Patents
Literature
39 results about "M13 bacteriophage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
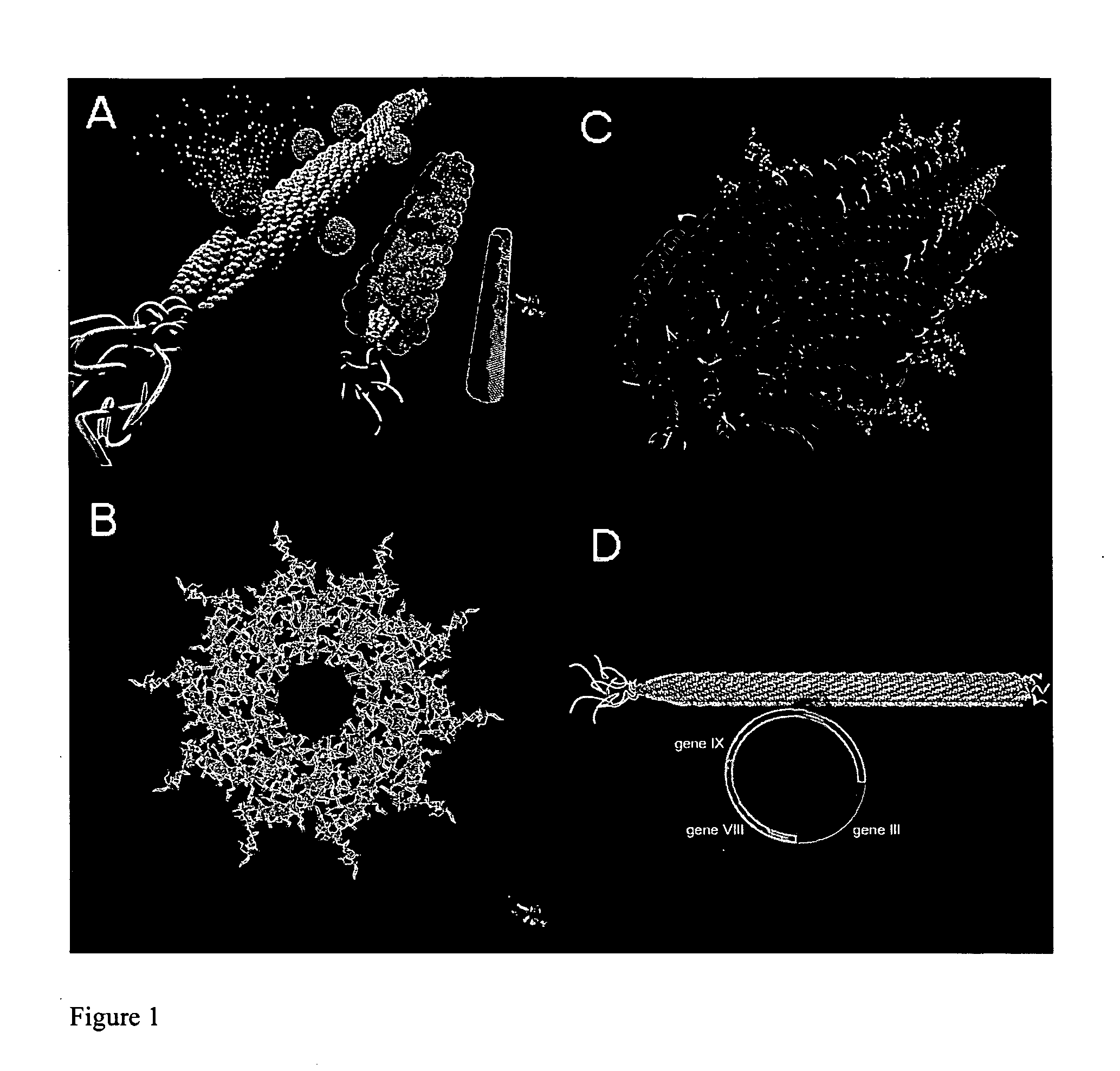
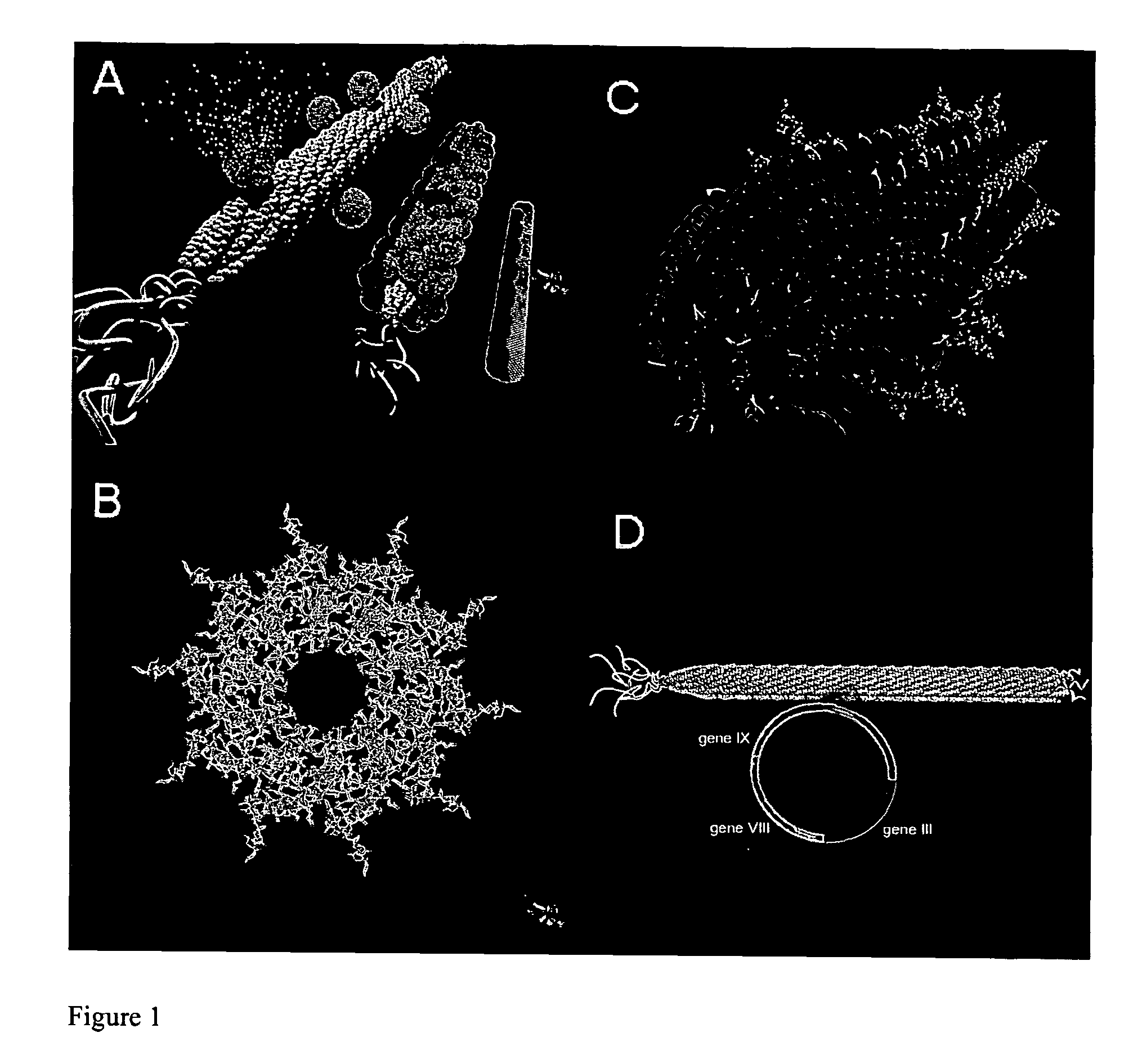
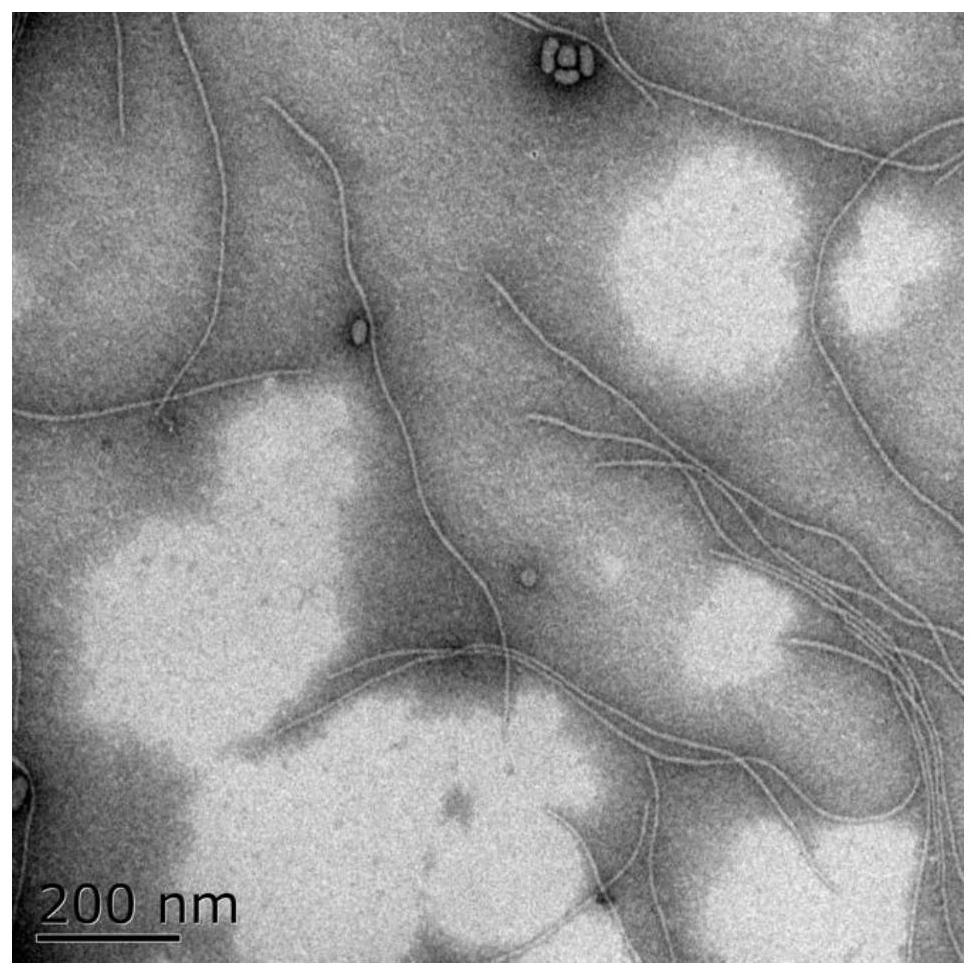
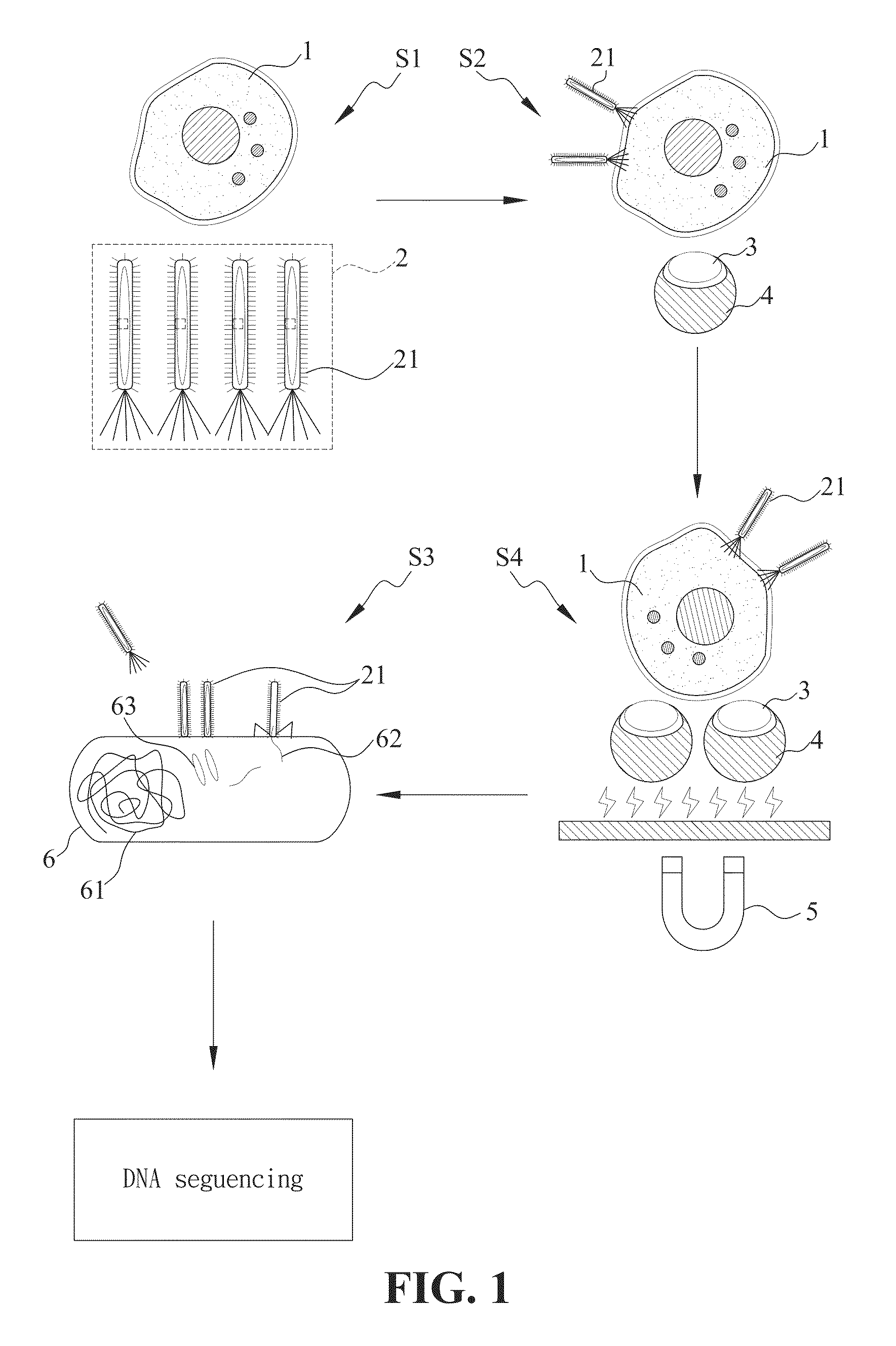
M13 is a filamentous bacteriophage composed of circular single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) which is 6407 nucleotides long encapsulated in approximately 2700 copies of the major coat protein P8, and capped with 5 copies of two different minor coat proteins (P9, P6, P3) on the ends. The minor coat protein P3 attaches to the receptor at the tip of the F pilus of the host Escherichia coli. Infection with M13 lysogenic phage. The infection causes turbid plaques in E. coli lawns, of intermediary opacity in comparison to regular lysis plaques. However, a decrease in the rate of cell growth is seen in the infected cells. M13 plasmids are used for many recombinant DNA processes, and the virus has also used for phage display, nanostructures and nanotechnology applications.
