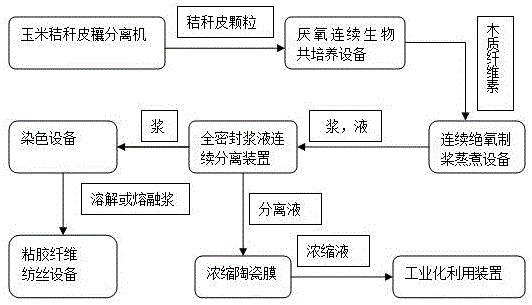
System for preparing viscose by pretreating corn straw through microbial co-culture
A technology of corn stalks and viscose fibers, which is applied to artificial filaments made of viscose, melt spinning, etc., can solve the problems of low yield of aerobic fermentation, long pretreatment period, high cost of enzyme preparations, etc. Effect of bleaching process, reduced cooking conditions, and reduced impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Using corn stalk husks separated from corn stalk leaves and husks as raw materials, the rumen fungus Neocallimastix frontalis isolated from the rumen of ruminant cattle and rumen bacteria Fibrobacter succinogenes were co-cultured to degrade hemicellulose and unstable fibers in straw husks. element; the domesticated co-cultivated microorganisms and the straw husks deprived of oxygen are fermented in an anaerobic continuous culture system, and the fermentation products are separated by the membrane separation device of the continuous culture system without antagonism, and the fermentation time is 48 hours. The pretreatment of corn stalk husks degrades the unstable cellulose and hemicellulose in corn stalk husks, and generates some monomers and highly crystalline lignocellulose; through regulation, the fermentation products can be separated in situ to realize the biological pretreatment of corn stalk husks, and the remaining The high crystalline lignocellulose; after anaero...
Embodiment 2
[0025]Corn stalk husks separated from corn stalk leaves and husks are used as raw materials, and rumen microorganisms are used for anaerobic co-cultivation with rumen microbial degradation products or metabolite utilization bacteria to degrade hemicellulose and unstable cellulose in straw husks; Co-cultivation of animal rumen fungus Neocallimastix frontalis and ethanologen Candida tropicalis; degradation of unstable cellulose and hemicellulose in corn stalk husks; domesticated co-cultured microorganisms and straw husks deprived of oxygen in an anaerobic continuous culture system Fermentation is carried out, and the fermentation product is separated by the membrane separation device of the continuous culture system without antagonism. The fermentation time is 36 hours, and the pretreatment of the corn stalk husk is completed; the fermentation product can be separated in situ through regulation, and the biological pretreatment of the corn stalk husk is realized. The remaining hig...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Using corn stalk husks separated from corn stalk leaves and husks as raw materials, the rumen fungus Neocallimastix frontalis and lactic acid bacteria Pediococcus acidilactic were co-cultured; the unstable cellulose and hemicellulose in corn stalk husks were degraded to generate some simple body and high crystalline lignocellulose; ferment the domesticated co-cultured microorganisms and the straw bark deprived of oxygen in an anaerobic continuous culture system, and the fermentation products are separated by the membrane separation device of the continuous culture system without antagonism. The time is 12 hours, and the pretreatment of corn stalk husks is completed. Through regulation, the fermentation product can be separated in situ, and the biological pretreatment of corn stalks can be realized. The remaining high-crystalline lignocellulose, after anaerobic fermentation, enters the anaerobic continuous cooking system under anaerobic conditions in a fully enclosed envi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com