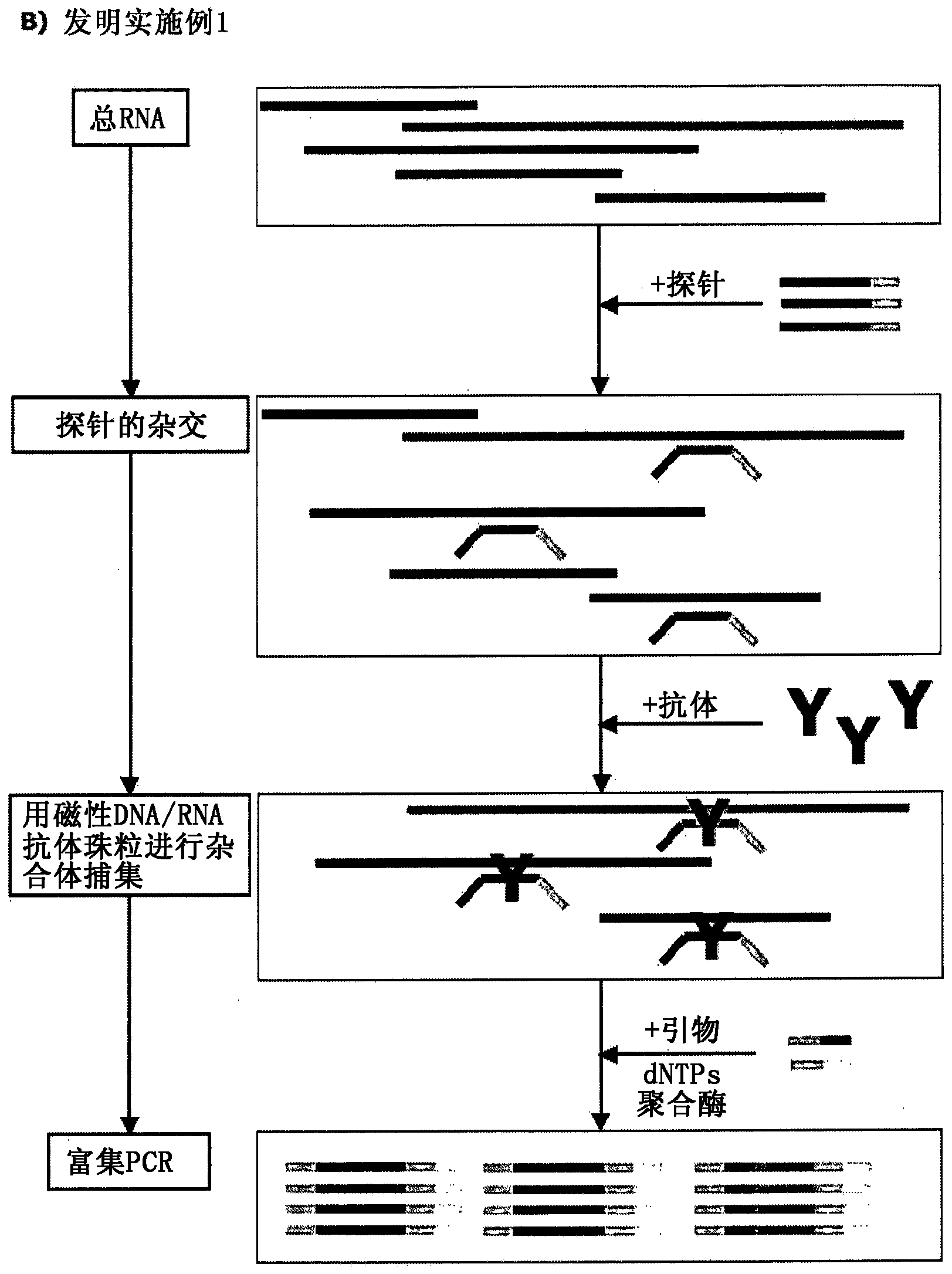
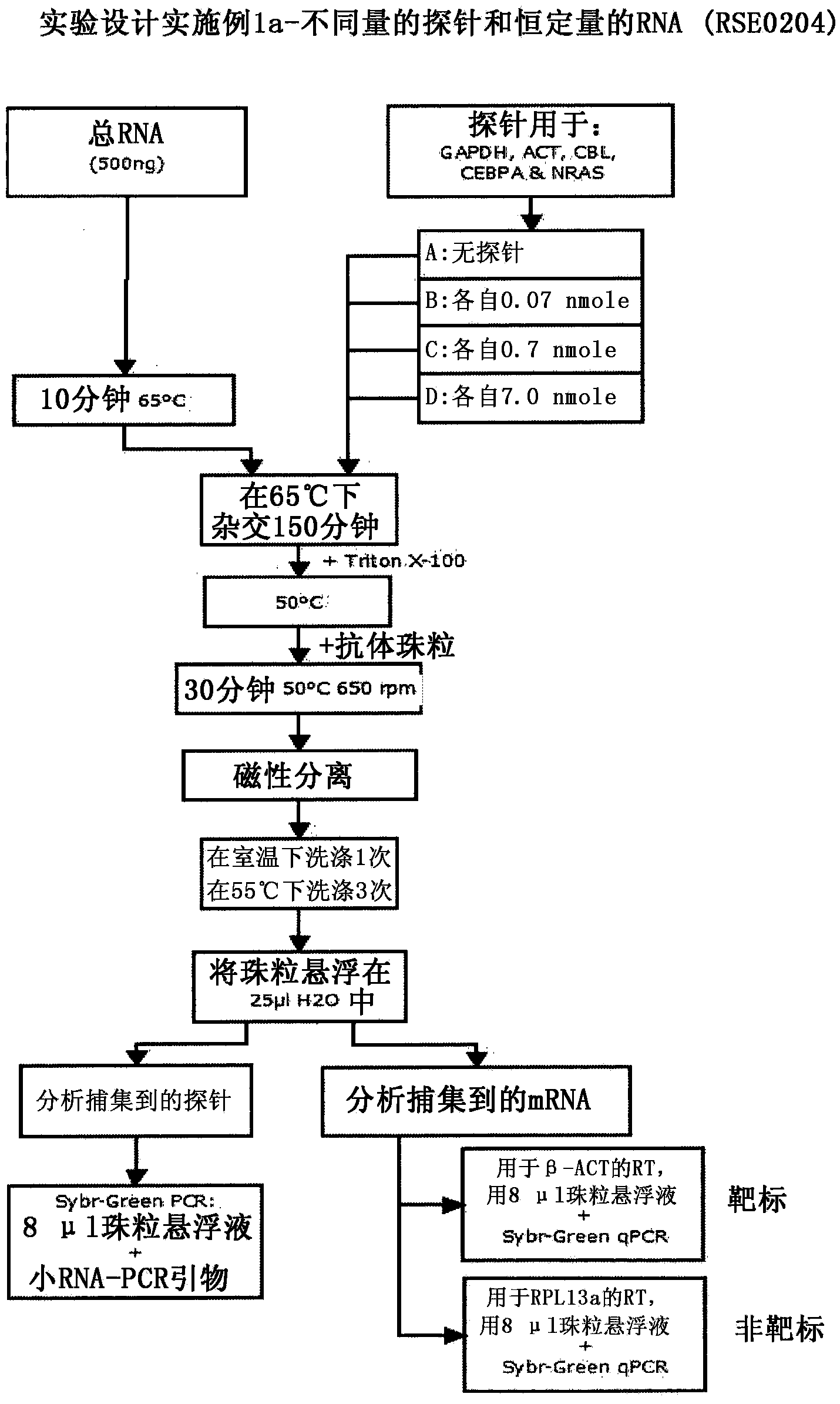
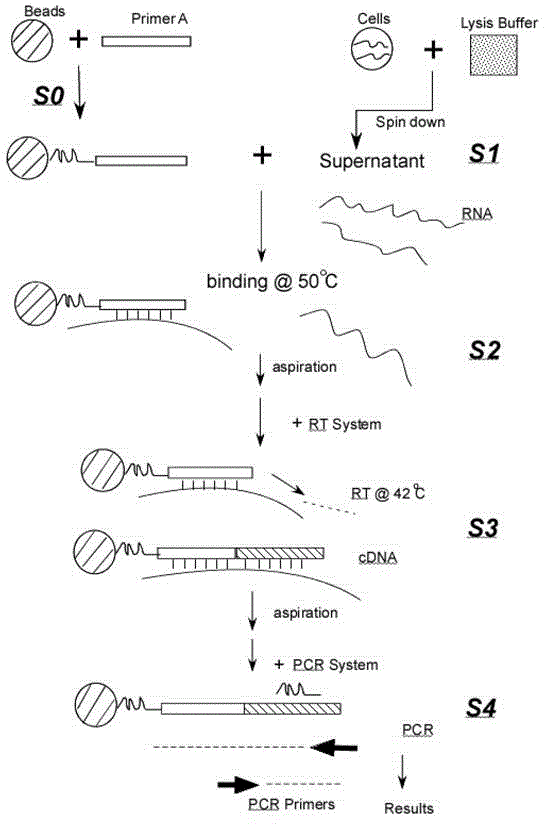
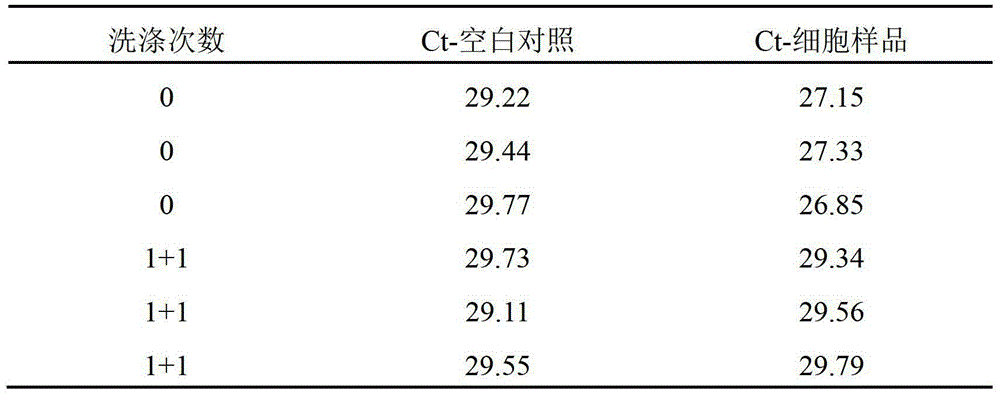
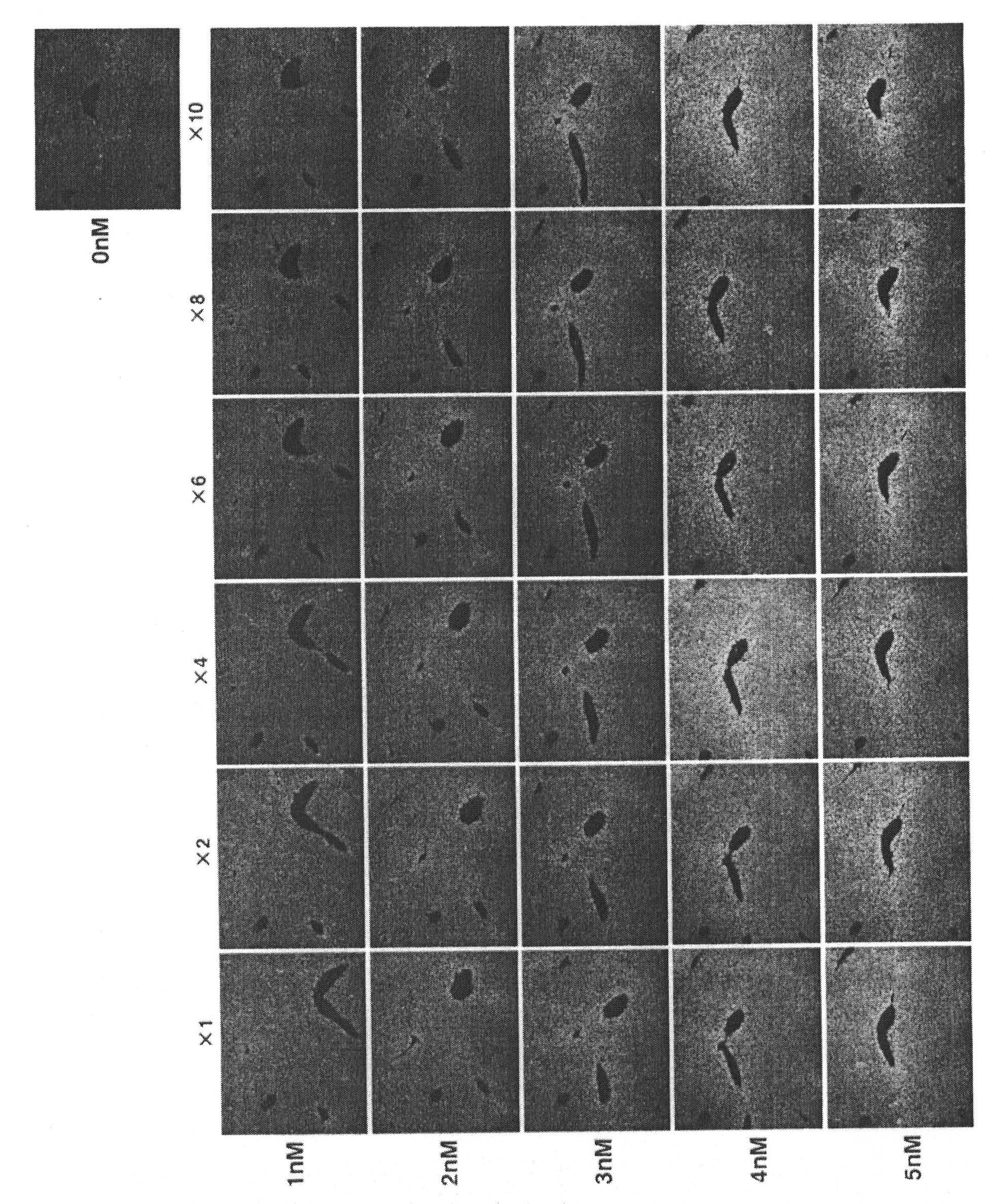
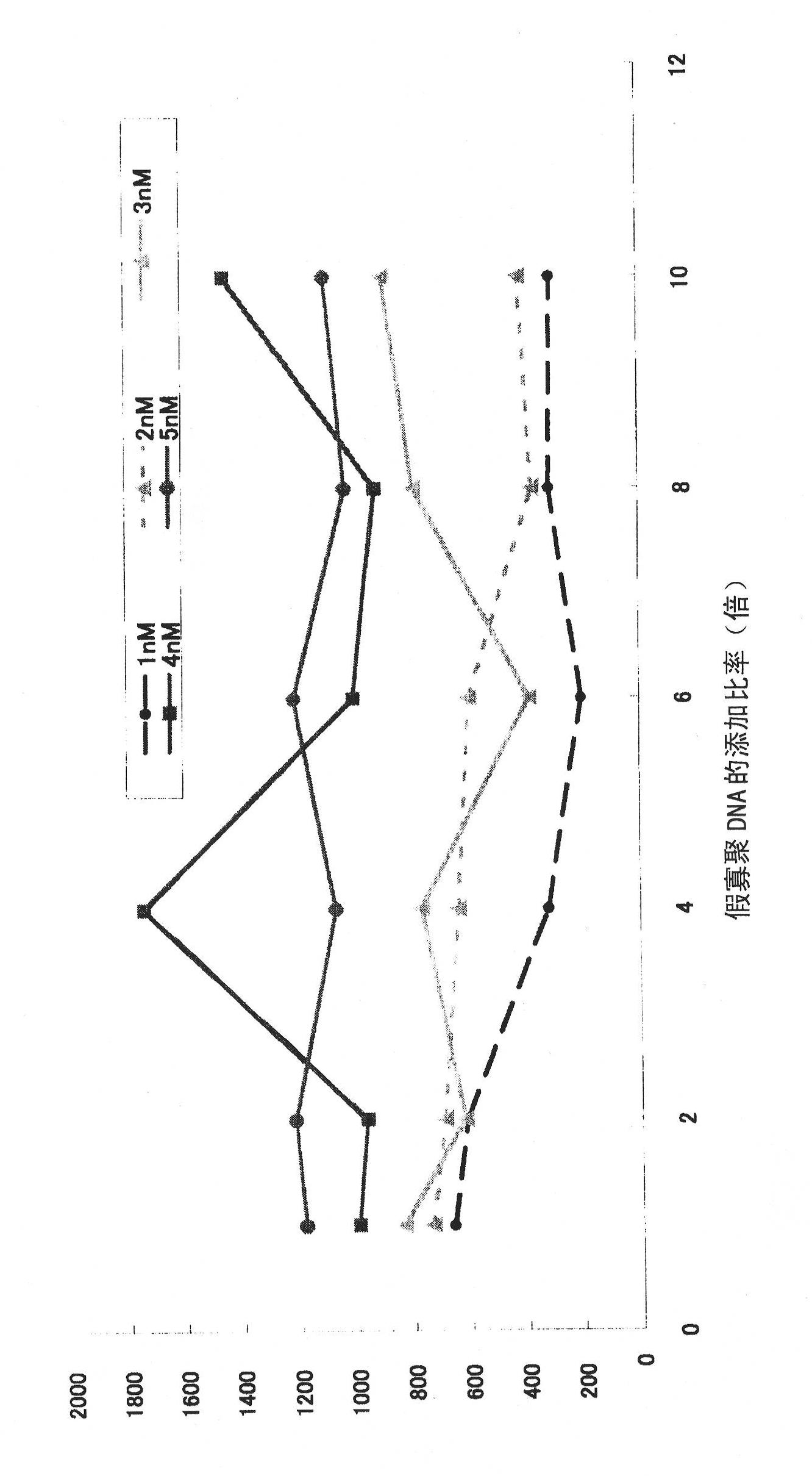
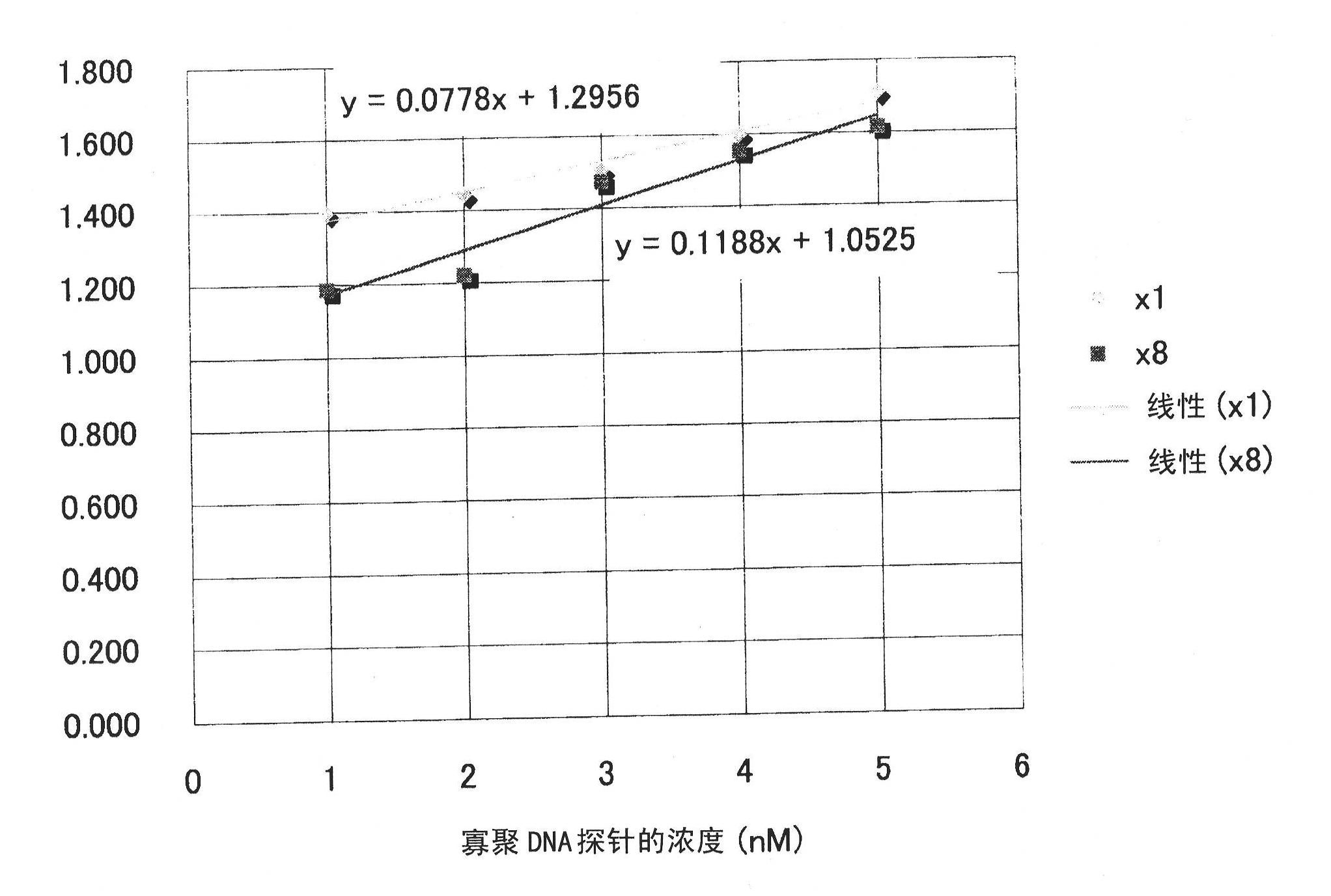
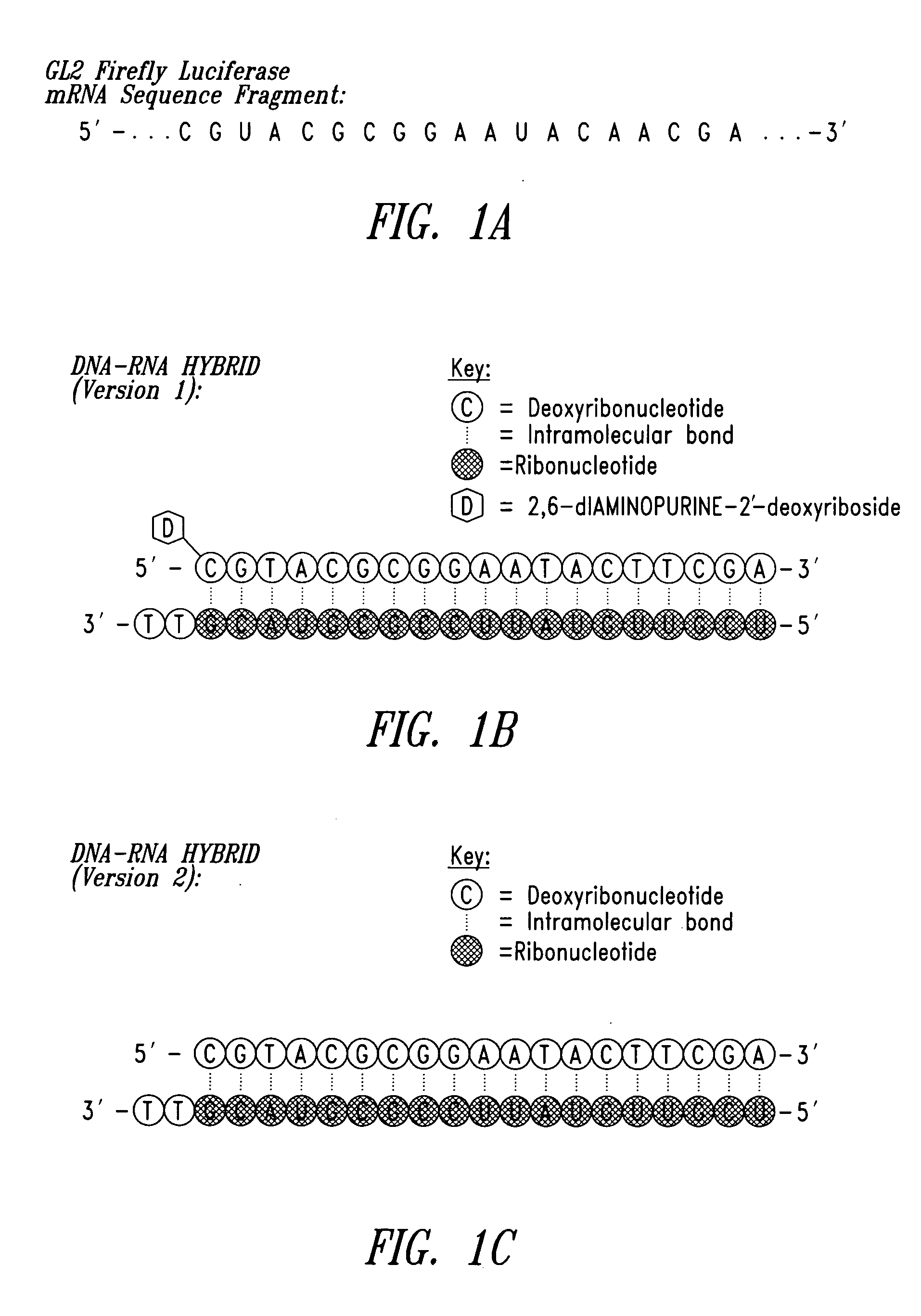
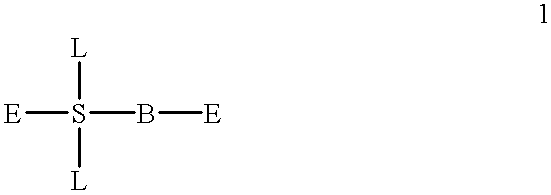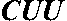Patents
Literature
46 results about "Rna hybridization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
RNA hybridization happens when one RNA strand combines, or hybridizes, with either another RNA strand or a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) strand.
Compound for detecting and modulating RNA activity and gene expression
InactiveUS6262241B1Tightly boundEfficient executionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsBond cleavageMinor groove
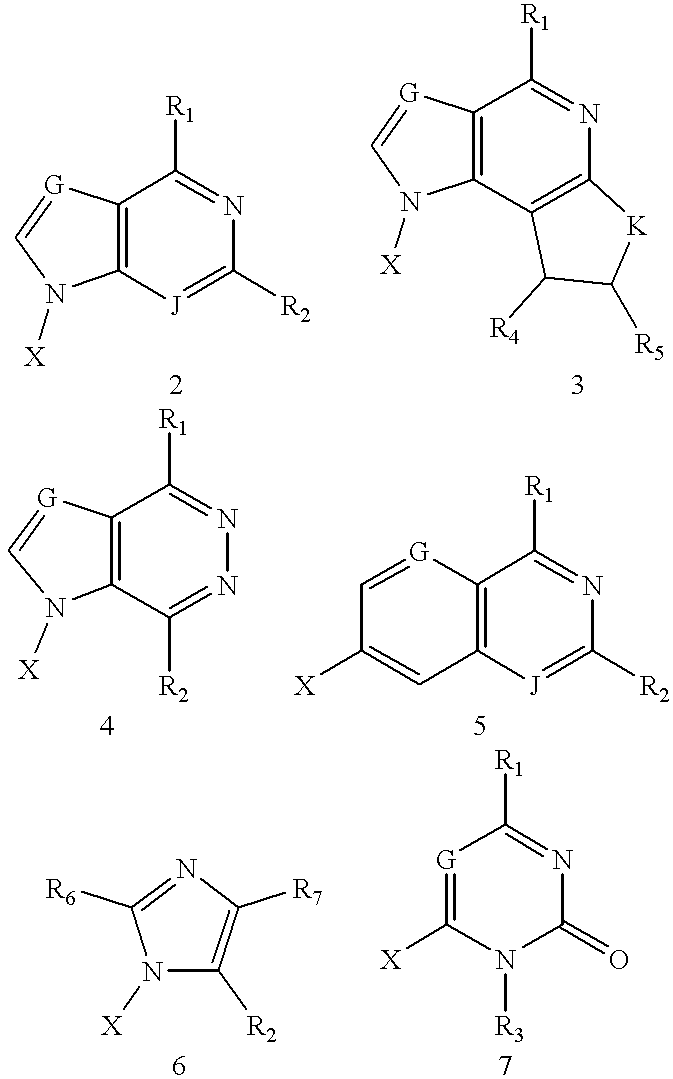
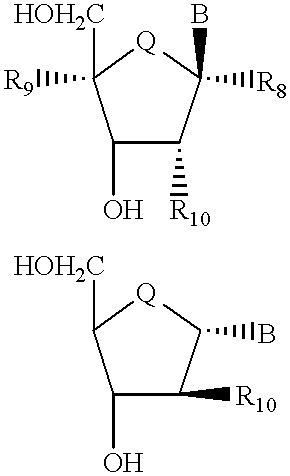
Compositions and methods for modulating the activity of RNA and DNA are disclosed. In accordance with preferred embodiments, antisense compositions are prepared comprising targeting and reactive portions. Reactive portions which act, alternatively, through phosphorodiester bond cleavage, through backbone sugar bond cleavage or through base modification are preferrably employed. Groups which improve the pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of the oligonucleotides are also useful in accordance with certain embodiments of this invention. Delivery of the reactive or non-reactive