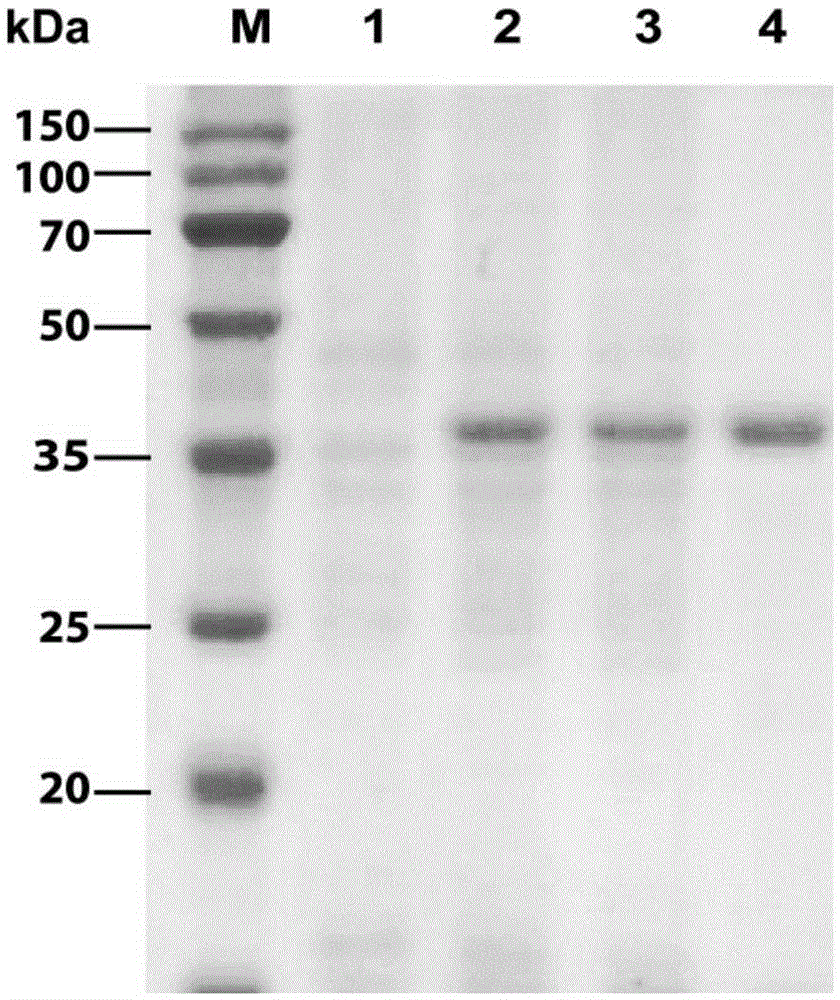
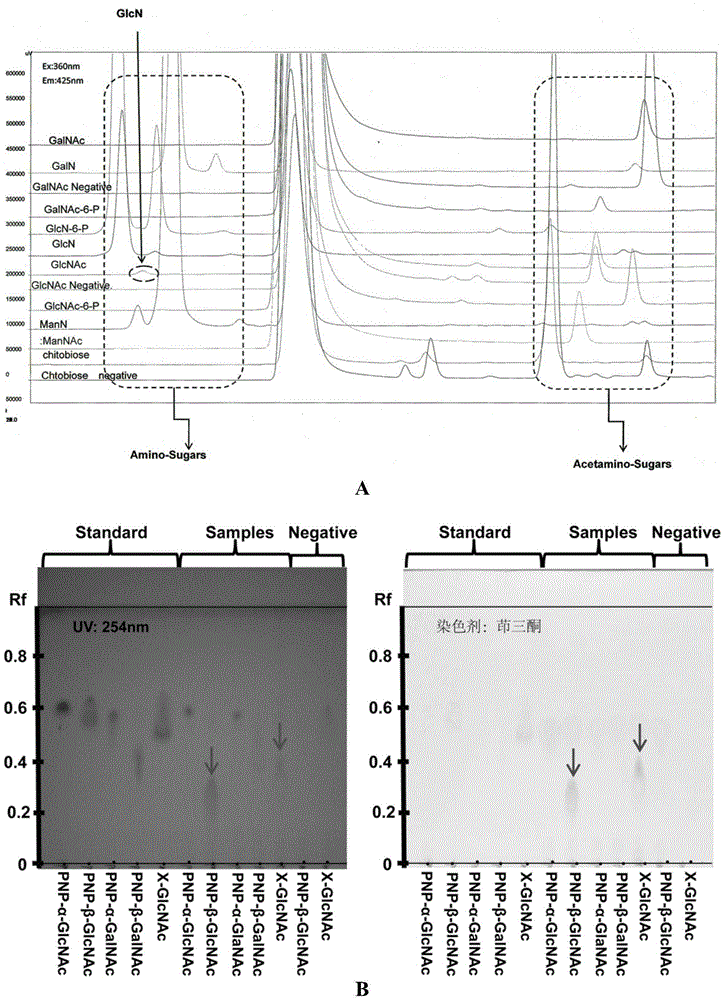
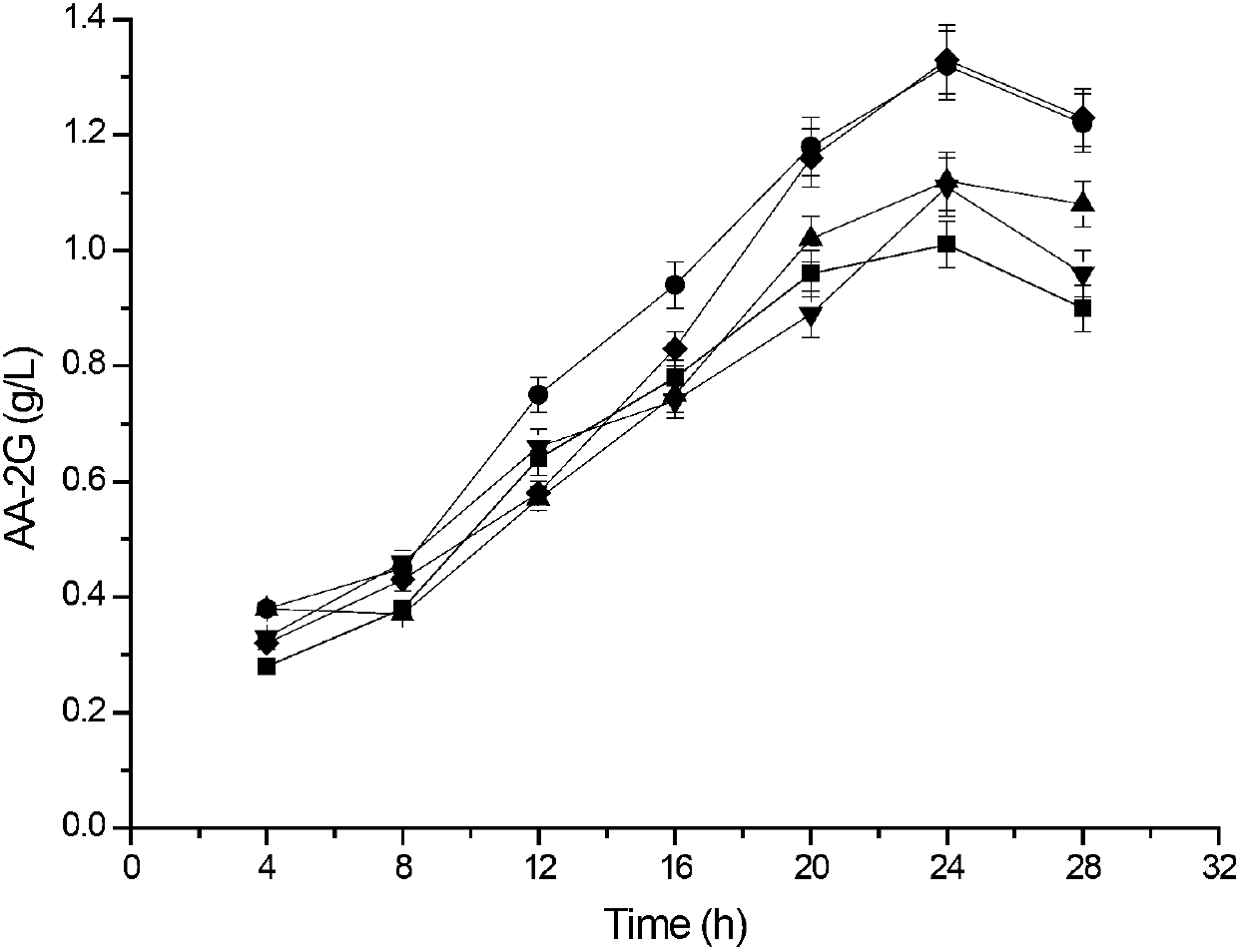
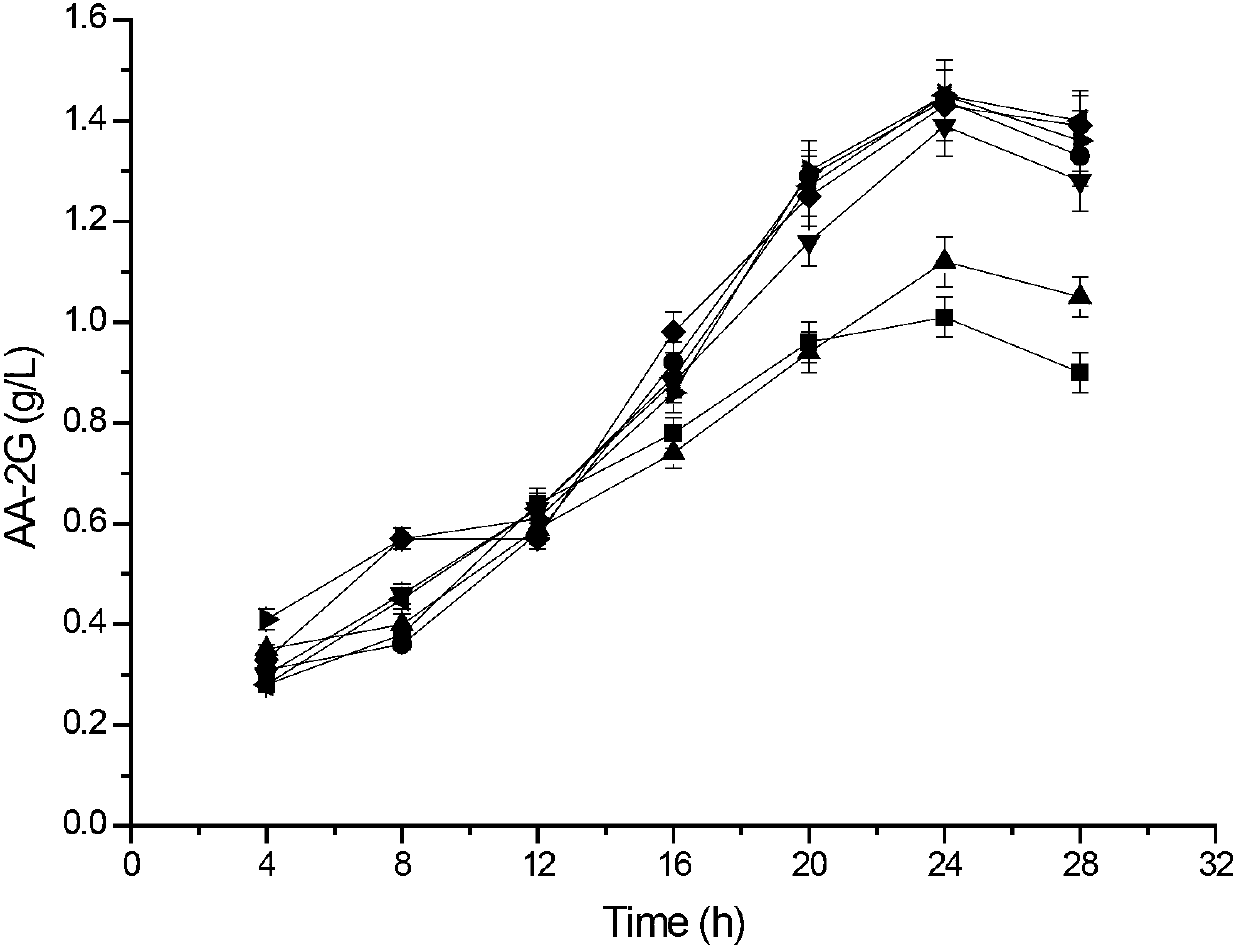
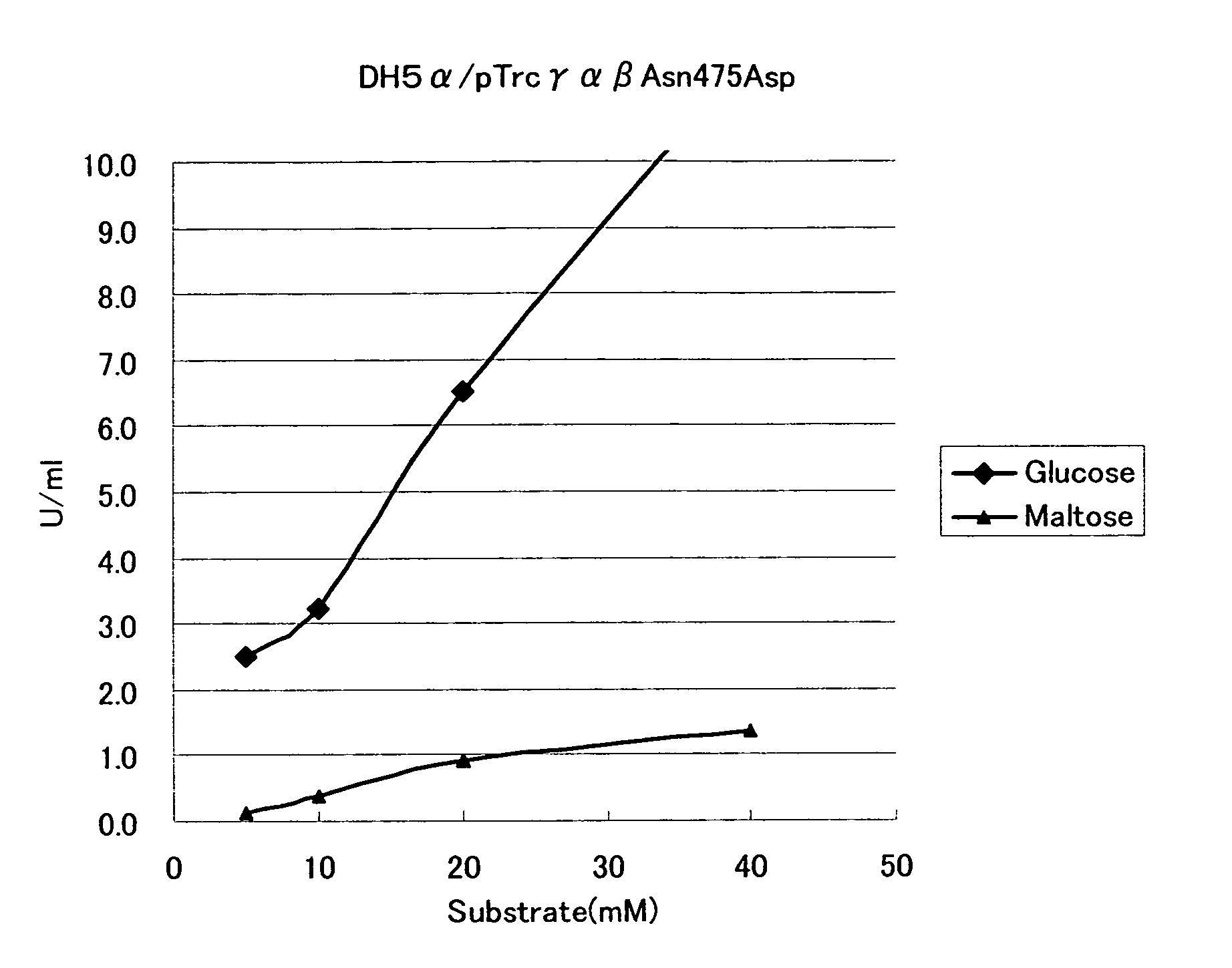
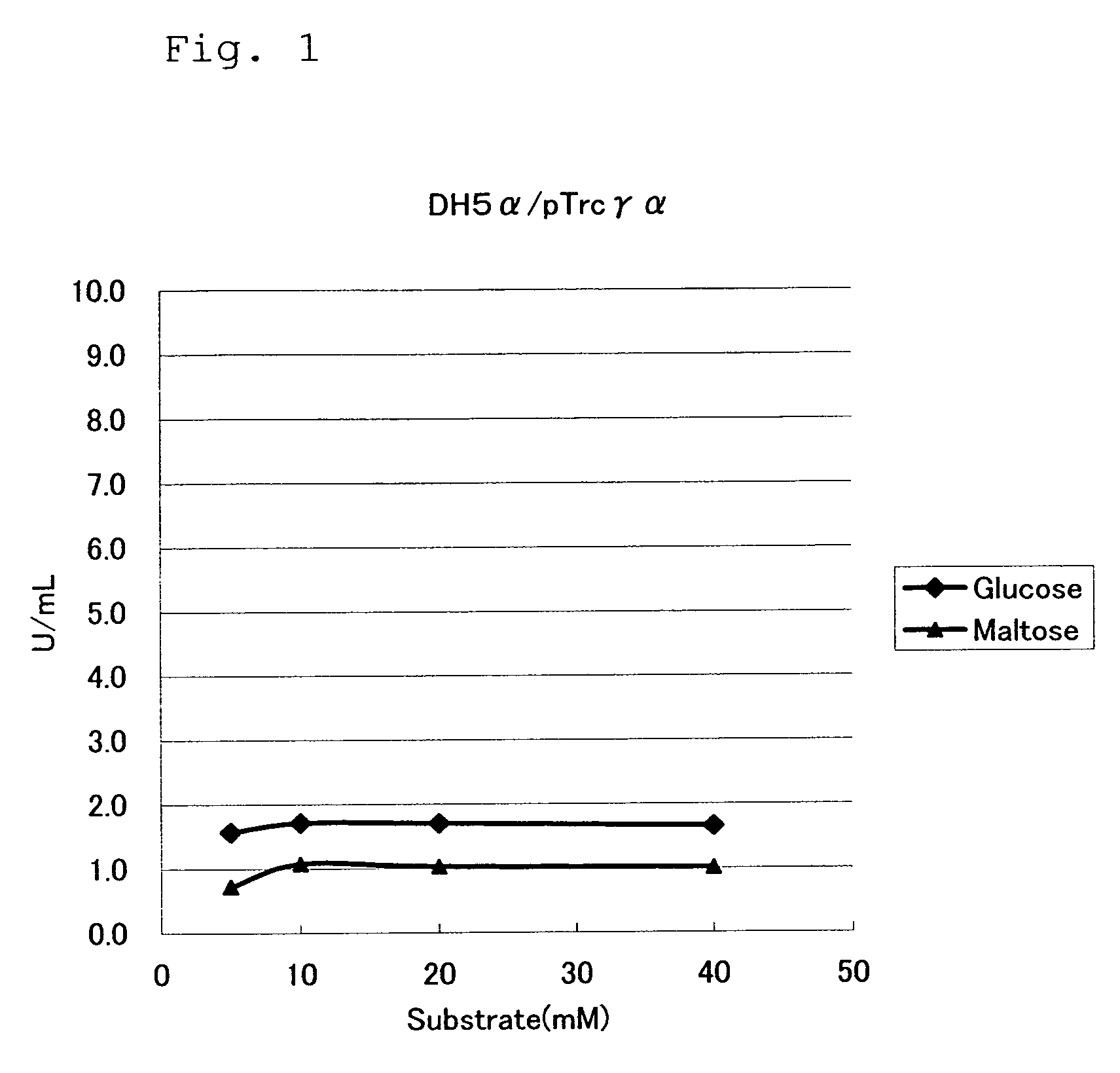
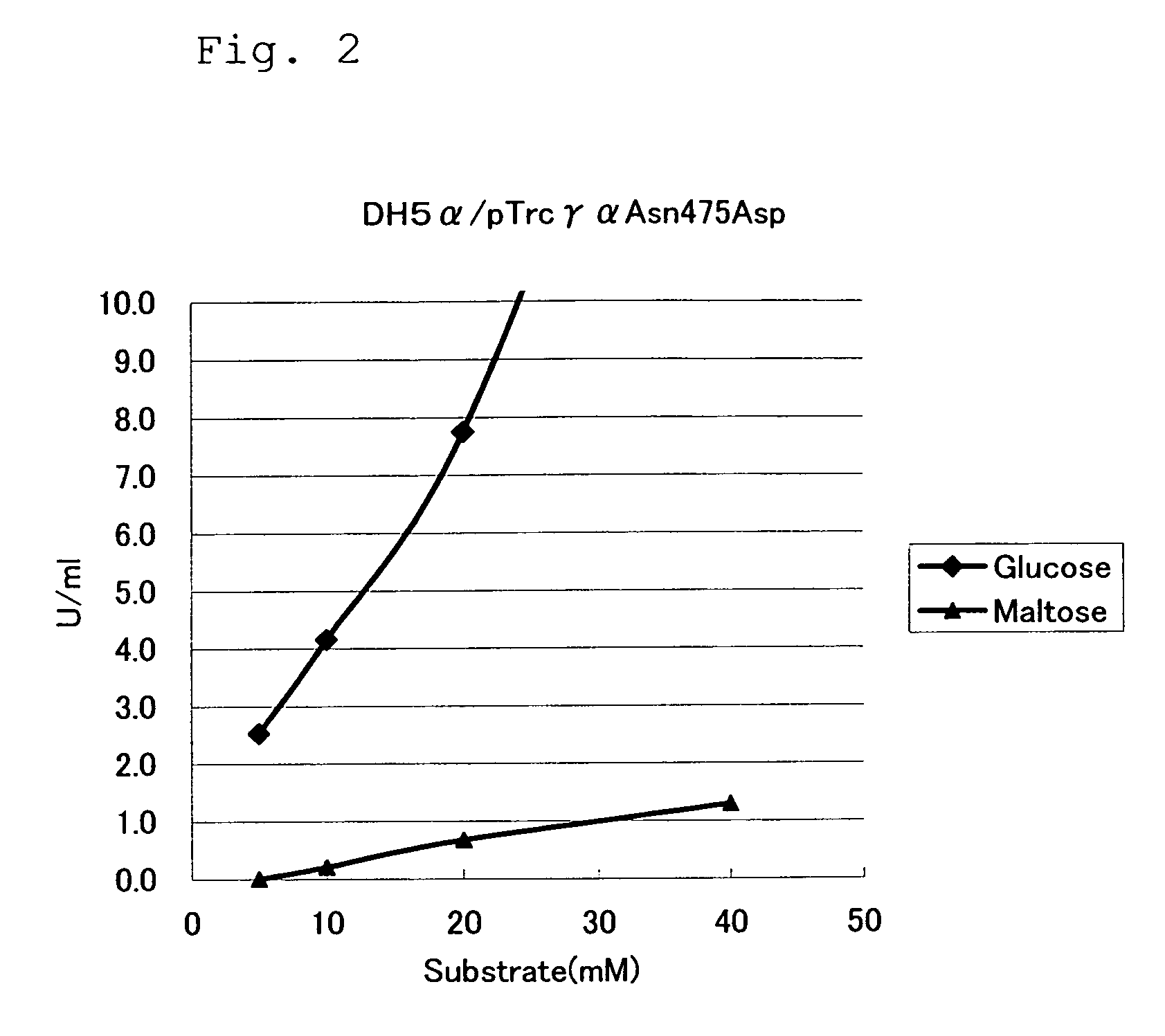
Patents
Literature
72 results about "Substrate Specificities" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Substrate specificities of g protein-coupled receptor kinase-2 and -3 at cardiac myocyte receptors provide basis for distinct roles in regulation of myocardial function. Vinge LE(1), Andressen KW, Attramadal T, Andersen GØ, Ahmed MS, Peppel K, Koch WJ, Freedman NJ, Levy FO, Skomedal T, Osnes JB, Attramadal H.
