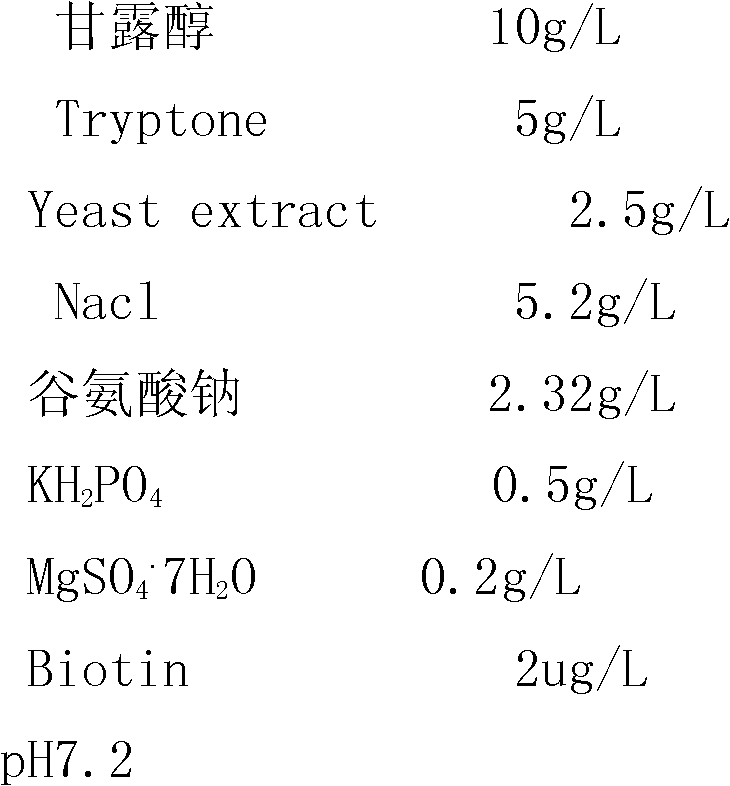
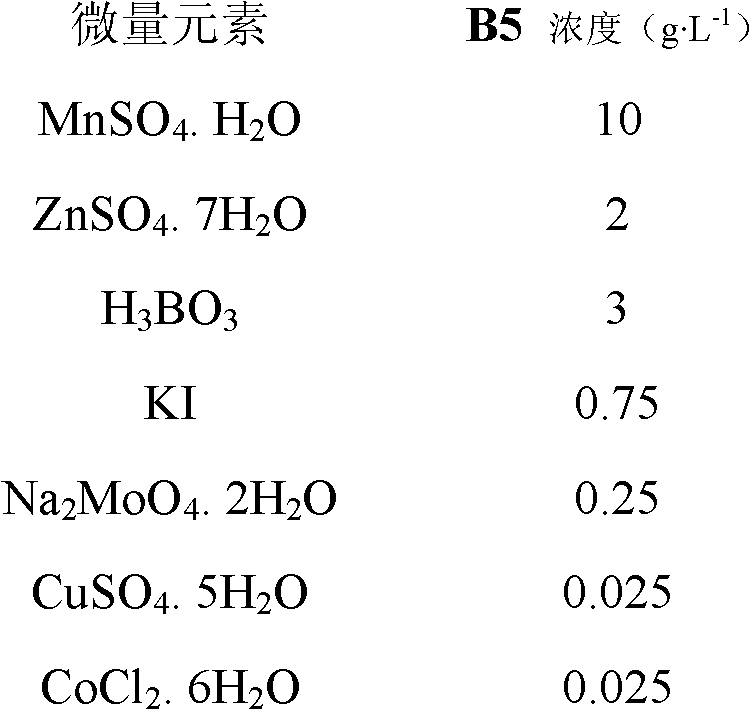
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Brachypodium distachyon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Brachypodium distachyon, commonly called purple false brome or stiff brome, is a grass species native to southern Europe, northern Africa and southwestern Asia east to India. It is related to the major cereal grain species wheat, barley, oats, maize, rice, rye, sorghum, and millet. It has many qualities that make it an excellent model organism for functional genomics research in temperate grasses, cereals, and dedicated biofuel crops such as switchgrass. These attributes include small genome (~270 Mbp) diploid accessions, a series of polyploid accessions, a small physical stature, self-fertility, a short lifecycle, simple growth requirements, and an efficient transformation system. The genome of Brachypodium distachyon (diploid inbred line Bd21) has been sequenced and published in Nature in 2010.
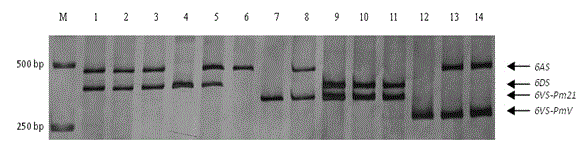
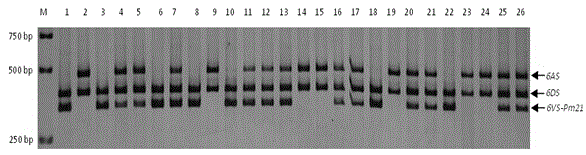
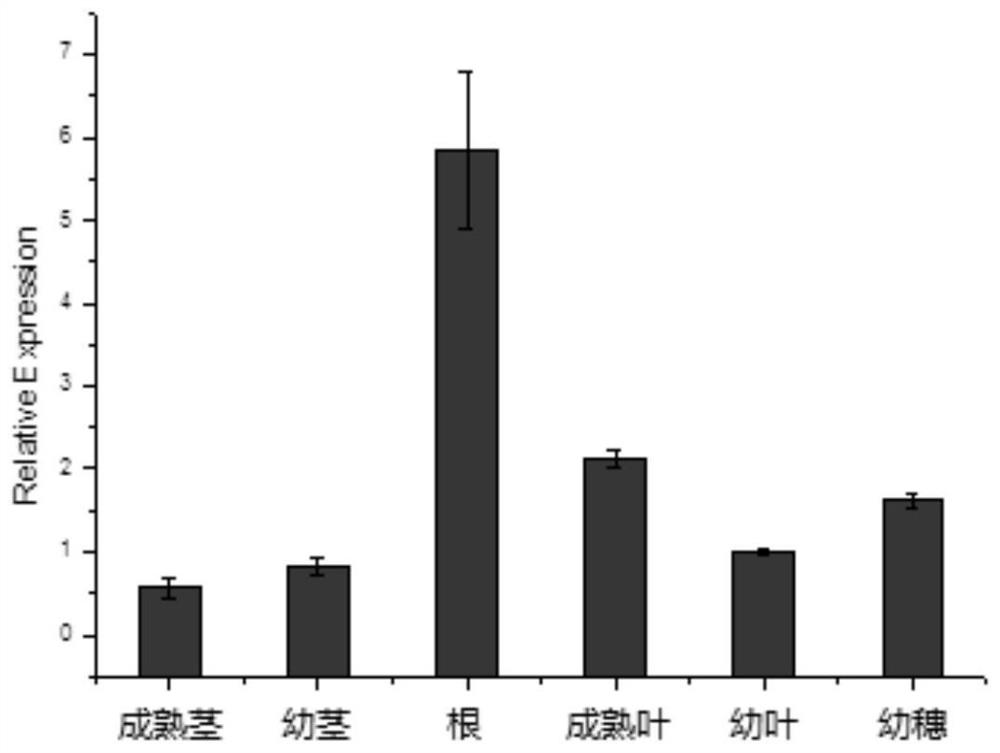
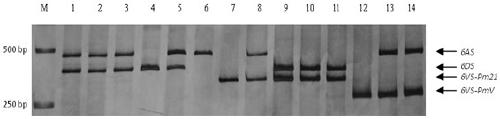
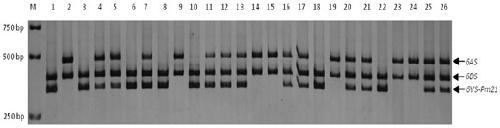
Haynaldia villosa's 6VS chromosome specific molecular marker 6VS-BH1 and application thereof
InactiveCN104877996AStrong brightnessWide range of annealing temperaturesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMarker-assisted selection
The invention relates to a haynaldia villosa's 6VS chromosome specific molecular marker 6VS-BH1 and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of molecular biology and genetic breeding science. The labeled primer 6VS-BH1 is developed on the basis of wheat-brachypodium distachyon comparative genomics means, and the specific sequence is 6VS-BH1F, as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and 6VS-BH1R, as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The molecular marker 6VS-BH1 has the advantages of wide annealing temperature range (60-66 DEG C), good stability, strong product brightness, high resolution and the like. The molecular marker 6VS-BH1, as a co-dominant marker, not only can be used for effectively tracing haynaldia villosa's 6VS chromosome in wheat background, but also can be used for distinguishing a homozygote and heterozygote and for distinguishing a Pm21 gene carried translocation line T6VS.6AL and a PmV gene carried translocation line T6VS.6DL. Therefore, the molecular marker 6VS-BH1 disclosed by the invention has an important practical value in the molecular marker-assisted selection breeding of wheat powdery mildew and the pyramiding breeding of Pm21 gene and PmV gene.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
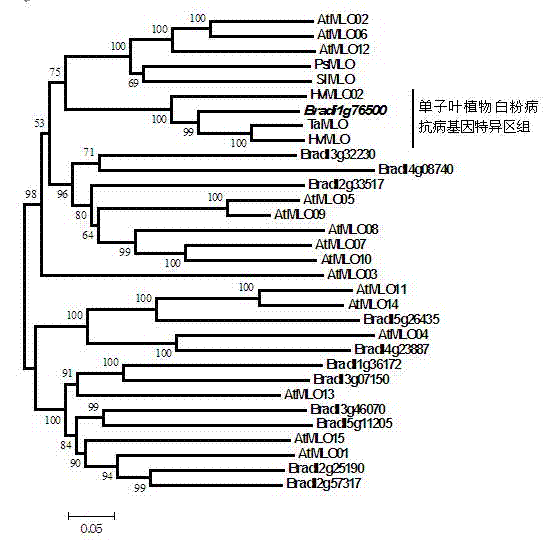
Rapid identification of anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon
InactiveCN102703462AShorten digging cycleRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyBrachypodium sylvaticum
The invention relates to rapid identification of anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon, relates to the knowledge of plant comparative genomics, genetics, biological information and other subjects, and belongs to the scientific field of plant biotechnology. The rapid identification of anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon comprises the main steps of: (1) downloading full genome sequences of Brachypodium distachyon and collecting MLO (mildew resistance locus o) type gene; (2) identifying the MLO type gene; (3) analyzing the MLO type gene historical development relation; and (4) comparing the MLO type powdery mildew gene. According to the rapid identification of anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon provided by the invention, the excavation period of the anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon is effectively shortened, and the rapid identification of the powdery mildew gene is facilitated; the identified powdery mildew gene can be used for developing corresponding coseparation functional markers (SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism), SCAR (sequence-characterized amplified region), and the like), and can also be rapidly used for assisted selection of molecule markers of anti-powdery-mildew gene, and the accuracy is high; development of multi-resistance breeding materials can be carried out by combining with other anti-disease gene molecule markers, the breeding time is shortened and the breeding efficiency is improved; and foundation is established for expounding the molecular mechanism of the anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon.