functionalities into the minor groove formed by the hybridization of the composition with the target RNA is also preferrably accomplished. Therapeutics, diagnostics and research methods and also disclosed. Synthetic nucleosides and nucleoside fragments are also provided useful for elaboration of oligonucleotides and oligonucleotide analogs for such purposes.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Methods and reagents for identifying rare fetal cells in the maternal circulation
Owner:SCHUELER PAULA A +6
Characterization of mRNA molecules
InactiveUS20160032273A1Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisReverse transcriptase
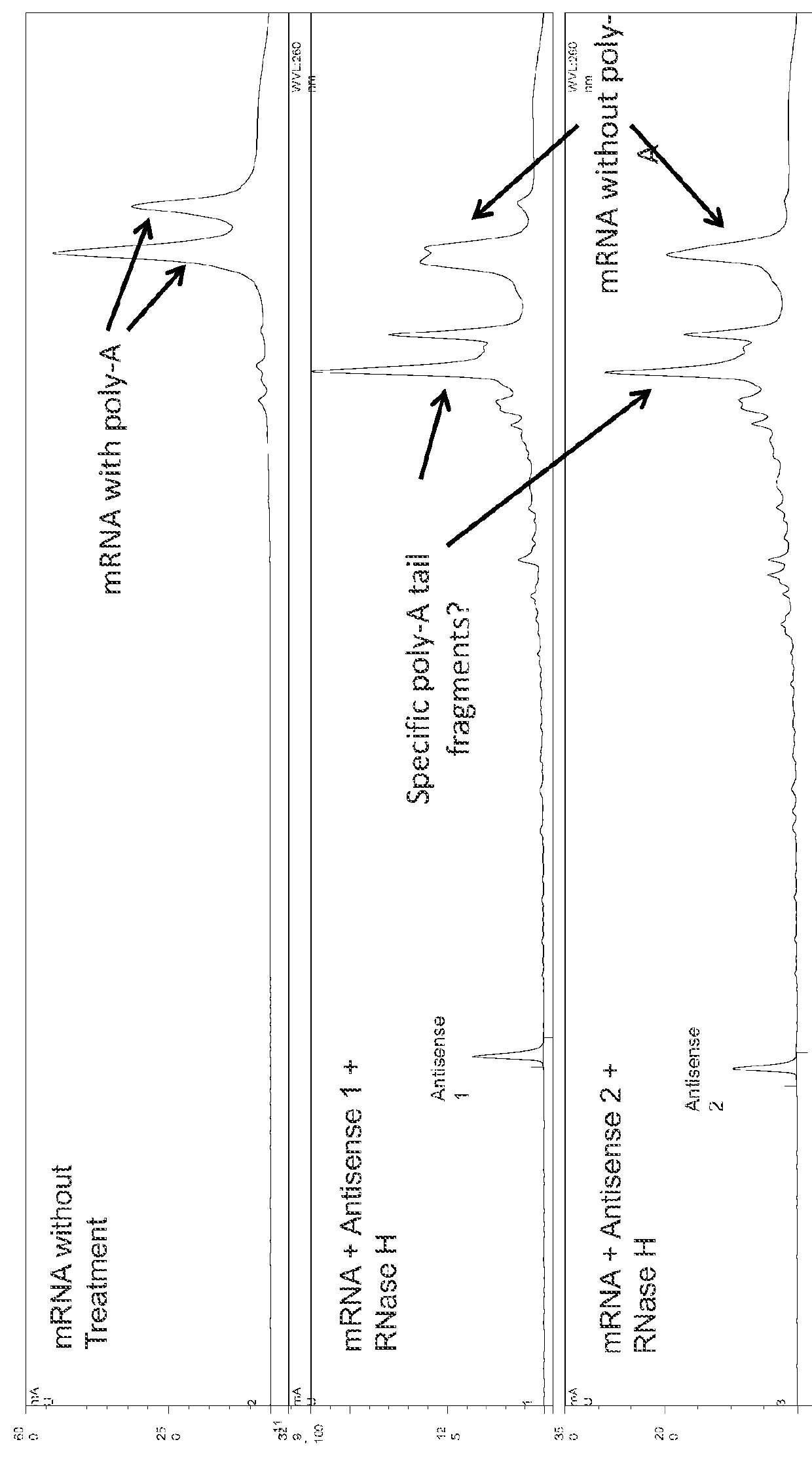
The present invention describes methods for the characterization of mRNA molecules during mRNA production. Characterizing mRNA includes processes such as oligonucleotide mapping, reverse transcriptase sequencing, charge distribution analysis, and detection of RNA impurities. Oligonucleotide mapping includes using an RNase to digest antisense duplexes from an RNA transcript, and then subjecting the digested RNA to reverse phase HPLC, anion exchange HPLC, and / or mass spectrometry analysis. Reverse transcriptase sequencing involves reverse transcription of an RNA transcript followed by DNA sequencing. Charge distribution analysis can comprise procedures such as anion exchange HPLC, or capillary electrophoresis. Detection of impurities includes detecting short mRNA transcripts, RNA-RNA hybrids, and RNA-DNA hybrids.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
