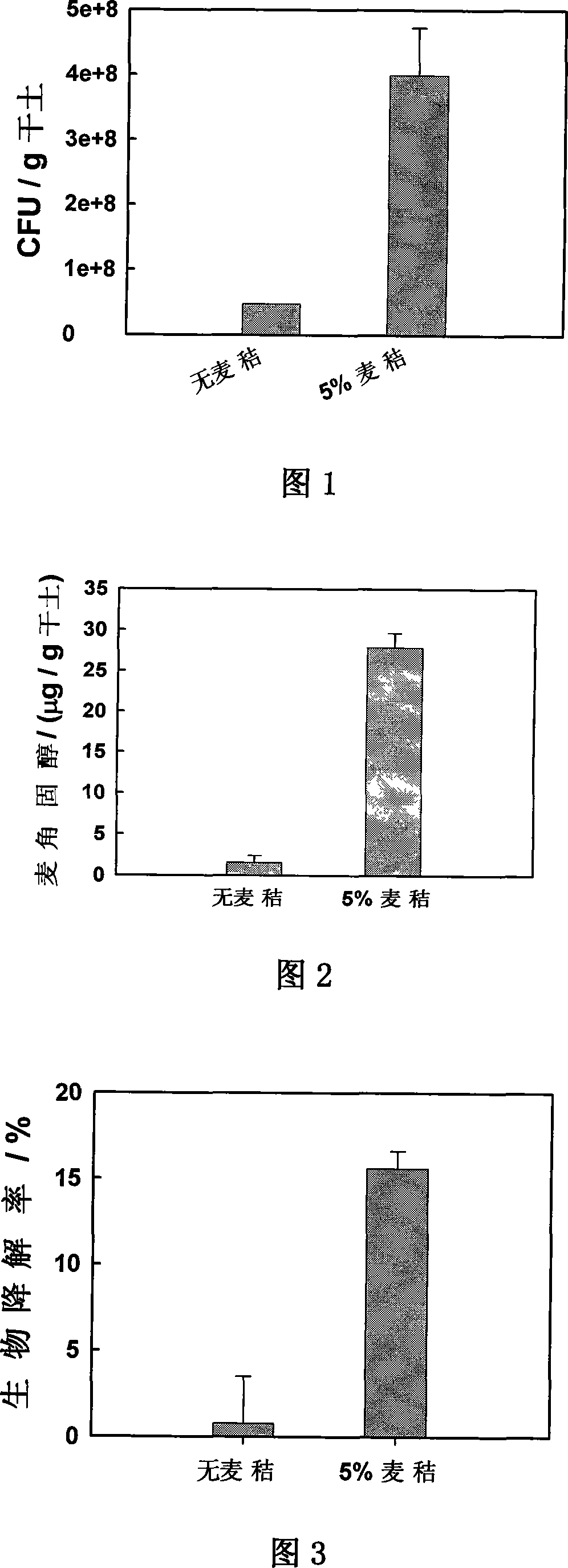
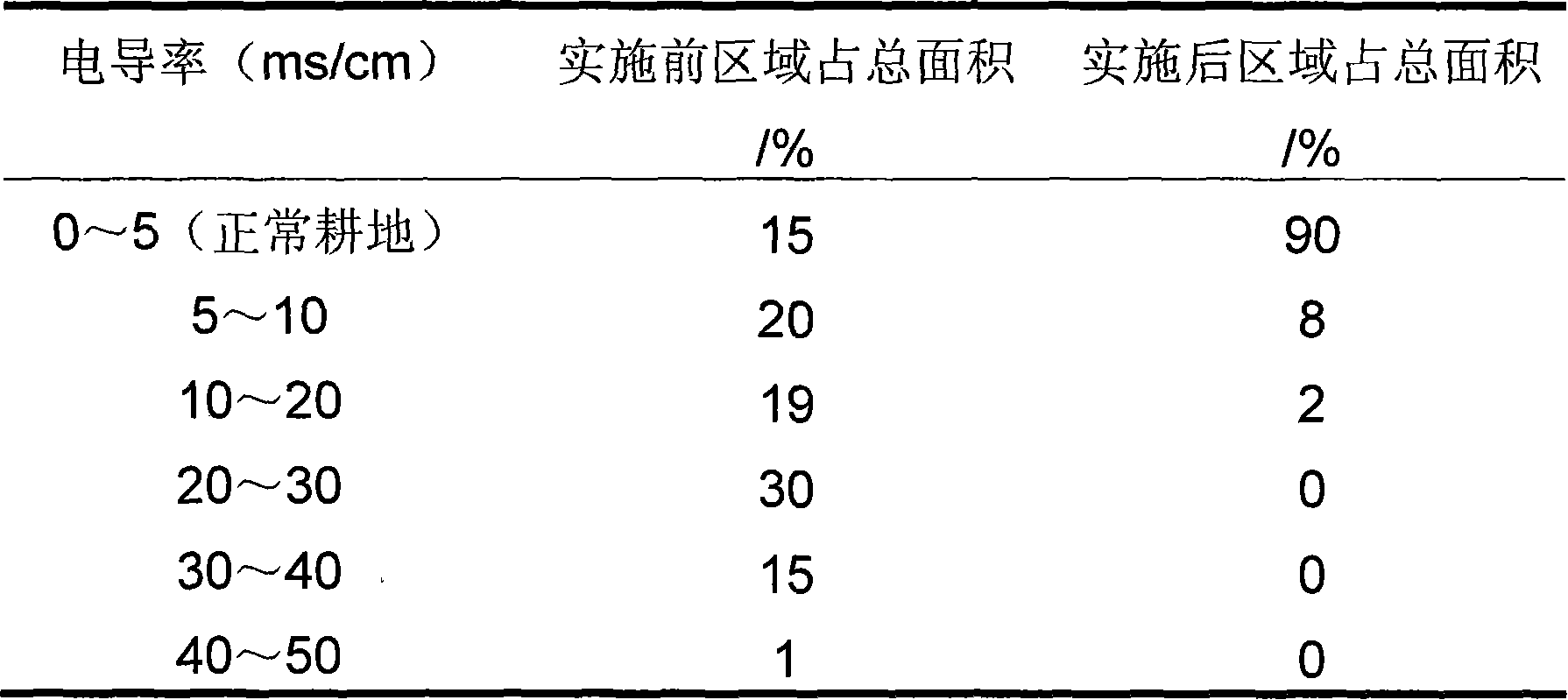
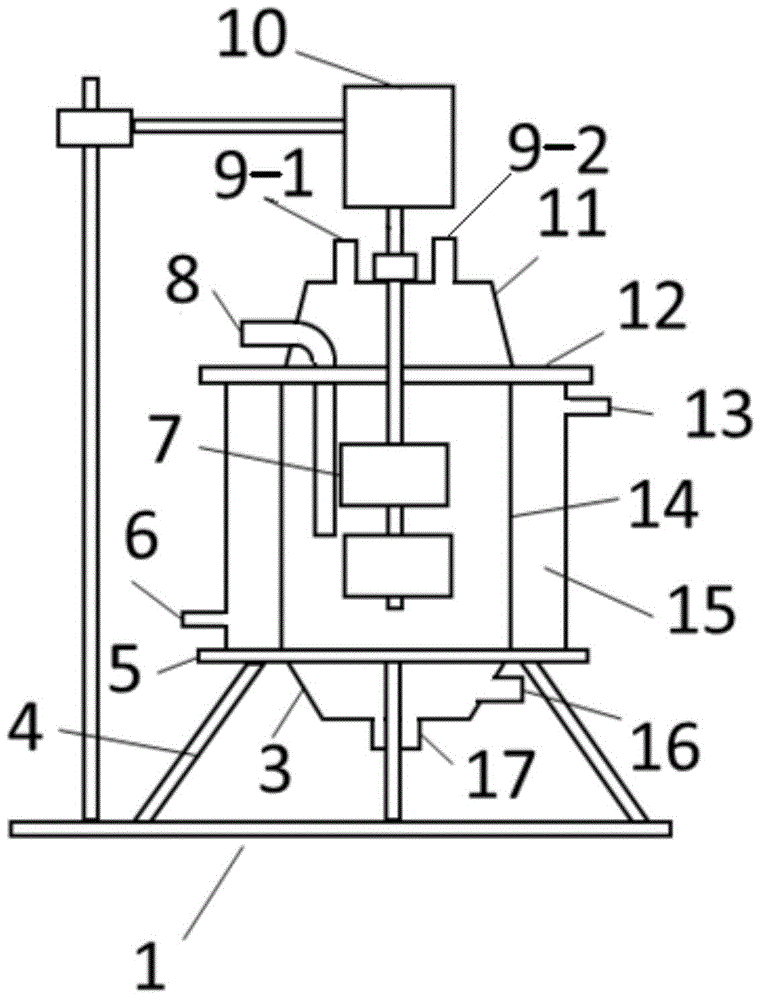
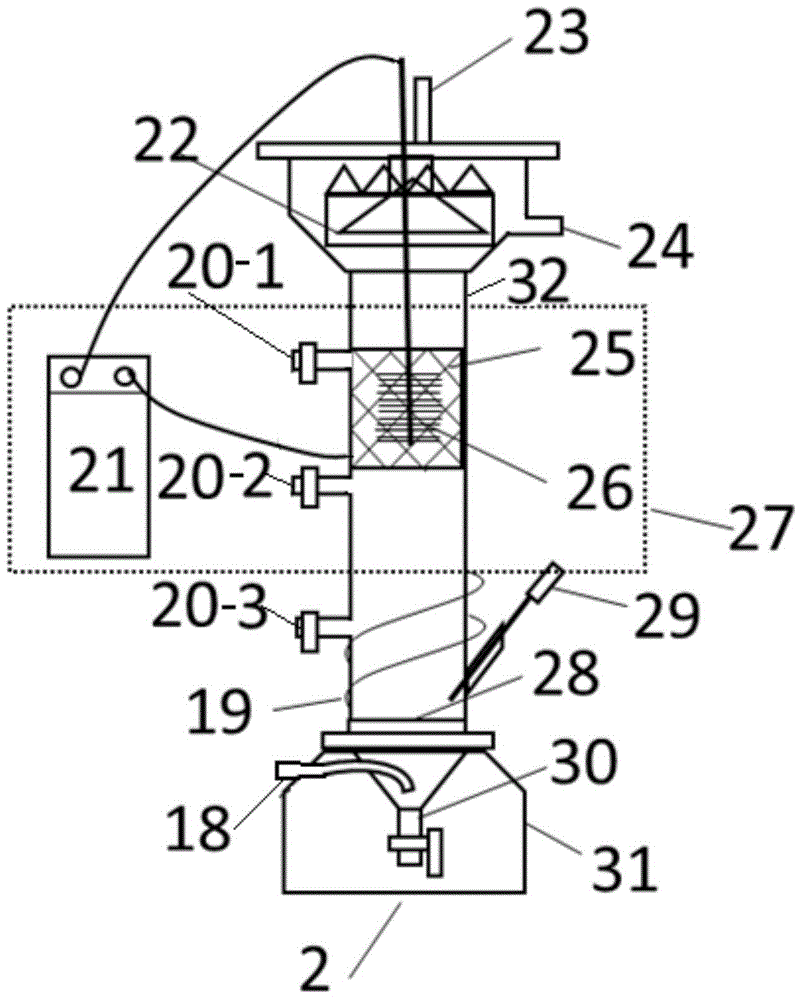
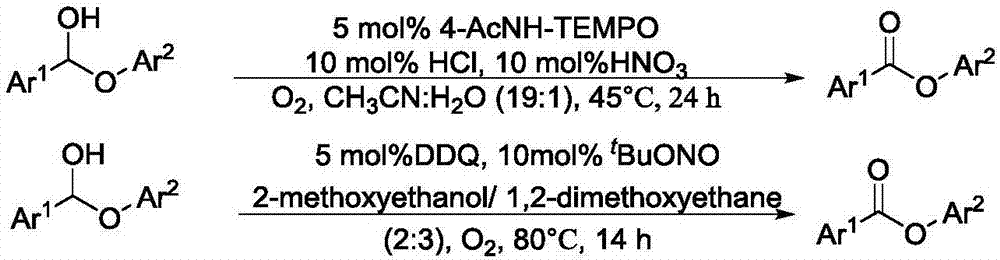
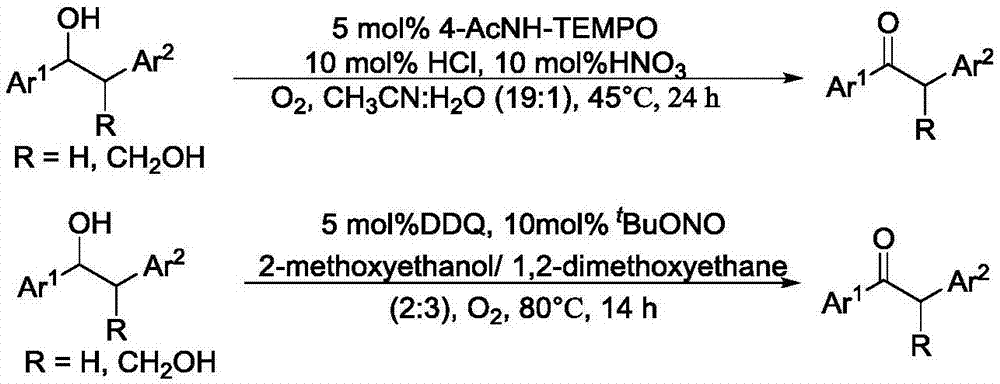
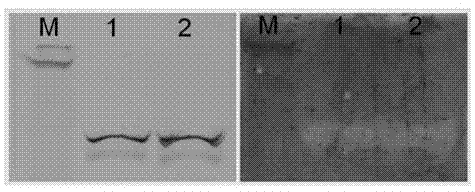
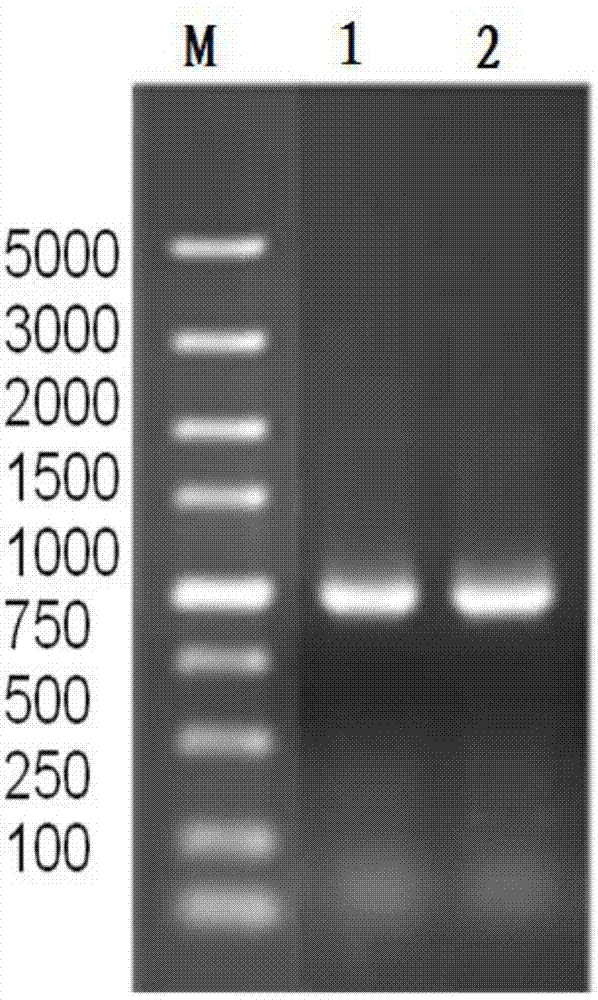
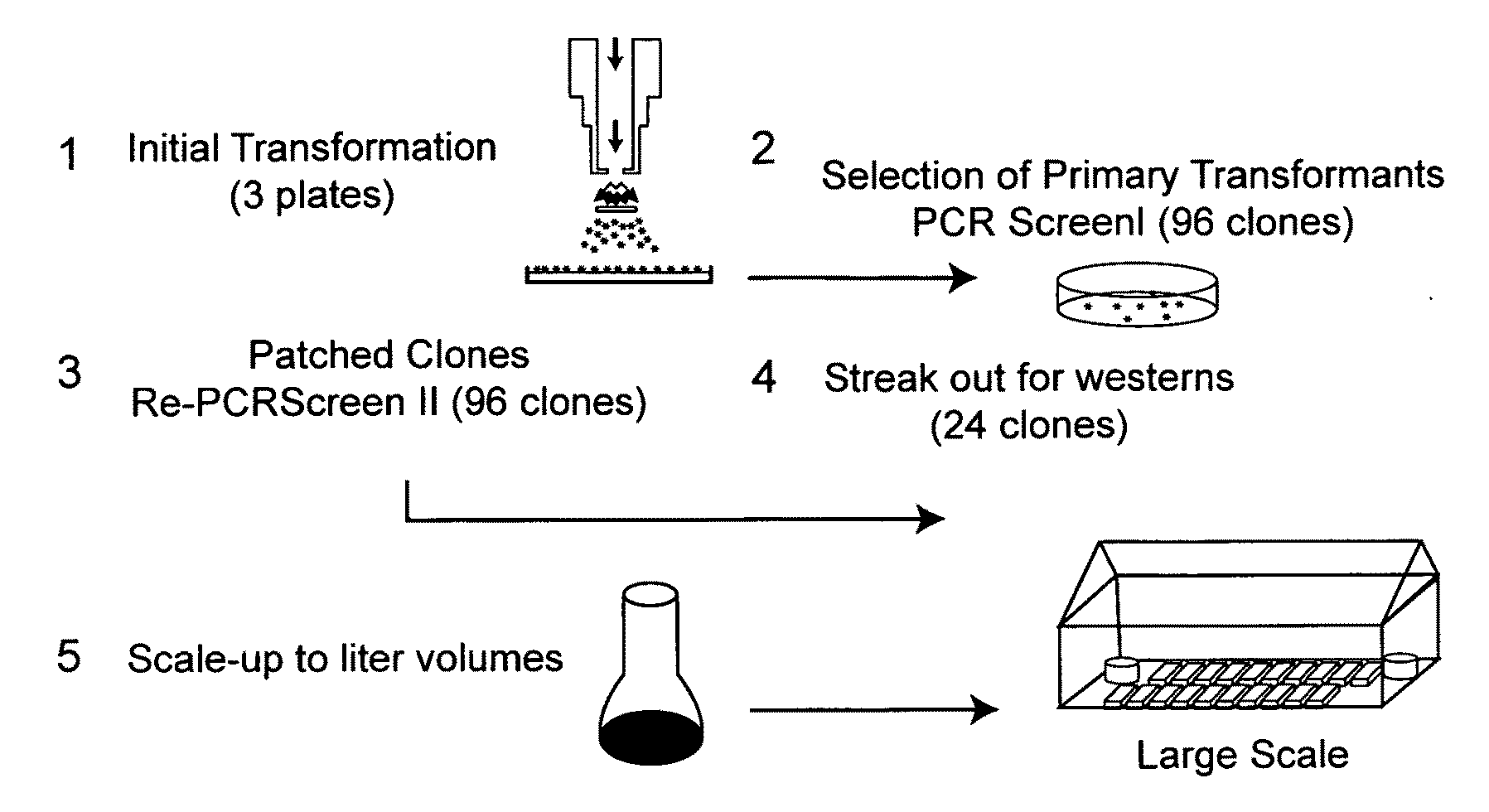
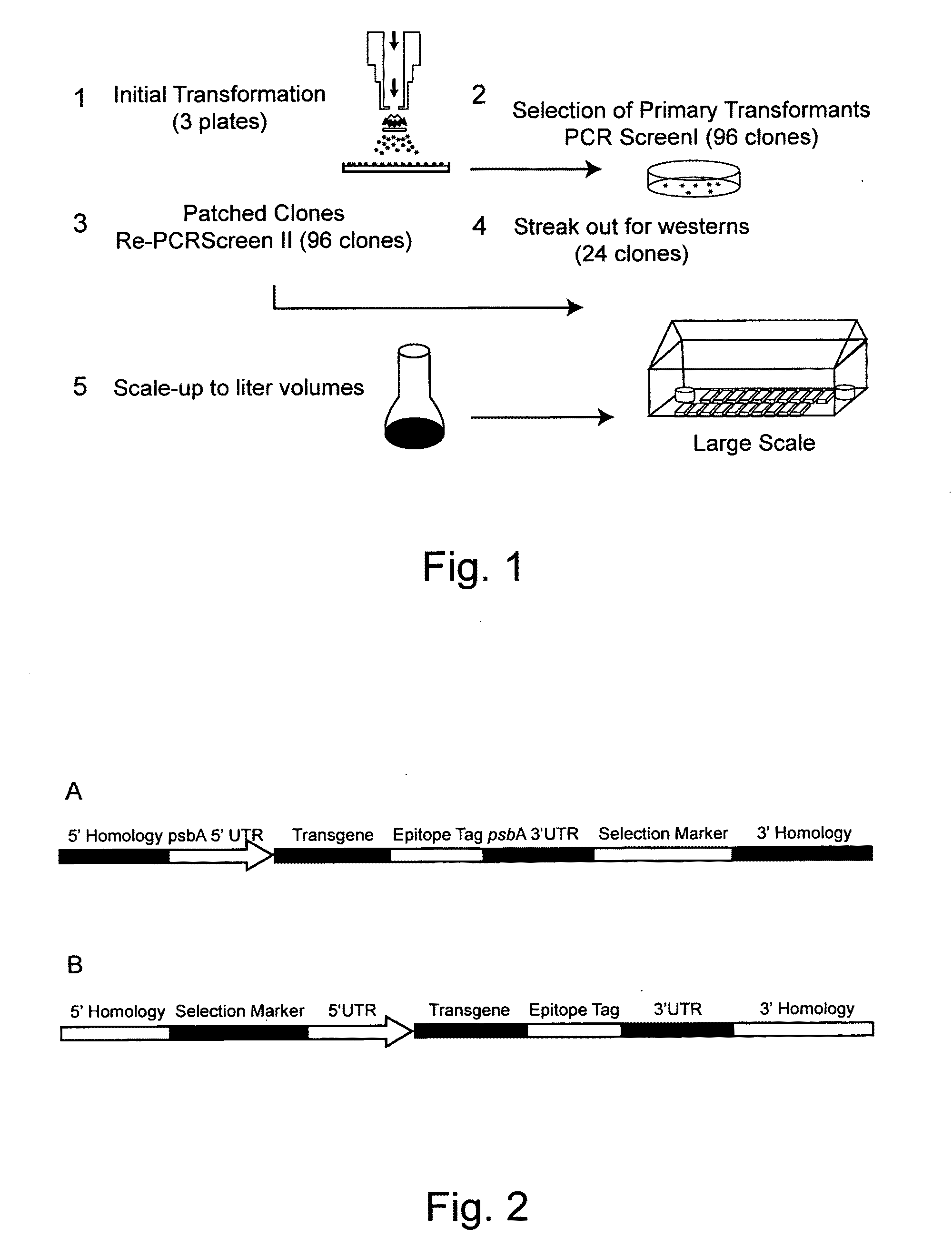
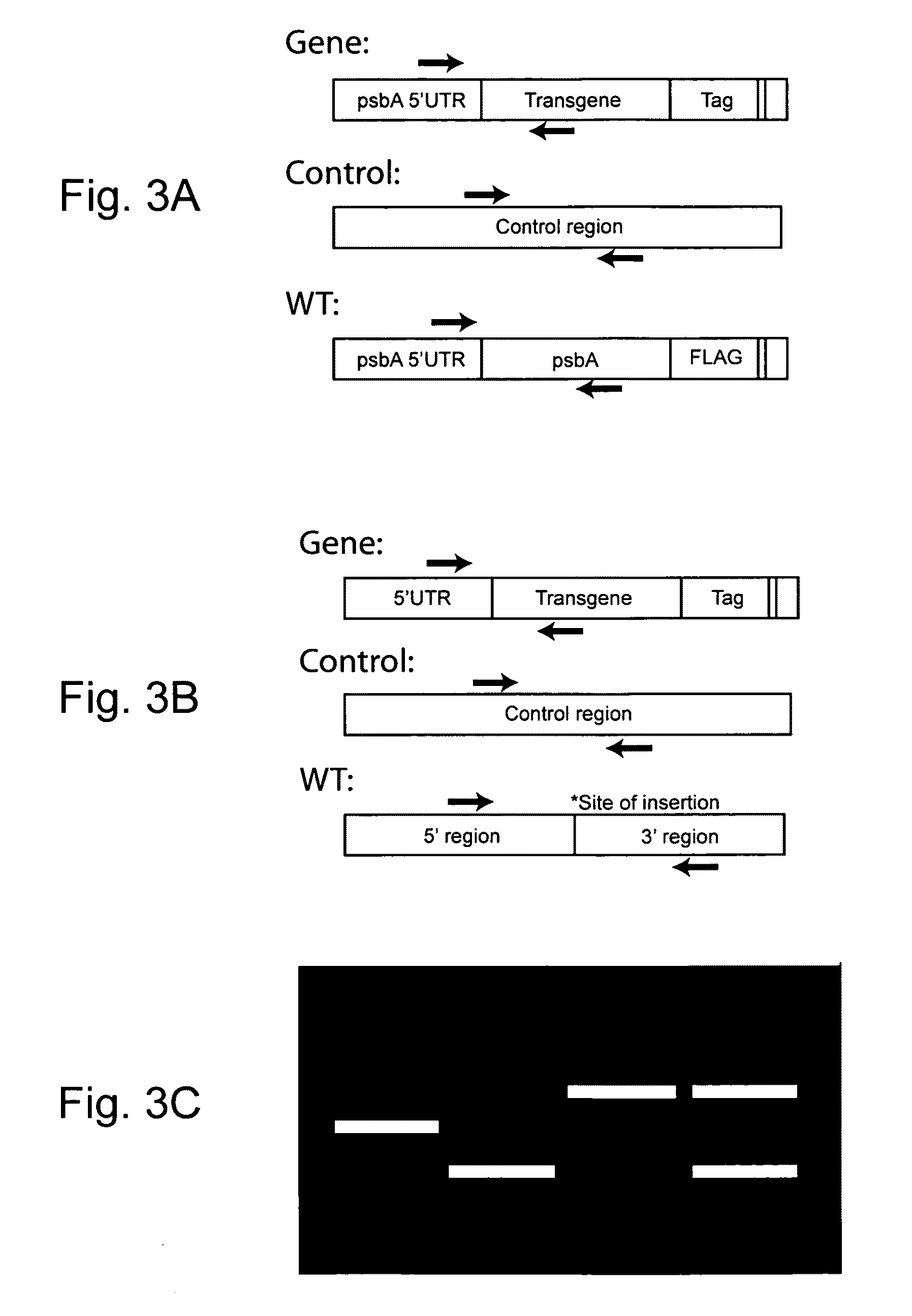
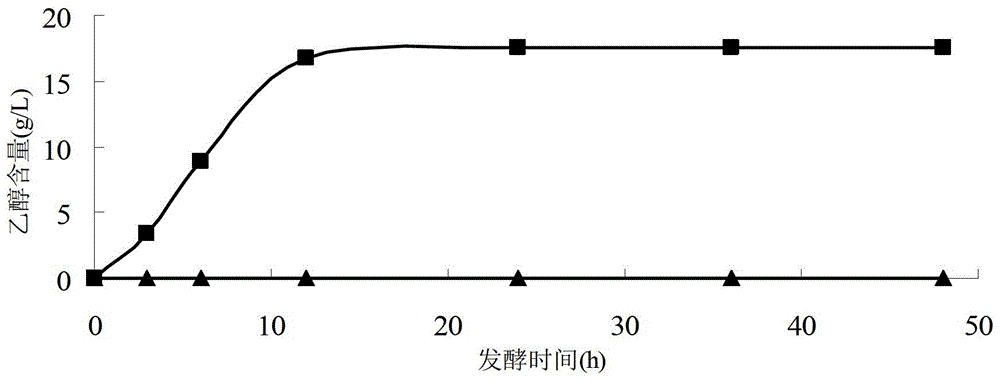
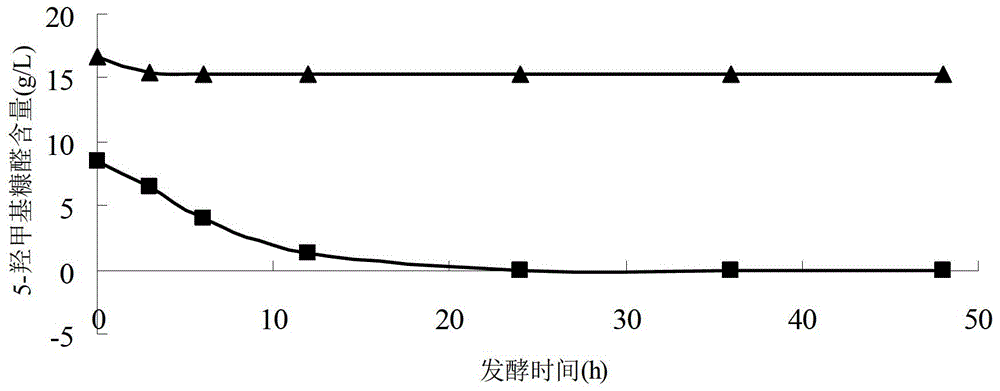
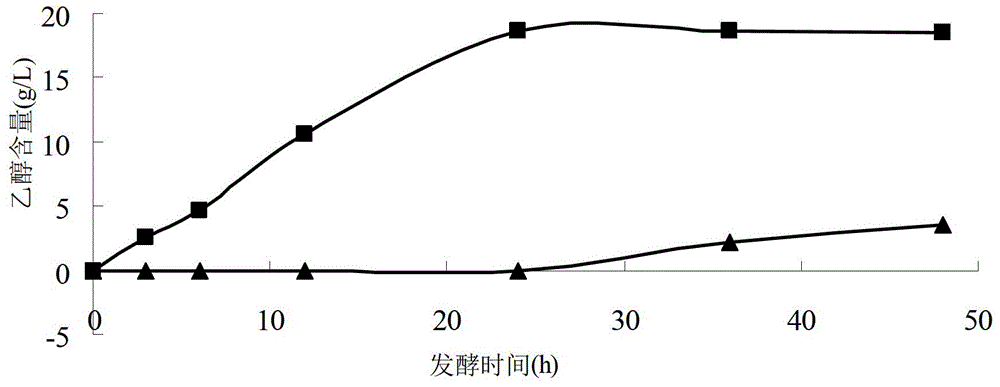
Patents
Literature
49 results about "Biomass degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In-situ biological repairing method for biomass intensified petroleum contaminative soil
ActiveCN101104177APromote accumulationIncrease intakeFungiBacteriaBiomass degradationIn situ bioremediation
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Biology in situ renovation method for biomass strengthen mix contaminated soil of stone oil-salt
InactiveCN101172286AImprove repair efficiencyImprove physiological and biochemical characteristicsFungiBacteriaBiomass degradationIn situ bioremediation
The invention discloses an in situ biological repairing method of biomass strengthening petroleum -salt-mixed contaminated soil, which is to add biomass degradation agent into biomass, and then the biomass degradation agent is plowed and landfilled under plough horizon, water logging and salt washing are utilized to reduce soil salt content, and then petroleum hydrocarbon degradation bacteria agent is added to degrade petroleum hydrocarbon, The invention utilizes the biomass to interdict capillary salt uprise phenomenon possibly generated; carbohydrate substance generated by biomass degradation can be taken as a good quality carbon source of the petroleum hydrocarbon degradation bacteria agent, so as to accelerate the growth of the petroleum hydrocarbon degradation bacteria agent; lignin generated by the biological degradation can absorb petroleum hydrocarbon pollutant, to prevent being diffused in the water logging and salt washing, bio surfactant generated by microorganism in the petroleum hydrocarbon degradation bacteria agent can accelerate the digestion of the petroleum hydrocarbon pollutant and further be converted into carbon dioxide and water by the petroleum hydrocarbon degradation bacteria agent biology. The efficiency of the degradative petroleum hydrocarbon pollutant of the invention method is high, and the speed is quick.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for synthesizing biomass-based polyurethane foam material by using papermaking waste liquor extract
The invention relates to a method for preparing a polyurethane foam material from biomass waste and papermaking black liquor extract serving as main raw materials. The low-cost and readily available biomass waste is taken as the raw material, the liquefaction product of the biomass waste is used for completely replacing polymer polyol, and waste produced in agricultural production is fully utilized; in addition, lignosulfonate is extracted from papermaking black liquor and added into biomass degradation liquor, a method for properly treating the papermaking black liquor is found while raw material cost is reduced, and the prepared polyurethane foam material has high degradation property due to the addition of a biomass component, and cannot pollute environment after being used. The waste in the agricultural production and the papermaking industry is effectively utilized, the raw material cost is greatly reduced, a new way is found for increasing the value of the waste produced in the agricultural production and the papermaking industry, inexhaustible plant resources can be fully utilized, and a road is opened up for recycling plants.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Microbial electrolysis two-section type sludge anaerobic digestion device and method for producing methane by using microbial electrolysis two-section type sludge anaerobic digestion device
ActiveCN104478178AImprove the breaking effectImprove utilization and removal rateSpecific water treatment objectivesWaste based fuelElectrolysisBiomass degradation
