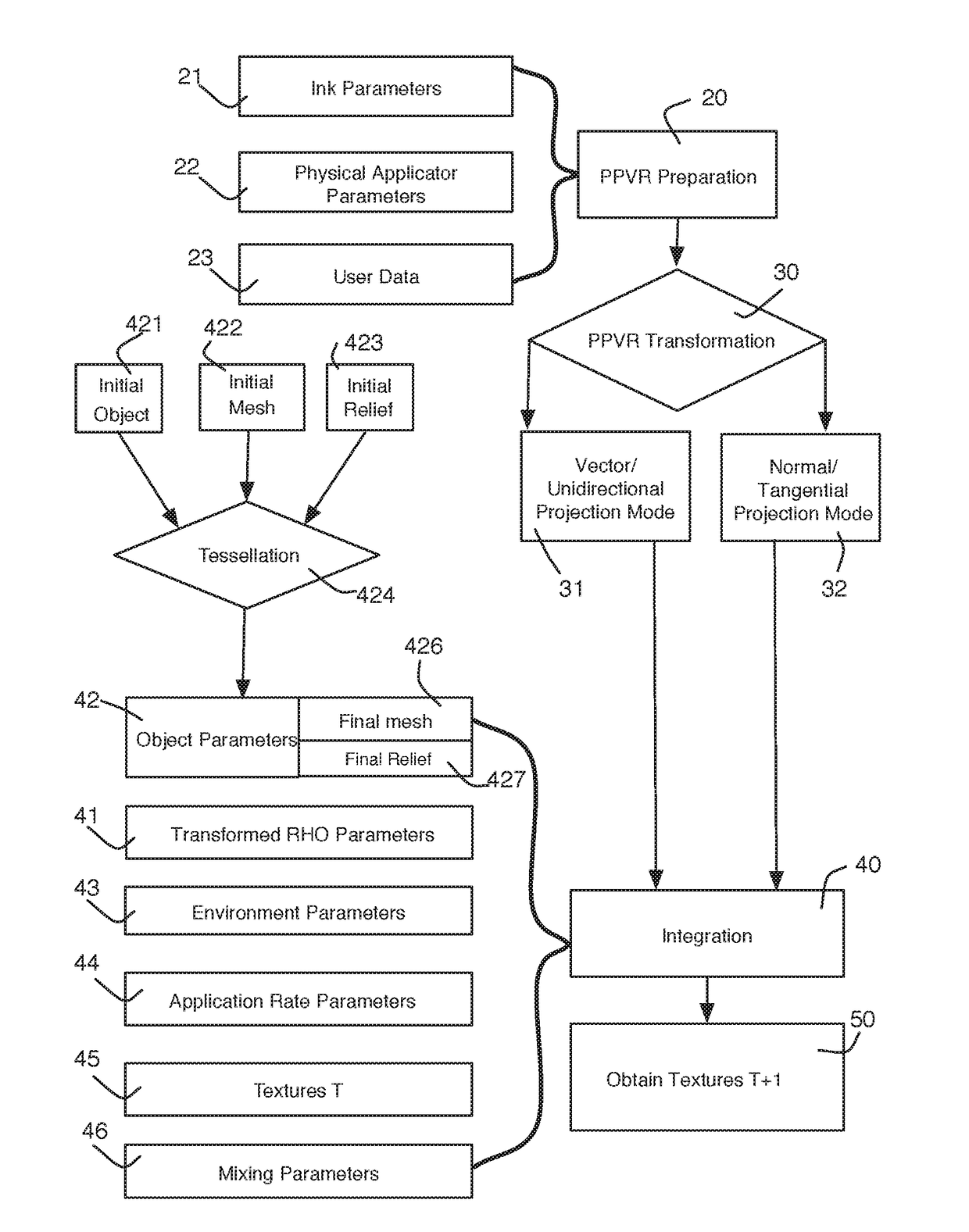
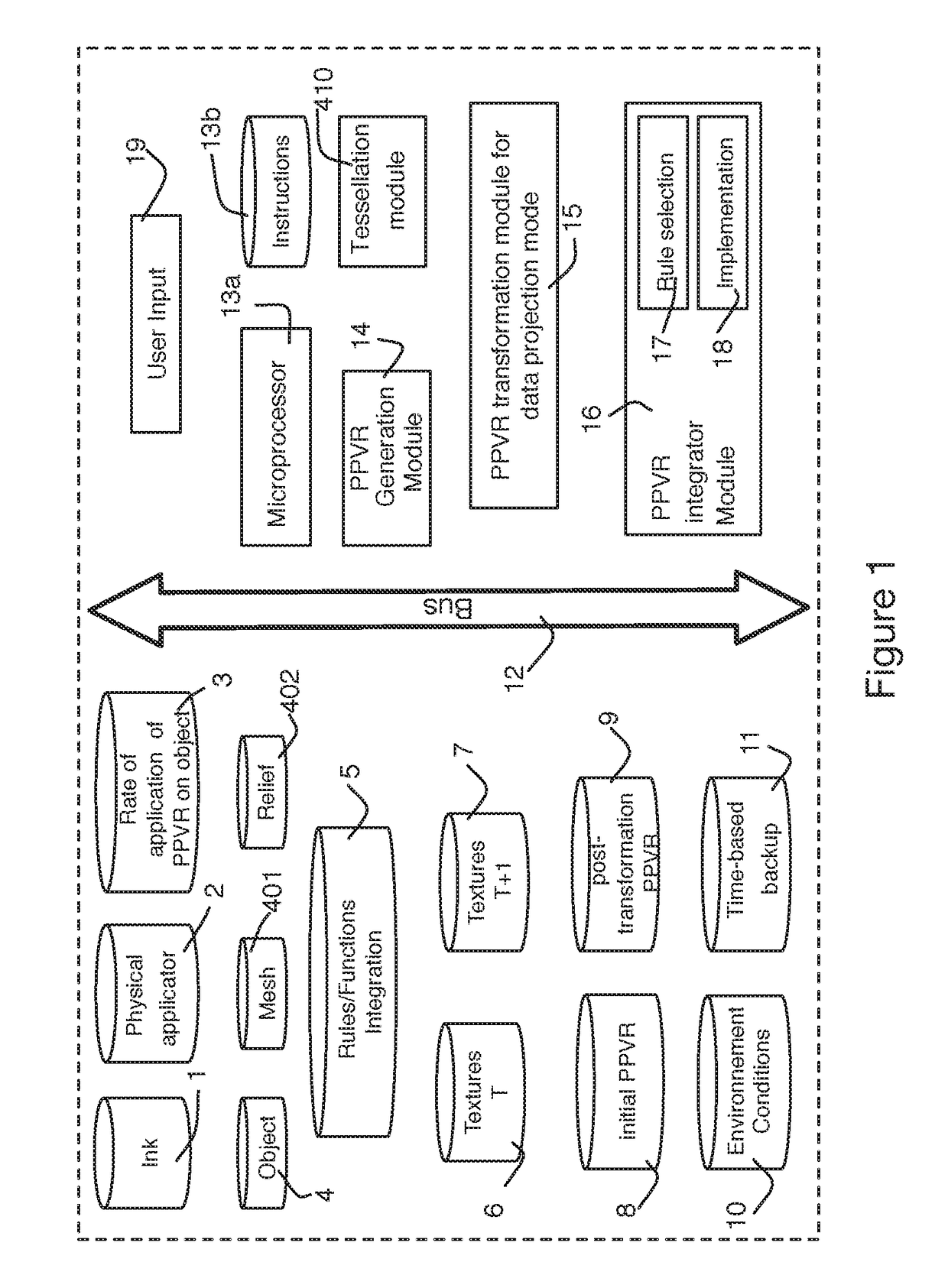
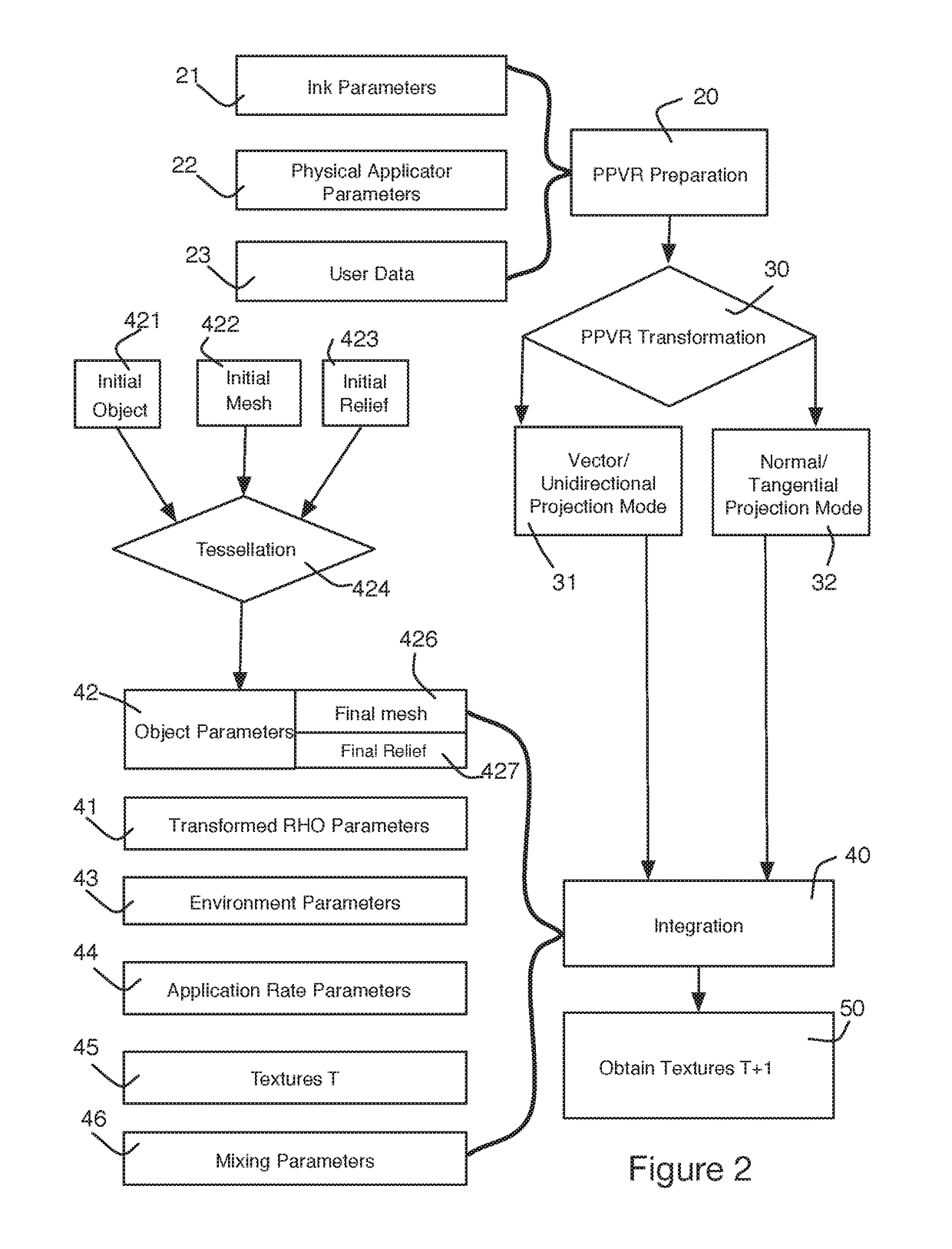
The invention relates to a system and method for generating procedural textures on an object on the basis of physical ink data and physical applicator data. The system includes: access to target object data having data for initial meshing and initial contouring of the target objects; access to data pertaining to mixture rules and mixture functions; access to physical data for initial textures T; a module for generating a pre-projection virtual rendering provided to combine the physical ink data with the physical applicator data; a module for tessellating the data of the target objects so as to convert the contours of the target objects into meshing; and an integrating module for the physical parameters, the integrating module being provided to generate a new set of textures T+I for the object(s).
Owner:ADOBE INC
Automatic wafer testing machine
PendingCN110239947AImplement automated testingImprove productivity and efficiencyConveyor partsTest fixtureTraining set
The invention discloses an automatic wafer testing machine, and belongs to the technical field of wafer testing. The automatic wafer testing machine comprises tray devices, a testing device and a transferring device, wherein the multiple tray devices are arranged, the multiple tray devices comprise to-be-tested tray devices and sorting tray devices, the to-be-tested tray devices are configured to carry trays with to-be-tested wafers to be placed thereon, the sorting tray devices are configured to carry trays with tested wafers placed thereon, the transferring device can be used for transferring the to-be-tested wafers on the to-be-tested tray devices to the testing device to complete testing, and the transferring device can also be used for transferring the tested wafers from the testing device to the sorting tray devices. According to the automatic testing machine, the automatic testing of the wafers is realized, the efficiency and the productivity of wafer testing are improved, and the labor intensity of working personnel production is reduced.