Inorganic nanowires
InactiveUS20050221083A1Good monodispersityHigh degreeMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsNanowireSingle crystal
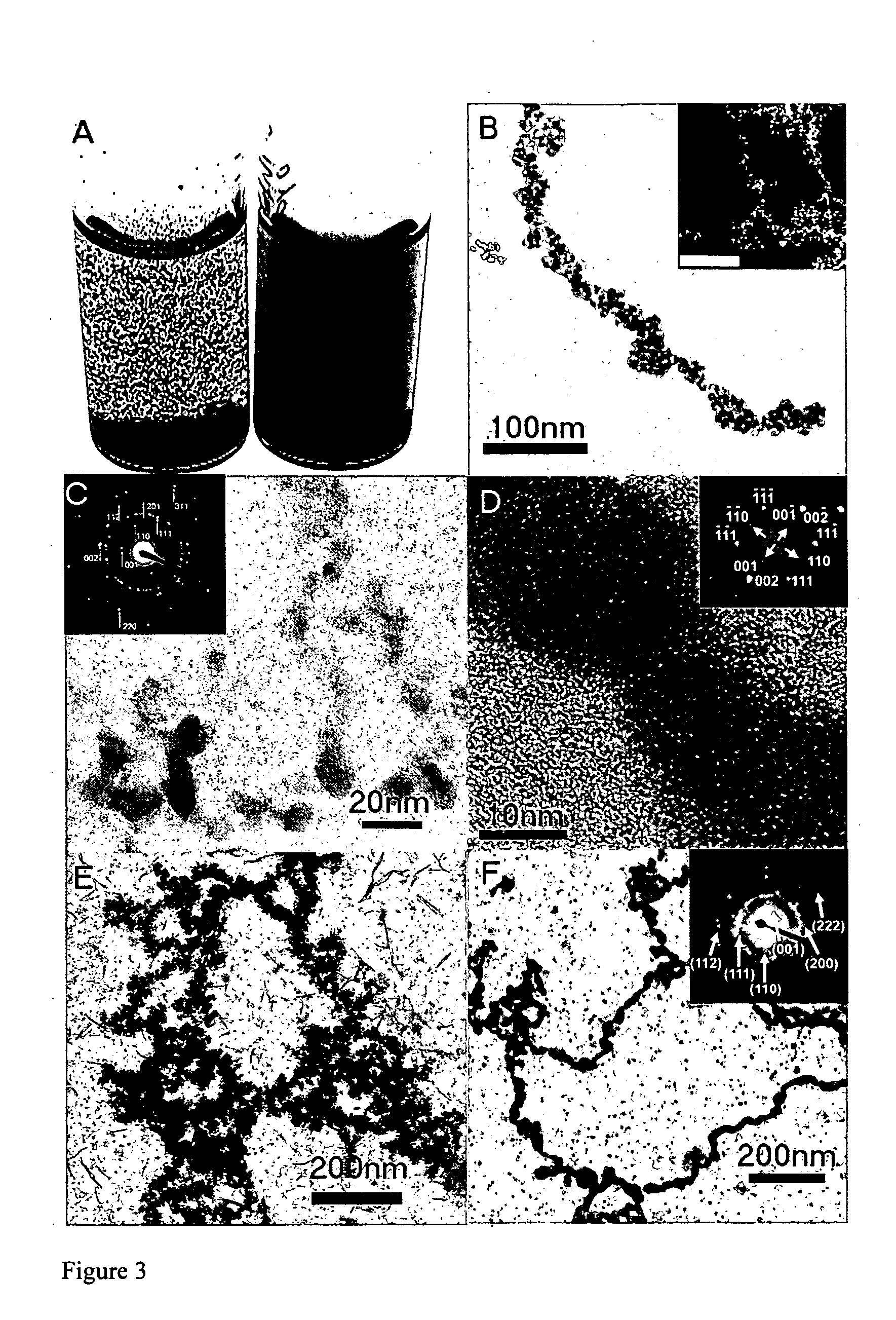
An inorganic nanowire having an organic scaffold substantially removed from the inorganic nanowire, the inorganic nanowire consisting essentially of fused inorganic nanoparticles substantially free of the organic scaffold, and methods of making same. For example, a virus-based scaffold for the synthesis of single crystal ZnS, CdS and free-standing L10 CoPt and FePt nanowires can be used, with the means of modifying substrate specificity through standard biological methods. Peptides can be selected through an evolutionary screening process that exhibit control of composition, size, and phase during nanoparticle nucleation have been expressed on the highly ordered filamentous capsid of the M13 bacteriophage. The incorporation of specific, nucleating peptides into the generic scaffold of the M13 coat structure can provide a viable template for the directed synthesis of a variety of materials including semiconducting and magnetic materials. Removal of the viral template via annealing can promote oriented aggregation-based crystal growth, forming individual crystalline nanowires. The unique ability to interchange substrate specific peptides into the linear self-assembled filamentous construct of the M13 virus introduces a material tunability not seen in previous synthetic routes. Therefore, this system provides a genetic tool kit for growing and organizing nanowires from various materials including semiconducting and magnetic materials.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
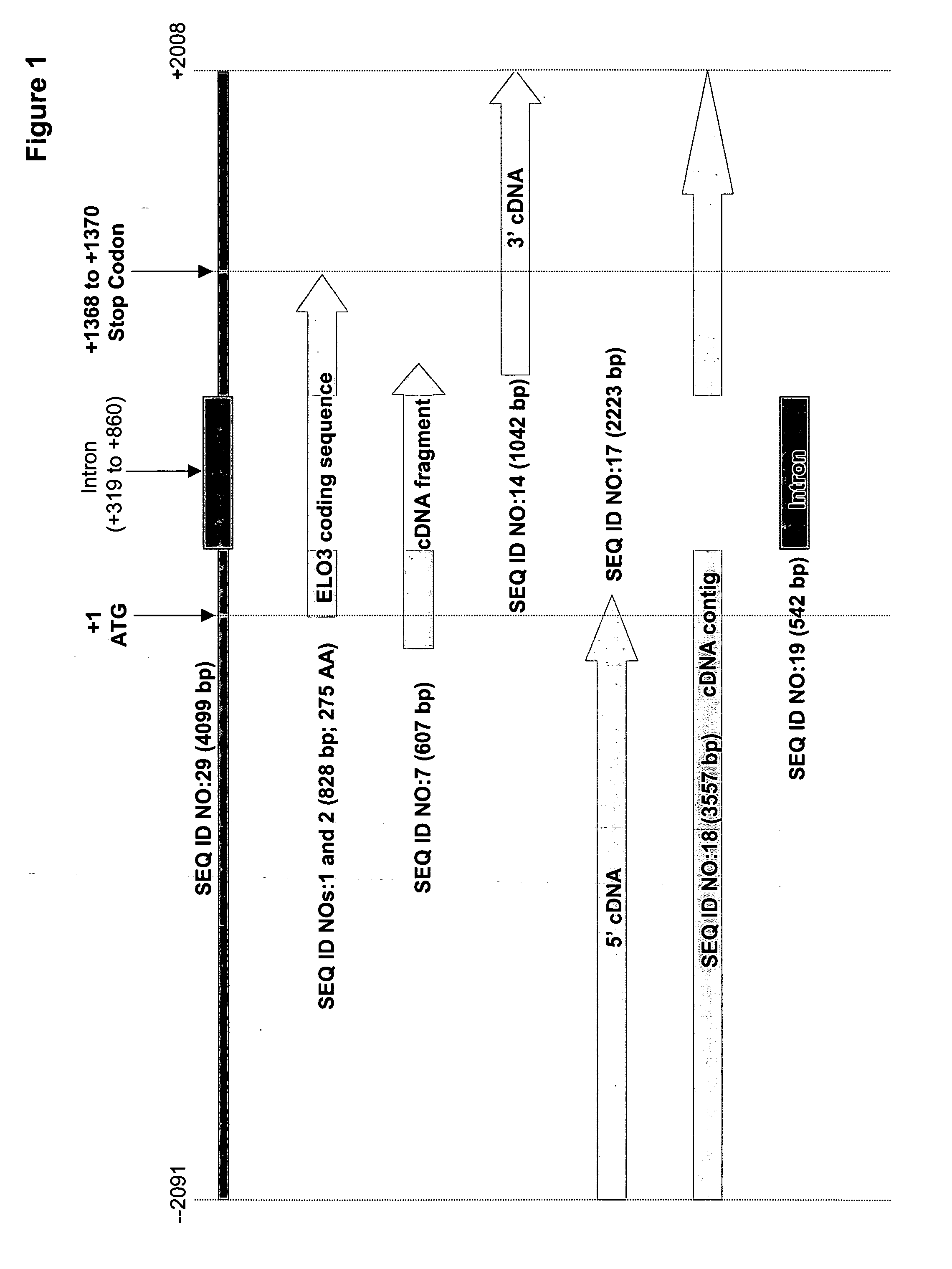
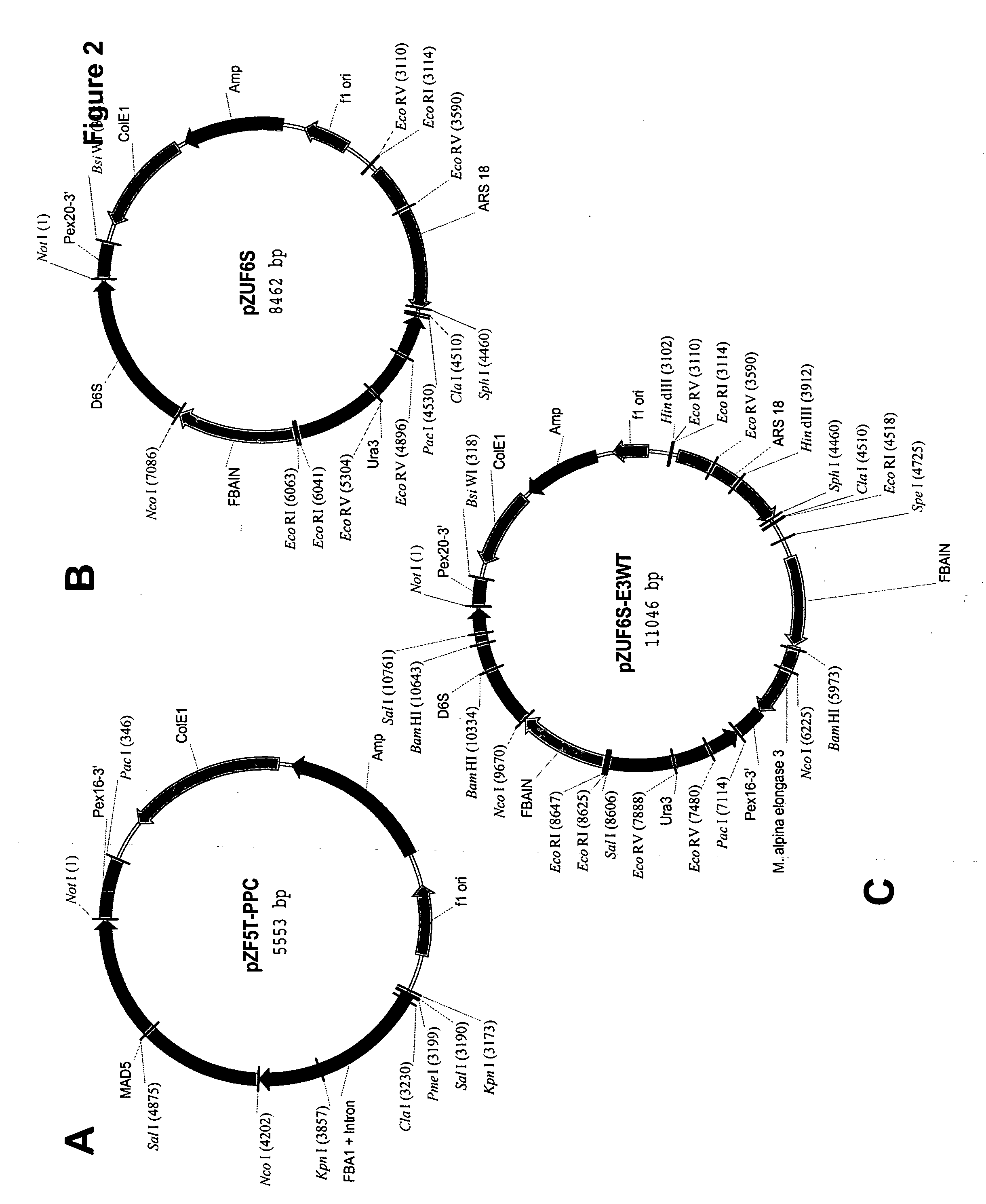
Mortierella alpina C16/18 fatty acid elongase
The present invention relates to a fungal C16 / 18 fatty acid elongase that is able to catalyze the conversion of palmitate (16:0) to stearic acid (18:0). Specifically, the nucleotide sequence of a Mortierella alpina C16 / 18 fatty acid elongase is provided (designated as “ELO3”). Methods of increasing microbial oil production, increasing carbon flux into the polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthetic pathway and increasing the content of polyunsaturated fatty acids by over-expression of the C16 / 18 fatty acid elongase are described herein. Most desirably, the substrate specificity of the instant ELO3 will be particularly useful to enable accumulation of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in oleaginous yeast, such as Yarrowia lipolytica.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
E. coli transformant, method for producing flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase using the same, and mutant flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenases
ActiveUS20130309750A1Accurate measurementEfficiently obtainedBacteriaOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliMicroorganism
A flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase (FAD-GDH) with high substrate specificity for D-glucose. A gene encoding a mutant FAD-GDH with its N-terminal region, containing an amino acid sequence corresponding to MKITAAIITVATAFASFASA that exists in the N-terminal region, deleted from the amino acid sequence of a wild-type FAD-GDH derived from Mucor is introduced into E. coli to obtain an E. coli transformant. Subsequently, this E. coli transformant is cultured to obtain an FAD-GDH with a specific N-terminal region deleted. The transformant allows the production of a large amount of GDH in a short time as compared with the original microorganism. An FAD-GDH that is less susceptible to the effects of dissolved oxygen and allows accurate measurement of glucose even in the presence of sugar compounds other than glucose in a sample.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Mortierella alpina C16/18 fatty acid elongase
ActiveUS20070087420A1Speed up the conversion processIncreased PUFA contentSugar derivativesBacteriaMicrobial oilNucleotide
The present invention relates to a fungal C16 / 18 fatty acid elongase that is able to catalyze the conversion of palmitate (16:0) to stearic acid (18:0). Specifically, the nucleotide sequence of a Mortierella alpina C16 / 18 fatty acid elongase is provided (designated as “ELO3”). Methods of increasing microbial oil production, increasing carbon flux into the polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthetic pathway and increasing the content of polyunsaturated fatty acids by over-expression of the C16 / 18 fatty acid elongase are described herein. Most desirably, the substrate specificity of the instant ELO3 will be particularly useful to enable accumulation of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in oleaginous yeast, such as Yarrowia lipolytica.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
DNA polymerase
InactiveUS20070020653A1Expanded substrate rangeImprove fidelitySugar derivativesHydrolasesPolymerase LSubstrate Specificities
The present invention relates to DNA polymerases. In particular the invention relates to a method for the generation of DNA polymerases exhibiting a relaxed substrate specificity. Uses of mutant polymerases produced using the methods of the invention are also described.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Method for producing epa-enriched oil and dha-enriched oil
InactiveUS20100190220A1Increase enzyme activityHigh yieldFatty acid esterificationFatty acids production/refiningSubstrate SpecificitiesGlyceride
Alcoholysis of oils and fats containing EPA and DHA is performed by a lipase having substrate specificity for fatty acids having 18 carbons or less and in the presence of a reaction additive such as magnesium oxide; then the glyceride fraction is separated; alcoholysis of the glyceride fraction is performed by a lipase having substrate specificity for fatty acids having 20 carbons or less and in the presence of a reaction additive such as magnesium oxide; and EPA-enriched oil and DHA-enriched oil are simultaneously obtained.