The invention discloses a microbial electrolysis two-section type sludge anaerobic digestion device and a method for producing methane by using the microbial electrolysis two-section type sludge anaerobic digestion device, relating to an improved two-section type anaerobic digestion device and a method for producing methanol from sludge. The purpose of the microbial electrolysis two-section type sludge anaerobic digestion device is to solve the technical problems of long fermentation cycle, low methanol yield and difficult biomass degradation and application in an existing residual sludge anaerobic digestion process. The microbial electrolysis two-section type sludge anaerobic digestion device consists of a continuous stirring type acidogenic reactor and a microbial electrocatalysis assisted upflow methane-producing reactor. The method comprises the following steps: starting a microbial catalytic electrolysis unit; producing acid by fermenting the residual sludge; and producing methanol. According to the microbial electrolysis two-section type sludge anaerobic digestion device and method disclosed by the invention, an acid production stage in a treatment process of the residual sludge only needs 5 to 8 days, a methanol production stage adopts continuous flow operation, the hydraulic retention time can be reduced to less than 1 day, and the operation cycle of sludge anaerobic digestion can be greatly shortened by adopting the device and method disclosed by the invention. The device and method disclosed by the invention belong to the field of sludge anaerobic digestion.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Use of genetically modified organisms to generate biomass degrading enzymes
InactiveUS20090253169A1Unicellular algaeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The present invention provides a method and compositions for high throughput screening of genetically modified photosynthetic organisms for plasmic state. The present invention provides methods of producing one or more proteins, including biomass degrading enzymes in a plant. Also provided are the methods of producing biomass degradation pathways in alga cells, particularly in the chloroplast. Single enzymes or multiple enzymes may be produced by the methods disclosed. The methods disclosed herein allow for the production of biofuel, including ethanol.
Owner:RENEW BIOPHARMA INC +1
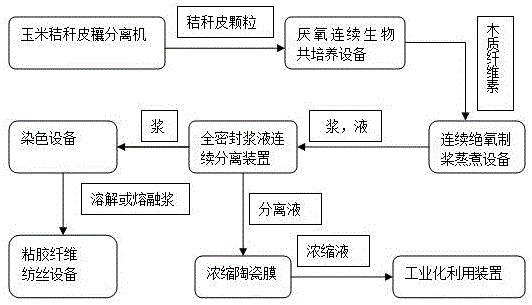
System for preparing viscose by pretreating corn straw through microbial co-culture
ActiveCN106087089AReduce usageReduce pollutionArtificial filaments from viscoseMelt spinning methodsMetaboliteBiomass degradation
The invention relates to a system for preparing viscose by pretreating corn straw through microbial co-culture. Corn straw peel obtained after corn straw stalks and leaves and peel are separated is used as a raw material, microbial co-culture of biomass degradation rumen microorganisms and a rumen microorganism degradation product or metabolite is achieved through fermentation of special equipment to degrade hemicellulose and unstable cellulose in the straw peel, the fermentation product can be separated in situ through regulation to achieve biological pretreatment on the corn straw peel, remaining high-crystallized lignocellulose is continuously cooked under the anaerobic environment to remove lignin and is subjected to cellulose dyeing or bleaching, viscose dissolution spinning is directly carried out on centrifuged cellulose pulp under the condition of certain water content, or melt spinning is carried out under the dry condition to prepare viscose. Usage of agentia for following cooking delignification is reduced through biological pretreatment, and then pollution is reduced; oxidization and blackening of pulp are reduced through anaerobic cooking, and then pollution is reduced; meanwhile, characteristics of fiber are kept to the maximum.
Owner:吉林中之林农业科技有限公司
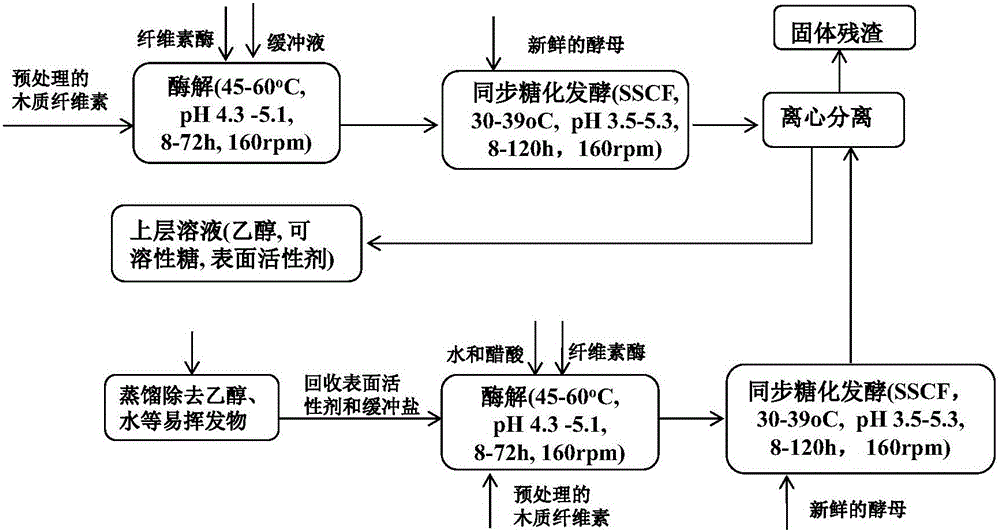
Lignocellulose simultaneous saccharification and fermentation process surfactant recovery technology
ActiveCN106520845AAchieve enrichmentAtom utilization is highProductsReagentsBiomass degradationEthanol fuel
