Patents
Literature
439 results about "Curved mirror" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
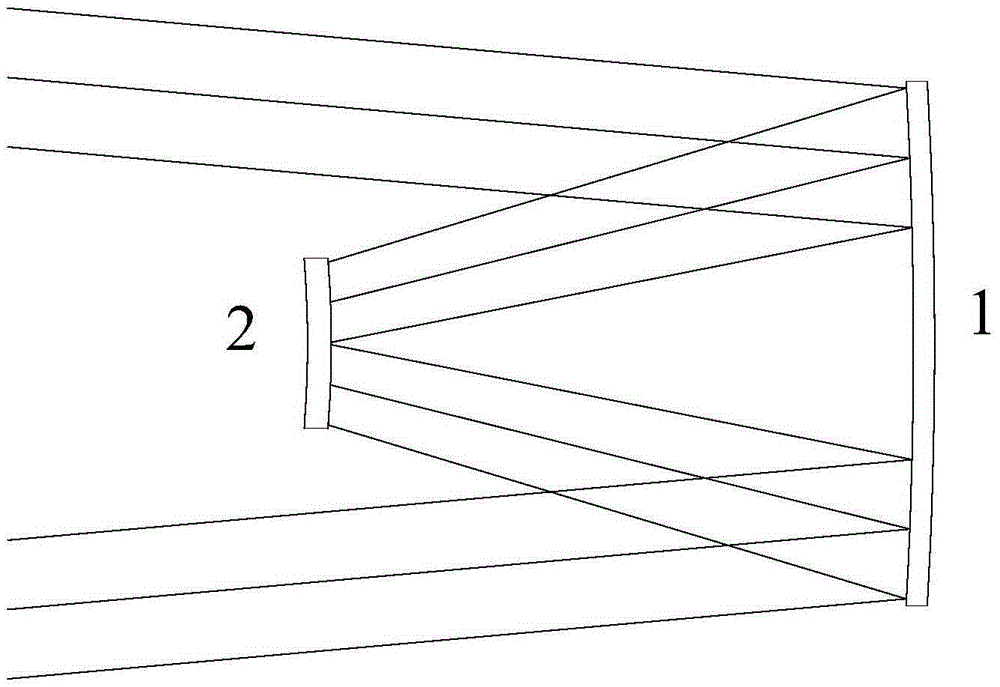
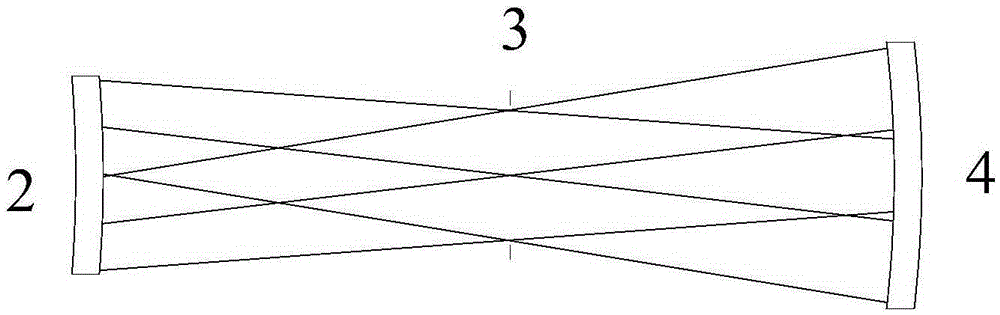
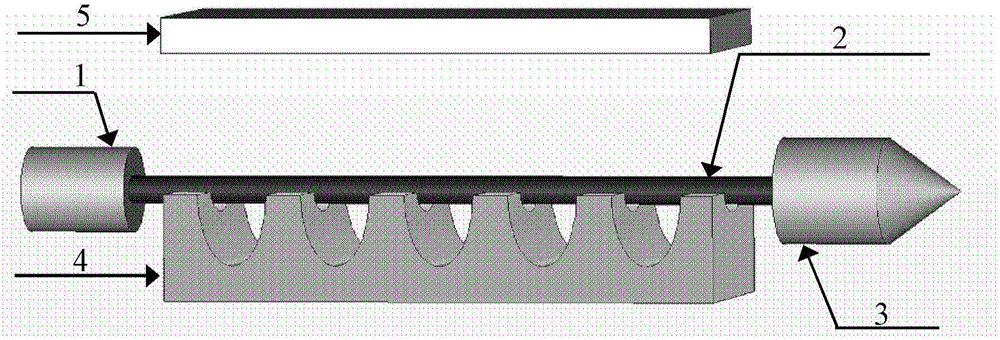
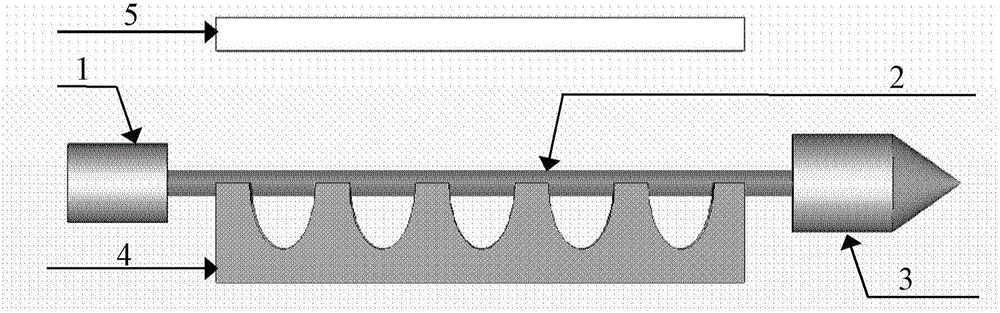
A curved mirror is a mirror with a curved reflecting surface. The surface may be either convex (bulging outward) or concave (recessed inward). Most curved mirrors have surfaces that are shaped like part of a sphere, but other shapes are sometimes used in optical devices. The most common non-spherical type are parabolic reflectors, found in optical devices such as reflecting telescopes that need to image distant objects, since spherical mirror systems, like spherical lenses, suffer from spherical aberration. Distorting mirrors are used for entertainment. They have convex and concave regions that produce deliberately distorted images. They also provide highly magnified or highly diminished images when the object is placed at certain distances.
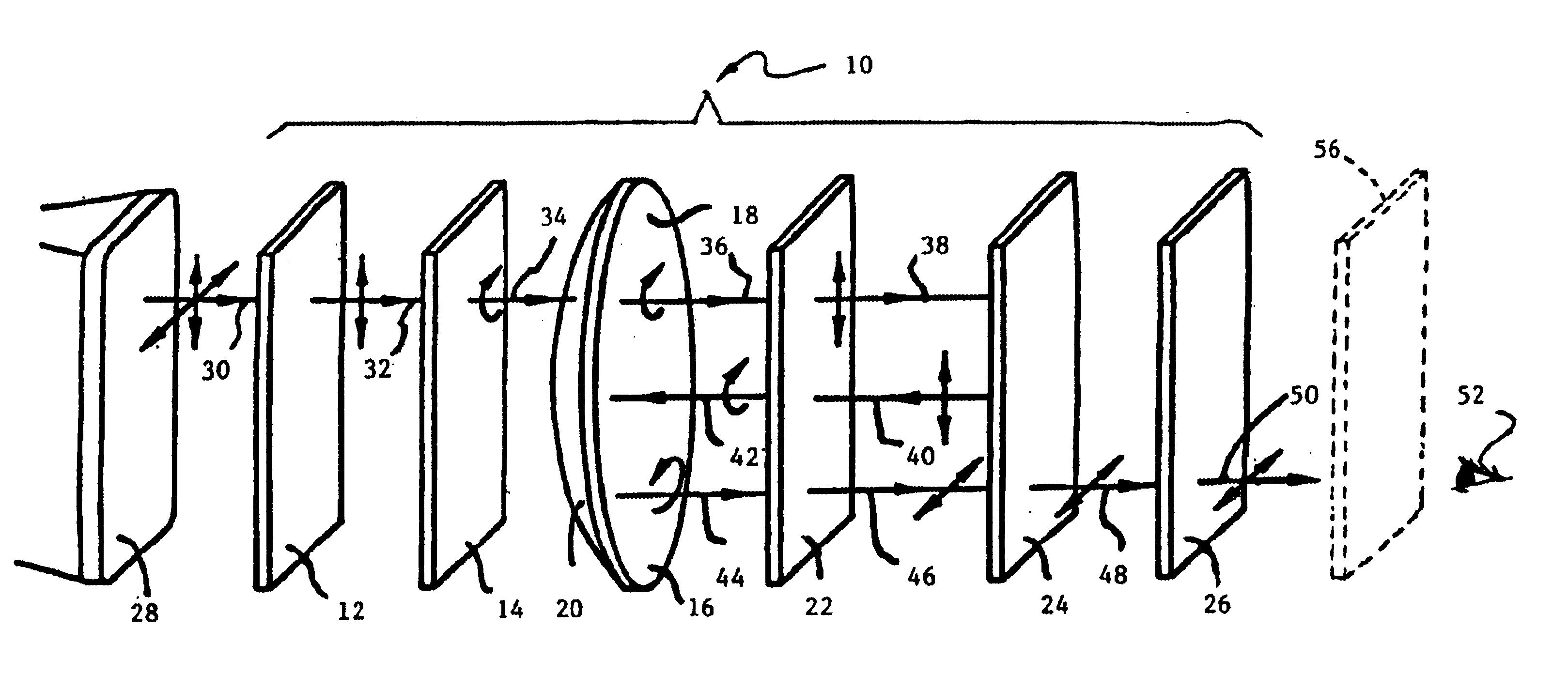
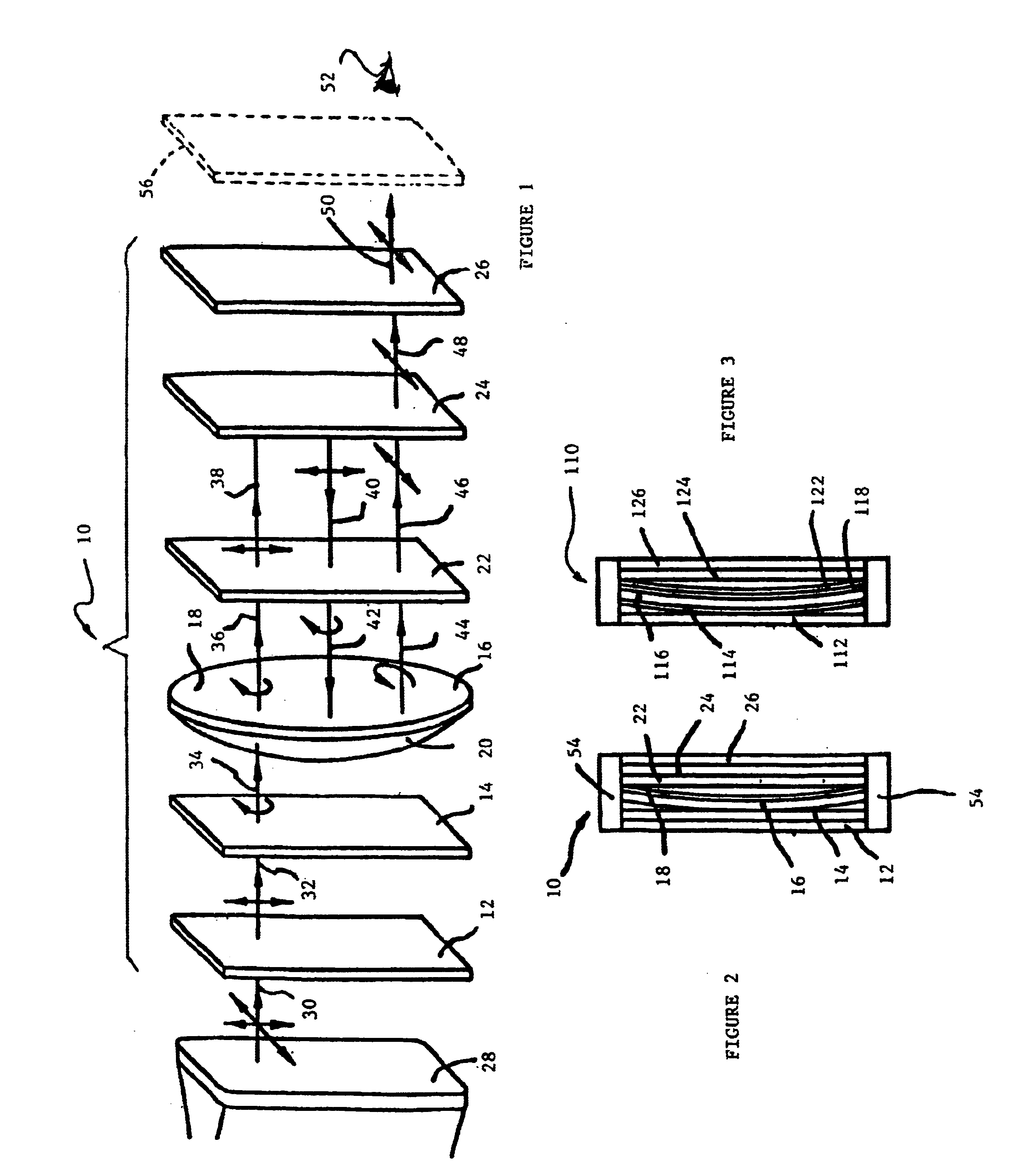
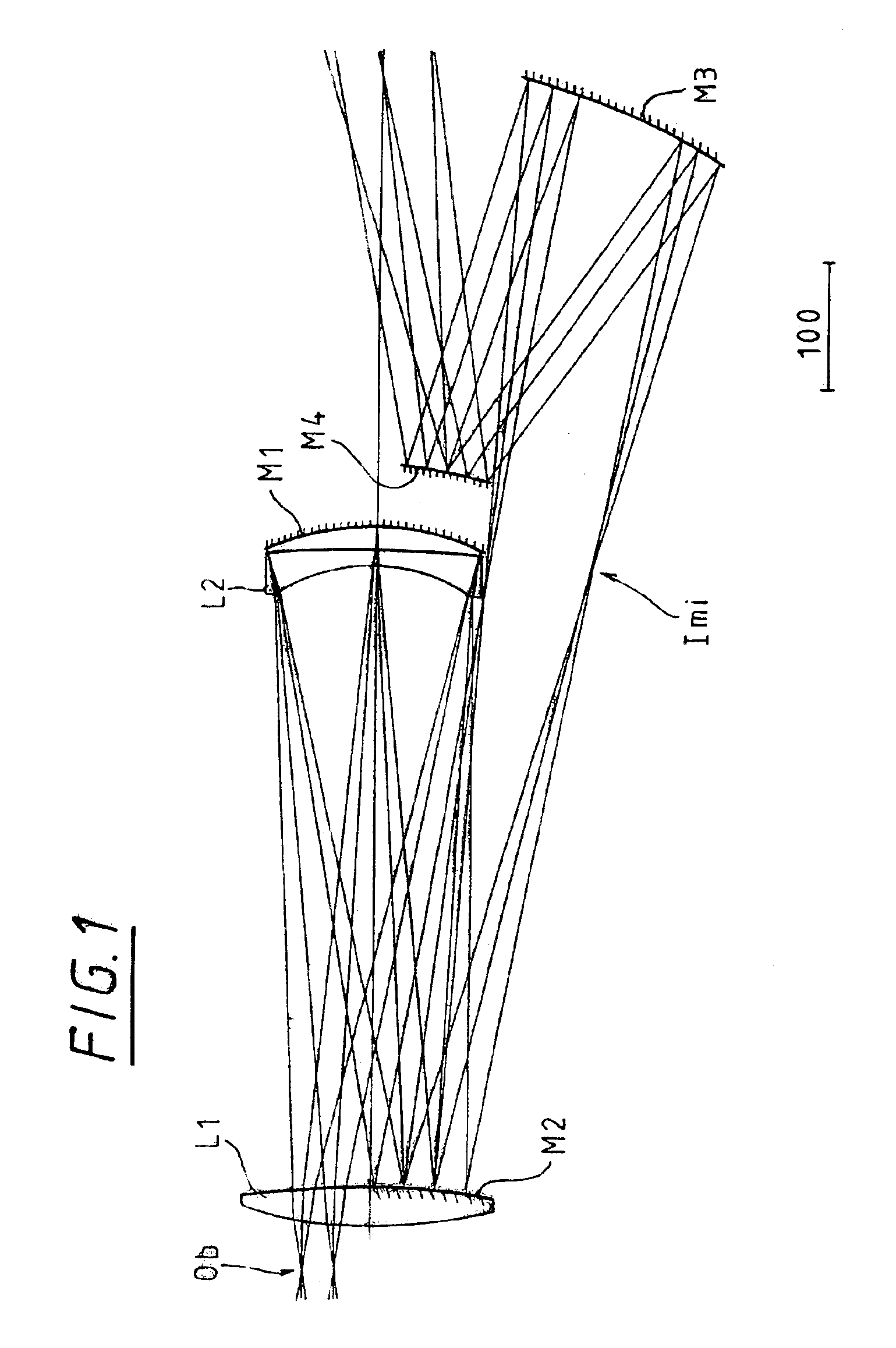
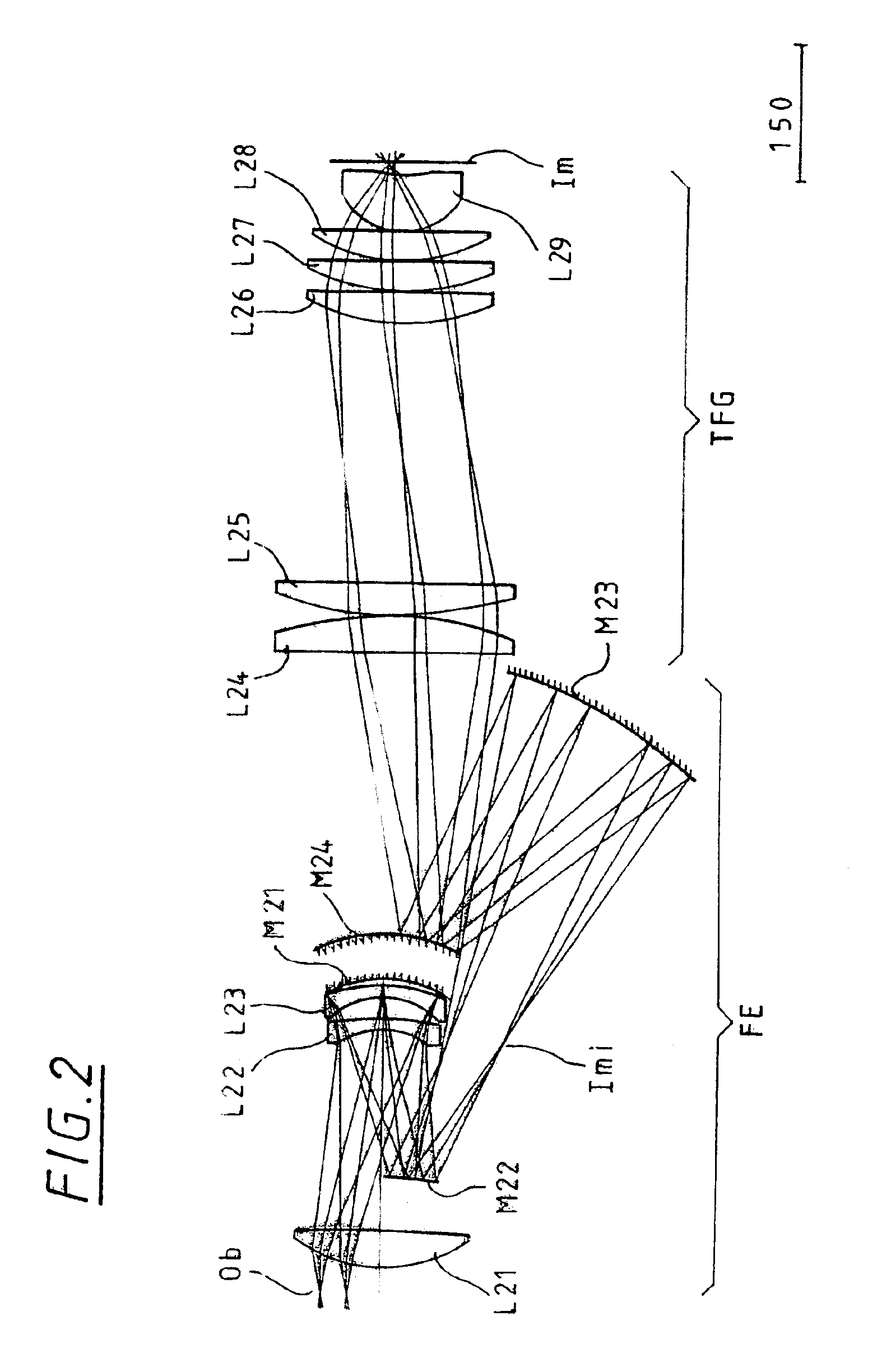
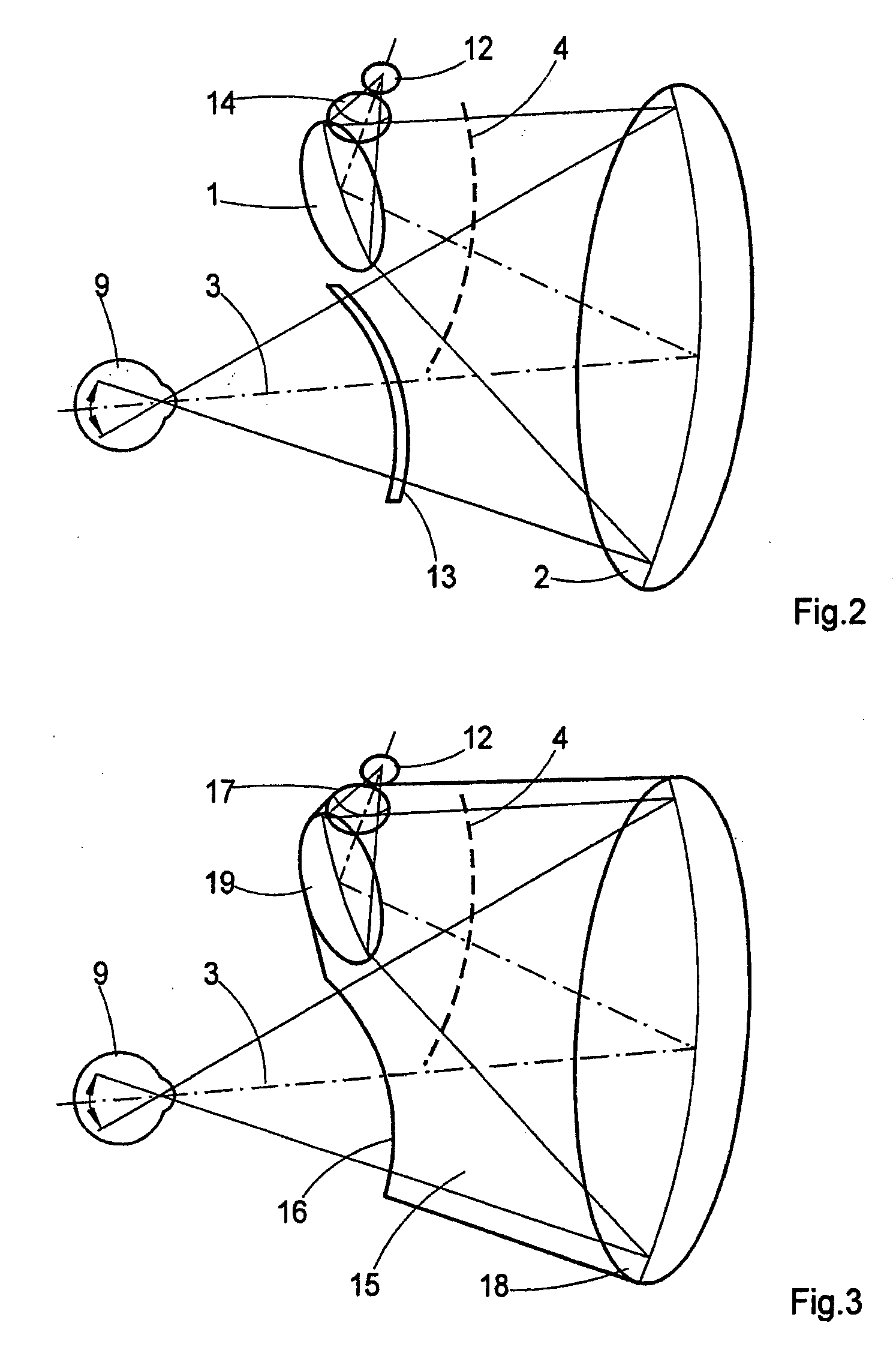
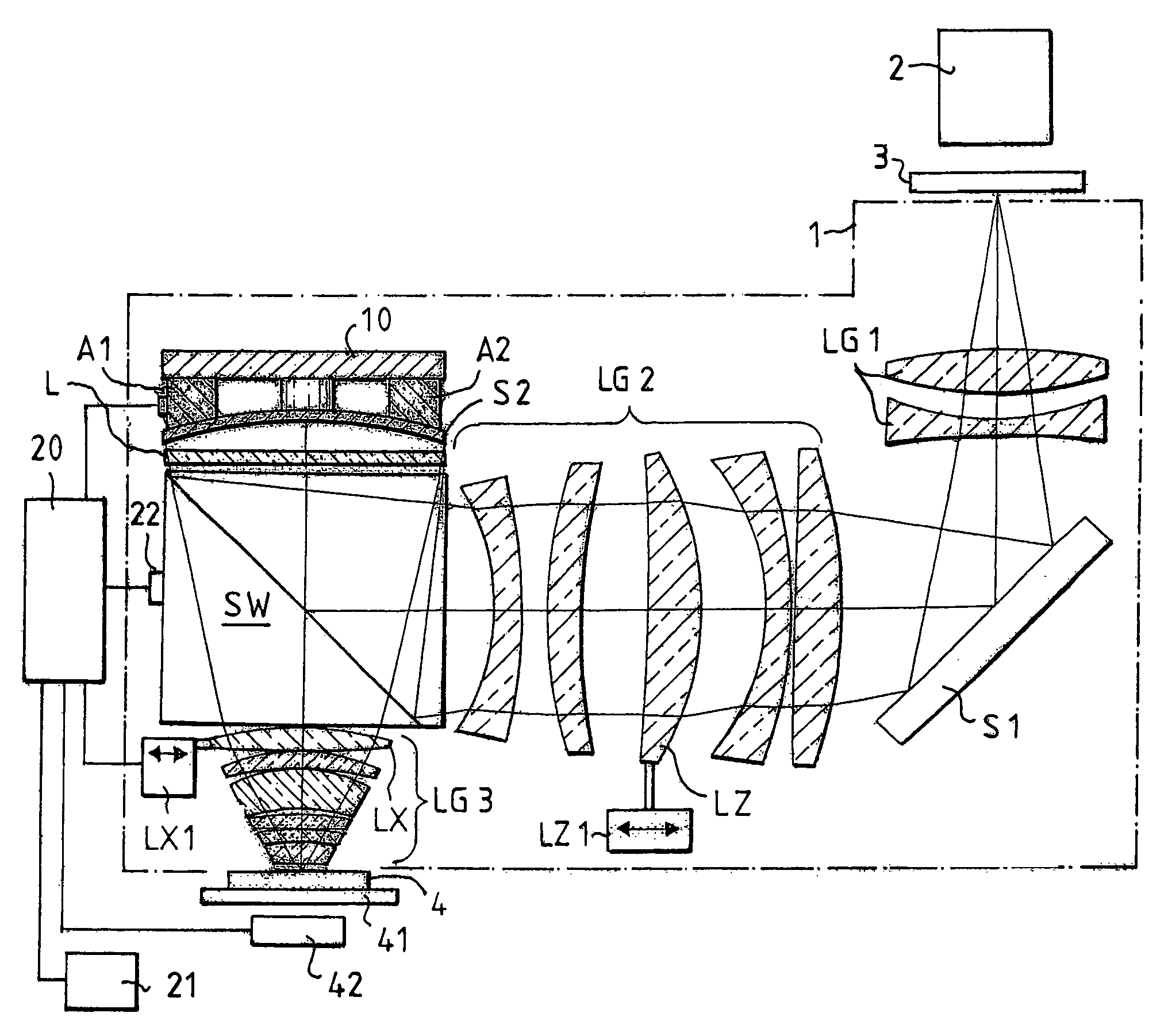
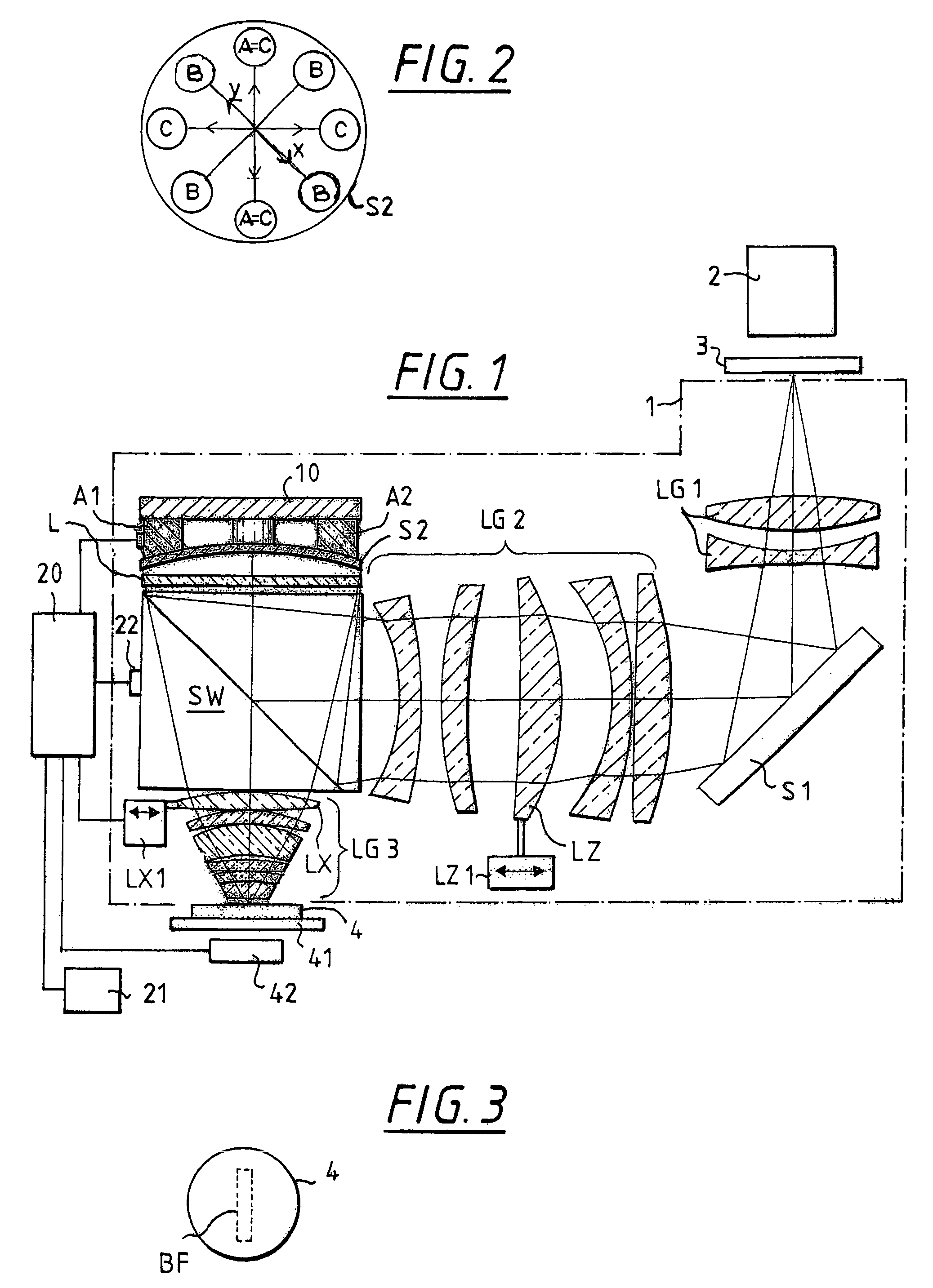
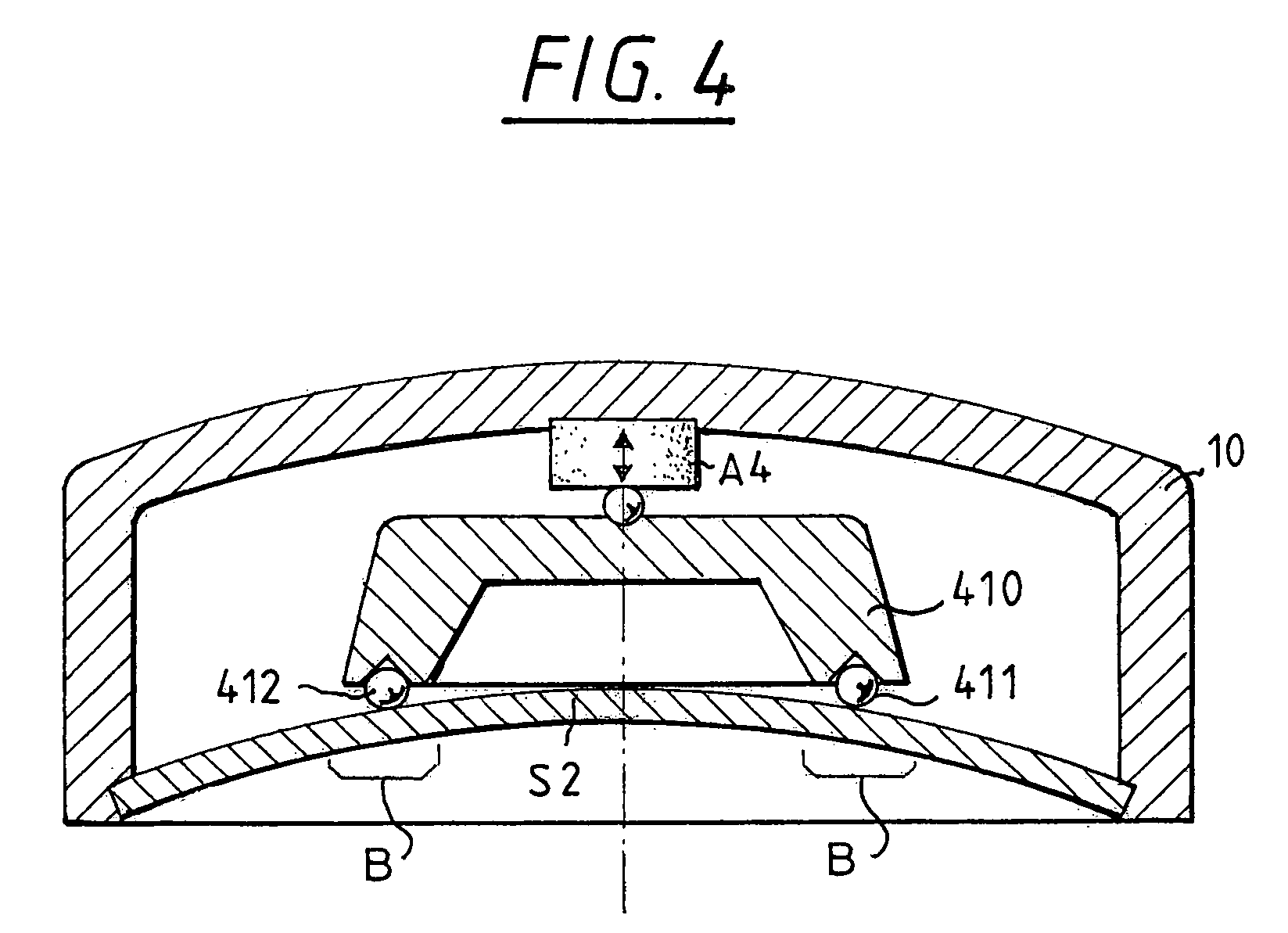
