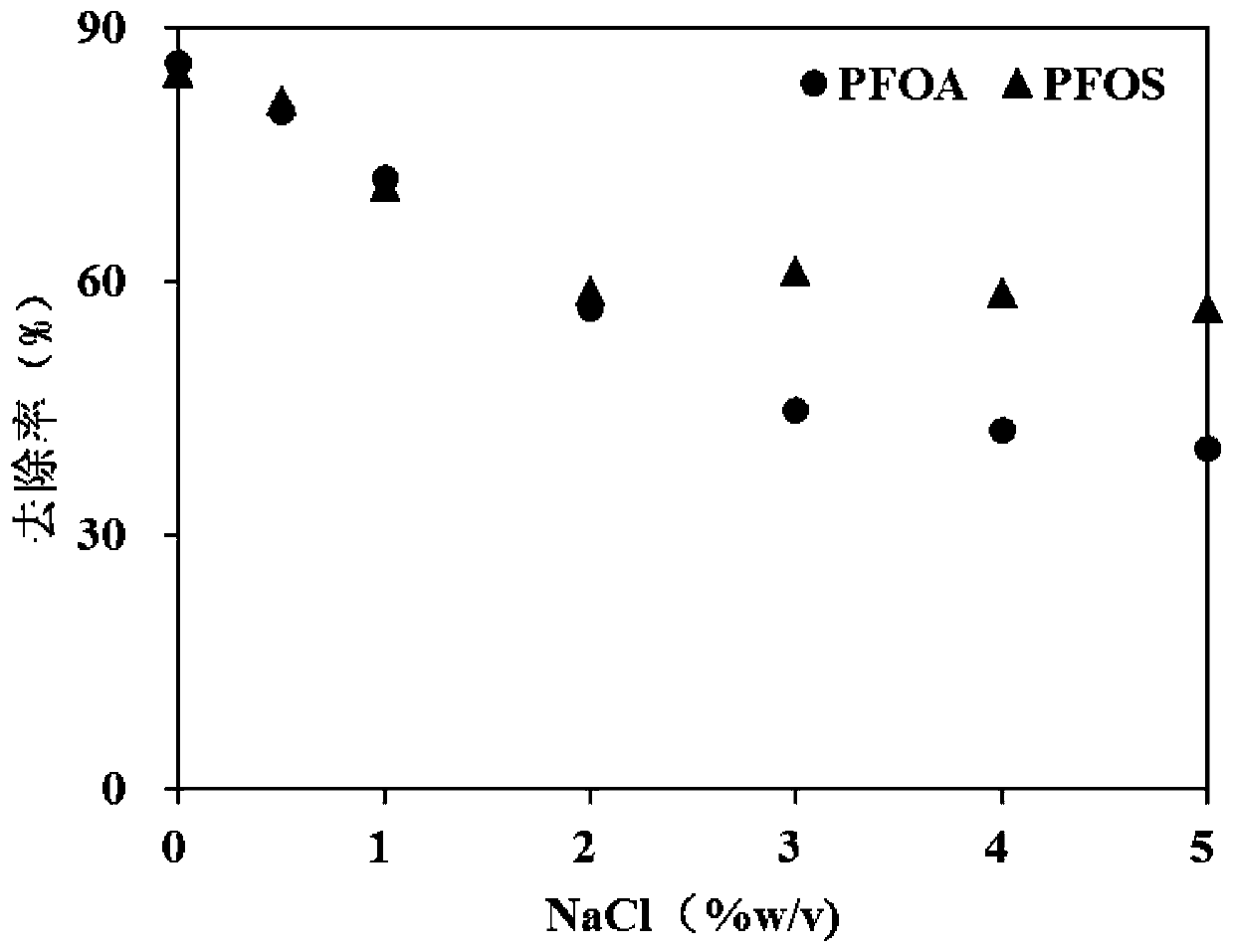
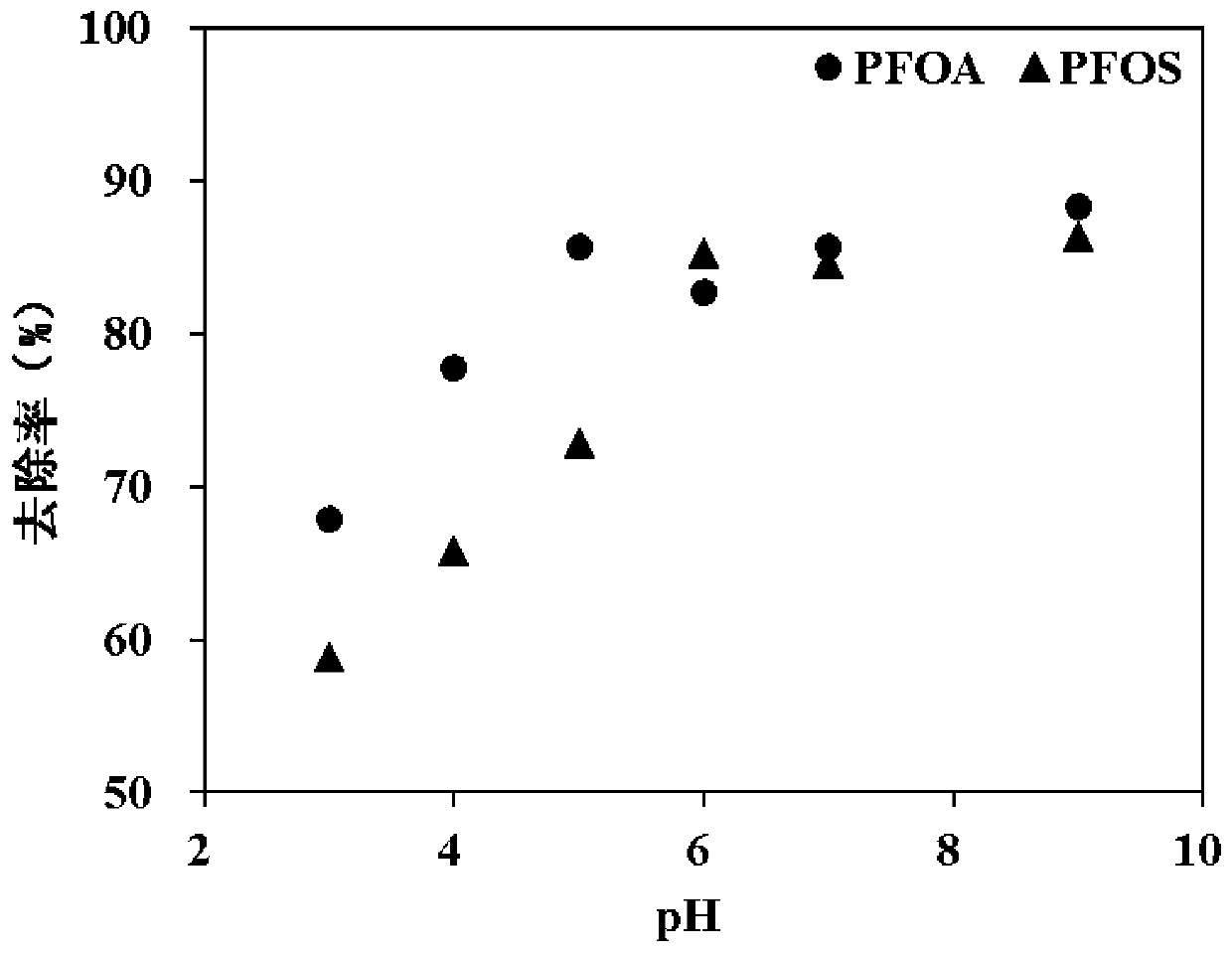
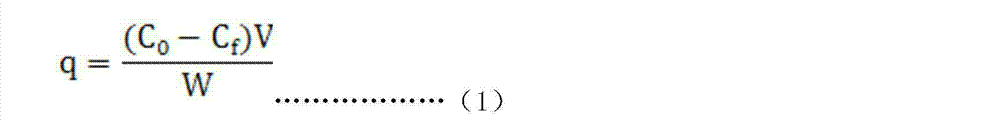Patents
Literature
116 results about "Membrane adsorption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Membrane adsorbent technology is a membrane integration technology that was developed in the mid-1980s (Avramescu et al. 2003, 2008). Adsorption is a mass transfer process by which a substance is transferred from the liquid phase to the surface of a solid, and becomes bound by physical and/or chemical interactions.
Membrane adsorbent for removing heavy metal ions from drinking water effectively and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101961648AImprove adsorption capacityImprove interception effectOther chemical processesWater contaminantsPolymer resinSorbent
The invention relates to a membrane adsorbent for removing heavy metal ions and a preparation method thereof, in particular to a method for preparing a membrane adsorbent for removing heavy metal ions from water by utilizing the process of membrane filtration. Casting membrane liquid for preparing the membrane adsorbent comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 70 / 30 to 20 / 80 percent of polymer / resin, 4 to 30 percent of additive and 30 to 75 percent of solvent, wherein the concentration sum of the polymer and the resin is between 20 and 55 percent, and the sum of components is 100 percent. According to the formula of the invention, the method of the membrane adsorbent comprises the following steps of: 1, preparing the casting membrane liquid; 2, preparing a membrane; and 3, performing aftertreatment. The surface of the membrane adsorbent has an opening structure, so the membrane adsorbent has the excellent adsorption function, can be used as filtering and adsorbing media, and is particularly suitable for removing the heavy metal ions from the water.
Owner:安徽森诺膜技术有限公司
Porous polymer membrane of inlaid molecular sieve with adsorption function
ActiveCN104492287AImprove adsorption capacityImprove interception effectSemi-permeable membranesOther chemical processesEutrophicationPorous polymer membrane
The invention provides a porous polymer membrane of an inlaid molecular sieve with an adsorption function, and particularly relates to a preparation method of the porous polymer membrane of the inlaid molecular sieve, which can remove heavy metal ions and nitrogen phosphorous and other pollutants in water by adopting membrane adsorption technology. A casting solution for preparing the porous polymer membrane of the inlaid molecular sieve comprises the following components in percentage by mass: polymer / molecular sieve adsorption material with the mass ratio being 90 / 10-10 / 90 and the concentration sum being 20%-50%, 4%-30% of pore-forming additives, 1%-5% of a particle dispersion-suspension stabilizer, 30%-75% of solvents, wherein the percentage sum of all the components is 100%. The molecular sieve adsorption material is evenly inlaid and dispersed into a porous membrane matrix material, the adsorption rate is high, the dynamic adsorption capacity is large, pollutants in water can be fast removed with a broad spectrum, and the eutrophication problem of a water body can be solved.
Owner:天津鼎芯膜科技有限公司
Purification processes for isolating purified vesicular stomatitis virus from cell culture
ActiveUS20070249019A1Improve Yield and PuritySsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideIon-exchange membranesBiology
Novel purification processes for obtaining vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) of improved purity from mammalian cell culture are described herein. More particularly, in certain embodiments, a process is described for purifying VSV from cell culture fluid of a mammalian cell culture infected with VSV, the process comprising: clarifying the cell culture fluid by low-speed centrifugation and recovering the VSV in the supernatant; filtering the supernatant through a 0.2 to 0.45 μm filter and recovering the VSV in the filtered solution; loading the VSV filtered solution onto a anion exchange membrane adsorber equilibrated with a first pH buffered salt solution, eluting the VSV from the anion exchange membrane adsorber with a second pH buffered salt solution and recovering the eluted VSV fractions; purifying the recovered VSV by tangential flow filtration (TFF) using a TFF membrane having a molecular weight cutoff between 300 kDa and 1,000 kDa and recovering the VSV in the retentate, and filtering the VSV retentate through a 0.2 to 0.22 μm filter and recovering the VSV in the filtered solution.