Owner:常熟市支塘镇新盛技术咨询服务有限公司
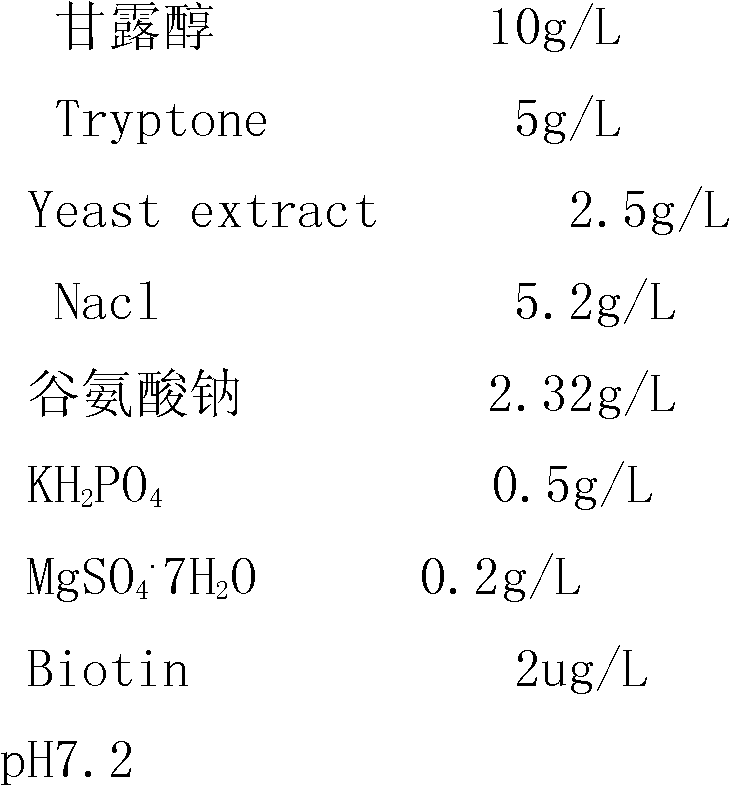
Culture medium for cultivating transgenic plant
The invention discloses a culture medium for cultivating a transgenic plant. The culture medium group comprises a callus induction culture medium, a subculture culture medium, a co-culture culture medium, a screening culture medium and a regeneration culture medium. Experiment results show that: with a transformation system and a transformation method of the present invention, average every 100 brachypodium distachyon immature embryos can produce about 103 positive transformation seedlings, wherein a positive seedling transformation rate achieves 103.4%, and is far higher than positive seedling transformation rates of the traditional and grain model plant rice, and the highest rice positive seedling transformation rate is 47.6% (Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2008, 25(3),322-331). With the efficient agrobacterium transformation system of the brachypodium distachyon, the important technology means is provided for temperate zone and grain plant gene function researches.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
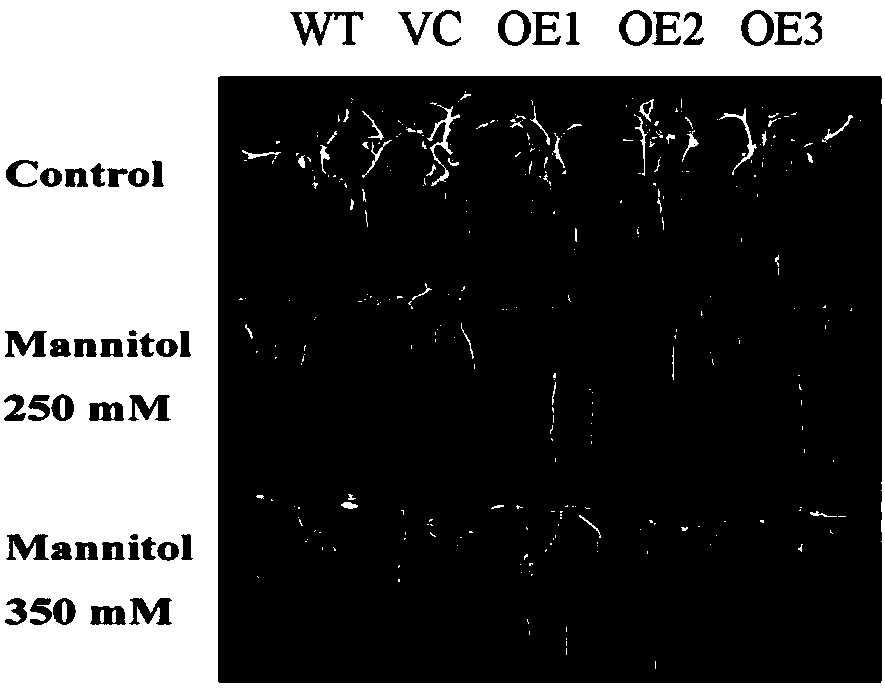
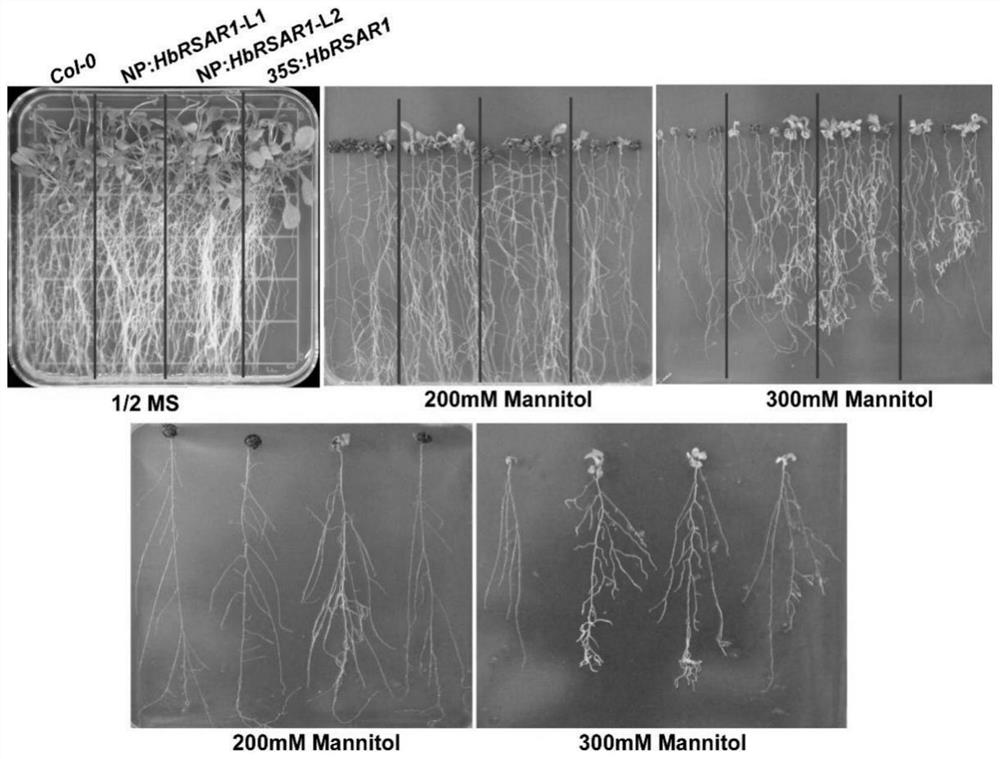
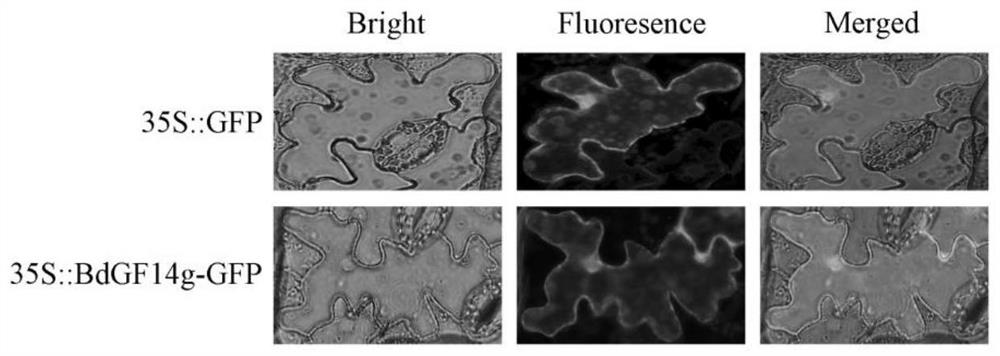
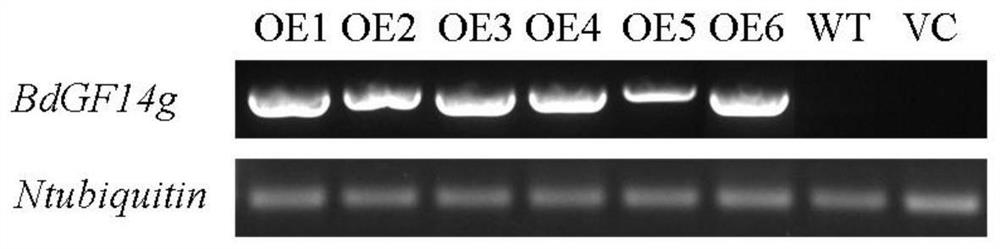
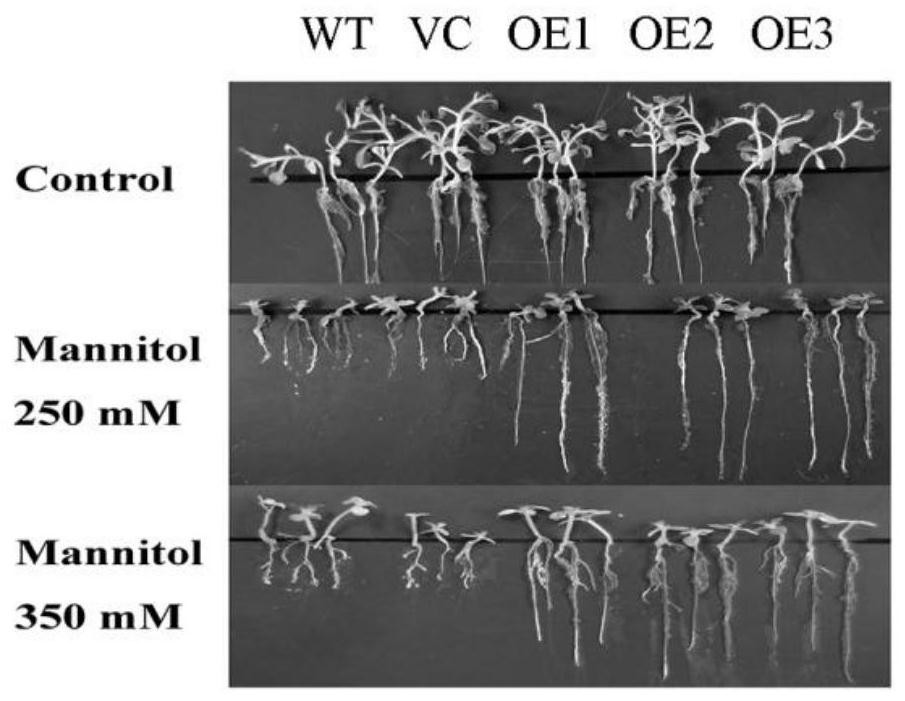
Brachypodium distachyon drought-resistant gene and expression vector as well as coding protein and application thereof
ActiveCN108103074AImprove toleranceGuaranteed absorptionBacteriaPlant peptidesBiotechnologyPeroxidase
The invention provides a brachypodium distachyon drought-resistant gene and an expression vector as well as coding protein and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is the sequenceshown by SEQ ID NO.1 or a nucleotide sequence complementary to the sequence shown by SEQ ID NO.1. The protein is obtained by coding the gene of claim 1, and the amino acid sequence of the protein is shown by SEQ ID NO.2. The gene is used for improving application of the plant tolerance to drought stress. The gene provided by the invention regulates the plant to close pores to reduce the moisture lost in transpiration; a stronger root system is obtained in a drought condition so as to guarantee moisture absorption; moreover, the gene can improve the activity of such enzymes as catalase, peroxidase and superoxide dismutase in the antioxidase system and eliminate reactive oxygen species (ROS) in time, thereby reducing the oxidative damage of cells caused by the ROS and improving the plant tolerance to drought.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
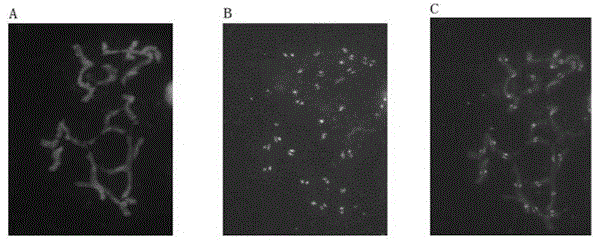
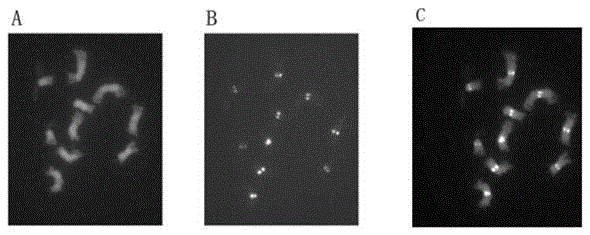
Brachypodium distachyon functional centromere antigen polypeptide and application
InactiveCN105461789ADiscuss formationDiscuss functionSerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against plantsNew Zealand white rabbitNucleotide
The invention provides a brachypodium distachyon functional centromere histone CENH3 and application. Firstly, the nucleotide sequence of a brachypodium distachyon functional centromere histone CENH3 gene is predicted through the bioinformatics sequence comparison method, a polypeptide is synthesized according to a segment of specific sequence of the N end of an amino acid sequence encoded by the nucleotide sequence, New Zealand white rabbits are conventionally immuned through the polypeptide, antiserums are prepared, and a CENH3 protein antibody is obtained through antigen affinity purification. The CENH3 antibody can be used for immunostaining experiments, physical positioning of centromere and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) experiments, the functional DNA sequence of a brachypodium distachyon functional centromere is obtained, positioning of centromere genome genetic maps and physical maps is carried out, and important tools and information are provided for research of centromere formation and function exercise mechanisms and building of artificial chromosomes.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
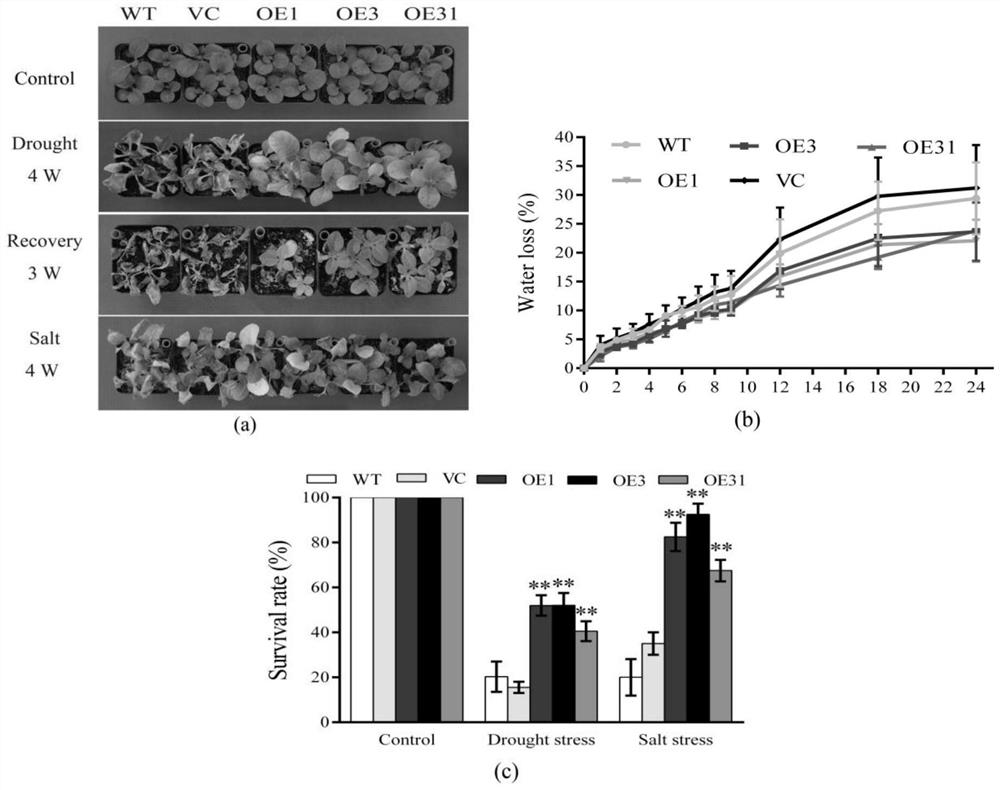
Drought resisting and salt resisting gene of brachypodium distachyon and coded proteins and application thereof
The invention provides an application of coded proteins of drought resisting and salt resisting gene of brachypodium distachyon. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is a sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 or a nucleotide sequence complementary as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The protein is obtained by coding the gene according to the claim 1, and the amino acid sequence of the protein is as shown in SEQ IDNO.2. The gene is applied to improving tolerance of plants to drought and salt resistance. The gene adjusted plant keeps cell moisture by accumulating through matters. ROS accumulation is reduced andthe cytomembrane oxidizing damage caused by active oxygen is reduced by improving the activity of an antioxidant enzyme system. By accelerating closing of pores under drought, the drought and salt resistance of transgenic tobacco is improved by way of reducing water damaged by means of transpiration, improving the expression level of stress related genes and the like. Drought and salt resisncve of the transgenic tobacco with the gene is dependent on adjustment of ABA synthesis and an ABA signal channel.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