Monitoring of gene expression by detecting hybridization to nucleic acid arrays using anti-heteronucleic acid antibodies
InactiveUS6232068B1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probeHybridization Array
Owner:TULARIK INC +1
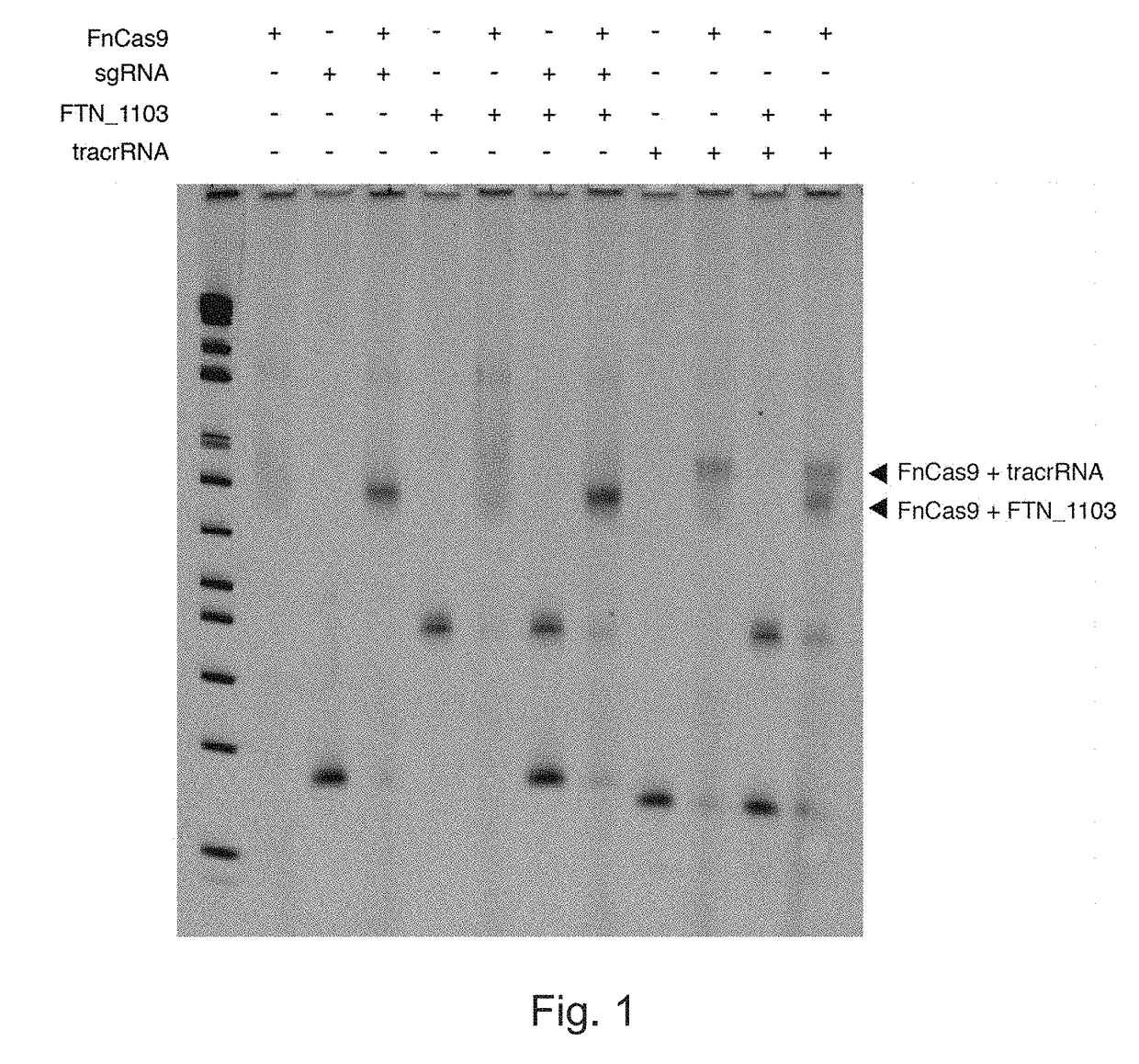
Rna-targeting system
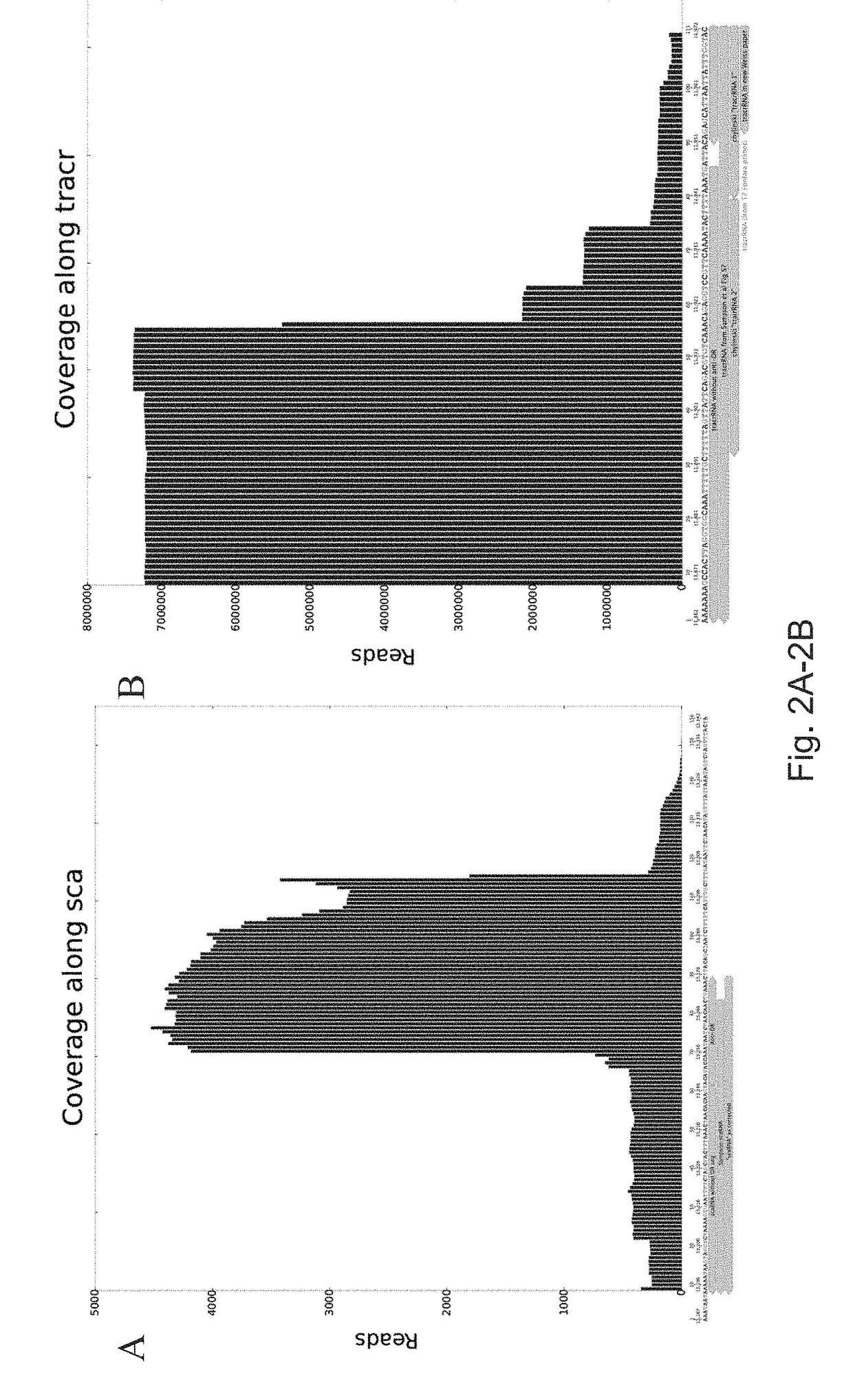
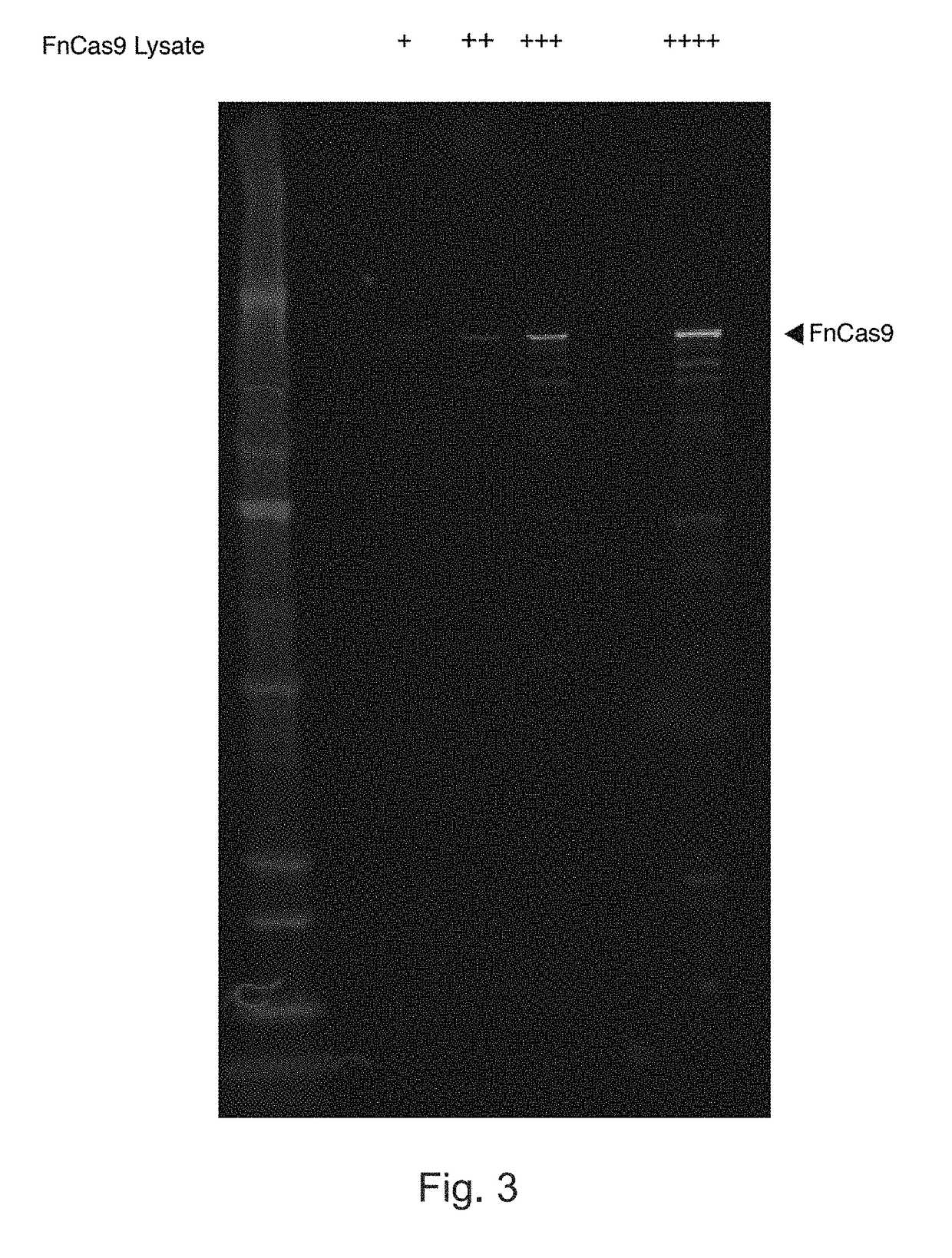
PendingUS20170306335A1Efficient use ofStrong specificityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHydrolasesGuide RNARna hybridization
The invention provides for systems, methods, and compositions for targeting RNA. In particular, the invention provides a non-naturally occurring or engineered RNA-targeting system comprising an RNA-targeting Cas protein and at least one RNA-targeting guide RNA, wherein said RNA-targeting guide RNA is capable of hybridizing with a target RNA in a cell.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
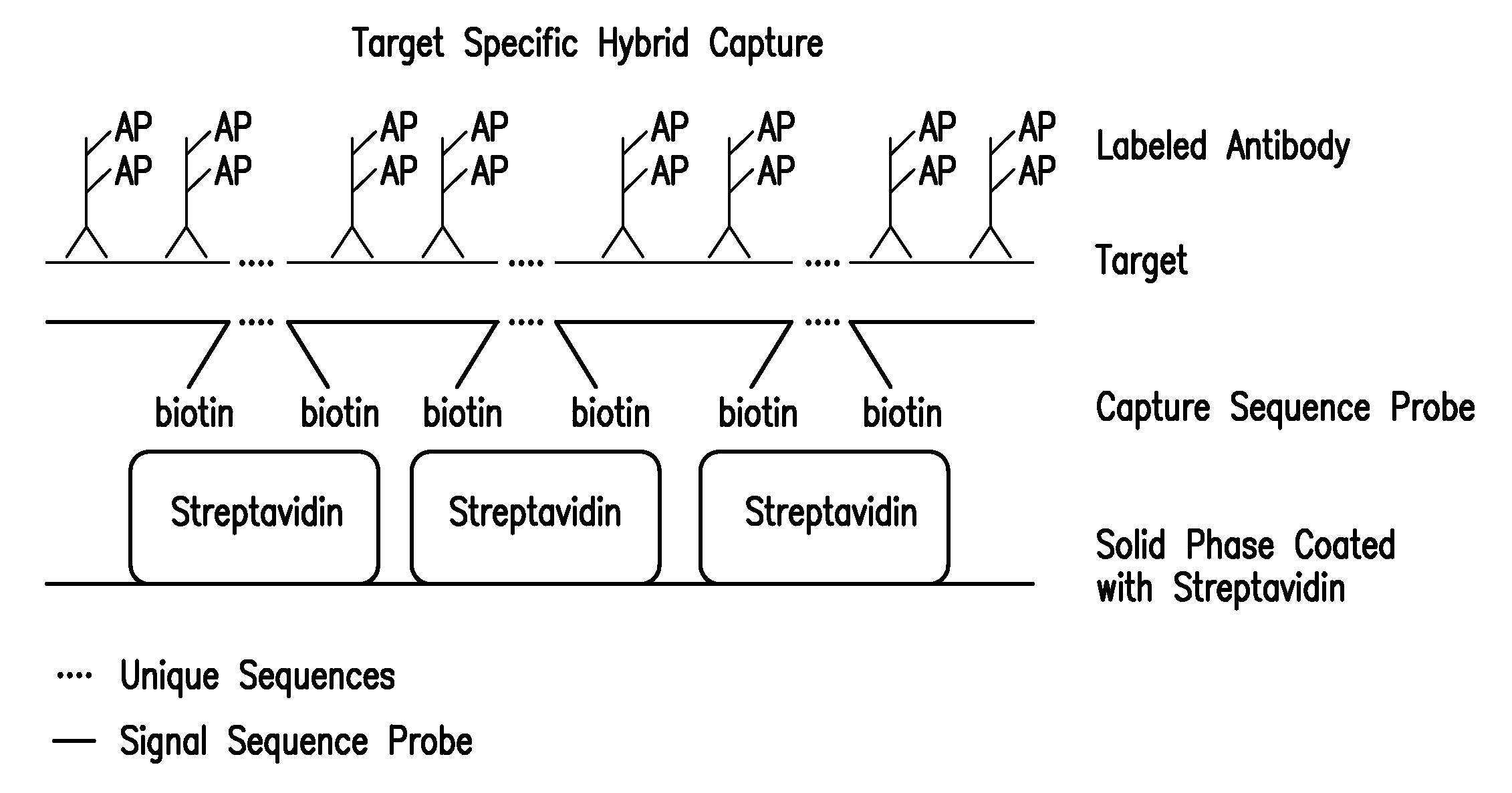
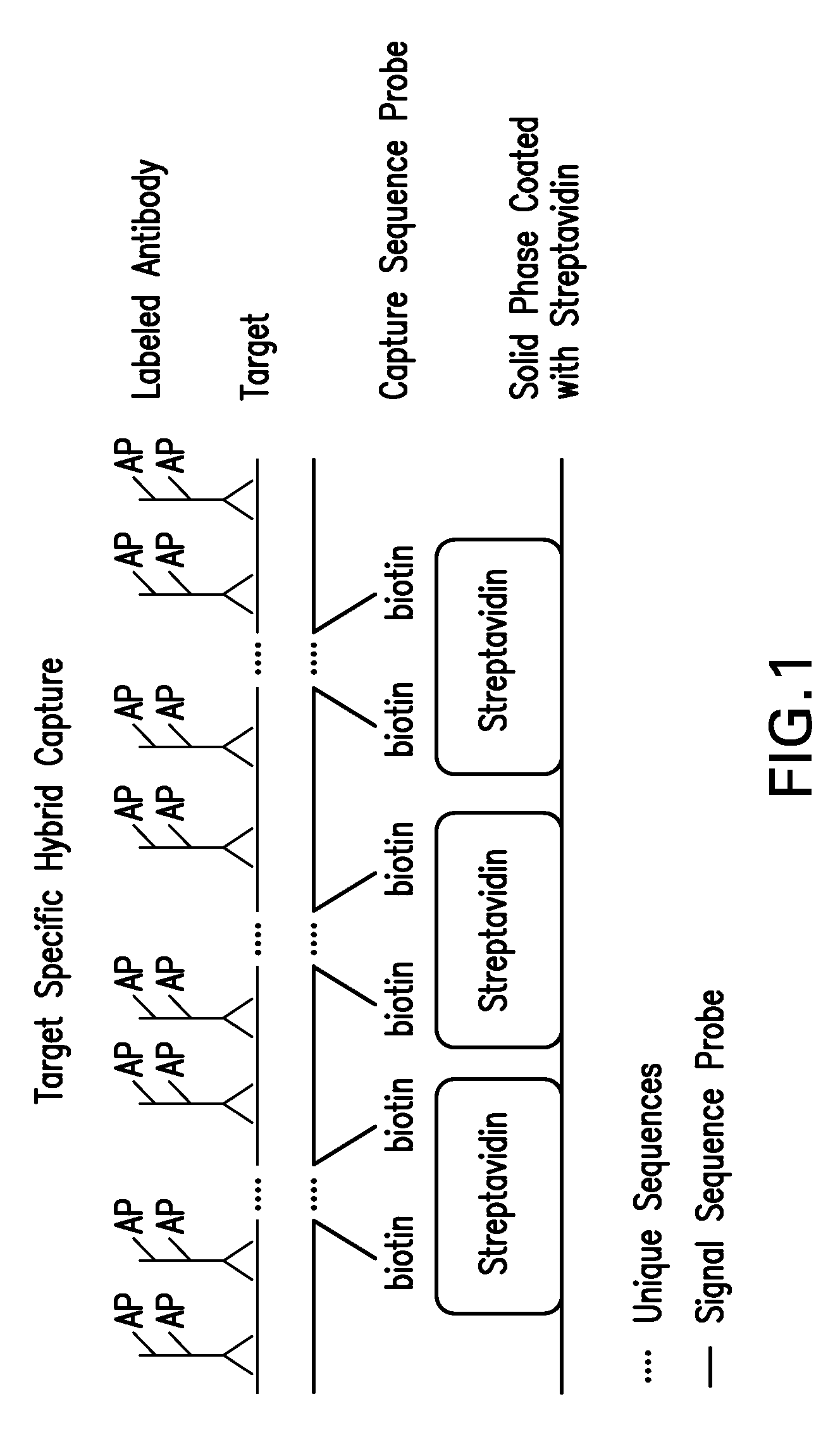
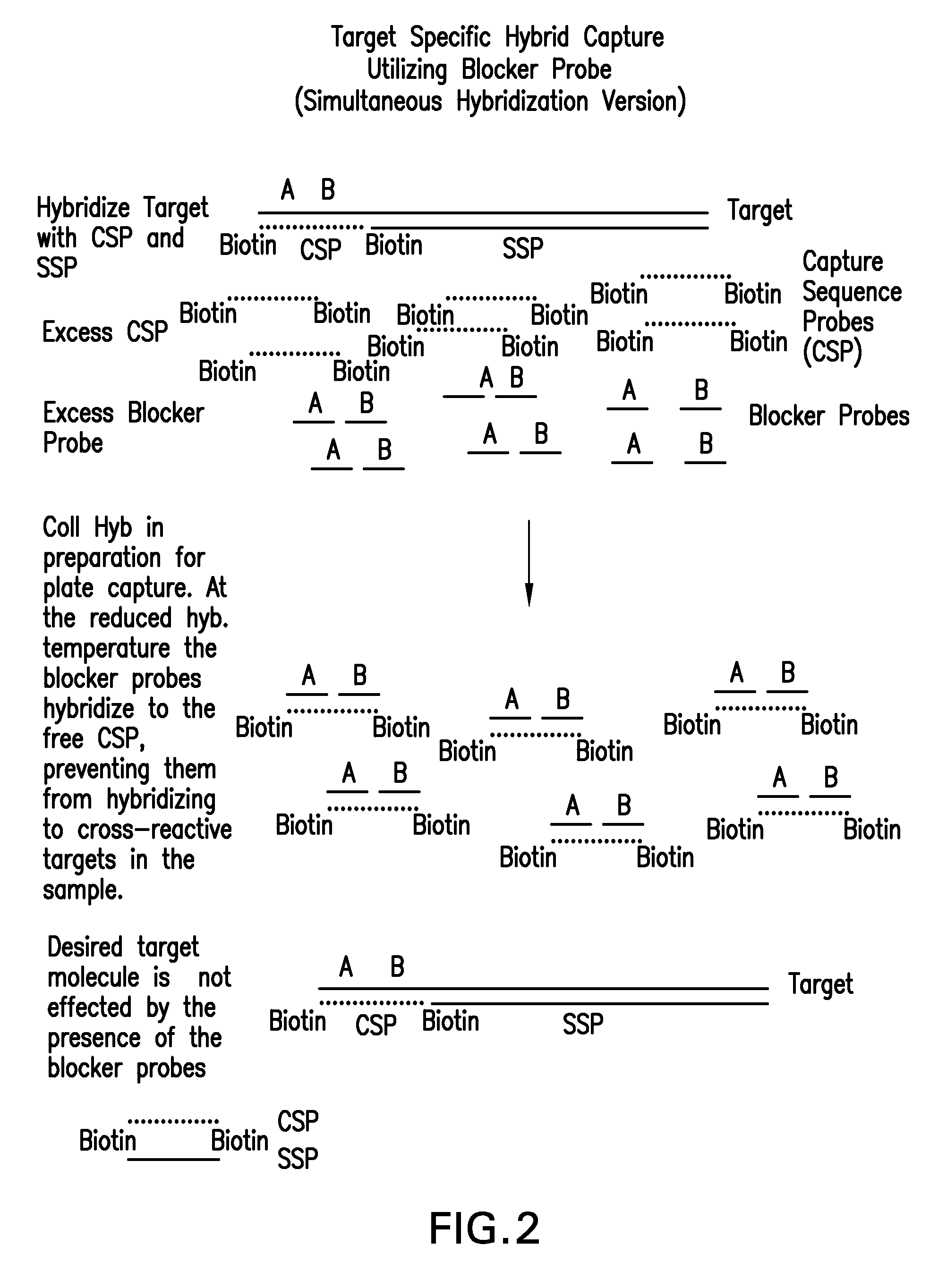
Detection of nucleic acids by target-specific hybrid capture method
InactiveUS7601497B2Rapid and sensitive and accurateFunction increaseSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionDNA
Target-specific hybrid capture (TSHC) provides a nucleic acid detection method that is not only rapid and sensitive, but is also highly specific and capable of discriminating highly homologous nucleic acid target sequences. The method produces DNA:RNA hybrids which can be detected by a variety of methods.