The present invention provides a lignocellulose simultaneous saccharification and fermentation process surfactant recovery technology, and belongs to the field of fuel ethanol production through biomass degradation fermentation. According to the technology, lignocellulose being subjected to acidolysis and steam blasting pretreatment is directly added with a surfactant and a buffer liquid without detoxification, pre-enzymolysis is performed, Saccharomyces cerevisiae is inoculated, ethanol fermentation is performed, the enrichment of the surfactant, the fermentation inhibitor and the buffer agent is achieved while the ethanol is distilled after the fermentation, and by extracting the fermentation inhibitor, the coupling separation recovery of the surfactant, the buffer agent and the fermentation inhibitor is achieved. According to the present invention, the recovered surfactant and the recovered fermentation inhibitor can be re-used so as to reduce the pollution and effectively reduce the cost; the recovered toxic inhibitor can be prepared into the high value chemical product through the chemical conversion so as to improve the atom utilization rate during the biomass conversion process; and with the lignocellulose simultaneous saccharification and fermentation process surfactant recovery technology, the industrialization of the cellulose ethanol is further promoted.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
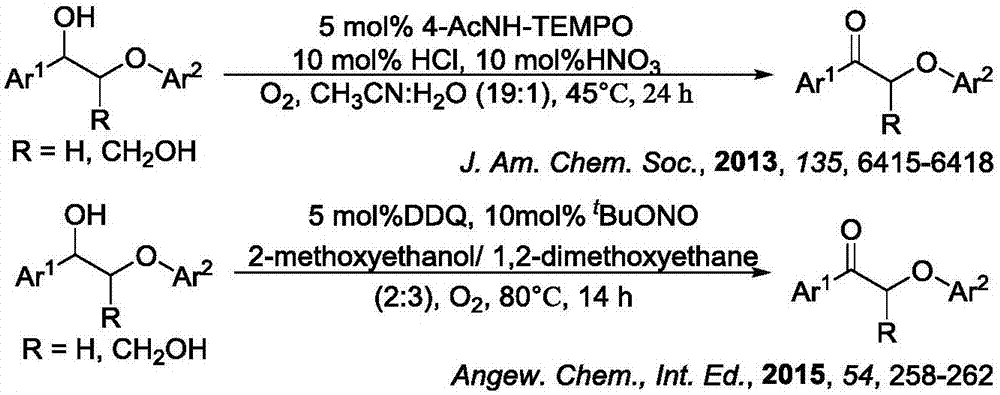
Method for degrading oxidation lignin into small molecular aromatic compound
InactiveCN106928053AMild reaction conditionsImprove conversion rateOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationBenzoic acidBiomass degradation
Belonging to the technical field of biomass degradation, the invention relates to a method for degrading oxidation lignin into a small molecular aromatic compound, and in particular relates to a method of breaking C-C bond by nontransition metal catalysis to degrade oxidation lignin into a small molecular aromatic compound. The method includes: firstly oxidizing oxidation lignin in an organic solvent with an oxidizing agent, then subjecting the obtained intermediate product to alcoholysis or hydrolysis under the action of a catalyst so as to obtain a small molecular aromatic compound, like methoxy substituted benzoic acid, methoxy substituted phenol, methoxy substituted benzoate and chain alcohol, etc. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple steps, mild reaction conditions, high conversion rate (up to 100%), no need for transition metals and the like, has effect on multiple connection modes of oxidation lignin, can reach the purpose of high selectivity and efficient degradation of lignin, and is conducive to large-scale industrial application.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for preparing pure biomass organophosphorus pesticide degradation agent
InactiveCN105617595AHigh degradation activityCompletely degradedChemical protectionActivated sludgeBiomass degradation
The invention discloses a method for preparing a pure biomass organophosphorus pesticide degradation agent and belongs to the field of pesticide degradation agents. According to the method, a large number of organophosphorus pesticide degrading bacteria are cultured, separated and screened out from mixed soil of earth surface sludge, activated sludge and common earth surface soil; hypha suspension liquid, humus and chitosan are mixed and aged to obtain a pasty mixture; and the pasty mixture, nano titanium dioxide and a garlic extract concentrated solution are mixed and pelletized. The organophosphorus pesticide degrading bacteria screened and acclimatized through the method have high degradation activity, and the temperature and pH applicable range is wide; the pure biomass organophosphorus pesticide degradation agent is combined with substances such as humic acid and can degrade organophosphorus pesticide more thoroughly and faster; allicin and alliin in the garlic extract concentrated solution have a degradation effect on the organophosphorus pesticide; degradation of the pesticide can be accelerated through photocatalysis of the nano titanium dioxide; moreover, the prepared pure biomass degradation agent is non-toxic, has no residues and is free of secondary pollution.
Owner:袁春华
Revegetation method for biomass landfill
The invention discloses a revegetation method for a biomass landfill. The revegetation method includes that planting soil mixed with organic fertilizer and turfy soil is added into a soil layer for planting pioneer plants to change secondary bare land with brushwood and bosk into forests; soil property of biomass-covered soil is improved by utilizing planting soil to guarantee planted plants not prone to death caused by the influence of gas, liquid and energy generated from biomass degradation; and meanwhile revegetation work amount and investment are reduced and soil utilization rate is increased, and harmful environmental effect from soil bareness is reduced.