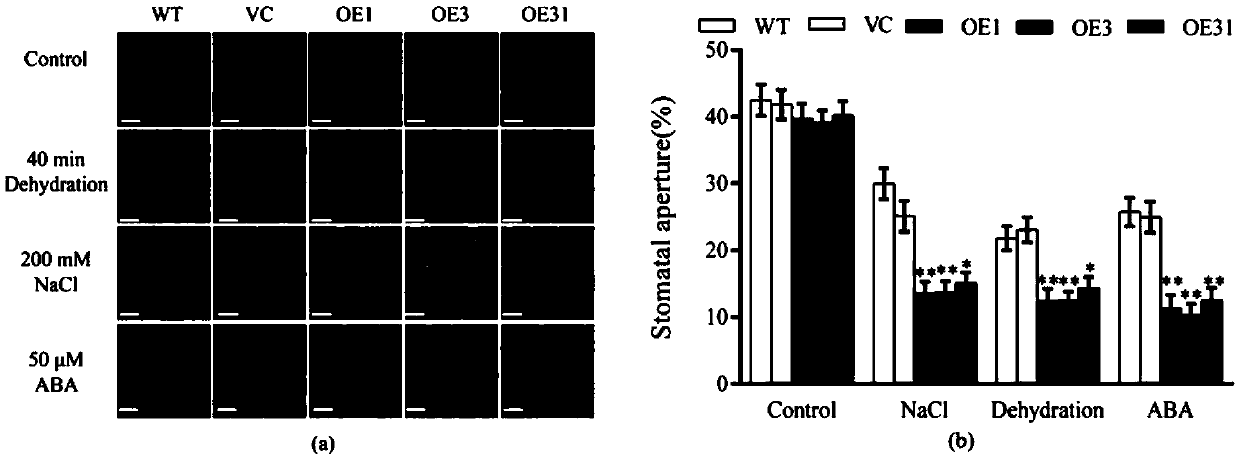
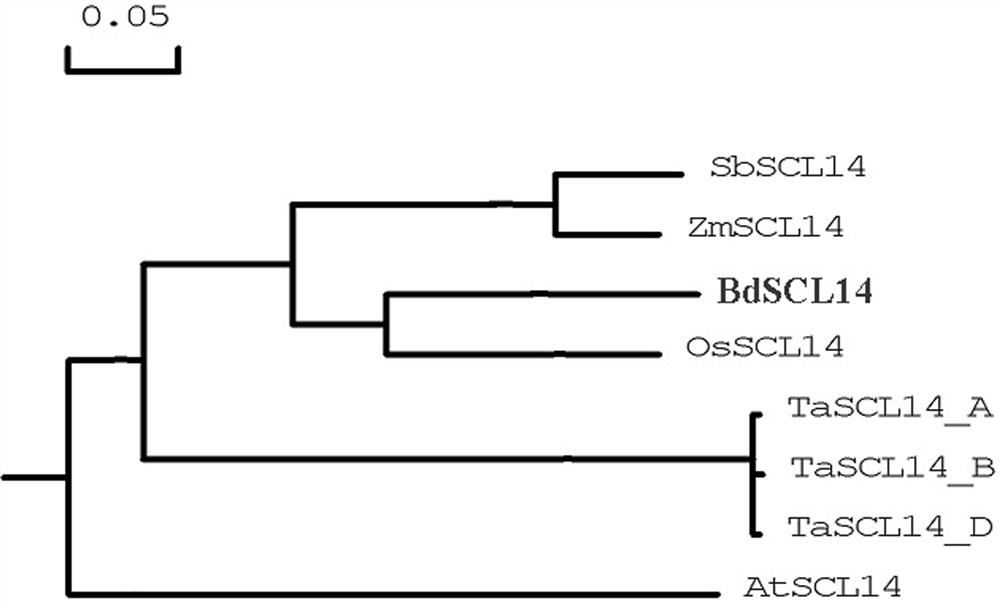
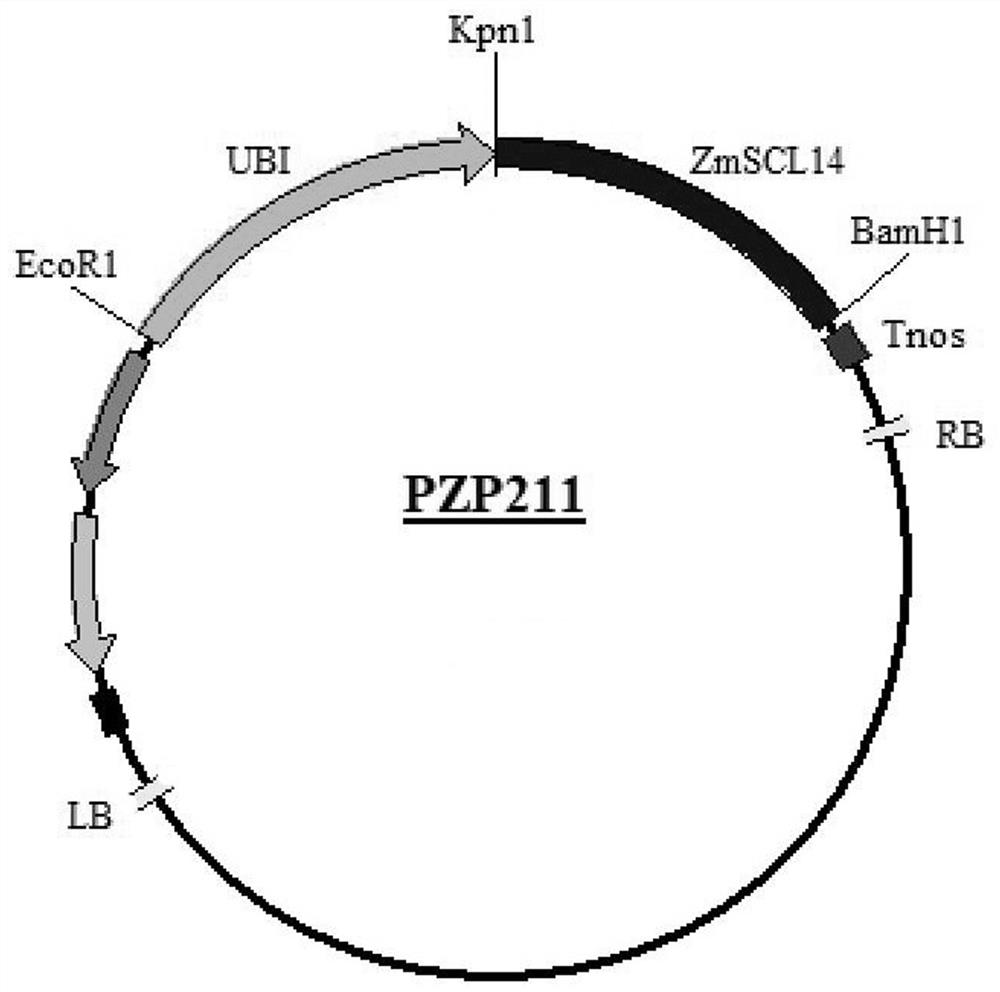
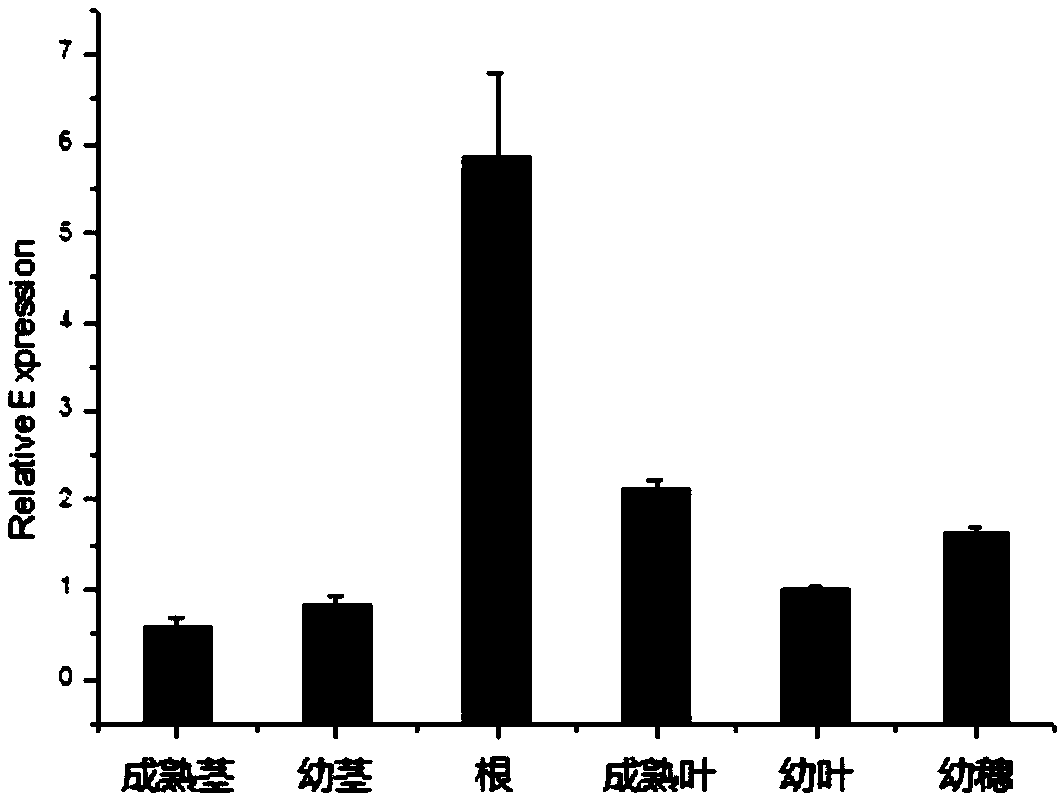
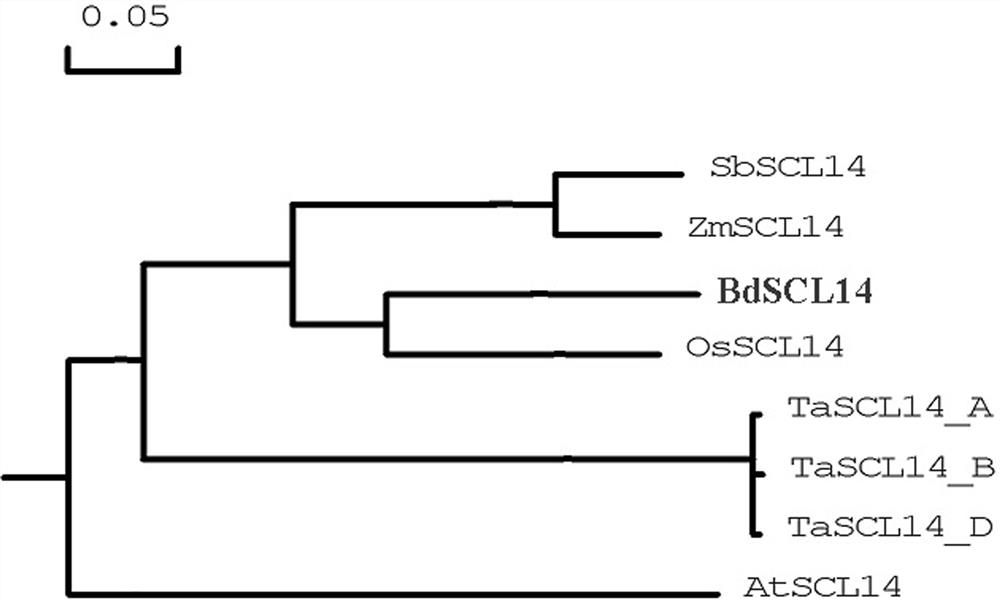
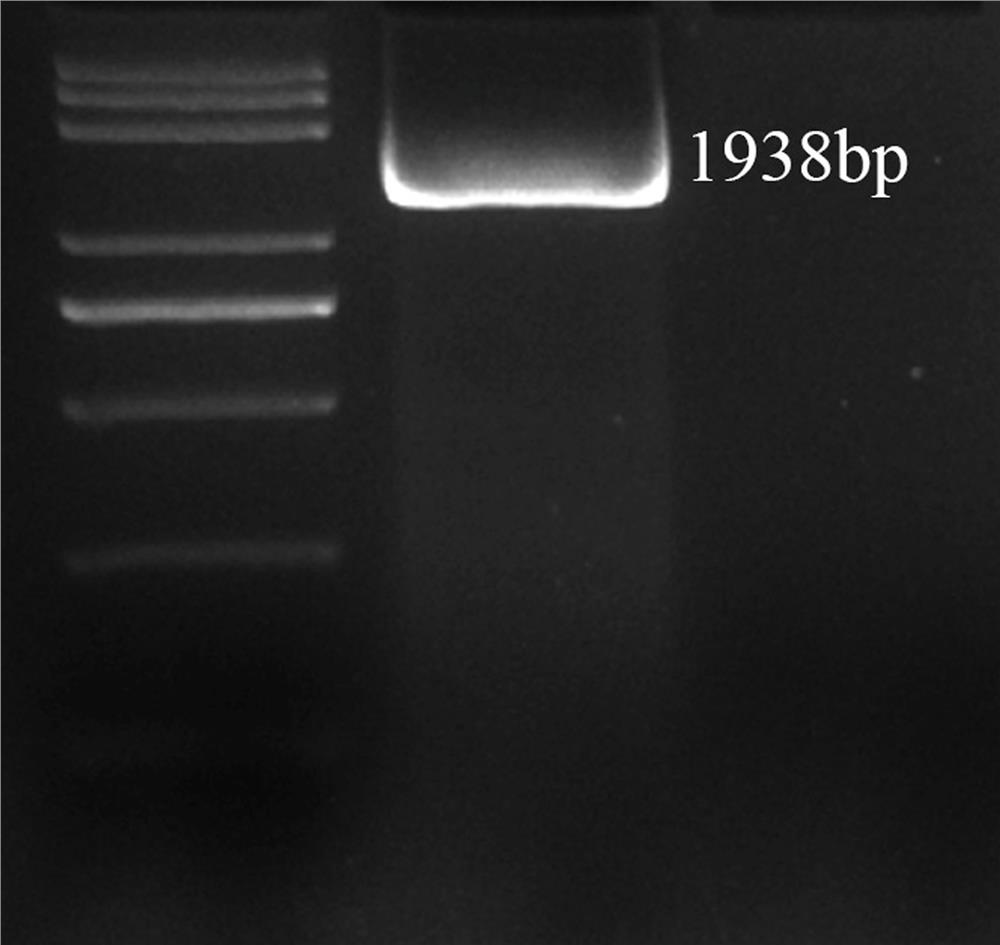
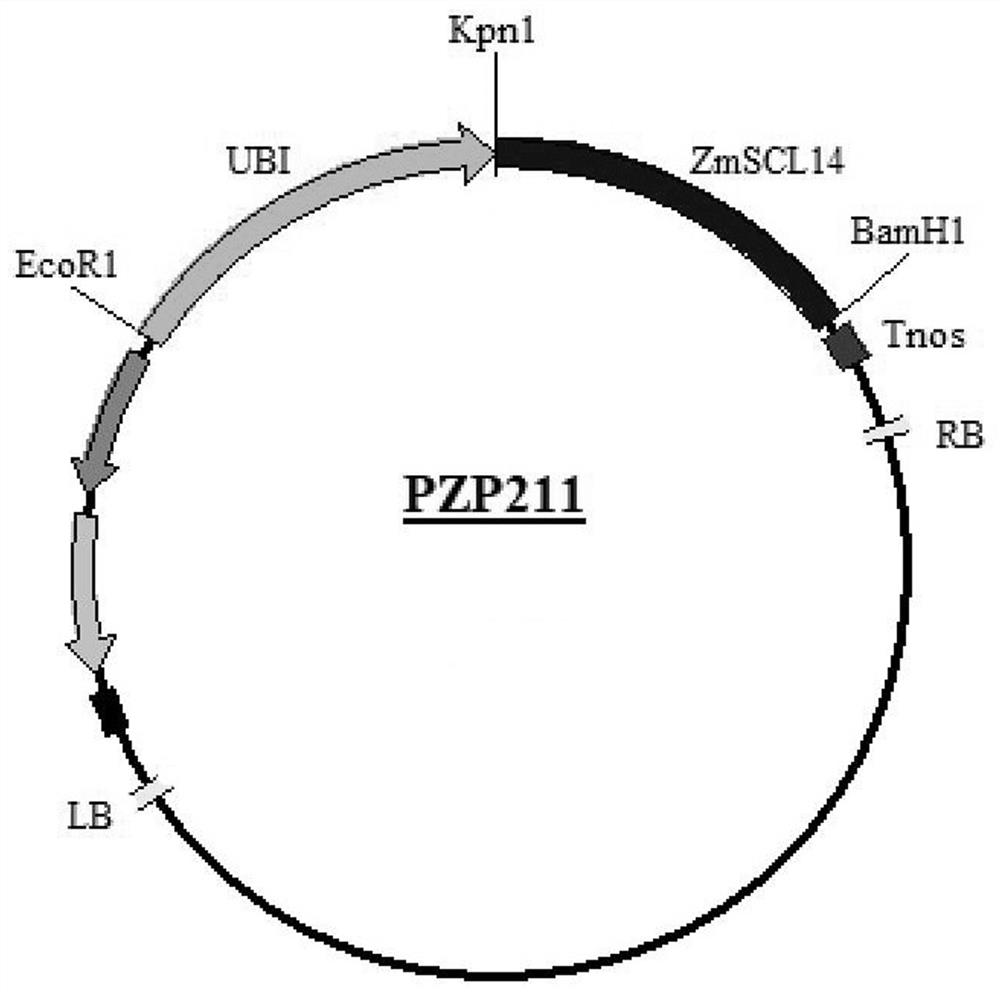
Application of corn gene ZmSCL14 in regulating and controlling flowering period of plants
ActiveCN112481276ADelayed floweringSlow growth ratePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyBrachypodium sylvaticum
The invention discloses an application of a corn gene ZmSCL14 in regulation and control of a flowering period of a plant. The nucleotide sequence of the corn gene ZmSCL14 is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1.According to the invention, a recombinant overexpression vector is obtained by utilizing the existing plant genetic engineering technology, then brachypodium distachyon callus is transformed by utilizing an agrobacterium infection transformation method, and a homozygous brachypodium distachyon plant of the overexpression ZmSCL14 gene is obtained through tissue culture, identification and screening. Compared with a wild type plant growing under the same condition, the brachypodium distachyon over-expressing the ZmSCL14 gene shows a late flowering phenotype, delays blooming of the brachypodium distachyon, can slow down the growth speed of the brachypodium distachyon plant and participates in regulating and controlling expression of blooming-related genes, so that the ZmSCL14 gene can be applied to cultivation of late flowers or dwarf varieties, and high agricultural application values are realized.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
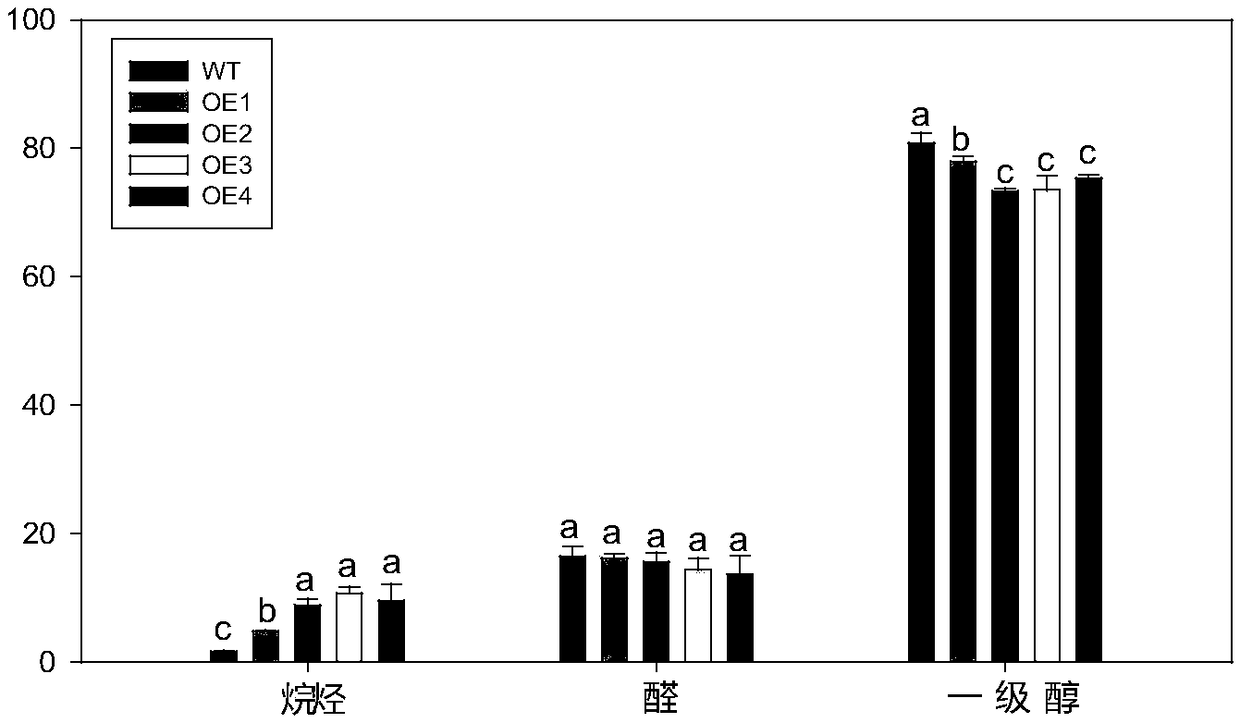
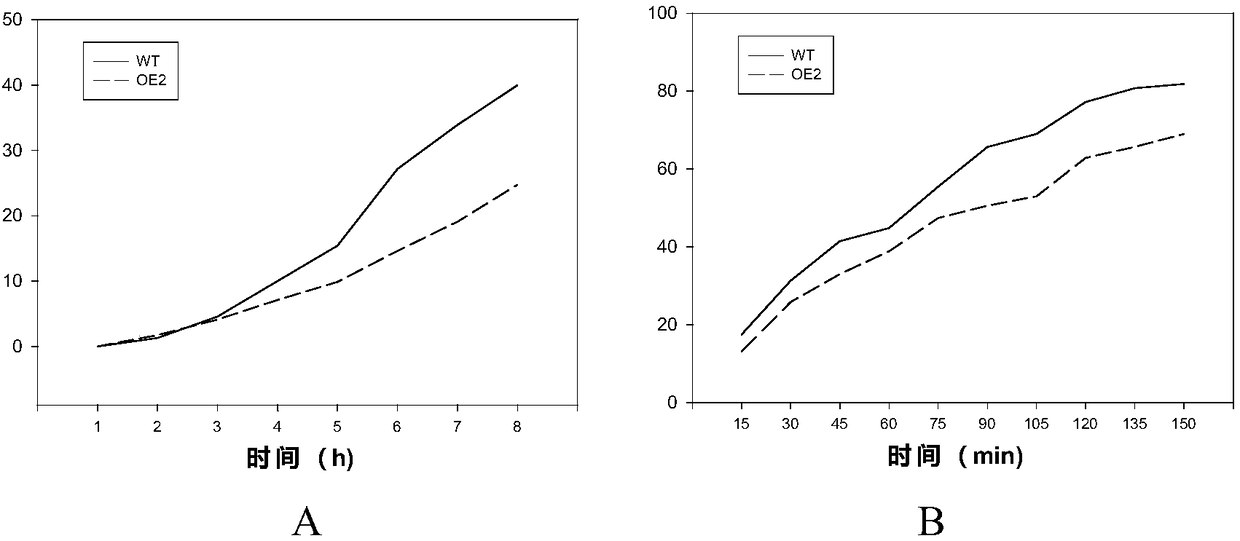
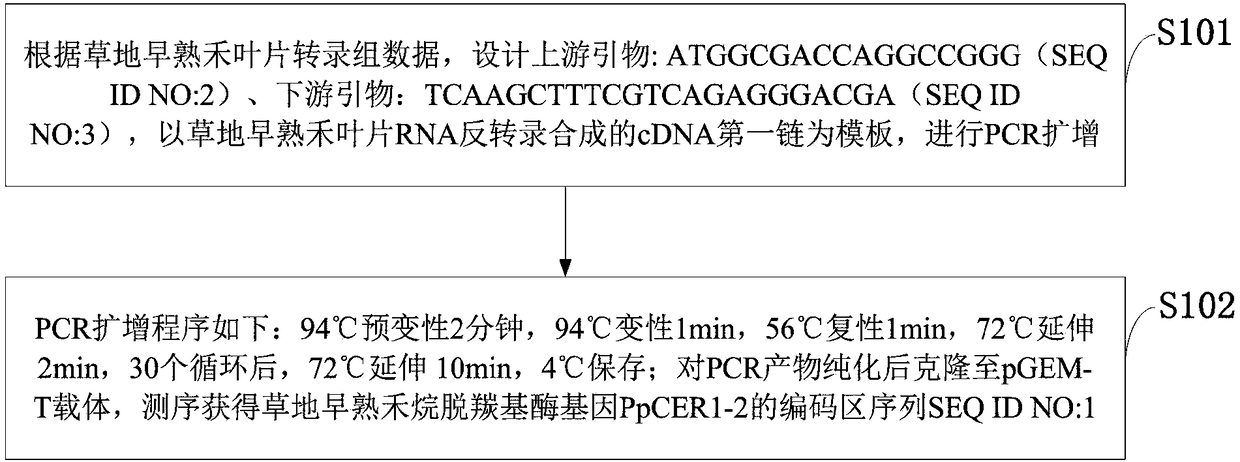
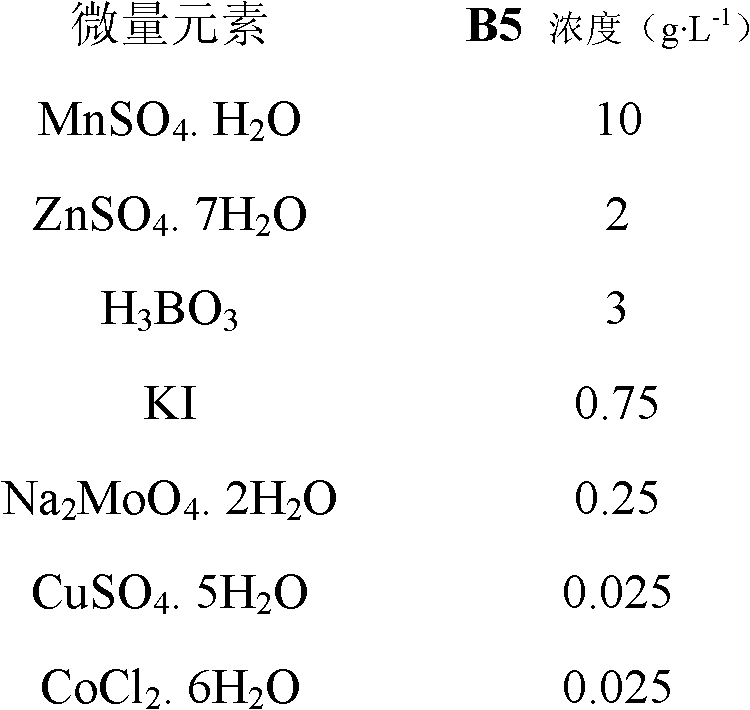
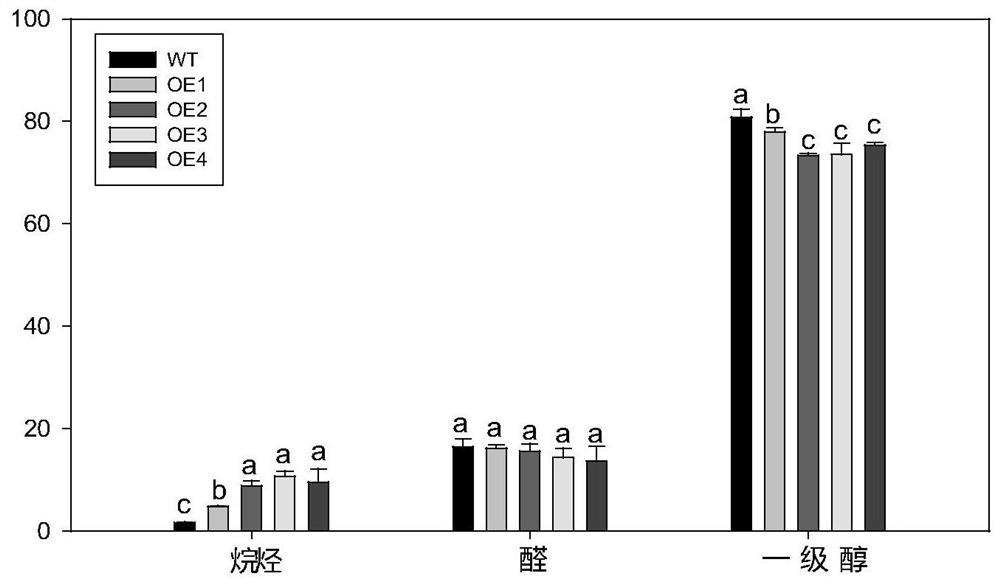
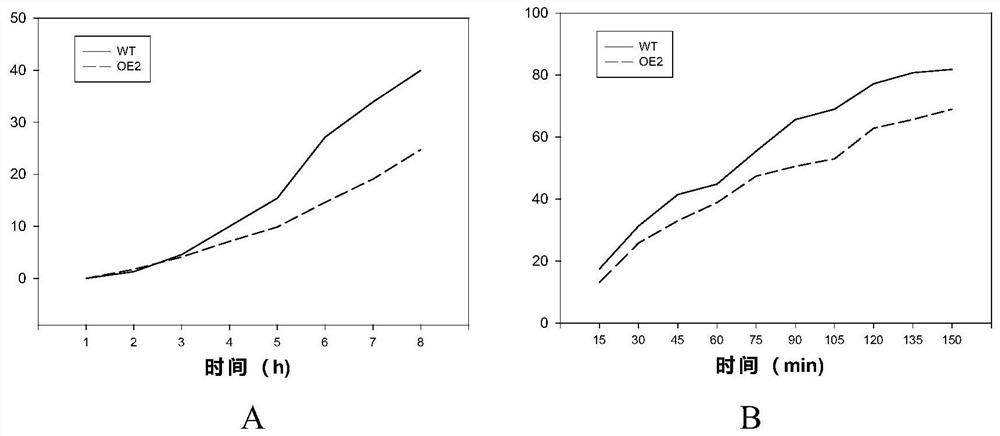
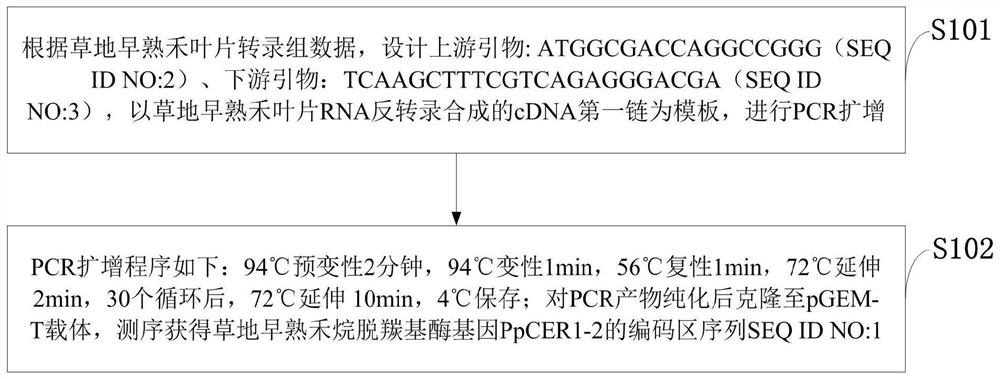
PpCER1-2 gene, vector and application of PpCER1-2 gene in improvement of drought resistance of gramineous plants
InactiveCN108531490AImprove drought resistanceReduce lossEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionCuticlePlant breeding
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant breeding and discloses a PpCER1-2 gene, a vector and application of the PpCER1-2 gene in improvement of the drought resistance of gramineous plants. The sequence of the PpCER1-2 gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The application of the PpCER1-2 gene in improvement of the drought resistance of the gramineous plants is provided. Experiments provethat cuticle alkane substances of a PpCER1-2 gene transferred and ultra-expressed Brachypodium distachyon blade are increased, the water loss of the surface of the blade is relieved, the chlorophyll leaching rate is reduced, and the growth condition of seedlings in drought environment also proves that the PpCER1-2 gene can effectively improve the drought resistance of the gramineous plants. The gramineous plants are important grain crops and garden green land plants, and after the drought resistance of the gramineous plants is improved by the PpCER1-2 gene, the use amount of irrigation water can be reduced, meanwhile, the problem of crop yield reduction caused by water shortage in the high-temperature weather in summer can be solved, and the application prospect is good.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
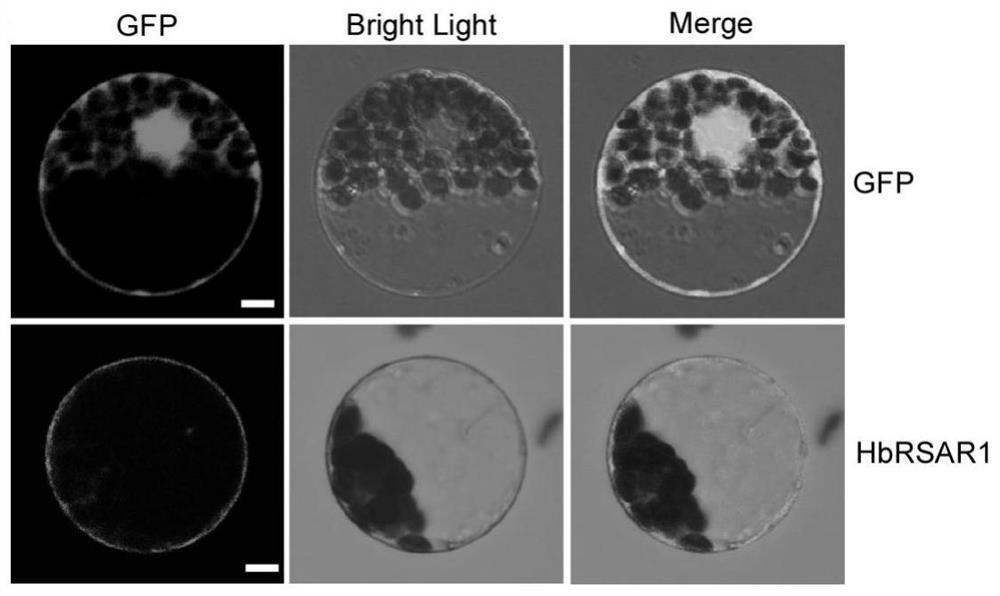
Potassium ion transporter protein HbRAR1 and application thereof in regulation and control of potassium transport of plants
ActiveCN113929758AImprove transport efficiencyClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesBrachypodium sylvaticumPlant roots
The invention discloses a high-efficiency potassium ion transporter HbRAR1 separated and identified from saline-grown wild barley as well as a related biological material and application of the high-efficiency potassium ion transporter HbRAR1. Transgenic experiments of introducing a gene coding the potassium ion transporter protein HbRAR1 into arabidopsis thaliana, brachypodium distachyon and potassium ion transport deficient yeast Cy162 prove that the potassium ion transport efficiency in an adversity environment, especially in a salt stress environment, is remarkably promoted by overexpression of the related gene, and meanwhile, the growth and development of plant roots under various stresses are promoted, comprising root hair elongation and lateral root growth. Therefore, the potassium ion transporter protein HbRAR1 is related to transport of potassium ions, can be used for promoting absorption and utilization of potassium by plants and increasing the yield of the plants.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