Inorganic nanowires
InactiveUS20050221083A1Good monodispersityHigh degreeMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsNanowireSingle crystal
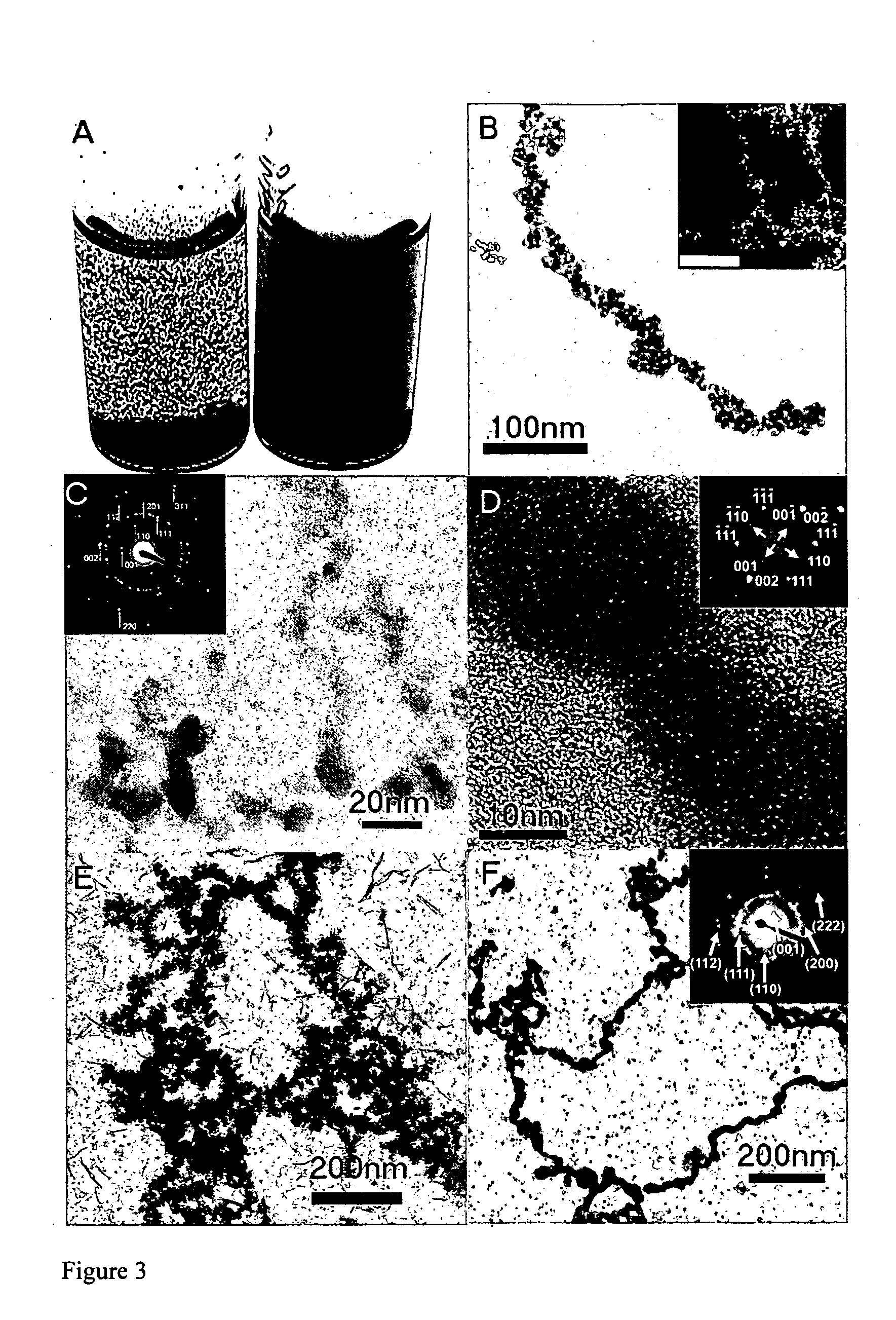
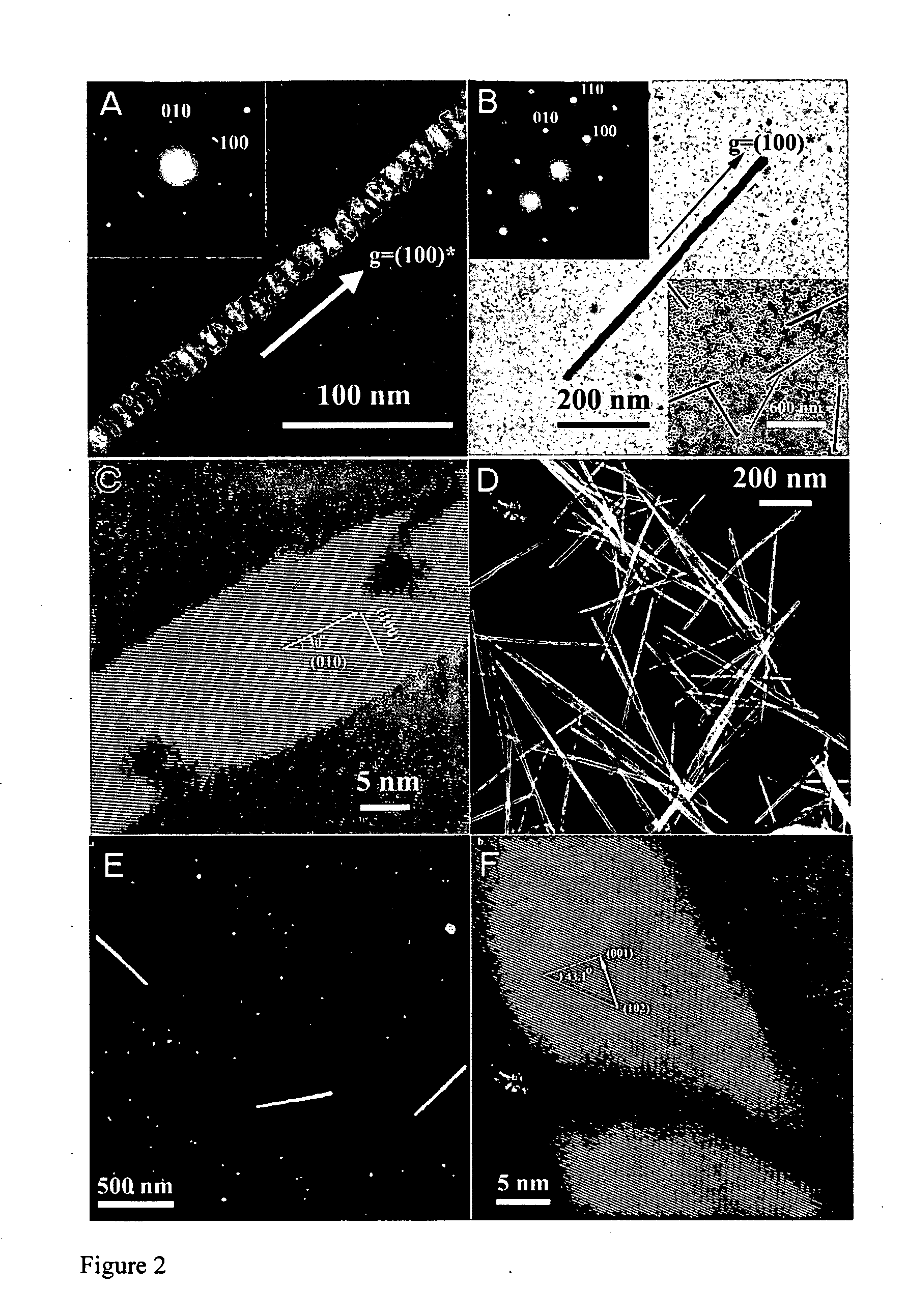
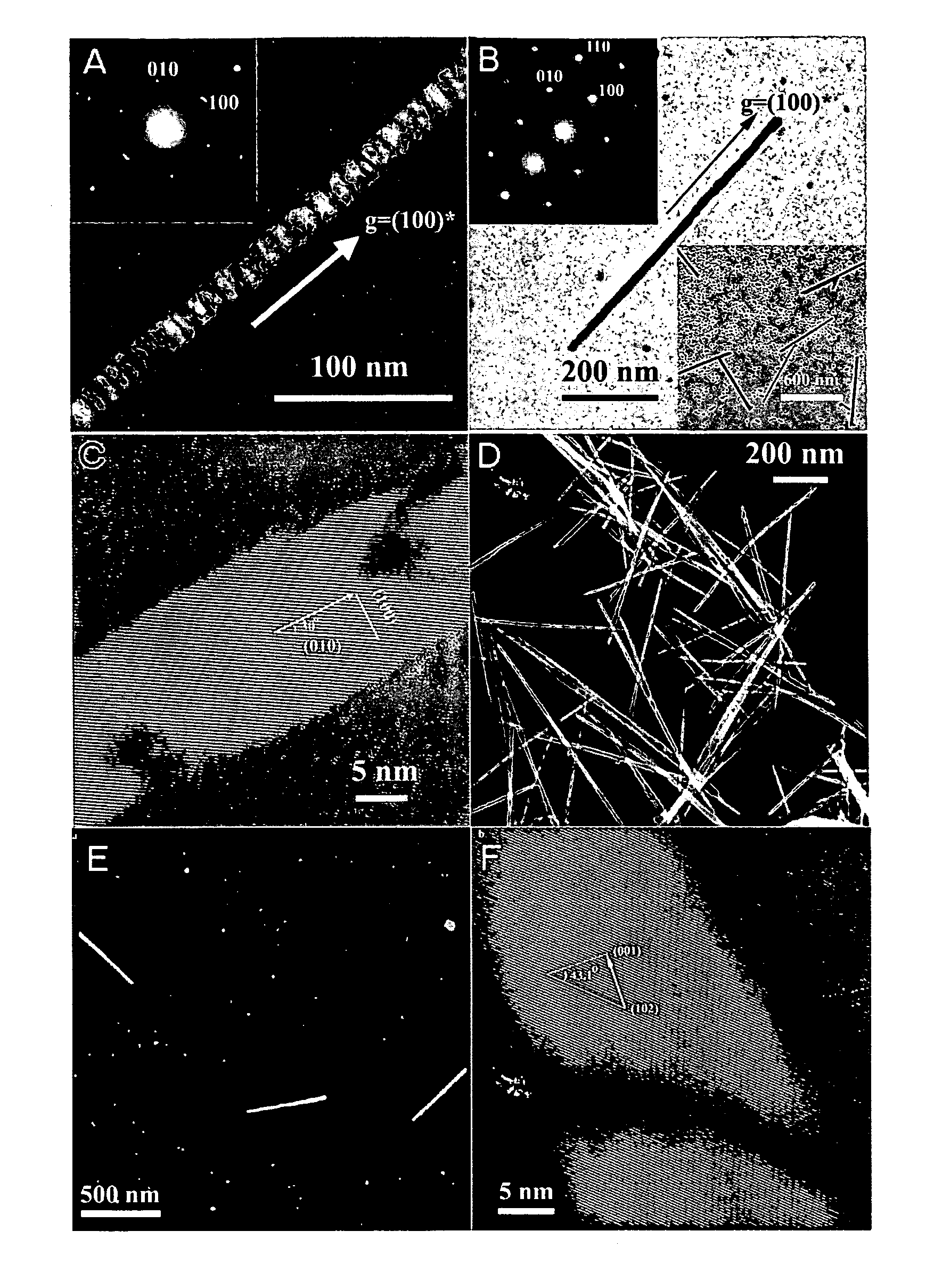
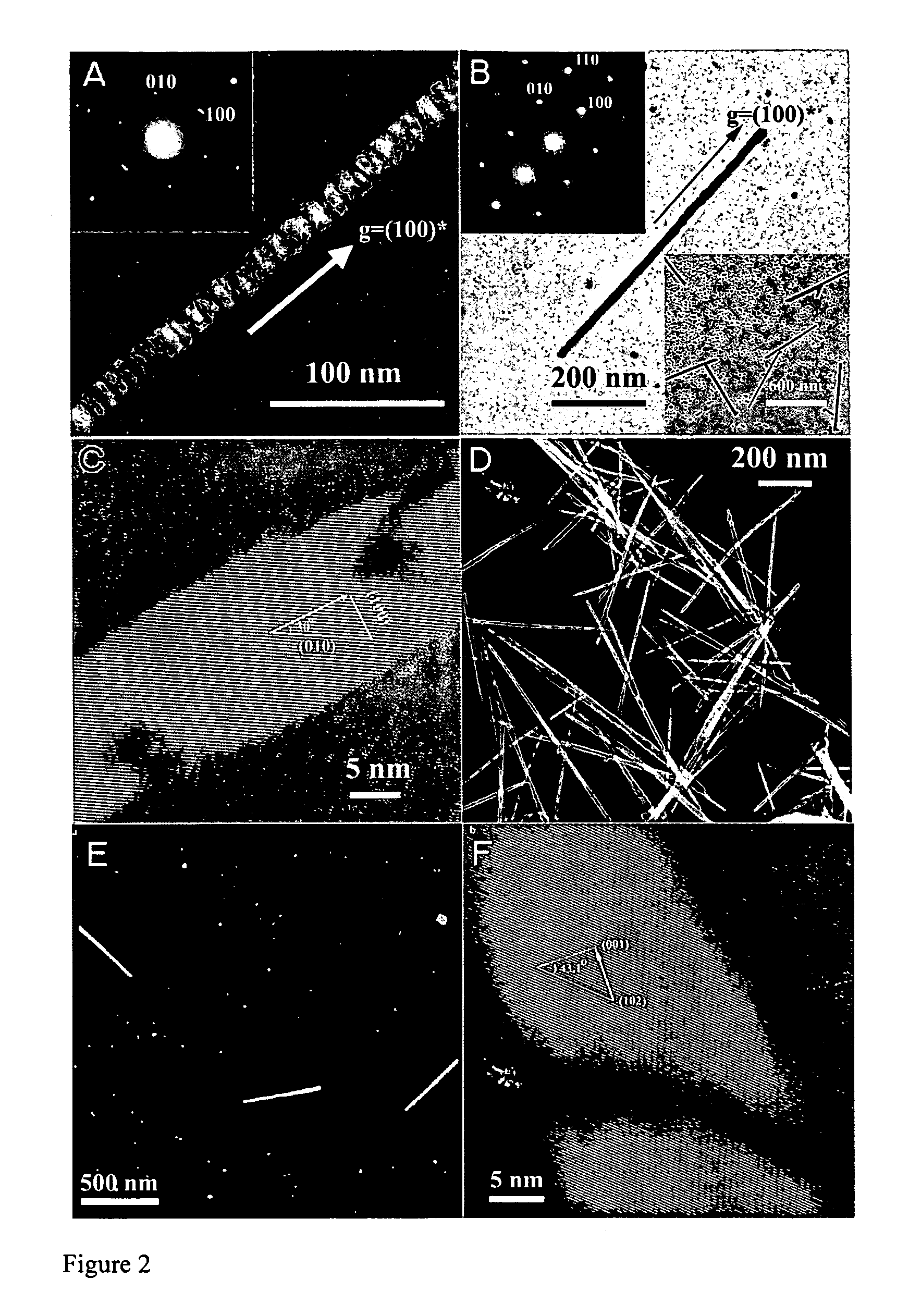
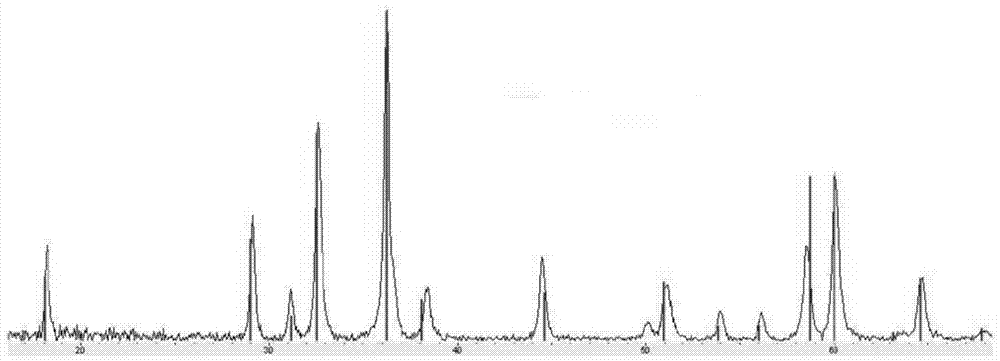
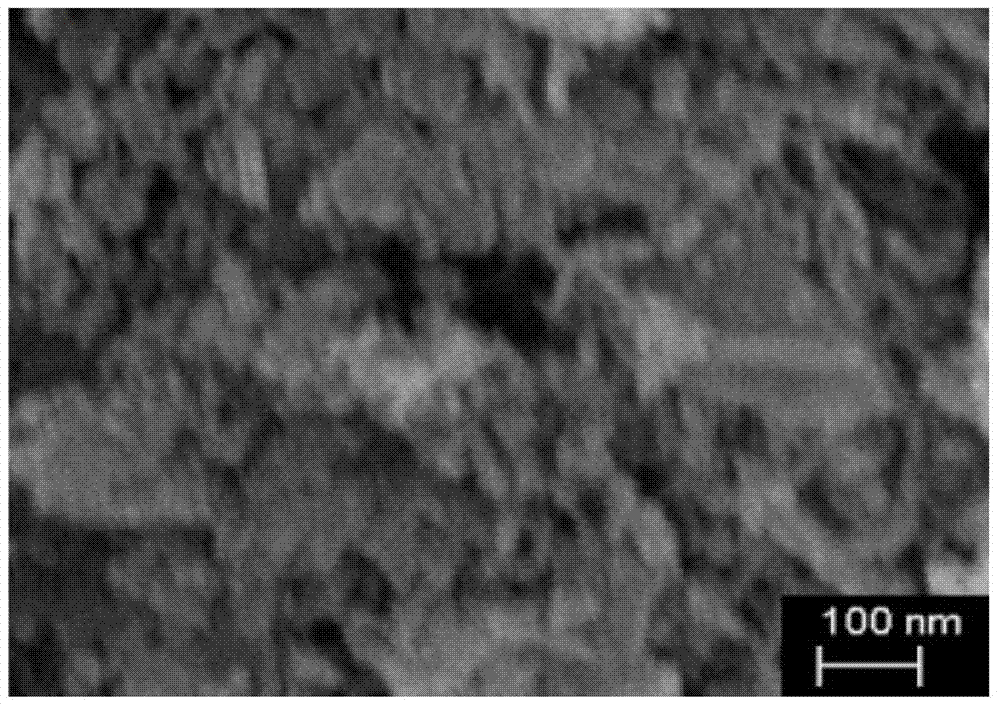
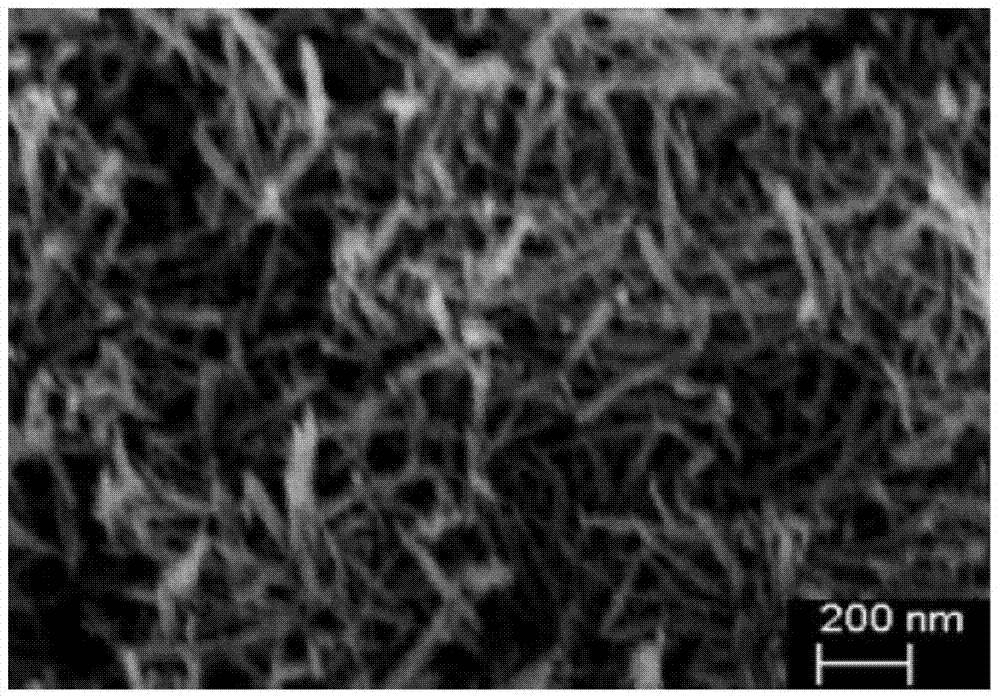
An inorganic nanowire having an organic scaffold substantially removed from the inorganic nanowire, the inorganic nanowire consisting essentially of fused inorganic nanoparticles substantially free of the organic scaffold, and methods of making same. For example, a virus-based scaffold for the synthesis of single crystal ZnS, CdS and free-standing L10 CoPt and FePt nanowires can be used, with the means of modifying substrate specificity through standard biological methods. Peptides can be selected through an evolutionary screening process that exhibit control of composition, size, and phase during nanoparticle nucleation have been expressed on the highly ordered filamentous capsid of the M13 bacteriophage. The incorporation of specific, nucleating peptides into the generic scaffold of the M13 coat structure can provide a viable template for the directed synthesis of a variety of materials including semiconducting and magnetic materials. Removal of the viral template via annealing can promote oriented aggregation-based crystal growth, forming individual crystalline nanowires. The unique ability to interchange substrate specific peptides into the linear self-assembled filamentous construct of the M13 virus introduces a material tunability not seen in previous synthetic routes. Therefore, this system provides a genetic tool kit for growing and organizing nanowires from various materials including semiconducting and magnetic materials.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Inorganic nanowires
InactiveUS7923109B2High degreeHigh of of modificationMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsNanowireSingle crystal
An inorganic nanowire having an organic scaffold substantially removed from the inorganic nanowire, the inorganic nanowire consisting essentially of fused inorganic nanoparticles substantially free of the organic scaffold, and methods of making same. For example, a virus-based scaffold for the synthesis of single crystal ZnS, CdS and free-standing L10 CoPt and FePt nanowires can be used, with the means of modifying substrate specificity through standard biological methods. Peptides can be selected through an evolutionary screening process that exhibit control of composition, size, and phase during nanoparticle nucleation have been expressed on the highly ordered filamentous capsid of the M13 bacteriophage. The incorporation of specific, nucleating peptides into the generic scaffold of the M13 coat structure can provide a viable template for the directed synthesis of a variety of materials including semiconducting and magnetic materials. Removal of the viral template via annealing can promote oriented aggregation-based crystal growth, forming individual crystalline nanowires. The unique ability to interchange substrate specific peptides into the linear self-assembled filamentous construct of the M13 virus introduces a material tunability not seen in previous synthetic routes. Therefore, this system provides a genetic tool kit for growing and organizing nanowires from various materials including semiconducting and magnetic materials.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Method of reducing cadmium ions by M13 phage-mediated nano-iron
ActiveCN103882064AEvenly dispersedImprove responseViruses/bacteriophagesFermentationMaterials preparationNanoparticle
The invention discloses a method of reducing cadmium ions by M13 phage-mediated nano-iron and belongs to the field of environmental pollution governance and nano material preparation. According to the method, iron-adsorbed special M13 phage is adopted to synthesize uniformly dispersed zero-valent nano-iron particles in a mediated manner, and adopts cadmium-adsorbed special M13 phage M13 (Cd-s) to uniformly disperse divalent cadmium ions; then, the zero-valent nano-iron mediated and dispersed by the M13 phage is taken as a reducing agent so as to efficiently reduce divalent cadmium ions uniformly dispersed on the surface of M13(Cd-s). The method disclosed by the invention is high in reducing efficiency, quick in reaction, capable of efficiently catalyzing the divalent ions to be reduced into zero-valent cadmium on the phage surface, so that cadnimum pollution in environment is removed, and nano-particles of zero-valent iron, iron oxide and zero-valent cadmium also can be quickly prepared.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