Owner:雷学军
Super-high-temperature-resistant and alkali-resistant beta-mannase gene, amino acid sequence and application of beta-mannase gene
The invention discloses a super-high-temperature-resistant and alkali-resistant beta-mannase gene. A base sequence of the beta-mannase gene is SEQ ID NO.1. The invention further discloses a nucleotide sequence SEQ ID NO.2 of super-high-temperature-resistant and alkali-resistant beta-mannase, and further discloses application of the super-high-temperature-resistant and alkali-resistant beta-mannase gene in preparation of the super-high-temperature-resistant and alkali-resistant beta-mannase. The obtained expression enzyme can widely endure alkaline (pH7-10) and high-temperature (80-100 DEG C) environments; and the specific activity of the purified expression enzyme can be up to 10400U / mg. The beta-mannase has super-high-temperature-resistant and alkali-resistant characteristics, and is suitable for application in the chemical industries such as biomass degradation, foods, feeds, papermaking and spinning.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
High throughput screening of genetically modified photosynthetic organisms
InactiveUS20090246766A1Stable transformationSugar derivativesUnicellular algaeHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsBiomass degradation
The present invention provides a method and compositions for high throughput screening of genetically modified photosynthetic organisms for plasmic state. The present invention provides methods of producing one or more proteins, including biomass degrading enzymes in a plant. Also provided are the methods of producing biomass degradation pathways in alga cells, particularly in the chloroplast. Single enzymes or multiple enzymes may be produced by the methods disclosed. The methods disclosed herein allow for the production of biofuel, including ethanol.
Owner:RENEW BIOPHARMA INC +1
Detoxification and fermentation method of large red algae biomass degradation liquid
The invention provides a detoxification and fermentation method of large red algae biomass degradation liquid. The detoxification and fermentation method comprises the following steps: degrading the large red algae biomass to obtain the degradation liquid, adding an appropriate amount of molecular-sieve or non-molecular-sieve adsorbent having adsorption property as a detoxifying agent into the degradation liquid to carry out double detoxification or multiple detoxification on the degradation liquid so as to remove substances of preventing the activities of microorganisms in the degradation liquid, finally removing the detoxifying agent and producing bio-fuels or chemical intermediates by fermentation of the corresponding fermentation microorganisms. By virtue of experimental verification, compared with the existing fermentation method of algae, the detoxification and fermentation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the treatment process of the degradation liquid is simple and consumes less time; the detoxifying agent is low in cost, wide in resources and can be recycled; the fermentation of the microorganisms has the advantages of high starting speed, short time, high yield and less byproducts and the fermented products are easily separated and purified.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for degrading lignin and model compound thereof through photocatalytic oxidation
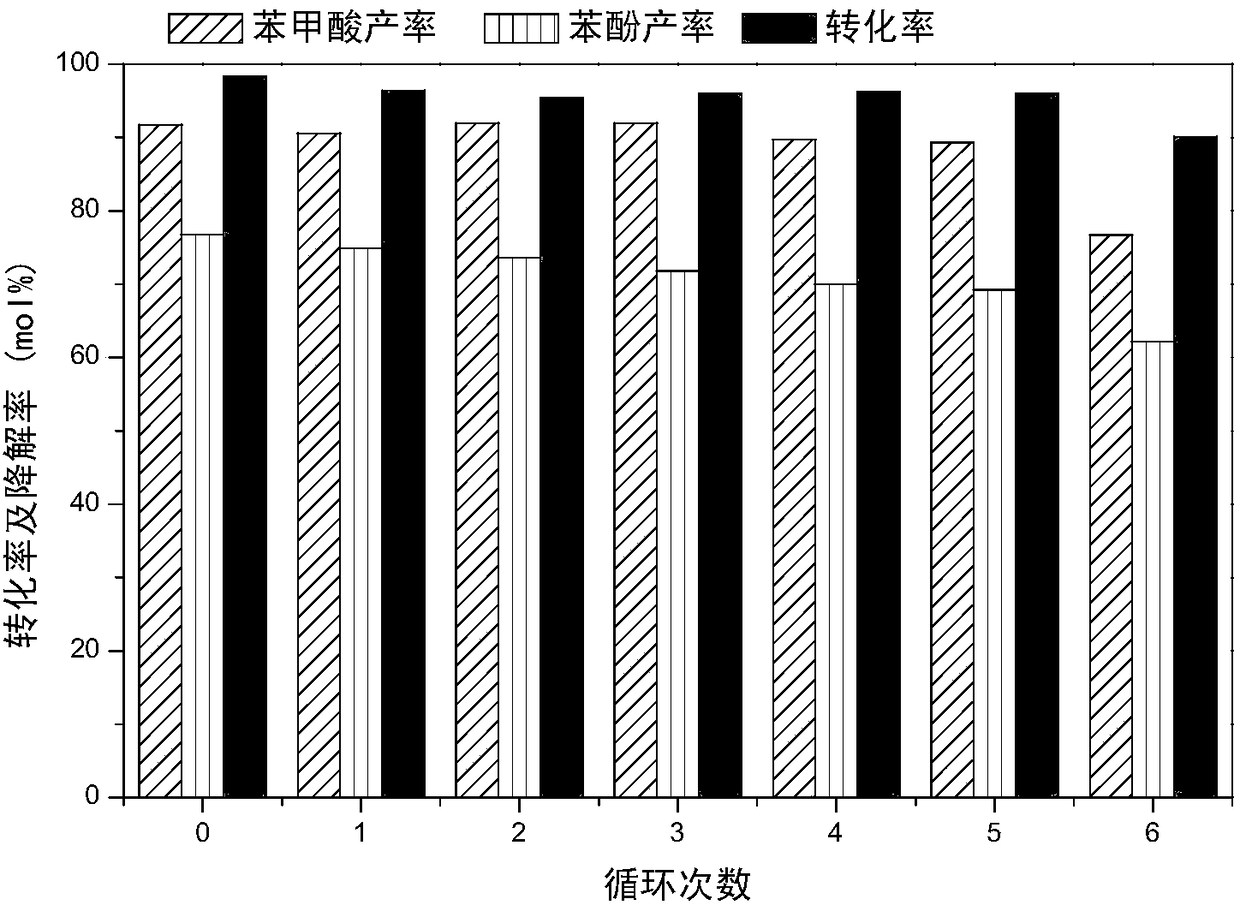
ActiveCN108276253AEfficient catalytic activityEasy to recycleOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationBenzoic acidAtmospheric air
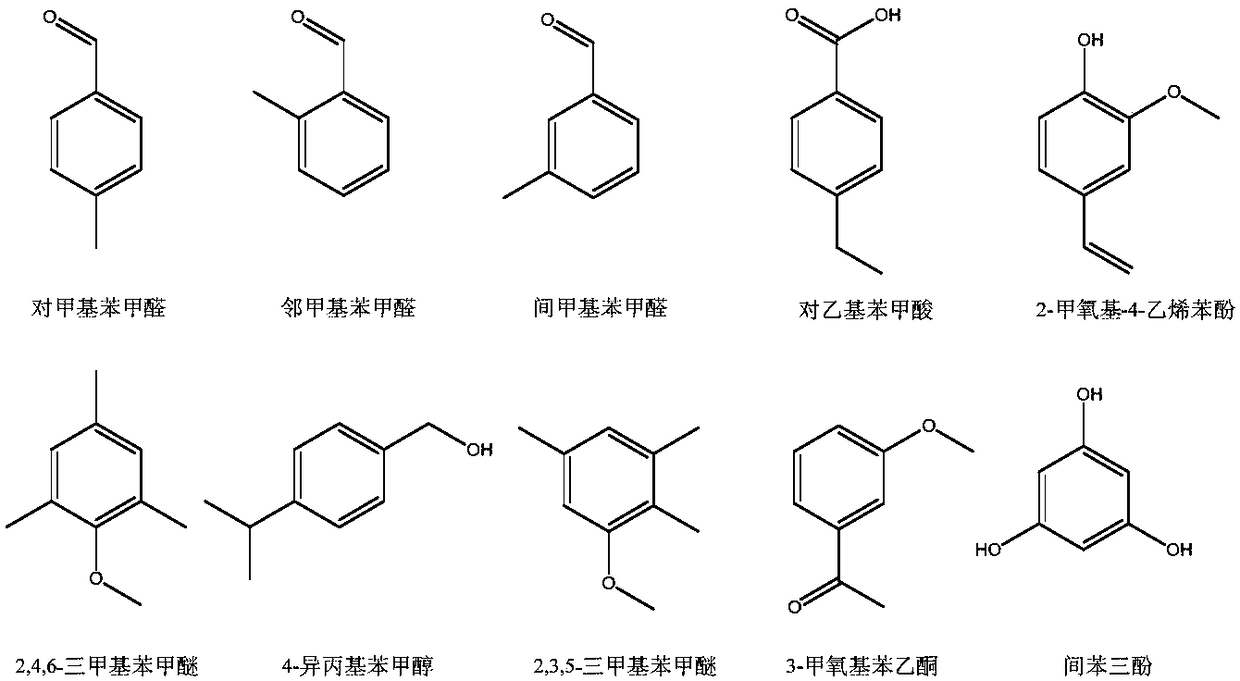
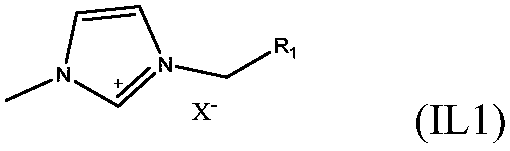
