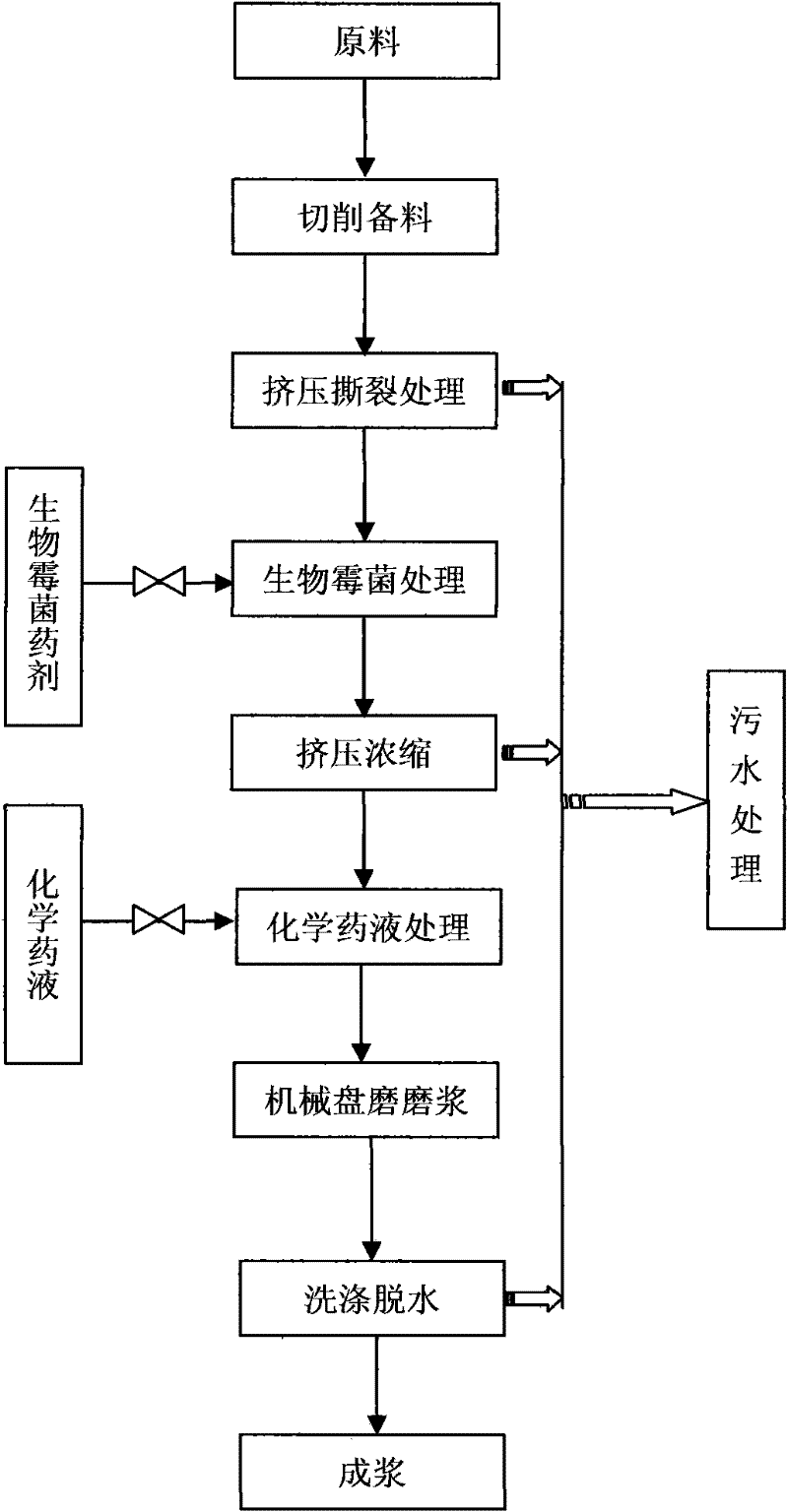
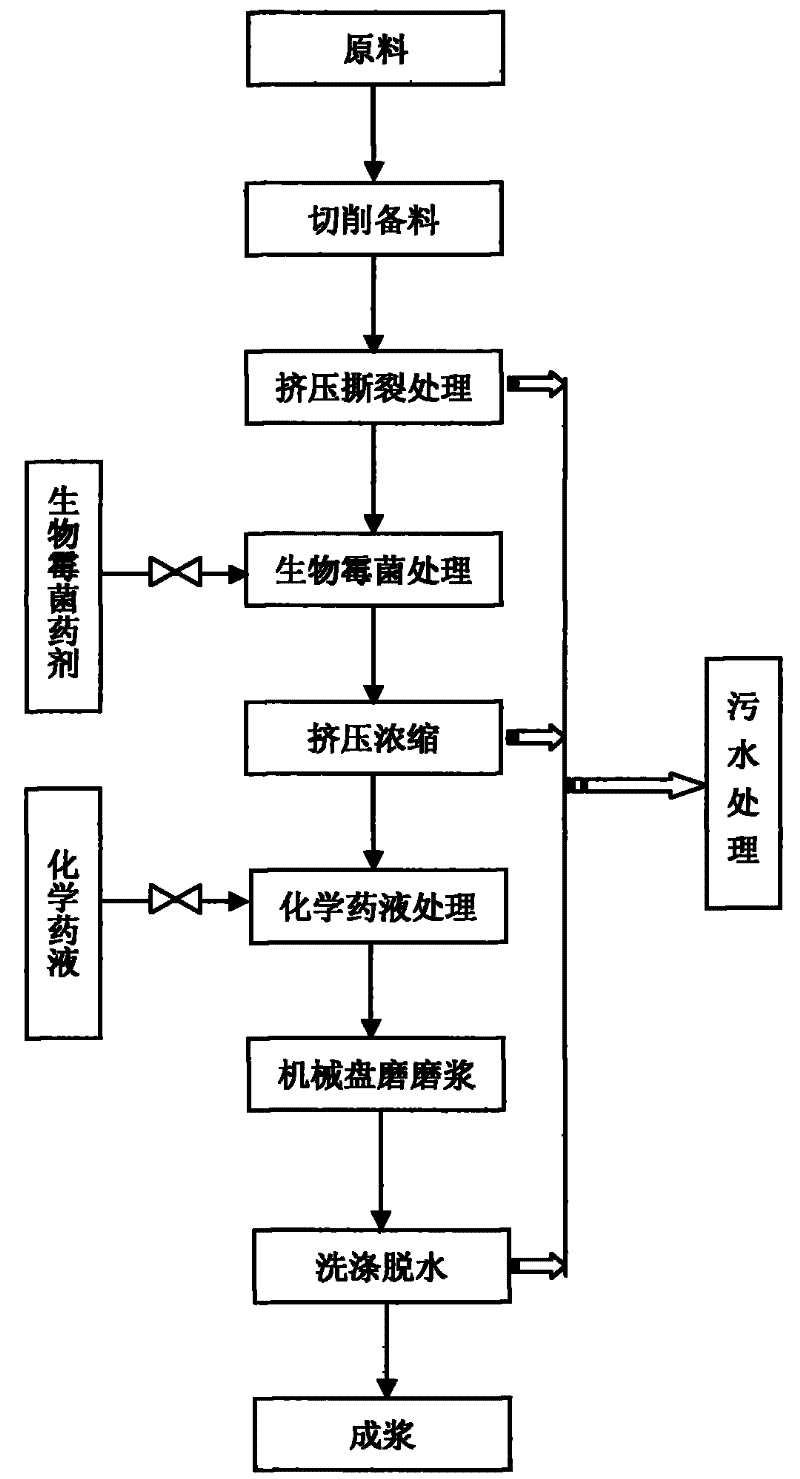
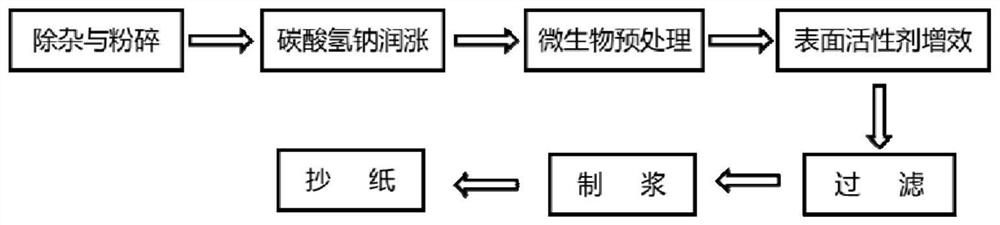
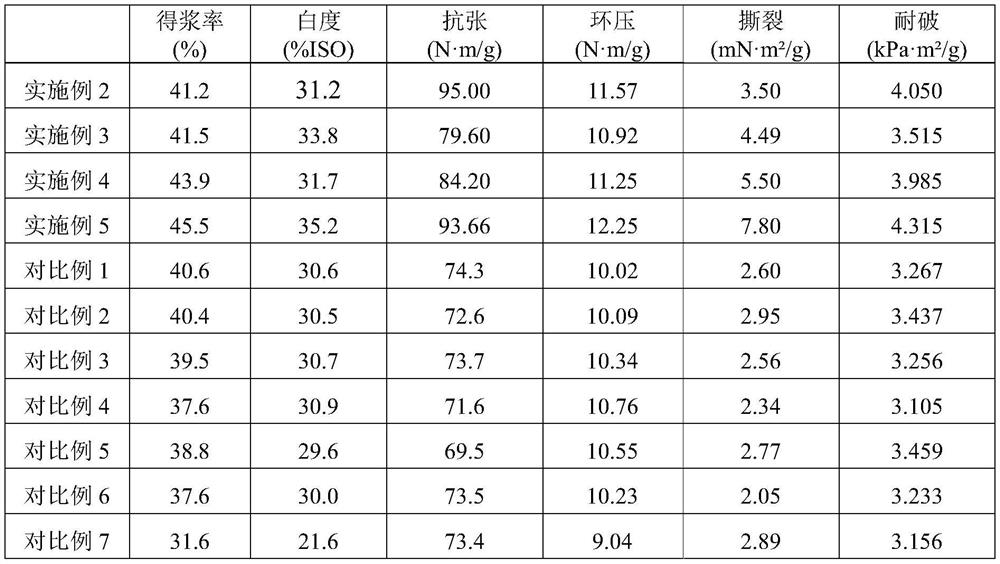
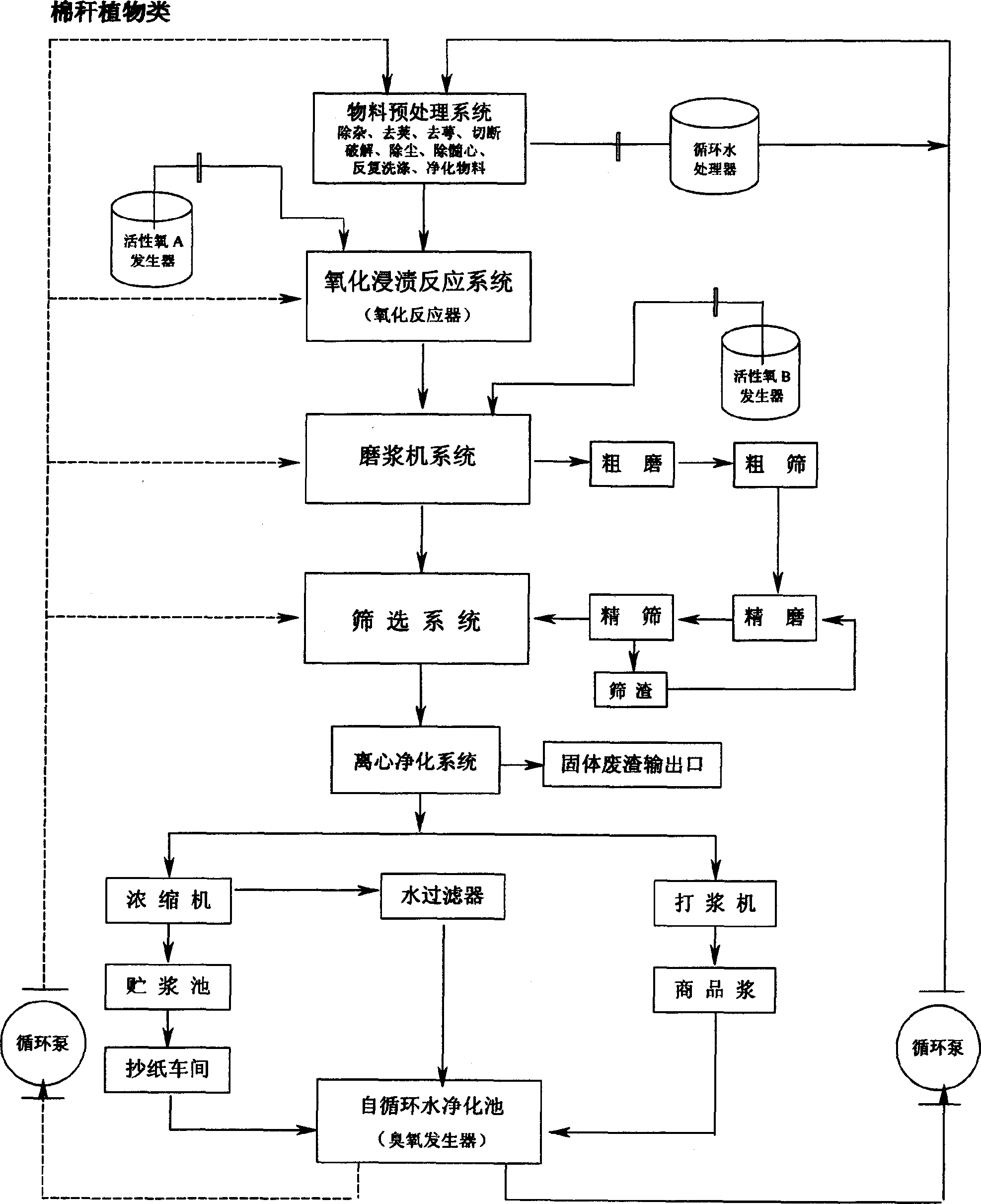
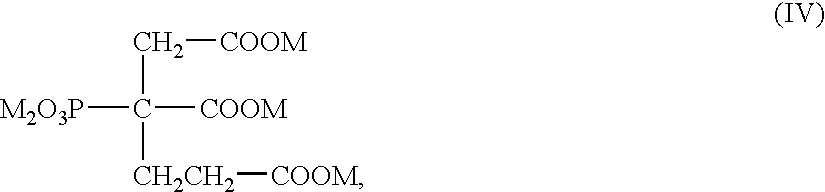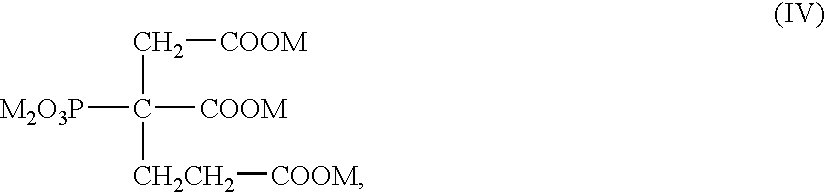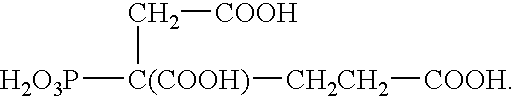Patents
Literature
124 results about "Chemical pulping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
