Patents
Literature
30 results about "Laser procedure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
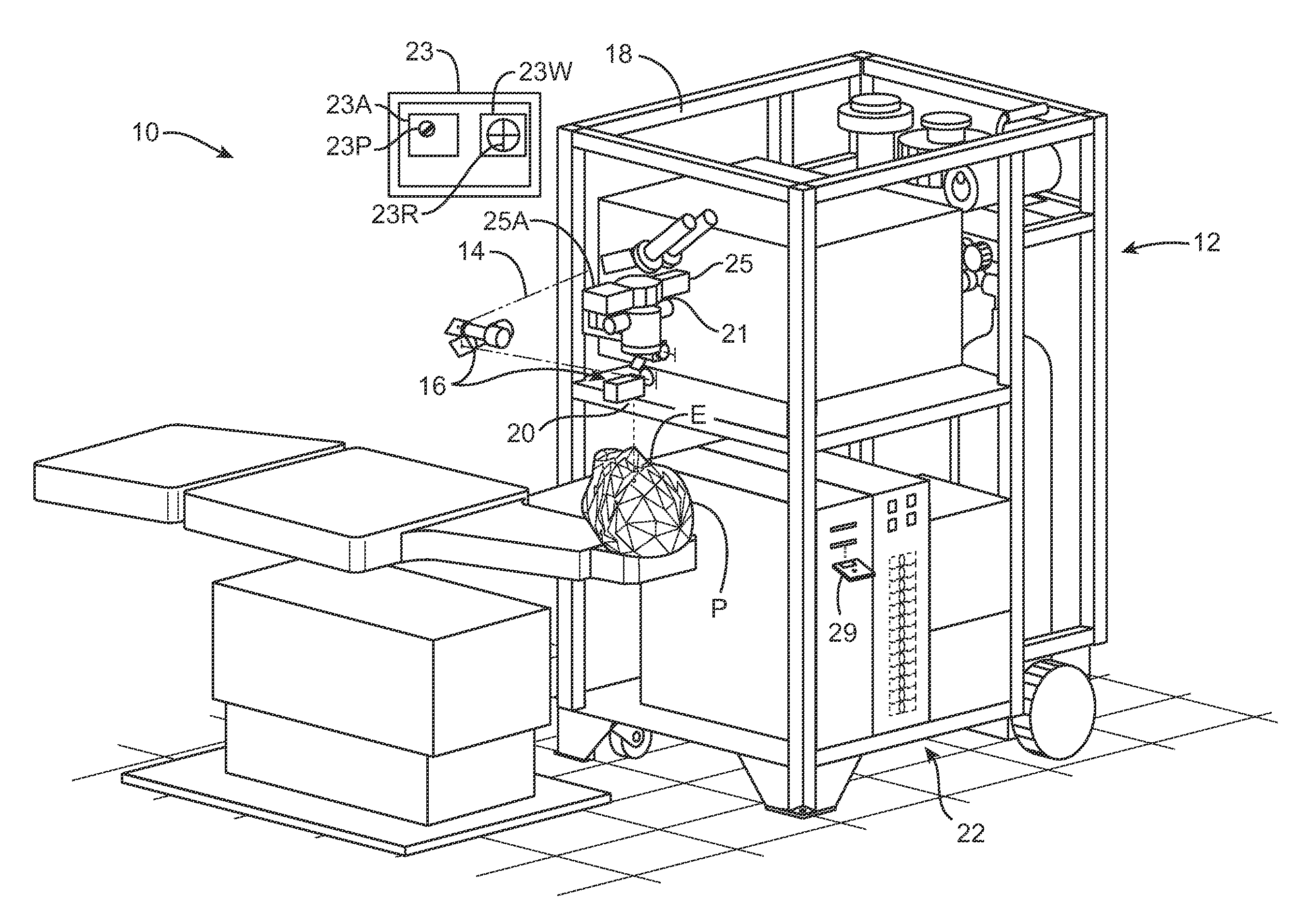
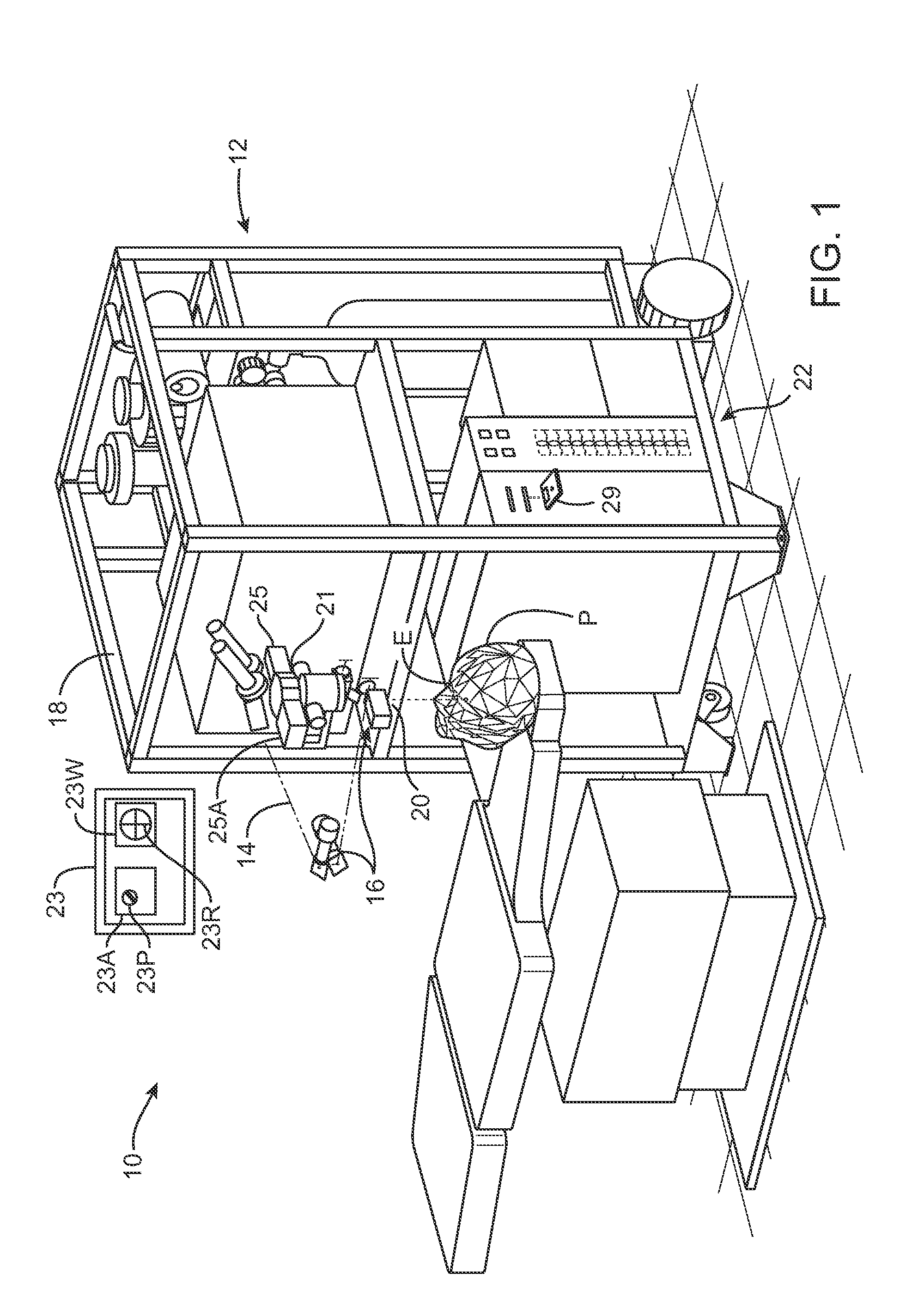
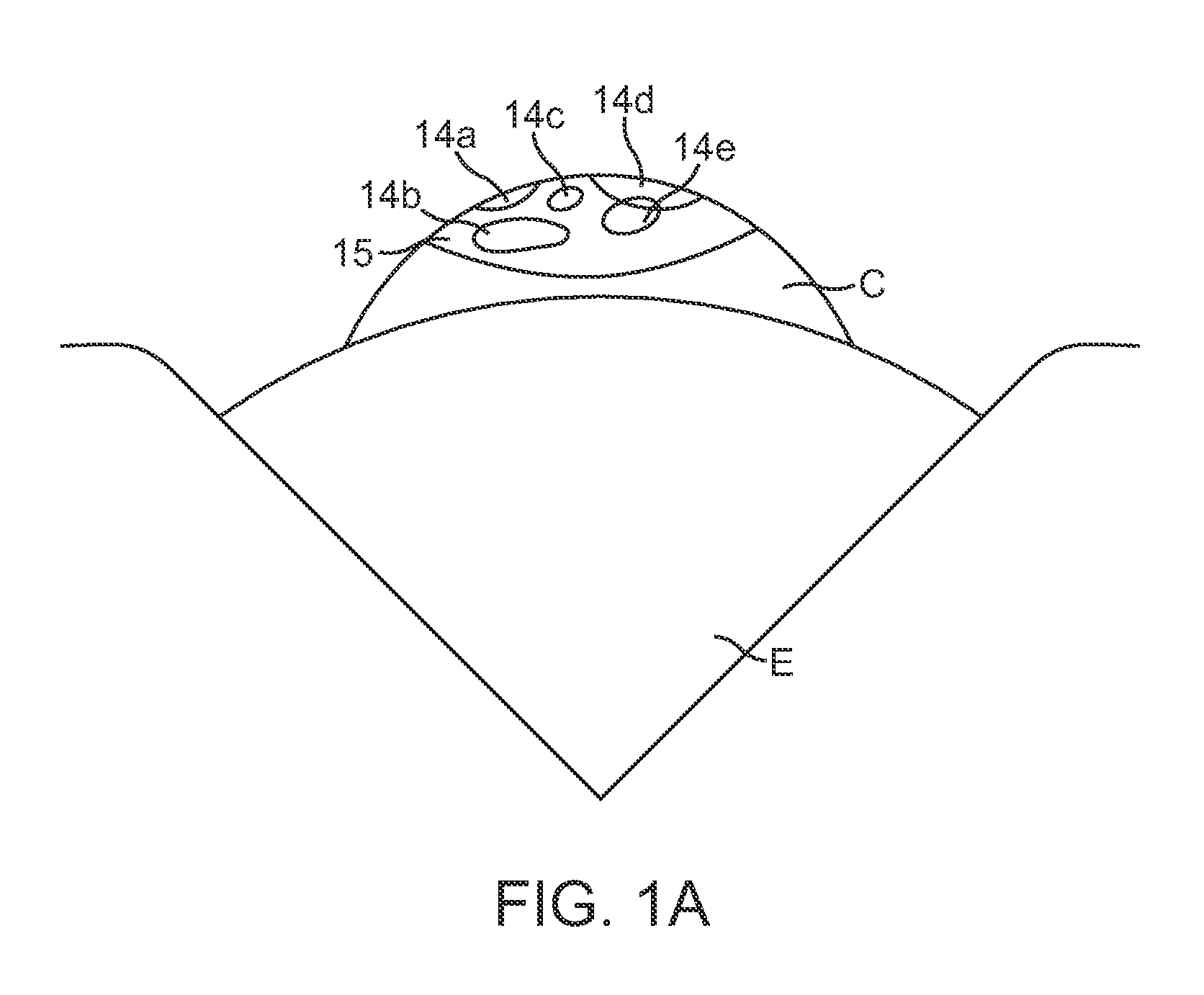
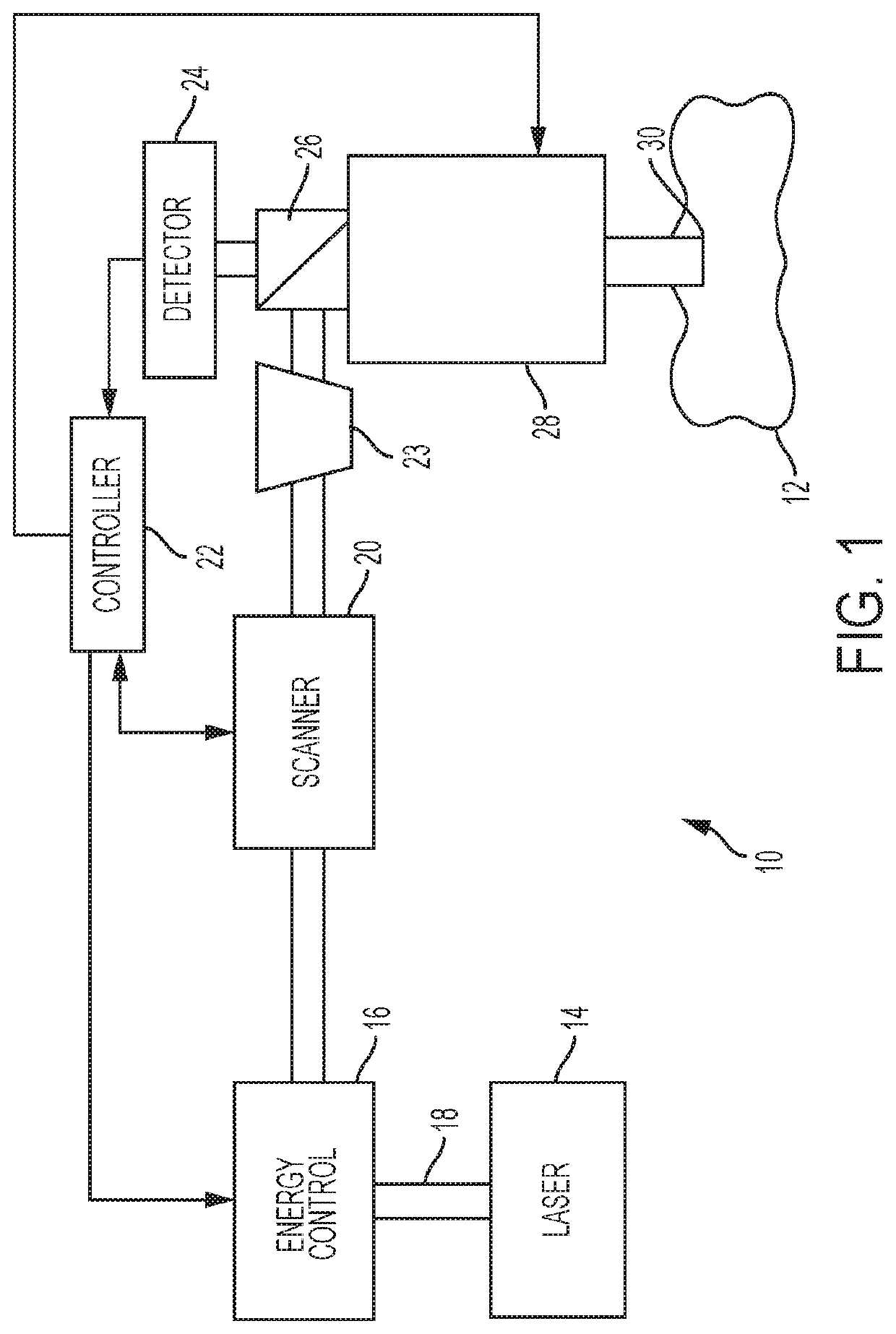
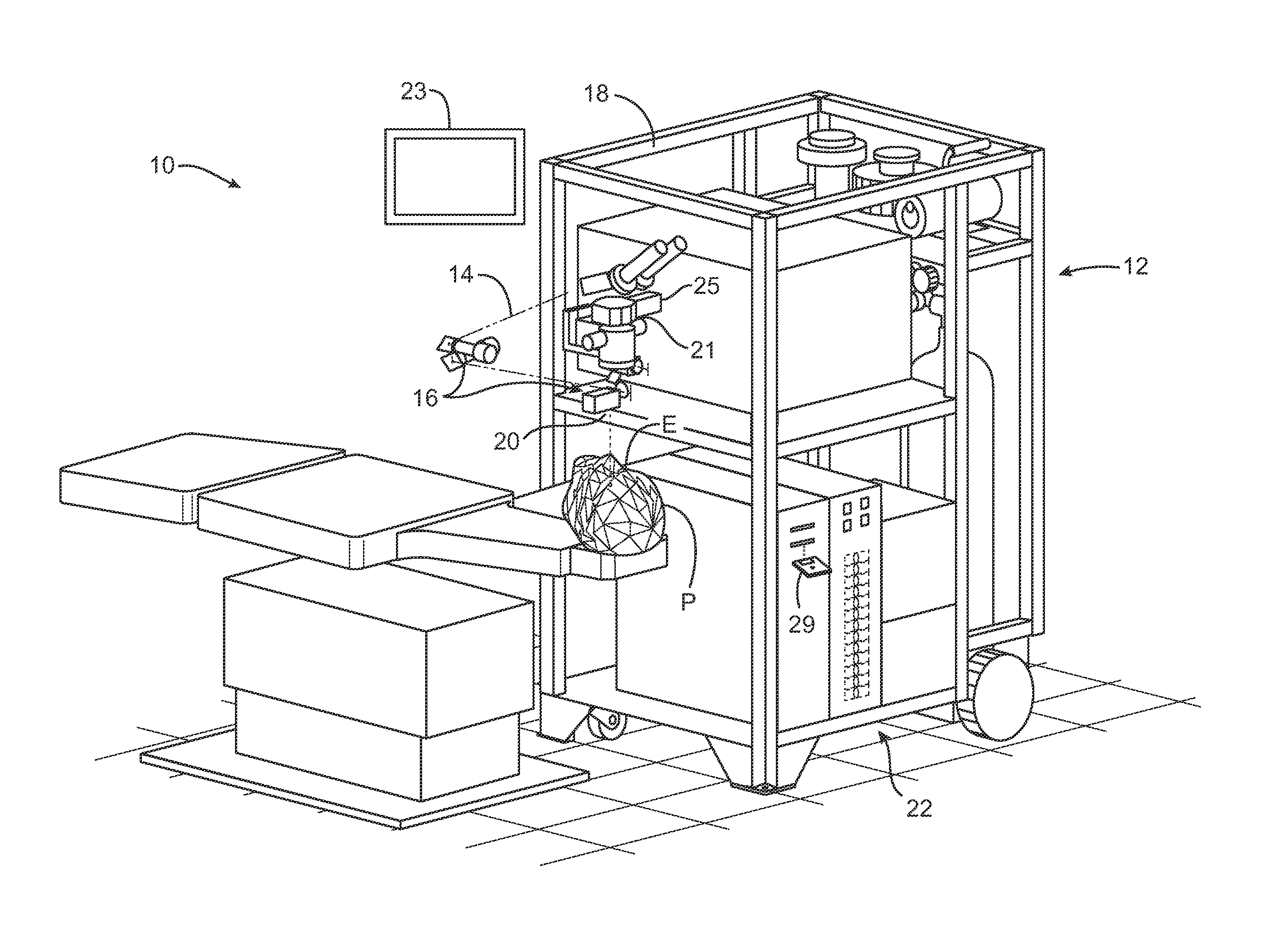
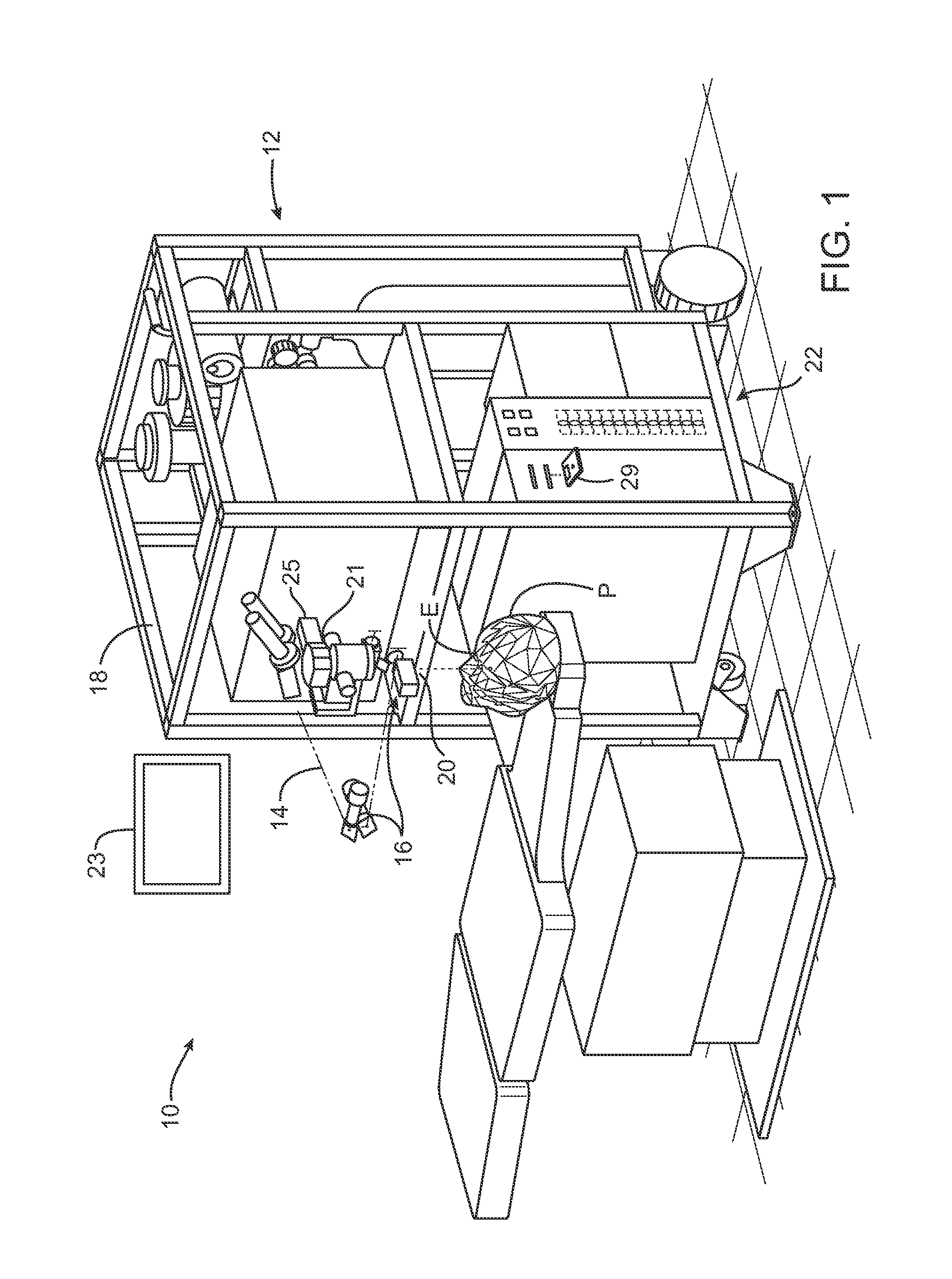
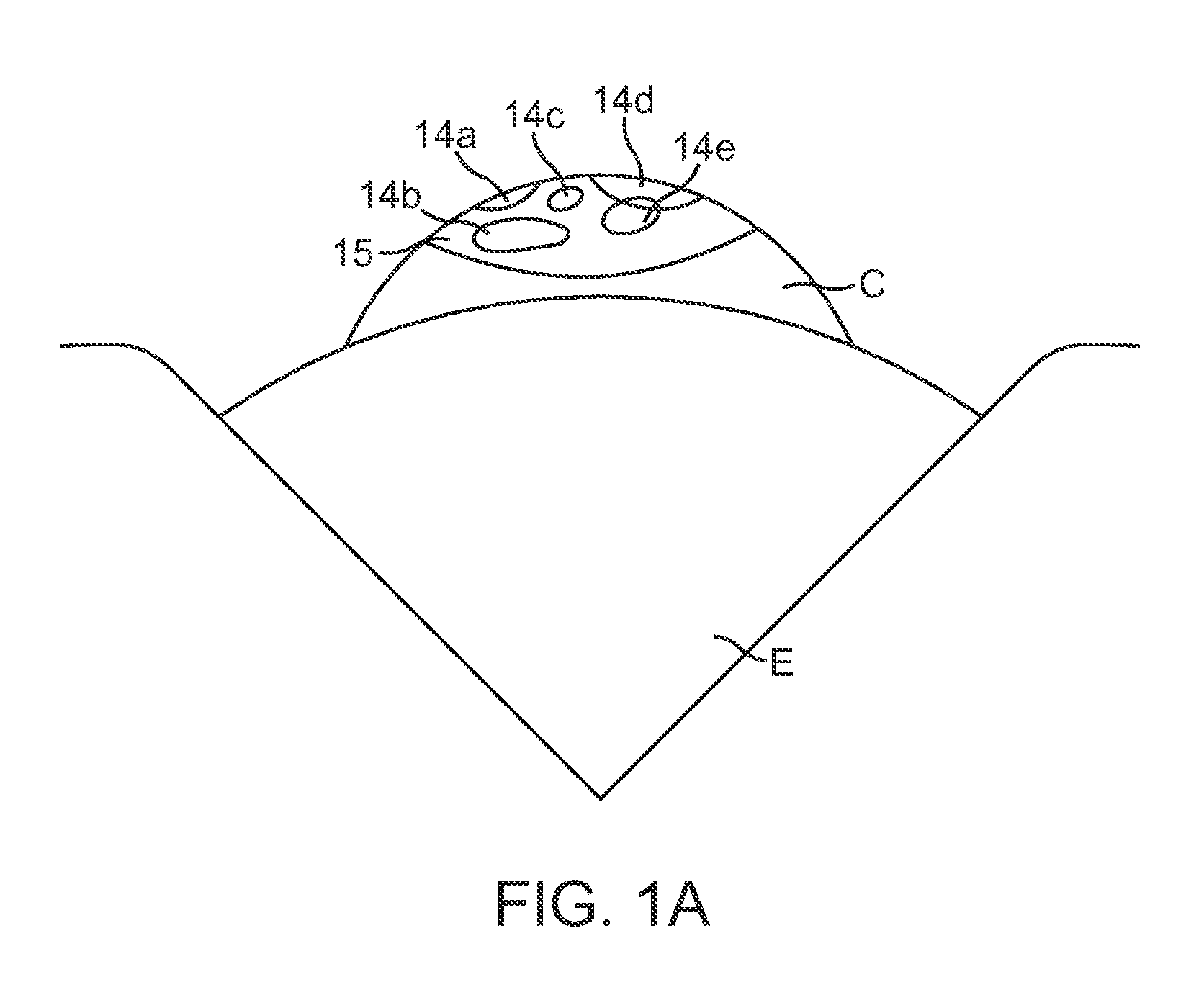
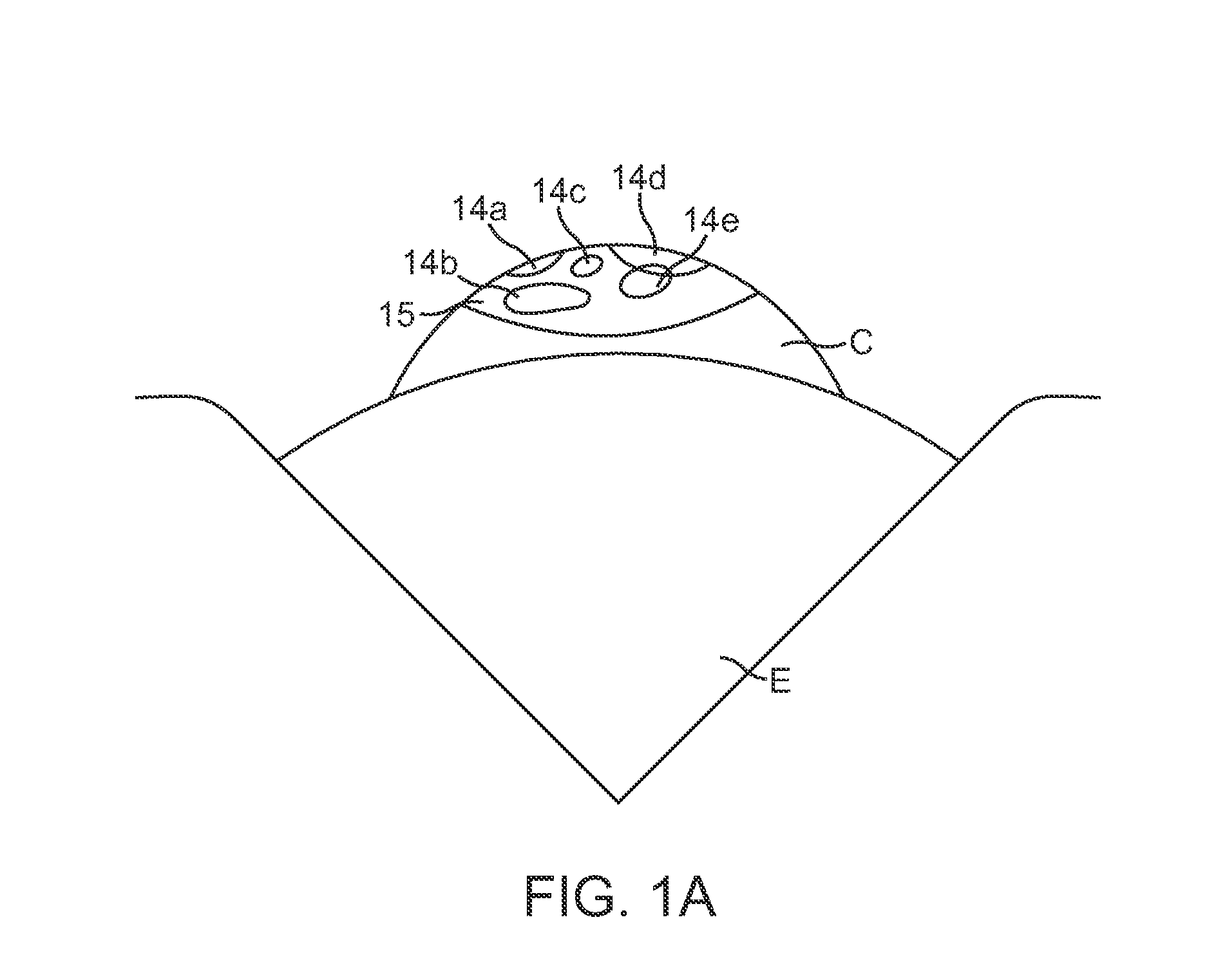
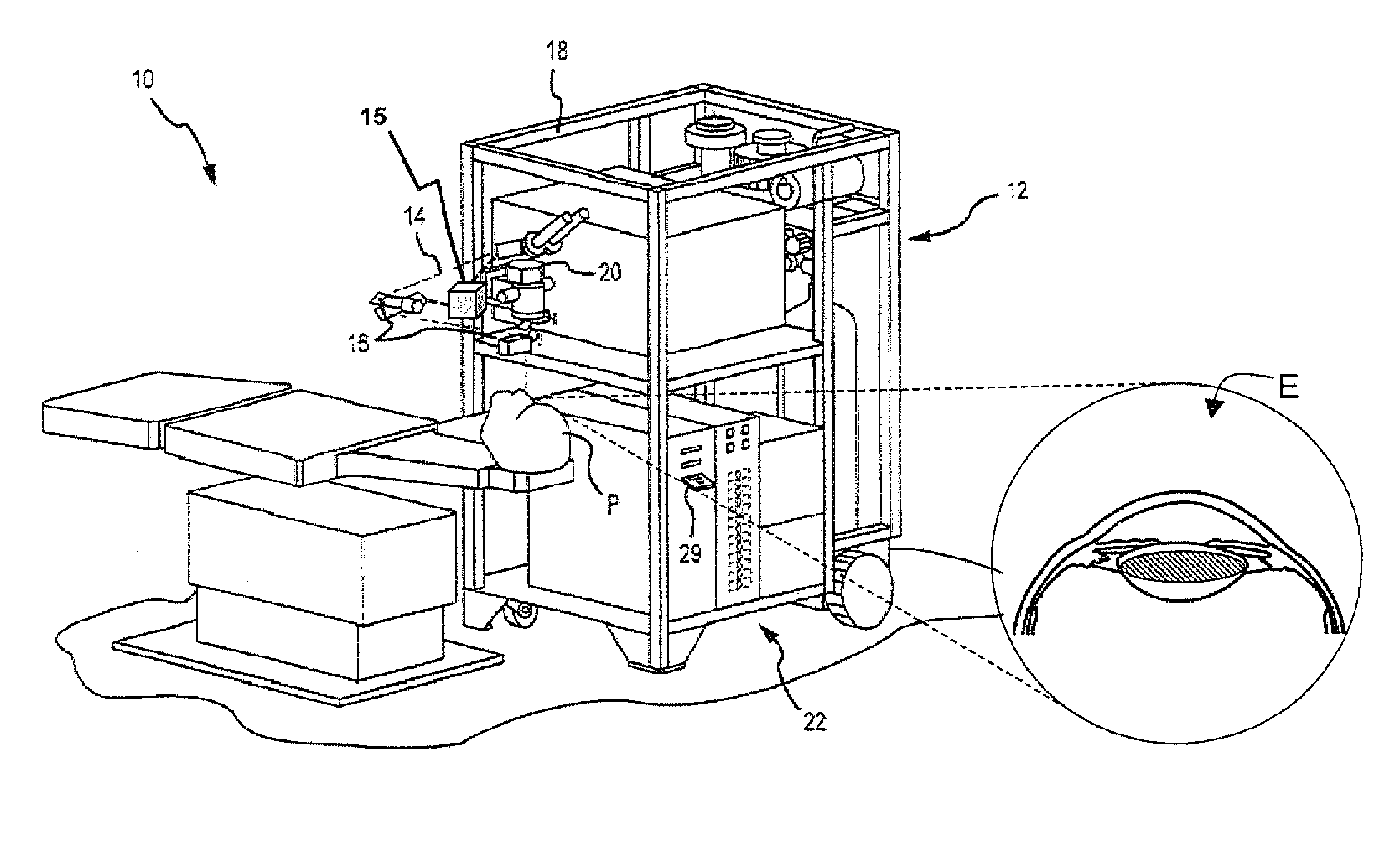
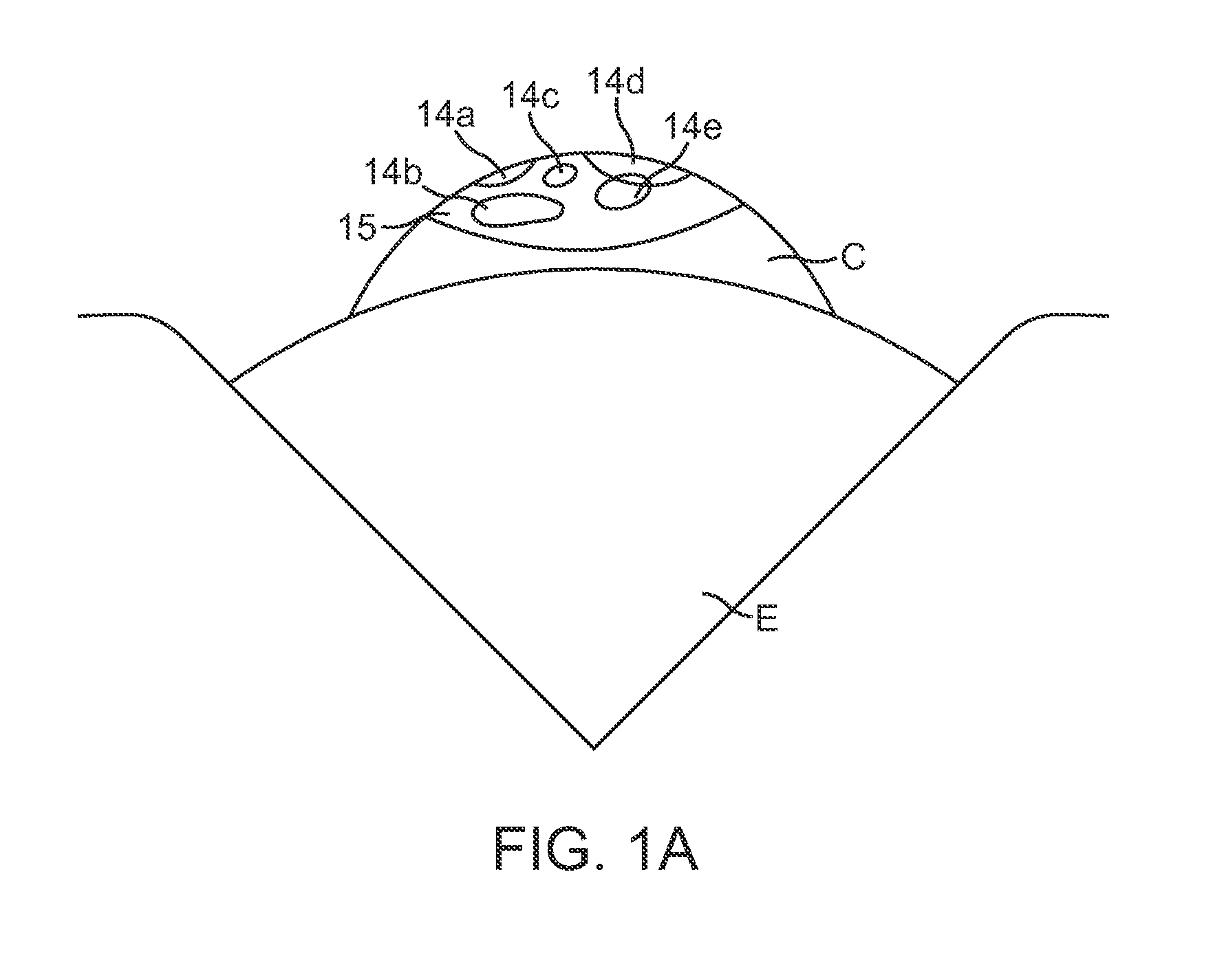
The Lase™ procedure is performed using a small needle and a catheter with a laser probe. Using low dose x-ray, the catheter is placed inside the broken disc. Once the probe is inserted, the laser vaporizes the broken parts of the disc.