Owner:NIPPON SUISAN KAISHA LTD
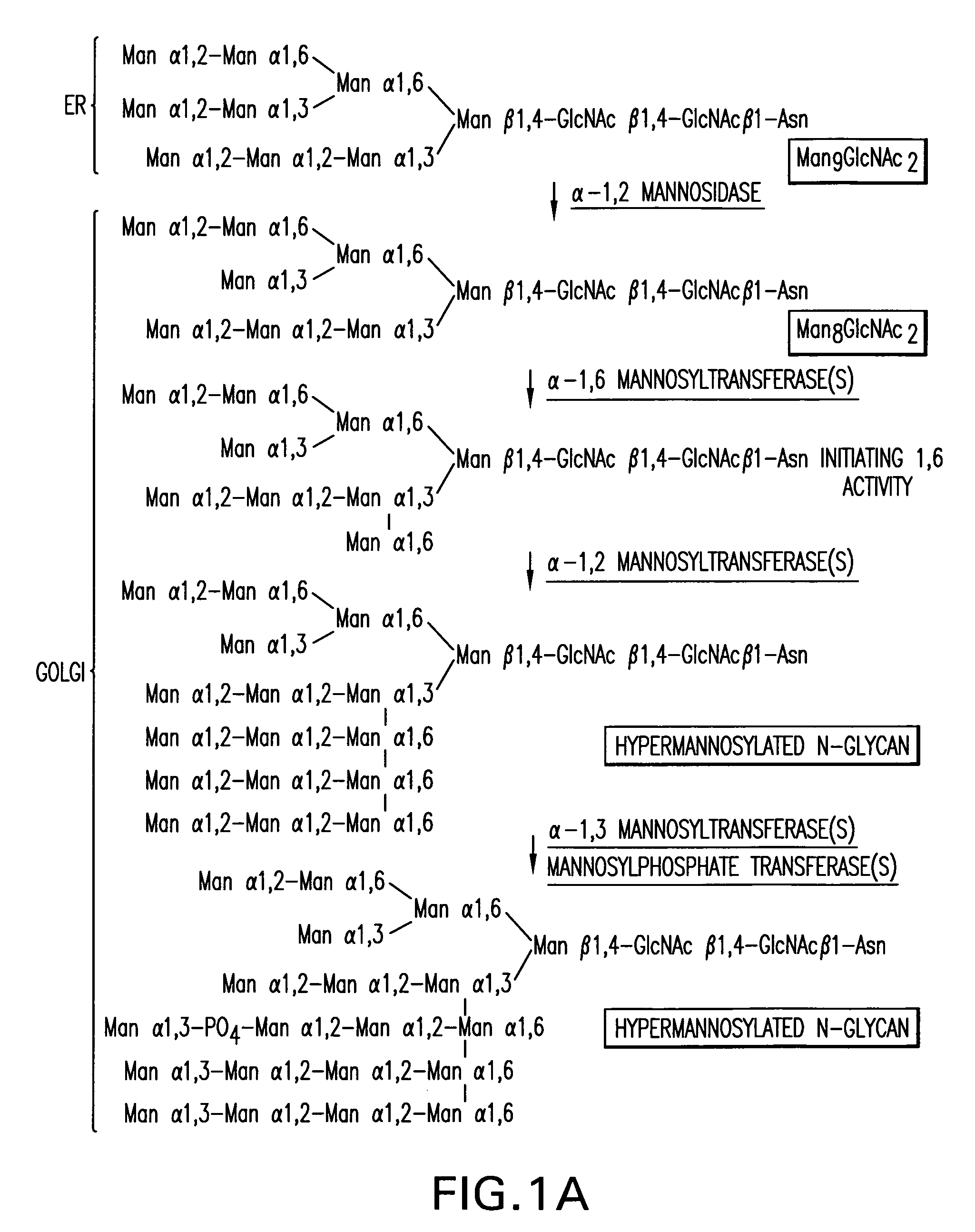
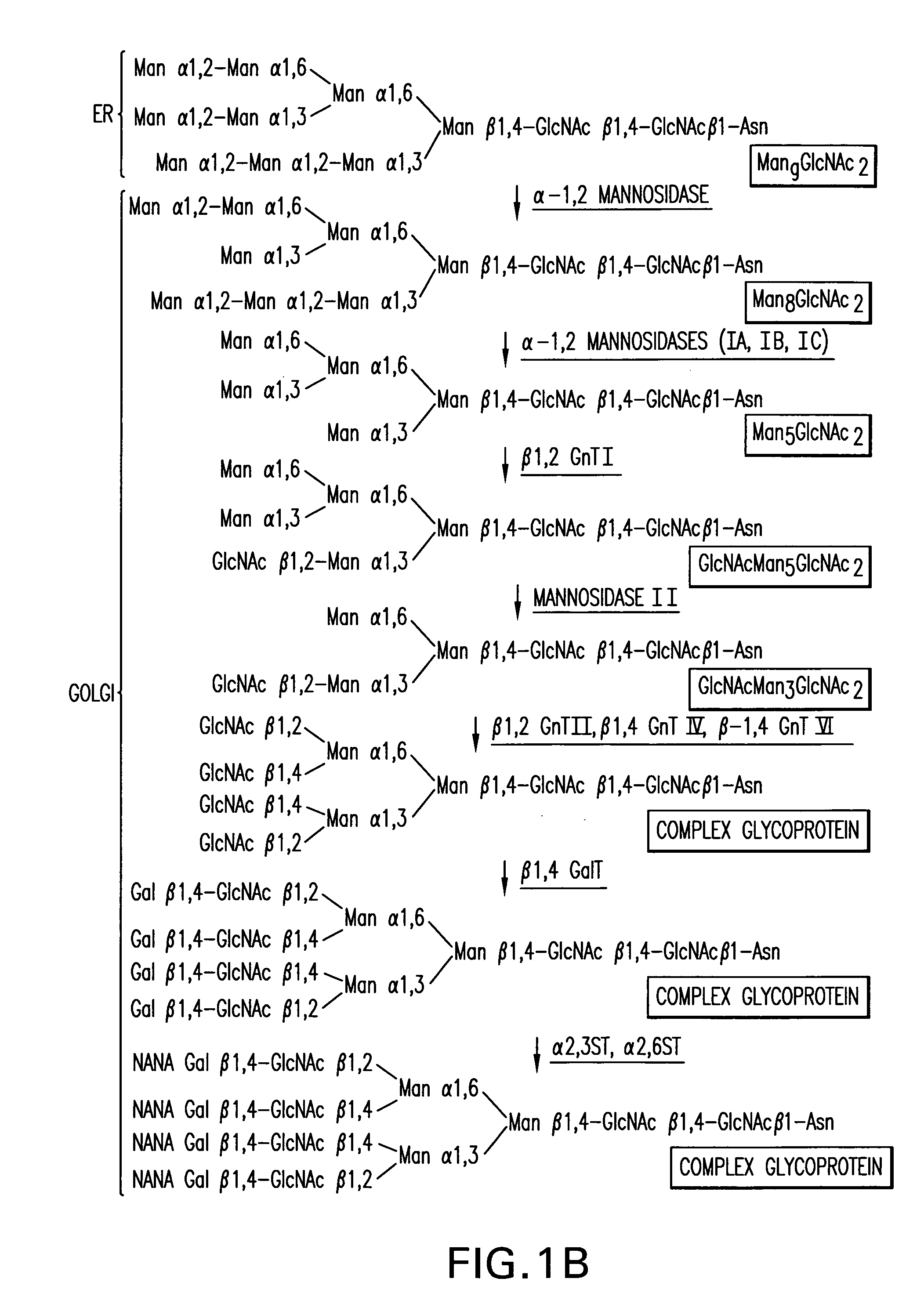
Expression of class 2 mannosidase and class III mannosidase in lower eukaryotic cells
A method for producing human-like glycoproteins by expressing a Class 2 α-mannosidase having a substrate specificity for Manα1,3 and Manα1,6 glycosidic linkages in a lower eukaryote is disclosed. Hydrolysis of these linkages on oligosaccharides produces substrates for further N-glycan processing in the secretory pathway.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenases
ActiveUS20110318810A1Accurate measurementAccurate blood glucose levelSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismLactose
A flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase with a high substrate specificity for D-glucose. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase which is derived from a microorganism belonging to the genus Mucor. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase has a low reactivity for maltose, D-galactose and D-xylose compared to its reactivity for D-glucose, and therefore is relatively unaffected by these saccharide compounds. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase is also relatively unaffected by dissolved oxygen, and allows accurate measurement of glucose amounts even in the presence of saccharide compounds other than glucose in samples.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
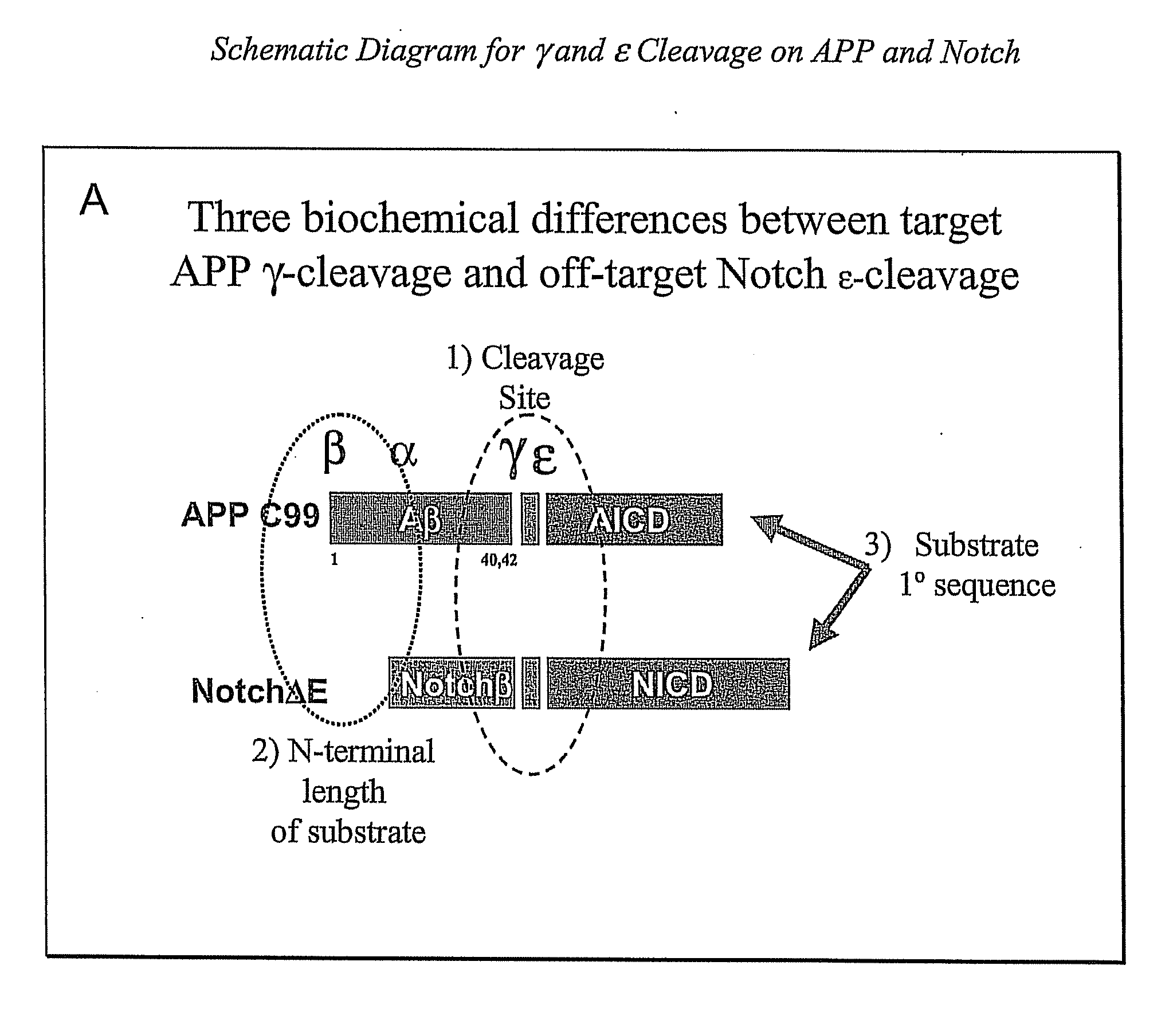
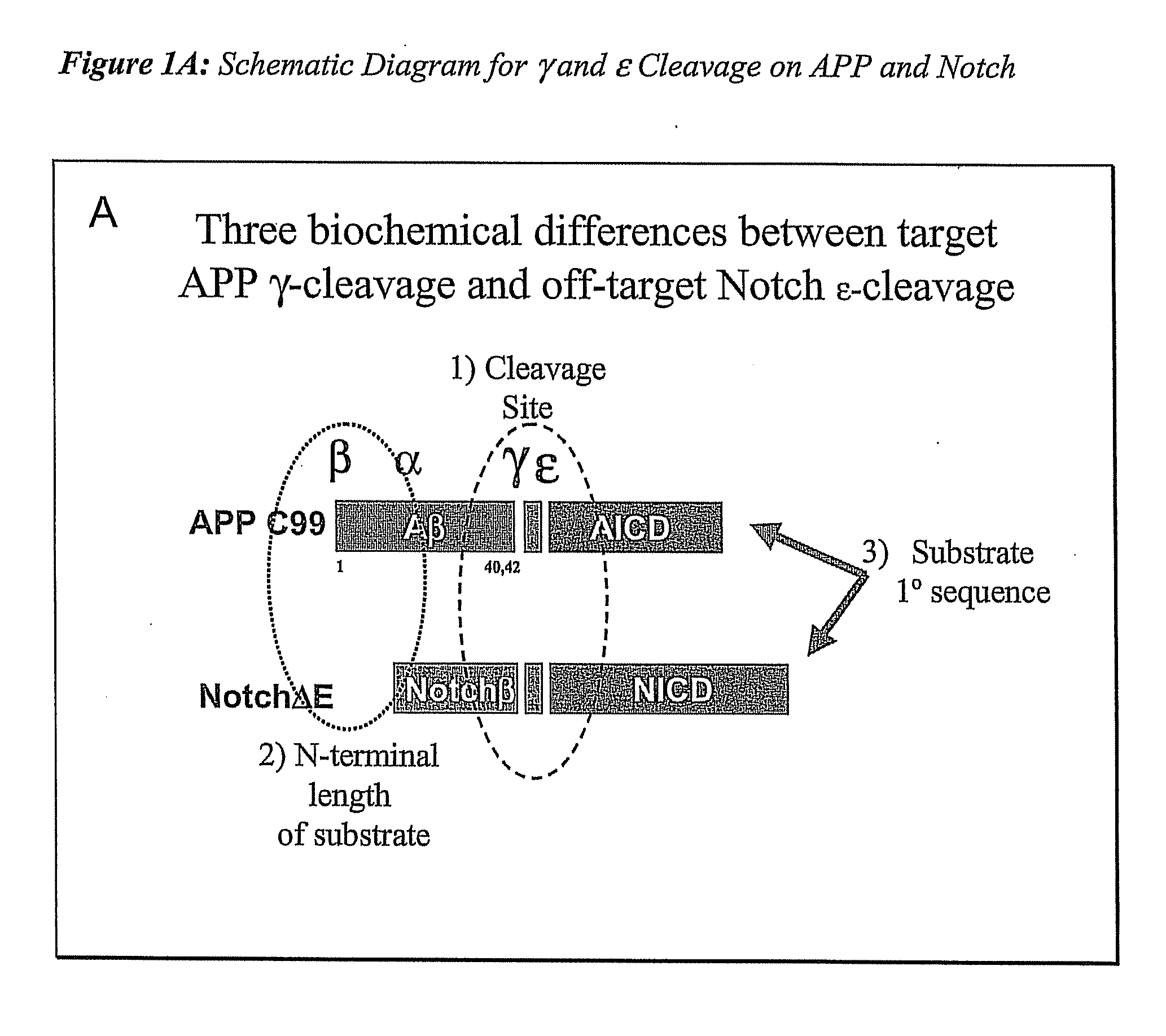
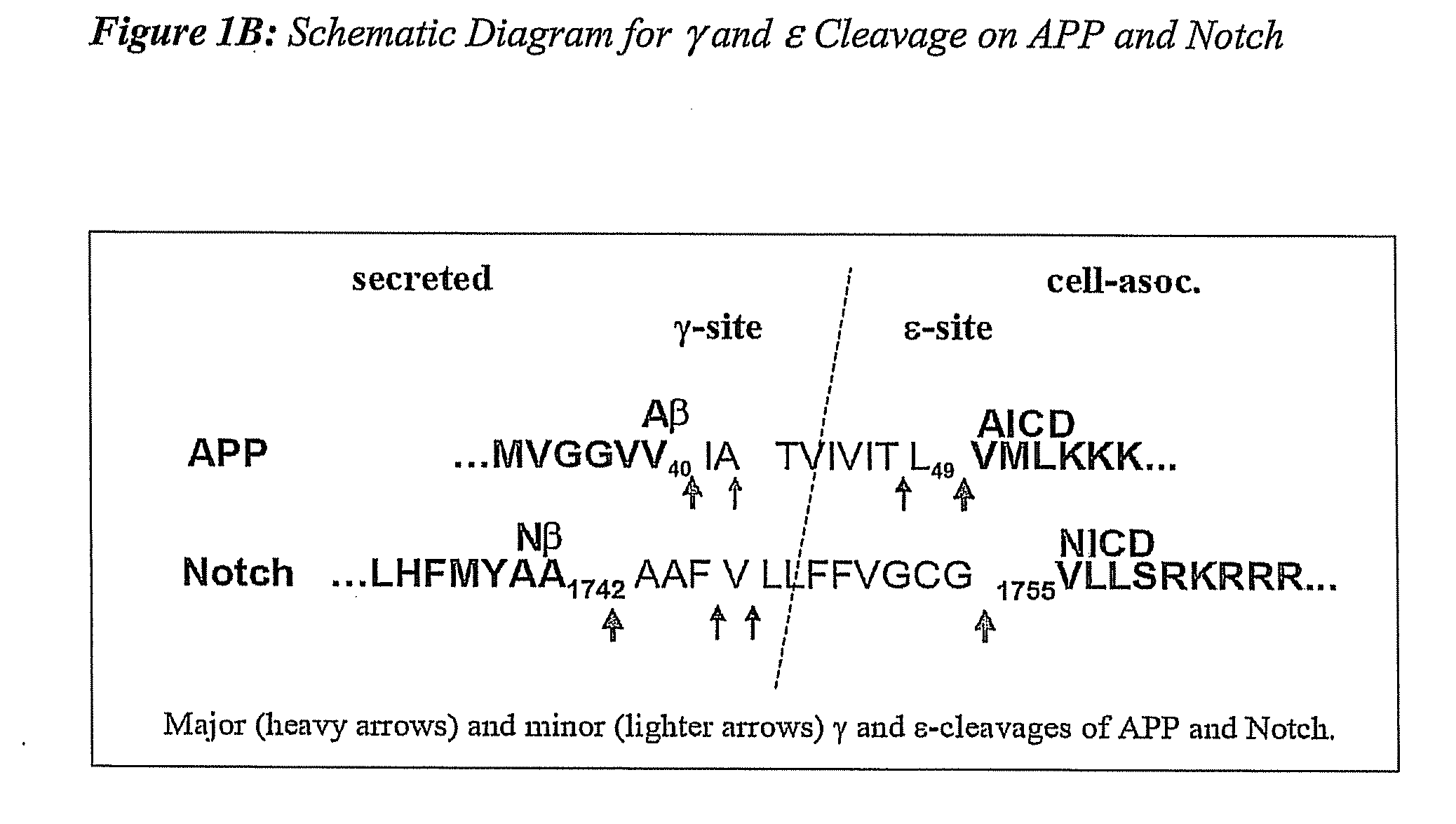
Compositions and Methods for Identifying Substrate Specificity of Inhibitors of Gamma Secretase
The invention provides assays and methods for determining the substrate specificity of gamma secretase inhibitors and for identifying substrate-selective (and substrate isoform-selective) inhibitors of gamma secretase. The invention provides assays and methods for determining whether a compound inhibits gamma secretase in a site specific or substrate specific manner. The invention provides isolated polypeptide sequences comprising modified gamma secretase substrates, and polynucleotide sequences encoding the polypeptide sequences. The invention also provides compounds that inhibit gamma secretase, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds, and methods of treating Alzheimer's disease using such compounds.