Owner:WYETH LLC
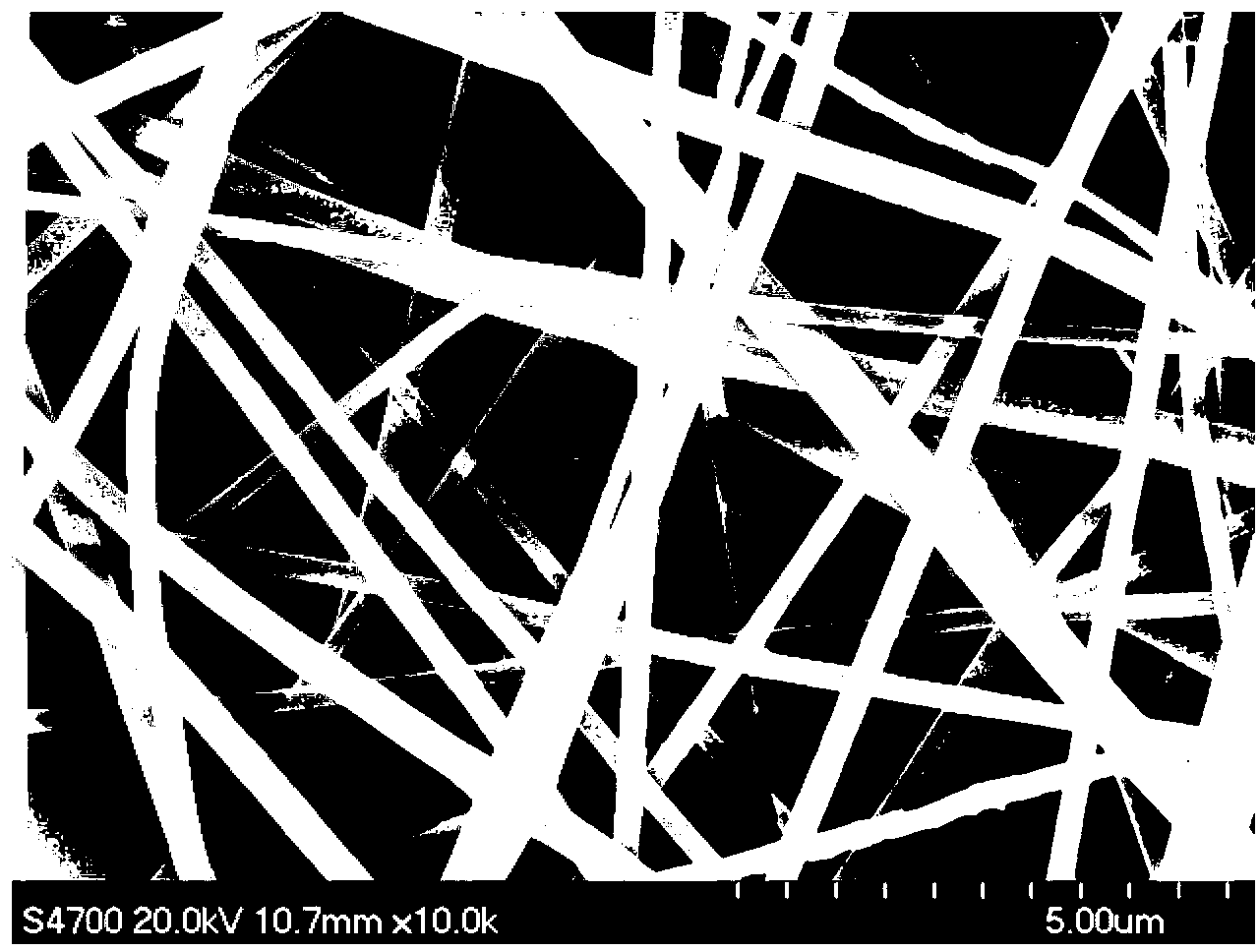
Nanofiber membrane and membrane adsorbing assembly for extracting uranium from seawater and brine water and application of nanofiber membrane and membrane adsorbing assembly
InactiveCN105080509AImprove adsorption efficiencyHigh mechanical strengthOther chemical processesProcess efficiency improvementIndustrial waste waterSpinning
The invention discloses a nanofiber membrane and a membrane adsorbing assembly for extracting uranium from seawater and brine water and application of the nanofiber membrane and the membrane adsorbing assembly. The nanofiber membrane is prepared by the steps: preparing polyacrylonitrile into a spinning solution; depositing polyacrylonitrile nanowires on a macromolecular non-woven fabric through an electrostatic spinning process to obtain a polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane; and then carrying out amidoximation on the polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane to obtain the nanofiber membrane. The membrane adsorbing assembly is prepared by the steps: preparing the nanofiber membrane into a rolled membrane assembly; and then carrying out amidoximation on the rolled membrane assembly to obtain the nanofiber membrane adsorbing assembly. The membrane adsorbing assembly disclosed by the invention is high in adsorption capacity, great in adsorption rate, stable in recycling performance and high in mechanical strength. The membrane adsorbing assembly not only is suitable for extracting uranium element from water bodies such as seawater or brine water and the like, but also is suitable for separating and recovering other noble metal or heavy metal ions from industrial wastewater, underground water and drinking water separately as well as removing metal ions from an organic phase.
Owner:和晶(上海)新能源科技有限公司
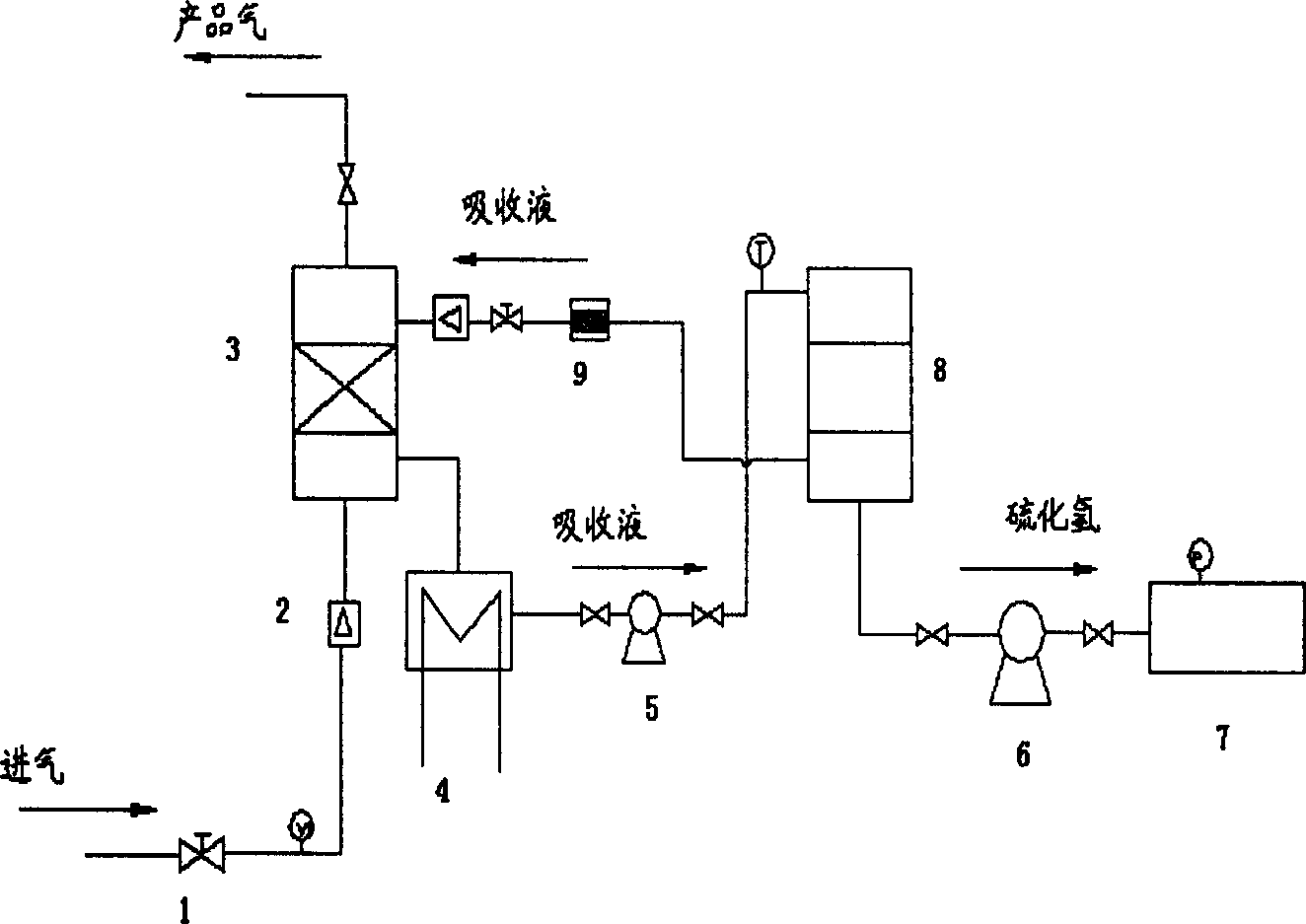
Membrane adsorption natural gas desulfur method
InactiveCN1785480AEffective contactLow investment costDispersed particle separationFiberHollow fibre membrane
A membrane absorption method for removing the acidic gas (H2S, organo-sulfur, etc) from the natural gas in oil-gas field by use of micro-pore hollow fiber membrane includes such steps as introducing natural gas to tubular cavity of membrane separator, penetrating H2S to outside of tubular cavity, absorbing it by absorptive liquid, heating the absorptive liquid by heat exchanger, and regenerating the absorptive liquid while releasing H2S, and pumping the H2S into tail gas tank by vacuum pump.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
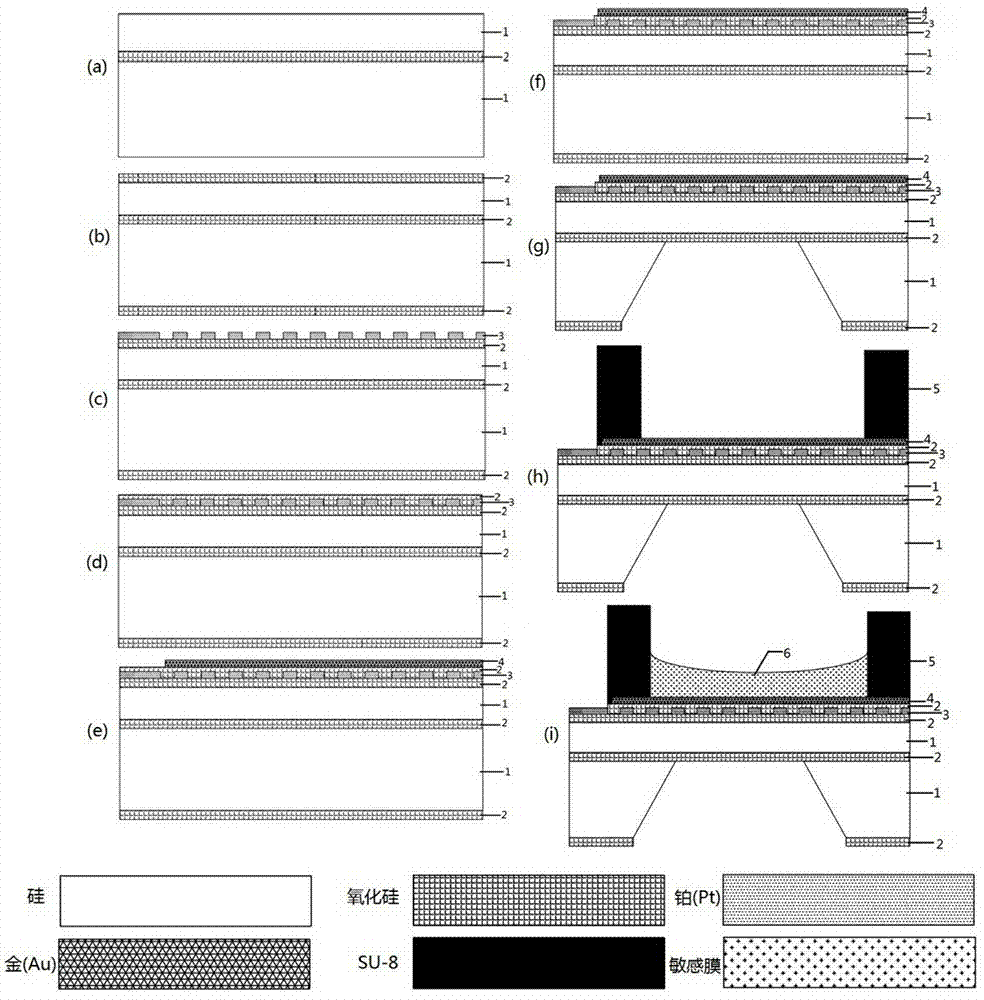
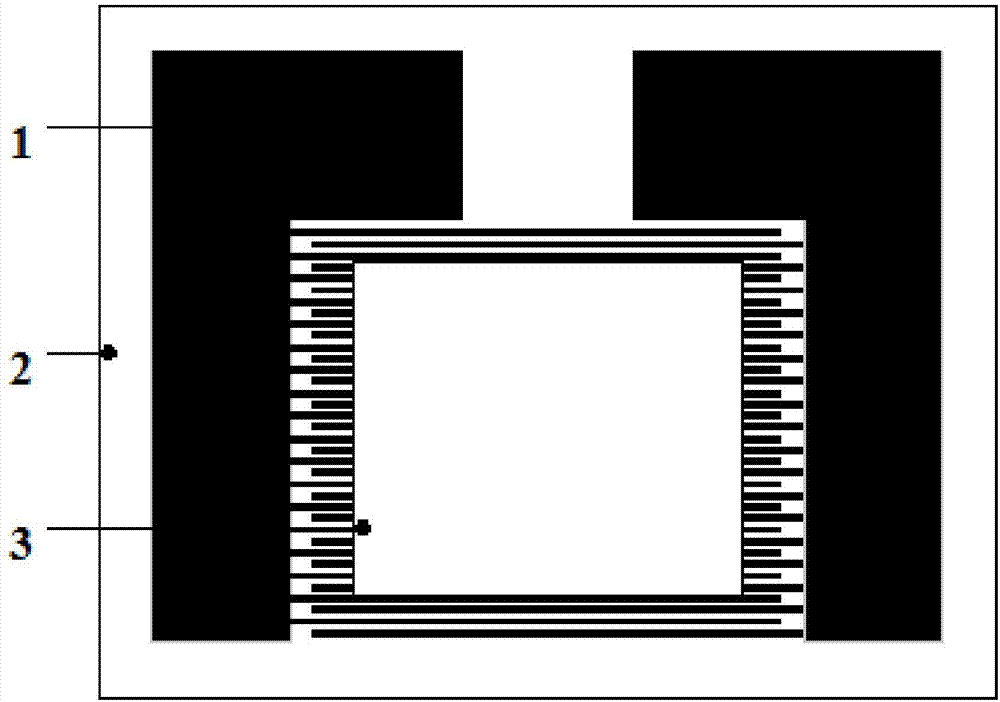
Micro-well based gas sensor array and its making method
ActiveCN102735712AAvoid cross contaminationHigh selectivityDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesSensor arrayMultilayer membrane
The invention discloses a micro-well based gas sensor array and its making method. According to the invention, (1) the gas sensor array adopts an MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) technology, an interdigital electrode is prepared on an SOI wafer surface, an SU-8 photoresist is used to make a micro-well isolation layer for preventing cross contamination of sensitive materials among different interdigital electrodes during sensitive membrane preparation, and each sensor array at least includes 4 interdigital electrode units; (2) an independent heating unit is located under each interdigital electrode, thus greatly improving the sensitivity and response recovery time of the sensor; (3) an organic membrane, an organic / inorganic composite membrane or an organic-inorganic multilayer membrane is taken as the sensitive membrane, and by determining the resistance change during gas adsorption of the sensitive membrane, qualitative and quantitative detection of a gas can be realized; and (4) using a droplet coating, gas jet or electronic injection technique to prepare the sensitive membrane. The gas sensor array has broad application prospects in the fields of atmospheric environment monitoring, aerospace sealed cabin air quality testing and food security, etc.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