Owner:范群意
Production technology of composite material product
The invention relates to a production technology of materials, in particular to a production technology of a composite material product. The production technology of the composite material product comprises the following steps that firstly, raw materials are made into rubber materials; secondly, the rubber materials are made into laminated materials; thirdly, the laminated materials are shaped through a mould, and are put into an outer sleeve, the outer sleeve is sleeved with a protection bag, and negative pressure is formed; fourthly, the product is put into a hot-pressing tank to be vulcanized, the pressure in the hot-pressing tank rises to 0.3 Mpa to 3.0 Mpa, the temperature of the hot-pressing tank rises to 60 DEG C to 300 DEG C, and after thermal forming is carried out for 15 minutes to 80 minutes, circulating cooling is carried out, and the product is taken out. According to the technology for producing the composite material product through the hot-pressing tank, the productivity and the efficiency are high, the yield is also high, and the size consistency of the product is good.
Owner:DONGGUAN FOUR DIMENSIONAL COMPOSITE PROD
Process of making a modifier for cement systems
InactiveUS20020169221A1Improve plasticizing effectReduce water consumptionPolishing compositionsSuperplasticizerEthylene Homopolymers
The disclosed process to obtain a modifier for cement systems comprises a synthesis of the modifier by a process of polymerization in a soft alkaline catalysis. This contributes to the formation of a product with a low molecular mass and viscosity. The concentration of the homogeneous aqueous solution is from 40-58% and the specific production of the process is Q=0.25 to 3.00 kg per hour in comparison with the specific production of the known prototype which is Q=0.03 to 0.04 kg per hour. One of the most important characteristics of the new process used to obtain the disclosed modifier is the fact that synthesis is achieved without external heat sources. Also, synthesis is achieved either by a periodic process or a continuous process. Another important characteristic of this process is the possibility to optimally combine a synergist in the form of a copolymer of formaldehyde with polycondensed desulfitade and the product of the aldonic condensation of the homopolymer in the presence of an alkaline starter. As a result, the required distribution of the molecular mass (DMM) is obtained and the temperature of the reactive mass is regulated during the final phase of the synthesis. The reactive mass temperature in the final phase is from 50-70° C.; the pH of the final product is auto-regulated without using special neutralizers, showing a value of 7.1-8.8 at a temperature of 20 + / - 2° C., and the average of the molecular mass will not exceed 340 Dalton. The unique properties of the final product insures the efficiency of the cement system modifiers with relatively low molecular mass. Synthesis occurs in a short period of time due to the combination of the high reactive capacity of the monomer, the high velocity of the elemental reactions and the growth of the polymeric chain. The absence of secondary products during the polymerization process results in a specific production of Q=0.25-3.0 kg per hour, which is one or two orders higher when compared with known technologies. In spite of the relatively low molecular mass, the disclosed modifier is distinguished by a high plasticizing effect and a reduction in water consumption in cement systems. The modifier is recommended for use in the clinker mill in order to substantially increase all the technical properties of cement and / or to increase the production of the mill of up to 45%, retaining the normal properties of the cement. The modifier can also be utilized for the production of relatively dry and self-leveling mortar and concrete mixes. In addition, the modifier can be used as a superplasticizer in cement systems. In addition, the modifier is a compactor of the microstructure, simultaneously increasing the strength of cement systems at all hardening ages and maintaining the value of the W / C ratio. If self-leveling mixes are used, the increase in strength of the components utilizing cement modified with the disclosed modifier can be increased up to 80%. From the above-mentioned properties, the conclusion is evident that the disclosed modifier represents a new technical solution related to the technology of its production and related to improved properties in cement systems.