Owner:ELAN PHARM INC
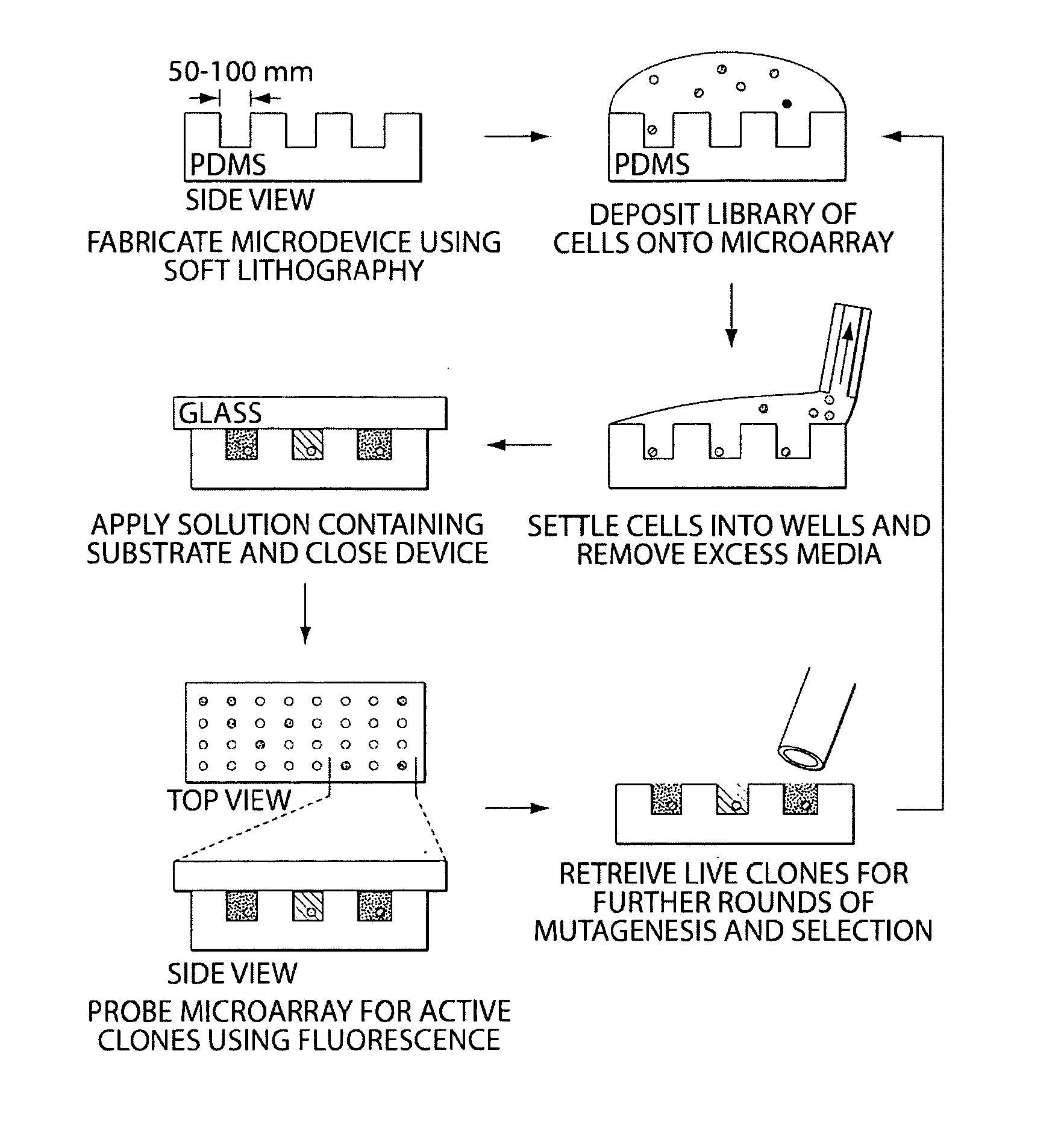
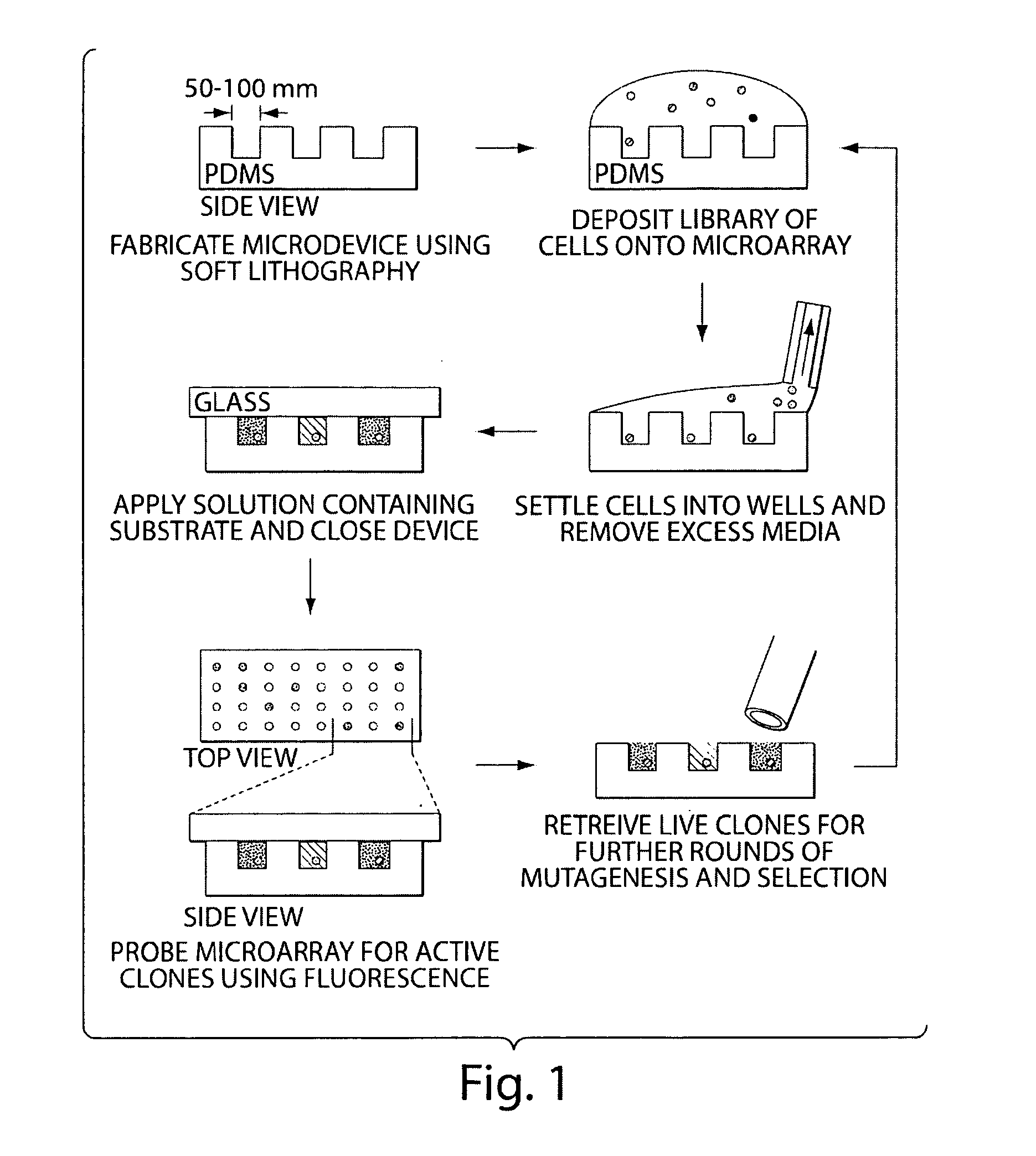
Compositions and Methods for Spatial Separation and Screening of Cells
InactiveUS20110124520A1Rapid mass productionAltered selectivityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMicroreactorSubstrate Specificities
The invention provides a method for isolating particular members from a library of variant cells in individual microreactors, wherein the phenotype of the biomolecule secreted by the cell is evaluated on the basis of multiple parameters, including substrate specificity and kinetic efficiency.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES +1
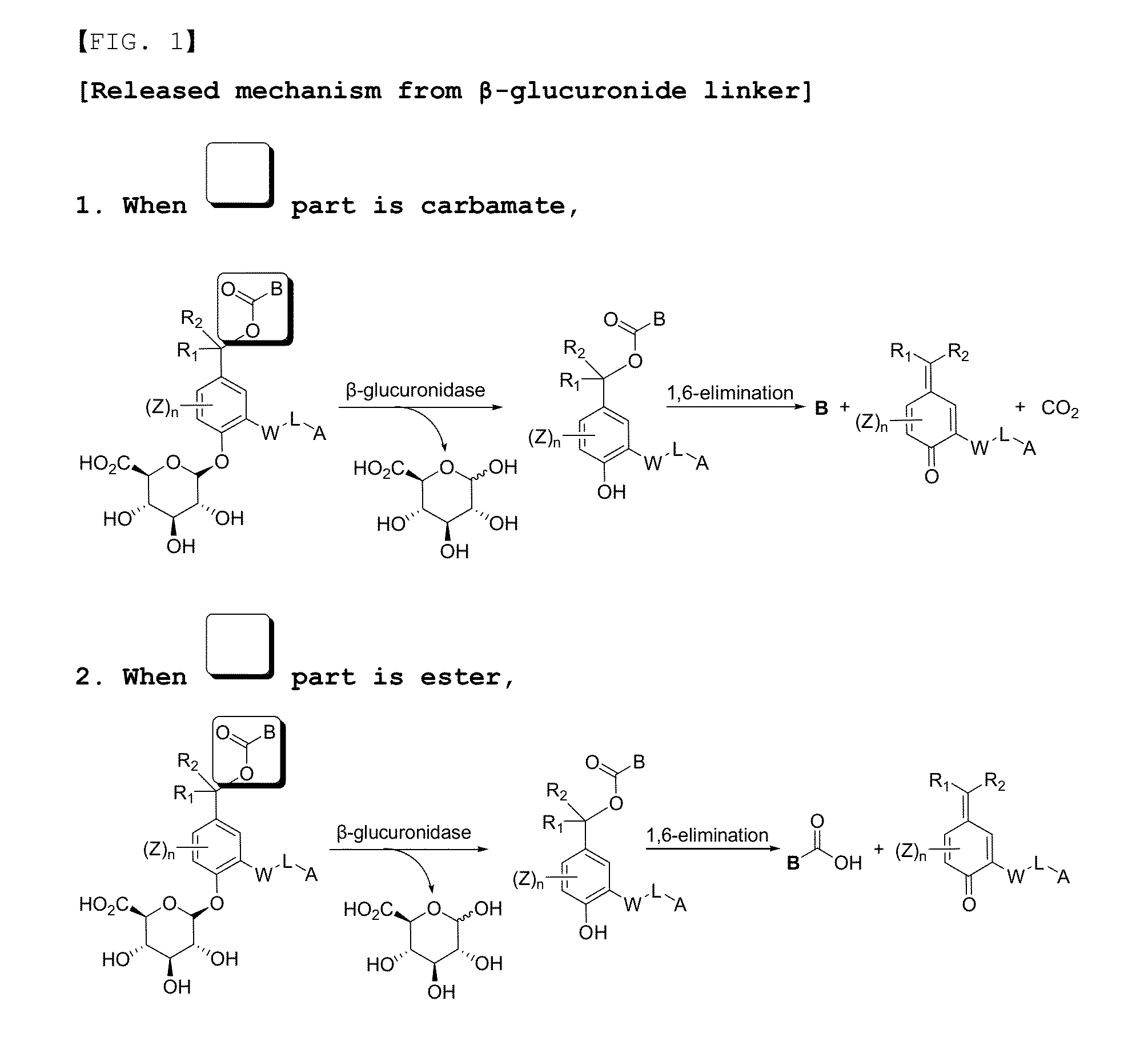
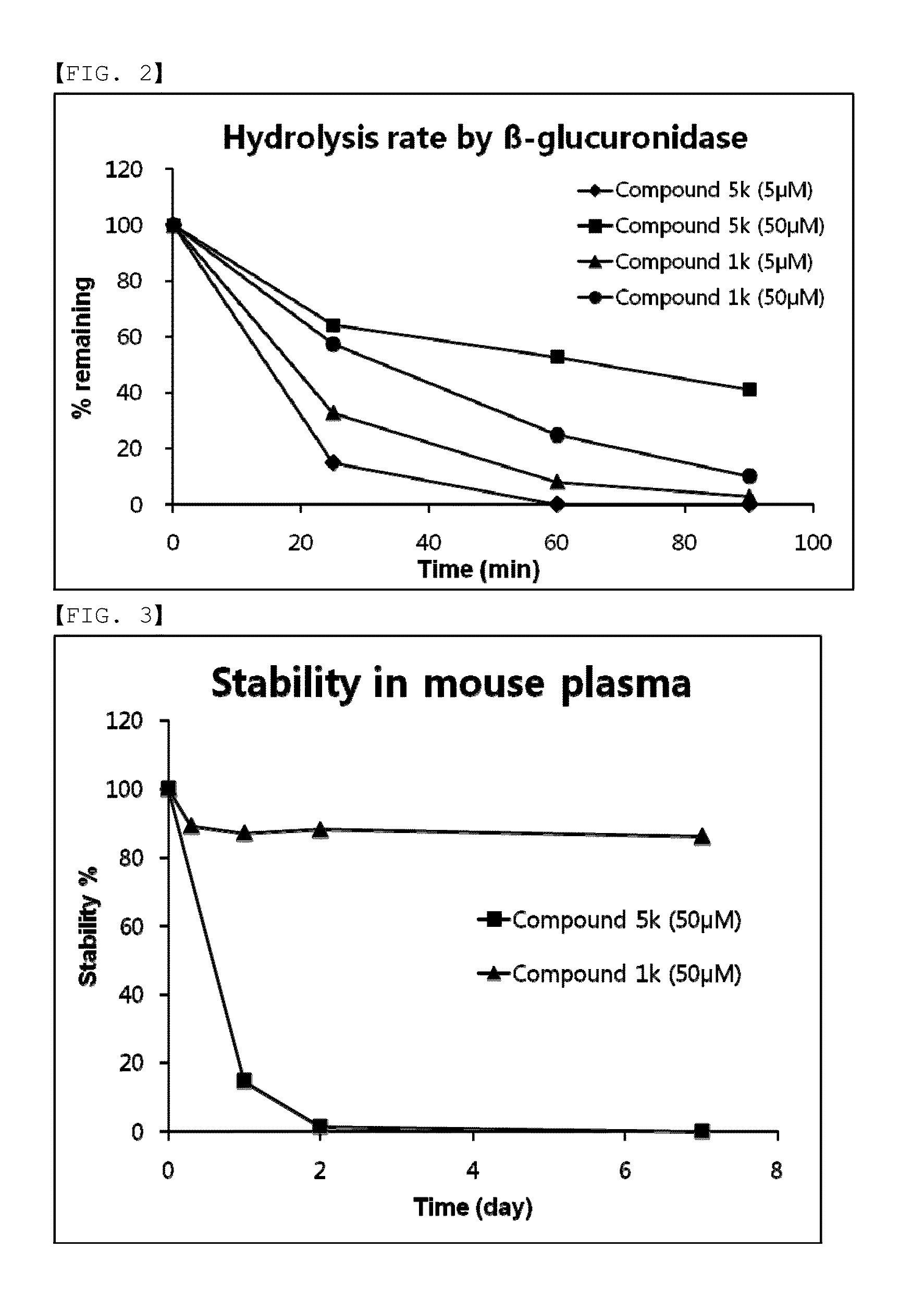
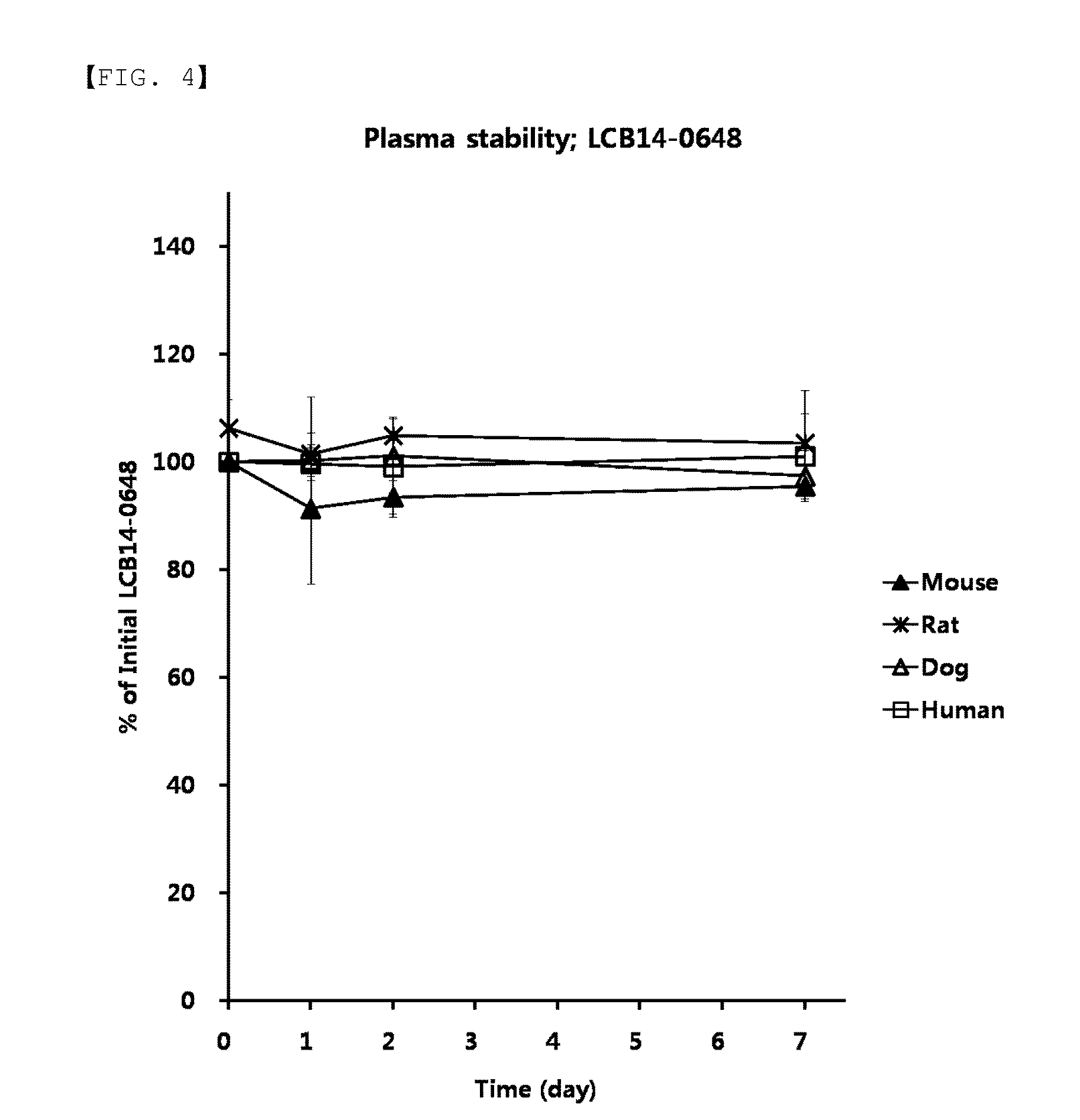
Compounds comprising self-immolative group
Provided are compounds comprising a self-immolative group, and the compounds comprising a self-immolative group according to the present invention may include a protein (for example, an oligopeptide, a polypeptide, an antibody, or the like) having substrate-specificity for a target and an active agent (for example, a drug, a toxin, a ligand, a detection probe, or the like) having a specific function or activity.
Owner:LEGOCHEM BIOSCIENCES INC
Method utilizing microalgae to produce biodiesel
ActiveCN103642579AHigh yieldOptimum Inoculation DensityFatty acid esterificationBiofuelsAlcoholBiodiesel
The invention belongs to the fields of biological engineering and energy, and specifically relates to a method utilizing microalgae to produce biodiesel. The method comprises the following steps: (1) culturing microalgae; (2) extracting the microalgae fat; (3) carrying out enzyme catalytic reactions so as to prepare microalgae biodiesel. An ester exchange method is adopted during the biodiesel preparation process, lipase is taken as the catalyst, the reaction conditions are mild, free aliphatic acids can be completely and directly esterified by lipase, the alcohol using amount is little, and furthermore the method adopts composite lipase to catalyze the reactions in order to effectively overcome the shortage of substrate specificity of single lipase and improve the ester exchange efficiency of biodiesel. The biodiesels prepared by the method all meet the GB / T20828-2007 standard of biodiesel for diesel engine fuel blending.