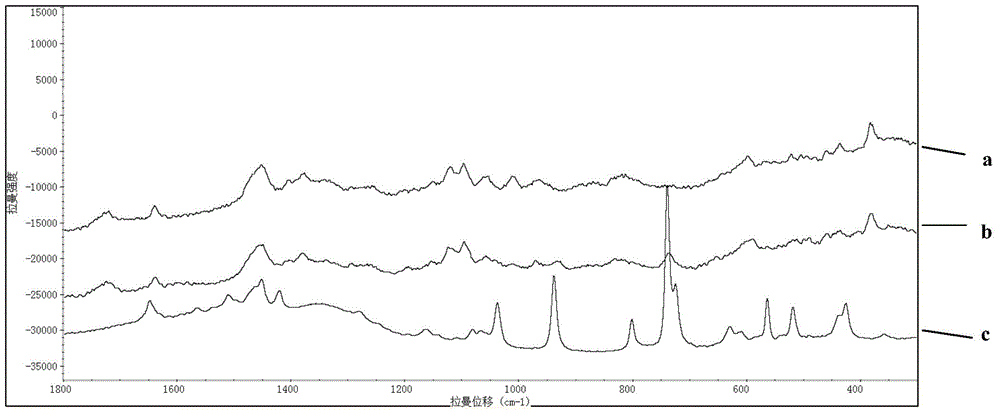
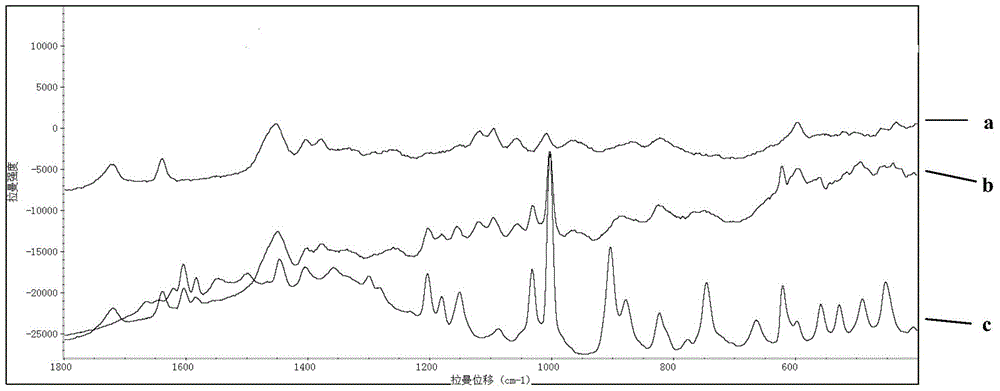
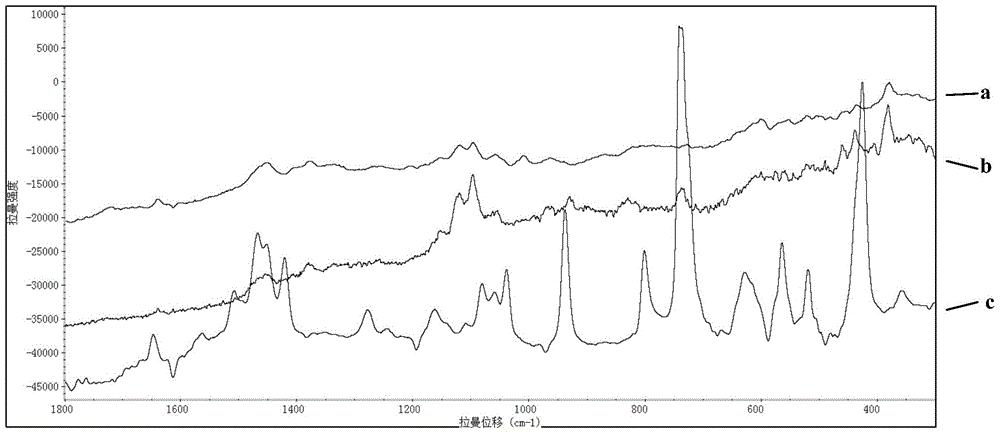
Rapid Raman spectrum detection method for molecularly imprinted membrane
InactiveCN104458695AAdsorptiveHigh strengthPreparing sample for investigationRaman scatteringFluorescenceSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
The invention relates to a Raman spectrum detection method for a molecularly-imprinted membrane (MIM) by use of a Raman spectrometer used as a detection means with the combination of a molecular imprinting technology and a membrane technology and is used for rapidly detecting target molecules-dimethylguanidine hydrochloride and the like in real time. According to the method, a piece of lens paper for an optical lens is used as a substrate (carrier), guanidine hydrochloride or 4-(2-amino ethyl) benzsulfamide is used as an imprinted template, nanogold / silver sol is added in a pre-polymerization solution, and a polymer is directly light-gathered on the lens paper, so as to be convenient to carry and detect. The addition of the nanogold / silver sol is similar to the surface enhanced raman spectroscopy in principle, the response strength of the Raman spectrum can be enhanced and the fluorescence signal interference is reduced; the molecularly-imprinted membrane after and before target adsorption is compared with a standard substance, so that the peaked change in the Raman spectrum can be observed and whether a practical sample contains a target molecule can be judged.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Amine modified fibrous membrane adsorption material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105195110ANot easy to knotThe response is not easy to controlOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesFiberFiltration
The invention discloses an amine modified fibrous membrane adsorption material and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of synthesis and application of environment function materials. Polyacrylonitrile powder is taken as a matrix, a liquid matrix is prepared through solid phase graft polymerization and amination, electrostatic spinning is performed, and the novel fibrous membrane adsorption material is prepared. The synthetic method is simple, the amination efficiency is high, a large quantity of swelling agents and amination reagents can be saved, and the prepared membrane adsorption material has a high hydrophilic surface and can be applied to a flat sheet membrane filtration assembly; when water passes through a fibrous membrane, surface groups can efficiently adsorb and remove multiple heavy metal ions in water, and the fibrous membrane which is saturated after adsorption can be reused after desorption and regeneration.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Preparation method and application of polyester nanofiber modified membrane adsorption material
InactiveCN103182296AEasy to operateMaintain nanofiber structureOther chemical processesFibre treatmentFiberPolyester
The invention relates to a preparation method and an application of a polyester nanofiber modified membrane adsorption material. The preparation method of the adsorption material comprises the following steps: adding polyethylene terephthalate spinning solution into electrostatic spinning equipment and preparing a polyester nanofiber membrane by using the electrostatic spinning equipment; and after carrying out low-temperature plasma grafting modification on the obtained polyester nanofiber membrane, performing cleaning and drying to obtain the polyester nanofiber membrane adsorption material. The nanofiber diameter is 200-500 nm before the adsorption material is modified, the nanofiber diameter after modification is increased, and after plasma treatment, if different grafting monomers are used, different nanofiber diameters are obtained. The preparation method of the adsorption material is simple to operate, and the obtained nanofiber membrane has the characteristics of hydrophilcity, low cost, large adsorption quantity, quick adsorption speed and wide raw material source. The adsorption material can efficiently and quickly adsorb heavy metal ions Cu (II).