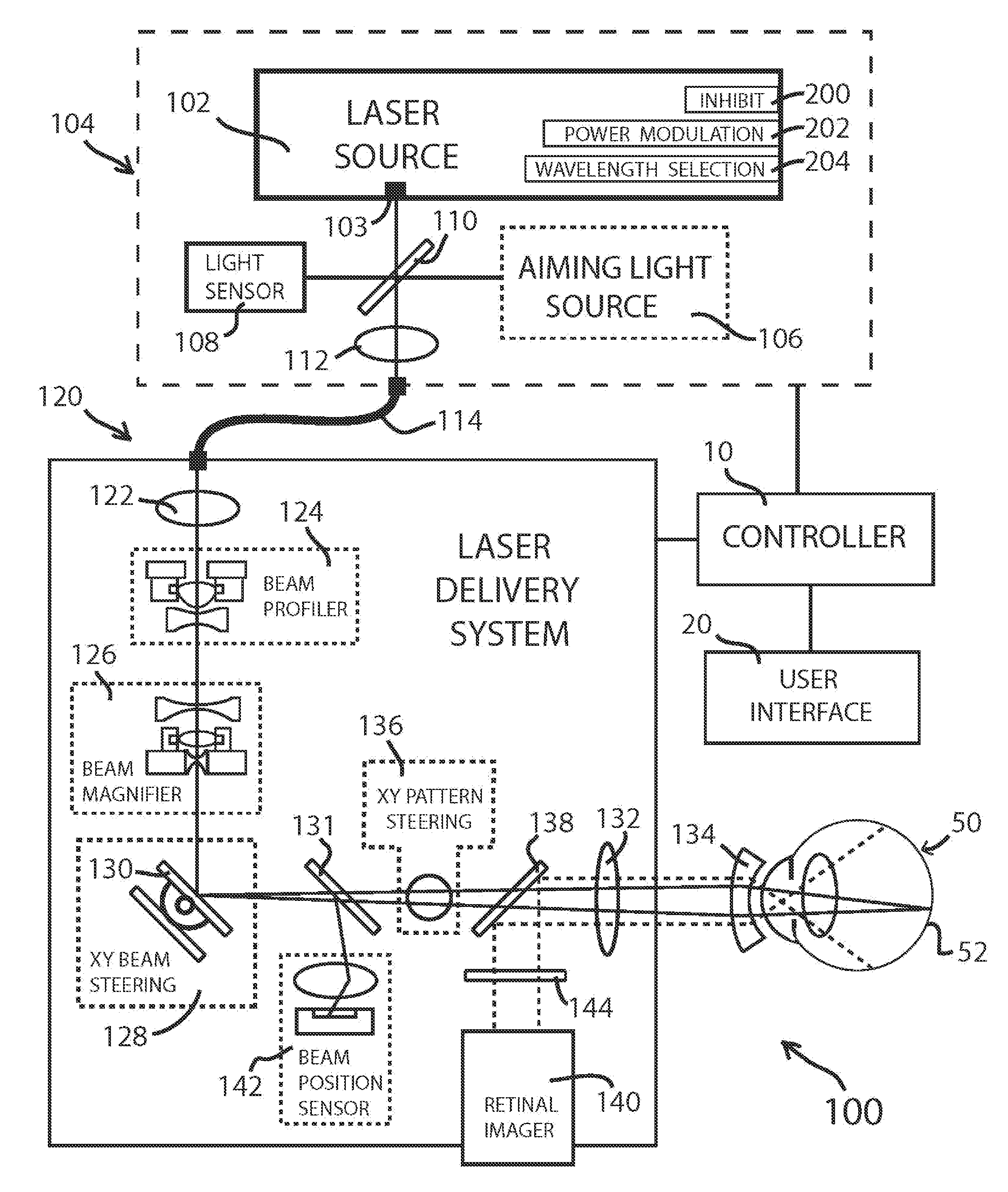
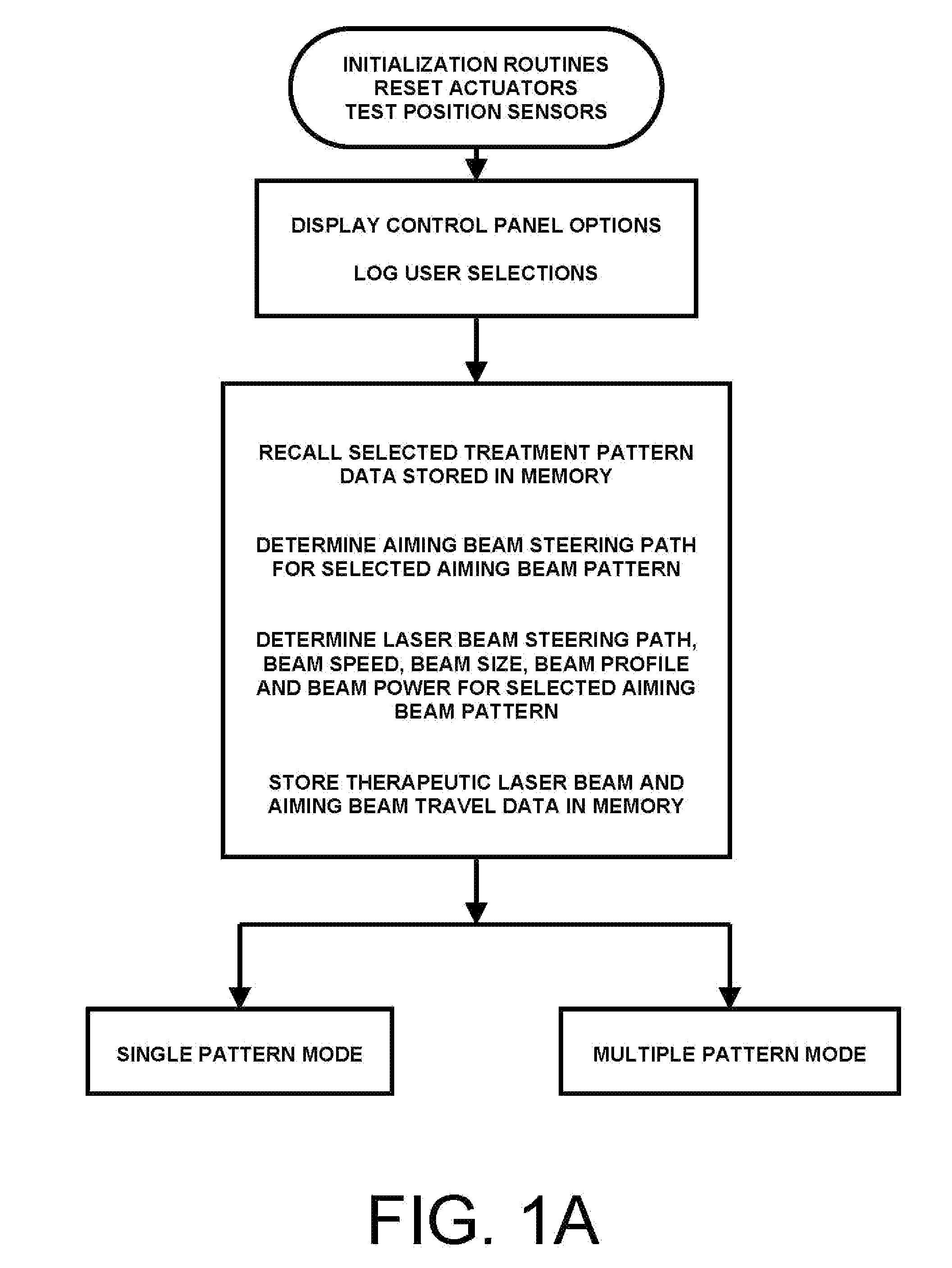
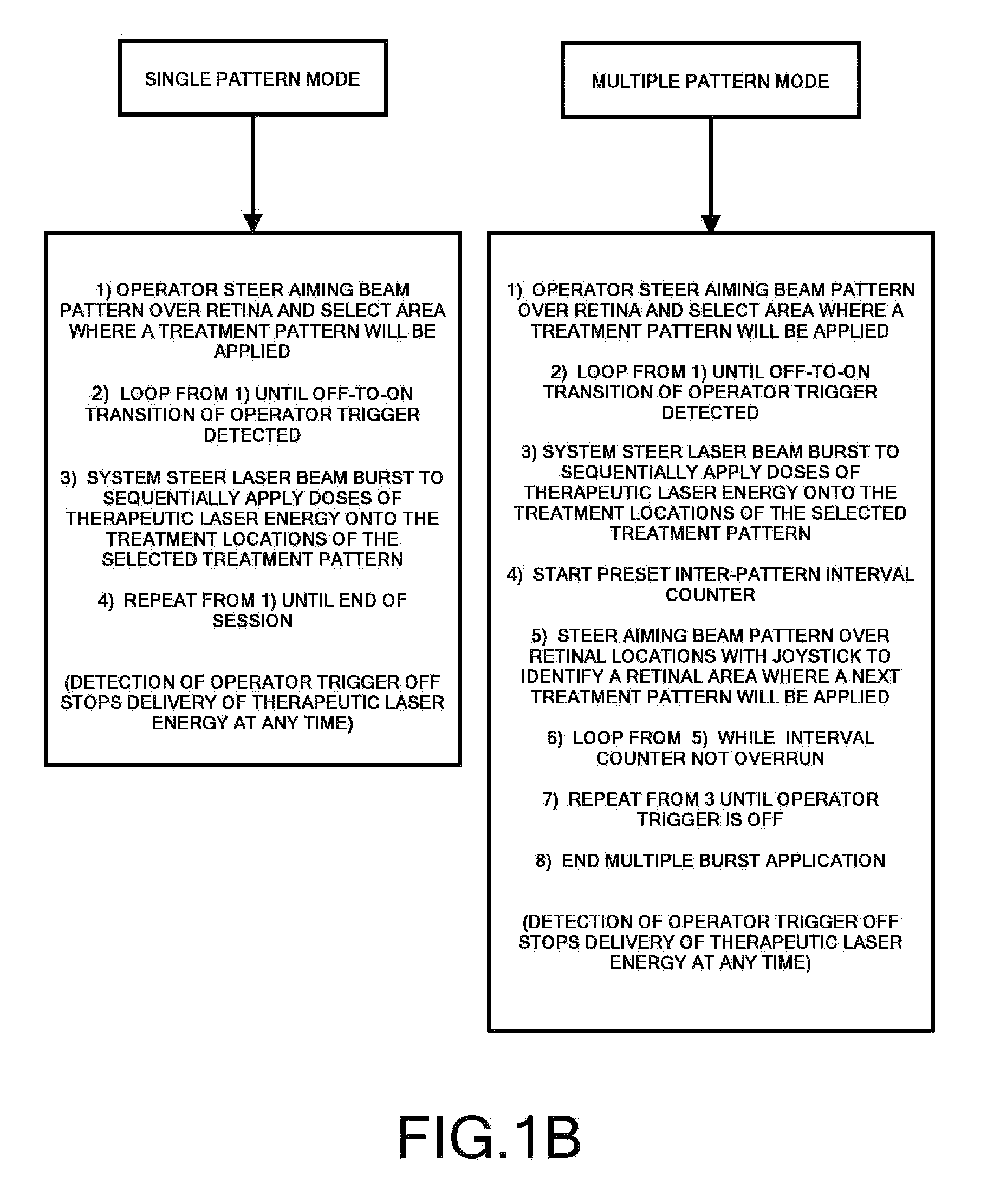
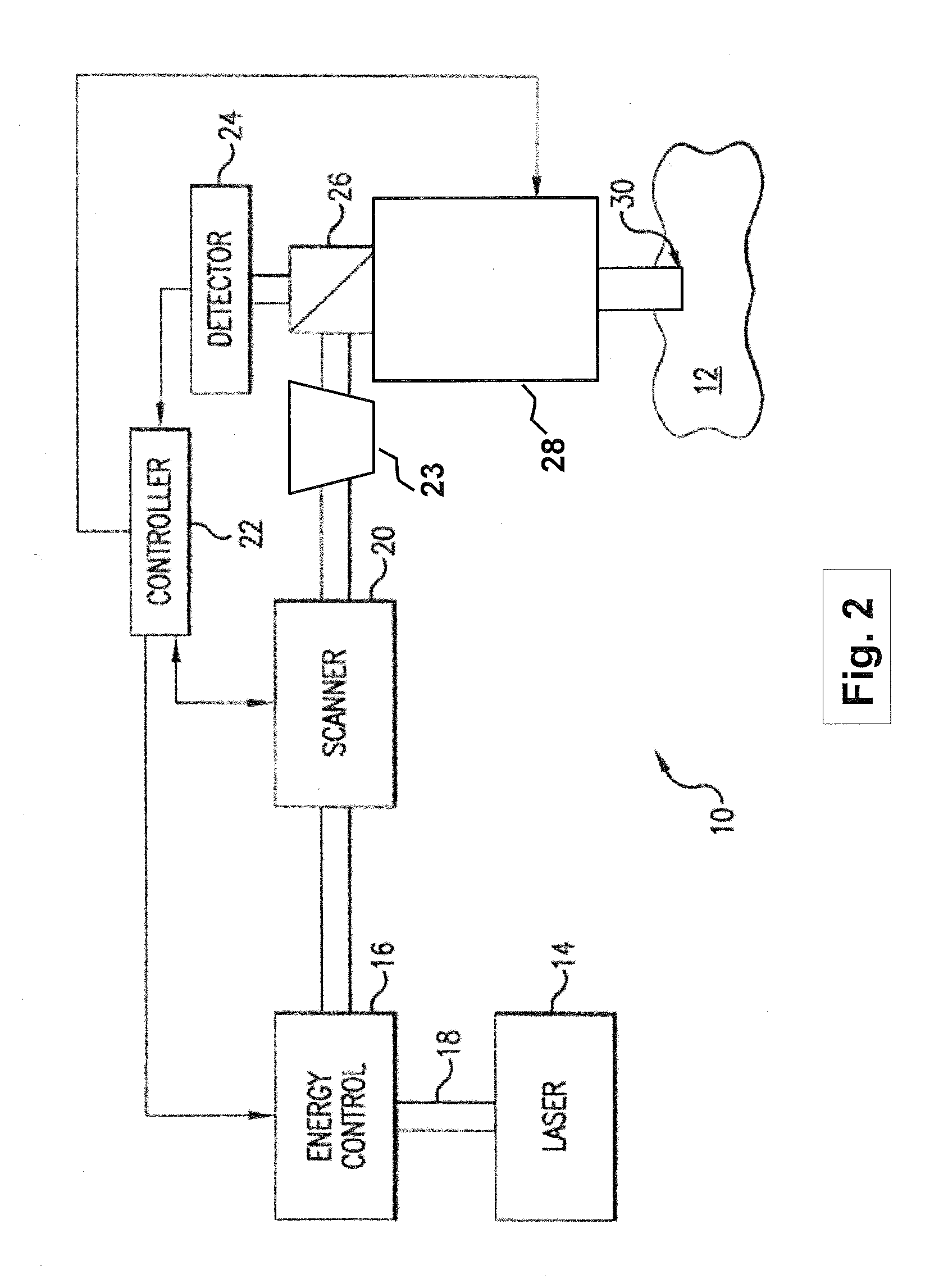
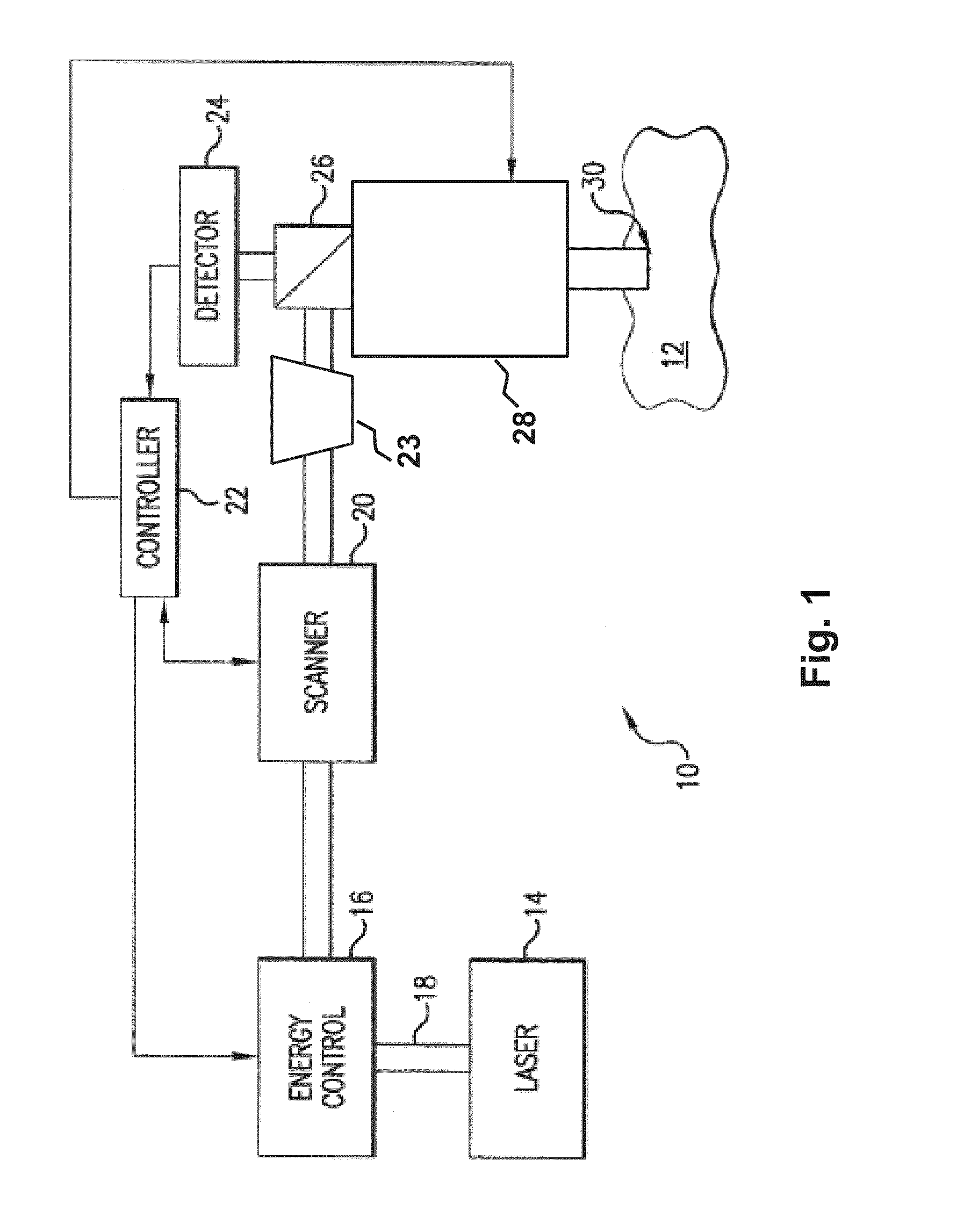
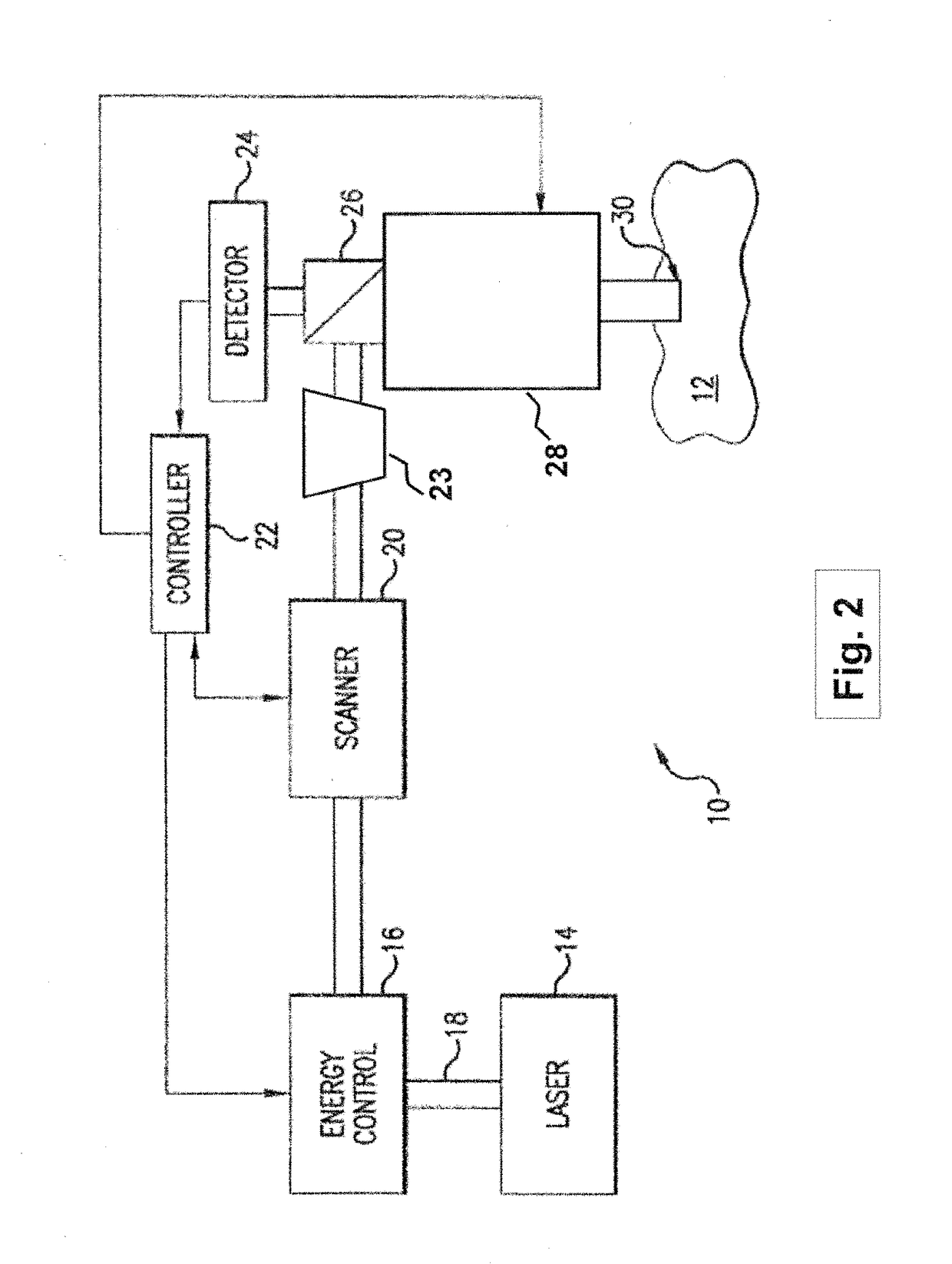
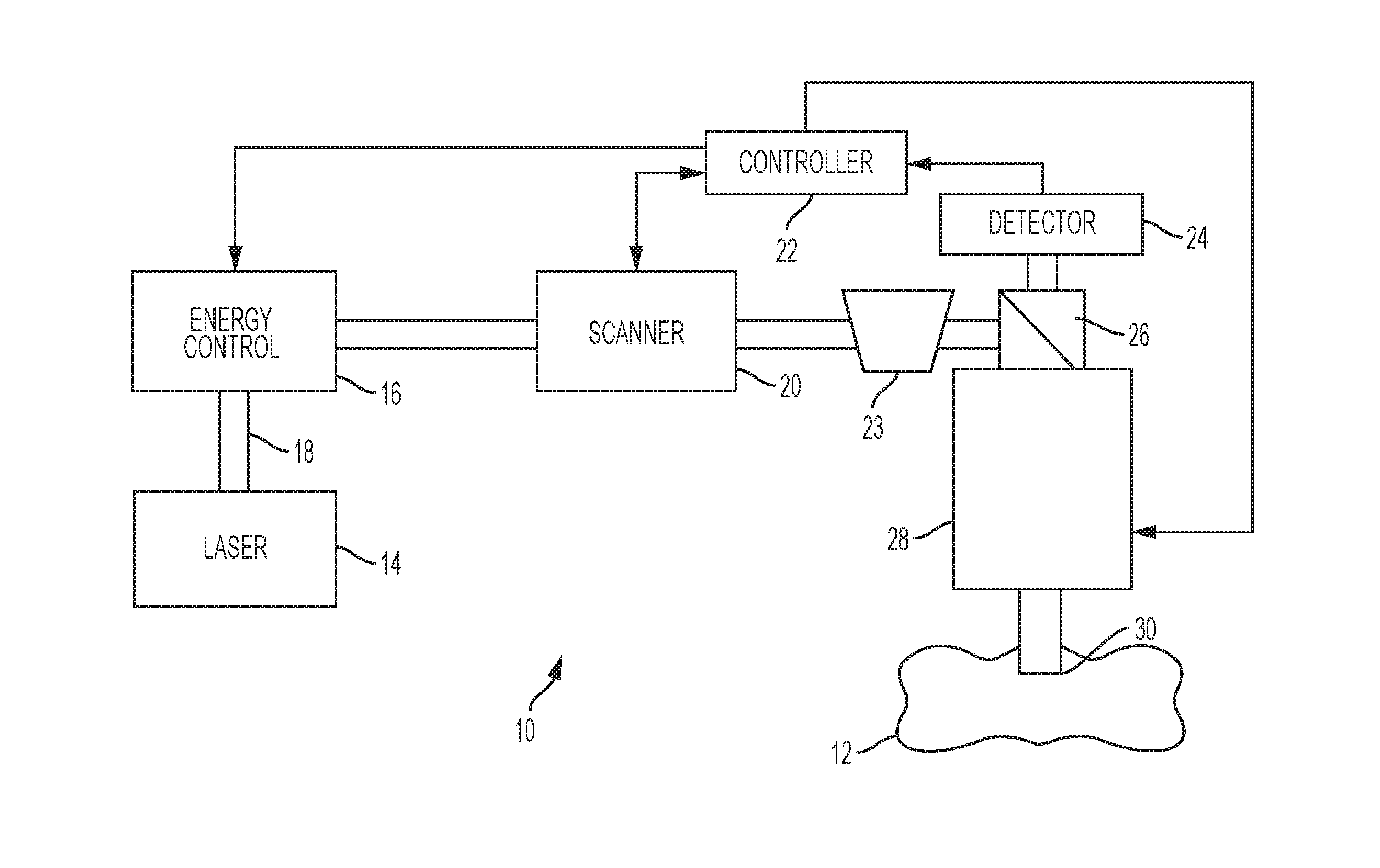
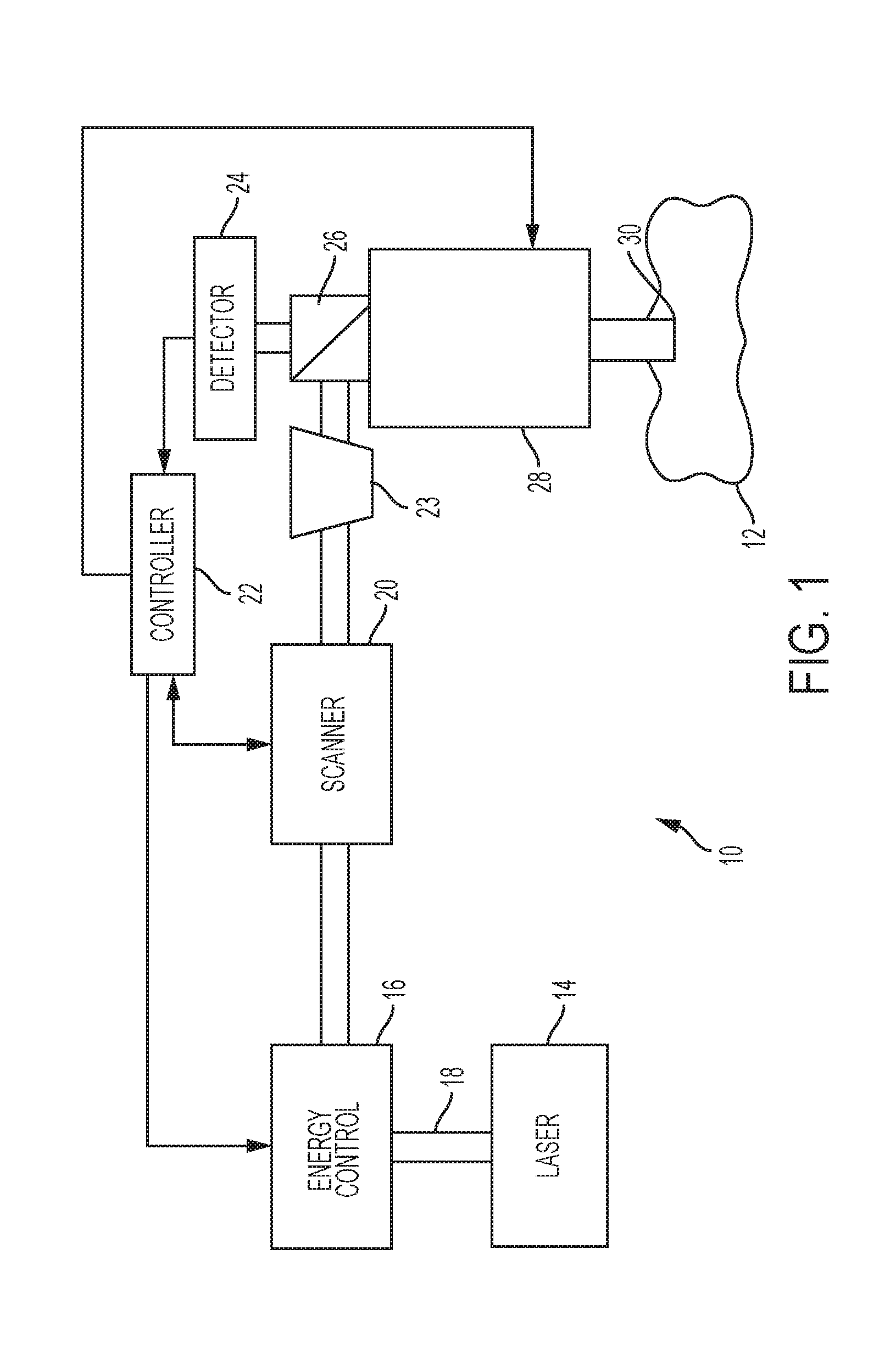
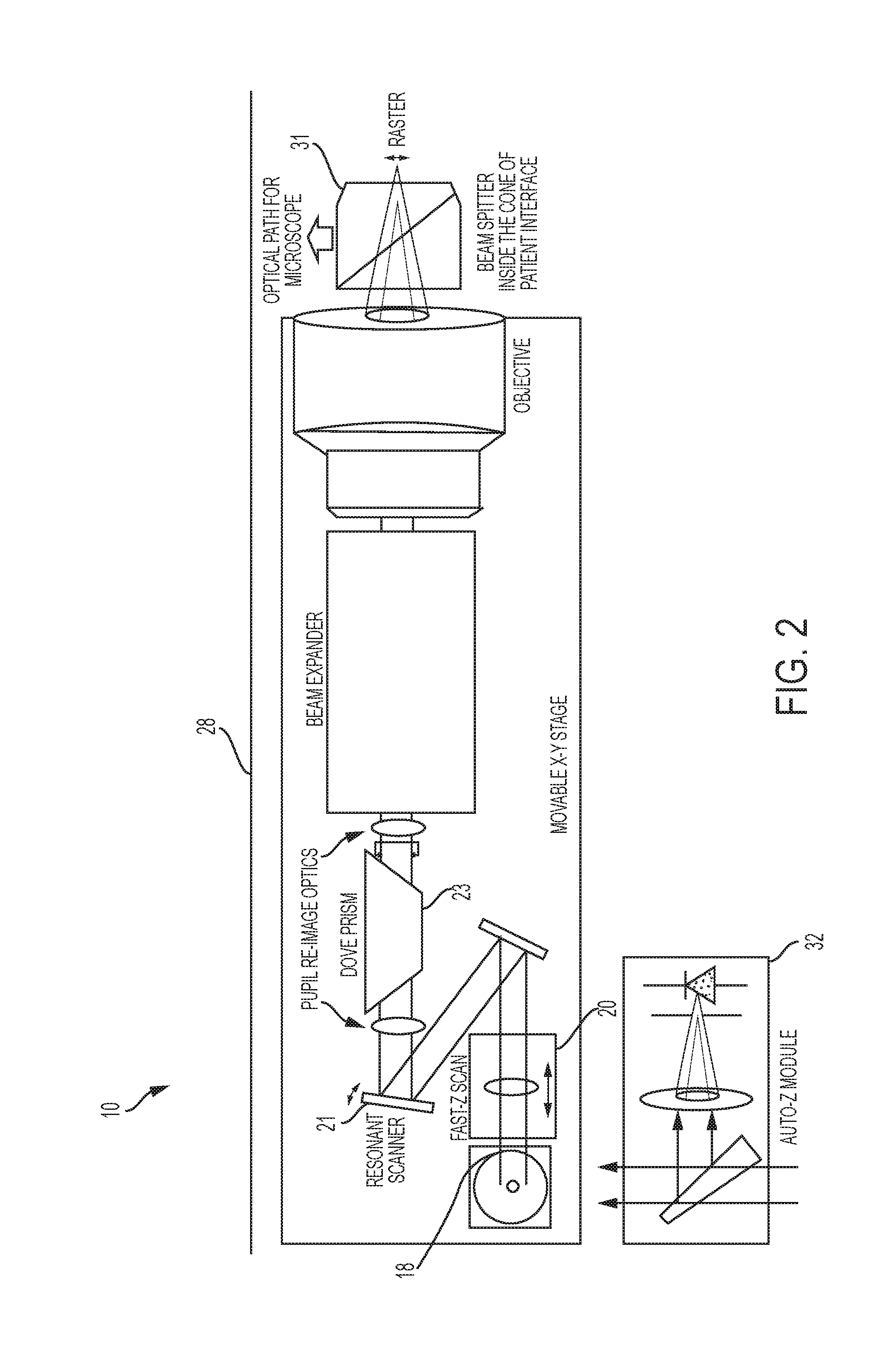
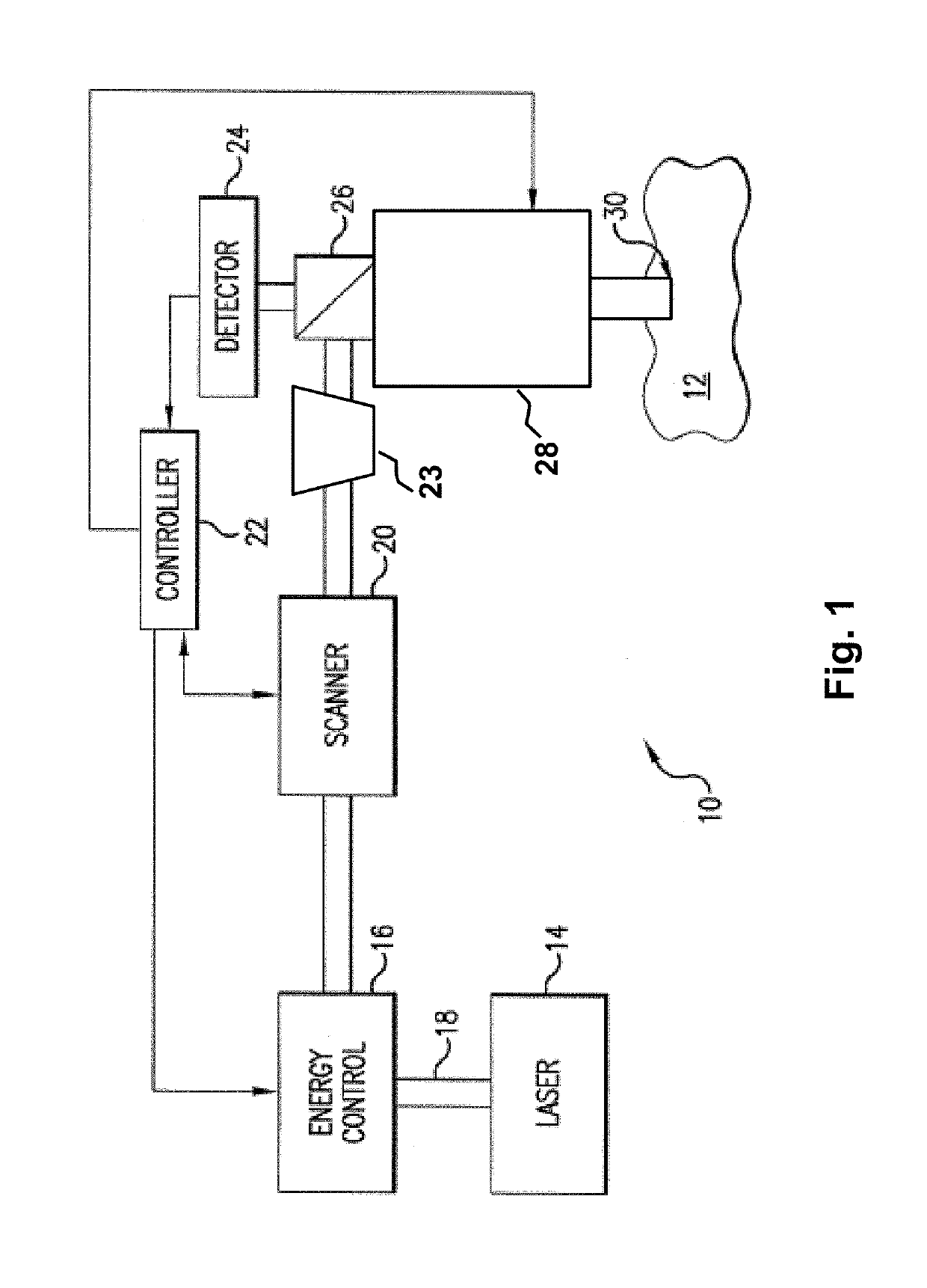
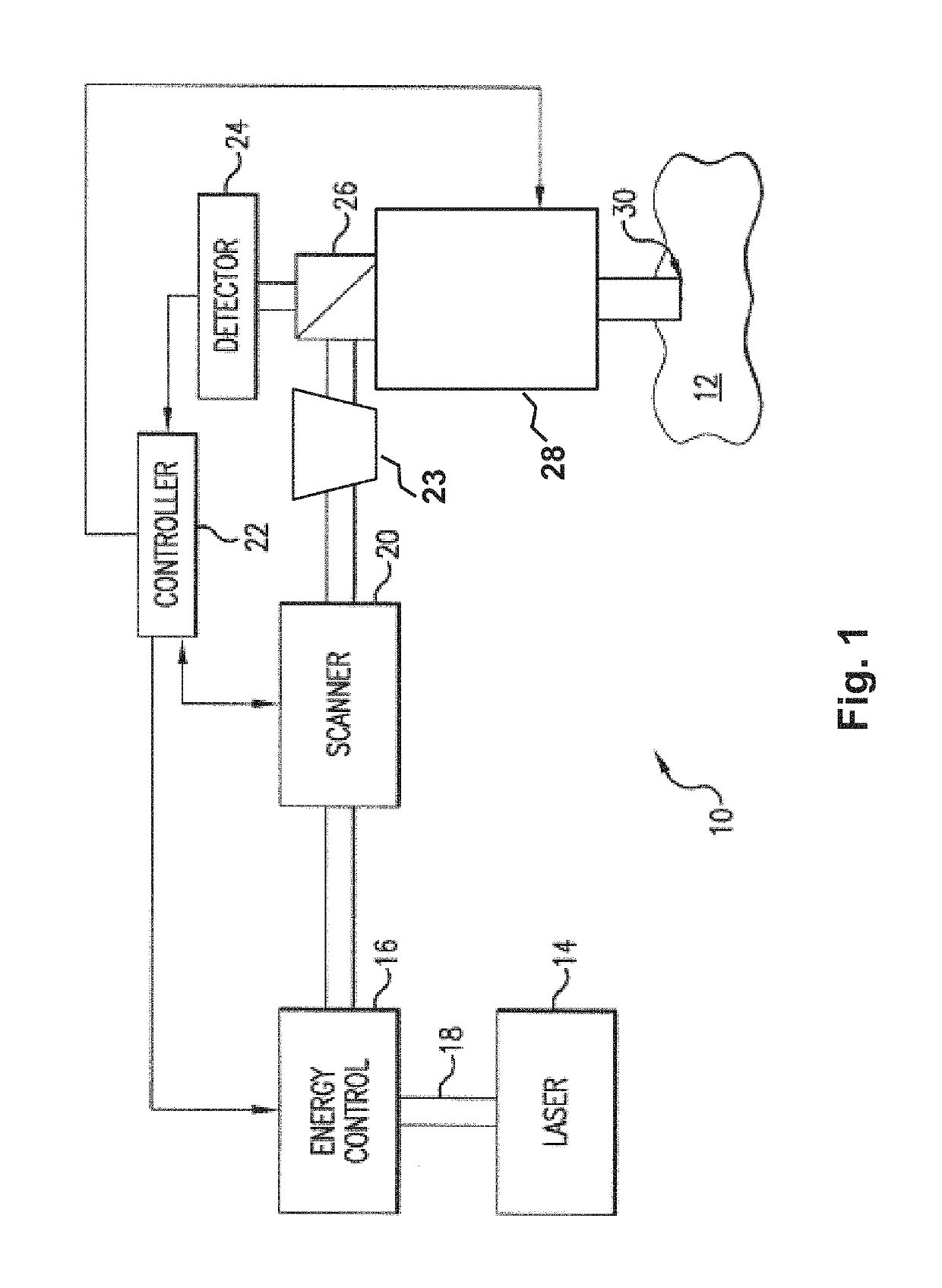
Steering laser treatment system and method of use
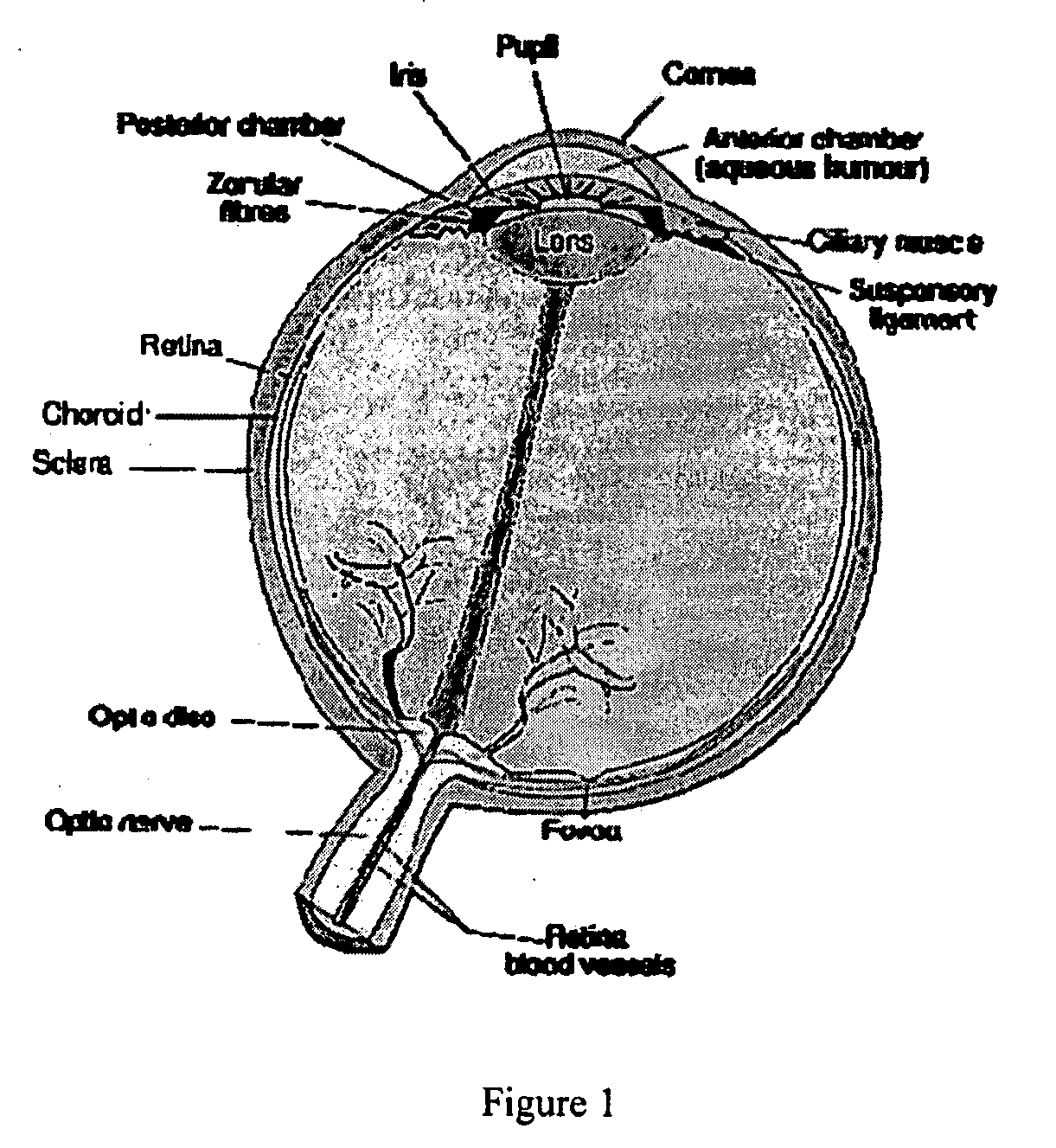
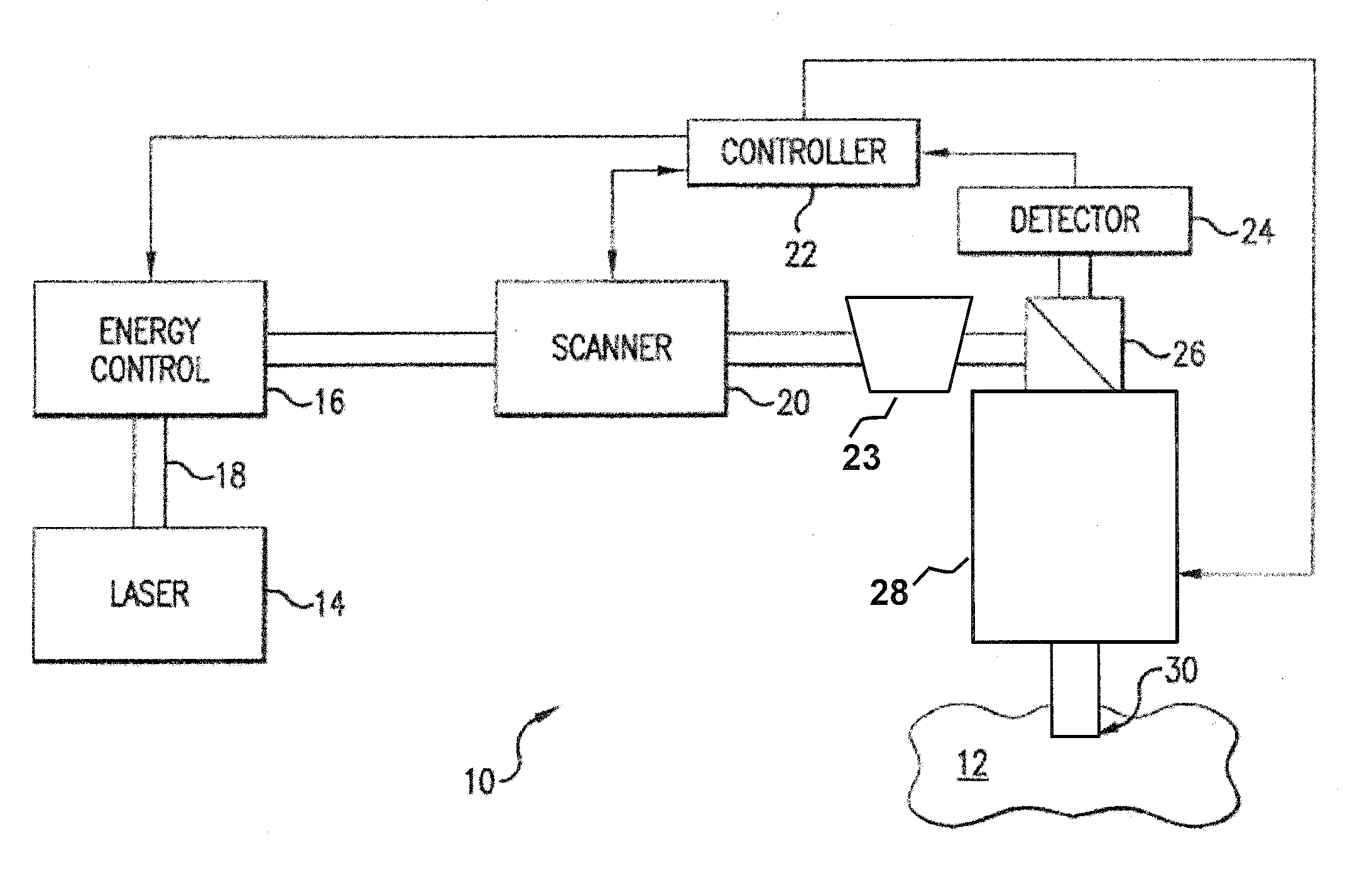
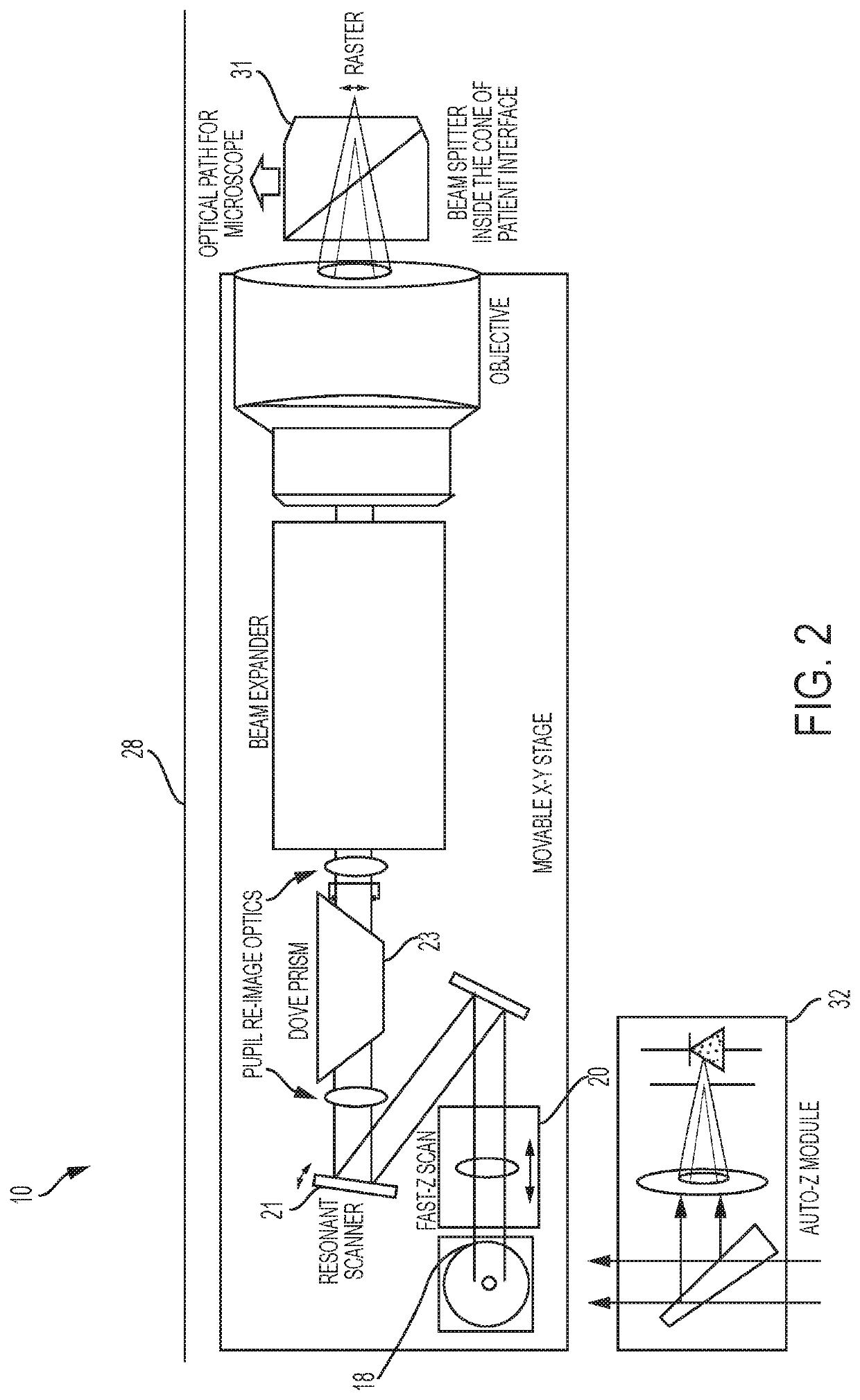
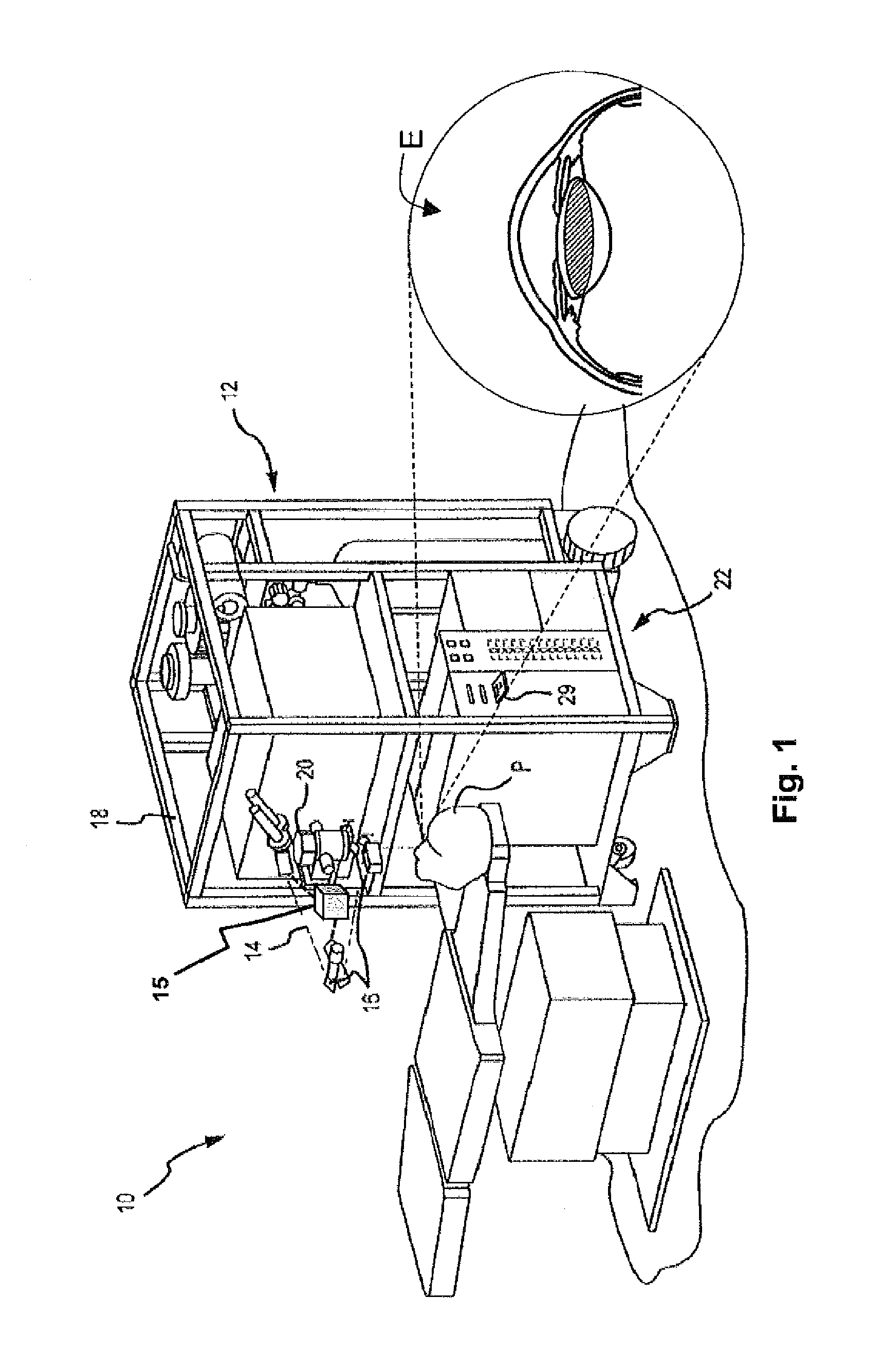
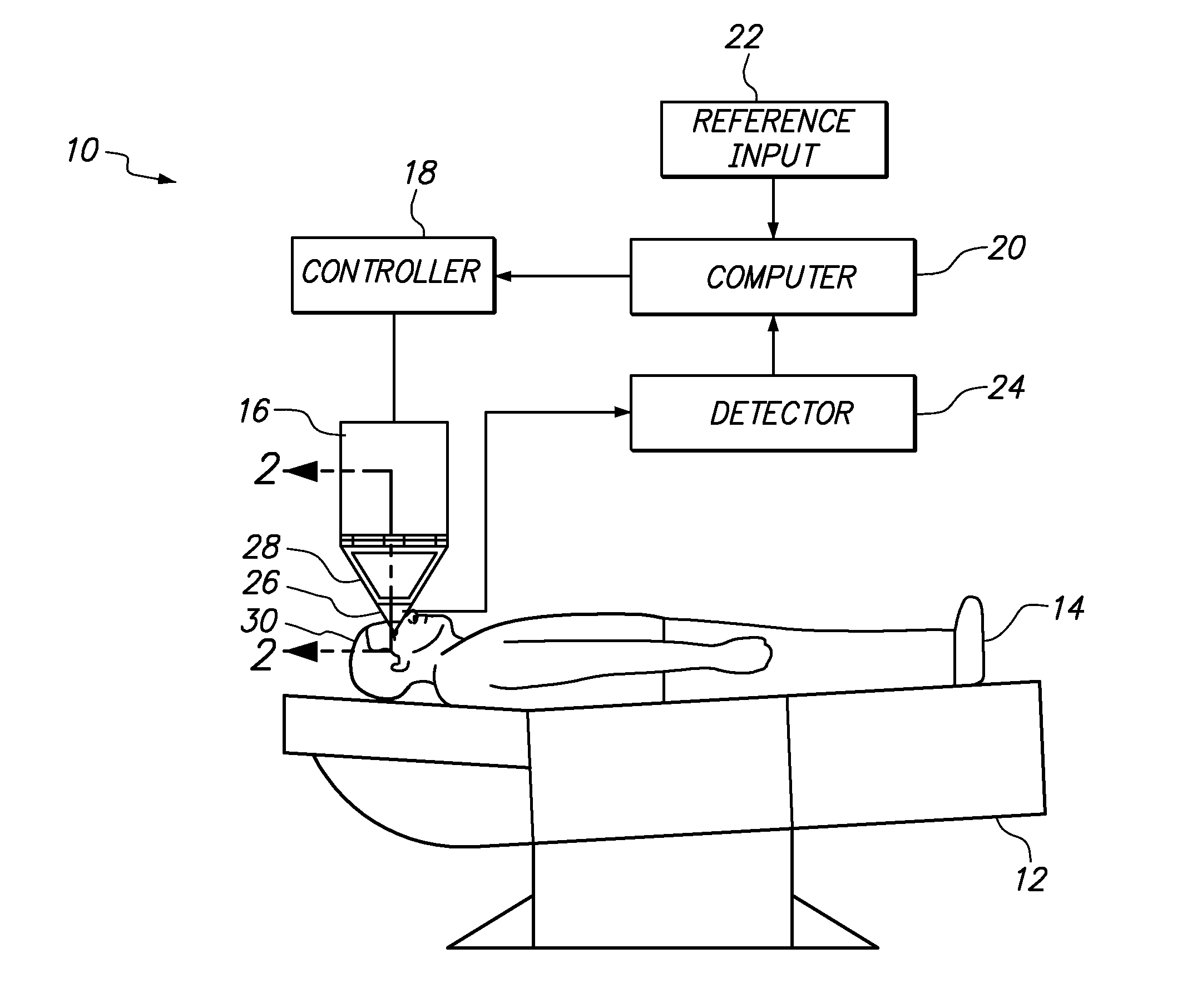
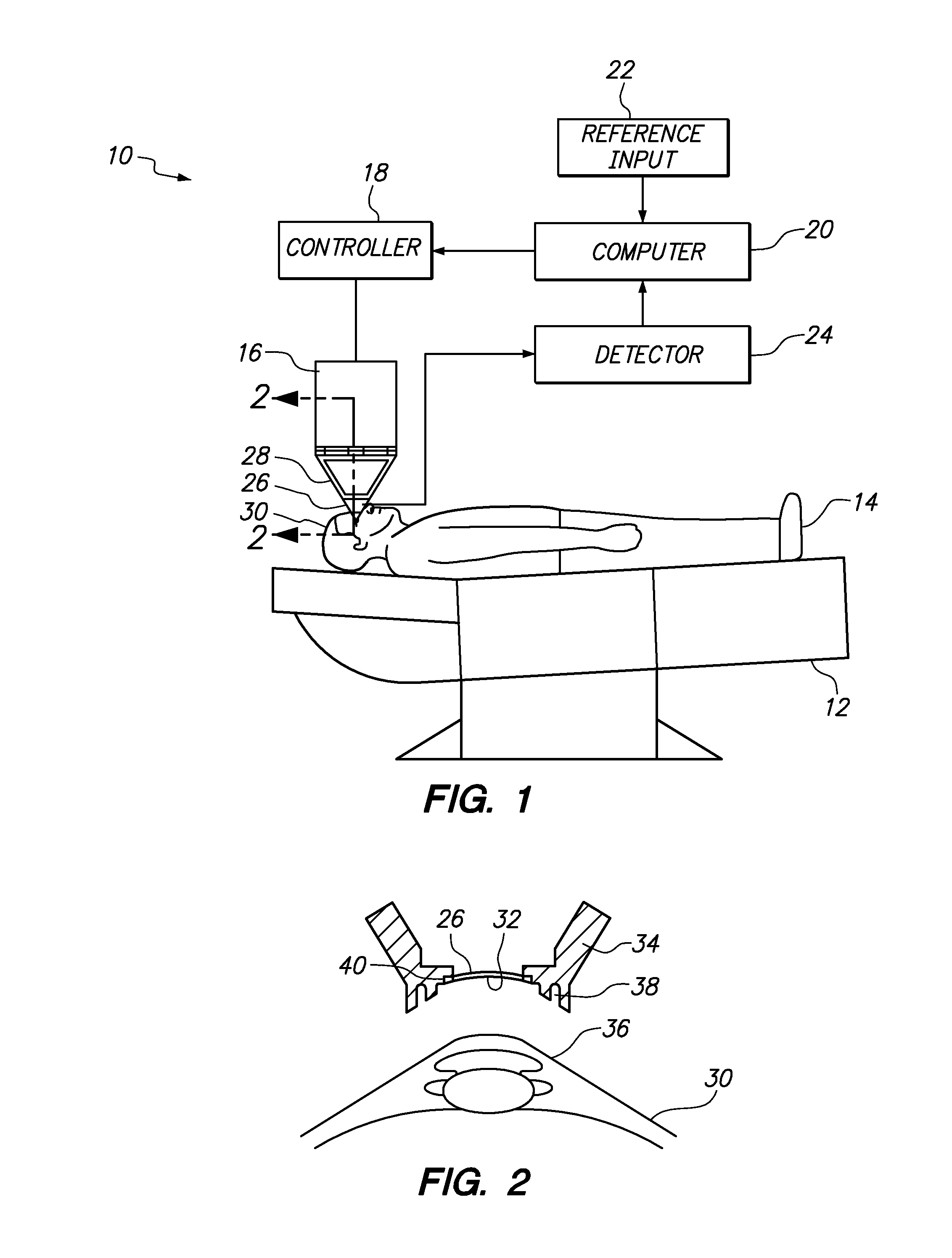
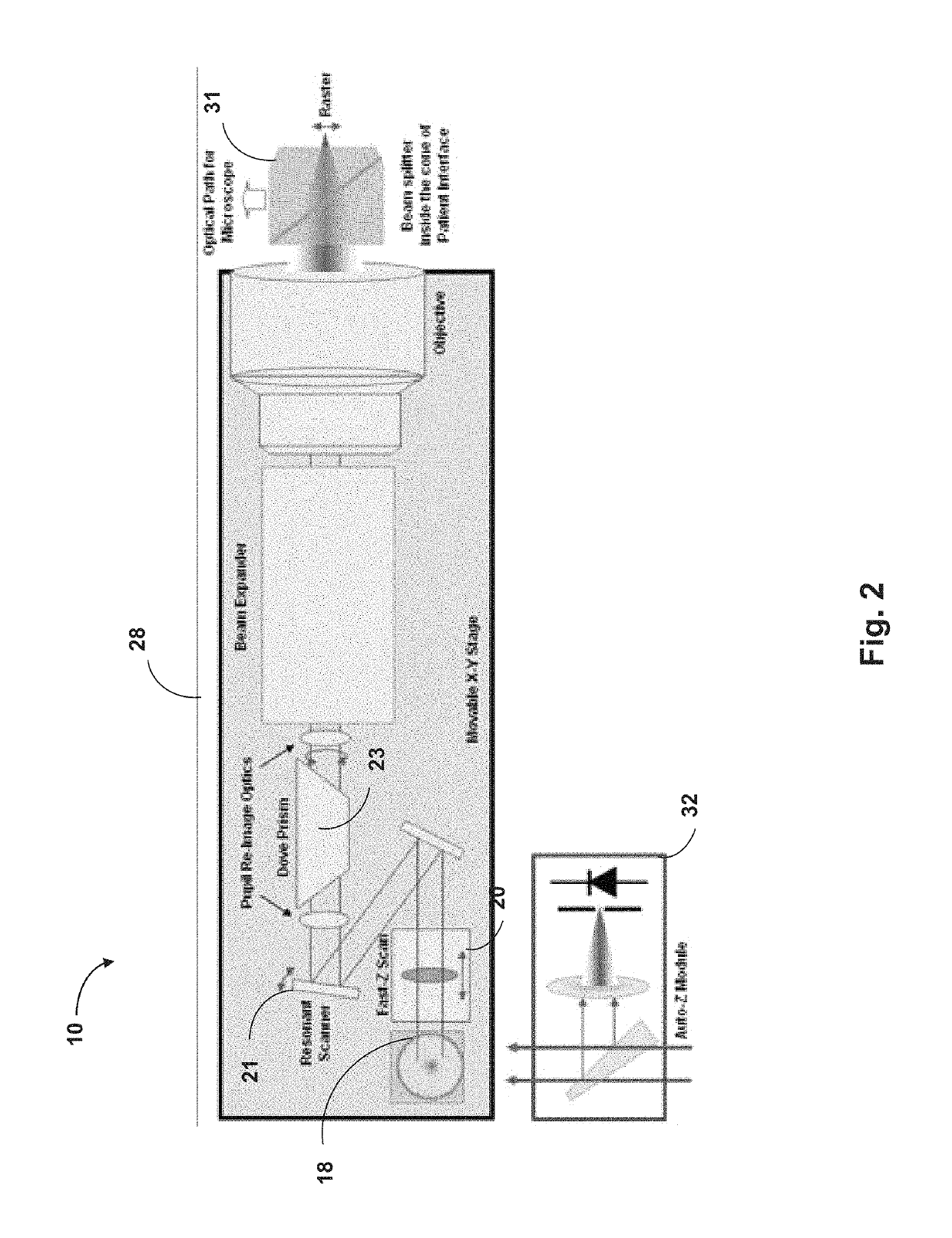
A system and method for delivering therapeutic laser energy onto selected treatment locations of the retina following a predetermined spatial distribution pattern using one single laser beam. A beam steering mechanism and control system delivers the laser energy sequentially to treatment locations forming a pre-selected treatment layout pattern. The invention allows time consuming therapeutic laser procedures such as pan-retinal photo-coagulation and segmental photocoagulation to be performed with increased accuracy and in a fraction of the time currently required for such procedures.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
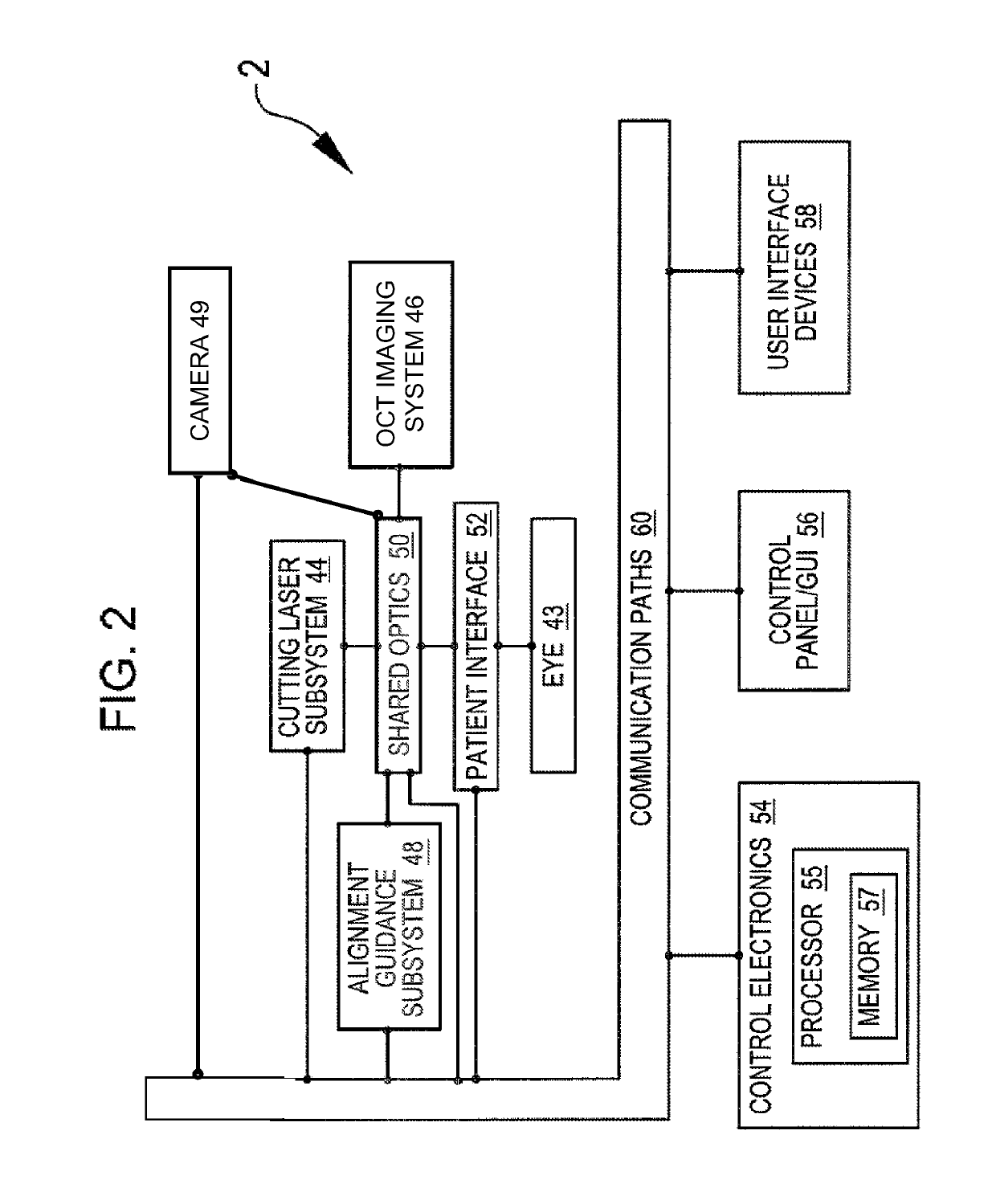
Method and apparatus to guide laser corneal surgery with optical measurement
InactiveUS20070282313A1Faster visual recoveryLess invasiveLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive errorPhototherapeutic keratectomy
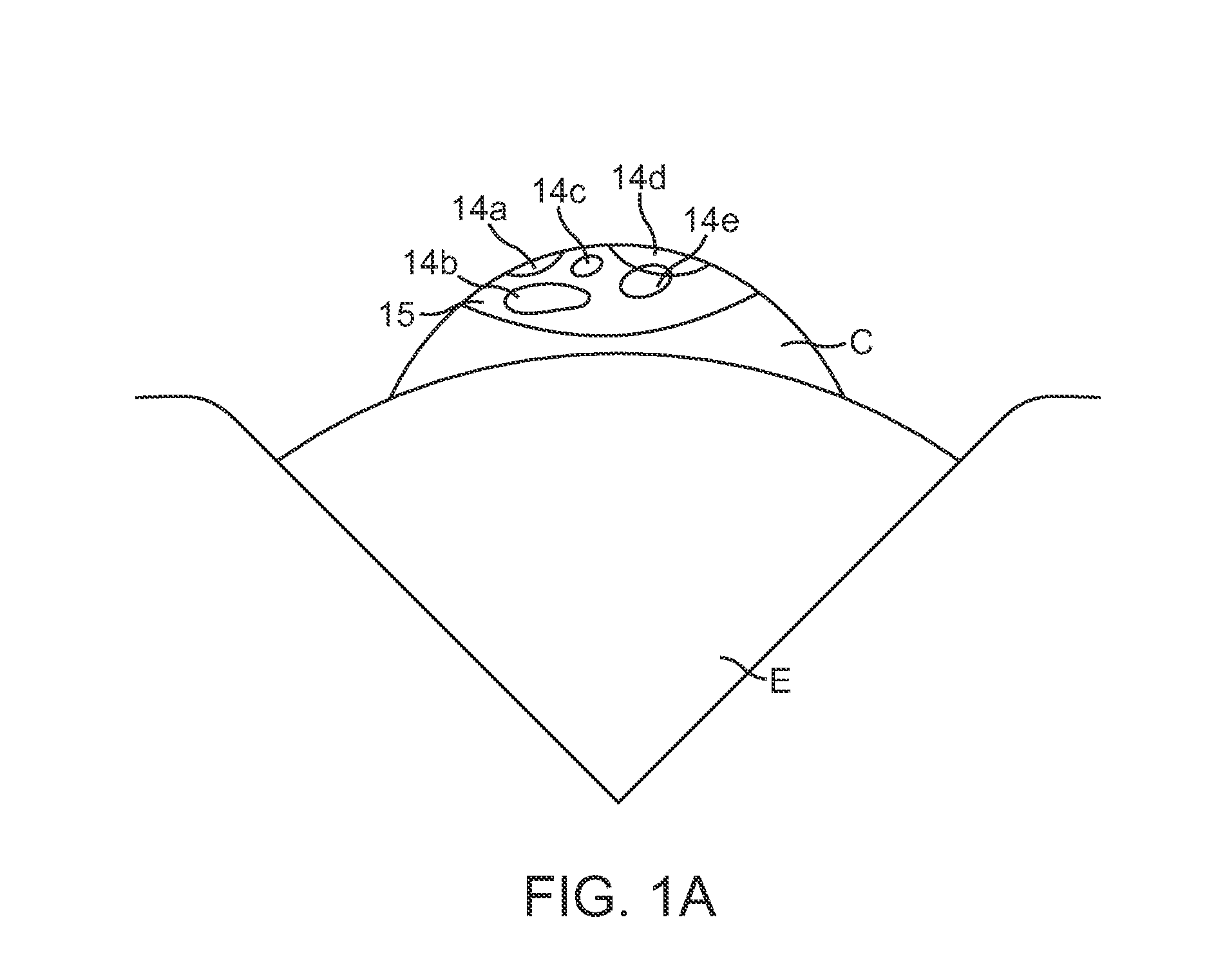
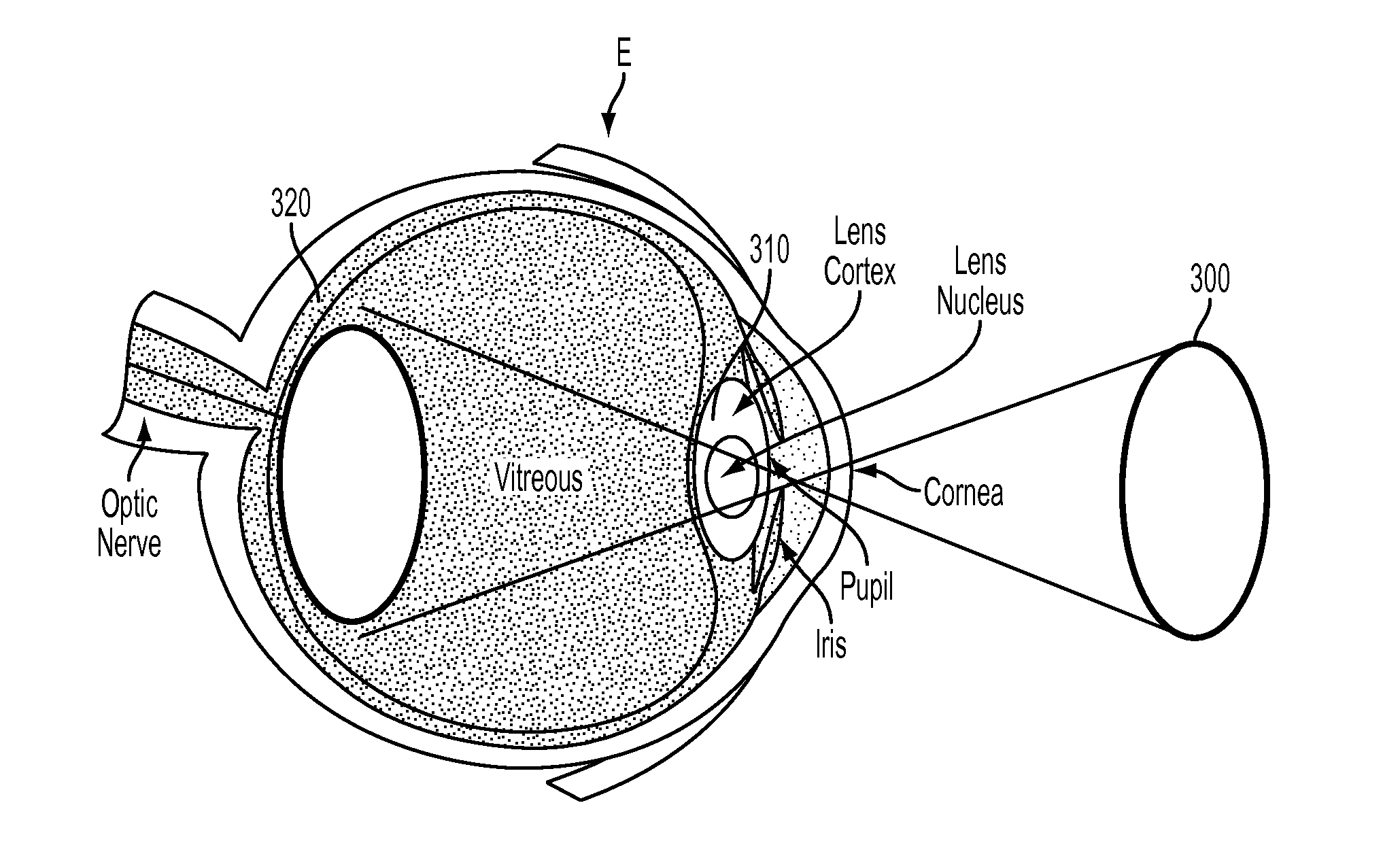