Owner:QIAGEN GAITHERSBURG
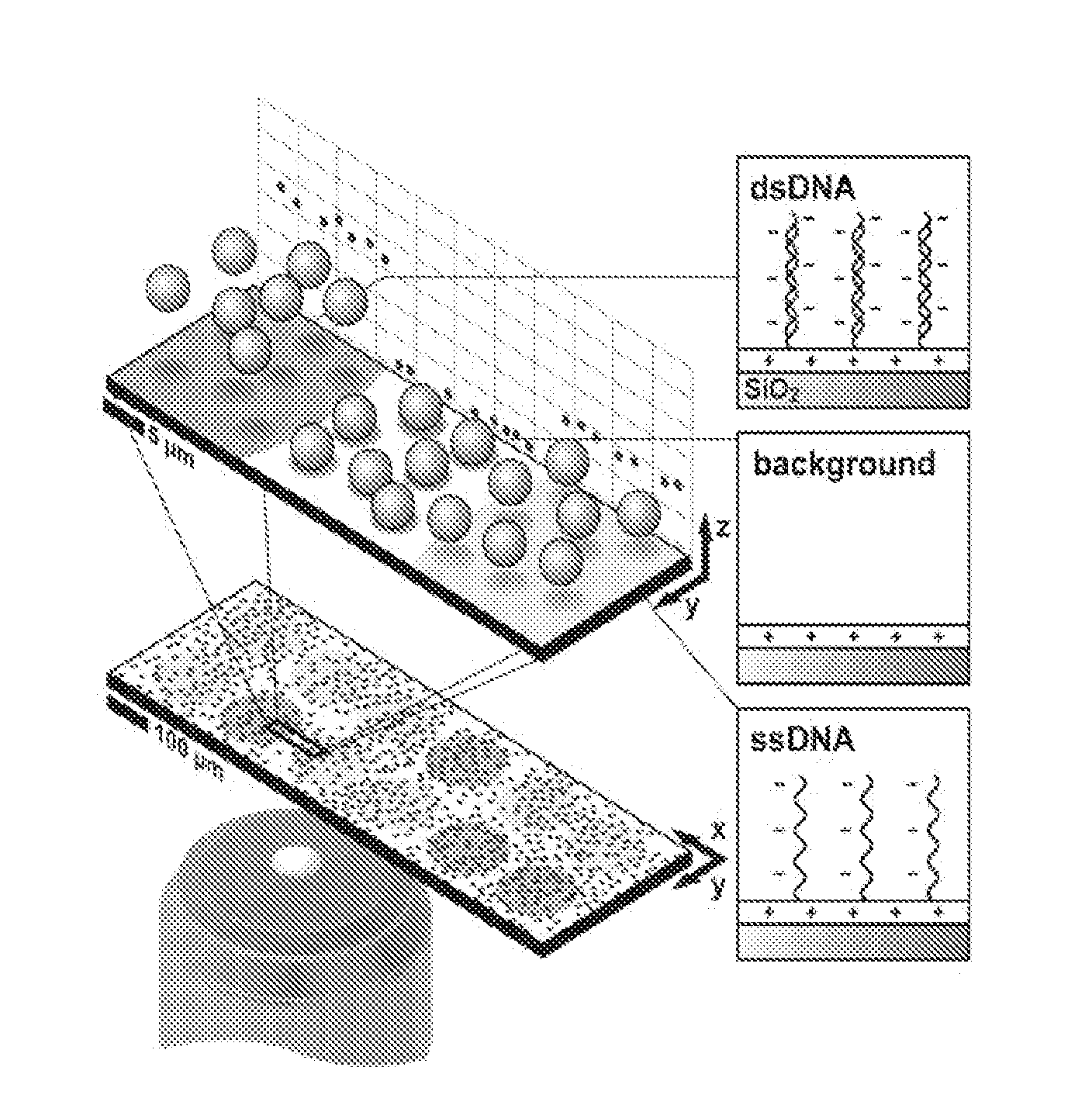
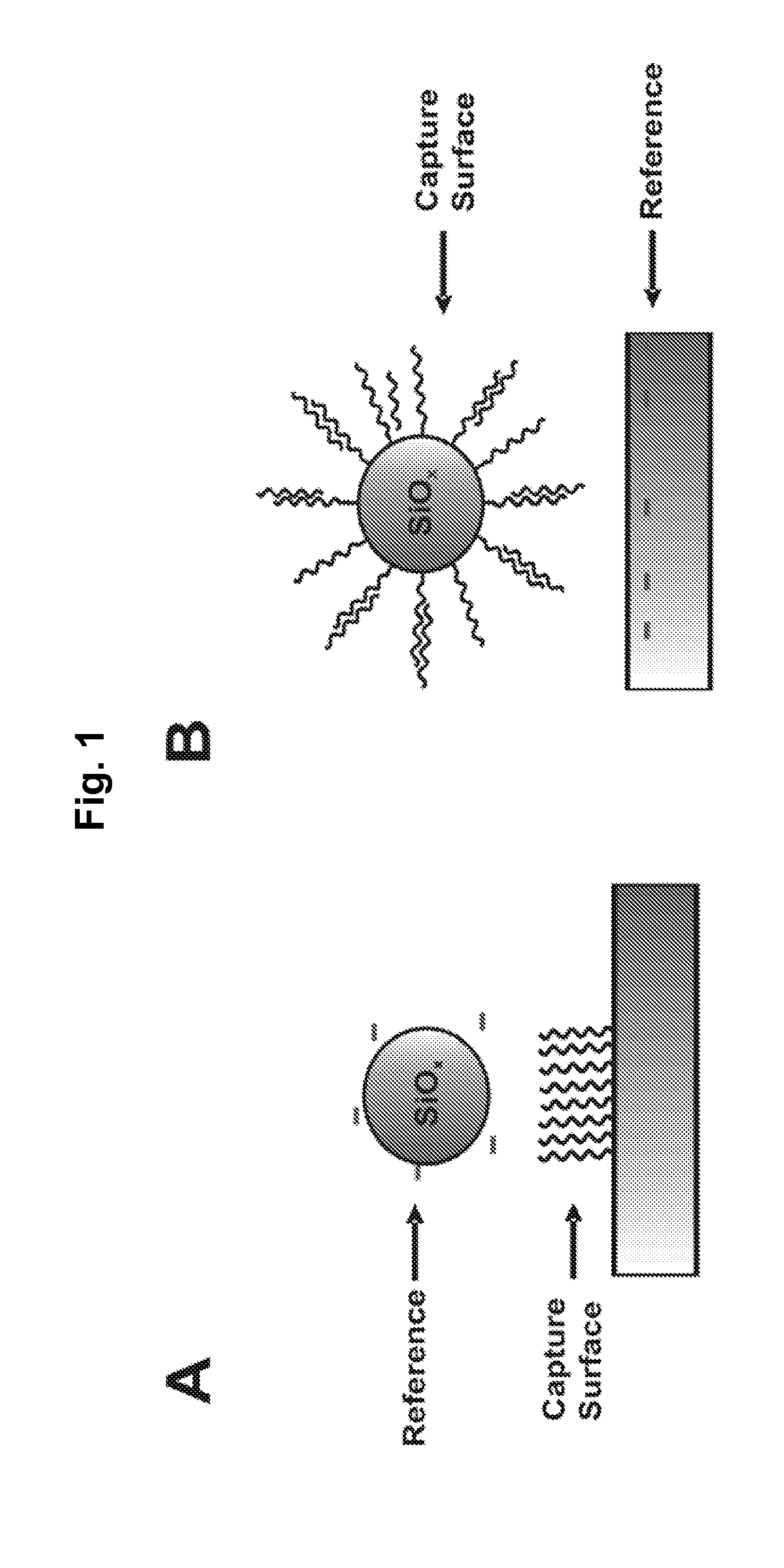
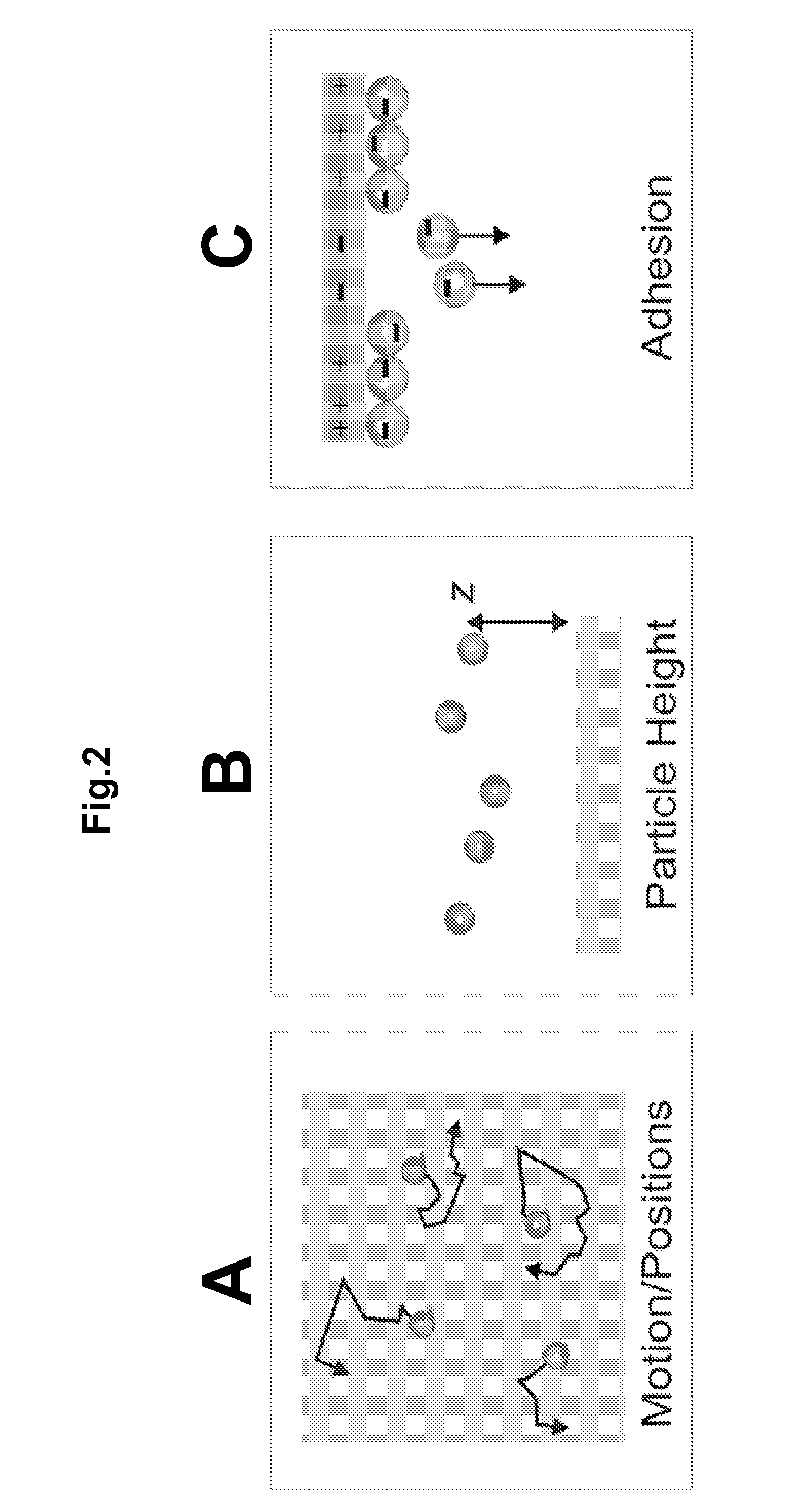
Particle-Based Electrostatic Sensing and Detection
InactiveUS20110140706A1Wide applicationMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMicrosphereMotion measurement
An apparatus and methods for electrostatic-based sensing and detection of charges and charged materials displayed on a surface. In a general embodiment, a method for electrostatically sensing charges or charged materials by comparing the electrostatic interaction between a capture surface and a reference surface. Assays to detect binding or interactions between a capture surface and a material to be detected are also described. We also describe a sensitive and label-free electrostatic readout of DNA or RNA hybridization in a microarray format and using a microfluidic device. The electrostatic properties of the hybridized particles are measured using the positions and motions of charged microspheres. This approach enables sensitive, non-destructive electrostatic imaging. Changes in surface charge density as a result of specific molecular interaction can be detected and quantified with great sensitivity, and in the presence of a complex background.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
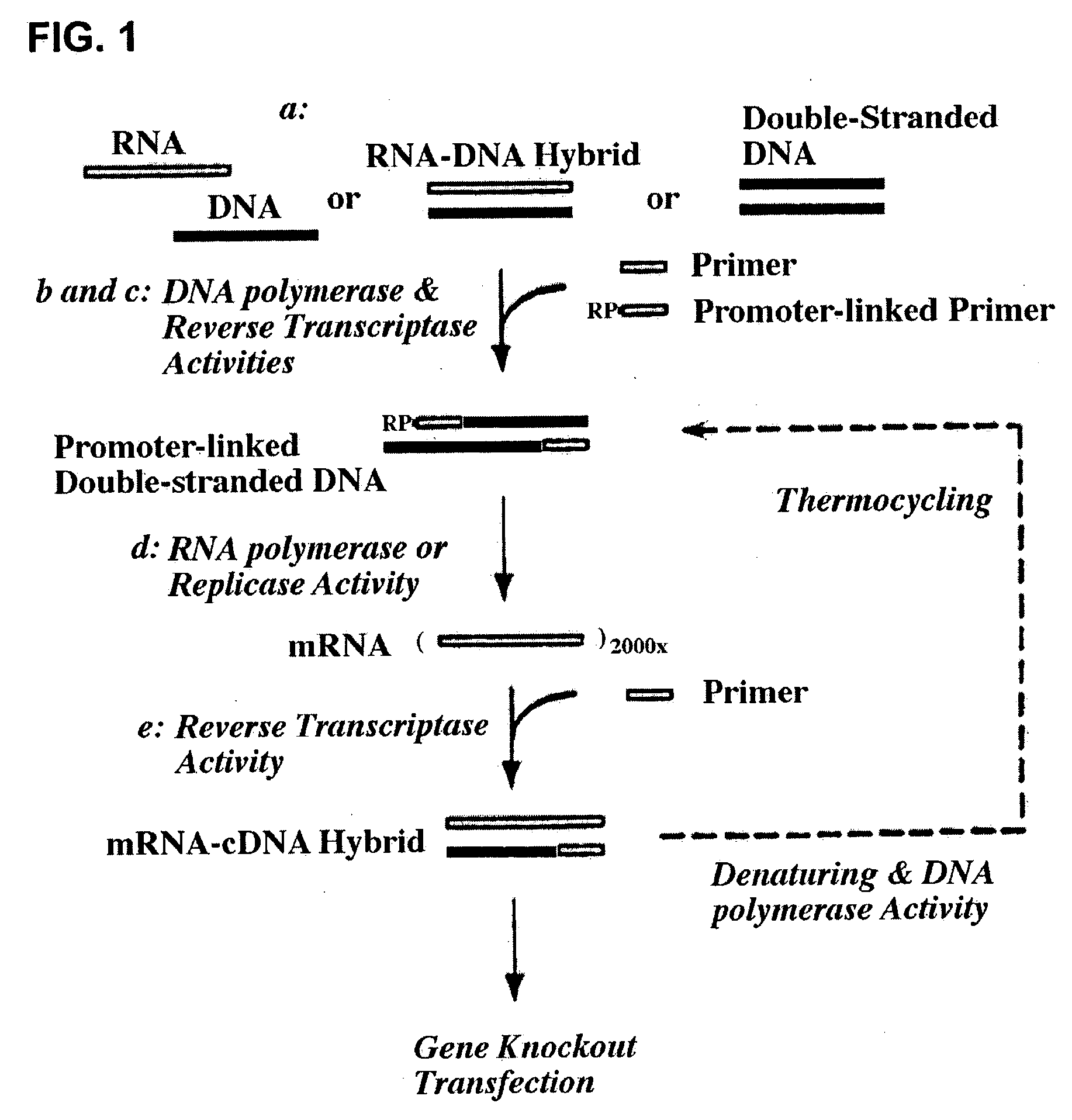
Therapeutically useful compositions of DNA-RNA hybrid duplex constructs
InactiveUS20040087526A1Inhibiting gene functionLower doseGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementGene silencingRna dna hybrids
The present invention provides novel compositions and methods for suppressing the expression of a targeted gene using RNA-DNA hybrid constructs. The invention further provides novel methods and compositions for generating or producing RNA-DNA hybrids, whose quantity is high enough to be used for the invention's gene silencing transfection and possibly in therapeutics applications. This improved RNA-polymerase chain reaction method utilizes thermocycling steps of promoter-linked DNA or RNA template synthesis, in vitro transcription and then reverse transcription to bring up the amount of RNA-DNA hybrids up to two thousand folds within one round of the above procedure for specific gene silencing.
Owner:EPICLONE
Use Of Low Doses Of Oligonucleotides Antisense To TGF-Beta, VEGF, Interleukin-10, C-Jun, C-Fos Or Prostaglandin E2 Genes In The Treatment Of Tumors
InactiveUS20090306176A1Improve securityLess side effectsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseInterleukin 10
This invention is related to the use of at least one oligonucleotide with a length of from about 8 to about 30 nucleotide building blocks for manufacturing a pharmaceutical preparation for the prophylaxis and / or the treatment of diseases, that are modulated by TGF-beta2, TGF-beta1, TGF-beta3, VEGF, interleukin-10, c-jun, c-fos, and / or prostaglandin E2 in a mammal, wherein said oligonucleotide hybridizes with a messenger RNA of a TGF-beta2, TGF-beta1, TGF-beta3, VEGF, interleukin-10, c-jun, c-fos and / or prostaglandin E2 gene and wherein said preparation comprises said oligonucleotide in a concentration of about 1 microM to about 25 microM.
Owner:ANTISENSE PHARMA GMBH
Antisense oligonucleotide inhibition of papillomavirus
InactiveUS6174870B1Rapid clearanceAltered sugar moieties or inter-sugar linkagesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMessenger RNAAlphapapillomavirus
Oligonucleotides and oligonucleotide analogs are provided which are capable of antisense interaction with messenger RNA of papillomavirus. Such oligonucleotides or oligonucleotide analogs can be used for diagnostics and therapeutics as well as for research purposes. In accordance with preferred embodiments of this invention, oligonucleotide or oligonucleotide analog is provided which is hybridizable with a messenger RNA from a papillomavirus. The oligonucleotide or oligonucleotide analog is able to inhibit the function of the RNA, and accordingly is useful for therapy for infections by such papillomavirus.In accordance with a preferred embodiment, portions of the papillomavirus are targeted for antisense attack. Thus oligonucleotides are preferably provided which hybridize with the E2, E1, E7, E6 or E6-7 messenger RNAs.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
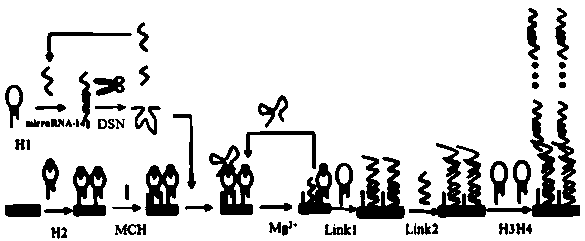
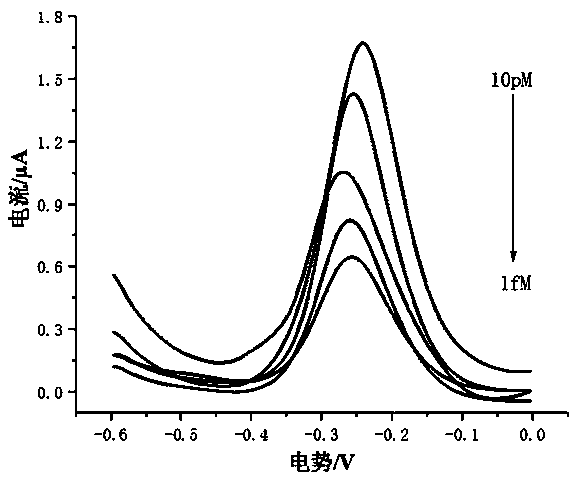
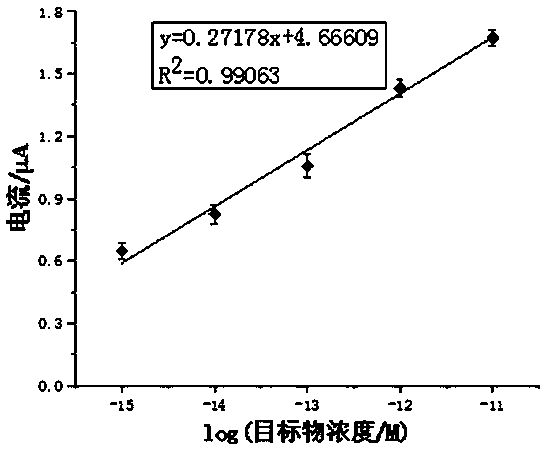
Method for preparing DNA self-assembly electrochemical biosensor through utilizing DSN and DNAzyme
ActiveCN110274941AAchieve multiple magnificationsRealize highly sensitive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemical biosensorComplementary pair
The invention discloses a method for preparing a DNA self-assembly electrochemical biosensor through utilizing DSN and DNAzyme. According to the method, the complementary pairing principle of DNA and RNA is utilized; a functional probe with a hairpin structure is designed; when a target object (a to-be-detected sample microRNA) exists, the specific endonuclease (DSN) cuts the DNA part of a DNA-RNA hybrid, so that 8-17 NDAzyme is obtained; the 8-17 NDAzyme specifically identifies and cuts adenine ribonucleotide rA site in an H2 sequence fixed onto an electrode surface; after the electrode surface is specifically cut by the NDAzyme, a DNA sequence which is connected with the electrode surface is sequentially assembled with a sequence Link 1, a sequence Link 2, a sequence H3 and a sequence H4, so that the electrochemical biosensor can be formed so as to be used for target detection. The established method has high sensitivity and can be used for directly detecting the microRNA of a complex system.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Efficient reduction of target rna's by single- and double-stranded oligomeric compounds
InactiveUS20100041047A1Inhibit RNA levelInhibits RNA levelSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRegion selectionRegulatory rna
The present invention provides, inter alia, methods of selecting a single-stranded oligomeric compounds for inhibiting RNA expression, methods of generating double-stranded oligomeric compounds, methods of identifying optimized double-stranded oligomeric compounds, methods of selecting optimized single-stranded oligomeric compounds, methods of selecting optimized double-stranded oligomeric compounds, methods of identifying multifunctional oligomeric compounds, methods for optimizing target region selection for modulation of RNA expression, methods of optimizing expression modulation of RNA, and the like. The present invention further provides oligomeric compounds, 8-80 nucleobases in length targeted to a target RNA, wherein said oligomeric compound hybridizes to said target RNA and inhibits RNA levels by at least 50% in both single-stranded and double-stranded forms, and multifunctional oligomeric compounds.
