Application of corn gene ZmSCL14 in regulating and controlling flowering period of plants
A gene and corn technology, applied in the application field of corn gene ZmSCL14 in regulating the flowering period of plants, to achieve high agricultural application value, slow down the growth rate, and delay the effect of flowering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1: corn ZmSCL14 Gene sequence analysis, cloning and vector construction
[0024] 1. Acquisition of maize ZmSCL14 gene
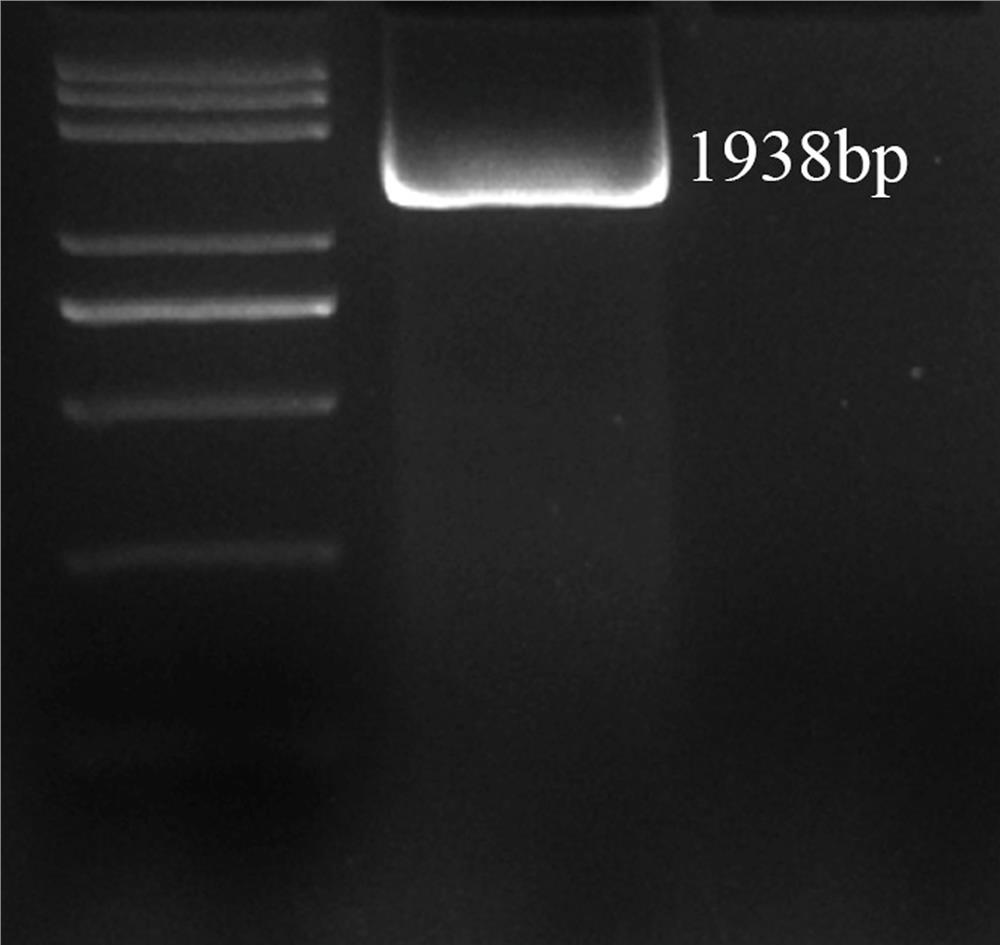
[0025] Use the corn genome database website gramene to find the gene GRMZM2G368909, named ZmSCL14 , ZmSCL14 The genome sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, the full length is 2421 bp, its CDS sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2, the length is 1938 bp, and it encodes 645 amino acids, and the encoded amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO. 3.