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is used to map the surface elevation and thickness of the cornea. The OCT maps are used to plan laser procedures for the treatment of an irregular, opacified or weakened cornea, and in the treatment of refractive errors. In the excimer laser phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK) procedure, the OCT data is used to plan a map of ablation depth needed to restore a smooth optical surface. In the excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy procedure, OCT mapping of epithelial thickness is used to achieve clean laser epithelial removal. In femtosecond laser anterior keratoplasty procedure, OCT data is used to plan the depth of femtosecond laser dissection to remove an anterior layer of the cornea, leaving a smooth recipient bed of uniform thickness to receive a disk of donated corneal tissue. The linkage of an OCT system to a precise laser surgical system enables the performance of new procedures that are safer, less invasive and produce faster visual recovery than conventional surgical procedures.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
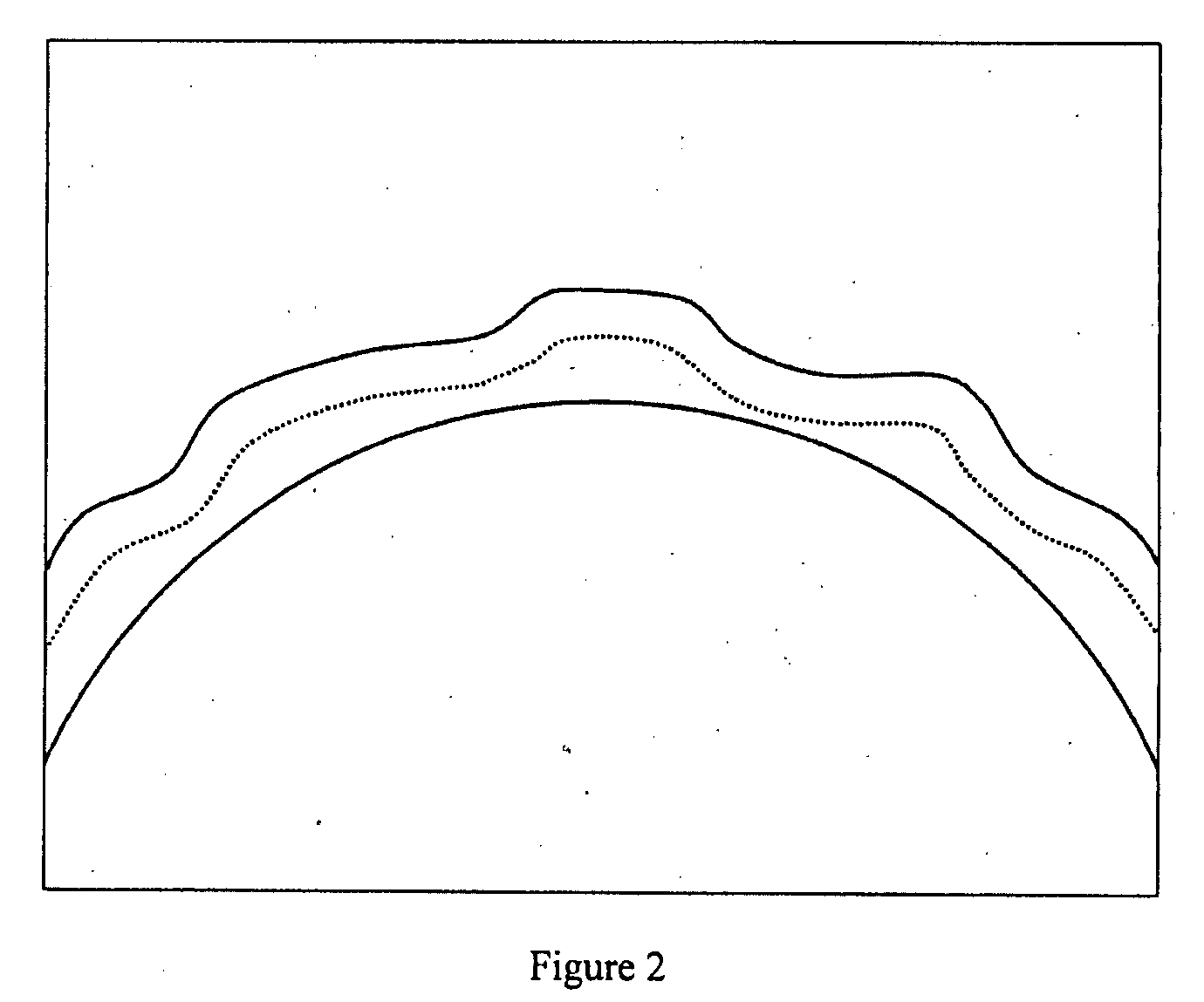
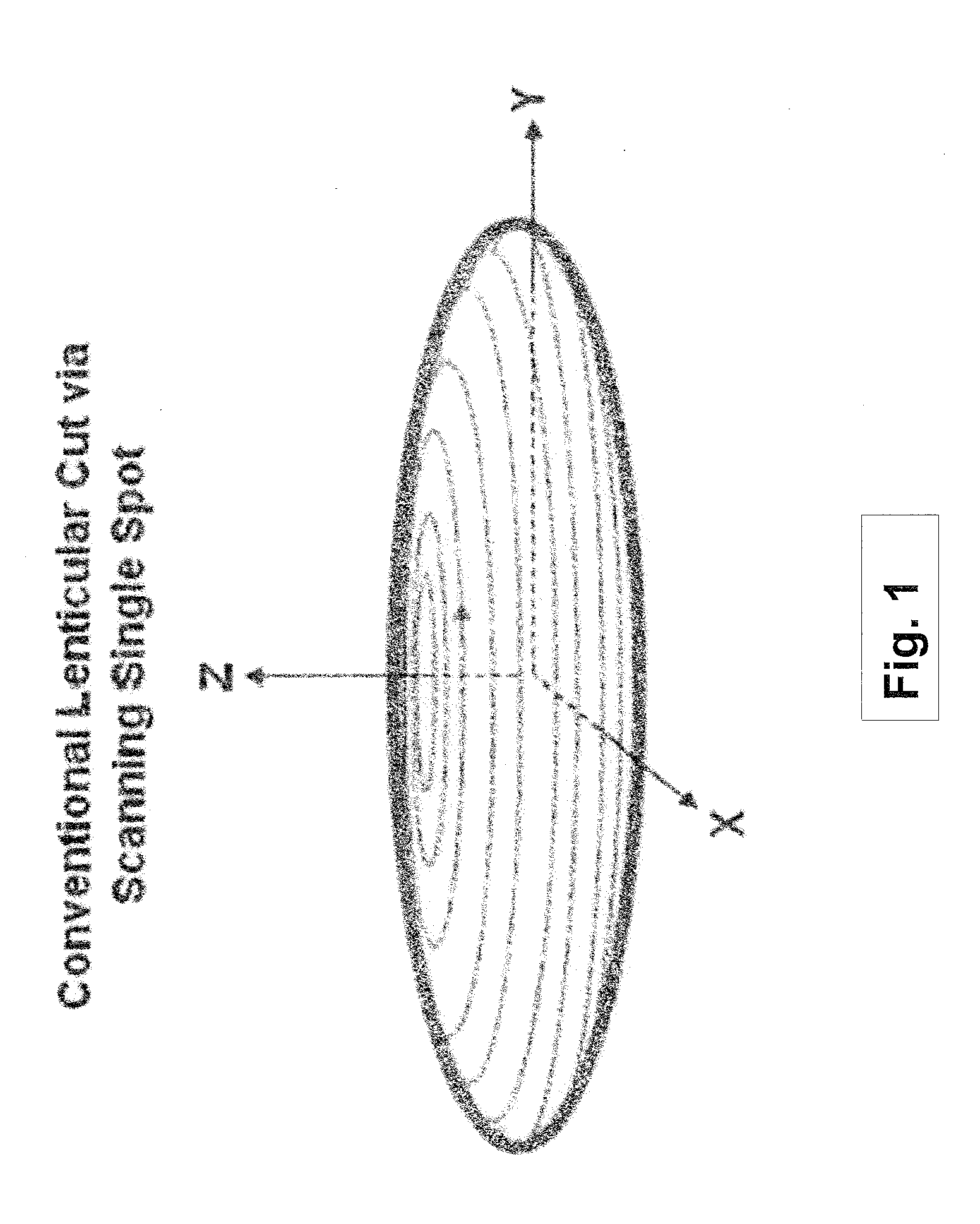
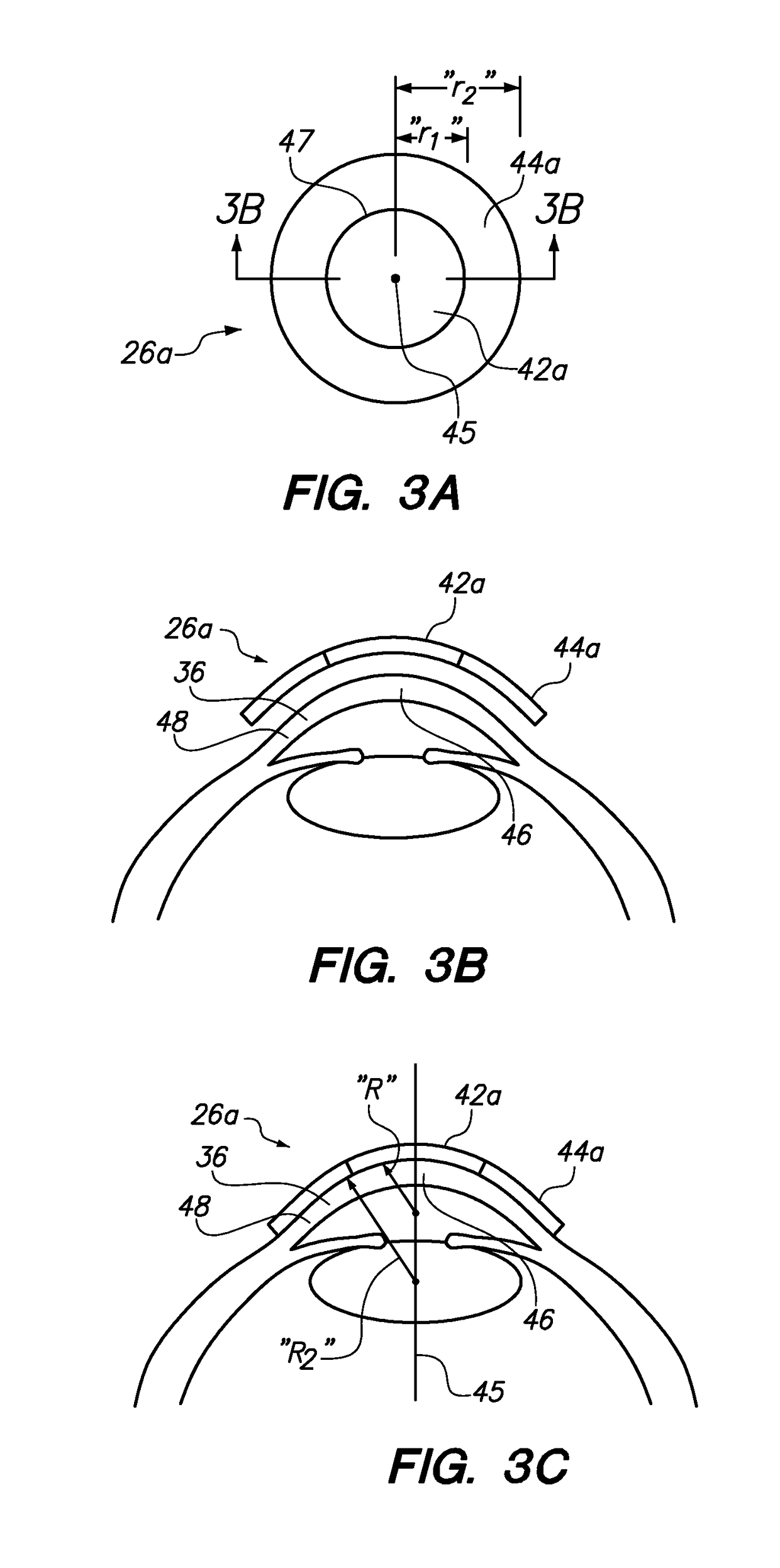
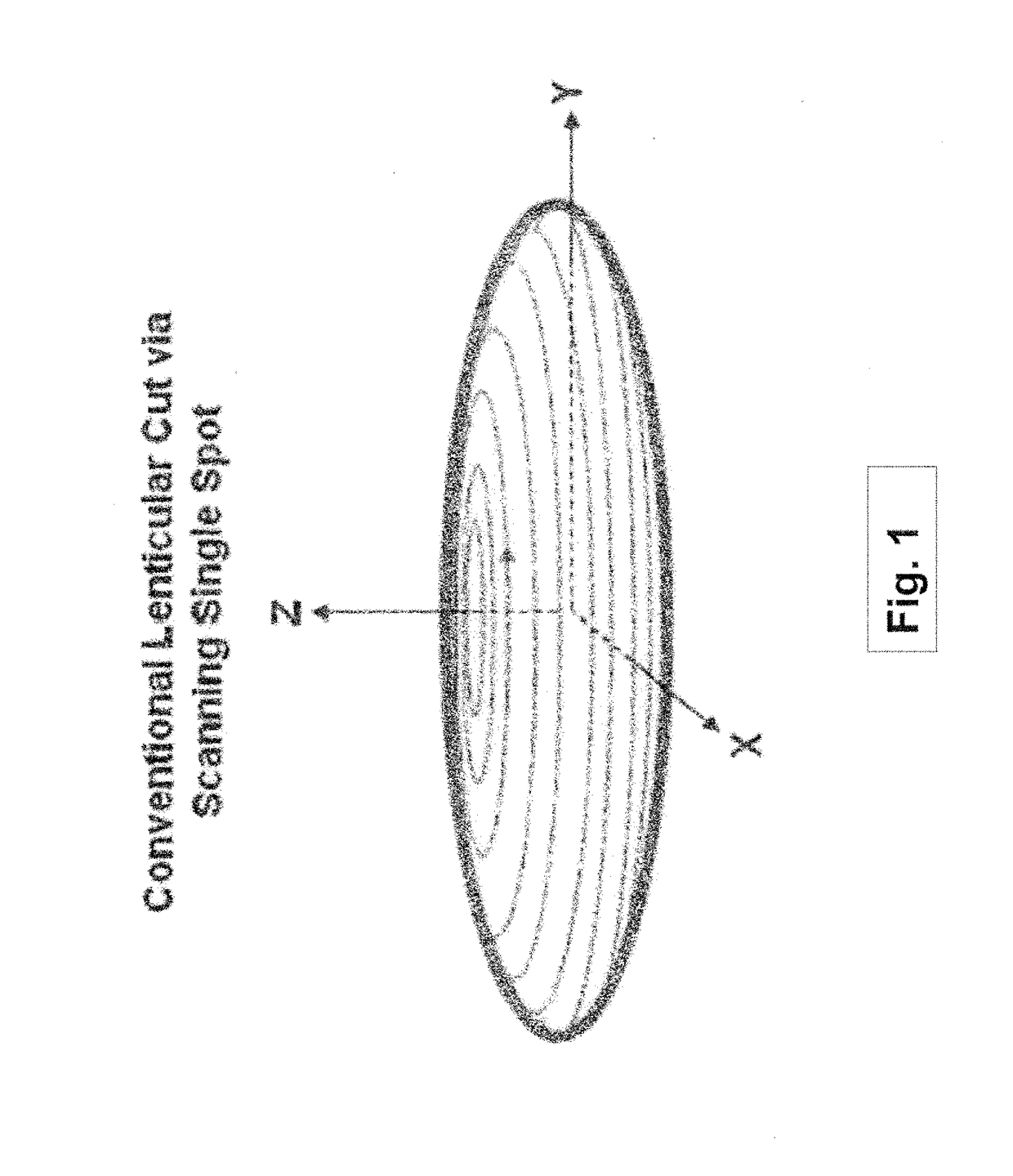
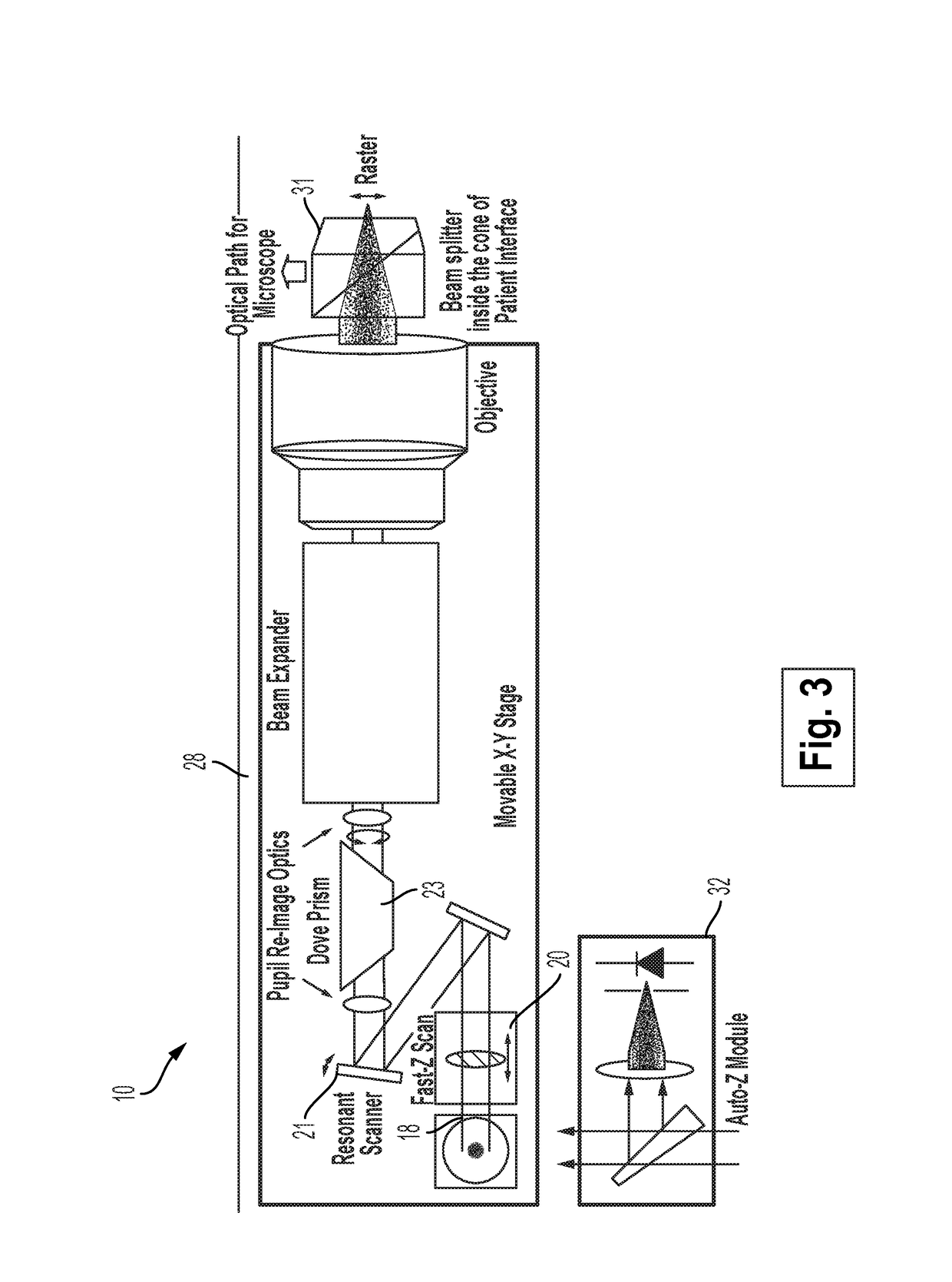
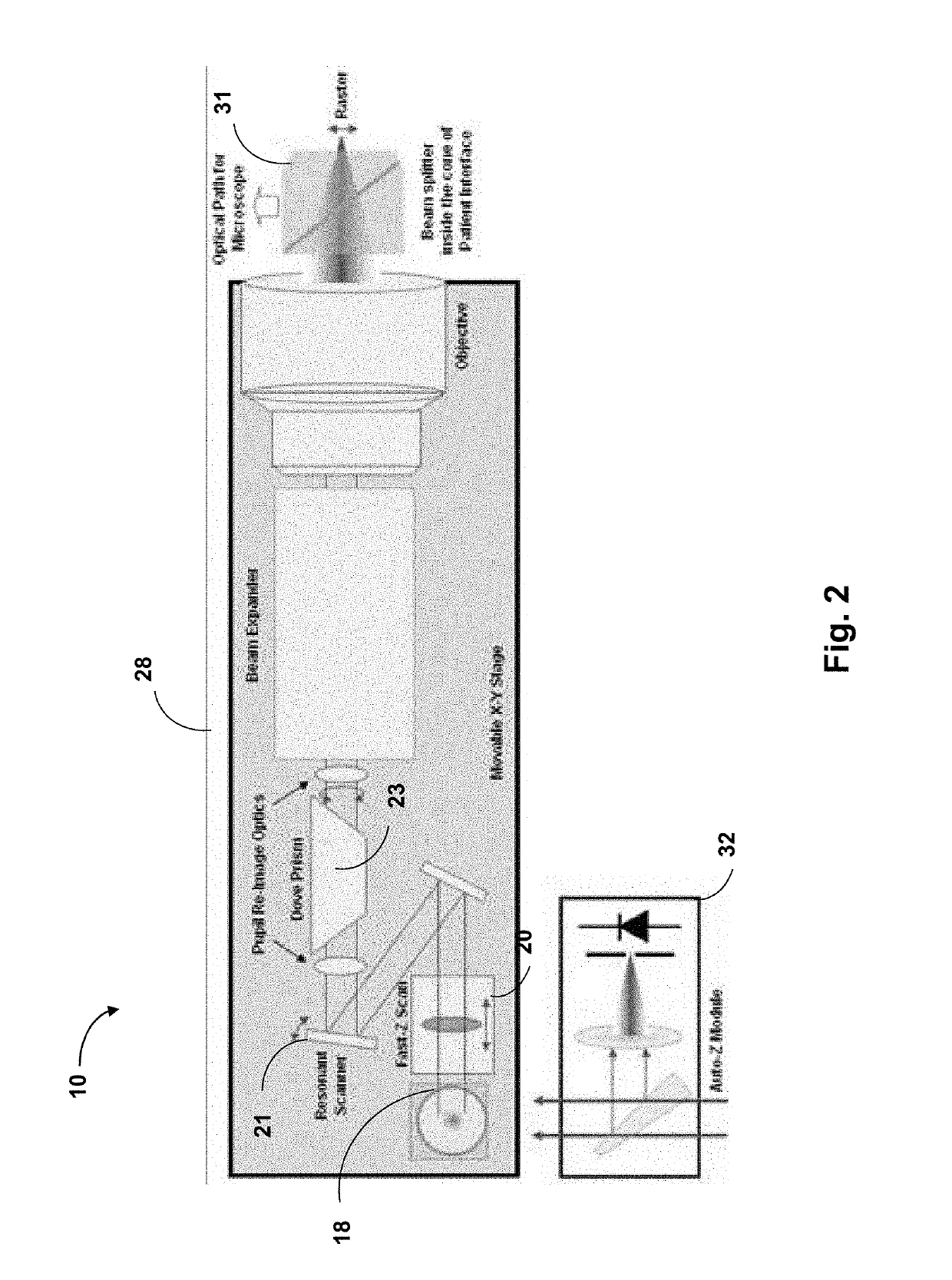
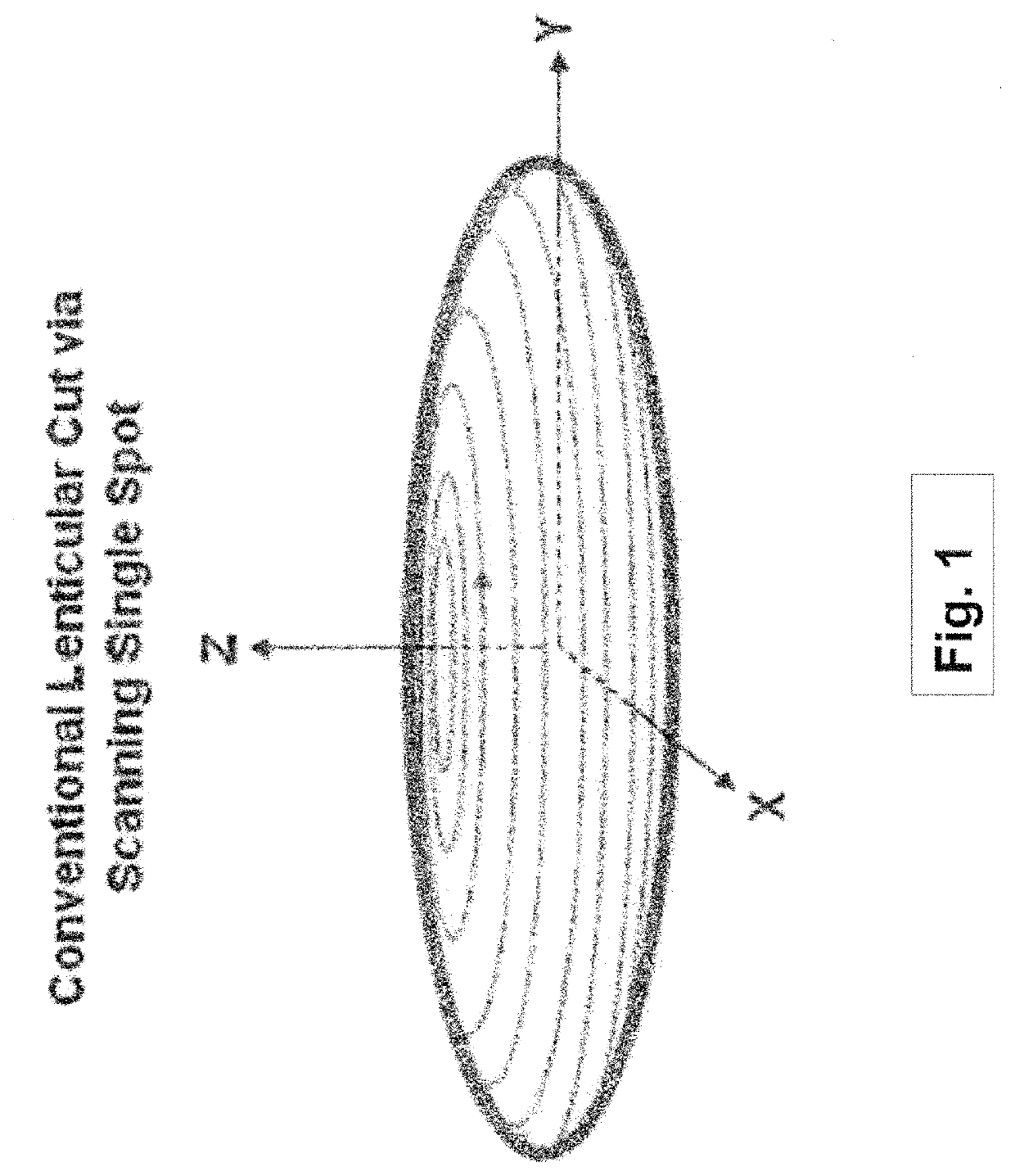
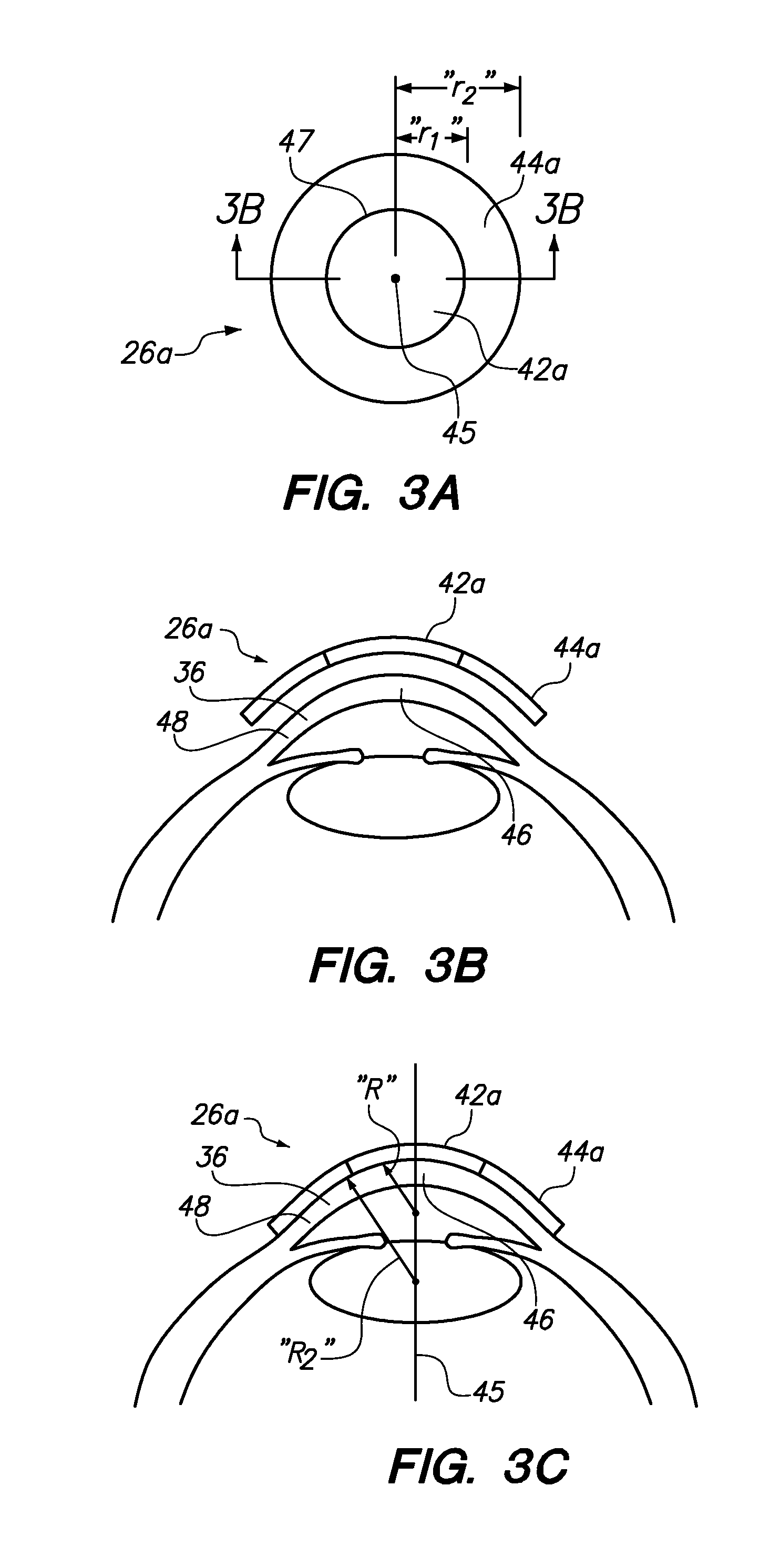
Systems and methods for lenticular laser incision