Owner:BEIJING EURO & AMERICAN INST OF SCI & TECH
DNA polymerase
InactiveUS20090305292A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LSubstrate Specificities
The present invention relates to DNA polymerases. In particular the invention relates to a method for the generation of DNA polymerases exhibiting a relaxed substrate specificity. Uses of mutant polymerases produced using the methods of the invention are also described.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
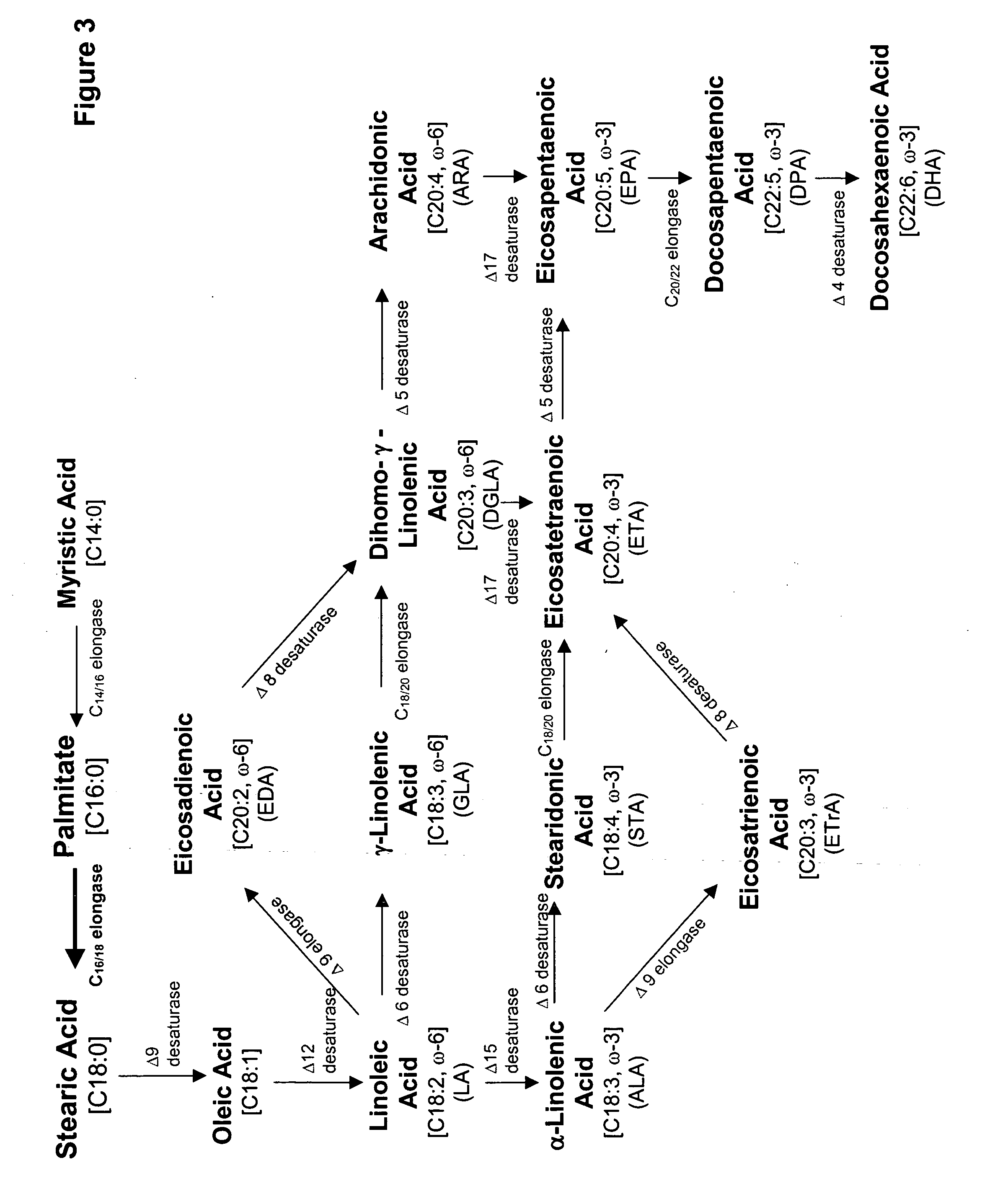
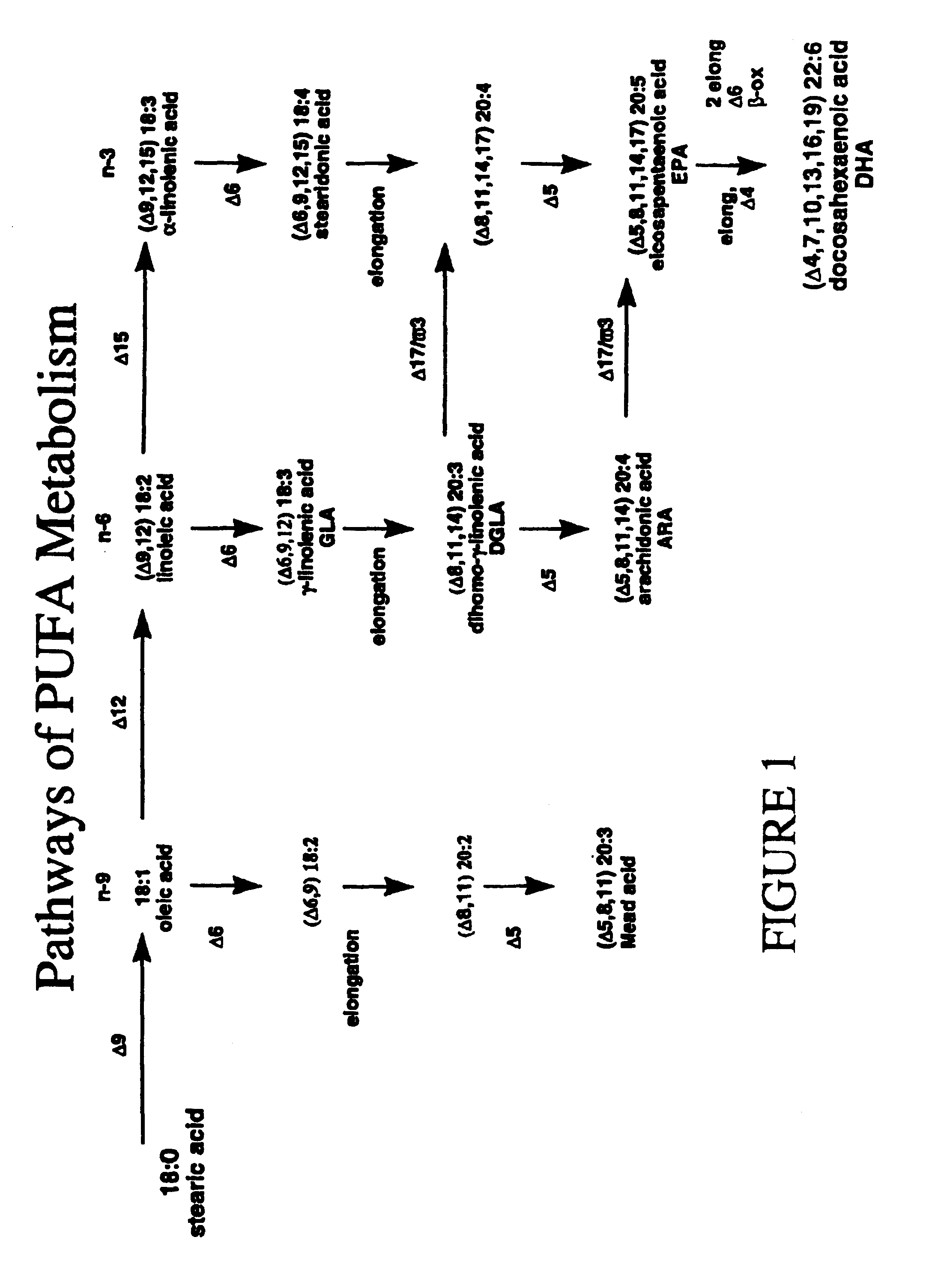
Polyunsaturated fatty acids in plants
InactiveUSRE41139E1Other foreign material introduction processesOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyDocosahexaenoic acid
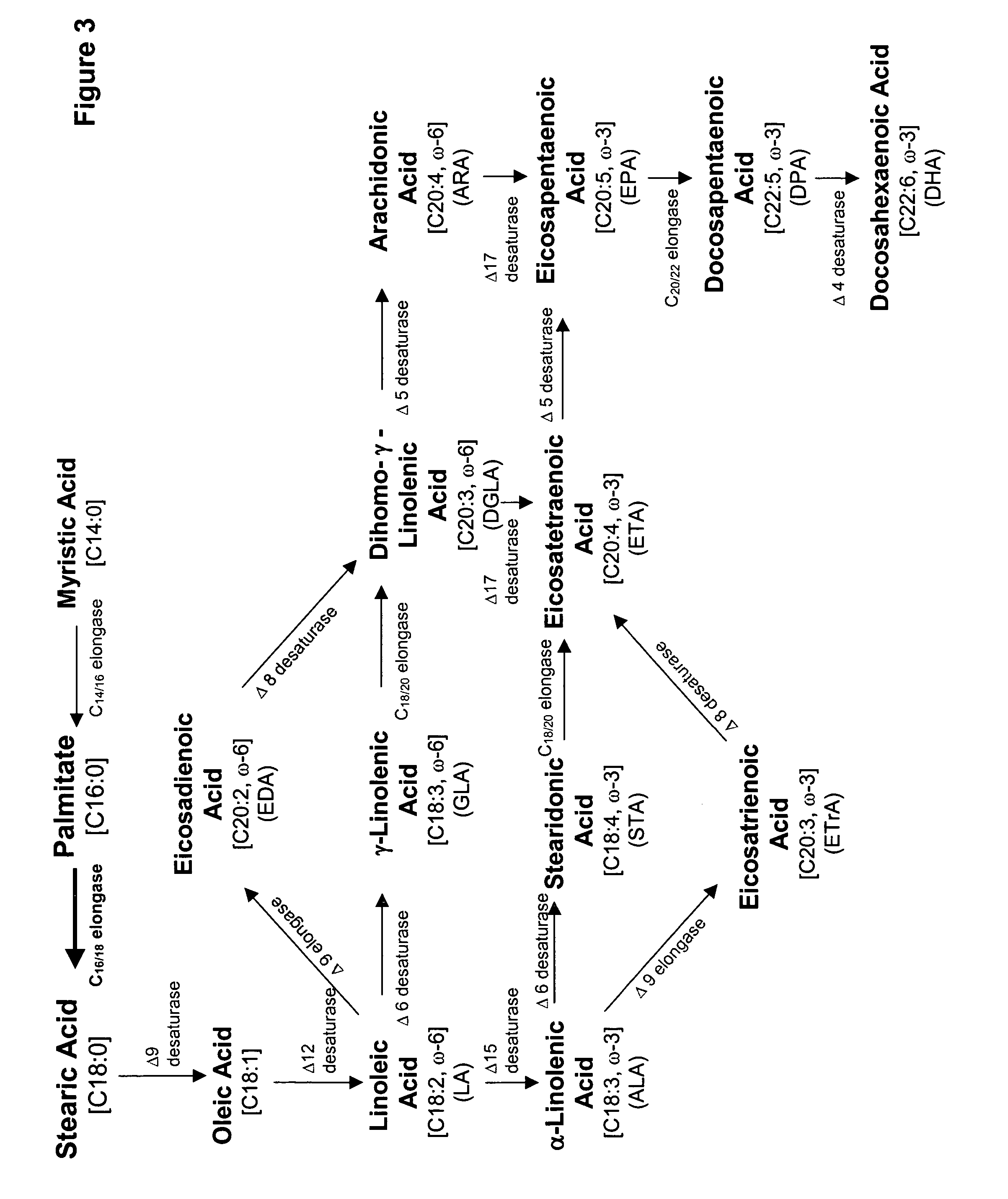
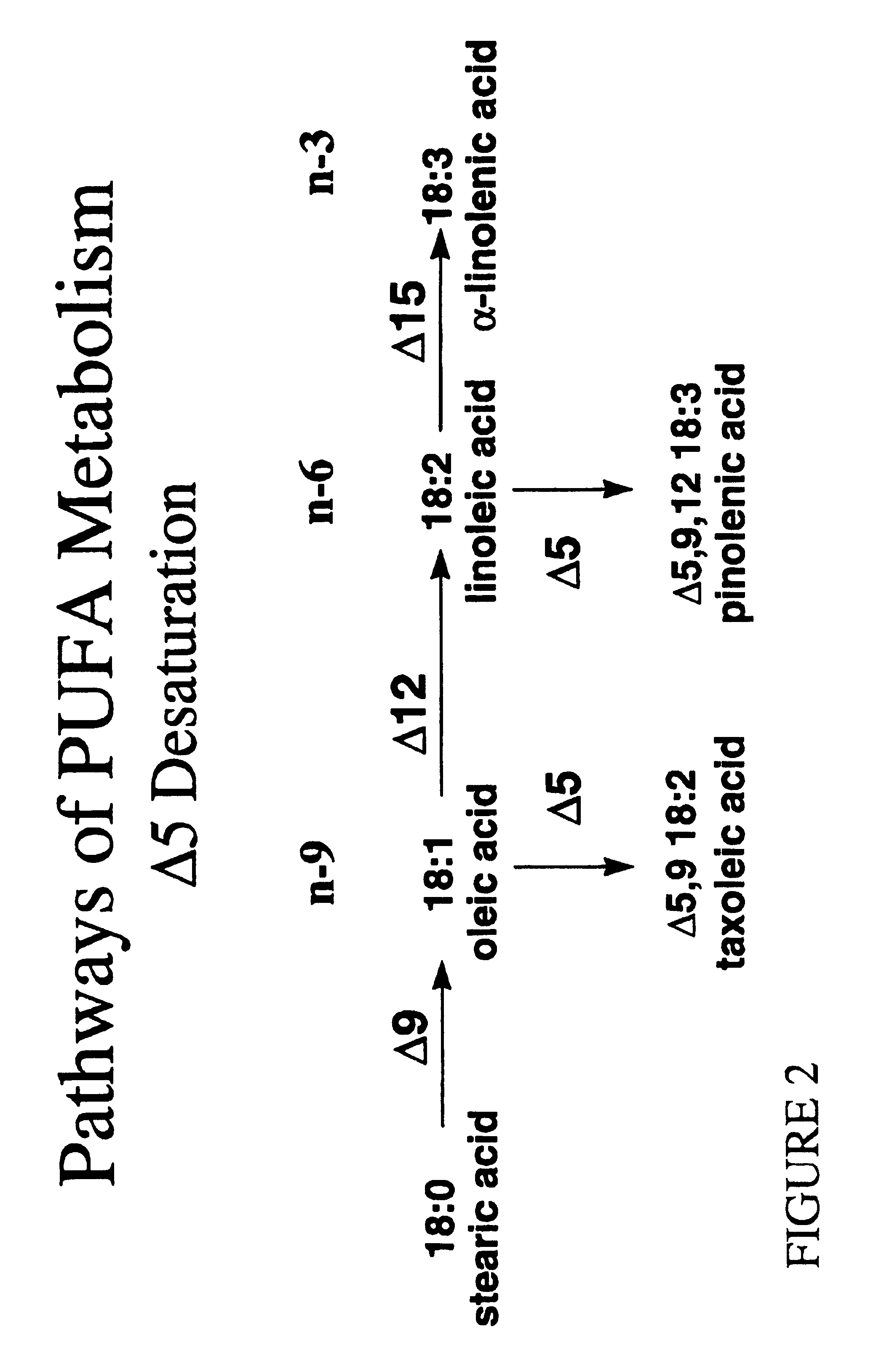
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for preparing polyunsaturated long chain fatty acids in plants, plant parts and plant cells, such as leaves, roots, fruits and seeds. Nucleic acid sequences and constructs encoding fatty acid desaturases, including Δ5-desaturases, Δ6-desaturases and Δ12-desaturases, are used to generate transgenic plants, plant parts and cells which contain and express one or more transgenes encoding one or more desaturases. Expression of the desaturases with different substrate specificities in the plant system permit the large scale production of polyunsaturated long chain fatty acids such as docosahexaenoic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid, α-linolenic acid, gamma-linolenic acid, arachidonic acid and the like for modification of the fatty acid profile of plants, plant parts and tissues. Manipulation of the fatty acid profiles allows for the production of commercial quantities of novel plant oils and products.
Owner:CALGENE LLC
Method of pre-treating sample for measuring saccharified amine and method of measuring saccharified amine
ActiveUS7449305B2Highly reliable measurementImprove accuracyHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteProteinase activity
The present invention provides a method of pretreating a sample containing a glycated amine as an analyte, thereby enabling highly reliable measurement of a glycated amine. A glycated amino acid in the sample is degraded by causing a fructosyl amino acid oxidase (FAOD) to act thereon, and thereafter, a FAOD further is caused to act on the glycated amine as the analyte in the sample to cause a redox reaction. The amount of the glycated amine is determined by measuring the redox reaction. The substrate specificity of the FAOD caused to act on the glycated amino acid may be either the same as or different from that of the FAOD caused to act on the glycated amine. When using the same FAOD, a FAOD is caused to act on the glycated amino acid to degrade it, and thereafter, the sample is treated with a protease to inactivate the FAOD and also to degrade the glycated amine. Then, the same FAOD further is added so that the FAOD acts on the degradation product obtained to cause a redox reaction, and the redox reaction is measured.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Glucose dehydrogenase
InactiveUS7494794B2Overcomes shortcomingSugar derivativesBacteriaHeat resistanceSubstrate Specificities
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Fructosylamine oxidase
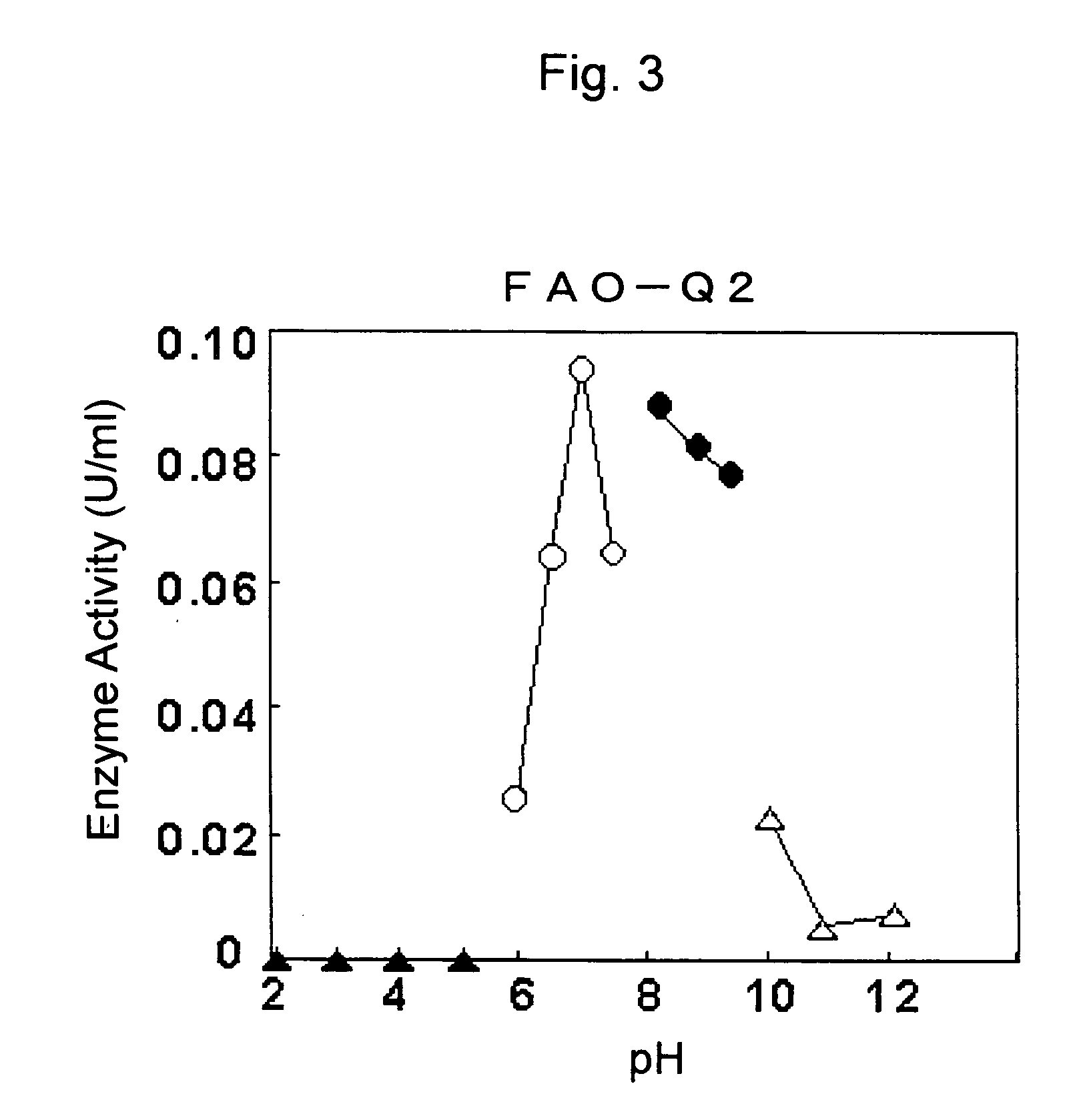
ActiveUS20060172367A1Accurate and efficient measurementFungiSugar derivativesSubstrate SpecificitiesLysinibacillus fusiformis
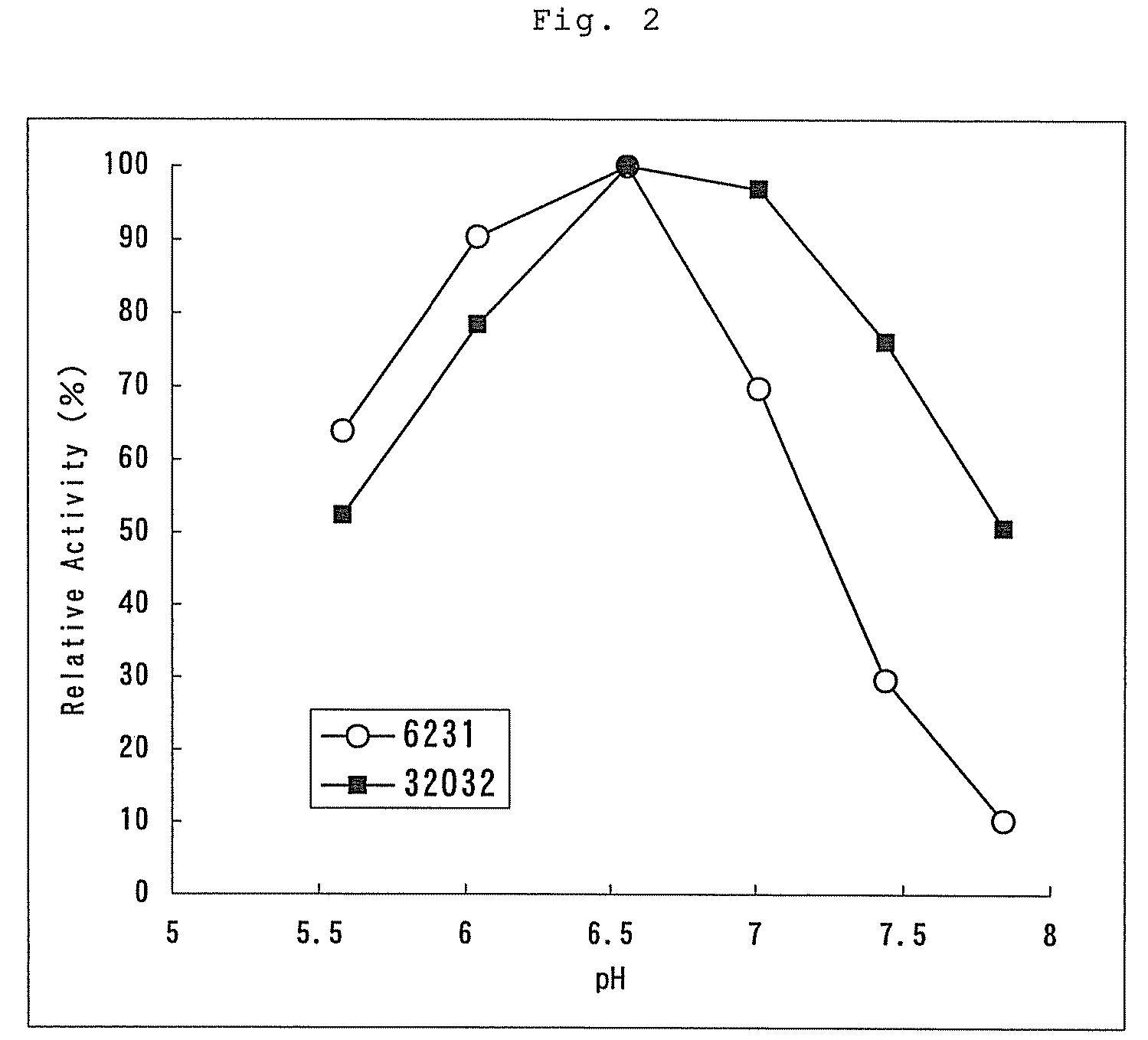
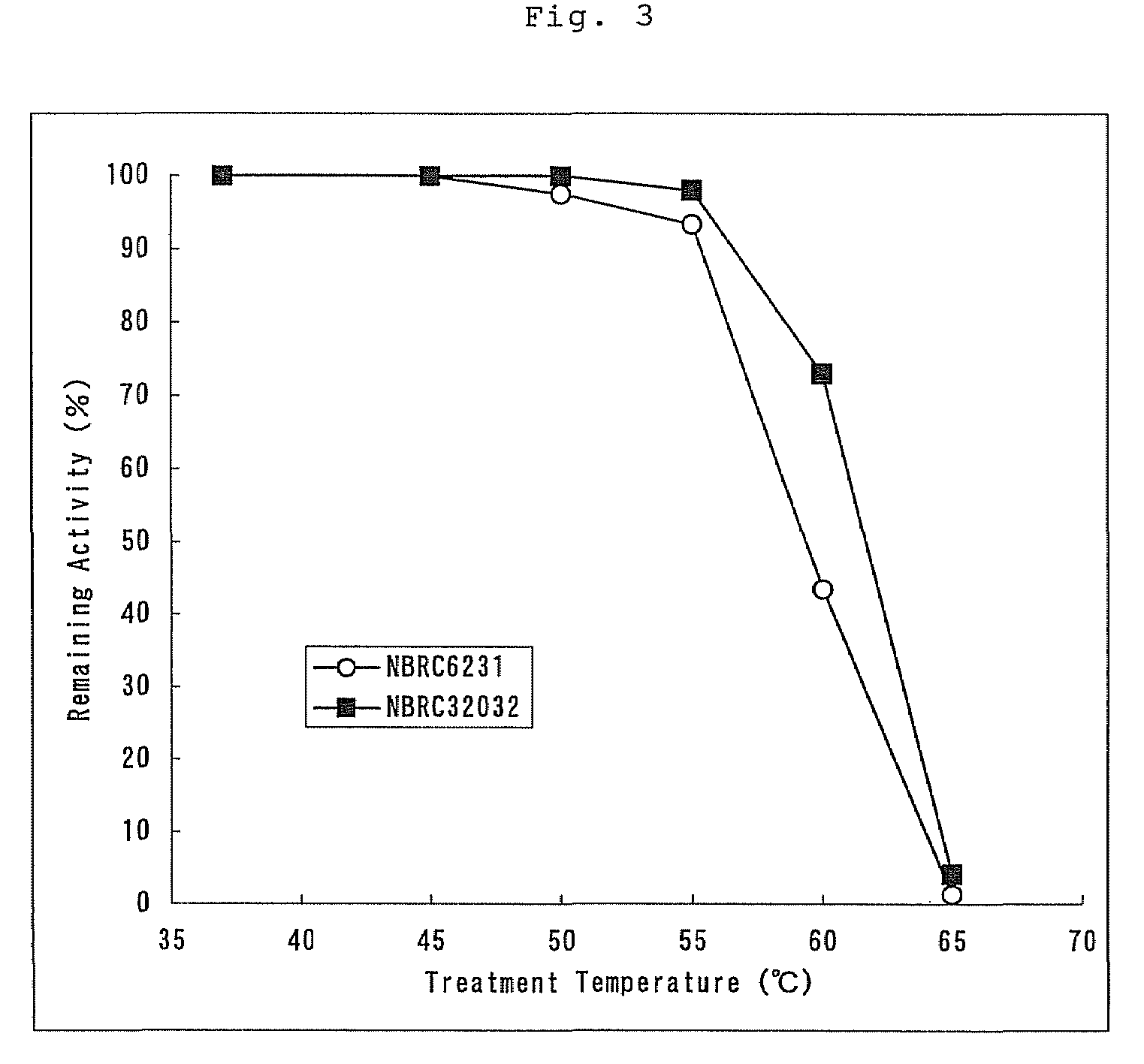
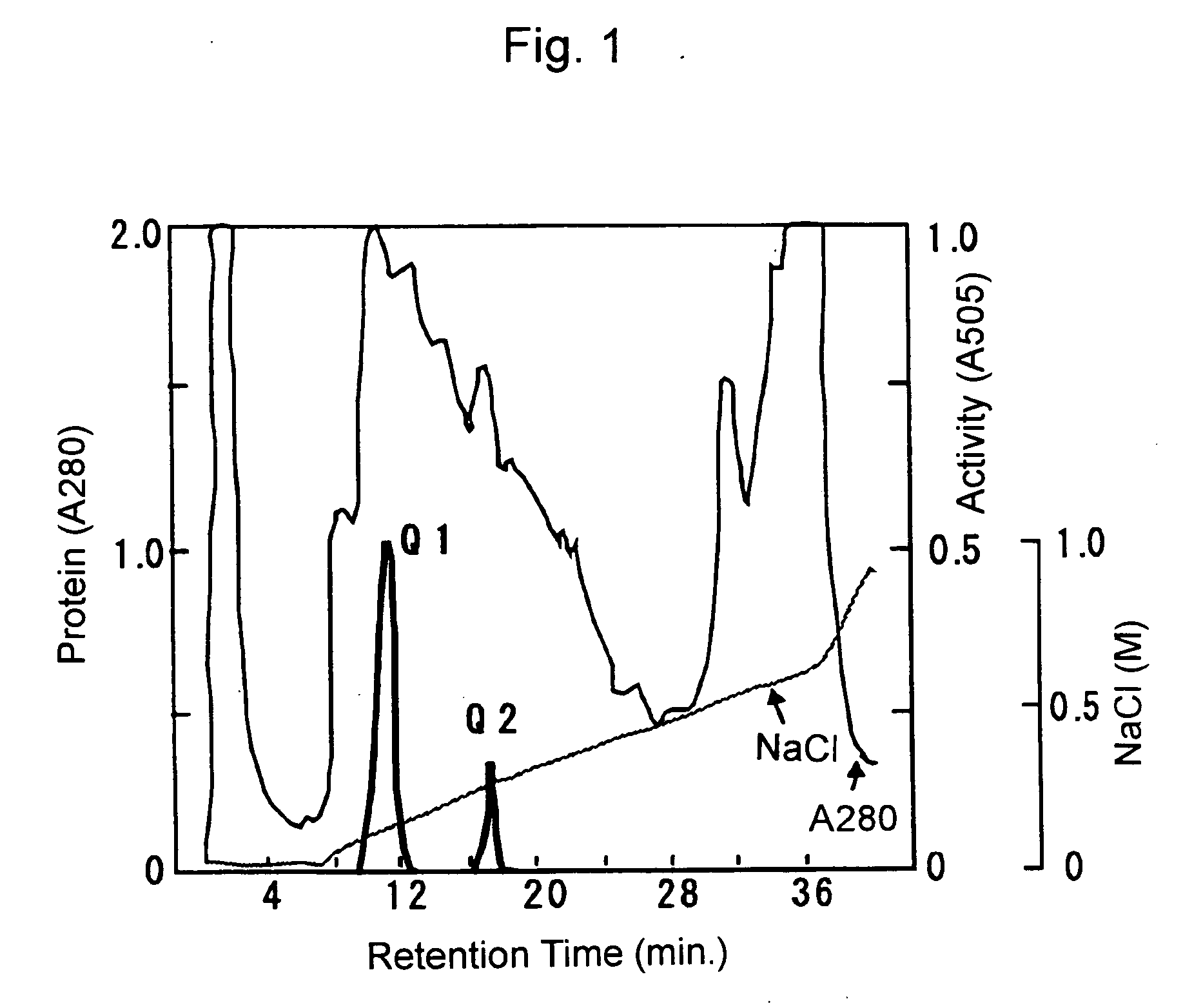
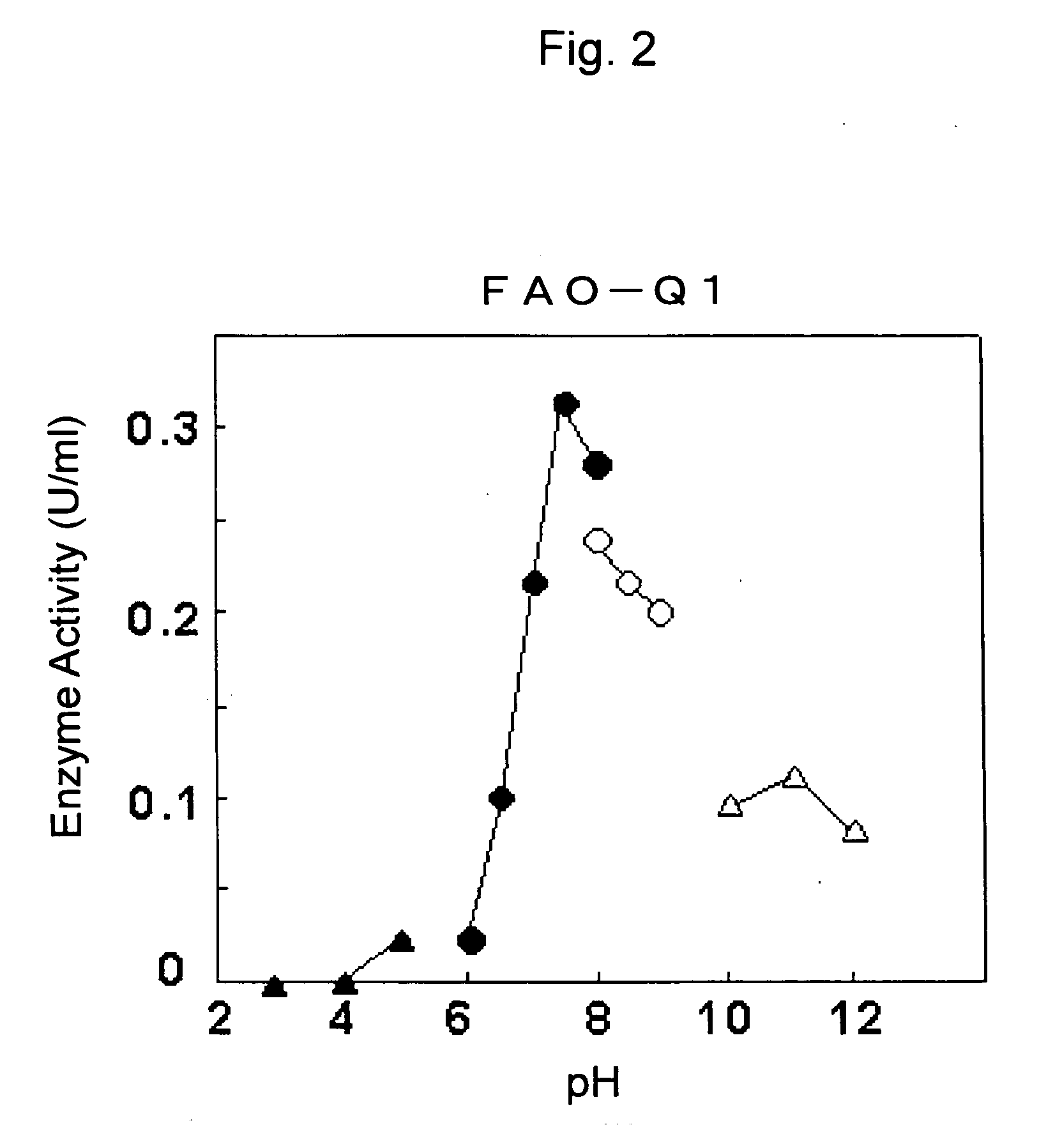
The present invention provides a fructosylamine oxidase which is obtainable by culturing Fusarium proliferatum, and purifying two types of fructosylamine oxidase (FAO) with different substrate specificities from the culture, and which is useful in the measurement of amadori compounds.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Isolation and composition of novel glycosidases
Substantially pure glycosidases capable for cleaving selected glycosidic bonds have been described including glycosidases isolated from Xanthomonas and recombinant glycosidases. Substrate specificity of isolated enzymes have been identified for GlcNacβ1-x, Galα1-3R, Galα1-6R, Galβ1-3R, Fucα-2R, Fucα1-3R, Fucα1-4R, Manα1-2R, Manα1-3R, Manα1-6R, Manβ1-4R, Xylβ1-2R, Glcβ1-4R, and Galβ1-4R providing improved capability for selectively cleaving a glycosidic linkage in a carbohydrate substrate and for forming modified carbohydrates.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Preparation method of biodiesel and compound enzyme used by preparation method