Collimating optical member for real world simulation
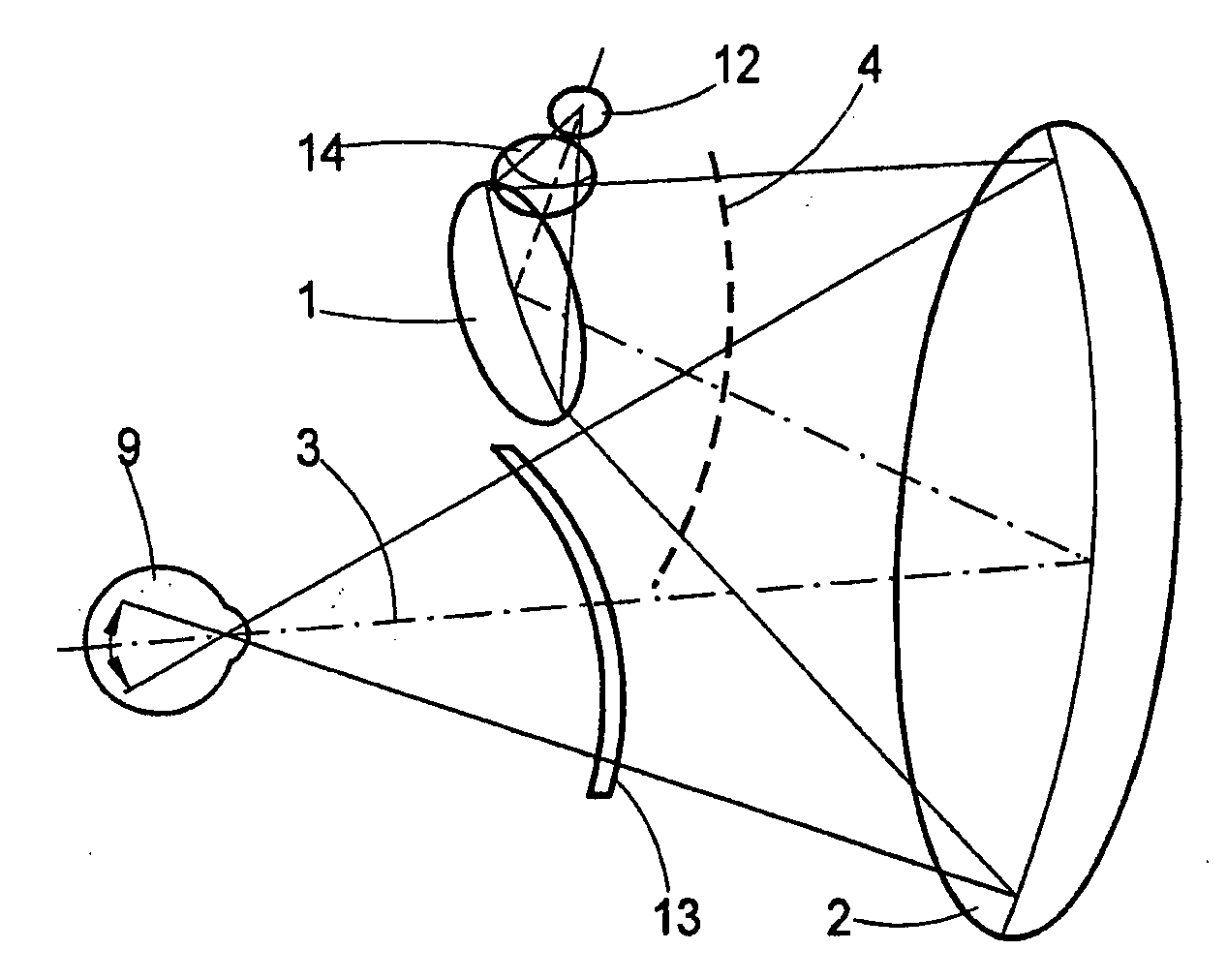
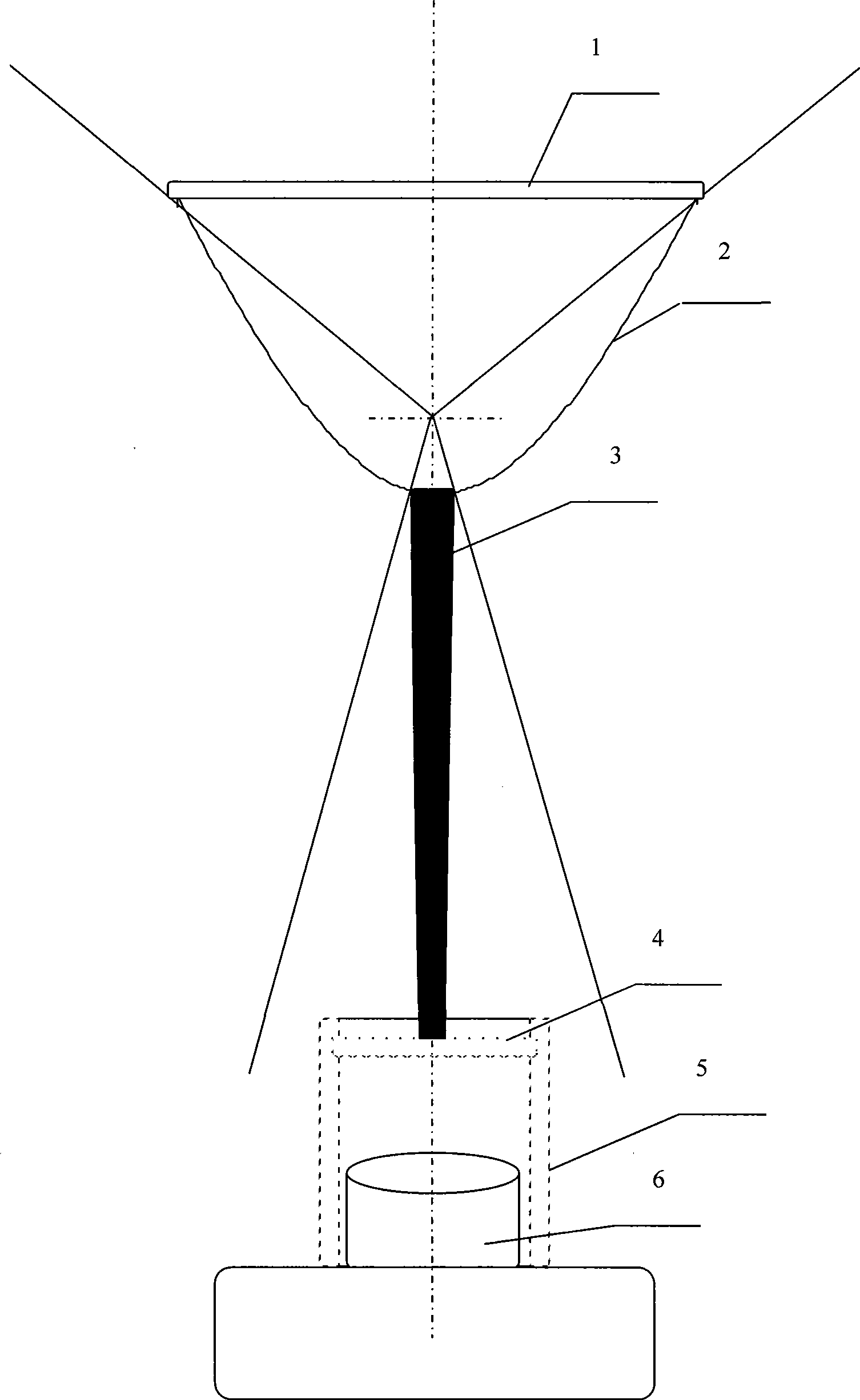
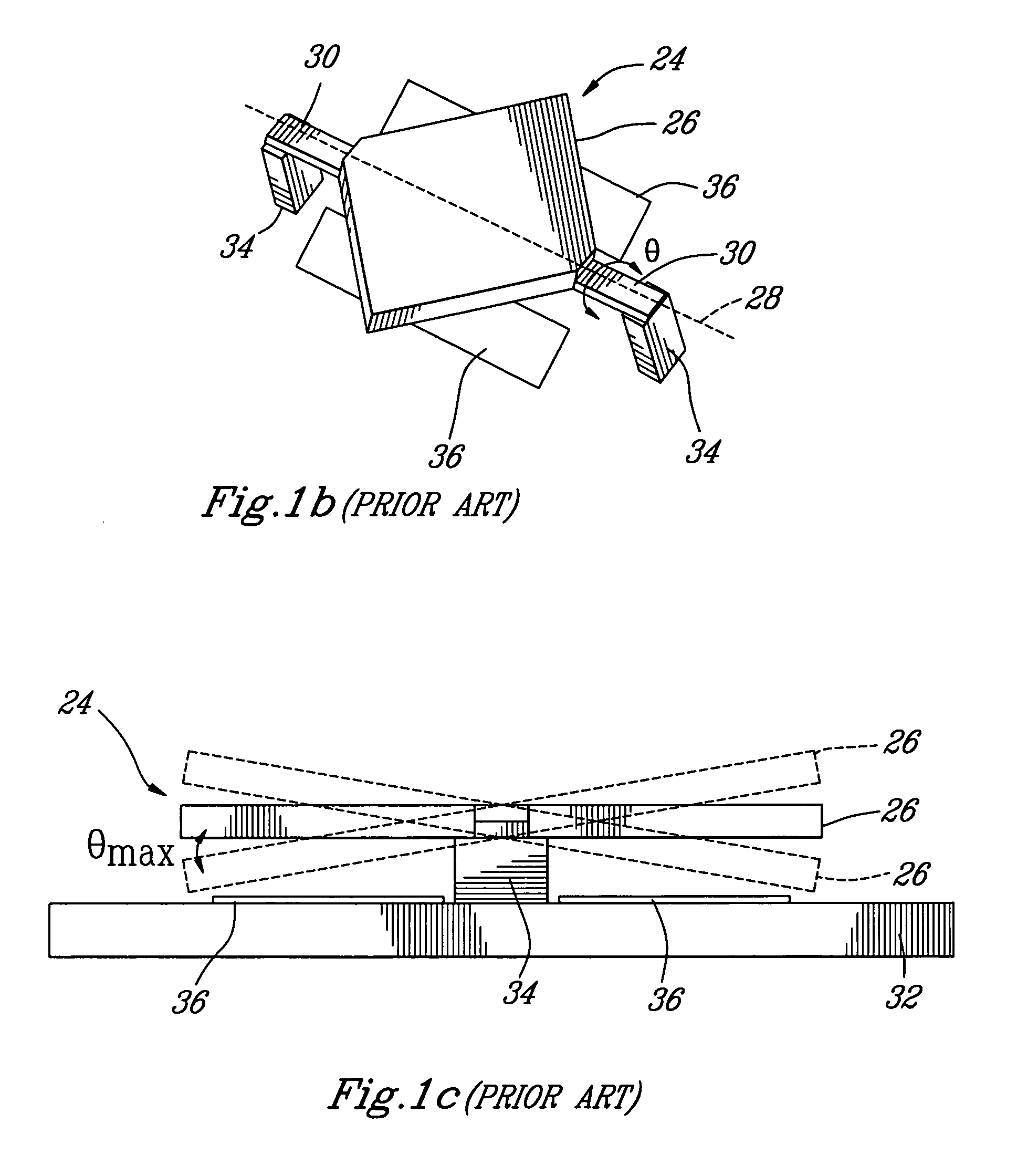
A collimating image-forming apparatus comprising a first linear polarizer is disclosed. A first quarter-wave plate is disposed adjacent the first polarizer and has its fast and slow axes at substantially 45° to the plane of polarization of the first polarizer. The apparatus further comprises a beam-splitting curved mirror having a convex surface adjacent the first polarizer and facing towards the first quarter-wave plate, a second quarter-wave plate adjacent the concave side of the curved mirror, the second quarter-wave plate having its having its fast and slow axes oriented with respect to the corresponding axes of the first quarter-wave plate at angles substantially equal to a first integral multiple of 90°, and a reflective-transmissive polarizing member adjacent the second quarter-wave plate. A second linear polarizer is adjacent the reflective-transmissive polarizing member, the second linear polarizer having its plane of polarization oriented with respect to the plane of polarization of the first linear polarizer at an angle substantially equal to a second integral multiple of 90°, both of the multiples being even or both being odd.