DNA origami structure, closing and releasing method of DNA origami structure and application of DNA origami structure as drug delivery system
InactiveCN112143727ASolve limitedSolve efficiency problemsMicrobiological testing/measurementInorganic non-active ingredientsGold particlesMedicine
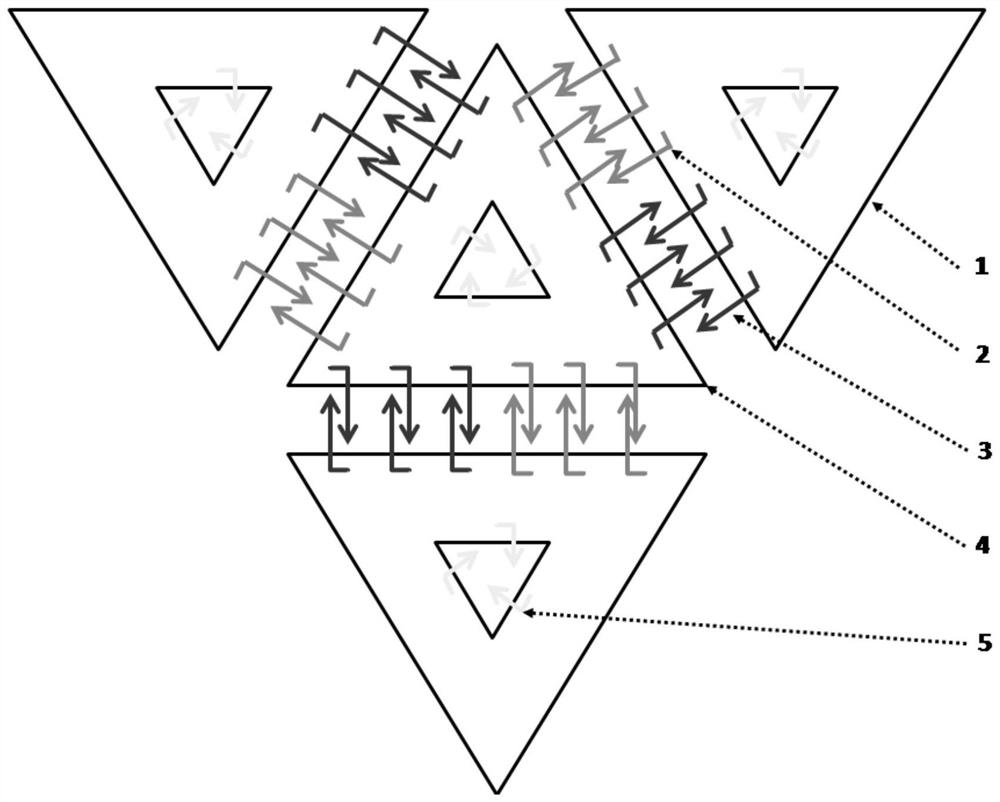
The invention relates to a DNA origami structure, a closing and releasing method of the DNA origami structure and an application of the DNA origami structure as a drug delivery system, and belongs tothe technical field of DNA nano drug delivery. The DNA origami structure is a DNA tetrahedron and comprises three side triangular origamis and a central triangular origami, and three sides of the central triangular origami are connected with the three side triangular origamis respectively; skeleton chains of the central triangular origami and the side triangular origamis are annular single-helix DNA chains of M13 bacteriophage; the central triangular origami and the side triangular origamis are occluded through base complementary pairing of respective internal staple chains and respective skeleton chains; the central triangular origami is complementarily paired with connecting staple chains of the side triangular origamis through a connecting staple chain; and the central triangular origami and the side triangular origamis capture nano-gold particles through capture chains, and the side triangular origamis and the central triangular origami form a three-dimensional tetrahedral origamistructure through traction of the nano-gold particles. According to the invention, the drug loading efficiency is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
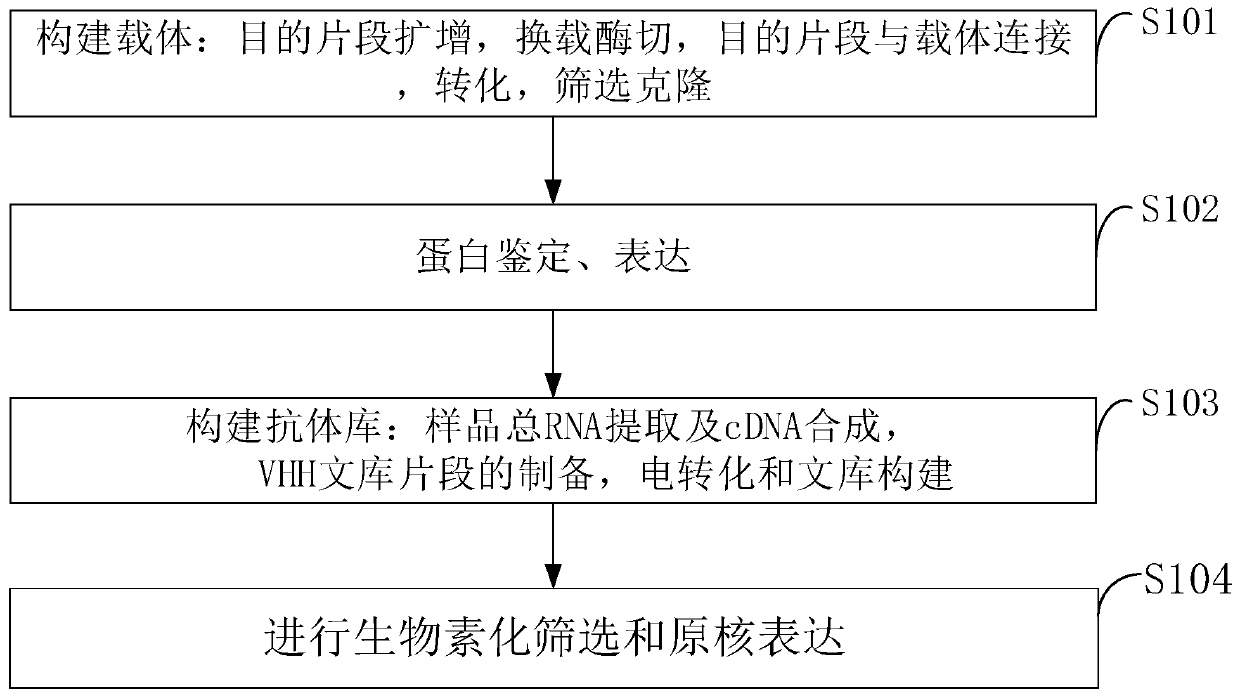
Method for preparing PD-L1 (programmed death-ligand 1) nanoantibody by immunizing alpacas with PD-L1 antigen
InactiveCN110256564ADifficult to identifyEvade captureMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsSequence signalAntigen
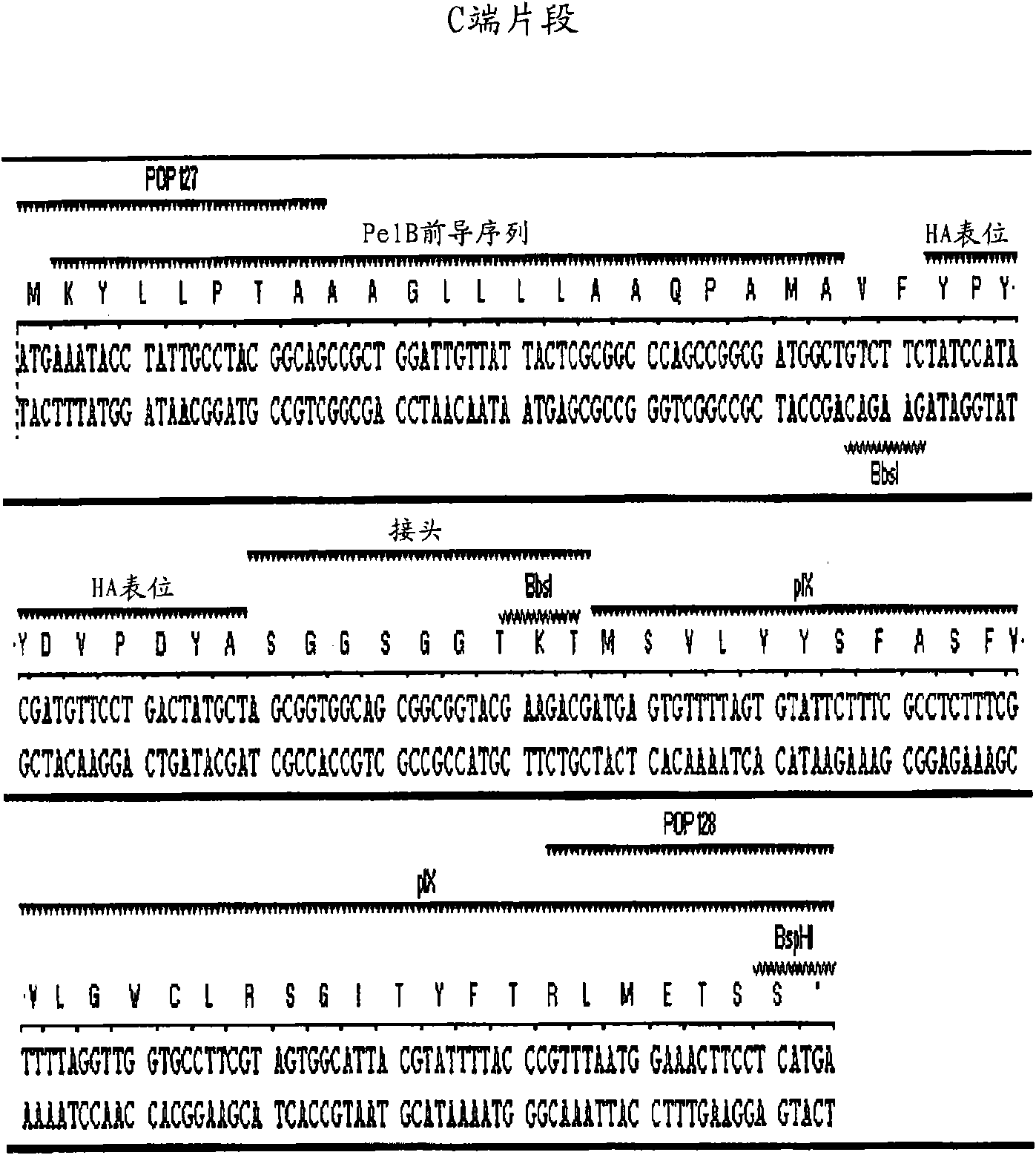
The invention belongs to the technical field of antibodies and discloses a method for preparing PD-L1 (programmed death-ligand 1) nanoantibody by immunizing alpacas with a PD-L1 antigen. The method comprises: designing two synthetic primers, amplifying by PCR (polymerase chain reaction) to obtain sufficient target products for enzyme digestion, linking target fragments to a vector, converting, and carrying out screening and cloning; carrying out protein verifying and expressing; constructing an antibody library; displaying a VHH antibody library through an M13 bacteriophage display system which is composed of a pMECS phagemid vector, E. coli TG1 and an M13KO7 helper phage. In the phasmid vector pMECS, a sequence before a Pst I enzyme digestion site is a coding sequence for part of amino acids in first frame regions of pelB secretory signal peptides and antibodies; the pelB signal peptides can guide subsequent polypeptides secreted to periplasmic cavities; a sequence after a Not I enzyme digestion site is a coding sequence for HA and 6*His tags; the method is suitable for purification or detection of fusion proteins.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Electrode composite material, preparation method thereof, anode possessing the electrode composite material and cell
ActiveCN104377350AInhibition of the shuttle effectInhibition lossMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesSulfurElectrochemistry
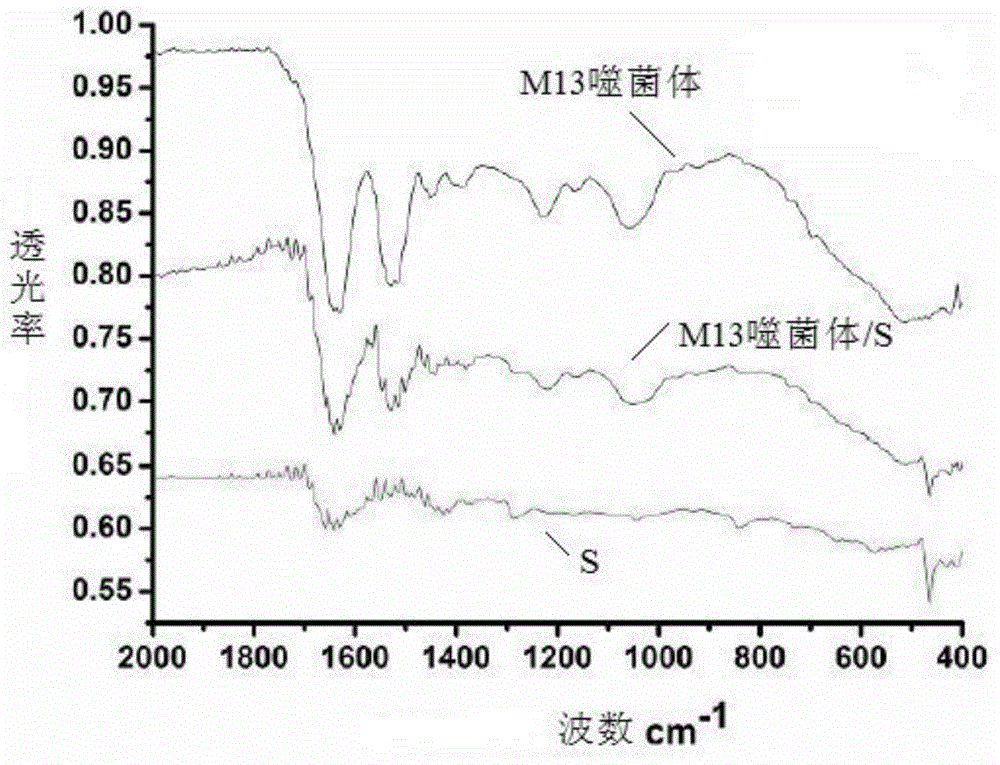
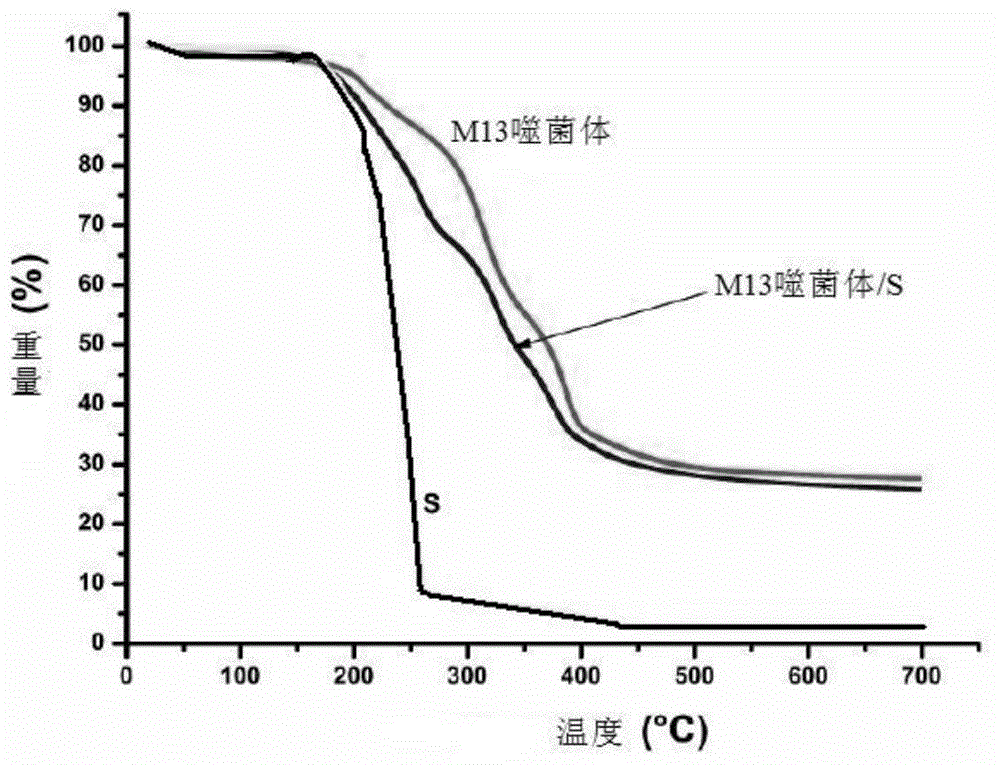
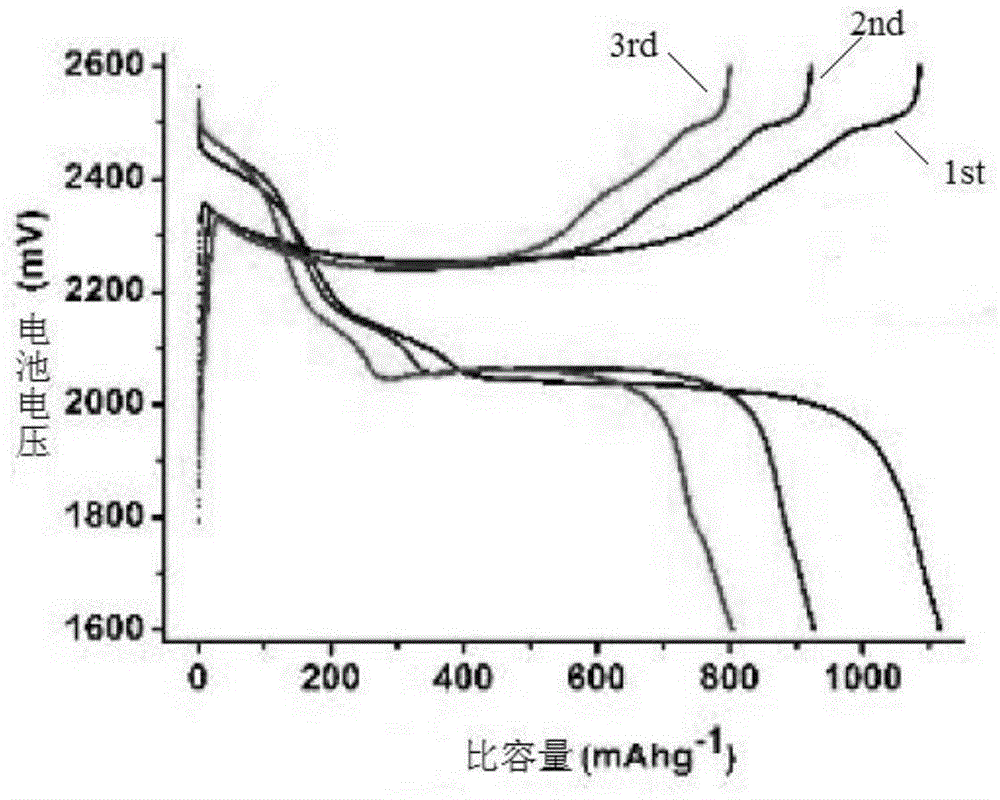
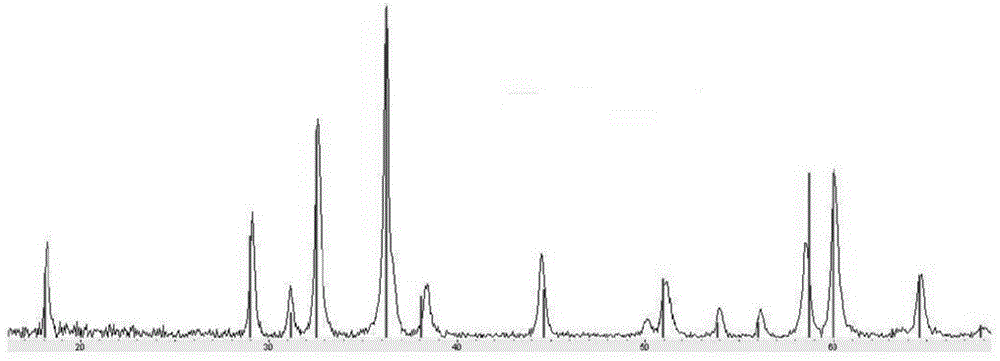
The invention provides an electrode composite material, which comprises M13 bacteriophage and elemental sulfur. The electrode composite material has good thermal stability and good electrochemistry performance, the problem of active material loss during charge and discharge process of cell can be effectively solved, and discharge capacity of the cell is increased. The invention also provides a preparation method of the electrode composite material, an anode possessing the electrode composite material and a cell.