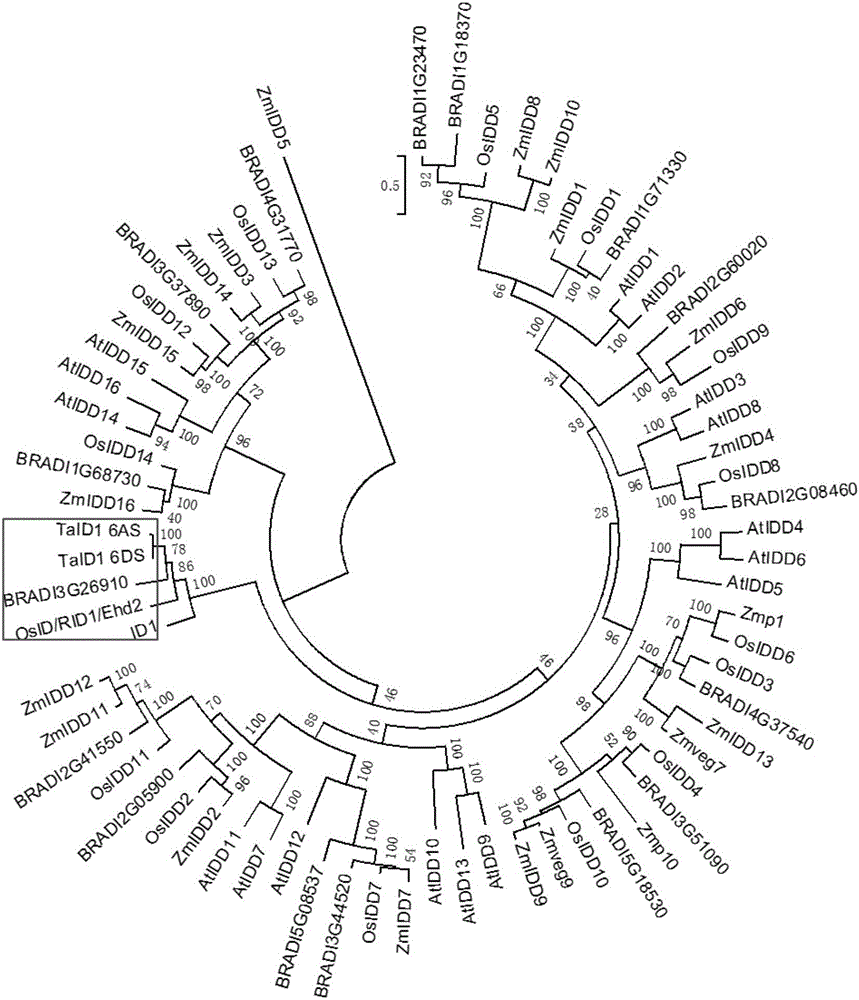
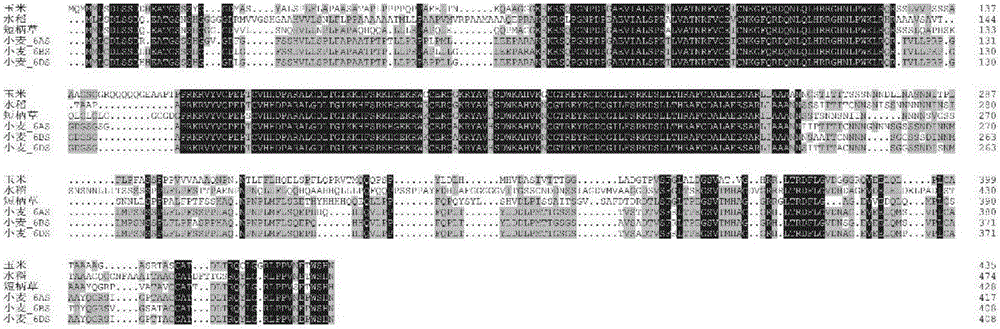
Clone and application of gene INDETERMINATE1 for regulating and controlling plant height of gramineous plants
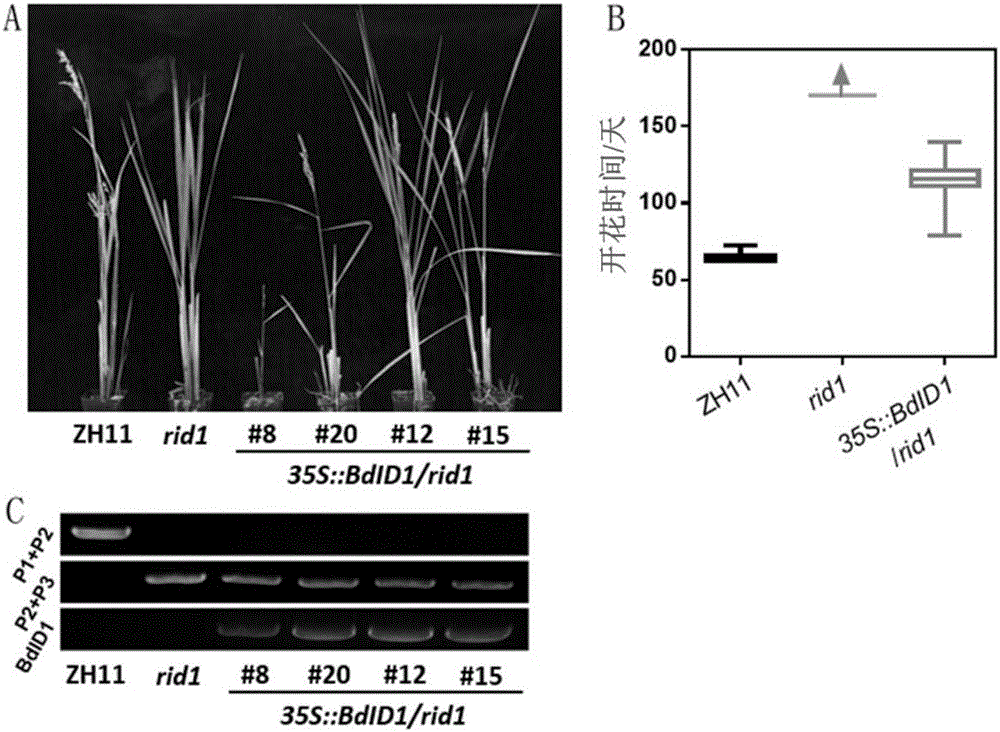
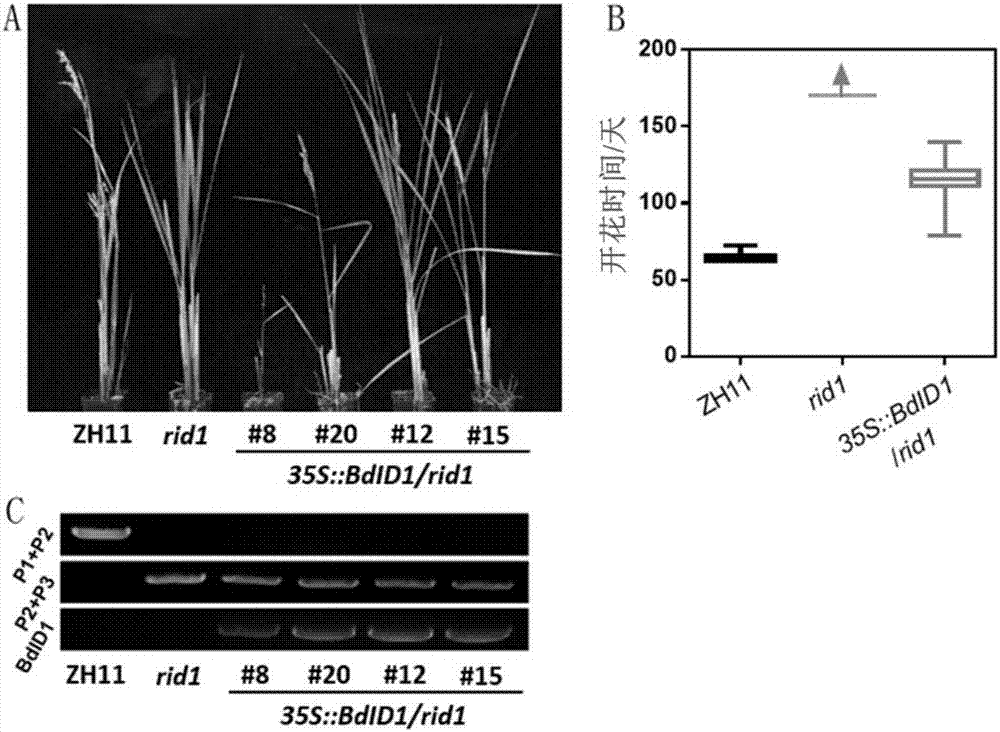
The invention relates to the technical field of plant biology, in particular to a clone and application of gene INDETERMINATE1 for regulating and controlling a plant height of gramineous plants. The inventor separated and cloned homologous ID1 genes from Brachypodium distachyon and wheat, and named the genes as BdID1 and TaID1, the inventor connected full length cDNA of the BdID1 and the TaID1 of A and B genomes to an expression vector initiated by an over expression vector, infected and converted Brachypodium distachyon with agrobacterium, and found that the genes enable Brachypodium distachyon to generate a dwarfing character.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
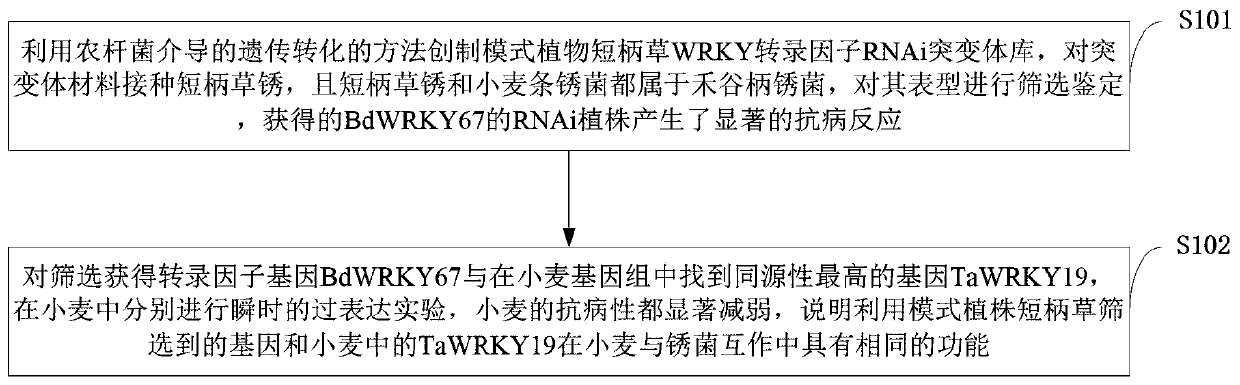
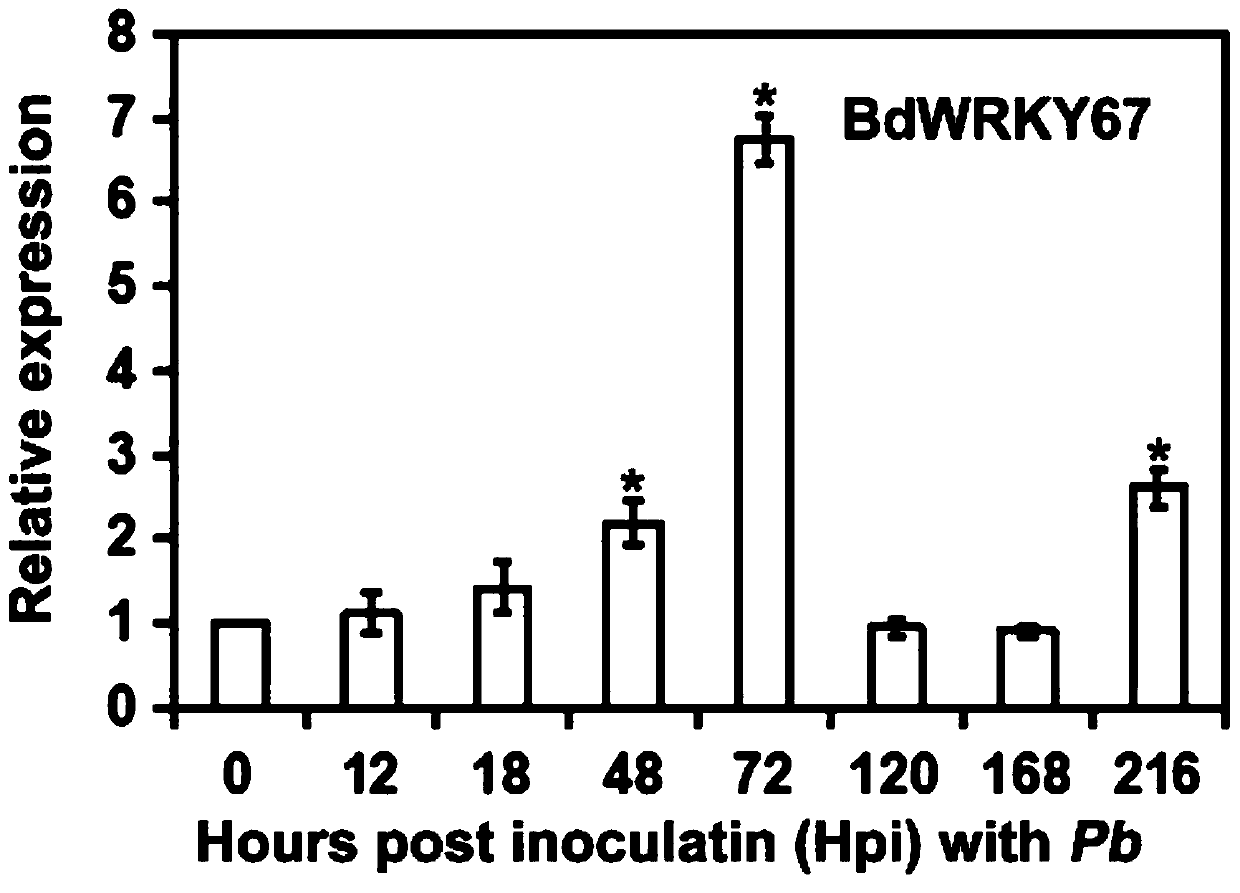
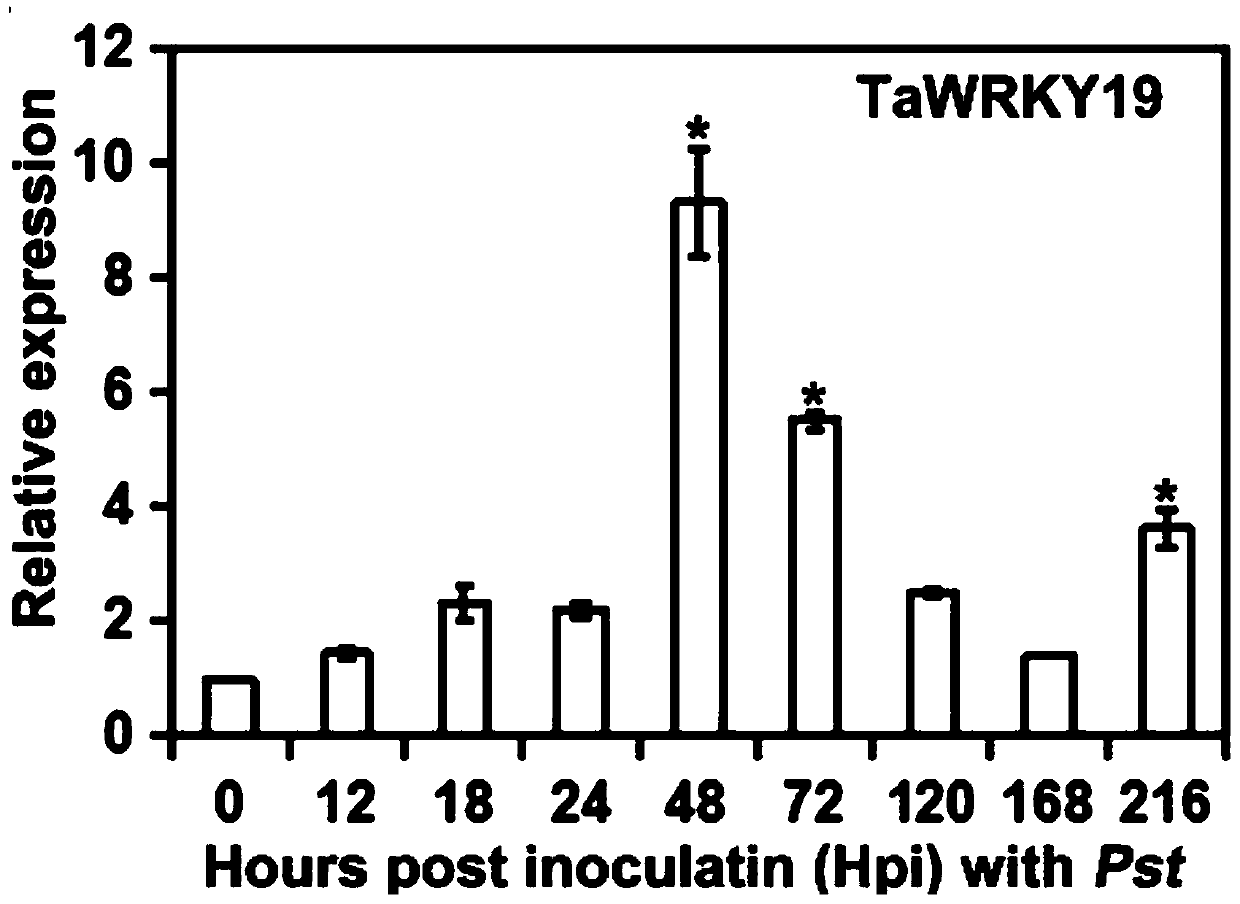
Transcription factor for improving rust disease resistant wheat varieties and screening and obtaining method of transcription factor
PendingCN110606877AIncrease resistanceReduce biomassMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBrachypodium sylvaticumBiotechnology
The invention belongs to the technical field of crop variety breeding, and discloses a transcription factor for improving rust disease resistant wheat varieties and a screening and obtaining method ofthe transcription factor. The transcription factor is TaWRKY19 and BdWRKY67 of a WRKY transcription factor in brachypodium distachyon, wherein the ORF coding sequence of the TaWRKY19 is SEQID NO:1, and the ORF coding sequence of the BdWRKY67 of the WRKY transcription factor gene in the brachypodium distachyon is SEQID NO: 2. An RNAi mutant of the WRKY transcription factor is obtained through agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated heredity and transformation, brachypodium sylvaticum is inoculated for disease resistance identification, and through the result, the inventor finds that the RNAi plantdisease resistance of the BdWRKY67 is notably improved. The disease resistance of plant wheat obtained through silencing of the TaWRKY19 transcription factor is notably improved, and the resistance ofplants subjected to instantaneous overexpression to puccinia striiformis is also obviously diminished, so that the transcription factor can be used for heredity improvement of stripe rust resistant wheat.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
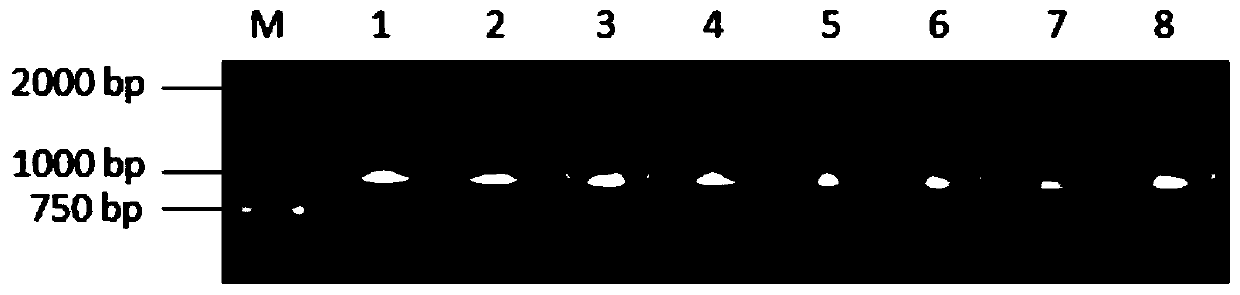
Endogenous reference gene suitable for brachypodium distachyon exogenous gene detection and copy number analysis, and application thereof
InactiveCN103525922ADemonstrating Species SpecificityIntraspecies nonspecificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationReference genesNucleotide
The invention discloses an endogenous reference gene suitable for brachypodium distachyon exogenous gene detection and copy number analysis, and application thereof. Through bioinformatics analysis and molecular biology experimental verification, a BDFIM gene serving as the endogenous reference gene for transgenic brachypodium distachyon qualitative and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection and copy number analysis is found from the brachypodium distachyon, and the nucleotide sequence of the gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The endogenous reference gene can be applied to qualitative and quantitative detection of the exogenous gene of the transgenic brachypodium distachyon, and also can be applied to analysis on the copy number of the exogenous gene in the transgenic brachypodium distachyon species.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHENSHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN
BdREF2 gene for regulating asafetide anabolism and application of BdREF2 gene
ActiveCN109055408AImprove degradation conversion efficiencyReduce contentOxidoreductasesFermentationCDNA libraryBiomass degradation
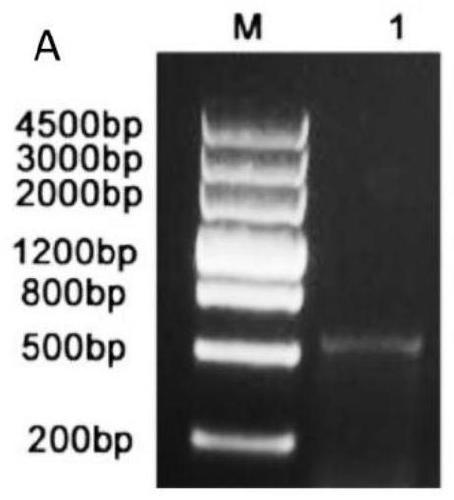
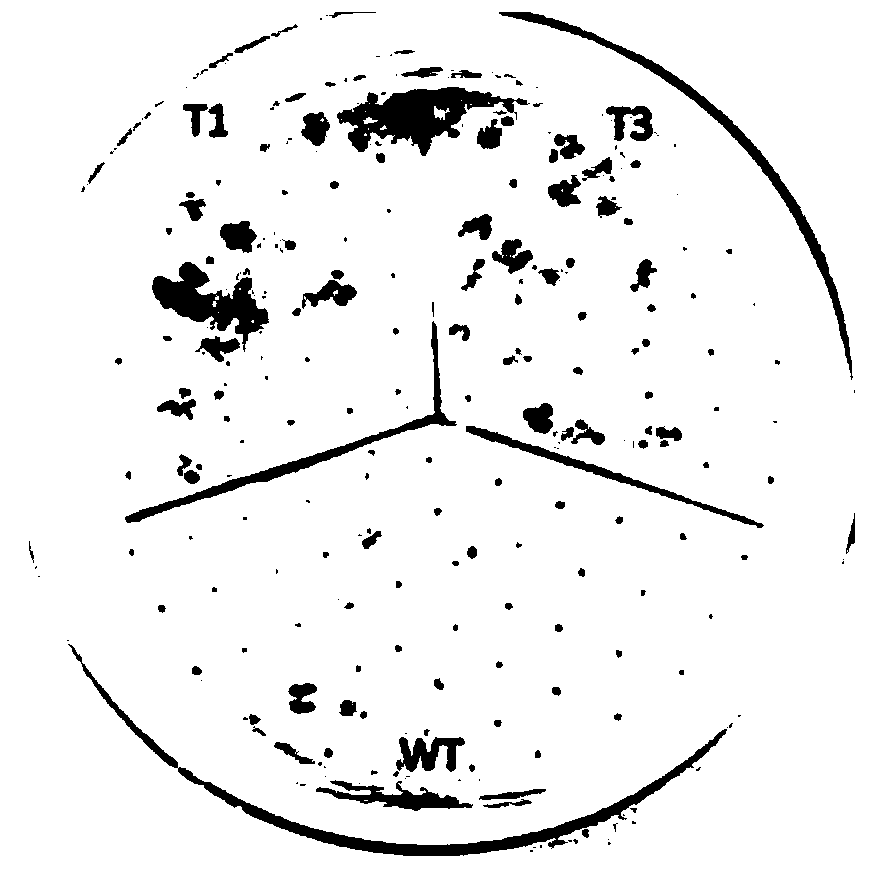
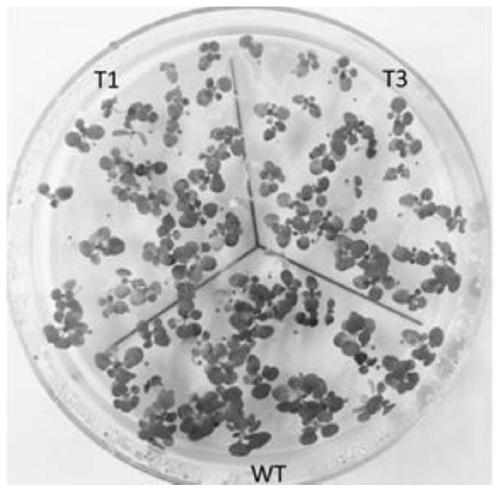
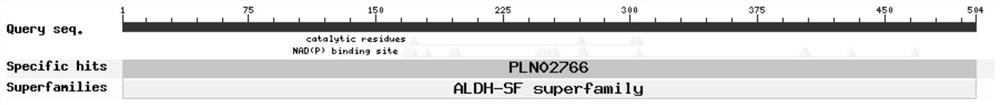
The invention relates to a BdREF2 gene for regulating asafetide anabolism and application of the BdREF2 gene, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. According to the BdREF2 gene disclosed by the invention, a coniferous aldehyde dehydrogenase gene named BdREF2 is separated from cDNA library of brachypodium distachyon; the BdREF2 gene in a brachypodium distachyon genome is knocked out by adopting a CRISPER / Cas9 gene editing system; it is found that the mutation of the BdREF2 can decrease the content of ferulic acid ester in plant cell walls while the degradation efficiency of biomass is obviously improved; the result indicates that the BdREF2 gene can be applied to biomass biodegradable genetic improvement of gramineous plants. It is firstly and directly proved that an REF homologousgene involved in regulating the biosynthesis of ferulic acid can be applied to improving the genetic improvement on biomass degradation and transformation efficiency of the gramineous plants, and hasimportant value for resource efficient utilization of biomass such as gramineae energy grass, forages and crop straws.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