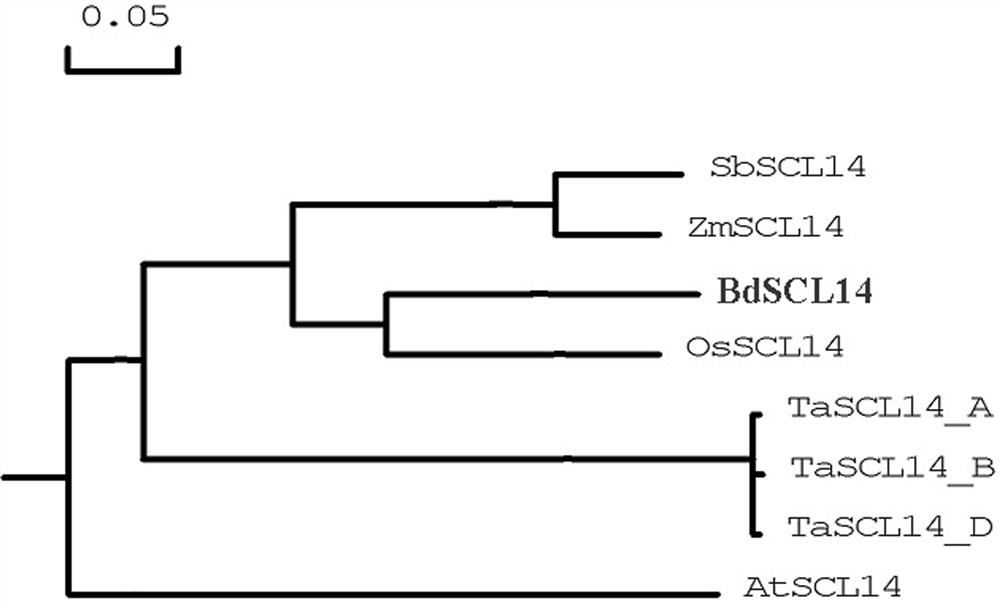
[0026] Will ZmSCL14 Amino acid sequence of Brachypodium distachyon, wheat, Arabidopsis, rice and Sorghum SCL14 protein to construct phylogenetic tree, such as figure 1 As shown, the homology of maize ZmSCL14 protein and sorghum SbSCL14 protein is relatively close.
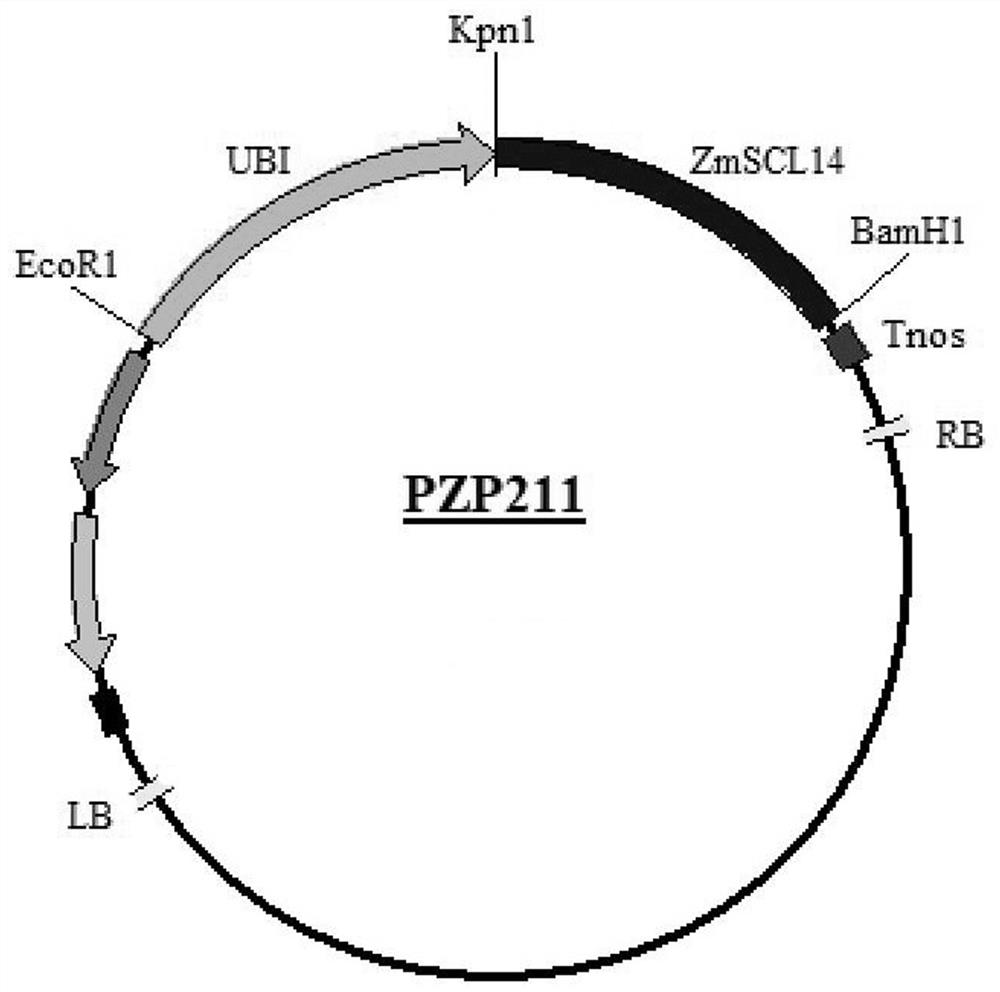
[0027] 2. Corn ZmSCL14 Gene cloning and vector construction
[0028] 1. Extraction of RNA: Extract the total RNA of corn with the whole gold TRIzon;
[0029] (1) Take fresh plant tissue material and grind it fully in liquid nitrogen, add...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2: Overexpression of Zm SCL14 Screening of Transgenic Brachypodium distachyon Positive Seedlings
[0049] 1. Brachypodium distachyon callus infection and tissue culture
[0050] (1) Configuration of solution and medium:
[0051] Infection solution formula (1L system): 10×Macro MS Salts 100mL; 100×Micro MS Salts 10μL; 200×Fe-EDTA 5mL; 100×M5 Vitamin 10mL; sucrose 30g; glucose 30g; 5.5, sterilized at 121°C for 20 minutes and stored in the refrigerator.
[0052] CIM medium formula (1L system): 10×Macro MS Salts 100mL; 100×Micro MS Salts 10mL; 200×Fe-EDTA 5mL; 100×M5 Vitamins 10mL; CuSO4 (8mg / mL) 7.5mL; 2,4-D ( 1mg / mL) 2.5mL; MES 0.5g; sucrose 30g; inositol 100mg; The bacteria bag is sealed for future use.
[0053] Germination medium formula (1L system): 10×Macro MS Salts 100mL; 100×Micro MS Salts 10mL; 200×Fe-EDTA 5mL; 100×M5 Vitamins 10mL; sucrose 30g; inositol 100mg; MES 0.5g; hydrolyzed casein 500mg; Kinetin (kinin KT 1mg / mL) 400μL; Phytagel 3g; dilute to...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3: Overexpression of Zm SCL14 Phenotypic Analysis of Transgenic Lines
[0070] 1. The homozygous T0 generation strain obtained in Example 2 and the differentiated wild-type Brachypodium distachyon T0 generation strain (control group, WT) were cultivated for seedlings, and numbered when transplanting the seedlings, according to the sequence of numbers Take a single plant for population analysis. If more than 40% of the single plants show the same phenotype, it is considered that the phenotype is a representative phenotype. From this, two representative transgenic lines were screened, numbered OE2 and OE3. ;
[0071]2. Count the flowering time and plant height of the homozygous plants of the T2 generation: the flowering time is the number of days from the germination of the T2 generation Brachypodium distachyda seeds under light conditions, using wet filter paper to dew (similar to wheat, two panicles) There are awns on the lemma of the panicle of Brachypodium,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com