The invention discloses a method for degrading lignin and model compound thereof through photocatalytic oxidation in a binary ionic liquid system, under a mild condition and by a one-pot method. In the method, binary ionic liquid comprises disubstituted imidazole ionic liquid and sulfo functionalized imidazole ionic liquid. The method is characterized in that the lignin model compound can be oxidatively degraded under the condition of low temperature (below 100 DEG C), atmospheric air and natural visible light irradiation, the highest conversion rate is 98.3%, products are benzoic acid and phenol, and the highest yields are 91.7% and 76.8% respectively; the natural lignin is oxidatively degraded to obtain acidic, phenolic and aldehydic aromatic products such as 4-ethylbenzoic acid, phloroglucinol and 4-methylphenylacetaldehyde. The method is environment-friendly and high-efficiency, the used ionic liquid can be recycled, the reaction operation condition is mild, the energy consumptionis low, and a technology is environment-friendly and safe; by the method, the problems of high energy consumption, high temperature, high pressure and a strict reaction condition in the conventional lignin oxidation method and the like are solved, and a novel method support is provided for industrialization of biomass degradation.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
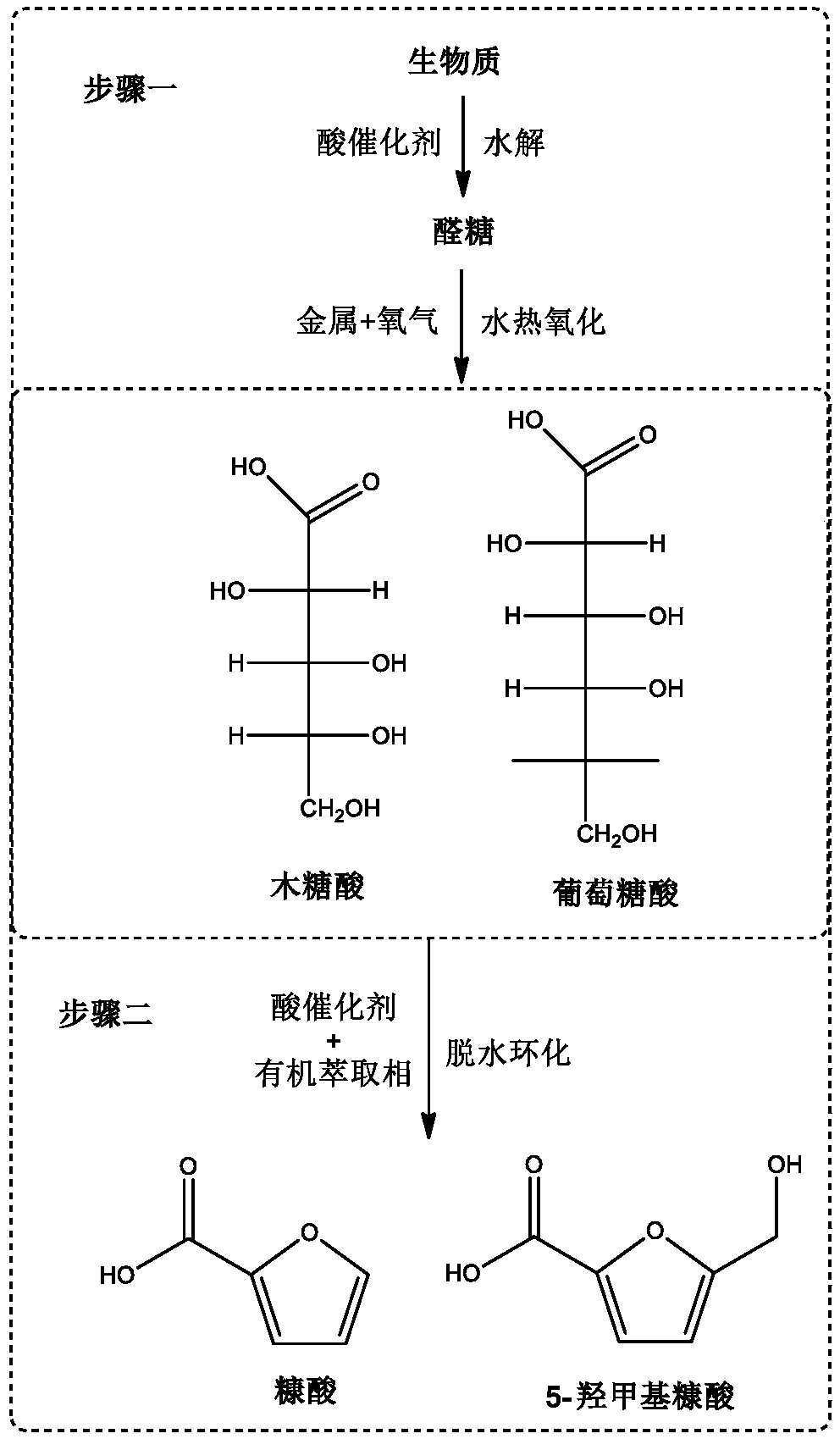
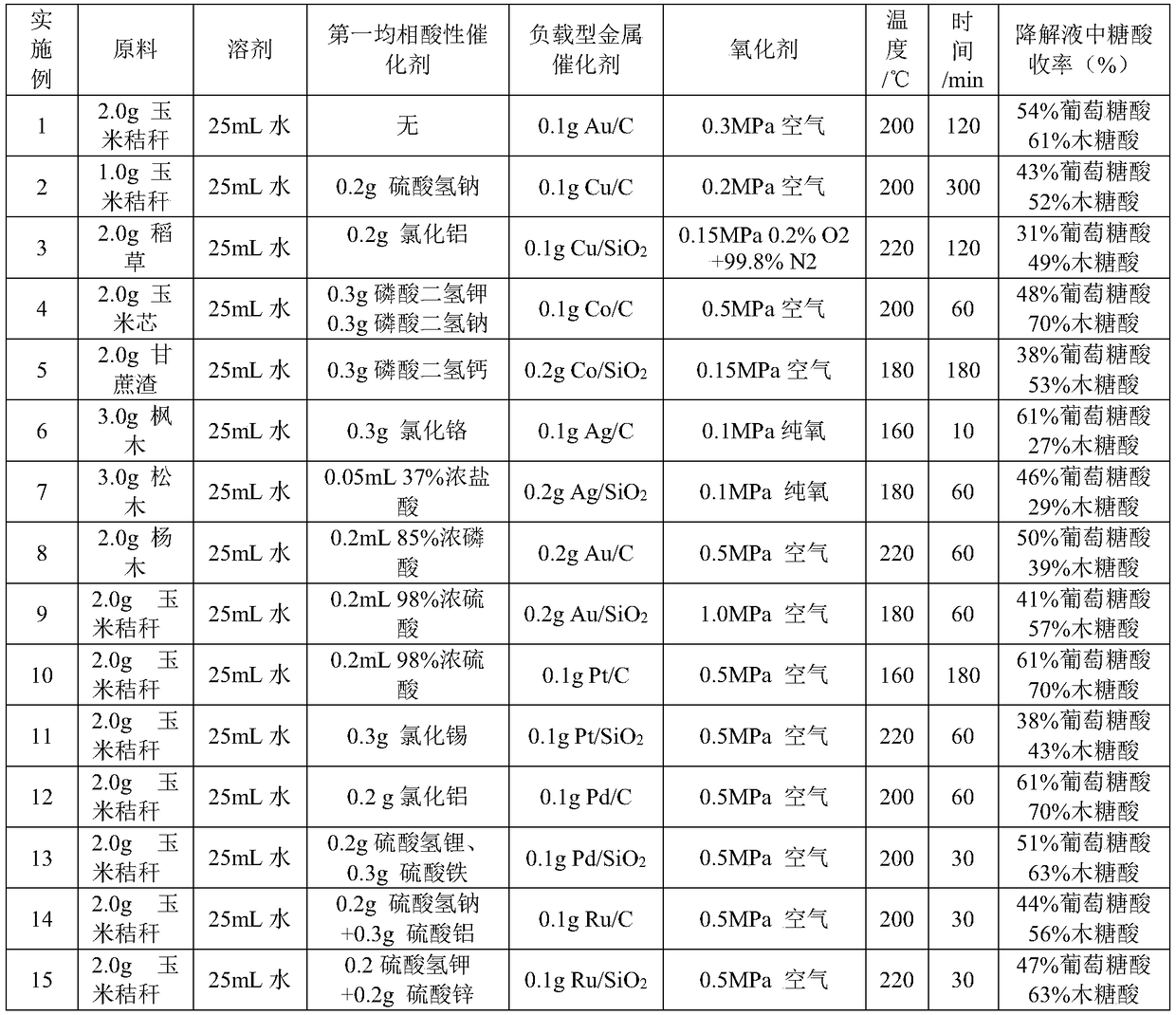
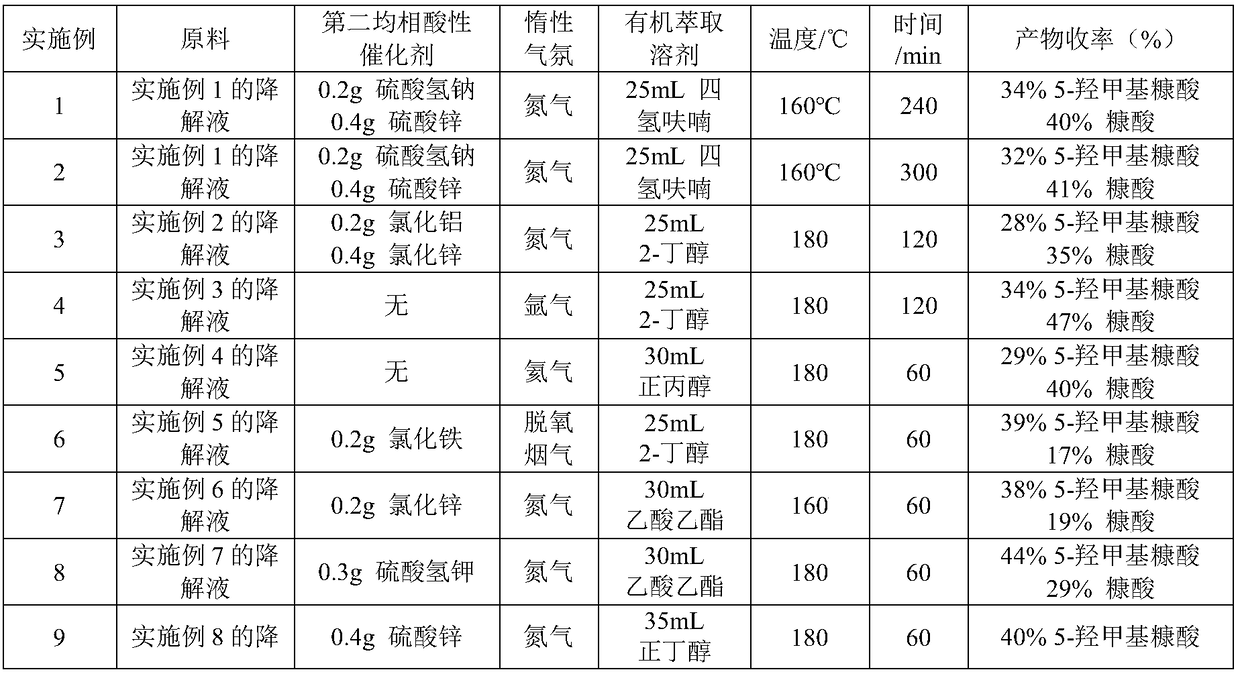
Method for preparing furoic acid and 5-hydroxymethyl furoic acid by biomasses
The invention discloses a method for preparing furoic acid and 5-hydroxymethyl furoic acid by biomasses. The method includes the steps: (1) taking oxygen-containing gas as an oxidizing agent, and converting the biomasses into degradation liquid containing gluconic acid and xylonic acid under hydrothermal reaction conditions through combined actions of a first homogeneous acid catalyst and a supported metal catalyst; (2) placing the degradation liquid containing the gluconic acid and the xylonic acid into an inert atmosphere, sequentially adding an organic solvent and a second homogeneous acidcatalyst to obtain mixed liquid, performing reaction on the mixed liquid to obtain the furoic acid and the 5-hydroxymethyl furoic acid. According to the method, a small amount of solid residue is generated in the whole reaction process, and the method avoids the problems of low target products, carbon deposition on device wall surface, pipeline blockage and the like caused by a lot of solid residue generated in traditional biomass degradation process.
Owner:GUIZHOU INST OF TECH
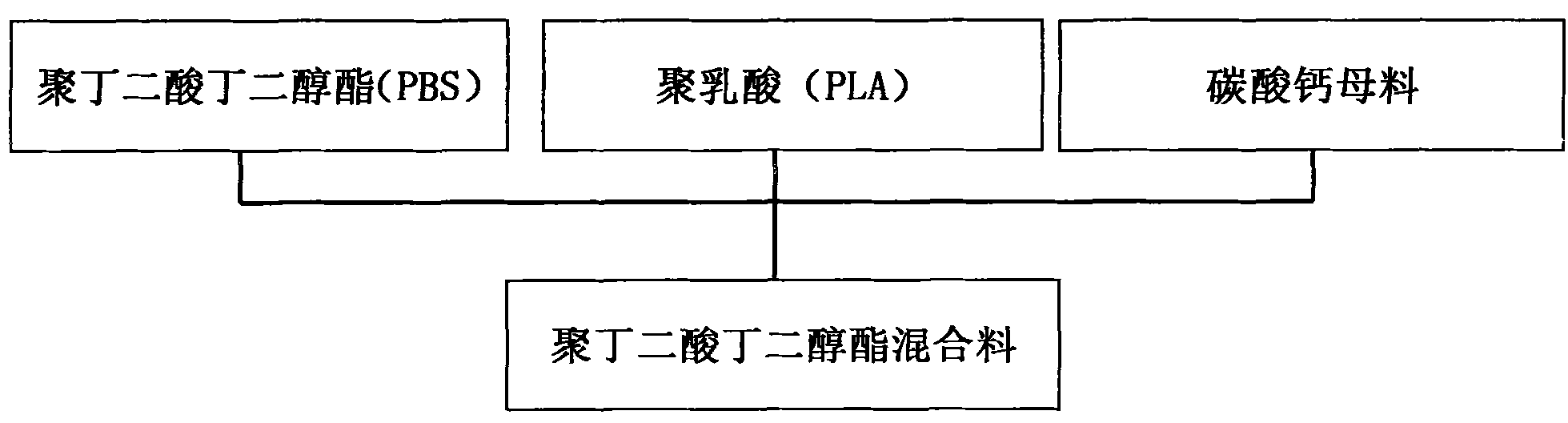
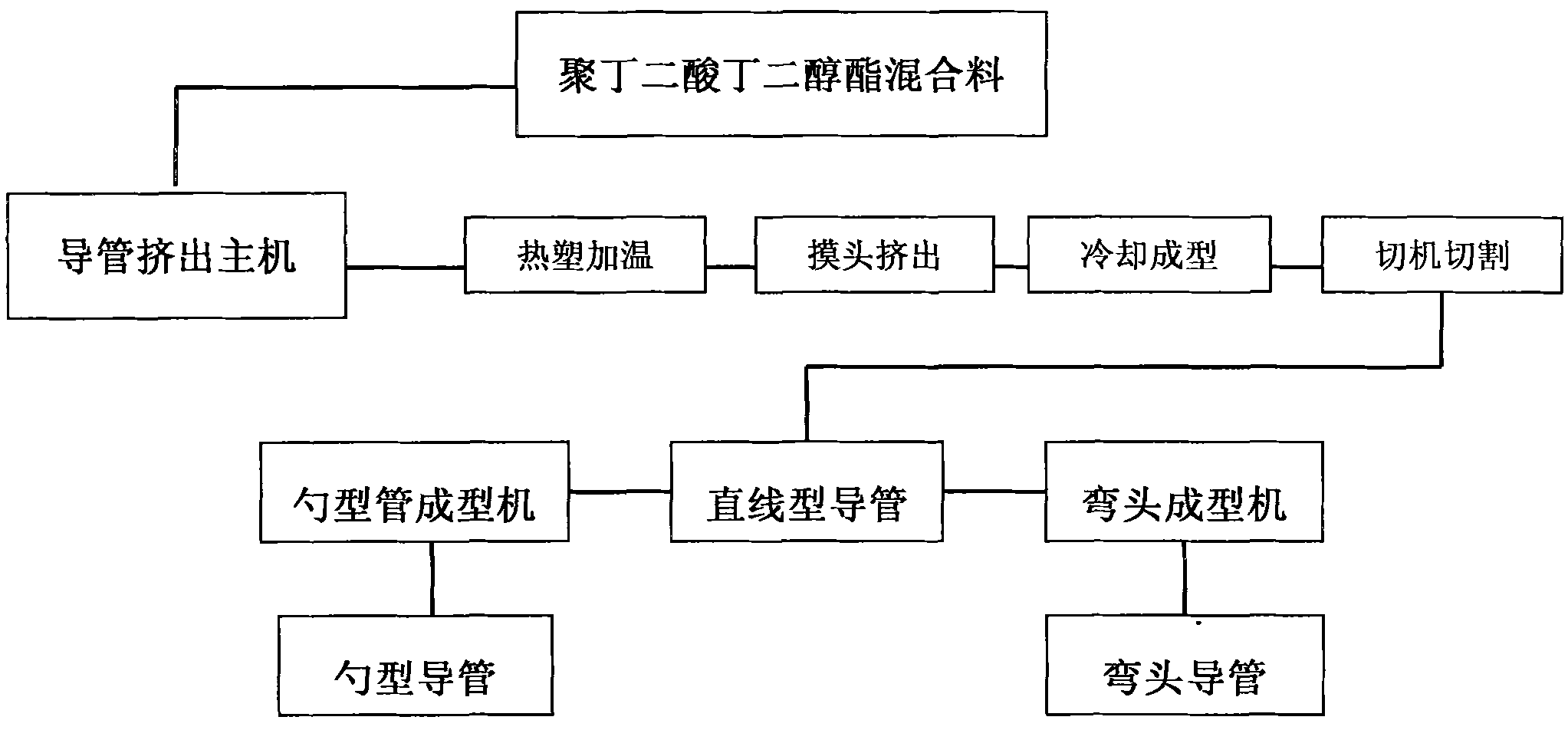
Preparation method for biomass degradation material and magnetic powder catheter
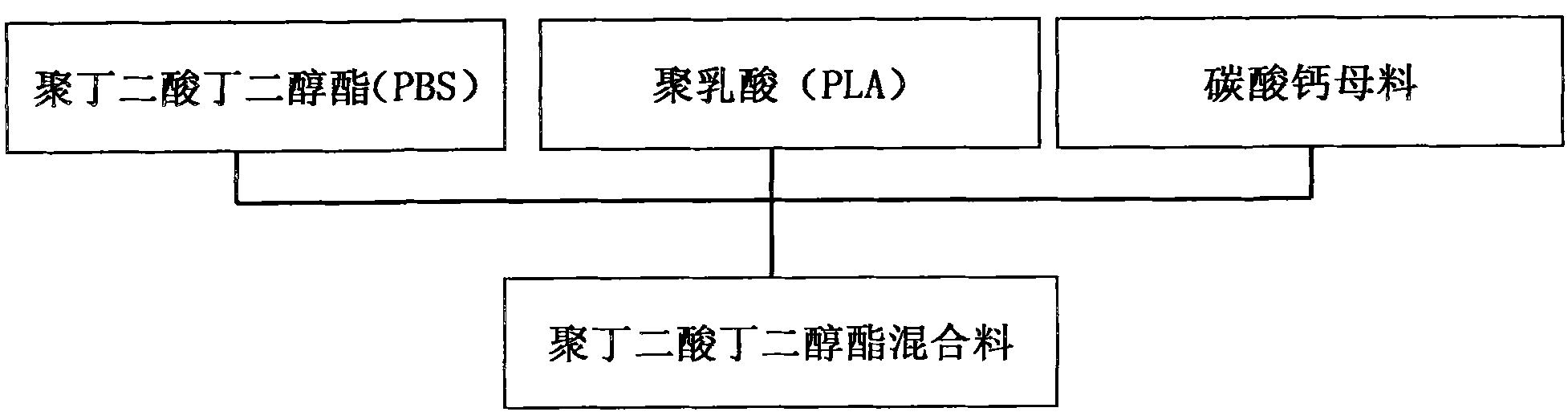
InactiveCN102140234AImprove impact resistanceGood flexibilityRigid pipesBiomass degradationFiller Excipient
The invention provides a preparation method for biomass degradation material, which comprises the following steps: (1) preparing raw materials: weighing the following compositions of raw materials by weight percentage: 40 to 60 of major ingredient poly( butylene succinate), 40 to 60 of modified material polylactic acid and 0.1 to 20 of filler calcium carbonate master batch; (2) mixing the compositions to form modified poly( butylene succinate) mixture; and (3) statically placing the modified mixture at low temperature for standby application. The invention also discloses a method for manufacturing a magnetic powder catheter by adopting the raw materials, which comprises the following steps: (4) preparing a magnetic powder catheter extrusion main machine and a round die head matched with the main machine for use; (5) feeding the modified poly( butylene succinate) mixture into the extrusion main machine so as to manufacture a continuous round hollow magnetic powder catheter; and (7) cutting the continuous round hollow magnetic powder catheter into magnetic powder catheter sections. The invention also provides the magnetic powder catheter prepared by the method. The materials provided by the invention can completely degrade. The method is scientific and reasonable; the production efficiency is high; the product performance is good; and the cost is low.