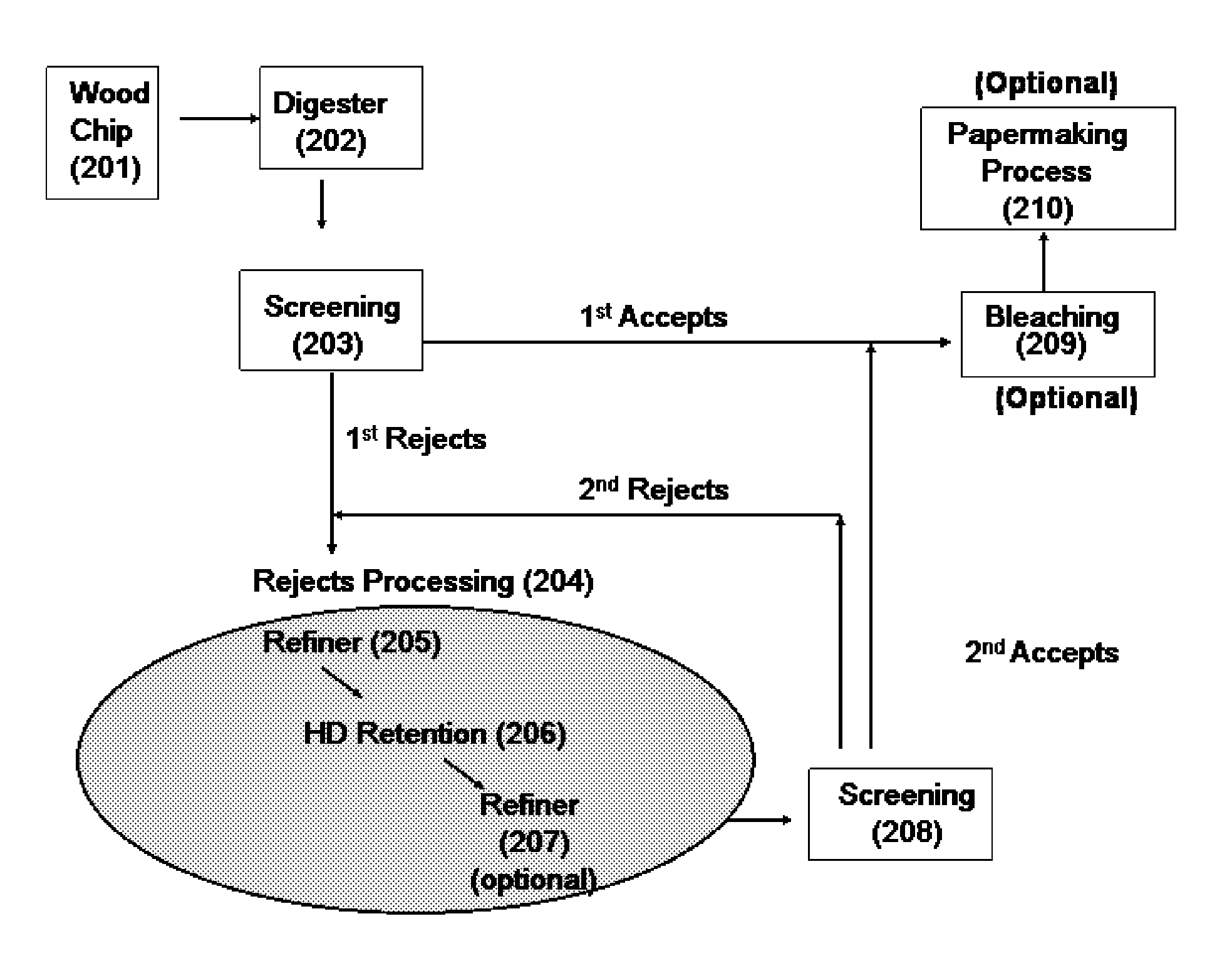
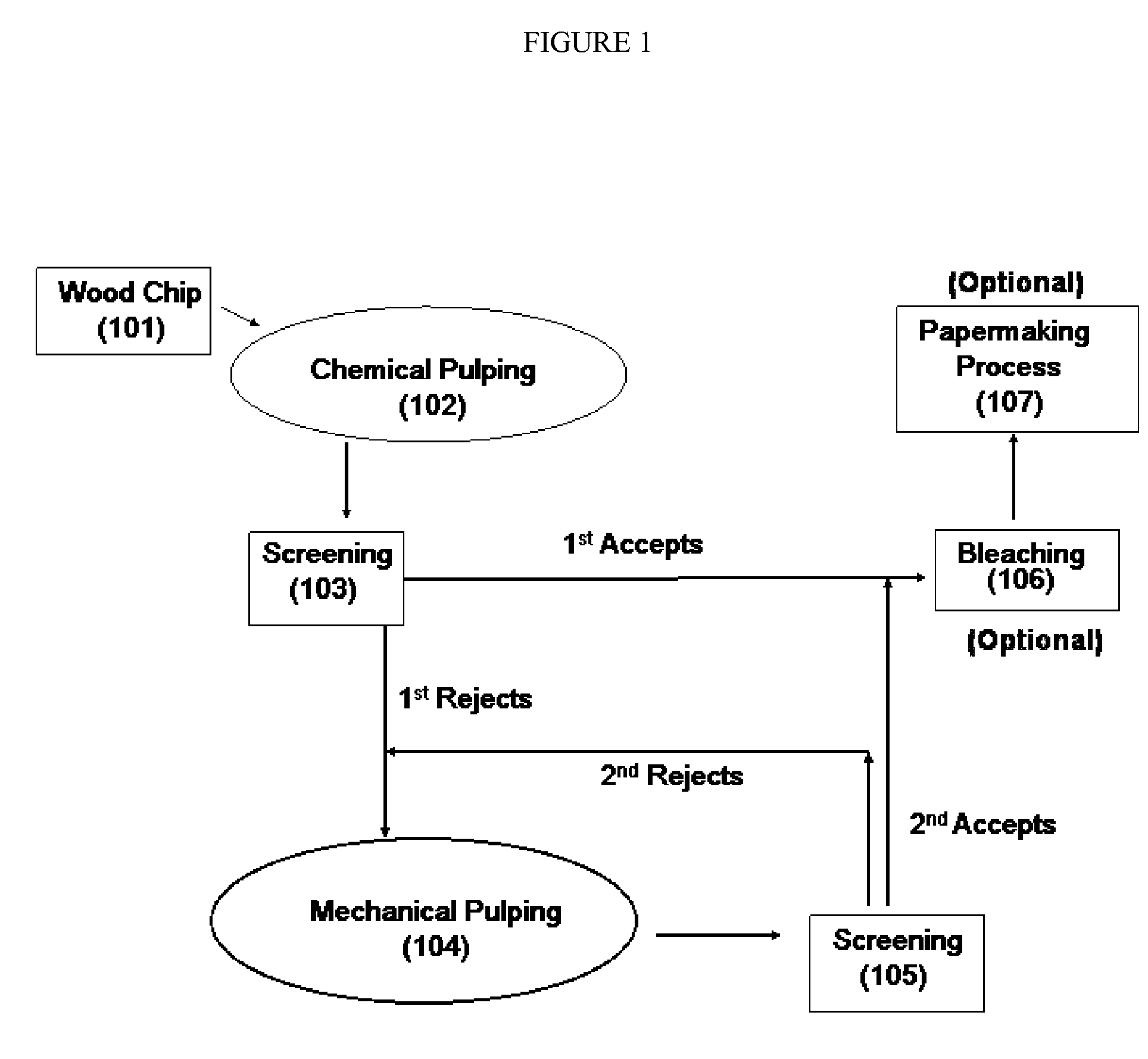
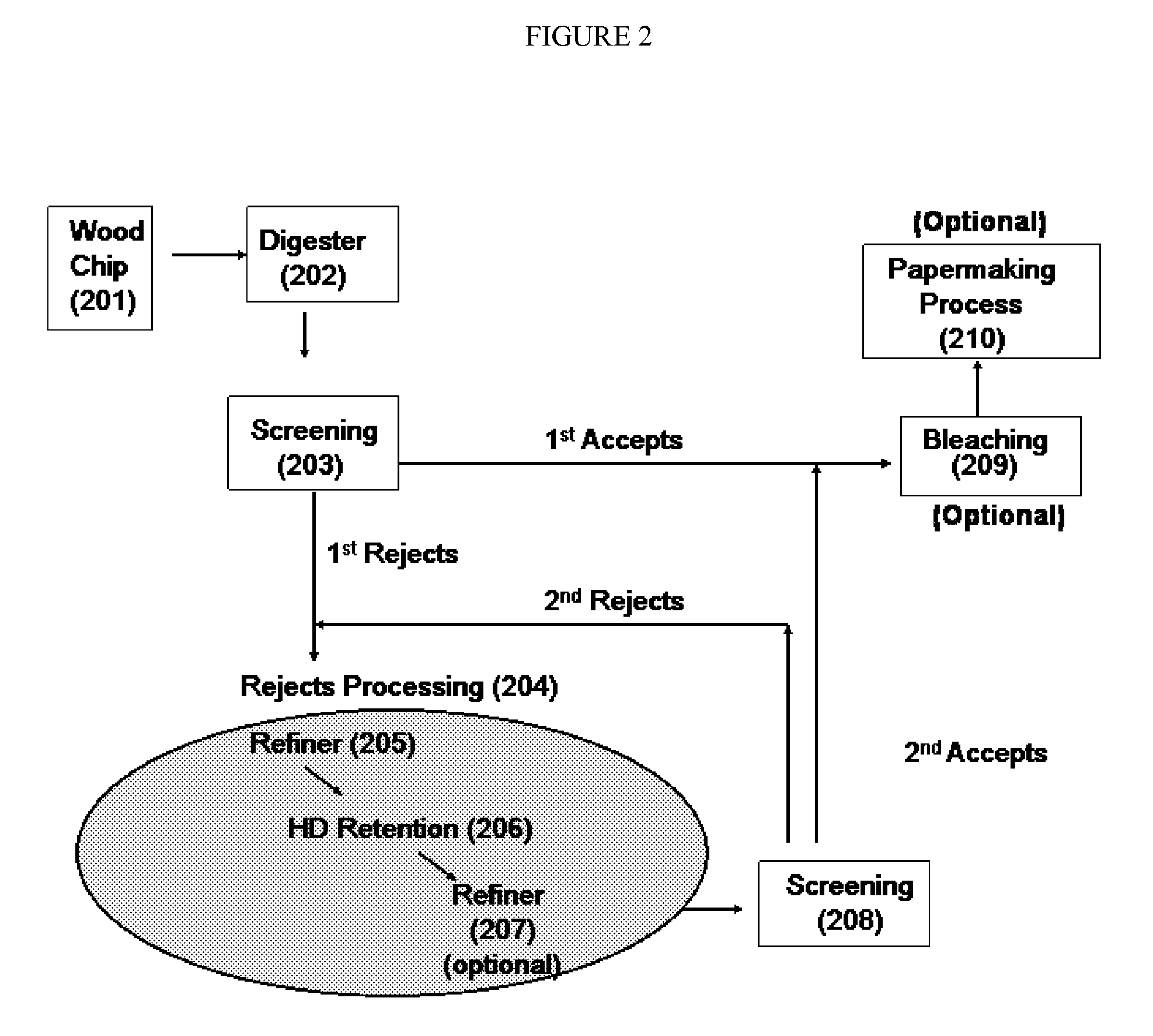
Chemical Pulping. A method of converting wood chips into paper pulp for use in papermaking accomplished by chemical cooking of the chips, as opposed to mechanical pulping. The purpose of pulping is to reduce wood (or other fibrous raw material) to individual cellulose fibers.