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Rhenium disulfide nanosheet array film adsorption sensor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107024516ASimple structureReduce volumeNanosensorsMaterial resistanceRheniumChemical vapor deposition
The invention discloses a rhenium disulfide nanosheet array film adsorption sensor and a preparation method thereof. The sensor comprises an electrode base and a sensitive material. The electrode base is composed of a gold electrode and a ceramic insulating sheet substrate, wherein the gold electrode is an interdigital electrode structure. The sensitive material is a rhenium disulfide nanosheet array film, and is synthesized by chemical vapor deposition method. Through design of the synthetic strategy, the rhenium disulfide nanosheet array film in an orientation perpendicular to the electrode base can be deposited on the electrode base so as to compose the adsorption sensor. The sensor has the characteristics of simple structure, small size, low preparation cost and simple synthesis. Because of the vertical orientation of the nanosheet, more gas molecules can be adsorbed on the surface, thus being beneficial to diffusion of molecules. Therefore, compared with the existing sensors, the sensor provided by the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, short response recovery time and good accuracy, and is very suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Polymer film, waterproof sound-permeable membrane, waterproof sound-permeable member, electronic device, electronic device case, waterproof sound transmission structure, waterproof gas-permeable membrane, waterproof gas-permeable member, waterproof ventilation structure, suction sheet, method for holding workpiece by suction on suction unit, method for producing ceramic capacitor, optical film, optical member, and composition
ActiveUS20170292000A1Avoid enteringMembranesSemi-permeable membranesCeramic capacitorPolymer thin films
The polymer film of the present invention has through holes extending from one principal surface of the polymer film to the other principal surface of the polymer film. The through holes are straight holes having a central axis extending straight, and have a shape in which the area of a cross-section perpendicular to the direction of the central axis increases from the one principal surface of the polymer film toward the other principal surface. This polymer film has passages in its thickness direction, has an unconventional structure, and can be used in various applications, such as in a waterproof sound-permeable membrane, in a waterproof gas-permeable membrane, and in a suction sheet. The ratio a / b of the opening diameter a of the through holes at the one principal surface to the opening diameter b of the through holes at the other principal surface is 80% or is less than 80%.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Preparation method of membrane adsorbent for removing ammonia nitrogen in wastewater
InactiveCN105032203AChange structureChange performanceSemi-permeable membranesOther chemical processesSludgePyrrolidinones
The invention provides a preparation method of a membrane adsorbent for removing ammonia nitrogen in wastewater. The preparation method comprises the following steps: treating modified pure water sludge; adding polyvinylpyrrolidone into a tapered bottle containing dimethyl acetamide; adding polyvinylidene fluoride after uniformly stirring; re-adding pure water sludge after dissolution; after fully stirring, sealing the bottle mouth and leaving the mixture to stand for defoaming to prepare a casting solution, wherein the addition of polyvinylpyrrolidone accounts for 2-4% of the mass of the casting solution, the total mass of polyvinylidene fluoride and sludge particles accounts for 17-20% of the mass of the casting solution, the mass ratio of polyvinylidene fluoride to the sludge particles is (3:7)-(7:3), and the rest is dimethyl acetamide; striking the casting solution on a glass plate to manufacture a flat sheet membrane; then placing the flat sheet membrane in a pure water precipitating bath; soaking in deionized water after film forming, and then taking out; placing the membrane in anhydrous ethyl alcohol to be soaked; taking out the membrane; naturally cooling to obtain the membrane adsorbent. The membrane adsorbent can absorb ammonia nitrogen in water and is renewable.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method and application of electrostatic spinning modified membrane adsorption material
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of an electrostatic spinning modified membrane adsorption material. A nanofiber membrane is prepared by adopting an electrostatic spinning instrument and is processed by a low-temperature plasma device, so that the electrostatic spinning nanofiber membrane is modified to obtain the electrostatic spinning modified membrane adsorption material. The PET (polyethylene glycol terephthalate) nanofiber membrane with uniform fiber morphology is prepared by adopting the electrostatic spinning instrument and then is subjected to surface modification by adopting the low-temperature plasma processing device in a plasma processing method combining gas phase and liquid phase, thus obtaining the PET nanofiber membrane with excellent hydrophilic performance. The modified membrane is applied to adsorption of heavy metal ions Cu (II). The electrostatic spinning modified membrane adsorption material can adsorb Cu (II) efficiently and rapidly.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Biomimetic membrane for removing aflatoxins, and preparation method and treatment method of biomimetic membrane
ActiveCN107927528AImprove stabilityExtension of timeLiquid surface applicatorsOn/in organic carrierBiomimetic membranesEnzyme catalysis
The invention provides a biomimetic membrane for removing aflatoxins, and a preparation method and treatment method of the biomimetic membrane. The biomimetic membrane comprises a microporous membrane, a dopamine coating coats the microporous membrane, polyethyleneimine is grafted to the dopamine coating, and enzyme molecules are adsorbed onto the polyethyleneimine. The method comprises the following steps of firstly coating the microporous membrane with poly-dopamine, then grafting the polyethyleneimine, and finally adsorbing the enzyme molecules through the polyethyleneimine. Enzymes adsorbed onto the biomimetic membrane can be unceasingly desorbed and released into feed liquid in the process of performing catalytic degradation on the aflatoxins, so that the polyethyleneimine is exposedto continue adsorbing the aflatoxins until a saturated state is obtained, and the total aflatoxins removing rate is greater than 80%. The adsorbed aflatoxins are eluted with aqueous alkali, so that regeneration and repeated use of the biomimetic membrane are realized, and 50% or above of the eluted aflatoxins can be degraded in the aqueous alkali. The preparation technology of the biomimetic membrane disclosed by the invention is simple, enzyme catalysis, enzyme slow release, membrane adsorption and alkali treatment are combined, and the removal rate of the aflatoxins can be increased.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Printing and dyeing wastewater deep treatment method