InactiveCN102911701ANo pollution in the processLow costFatty acid esterificationBiofuelsAlcoholOrganic solvent
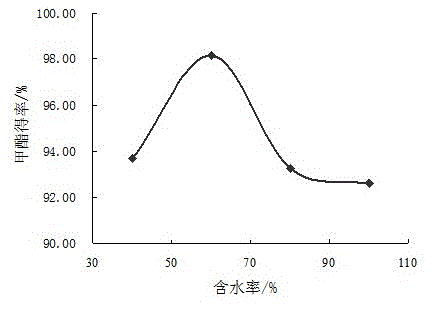
The invention discloses a preparation method of biodiesel and compound enzyme used by the method. The method comprises the following steps of: adding short-chain alcohol, oil, water and the compound enzyme into a reaction vessel, controlling the temperature at 30-50 DEG C, and reacting for 48-72hours to prepare the biodiesel, wherein the molar ratio of the short-chain alcohol to the oil is (3-5): 1, the use level of the water is 40-100% as heavy as that of the oil, and the use level of the compound enzyme is 4-22U / g of soybean oil. The method is environment-friendly without adding any organic solvents, can express the compound enzyme by utilizing recombinant bacteria, does not need to purchase the commercial enzyme, and the compound lipase is adopted to cooperatively catalyze, so that the substrate specificity of single lipase can be overcome, the ester converting efficiency when the biodiesel is prepared by an enzyme method can be improved, and products are easy to separate. After the method for catalysis by using the compound lipase is used, the use level of the required enzyme is reused by more than 50% of the use level of the single lipase, and the yield of the active ingredients in the biodiesel, i.e., the fatty acid methyl ester, is 98%, so that the production cost can be greatly reduced. The preparation method is very good in industrialized prospect.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Recombinant pichia pastoris, construction method and application of recombinant pichia pastoris
InactiveCN106047738ALow substrate specificityHigh catalytic activityFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisPrenylation
The invention discloses recombinant pichia pastoris (GS115-ppic9-novQ) preserved in CCTCC (China center for type culture collection) on March 11, 2016 with the preservation number of CCTCC M 2016105. The invention further discloses a construction method of the recombinant pichia pastoris and an application in production of aromatic prenyltransferase. By means of induction culture of the engineering bacterium, soluble recombinant aromatic prenyltransferase NovQ with biological activity can be directly obtained in supernatant of a fermentation liquid, and processes such as cell collection, cell disruption and the like are omitted, accordingly, the production process is simplified. Compared with enzymes from other sources, the aromatic prenyltransferase has the advantages that the activity does not depend on structures such as a living cell or a biological membrane, the substrate specificity is low, prenylation of multiple substrates can be catalyzed, the catalytic activity is high and the like.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
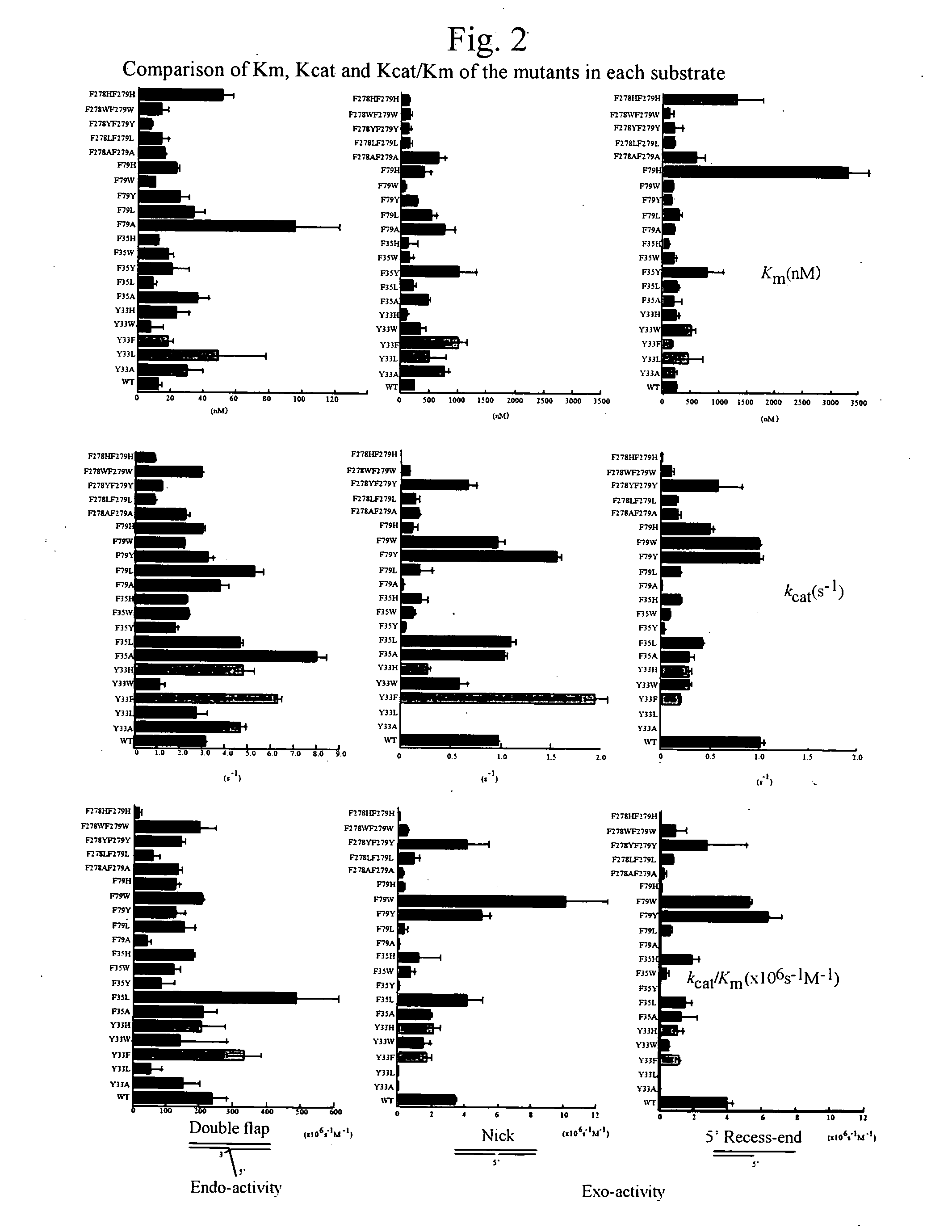
Flap Endonuclease Mutants
InactiveUS20080118922A1Sensitive and accurateBacteriaSugar derivativesBinding siteSubstrate Specificities
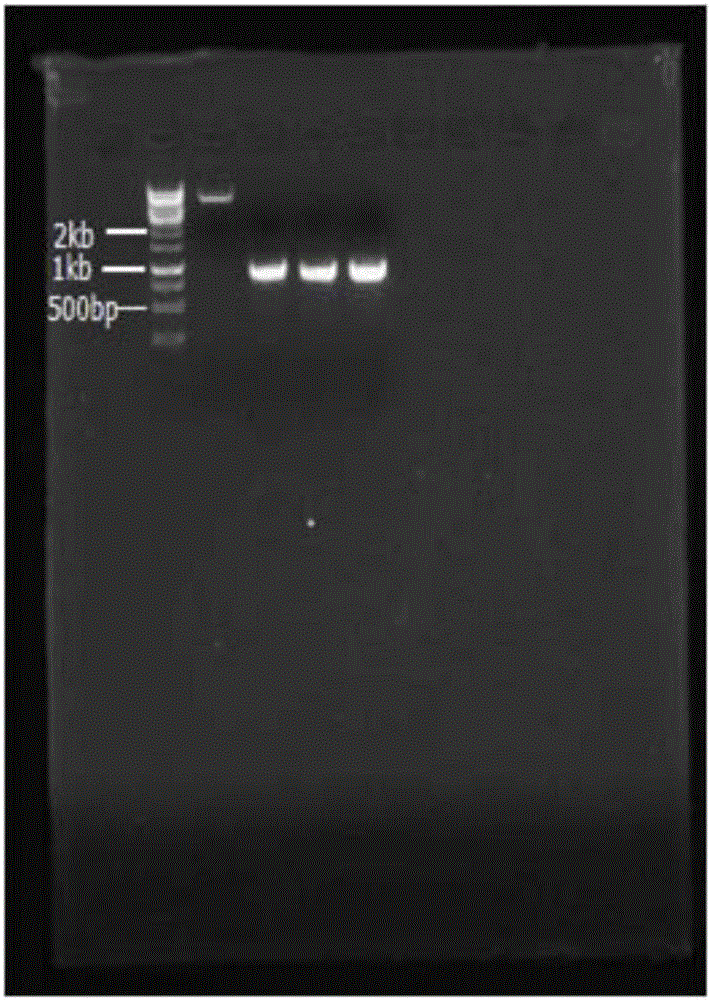
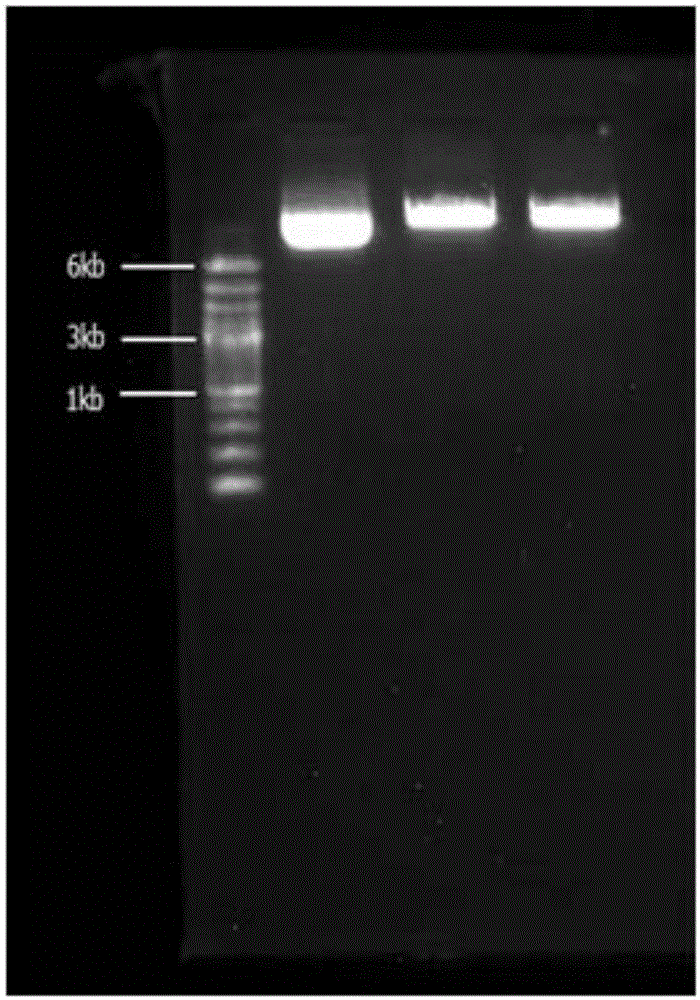
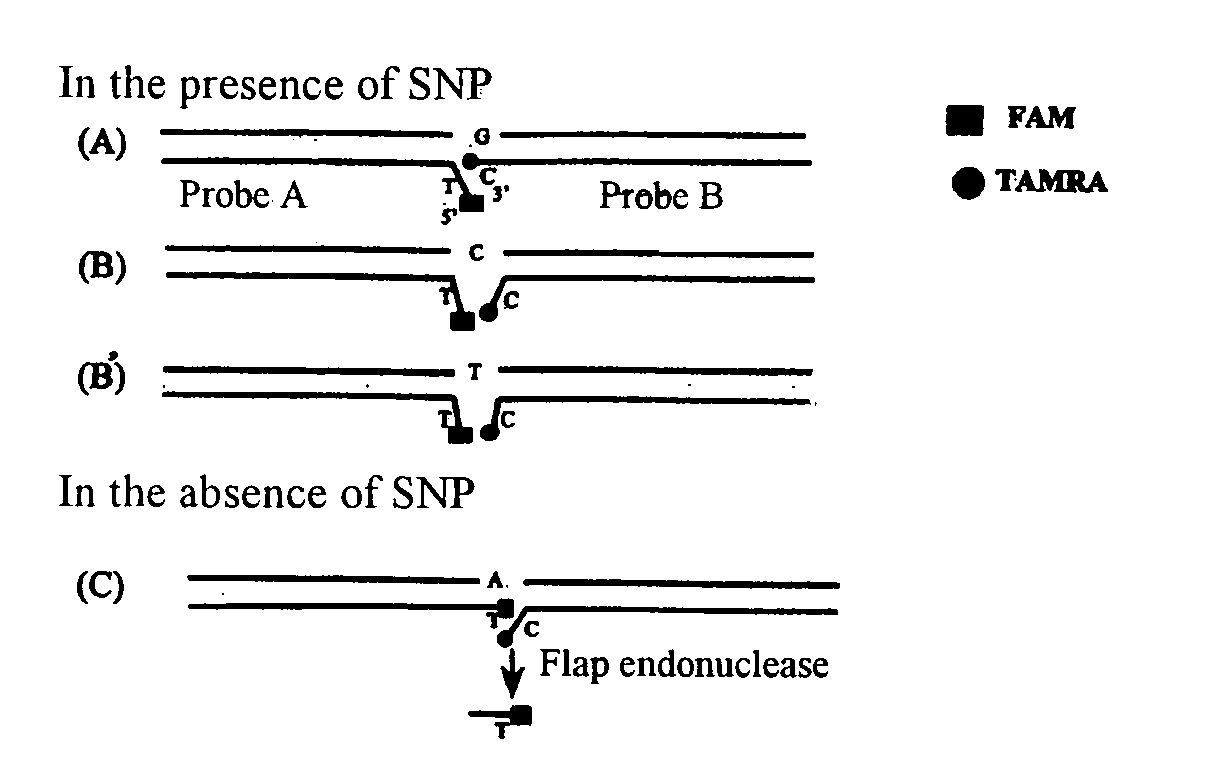
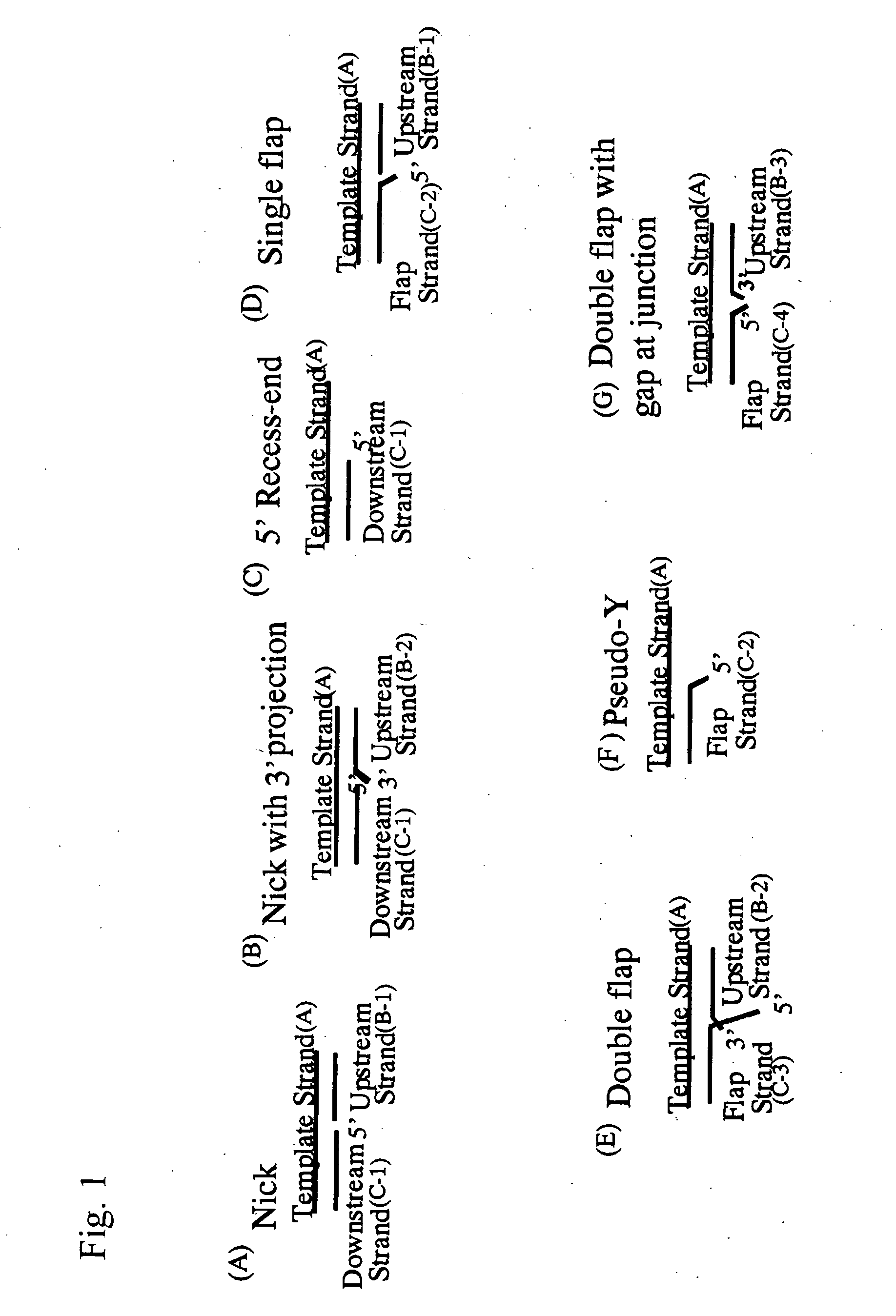
A mutation is introduced into the substrate-binding site of flap endonuclease to prepare a mutant with modified substrate specificity. Using the mutant as a reagent for the analysis of genetic polymorphism, the analysis of genetic polymorphism can be performed more accurately, easily and sensitively as compared with conventional methods.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
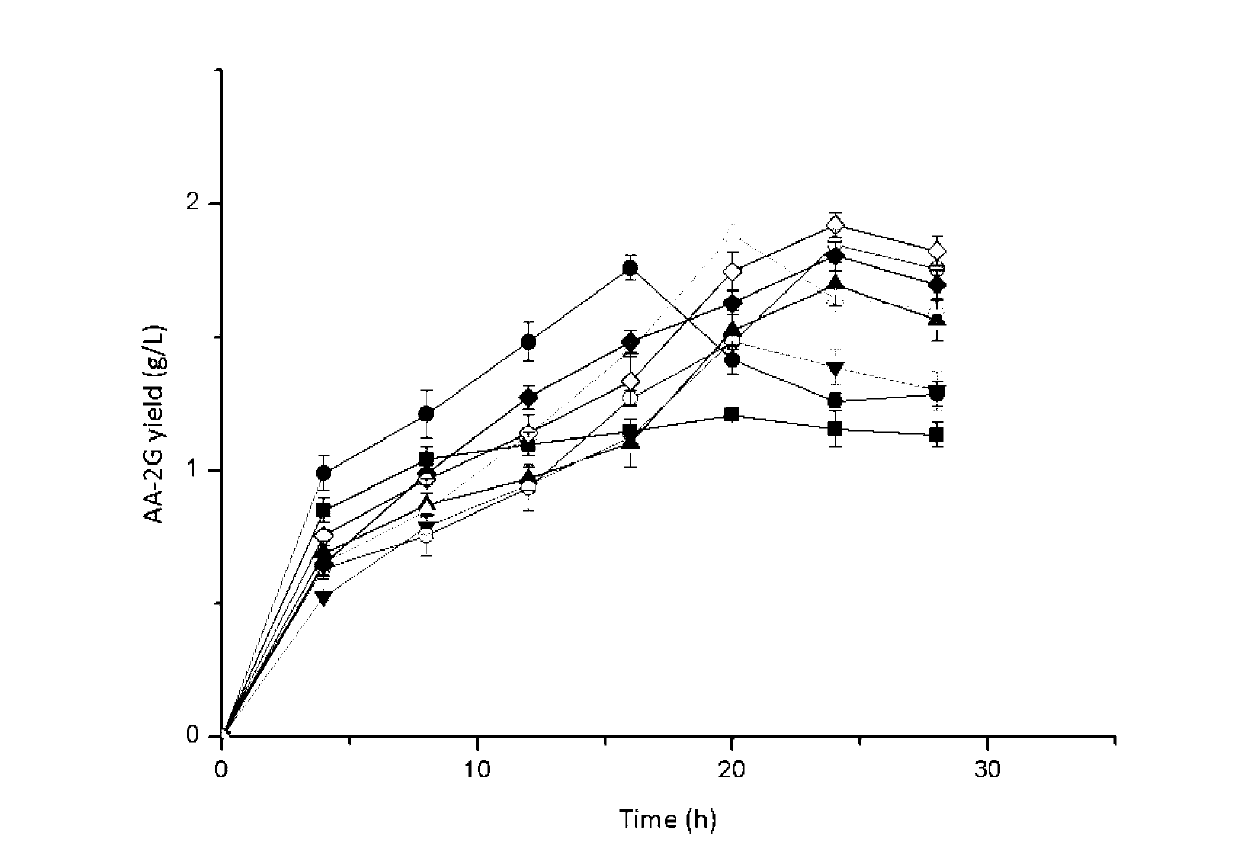
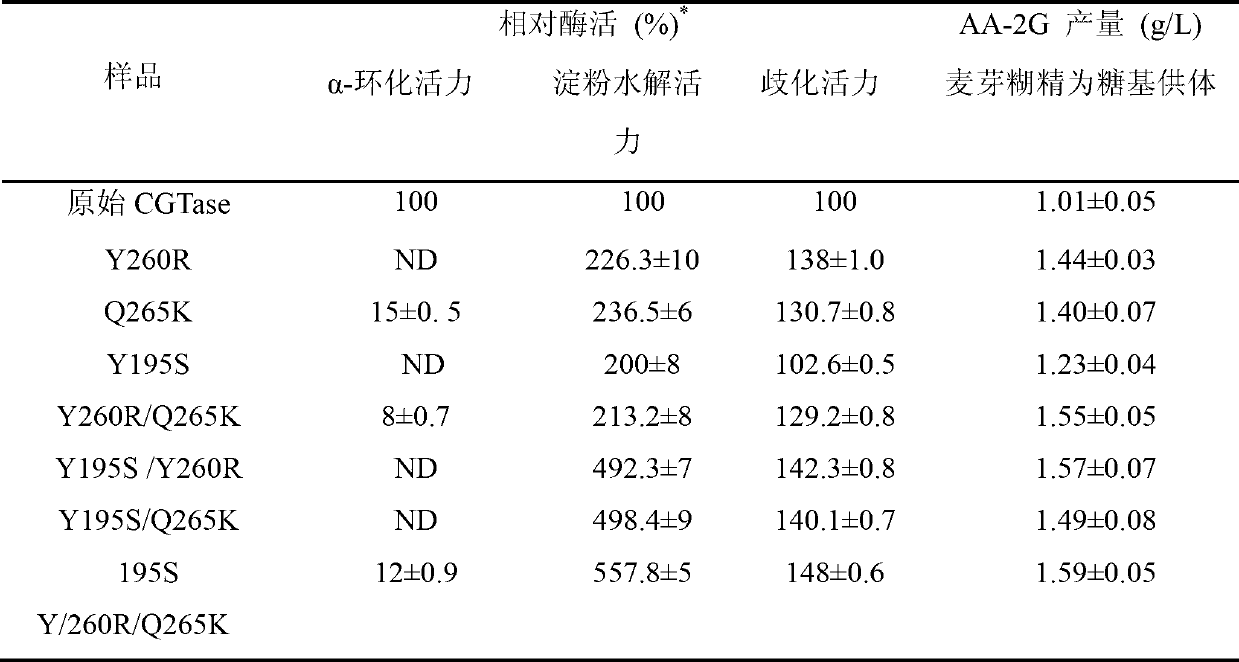
Cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase with improved maltodextrin substrate specificity and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102994468AIncreased substrate specificityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesArginineWild type
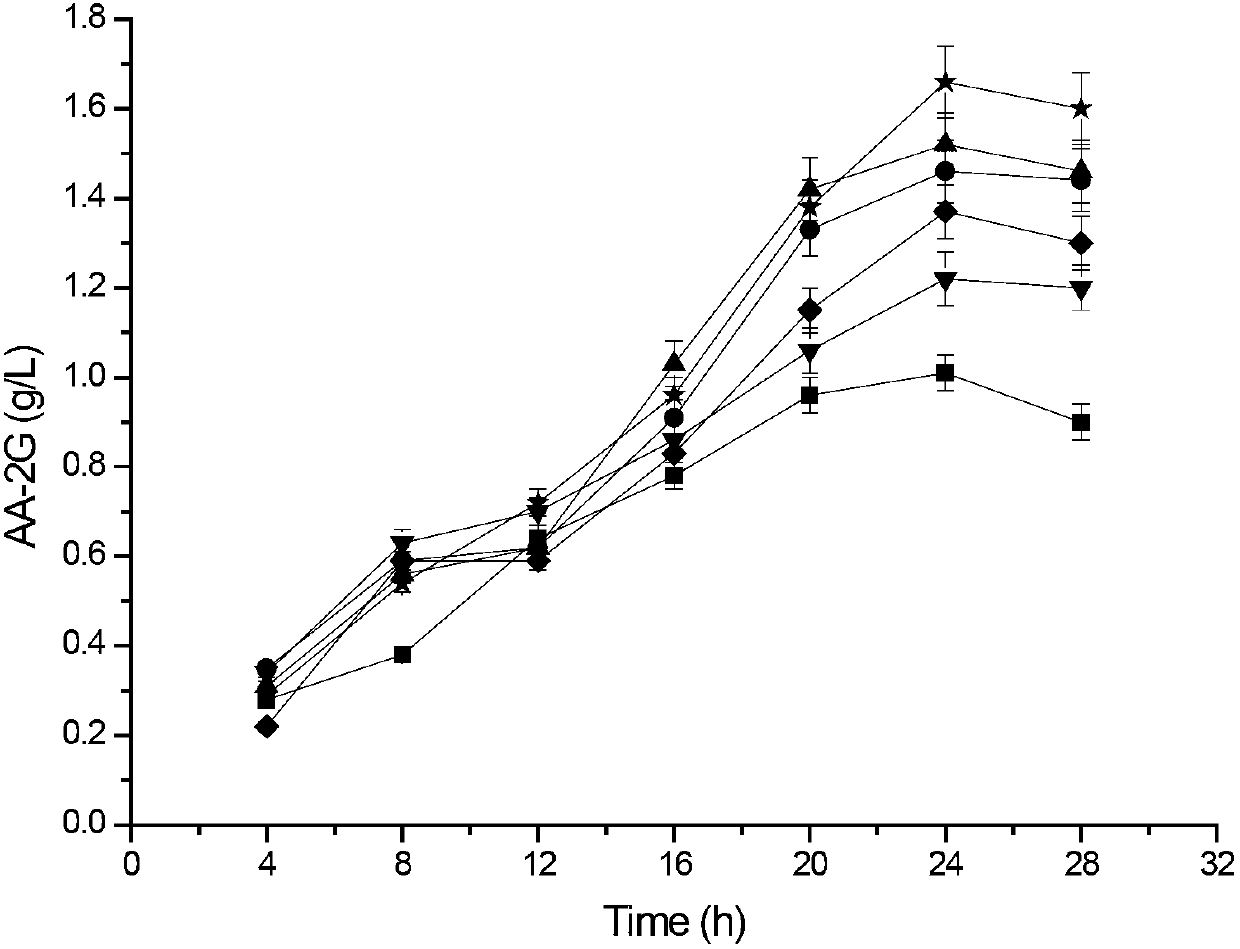