Embodiments of this invention generally relate to ophthalmic laser procedures and, more particularly, to systems and methods for lenticular laser incision. In an embodiment, an ophthalmic surgical laser system comprises a laser delivery system for delivering a pulsed laser beam to a target in a subject's eye, an XY-scan device to deflect the pulsed laser beam, a Z-scan device to modify a depth of a focus of the pulsed laser beam, and a controller configured to form a top lenticular incision and a bottom lenticular incision of a lens in the subject's eye.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Optical fiber-handpiece combination for medical laser treatments
InactiveUS6574401B2Safe and practical and economical for medical laser treatmentAvoid vertical movementDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsFiberAdhesive
Owner:BIOLITEC PHARMA MARKETING
Operator-controlled scanning laser procedure designed for large-area epithelium removal
ActiveUS20080287928A1Improve accuracyImprove efficacyLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsEpitheliumPulse beam
Systems and methods for removing an epithelial layer disposed over a stromal layer in a cornea irradiate a region of the epithelial layer with a pulsed beam of ablative radiation. The ablative radiation is scanned to vary the location of the beam within the region in accordance with a pulse sequence. The pulse sequence is arranged to enhance optical feedback based on a tissue fluorescence of the epithelial layer. The penetration of the epithelial layer is detected in response to the optical feedback. The use of scanning with the pulse sequence arranged to enhance optical feedback allows large areas of the epithelium to be ablated such penetration of the epithelial layer can be detected.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Systems and methods for synchronized three-dimensional laser incisions