Owner:OPTICAL RESOLUTIONS +1
Context and Epsilon Stereo Constrained Correspondence Matching
InactiveUS20130002828A1Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionParallaxGreek letter epsilon
A catadioptric camera having a perspective camera and multiple curved mirrors, images the multiple curved mirrors and uses the epsilon constraint to establish a vertical parallax between points in one mirror and their corresponding reflection in another. An ASIFT transform is applied to all the mirror images to establish a collection of corresponding feature points, and edge detection is applied on mirror images to identify edge pixels. A first edge pixel in a first imaged mirror is selected, its 25 nearest feature points are identified, and a rigid transform is applied to them. The rigid transform is fitted to 25 corresponding feature points in a second imaged mirror. The closes edge pixel to the expected location as determined by the fitted rigid transform is identified, and its distance to the vertical parallax is determined. If the distance is not greater than predefined maximum, then it is deemed correlate to the edge pixel in the first imaged mirror.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Process for fabricating MEMS membrane with integral mirror/lens
InactiveUS7208333B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffraction gratingsOptical surfaceDiffractive lens
An optical membrane device and method for making such a device are described. This membrane is notable in that it comprises an optically curved surface. In some embodiments, this curved optical surface is optically concave and coated, for example, with a highly reflecting (HR) coating to create a curved mirror. In other embodiments, the optical surface is optically convex and coated with, preferably, an antireflective (AR) coating to function as a refractive or diffractive lens.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Ultraviolet sterilizer for surgery
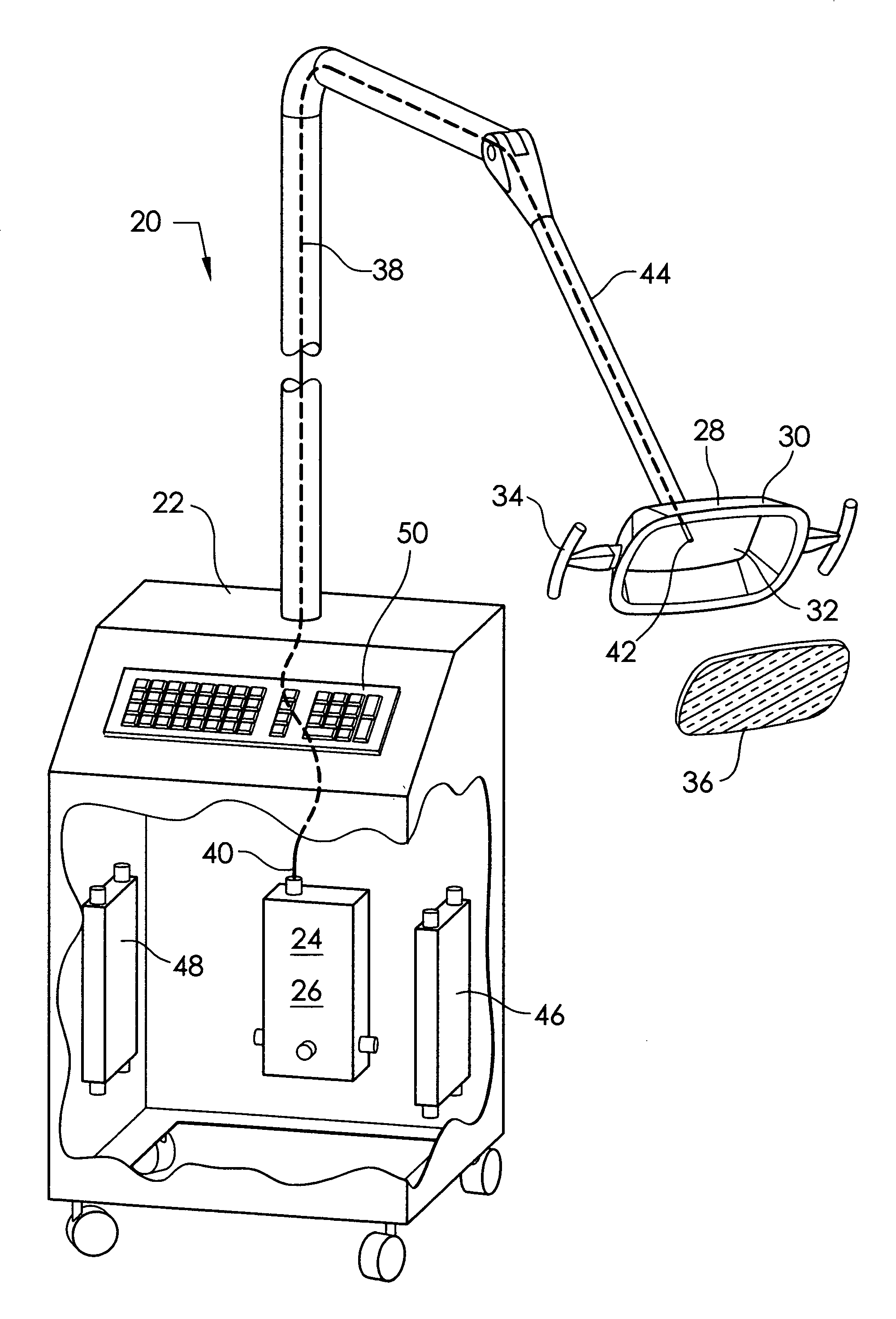
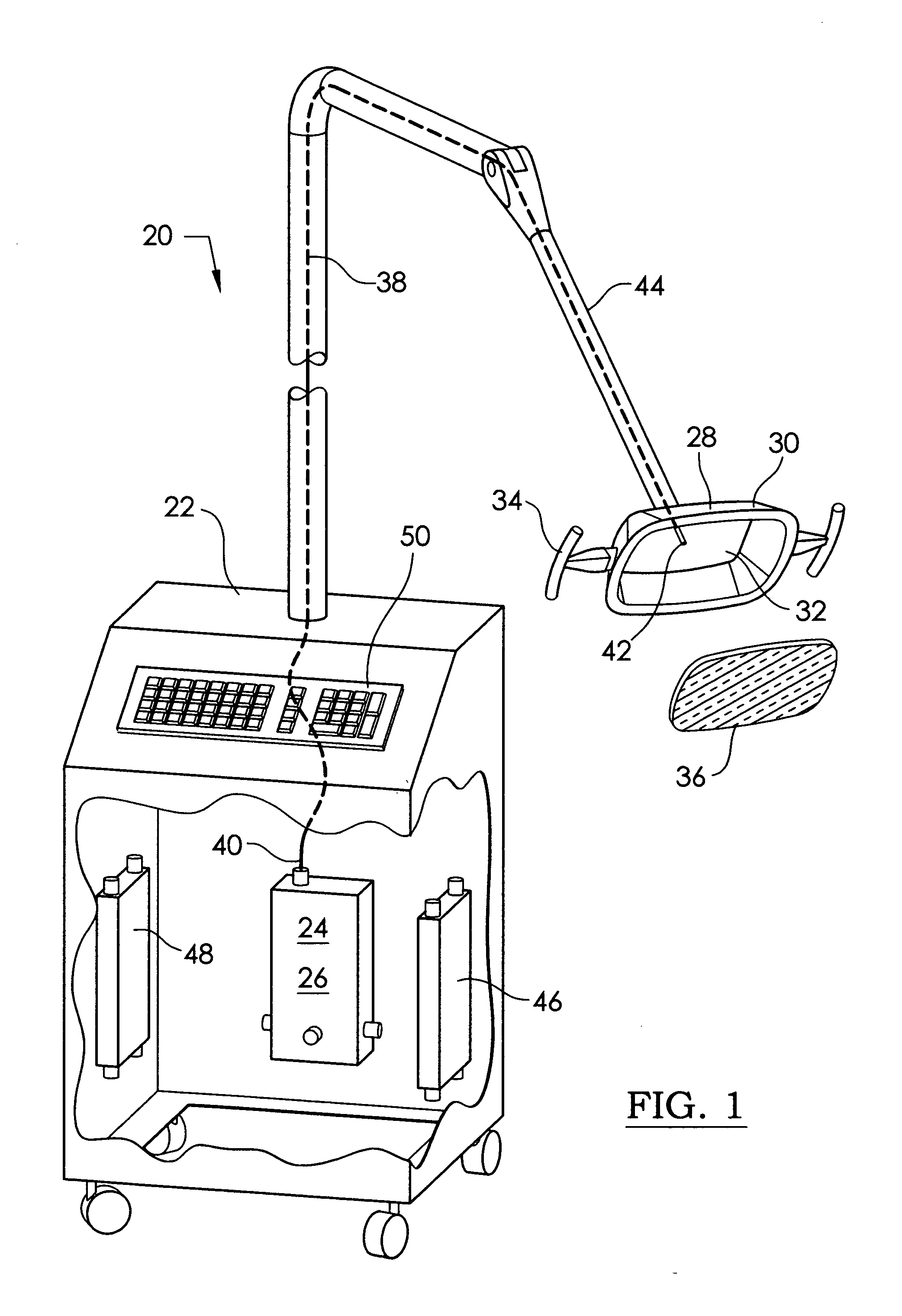
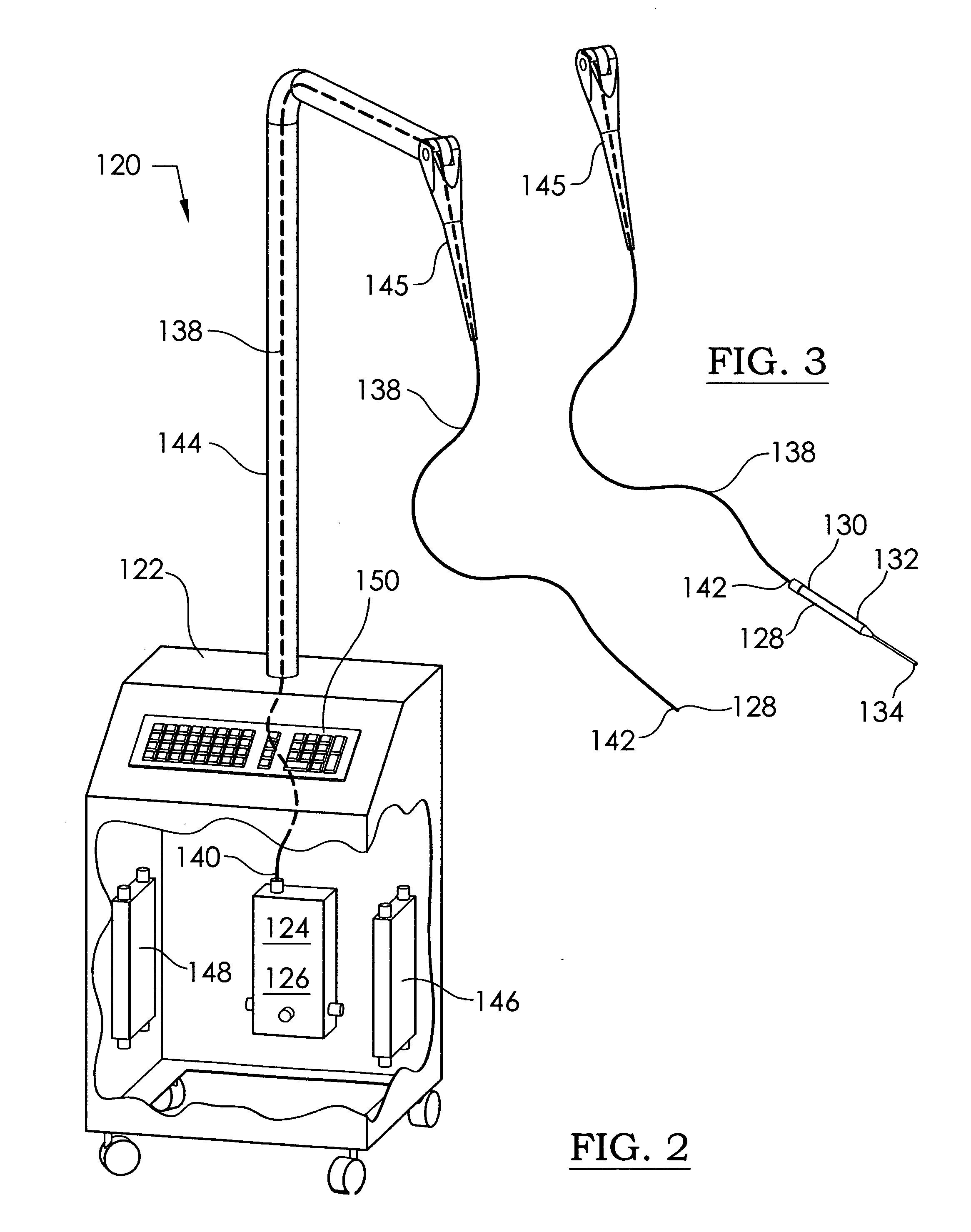
InactiveUS20110054574A1Prevent moistureAvoid burnsLight therapyRadioactive sourcesUv disinfectionArthroscopy
An ultraviolet sterilizer for use during surgery is mounted in a base cabinet. The UV light source can be a laser, or an LED. An optical frequency multiplier can be used that outputs UV of less than 280 nm, or greater than 320 nm, to avoid burning the patient. A visible LED aiming light directs the UV light toward the surgery. A crosshair image can be projected to position the light.One lamp has a housing, a cavity, a handle, and an ocular plate to pass the UV and the aiming light. An articulated arm allows selective positioning of the lamp. Another lamp has a stylus, a handle, and a tip small enough for easy insertion into a small incision for arthroscopy. A fiber optic cable connects the UV and the aiming light to the lamp. Lenses or filters can be used with the fiber optic cable.An electronic power supply and a CPU connect to the UV and the aiming light sources. A keyboard inputs commands to the CPU. A sensor provides feedback.Another UV sterilizer is mounted on a ceiling of the operating room. A lamp has a housing with a cavity. Either a curved or a flat substrate is mounted in the cavity. Solid state UV elements are arrayed on the substrate, along with visible LEDs for aiming. Either a curved or a flat mirror is disposed behind the substrate. An ocular plate passes the UV and the aiming light, and protects the elements from damage. The ocular plate is a diffuser, a filter, or a fresnel lens.
Owner:FELIX PERRY
Microlithographic reduction projection catadioptric objective
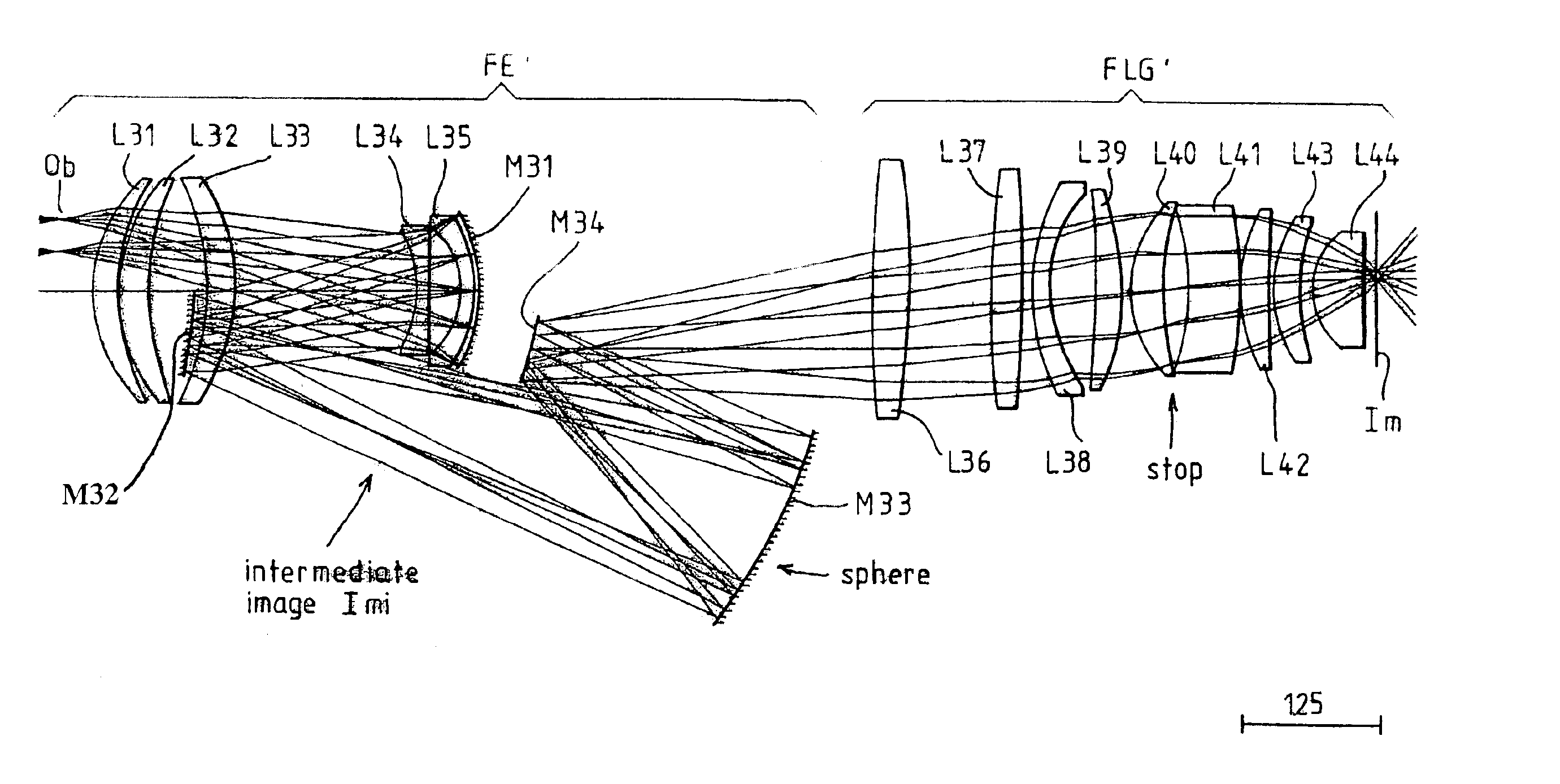
InactiveUS6873476B2Reduce complexityIncrease the number ofProjectorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIntermediate imageVirtual image
The invention concerns a microlithographic reduction projection catadioptric objective having an even number greater than two of curved mirrors, being devoid of planar folding mirrors and featuring an unobscured aperture. The objective has a plurality of optical elements, and no more than two optical elements deviate substantially from disk form. The objective has an object side and an image side, and has in sequence from the object side to the image side a catadioptric group providing a real intermediate image, a catoptric or catadioptric group providing a virtual image, and a dioptric group providing a real image.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH +1
Light modulating microdevice
A light modulator comprises a mirror, a substrate provided with at least one electrode, and at least one hinge extending between the substrate and the mirror. The mirror is flexible with the hinge being displaceable for allowing for the displacement and / or the deformation of the mirror. Typically, there are two symmetrically disposed hinges, each including upper and lower arms that define an angle therebetween. The upper arm is connected to the mirror, and the lower arm is mounted to the substrate. The upper and lower arms are adapted to pivot relative to one another thereby allowing the angle to vary and thus allowing the mirror to at least one of displace and deform. When unbiased, the mirror may be plane, convex or concave. When biased, the plane mirror adopts a curved attitude, whereas the curved mirror changes its curvature. The upper and lower arms of each hinge are V-shaped and define an apex. The apexes extend inwardly in a facing relationship.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT +1
Image projection system and method
ActiveUS7384158B2Improve image qualityShorten the optical path lengthTelevision system detailsMirrorsOptical reflectionImaging processing
An image projection system and method is presented for optically projecting an image onto a display surface with visually correct geometry and optimum image quality. The projection system includes an image processing unit for receiving the input image data and generating distortion-compensated image data to compensate for ensuing spatial distortions in the projection system, a projection light engine for receiving the distortion-compensated image data and projecting a distortion-compensated optical image that corresponds to the distortion-compensated image data; and, an optical reflection assembly comprising at least one curved mirror positioned in the optical path of the distortion-compensated optical image emerging from the projection light engine for producing a displayed optical image with reduced distortion on the display surface. The image processing unit distortion-compensates the input image data such that the optical and spatial distortions associated with the projection light engine and optical reflection assembly are substantially reduced in the displayed optical image.