Owner:POSITEC POWER TOOLS (SUZHOU) CO LTD +1
Electrode composite material, preparation method of electrode composite material, as well as negative electrode and battery with electrode composite material
ActiveCN104425801ALow costWith mass productionMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesNanostructureLithium-ion battery
The invention provides an electrode composite material which comprises a M13 bacteriophage and Mn3O4. The electrode composite material has a good nano structure and a good electrochemical performance, and can be used as a negative electrode material of a lithium ion battery; moreover, a preparation method of the electrode composite material is simple and feasible, and can be implemented at low temperature. The invention also provides the preparation method of an electrode composite material, and a negative electrode and a battery which comprise the electrode composite material.
Owner:POSITEC POWER TOOLS (SUZHOU) CO LTD +1
Preparation method of RGD-M13 bacteriophage/oxidized regenerated cellulose composite hemostatic material
ActiveCN105435295AHigh grafting rateImprove adhesionPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAbsorbent padsMedicineUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a preparation method of a RGD-M13 bacteriophage / oxidized regenerated cellulose composite hemostatic material, and relates to a preparation method of a hemostatic material. The invention aims to solve the problems that in the prior art, after the modification of conventional oxidized regenerated cellulose, the hemostatic time is slightly prolonged, while the mechanical strength and biological absorbability of oxidized regenerated cellulose are both reduced. The preparation method comprises the following steps: step one, activating oxidized regenerated cellulose; step two, soaking the activated oxidized regenerated cellulose in RGD-M13 bacteriophage suspension so as to obtain the RGD-M13 bacteriophage / oxidized regenerated cellulose composite hemostatic material. The prepared RGD-M13 bacteriophage / oxidized regenerated cellulose composite hemostatic material can be used to stop bleeding, and hemostatic time is shortened by 10.4 to 32.9%. The provided prepared method can obtain a RGD-M13 bacteriophage / oxidized regenerated cellulose composite hemostatic material.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Recombinant phages
The present invention relates to bacteriophages for use in the treatment or prophylaxis of bacterial infections, especially mucosal bacterial infections such as Heliobacter pylori infections, in particular, it relates to modified filamentous bacteriophages, e.g. M13 phages, for such use, which bacteriophages present at the surface a recombinant protein comprising (i) a first component derived from a bacteriophage surface protein; and (ii) a second component comprising variable region sequences of an antibody to provide a bacterial antigen binding site, said second component rendering said bacteriophage capable of binding to and thereby inhibiting growth of bacterial cells involved in the etiology of said infection.
Owner:M ANG RDH SVEN
Preparation method of RGD-M13 phage/polylysine/oxidized regenerated cellulose composite haemostatic material
ActiveCN105477675AGood hemostatic effectNo damage to mechanical strengthPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAbsorbent padsPolymer sciencePolyphage
The invention discloses a preparation method of an RGD-M13 phage / polylysine / oxidized regenerated cellulose composite haemostatic material, and relates to a preparation method of a haemostatic material. The invention aims at solving the problems of an existing oxidized regenerated cellulose modified haemostatic material that a haemostatic time is lightly improved, and the mechanical strength and bio-absorbing property of the oxidized regenerated cellulose are decreased. The method comprises the following steps: I. self-assembly of polylysine; II. self-assembly of an RGD-M13 phage; and III. cleaning and drying, so that the RGD-M13 phage / polylysine / oxidized regenerated cellulose composite haemostatic material is obtained. The RGD-M13 phage / polylysine / oxidized regenerated cellulose composite haemostatic material prepared by the invention, when applied to haemostasis, can shorten the haemostatic time by 25.17%-41.95%. The invention provides the RGD-M13 phage / polylysine / oxidized regenerated cellulose composite haemostatic material.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Modified ITO electrode for improving electricity production efficiency of electricity producing bacteria and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106226372AEasy to transformImprove electricity production efficiencyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPlatinumElectricity
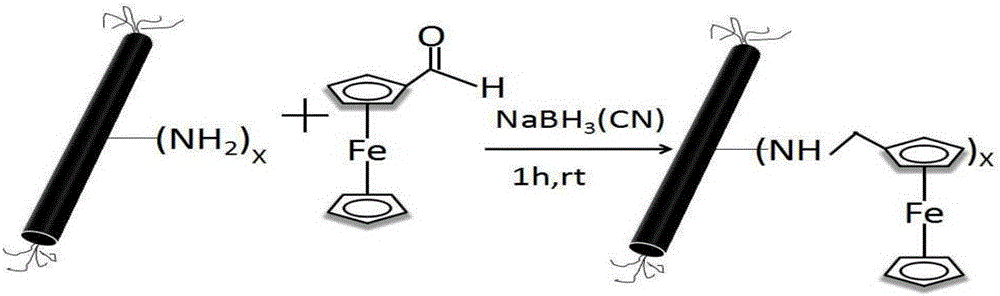
The invention discloses a modified ITO electrode for improving electricity production efficiency of electricity producing bacteria and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: reacting the amine group on a protein shell of M13 bacteriophage with ferrocene formaldehyde for connection, and uniformly coating the surface of ITO; assembling a three-electrode reactor and conducting electrochemical parameters scanning by an electrochemical workstation; and using the modified electrode as a working electrode, Ag / AgCl as a reference electrode and platinum wire as a negative electrode. In this environment, the electron transfer efficiency and capacity of the electricity producing bacteria can be accelerated. The electrode modification method is more simple and feasible compared to gene reconstruction on electricity producing bacteria for improvement of electricity producing capability, and has good development space.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
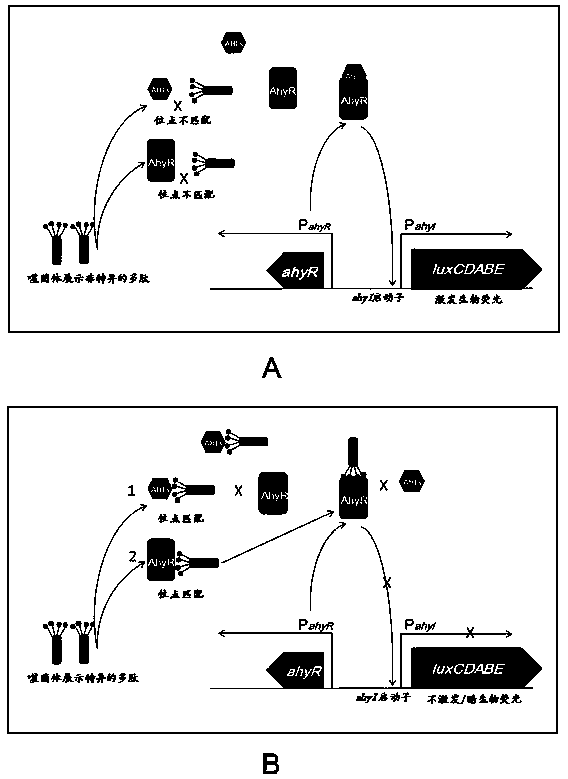
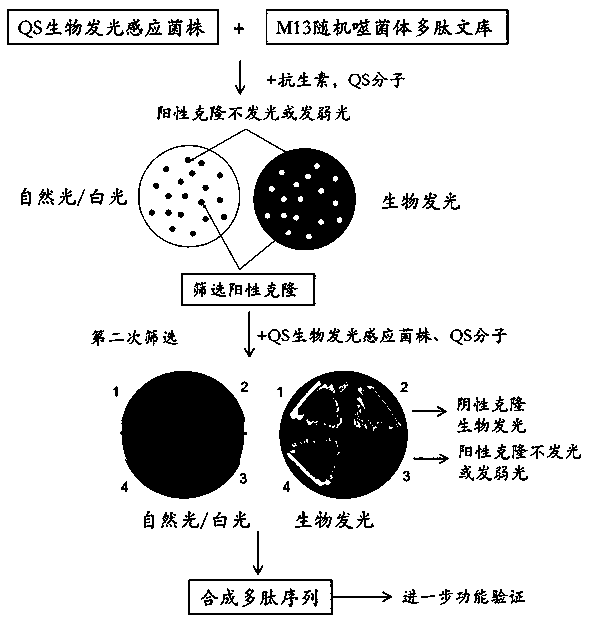
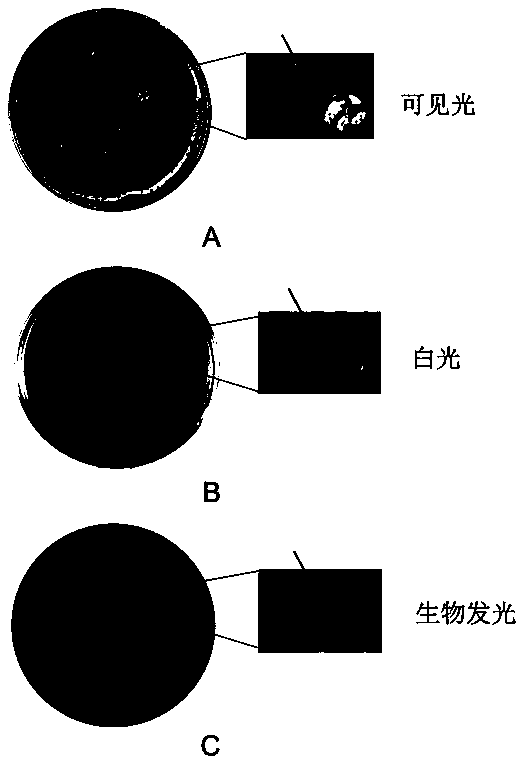
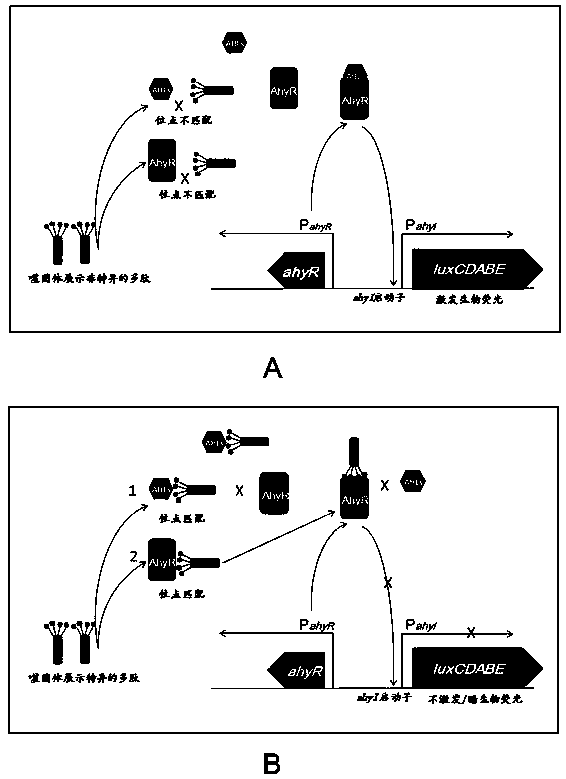
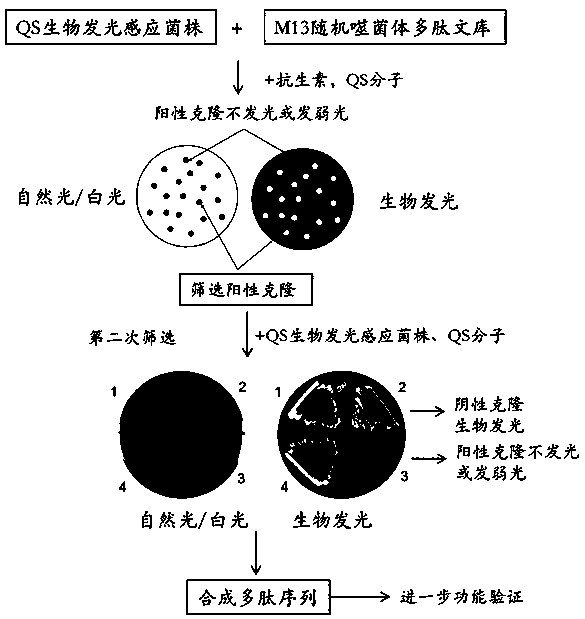
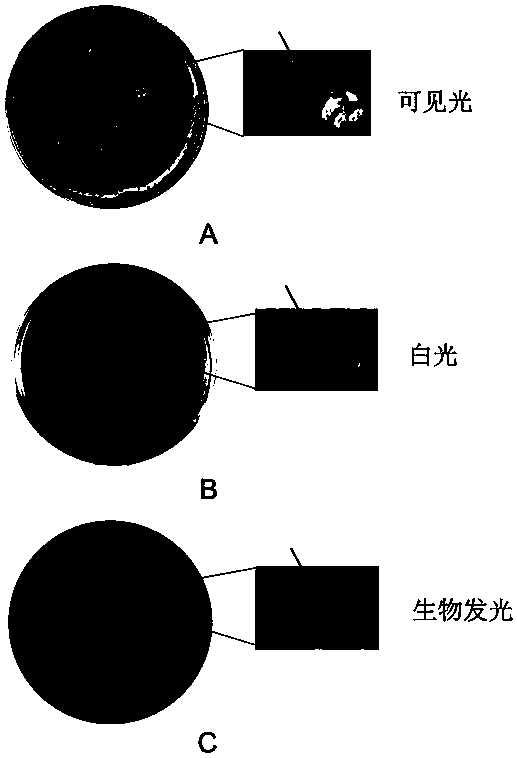
Method for rapidly screening bacterial quorum sensing inhibitor (QSI) by utilizing luminescence method
ActiveCN105504001AEliminate blind selection of materialsEliminate cumbersome processing stepsPeptide preparation methodsEscherichia coliAmpicillin
The invention provides a method for rapidly screening a bacterial quorum sensing inhibitor (QSI) by utilizing a luminescence method. The method is characterized by infecting escherichia coli ER2738 carrying pSB536 by utilizing the characteristic that a phage M13 does not lyse a host bacterium and can be secreted outside cells and then screening a bacterial clone which is blue under visible light and does not emit or emits weak biological fluorescent light under exciting light in a plate to which a C4-AHL molecule, tetracycline, ampicillin and X-gal / IPTG are added; then amplifying the phage, carrying out streak culture in the plate to which the substances are added, verifying the functions of the QSI by a method of inhibiting bioluminescence and finally obtaining specific QSI polypeptide sequences through sequencing. The method is simple in steps, and multiple QSI candidate polypeptides can be obtained only within three days to about one weak, so that the method has very obvious advantages.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
A human non-antibody peptide or protein phage library
InactiveCN101970691AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism librariesADAMTS ProteinsM13 bacteriophage
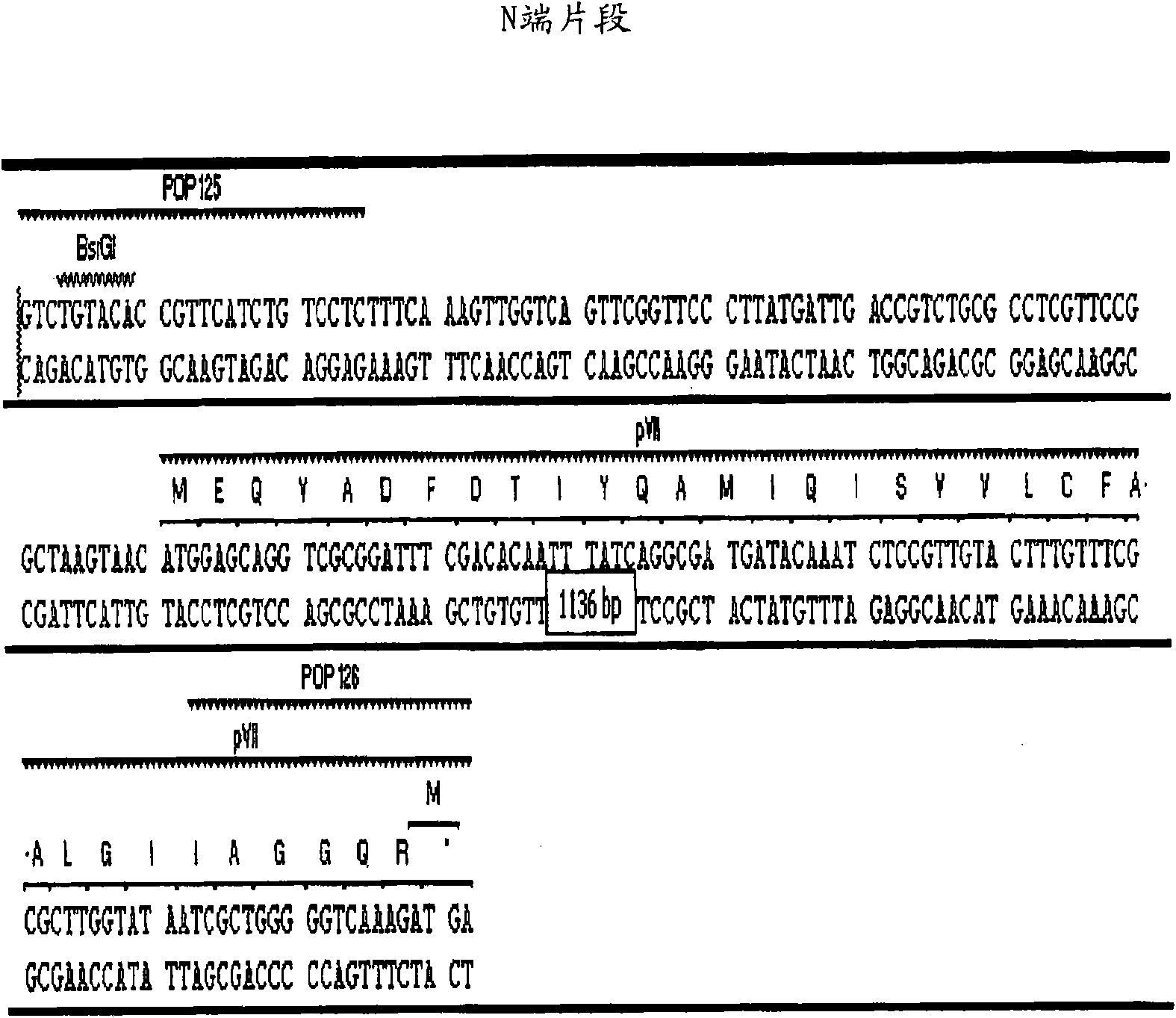
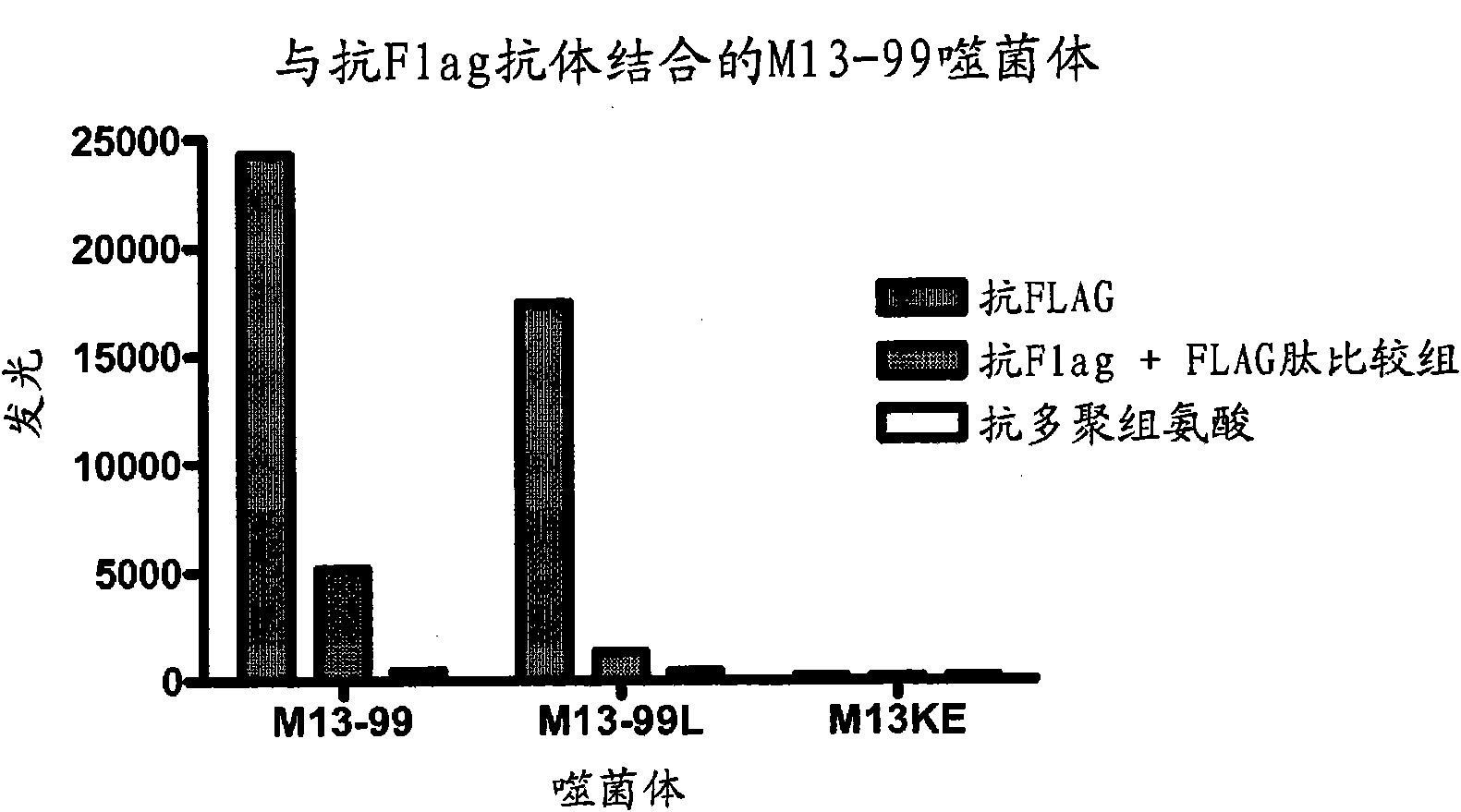
The invention relates to a compositions and methods for generating and using pIX phage display libraries for producing non-antibody peptide or protein proteins or peptides using engineered hybrid phage vectors derived from pIX of M 13 phage.
