Nucleic acid for detecting Zika virus, real-time fluorescence RPA kit and method
A Zika virus and real-time fluorescence technology, applied in the field of biotechnology detection, can solve the problems of difficult to achieve detection results, difficult design of primers and probes, etc., to avoid non-specific amplification problems, overcome long detection time, and simplify operations The effect of the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] The design of embodiment 1 primer, probe
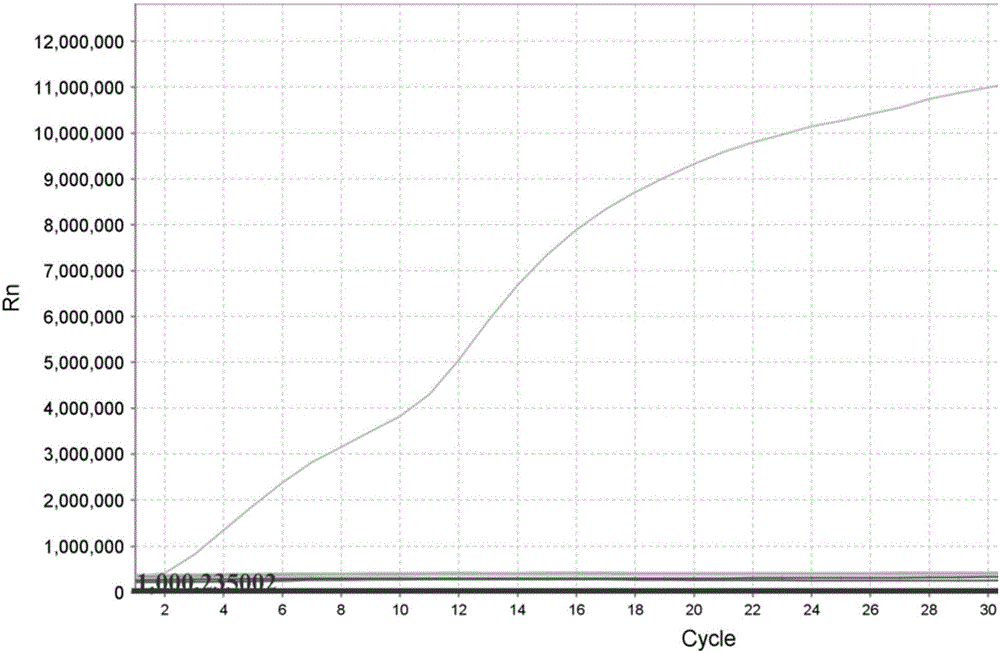
[0036] In the present invention, adopting recombinase polymerase amplification technology (RPA) to detect Zika virus, the design of primers and RPA probes is particularly critical, and the primers and probes of this technology are designed without special software. It can only rely on artificial design, and mark a fluorescent group and a fluorescent quenching group on the two thymine nucleotides in the middle of the RPA probe, and design an abasic site between the two groups ( dSpacer), this site can be recognized and cut by exonuclease III with 3'-5' exonuclease activity, freeing the fluorescent group, thereby emitting a fluorescent signal and then captured by a fluorescent detection instrument. The design of RPA probes is particularly important, which is related to the success of the entire experiment. The success of its design not only needs to be designed based on experience, but also requires a large number of experimental...
Embodiment 2
[0043] The construction of embodiment 2 plasmid
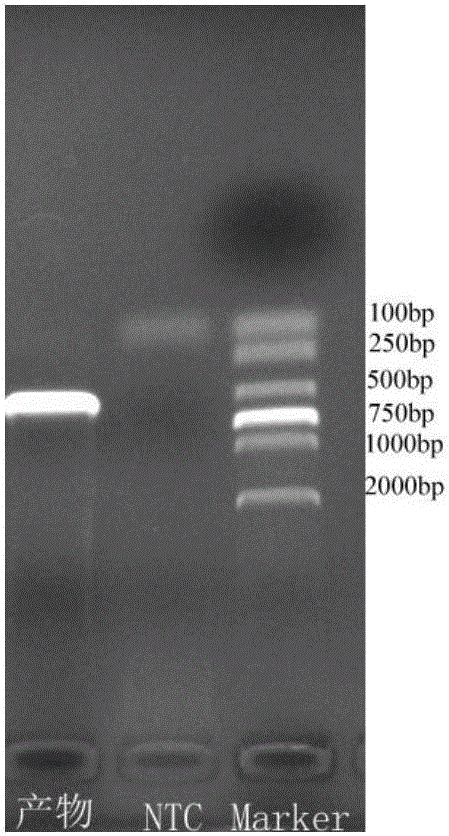
[0044] Compare the whole genome sequence of Zika virus in Genebank, select a relatively conservative sequence segment (membrane protein gene, position 1584-2107), and insert the SP6 promoter sequence at the 5' end of position 1584: ATTTAGGTGACACTATAG, in A 6×His tag sequence was introduced at the 3' end of the 2107 site. The reason for the primer SP6 promoter is that after the successful construction of the plasmid, the above-mentioned recombinant sequence was amplified by PCR method, and the artificially synthesized sequence was transcribed into RNA in vitro to simulate the nucleic acid of Zika virus by using the transcription kit. The purpose of using the 6×His tag sequence is to distinguish the positive quality control from the real Zika virus nucleic acid in the sample.