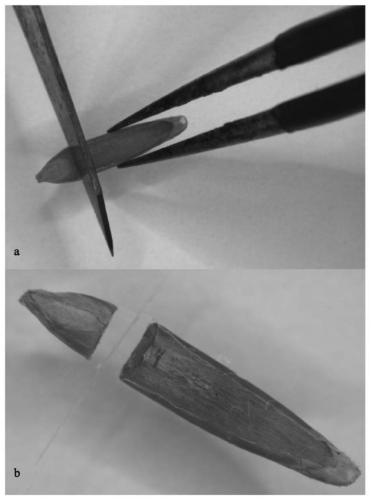
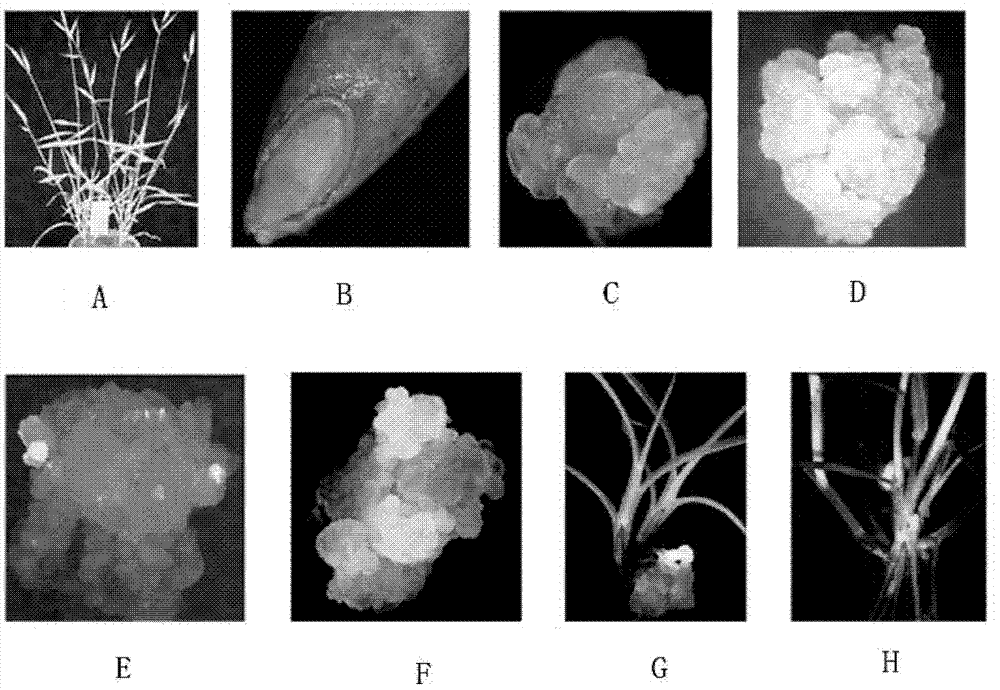
Culture medium and method for rapidly inducing seeds of brachypodium distachyon to generate calluses
InactiveCN111448992AConvenient researchInduced fastHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologyBrachypodium distachyon
The invention discloses a culture medium and a method for rapidly inducing seeds of brachypodium distachyon to generate calluses. Filexide (FPX) and CuSO4 are added to an MS basic culture medium. Theseeds of brachypodium distachyon are cut by a surgical knife to break dormancy of the seeds, the rapid calluses of the seeds of brachypodium distachyon are obtained under the synergistic action of FPX, and the induction rate is as high as 98.3%. The culture medium and method can be directly used for induction of the calluses of the seeds of brachypodium distachyon, shorten time of plant tissue culture, and lay a foundation for accelerating plant transgenic breeding.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
corn gene zmscl14 Application in regulating plant flowering period
ActiveCN112481276BDelayed floweringSlow growth ratePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a corn gene ZmSCL14 Application in regulating flowering period of plants. The maize gene ZmSCL14 The nucleotide sequence of is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The present invention utilizes the existing plant genetic engineering technology to obtain the recombinant overexpression vector, and then uses the Agrobacterium infection transformation method to transform the Brachypodium distachyon callus, and obtains the homozygous overexpression vector through tissue culture, identification and screening. ZmSCL14 Genes of Brachypodium distachyon plants. To compare it with wild-type plants grown under the same conditions, overexpressing ZmSCL14 The Brachypodium distachyon of the gene exhibits a late flowering phenotype, delays the flowering of Brachypodium distachyon, and can also slow down the growth rate of Brachypodium distachyon plants, and participates in the regulation of the expression of genes related to flowering, so ZmSCL14 The gene can be used to breed late-flowering or dwarf varieties, and has high agricultural application value.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Brachypodium distachybes functional centromere antigen polypeptide and its application
InactiveCN105461789BSerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against plantsNucleotideNew Zealand white rabbit
The invention provides a brachypodium distachyon functional centromere histone CENH3 and application. Firstly, the nucleotide sequence of a brachypodium distachyon functional centromere histone CENH3 gene is predicted through the bioinformatics sequence comparison method, a polypeptide is synthesized according to a segment of specific sequence of the N end of an amino acid sequence encoded by the nucleotide sequence, New Zealand white rabbits are conventionally immuned through the polypeptide, antiserums are prepared, and a CENH3 protein antibody is obtained through antigen affinity purification. The CENH3 antibody can be used for immunostaining experiments, physical positioning of centromere and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) experiments, the functional DNA sequence of a brachypodium distachyon functional centromere is obtained, positioning of centromere genome genetic maps and physical maps is carried out, and important tools and information are provided for research of centromere formation and function exercise mechanisms and building of artificial chromosomes.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Transgenic plant and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110438147AMade preciselyConvenient researchVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyForward primer
The invention discloses a transgenic plant and a preparation method thereof. The transgenic plant comprises a DREB1-like gene shown as SEQ ID NO:1 in a sequence table. The preparation method comprisesthe steps that RNA of brachypodium distachyon is extracted; the RNA is subjected to inverse transcription into cDNA; the cDNA is taken as a template, and a first forward primer and a first reverse primer are utilized for PCR amplification to obtain an amplification product; the amplification product is connected with a carrier to obtain a connected product; the connected product is transferred into a competent cell to obtain a converted product; positive monoclone is screened from the converted product to obtain recombinant plasmid; the DREB1-like gene on the recombinant plasmid is inserted into a skeleton carrier to obtain a recombinant carrier; the recombinant carrier is transferred into agrobacterium to obtain recombinant bacteria; the recombinant bacteria are transferred into a plantto obtain the T0 generation of transgenic plant; and the T0 generation of positive transgenic plant is screened. The transgenic plant comprises the DREB1-like gene, and the DREB1-like gene can give the transgenic plant the characteristic of resisting oxidative stress.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