The invention discloses cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase with improved maltodextrin substrate specificity and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. 195-bit tyrosine (Tyr) of CGTase of P.macerans strain JFB05-01 (CCTCC NO:M208063) is replaced by serine (Ser), 260-bit tyrosine (Tyr) is replaced by arginine (Arg), and 265-bit glutamine (Gln) is replaced by lysine (Lys), so that the AA-2G yield is respectively improved by 23 percent, 44 percent and 40 percent. According to combined mutation of the mutant strains, double mutants Y195S / Y260R, Y195S / Q265K and Y260R / Q265K and A three-point mutant Y195S / Y260R / Q265K are obtained. A Glycosyl donor is produced by the maltodextrin, so that the AA-2G yield is respectively improved by 57 percent, 49 percent, 55 percent and 59 percent; and compared with the mild type CGTase, the mutant strains facilitate the production of the AA-2G for glycosyl donors by using maltodextrin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
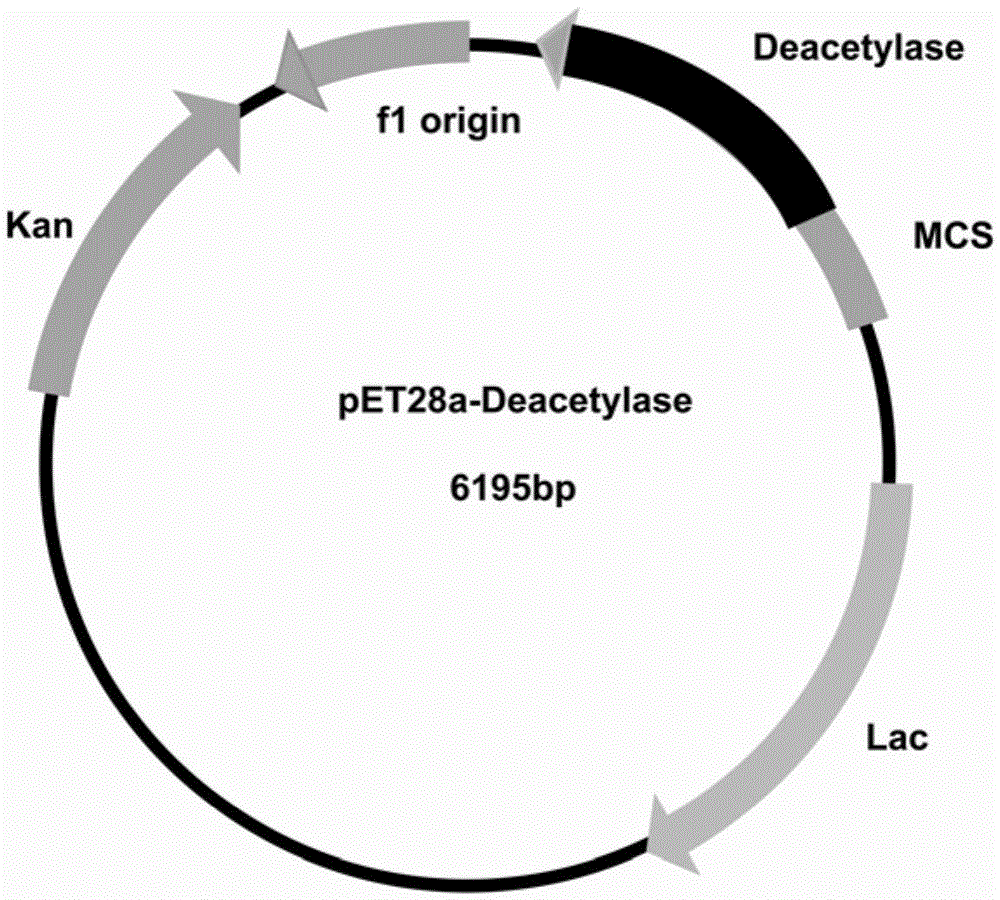
D-acetylglucosamine deacetylase heterologous expression and application
InactiveCN105274081AGreat potential for industrializationStrong substrate specificityBacteriaHydrolasesHeterologousBio engineering
The present invention belongs to the field of biological engineering, and specifically discloses high-quality D-acetylglucosamine deacetylase heterologous expression and application. The amino acid sequence of the D-acetylglucosamine deacetylase is as shown in SEQNO. 1. Through enzymatic activity measurement and substrate specificity analysis, the D-acetylglucosamine deacetylase is strong in substrate specificity, and in the substrate for researches, D-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) and beta-bonded D-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) are deacetylated targetedly to generate D-glucosamine (GlcN) or beta-bonded glucosamine (GlcN). Recombinant D-acetylglucosamine deacetylase is expressed by use of genetic engineering cloning, the D-acetylglucosamine deacetylase can be strongly expressed, and high-quality D-acetylglucosamine deacetylase can be obtained.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Modified sarcosine oxidase, process for producing the same and reagent composition using the same
The present invention discloses a protein, which still has sarcosine oxidase activity after being modified by adding, deleting, inserting or replacing at least one amino acid in the amino acid sequence constituting the protein having sarcosine ammoniaase activity, characterized by Improved stability in liquid compared to unmodified protein and / or reduced effect on L-proline compared to unmodified protein. Sarcosine oxidase has at least one of the following characteristics, namely, based on the effect of creatine on L-proline, measured at 37°C and pH 8.0, is 0.7% or less and the Km of L-proline The value is 150 mM or more; the method for producing sarcosine oxidase having excellent substrate specificity comprises culturing a microorganism capable of producing sarcosine oxidase and collecting sarcosine oxidase from the culture medium; and containing sarcosine A reagent for the detection of creatinine for amino acid oxidase.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase with improved maltodextrin substrate specificity and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103122341AIncreased substrate specificityIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesCyclodextrinWild type
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase with improved maltodextrin substrate specificity and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the invention, for CGTase derived from peanibacillus macerans, lysine at a 47th site, tyrosine at a 89th site, asparaginate at a 94th site and aspartic acid at a 196th site are respectively mutated into leucine K47L, phenylalanine Y89F, praline N94P and tyrosine D196Y, so that AA-2G yields are respectively increased by 30.7%, 10.9%, 10.0% and 31.7%. Complex mutation is carried out on the mutant strains to obtain double mutants namely K47L / Y89F, K47L / N94P, K47L / D196Y, Y89F / N94P, Y89F / D196Y and N94P / D196Y, three-point mutants namely K47L / Y89F / N94P, K47L / Y89F / D196Y, K47L / N94P / D196Y and Y89F / N94P / D196Y and a four-point mutant namely K47L / Y89F / N94P / D196Y. Yields of AA-2G produced by the mutants while maltodextrin is utilized as a glycosyl donor are respectively increased by 42.6%, 11.0%, 37.6%, 43.6%, 43.6%, 41.6%, 44.5%, 50.5%, 20.8%, 35.6% and 64.4%. Compared with the wild type CGTase, the mutants is more beneficial to production of the AA-2G while the maltodextrin is utilized as the glycosyl donor.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Butanedione reductase application
InactiveCN106337068AHigh enzymatic activityIncreased substrate specificityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionEnterobacter cloacaeSubstrate Specificities