Owner:VICKERS TIMOTHY +5
Rnase h-based RNA profiling
InactiveUS20130231261A1Easy to reuseMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningRna profilingA-DNA
Methods for determining the presence, absence and / or amount and / or identity of RNA in a biological or other sample employs capturing and separating a DNA:RNA hybrid formed by a DNA probe and the RNA of interest from unhybridized DNA and RNA with an RNase H under conditions wherein the nuclease activity of the RNase H is inhibited, releasing the DNA probe by altering the conditions so that the nuclease activity is restored, and determining the presence or amount, and, for multiplex samples, nature of the DNA released. The method can be used to determine RNA of various types, including RNA comprising transcriptomes.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS BIOLOGY
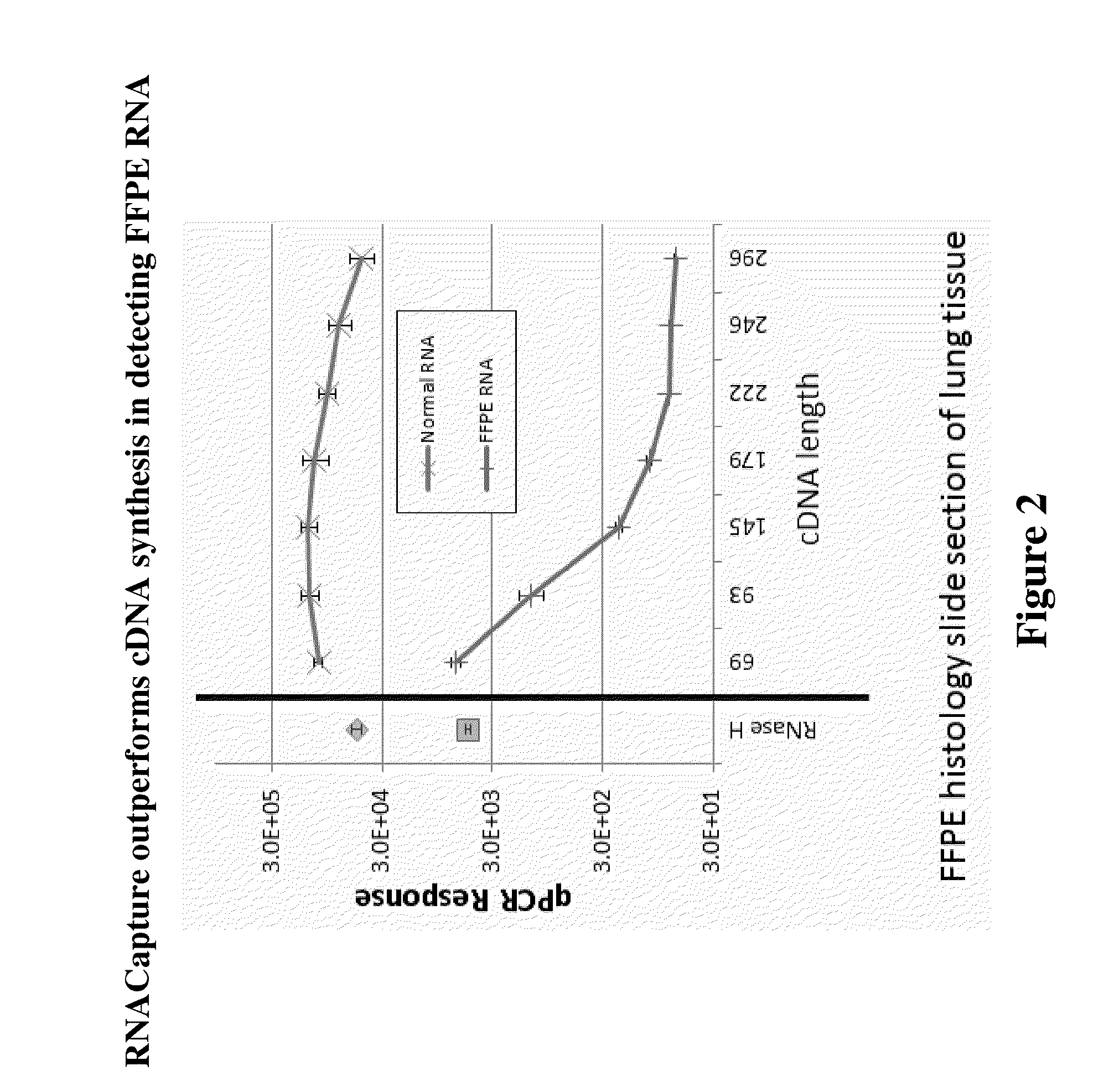
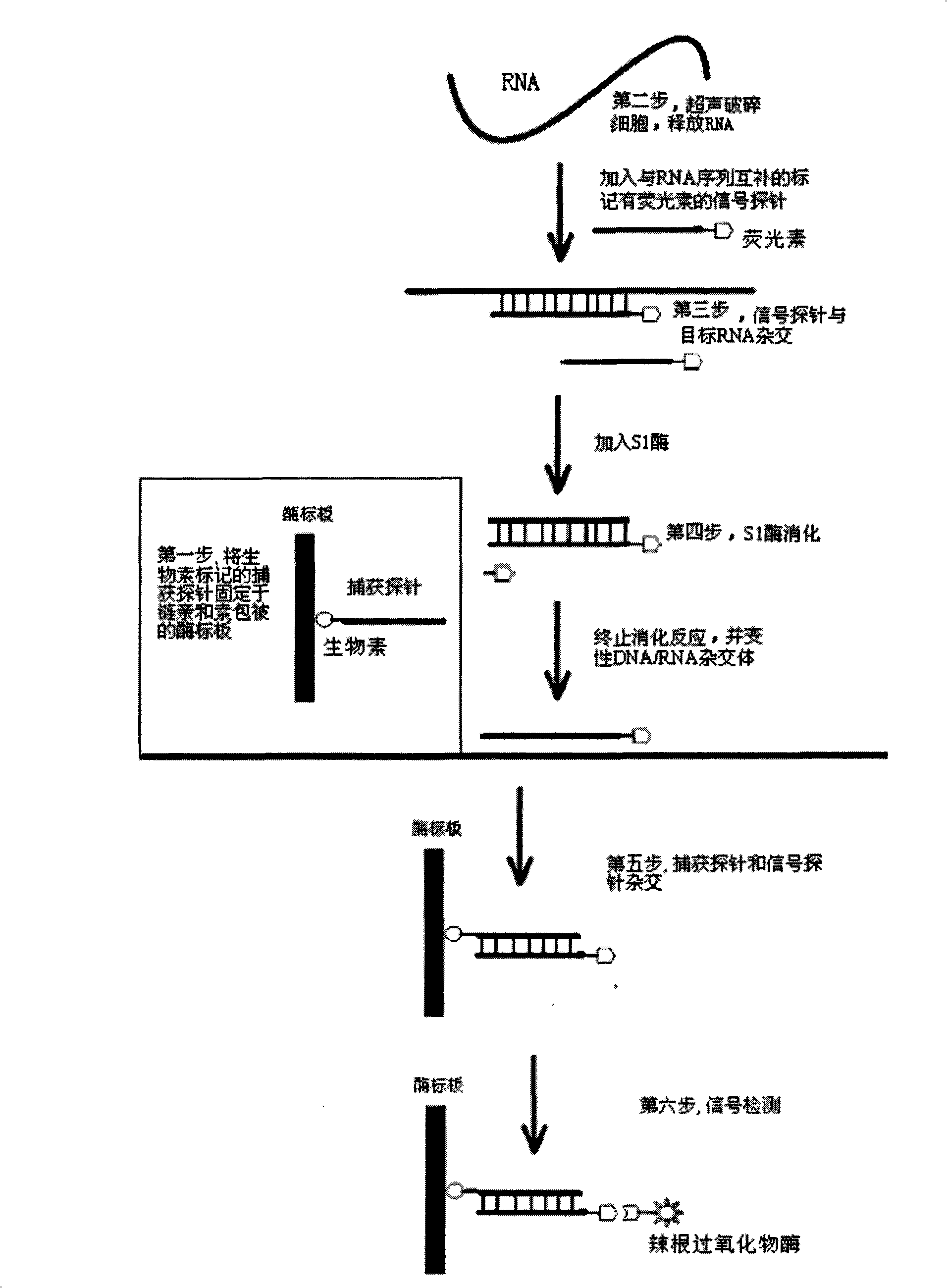
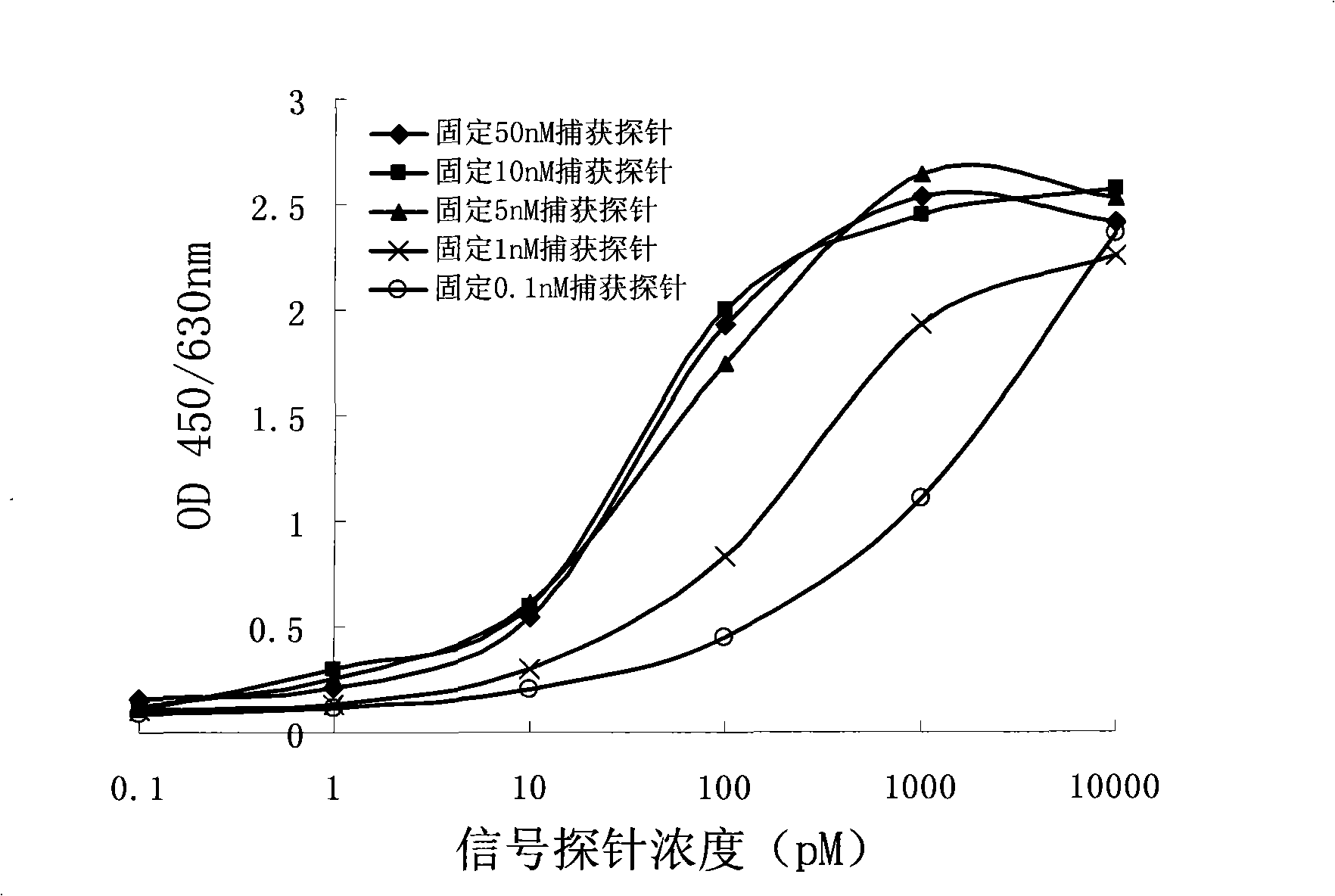
RNA quantitative determination method utilizing S1 enzyme cutting single-chain nucleic acid characteristic
InactiveCN101260432ASimple methodEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotin-streptavidin complexSingle-Stranded RNA
The invention discloses an RNA quantitative detection method using the cutting single strand nucleic acid characteristic of S1 enzyme. The method mainly comprises the following steps: first, fixing a capture probe with proper concentration to a enzyme label plate precoated by the streptavidin for further use; then ultrasonically lysising the cell and releasing RNA from the cell, filling in signal probe and hybridizing with targeting RNA; after hybridizing, filling in S1 enzyme to cut the single strand part in the single RNA,DNA and RNA / signal probe crossbreed, obtaining the complete complementary targeting RNA / signal probe crossbreed; hybridizing between the capture probe and the signal probe after the rest crossbreed is denaturated, finally amplifying the signal by horseradish peroxidase. The invention has simple operation and strong specificity. The RNA quantitative detection can be finished under conventional experimental conditions.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Tropical plant polysaccharide and polyphenol small RNA extraction method
The present invention discloses a tropical plant polysaccharide and polyphenol small RNA extraction method, which comprises: sampling tropical plant leaves, freezing in liquid nitrogen, and storing at a temperature of -80 DEG C; preparing small RNA extraction reagents, wherein the reagents comprise a CTAB lysis buffer solution, a PEG8000 precipitation buffer solution, an EDC cross-linking buffer solution, a miRNA Northern blotting hybridization buffer solution, 7% dPAGE, and Washing Buffer; according to small RNA extraction pretreatment, Trizol extraction, fractional precipitation of high molecular weight RNA, and small RNA precipitation, extracting small RNA; according to 17% dPAGE separation, trarsmembrane and cross-linking, miRNA hybridization and washing of membrane, small RNA hybridization and washing of membrane, and exposure and storage, achieving RNA hybridization; carrying out miRNA stem-loop RT-PCR amplification; and carrying out extraction and detection analysis on polysaccharide and polyphenol plant small RNA. According to the present invention, the defects in the current plant small RNA extraction method are overcome, characteristics of fastness, stability and easy operation are provided, rapid extraction and detection analysis can be performed on miRNA and siRNA, and broad application prospects are provided.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Detection of nucleic acids by target-specific hybrid capture method
InactiveUS20100036104A1Rapid and sensitive and accurateFunction increaseSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionDNA
Target-specific hybrid capture (TSHC) provides a nucleic acid detection method that is not only rapid and sensitive, but is also highly specific and capable of discriminating highly homologous nucleic acid target sequences. The method produces DNA:RNA hybrids which can be detected by a variety of methods.