ActiveCN107311387ALarge adsorption capacityImprove adsorption capacitySemi-permeable membranesMembranesTextile printerPhotocatalytic reaction
The invention discloses a printing and dyeing wastewater deep treatment method which includes the steps: first, medium filtration; second, magnetic hydrogel micro-sphere adsorption; third, photocatalytic reaction; fourth, electrostatic spinning nanofiber membrane filtration; fifth, ultrafiltration membrane segment. According to the printing and dyeing wastewater deep treatment method, most impurities, organic matters and heavy metal ions are adsorbed by magnetic hydrogel micro-spheres with excellent performances, the organic matters are directly mineralized by a photocatalytic reactor, and most inorganic salts are removed by ultrafiltration membranes through polyvinyl alcohol / chitosan electrostatic spinning nanofiber membrane adsorption. The printing and dyeing wastewater deep treatment method is simple to operate, high in efficiency, free from secondary pollution and low in cost, and the water quality of obtained recycled water meets textile printing and dyeing industrial water standards.
Owner:金华雅帅纺织有限公司
Polyurethane cervix uterus repairing film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108159025AGuaranteed continued dosingGood treatment effectPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSexual disorderPolyurethane membraneEngineering
The invention provides a polyurethane cervix uterus repairing film which is characterized by being prepared from a medical polyurethane membrane and a membrane conveying device, wherein the membrane conveying device comprises an injector casing, a push rod sealing plug and a push rod; the push rod sealing plug is arranged in the injector casing, the rear end of the push rod sealing plug is fixedlyconnected with the push rod, the rear end of the push rod extends out of the rear end of the injector casing, and a membrane adsorption opening is formed in the front end of the injector casing. Before the polyurethane cervix uterus repairing film is utilized, the medical polyurethane membrane is adsorbed by the membrane adsorption opening; when the polyurethane cervix uterus repairing film is utilized, the membrane conveying device pushes the medical polyurethane membrane to be attached to the surface of the cervix uterus.
Owner:SUZHOU NANOCRYSTAL PHARMA
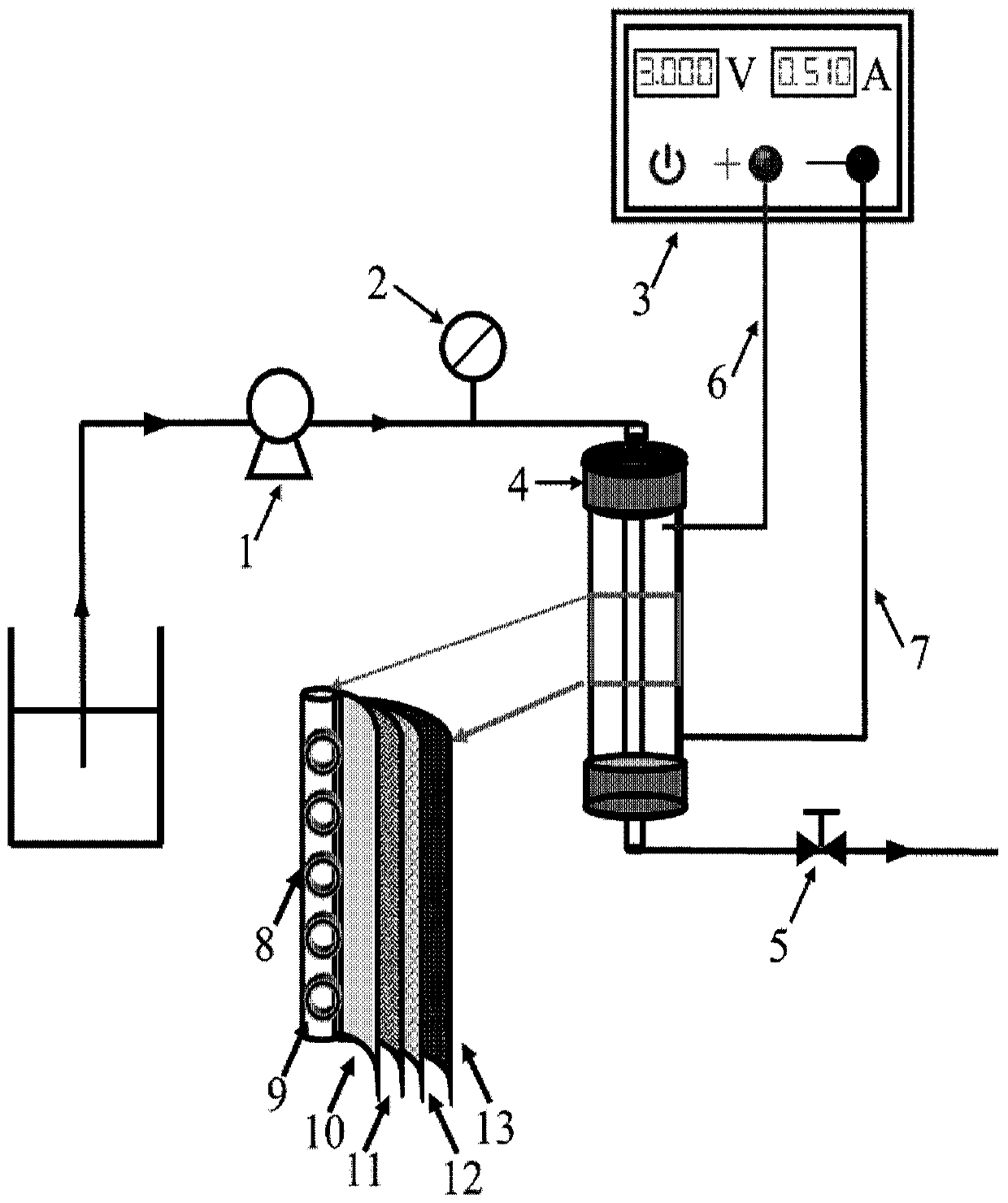
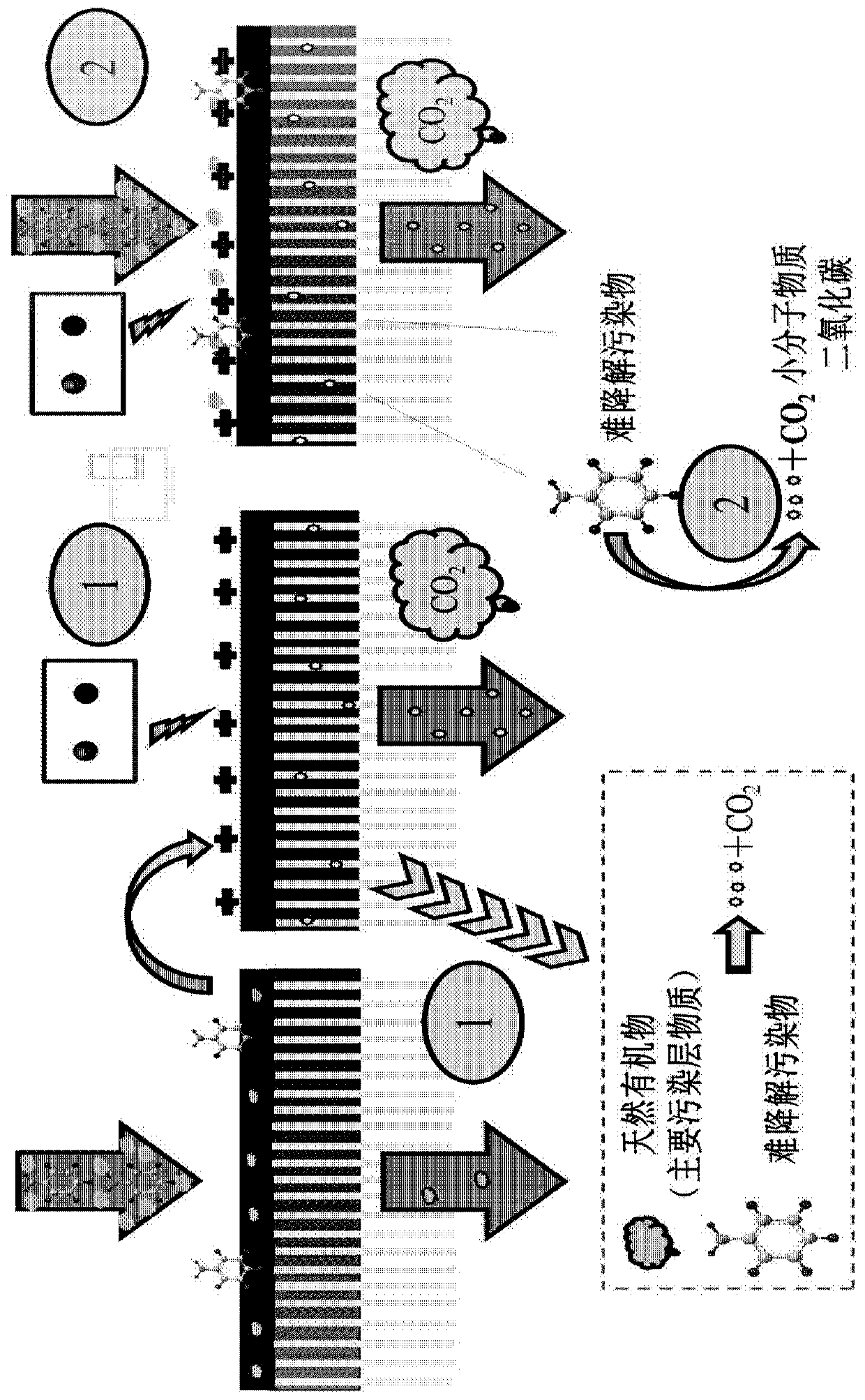
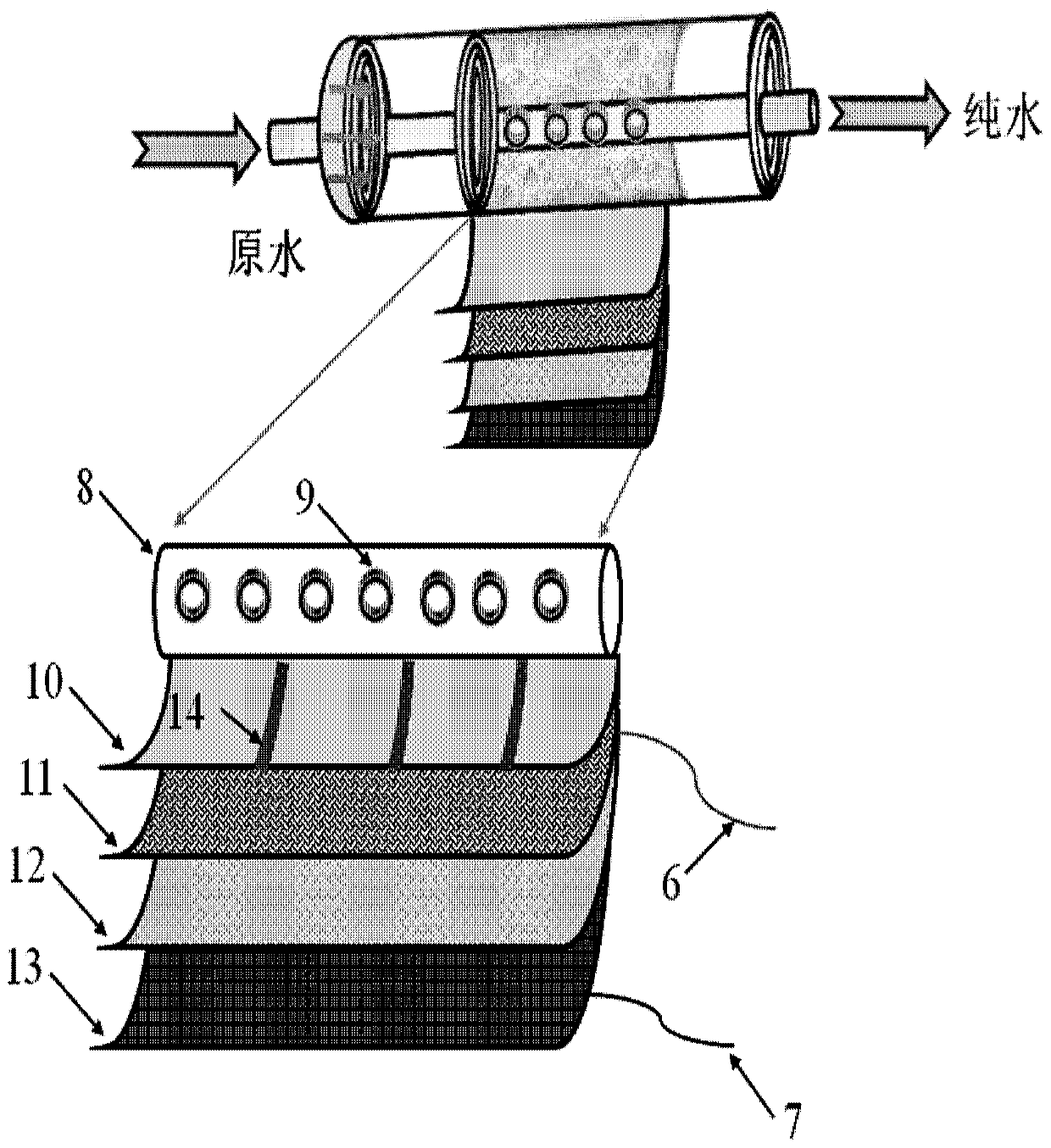
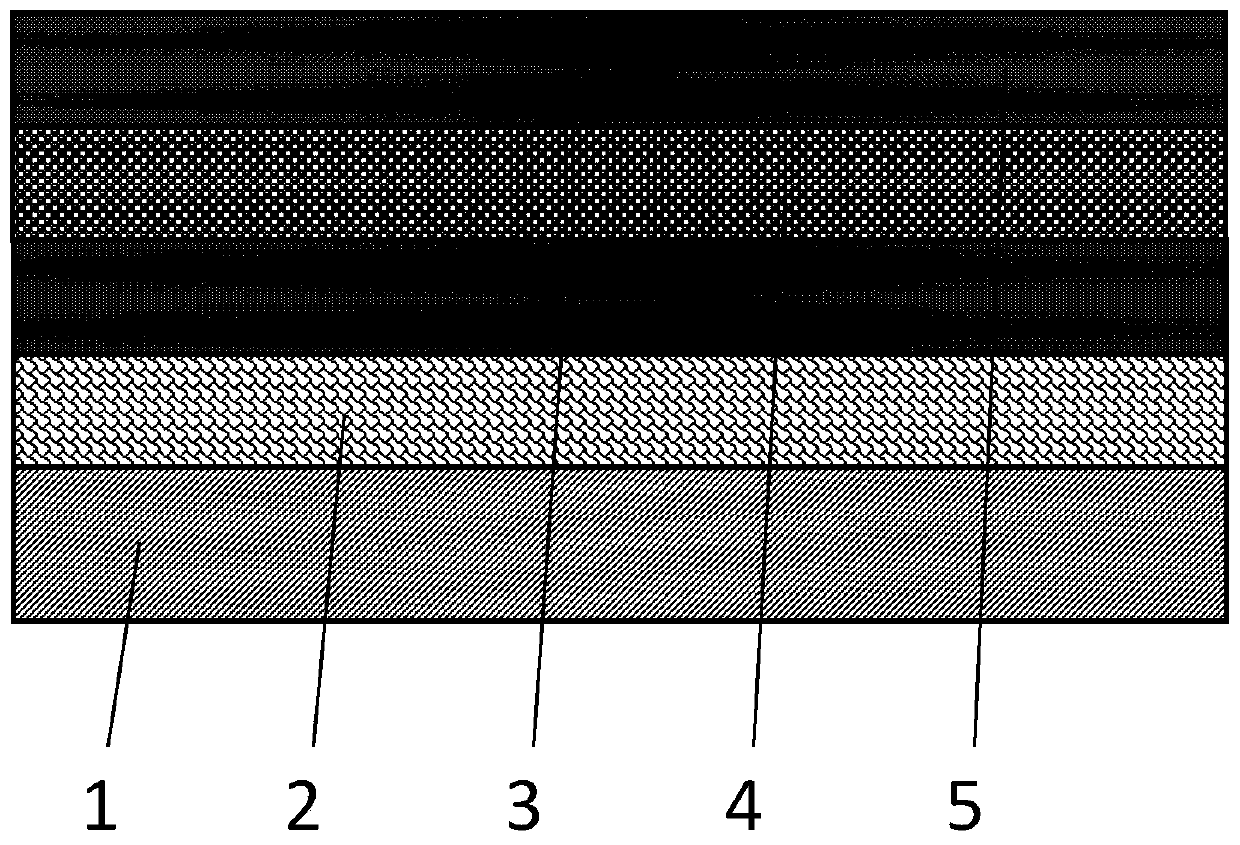
Membrane adsorption assembly, regenerable membrane adsorption reactor, liquid treatment apparatus and method
ActiveCN110002530AEfficient couplingLow area costSpecific water treatment objectivesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisCouplingMembrane adsorption
The invention discloses a membrane adsorption assembly, a regenerable membrane adsorption reactor, a liquid treatment apparatus and method. The membrane adsorption assembly comprises a central tube and a membrane adsorption roll, the central tube is provided with a plurality of tube holes for water discharge, the membrane adsorption roll is sleeved on the central tube, the membrane adsorption rollcomprises at least one membrane adsorption layer, and each membrane adsorption layer sequentially comprises a filtering film, a conductive anode, an insulation partition net and a conductive cathodefrom inside to outside. The high-efficiency coupling of membrane separation, adsorption and electrochemical advanced oxidation is realized, and the land occupation area and maintenance cost is reduced; and the in-situ green regeneration of the conductive anode is realized, the use of chemical reagents is reduced, the cost is reduced, and the wide popularization and application is relatively conducive.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Heating carbon film-adsorption-catalysis composite air purification filter screen and application thereof
InactiveCN110975416AImprove heating efficiencyIncrease flexibilityBreathing filtersMembrane filtersCarbon filmAir decontamination
The invention discloses a heating carbon film-adsorption-catalysis composite air purification filter screen and application thereof. The composite air purification filter screen consists of a substrate layer, a heating carbon film, an adsorption layer, a catalytic layer and a filter layer, wherein the substrate layer mainly plays a role in supporting and protecting; the adsorption layer is mainlyused for rapidly adsorbing harmful gas components; the catalytic layer is used for decomposing gaseous organic matters; the heating carbon film is used for heating the adsorption layer and the catalytic layer, so the adsorption layer is regenerated and the activity of the catalytic layer is improved; and the filtering layer is mainly used for intercepting particles. The composite filter screen disclosed by the invention has the function of simultaneously and efficiently removing gaseous pollutants and particulate matters and the functions of desorption regeneration and environmental low temperature resistance, and can heat air to a certain extent; the flexible substrate is adopted, so bending can be achieved; meanwhile, heating efficiency and the adaptability of a purification module are improved, so the composite air purification filter screen can be used for masks, air purifiers and fresh air systems.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Flying ash desalination and water washing device
The invention relates to a flying ash desalination and water washing device. One end of a feeding pipeline is connected with a warehouse; the other end of the feeding pipeline is connected with a feeding device; the feeding device feeds flying ash and water onto filter cloth of a vacuum belt conveyor according to a solid-to-liquid ratio being 1:4 in a mixed way; a vacuum box is arranged in the vacuum belt conveyor; a conveying belt of the vacuum belt conveyor is filter cloth; the filter cloth covers the vacuum box; a microporous membrane is used on the filter cloth for membrane adsorption; a filter cloth tensioning device, a filter cloth deviation rectifying device and an ultrasonic cleaning device are also arranged in the vacuum belt conveyor; a vacuum suction device comprises a vacuum pump and five groups of liquid discharge tanks; the five groups of liquid discharge tanks are connected with the vacuum pump and are sequentially distributed from left to right; the vacuum box is in a vacuum state through the vacuum pump; the atomizing type mixing is performed through the liquid discharge tanks; in addition, a chaotropic agent with 1 mass percent of flying ash is added, so that mixtures on the filter cloth are uniformly mixed; a water solution in a flying ash solution subjected to water washing is sucked away through suction, so that the solid-liquid separation effect is achieved; ash water is separated into a salt-containing solution and wet ash with the water content being about 30 percent.