Owner:WATERLIGHT CEMENT
System and method for generating procedural textures with the aid of particles
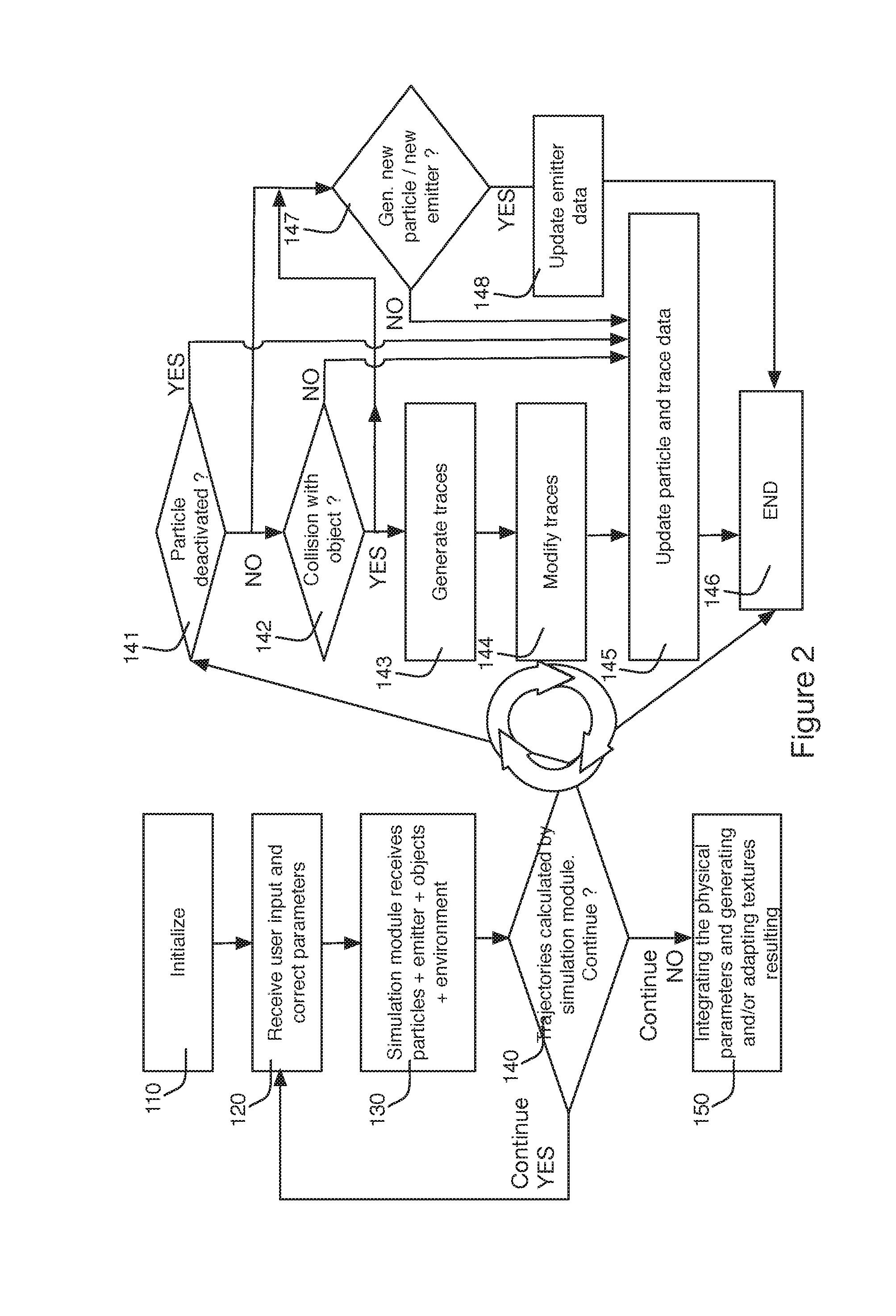
ActiveUS20160247297A1Improve productivity and efficiencyImprove realismImage analysisTexturing/coloringGraphicsObject based
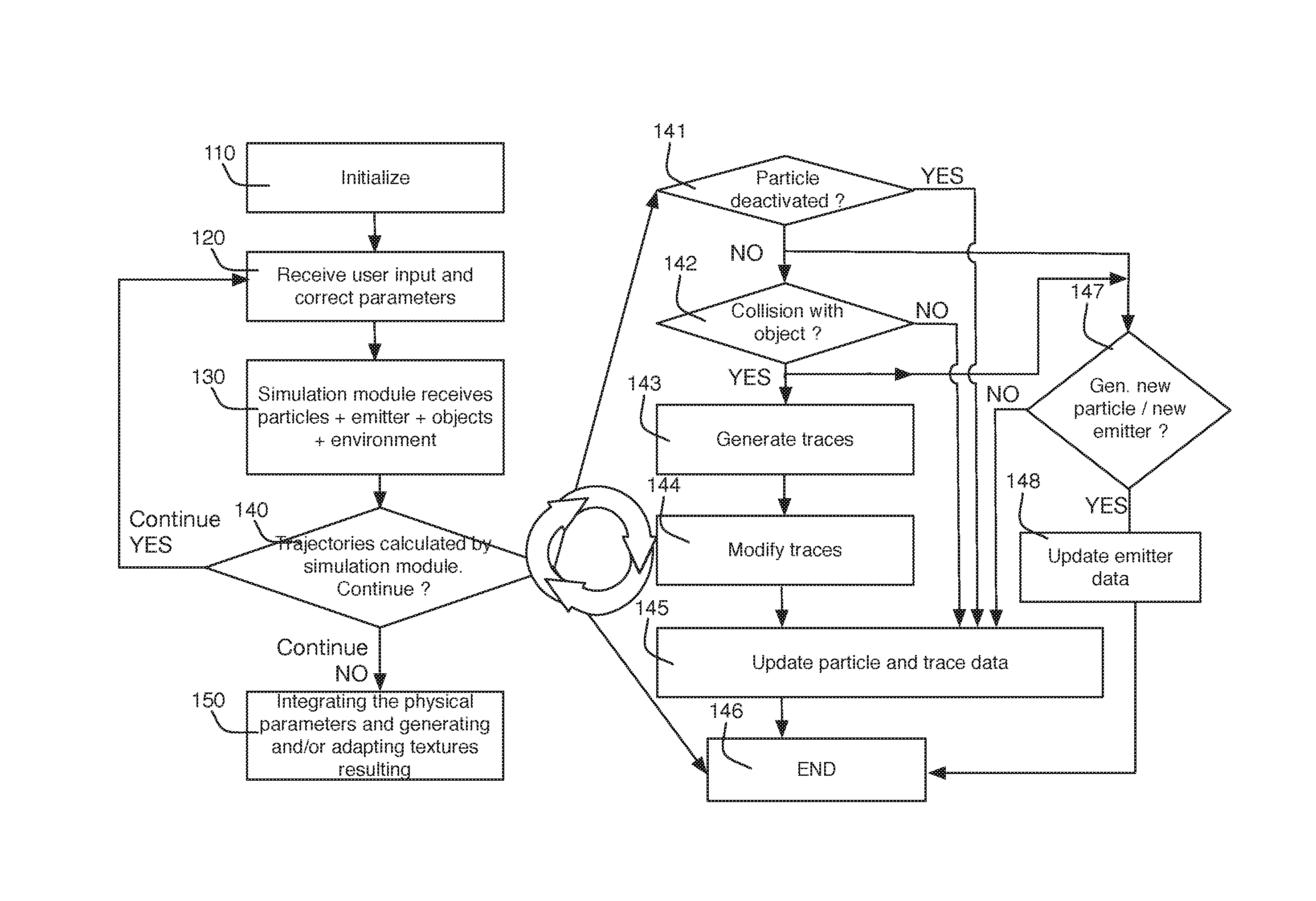
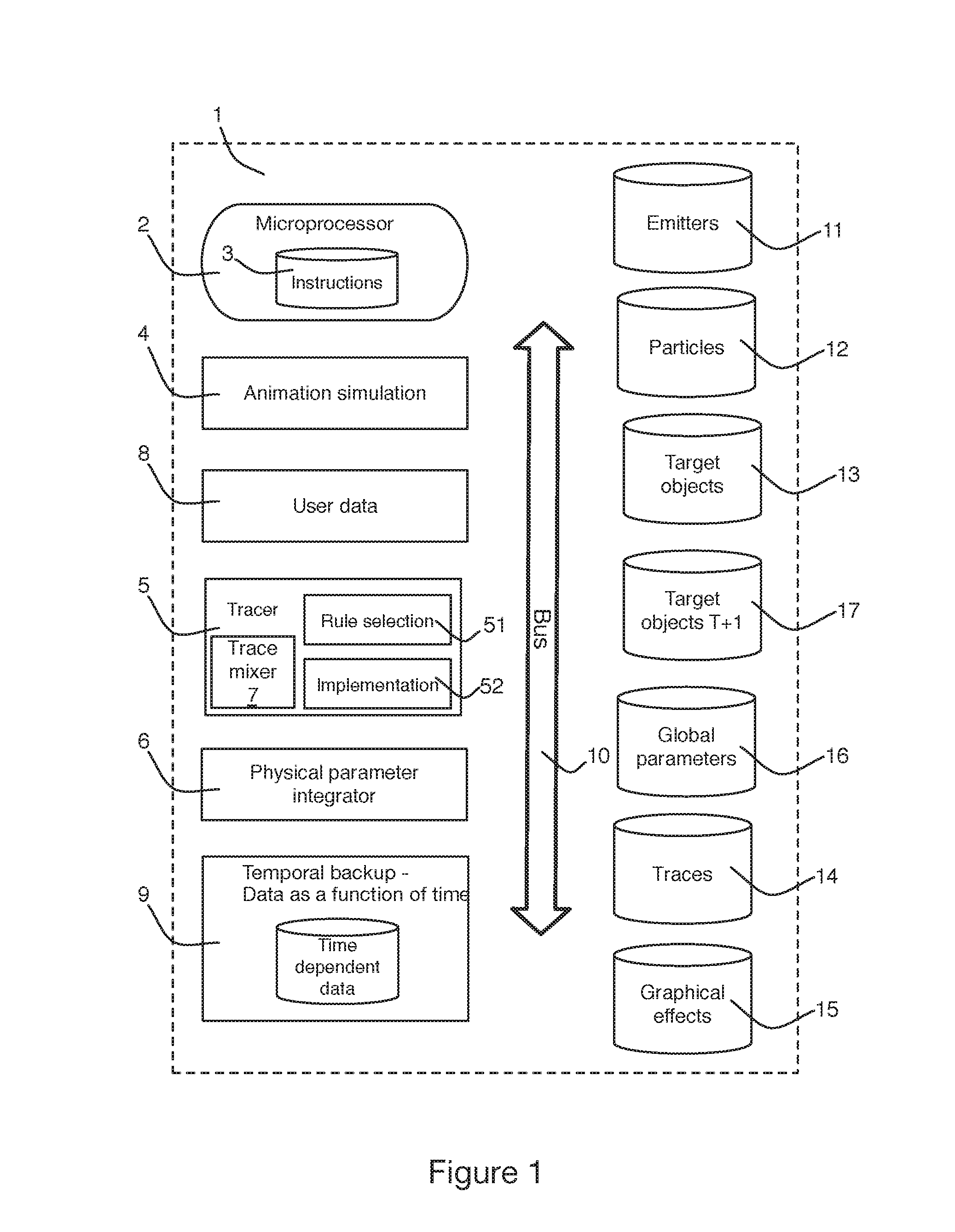
System for generating textures on an object based on the particles emitted by a particle engine, including an access to data of a particles emitter, of particles emitted, of target object, of traces, and of graphical effects; an animation simulation module provided so as to perform a simulation of emission and of displacement for each of the particles provided; a tracer module provided for generating a trace on the surface of a target object corresponding to the displacement of a particle along said surface after an impact of the particle against the target object with the aid of the traces data and of the target object data; a physical parameters integrator module provided for generating a new set of textures for said object taking into account the data of the object, the data of each now or modified trace, and the data of the corresponding graphical effects. Corresponding method for generating textures.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Metal substrate and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20160316568A1Improve structural strengthIncrease productionPrinted circuit secondary treatmentAdhesivesSurface roughnessOptoelectronics
A metal substrate includes a first insulating substrate, a second insulating substrate, a first metal layer, a second metal layer and a release layer. The first insulating substrate has a first modified surface and a second surface opposite to the first modified surface. The first metal layer faces the second surface. The release layer is bonded on the first modified surface. The second insulating substrate is bonded on a side of the release layer, such that the release layer is between the first modified surface and the second insulating substrate. The second metal layer is disposed on a side of the second insulating substrate, such that the second insulating substrate is between the release layer and the second metal layer. An original surface roughness of the first modified surface has a variation substantially less than 10% after the first modified surface is released from the release layer.
Owner:AZOTEK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com