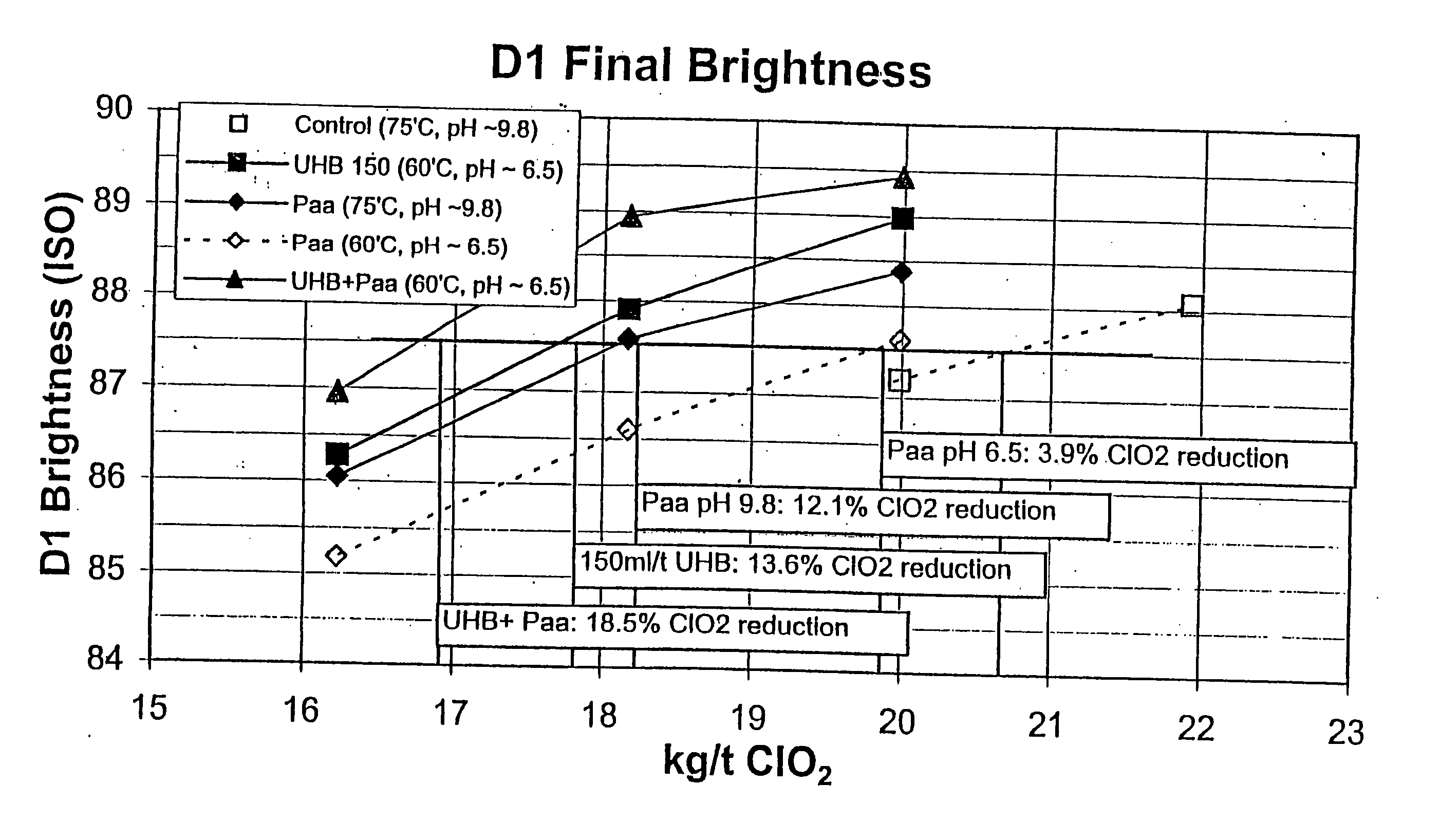
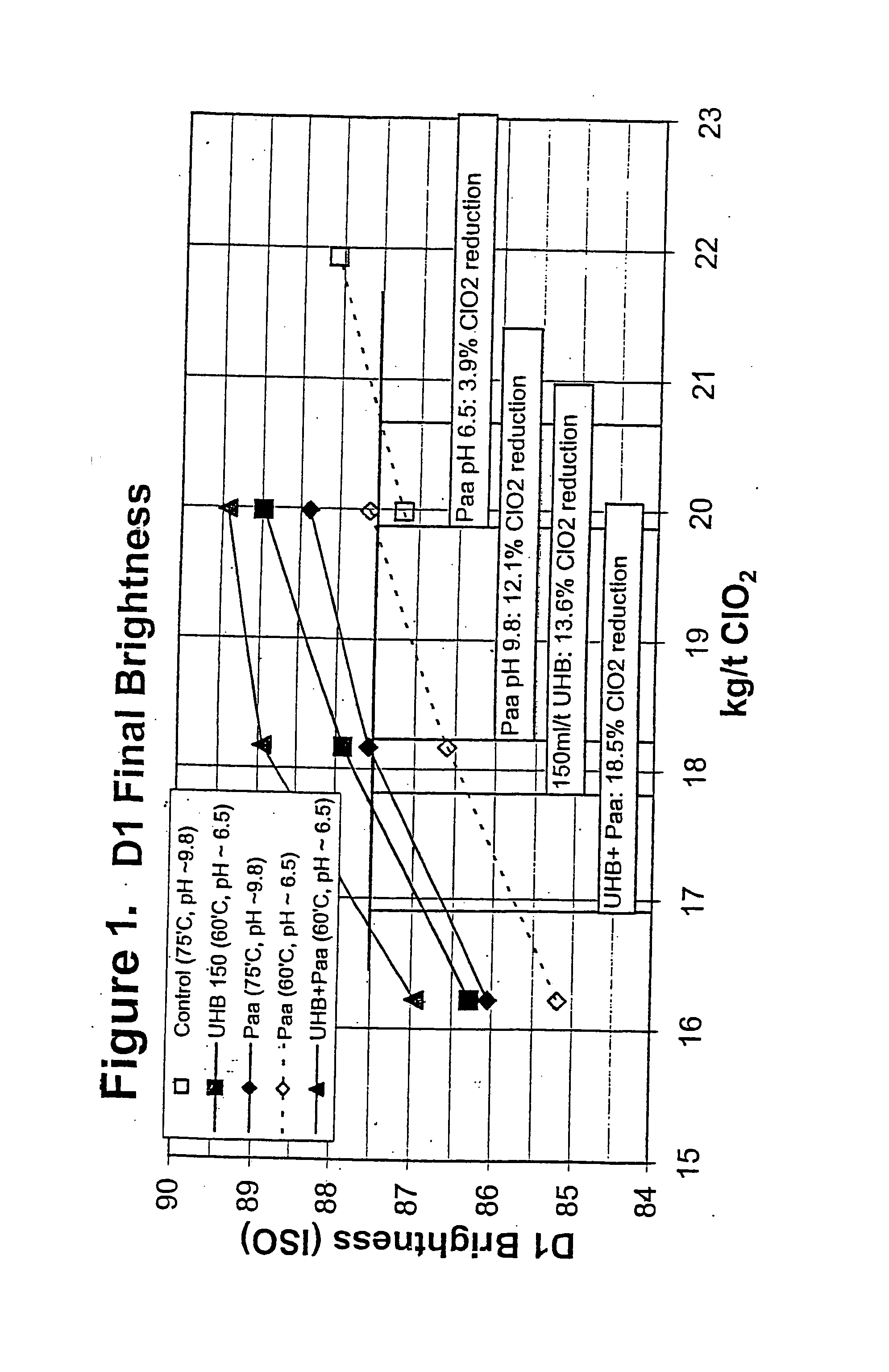
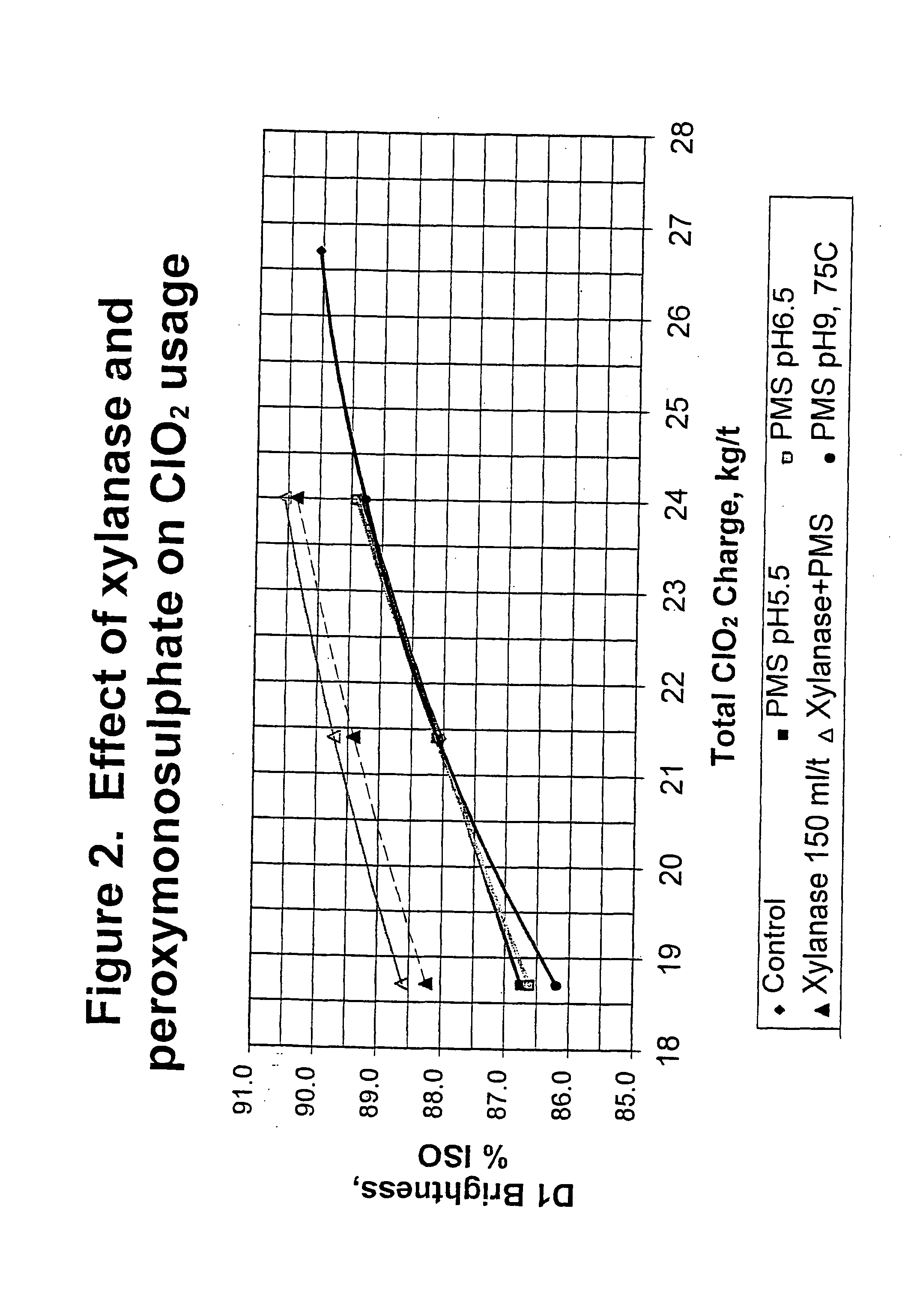
Bleaching stage using xylanase with hydrogen peroxide, peracids, or a combination thereof
a technology of hydrogen peroxide and bleaching stage, which is applied in the direction of multi-stage pulping process, cellulose treatment using microorganisms/enzymes, and inorganic base pulping, etc. it can solve the problems of inability to remove all lignin without, harsh pulp, and destruction of some cellulose fibers in pulp, so as to reduce the use of chlorine-containing bleaching chemicals and less costly bleaching operations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Determination of Kappa Number
[0077] The kappa number of the pulp is determined using the protocol described in: TAPPI method for Kappa number of pulp (T 236 cm-85) from TAPPI Test Methods 1996-1997, which is herein incorporated by reference. Briefly, the kappa number is the volume (in milliliters) of a 0.1 N potassium permanganate solution consumed by one gram of moisture-free pulp under the conditions specified in the method. The results are corrected to 50% consumption of the permanganate added.