Owner:广州高馨能生物科技有限公司
Biomass direct power generation fuel cell and CO2 utilization system and method
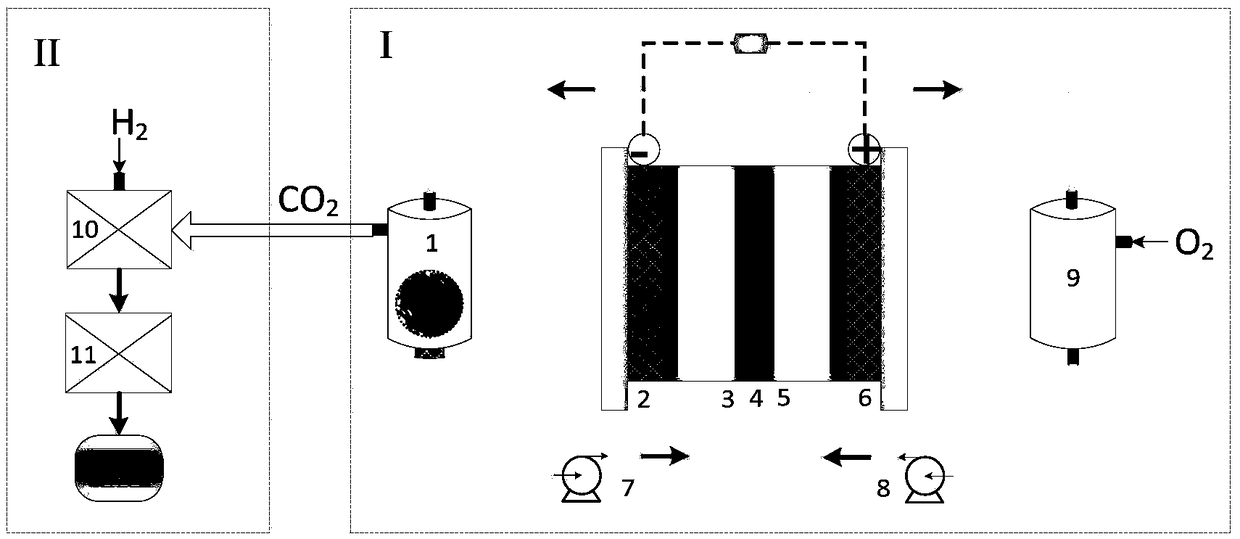
InactiveCN108808041AReduce usageSimple processElectrolyte stream managementWaste based fuelAlkaneBiomass degradation
The invention provides a biomass direct power generation fuel cell and a CO2 utilization system and method. The system comprises a biomass direct power generation fuel cell system I and a CO2 utilization system II, and is used for converting chemical energy in biomass into electrical energy and converting CO2 gas generated by the biomass direct power generation fuel cell system I into hydrocarbonfuel highly selectively and directionally. The method comprises the following steps: the biomass degradation process is accompanied with reduction of Fe<3+>, electrons are provided while Fe<2+> on ananode is oxidized, electrons are received on a cathode, VO<2+> is reduced, and currents are generated by directional movement of electrons; CO2 produced in the process of biomass degradation is hydrogenated to produce methanol, and methanol is subjected to C-C coupling reaction, and C<5+> alkane is produced. With the adoption of the method, chemical energy of biomass is directly converted into electric energy, and CO2 waste gas is converted into high-value fuel.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
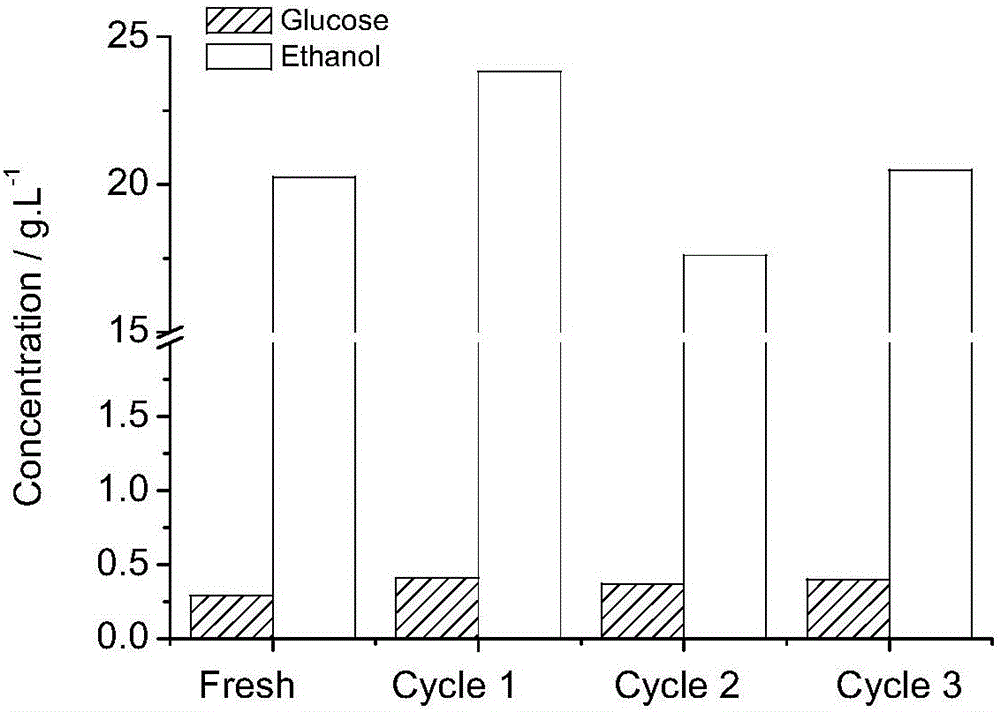
Surfactant recovery technology for lignocellulose hydrolysate fermentation process
ActiveCN106188612APromote the industrialization of ethanolAchieve enrichmentEther separation/purificationPlastic recyclingDistillationBiomass degradation
The invention provides a surfactant recovery technology for a lignocellulose hydrolysate fermentation process, and belongs to the field of biomass degradation fermentation production of fuel ethanol. According to the technology, detoxification treatment is not required to be performed on a lignocellulose hydrolysate subjected to thermochemical pretreatment such as acid hydrolysis or steam explosion, the pH value is directly regulated, a surfactant is added, brewer yeasts are added for ethanol fermentation, and then yeast cells are directly separated and recovered; enrichment of the surfactant, a fermentation inhibitor and a buffering agent is implemented at the same time of ethanol distillation; the fermentation inhibitor is extracted to implement coupling separation and recovery of the surfactant, the buffering agent and the fermentation inhibitor. The technology has the advantages that not only is the cyclic utilization efficiency of the yeasts improved, but also coupling recovery of the surfactant, the buffering agent and the fermentation inhibitor is implemented; relative to an ethanol distillation process, no energy consumption is added by surfactant recovery, a recovery process is simple, pollution is effectively reduced, the cost is lowered, and the industrialization process of cellulosic ethanol is further promoted.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing organic acid by oxidative degradation of biomass and prepared organic acid
InactiveCN107827732ANot suitable for storageReduce energy consumptionOrganic compound preparationLignin derivativesWater bathsAcetic anhydride
The invention discloses a method for preparing organic acid by oxidative degradation of biomass and a prepared organic acid, which relate to the field of biomass reuse and solve the problems of high energy consumption, high cost, harsh reaction conditions, large residue amount and environment pollution existing in conventional biomass degradation and utilization methods. The method comprises the following steps: biomass and acetic anhydride are uniformly mixed according to a solid-liquid ratio of 1g:(5ml to 30ml) under magnetic stirring, and 30 percent of hydrogen peroxide is dripped by a constant-pressure drop funnel; the mixture is oxidized under the condition of 35 DEG C to 85 DEG C for 6 to 48 hours; filtration is performed to obtain an oxidized solution; the oxidized solution is driedby evaporation in water bath, so as to obtain residue; and the residue is separated by column chromatography, so that the organic acid is obtained. By oxidatively degrading an organic matter in the biomass under mild conditions, the chemical with high added value-the organic acid can be obtained, establishing a novel method for the application of biomass. The method has the advantages of low energy consumption, low cost, less residue and no environment pollution.
Owner:JILIN AGRI SCI & TECH COLLEGE
BdREF2 gene for regulating asafetide anabolism and application of BdREF2 gene
ActiveCN109055408AImprove degradation conversion efficiencyReduce contentOxidoreductasesFermentationCDNA libraryBiomass degradation
The invention relates to a BdREF2 gene for regulating asafetide anabolism and application of the BdREF2 gene, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. According to the BdREF2 gene disclosed by the invention, a coniferous aldehyde dehydrogenase gene named BdREF2 is separated from cDNA library of brachypodium distachyon; the BdREF2 gene in a brachypodium distachyon genome is knocked out by adopting a CRISPER / Cas9 gene editing system; it is found that the mutation of the BdREF2 can decrease the content of ferulic acid ester in plant cell walls while the degradation efficiency of biomass is obviously improved; the result indicates that the BdREF2 gene can be applied to biomass biodegradable genetic improvement of gramineous plants. It is firstly and directly proved that an REF homologousgene involved in regulating the biosynthesis of ferulic acid can be applied to improving the genetic improvement on biomass degradation and transformation efficiency of the gramineous plants, and hasimportant value for resource efficient utilization of biomass such as gramineae energy grass, forages and crop straws.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Garbage treatment equipment for biodegradation
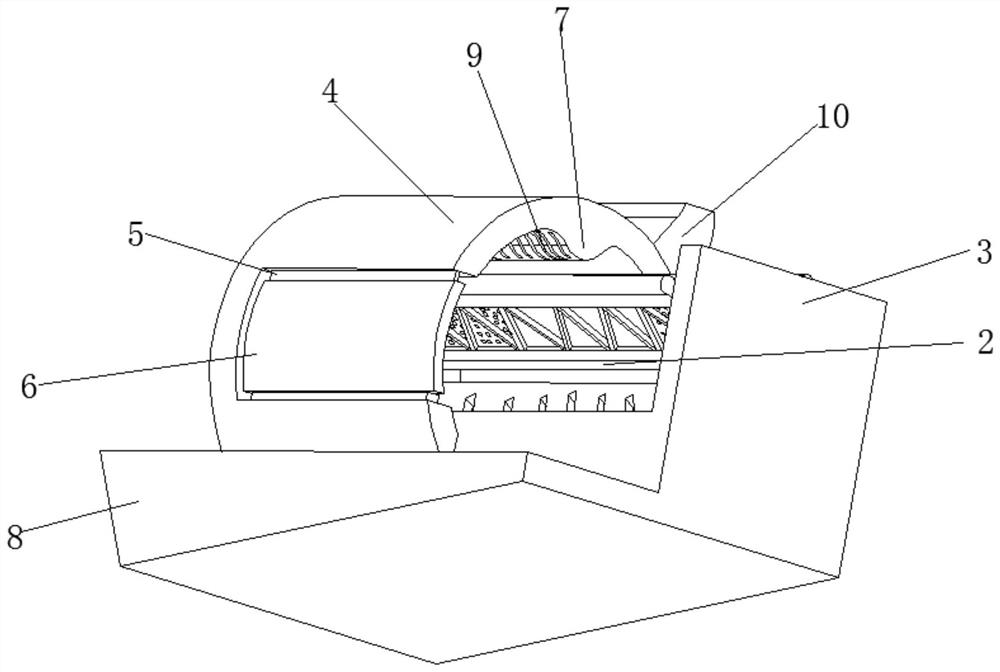
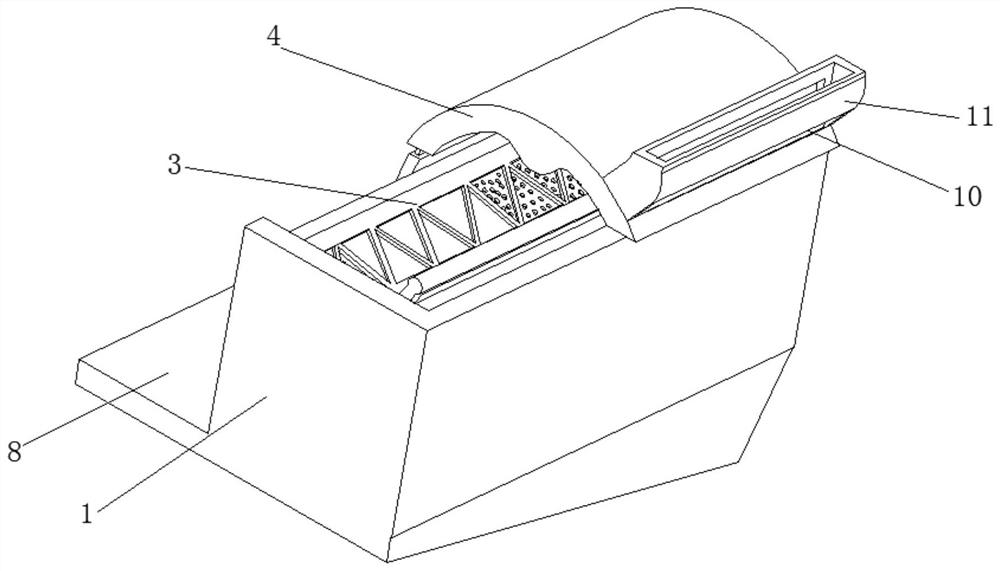
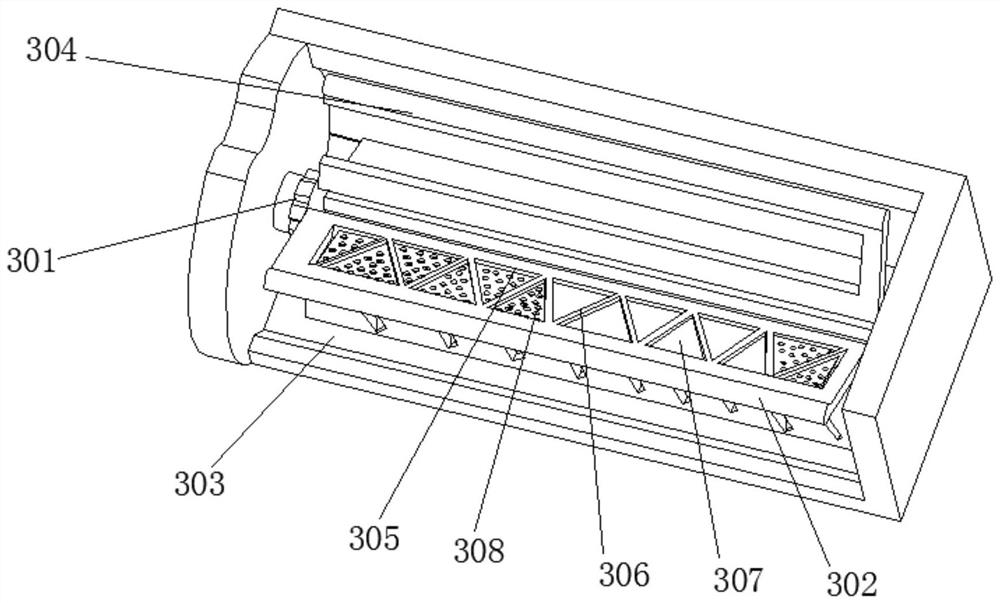
InactiveCN113879720ATake advantage ofRelieves rising and falling forcesWaste collection and transferRefuse receptaclesRefuse collectionBiomass degradation
The invention discloses garbage treatment equipment for biodegradation, and relates to the technical field of biomass degradation and conversion equipment. The garbage treatment equipment for the biodegradation comprises a recycling barrel, a relieving mechanism is arranged on the inner surface of the recycling barrel, a collecting barrel is slidably connected to the inner surface of the recycling barrel, a through groove is arranged on the inner surface of the collecting barrel, a screening window is slidably connected to the inner surface of the through groove, and a one-way mechanism is arranged on the inner surface of the screening window. The collecting barrel capable of moving up and down to separate solid from liquid is additionally arranged in a barrel for containing garbage in a centralized mode, solid-liquid separation is carried out on the garbage through vertical movement of the collecting barrel and centrifugal force generated by operation of internal components, force capable of relieving ascending and descending is added at the lifting position, the safety of equipment in the using process is further improved, the functionality of the equipment is also improved, and after the garbage is collected, solid-liquid separation can be directly carried out, and the garbage can be compacted, so that the internal space of the equipment can be fully utilized during collection.