Owner:APPLE INC +1
Sensitization of photo-thermo-refractive glass to visible radiation by two-step illumination
InactiveUS7326500B1High resolutionReduce noiseHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesPhotomechanical apparatusRefractive indexWaveguide
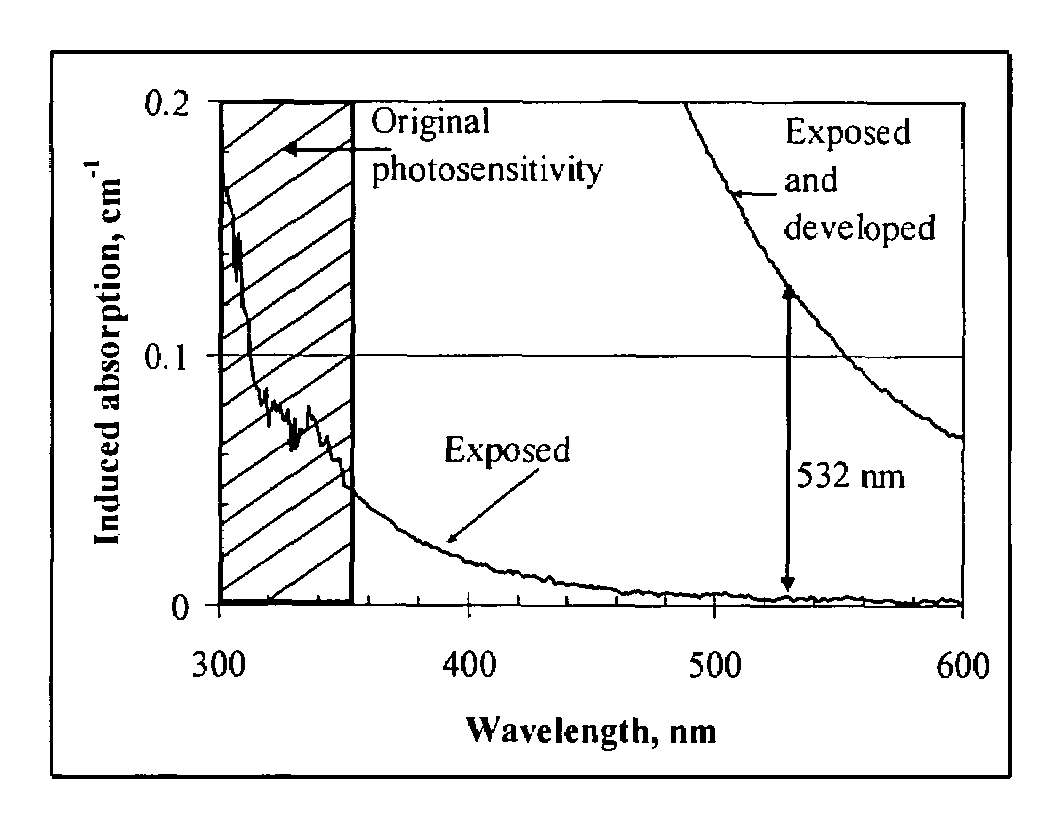
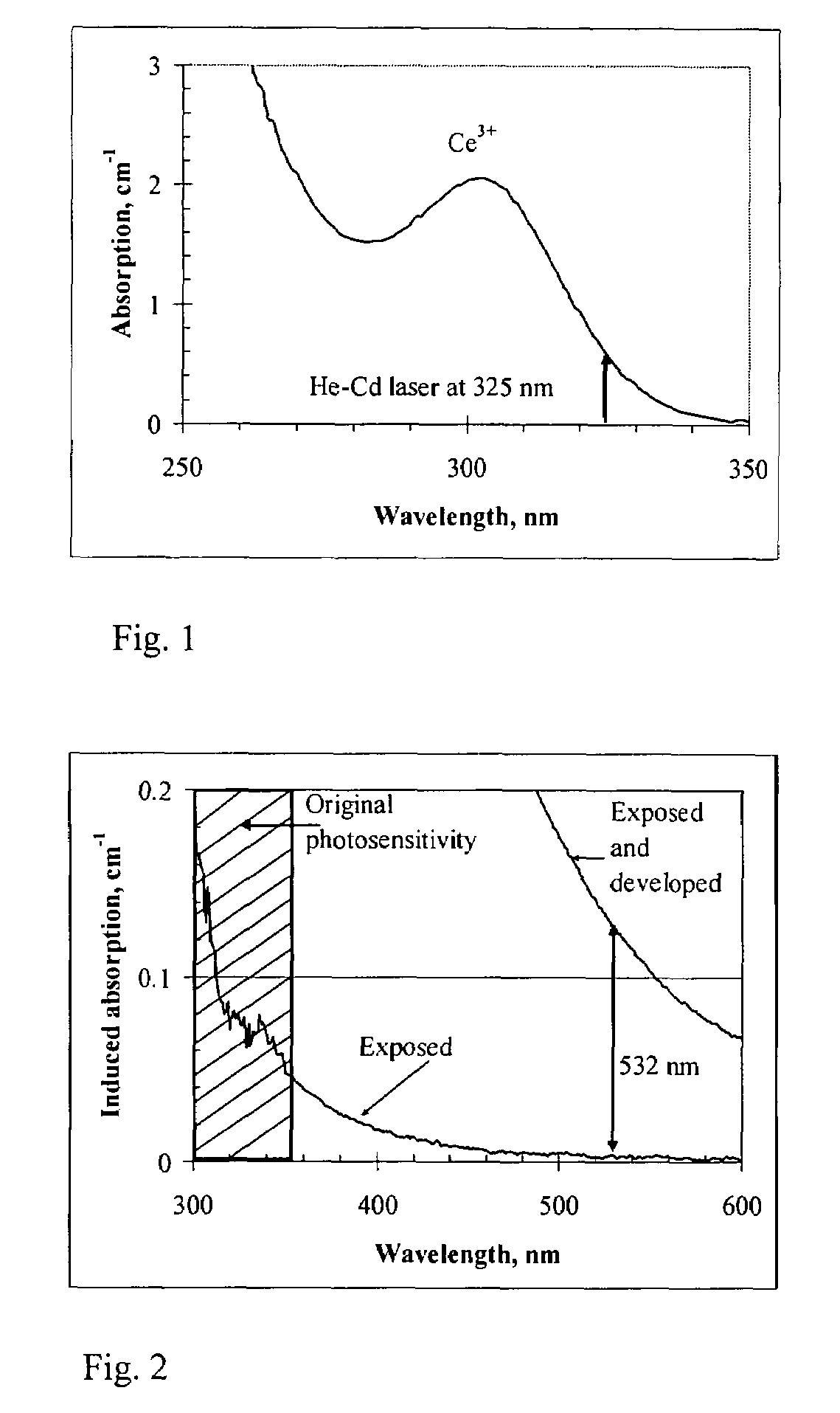
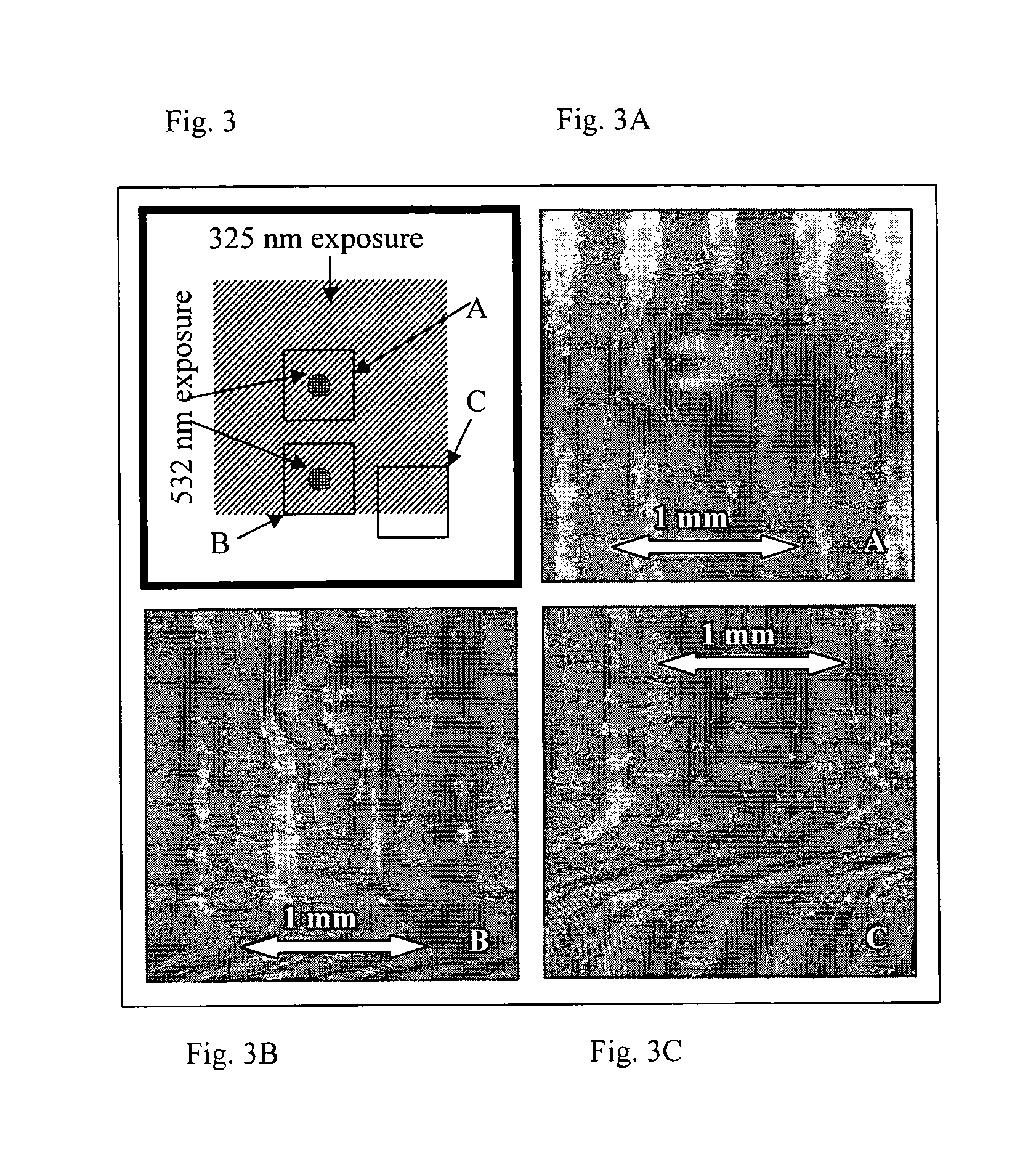
Photo-thermo-refractive (PTR) glass is a multi-component silicate glass having photosensitivity in rear UV region. A novel process is disclosed for PTR glass sensitization to visible region by means of two-step illumination followed by thermal development. This disclosed process utilizes a first illumination at approximately 325 nm followed by a second illumination with radiation in the visible spectral region out of the region of original photosensitivity of the PTR glass which enables fabrication of complex holographic optical elements for visible region such as plane elements, lenses, curved mirrors, combinations of complex elements and optical correlators. The same process provides a positive increment of refractive index in the bulk of the PTR glass and, therefore, can be used for refractive optical elements recording, such as lenses and waveguides.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Optical system for a fundus camera
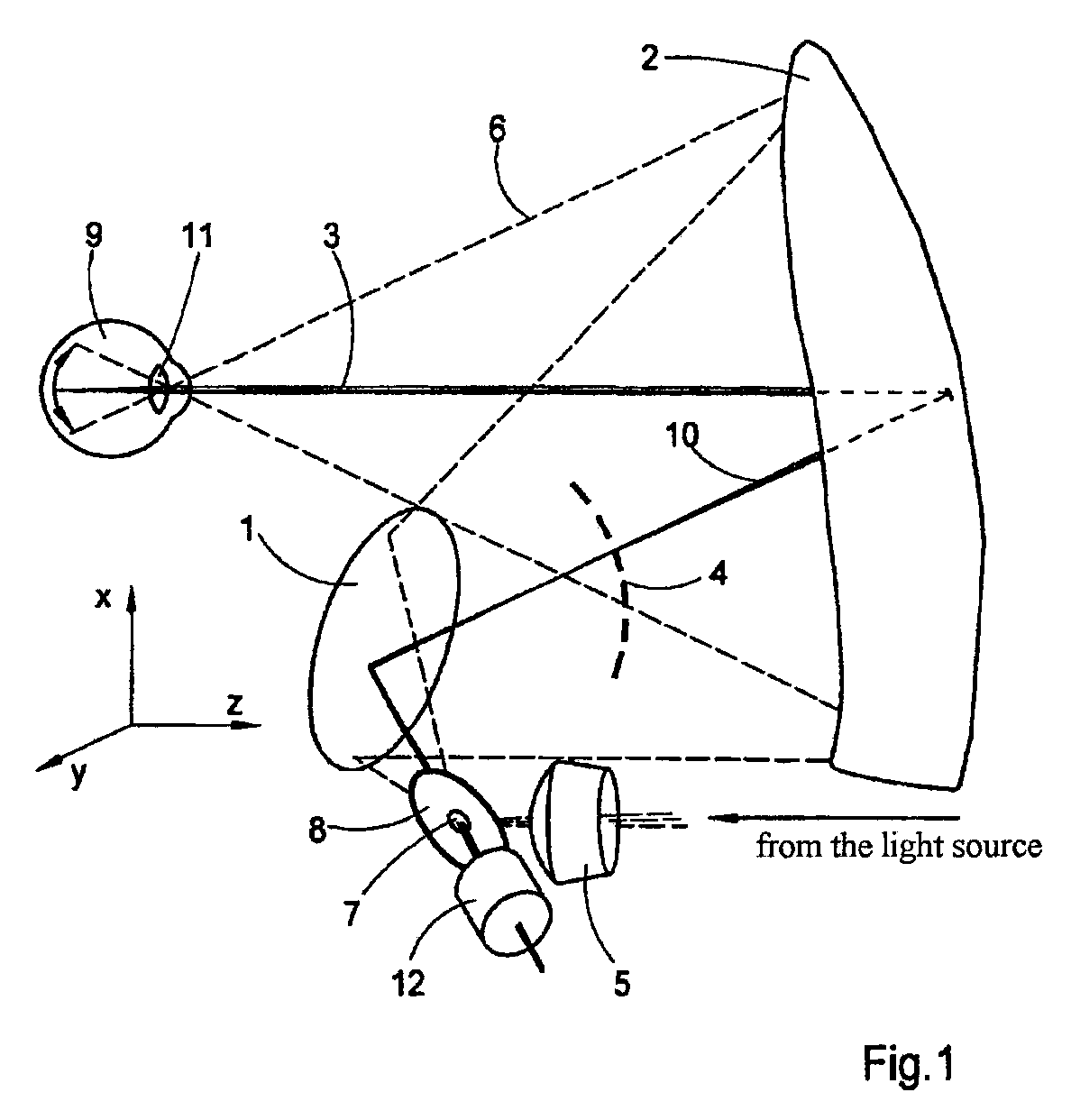
InactiveUS20100014052A1Suppression of blurDimension of can be minimizeEye diagnosticsOptical elementsCatoptricsDioptre
The invention is directed to an optical system for a fundus camera for reflection-free opthalmoscopy having a beam path with refractive and reflective optical elements which are used substantially in common for illumination and observation or recording. An imaging mirror system substantially comprising a plurality of reflecting optical elements in the form of mirrors and is provided for illuminating and imaging the fundus. At least one optical element, for example, mirror, is formed as a freeform mirror with an imaging, reflecting freeform surface. The optical elements are arranged in a housing in a precisely defined position and attitude relative to one another in such a way that an imaging of the reflecting surfaces of the optical elements on the image of the imaged retina is prevented within a wide diopter range of the patient's eye to be examined.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Collimating optical member for real world simulation
A collimating image-forming apparatus comprising a first linear polarizer is disclosed. A first quarterwave plate (14) is disposed adjacent the first polarizer (12) and has its fast and slow axes at substantially 45° to the plane of polarization of the first polarizer. The apparatus further comprises a beam-splitting curved mirror (16) having a convex surface adjacent the first polarizer and facing towards the first quarter-wave plate, a second quarter-wave plate (22) adjacent the concave side of the curved mirror, the second quarterwave plate having its having its fast and slow axes oriented with respect to the corresponding axes of the first quarter-wave plate at angles substantially equal to a first integral multiple of 90°, and a reflective-transmissive polarizing member (24) adjacent the second quarter-wave plate. A second linear polarizer (26) is adjacent the reflective-transmissive polarizing member, the second linear polarizer having its plane of polarization oriented with respect to the plane of polarization of the first linear polarizer at an angle substantially equal to a second integral multiple of 90°, both of the multiples being even or both being odd.
Owner:OPTICAL RESOLUTIONS +1
Guide
InactiveUS20040083869A1Metal sawing accessoriesMeasurement/indication equipmentsLight beamOptoelectronics
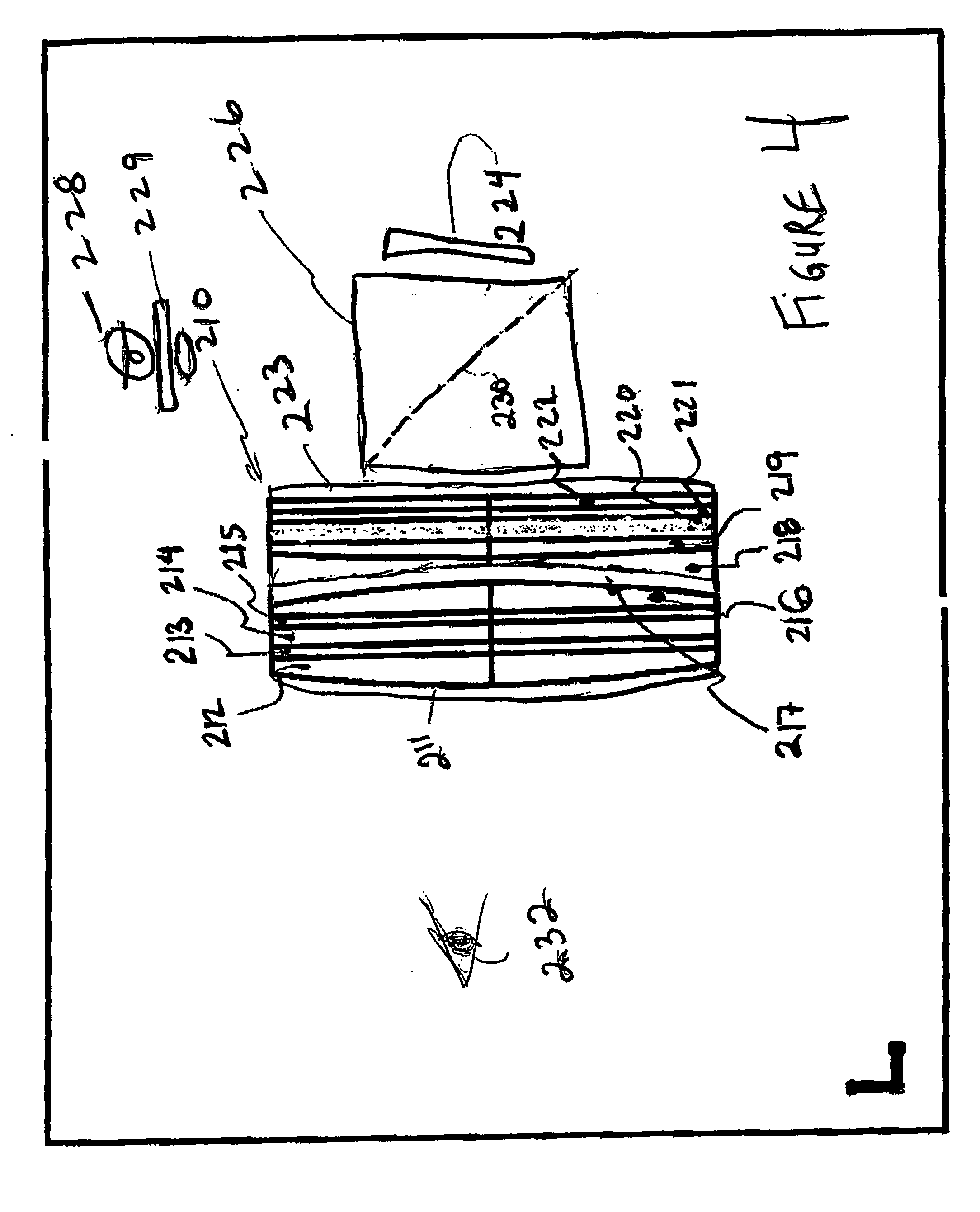
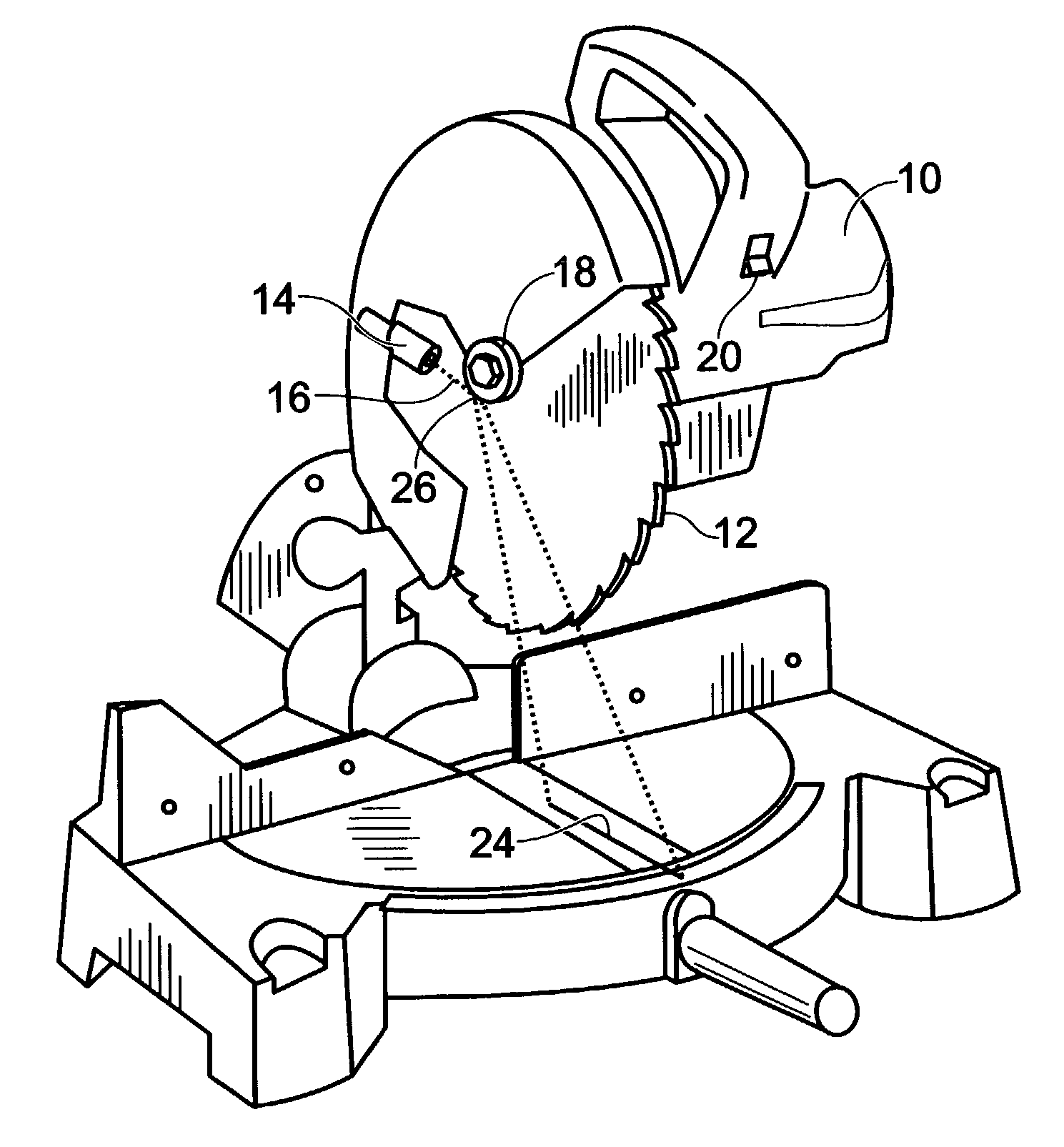
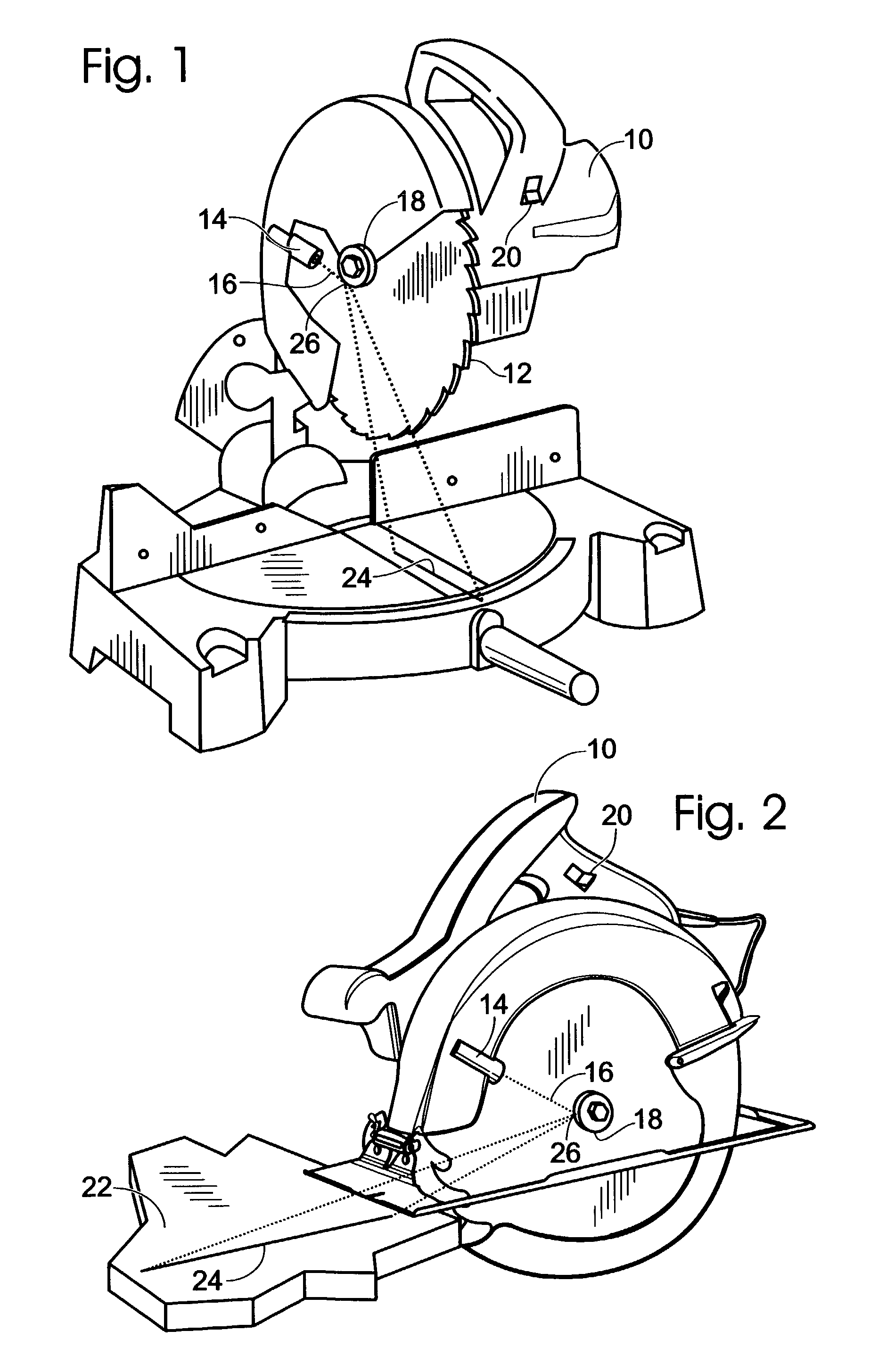
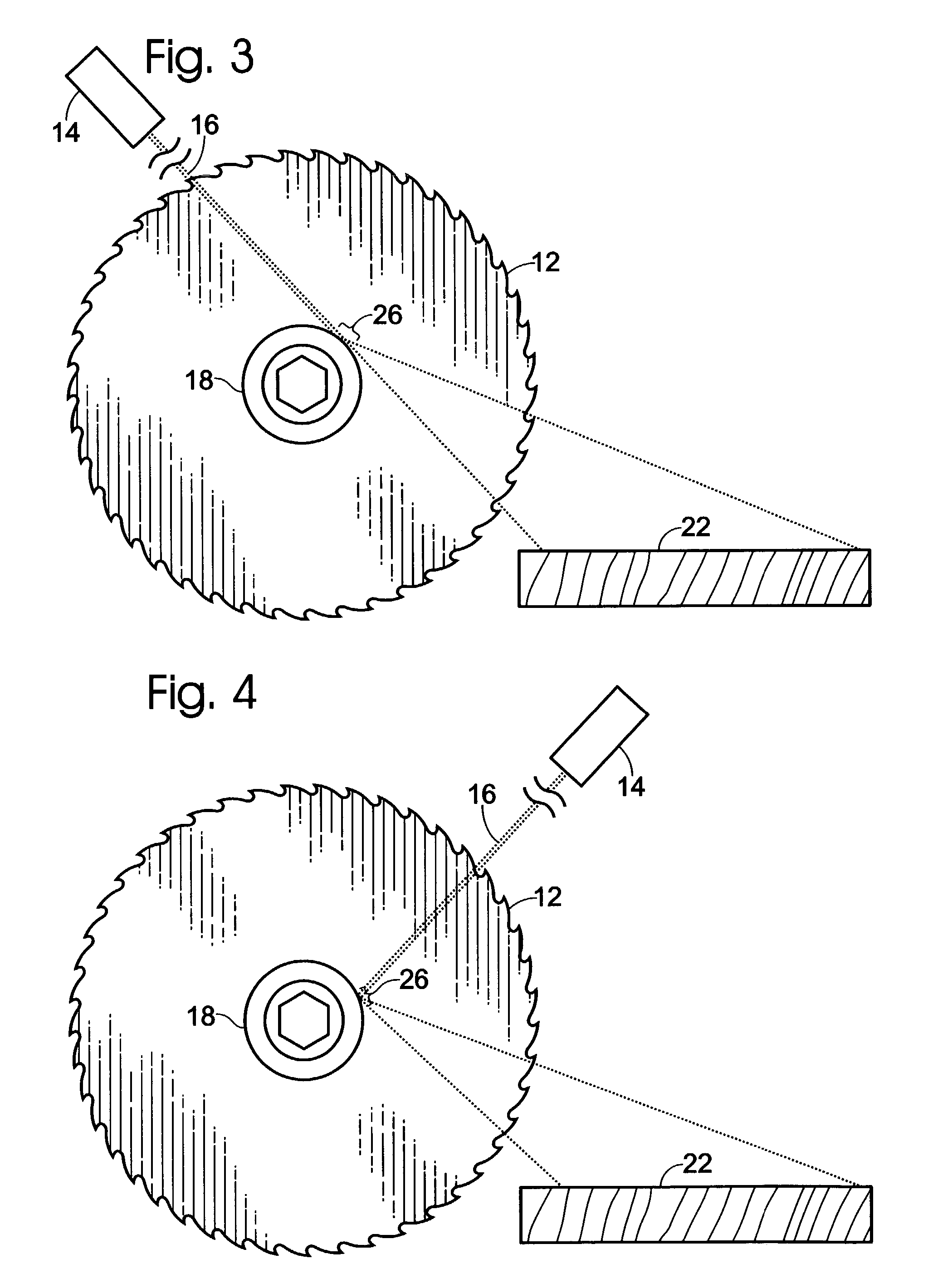
A method and apparatus for providing a guide for use with rotary components such as a rotary saw. In the preferred embodiment the invention is comprised of a rotary saw with a blade, a reflector affixed adjacent and coaxial to said blade, a light beam source, preferably a laser projecting a beam of light co-planer to and at said reflector. The reflector acts as a curved mirror to fan the beam of light creating a guideline coplanar with the rotary component or blade of the rotary saw.
Owner:AZIZ EDMUND J +1
AR or VR imaging method and glasses capable of being used for AR or VR
The invention provides an AR or VR imaging method and glasses capable of being used for AR or VR in order to solve the technical problems that an existing AR imaging method and AR glasses images deform, the gravity center of the AR glasses are near the front, and a display screen is large. The glasses comprise a head-mounted support, a display unit arranged on the head-mounted support, a reflecting unit and a central beam splitter. The reflecting unit comprises a holophote, a Fresnel lens and cambered lenses which are arranged on a light path of the display unit. The cambered lenses are arranged in front of the eyes of a user; the holophote reflects VR split screen images and carries out secondary amplifying or shrinking, and imaging is carried out in the eyes of the user; the cambered lenses reflect the AR split screen images respectively and carry out secondary amplifying or shrinking, imaging is carried out in the eyes of the user, scenes in front of the eyes of the user are transmitted into the eyes of the user, and it is guaranteed that image deformation is small under the condition that the gravity center of the AR glasses is close to the forehead. A small focal distance is adopted, the height of a display screen is half of that in the prior art, and the load bearing feeling is small when the user wears the glasses.