Embodiments of this invention generally relate to ophthalmic laser procedures and, more particularly, to systems and methods for creating synchronized three-dimensional laser incisions. In an embodiment, an ophthalmic surgical laser system comprises a laser delivery system for delivering a pulsed laser beam to a target in a subject's eye, an XY-scan device to deflect the pulsed laser beam, a Z-scan device to modify a depth of a focus of the pulsed laser beam, and a controller configured to synchronize an oscillation of the XY-scan device and an oscillation of the Z-device to form an angled three-dimensional laser tissue dissection.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
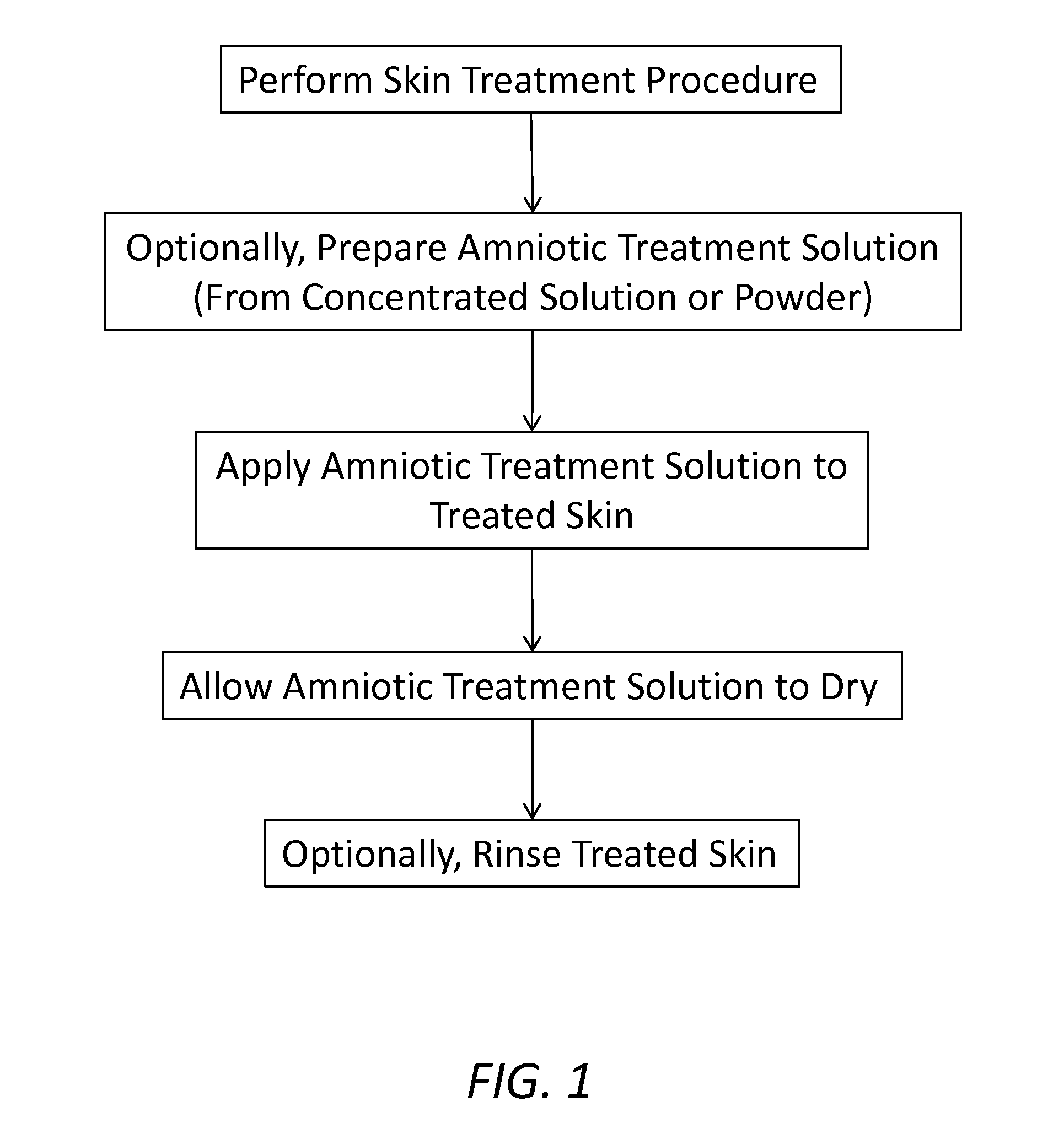
Skin treatment protocol utilizing amniotic solution
InactiveUS20150140114A1Skin healthGenerate fastCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsDermabrasionSkin treatments
A skin treatment method, including: performing a skin treatment procedure on the skin of a patient, wherein the skin treatment procedure includes one of a chemical peel procedure, a dermabrasion procedure, a micro-needling procedure, and a laser procedure; and subsequently, applying a preparation including one or more of amniotic fluid and amniotic membrane material to the treated skin of the patient to promote healing and collagen rejuvenation, wherein the preparation including the one or more of amniotic fluid and amniotic membrane material is prepared from one or more of amniotic fluid, a concentrated amniotic membrane solution, and an amniotic membrane powder. The preparation comprising the one or more of amniotic fluid and amniotic membrane material also includes sterile water or saline. The treated skin of the patent preferably includes one or more of the skin of the face and the skin of the neck.