Bleaching stage using xylanase with hydrogen peroxide, peracids, or a combination thereof
InactiveUS20040112555A1Less-costly bleaching operationReduce usagePulp bleachingPulping with inorganic basesChlorine dioxideXylanase Y
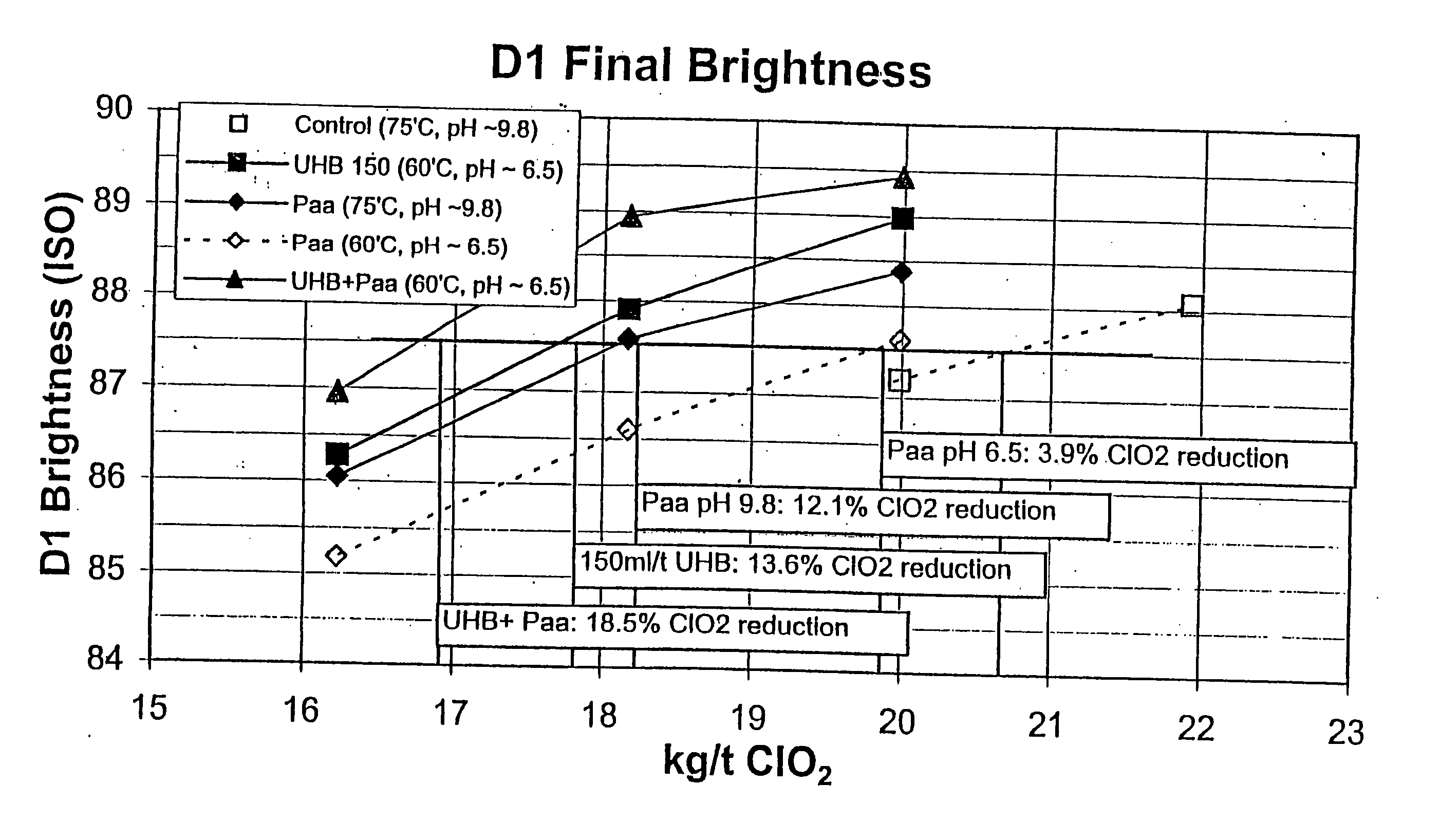
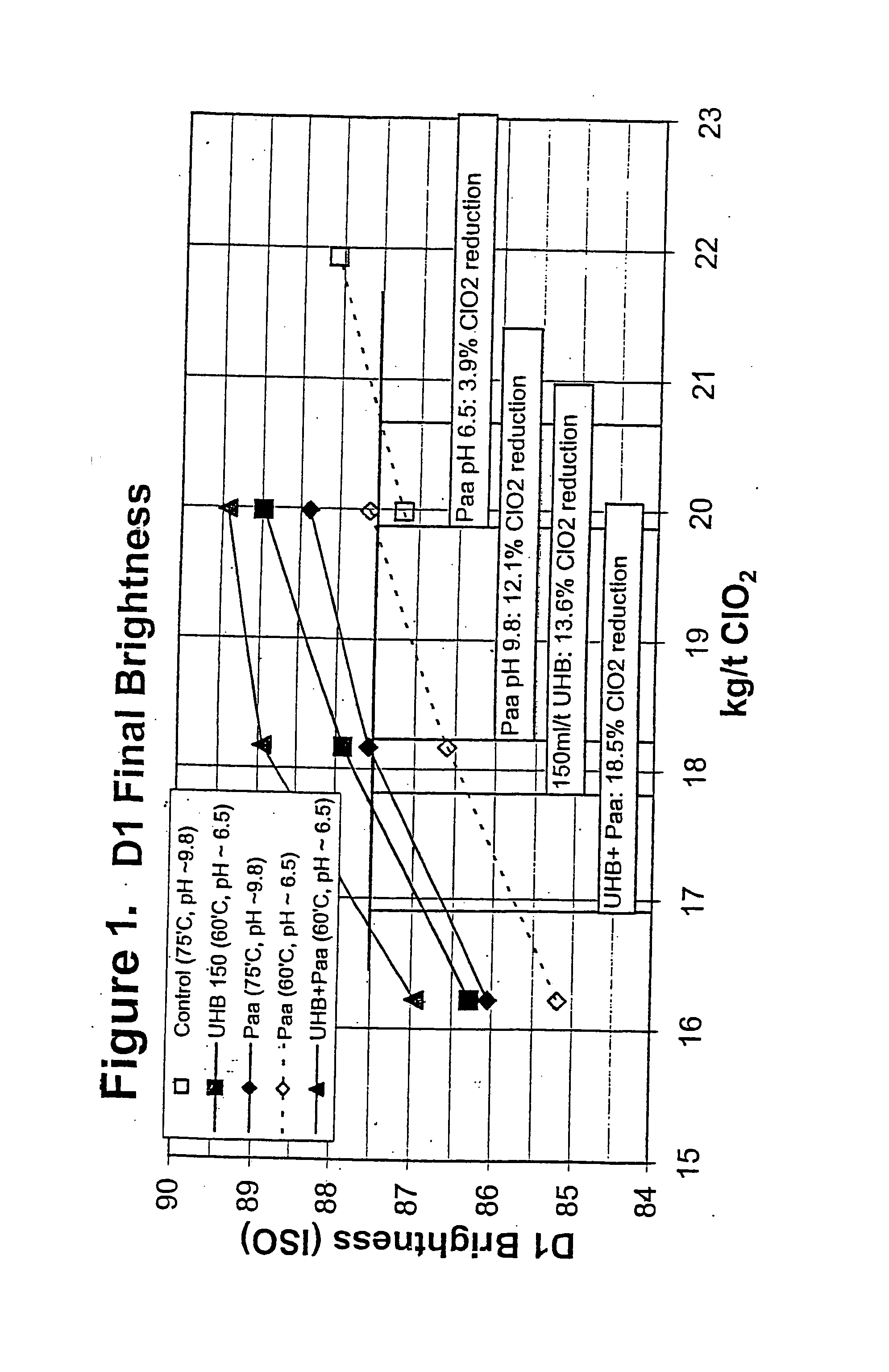
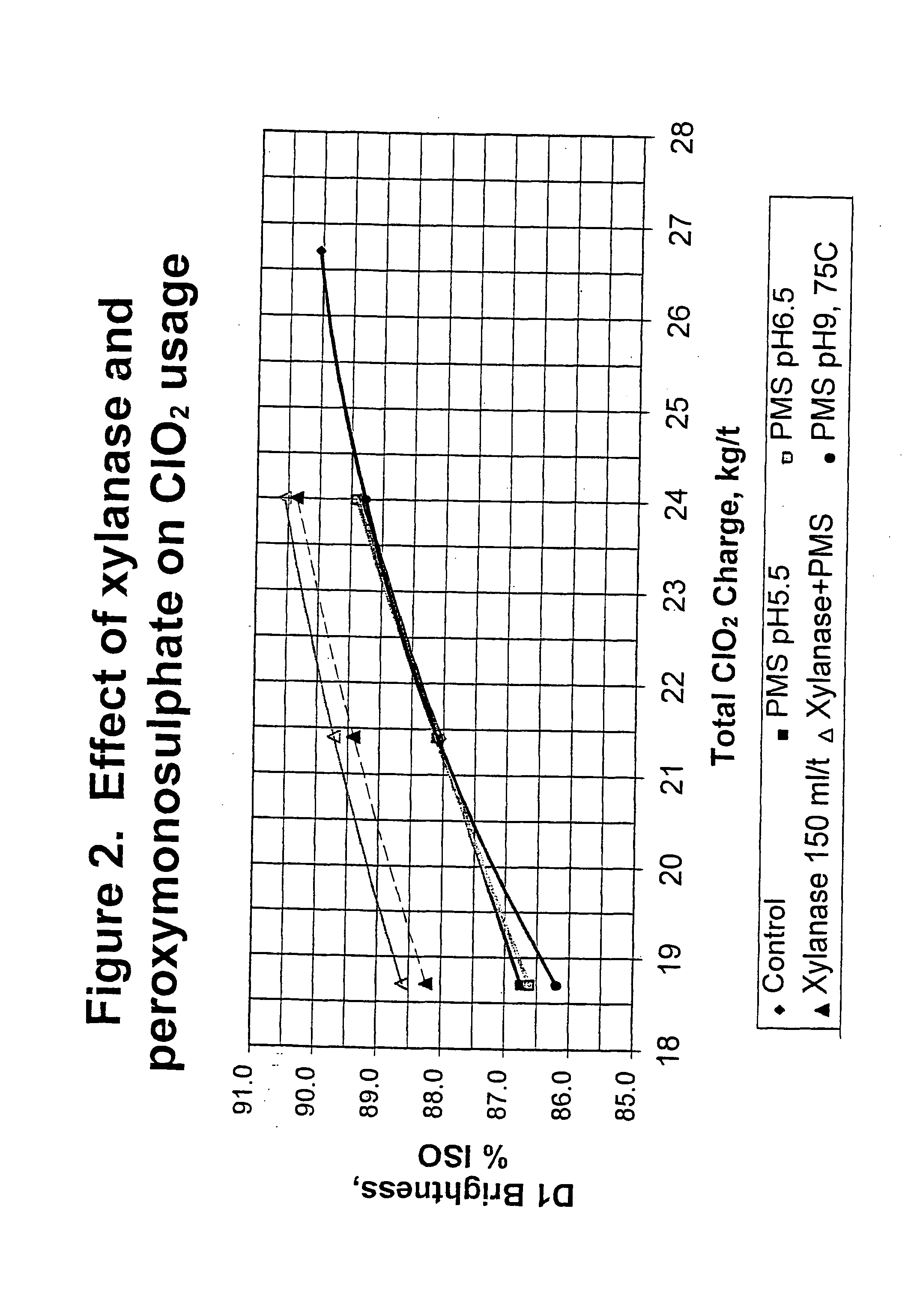
The present invention discloses methods of bleaching chemical pulp that combine xylanase enzymes with hydrogen peroxide, peracids, or a mixture. The method comprises the steps of carrying out a chemical pulping operation, optionally followed by delignifying the pulp with oxygen, then combining xylanase enzymes with hydrogen peroxide, peracids, or a mixture to bleach the pulp. The method allows the mill to use both xylanase and peracids in a single bleaching tower to decrease the usage of chlorine dioxide and other bleaching chemicals. The pulp bleaching method of the present invention may be performed in a pulp mill as part of a complex pulp bleaching process.