Owner:XIAN KISSFUTURE NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Two-dimensional micro optical scanner
InactiveUS20080130077A1Reduce scan angleLight would become directionalPictoral communicationOptical elementsOptical scannersLight scan
A two-dimensional micro optical scanner is provided. The two-dimensional micro optical scanner includes a first scanner with a first mirror pivoted in a first direction; a second scanner with a second mirror pivoted in a second direction; and an optical path changing member with a curved mirror. The optical path changing member directs light scanned by the first scanner to the second scanner.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Image display apparatus and object apparatus
ActiveUS20160320616A1Geometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsProjection imageImage formation
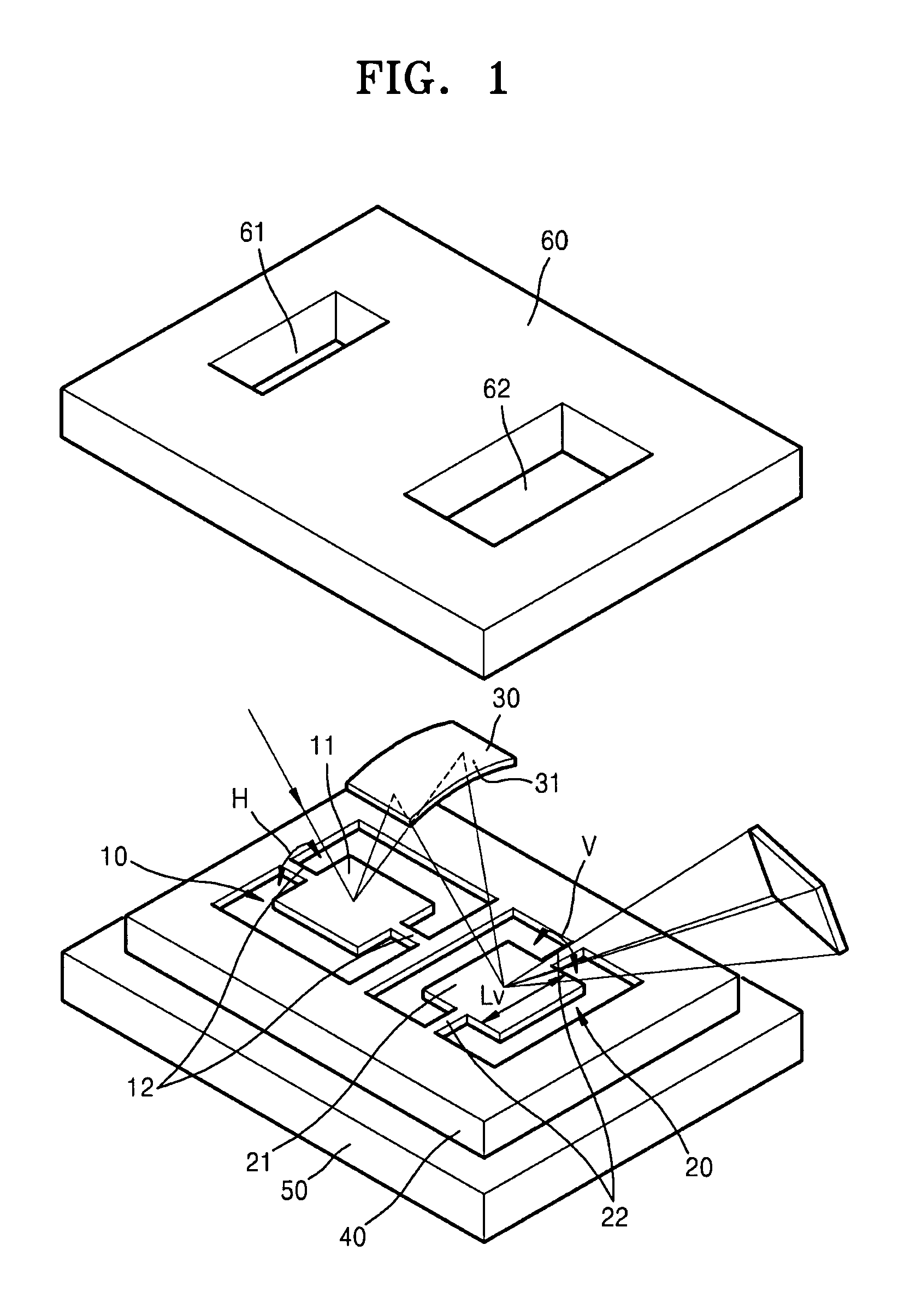
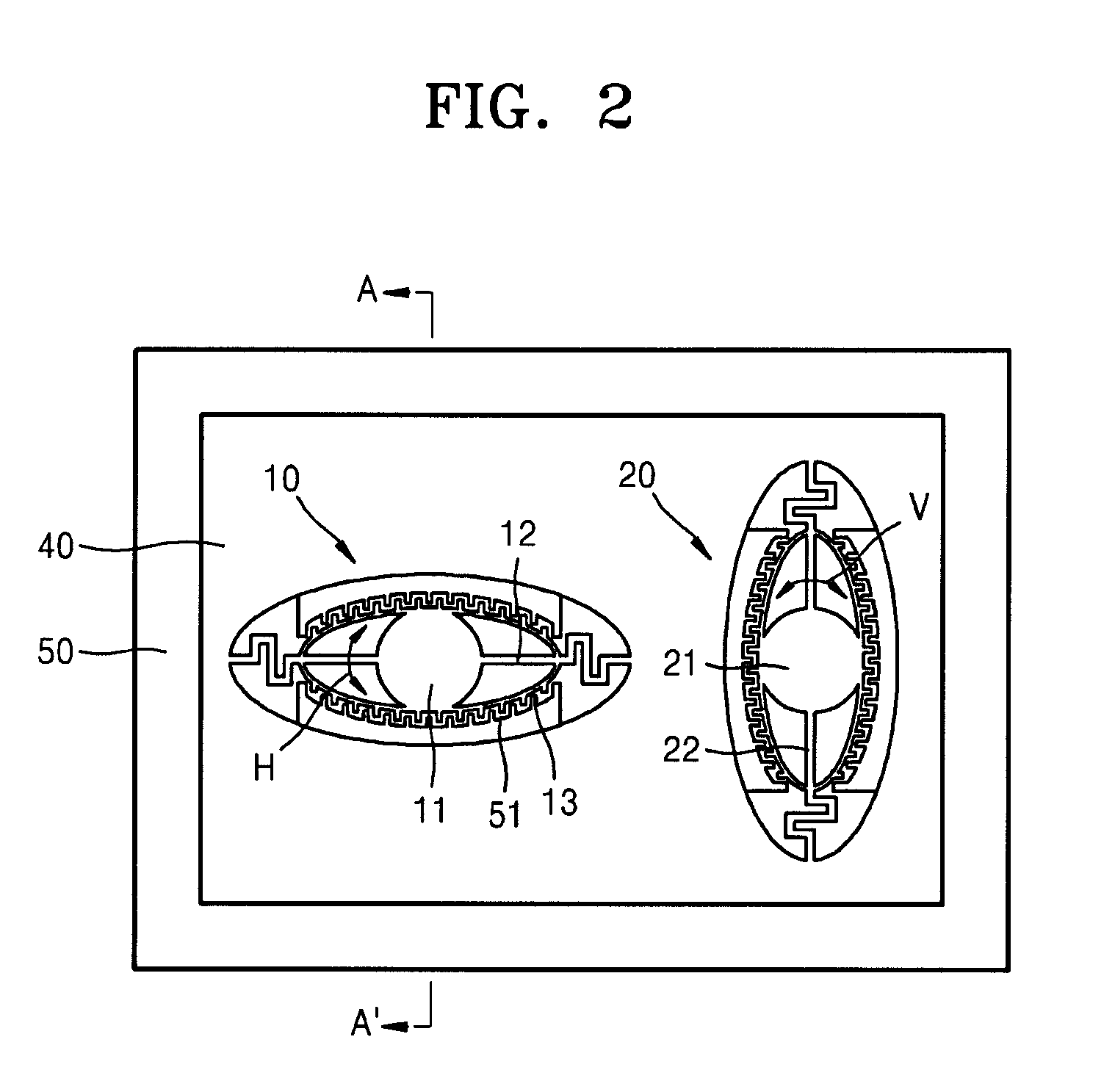
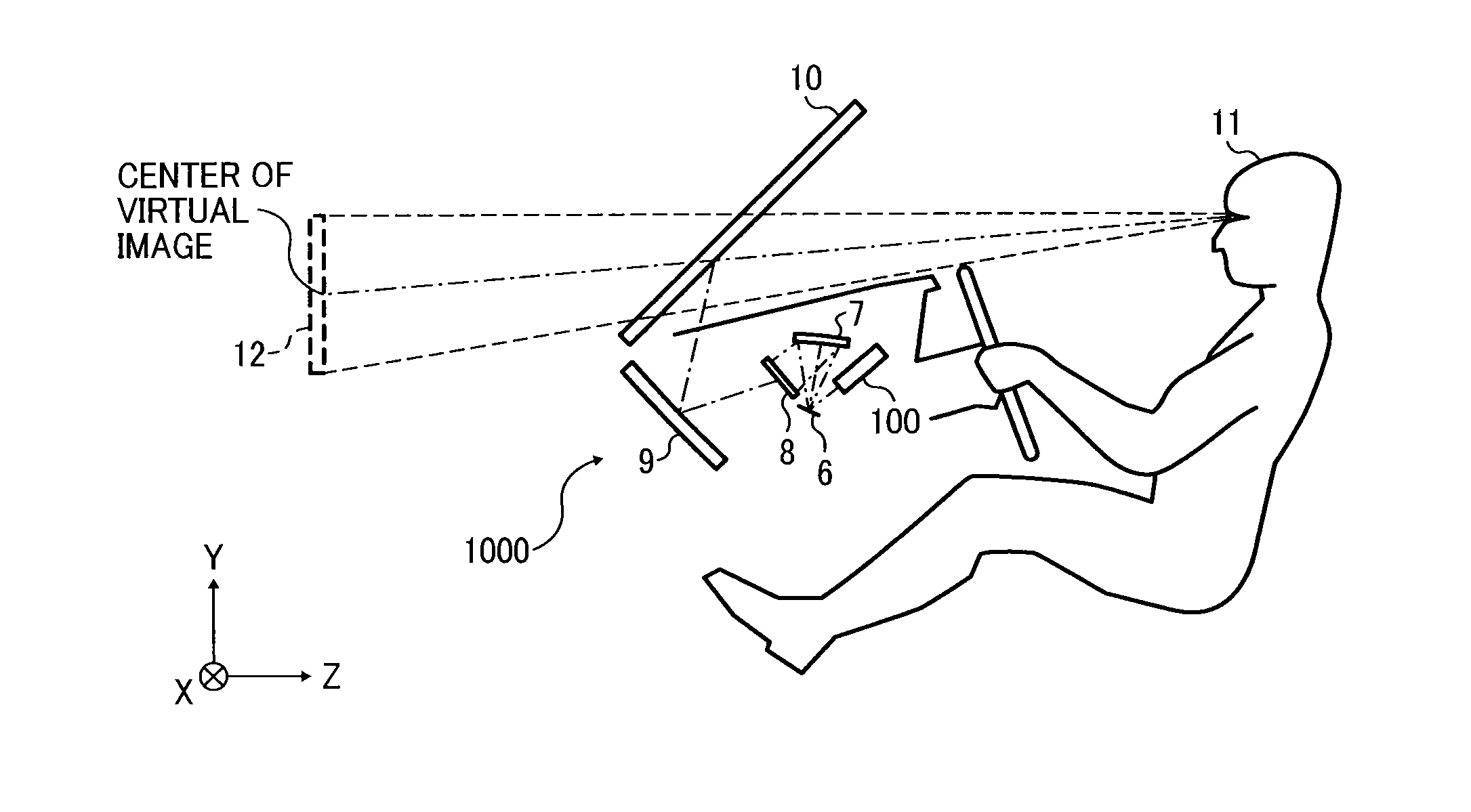
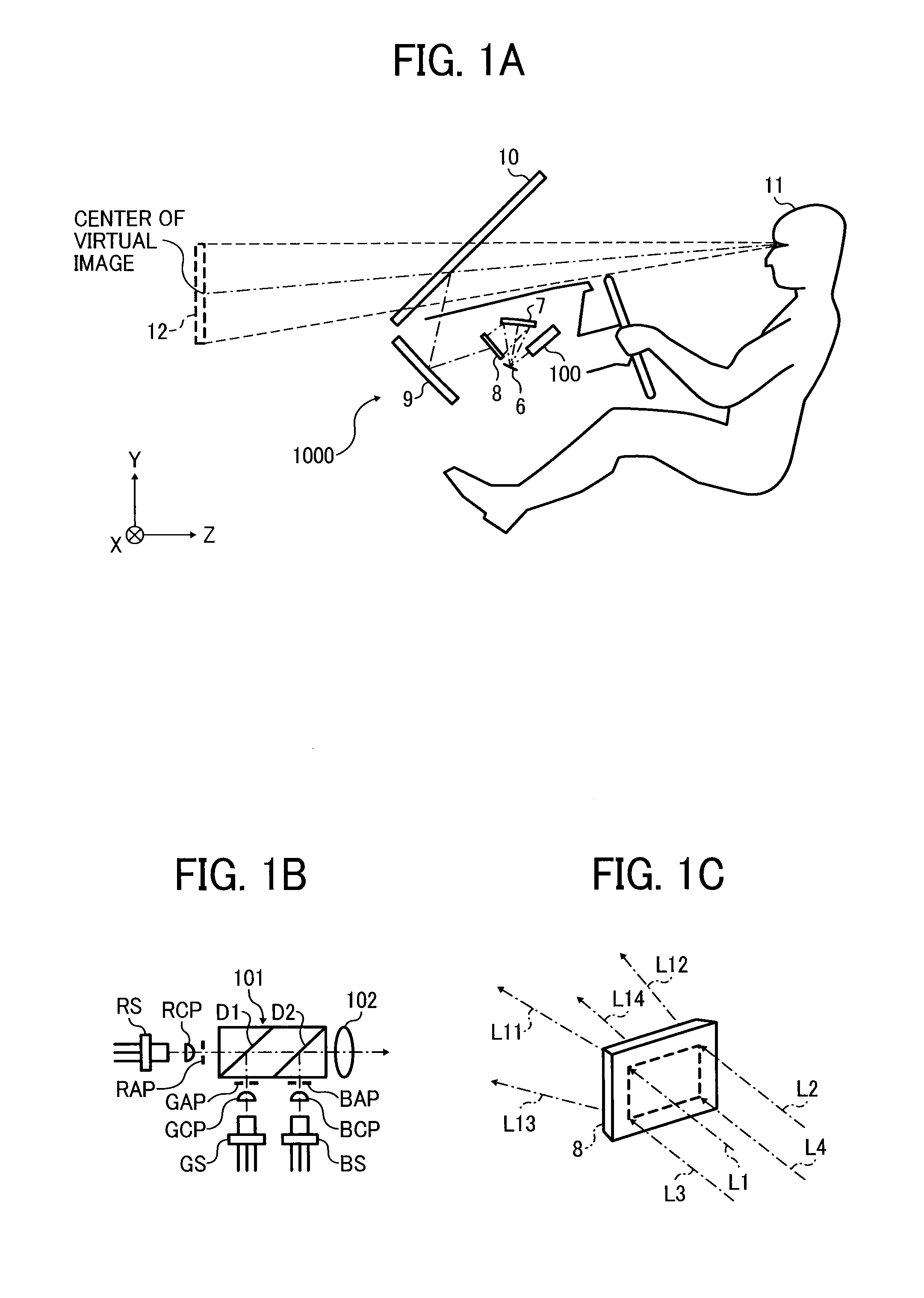
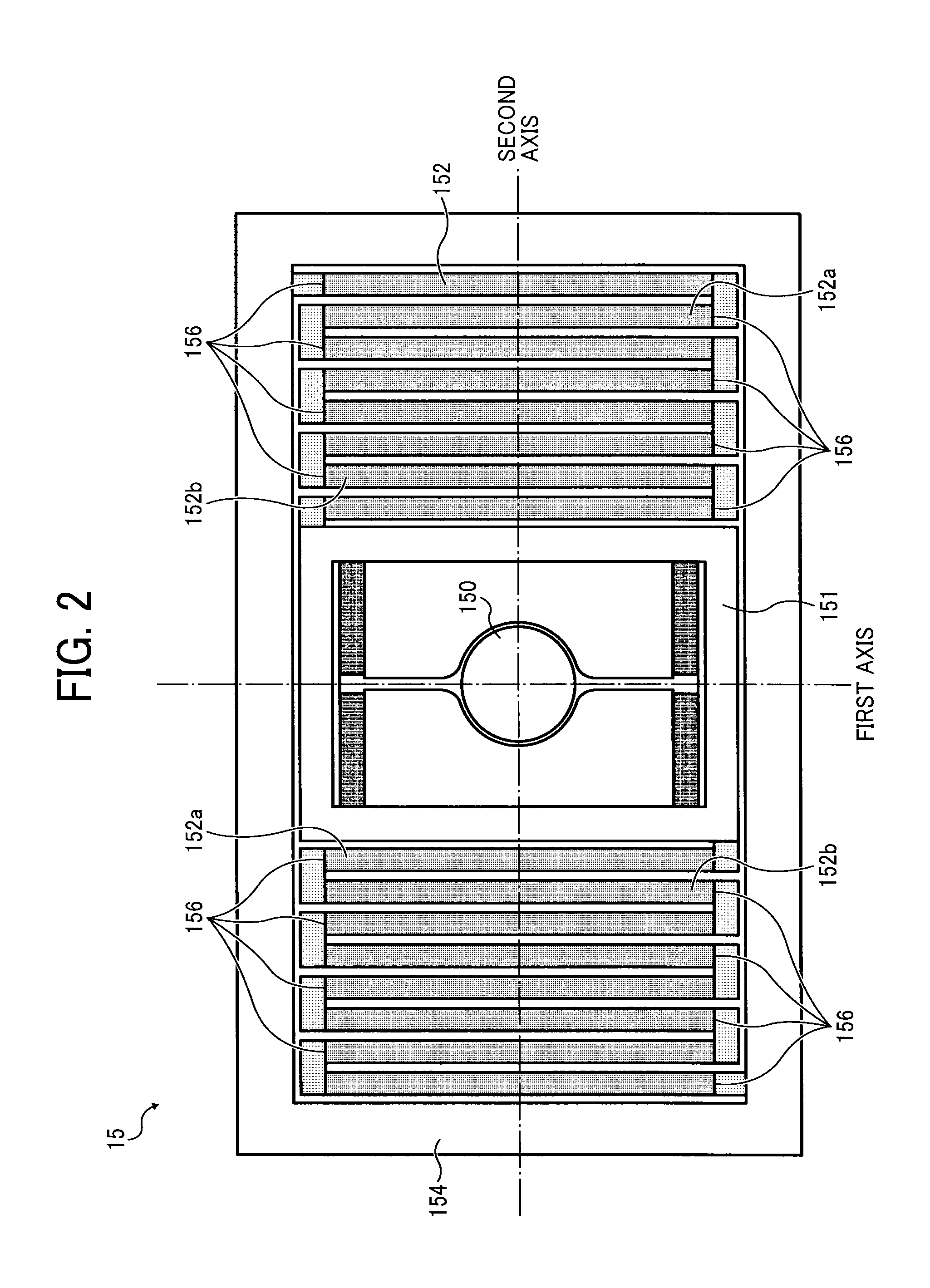
An image display apparatus (1000) mounted on an object or attached to a human body, includes: an image forming unit (200) to form an image with light; an optical system including a curved mirror (9) that reflects the light forming the image toward a bent transmission and reflection member; and a rotator (310) to rotate the curved mirror (9) about a prescribed axis. A first projection image, which is a projection image on an XY plane of the image, forms an angle θ1 with respect to an X direction. A second projection image, which is a projection image on an XY plane of the prescribed axis, forms an angle θ2 with respect to the X direction. The X denotes a lateral direction of the object or the human body and the Y direction denotes a vertical direction of the object or the human body.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical element for vertical external-cavity surface-emitting laser
InactiveUS20130223466A1Increase brightnessLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionOptical radiationLength wave
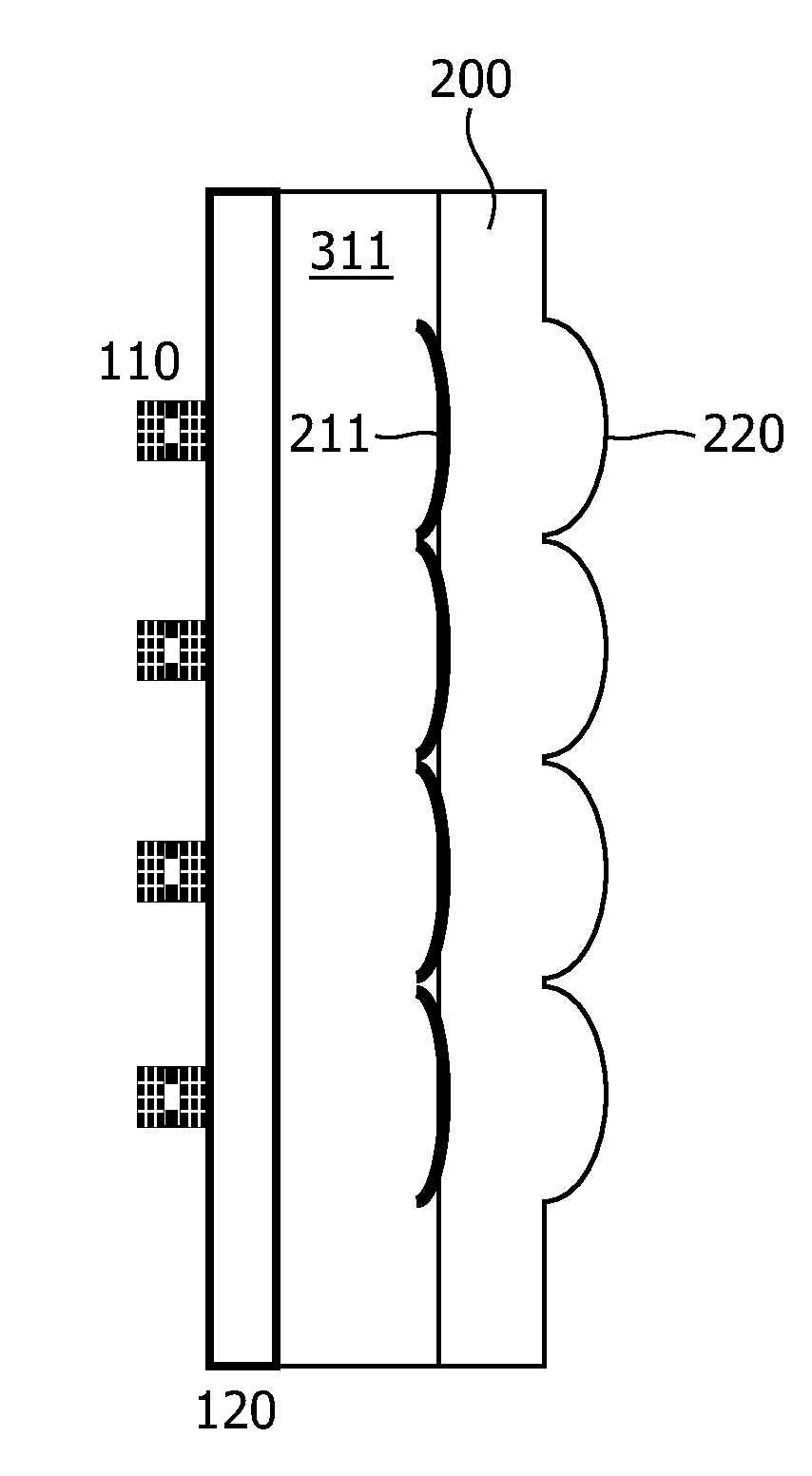
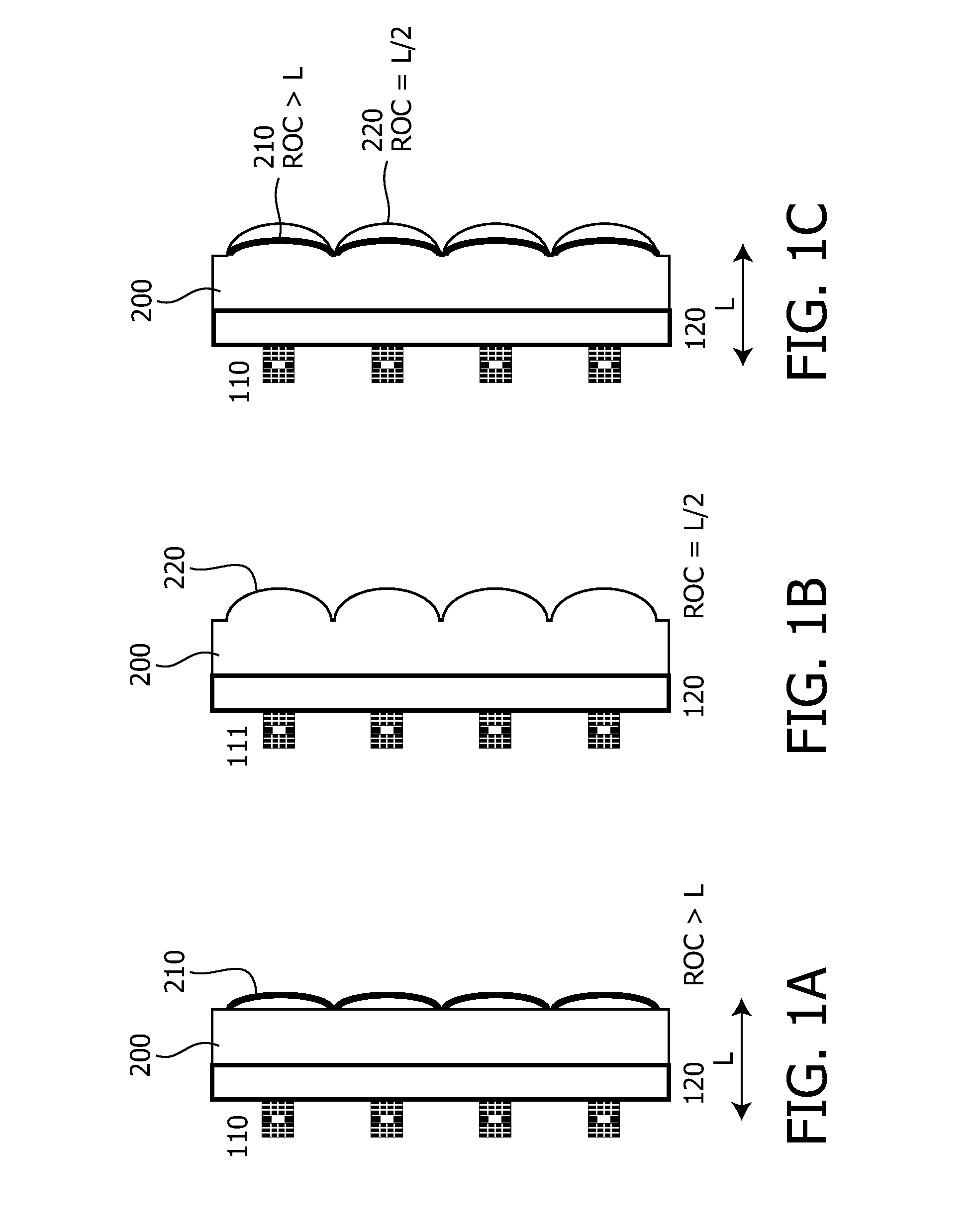
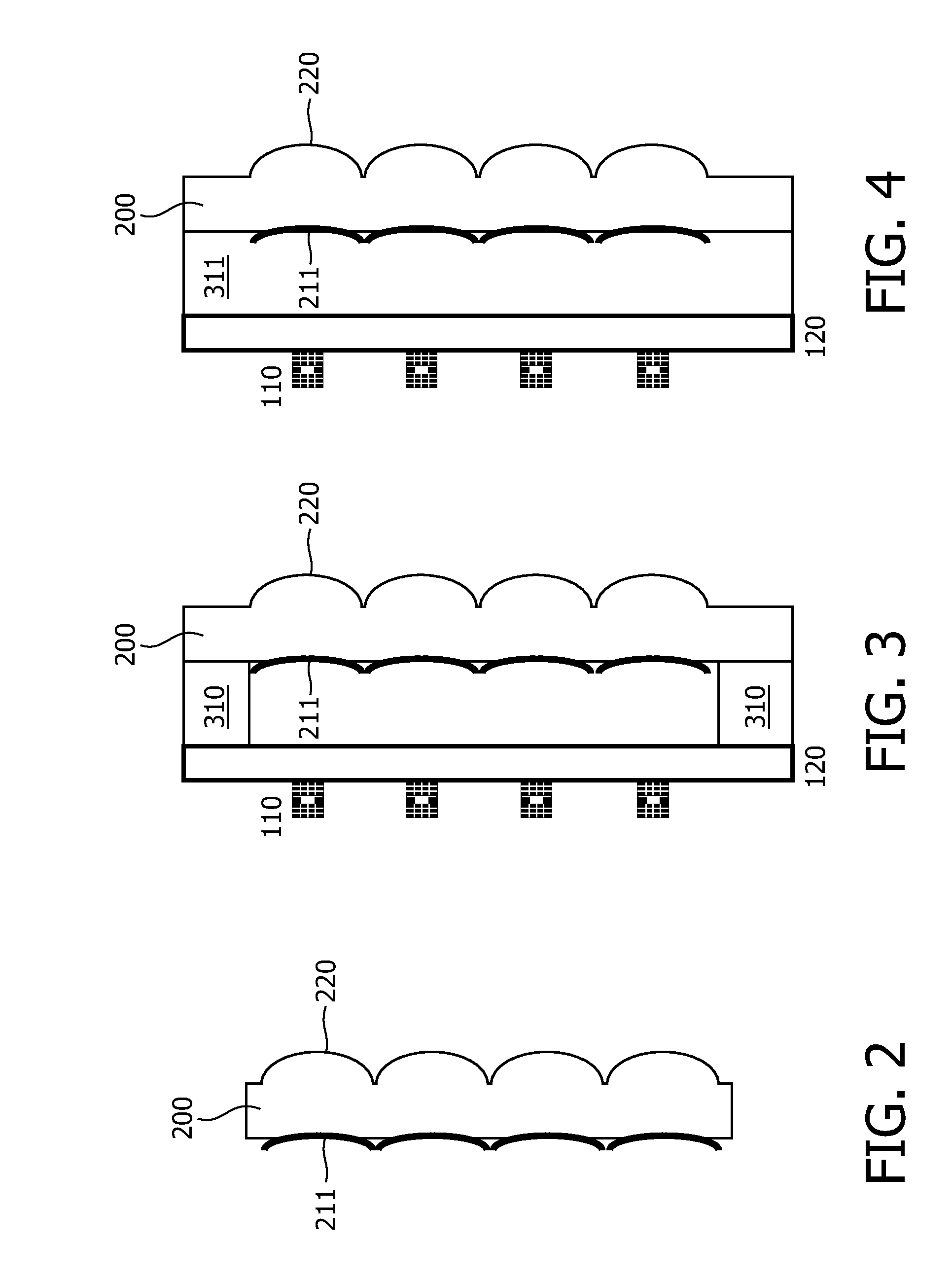
The present invention relates to an optical element for VEC-SELs or VECSEL arrays. The optical element is formed of a substrate (200) which is transparent at least in a wavelength region of optical radiation. A first interface of the- substrate (200) comprises one or several curved regions forming part of an optical lens or of an array of optical lenses (220) integrated in the substrate (200). The substrate (200) further comprises one or several optical mirrors (210) formed on a second interface of the substrate (200) opposing the first interface or embedded in the substrate (200). The optical mirrors (210) are arranged and designed to back reflect a fraction of optical radiation incident on the first or second interface. The optical mirrors (210) are flat mirrors or curved mirrors having a radius of curvature different from the radius of curvature of the curved region (220). The optical element allows the fabrication of a VECSEL or VECSEL array having a high brightness without the requirement of additional adjustments during fabrication. The VECSEL are arranged at a distance (L) to the optical mirrors (210) and this equals the length of the external cavity. The ROC of the optical lens may be chosen to ROC=L / 2 and for the optical mirror ROC>L. The cavity length may be adjusted by a monolithic spacer (120)
Owner:TRUMPF PHOTONIC COMPONENTS GMBH
Vehicle blind spot mirror
A vehicle blind spot mirror with a mirror having a single plane outwardly curved surface, an extension member attached to the rear portion of the outwardly curved mirror and having a double stick foam tape attachment means on the opposite surface of the extension, allowing the extension and attached blind spot mirror to be affixed to a vehicle's existing rear view mirror even if the rear view mirror is set in a recessed frame, thereby allowing for a larger blind spot mirror than the original rear view mirror. A preferred embodiment includes wherein said outwardly curved mirror is approximately seven and one half inches wide and five inches tall and is radially curved in such a way that the vertical center axis of said mirror is raised between thirty and eighty thousandths of an inch higher than the right or left edge. An alternate embodiment wherein the outwardly curved mirror is installed in place of a traditional flat plane driver's side rear view mirror found in current motor vehicles.
