Application of EB1 gene to detection of nosema bombycis
A microsporidia and silkworm technology, applied in the application field of EB1 gene in the detection of silkworm microsporidia, can solve the problems of interference with effective amplification of PCR, etc., and achieve the effects of strong specificity, high sensitivity, convenient use and industrial production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1 EB1 Gene function research
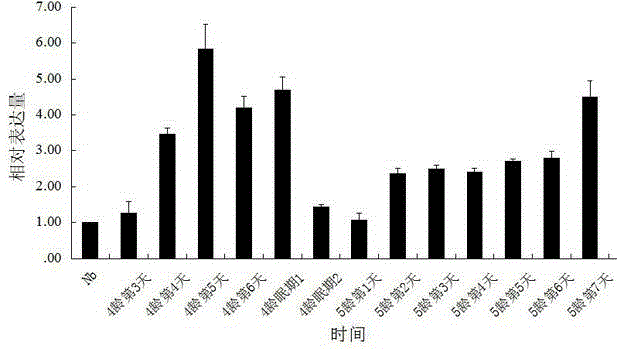
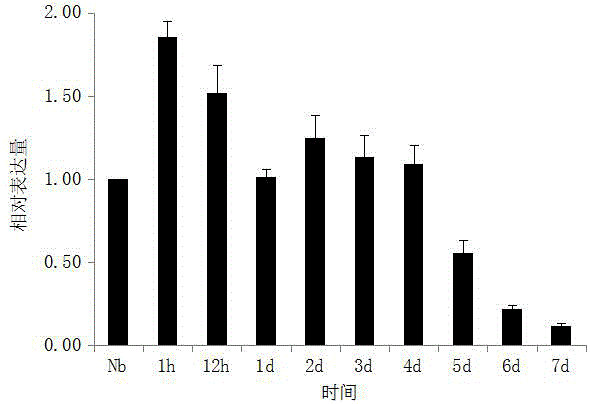
[0032] Microsporidium Bombyx mori N. bombycis (Guangdong strain) on the basis of transcriptomics research, identified for the first time that it may be related to N. bombycis related to infection and reproduction EB1 gene (Accession No. KF421134), and against infection with Microsporidium silkworm N. bombycis Bombyx mori tissues of different development stages such as silkworm larvae and eggs were carried out EB1 Analysis of expression differences.
[0033] The test method is: silkworms from the 4th instar (bombyx mori variety: Liangguang No. 2) are fed with No. spp. silkworm, once in the morning and once in the evening, and then normally reared. Every day after the poisoning (from the first day of the fourth instar to the fifth instar mature silkworms), the silkworms reared with the poisoning were randomly selected, and the silkworms were dissected with sterile vessels, sterile water and a new wax dish, and the midgut wa...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2 EB1 Application of the gene as a target gene to detect whether silkworm eggs are infected with Microsporidium mori
[0042] 1. Extraction of total DNA from silkworm eggs
[0043] Genomic DNA was extracted using the DNeasy Plant mini kit produced by QIAGEN, and the steps were as follows:
[0044] (1) Take 20 silkworm eggs and put them into a mortar, grind them thoroughly with liquid nitrogen, and collect the ground powder into a 1.5mL centrifuge tube;
[0045] (2) Add 400 μL AP1 and 4 μL RNase, and vortex to mix (do not mix 400 μL APL and 4 μL RNase before use); after mixing, incubate at 65°C for 10 min (invert the test tube up and down for 2~ 3 times);
[0046] (3) Add 130 μL AP2, mix and place in ice bath for 5 minutes; then centrifuge at 14 000 rpm for 5 minutes;
[0047] (4) Pipette the supernatant into the collection tube in the QIA shredder spin column, centrifuge at 14 000rpm for 2min;
[0048] (5) Transfer the supernatant in the ce...
Embodiment 3 Embodiment 2
[0060] The specific detection of the primer described in embodiment 3 embodiment 2
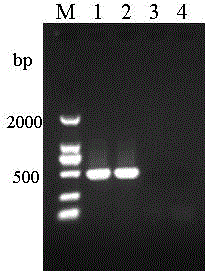
[0061] Take 30 "poisonous" silkworm eggs, healthy silkworm eggs and purified Nosporum silkworm respectively, extract total DNA according to the method in Example 2, then carry out PCR amplification, and use agarose gel electrophoresis to detect the results. Test results such as figure 1 Shown: DNA fragments of 496bp were detected in "poisonous" silkworm eggs and purified No. Except for the N.b specific target band of about 496bp, there are no other bands with sizes different from the target fragment. Therefore, the EB1 As the target gene for detection, the inhibitory substances in the silkworm egg extract will not interfere with the effective PCR amplification of pathogenic gene DNA, and the detection results are more accurate and sensitive. It can quickly detect whether it is infected with No. spp. silkworm. The above results show that the primers described in Example 2 have good specif...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com