Owner:IOGEN BIO PRODUCKTS CORP
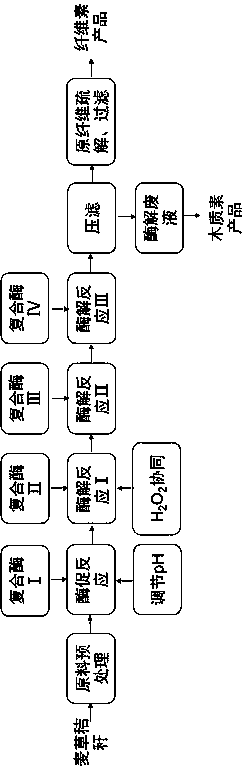
Enzymatic straw material pulping process
InactiveCN1421570AWell mixedChemical/chemomechanical pulpNon-woody plant/crop pulpLignin peroxidaseXylanase Y
The enzymatic straw material pulping process includes three stages of mechanical pre-treatment, enzyme treatment and chemical pulping or chemical-mechanical pulping. After being pretreated mechanically in a pulp grinder, the straw material is treated with hemicellulase liquid or mixed enzyme liquid comprising hemicellulase and lignin peroxidase at pH 3.5-6.5 and 40-60 deg.c for 1-10 hr. In chemical pulping, the material is presoaked with waste pulp-making liquor before extruding out wastes liquor and digested; and in chemical-mechanical pulping, the material is first treated with EDTA, NaOH and H2O2 at 40-80 deg.c for 30-120 min and then ground to form the pulp. The present invention is used in papermaking enterprises with straw as material and has the advantages of low pollution load, high, paper pulp quality, easy-to-process waste liquor, etc.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Fiber blend having high yield and enhanced pulp performance and method for making same
InactiveUS20080308239A1Increase stiffnessHigh strengthFibreboardPulp properties modificationFiberKappa number
The present disclosure relates to producing paper or paperboard having improved stiffness and strength, compared to the conventional paperboard at the same basis weight. It also discloses a method of wood pulping having a significantly increased yield and providing fiber pulps with enhanced properties such as strength and stiffness. Wood chips are chemically pulped to a high kappa number, providing a rejects component and an accepts component. The rejects component is subjected to a substantially mechanical pulping process, optionally in a presence of bleaching agent, prior to blending back into the accepts component. The resulting fiber blend is washed, optionally bleached, and subjected to a papermaking process to provide paper or paperboard with enhanced strength and stiffness at low basis weight.
Owner:MEADWESTVACO CORP
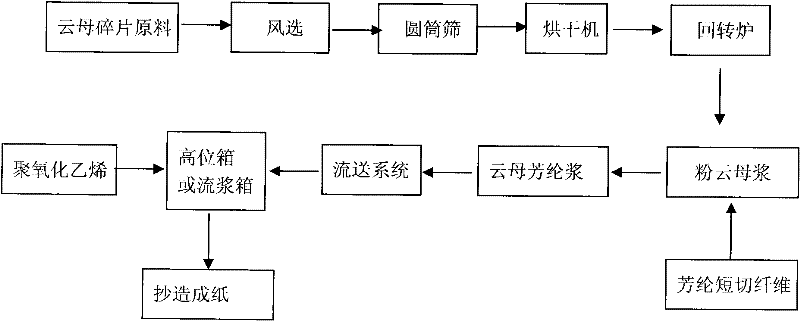
Method for making mica paper by reinforcement of aramid short fiber and chemical pulping
InactiveCN101748648AHigh strengthHigh dielectric strengthSynthetic cellulose/non-cellulose material pulp/paperPulp material addition processesEngineeringRotary furnace
The invention relates to a method for making mica paper by reinforcement of aramid short fiber and chemical pulping. The method comprises the following steps: cleaning mica flakes to remove impurities; putting the mica flakes to an intermittent heating rotary furnace for calcination to remove a part of crystal water in the crystal of mica and generate remarkable expansion and delamination along the vertical direction of a cleavage plane so as to make the mica loose and flexible; dipping the mica in acid or alkali solution at a certain concentration, delaminating into mica sheets, and classifying the mica sheets into chemical mica pulp with certain beating degree; and adding 3 to 15 percent of aramid fiber (based on the mass of the mica flakes) into the pulp, preparing mica aramid pulp, and making the mica aramid pulp into paper by a paper machine. The framework effect of the aramid improves the strength of the mica paper.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Oil-tea camellia fruit shell semi-chemical pulp preparing process
InactiveCN103696306ASolve the use problemAlleviate resource constraintsFibrous raw materialsFiberCamellia oleifera
The invention discloses an oil-tea camellia fruit shell semi-chemical pulp preparing process, comprising main steps of preprocessing, boiling, black liquid extracting, washing, mechanical pulp grinding, abeyance eliminating, purifying and screening. Oil-tea camellia fruit shell waste with rich resources is used as a new pulping raw material to produce semi-chemical pulp, so the comprehensive use problem of the oil-tea camellia fruit shell waste is effectively solved, the condition of fiber resource shortage in the paper making industry is relieved, the wood resource consumption in pulping and papermaking is reduced, and the natural environment is protected; the oil-tea camellia fruit shell semi-chemical pulp preparing process overcomes the negative influence of chemical composition of oil-tea camellia fruit shells to the pulping performances, a semi-chemical pulping method massively retaining lignin and hemicellulose is adopted, and the prepared oil-tea camellia fruit shell semi-chemical pulp is less in chemical medicine consumption, high in paper pulp yield, good in strength and low in cost. The oil-tea camellia fruit shell semi-chemical pulp preparing process is strong in operability, low in production cost and easy for realizing large-scale production.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Method for reclaiming lignin and alkali from boiling black liquor
InactiveCN101157459AIncreased recycling profitMake full use ofAlkali metal sulfides/polysulfidesLignin derivativesLiquid wasteCombustion
The invention relates to a method for reclaiming lignin and alkali from steamed black liquor in chemical pulping. The invention adopts addition of H2SO4 solution into the black liquor to precipitate lignin thereof, and after separation, eylogen with high added value is obtained; then NaOH solution is added into the black liquor to adjust the pH value followed by procedures such as evaporation, combustion, causticization, etc. to reclaim alkali and heat energy. The added H2SO4 reacts with NaOH to produce Na2SO4, which can partially or completely substitute replenished mirabilite in the process of alkali reclamation and then transform into NaOH and Na2S for reuse as steaming drugs in production. The invention solves the problems that the combustion method for reclamation of alkali and heat energy from the black liquor does not rationally utilize the lignin resource thereof, and the alkali and the heat energy in the black liquor are not rationally reclaimed in the traditional acid extracting lignin process, as well as waster liquor is difficult to dispose further. The invention has prominent social, environmental and economic benefits; additionally, the method of the invention does not produce harmful substances and has no secondary pollution.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
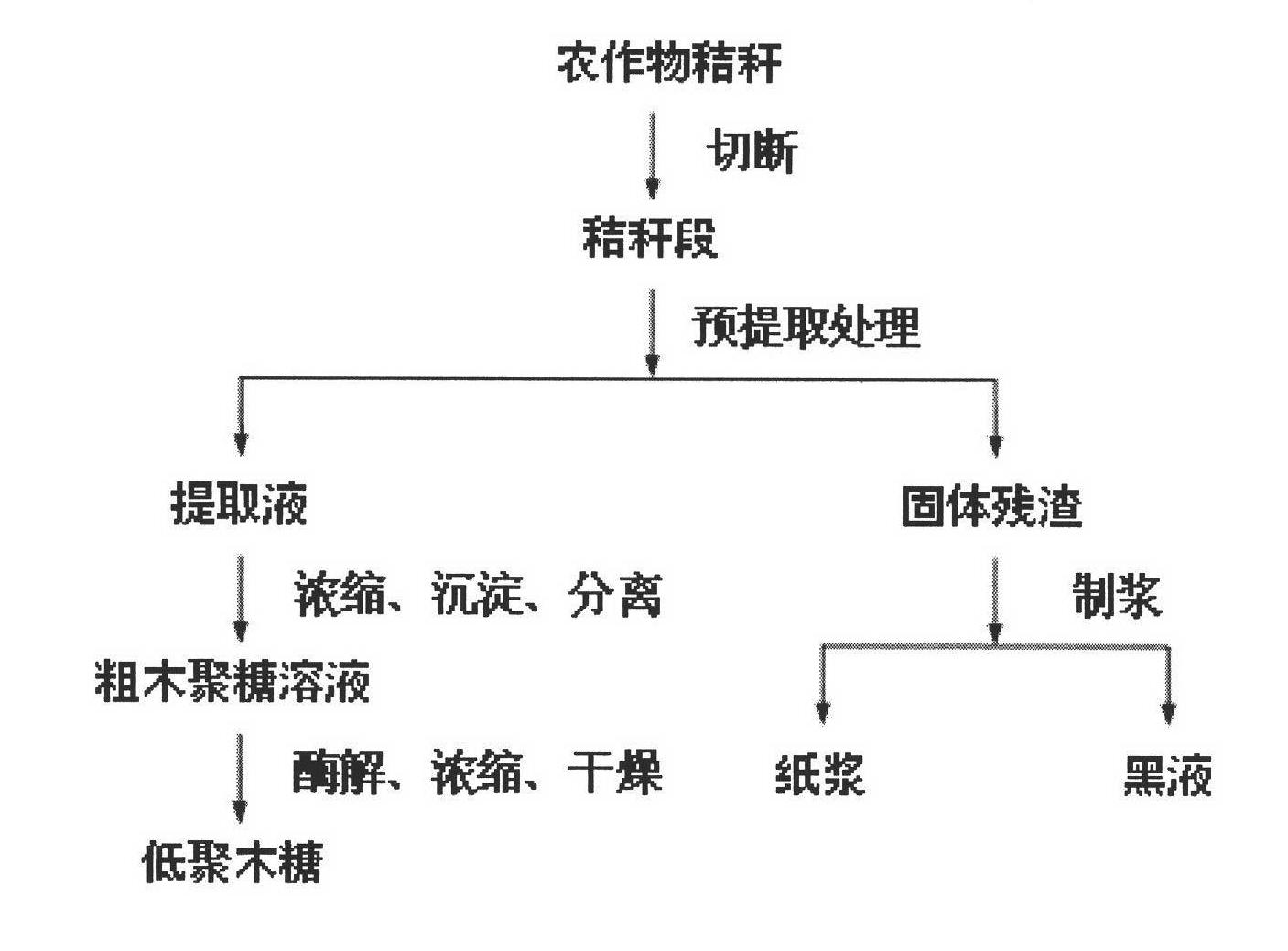
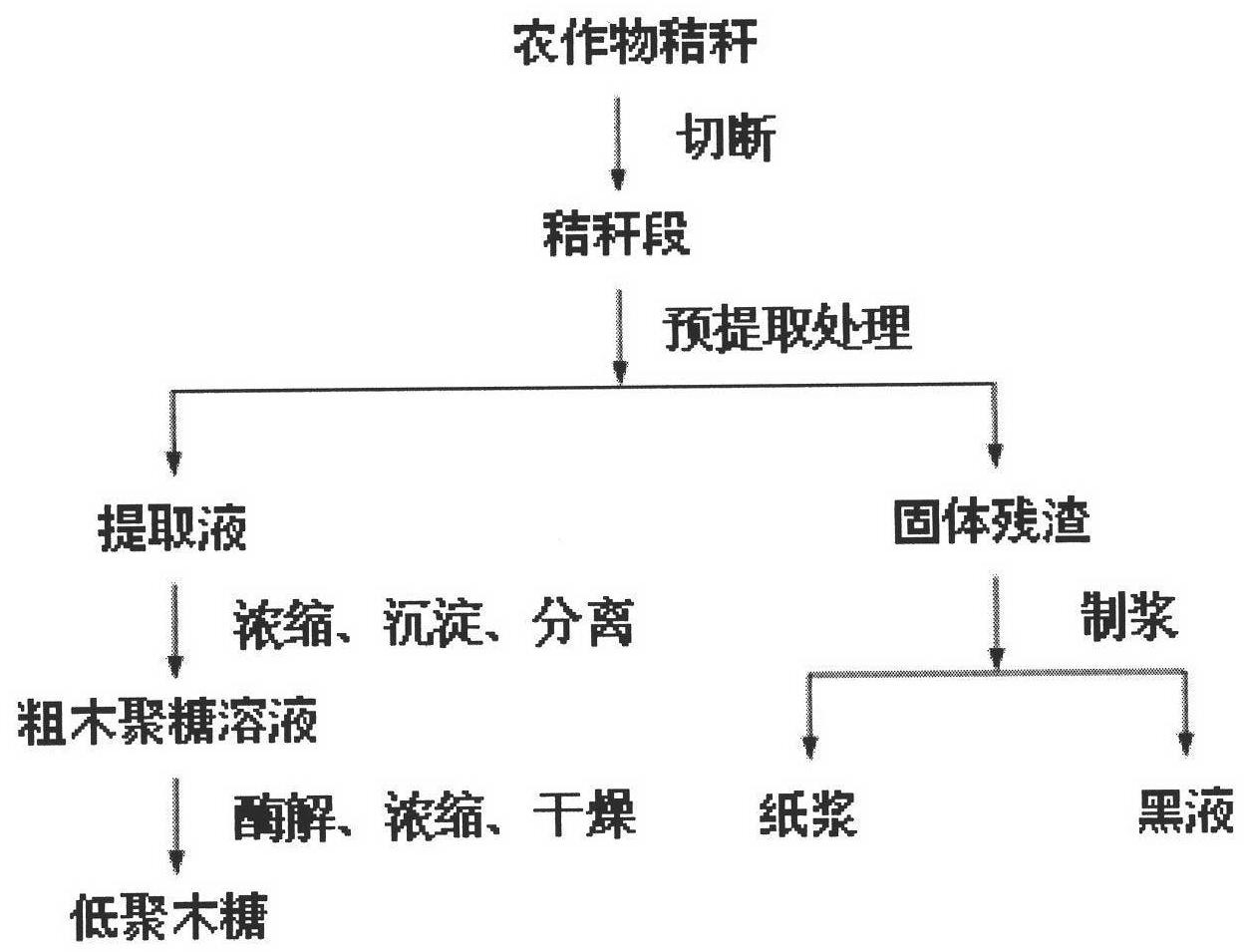
A kind of method for preparing xylo-oligosaccharide and paper pulp
ActiveCN102277761AImprove fiber qualityImprove physical performance indicatorsPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsPulping with inorganic basesFiberOligosaccharide
The invention discloses a method for preparing oligosaccharide and paper pulp, belonging to the technical fields of pulping and the comprehensive utilization of pulping. The method comprises the steps of: using crop straws as raw materials, pre-treating the raw materials to obtain a pre-extracting solution, concentrating the pre-extracting solution by a membrane separation method, then obtaining a crude xylan solution via precipitation and centrifugal separation, and then preparing oligosaccharide via enzymolysis, vacuum concentration and frozen-drying. The pre-treated solid residues are stewed via an alkaline process so as to prepare unbleached paper pulps of which the indexes such as fiber length, whiteness, fracture length, tear resistance, folding strength and the like are all improved. The generated black liquid has the characters of low viscosity and high heat productivity. The method for preparing oligosaccharide and paper pulp integrates the comprehensive utilization method with the biomass transformation method on the premise of optimizing the traditional alkaline chemical pulping technique to prepare products with high additional values, namely oligosaccharide, thereby increasing the quality of the paper pulp and the extraction, vaporization and combustion performances of the black liquid.