Owner:于辰辉
Bacteria with reconstructed transcriptional units and the uses thereof
InactiveUS20140356923A1High activityIncrease regulatory acceptanceBacteriaBiofuelsBiotechnologyBiomass degradation
The present invention relates to recombinant bacteria and the uses thereof, particularly for the production of ethanol. The invention also relates to methods for the production of such bacteria, as well as to nucleic acid constructs suitable for such production. The invention specifically relates to bacteria having a reconstructed biomass degradation unit.
Owner:DEINOVE SA
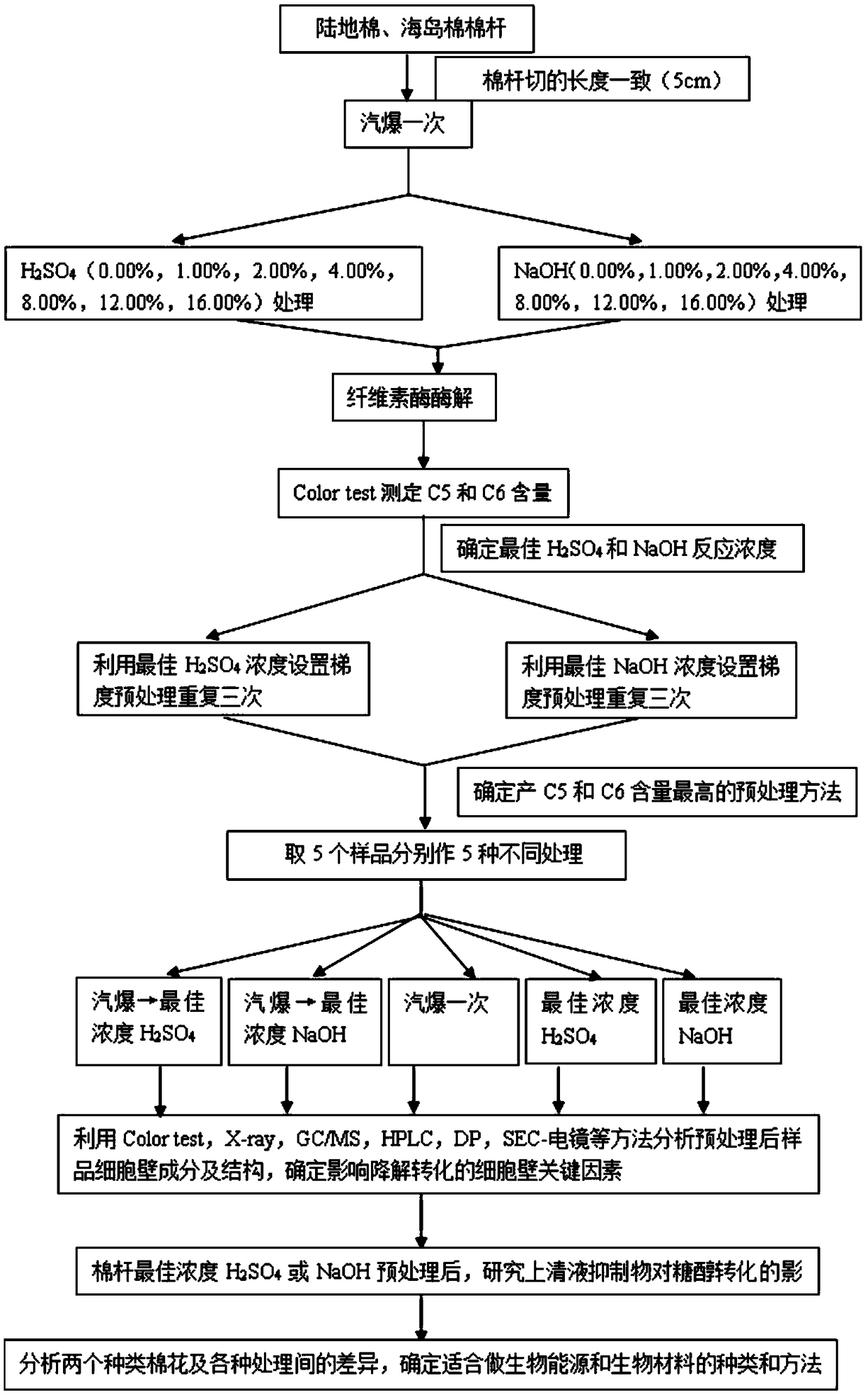
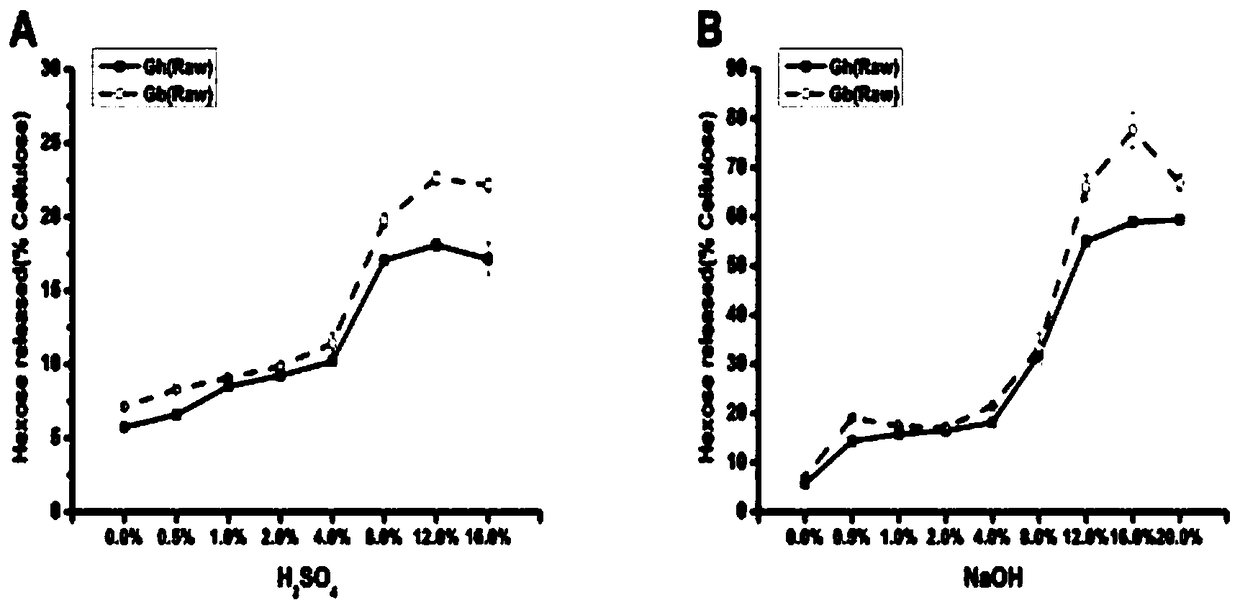
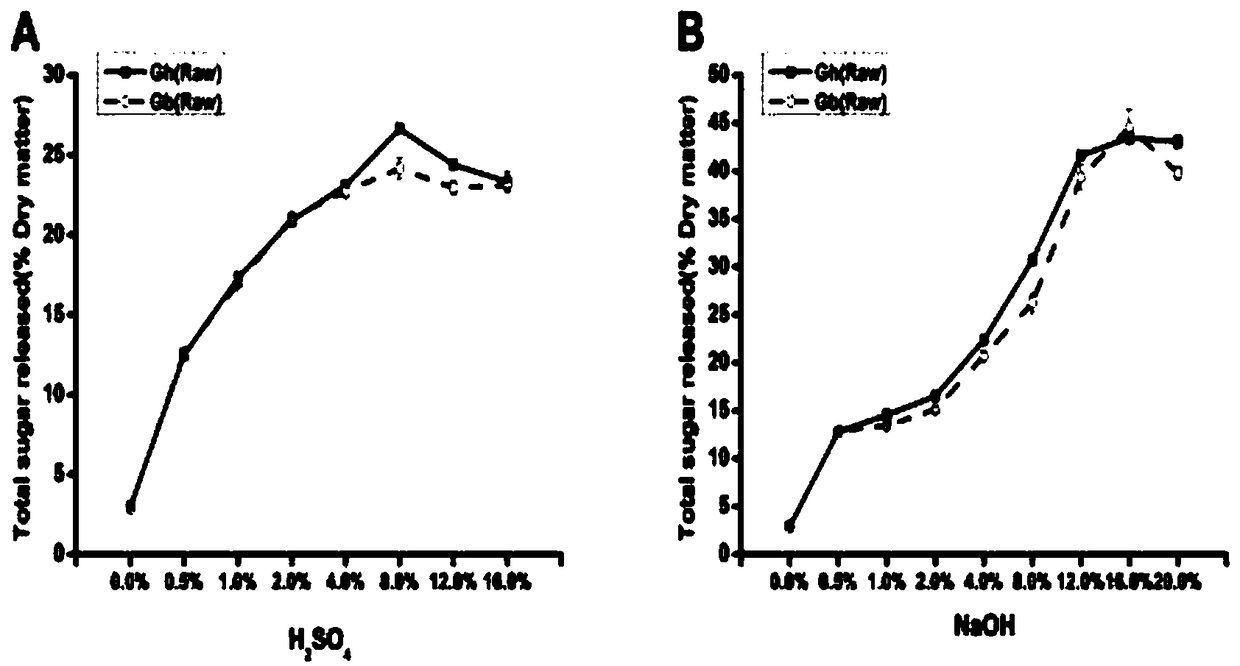
Research method for improving biomass degradation and sugar alcohol conversion efficiency of cotton stalk
InactiveCN109371076AReduce the degree of polymerizationDegradation efficiency is improvedBiofuelsFermentationFine structureCellulose
The invention discloses a research method for improving biomass degradation and sugar alcohol conversion efficiency of cotton stalk. Straw cell wall components and fine structures thereof and pretreatment degradation efficiency after steam explosion are studied, the relationship between the straw cell wall components and fine structures thereof and pretreatment degradation efficiency is discussedand analyzed, and a theoretical basis is provided for the effective use of the cotton stalk. It is found by the research and study of upland cotton and island cotton stalk, the island cotton is more suitable for serving as an energy plant compared with the upland cotton, and bioethanol is produced by using biomass energy. It is determined that a key structural factor of the cell wall component that affects the degradation efficiency of the cotton stalk is the degree of polymerization of cellulose. A steam explosion +0.25% H2SO4 two-step method improves the degradation efficiency of an originalsample by 5-6 times by greatly reducing the polymerization degree of the cellulose.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Production technology of cello-oligosaccharide
The invention discloses a production technology of cello-oligosaccharide. The technology comprises the following basic steps: (1) crushing a biomass raw material (2) uniformly mixing the crushed sample and a reaction solution; (3) letting the reaction system react at room temperature for a certain period of time; (4) adding water to dilute a reaction liquid; (5) hydrolyzing the reaction system at high temperature for a period of time; (6) carrying out solid-liquid separation, and neutralizing a liquid part by the use of alkali; and (7) carrying out sugar-salt separation to obtain cello-oligosaccharide. The operation method is simple, and the problem that molecular weight cannot be manually controlled at a stage by pure biomass degradation is solved. The production technology makes it possible to realize industrial large-scale production of cellulose-enriched biomass and obtain high-purity cello-oligosaccharide.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
GH10 family high-temperature-resistant xylanase mutants and application thereof
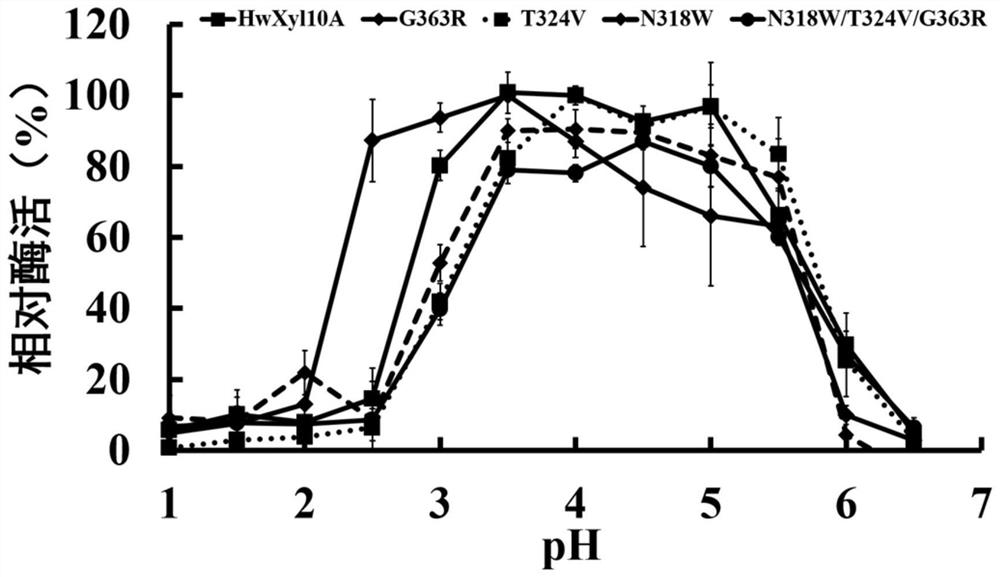
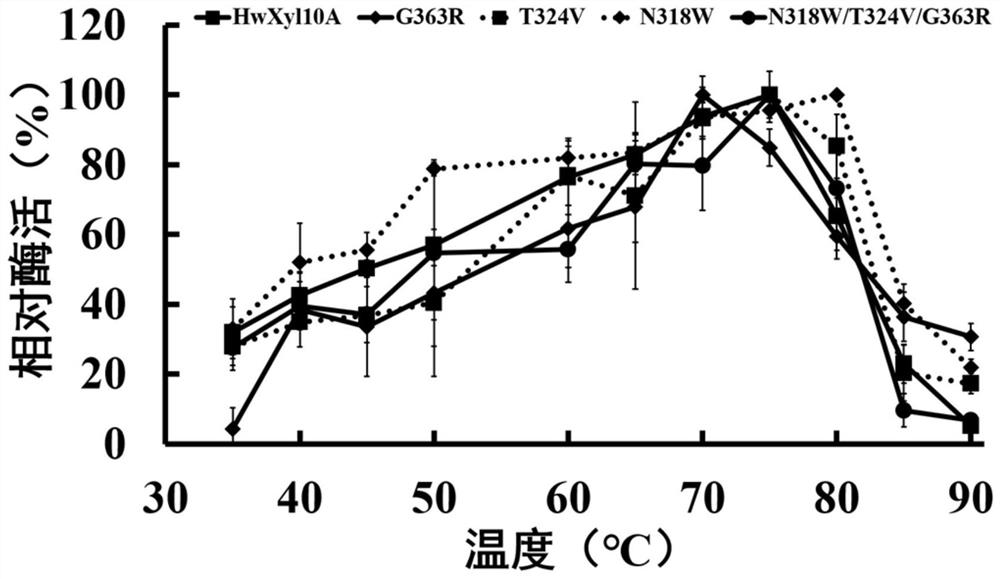
The invention provides GH10 family high-temperature-resistant xylanase mutants and application thereof. The mutants are HwXyl10A-G363R, HwXyl10A-T324V, HwXyl10A-N318W and HwXyl10A-N318W / G363R / T324V mutants; and the half-life periods of the four mutants at 75 DEG C are prolonged by 12min, 20min, 24min and 38min respectively compared with those of wild mutants. The xylanase mutants have high catalytic activity and excellent thermal stability at animal body temperature and have great application potential in feed addition and biomass degradation.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
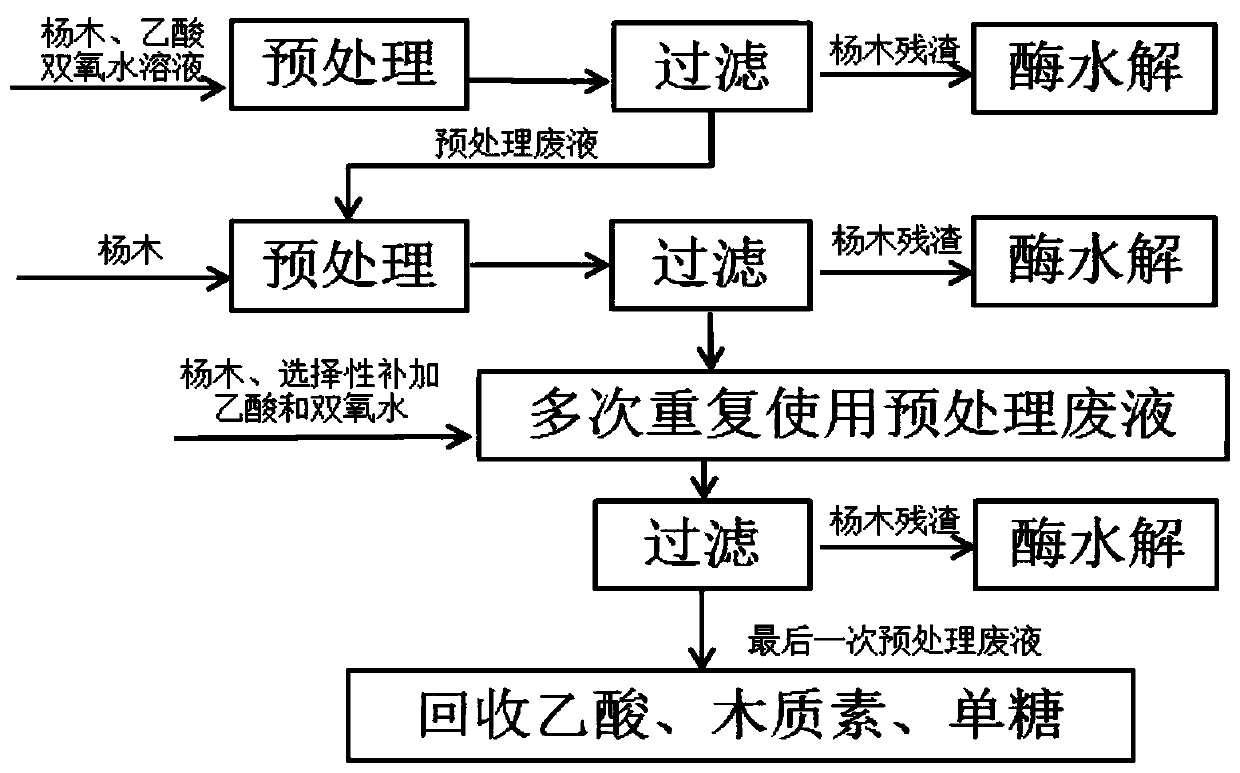
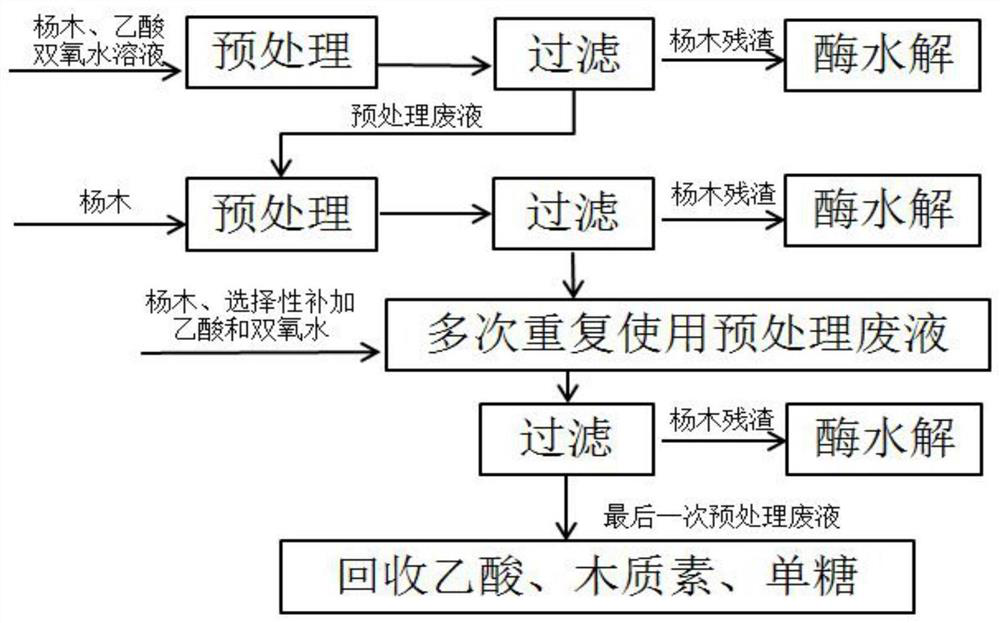
Method for removing poplar lignin by cyclic utilization of acetic acid-hydrogen peroxide pretreatment liquid
ActiveCN111576070AReduce consumptionReduce pretreatment costsPaper material treatmentAcetic acidEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention provides a method for removing poplar lignin by cyclic utilization of acetic acid-hydrogen peroxide pretreatment liquid, and belongs to the technical field of forestry biomass degradation and conversion. The method comprises the following steps: mixing an acetic acid-hydrogen peroxide solution with poplar and sulfuric acid to obtain a mixture; treating the mixture at 60-80 DEG C for2 hours, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain a liquid, namely a pretreatment liquid; and mixing the pretreatment solution with the poplar, and repeating for 3-4 times to realize cyclicutilization of the pretreatment solution. According to the method, the poplar is treated with the acetic acid-hydrogen peroxide pretreatment liquid, consumption of acetic acid-hydrogen peroxide is reduced, and the pretreatment cost is reduced; acetic acid and hydrogen peroxide are added into the pretreatment liquid to prolong the use frequency of the pretreatment liquid, and the supplemented reagents are non-toxic and harmless; the problems of complex recovery process, high cost and serious pollution of the pretreatment liquid are solved; 57% of poplar lignin can still be removed after the pretreatment liquid is repeatedly used for three times, and the yield of enzyme hydrolysis glucose of the pretreated poplar can reach 90.0% or above.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
A method for removing poplar lignin by recycling acetic acid-hydrogen peroxide pretreatment solution