The invention provides an application of butanedione reductase BDH of enterobacter cloacae subsp. dissolvens SDM. Through enzymology analysis, the BDH has the advantages of high enzyme activity, good substrate specificity, and single optical selectivity, and has wide industrial application prospect. According to the specific property of the BDH, The invention provides a plurality of applications of BDH or cell organism containing the BDH coding gene bdh to carry out catalyzed synthesis to obtain the chiral pure (S)-acetoin, (R)-acetoin, (S,S)-2,3-butylene glycol, meso-2,3-butylene glycol and ethyl lactate, and the butanedione reductase has important meaning for researching synthesis of chiral pure (S)-acetoin / (R)-acetoin and (S,S)-2,3-butylene glycol / meso-2,3-butylene glycol.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Mutant Glucose Dehydrogenase
ActiveUS20080280312A1Increased substrate specificityReduced responseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGlucose polymersSubstrate Specificities
Substrate specificity for glucose of a glucose dehydrogenase having the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 13 is improved by substituting another amino acid residue for the amino acid residue at position 472 and / or 475.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Active-site engineering of nucleotidylyltransferases and general enzymatic methods for the synthesis of natural and “unnatural” UDP- and TDP-nucleotide sugars
InactiveUS7122359B2Method is fastEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesAlkanePresent method
The present invention provides mutant nucleotidylyl-transferases, such as Ep, having altered substrate specificity; methods for their production; and methods of producing nucleotide sugars, which utilize these nucleotidylyl-transferases. The present invention also provides methods of synthesizing desired nucleotide sugars using natural and / or modified Ep or other nucleotidyltransferases; and nucleotide sugars sythesized by the present methods. The present invention further provides new glycosyl phosphates, and methods for making them.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
Glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveCN101454449AEfficient productionImprove heat resistanceFungiBacteriaLiquid stateAspergillus oryzae
The invention provides a glucose dehydrogenase which is excellent in thermostability and substrate specificity and is not affected by dissolved oxygen. More particularly, the invention relates to the glucose dehydrogenase which is derived from a eukaryote and is characterized by maintaining 90% or more activity after a heat treatment at 55 DEG C for 15 minutes in a liquid state compared to the activity before the heat treatment. The invention efficiently produces a glucose dehydrogenase derived from Aspergillus oryzae and provides a more practical glucose dehydrogenase. The invention providesa method for producing a filamentous fungus-derived FAD-GDH with excellent substrate specificity by high expression in a recombinant, a FAD-GDH protein obtained by the method and a glucose assay reagent utilizing the protein. The invention relates to a method of improving the stability of a composition containing a soluble glucose dehydrogenase (GDH). As the soluble GDH, the filamentous fungus-derived FAD-dependent GDH is preferable, and particularly, the best effect has been observed in an A. oryzae-derived FAD-GDH or an A. terreus-derived FAD-GDH.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Mutant firefly luciferase
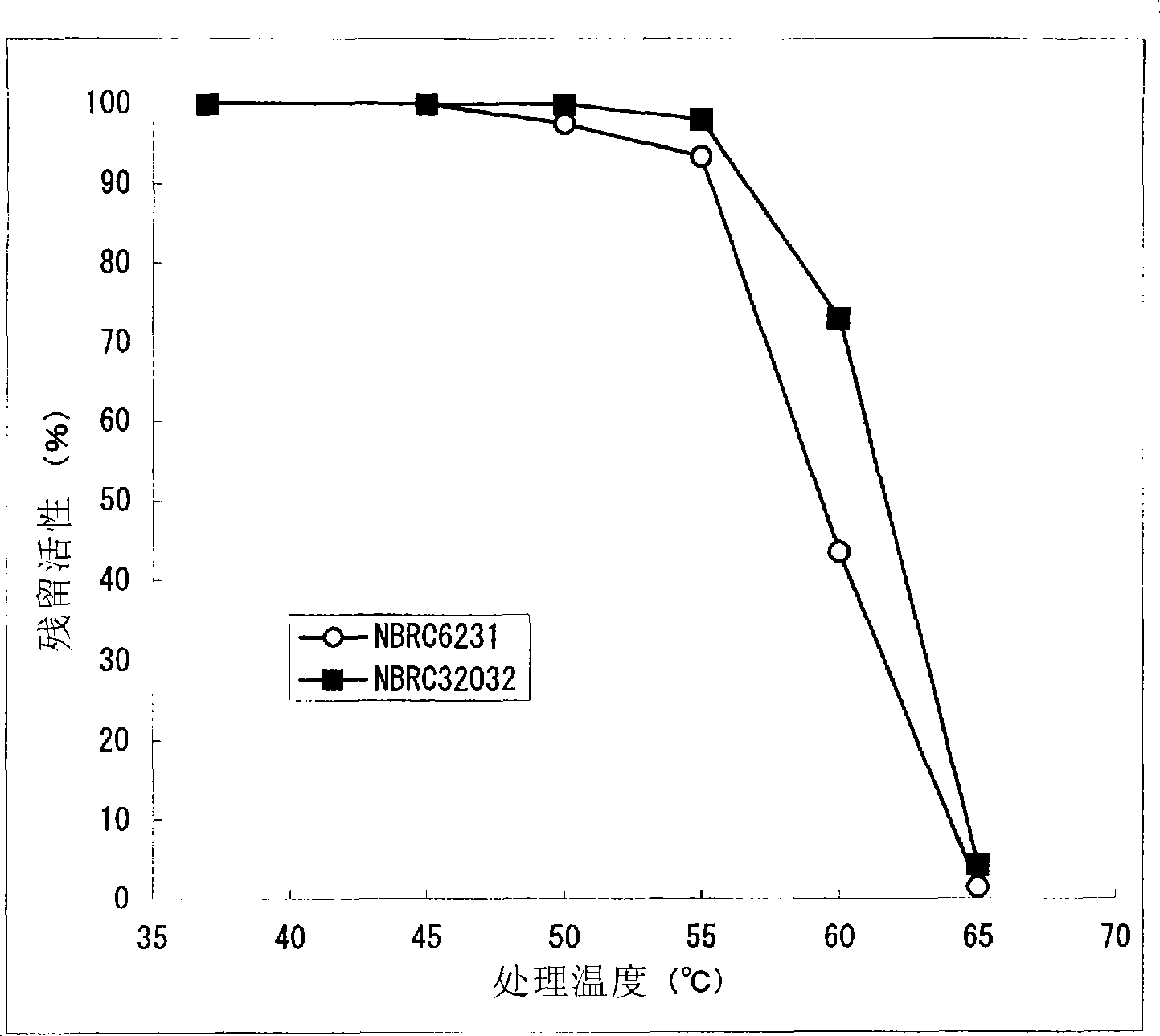
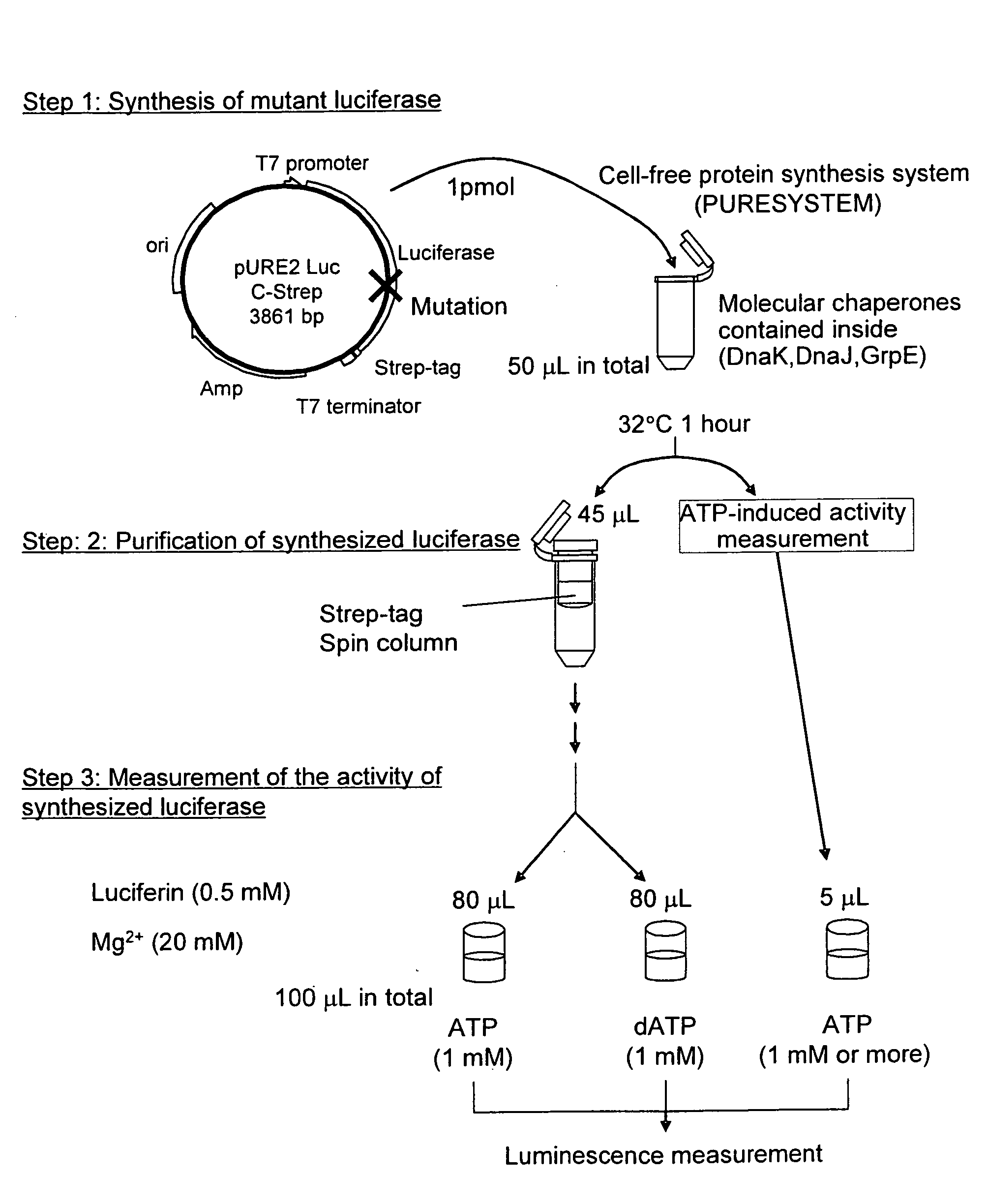
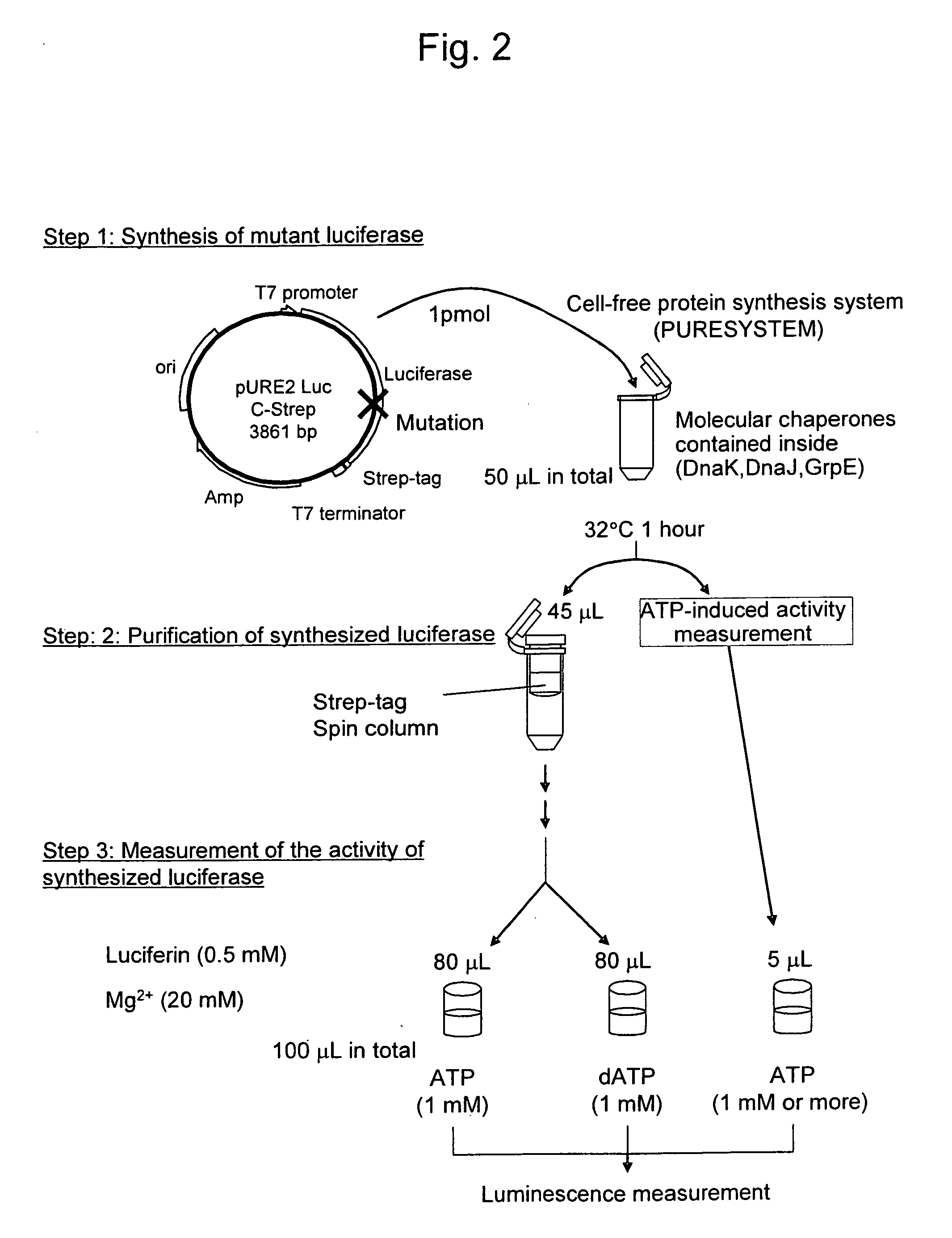
InactiveUS20090081680A1Reduce the ratioSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceWild type
This invention relates to: the development of a mutant firefly luciferase in order to use dATP as a DNA polymerase substrate upon pyrosequencing, such luciferase being subjected to substrate specificity modification in a manner such that the dATP-induced activity alone is decreased while the ATP-induced activity is maintained; and a mutant firefly luciferase for which the proportion of activity induced by dATP to activity induced by ATP (dATP / ATP) is lower than that for the wild-type firefly luciferase, in which an amino acid identified based on homology analysis as corresponding with the 421st amino acid (glycine) of the amino acid sequence of the wild-type North American firefly (Photinus pyralis) luciferase has been substituted with a polar amino acid.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com