Owner:CHINA NAT PULP & PAPER RES INST CO LTD
Paper-making technique employing bio-fermentation pulping method instead of chemical pulping technique
InactiveCN101225614ASolve pollutionRealize cleaner productionDigestersPaper-making machinesFiberChemical treatment
The invention discloses a paper making craft which replaces the chemical pulp making with biological fermentation pulp making, comprising process sections of pulp making and paper making. The procedures can be described as follows: (1) material preparation: fiber plants are grinded; (2) dissociation of the fiber: the grinded fiber plants are sterilized through steaming and boiling; after being cooled, mould that can decompose cellulose and lignin is added in; then the mixture is evenly stirred and put into a fermentation tank to be fermented; when the fiber plants are dissociated fluffy, the paper pulp is made. Since a plurality of chemical treating procedures are avoided due to the spare of chemical source materials, more than twenty procedures in previous paper making process are reduced into only several procedures, therefore, the paper making procedures are greatly simplified and a large amount of producing materials and energy is saved; thus the paper making craft has the advantages of greatly reduced production cost, source-saving and energy-saving effects.
Owner:陈淑华 +1
Pulp-making process using biological fermentation method
InactiveCN1395002AEliminate pollutionNo input requiredCellulose material pulpingBiotechnologyBlack liquor
The pulp-making process by using microbial fermentation process is mainly aimed at solving the problem of black liquor polluting environment, and incldues the following steps: cutting wheat (rice) straw or wood material, moistening cut wheat (rice) straw or wood material, inoculating the moistened cut wheat (rice) straw or wood material with bacteria or actino mycetes, fermenting and heating, continuously fermenting and zymolysis so as to obtain straw (wood) pulp.
Owner:姜占定
Environment protection type coal water slurry and preparation thereof
The invention relates to environment-friendly water-coal slurry and a method for preparing the same. The aim of the invention is to prepare the environment-friendly water-coal slurry by using wheat straw chemical pulping paper-making black liquor waste water and coal slurry as raw materials. The mixture ratio of the water-coal slurry is as follows: 57 to 62 percent of the (dried) coal slurry, 15 to 20 percent of the pulping paper-making black liquor, and 20 to 27 percent of pulping paper-making medium wastewater; and the total weight of various components is 100 percent. The method comprises the following steps: pumping the pulping paper-making black liquor subjected to sulfonating treatment into a strong stirring barrel; feeding the coal slurry into the strong stirring barrel through a feeder; pumping the pulping paper-making medium wastewater into the strong stirring barrel; starting the strong stirring barrel so that the materials are further dispersed and mixed; and filtering the mixture to remove impurities, and then pumping the mixture into a slurry storage tank through a screw pump for standby.
Owner:何秀院
Lignin sand-fixation agent
A sand-fixation lignin chemical is prepared from the waste digestion liquid generated in chemical pulping step through reaction on aldehyde compound, adding less cross-linking agent and condensating reaction on urea. It is applied by spraying it on ground surface for preserving water, improving soil and increasing the survival rate of vegetation.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
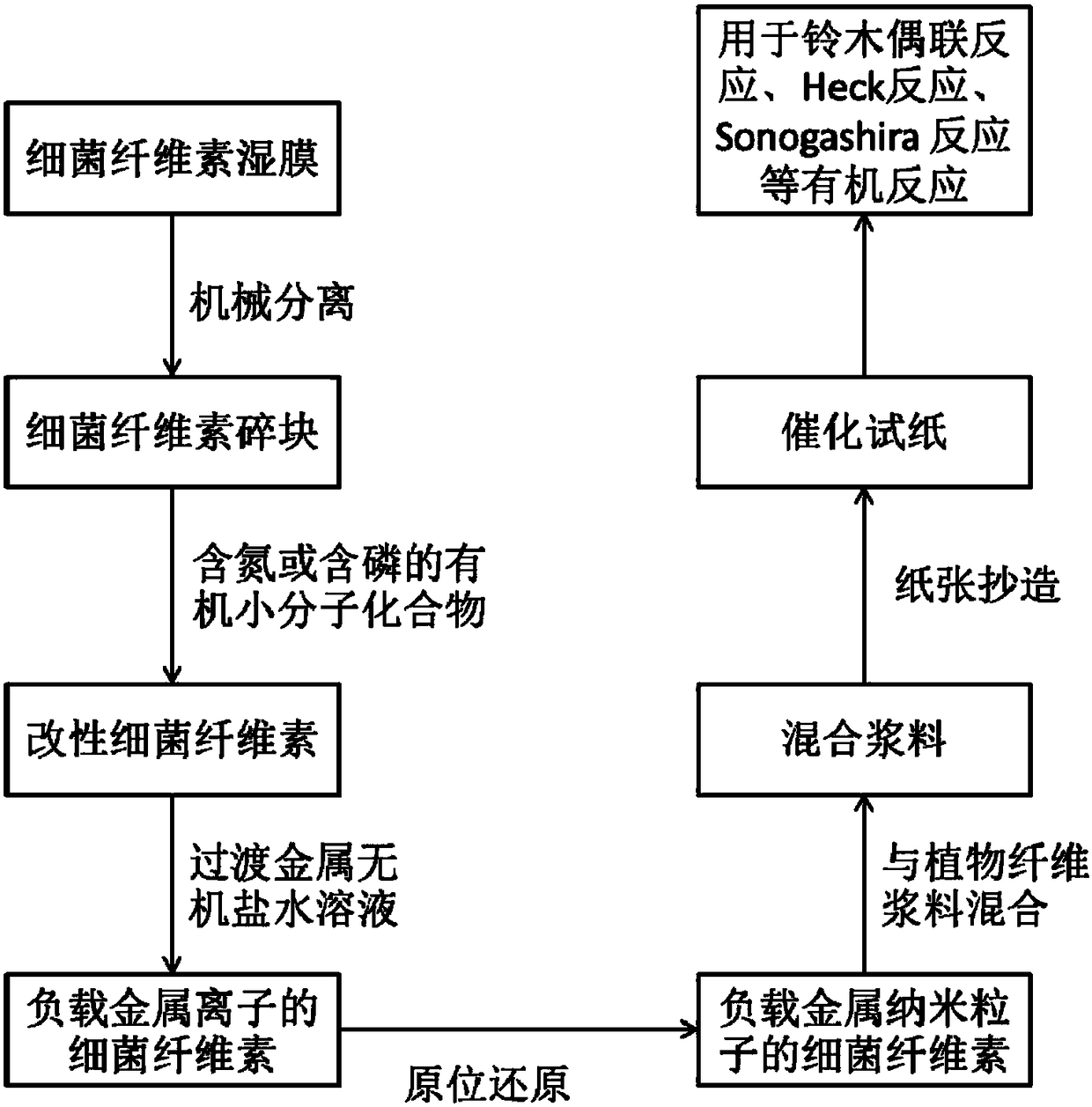
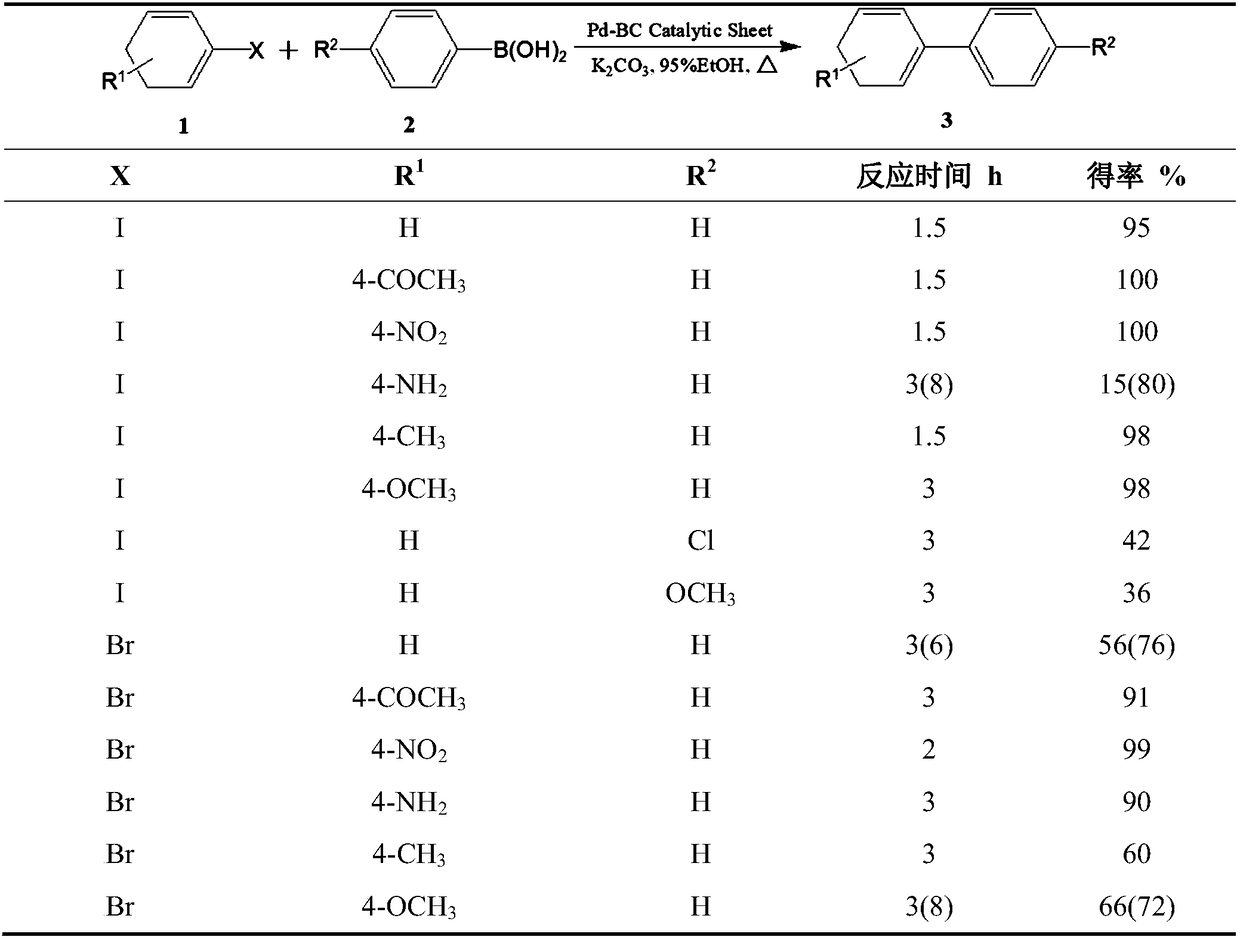
Catalytic test paper produced by compounding bacterial cellulose-supported metal particles with plant fibers, and production method thereof
ActiveCN108543547AGuaranteed mechanical strengthGuaranteed responseHydrocarbon by hydrocarbon and non-hydrocarbon condensationAmino-hyroxy compound preparationFiberPapermaking
The invention discloses a atalytic test paper produced by compounding bacterial cellulose-supported metal particles with plant fibers, and a production method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: bonding the hydroxyl groups of bacterial cellulose with a nitrogen-containing or phosphorus-containing organic small molecule compound, stably loading metal nano-particles having a catalysiseffect on the surface of the bacterial cellulose by the nano-pore structure on the surface of the bacterial cellulose and the chelation effect between nitrogen or phosphorus and a metal, compoundingthe bacterial cellulose with the plant fibers, and carrying out a papermaking process to produce the catalytic test paper. The bacterial cellulose is cellulose secreted and synthesized by bacterial microorganisms. Transition metal is palladium, chromium, nickel, silver, copper, gold or other metal having a catalytic performance. A plant fiber slurry is a papermaking raw material prepared by a mechanical or chemical pulping process of wood fibers, non-wood plant fibers or secondary fibers. The catalytic test paper has the advantages of high convenience in use and recovery, high reusability, simple design, low manufacturing cost, high catalytic efficiency, and green and degradable carrier material.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A combined pulping method
InactiveCN102268826AImprove efficiencyReduce pollutionPulping with inorganic basesPulp beating/refining methodsMature technologyPulp industry
A combined pulping method, using bamboo wood as raw material. The present invention relates to a combined pulping method, in particular to a biological, chemical and mechanical combined pulping method, which belongs to the technical field of pulping and papermaking, especially biochemical and mechanical Combined pulping technology. The present invention combines the current advanced biotechnology, mature chemical pulping technology and high-efficiency mechanical pulping technology through organic integration, comprehensively utilizes the advantages of the above technologies, conducts targeted combination, and develops a new pulping method. The method of the invention reduces the pollution of the pulping industry and improves the economic benefits of the pulping industry. The combined pulping method has strong raw material adaptability, good pulping performance, and good pulp is suitable for compounding various papers.
