Primers for detecting plurality of newborn inherited metabolic disease causing genes and kit
A technology for genetic metabolic diseases and neonates, applied in the field of genetic detection of neonatal genetic metabolic diseases, can solve the problems of low throughput and small genetic metabolic disease screening, achieve early diagnosis and early treatment, and reduce fatalities rate and disability rate, effect of reducing burden
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Example 1: In this example, six genes including non-syndromic deafness-related pathogenic genes GJB2, GJB3, SLC26A4, 12SrRNA, COCH and DFNA5 were selected.
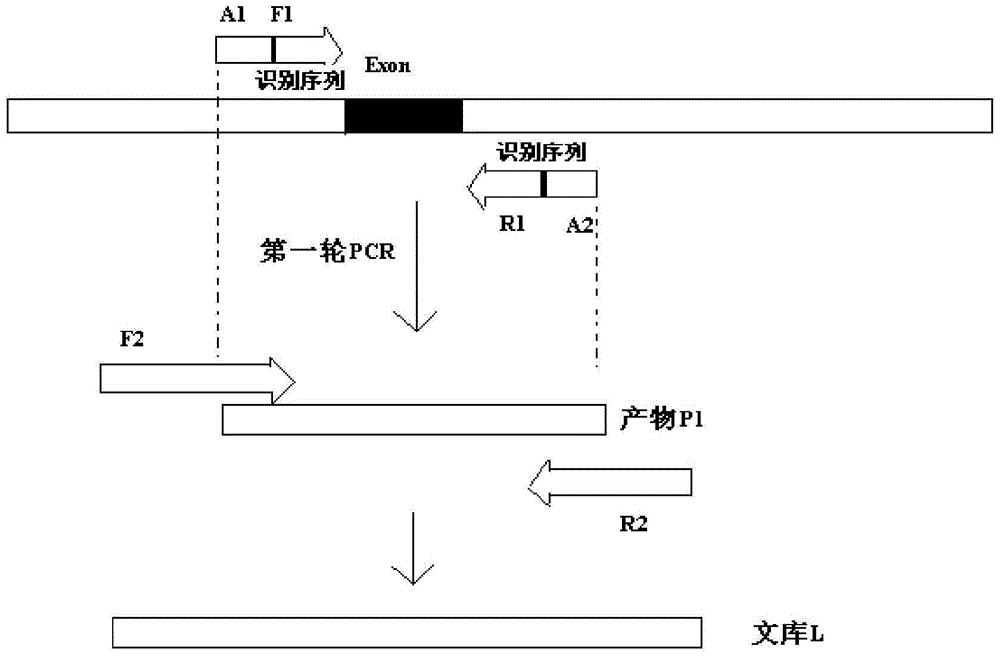
[0068] 1. Sample preparation (acquisition of sequencing library)
[0069] The steps of performing two rounds of PCR amplification on the exon and exon-intron binding region of the gene to obtain the sequencing library are as follows:
[0070] 1. Acquisition of disease-causing gene information.
[0071] Search for non-syndromic deafness on the OMIM (Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man) website or NCBI's OMIM database to obtain hotspot pathogenic genes related to it and obtain information on related mutation sites.
[0072] 2. Search the sequence and position information of the exons and introns of each relevant pathogenic gene in NCBI.
[0073] 3. Multiplex PCR primer design and synthesis
[0074] Corresponding PCR primers were designed for the exons of the above genes. According to the aforementioned design prin...
Embodiment 2
[0121] Embodiment 2: Referring to the method of Example 1, for a certain glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency patient, the primers were designed using the method of the present invention, and the first round of primer sequences are as follows in Table 2:
[0122] Table 2, G6PD gene first-round PCR primer sequence list
[0123]
[0124]
[0125] After the first round of PCR was completed, high-throughput sequencing was carried out after the second round of PCR (see Example 1 for specific steps and methods), and the results obtained were as follows:
[0126] The high-throughput sequencing results of patients with G6PD deficiency are:
[0127]
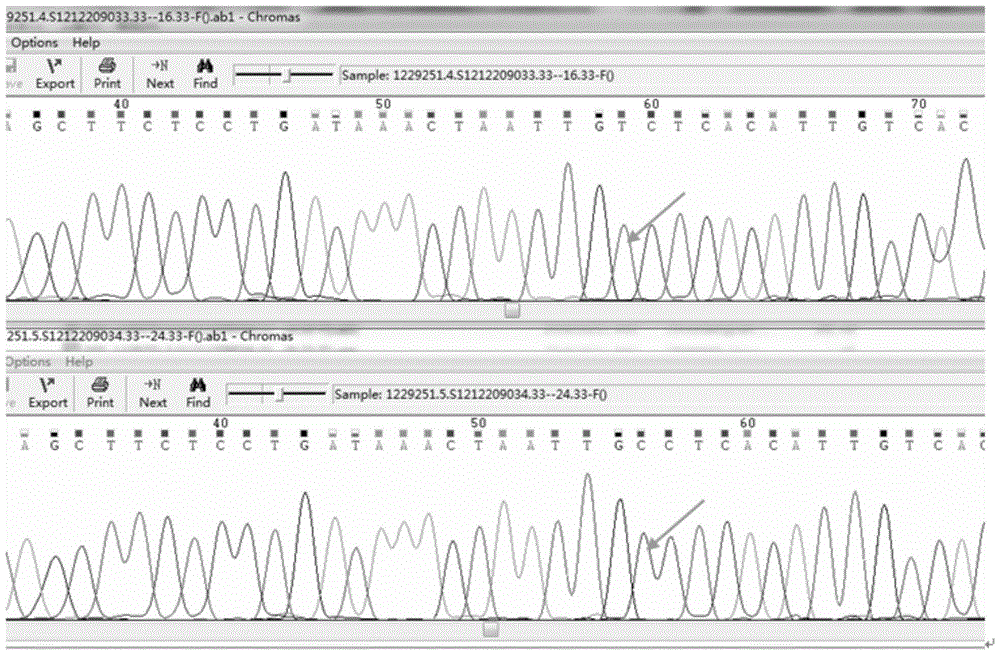
[0128] The c.678C>G mutation site of the G6PD gene is verified with the gold standard Sanger method (with normal people as a control), and it is found that it is completely consistent with the mutation type detected by the present invention, such as Figure 5 Shown:
[0129] Figure 5 It is the Sanger sequencing result...
example 3
[0133] Example 3: with reference to the method of Example 1, to a newborn of a certain Gitelman syndrome patient, utilize the method of the present invention to related disease-causing gene SLC12A3 gene design primer (the primer of first-round PCR is as table 3) carries out PCR amplification high Through-put sequencing was used to determine whether the patient's son suffered from Gitelman syndrome, and the following results were obtained:
[0134] Table 3, SLC12A3 gene first-round PCR primer sequence list
[0135]
[0136]
[0137] The results of high-throughput sequencing of newborns of patients with Gitelman syndrome are:
[0138]
[0139] The C.176_179delACAAA deletion mutation site of the SLC12A3 gene was verified by the gold standard Sanger method, and it was found to be completely consistent with the mutation type detected in the present invention. After the ACAAA sequence was deleted, a frameshift mutation was caused, and it was heterozygous at the same time, r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com