A kind of bdref2 gene that regulates the synthesis and metabolism of plant ferulic acid and its application
ActiveCN109055408BReduce contentImprove degradation efficiencyOxidoreductasesFermentationCDNA libraryBiomass degradation
The invention relates to a method for regulating the synthesis and metabolism of plant ferulic acid BdREF2 The gene and its application belong to the field of genetic engineering; the present invention isolates a coniferous aldehyde dehydrogenase gene from the Brachypodium distachyon cDNA library, named as BdREF2 ; using the CRISPER / Cas9 gene editing system to convert the Brachypodium distachyon genome BdREF2 gene knockout, discovery BdREF2 The mutation of the plant can reduce the content of ferulic acid esters in the cell wall of the plant, and the degradation efficiency of the biomass is significantly improved, indicating that BdREF2 The gene can be applied to the genetic improvement of grass biomass degradability; the present invention directly proves for the first time that the REF homologous gene involved in the regulation of ferulic acid biosynthesis can be applied to the genetic improvement of grass biomass degradation conversion efficiency , which is of great value for the efficient utilization of biomass resources such as gramineous energy grasses, forage grasses, and crop straws.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Trichophyllum 6vs chromosome-specific molecular marker 6vs-bh1 and its use
InactiveCN104877996BStrong brightnessWide range of annealing temperaturesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMarker-assisted selection
The invention relates to a haynaldia villosa's 6VS chromosome specific molecular marker 6VS-BH1 and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of molecular biology and genetic breeding science. The labeled primer 6VS-BH1 is developed on the basis of wheat-brachypodium distachyon comparative genomics means, and the specific sequence is 6VS-BH1F, as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and 6VS-BH1R, as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The molecular marker 6VS-BH1 has the advantages of wide annealing temperature range (60-66 DEG C), good stability, strong product brightness, high resolution and the like. The molecular marker 6VS-BH1, as a co-dominant marker, not only can be used for effectively tracing haynaldia villosa's 6VS chromosome in wheat background, but also can be used for distinguishing a homozygote and heterozygote and for distinguishing a Pm21 gene carried translocation line T6VS.6AL and a PmV gene carried translocation line T6VS.6DL. Therefore, the molecular marker 6VS-BH1 disclosed by the invention has an important practical value in the molecular marker-assisted selection breeding of wheat powdery mildew and the pyramiding breeding of Pm21 gene and PmV gene.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
A wheat promoter induced by rust fungus
ActiveCN104878014BVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideTriticeae
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
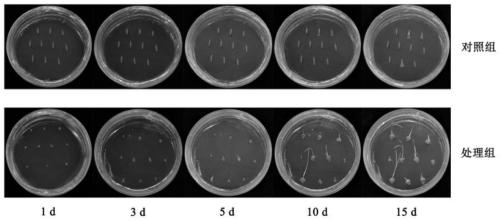
A method for genetically transforming Brachypodium distachyon by inflorescence dipping
InactiveCN110669781BAvoid high demandsGood genetic stabilityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyBrachypodium sylvaticum
The invention discloses a method for genetically transforming Brachypodium distachyon by inflorescence dipping, comprising: A, transformation of Agrobacterium EHA105 and identification of positive clones; B, dipping of Agrobacterium inflorescences of Brachypodium distachyon; C, transgenic two Positive plants of T0 generation of Brachypodium paniculata were obtained. The invention avoids the culture process of the callus through the genetic transformation method of the inflorescence mediated by the agrobacterium, saves a lot of time, and provides an effective and fast method for obtaining transgenic plants for the genetic improvement of crops.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHENSHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN
Genetic transformation method of brachypodium distachyon
PendingCN111500622AHigh regeneration rateHigh rate of callus inductionHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologyBrachypodium sylvaticum