Owner:HUZHOU SENNUO MEMBRANE TECH ENG
Method for rapidly removing perfluoro/polyfluoro compounds in environmental water
ActiveCN111252859AImprove extraction efficiencyGood choiceWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisEnvironment waterPolyvinylidene difluoride
The invention belongs to the field of chemical analysis technology and environmental protection, and provides a polyvinylidene fluoride filter membrane adsorption removal method for removing perfluorinated compounds in environmental water. An adsorption medium provided by the invention is a highly fluorinated polyvinylidene fluoride filter membrane, a sample solution can quickly flow through the adsorption medium due to the large diameter of the adsorption medium, and the adsorption medium has high adsorption capacity and good selectivity on perfluorinated compounds based on the fluorine-fluorine affinity effect, and is especially suitable for enrichment and / or purification of long-chain perfluorinated compounds in environmental water samples. The adsorption medium used in the method doesnot need to be synthesized and is low in price and convenient to operate.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Purification processes for isolating purified vesicular stomatitis virus from cell culture
A process is described for purifying vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) from cell culture fluid of a mammalian cell culture infected with VSV, the process comprising: clarifying the cell culture fluid by low-speed centrifugation and recovering the VSV in the supernatant; filtering the supernatant through a 0.2 to 0.45 μm filter and recovering the VSV in the filtered solution; loading the VSV filtered solution onto a anion exchange membrane adsorber equilibrated with a first pH buffered salt solution, eluting the VSV from the anion exchange membrane adsorber with a second pH buffered salt solution and recovering the eluted VSV fractions; purifying the recovered VSV by tangential flow filtration (TFF) using a TFF membrane having a molecular weight cutoff between 300 kDa and 1,000 kDa and recovering the VSV in the retentate, and filtering the VSV retentate through a 0.2 to 0.22 μm filter and recovering the VSV in the filtered solution.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Method for separating and preparing exosome
InactiveCN109266613AImproved separation and preparation methodsHigh purityCell dissociation methodsTumor/cancer cellsCellular DebrisCentrifugation
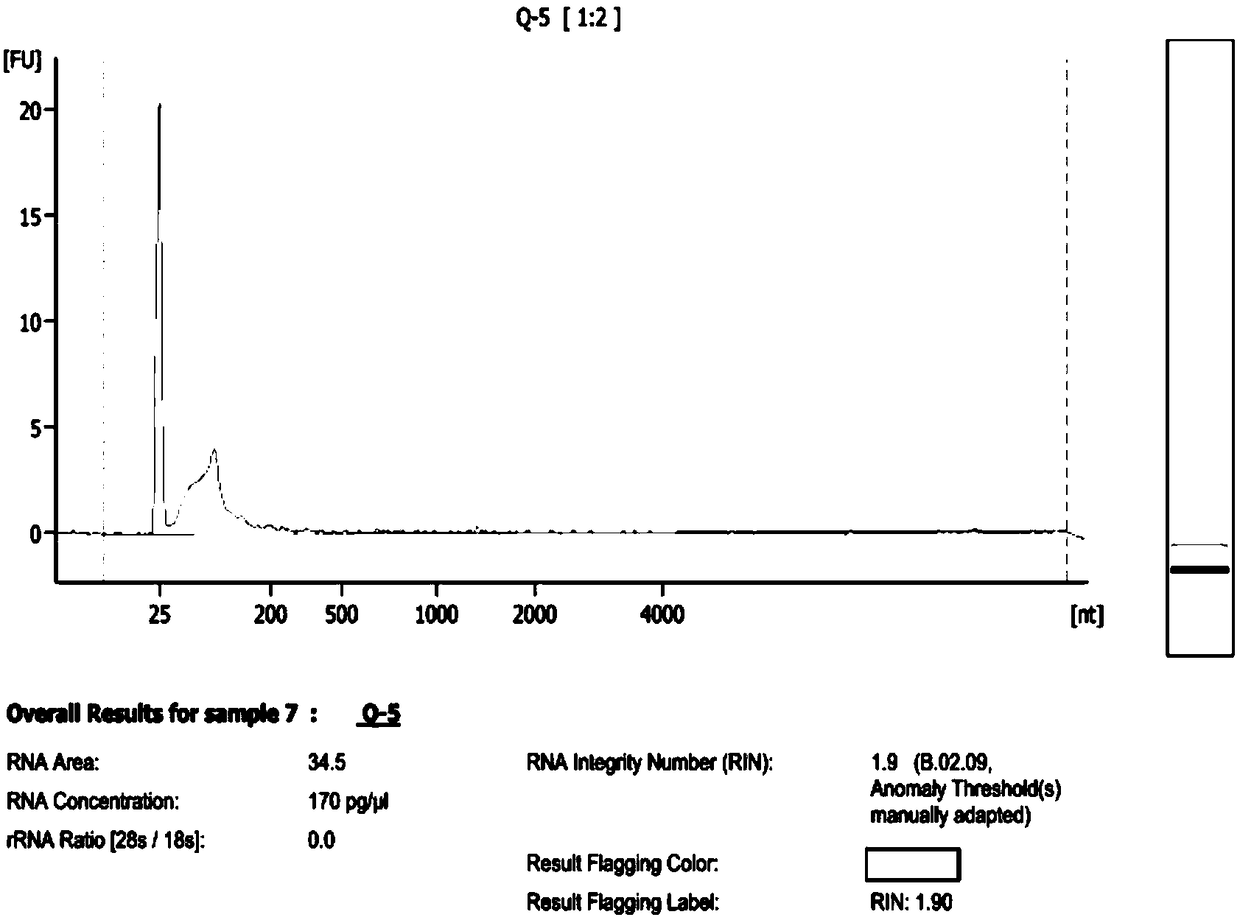
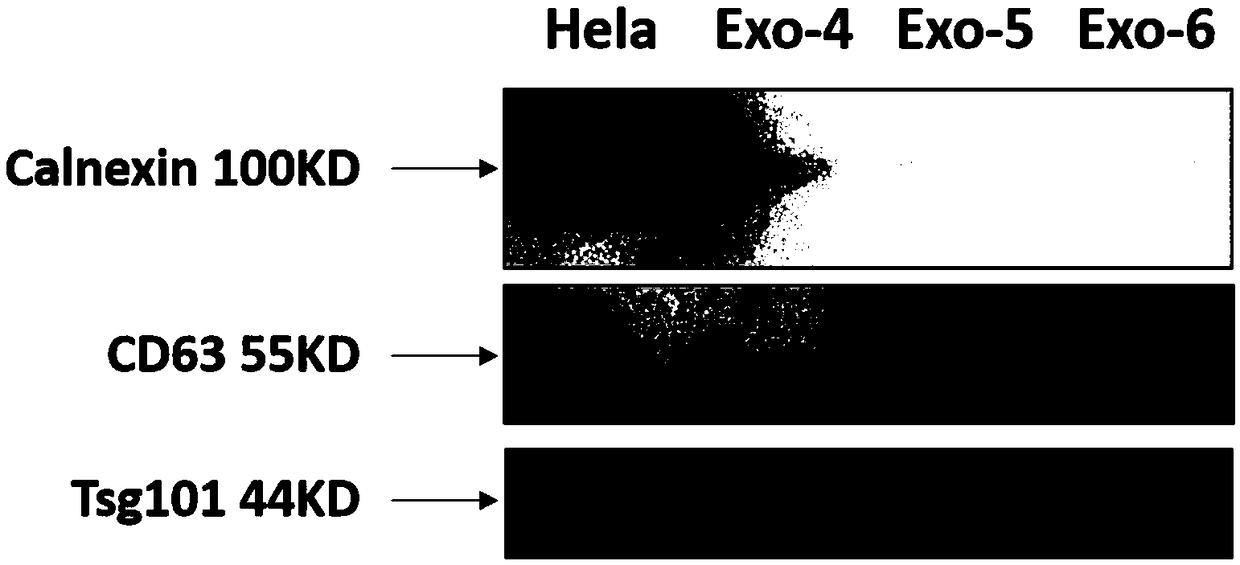
The invention relates to a method for separating and preparing exosomes, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The method for separating and preparing exosome comprise that following steps: 1) removing cellular impurities by centrifugation; 2) centrifuging to remove cellular debris and large protein impurities; 3) transferring that supernatant into a new centrifugal tube, centrifuging to discard the precipitate and leave the supernatant; 4) filtering that supernatant and transferring; 5) mixing that reagent XBP and the sample, transferring the reagent XBP into a membrane adsorption column,centrifuging, and discarding the liquid at the bottom of the tube; 6) centrifuging to remove liquid remaining on that membrane; 7) adding reagent XWP, centrifuging, discarding that liquid at the bottom of the tube, and changing the column into a new centrifugal tube; and 8) adding that reagent XE to the column, centrifuging and eluting the exocrine body to obtain the liquid containing the exocrinebody. The RNA purity of the extracted exocrine body is improved, the impurity is less, the biological sample volume of the initially extracted exocrine body can be reduced, and the yield of the circulating exocrine body can be improved.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Succinyl-beta-cyclodextrin modified PAN film adsorbing material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109985609AIncrease negative chargeImprove hydrophilic abilityOther chemical processesRadioactive contaminantsBeta-CyclodextrinsUranium
