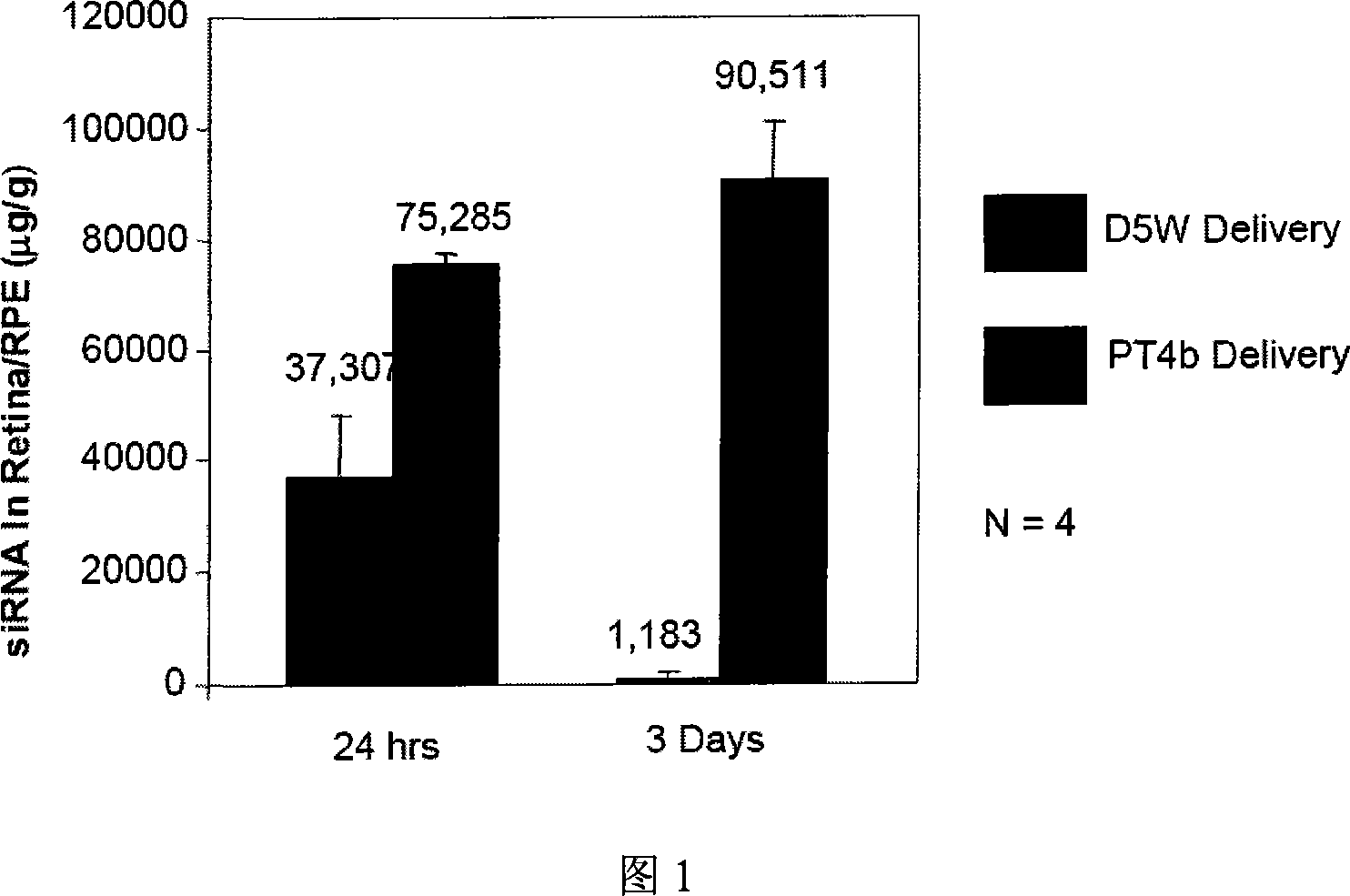
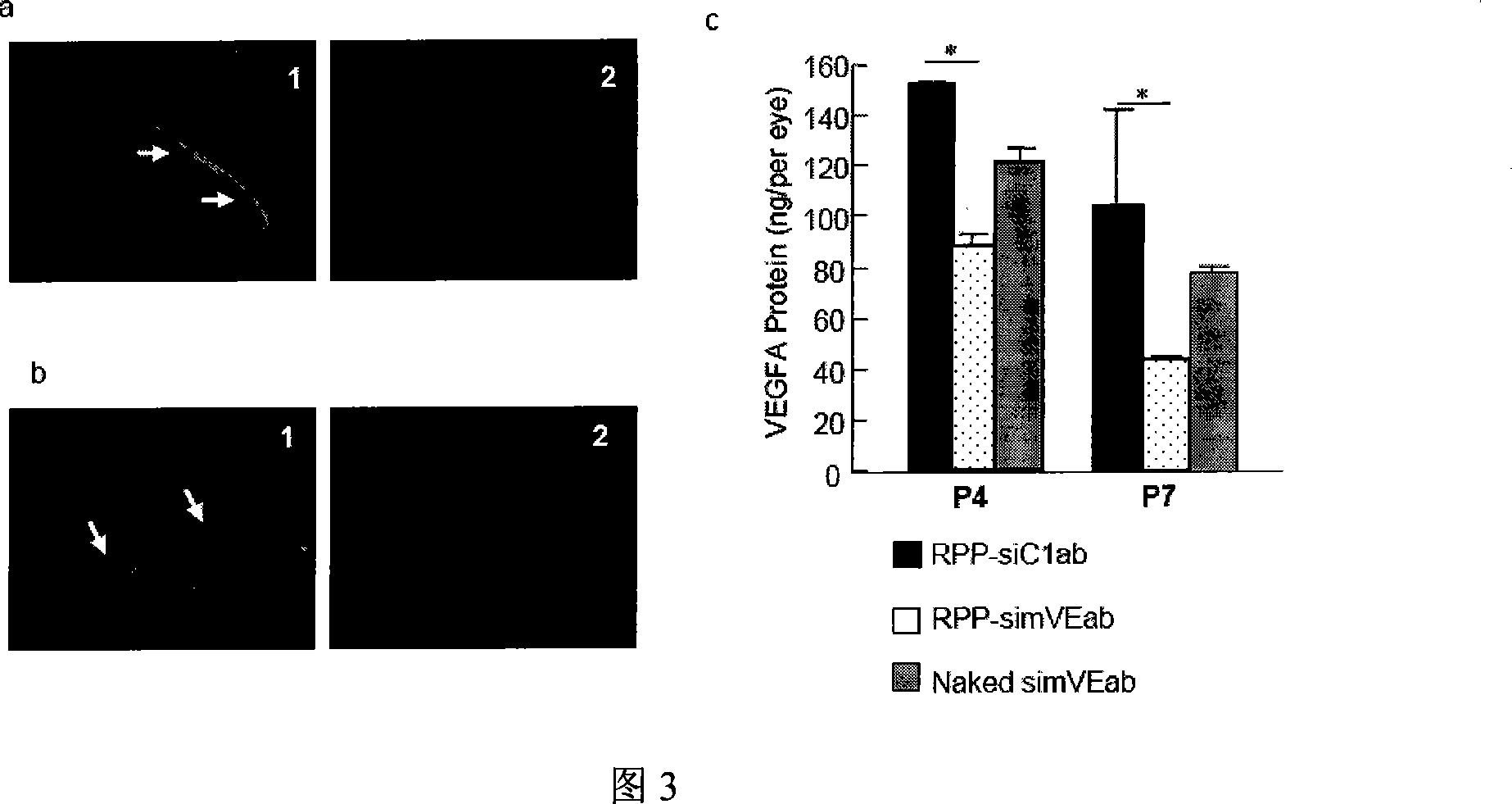
Multiple target point small interference RNA cocktail agent for treating ophthalmic disease and preparing method thereof
An ophthalmic disease, small interference technology, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, gene therapy, etc., can solve the problem of no way to ensure siRNA and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
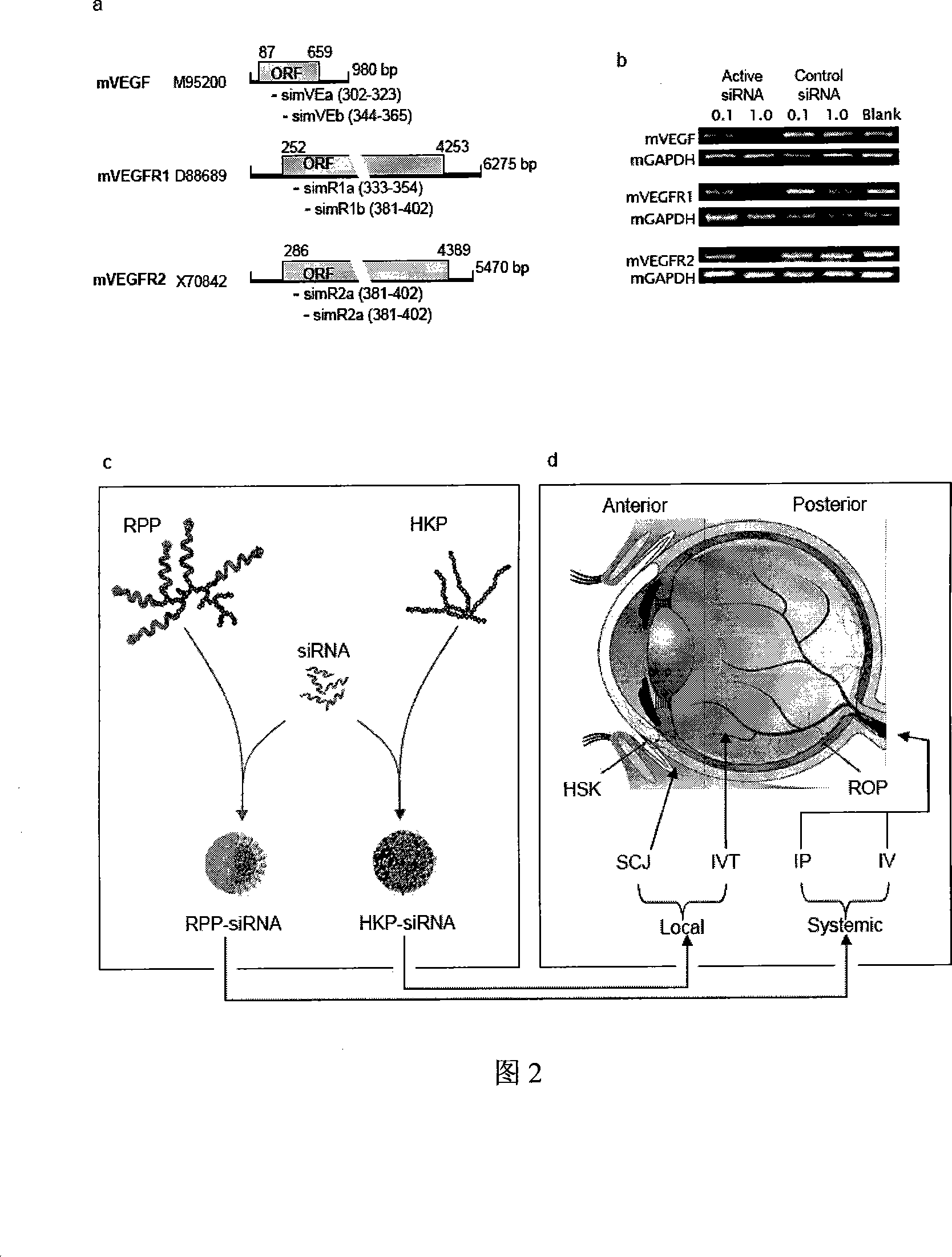
[0196] Example 1 Design of siRNA double-stranded molecules against VEGF, VEGF-R1, VEGF-R2
[0197] Six siRNA double-stranded molecules were designed for each gene, and a total of 18 siRNAs were chemically synthesized at Qiagen (Germantown, MD). All siRNAs have a dTdT overhang at the 3' end, and there are no other modifications. After screening in the cell model, two siRNAs with the best activity were selected from every six siRNAs, and the siRNAs were mixed in equal proportions. The siRNA sequence is as follows:
[0198] mVEGF-siRNA (a): (forward) 5'-GCCGUCCUGUGUGCCGCUGdtdt-3', (reverse)