Owner:SASKO JOHN R
Topical numbing composition for laser therapy
A method for decreasing patient discomfort and anesthetizing the skin of a patient for a dermatologic laser procedure is described. A composition is also described for topical administration of at least one anesthetic agent to the skin of a patient prior to dermatologic laser application.
Owner:MCCARTT MARY DUKE +2
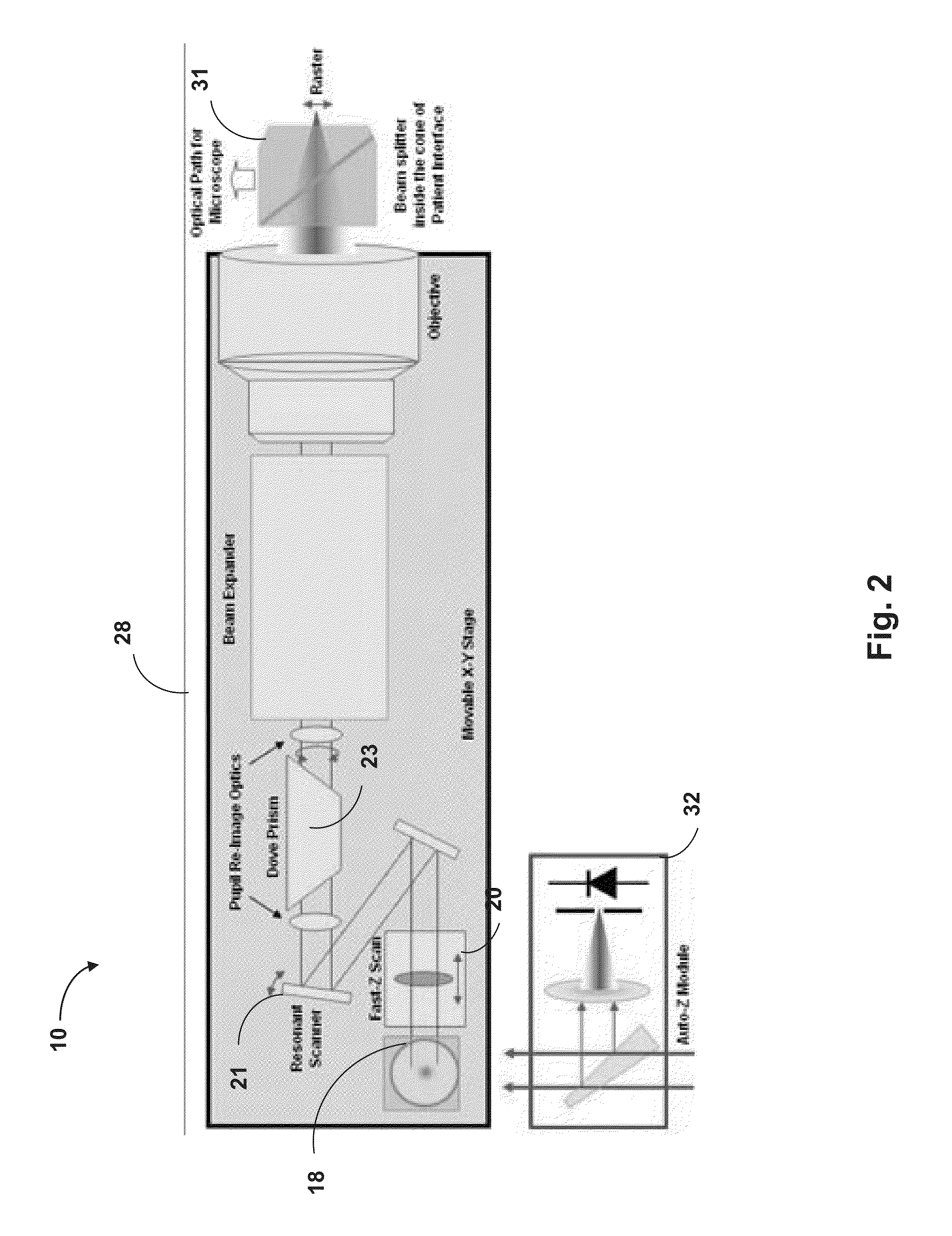
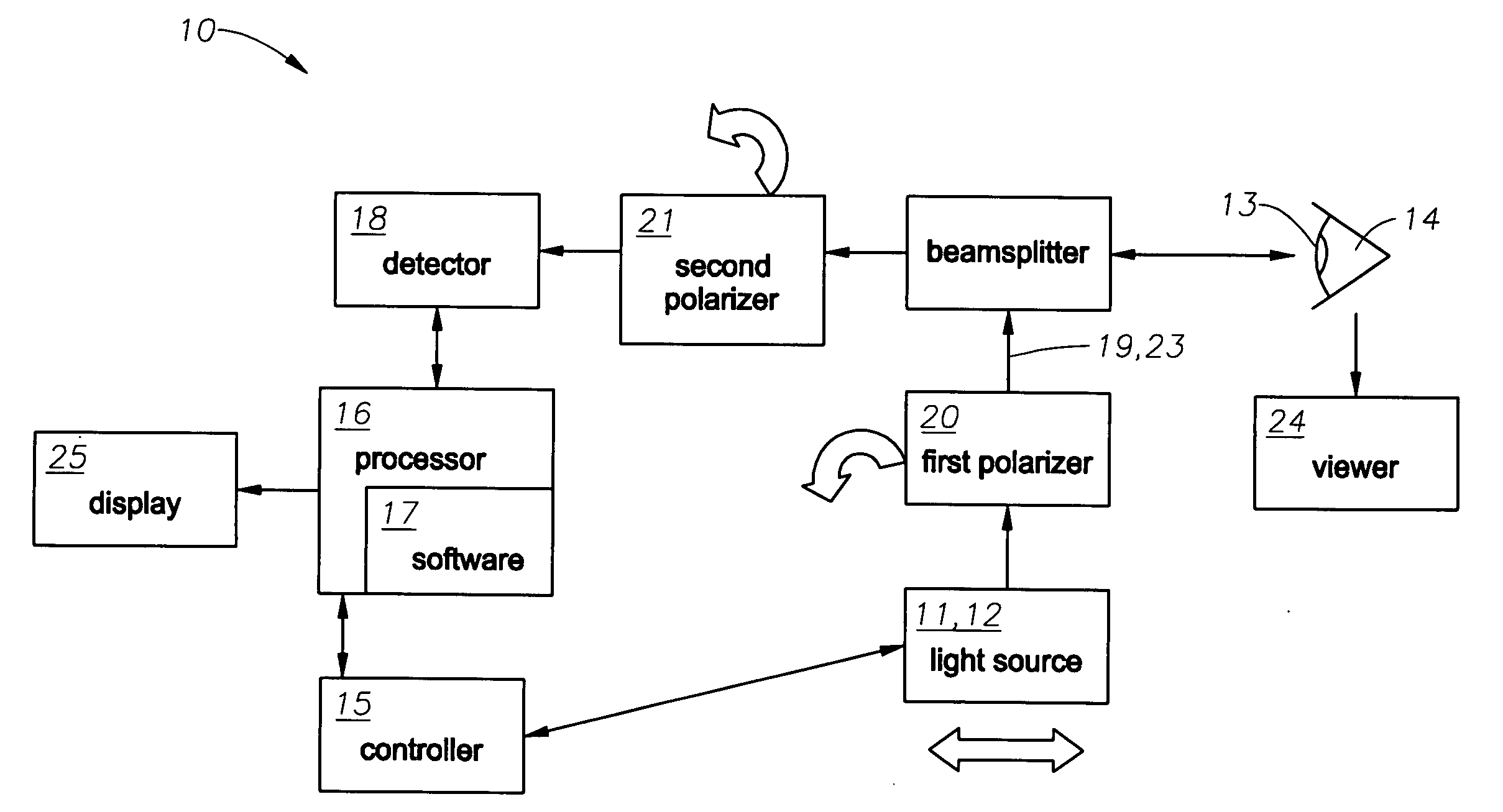
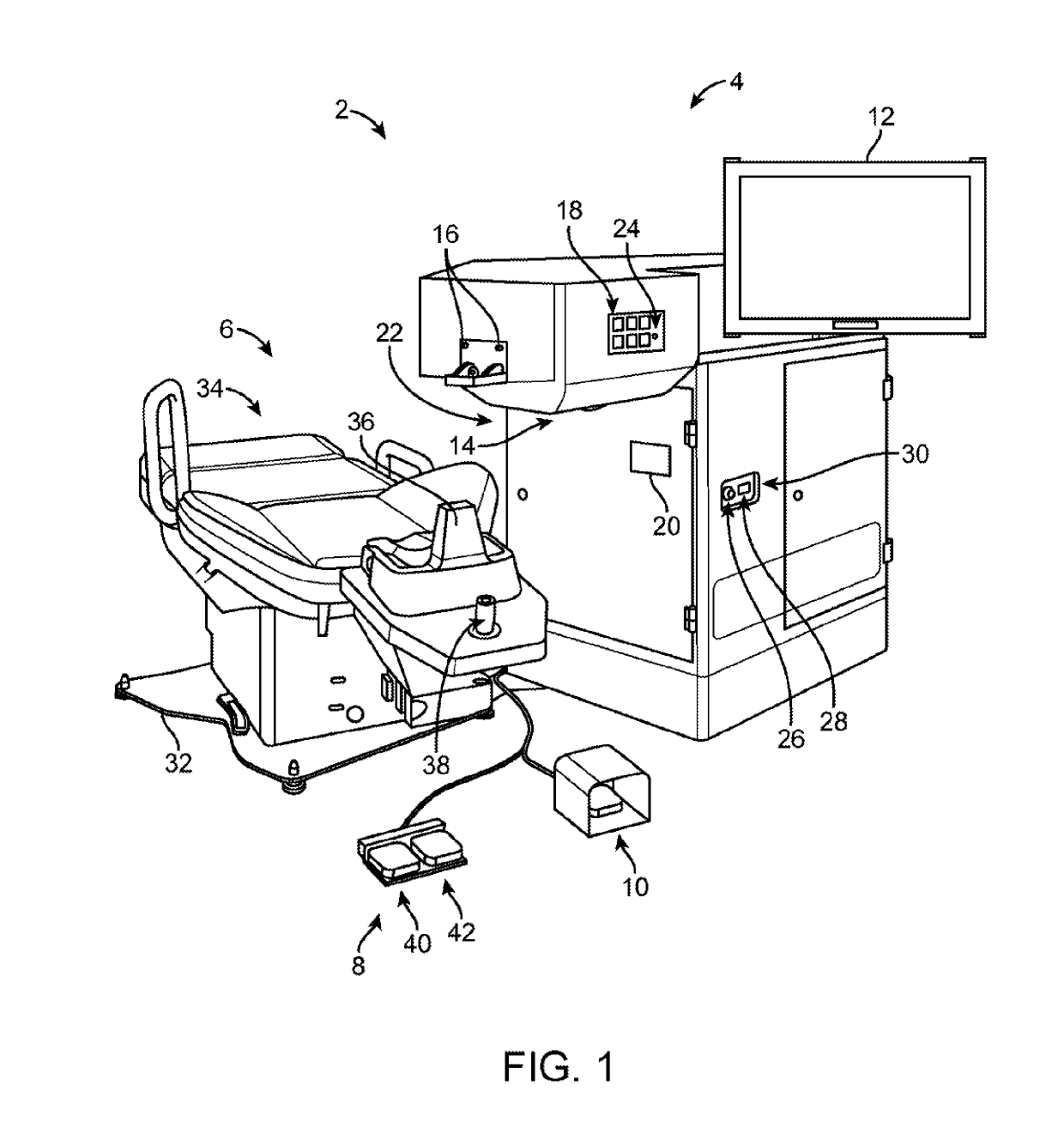
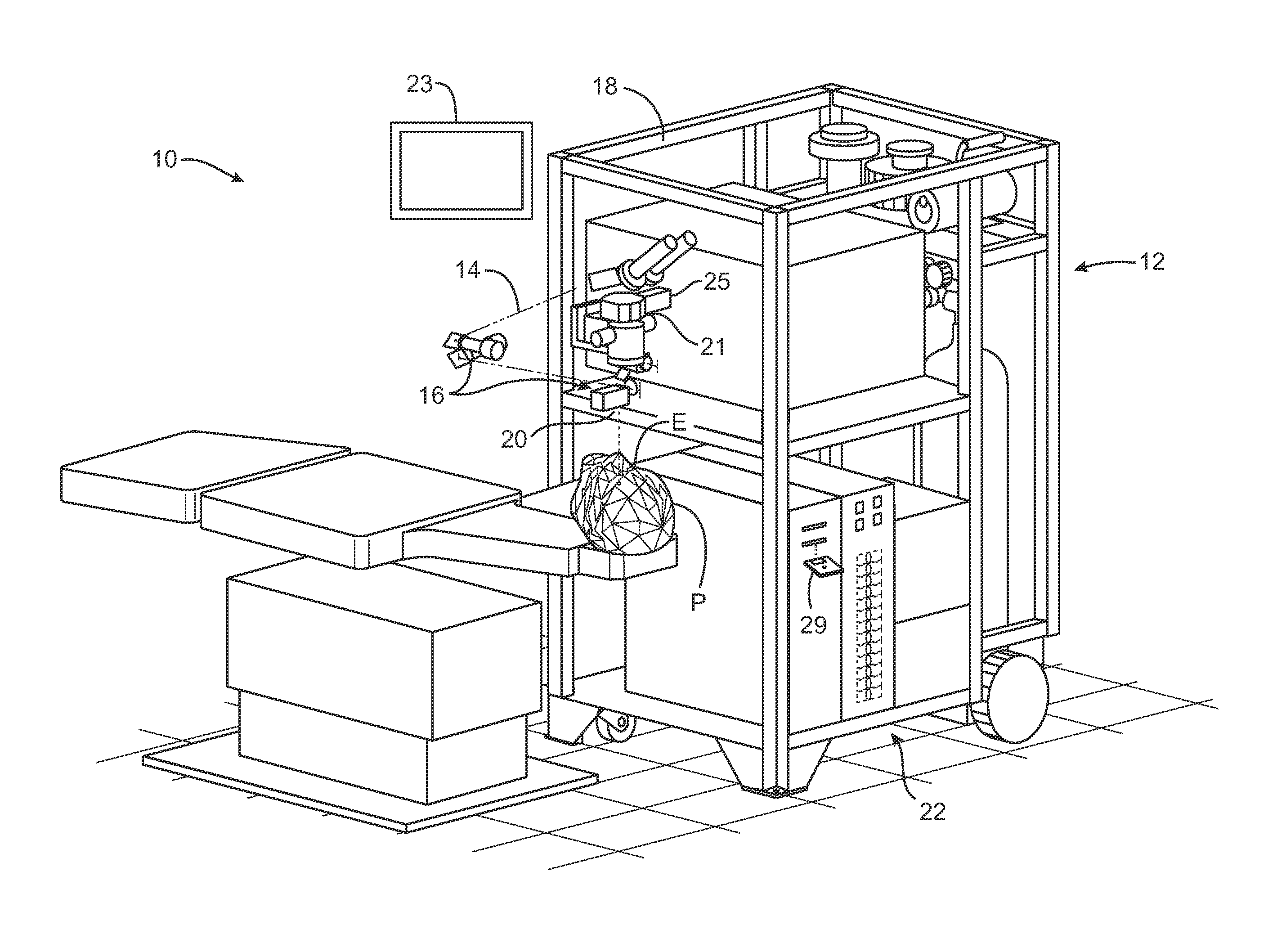
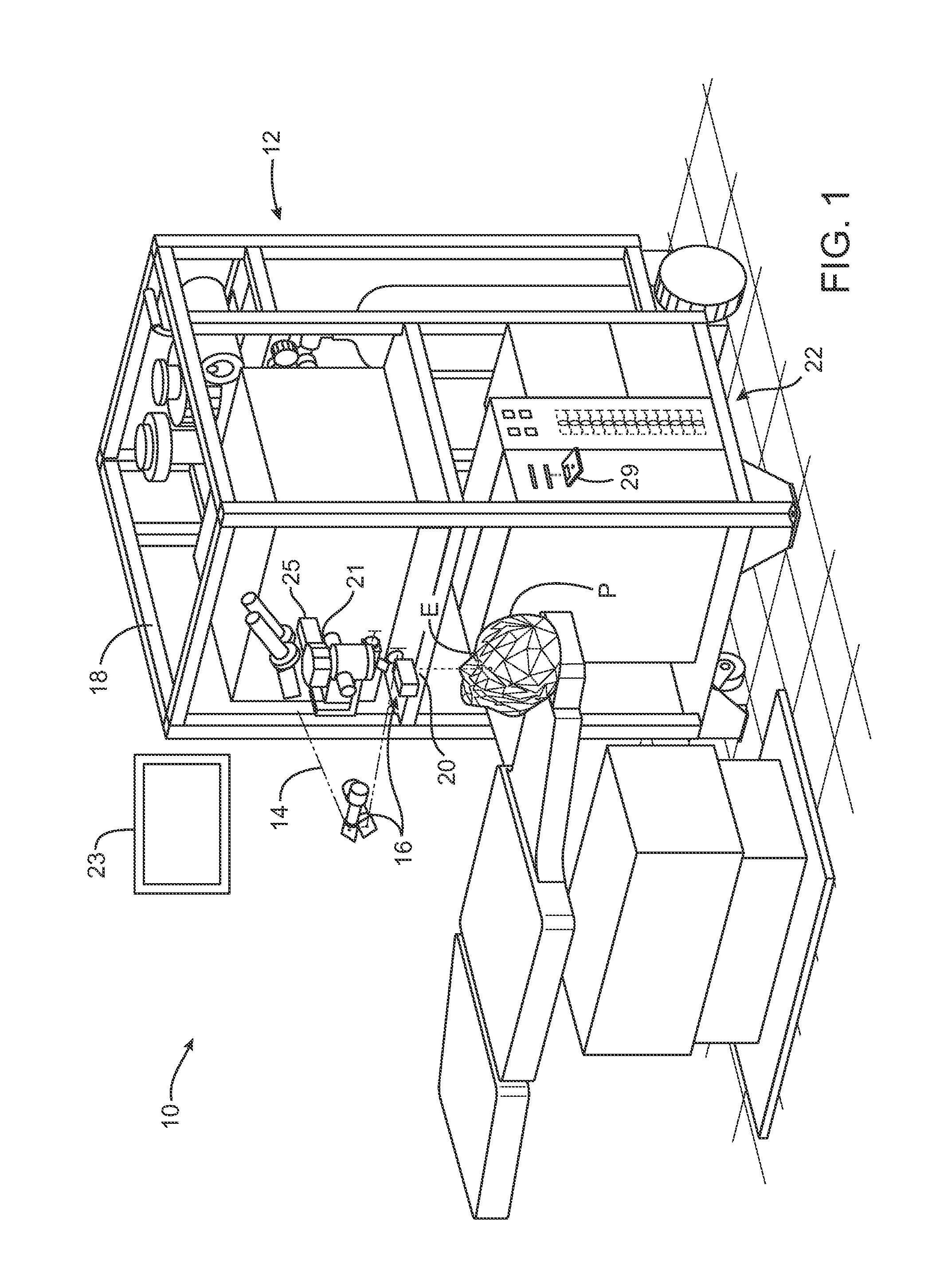
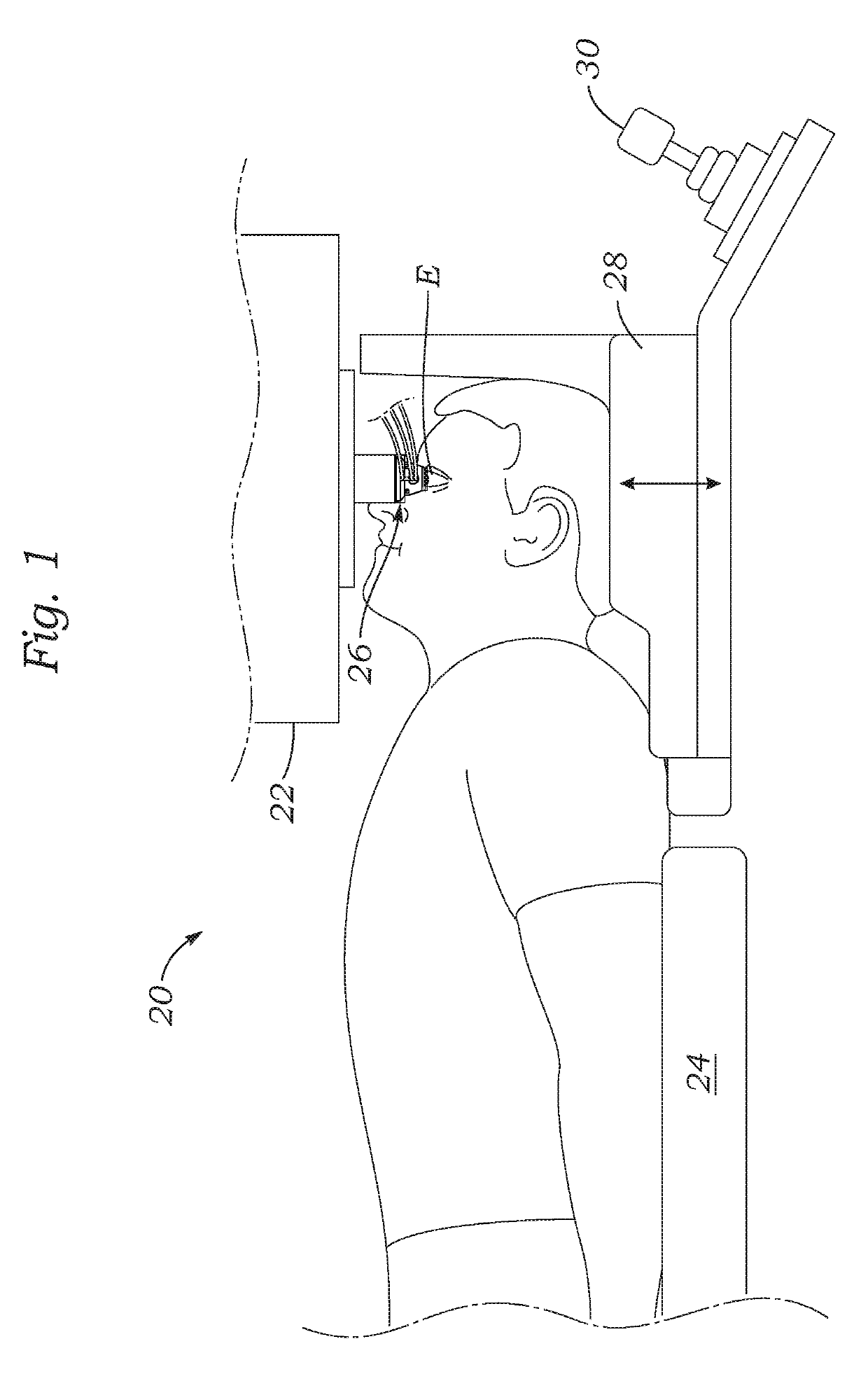
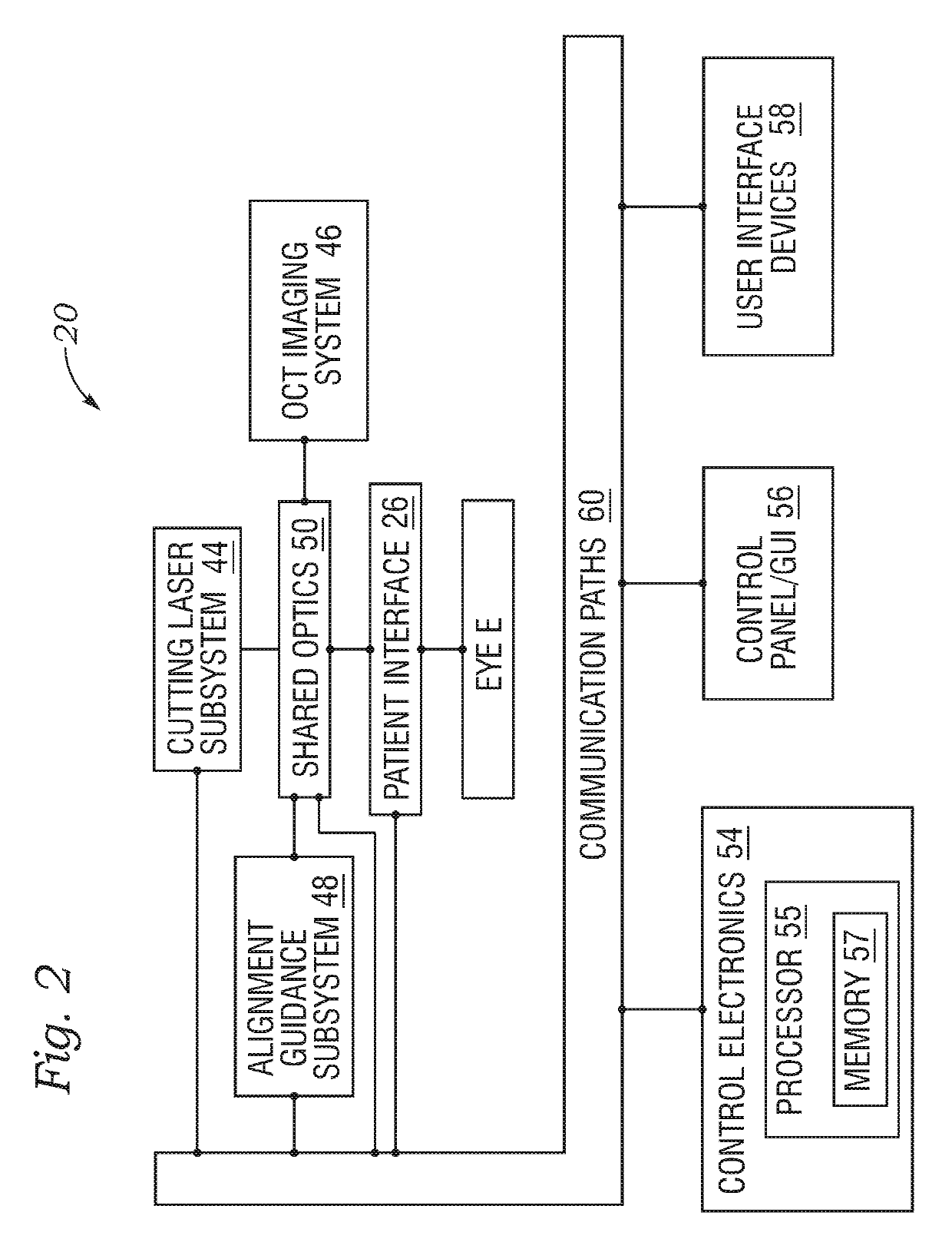
Illumination characteristic selection system for imaging during an ophthalmic laser procedure and associated methods
InactiveUS20070146634A1Particular polarization propertyGood effectLaser surgeryEye diagnosticsImaging processingLaser procedure
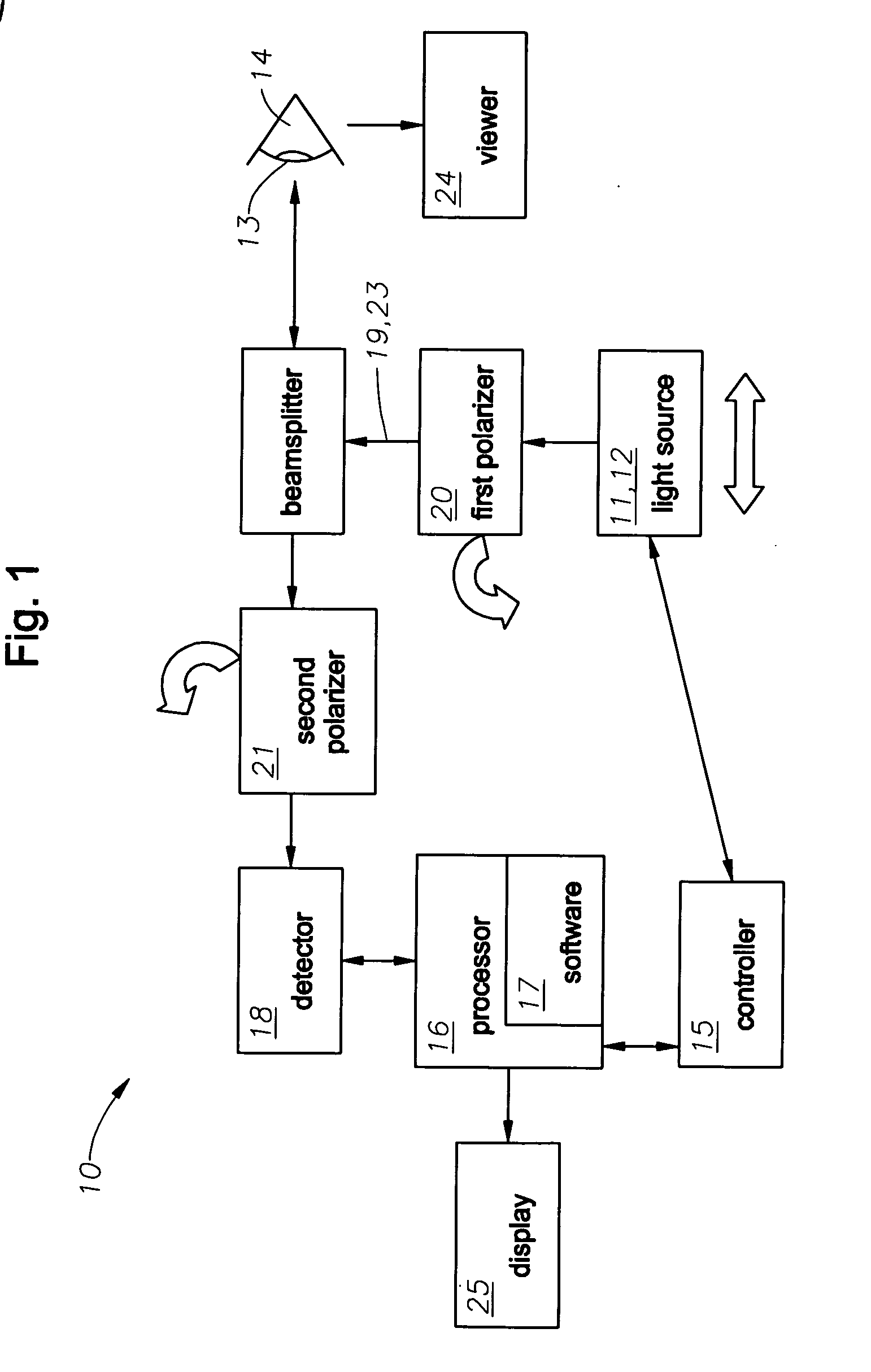
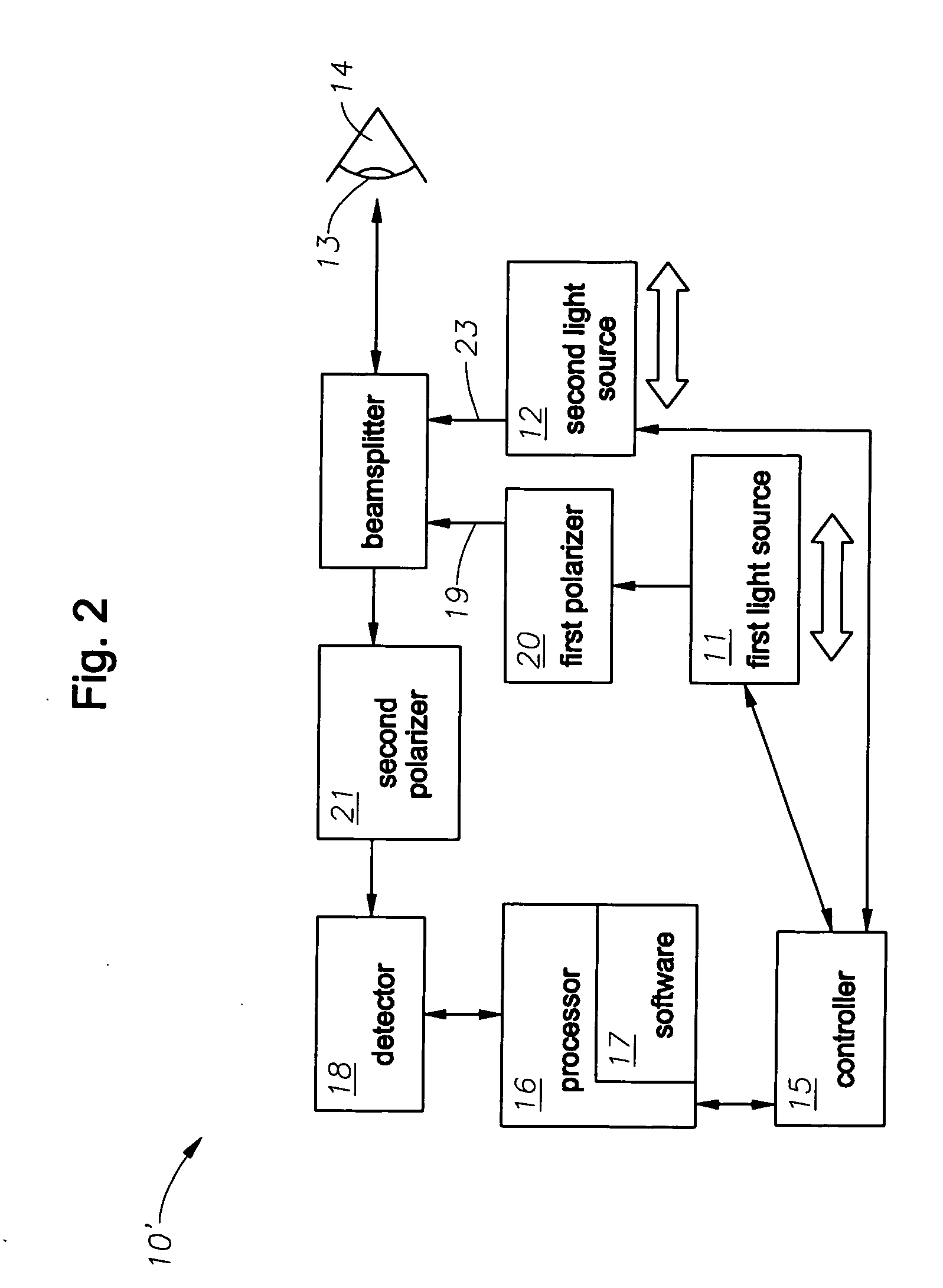
A system for optimizing the effects of light sources on viewing and image processing, and for imaging an illuminated object takes advantage of the fact that specularly reflected light has particular polarization properties compared with diffusely scattered light. The system includes a polarized light source to illuminate an object with a polarized beam and an unpolarized light source for delivering unpolarized light to illuminate the object with an unpolarized beam. A detector is positioned to receive light from the beams reflected from the object. A polarizer is oriented for substantially filtering out specular reflection from the object and for permitting at least a portion of diffuse reflection from the object to pass therethrough. The polarized and unpolarized light sources and the polarizer are controllable for selectively illuminating the object with and detecting light having a selected polarization characteristic as a function of a portion of a procedure being performed.
Owner:ALCON REFRACTIVEHORIZONS
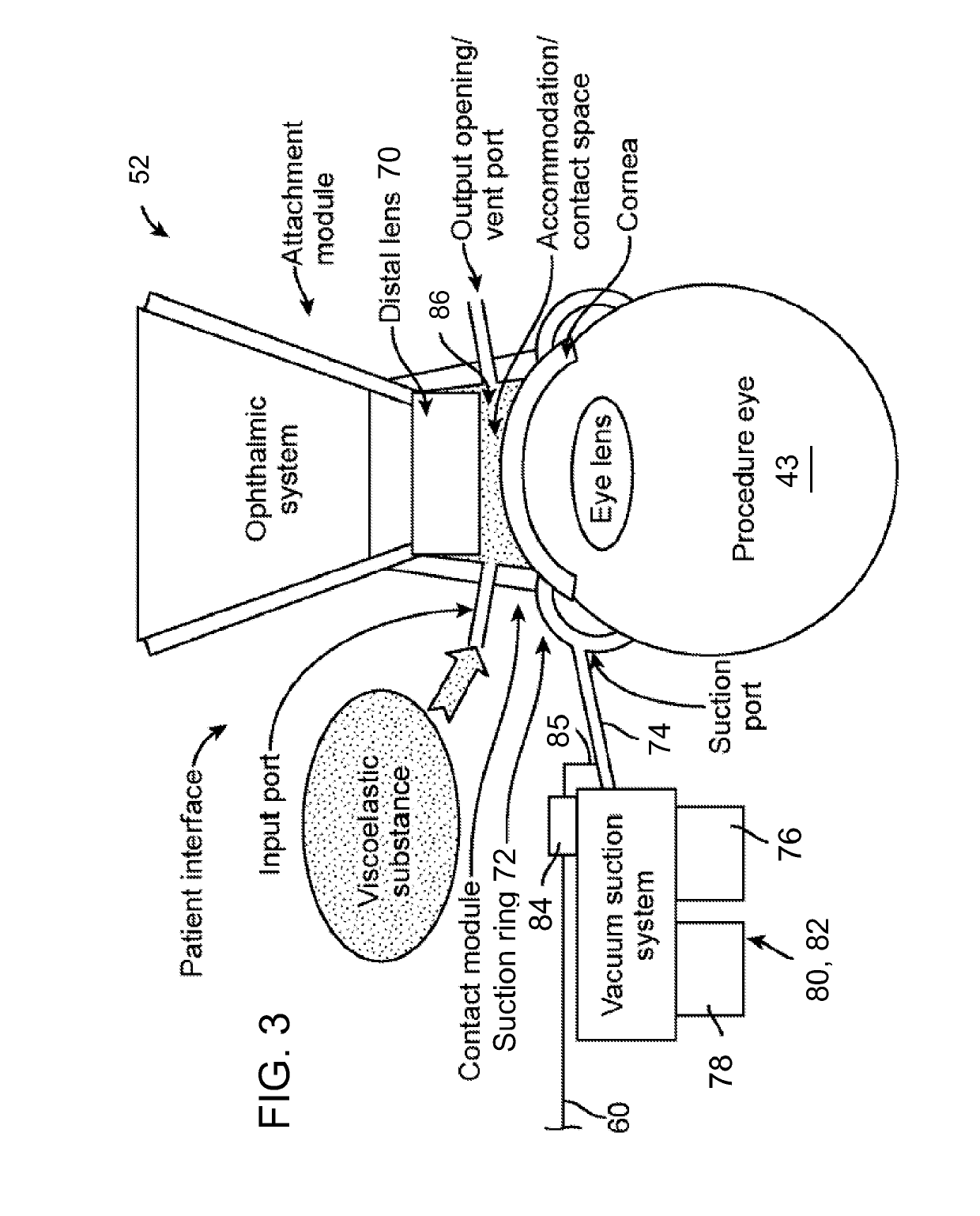
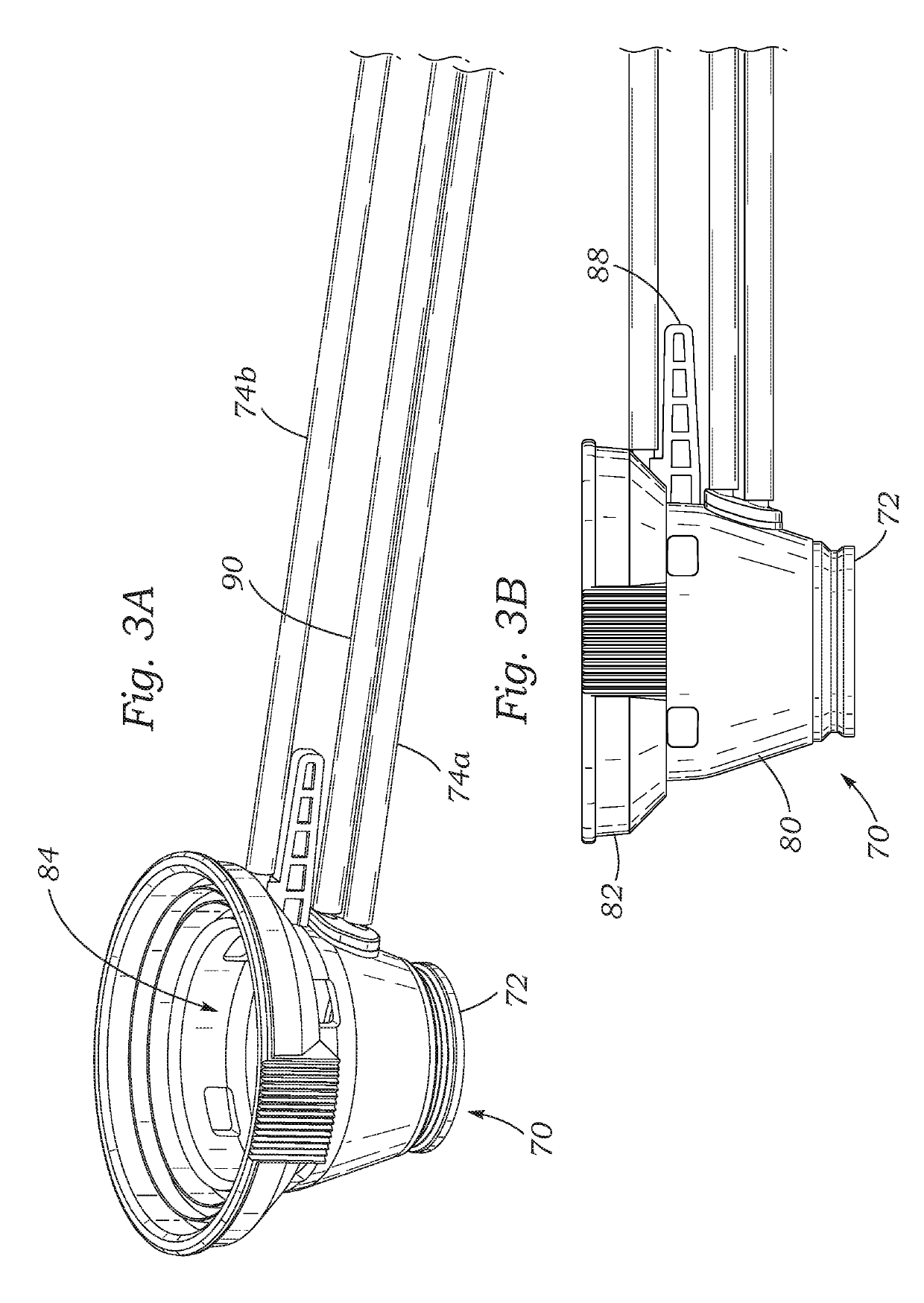
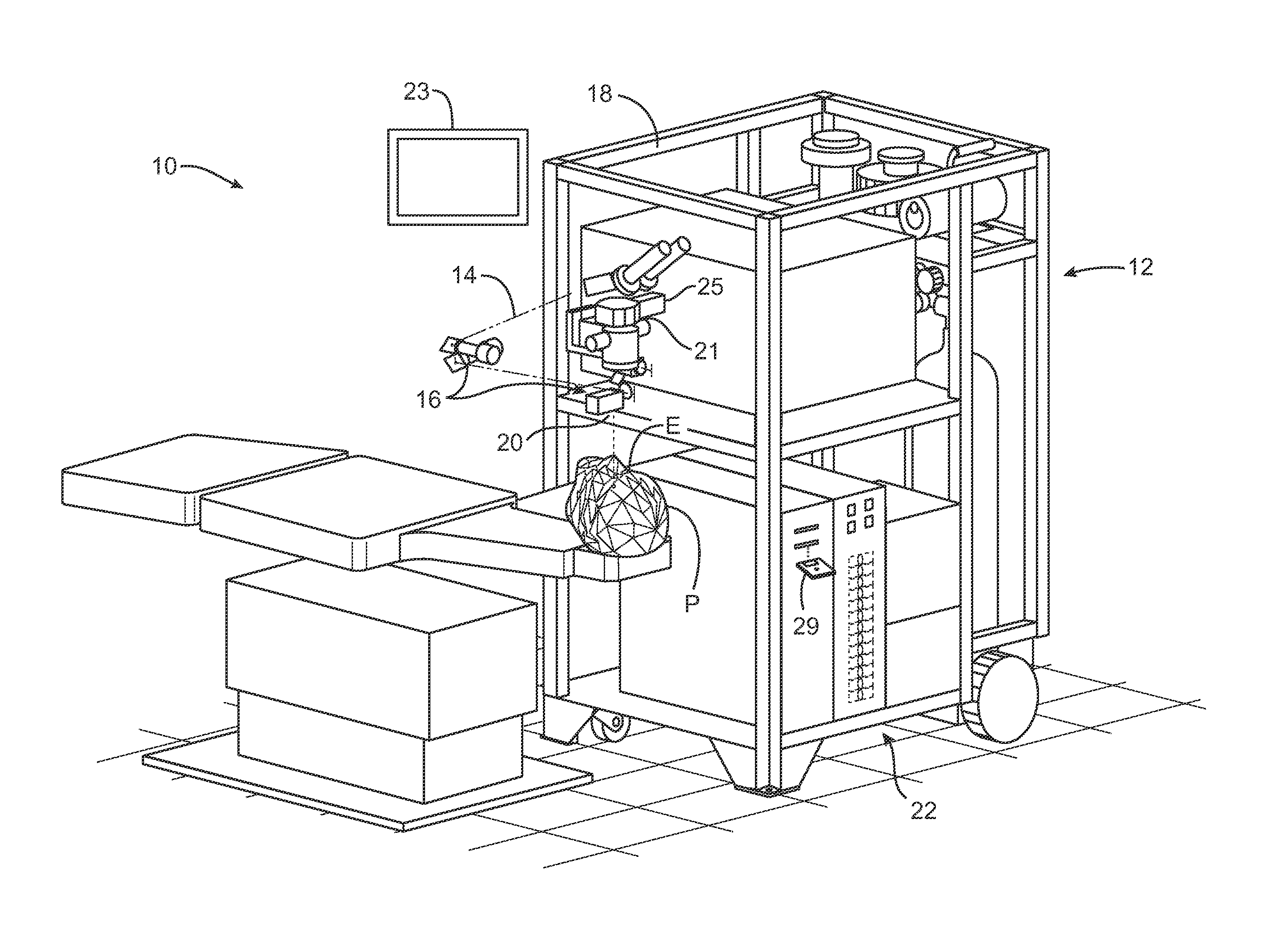
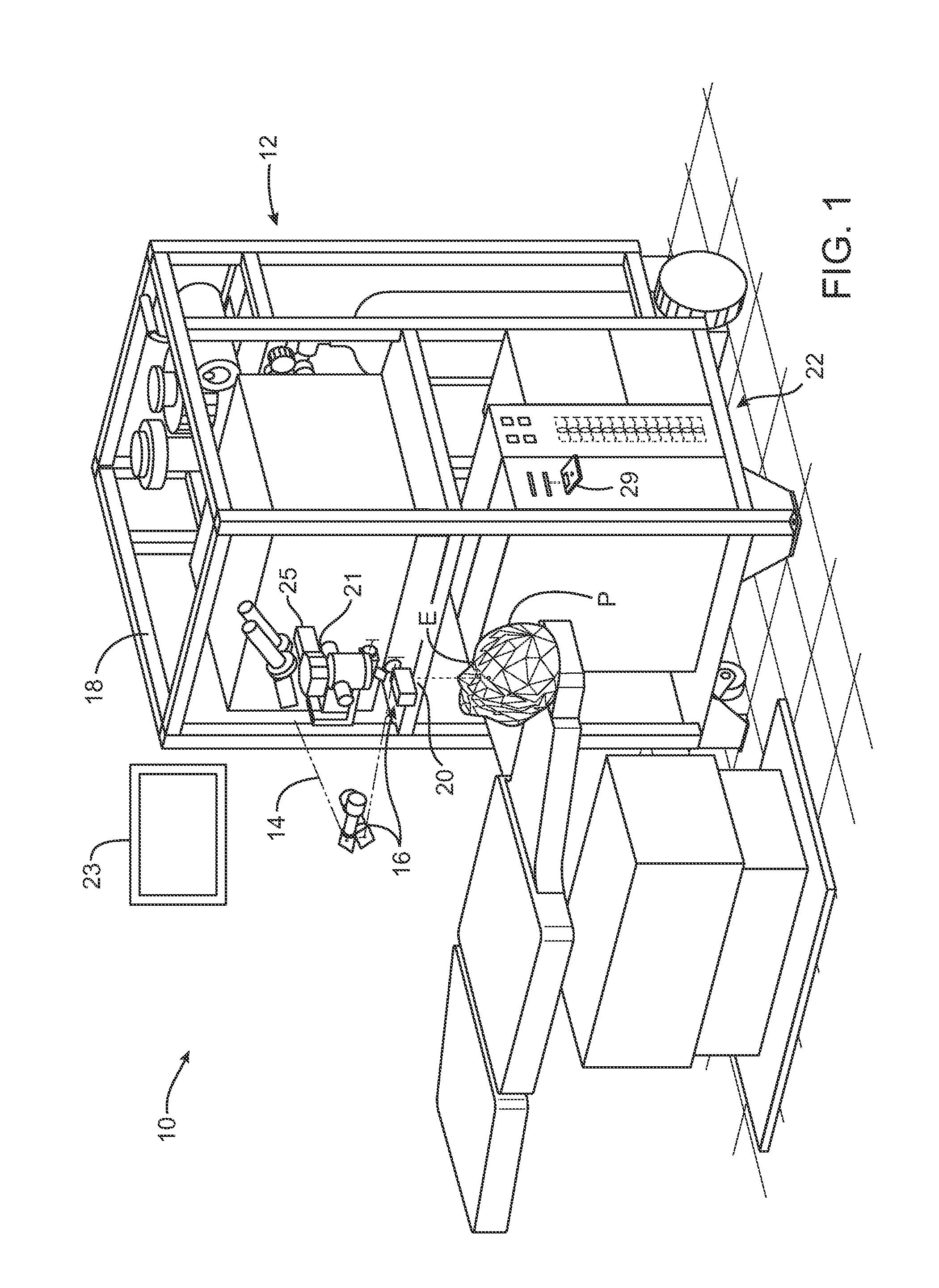
Adaptable patient interface
InactiveUS9603744B2Reduce and eliminate eye movementMinimize distortionLaser surgerySurgeryAnterior surfaceLaser procedure
Systems and methods are described for stabilizing an eye for an ocular laser procedure while minimizing corneal distortions which can adversely affect a surgical laser beam. For the systems, a patient interface includes a contact element for stabilizing the eye and establishing a conformal interface with the anterior surface of the cornea. More specifically, devices are disclosed which overlay both a central corneal region and a peripheral corneal region. In some embodiments, a first material is used in the contact element to overlay the central corneal region and a second material is used in the contact element to overlay the peripheral corneal region. Typically, the first and second materials differ in terms of hardness and deformability. In another embodiment disclosed herein, a contact element having a viscoelastic material for stabilizing an eye for a laser procedure is described.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
Systems and methods for lenticular laser incision
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Vacuum loss detection during laser eye surgery
ActiveUS20190151145A1Avoids imparting undesirable forceImproved laser eye surgery systemsLaser surgerySurgeryLiquid mediumLaser procedure
A laser eye surgery system that has a patient interface between the eye and the laser system relying on suction to hold the interface to the eye. The patient interface may be a liquid-filled interface, with liquid used as a transmission medium for the laser. During a laser procedure various inputs are monitored to detect a leak. The inputs may include a video feed of the eye looking for air bubbles in the liquid medium, the force sensors on the patient interface that detect patient movement, and vacuum sensors directly sensing the level of suction between the patient interface and the eye. The method may include combining three monitoring activities with a Bayesian algorithm that computes the probabilities of an imminent vacuum loss event.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Systems and methods for lenticular laser incision
Embodiments of this invention generally relate to ophthalmic laser procedures and, more particularly, to systems and methods for lenticular laser incision. In an embodiment, an ophthalmic surgical laser system comprises a laser delivery system for delivering a pulsed laser beam to a target in a subject's eye, an XY-scan device to deflect the pulsed laser beam, a Z-scan device to modify a depth of a focus of the pulsed laser beam, and a controller configured to form a top lenticular incision and a bottom lenticular incision of a lens in the subject's eye, where each of the top and bottom lenticular incision includes a center spherical portion and an edge transition portion that is not located on the same spherical surface as the spherical portion but has a steeper shape.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Operator-Controlled Scanning Laser Procedure Designed for Large-Area Epithelium Removal
Systems and methods for removing an epithelial layer disposed over a stromal layer in a cornea irradiate a region of the epithelial layer with a pulsed beam of ablative radiation. The ablative radiation is scanned to vary the location of the beam within the region in accordance with a pulse sequence. The pulse sequence is arranged to enhance optical feedback based on a tissue fluorescence of the epithelial layer. The penetration of the epithelial layer is detected in response to the optical feedback. The use of scanning with the pulse sequence arranged to enhance optical feedback allows large areas of the epithelium to be ablated such that an operator can detect penetration of the epithelial layer.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Systems and methods for femtosecond laser photorefractive keratectomy
ActiveUS20160250074A1Correct distortionConvenient treatmentLaser surgeryFemto second laserLaser procedure
Embodiments of this invention generally relate to ophthalmic laser procedures and, more particularly, to systems and methods for photorefractive keratectomy. In an embodiment, an ophthalmic surgical laser system comprises a laser source generating a pulsed laser beam and a laser delivery system delivering the pulsed laser beam to a cornea of an eye. A patient interface couples to and constrains the eye relative to the laser delivery system. A controller controls the laser delivery system to perform an anterior surface volume dissection on the cornea.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