[0078] The kappa number determination is performed at a constant temperature of 25.degree. C..+-.0.2.degree. C. with continuous agitation. However, it is possible to correct for variations in temperature as is described below.
[0079] The moisture content of the pulp is determined in accordance with TAPPI T 210 "Sampling and Testing Wood Pulp Shipments for Moisture" which is herein incorporated by reference. Briefly, the pulp specimen is disintegrated in about 800 mL of distilled water and st...
example 2
Standard Assay for the Measurement of Xylanase Activity
[0092] The endo-xylanase assay is specific for endo-1,4-beta-D-xylanase activity. On incubation of azo-xylan (oat) with xylanase, the substrate is depolymerized to produce low-molecular weight dyed fragments which remain in solution on addition of ethanol to the reaction mixture. High molecular weight material is removed by centrifugation, and the colour of the supernatant is measured. Xylanase activity in the assay solution is determined by reference to a standard curve.
[0093] Substrate: The substrate is purified (to remove starch and beta-glucan). The polysaccharide is dyed with Remazolbrilliant Blue R to an extent of about one dye molecule per 30 sugar residues. The powdered substrate is dissolved in water and sodium acetate buffer and the pH is adjusted to 4.5.
[0094] Assay: Xylanase is diluted in 0.5 M acetate buffer at pH 4.5. Two millilitres of the solution is heated at 40.degree. C. for 5 minutes....
example 3
Preparation of Chlorine Dioxide
[0098] Chlorine dioxide was made in the lab by the standard procedure of passing a mixture of chlorine gas and nitrogen through a series of columns containing sodium chlorite, and collecting the evolved gas in cold water. The chlorine dioxide was stored refrigerated at a concentration of 10.4 grams per litre in water. Further details regarding the preparation of chlorine dioxide may be found in Chlorine Dioxide Generation published by Paprican, Pointe Claire, Qubec (which is herein incorporated by reference).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com