Owner:GERDES HARTMUT H
Novel binocular stereo vision measuring device
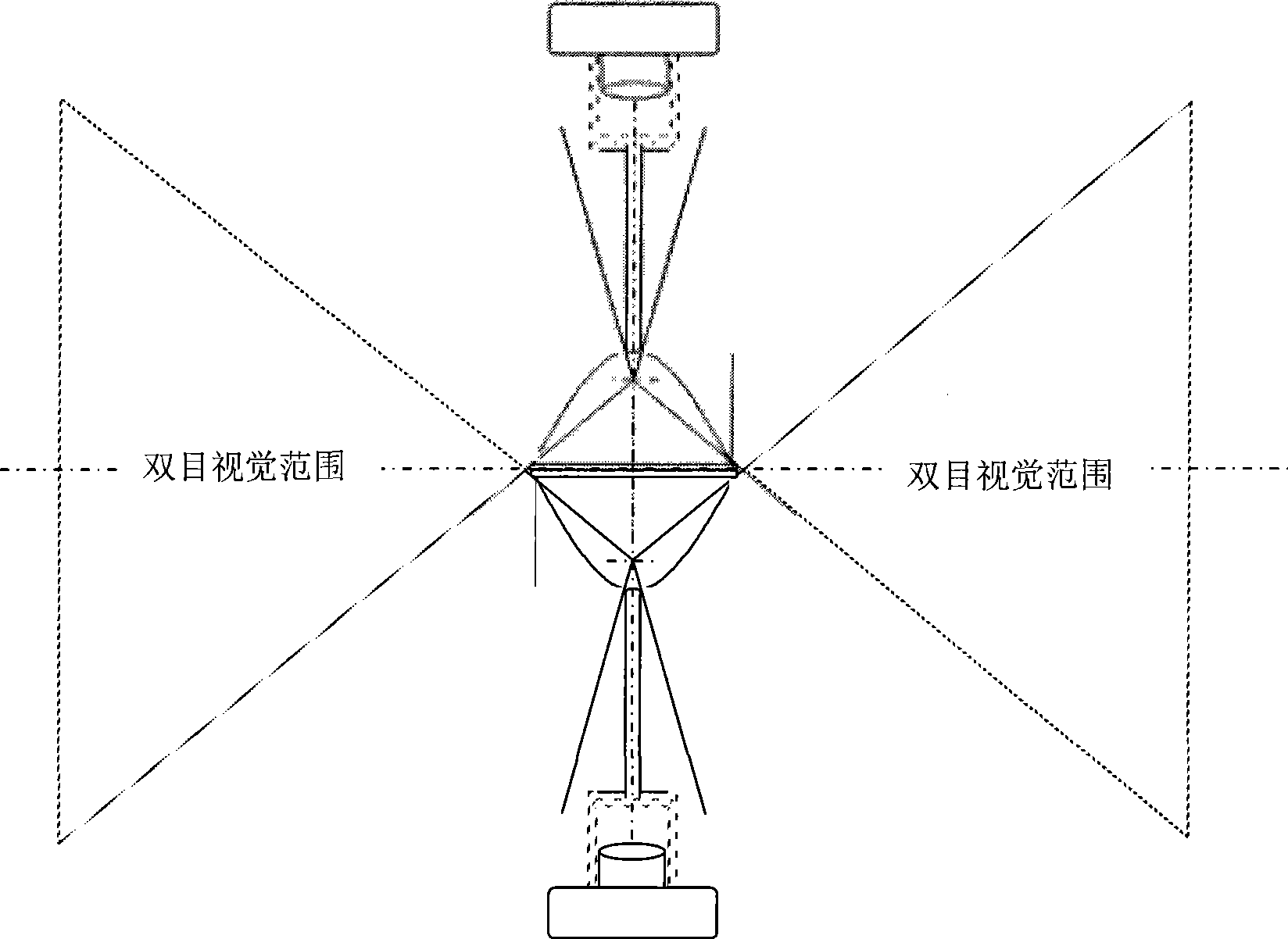
The invention relates to a novel binocular stereoscopic vision measuring device, which comprises two omnibearing vision sensors provided with the same imaging parameters, a connecting unit and a microprocessor which is used for performing three-dimensional stereoscopic vision reconstruction on images of the two omnibearing vision sensors, wherein the omnibearing vision sensors comprise hyperbolic mirror surfaces, upper covers, stand bars, transparent glass surfaces, supplementary lens frames and image units; the upper covers are arranged on the hyperbolic mirror surfaces; the stand bars are round platforms with thick upper parts and thin lower parts; upper ends of the stand bars are arranged inside small holes in bottom centers of the hyperbolic mirror surfaces, and lower ends of the stand bars are arranged inside mounting holes in the centers of the transparent glass surfaces which are embedded into the supplementary lens frames; the stand bars are perpendicular to the transparent glass surfaces; and the image units are positioned inside the supplementary lens frames. The novel binocular stereoscopic vision measuring device simplifies the complexity of calculation of stereo matching and so on, saves the operation of camera calibration, is convenient to perform feature extraction, is easy to realize stereo image matching, and finally achieves the aim of high-efficiency, real-time and accurate stereoscopic vision measurement.
Owner:汤一平
Laser beam generating apparatus
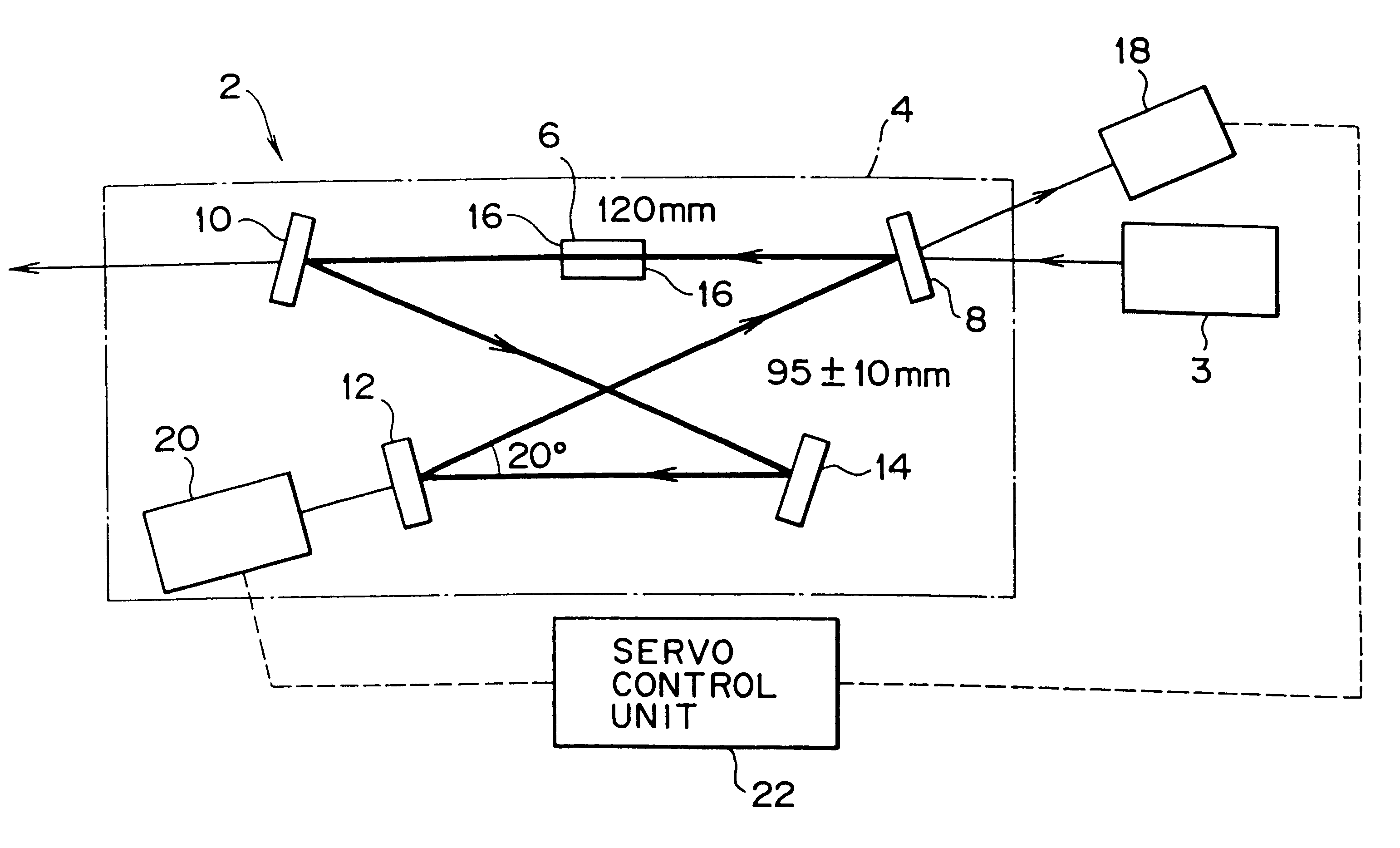
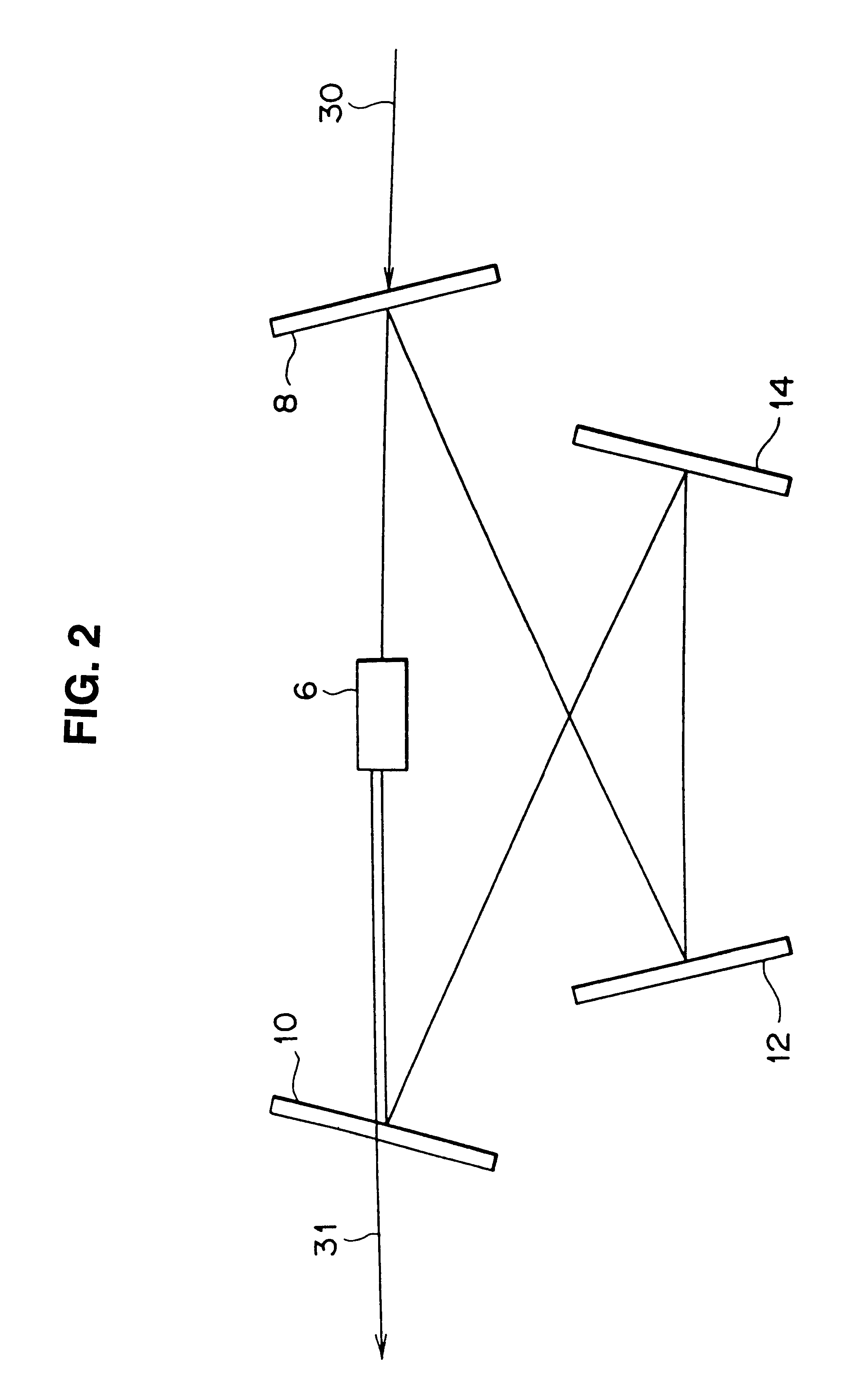
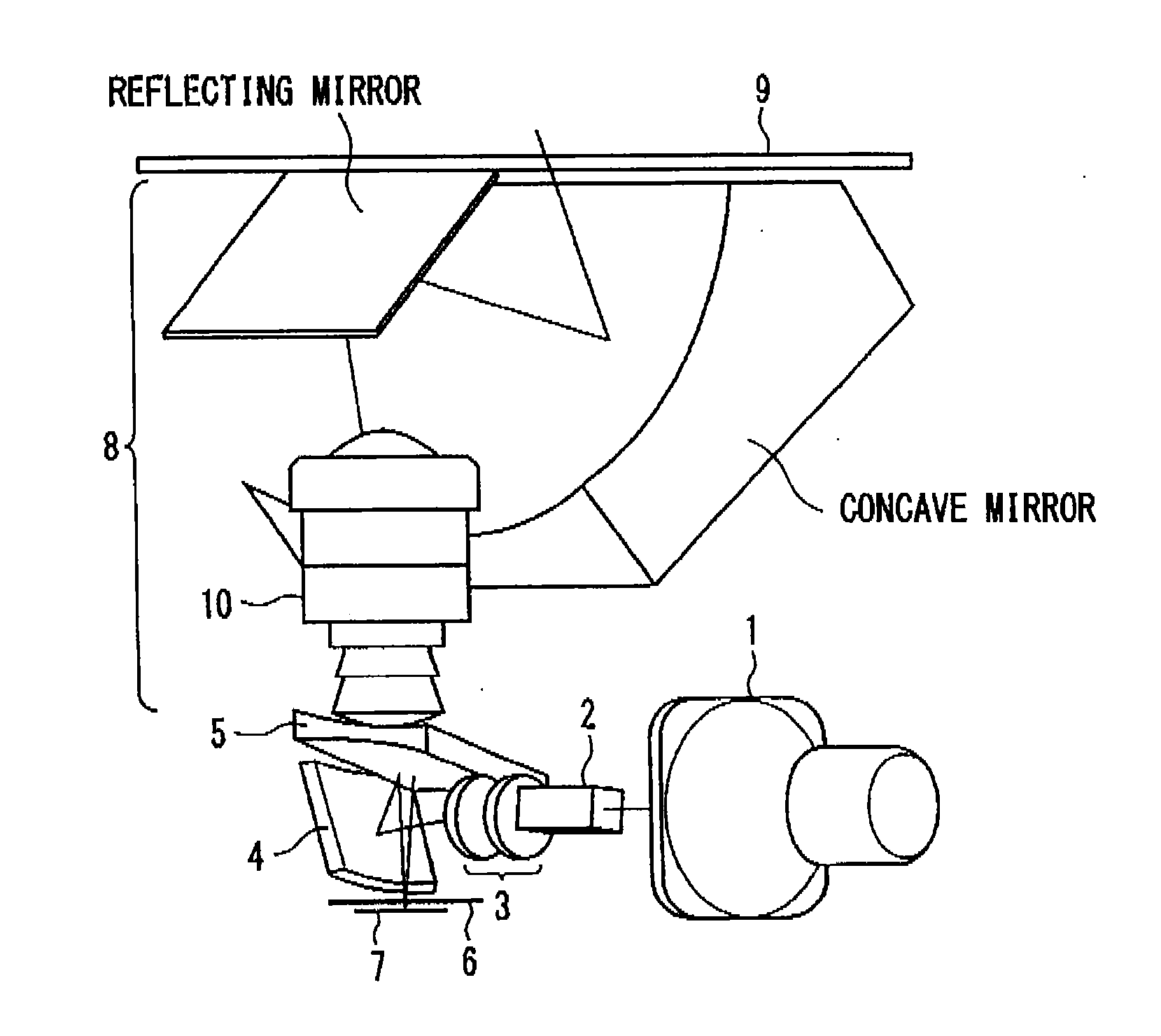
A laser beam in the ultraviolet region is generated at high power for along period. A green laser beam generated by a laser oscillator comes incident into a resonator from behind a first curved mirror, and circulates there, reflected by each mirror. By passing a barium borate crystal, it causes a secondary harmonic (a laser beam in the ultraviolet region) to be generated, which is taken out of the resonator via a second curved mirror. The beam waist of the laser beam passing the barium borate crystal is set to 46 mum, about double the conventional thickness, by adjusting the distance between the first curved mirror and a second flat mirror. As a result, the power density of the laser beam in the barium borate crystal is reduced to ¼ of the value according to the related art, and it is made possible to avoid rapid degradation of the barium borate crystal by excessive squeezing of the laser beam.