The invention provides a genetic transformation method of brachypodium distachyon. The genetic transformation method at least comprises the following steps: 1) carrying out callus induction on immature embryos of brachypodium distachyon by utilizing an induction culture medium to obtain calluses, and carrying out subculture; 2) co-culturing the subcultured callus and agrobacterium tumefaciens, andinfecting the callus with the agrobacterium tumefaciens by using an infection solution; 3) screening the co-cultured calluses by using a screening culture medium to obtain calluses which grow well and are not browned; and (4) culturing the calluses obtained in step (3) by utilizing a regeneration culture medium until the calluses are differentiated and germinated so as to obtain brachypodium distachyon seedlings. Compared with an existing brachypodium distachyon transformation system, the brachypodium distachyon transformation system of the invention has the following advantages: the callus induction rate can be increased to 85.4% or above, and the regeneration rate of transgenic plants is increased. The efficient agrobacterium tumefaciens genetic transformation system established by theinvention provides certain technical guidance for exploring the gene function of brachypodium distachyon and provides a basis for gene improvement of gramineous crops.
Owner:山西师范大学
Brachypodium distachyon Drought Tolerance Tolerance Gene And Its Encoded Protein And Its Application
ActiveCN109517827BImprove tolerancePromote accumulationFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyBrachypodium sylvaticum
The invention provides an application of coded proteins of drought resisting and salt resisting gene of brachypodium distachyon. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is a sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 or a nucleotide sequence complementary as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The protein is obtained by coding the gene according to the claim 1, and the amino acid sequence of the protein is as shown in SEQ IDNO.2. The gene is applied to improving tolerance of plants to drought and salt resistance. The gene adjusted plant keeps cell moisture by accumulating through matters. ROS accumulation is reduced andthe cytomembrane oxidizing damage caused by active oxygen is reduced by improving the activity of an antioxidant enzyme system. By accelerating closing of pores under drought, the drought and salt resistance of transgenic tobacco is improved by way of reducing water damaged by means of transpiration, improving the expression level of stress related genes and the like. Drought and salt resisncve of the transgenic tobacco with the gene is dependent on adjustment of ABA synthesis and an ABA signal channel.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
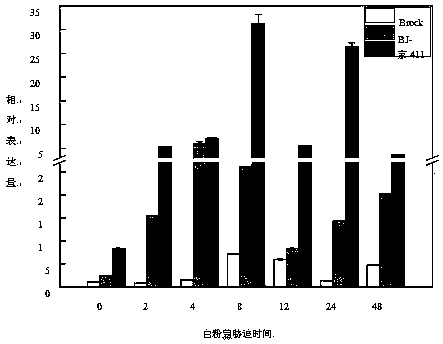
Triticum aestivum PITP TaSec14 gene and application thereof
InactiveCN111138520AIncrease resistanceBreeding for improved resistancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses a cDNA sequence and an amino acid sequence of a PITP (Phosphatidylinositol Transfer Protein) gene TaSec14 cloned in powdery mildew infected triticum aestivum variety of Jing 411. The cDNA full length of the gene is 1546 bp; the DNA full length is 2186 bp; an open reading frame is 1212 bp; 403 amino acids are coded; 80.45-percent homology is realized with PITP3(XP_010236107.1) in Bd (Brachypodium Distachyon); SEC14 conserved domains are contained; and the gene is named as TaSec14. After inoculation with the powdery mildew, the TaSec14 has the consistent expression trendin Jing 411 and a near-isogenic line BJ-1 thereof, and the expression amount is respectively higher than that of a disease-resistant triticum aestivum variety of Brock. A virus induced gene silencingtechnology is used for knocking down the Tasec14 gene in Jing 411; through the expression reduction of the TaSec14 gene, the resistance of the diseased triticum aestivum Jing 411 on the powdery mildewcan be improved to a certain degree; and the TaSec14 gene has the regulation and control effects in the interaction process of the triticum aestivum with the powdery mildew. The invention provides anovel genetic resource for the triticum aestivum powdery mildew resistance mechanisms and disease resistance breeding.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Brachypodium distachyon drought resistance gene, expression vector, encoded protein and application thereof
ActiveCN108103074BImprove toleranceGuaranteed absorptionBacteriaPlant peptidesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention provides a brachypodium distachyon drought-resistant gene and an expression vector as well as coding protein and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is the sequenceshown by SEQ ID NO.1 or a nucleotide sequence complementary to the sequence shown by SEQ ID NO.1. The protein is obtained by coding the gene of claim 1, and the amino acid sequence of the protein is shown by SEQ ID NO.2. The gene is used for improving application of the plant tolerance to drought stress. The gene provided by the invention regulates the plant to close pores to reduce the moisture lost in transpiration; a stronger root system is obtained in a drought condition so as to guarantee moisture absorption; moreover, the gene can improve the activity of such enzymes as catalase, peroxidase and superoxide dismutase in the antioxidase system and eliminate reactive oxygen species (ROS) in time, thereby reducing the oxidative damage of cells caused by the ROS and improving the plant tolerance to drought.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