Owner:CHINA NAT PULP & PAPER RES INST CO LTD
Method for pulping through micro-biological degradation of plant straws
ActiveCN108277673ANo pollution in the processAchieve energy savingCane mechanical workingCellulose treatment using microorganisms/enzymesDry weightRubbing
The invention discloses a method for pulping through micro-biological degradation of plant straws. The method comprises the steps of cutting and removing a root part and a tip part of a bamboo, and remaining 2 to 3 meters of a middle section for standby use; peeling and slicing the bamboo to obtain bamboo slices; cleaning; squeezing the bamboo slices into bamboo residues; feeding the bamboo residues into a degradation pond, adding a polysaccharide compound myxomycete cluster with the mass accounting for 25 percent to 40 percent of dry weight of the bamboo residues into the degradation pond, and degrading at 10 to 30 DEG C for 48 to 120h until thoroughly dissolving the bamboo residues; after degrading, discharging degradation liquid from the degradation pond, discharging into a stainless steel heat-insulation water pond through a 100-mesh stainless steel filter mesh, and reserving for standby use; concentrating the degradation liquid to obtain a concentrated solution with the dryness fraction being 80 percent to 90 percent; pumping the concentrated solution with the dryness fraction being 80 percent to 90 percent into a stainless steel centrifugal spray dryer, drying, and then packaging; rubbing and splitting bamboo pulp discharged from the degradation pond, high consistency grinding, and squeezing water for drying. The method provided by the invention belongs to an environment-friendly technology, adopts micro-biological degradation of the plant straws to replace chemical pulping in the prior art, and is energy-saving and environmentally friendly without pollution.
Owner:江西鼎宏生物科技有限公司
Alkali-resistant compound microorganism pretreatment fungicide for pulping wheat straw and application of alkali-resistant compound microorganism pretreatment fungicide
ActiveCN113151098AEfficient degradationEmission reductionBacteriaPaper recyclingBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention relates to an alkali-resistant compound microorganism pretreatment fungicide for pulping wheat straw and application of the alkali-resistant compound microorganism pretreatment fungicide. The alkali-resistant compound microorganism pretreatment fungicide comprises bacillus licheniformis, alcaligenes faecalis, Lysinibacillus sp., bacillus subtilis and bacillus cereus, the mass ratio of all bacterial strains to bacterial liquid is (1-3): (1-3): (1-2): (1-3): (1-3), in biological pretreatment of wheat straw, all the bacterial strains are mutually beneficial, symbiotic and synergistic interaction is achieved, and the efficient degradation of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin is jointly promoted. According to the method, the biological pretreatment chemical pulping method is adopted for pulping, and the alkali-resistant compound microorganism pretreatment fungicide is used for biological pretreatment pulping, so that the use of a large amount of chemical preparations is avoided, the discharge of wastewater in the traditional chemical pulping process is reduced, the production cost of an enterprise is reduced, and the method is advanced in technology and environment-friendly at the same time.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing active carbon by waste water sludge from chemical pulping and paper mill
InactiveCN102344136AResolve disposal issuesNo emissionsSludge treatment by pyrolysisPotassium hydroxidePapermaking
A method for preparing active carbon by waste water sludge from chemical pulping and paper mills relates to the following steps: drying, pulverizing and screening papermaking waste water sludge, performing dipping treatment by potassium carbonate or sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide solutions for 10-30 hours, adding into an activation furnace, heating to 500-900 DEG C under an anaerobic condition for pyrolysis, wherein the whole course takes 1-4 hours and the heating rate is 5-20 DEG C / min; rinsing and drying the activated product with distilled water to obtain active carbon; wherein the alkali liquor is recyclable. The active carbon prepared by the invention has a methylene blue adsorption value of 4-9 mg / 0.1 g, is applicable to waste water treatment in paper mills, and has good effect; during the active carbon preparation process of the invention, no waste water or waste gas is discharged. The invention solves the disposal problem of papermaking sludge, and the prepared active carbon can reduce cost of papermaking waste water treatment. The invention belongs to the technical field of pulping papermaking.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
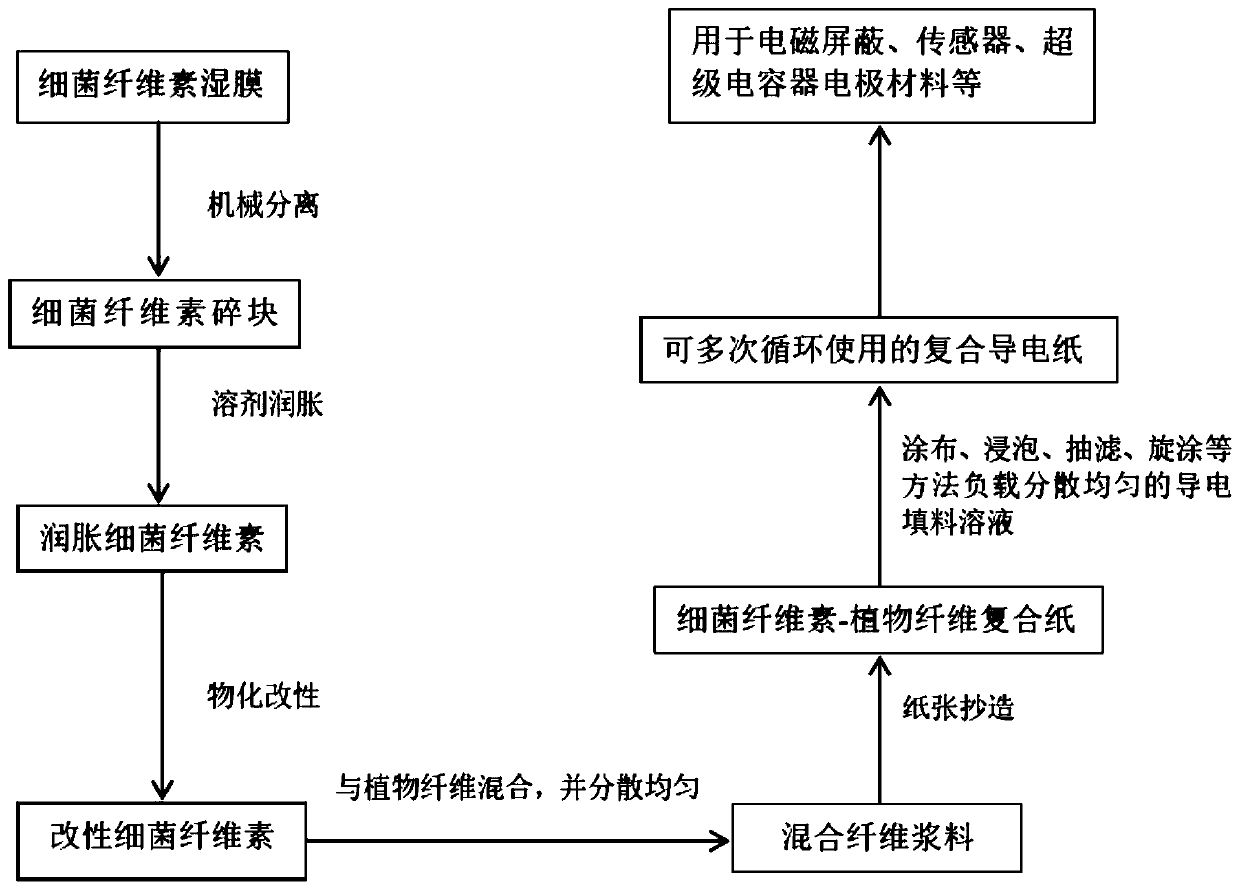
Bacterial cellulose-plant fiber composite conductive paper as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111074669AImprove bindingImprove uniformityHybrid capacitor electrodesNon-macromolecular organic additionCarbon fibersPlant fibre
The invention discloses bacterial cellulose-plant fiber composite conductive paper as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. According to the method, bacterial cellulose and plant fibers are compounded into paper, and then conductive filler is loaded on the composite paper through an impregnation method or a coating method to prepare the conductive paper. The bacterial celluloseis cellulose secreted and synthesized by bacterial microorganisms or modified bacterial cellulose. The conductive filler is the filler with conductivity such as carbon nanotubes, silver nanowires, carbon fibers and graphene. The plant fiber pulp is a papermaking pulp raw material prepared from wood fibers, non-wood plant fibers or secondary fibers through a mechanical or chemical pulping method and the like, and comprises hardwood pulp, softwood pulp, bagasse pulp, bamboo pulp, straw pulp, secondary fiber pulp and the like. The conductive paper prepared by the method has the advantages of simplicity in preparation, strong conductivity, high mechanical stability, low leaching rate of the conductive filler, strong recycling capability and the like, and has excellent performance in application of paper-based conductors, paper-based electrodes, paper-based capacitors and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing paper pulp by adopting cotton stalk peel as raw material
InactiveCN101831822APromote degradationEfficient removalPulp beating/refining methodsCellulose material pulpingPectinaseChemical pulp
The invention relates to a method for producing paper pulp by adopting cotton stalk peel as raw material, which adopts an enzyme-ammonium sulfite method. The enzyme-ammonium sulfite method comprises the steps of: firstly, removing pectin of the cotton stalk peel and degrading lignin by using degumming enzyme and then, preparing coarse pulp by an ammonium sulfite boiling step, and finally processing the coarse pulp by a conventional production method to obtain finished product pulp, wherein the degumming enzyme is prepared by compounding pectinase, laccase and lignin enzyme in the weight ratio of 1-3:1:1, and a degumming enzym solution is prepared by compounding the degumming enzyme, urea and water in the weight ratio of 5:5:1000-15:15:1000; the cotton stalk peel is soaked in the sealed degumming enzyme solution for 24-48 hours in the static state at the temperature of 20-30 DEG C. The weight ratio of the ammonium sulfite to the oven dry cotton stalk peel in a boiling solution is 10-13 percent, and the pH value of the boiling solution is 7-9. In the invention, the pectinase is added in the degumming enzyme, which effectively remove pectic substances and solves the problem that subsequent processing is influenced by the existence of the pectin and industrialized production can not be realized. The invention can produce the paper pulp meeting standards. Compared with the traditional chemical pulp producing method, the invention has the advantages of high pulp yield, energy saving, cost reduction and recycled black liquor.
Owner:凌受明
Production method and applications of compound enzyme liquid used in papermaking and pulping process of wheat straws and rice straws
ActiveCN103540581AImprove catalytic performanceImprove accessibilityMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesCellulosePectinase
The invention discloses a production method of a compound enzyme liquid used in the papermaking and pulping process of wheat straws and rice straws. The production method is characterized by comprising the steps of weighing each component enzyme, mixing and compounding all the component enzymes in a compounding pot, performing corrosion prevention, inspecting, packaging, and storing in a warehouse with the temperature of 5 DEG C, wherein the component enzymes are alkaline pectinase and xylanase, or are alkaline pectinase, xylanase, mannose and ligninase. The application of the compound enzyme liquid in the papermaking and pulping process of wheat straws and rice straws comprises the following steps: papermaking raw materials are pre-treated and then sent into a digester for enzyme treatment, namely the raw materials are soaked with the compound enzyme liquid, wherein the enzyme treatment conditions are as follows: the temperature ranges from 40 DEG C to 60 DEG C, the mass ratio of an absolute dry raw materials to the compound enzyme liquid is 100:(1.2-1.8) and the enzyme soaking time ranges from 20 minutes to 60 minutes; after enzyme treatment, the papermaking raw materials are digested in the digester. Each component enzyme in the compound enzyme liquid is high in activity but has no activity to crystalline cellulose and carboxymethyl cellulose; and compared with the traditional chemical pulping method, the production method has the advantages that the use amount of alkali is lowered by about 50%, the content of COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) in waste water is lowered by over 30%, the production cost is lowered by about 20% and the quality of paper products is enhanced.