Owner:SONY CORP
Catadioptric projection objective with adaptive mirror and projection exposure method
InactiveUS7112772B2Improve image qualityPhotometry using reference valueMirrorsDeformable mirrorAstigmatism
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
No-blocking pure reflection optical system
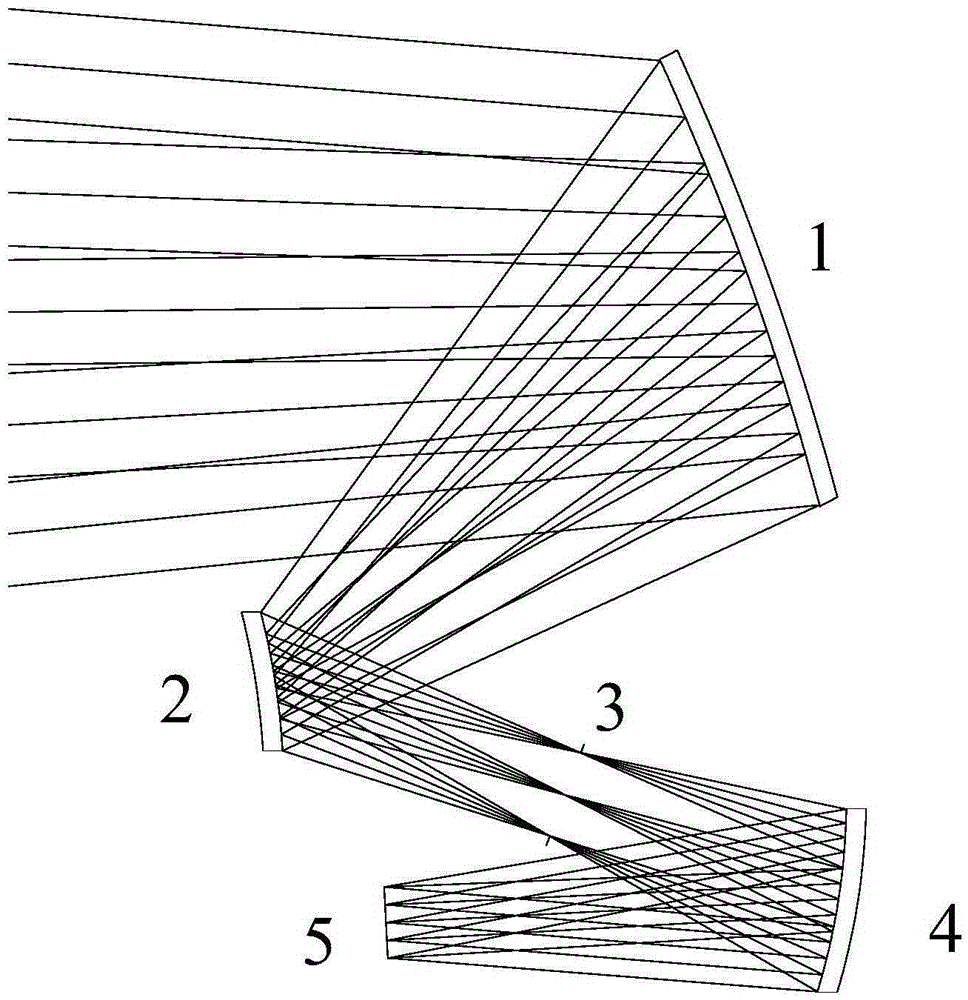
The invention relates to a no-blocking pure reflection optical system. The system is of an eccentric three-mirror structure and comprises a primary mirror, a secondary mirror, an aperture diaphragm, a ternary mirror and a detector focal plane which are arranged along the optical path from the object space to the image space in sequence, wherein the primary mirror, the secondary mirror and the ternary mirror are all reflecting mirrors, the primary mirror is a concave-paraboloid mirror, the secondary mirror is a convex hyperboloidal mirror, and the ternary mirror is a free-form-surface mirror; light is reflected on the surface of the primary mirror, the surface of the secondary mirror and the surface of the ternary mirror in sequence and blocking is avoided, and light reflected by the three mirrors irradiates on the focal plane perpendicularly. The system has the advantages of being wide in wave band, large in visual field, small in distortion, small in F number, free of blocking, telecentric in image space, free of chromatic aberration or thermal aberration and the like and is suitable for high-resolution observation.
Owner:LUOYANG INST OF ELECTRO OPTICAL EQUIP OF AVIC
THz wave radiation source with oval groove grating structure
The invention provides a THz wave radiation source with an oval groove grating structure. The oval groove grating with periodicity is adopted as a beam-wave interaction structure of the radiation source. When an electron beam passes through the structure at a certain speed, the electron beam and surface slow waves interact to be clustered and generate an electron beam cluster, then Smith-Purcell coherent radiation is stimulated, radiation is collected through a flat plate or a curved mirror (metal or medium) to generate tunable, compact and high-power THz waves, and therefore the THz wave radiation source can be easily applied to communication, radars, electronic countermeasures, electromagnetic weapons, astronomy, medical imaging, nondestructive detection, safety inspection and other aspects.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Heliostat with glass micro-arc curved surface mirror forming process structure
InactiveCN101058474AReduce mold costEasy to operateSolar heat devicesGlass reforming apparatusHeliostatEngineering
The invention discloses a heliostat through glass micro-arc mirror shaping technique in the solar utilizing technical domain, which is composed of curved mirror composite adjusting device and a group of single-chip glass micro-arc curved mirror shaping adjusting device, wherein the glass mirror rack of the single-chip glass micro-arc curved mirror shaping adjusting device is connected with the glass mirror through three groups of adjustable connecting devices at two ends or in the middle; two ends of each single-chip glass micro-arc curved mirror shaping adjusting device are fixed on the main frame of the curved mirror composite adjusting device through at least two groups of locking fixing piece, which are arranged adjacently; the incidence adjusting device is loaded near two groups of locking fixing piece adjacent to the main frame.
Owner:张耀明 +2
MEMS membrane with integral mirror/lens
InactiveUS20020126726A1Optical resonator shape and constructionDiffraction gratingsOptical surfaceDiffractive lens
An optical membrane device and method for making such a device are described. This membrane is notable in that it comprises an optically curved surface. In some embodiments, this curved optical surface is optically concave and coated, for example, with a highly reflecting (HR) coating to create a curved mirror. In other embodiments, the optical surface is optically convex and coated with, preferably, an antireflective (AR) coating to function as a refractive or diffractive lens.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
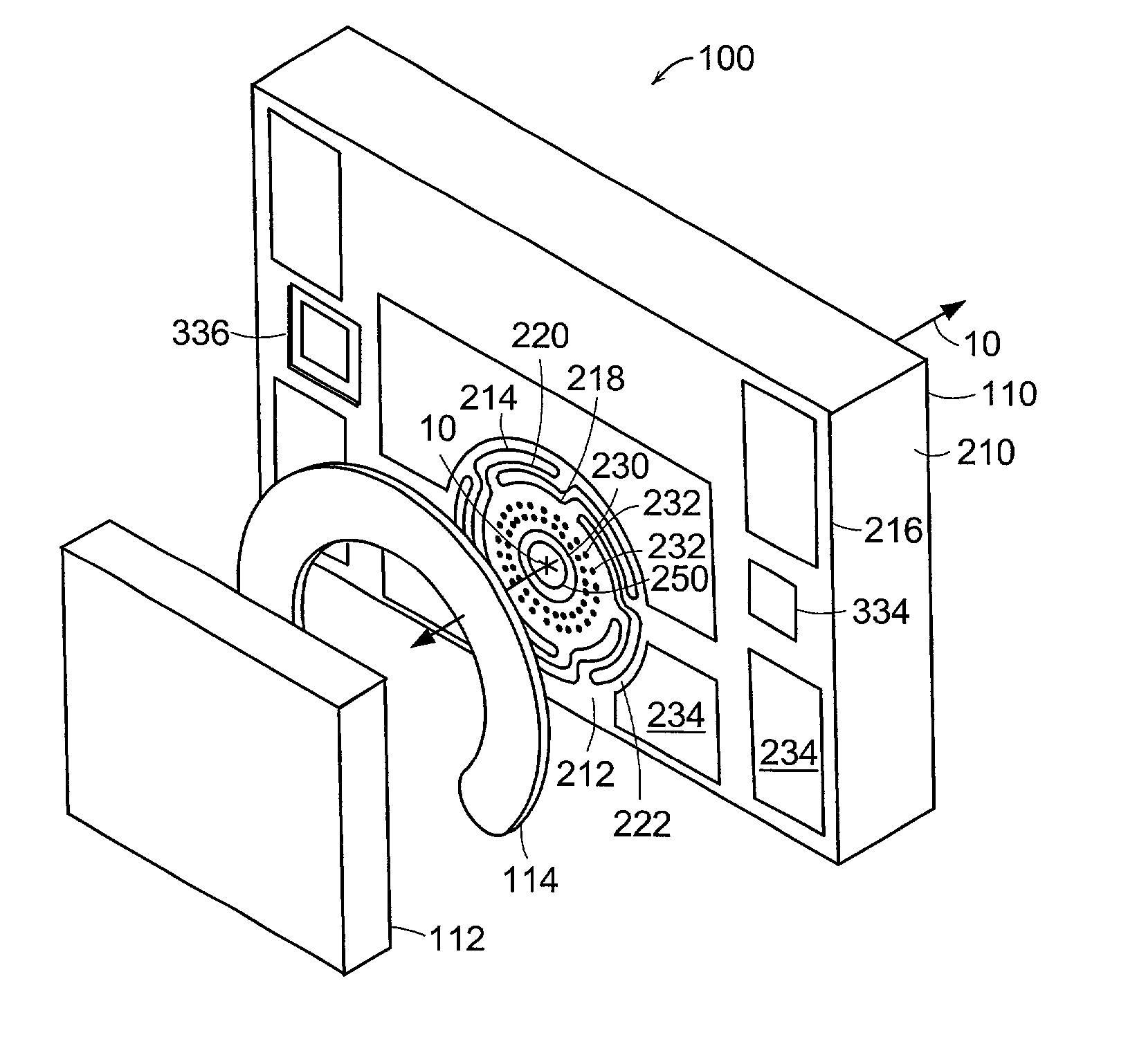
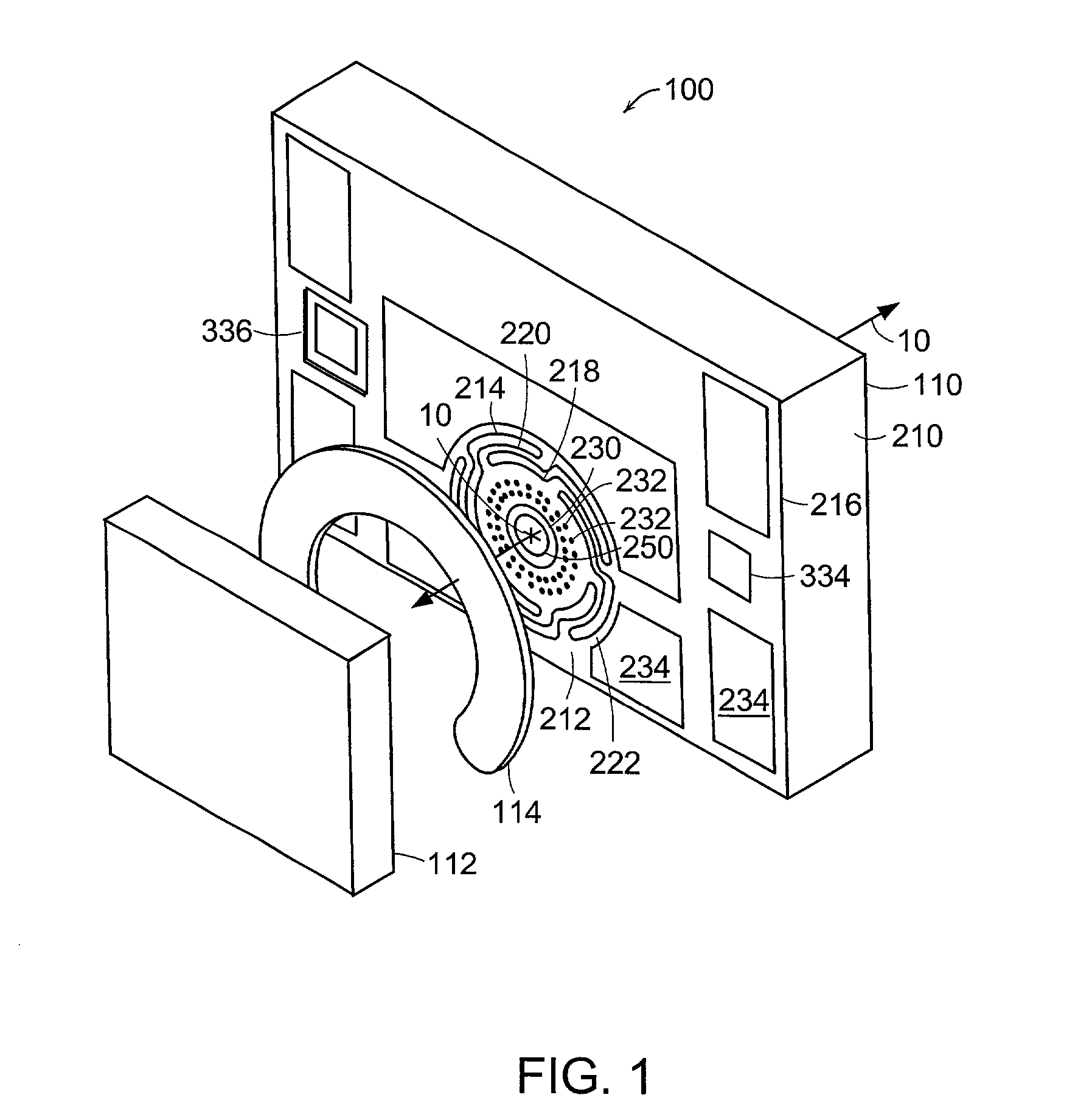
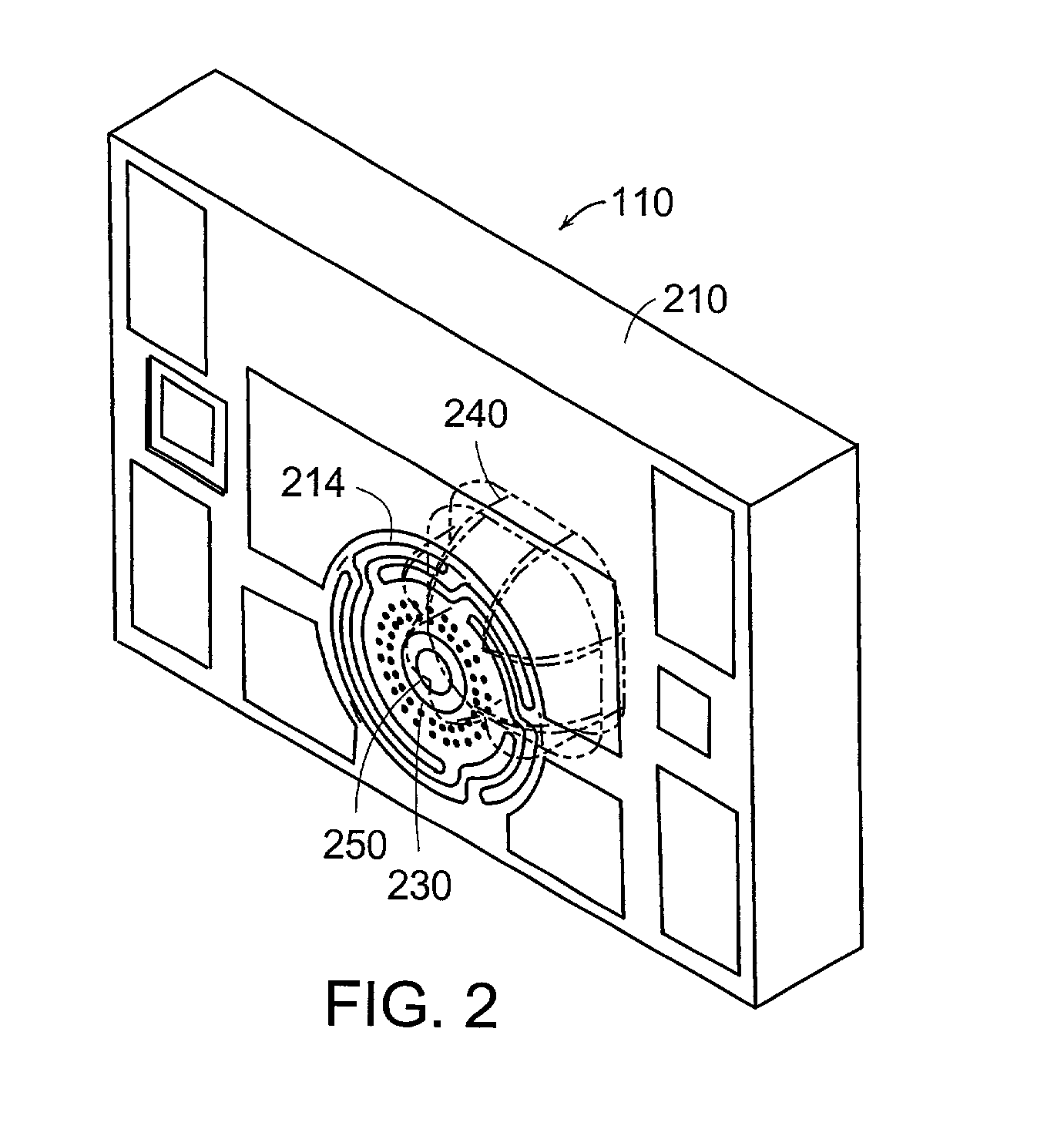
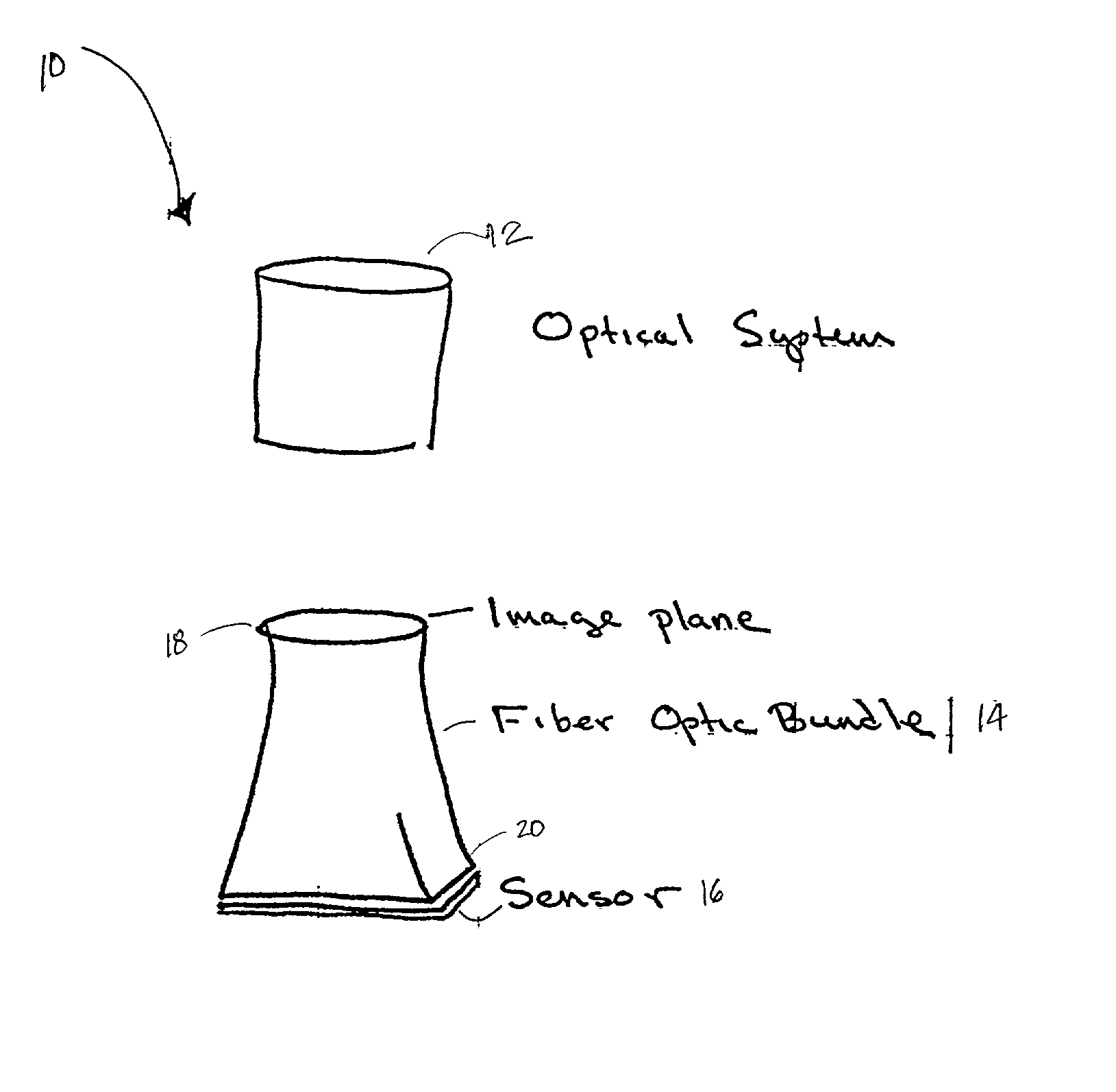
Fiber optic image mapping apparatus and method
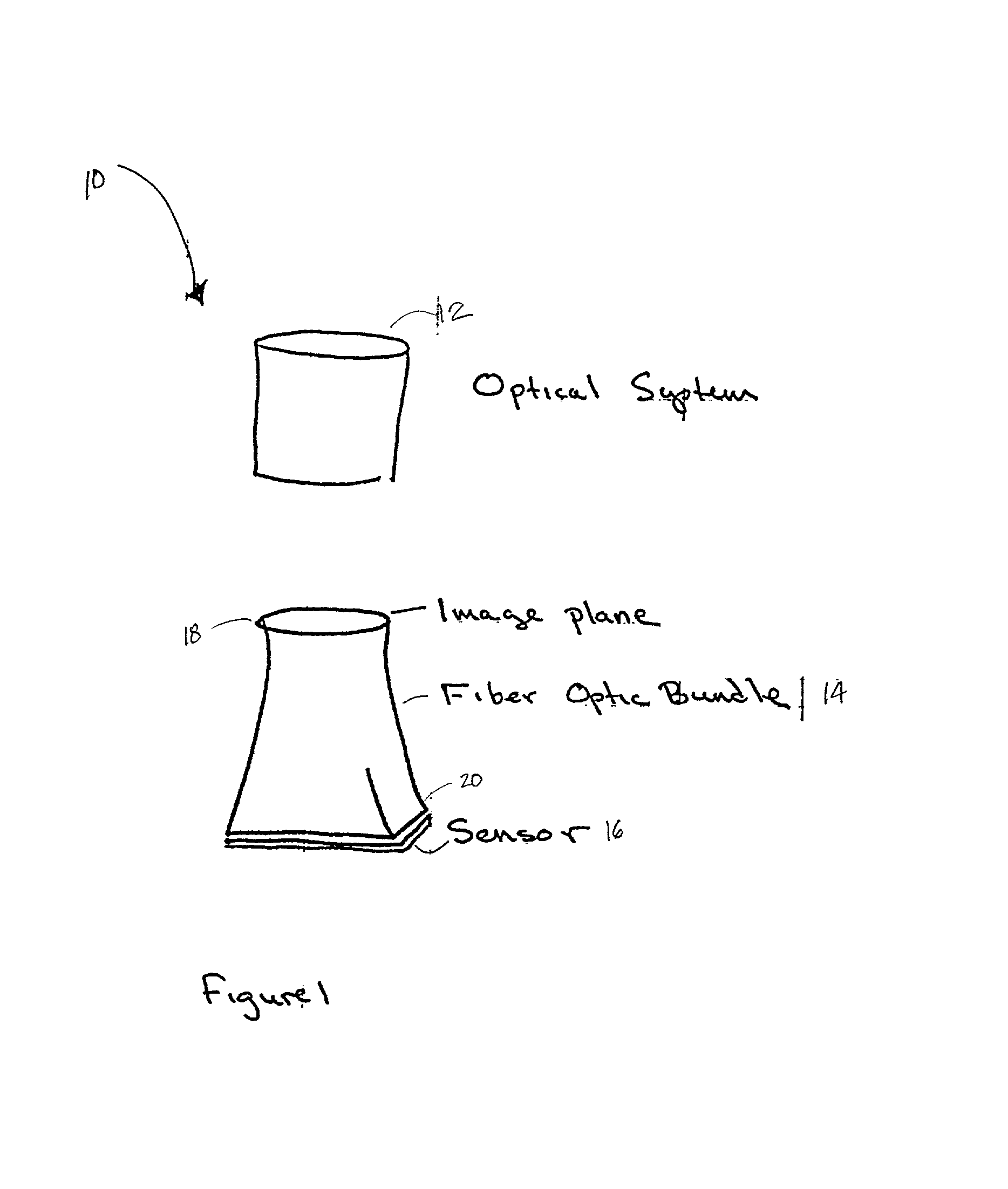
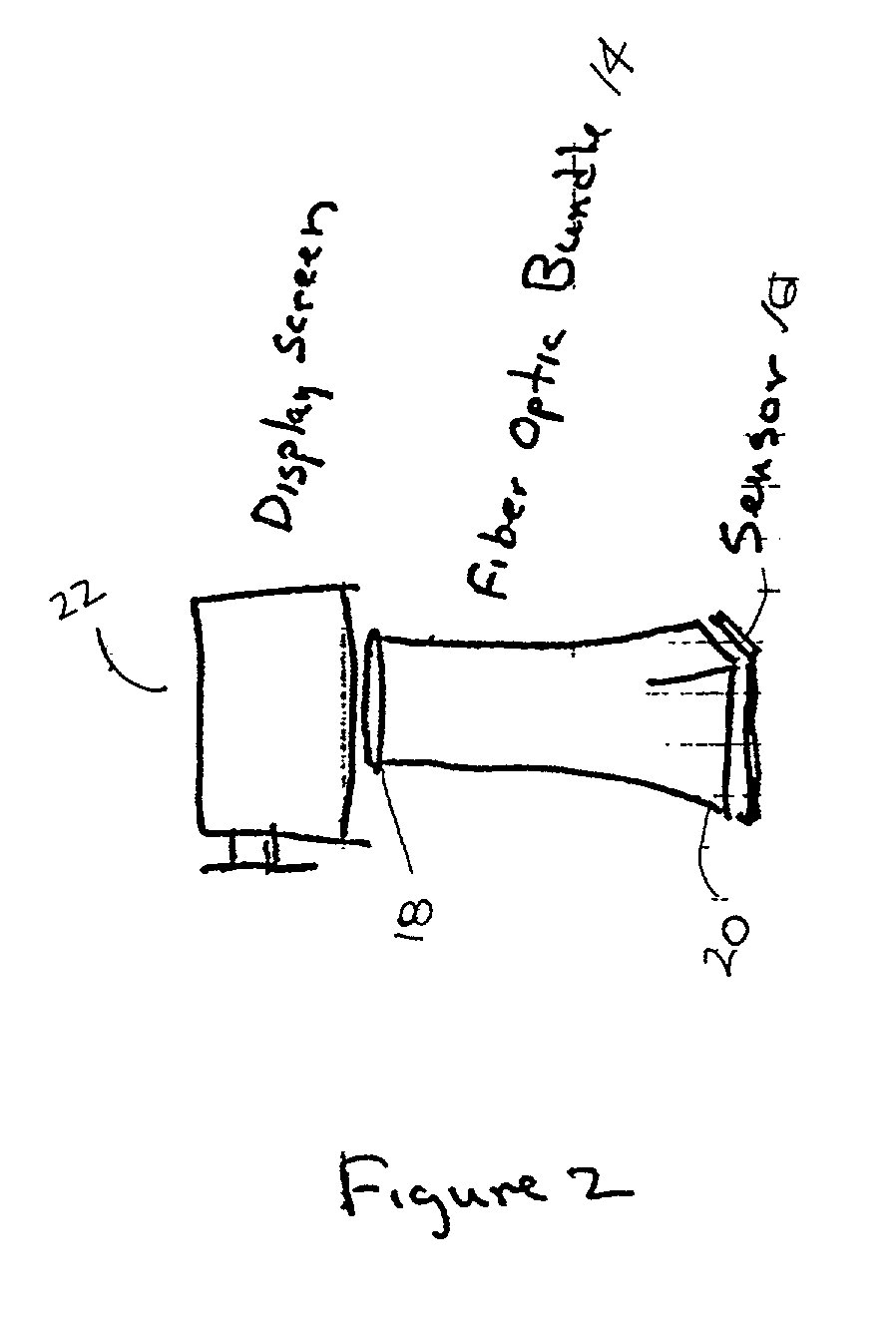
An apparatus for transforming the shape of an image in a way that utilizes substantially all the available pixels for both the image generated and the sensor to which the image is projected, is disclosed. Also disclosed is an apparatus and method to reduce or eliminate substantially any blurring associated with a non-planar focal plane associated with an image generated from a curved mirror, particularly when some portions of the image are focused on the plane of the sensor and other portions are blurred. Loss of image resolution is eliminated, thereby achieving desired fiber optic image mapping, by the present invention for coherent and incoherent fiber optic cables.