Owner:CENTOCOR ORTHO BIOTECH
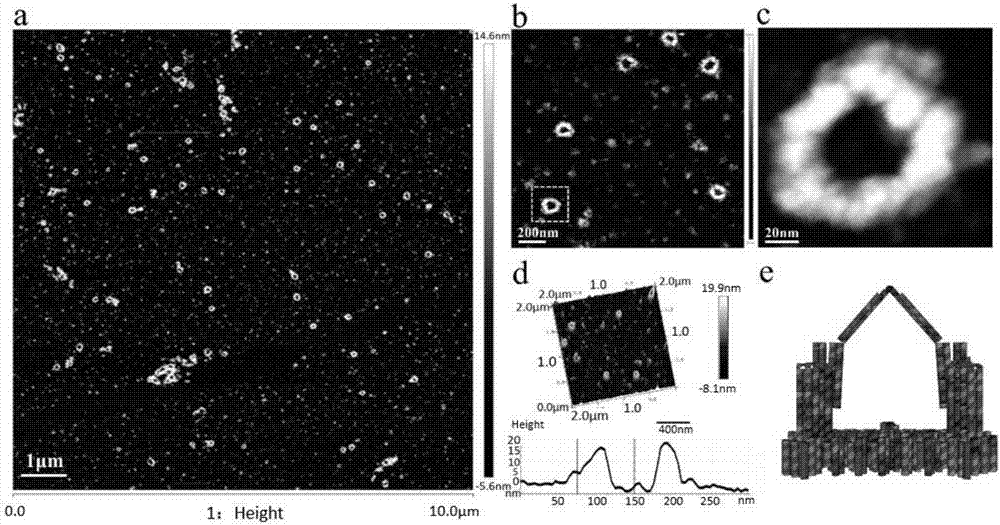
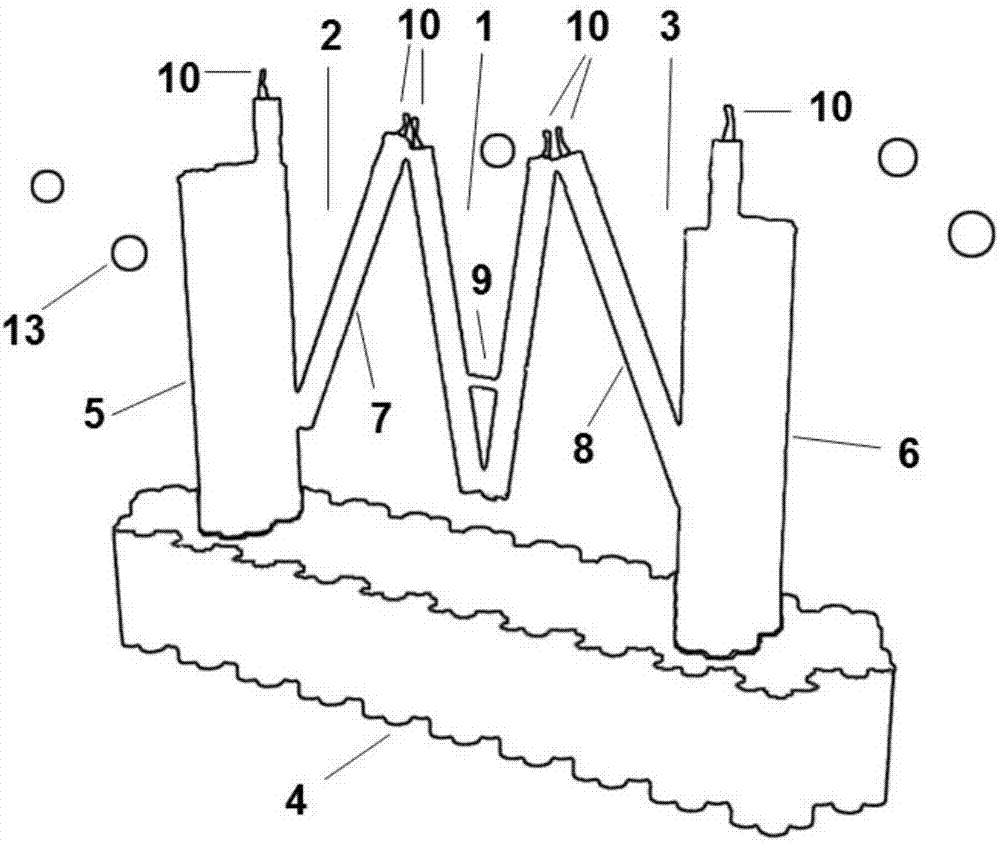
Novel micro-environment biological macromolecule general oscillator as well as synthesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN107083389AAchieve captureAchieve releaseOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderReaction rateFree protein
The invention discloses a novel micro-environment biological macromolecule oscillator. The oscillator relies on DNA origami, uses single-stranded-base genes of a M13 phage as a skeleton, uses more than 100 kinds of single-stranded oligonucleotide primers to fold skeleton nucleic acid into a stable trigeminy clip structure, and combines with the affinity of aptamer on biological macromolecules, the closing and opening of clips can dynamically capture and release free proteins to achieve a regulatory function of the concentration of micro-environment biological macromolecules. The opening and closing state of an outer clip and a middle clip are always different. When the oscillator adjusts the concentration of a pair of macromolecules with antagonistic functions, the metabolic reaction rate and the reaction direction can be controlled. The structure of a DNA device is observed by an atomic force microscope, and the ability to regulate and control protein molecules is demonstrated by experiments such as in vitro blood coagulation.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Defense peptides against fungal infection and method of their use
InactiveUS9051581B2High recovery rateRapidly identify new defense peptidesSugar derivativesBacteriaBiotechnologyAsian soybean rust
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Method for directly counting H9N2 avian influenza virus by naked eyes
PendingCN110187114ATiter accurate quantificationEasy to operateBiological material analysisNanoparticleAvian influenza virus
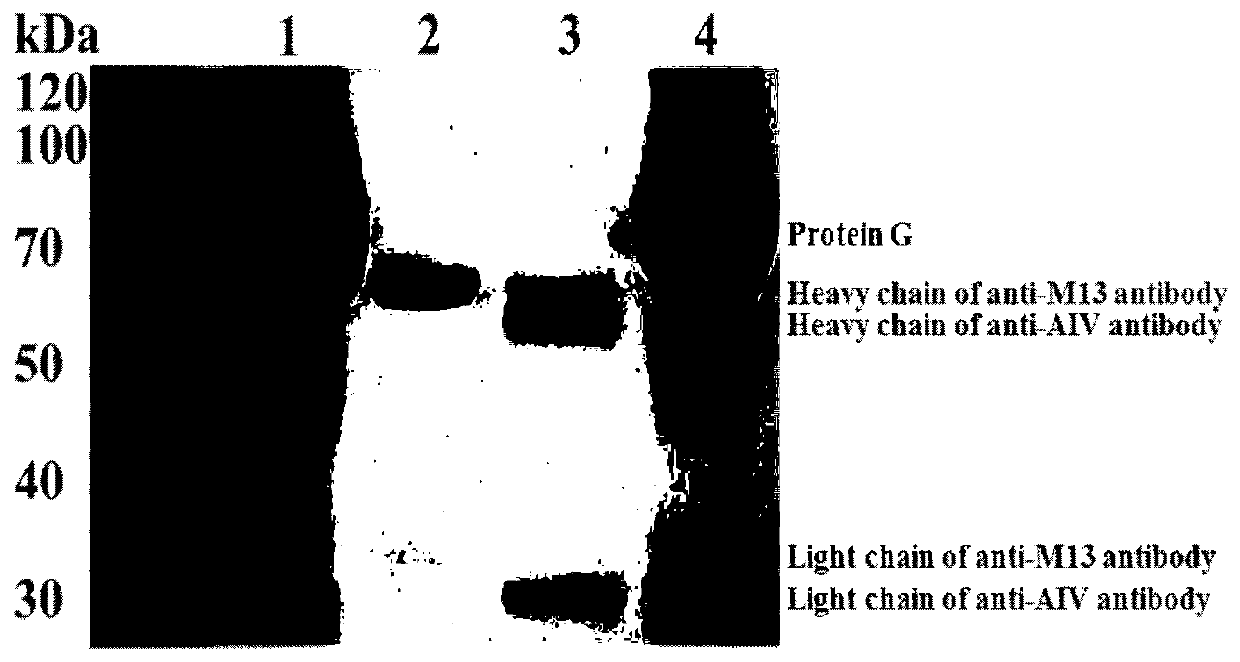
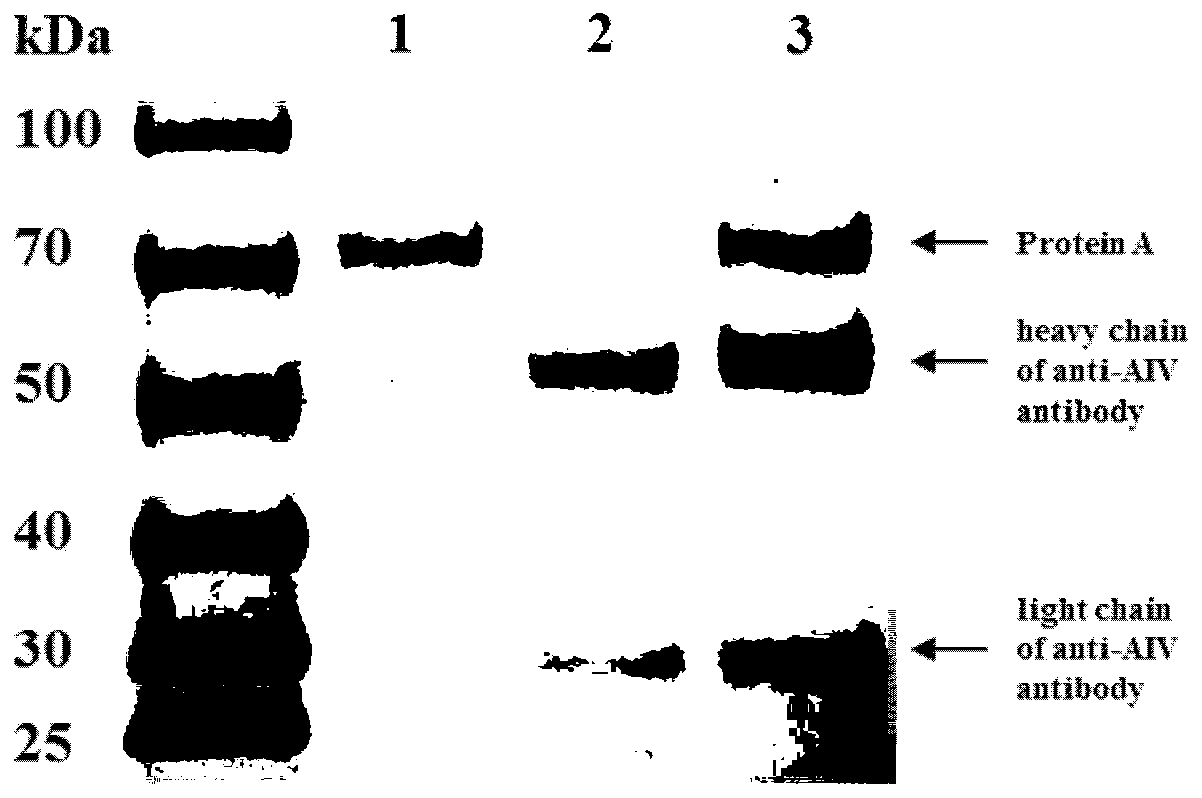
The invention discloses an M13@GNP indicator probe and a preparation method thereof, wherein the M13@GNP indicator probe is a protein G-coated gold nanoparticle combined with an M13 monoclonal antibody and a H9N2 monoclonal antibody, and then combined with the M13 phage. The invention also discloses a method for directly counting H9N2 avian influenza virus by naked eyes. The object of the invention is to establish a detection method for directly counting H9N2 influenza virus based on phage@gold nanoprobe, which can detect and quantify H9N2 influenza virus in a sample, shorten the detection period, simplify the detection process, improve the universal applicability of detection methods and is conducive to on-site inspection, so that the detection of H9N2 influenza virus is accurate, sensitive and simple, and timely prevention and control is of great significance.