Owner:QIAGEN GAITHERSBURG INC
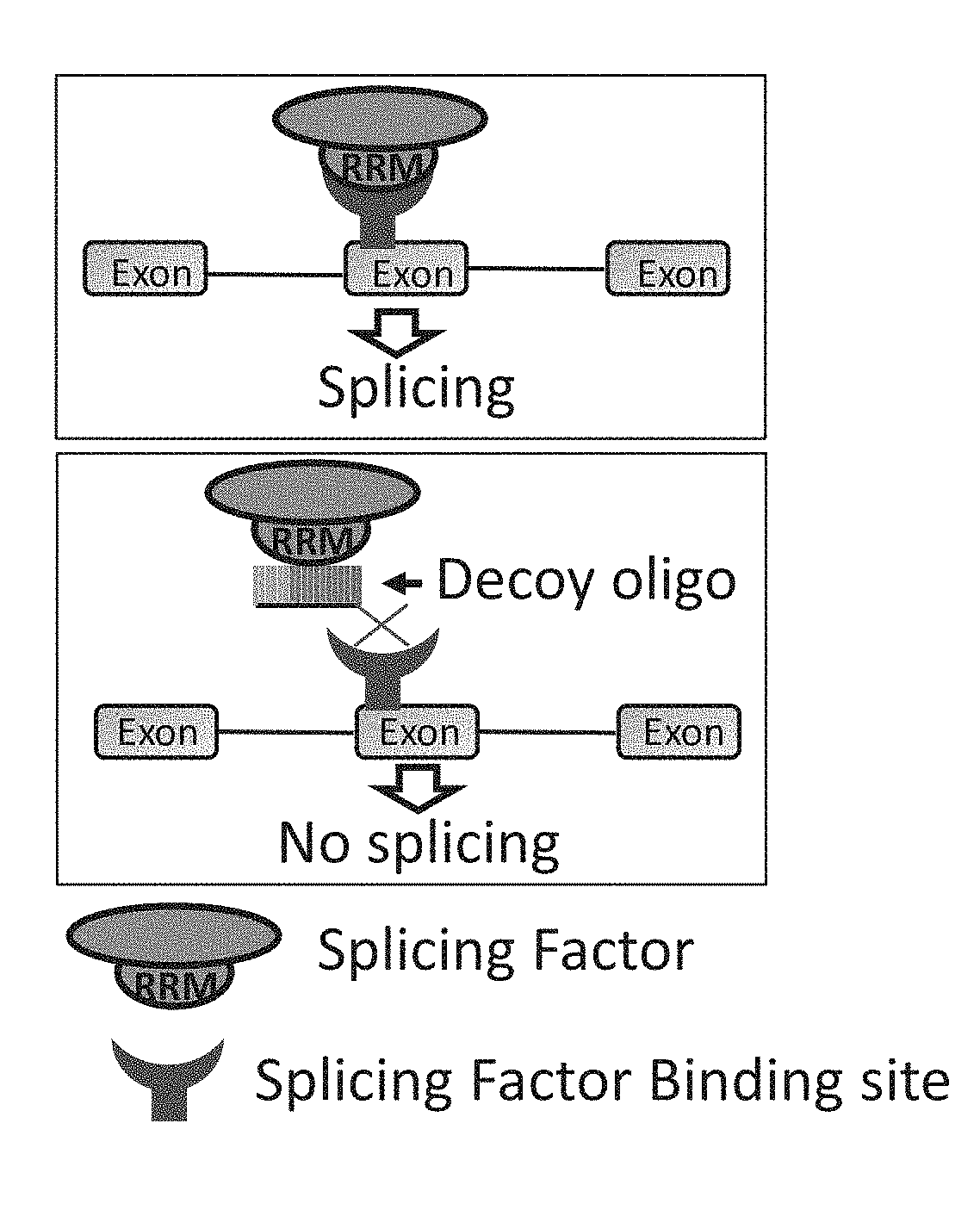
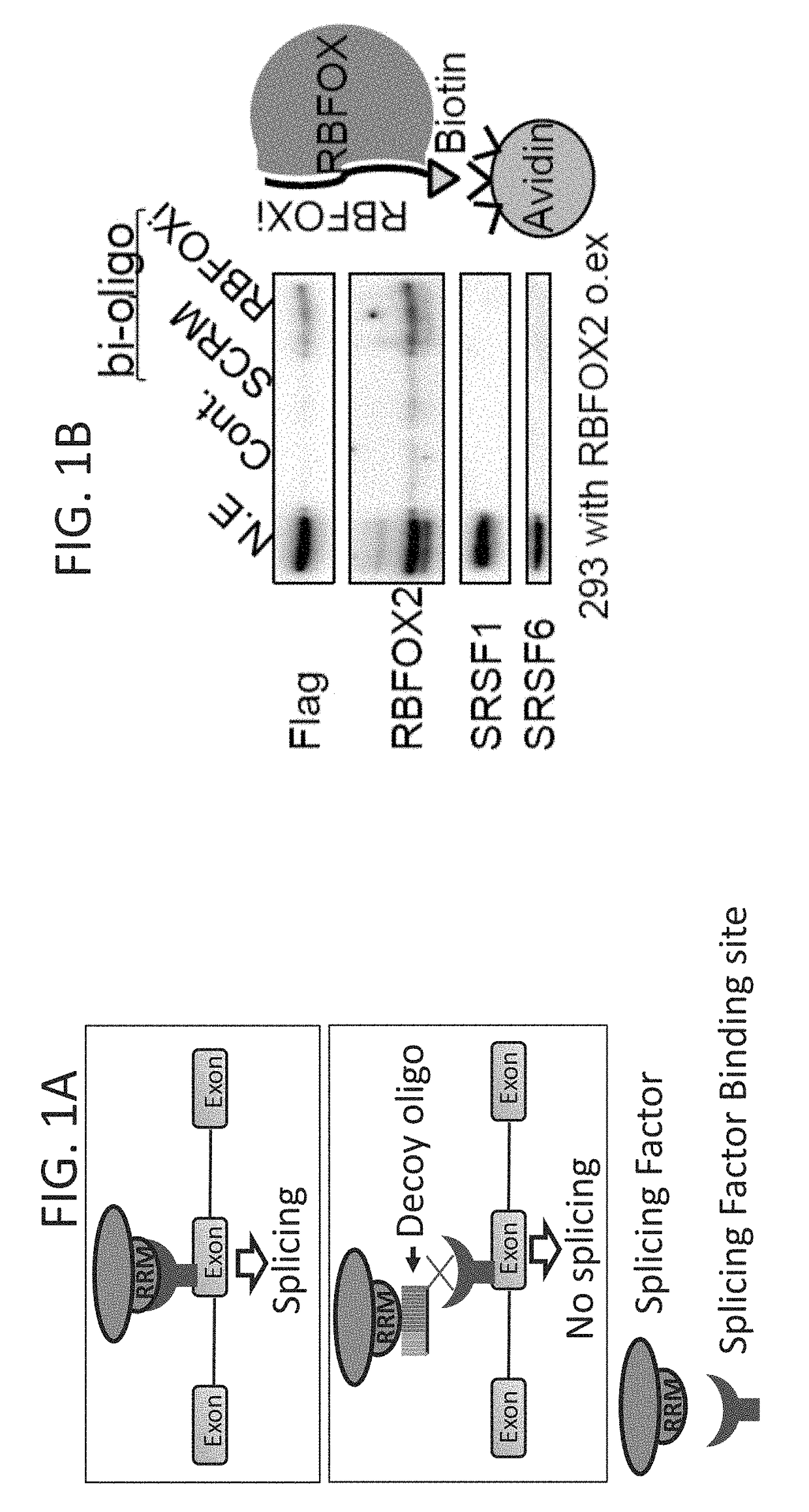
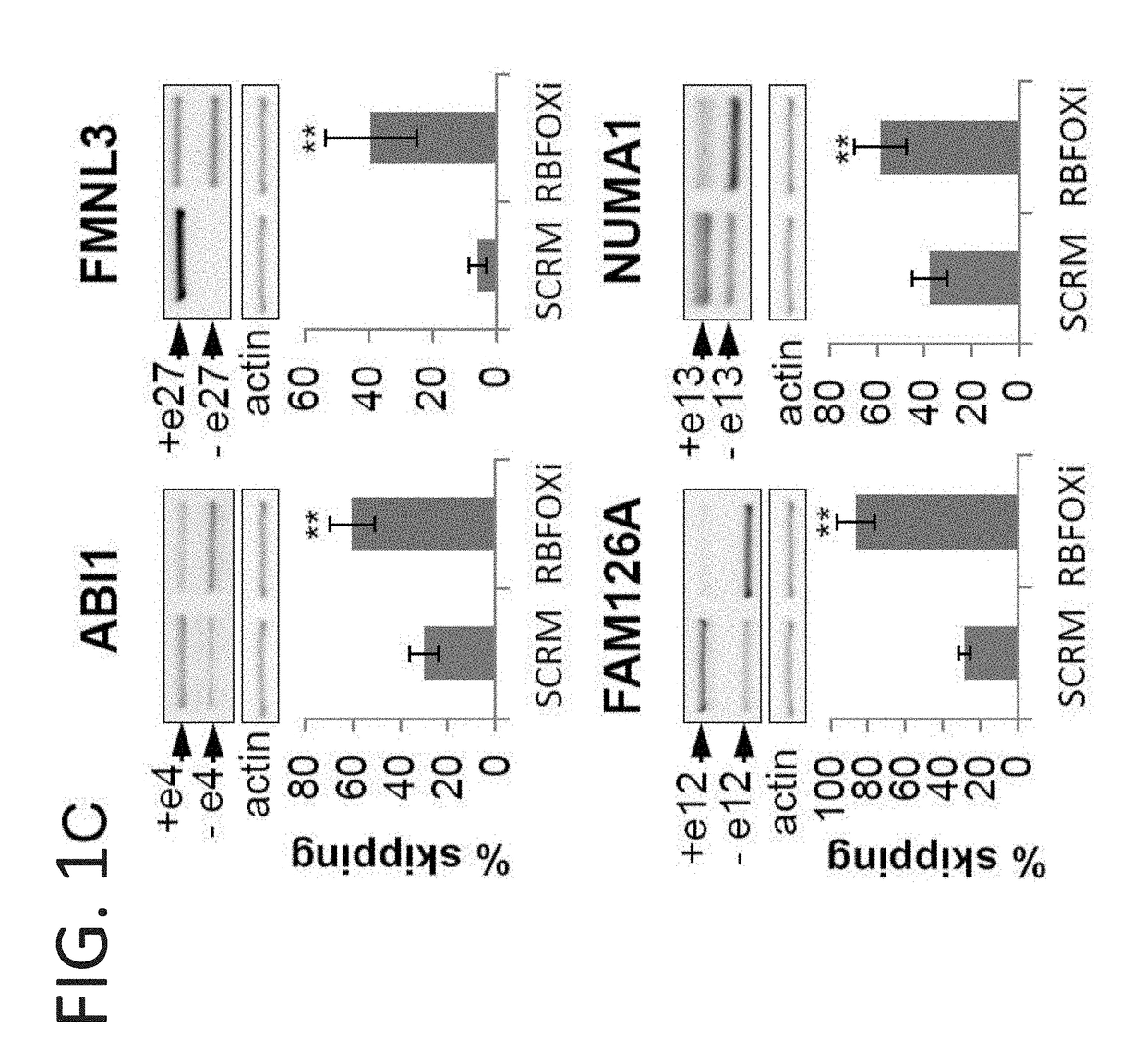
Decoy oligonucleotides for the treatment of diseases
An isolated oligonucleotide comprising ribonucleotides is disclosed. The oligonucleotide comprises a nucleic acid sequence which encodes at least one copy of a splicing-factor binding site. The oligonucleotide is no more than 150 bases and may be devoid of a sequence that allows hybridization thereof to cellular RNA under physiological conditions. The oligonucleotide inhibits overall cellular splicing activity of a specific splicing factor. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the oligonucleotide and uses thereof are further disclosed.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Nucleic acid ladders
The present invention provides nucleic acid molecules which may be used as standards for estimating the size (in base pairs) and mass of linear, double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acid molecules separated by size. The nucleic acid molecules of the invention may be DNA molecules, RNA molecules or DNA / RNA hybrid molecules, and may be double-stranded or single-stranded. The invention also provides methods for producing nucleic acid sizing ladders from these nucleic acid molecules, ladders produced by such methods, and methods for estimating the size and mass of nucleic acid molecules by comparison to these nucleic acid sizing ladders.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method and kit for detecting small RNA
InactiveCN101633957AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationInterference resistanceBench test
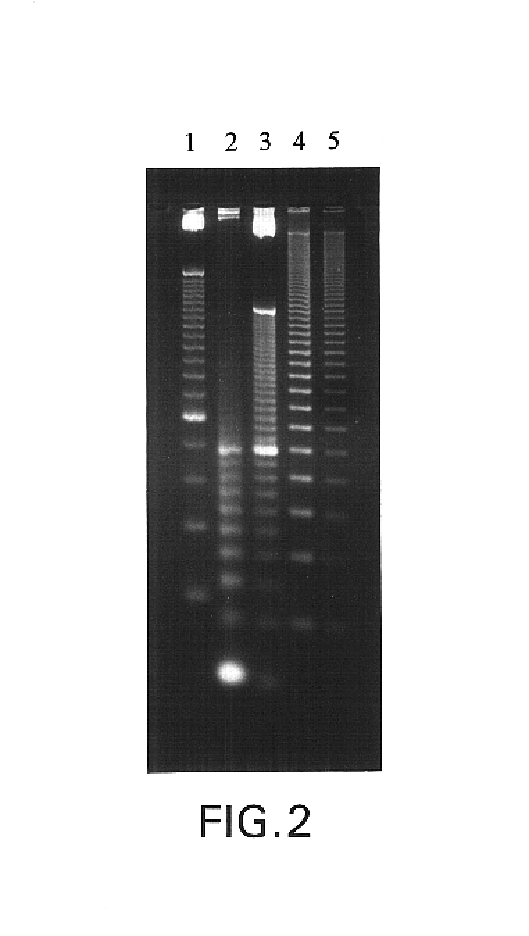
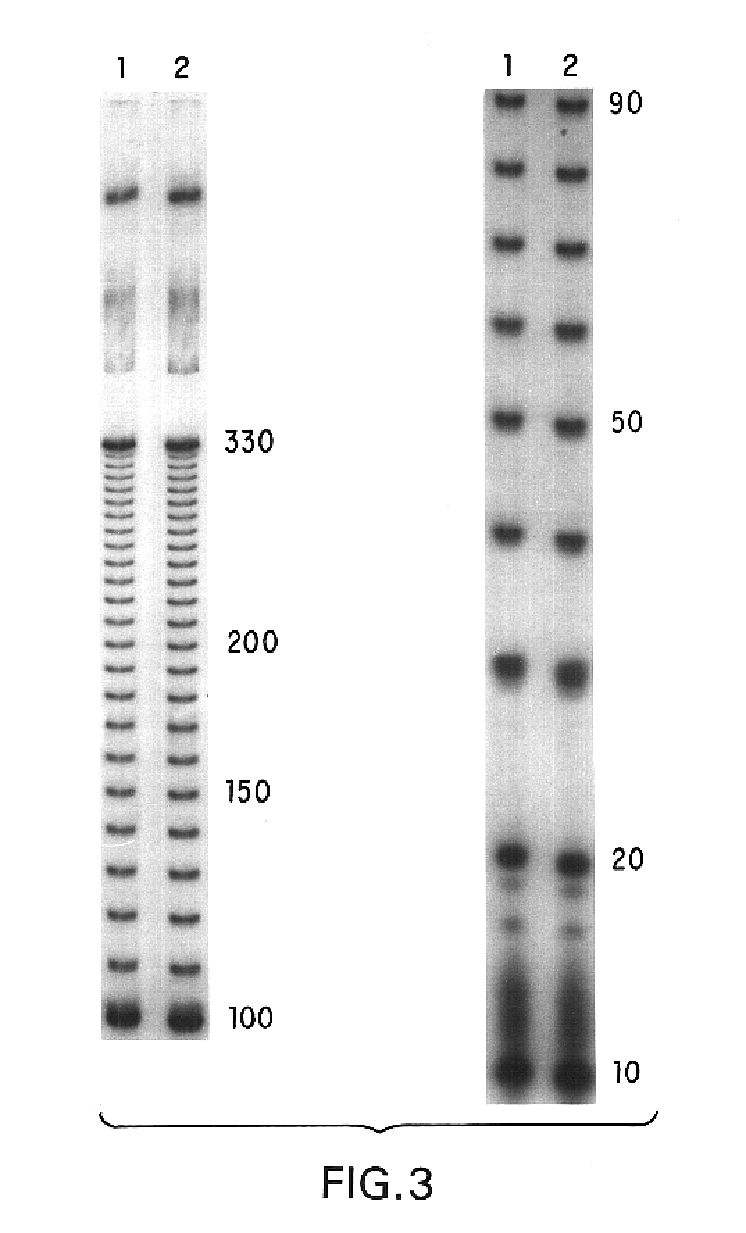
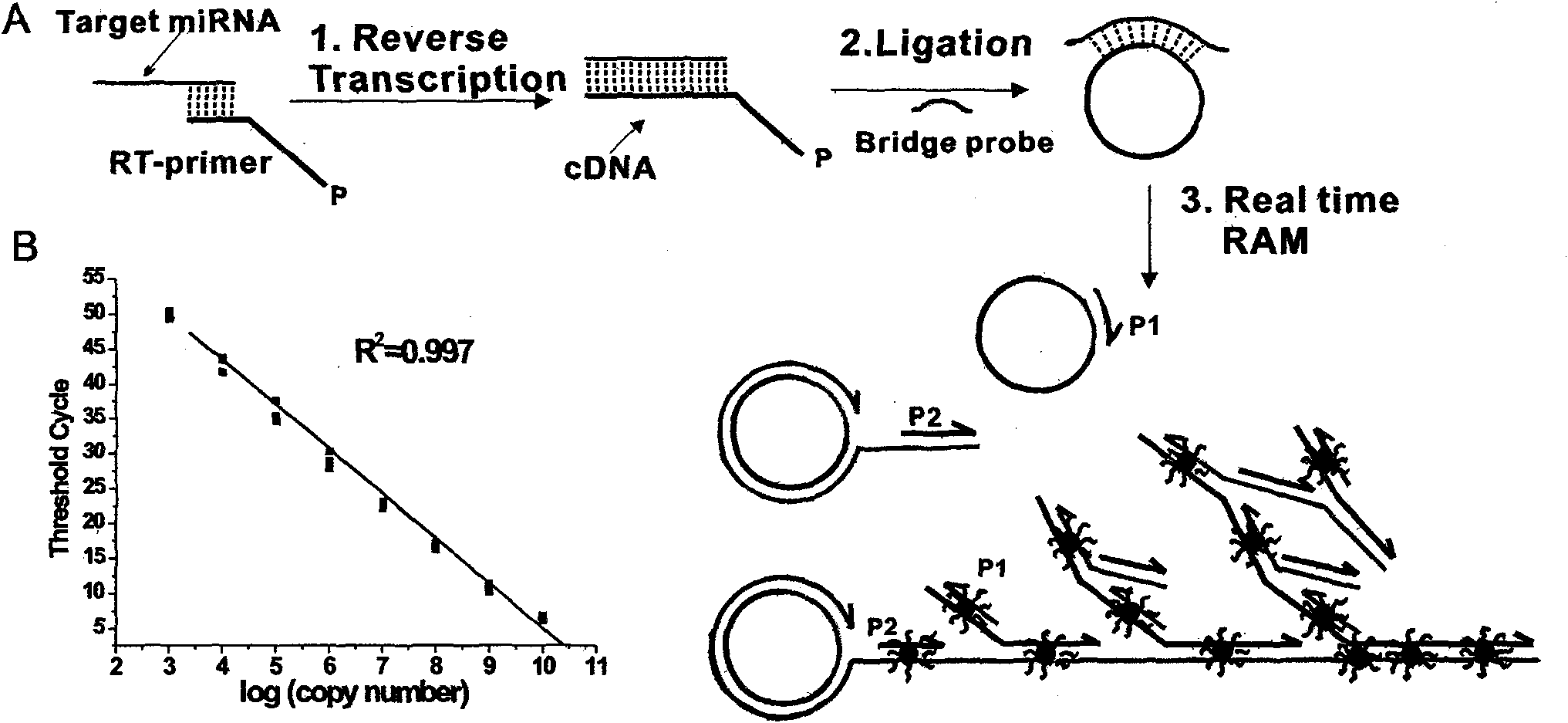
The invention relates to a method and a kit for detecting a small RNA, belonging to the field of detection of small RNAs. The method for detecting the small RNA comprises the following steps: 1. hybridizing an RT-primer and a target small RNA; 2. reversely transcribing; 3. connecting the head and the tail of a reversely transcribed DNA chain to form a ring by the mediation of a bridge probe; and 4. carrying out branch amplification real-time quantitative detection under the actions of DNA polyase, a first primer and a second primer. The method for detecting the small RNA has the advantages of high sensitivity, large dynamic range, high interference resistance, and the like and has wide application prospect in a plurality of fields of scientific experiment, clinical diagnosis, spot test, benchmark test, and the like relevant to the small RNA.