The invention relates to a succinyl-beta-cyclodextrin modified PAN film adsorbing material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: firstly forming a dense polydopamine intermediate layer on a PAN film, wherein the polydopamine intermediate layer contains a large amount of hydrophilic hydroxyl and amino functional groups, and performing dehydration condensation on the amino of the polydopamine intermediate layer and carboxyl of succinyl-beta-cyclodextrin to obtain the succinyl-beta-cyclodextrin modified PAN film adsorbing material. The adsorbing material provided by the invention has good adsorption performance on hexavalent uranium through enveloping action of a hollow cavity of the cyclodextrin and uranium and action of carboxyl of succinyl and the hexavalent uranium, greatly improves the removal efficiency of the hexavalent uranium, and is easy to recover and recycle; and the succinyl-beta-cyclodextrin particles are firmly loaded and not easily disembedded, and have uniform loading, thereby increasing the contact area with pollutants, and improving the treatment efficiency.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
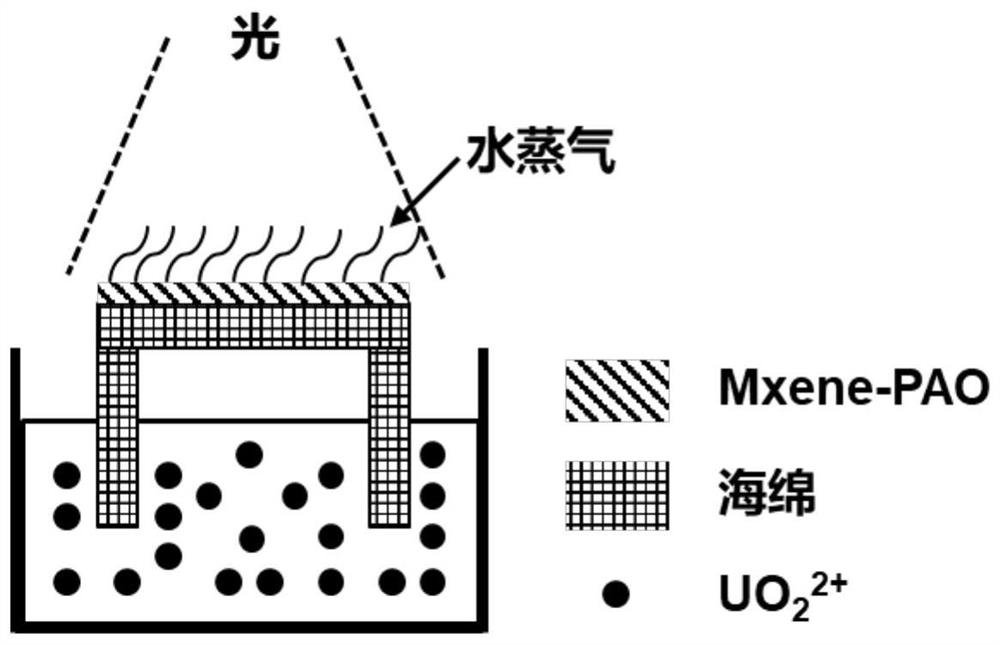
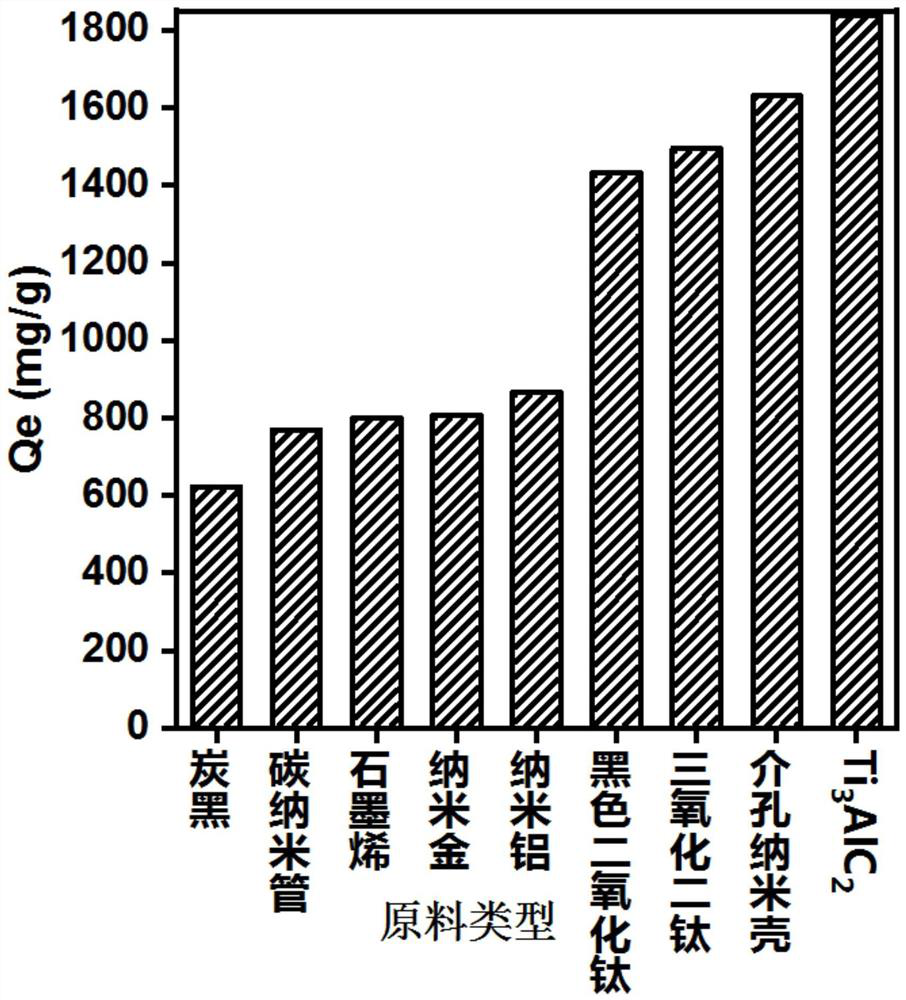
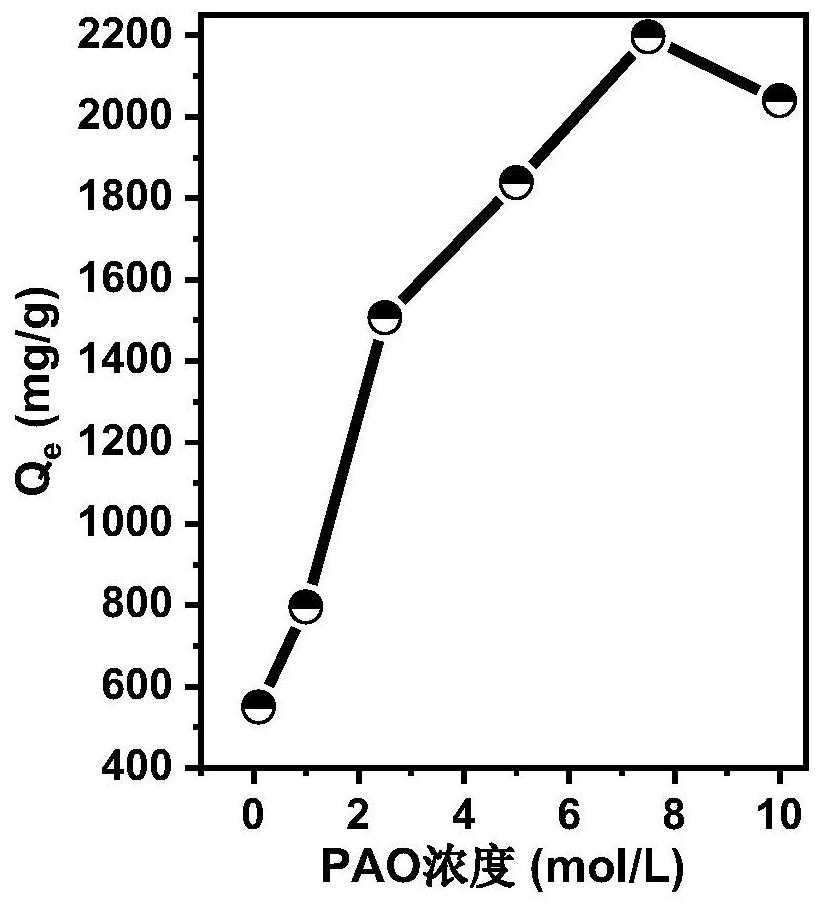
Preparation method of Mxene membrane adsorption material based on polyamidoxime and uranium extraction method
ActiveCN112973653ARich varietyWide range of sourcesGeneral water supply conservationOther chemical processesNuclear chemistryMembrane adsorption
The invention discloses a preparation method of an Mxene membrane adsorption material based on polyamidoxime and a uranium extraction method. The method comprises the following steps: treating the raw materials with HF at a certain temperature and under certain conditions; soaking in a DMSO solution, and carrying out ultrasonic suction filtration to form an Mxene membrane; soaking the Mxene membrane in a polyamidoxime solution, carrying out vacuum suction filtration to remove the polyamidoxime solution after soaking is finished, washing with pure water, and then drying to obtain an amidoximation modified Mxene membrane; flatly placing the Mxene membrane on the surface of the upper portion of the sponge, placing the Mxene membrane and the sponge into a uranyl ion solution together under illumination, and enabling the upper portion of the sponge to contact with the Mxene membrane. The method is simple, raw materials are rich, reaction conditions are mild, energy consumption is low, and the prepared material is good in adsorption performance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
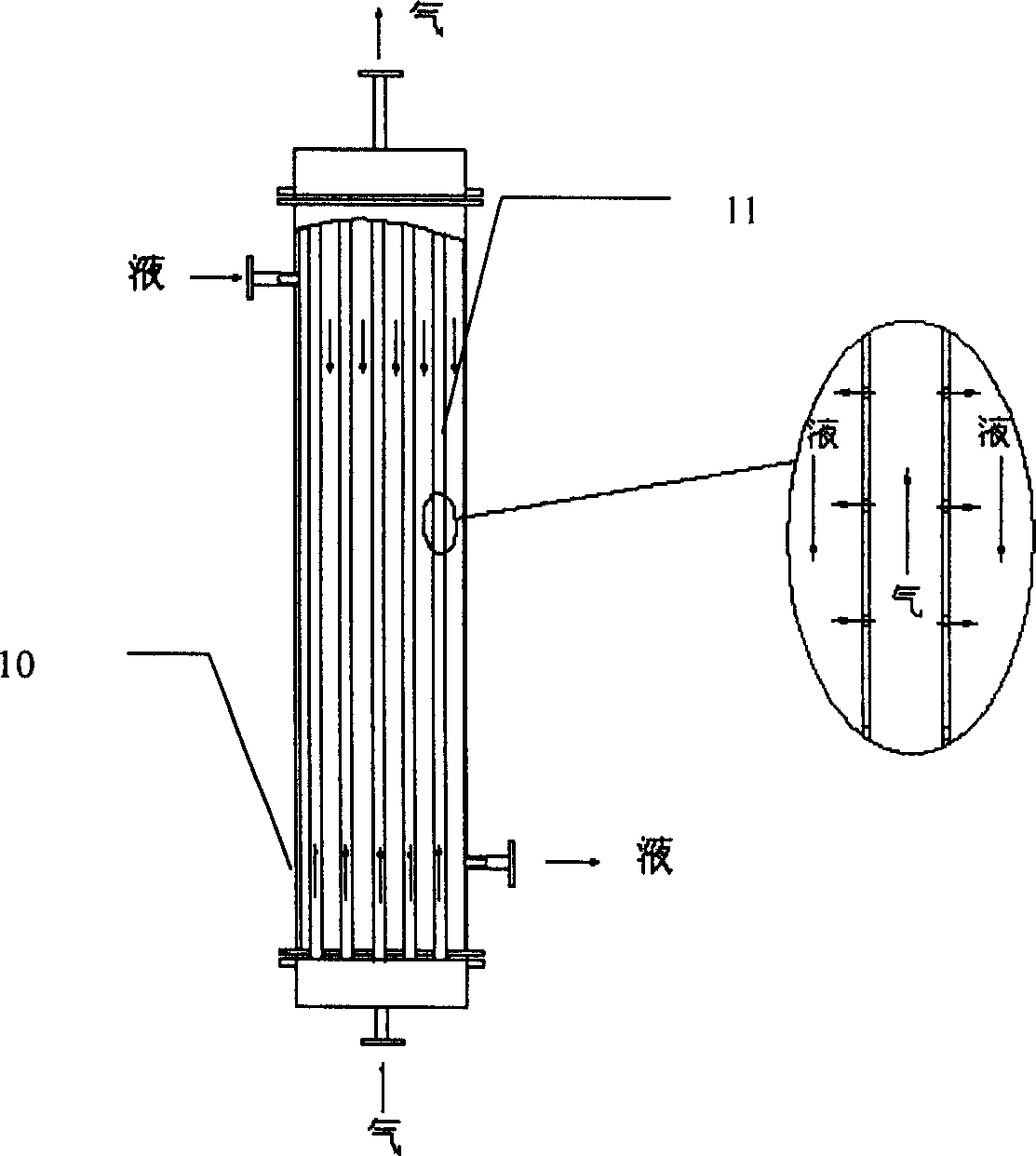
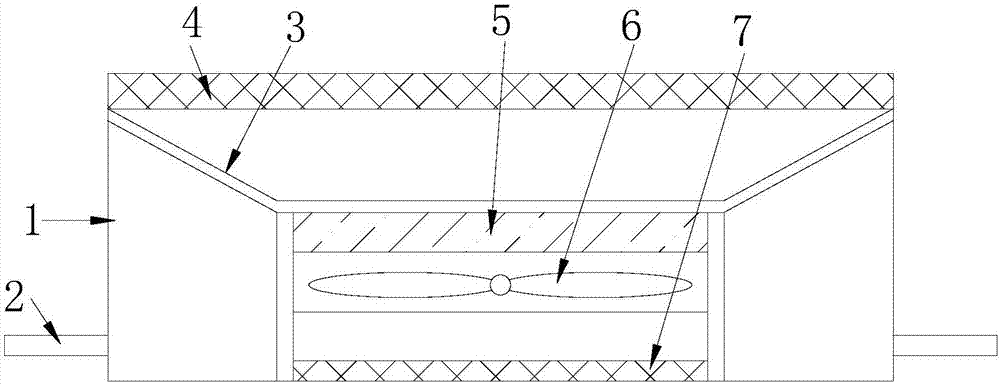
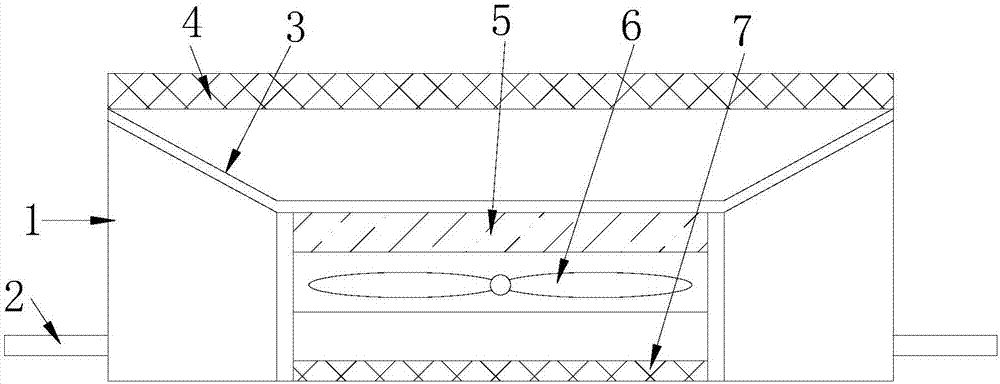
Membrane adsorption device
InactiveCN107986020AImprove adsorption capacityImprove stabilityPump componentsPumpsPulp and paper industryMembrane adsorption
The invention discloses a membrane adsorption device and relates to the technical field of automation. Mounting plates are mounted at two ends of a frame, an adsorption support net is mounted at the upper end of the frame, a wind gathering cover is mounted at the lower end of the adsorption support net, a wind gathering barrel is mounted at the lower end of the wind gathering cover, a filter is mounted at the inner upper end of the wind gathering barrel, an adsorption fan is mounted at the lower end of the filter, and a wind outlet filter net is mounted at the lower end of the adsorption fan.The device facilitates rapid adsorption and is convenient to use and simple to operate, the stability can be improved and time can be saved.
Owner:中子星电子科技(苏州)有限公司
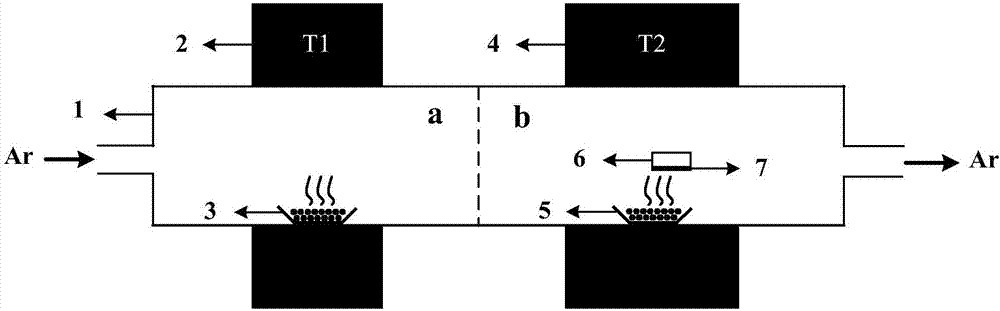
Method and device for continuous membrane adsorption
A method and system is provided for yielding biopharmaceutical products involving a chromatographic separation process. The method comprises: providing a plurality of membrane adsorber cartridges; providing a plurality of valves, communicatively coupled to said plurality of membrane adsorber cartridges; and switching the valves, so as to interconnect said membrane adsorber cartridges to operate in a countercurrent flow mode. The system comprises multiple membrane adsorber cartridges that are interconnected and configured to operate in a countercurrent flow mode. Furthermore, the configuration comprises a valve assembly that allows the cartridges to be subjected to different steps in the process by automatic switching of the valves. In this way, cartridges are recycled many times during the purification of a batch.
