Wheat straw fibers and technology for separating films by biological enzyme method thereof
A technology for separating fibers and wheat straw, which is applied in the field of bioenzymatic separation of wheat straw fibers, and can solve problems such as secondary pollution, difficult-to-cook black liquor, and reduction in pulp rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
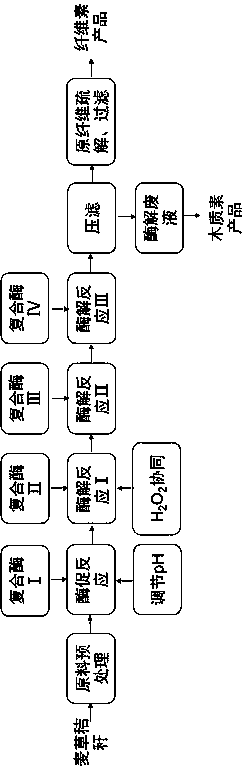
[0086] Chop the wheat straw raw material into 3-5cm, clean it, put it into the enzymolysis reactor, the solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:4, add compound enzyme I, raise the temperature and keep the temperature at 80°C, and stir evenly in the enzymolysis reactor, The pH value was adjusted with NaOH, and the pH was maintained at 12 during the reaction period to neutralize the acidic substances produced during the straw heating process and maintain the high active pH range of the complex enzyme I. Based on the enzyme activity of 80000U / g, the compound enzyme Ⅰ is converted into the mass number of added enzyme per ton of straw raw material: 40g of high-temperature amylase, 44g of alkaline high-temperature xylanase, and the reaction time is 150min. Then add compound enzyme II, stir evenly, and maintain the temperature at 70°C. Compound enzyme II is based on the enzyme activity of 80000U / g, and the mass number of added enzymes converted to tons of straw raw materials is: 80g of high-tempe...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Chop the wheat straw raw material into 3-5cm, clean it, put it into the enzymolysis reactor, the solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:4, add compound enzyme I, raise the temperature and maintain the temperature at 95°C, stir evenly in the enzymolysis reactor, The pH value was adjusted with NaOH, and the pH was maintained at 12 during the reaction period to neutralize the acidic substances produced during the straw heating process and maintain the high active pH range of the complex enzyme I. Based on the enzyme activity of 80000U / g, the compound enzyme I converted the mass number of added enzymes per ton of straw raw material into: high-temperature amylase 40g, alkaline high-temperature xylanase 44g, and the reaction time was 120min. Then add compound enzyme II, stir evenly, and maintain the temperature at 95°C. Compound enzyme II is based on the enzyme activity of 80000U / g, and the mass number of added enzymes converted to tons of straw raw materials is: 80g of high-temperature ...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Chop the wheat straw raw material into 3-5cm, clean it, put it into the enzymolysis reactor, the solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:4, add compound enzyme I, raise the temperature and maintain the temperature at 95°C, stir evenly in the enzymolysis reactor, The pH value was adjusted with KOH, and the pH was maintained at 12 during the reaction period to neutralize the acidic substances produced during the straw heating process and maintain the high active pH range of the complex enzyme I. Based on the enzyme activity of 80000U / g, the compound enzyme I converted the mass number of added enzymes per ton of straw raw material into: high-temperature amylase 40g, alkaline high-temperature xylanase 44g, and the reaction time was 120min. Then add compound enzyme II, stir evenly, and maintain the temperature at 95°C. Compound enzyme II is based on the enzyme activity of 80000U / g, and the mass number of added enzymes converted to tons of straw raw materials is: 80g of high-temperature x...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com