[0199] 5'-CAGCGGCACACAGGACGGCdtdt-3'; mVEGF-siRNA(b): (forward)
[0200] 5'-CGAUGAAGCCCUGGAGUGCdtdt-3', (reverse)
[0201] 5'-GCACUCCAGGGCUUCAUCGdtdt-3'; mVEGFR1-siRNA(a): (forward)
[0202] 5'-GUUAAAAGUGCCUGAACUGdtdt-3', (reverse)
[0203] 5'-CAGUUCAGGCACUUUUAACdtdt-3'; mVEGFR1-siRNA(b): (forward)
[0204] 5'-GCAGGCCAGACUCUCUUUCdtdt-3', (reverse)
[0205] 5'-GAAAGAGAGUCUGGCCUGCdtdt-...
Embodiment 2
[0218] Example 2 Screening Candidate siRNA Double-Strand Molecules on Cell Model
[0219]Candidate mouse VEGF siRNA was screened using RAW264.7 gamma NO(-) cells (ATCC, CRL-2278), cell culture condition: RPMI containing 10% FBS. Candidate mouse VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 were screened using SVR cells (ATCC, CRL-2280), cell culture conditions: DMEM containing 5% FBS. The cells were planted in 6-well plates, and the transfection reagent was LipofectAmine (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). After 24 hours or 48 hours, RNA was extracted, and RNA copy number changes were analyzed by RNA-specific PCR (RS-PCR).
Embodiment 3
[0220] Embodiment 3 prepares siRNA / polymer nanoparticle
[0221] A branched lysine-histidine polypeptide complex (HKP) was synthesized on a Ranin Voyager synthesizer (PTI, Tucson, AZ). The HKP polypeptide used here is PT73, and its structural characteristics are (R)K (R)-K(R)-(R)K(X), where R=KHHHKHHHNHHHNHHHN, X=C(O)NH2, K=lysine, H=histidine and N=Asperagine. PT73 and siRNA were respectively dissolved in water and mixed at a mass ratio of 4:1 to form nanoparticles with an average diameter of 150-200 nm. The targeted nano-conjugated polymer carrier RPP for systemic administration is an amphiphilic three-segment chimera, and its structural feature is RGD-PEG-PEI, wherein RGD is an adhesion protein whose sequence is H-ACRGDMFGCA-OH, PEG is polyethylene glycol, and PEI is polyethyleneimine. RPP and siRNA were dissolved in water respectively, and mixed according to the molar ratio of 2:1, which can self-assemble to form 120-150nm nanoparticles. The ζ-potential analysis showed t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com