Owner:SHAOXING INST OF TECH COLLEGE OF ENG PEKING UNIV BIOENG CENT
Probe set for detecting small RNA and method for detecting small RNA using same
InactiveCN101591709AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideGel electrophoresis
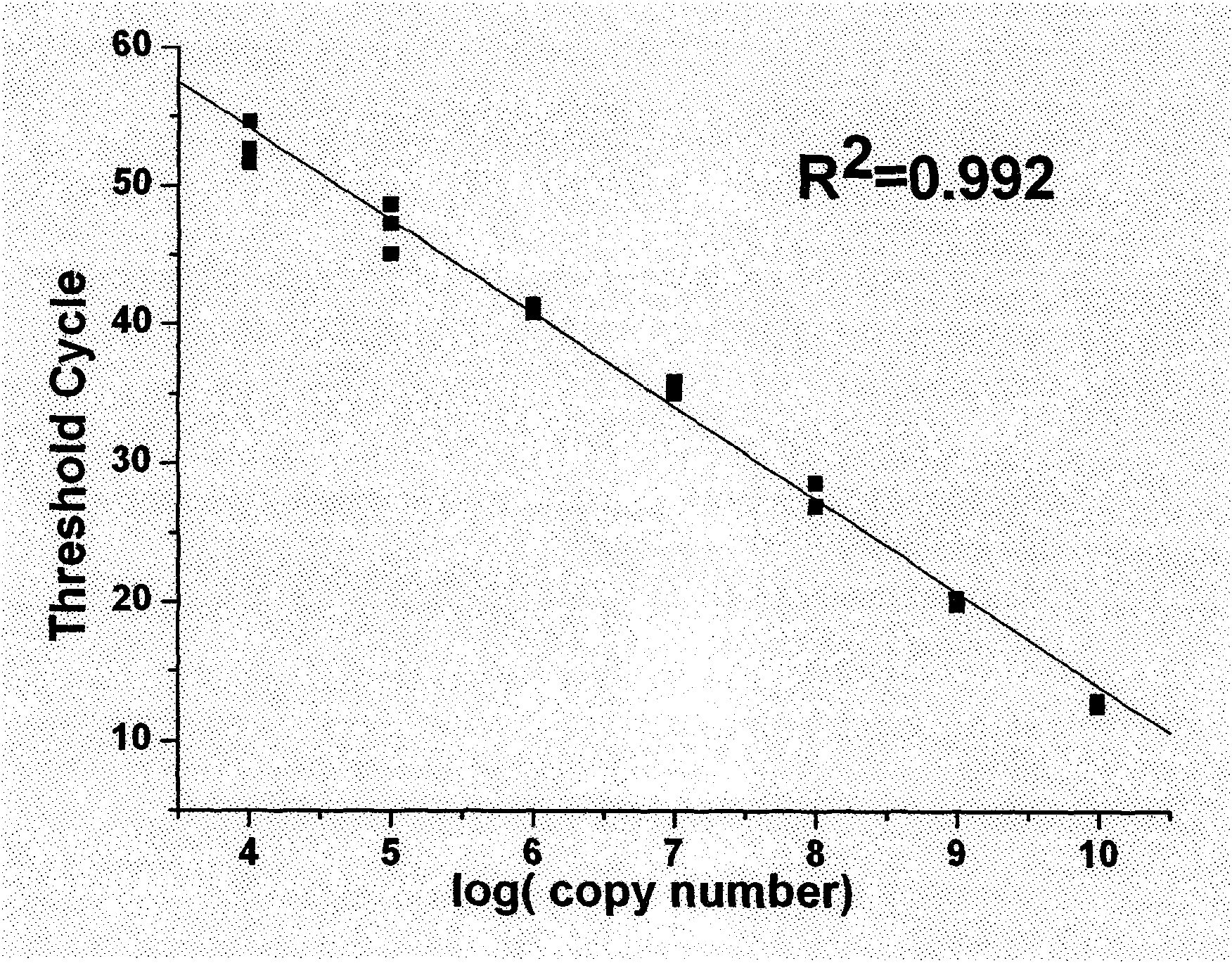
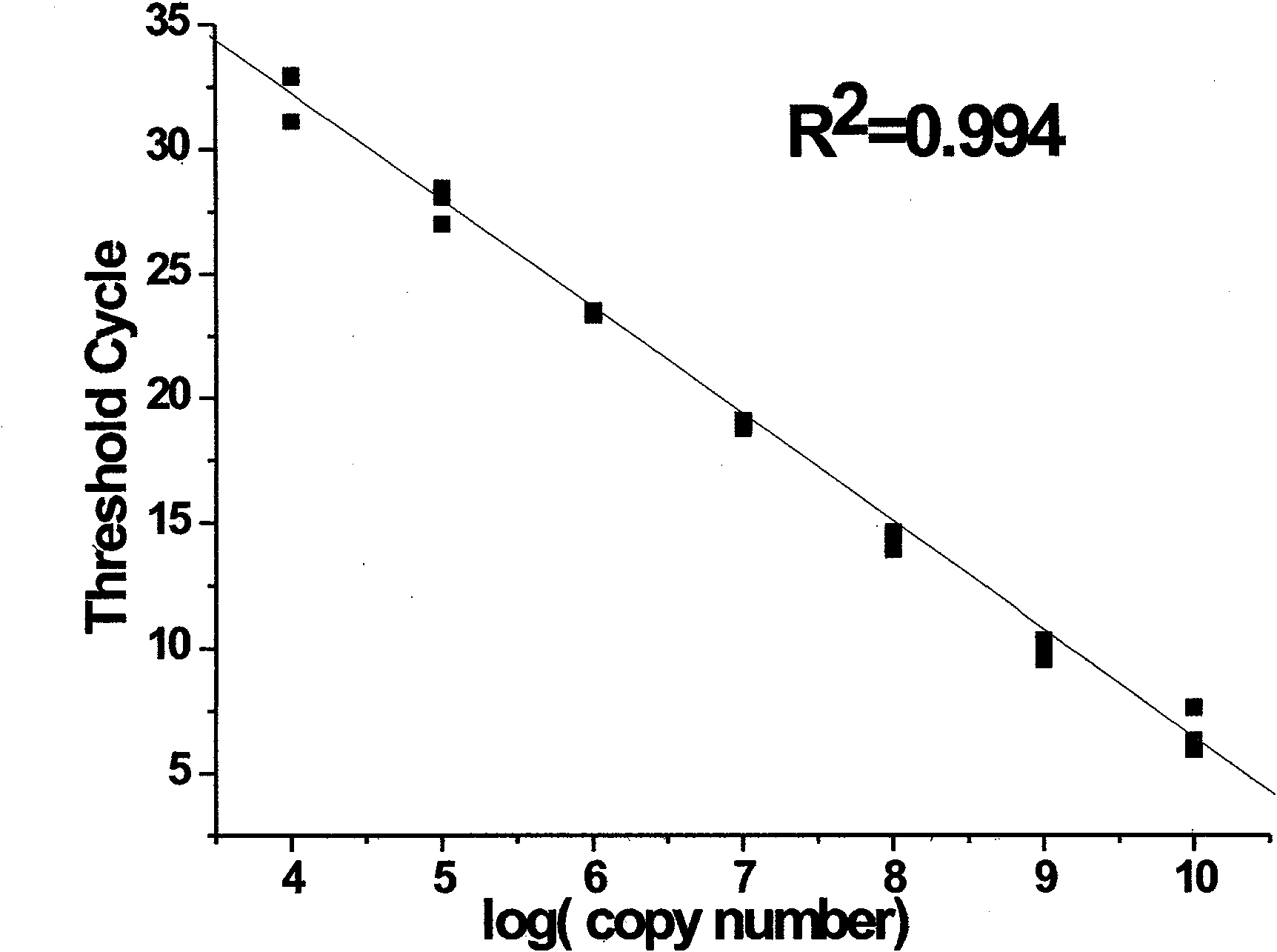
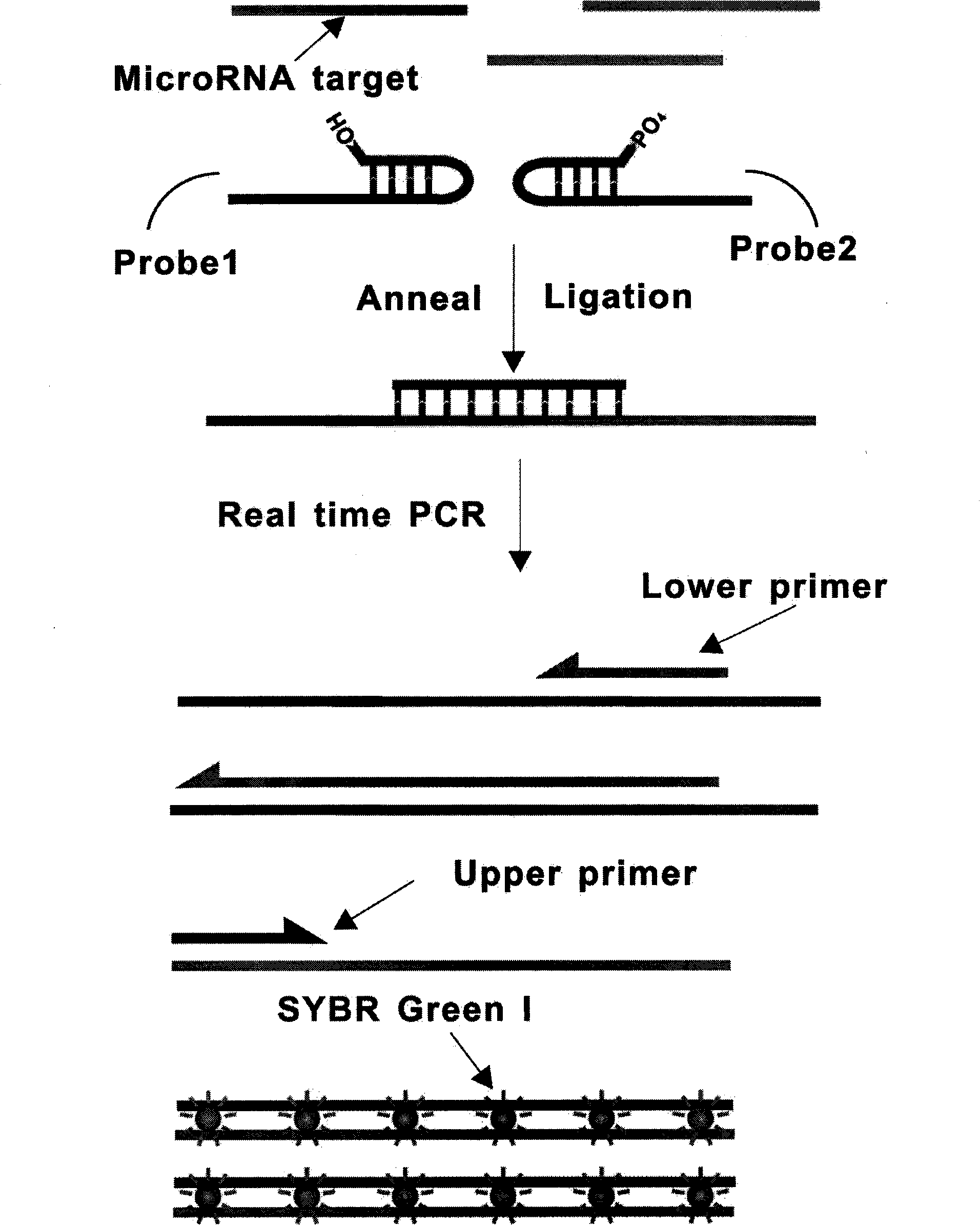
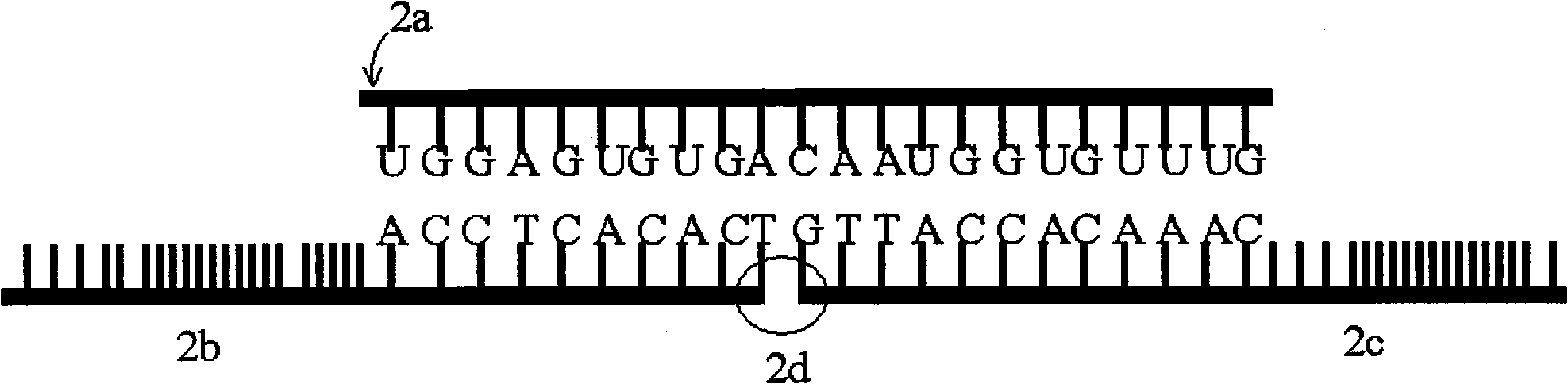
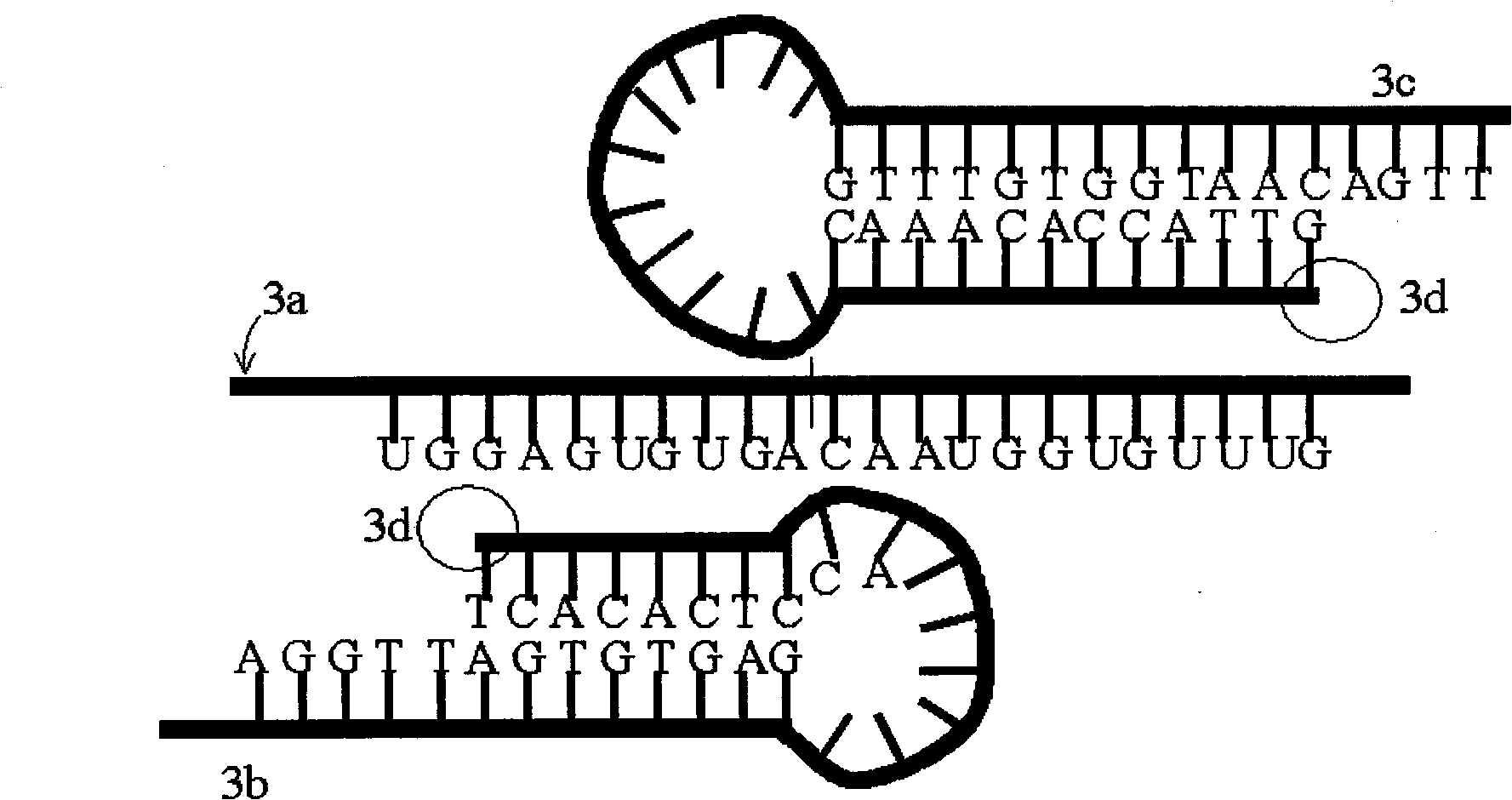
The invention relates to a probe set for detecting a small RNA and a method for detecting the small RNA by using the same and belongs to the field of small RNA detection. The DNA probe set for detecting the small RNA of the invention comprises at least two probes, wherein a segment of nucleotide sequence containing all connections of the connected at least two probes is complementary to the nucleotide sequence of a target small RNA molecular. The method for detecting the small RNA of the invention comprises the following steps: making the probes and the target small RNA first crossed and then connected under the action of a ligase; and finally, detecting the target small RNA by gel electrophoresis, real-time polymerase chain reaction and the like. The method for detecting the small RNA of the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, large dynamic range, strong anti-interface capacity, low price and the like, and has wide application prospects in various fields related to small RNA detection, such as scientific experiments and clinical diagnosis.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Detection of nucleic acids by type specific hybrid capture method
InactiveUS20090162851A1Reduce background signalHigh detection specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionType specific
Target-specific hybrid capture (TSHC) provides a nucleic acid detection method that is not only rapid and sensitive, but is also highly specific and capable of discriminating highly homologous nucleic acid target sequences. The method produces DNA-RNA hybrids which can be detected by a variety of methods.
Owner:QIAGEN GAITHERSBURG
Probe microscope system suitable for observing sample of long body
InactiveUS7507957B2Smooth startMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationNanomedicineFluorescence microscopeScanning probe microscopy
Owner:HITACHI HIGH TECH SCI CORP
Systemic displacement polymerase lymerase chain reaction
InactiveCN101063159AAvoid recontaminationDetection fitMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDirect testFluorescence
The invention discloses a 'system displacement polymerase lymerase chain reaction', which is characterized by the following: displacing program PCR system with above one indicating PCR system; setting the each indicating PCR system augment as small part crossing sequence of independence indicator board and program mold; possessing non-homologous sequence in indicator board with program mold; inverting the program specimen PCR to about ten non-interference indicated PCR system; changing to another system when polluted; avoiding twice pollution of PCR product; crossing the indicated DNA with program DNA; or crossing with program RNA; augmenting directly; fitting for direct test of RNA specimen; co-using with fluorescence molecular beacon (Molecular beacon); fitting for quantitative determination of the program mold.
Owner:北京万达因生物医学技术有限责任公司
Pool and superpool matrix coding and decoding designs and methods
InactiveUS20040224346A1Shorten analysis timeReduce materialPeptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementImage resolutionProtein hybridization
This application pertains to construction of pooled biological material such as DNA, RNA, proteins and the like that are able to be screened by a wide variety of methods such as PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), DNA / DNA hybridization, DNA / RNA hybridization, RNA / RNA hybridization, single strand DNA probing, protein / protein hybridization and a wide variety of additional methods. Our new method for construction of pools and superpools for screening differs in that the complete set is systematically divided into a variety of smaller subsets which are then re-pooled to make the final screening pools. This pooled material can be from individual samples or a population of samples. In order to reduce the analysis time, materials and expense, the pooling of high resolution small pools in a matrix allows for a lower number of user experiments to have higher resolution (as if the researcher had analyzed the complete set of small pools).