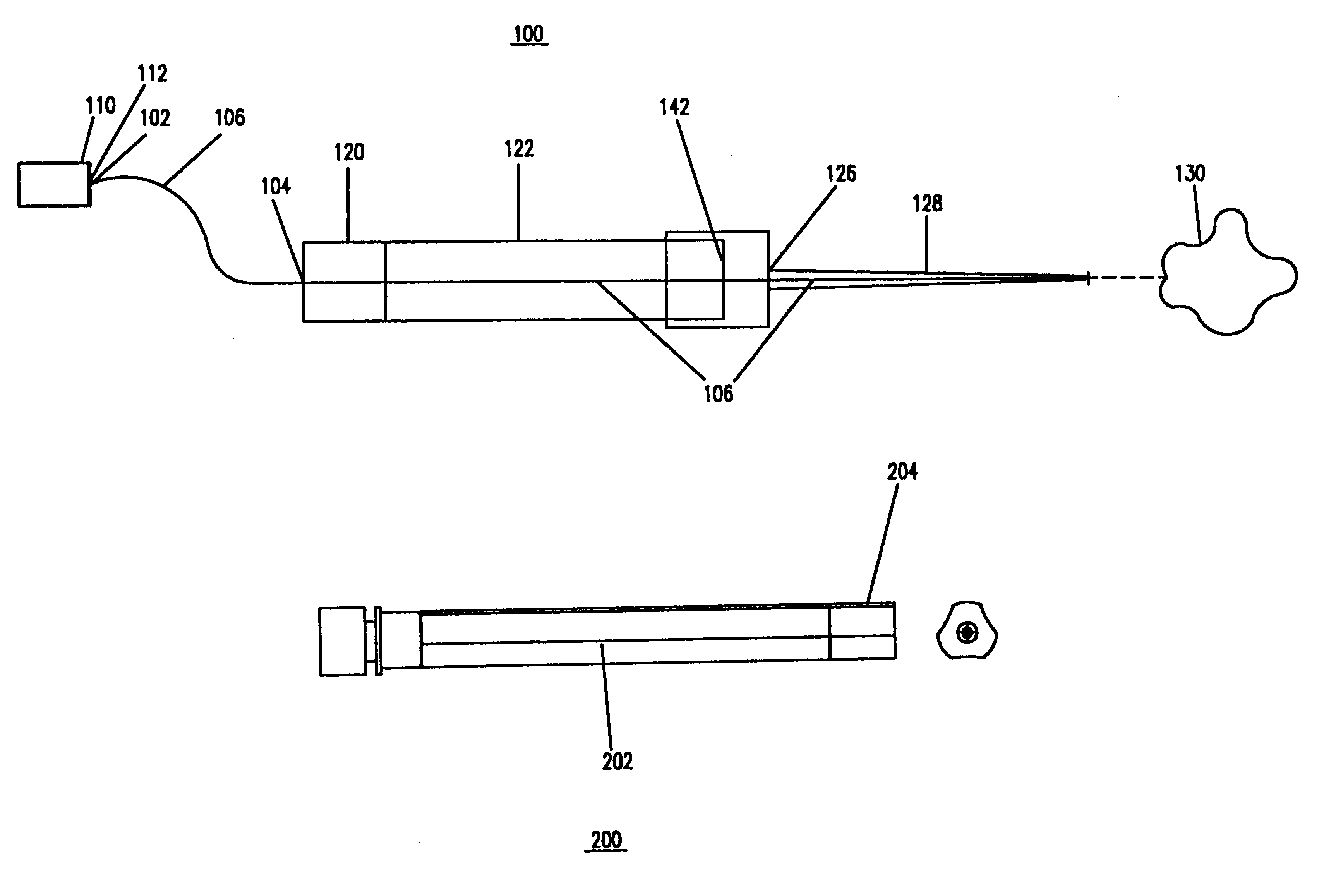
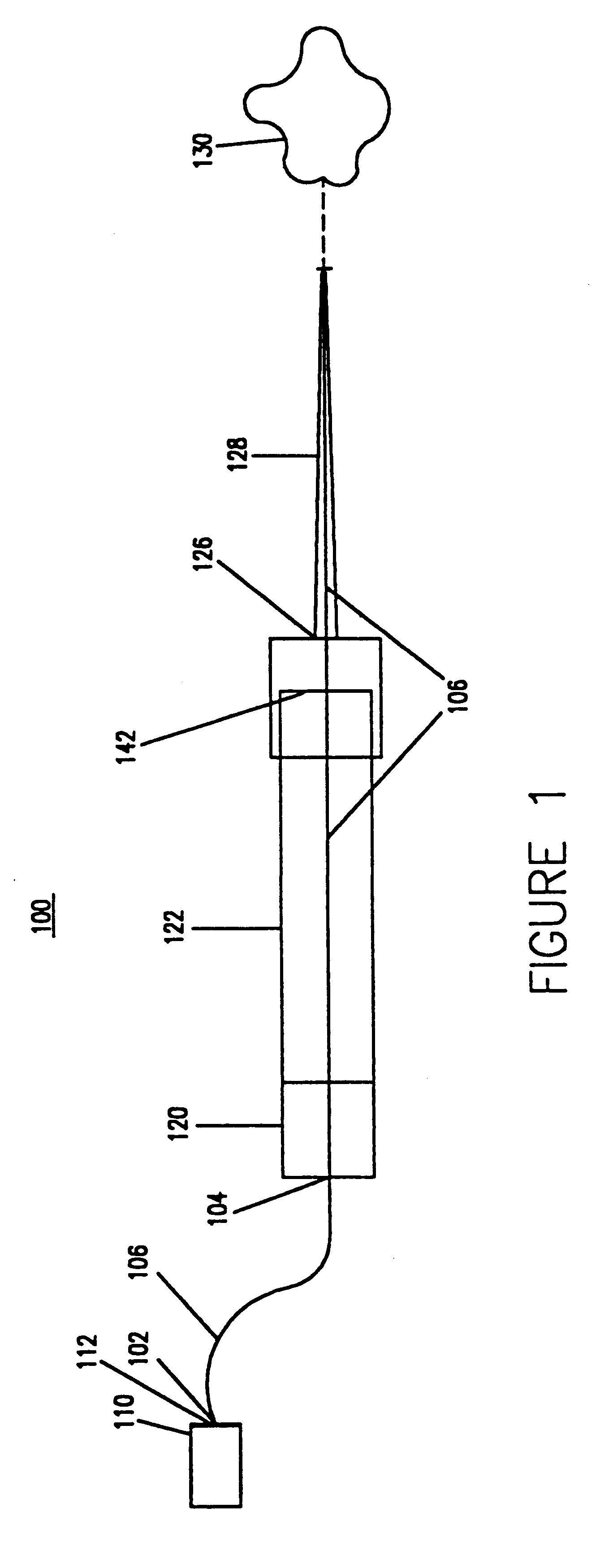
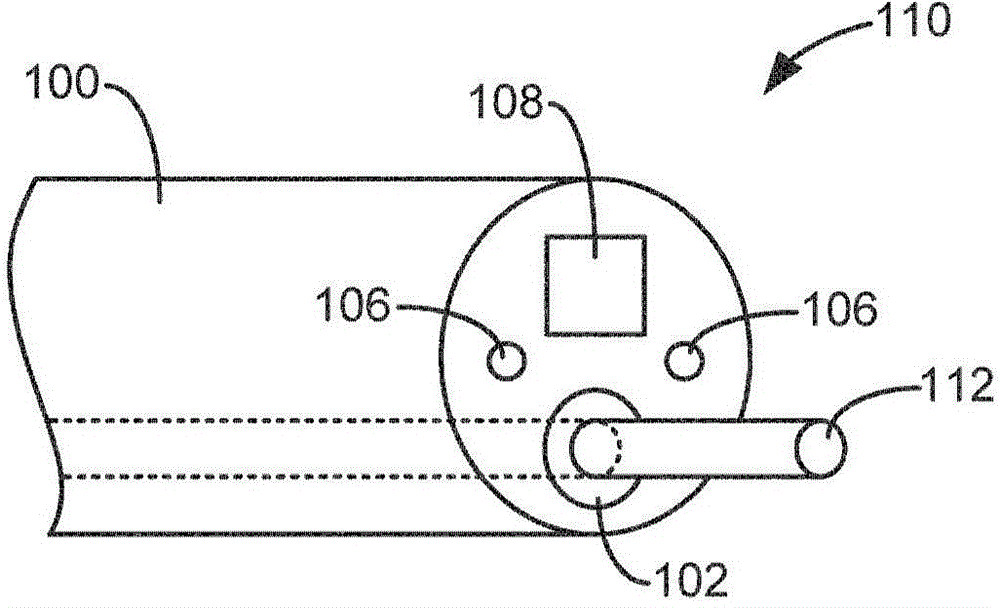
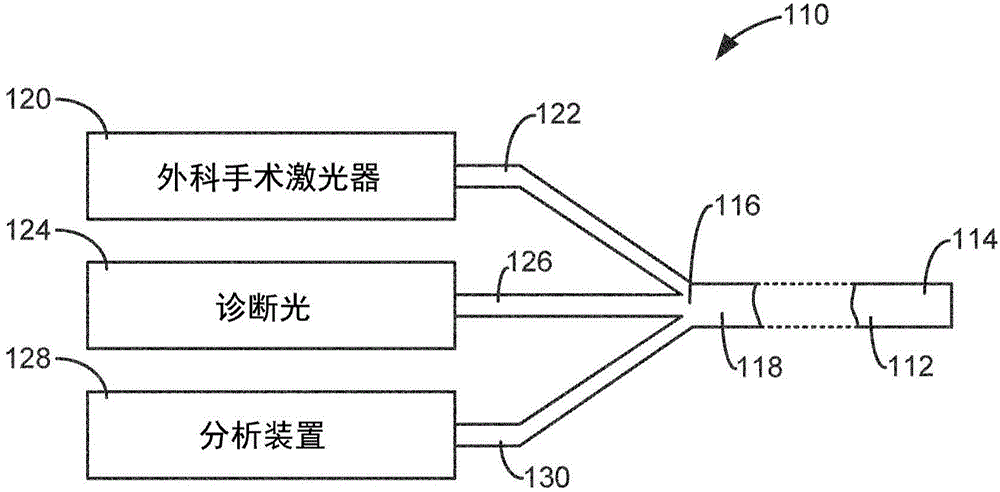
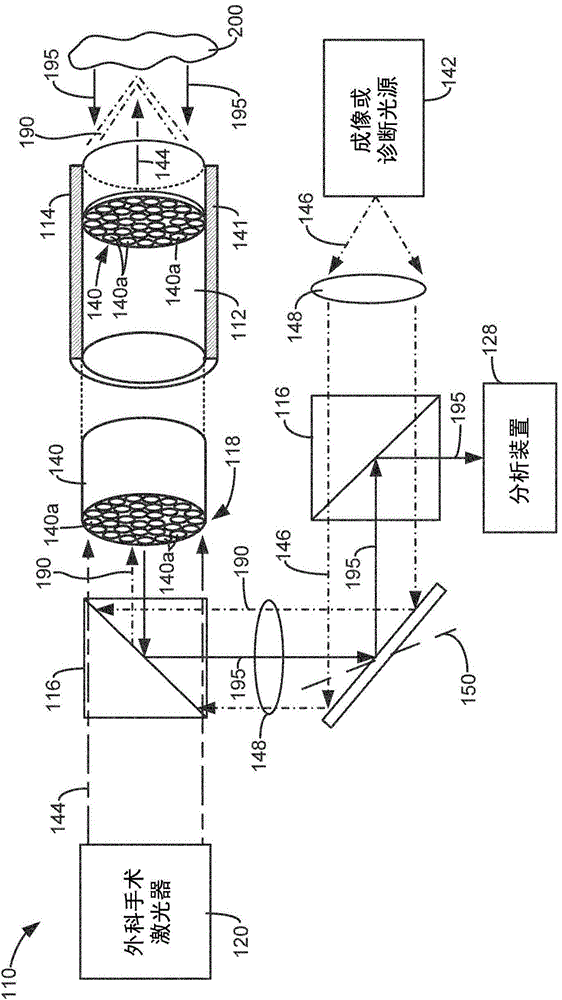
Surgical laser tool
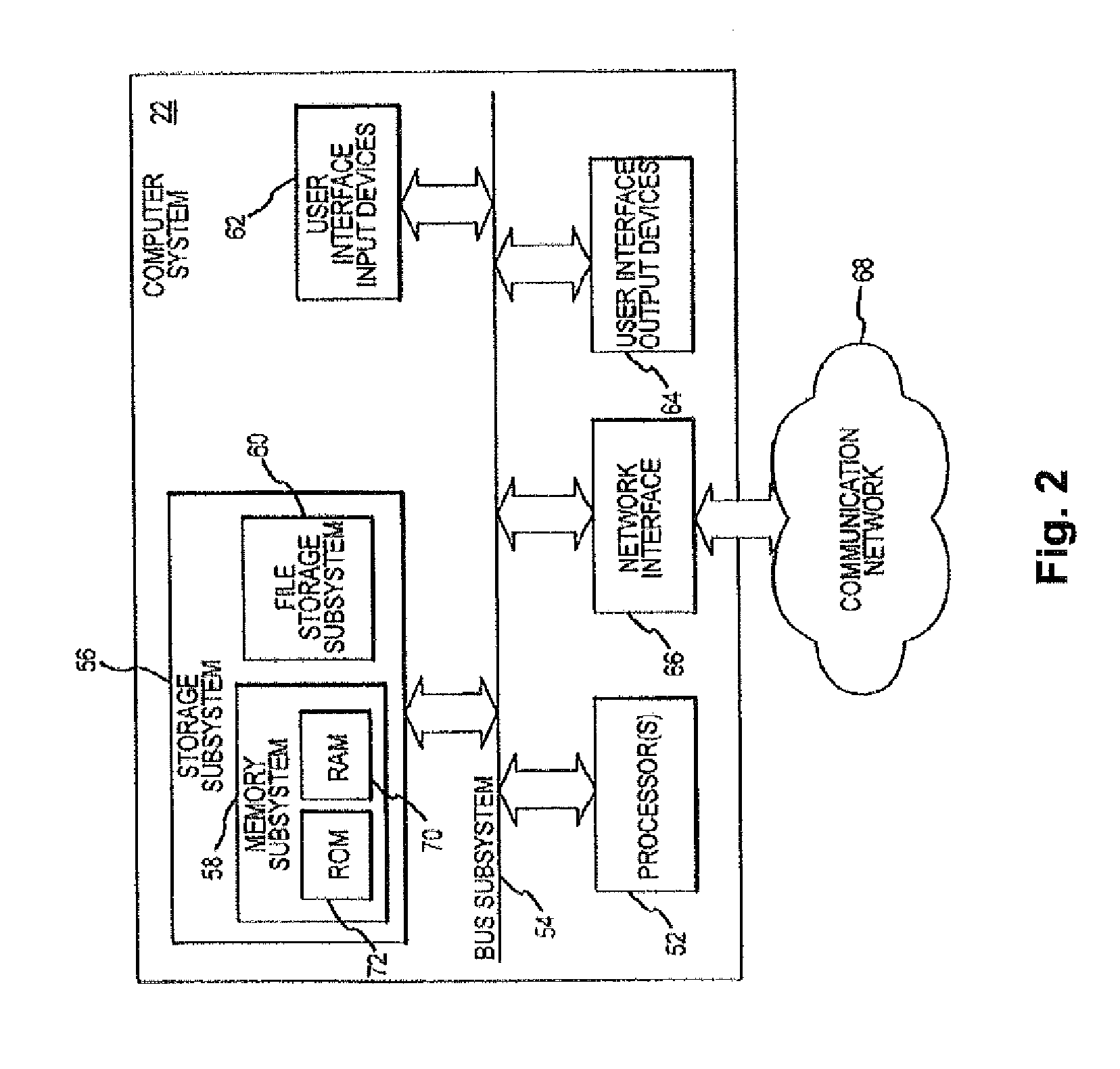
A surgical laser tool for performing a laser procedure at a treatment site is provided. The surgical laser tool includes a laser source, a fiber catheter, and an analytical device. The laser source is configured to generate laser energy. The fiber catheter is configured to (i) acquire optical feedback from the treatment site and (ii) deliver the laser energy to the treatment site. The analytical device is configured to analyze reflected light from the treatment site in order to allow a physician to perform a diagnosis on the treatment site.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Systems and methods for femtosecond laser photorefractive keratectomy
ActiveUS10716705B2Convenient treatmentCorrect distortionLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsFemto second laserLaser procedure
Embodiments of this invention generally relate to ophthalmic laser procedures and, more particularly, to systems and methods for photorefractive keratectomy. In an embodiment, an ophthalmic surgical laser system comprises a laser source generating a pulsed laser beam and a laser delivery system delivering the pulsed laser beam to a cornea of an eye. A patient interface couples to and constrains the eye relative to the laser delivery system. A controller controls the laser delivery system to perform an anterior surface volume dissection on the cornea.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Operator-controlled scanning laser procedure designed for large-area epithelium removal
Systems and methods for removing an epithelial layer disposed over a stromal layer in a cornea irradiate a region of the epithelial layer with a pulsed beam of ablative radiation. The ablative radiation is scanned to vary the location of the beam within the region in accordance with a pulse sequence. The pulse sequence is arranged to enhance optical feedback based on a tissue fluorescence of the epithelial layer. The penetration of the epithelial layer is detected in response to the optical feedback. The use of scanning with the pulse sequence arranged to enhance optical feedback allows large areas of the epithelium to be ablated such that an operator can detect penetration of the epithelial layer.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Operator-controlled scanning laser procedure designed for large-area epithelium removal
ActiveUS8926600B2Improve accuracyImprove efficacyLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsPulse beamEpithelium
Systems and methods for removing an epithelial layer disposed over a stromal layer in a cornea irradiate a region of the epithelial layer with a pulsed beam of ablative radiation. The ablative radiation is scanned to vary the location of the beam within the region in accordance with a pulse sequence. The pulse sequence is arranged to enhance optical feedback based on a tissue fluorescence of the epithelial layer. The penetration of the epithelial layer is detected in response to the optical feedback. The use of scanning with the pulse sequence arranged to enhance optical feedback allows large areas of the epithelium to be ablated such penetration of the epithelial layer can be detected.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Femtosecond laser system and methods for photorefractive keratectomy
ActiveUS20190125584A1Minimize disruptionLess discomfortLaser surgeryFemto second laserLaser procedure
Embodiments of this invention generally relate to ophthalmic laser procedures and, more particularly, to systems and methods for lenticular laser incision. In an embodiment, an ophthalmic surgical laser system comprises a laser delivery system for delivering a pulsed laser beam to a target in a subject's eye, an XY-scan device to deflect the pulsed laser beam, a Z-scan device to modify a depth of a focus of the pulsed laser beam, and a controller configured to form a top lenticular incision and a bottom lenticular incision of a lens in the subject's eye, or just a bottom lenticular incision.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Drive motor sealing barrel laser welding manufacturing method
ActiveCN107598373AGood pressure tightnessImprove efficiencyWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusHigh power lasersLaser procedure
The invention discloses a drive motor sealing barrel laser welding manufacturing method. A high power laser beam is subject to single-face welding and double-face molding welding, an annular rigid clamp in special design and a V-shaped groove type on the back face are adopted in the welding process, laser spot welding positioning is firstly carried out according to the sealing barrel special structure after clamping, a high-frequency impulse modulation laser procedure is adopted for welding, a welding seam track is subject to symmetrical welding, machining is carried out after welding to remove surface welding seam sinking parts and welding seam roots, and a control rod drive motor sealing barrel with a certain wall thickness is obtained. According to the drive motor sealing barrel laser welding manufacturing method, effective welding seam fusion depth is larger than 10 mm, the welding seam width is smaller than 1.5 mm, and the good pressure-resistant sealing performance is achieved.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Systems and methods for dynamic patient fixation system
The field of the invention relates to systems and methods for ophthalmic laser procedure and, more particularly, to systems and methods for dynamic fixation used in the fixation of the eye(s) of a patient during laser-assisted ophthalmic surgery and / or ophthalmic diagnostic and measurement systems where visualization and concentration on a target are desired. The invention generally enhances the alignment between the eye and a laser beam of a laser eye surgery system using visual fixation system and laser delivery optics. The visual fixation system allows a patient's eye(s) to be accurately focused at one or more fixation targets.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Systems and methods for lenticular laser incision