Owner:PROPHARMA GRP EURO BV
Novel method for detecting pathogenic microorganisms
InactiveCN110438199AGuaranteed reliabilityGuaranteed accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisSingle strandA-DNA
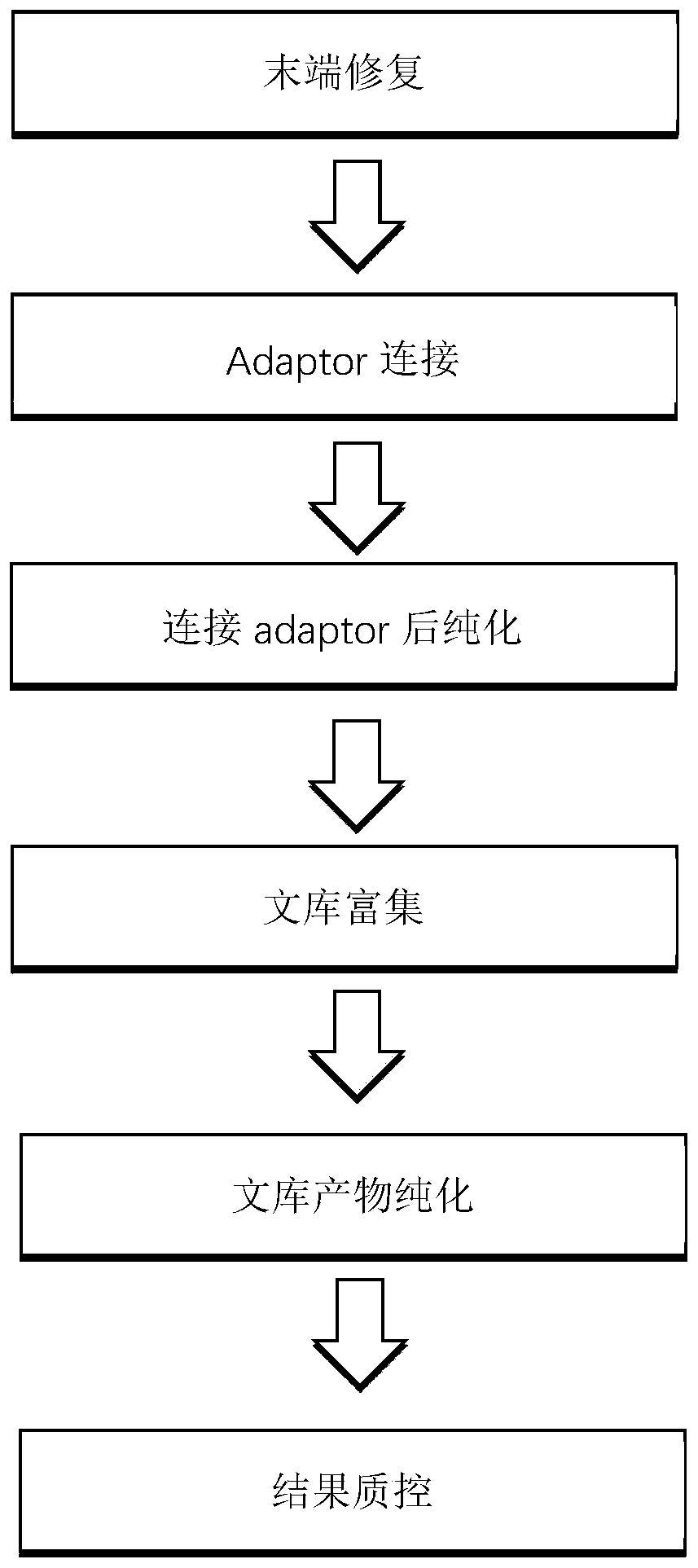
The invention discloses a novel method for detecting pathogenic microorganisms. The method comprises: a collection step of samples such as cerebrospinal fluid and alveolar lavage fluid; a collection steps of peripheral blood samples; a DNA extraction step; a library construction step; a sequencing step; and an analysis step. The DNA extraction step comprises: taking 400 [mu]l sample for detection,adding reaction reagents of buffer GB, Lysis Enzyme K, RNA, Carrier to the sample, conducting reaction at 56 DEG C for 10 minutes to obtain a reaction solution, purifying the reaction solution by silica gel membrane adsorption column to remove salt ions and organic reagents, and obtaining DNA with total amount and purity meeting the requirements. The library construction step comprises: conducting terminal repair, linker connection, library amplification and enrichment, purification and quality control of the DNA to complete the library construction. The sequencing step comprises: denaturingthe library into a single strand by NaOH, then binding the library to a sequencing chip, enriching each single strand DNA into a cluster by bridge amplification, and obtaining sequencing data by usingIllumina SBS sequencing method to read the sequence. The analysis step comprises: filtering the sequencing data, removing the human source and the linker sequence, and comparing the remaining data with a microbial reference database.
Owner:深圳谱元科技有限公司
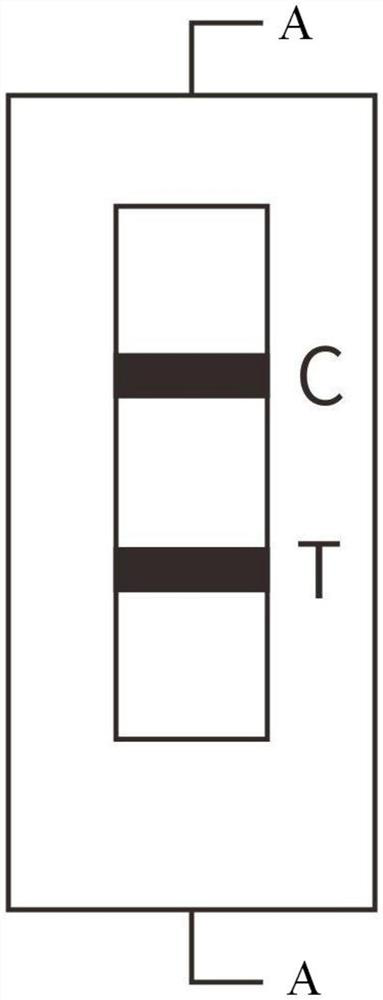
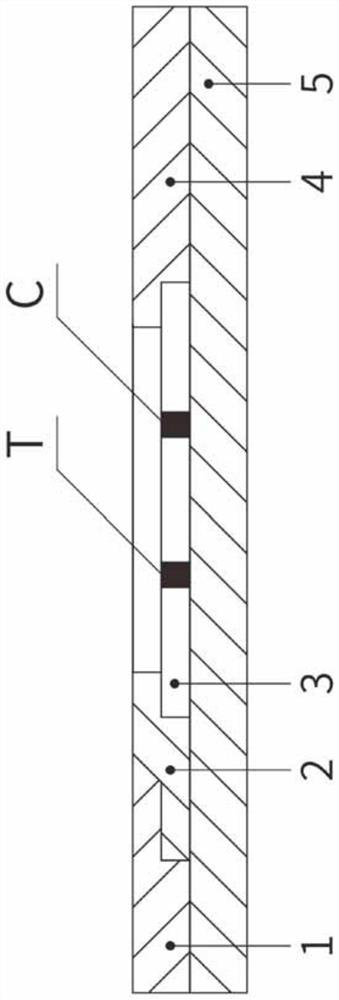
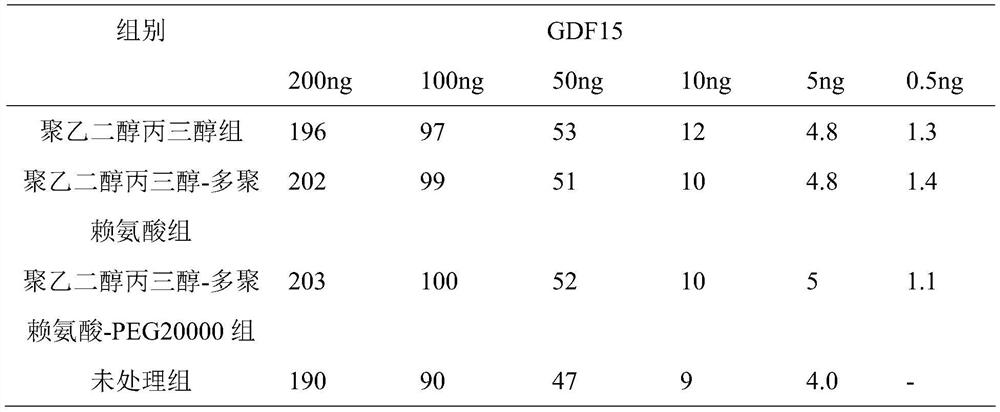
GDF15 rapid quantitative fluorescent microsphere detection device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111638364ANovel structureStrong specificityBiological material analysisBiological testingCellulosePolythylene glycol
The invention relates to a GDF15 rapid quantitative fluorescent microsphere detection device and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of medical detection. The device is prepared byadhering a nitrocellulose membrane with a solid phase containing a GDF15 antibody and a goat-anti-mouse IgG polyclonal antibody, glass fiber adsorbed with a fluorescent microsphere labeled GDF15 antibody, a sample pad, absorbent paper and other auxiliary materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps: pretreating a nitrocellulose membrane by adopting a polyethylene glycol glyceroltreatment solution; combining a GDF15 antibody firstly with oleic acid modified zinc sulfide nanoparticles and then adsorbing to a nitrocellulose membrane; and preparing the proper buffer solution and the sample pad treatment solution. The reaction sensitivity is effectively improved on the basis of ensuring complete release of the immunofluorescence microsphere, and under the same threshold value, the dosage of the immunofluorescence microsphere can be reduced, the cost is saved, and the complexity of production operation is not increased. The test paper is high in sensitivity, strong in specificity, simple and convenient to operate, time-saving and strong in practicability.
Owner:JILIN PROVINCE GERUISITE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Biological detection chip, biosensor and preparation method thereof and application
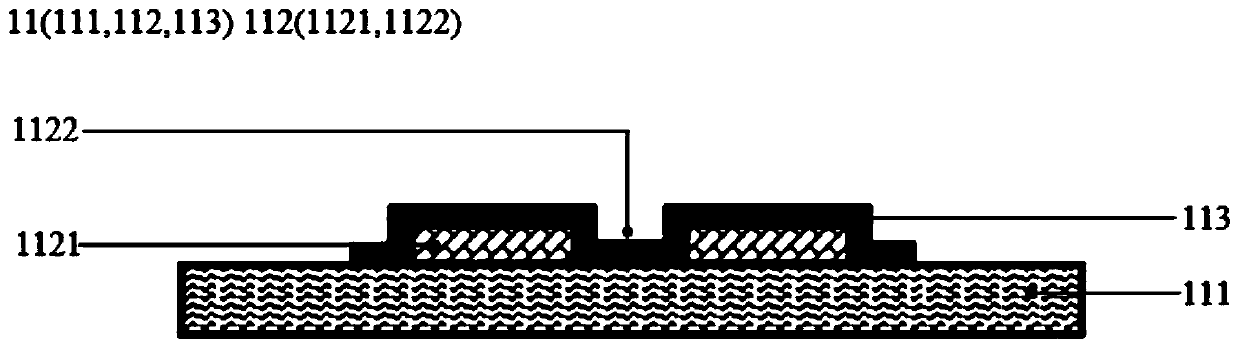
PendingCN111060469AEasy to detectReal-timeColor/spectral properties measurementsMembrane surfaceIr absorption
The invention discloses a biological detection chip. The biological detection chip comprises a substrate, a metal array layer and a film adsorption layer which are stacked, wherein the metal array layer is positioned on the substrate and is provided with a spacing region for exposing the substrate; the film adsorption layer wraps the metal array layer and the surface of the substrate located in the spacing region, and the film adsorption layer is provided with a hydrophilic surface. Cells and organelles with biological film structures can be adsorbed by utilizing the hydrophilic surface of thefilm adsorption layer, target biomolecules are loaded on a biological film, the surface enhanced infrared absorption spectrum of the target biomolecules can be obtained, and detection and analysis ofthe target molecules are realized. The invention discloses a biosensor, which comprises the biological detection chip, is suitable for detecting film surface biomolecules with complex types, does notdestroy the molecular structure, and is suitable for research of various physiological and pathological processes, drug screening diagnosis and the like. The invention discloses a preparation methodof a biological detection chip, which is simple in preparation process and suitable for preparing the chip for detecting the biomolecules on the surfaces of various films.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Composite method oil and gas recycling method
InactiveCN106139630AEliminate potential safety hazardsReduce dosageDispersed particle separationVapor condensationActivated carbonWater vapor
The invention discloses a composite method oil and gas recycling method. The problem how to match separation membrane adsorption with condensate absorption for oil gas to improve the oil recycling rate is solved. Oil gas with no steam is fed into an oil gas separation membrane separation device to be subjected to oil gas and air separation, and oil gas adsorbed to the oil gas separation membrane is conveyed into an absorption tower through a vacuum pump; oil gas not adsorbed to the oil gas separation membrane is fed into an activated carbon adsorption tank for separation of oil gas and air, the oil gas adsorbed to the activated carbon is conveyed into an absorption tower through a vacuum pump; gasoline for spraying is subjected to cooling through a condensing unit, the temperature is decreased to about 15 DEG C; the cooled sprayed gasoline is fed into an absorption tower, the gasoline fed into the absorption tower is subjected to spraying, and oil gas is converted into gasoline; oil gas of the unconverted gasoline is discharged into a condensate tank till the oil gas concentration meets the evacuation requirement. The oil gas absorption rate is improved, and potential safety hazards of static electricity likely to be generated by membrane separation are eliminated.
Owner:SHANXI FENXI ELECTROMECHANICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com