An internal standard gene suitable for the detection and copy number analysis of Brachypodium distachyon exogenous genes and its application
InactiveCN103525922BReduce the number of copiesMeet the standardsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrachypodium sylvaticumReference genes
The invention discloses an endogenous reference gene suitable for brachypodium distachyon exogenous gene detection and copy number analysis, and application thereof. Through bioinformatics analysis and molecular biology experimental verification, a BDFIM gene serving as the endogenous reference gene for transgenic brachypodium distachyon qualitative and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection and copy number analysis is found from the brachypodium distachyon, and the nucleotide sequence of the gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The endogenous reference gene can be applied to qualitative and quantitative detection of the exogenous gene of the transgenic brachypodium distachyon, and also can be applied to analysis on the copy number of the exogenous gene in the transgenic brachypodium distachyon species.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHENSHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN
Cloning and application of a gene indeterminate1 regulating plant height in Gramineae
The present invention relates to the field of plant biotechnology, in particular to the cloning and application of a gene INDETERMINATE1 (ID1) regulating the plant height of gramineous plants. The inventors isolated and cloned a homologous ID1 gene from Brachypodium distachyon and wheat, and incorporated They were named BdID1 and TaID1. The inventors connected the full-length cDNA of BdID1 and TaID1 of the A and B genomes to the expression vector initiated by the overexpression vector, and transformed Brachypodium distachyon by Agrobacterium infection, and found that the above-mentioned genes can make the two Brachypodium tachypodium appeared dwarf traits.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for rapid and efficient genetic transformation of brachypodium distachyon by inflorescence dip dyeing
InactiveCN110669781AAvoid high demandsGood genetic stabilityVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyBrachypodium sylvaticum
Owner:SHANGHAI CHENSHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN
Culture medium for cultivating transgenic plant
The invention discloses a culture medium for cultivating a transgenic plant. The culture medium group comprises a callus induction culture medium, a subculture culture medium, a co-culture culture medium, a screening culture medium and a regeneration culture medium. Experiment results show that: with a transformation system and a transformation method of the present invention, average every 100 brachypodium distachyon immature embryos can produce about 103 positive transformation seedlings, wherein a positive seedling transformation rate achieves 103.4%, and is far higher than positive seedling transformation rates of the traditional and grain model plant rice, and the highest rice positive seedling transformation rate is 47.6% (Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2008, 25(3),322-331). With the efficient agrobacterium transformation system of the brachypodium distachyon, the important technology means is provided for temperate zone and grain plant gene function researches.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
ppcer1-2 gene, carrier and its application in improving the drought resistance of gramineous plants
InactiveCN108531490BImprove drought resistanceReduce lossEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyArid
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant breeding, and discloses a PpCER1-2 gene, a carrier and its application in improving the drought resistance of gramineous plants; the sequence of the PpCER1-2 gene is: SEQ ID NO:1. The present invention provides the application of PpCER1-2 gene in improving the drought resistance of gramineous plants; experiments prove that the PpCER1-2 gene has been transferred into and overexpressed Brachypodium distachyon leaves cuticle alkanes increase, and the water loss on the leaf surface slows down , the chlorophyll extraction rate decreased, and the growth of its seedlings in a drought environment also proved that the PpCER1‑2 gene can effectively improve the drought resistance of plants. Grasses are important food crops and garden green space plants. After improving the drought resistance of grasses through the present invention, the amount of irrigation water can be reduced, and at the same time, the problem of crop yield reduction caused by water shortage in summer high temperature weather can be enhanced, which has good application prospect.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com