Embodiments of this invention generally relate to ophthalmic laser procedures and, more particularly, to systems and methods for lenticular laser incision. In an embodiment, an ophthalmic surgical laser system comprises a laser delivery system for delivering a pulsed laser beam to a target in a subject's eye, an XY-scan device to deflect the pulsed laser beam, a Z-scan device to modify a depth of a focus of the pulsed laser beam, and a controller configured to form a top lenticular incision and a bottom lenticular incision of a lens in the subject's eye, where each of the top and bottom lenticular incision includes a center spherical portion and an edge transition portion that is not located on the same spherical surface as the spherical portion but has a steeper shape.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
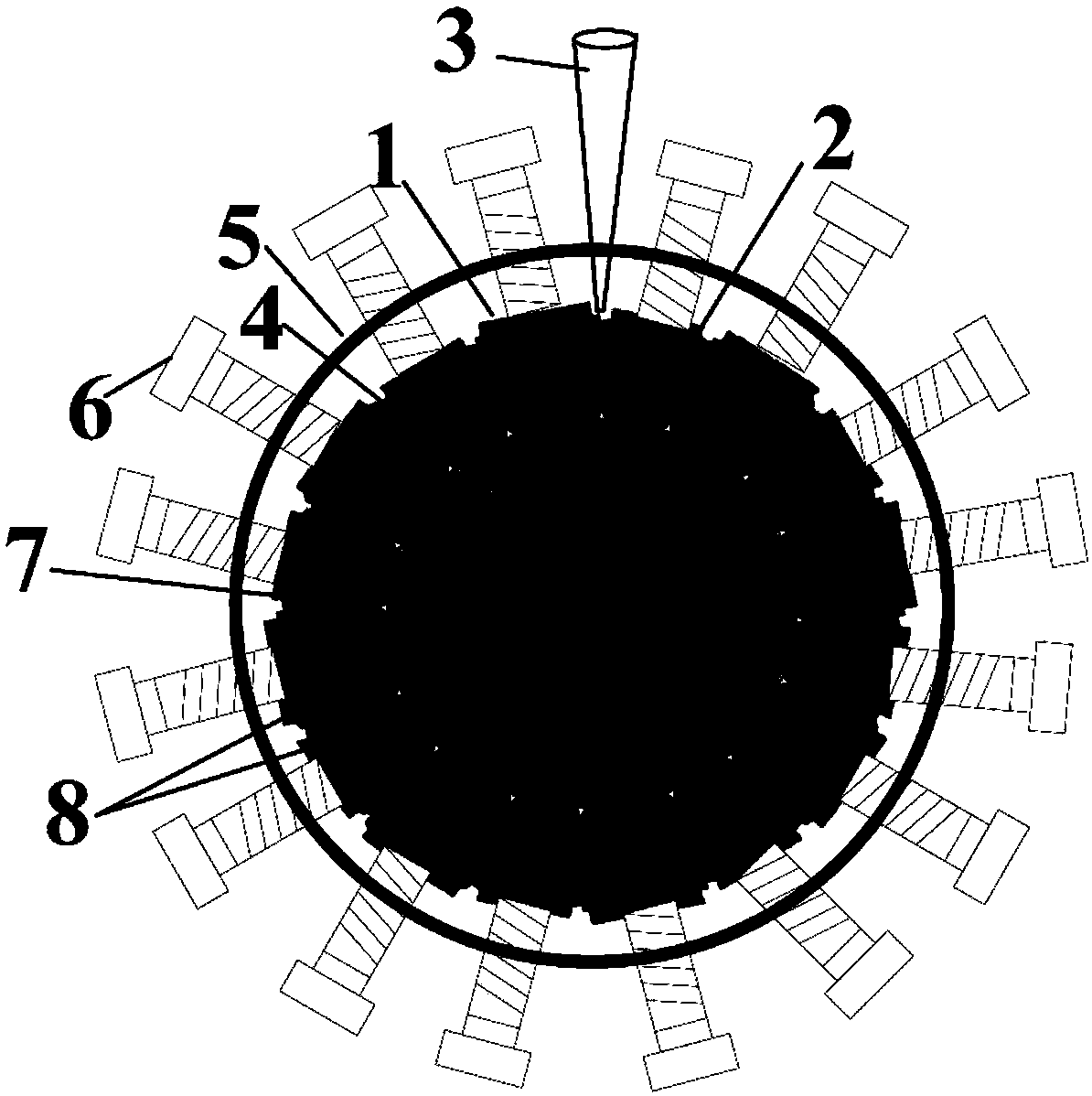
A docking interface device
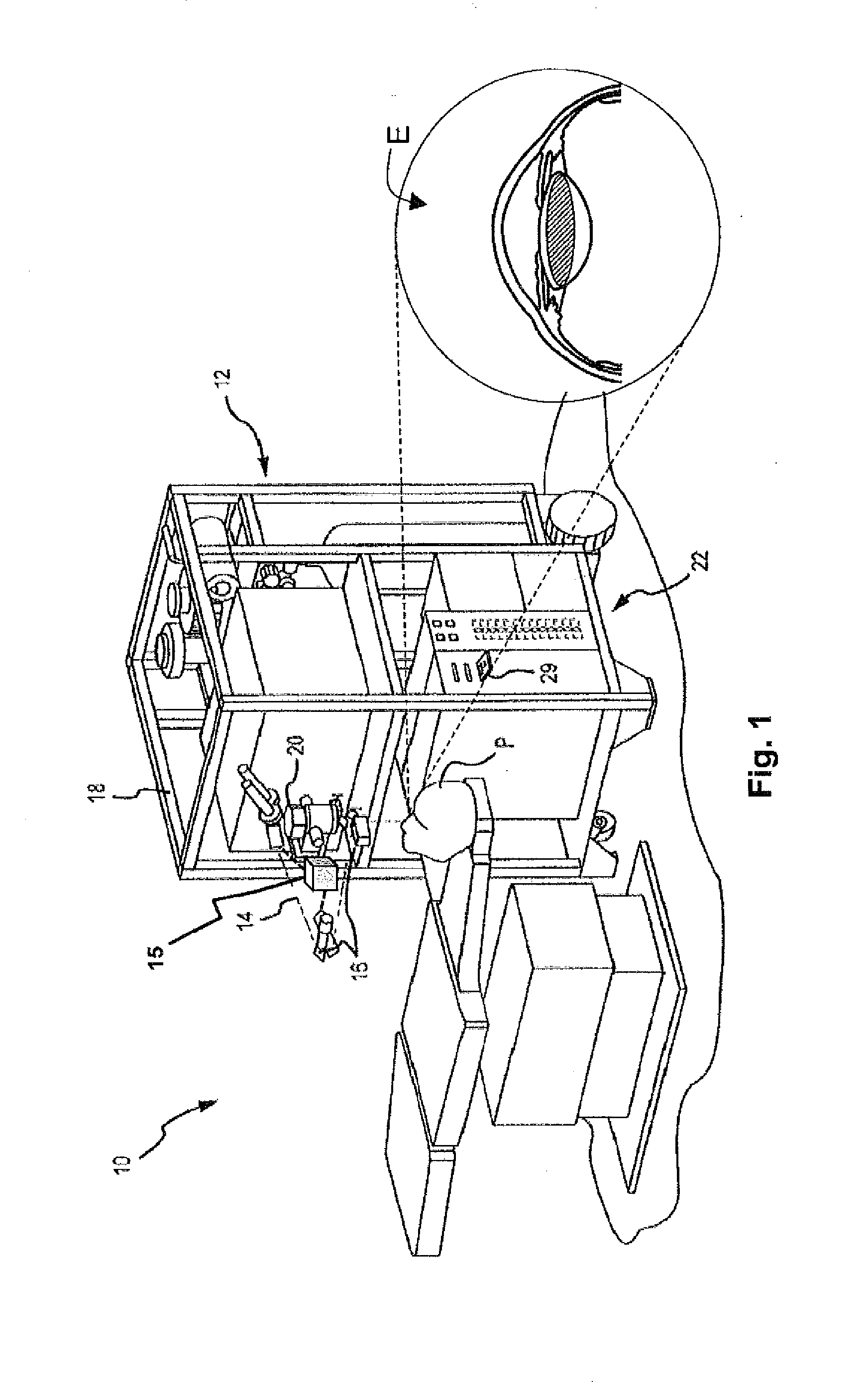
The invention relates to a butt joint interface device for establishing a stable docking of a laser beam with an eye during a laser procedure, which includes an attachment device, a suction ring, a pressure distribution ring, and a vacuum device interface. The attachment device is connected to a laser light path outlet of the ophthalmologic operation equipment. The vacuum device interface is connected with an external vacuumizing device; the suction ring is in direct contact with the eyes, and negative pressure generated by the external vacuumizin device is distributed to the surfaces of theeyeballs through the pressure distribution ring, so that the vacuum pressure is prevented from directly acting on the eyeballs, corneal deformation can be reduced, pressure applied to the eyeballs bythe butt joint interface device is reduced, corneal deformation and corneal wrinkles are reduced, and operation safety is improved. According to the butt joint interface device, stable butt joint canbe established between a treatment laser beam and the eye during an ophthalmologic laser operation, a flattening lens is not in direct contact with the cornea of the eye in the butt joint process, optical path connection between the focusing lens and the front surface of the eye is completed through a liquid medium, and therefore rising of intraocular pressure caused in the butt joint process is reduced.
Owner:JIHUA LAB
Systems and methods for dynamic patient fixation system
The field of the invention relates to systems and methods for ophthalmic laser procedure and, more particularly, to systems and methods for dynamic fixation used in the fixation of the eye(s) of a patient during laser-assisted ophthalmic surgery and / or ophthalmic diagnostic and measurement systems where visualization and concentration on a target are desired. The invention generally enhances the alignment between the eye and a laser beam of a laser eye surgery system using visual fixation system and laser delivery optics. The visual fixation system allows a patient's eye(s) to be accurately focused at one or more fixation targets.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Laser patch and laser patch procedure set including same
The present invention relates to a laser patch. According to an embodiment of the present invention, the laser patch comprises: a plate-like patch body having a through-hole for penetration of a laser; a circuit board disposed in the patch body; a built-in battery disposed in the patch body; and a laser diode element electrically connected to the circuit board, and supplied with power from the built-in battery to emit the low output laser to the outside of the patch body. The laser diode element comprises: a first element emitting the low output laser having a wavelength range of 630-680 nm; and a second element emitting the low output laser having a wavelength range of 780-990 nm.
Owner:WELLSCARE CO LTD
Adaptable patient interface
InactiveUS20140135750A1Reduce and eliminate eye movementMinimizing corneal distortionLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsLaser procedureAnterior surface
Systems and methods are described for stabilizing an eye for an ocular laser procedure while minimizing corneal distortions which can adversely affect a surgical laser beam. For the systems, a patient interface includes a contact element for stabilizing the eye and establishing a conformal interface with the anterior surface of the cornea. More specifically, devices are disclosed which overlay both a central corneal region and a peripheral corneal region. In some embodiments, a first material is used in the contact element to overlay the central corneal region and a second material is used in the contact element to overlay the peripheral corneal region. Typically, the first and second materials differ in terms of hardness and deformability. In another embodiment disclosed herein, a contact element having a viscoelastic material for stabilizing an eye for a laser procedure is described.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
Liquid loss detection during laser eye surgery
ActiveUS10406032B2Avoid undesirable forceImproved laser eye surgery systemsLaser surgeryControl electronicsLaser procedure
A laser eye surgery system that has a patient interface between the eye and the laser system relying on suction to hold the interface to the eye, the patient interface using liquid used as a transmission medium for the laser. During a laser procedure sensors monitor the level of liquid within the patient interface and send a signal to control electronics if the level drops below a threshold value. The sensor may be mounted on the inside of the patient interface, within a fluid chamber. Alternatively, a gas flow meter may be added to a suction circuit for the patient interface that detects abnormal suction levels indicating low fluid level.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Systems and methods for synchronized three-dimensional laser incisions
Embodiments of this invention generally relate to ophthalmic laser procedures and, more particularly, to systems and methods for creating synchronized three-dimensional laser incisions. In an embodiment, an ophthalmic surgical laser system comprises a laser delivery system for delivering a pulsed laser beam to a target in a subject's eye, an XY-scan device to deflect the pulsed laser beam, a Z-scan device to modify a depth of a focus of the pulsed laser beam, and a controller configured to synchronize an oscillation of the XY-scan device and an oscillation of the Z-device to form an angled three-dimensional laser tissue dissection.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com