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Engineered hybird phage vectors for the design and the generation of a human non-antibody peptide or protein phage library via fusion to pix of m13 phage
The invention relates to a compositions and methods for generating and using pIX phage display libraries for producing non-antibody peptide or protein proteins or peptides using engineered hybrid phage vectors derived from pIX of M 13 phage.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Bacteriophage electrochemical luminescence signal amplification probe and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107418559AImprove signal amplification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLuminescent compositionsAntigenBiotin-streptavidin complex
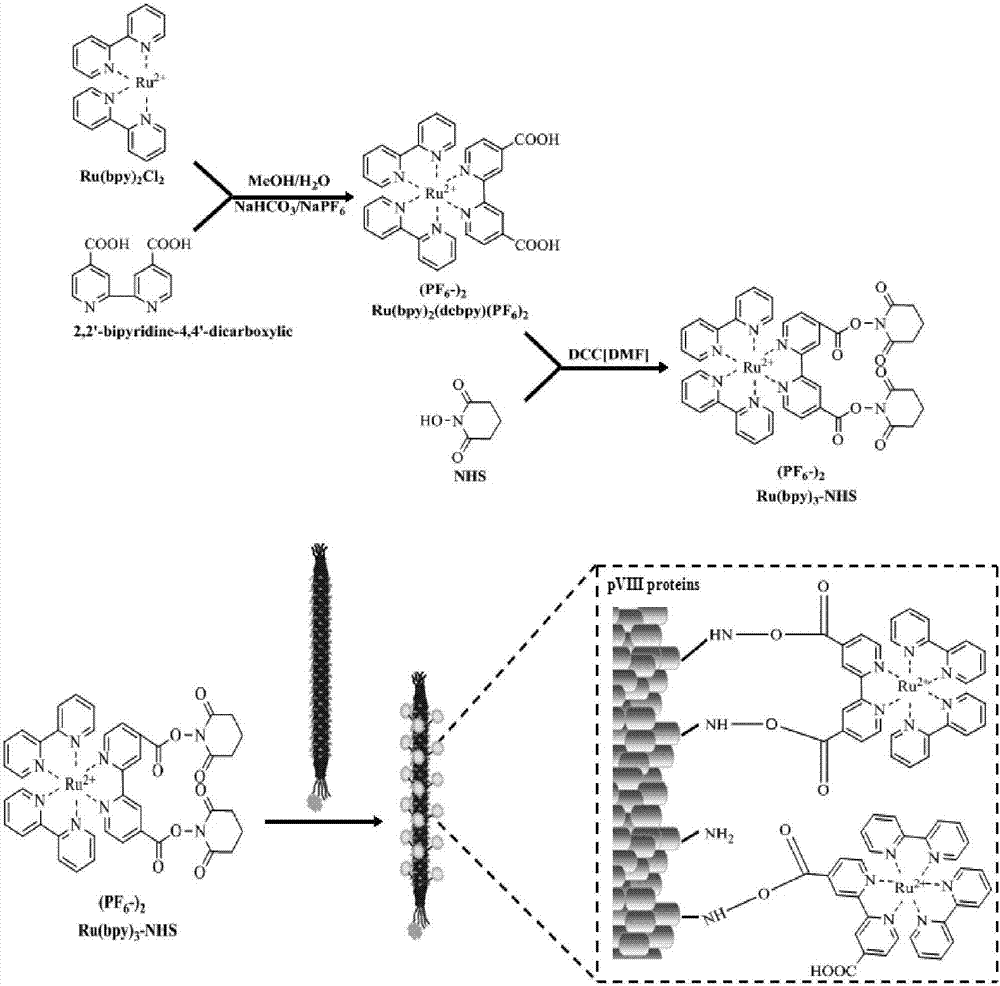
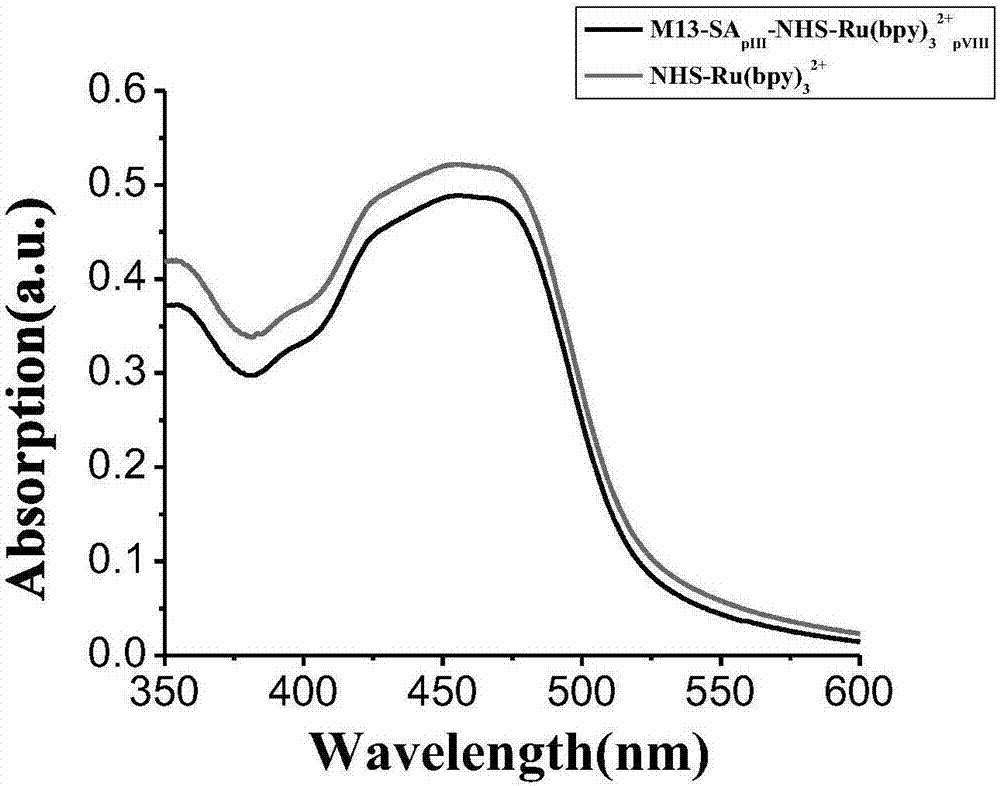
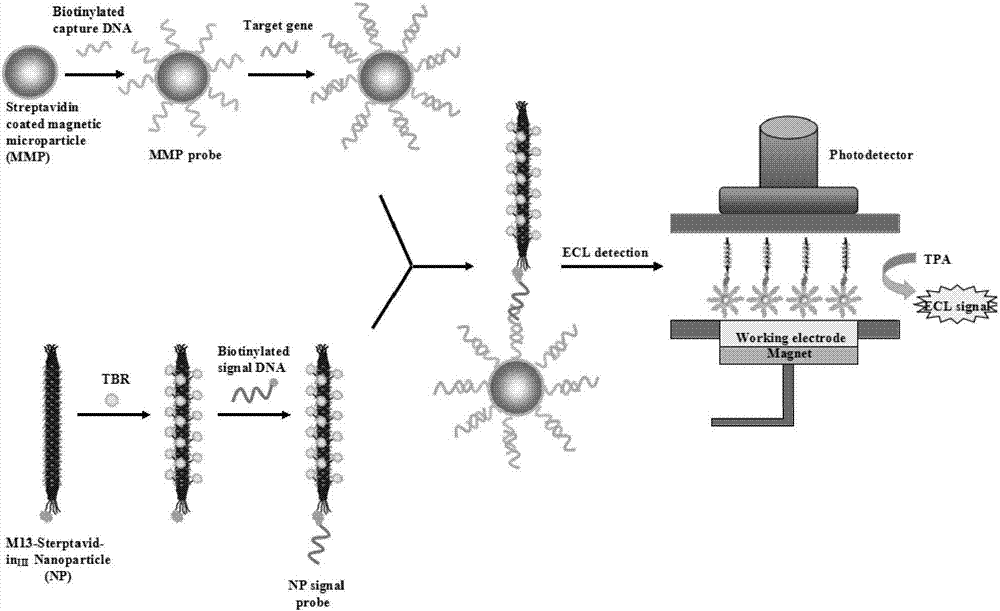
The invention discloses a bacteriophage electrochemical luminescence signal amplification probe and a preparation method and application thereof. The bacteriophage electrochemical luminescence signal amplification probe comprises M13 bacteriophage, streptavidin expressed in the M13 bacteriophage in a fusion manner and tris-(bipyridyl) ruthenium which is covalently connected to the M13 bacteriophage. According to the bacteriophage electrochemical luminescence signal amplification probe, the M13 bacteriophage is used as a connecting skeletion for amplifying tris-(bipyridyl) ruthenium signals, and has the advantages of stable system, difficulty in gathering, easiness in storage and the like. The prepared signal amplification probe has the advantages of simplicity, controllability, high signal amplification efficiency and the like, and can be used for quantitative detection of nucleic acid or antigen and the like.
Owner:广州博徕斯生物科技股份有限公司
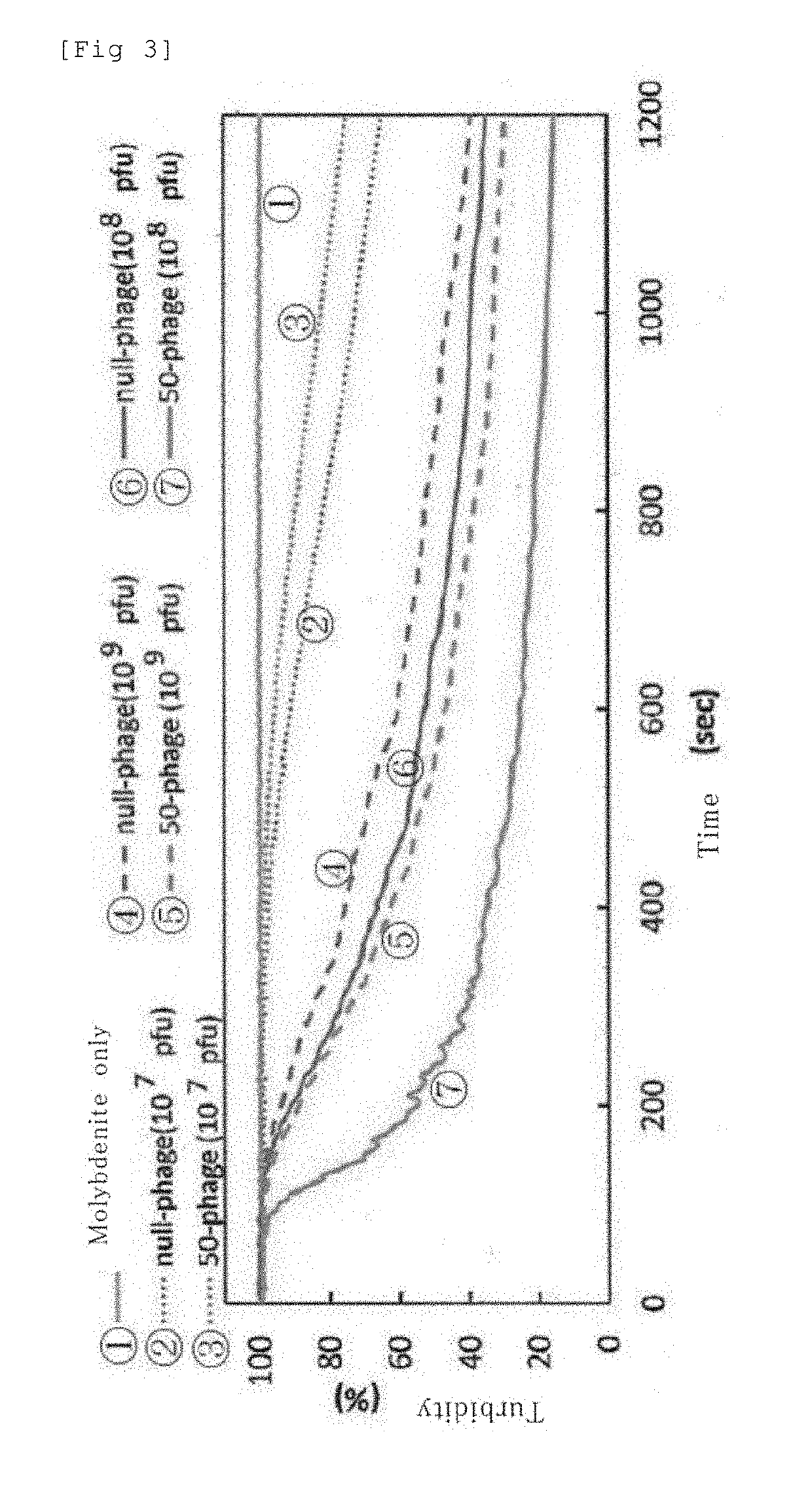
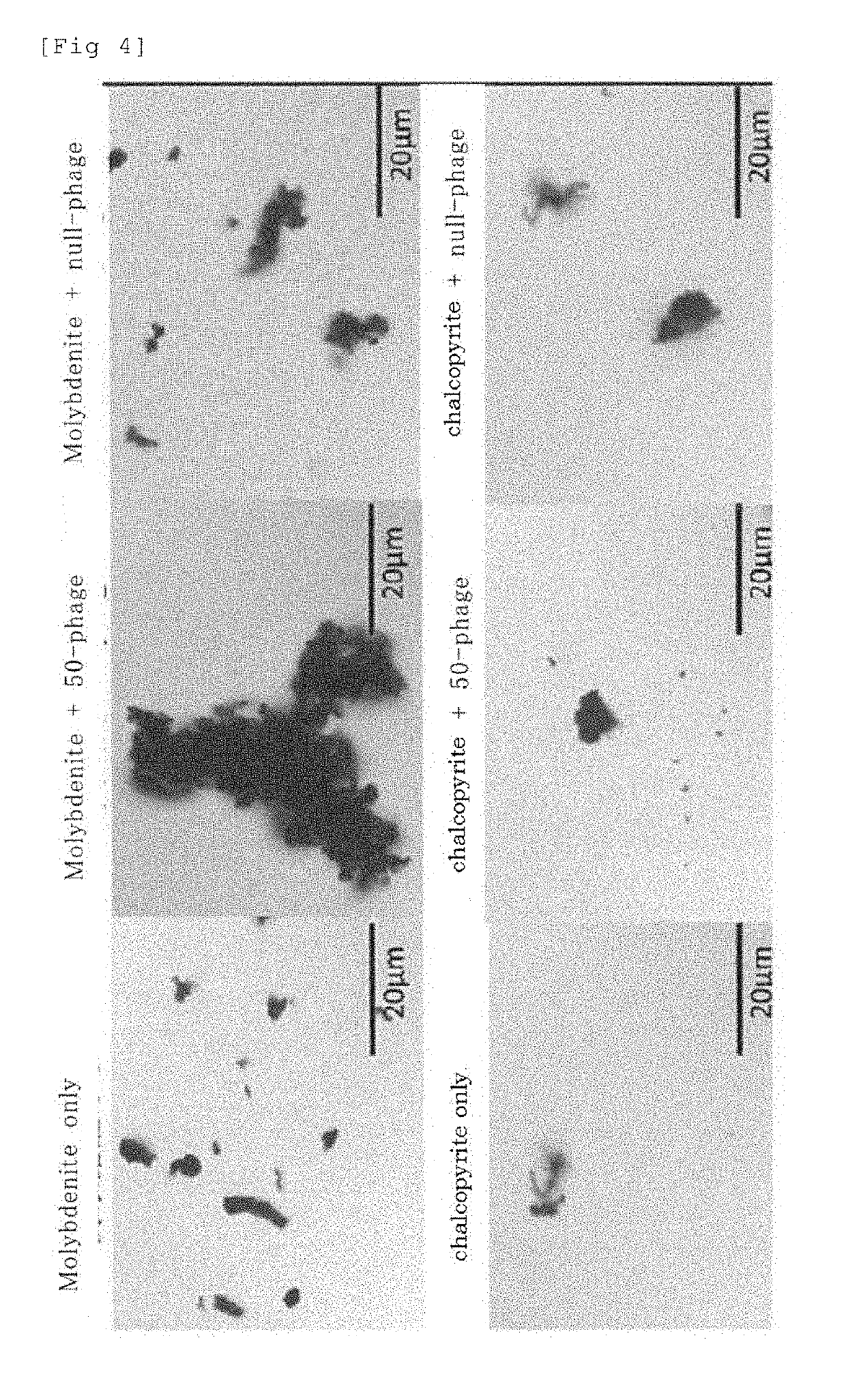
Virus composition and method for separation using same
ActiveUS20190309325A1Safe isolationEffective isolationIon-exchange process apparatusGas treatmentVirusM13 bacteriophage
(Technical problems to be solved) To provide a method for selecting mineral of molybdenum.(Means for solving the problems) Composition comprising M13 phage for separating a substance containing molybdenum.