Owner:AMPLICON EXPRESS
Method and kit for characterizing rna in a composition
The invention relates to a kit and a method for determining the sequence and / or quantity of a ribonucleic acid in a composition, comprising the steps of: . i. providing a composition comprising one or more ribonucleic acids molecules (RNA), . ii. hybridizing to said one or more RNAs, one or more two-part nucleic acid hybridization probes, wherein each probe comprises, . a. a first nucleic acid molecule with a 3'-tail wherein said tail does not hybridize to an RNA in the composition, . b. a second nucleic acid molecule with a 5'-tail wherein said tail does not hybridize to an RNA in the composition, . c. wherein said first and said second nucleic acid molecules when and if hybridized to their target RNA lie on one single stranded RNA molecule separated from each other by between 2 and 1000 nucleotides, . iii. covalently linking the hybridized 5'-tail of said first nucleic acid molecule to the hybridized 3'-tail of said second nucleic acid, wherein the linking is done by means of reverse transcription and subsequent ligation, . binding the RNA-DNA hybrids to duplex-specific antibodies, . iv. amplifying the linked molecules with primers that are specific for said first 3'-tail of said first nucleic acid molecule and said second 5'-tail of said second nucleic acid molecule and, . v. sequencing the amplification products by means of next generation sequencing. . The kit comprises primers, antibodies and ligase or reverse transcriptase.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
RNA one-step-lysis and one-tube RT-PCR detection method
ActiveCN103333955AEasy to operateReduce non-specific reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceLysisFluorescence
The invention provides a RNA one-step-lysis and one-tube RT-PCR (one-Step-lysis and One-tube RT-PCR, SORT-PCR) detection method. Compared to the conventional RT-PCR method, the RNA one-step-lysis and one-tube RT-PCR method does not need to purify and extract RNA, RNA is hybridly combined to a fixed specific primer or Oligo primer after cell lysis, other components in the cell lysis solution supernatant are washed away, then the RNA is added into a RT reaction system to perform RT reactions. After being dried again, the RNA is added into a PCR reaction system to perform PCR reactions, and the result can be detected by the fluorescence real-time quantitative analyzing method. The RNA one-step-lysis and one-tube RT-PCR detection method shortens the RNA detection process of more than 3 hours to 2 hours, and has the advantages of simple operation, high detection sensitivity and specificity, and suitability for detecting RNA from various sources of sample lysis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JFK BIOLOGICAL TECH
Manipulation of flavonoid biosynthetic pathway
InactiveUS20120204289A1Increased PAIncrease nutritionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningProanthocyanidinFlavonoid biosynthesis
The present invention relates to a method of identifying a gene encoding a polypeptide or polypeptide isoform which is substantially more active in either a proanthocyanidin (PA) or anthocyanin (ANT) pathway of a plant, said method including providing material from said plant; and an oligonucleotide probe capable of hybridizing with RNA from a gene encoding a polypeptide which is active in a flavonoid biosynthetic pathway; extracting RNA from said plant material; hybridizing the oligonucleotide probe with the RNA to generate an expression profile; measuring PA and / or ANT levels in said plant material to generate a metabolic profile; comparing said expression profile with said metabolite profile to identify said gene encoding a polypeptide or polypeptide isoform which is substantially active in either a PA or ANT pathway.
Owner:AGRI VICTORIA SERVICES PTY LTD
RNA in situ hybridization
InactiveCN102037137AImprove diagnostic accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyNucleotideTissue sample
The invention provides an RNA in situ hybridization which is characterized by identifying the presence of target gene mRNA by hybridizing the target gene mRNA expressed in a tissue sample with at least one oligonucleic acid probe and detecting a low-molecular-weight compound label added to at least one nucleotide in the oligonucleic acid probe. In the method, the tissue sample is pretreated with at least one dummy oligonucleic acid (prehybridization), and subsequently the oligonucleic acid probe is contacted with the tissue sample to hybridize the oligonucleic acid probe with the target gene mRNA, or alternatively, a mixed solution of the oligonucleic acid probe and the dummy oligonucleic acid is contacted with the tissue sample to hybridize the oligonucleic acid probe with the target gene mRNA. The dummy oligonucleic acid has almost the same length as that of the oligonucleic acid probe. The dummy oligonucleic acid cannot hybridize with a region on the target gene mRNA with which the oligonucleic acid probe can hybridize, and cannot hybridize with the oligonucleic acid probe.
Owner:CELISH FD
Modulation of gene expression using DNA-RNA hybrids
InactiveUS20050164212A1Determining effectInhibit expressionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDna rna hybridsA-DNA
The present invention is directed to novel DNA-RNA hybrids comprising either a DNA sense strand and an RNA antisense strand, or an RNA sense strand and a DNA antisense strand. The compounds of the invention, and compositions and arrays comprising the same, may be used for a variety of purposes, including inhibiting gene expression, treating disease and infection, determining the function of genes, and identifying and validating novel drugs and their targets.
Owner:HALO BIO RNAI THERAPEUTICS
Integrated electrochemical detection and purification of nucleic acid biomarkers
ActiveUS20190137434A1Improve ultimate sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesBiomarker (petroleum)Rna targeting
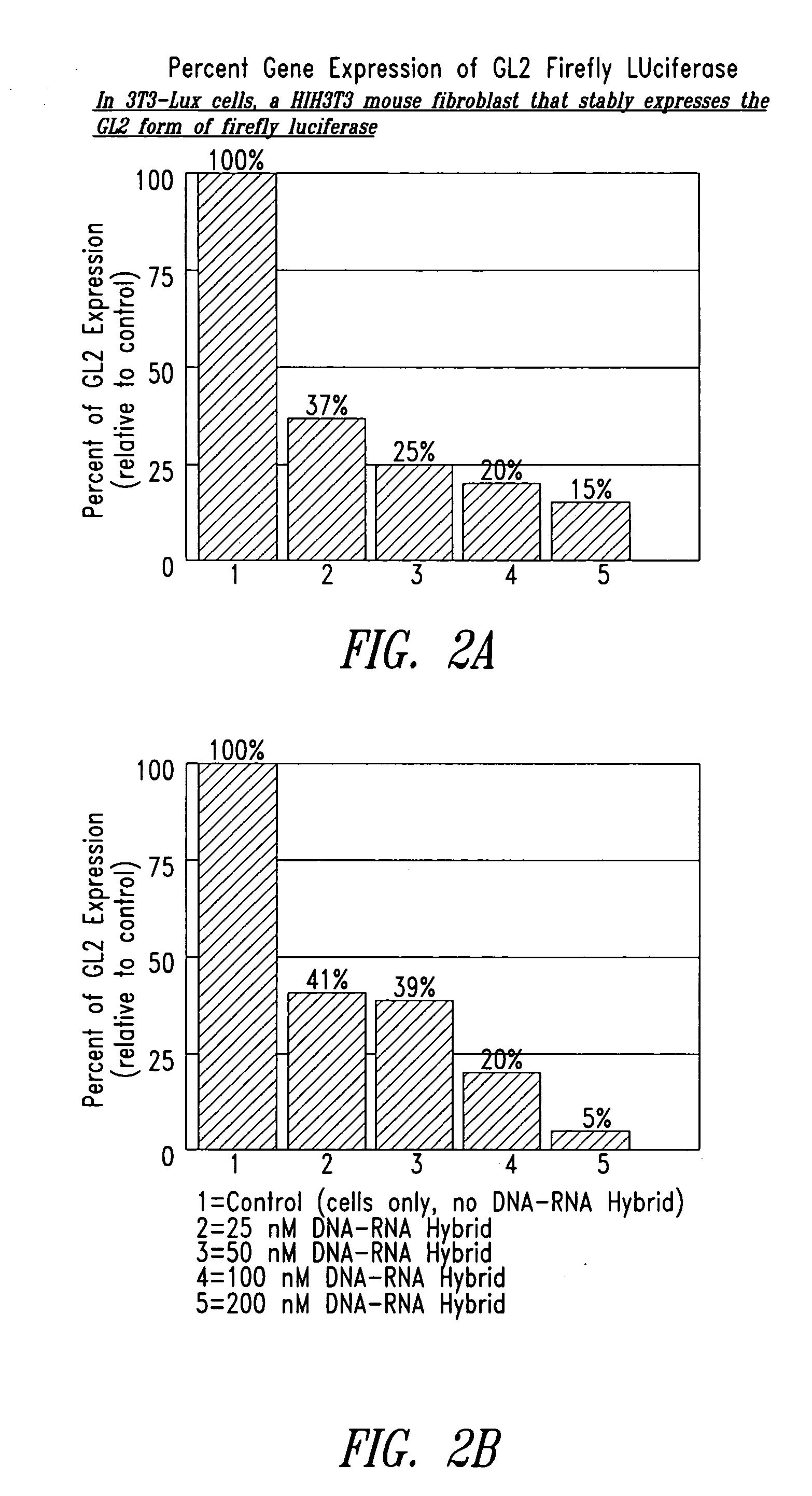
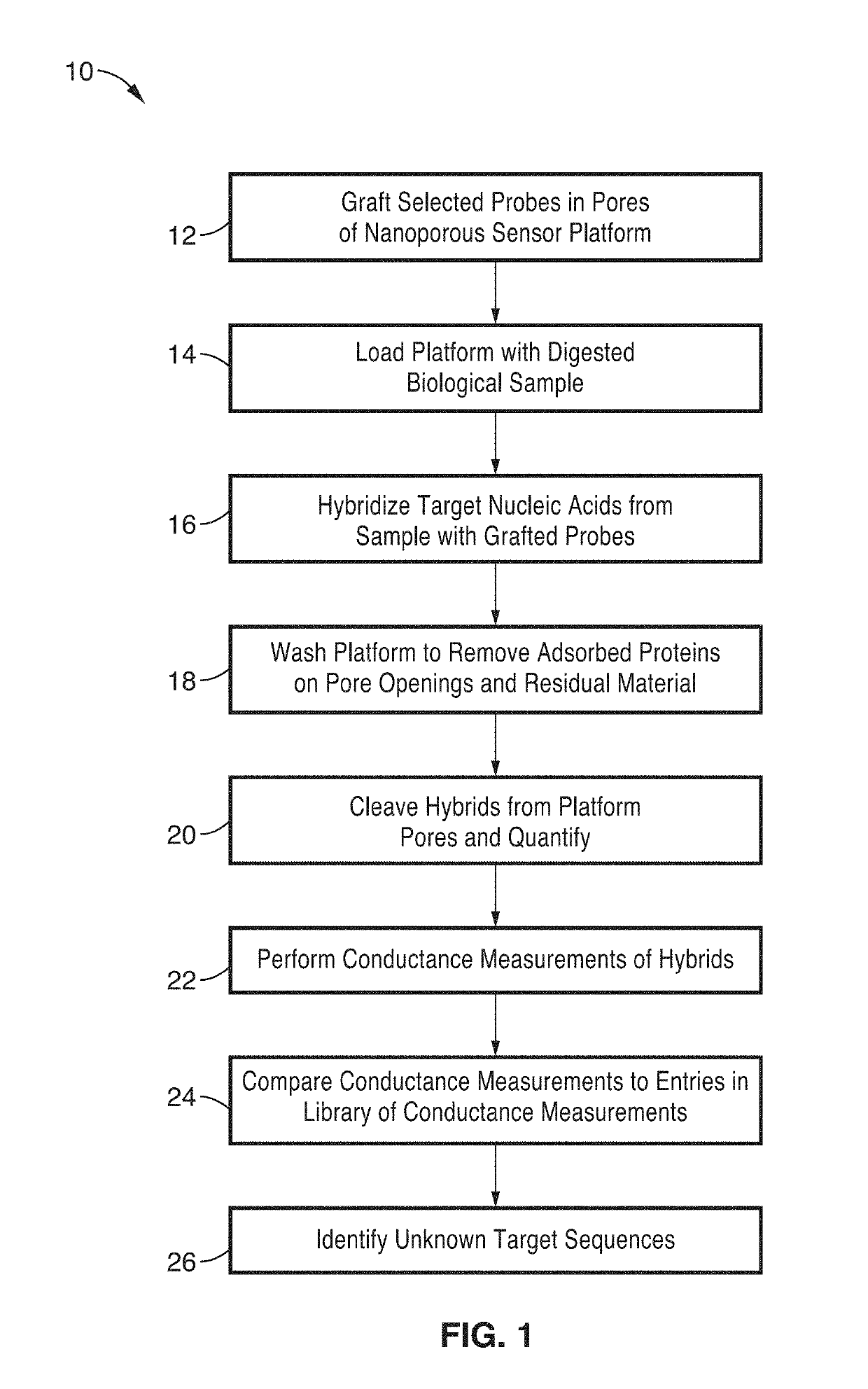
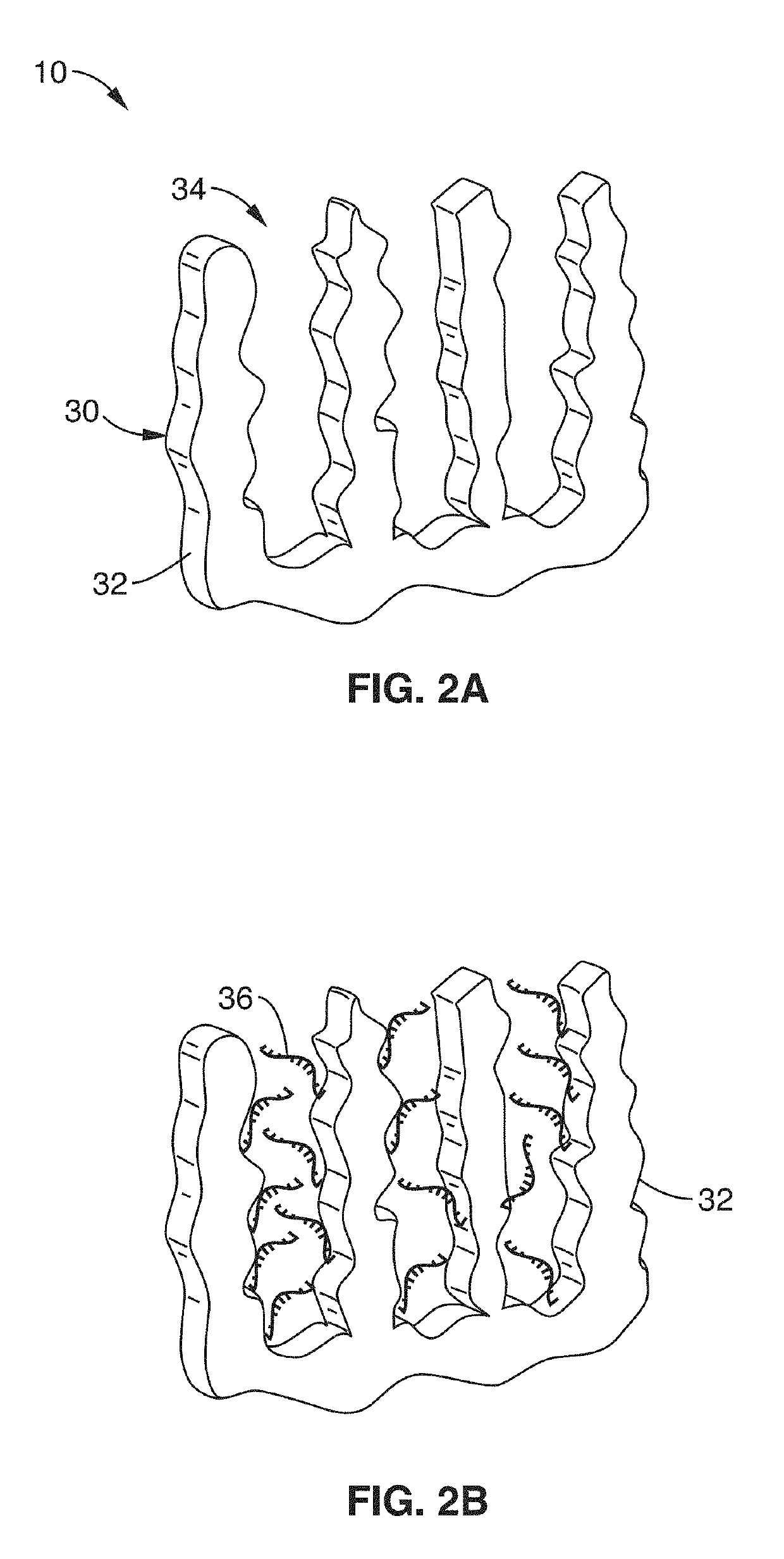
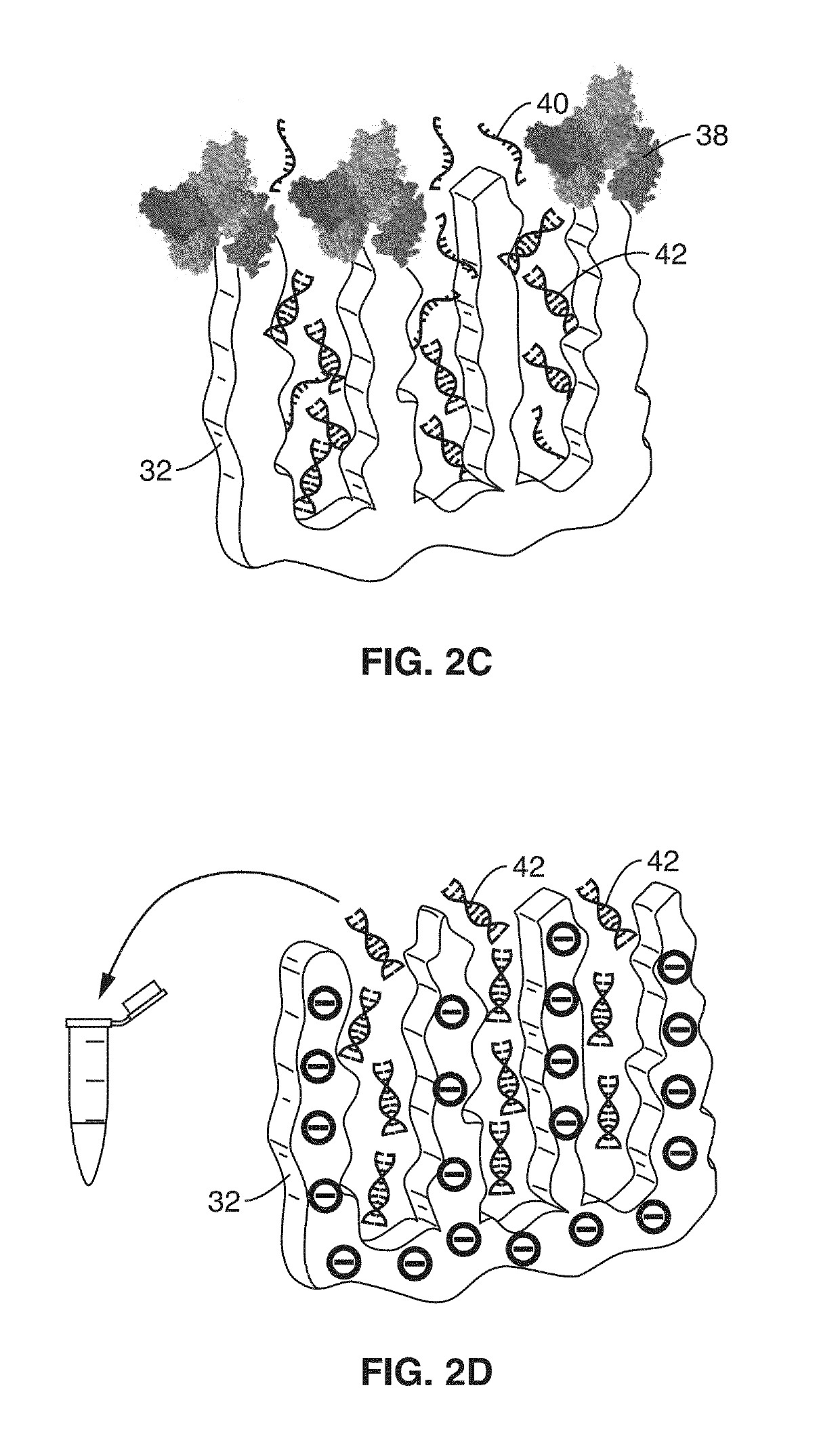
A biosensor platform apparatus and method are provided that can detect, purify and identify nucleic acid (DNA and RNA) biomarkers in complex biological fluids. The methods use a two-stage molecular based approach. The first stage screens for specific nucleic acid-based biomarkers in complex biological fluids by electrochemical detection of DNA:RNA hybridization and facilitates the removal of remaining complex media constituents. The first stage utilizes probes within a tunable nanoporous electrode. The second stage identifies the purified specific hybrids by single-molecule conductance measurements via break junction scanning. Identification can be assisted with a library of conductance measurements. The methods can provide strain level information that can be used for identifying anti-microbial resistance in detected pathogens. Collection of RNA targets allows for biomarker detection and identification without the need for amplification and can provide information about the viability of the sample organism.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com