[0045] details as follows:
[0046] (1) The artificially synthesized sequence (SEQ ID No.4) is as follows:
[0047] 5′- ATTTAGGTGACACTATAG CATTGGTTGG...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Embodiment 3 Zika virus isothermal amplification detection method
[0058] In the method established by the present invention, in order to avoid the failure or contamination of the reagents used, a positive control and a negative control reagent are provided, and the negative control uses nuclease-free water;
[0059] The positive control adopts the plasmid DNA carrying the amplified product, and the nucleotide sequence of the amplified product contains the sequence shown in SEQID No.4.
[0060] The design of the negative control can effectively verify whether the reagents used are contaminated and avoid the occurrence of false positives. The design of the positive control can effectively verify the effectiveness of the reagents used and avoid the occurrence of false negatives.
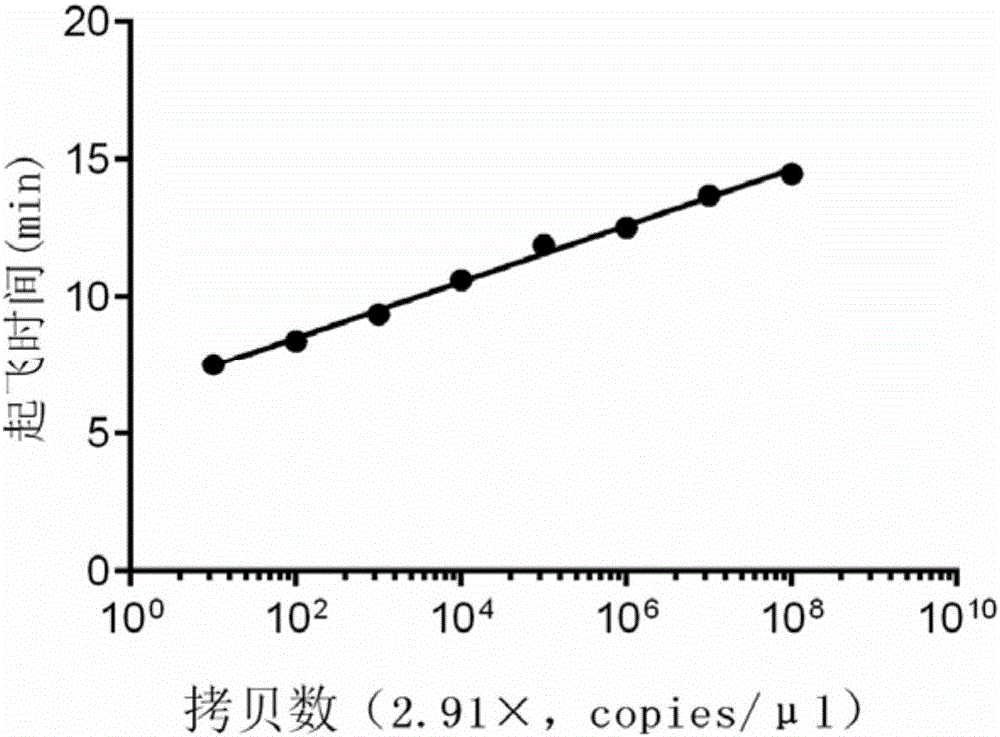
[0061] After multiple optimization experiments, the following method was determined to be used for detection.
[0062] The method for detecting Zika virus by isothermal amplification comprises...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com