Owner:SHIBAURA INST OF TECH +1
Linear neutralizing epitope polypeptide of fowl reticuloendotheliosis virus gp90 protein and application thereof
InactiveCN102584942BMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiopanningSequence comparison
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Micro-electrolysis system and its preparation method and application
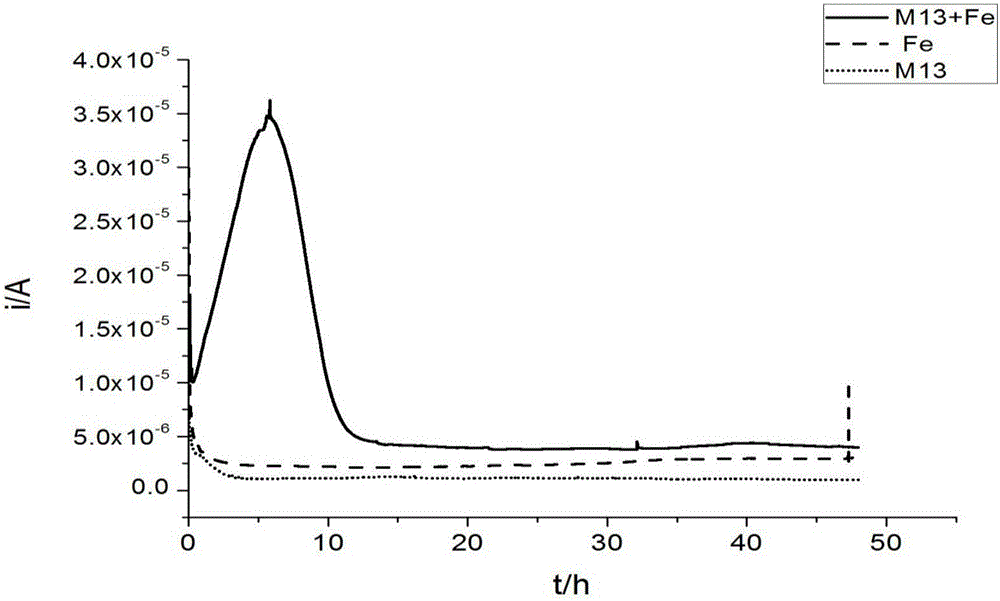
The invention provides a microelectrolysis system as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The microelectrolysis system comprises bacteriophage M13, first metal and second metal, wherein the first metal and the second metal are distributed on the surface of the bacteriophage M13 and have a potential difference. The first metal and the second metal have the potential difference, so that the microelectrolysis system can be formed effectively and can be used for performing reductive treatment on organic pollutants or heavy metal ions in sewage, the reduction rate is high, required time is short, treatment can be performed at normal temperature and normal pressure, and the microelectrolysis system does not need a noble metal catalyst and is lower in cost.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Defense peptides against fungal infection and method of their use
InactiveUS20110271400A1High expressionHigh recovery rateFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyAsian soybean rust
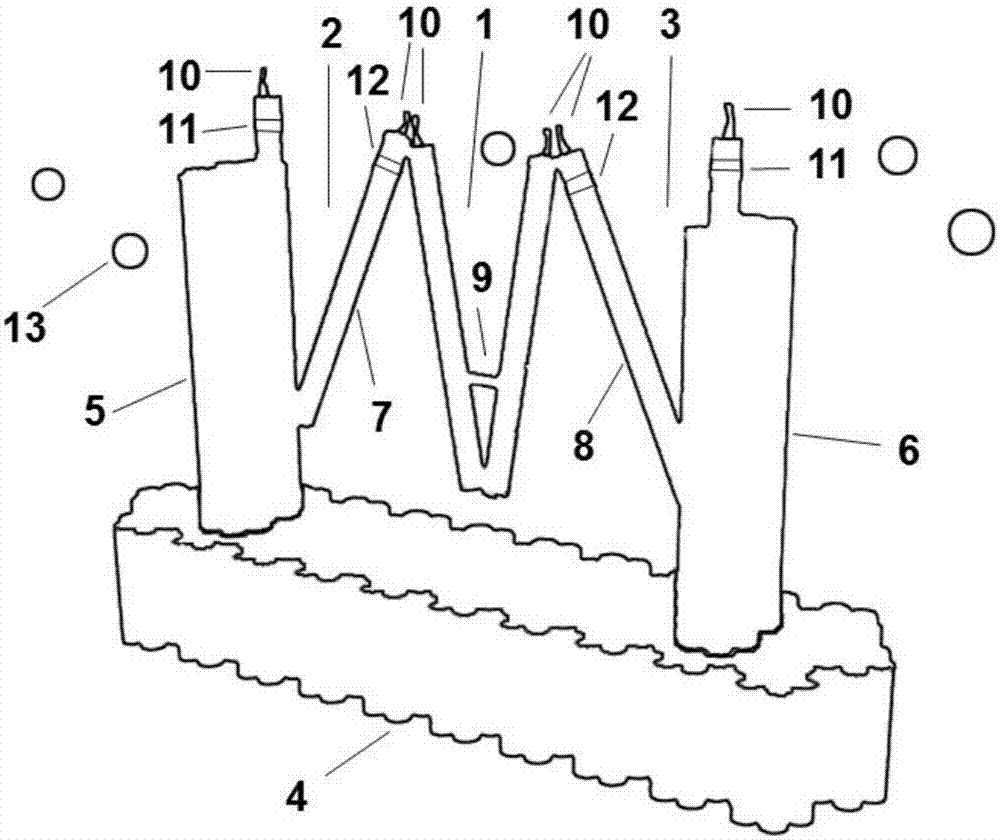
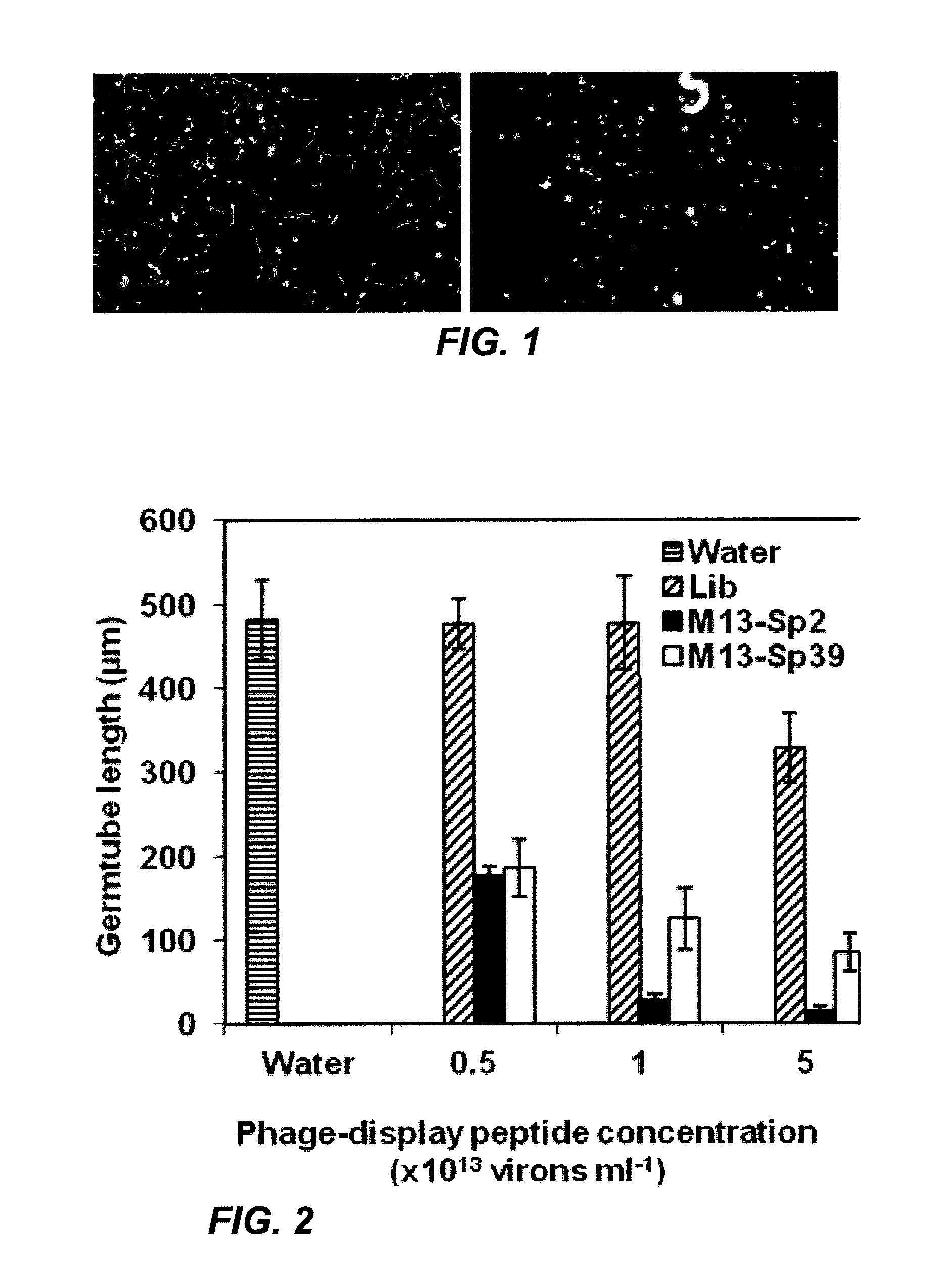
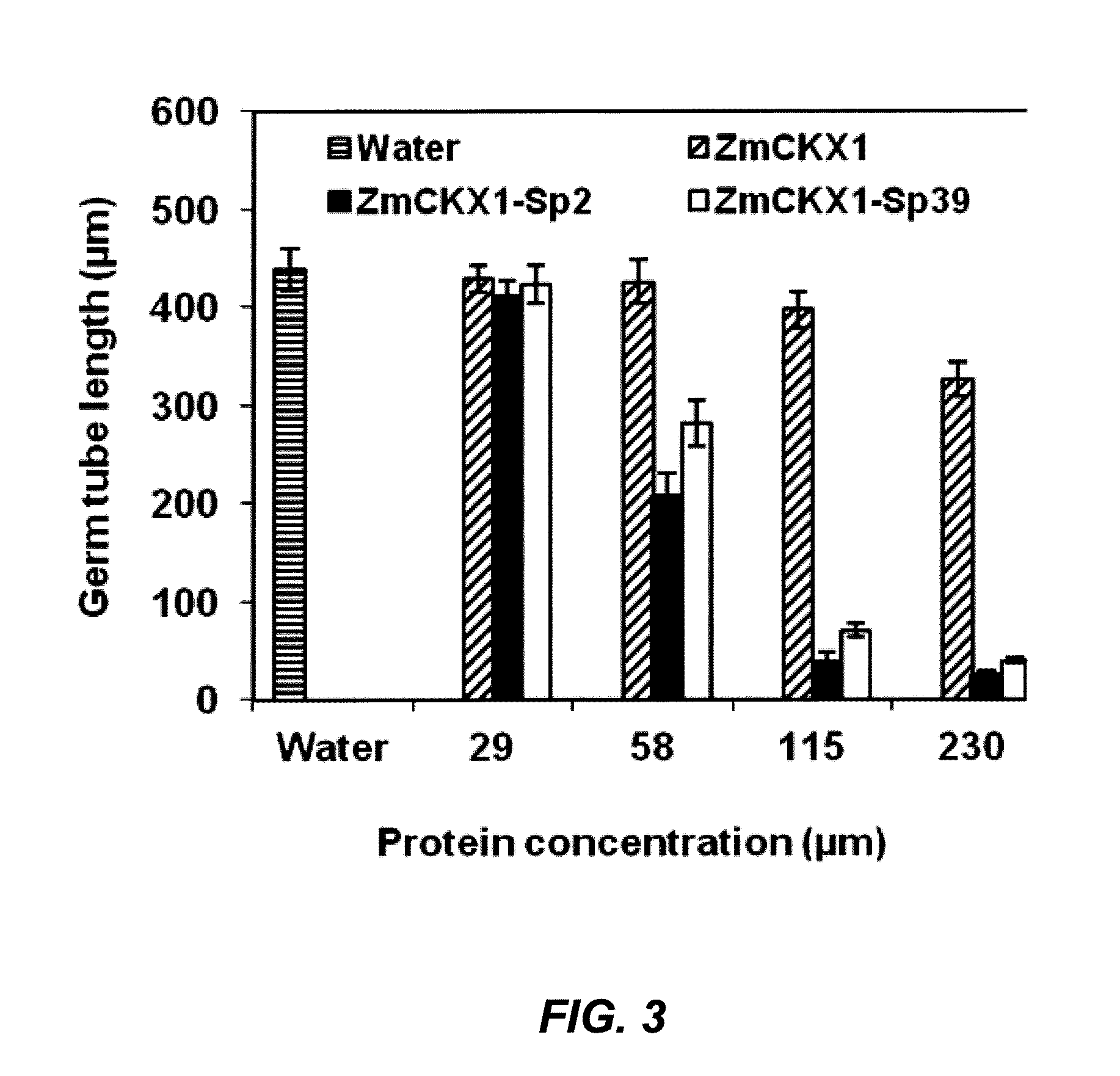
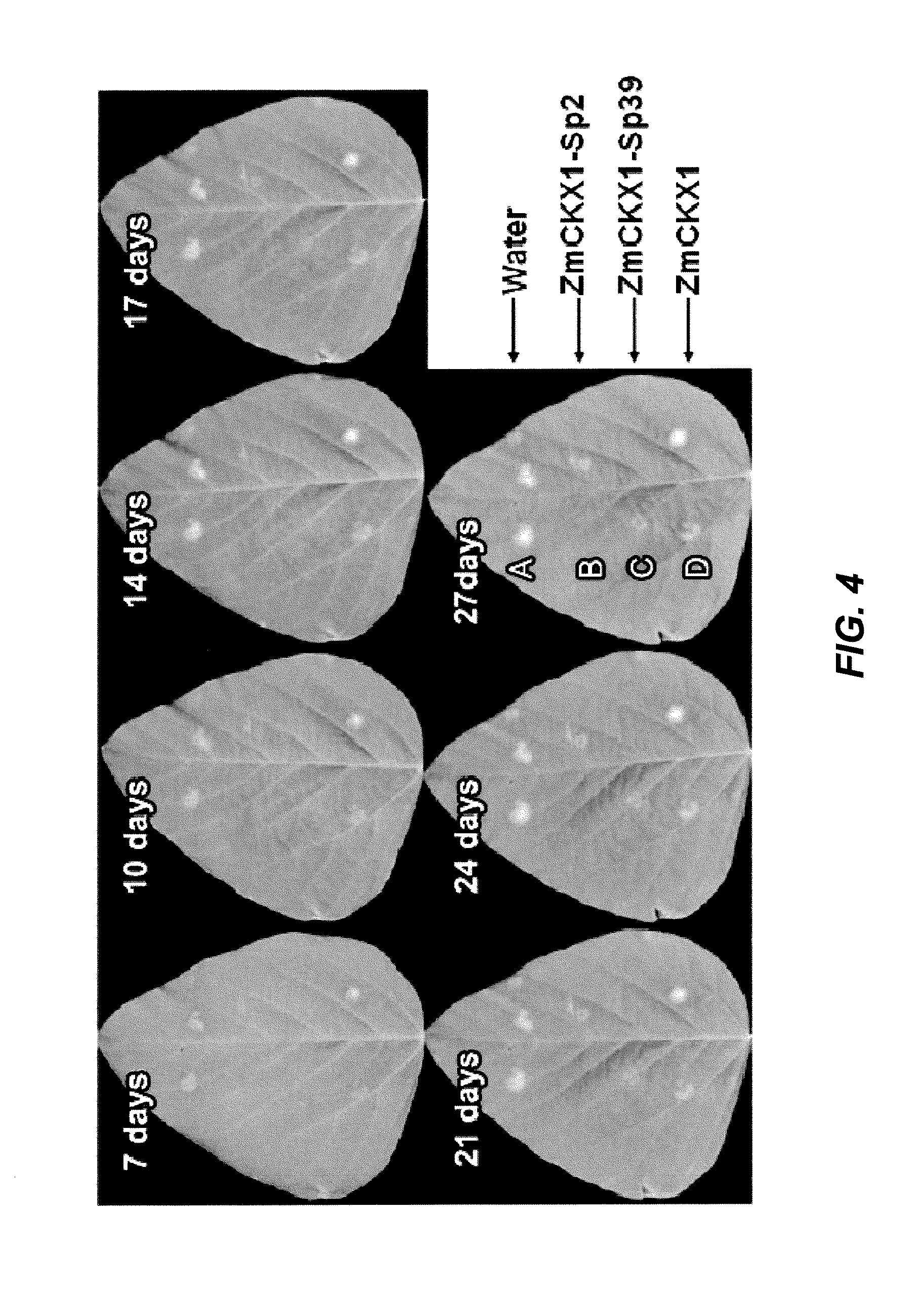
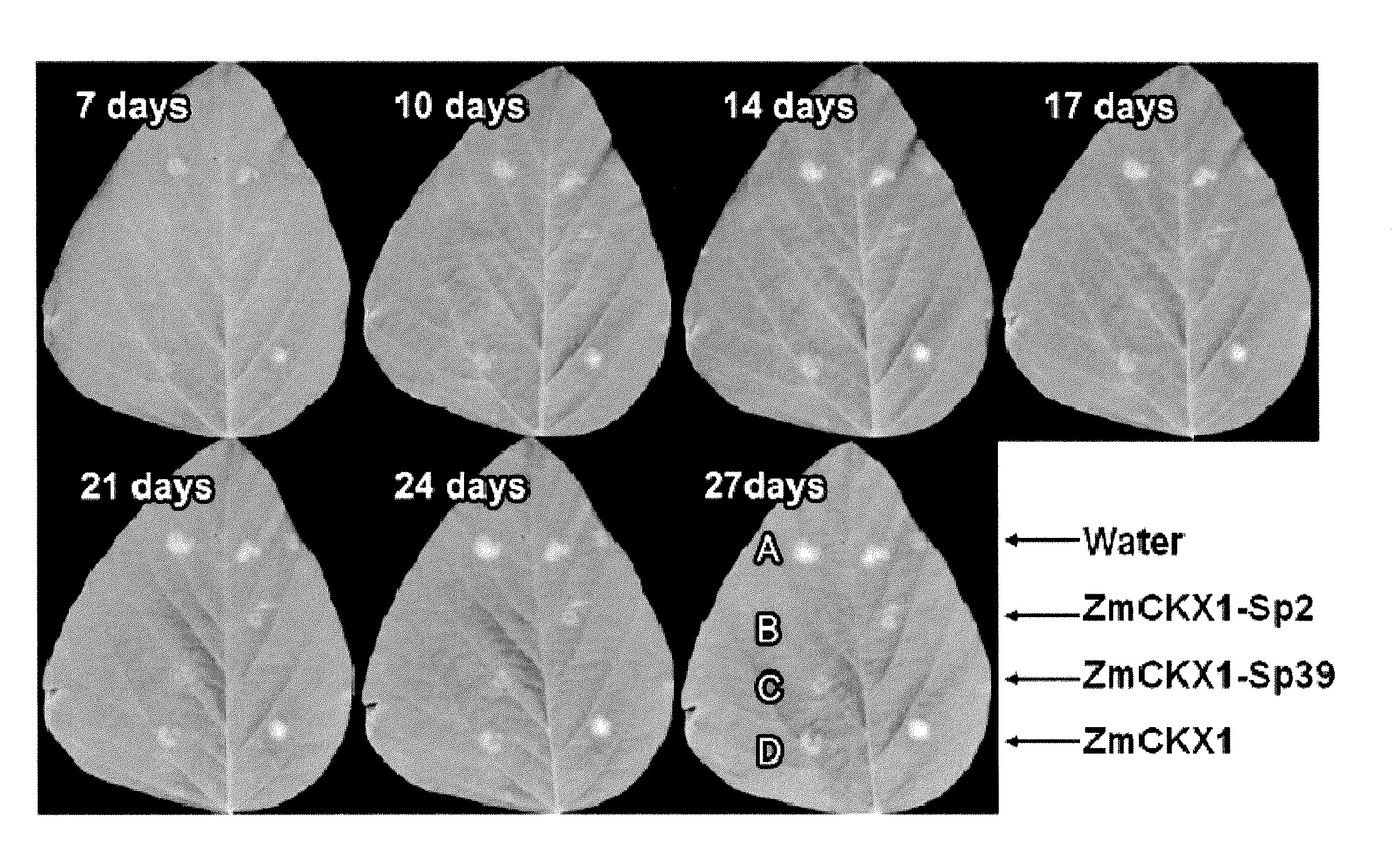
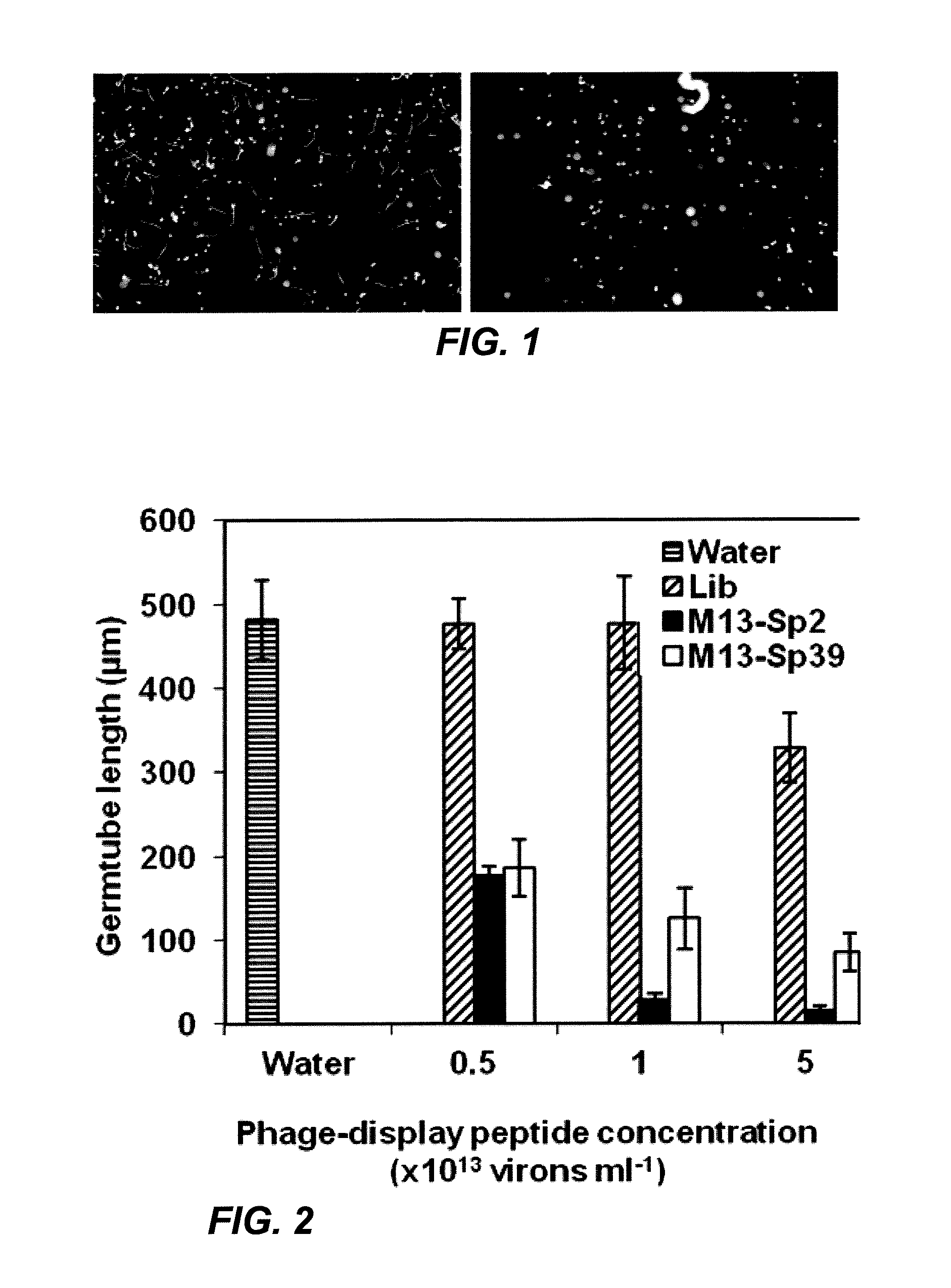
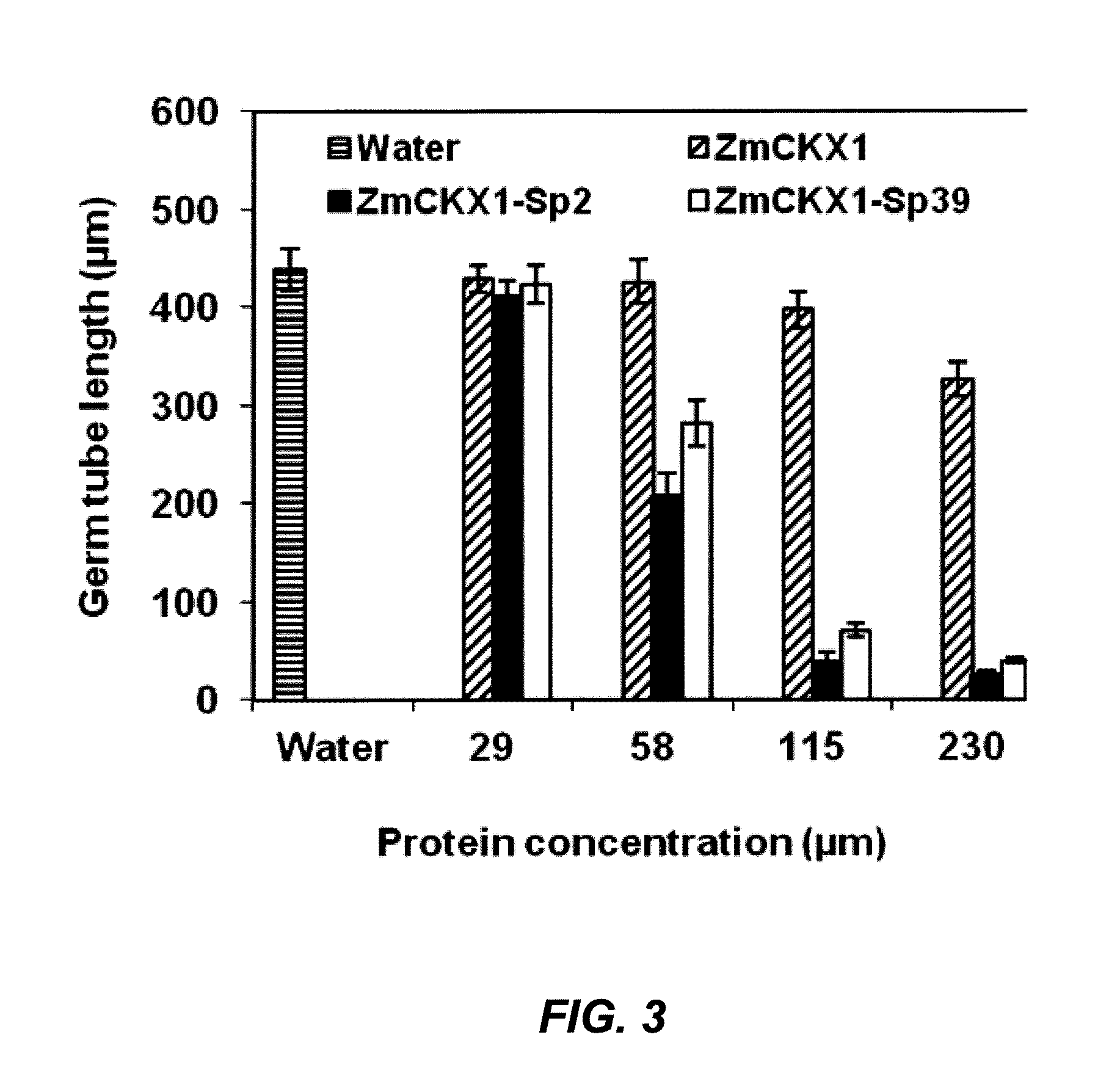
Phakopsora pachyrhizi, the fungal pathogen that causes Asian soybean rust, has the potential to cause significant losses in soybean yield in many production regions of the U.S. To assist the development of new modes of soybean resistance to fungal infection, peptides were identified from combinatorial phage-display peptide libraries which inhibit germ tube growth from urediniospores of P. pachyrhizi. Two peptides, Sp2 and Sp39, were identified that inhibit germ tube development when displayed as fusions with the coat protein of M13 phage or as fusions with maize cytokinin oxidase / dehydrogenase (ZmCKX1). These peptides may be used in vitro to help control fungal infection. These peptides may also be expressed as transgenes in a plant to help the resulting transgenic plant defend against the fungi
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
M13 bacteriophage nanoprobe and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113308484AHigh biosecurityImprove stabilityVirus peptidesFermentationNanoparticleM13 bacteriophage
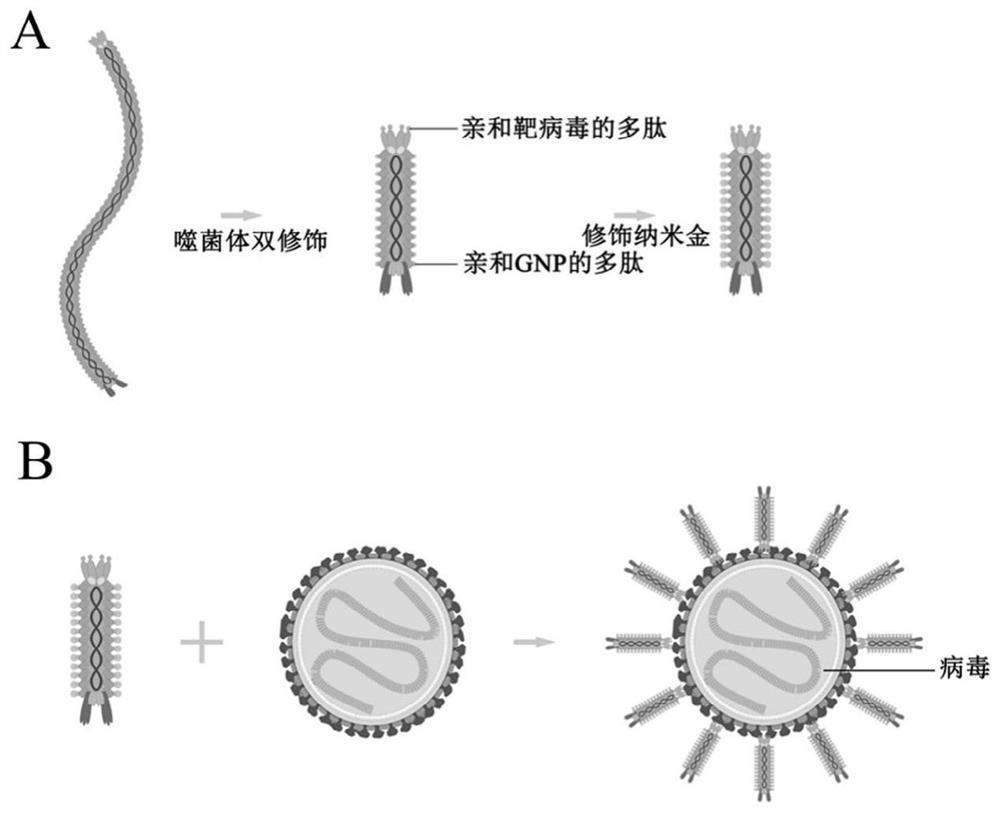
The invention discloses a bacteriophage nanoprobe and a preparation method thereof. The bacteriophage nanoprobe is an M13 bacteriophage derivative, firstly, polypeptide of an affinity virus is displayed at an N end of P3 protein of a helper bacteriophage M13KO7, polypeptide of an affinity nanoparticle is displayed at an N end of P8 protein, the polypeptide of the affinity nanoparticle is displayed at an N end of P8 protein, and then, the modified helper phage M13KO7 is used for infecting a phage liquid containing a replication starting point ori(+) and a packaging signal, so that the phage is packaged by the modified helper phage M13KO7, and the phage nano probe which is 50-100 nm long and is used for virus detection is assembled. The product prepared by the invention has the characteristics of high specificity, good sensitivity, high biological safety, capability of realizing visual detection of viruses, wide application field and the like, in addition, the process is simple and convenient, the cost is relatively low, a result can be observed by naked eyes, and an electrochemical signal can be generated by utilizing a biosensor, so that the product has a very good popularization prospect.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Electrode composite material and preparation method thereof, and negative electrode and battery having the electrode composite material
ActiveCN104425801BLow costLarge-scale production potentialMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesNanostructureLithium-ion battery
Owner:POSITEC POWER TOOLS (SUZHOU) CO LTD +1
A preparation method of rgd-m13 phage/oxidized regenerated cellulose composite hemostatic material
ActiveCN105435295BGood hemostatic effectNo damage to mechanical strengthPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAbsorbent padsMedicineUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a preparation method of a RGD-M13 bacteriophage / oxidized regenerated cellulose composite hemostatic material, and relates to a preparation method of a hemostatic material. The invention aims to solve the problems that in the prior art, after the modification of conventional oxidized regenerated cellulose, the hemostatic time is slightly prolonged, while the mechanical strength and biological absorbability of oxidized regenerated cellulose are both reduced. The preparation method comprises the following steps: step one, activating oxidized regenerated cellulose; step two, soaking the activated oxidized regenerated cellulose in RGD-M13 bacteriophage suspension so as to obtain the RGD-M13 bacteriophage / oxidized regenerated cellulose composite hemostatic material. The prepared RGD-M13 bacteriophage / oxidized regenerated cellulose composite hemostatic material can be used to stop bleeding, and hemostatic time is shortened by 10.4 to 32.9%. The provided prepared method can obtain a RGD-M13 bacteriophage / oxidized regenerated cellulose composite hemostatic material.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Immunochromatographic test paper and preparation method for detecting ochratoxin a based on m13 phage
ActiveCN103969444BAvoid harmStrong specificityBiological material analysisBiological testingCelluloseEpitope