ActiveCN111576070BReduce consumptionReduce pretreatment costsPaper material treatmentAcetic acidEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention provides a method for recycling acetic acid-hydrogen peroxide pretreatment solution to remove poplar lignin, belonging to the technical field of forestry biomass degradation and conversion, comprising mixing acetic acid-hydrogen peroxide solution with poplar and sulfuric acid to obtain a mixture; After treatment at 60-80 ℃ for 2 hours, after solid-liquid separation, the obtained liquid is the pre-treatment liquid; the pre-treatment liquid is mixed with poplar and repeated 3-4 times to realize the recycling of the pre-treatment liquid. The invention utilizes acetic acid-hydrogen peroxide pretreatment solution to treat poplar, reduces the consumption of acetic acid-hydrogen peroxide, and reduces the cost of pretreatment; the pretreatment solution prolongs the use times of the pretreatment solution by adding acetic acid and hydrogen peroxide, and the added reagents are all non-toxic It is harmless; it solves the problems of complex recovery process, high cost and serious pollution of its pretreatment liquid; after repeated use of the pretreatment liquid for 3 times, 57% of poplar lignin can still be removed, and the enzymes of poplar wood after pretreatment can still be removed. The yield of hydrolyzed glucose can reach more than 90.0%.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Sewage treatment equipment for biomass degradation
InactiveCN113716735AReduce the smellAvoid inhalationWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationTreatment involving filtrationSludgeBiomass degradation
The invention discloses sewage treatment equipment for biomass degradation, and relates to the technical field of biomass degradation and conversion equipment. The sewage treatment equipment for biomass degradation comprises a processing box, the inner surface of the processing box is rotatably connected with a rotating main shaft, the outer surface of the rotating main shaft is fixedly connected with a separation mechanism, the outer surface of the rotating main shaft is rotatably connected with an arc-shaped machine cover, and the outer surface of the arc-shaped machine cover is slidably connected with the inner surface of the processing box. A separation mechanism and a flapping mechanism are additionally arranged in the equipment, the traditional natural separation and natural filtration steps of the equipment are changed, a whole processing bin above the equipment is rotated, sludge, garbage and sewage are separated and spin-dried through centrifugal force, and in the separation process, after being extruded, internal garbage can be mixed with a macromolecular coagulant for filtering and washing, and when the sewage amount is large, the odor emitted by the sewage can be controlled to be reduced, so that a large amount of odor is prevented from being directly inhaled into the mouth and nose of a worker.
Owner:于辰辉
Cracking polysaccharide monooxygenase and application thereof
PendingCN114410596AImprove degradation efficiencyIncreased reducing sugar yieldOxidoreductasesFermentationBiomass degradationEnzyme system
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and particularly relates to a bacterial-derived lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the PlLPMOCB3 is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 in a sequence table. The PlLPMOCB3 not only has the capability of degrading biomass polysaccharides such as cellulose, xylan, chitin and the like, but also has a synergistic effect with commercial cellulase, xylanase or chitinase to improve the degradation efficiency of cellulose, lignocellulose, xylan and chitin substrates. Wherein when PlLPMOCB3 and commercial cellulase act together, the synergy degree of cellulose and corncob substrates can reach 1.43 and 1.22 respectively; when the xylanase acts together, the synergy degree reaches 4.57; and the synergism degree is up to 1.70 when the bacillus subtilis and chitinase act together. And a new way is provided for enriching a lysable polysaccharide monooxygenase library and artificially compounding a biomass degradation efficient compound enzyme system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing methane by combined fermentation of enteromorpha and straw biomass
ActiveCN102876727BImprove conversion rateIncrease productionWaste based fuelFermentationBiomass degradationResource utilization
The invention discloses a method for preparing methane by the combined fermentation of enteromorpha and straw biomass. The method comprises the steps of fermenting fresh enteromorpha as raw materials to obtain enteromorpha biomass degradation liquid; collecting and fermenting straw solid compost to obtain a straw biomass degradation matrix; compounding the enteromorpha biomass degradation liquid and the enteromorpha degradation matrix according to the proportion, and conducting acidized fermentation to obtain an acidized matrix; putting the acidized matrix into a methane fermenting device, conducting water sealing, and fermenting the methane with constant pressure; and supplementing materials and discharging slag to conduct a new round of fermentation when the daily methane generating amount is smaller than daily average methane amount by 5%. According to the method disclosed by the invention, organic matters, namely the enteromorpha and straws, are complemented with each other, so that the buffering capability of a system is improved. According to the process, a two-step fermentation method is implemented, the fermentation starting is quick, the methane generating peak is ahead of schedule, the methane fermentation period is shortened, and the methane generating amount is high. Meanwhile, the utilization ratio of equipment is increased, and the energy consumption is lowered. According to the method, the resource utilization of the enteroporpha and the straw is realized, the sea environment is improved, the environment event formed by burning the straws can be reduced, the clean methane energy resource is produced, the multiple purposes of turning waste into wealth, saving energy and reducing emission are achieved, and the social and economical benefits are good.
Owner:连云港忠华农业科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com