Owner:江苏富星纸业有限公司
A kind of preparation method of offset paper or electrostatic copy paper
InactiveCN102277786AHarm reductionLess investmentNon-fibrous pulp additionSpecial paperSulfurWastewater
The invention relates to a preparation method of offset paper or electrostatic copy paper. The method belongs to the field of pulp and paper making. The method uses chemical pulping without sulfur compounds. The obtained chemical pulp is mixed with other pulp and additives are added to prepare paper. The paper is surface-sized to obtain finished paper, and the finished paper is friendly to human eyesight. During the implementation of the present invention, no environmentally harmful chemical raw materials such as sulfides and chlorine-containing compounds are used, and no highly harmful bleaching wastewater is produced. The present invention saves investment and operating costs, and reduces the amount of fresh water used for preparation. The method of the present invention is environmentally friendly. Friendly and strong.
Owner:CHINA NAT PULP & PAPER RES INST CO LTD
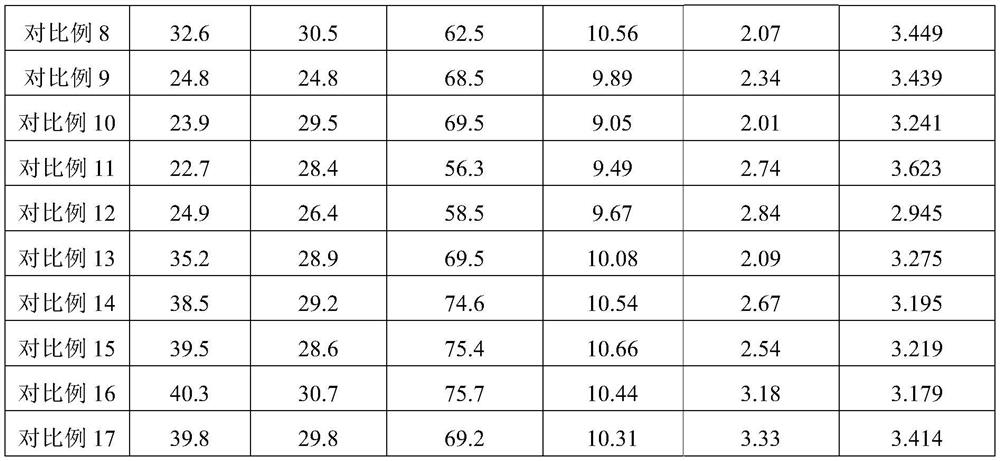
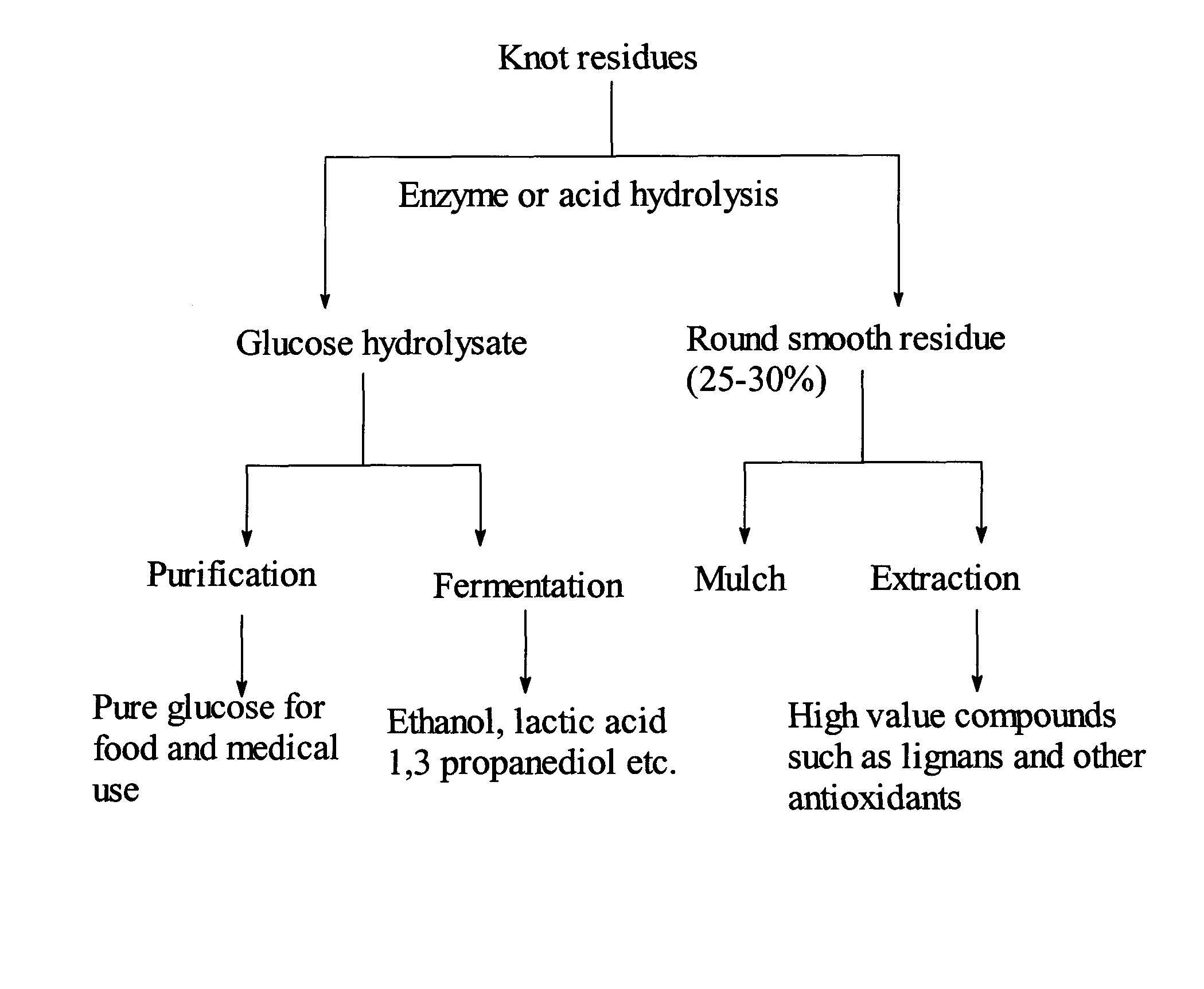
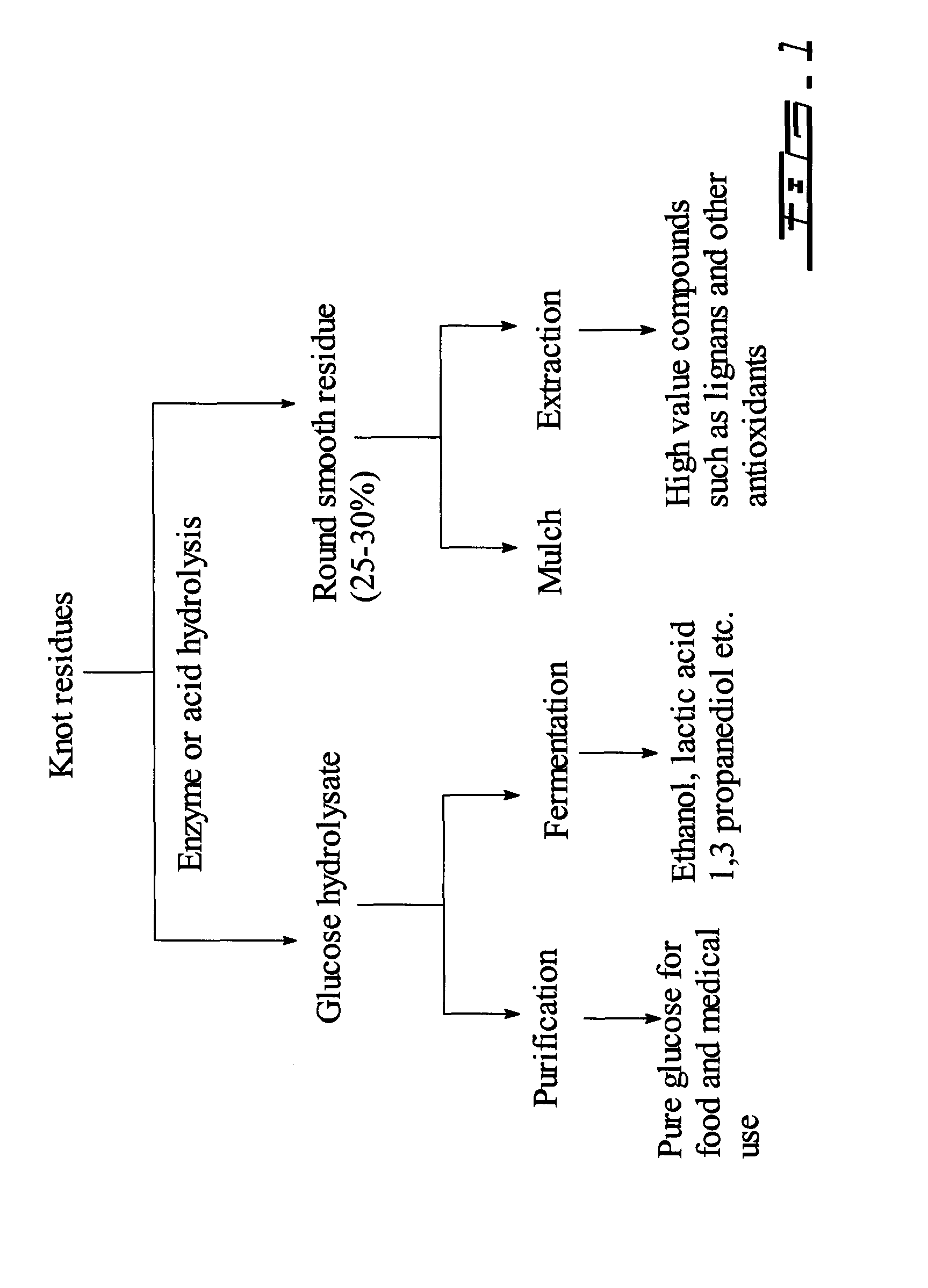
Conversion of knot rejects from chemical pulping
InactiveUS20100240104A1Increase valueMore amenableCellulosic pulp after-treatmentFood ingredient as antioxidantEnzymatic hydrolysisHydrolysate
Knot rejects from chemical pulping processes are subjected to acid hydrolysis or an enzymatic hydrolysis treatment. The resultant hydrolysate is enriched with glucose, representing a value-added raw material for products using hexoses. The residue, separated from the said hydrolysate after the acid hydrolysis or enzyme treatment, consists of mainly knots or chips. The residue has a much improved aesthetic appearance which can be readily used as value-added raw materials for mulch or similar applications. The residue could also be extracted to obtain high value antioxidants and other nutraceutical chemicals such as lignans or can be utilized according to currently known practices including recooking, burning and depositing.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Composition for the production of improved pulp
InactiveUS6890404B2Improve propertiesReducing digester cycle timePulp liquors combustionDigestersCarboxylic acidCycle time
Compositions and method for improving properties of pulp produced or reducing the digester cycle time in alkaline chemical pulping processes in which an effective amount of at least one selected phosphonate or carboxylate compound or mixtures thereof is admixed with the alkaline aqueous mixture in the digester of the chemical pulping process. The compositions and method are especially well suited for use in the Kraft pulping process.
Owner:ITALMATCH KEMIKALS SPA
Method and system for semi-chemical pulping
InactiveCN101387087AAvoid stickingDigestersPulping with inorganic basesWhite liquorPulp and paper industry
Provided is a method and an apparatus for minimizing adherence of lignin to an extraction screen in a semi-chemical pulping process. The method and apparatus generally relate to supplying white liquor and NaOH to as to increase the pH of cooking liquor at or near an extraction screen.