The invention discloses an immunochromatography test paper for testing ochratoxin A based on an M13 phage and a preparation method of the immunochromatography test paper. A test paper adsorbing layer comprises an adsorbing fiber layer, a gold-labeled antibody fiber layer, a cellulose membrane layer and a water absorbing material layer, wherein a testing blot used for showing OTA mimic epitope and blotted by the M13 phage and a contrasting blot using a goat anti-mice IgG antibody solution are arranged on the cellulose membrane layer; a gold-labeled antibody is a collaurum-labeled OTA monoclonal antibody or polyclonal antibody. According to the invention, the application of immunochromatography technique based on the M13 phage on quick OTA residue testing is realized, OTA conjugate blotted on the testing blot of a traditional test strip is replaced with the M13 phage shown with the OTA mimic epitope, harm of the OTA conjugate to a test paper producer, an experimenter and environment is avoided, and the test paper is strong in specificity and high in sensitivity during testing, and is simple and convenient to test, straightforward, accurate, low in cost, and wide in application range.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A preparation method of rgd-m13 phage/polylysine/oxidized regenerated cellulose composite hemostatic material
ActiveCN105477675BGood hemostatic effectNo damage to mechanical strengthPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAbsorbent padsPolymer scienceUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a preparation method of an RGD-M13 phage / polylysine / oxidized regenerated cellulose composite haemostatic material, and relates to a preparation method of a haemostatic material. The invention aims at solving the problems of an existing oxidized regenerated cellulose modified haemostatic material that a haemostatic time is lightly improved, and the mechanical strength and bio-absorbing property of the oxidized regenerated cellulose are decreased. The method comprises the following steps: I. self-assembly of polylysine; II. self-assembly of an RGD-M13 phage; and III. cleaning and drying, so that the RGD-M13 phage / polylysine / oxidized regenerated cellulose composite haemostatic material is obtained. The RGD-M13 phage / polylysine / oxidized regenerated cellulose composite haemostatic material prepared by the invention, when applied to haemostasis, can shorten the haemostatic time by 25.17%-41.95%. The invention provides the RGD-M13 phage / polylysine / oxidized regenerated cellulose composite haemostatic material.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
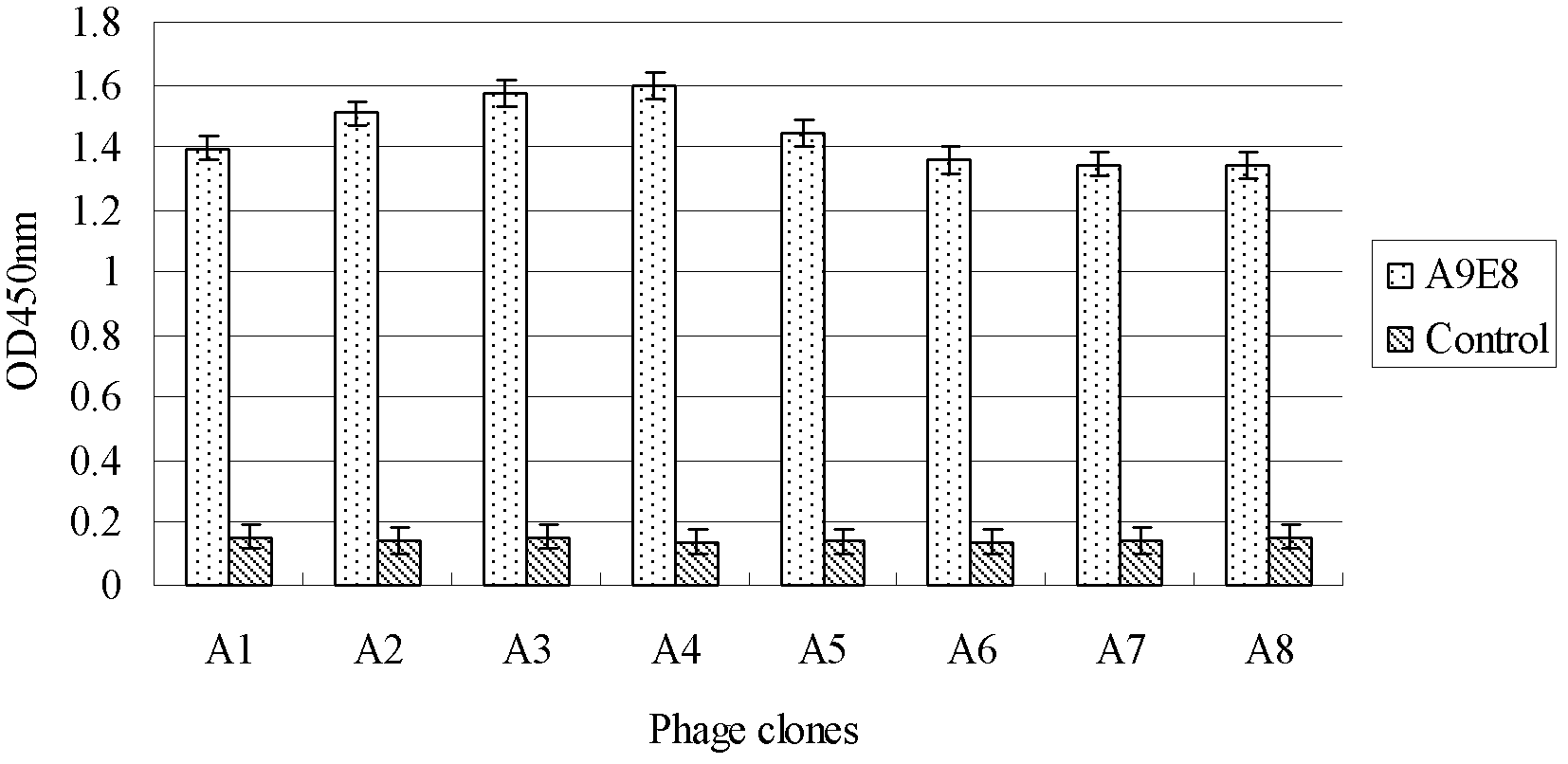
Peptide specific for ovarian cancer and applications
ActiveUS9170261B2Strong specificityRapid cancer screeningCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesMaterial analysisMedicineMagnetic bead
The present invention provides a novel peptide with high specificity for recognition of ovarian cancer. The peptide is selected using M13 phage display library and epithelial-enrich-conjugated magnetic beads. Only a small amount of the peptide is required to establish over 80% binding activity to ovarian cancer comparing to low binding activities to other cancers, showing high specificity for ovarian cancer. Thus the peptide of the present invention can be effective in early detection of ovarian cancer.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
A method for rapid screening of bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors using luminescence
ActiveCN105504001BEliminate blind selection of materialsEliminate cumbersome processing stepsPeptide preparation methodsEscherichia coliAmpicillin
The invention provides a method for rapidly screening a bacterial quorum sensing inhibitor (QSI) by utilizing a luminescence method. The method is characterized by infecting escherichia coli ER2738 carrying pSB536 by utilizing the characteristic that a phage M13 does not lyse a host bacterium and can be secreted outside cells and then screening a bacterial clone which is blue under visible light and does not emit or emits weak biological fluorescent light under exciting light in a plate to which a C4-AHL molecule, tetracycline, ampicillin and X-gal / IPTG are added; then amplifying the phage, carrying out streak culture in the plate to which the substances are added, verifying the functions of the QSI by a method of inhibiting bioluminescence and finally obtaining specific QSI polypeptide sequences through sequencing. The method is simple in steps, and multiple QSI candidate polypeptides can be obtained only within three days to about one weak, so that the method has very obvious advantages.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
A novel microenvironment biomacromolecule universal oscillator, its synthesis method and application
InactiveCN107083389BAchieve captureAchieve releaseOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderProtein moleculesSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a novel micro-environment biological macromolecule oscillator. The oscillator relies on DNA origami, uses single-stranded-base genes of a M13 phage as a skeleton, uses more than 100 kinds of single-stranded oligonucleotide primers to fold skeleton nucleic acid into a stable trigeminy clip structure, and combines with the affinity of aptamer on biological macromolecules, the closing and opening of clips can dynamically capture and release free proteins to achieve a regulatory function of the concentration of micro-environment biological macromolecules. The opening and closing state of an outer clip and a middle clip are always different. When the oscillator adjusts the concentration of a pair of macromolecules with antagonistic functions, the metabolic reaction rate and the reaction direction can be controlled. The structure of a DNA device is observed by an atomic force microscope, and the ability to regulate and control protein molecules is demonstrated by experiments such as in vitro blood coagulation.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com