Owner:CYCLOVISION TECH
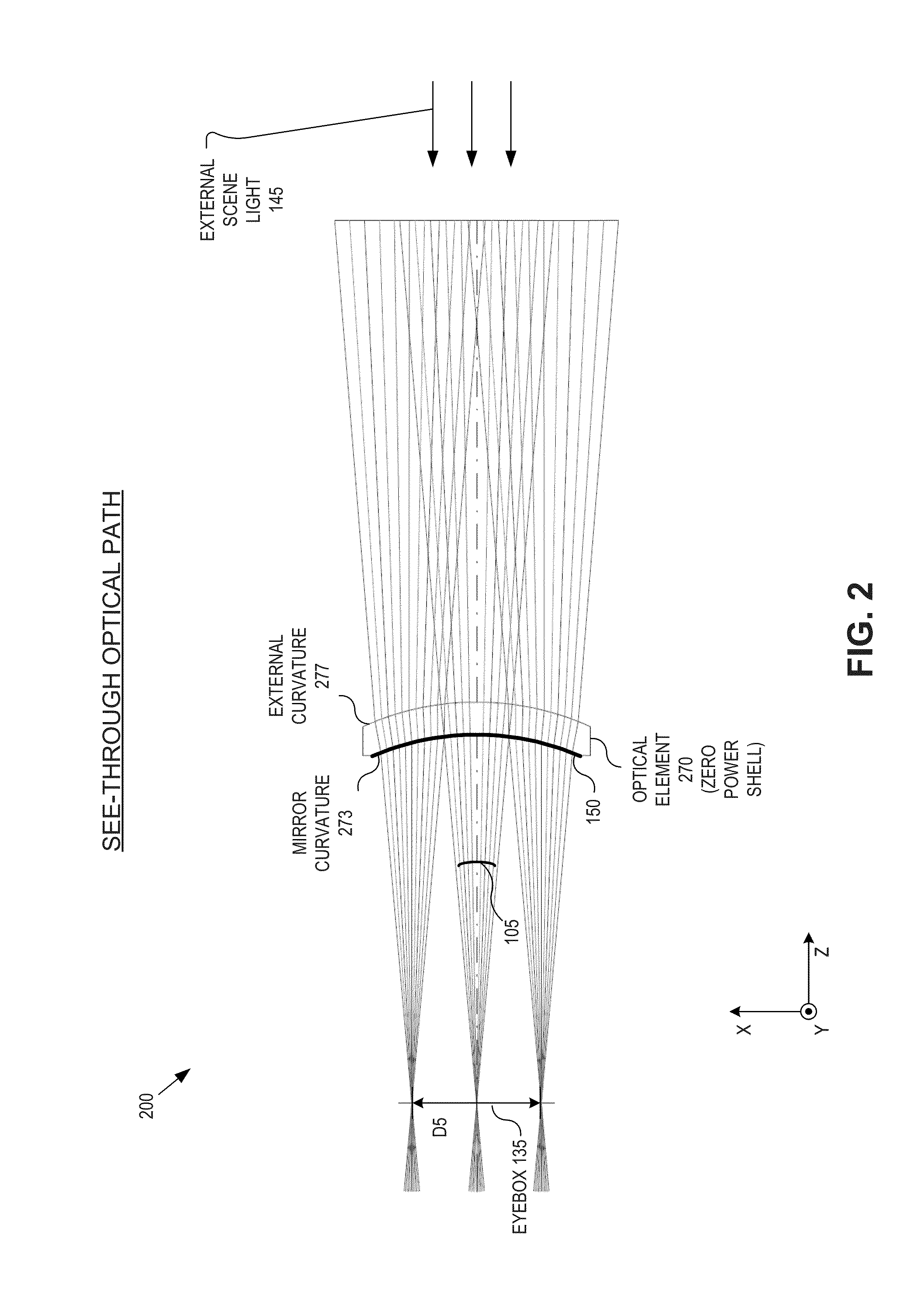
Transparent microdisplay in head mountable displays
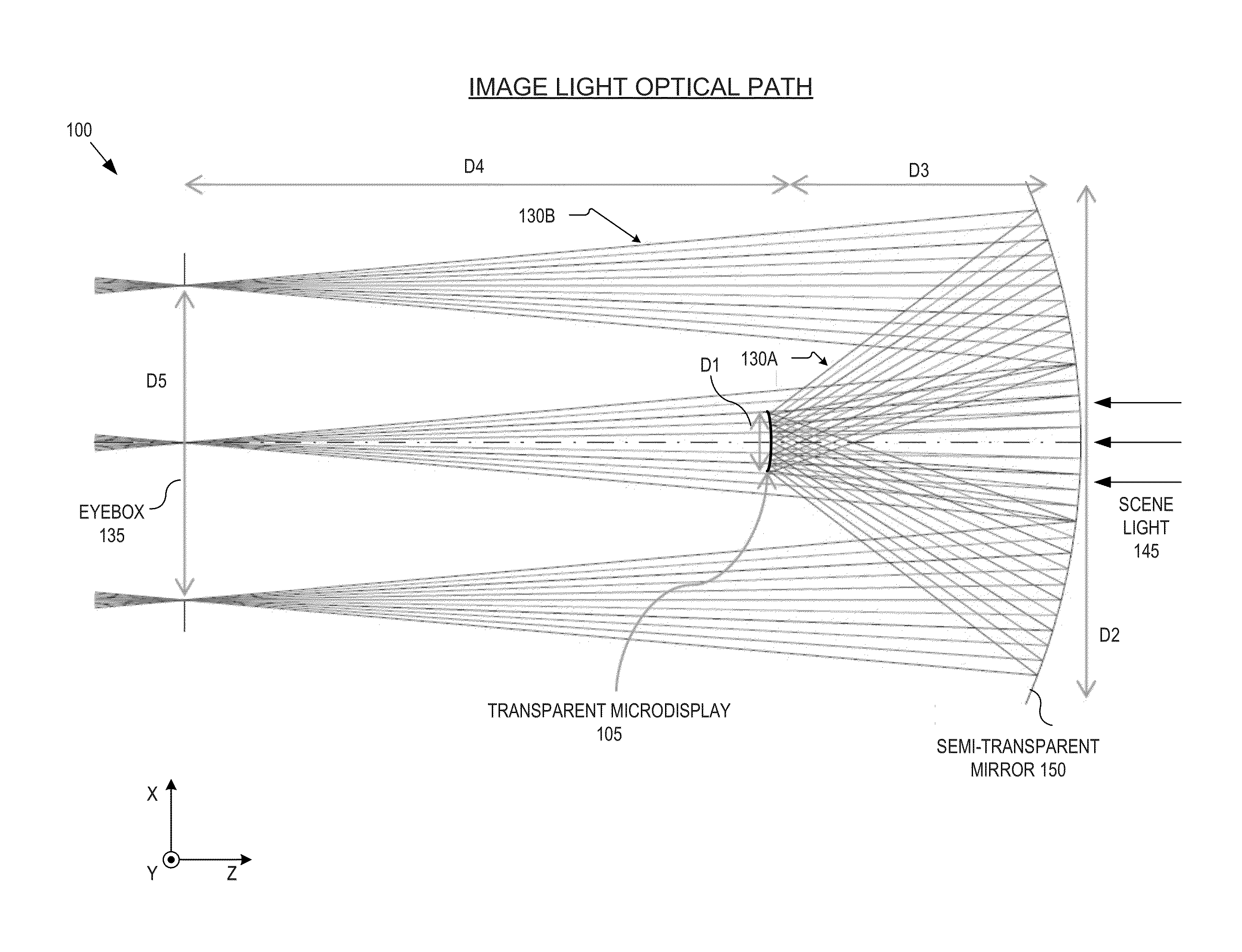
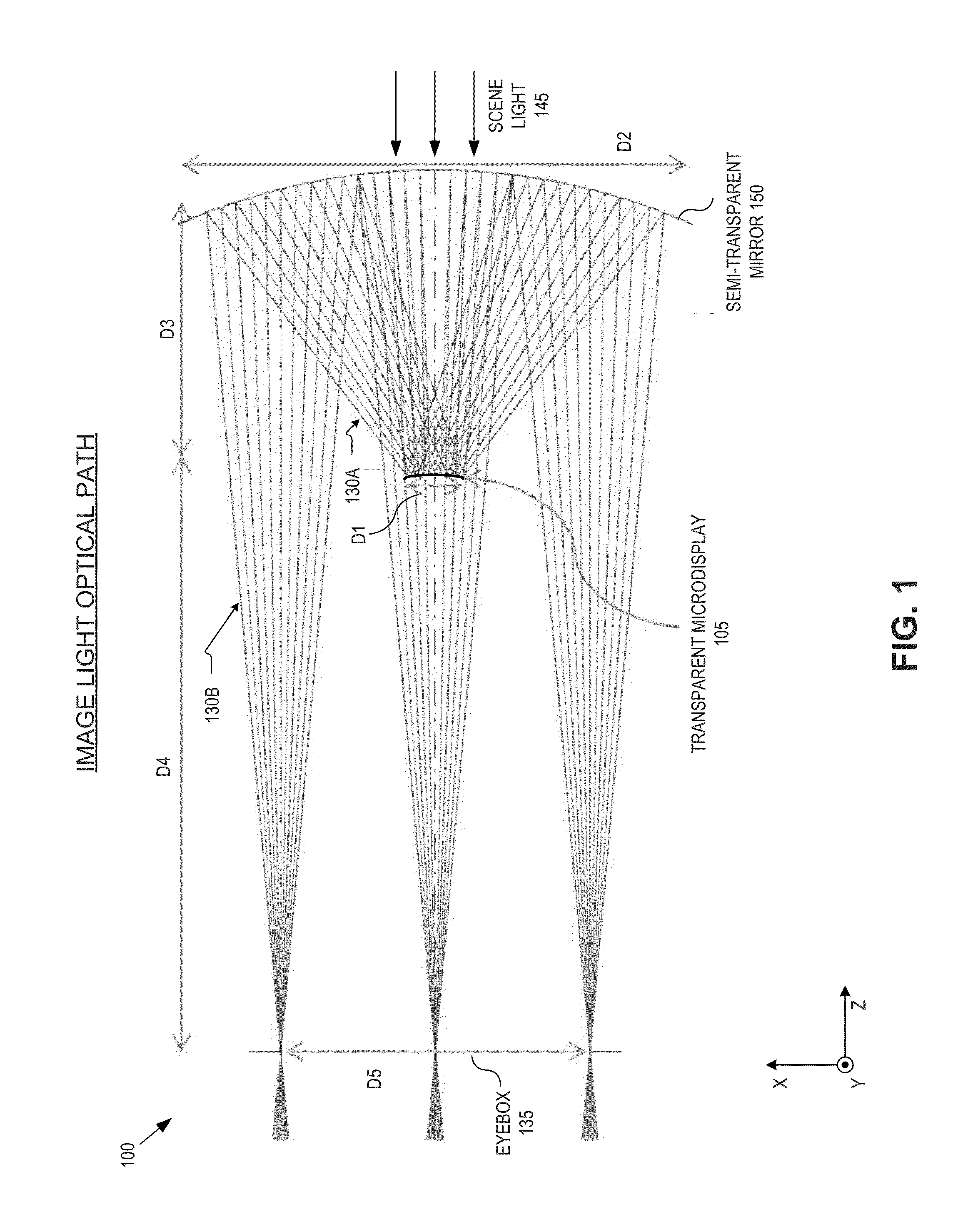
An optical apparatus includes a transparent microdisplay and a curved mirror. The transparent microdisplay has an array of self-illuminating emitters configured to emit image light propagating in an external direction. The curved mirror is positioned to reflect the image light toward an eye-ward side of the optical apparatus. A first curvature of the curved mirror has an optical power configured to focus the image light reflected by the curved mirror within an eyebox sized area. The transparent microdisplay is disposed between the curved mirror and the eyebox sized area.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Backlight
A backlight is provided for an at least partially transmissive display or another lighting application. The backlight comprises an array of primary light sources that emit downwards towards an arrangement of curved mirror surfaces. The light reflected by the mirror surfaces is collimated by an arrangement of lenses. The mirror surface shape, lens shape, primary light source positions and the separation between the lens and mirror surfaces are chosen to ensure a high degree of spatial uniformity as well as collimation.
Owner:SHARP KK
Sample inspection system
InactiveUS20050174568A1Reduce positioning errorsRadiation pyrometrySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementLight beamCombined use
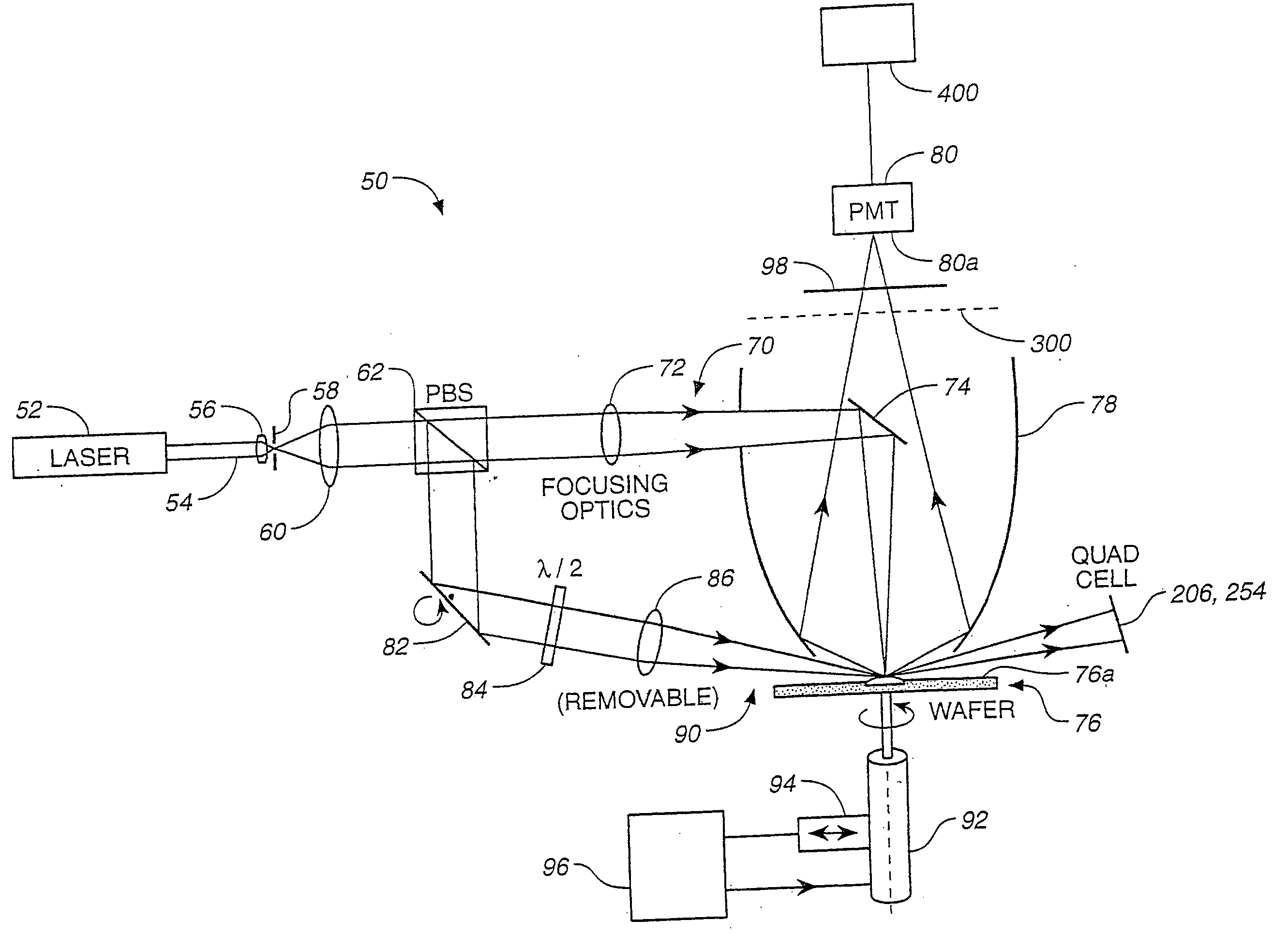
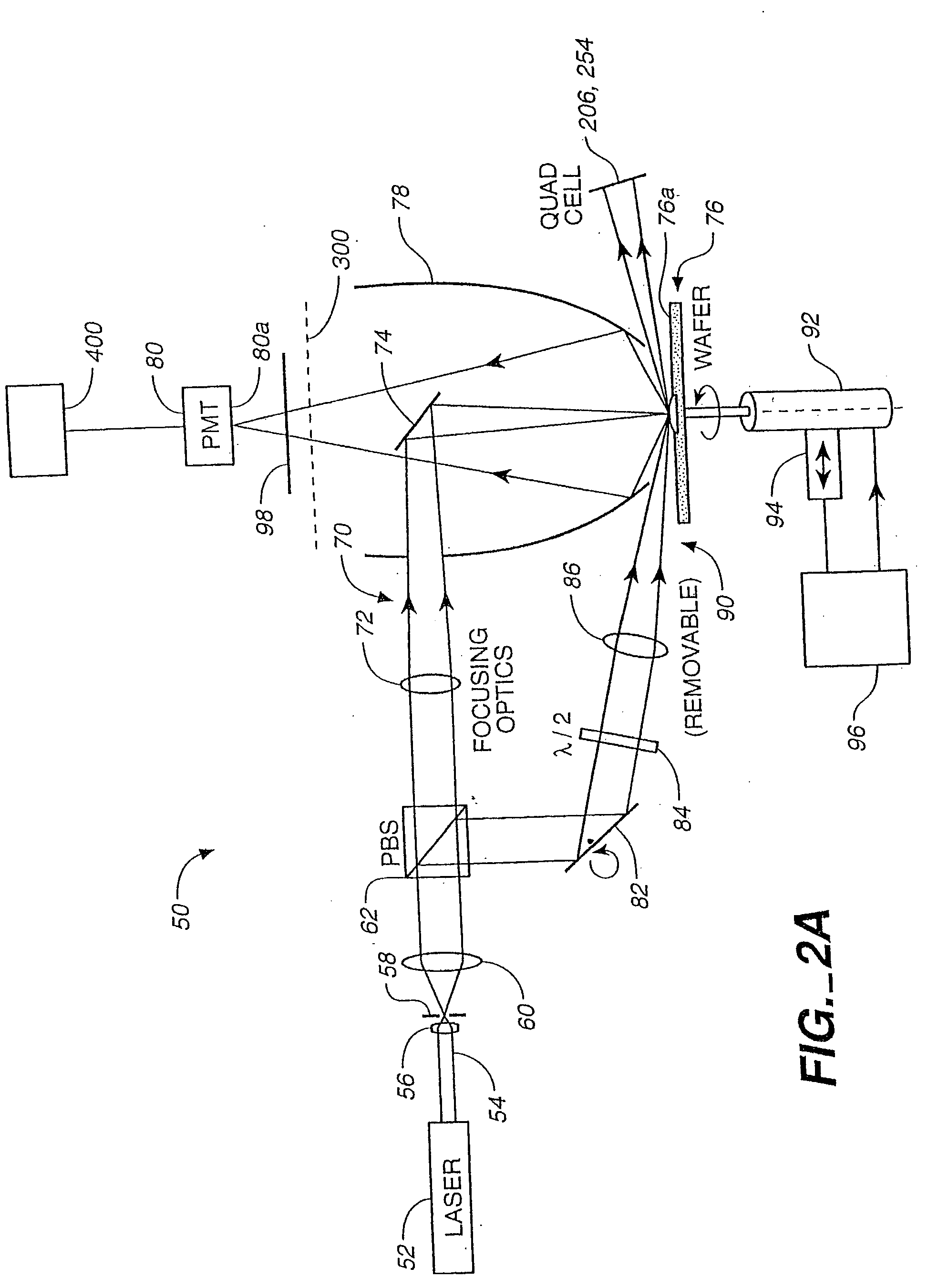
A curved mirrored surface is used to collect radiation scattered by a sample surface and originating from a normal illumination beam and an oblique illumination beam. The collected radiation is focused to a detector. Scattered radiation originating from the normal and oblique illumination beams may be distinguished by employing radiation at two different wavelengths, by intentionally introducing an offset between the spots illuminated by the two beams or by switching the normal and oblique illumination beams on and off alternately. Beam position error caused by change in sample height may be corrected by detecting specular reflection of an oblique illumination beam and changing the direction of illumination in response thereto. Butterfly-shaped spatial filters may be used in conjunction with curved mirror radiation collectors to restrict detection to certain azimuthal angles.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Electromagnetic coupling field-induced rheological polishing tool
InactiveCN101774151AExquisite structureImprove securityPolishing machinesLow voltageOptical processing
The invention belongs to the technical field of precise optical working and relates to an electromagnetic coupling field-induced rheological polishing tool. Based on electro-rheological and magneto rheological effect, the invention utilizes ferro magnetic material as a polished shaft; when direct current low voltage is applied on an electromagnetic coil, the polished shaft is magnetized to form an electromagnet with the electromagnetic coil, and a vertically distributed magnetic field is produced near the tip of the polished shaft; when direct current high voltage is applied on a taper sleeve and two ends of the polished shaft, a horizontal electric field can be provided to obtain a cross field near a polishing head; when direct current high voltage is applied on a sheet metal and the polishing shaft, a vertical electric field can be obtained, and a parallel field is obtained near the polishing head. Electromagnetic rheological liquid generates rheological effect under the action of externally applied electric and magnetic fields; liquid particles are distributed in chain and intensively attached near the polishing head to form a small-size flexible liquid polishing head which forms relative shearing movement with workpiece surface under the drive of a motor, thus finishing the ultrasmooth polishing of minor-caliber aspherical mirrors, heteromorphic mirrors and free curved mirrors.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Light modulating microdevice
A light modulator comprises a mirror, a substrate provided with at least one electrode, and at least one hinge extending between the substrate and the mirror. The mirror is flexible with the hinge being displaceable for allowing for the displacement and / or the deformation of the mirror. Typically, there are two symmetrically disposed hinges, each including upper and lower arms that define an angle therebetween. The upper arm is connected to the mirror, and the lower arm is mounted to the substrate. The upper and lower arms are adapted to pivot relative to one another thereby allowing the angle to vary and thus allowing the mirror to at least one of displace and deform. When unbiased, the mirror may be plane, convex or concave. When biased, the plane mirror adopts a curved attitude, whereas the curved mirror changes its curvature. The upper and lower arms of each hinge are V-shaped and define an apex. The apexes extend inwardly in a facing relationship.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT +1
Magnification optical system
A magnification optical system forms an enlarged image of an object. It includes a refractive optical system including a plurality of lens groups; and a mirror train including a curved mirror, arranged in this order from an object side, a first focus structure configured to move the respective lens groups of the refractive optical system by different amounts along a normal line of a conjugate surface on the object side, and a second focus structure configured to move the respective lens groups along the normal line of the conjugate surface on the object side by different amounts from those of the first focus structure.
Owner:RICOH KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com