Owner:ANDRITZ AG
Method for plant pulping and co-producing organic fertilizer
InactiveCN102838403AImprove qualityGood fertilizer effectSewage/sludge fertilisersFertilizer mixturesFiberPlant growth
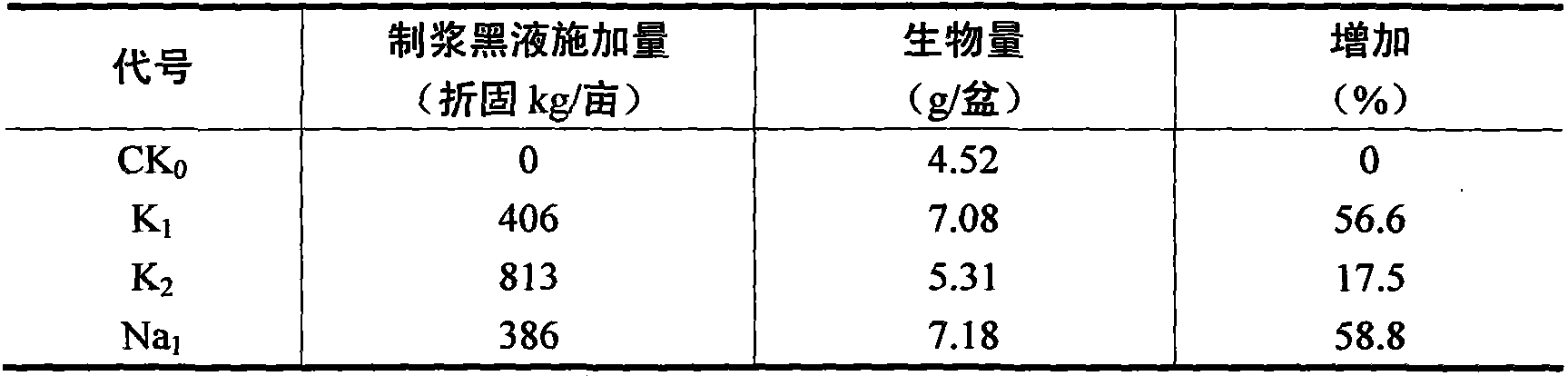
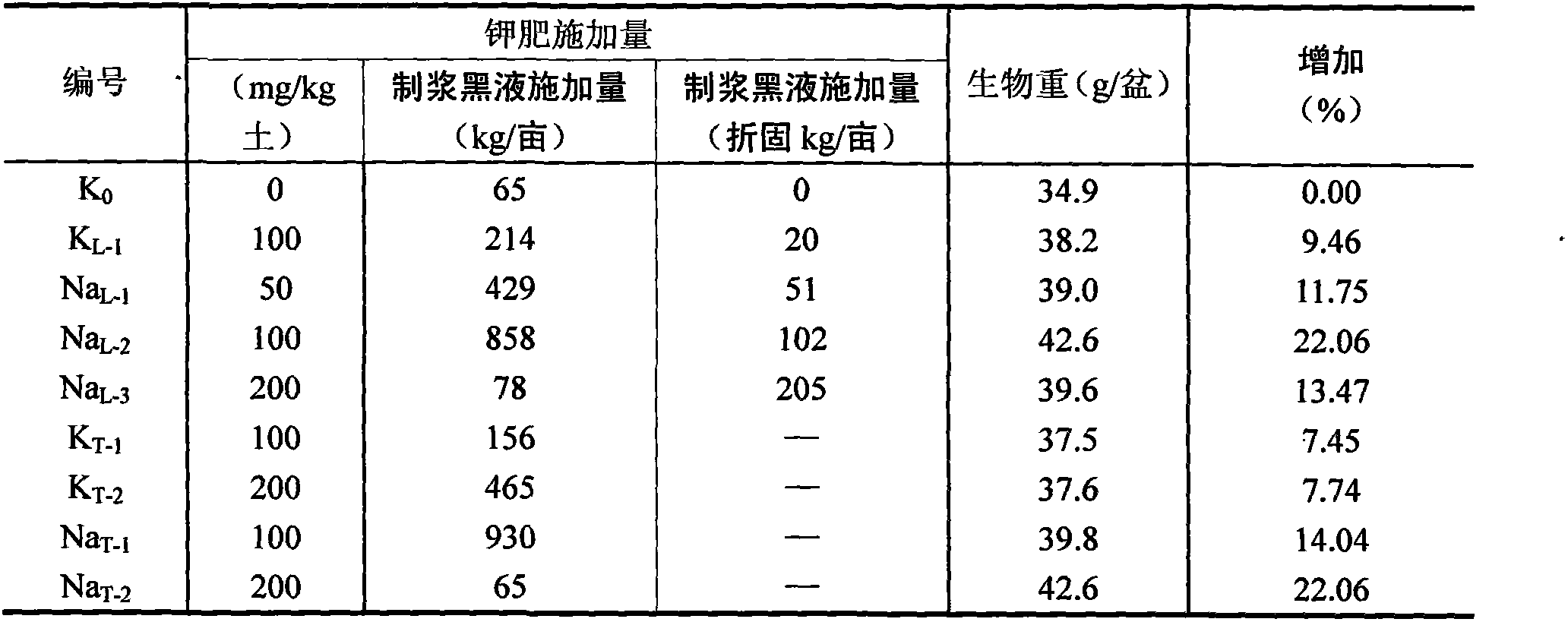
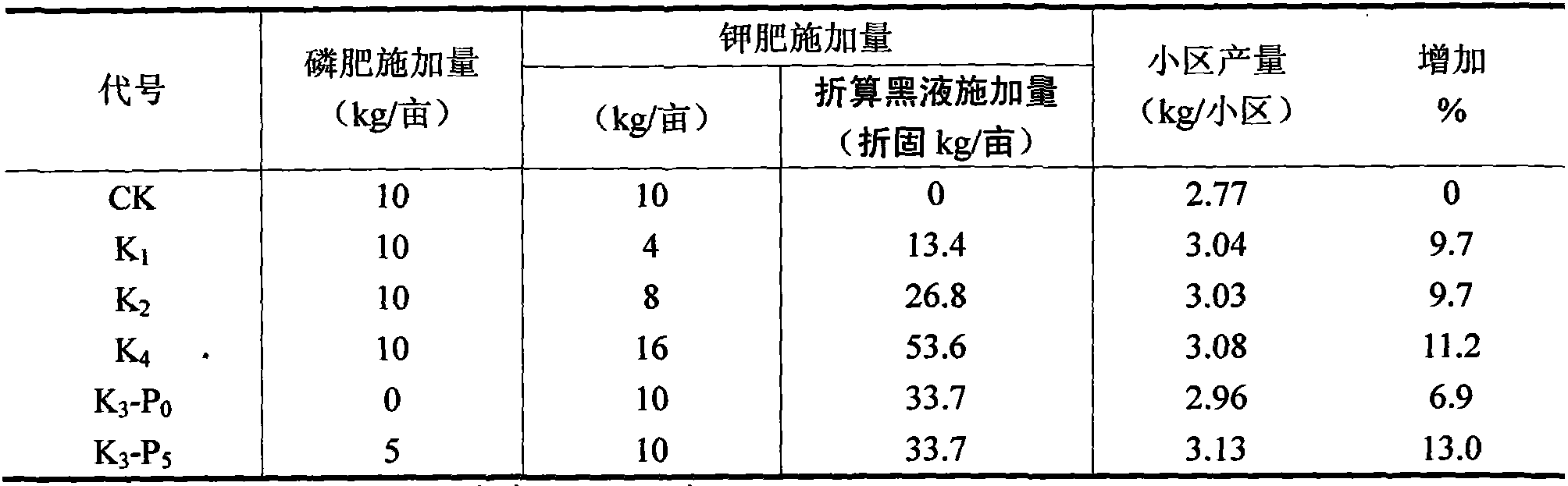
The invention relates to a method for co-producing an organic fertilizer source by utilizing a novel chemical pulping technology, characterized in that: a new technology alkaline pulping black liquor has a high content of potassium, contains no sulfide, anthraquinone, etc., and simultaneously contains humic acid, lignin and other organic matters which are helpful for raising the physical and chemical property of soil. A lot of plant cultivation tests show that: after being subject to pH adjustment, the new technology pulping black liquor can be directly used as a potassium-containing organic fertilizer or an organic-inorganic compound fertilizer or be used as a potassium-containing organic fertilizer or an organic-inorganic compound fertilizer after lignin is extracted or being condensed in a solid state, and the effect is significant; a proper amount of the new technology pulping black liquor has no side effect to plant growth, is beneficial for plant growth, has a fertilizer efficiency as much as that of an inorganic potash fertilizer, and simultaneously has the effect of releasing phosphor and saving fertilizer. The new technology pulping black liquor can be individually applied, or be applied with inorganic fertilizers, or be compounded with weathered coal, fiber, etc. The invention provides a method for the green utilization of the new technology pulping black liquor.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY +1
Straw fiber and process for separating straw fiber by bio-enzyme method
InactiveCN108286200AImprove fiber qualityQuality improvementCellulose treatment using microorganisms/enzymesNon-woody plant/crop pulpCelluloseBlack liquor
The invention belongs to the field of biological pulping and provides straw cellulose. The straw cellulose is characterized in that straw stalk fiber cut and separated by enzyme molecules directionally is well preserved, the result that fine fiber is damaged in the traditional chemical pulping is overcome, the length-weight average value is 0.70 to 1.10 mm, and the quality-weight average value is1.10 to 1.40 mm. The invention further provides straw fiber. The straw fiber comprises the fiber structure of the straw cellulose; the quality of the straw stalk fiber is as follows: the brightness (whiteness) is 57 to 75 percent, the hardness is 7 to 26 K, the folding resistance is 30 to 78 times, the tearing index is 3.0 to 5.5 mN.m<2> / g, and the tensile index is 41.0 to 62.0 N.m / g. The invention further provides a process for separating fiber from straws and application of the straw fiber. High-temperature chemical cooking black liquid is not generated in the production process, the fiber quality (length, whiteness, short fiber content and the like) is obviously more excellent than the quality of the traditional chemical pulping, the pulp yield is increased by 25 percent or higher whenbeing compared with that of the traditional chemical pulping rate, and water consumption and energy consumption in the production process are reduced by 30 percent or higher when being compared with those of the traditional chemical pulping.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing paper pulp by fiber residue generated during microorganism product fermentation
The invention discloses a technique method for preparing paper pulp from fiber residua of fermentation products preparation from crop castoff by microorganism fermenting, which makes production of the paper pulp more economic than production direct from crop castoff by comprehensively utilizing microorganism fermentation and mechanical working. The method includes steps: crushing, acid (including organic acid and inorganic acid) or basic hydrolyzing, and enzymatic hydrolyzing crop castoff to obtain fiber residua, microorganism fermenting, distilling, solid-liquid separating, pulp grinding, pulp screening, and pulp extruding. The crop castoff includes processed castoff of corn straw, wheat straw hood, haulm, reed, medulla junci, bagasse, bamboo and forest. Advantages of the invention are: producing process has no pollution, less water is used, cost of the method is 35% of cost of chemical pulp preparation, and the method can be used to prepare food packaging paper and medicine packaging paper.
Owner:徐佳珊
Composition for inhibiting calcium salt scale
InactiveUS6869503B2Cellulosic pulp after-treatmentPulp liquors combustionBlack liquorChemical pulping
Compositions and method of improving inhibition of calcium salt scale formation under the conditions found in chemical pulp processes in which an effective amount of selected phosphonates or phosphonate blends is admixed with the black liquor composition recovered from the digester in a chemical pulping process. The compositions and method are especially well suited for use in the Kraft pulping process.
Owner:THERMPHOS TRADING GMBH
Oxidation method prepared whole-cotton stalk newspaper pulp and its preparation method
The invention discloses a full-cotton stalk news pulp and preparing method through full-sealing, non-polluting, self-circulating and zero-discharge oxidizing method, which is characterized by the following: utilizing electron reducing reaction in the ion reaction of oxygen molecular to produce free radical of active oxygen to transmit and separate lignin; making chromogenic gene change in the plant cell interlayer to obtain pulp. The invention changes chemical pulping technology without polluting acid, alkaline and anthraquinone, which saves boiling and bleaching procedures.
Owner:梅秀泉
Paper pulp production method by utilizing alternaria tenuis to biodegrade lignin
The invention relates to a paper pulp production method by utilizing alternaria tenuis to biodegrade lignin. Combined with machining, the method comprises steps of: immersing fragmented raw materials into a water tank containing alternaria tenuis bacterial liquid; maintaining a temperature at 30-45 DEG C; and decomposing for 6-48 h. The production process of the invention uses no chemical, generates no pollution, saves water, has low material loss, low energy consumption and a cost only 40% of that of an existing chemical pulping method. The method can be used to produce paper pulp using raw materials of wheat straw, straw, reed, Chinese alpine rush, bagasse, bamboo and timber, etc., and realizes zero discharge of water for paper pulp production. Produced paper pulp has excellent quality and no chemical toxin, and can be used for manufacturing of daily used paper like food package paper and medicine packing paper, etc.; besides the production process has no pollution. The method has high economic benefit and social benefit, and is a high-tech with value for ecological balance.
Owner:张健
Wheat straw fibers and technology for separating films by biological enzyme method thereof
InactiveCN108286201AImprove fiber qualityQuality improvementCellulose treatment using microorganisms/enzymesNon-woody plant/crop pulpCelluloseBiotechnology
The invention belongs to the field of bio-pulping, provides wheat straw cellulose, and aims at storing straw fibers which are subjected to directional cutting and separating by enzyme molecules and overcoming the result of damage to fine fibers in traditional chemical pulping. The wheat straw cellulose is 0.80-1.10mm in average length based on length-weight ratio and is 1.20-1.50mm in average length based on mass-weight. The invention also provides wheat straw fibers comprising the fiber structure of the abovementioned wheat straw cellulose. The quality of the wheat straw fibers meets that thebrightness (whiteness) is 53-75%; the hardness is 8-26K; the folding strength is 30-75 times; the tearing index is 3.3-5.5mN.m<2> / g; and the tensile index is 45.0-62.0N.m / g. The invention also provides a wheat straw fiber separating technology and application of the wheat straw fibers. According to the technology, high-temperature chemical boiling black liquid is not produced in the production process; the fiber quality (length, whiteness, short fiber content, etc.) is obviously superior to that of traditional chemical pulping fibers; the pulp yield is increased by more than 25% by being compared with traditional chemical pulping yield; the water consumption and the energy consumption in production are decreased by more than 30% by being compared with those in traditional chemical pulping.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com