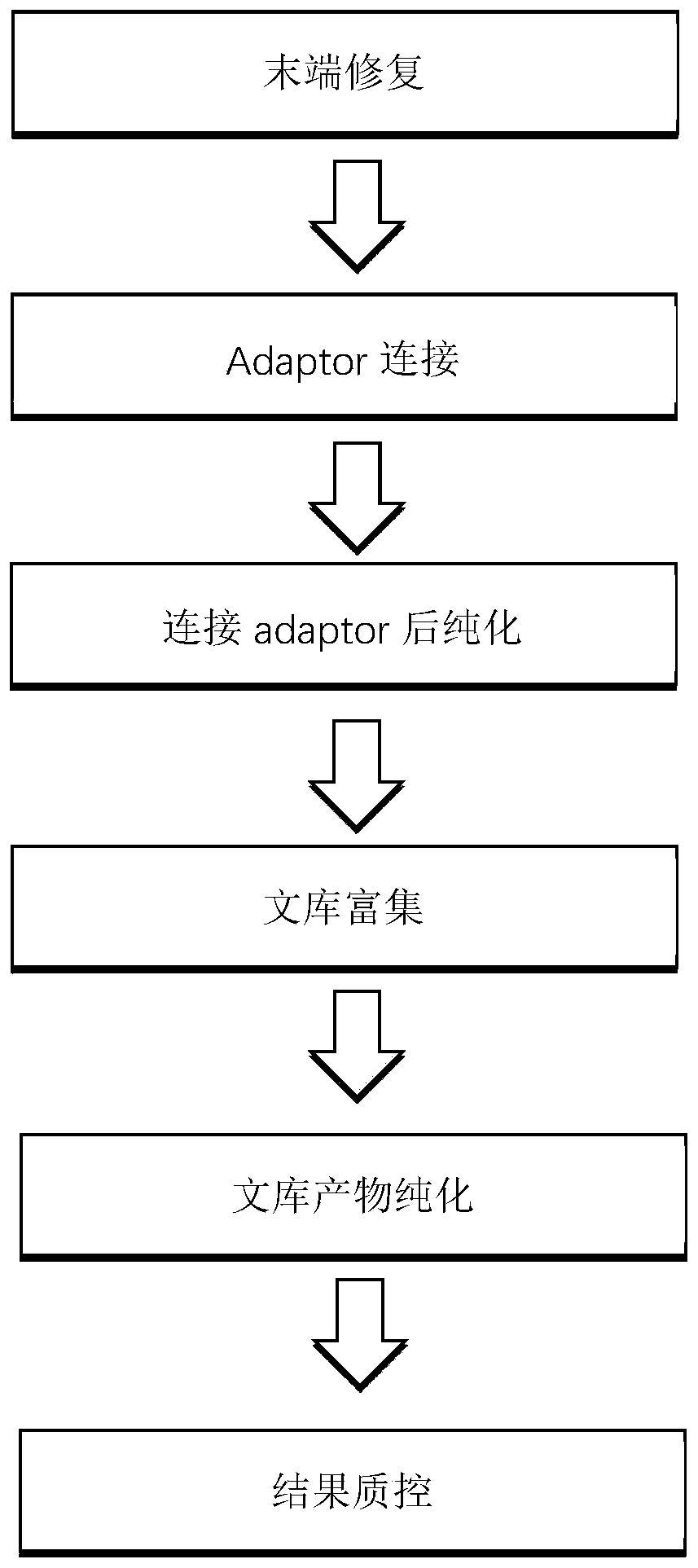
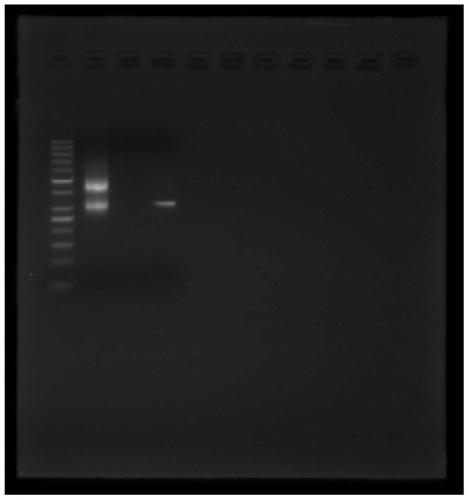
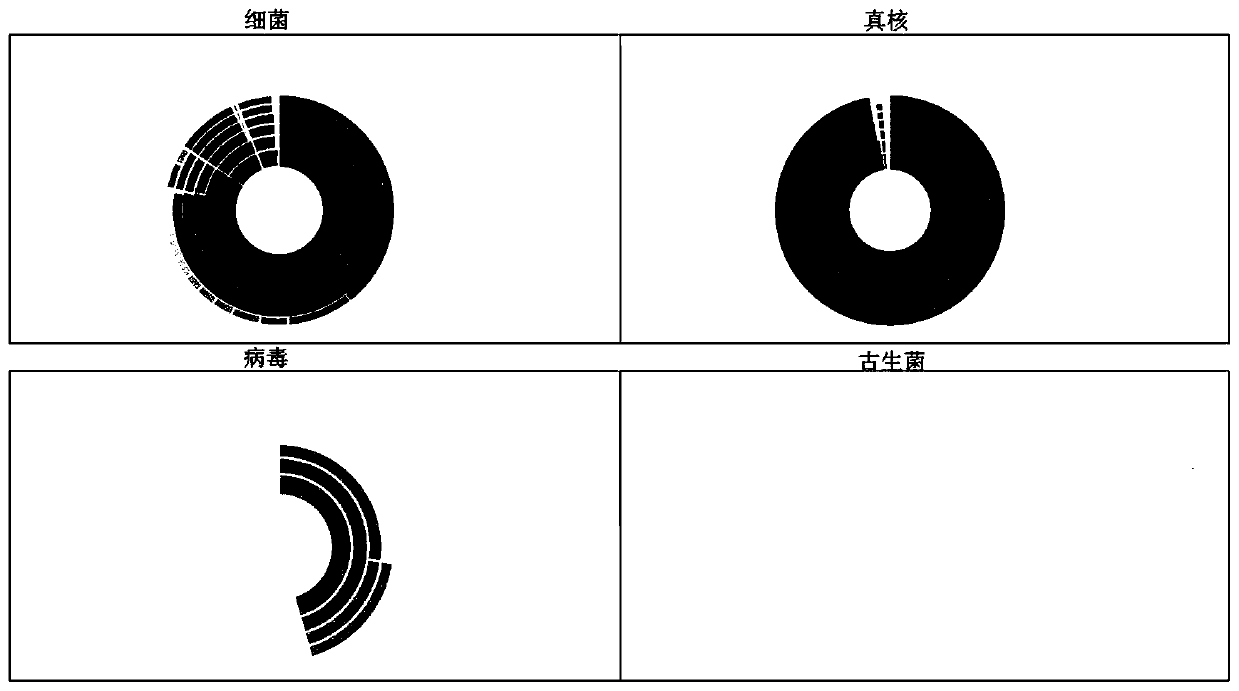
Novel method for detecting pathogenic microorganisms
A pathogenic microorganism and microbial technology, applied in the fields of molecular biology and molecular genetics, can solve problems such as dependence on cultivation, low identification accuracy, inability to deal with unknown or mutated pathogens, and achieve the effect of ensuring reliability and accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1: 1 part of plasma sample B1 pathogenic microorganism detection
[0050] Using the detection method of the present invention, its plasma sample B1 is detected, and a parallel quality control is added. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0051] 1 DNA extraction: Add absolute ethanol to buffer GD and rinse solution PW before use.
[0052] 1.1 Take 400μl sample to a 2ml centrifuge tube.
[0053] 1.2 Add 40 μl Lysis Enzyme K solution and vortex evenly.
[0054] 1.3 Add 400μl buffer GB and 5ul Carrier RNA, mix gently by inversion, incubate at 56°C for 10min, and shake the sample from time to time. Centrifuge briefly to remove droplets from the inside of the cap.
[0055] Among them, when buffer GB is added, a white precipitate may be produced, which generally disappears when placed at 56°C, and will not affect subsequent experiments. If the solution does not become clear, it means that the lysis is not complete, which may lead to a small amount ...
Embodiment 2
[0114] Example 2: Detection of pathogenic microorganisms in 1 part of cerebrospinal fluid and 1 part of blood
[0115] Using the method of the present invention to detect two samples, and add parallel quality control. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0116] 1 DNA extraction: Please add absolute ethanol to buffer GD and rinse solution PW before use.
[0117] 1.1 Take 400ul sample to a 2ml centrifuge tube.
[0118] 1.2 Add 40ul Lysis Enzyme K solution and vortex evenly.
[0119] 1.3 Add 400ul buffer GB and 5ul Carrier RNA, mix gently by inversion, incubate at 56°C for 10min, and shake the sample from time to time. Briefly centrifuge to remove the liquid droplets on the inner wall of the tube cap; among them, white precipitate may be produced when buffer GB is added, which will disappear when placed at 56°C and will not affect subsequent experiments. If the solution does not become clear, it means that the lysis is not complete and may The amount of extract...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com